Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Raise temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exhaust emission aftertreatment
InactiveUS6857264B2Raise temperatureImprove utilityElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gasExhaust fumes
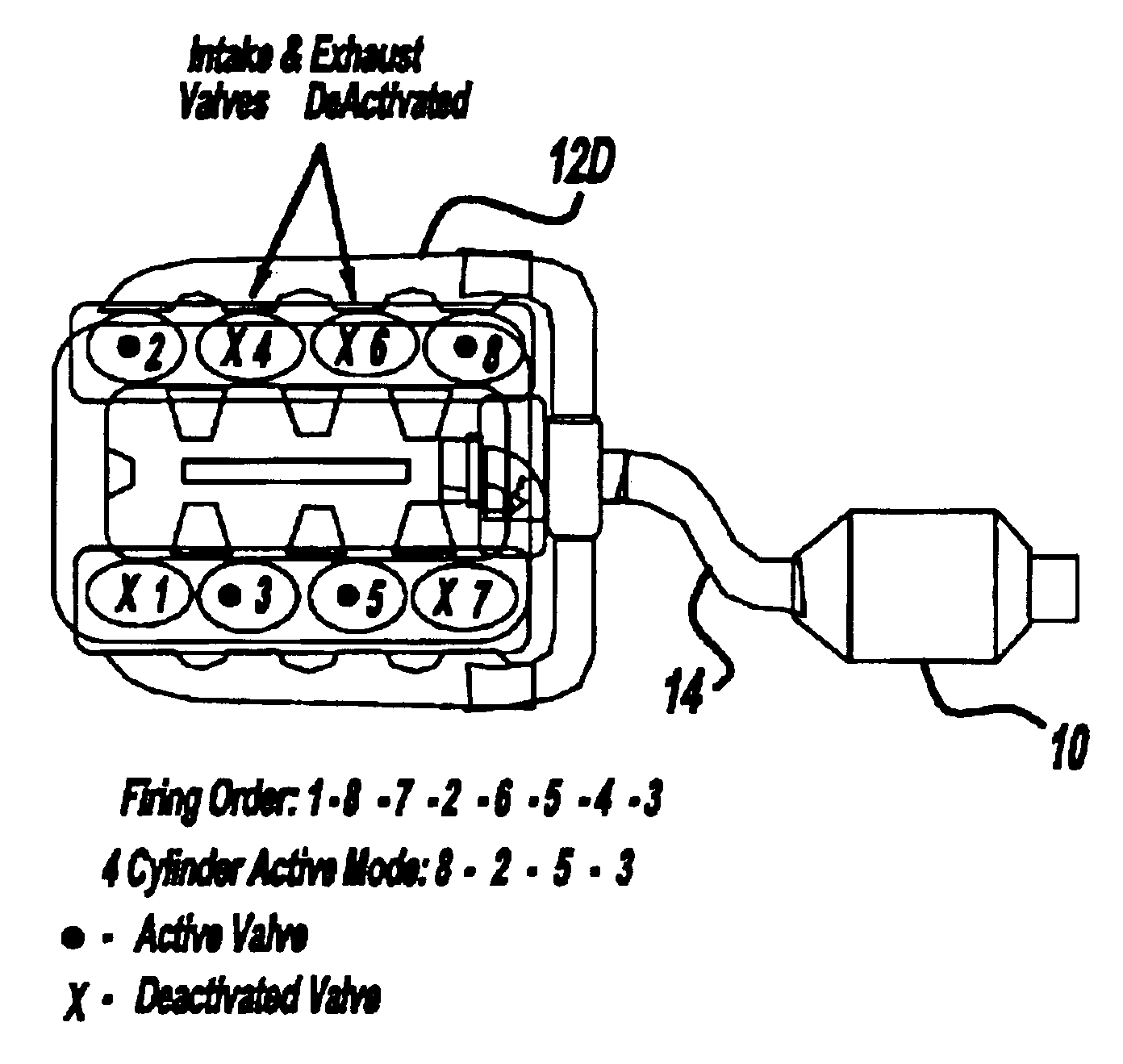
An engine control system in a vehicle including a variable displacement internal combustion engine, a controller for controlling the displacement of the variable displacement internal combustion engine, and where the controller operates the variable displacement internal combustion engine in a partially displaced operating mode upon startup to increase exhaust gas temperature.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Washing machine
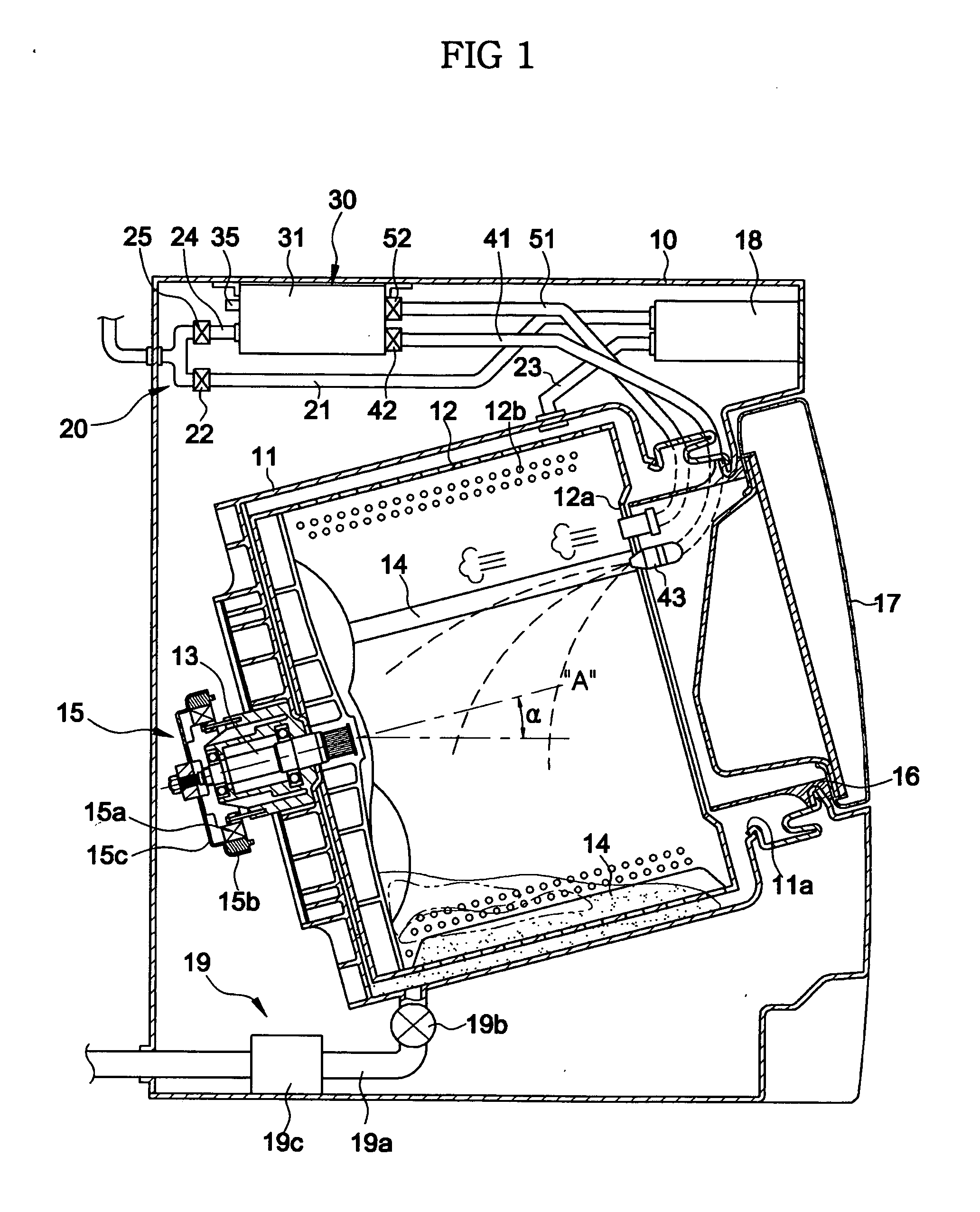
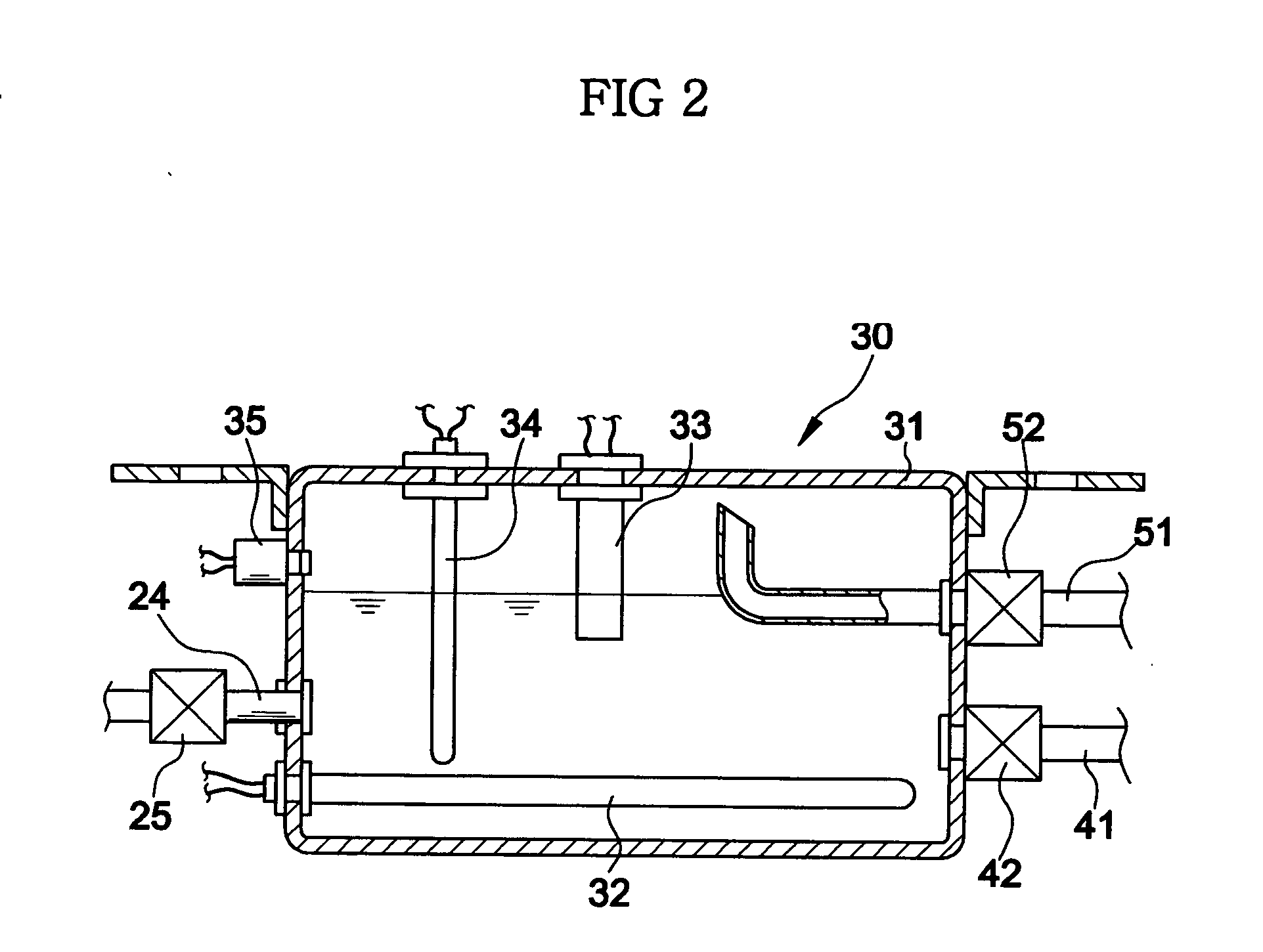
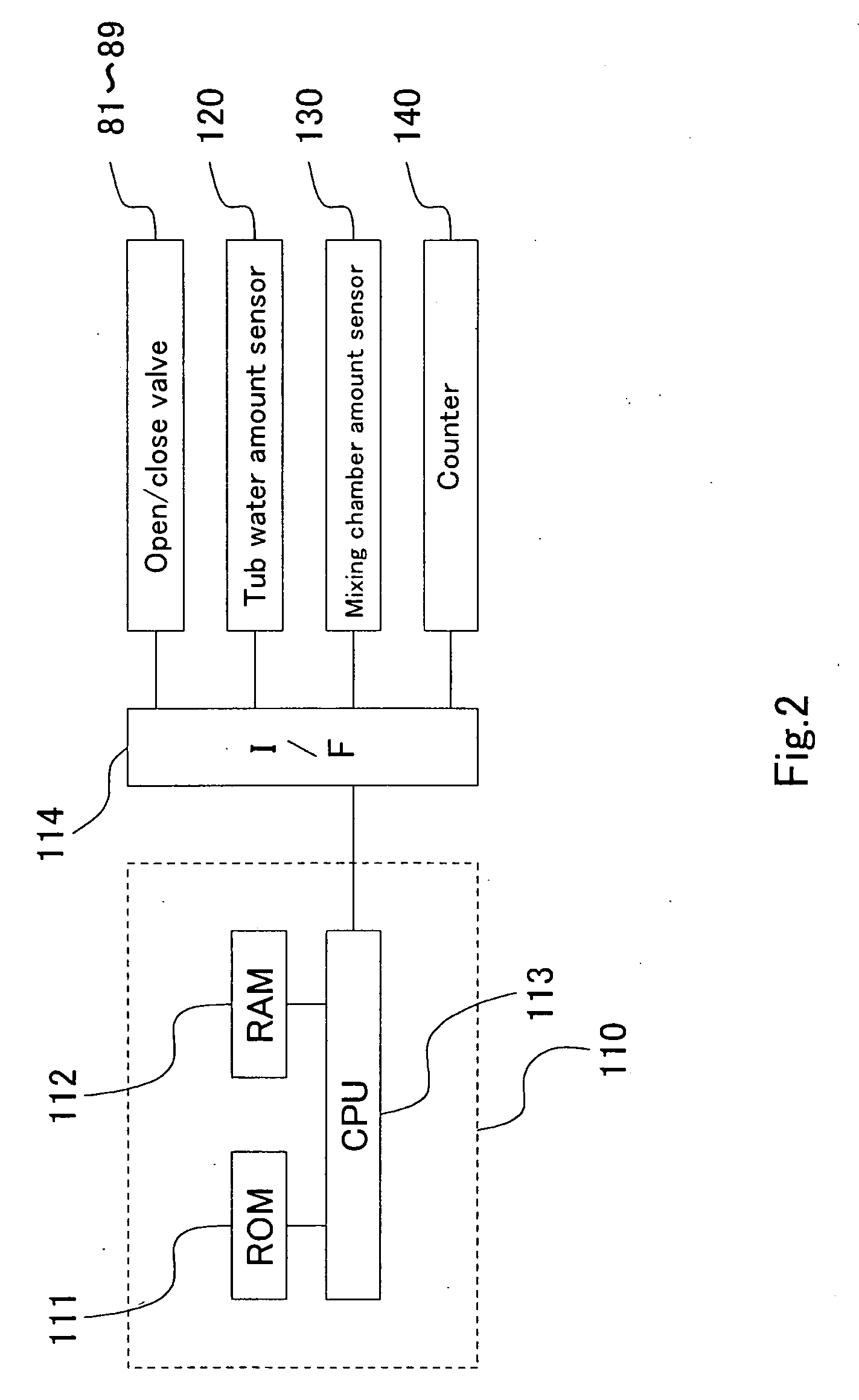
ActiveUS20050132756A1Raise temperatureWash time be reduceOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusProcess engineeringGenerating unit
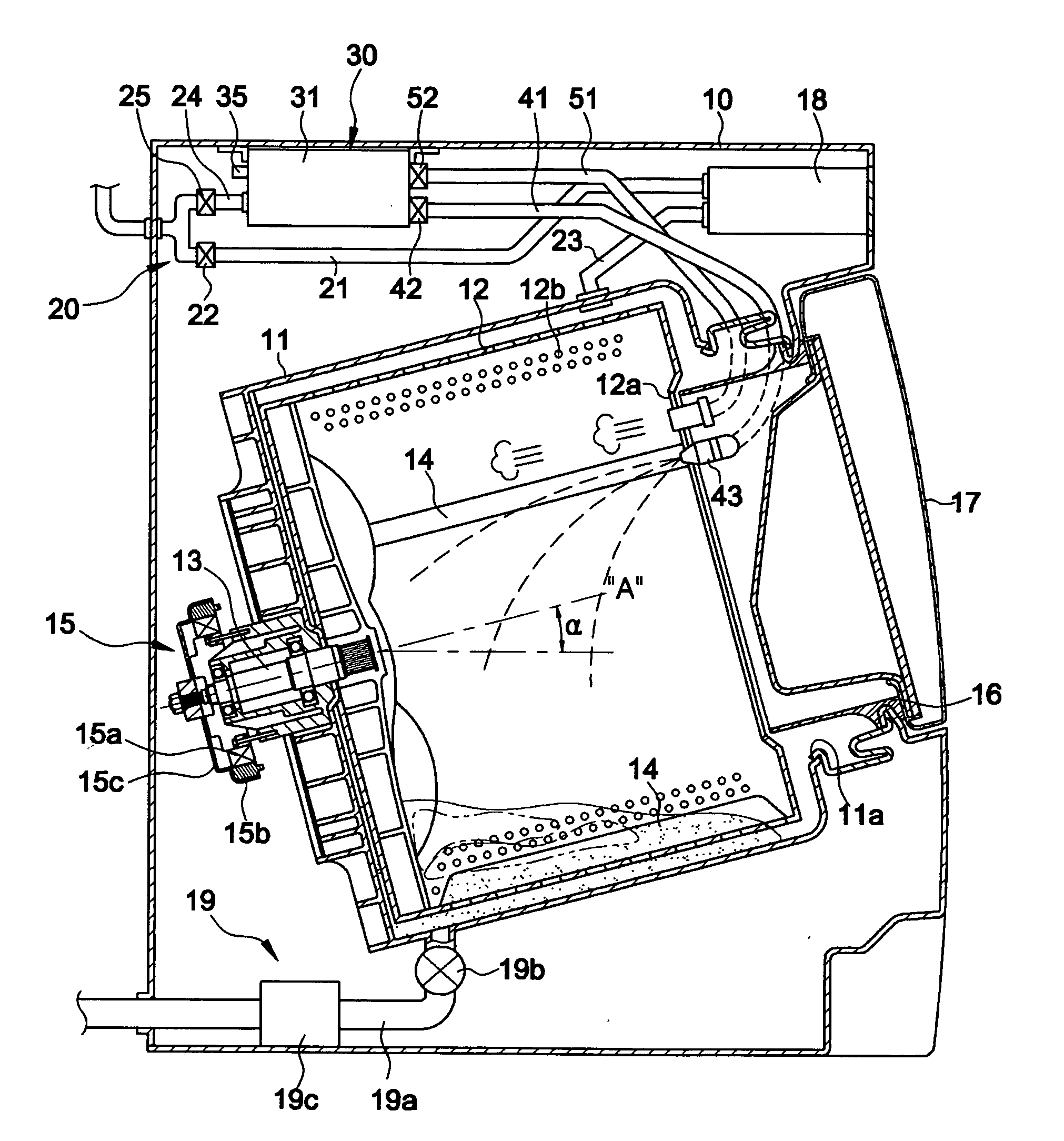
A washing machine in which steam and hot water are supplied to heat wash water. The washing machine includes a water tub for containing wash water, a steam generating unit for heating water supplied thereto, thereby generating steam, a water supply unit for supplying water into the water tub and the steam generating unit, a steam supply unit for supplying the steam generated from the steam generating unit into the water tub, and a hot water supply unit for supplying hot water from the steam generating unit into the water tub. In the washing machine, the temperature of wash water can be rapidly increased in accordance with steam and hot water supplied into the water tub. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce the overall wash time while reducing the amount of wash water to be used. The energy consumed to heat the wash water can also be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
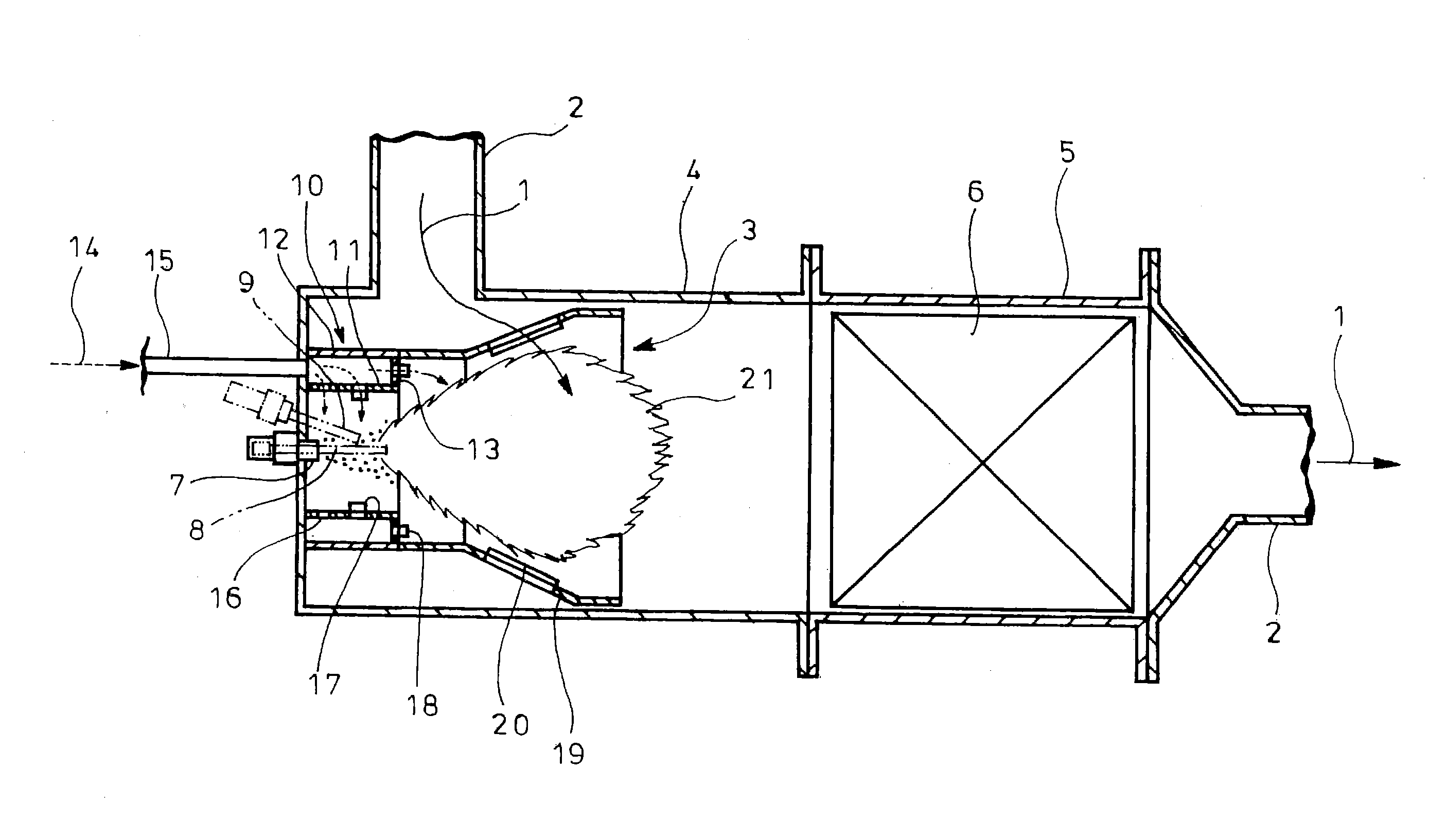
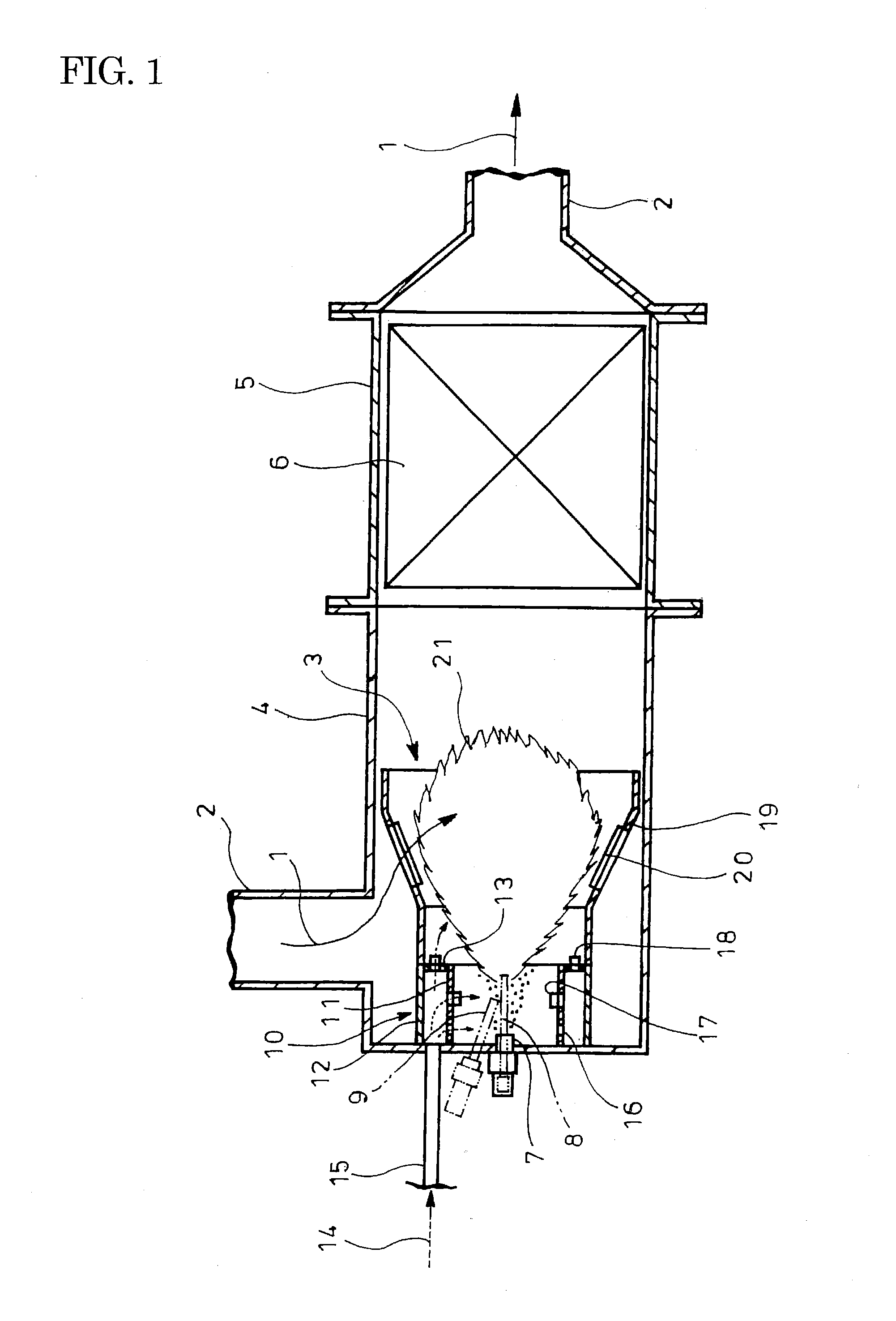
Combustion appliance for raising the temperature of exhaust gas
InactiveUS20120322012A1Raise temperatureFacilitate mixingBurnersSilencing apparatusExhaust gasExhaust fumes
Injection nozzle 7 and electrode rods 8 and 9 (ignitor) are surrounded by double-cylinder flame stabilizer 10. Toroidal blocking plate 13 closes between inner and outer cylinders 11 and 12 of the stabilizer at its distal end whose proximal end is connected with line 15 for introducing combustion air 14 to between the cylinders. Inflow holes 16 are formed throughout the inner cylinder at its proximal end. Peripheral fins 17 are formed peripherally on the inner cylinder radially inwardly through cutting and bending-up at positions shifted from the inflow holes toward the distal end of the inner cylinder such that combustion air is introduced from circumferentially to form swirling flow inside the inner cylinder. End fins 18 are formed on the blocking plate in fuel injection direction through cutting and bending-up such that combustion air is discharged circumferentially to form swirling flow around flame 21.
Owner:HINO MOTORS LTD
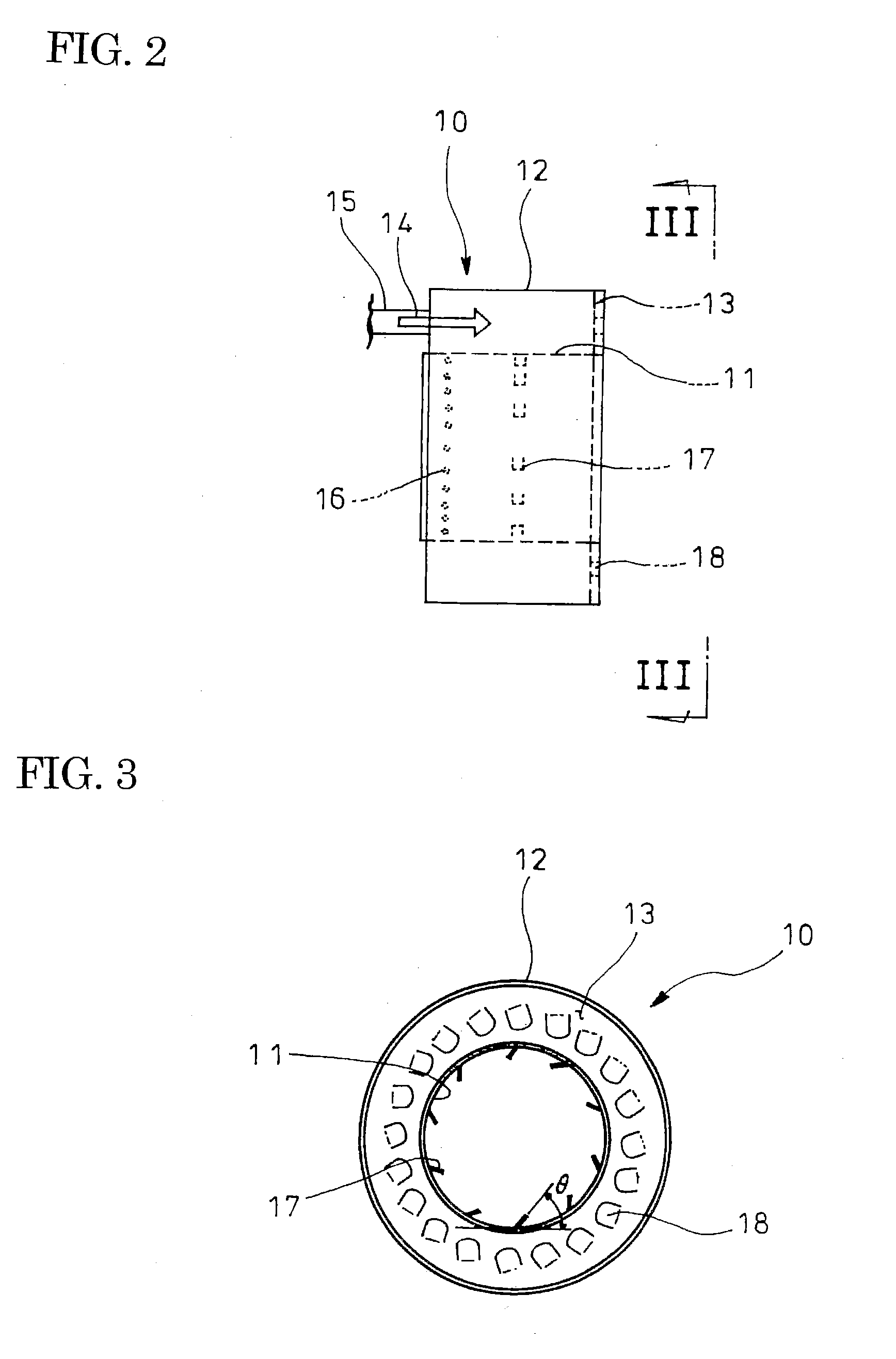
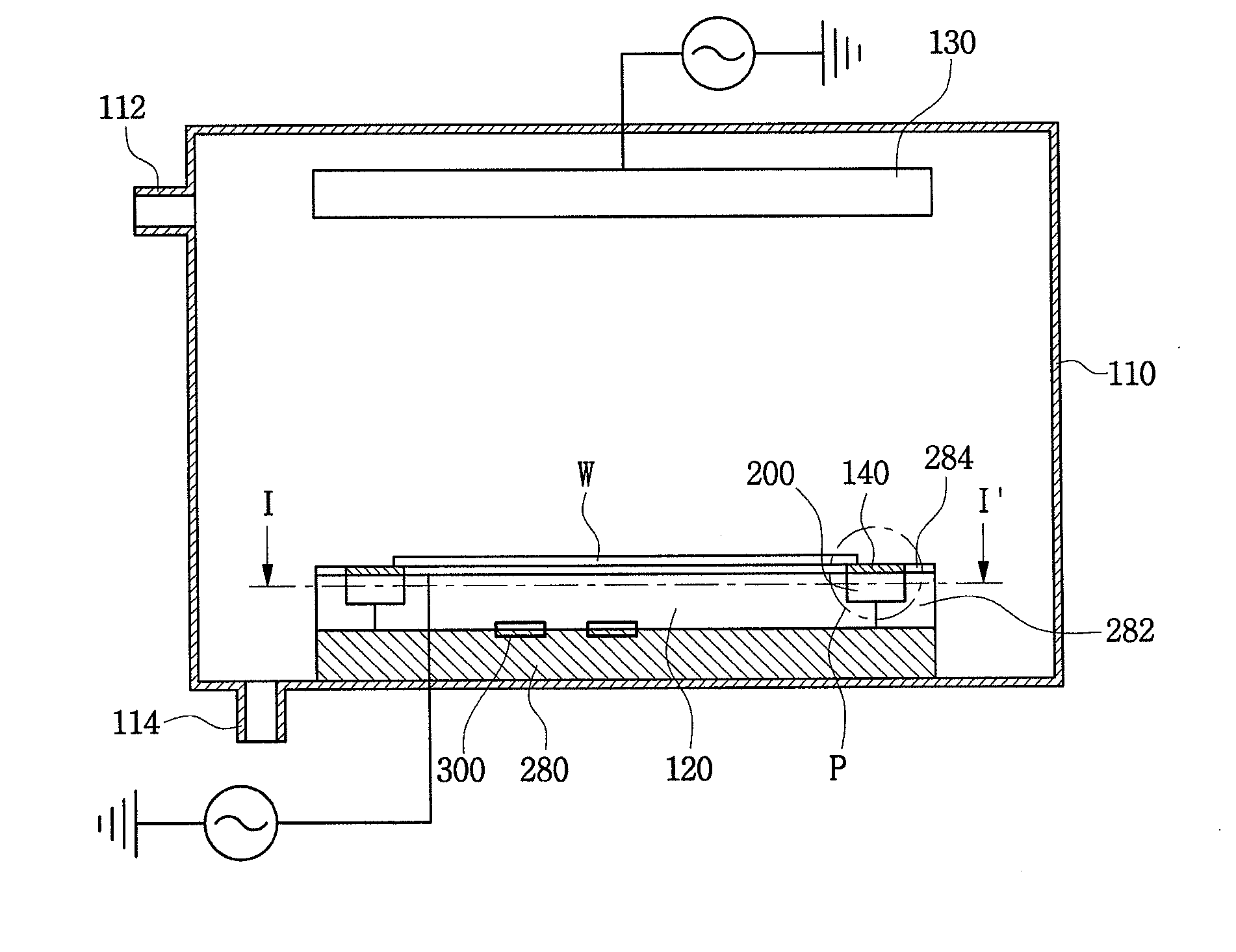
Plasma dry etching apparatus having coupling ring with cooling and heating units
ActiveUS20100326600A1Temperature dropRaise temperatureElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadio frequencyCooling Units
A plasma dry etching apparatus includes a pedestal in a process chamber, the pedestal being configured to support a wafer, a cathode electrode and a plate electrode in the process chamber, the cathode and plate electrodes being configured to apply radio-frequency (RF) power, an edge ring on an edge of the pedestal, a coupling ring having a first side on the pedestal and a second side on the edge ring, an edge cooling unit in the coupling ring, the edge cooling unit being configured to cool the edge ring to drop a temperature of an extreme edge of the wafer, and an edge heating unit in the coupling ring, the edge heating unit being configured to heat the edge ring to raise the temperature of an extreme edge of the wafer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
NANO composite with superhydrophobic surface and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130115420A1Raise temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsNanometreNanocomposite
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Remotely RF powered conformable thermal applicators
ActiveUS20070168001A1Raise temperatureElectrotherapyEnergy modified materialsSuperparamagnetismCompound (substance)
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to apparatus and methodology of thermal applicators in cancer therapy. In particular, the present embodiments are directed to a technique called “nanoparticle ferromagnetic resonance heating,” where ferromagnetic resonance heating in addition to an RF hyperthermia treatment is used to cause cell apoptosis and necrosis. An apparatus for carrying out a ferromagnetic resonance heating treatment of a tumor, comprises a volume concentration of super paramagnetic particles contained within the interior of the tumor, the concentration ranging from about 0.1 to about 1 percent; a magnetic field source configured to deliver a gradient DC magnetic field to the region of the tumor; and an energy source configured to deliver to the tumor an RF field at a frequency ranging from about 100 to 200 MHz. The apparatus of claim 1, wherein the super paramagnetic particles are selected from the group consisting of maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) based compounds, and yttrium iron garnet (Y3Fe5O12) based compounds.
Owner:INTEMATIX
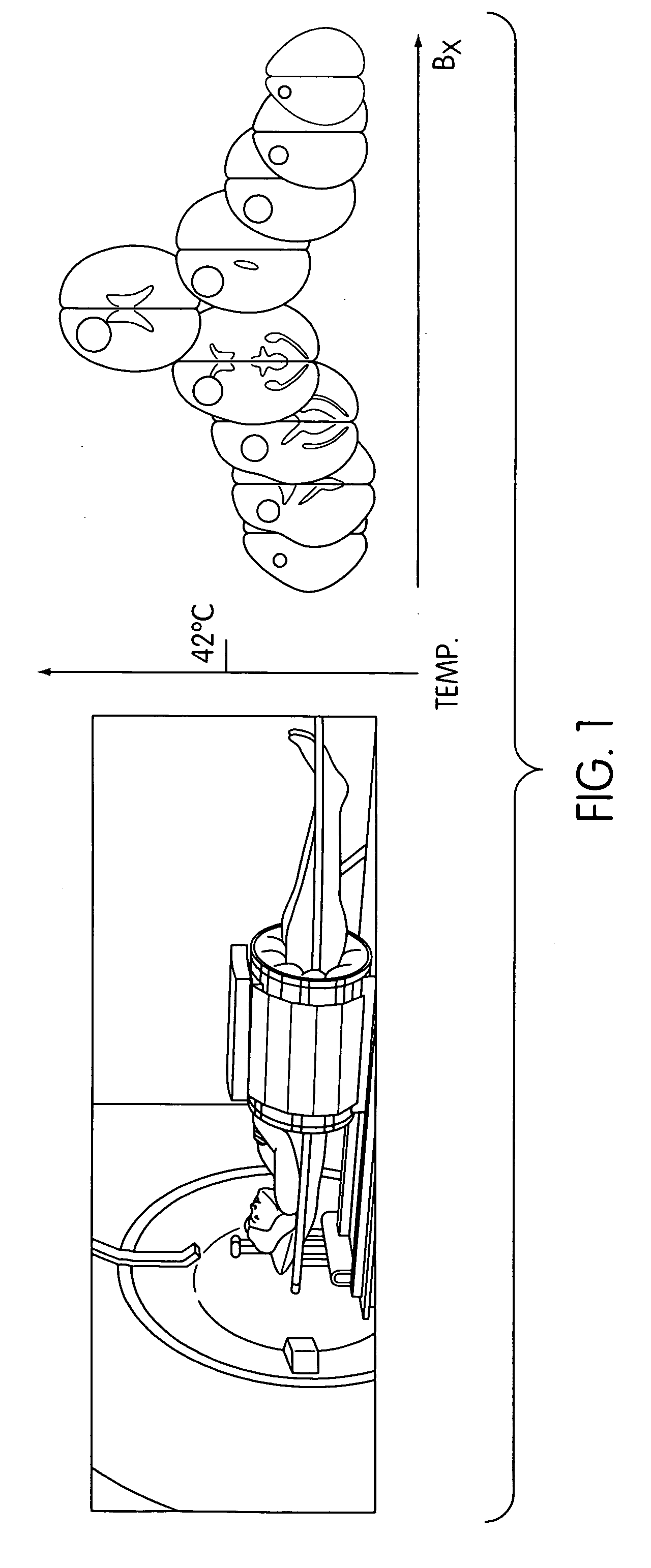
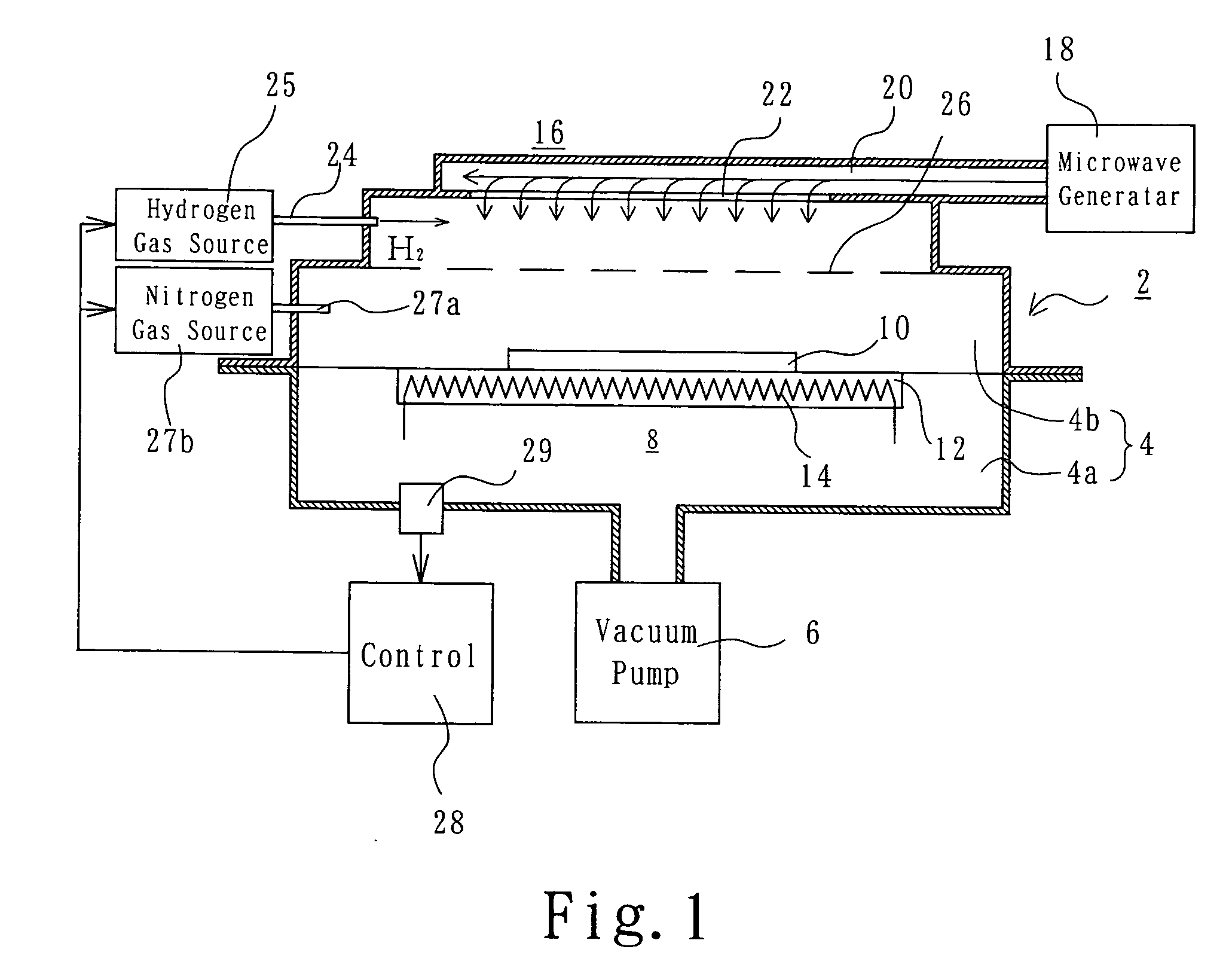
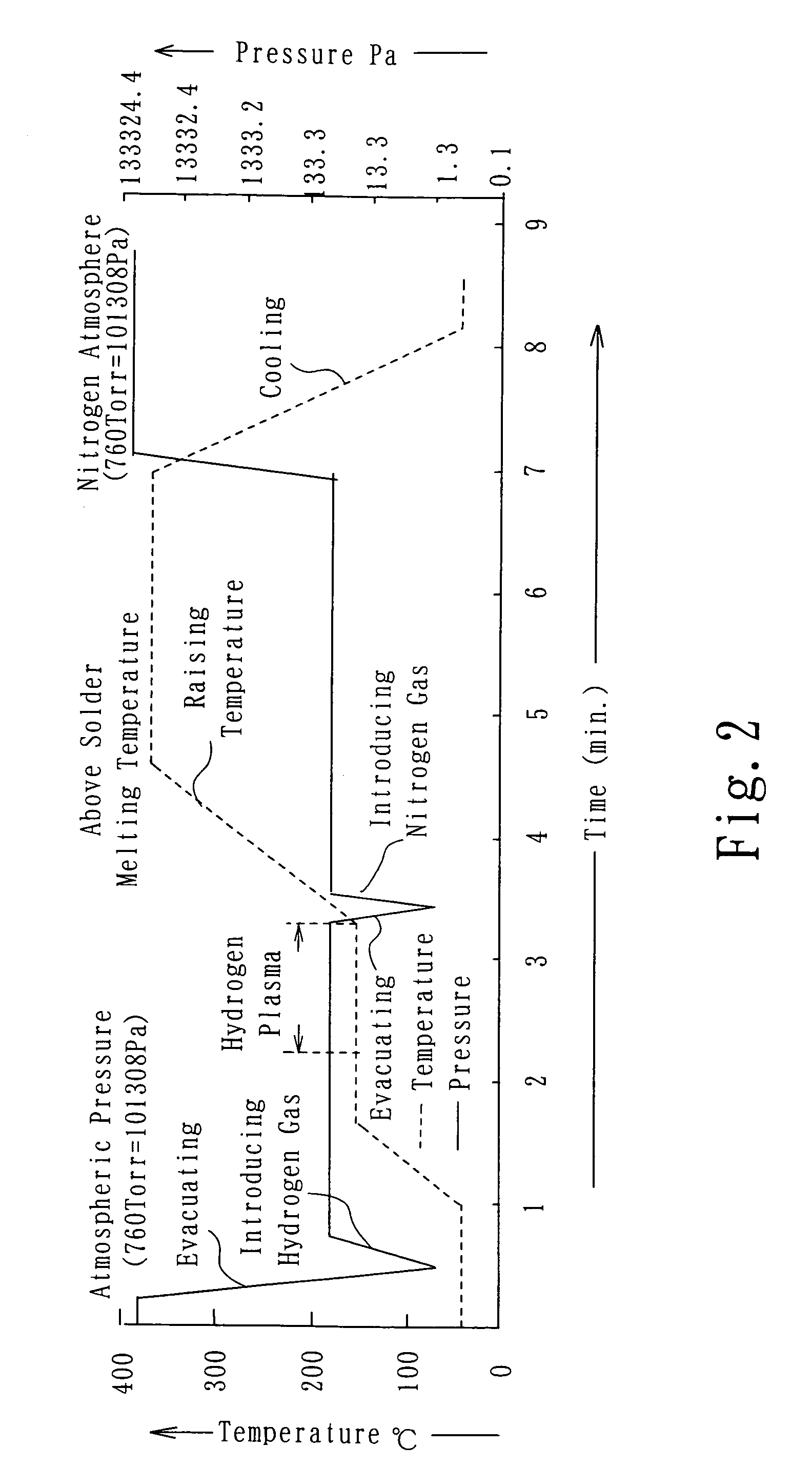
Soldering method
InactiveUS20070170227A1Raise temperaturePrinted circuit assemblingCooking-vessel materialsIndiumSoldering
An object of the invention is to provide a high-quality soldering method, by reducing, to a vacuum, the pressure in a vacuum room (2) in which a workpiece (10) having solid solder placed thereon consisting solely of tin or including tin and one or more components selected from silver, lead, copper, bismuth, indium and zinc is disposed. A free-radical gas is generated to remove an oxide film on the solder, and, after that, the generation of the free-radical gas is stopped, and the temperature of the solder is raised to a temperature above the melting point of the solder to melt the solder in the non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Owner:SHINKO SEIKI CO LTD
Fuel cell cogeneration system
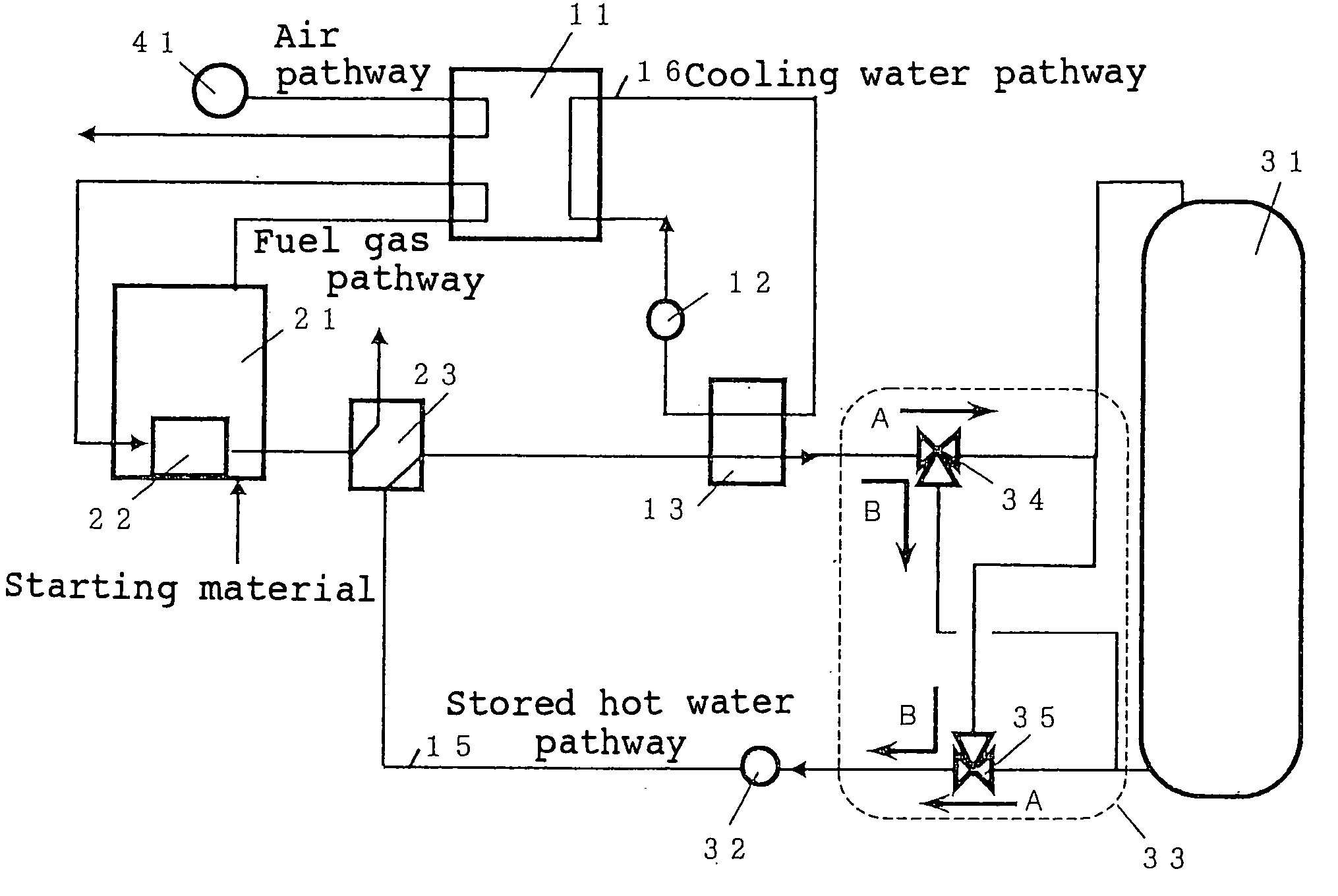
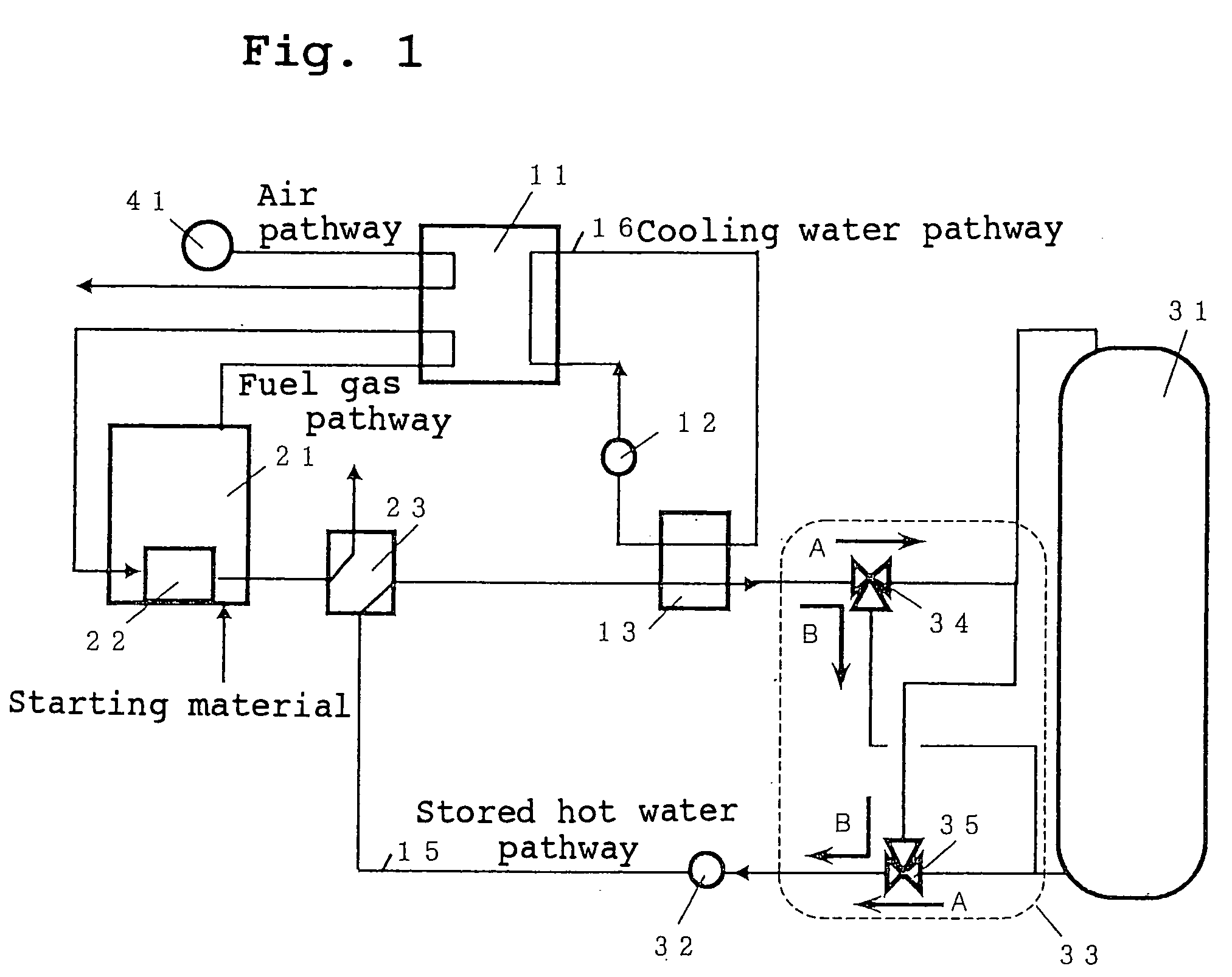
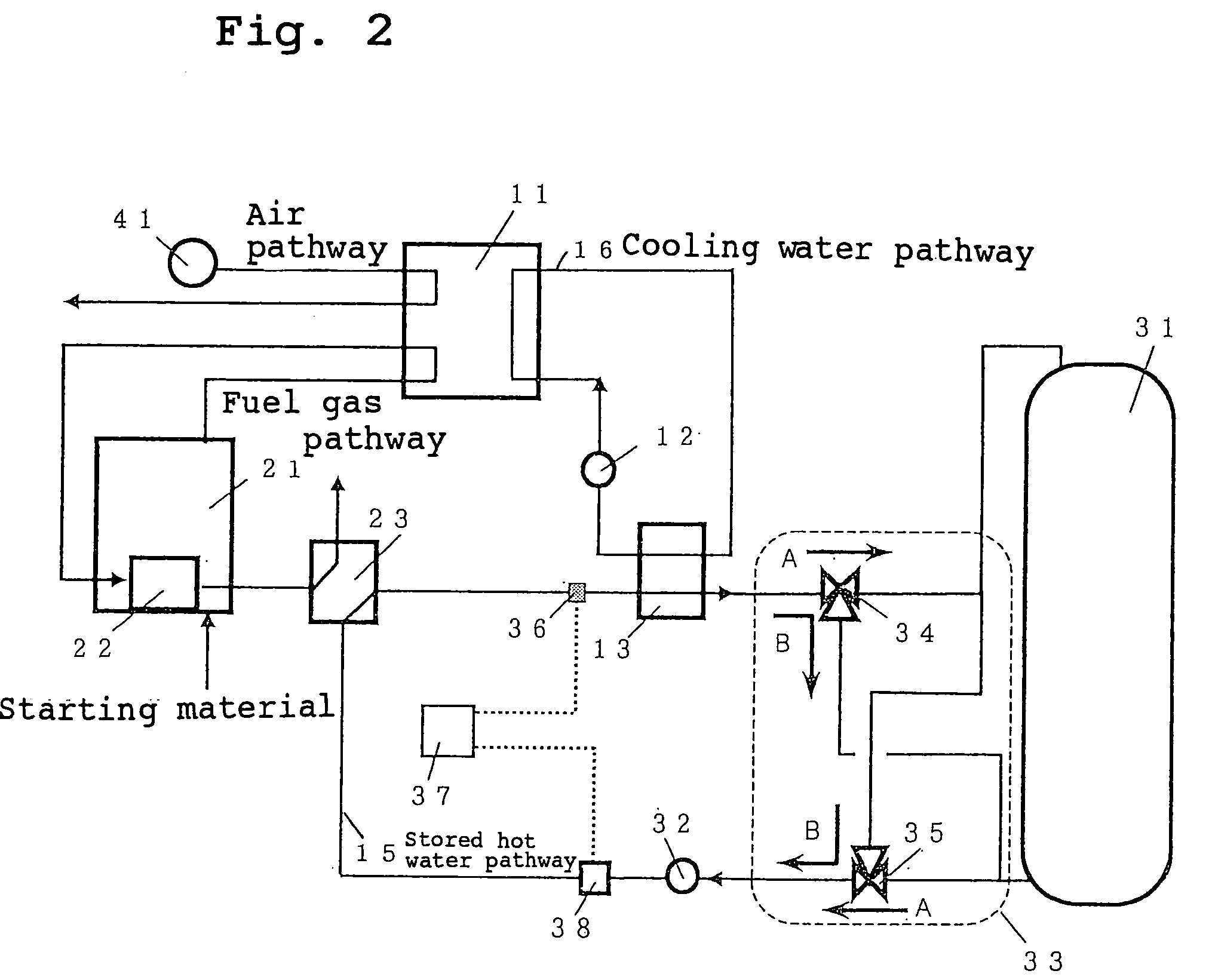
InactiveUS20050164056A1Raise temperatureReduce timeFuel cell auxillariesFuel cell applicationsCogenerationWater tanks
A fuel cell cogeneration system includes a fuel cell, a cooling water heat exchanger provided on a cooling water pathway, a stored hot water pathway through which stored hot water that exchanges heat with cooling water flows, a stored hot water tank, a stored hot water controlling device, a stored hot water temperature measuring device, a stored hot water flow rate adjusting device, a flow rate controlling device of controlling the stored hot water flow rate adjusting device and an exhaust gas heat exchanger of exchanging heat between exhaust gas from fuel processing devices and stored hot water. The flow rate controlling device controls the stored hot water adjusting device to reduce the flow rate of stored hot water flowing through the stored hot water pathway when the temperature of stored hot water is a first predetermined temperature or less during the starting of operation of the fuel cell.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Grain refining method of high-strength long-service-life gear steel
The invention relates to a grain refining method of high-strength long-service-life gear steel. The grain refining method of the high-strength long-service-life gear steel comprises the following steps of controlling the steel 0. 020%-0.030% of Al, 0.010%-0.060% of Nb, 0.0060%-0.0100% of N, Ti is less than or equal to 0.035%, O is less than or equal to 0.012%, the content of Al and Ti is reduced,Nb is increased, a part of N is matched, and the crystal grains are refined by the co-action of Al+Nb+N. The rolling process has a key influence on grain refinement, in the aspect of rolling, according to the melting of AlN, NbC, NbN, Nb (C, N), the research on the precipitation temperature and the precipitation phase is improved in a targeted manner, during heating, Nb, C, Al and N are fused intogamma-Fe, a large compression ratio is adopted for the first several times of rolling, so that large deformation is formed; the tissue is refined, tissue preparation is provided for separation of theposterior particle AlN and NbC; the final rolling temperature is controlled, so that a large amount of particles such as NbC, AlN and the like after rolling are separated out; after rolling, slow cooling is carried out, the cooling speed is less than or equal to 8 DEG c. / min, the precipitation time of Al, Nb carbide, nitride or carbonitride is prolonged, through the above improvement, the grainsize of the gear steel is ensured to be fully refined.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Combustion process applicable to the manufacture of cement
Combustion process especially applicable to cement works, in which process it is desired to use fuels which are difficult to ignite. To do so, a flame comprising a primary zone and a secondary zone is created. The hot primary zone is created using an oxy-fuel flame, which makes it possible to preheat the fuel which is difficult to ignite so as to raise it to the suitable temperature in the secondary zone where it burns, with air, in order to create the main flame. Applications: cement, metallurgy, glass, etc.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Heater
ActiveUS20130287378A1Raise temperatureImprove sealabilityBeverage vesselsLiquid transferring devicesHoneycomb structureBiomedical engineering
The heater includes a heater main body, a housing storing the heater main body therein, and a coating material arranged in at least a part between the heater main body and the housing and covering at least a part of the heater main body. The coating material is a material containing at least one of ceramic and glass, the heater main body has a cylindrical honeycomb structural portion having partition walls separating and forming a plurality of cells and a pair of electrode portions disposed on a side face of the honeycomb structural portion, the housing contains the heater main body so as to cover the side face side of the heater main body, and the partition walls of the honeycomb structural portion is of a material containing ceramic as the main component and produces heat by energization.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Heater
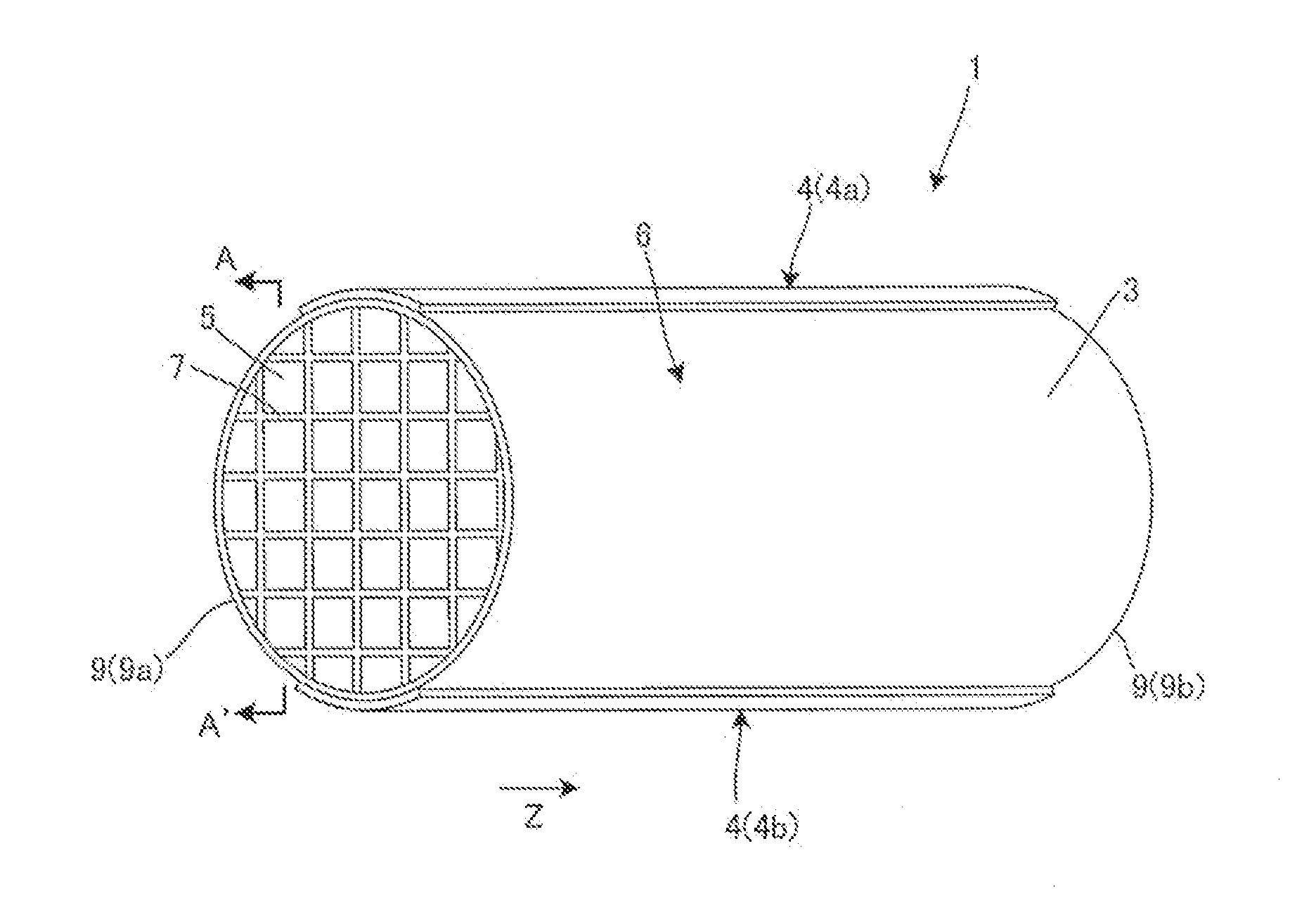
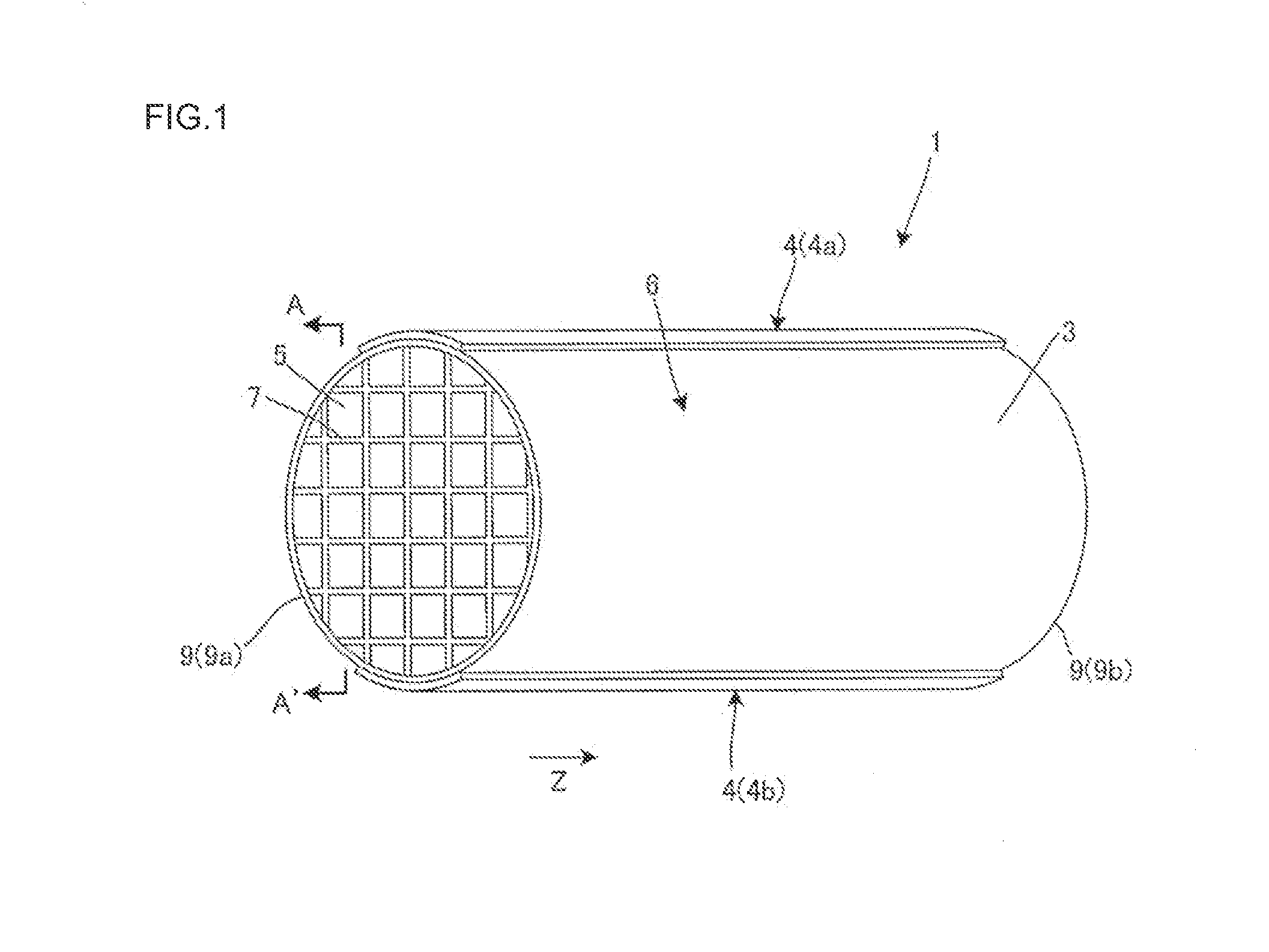
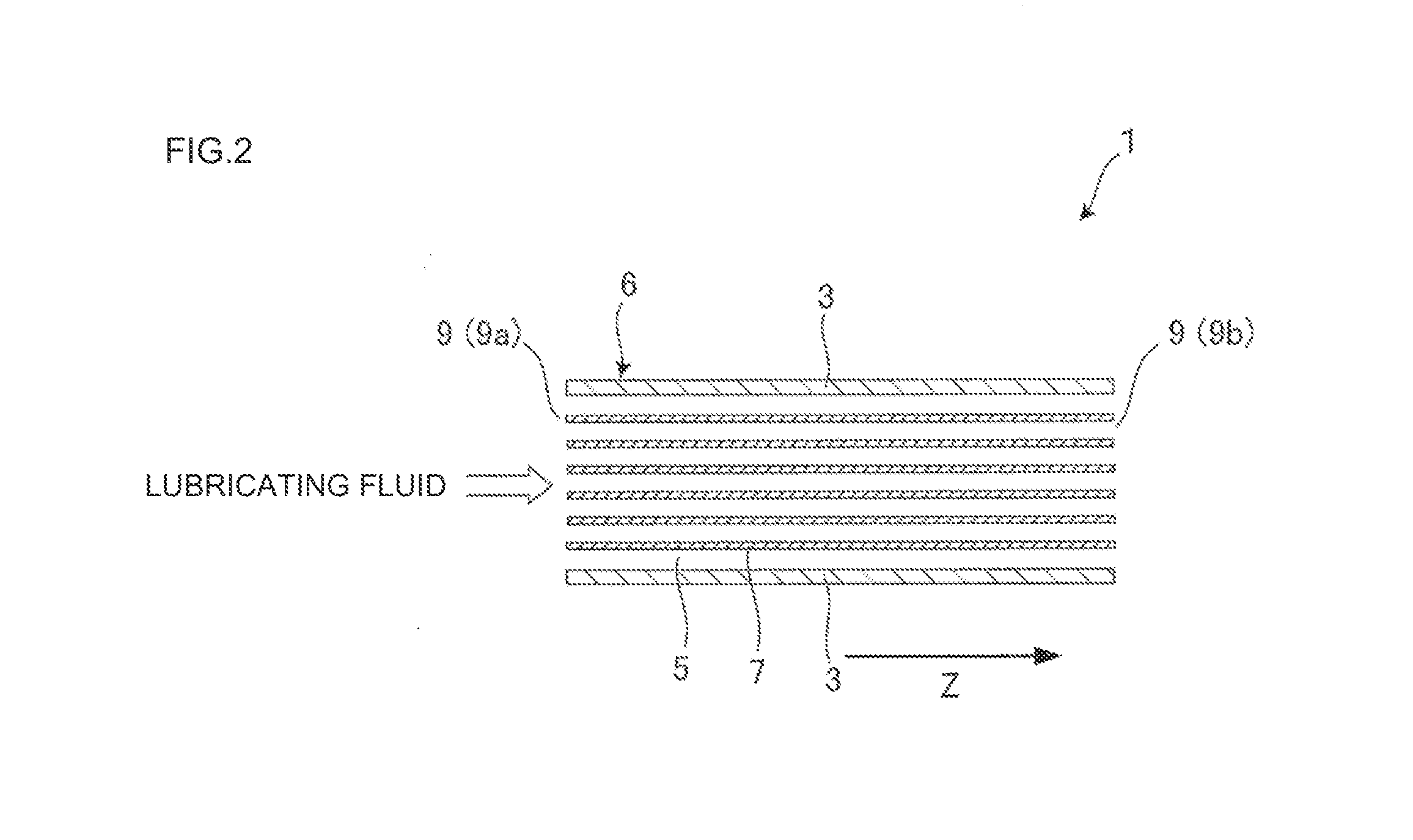
ActiveUS20120241439A1Raise temperatureGrow fastOhmic-resistance electrodesHeater elementsCeramicHoneycomb structure
There is disclosed a heater which does not excessively heat a lubricating fluid but can rapidly raise a temperature of the lubricating fluid, even when a size thereof is small. A heater 1 includes a honeycomb structure section 6 including partition walls 7 which contain a ceramic as a main component and generate heat by electrical conduction, and a plurality of cells 5 which are partitioned and formed by the partition walls 7 and extend through the honeycomb structure section from one end 9a to another end 9b to become through channels of a lubricating fluid; and a pair of electrodes 4 which become an anode 4a and a cathode 4b to come in contact with the honeycomb structure section 6, thereby conducting the electricity through the partition walls 7 of the honeycomb structure section 6.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Apparatus and method for preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide
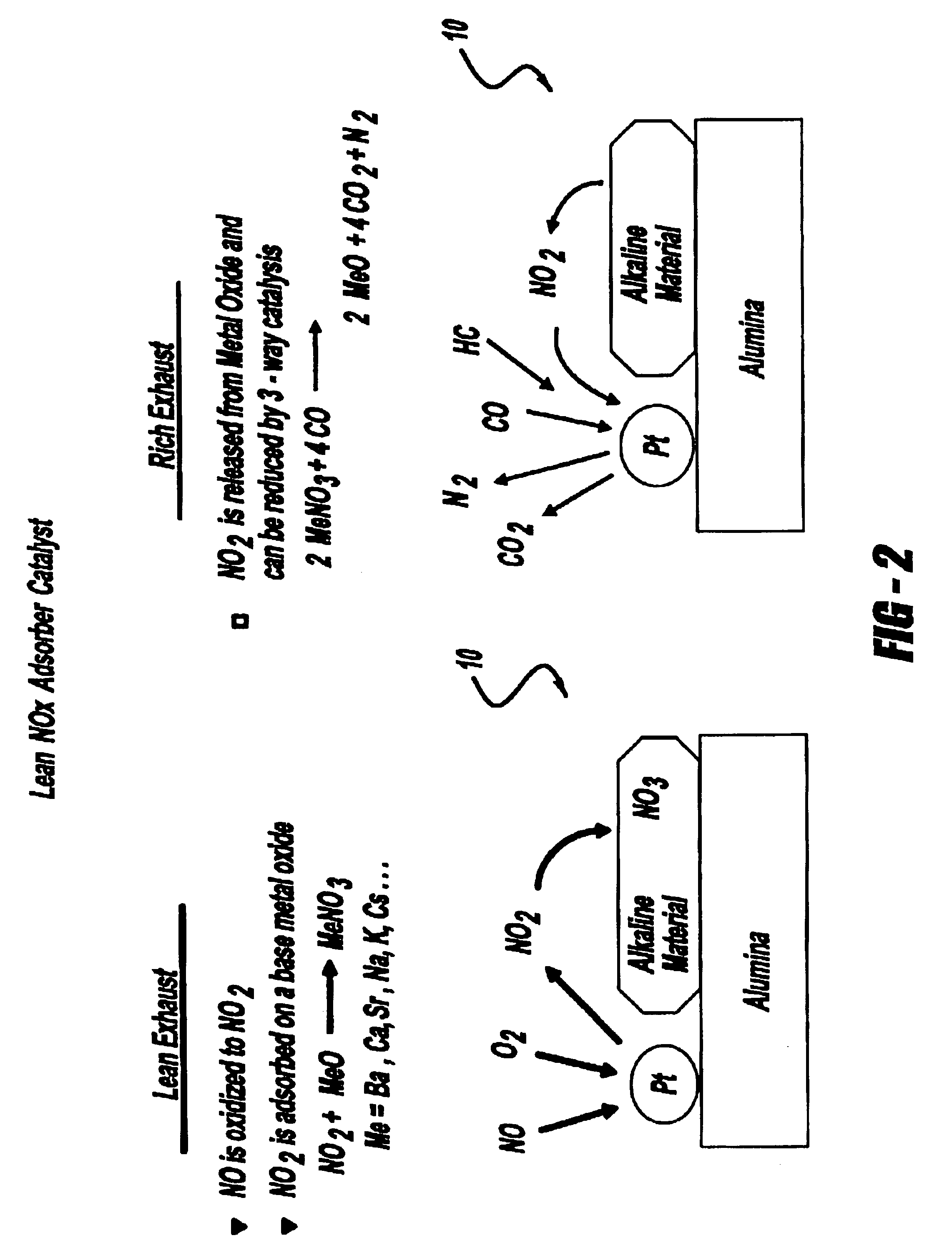
InactiveUS20060067863A1Raise temperatureHydrogenPhysical/chemical process catalystsChemistryHigh pressure
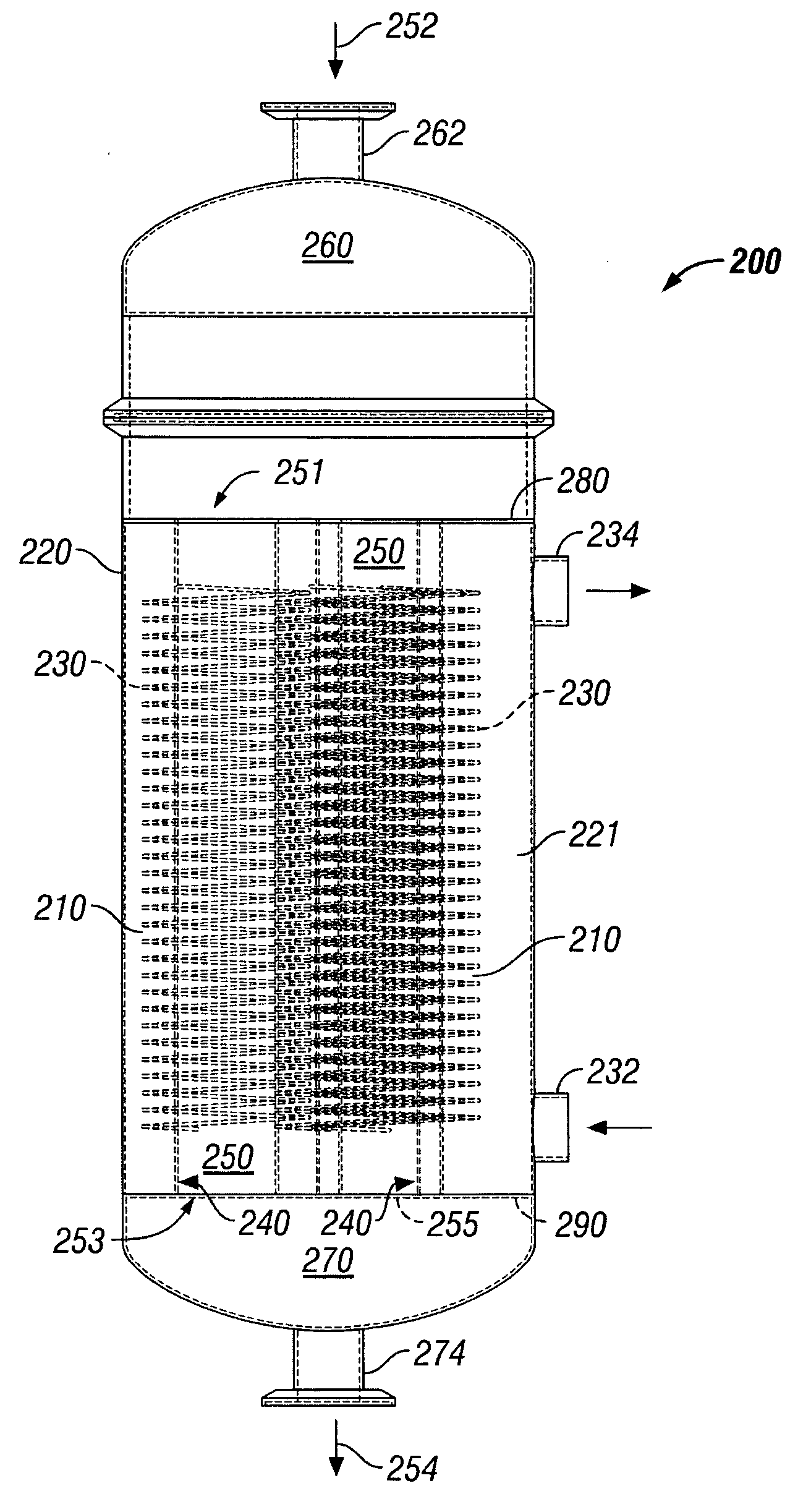
An apparatus and method for the preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide in a hydrogen-rich fluid. The apparatus utilizes one or more reactors that are dimensioned to optimize the exothermic oxidation reaction and the transfer of heat to and from the catalyst bed. A reactor of the apparatus has an elongated cylindrical catalyst bed and heat transfer means adjacent the catalyst bed. The heat transfer means is suitable for pre-heating the catalyst bed during start-up operations and for removing the heat from the catalyst bed during the oxidation reaction. One or more reactors of different dimensions may be utilized depending upon the pressure of the hydrogen-rich fluid to be directed into the apparatus and the pressure requirements for the carbon monoxide-depleted fluid exiting the apparatus. For instance, in low pressure operations where it may be desirable to minimize the pressure drop across the apparatus, two or more reactors having relatively smaller dimensions can be utilized. In higher pressure operations where pressure drop across the preferential oxidation apparatus is of less concern, a single reactor having larger dimensions may be utilized. The relatively narrow dimension of the catalyst bed coupled with the relatively large surface are used for heat transfer provides for more uniform temperatures within the catalyst bed and improved temperature control of the bed.
Owner:TEXACO INC
Methods and systems for controlling catalyst temperature
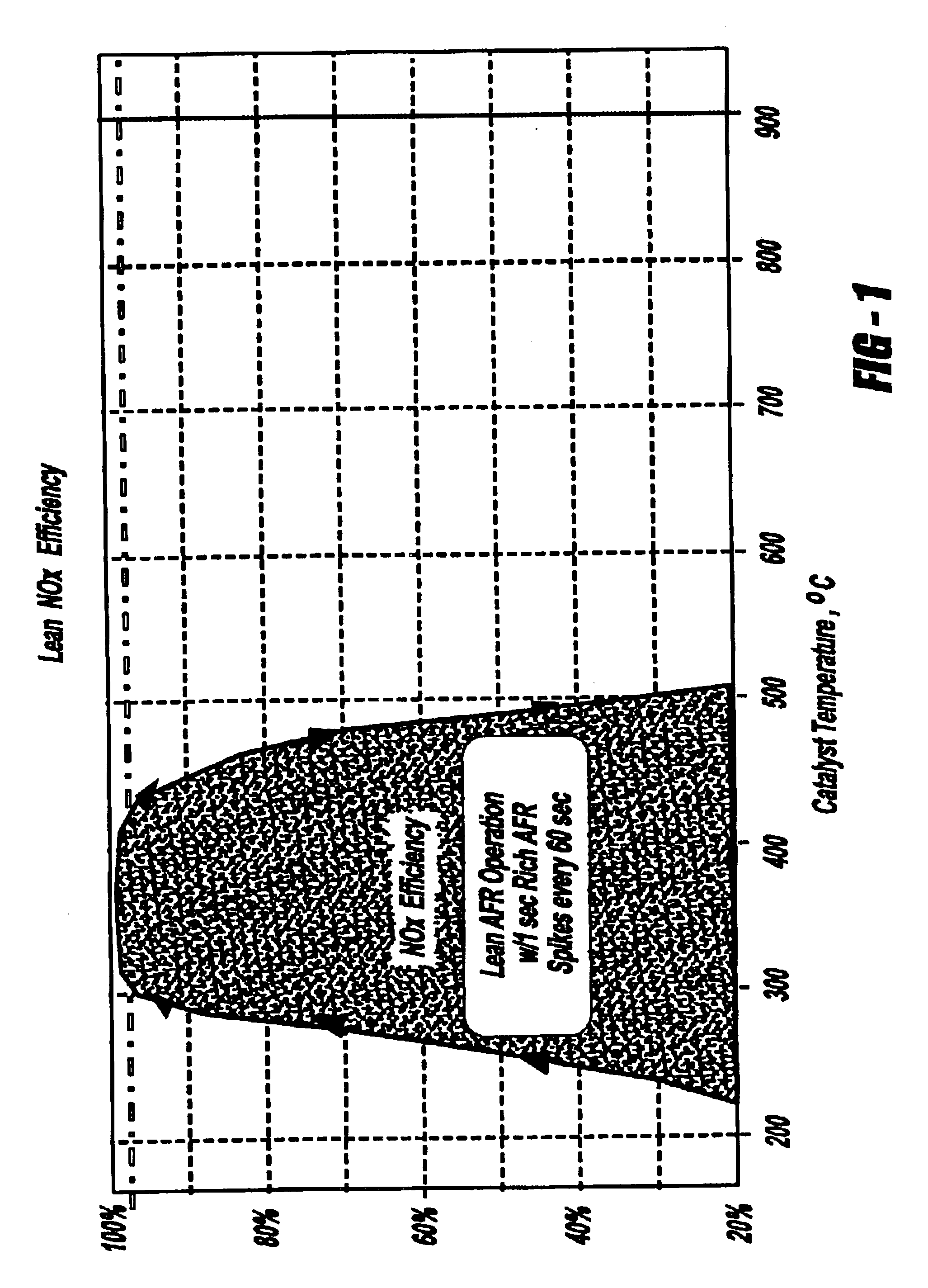
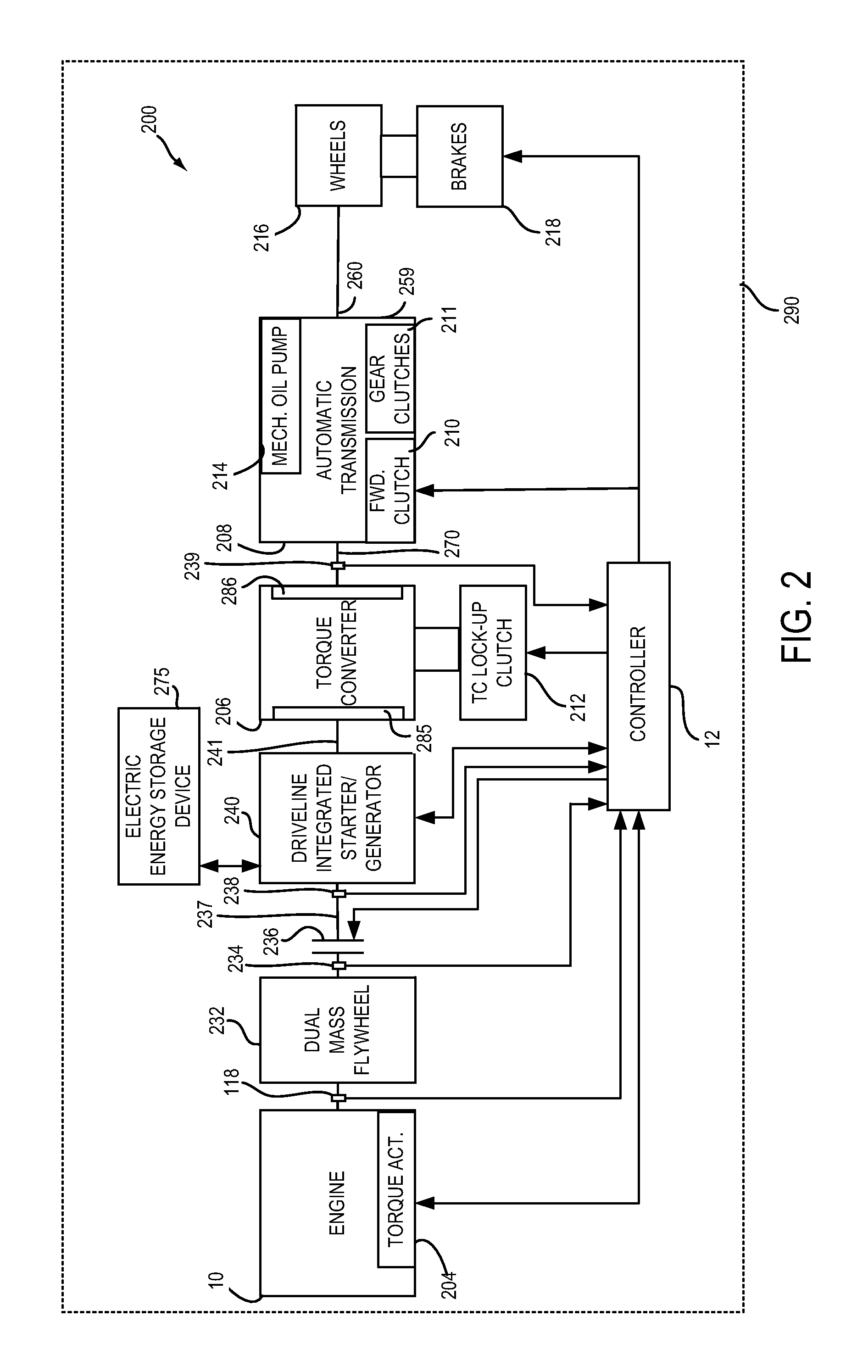
ActiveUS20150045185A1Efficient propulsionRaise temperatureHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesClutchProcess engineering
Systems and methods for improving operation of a hybrid vehicle are presented. In one example, operation of a driveline disconnect clutch is based on temperature conditions of a catalyst. The driveline disconnect clutch may not be opened if catalyst temperature is greater than a threshold temperature so that the catalyst may be cooled.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for Growing Group III-Nitride Crystals in Supercritical Ammonia Using an Autoclave
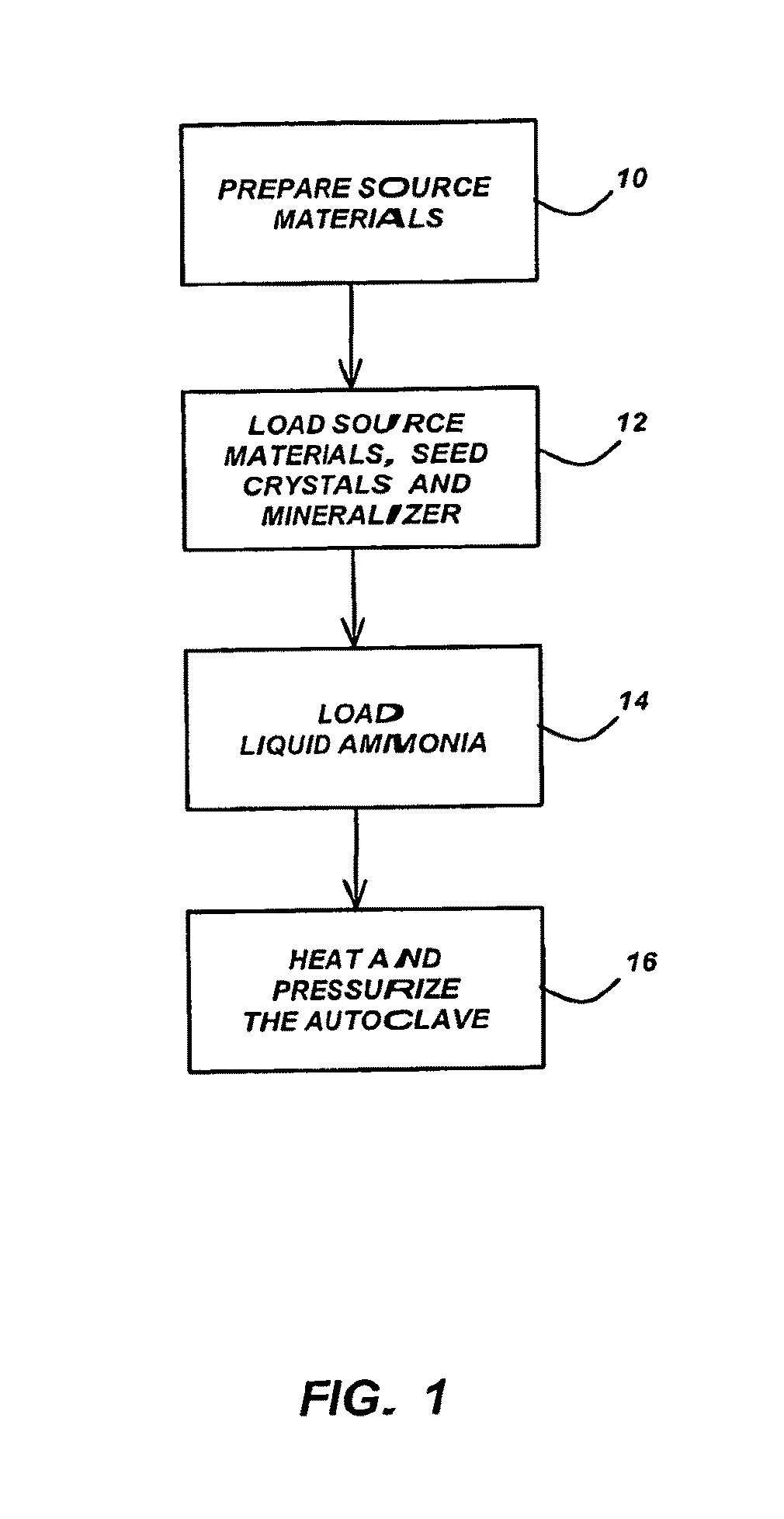
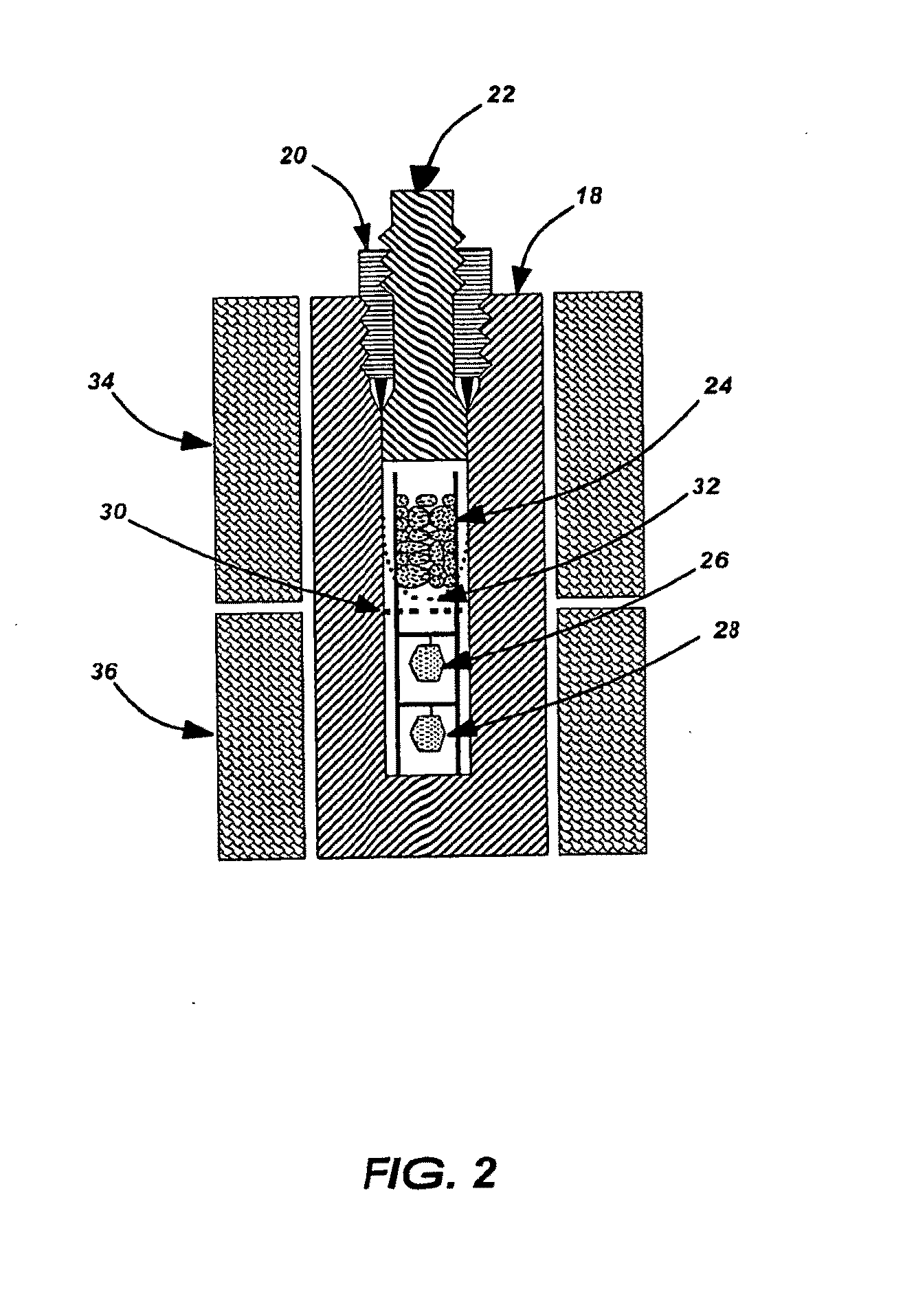
ActiveUS20100158785A1Raise temperaturePrevent transferPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNutrientSource material
A method of growing high-quality, group-III nitride, bulk single crystals. The group III-nitride bulk crystal is grown in an autoclave in supercritical ammonia using a source material or nutrient that is a group III-nitride polycrystals or group-III metal having a grain size of at least 10 microns or more and a seed crystal that is a group-III nitride single crystal. The group III-nitride polycrystals may be recycled from previous ammonothermal process after annealing in reducing gas at more then 600° C. The autoclave may include an internal chamber that is filled with ammonia, wherein the ammonia is released from the internal chamber into the autoclave when the ammonia attains a supercritical state after the heating of the autoclave, such that convection of the supercritical ammonia transfers source materials and deposits the transferred source materials onto seed crystals, but undissolved particles of the source materials are prevented from being transferred and deposited on the seed crystals.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
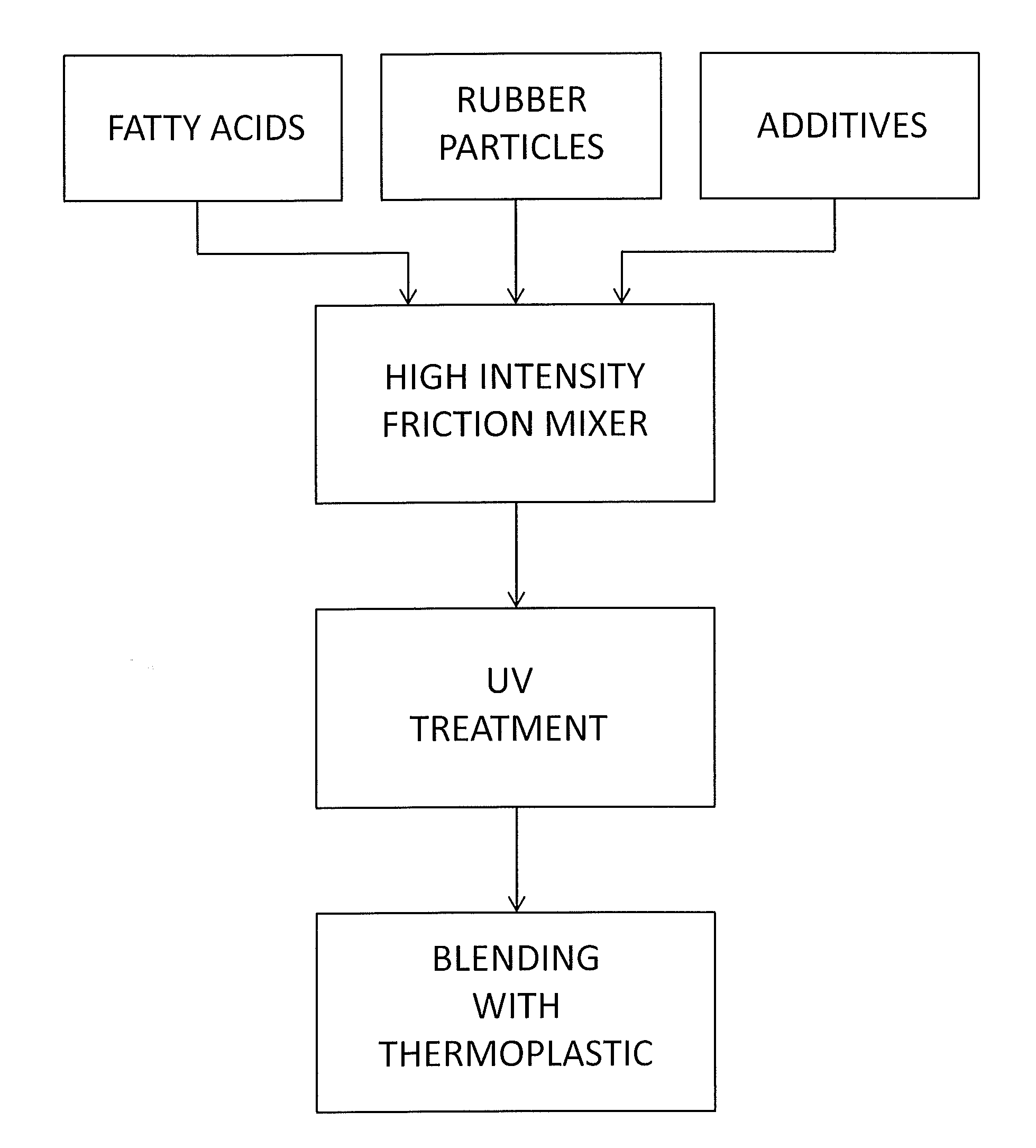
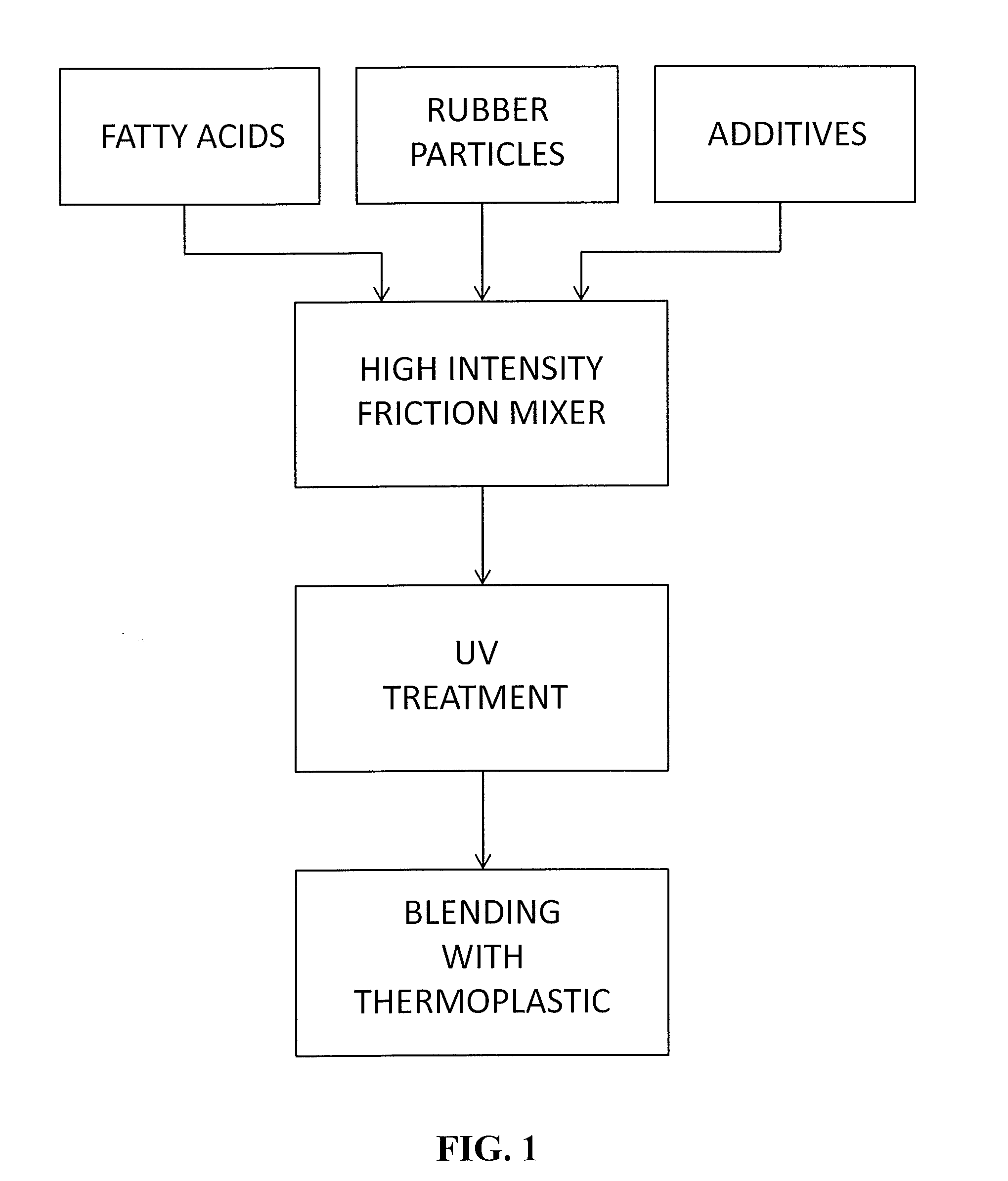
Method and System for Treating Elastomers and Articles Made Therefrom
A method and system for treating rubber-containing elastomers to produce materials suitable for blending with thermoplastic or thermoset polymers are disclosed. The elastomers may comprise virgin or recycled particulate rubber such as from used tires. The blended rubber and polymer materials possess thermoplastic properties and can be reused many times.
Owner:PRIME ELASTOMERS
Self-contained temperature-change container assemblies
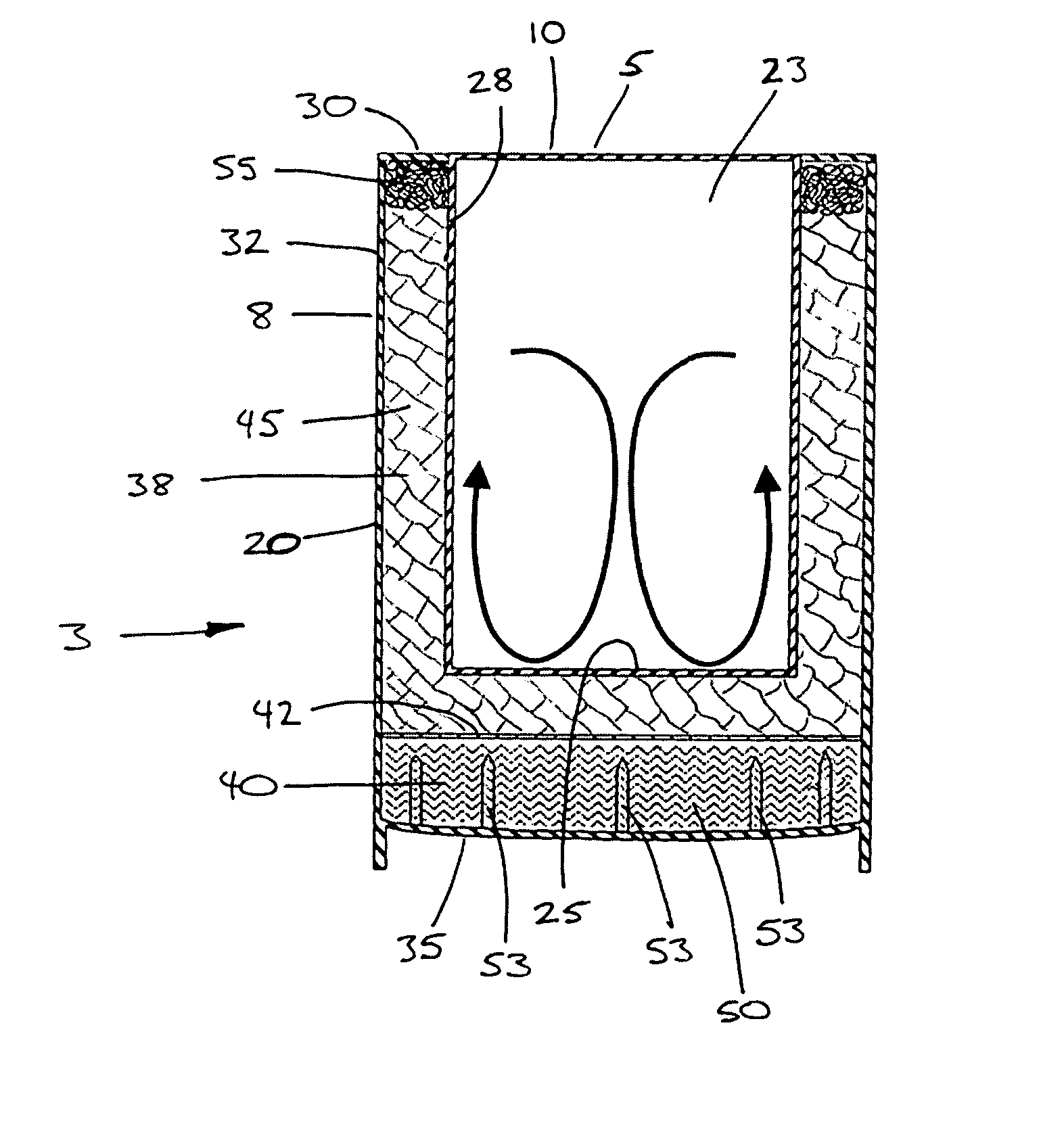
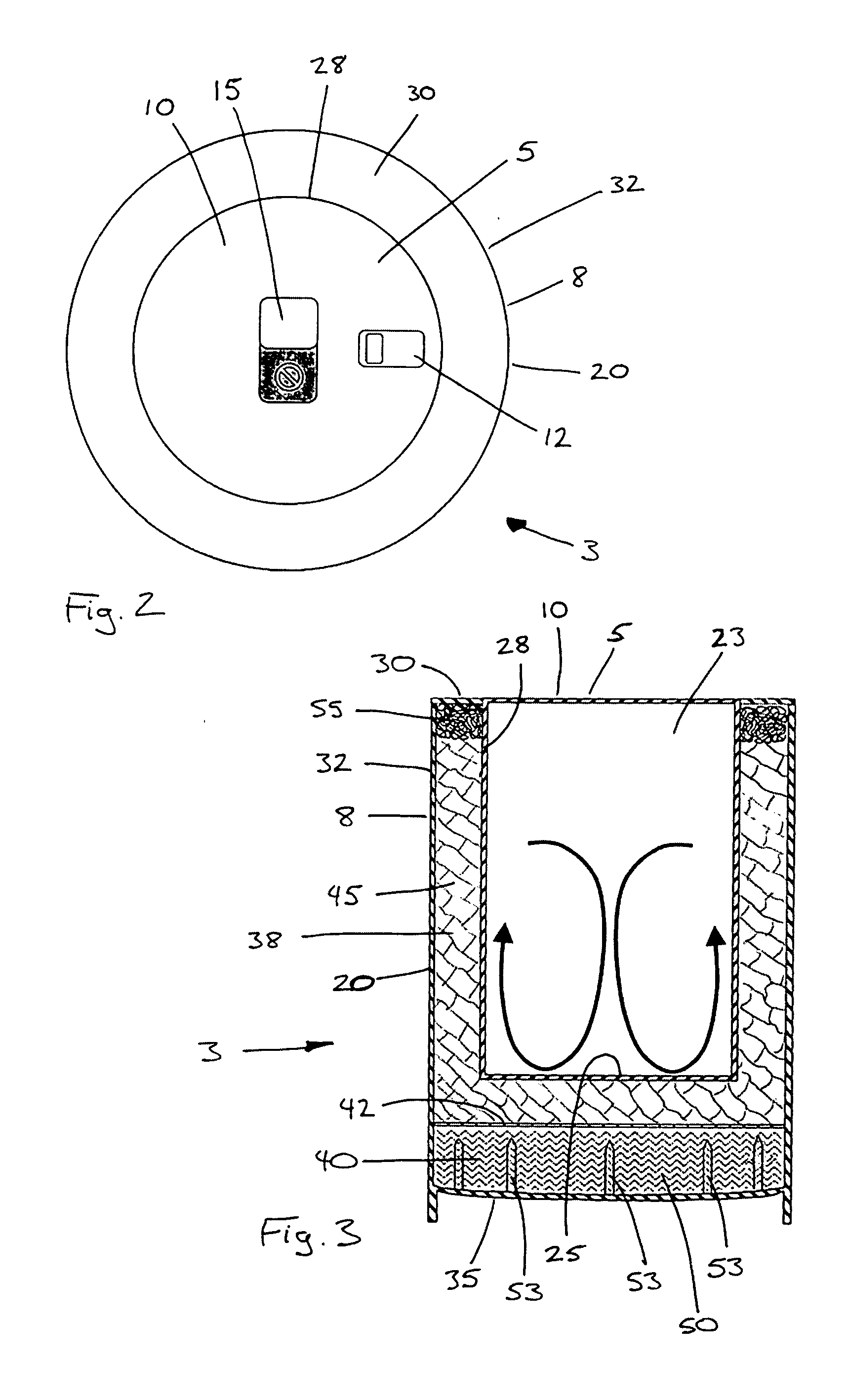
InactiveUS20050000506A1Raise temperatureLarge surface areaExothermal chemical reaction heat productionOther heat production devicesMechanical engineeringSteel wool
A container assembly heats or cools a product inside an inner container. An outer jacket at least partially surrounds the inner container, with a first internal volume and a second internal volume in the space between the outer jacket and the inner container. A first temperature-change reagent is contained inside the first internal volume, and a second temperature-change reagent is held in the second internal volume, with a reagent separator between the two. Several penetrators are disposed to penetrate the reagent separator to produce openings through the separator and through which the two reagents can mix. Steel wool inside the first internal volume acts as a steam condenser. The outer jacket includes a jacket top ring secured around an upper surface of a standard can, a jacket body secured to the jacket top, and a flexible jacket bottom that carries several spikes molded onto the jacket bottom.
Owner:SELF HEATING TECH CORP
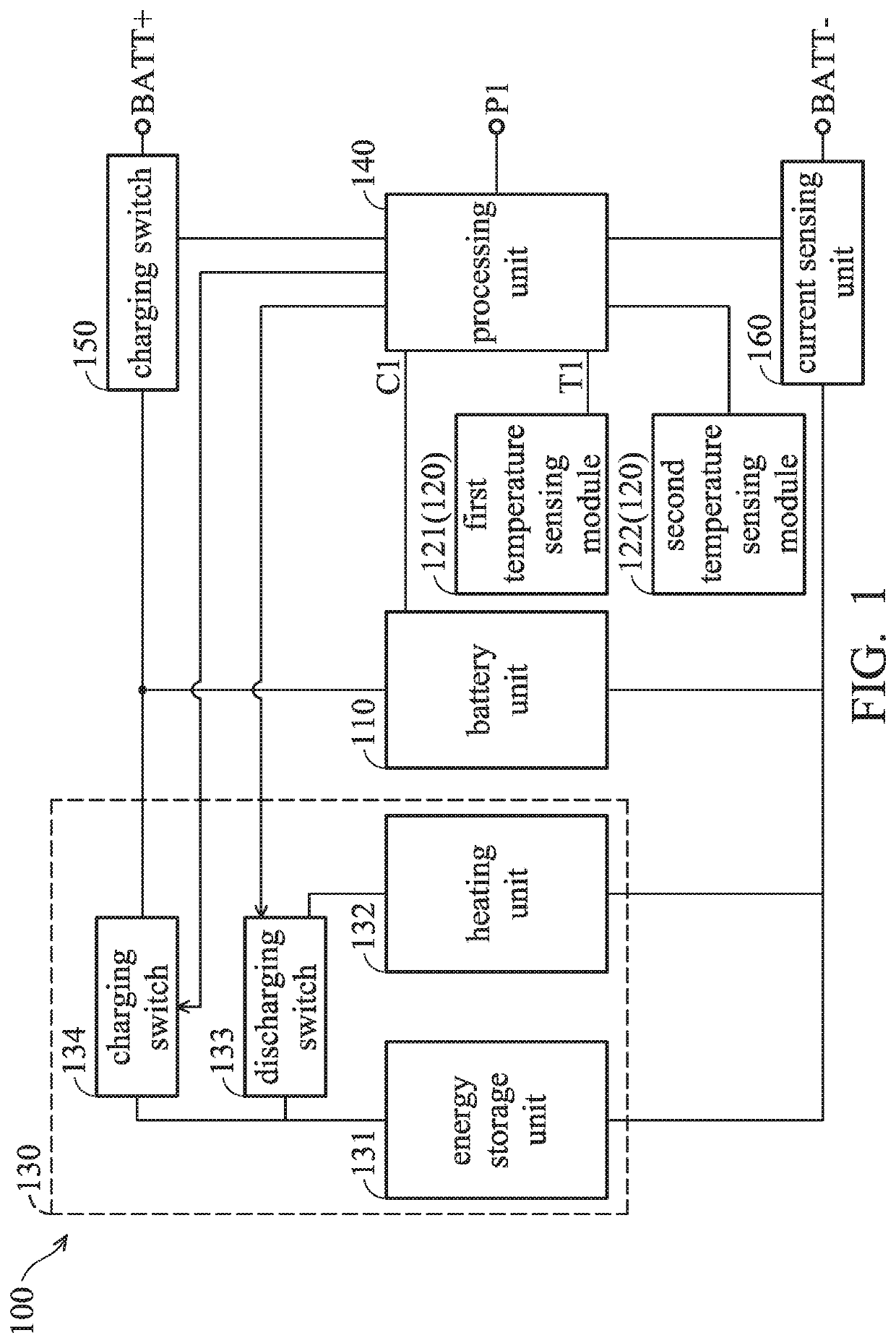
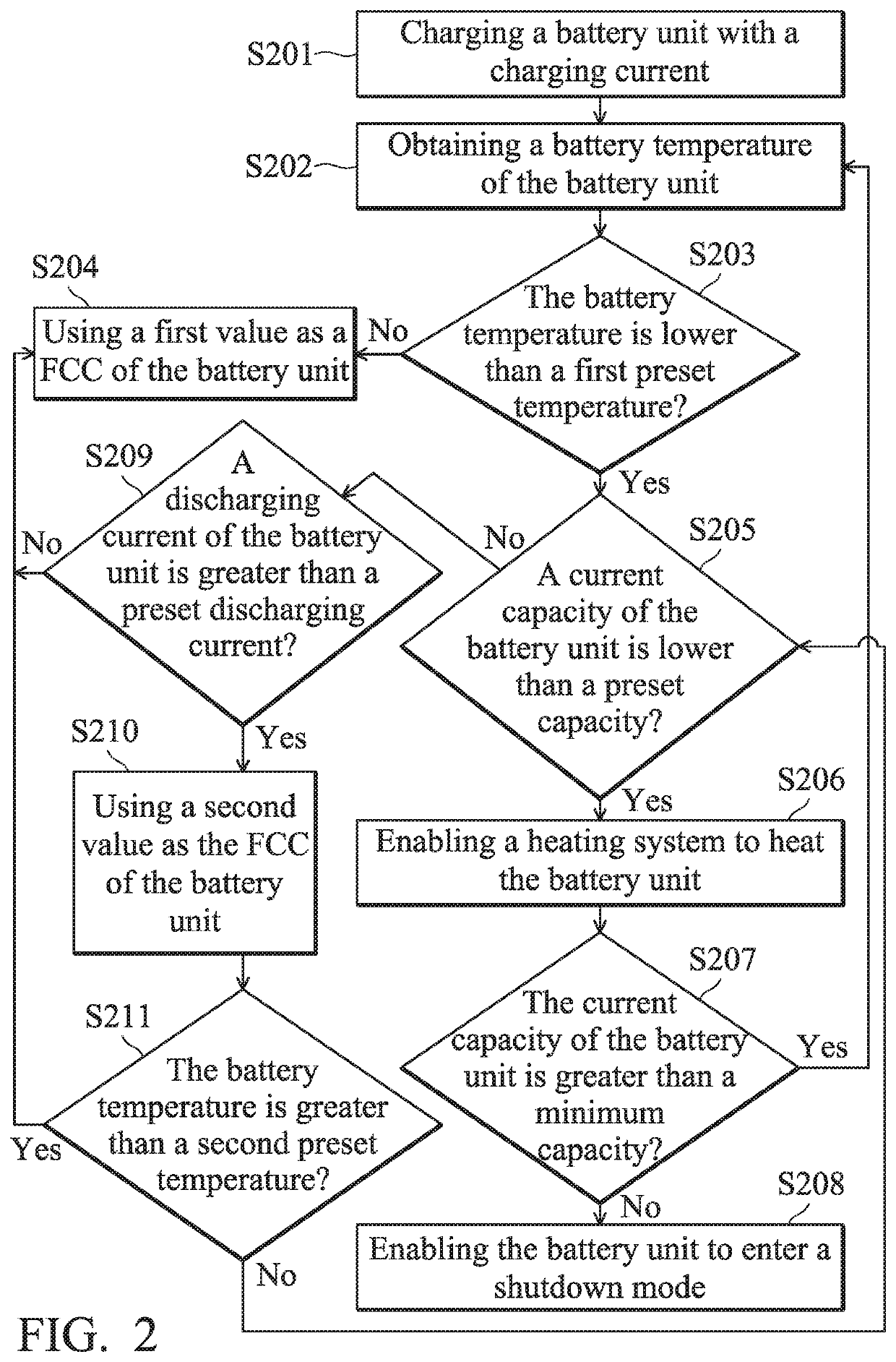
Smart battery device and charging method
ActiveUS20200403416A1Raise temperatureCircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingProcess engineeringHeating system
The present invention provides a smart battery device and a charging method. The charging method includes: obtaining a battery temperature of a battery unit; determining whether the battery temperature is lower than a first preset temperature; determining whether a current capacity of the battery unit is lower than a preset capacity when the battery temperature is lower than the first preset temperature; and enabling a heating system to increase the battery temperature when the current capacity of the battery unit is lower than the preset capacity.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
Microwave heating honeycomb zeolite adsorbent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108940244ARaise temperature ℃Improve removal efficiencyGas treatmentAluminium silicatesAdhesiveMullite
The invention discloses a microwave heating honeycomb zeolite adsorbent and a preparation method thereof. The microwave heating honeycomb zeolite adsorbent comprises a zeolite honeycomb body. A framework, a microwave adsorption layer and a zeolite adsorption layer are arranged on the zeolite honeycomb body; the zeolite honeycomb body comprises a framework which is selected from cordierite and mullite. The microwave absorption layer which is 100-500 microns is coated to the outer layer of the framework. By adding B2O3 and ZnO as a doping material into SiC and being bonded by an aluminum oxide and silicon oxide adhesive, the microwave absorption layer is prepared from zinc oxide and silicon carbide. A zeolite adsorption layer which is 200-1000 microns thick is coated to the outer surface ofthe wave absorption layer. The zeolite adsorption layer is prepared from 80-90% by mass of a molecular sieve, 2-5% by mass of SiO2, 3-6% by mass of Al2O3 and 5-10% by mass of SiC. According to the microwave heating honeycomb zeolite adsorbent, the wave absorption layer in the zeolite honeycomb body gnerates heat to quickly increase the temperature of zeolite so as to desorb VOCs.
Owner:南通斐腾新材料科技有限公司
Heat-generating tooling systems and methods
ActiveUS20210001519A1Raise temperatureDomestic articlesManufacturing engineeringMechanical engineering
Methods of manufacturing composite workpieces that include positioning a heat-generating element proximate to an uncured composite workpiece, triggering the heat-generating element to produce an exothermic chemical reaction or exothermic physical reaction so that the temperature of the uncured composite workpiece is raised to a predetermined first temperature, and curing the composite workpiece while it is at a temperature that is at least the predetermined first temperature.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Apparatus and Method for Identifying and Operating Air Purge in Safe Mode and Having a Dip Tube
ActiveUS20130118198A1Raise temperatureValve members for heating/coolingPipe heating/coolingRefrigerantVapor pressure
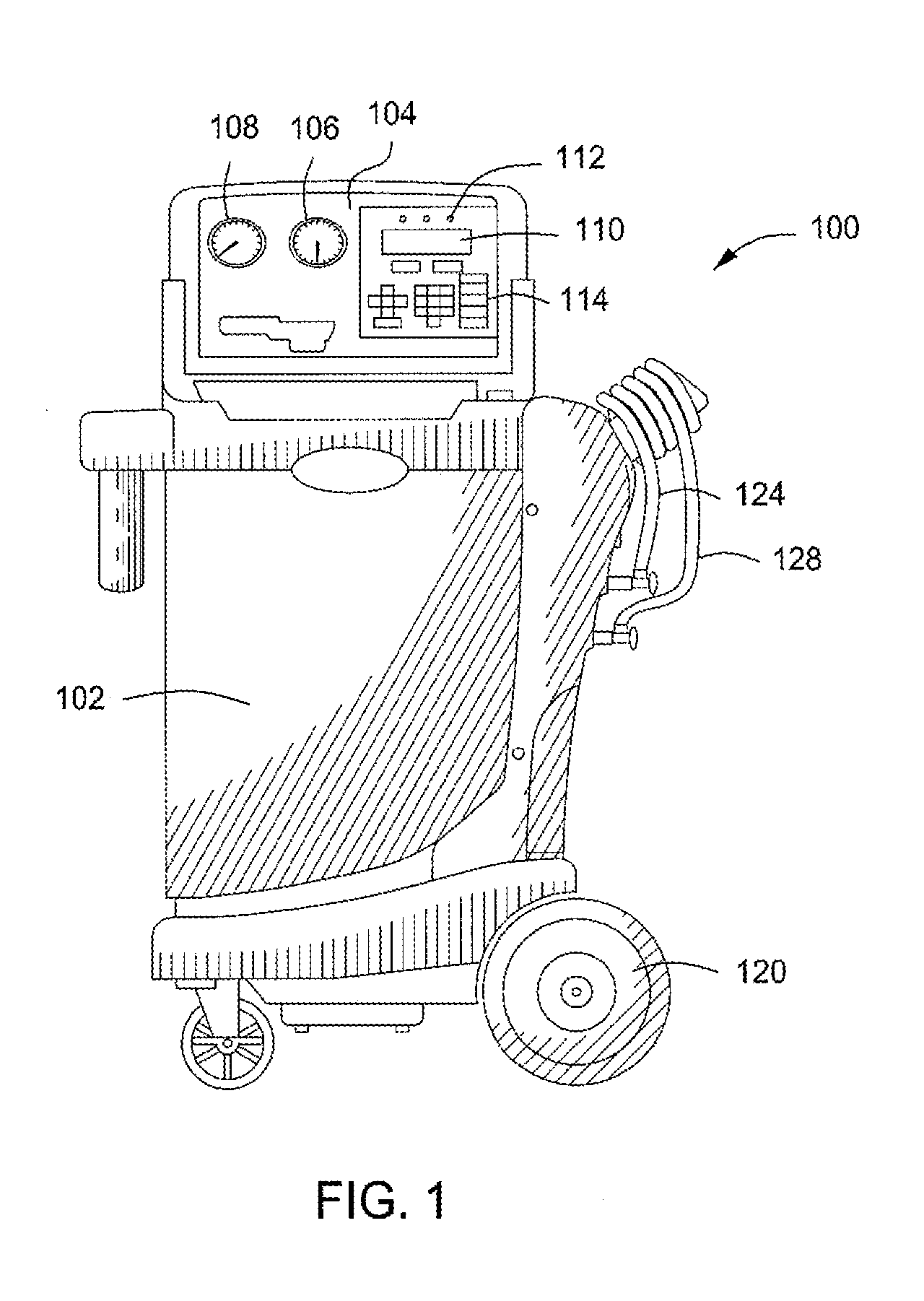
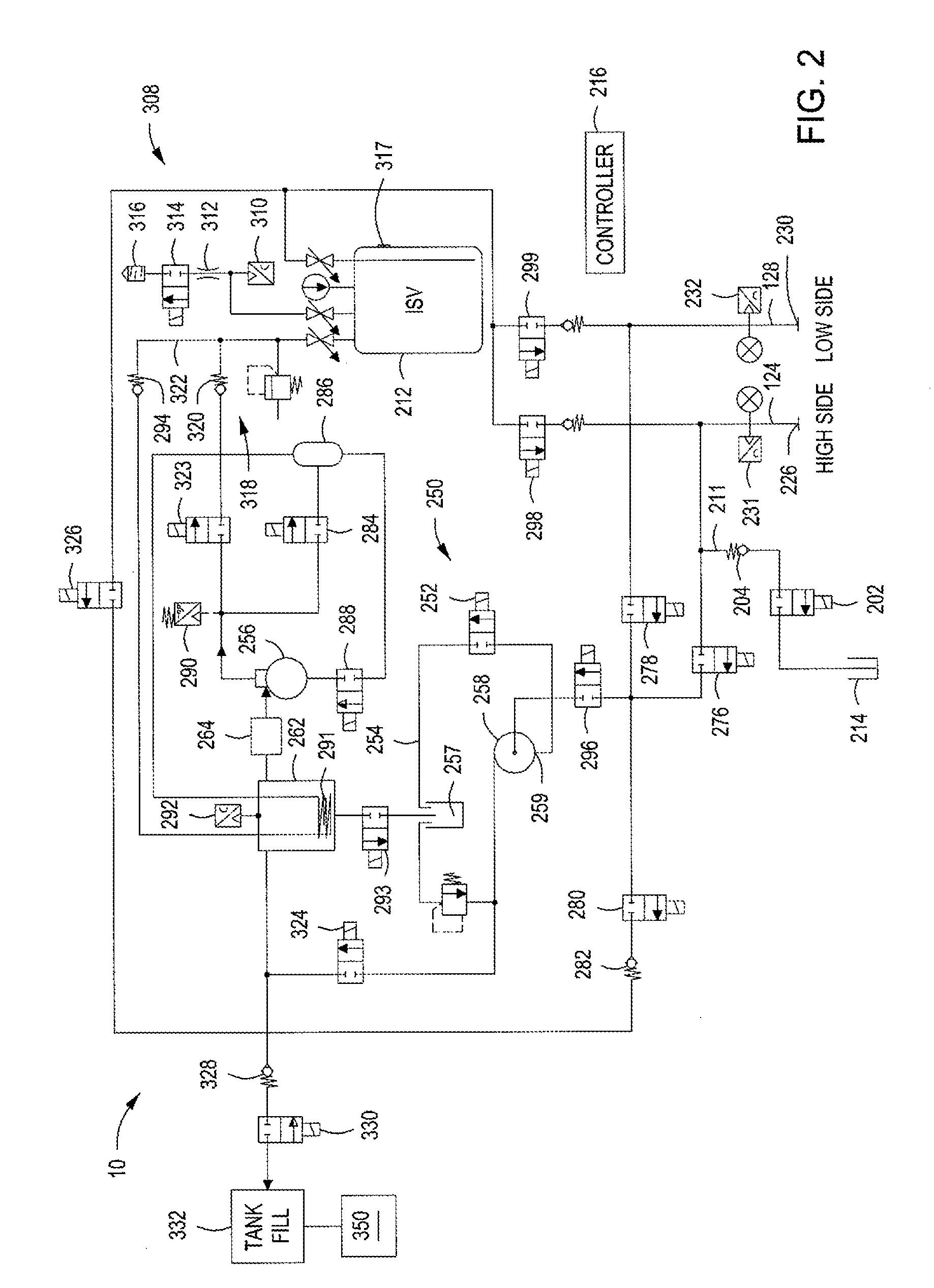
A refrigerant recovery unit is provided and includes a safe purging mode. The safe purging mode allows non-condensable gases to be incrementally purged from a storage tank when the determined ideal vapor pressure is high, such as 40 p.s.i., in order to minimize refrigerant loss during purging. The purging can be done in small increments of time, pressure or mass. The storage tank can include a dip tube that extends into the liquid portion of the refrigerant in order to heat up the refrigerant in the tank with the heated recovered refrigerant.
Owner:BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE SERVICE SOLUTIONS
Fluid mixing device for tub and bath fluid mixing apparatus
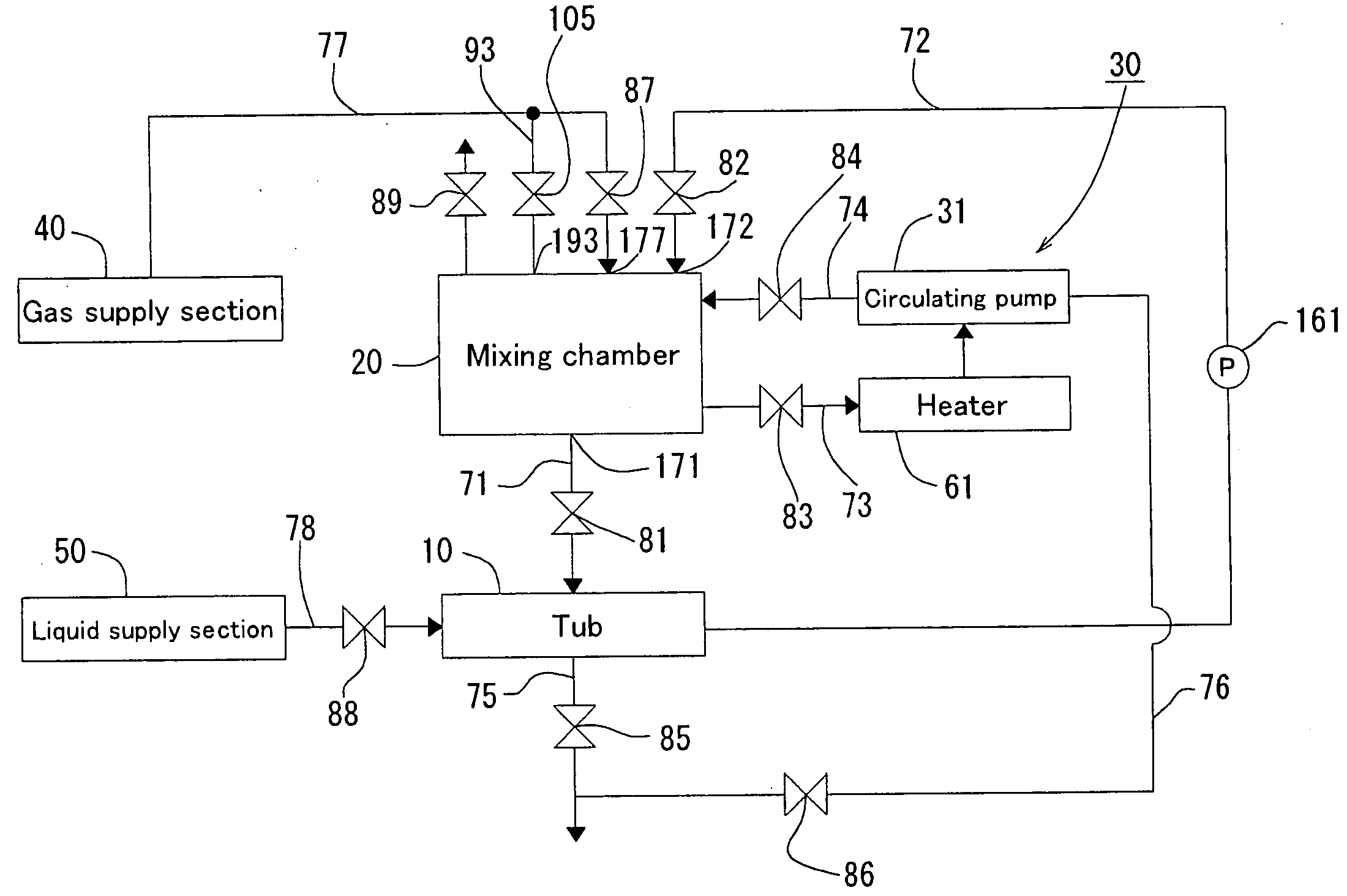
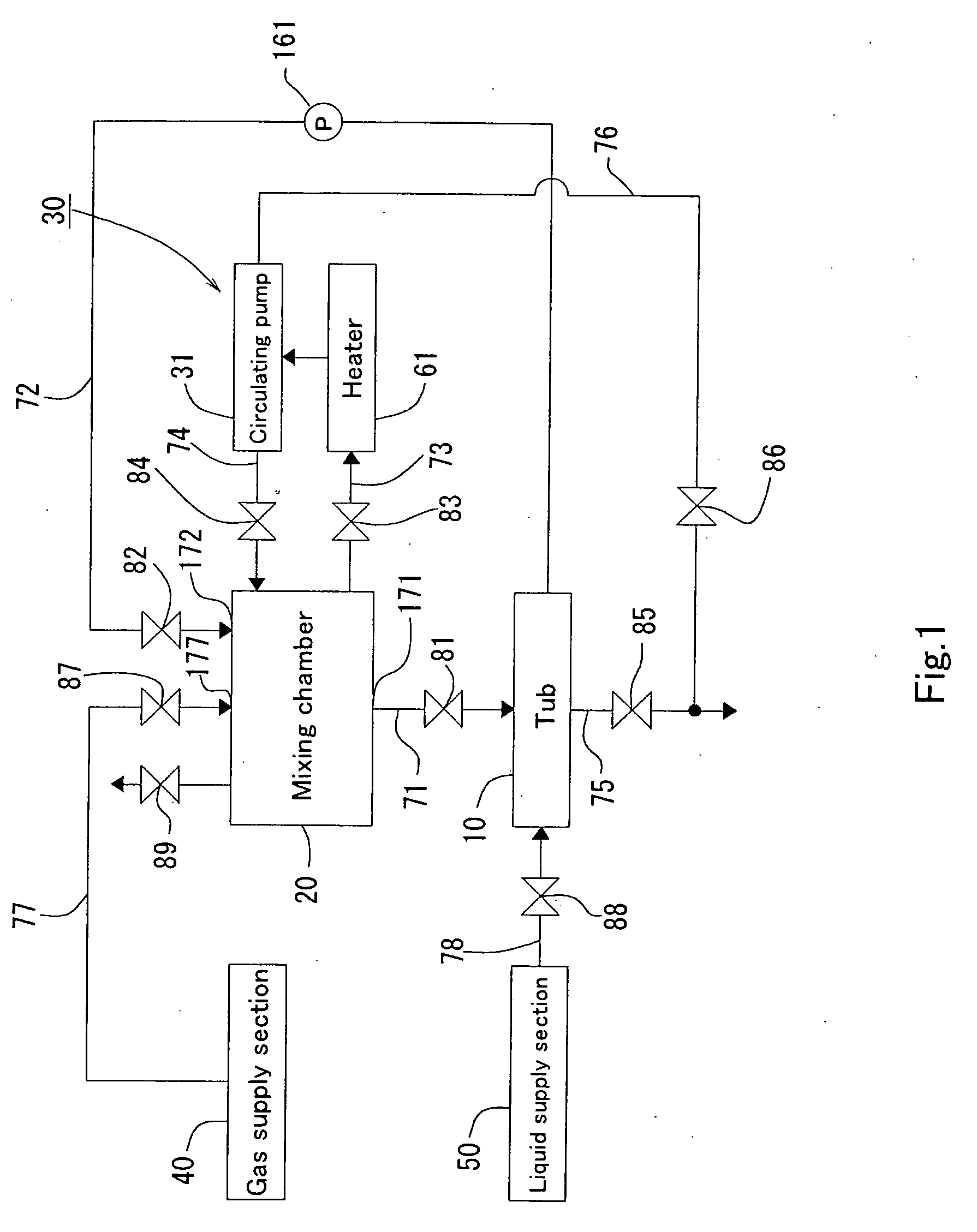
InactiveUS20060208370A1Elevate warm bath effectRaise temperatureUsing liquid separation agentMixing methodsEngineeringMixing chamber
A fluid mixing device for a tub includes a closed mixing chamber having: a liquid inlet for introducing liquid into the mixing chamber; a gas inlet for introducing gas into the mixing chamber; and a gas-containing liquid outlet for discharging gas-containing liquid from the mixing chamber to a tub.
Owner:MASUDA MASATOSHI
Use of a q&p steel for producing a shaped component for high-wear applications
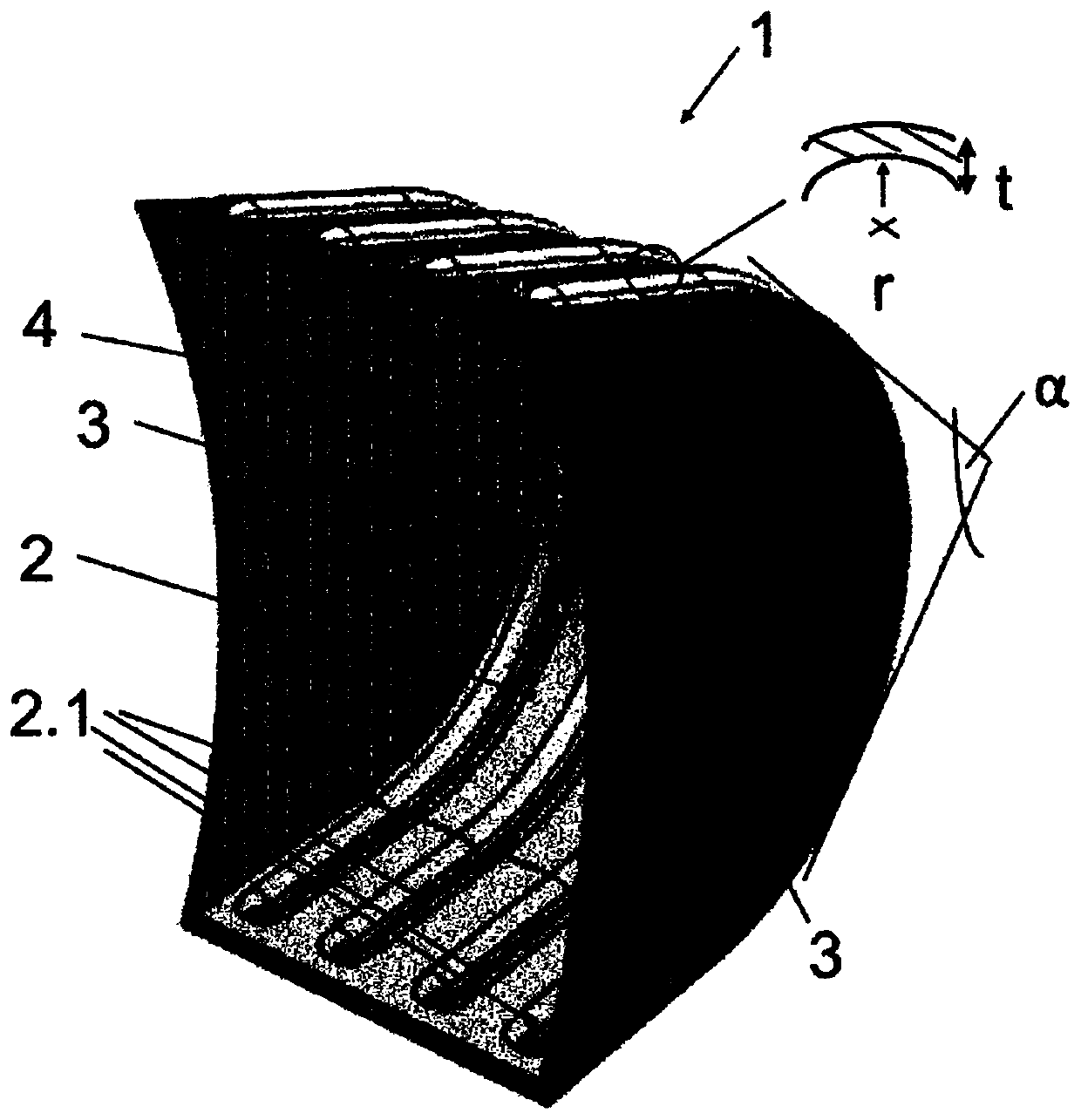
ActiveCN110997961ARaise temperatureAvoid casting technical problemsSuperimposed coating processPolymer scienceBend radius
The invention relates to a use of a Q&P steel for producing a shaped component (2) for high-wear applications, wherein the Q&P steel has a hardness of at least 230 HB, in particular at least 300 HB, preferably at least 370 HB, and a bending angle [alpha] of at least 60 DEG C, in particular at least 75 DEG C, preferably at least 85 DEG C, determined according to VDA238-100, and / or a bending ratio of r / t<2.5, in particular r / t<2.0, preferably r / t<1.5, wherein t corresponds to the material thickness of the steel and r corresponds to the (inner) bending radius of the steel.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG +1
Rotary kiln low-nitrogen combustion device and production method
InactiveCN113465366AEmission reductionLong conveying distanceRotary drum furnacesWaste heat treatmentCombustorProcess engineering
The invention relates to a rotary kiln low-nitrogen combustion device and a production method. The rotary kiln low-nitrogen combustion device comprises a cooler, a low-nitrogen combustor, a secondary air pipe, a rotary kiln, a decomposing furnace and a preheater, the lower furnace body of the decomposing furnace is provided with a lower coal feeding device and a lower tertiary air pipe, and the middle lower part of the upper furnace body is provided with an upper coal feeding device and an upper tertiary air pipe; a feeding hole of the preheater communicates with the decomposing furnace, an air outlet of the preheater communicates with an air inlet of the cooler, and an air outlet of the cooler respectively communicates with the secondary air pipe, the lower tertiary air pipe and the upper tertiary air pipe; a spiral ventilation channel is formed in the secondary air pipe; and one end of the secondary air pipe enters the rotary kiln from the kiln head of the rotary kiln and is tightly attached to the kiln wall. The preheater, the cooler, the rotary kiln and the decomposing furnace are used as a whole, the low-nitrogen combustor, staged combustion and O2 / CO2 combustion technologies are combined, generation of NOx in the rotary kiln and the decomposing furnace is controlled at the same time, reduction of existing NOx is enhanced, NOx in the whole process is controlled, and the emission amount of NOx is greatly reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Thermal treatment process for X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 grain refinement
The invention provides a thermal treatment process for X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 grain refinement. According to the thermal treatment process, the amount of acicular austenite is decreased as much as possible by increasing the heating speed, and the amount of spherical austenite is increased, so that grain refinement is achieved, the grain size can meet the technical requirement, and the using range of X12CrMoWVNbN10-1-1 is enlarged. Fed materials are forged into workpieces, the workpieces are sequentially subjected to high-temperature normalizing, high-temperature tempering, conventional normalizingand high-temperature tempering, and then the workpiece subjected to high-temperature tempering are subjected to subsequent processing treatment. In the high-temperature normalizing process, the temperature increasing speed of the workpieces in an alpha and gamma two-stage region is increased, the workpieces can pass through the two-stage region rapidly, and the spherical austenite can be obtainedas much as possible. On one hand, the orientation relationship of crystallography is broken through to a greater extent, namely, the K--S relationship; and on the other hand, the nucleation rate of the austenite can be increased by increasing the heating speed. The high-temperature tempering process particularly comprises the steps that heat preservation is conducted for 15-20 h at the environmental temperature of 700 DEG C to enable carbides to be dissolved as many as possible to further destroy the orientation relationship of metallography, and then air cooling is conducted.
Owner:WUXI HONGDA HEAVY IND
Dryer appliance with accelerated refrigerant cycle
InactiveUS20130047638A1Reduce pressure of refrigerantRaise temperatureHeat pumpsCompression machines with cascade operationRefrigerantProcess engineering
An appliance heat pump dryer is provided that has an accelerated refrigerant cycle for providing heat to the articles being dried. The heat source, such as an electrical heating element, provides heat to the evaporator so that the appliance can reach steady state operating conditions more rapidly and thereby reduce the overall cycle operating time. Options can be provided for the user to select whether the drying cycle will be accelerated.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
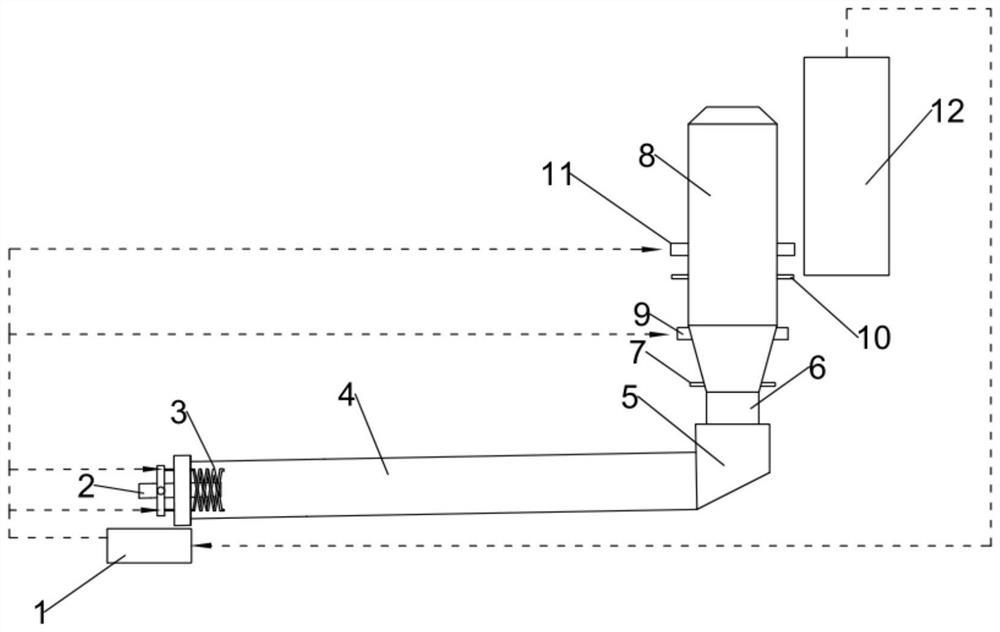
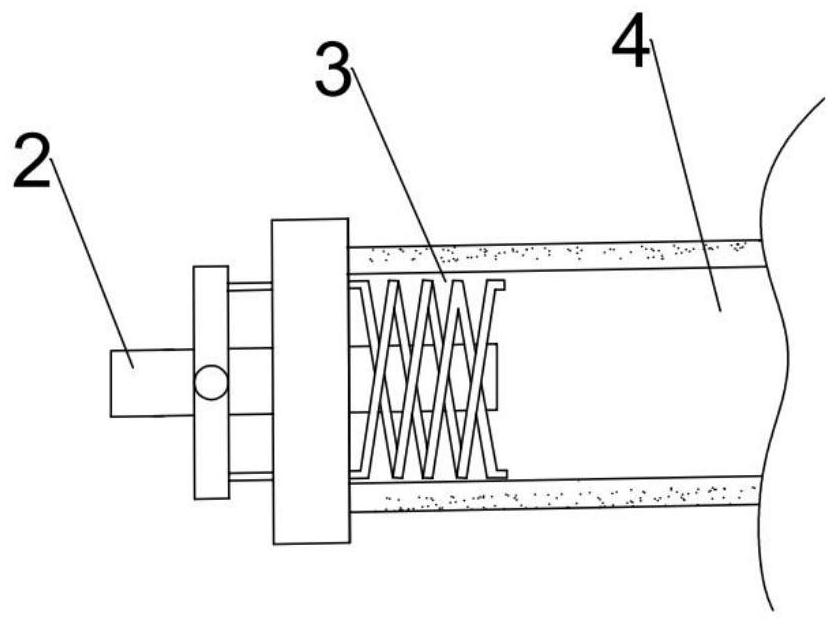
Internal combustion engine with gas-liquid separator for blowby gas
ActiveUS20190277172A1Raise temperatureIncrease in sizeCasingsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion engineVapor–liquid separator
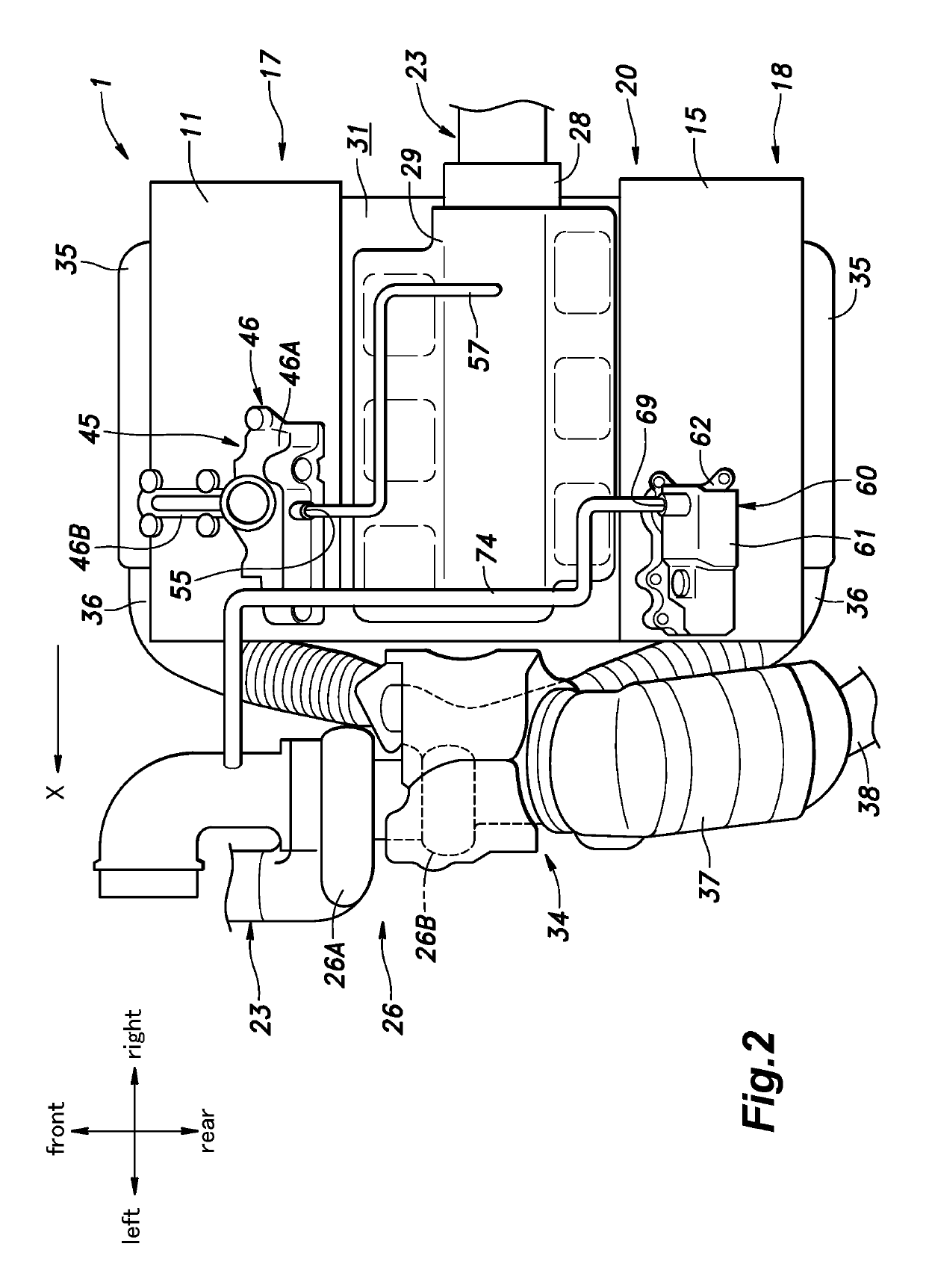
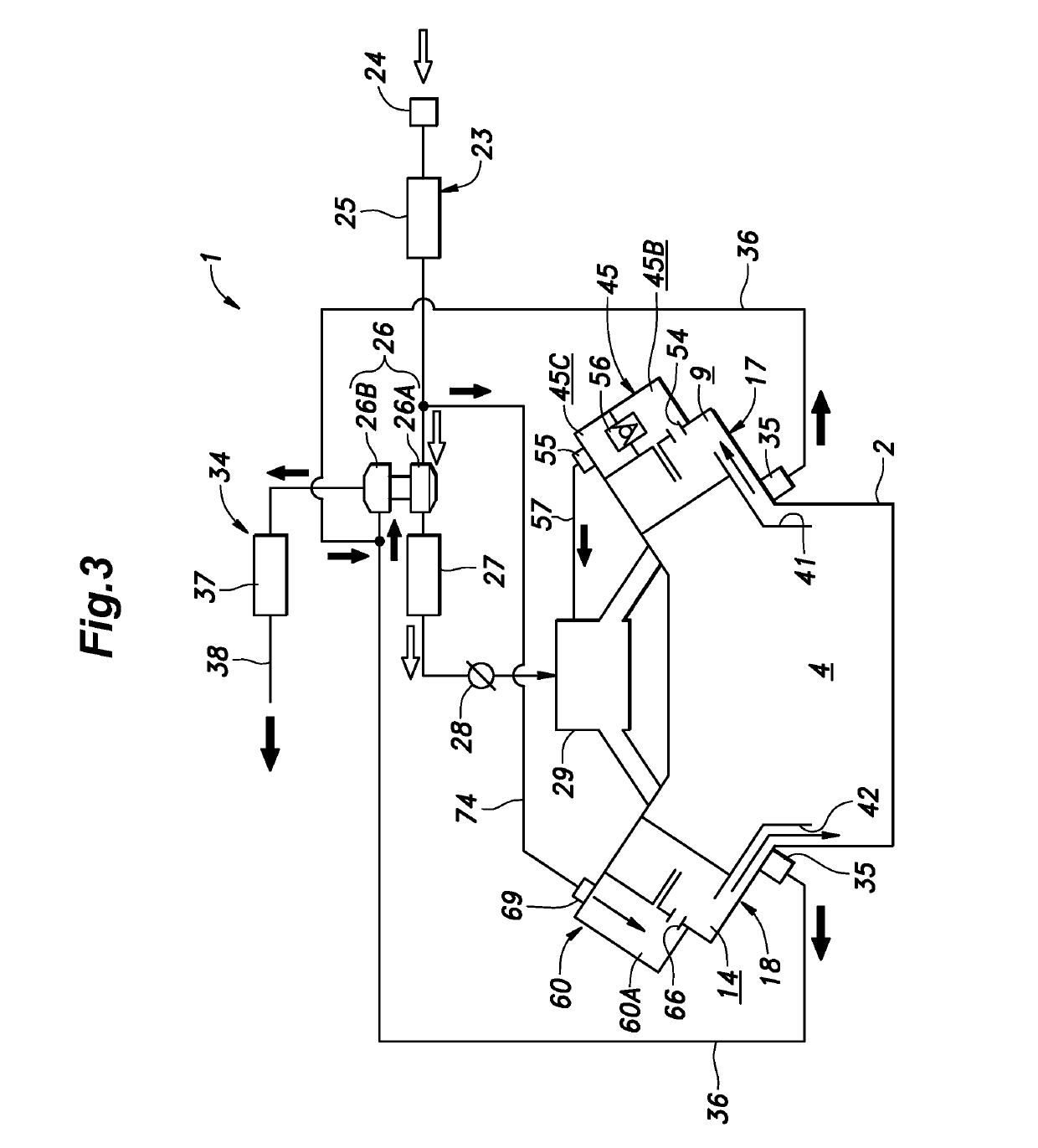
An internal combustion engine (1) includes an internal combustion engine main body (20), a head cover (11, 15) attached to an upper end part of the internal combustion engine main body, and an exhaust system (34) connected to the internal combustion engine main body, and a gas-liquid separator (45, 60) for blowby gas provided in the head cover. A part of the exhaust system is positioned adjacent to the internal combustion engine main body in a first direction (X) along a cylinder row, and the gas-liquid separator is positioned in the head cover so as to be offset in the first direction.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Coated fertilizer as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109438125APromote decompositionIncrease the number ofCalcareous fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserPhosphateFerric-edta
The invention relates to a coated fertilizer as well as a production method and application thereof. The coated fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10 to 15 parts of potassium fulvate, 5 to 10 parts of fulvic acid, 30 to 35 parts of potassium nitrate, 20 to 25 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3 to 5 parts of EDTA ferric sodium salt, 1 to 3 parts of manganese disodium EDTA trihydrate, 1 to 3 parts of copper disodium EDTA, 3 to 5 parts of zinc disodium EDTA and 1 to 3 parts of ammonium molybdate. The coated fertilizer according to the invention canprovide nutrition for crops, also can activate various synthetases in crops and improve cell membrane permeability, thereby improving nutrient absorption and fertilizer utilization rate. The coated fertilizer has a very good biological stimulation effect under harsh conditions such as high temperature, low temperature and drought.
Owner:SICHUAN TIANHUA
Methods for Amplifying Fragmented Target Nucleic Acids Utilizing an Assembler Sequence
InactiveUS20160068900A1Raise temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
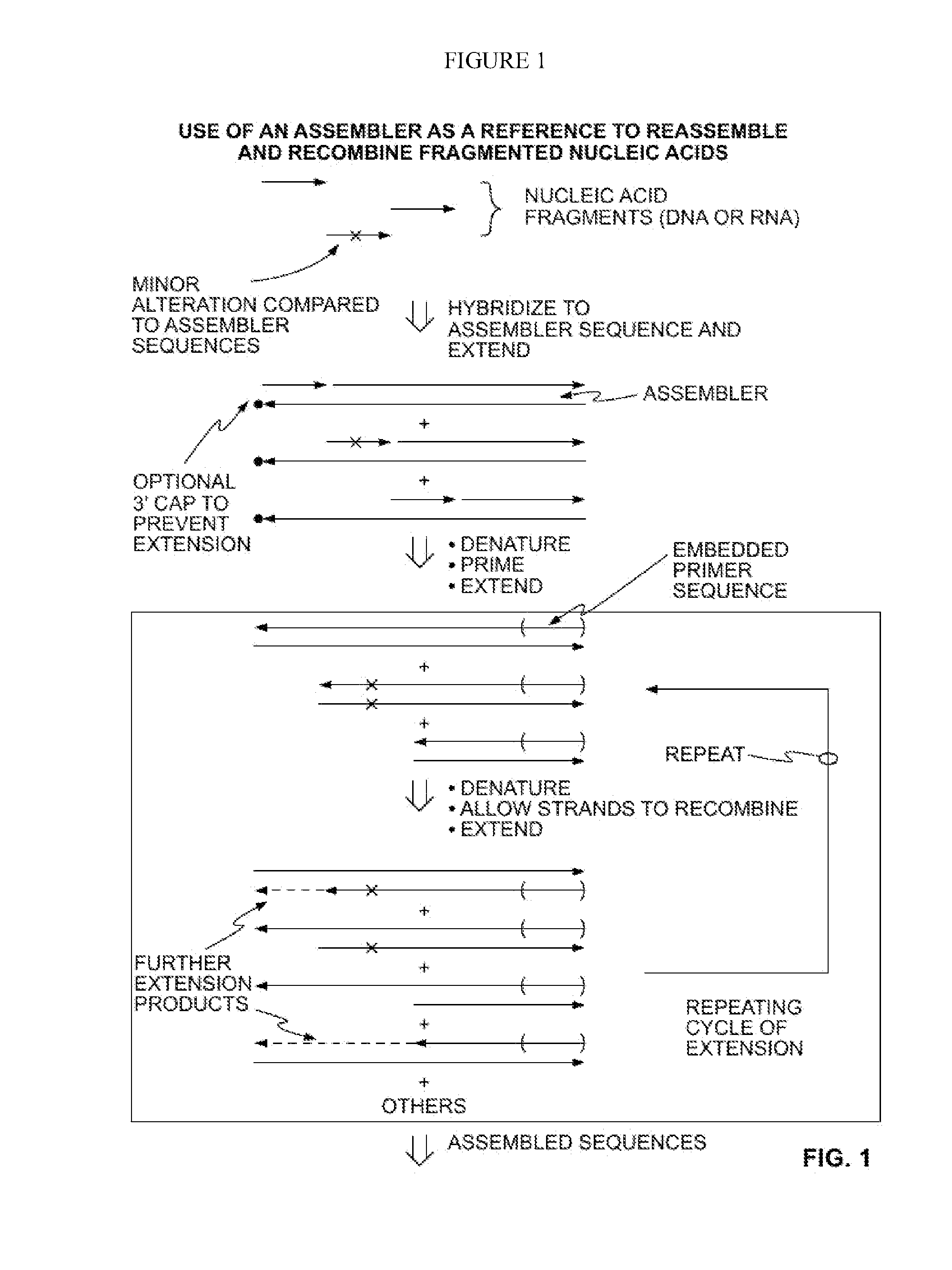
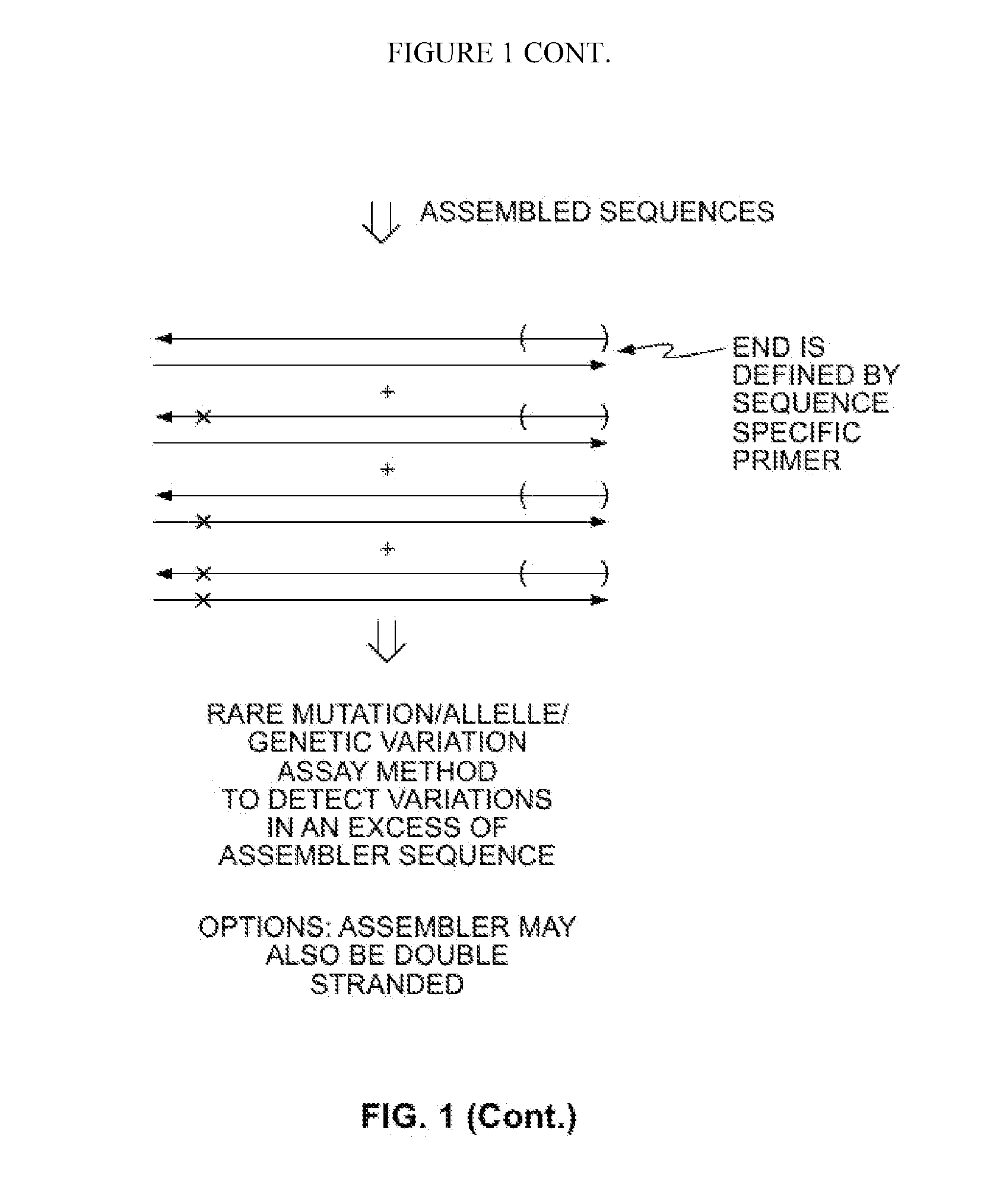
The present invention provides methods of amplifying a fragmented target nucleic acid containing short target nucleic acid fragments utilizing an assembler sequence to convert these short fragments into longer sequences enabling their identification and interrogation. This is particularly important when attempting to identify small genetic variations, such as SNVs, present in highly fragmented nucleic acid samples. Amplification is accomplished by hybridizing the short target nucleic acid sequences to the assembler sequence, where these short sequences serve as primers for extension. Since the fragmented target nucleic acids that contain SNVs are utilized as primers on the assembler sequence they are preserved during amplification and can be detected.
Owner:AEGEA BIOTECH
Method of producing resin varnish for printing ink
ActiveUS6894096B2Easily produceRaise temperatureInksNatural resin chemical modificationSolventChemistry
A resin varnish for printing ink is produced by condensing phenol and formaldehyde in an ink solvent to obtain an ink solvent solution of resole initial condensate, after which the resole initial condensate and a rosin ester containing 30-60 wt % non-aromatic conjugate resin acid and 20-60 wt % aromatic resin acid are reacted at 100-250° C. in a system containing ink solvent or in a system containing ink solvent and drying oil. A high-viscosity, high-molecular-weight ink resin is produced efficiently by reacting, with resole initial condensate in ink solvent, a rosin ester containing specified contents by percentage of conjugate acid and aromatic resin acid. The resin varnish obtained has very few decomposition components and nonuniformly gelled components, so it also is suitable for screen printing ink and letterpress printing ink, in addition to offset printing ink.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com