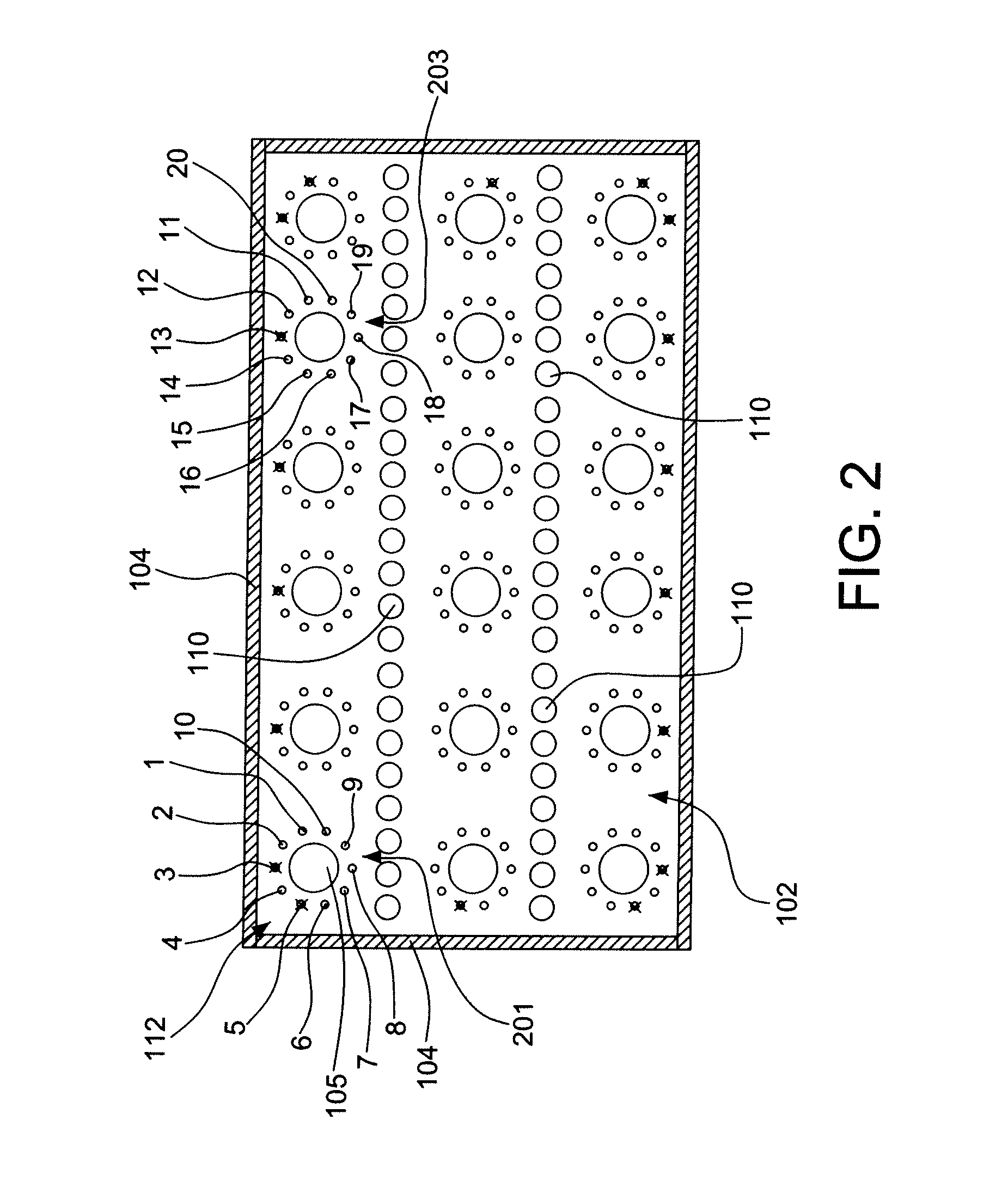
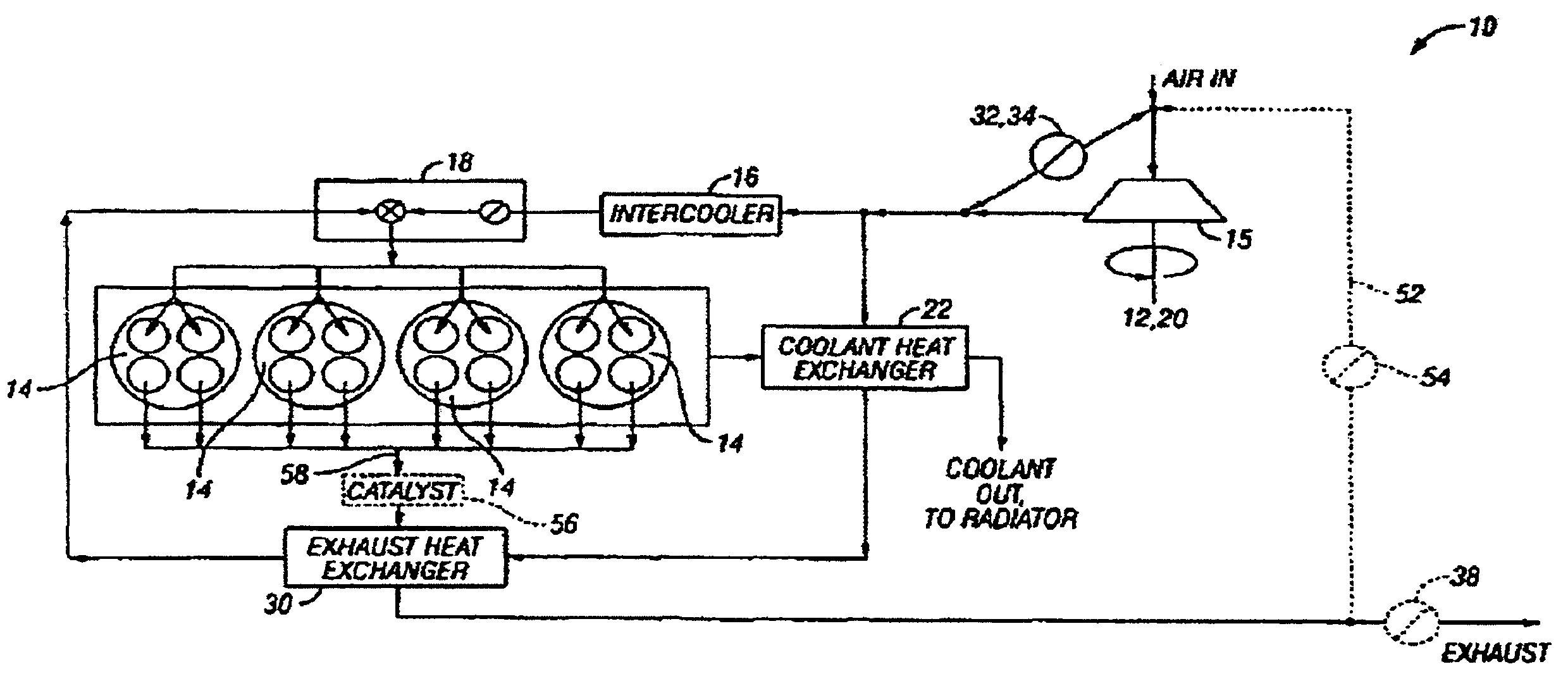
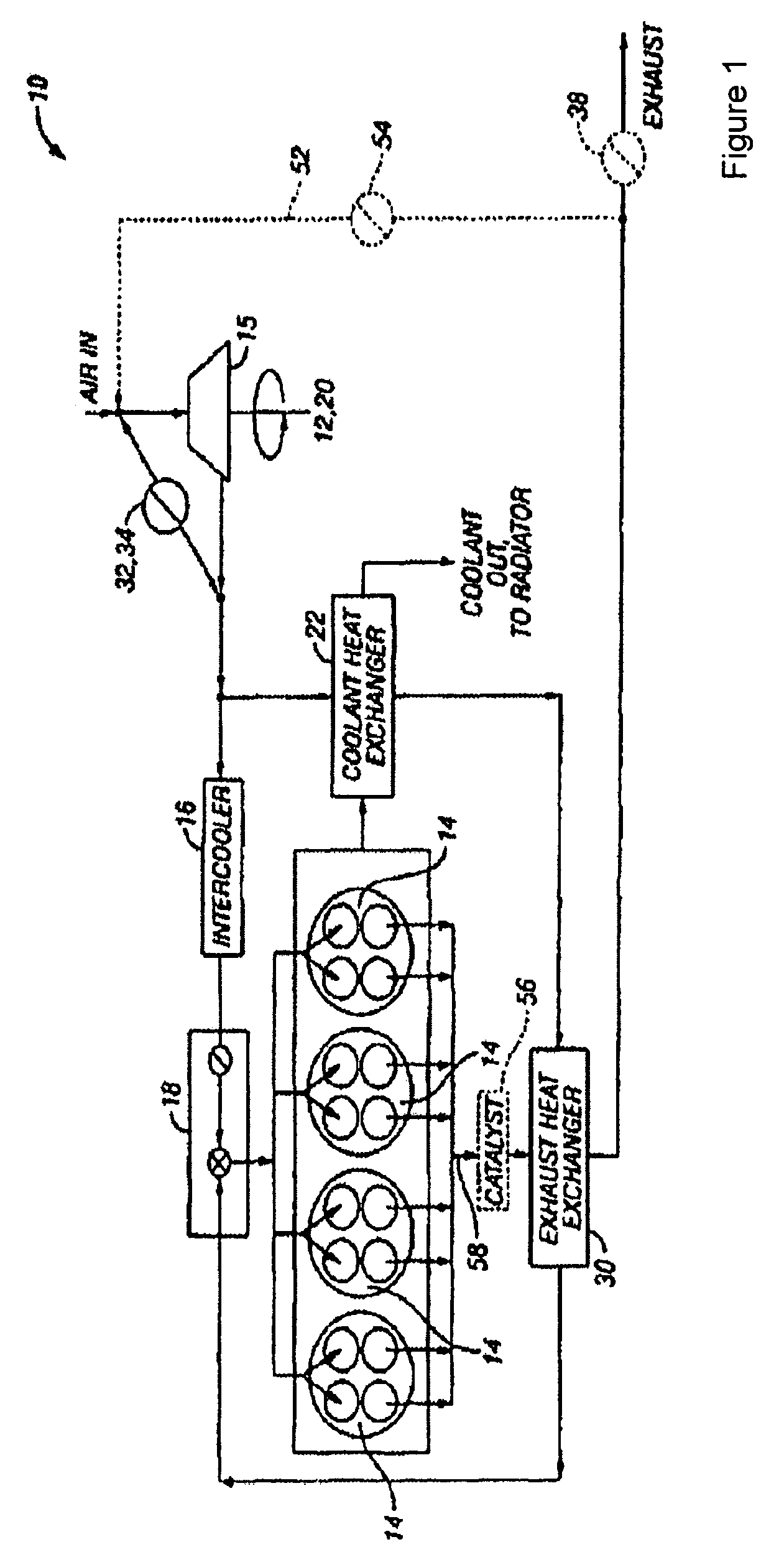
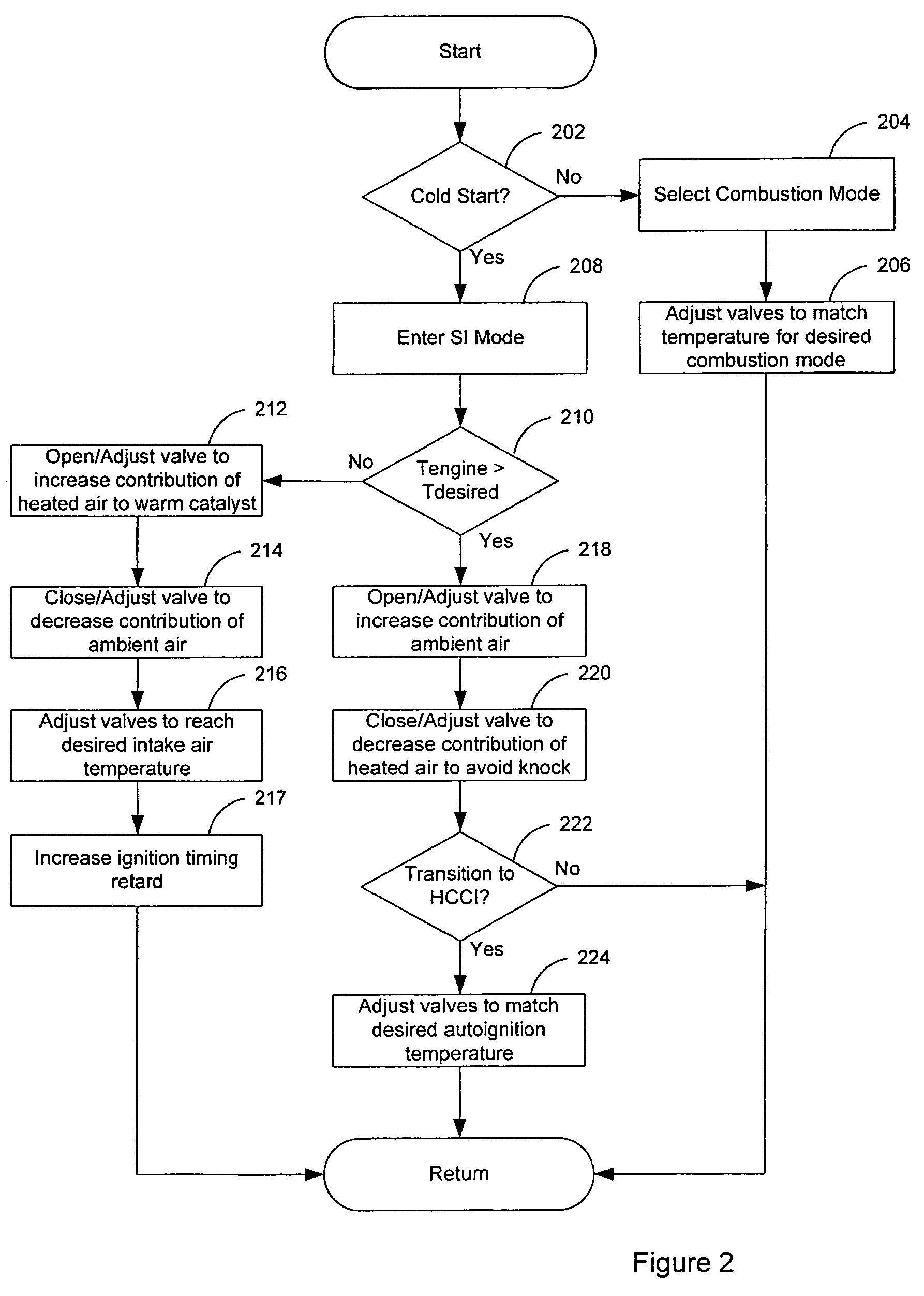
Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Reduce the production of nitrogen oxides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
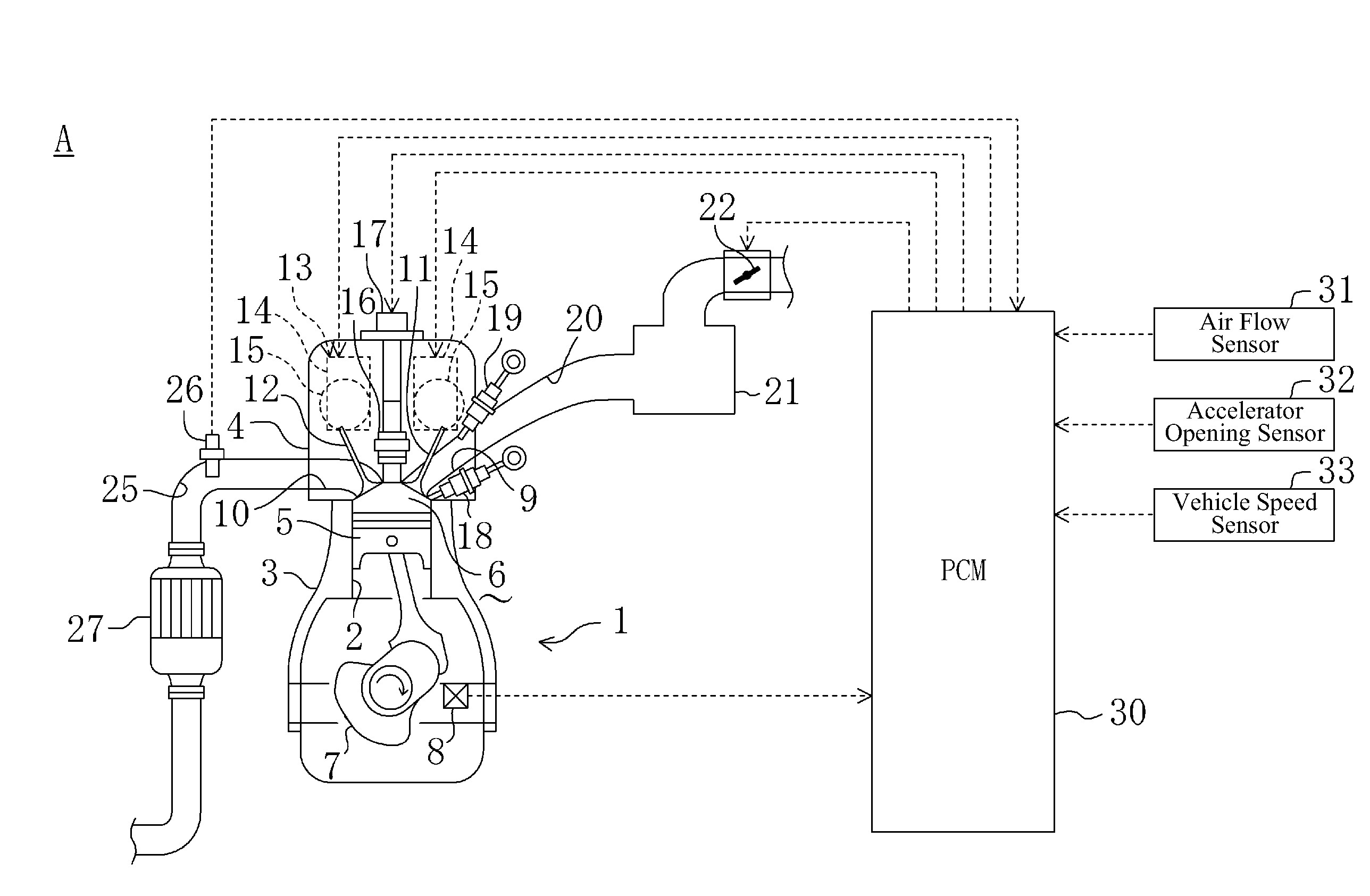
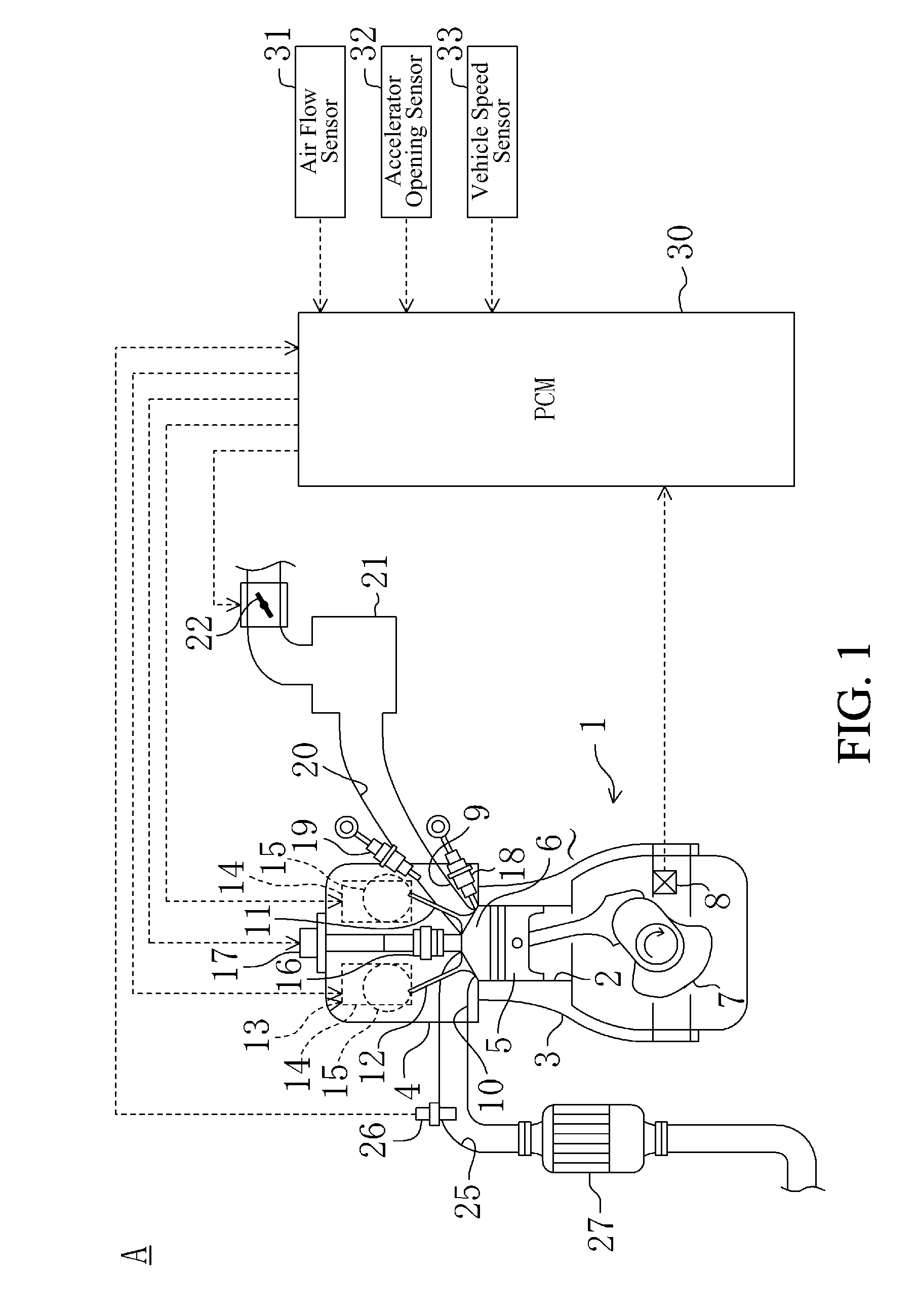
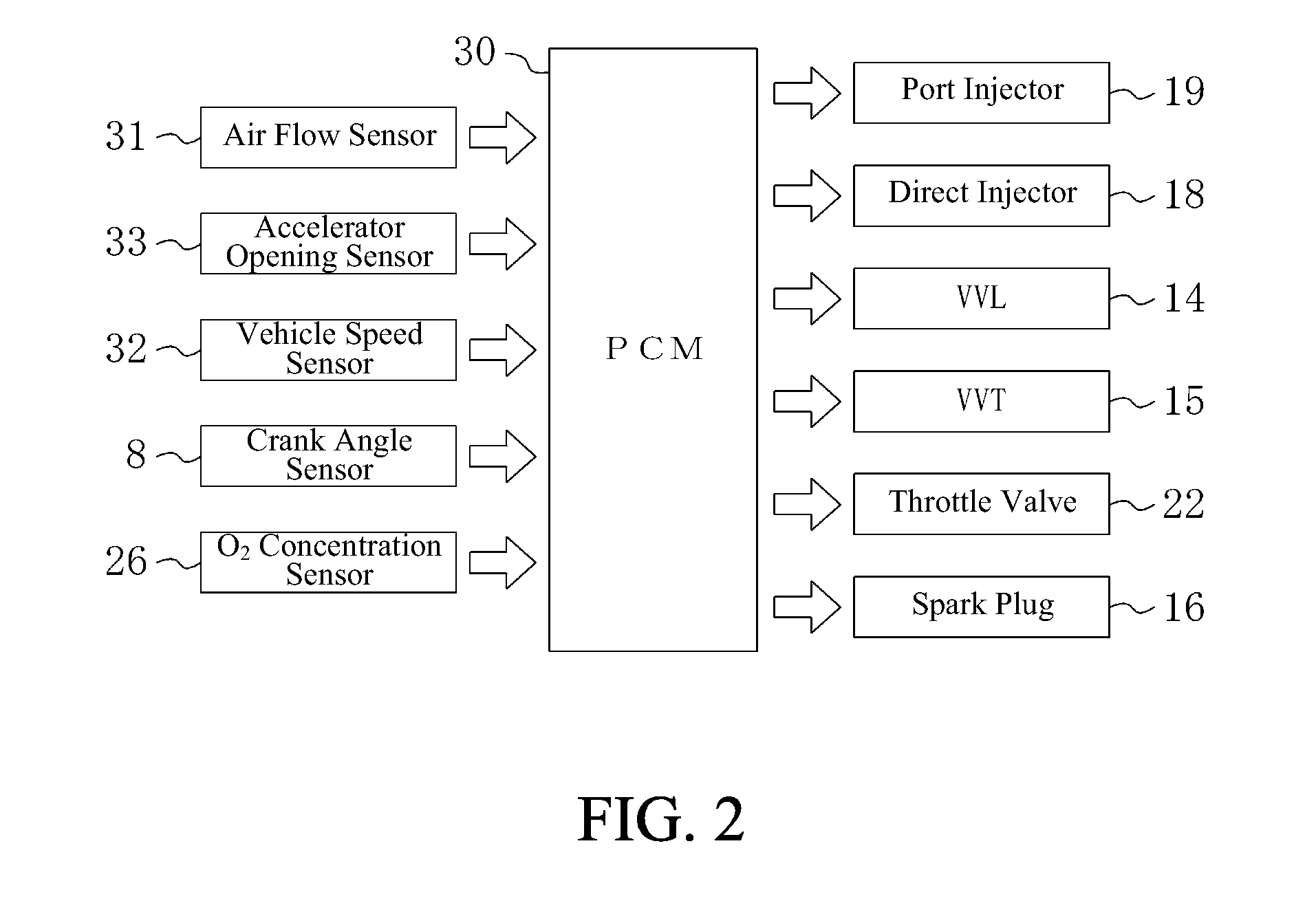
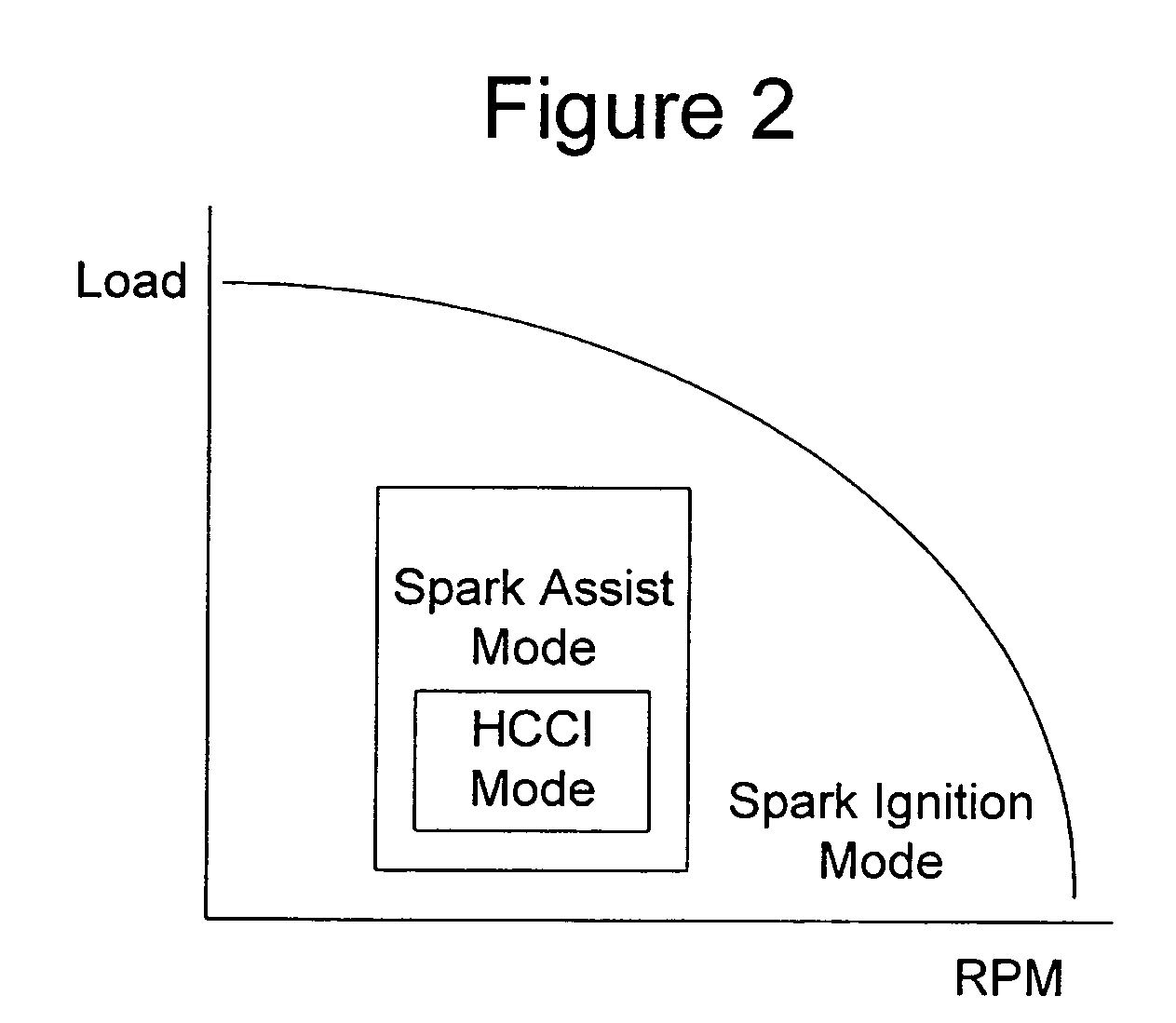
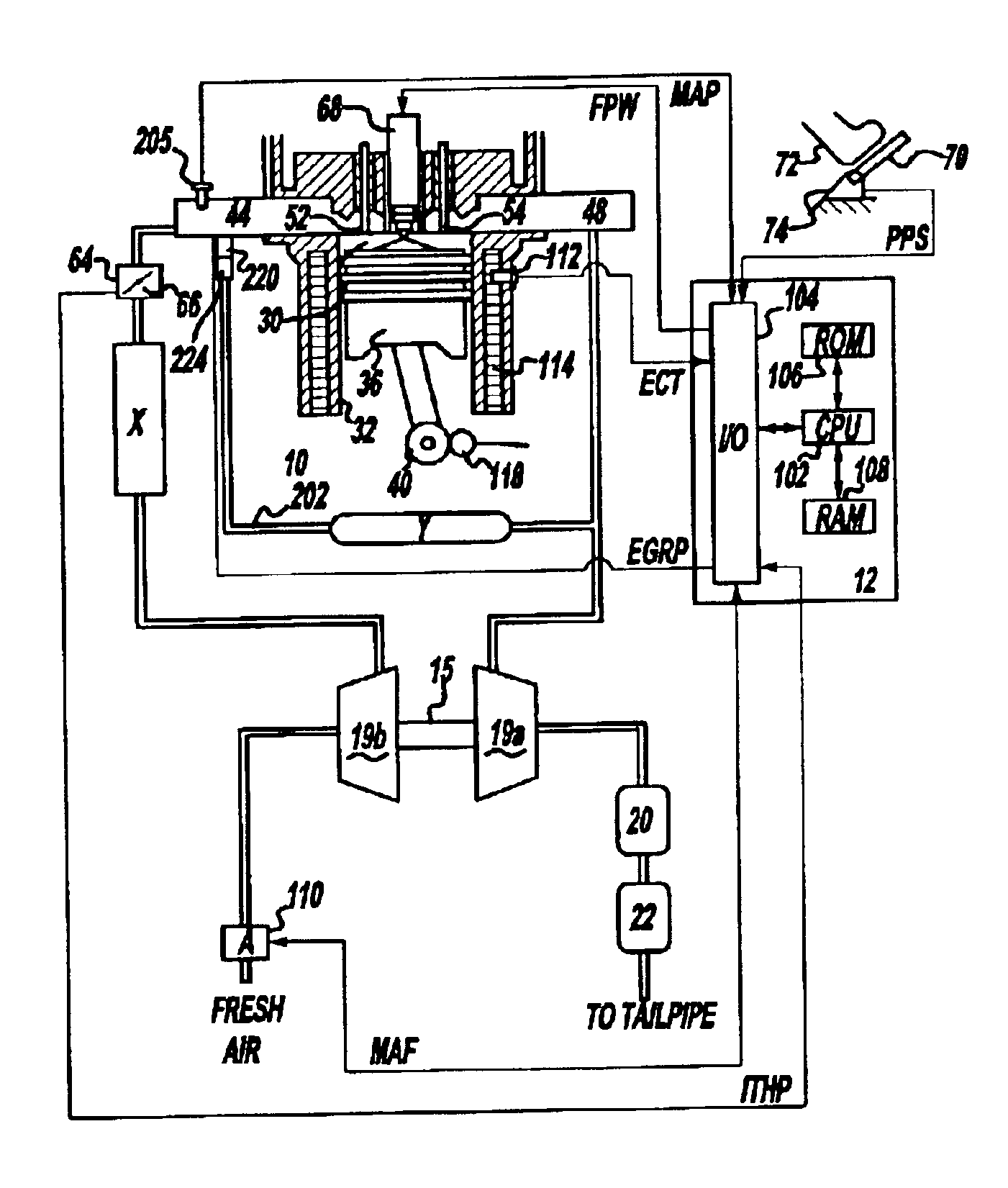
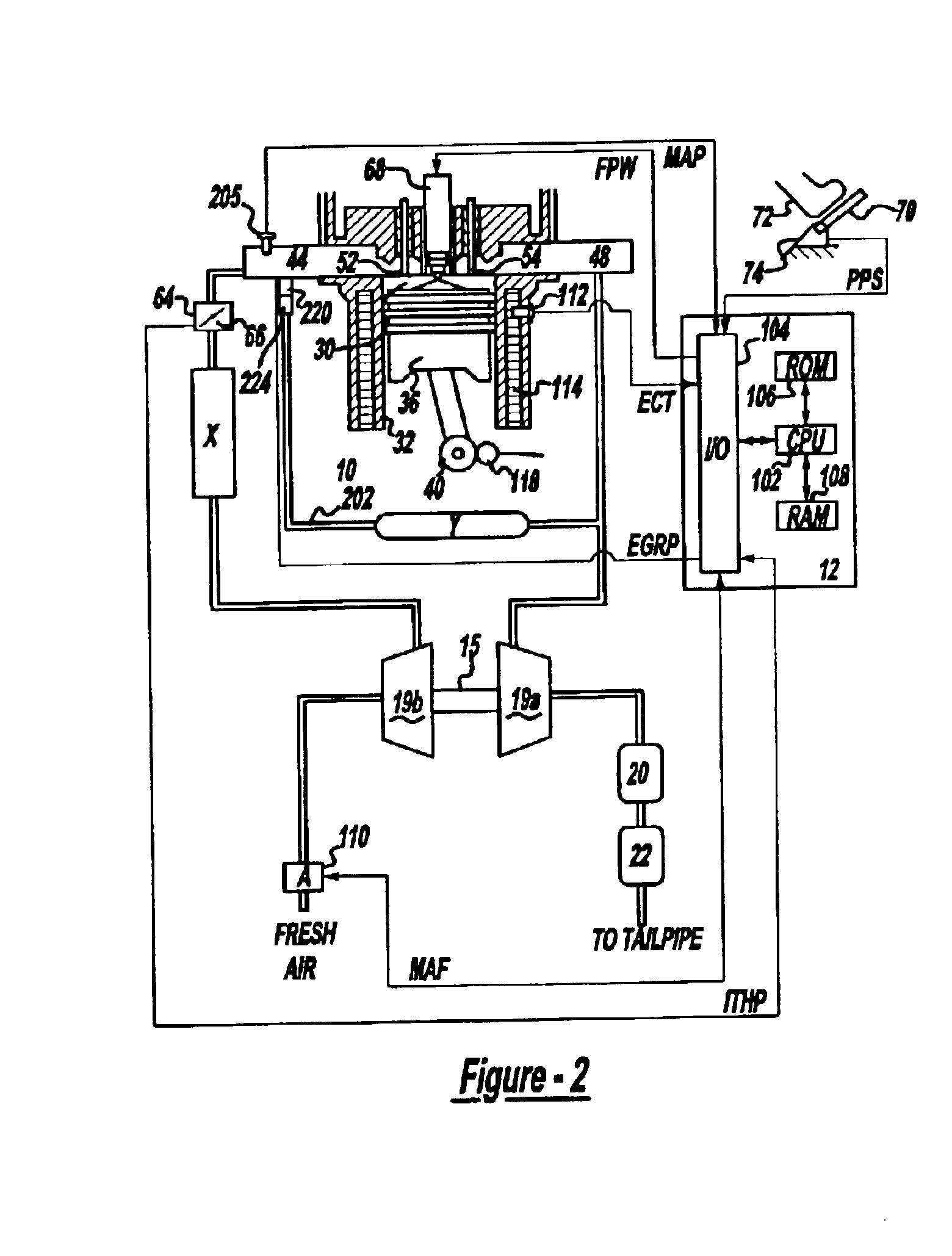
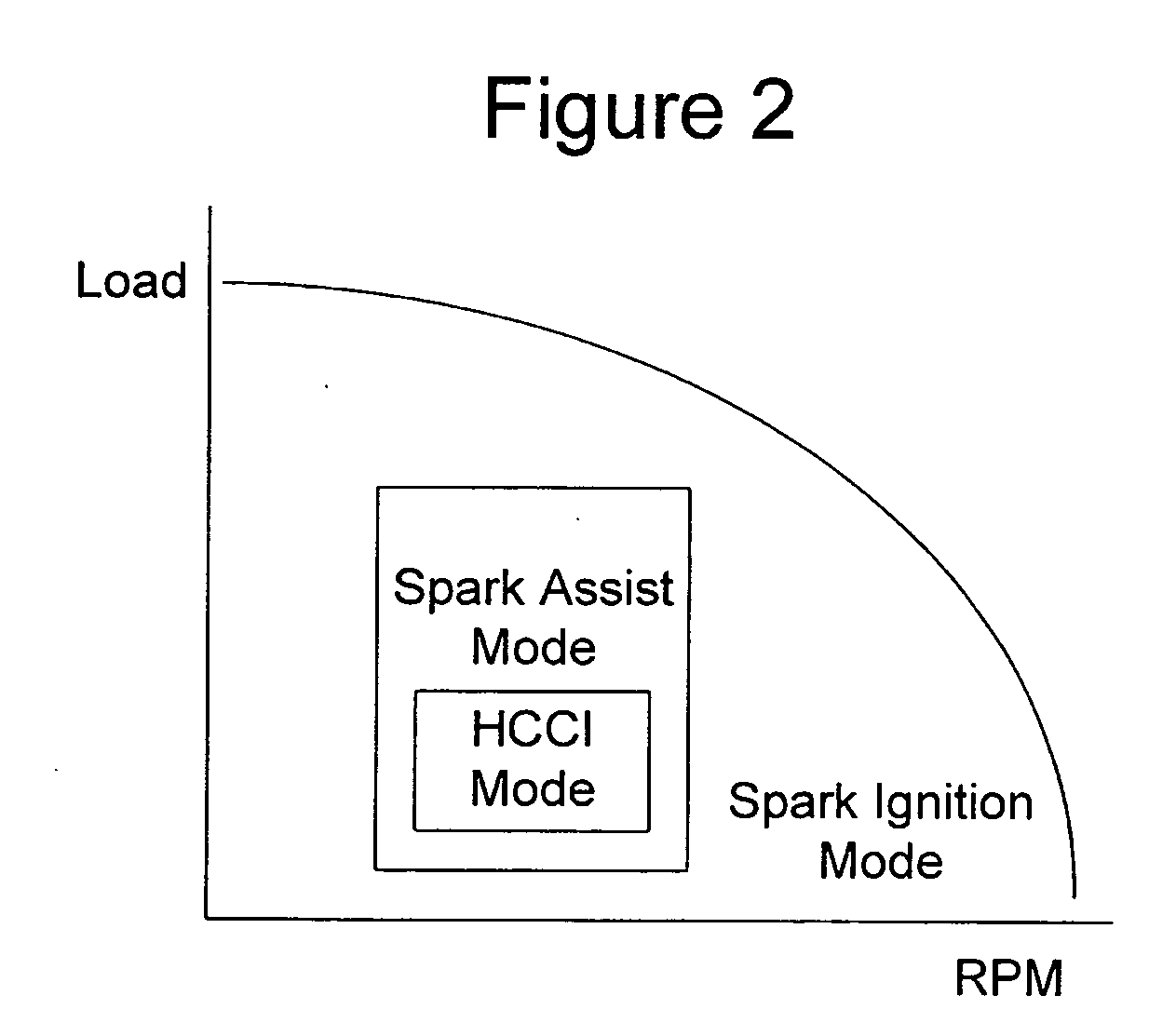
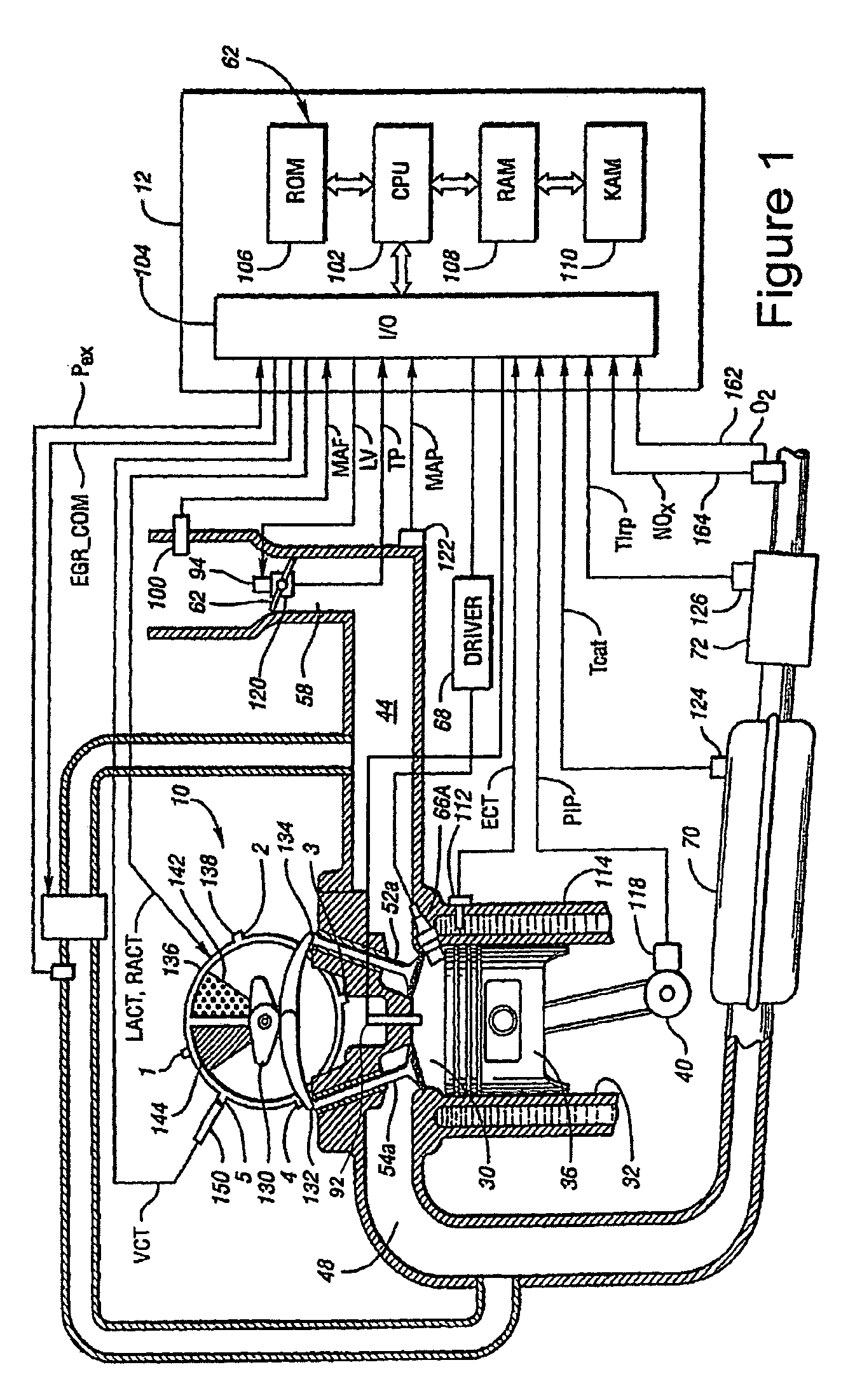
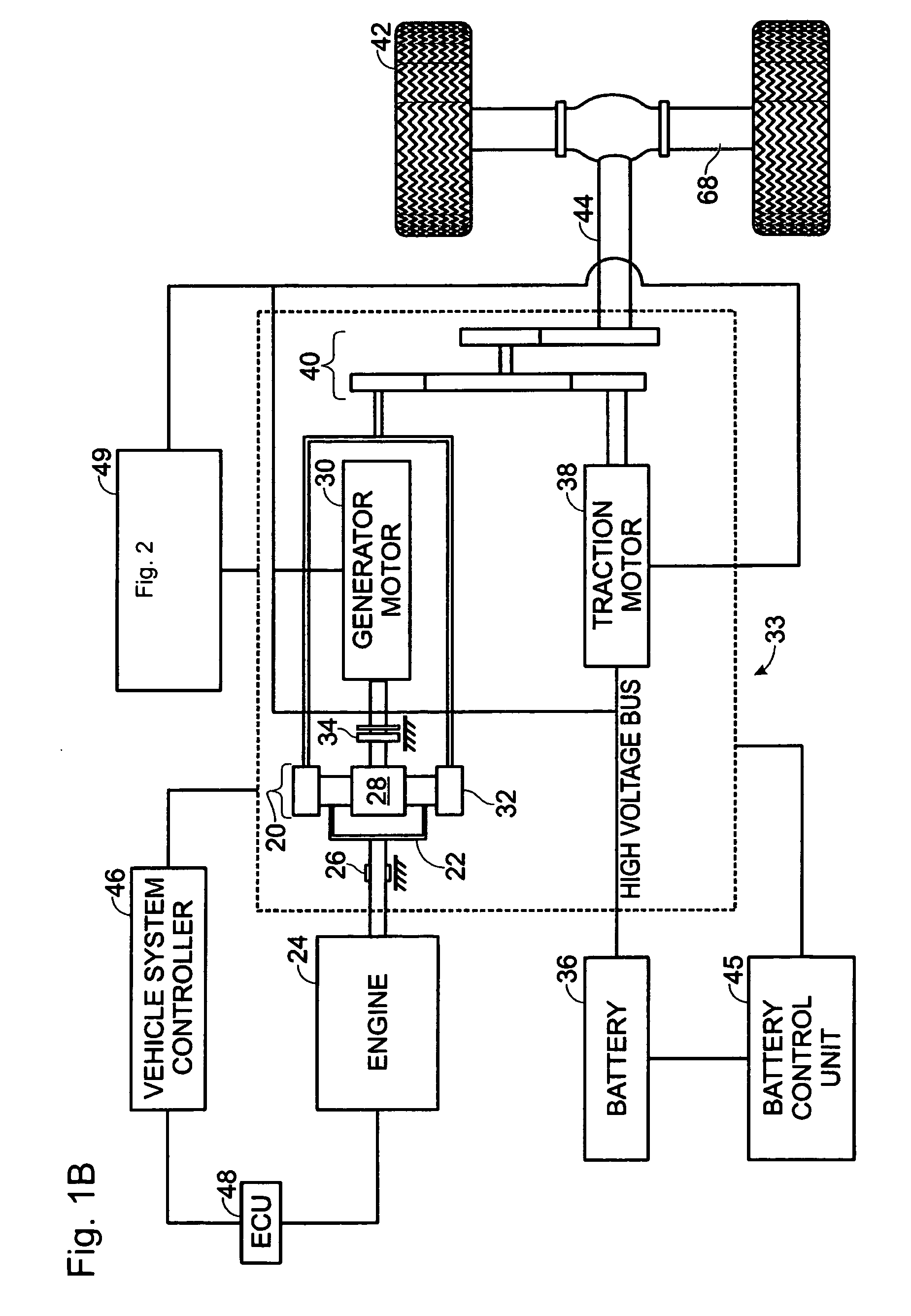
Multiple Combustion Mode Engine Using Direct Alcohol Injection
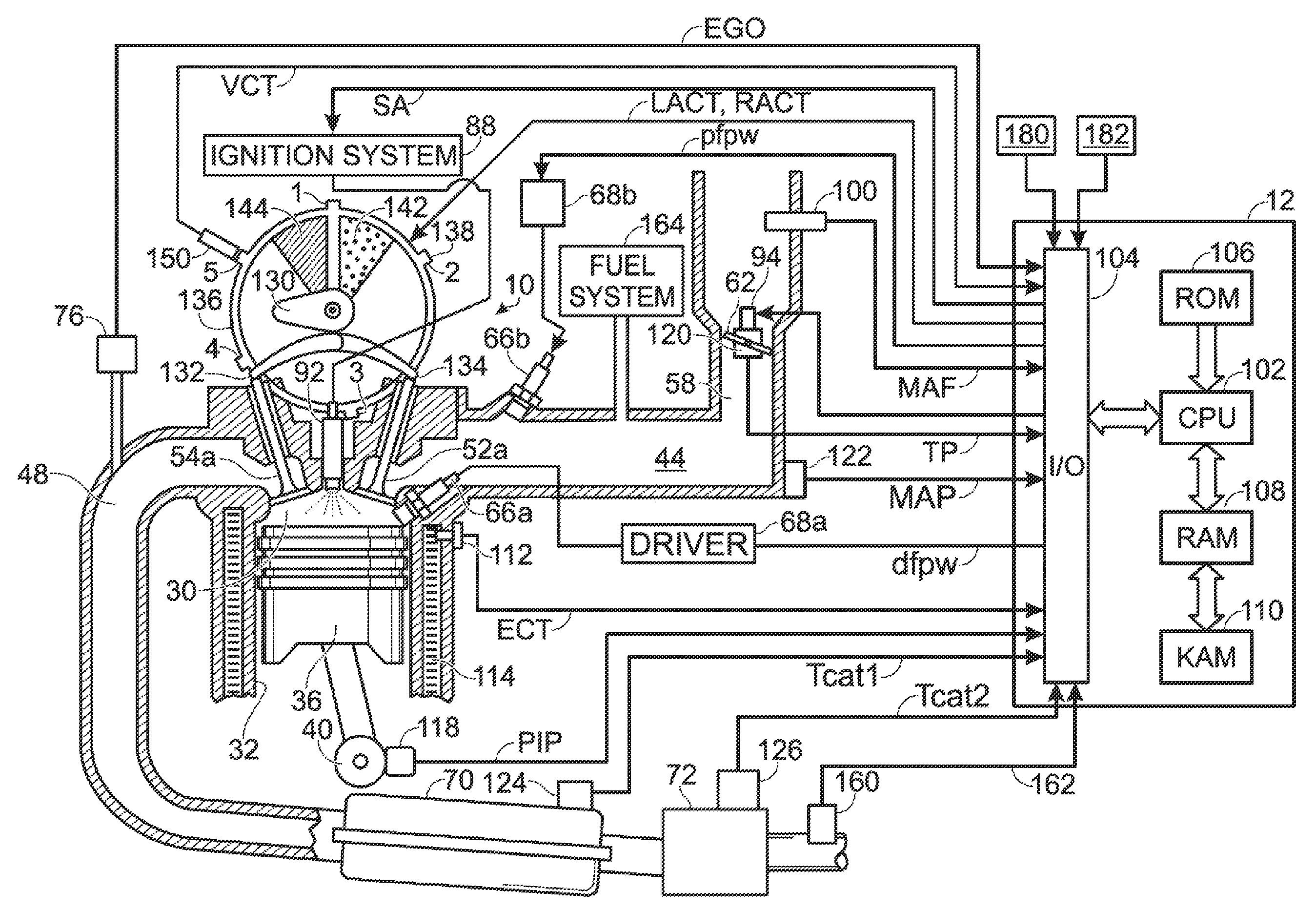
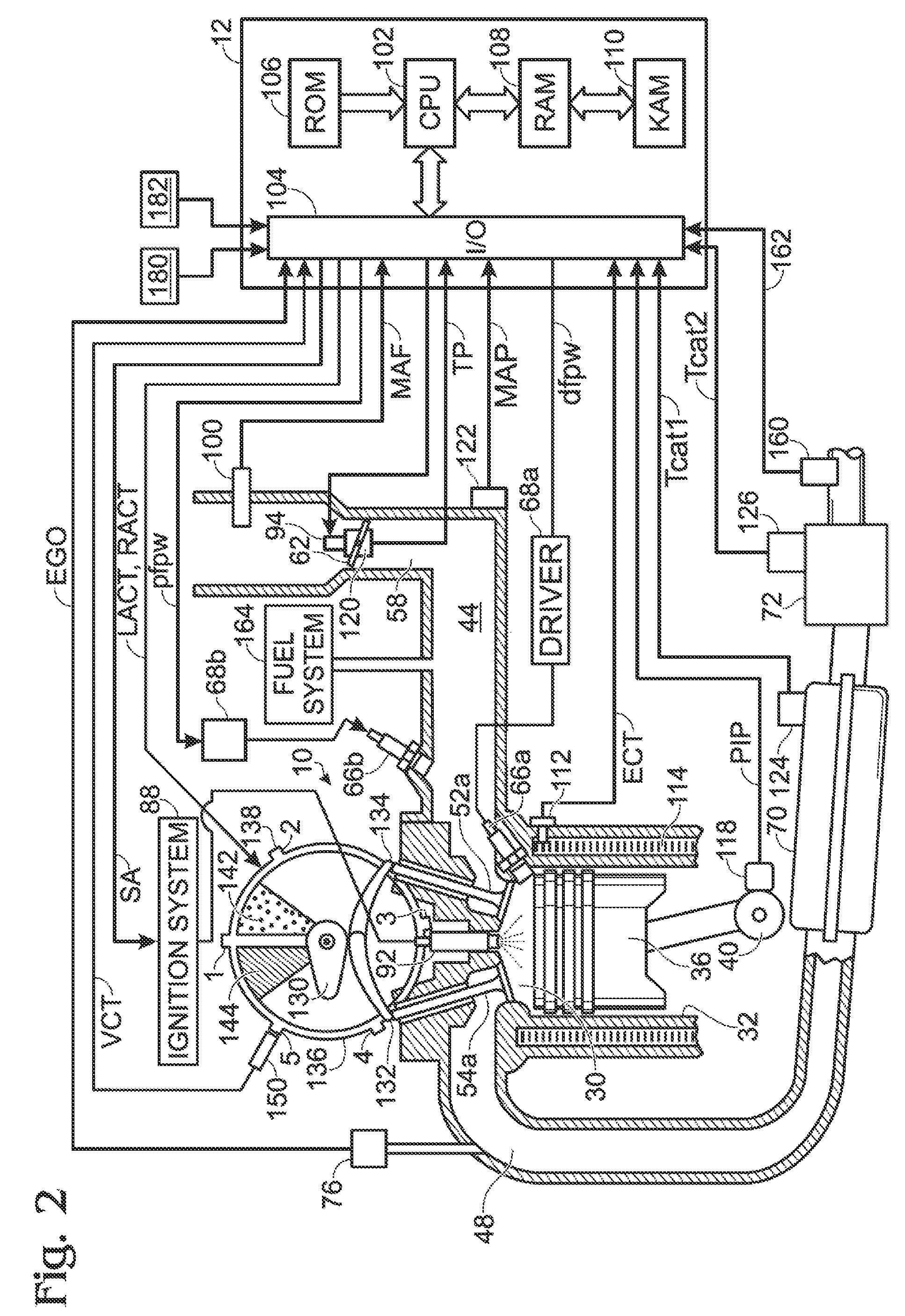
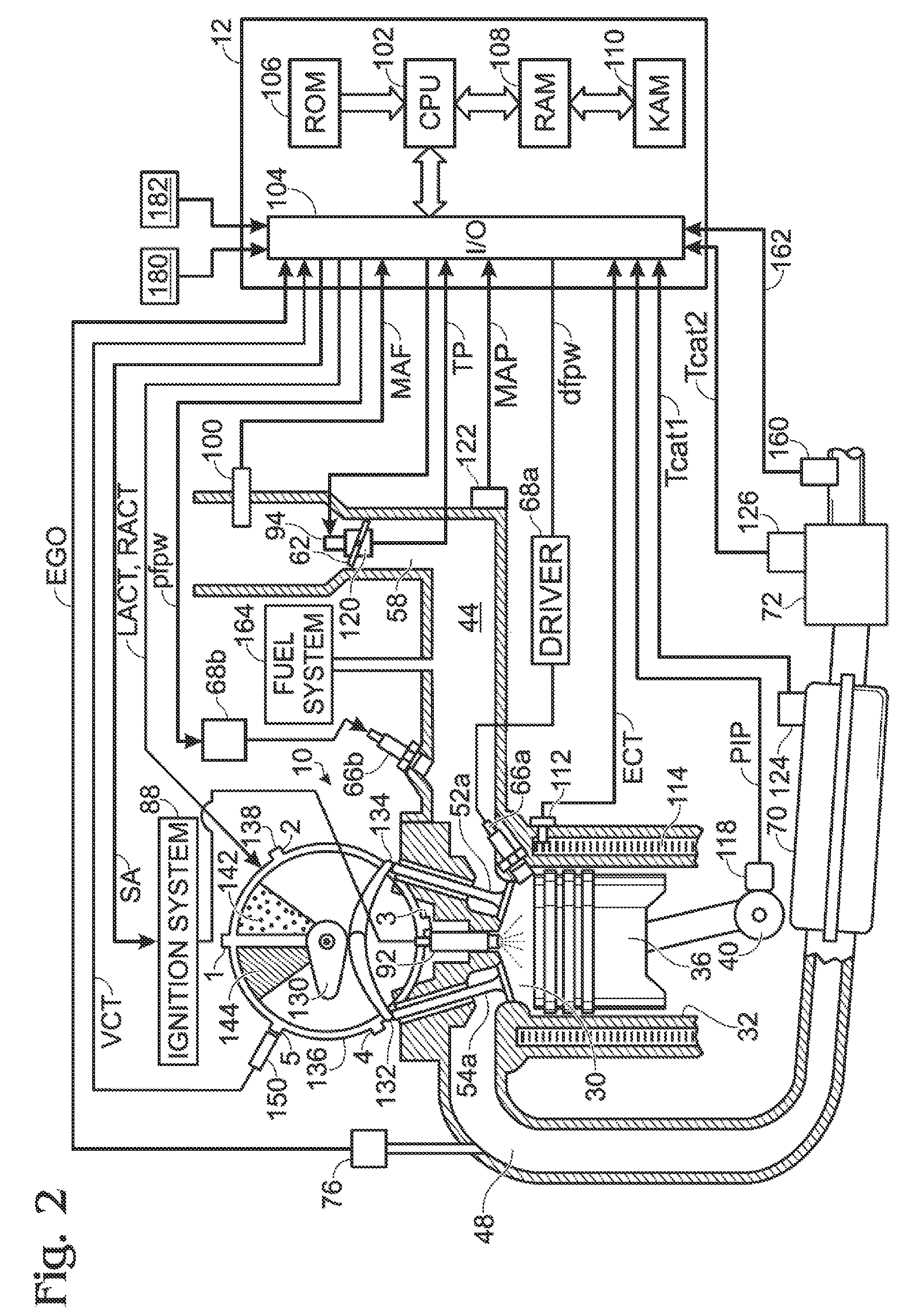
ActiveUS20080127933A1Improve operation and transient performanceDesign range be expandAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlAutomotive engineeringSpark-ignition engine
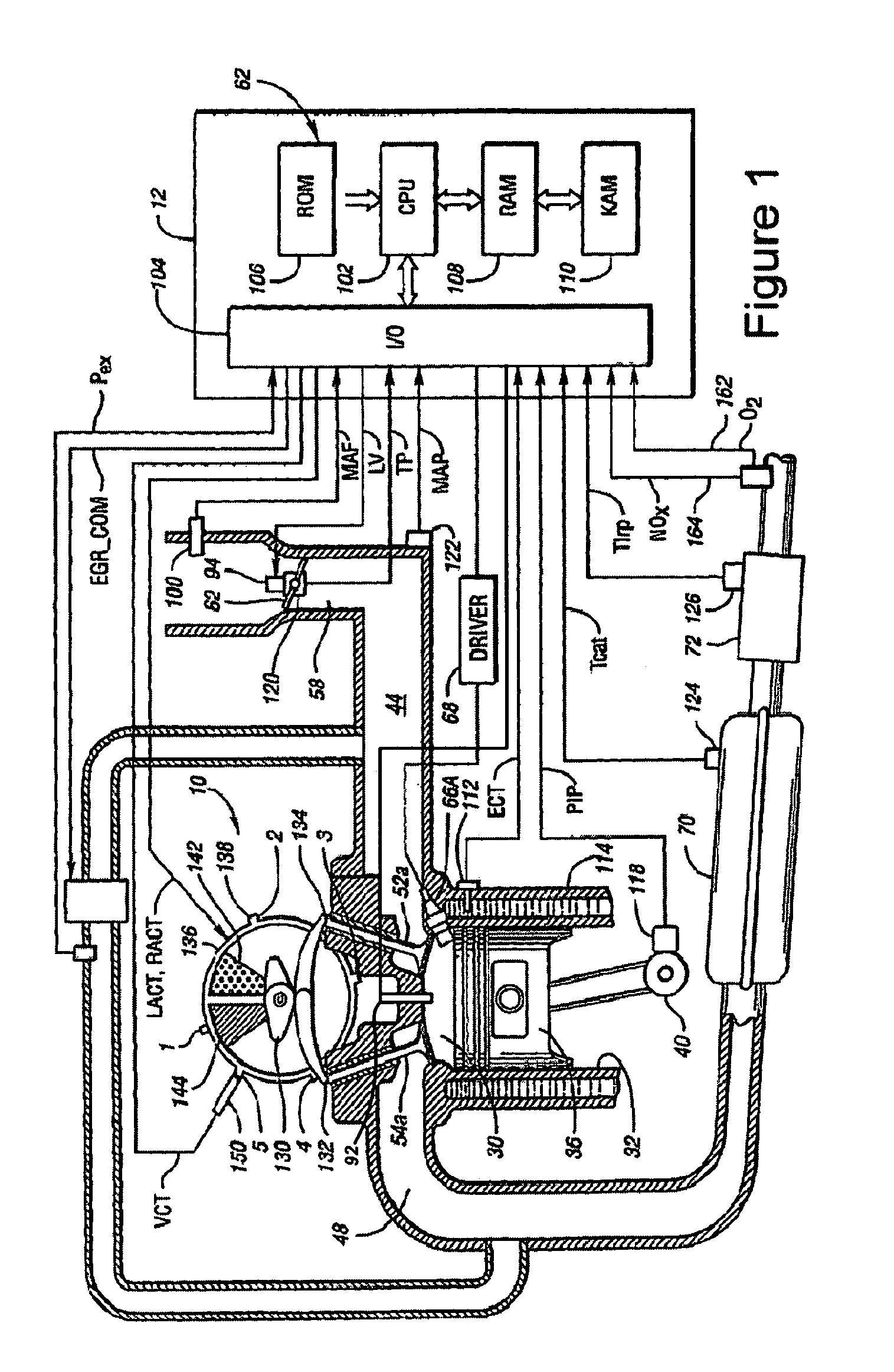
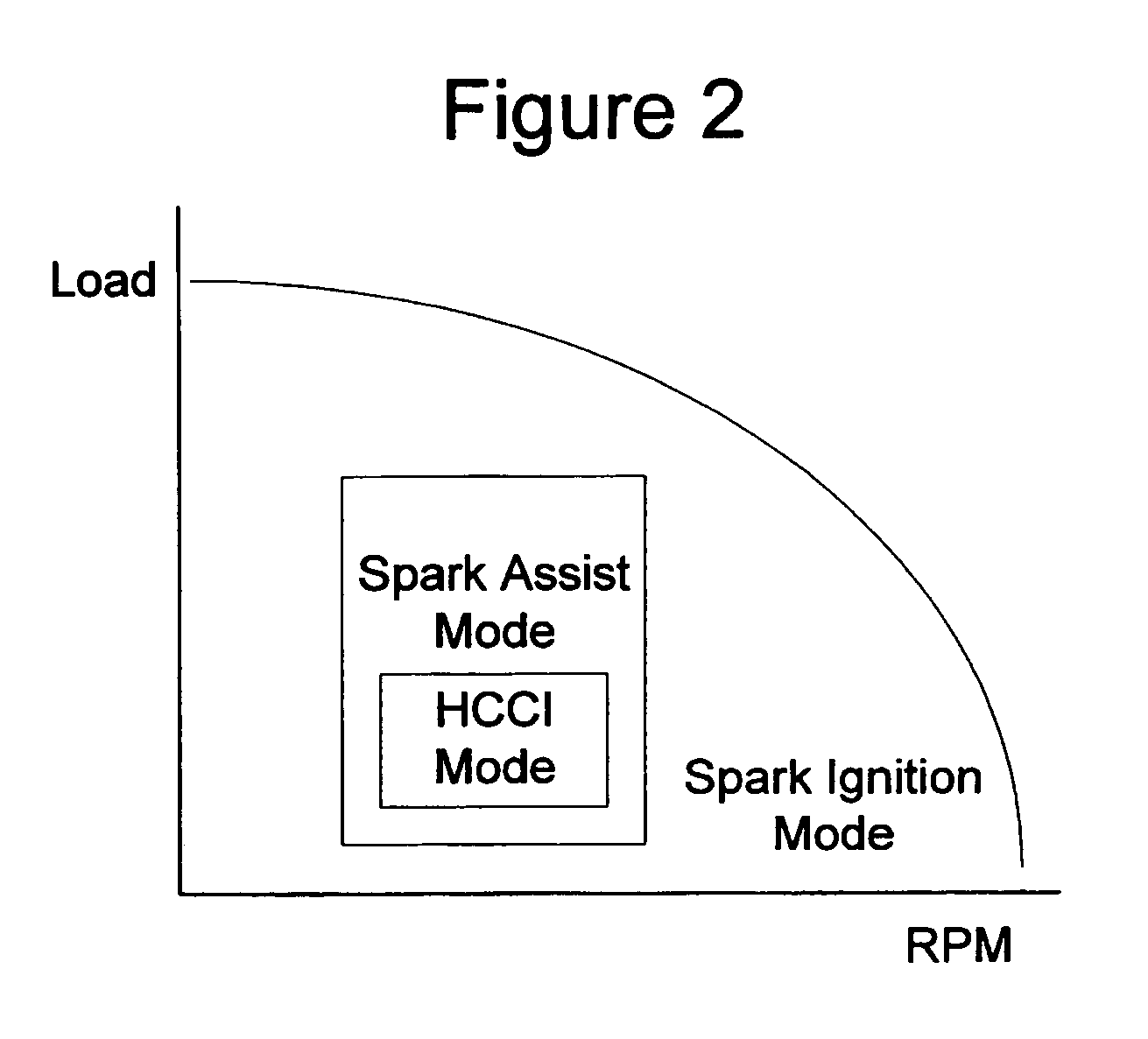
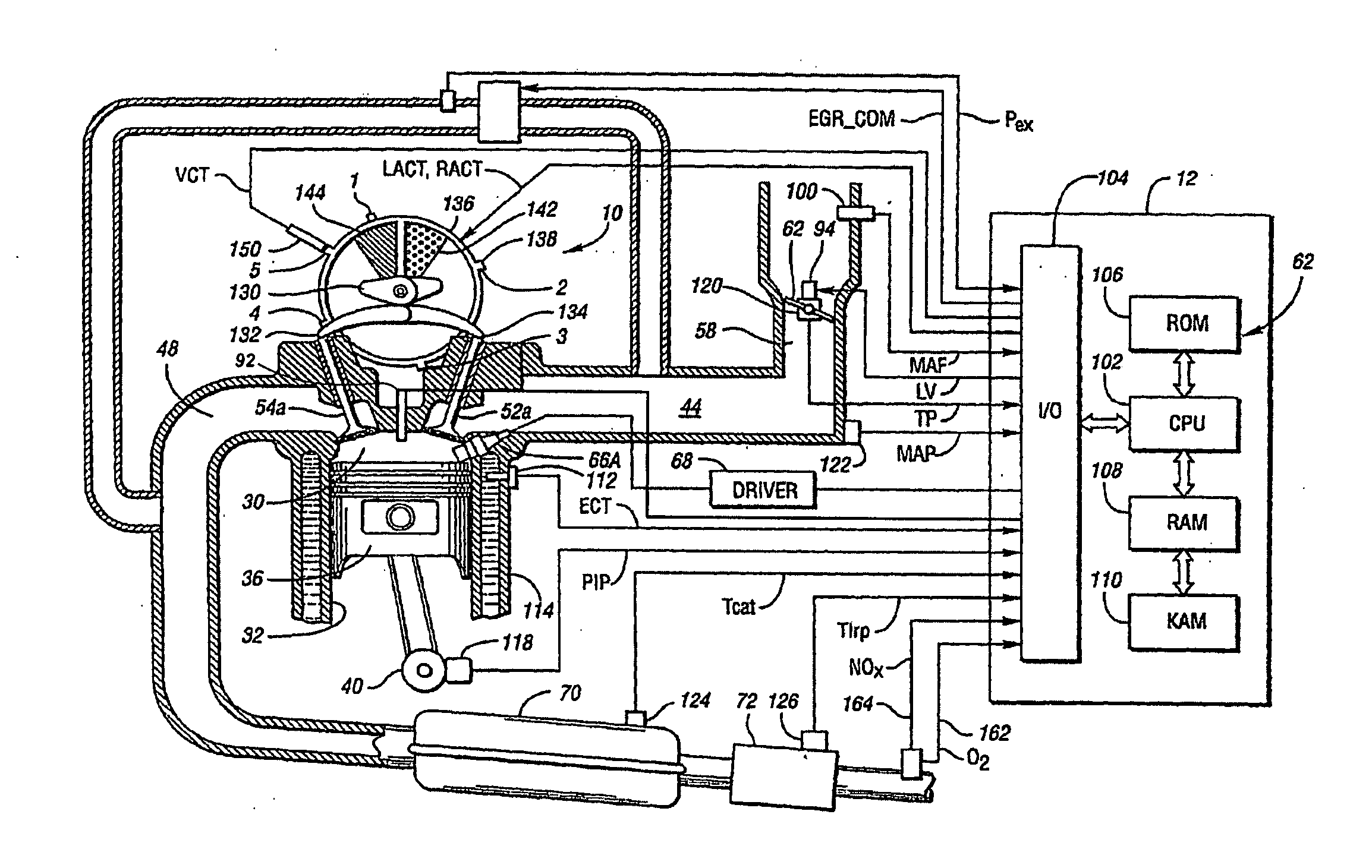
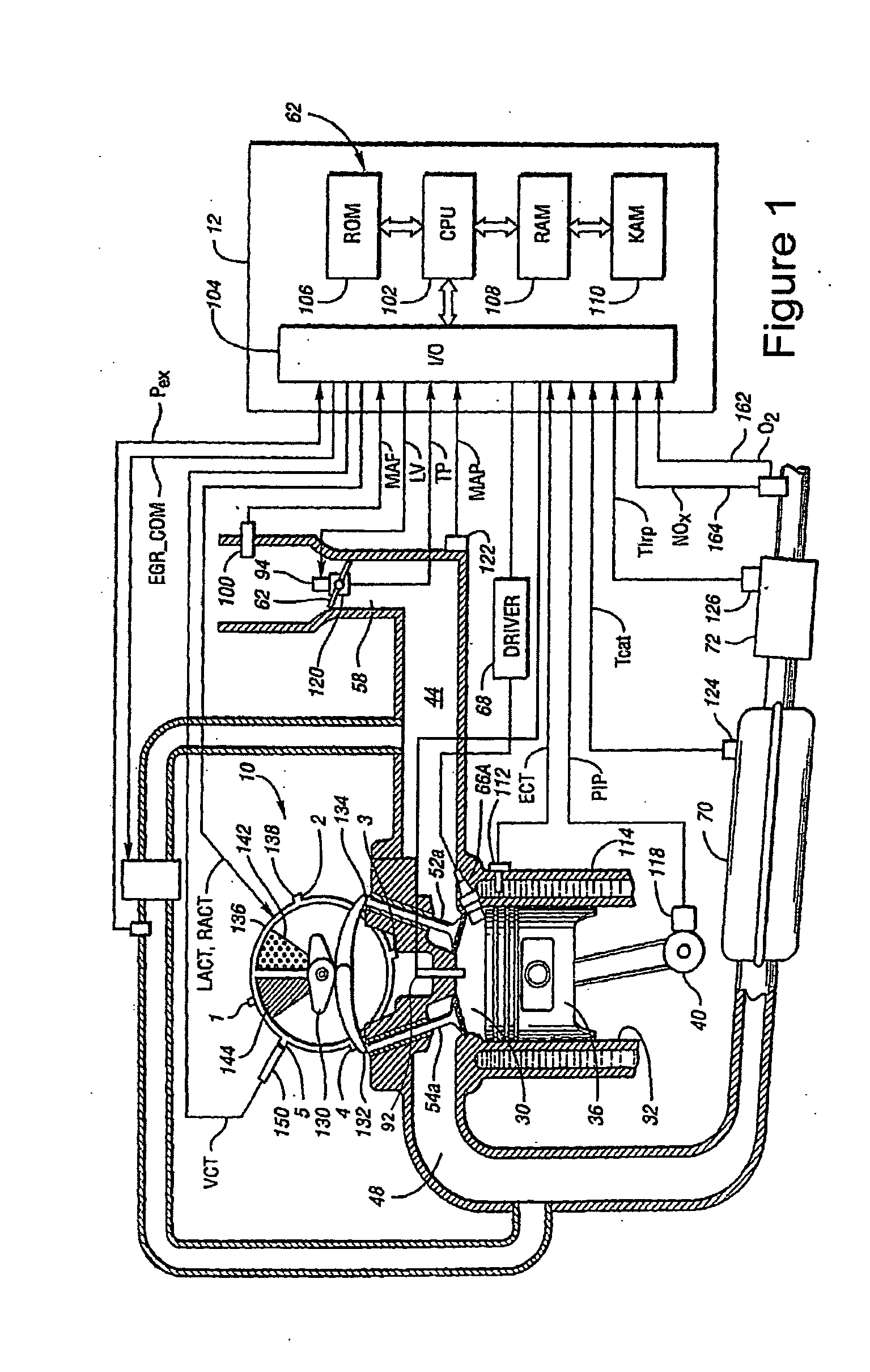
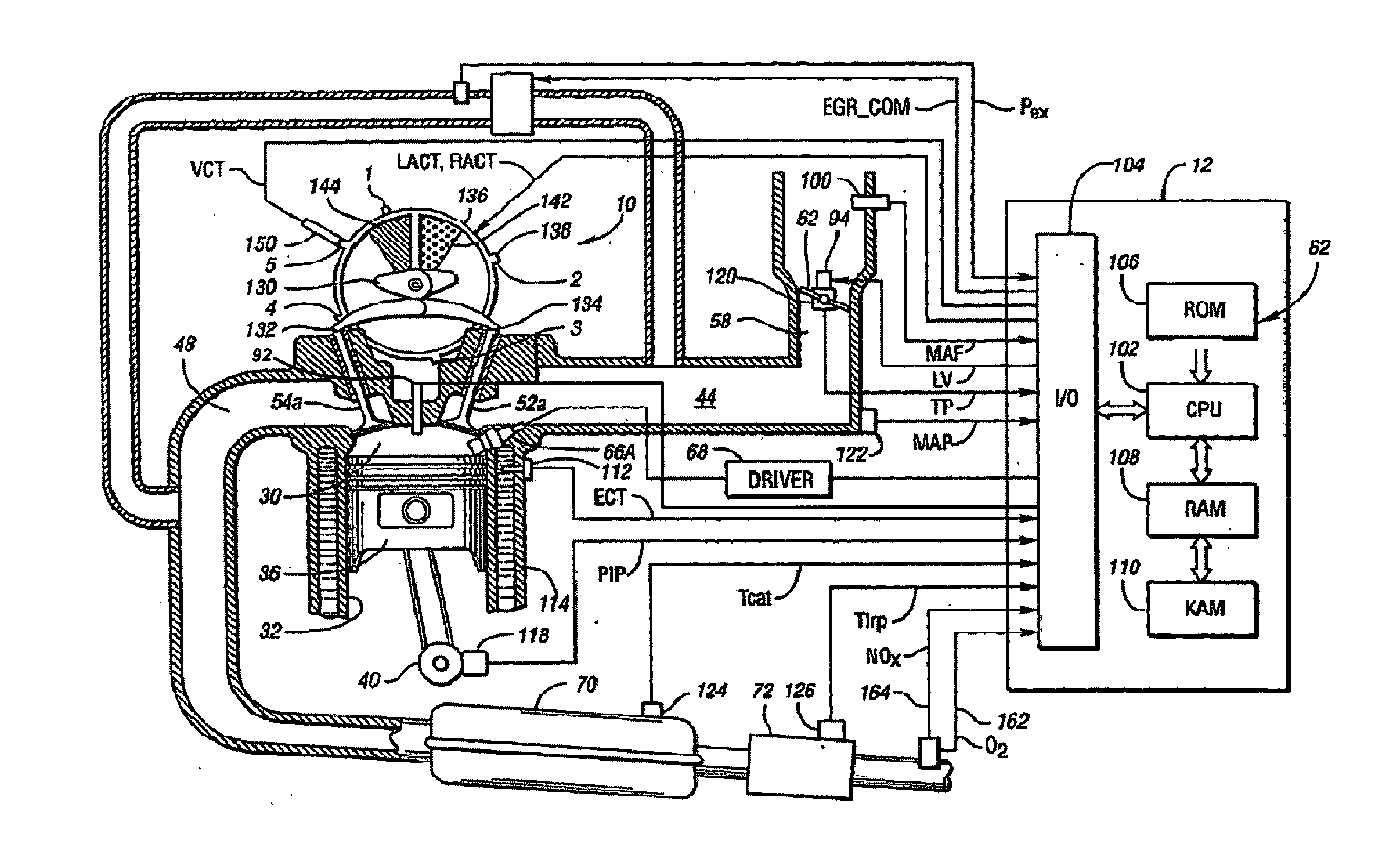
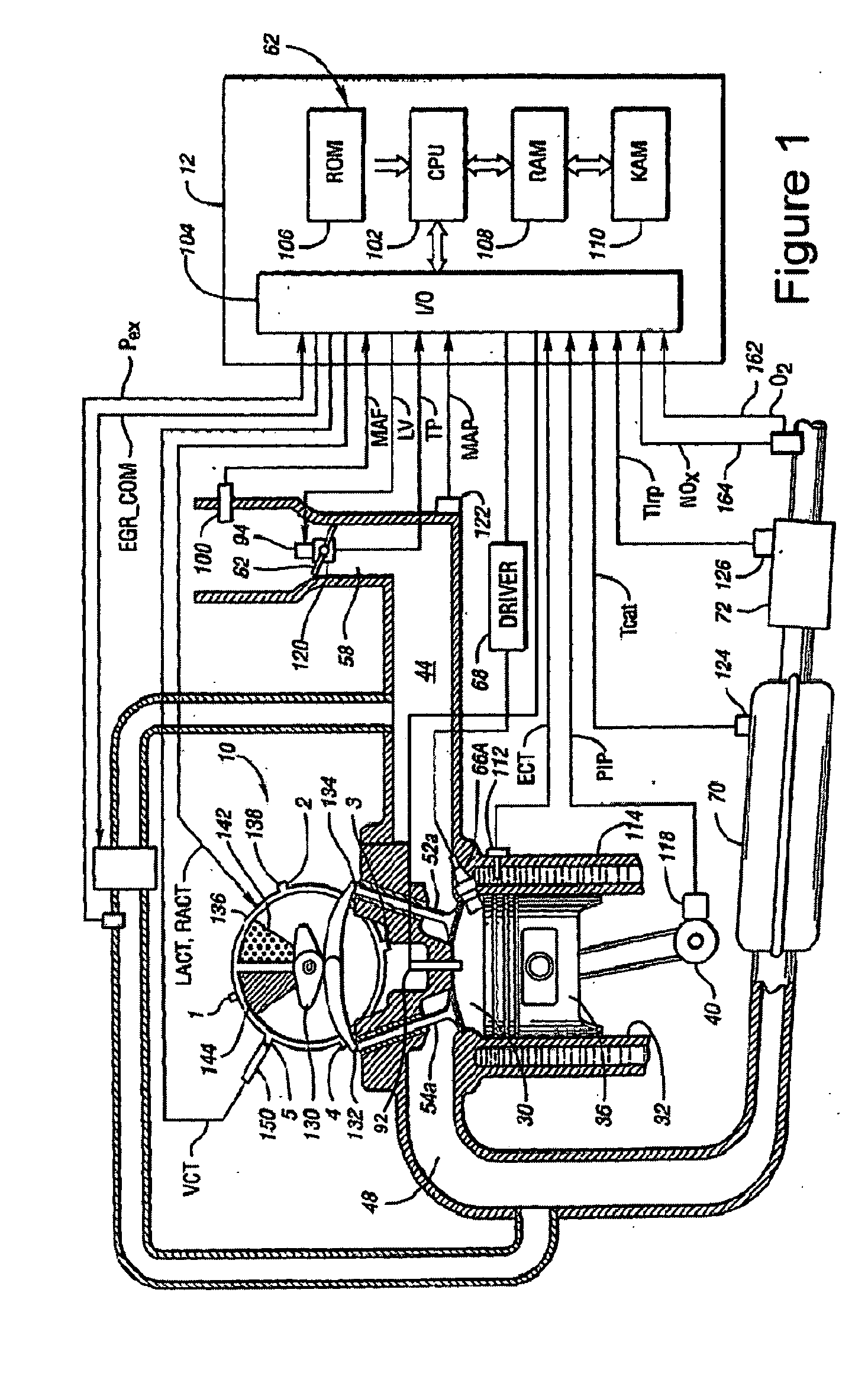
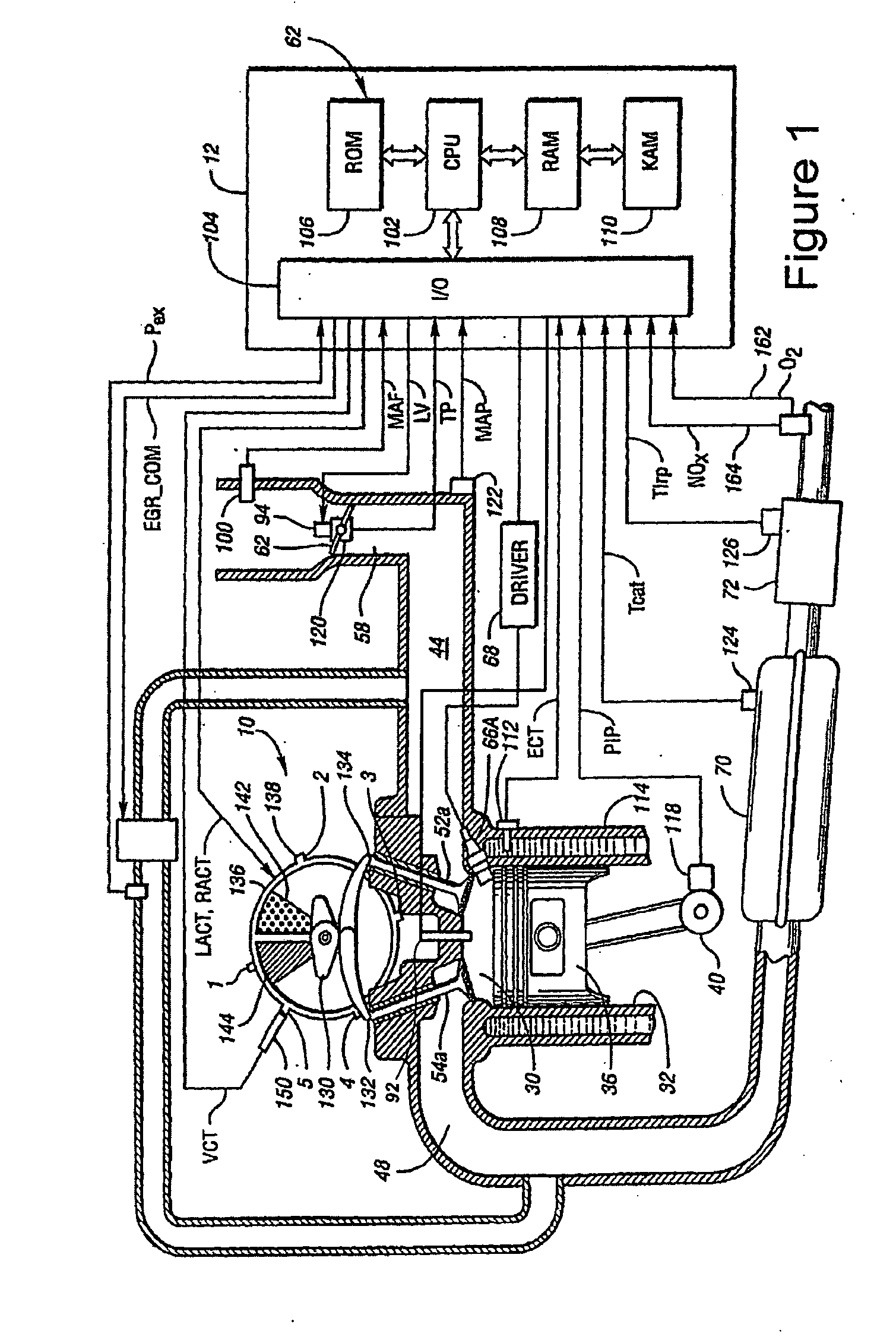
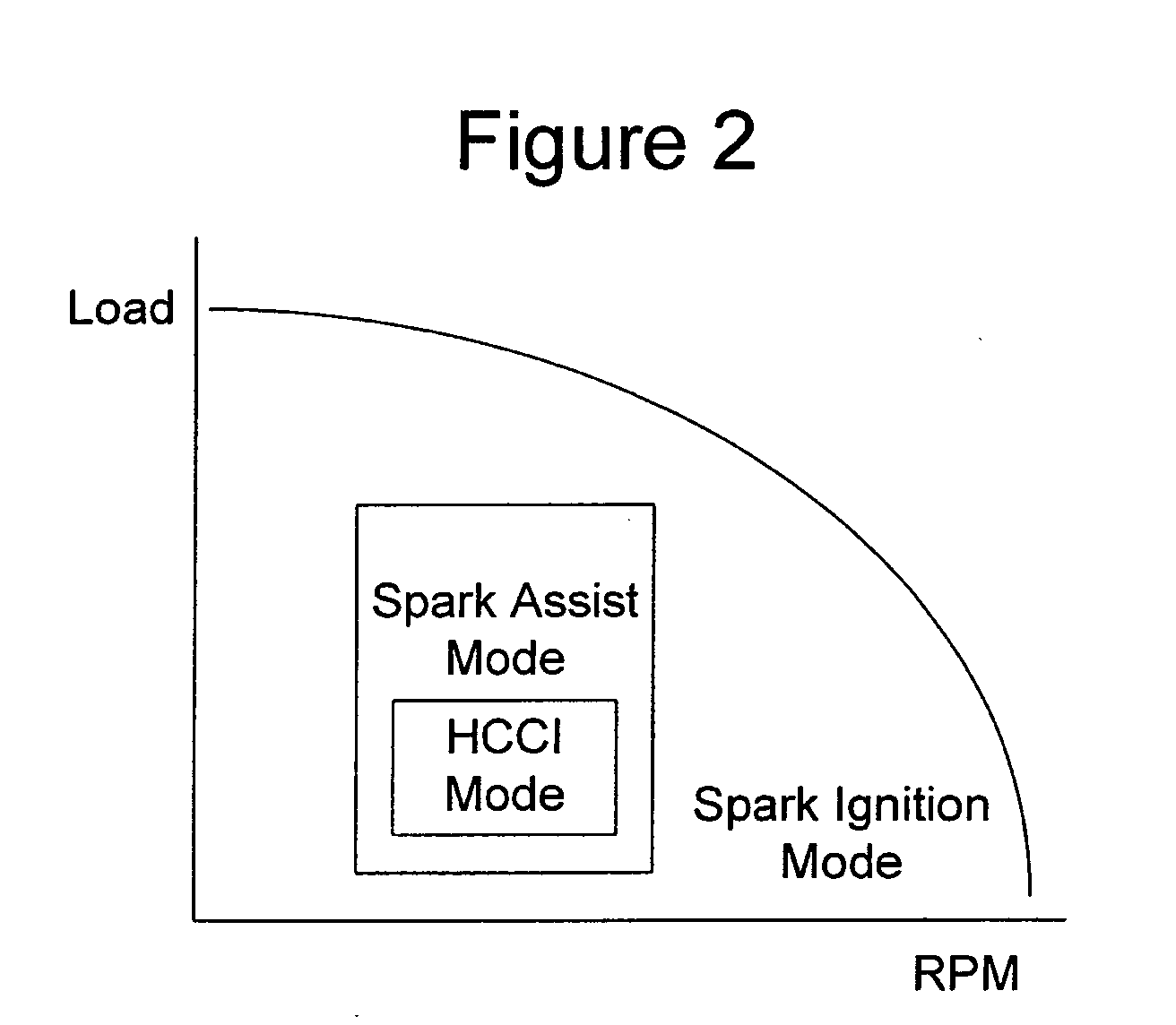
A method of operating an engine, comprising of performing homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion during a first operating condition, and performing spark ignition combustion during a second operating condition, where an amount of directly injected alcohol in at least one of said homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion and said spark ignition combustion is varied in response to at least an operating parameter.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
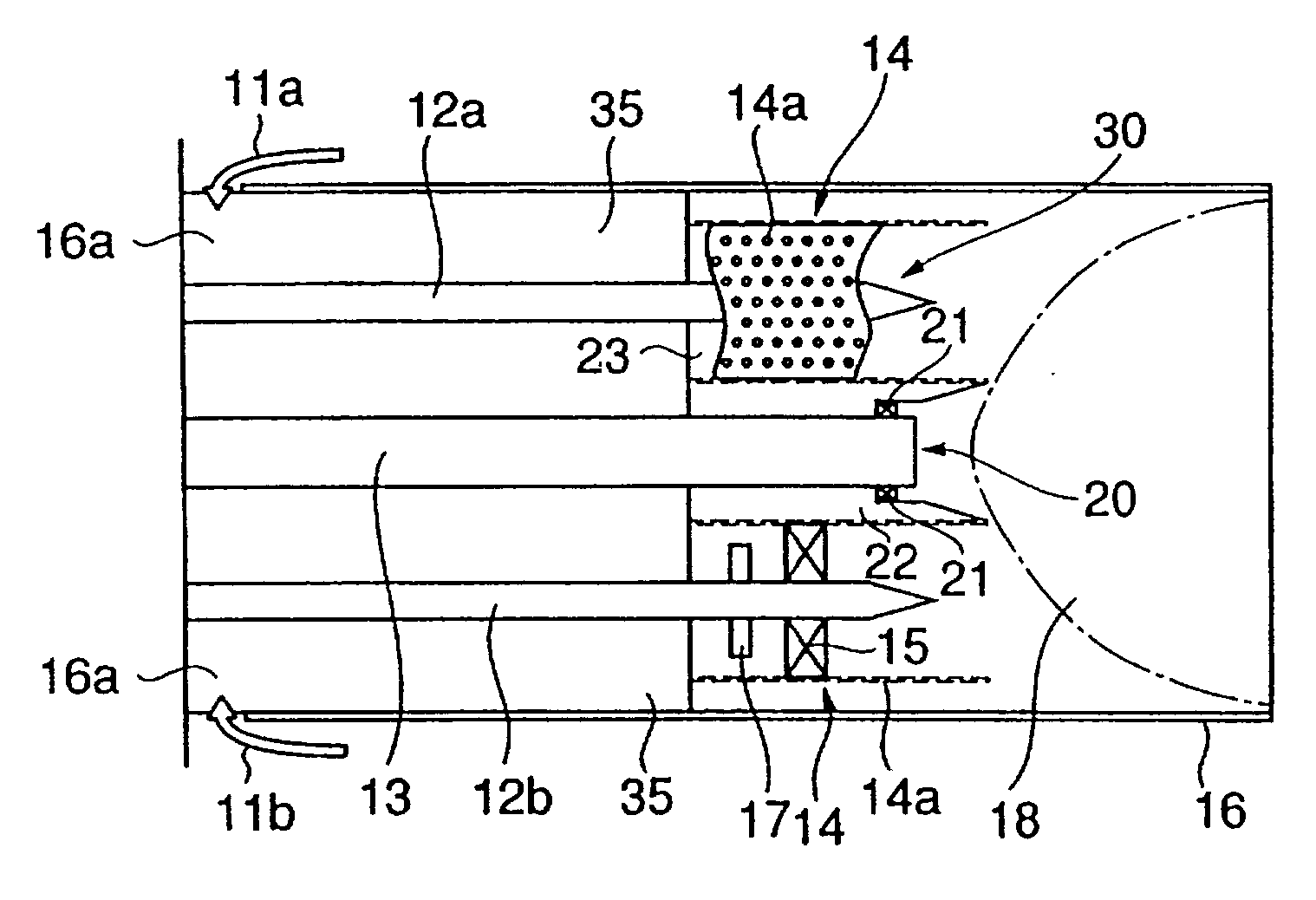
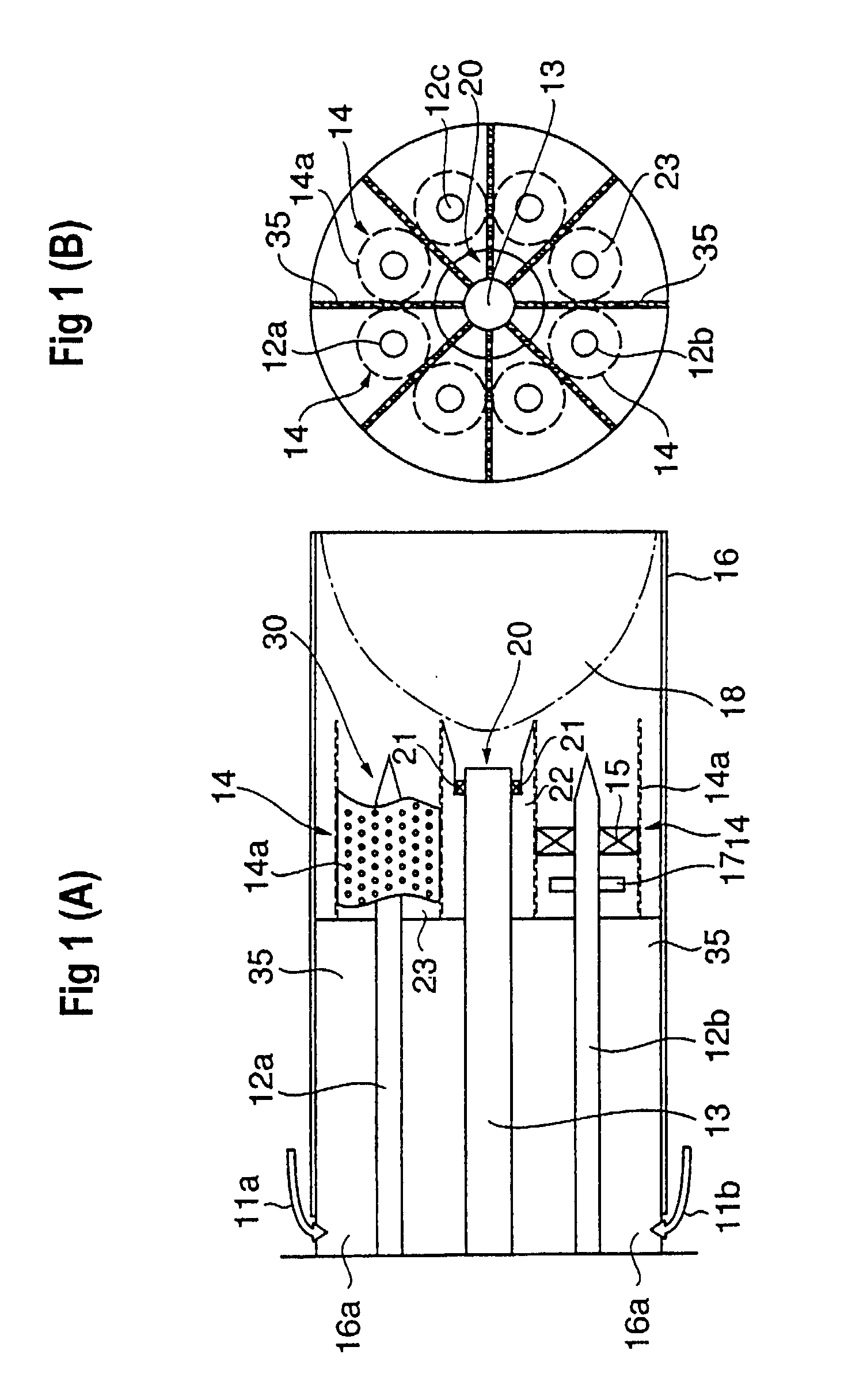
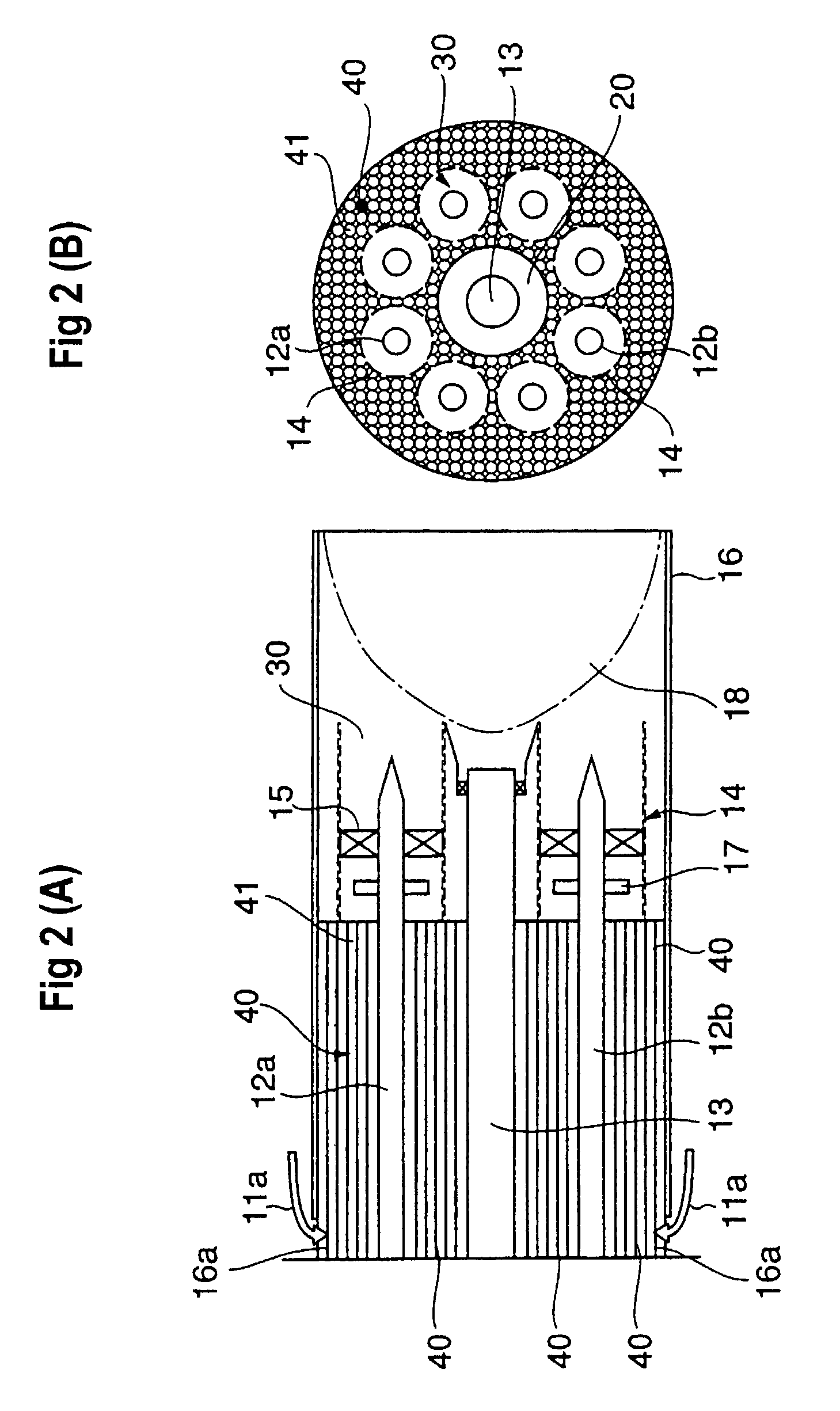
Air staged low-NOx burner
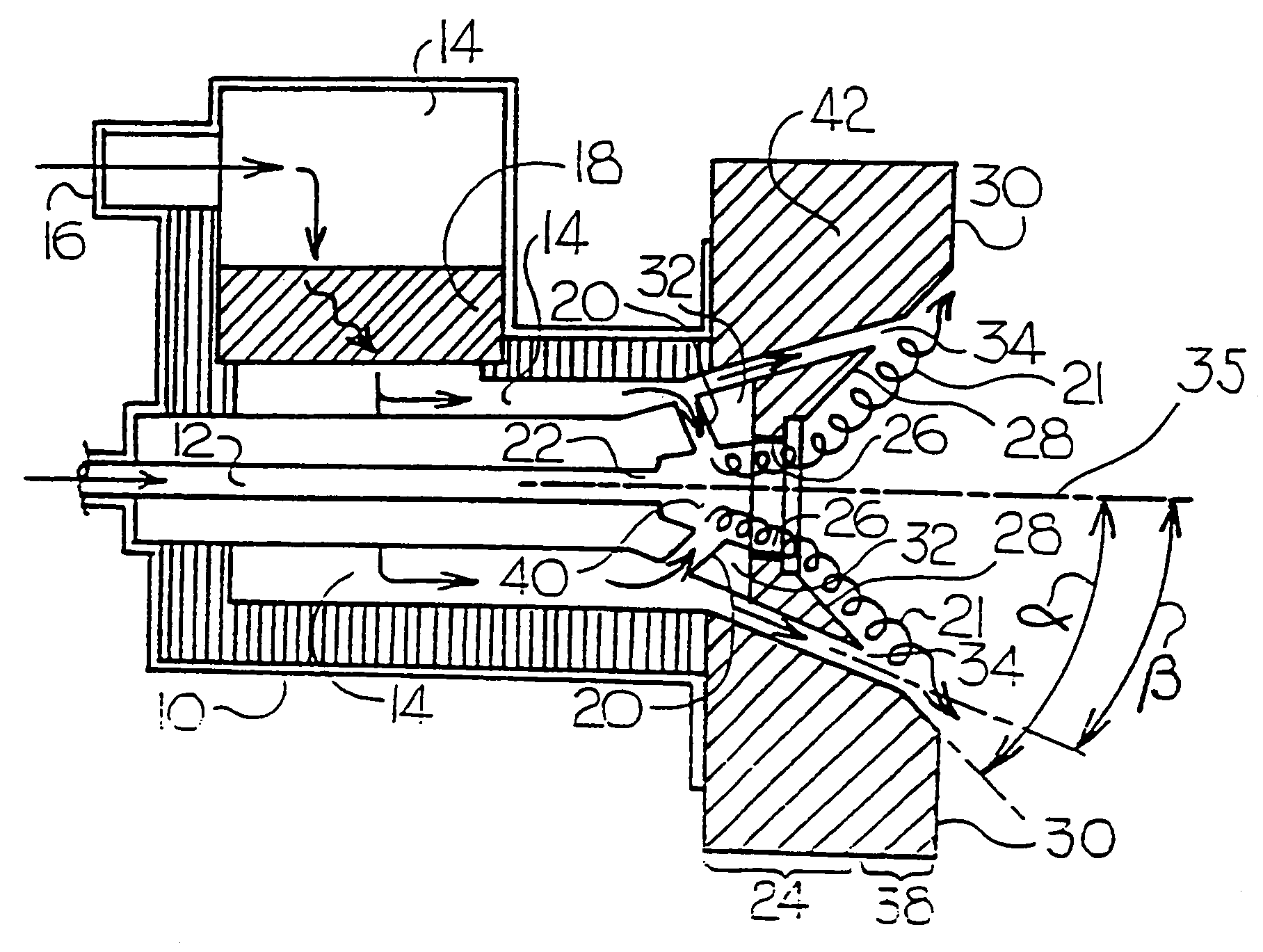
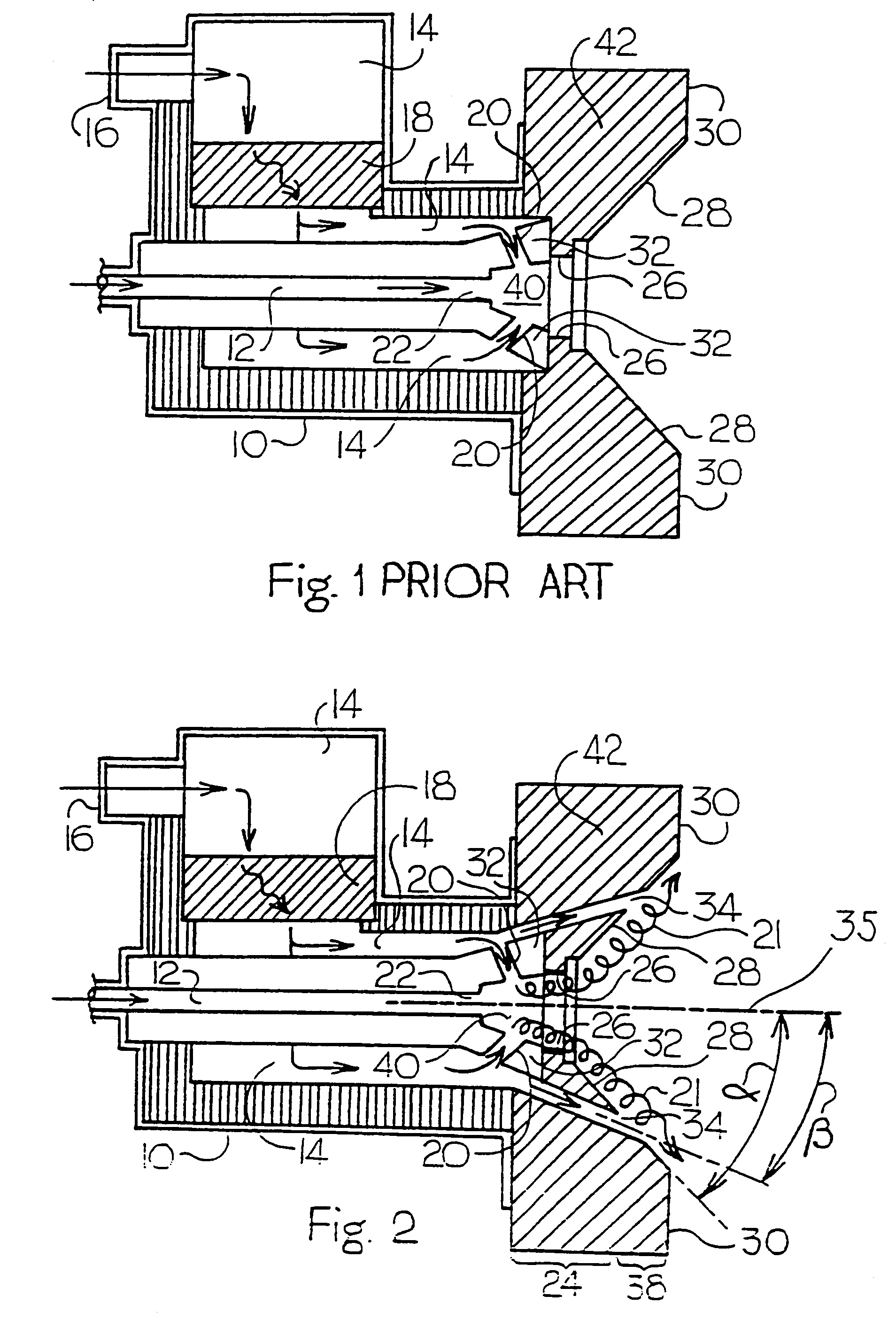
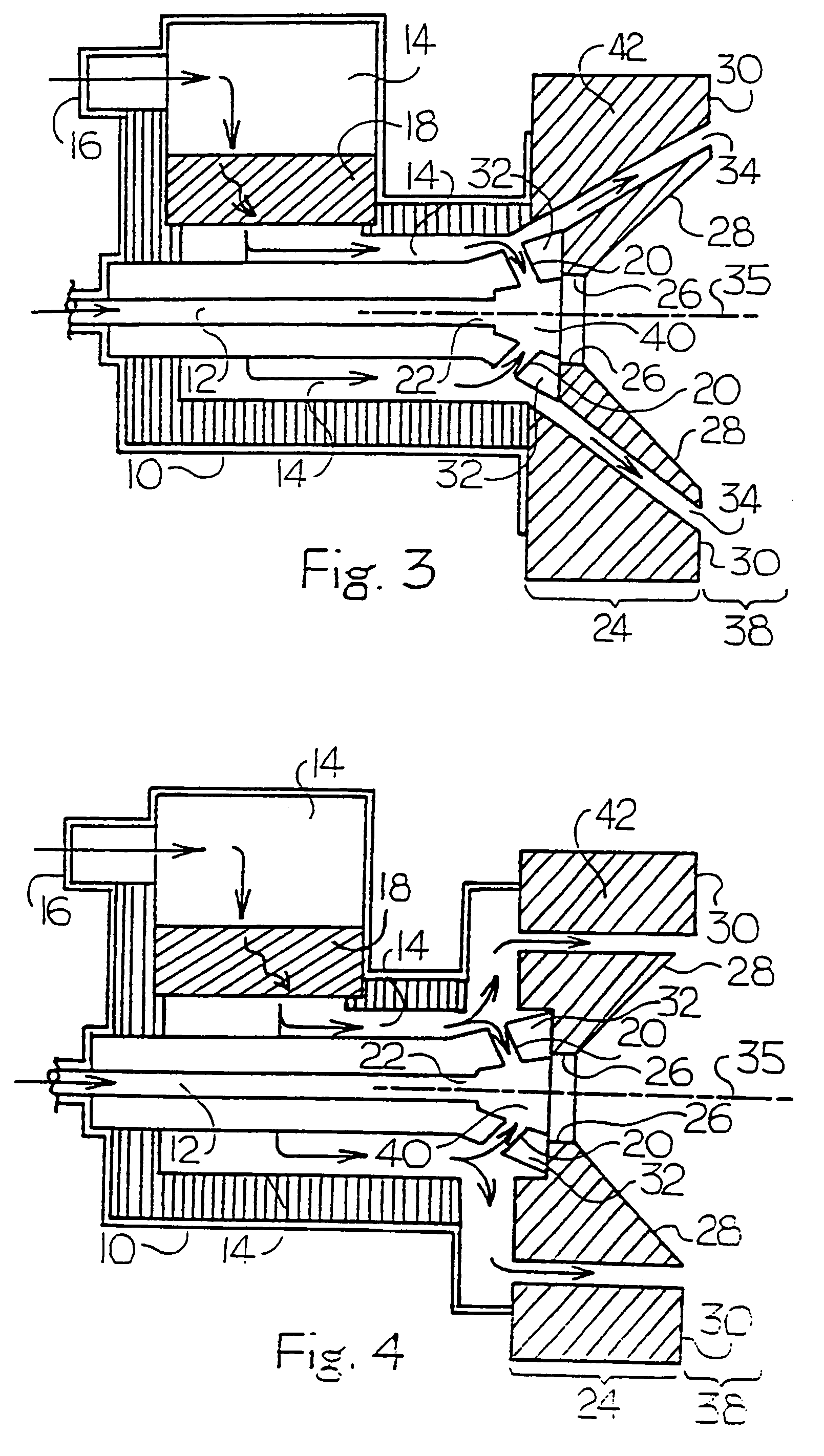
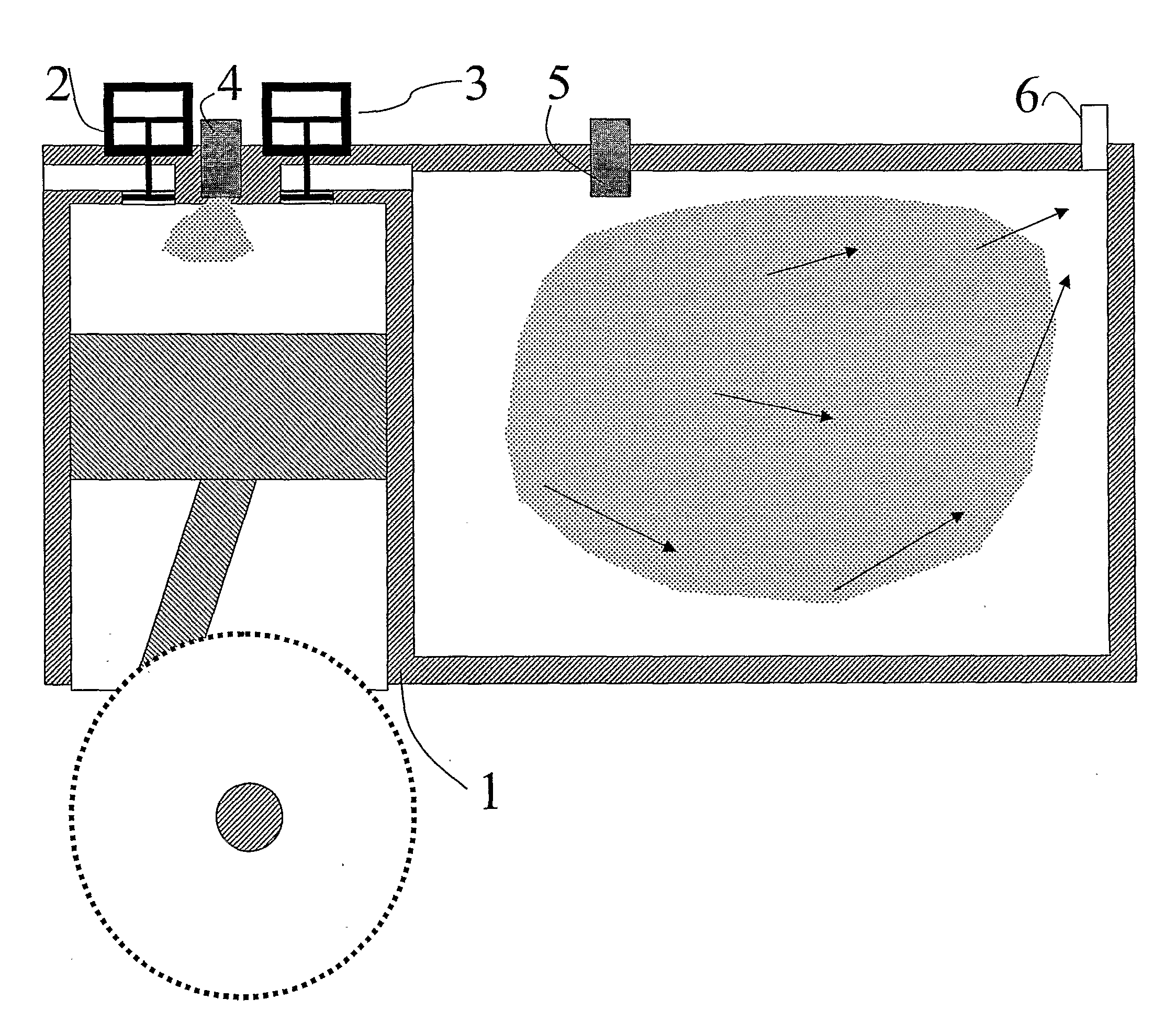
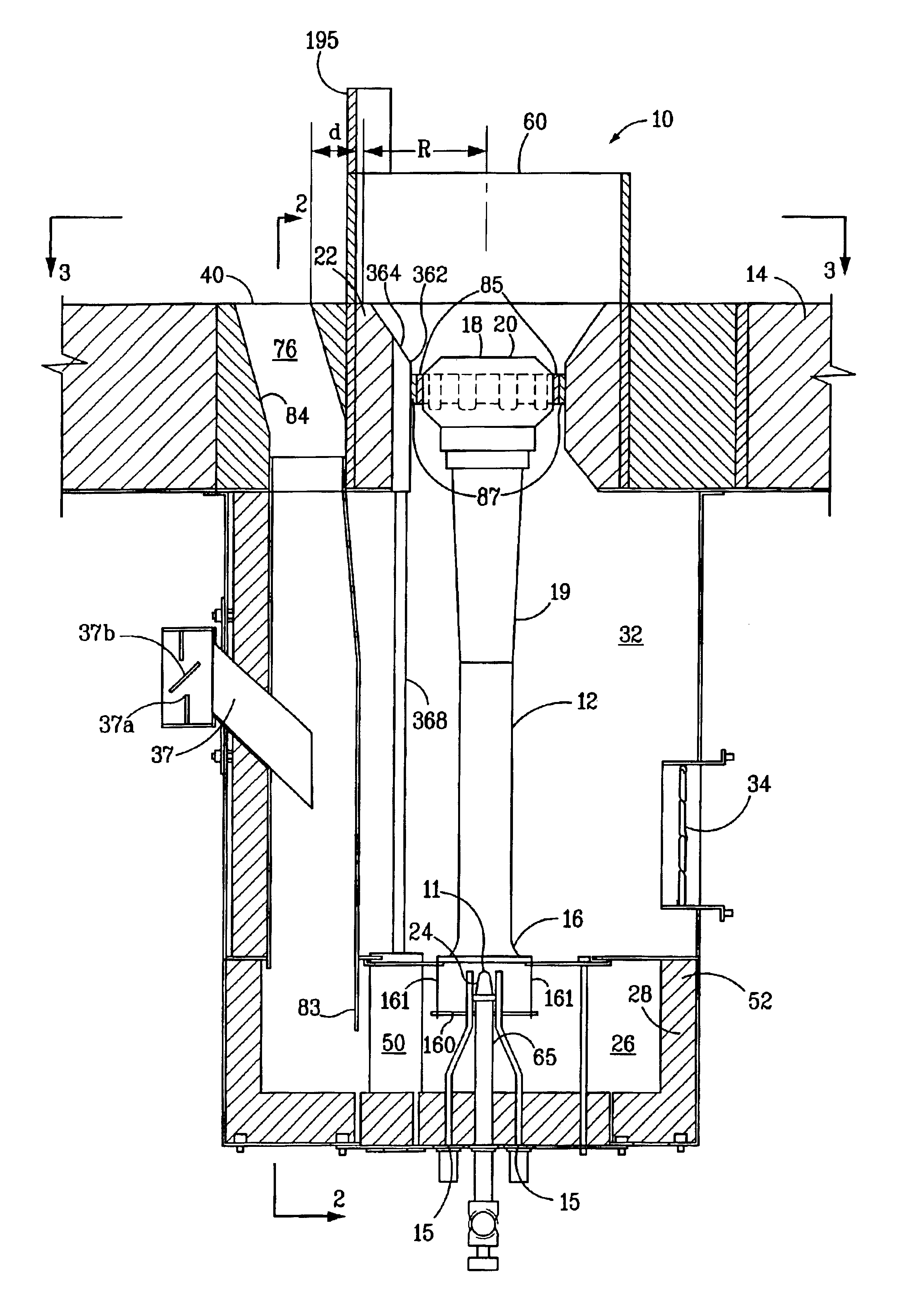
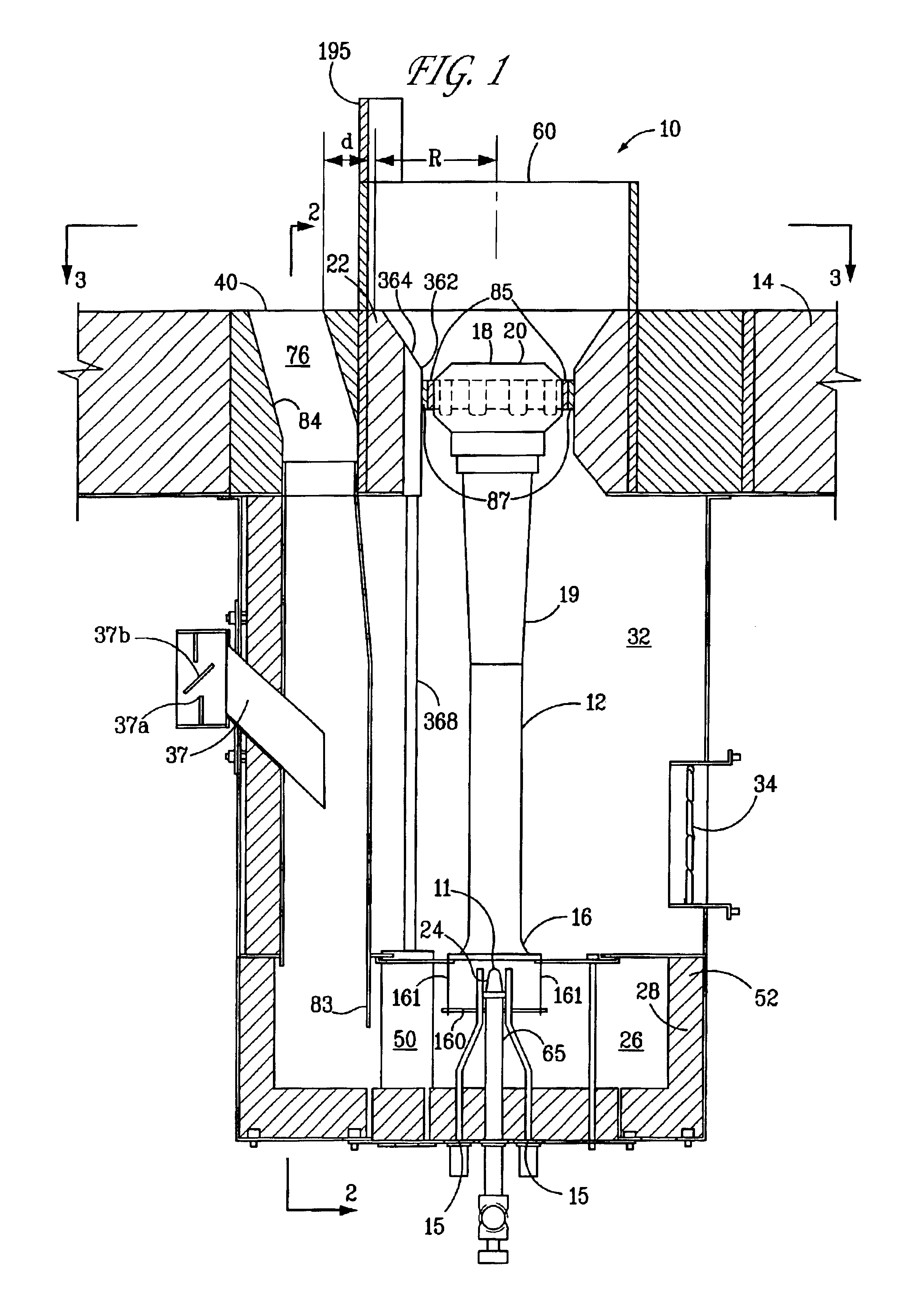
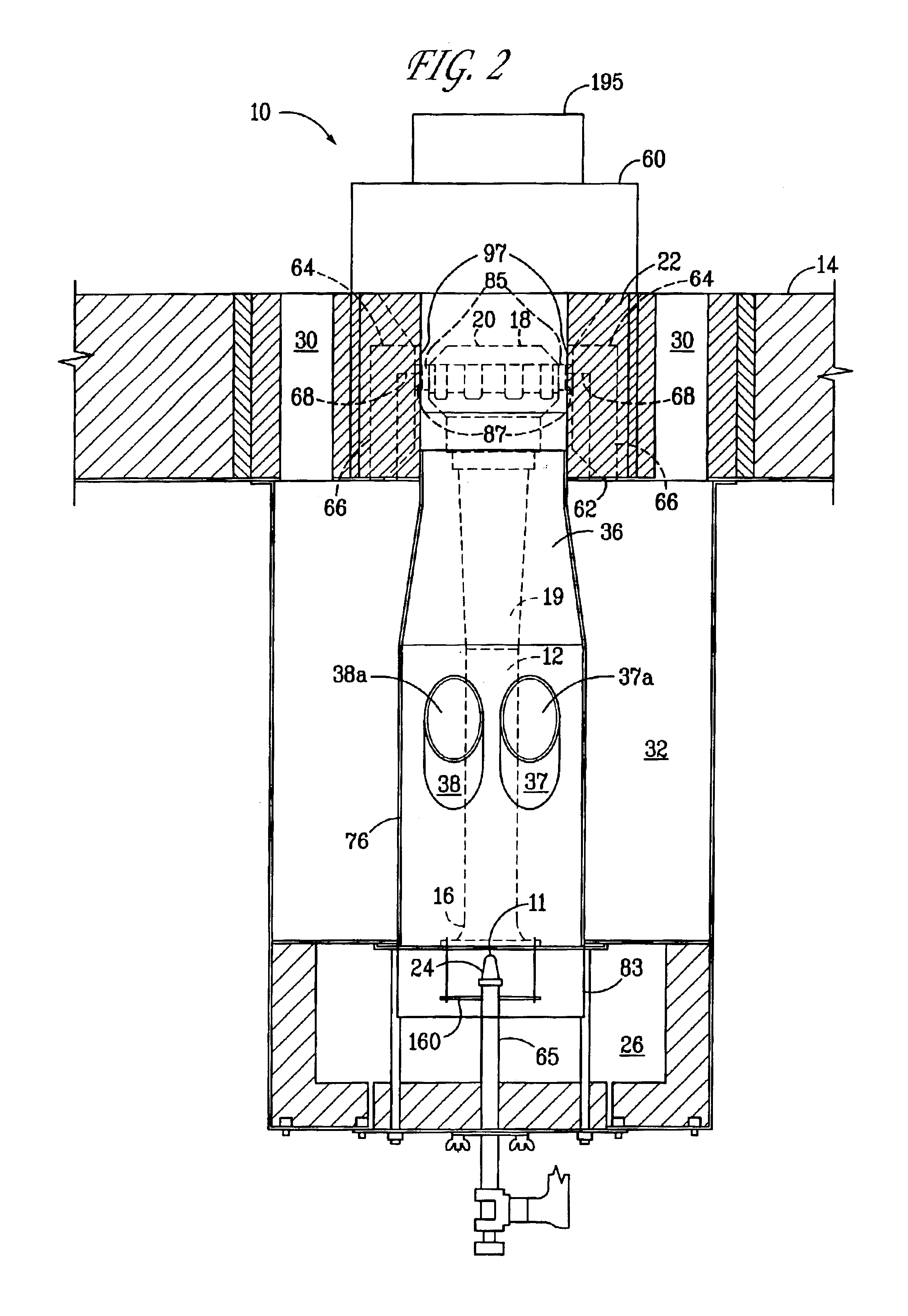
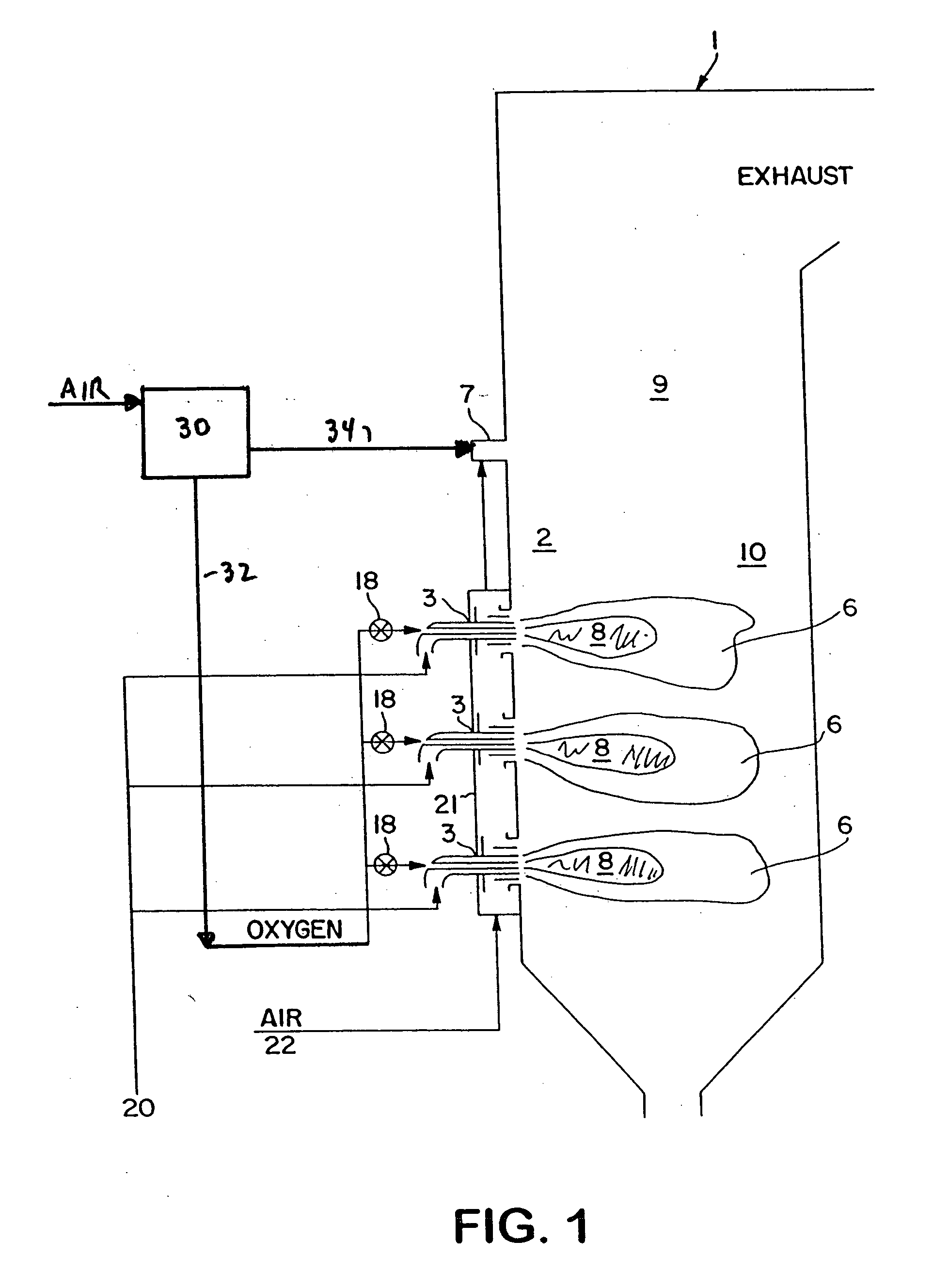
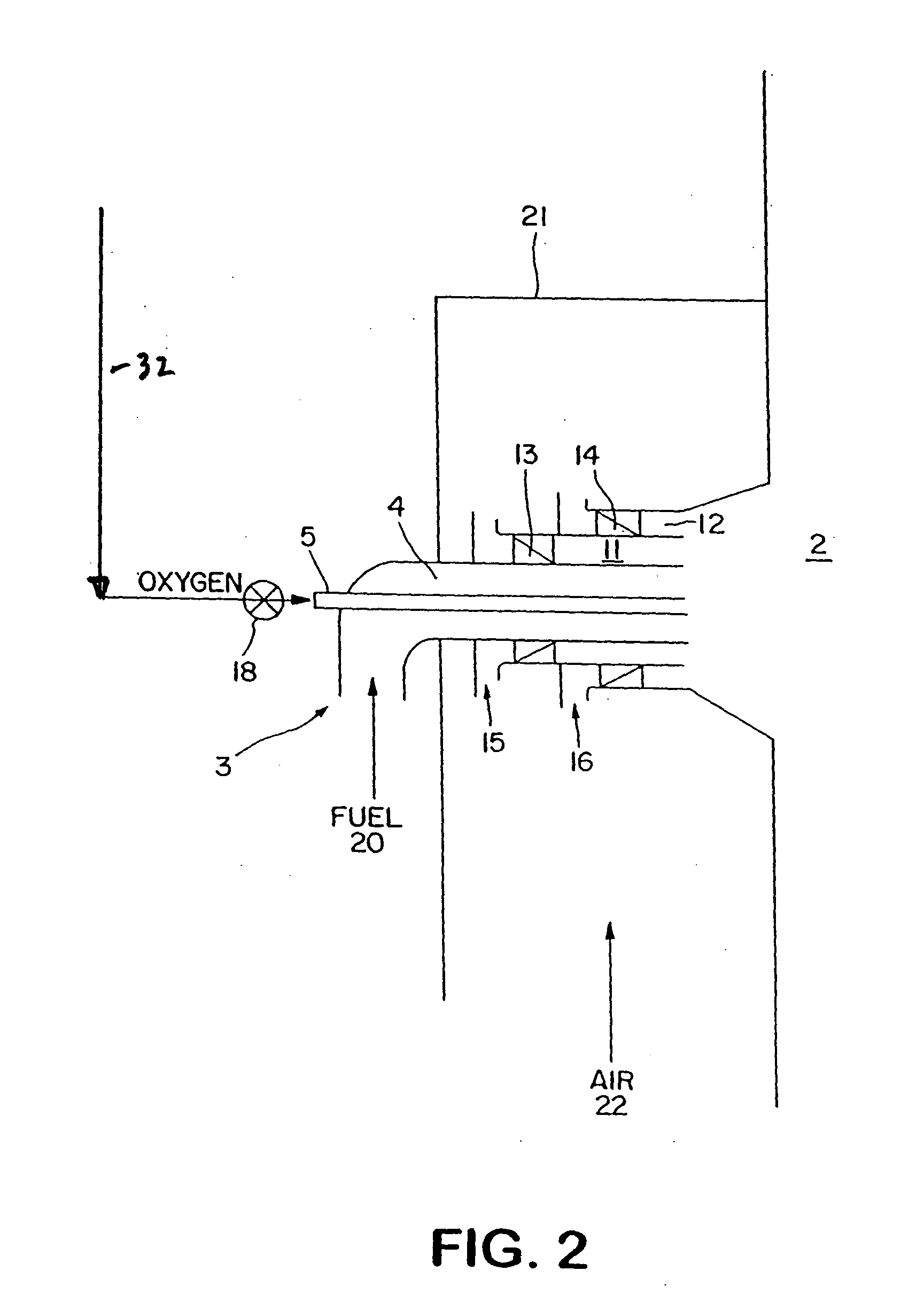
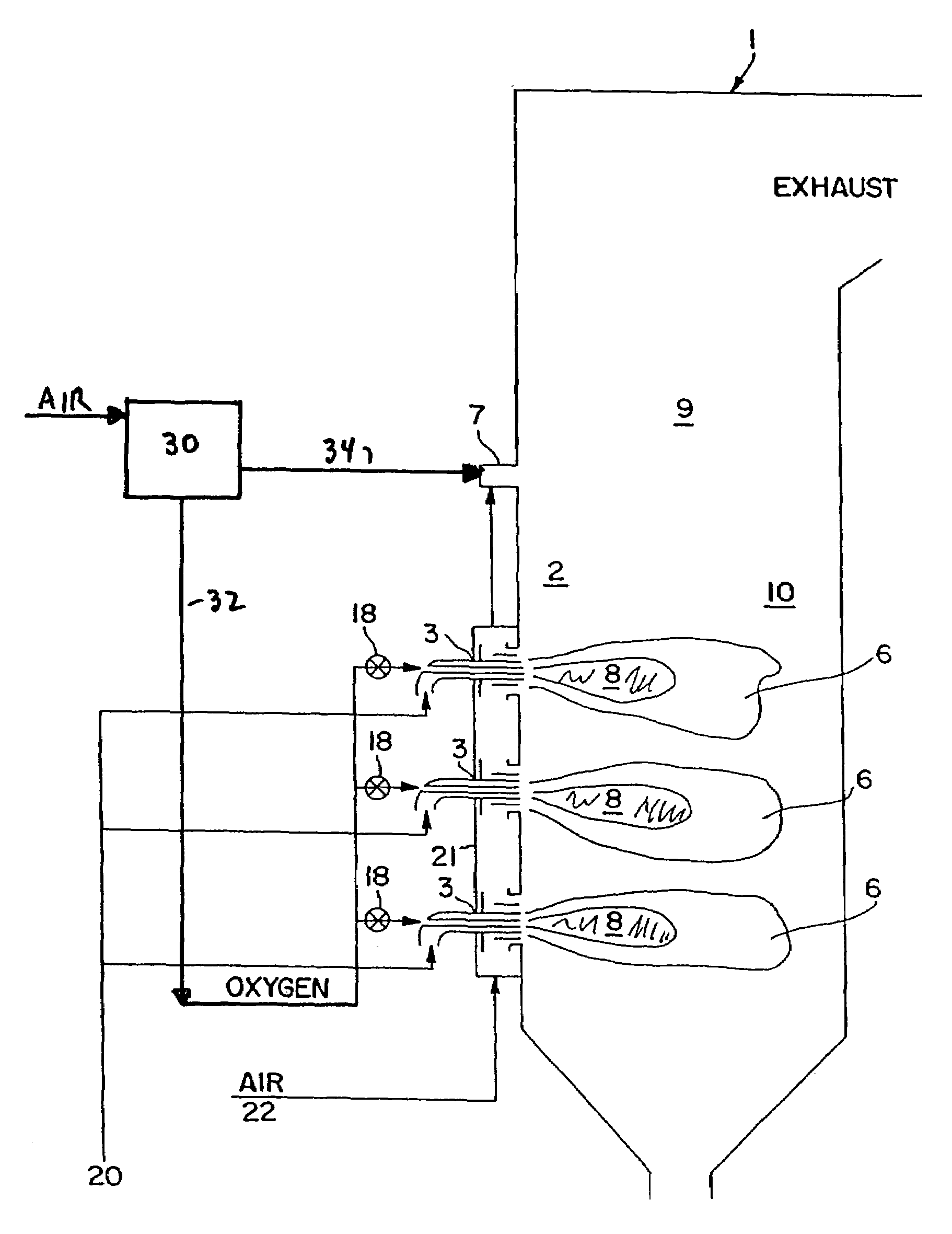
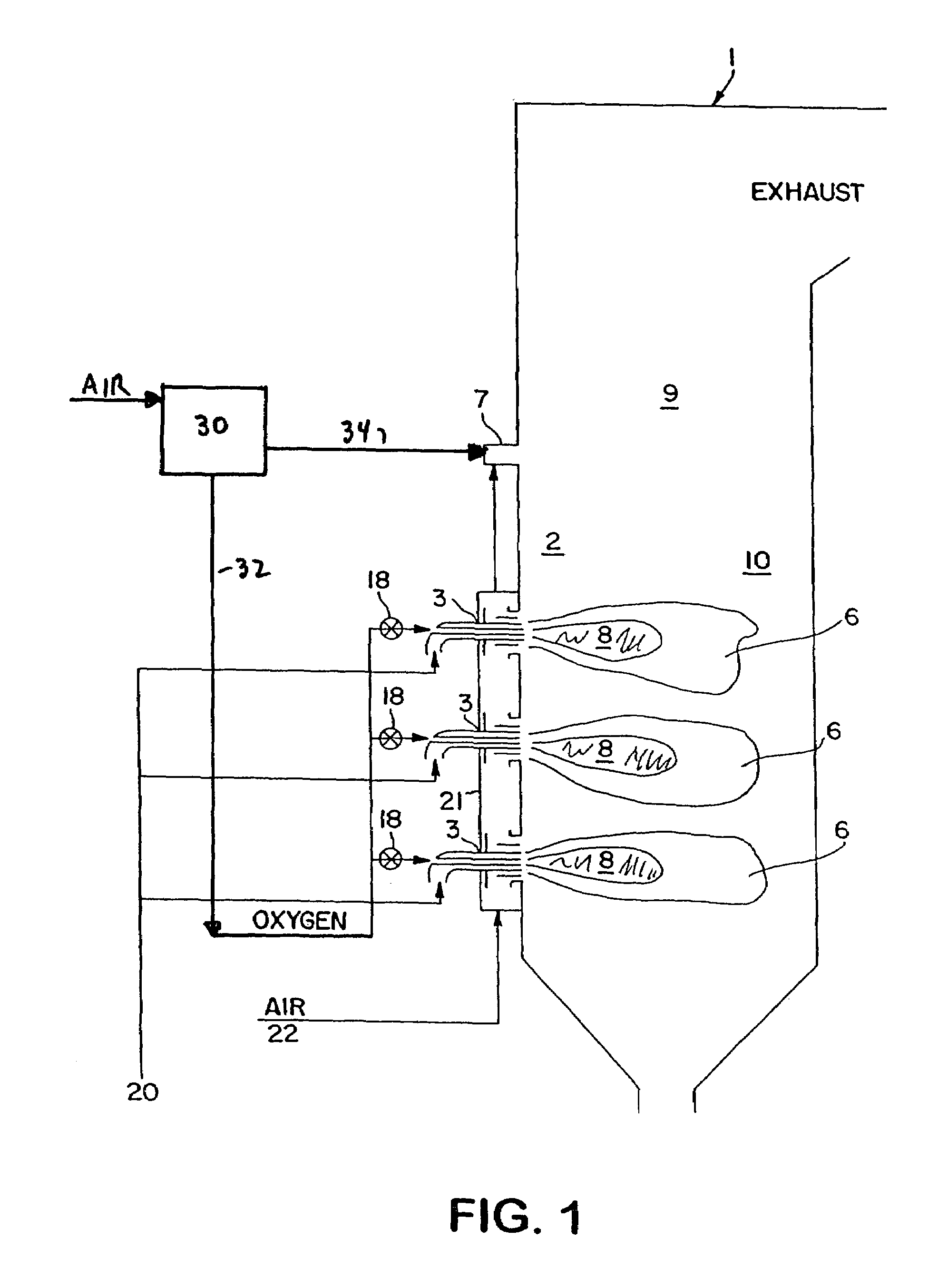
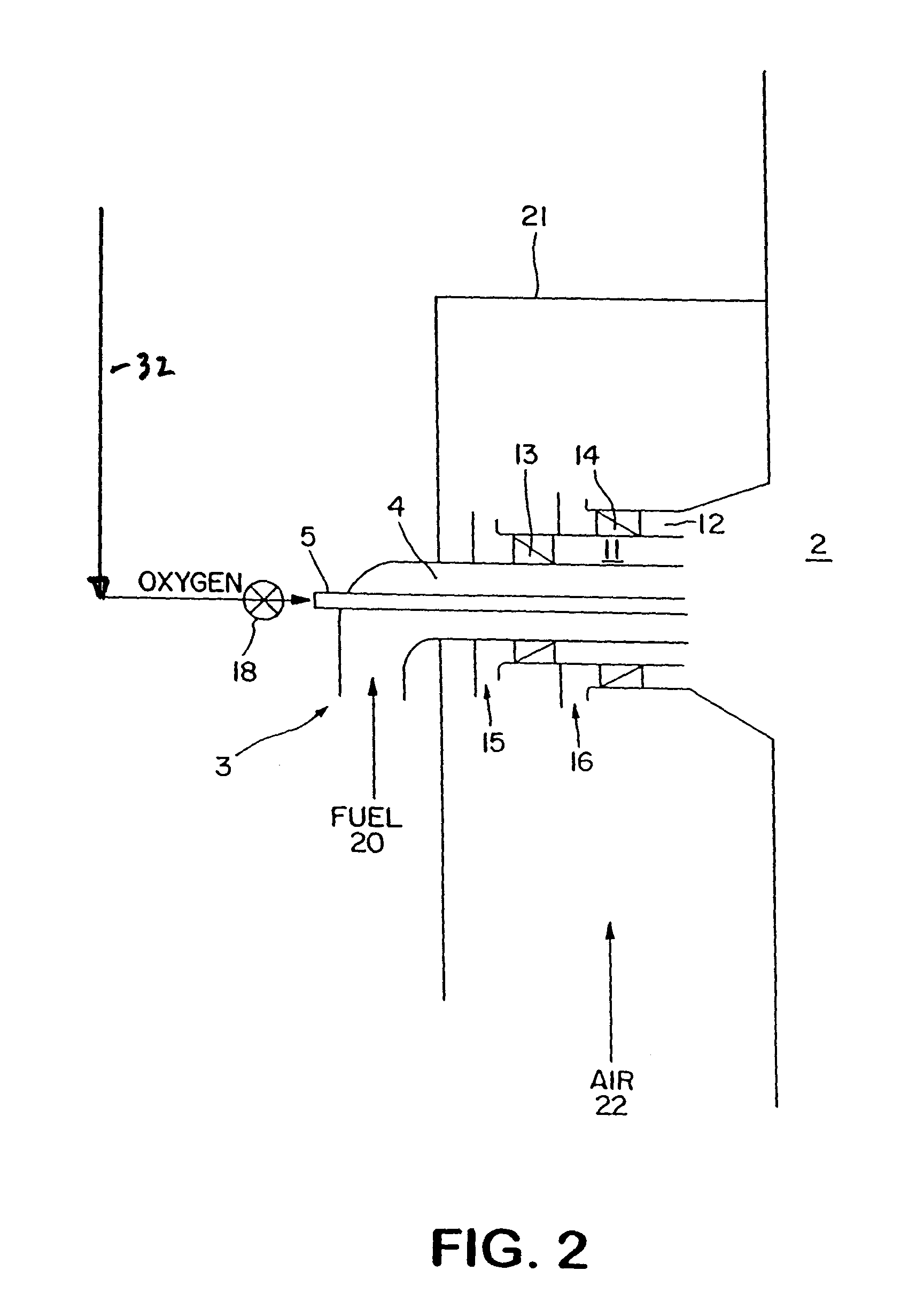
InactiveUS7175423B1Reduce the production of nitrogen oxidesReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelCombustorEngineering
An apparatus and method for using staged air combustion. The apparatus includes a burner body (10) secured to a port block (42), and a fuel passageway (12) extending through the burner body (10), terminating in a fuel nozzle (22), which injects fuel into the burner throat (40). Primary air jets (20) are configured to inject primary air into a primary combustion region (24), which is normally in the burner throat (40). A dish with a dish surface (28) is connected to the burner throat (40); the dish surface (28) extending in a divergent angle with respect to a burner centerline (35). Secondary air jets (34) are connected to the air passageway (14) and extend through the port block (42). The secondary air jets (34) inject secondary air into a secondary combustion region (38), which may be at the dish surface (28) or the hot face (30) of the burner.
Owner:BLOOM ENG
Multiple combustion mode engine using direct alcohol injection
ActiveUS7461628B2Improve efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlHomogeneous charge compression ignitionAlcohol
A method of operating an engine, comprising of performing homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion during a first operating condition, and performing spark ignition combustion during a second operating condition, where an amount of directly injected alcohol in at least one of said homogeneous charge compression ignition combustion and said spark ignition combustion is varied in response to at least an operating parameter.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
Method and a system for control of a device for compression
InactiveUS20070151528A1Work lessImprove efficiencyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesSteam pressureCombustion chamber
A method of compressing a medium in the combustion chamber of a combustion engine, wherein a liquid spray is introduced into the compression chamber during a compression stroke, the liquid is pressurized and heated before introduction into the compression chamber to such a degree that at least a part of the droplets of the spray explode spontaneously upon entrance in the compression chamber. The pressurized liquid has a steam pressure that is above the pressure in the compression chamber, and the liquid has a temperature that exceeds the boiling point of the liquid for the temperature and the pressure that, at the moment of introduction, exists in the compression chamber, and the heat being water. The liquid is heated to such an extent that, at the moment of introduction, it has a temperature that is below the temperature of the medium at the moment of introduction of the liquid.
Owner:CARGINE ENG AB
Burner with low NOx emissions
InactiveUS6877980B2Reduce the production of nitrogen oxidesDecrease in burner stabilityDomestic stoves or rangesBurner ignition devicsEngineeringCombustor
A burner for use in furnaces such as in steam cracking. The burner includes a primary air chamber; a burner tube having an upstream end, a downstream end and a venturi intermediate said upstream and downstream ends, said venturi including a throat portion having substantially constant internal cross-sectional dimensions such that the ratio of the length to maximum internal cross-sectional dimension of said throat portion is at least 3; a burner tip mounted on the downstream end of said burner tube adjacent a first opening in the furnace, so that combustion of the fuel takes place downstream of said burner tip; and a fuel orifice located adjacent the upstream end of said burner tube, for introducing fuel into said burner tube.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
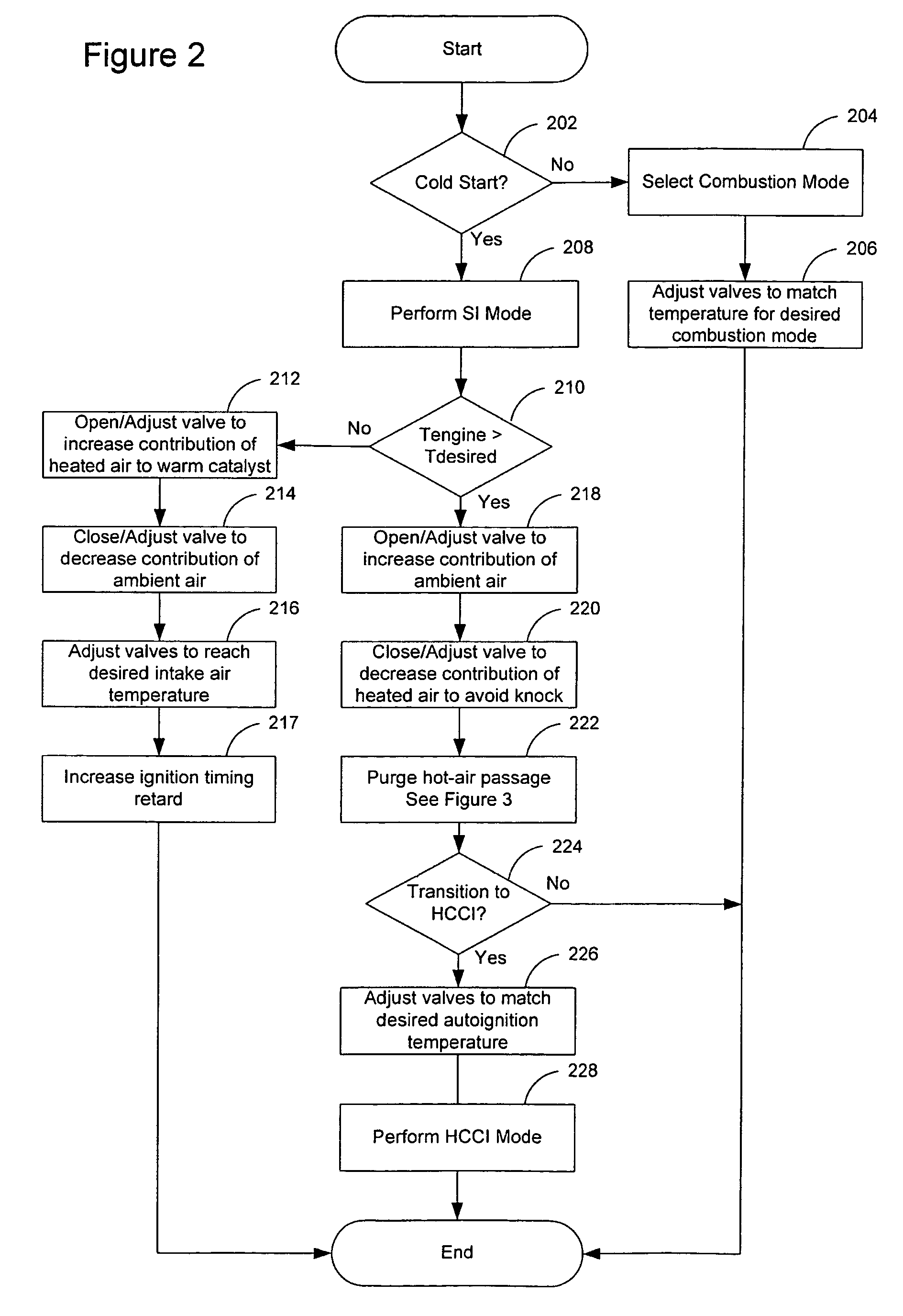
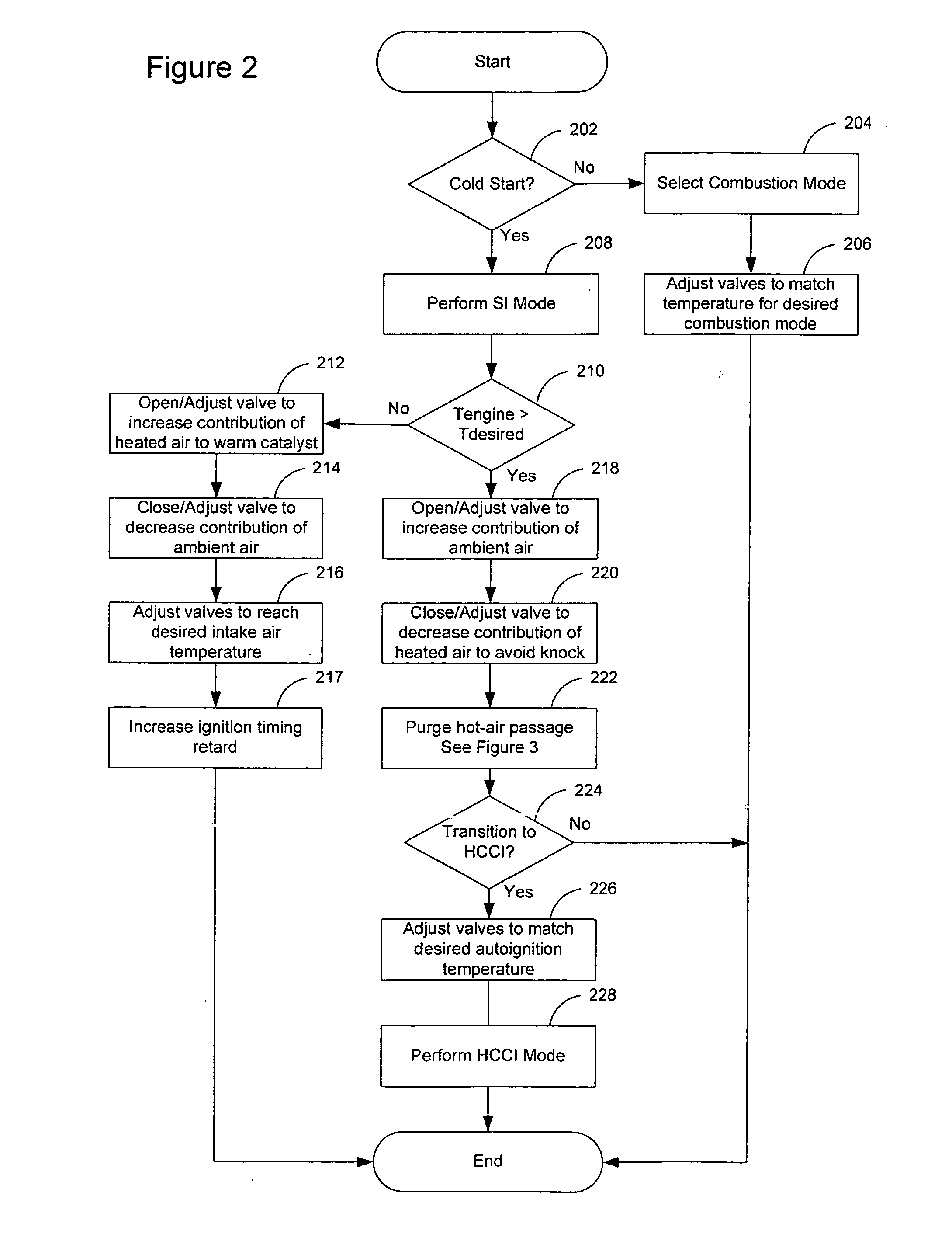
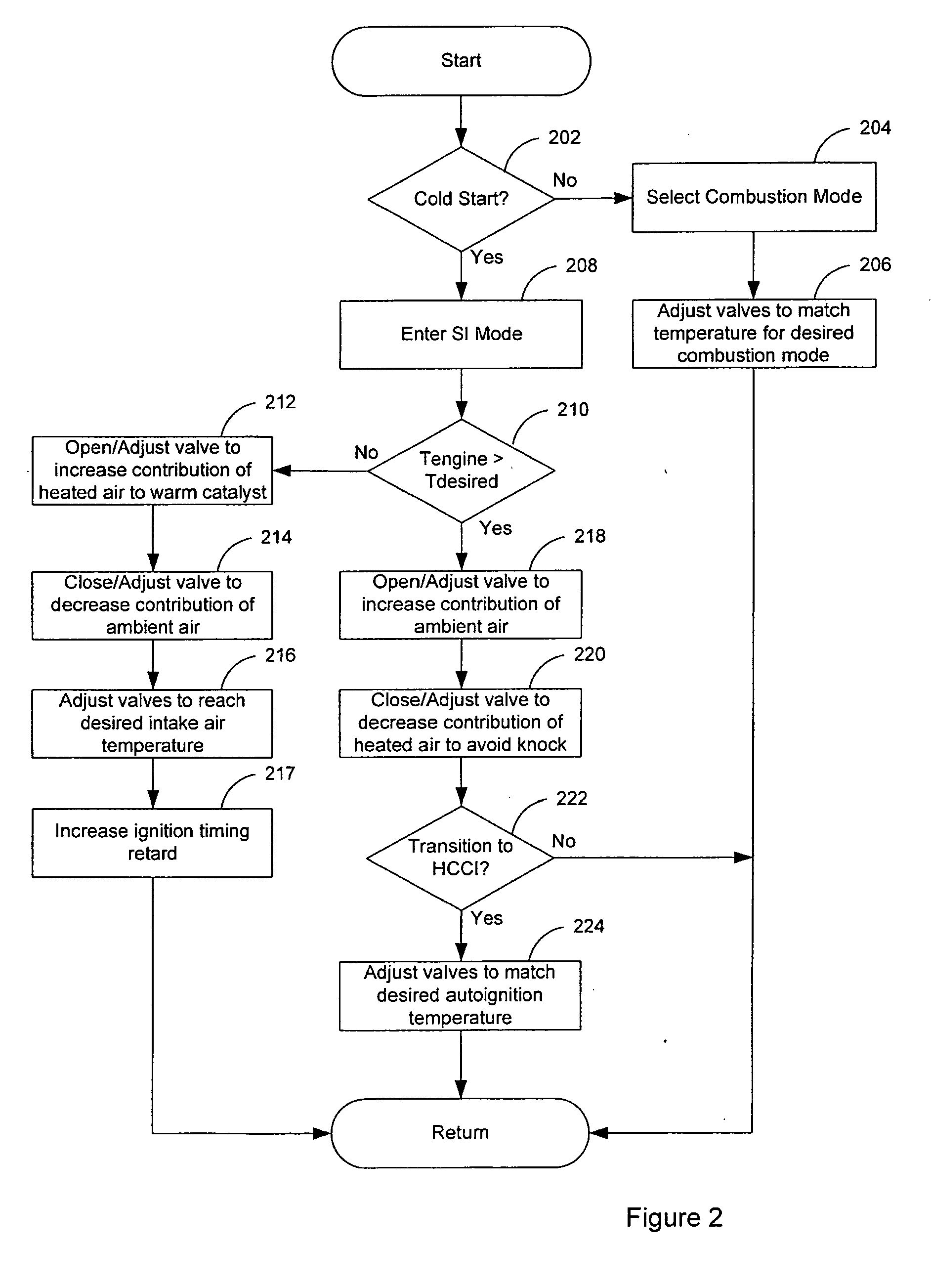
Method of operating an internal combustion engine
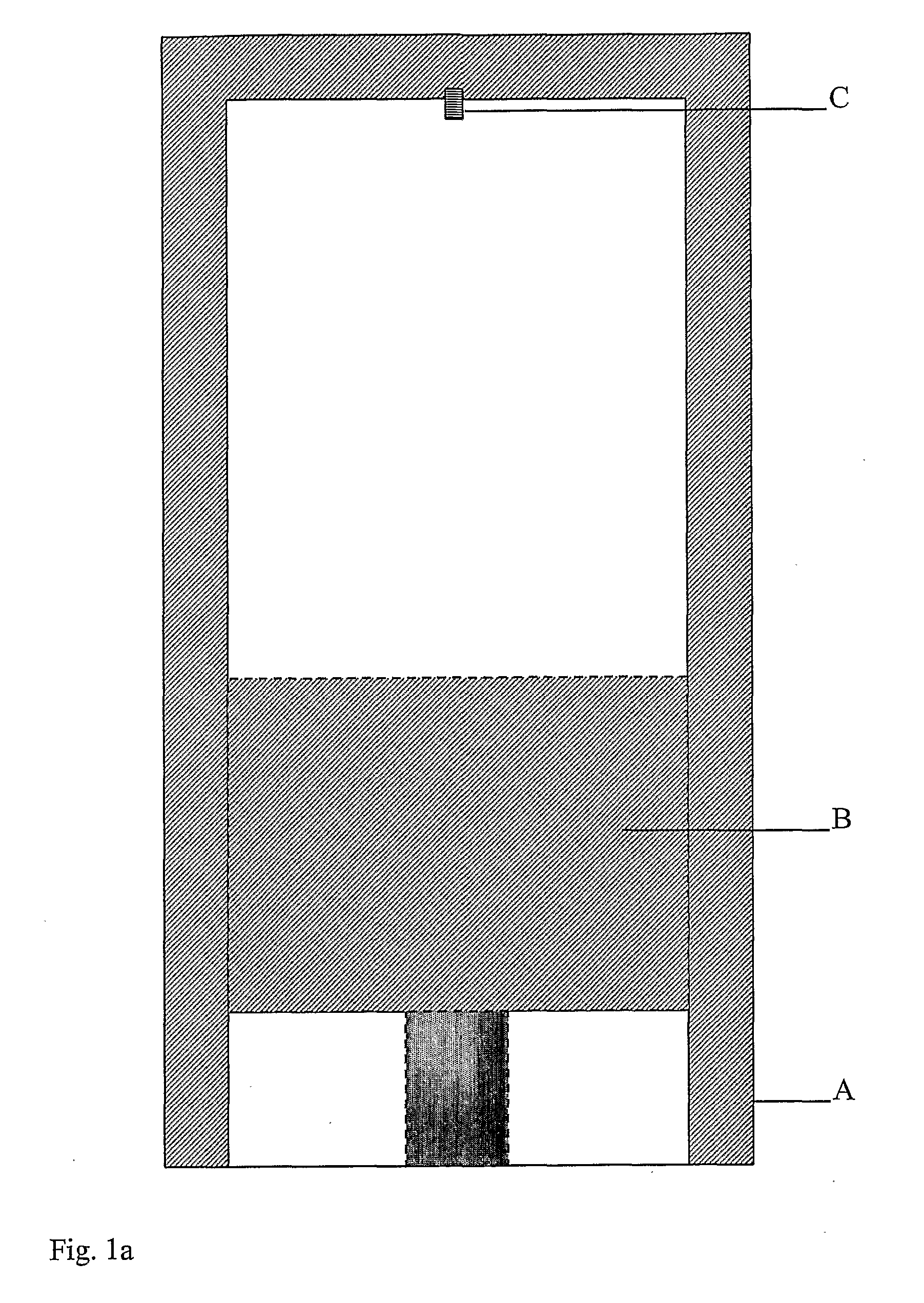
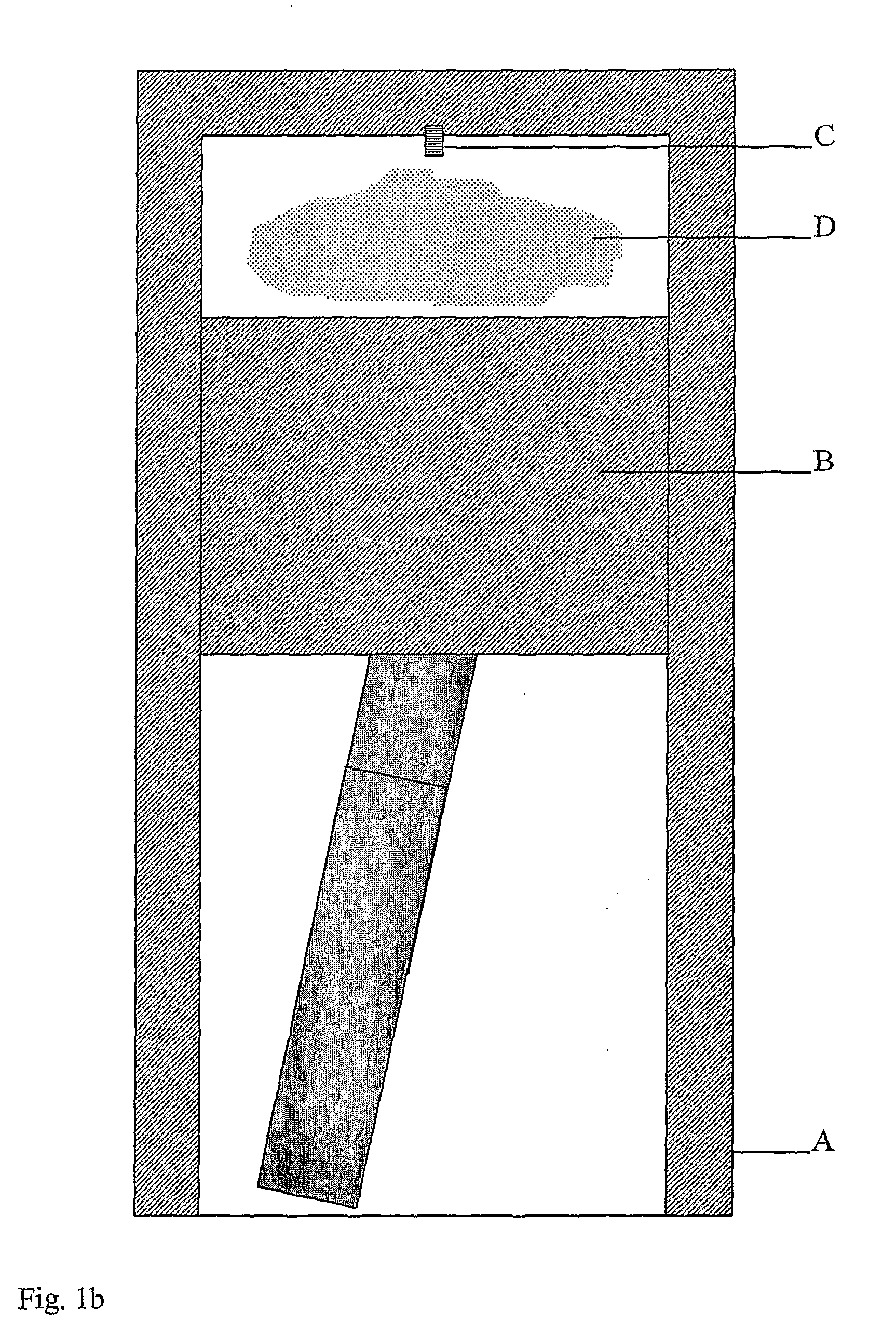
ActiveUS20080178836A1Overcome disadvantagesAccelerate emissionsValve arrangementsElectrical controlExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
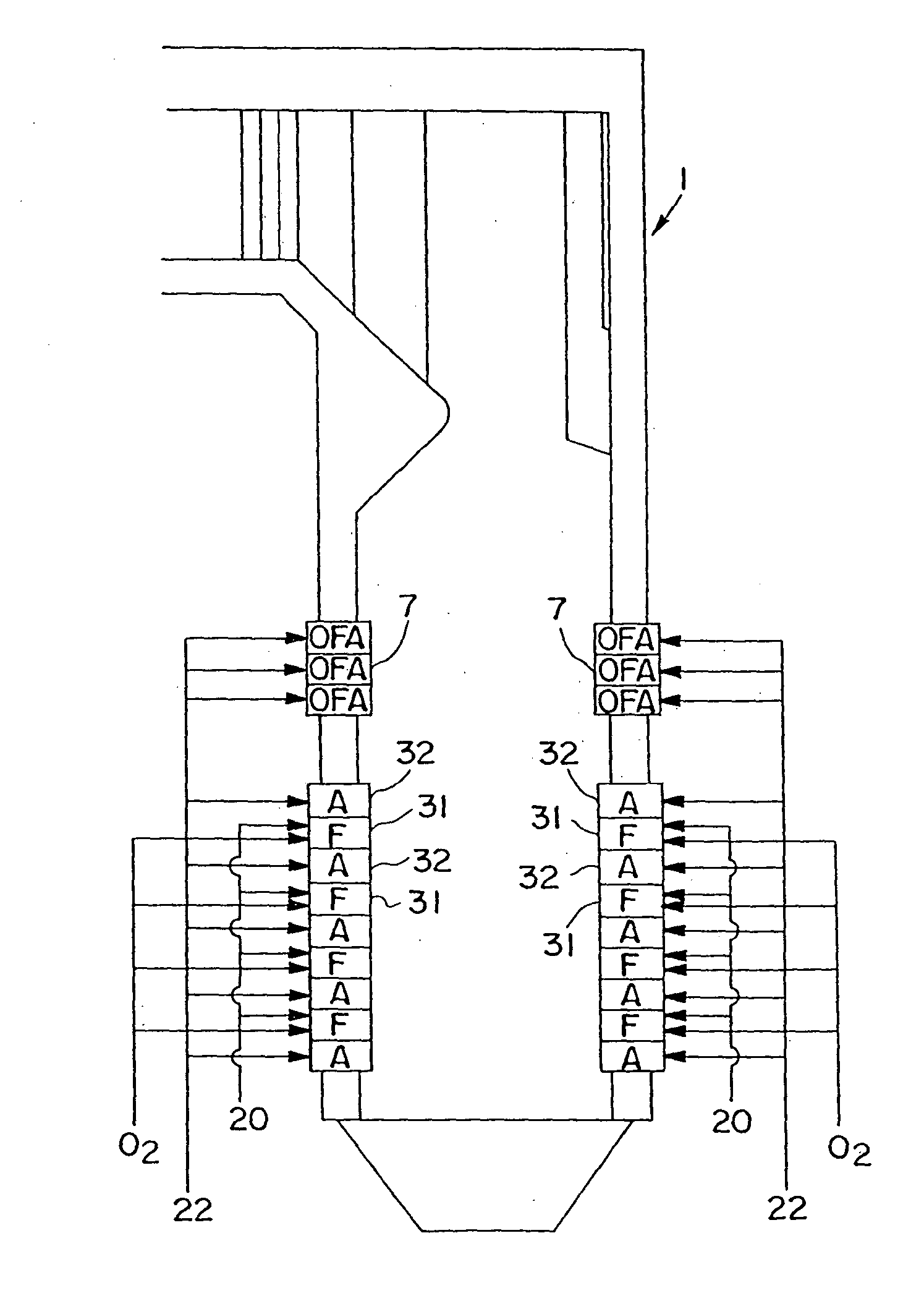
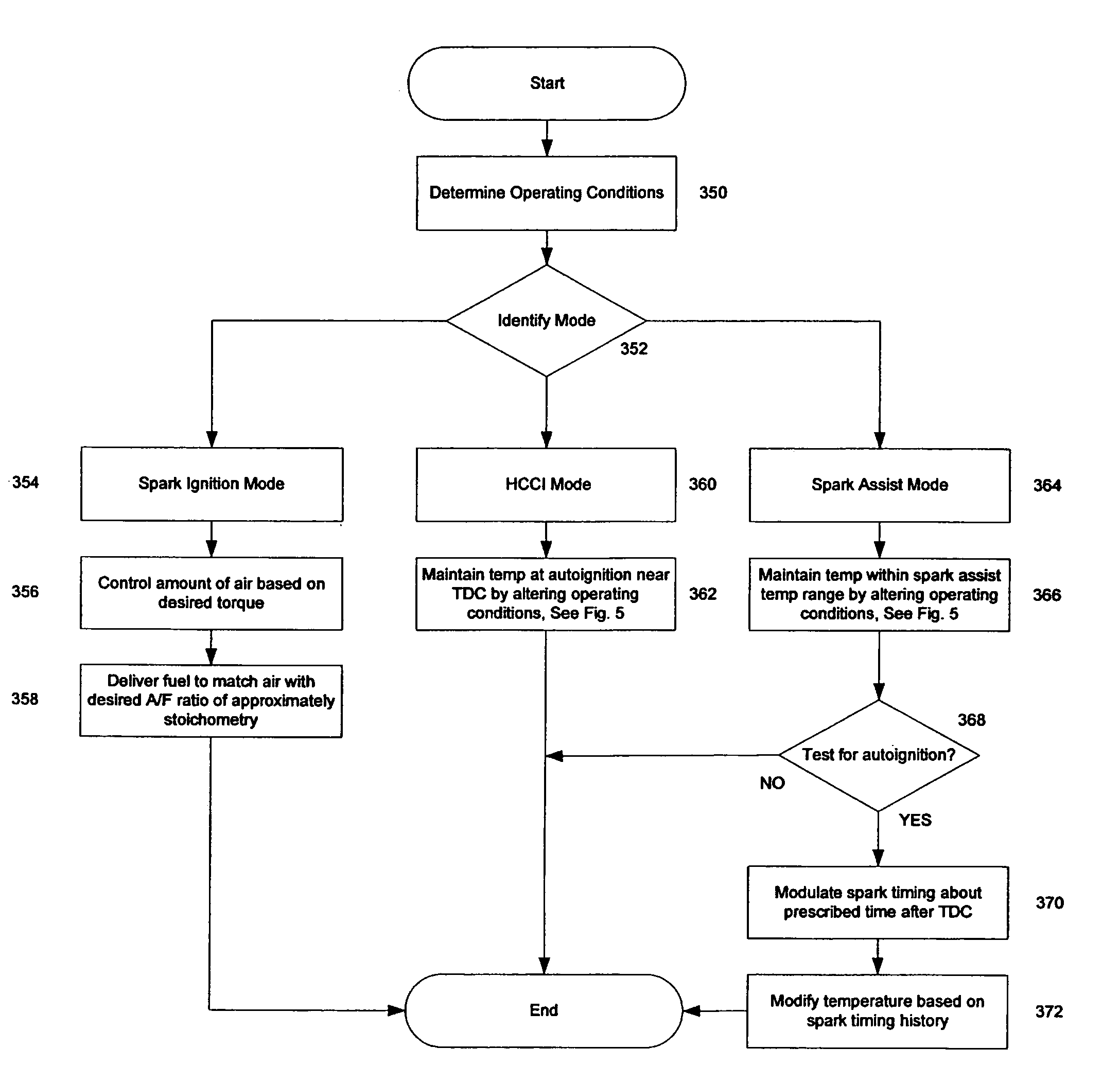
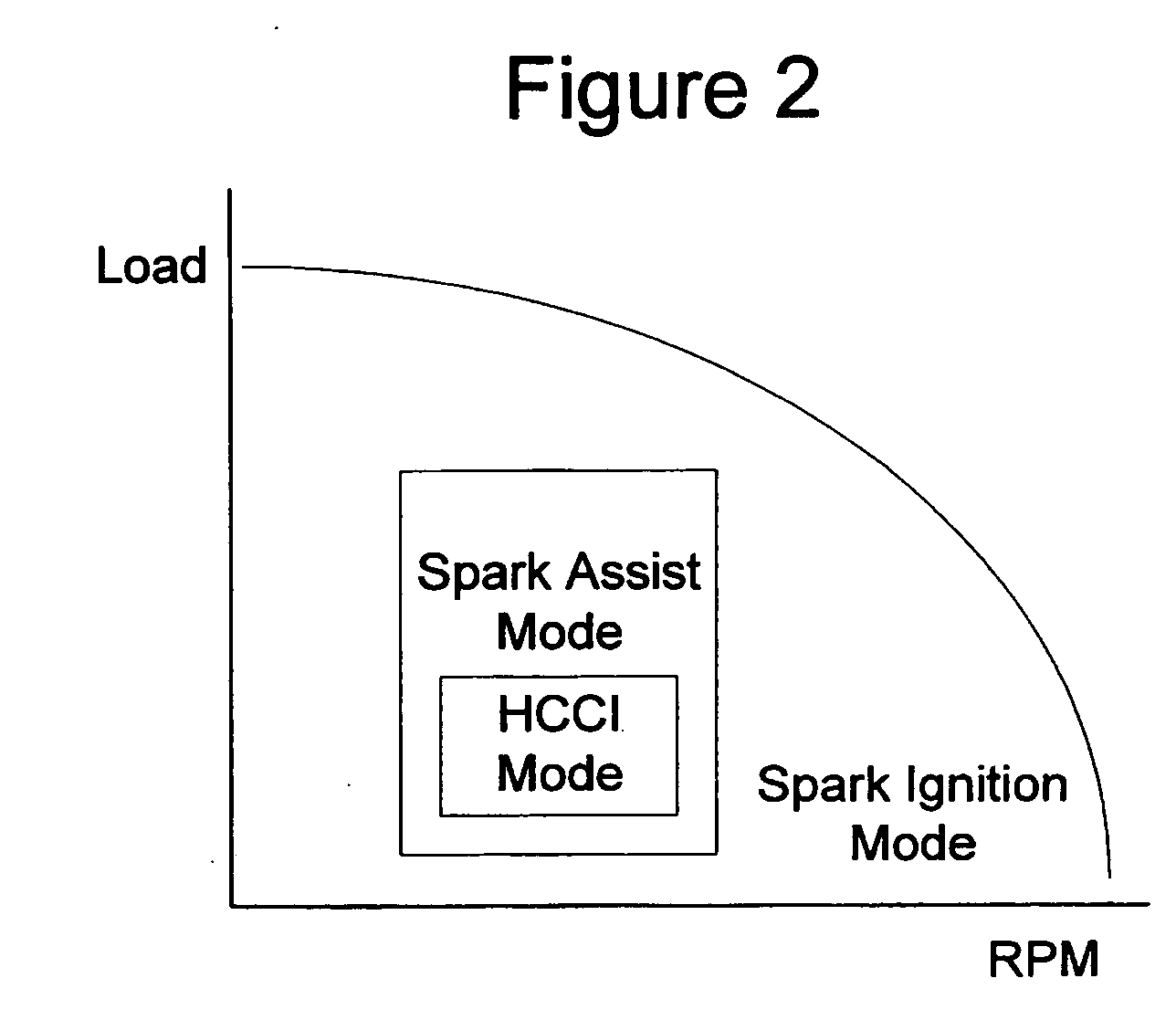
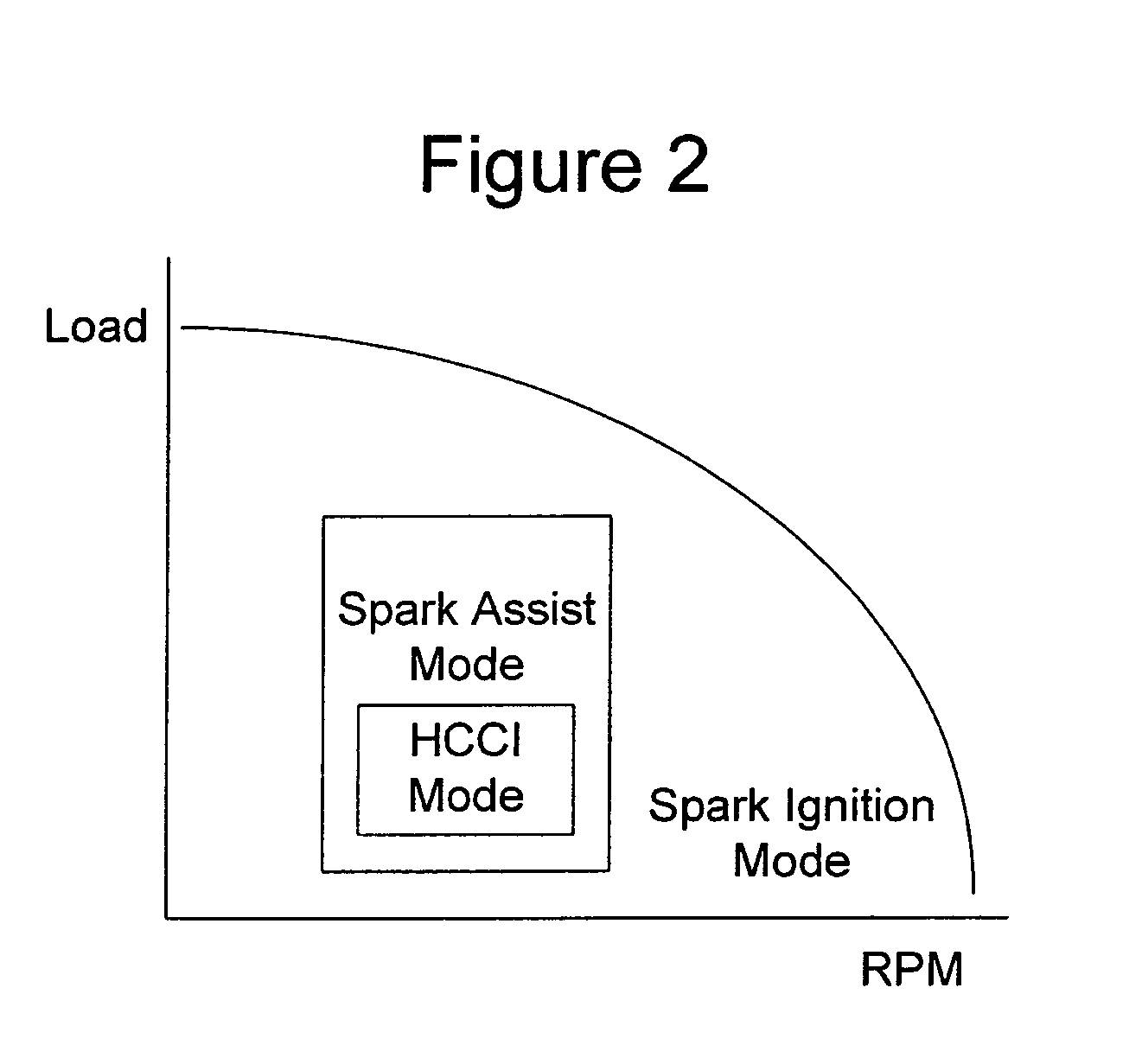
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston and a spark plug, comprising during a first mode, bringing the temperature of the combustion chamber to auto-ignition temperature by adjusting engine operating conditions and producing auto-ignition in said combustion chamber without requiring spark from said spark plug; and during a second mode, bringing the temperature of the combustion chamber close to auto-ignition temperature by adjusting engine operating conditions, forming a small cloud of stratified air-fuel mixture near said spark plug, igniting said fuel cloud by a spark form said spark plug, and then causing cylinder pressure to rise, thereby producing auto-ignition at other sites in said combustion chamber wherein said first mode is implemented in a first operating range and said second mode is implemented only in a second operating range where engine speed and load are lower than said first operating range.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
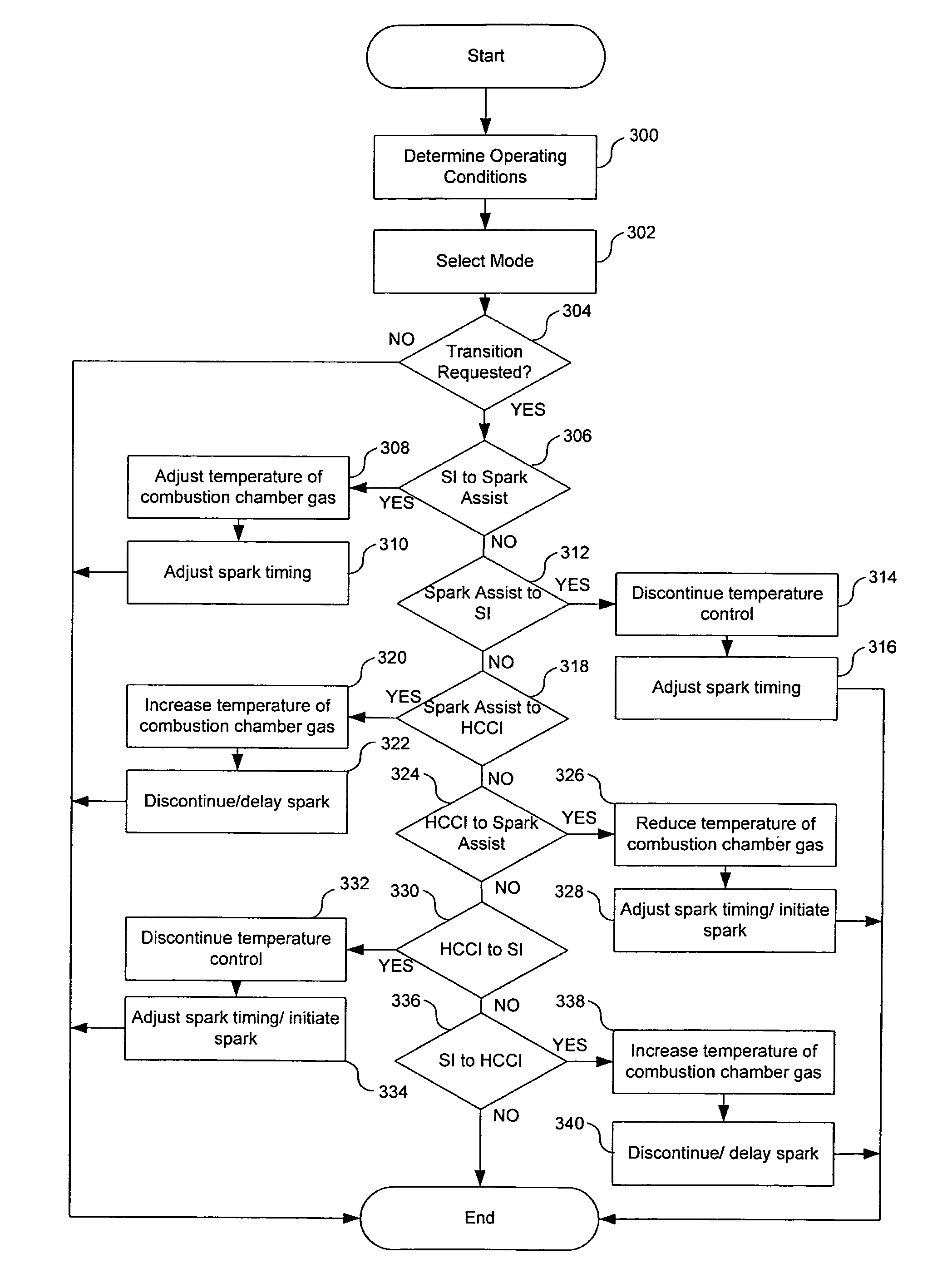
Transition strategy for engine operation with spark ignition and homogeneous charge compression ignition modes
ActiveUS7240659B2Improve efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionExternal combustion engine
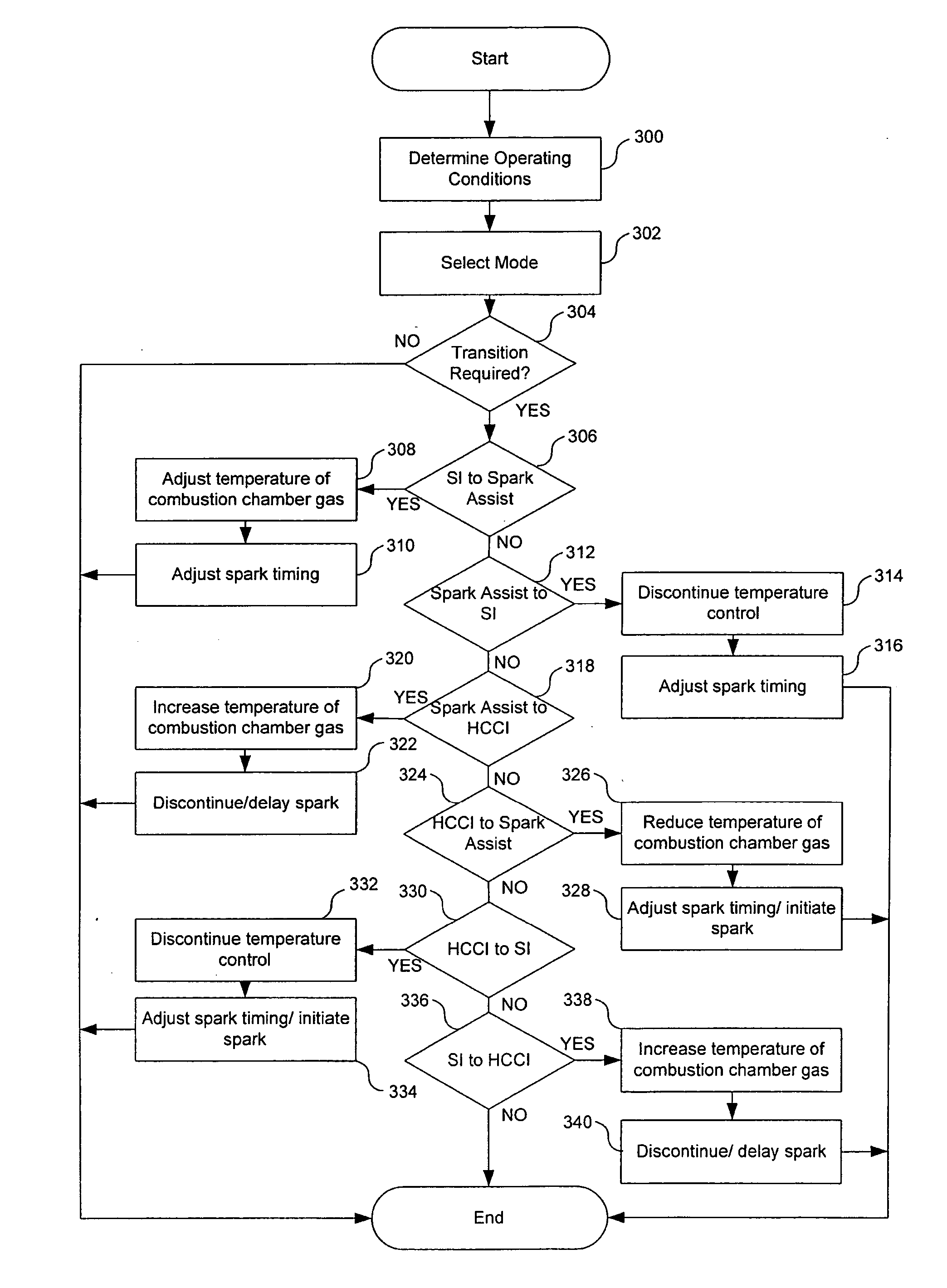
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston and a spark plug, when transitioning between spark ignition combustion and autoignition combustion, creating a first mixture of air and fuel, adjusting an operating condition of the engine so that said first mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber approaches, but does not achieve, the autoignition temperature, and performing a spark from the spark plug so that at least a portion of said first mixture combusts to raise a remaining portion of said first mixture to said autoignition temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
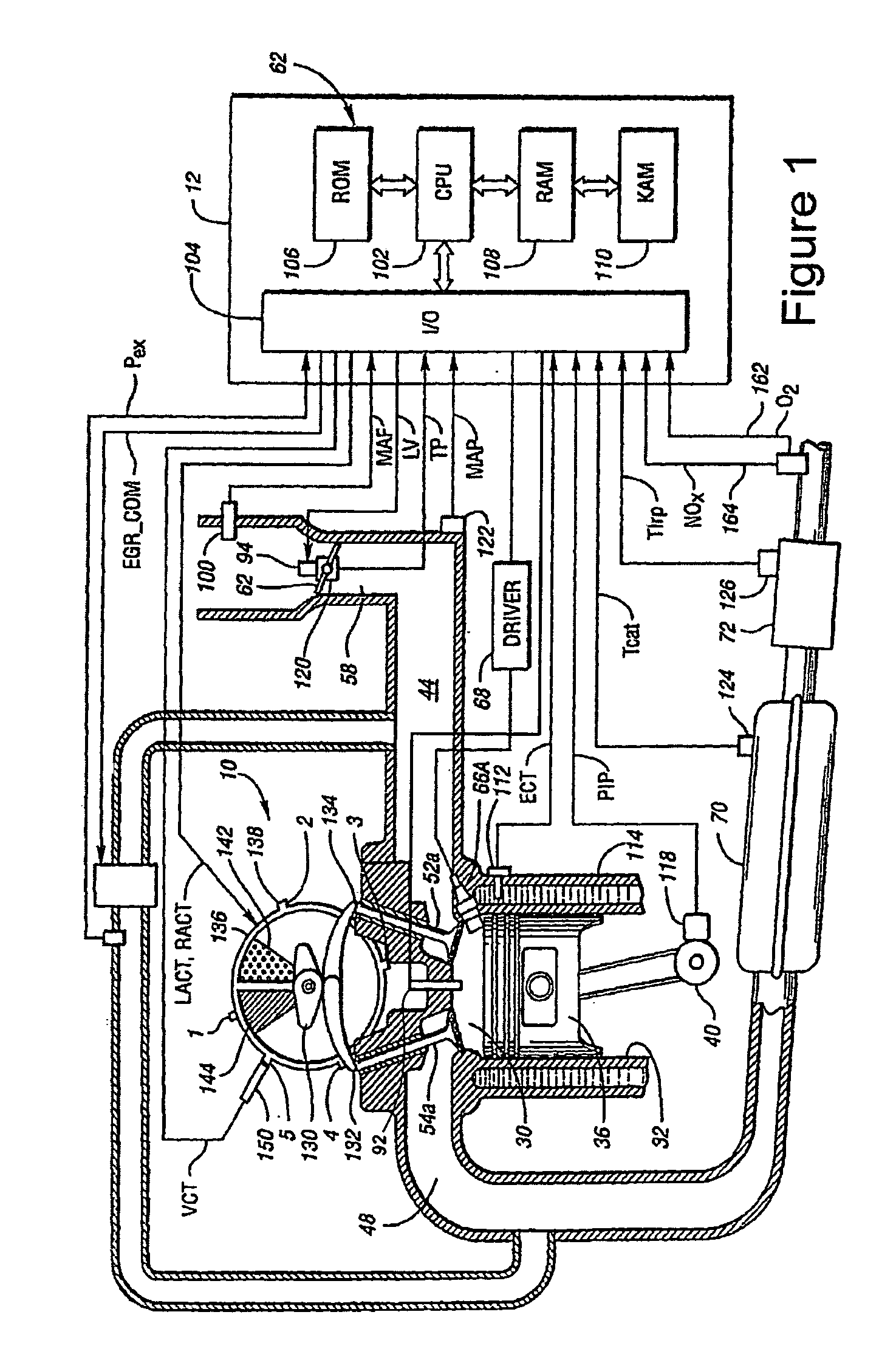
System and method for reducing NOx emissions during transient conditions in a diesel fueled vehicle
InactiveUS6863058B2Accurately controlReduce nitrogen oxide emissionsElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion chamberManifold vacuum
The present invention is a dual-stage fuel injection strategy for compression ignition engines in which 15-40% of the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber no later than about −20 to −30 CA ATDC and as early as IVC. The rest of the fuel is then injected in one or more fuel pulses, none of which start before about −20 to −30 CA ATDC. The fuel injected early in the compression stroke forms a lean mixture that burns with low soot and low NOx emissions. The combustion of that fuel serves to increase in-cylinder temperature such that the ignition delay of subsequent fuel injection pulses is short. This mode is utilized when it is predicted that a NOx spike is imminent. Various other alternative methods for reducing NOx spikes are also disclosed such as specialized EGR systems that can provide EGR with low manifold vacuum.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Low NOx combustion using cogenerated oxygen and nitrogen streams
InactiveUS20050058958A1Minimize fuel NOx formationReduce temperature and oxygen concentrationCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelChemistryAir separation
Combustion of hydrocarbon fuel is achieved with less formation of NOx by feeding the fuel into a slightly oxygen-enriched atmosphere, and separating air into oxygen-rich and nitrogen-rich streams which are fed separately into the combustion device.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
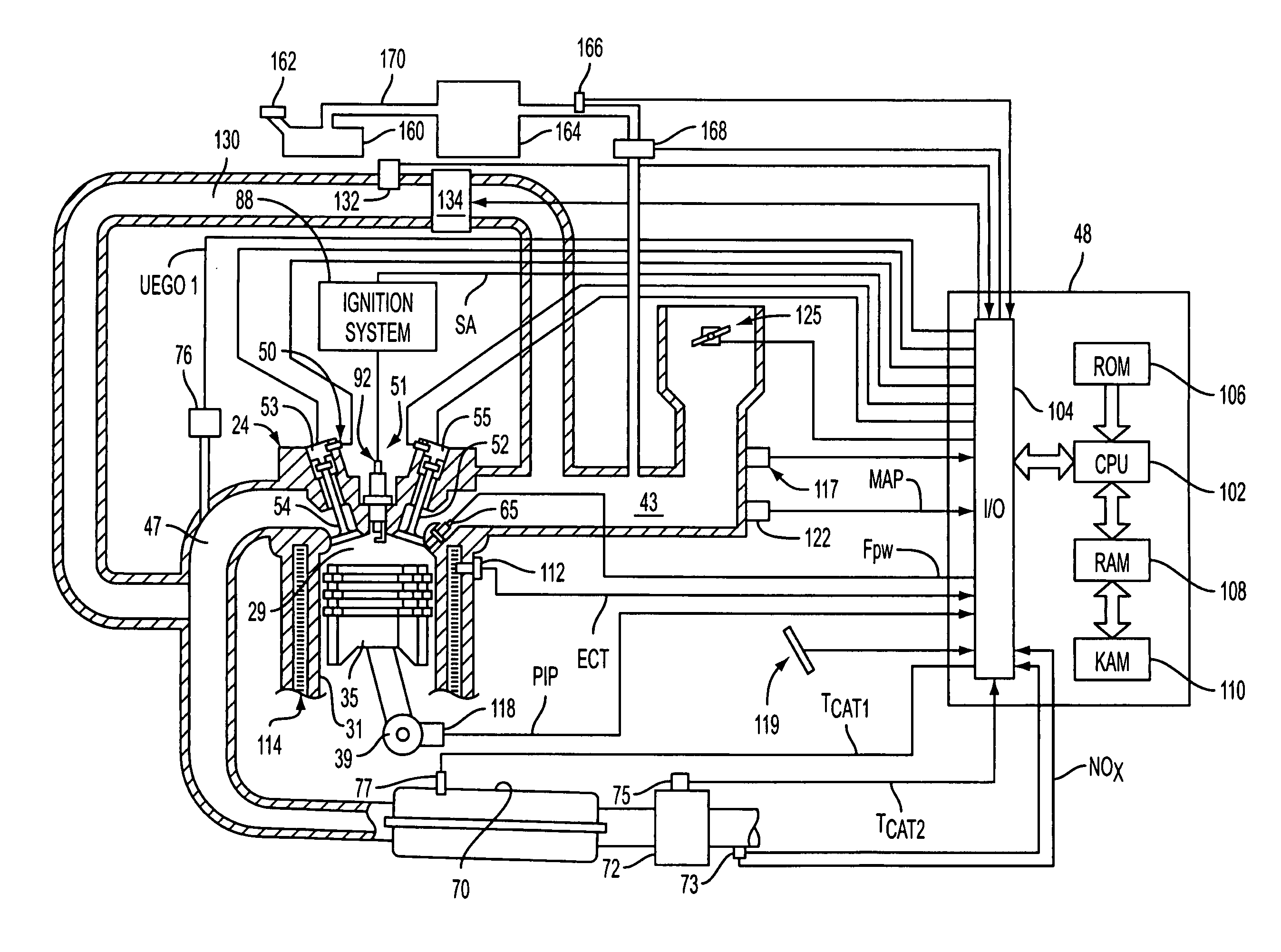
System and method for engine operation with spark assisted compression ignition
InactiveUS7234438B2Improve efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesElectrical controlCombustion enginesCombustion chamberTop dead center
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston is disclosed. The method comprising during a first mode, adjusting an operating condition of the engine so that a first mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber attains an autoignition temperature and therefore combusts without performing a spark from the spark plug; and during a second mode, adjusting said operating condition of the engine so that a second mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber approaches, but does not achieve, said autoignition temperature; and performing a spark from the spark plug after top dead center of piston position so that said second mixture combusts.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Transition strategy for engine operation with spark ignition and homogeneous charge compression ignition modes
ActiveUS20070062483A1Improve fuel efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPistonAutoignition temperature
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston and a spark plug, when transitioning between spark ignition combustion and autoignition combustion, creating a first mixture of air and fuel, adjusting an operating condition of the engine so that said first mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber approaches, but does not achieve, the autoignition temperature, and performing a spark from the spark plug so that at least a portion of said first mixture combusts to raise a remaining portion of said first mixture to said autoignition temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Gasturbine and the combustor thereof
InactiveUS20030051478A1Reduce the production of nitrogen oxidesSuppress pressure fluctuationsContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustorHoneycomb
The objective is to provide a gas turbine and the combustor thereof in which super high frequency combustion oscillation and the generation of NOx are reduced. The fluctuation in pressure which induces the fluctuation in heat liberation is suppressed in the gas turbine combustor comprising a plurality of main fuel supply nozzles, each having a premixing nozzle at the top end part thereof, by providing in the space upstream from the premixing nozzles partition elements for dividing the space along the axis of the combustor or a honeycomb element having air passages in the axial direction, or by providing premixing nozzles composed of cylindrical elements with many holes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
System and method for engine operation with spark assisted compression ignition
InactiveUS20070062486A1Improve fuel economyEmission reductionElectrical controlCombustion enginesCombustion chamberTop dead center
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston is disclosed. The method comprising during a first mode, adjusting an operating condition of the engine so that a first mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber attains an autoignition temperature and therefore combusts without performing a spark from the spark plug; and during a second mode, adjusting said operating condition of the engine so that a second mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber approaches, but does not achieve, said autoignition temperature; and performing a spark from the spark plug after top dead center of piston position so that said second mixture combusts.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for engine operation with spark assisted compression ignition
ActiveUS20070062484A1Reliable spark assisted HCCI operationImprove fuel economyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston, comprising of adjusting an operating parameter of the engine so that a mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber approaches, but does not achieve, an autoignition temperature, and performing a spark from the spark plug so that said second mixture combusts; adjusting a timing of said spark from the spark plug; and adjusting an operating parameter to increase a correlation between said adjusted spark timing and timing of said combustion.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Reformer and Method of Operating the Reformer
ActiveUS20110220847A1Lower capital expenditureEqual or increased NOx reductionChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesGaseous fuel burnerCombustorEngineering
A method of combustion and a reformer. The method includes combusting a fuel in combustion region of an up-fired or down-fired reformer and forming non-uniform injection properties with a wall-bound burner. The combusting is performed in a combustion region by burners, wherein at least one of the burners is the wall-bound burner forming the non-uniform injection properties. The non-uniform injection properties generate a heat profile providing a first heat density proximal to a wall and a second heat density distal from the wall, the second heat density being greater than the first heat density. The non-uniform injection properties are formed by injection properties selected from an angle of one or more injectors, a flow rate of one or more injectors, an amount and / or location of oxidant injectors, an amount and / or location of fuel injectors, and combinations thereof.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
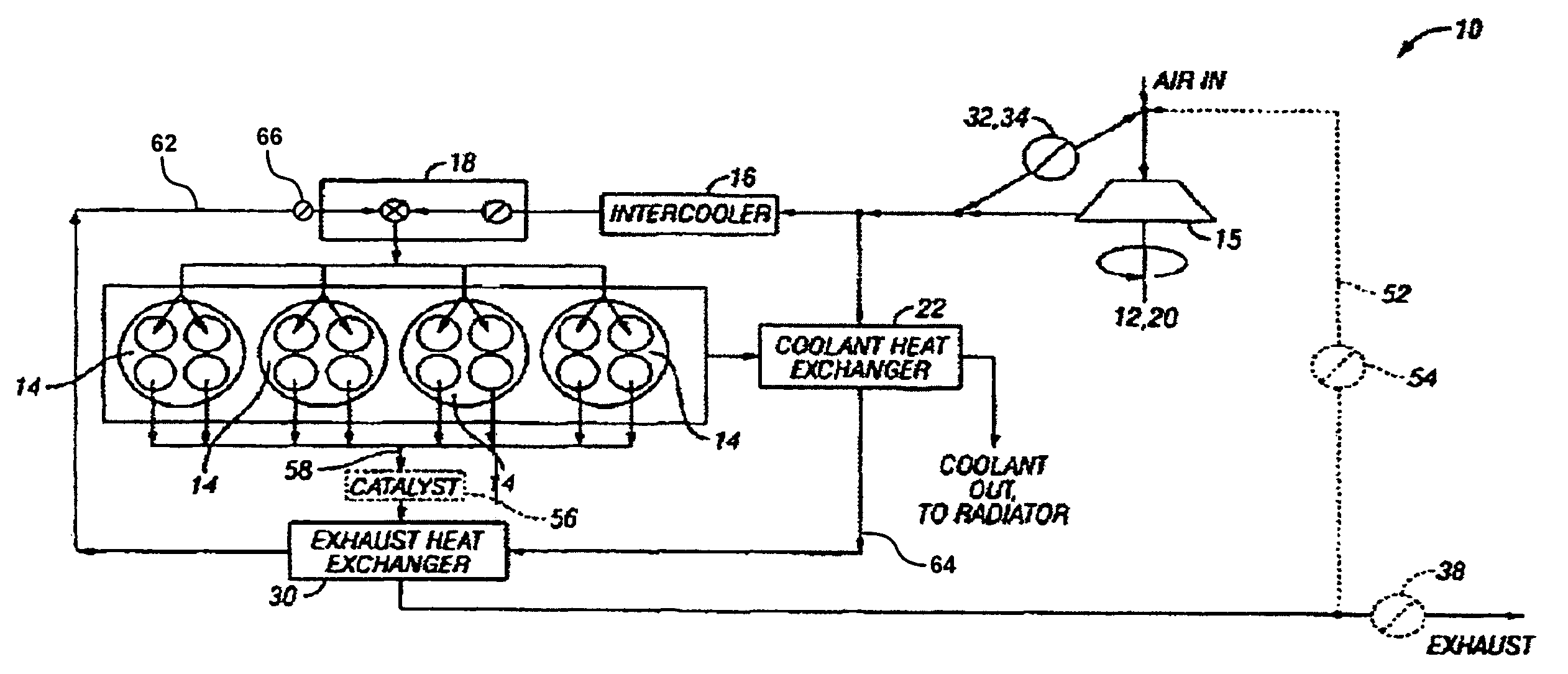
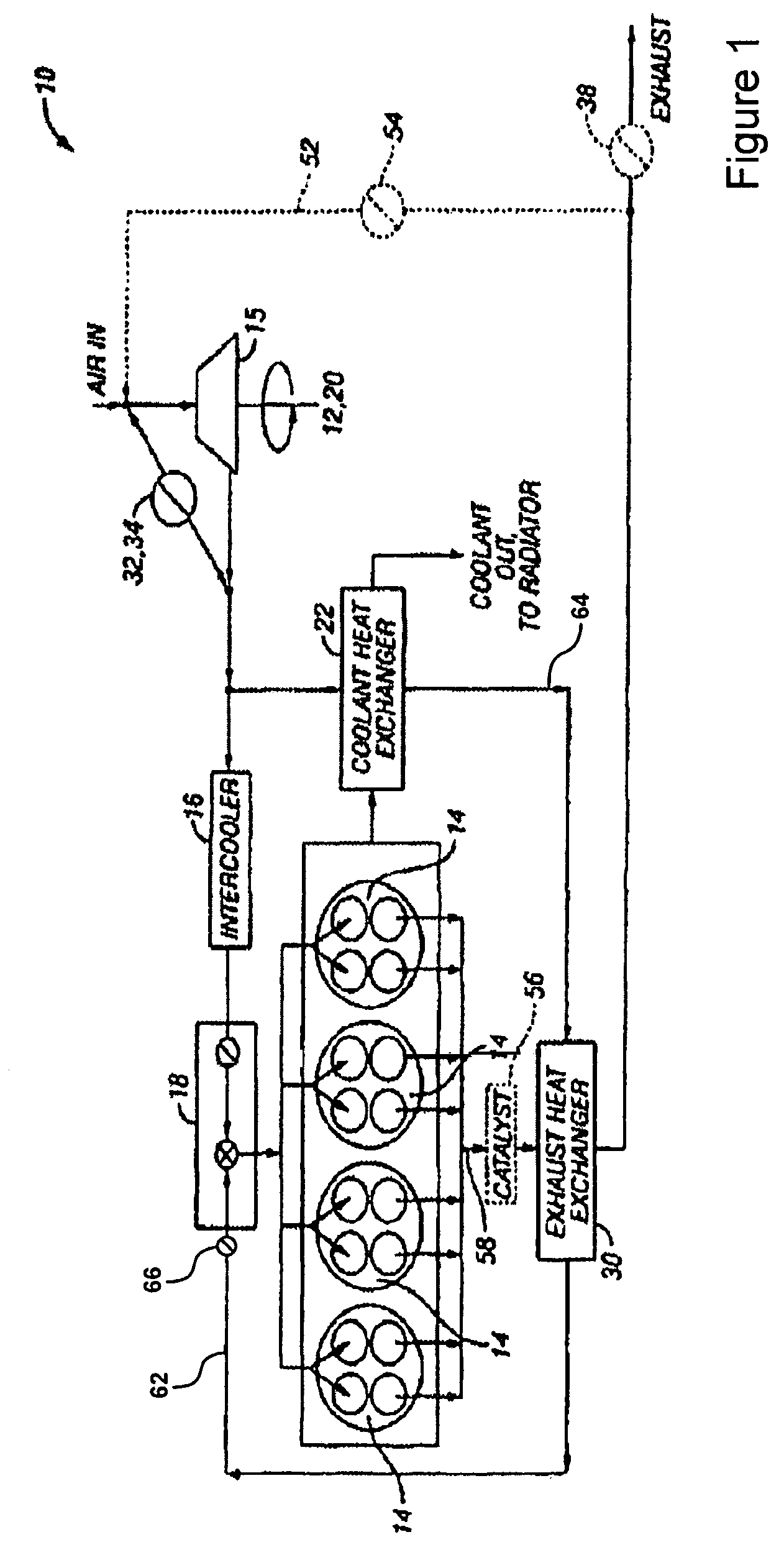
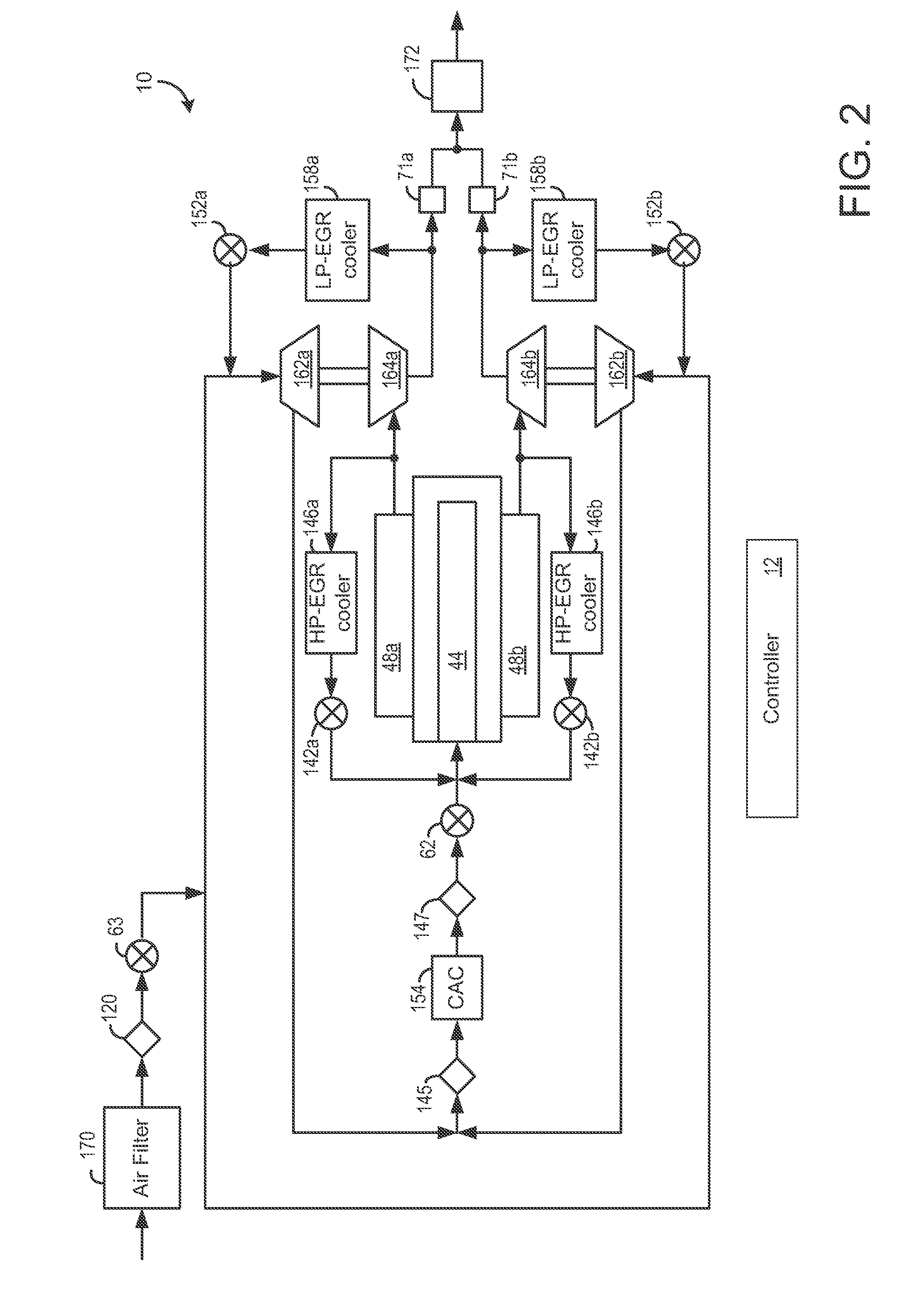
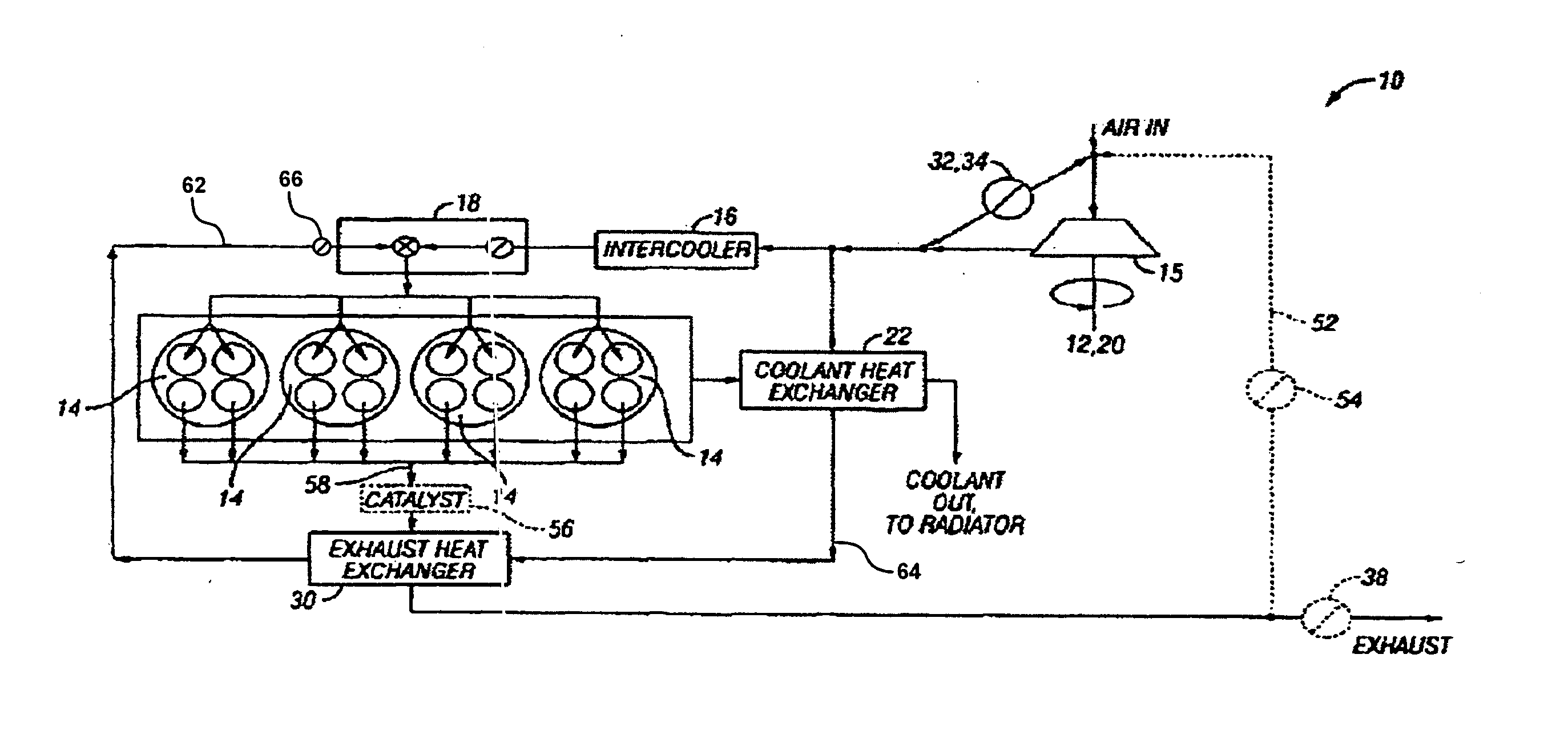
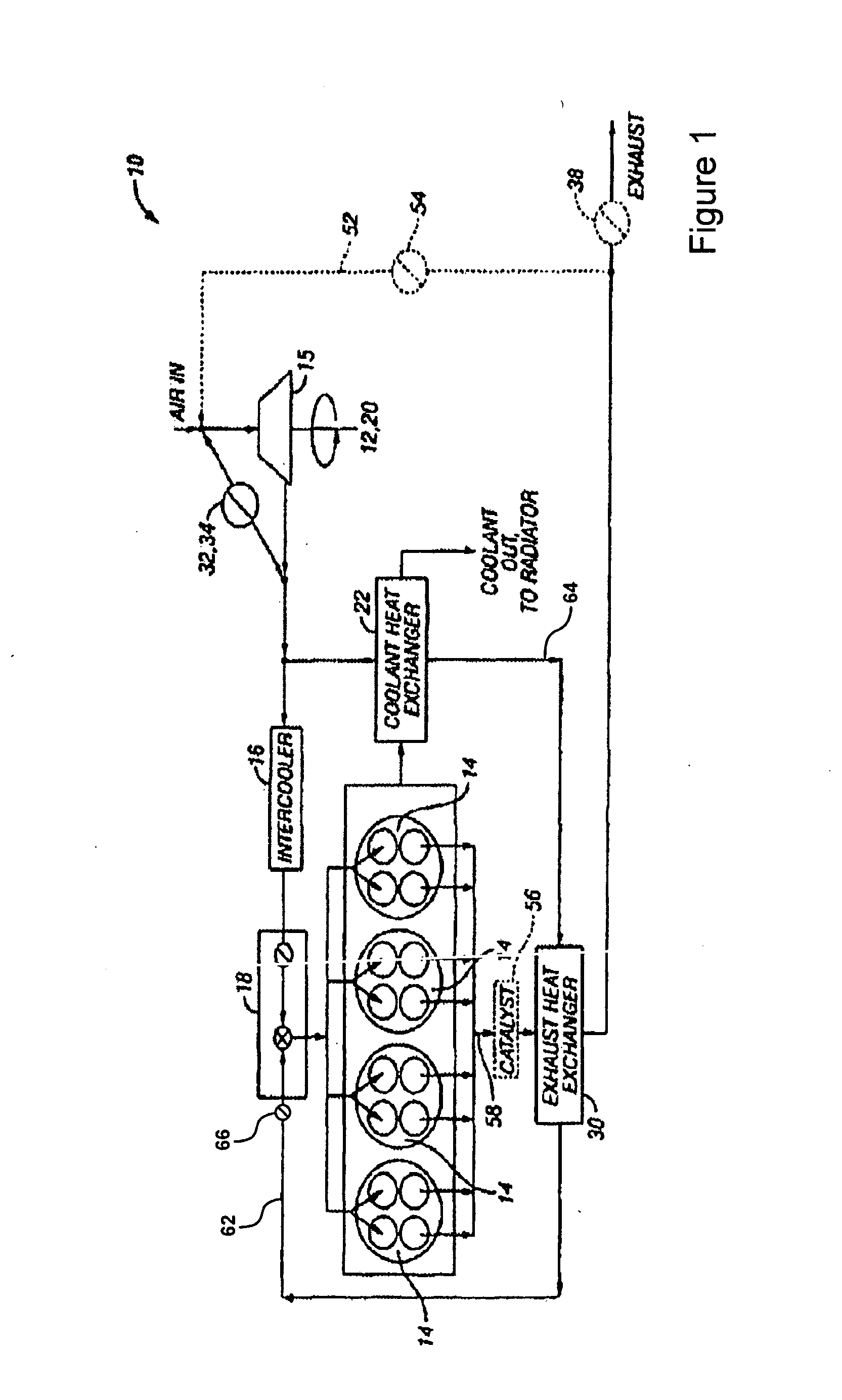
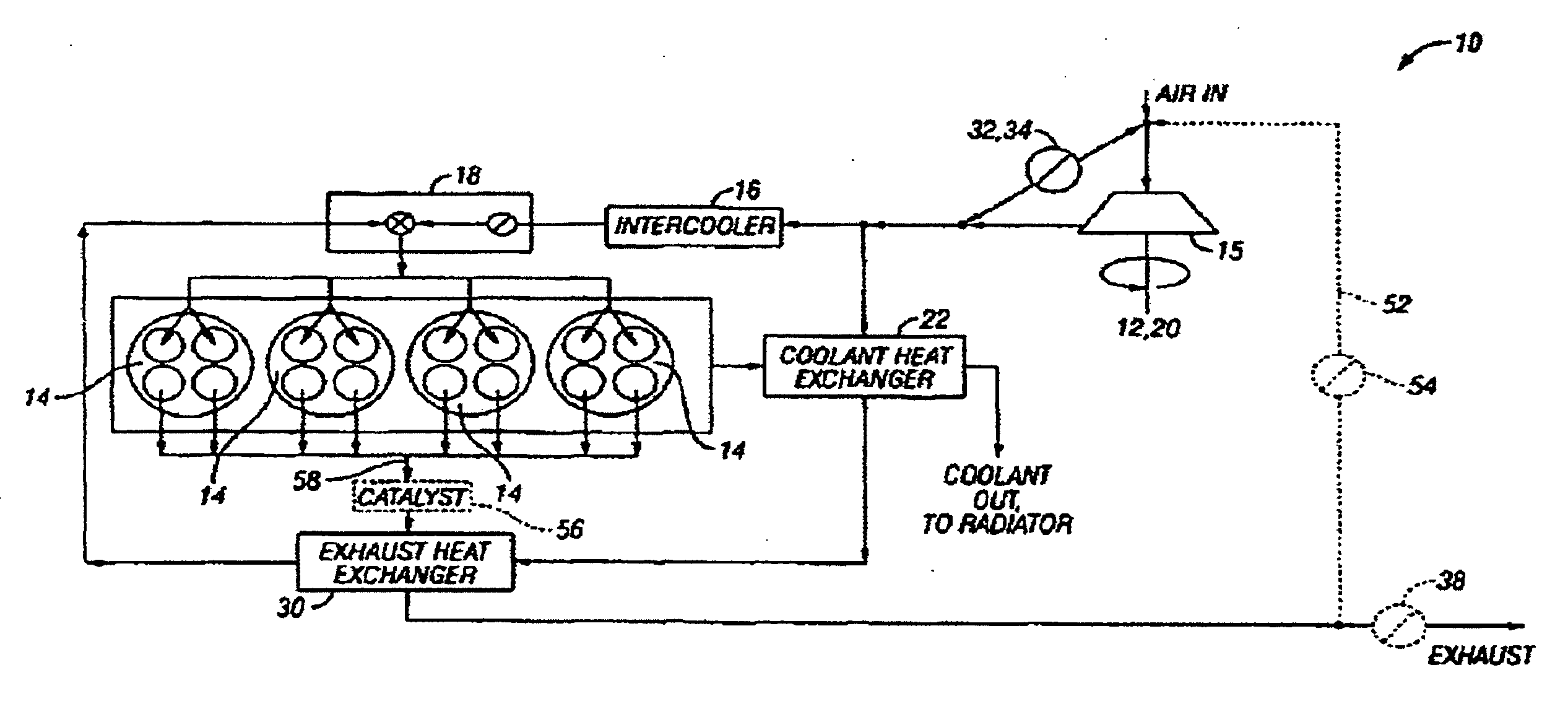
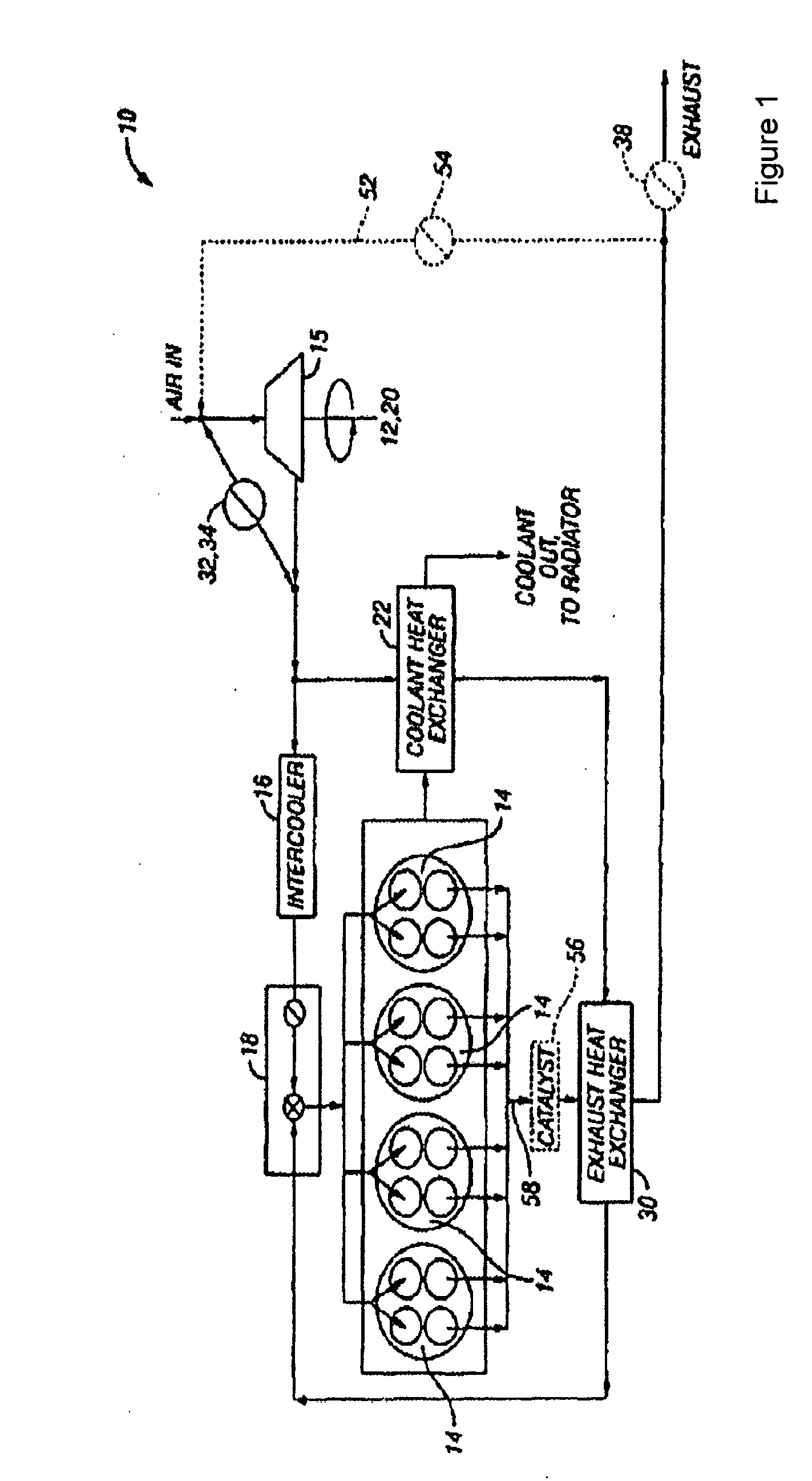
System and method for improved engine starting using heated intake air
InactiveUS7287521B2Improve efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHeat exchangerSpark plug
A system for an internal combustion engine, the engine having an intake and exhaust manifold, the system comprising of a heat exchanger configured to extract energy from engine exhaust gases; a catalyst coupled between said heat exchanger and the exhaust manifold of the engine; a spark plug in a cylinder of the engine; and a controller to operate the engine to perform spark ignition of a mixture of air and fuel in said cylinder during an engine cold start, where said air is heated with the energy before being inducted into said cylinder.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for maintaining heated intake air
InactiveUS7213585B2Improve efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesInternal combustion piston enginesThermal treatment of fuelFlame propagationInlet manifold
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
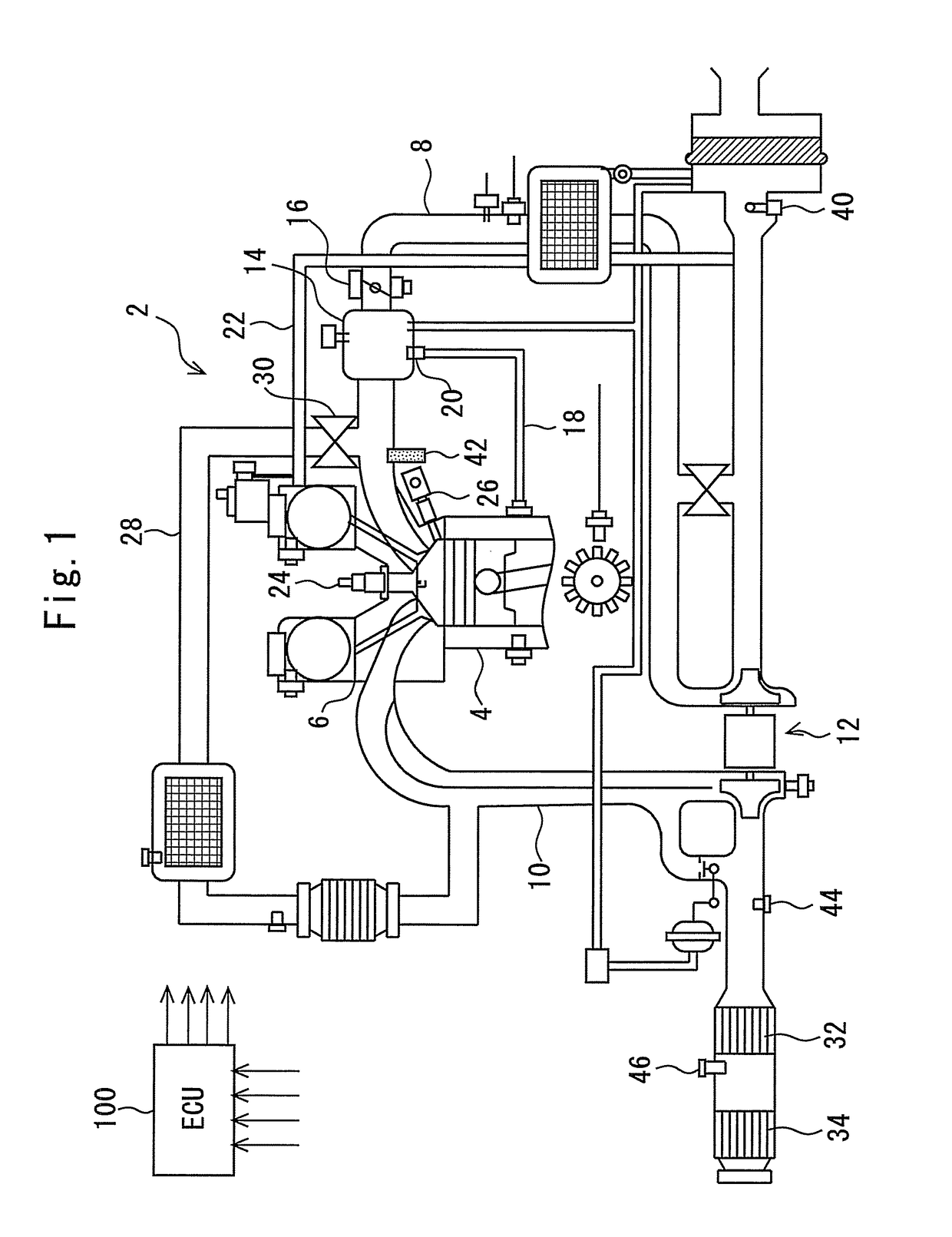
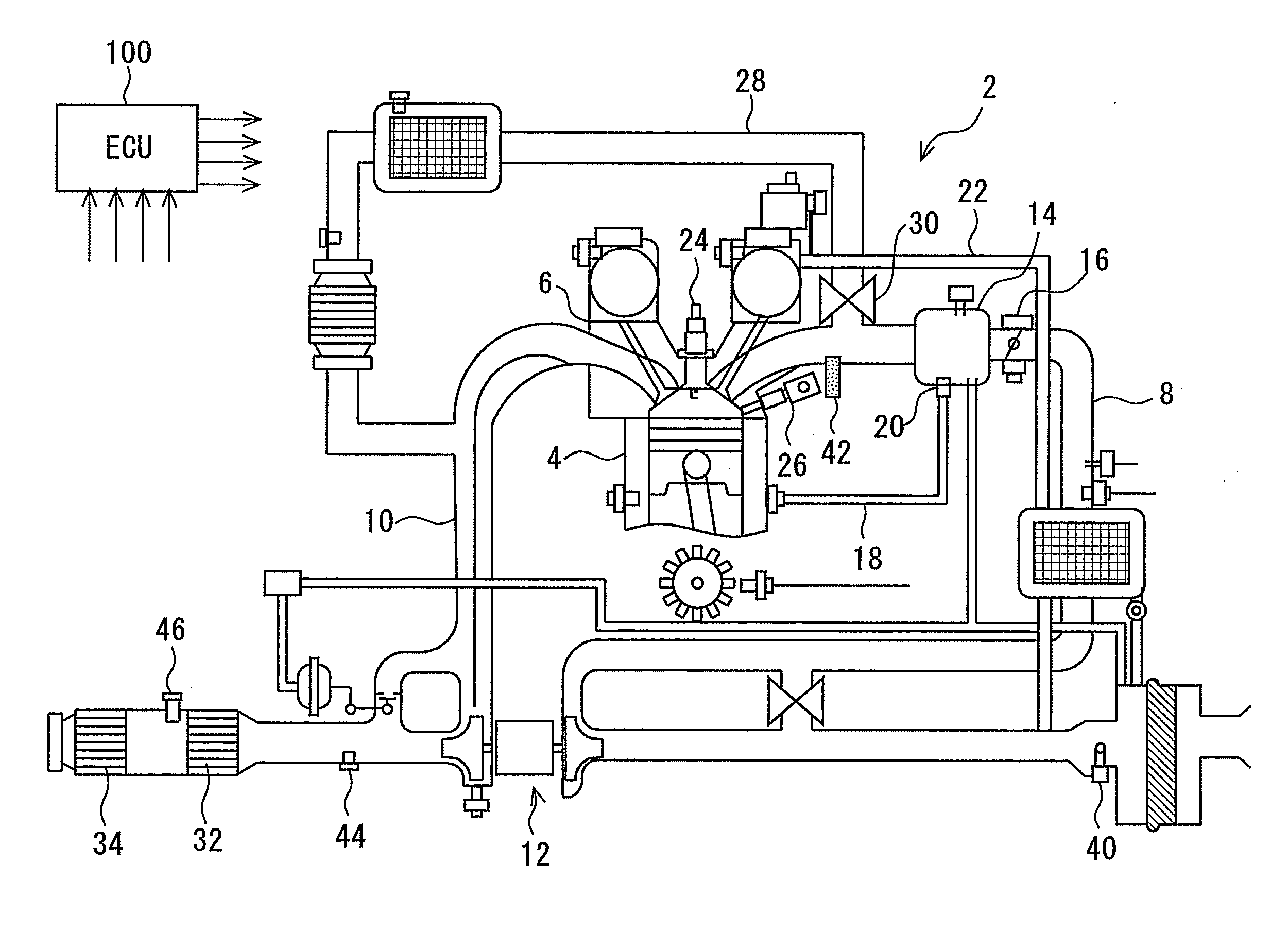
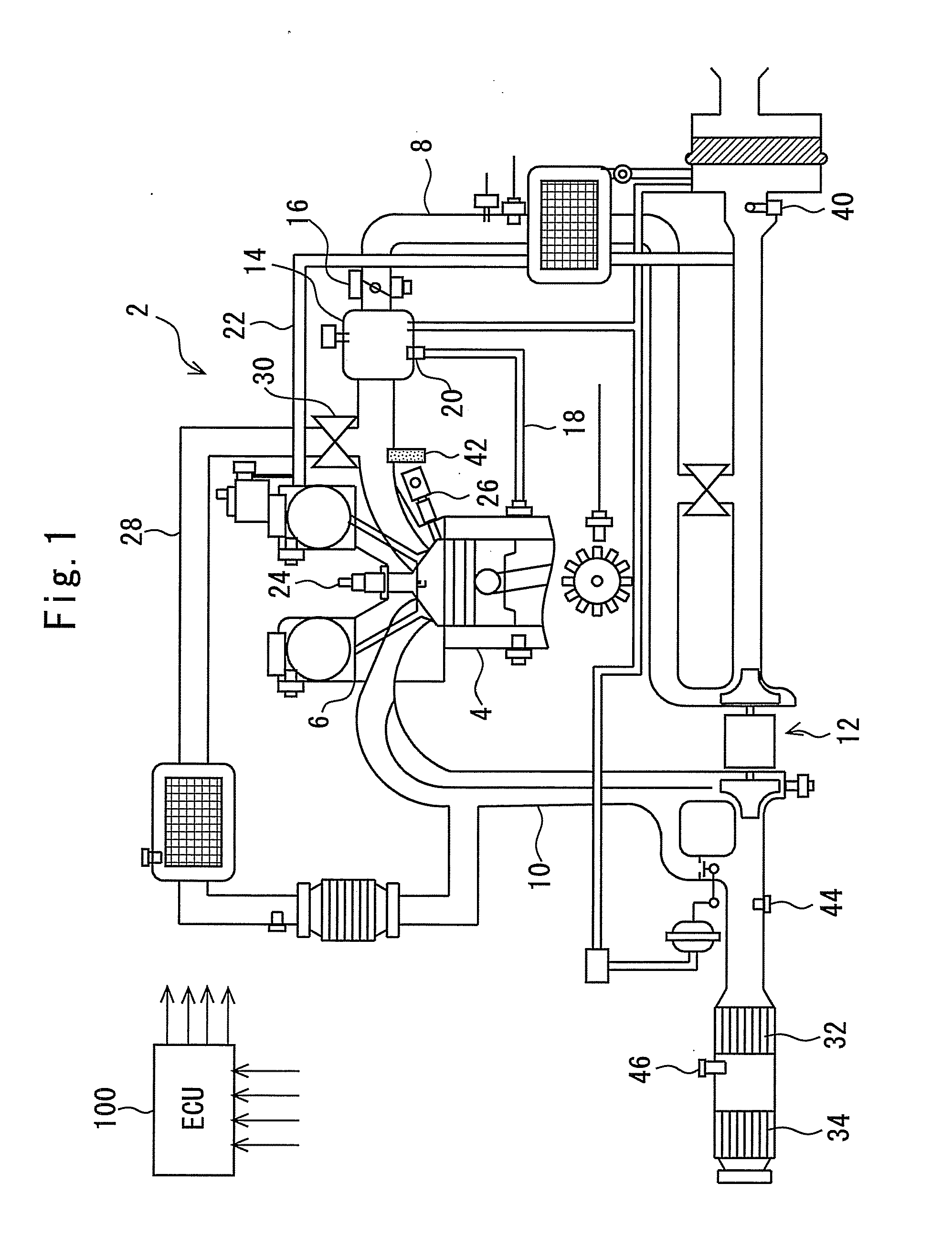
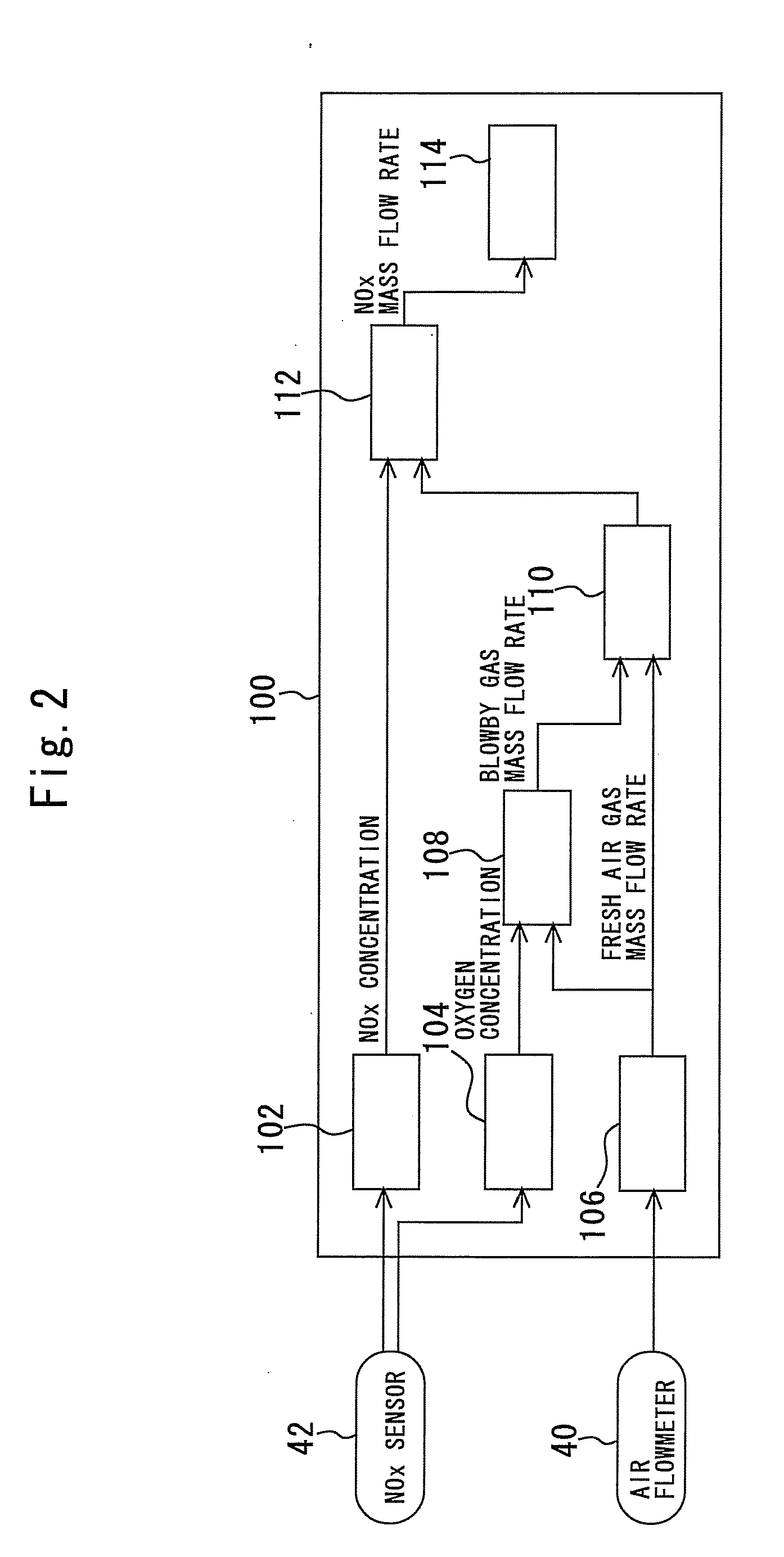
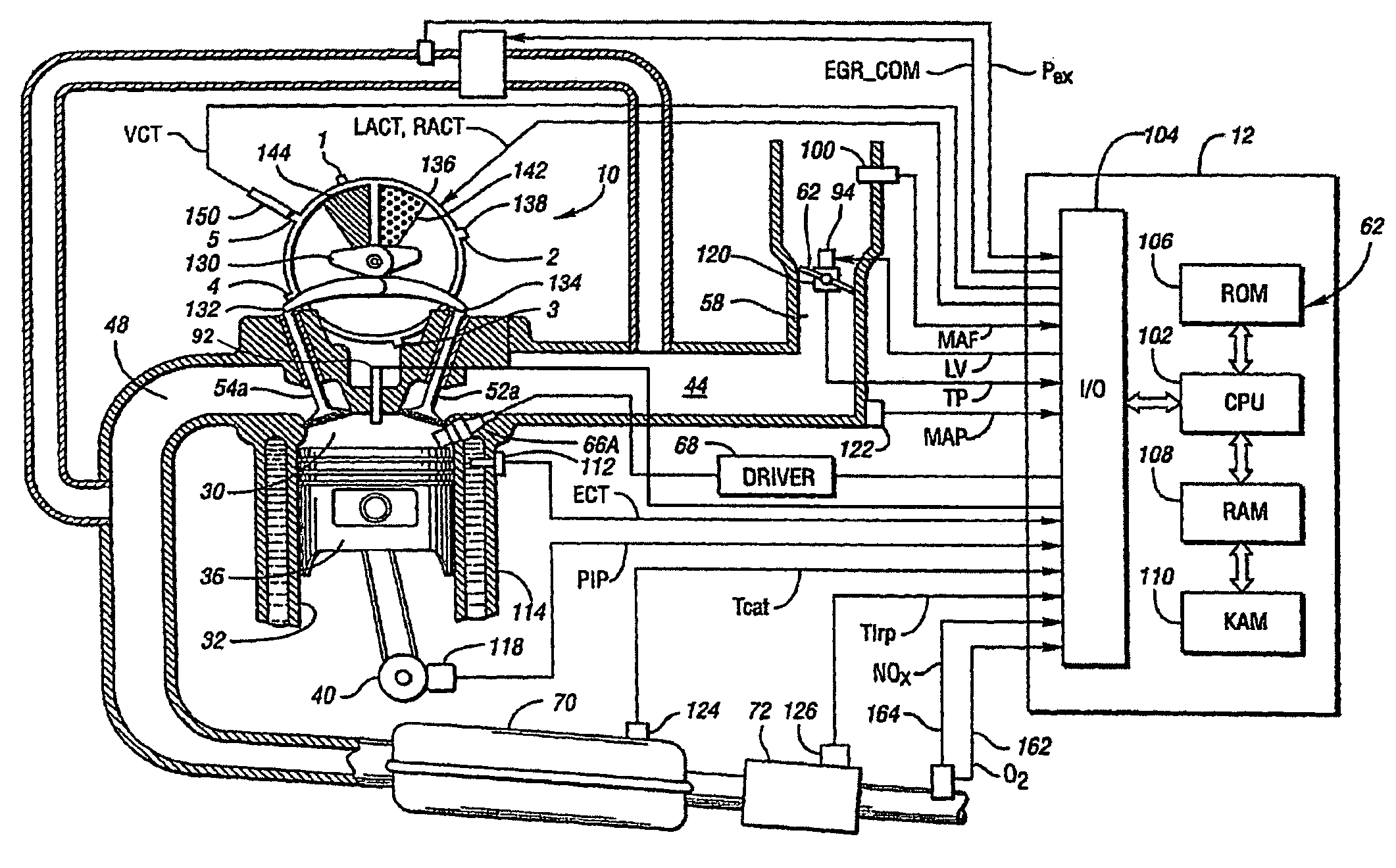
Control device for internal combustion engine and measuring device of mass flow rate of NOx recirculated to intake passage with blowby gas
InactiveUS8469010B2Improve accuracyGuaranteed true stateVehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingMeasurement deviceExternal combustion engine
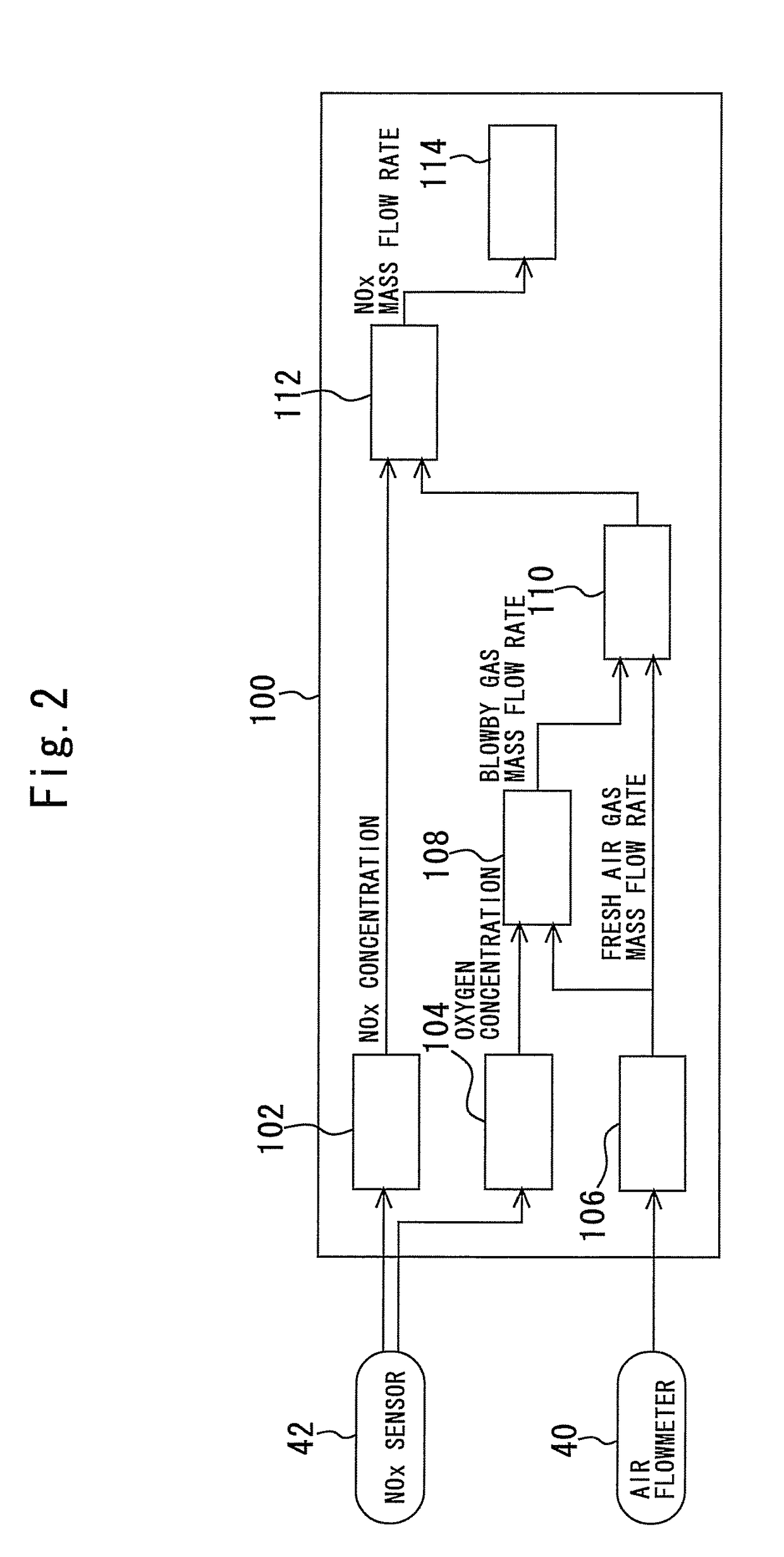
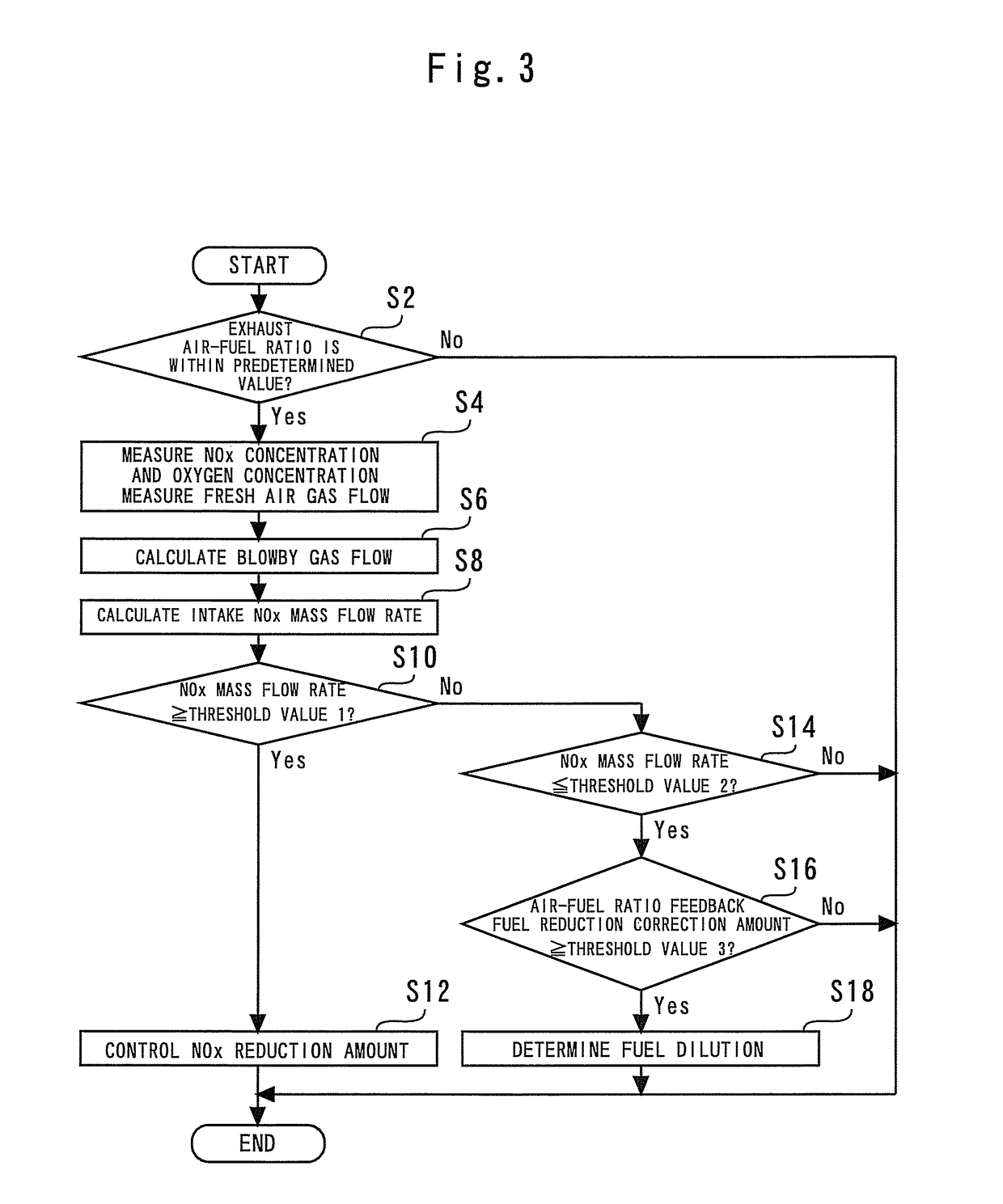
A mass flow rate of NOx which is recirculated to an intake passage with a blowby gas is obtained with high precision, and based on the result, a state of an internal combustion engine can be accurately diagnosed. A control device for an internal combustion engine of the present invention measures a NOx concentration in an intake passage downstream from a position where the blowby gas is recirculated, and similarly measures an oxygen concentration in the intake passage downstream from the aforesaid position. Further, the control device measures a mass flow rate of fresh air taken into the intake passage. The control device calculates a mass flow rate of the blowby gas recirculated to the intake passage from the oxygen concentration and the mass flow rate of the fresh air. Next, the control device calculates a mass flow rate of all gases in the intake passage from the mass flow rate of the fresh air and the mass flow rate of the blowby gas. Subsequently, the control device calculates the mass flow rate of NOx in the aforesaid intake passage from the mass flow rate of all the gases and the NOx concentration. The present control device diagnoses the state of the internal combustion engine based on the mass flow rate of NOx thus calculated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
NOx FEEDBACK FOR COMBUSTION CONTROL
ActiveUS20130118461A1Reduce the production of nitrogen oxidesEmission reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionAutomotive engineering
A method for controlling combustion in an engine is provided. The method comprises under a first condition, adjusting an EGR amount of a total cylinder charge in response to engine out NOx levels being below a first threshold. In this way, NOx levels may be used as feedback to control combustion stability.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and method for maintaining heated intake air
InactiveUS20070062490A1Improve fuel efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersFlame propagationSpark plug
A system for an internal combustion engine, the engine having an intake and exhaust manifold, the system comprising a heat exchanger configured to extract energy from at least a heat source that heats a first portion of intake air, a spark plug coupled to the engine, an intake passage configured to deliver said first portion of heated intake air to the engine and to deliver a second portion of intake air which bypasses said heat source, and a controller configured to direct said second portion of intake air to the engine at least when utilizing said spark plug to initiate combustion and flame propagation of an air-fuel mixture, and to at least temporarily cause said first portion of intake air to flow during said spark ignition combustion so that a temperature of said first portion of intake air is maintained above a selected value.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
CONTROL DEVICE FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE AND MEASURING DEVICE OF MASS FLOW RATE OF NOx RECIRCULATED TO INTAKE PASSAGE WITH BLOWBY GAS
InactiveUS20110282539A1Improve accuracyGuaranteed true stateVehicle testingInternal-combustion engine testingExternal combustion engineEngineering
A mass flow rate of NOx which is recirculated to an intake passage with a blowby gas is obtained with high precision, and based on the result, a state of an internal combustion engine can be accurately diagnosed. A control device for an internal combustion engine of the present invention measures a NOx concentration in an intake passage downstream from a position where the blowby gas is recirculated, and similarly measures an oxygen concentration in the intake passage downstream from the aforesaid position. Further, the control device measures a mass flow rate of fresh air taken into the intake passage. The control device calculates a mass flow rate of the blowby gas recirculated to the intake passage from the oxygen concentration and the mass flow rate of the fresh air. Next, the control device calculates a mass flow rate of all gases in the intake passage from the mass flow rate of the fresh air and the mass flow rate of the blowby gas. Subsequently, the control device calculates the mass flow rate of NOx in the aforesaid intake passage from the mass flow rate of all the gases and the NOx concentration. The present control device diagnoses the state of the internal combustion engine based on the mass flow rate of NOx thus calculated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and method for engine operation with spark assisted compression ignition
ActiveUS7213572B2Improve efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberInternal combustion engine
A method of operating an internal combustion engine having a combustion chamber with a piston, comprising of adjusting an operating parameter of the engine so that a mixture of air and fuel in the combustion chamber approaches, but does not achieve, an autoignition temperature, and performing a spark from the spark plug so that said second mixture combusts; adjusting a timing of said spark from the spark plug; and adjusting an operating parameter to increase a correlation between said adjusted spark timing and timing of said combustion.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
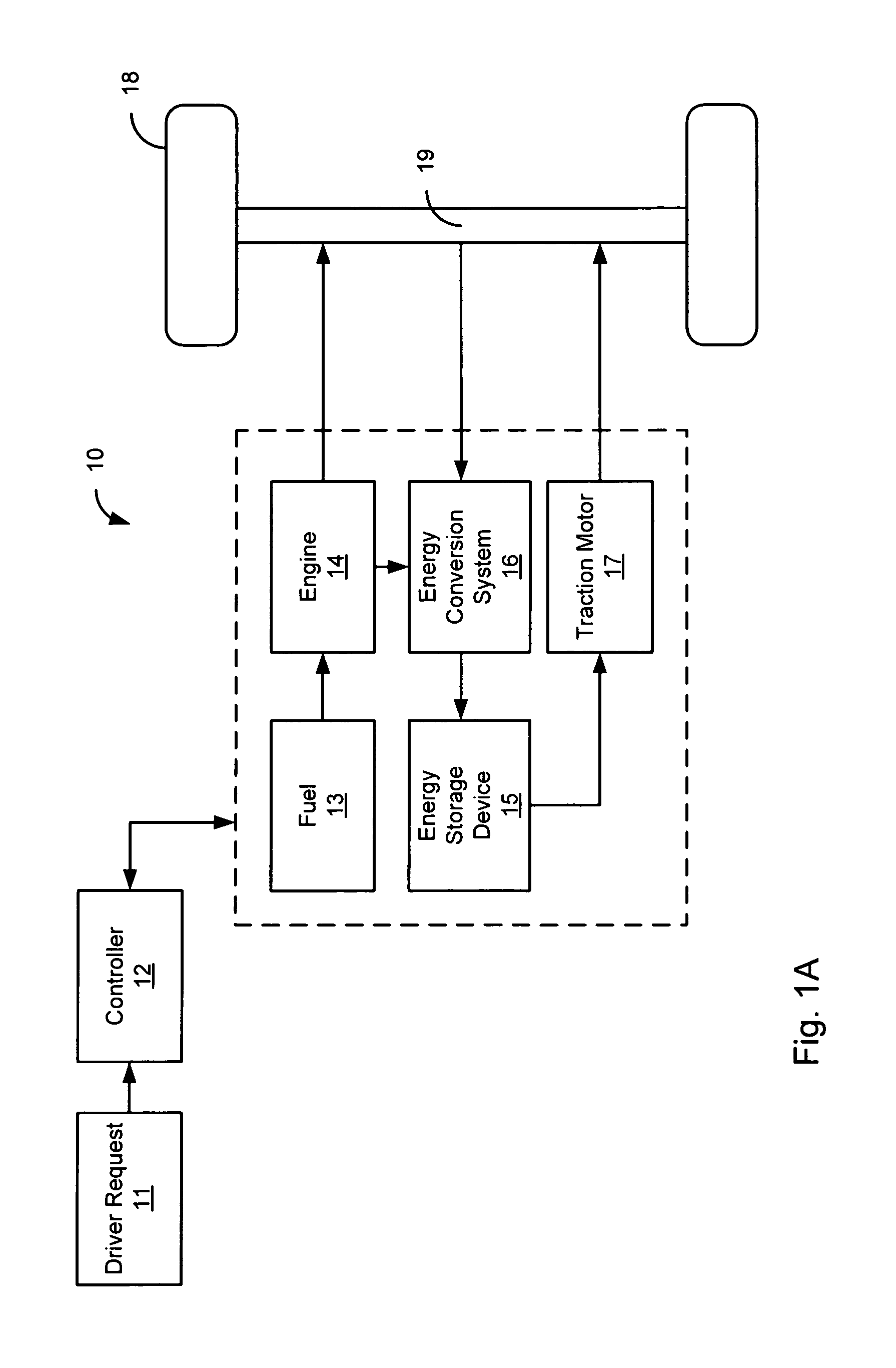
System and method for controlling vehicle operation in response to fuel vapor purging
ActiveUS20070204838A1Reduce advantageLimit its operationHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlAutomotive engineeringSpark-ignition engine
A hybrid vehicle propulsion system, comprising of an engine having at least one combustion cylinder configured to selectively operate in one of a plurality of combustion modes, wherein a first combustion mode is a spark ignition mode and a second combustion mode is a homogeneous charge compression ignition mode, an energy storage device configured to store energy, a motor configured to absorb at least a portion of an output produced by the engine and convert said absorbed engine output to energy storable by the energy storage device and wherein the motor is further configured to produce a motor output, a fuel tank vapor purging system coupled to the engine, and a controller configured to vary fuel vapors supplied to the engine during different combustion modes of the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
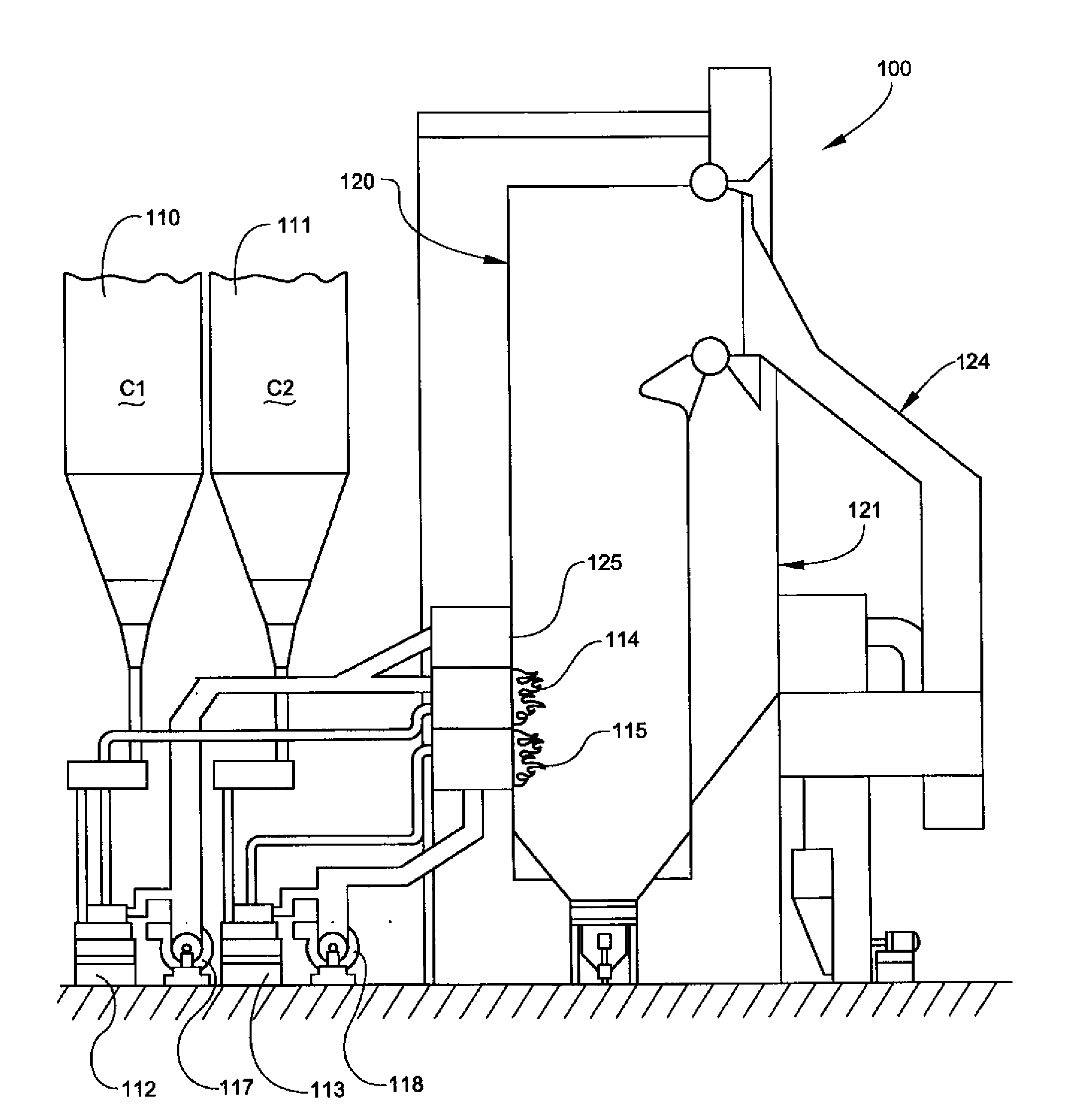
Method for decreasing nitrogen oxides of a pulverized coal boiler using burners of internal combustion type
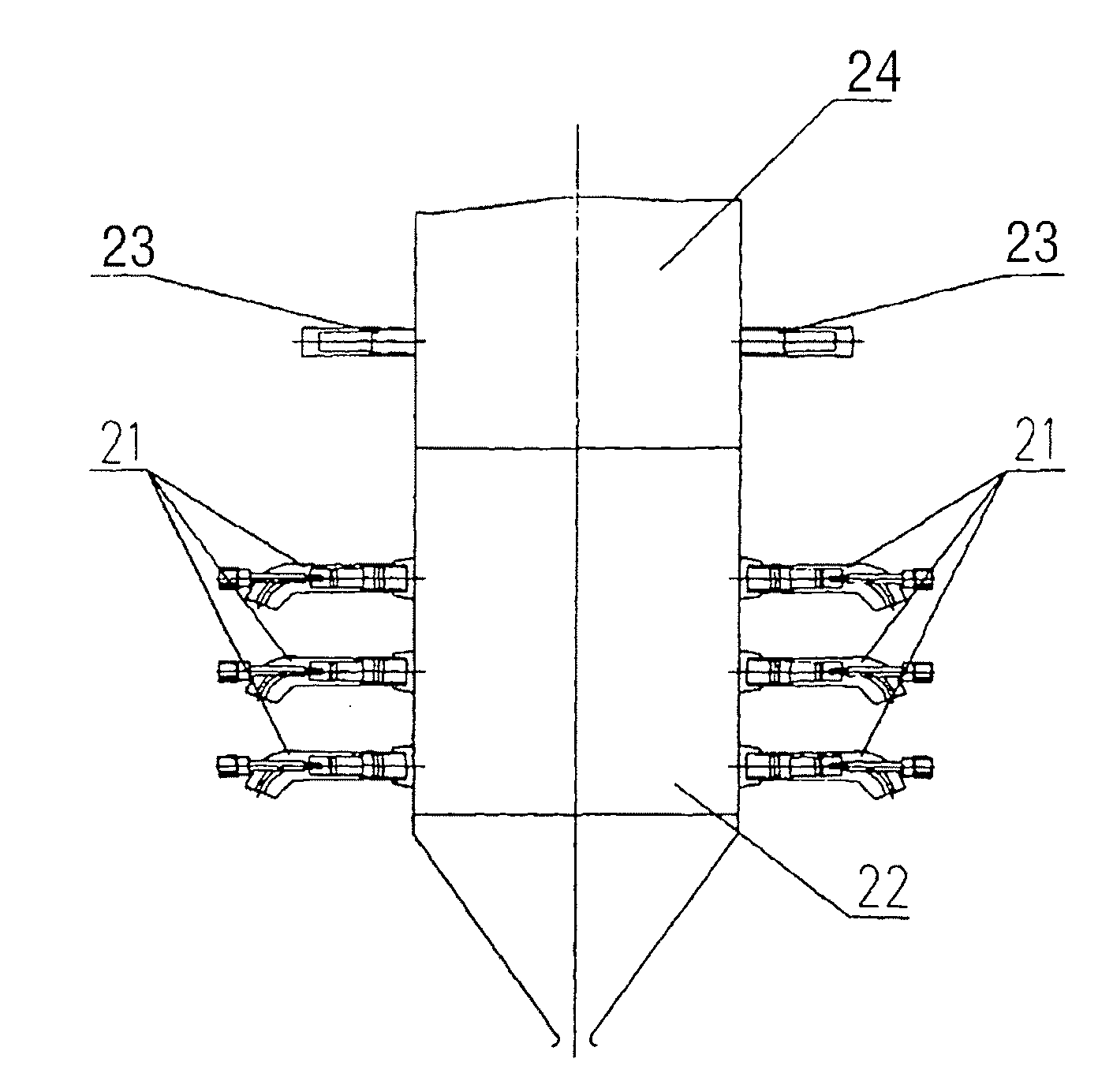
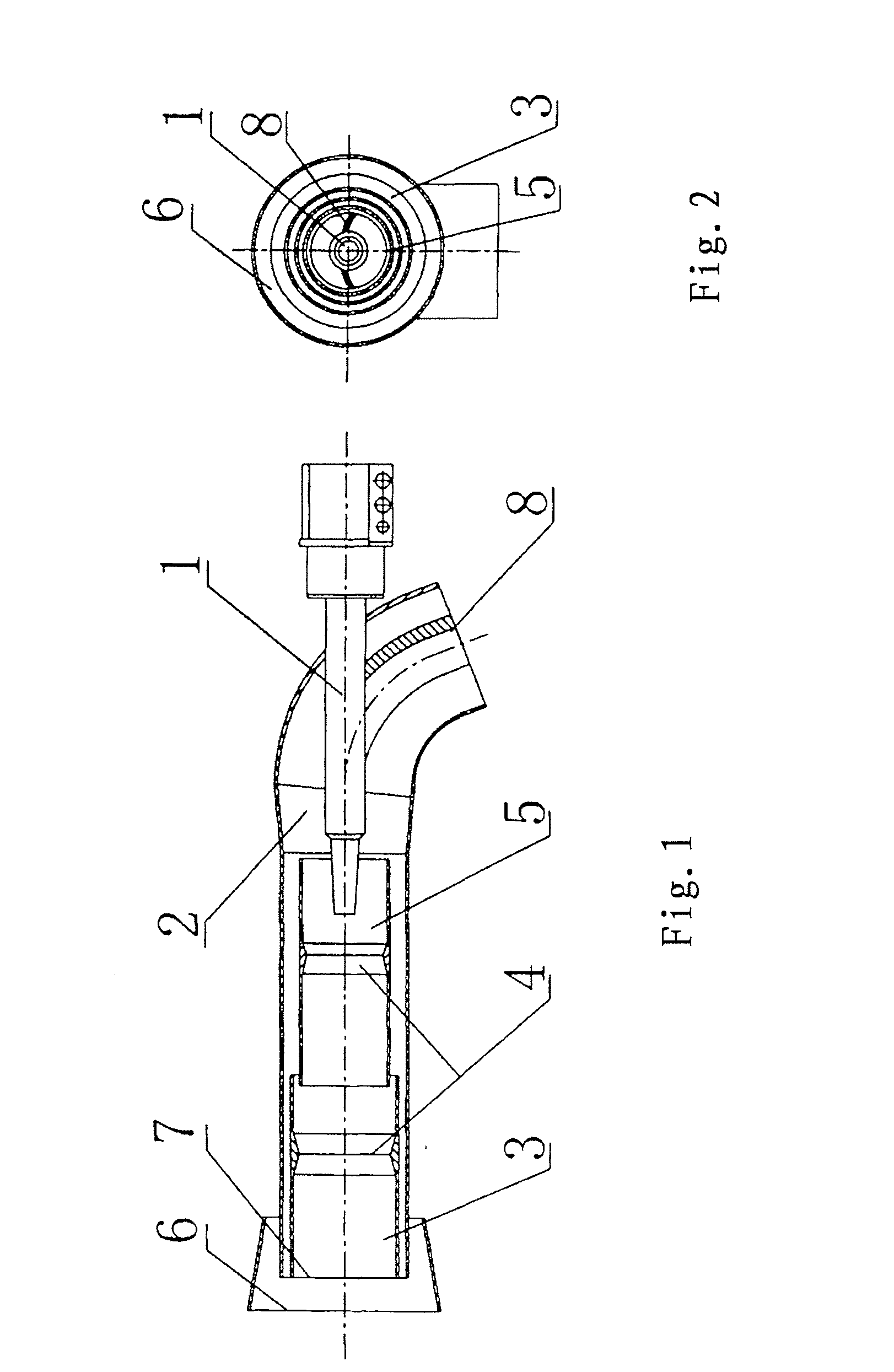
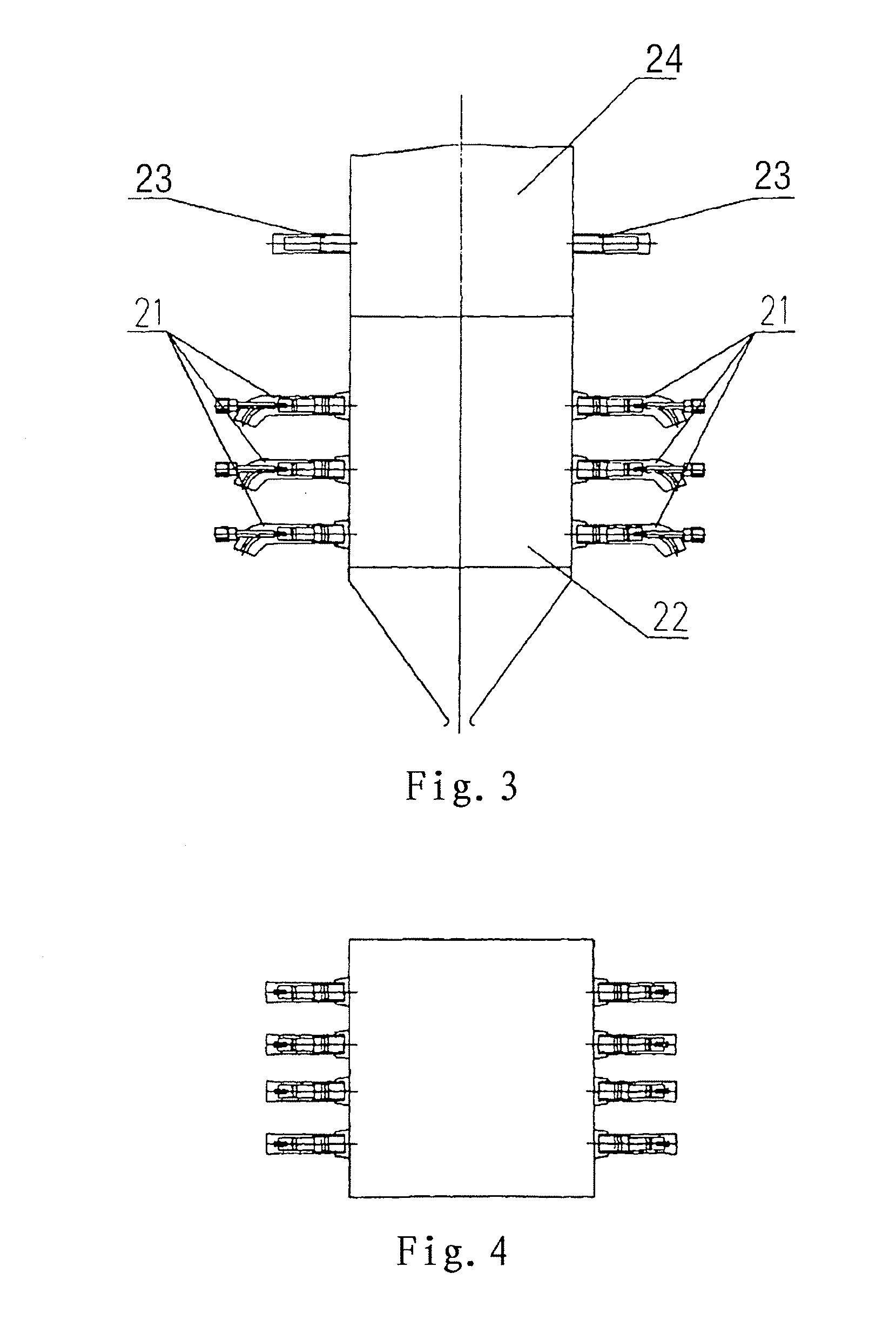
ActiveUS20110033807A1Reduce NOx generationAvoid generatingStaged combustionPulverulent fuel combustion burnersBoiler efficiencyCombustion chamber
A method for decreasing nitrogen oxides of a pulverized coal boiler using burners (2) of internal combustion type comprising: designing or changing all or part of burners of the pulverized coal boiler as internal combustion type burners (2), in which the ignition sources may be plasma generators (1) or ignition devices such as small oil guns etc., and the power thereof can be adjusted for controlling the ignition intensity in the burners (2). The burners (2) are interiorly divided into several stage combustion chambers (5) and are provided with pulverized coal concentrators (4) which do deep fuel staging in the burners (2). During the operation of the boiler, the ignition sources always keep in a working state, and the pulverized coal in the burners (2) is ignited stage by stage and is burnt in advance; decreasing the secondary air amount in the primary combustion zone (22) so that the primary combustion zone (22) is in a relatively strong reducing atmosphere and a high temperature and oxygen-deficient condition for inhibiting the generation of NOx is created; and supplying the remaining air from the upper of furnace of the boiler in the form of over-fire air, so that a deep air staging is carried out in the total furnace. Thus, the NOx generation of combustion can be effectively controlled on the premise of not decreasing the boiler efficiency.
Owner:YANTAI LONGYUAN POWER TECH
System and method for improved engine starting using heated intake air
InactiveUS20070062178A1Improve fuel efficiencyReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInlet manifoldCylinder (engine)
A system for an internal combustion engine, the engine having an intake and exhaust manifold, the system comprising of a heat exchanger configured to extract energy from engine exhaust gases; a catalyst coupled between said heat exchanger and the exhaust manifold of the engine; a spark plug in a cylinder of the engine; and a controller to operate the engine to perform spark ignition of a mixture of air and fuel in said cylinder during an engine cold start, where said air is heated with the energy before being inducted into said cylinder.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Staged-coal injection for boiler reliability and emissions reduction
InactiveUS20080105176A1Reduces fireside corrosionEmission reductionStaged combustionPulverulent fuel combustion burnersEngineeringCoal fired
A staged-coal injection procedure for coal-fired boilers used in power generation. The procedure includes the steps of combusting a first type of coal in a first zone of a furnace; and combusting a second type of coal in a second zone of the furnace. The second zone is at a position separate from the first zone.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
Diesel engine exhaust purifier
InactiveUS20100263623A1Reduce the production of nitrogen oxidesReduce the temperatureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberSteep slope
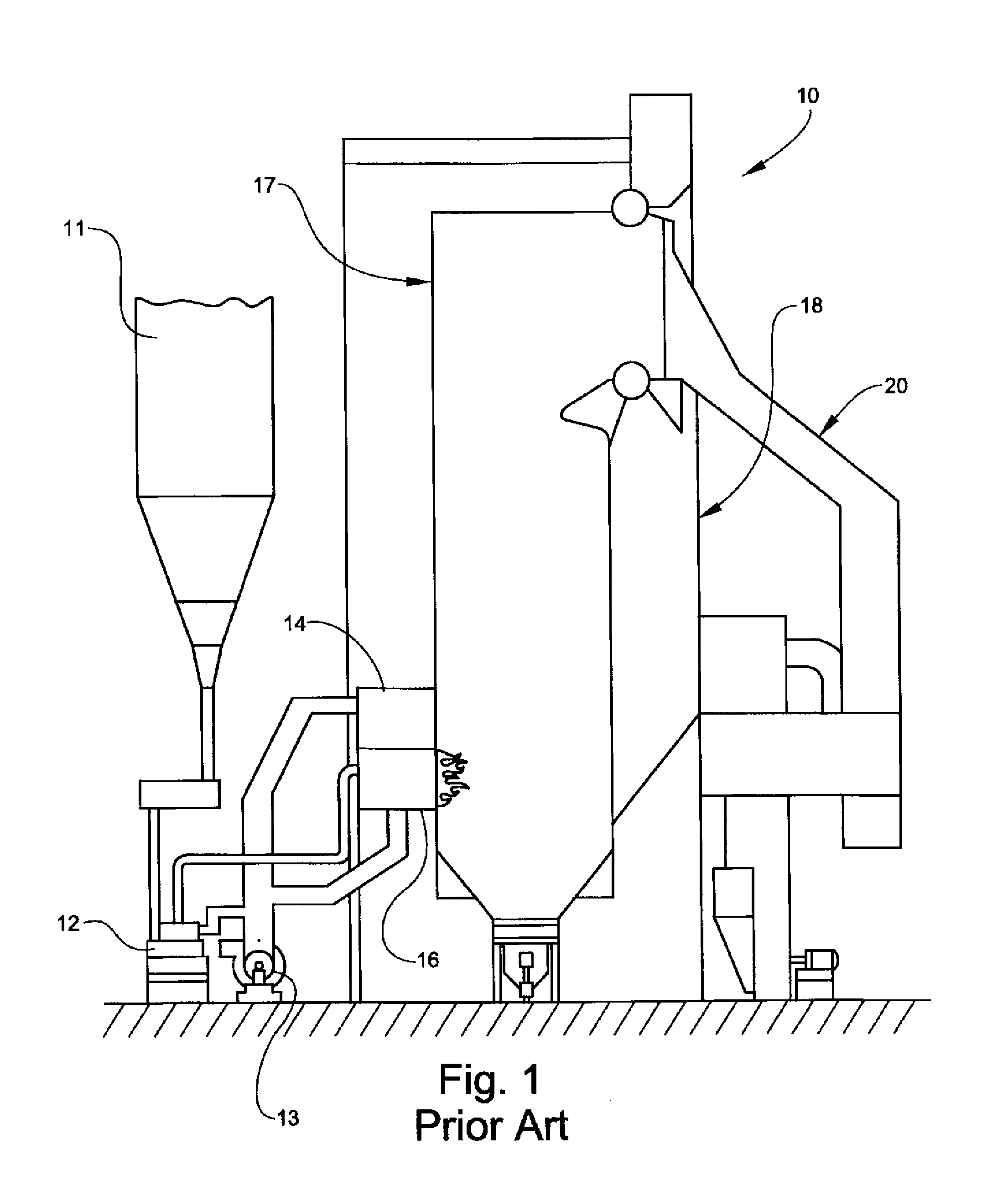
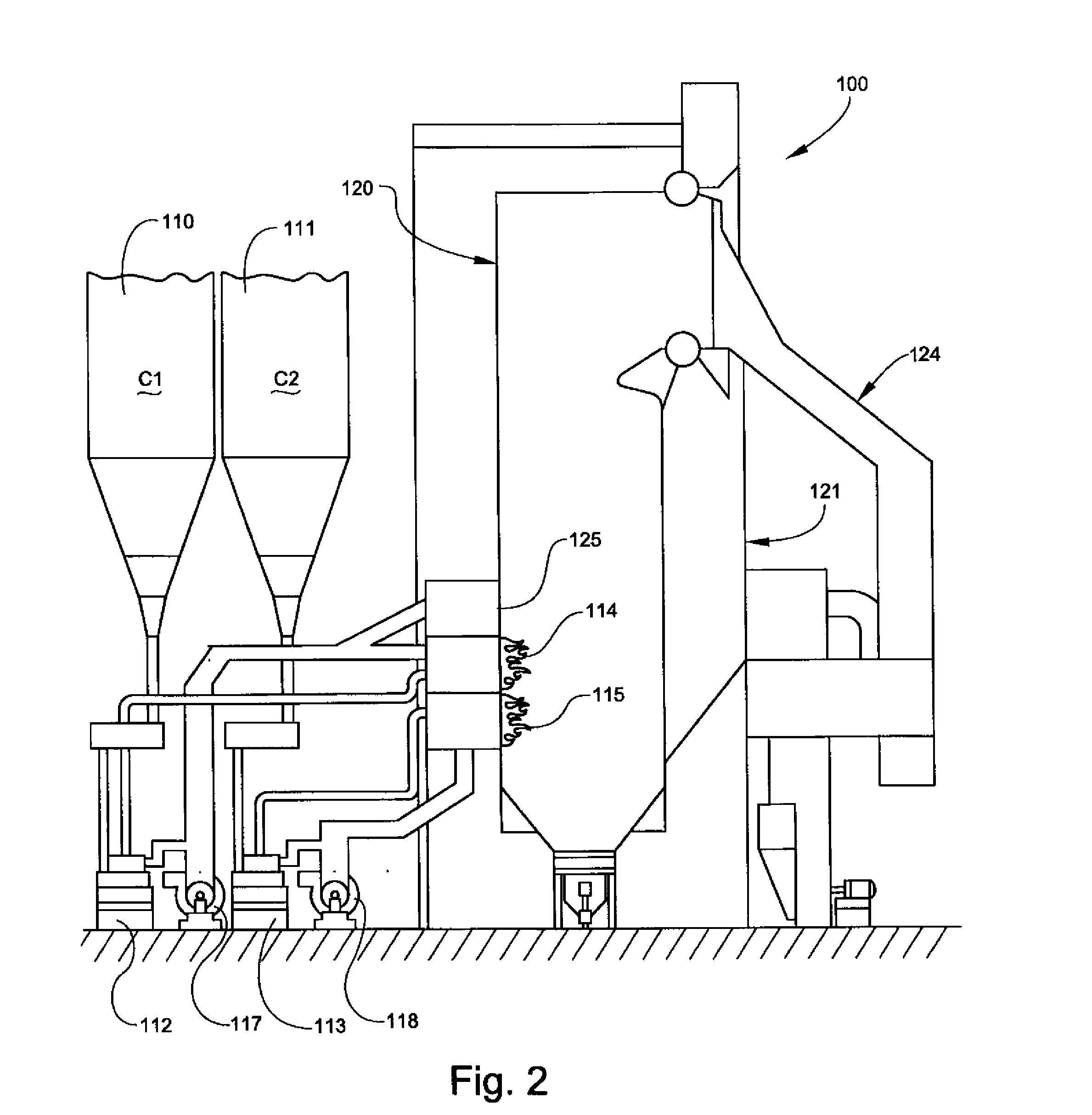
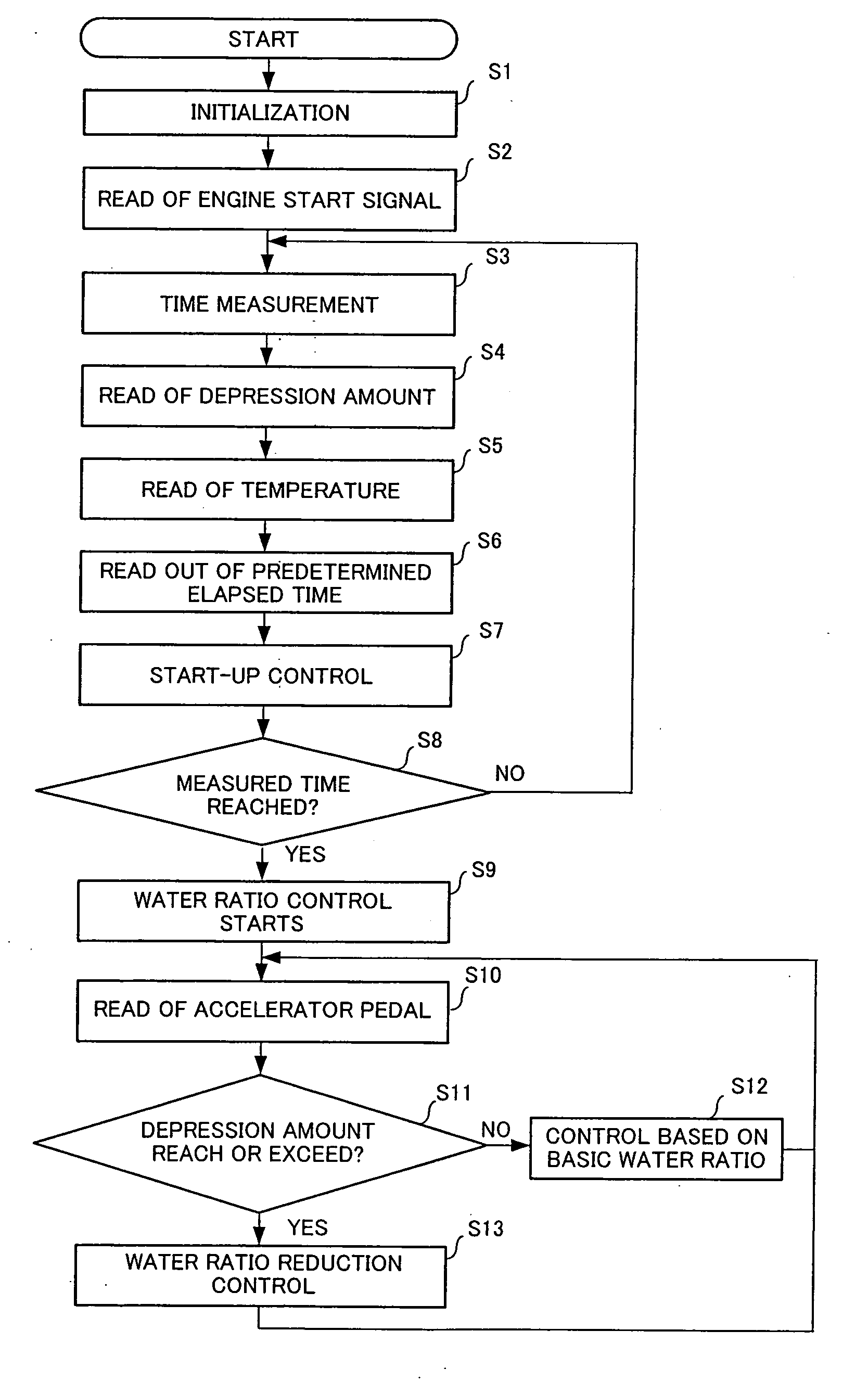
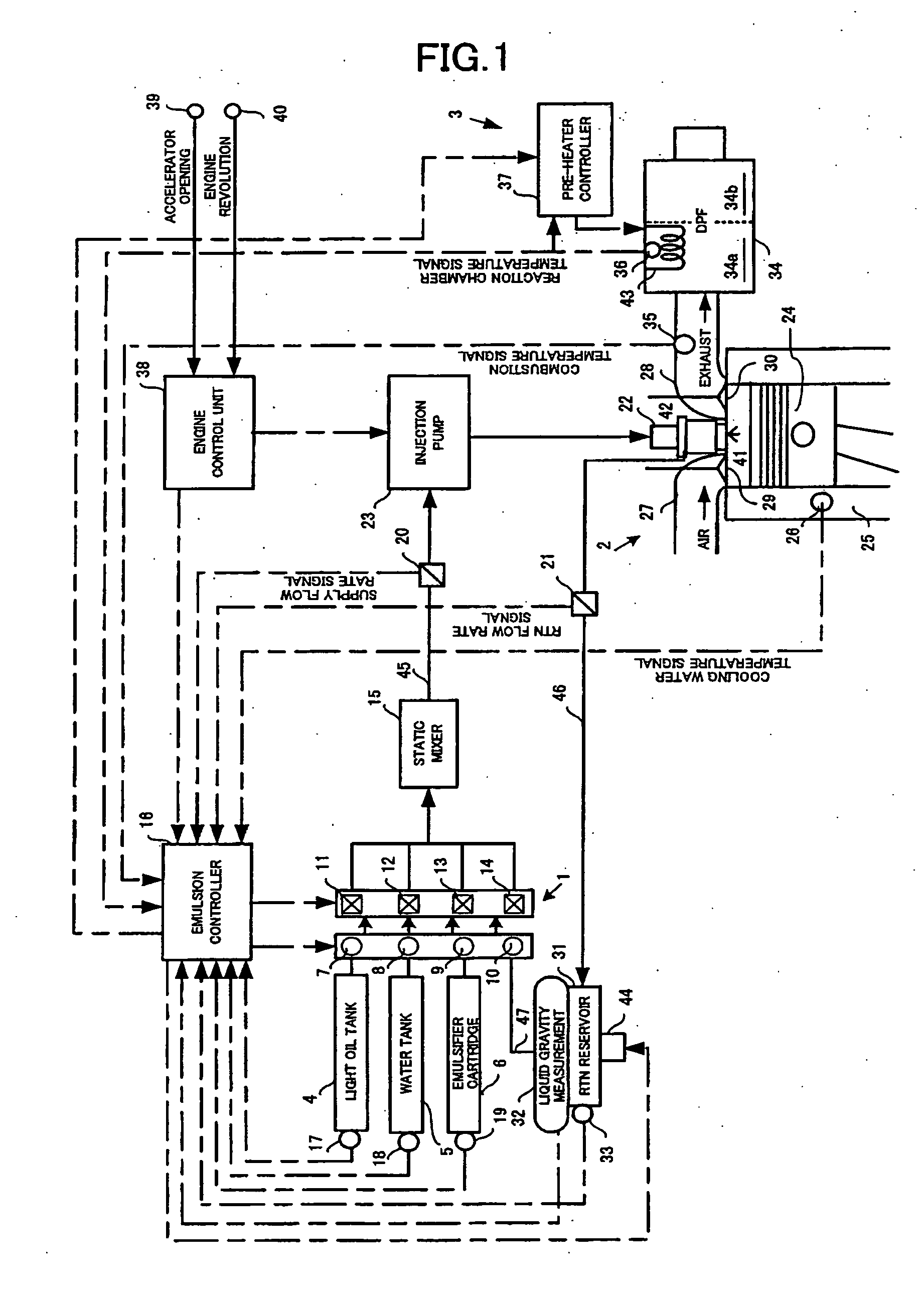
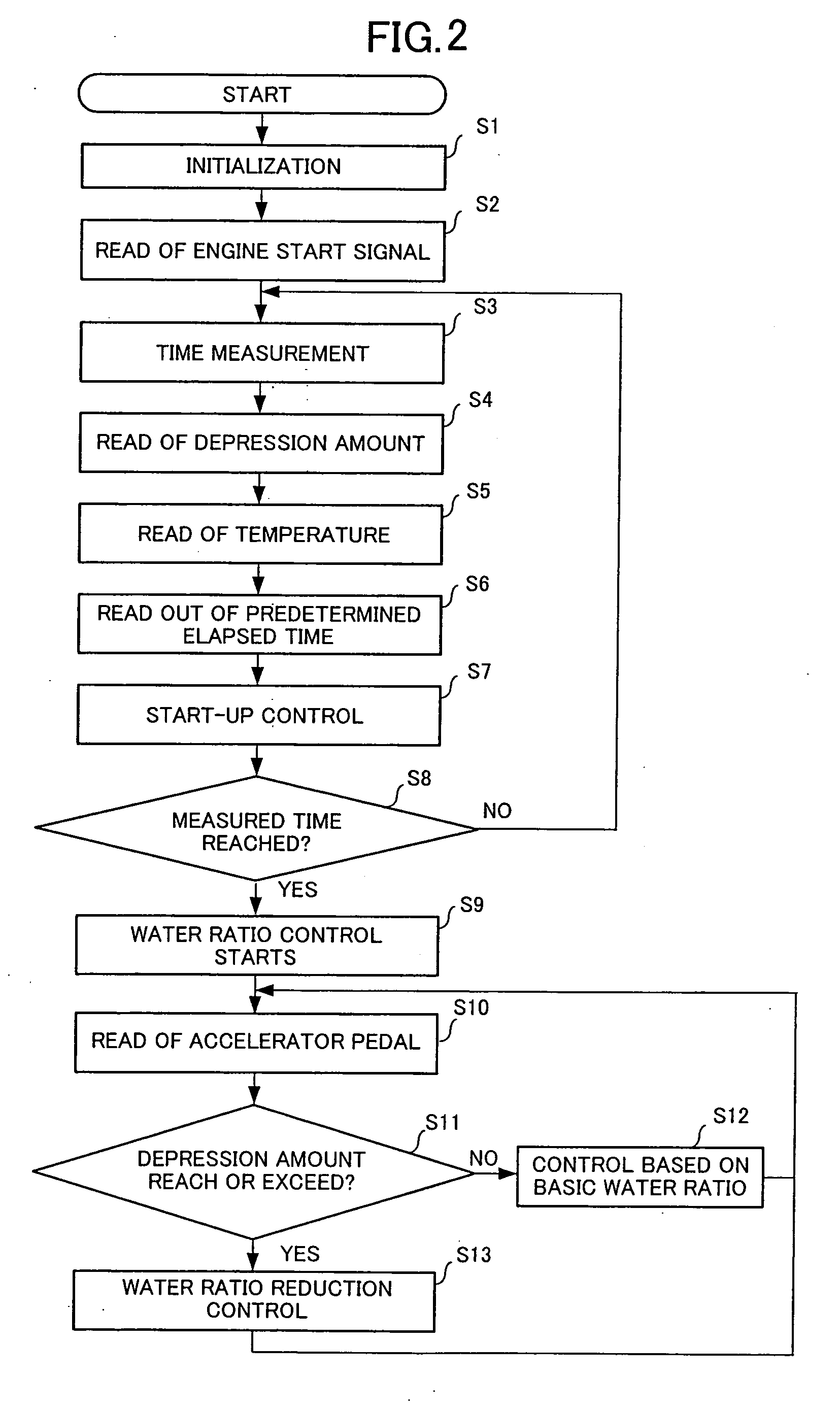
An exhaust emission control apparatus for diesel engines is offered which is capable of achieving better power performance and exhaust emission purification efficiency in an optimally reconciled manner, and from which torque deficiency during hill climbing on a steep slope is eliminated. Emulsified fuel including light oil, water and emulsifier supplied respectively from a light oil tank 4, a water tank 5 and an emulsifier cartridge 6, of which the water ratio is adjusted by flow variable control valves 11-13, is supplied to a combustion chamber 4. The water ratio is normally set to a basic water ratio corresponding to the signal of an accelerator opening sensor 39 (Step S32). However, when a difference between target acceleration and actual acceleration of a vehicle corresponding to the accelerator pedal opening exceeds a predetermined value (Step S36), the basic water ratio is corrected so as to reduce the water ratio (Step S37).
Owner:LENZ ENVIRONMENTAL RESOURCES
Low NOx combustion using cogenerated oxygen and nitrogen streams
InactiveUS7484956B2Reduce the amount requiredMinimizing NOx formationCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelCombustion using liquid and pulverulent fuelNitrogen richOxygen rich
Combustion of hydrocarbon fuel is achieved with less formation of NOx by feeding the fuel into a slightly oxygen-enriched atmosphere, and separating air into oxygen-rich and nitrogen-rich streams which are fed separately into the combustion device.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Fuel injection device for gas turbine
ActiveUS20160169160A1Simple structureReduce the production of nitrogen oxidesContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustion chamberWater vapor
A fuel injection device, for a gas turbine, which enhances uniform distribution in concentration of fuel gas and water vapor in a combustion chamber with simple structure and at low cost to effectively reduce NOx, is provided. The fuel injection device with a fuel nozzle to mix fuel gas and water vapor and inject the fuel gas and water vapor into a combustion chamber, includes: a nozzle housing having a mixing chamber thereinside; a first introduction passage to introduce the fuel gas into the mixing chamber from outside of the nozzle housing; and a second introduction passage to introduce the water vapor into the mixing chamber from an outside of the nozzle housing; and a plurality of reverse passages communicating with a downstream end of the mixing chamber and configured to allow for a plurality of reverses of flow of mixed gas from the mixing chamber.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
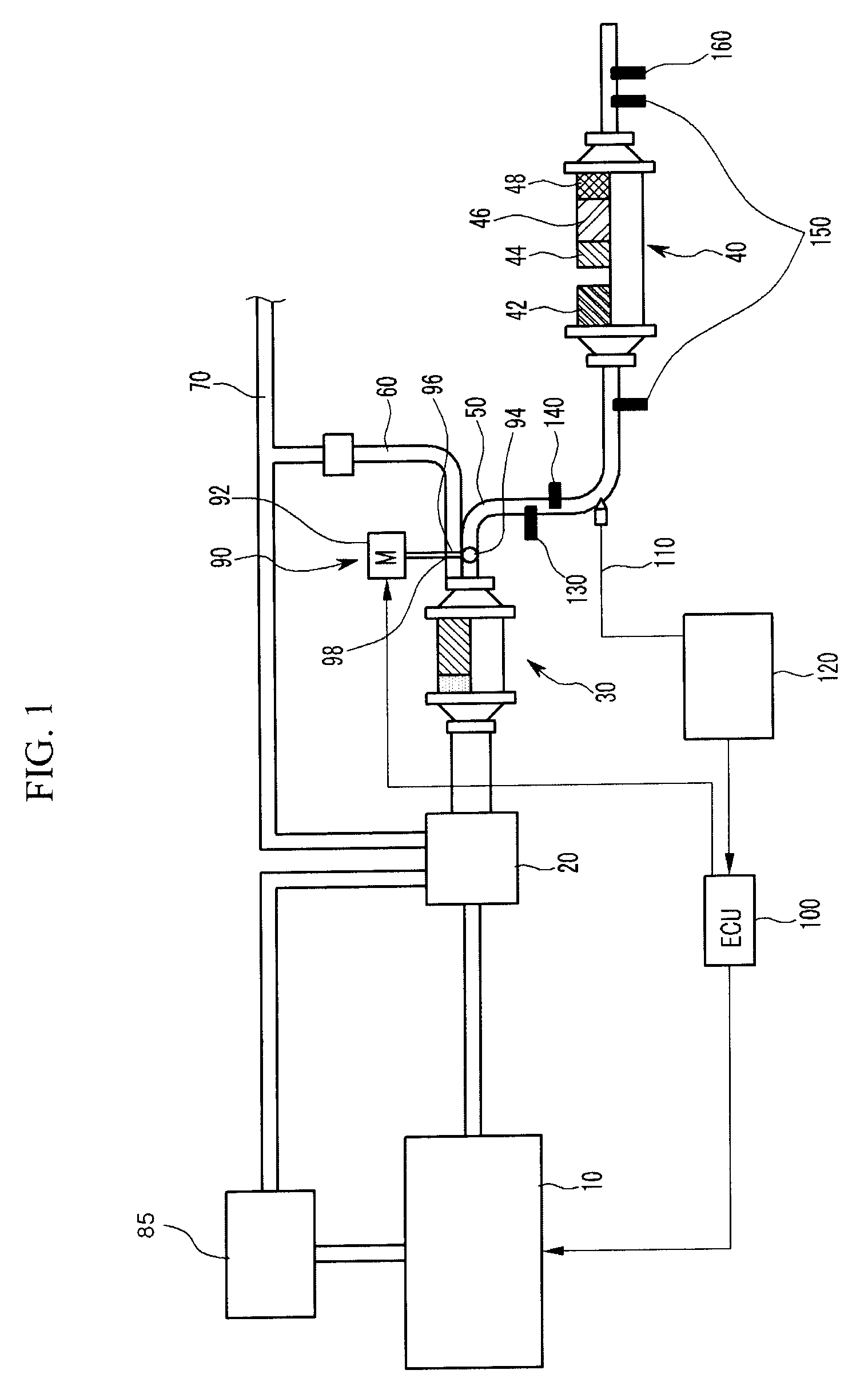
Purification system for variable post injection in LP EGR and control method for the same
InactiveUS8341939B2Reduce materialImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelParticulatesTurbocharger
A purification system for variable post injection in LP EGR, the system includes a turbo charger disposed downstream of a diesel engine, a DPF (catalyzed particulate filter) disposed downstream of the turbo charger, a NOx reduction apparatus disposed upstream or downstream of the DPF, a bypass line diverged from the DPF for mixing exhaust gas and air inflowing the turbo charger, a exhaust gas control portion disposed downstream of the DPF for controlling flowing of the exhaust gas and a lean / rich controlling portion for controlling lean / rich of the exhaust gas.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com