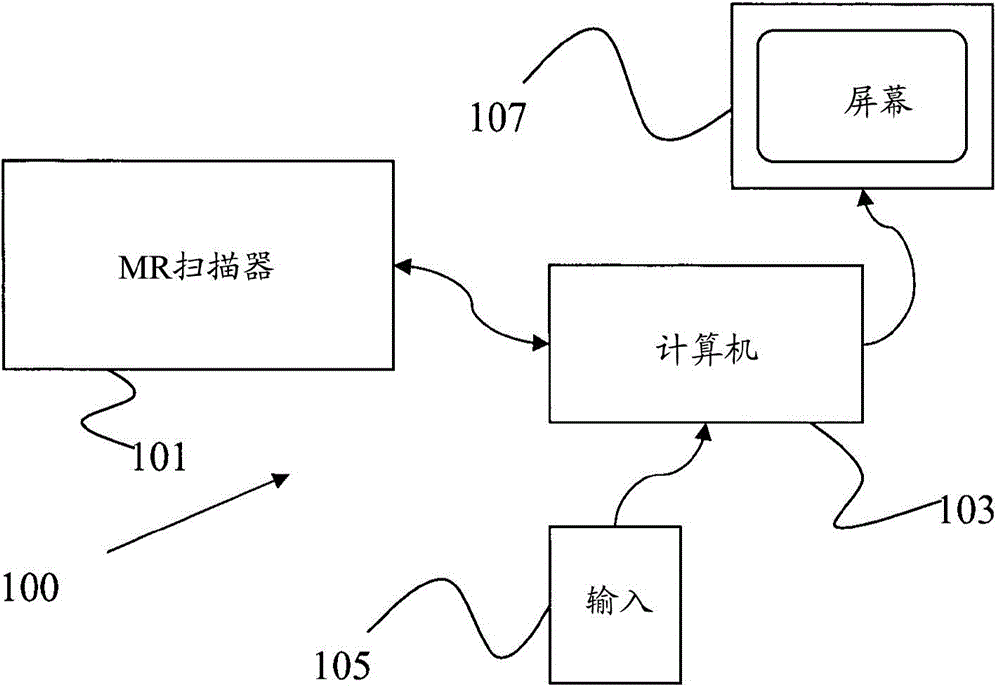
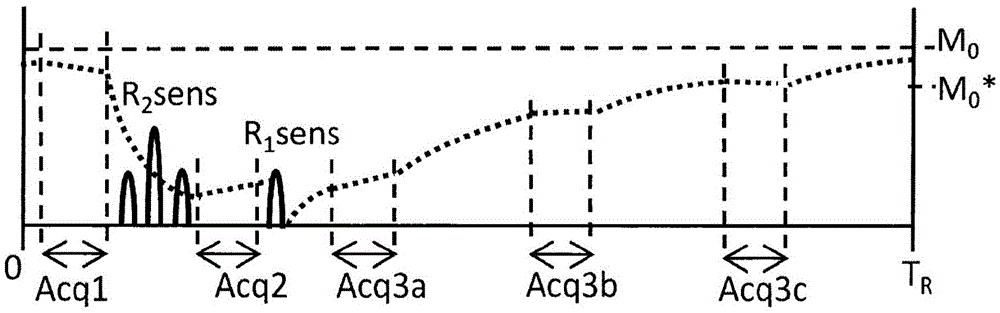
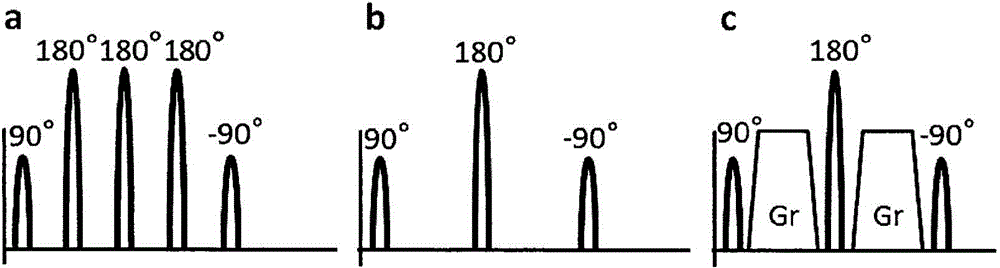
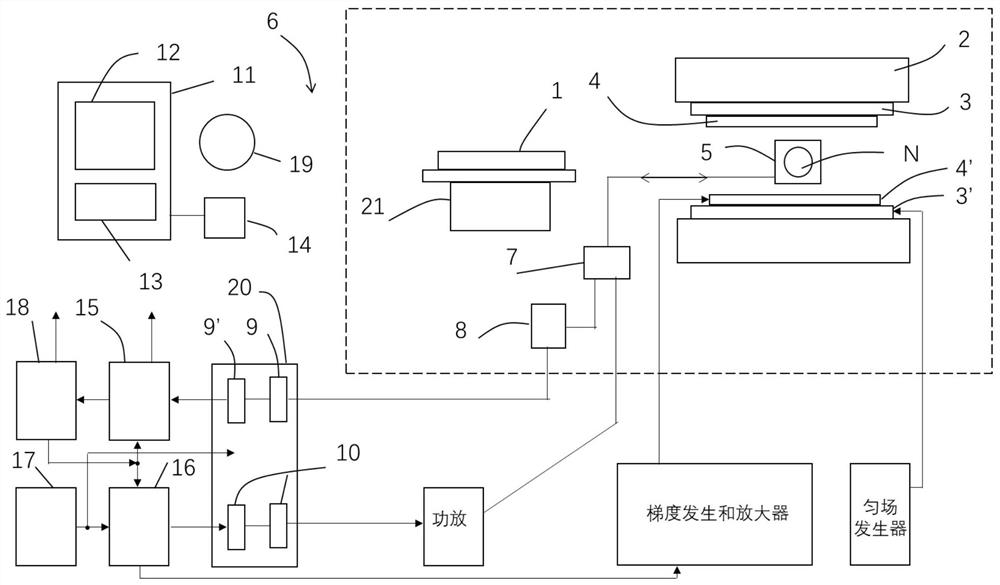
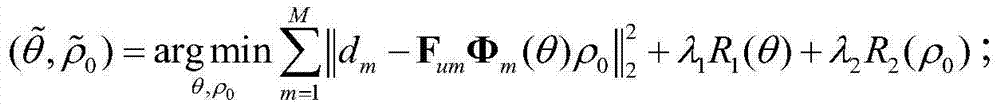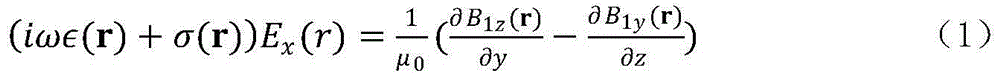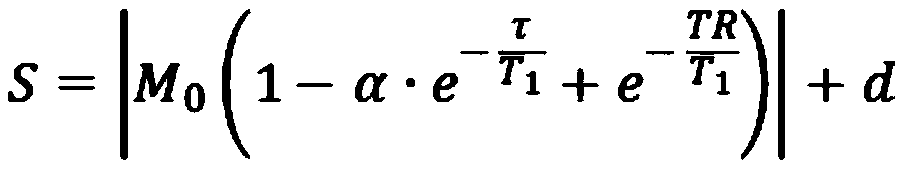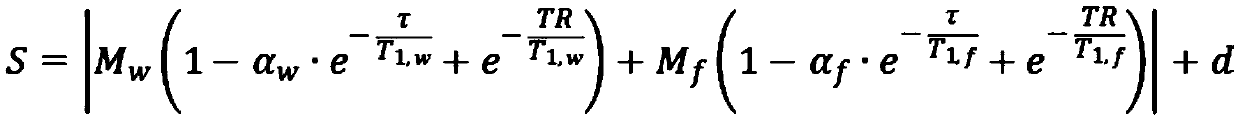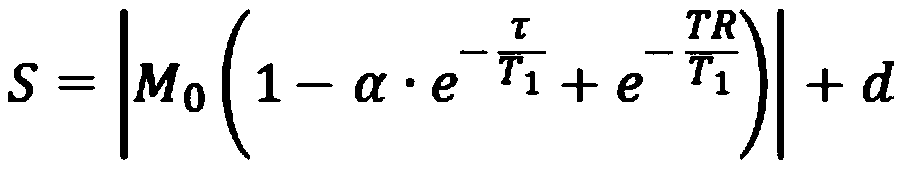Patents
Literature
50 results about "Proton density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
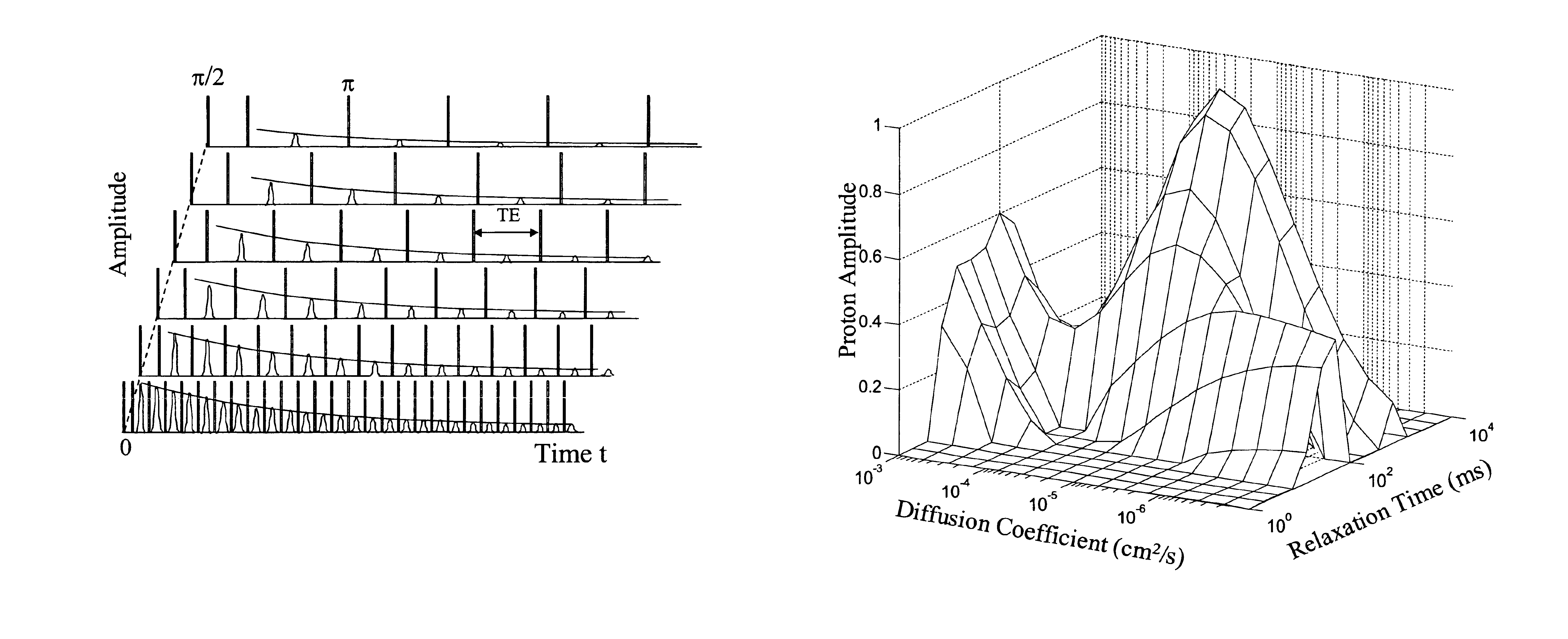
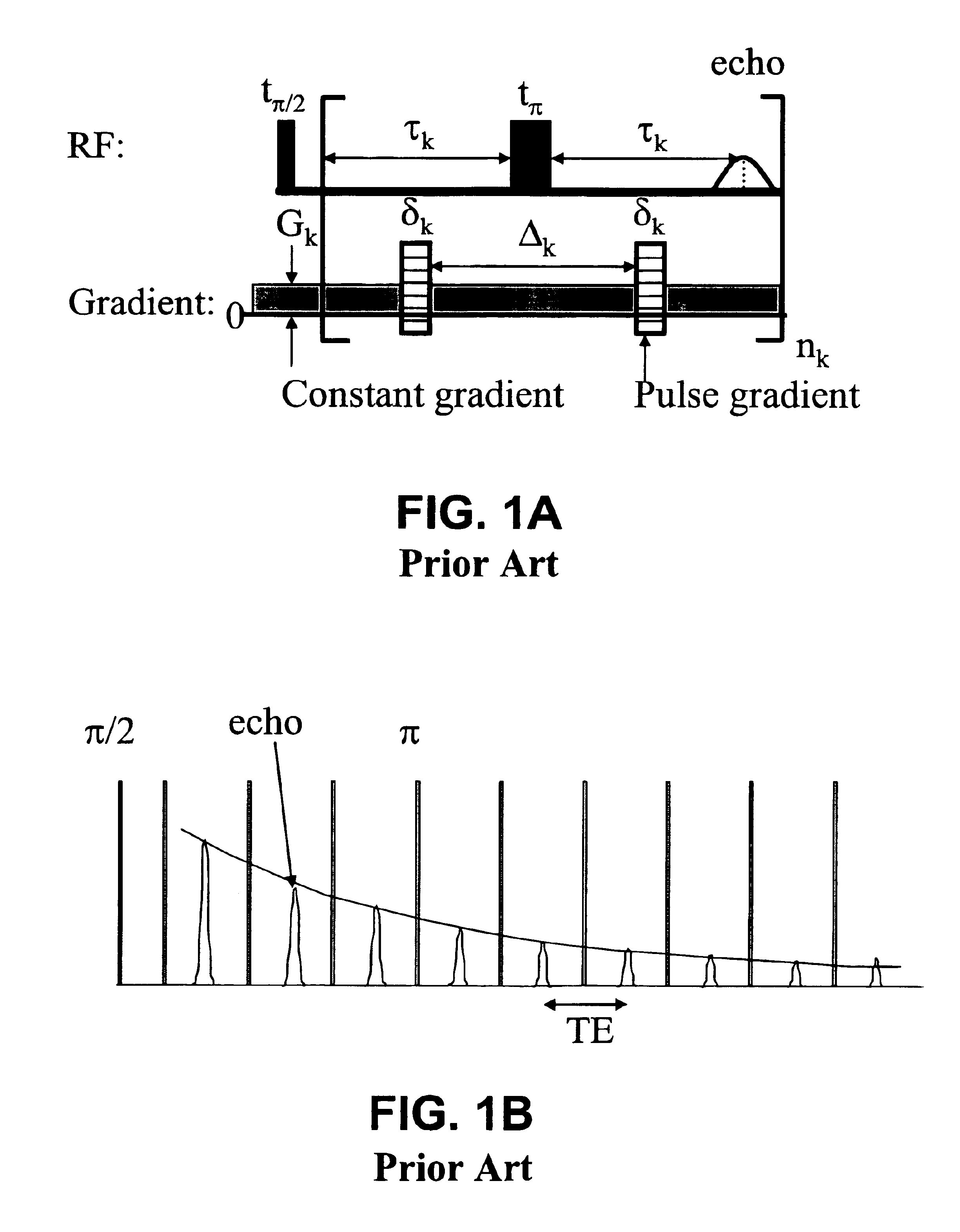
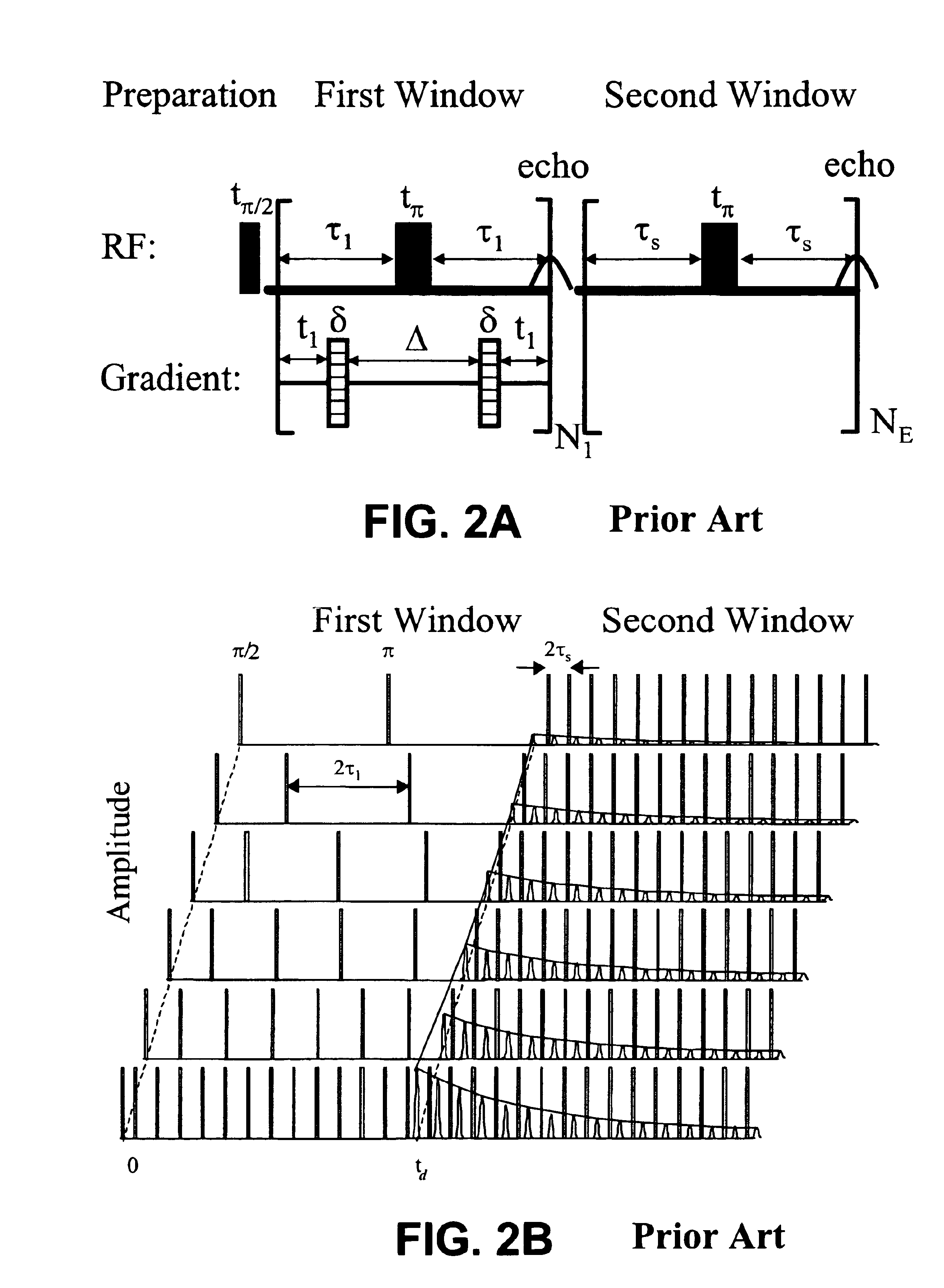
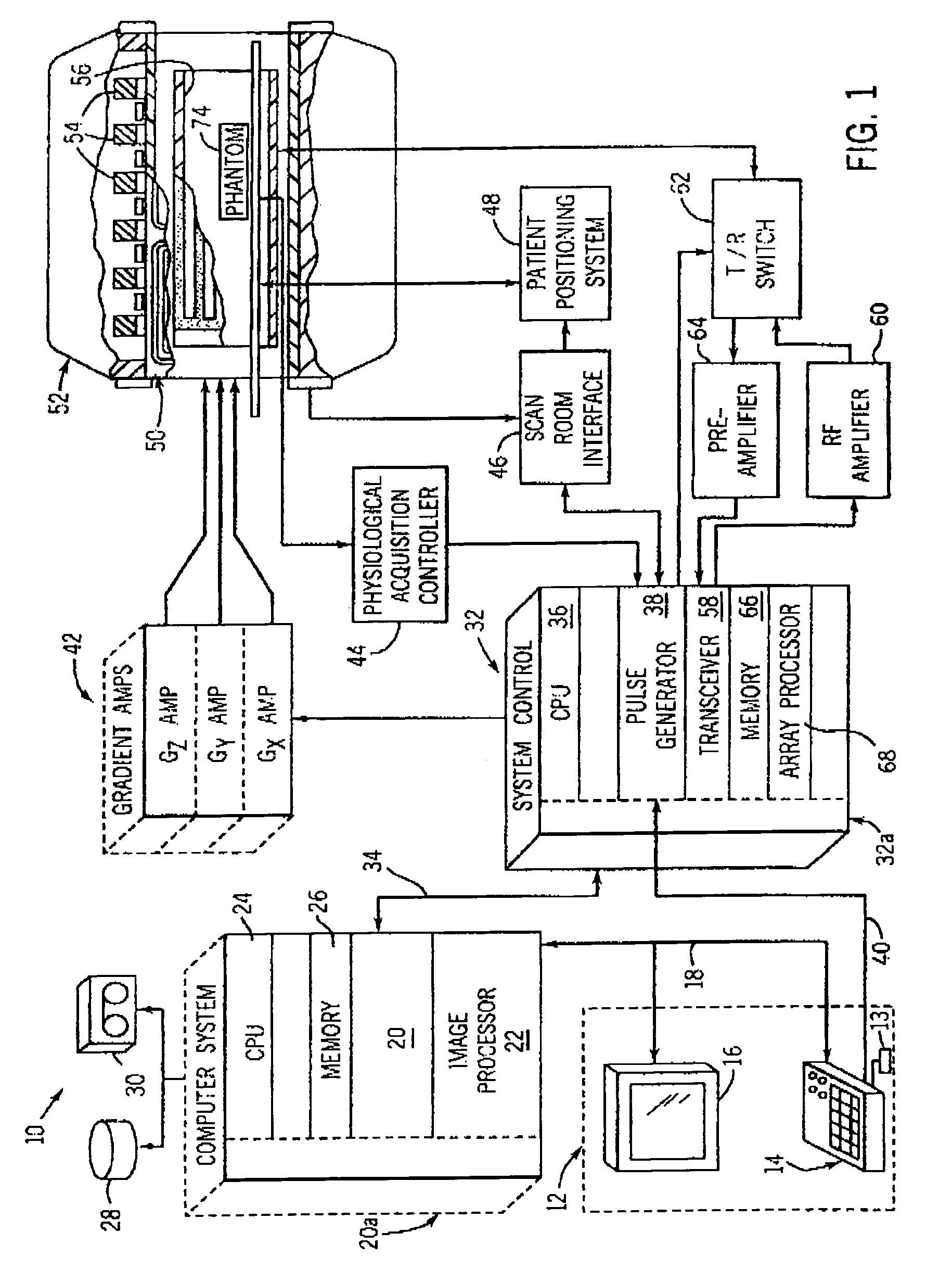
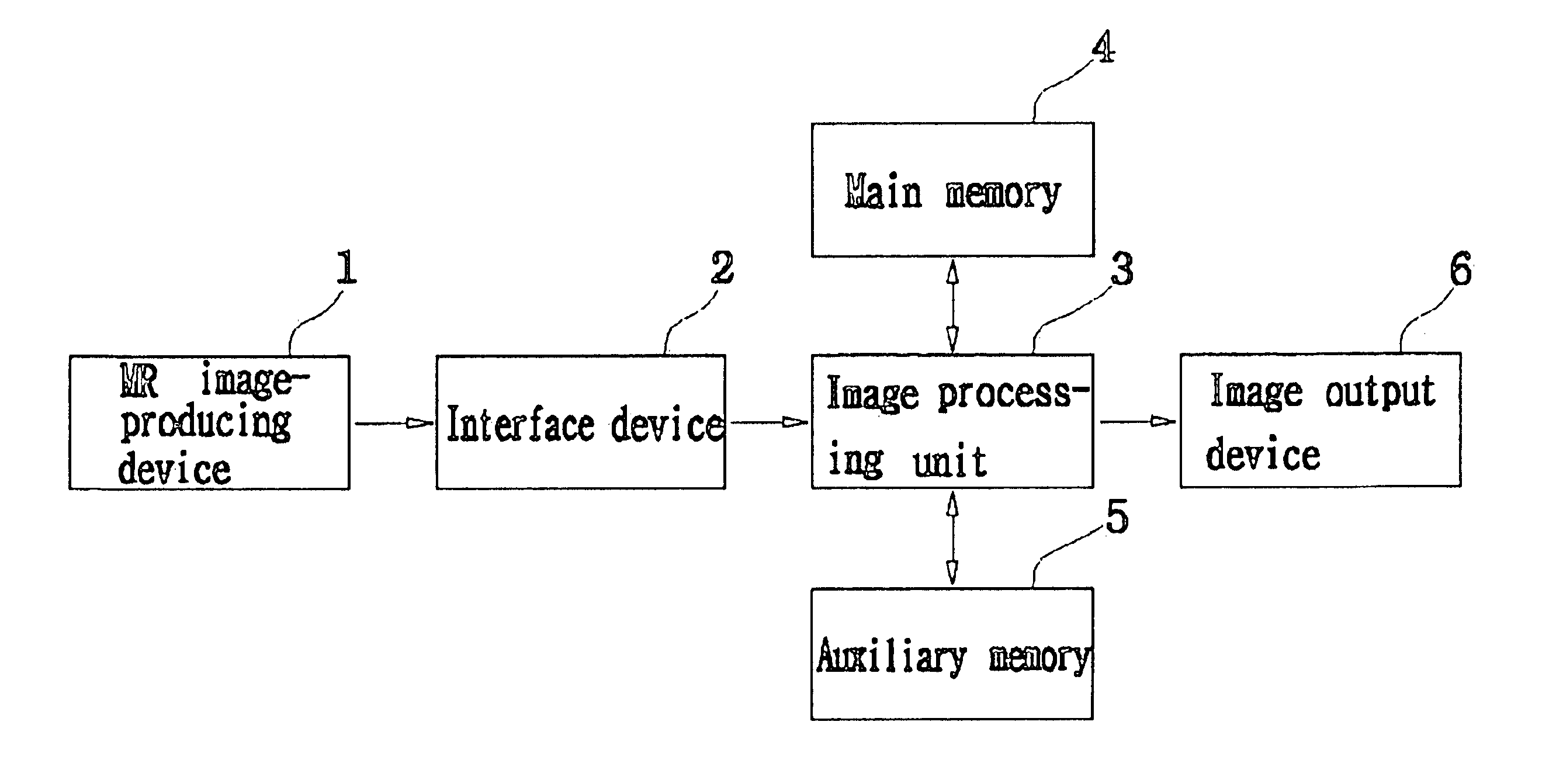
Method for obtaining multi-dimensional proton density distributions from a system of nuclear spins
InactiveUS6937014B2Slow solutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic property measurementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePorous medium
The present invention provides a method for obtaining a multi-dimensional proton density distribution from a system of nuclear spins. A plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data is acquired from a fluid containing porous medium having a system of nuclear spins. A multi-dimensional inversion is performed on the plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance data using an inversion algorithm to solve a mathematical problem employing a single composite kernel to arrive at a multi-dimensional proton density distribution. Ideally, the mathematical problem can be cast in the form of a Fredholm integral of the first kind wherein a two or more kernels can be reduced to a single composite kernel for ease of solution. Preferably, a series of conventional CPMG pulse sequences, using a conventional NMR tool, can be used to excite the system of nuclear spins. The present invention further includes a regression method which reduces computational efforts by retaining only those grid points, and preferably their neighboring grid points, which have non-zero values, during subsequent iterations of solving for the multi-dimensional proton density distribution. This regression process can be repeated until the density distribution is satisfactorily smooth.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
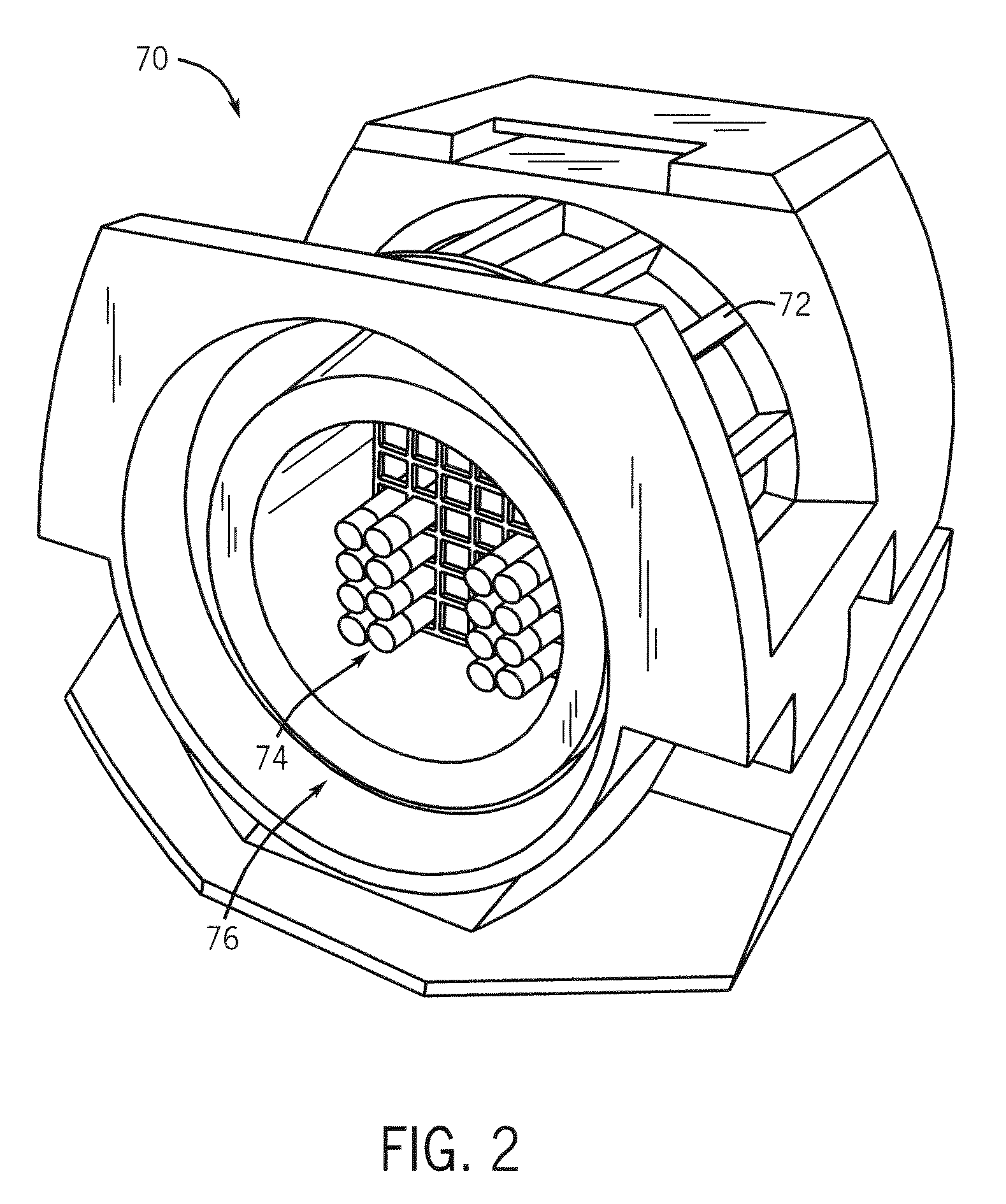
Apparatus to simulate MR properties of human brain for MR applications evaluation
InactiveUS6965235B1Increase contrastImproves white matterMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionVolumetric Mass DensityT1 weighted
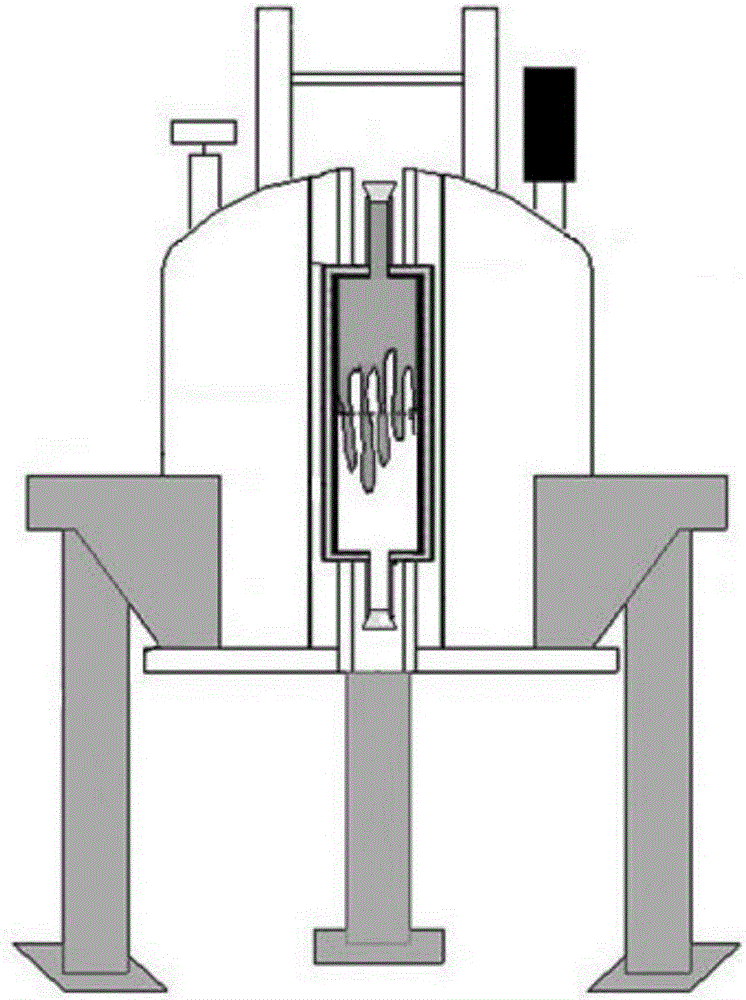
A system and method for mimicking a human brain for MR imaging at various magnetic field strengths is disclosed. A phantom is constructed of a structure having a number of sections. A first section contains a mixture of nickel chloride, agarose gel powder, potassium sorbate, deuterium oxide, and water such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the first section mimic white matter of the human brain. A second section contains different amounts of the same components such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the second section mimic gray matter of the human brain. As such, when the phantom is scanned in an MR imaging machine, an optimized flip angle for T1-weighted imaging to improve contrast between white matter and gray matter of the human brain that takes into account proton density differences therebetween can be determined.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
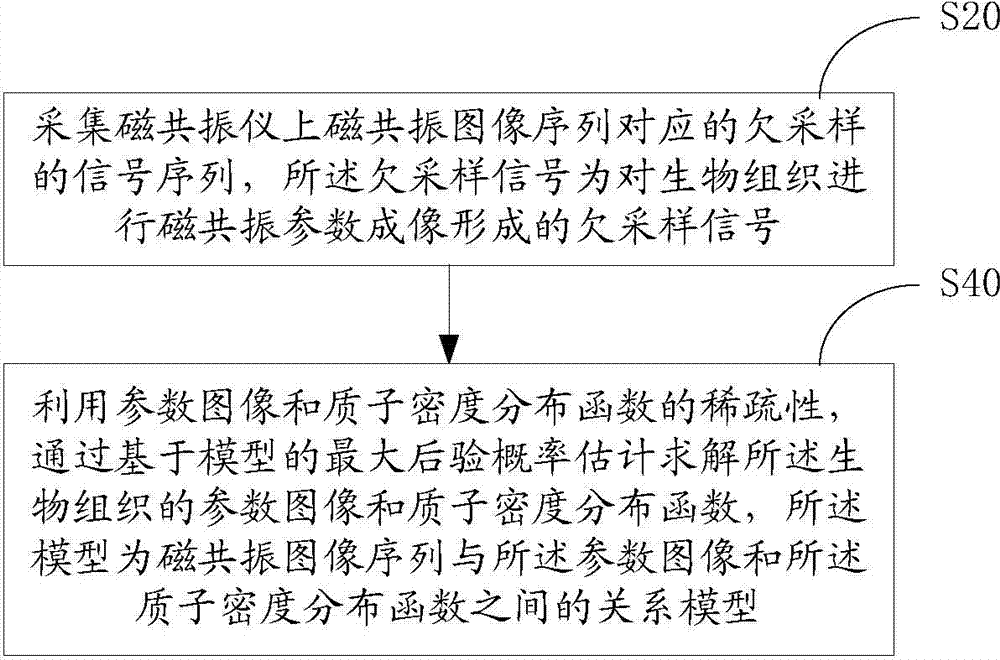
Magnetic resonance parameter imaging method and system
ActiveCN103705239AImaging is fast and accurateAvoid error propagationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRelational modelMaximum a posteriori estimation
A magnetic resonance parameter imaging method includes the steps of acquiring an under-sampling signal corresponding to a magnetic resonance image sequence on a magnetic resonance imager; estimating and solving a parameter image and proton density distribution function of biological issue through sparsity in parameter image and proton density distribution functions and model-based maximum posterior probability. The under-sampling signal is formed by application of magnetic resonance parameter imaging on the biological issue. A model for maximum posterior probability is a model of relation between the magnetic resonance image sequence and the parameter image and proton density distribution function. The method has the advantages that the parameter image and proton density distribution function of the biological tissue is directly estimated through the under-sampling signal and error propagation caused by the application of an under-sampling rebuilt magnetic resonance image in estimating biological tissue parameters is avoided. The sparsity in the parameter image and proton density distribution function is introduced, and image artifacts caused by under-sampling can be effectively suppressed. In addition, the invention further provides a magnetic resonance parameter imaging system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Device and method for detecting gas-liquid diffusion processes by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique
ActiveCN102879306ADensity determinationReal-time monitoring of density changesSurface/boundary effectLiquid diffusionTransverse relaxation
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting gas-liquid diffusion processes by using an MRI technique, and belongs to the technical field of chemical engineering and petroleum engineering. The device comprises a magnetic resonance imaging system and a dual chamber pressure attenuation system. The magnetic resonance imaging system is provided with a rock core clamper in a magnetic resonance imaging instrument which is electrically connected with a data acquisition and processing system. According to the device and the method for detecting gas-liquid diffusion processes by using the MRI technique, proton density images, longitudinal and transverse relaxation and diffusion tensor distribution images of fluids in porous media can be measured in real time, visually and with no damage through the MRI technique. Quantitative analysis can be performed on porous medium porosity, permeability, saturation level and the like; an improved dual chamber pressure attenuation method can reduce the leakage rate, and confirm the initial gas density conveniently and accurately; and a magnetic suspension balance can monitor gas density changes in real time, and accordingly, deficiencies of traditional dual chamber pressure attenuation methods are compensated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Markers, phantoms and associated methods for calibrating imaging systems
Embodiments of the present invention provide markers, phantoms, and associated methods of calibration which are suitable for use in both magnetic resonance imaging and radiographic imaging systems. A marker includes a first marker component having a first hydrogen proton density and a first mass density; and a second marker component having a second hydrogen proton density different than the first hydrogen proton density, and a second mass density different than the first mass density. The first marker component and the second marker component are non-magnetic.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
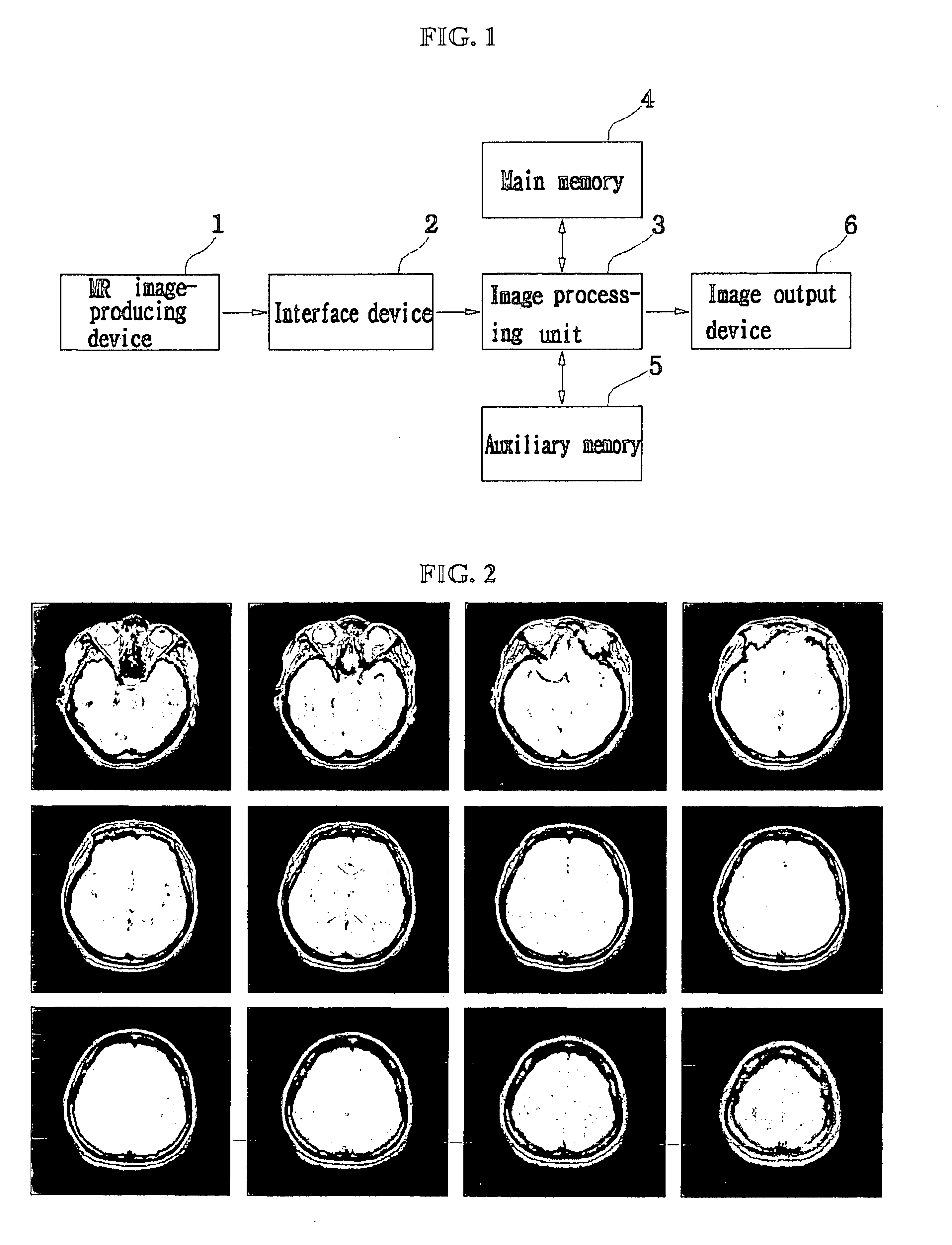
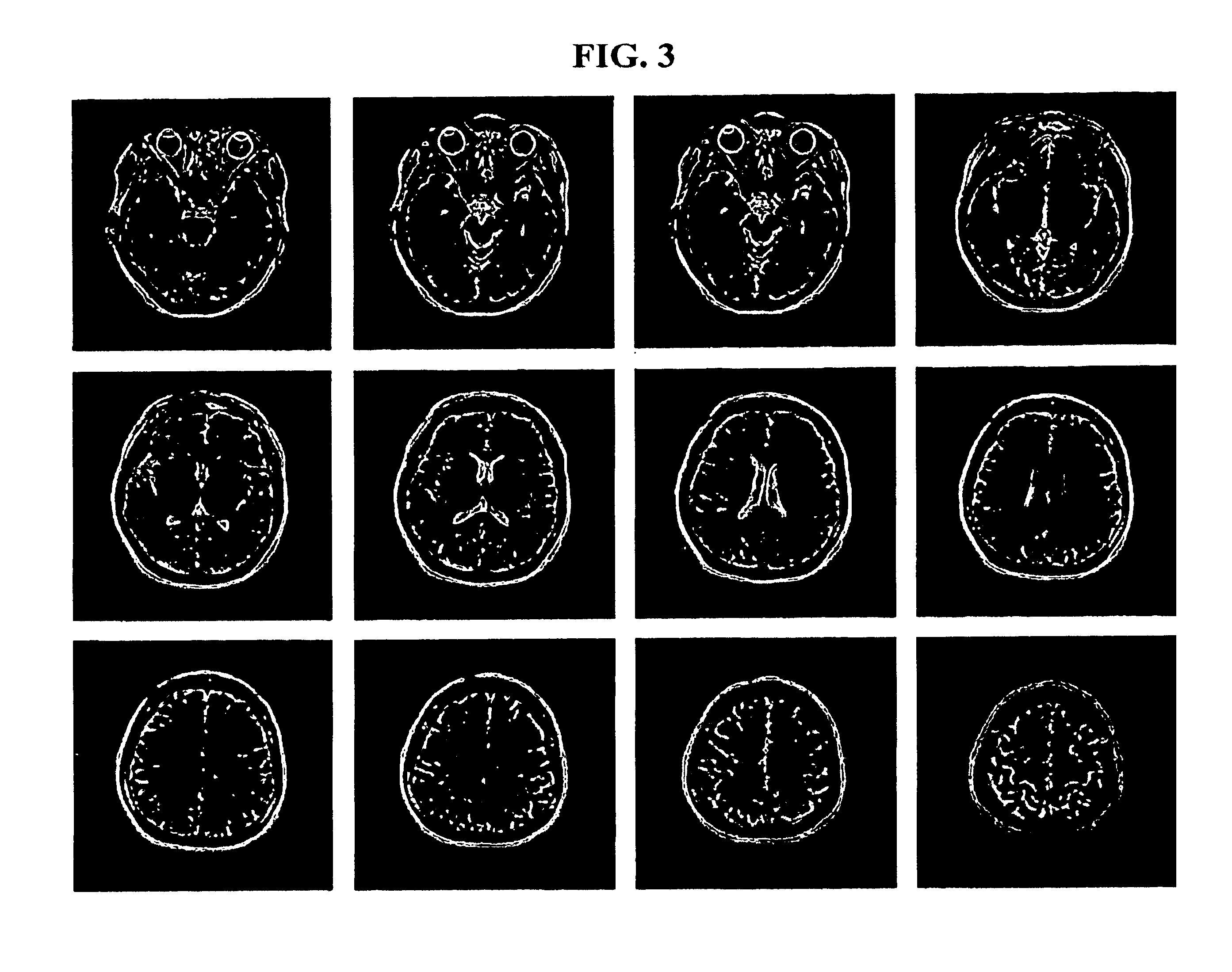
Method for segmentation and volume calculation of white matter, gray matter, and cerebral spinal fluid using magnetic resonance images of the human brain
InactiveUS6895107B2Reduce blurAssisted identificationImage enhancementImage analysisVisual recognitionGrey matter
A fully-automated method for segmentation of white matter, gray matter, and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and for calculating their respective volumes is disclosed. The technique preferably uses a T2-weighted scan and a proton-density scan. The T2-weighted scans are used to highlight those portion of the brain corresponding to CSF. Thereafter, the proton density images are separated in CSF-containing and CSF-free portions, in accordance with the T2-weighted images. The CSF-free portion is then segmented into white matter and gray matter portions. The CSF-containing portion is further segmented into pure CSF-regions, and regions containing a mixture of gray and white matter and CSF. After CSF is segmented from this mixture, the white and gray matter and again segmented, and the respective volumes of white matter, gray matter, and CSF are calculated. A technique for determining a threshold gray scale value for segmenting the white and gray matter to assist in the visual identification of such regions is also disclosed.
Owner:PARK JONG WON
Mr imaging with cest contrast enhancement
InactiveCN102257399AMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic variable regulationMagnetic field gradientMedicine
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
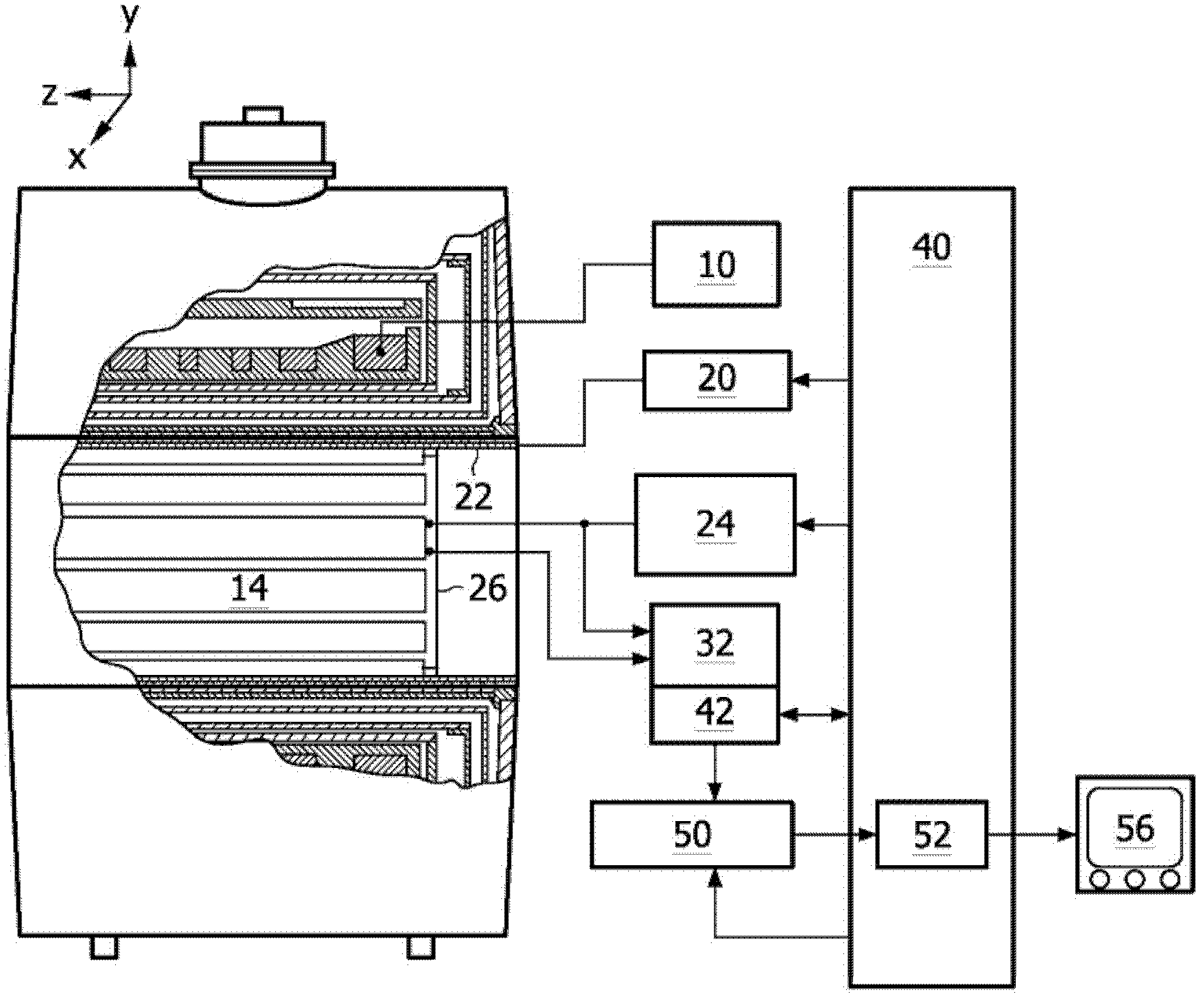
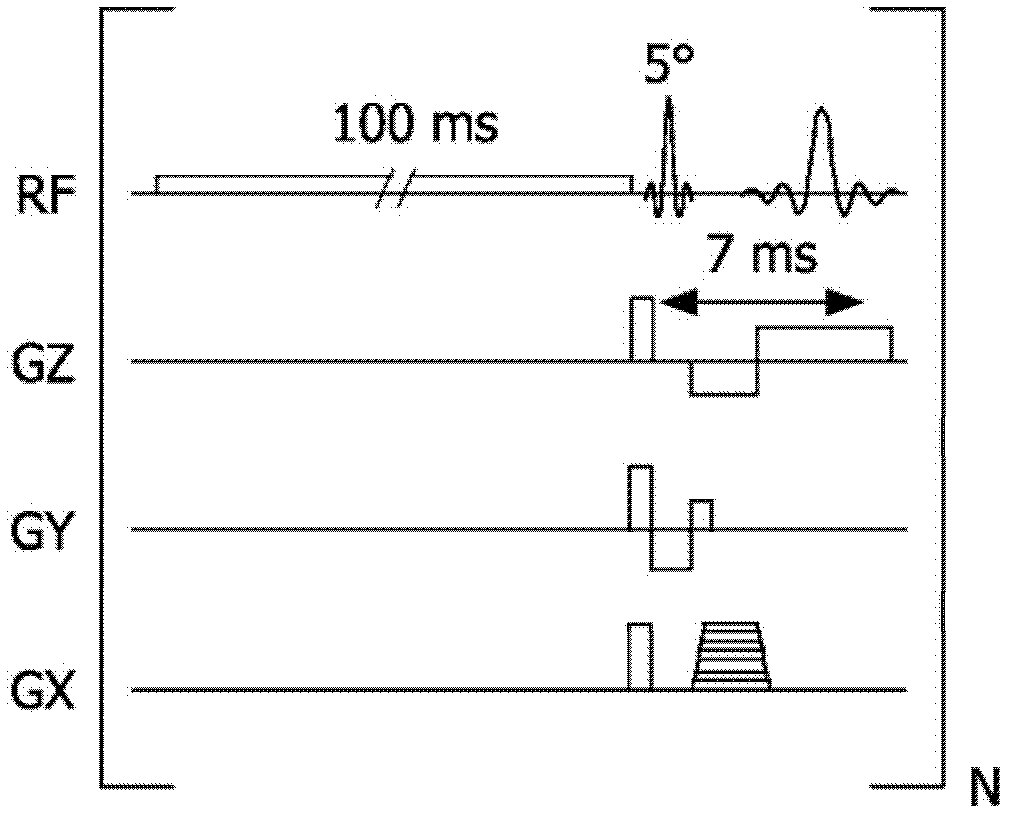
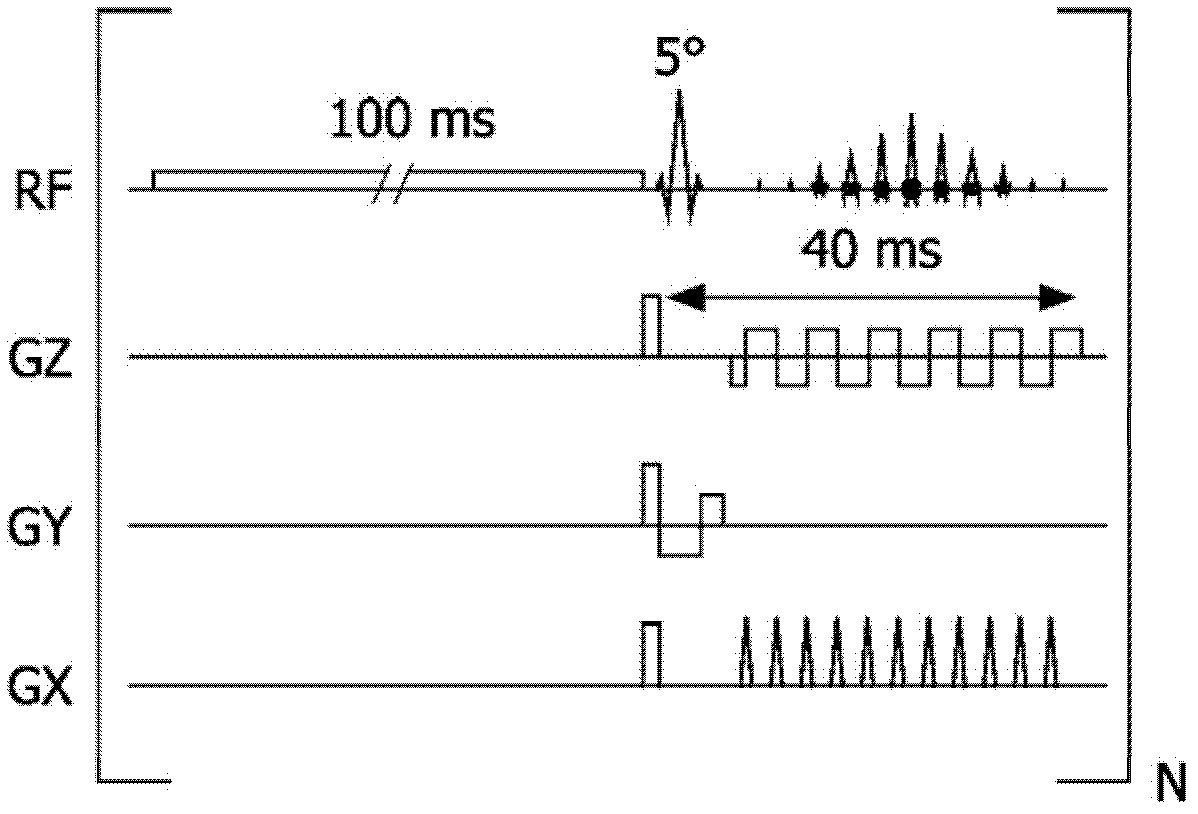
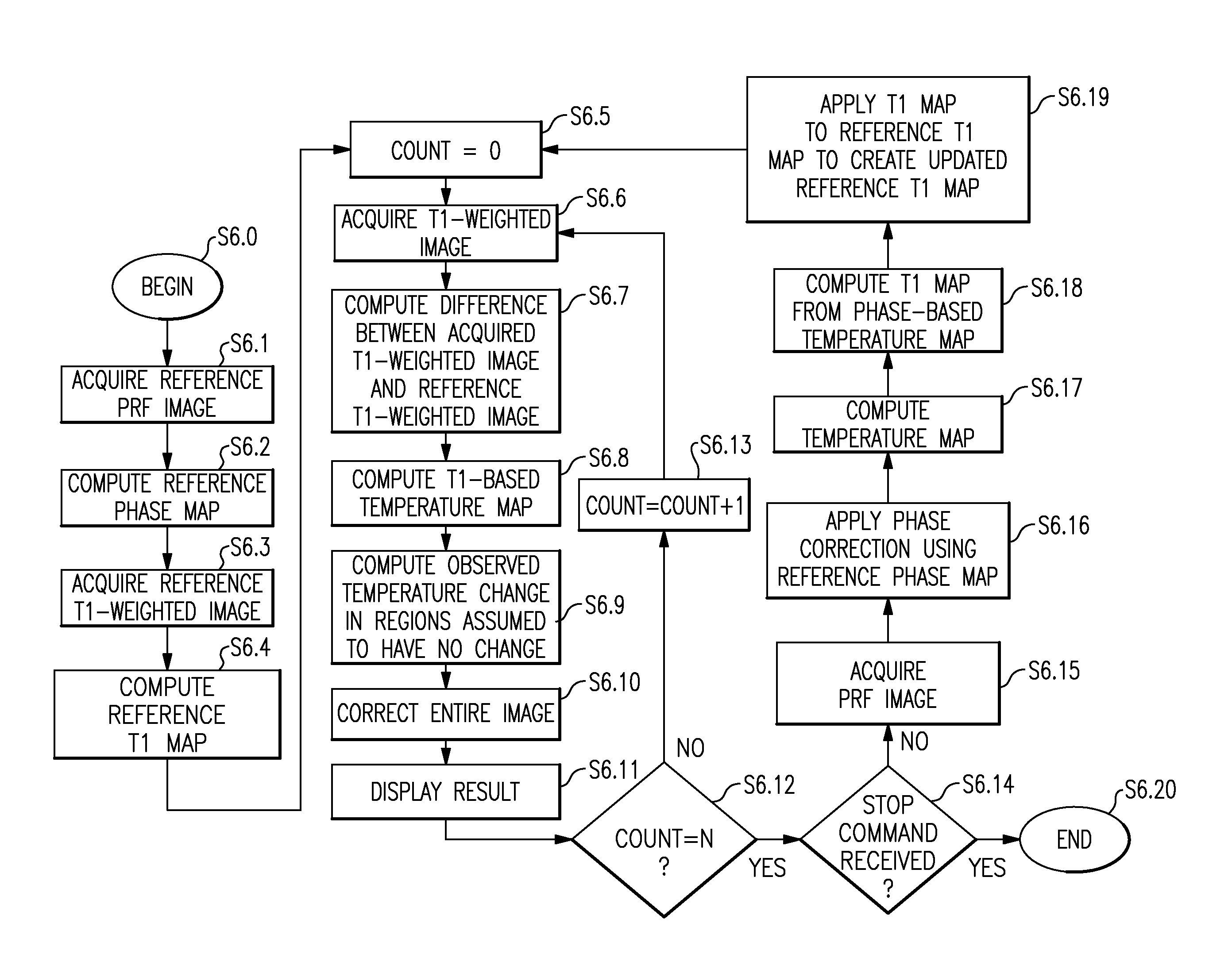
T1-corrected proton resonance frequency shift thermometry
InactiveUS8024025B2Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionResonanceProton resonance frequency
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Direct and Indirect Surface Coil Correction for Cardiac Perfusion MRI
InactiveUS20110208039A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringRadiologySurface coil
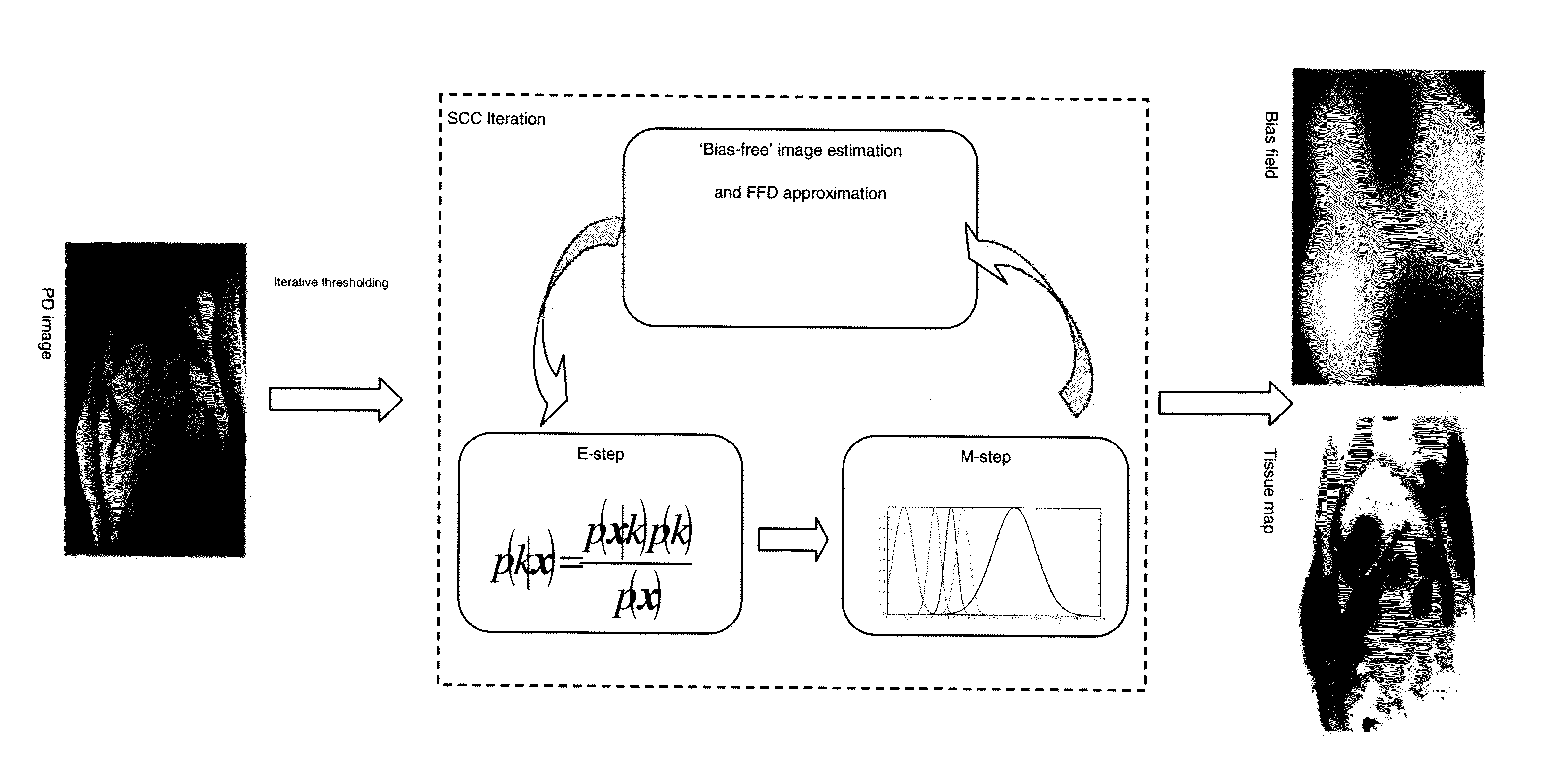
Method of correcting cardiac perfusion MR imaging for inhomogeneities (430) caused by non-uniform receiver coil fields using proton density weighted images (410) and B-Spline Free-Form Deformation (425).
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
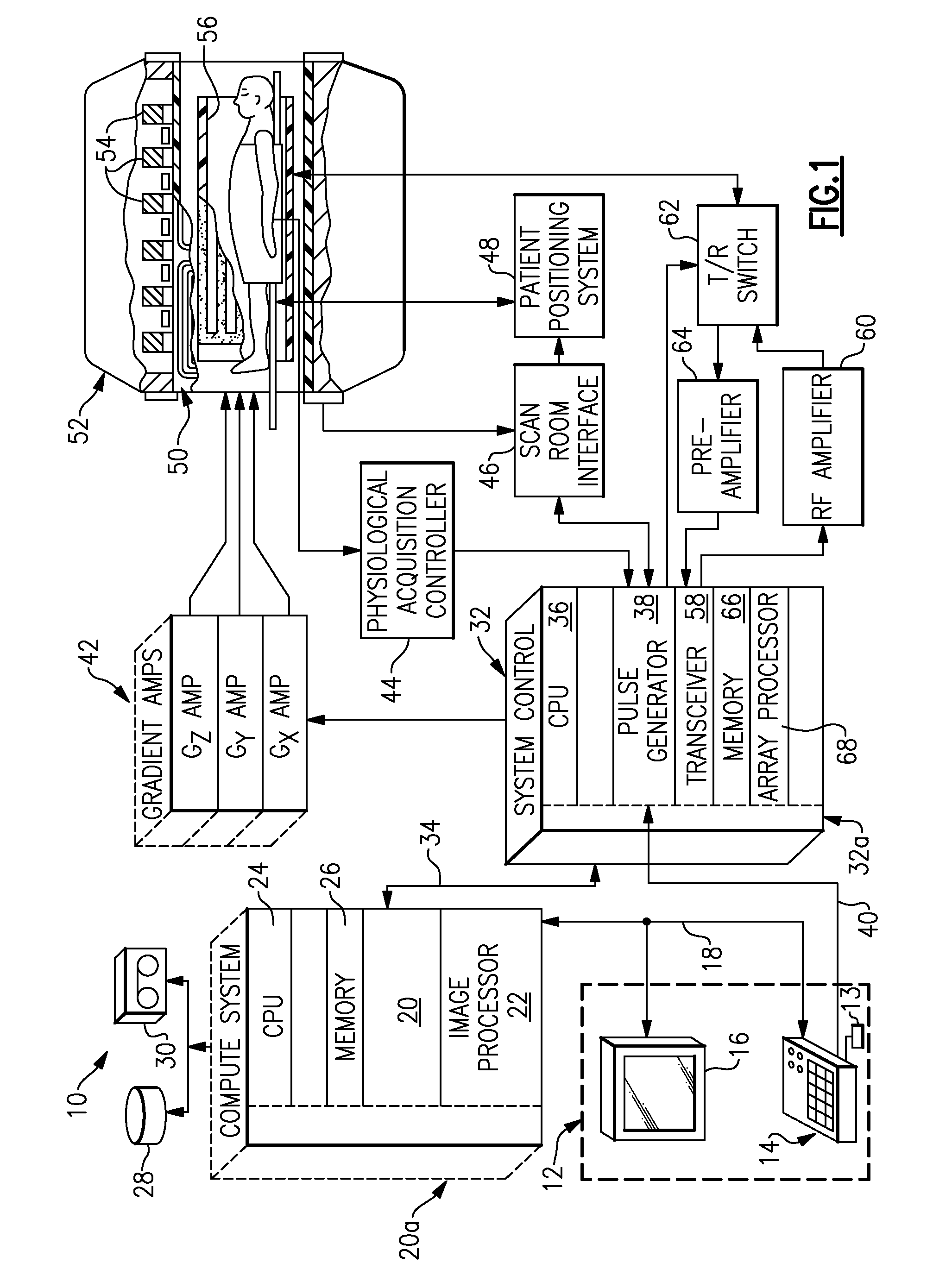
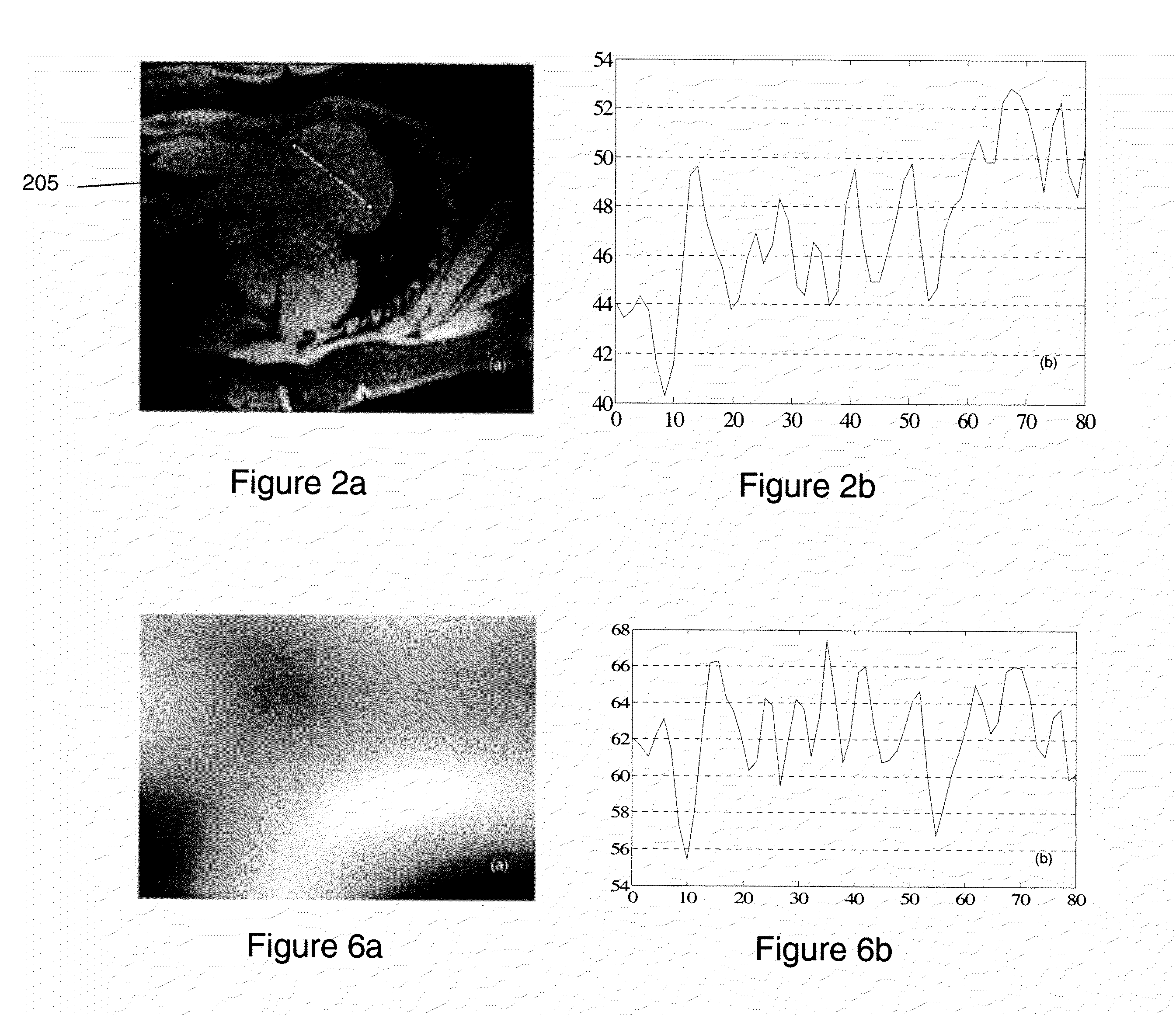
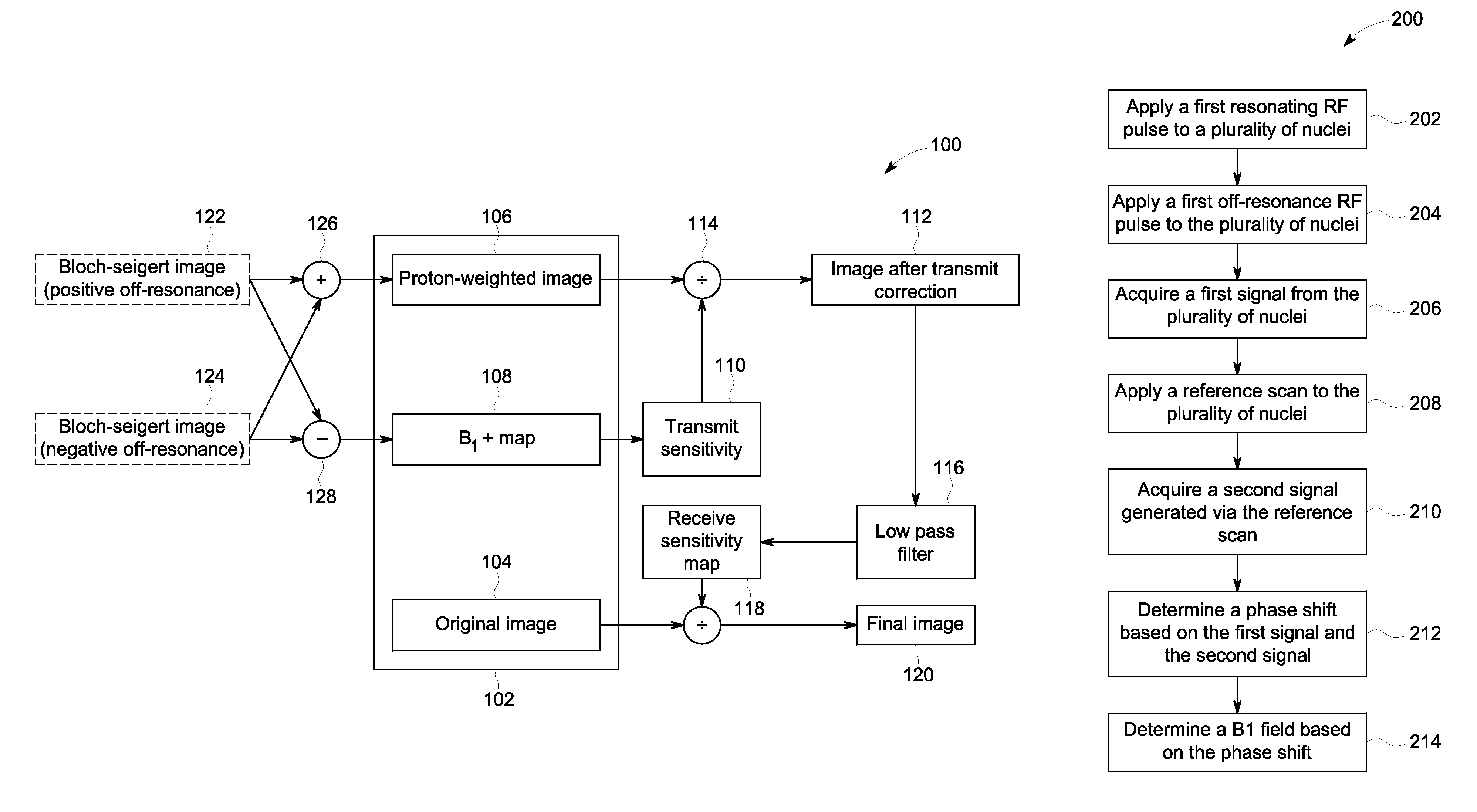
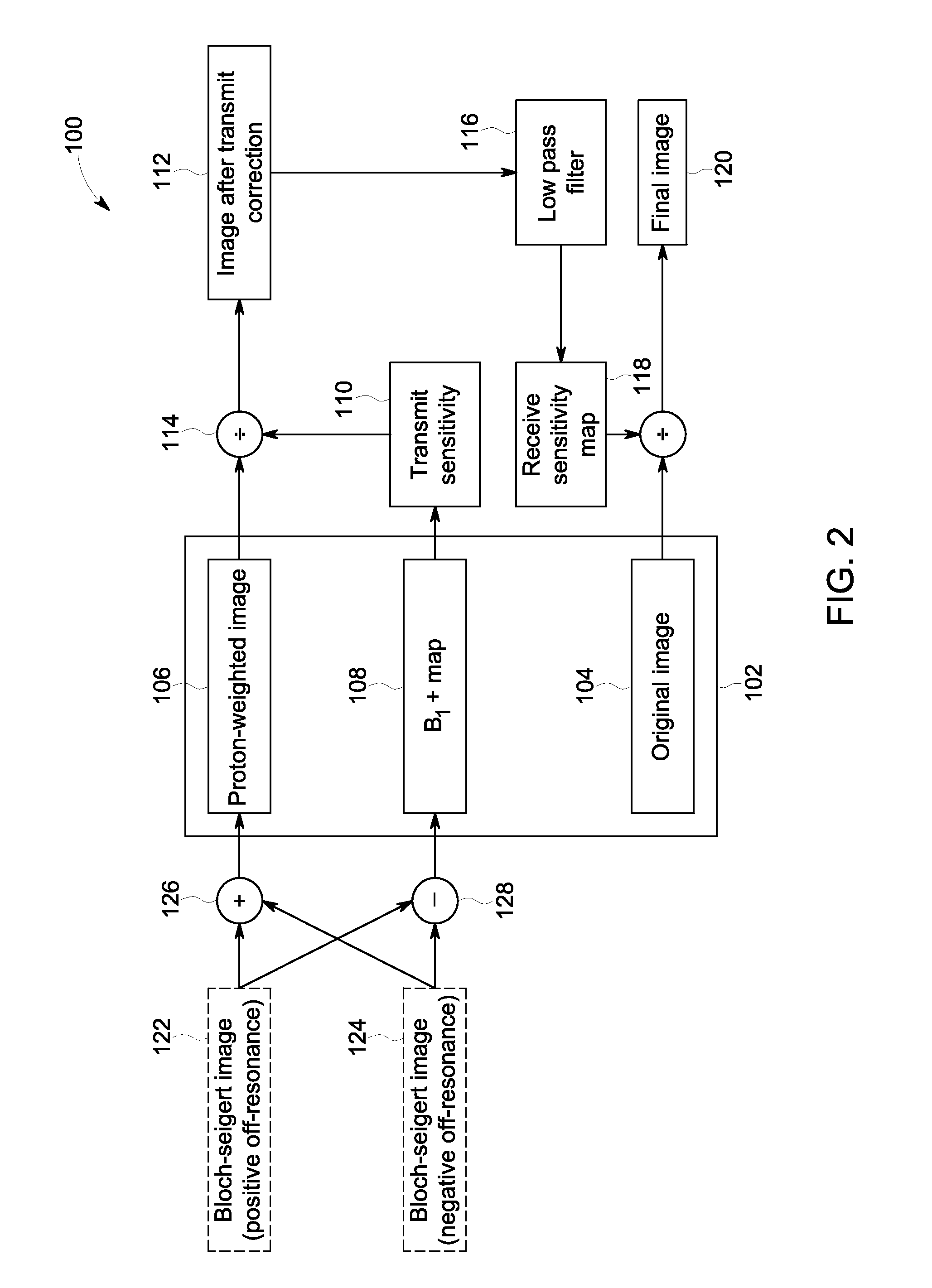
System and method of receive sensitivity correction in MR imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus includes a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system having a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet, and an RF transceiver system and an RF switch controlled by a pulse module to transmit RF signals to an RF coil assembly to acquire MR images, and a computer programmed to generate an original image of an object, generate a proton density weighted image of the object, generate a B1+ field map of the object, generate a transmit-corrected image based on the B1+ field map and based on the proton density weighted image, electronically filter the transmit-corrected image to generate a receive sensitivity map, and revise the original image using the receive sensitivity map.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Methods and systems for improved magnetic resonance acquisition
ActiveCN104412118AMeasuring Physical PropertiesDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceProton
Magnetic resonance imaging methods and apparatus for simultaneous measurement of the physical properties R1 and R2 relaxation rate, proton density, and apparent diffusion coefficient using a single magnetic resonance acquisition.
Owner:SYNTHETICMR
Magnetic resonance quantitative imaging method and device based on gradient echoes
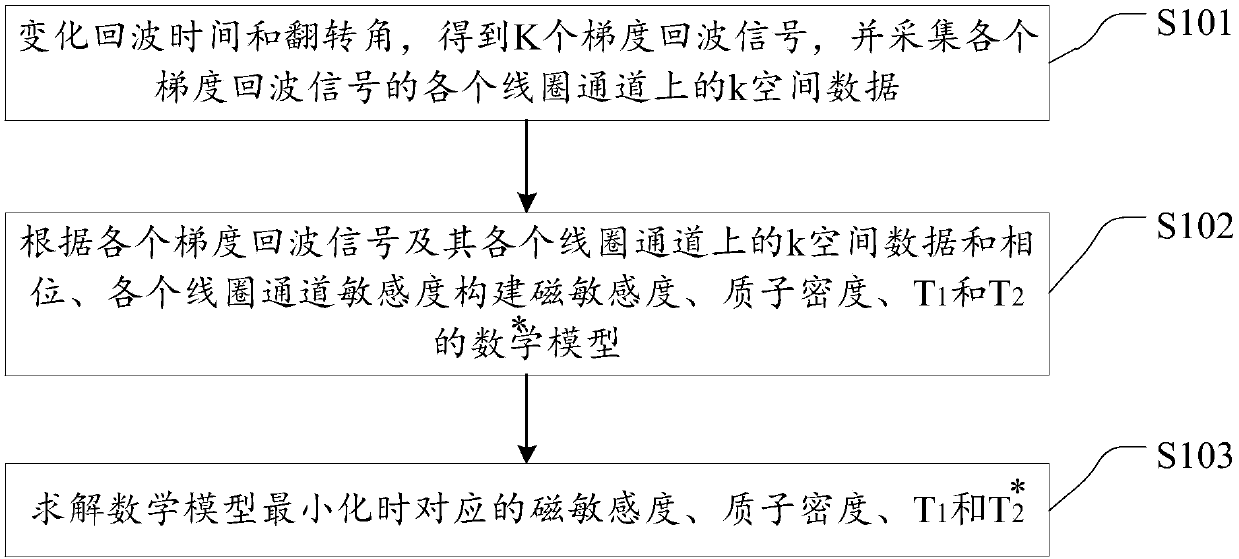
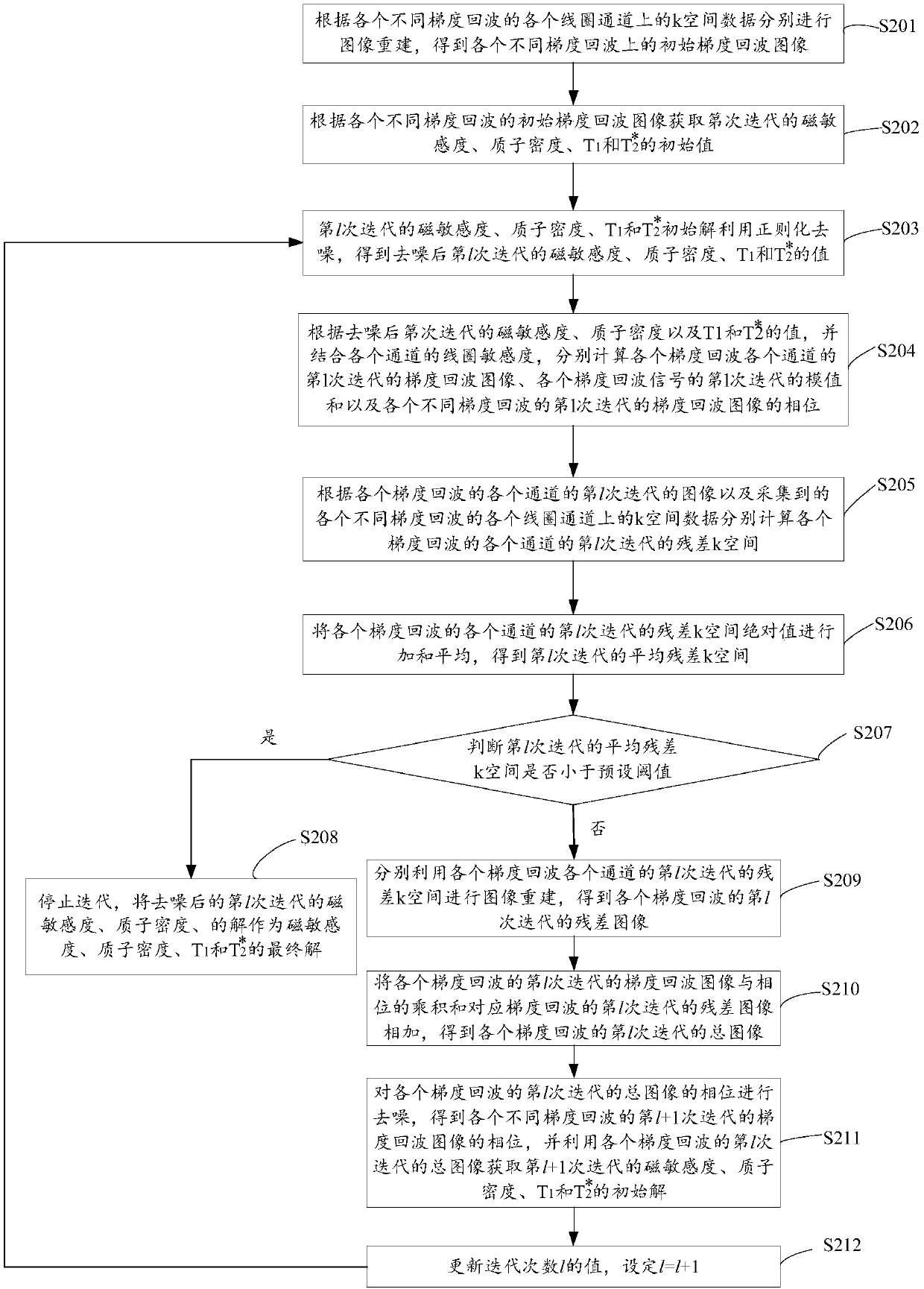
ActiveCN108802648AHigh precisionImprove accuracyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMathematical modelResonance
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance quantitative imaging method and device based on gradient echoes. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, changing the echo time and the turnoverangle for many times to obtain K gradient echo signals, and acquiring the k space data on each coil channel of each gradient echo signal; and then according to the gradient echo signals, k space dataand phases on each coil, and the sensitivity of each coil channel, establishing unknown factors including a mathematical model of magnetic sensitivity, proton density, T1, and T*2, and finally solving the magnetic sensitivity, the proton density, T1, and T*2 corresponding to the minimization of the mathematical model. The magnetic resonance quantification is directly solved as the unknown in themathematical model, and the regularization is directly directed to the resonance quantification, a magnetic resonance quantitative value is obtained by solving an equation solution, and more accurateresults can be obtained. According to the method, the accuracy and accuracy of magnetic resonance quantification can be improved, and the accuracy of clinical diagnosis is further improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEUSOFT MEDICAL TECH LTD
Single scan space-time coding imaging reconstruction method based on residual network
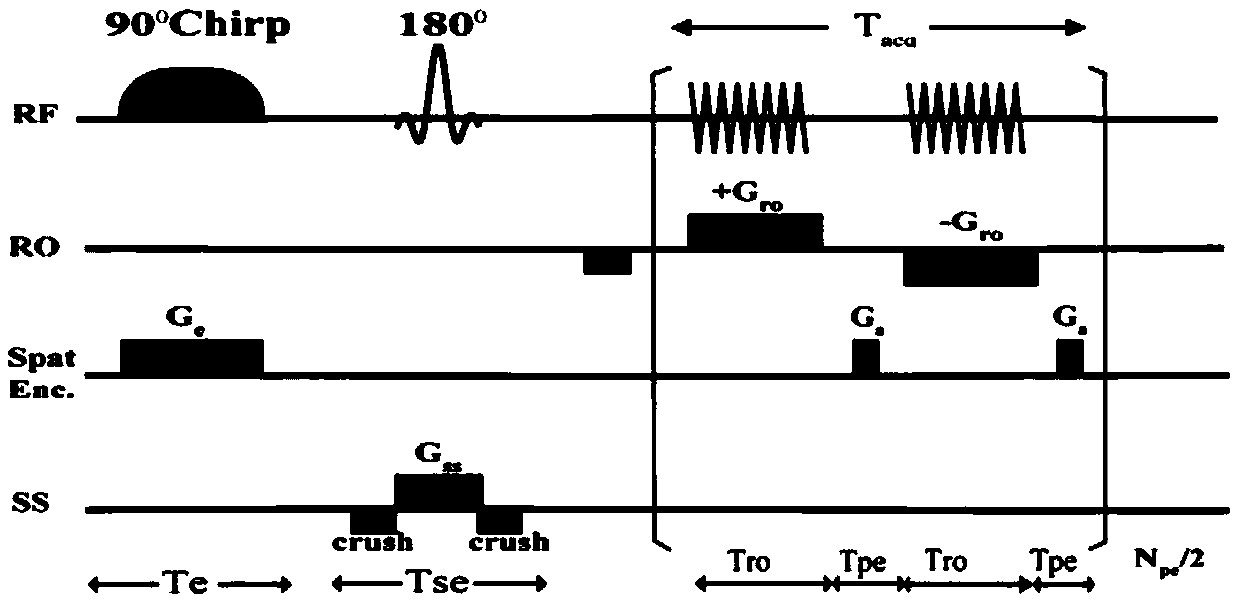
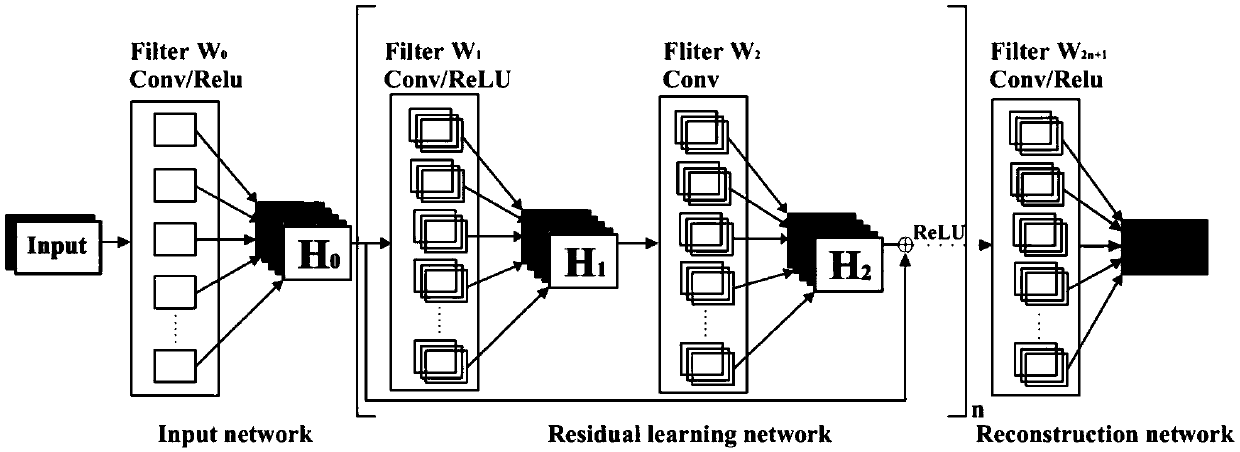
ActiveCN109597012AResistance to distortionHigh-resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsReconstruction methodStudy methods
The invention discloses a single scan space-time coding imaging reconstruction method based on the residual network, which relates to a magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction technique based on a deep learning network. The invention provides a single scan space-time coding imaging reconstruction method based on a residual network for obtaining a two-dimensional image in a single scan and reconstructing by a deep learning method. The excitation pulse is replaced by a linear sweep pulse, which effectively resists image distortion caused by the nonuniform magnetic field and chemical shift, andat the same time obtains imaging speed, resolution and signal-to-noise ratio similar to EPI. The SPEN imaging is undersampled along the phase encoding direction. Although the space-time coding imaging signal itself can reflect the contour of the imaged object without reconstruction, the inherent resolution of the contour is typically very low. The single scan space-time coding imaging reconstruction method based on residual network utilizes deep learning to reconstruct SPEN images from low-resolution signal space, greatly improves image resolution, exhibits proton density distribution, and obtains high signal-to-noise ratio while obtaining a resolution similar to conventional deconvolution reconstruction methods.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for measuring convective mixing process velocity field in porous medium based on nuclear magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN106124798AWon't disturbHydrodynamic testingFull-field flow measurementPorous mediumStationary state
The invention relates to a method for measuring a convective mixing process velocity field in a porous medium based on nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, and the method belongs to the technical field of convective mixing process velocity field measurement. The method comprises the steps of carrying out upper-lower layered saturation on two kinds of solutions with different densities in the porous medium at first, placing a sand-filled pipe saturating the two kinds of solutions with different densities in an inverted manner and then placing the sand-filled pipe into a nuclear magnetic probe quickly, adopting a spin echo sequence method added with phase encoding gradient pulses to obtain a proton density image of a fluid and converting the proton density image into a phase image, making difference between the phase image and a stationary state phase image under the same pulsed gradient to obtain a phase shifting image, and measuring to obtain a porous medium convective mixing process velocity field by adopting a phase method. The method realizes the unconventional fluid distribution situation required by convective mixing, is applied to the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging technology, carries out visual observation on the convective mixing process velocity field by non-contact and non-interference means, and does not disturb flow of the fluid.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic resonance human tissue electrical characteristic tomography method
ActiveCN104352239AHigh resolutionHigh precisionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyPermittivity
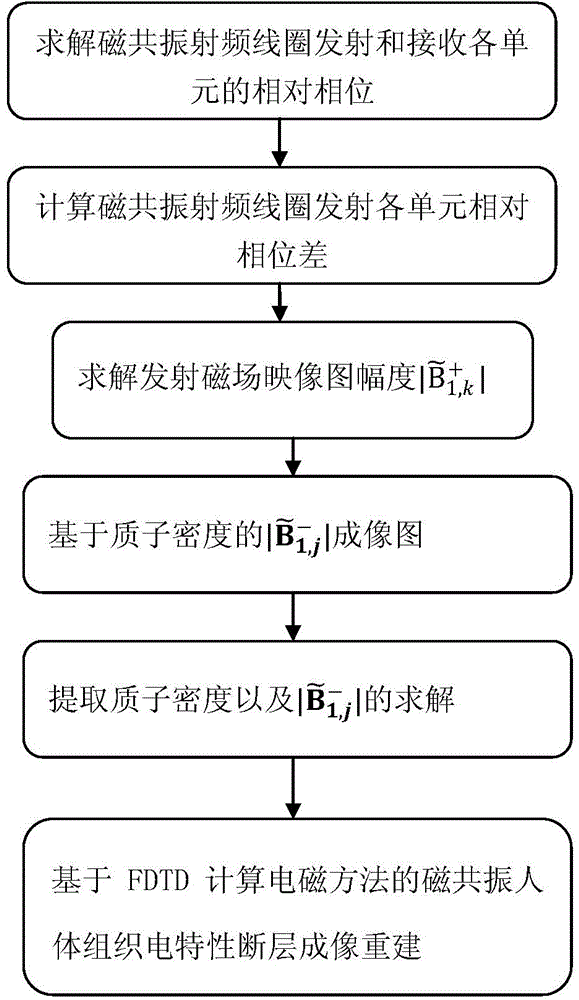
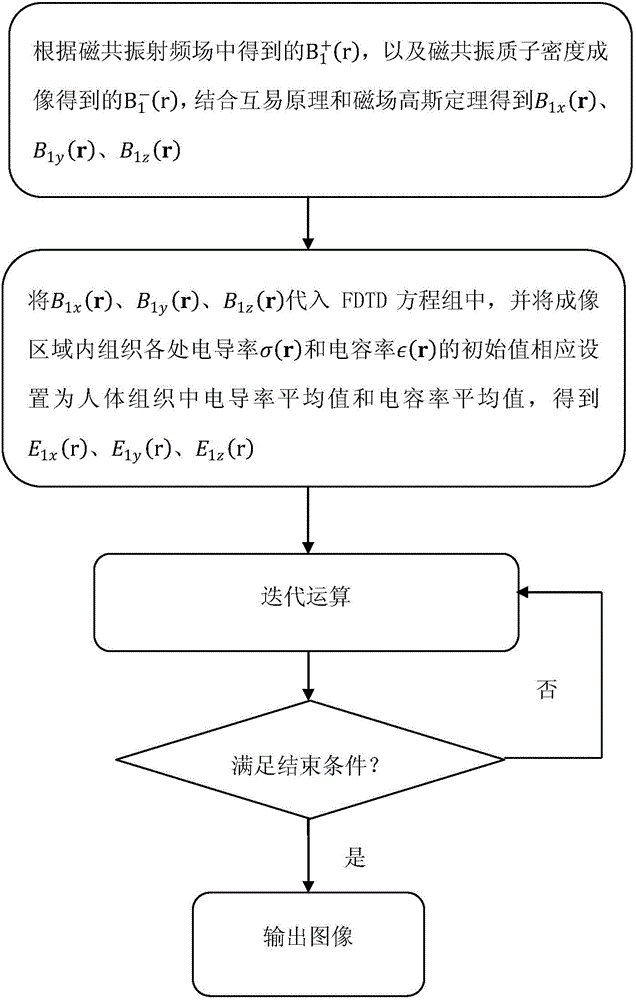
The invention relates to a human tissue physical characteristic parameter magnetic resonance tomography method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) calculating B1x(r), B1y(r) and B1z(r) according to B1<+>(r) obtained in a magnetic resonance radiofrequency field and B1<->(r) obtained through magnetic resonance proton density imaging in combination with a reciprocity principle and a magnetic field Gauss theorem; (2) substituting B1x(r), B1y(r) and B1z(r) into a magnetic resonance time-harmonic radiofrequency electromagnetic field FDTD (Finite Difference Time Domain) equation set, and correspondingly setting the initial values of the conductivity sigma(r) and capacity belong to (r) of each tissue in an imaging region as the average conductivity value and average capacity value of human body tissues to obtain E1x(r), E1y(r) and E1z(r); (3) performing repeated iterative operation till algorithm convergence, wherein the distribution of sigma(r) and belong to (r) of each tissue in the imaging region is the evaluated tissue electrical characteristic parameter distribution result; (4) outputting an image according to the tissue electrical characteristic parameter distribution result in the imaging region.
Owner:SHENZHEN BASDA MEDICAL APP
Acquisition method and device of magnetic resonance quantitative information graphs
ActiveCN108294753AIncrease data acquisition rateNo image mismatch issuesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAlgorithmResonance
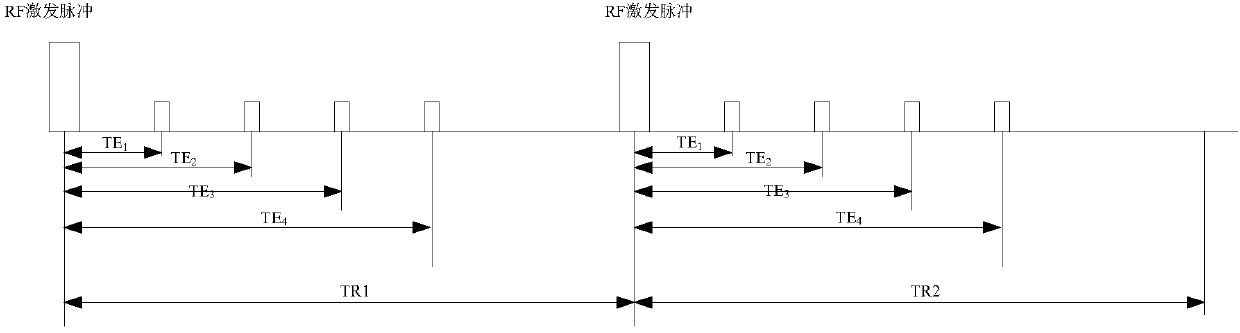
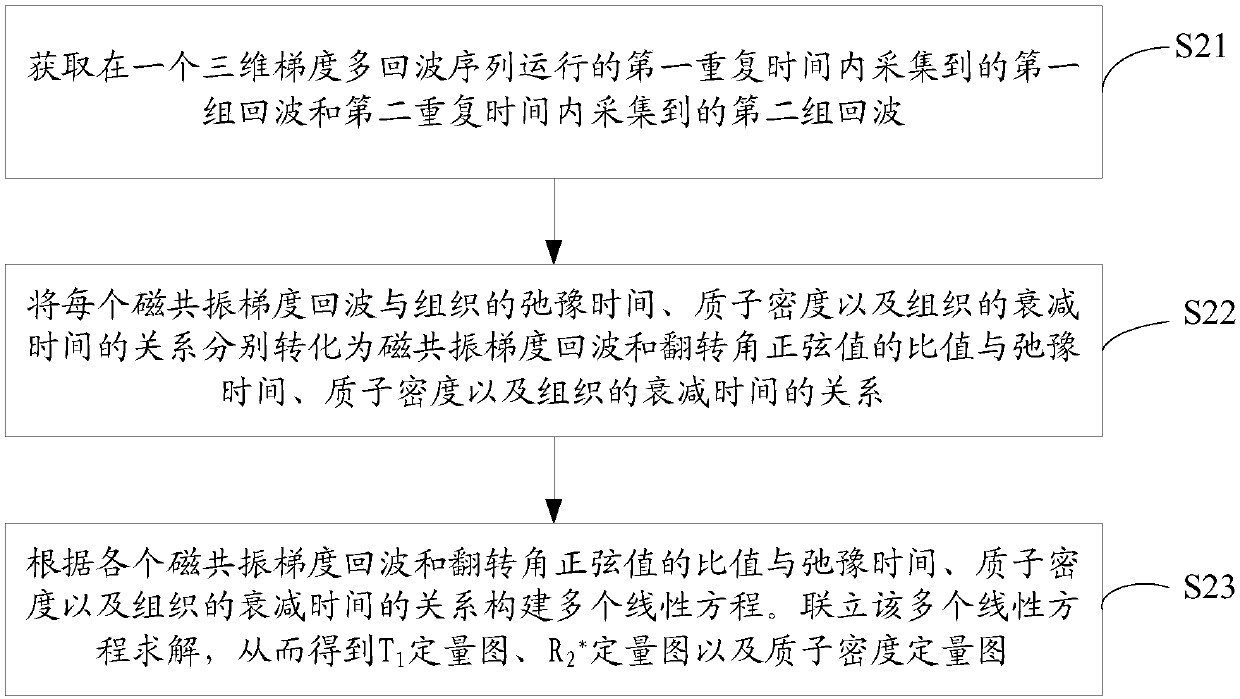
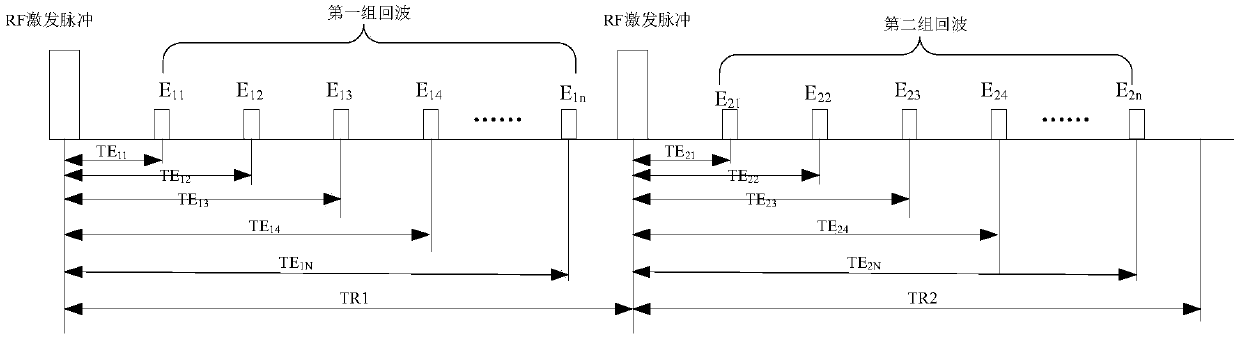
According to the embodiment, the invention discloses an acquisition method and an acquisition device of magnetic resonance quantitative information graphs. The method comprises the following steps: onthe basis of two groups of echos which are acquired within two different repetition times during running of a three-dimensional gradient multi-echo sequence, constructing a plurality of linear equations that unknowns are T1, Formula (shown as the Description) and / or proton density, and guaranteeing that the number of the constructed linear equations is no less than the number of unknowns in the linear equations; and through a mode of solving solutions of the linear equations, acquiring a T1 quantitative graph, a quantitative graph of the Formula and a proton density quantitative graph. Therefore, according to the acquisition method of the magnetic resonance quantitative information graphs provided by the embodiment, a process of acquiring the quantitative information graphs into a processof solving a linear equation group, and the acquisition method has the characteristic that three quantitative information graphs can be simultaneously acquired through one-time data acquisition. Eachquantitative information graph can be acquired just by conducting one-time acquisition on a patient instead of scanning the patient for several times, so that a great amount of data acquisition timeis saved and a data acquisition rate is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEUSOFT MEDICAL TECH LTD
Nondestructive testing method for water distribution in drying process of roots of red-rooted salvia
ActiveCN107091852AReduce water contentReduce energy exchangeWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBound waterRoom temperature
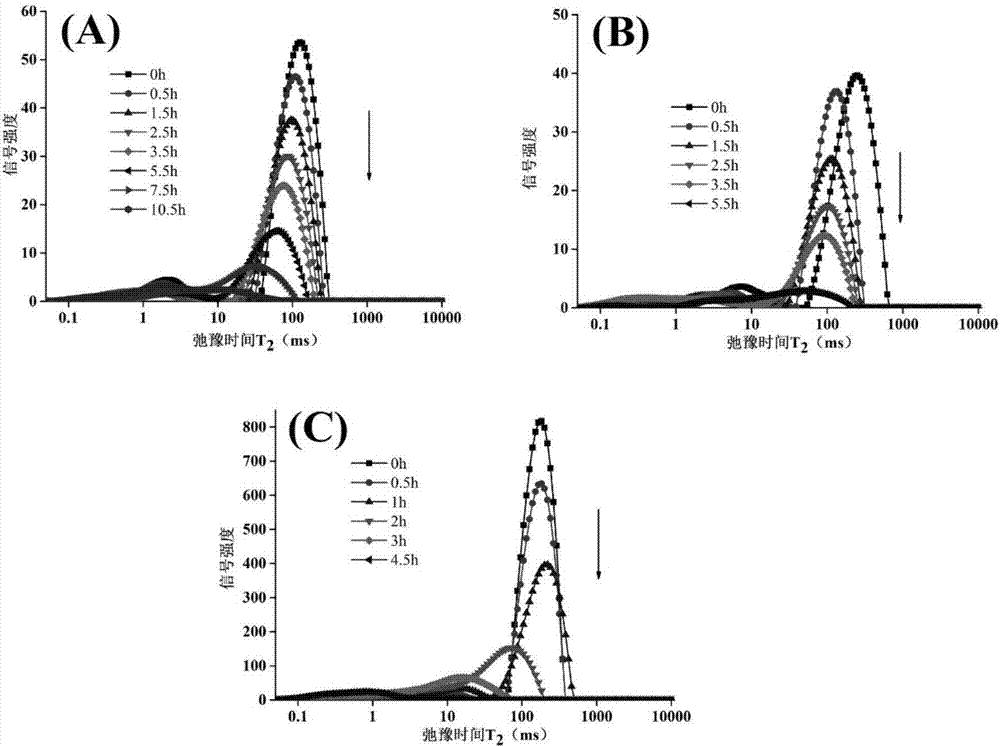
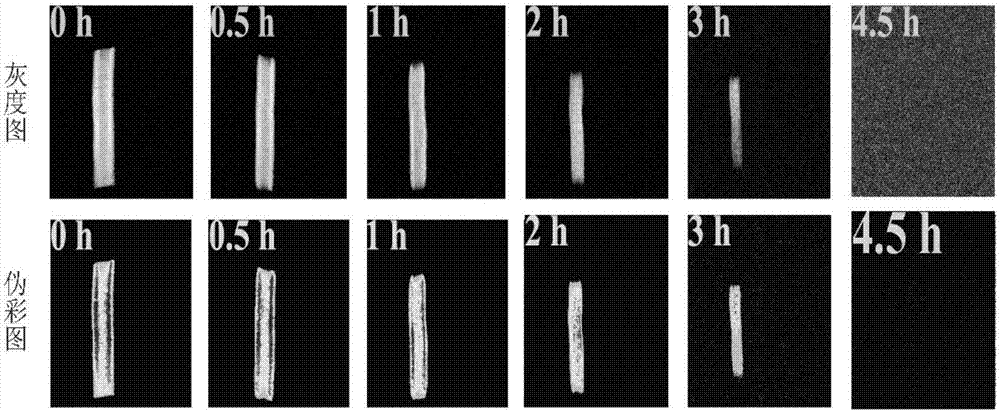
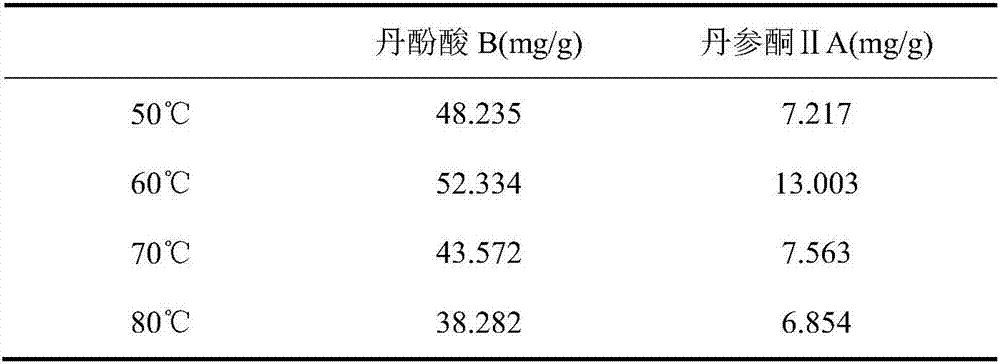
The invention discloses a nondestructive testing method for water distribution in the drying process of roots of red-rooted salvia. Roots of red-rooted salvia samples with different drying times and different drying temperatures are coated with thread seal tapes in a sealed mode, and the coated roots of red-rooted salvia samples are placed for 3-5min at room temperature; a T2 spectrogram and proton density weighed images are obtained through the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology, the positions of 10 ms and 100 ms in the T2 spectrogram serve as boundaries, bound water exists at the positions of 0.1-10 ms, water not likely to flow exists at the positions of 10-100 ms, free water exists at the positions of 100-1,000 ms, the peak integral area serves as the relative content of the water, and therefore the relative content of the bound water, the relative content of the water not likely to flow and the relative content of the free water are obtained; distribution positions of the water in the roots of red-rooted salvia samples in the roots of red-rooted salvia samples are obtained according to the proton density weighed images, therefore, the distribution states of the bound water, the water not likely to flow and the free water of the roots of red-rooted salvia samples with the different drying times and the different drying temperatures are obtained, and then the water distribution in the drying process of the roots of red-rooted salvia is obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG ANALYSIS & TEST CENT
Markers, phantoms and associated methods for calibrating imaging systems
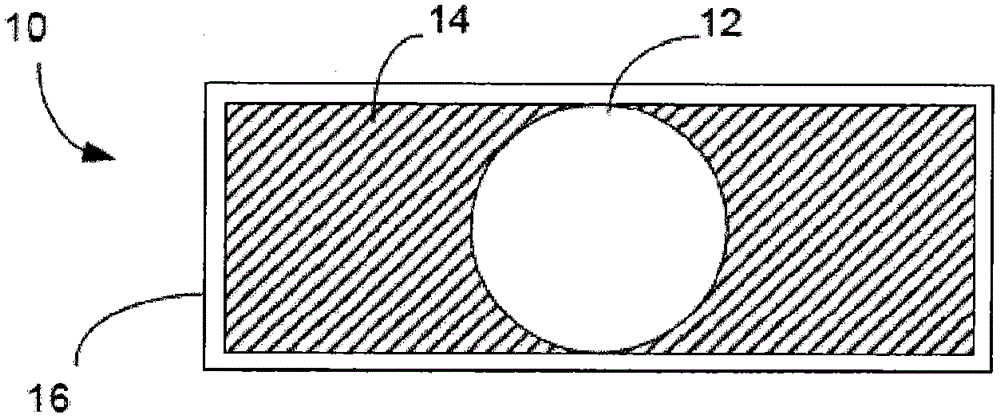
Embodiments of the present invention provide markers, phantoms, and associated methods of calibration which are suitable for use in both medical resonance imaging and radiographic imaging systems. A marker (10) includes a first component (12) having a first hydrogen proton density and a first mass density; and a second component (14) having a second hydrogen proton density different than the first hydrogen proton density, and a second mass density different than the first mass density. The first and second components are non magnetic.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Catalyst Composition
InactiveUS20090286670A1Promote catalysisEnhance alkylationMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystMolecular sieveAlkyl transfer
The present invention provides an improved catalyst and a method for its manufacture. The catalyst comprises an acidic, porous crystalline material and has a Proton Density Index of greater than about 1.0, for example from greater than 1.0 to about 2.0, e.g. from about 1.01 to about 1.85. This catalyst may be used to effect conversion in chemical reactions, and is particularly useful in a process for selectively producing a monoalkylated aromatic compound comprising the step of contacting an alkylatable aromatic compound with an alkylating agent under at least partial liquid phase conditions. The acidic, porous crystalline material of the catalyst may comprise an acidic, crystalline molecular sieve having the structure of zeolite Beta, an MWW structure type material, e.g. MCM-22, MCM-36, MCM-49 MCM-56, or a mixture thereof.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Organic compound conversion process
ActiveUS8222468B2Hydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionMolecular sieveOrganic compound
The present invention provides a process for conversion of feedstock comprising organic compounds to desirable conversion product at organic compound conversion conditions in the presence of catalyst comprising an acidic, porous crystalline material and having a Proton Density Index of greater than 1.0, for example, from greater than 1.0 to about 2.0, e.g. from about 1.01 to about 1.85. The acidic, porous crystalline material of the catalyst may comprise a porous, crystalline material or molecular sieve having the structure of zeolite Beta, an MWW structure type material, e.g. MCM-22, MCM-36, MCM-49, MCM-56, or a mixture thereof.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
T1 parameter diagram imaging method and magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN108742626AReduce scan timeImprove scanning efficiencyDiagnostic signal processingSensorsProtonMagnetization
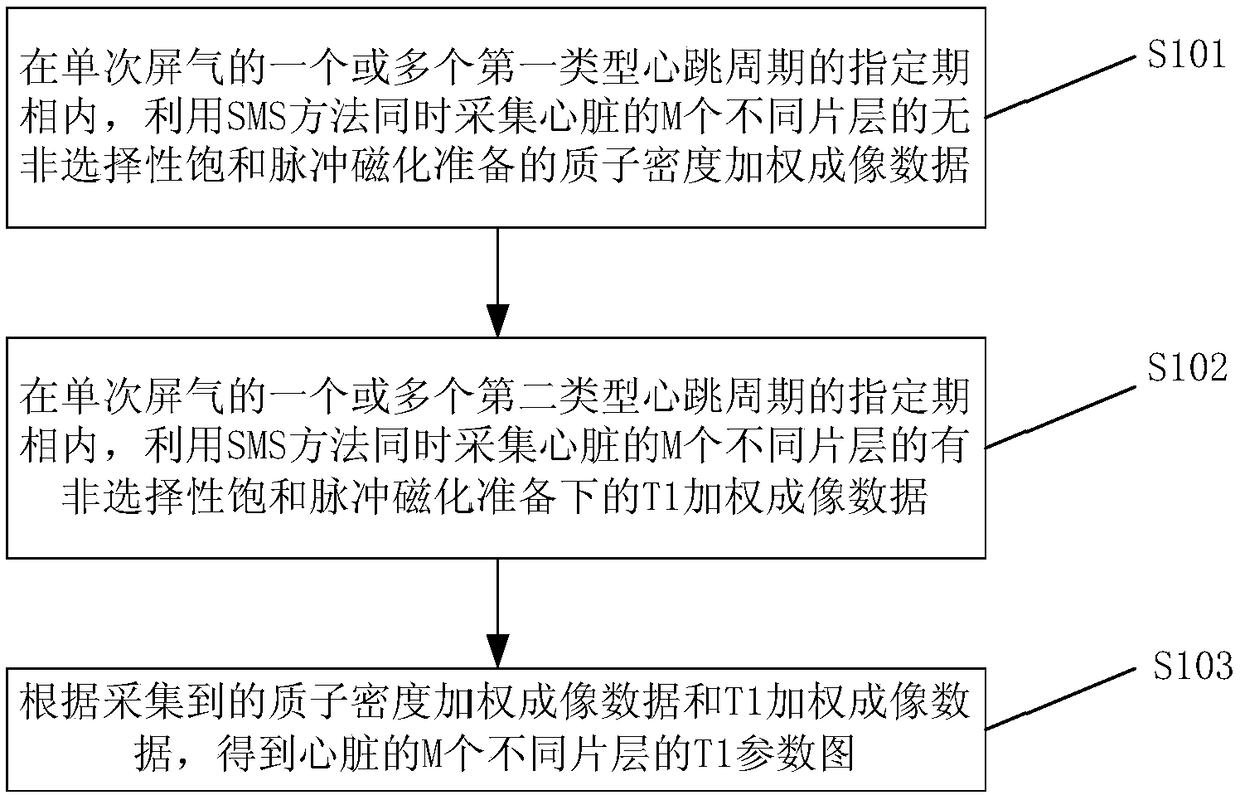
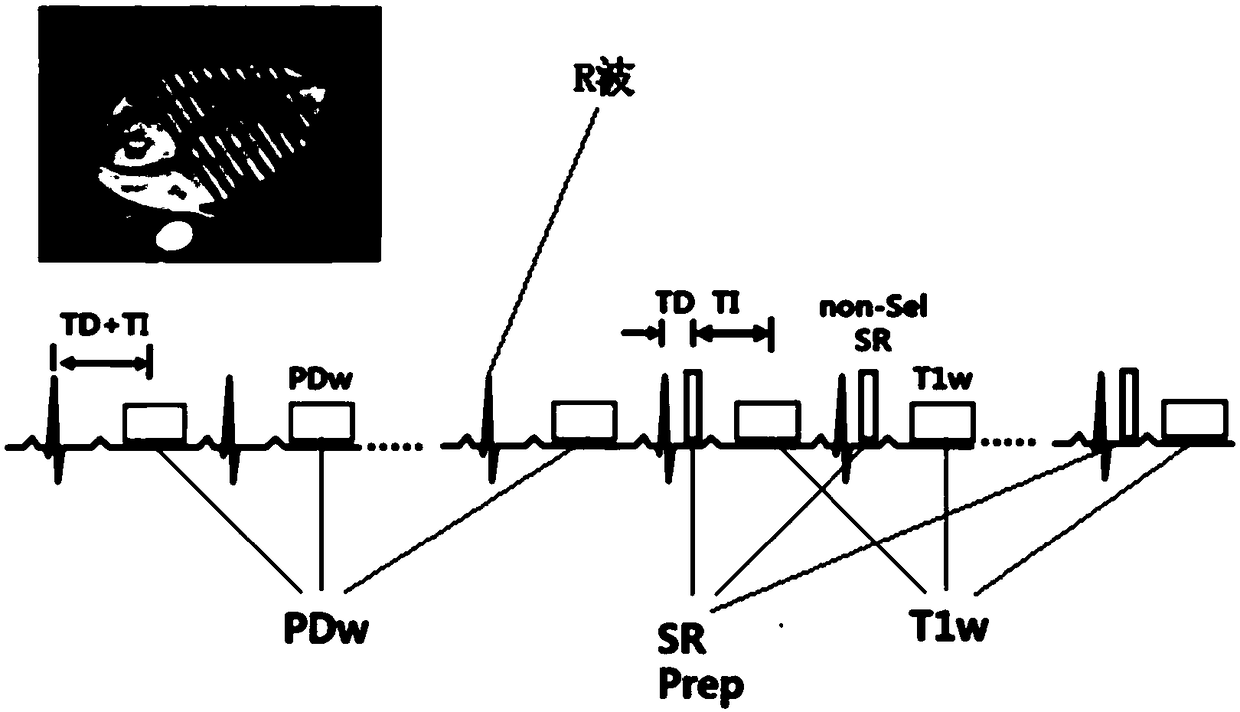
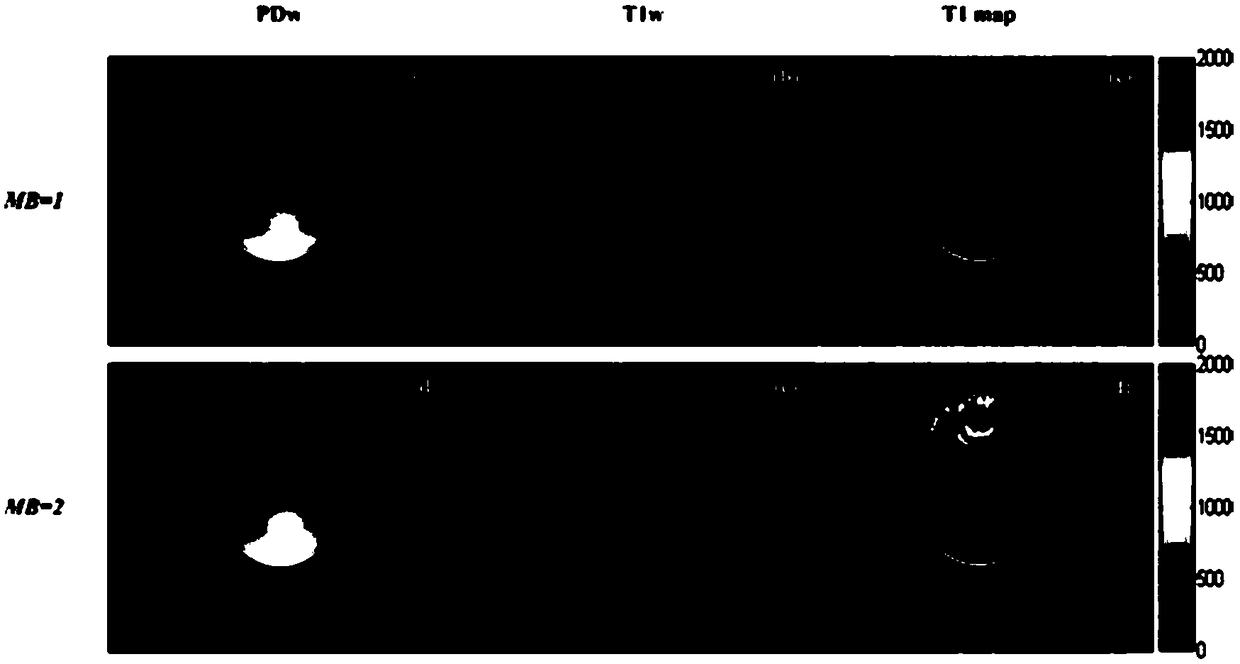
The embodiment of the invention provides a T1 parameter image imaging method and a magnetic resonance imaging system. The method comprises the following steps: during the specified period of one or more first-type heart beat cycles with a single breath hold, proton density weighted imaging data of heart different M layers prepared by non-selective saturated pulse magnetization are collected simultaneously by using SMS method, during the specified period of one or more second-type heart beat cycles with a single breath hold, T1-weighted imaging data of heart different M layers prepared by non-selective saturated pulse magnetization are collected simultaneously by using SMS method, according to the proton density weighted imaging data and T1-weighted imaging data, the T1 parameters of the heart are obtained, by using SMS technology, two or more images in the same period can be acquired simultaneously in one heartbeat cycle, which enlarges the space coverage of T1 parameter map in singlebreath hold, and achieves the whole heart T1 parameter map, thus solving the problem of small space coverage of T1 parameter map in single breath hold.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method for measuring inversion-recovery sequence T1 under water-fat mixed system
PendingCN110786854AAddressing measurement deficienciesDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMedicineMR - Magnetic resonance
The invention provides a method for measuring an inversion-recovery sequence T1 under a water-fat mixed system and relates to the technology of magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting a multi-echo image, performing water-fat separation on the image, calculating the fat proton density percentage of each pixel or ROI; 2, collecting a free attenuation signal; 3, performing multi-parameter fitting on the collected free attenuation signal after the fat proton density percentage of the pixel or ROI is calculated, and calculating relaxation features of water and fat to solve the defect that traditional inversion-recovery T1 measurement cannot complete tissue T1 measurement under the situation of fat existence. The method can be used for measuring the T1of a water tissue and the T1 of fat under the situation of a sufficient proportion of a fat signal.
Owner:广州互云医院管理有限公司
Method and device for imaging magnetic resonance electromagnetic characteristic parameters of human body biological tissues
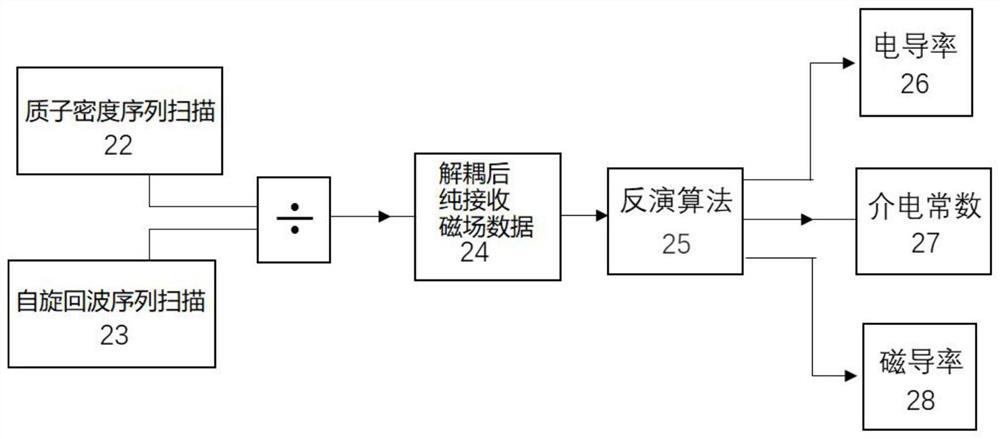
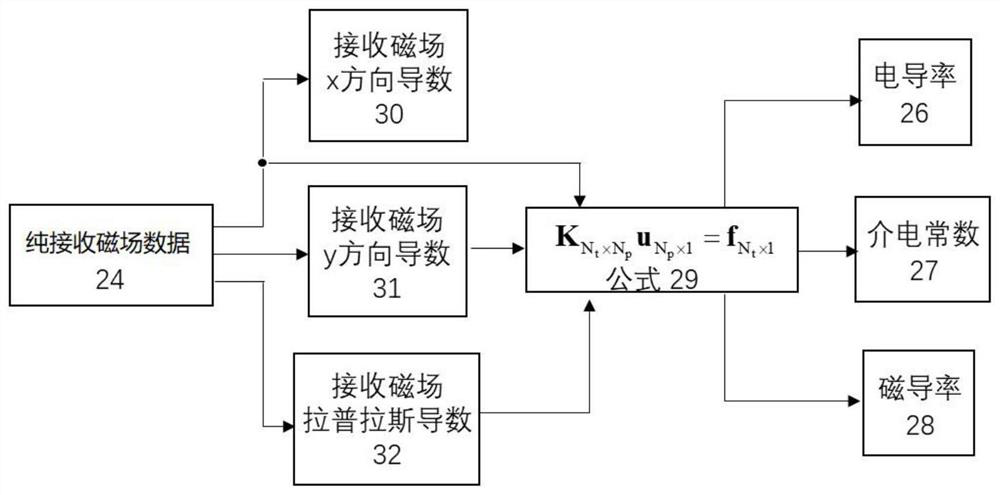
ActiveCN113406544AThe inversion result is accurateLow costWater resource assessmentMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDielectricMagnetic field amplitude
The invention relates to a method and a device for imaging magnetic resonance electromagnetic characteristic parameters of human body biological tissues. The method comprises the following steps of respectively carrying out spin echo and proton density imaging sequence scanning to obtain image data, dividing the spin echo reconstruction image data by the proton density image data to obtain decoupled pure receiving magnetic field data, and on the basis of pure receiving magnetic field data, conducting synchronous reconstruction by utilizing a convection-reaction-diffusion or gradient indirect inversion algorithm to obtain parameter value distribution of the electrical conductivity, the dielectric constant and the magnetic conductivity of the tissue. A result obtained by utilizing the spin echo sequence and receiving magnetic field amplitude and phase component inversion does not contain contribution of quasi-static frequency components related to main magnetic field uniformity distortion in image data acquisition. The measurement process is noninvasive, and the obtained measured value does not need to be assisted by a contrast agent.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
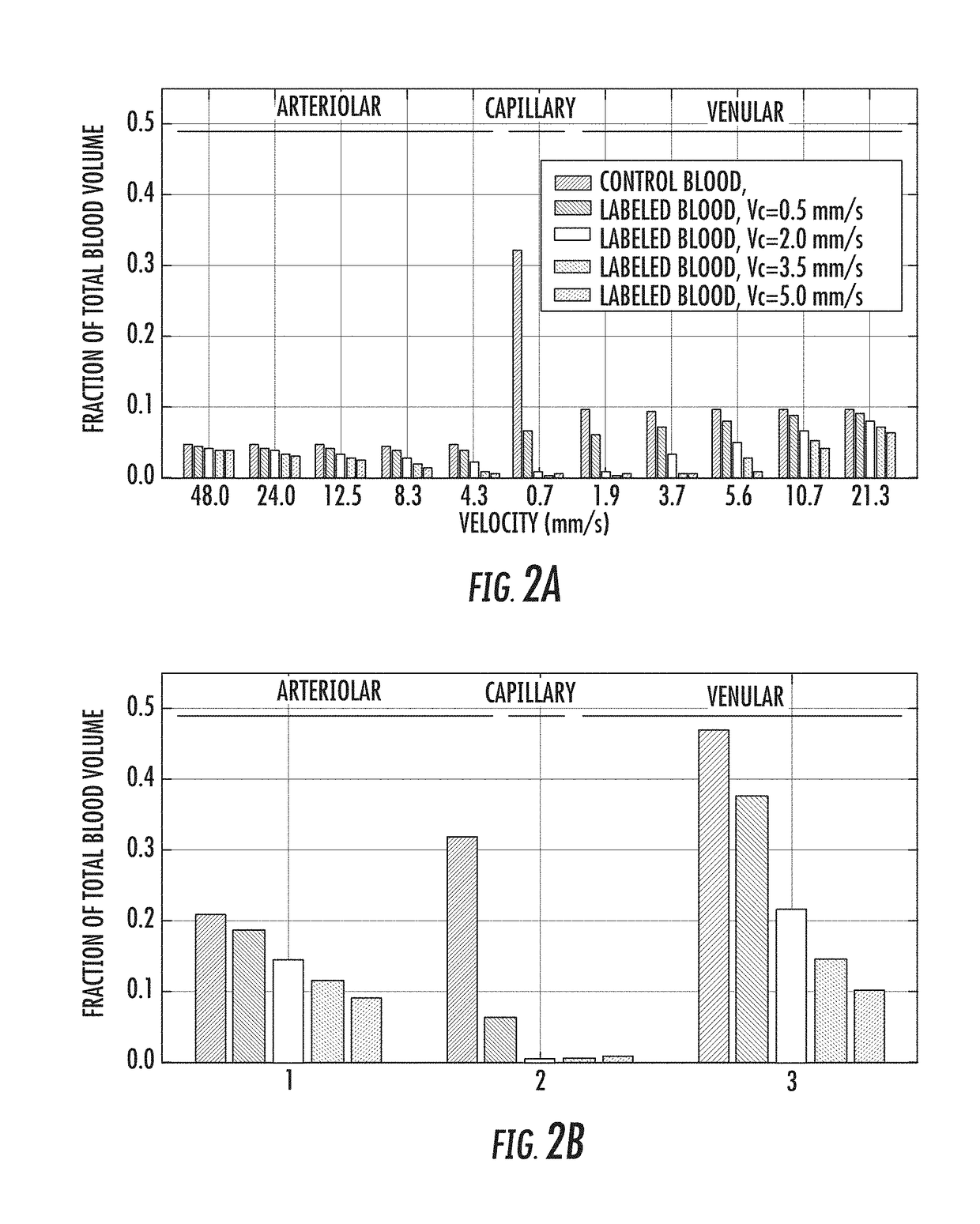
Measurement of blood volume using velocity-selective pulse trains on MRI
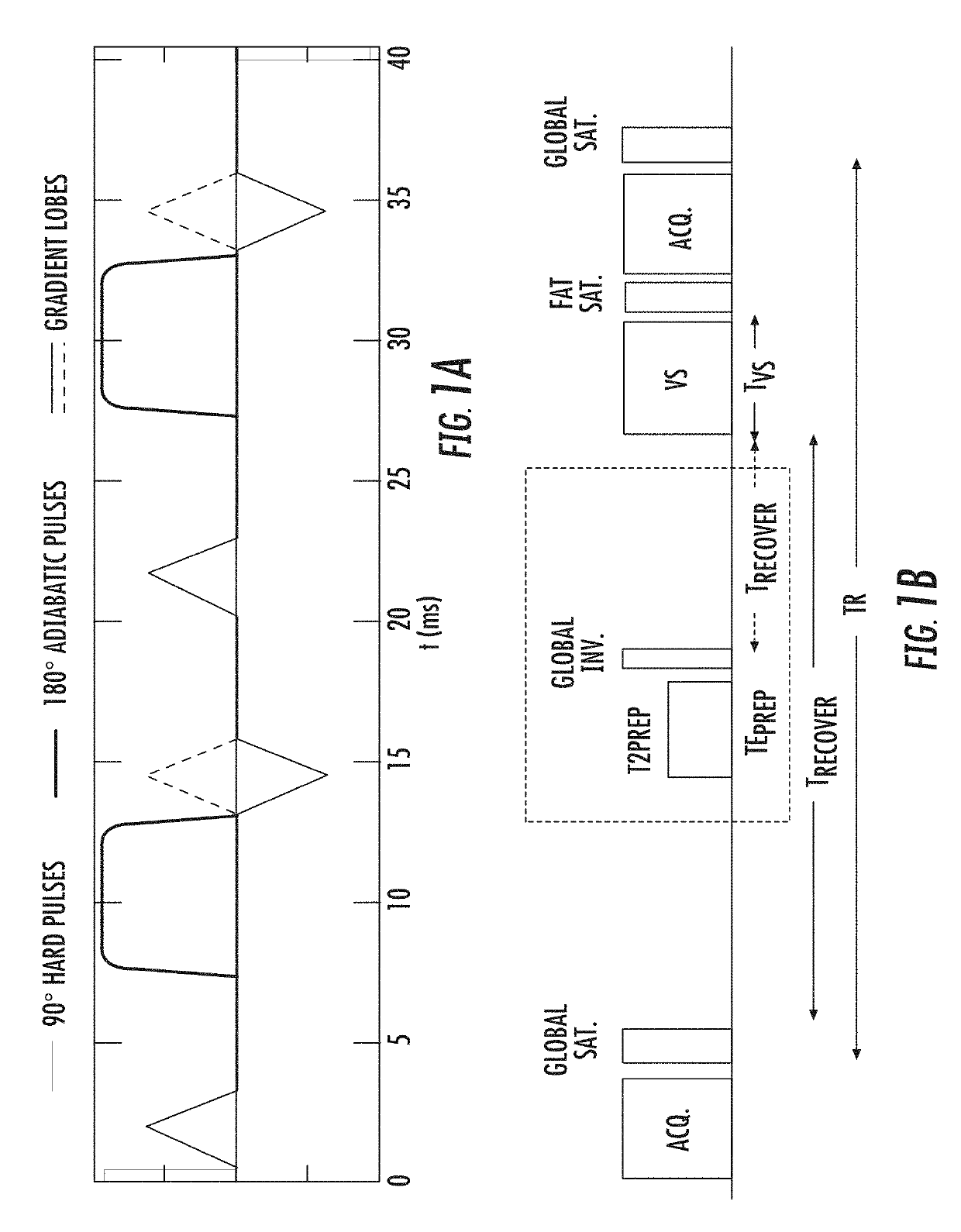
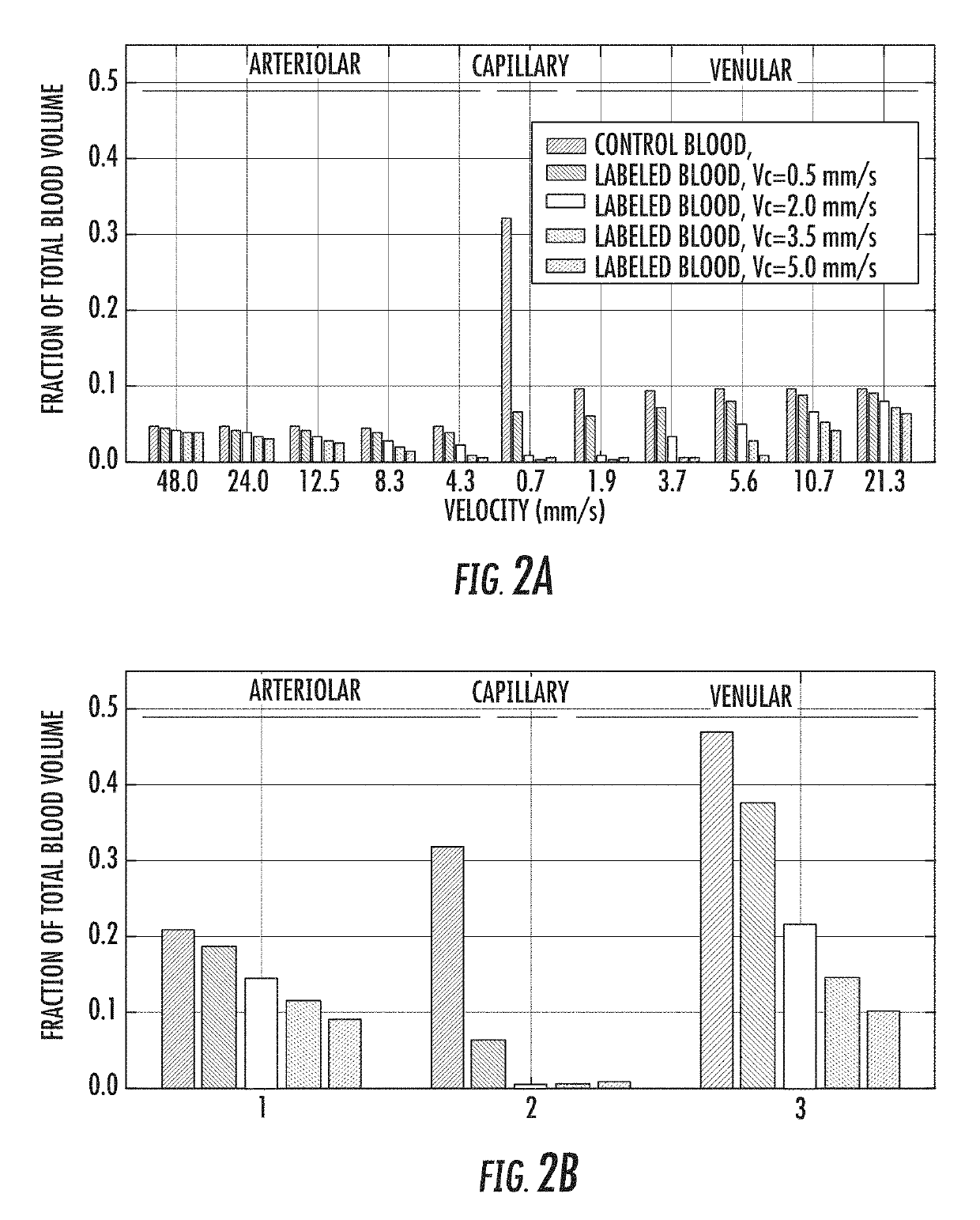
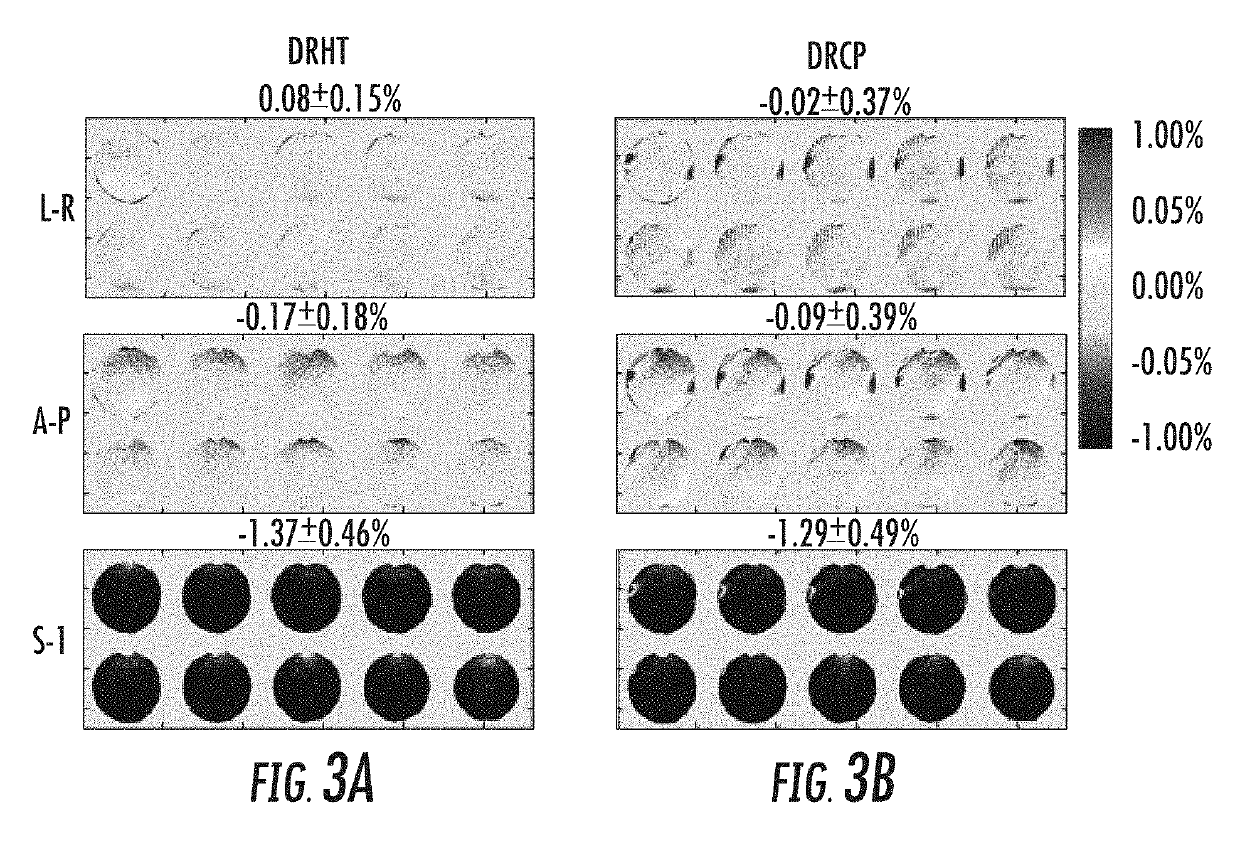
The present invention is directed to a system and method for measuring blood volume using non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. The method of the present invention includes a subtraction-based method using a pair of acquisitions immediately following velocity-sensitized pulse trains for the label module and its corresponding control module, respectively. The signal of static tissue is canceled out and the difference signal comes from the flowing blood compartment above a cutoff velocity. After normalizing to a proton density-weighted image acquired separately and scaled with the blood T1 and T2 relaxation factors, quantitative measurement of blood volume is then obtained.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of treating cells with drug and radiation according to proton density
Owner:KUMAR RAJAH VIJAY
Method and magnetic resonance device for the automated classification of an image property of a magnetic resonance image
ActiveCN103809142ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMri image
A method is disclosed for the automated classification of an image property of a magnetic resonance image(6). In an embodiment, the method includes determining at least the parameters T1, T2 and proton density of at least two tissues imaged in the magnetic resonance image(6) or prespecifying at least two sets of at least these parameters; calculating the signal intensity in the center of the k-space for each imaged tissue or each set of parameters; and classifying the image property as a function of the calculated signal intensities. A magnetic resonance device is also disclosed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
High-quality magnetic resonance image synthesis method
ActiveCN109938733AImprove image qualityReduce the influence of tissue contrast resultsDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsObservational errorSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a high-quality magnetic resonance image synthesis method. The method comprises the steps that the value range of echo time TE and sweeping repetition time TR in a magnetic resonance signal generation formula is expended to a negative number interval, and the contribution of proton density PD parameters is expanded to negative power. According to the method, the influence ofmeasurement errors of quantitative tissue parameters of magnetic resonance on the tissue contrast results of synthetic magnetic resonance images can be effectively reduced, and the tissue contrast ofthe synthetic magnetic resonance images can be significantly improved. By means of the method, the imaging quality of synthetic magnetic resonance can be significantly improved, and the detection effect in neuroscience and clinical pathological changes is promoted. The method is expected to improve the imaging quality of the synthetic magnetic resonance and promote its detection effect in neuroscience and clinical pathological changes finally.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Markers, phantoms and associated methods for calibrating imaging systems
Embodiments of the present invention provide markers, phantoms, and associated methods of calibration which are suitable for use in both medical resonance imaging and radiographic imaging systems. A marker includes a first component having a first hydrogen proton density and a first mass density; and a second component having a second hydrogen proton density different than the first hydrogen proton density, and a second mass density different than the first mass density. The first and second components are non-magnetic.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Dual contrast vessel wall MRI using phase sensitive polarity maps
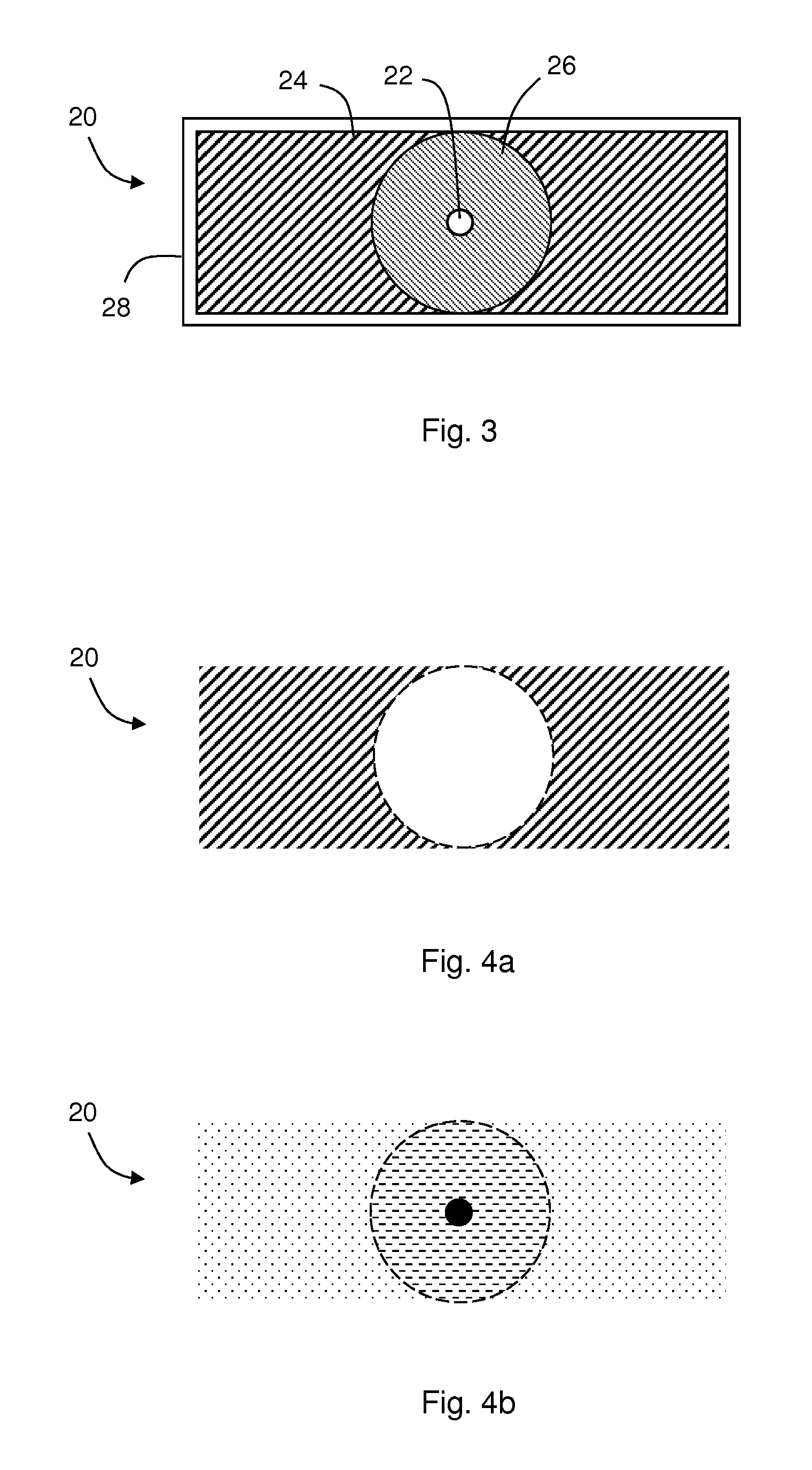
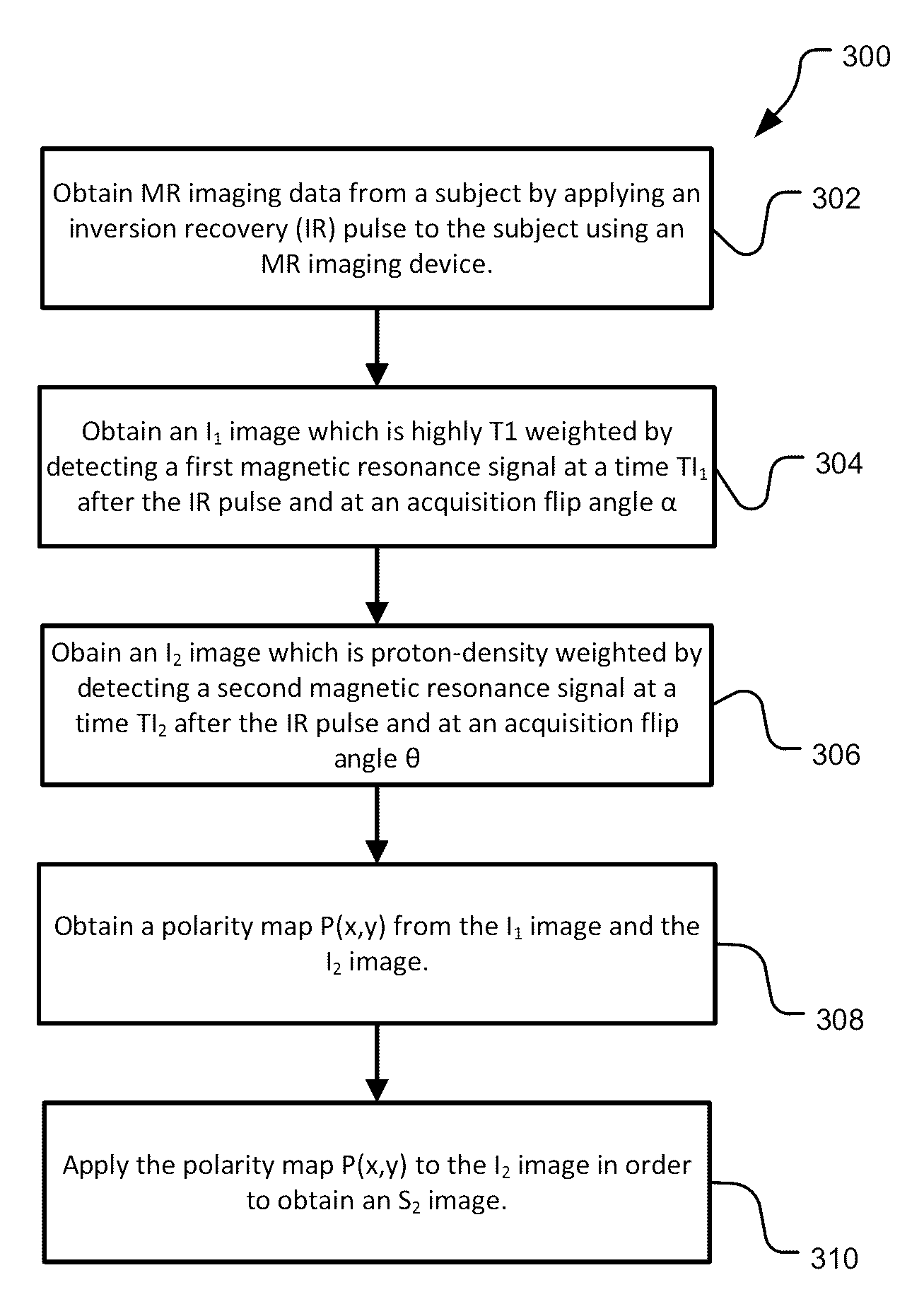
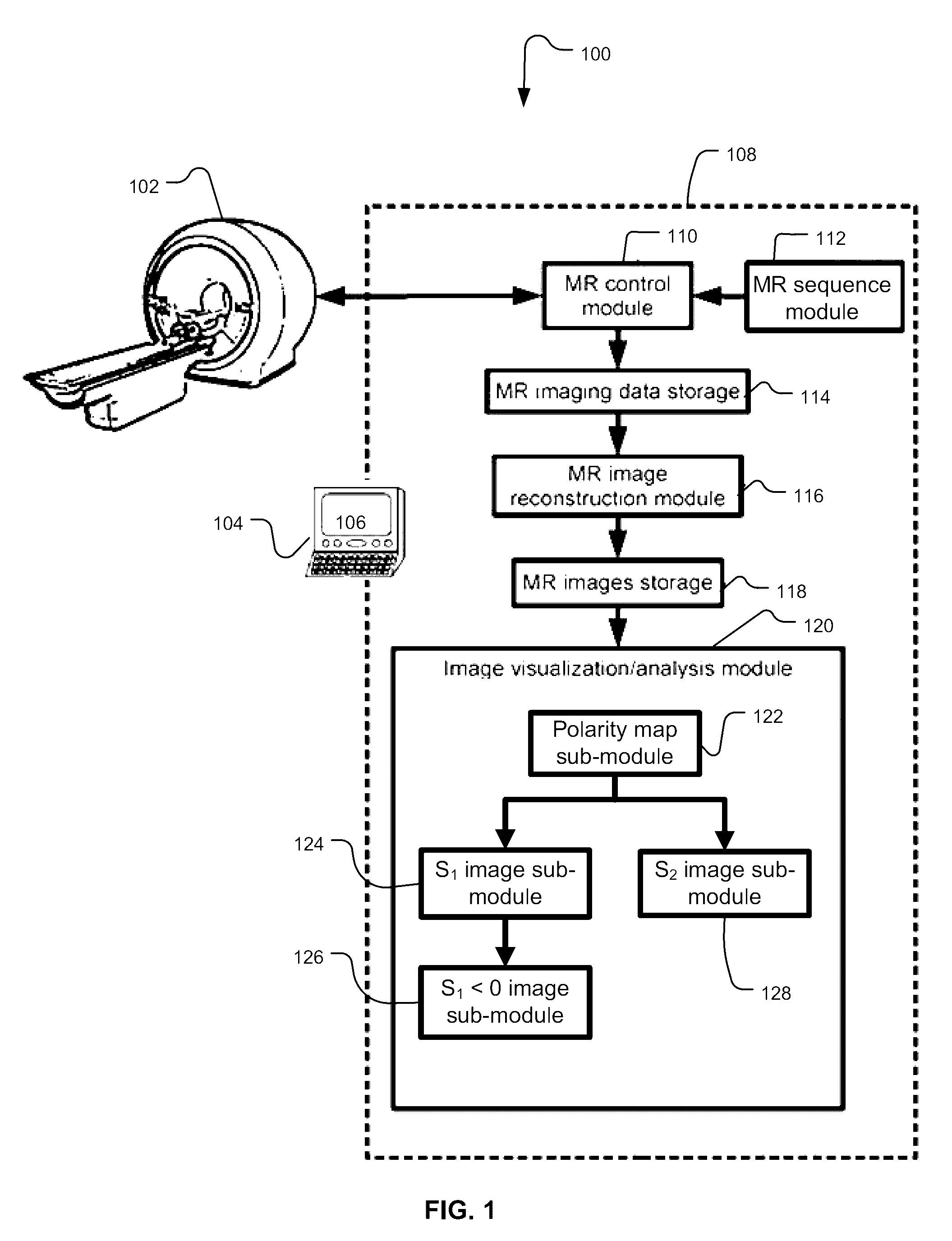
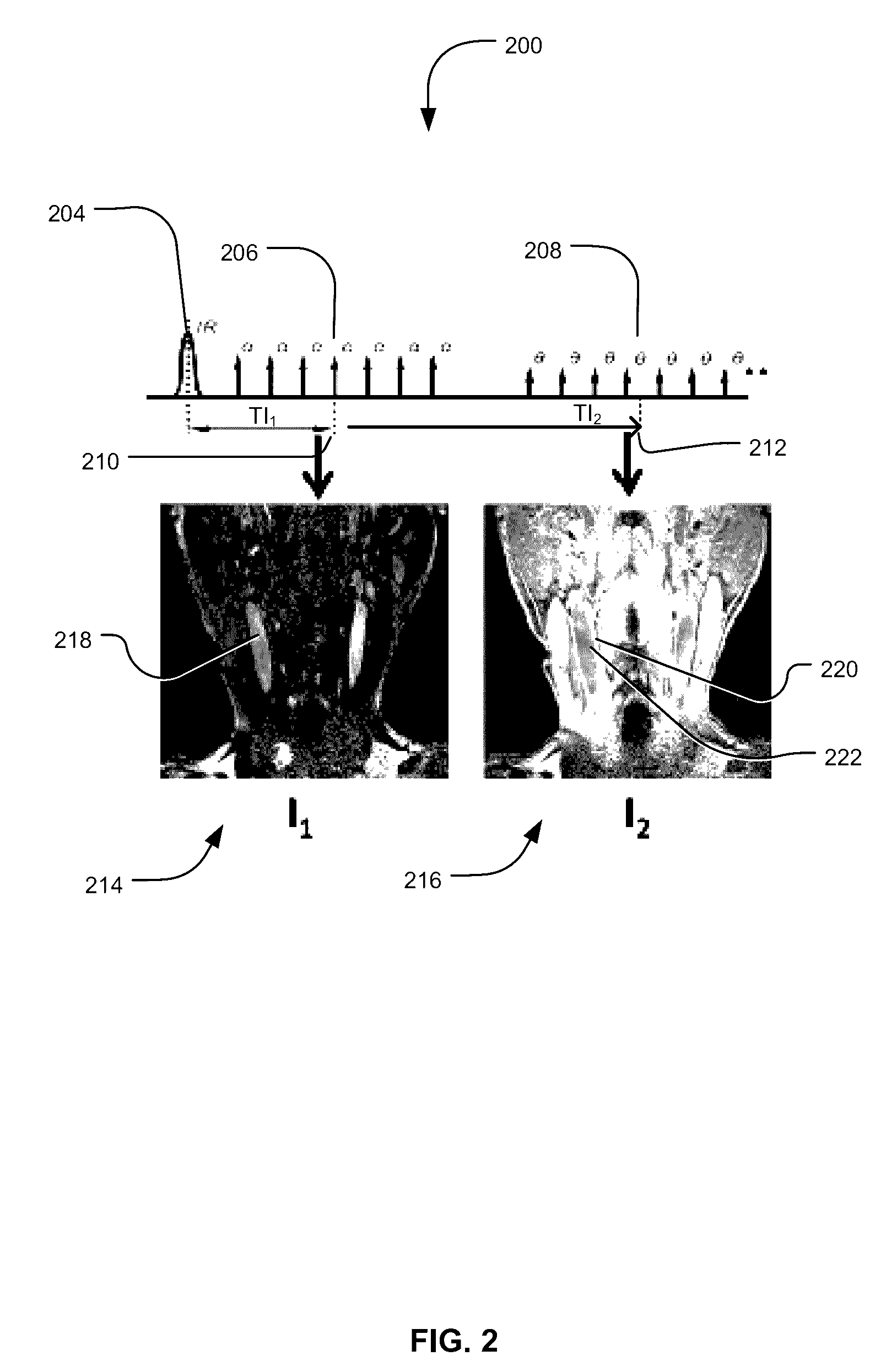
InactiveUS9557396B2Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionInversion recoveryVoxel
Methods and systems for using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging include obtaining a T1-weighted MR image and a proton-density (PD) weighted MR image from a dual-image acquisition following an inversion-recovery (IR) pulse. The T1-weighted and PD-weighted images are used to obtain a polarity function describing a positive or negative polarity at individual voxels, which is used to reconstruct a polarity-enhanced PD-weighted image from the PD-weighted image. The polarity-enhanced PD-weighted image can be used for assessing at least plaque burden and juxtaluminal calcification (JCA).
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Measurement of blood volume using velocity-selective pulse trains on MRI
ActiveUS10330762B2Minimize impactMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNormal blood volumeProton
The present invention is directed to a system and method for measuring blood volume using non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. The method of the present invention includes a subtraction-based method using a pair of acquisitions immediately following velocity-sensitized pulse trains for the label module and its corresponding control module, respectively. The signal of static tissue is canceled out and the difference signal comes from the flowing blood compartment above a cutoff velocity. After normalizing to a proton density-weighted image acquired separately and scaled with the blood T1 and T2 relaxation factors, quantitative measurement of blood volume is then obtained.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com