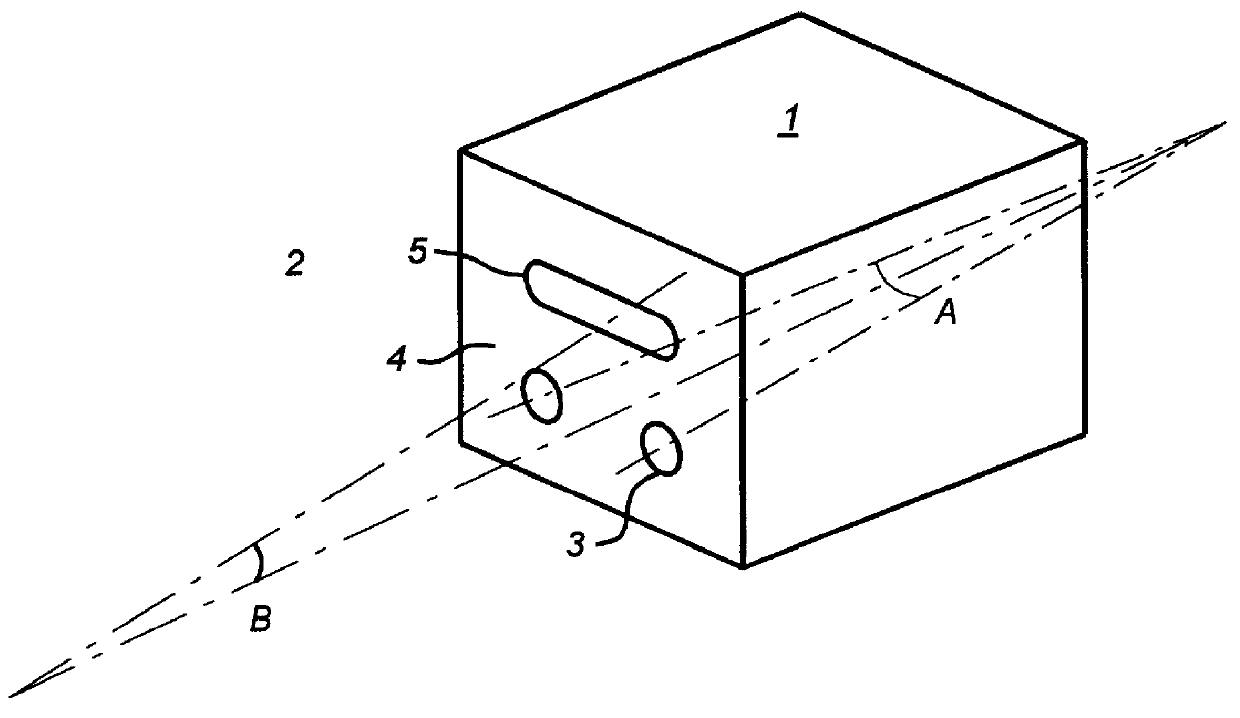
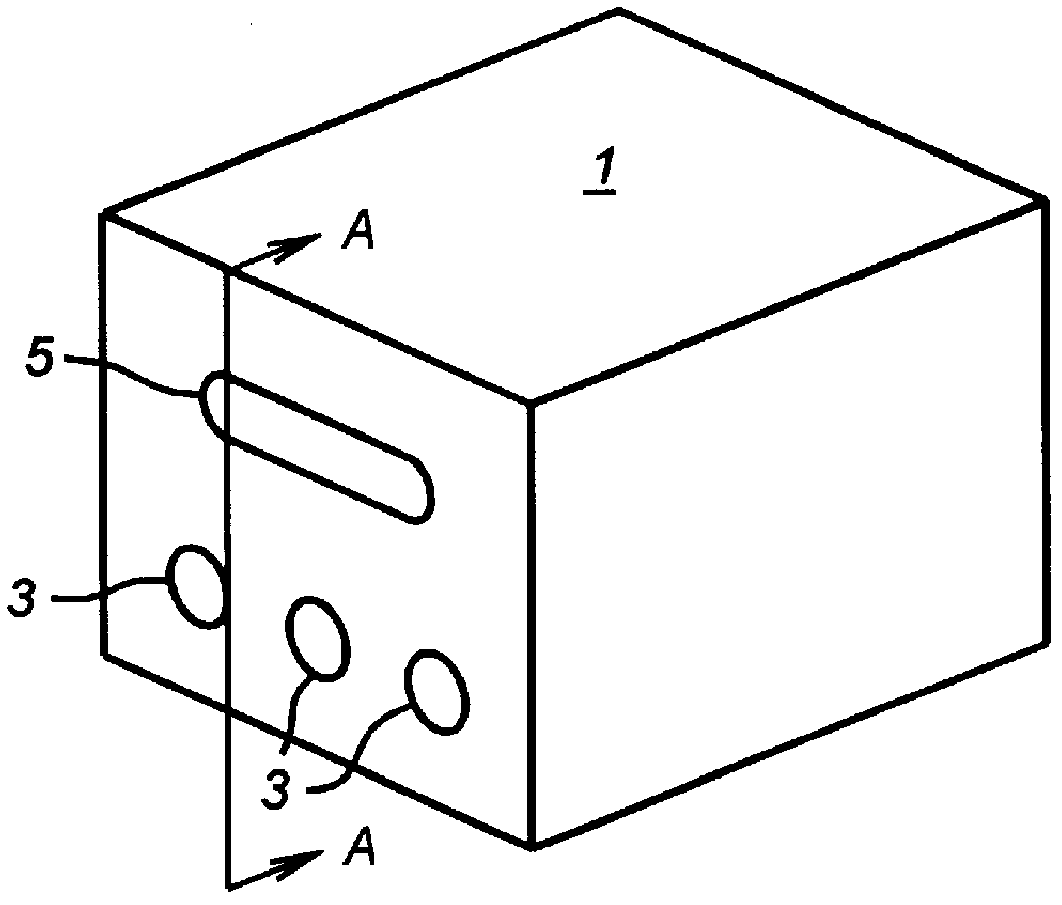
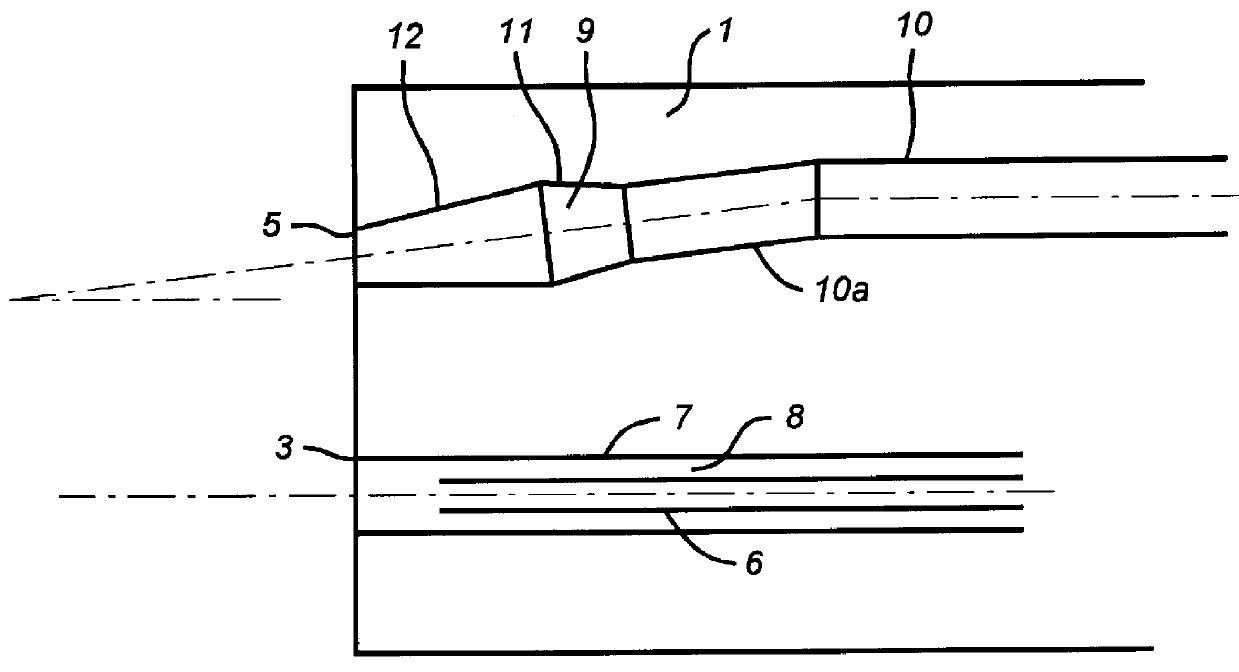
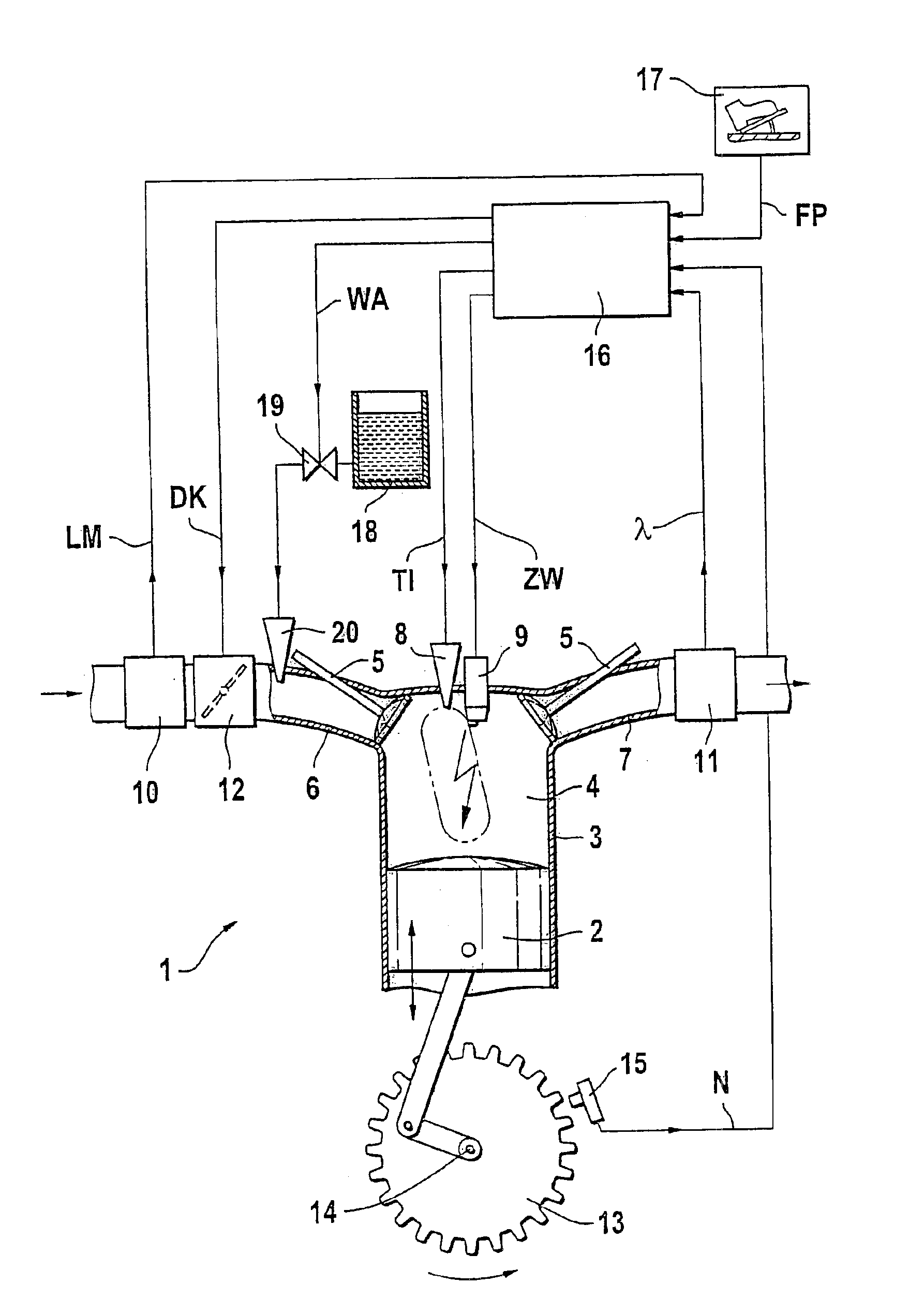
Patents
Literature
428results about How to "Reduce nitrogen oxide emissions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
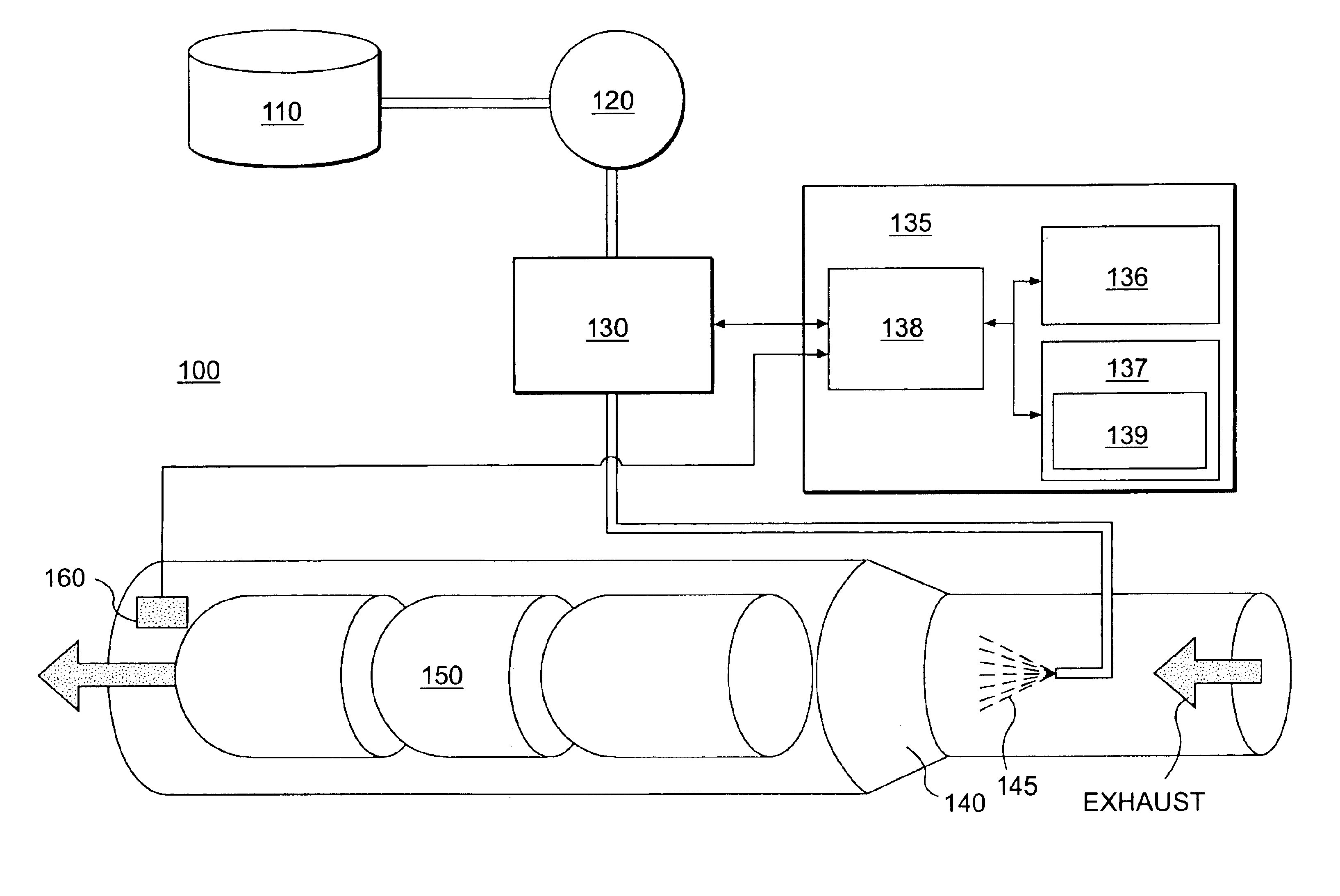
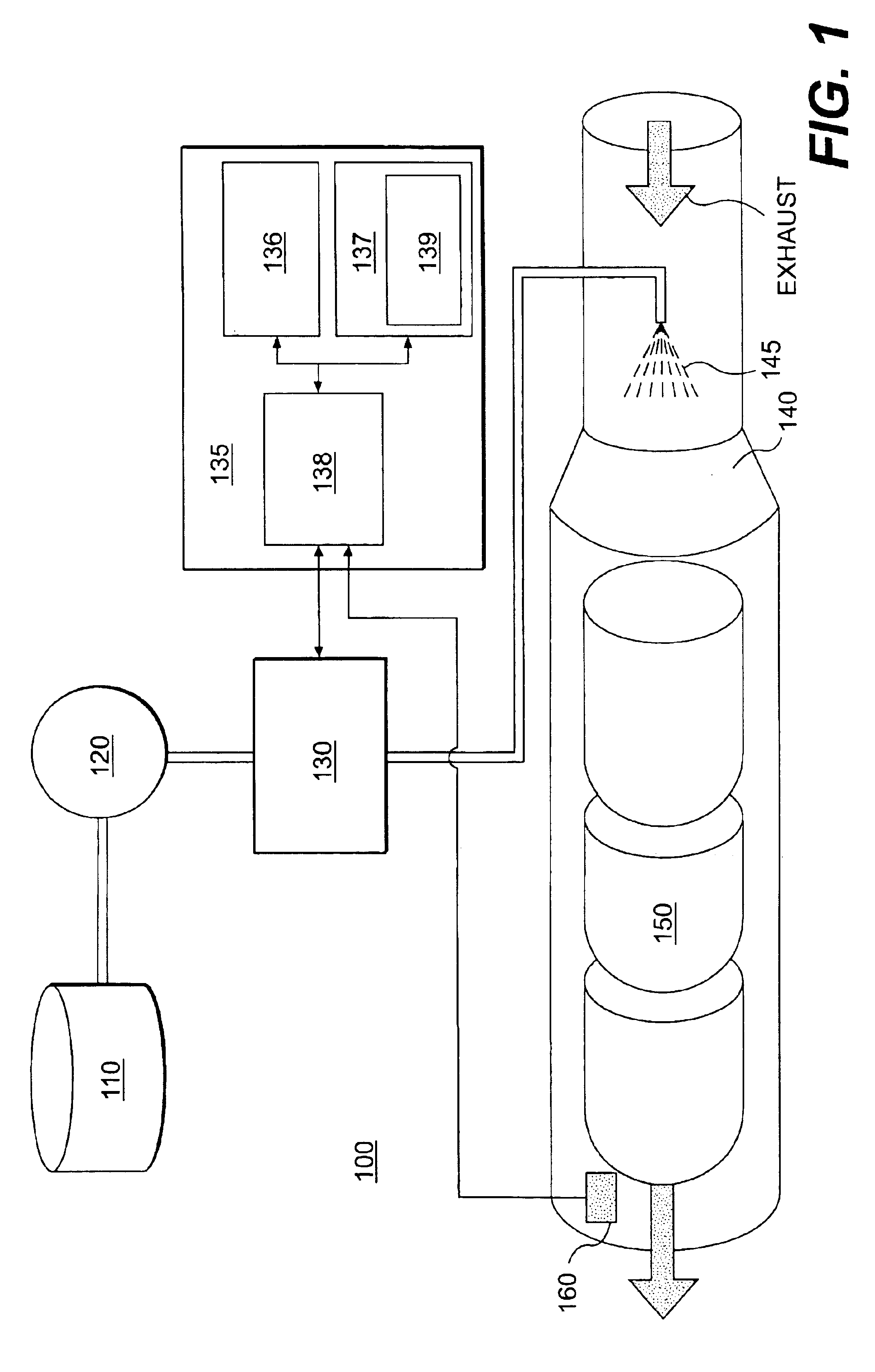
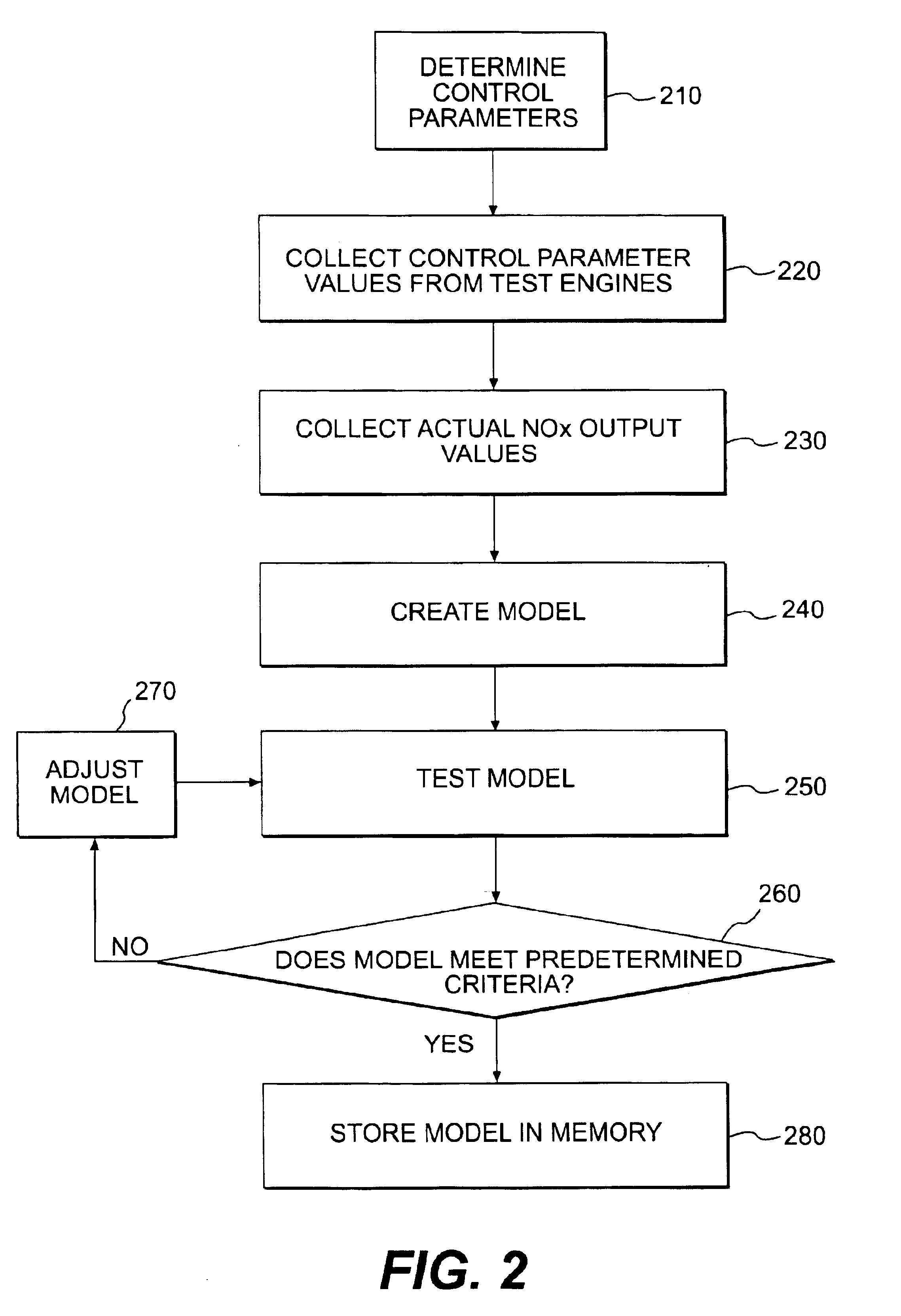
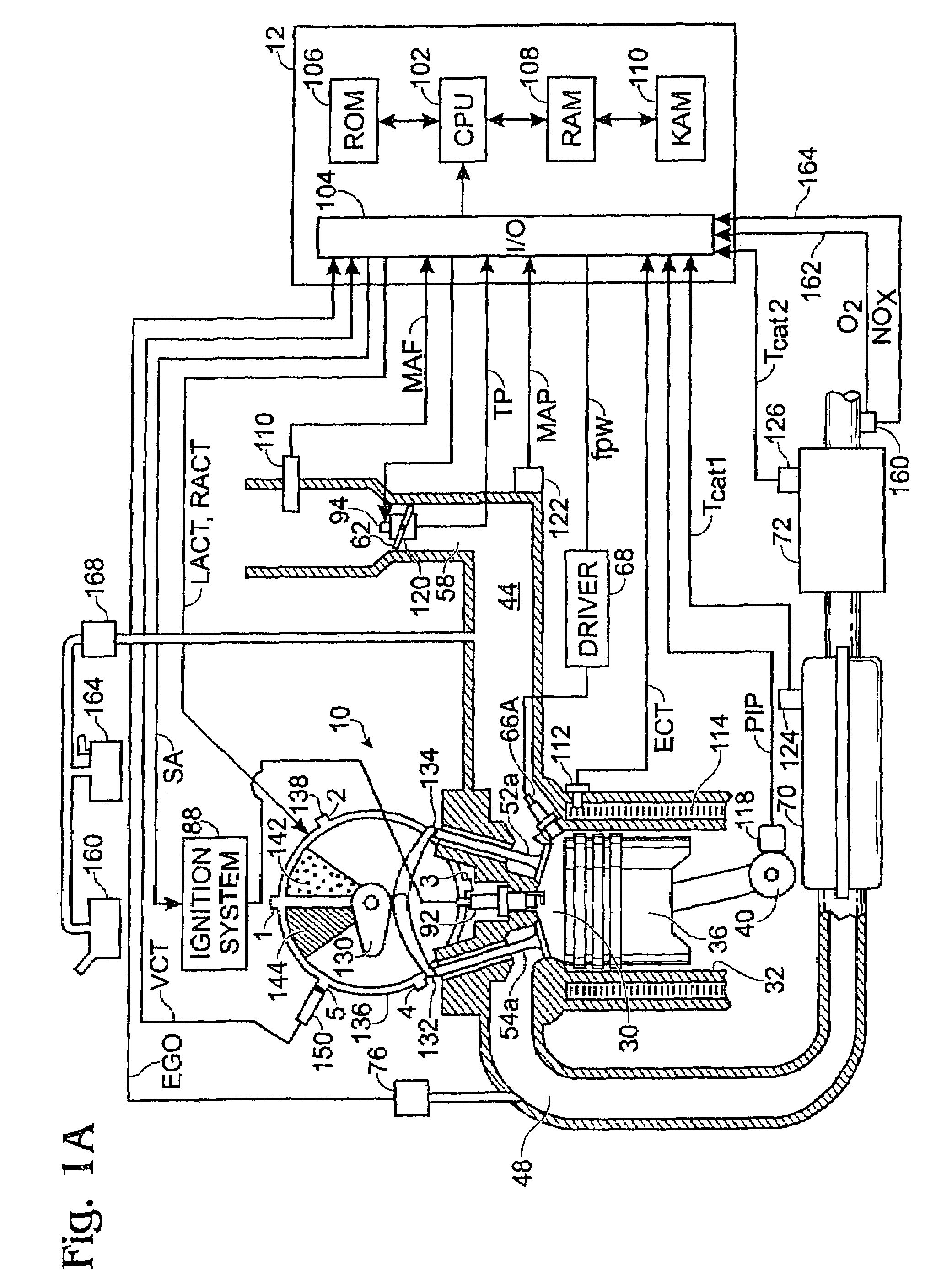
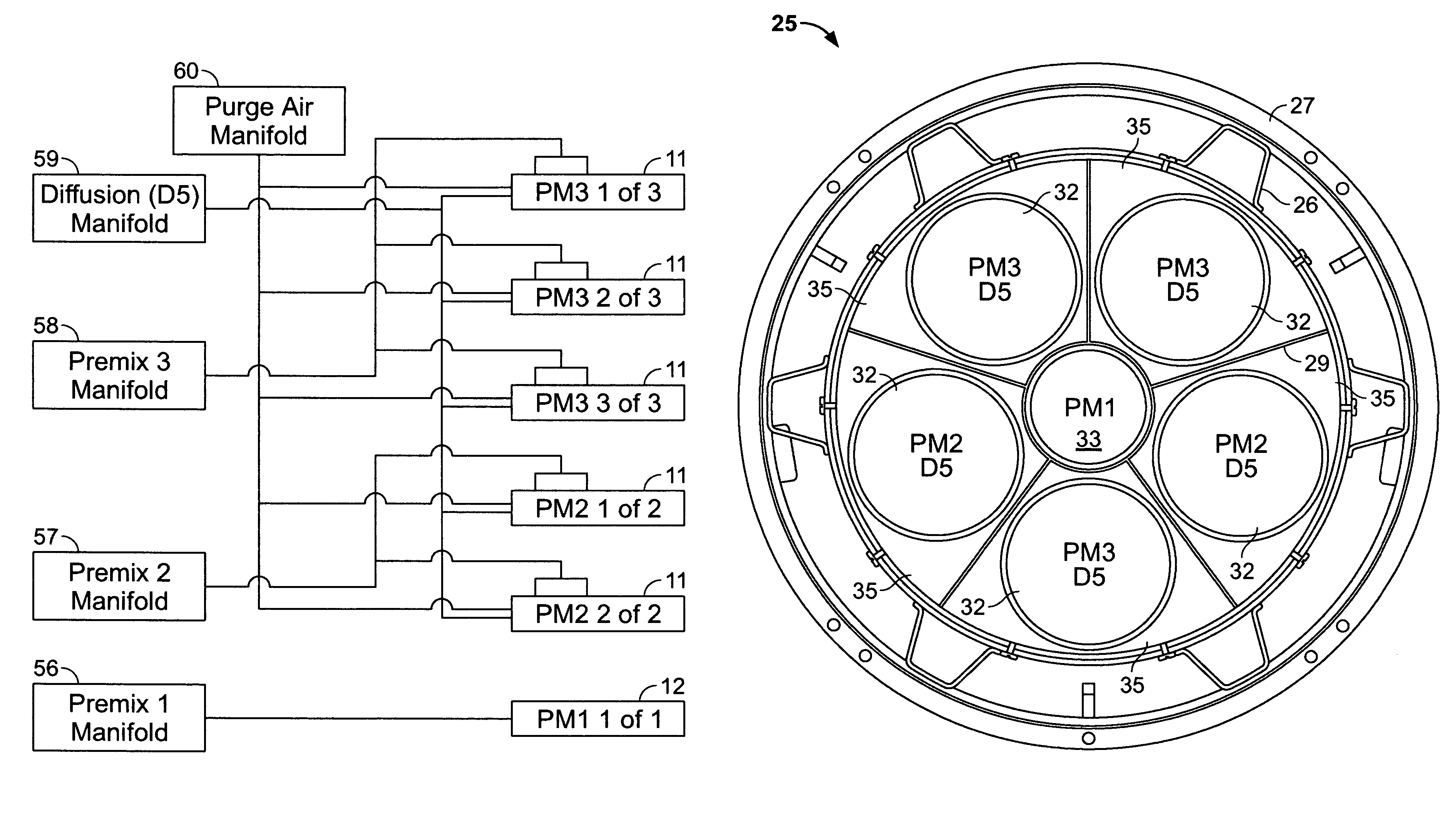
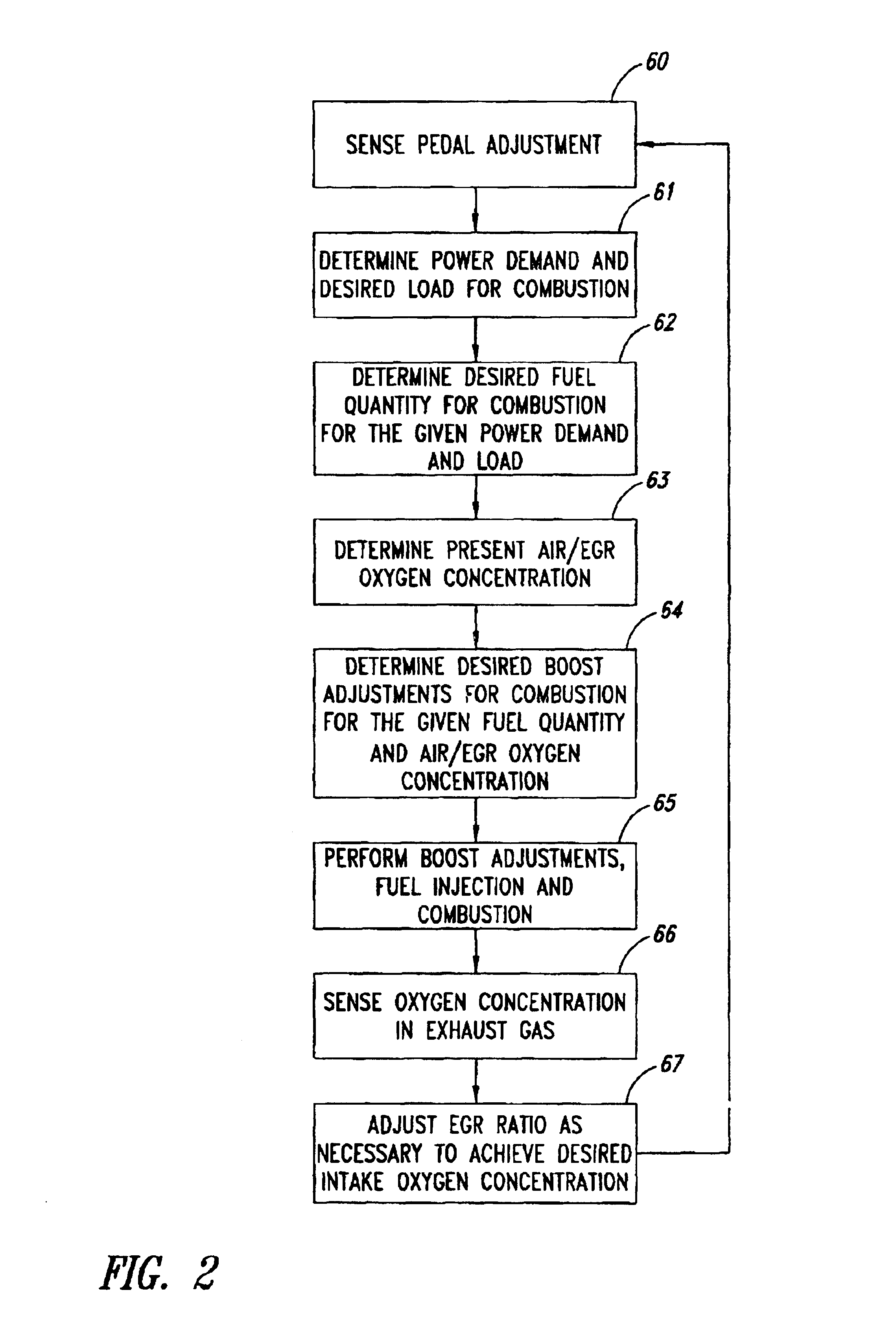
NOx emission-control system using a virtual sensor
InactiveUS6882929B2Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsAmbient humidityControl system
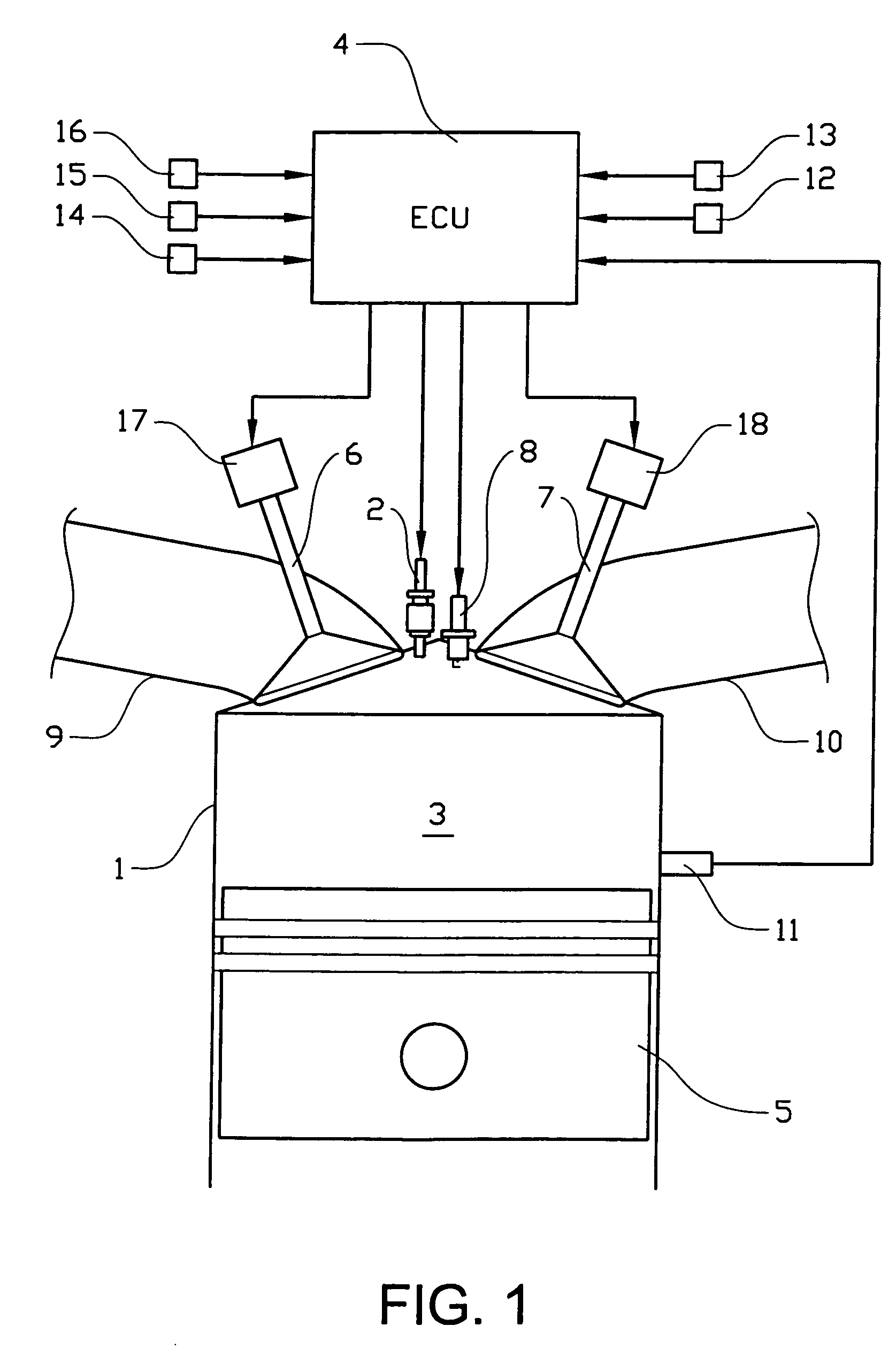
A method and system may be provided to perform a process for controlling NOx emissions of an target engine. In one embodiment of the invention, the process may include determining predicted NOx values based on a model reflecting a predetermined relationship between control parameters and NOx emissions, wherein the control parameters include ambient humidity, manifold pressure, manifold temperature, fuel rate, and engine speed associated with the engine. Further, the process may include adjusting the model based on a determination of whether the predicted NOx values meet a predetermined criteria associated with actual NOx values. The adjusted model may be stored in a memory associated with the engine whereby NOx emissions exhausted from the engine may be reduced based on virtual NOx emission values determined from the adjusted model.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
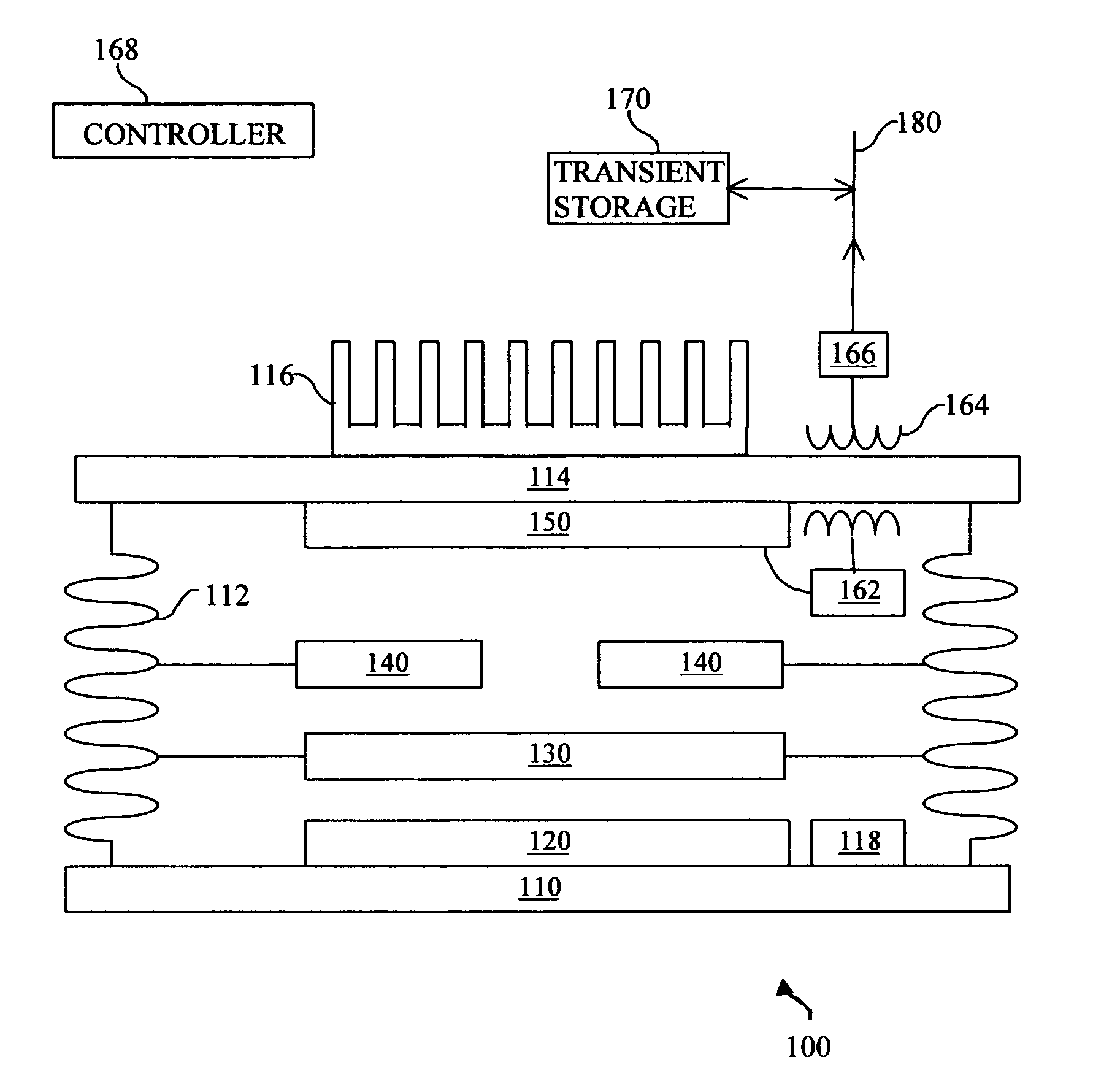
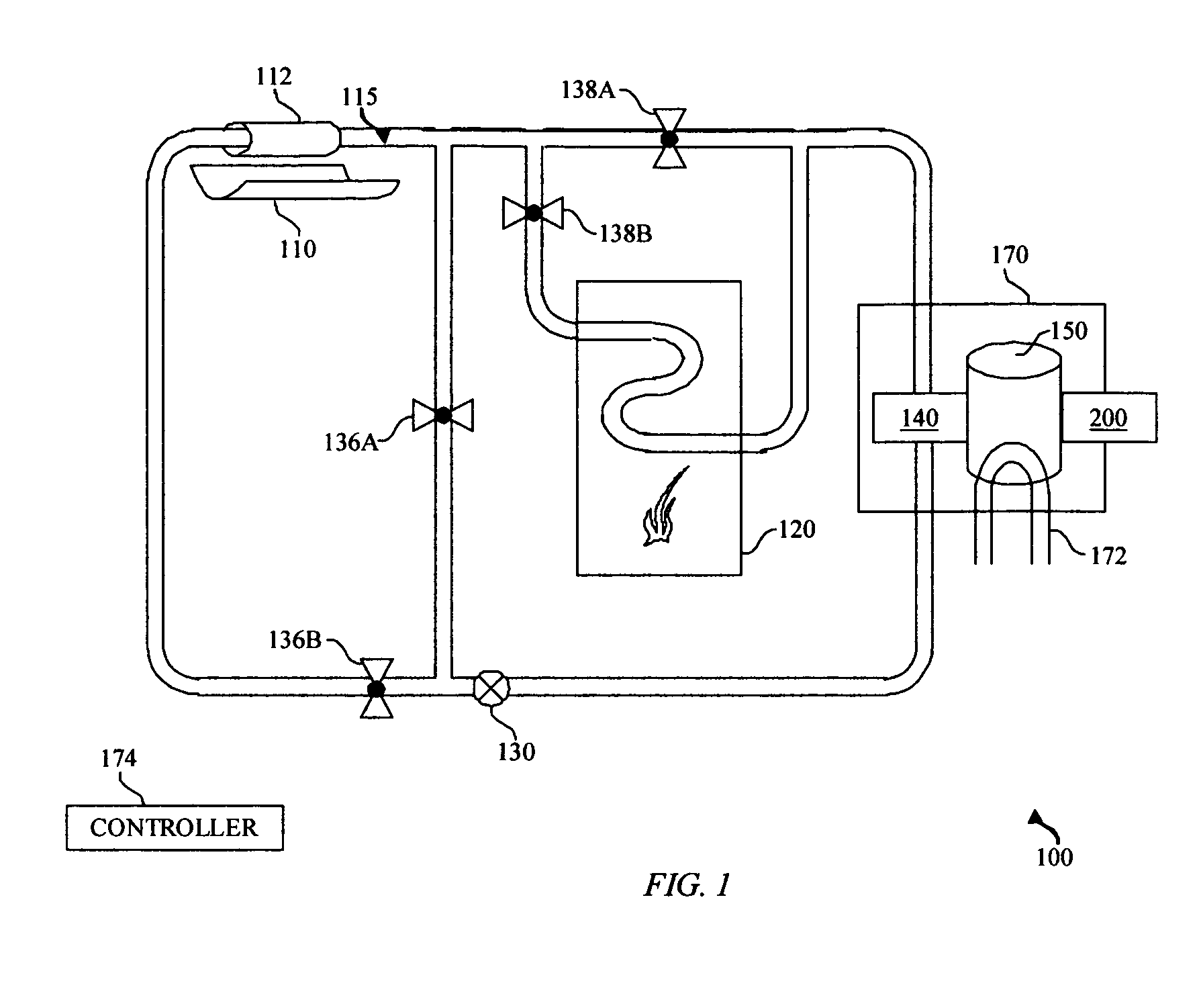
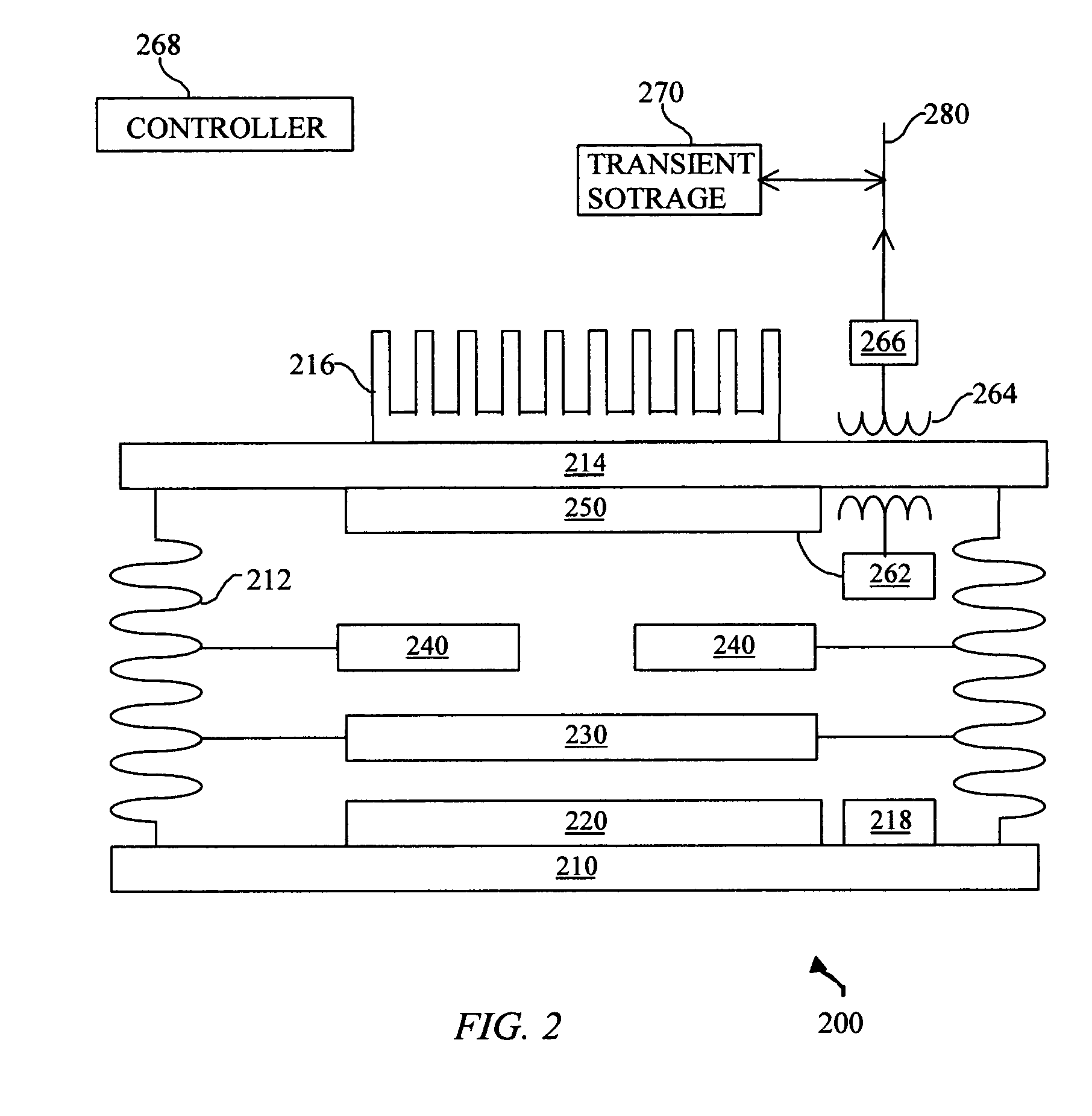
System and method for enhanced thermophotovoltaic generation
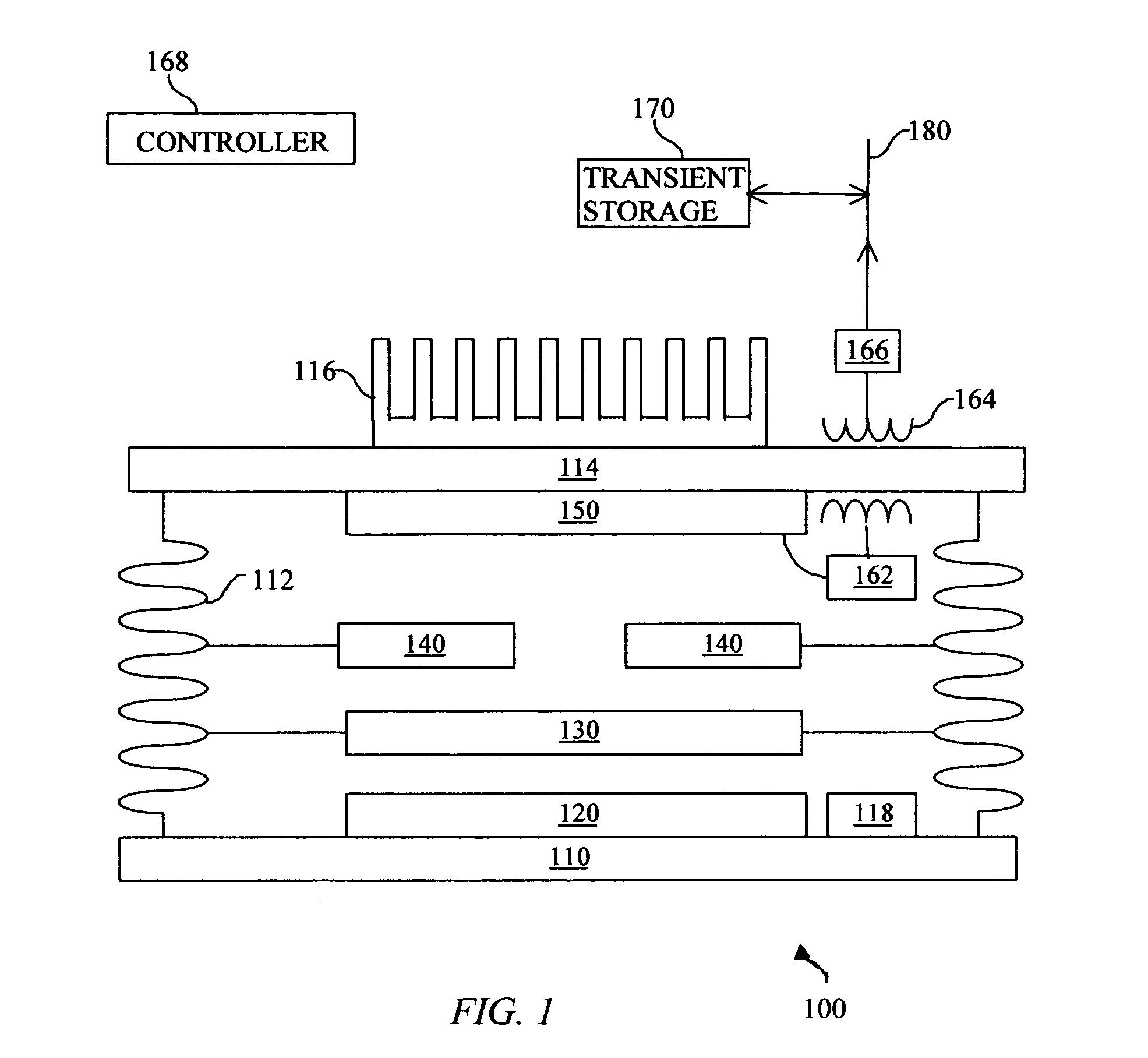
InactiveUS20050109386A1Reduce fossil fueled NOx emissionIncreasing burner efficiencyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPV power plantsThermophotovoltaicDistributed generation
A system and method for lower cost, high efficiency, thermophotovoltaic distributed generation includes: an emitter, a photovoltaic cell, and transient electrical energy storage.
Owner:PRACTICAL TECH
Engine system and method with cylinder deactivation
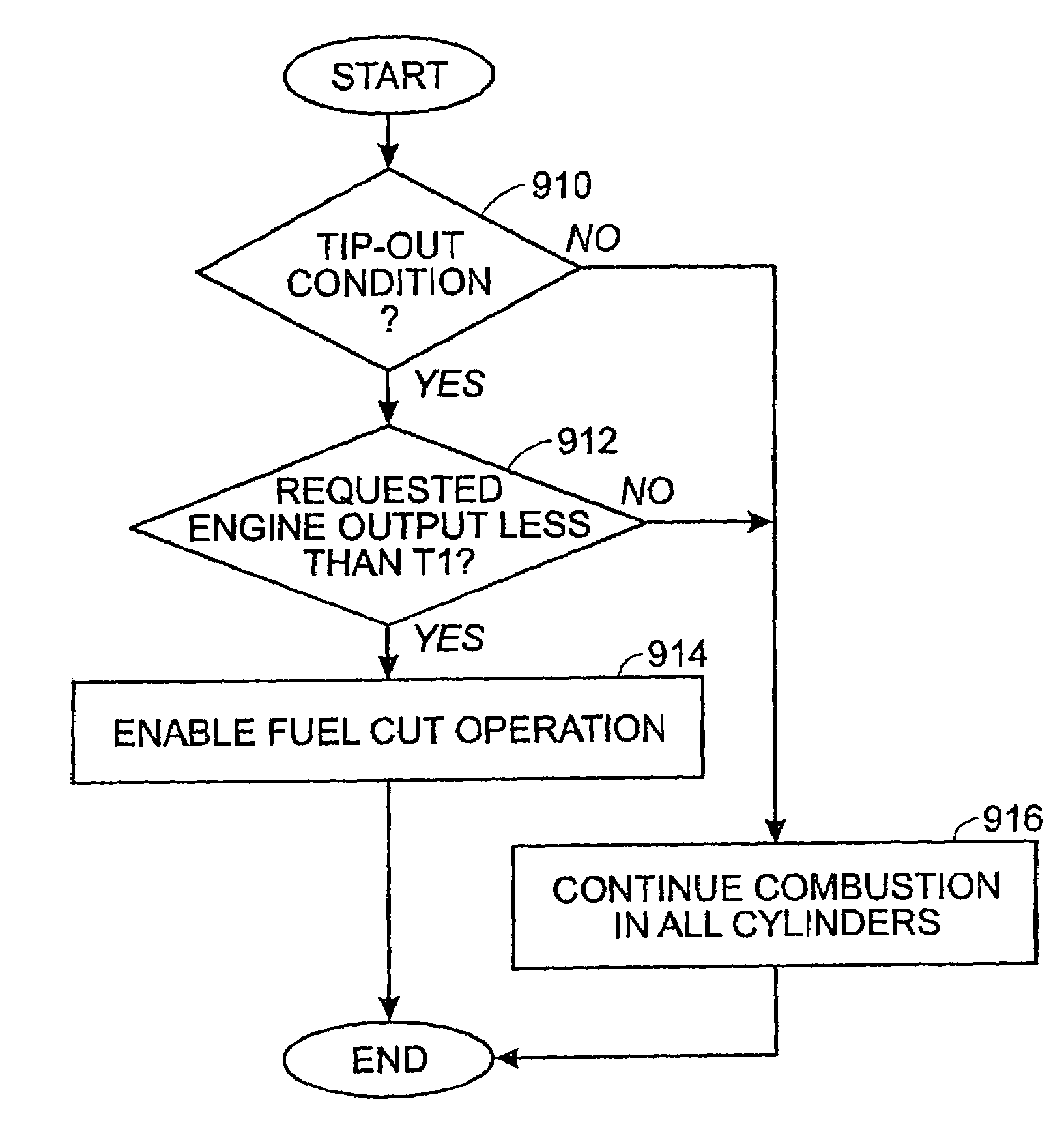
ActiveUS6978204B2Increase varietyEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSystems designFuel vapor
Various systems and methods are disclosed for carrying out combustion in a fuel-cut operation in some or all of the engine cylinders of a vehicle. Further, various subsystems are considered, such as fuel vapor purging, air-fuel ratio control, engine torque control, catalyst design, and exhaust system design.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
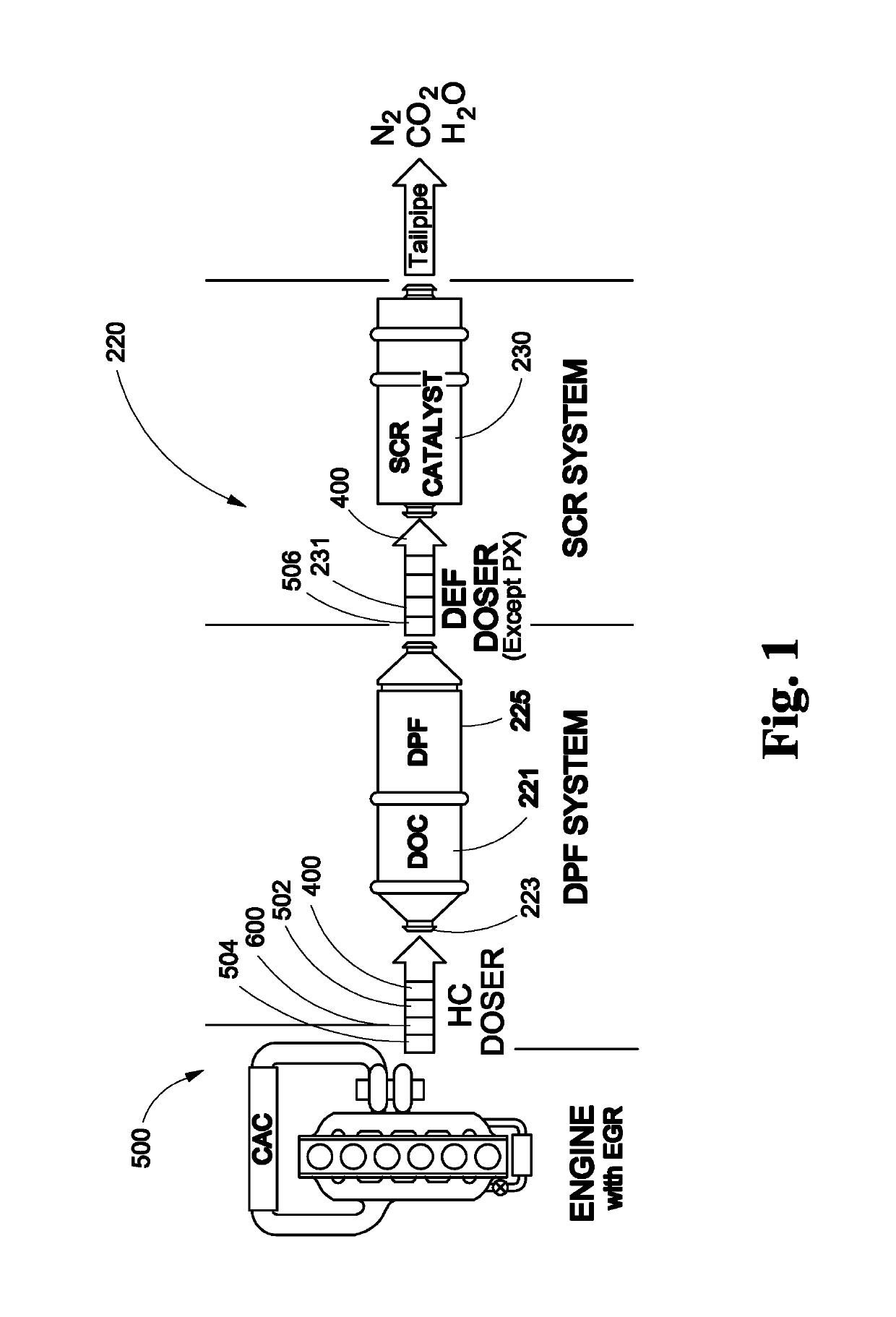
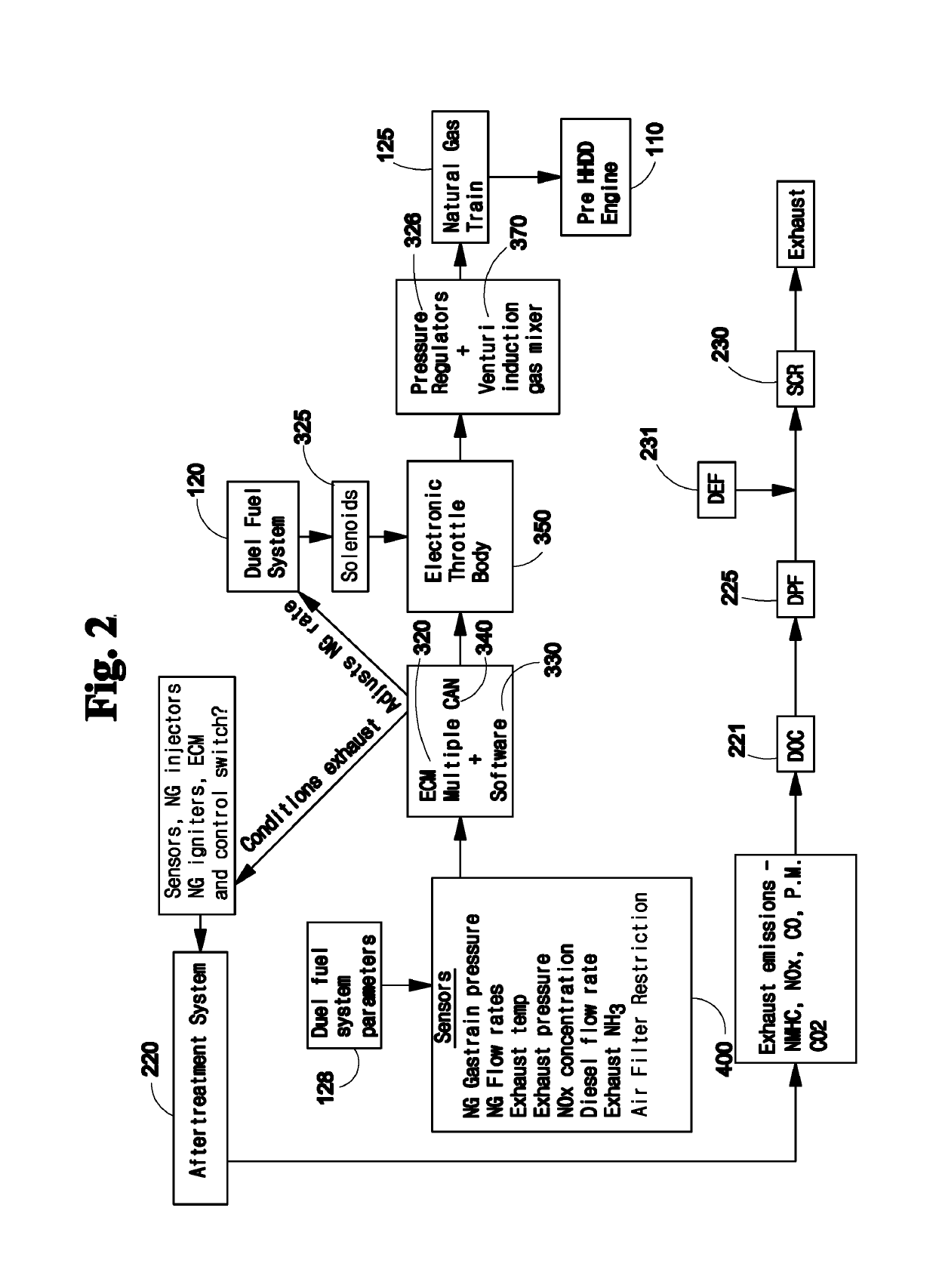
System comprising duel-fuel and after treatment for heavy-heavy duty diesel (HHDD) engines
ActiveUS10287943B1Eliminating of time lapseFast heatingInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusDecreased carbon dioxideExhaust emission
The present invention provides up-fit after treatment technology for bringing Heavy-Heavy Duty Diesel (HHDD) engine powered vehicles into compliance with the Title 13 CCR, Part 2025 mandate (meeting 2010 criteria emission standards). It also includes a Dual Fuel system, Exhaust Thermal Management System further reducing: NOx constituents, consumption of diesel fuel, particulate matter and CO2 emissions. The invention further comprises multiple sensors that provide data to electronic control module(s). The APGV6000 enables rapid after-treatment thermal activation, compares “real-time” sensor data with target data, and adjusts the after treatment system and / or dual fuel system and / or Exhaust Thermal Management system to produce exhaust emissions well below 2010 exhaust emission standards. For 2010 and newer HHDD engine applications, the V6000 comprises the Dual Fuel and exhaust thermal management system to affect rapid after-treatment activation, reduced NOx emissions well below, 2010 (current) standards, reduce diesel fuel usage and reduce CO2 emission.
Owner:CLEAN POWER TECH LLC
Combustion process and apparatus therefore containing separate injection of fuel and oxidant streams
InactiveUS6074197AReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsAvoid chemical reactionsCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelCombustorCombustion chamber
A burner assembly having improved flame length and shape control is presented, which includes in exemplary embodiments at least one fuel fluid inlet and at least one oxidant fluid inlet, means for transporting the fuel fluid from the fuel inlet to a plurality of fuel outlets, the fuel fluid leaving the fuel outlets in fuel streams that are injected into a combustion chamber, means for transporting the oxidant fluid from the oxidant inlets to at least one oxidant outlet, the oxidant fluid leaving the oxidant outlets in oxidant fluid streams that are injected into the combustion chamber, with the fuel and oxidant outlets being physically separated, and geometrically arranged in order to impart to the fuel fluid streams and the oxidant fluid streams angles and velocities that allow combustion of the fuel fluid with the oxidant in a stable, wide, and luminous flame. Alternatively, injectors may be used alone or with the refractory block to inject oxidant and fuel gases. The burner assembly affords improved control over flame size and shape and may be adjusted for use with a particular furnace as required.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC +1
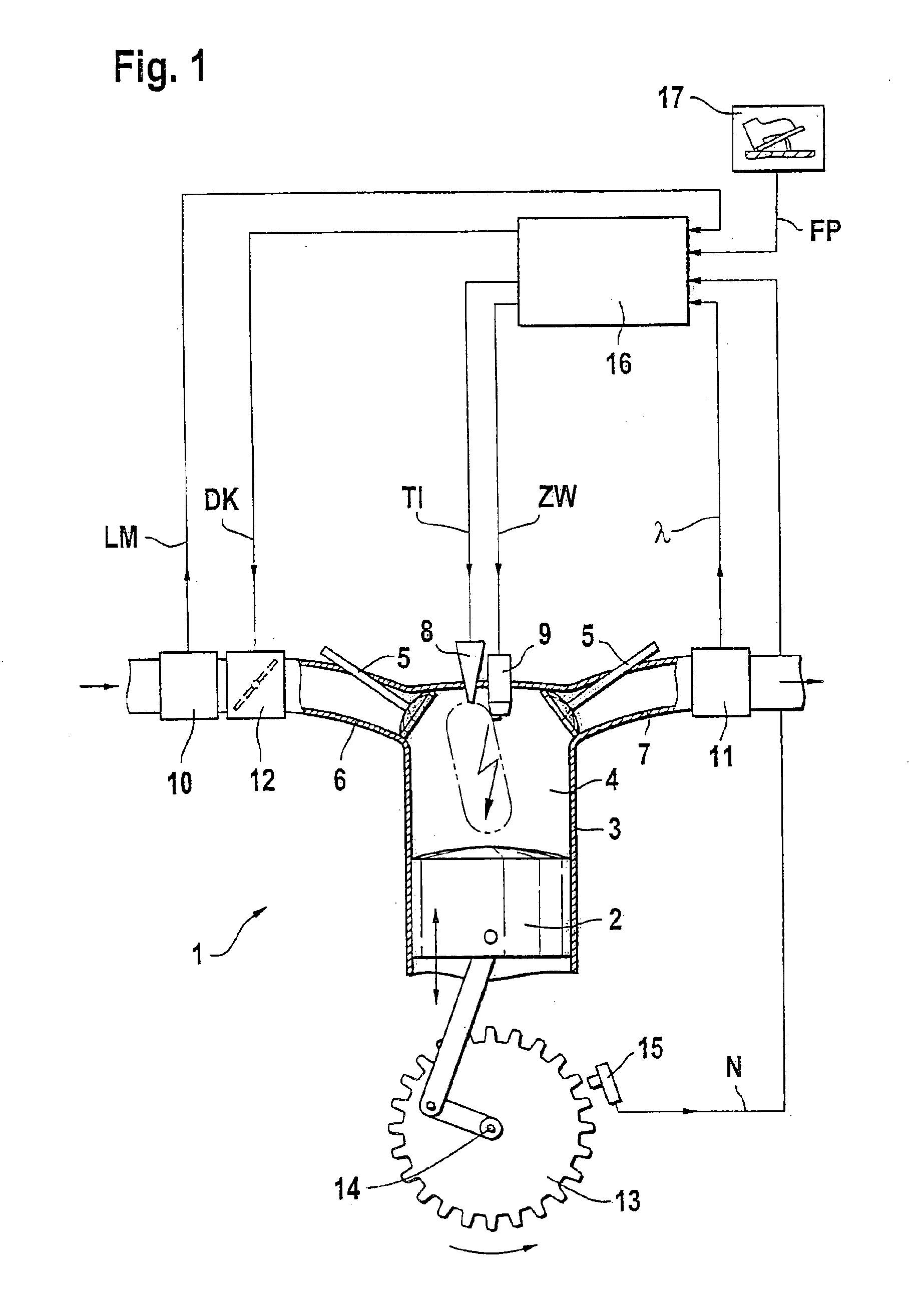
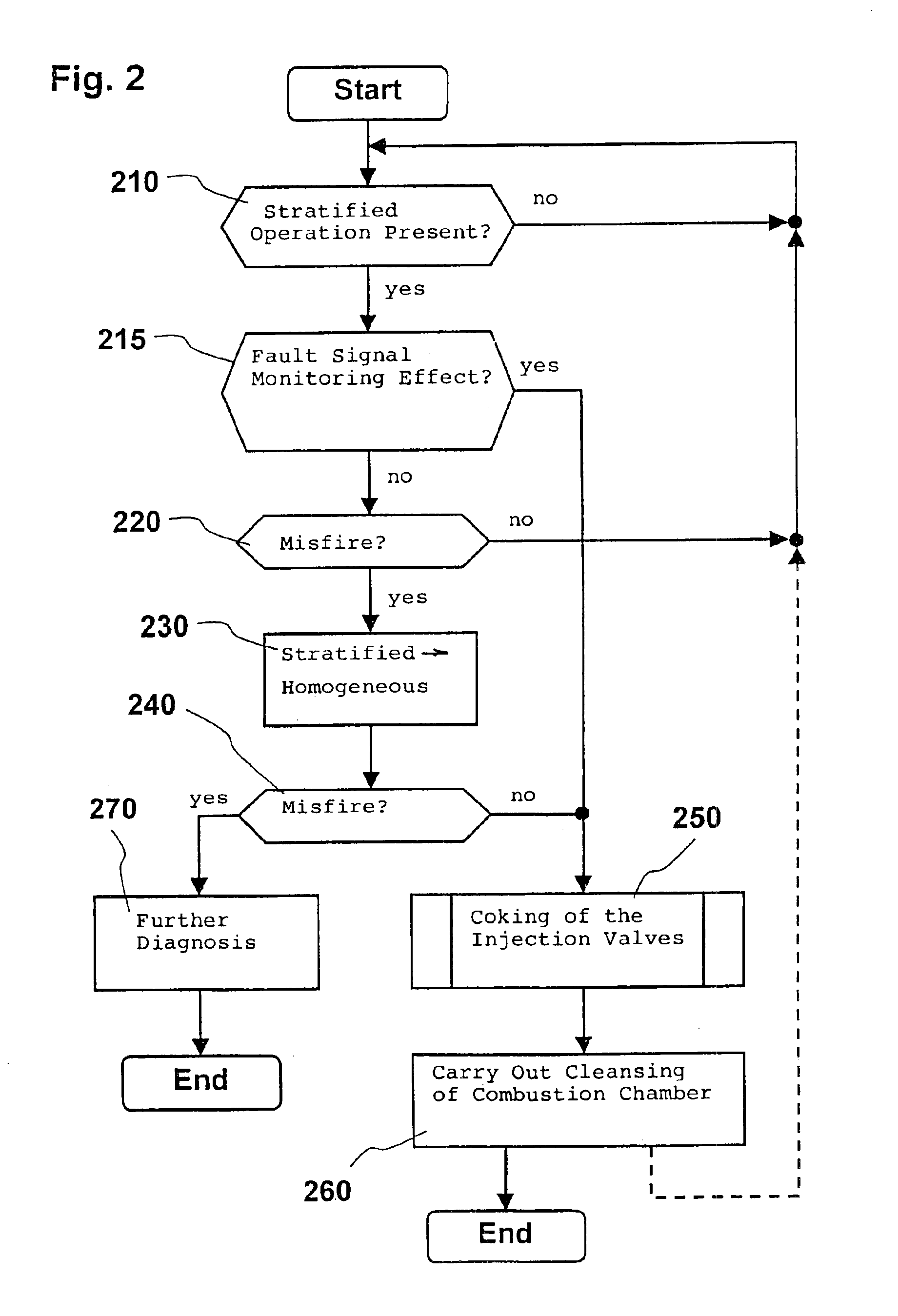
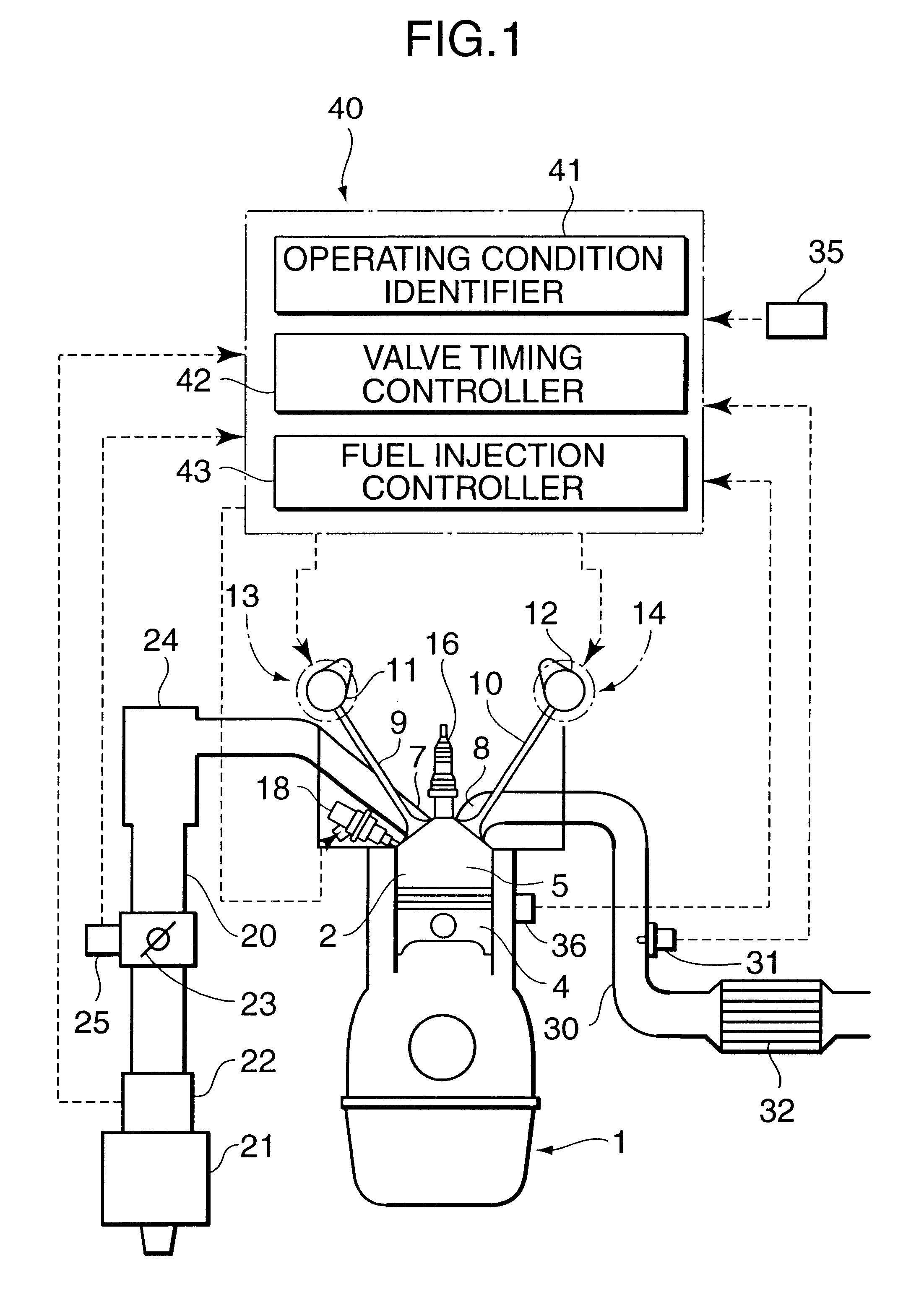
Method for operating an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6892691B1Simple meansPromote combustionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
The operation of an internal combustion engine under unfavorable operating conditions can lead to the formation of deposits in the combustion chamber (4). A method and an arrangement for operating an internal combustion engine (1), especially of a motor vehicle, is suggested, wherein fuel is conducted into a combustion chamber (4) and is there combusted. When deposits are detected in the combustion chamber (4), measures are initiated in a targeted manner for cleansing the combustion chamber (4). A knocking combustion is especially introduced and / or a cleansing liquid is added to the inducted combustion air.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
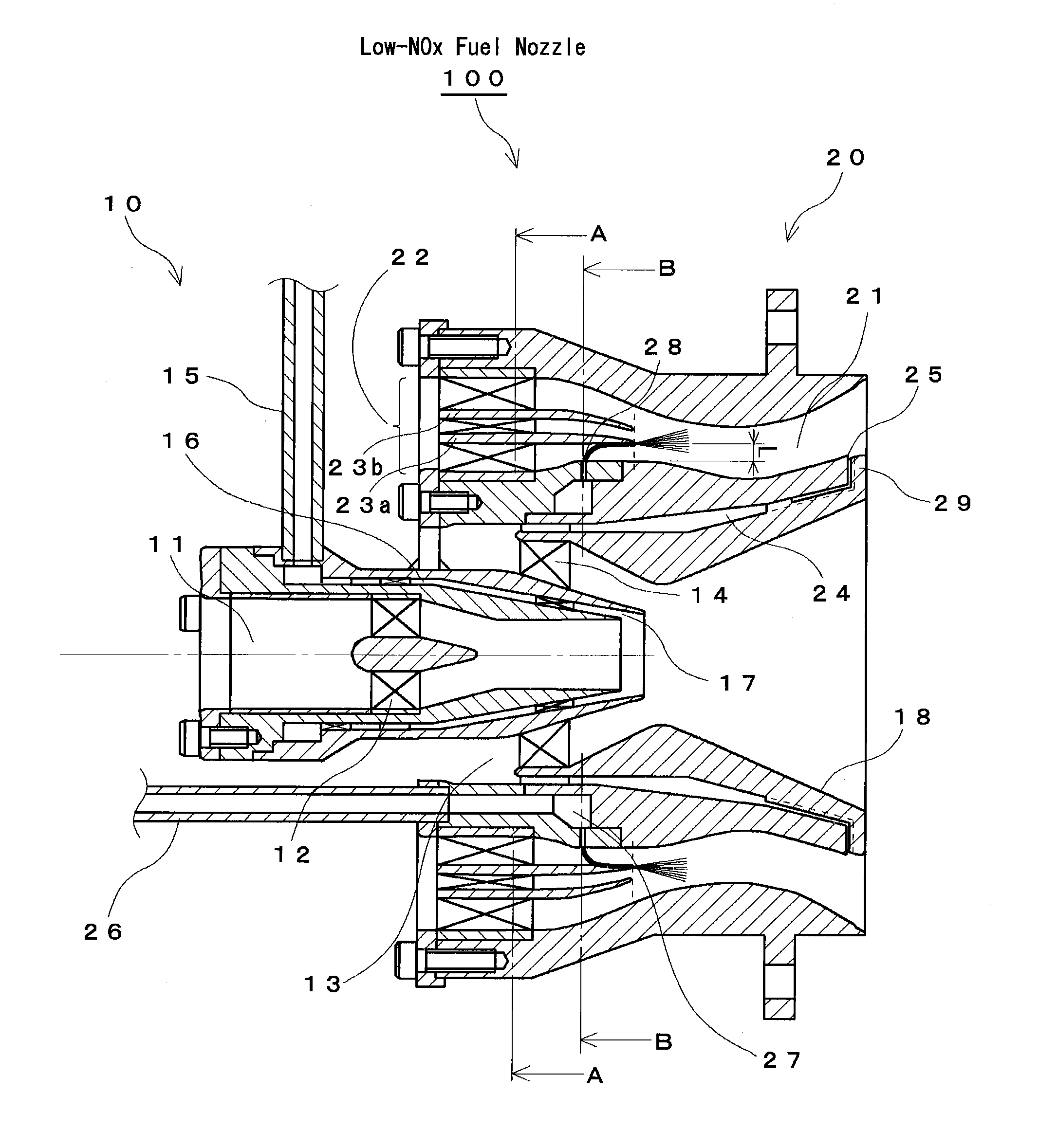
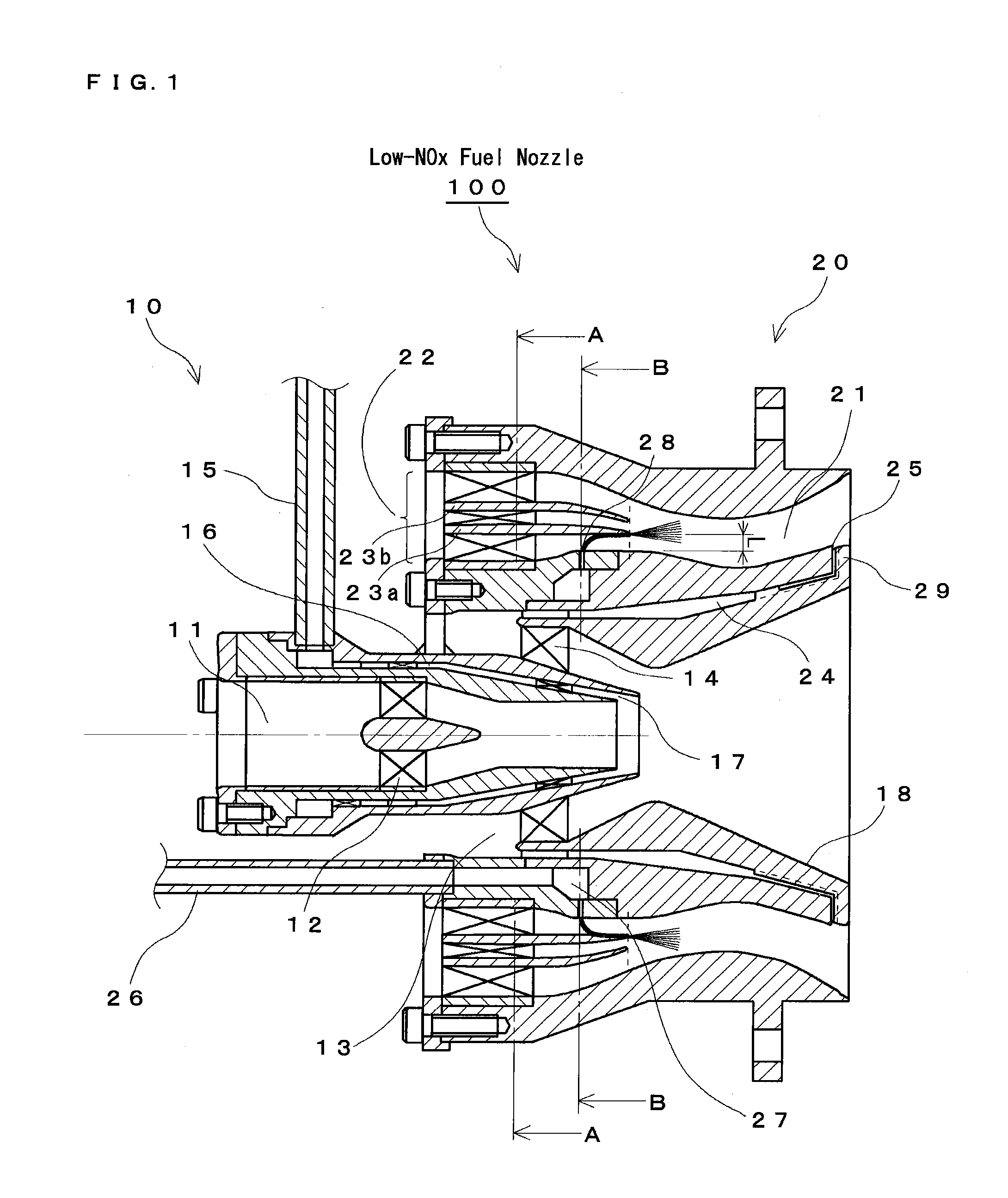
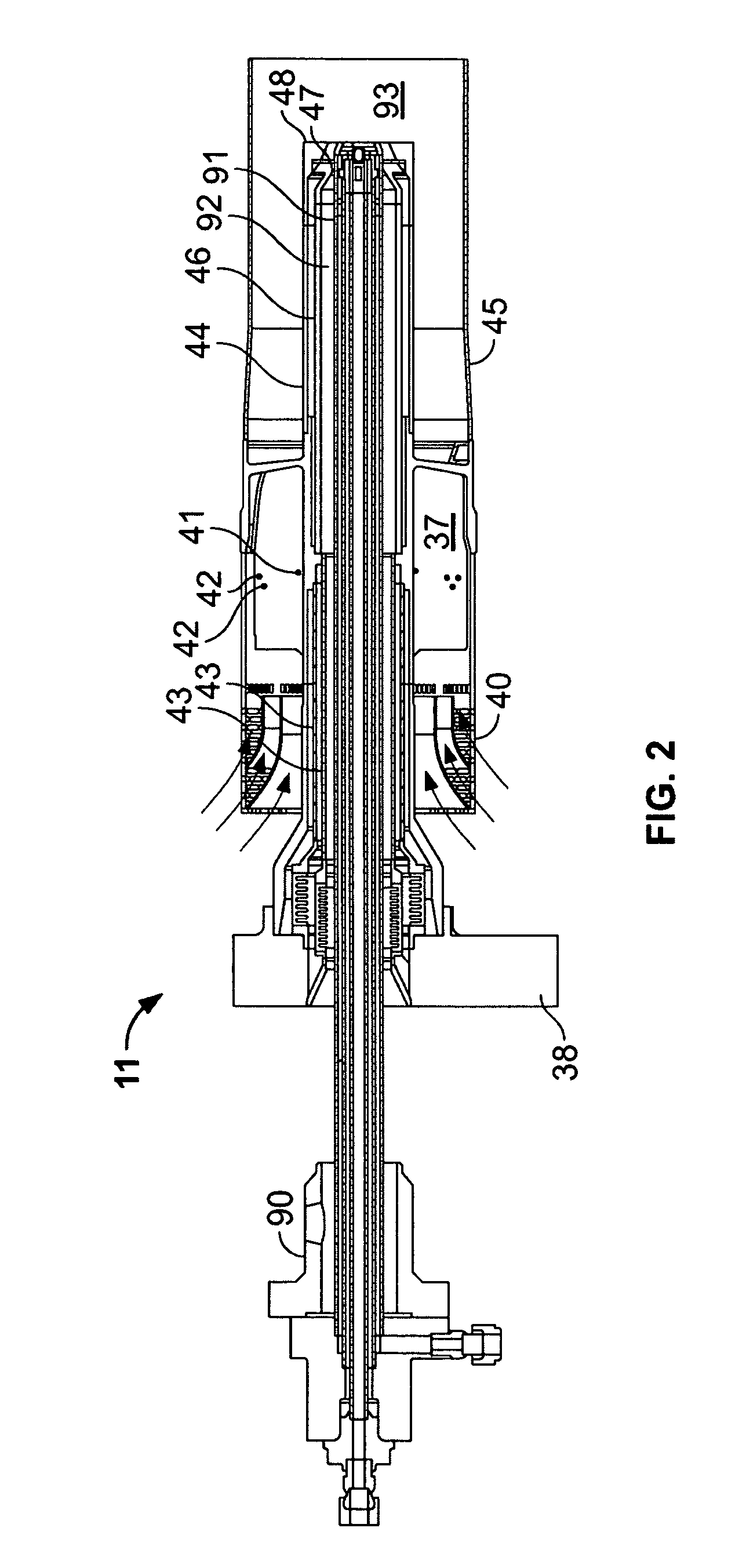
Staging fuel nozzle
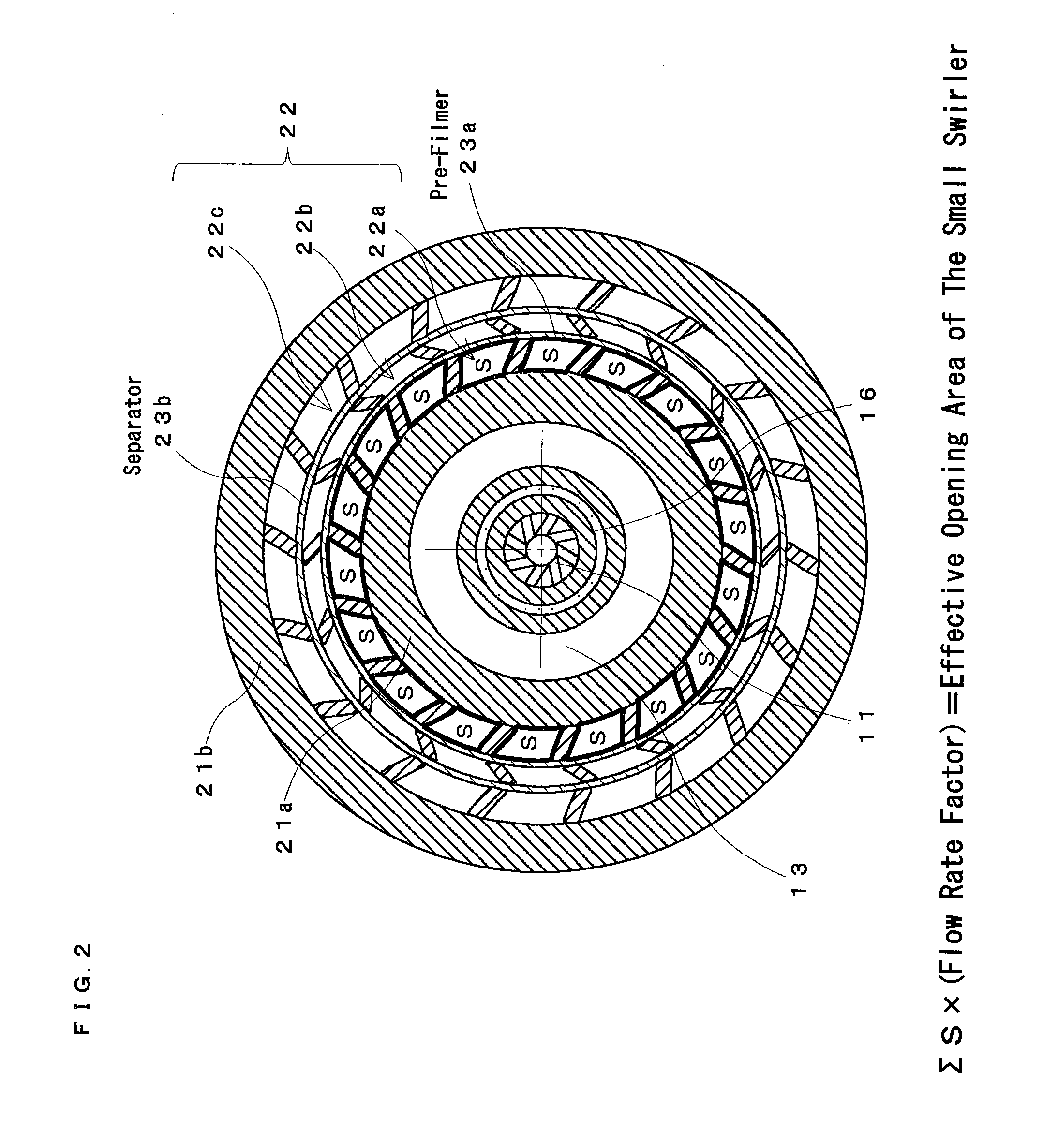
ActiveUS20100308135A1Reduce amount of NOx generateHigh degree of atomizationBurnersTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsEngineeringFuel injection
A main swirler of a triple annular configuration that is partitioned by a pre-filmer and a separator is installed in an inlet port of a main air flow channel. The vicinity of the inner wall of the main air flow channel provided with a main fuel injection port is bulged radially outward from the innermost surface (innermost surface of a small swirler) of a main swirler. Further, a distance from the main fuel injection port and the pre-filmer is set such that an effective opening area between the pre-filmer and “the inner wall of the main air flow channel provided with the main fuel injection port” is equal to an effective opening area of the small swirler. The swirling directions of the swirlers of the main swirler are “clockwise”-“counter-clockwise”-“clockwise” respectively along the radial outward direction when the swirling direction of the innermost swirler is taken as “clockwise”.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Combustion equipment and burner combustion method
InactiveUS20080268387A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsIncrease flow rateCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelContinuous combustion chamberCombustion chamberCombustor
Combustion equipment of a coaxial jet combustion scheme is provided that includes: a burner plate in which fuel and air are mixed with each other while the fuel and air pass through an air hole; a burner plate extension which is a portion of the burner plate and extends toward a combustion chamber side spaced apart from the air hole; and a protrusion disposed on the combustion chamber side of the burner plate extension so as to protrude in a direction where flow of the fuel moves. In the combustion equipment, a gap between opposite portions of the protrusion is greater than a diameter of the air hole and a flame source forming area is defined between the burner plate, the burner plate extension and the protrusion. The combustion equipment of a coaxial jet combustion scheme can achieve a further reduction in NOx emissions.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electric flame control using corona discharge enhancement
InactiveUS7243496B2Increased ionizationPromote combustionTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionElectricityCombustor
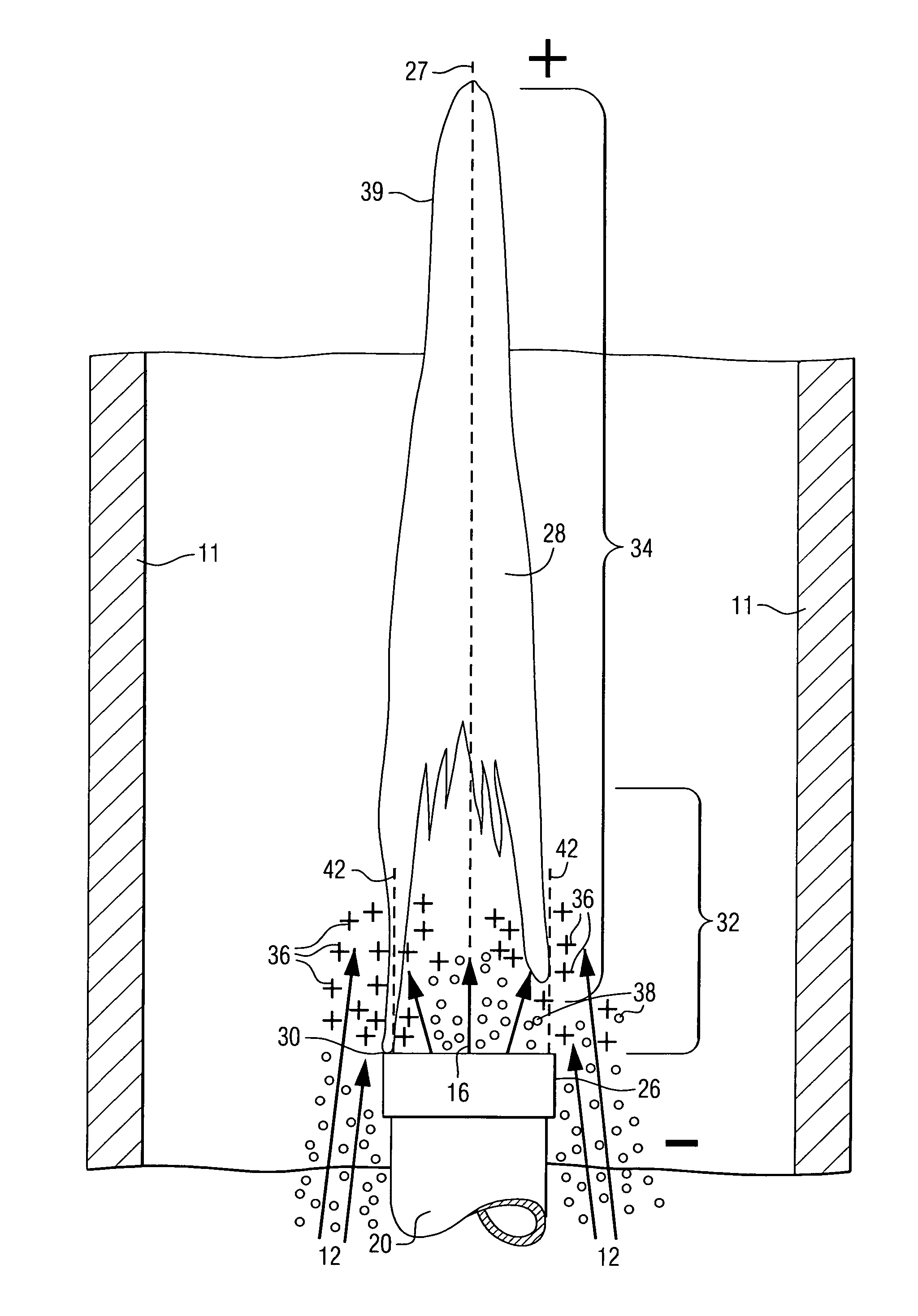
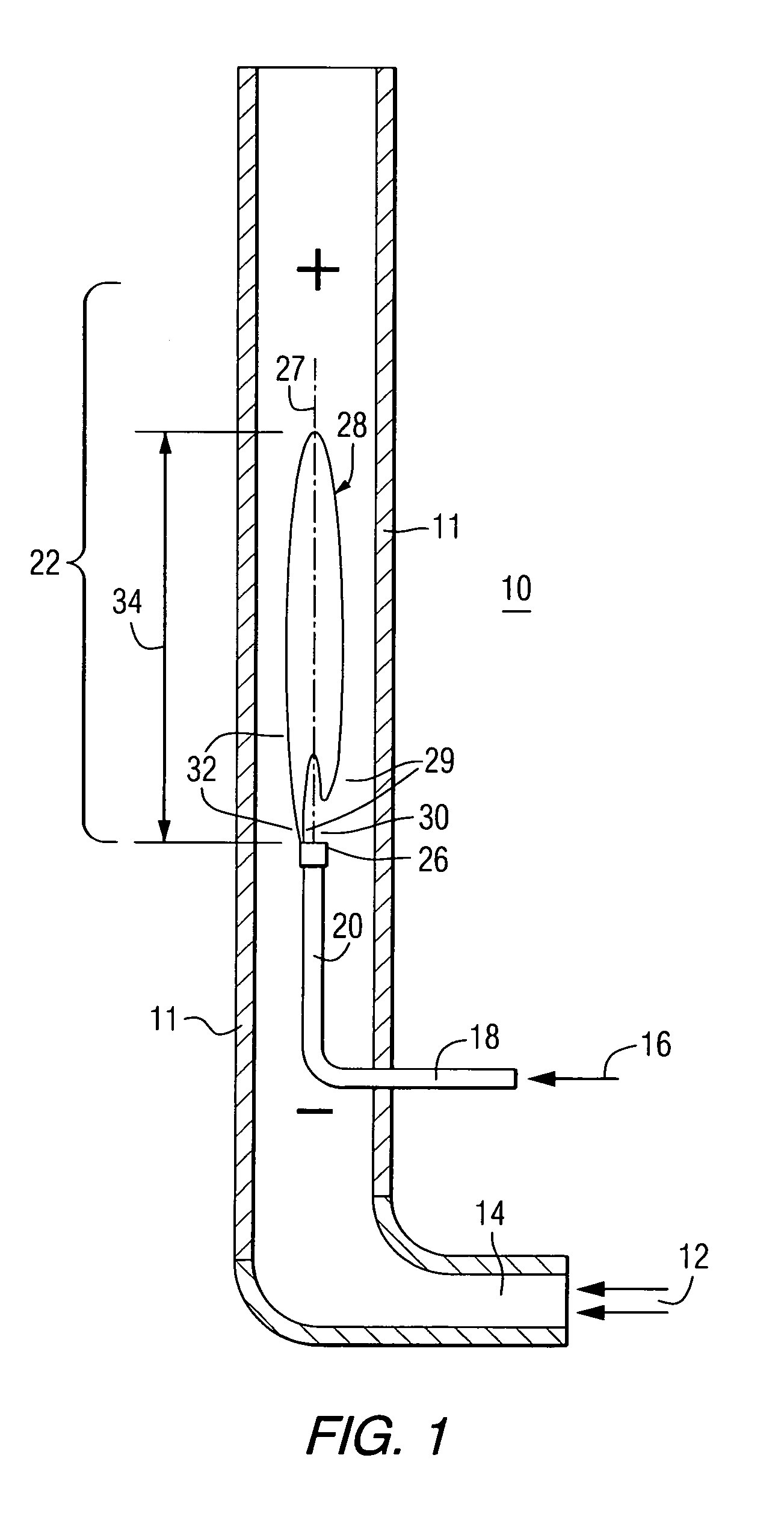
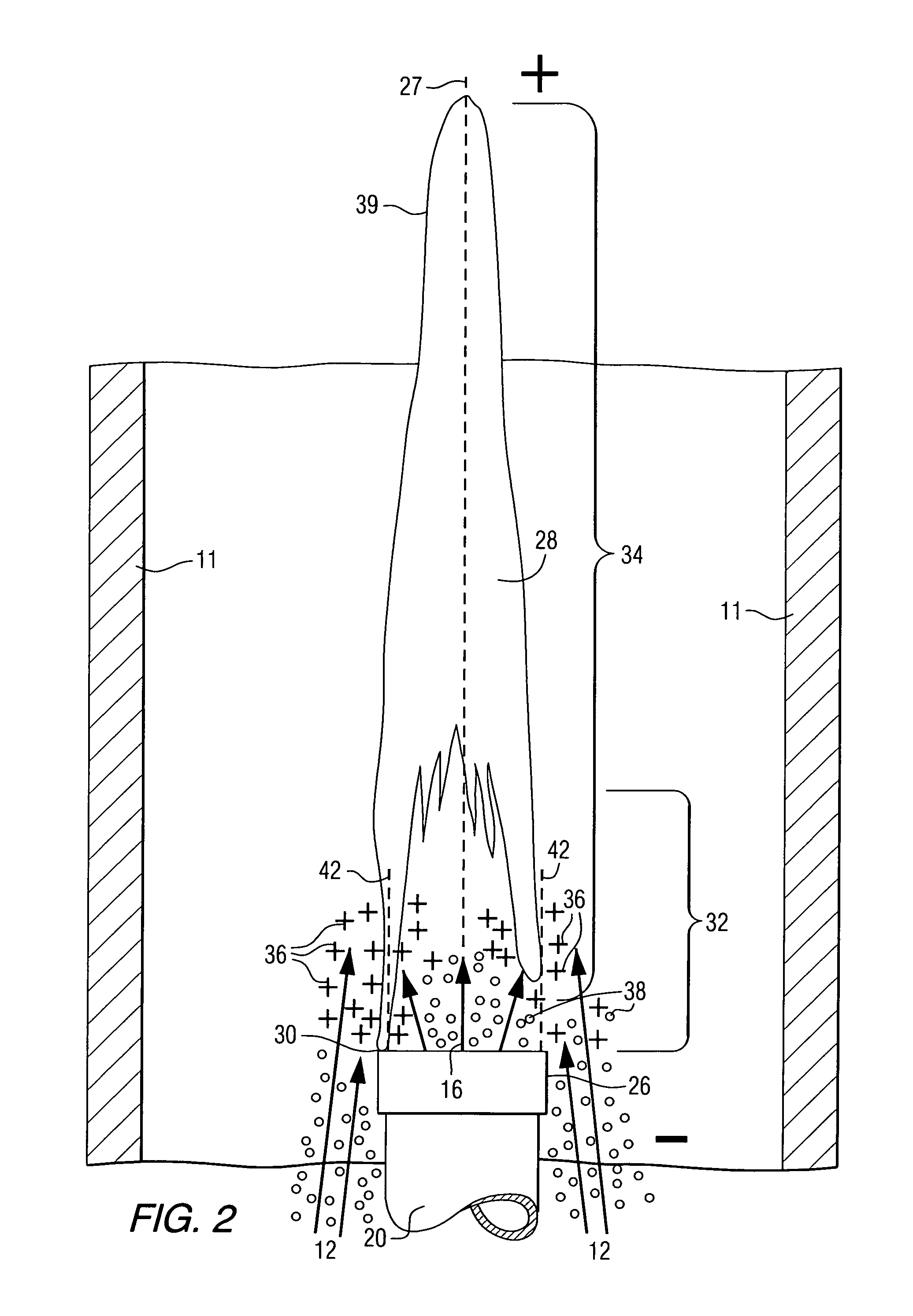
A method of operating a combustor (10), to provide intimately mixed hot combusted gas (44) for a gas turbine (46), includes feeding gaseous oxidant (12) and gaseous fuel (16) into the combustor (10) near a combustion flame (28) which has a tip end (39) and a root end (29), where corona discharge occurs through adjustment of an electric field (34), and where the corona discharge causes ionized particles (36) to form and also causes intimate turbulent mixing of the gases.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
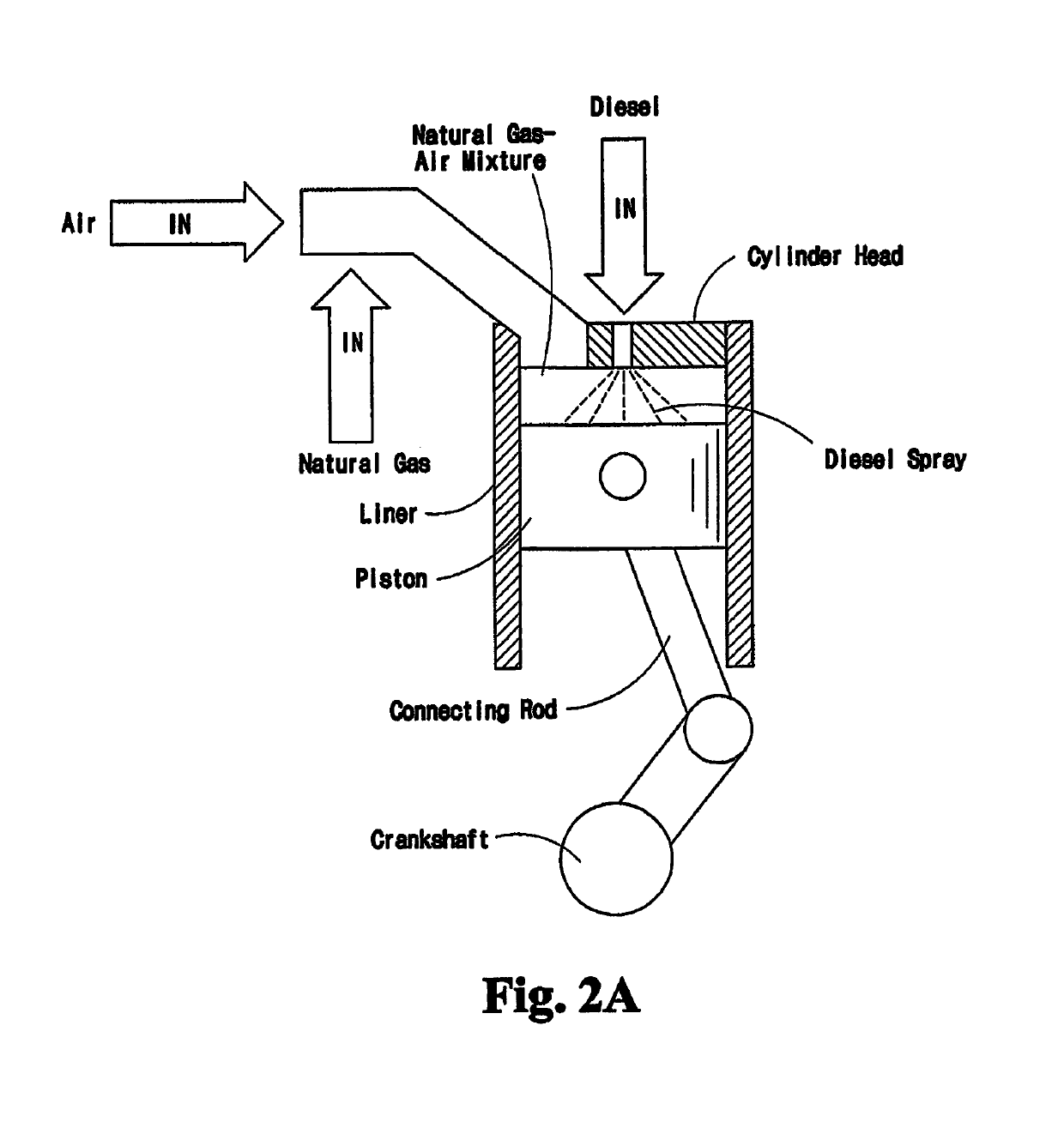
Internal combustion engine with injection of gaseous fuel
InactiveUS6854438B2Reduce modificationReduce manufacturing costIncandescent ignitionInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineFuel injection
An internal combustion engine comprises a fuel injection nozzle for injecting a gaseous fuel directly into the combustion chamber. shield, is installed in close proximity to the fuel injection nozzle, provides a shielded space around a hot surface igniter and restricts flow between the shielded space and the combustion chamber. The nozzle comprises a fuel injection port oriented to direct a fuel spray against a surface of the sleeve An inlet in the sleeve allows air and fuel to enter the shielded space to form a combustible mixture therein. The sleeve contains a substantial amount of the combustible mixture within the shielded space until it ignites and pressure builds within the shielded space to propel a combustion flame through at least one discharge opening and into contact with the fuel sprays emerging from the fuel injection nozzle.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Combustor
ActiveUS20110076628A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsMaintains combustion stabilityFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberCombustorCombustion chamber
This invention is directed to supply a combustor having a structure that reduces NOx emissions while maintaining combustion stability. The combustor has a chamber into which fuel and air are supplied. An air hole plate having a plurality of air holes upstream of the chamber is also disclosed, and fuel nozzles supplying fuel to the air holes of the air hole plate are further disclosed. In the combustor, a center of a chamber-side of the air hole plate is closer to the chamber than exits of outermost peripheral air holes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
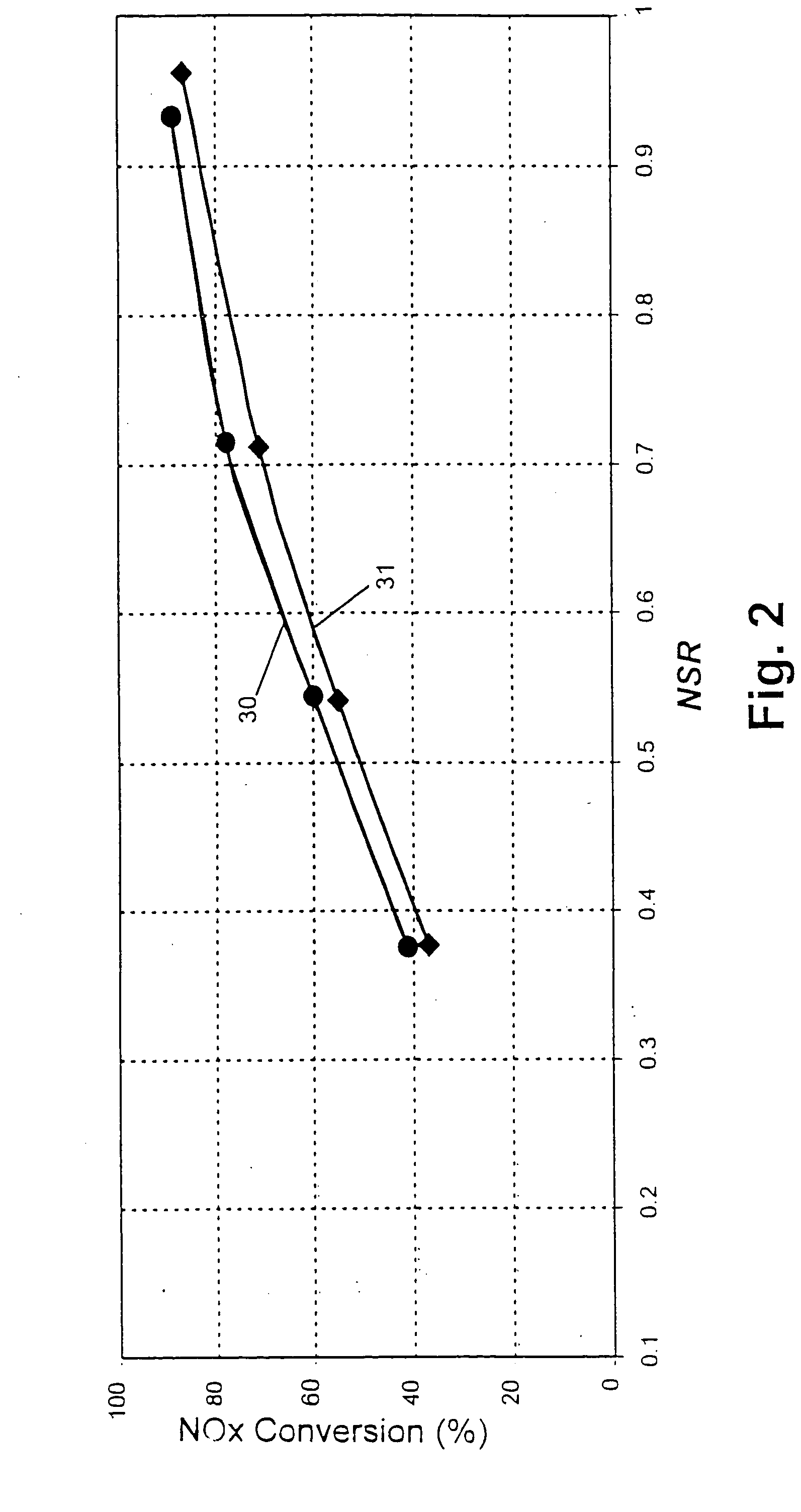
Reactor system for reducing NOx emissions from boilers
ActiveUS7943097B2Low costEasy maintenanceCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsCombustorReactor system
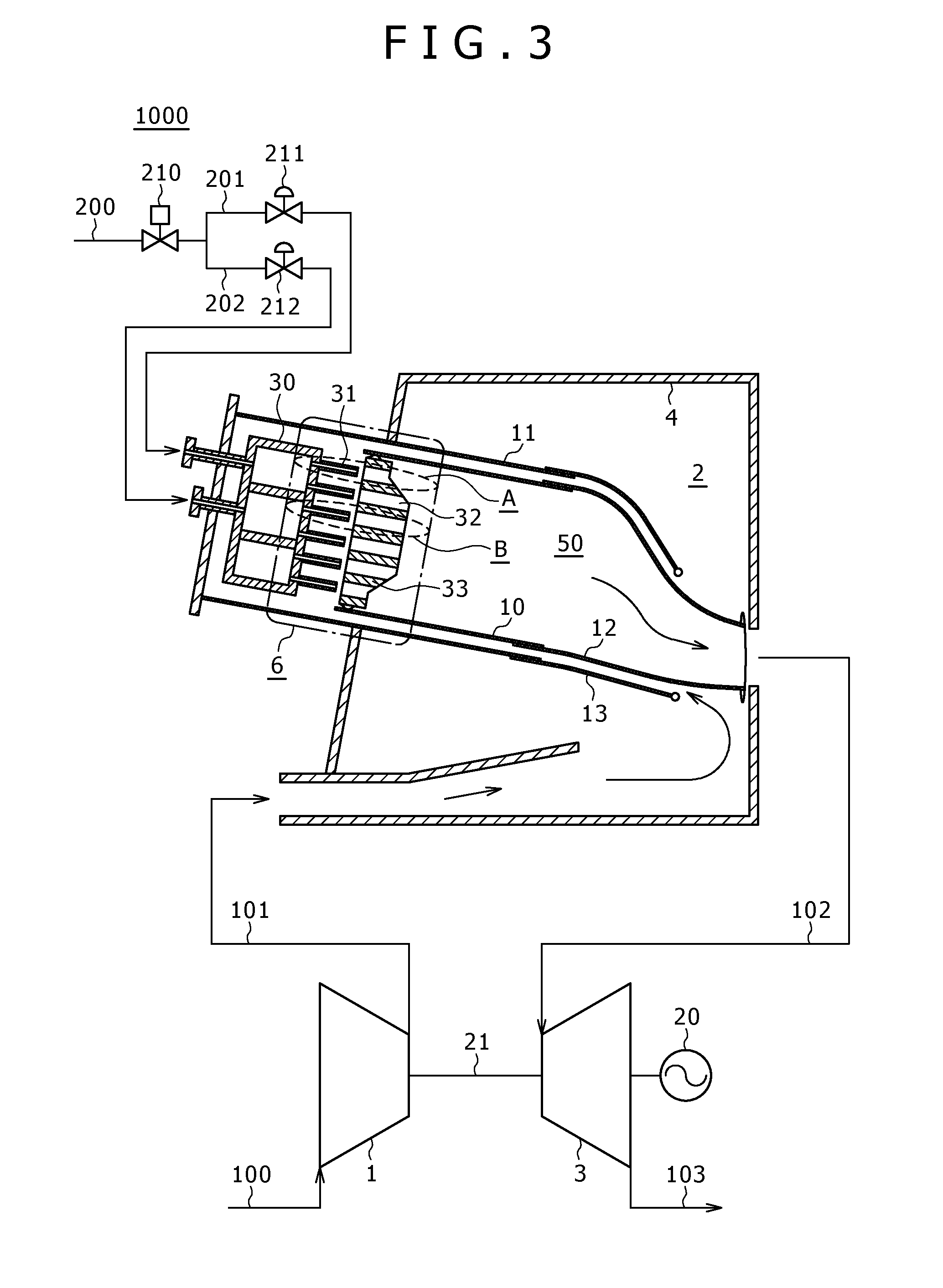
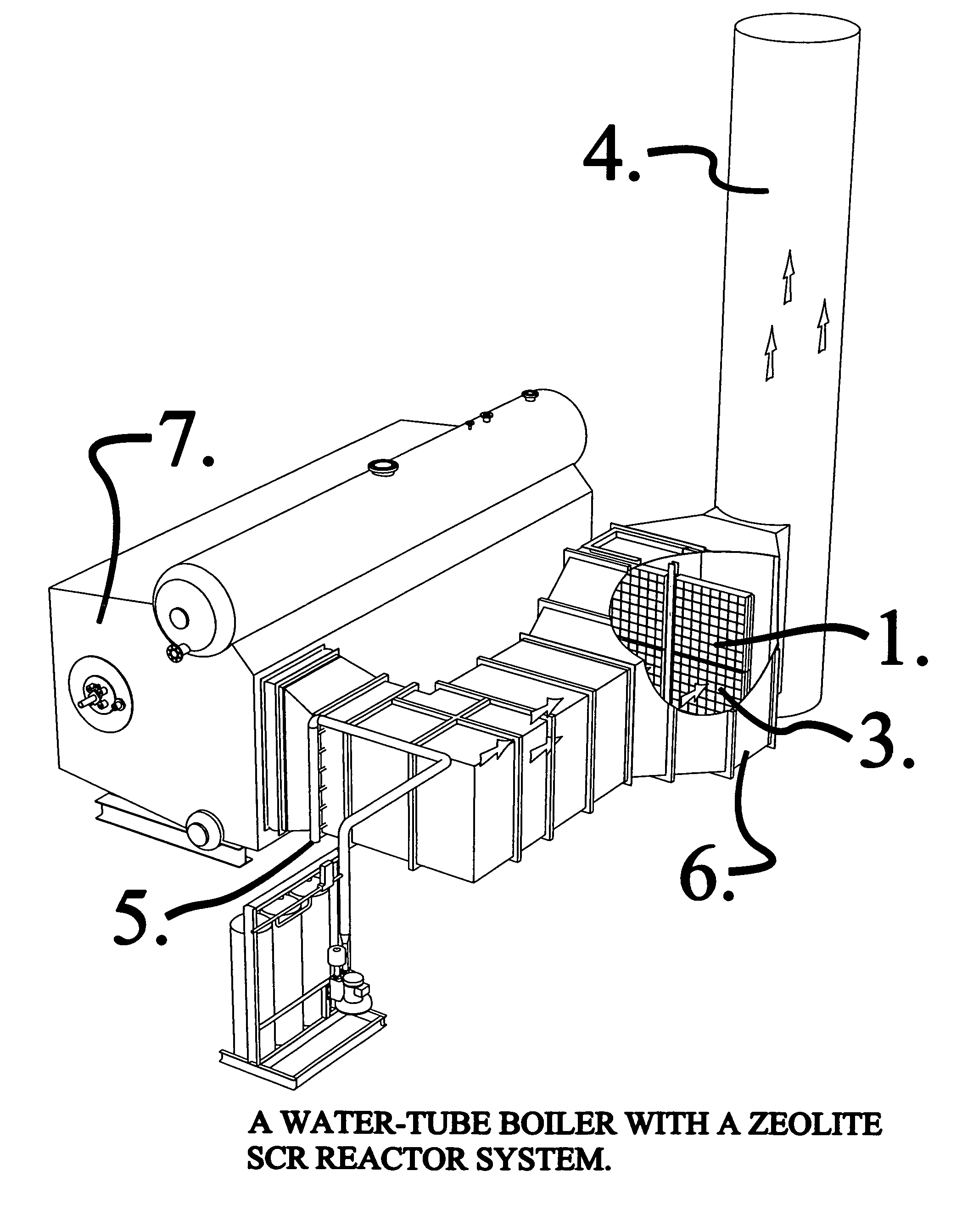
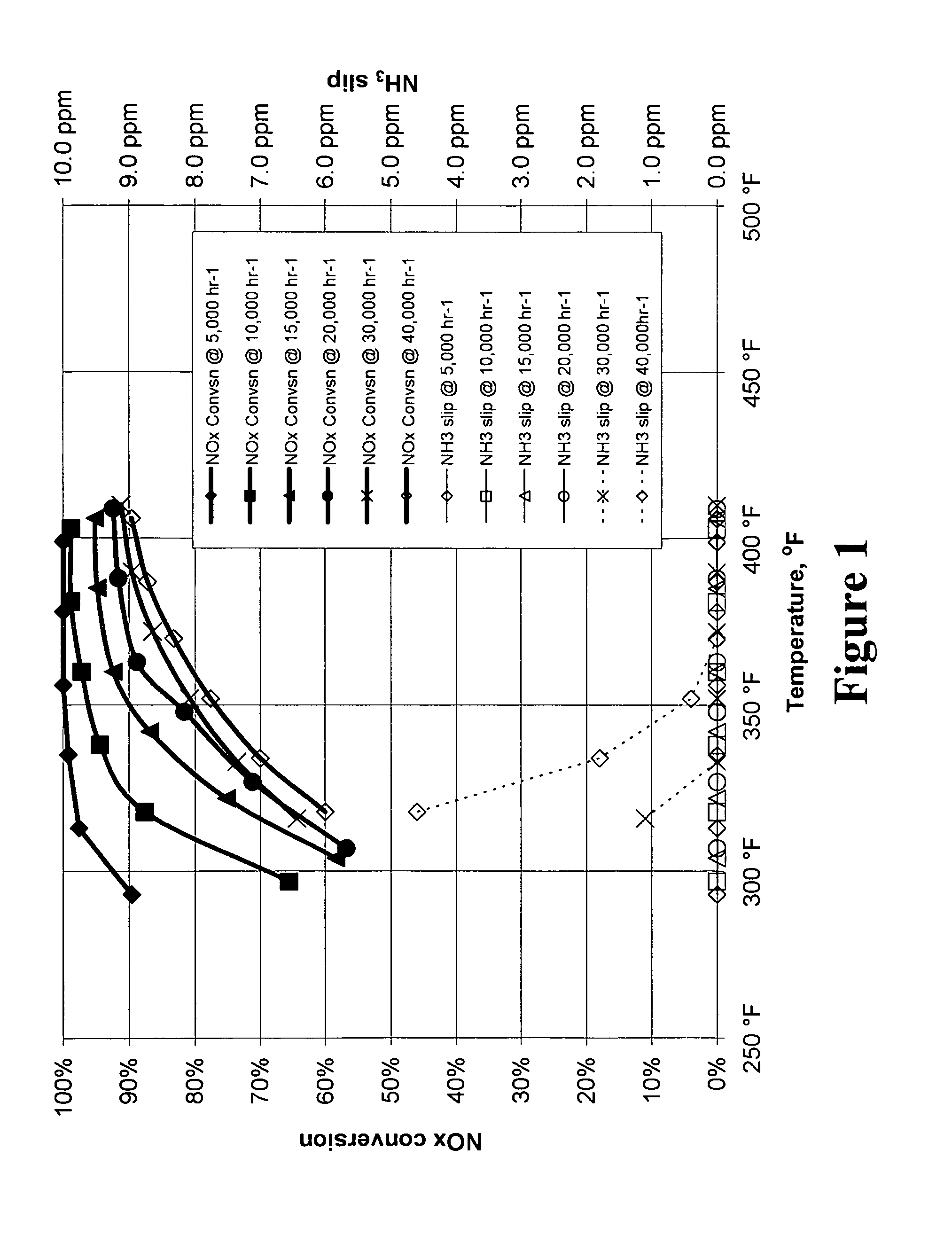
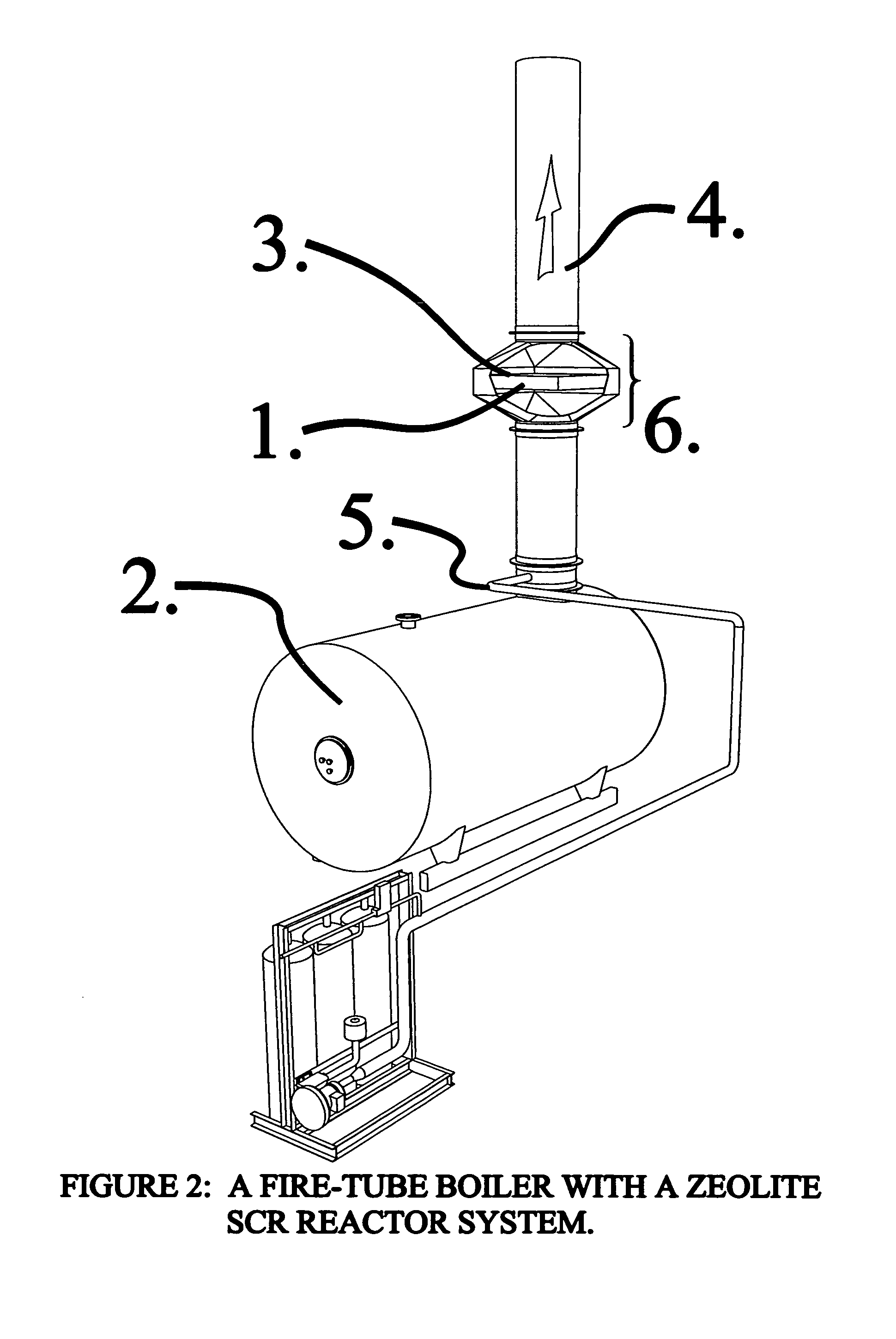
A zeolite based SCR catalyst for NOx reduction using a reducing agent for treating exhaust streams from industrial and commercial boilers is provided. The reactor system has a zeolite based catalyst arranged in catalyst cassettes in a modular fashion where the reactor containing the zeolite based SCR catalyst cassettes is placed in a perpendicular direction to the exhaust exiting the industrial and / or commercial boiler. The catalyst selectively reduces nitrogen oxides to nitrogen with a reducing agent at low to medium temperatures. The reactor results in high NOx conversions and very low ammonia slip and is active for a wide range of boiler firing conditions. Boilers with low NOx and / or ultra low NOx burners can be replaced with a standard conventional burner for overall emissions reduction performance, efficiency improvements and energy savings. Boilers with low NOx and ultra low NOx burners can also be fitted with this zeolite based SCR catalyst reactor for additional NOx reductions and energy savings.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
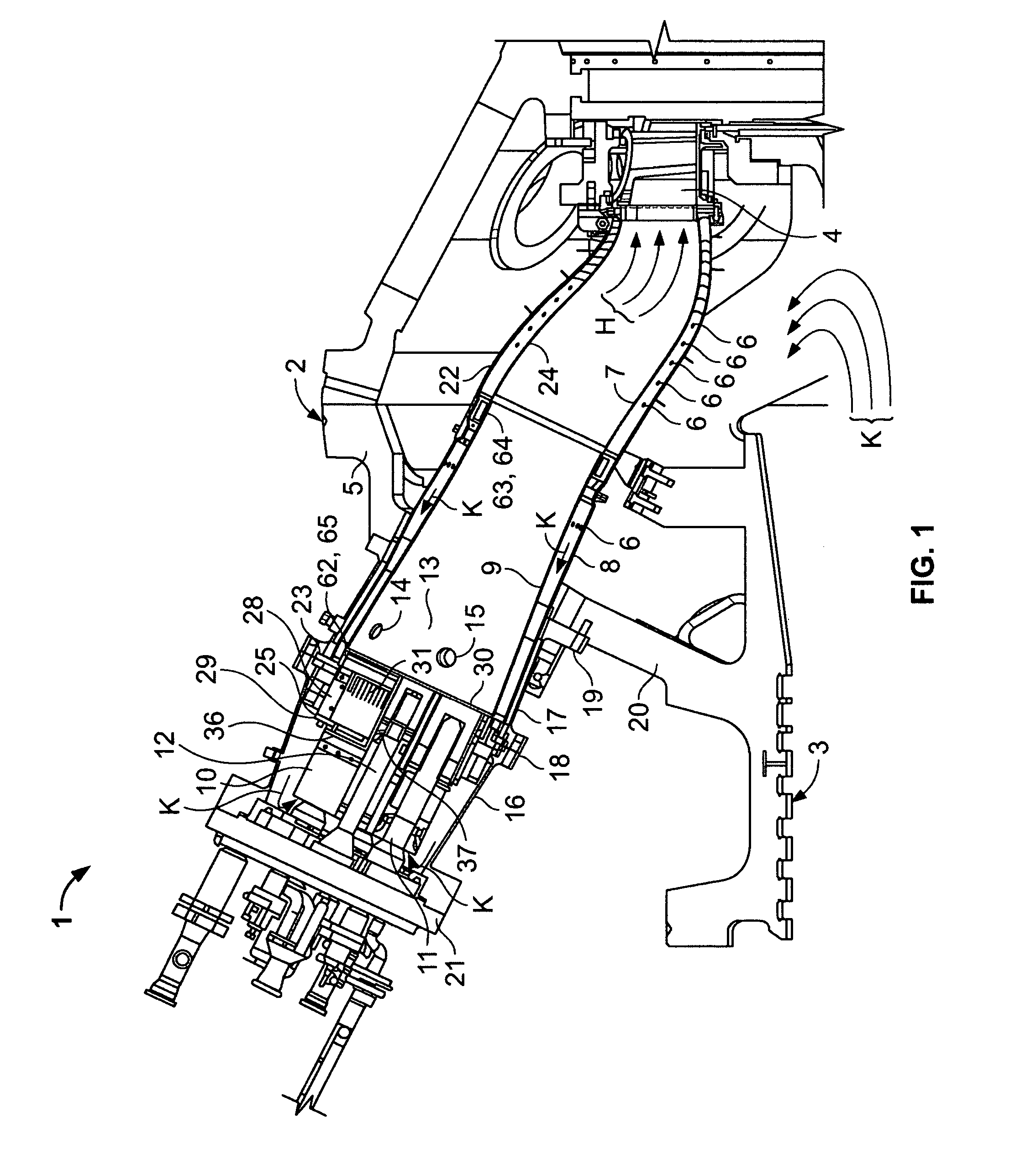
Methods and apparatus for low emission gas turbine energy generation
ActiveUS20050268617A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberEngineeringLow emission
A low-emission method for producing power using a gas turbine includes premixing a plurality of fuel and air mixtures, injecting the fuel and air mixtures into a combustion chamber using a plurality of fuel nozzles, and adjusting a ratio of fuel and air injected by at least one of the nozzles to control a fuel / air concentration distribution within the combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for thermal to electric conversion
InactiveUS20050109387A1Efficient storageLow costSolar heating energySolar heat devicesElectricityEngineering
A system and method for lower cost, solar thermal generation includes a thermal input block, and an energy storage block.
Owner:PRACTICAL TECH
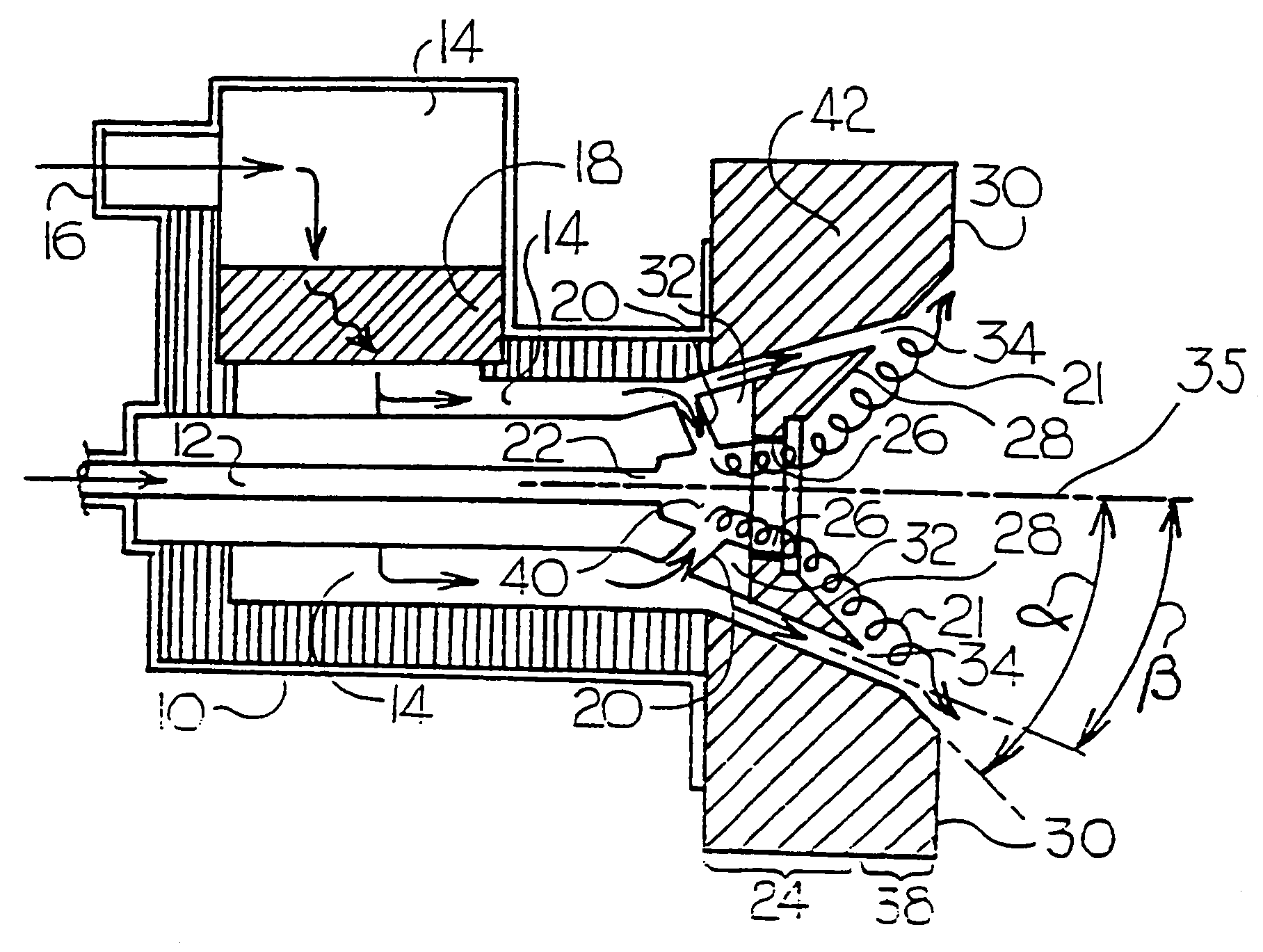
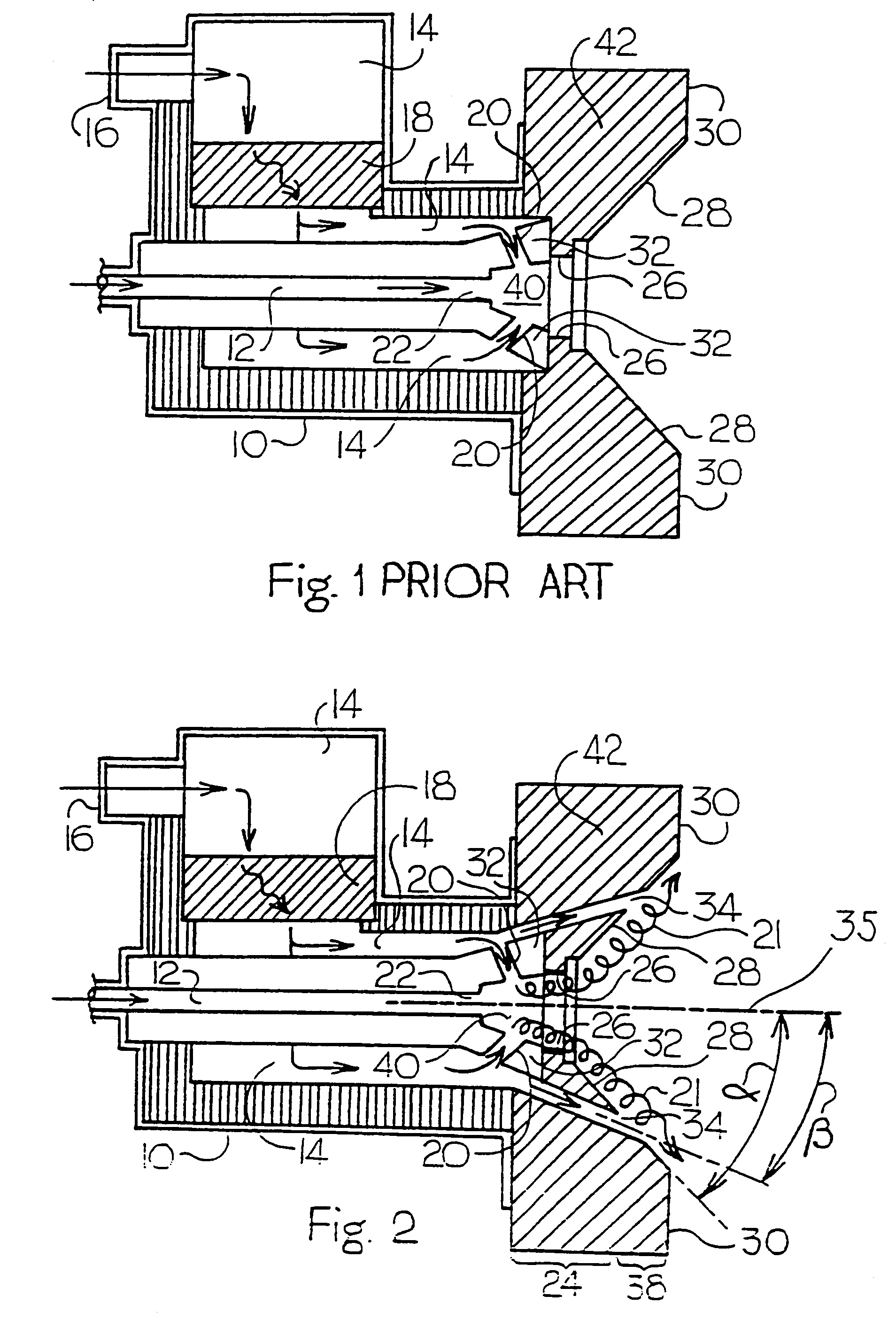
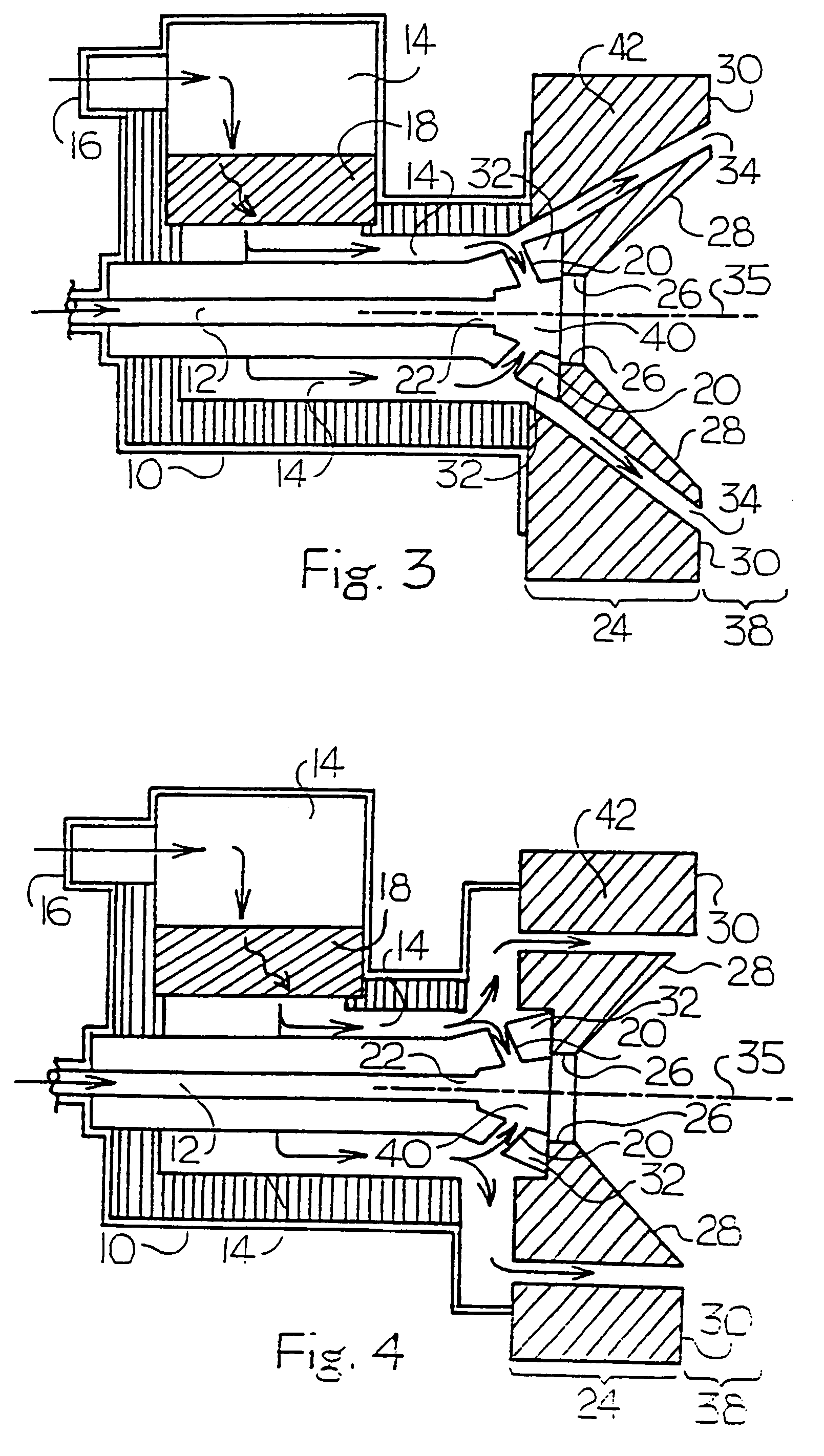
Air staged low-NOx burner
InactiveUS7175423B1Reduce the production of nitrogen oxidesReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelCombustorEngineering
An apparatus and method for using staged air combustion. The apparatus includes a burner body (10) secured to a port block (42), and a fuel passageway (12) extending through the burner body (10), terminating in a fuel nozzle (22), which injects fuel into the burner throat (40). Primary air jets (20) are configured to inject primary air into a primary combustion region (24), which is normally in the burner throat (40). A dish with a dish surface (28) is connected to the burner throat (40); the dish surface (28) extending in a divergent angle with respect to a burner centerline (35). Secondary air jets (34) are connected to the air passageway (14) and extend through the port block (42). The secondary air jets (34) inject secondary air into a secondary combustion region (38), which may be at the dish surface (28) or the hot face (30) of the burner.
Owner:BLOOM ENG
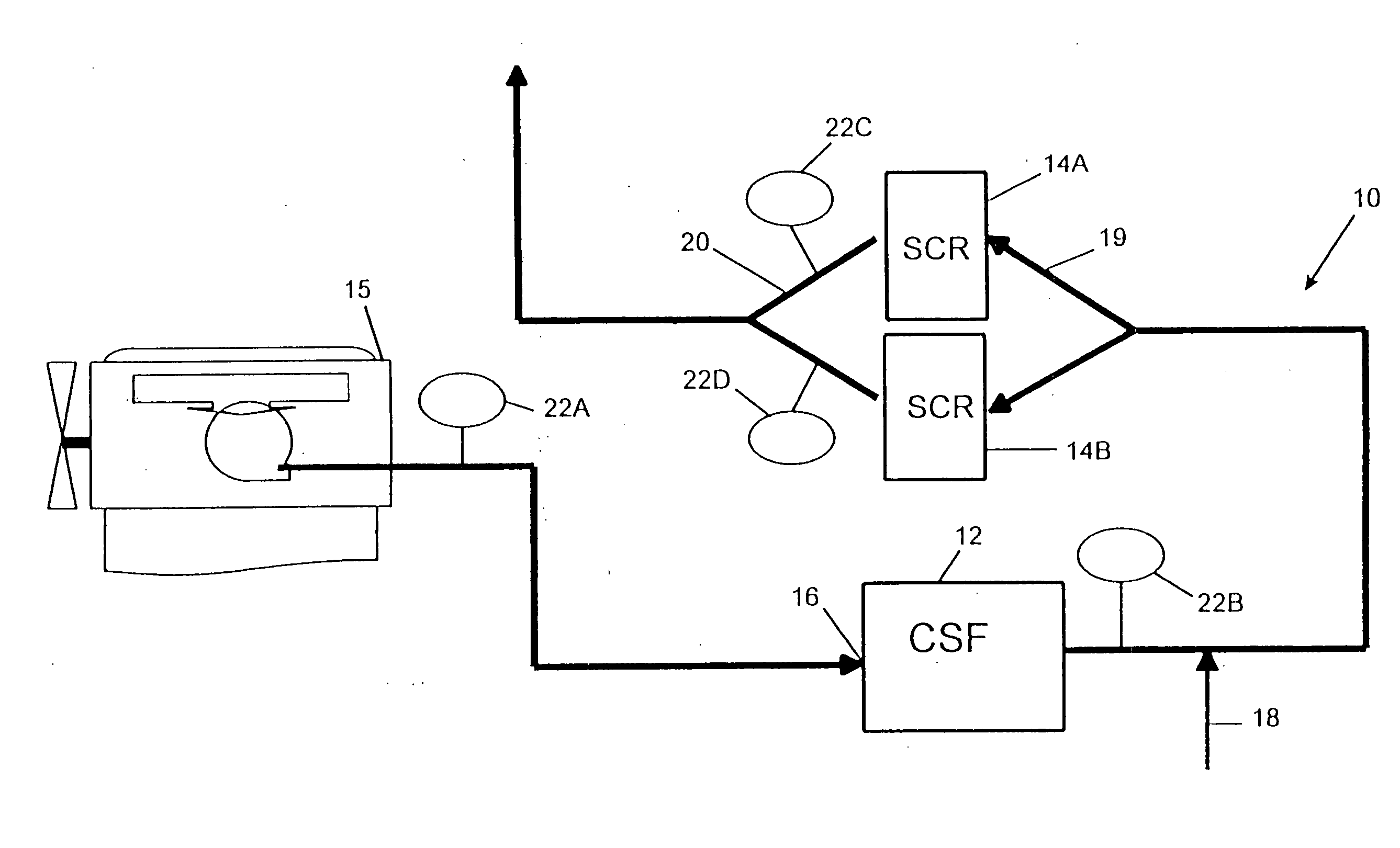
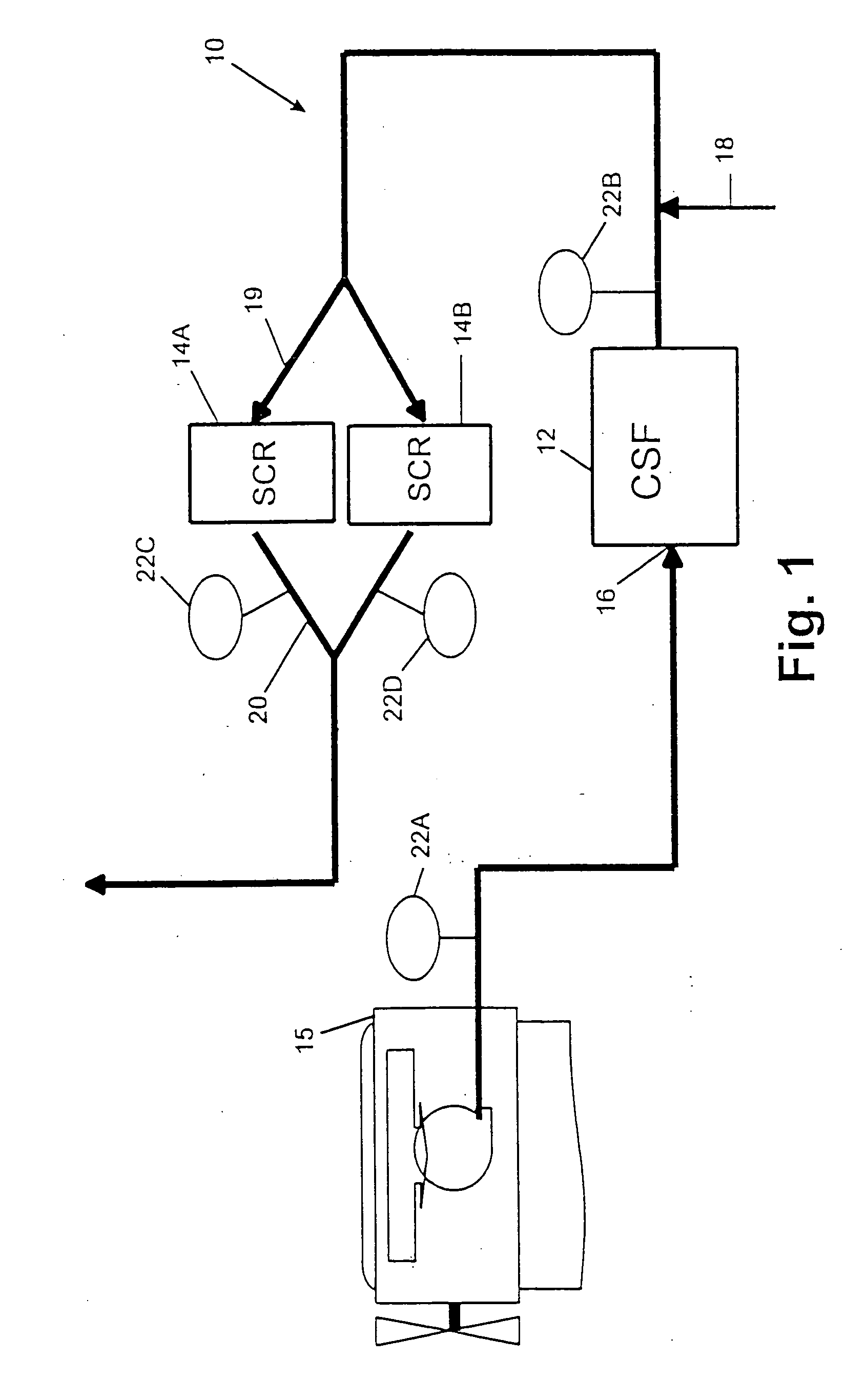
Exhaust system for enhanced reduction of nitrogen oxides and particulates from diesel engines
InactiveUS20050056004A1Well nox conversion performancePromote conversionNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentNitrogen oxidesUrea
A diesel engine aftertreatment exhaust system uses catalyzed soot filters for particulate matter reduction and urea SCR catalysts for NOx reduction on diesel engines in a combined system to lower particulate matter and NOx at the same time. With this integral emission control system, diesel engines are able to meet ultra low emission standards.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
Methods and apparatus for low emission gas turbine energy generation
ActiveUS7284378B2Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsFuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberCombustion chamberLow emission
A low-emission method for producing power using a gas turbine includes premixing a plurality of fuel and air mixtures, injecting the fuel and air mixtures into a combustion chamber using a plurality of fuel nozzles, and adjusting a ratio of fuel and air injected by at least one of the nozzles to control a fuel / air concentration distribution within the combustion chamber.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
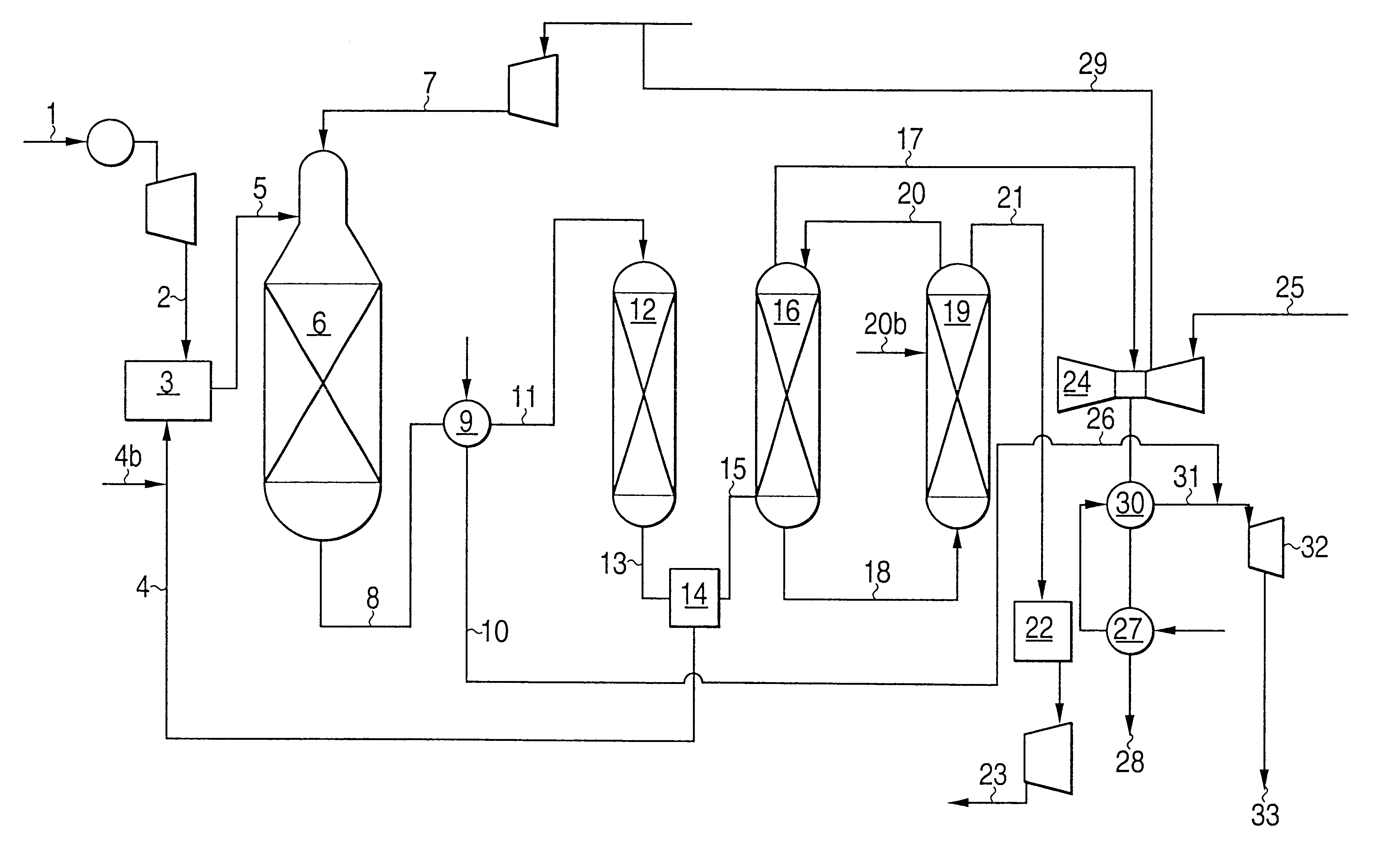
Process for generating electric energy, steam and carbon dioxide from hydrocarbon feedstock
InactiveUS6505467B1Acceptable power generationMaintain normal flowCarbon compoundsFinal product manufactureSyngasChemistry
A process producing electric energy, steam and carbon dioxide in concentrated form from a hydrocarbon feedstock. The process includes forming synthesis gas in an air driven autothermal reactor unit (ATR), heat exchanging the formed synthesis gas and thereby producing steam, treating at least part of the synthesis gas in a CO-shift reactor unit and carbon dioxide separation unit for formation of concentrated carbon dioxide and a lean hydrogen containing gas which is combusted in a combined cycle gas turbine for production of electric energy, and where air from the turbine is supplied to the ATR unit. The exhaust from the gas turbine is heat exchanged for the production of steam which together with steam generated upstream said unit is utilized in a power generator for production of substantially CO2-free electric energy. Steam may be fed to the gas turbine for diluting the hydrogen containing gas mixture. The process may also be combined with the production of synthesis gas products such as methanol and / or ammonia. Part of the gas from the carbon dioxide removal unit may be utilized in a fuel cell.
Owner:STATOIL ASA PETRO SA (NO)
Low emission diesel combustion system with low charge-air oxygen concentration levels and high fuel injection pressures
InactiveUS6857263B2Cost effectiveLower Level RequirementsLiquid coolingEngine sealsLow loadMass ratio
This invention sets forth a commercially viable diesel combustion system that meets environmentally acceptable levels of NOx emissions (i.e. 0.2 g / bhp-hr or lower across a full map of engine speeds and loads) without the need for use of NOx aftertreatments, and simultaneously maintains engine-out PM emissions relatively close (e.g. with smoke levels at or below 3 BSN) to environmentally acceptable PM post-aftertreatment levels. The invention achieves these results by operating within a unique combination of parameters. These parameters comprise: (1) charge-air oxygen concentration below 16%, preferably between 10% and 15%, more preferably between 11% and 14%, and most preferably between 12% and 13.5% for virtually all engine operating conditions (but not necessarily at no-load or low load conditions), (2) fuel injection pressures at or exceeding 1800 bar, preferably exceeding 2100 bar, more preferably exceeding 2300 bar, and most preferably exceeding 2500 bar, at most engine speeds and loads, and (3) charge-air mass / fuel mass ratio between 25:1 and 45:1 for medium and high loads. Furthermore, the system is preferably run continuously slightly lean of stoichiometry, providing just enough excess oxygen to facilitate completeness of combustion and to maintain an exhaust oxygen level sufficient for continuous trap regeneration at a balance point in operation.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
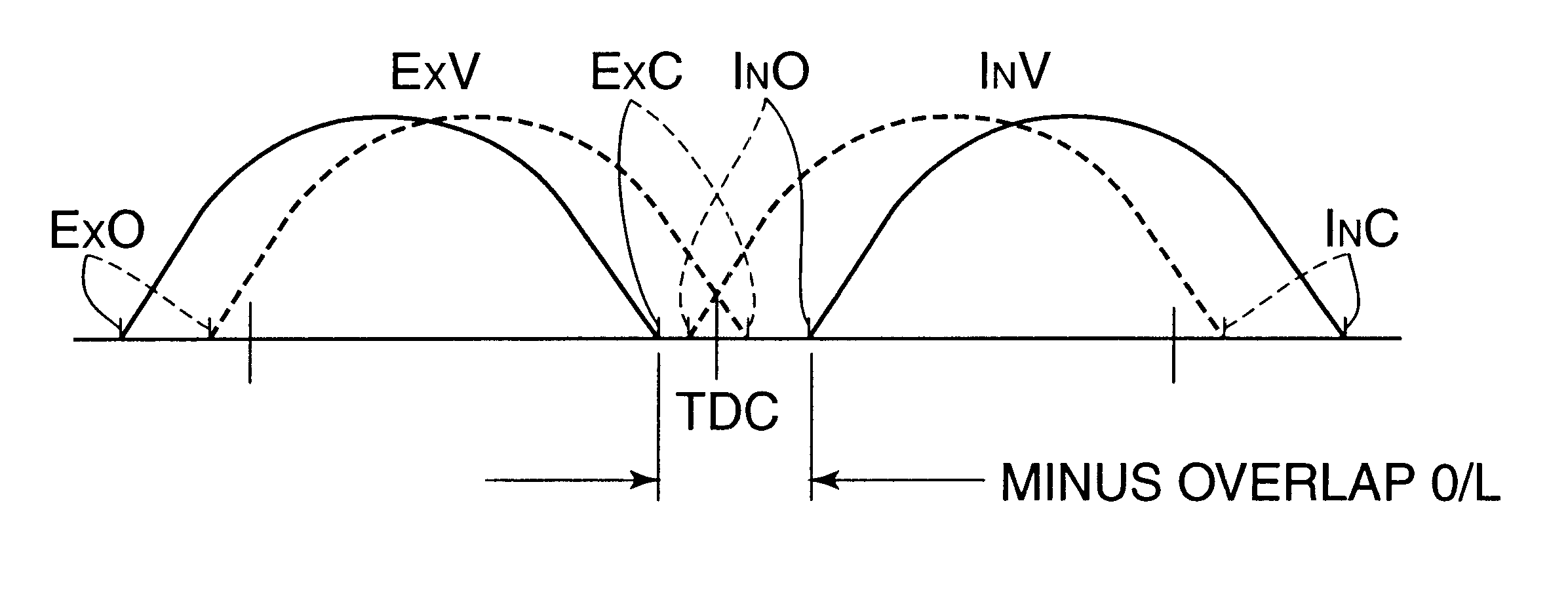
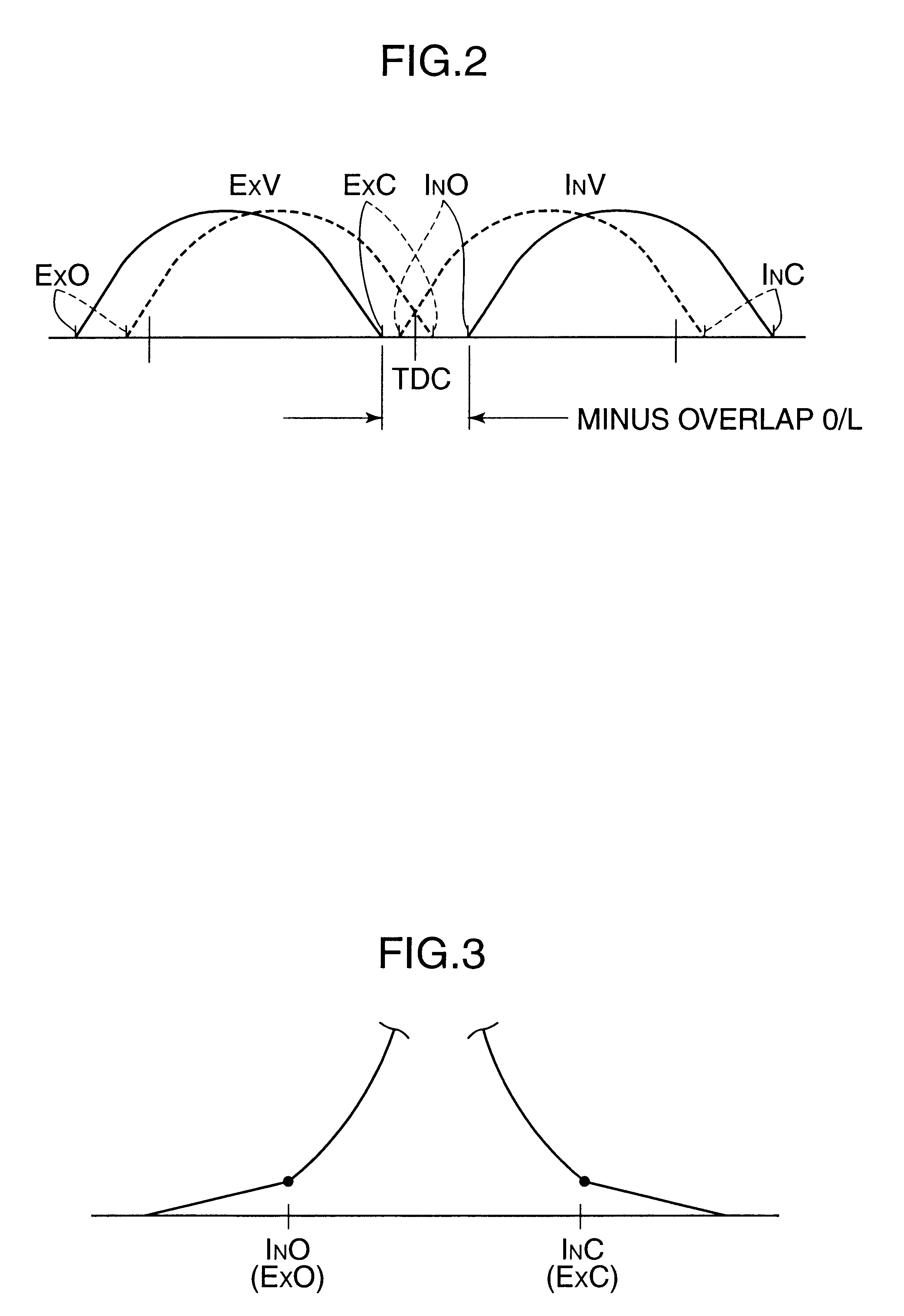
Automotive four-cycle engine
InactiveUS6626164B2Sufficient effectAvoid increase in combustion temperature and exhaust gas temperatureValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveTop dead center
A four-cycle engine is provided with valve timing adjusters for adjusting opening and closing timing an and an exhaust valve. In medium- to high-speed ranges in medium- to high-load regions of the engine, a closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve defined as a point of transfer from an acceleration portion to a constant speed portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point a specific period before an intake top dead center, and an opening point (InO) of the intake valve defined as a point of transfer from a constant speed portion to an acceleration portion on its valve lift characteristics curve is set to a point after the intake top dead center. In addition, the period from the closing point (ExC) of the exhaust valve to the opening point (InO) of the intake valve is made longer in the medium-speed range than in the high-speed range in the medium- to high-load regions of the engine.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Diesel combustion chamber
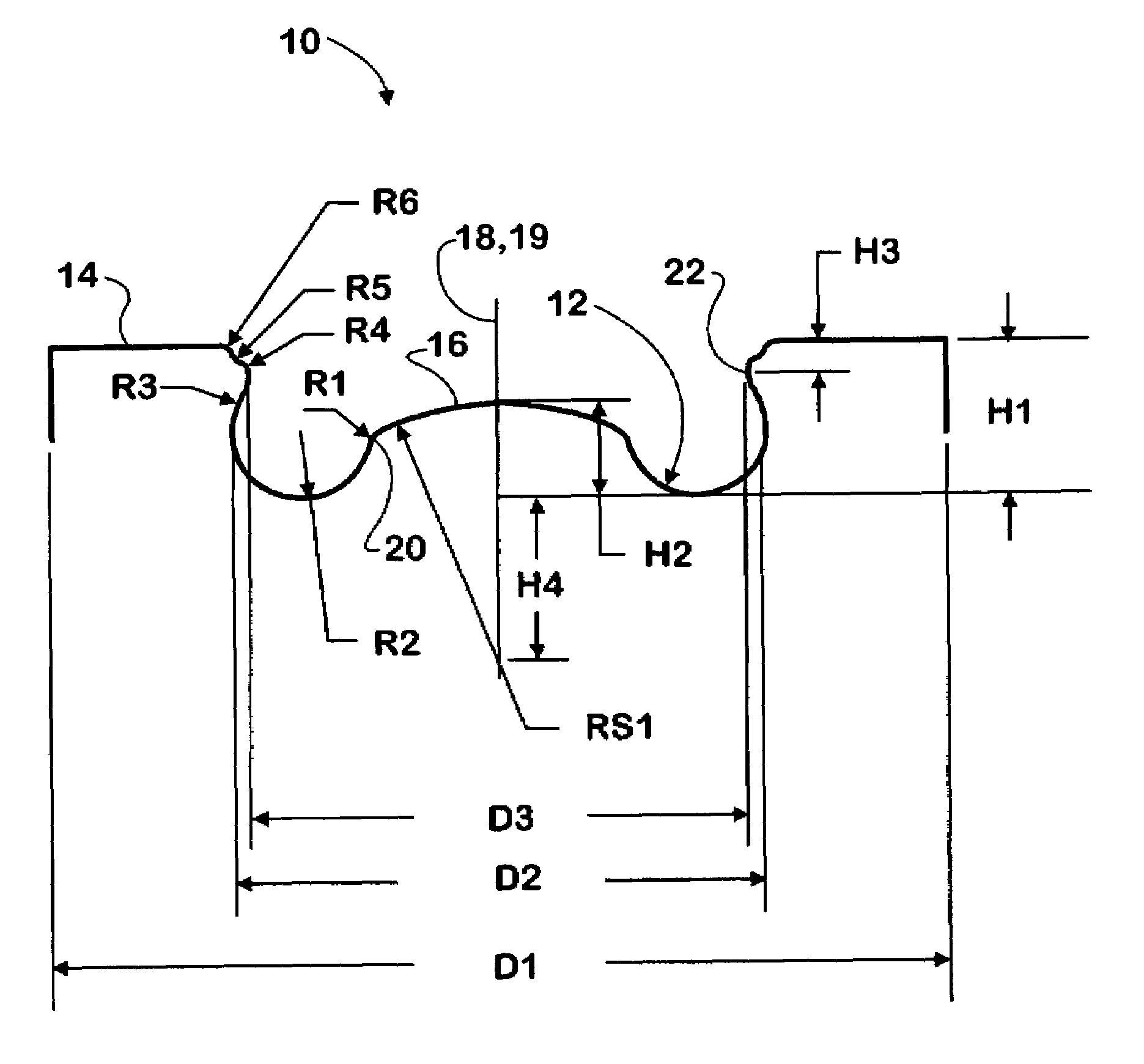
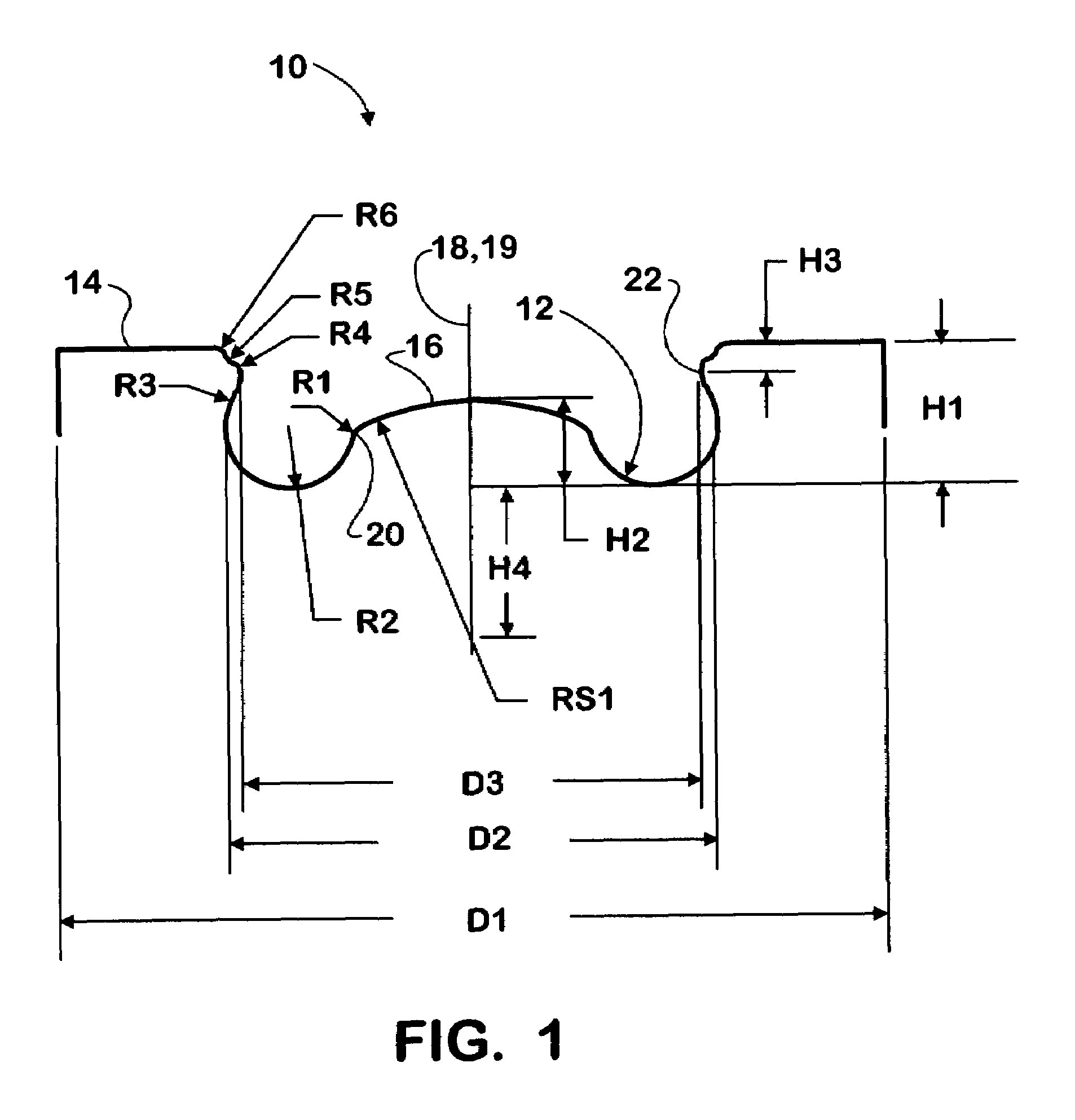
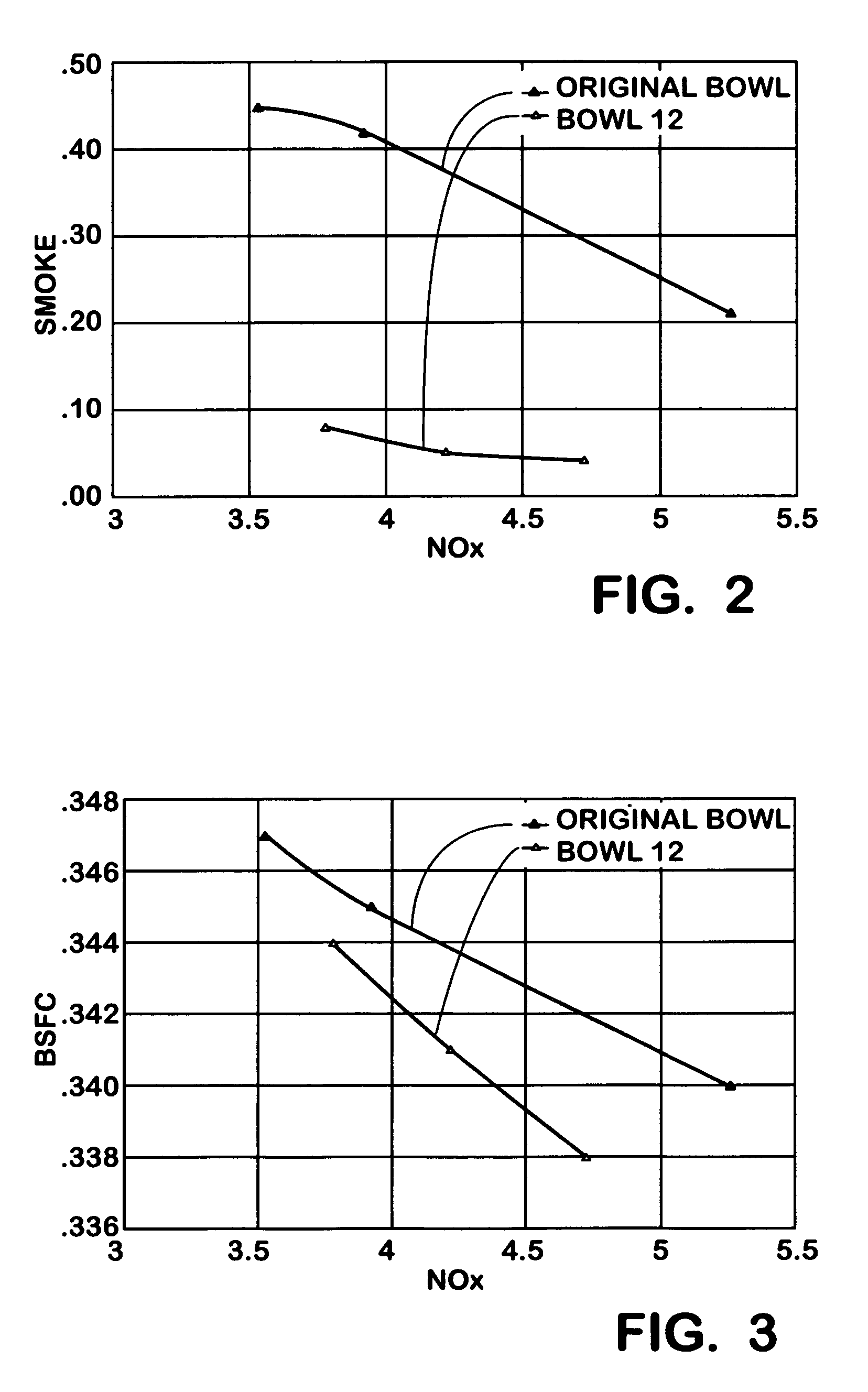
ActiveUS6997158B1Increase kinetic energyEasily formInternal combustion piston enginesPistonsPistonCombustion chamber
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Exhaust emission aftertreatment
InactiveUS6857264B2Raise temperatureImprove utilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gasExhaust fumes
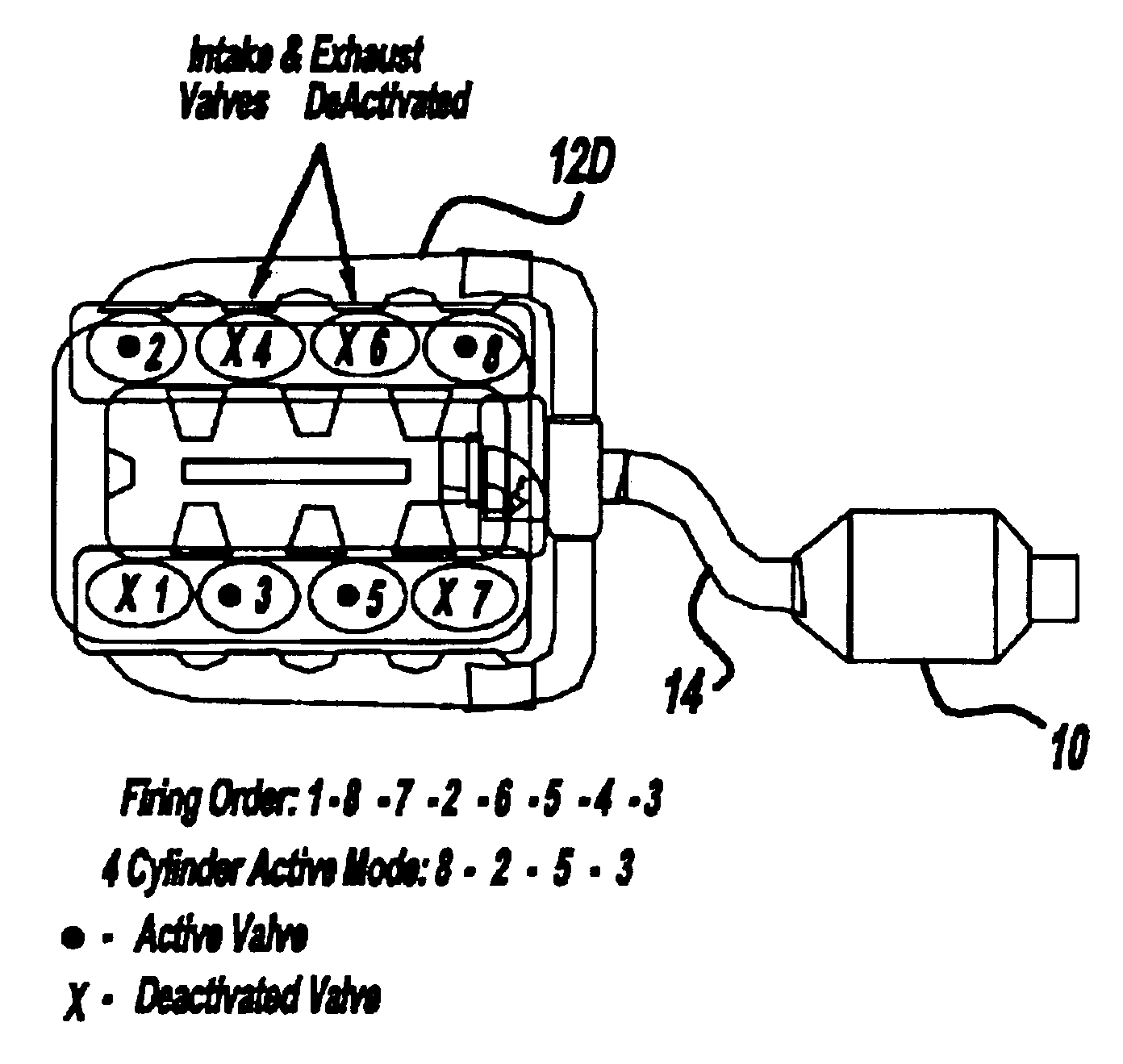
An engine control system in a vehicle including a variable displacement internal combustion engine, a controller for controlling the displacement of the variable displacement internal combustion engine, and where the controller operates the variable displacement internal combustion engine in a partially displaced operating mode upon startup to increase exhaust gas temperature.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Combustion emission-reducing method
InactiveUS8206470B1Reduce the amount requiredReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsCyanogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionFuel efficiency
In one embodiment, a fluid mixture composition is used at least in part as a fuel for engine-powered transportation vehicles, the mixture comprising an initial concentration of an ammonia-like reductant component and an initial concentration of an ammonia-like carrier component. The mixture may also include an optional third hydrocarbon component, e.g., gasoline or diesel fuel, with modified properties when compared to conventional gasolines or diesel fuels. The mixture is separated into a first and a second stream, with the majority of the first stream being used as a fuel for the engine and at least a first portion of the second stream being injected into the engine exhaust gases to reduce NOx emissions. A second portion of the second stream is aspirated into the engine and a lean air / fuel ratio may be used to improve fuel efficiency.
Owner:JACOBSON WILLIAM O
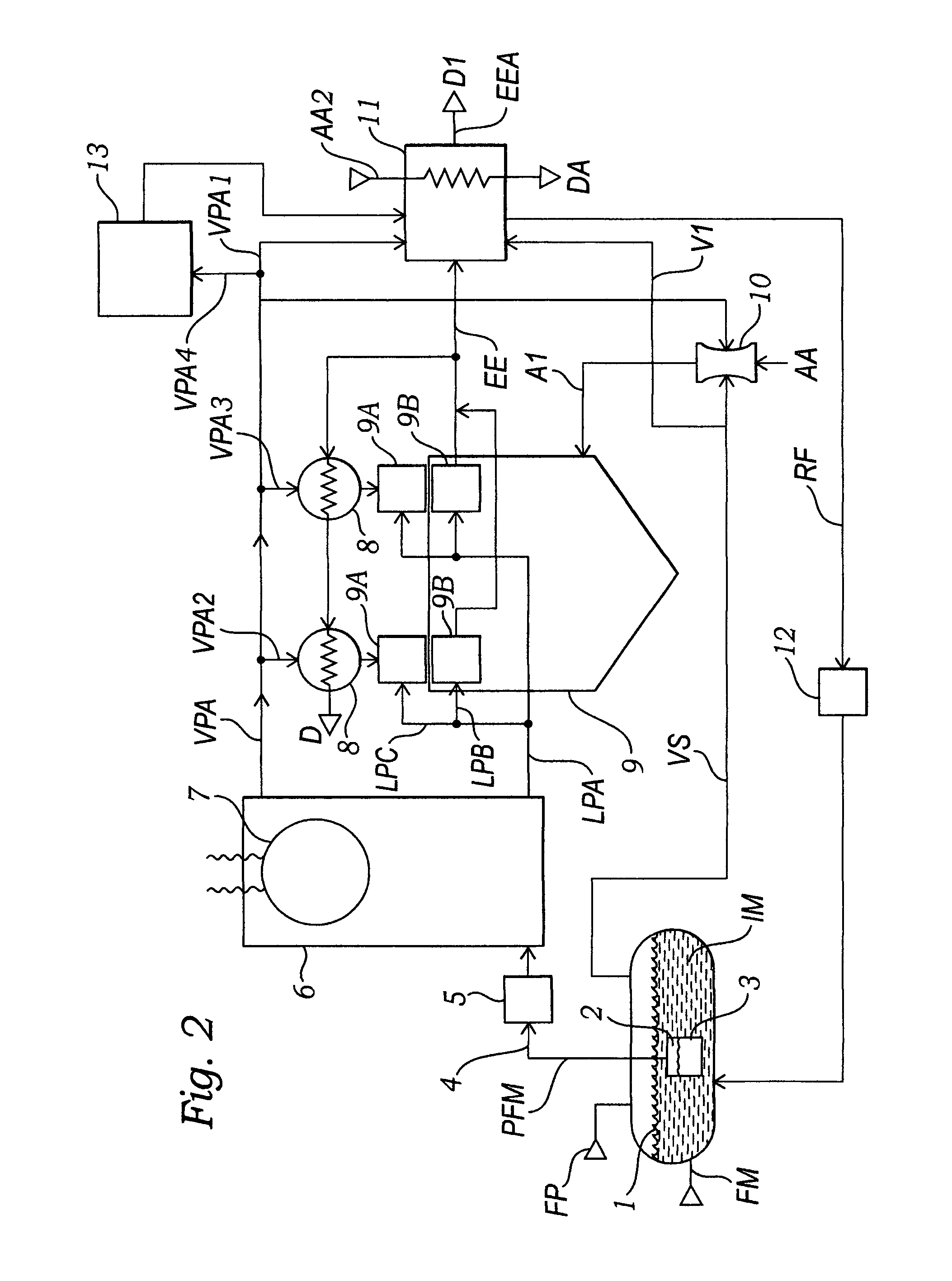
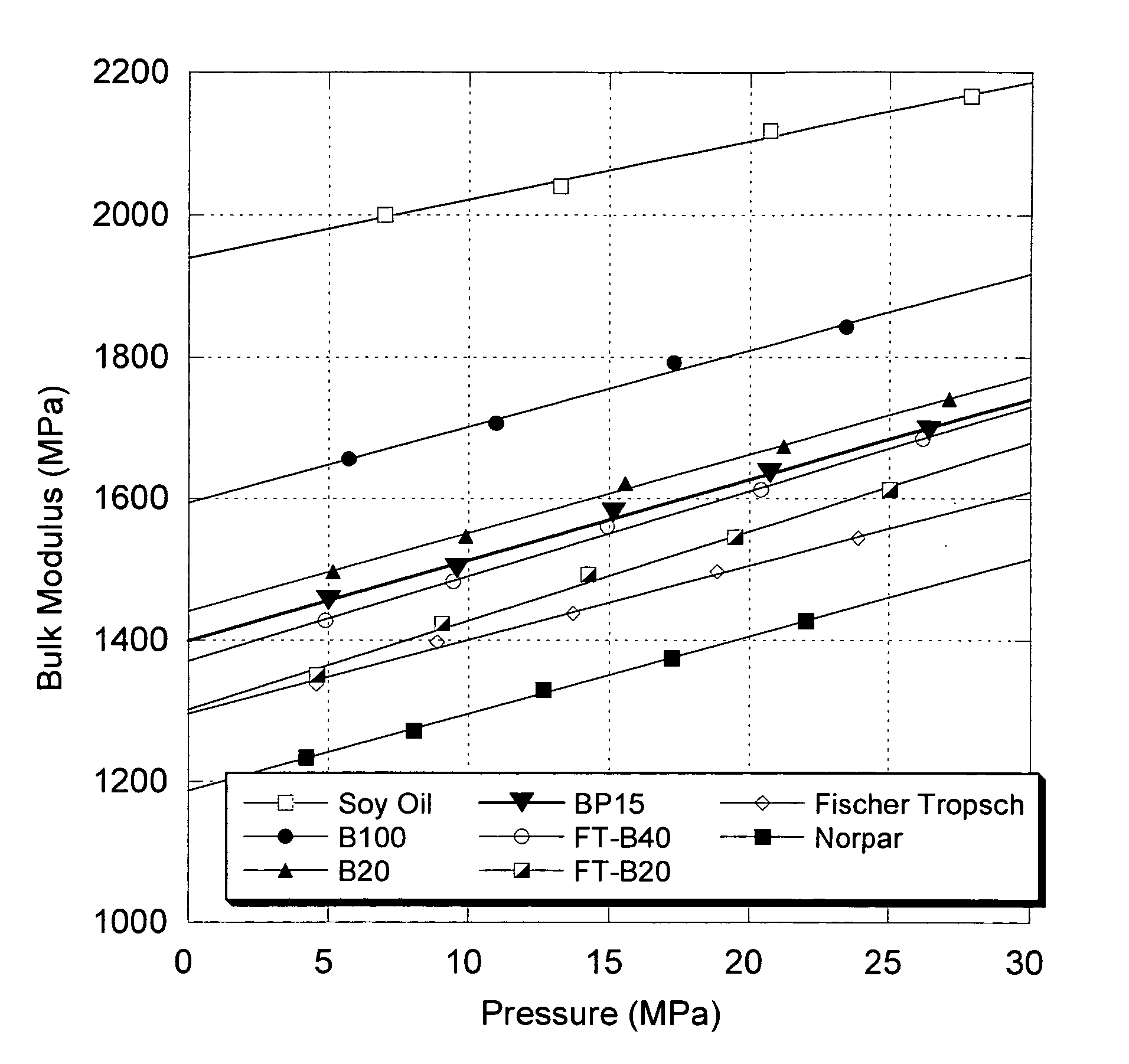
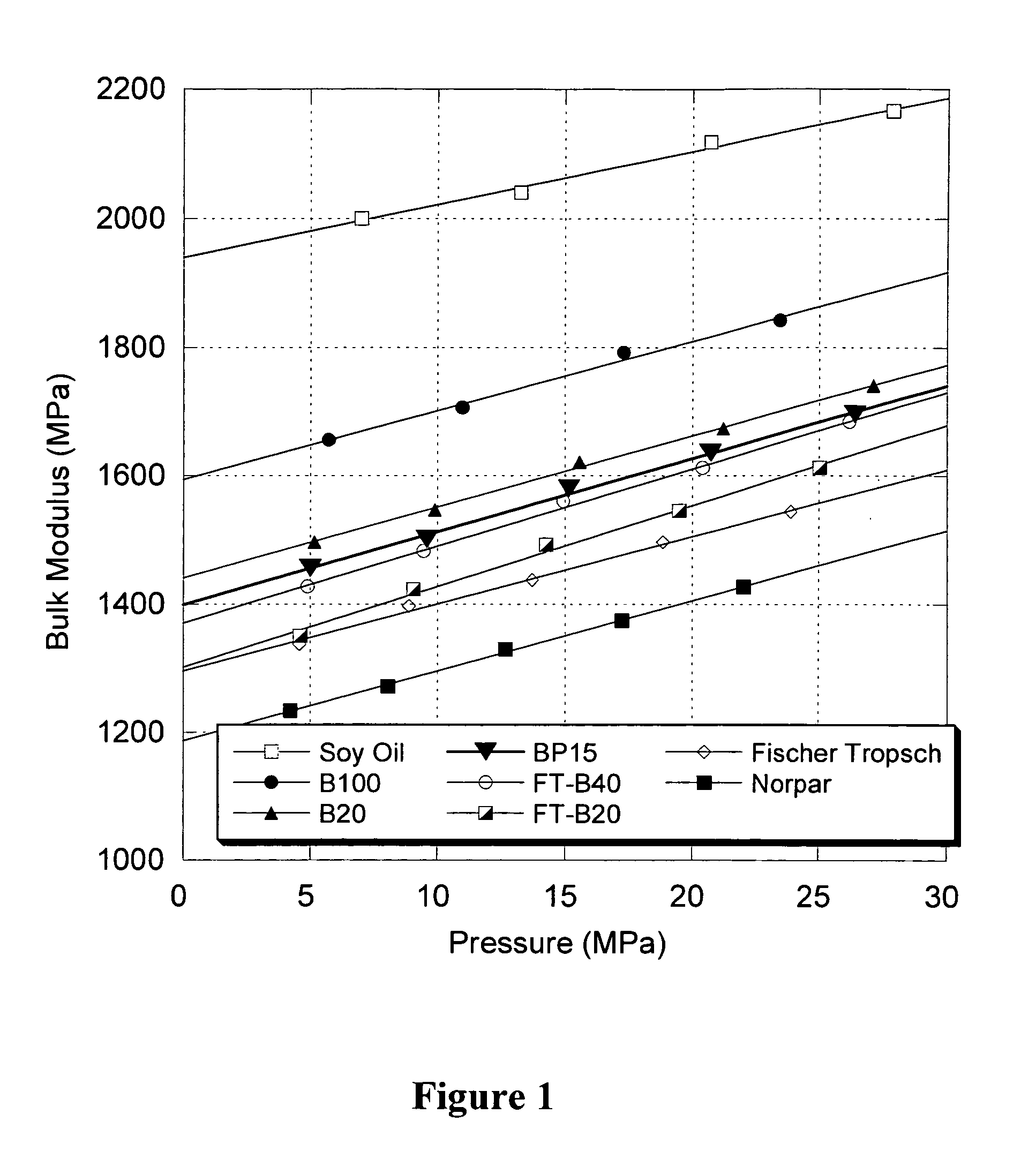
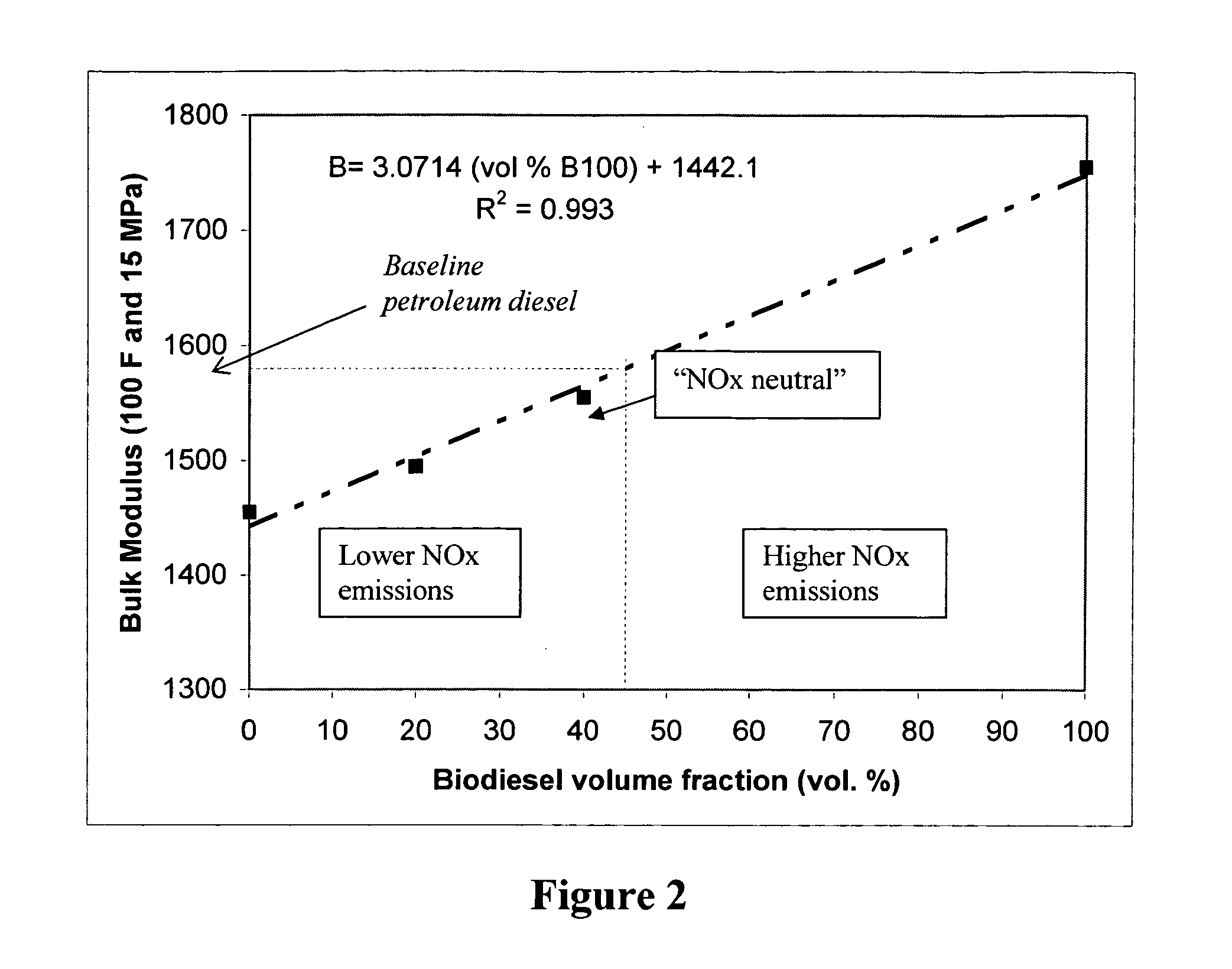
Blends of synthetic distillate and biodiesel for low nitrogen oxide emissions from diesel engines
InactiveUS20050210739A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsReduced NO<sub>xBiofuelsSolid fuelsAlkaneBiodiesel
This invention shows how to make and use a biodiesel-based fuel in diesel engines without incurring the NOx penalty. Embodiments primarily relate to an optimum range of bulk modulus of compressibility for biodiesel blends, which results in generating “NOx neutral” biodiesel blends or to formulate biodiesel blends with lower NOx emissions than conventional petroleum diesel fuel. These biodiesel blends preferably comprise synthetic paraffinic middle distillate derived from a hydrocarbon synthesis to generate synthetic environmentally-friendly diesel fuels.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO +1
Urea solution tank assembly
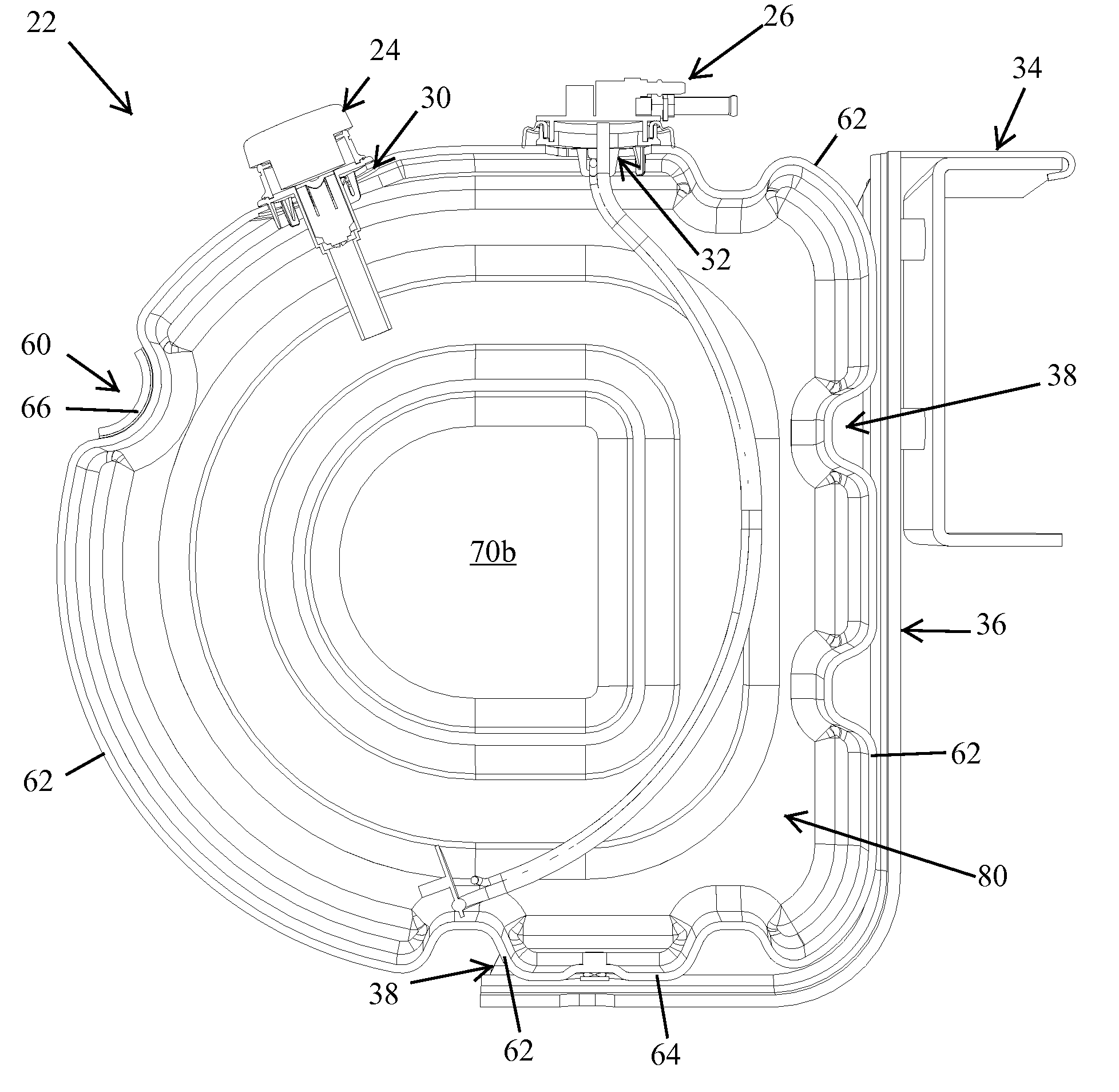
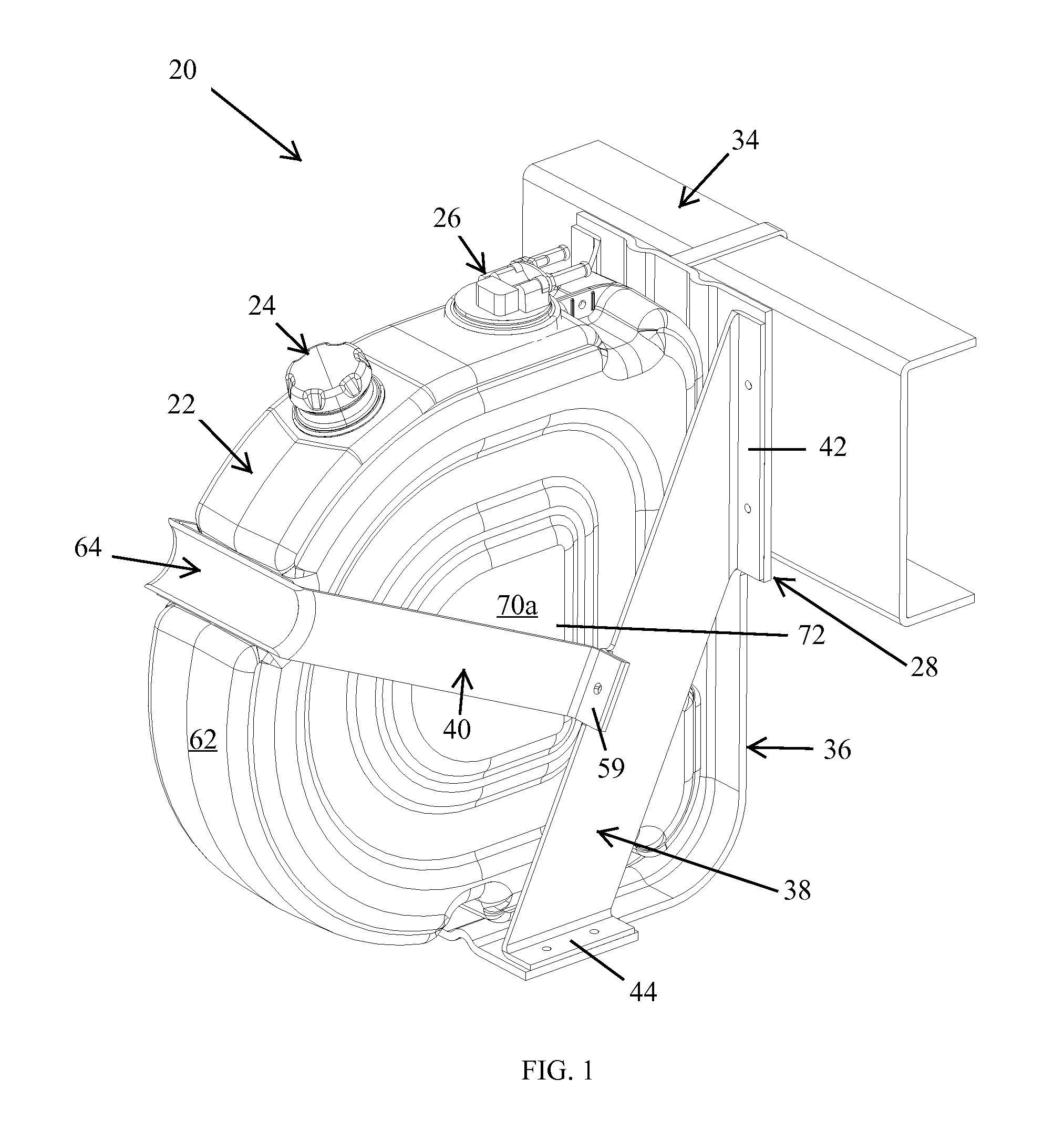
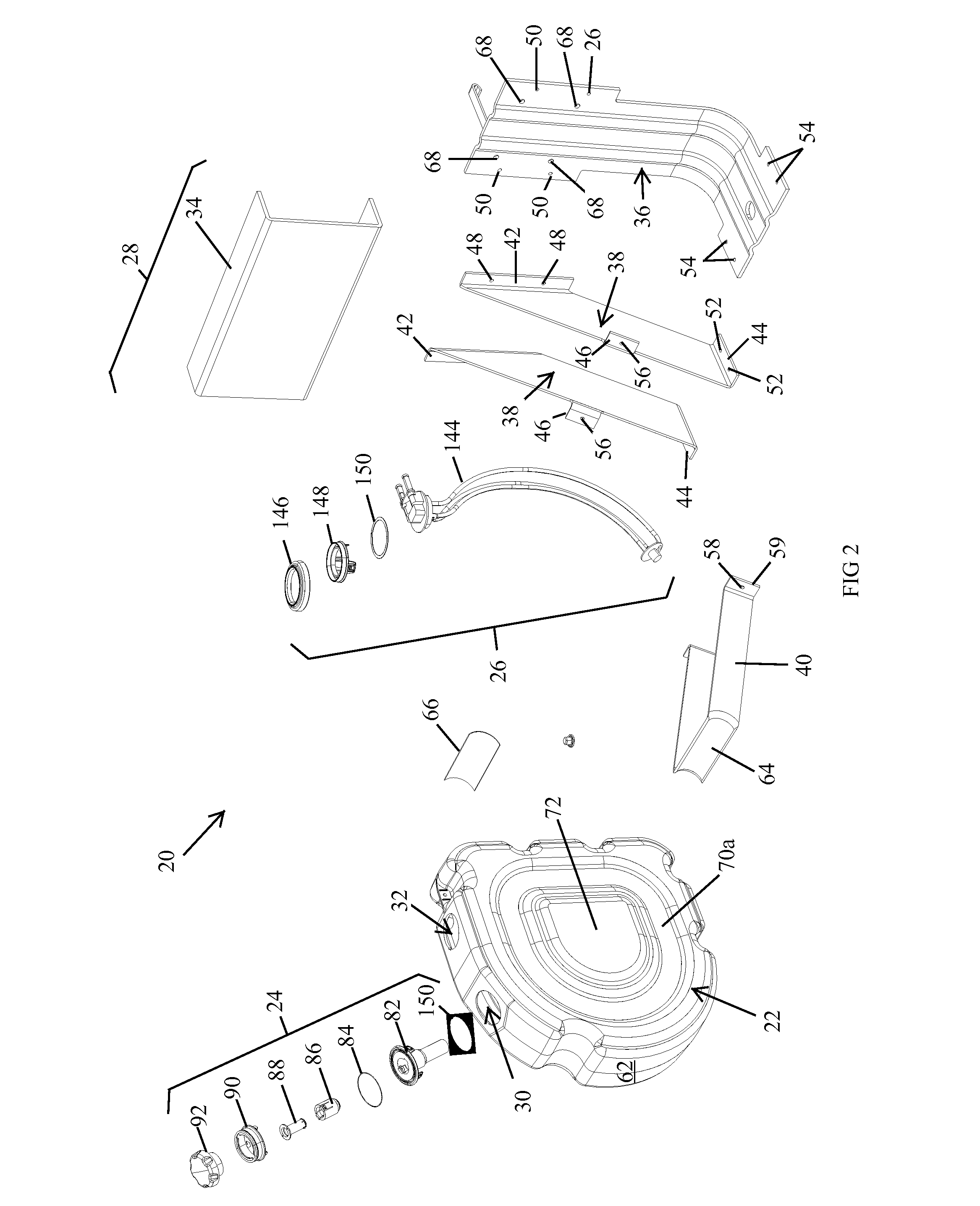
InactiveUS20090188923A1Easy to manufactureEasy to solveInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusVehicle frameDiesel fuel
A tank for storing urea solution and a tank assembly for storing disparate fluids, such as diesel fluid and urea solution, are disclosed. The tank may further include a filler assembly and / or a sensor assembly, either of which are adapted to be connected to the tank without the use of separate fasteners, The tank assembly may include a reservoir and a sensor for automatically diverting non-conforming urea solution to the reservoir. A recess may be defined in the tank body in order to accommodate a strap for securing the tank to the frame of vehicle. The tank may include parallel sidewalls that include a projection on one and a corresponding indentation on the other in order to allow the tanks to be easily stacked during assembly.
Owner:FUEL SYST
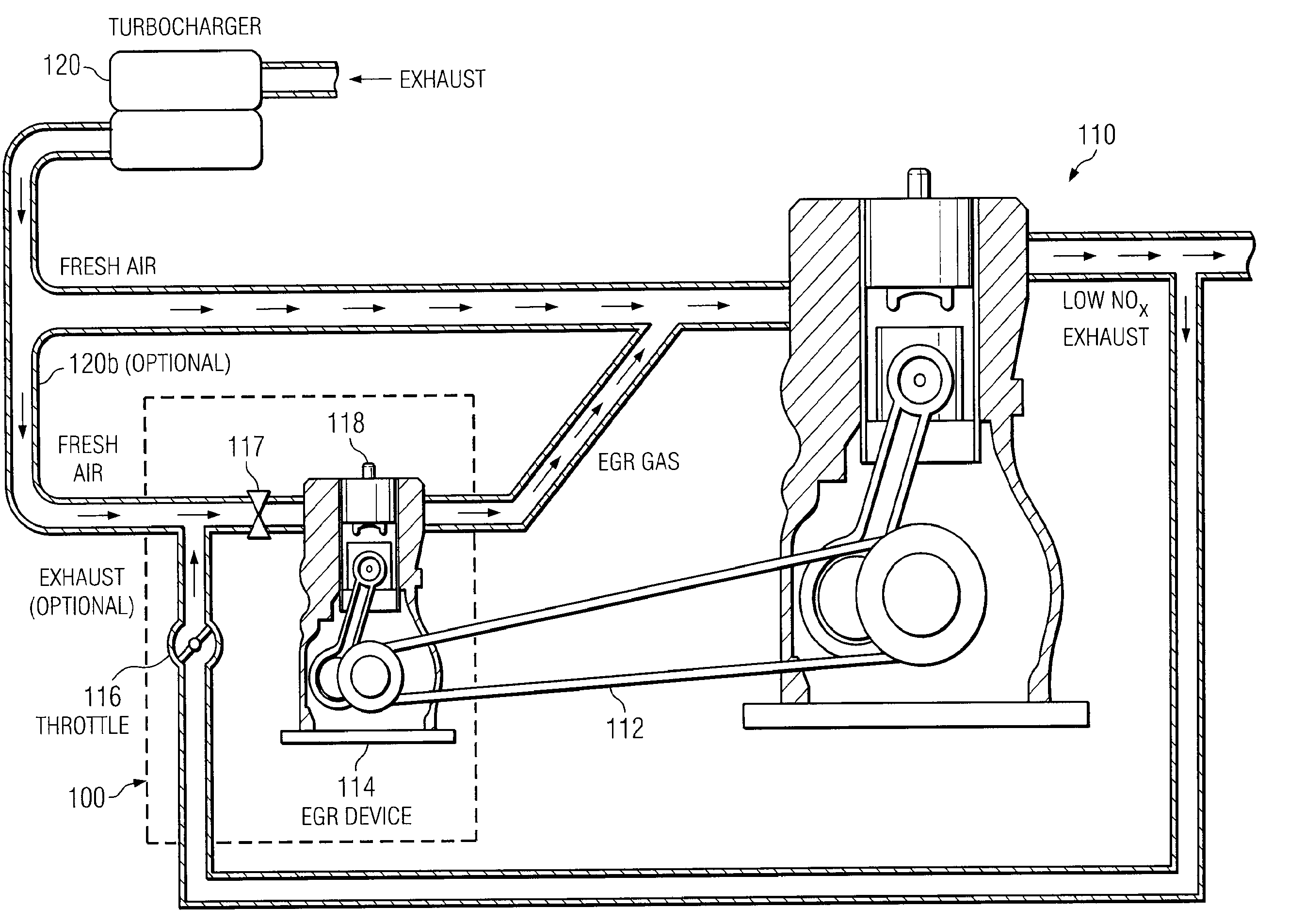
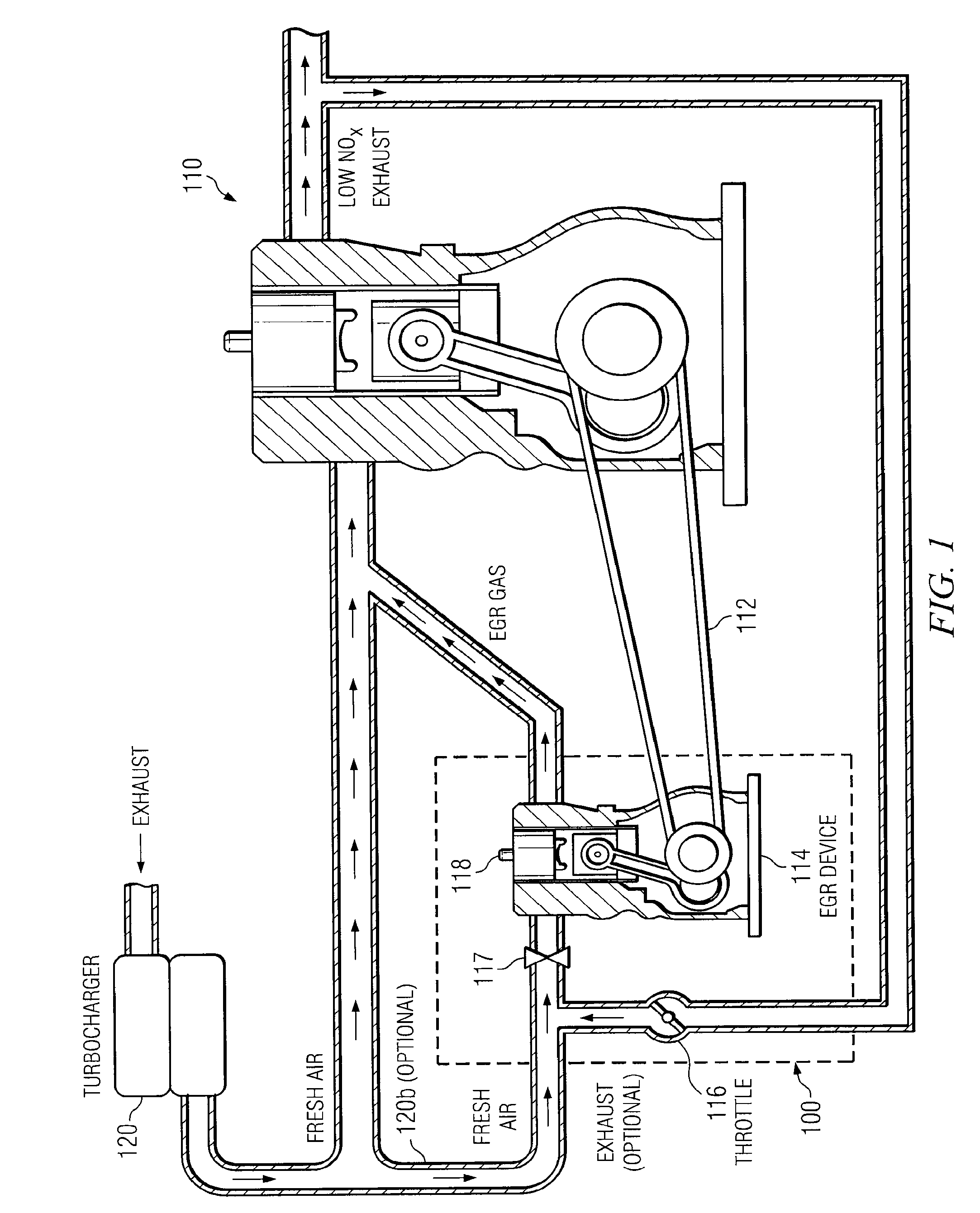
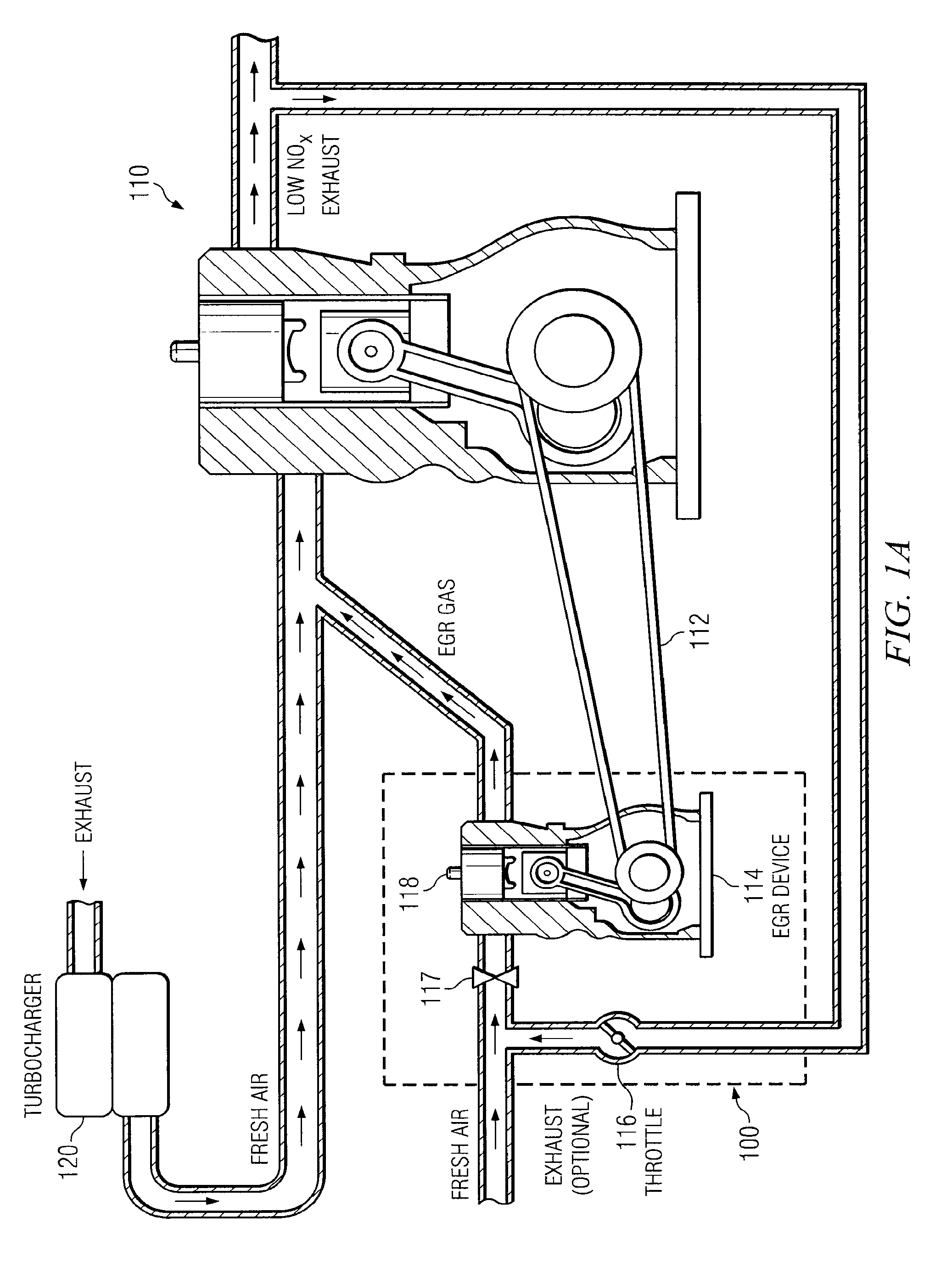
Secondary internal combustion device for providing exhaust gas to EGR-equipped engine
ActiveUS7721541B2Alleviate challengeReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustionEngineering
A system and method for providing exhaust gas to an EGR-equipped lean burn diesel engine (the primary engine). The exhaust gas is provided by a secondary internal combustion device, whose configuration, thermal cycle, and operating conditions may be different from that of the primary engine. The secondary internal combustion device may receive recirculated exhaust gas, fresh air, or some combination of both.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Combustion process and apparatus therefore containing separate injection of fuel and oxidant streams
InactiveUS6331107B1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsAvoid chemical reactionsCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelCombustorCombustion chamber
A burner assembly having improved flame length and shape control is presented, which includes in exemplary embodiments at least one fuel fluid inlet and at least one oxidant fluid inlet, means for transporting the fuel fluid from the fuel inlet to a plurality of fuel outlets, the fuel fluid leaving the fuel outlets in fuel streams that are injected into a combustion chamber, means for transporting the oxidant fluid from the oxidant inlets to at least one oxidant outlet, the oxidant fluid leaving the oxidant outlets in oxidant fluid streams that are injected into the combustion chamber, with the fuel and oxidant outlets being physically separated, and geometrically arranged in order to impart to the fuel fluid streams and the oxidant fluid streams angles and velocities that allow combustion of the fuel fluid with the oxidant in a stable, wide, and luminous flame. Alternatively, injectors may be used alone or with the refractory block to inject oxidant and fuel gases. The burner assembly affords improved control over flame size and shape and may be adjusted for use with a particular furnace as required.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Internal combustion engine and method for auto-ignition operation of said engine
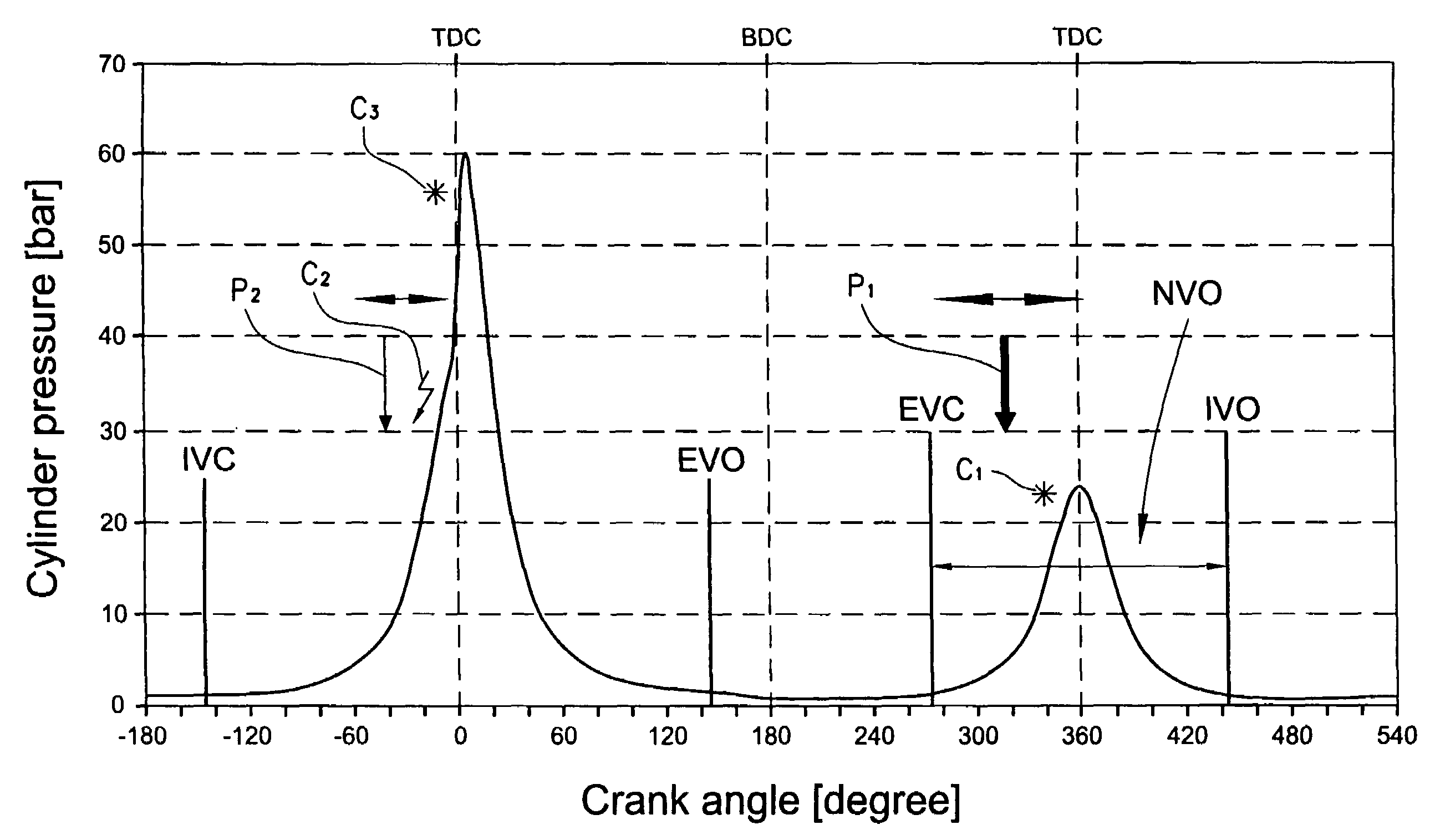
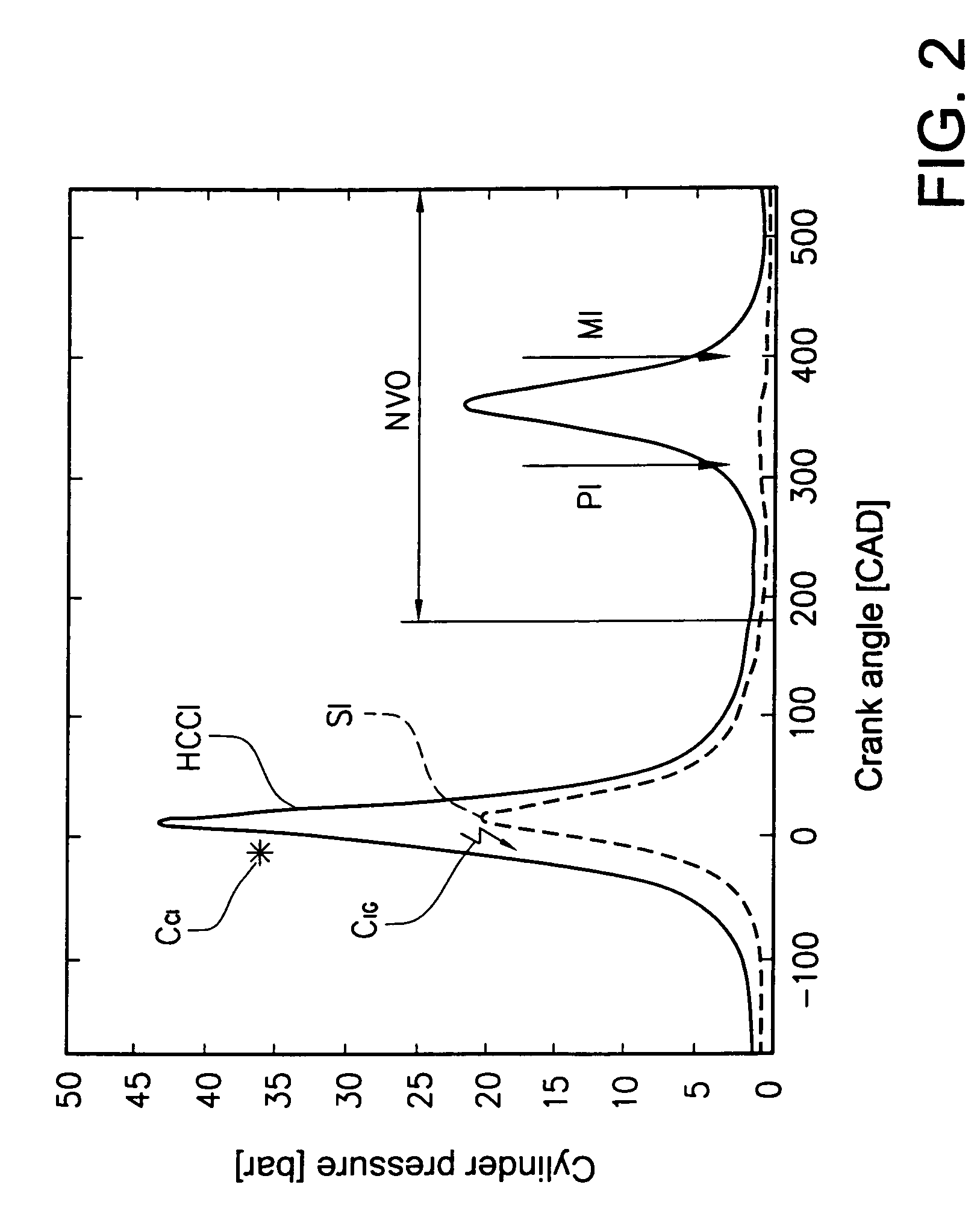
ActiveUS7194996B2Improve thermal efficiencyImprove flammabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCompression actionTop dead center
The invention relates to an internal combustion engine that can be operated in compression ignition mode, the engine comprising a fuel injector for each cylinder; a fuel injection controller for controlling fuel injection quantity and a piston in each cylinder whose compression action causes a mixture of air and fuel to be ignited. The engine is further provided with inlet and outlet valves and sensors for measuring various engine operating parameters. During compression ignition mode, the control unit controls the fuel injector to perform a first fuel injection before top dead center of the exhaust stroke during a period of negative valve overlap, and a second fuel injection during the piston compression stroke. The control unit may perform a switch between a first fuel injection strategy and at least one further fuel injection strategy in response to a change in load demand on the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for reducing gas turbine engine emissions
InactiveUS20080016876A1Emission reductionReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsContinuous combustion chamberEngine manufactureCombustorEngineering
A low emission turbine includes a reverse flow can-type combustor that generally includes a primary and secondary fuel delivery system that can be independently controlled to produce low CO, UHC, and NOx emissions at design set point and at conditions other than design set point. The reverse flow can-type combustor generally includes an annularly arranged array of swirler and mixer assemblies within the combustor, wherein each swirler and mixer in the array includes a primary and secondary fuel delivery system that can be independently controlled. Also disclosed herein is a can-type combustor that includes fluid passageways that perpendicularly impinge the backside of a heat shield. Processes for operating the can-type combustors are also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
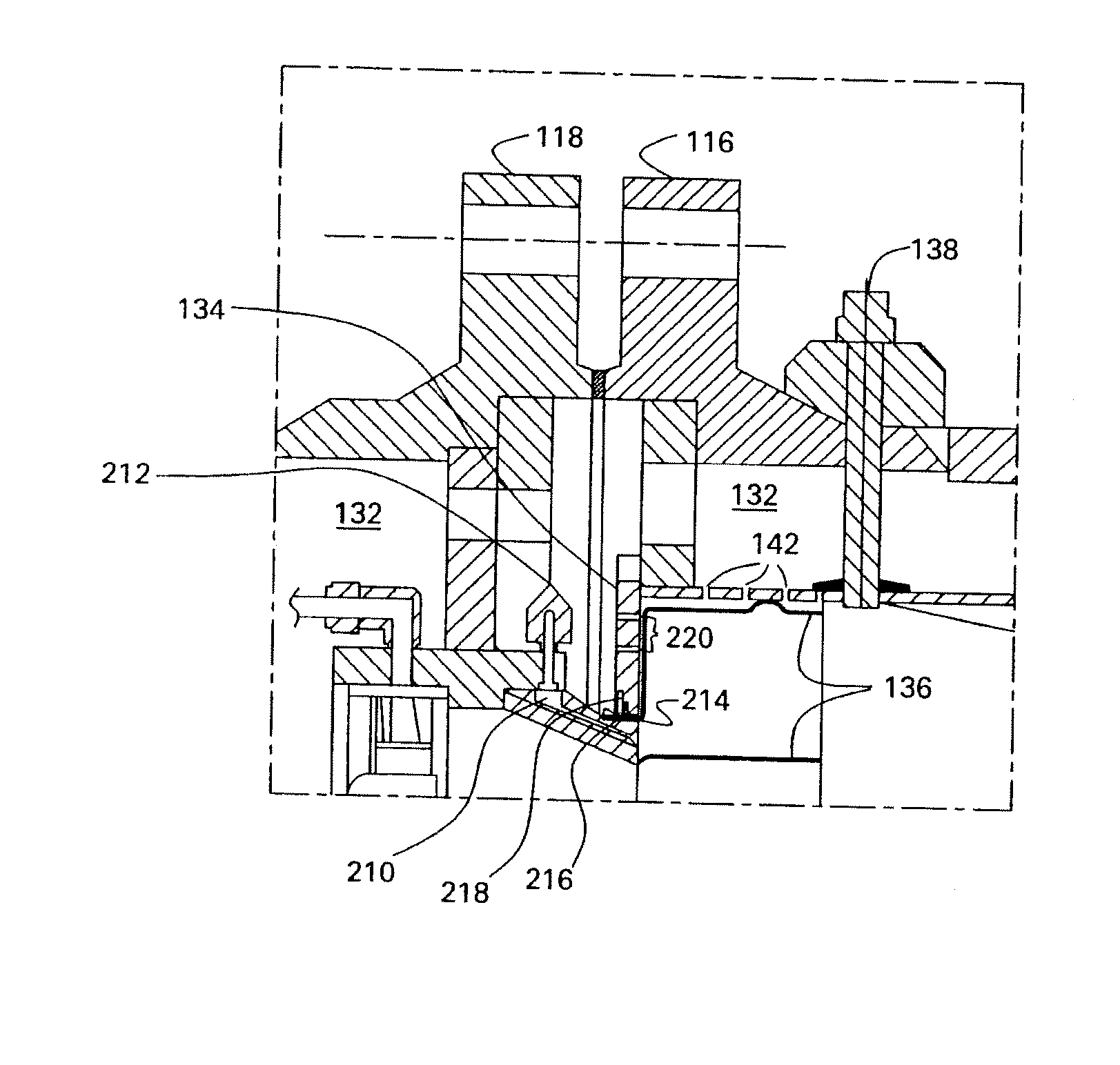
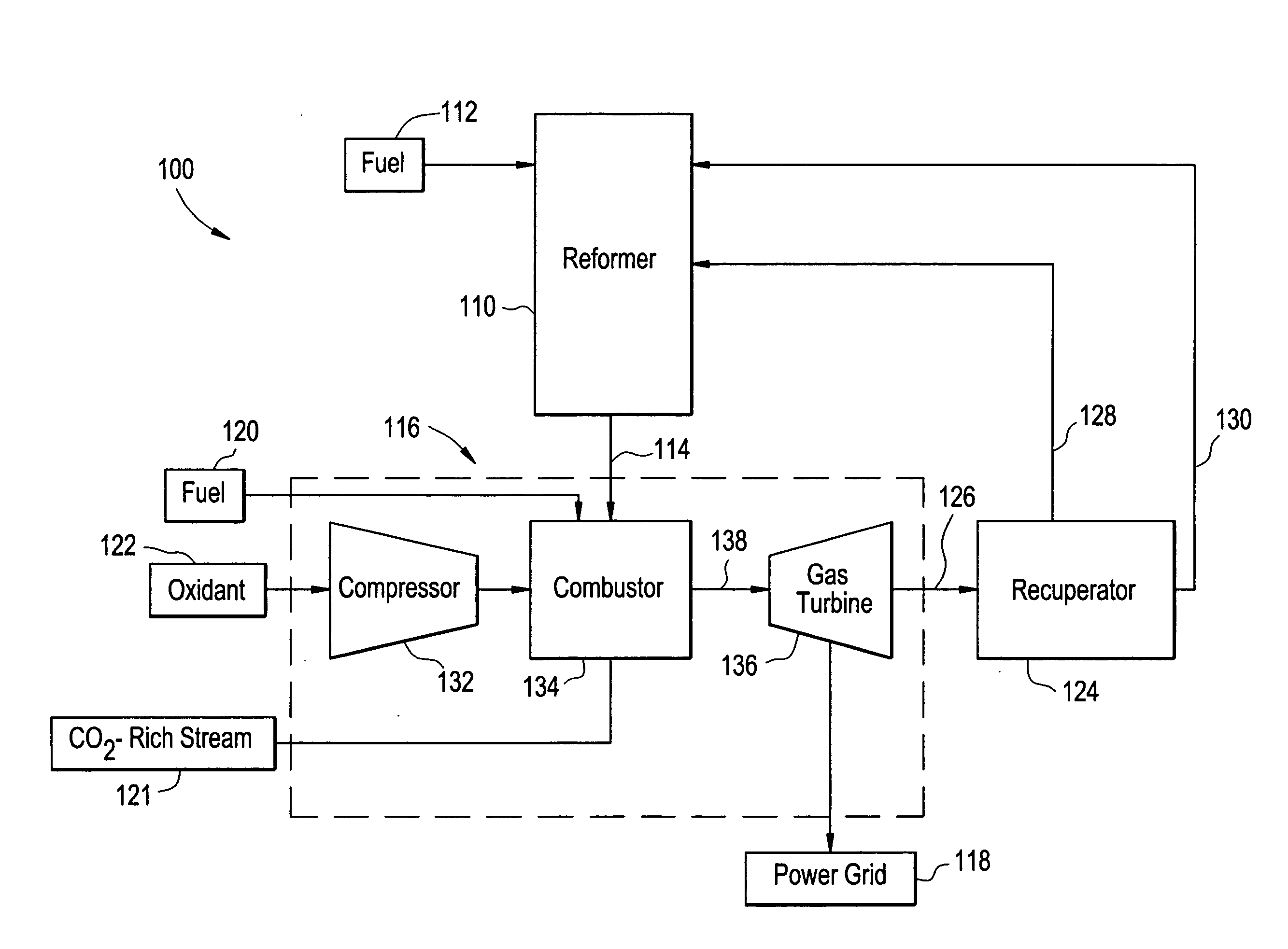
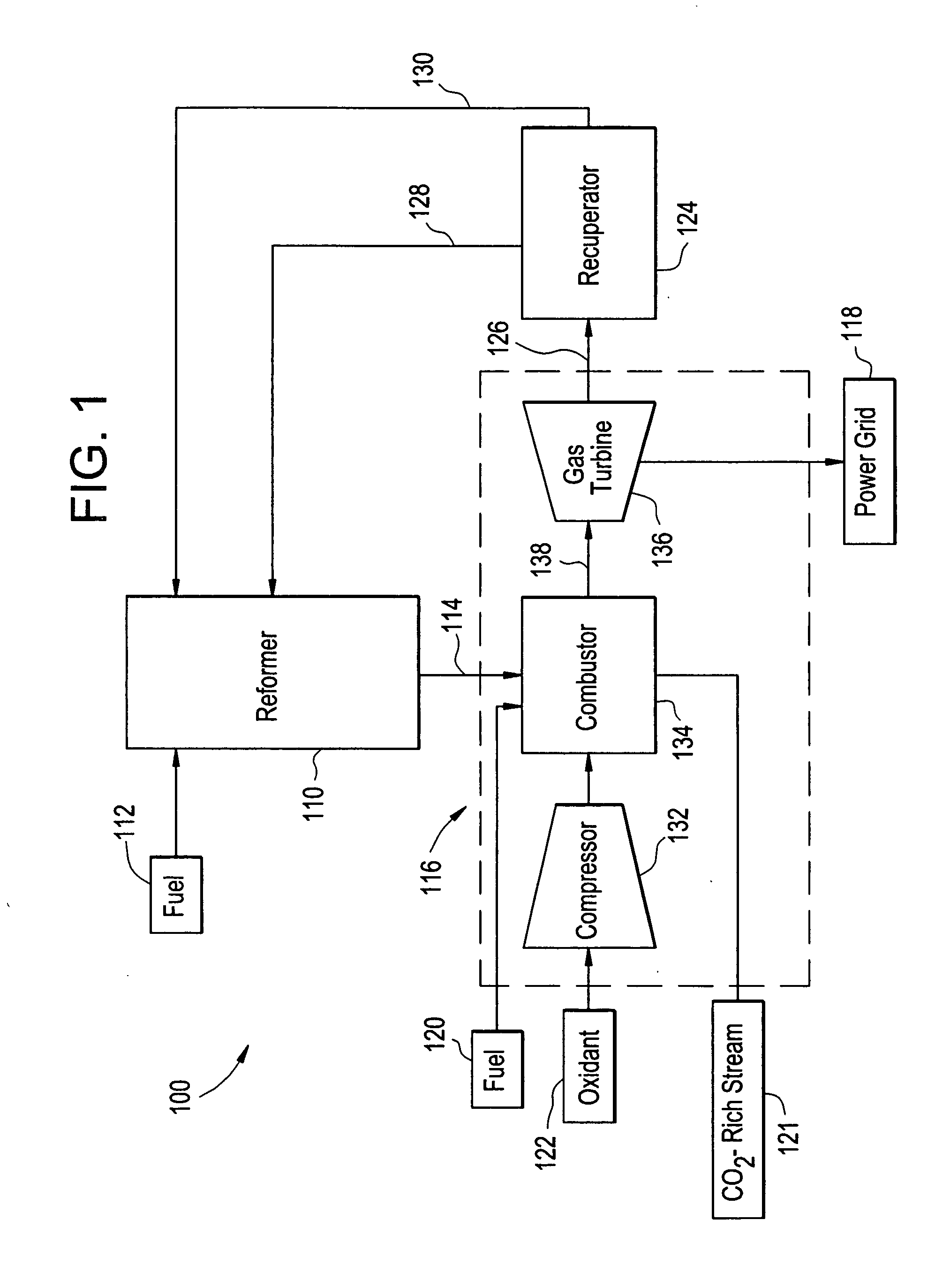
Systems and processes for reducing NOx emissions
ActiveUS20080141643A1Reduce harmful emissionsReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsGas treatmentDispersed particle separationElectricityCombustion system
A system for reducing NOx emissions, includes a reformer configured to receive a fuel and produce a hydrogen-enriched stream, a combustion system configured to burn the hydrogen enriched-stream and produce electricity and an exhaust stream, and a recuperator configured to recover heat from the exhaust stream, wherein the recovered heat is recycled back to the reformer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com