Patents
Literature
122results about How to "Extended imaging range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
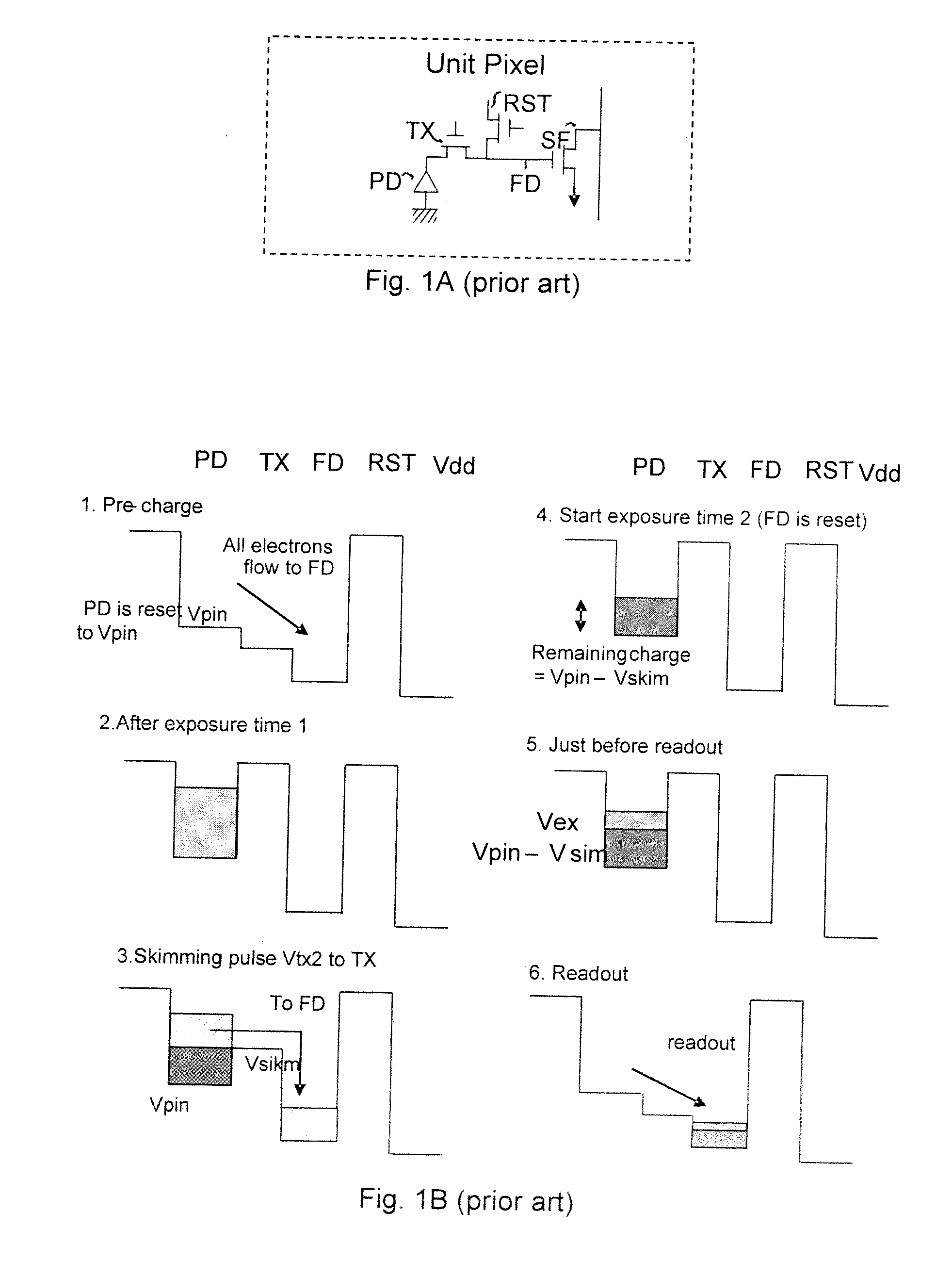
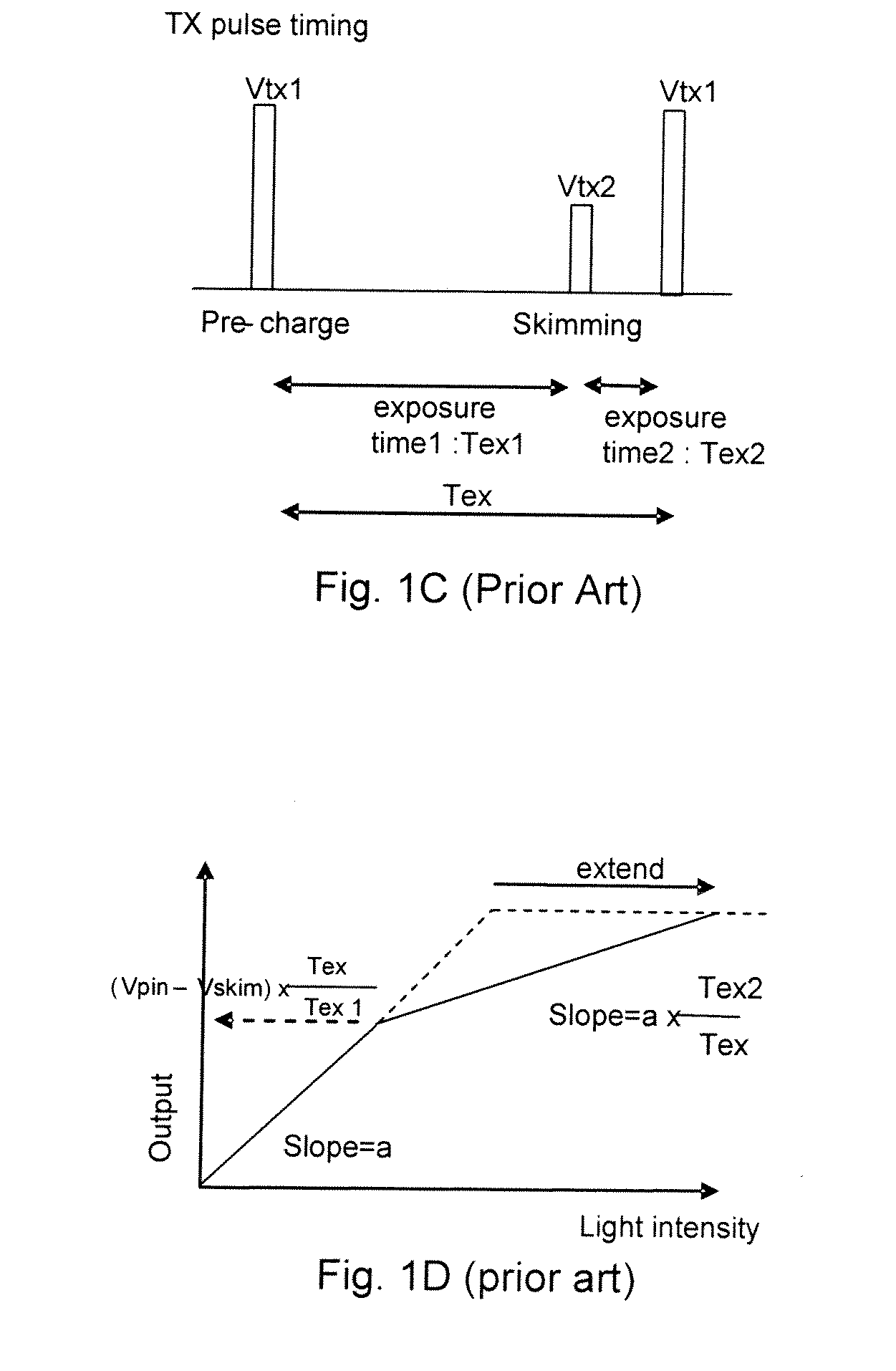
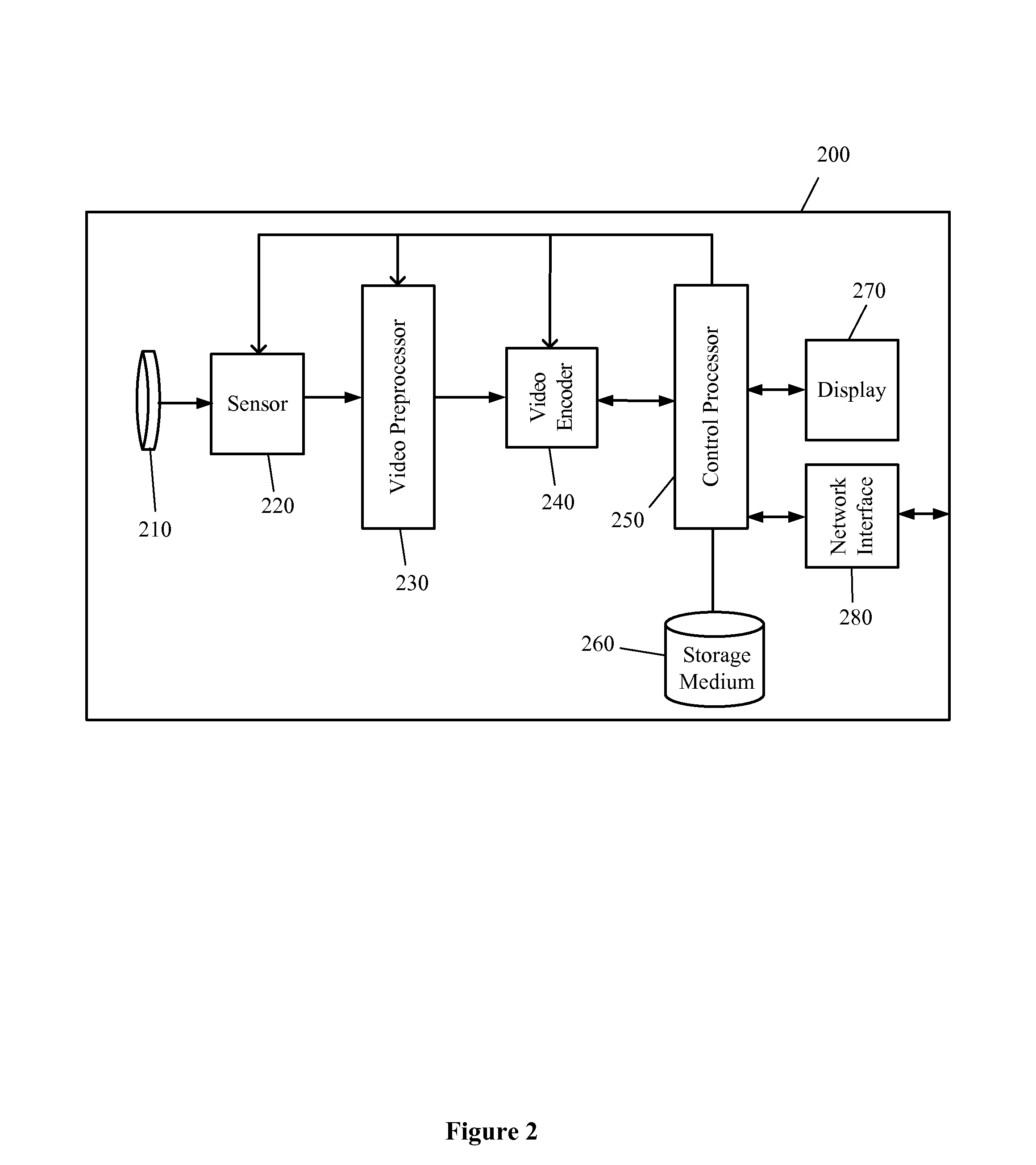
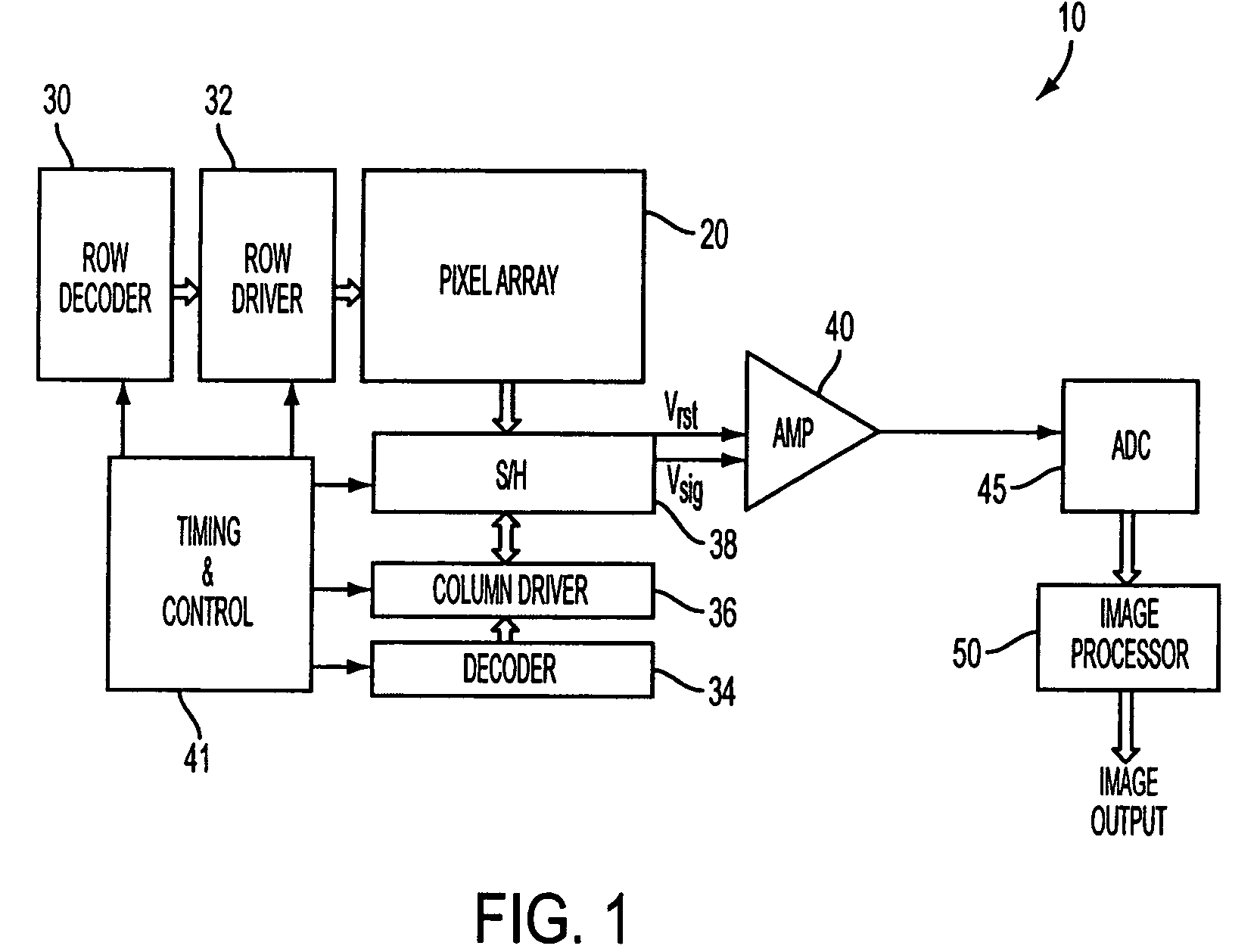
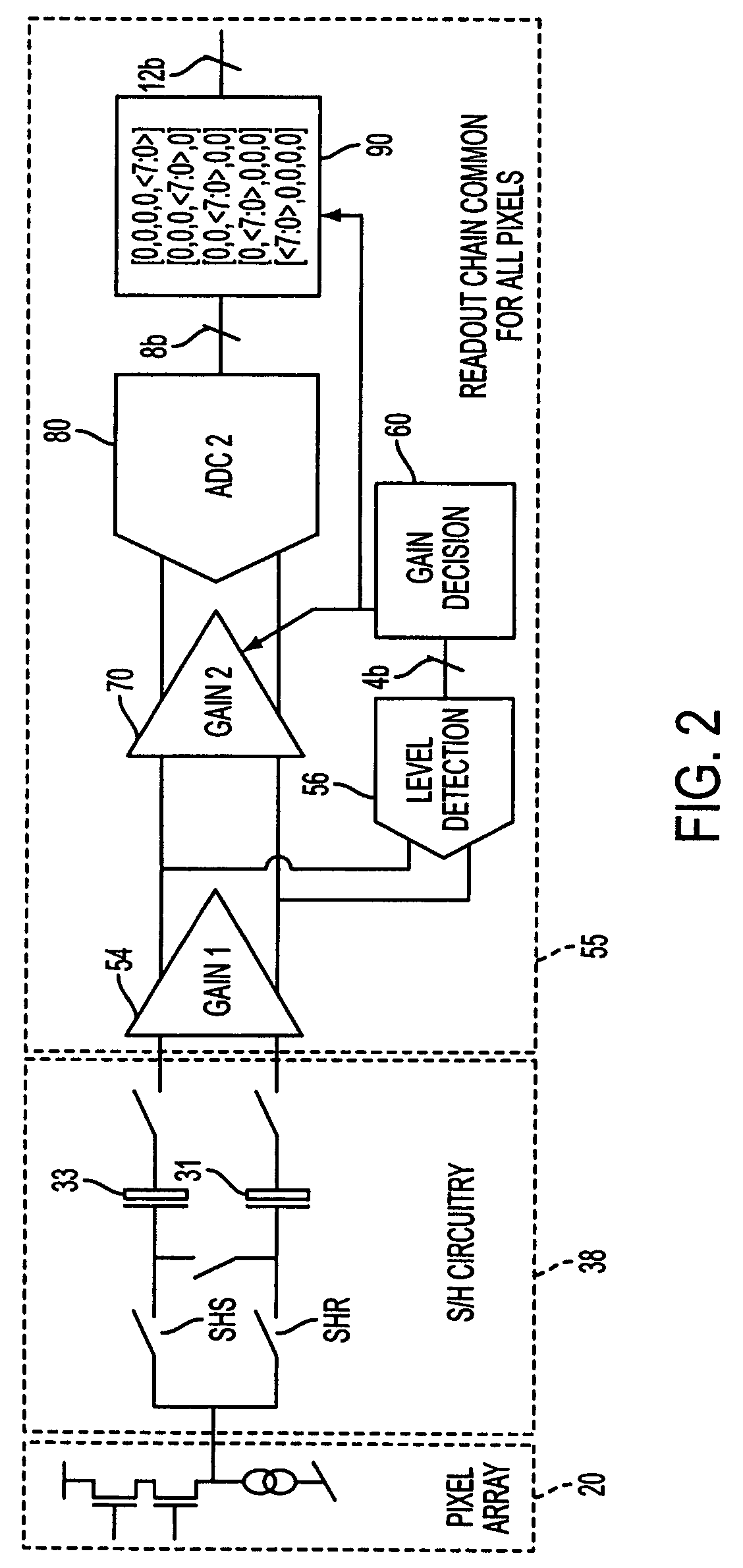
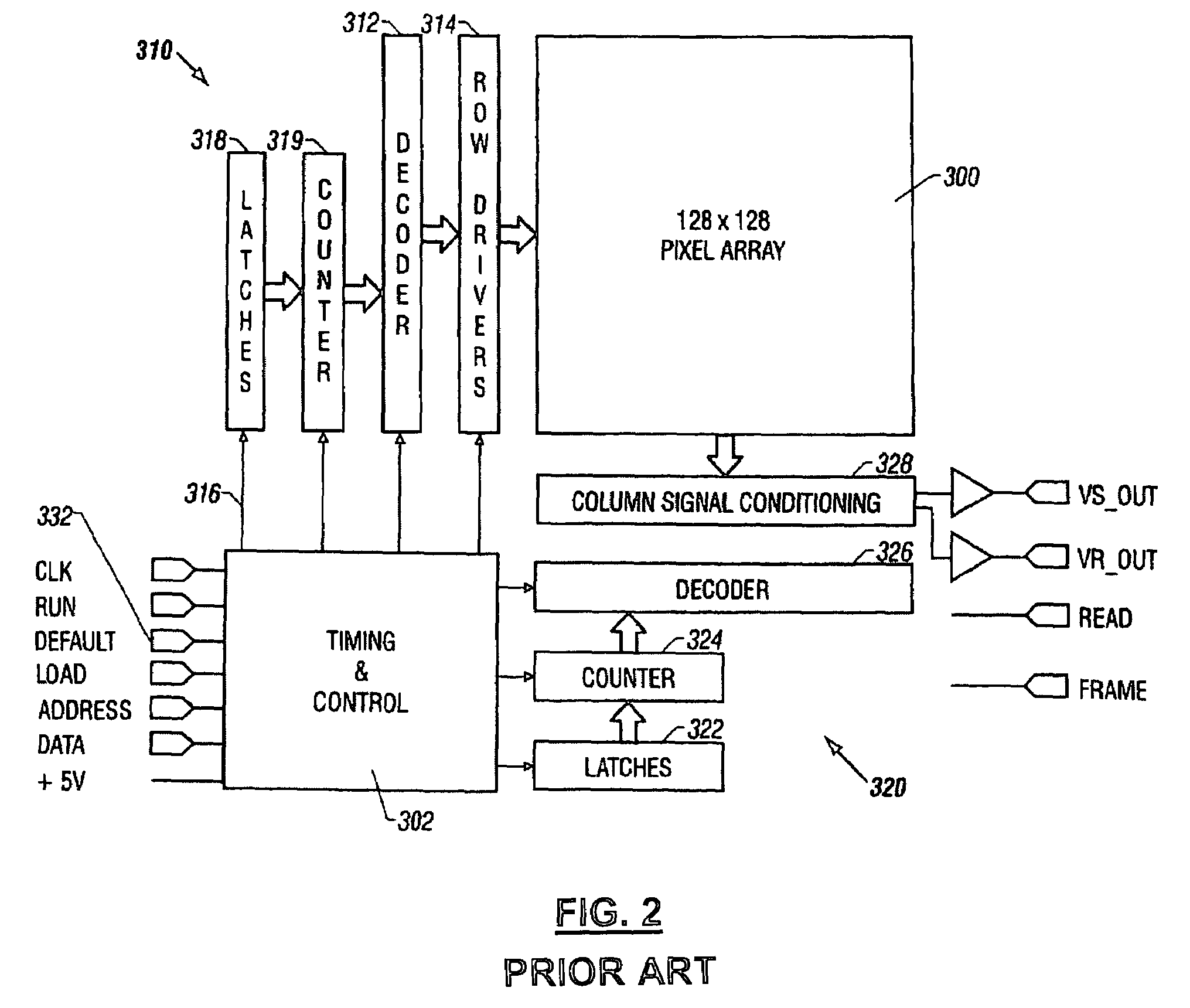
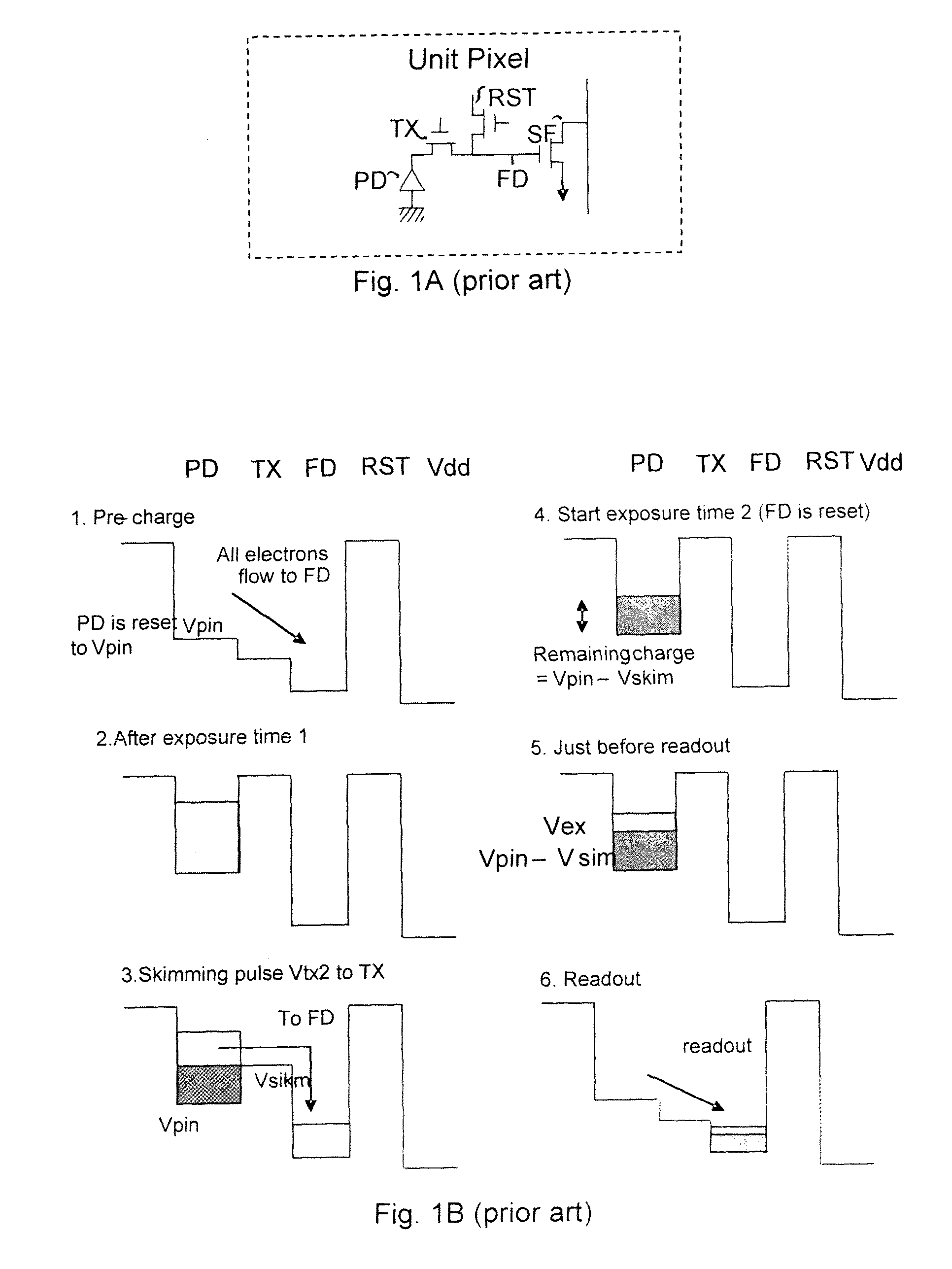
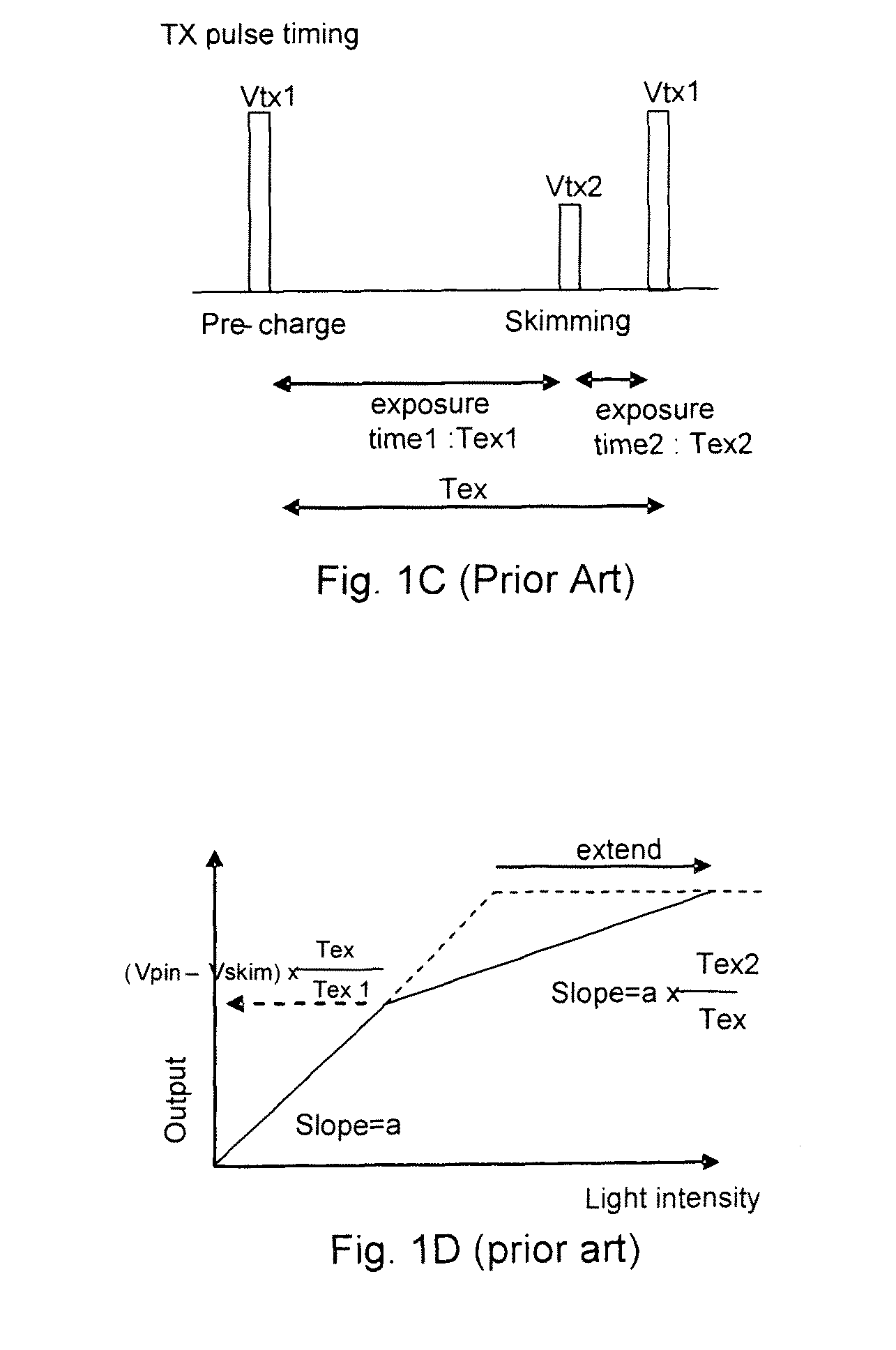
Readout technique for increasing or maintaining dynamic range in image sensors
ActiveUS20060214085A1Extended imaging rangeReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system detailsNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
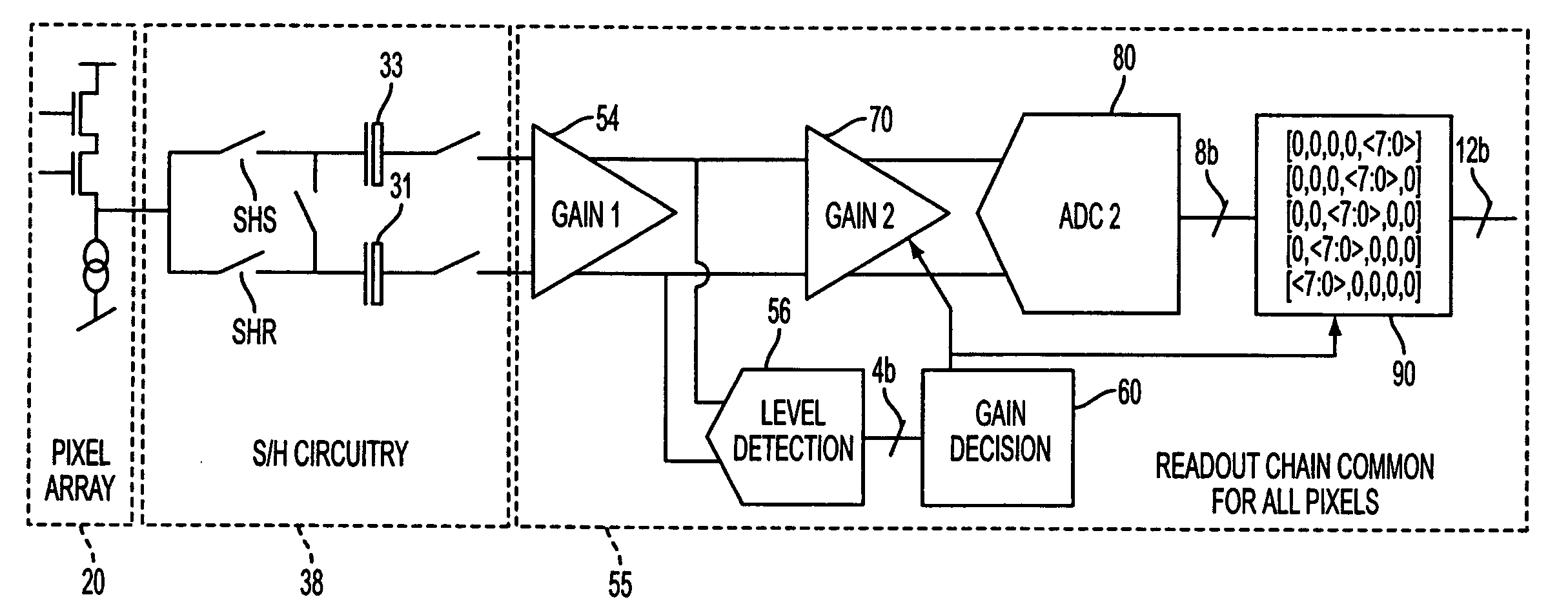
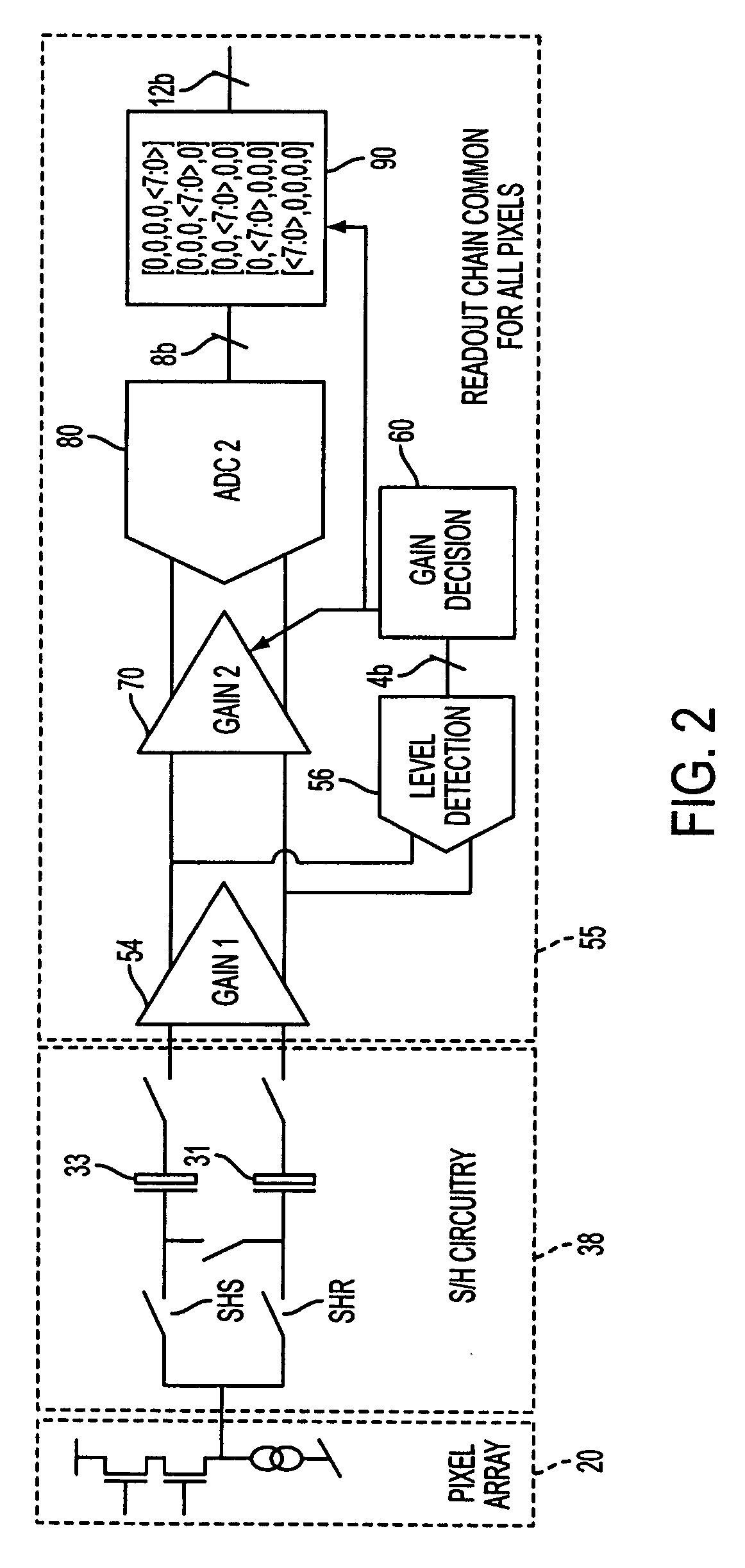
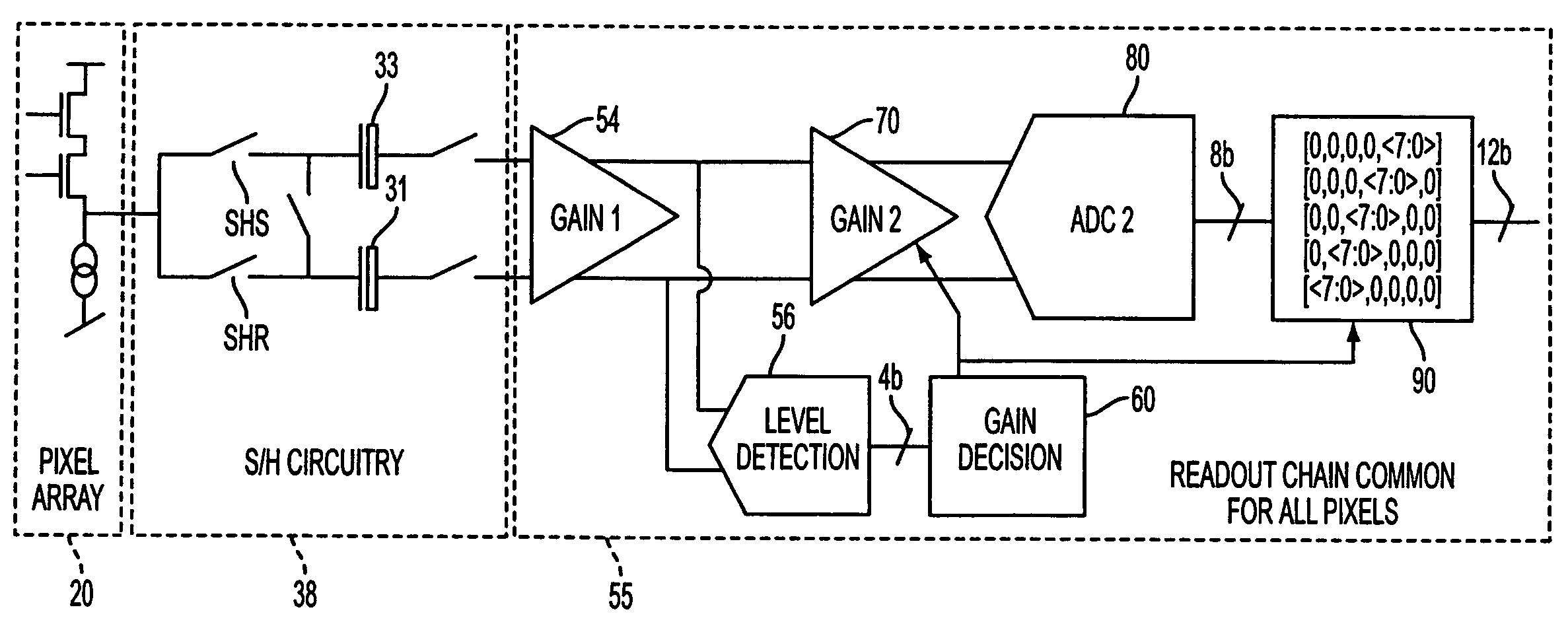
The apparatus and method provide a readout technique and circuit for increasing or maintaining dynamic range of an image sensor. The readout technique and circuit process each pixel individually based on the magnitude of the readout signal. The circuit includes a gain amplifier amplifying the readout analog signal, a level detection circuit for determining the signal's magnitude, a second gain amplifier applying a gain based on the signal magnitude and an analog-to-digital converter digitizing the signal and a circuit for multiplying or dividing the signal. The method and circuit allow for a lower signal-to-noise ratio while increasing the dynamic range of the imager.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
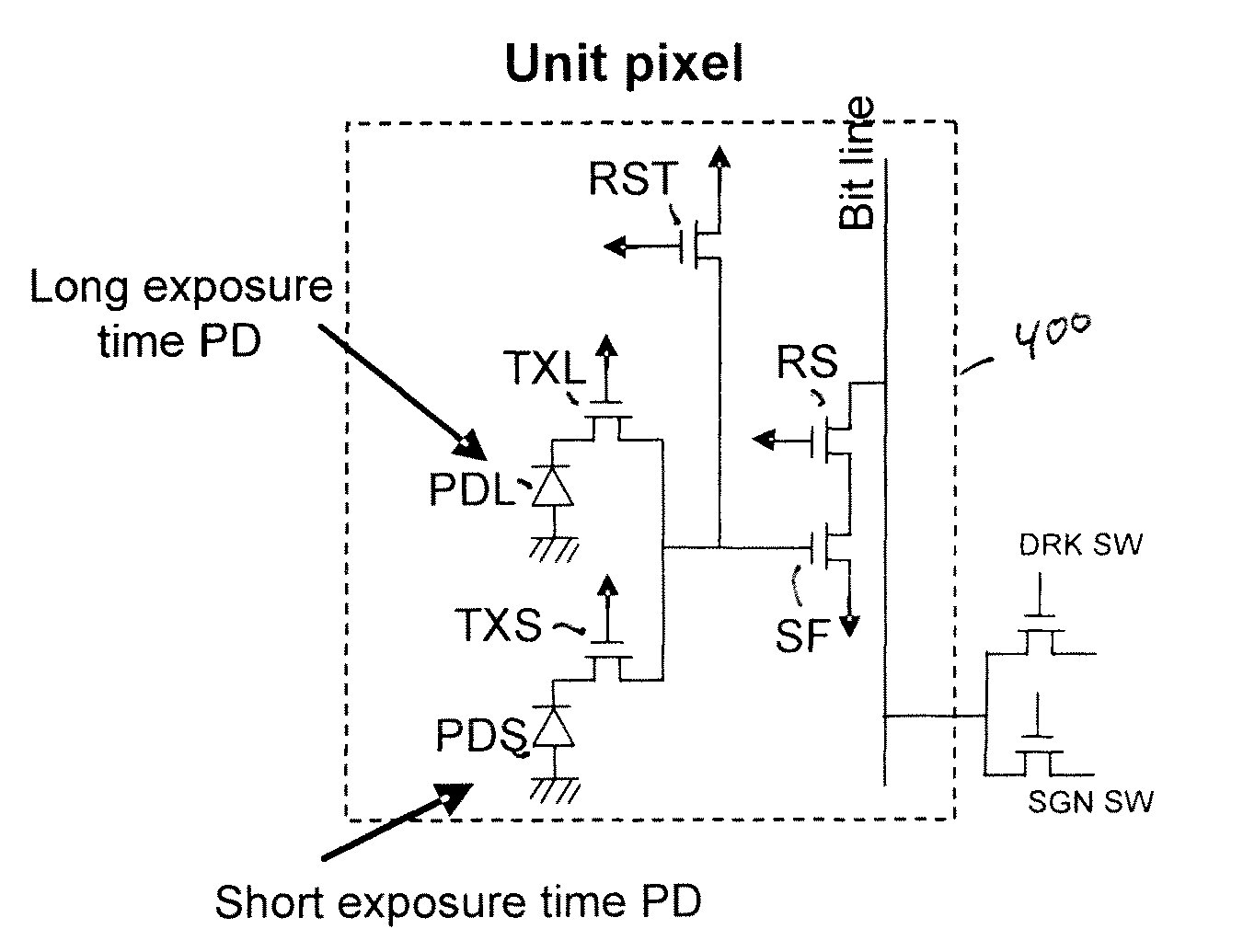
High dynamic range sensor with blooming drain
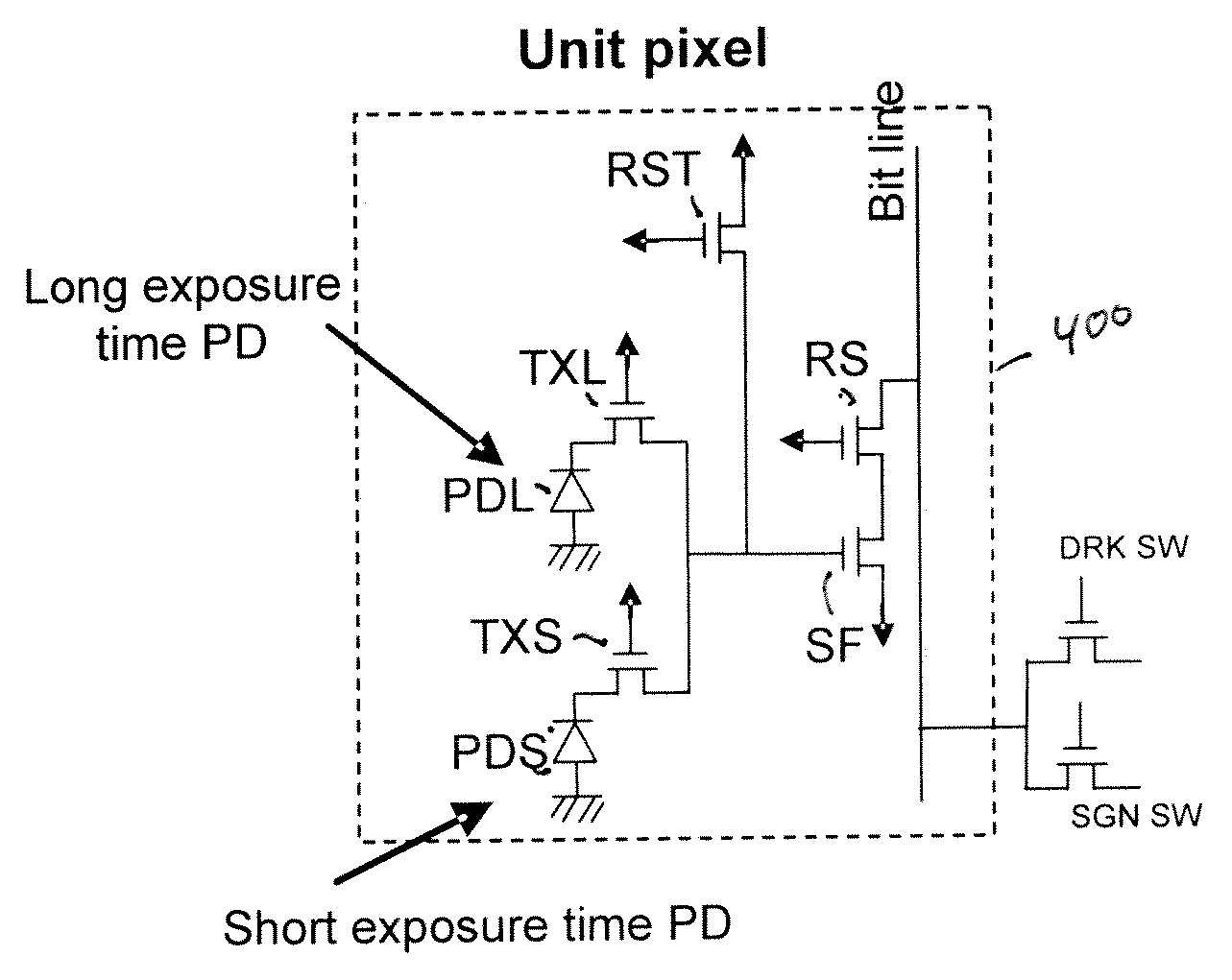
ActiveUS20090002528A1High sensitivityExtended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsEngineeringPhotodiode
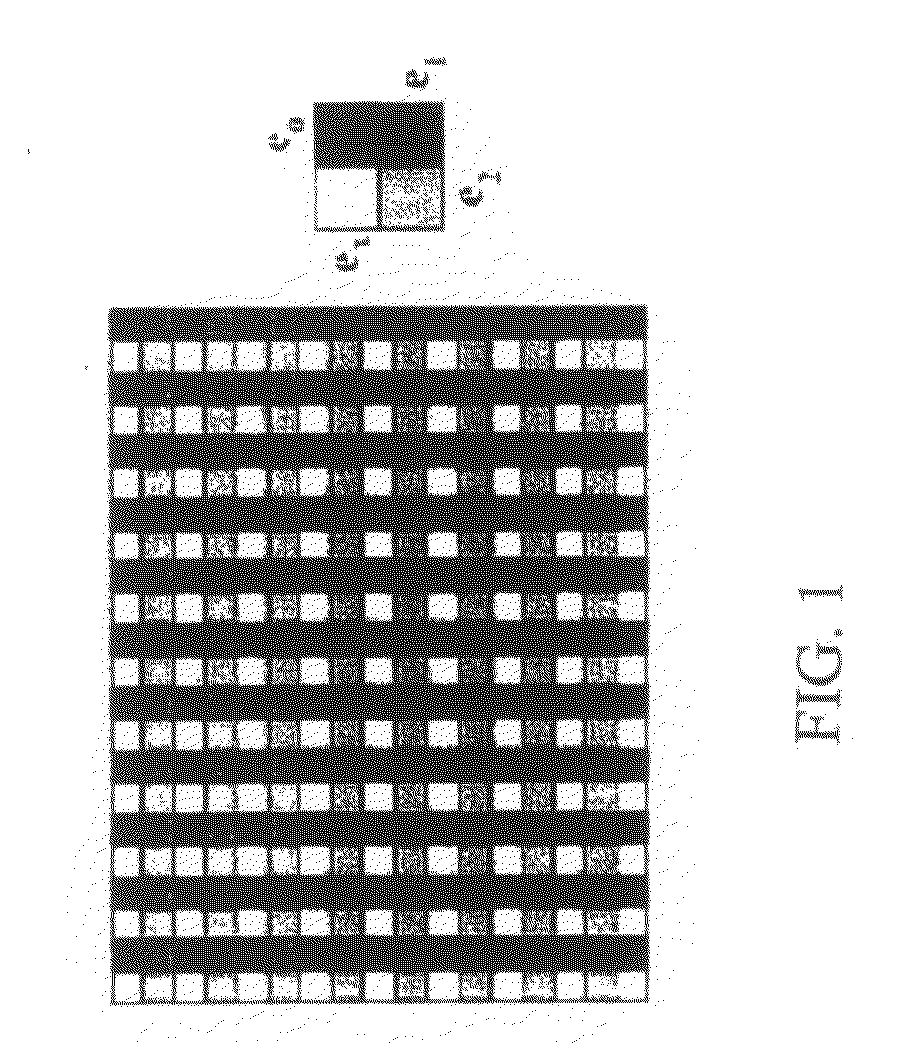
An image sensor has at least two photodiodes in each unit pixel. A high dynamic range is achieved by selecting different exposure times for the photodiodes. Additionally, blooming is reduced. The readout timing cycle is chosen so that the short exposure time photodiodes act as drains for excess charge overflowing from the long exposure time photodiodes. To improve draining of excess charge, the arrangement of photodiodes may be further selected so that long exposure time photodiodes are neighbored along vertical and horizontal directions by short exposure time photodiodes. A micro-lens array may also be provided in which light is preferentially coupled to the long exposure time photodiodes to improve sensitivity.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Image sensor with wide dynamic range
ActiveUS20110063483A1Wide dynamic rangeKeep for a long timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsWide dynamic rangeSensor system
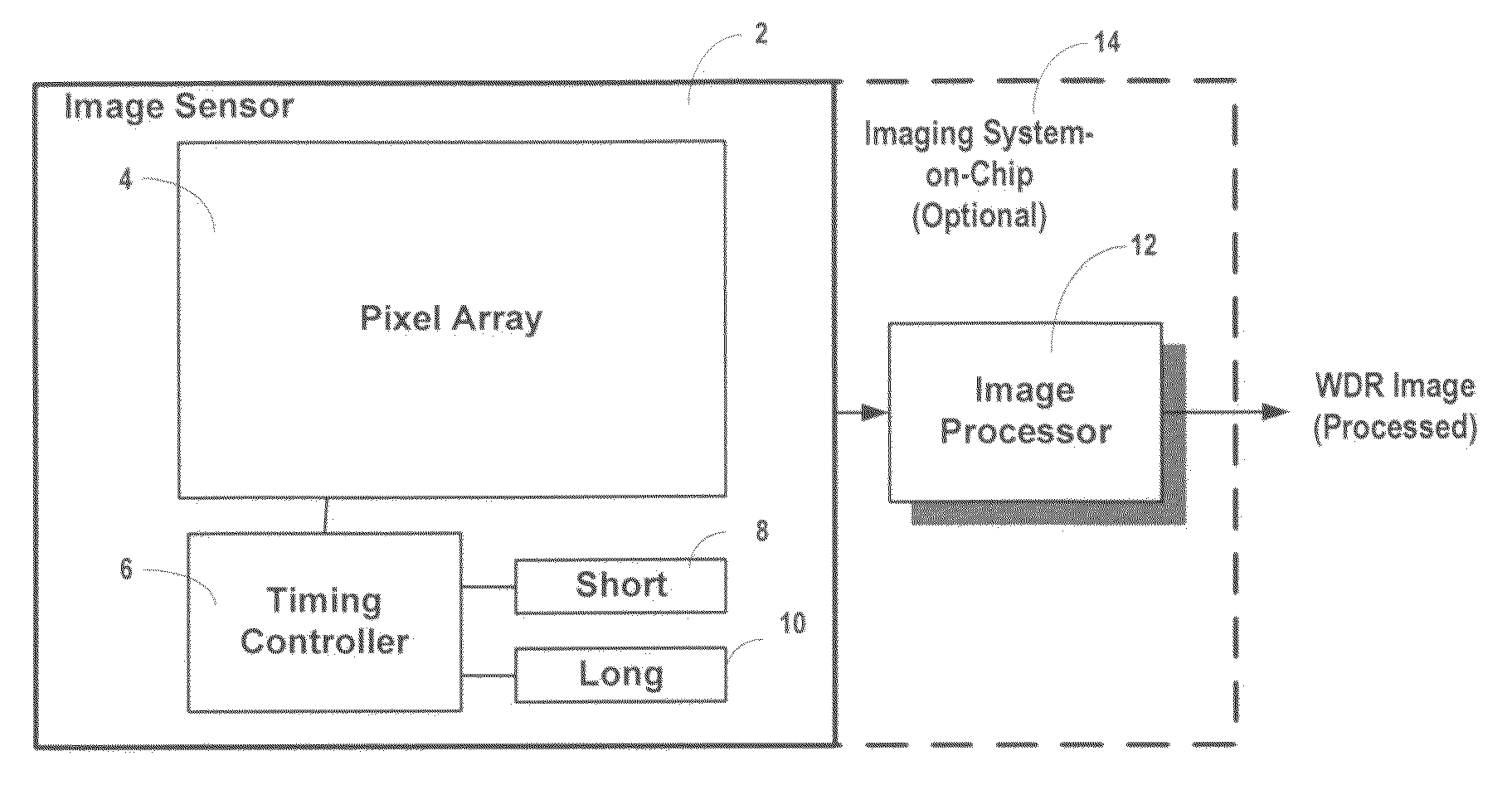
An image sensor, system and method that alternates sub-sets of pixels with long exposure times and pixels with short exposure times on the same sensor to provide a sensor having improved Wide Dynamic Range (WDR). The sub-sets of pixels are reset at different time intervals after being read, which causes the respective integration times to vary. By combining information contained in the both the short and long integration pixels, the dynamic range of the sensor is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of displaying a low dynamic range image in a high dynamic range
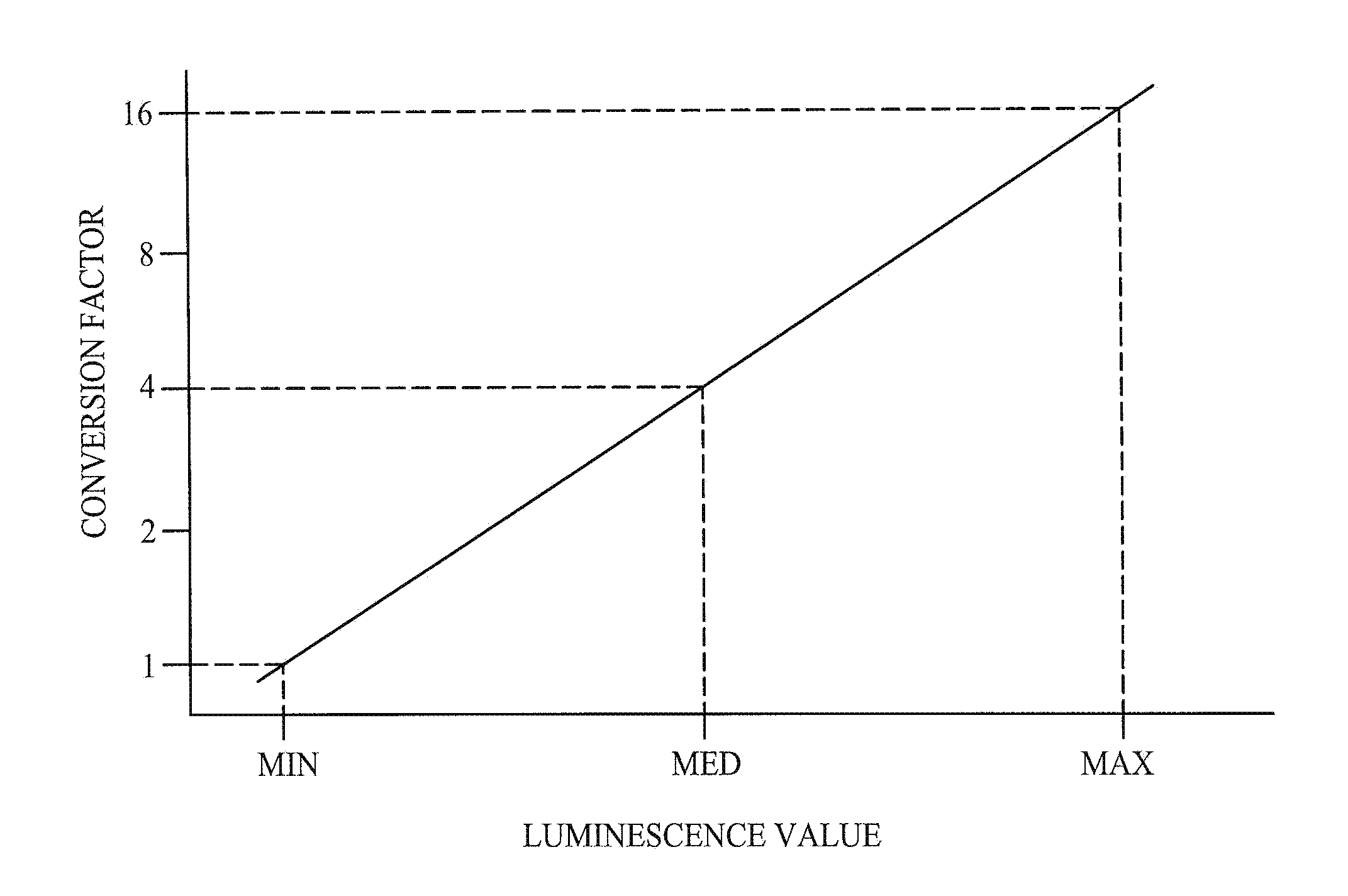
ActiveUS20080297460A1Extended imaging rangeImprove viewable contest and detailCathode-ray tube indicatorsConversion factorLightness
A method of increasing the dynamic range of an image comprising a plurality of pixels each having a luminance value within a first luminance dynamic range. The method includes determining a background luminance value for each pixel of the image and determining a minimum and a maximum of the background luminance values. A conversion factor is then determined for each pixel of the image based on the minimum and maximum of the background luminance values. The image id converted from the first luminance dynamic range to a second luminance dynamic range by multiplying the luminance value of each pixel of the image by its conversion factor.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Positioning and locating device for radiotherapy and positioning method of dynamic target region
ActiveCN104587609AFast cross imagingExpand the scope of useComputerised tomographsTomographyEngineeringX ray image
The invention discloses a positioning and locating device for radiotherapy and a positioning method of a dynamic target region. A therapy robot has an operating arm, wherein a compact linear electronic accelerator is arranged at one end of an operating arm of the therapy robot, and a secondary collimator is installed at one end of the compact linear electronic accelerator; a robot treatment table is arranged on a corresponding position of a double-image C-arm system, an C-arm sliding rail laser locator is arranged inside the double-image C-arm system, and a left side locator for an C-arm installation space is arranged on a corresponding position at the outer part of the double-image C-arm system. The positioning and locating device provided by the invention is provided with two groups of X-ray image systems, so as to realize binocular imaging; when the C-arm sliding rail rotates and a group of X-ray image systems is started, and CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) imaging can be realized; according to the positioning method, different imaging ways are adopted for a static target region and a dynamic target region, the rapidity and timeliness of the binocular imaging, the high quality, high definition and image registration of the CBCT imaging can be fully exerted.
Owner:RADIATION THERAPY MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Pixels for CMOS image sensors
InactiveUS20060261431A1Improve charge transfer efficiencyRaise the voltage differenceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl signalEngineering
A unit pixel of a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor includes a photoelectric conversion element, a transfer transistor, a boosting capacitor and a signal transfer circuit, where the photoelectric conversion element generates a charge based on incident light, the transfer transistor transfers the charge to a floating diffusion node in response to a transfer control signal, the boosting capacitor is disposed between a gate of the transfer transistor and the floating diffusion node, the signal transfer circuit transfers an electric potential of the floating diffusion node in response to a selection signal, and a dynamic range of the electric potential of the floating diffusion node may be widened and a drain-source voltage difference of the transfer transistor may be increased so that the charge transfer efficiency may be enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
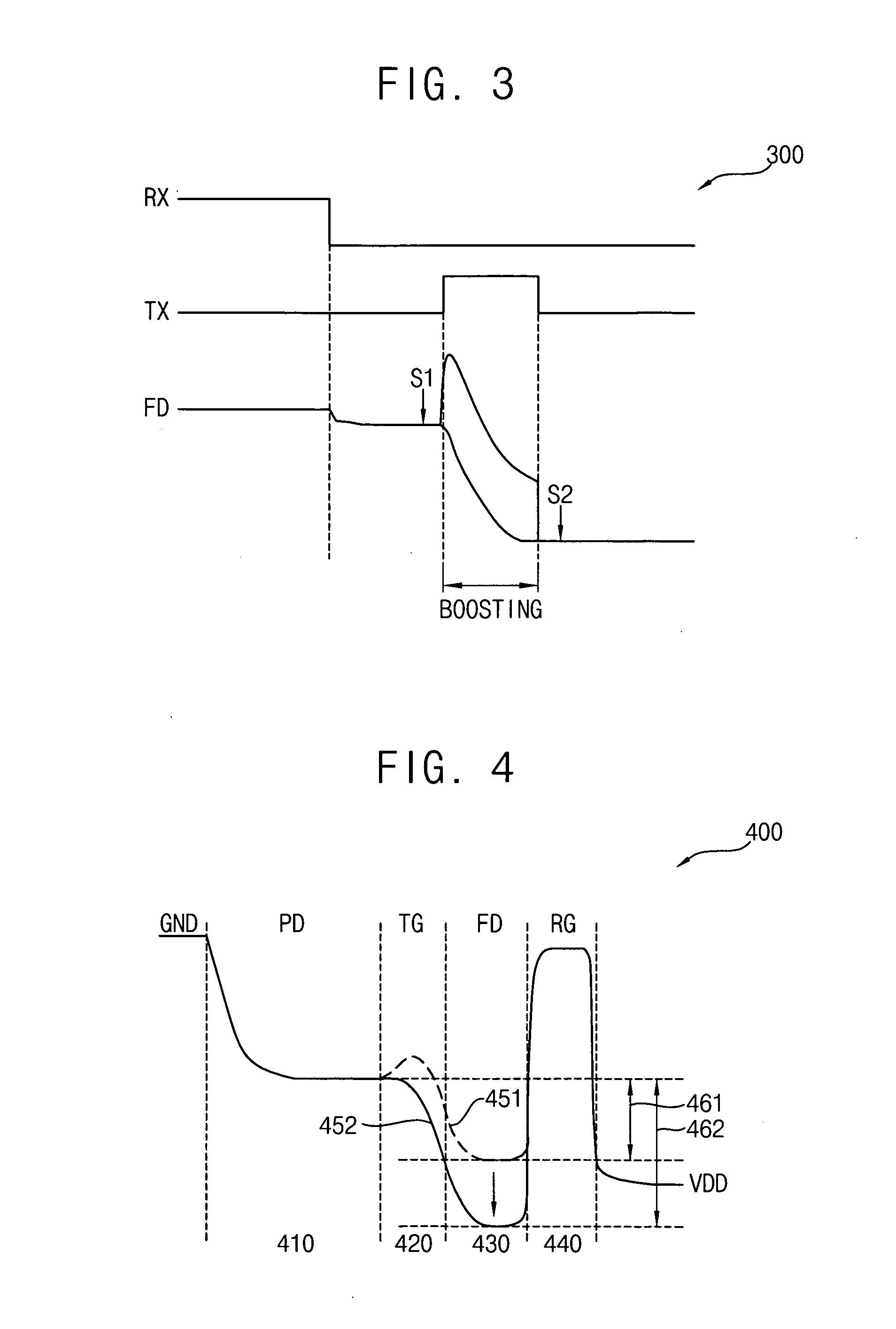
Method and apparatus for increasing dynamic range of image by using electronic shutter
InactiveUS20110050946A1Improve dynamic rangeExtended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectronic shutterElectron
A method for increasing a dynamic range of an image by using an electronic shutter of a camera, the method including initiating exposure of an image sensor by moving a mechanical front curtain included in the camera; moving an electronic front curtain with respect to at least one pixel of the image sensor according to a control pulse signal of the electronic shutter; and blocking the exposure of the image sensor by moving a mechanical rear curtain included in the camera.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for forming an image
InactiveUS6927793B1Extended imaging rangeImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer scienceWide dynamic range
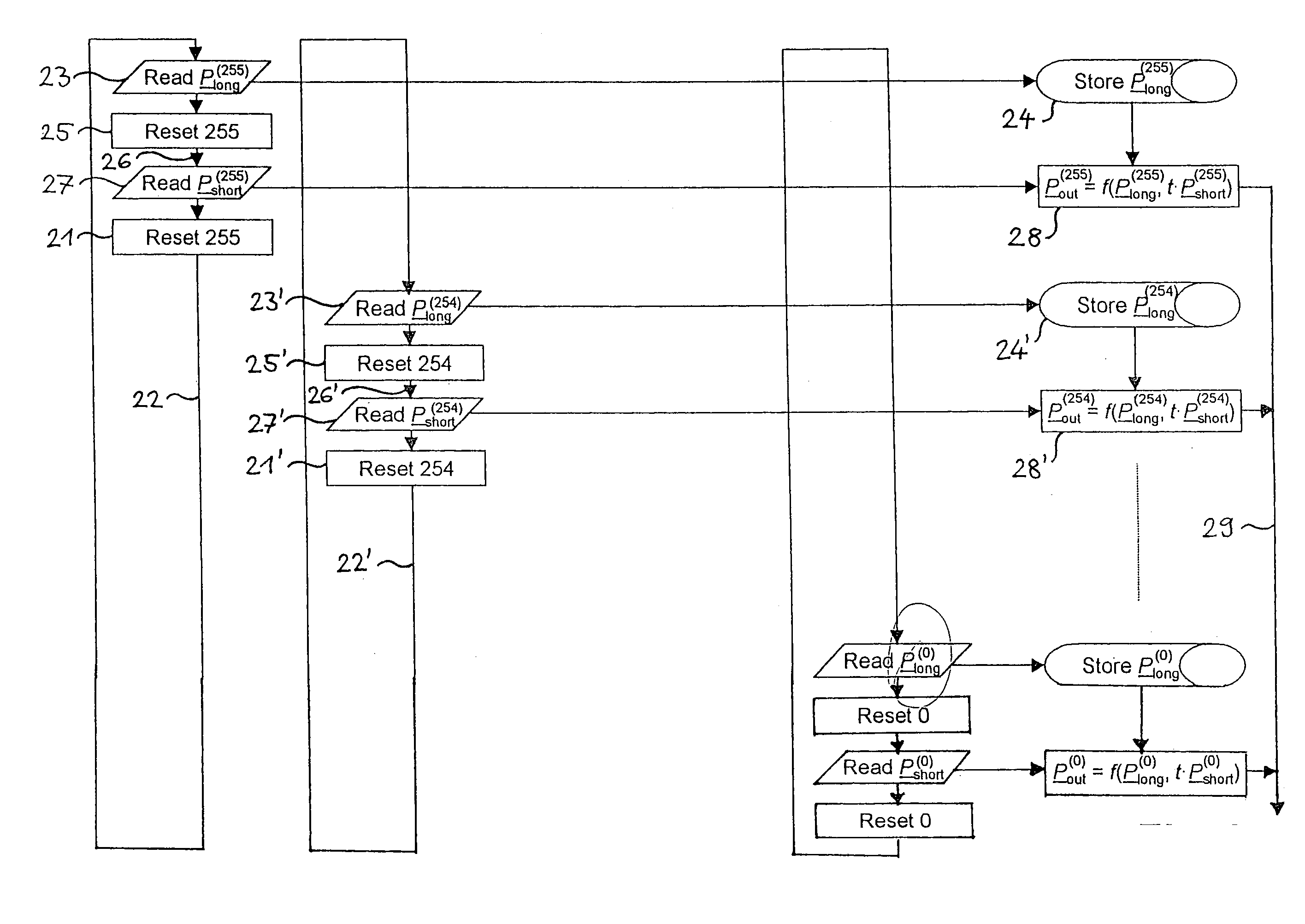
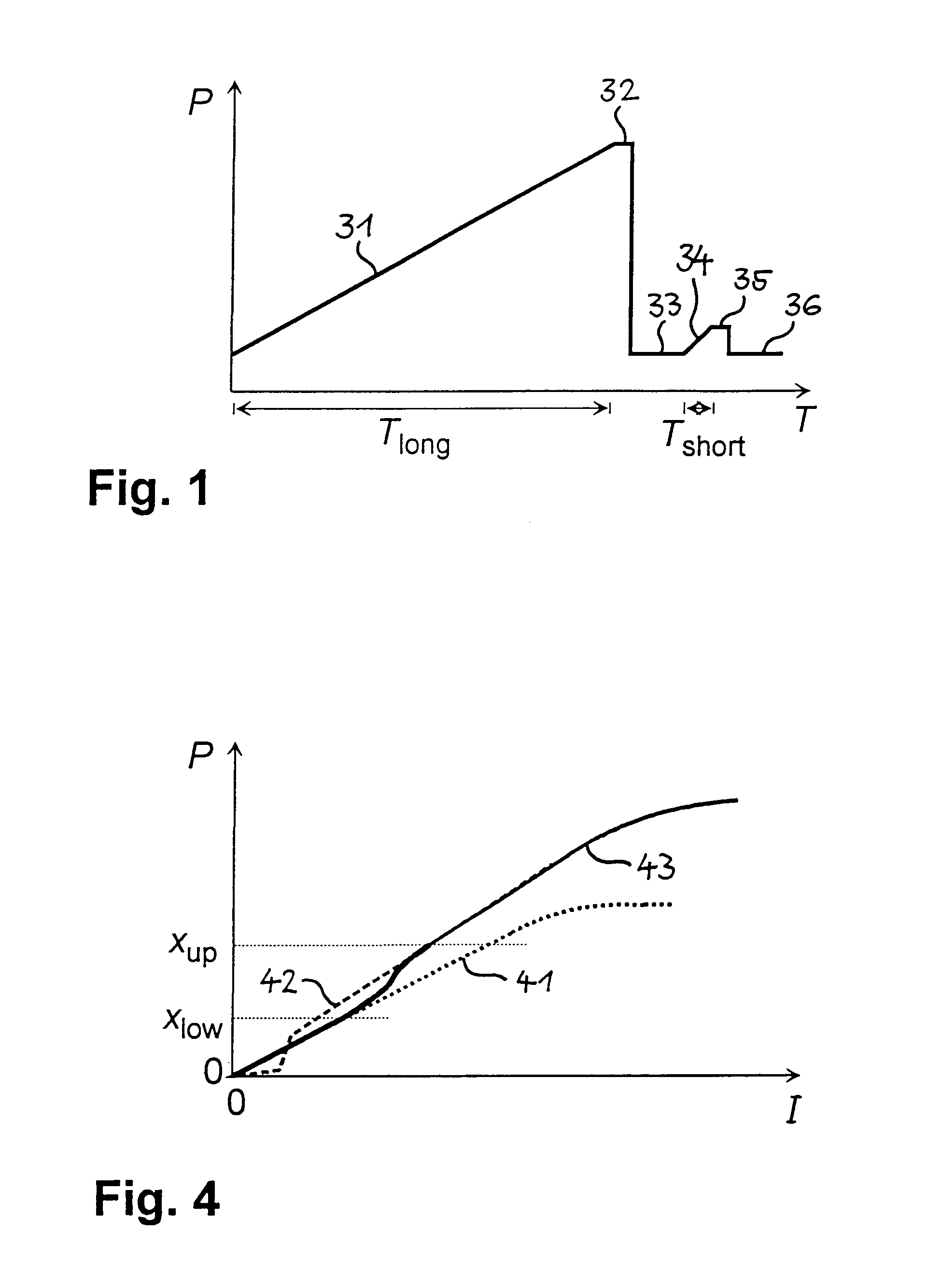
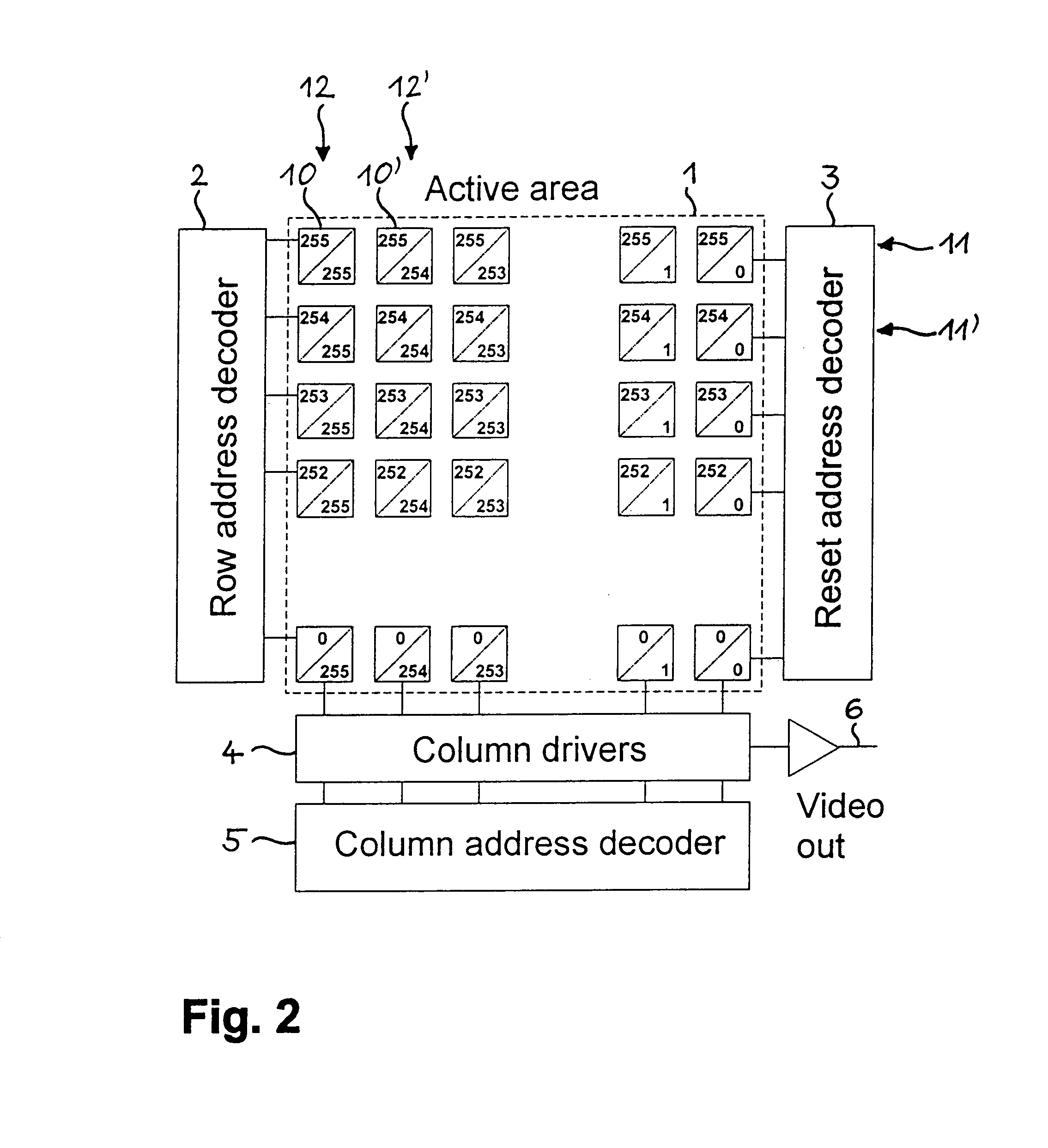
The method for forming an image with a wide dynamic range makes use of an image sensor containing subsets of pixels that can be individually reset. After an initial reset (21), a pixel or row of pixels is exposed (22) for a first time interval and the gray value(s) (Plong(255)) are read out (23) and stored (24). The pixel or row of pixels is then reset (25) and exposed (26) for a second, shorter time interval. The second gray value(s) (Pshort(255)) is / are read out (27) and either stored or immediately combined (28) with the first gray value(s) (Plong(255)) by means of a merging function (ƒ). The merging function (ƒ) ensures a monotonic, smooth change in output from the lowest to the highest gray values. The procedure is repeated for all pixels or rows of pixels in the image sensor, thus obviating the need for the storage of complete images. The method reduces temporal aliasing to a minimum and eliminates spatial aliasing.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Image sensor with wide dynamic range
ActiveUS8605177B2Keep for a long timeTime can be short and longTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsWide dynamic rangeShort exposure
An image sensor, system and method that alternates sub-sets of pixels with long exposure times and pixels with short exposure times on the same sensor to provide a sensor having improved Wide Dynamic Range (WDR). The sub-sets of pixels are reset at different time intervals after being read, which causes the respective integration times to vary. By combining information contained in the both the short and long integration pixels, the dynamic range of the sensor is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
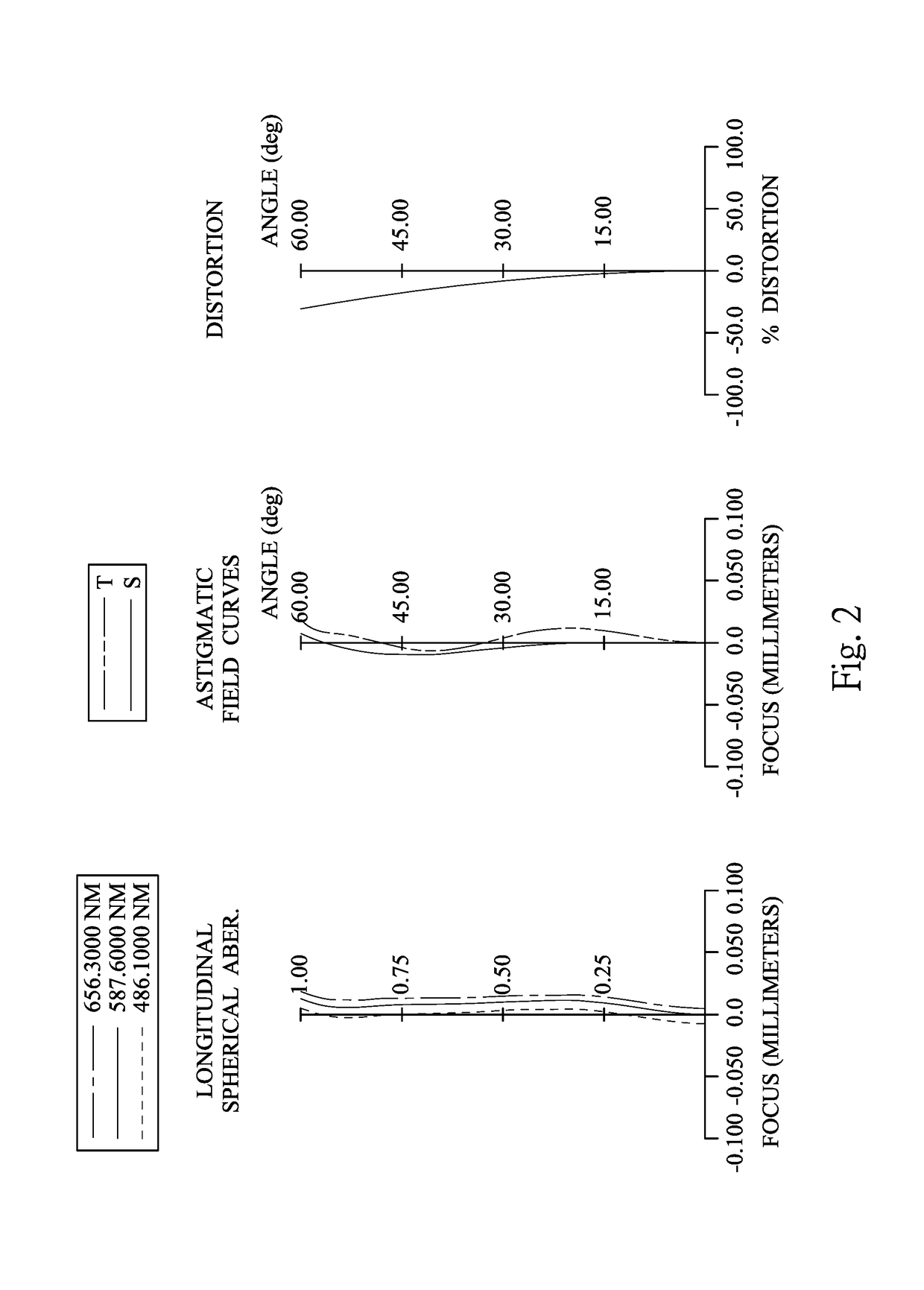
Optical imaging lens assembly, image capturing apparatus and electronic device
An optical imaging lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element, a fifth lens element, a sixth lens element and a seventh lens element. The first lens element has negative refractive power. The second lens element has negative refractive power. The third lens element has positive refractive power. The fourth lens element has positive refractive power. The fifth lens element has negative refractive power. The seventh lens element has an object-side surface and an image-side surface being both aspheric, wherein at least one of the object-side surface and the image-side surface of the seventh lens element includes at least one inflection point.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Constructing three-dimensional model apparatus
InactiveUS8442303B2Extended imaging rangeHigh accurate three-dimensionalImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingDimensional modeling
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
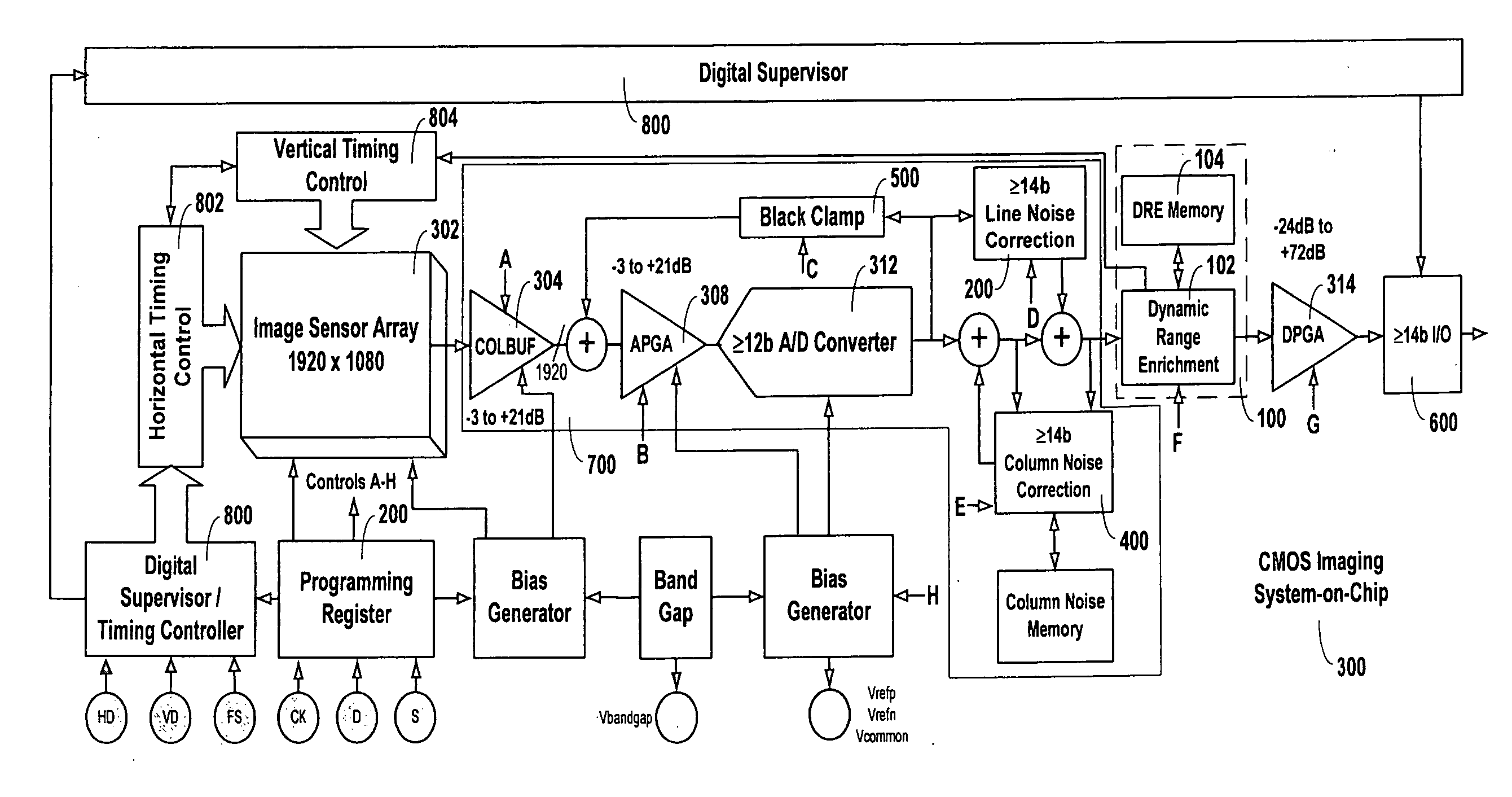
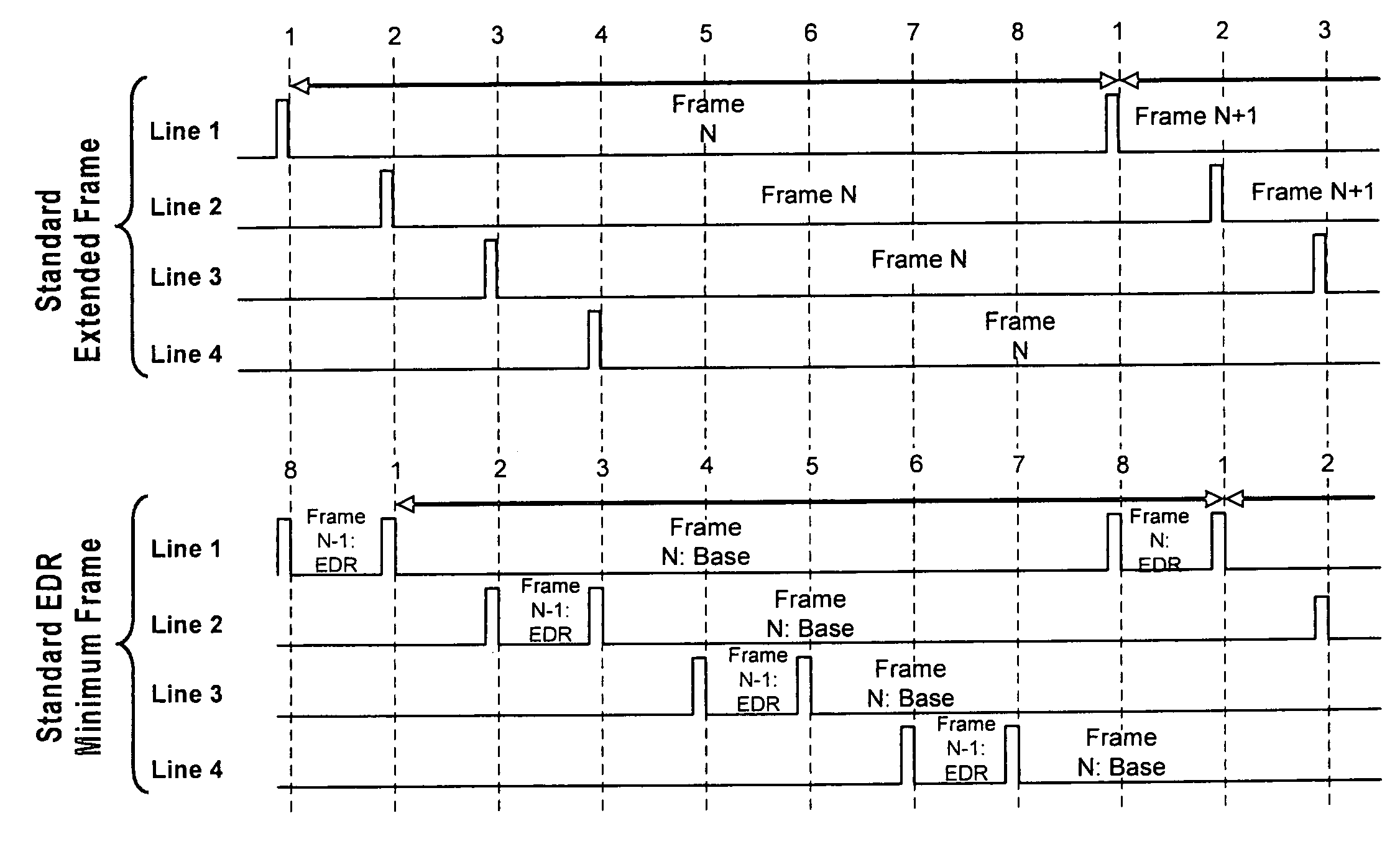
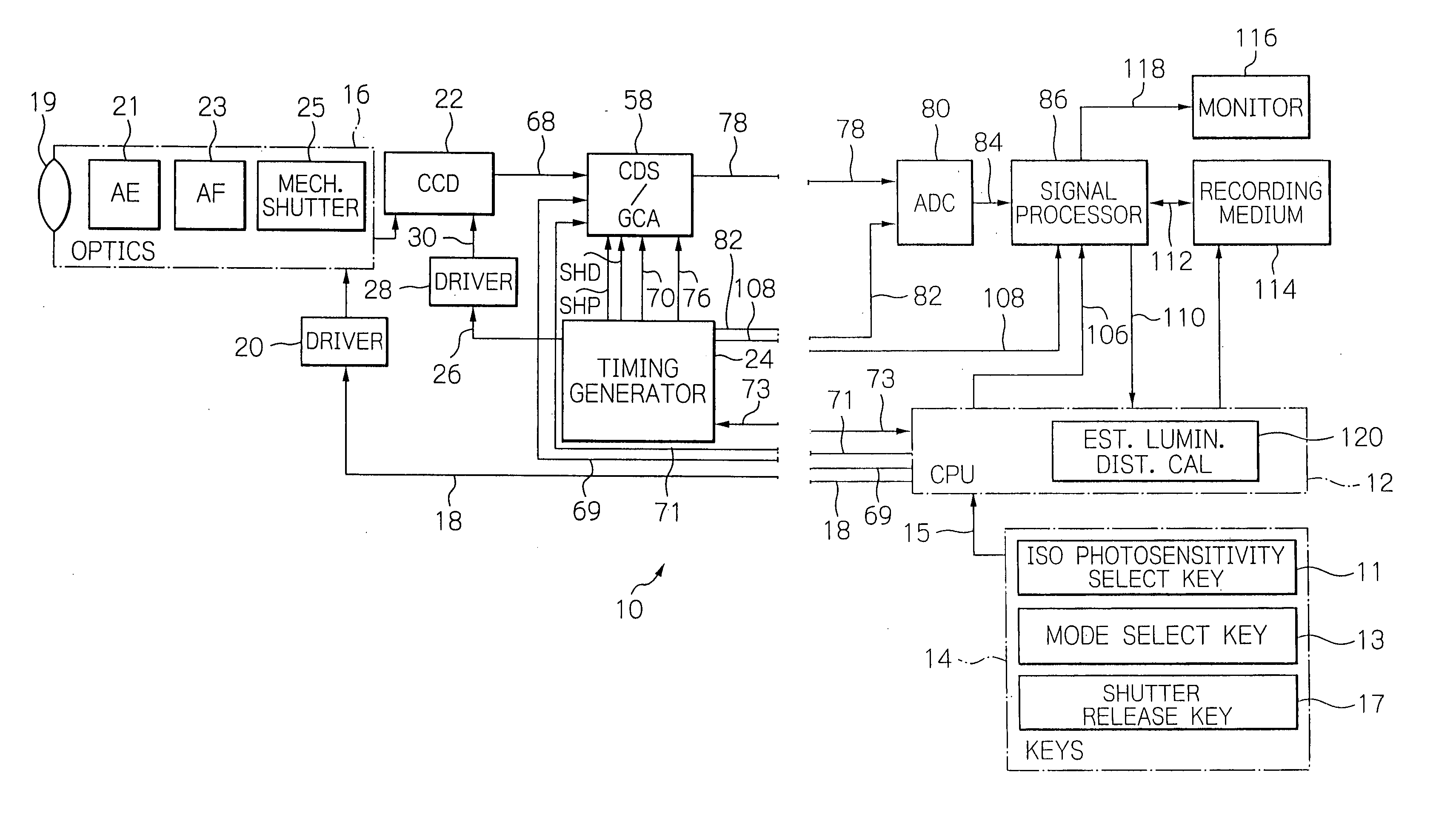
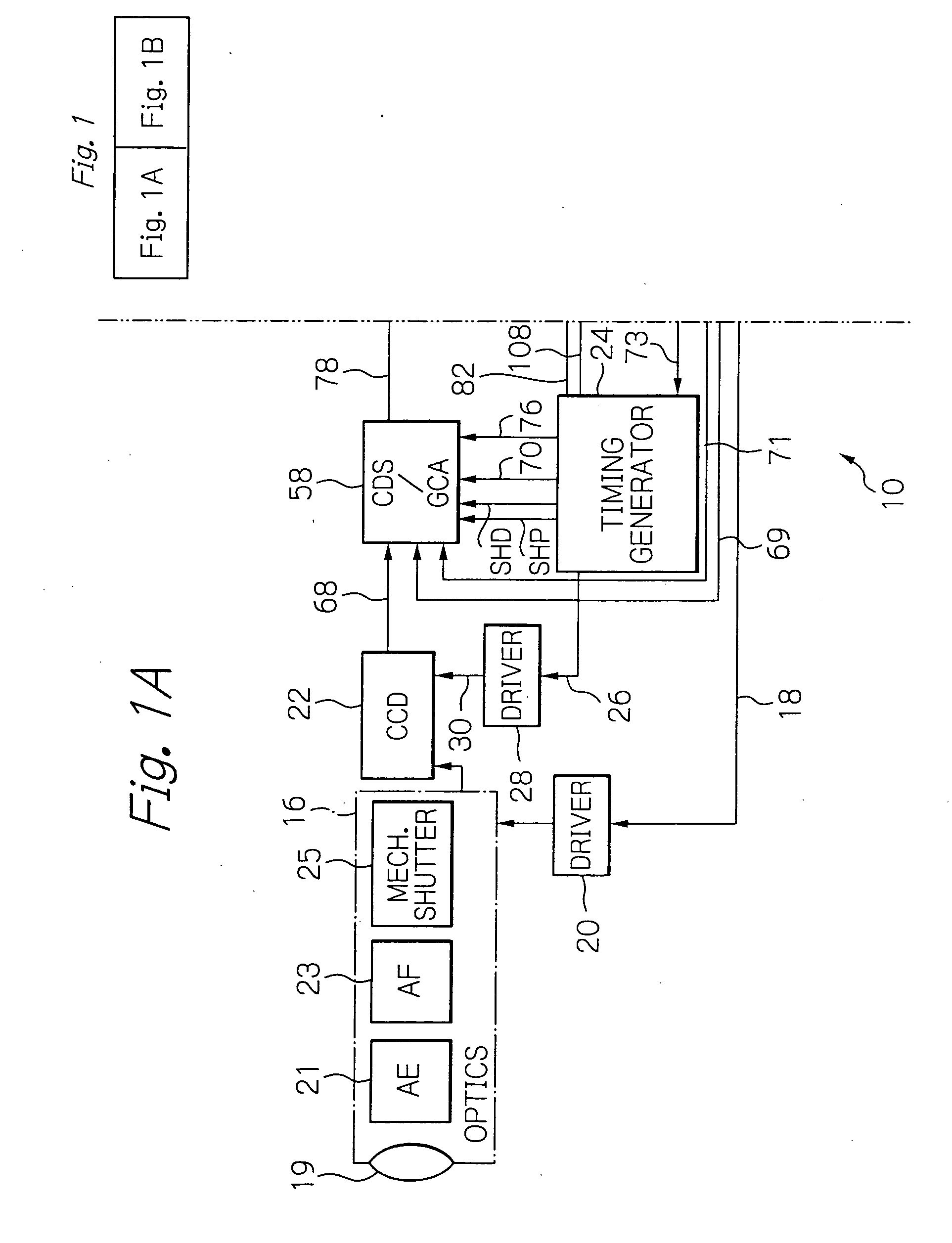
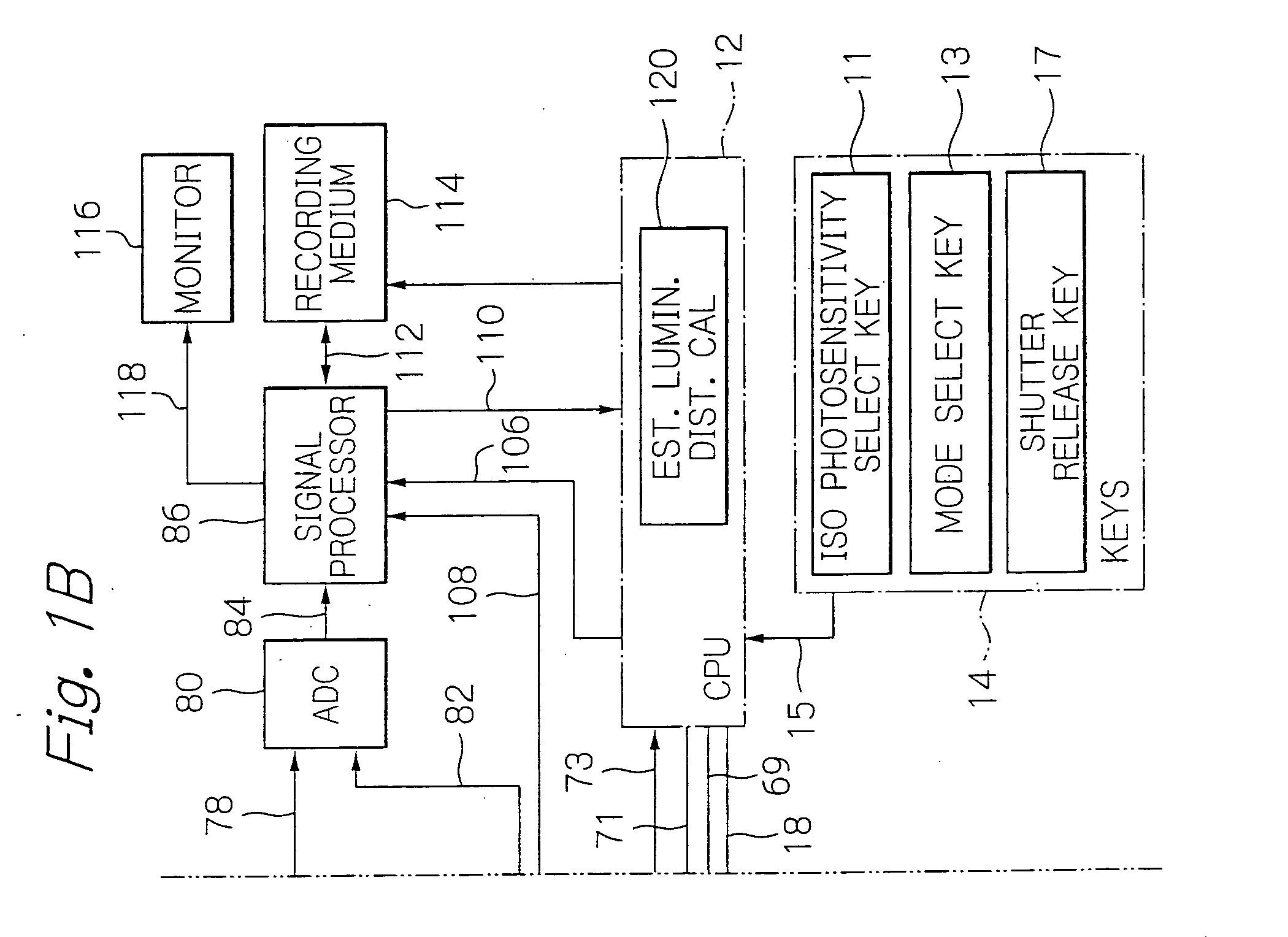
Method and apparatus for improving and controlling dynamic range in an image sensor
ActiveUS20080218602A1Good curative effectImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl signalA d converter
A method and apparatus for an electronic image sensor having a base exposure, followed by a second or multiple exposures that are formed during signal readout. A timing controller controls the signal readout, such that as each line is read, the second and subsequent exposures are subsequently added to the base exposure to enrich the dynamic range. The image sensor may further include an analog-to-digital converter and noise suppression to further enhance the efficacy of the dynamic range enrichment. The system may also include additional signal processing and scaling functions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
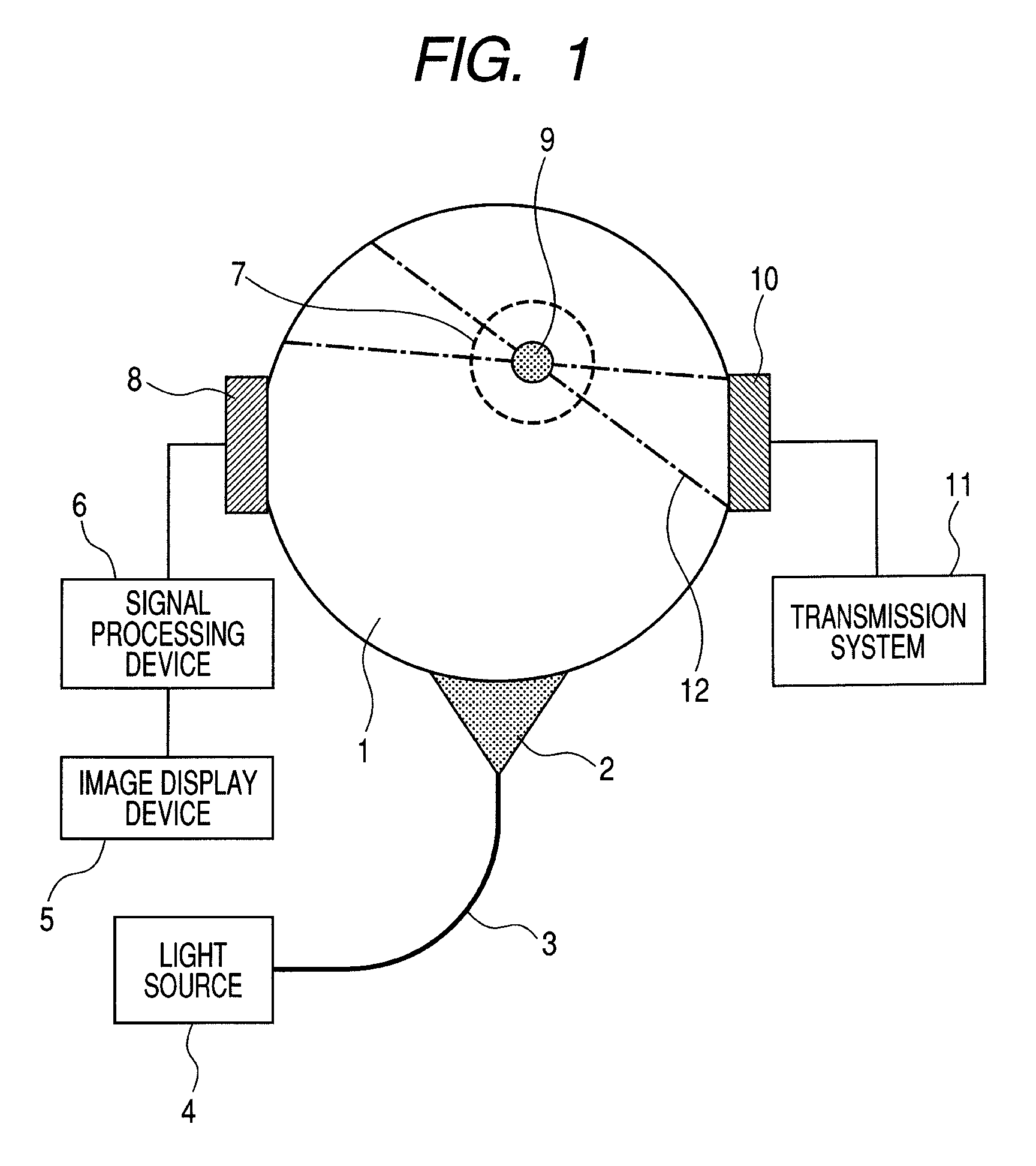
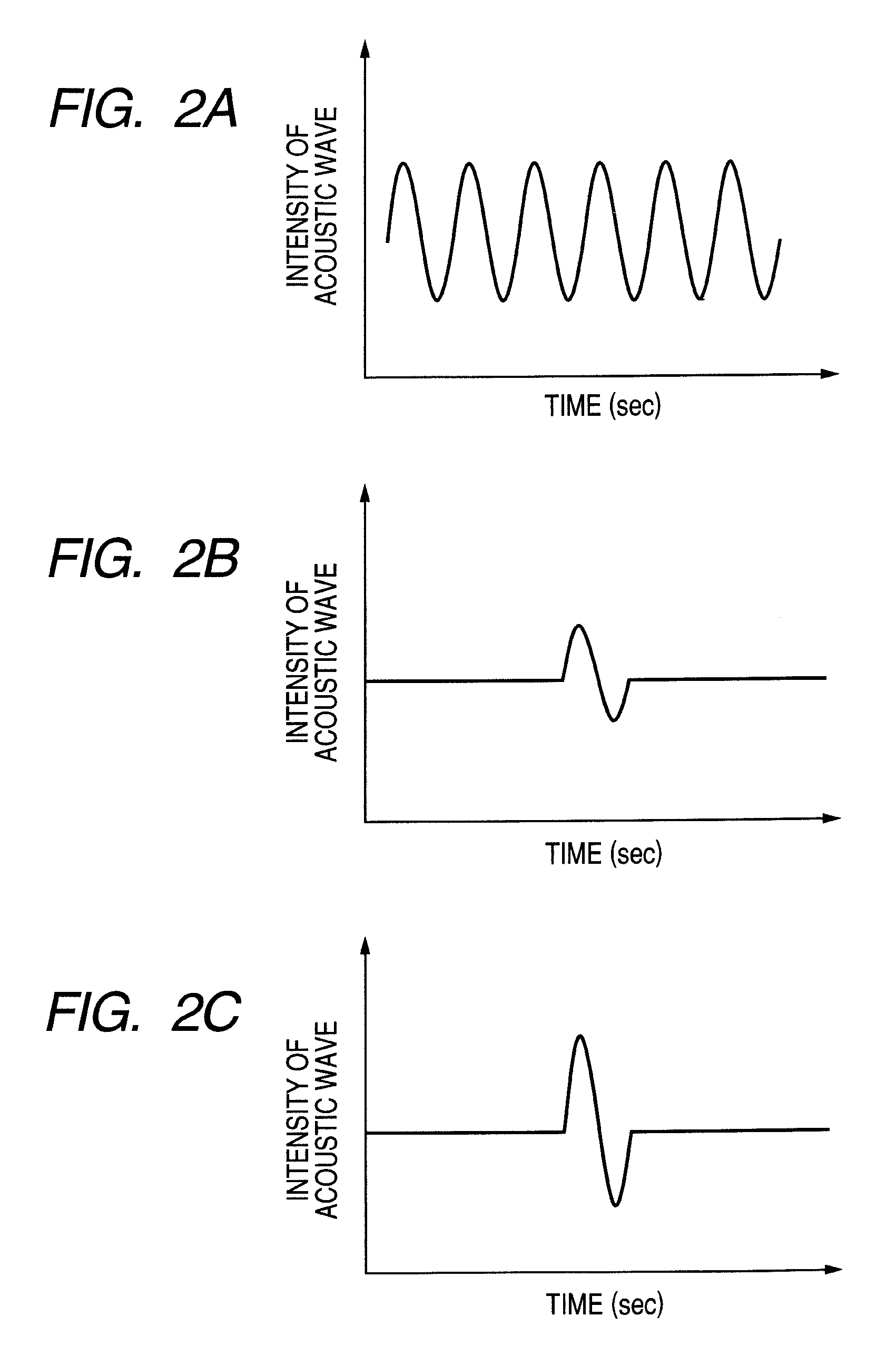
Biological information imaging apparatus and method for analyzing biological information
InactiveUS9131851B2High sensitivityExtended imaging rangeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionLiving bodyLight source
There are provided a biological information imaging apparatus that can measure ultrasound generated from an optical absorber in a deep part of a subject living body with high sensitivity, and a method for analyzing biological information using the biological information imaging apparatus. The biological information imaging apparatus that detects ultrasound and images biological information, includes: a light source that irradiates the subject with light for generating ultrasound from an optical absorber existing in the subject; an ultrasound transmission unit that transmits focused ultrasound to a specific region where the optical absorber exists; and an ultrasound detection unit that detects an ultrasound synthesized signal due to interaction between ultrasound generated from the optical absorber that absorbs the light and the focused ultrasound transmitted to the specific region.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for imaging an object
InactiveUS20150116538A1Enlarge dynamic rangeExtended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage sensorMatrix Array
An apparatus for imaging an object has an image sensor that comprises a plurality of pixels. The plurality of pixels is matrix-arrayed along vertical and horizontal directions. The apparatus also has an image sensor driver that drives the image sensor, and the image sensor driver is capable of reading image-pixel signals of neighboring pixels among the plurality of pixels while mixing the image-pixel signals. The apparatus also has a pixel addition setting processor that sets the number of pixel addition with respect to at least one of at least one row and at least one column. The pixel addition setting processor sets different numbers of pixel addition to different pixel areas. The image sensor driver reads the image-pixel signals in response to the set number of pixel addition.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
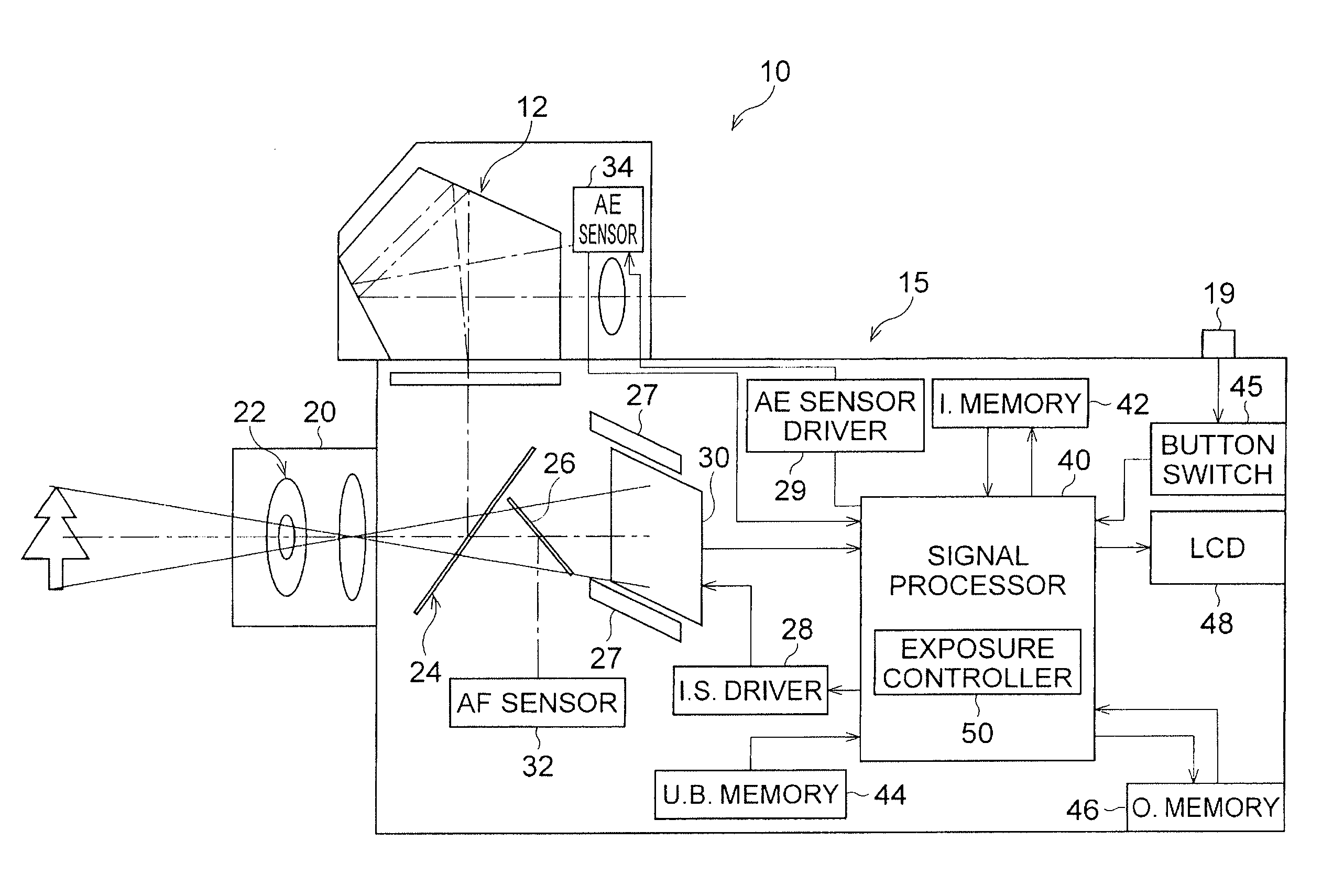
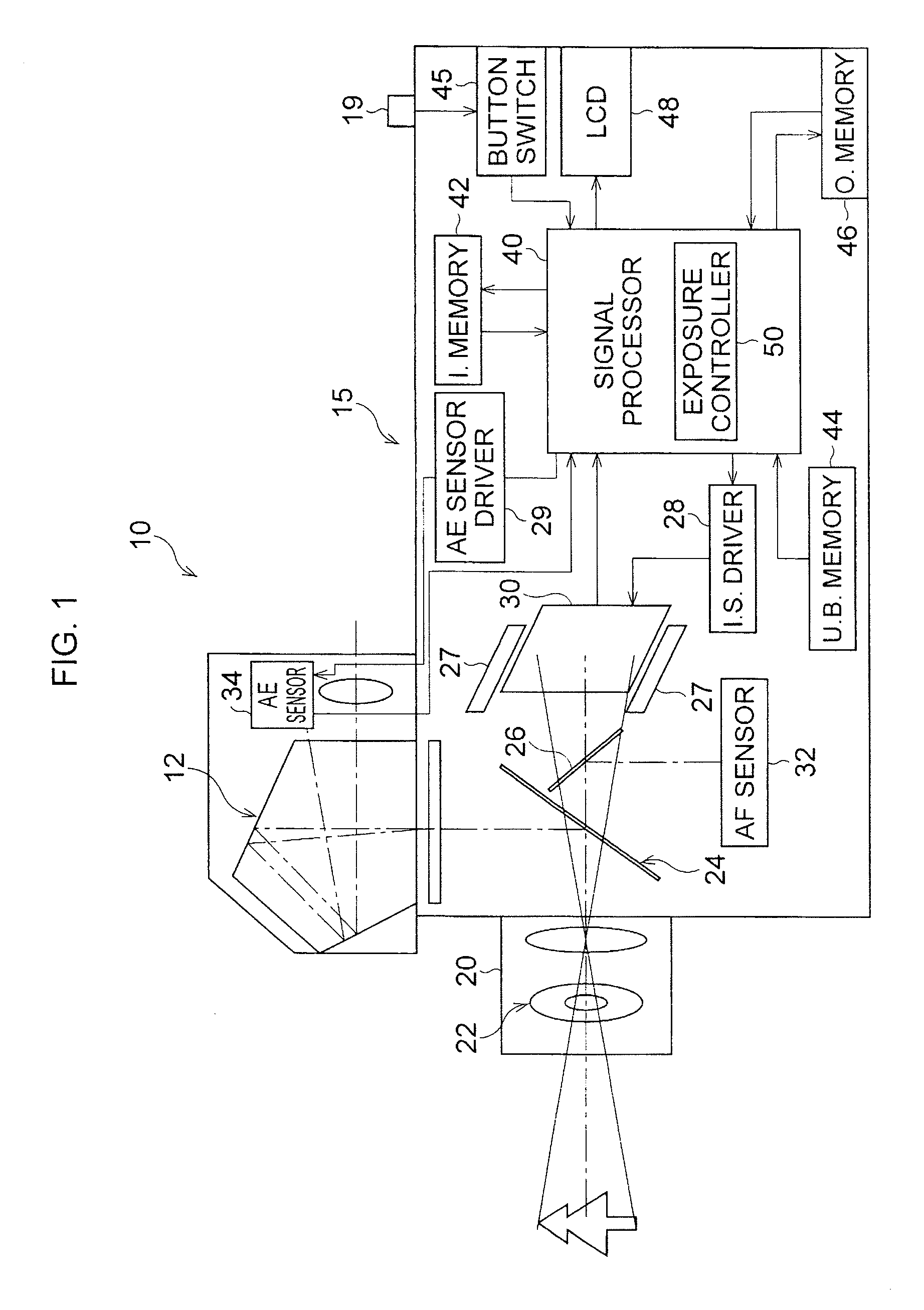
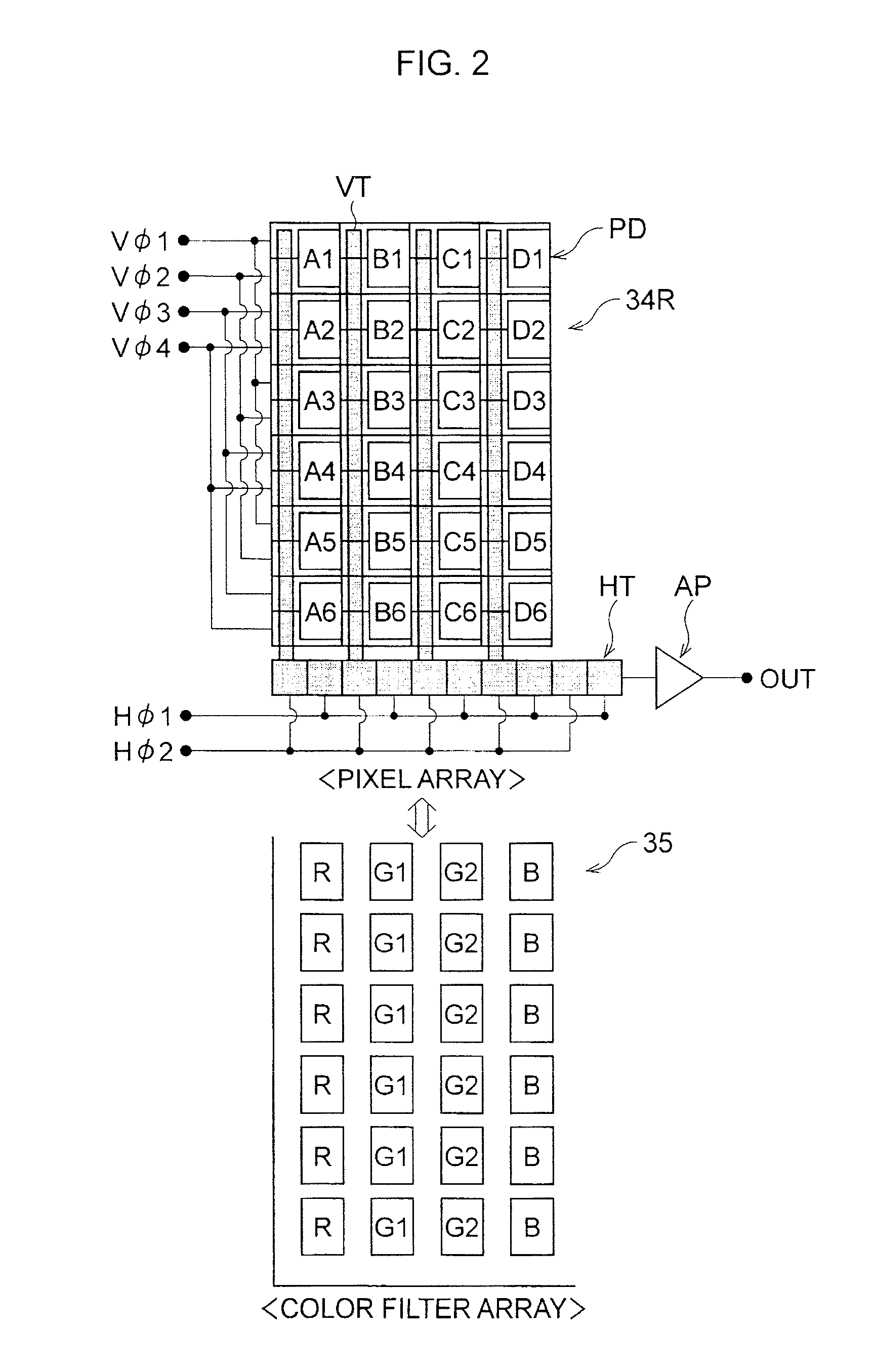
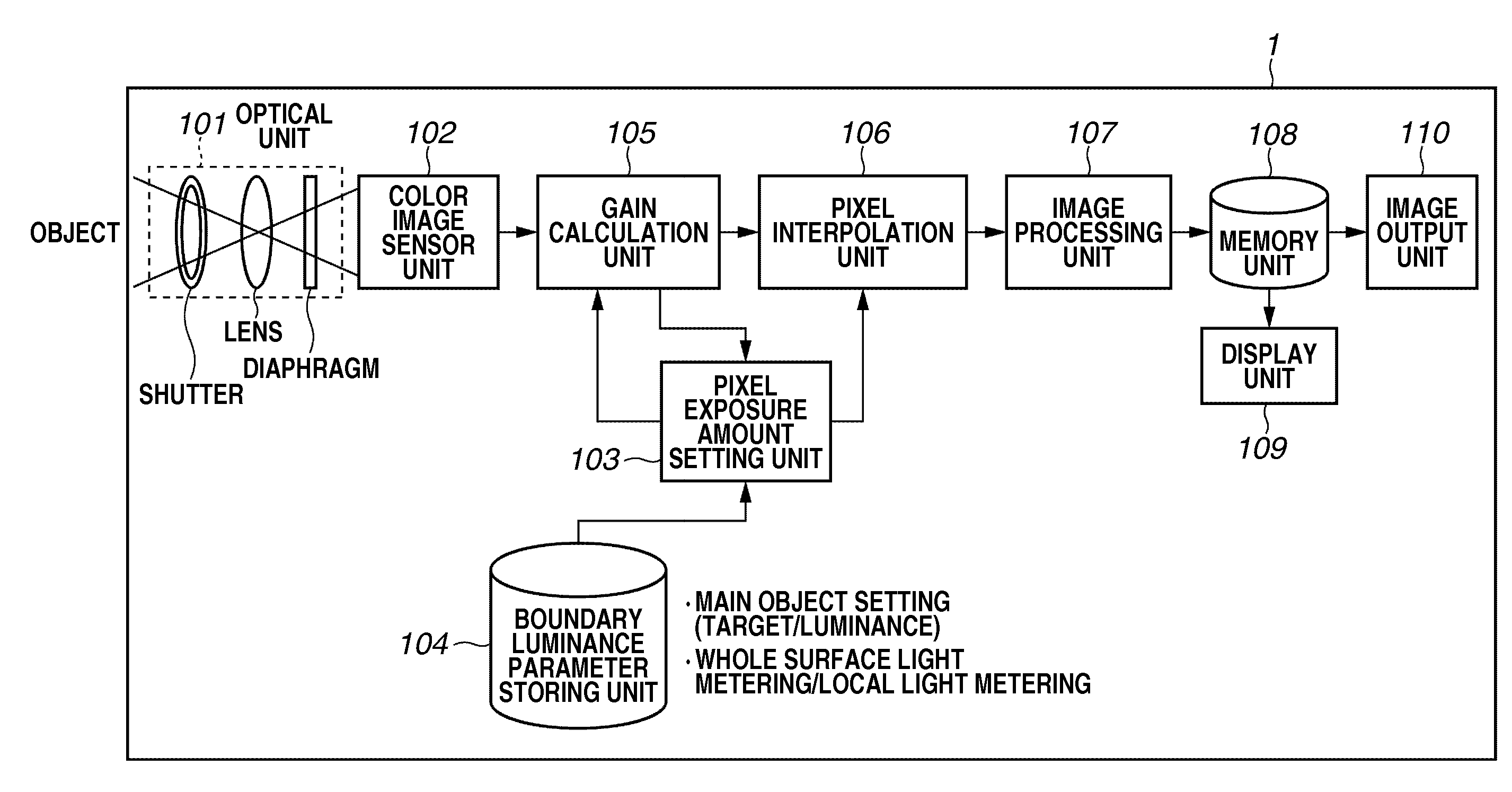
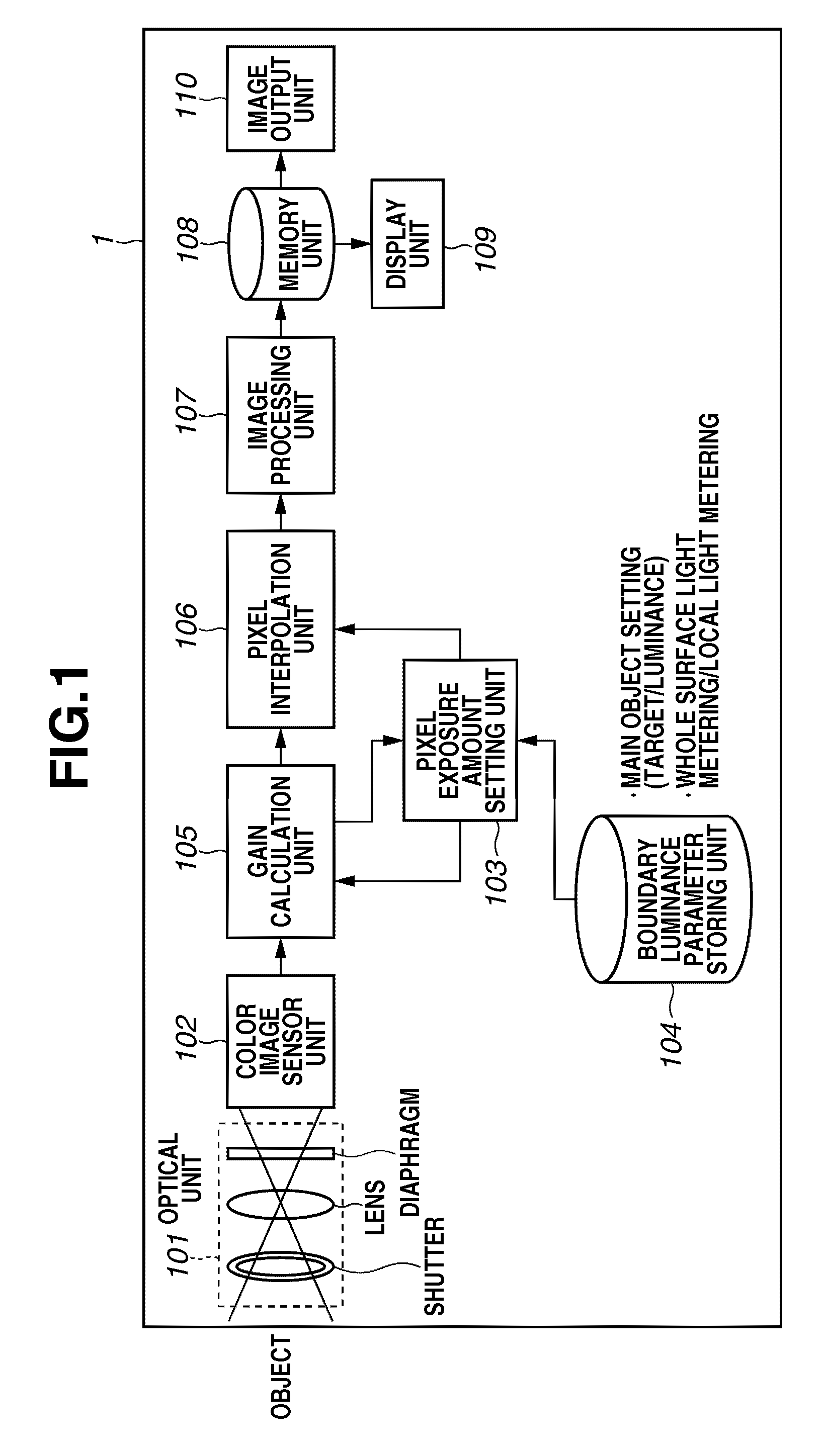
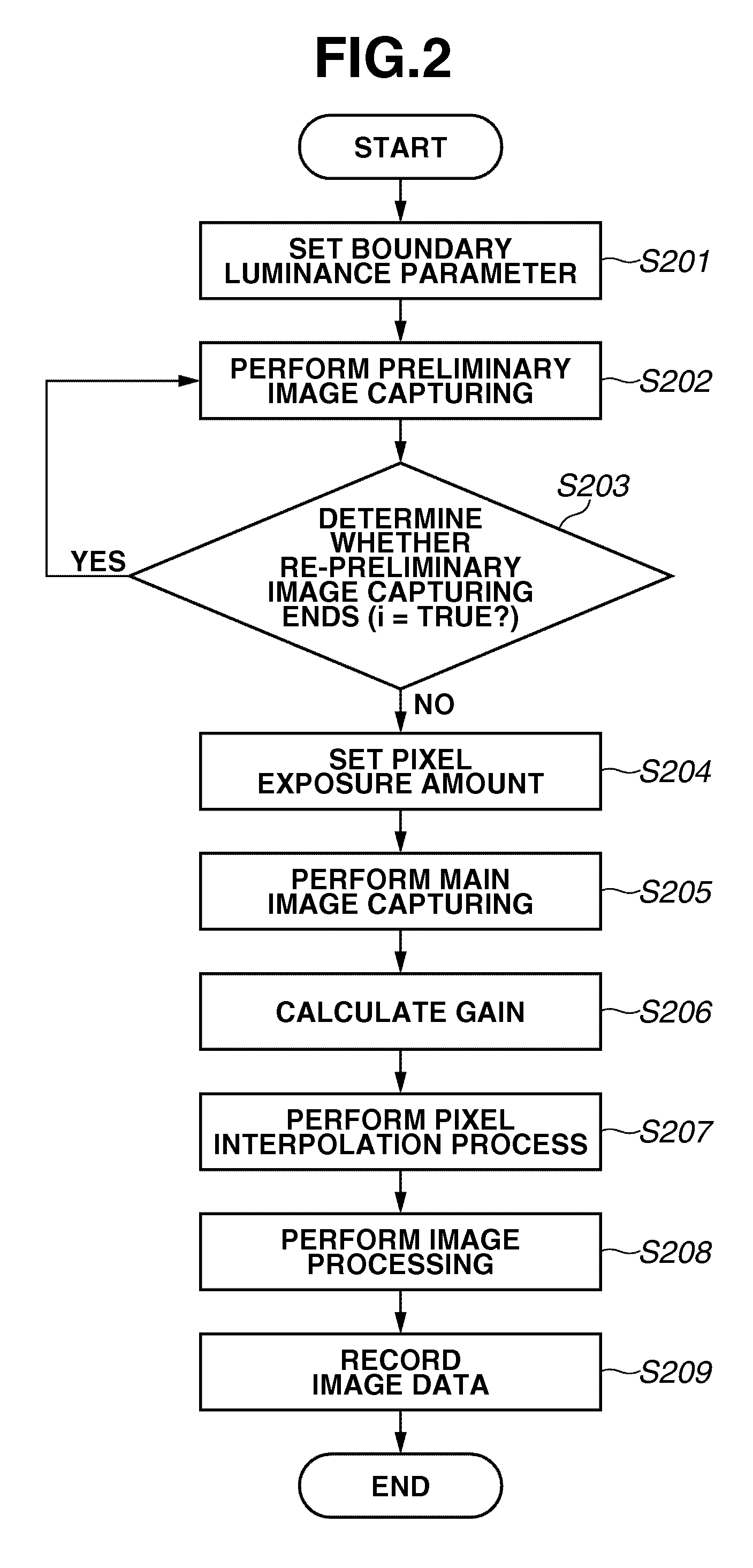
Image capturing apparatus and image capturing method
InactiveUS20100141792A1Extended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExposure controlPhotoelectric conversion
An image capturing apparatus includes an image capturing unit including a plurality of pixels adjacently disposed in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction and configured to perform photoelectric conversion on received light to accumulate electric charge, and a pixel exposure control unit configured to set an exposure amount of each of the plurality of pixels based on a result of capturing an image by the image capturing unit and to control an exposure time of each of the plurality of pixels.
Owner:CANON KK
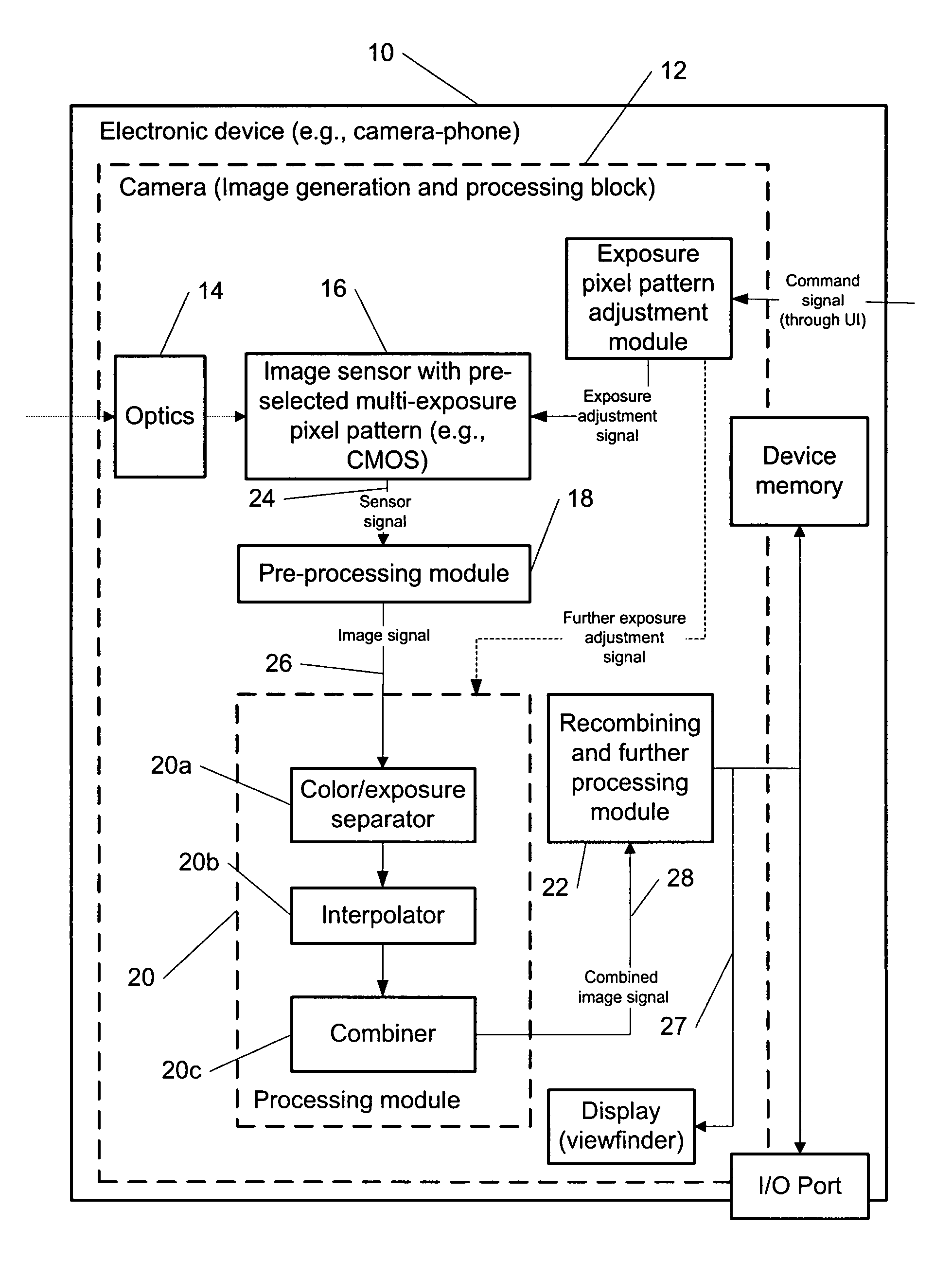
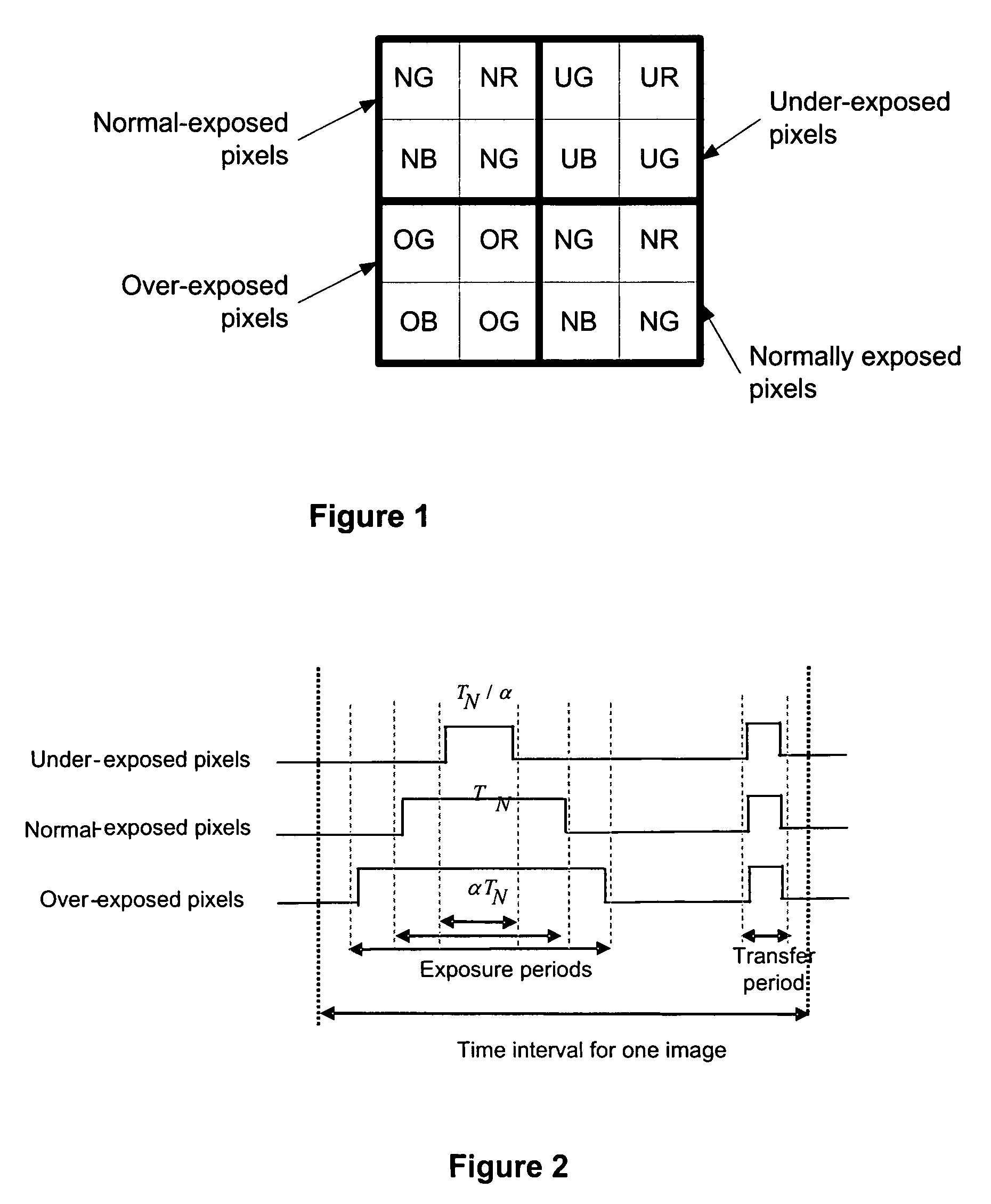
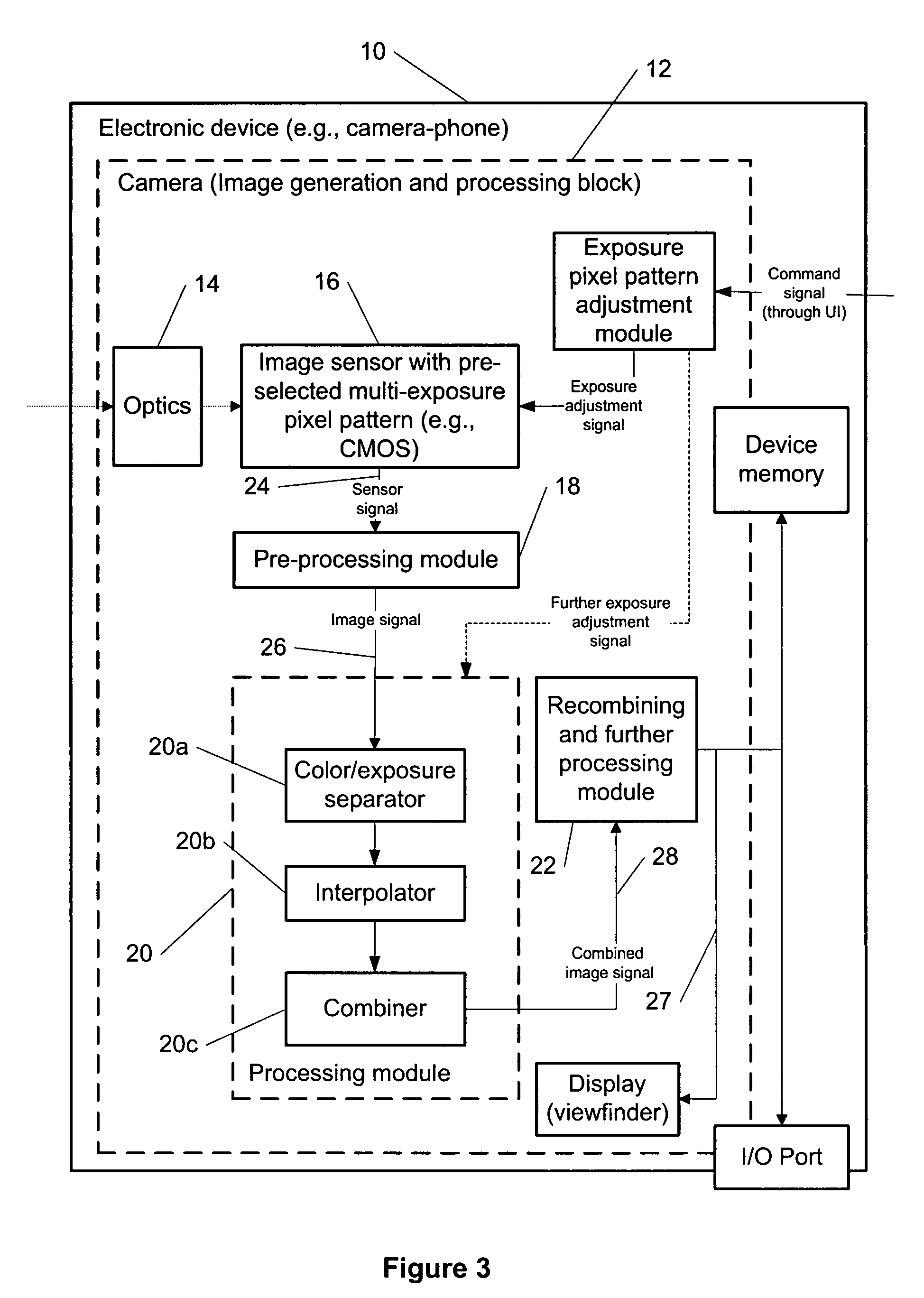
Multi-exposure pattern for enhancing dynamic range of images
ActiveUS7940311B2Extended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsViewfinderUser interface
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for enhancing a dynamic range of an image with a multi-exposure pixel pattern taken by an image sensor of a camera for one or more color channels, wherein a plurality of groups of pixels of the image sensor have different exposure times (e.g., pre-selected or adjusted by a user through a user interface using a viewfinder feedback, or adjusted by a user through a user interface after taking and storing RAW image, etc.). Processing of the captured image for constructing an enhanced image of the image for each of the one or more color channels can be performed using weighted combination of exposure times of pixels having different pre-selected exposure times according to a predetermined criterion.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
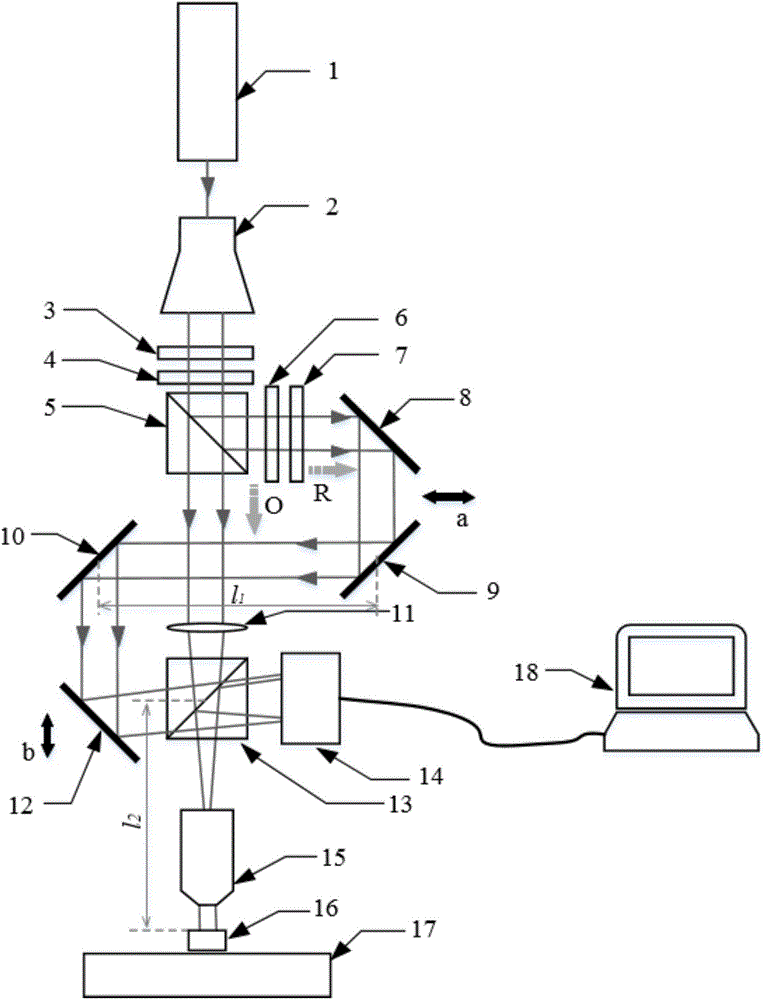
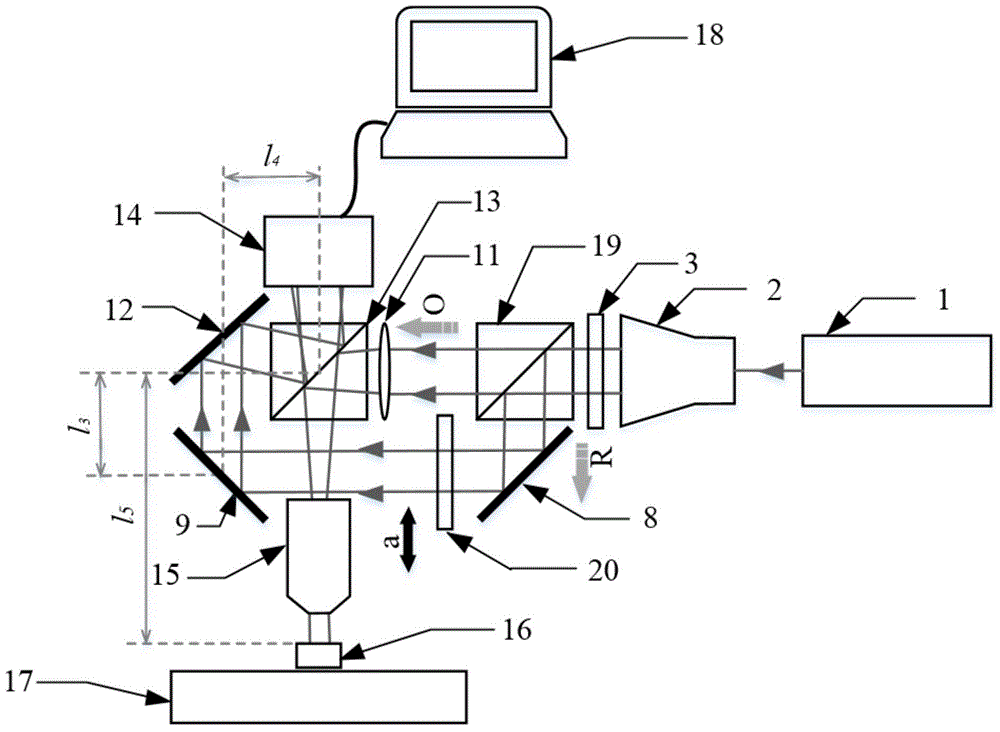
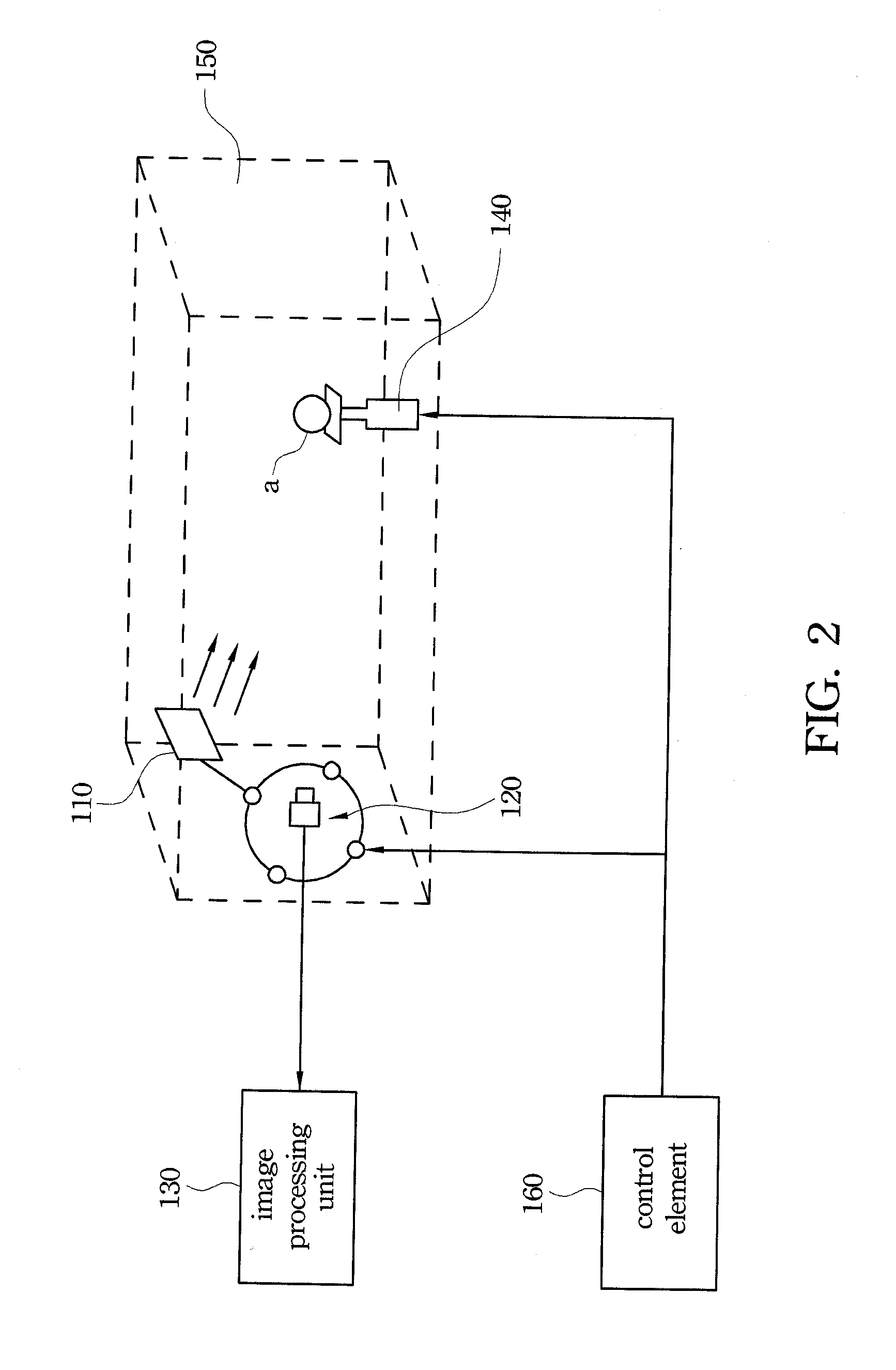
Reflection-type off-axis digital holographic microscopy measurement device
InactiveCN106292238AReduce usageOvercome the problems of complex structure, not compact and difficult instrumentationUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceImaging processing
The invention discloses a reflection-type off-axis digital holographic microscopy measurement device, which comprises a light source unit, an object light adjusting unit, a reference light adjusting unit and an image processing unit. The reference light adjusting unit comprises an optical path adjustment reflector group and an optical path guidance reflector group. The optical path adjustment reflector group comprises a first reflector and a second reflector, the positions of which are relatively fixed. The first reflector is used for reflecting the reference light R to the second reflector; the second reflector is used for reflecting the input reference light R to the optical path guidance reflector group; the optical path of the reference light R can be adjusted by moving the optical path adjustment reflector group wholly; the optical path guidance reflector group can guide the reference light R, the optical path of which is adjusted, to be input to the image processing unit to have interference with reflected light O'; and the image processing unit is used for processing interference fringes to obtain a sample three-dimensional image. The device can improve the quality of the holographic image.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for video processing for improved video compression
InactiveUS20120002000A1Efficient communicationOvercome deficienciesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTelecommunications linkVideo processing
Systems, apparatuses, and methods are provided for processing video. In one method, analog image information is acquired over an exposure period, and digital image information is generated from the analog image information at a frame period where the exposure period is greater than the frame period. In another method, stored characteristic information such as images of parties are compared to a received characteristic information. If there is a match, a communication link is established between the parties.
Owner:VIBARE
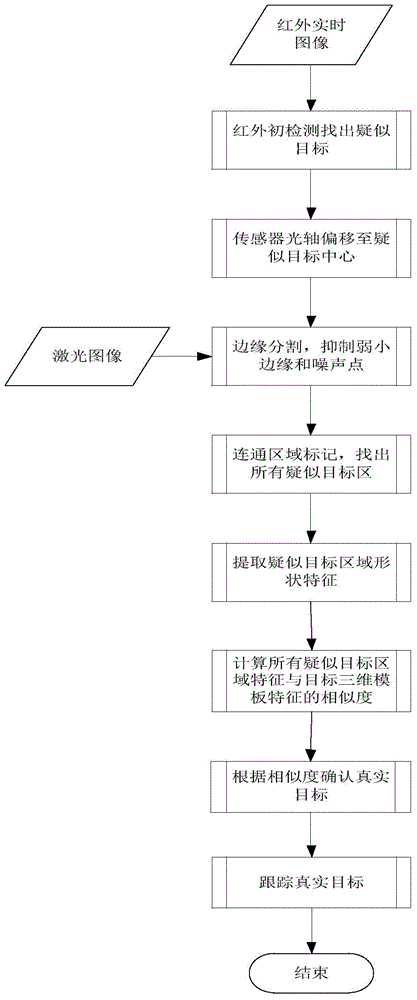
Laser infrared composite ground building recognition and navigation method
ActiveCN104536009ALarge field of viewIncrease frame rateCharacter and pattern recognitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser imagingEngineering
The invention provides a laser infrared composite ground building recognition and navigation method. The method includes the following steps that (1) a ground infrared image is acquired through aerial photography; (2) the infrared image is detected, so that a suspected target is located and determined; (3) the suspected target is aligned for laser imaging; (4) range gating is conducted on laser imaging so that foreground and background interference can be filtered out; (5) a shape feature of the suspected target is extracted from an image acquired after interference of laser imaging is filtered out, serves as a target matching element and is matched with a target shape feature template, and therefore the target is recognized. By the adoption of the method, laser imaging is fused to infrared imaging target localization, the advantage that the range of infrared imaging is large is used, three-dimensional distance information of laser imaging is adopted, and the locating accuracy of a building is effectively improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
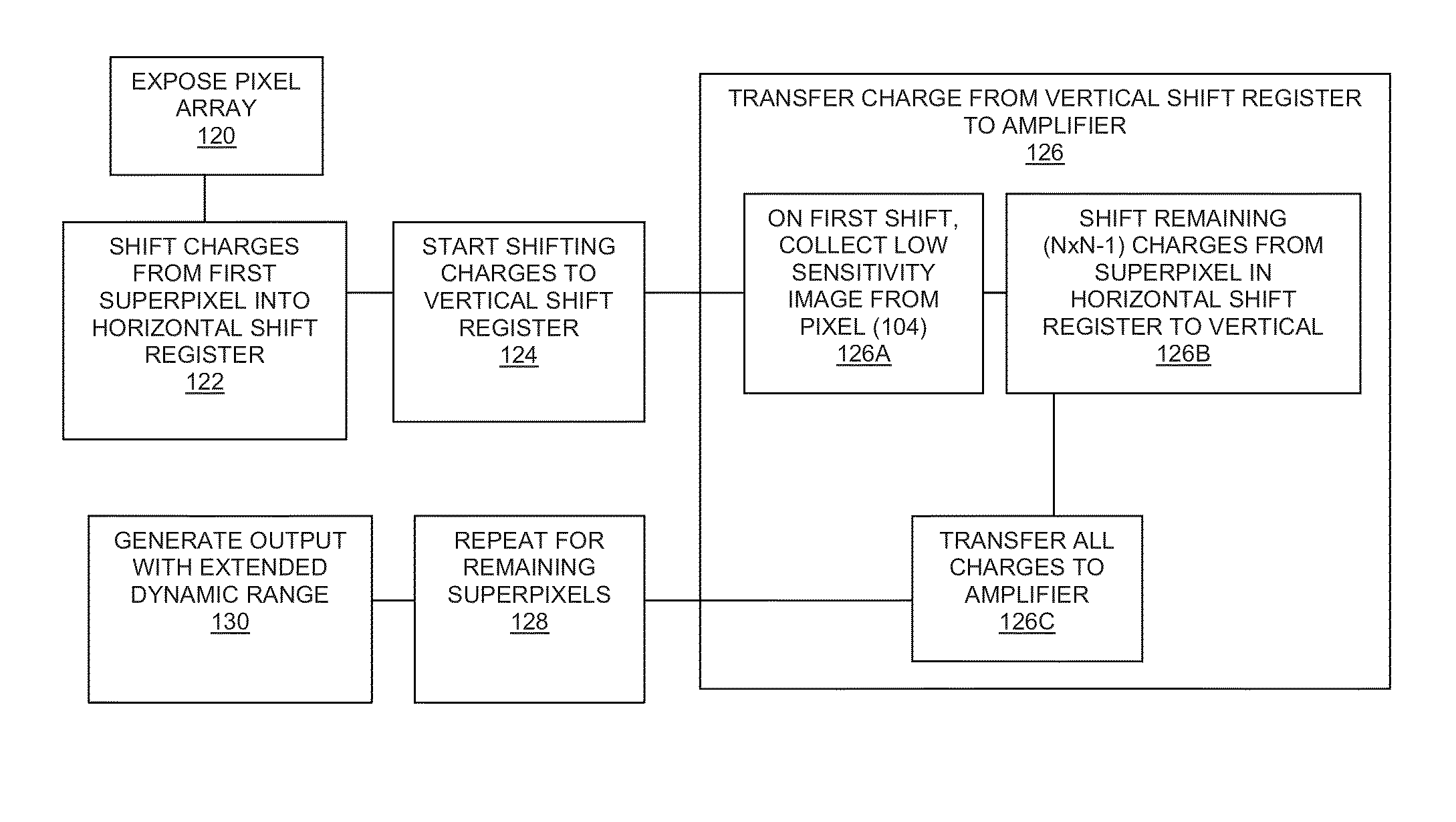
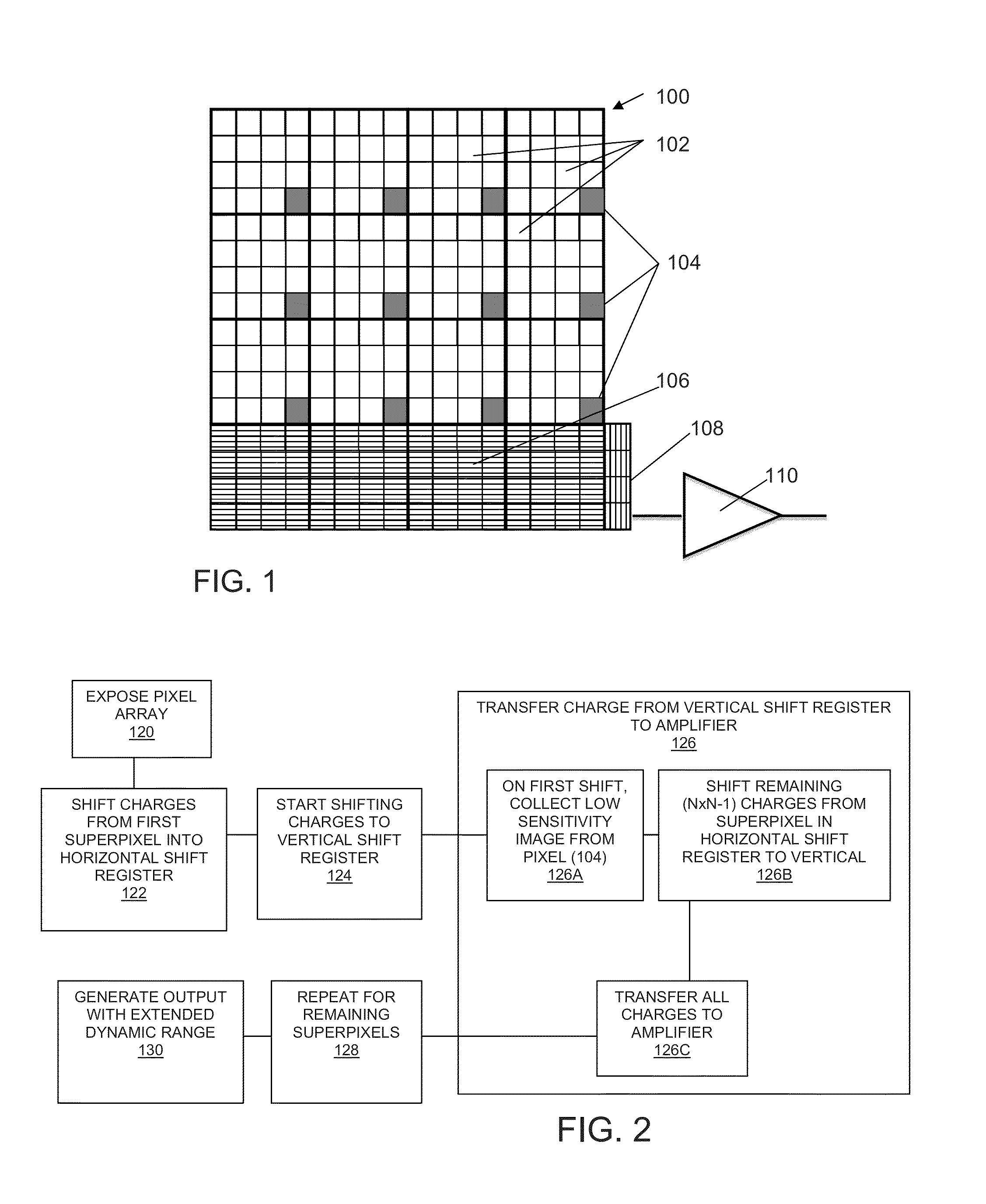
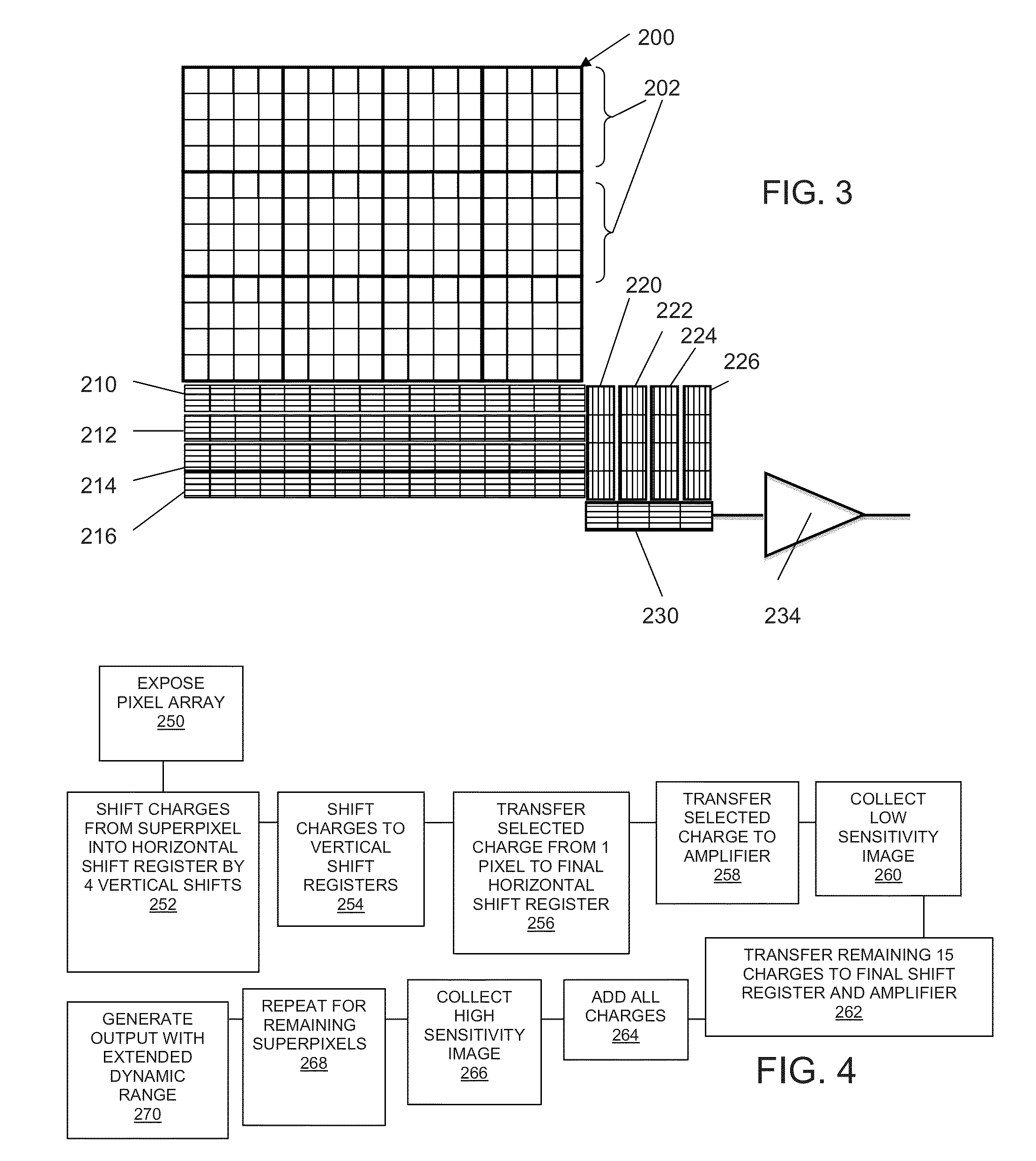
Device and method for extending dynamic range in an image sensor
ActiveUS20140118588A1Detectability enhanceExtended imaging rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPixel arrayAudio power amplifier
An image sensor comprises a pixel array having a plurality of pixel regions, wherein the pixel array is adapted to generate at least one signal from each pixel region and a separate signal from a subset of pixels within each pixel region, both during a single exposure period. In one embodiment, the sensor is in communication with a shift register which accumulates the separate signal and transfers the separate signal to an amplifier. The shift register further accumulates the at least one signal from the pixel region after the separate signal has been transferred to the amplifier and transfers the at least one signal to the amplifier.
Owner:PIXON IMAGING
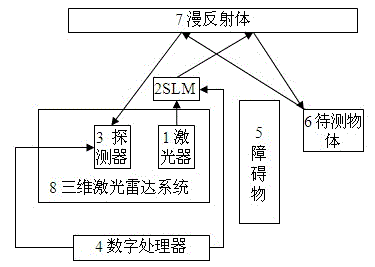
Reflective imaging method and system for modulation-type diffuse reflection surface according to flight time principle
InactiveCN103558604AEfficient detectionExtended imaging rangeElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpatial light modulatorRadar systems
The invention discloses a reflective imaging method and system for a modulation-type diffuse reflection surface according to the flight time principle. Laser emitted by a laser device is reflected to an object to be detected after passing through a spatial light modulator and the surface of a diffuse reflection body. After reflective light of the object to be detected is re-reflected through the surface of the diffuse reflection body, the reflective light is received by a detector controlled by a digital processor at different photonic flight times, and the object to be detected, which is sheltered by a barrier can be restored according to the elliptical distribution conditions of a contour map of an image. The digital processor is connected with the spatial light modulator, the laser device and the detector, and the laser device is connected with the spatial light modulator. The barrier is arranged between a three-dimensional laser radar system and the object to be detected. Output light, modulated through the spatial light modulator, of the laser device irradiates on the object to be detected by passing the diffuse reflection body, and the reflective light of the object to be detected is received by the detector by passing the diffuse reflection body. A non-direct-view object which can not be detected by an imaging system of a traditional optical system can be detected through the reflective imaging method and system, and therefore the imaging range of a three-dimensional laser radar is expanded.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multi-focus scanning three-dimensional imaging method and system based on double-helix-point spread function
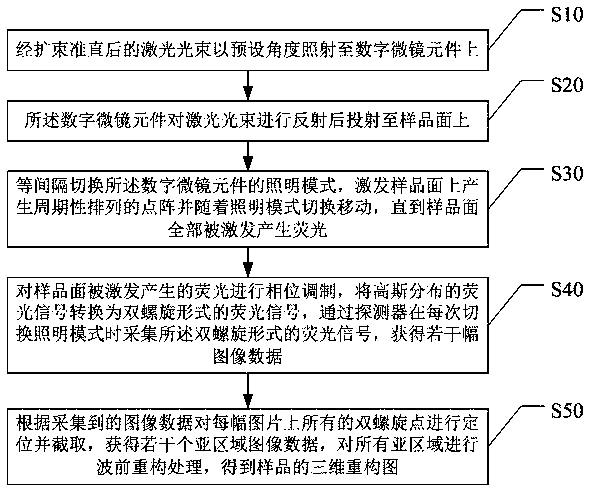
ActiveCN108982452AReduce acquisition timeImprove time resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceDiffusion function
The invention discloses a multi-focus scanning three-dimensional imaging method and system based on a double-helix-point spread function. The method comprises the following steps: irradiating a laserbeam on a digital micromirror element at a preset angle; reflecting the laser beam by the digital micromirror element, and projecting onto the sample surface; switching the illumination mode of the digital micromirror element at equal intervals, exciting the generation of periodic arrays on the sample surface to move along with the switching of the illumination mode; performing phase modulation onfluorescent light generated by excitation of the sample surface, converting a fluorescence signal of Gaussian distribution into a fluorescence signal of a double-helix form, acquiring a fluorescencesignal of the double-helix form by a detector, and acquiring a plurality of image data; locating and intercepting all double helix points on each image according to the acquired image data to obtain aplurality of sub-regions, and performing wavefront reconstruction processing on all sub-regions to obtain a three-dimensional restructuring graph of a sample. The sample is excited simultaneously through multiple focus points, so that the sample acquisition time is reduced, and the time resolution of a three-dimensional image scanning microscopy system is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Readout technique for increasing or maintaining dynamic range in image sensors
ActiveUS7297917B2Extended imaging rangeImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Audio power amplifier
The apparatus and method provide a readout technique and circuit for increasing or maintaining dynamic range of an image sensor. The readout technique and circuit process each pixel individually based on the magnitude of the readout signal. The circuit includes a gain amplifier amplifying the readout analog signal, a level detection circuit for determining the signal's magnitude, a second gain amplifier applying a gain based on the signal magnitude and an analog-to-digital converter digitizing the signal and a circuit for multiplying or dividing the signal. The method and circuit allow for a lower signal-to-noise ratio while increasing the dynamic range of the imager.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Method and apparatus for improving and controlling dynamic range in an image sensor
ActiveUS7616243B2Good curative effectImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl signalA d converter
A method and apparatus for an electronic image sensor having a base exposure, followed by a second or multiple exposures that are formed during signal readout. A timing controller controls the signal readout, such that as each line is read, the second and subsequent exposures are subsequently added to the base exposure to enrich the dynamic range. The image sensor may further include an analog-to-digital converter and noise suppression to further enhance the efficacy of the dynamic range enrichment. The system may also include additional signal processing and scaling functions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Free-form surface-based spectral imaging system
InactiveCN106289524AOvercome the problems of low diffraction efficiency and overlapping spectral linesReduce volumeSpectrum investigationFree formImaging quality
The invention discloses a free-form surface-based spectral imaging system, which is characterized by comprising an incident slit, a curved prism, a free-form surface reflector, a plane reflector and a detector image plane. The incident slit serves as the object plane of the spectral imaging system. Light rays, far from the heart of an object space, inject onto the curved prism through the incident slit. After the transmission process, the light rays are reflected by the free-form surface reflector, then transmitted through the curved prism again, and finally imaged on the detector image plane after being reflected by the plane reflector. According to the technical scheme of the invention, based on the non-rotation symmetry of the free-form surface, the defect that a grating is low in diffraction efficiency and overlapped in spectral orders can be effectively overcome. Meanwhile, only one reflector and one prism are adopted, so that the aberration caused by the increased field of view can be effectively balanced. The imaging range of the system is enlarged, and the imaging quality of the system is improved. In addition, both the size and the weight of a spectrometer are reduced, and the system is simplified. The system can be applied to airborne applications large in field of view, large in relative aperture and wide in spectrum.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of displaying a low dynamic range image in a high dynamic range
ActiveUS8207931B2Extended imaging rangeImprove viewable contest and detailCathode-ray tube indicatorsConversion factorLightness
A method of increasing the dynamic range of an image comprising a plurality of pixels each having a luminance value within a first luminance dynamic range. The method includes determining a background luminance value for each pixel of the image and determining a minimum and a maximum of the background luminance values. A conversion factor is then determined for each pixel of the image based on the minimum and maximum of the background luminance values. The image id converted from the first luminance dynamic range to a second luminance dynamic range by multiplying the luminance value of each pixel of the image by its conversion factor.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
High dynamic range sensor with blooming drain
ActiveUS7825966B2Extended imaging rangeHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringPhotodiode
An image sensor has at least two photodiodes in each unit pixel. A high dynamic range is achieved by selecting different exposure times for the photodiodes. Additionally, blooming is reduced. The readout timing cycle is chosen so that the short exposure time photodiodes act as drains for excess charge overflowing from the long exposure time photodiodes. To improve draining of excess charge, the arrangement of photodiodes may be further selected so that long exposure time photodiodes are neighbored along vertical and horizontal directions by short exposure time photodiodes. A micro-lens array may also be provided in which light is preferentially coupled to the long exposure time photodiodes to improve sensitivity.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Method for Constructing Three-Dimensional Model and Apparatus Thereof
InactiveUS20090310852A1Improve accuracyEasy to operateImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingComputer science
Disclosed are a method and an apparatus for constructing an accurate three-dimensional model. The apparatus includes a plurality of light sources, an image-capturing element and an image-processing unit. The present invention is used to integrate the two-dimensional images from different views of an object into a high accurate three-dimensional model. Compared with conventional apparatuses, the apparatus of the present invention is useful without safety problems, relatively easily manipulated, and capable of quick image reconstruction.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Dynamic range broadening method for a solid-state image sensor including photosensitive cells each having a main and a subregion
InactiveUS20050099508A1Efficiently reading out signal chargeImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodiodeDigitization
A method of broadening a dynamic range is applied to a solid-state image sensor of the type including photodiodes each being divided into a main and a subregion different in photosensitivity from each other. While the quantity of light to be incident on a photodiode is reduced, a signal charge is read out only from the main region of the photodiode. The signal charge is digitized and then written to two image memories. Digital signals thus stored in the image memories are respectively amplified by white balance gain circuits with different gains. The resulting digital signals are combined by an image synthesizer. The method can therefore broaden the dynamic range of the image sensor by using only the main regions of the photodiodes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Laser distance measuring sensor
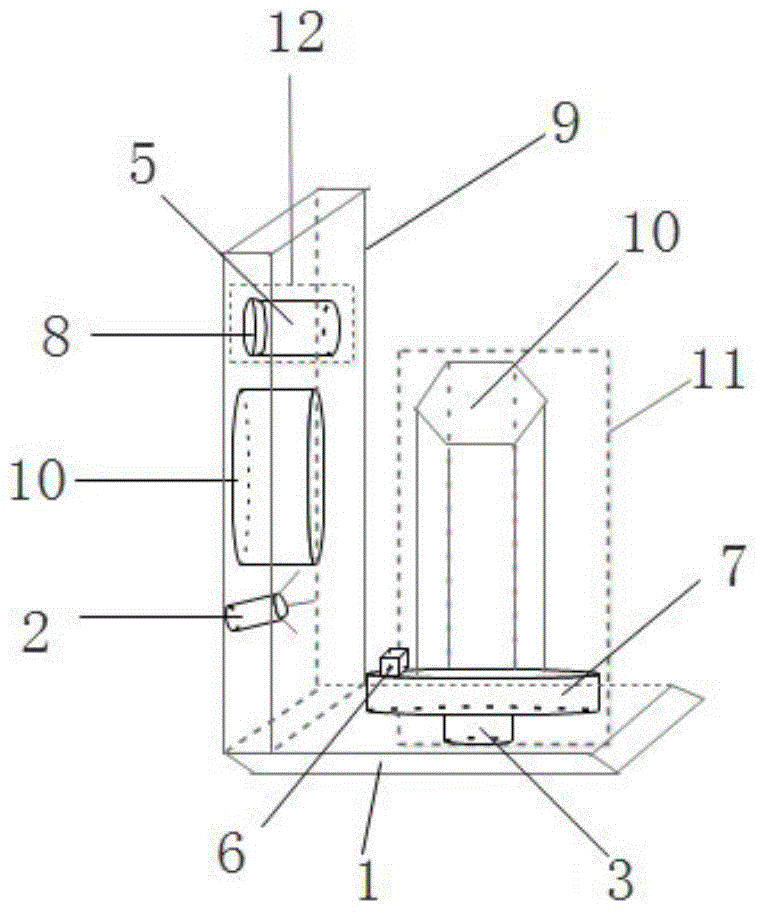
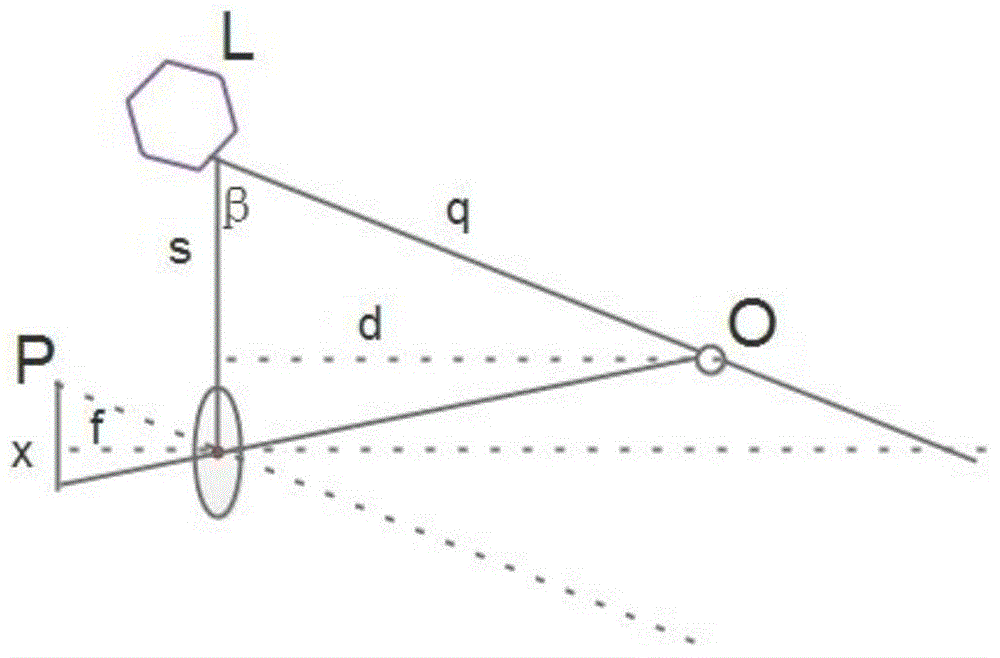
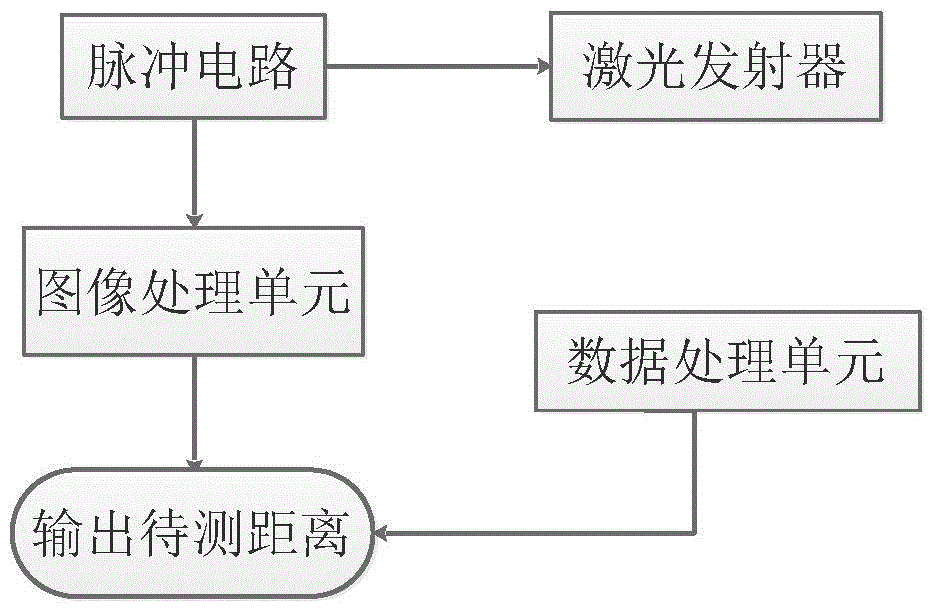
InactiveCN105698749AReduce frictionAvoid vibrationOptical rangefindersMain processing unitLaser transmitter
The invention provides a laser distance measuring sensor which comprises a base, a laser transmitter, a scanning unit, an image processing unit and a data processing unit. The scanning unit comprises a motor connected with the base and a prism connected with the motor, and the motor is fixed on the base; the prism synchronously rotates with the motor and reflects and scans light beams emitted by the laser transmitter; the image processing unit comprises an ordinary CCD image sensor and a cylindrical concave mirror; the data processing unit is connected with the motor and records rotating angle information of the prism. Compared with a traditional laser distance measuring sensor, the laser distance measuring sensor is higher in measurement precision and sensitivity, smaller in size, lighter in weight, lower in cost and longer in working life and has large application value in the field of low-cost intelligent consumption.
Owner:BEIJING ROBOTLEO INTELLIGENT TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com