Patents
Literature
226results about How to "Reduce NOx" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
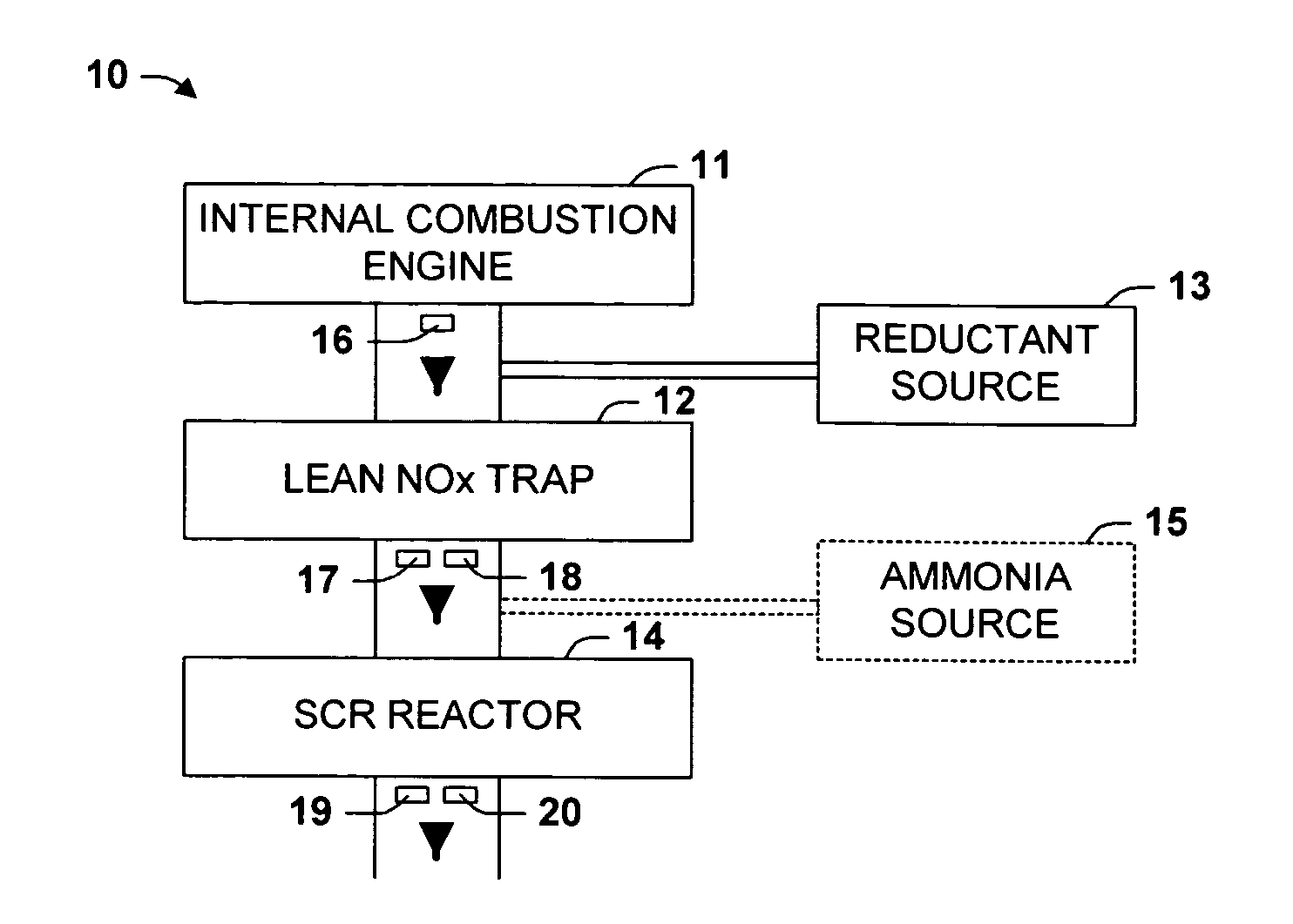
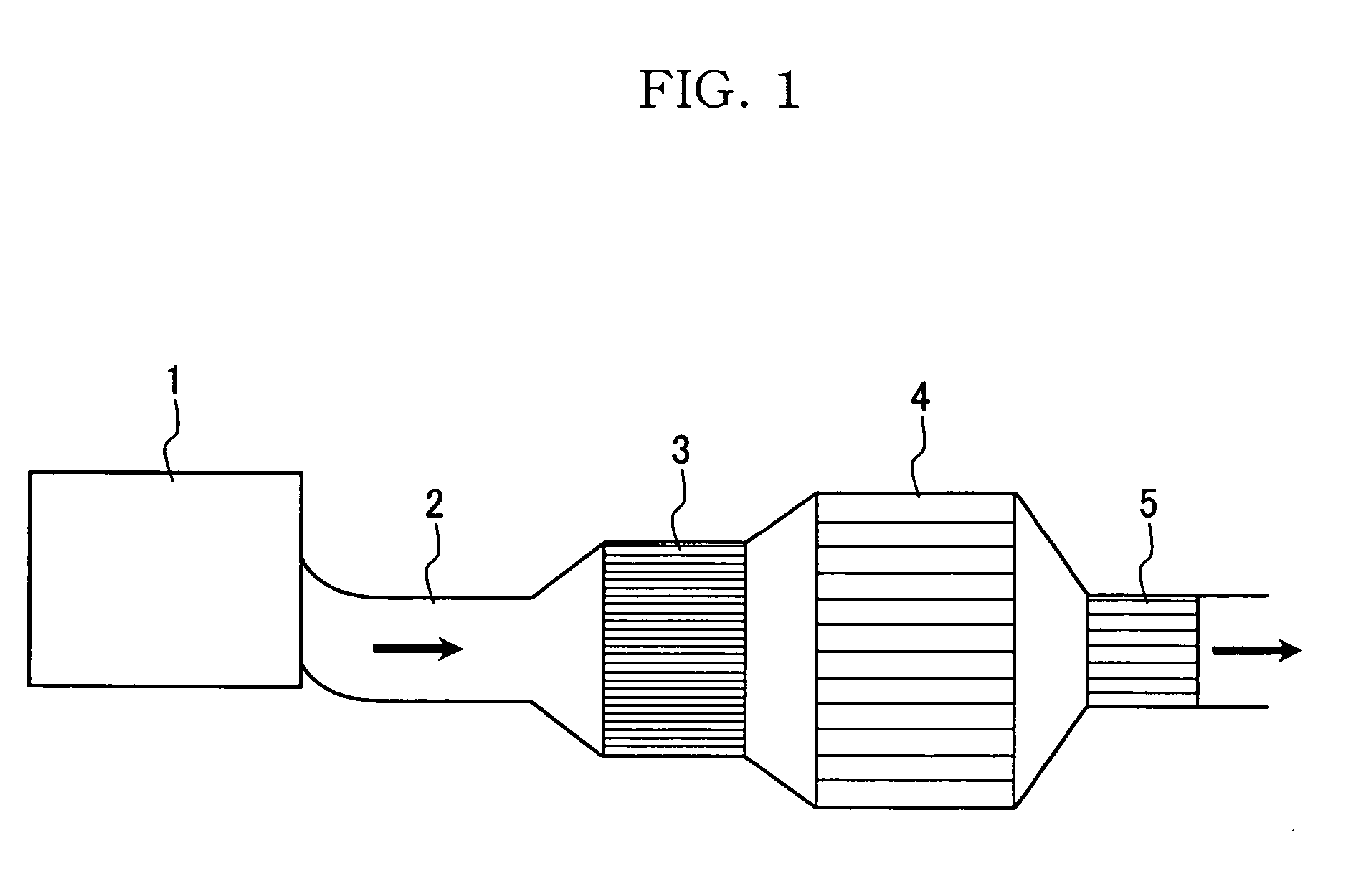
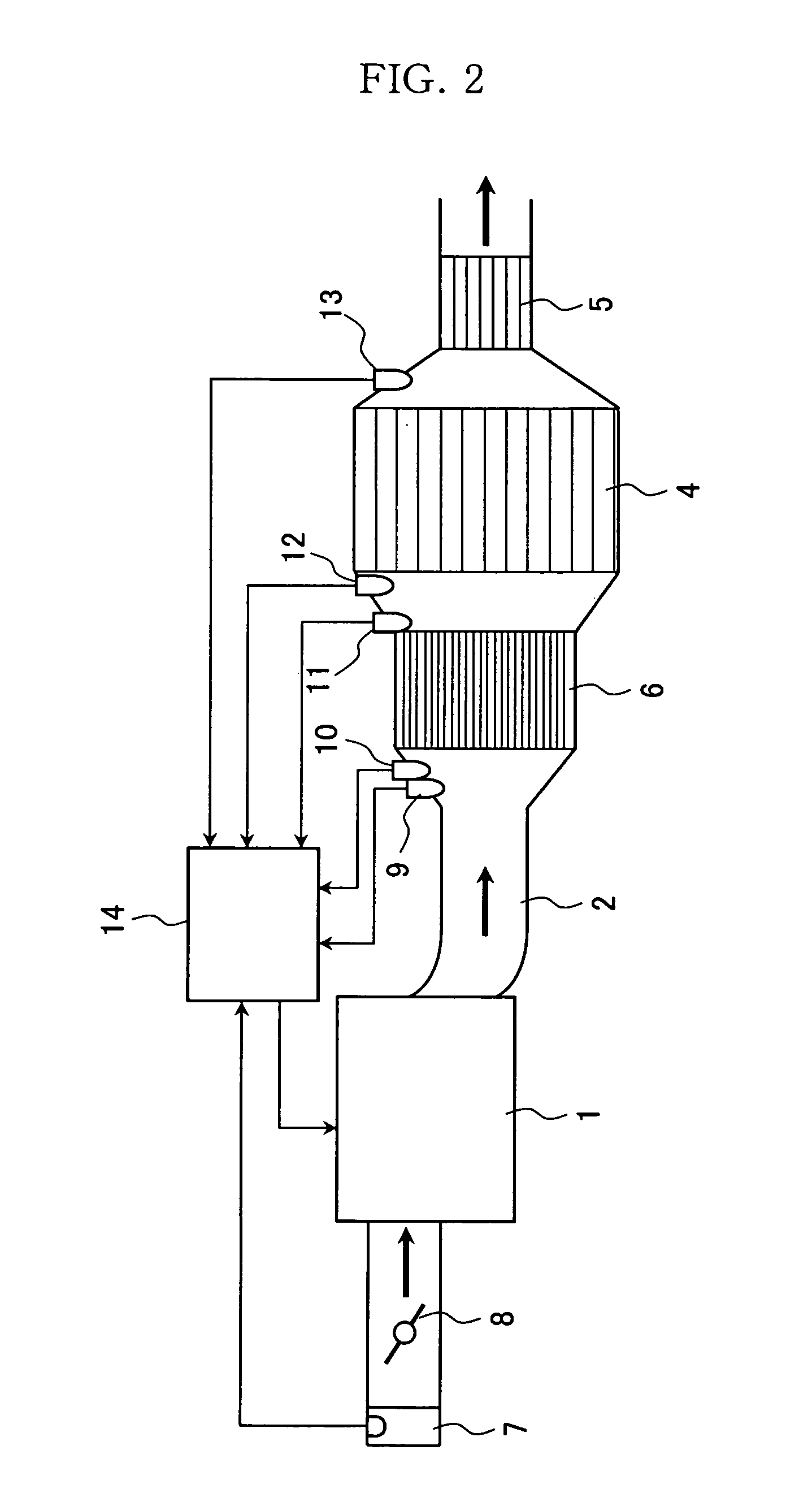
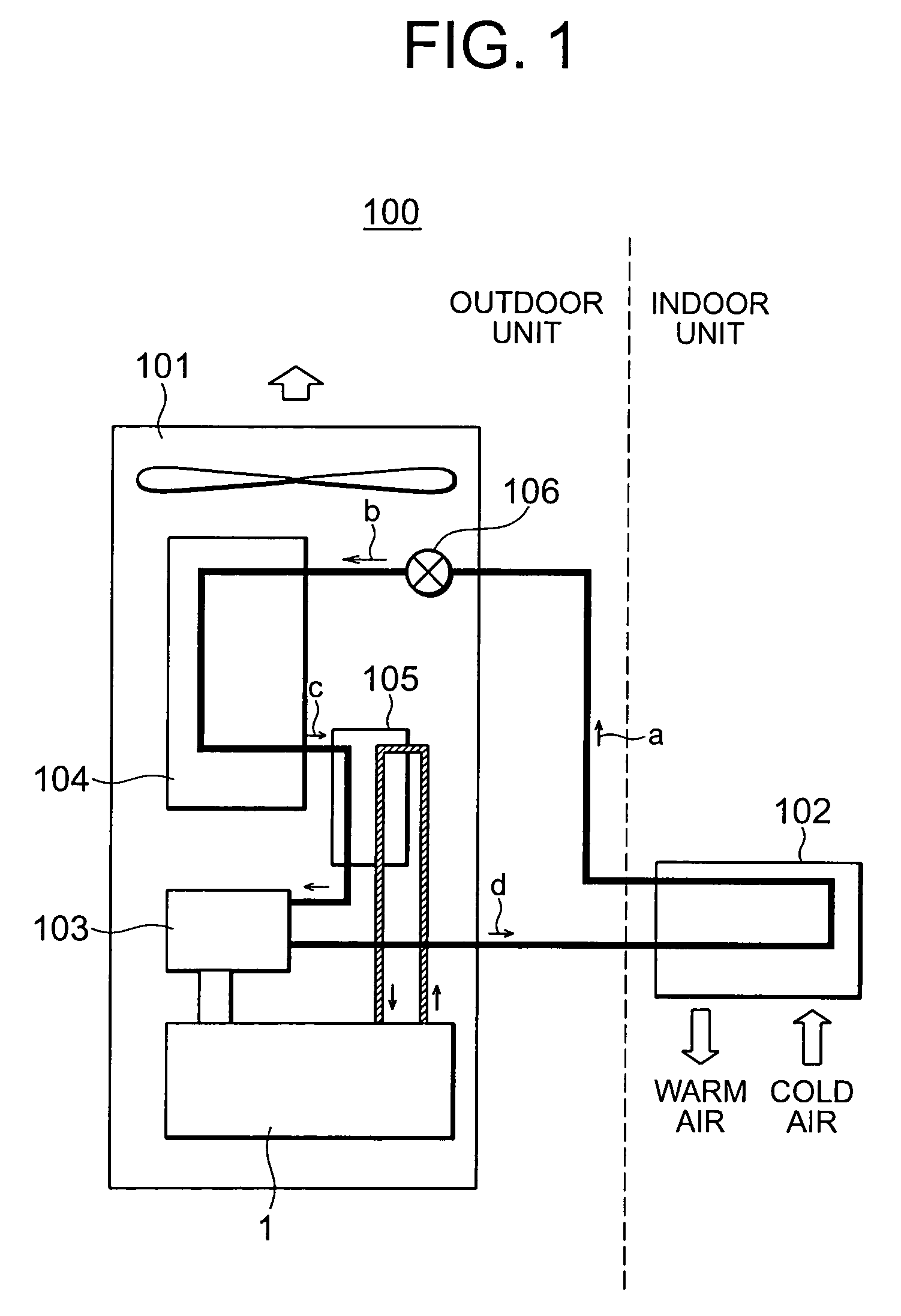
Hybrid catalyst system for exhaust emissions reduction
InactiveUS20060010857A1Improve efficiencySpeed up the conversion processHydrogenGas treatmentExhaust fumesEngineering
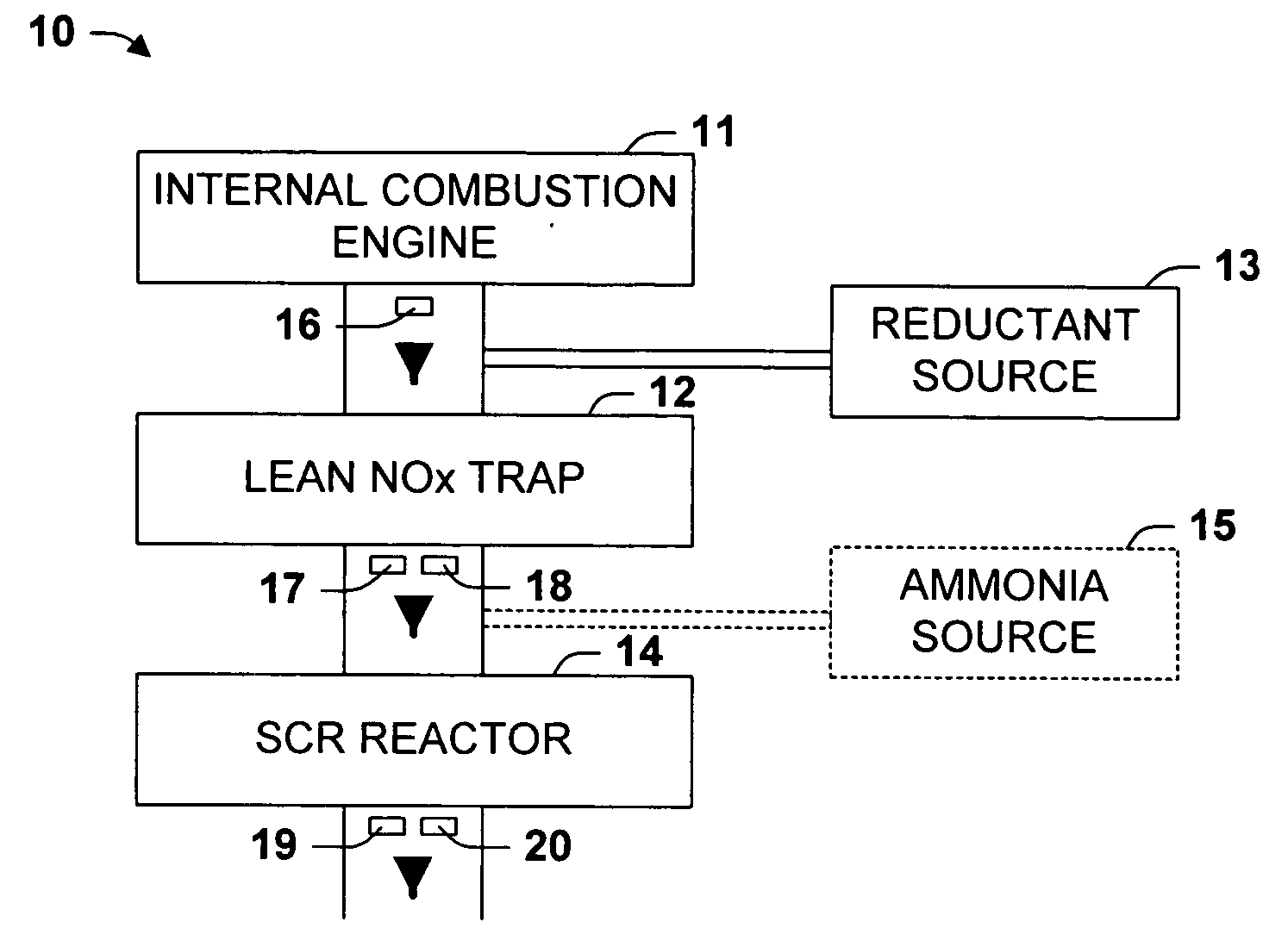
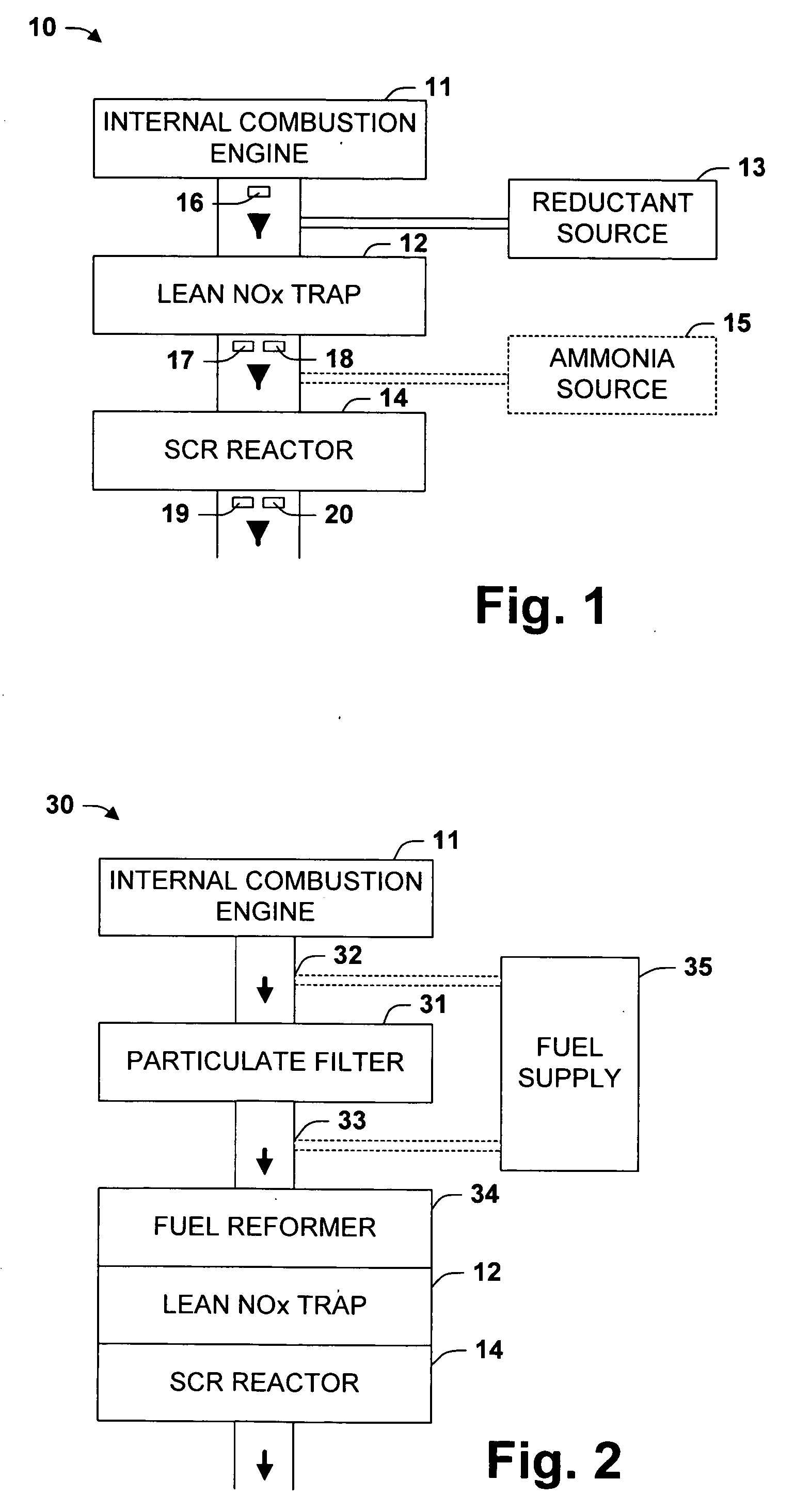
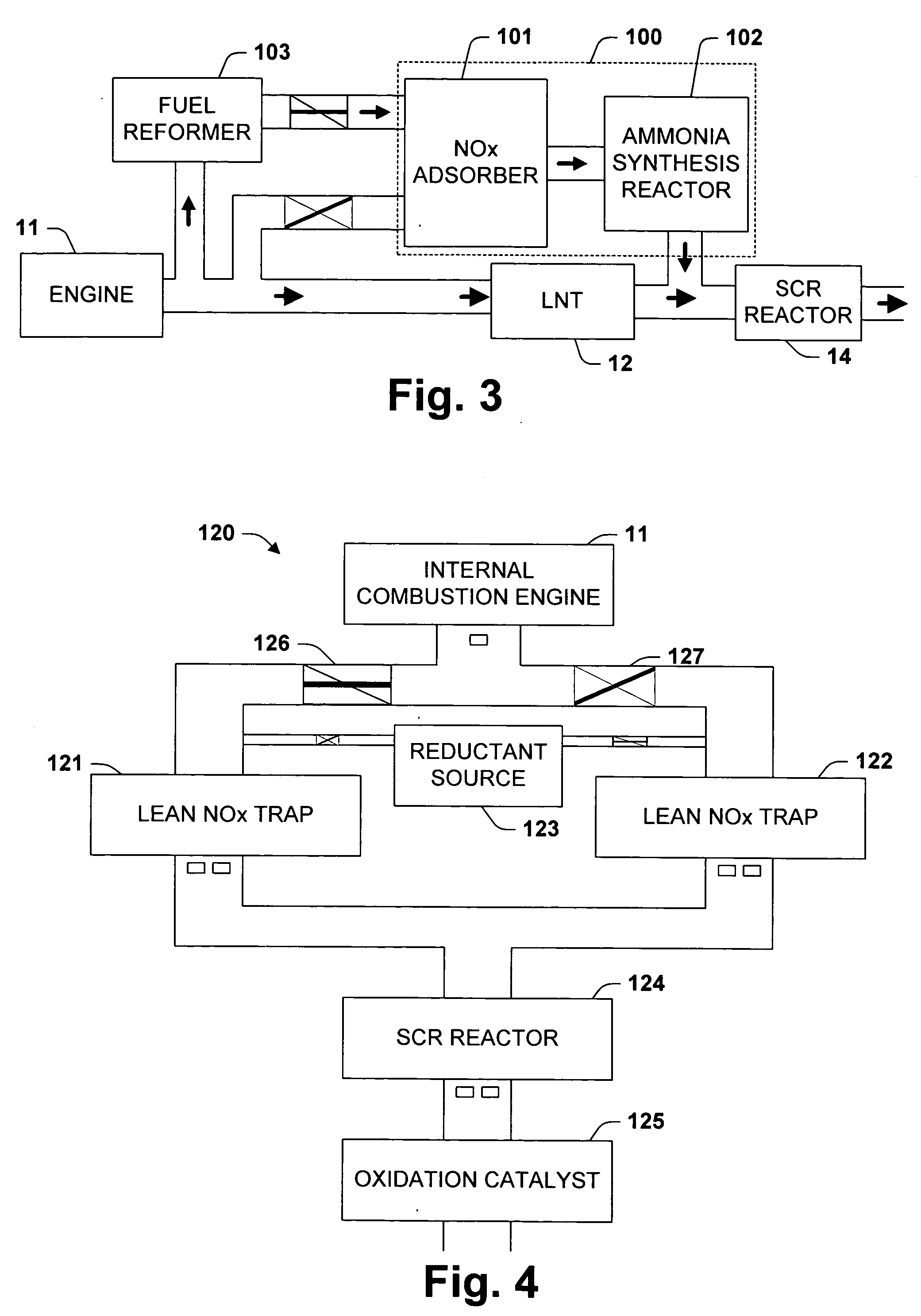
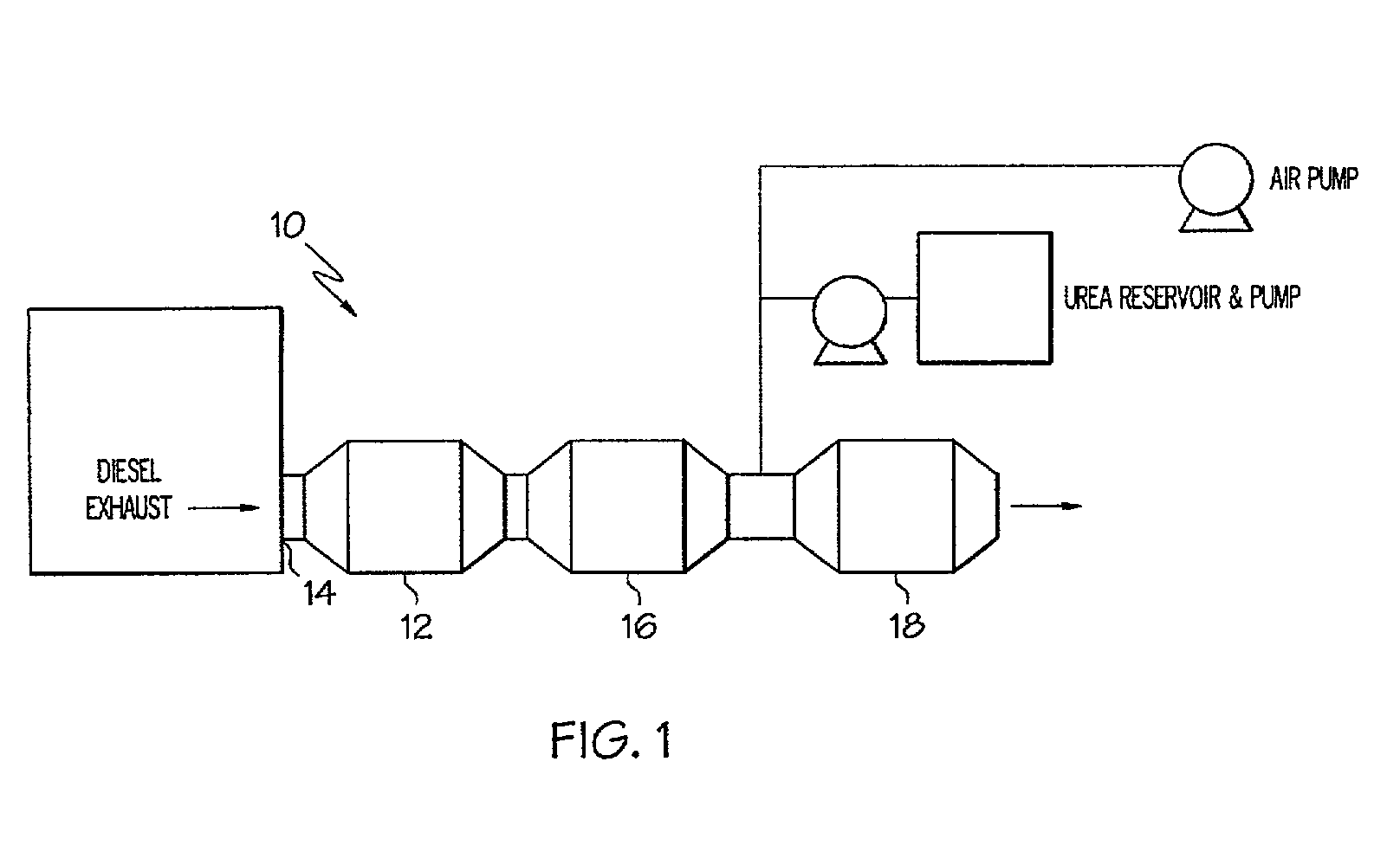
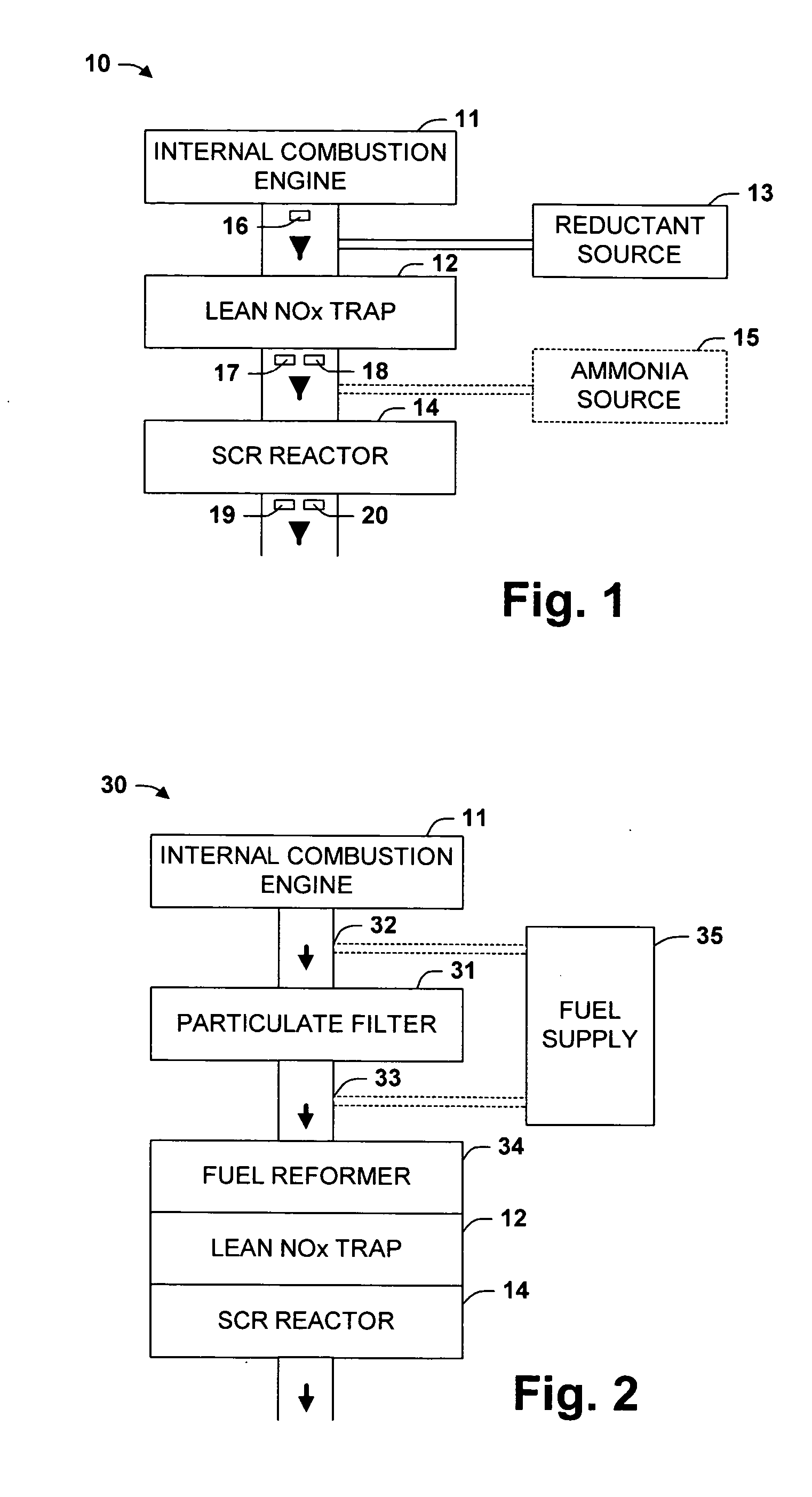
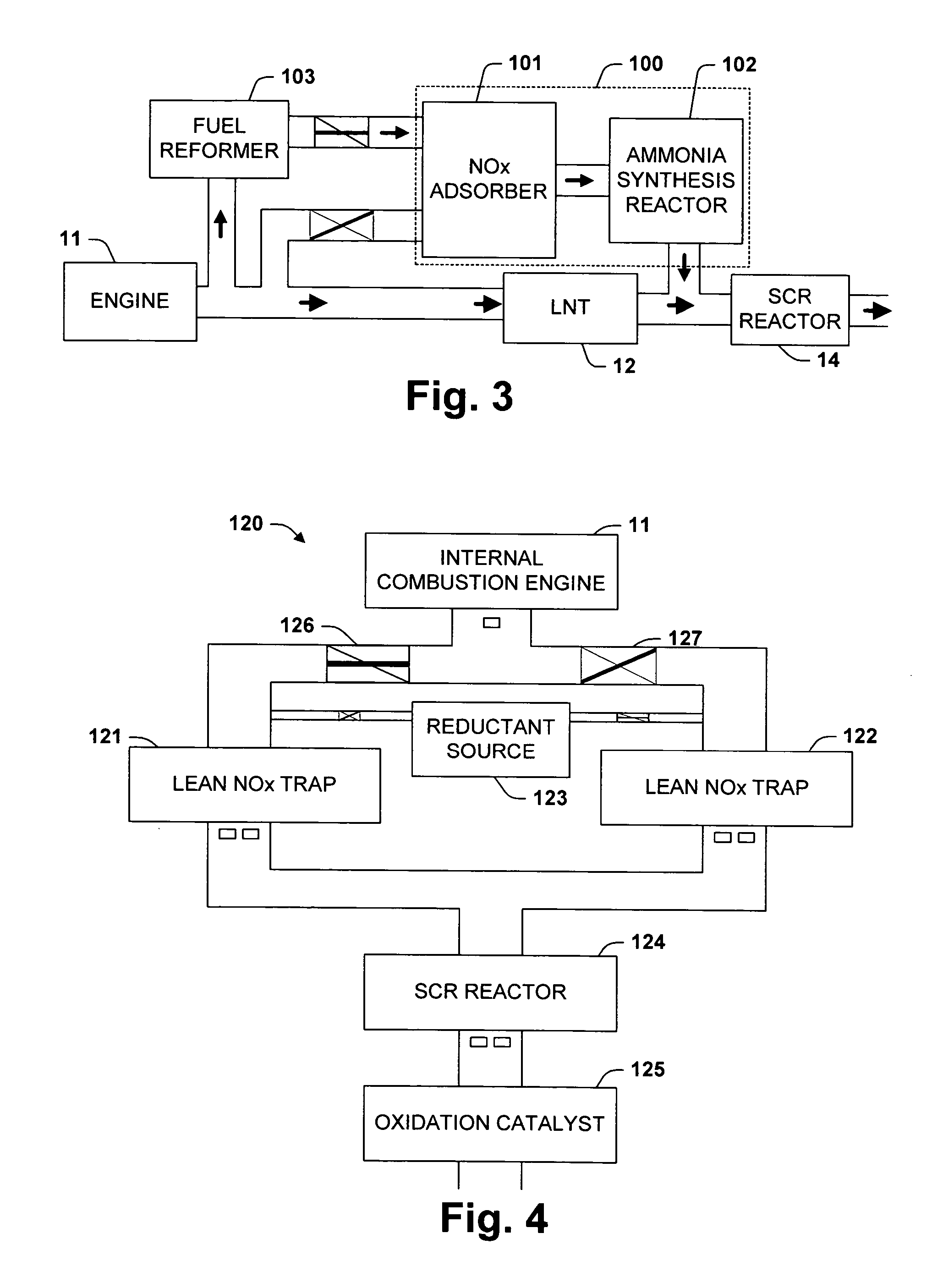
One aspect of the invention relates an exhaust treatment system having an SCR reactor following a NOx adsorber. Syn gas is used to regenerate the NOx adsorber. Another aspect relates to an LNT / SCR provided with an ammonia source separate from the LNT. A further aspect relates to a system comprising first and second LNTs and one or more SCRs downstream of the LNTs. A still further aspect relates to a device comprising first and second NOx adsorbers contained in a single housing. Another aspect relates to coating a surface of a moving part in an exhaust system with an oxidation catalyst to mitigate fouling. Additional aspects of the invention relate to strategies for controlling one or more of the time to initiate a regeneration cycle, the time to terminate a regeneration cycle, and the reductant injection rate during regeneration of LNT / SCR exhaust treatment systems.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
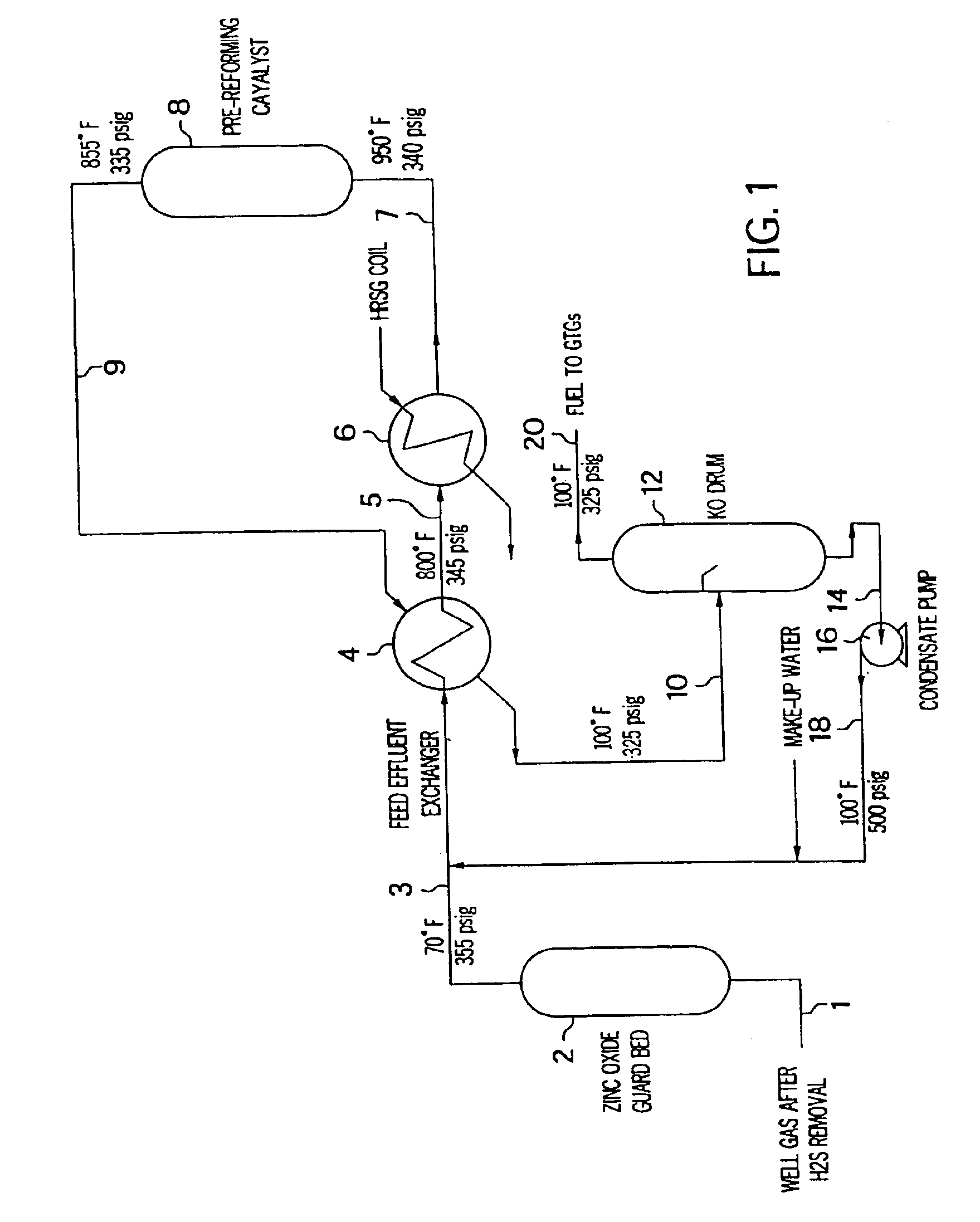
Method for utilizing gas reserves with low methane concentrations and high inert gas concentrations for fueling gas turbines
InactiveUS6907737B2Improve flammabilityLow costSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringCurrent technology
The invention is directed to a method of fueling gas turbines from natural gas reserves with relatively low methane concentrations. The invention uses such reserves to generate electric power. The invention permits the use of these reserves at significantly lower cost than by producing pipeline natural gas to fuel gas turbines to generate electric power. These reserves currently generally are used only after the removal of impurities to produce pipeline natural gas quality turbine fuel. The latter current technology is capital intensive, and at current natural gas prices, economically unattractive. The process of the invention can remove the impurities from the gas from the natural gas reserve necessary for protection of the environment, and leaves inert gasses in the fuel in an amount which will increase the output of a gas turbine for the generation of power by about 5 to about 20%.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Gas turbine combustor, and gas turbine with the combustor
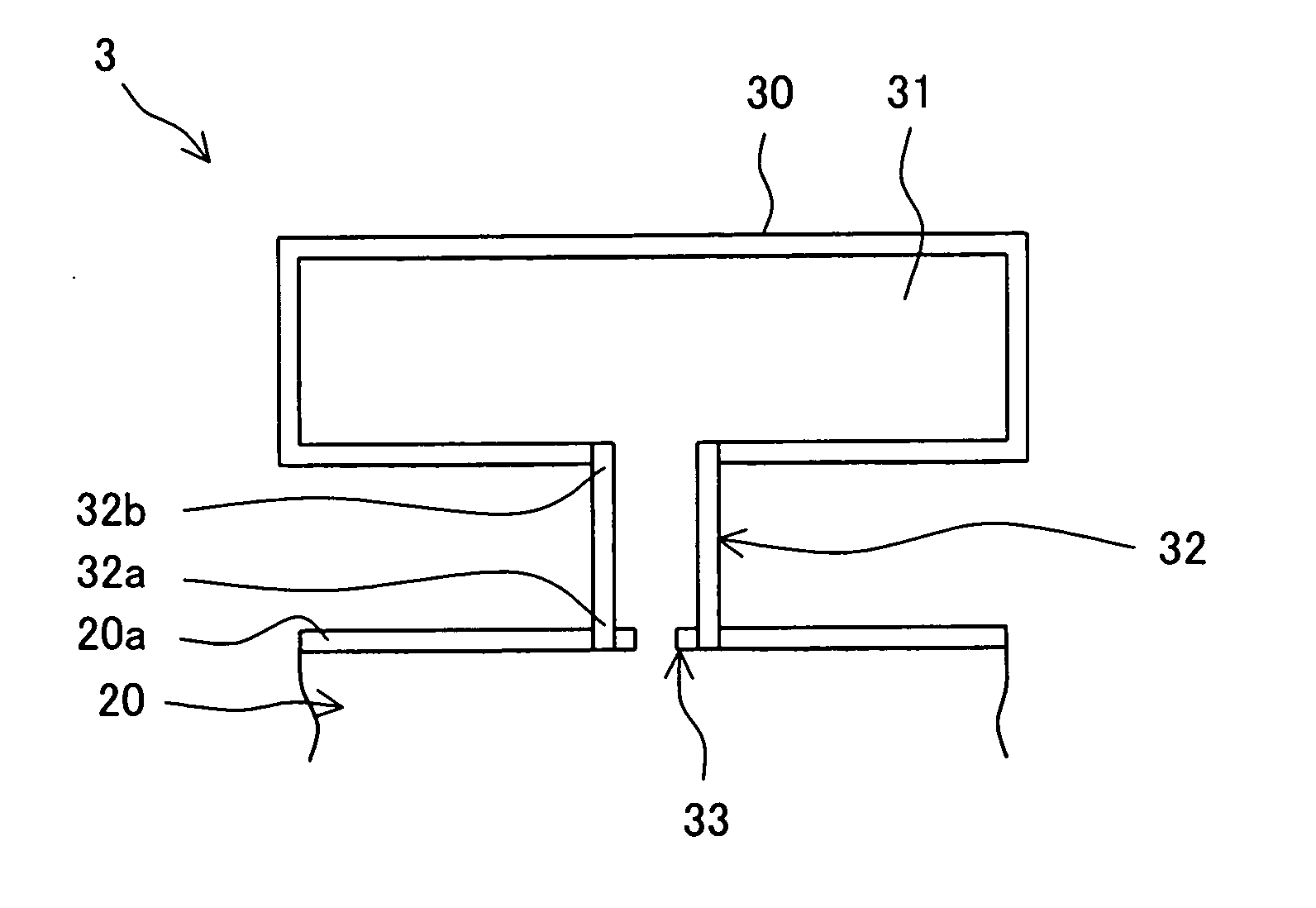
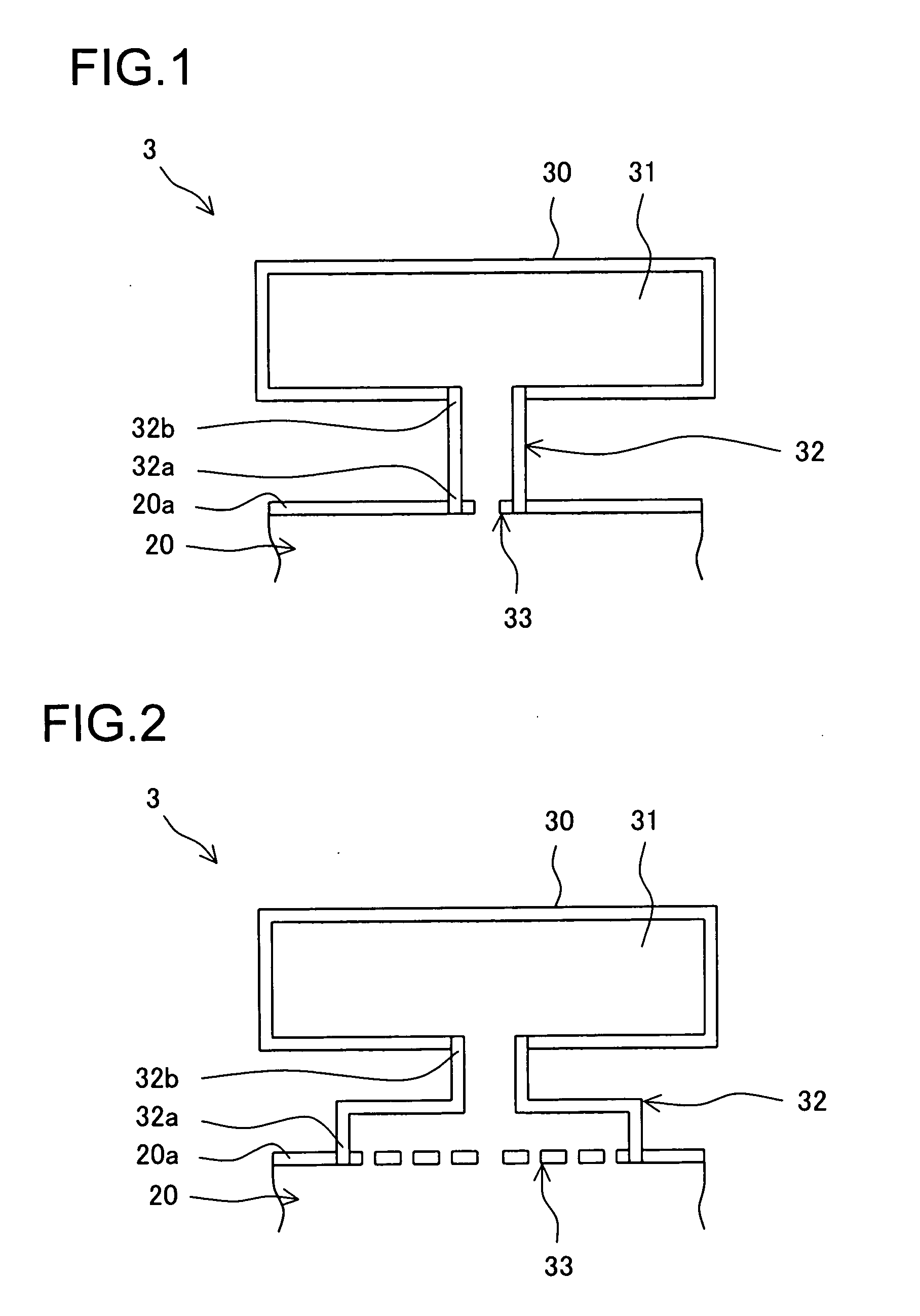
ActiveUS20050223707A1Reduce vibrationReduce NOxContinuous combustion chamberEngine fuctionsVibration amplitudeCombustor
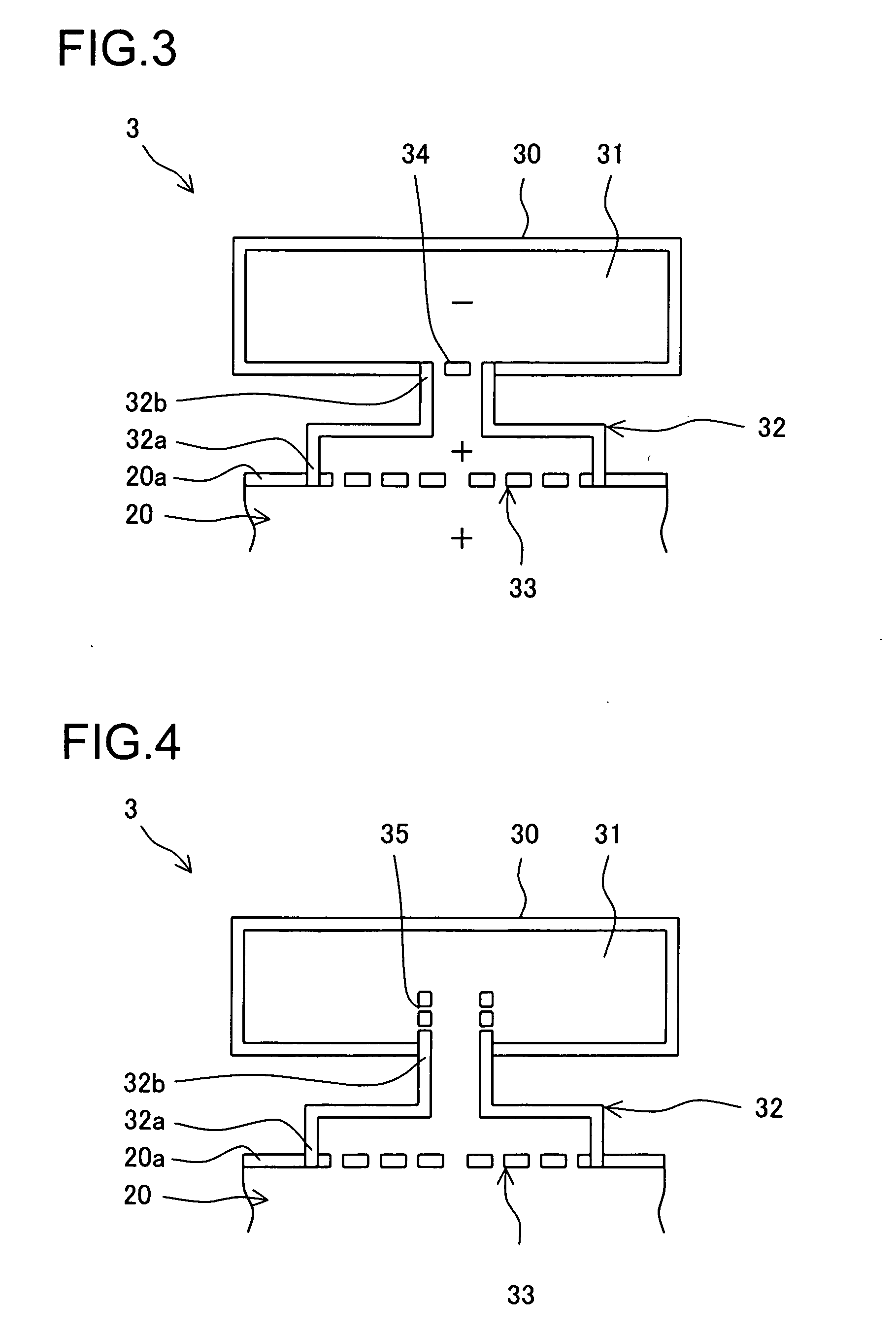
In order to realize a stable decrease in NOx, a gas turbine combustor is supplied which can reduce combustion vibration. A combustor (3) is provided with a first box body (30), which is installed outside an object body (20) such as a combustor basket (6), a transition piece (7) or a bypass duct (11) so as to form a first internal space (31) having a predetermined capacity; and a first throat (32) having a predetermined length which has one end (32a) open to a side wall (20a) of the object body (20) and has the other end (32b) open to a first internal space (31); wherein, a first resistive element (33) having a multiple number of through-holes is inserted and engaged to one end (32a). Fluid particles serving as vibration elements of combustion vibration caused in a combustion region are effectively trapped by the first resistive element (33) and at the same time resonate with the air of the first internal space (31) being connected through the first throat (32) and vibrate in the neighborhood of the first resistive element (33), thereby damping vibration amplitude thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
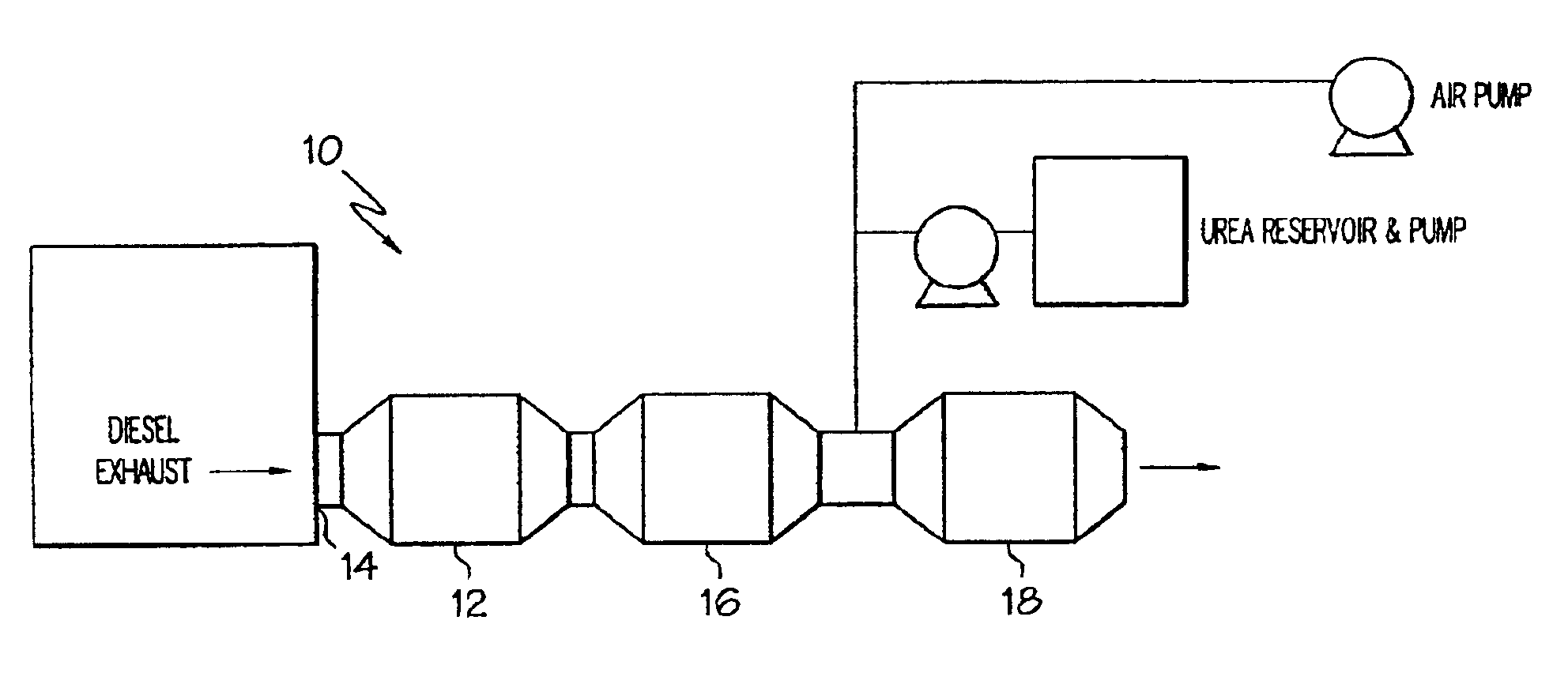
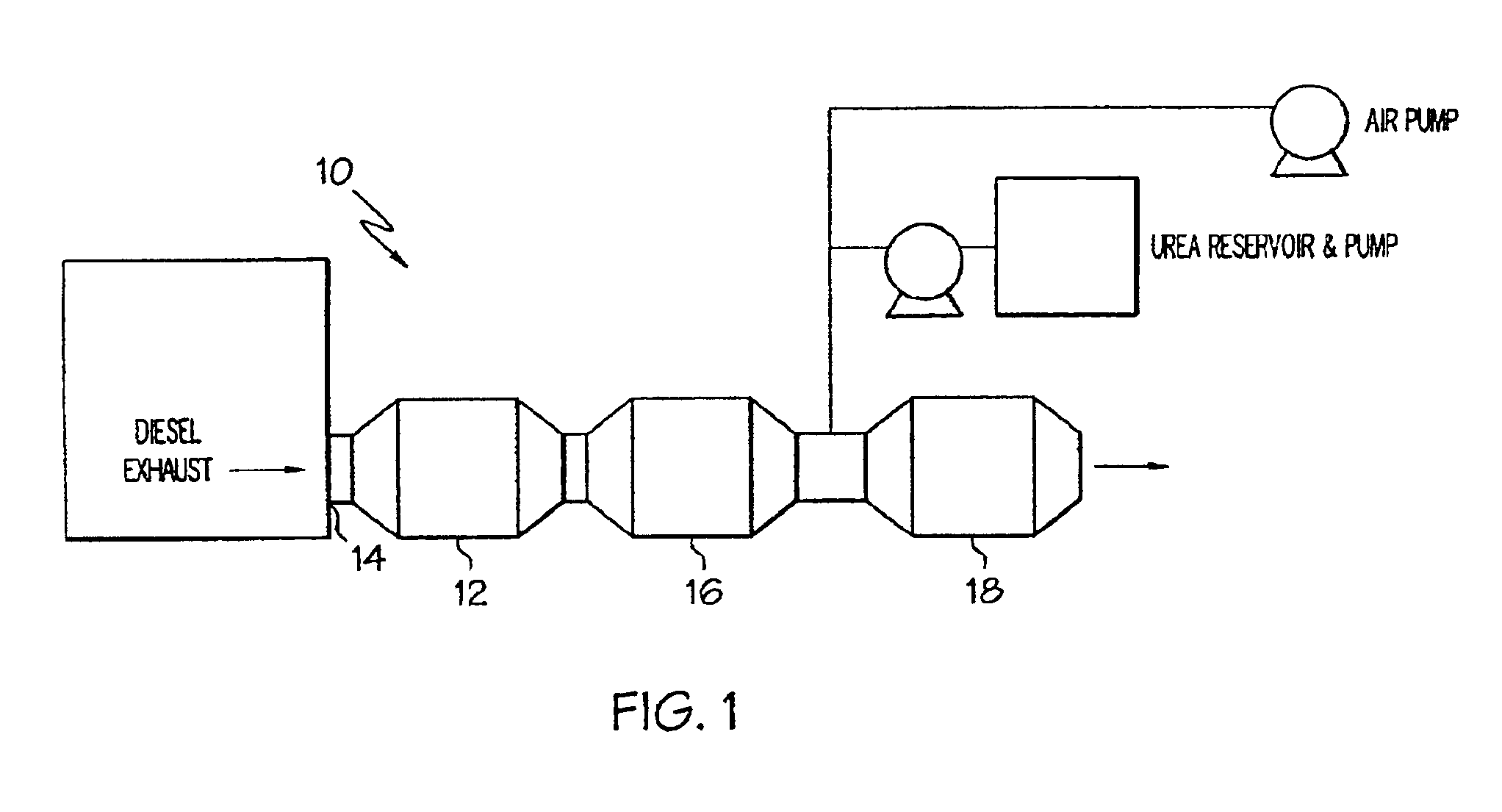
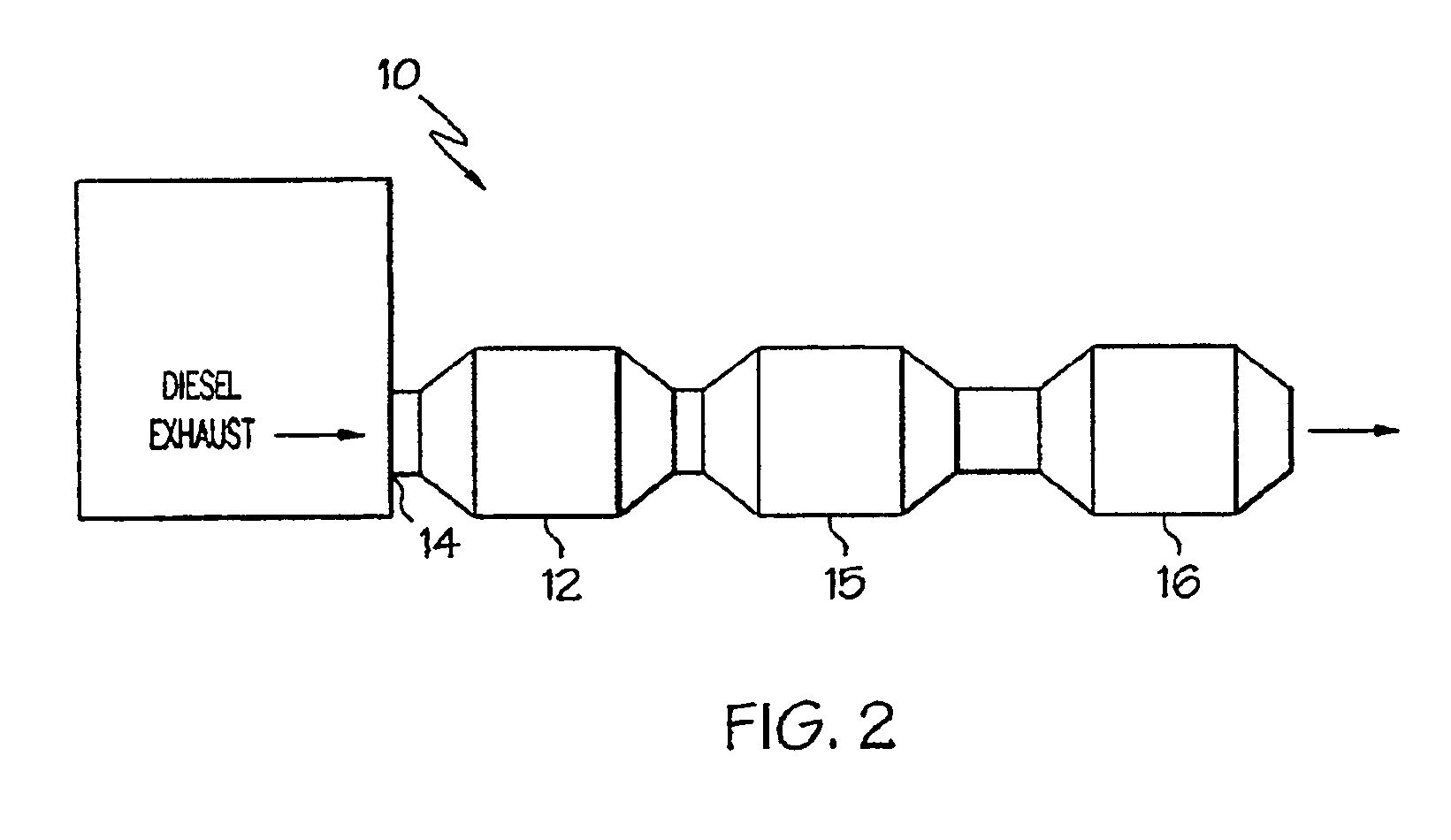
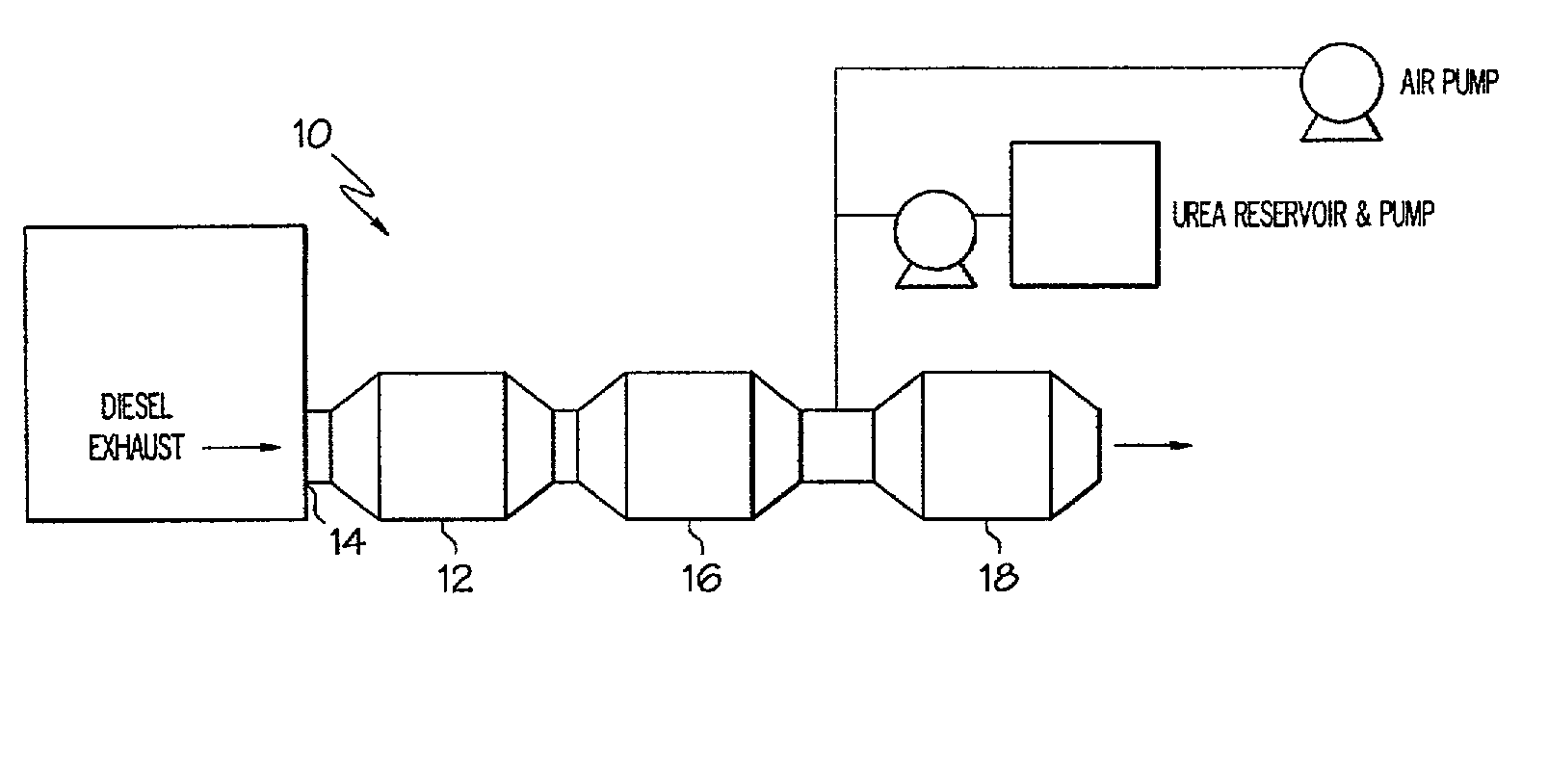
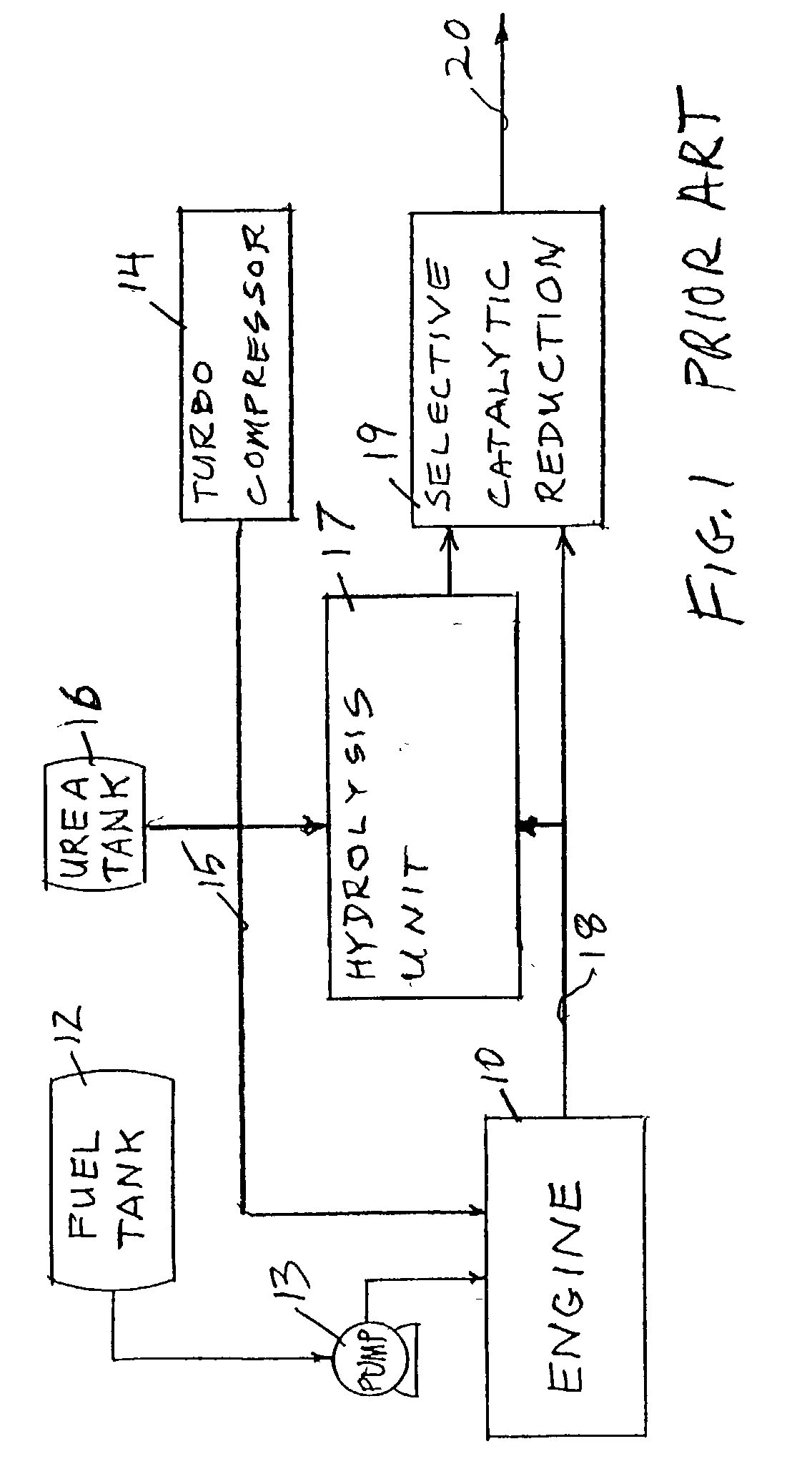
Method of treating diesel exhaust gases
InactiveUS6813884B2Promote regenerationReduce NOxExhaust apparatusDispersed particle separationParticulatesNitrogen
A diesel exhaust treatment system and method of oxidizing NO to NO.sub.2 at low temperatures are provided. The system utilizes a platinum catalyst on a zirconia-stabilized silica support which oxidizes NO in the exhaust gas to NO.sub.2 and uses the NO.sub.2 in an amount sufficient to oxidize particulate trapped on a particulate filter. The catalyst is preferably pre-treated at a temperature of between about 500 to 650.degree. C. in a NO-oxygen-nitrogen mixture to increase conversion at low temperatures. The catalyst preferably includes an additional oxide component selected from the group consisting of TiO.sub.2, P.sub.2 O.sub.5, WO.sub.3, B.sub.2 O.sub.3, and Al.sub.2 O.sub.3. or a heteropolyacid component to further increase activity at low temperatures or to decrease platinum loading at the same level of performance.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
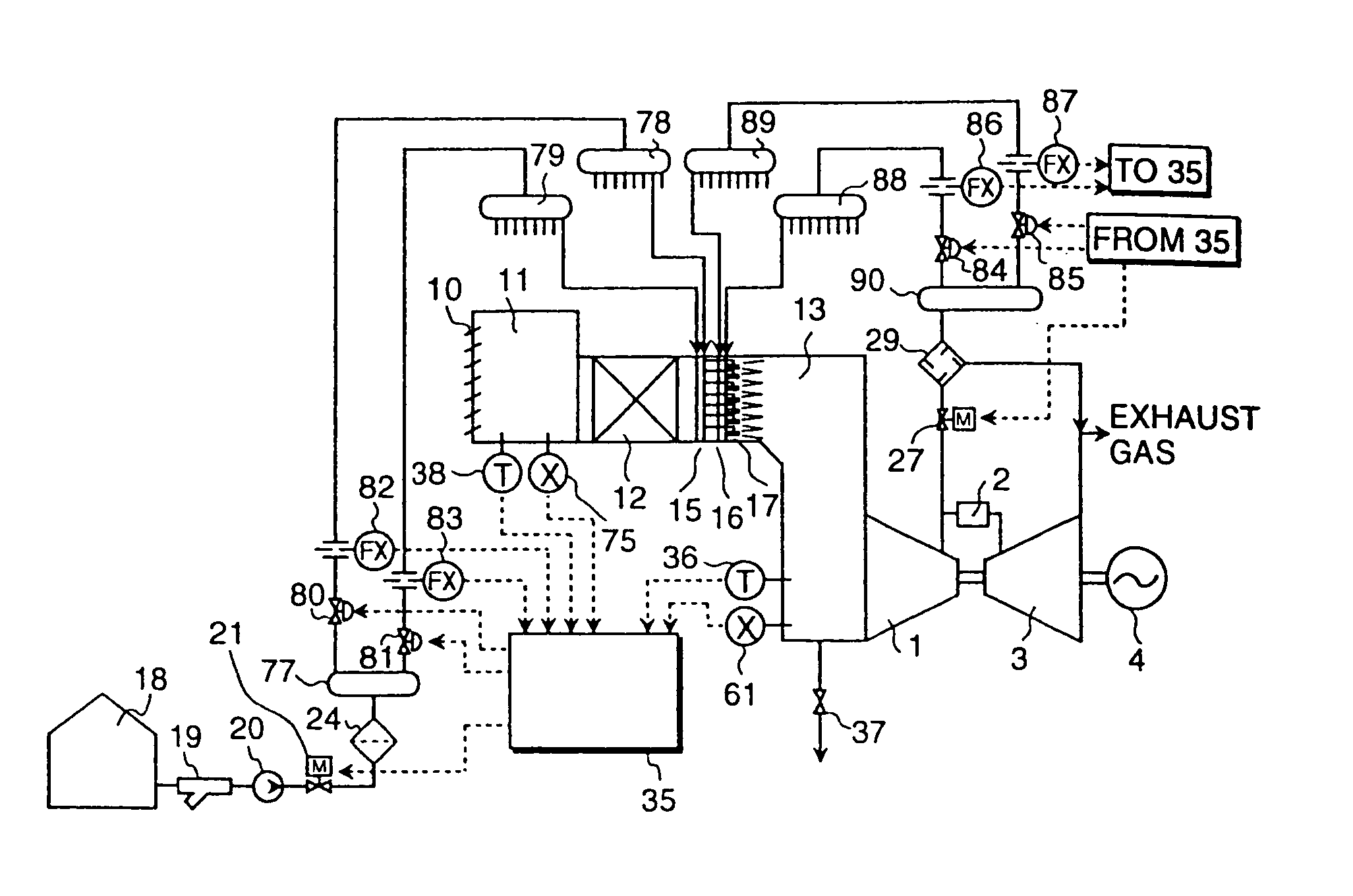
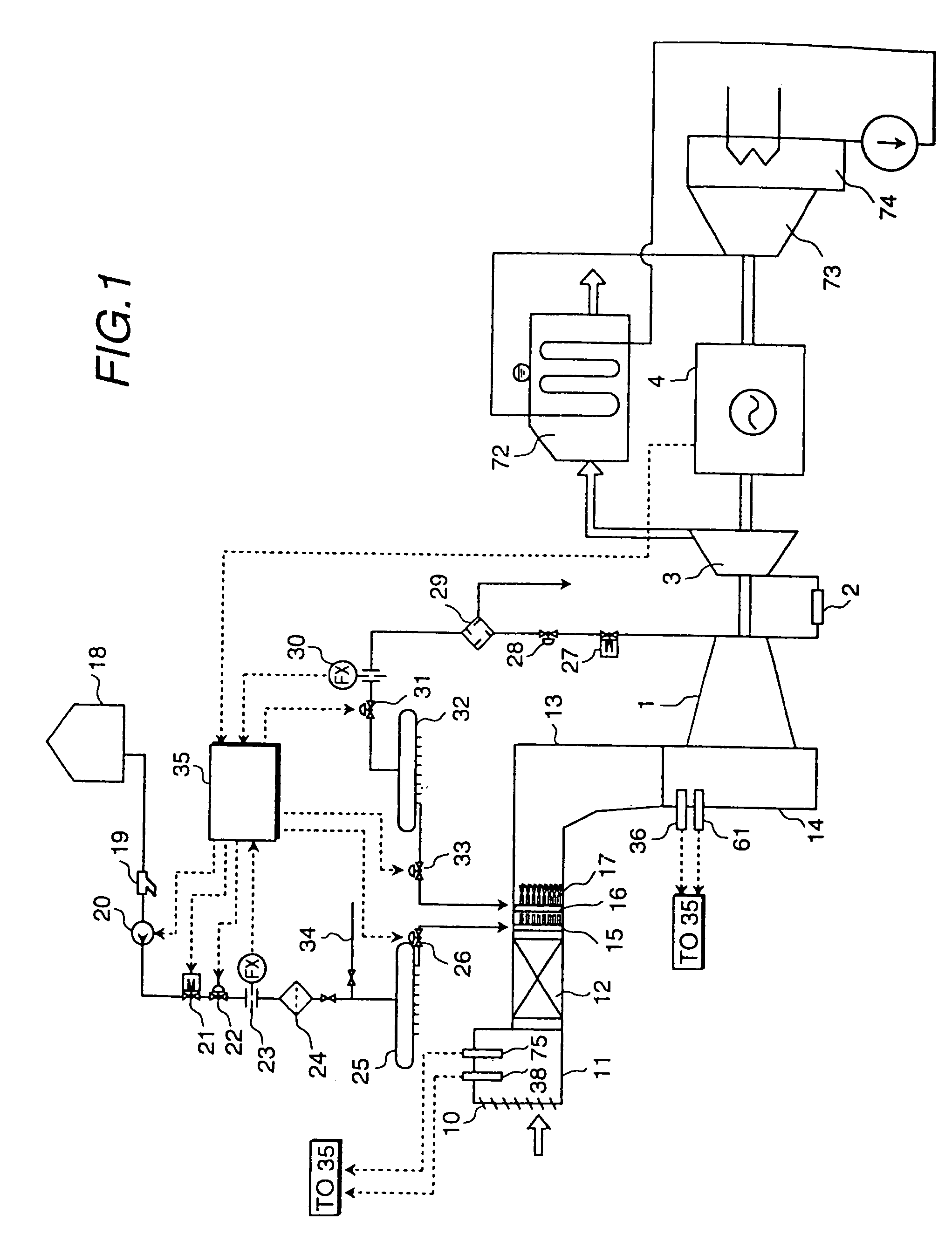
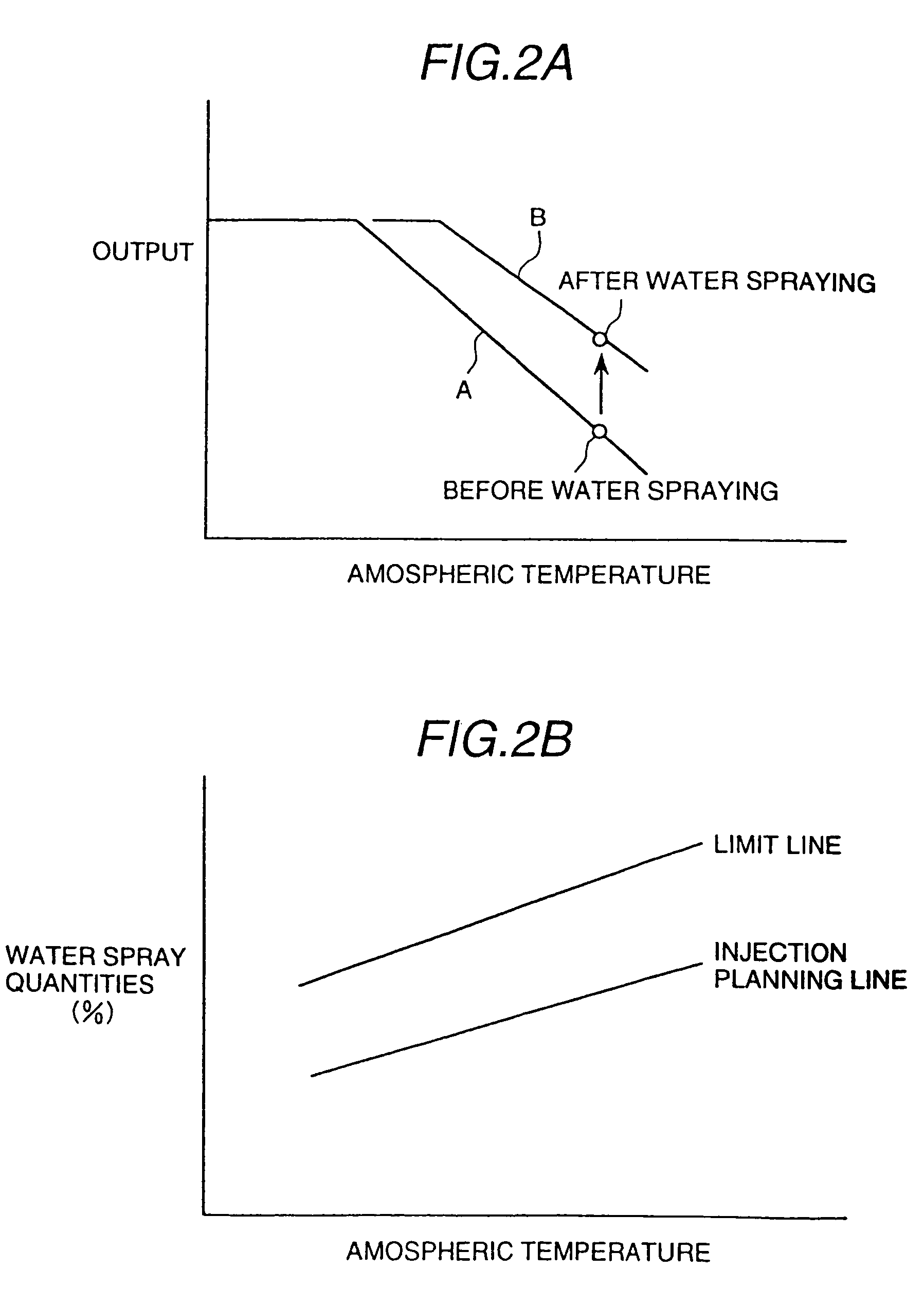
Gas turbine having water injection unit
InactiveUS7040083B2Low temperature of airIncrease productionTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionCombustorAtmospheric temperature
A gas turbine comprises a compressor for compressing a gas supplied therein and discharging the compressed gas, a combustor in which the discharged gas from the compressor and a fuel are combusted, a turbine to be driven by a combustion gas from the combustor, and a water injection unit which injects water into the gas to be supplied to the compressor, thereby lowering the temperature of the gas to be introduced into the compressor to a temperature lower than the atmospheric temperature, and causing water droplets having been injected in the gas and within the compressor to be vaporized while flowing down therein, wherein the quantity of water spray injection is controlled while monitoring operational conditions of the gas turbine.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method of treating diesel exhaust gases
InactiveUS20030140620A1Add supportHigh catalytic activityExhaust apparatusDispersed particle separationParticulatesNitrogen
A diesel exhaust treatment system and method of oxidizing NO to NO2 at low temperatures are provided. The system utilizes a platinum catalyst on a zirconia-stabilized silica support which oxidizes NO in the exhaust gas to NO2 and uses the NO2 in an amount sufficient to oxidize particulate trapped on a particulate filter. The catalyst is preferably pre-treated at a temperature of between about 500 to 650° C. in a NO-oxygen-nitrogen mixture to increase conversion at low temperatures. The catalyst preferably includes an additional oxide component selected from the group consisting of TiO2, P2O5, WO3, B2O3, and Al2O3. or a heteropolyacid component to further increase activity at low temperatures or to decrease platinum loading at the same level of performance.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
CATALYSTS, SYSTEMS, AND METHODS FOR REDUCING NOx IN AN EXHAUST GAS
InactiveUS20100101221A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsReduce NOxGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsExhaust fumesAmmonia
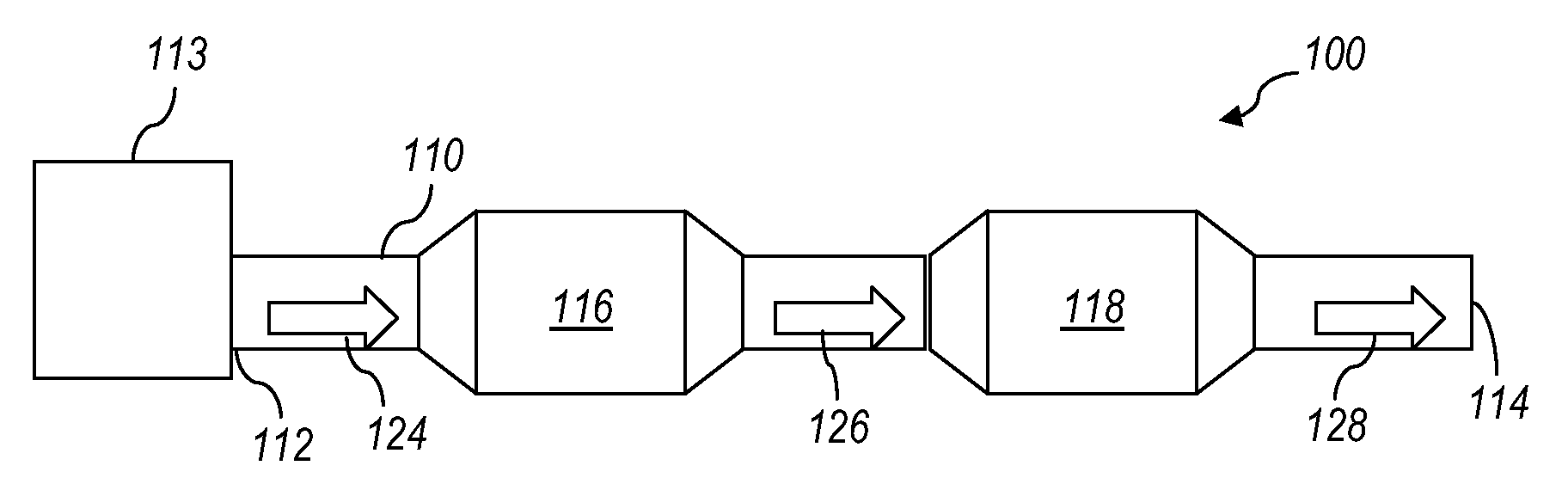
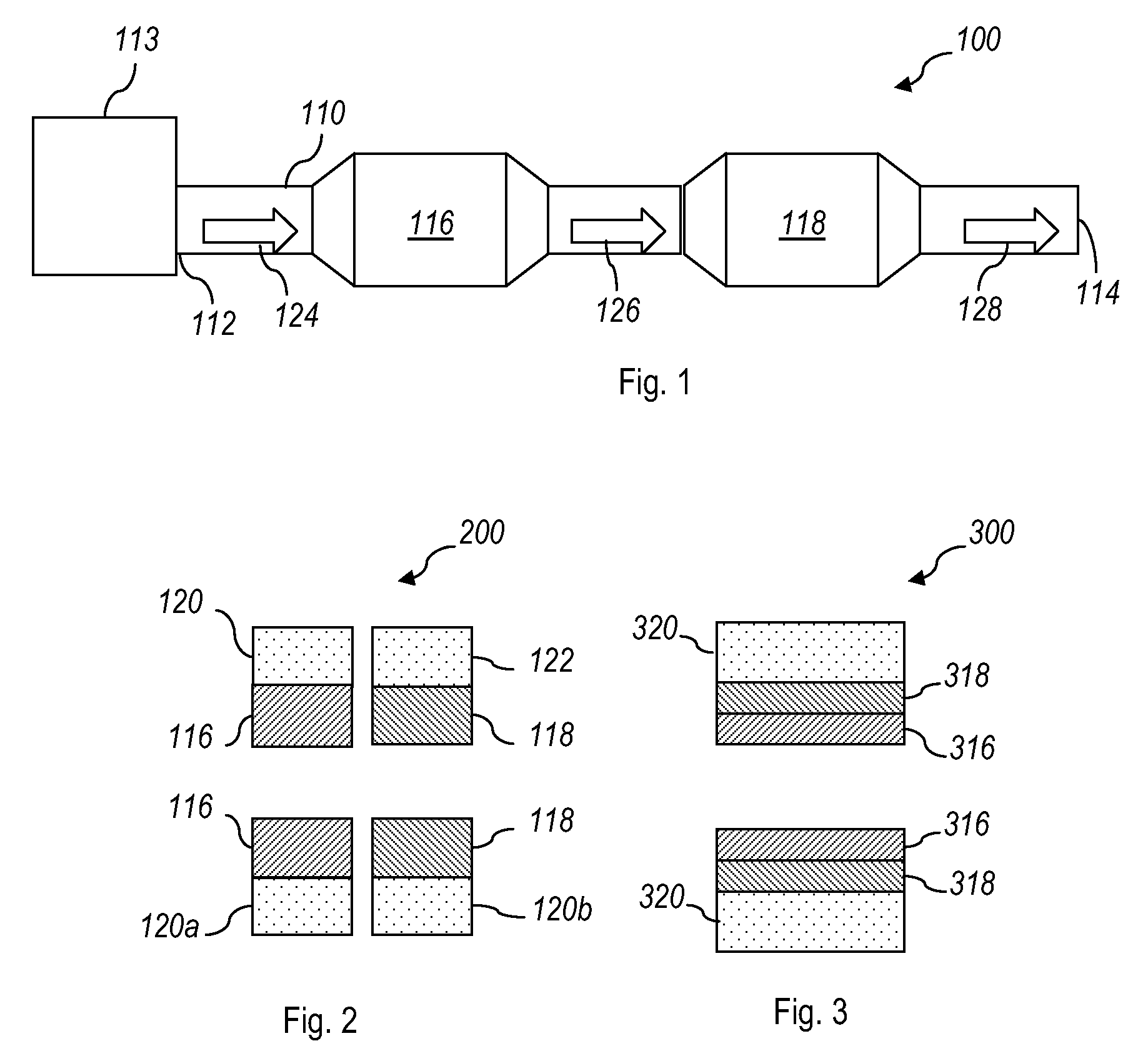
Catalysts, systems, and methods disclosed herein provide for reduced NOx emissions in the exhaust stream of a lean burning engine. The catalysts include two different types of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts (i.e., two different types of catalysts that may catalytically reduce NOx using a reductant). The first SCR catalyst (116) is an SCR catalyst having a composition that produces a reductant (e.g., an HC-SCR catalyst that produces ammonia) and the second catalyst (118) is an SCR catalyst (e.g., NH3-SCR) having a composition that reduces NOx using the reductant produced by the first SCR catalyst (116).
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
System and method for reducing NOx emissions in an apparatus having a diesel engine
InactiveUS20070062179A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsIncrease exhaust temperatureElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberExhaust valve
In a mechanical apparatus having a diesel engine including a combustion chamber, the mechanical apparatus also having an aftertreatment device configured to treat emissions from the diesel engine, an intake valve for passing air into the combustion chamber, and an exhaust valve for passing exhaust out of the combustion chamber, a method of operating the engine, wherein the method includes performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a first exhaust valve timing and a first intake valve closure timing; determining a temperature of the exhaust gas that enters the aftertreatment device; and if the temperature of the exhaust gas is equal to or below a preselected temperature threshold, then performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a second, earlier exhaust valve closure timing and a second later intake valve opening timing to thereby increase the internal exhaust gas recirculation and the temperature of exhaust emitted by the diesel engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
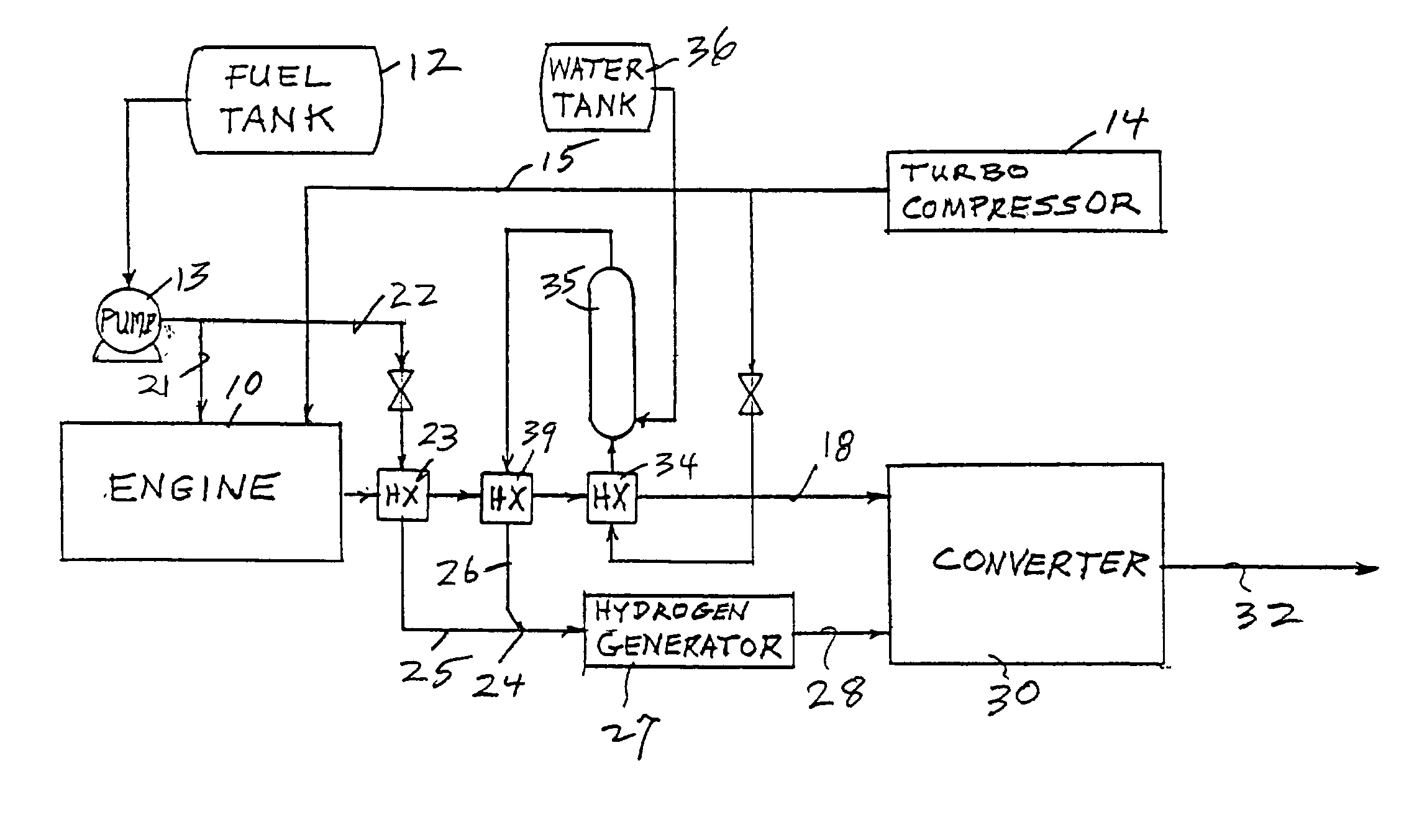
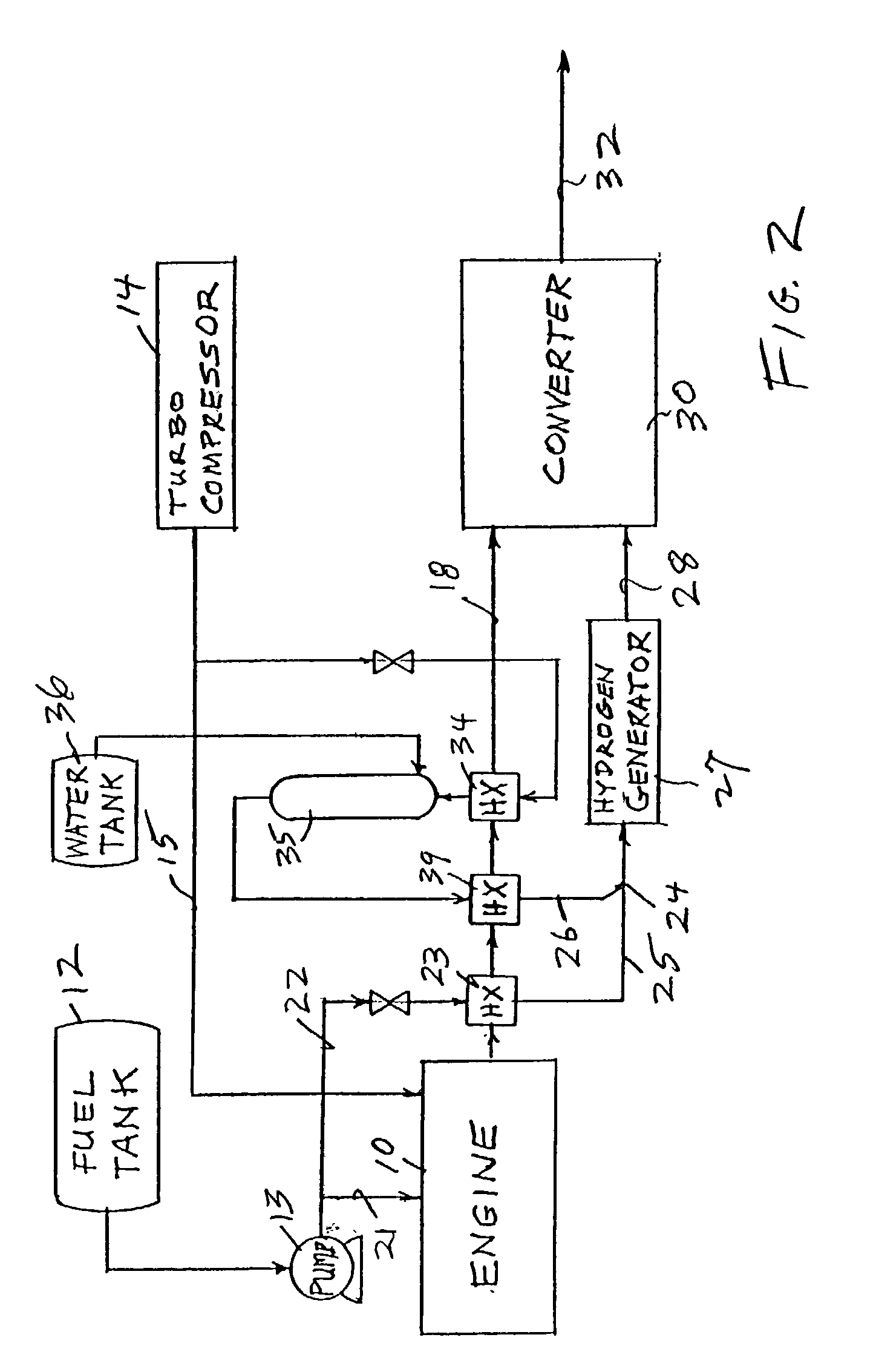
Reducing oxides of nitrogen using reformate generated from engine fuel, water and/or air
InactiveUS20030226350A1Reduce additionalSimple and low-cost hydrogen generationHydrogenInternal combustion piston enginesMethaneCatalytic converter
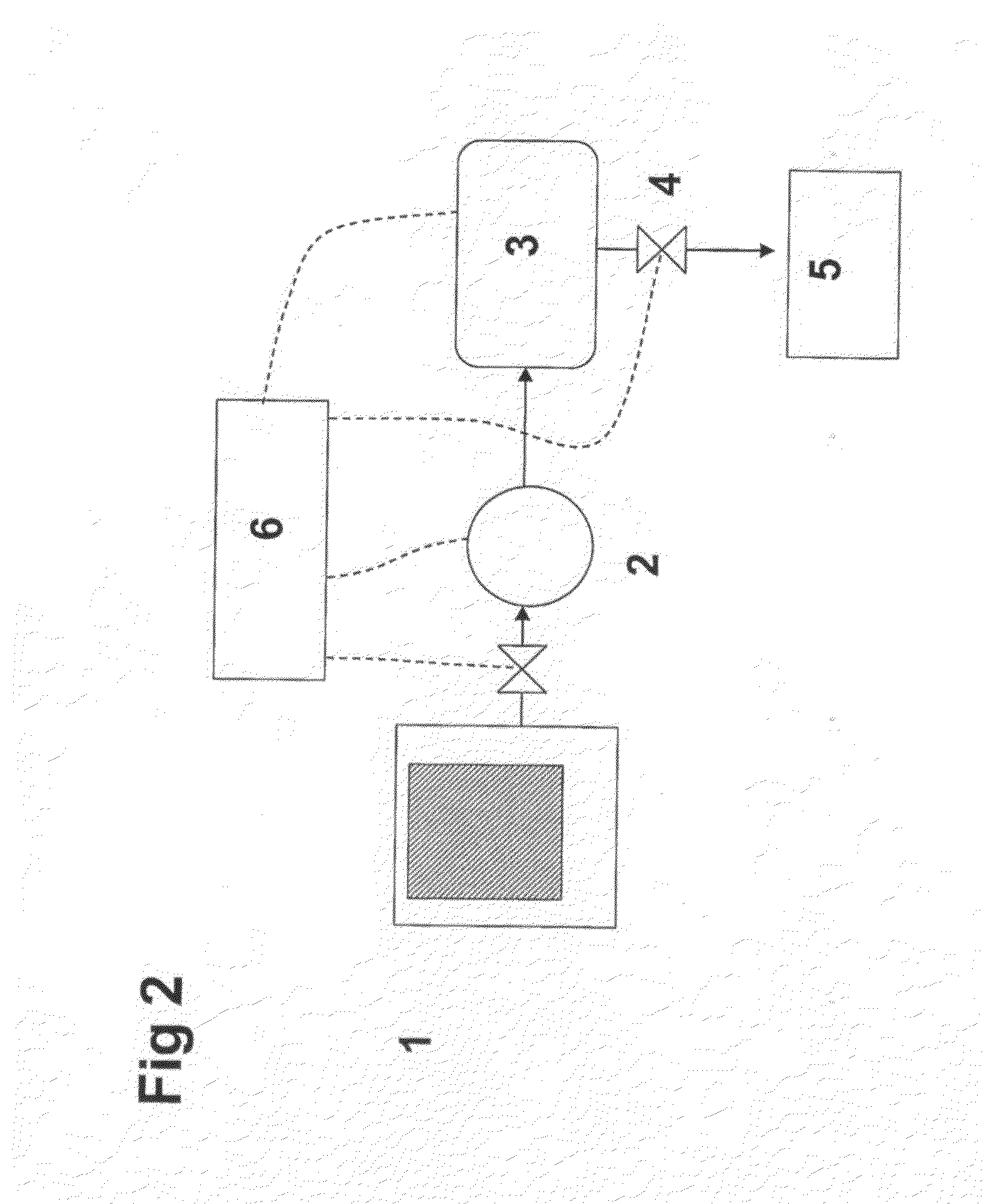
Inlet air (15) humidified in an air bubbling (or other) humidifier (35) that receives water from a tank (36) is sent to a hydrogen generator (27) along with vaporized (23) diesel fuel (22) to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide (28) for either (a) mixing with the mainstream of exhaust (18) fed to a catalytic converter (30) or (b) regenerating a pair of NOx adsorption traps (38, 39), thereby reducing oxides of nitrogen (NOx), to provide system exhaust (32) which may have less than 0.40 grams / bhp / hr of NOx and 0.28 grams / bhp / hr of non-methane hydrocarbons. In other embodiments, unhumidified air mixed with fuel feeds a homogeneous non-catalytic partial oxidizer (27) to provide the required hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Hybrid catalyst system for exhaust emissions reduction
InactiveUS20070033928A1Improve efficiencySpeed up the conversion processHydrogenGas treatmentExhaust fumesEngineering
One aspect of the invention relates an exhaust treatment system having an SCR reactor following a NOx adsorber. Syn gas is used to regenerate the NOx adsorber. Another aspect relates to an LNT / SCR provided with an ammonia source separate from the LNT. A further aspect relates to a system comprising first and second LNTs and one or more SCRs downstream of the LNTs. A still further aspect relates to a device comprising first and second NOx adsorbers contained in a single housing. Another aspect relates to coating a surface of a moving part in an exhaust system with an oxidation catalyst to mitigate fouling. Additional aspects of the invention relate to strategies for controlling one or more of the time to initiate a regeneration cycle, the time to terminate a regeneration cycle, and the reductant injection rate during regeneration of LNT / SCR exhaust treatment systems.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Exhaust gas purifier for use in internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20040154288A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsSuppressing impairment in THE exhaust gas performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesReduction driveExhaust fumes
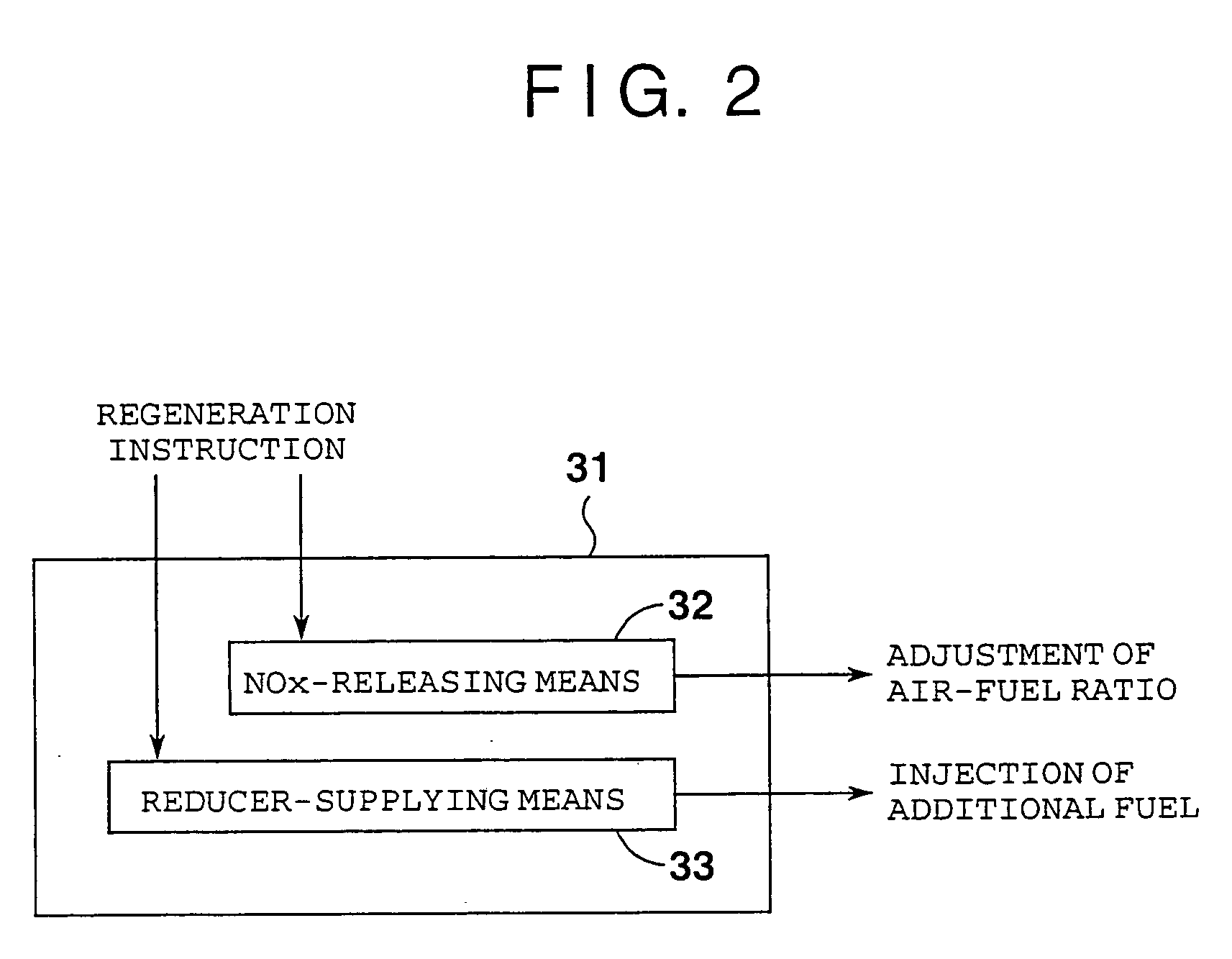
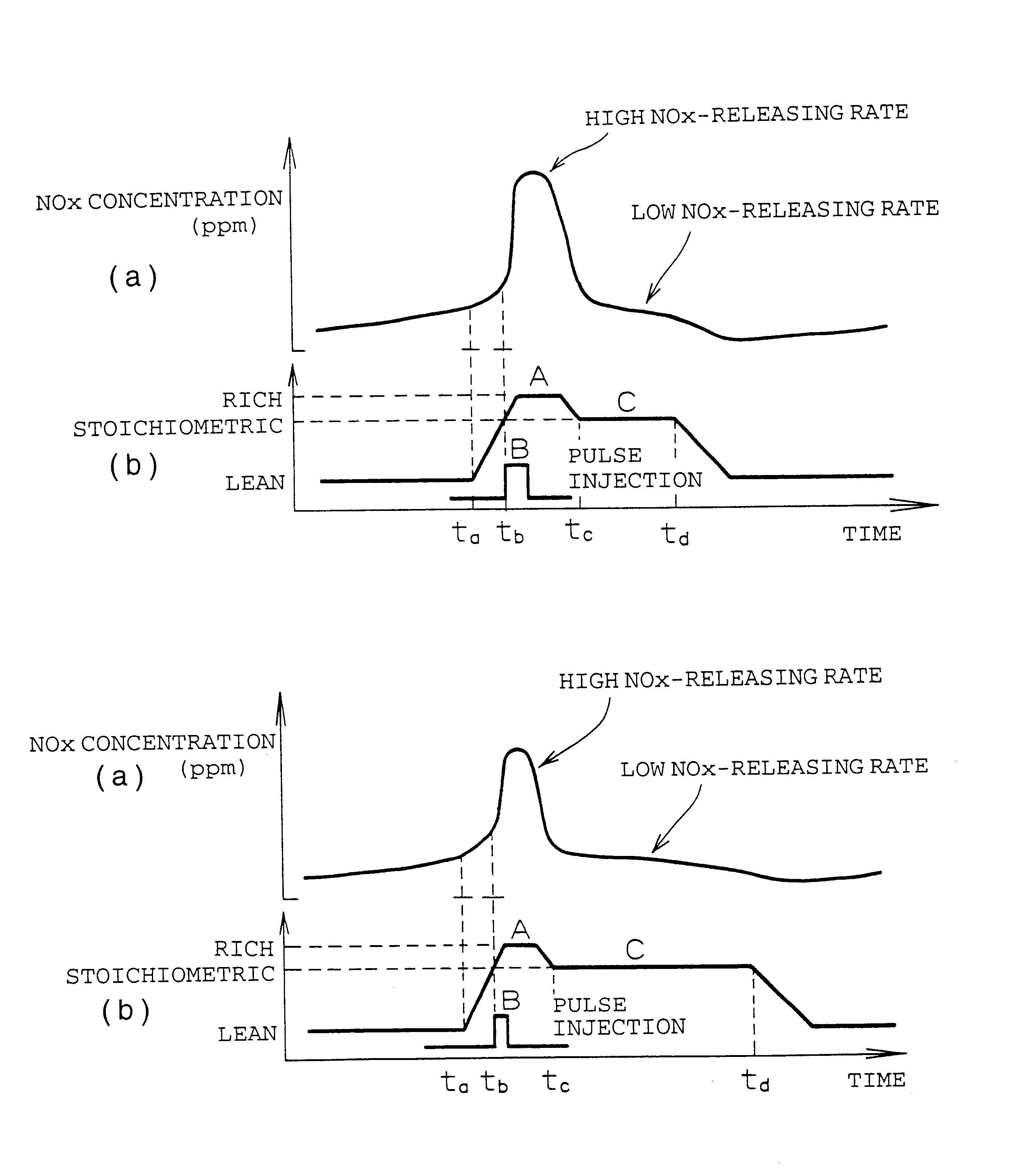
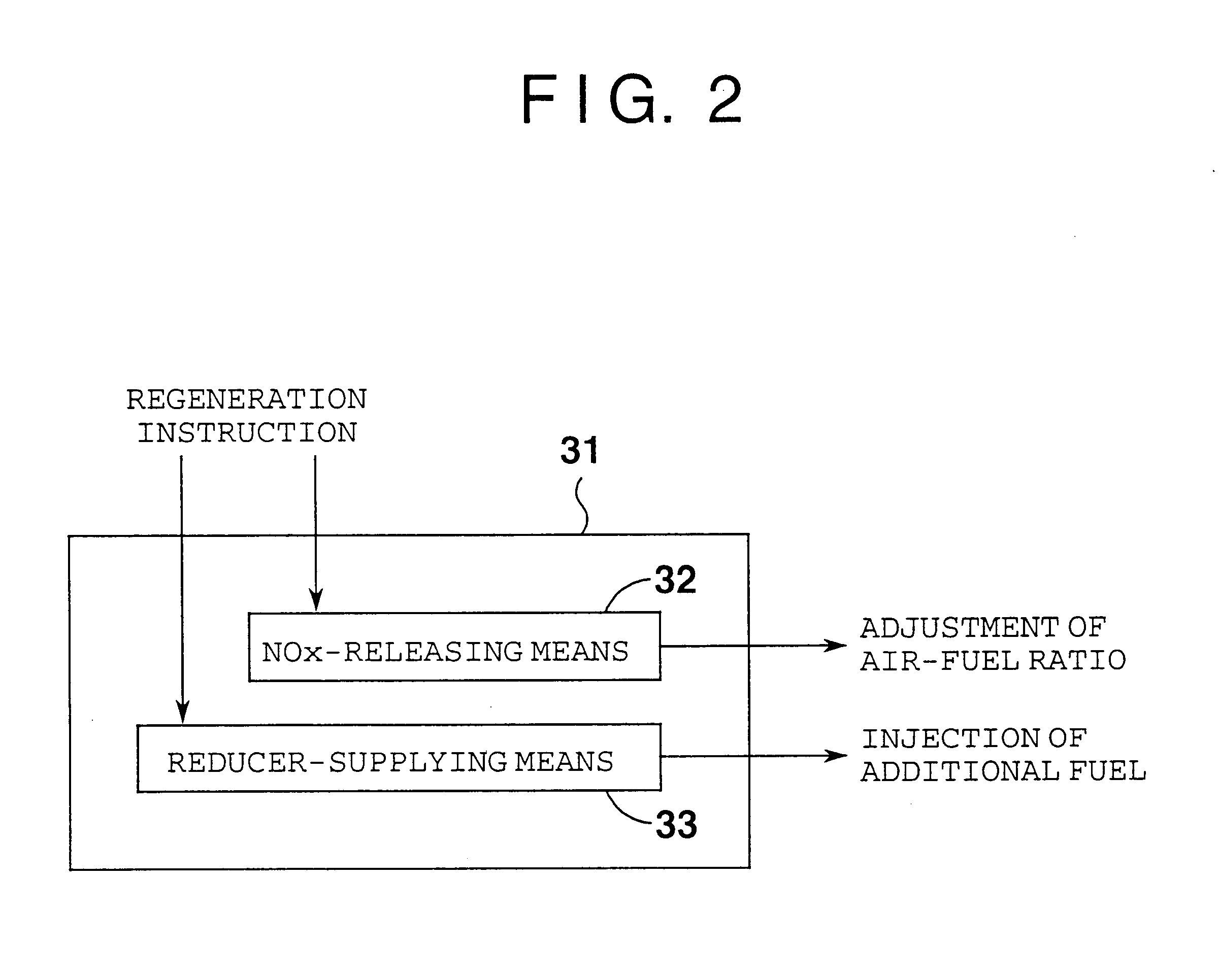
When a NOx-releasing unit is operated to change an air-fuel ratio to a rich side to thereby establish a low-oxygen-concentration atmosphere of an exhaust gas such that NOx is released from a NOx catalyst, a reducer-supplying unit additionally supplies a reducer during an operating period of the NOx-releasing unit for reducing NOx released into an exhaust path such that release of NOx balances with reduction of NOx, thereby reducing NOx released from the NOx catalyst and thus suppressing worsening of exhaust gas performance.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Multi-fuelling an engine
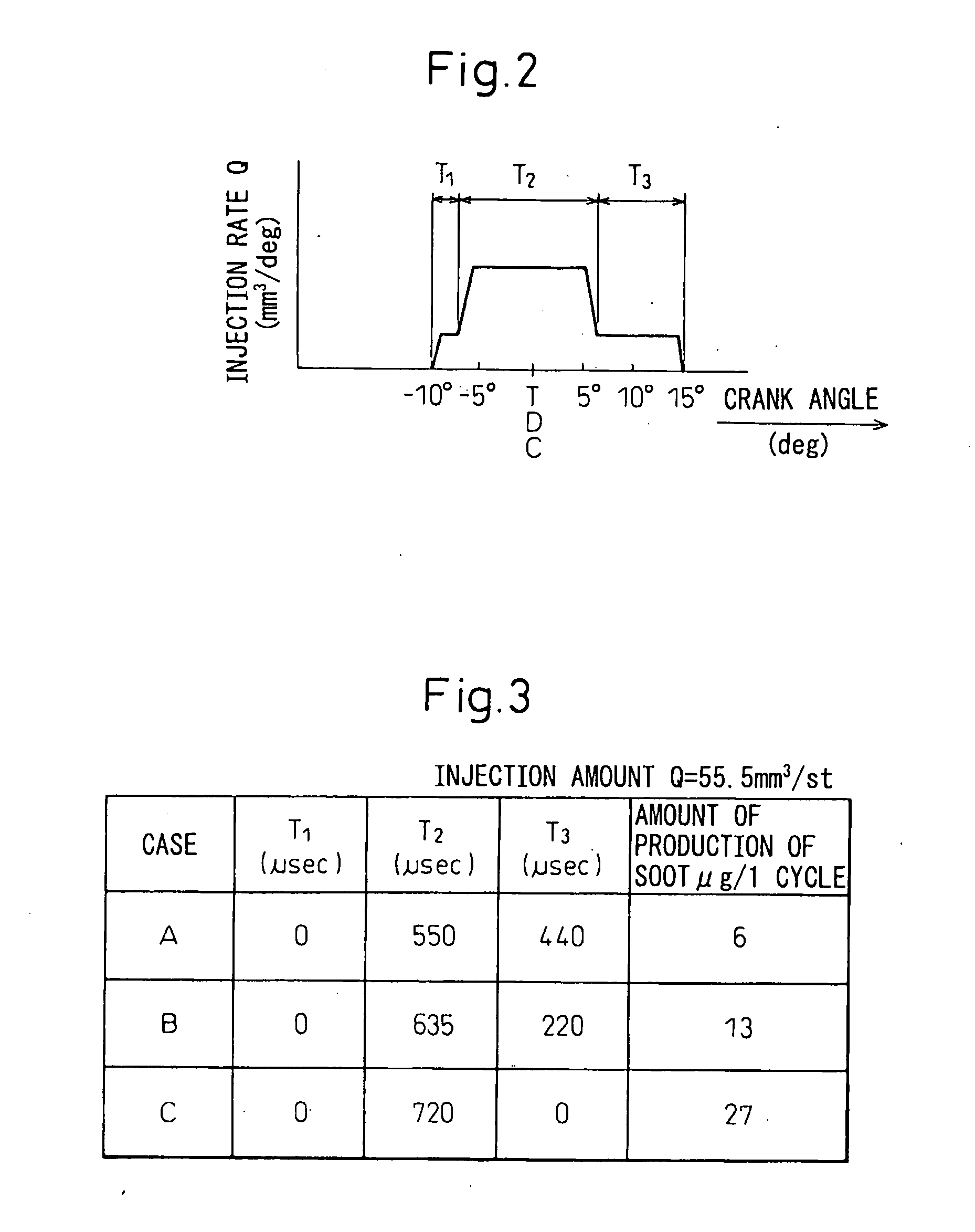
InactiveUS20110088654A1Reduce NOxReduce soot emissionsElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBiodieselCombustion chamber
A compression ignition engine is supplied with a first fuel in a flow of air and a second fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The first fuel comprises a more volatile fuel than diesel such as ethanol, LPG or other combustible gas; the second fuel comprises diesel or biodiesel; and the second fuel is injected in multiple pulses in each ignition cycle with the first pulse acting as a pilot pulse to trigger ignition, and the timing of the second pulse being such as to modify the temperature through evaporation of the second fuel and thereby reduce the combustion temperature and mitigate knock susceptibility. Preferably the pilot pulse is followed by a single further pulse of the second fuel in the ignition cycle. The engine may be controlled to operate in two different modes, one mode for light and medium load conditions when there is only a pilot pulse injection of the second fuel which reduces NOx and soot emissions, and the other mode for higher load conditions when there is a pilot pulse injection followed by a main pulse injection of the second fuel. The first fuel may comprise bioethanol and or one or more of the following: ethanol, butanol, propanol, lpg, natural gas, hydrogen.
Owner:G VOLUTION
Two-shaft gas turbine
ActiveUS20090320438A1Avoid excessive rotationLow efficiencyEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsWorking fluidCombustor
Provided is a two-shaft gas turbine with improved reliability that improves output power and efficiency and is stably operated by establishing a balance between the driving force of a compressor and the output power of a high-pressure turbine in the case where the two-shaft gas turbine is applied to a system in which the flow rate of fluid flowing into a combustor is increased compared with a simple cycle gas turbine.A portion of working fluid driving the high-pressure turbine is allowed to flow not into the high-pressure turbine but into a low-pressure turbine.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Apparatus and method for clarifying exhaust gas of diesel engine
InactiveUS20060107649A1Speed is fastShorten speedCombination devicesElectrical controlDiesel particulate filterExhaust fumes
An apparatus for purifying an exhaust gas of a diesel engine, characterized in that it has an NOx adsorption and reduction type catalyst and a diesel particulate filter for oxidizing and removing particulate matters in the exhaust gas, which are provided in the flow route for the exhaust gas and are arranged in the above described order from the upstream of the flow of the exhaust gas. The above arrangement allows the elevation of the temperature of the catalyst with ease and the precise control of the temperature and atmosphere therein, resulting in the achievement of satisfactory NOx purification performance, and the employment of the NOx adsorption and reduction type catalyst allows the enhancement of the rate of reduction of the NO2 captured, which shortens the time to keep a stoichiometric-rich atmosphere to a time of several seconds to several minutes.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and device for safe and controlled delivery of ammonia from a solid ammonia storage medium
InactiveUS20100293927A1Facilitated releaseReduce the temperatureInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusGas phaseDesorption
Solid metal ammine complexes are applied for safe and high-density storage of ammonia to be released for use as reducing agent in selective catalytic reduction of NOx in exhaust gases. The compositional formula of the metal ammine complexes is M(NH3)nXz, where MZ+ represents one or more metal ions capable of binding ammonia, X represents one or more anions, n is the coordination number (from 2 to 12), and z the valency of the metal ion (and thus the total number of compensating anion charges). Ammonia is released by generating a reduced gas-phase pressure of ammonia inside the container, which is below the equilibrium desorption pressure of ammonia at the operating temperature of the storage material thus enabling the unit to be operated is a safe manner with lower operating temperature and pressure.
Owner:AMMINEX
Injection methods to reduce nitrogen oxides emission from gas turbines combustors
InactiveUS20050000220A1Inhibition formationHigh nitrogen oxide reductionDispersed particle separationGas turbine plantsCombustorNitrogen oxides
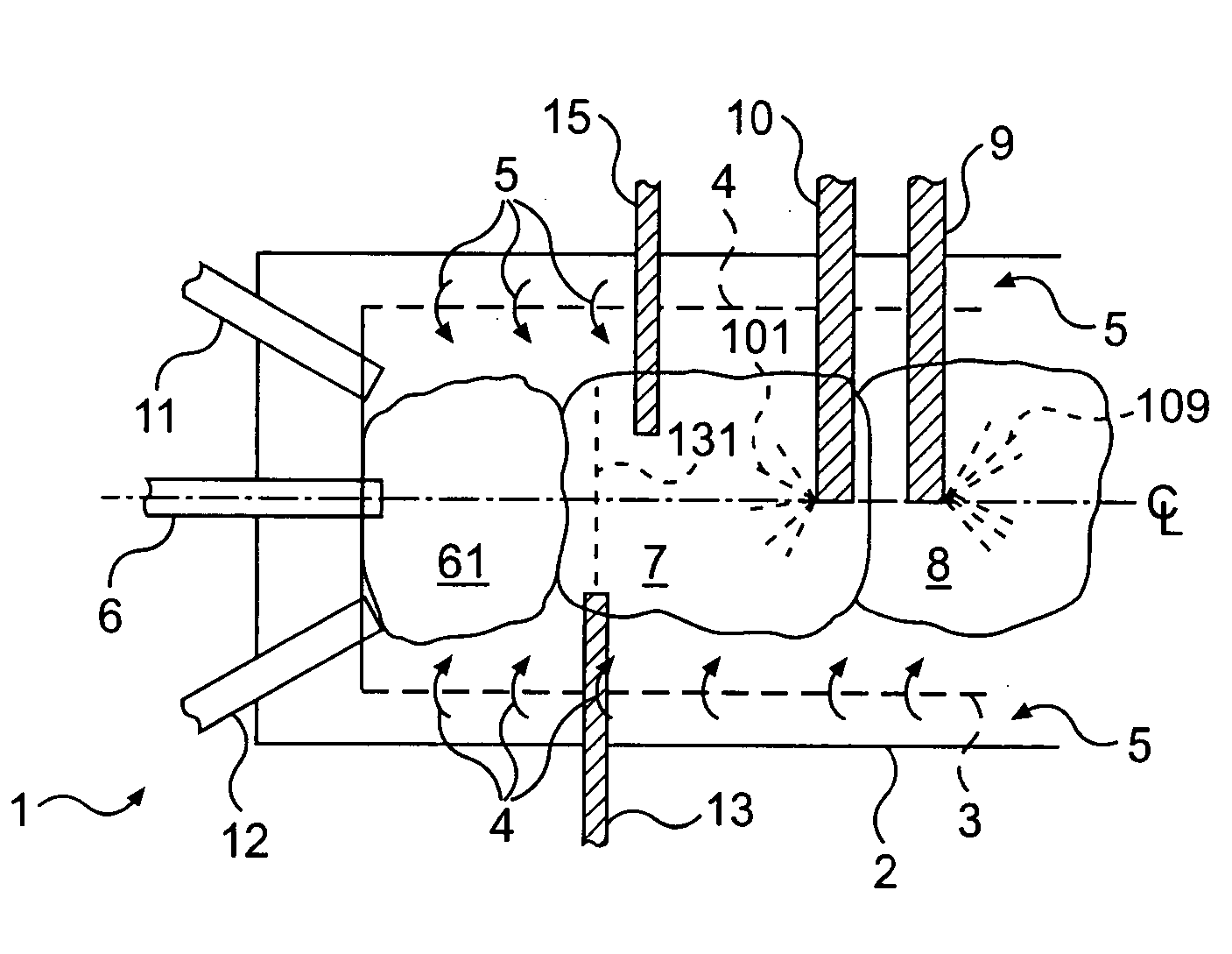
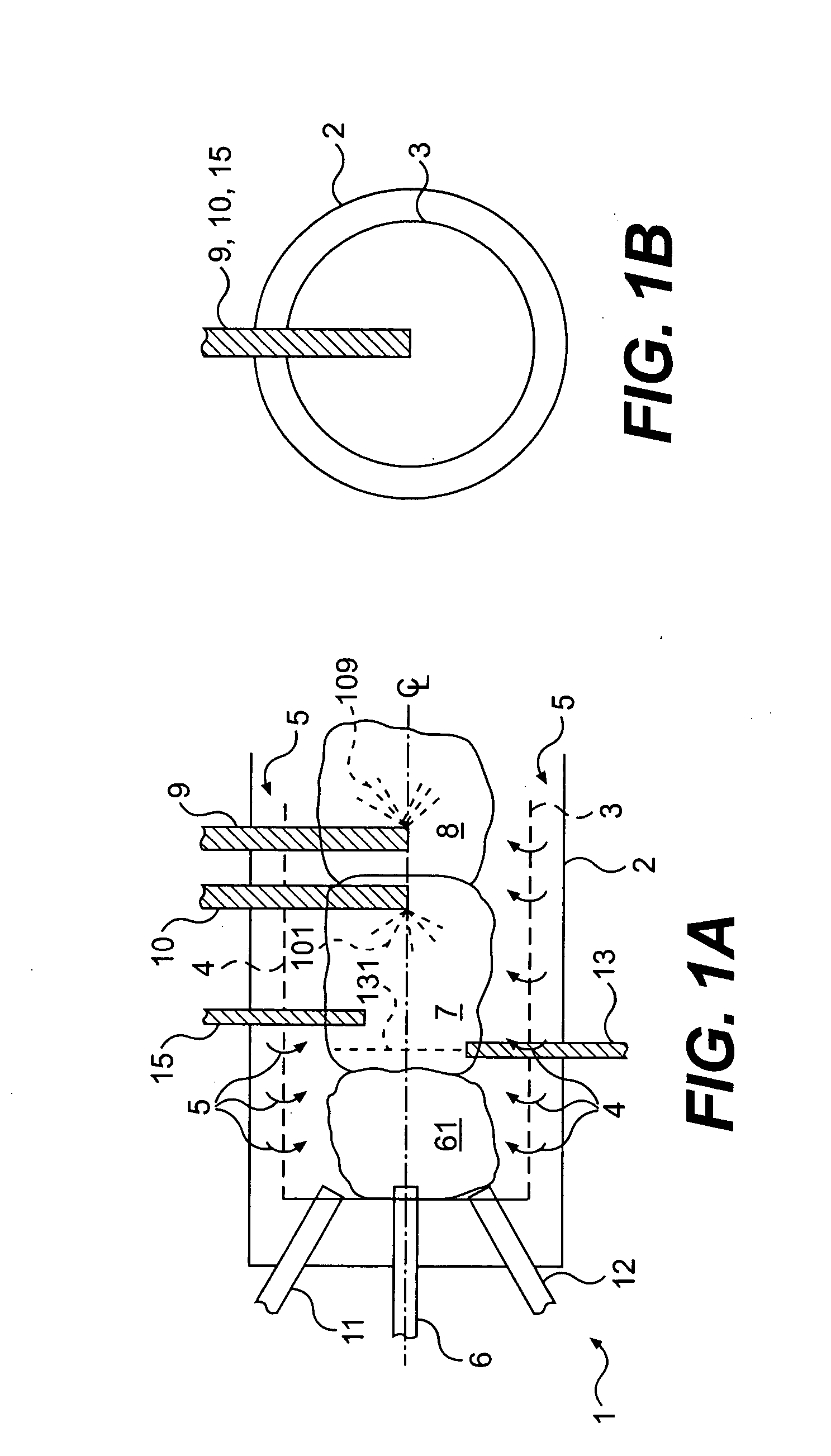
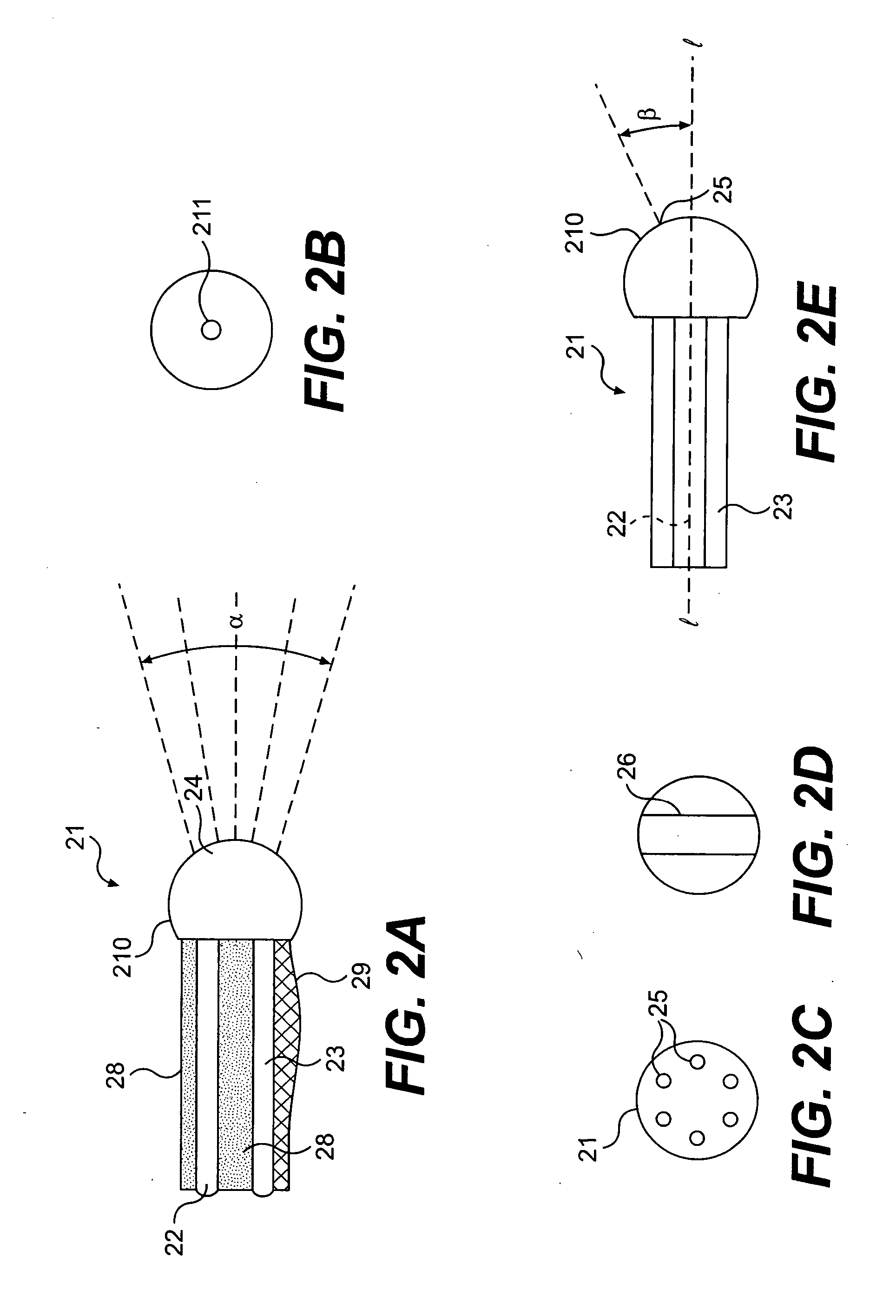
A process having three steps utilized individually or in combination to reduce nitrogen oxides, NOx, emissions from gas turbines. One or more injectors disperse very fine fuel droplets to achieve rapid and complete combustion in zone one immediately downstream of the fuel injectors. The second step uses one or more injectors inserted into the combustor to disperse water droplets throughout zone two, immediately downstream of zone one, to lower the gas temperature and suppress formation of thermal NOx,. The third step uses one or more injectors to disperse aqueous droplets containing a dissolved NOx reducing agent throughout zone three, immediately downstream of zone two, and whose gas temperature favors the reduction of NOx. Alternatively, the dissolved NOx reducing agent can be mixed with a liquid fuel to convert zone three into slightly fuel rich conditions, enabling nitrogen oxide reduction at higher gas temperatures.
Owner:ZAUDERER BERT
Method for engine condition control with turbocompressor controllable bypass
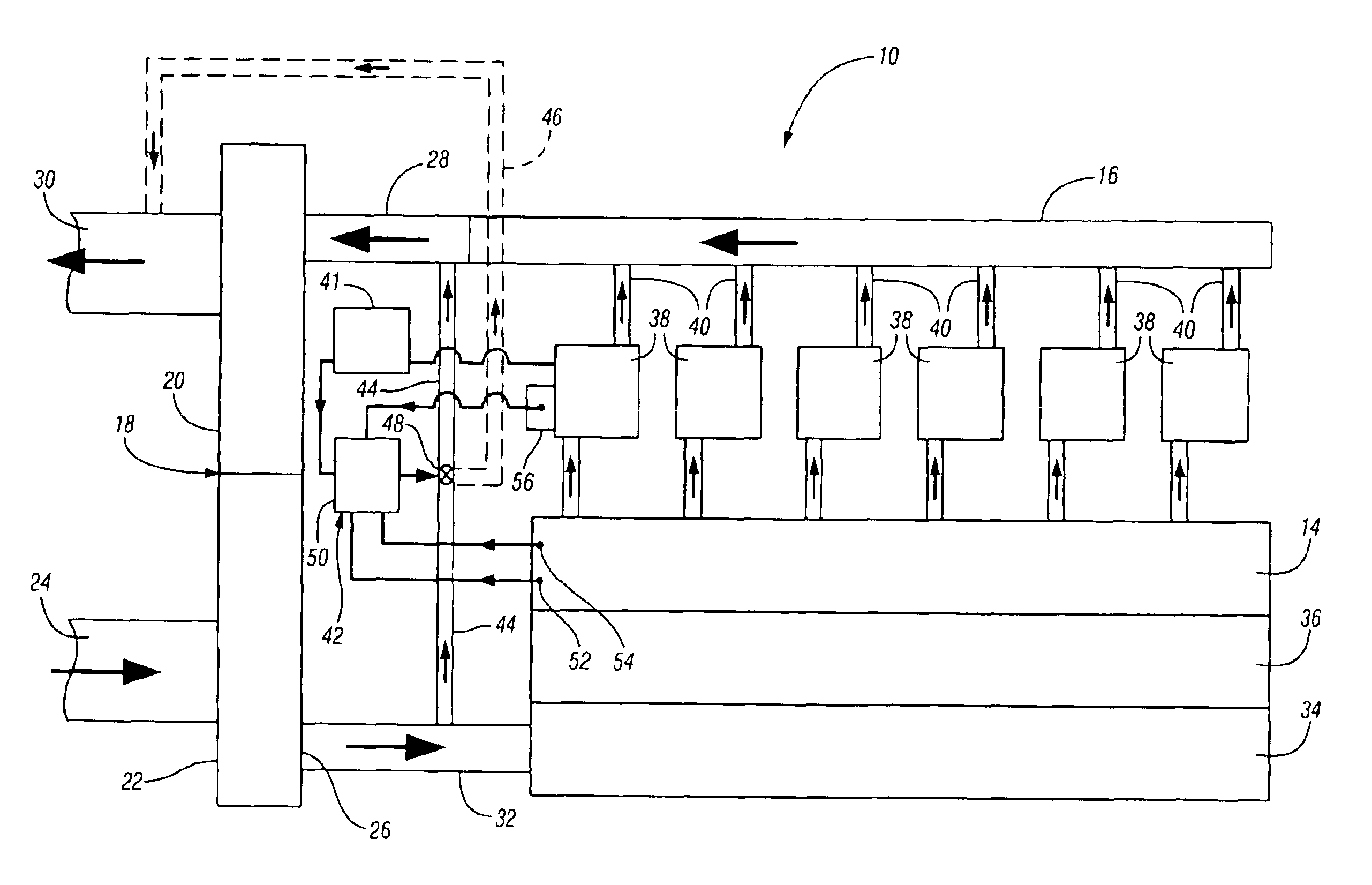
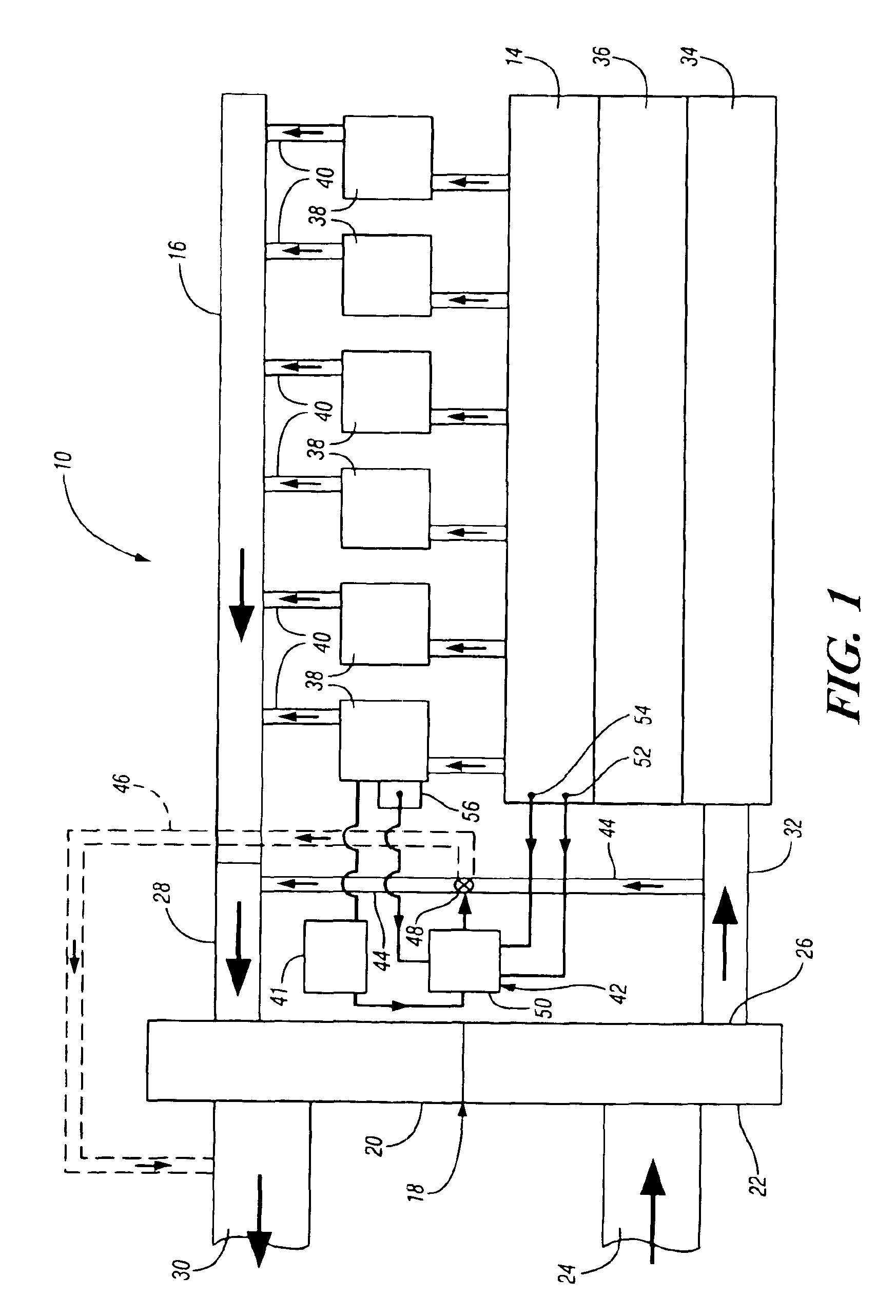
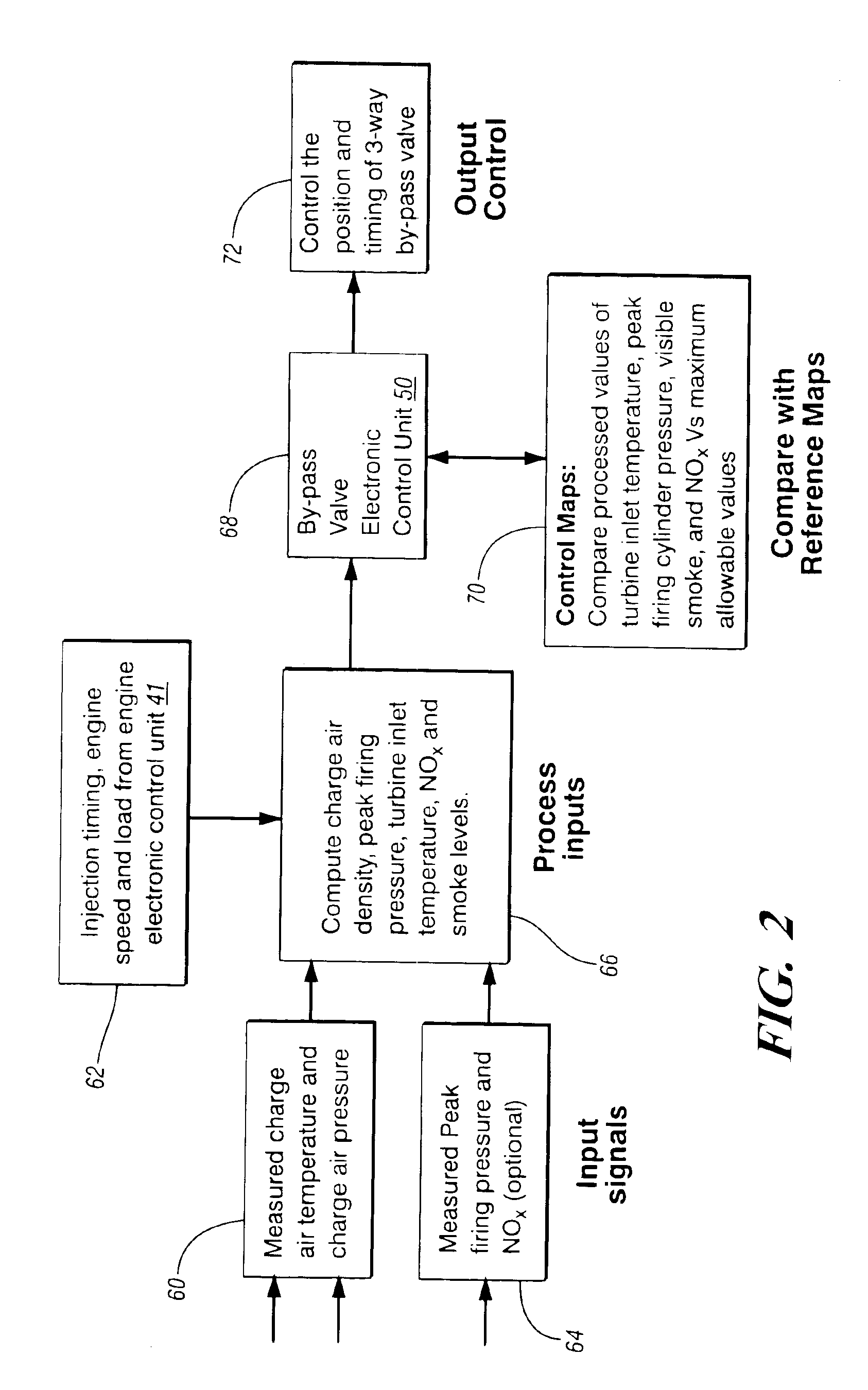
InactiveUS6912852B2Fast dynamic responseHigh pressureInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersTurbochargerExhaust fumes
A system for a turbocharged internal combustion engine includes an engine having a charge inlet connected to the compressor outlet and an exhaust outlet connected to the turbine inlet for driving the turbocharger with hot exhaust gas and supplying compressed air to the engine for combustion. A bypass duct connects the compressor outlet to the turbine inlet for diverting a portion of the compressed air around the engine to the turbine inlet or exhaust. A control device selectively controls the diversion of air. An operating method for the system involves controlling peak cylinder firing pressure and / or maximum turbine inlet temperature, optionally with exhaust NOx and smoke in order to limit these variables to acceptable limits with a minimum of operational limitations.
Owner:ELECTRO-MOTIVE DIESEL
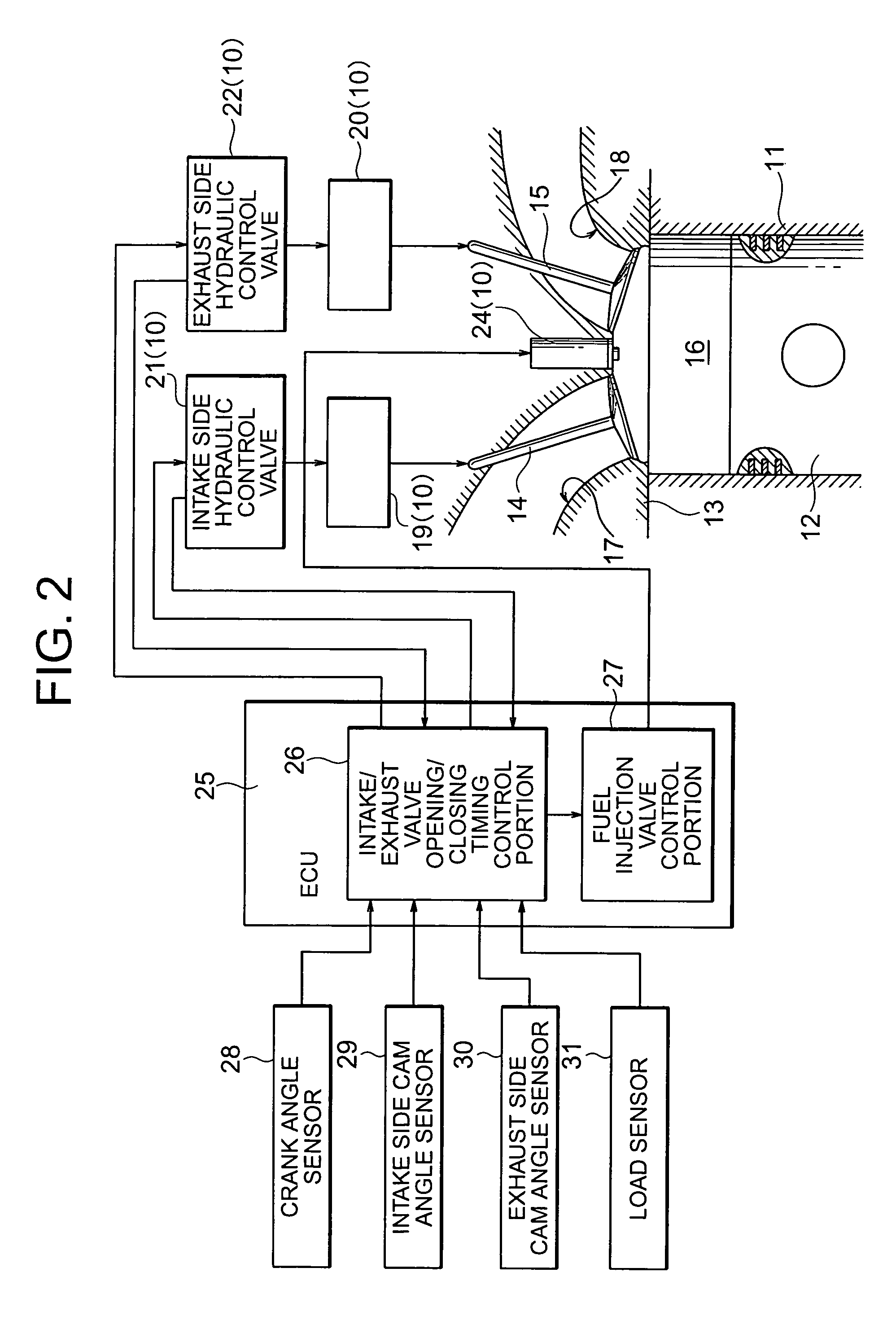
Internal combustion engine and control device for the internal combustion engine
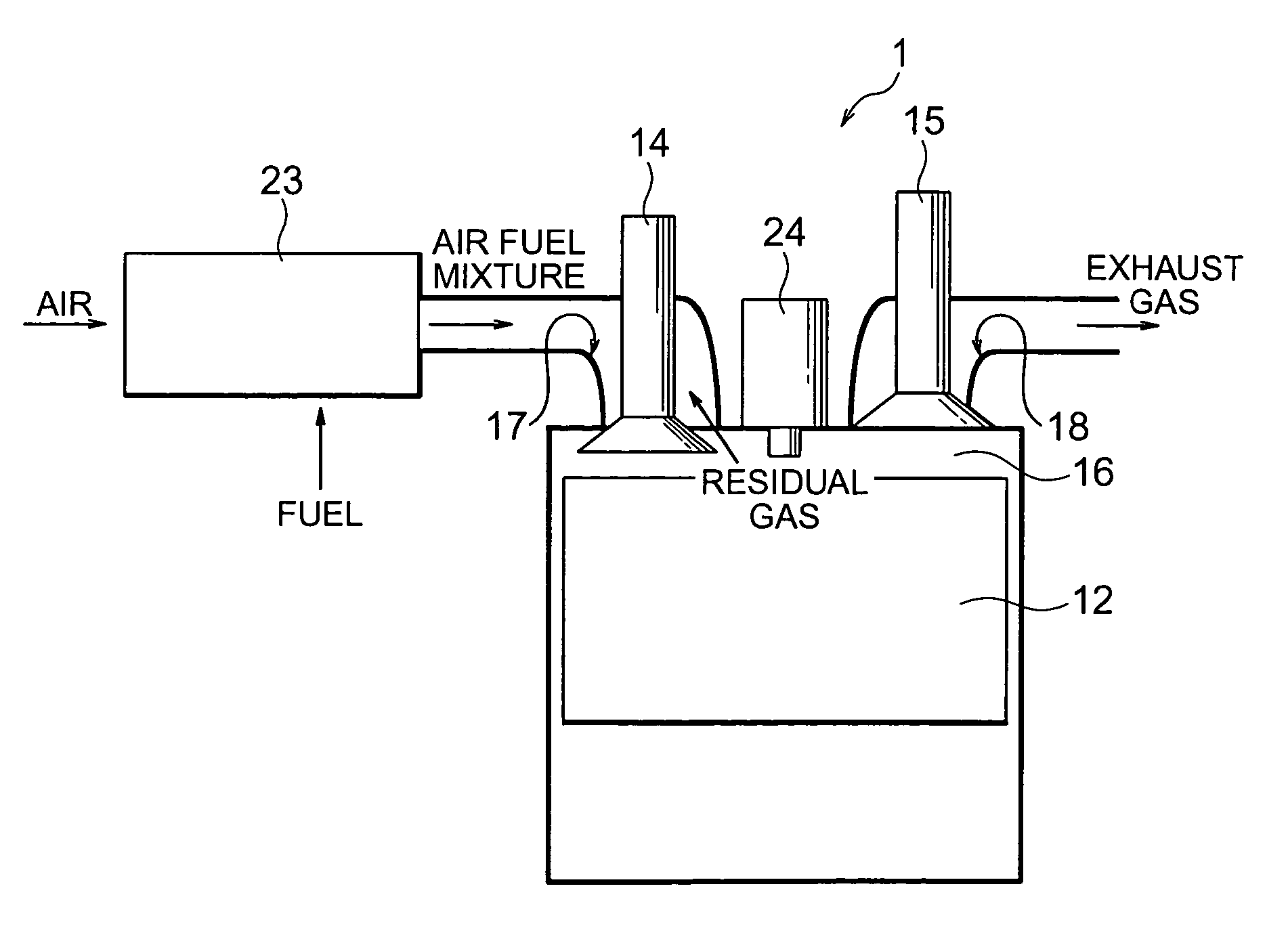
ActiveUS7051700B2Improve thermal efficiencyImprove flammabilityValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberExhaust valve
Disclosed is an internal combustion engine in which it is possible to provide, from the exhaust stroke to the intake stroke, a period T during which both an intake valve (14) and an exhaust valve (15) remain closed, the internal combustion engine being equipped with a fuel injection valve (24) capable of injecting fuel into a combustion chamber (16), the closing time EVC for the exhaust valve (15) being set to be on the advance side with respect to the intake top dead center, the fuel injected from the fuel injection valve (24) being pressurized together with a residual gas inside the combustion chamber (16) during the period T in which both the intake valve (14) and the exhaust valve (15) remain closed.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
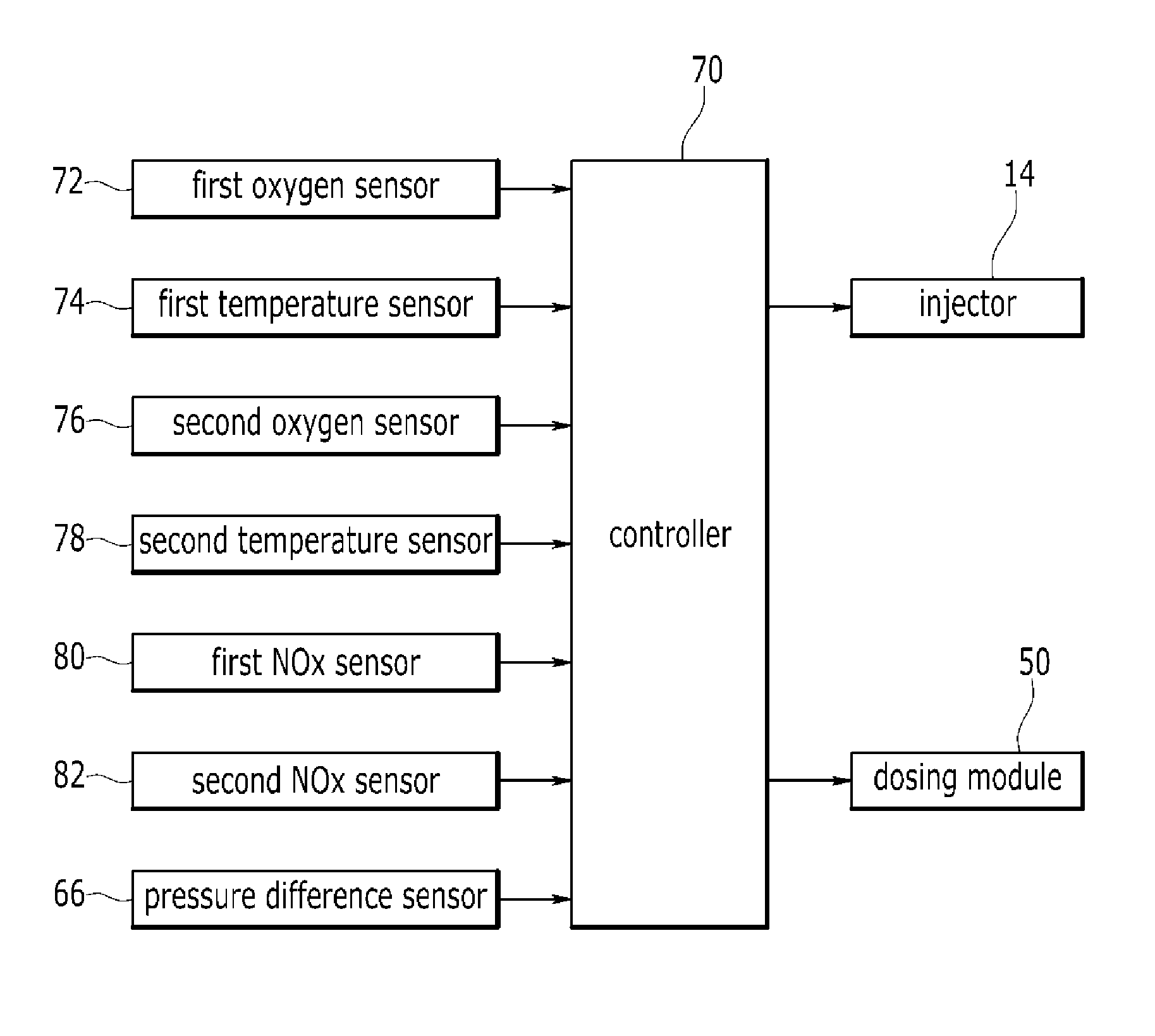
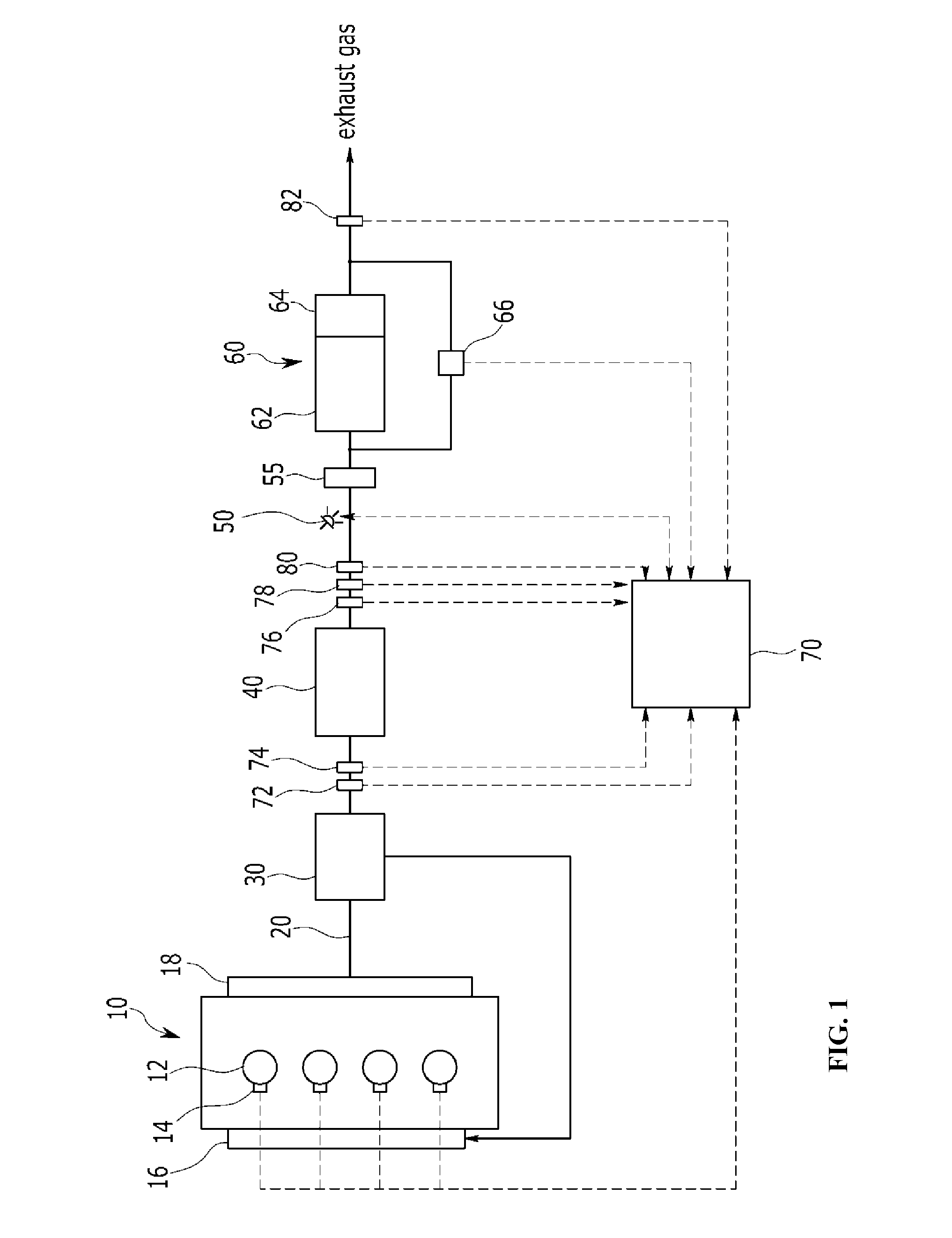
System and method of purifying exhaust gas
InactiveUS20150143798A1Improve purification efficiencyReduce NOxElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesNitrogen oxide
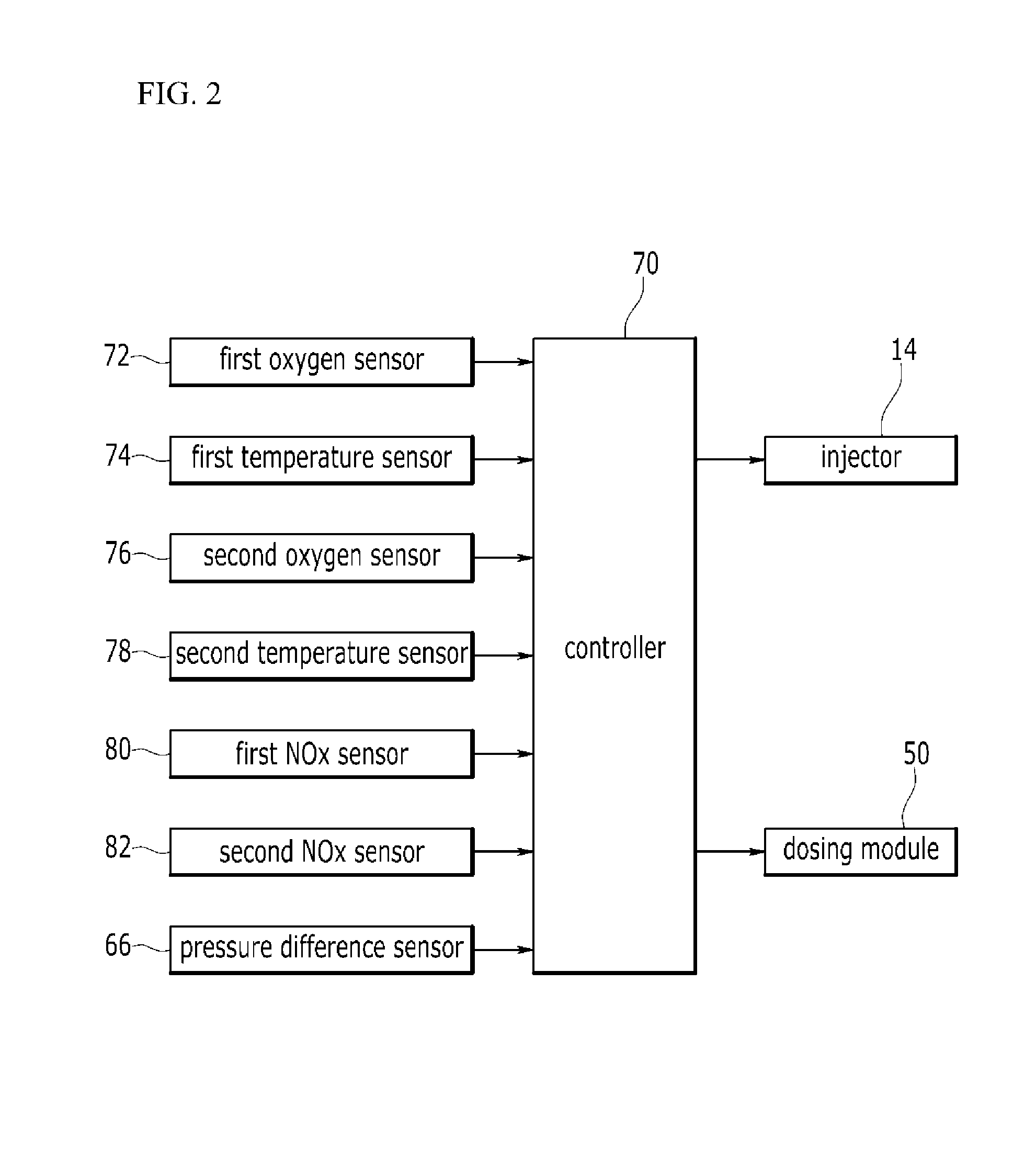
A system of purifying exhaust gas may include an engine including an injector, a lean NOx trap (LNT) adapted to absorb nitrogen oxide (NOx) contained in the exhaust gas at a lean air / fuel ratio, to release the absorbed nitrogen oxide at a rich air / fuel ratio, and to reduce the nitrogen oxide contained in the exhaust gas or the released nitrogen oxide, a dosing module adapted to inject reducing agent into the exhaust gas, a selective catalytic reduction catalyst on a diesel particulate filter (SDPF) adapted to trap particulate matter and to reduce the nitrogen oxide using the reducing agent injected through the dosing module, and a controller performing denitrification (DeNOx) using the LNT when temperature of the exhaust gas may be lower than transient temperature, and performing denitrification using the SDPF when the temperature of the exhaust gas may be higher than or equal to the transient temperature.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
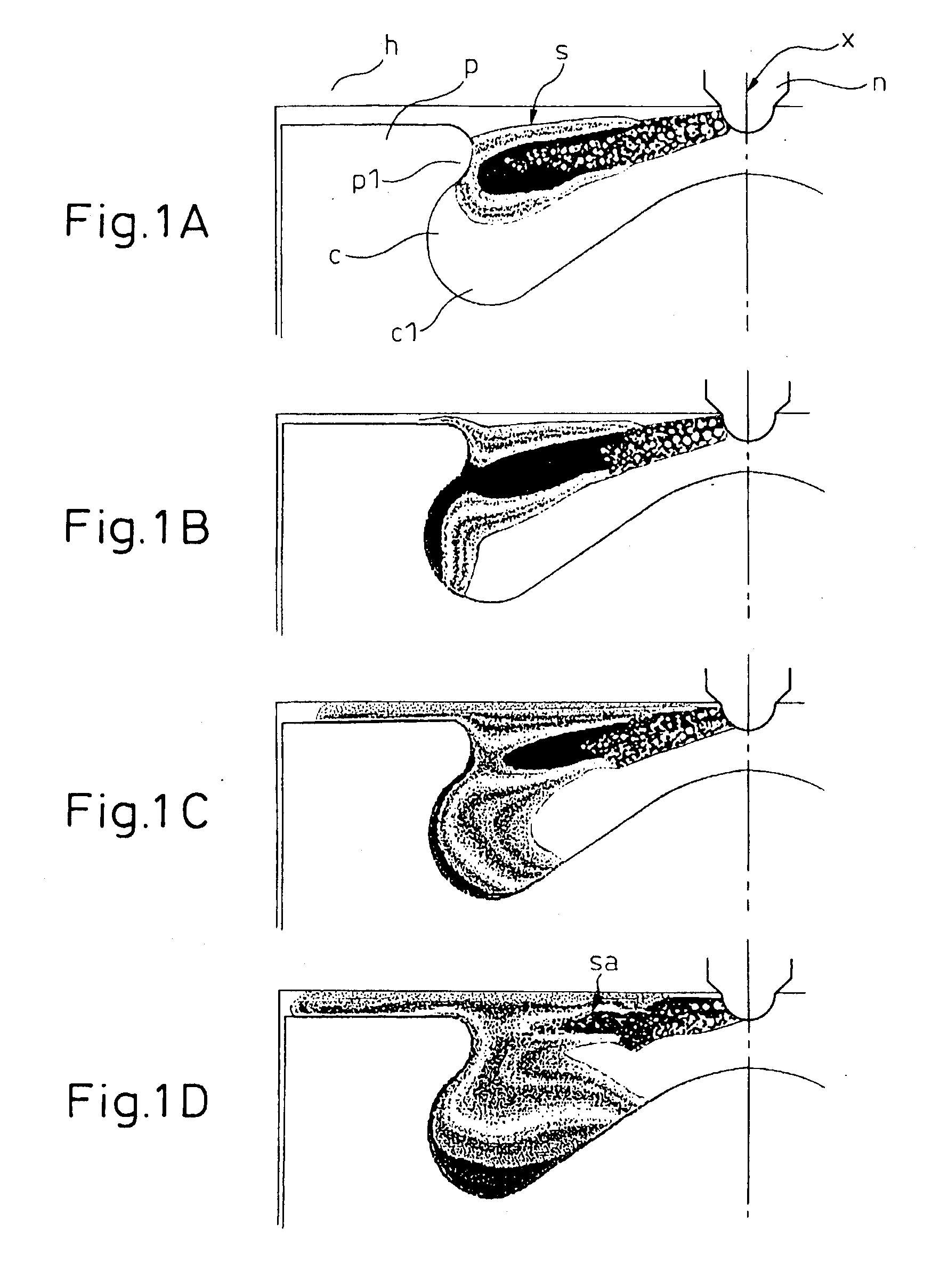
Combustion Chamber with Double Convex Surfaces and Double Concave Surfaces
InactiveUS20100108044A1Reduce NOxReduce soot emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
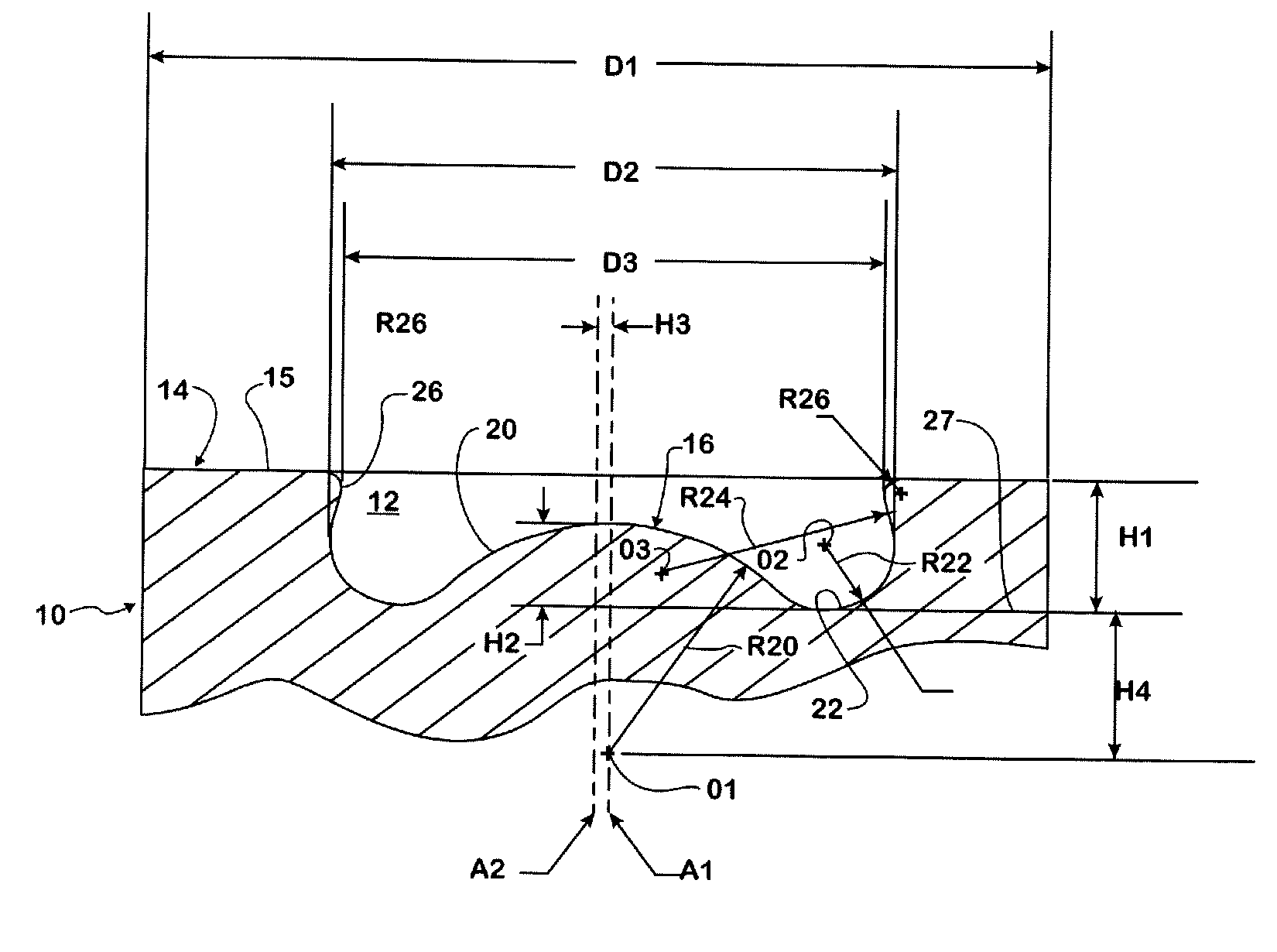
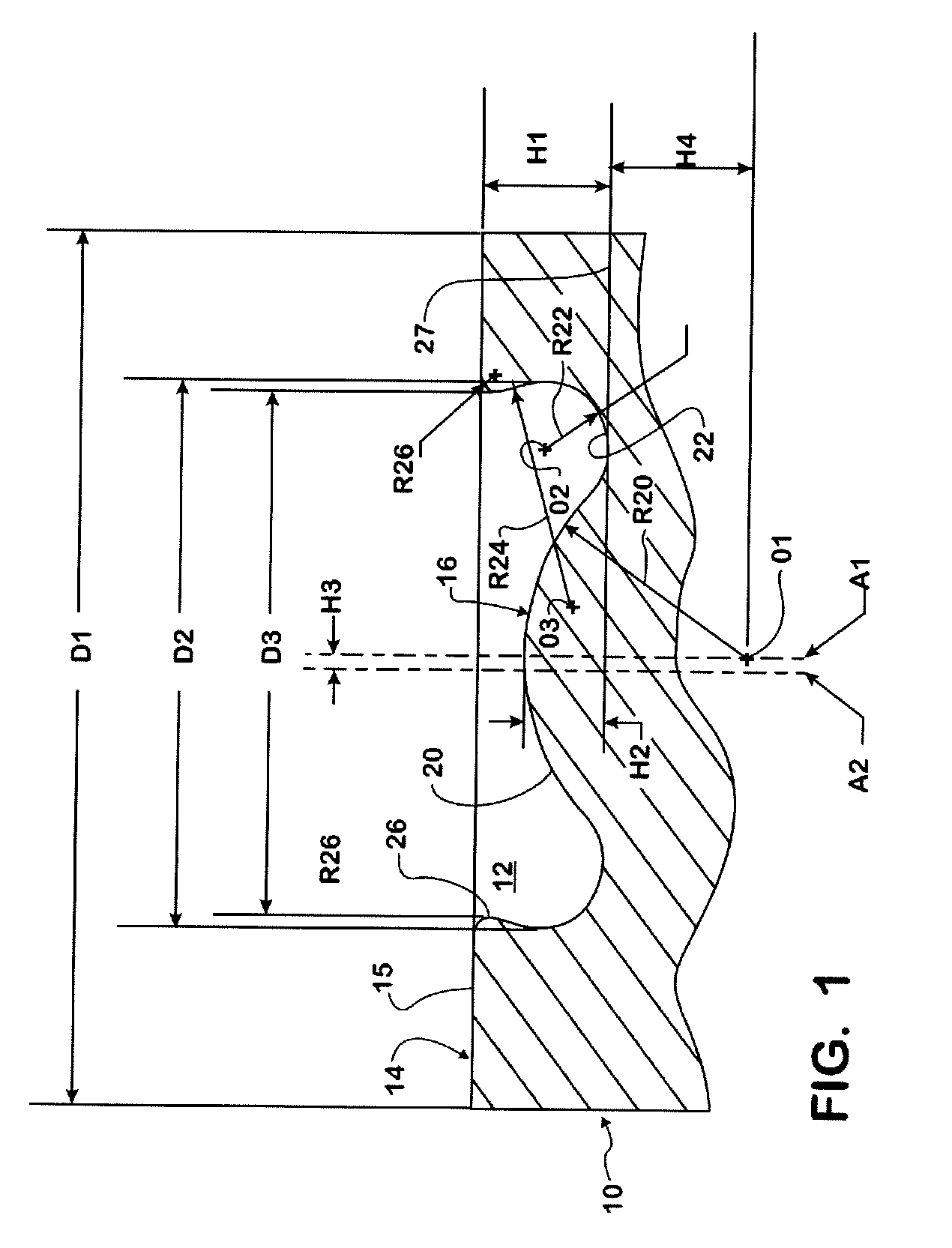
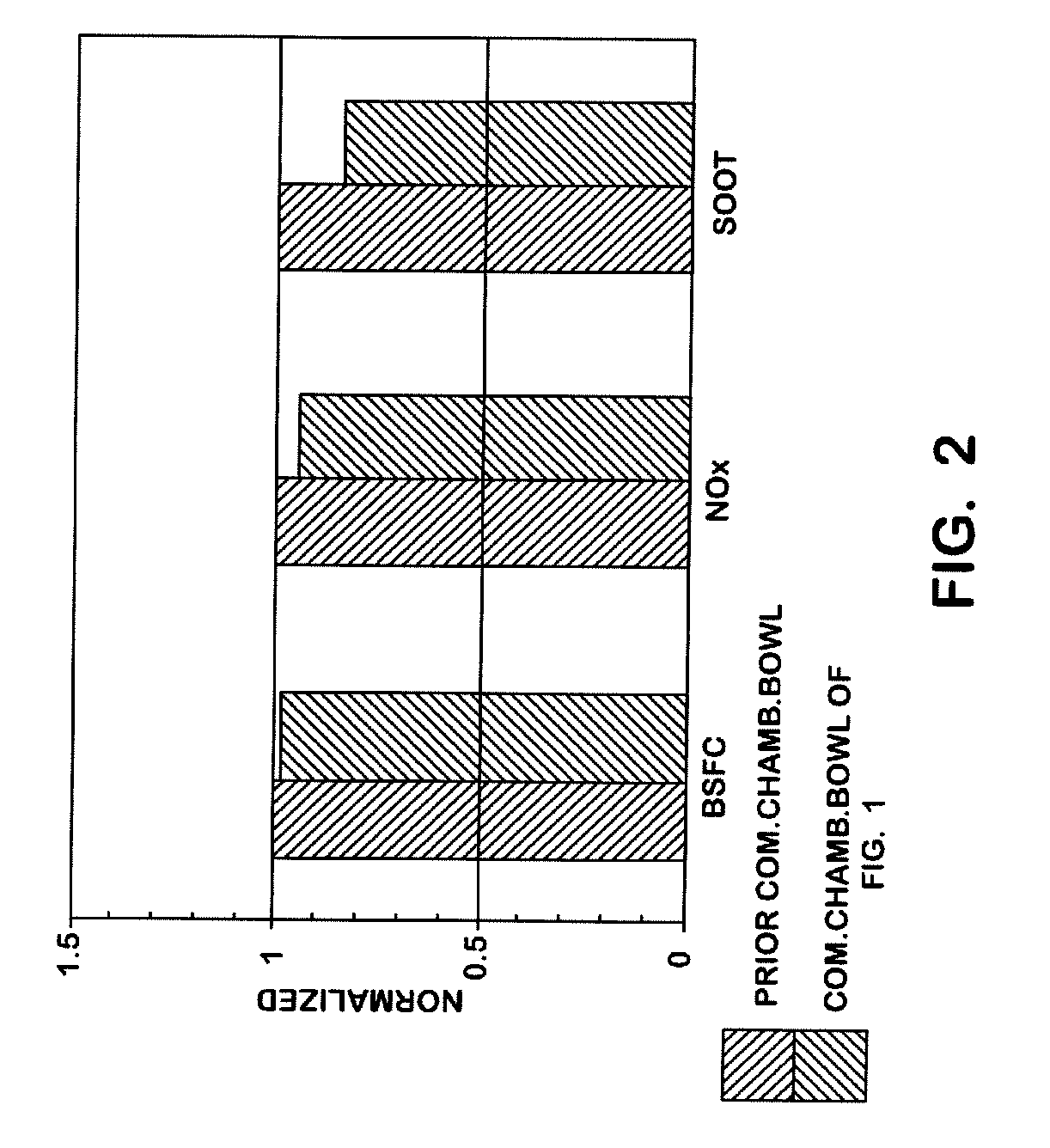
A combustion chamber bowl is defined in a crown of a piston for use in a cylinder of a diesel engine. The combustion chamber bowl includes a center convex spherical portion, first and second annular concave portions and an annular convex portion. The center convex spherical portion is elevated relative to a bottom plane of the combustion chamber bowl and smoothly transitions into the first concave annular portion which transitions smoothly into the second concave annular portion. The second concave annular portion smoothly transitions into the convex annular portion which smoothly transitions into the top surface of the piston crown.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
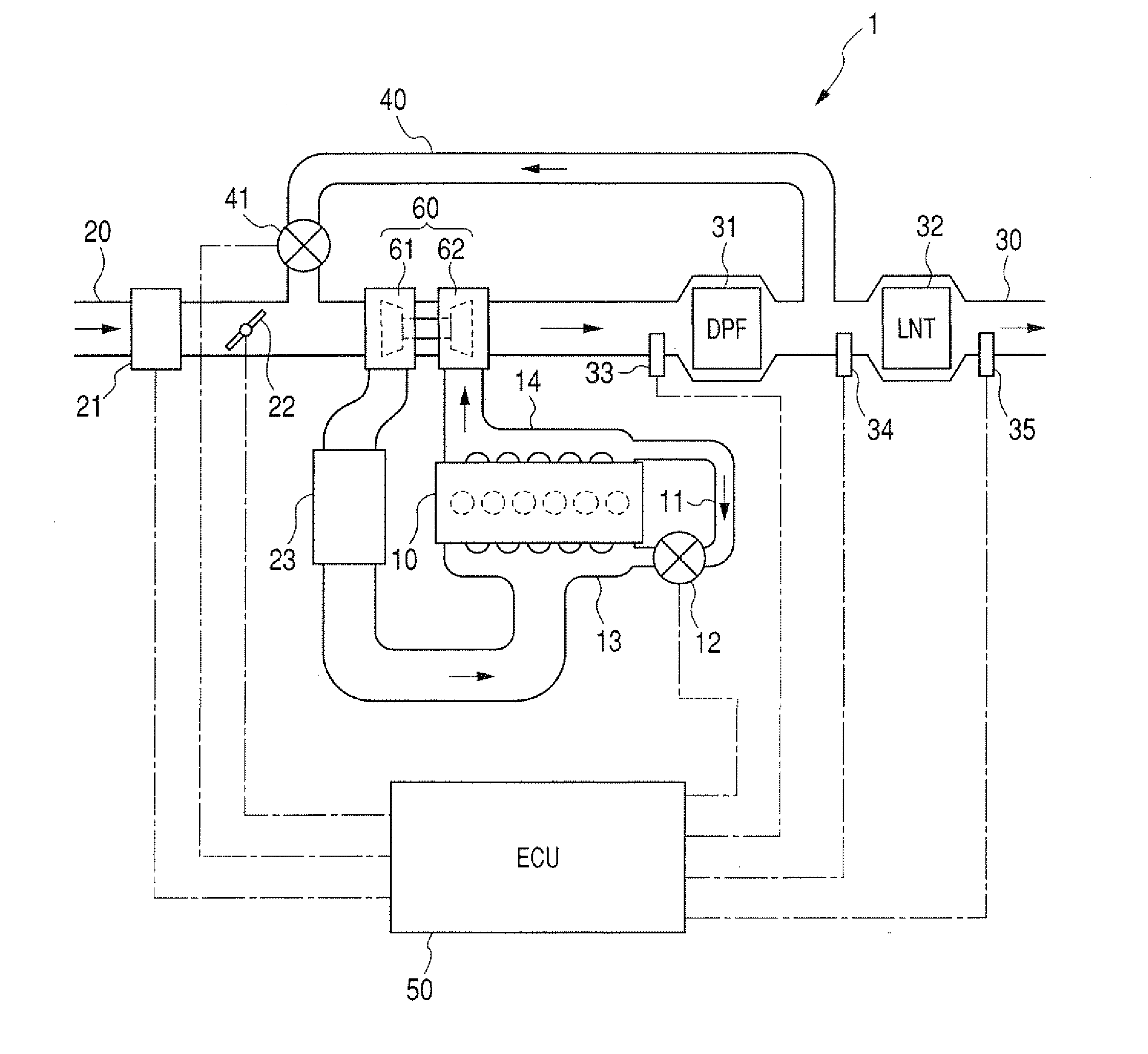
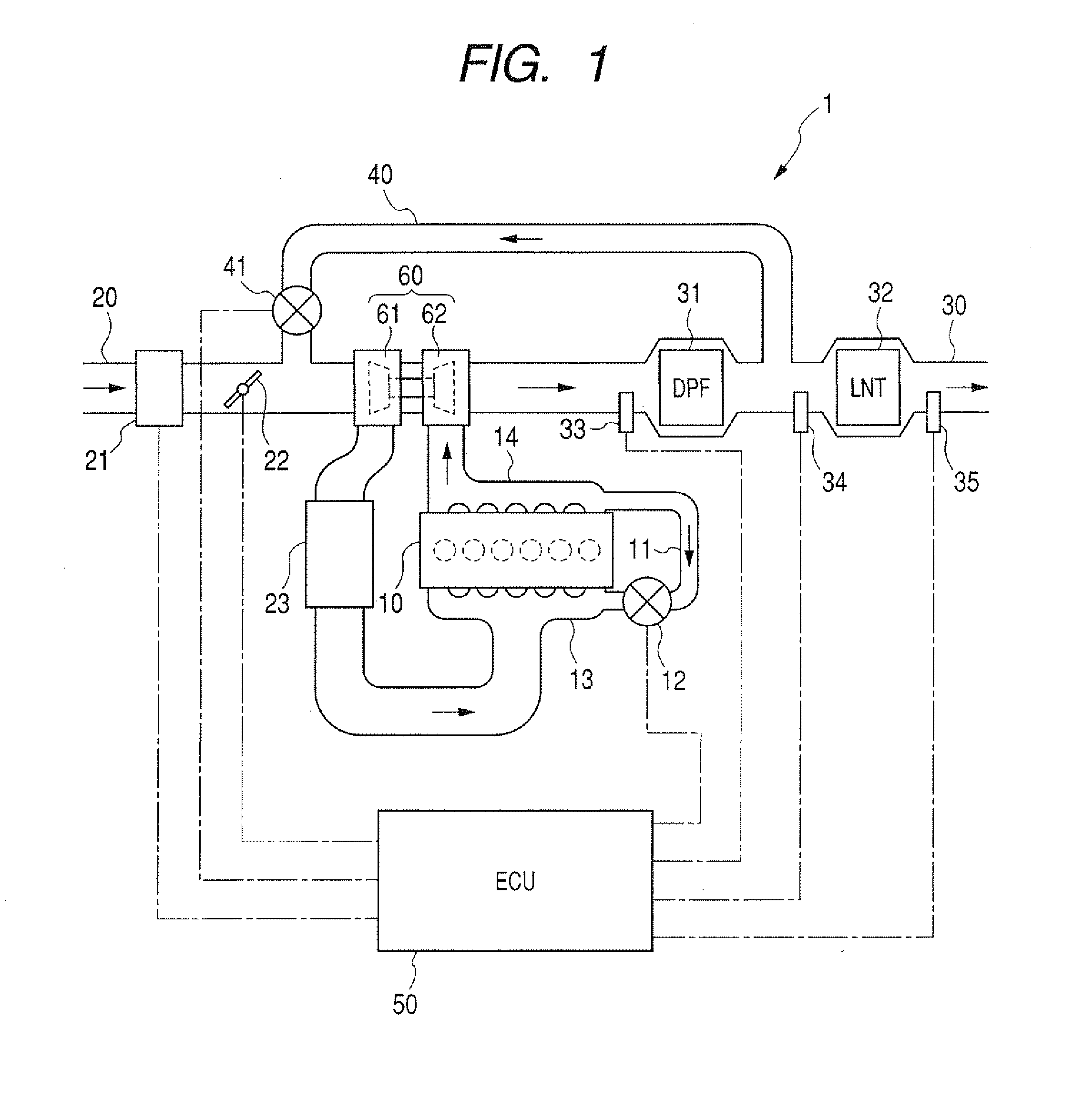
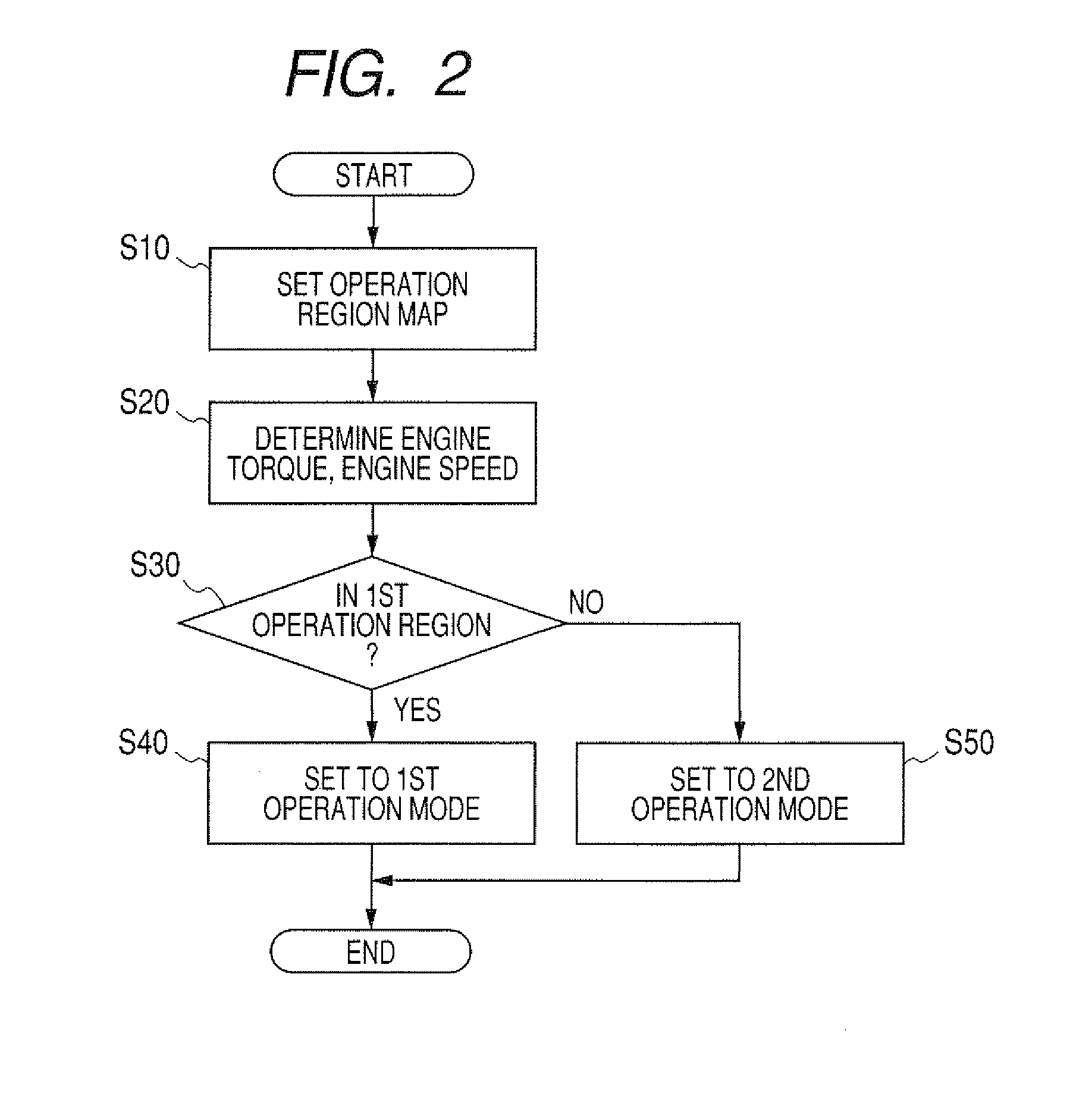
Operating Method for a Motor Vehicle Diesel Engine Having an Exhaust Emission Control System
InactiveUS20140041367A1Reduced operating requirementsLow pollutant emissionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemDiesel engine
An operating method is provided for a motor vehicle diesel engine having an exhaust emission control system that includes a three-way catalytic converter and an SCR catalytic converter situated one behind the other in the flow direction of the exhaust gas. The diesel engine is operated, at least intermittently, with an air-fuel ratio of approximately λ=1.0 in a first operating range in which the SCR catalytic converter falls below a predefinable minimum temperature and with excess air that is typical for normal diesel engine operation in a second operating range in which the SCR catalytic converter exceeds the predefinable minimum temperature. An output signal of an exhaust gas sensor situated downstream from the three-way catalytic converter and which is correlated with a NOx concentration of the exhaust gas is used to set the air-fuel ratio in the first operating range.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Catalyzed filter for treating exhaust gas
InactiveUS20120258032A1Less-optimal interactionThermal expansion is very limitedCombination devicesGas treatmentMolecular sieveMetal
Provided is a wall-flow filter coated with an SCR catalyst composition, wherein the catalyst composition contains transition metal promoted molecular sieve crystals, and wherein (i) the crystals have a mean crystalline size of about 0.5 μm to about 15 μm, (ii) the crystals are present in said composition as individual crystals, agglomerations having a mean particle size of less than about 15 μm, or a combination of said individual crystals and said agglomerations; and (iii) said molecular sieve is an aluminosilicate or a silico-aluminophosphate of a Framework Type having a maximum ring size of eight tetrahedral atoms.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
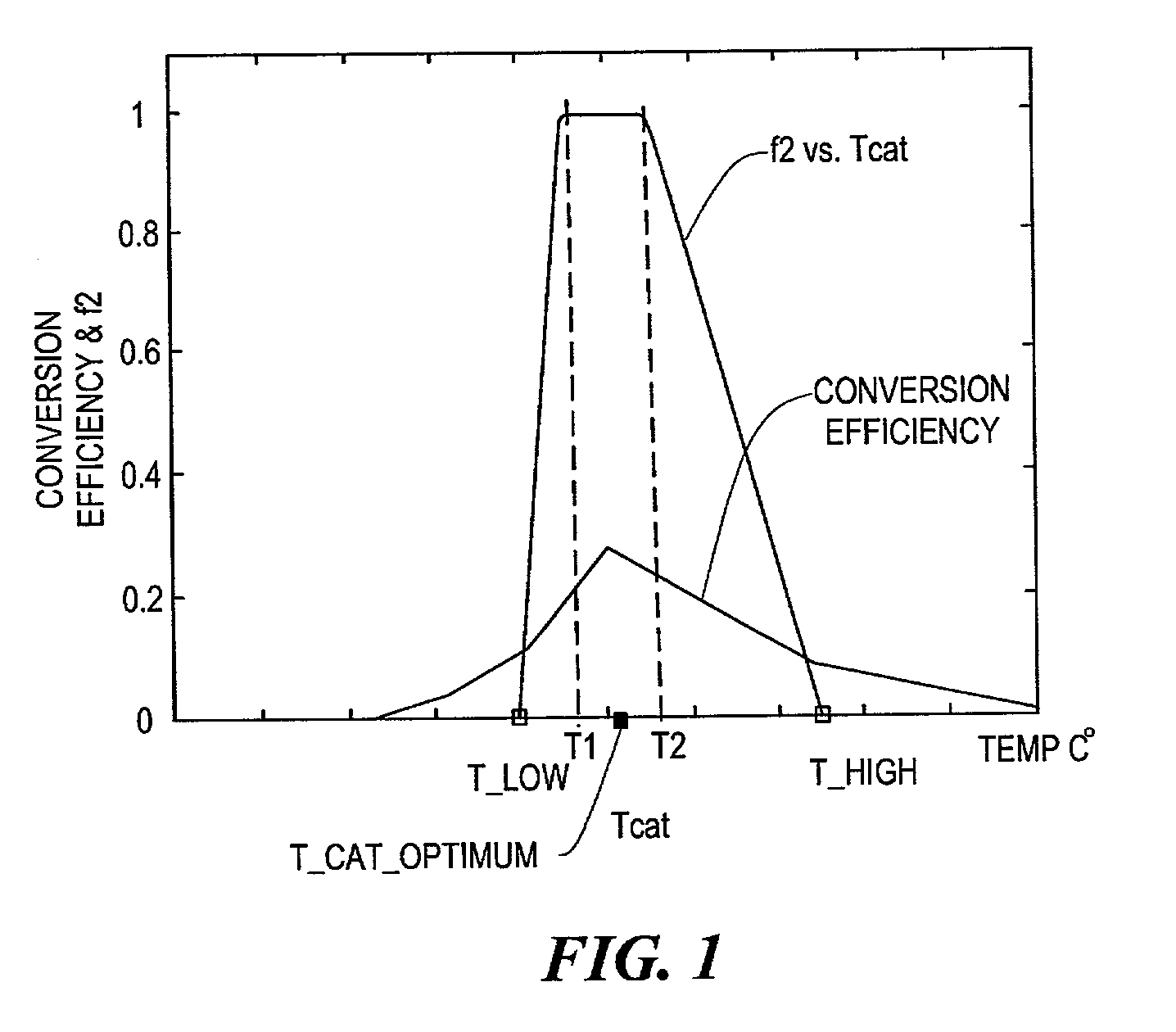
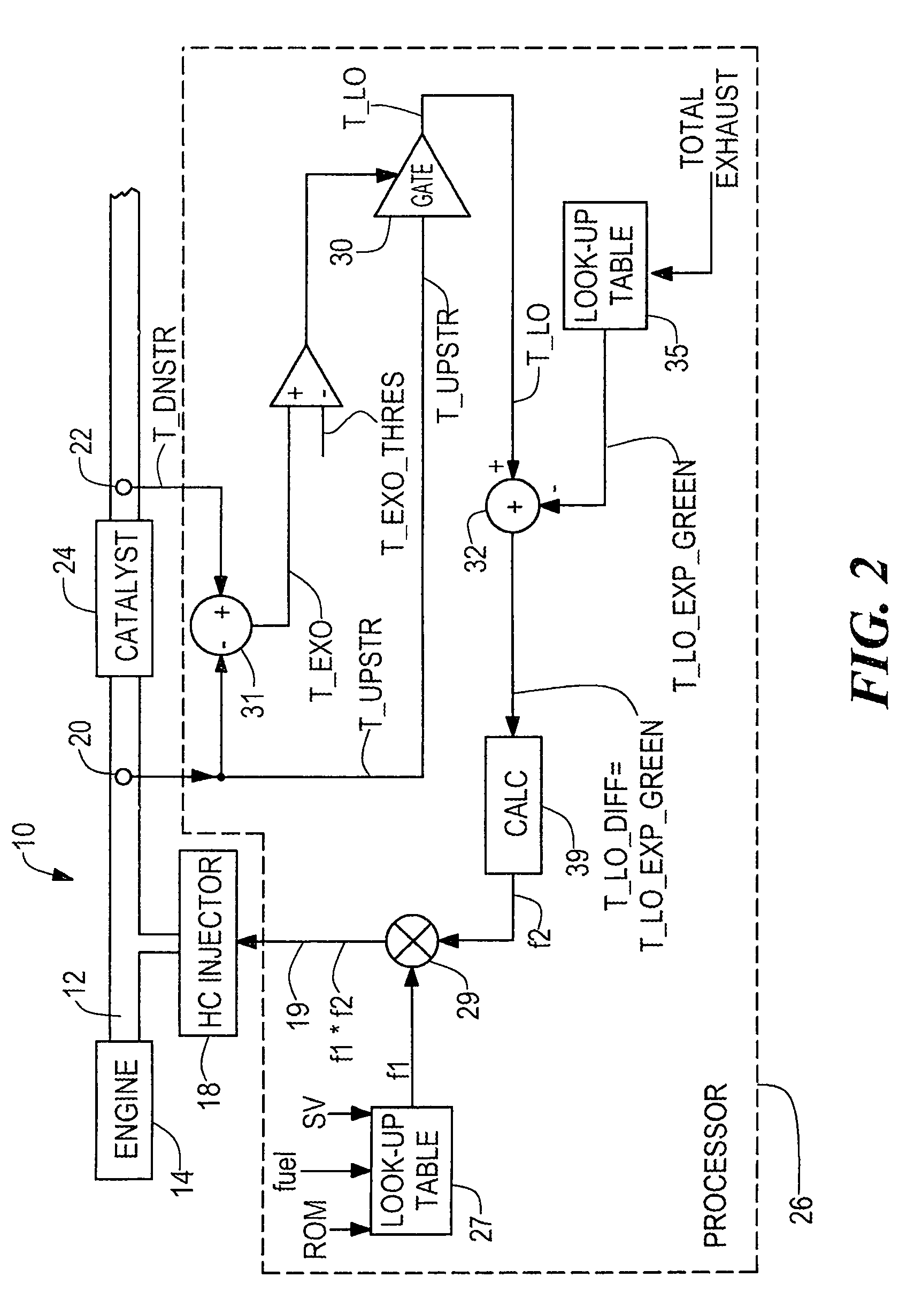
Method and apparatus for controlling hydrocarbon injection into engine exhaust to reduce NOx
InactiveUS7121085B2Reduce NOxEfficient conversionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringExothermic reaction
A method and system for controlling hydrocarbon injection into engine exhaust to reduce NOx. The method and system inject the hydrocarbon into the engine exhaust in accordance with detection of a light-off event. The light-off event can be detected because when there is this hydrocarbon-O2 reaction, such reaction is an exothermic reaction and thus heat is generated and given off. The generation of such heat may be detected by measuring the difference in temperature across the catalyst. The peak in NOx conversion efficiency temperature changes with age. However, because the peak in NOx conversion efficiency temperature occurs at substantially the same light-off temperature, a determination of light-off by the system and method enables adjustment in the hydrocarbon injection level for maximum NOx reduction efficiency.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas purifying catalyst and process for purification of exhaust gas
ActiveUS20060014630A1Reduce NOxHigh repressionOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideOrganic chemistryNitrogen oxidesExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas purifying catalyst has a catalytic component including copper, ZSM-5, and β zeolite. This exhaust gas purifying catalyst reduces nitrogen oxides even from low temperature range and exhibits durability even under a thermal load of high temperature.
Owner:UMICORE SHOKUBAI USA +1
Gas Turbine Combustor
InactiveUS20110185703A1Low NOx combustionImprove power generation efficiencyContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberCombustor
A gas turbine combustor includes plural multi-coaxial-injection-hole burners in which plural fuel nozzles and plural air holes provided in an air plate to correspond to the respective fuel nozzles are coaxially arranged. Each of the multi-coaxial-injection-hole burners includes a first coaxial injection burner disposed on an inner circumferential side, and a second coaxial injection burner disposed on an outer circumferential side, and a diameter of the air holes of the first coaxial injection burner is smaller than a diameter of the air holes of the second coaxial injection burner. Combustion for carrying out flame holding of a gas turbine combustor is performed by the first coaxial injection burner, and low NOx combustion of the gas turbine combustor is performed by the second coaxial injection burner.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Exhaust purification device for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20080307772A1Accurate acquisitionReduce catalysisElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesEngineering
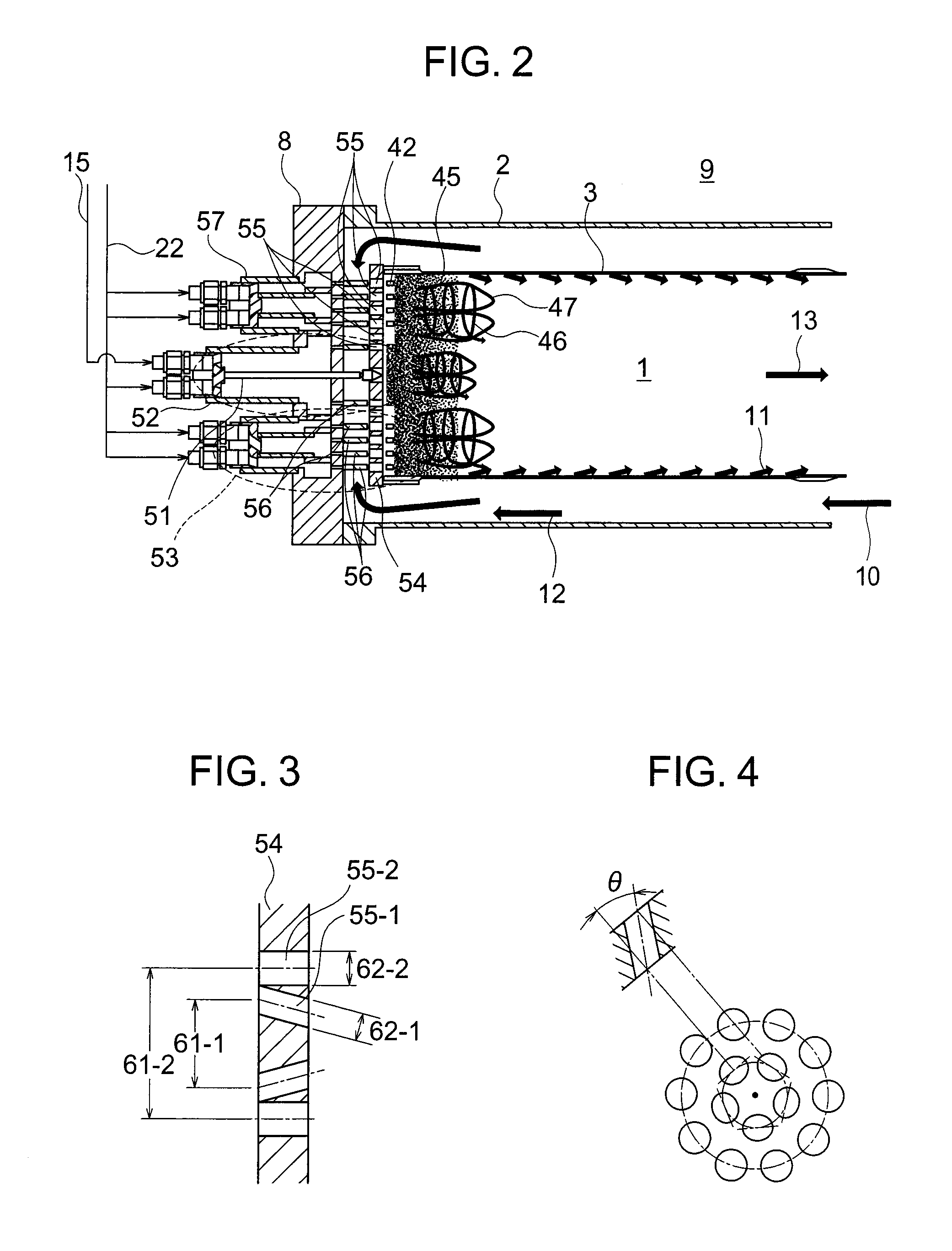
When it is determined that fuel in use is low-cetane fuel or a present location point is at a high altitude, a map of rich combustion, exhaust gas fuel addition or a post-injection is rewritten on the occasion of reduction of NOx to inhibit a misfire. Also, deterioration of fuel consumption due to regeneration of a diesel particulate filter is inhibited by suppressing excessive discharge of smoke due to the rich combustion. Thus, an exhaust purification device of an internal combustion engine capable of achieving both of inhibition of the deterioration in the fuel consumption due to the regeneration of the diesel particulate filter and inhibition of torque shock accompanying the misfire during the rich combustion for the NOx reduction is provided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Exhaust gas purifier for use in internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6718756B1Reduce NOxSuppressing impairment in THE exhaust gas performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesReduction driveExhaust fumes
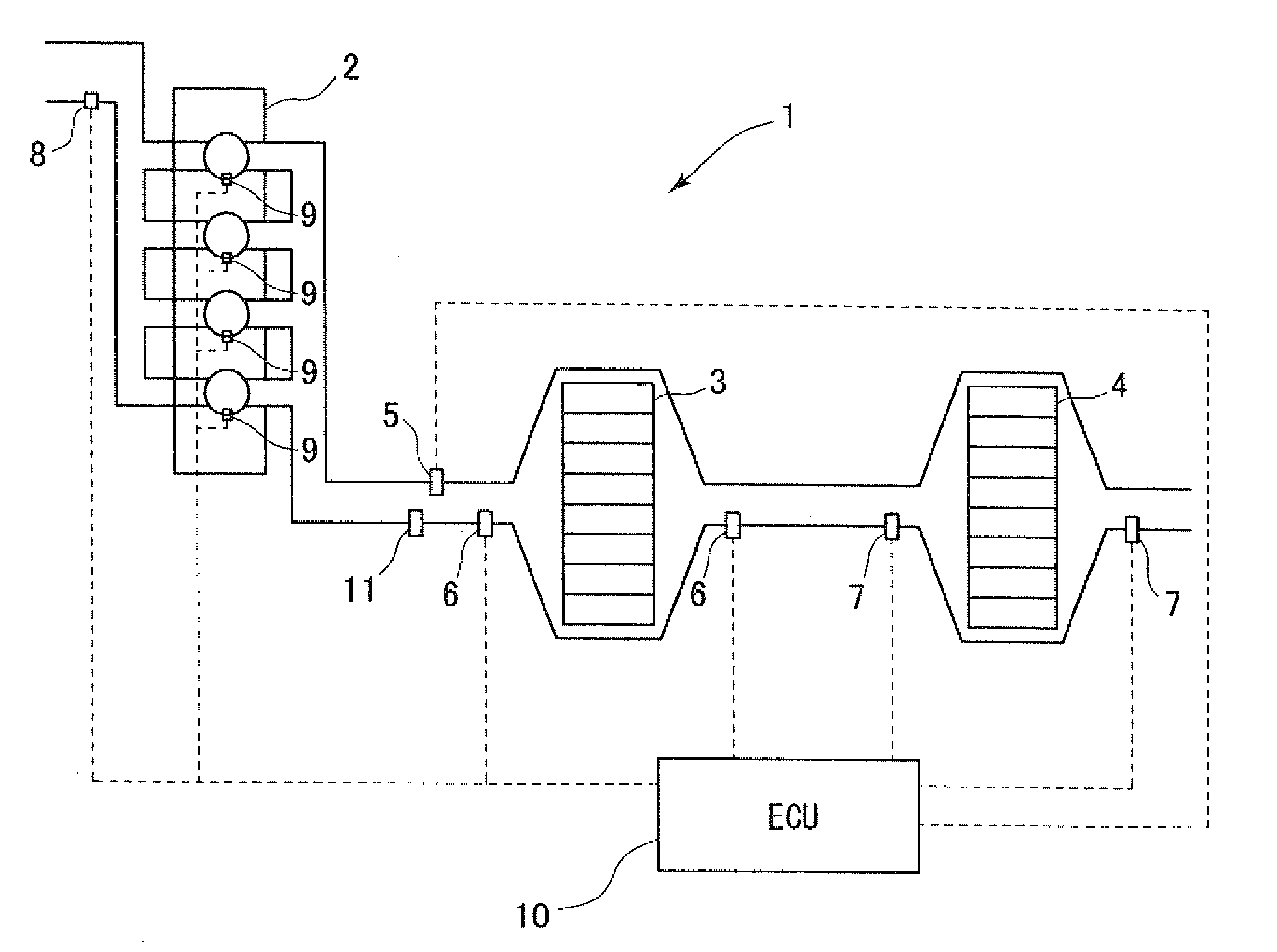
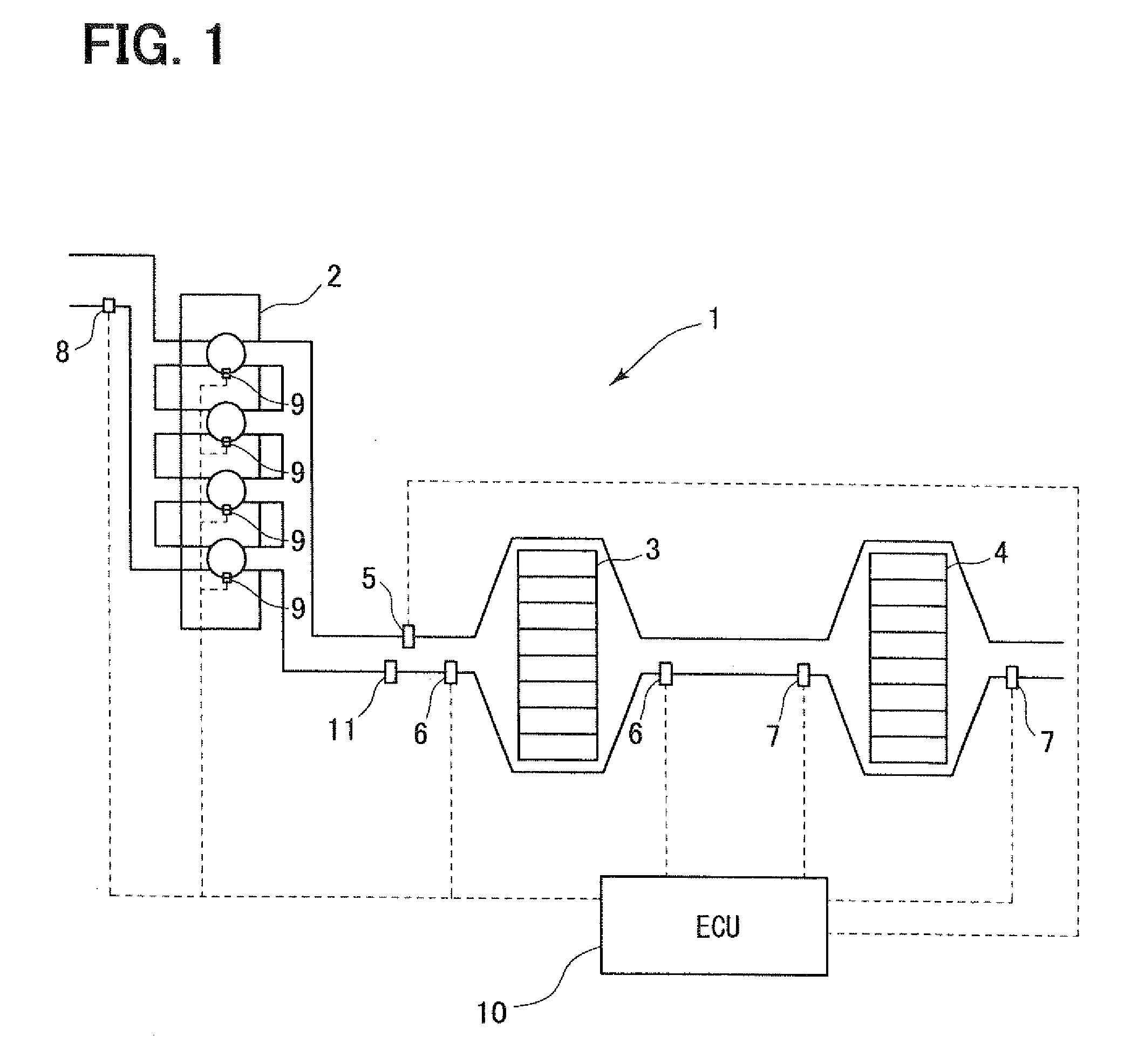
When a NOx-releasing unit is operated to change an air-fuel ratio to a rich side to thereby establish a low-oxygen-concentration atmosphere of an exhaust gas such that NOx is released from a NOx catalyst, a reducer-supplying unit 33 additionally supplies a reducer during an operating period of the NOx-releasing unit for reducing NOx released into an exhaust path such that release of NOx balances with reduction of NOx, thereby reducing NOx released from the NOx catalyst and thus suppressing worsening of exhaust gas performance.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Fuel Injection System of Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20080053408A1Improve combustionReduce NOxElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInjection pressureInjection port
A fuel injection system deliberately utilizing after injection so as to improve the engine combustion and reduce soot and NOx, wherein at least one operating valve is provided for operating a first injection port group and second injection port group, after injection is performed consecutively after main injection in a high load region, fuel is injected from the first injection port group and second injection port group at the time of main injection, fuel is injected from the first injection port group at the time of after injection, the actual injection pressure near the first injection port during the after injection period is higher than the actual injection pressure near the first injection port during the main injection period, the operating valve opens the first injection port group to start the injection, then the operating valve opens the second injection port group simultaneously or in a short time as well to perform the main injection, the operating valve closes the second injection port group, then performs the after injection, and the operating valve closes the first injection port group and ends the injection after the elapse of a time longer than simultaneously or a short time from after start of after injection.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and method for urea decomposition to ammonia in a side stream for selective catalytic reduction
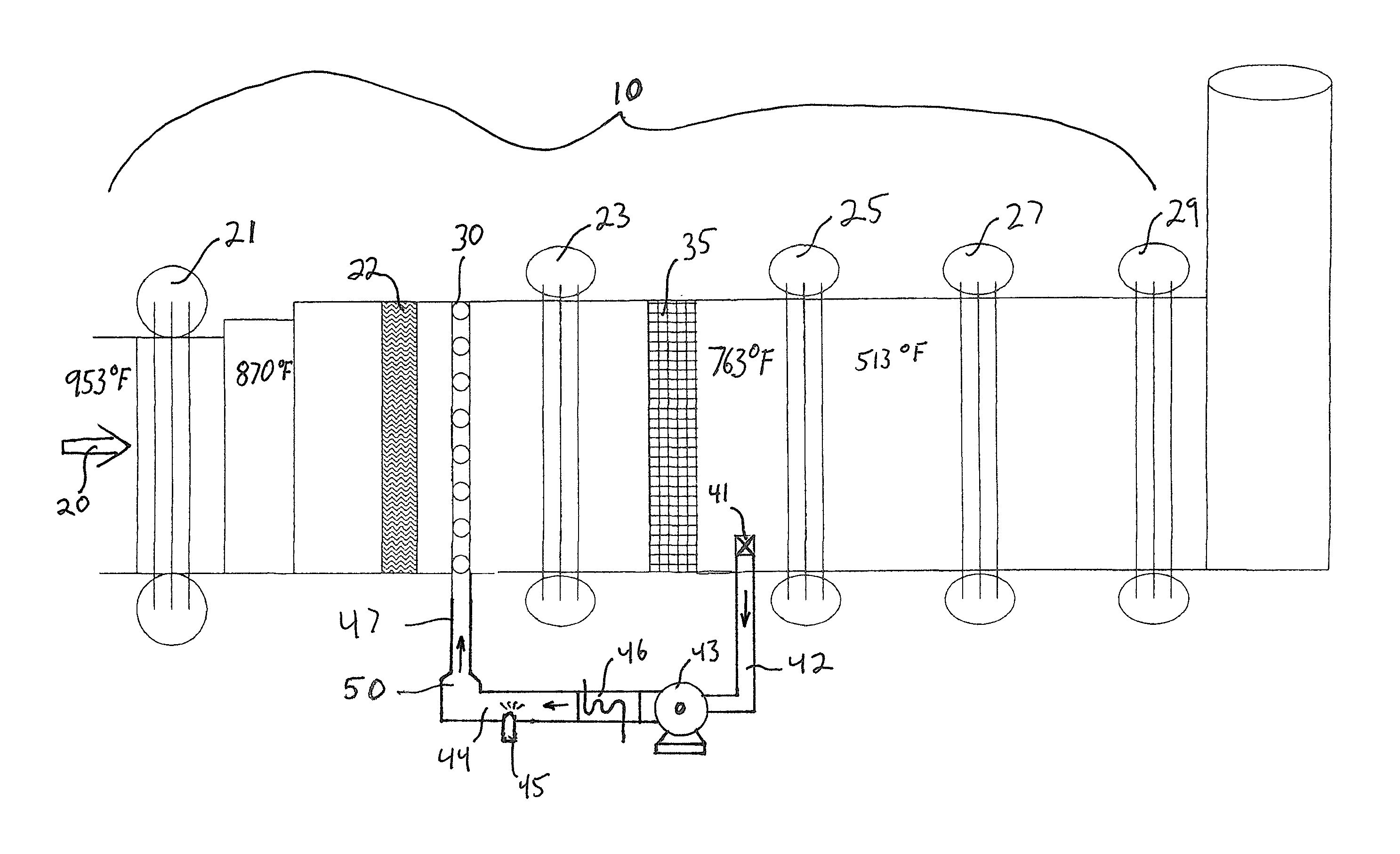
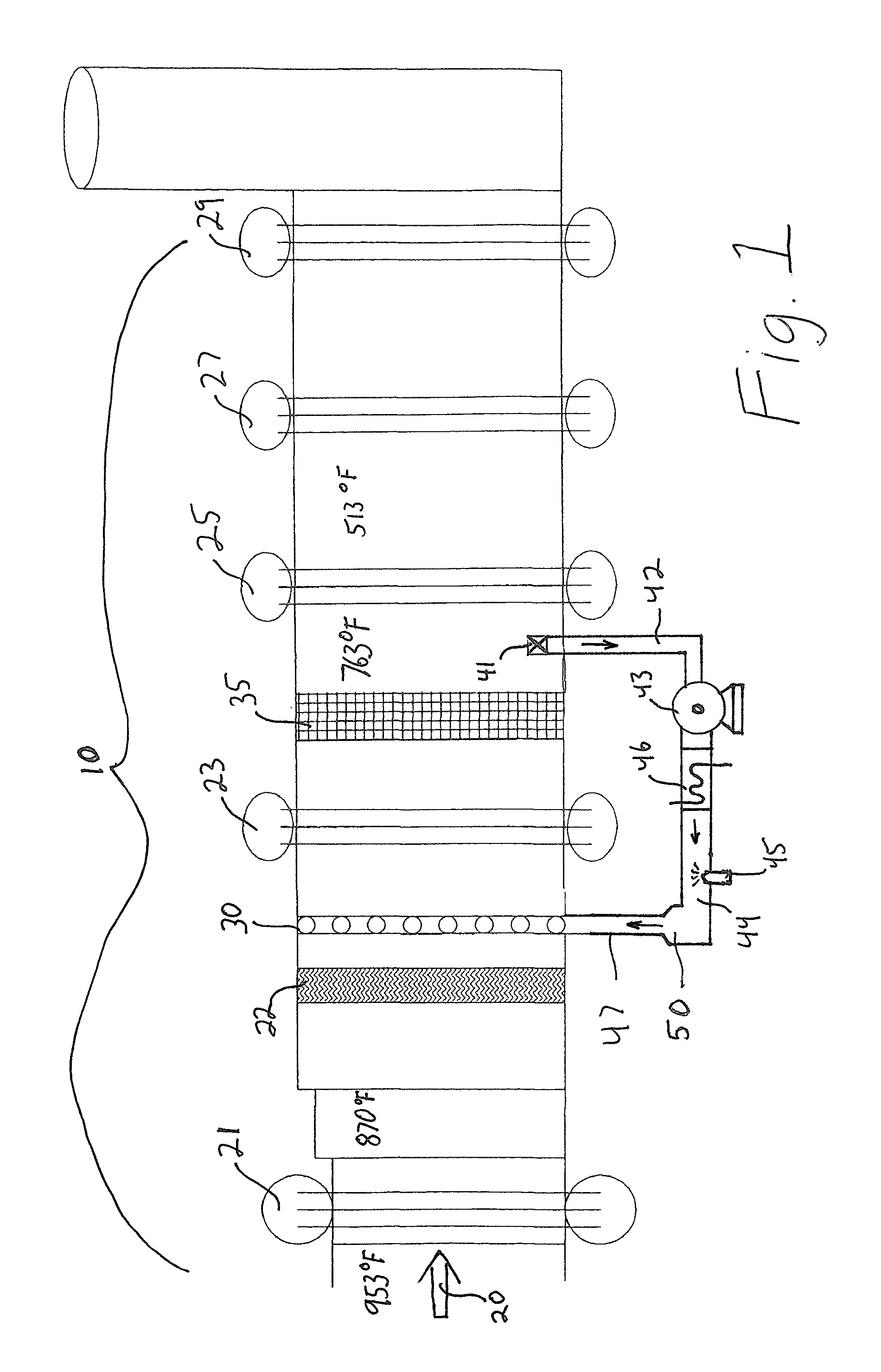
ActiveUS20140096532A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsReduce NOxExhaust apparatusEmission preventionRecovery boilerAmmonia gas
A method for reducing NOx emissions in the exhaust of a combined cycle gas turbine equipped with a heat recovery boiler and a catalyst effective for NOx reduction, wherein a slip stream of hot flowing exhaust gases is withdrawn from the primary gas flow after the catalyst at a temperature of 500° F. to 900° F. and directed through a fan to a continuous duct into which an aqueous based reagent is injected for decomposition to ammonia gas and the outlet of the continuous duct is connected to an injection grid positioned in the primary exhaust for injection of ammonia gas into the primary exhaust stream at a location upstream of the catalyst.
Owner:CECO ENVIRONMENTAL IP INC
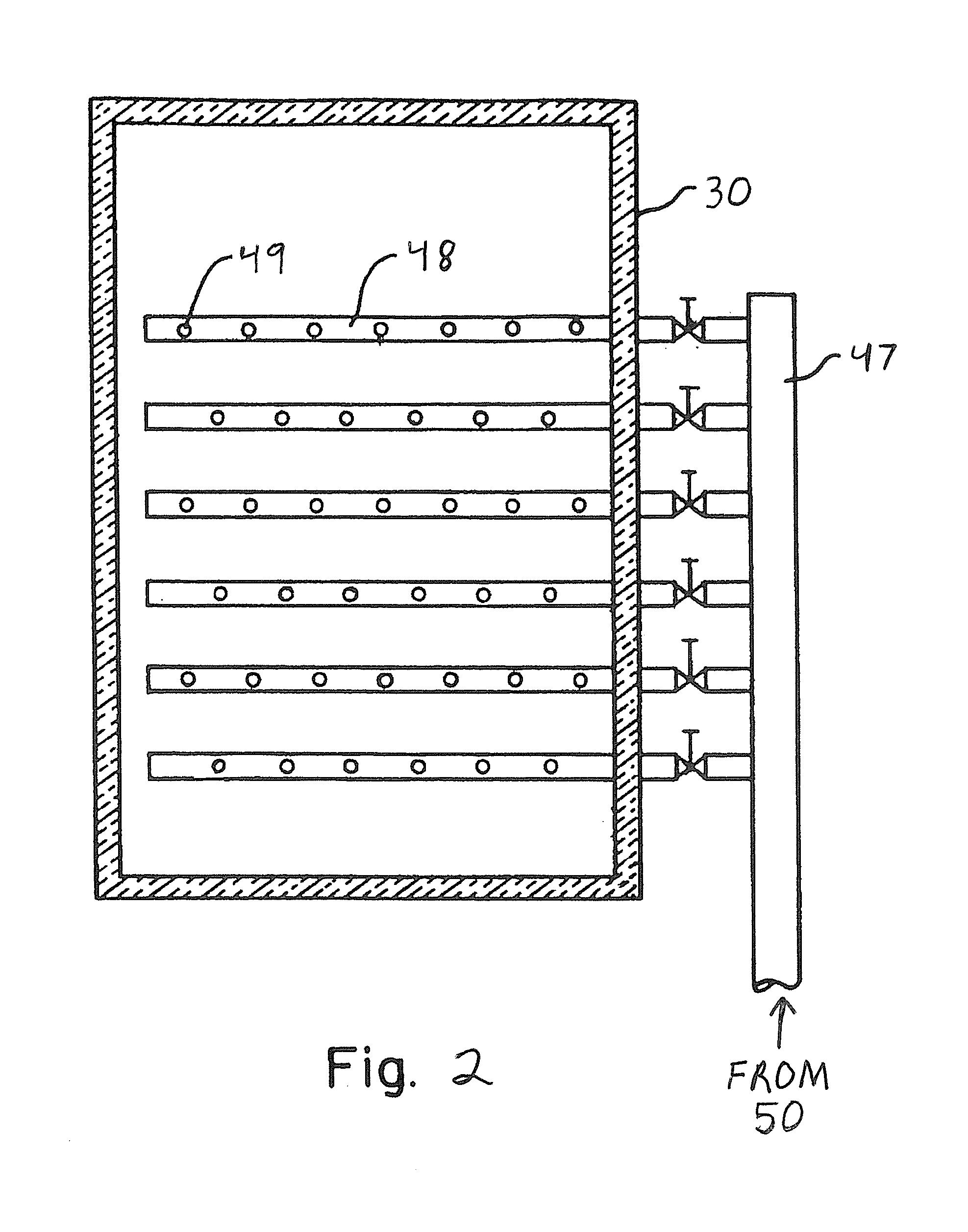
Exhaust gas cleaning apparatus for lean burn internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20080314036A1Temperature of engine increaseStrong reduction performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineExhaust fumes
An exhaust gas cleaning apparatus includes a LNT, a fuel adding device, an exhaust gas returning passage, and a controller. The LNT is provided in an exhaust gas passage of an engine. The fuel adding device is located upstream of the LNT to add fuel to exhaust gas flowing through the exhaust pipe. The exhaust gas returning passage branches off from the exhaust gas passage at a position downstream of the fuel adding device. The controller controls the apparatus to selectively operate in one of first and second modes according to the operating condition of the engine. In the first mode, the fuel adding device adds the fuel to the exhaust gas with the exhaust gas returning passage closed; in the second mode, the exhaust gas is partially returned to an intake air passage through the exhaust gas returning passage without the fuel being added by the fuel adding device.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com