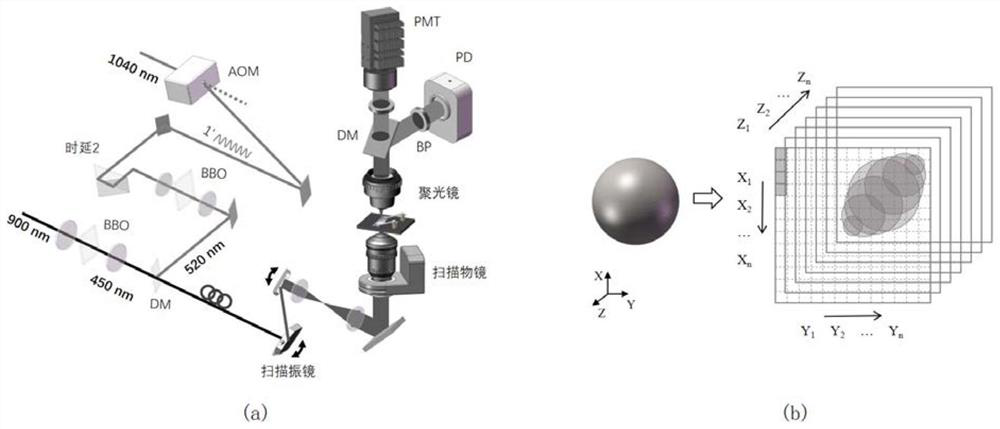
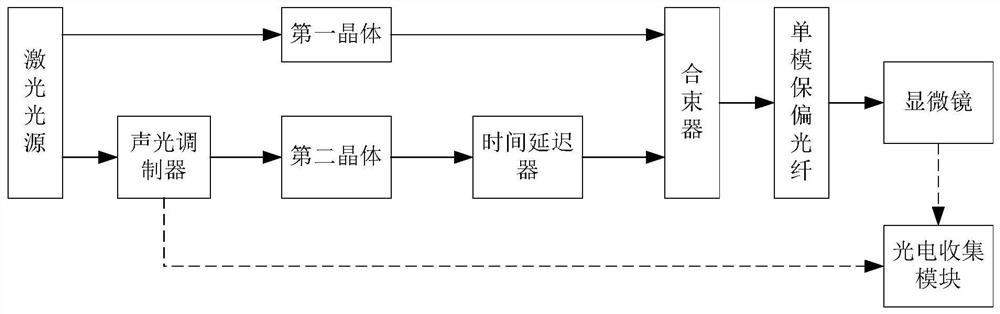
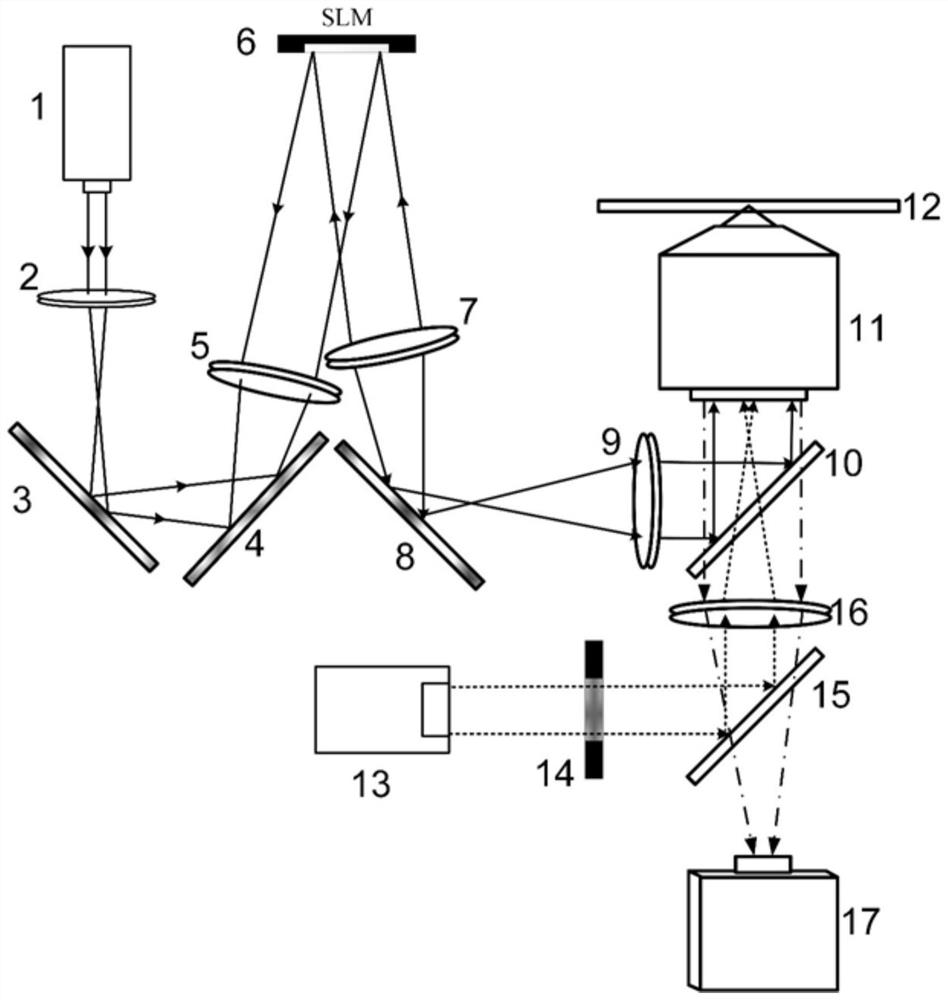
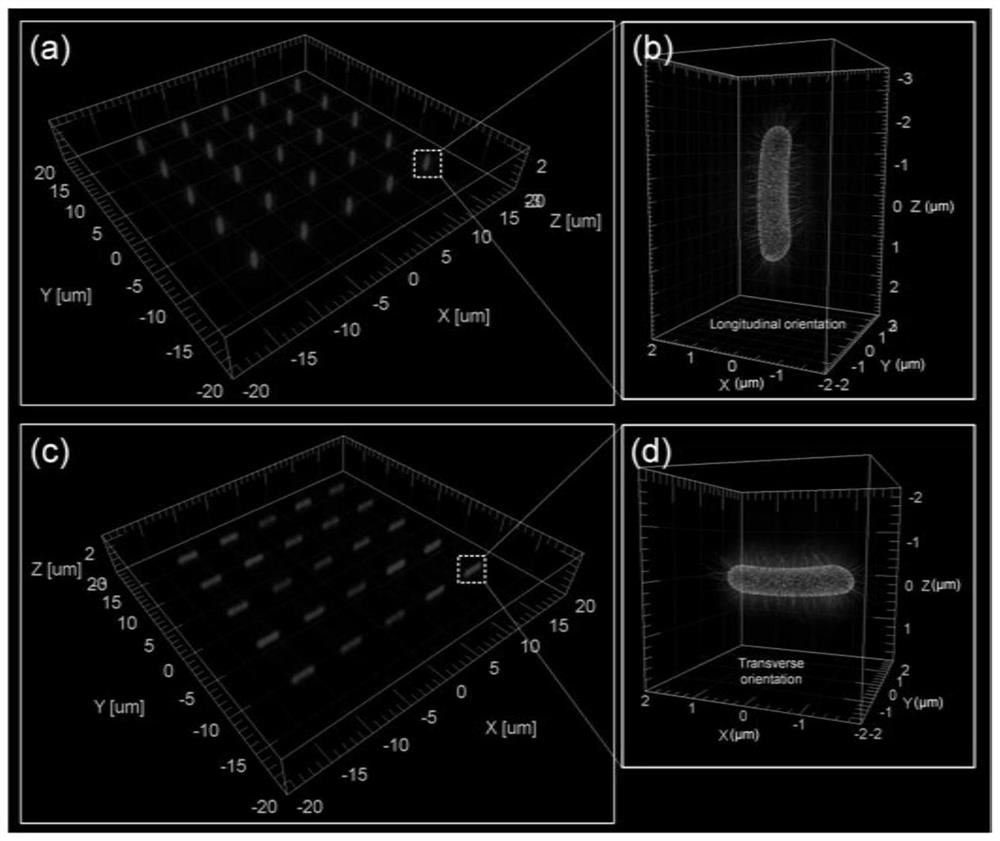
Patents
Literature
76results about How to "Achieving super-resolution imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
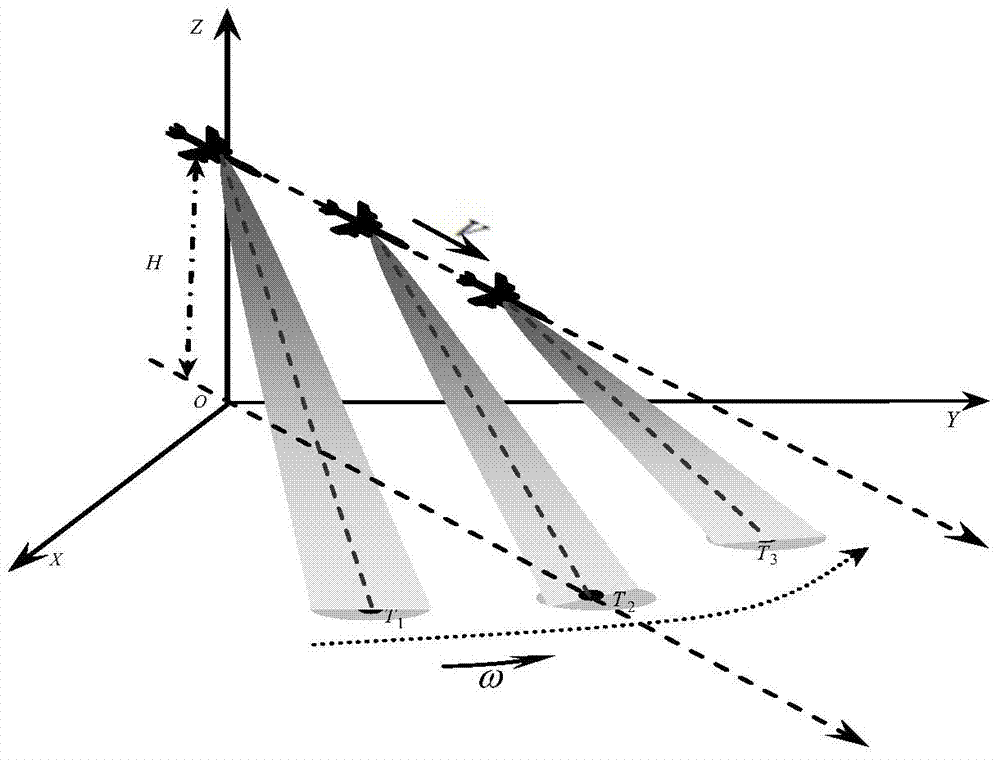
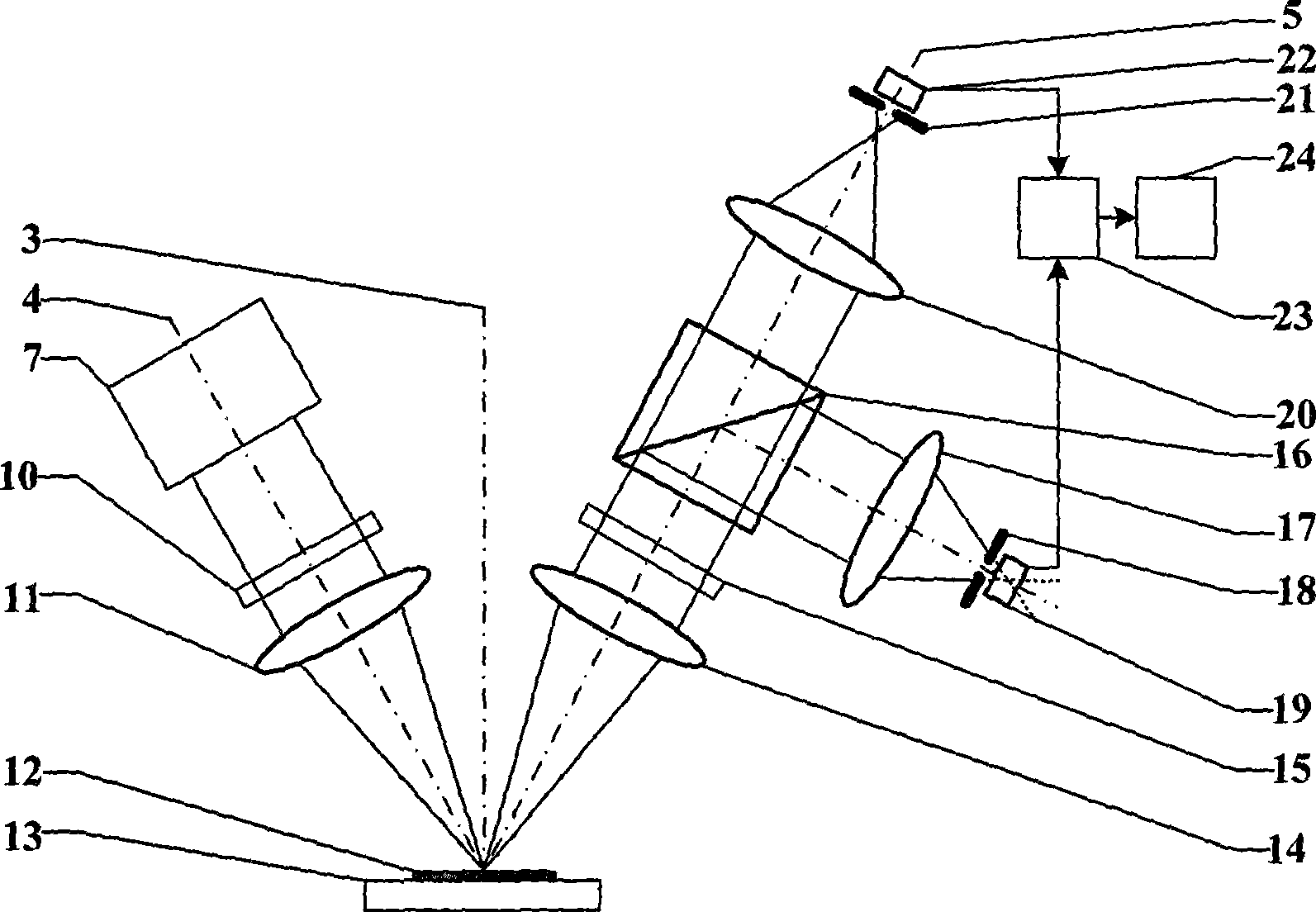
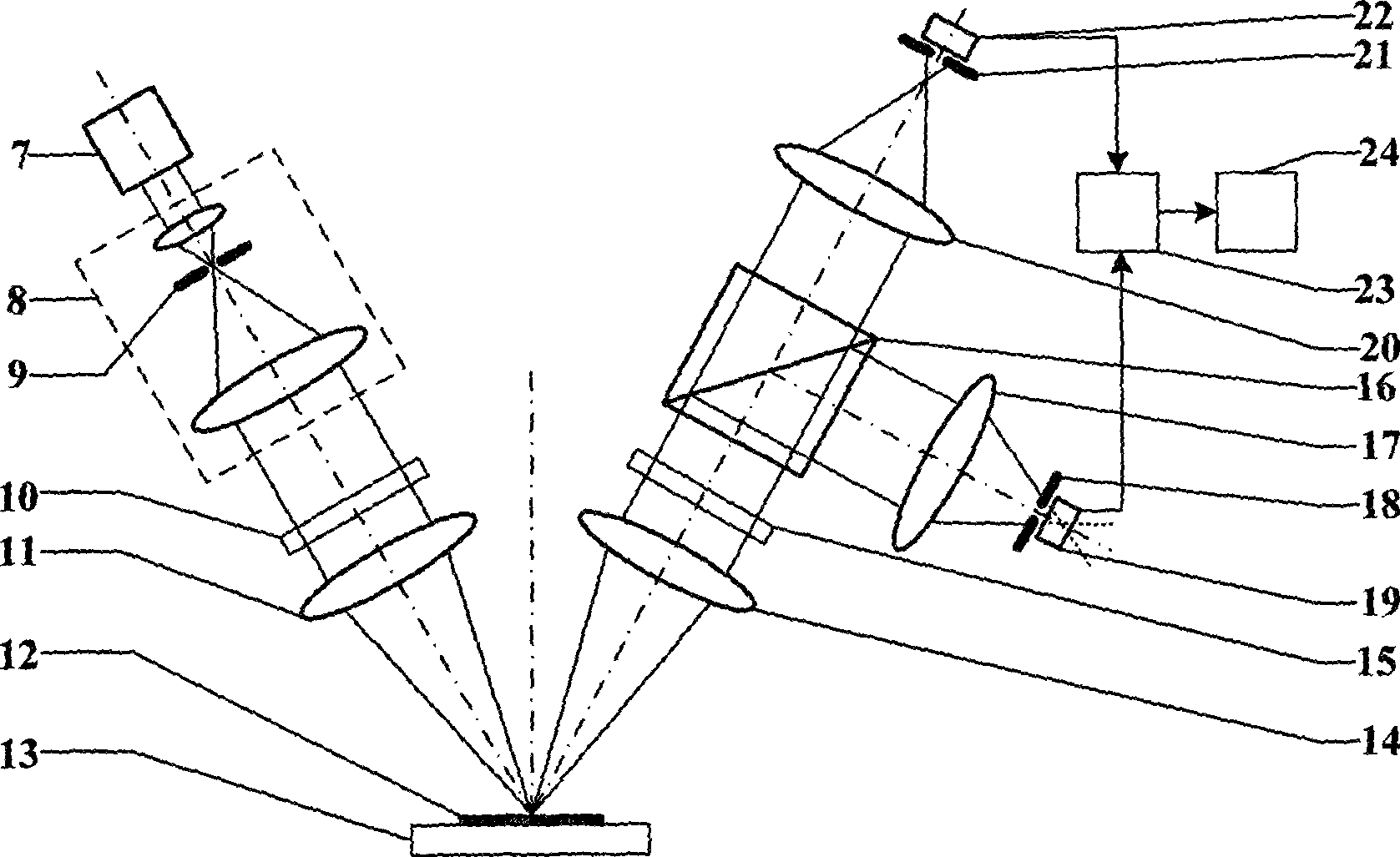
Real beam scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging method
ActiveCN106908787AAchieving super-resolution imagingRealization of super-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSample sequenceBeam scanning
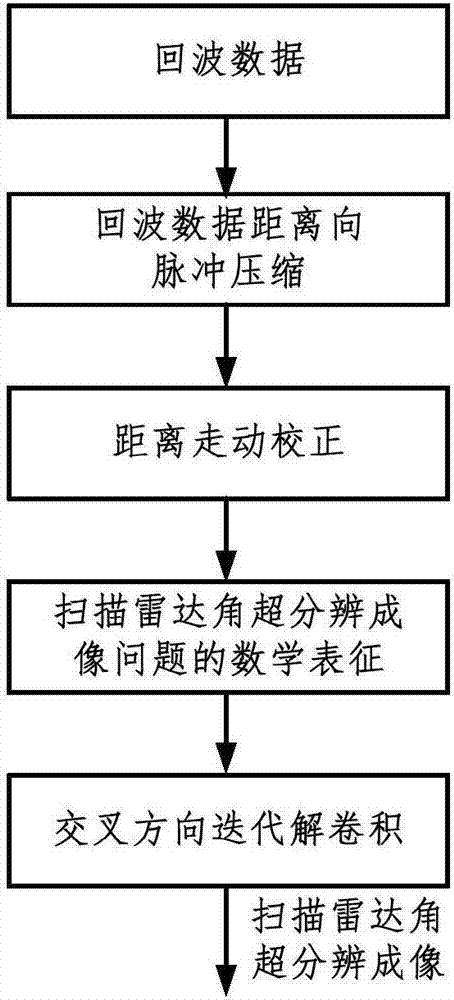
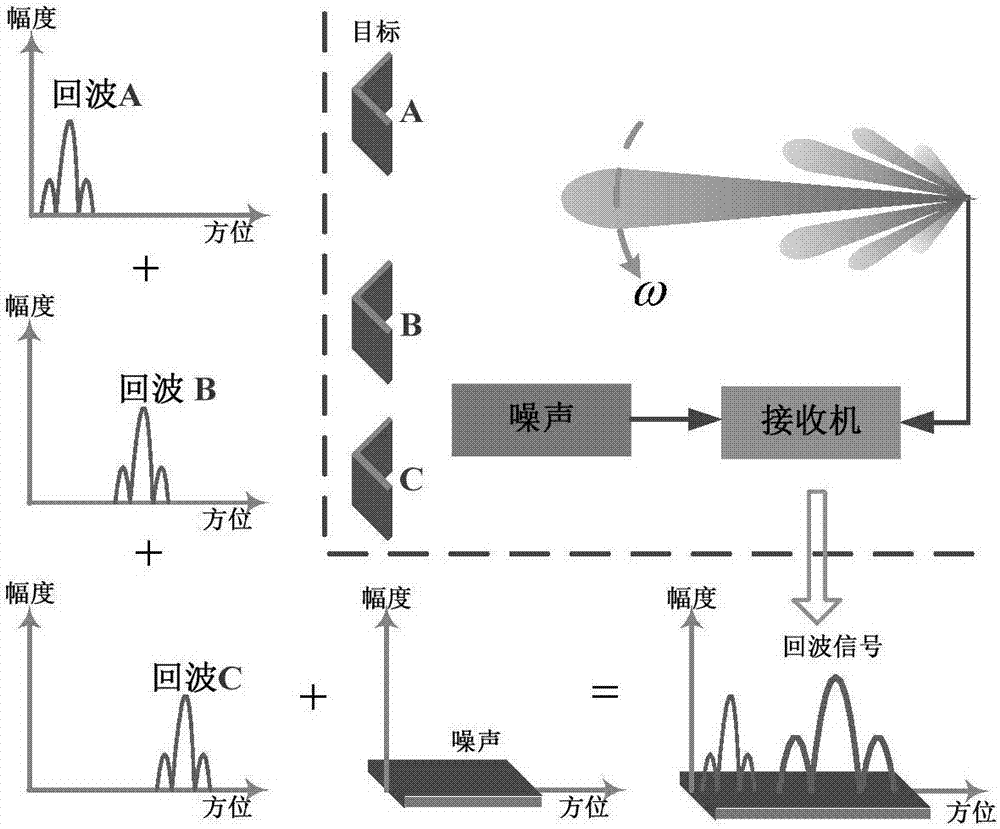
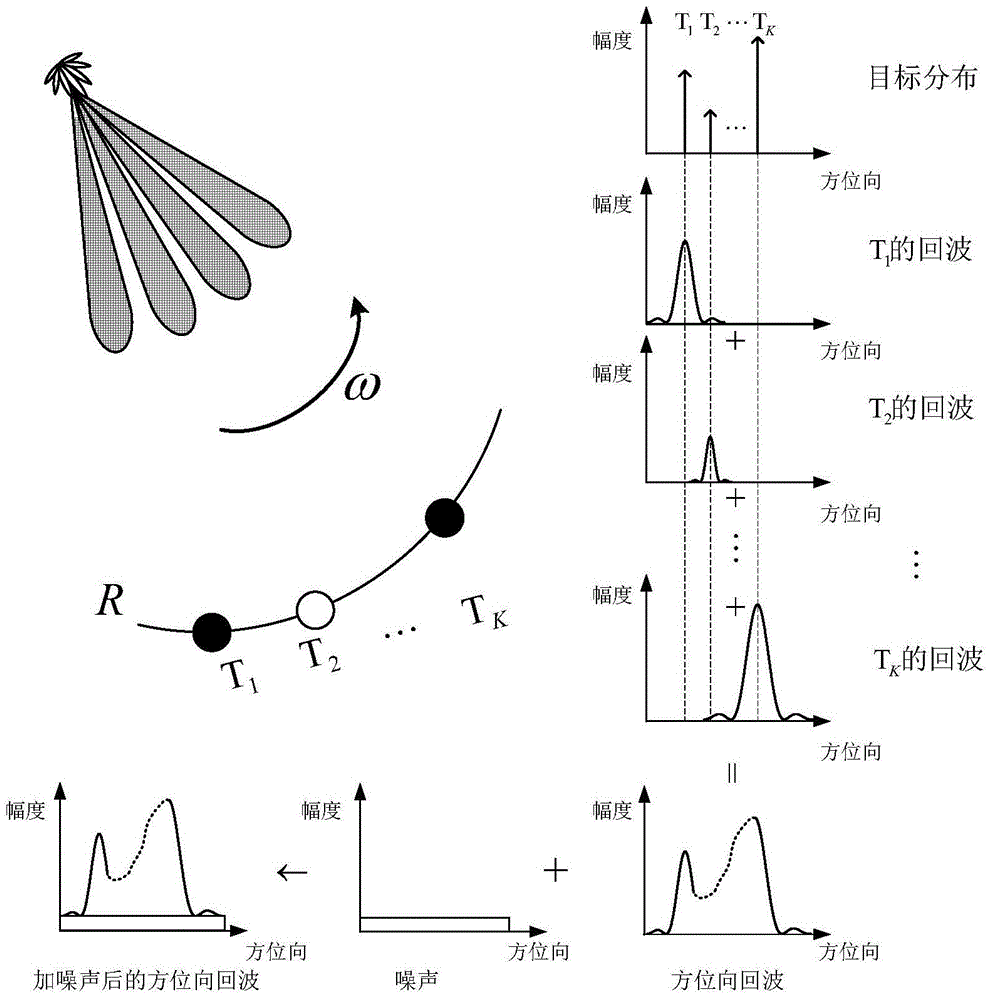
The invention discloses a real beam scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging method, which belongs to a method for realizing scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging by using the total variation functional of the scattering coefficient of an imaging region as de-convolution of priori information. A scanning radar azimuth echo signal is modeled into a result obtained by superimposing noise onto the convolution of a sampling sequence of antenna beam along the azimuth and a sampling sequence of a target reflectance distribution function along the azimuth, and a problem of scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging is converted into a de-convolution problem; then, the total variation functional of the scattering coefficient of an imaging region is integrated into priori information of the de-convolution problem, and the de-convolution problem is converted into a constrained optimization problem; and finally, a global optimal solution to the constrained optimization problem is obtained through a cross iteration method, and scanning radar front-view super-resolution imaging is realized.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Light activated fluorescent probe having protein label positioning function as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104745177AWide variety of sourcesLow application costOrganic chemistryIn-vivo testing preparationsQuantum yieldFluorescent imaging
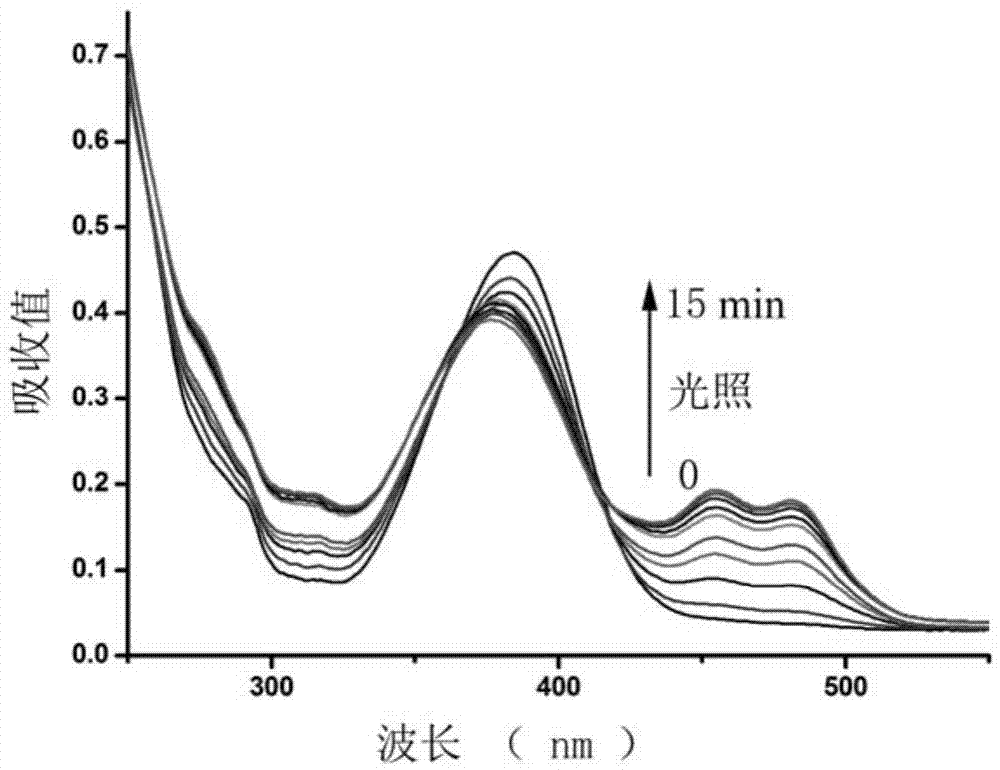
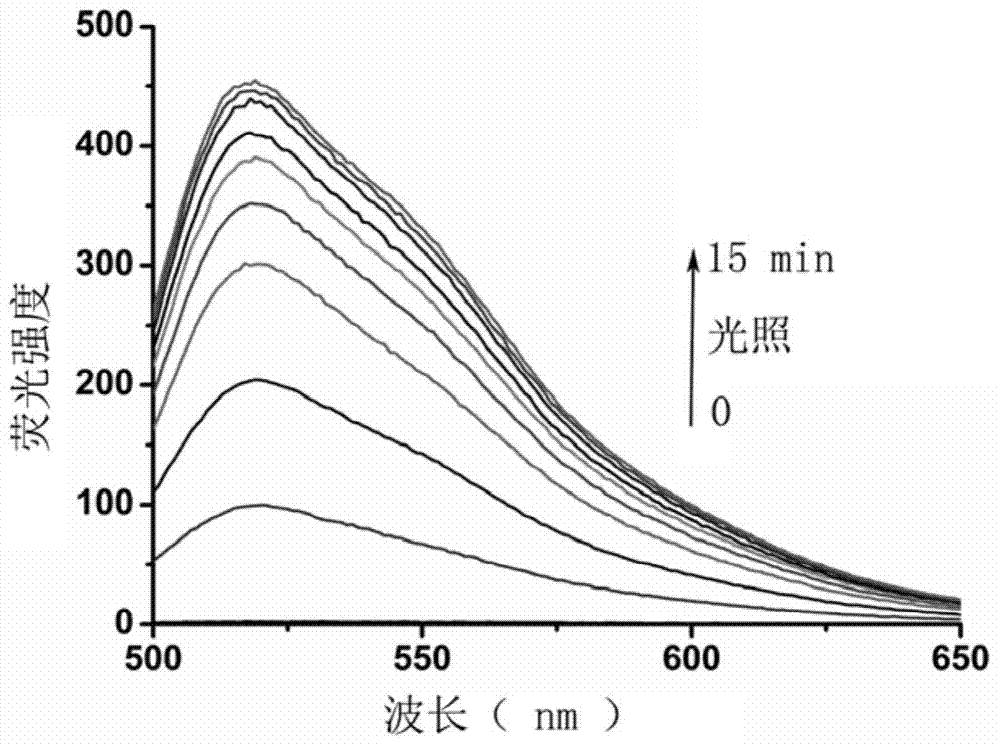
The invention discloses a light activated fluorescent probe having a protein label positioning function, and further discloses a preparation method and application thereof. The light activated fluorescent probe having the protein label positioning function has excellent photophysical properties, such as high-efficiency light control property and high fluorescence quantum yield, and characteristics, such as simple small molecule dye synthesis; furthermore, in combination with a chemical label technology, the light activated fluorescent probe is capable of positioning target molecular specificity in living cells precisely; real-time super-resolution fluorescence imaging in the living cells can be realized; and therefore, the light activated fluorescent probe has important application value in the field of super-resolution, especially super-resolution imaging in the living cells.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Laser radar based on highly-correlated quantum imaging principle
InactiveCN101846745AReduce lossRealize ultra-long-distance detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime delaysDistance detection
The invention discloses laser radar based on a highly-correlated quantum imaging principle, which consists of a pulse laser, a parameter down-conversion non-linear device, a receiving lens, a photon detector, an imaging lens, an area-array detector, a time delay correlator and a signal processor. The pulse laser transmits laser pulse to generate two laser beams having different wavelengths and the highly correlation by parameter down-conversion non-linear device, one path of laser beam with long wavelength is irradiated on a measured object and is focused on a photon detector through a receiving lens to detector after being reflected, and a switch signal indicative of the detecting result of the photon is output; the other path of laser beam with short wavelength is irradiated to the area-array detector through an imaging lens to acquire a two-dimension photon image signal; and two paths of signals are correlated and integrated by the signal processor to acquire image and distance information of the measured object. The laser radar effectively solves the problem of transmission loss by using the laser with the long wavelength in an atmosphere window to realize the ultra-long distance detection and realize the super-resolution detection by using the highly-correction effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
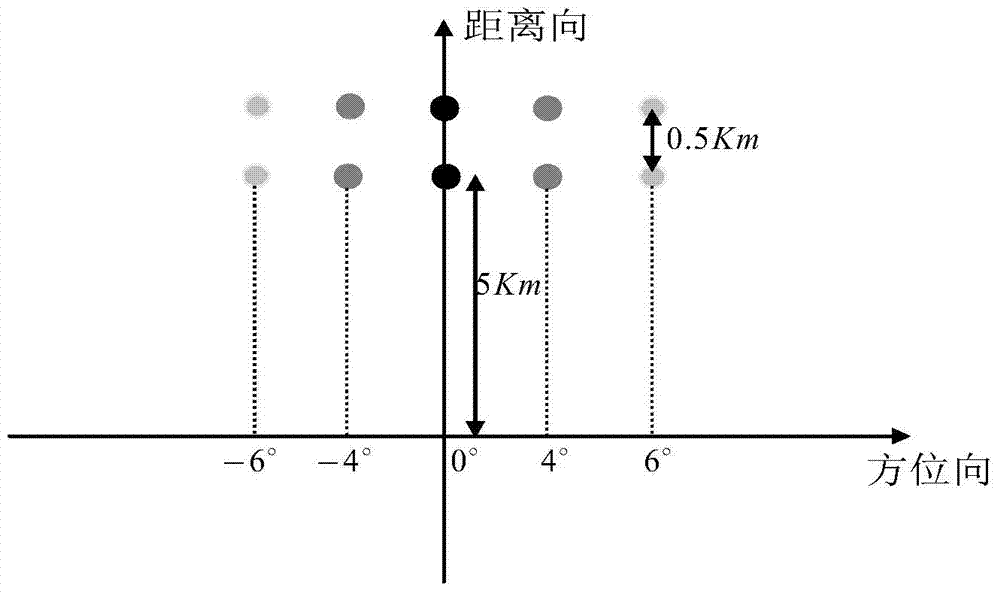
Deconvolution method for realizing scanning radar azimuth super-resolution imaging
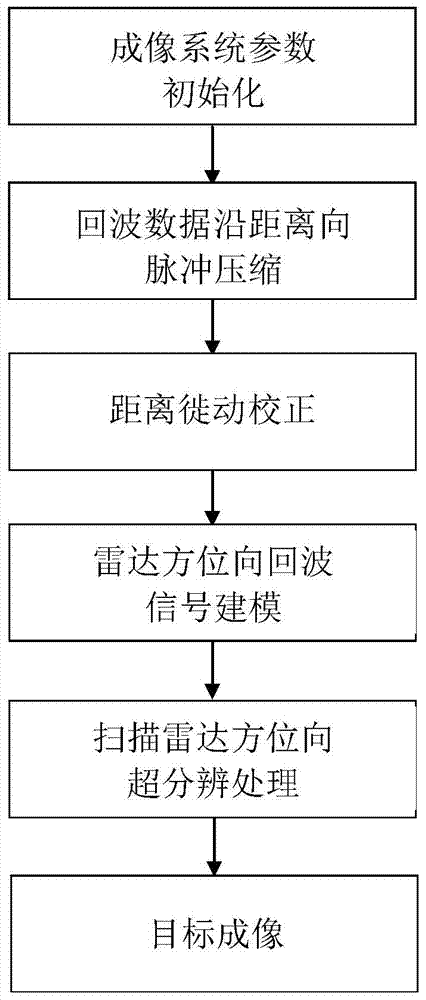
ActiveCN104977582AAchieving super-resolution imagingOvercome Spectrum LossRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumMaximum a posteriori estimation
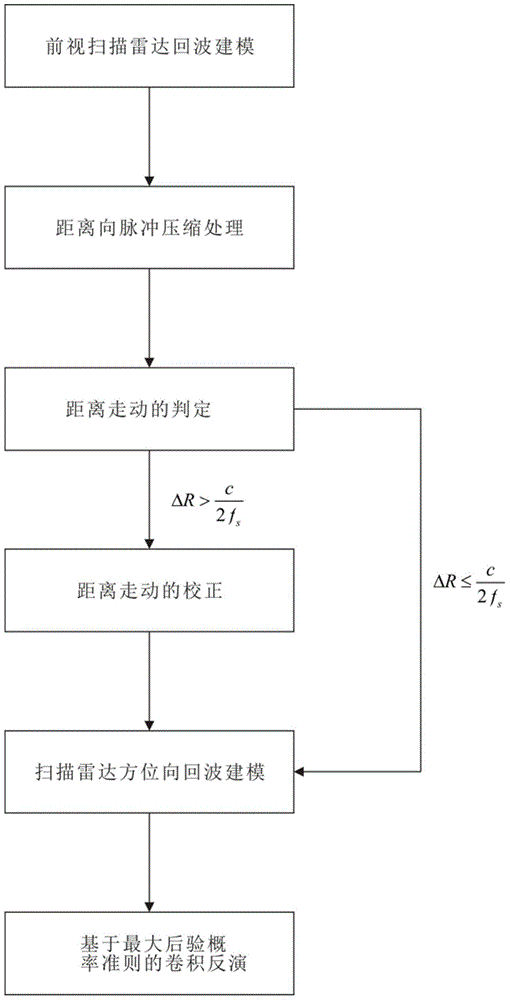
The invention discloses a deconvolution method for realizing scanning radar azimuth super-resolution imaging. Step one, forward-looking scanning radar echo modeling is performed; step two, range direction pulse compression processing is performed; step three, range wall determination is performed; step four, range walk correction is performed; step five, scanning radar azimuth direction echo modeling is performed; and step six, convolution inversion based on the maximum posterior probability criterion is performed. The beneficial effects are that an azimuth echo convolution model is established, an algorithm iteration expression is derived based on the maximum posterior probability criterion through combination of prior information and a likelihood function, low frequency is reconstructed, high frequency is recovered, an iterative solution is obtained by utilizing frequency spectrum extrapolation property, a problem of spectrum loss caused by noise and antenna low-pass property is overcome, a high-frequency component is acquired by utilizing nonlinear operation separation and super-resolution imaging is realized. Besides, frequency domain spectrum width and a change trend diagram of frequency domain integral sidelobe comparison number of iterations are provided by utilizing the frequency spectrum extrapolation property, and finally convolution inversion is realized and the inversion result is used for realizing scanning radar super-resolution imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Monitoring method and monitoring device of movable ultrasonic image with high resolution
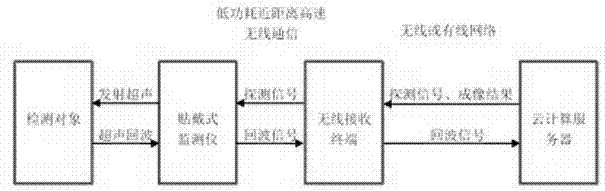
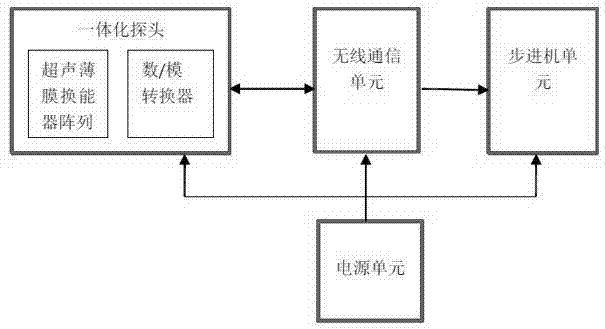
InactiveCN103169495ASimple structureLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingImage resolution
The invention discloses a monitoring method and a monitoring device of a movable ultrasonic image with high resolution. The device comprises an ultrasonic monitor, a wireless receiving terminal and a Cloud calculation server. The ultrasonic monitor is connected with the wireless receiving terminal through a low-power-consumption wireless communication technique, and the wireless receiving terminal is connected with the Cloud calculation server through a wireless or wiring network. According to the method, a rotary probe of a step motor inside the monitor is used for carrying out full-automatic and all-around compound scanning along a specific rail, collected data are transmitted to the Cloud calculation server through ultrasonic reflection echo information received by the probe by means of the wireless communication technique, the Cloud calculation server reconstructs an algorithm by means of super resolution, repeated superposition is carried out on a series of low-resolution signals or images of multiple frames repeatedly, areas are repeatedly divided, judgment and subdivision are carried out, the signals or the images with high resolution are reconstructed, and high-precision ultrasonic imaging is achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FENGPU INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Airborne scanning radar imaging method in iteration compression mode
ActiveCN103487803AAchieving super-resolution imagingEfficient integrationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPrior informationMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention discloses an airborne scanning radar imaging method in an iteration compression mode. The airborne scanning radar imaging method is characterized in that an azimuth-direction super-resolution imaging back model is built under the Bayesian theory framework, and the model built under the Bayesian theory can effectively fuse prior information of a target. When the super-resolution imaging back model is built, the assumption of a radar imaging basic idea on the noise statistical property is followed, and the Gaussian distribution function is adopted in the model to describe the noise statistical property. Due to the fact that target scattering has sparsity relative to an imaging background, the prior information of target scattering is described through the Laplace distribution function, radar super-resolution imaging is precisely converted into the maximum posterior probability problem in mathematics, corresponding target information when the posterior probability is maximum is solved, then the target information is reconstituted, and therefore the radar super-resolution imaging is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wide field super-resolution microscopic imaging method and wide field super-resolution microscopic imaging apparatus based on total internal reflection structure illumination
ActiveCN106950208AEasy to operateImprove the utilization rate of incident light energyFluorescence/phosphorescenceLight energyFluorescence intensity
The present invention discloses a wide field super-resolution microscopic imaging method based on total internal reflection structure illumination. The wide field super-resolution microscopic imaging method comprises that a laser beam is divided into two linearly polarized light beams having symmetrical propagation directions and perpendicular vibration directions; the two linearly polarized light beams are converted into two tangential linearly polarized light beams, the two tangential linearly polarized light beams are projected on a fluorescent sample, total reflection is generated and mutual interference is generated to produce a fringe structure illumination pattern; the fluorescent signal emitted by the sample is collected to obtain fluorescent intensity information; by sequentially rotating the direction of the interference fringe of the structure illumination pattern, the phase of the interference fringe is changed a plurality of times in various directions to obtain a plurality of fluorescent intensity images under the corresponding phases in various directions; and data processing is performed on the plurality of the fluorescent intensity images, and re-construction is performed to obtain the super-resolution image. The present invention further discloses a wide field super-resolution microscopic imaging apparatus based on total internal reflection structure illumination. According to the present invention, the incident light energy utilization rate is high, the interference fringe contrast is high, and the resolution exceeding the diffraction limit under the low incident light power condition can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
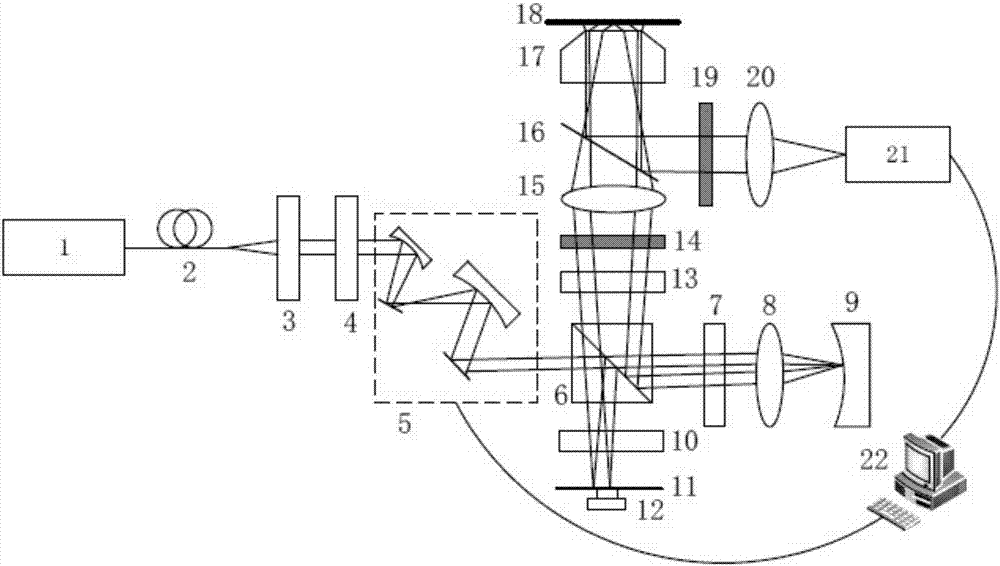
Device and method for measuring smooth free-form surface sample based on differential STED
ActiveCN104296685AAchieving super-resolution imagingSuppression of common mode noiseUsing optical meansLight spotFree form
The invention provides a device and method for measuring a smooth free-form surface sample based on differential STED, and belongs to the field of optical microscopic measurement. The surface of the smooth free-form surface sample is plated with a fluorescent film, and by the utilization of the characteristic that the fluorescent film radiates fluorescence in various directions under laser radiation, the problem that signal light is difficult to collect due to specular reflection of light beams on a smooth free-form surface is solved; meanwhile, by the adoption of the STED microscopy principle, light spots formed by collecting two pulse laser beams of different wavelengths coincide with each other, the portions, located in the center regions of the light spots, of the fluorescent film on the sample excite fluorescence, the portions, located in the light spots but not located in the center regions of the light spots, of the fluorescent film generate back excitation and do not emit fluorescence, and therefore super-resolution imaging of the sample is achieved; by the adoption of a differential detection structure, differential operation is conducted on two paths of collected signals, a differential response curve is acquired, the surface position of the sample is determined through a zero point of the differential response curve, and finally the purpose of measuring the smooth free-form surface sample shape with the large curvature at high accuracy is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method
InactiveCN103310427AImprove image qualityHigh resolutionImage enhancementImaging qualityHorizontal and vertical
The invention provides an image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method and relates to the technical field of digital image processing in a space remote sensing imaging system. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method solves the problems that optimization elements which can be utilized are less, the improvement space of the image quality is limited, and accordingly the image quality cannot be effectively improved in the existing Wiener filtering image restoration method. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method comprises utilizing a light beam splitter to collect in-focus images and out-of-focus images in two channels respectively and collect N staggered in-focus images which enable 1 / N pixels to be staggered in the horizontal and vertical direction relative to the in-focus images; performing PD (Phase Diversity) processing on the in-focus images and the out-of-focus images; utilizing a conjugate gradient algorithm to obtain an aberration coefficient; obtaining restored target images after the PD processing and calculating an objective function; performing Wiener filtering processing on the staggered in-focus images and the restored target images; and performing sub-pixel integration on the two restored images to obtain a restored image with ultrahigh resolution. The image super-resolution and image quality enhancement method achieves super-resolution and high definition of images and improves the resolution by 1.4 times.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultra-resolution dual shaft differential confocal measurement method and device
InactiveCN101458071AEffective balance space sizeImprove resolutionUsing optical meansDual axis confocalLight beam
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical precise measurement and relates to a super-resolution double-shaft differential confocal measuring method and a super-resolution double-shaft differential confocal measuring device. In the method and the device, pupil filtering technology is fused in a double-shaft confocal measuring structure, and a differential treatment method is used for receiving a measured light beam and carrying out treatment, thereby achieving the aims of improving resolution, expanding working distance, improving anti-interference capability and improving linear range. The invention can be used for precise measurement in such fields as micro-electronics, materials, industrial precise detection, biomedicine, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
STED (stimulated emission depletion)-based device and method for measuring smooth free-form surface sample
InactiveCN104279982ARealize the collectionAchieving super-resolution imagingUsing optical meansPicosecond pulsed laserMirror reflection
The invention relates to an STED (stimulated emission depletion)-based device and method for measuring a smooth free-form surface sample, belonging to the field of the optical microscopic measurement. The device comprises a first picosecond pulse laser, a first conduction optical fiber, a first collimator objective, a first plane reflecting mirror, a second picosecond pulse laser, a second conduction optical fiber, a second collimator objective, a second plane reflecting mirror, a vortex-shaped phase modulation plate, a half-wave plate, a first dichroscope, a second dichroscope, a quarter-wave plate, a focusing object lens, a coating sample, a three-dimensional micro-displacement carrier table, an optical filter, a collection object lens, a pin hole and a photoelectric detector. The surface of the sample is coated with a fluorescent membrane, so that an industrial sample can be measured by utilizing the STED microscopy; meanwhile, the fluorescent membrane radiates fluorescence in different directions under the illumination of the laser, so that the problem that the signal light is difficult to collect caused by the mirror reflection of the light beam on a smooth free-form surface can be avoided. By adopting the device and method, the surface appearance of the smooth sample with a large angle between a normal and the optical axis direction can be high precisely measured.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
THz radiation reinforcing method through light line array
ActiveCN103411903AIncreased Radiation PowerHigh light wave powerOptical detectionColor/spectral properties measurementsFemto second laserMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a THz radiation reinforcing method through a light line array, which comprises the following steps: calibrated femtosecond laser are focused by a focusing lens to generate light line; a BBO crystal is mounted behind the focusing lens to generate a two-color field; a step-type phase plate is mounted in front of the focusing lens to generate controllable light line array to reinforce the THz radiation. Compared with the conventional THz radiation reinforcing method, the method provided by the invention has the advantage that a simple, compact, and feasible structure is provided; the generated THz is impulse light wave, has higher average power and signal-to-noise ratio compared with THz generated without the phase plate, and can be applied to THz remote detection; the THz radiation reinforcing method can reinforce THz radiation power, increases the signal-to-noise ratio, and can be applied to THz spectral analysis.
Owner:天津理特光电科技有限公司
Optimization method for improving imaging quality of single-pixel camera through image reconstruction algorithm based on deep learning
ActiveCN110288526AIncrease flexibilityImprove performanceImage enhancementInternal combustion piston enginesImaging qualityImage resolution
The invention discloses an optimization method for improving the imaging quality of a single-pixel camera through an image reconstruction algorithm based on deep learning. With the development of a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN), the application of the DCNN in the field of super-resolution imaging also develops. Based on the basic principles of the compressed sensing and the single-pixel camera imaging, a deep learning network structure model for image super-resolution reconstruction is designed, a novel deep learning image reconstruction algorithm is embedded into a single-pixel imaging system, and a deep learning technology and a single-pixel camera super-resolution imaging technology are combined. Compared with a traditional matching pursuit algorithm, a minimum L1 norm algorithm and an iteration threshold algorithm for compressed sensing image reconstruction, the novel deep learning algorithm effectively improves the image reconstruction precision and the imaging quality and effect of the single-pixel camera. The effectiveness of the imaging optimization of the single-pixel camera is verified through the simulation and the actual imaging experiments in the deep learning manner.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Super-resolution Bessel micro-imaging device and method based on multi-focus light illumination
ActiveCN110487762AExtended imaging rangeReduce acquisition timeRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Fluorescence
The invention provides a super-resolution Bessel micro-imaging device and method based on multi-focus light illumination. The method comprises a laser light source, a beam-expanding collimating and reflecting component, a Gaussian fluorescence generation component which excites a sample surface to generate a Gaussian-distributed fluorescence signal according to an introduced illumination mode of equal interval switching, a Bessel fluorescence generation component which converts the Gaussian-distributed fluorescence signal into a Bessel-distributed fluorescence signal and obtains image data, and a control terminal which performs image reconstruction on image data to obtain a super-resolution sample two-dimensional information image. According to the invention, a sample is simultaneously excited through multiple focus points, the imaging range of the microscopic imaging device is improved, the sample collection time is reduced, the Gaussian-distributed fluorescence signal is converted into the Bessel-distributed fluorescence signal, the image data of the collected Bessel-distributed fluorescence signal is subjected to image reconstruction, and the super-resolution imaging at a largeworking distance can be achieved while the high signal-to-noise ratio is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
High speed adaptive optical ring spot correction system and method based on machine learning
PendingCN109212735AQuick correctionFix resolution dropMicroscopesIncreasing energy efficiencySpatial light modulatorFluorescence
The invention discloses a high speed adaptive optical ring spot correction system and method based on machine learning. According to the system and the method, a learning model is established, a mapping relationship between distorted ring spot forms and phase reconstruction coefficients required for correcting deformation is established, a to-be-tested distorted ring spot is input into a trained model, the phase reconstruction coefficient for correcting the distortion can be solved, and further correction phase reconstructed by the phase reconstruction coefficient is loaded to a spatial lightmodulator, so the distortion can be corrected. According to the system and the method, rapid correction can be carried out on ring spot aberration in a stimulated emission depletion (STED) fluorescence microscopy, precision is high, the system is simple and is easy to operate, and the resolution reduction problem resulting from the aberration and scattering generated when sample deep layer imagingis carried out in an STED super-resolution microscopy imaging technology is solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Super-resolution microscopic CT imaging system
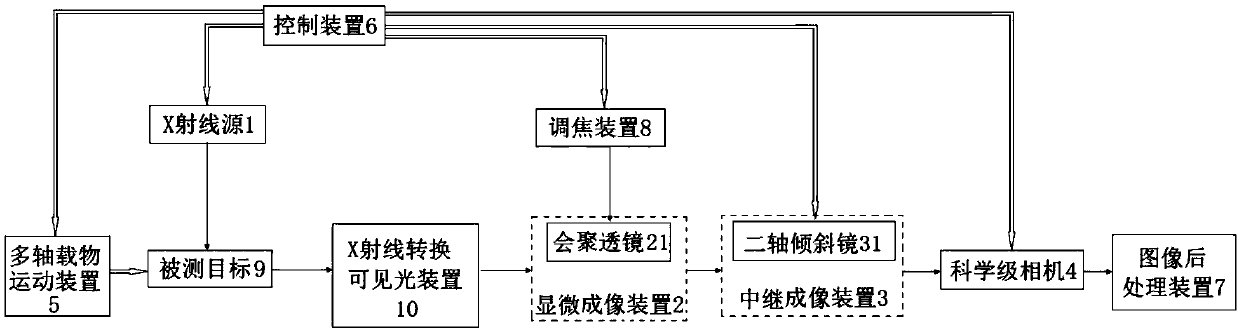
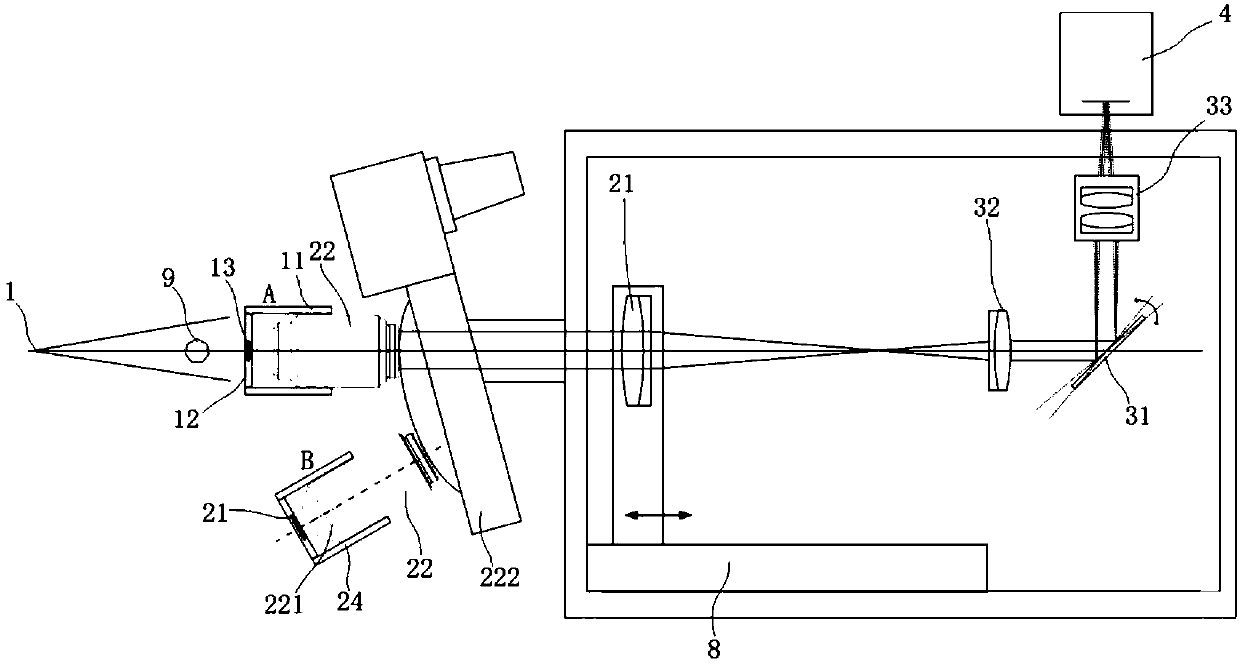
The invention discloses a super-resolution microscopic CT imaging system. The system includes an X-ray source, an X-ray conversion visible light device, a microscopic imaging device, a relay imaging device, a scientific grade camera, a multi-axis loading motion device, and a control device. An X-ray emitted by the X-ray source penetrates a measured object, and is converted into a 2D visible lightfield distribution by the X-ray conversion visible light device. The 2D visible light field distribution is propagated backward from the exit surface of the X-ray conversion visible light device and is projected as the object side onto the microscopic imaging device, and first microscopic amplification imaging is carried out on the 2D visible light field distribution via the microscopic imaging device. Then, the 2D visible light field distribution is projected onto the relay imaging device, and second relay amplification imaging is carried out on the 2D visible light field distribution via therelay imaging device. The relay imaging device includes a sub-pixel scanning member disposed on a parallel light path of the relay imaging device. The sub-pixel scanning member is used for making anoverall 2D image on the imaging plane of the relay imaging device carry out sub-pixel 2D translation in a vertical axis plane, so as to get a series of 2D images with pixels subdivided. The limitationcaused by the original imaging hardware of the system is broken, and super-resolution imaging is realized.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Broadband low-loss terahertz far field super lens and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN106950621AFrequency has little effectAchieving super-resolution imagingLensUltrasound attenuationGrating
The present invention discloses a broadband low-loss terahertz far field super lens and an imaging method thereof. Transmission-type metal gratings with angle period distribution are employed, electromagnetic waves can be only existed in a TEM mode, evanescent waves can be converted to TEM cylindrical waves in a gradually opening planar waveguide to allow all the information to perform transmission without attenuation along the radial direction so as to realize super-resolution imaging through the channel transportation of the evanescent waves; the energy flow direction of the electromagnetic waves is along the radial direction, according to the angular momentum conservation, the tangential wave vectors of the evanescent waves are subjected to equal proportion compression to allow the evanescent waves to gradually convert to transmission waves and go on transmission after the electromagnetic waves capable of bearing target detail information departs from a lens so as to realize far field imaging; and when the Fabry-Perot oscillation happens, waves having different tangential wave vectors have the same transmissivity so as to realize complete work point of the lens. The broadband low-loss terahertz far field super lens and the imaging method thereof can effectively reduce the transmission loss, are easy to process and small in frequency influence on the lens electromagnetic parameters, and realize broadband imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
STED (stimulated emission depletion) parallel microscopic imaging system based on uniform structured illumination
ActiveCN108181235AImprove imaging resolutionFast imagingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLight laserOptoelectronics
The invention provides an STED (stimulated emission depletion) parallel microscopic imaging system based on uniform structured illumination. By designing an illumination module, an exciting light beamemitted by an exciting light laser is divided into two coherent light beams, a depletion light beam of Gaussian distribution is modulated into a flattened beam by a flattened Gaussian beam shaper andis divided into two coherent light beams, uniformly distributed streaky exciting structured light and depletion structured light are obtained respectively by interference, excitation and depletion are performed on a sample, STED parallel microscopic imaging is performed, then image reconstruction is performed with an STED coordinate positioning method and an SIM frequency domain and spectrogram fusion method, super-resolution imaging is realized, and the field range and the imaging speed of the STED microscopic system can be increased.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOKE MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD +1
STED parallel microscopic imaging system based on structural light illumination
ActiveCN108121059AExpanded field of view and imaging speedAchieving super-resolution imagingMicroscopesVisual field lossLight laser
The invention provides an STED parallel microscopic imaging system based on structural light illumination. Through designing an illuminating module, one laser beam which is transmitted from an existing laser is divided into two coherent light beams; one loss light beam which is transmitted from a loss light laser is divided into two coherent light beams; exciting structural light and loss structural light which are uniformly distributed are respectively obtained through interference; the exciting structural light and the loss structural light respectively perform excitation and loss on a sample; STED parallel microscopic imaging is performed; then image reconstruction is performed through an STED coordinate positioning method and an SIM frequency domain frequency spectrum graph fusion method, thereby realizing super-resolution imaging and facilitating improvement of visual field range and imaging speed of an STED microscopic system.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOKE MEDICAL TECH DEV CO LTD +1
Super-resolution imaging method and implementation device on the basis of Fresnel zone plate coding
ActiveCN105674923AAchieving super-resolution imagingReasonable ideaTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceSuperresolution
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
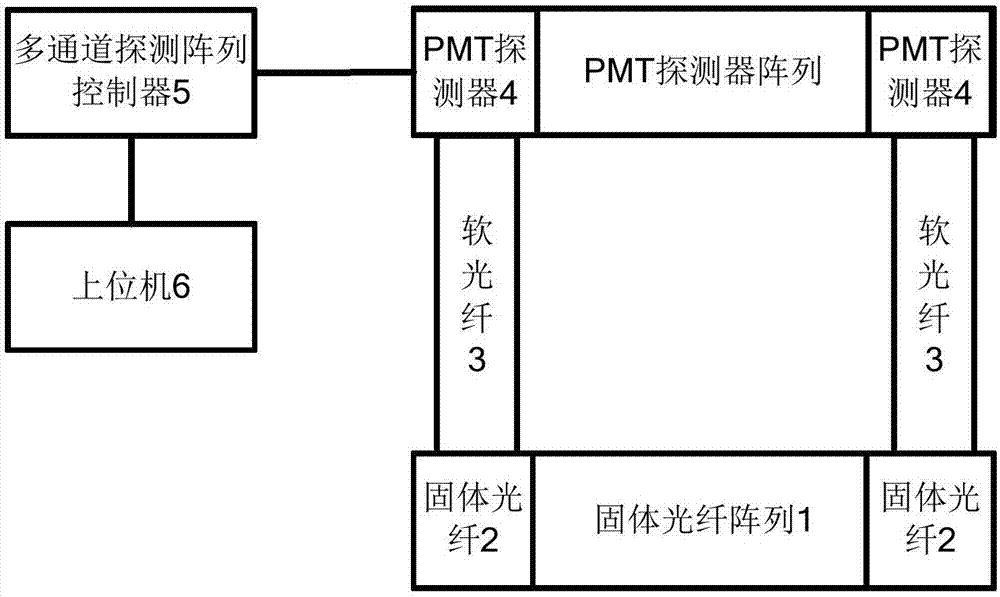
Fiber-array-based multi-channel fluorescence detection system
InactiveCN107229114AAchieving super-resolution imagingMicroscopesPhotometry using multiple detectorsFluorescenceFiber array
The invention provides a fiber-array-based multi-channel fluorescence detection system. A solid-state optical fiber array receives a fluorescence signal and transmits the signal to a flexible fiber; and the flexible fiber is connected to a PMT detection array and transmits the signal to the PMT array. An upper computer controls the multi-channel PMT array to receive an optical signal and transform the optical signal into an analog signal; and a data acquisition card converts the analog signal into a digital signal and returns the digital signal to a main controller. The fixed fiber is used for replacing the pinhole in the traditional confocal system and the fiber array forms the pinhole surface of the confocal system, thereby realizing super-resolution imaging of the confocal system.
Owner:上海戴泽光电科技有限公司
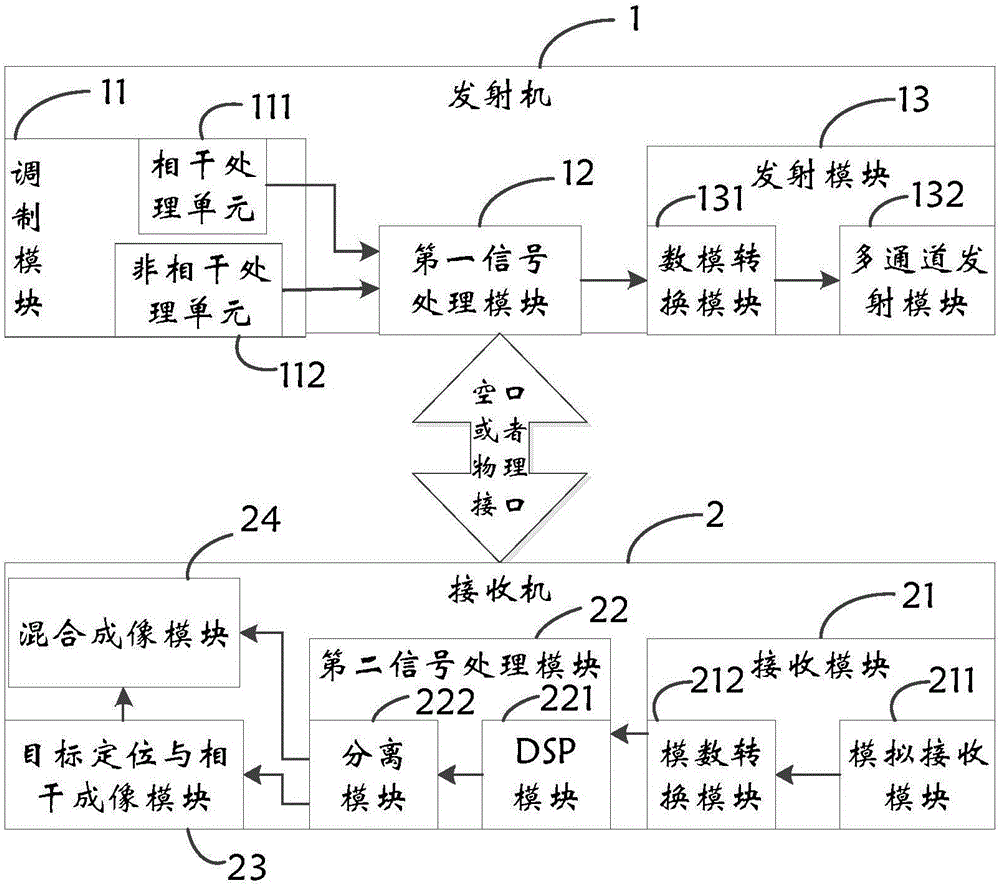
Mixing mode imaging device and mixing mode imaging method
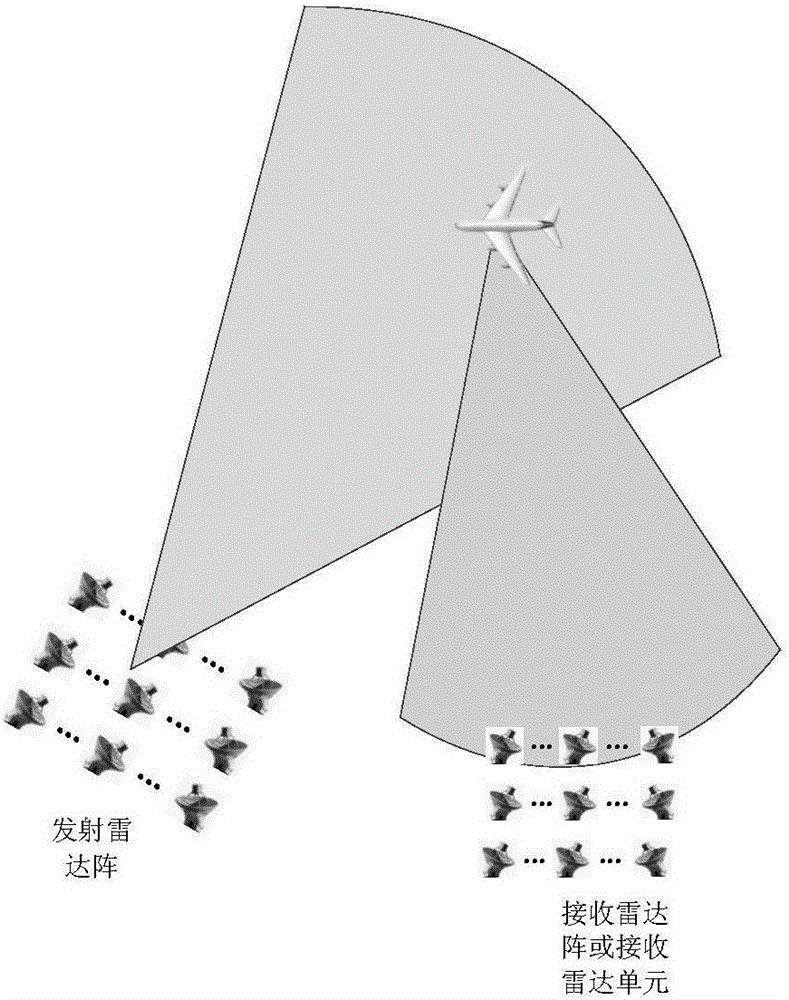
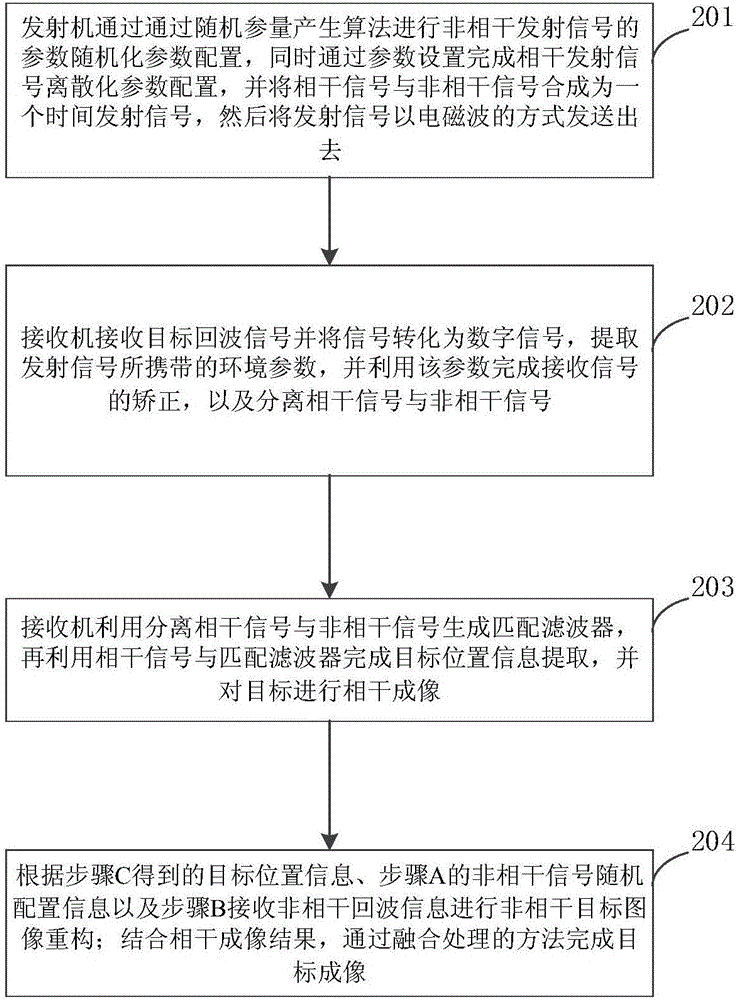
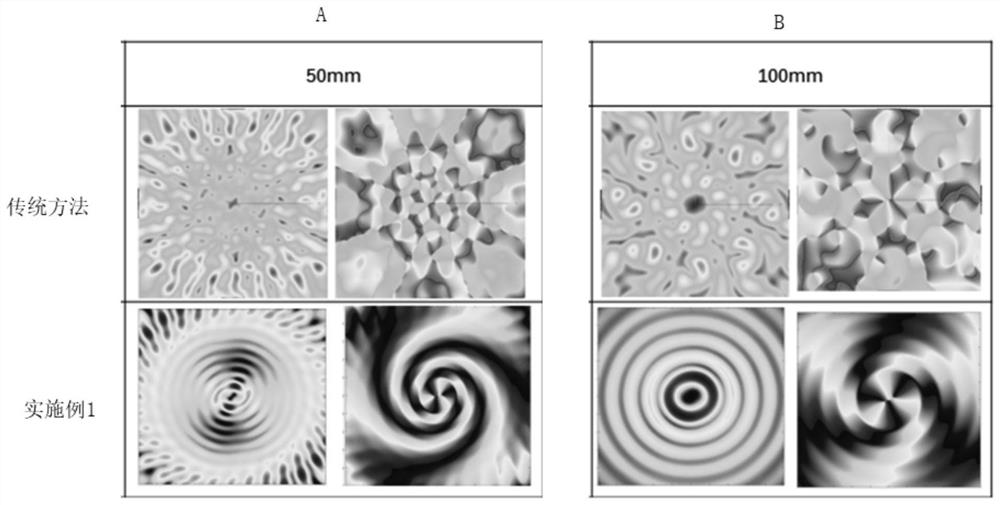
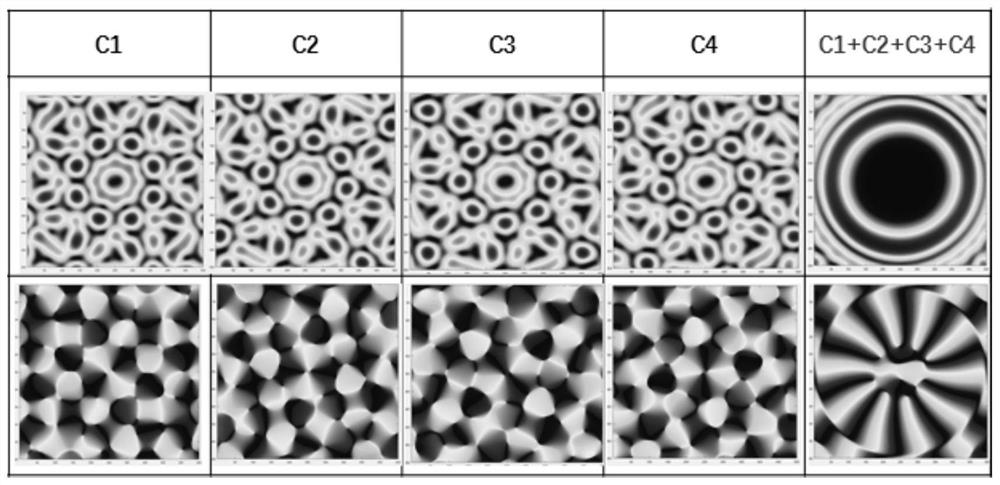
InactiveCN106291544AWith target positioning functionImprove image qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionRadar imaging
The invention discloses a mixing mode imaging device and a mixing mode imaging method. The imaging device comprises a transmitter and a receiver, which are connected together by a physical interface. The transmitter comprises a modulation module, a first signal processing module, and a transmitting module. The receiver comprises a receiving module, a second signal processing module, a target positioning and coherent imaging module, and a mixing imaging module. The mixing imaging module is used to estimate a target characteristic parameter according to an incoherent transmitting signal, an incoherent receiving signal, a target positioning signal acquired by the target positioning and coherent imaging module, and an environmental parameter output by the second signal processing module, and is used to complete target imaging by combining with a coherent imaging result and adopting a fusion processing method. Advantages of a coherent radar imaging system and an incoherent radar imaging system are kept at the same time, and the imaging system is provided with a target positioning function, and imaging resolution is capable of breaking through a limitation of a radar aperture.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for synthesizing vortex electromagnetic field with high orbital angular momentum mode number
ActiveCN111740223ANot limited by timeHigh-resolutionParticular array feeding systemsAntenna supports/mountingsRadar imagingImage resolution
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a vortex electromagnetic field with a high orbital angular momentum mode number. The method for synthesizing the vortex electromagnetic field comprises the following steps: N antenna units form a circular antenna array, and by rotating the circular antenna array and regulating and controlling the phase of each antenna unit, the vortex electromagnetic field is synthesized, wherein N is an integer larger than or equal to 1. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, the synthesized vortex electromagnetic field with the target mode numbercan be generated as required, and the vortex electromagnetic field with the high mode number is directly synthesized by rotating the antenna array and regulating and controlling the phase of each antenna unit under the condition of a small number of antennas, so that the resolution of the imaging system in the azimuth direction is increased. The vortex electromagnetic field synthesized by using the method disclosed by the invention not only is beneficial to realizing super-resolution imaging, but also has remarkably improved modal purity, and has a very good application prospect in the fieldsof super-resolution biomedical imaging, radar imaging, wireless communication and the like.
Owner:中科星河(山东)智能科技有限公司
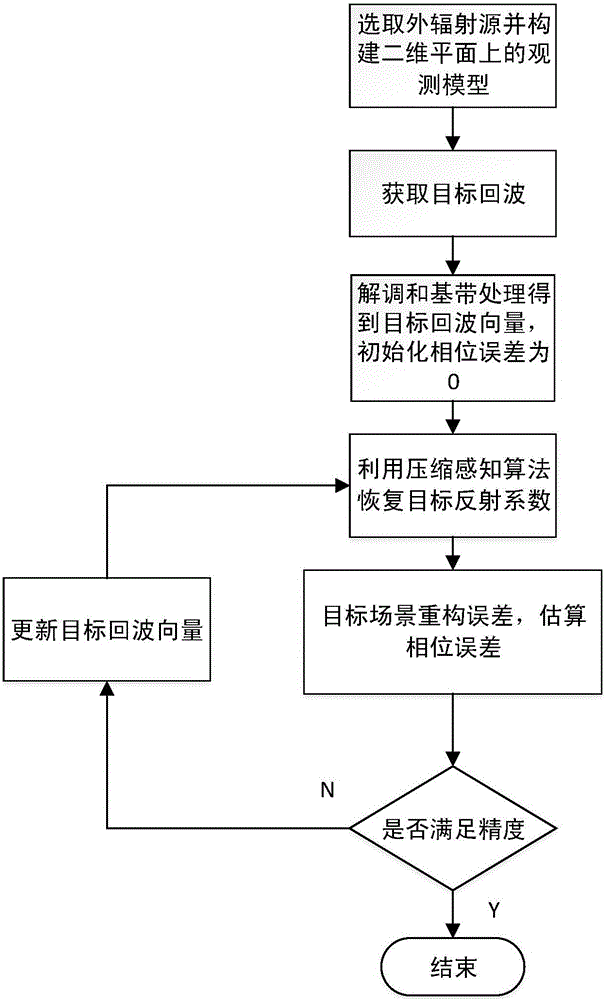
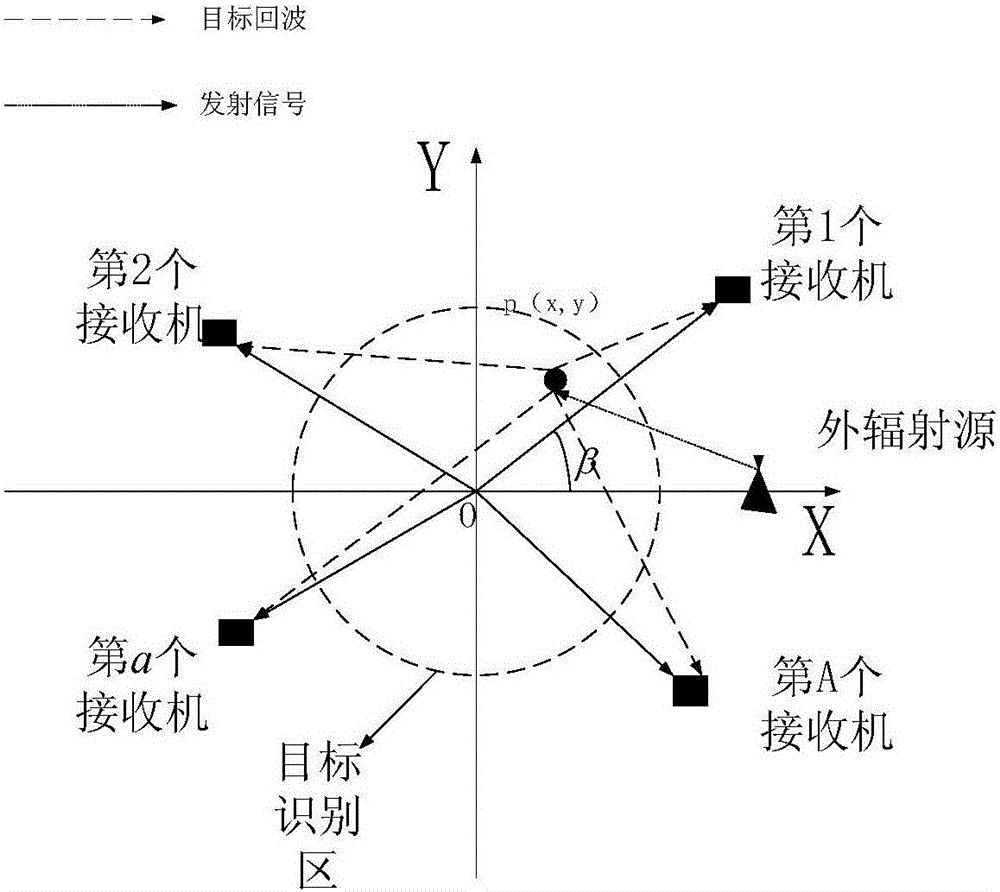
Self-focusing method of multi-base outer radiation source radar imaging system
ActiveCN105974413AHigh image resolutionOvercoming Image Defocus ProblemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhysicsReflection coefficient
The invention discloses a self-focusing method of a multi-base outer radiation source radar imaging system, wherein the self-focusing method mainly settles a problem of image defocusing caused by direct recovery of a target scene on condition of no consideration of a phase error in a traditional compression sensing algorithm. The self-focusing method comprises the realizing processes of 1), selecting an outer radiation source signal, establishing an observation model; 2), initializing a phase difference to zero, and acquiring a target echo vector; 3), applying the compression sensing algorithm on the target echo vector for estimating a target reflection coefficient vector, establishing a reconstruction error of the target scene according to the target reflection coefficient vector in two adjacent iterations; 4), calculating a phase error through the minimizing condition of the reconstruction error of the target scene; and 5), calculating whether the phase error satisfies an iteration stopping condition, if yes, stopping iteration for obtaining a phase error, and otherwise, returning the step 3) after the target echo vector is updated. The self-focusing method improves imaging resolution and can be used for performing high-resolution imaging on the multi-base outer radiation source radar imaging system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
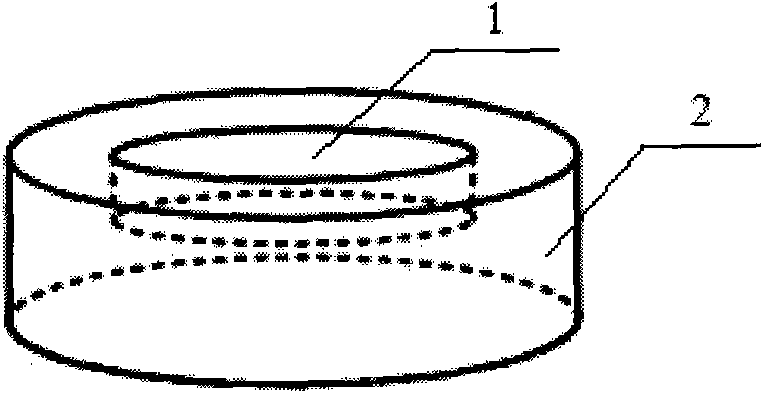
Super-resolution optical imaging device and method
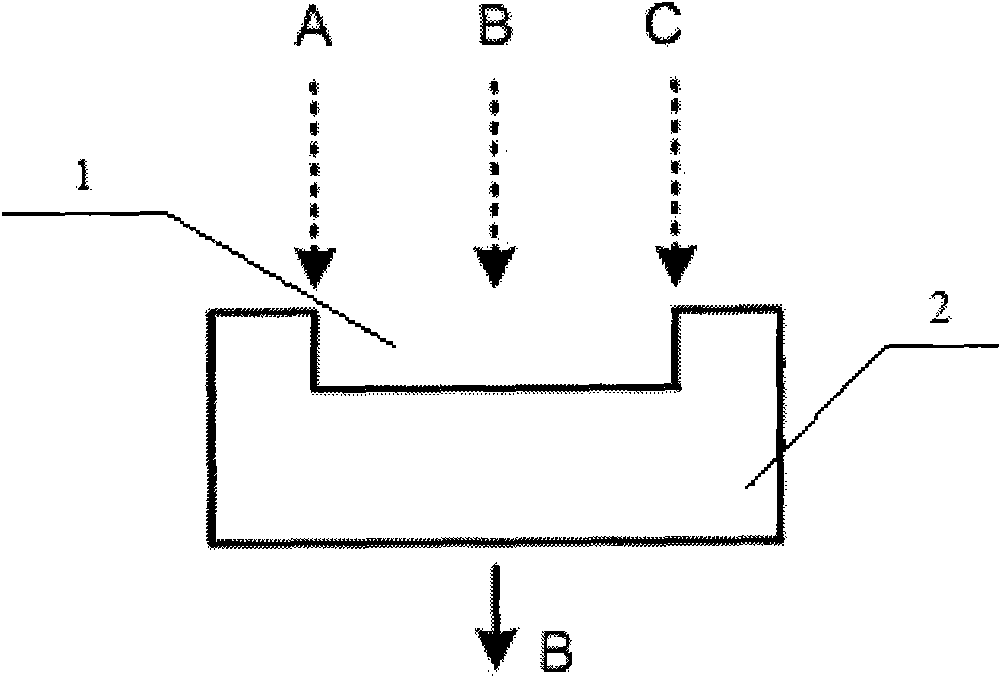
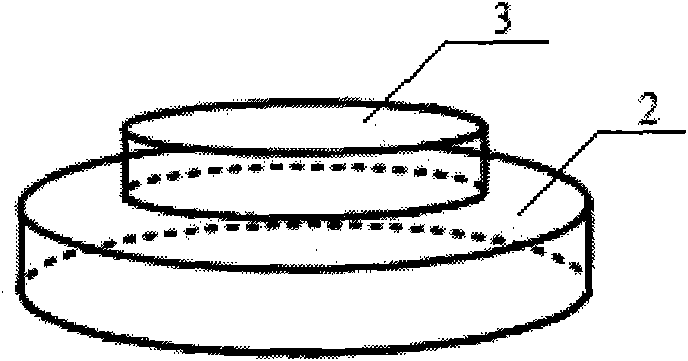
The invention discloses super-resolution optical imaging device and method. The super-resolution optical imaging device comprises a base. The base is provided with a groove (a step); the difference of optical paths passing through the groove (the step) and the edge of the groove (the outside of the step) is a half of the length of a light wave emitted by an imaging object due to the design of the depth of the groove (the height of the step); light beams positioned right above the groove (the step) are emitted to the bottom surface of the groove (the surface of the step); half of other light beams pass through the bottom surface of the groove (the surface of the step), the other half of the same pass through the edge of the base, and the light beams passing through the bottom surface of the groove (the surface of the step) and the edge of the base carry out self-mixing interference cancellation to obtain the information of the light beams positioned right above the groove on the base so as to break through a diffraction limit. The invention has small size and simple structure and realizes the super-resolution imaging.
Owner:NANJING FANGYUAN GLOBAL DISPLAY TECH
Real-time imaging method of super-resolution millimeter wave MIMO array
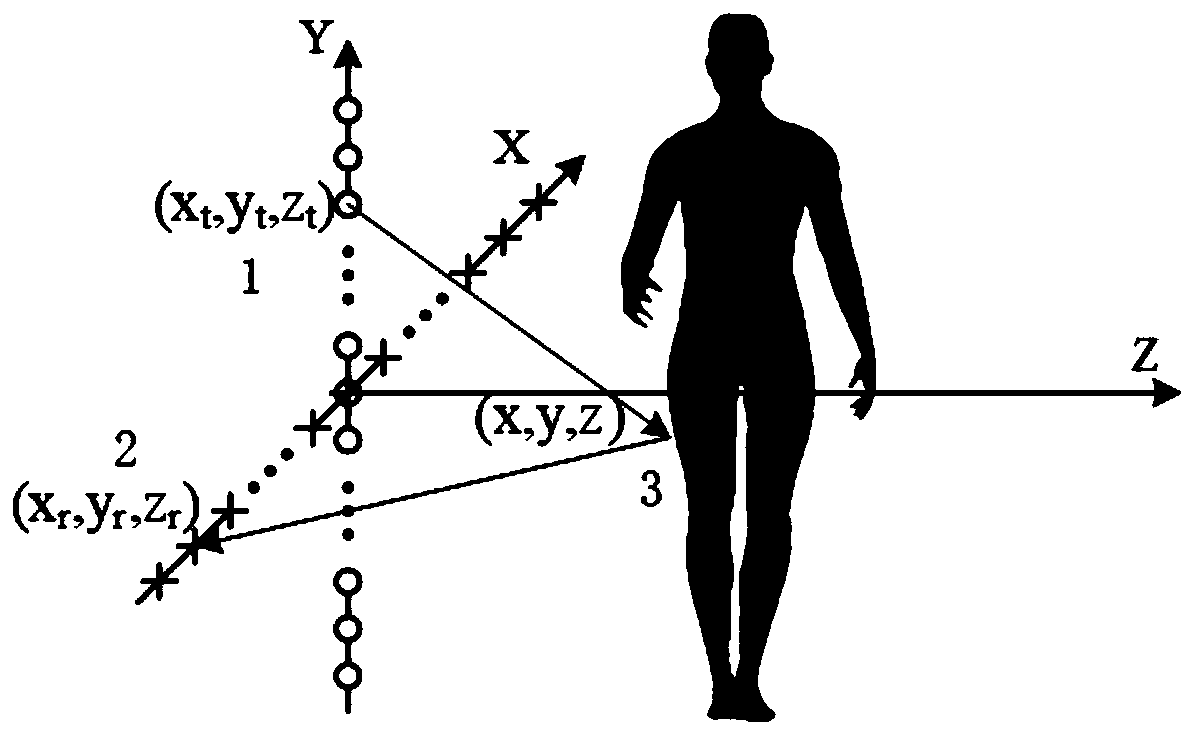
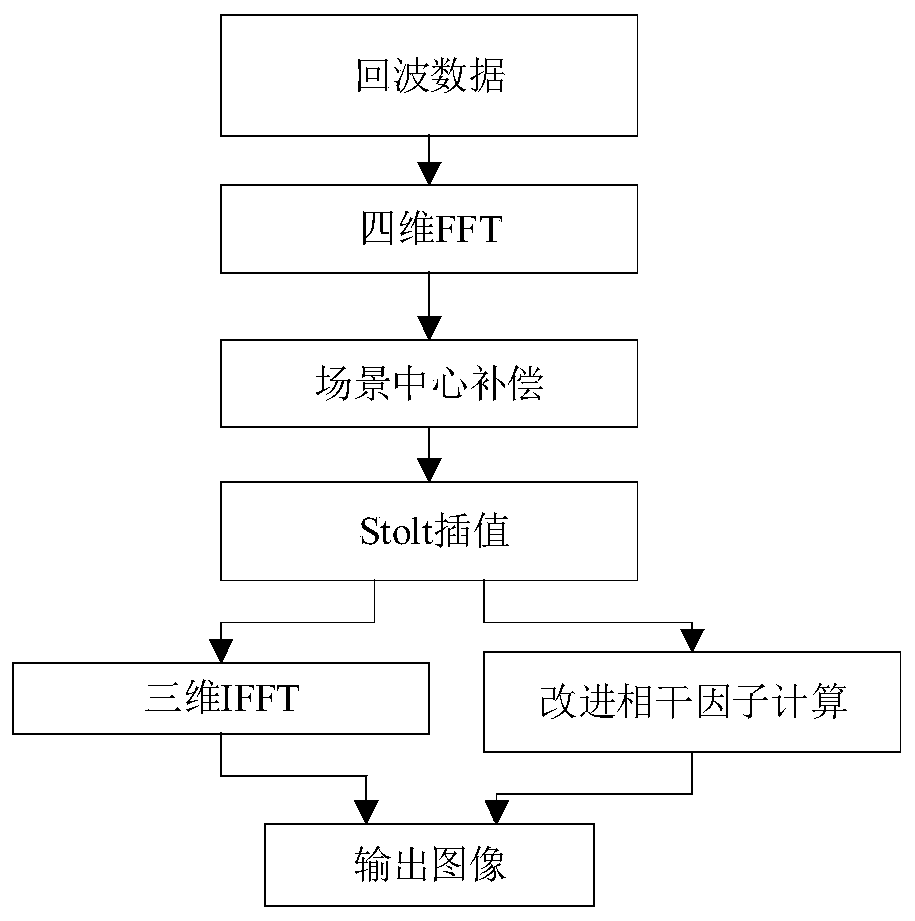
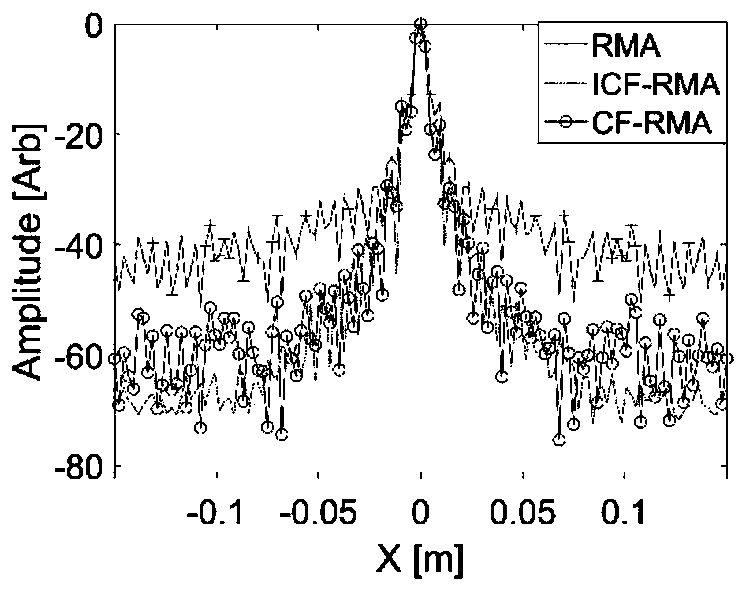
PendingCN110764089AImprove performanceReduce noise levelRadio wave reradiation/reflection3d imageSoftware engineering
The invention provides a real-time imaging method of a super-resolution millimeter wave MIMO array. The method comprises the steps of: step (1) performing, by the MIMO array, echo data sampling, and recording a broadband response signal; step (2): obtaining a three-dimensional image of a reflectivity function for a frequency domain response signal by using MIMO RMA, and meanwhile, figuring out animproved coherence factor in a wave number domain; and step (3): correcting the three-dimensional image of the reflectivity function obtained in the step (2) by using the improved coherence factor obtained in the step (2). By adopting the method, the incoherent power of the reflectivity function is re-defined in the wave number domain, so that the calculation of the coherence factor can be completed quickly in one step of three-dimensional IFFT, thereby further improving the imaging speed. In addition, the method still retains the super-resolution performance, comprising improving the spatialresolution, reducing the sidelobe and base noise levels of the image, and significantly improving the dynamic range of the image.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Overlapped compound eye
InactiveCN113141493AImage quality impactImprove imaging resolutionTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsOphthalmology
The overlapped compound eye comprises m sub-eye micro lenses arranged on a sub-eye arrangement surface, and further comprises a projection module and a photoelectric detector, the projection module is fixed on the curved surface of the compound eye, and the projection module projects a preset coding pattern to a target object; and the sub-eye micro lens is connected with the photoelectric detector through the transmission module. According to the method, a curved image detector which is highly matched with a curved compound eye and is difficult to process and manufacture does not need to be manufactured, only one photoelectric detector without spatial resolution is used for recording light intensity information, imaging is calculated through a single-pixel technology, and the design and manufacturing cost of a high-precision optical part is greatly saved; the imaging resolution of the compound eye is not limited by hardware such as the number of the sub-eyes and the clear aperture size of the sub-eyes any more, the imaging resolution is improved by two orders of magnitude, and the super-resolution imaging capacity is achieved; according to the method, the complete recognizable image of the target can still be obtained under the condition that part of the sub-eyes are damaged or shielded and cannot work normally, and the robustness is greatly improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
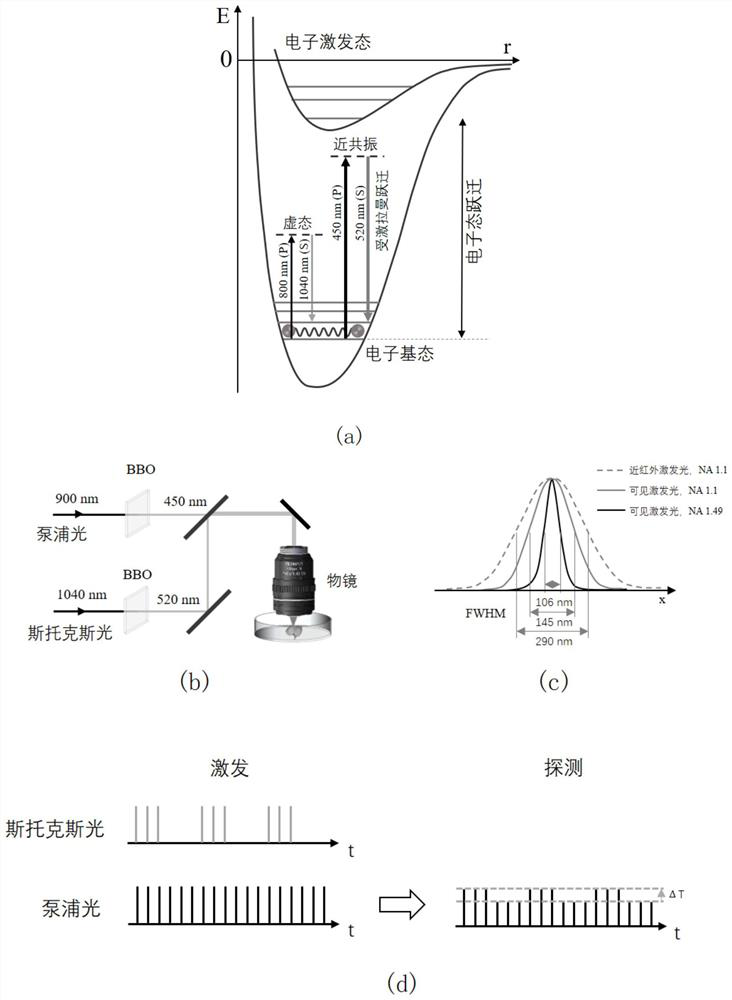
Super-resolution stimulated Raman microimaging method and device for realizing near resonance enhancement
ActiveCN112240880AGuaranteed collinearityGuaranteed stabilityRaman scatteringMicroscopic imageMicro imaging
The invention discloses a super-resolution stimulated Raman microimaging method and device for realizing near resonance enhancement. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a first pulse light source lambda 1 and a second pulse light source lambda 2 which are synchronous and phase-locked; (2) carrying out frequency multiplication processing on the first pulse light source lambda 1,and carrying out frequency multiplication processing on the second pulse light source lambda 2 subjected to intensity modulation, so as to halve the wavelength of the second pulse light source lambda2 and obtain third pulse laser lambda 3 and fourth pulse laser lambda 4; (3) carrying out delay processing on the fourth pulse laser lambda4 to realize time domain matching with the third pulse laserlambda3, and carrying out beam combination processing on the third pulse laser lambda3 and the fourth pulse laser lambda4 which are matched in time domain to realize complete matching of a spatial domain; (4) simultaneously coupling the combined third pulse laser lambda 3 and fourth pulse laser lambda 4 into a single-mode polarization maintaining optical fiber; and (5) processing an optical signal generated after the light transmitted by the single-mode polarization maintaining optical fiber and the sample act, and obtaining a microscopic image. According to the invention, the spatial resolution is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Holographic optical tweezer fusion structure illumination microscopic system and method
ActiveCN113568294AHigh spatial frequencyRealize 3D super-resolution imagingMicroscopesNeutron particle radiation pressure manipulationSpatial light modulatorControl system
The invention provides a holographic optical tweezers fusion structured illumination microscopic system and method, and belongs to the technical field of optical microsystems, the holographic optical tweezers fusion structured illumination microscopic system comprises a holographic optical tweezers micro-control system and a structured illumination microscopic system, the holographic optical tweezers micro-control system comprises a laser generating device, a light beam expanding unit and a light modulation unit; the light beam expanding unit comprises a first lens and a second lens which are sequentially arranged in the light emitting direction of the laser generating device, and the light modulation unit comprises a light spatial light modulator arranged in the light emitting direction of the second lens, and a third lens, a fourth lens, a first dichroic mirror and an objective lens which are sequentially arranged in the light emitting direction of the light spatial light modulator. And the structured illumination microscopic system comprises an illumination light source, and a structured light generator, a second dichroic mirror, a fifth lens, a first dichroic mirror and an objective lens which are sequentially arranged along the light emitting direction of the illumination light source.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Super-resolution imaging system and method based on filtering incoherent light field intensity high-order autocorrelation
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging system and method based on filtering incoherent light field intensity high-order self-correlation. The super-resolution imaging system comprises an incoherent light source, an imaging lens, an area array detector, a space threshold filter and a high-order intensity self-correlation operation system. The light emitted by the incoherent light source irradiates a target object, and the light transmitted or reflected and scattered by the object passes through the lens with the focal length F and then is imaged on the area array detector with the spatial resolution capability. The area array detector controls a data acquisition time sequence through external triggering, acquires an instant area array intensity signal at each moment, inputs the instant area array intensity signal to the intensity space filter with a set proper threshold value for filtering operation, and performs high-order intensity self-correlation operation according to the filtered spatial intensity distribution area array data to reconstruct an image of the target object. The method has the capability of resisting atmospheric disturbance, turbulence and other severe weather influences, can realize super-resolution imaging, and has important significance in various fields needing high-resolution imaging, such as microscopic imaging and remote sensing.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com