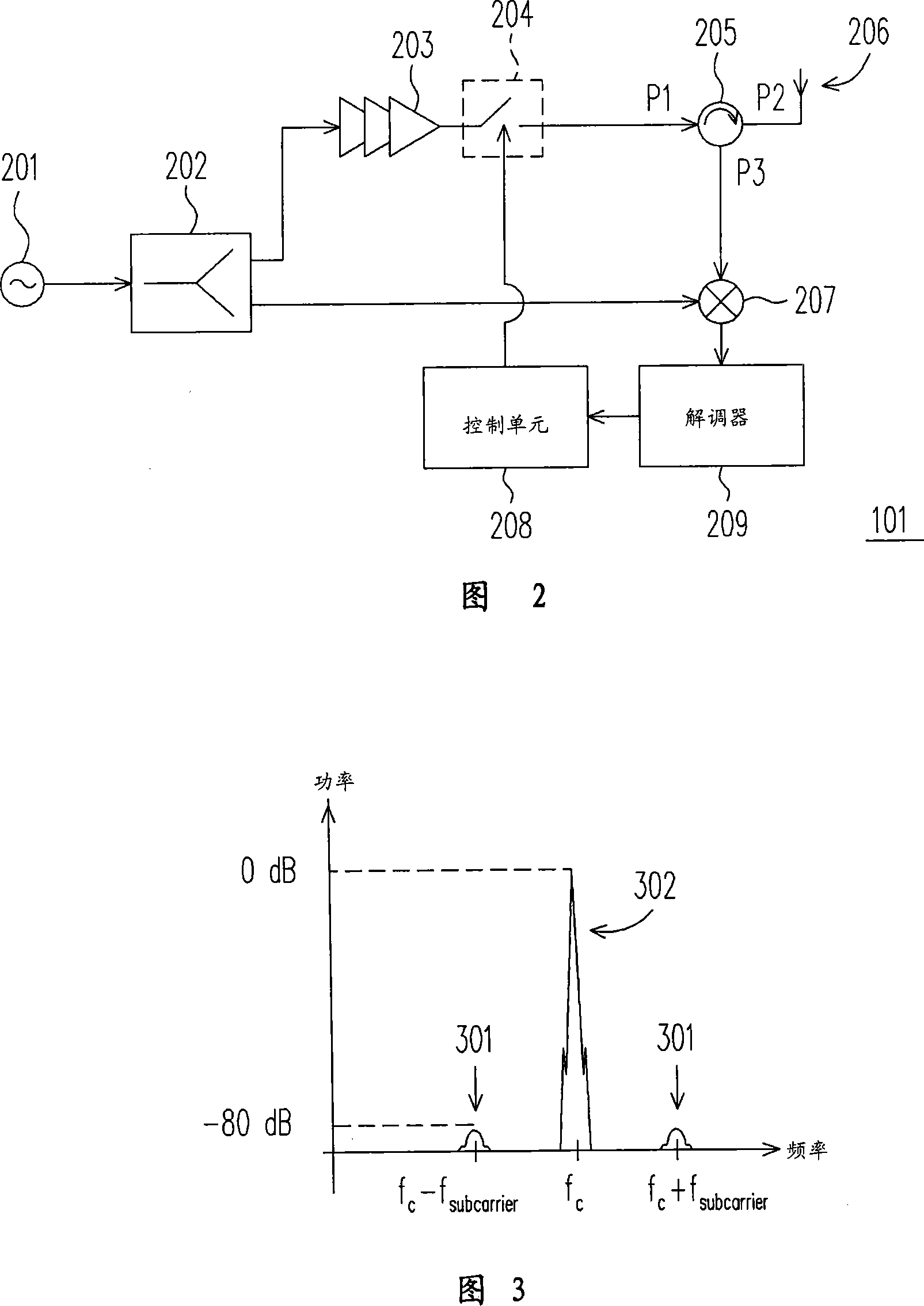
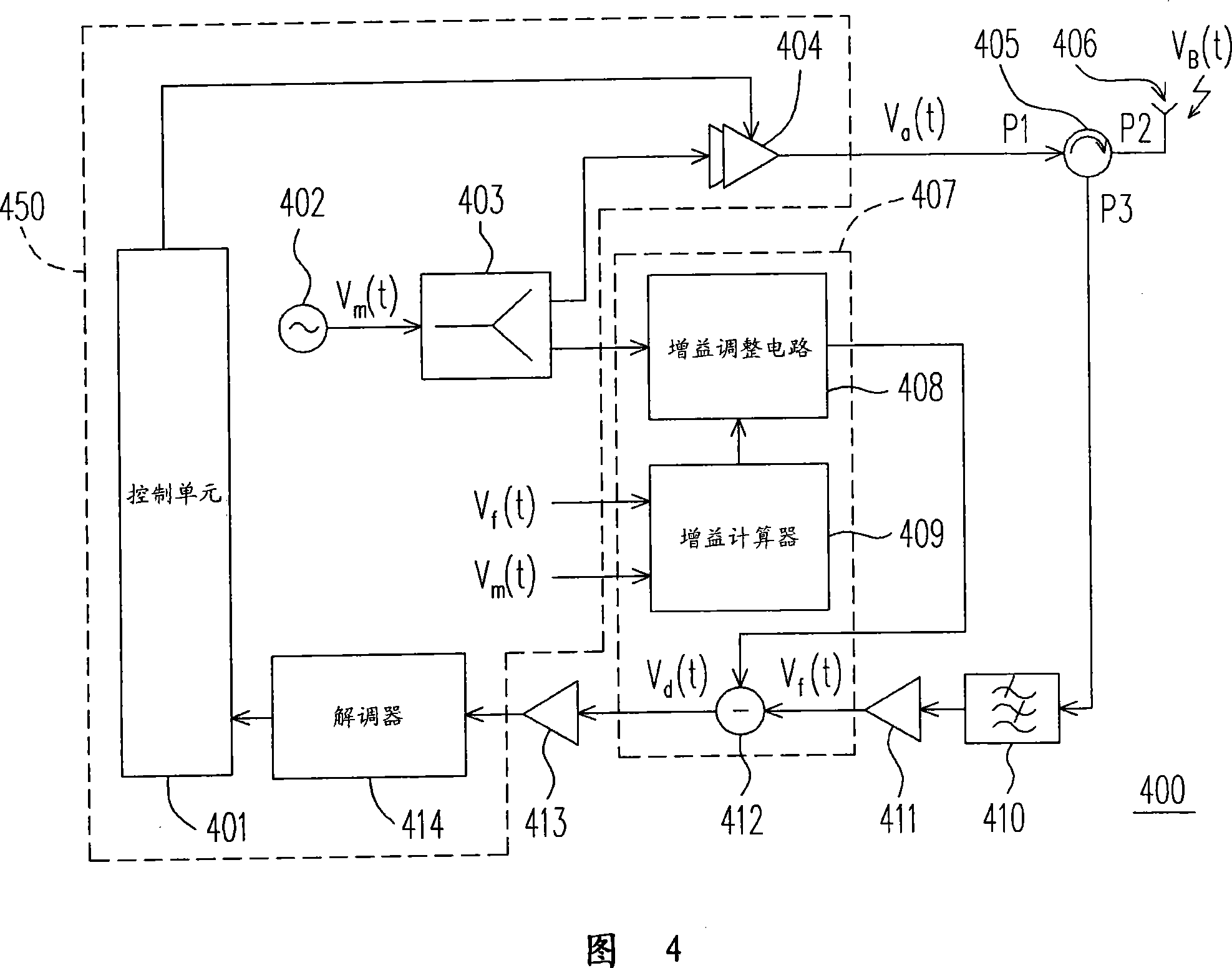
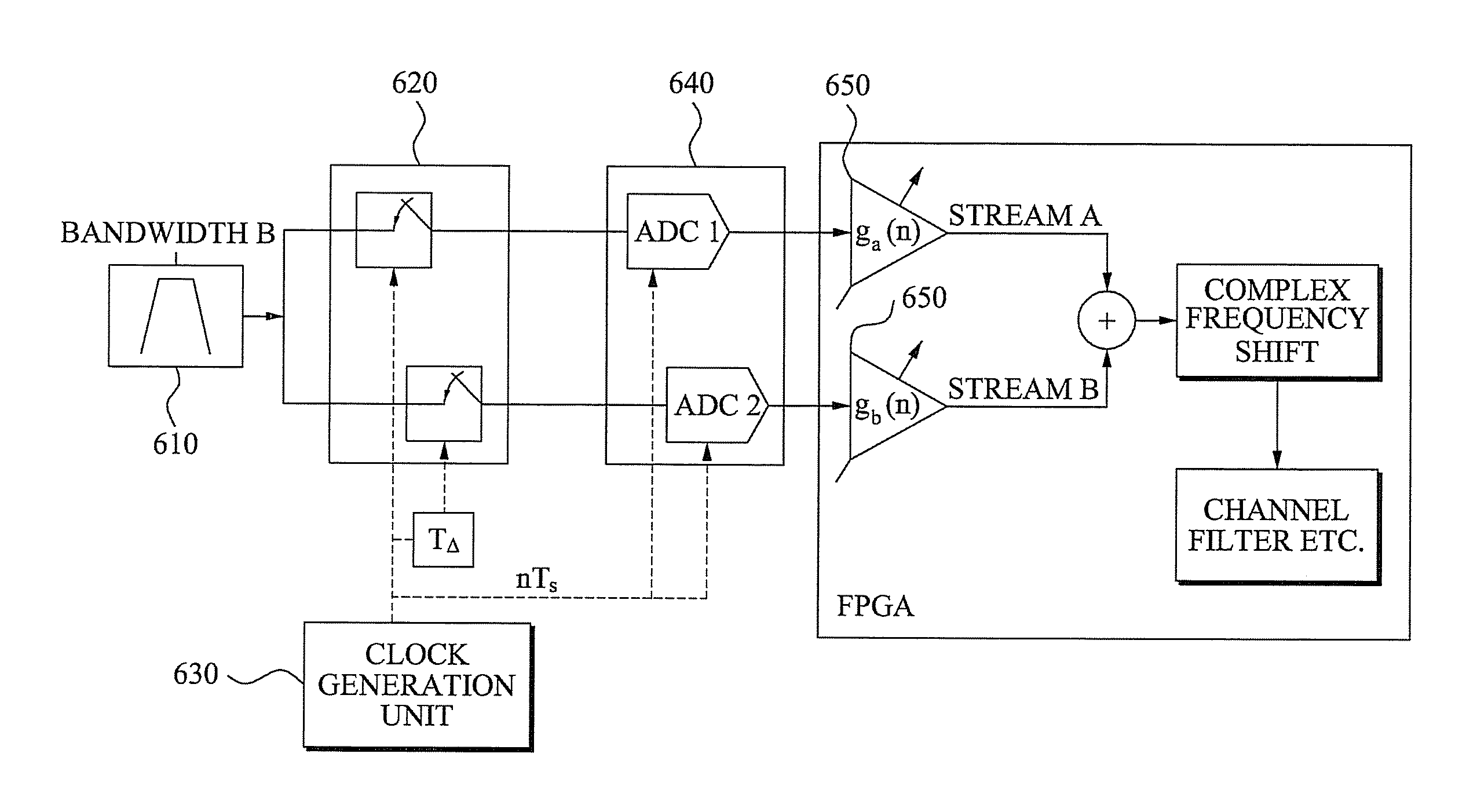
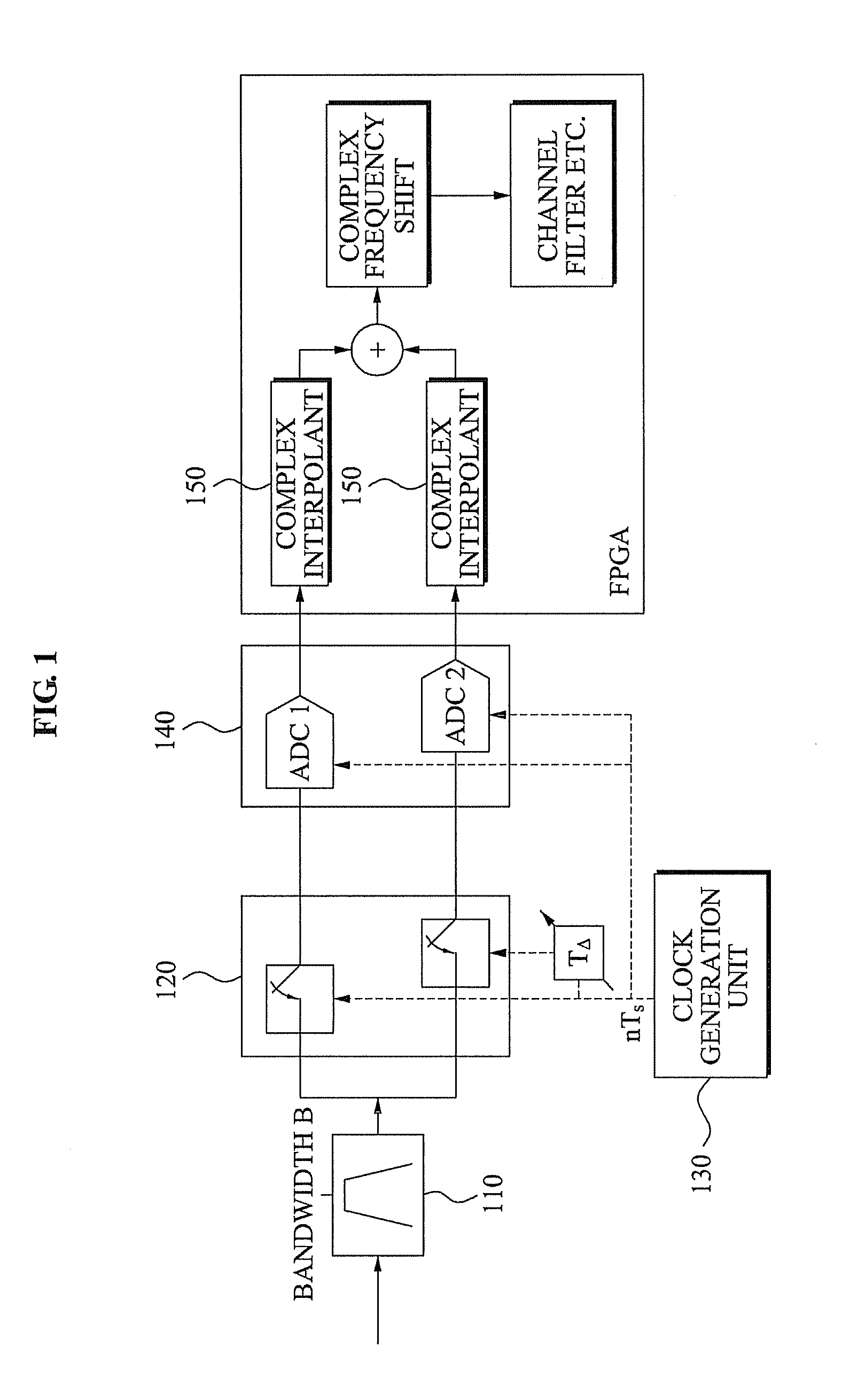
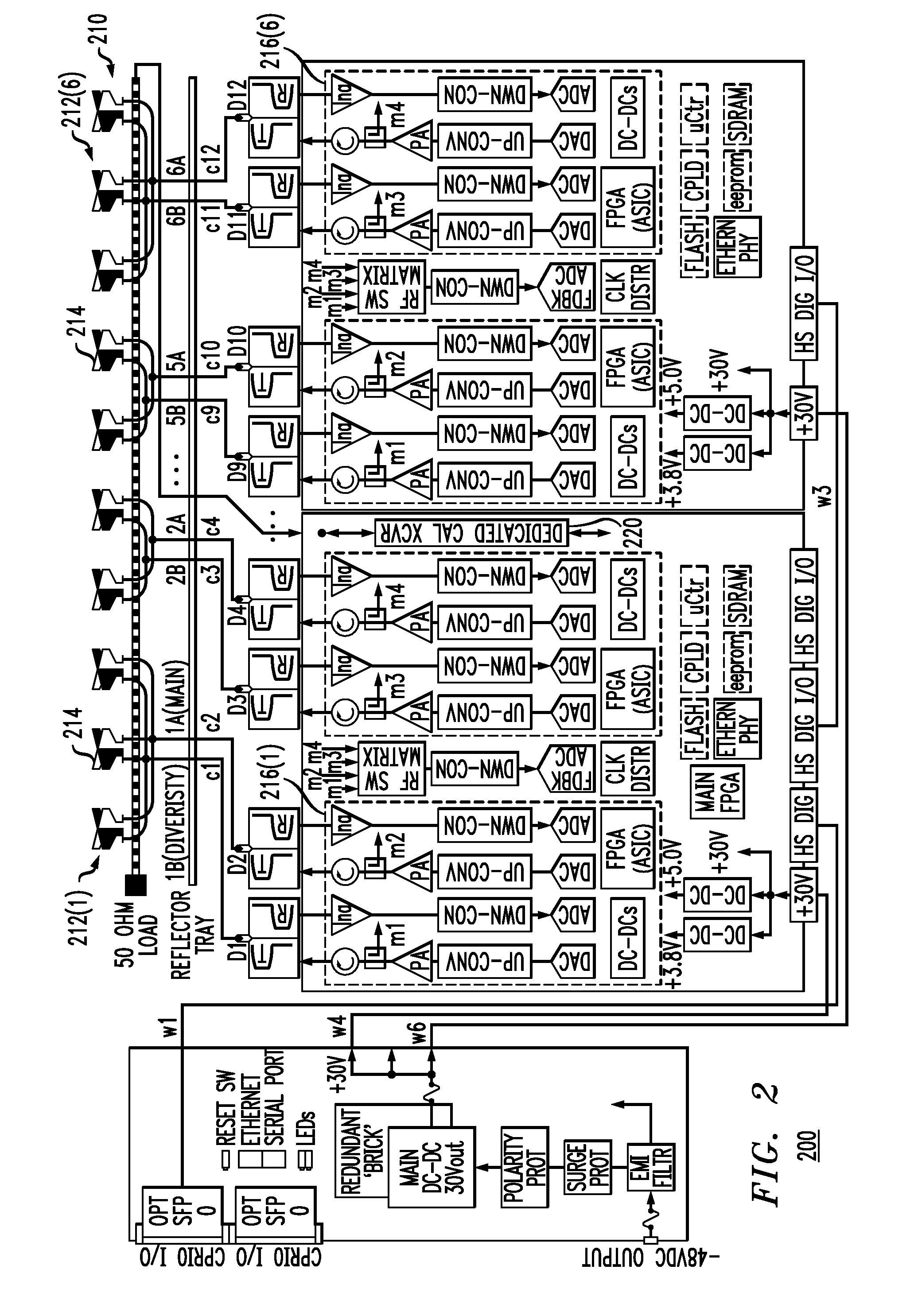
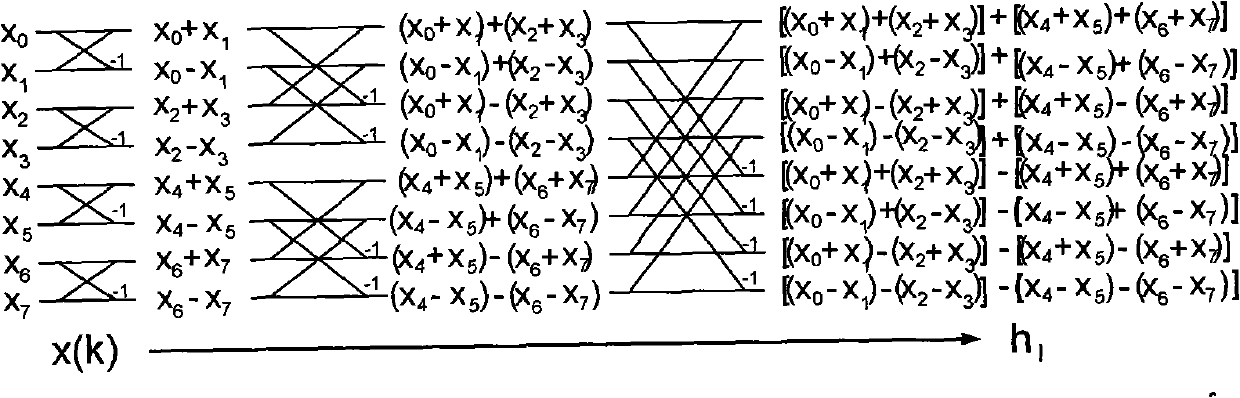Patents
Literature
66 results about "Complex gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
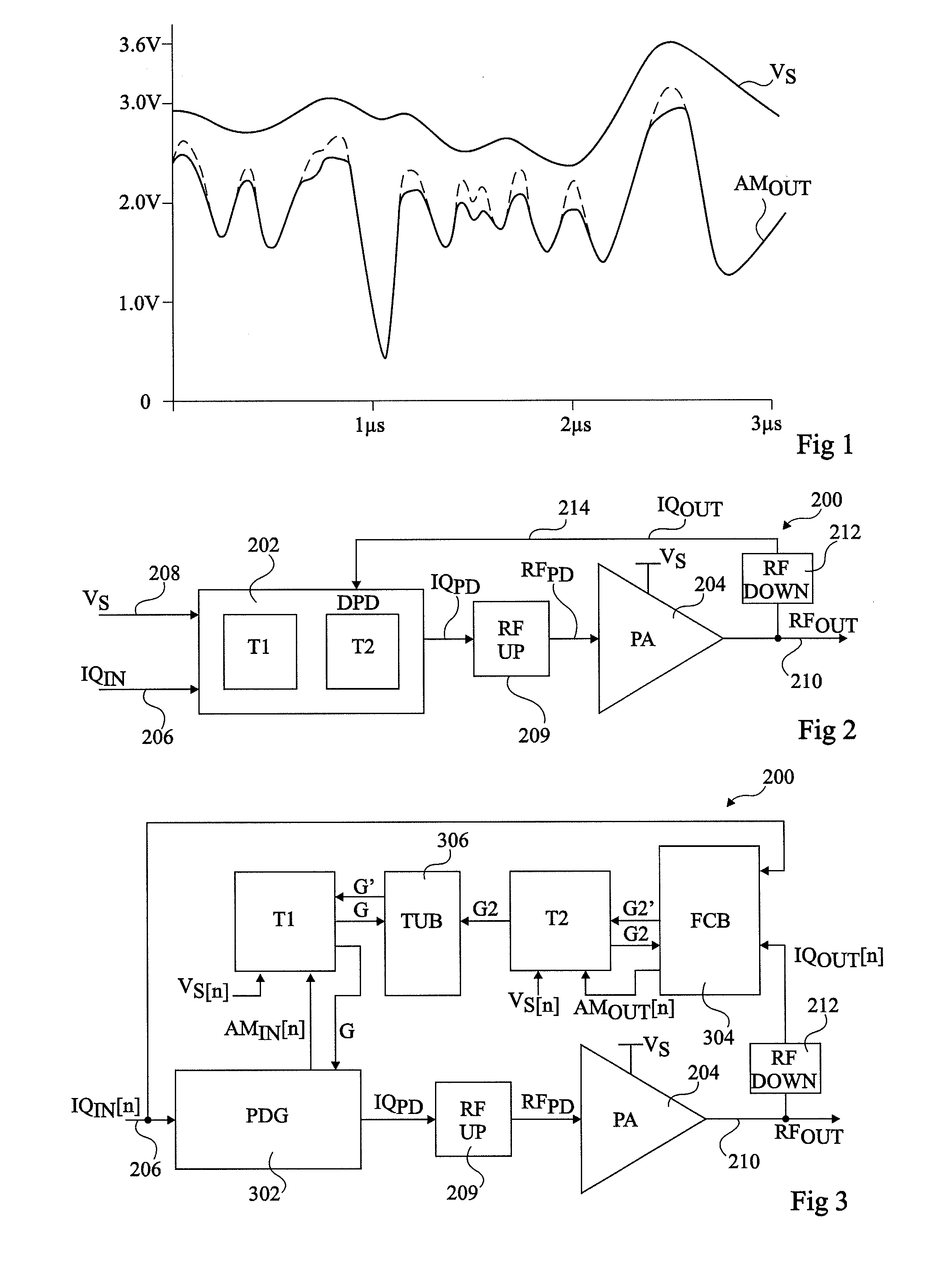
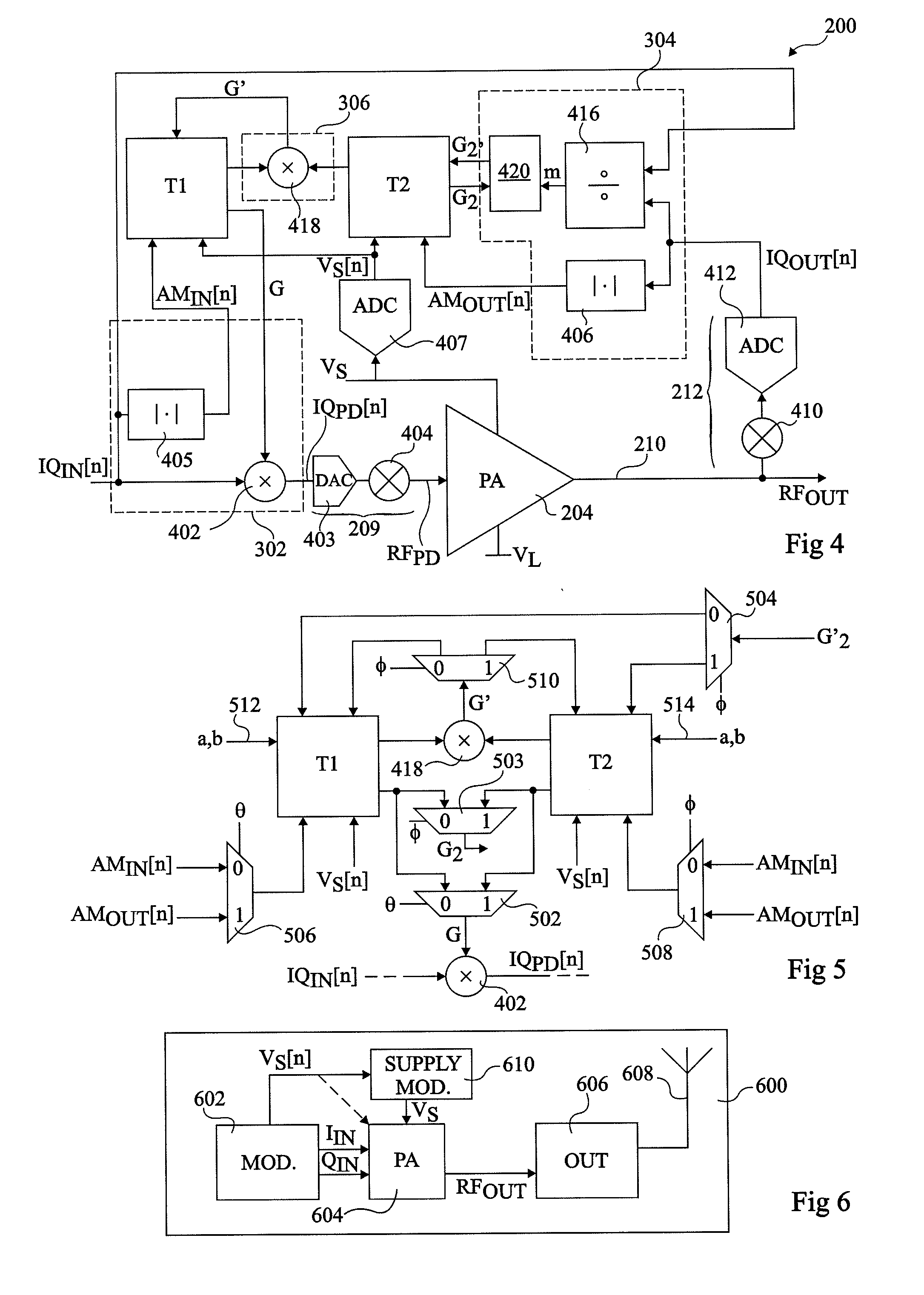
In electronics, complex gain is the effect that circuitry has on the amplitude and phase of a sine wave signal. The term complex is used because mathematically this effect can be expressed as a complex number.
Analog compensation circuit and method
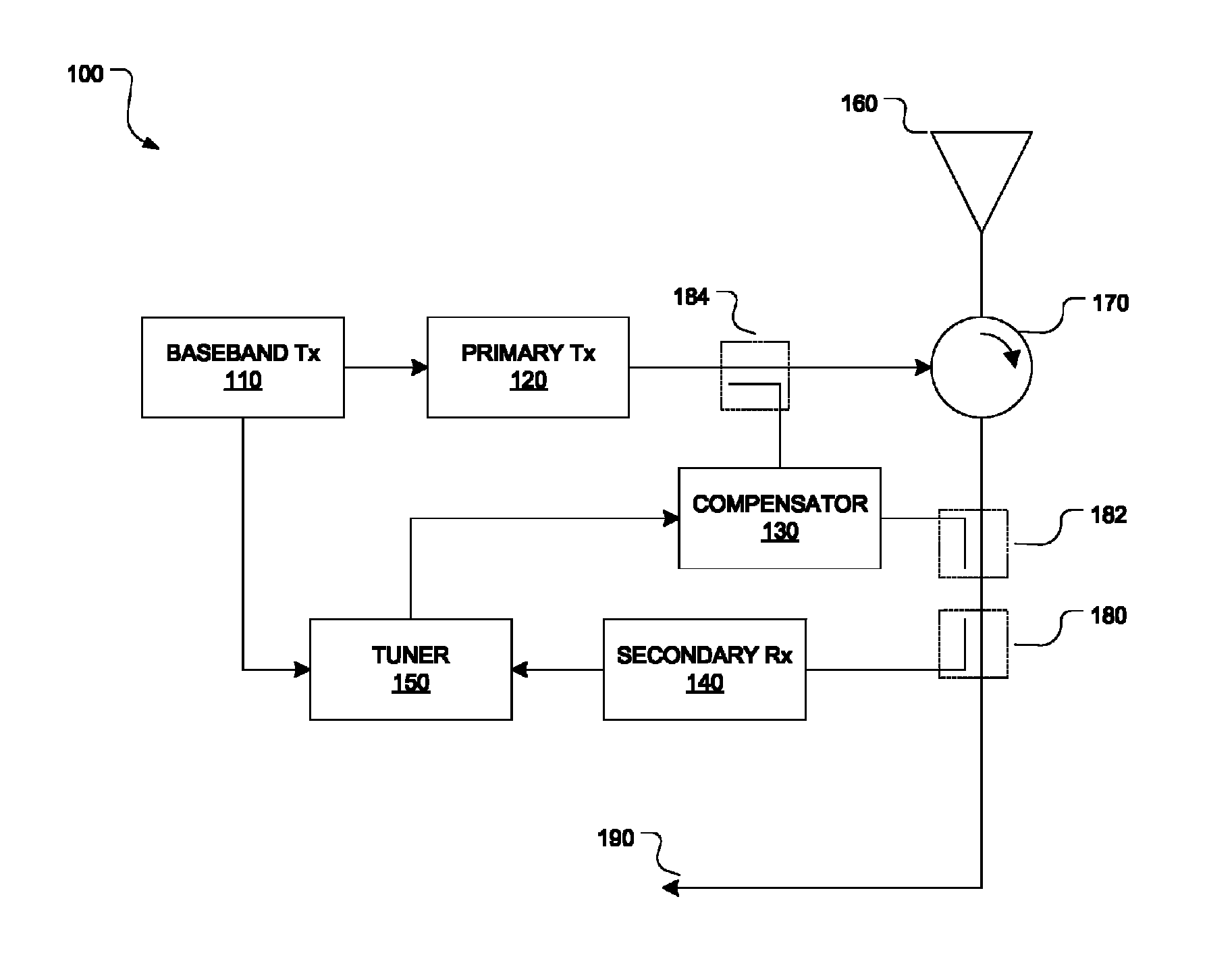
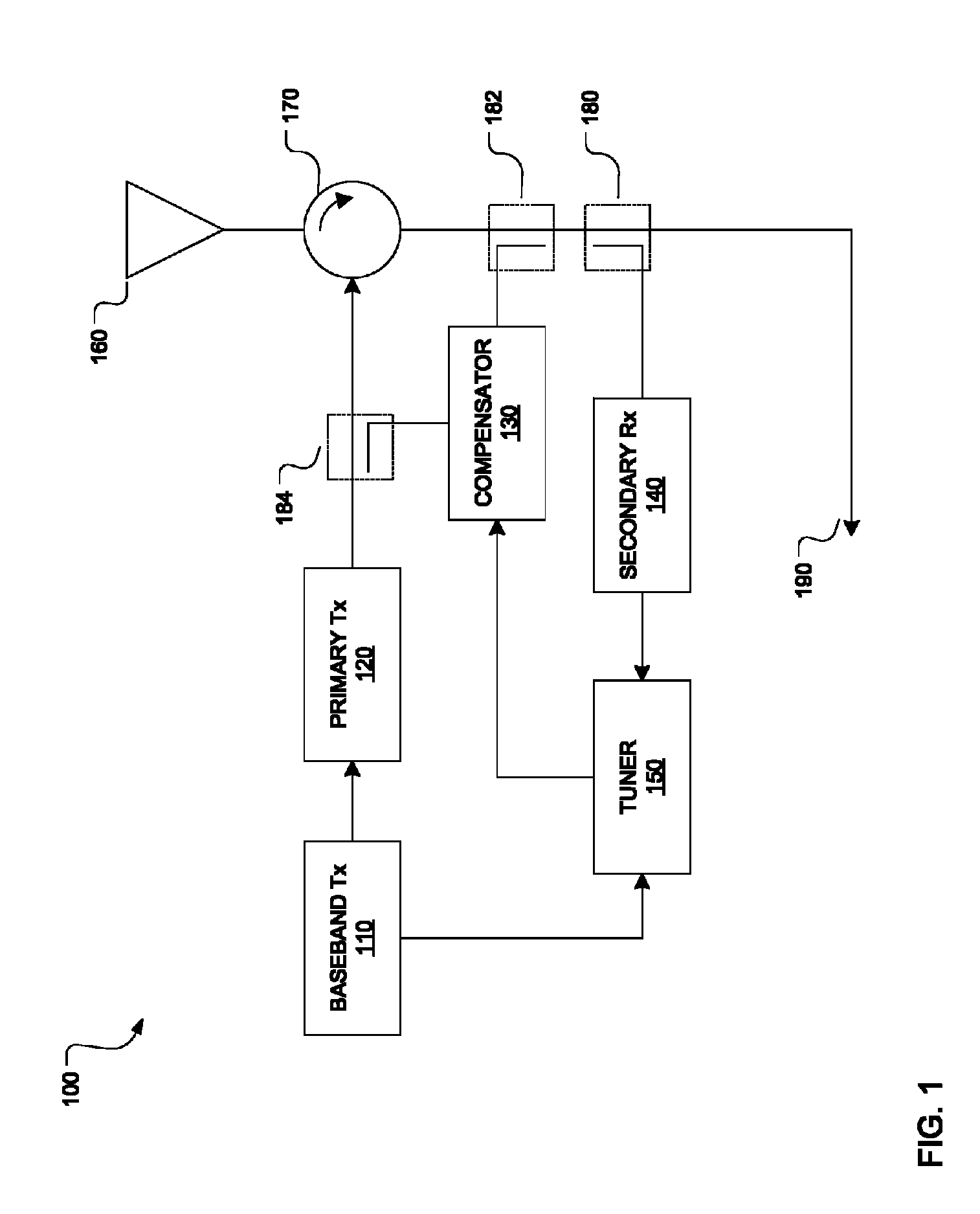
Disclosed herein are an analog compensation circuit and a method for tuning an analog compensator in full-duplex transmission systems. An embodiment analog compensation circuit includes a secondary receiver configured to receive and convert a sampled self-interference signal to a baseband self-interference signal. A tuner is coupled to the secondary receiver and configured to receive a baseband transmit signal and the baseband self-interference signal, and to compute complex gains according to the baseband transmit signal and the baseband self-interference signal. An analog compensator is coupled to the tuner and has multiple branches. The analog compensator is configured to receive the complex gains and use them to adjust respective attenuators and phase shifters of the branches. The analog compensator is further configured to process a sample of a transmit signal using the branches, the transmit signal being up-converted from a new baseband transmit signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
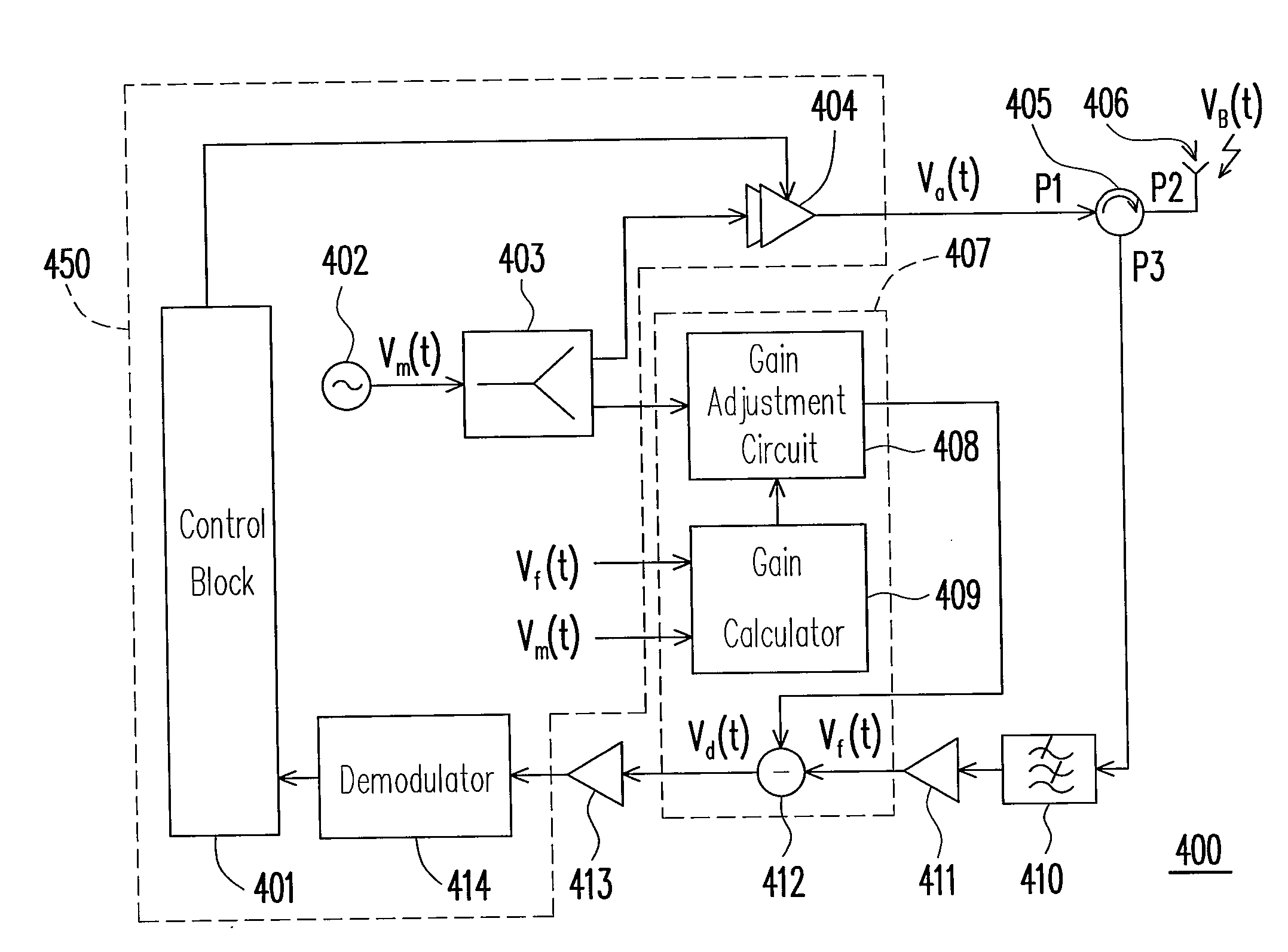
Rfid reader and circuit and method for echo cancellation thereof
InactiveCN101201891AMemory record carrier reading problemsLine-transmissionCarrier signalComplex gain
An echo cancellation circuit for an RFID reader and the method thereof are provided. The echo cancellation circuit includes a gain calculator, a gain adjustment circuit, and a subtraction circuit. The gain calculator provides a complex gain value according to a carrier signal and a received signal through an adaptive algorithm. The gain adjustment circuit is coupled to the gain calculator. The gain adjustment circuit multiplies the carrier signal by the complex gain value, and outputs the result of the multiplication. The subtraction circuit is coupled to the gain adjustment circuit. The subtraction circuit subtracts the output of the gain adjustment circuit from the received signal, and then provides the result of the subtraction as the output signal of the echo cancellation circuit.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Digital direct conversion receiving apparatus and method
InactiveUS20100156690A1InhibitionElectric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsPhase conversionPhase difference
A digital direct conversion receiving apparatus, including: a phase conversion unit to down-convert a Radio Frequency (RF) signal into a plurality of sample signals, and generate a certain phase difference among the plurality of sample signals when the RF signal is down-converted; and a variable complex gain unit to remove an image component from the plurality of sample signals using the generated phase difference.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
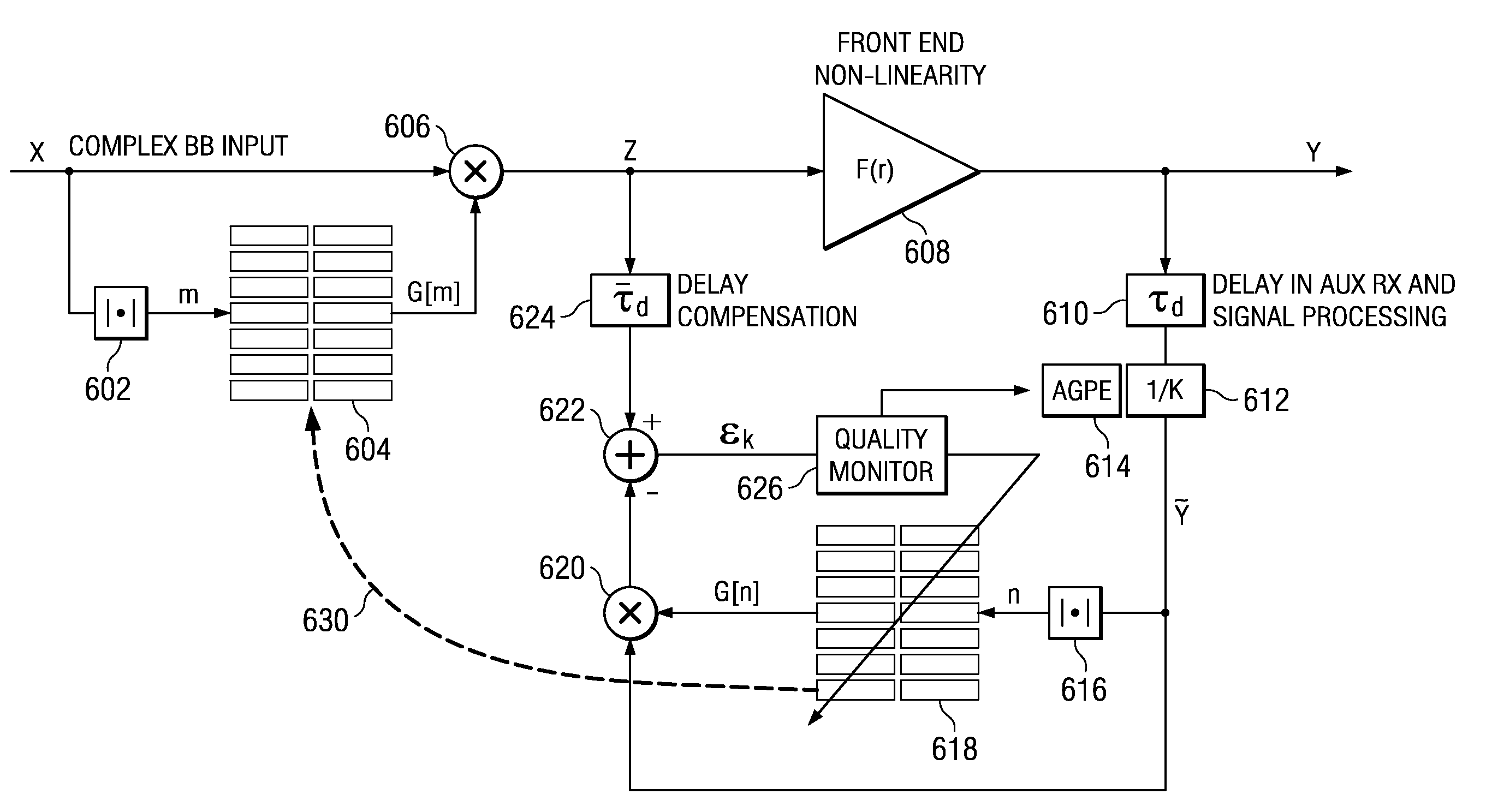
Adaptive Complex Gain Predistorter for a Transmitter
ActiveUS20100035554A1Resonant long antennasPower amplifiersLinear regionIn-phase and quadrature components
Symbols are transmitted in a Cartesian transmitter by pre-distorting an input signal X having in-phase and quadrature components using a first compensation lookup table operable to hold complex valued entries to carry out in-phase and quadrature compensation pre-distortion with respect to the input signal to form a pre-distorted signal Z. The pre-distorted signal Z is processed to form an output signal Y using a nonlinear element. A complex gain normalization parameter adaptively updated to reflect varying gain of a linear region of the nonlinear element. A normalized feed back signal {tilde over (Y)} is formed using the adaptively updated complex gain normalization parameter. The first compensation lookup table is updated based on the pre-distorted input signal Z and the adaptively normalized feedback signal {tilde over (Y)}.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
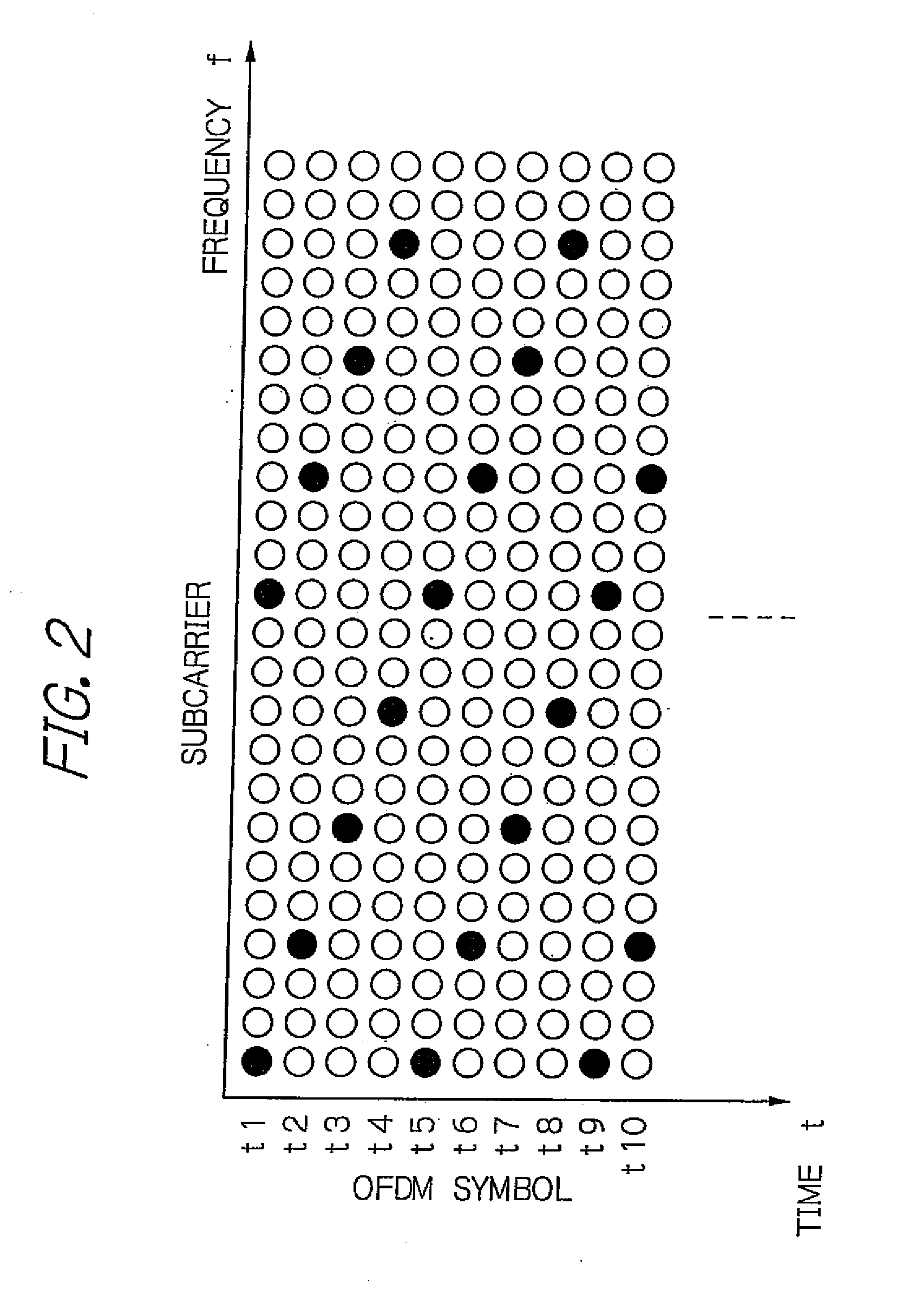
Transmit diversity technique based on channel randomization for OFDM systems
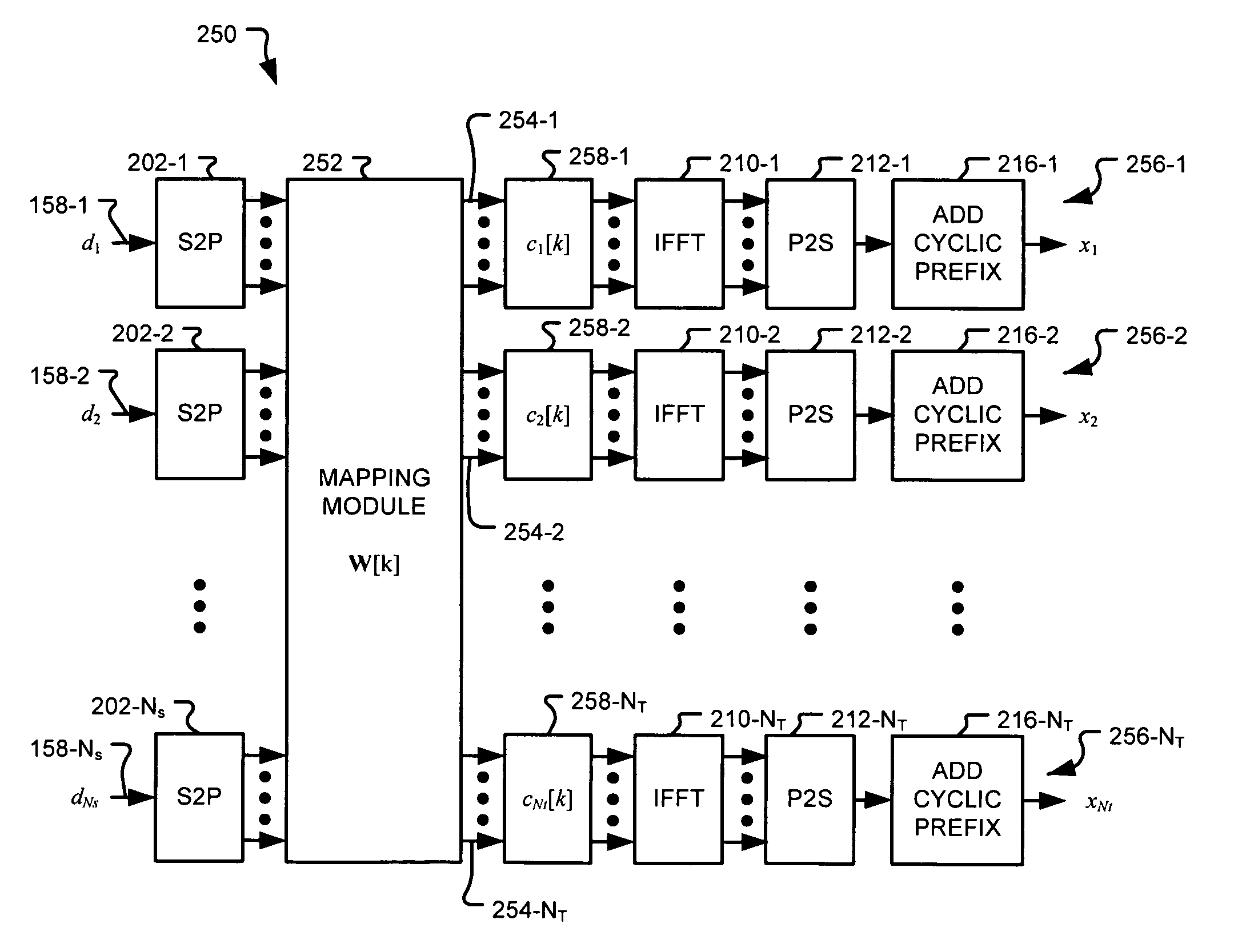
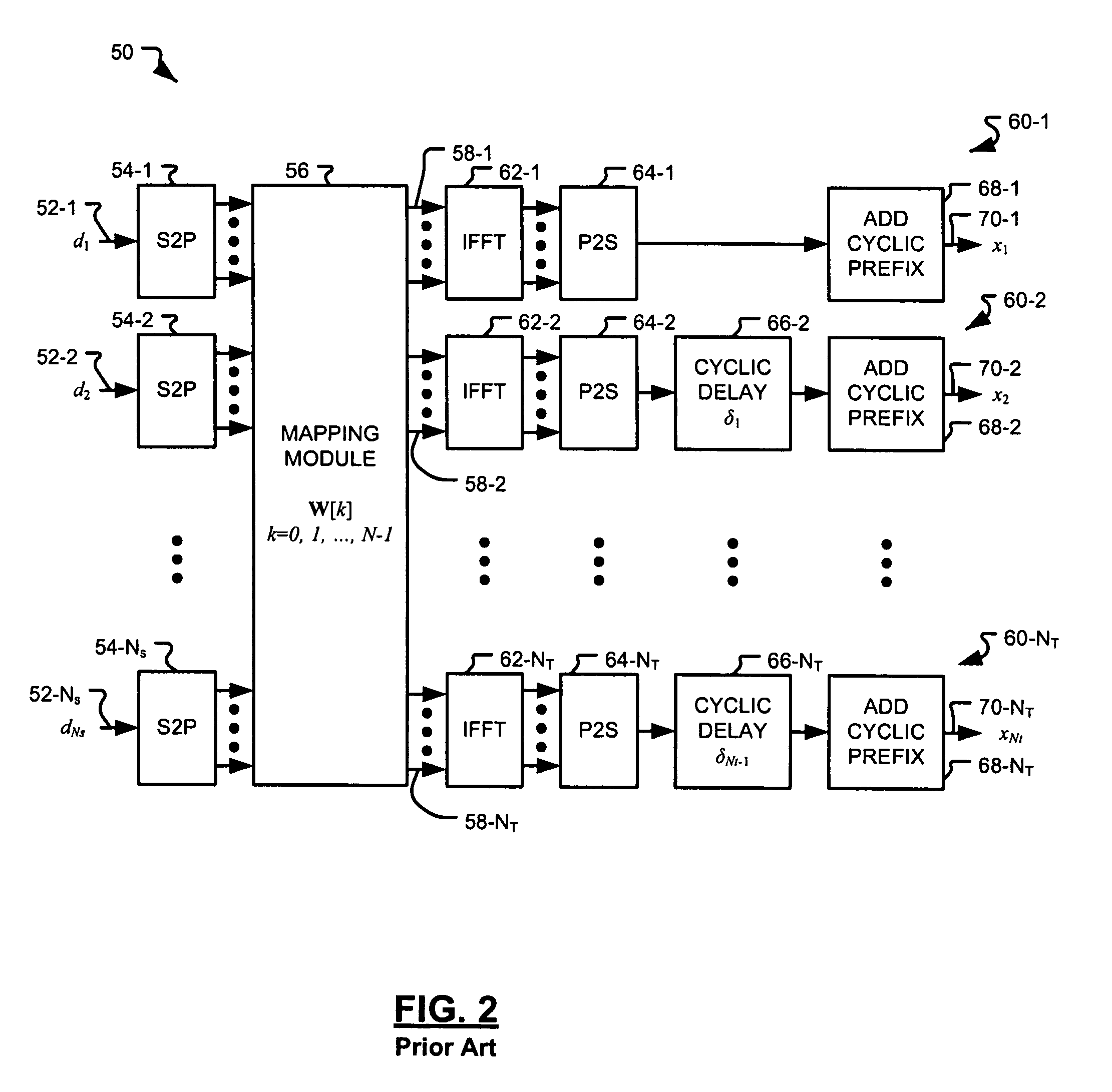
A physical layer (PHY) module includes NT radio frequency (RF) channels and a mapping module. The NT RF channels each include N subcarriers. The mapping module includes Ns inputs receiving corresponding ones of NS data streams. The mapping module further includes NT outputs communicating with corresponding ones of the NT RF channels. Each of the NT outputs includes N outputs. The mapping module further includes a mapping matrix that maps the NS data streams to the NT outputs. NT, NS, and N are integers greater than or equal to 2. The NT RF channels include NT gain modules that apply NT different complex gains to the NT outputs, respectively. One of the NT different complex gains is applied to each of the N outputs of a corresponding one of the NT outputs. The NT different complex gains correspond to NT transmit antennas of the NT RF channels, respectively.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Channel estimation in cdma communications systems using both lower power pilot channel and higher power date channel
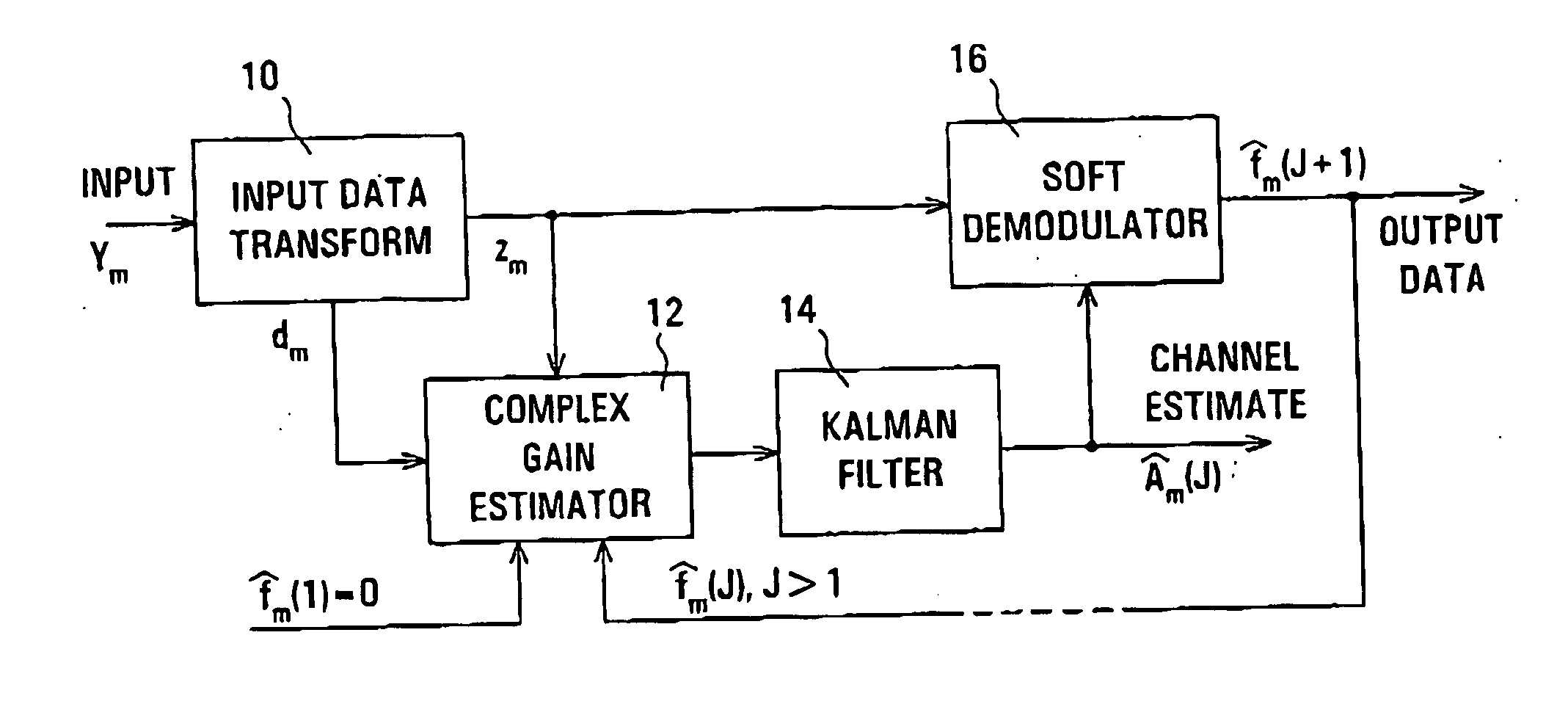
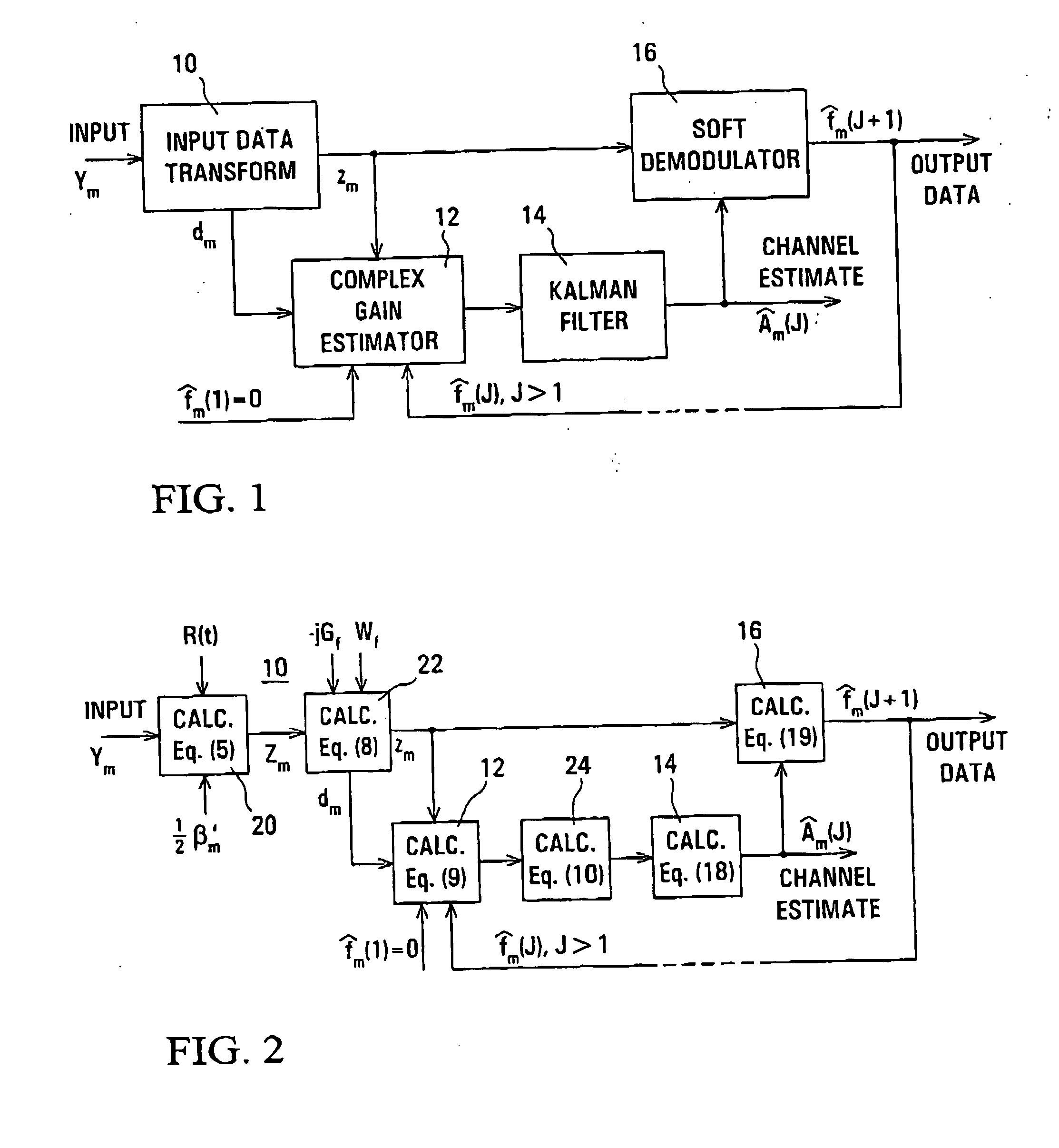
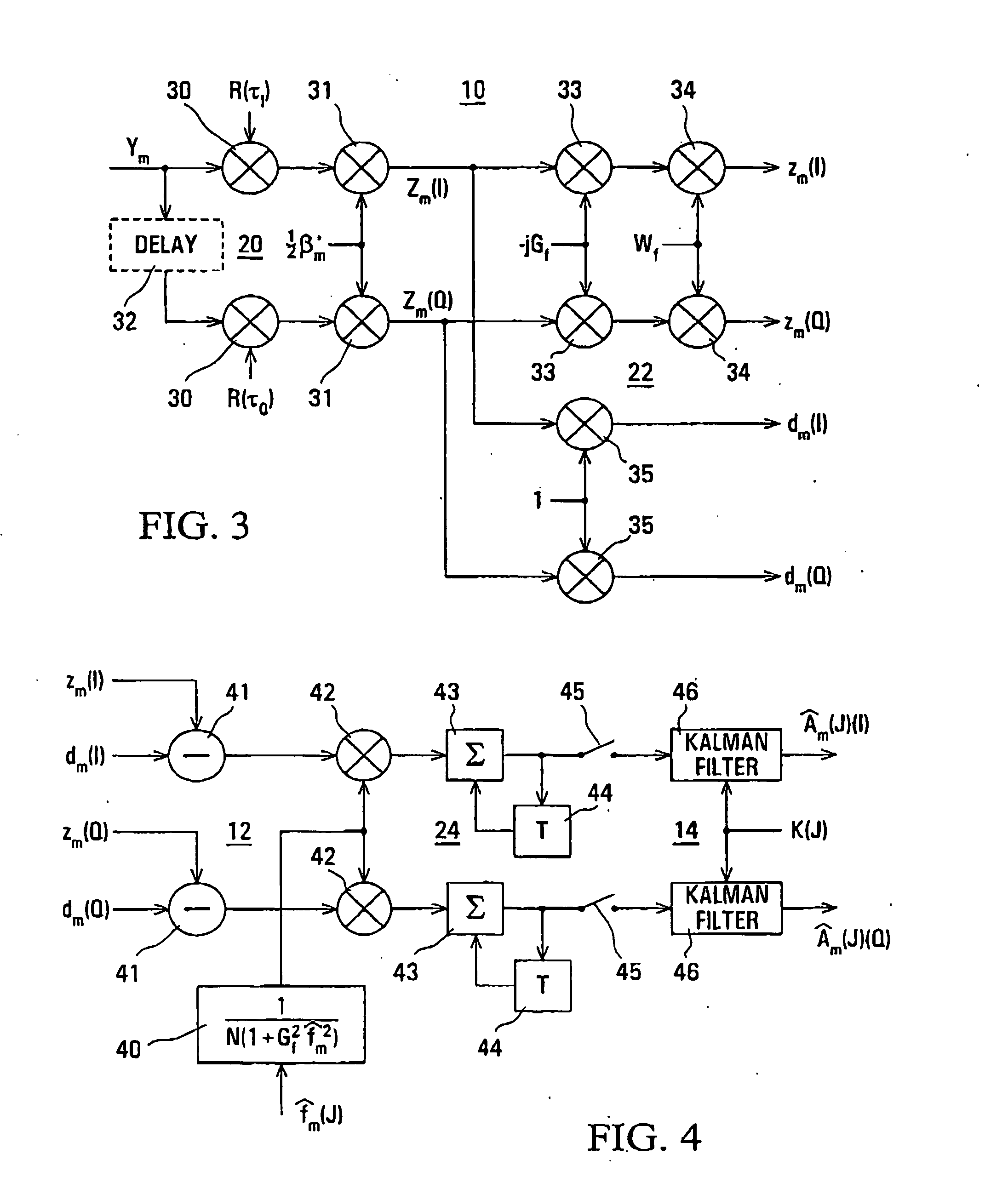
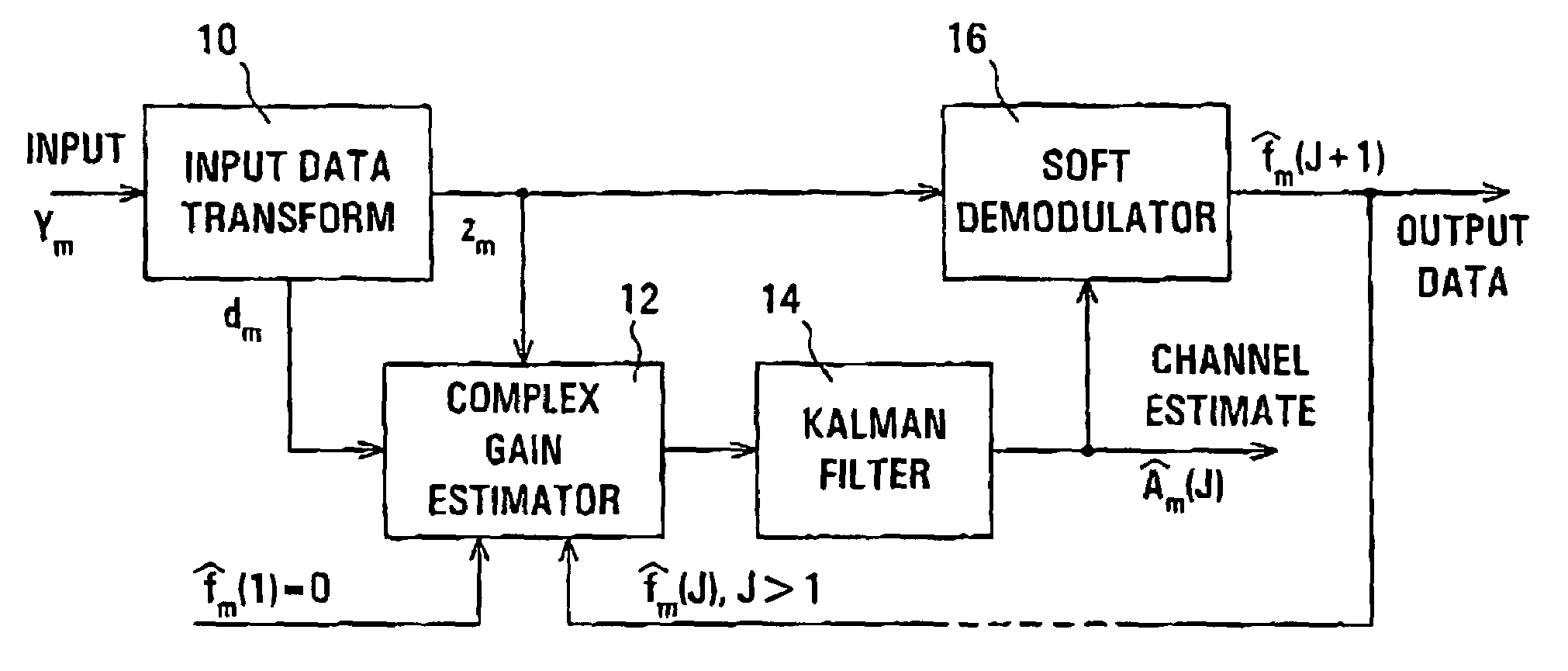
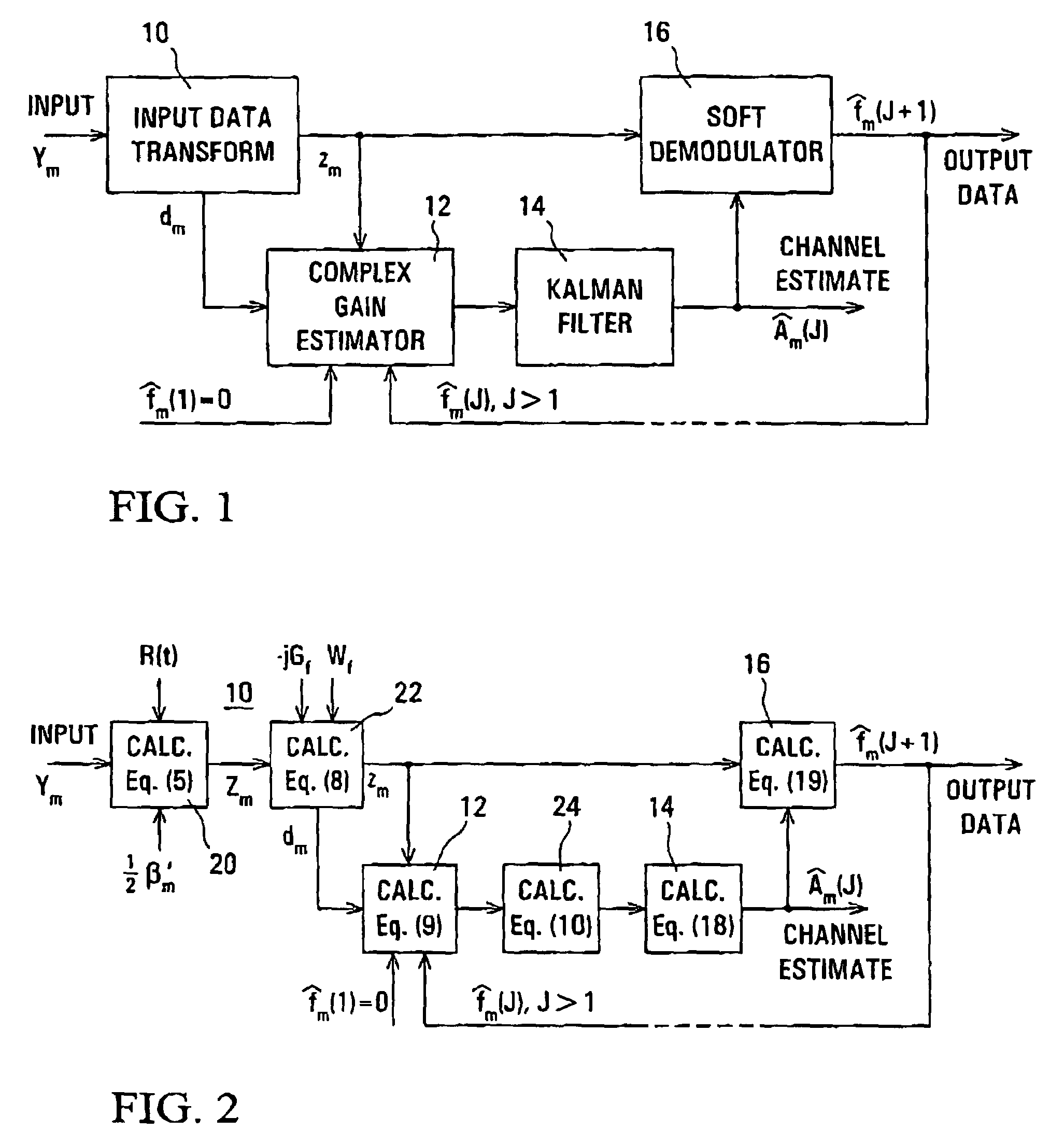
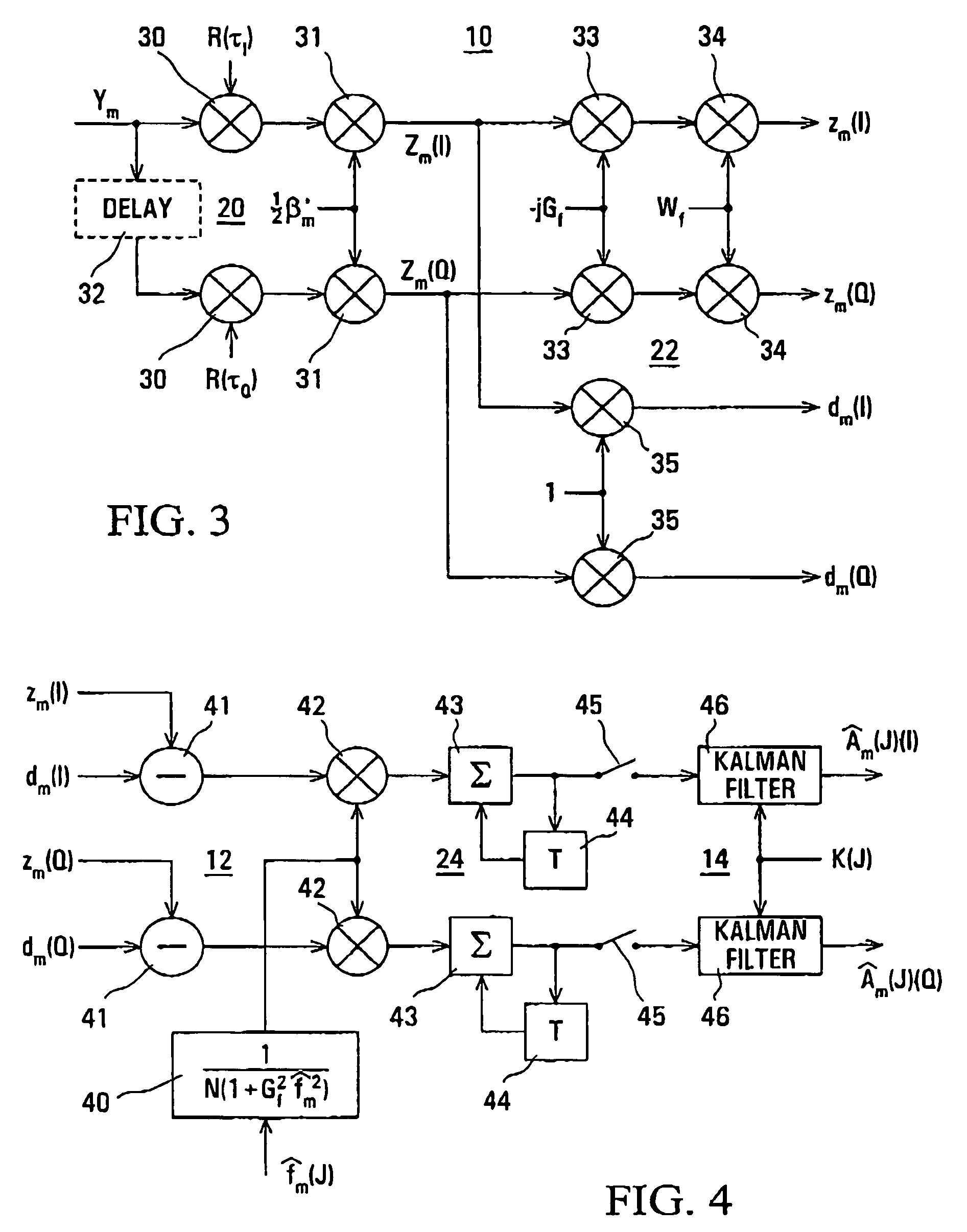
InactiveUS20070030827A1Improving estimated complex gain of communication channelAccurate estimateMultiple-port networksError preventionKaiman filterCommunications system
An iterative arrangement of channel estimator (12), a Kalman filter unit (14), and a soft demodulator (16) is provided for producing an estimate of complex gain of a CDMA communications channel carrying data and pilot channels, and demodulated data of the data channel. An initial channel estimate is produced by the estimator (12) using only the low-power pilot channel. This later is improved by the iterative process using the data channel. The complex gains is represented by a sum of sinusoidal signals with different frequencies and randomly variable amplitude and phase.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
Channel estimation method for improving receiving sensitivity of OQAM (Offset Quadrate Amplitude Modulation)-OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) light transmission system
InactiveCN104506467AAccurate estimateEliminate distractionsBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainPhase response
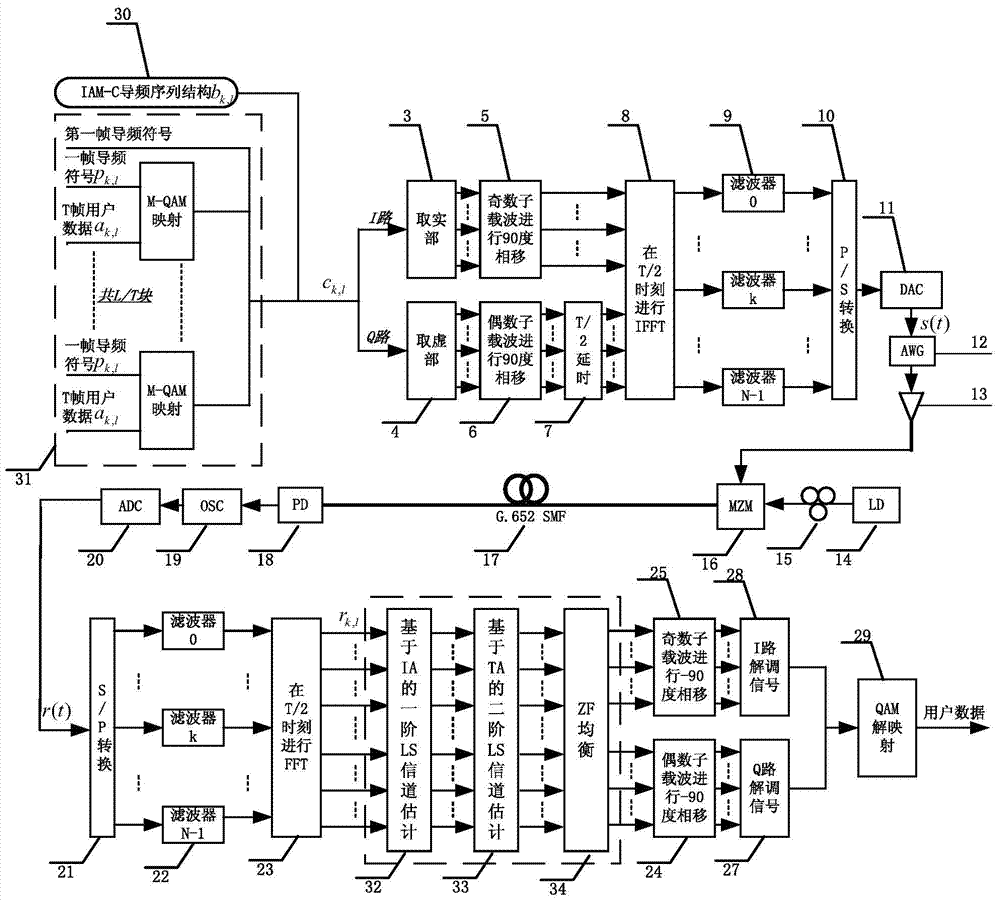
The invention provides a channel estimation method for improving receiving sensitivity of an OQAM (Offset Quadrate Amplitude Modulation)-OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) light transmission system, and aims at solving the problems that the traditional channel estimation algorithm for the light OQAM-OFDM cannot treat intersymbol interference and inter-subcarrier interference caused by the orthogonal damage of a subcarriers, and the decrease of the receiving sensitivity of the system caused by the accompanying gaussian noise and the like produced by devices in the system is ignored. The channel estimation method has the advantages that the interference approximating utilization based time-domain averaging channel estimation method (IATA-CE) comprising the steps of first-order LS channel estimation, second-order LS channel estimation and ZF balancing is performed during receiving to accurately estimate complex gain and phase response of a fiber channel; in addition, the interference from gaussian noise produced by the devices in the system can be resisted well; therefore, accurate channel estimation coefficients can be obtained, and as a result, the BER performance and receiving sensitivity of the system can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Adaptive controller for linearization of transmitter
ActiveUS7251290B2Reduce sensitivityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasOrthogonal coordinatesEngineering
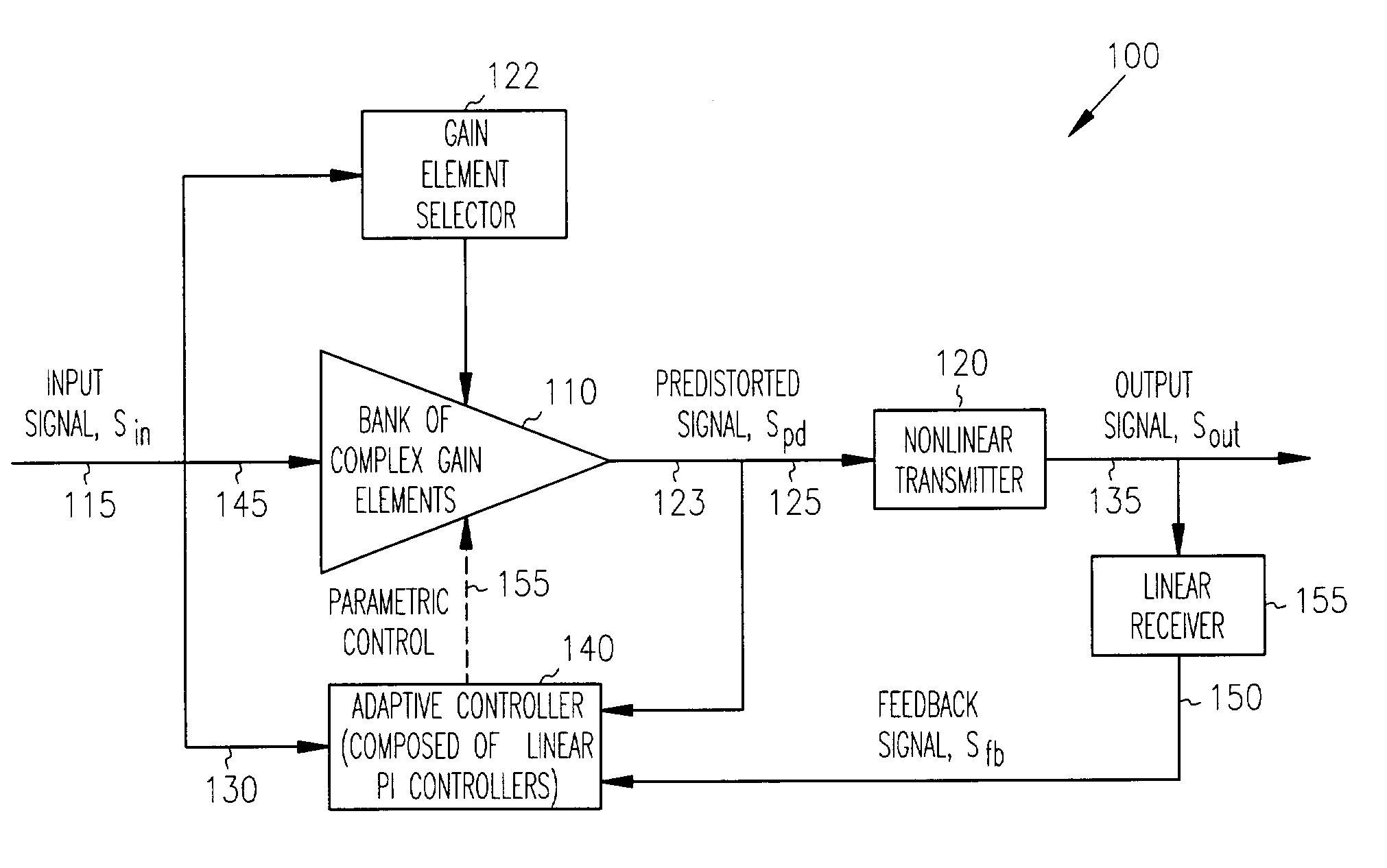
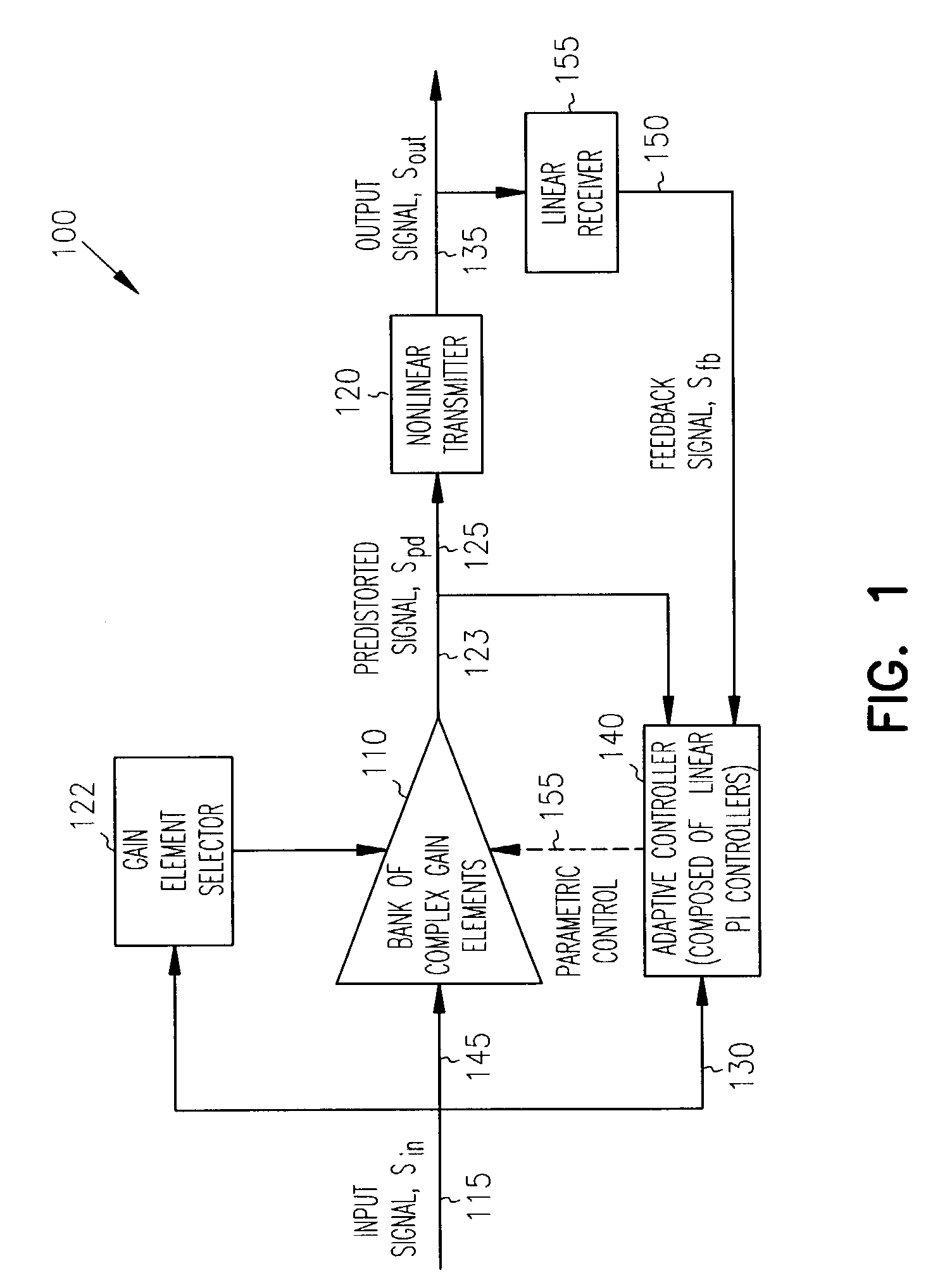
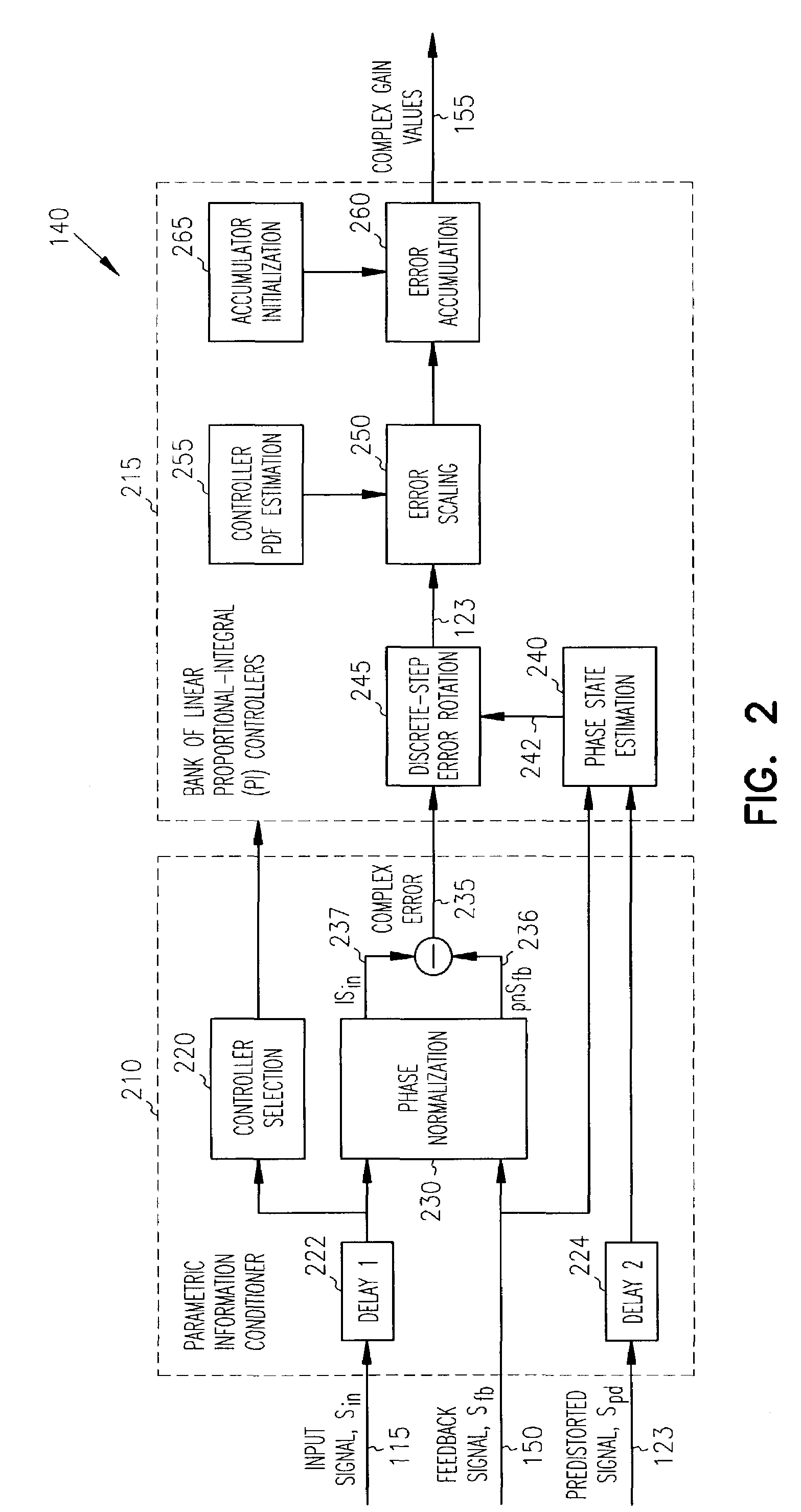
A bank of complex gain elements is used to provide a step-wise approximation of an arbitrary complex-gain predistortion function for a nonlinear transmitter. The bank of gain elements is in an adaptive loop realizing adaptive control. The adaptive loop is closed between an Input of the gain bank and an output of the transmitter through a linear receiver at an adaptive controller composed of a bank of proportional-integral (PI) controllers. The real and imaginary parts of each predistortion gain element are controlled by a corresponding adaptive PI controller. The signals processed by the adaptive controller are represented in orthogonal coordinates in terms of real and imaginary number pairs of complex numbers. The adaptive controller achieves unconditionally stable operation independently from the arbitrary phase rotation in the input signal or the adaptive loop.
Owner:APPLE INC
Analog Compensation Circuit and Method
Disclosed herein are an analog compensation circuit and a method for tuning an analog compensator in full-duplex transmission systems. An embodiment analog compensation circuit includes a secondary receiver configured to receive and convert a sampled self-interference signal to a baseband self-interference signal. A tuner is coupled to the secondary receiver and configured to receive a baseband transmit signal and the baseband self-interference signal, and to compute complex gains according to the baseband transmit signal and the baseband self-interference signal. An analog compensator is coupled to the tuner and has multiple branches. The analog compensator is configured to receive the complex gains and use them to adjust respective attenuators and phase shifters of the branches. The analog compensator is further configured to process a sample of a transmit signal using the branches, the transmit signal being up-converted from a new baseband transmit signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Adaptive complex gain predistorter for a transmitter
ActiveUS8055217B2Resonant long antennasPower amplifiersLinear regionIn-phase and quadrature components
Symbols are transmitted in a Cartesian transmitter by pre-distorting an input signal X having in-phase and quadrature components using a first compensation lookup table operable to hold complex valued entries to carry out in-phase and quadrature compensation pre-distortion with respect to the input signal to form a pre-distorted signal Z. The pre-distorted signal Z is processed to form an output signal Y using a nonlinear element. A complex gain normalization parameter adaptively updated to reflect varying gain of a linear region of the nonlinear element. A normalized feed back signal {tilde over (Y)} is formed using the adaptively updated complex gain normalization parameter. The first compensation lookup table is updated based on the pre-distorted input signal Z and the adaptively normalized feedback signal {tilde over (Y)}.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
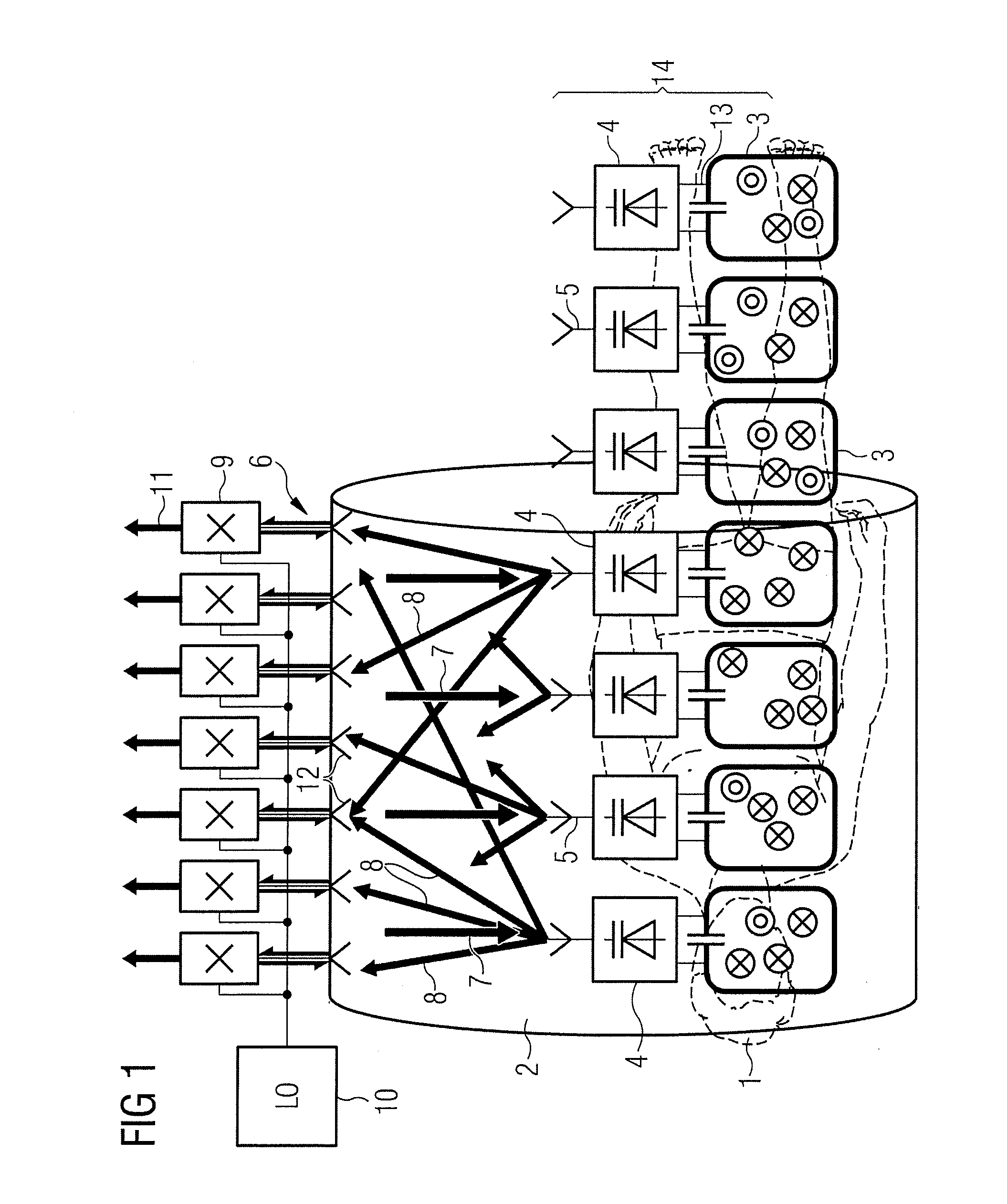
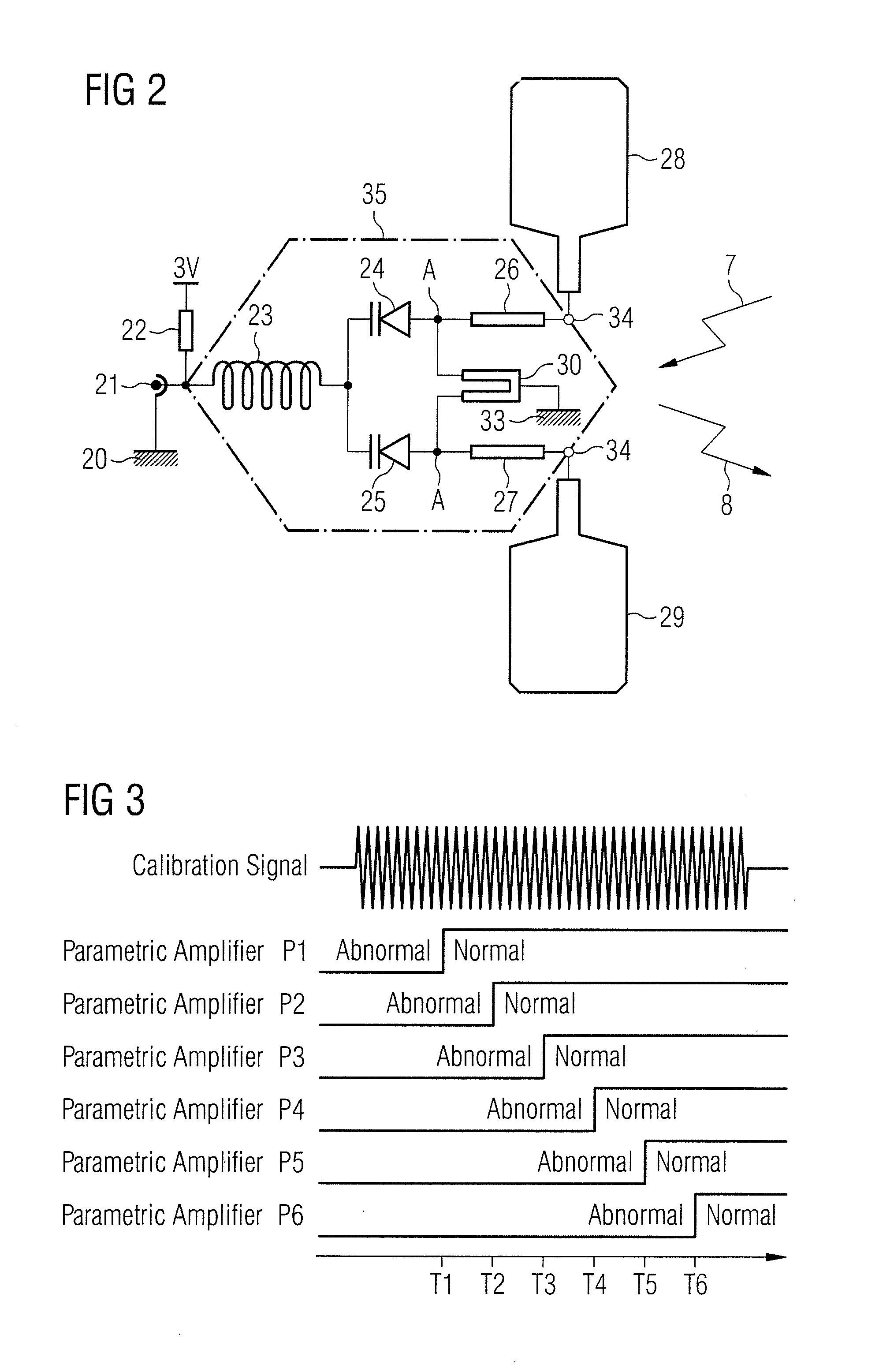
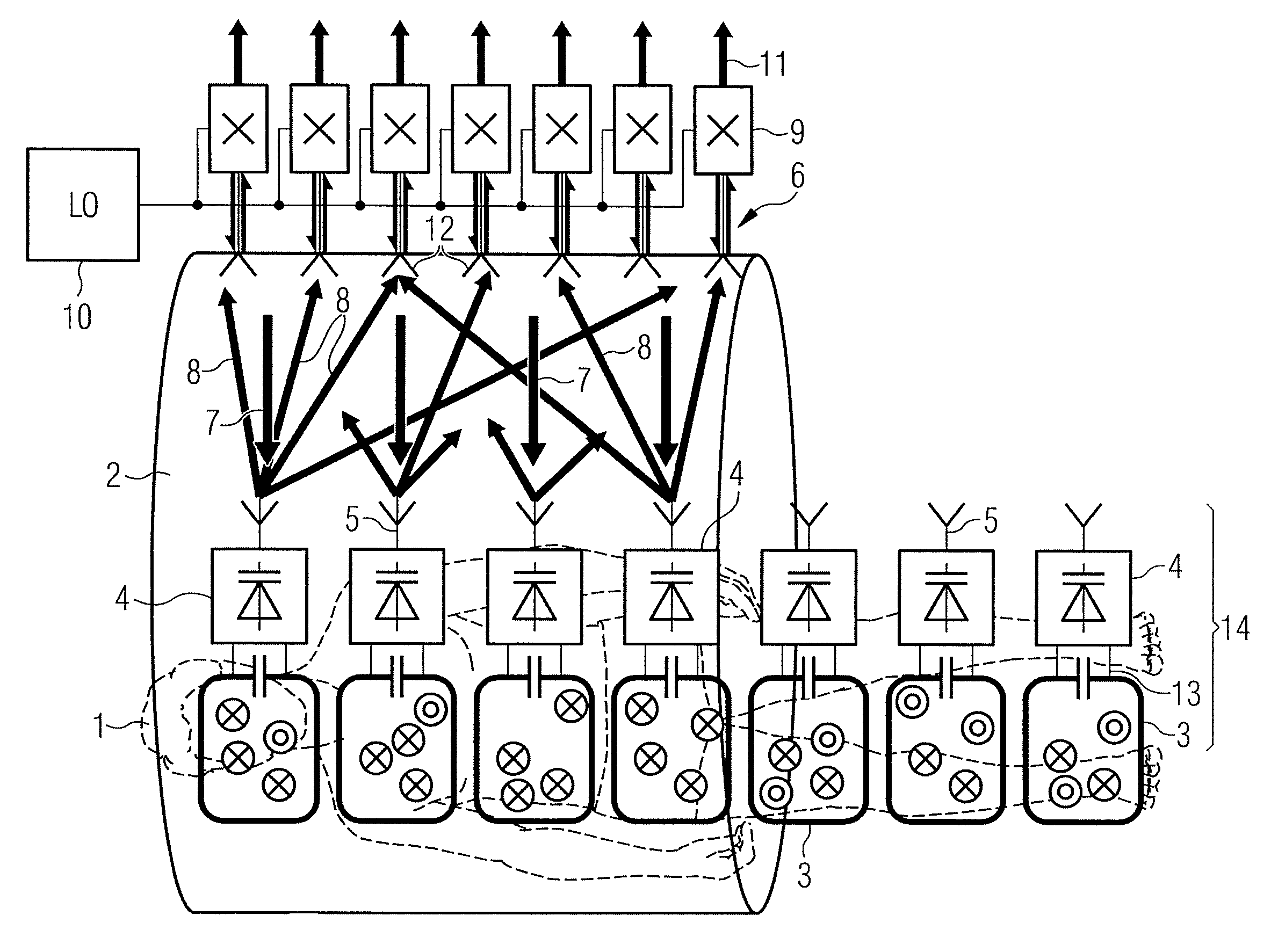
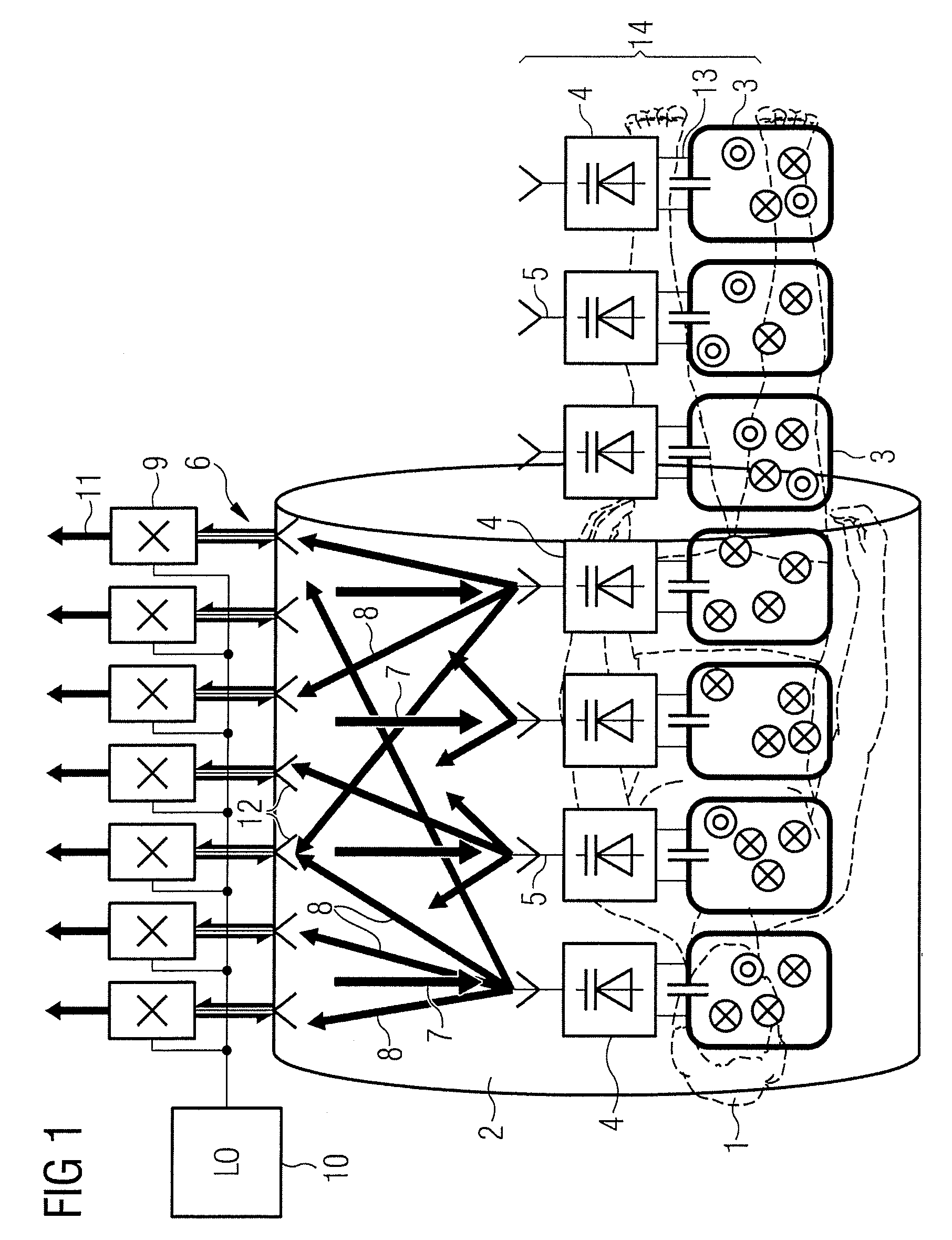
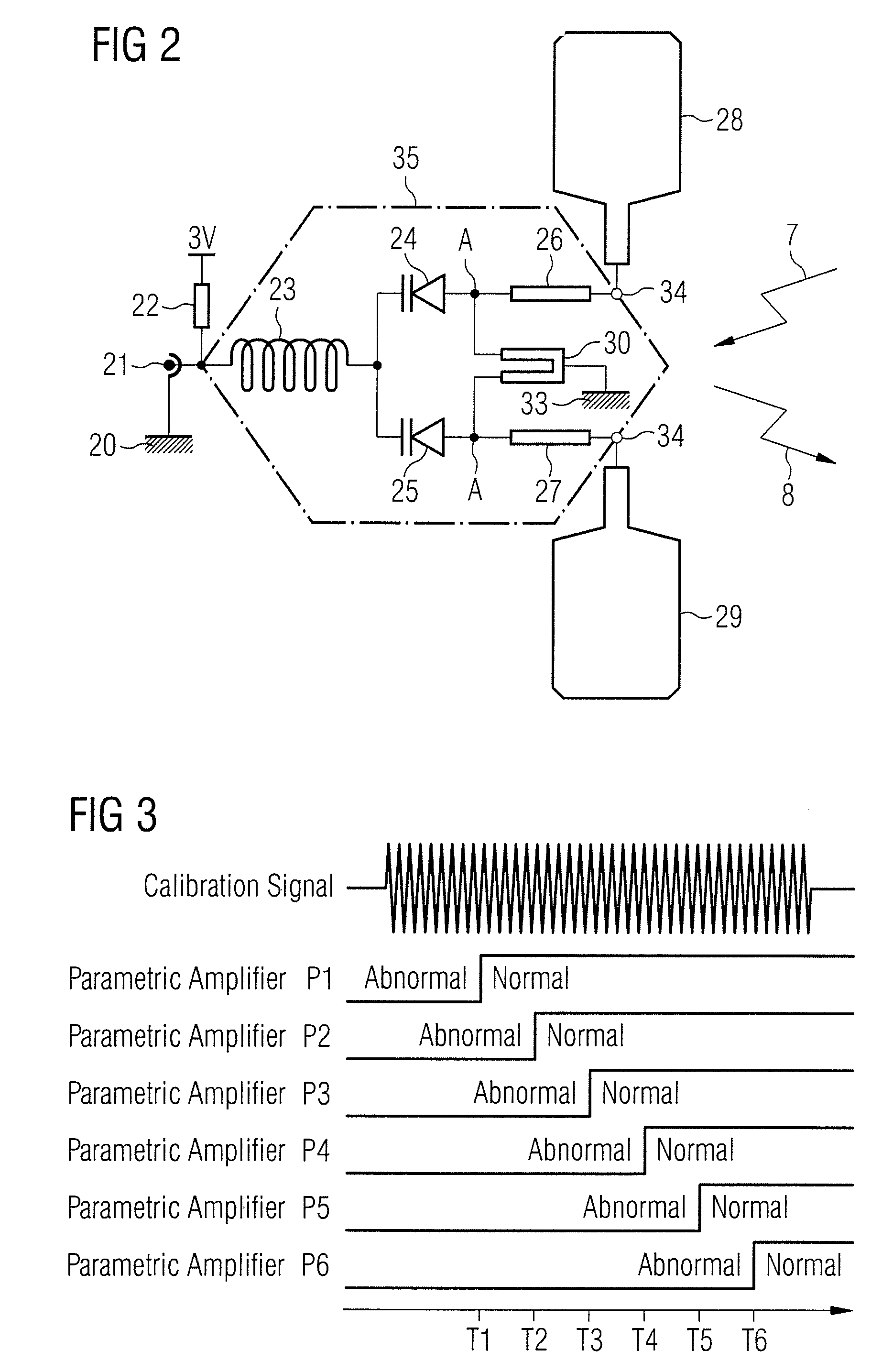
Calibration method
A method for calibration of a magnetic resonance imaging system having a bore, a body coil mounted in the bore, a patient mat, a number of local coils mounted in the patient mat, an upconversion stage having a number of upconverters, and a processing stage, includes the steps of generating a calibration signal in the body coil; receiving the calibration signal at the local coils, upconverting the signal from the local coils in the upconversion stage, transmitting the upconverted signal to the processing stage, synchronously downconverting the signal in the processing stage using the calibration signal generated in the body coil, and processing the downconverted signal to generate an overall path complex gain.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Channel estimation system and method thereof
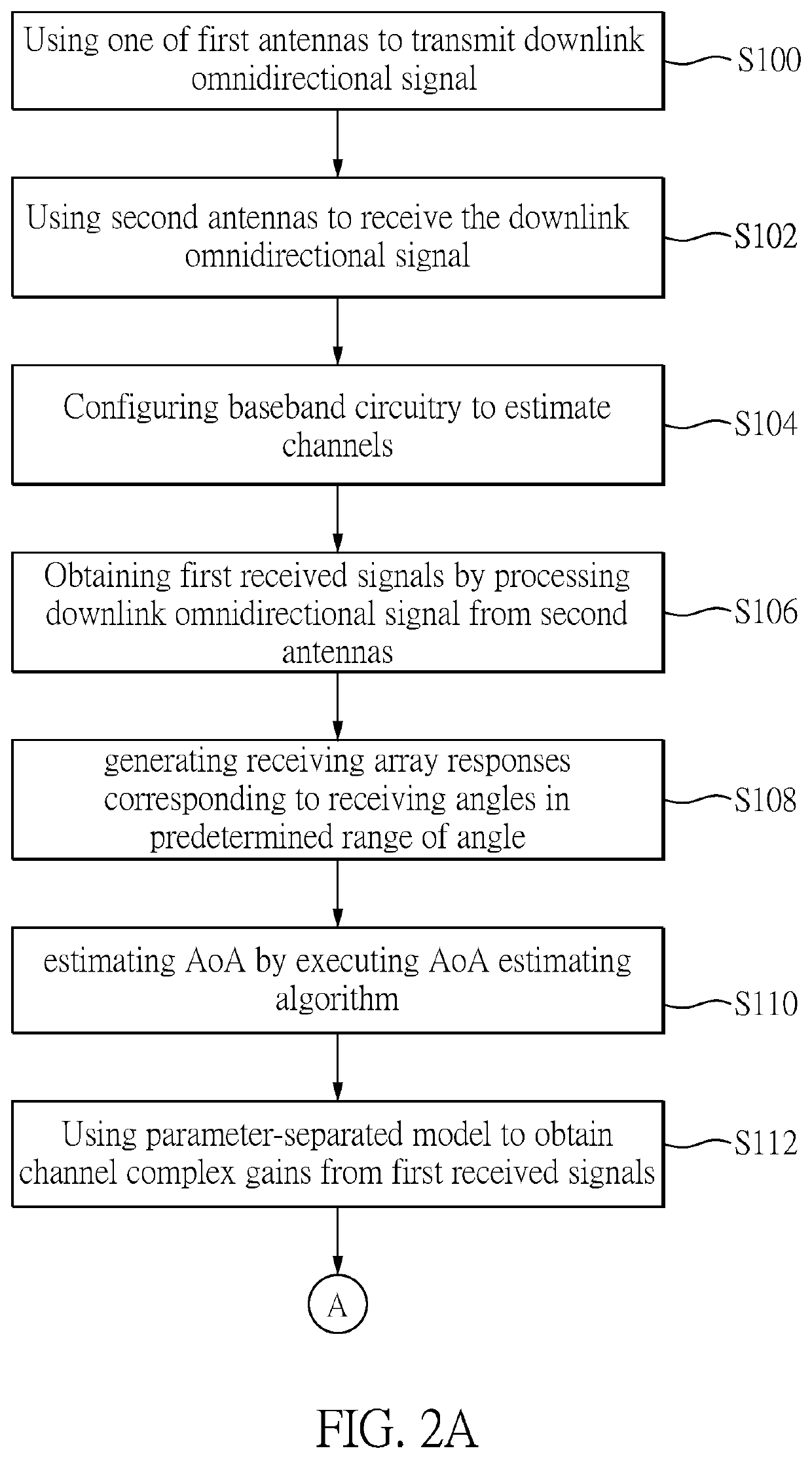
ActiveUS10594517B1Avoid mistakesInaccurate estimationSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationEngineeringMillimetre wave
A channel estimation system and method thereof is provided. By utilizing the nature of the millimeter-wave channel with sparse path, the channel estimation problem is transformed from estimating the entire channel matrix to estimating independent parameters of the millimeter-wave channel. These parameters are angle of arrival (AoA) and angle of departure (AoD), and complex gain of the channel paths.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Method for implementing rapid channel estimation using FWT in DMB-T system
ActiveCN101330482AImprove practicalityReduce computational complexityBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainChannel impulse response
The invention discloses a method for realizing fast channel estimation in a DMB-T system by using an FWT, which realizes multipath acquisition by using the FWT. The steps for related to the matching of a PN sequence are as follows: a cyclic convolution with length of N receives signal vector sequence r, and the signal vector sequence r is transformed into time-domain channel impulse response h; the strong number S and the corresponding impulse response hsi are obtained. The interference cancellation steps are as follows: as for all strong impulse response complex gains, the interference is entirely cancelled through all strong interference components hsi, and a real channel impulse response sequence h and the channel transmission function H (omega) are obtained. The method has the advantages that the computational complexity can be effectively reduced, the hardware realization is simple, and the method is suitable for matching related system by using by using the periodic PN sequence, for example, the receiving system of DMB-T digital terrestrial broadcasting.
Owner:麦克盛科技(香港)有限公司
RFID reader and circuit and method for echo cancellation thereof
InactiveUS20080136645A1High sensitivityBroad SFDRMemory record carrier reading problemsSubstation equipmentCarrier signalComplex gain
An echo cancellation circuit for an RFID reader and the method thereof are provided. The echo cancellation circuit includes a gain calculator, a gain adjustment circuit, and a subtraction circuit. The gain calculator provides a complex gain value according to a carrier signal and a received signal through an adaptive algorithm. The gain adjustment circuit is coupled to the gain calculator. The gain adjustment circuit multiplies the carrier signal by the complex gain value, and outputs the result of the multiplication. The subtraction circuit is coupled to the gain adjustment circuit. The subtraction circuit subtracts the output of the gain adjustment circuit from the received signal, and then provides the result of the subtraction as the output signal of the echo cancellation circuit.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Predistortion feedback method, apparatus and system
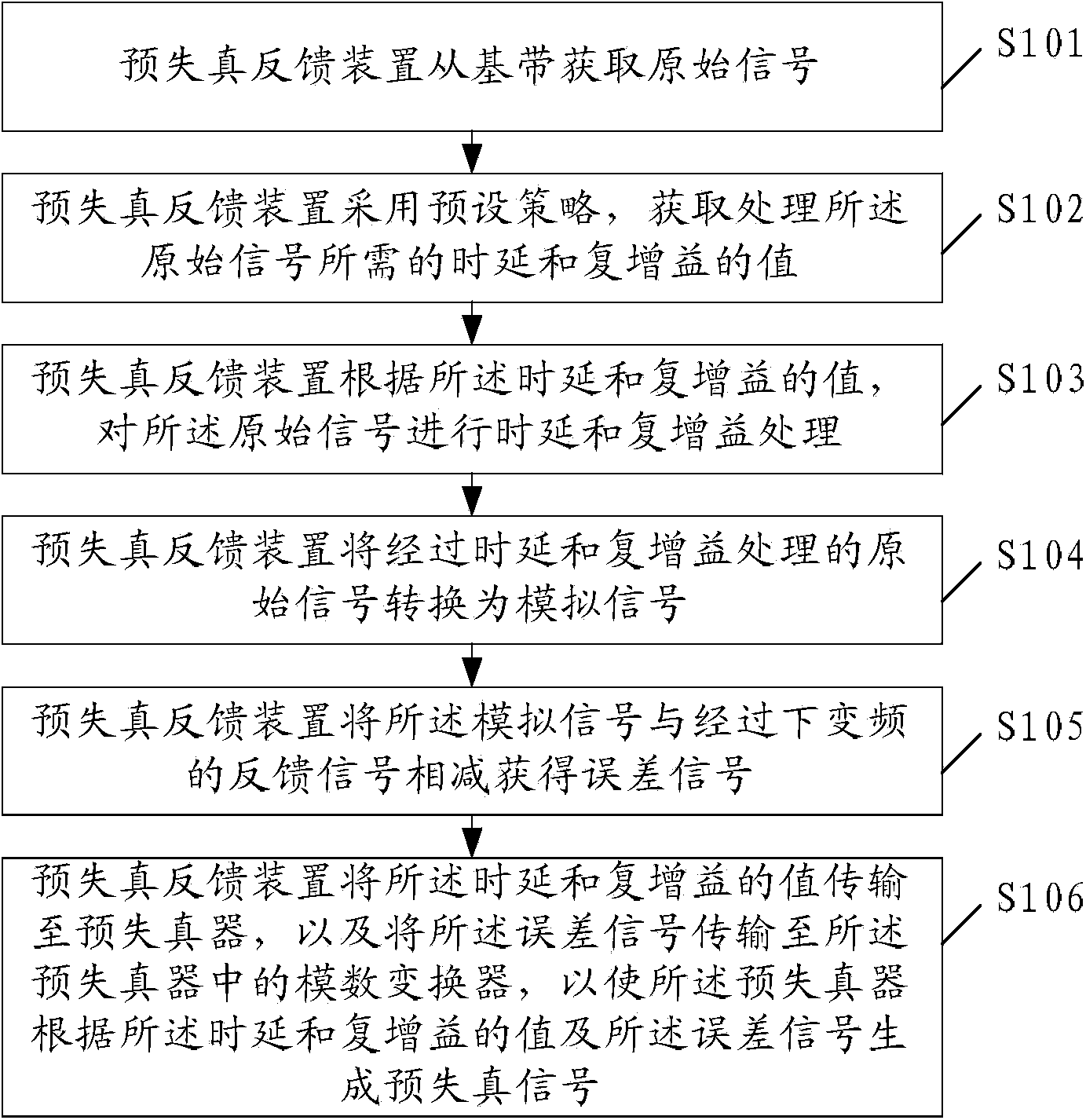
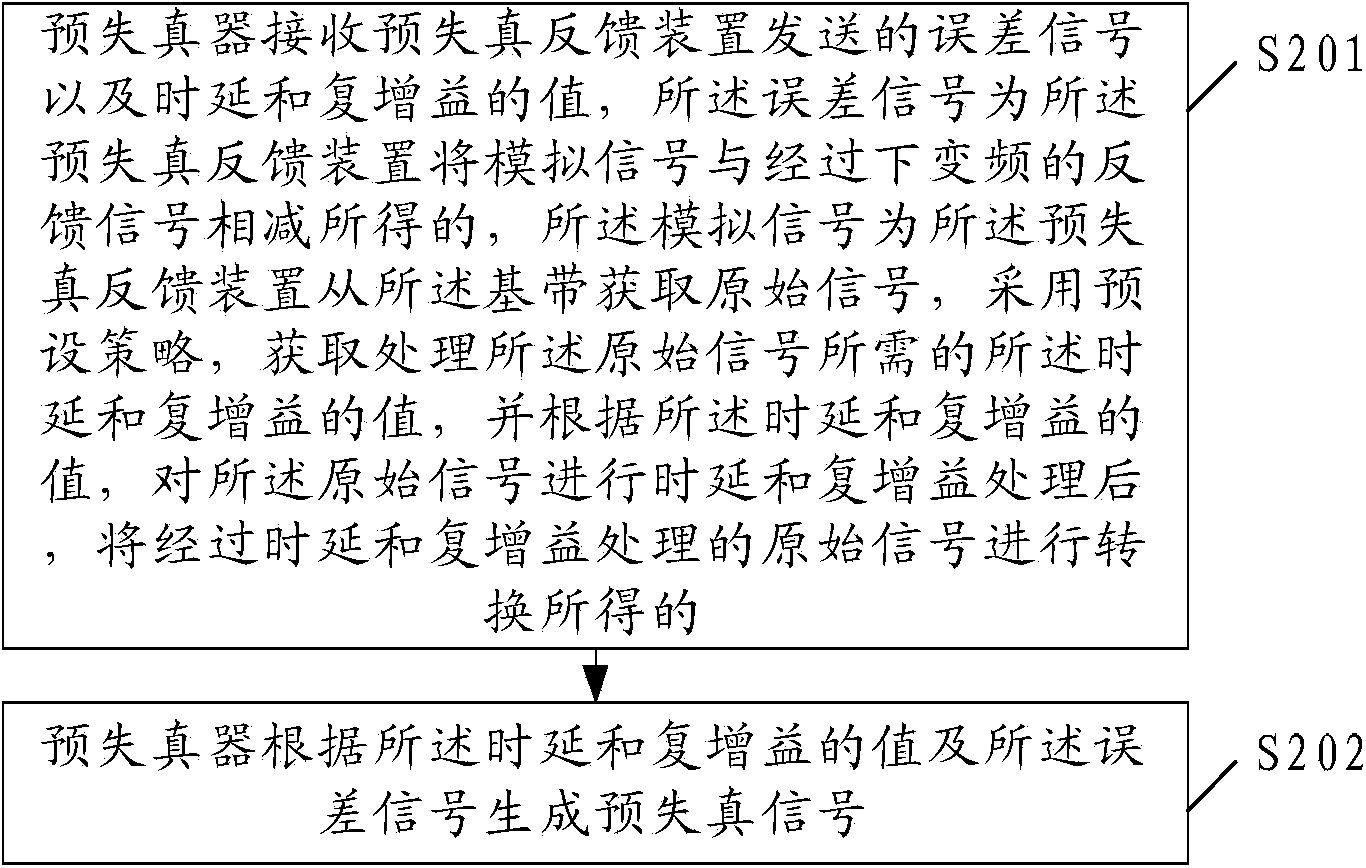
ActiveCN103858397AEliminate linear componentsLow costSynchronous/start-stop systemsTime delaysAnalog signal
The embodiment of the invention provides a predistortion feedback method, an apparatus and a system, relating to the communication field, which reduces bandwidth of an AD converter in a predistorter and further reduces cost of the predistortion technology. The predistortion feedback method of the embodiment comprises: acquiring original signals from a base band; adopting preset strategy, acquiring values of time delay and complex gain demanded for processing the original signals; according to the values of time delay and complex gain, performing time delay and complex gain on the original signals; converting the original signals through time delay and complex gain into the simulation signals; substracting the feedback signals through down-conversion from the simulation signals to obtain the error signals; transmitting the values of the time delay and the complex gain to the predistorter, transmitting the error signals to the AD converter in the predistorter, to cause the predistorter to generate the predistortion signals according to the values of the time delay and the complex gain.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
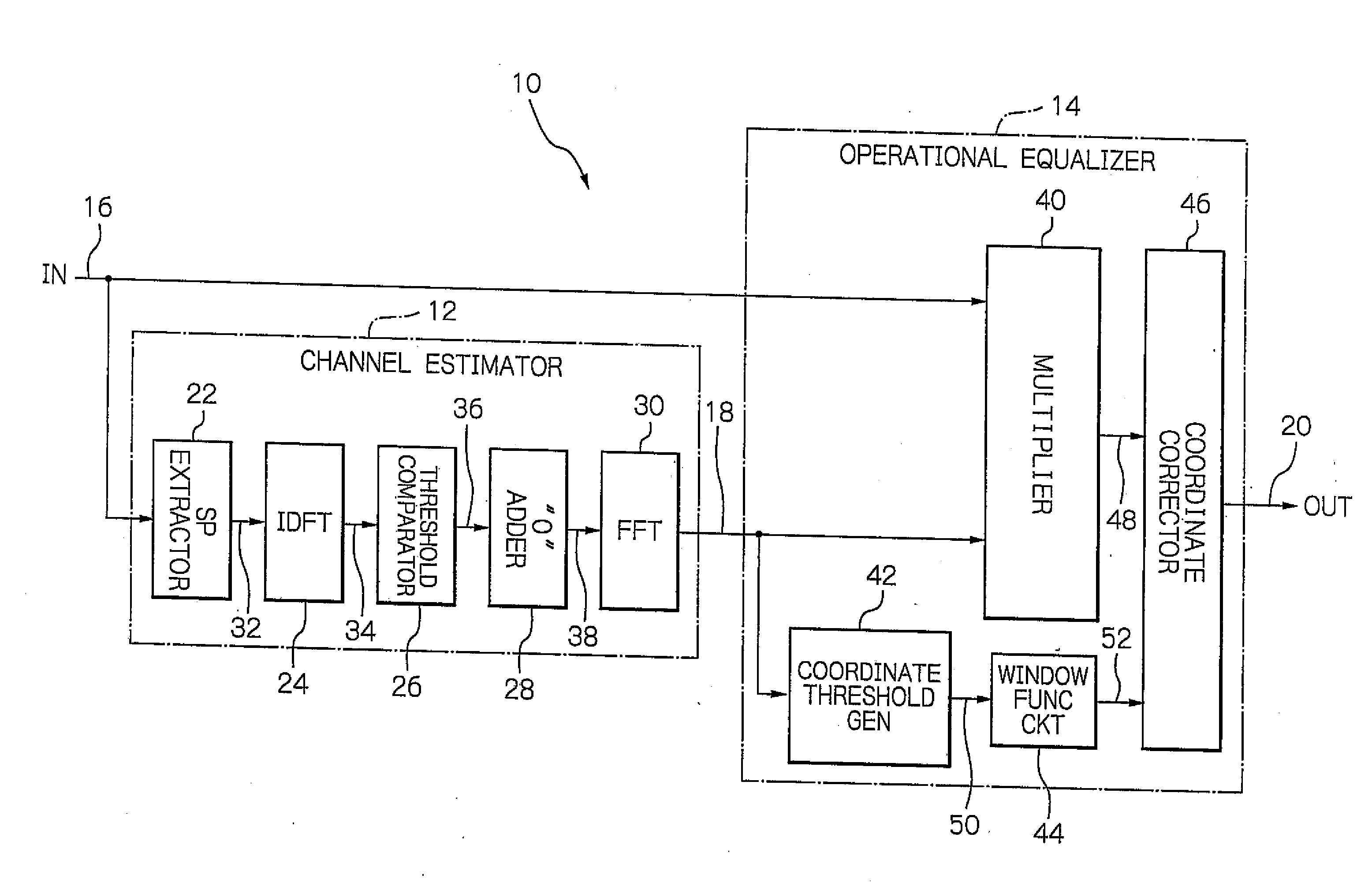
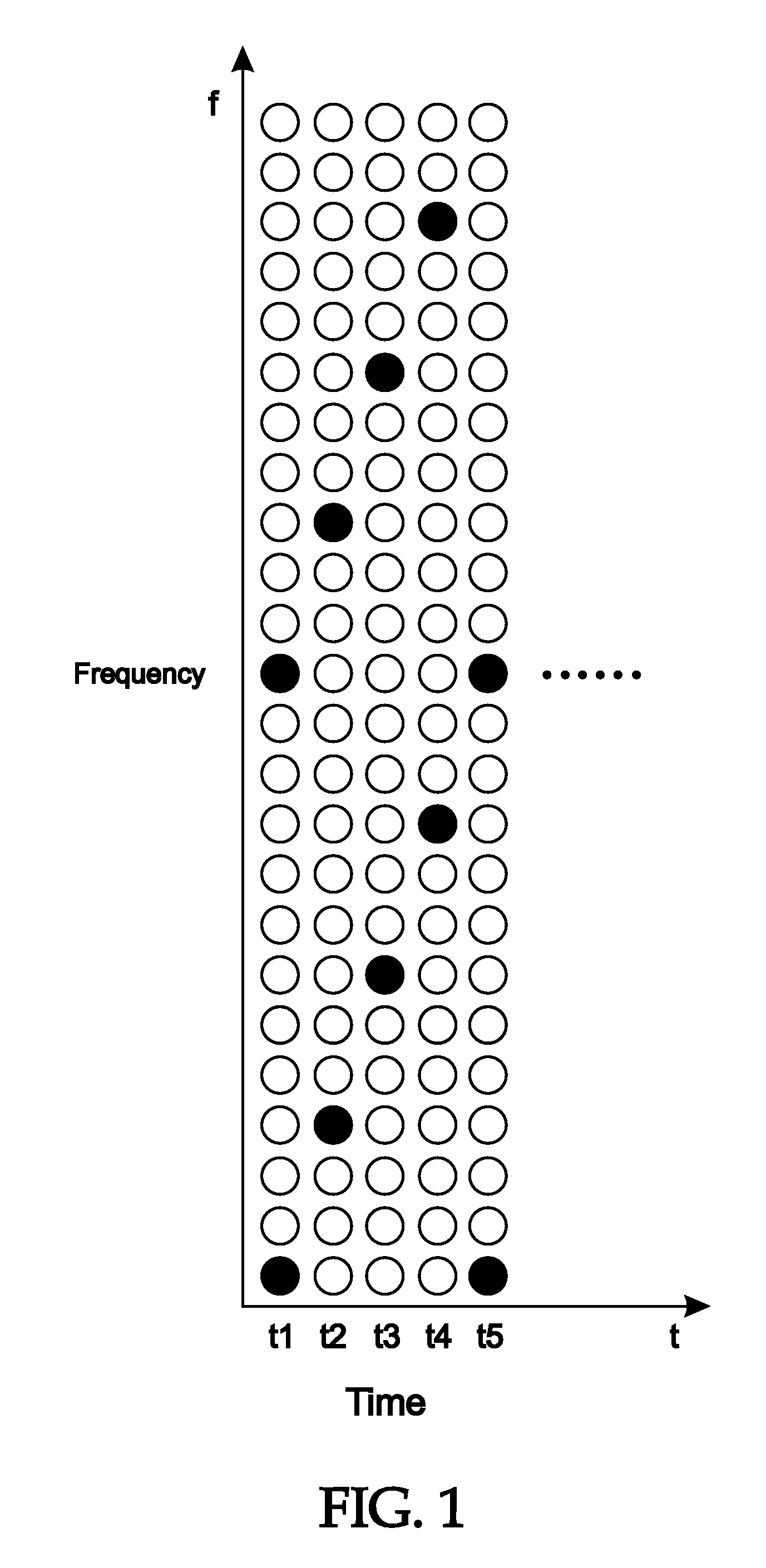
Orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM) signal equalizier
An equalizer equalizes a received orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM) signal which includes periodic pilot symbols. The equalizer includes a channel estimation unit which estimates a frequency response the received OFDM signal, and an equalization circuit which equalizes the received OFDM signal in accordance with the frequency response estimated by the channel estimation circuit so as to output a resultant equalized OFDM signal. The channel estimation circuit determines complex gain amounts of respective propagation channels of the OFDM signal based on the pilot symbols, applies the complex gain amounts to a window function circuit which passes given complex gain amounts among the complex gain amounts which are contained within a predetermined time region window, and computes the frequency response based on the given complex gain amounts which are contained within the predetermined time region window.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
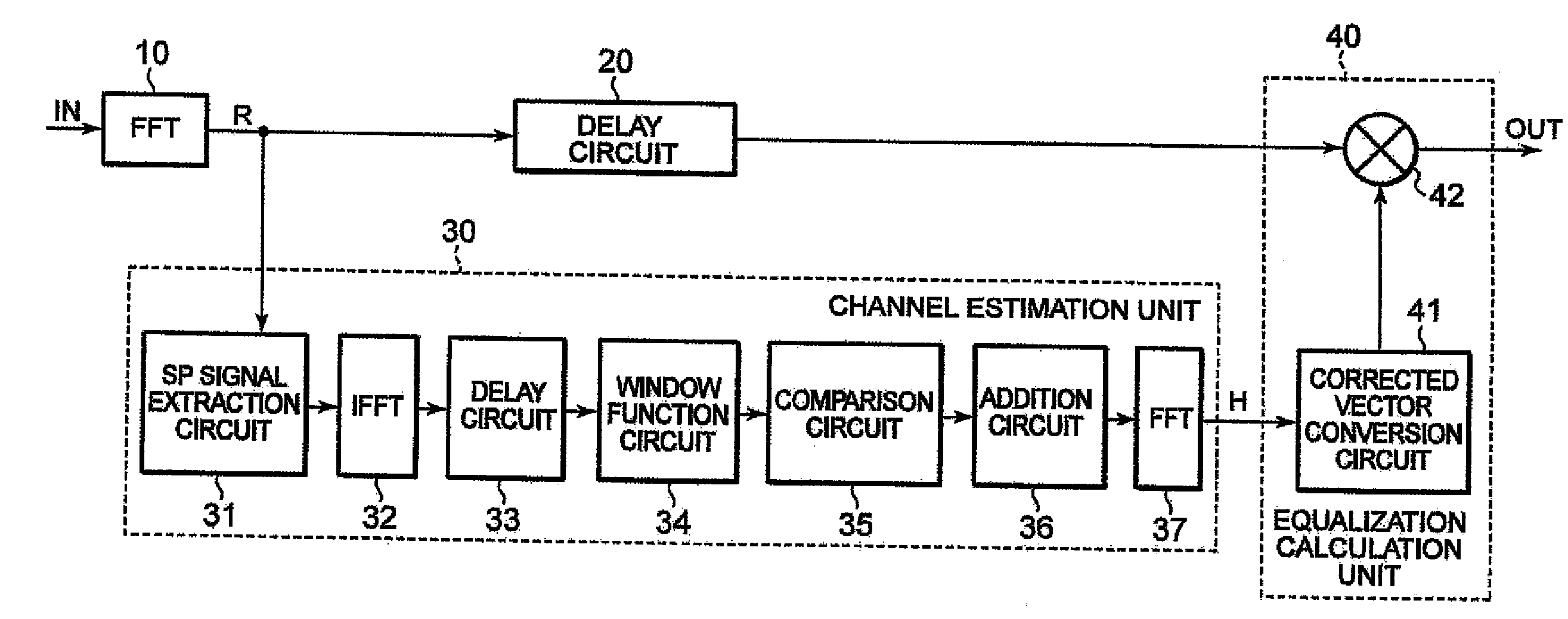
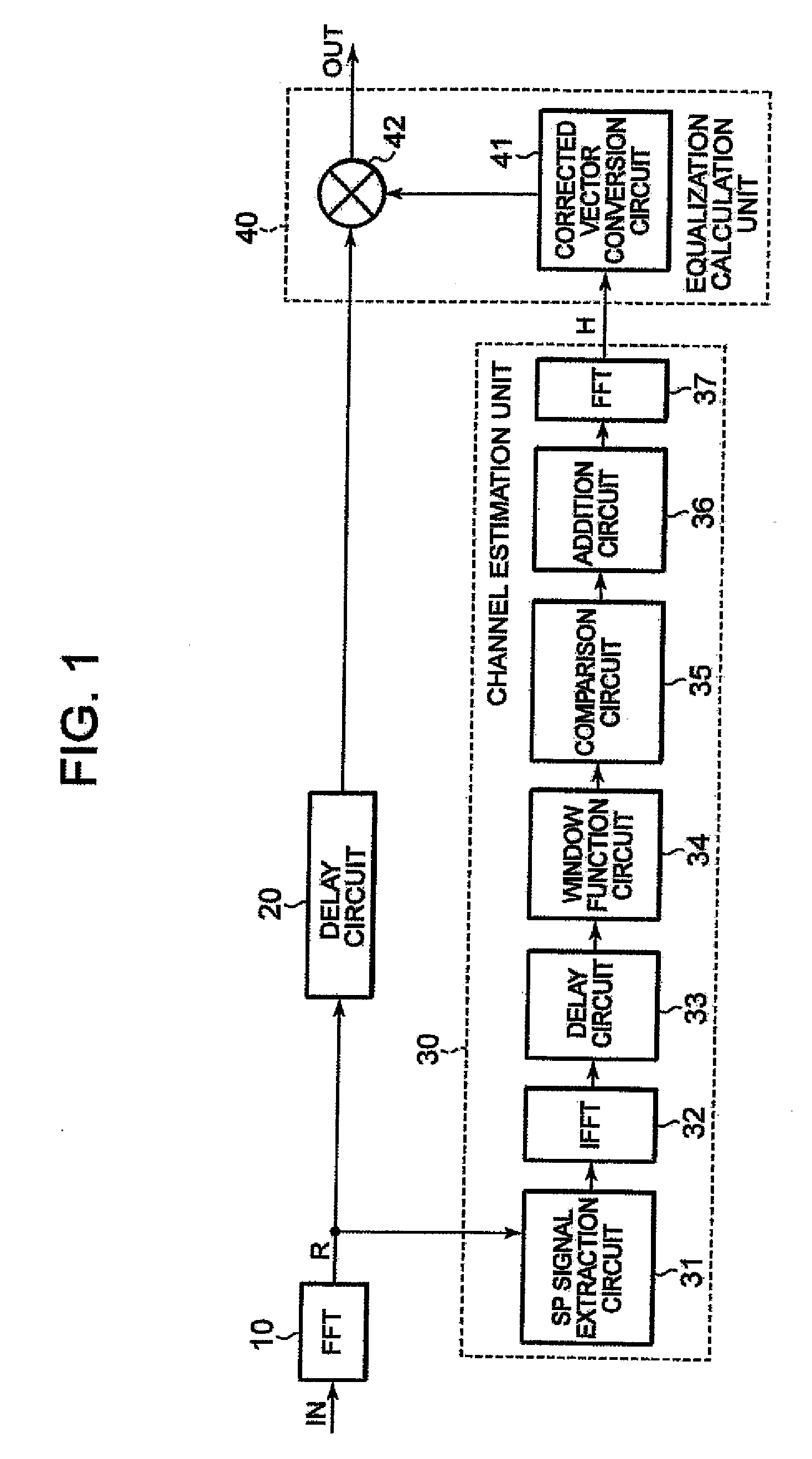
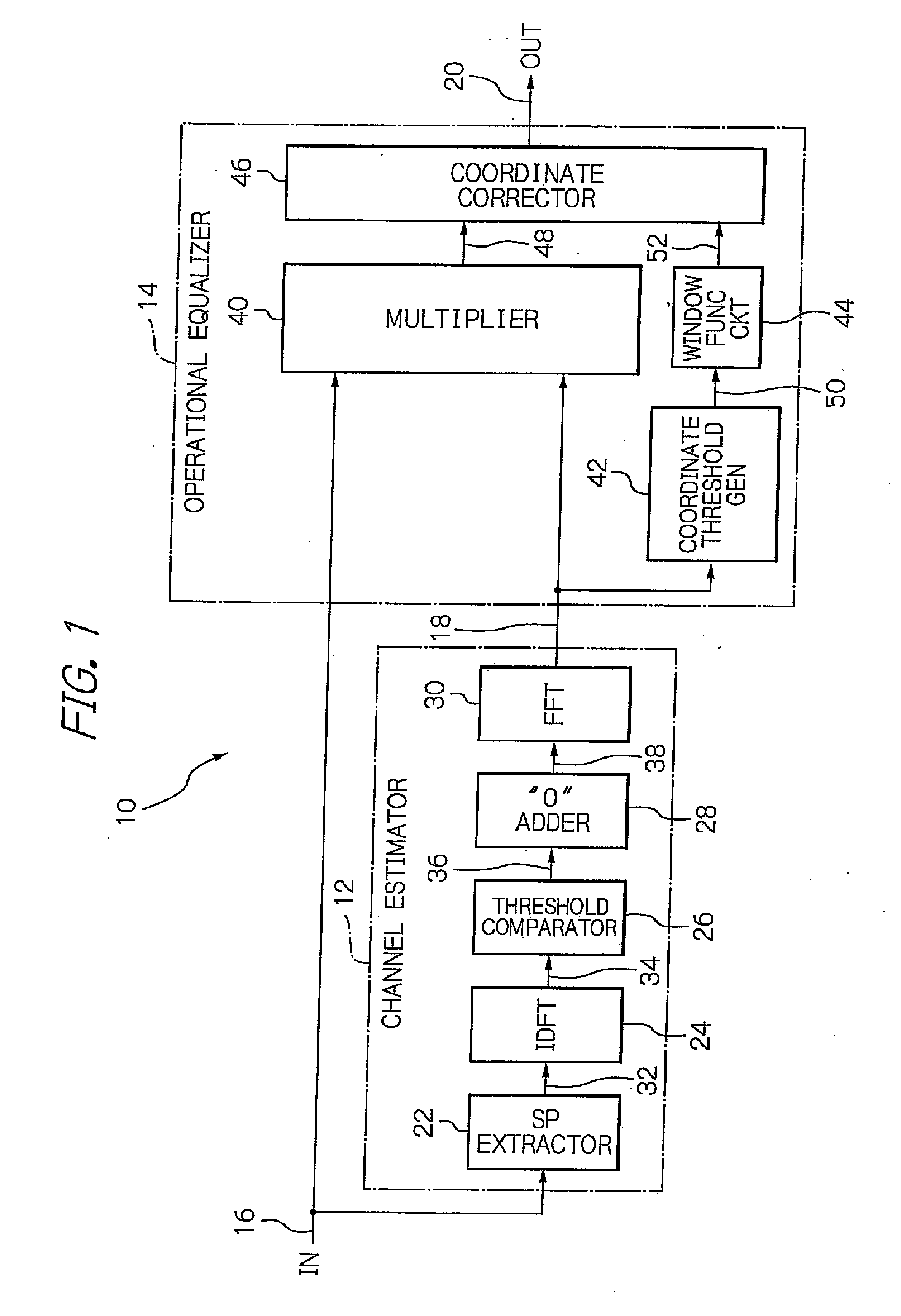
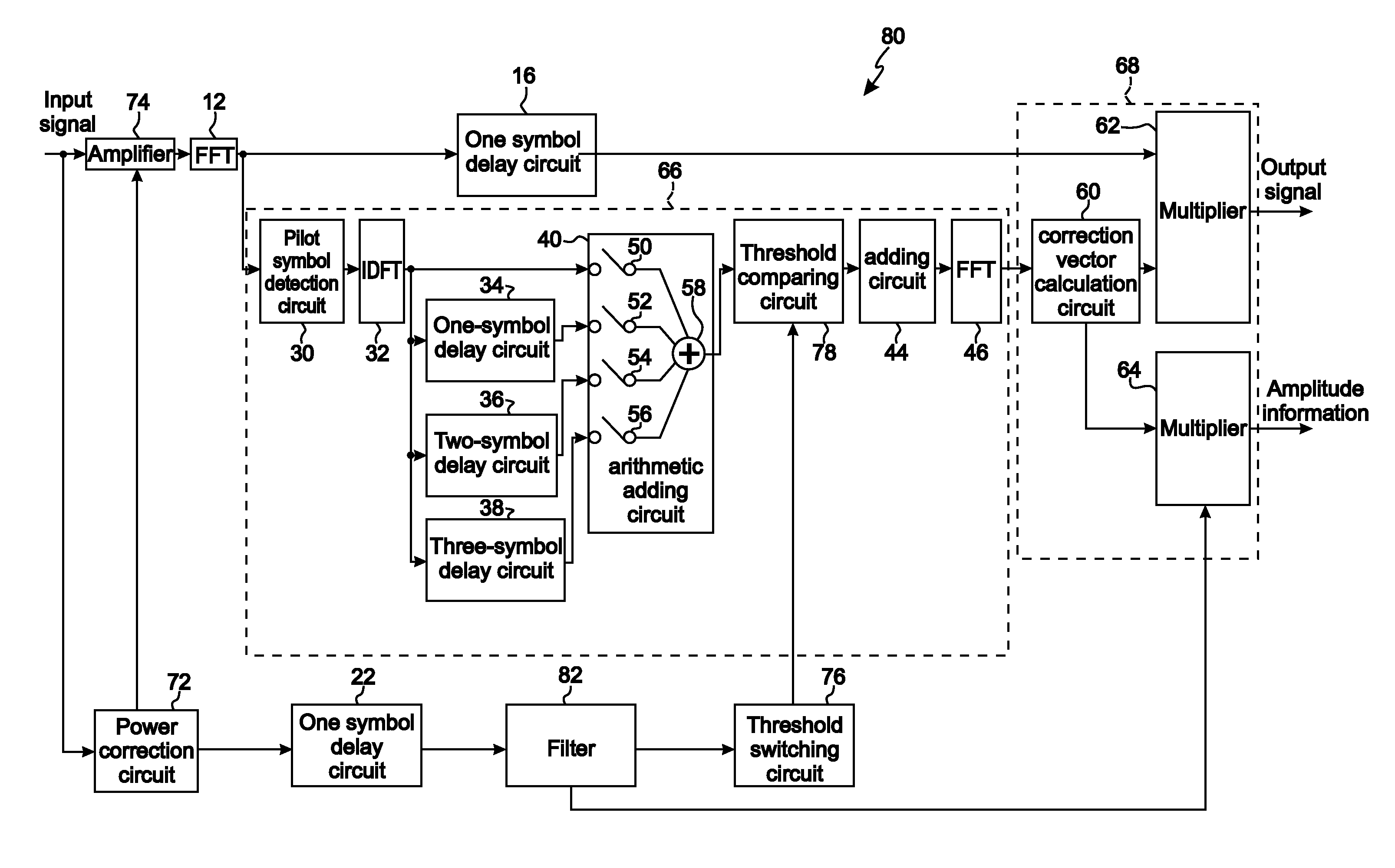
Equalizer demodulating a signal including sp symbols and an equalization method therefor
InactiveUS20080063040A1Relatively small errorReduce degradationMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFourier transform on finite groupsEqualization
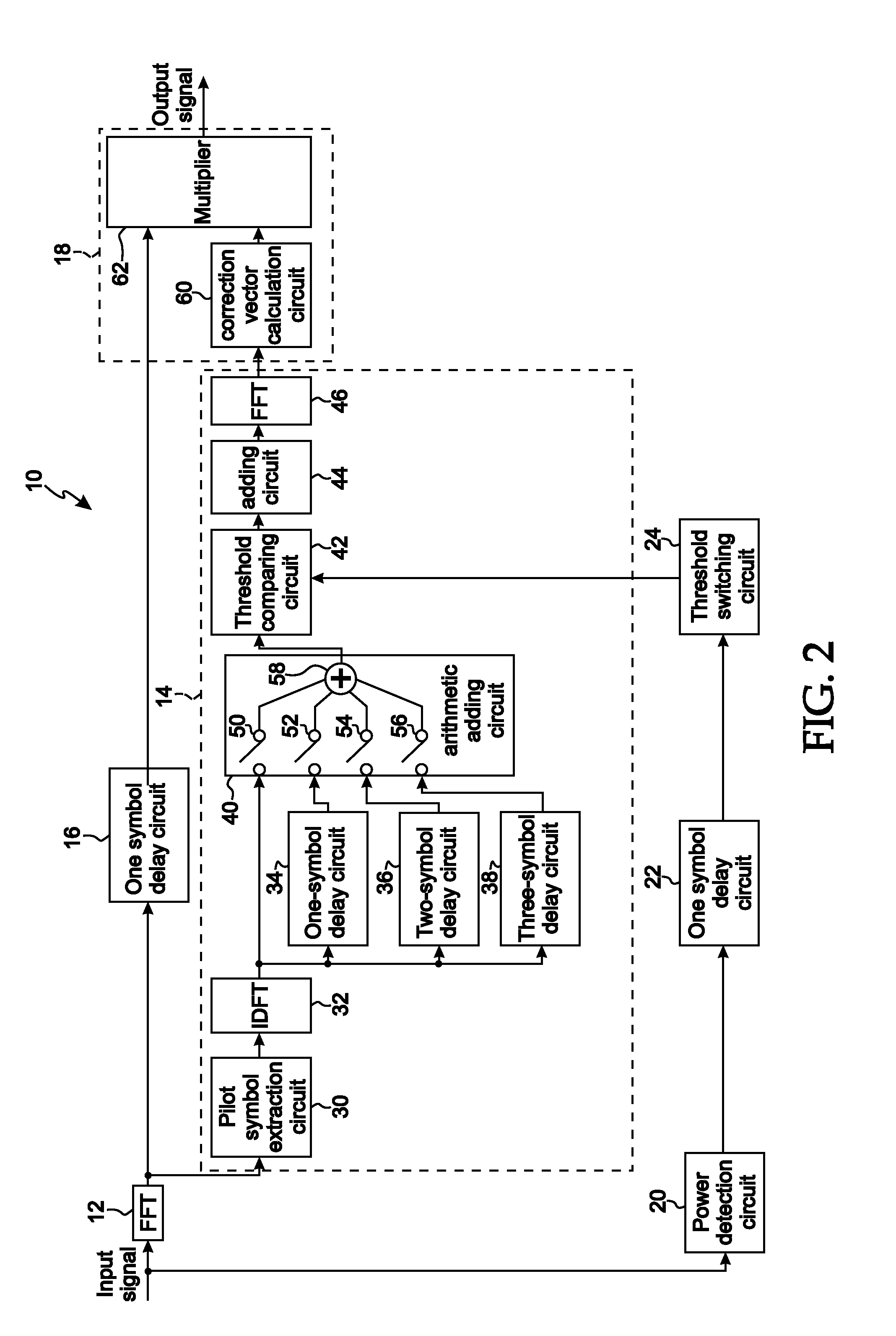
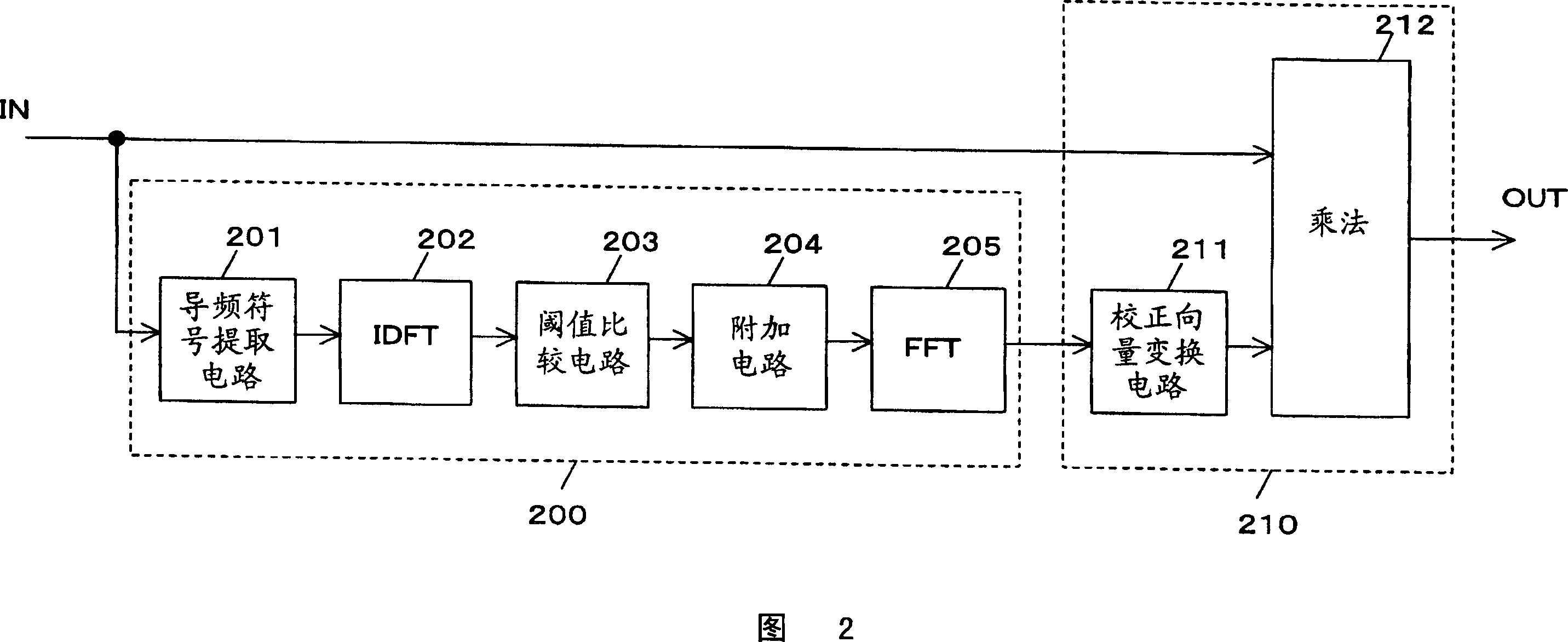
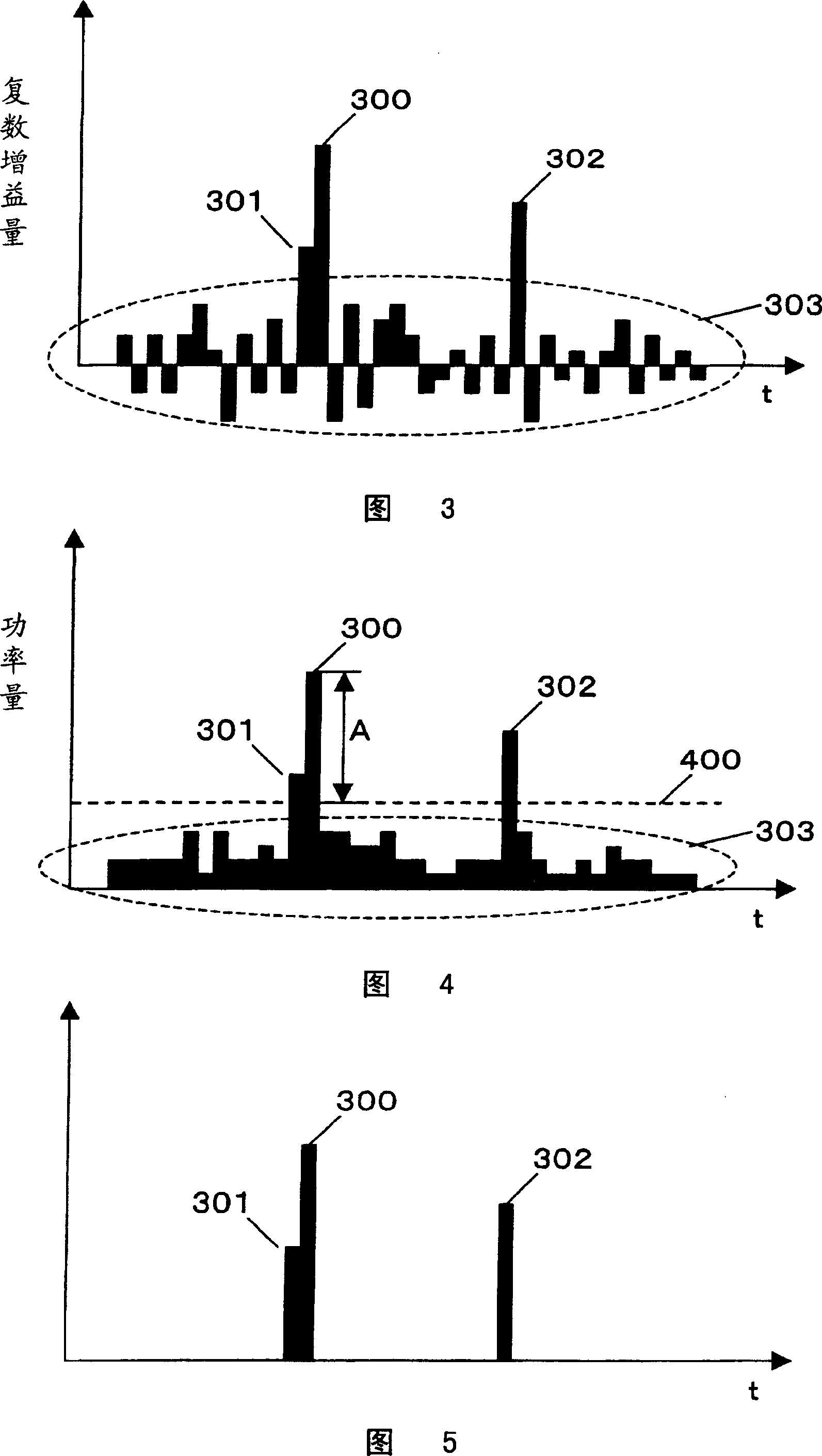
In an equalizer, an scattered pilot (SP) extractor in a channel estimator extracts an SP symbol from an input signal, an IDFT circuit calculates from the SP a complex gain of each path, and a threshold comparator and a “0” addition circuit extract signals of paths. An FFT circuit Fourier-transforms signals of the paths. A multiplier in an operational equalizer multiplies a complex conjugate signal of a transmission line estimation in the path on which the Fourier-transform was made and the input signal to output the product to the coordinate corrector. A coordinate threshold generator multiplies the transmission line estimation by the complex conjugate signal to generate power of a coordinate threshold to output the power to a window function circuit, which corrects the power value to supply the value to the coordinate corrector. The corrector corrects the amplitude of the modulation coordinate in the product to output the amplitude.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
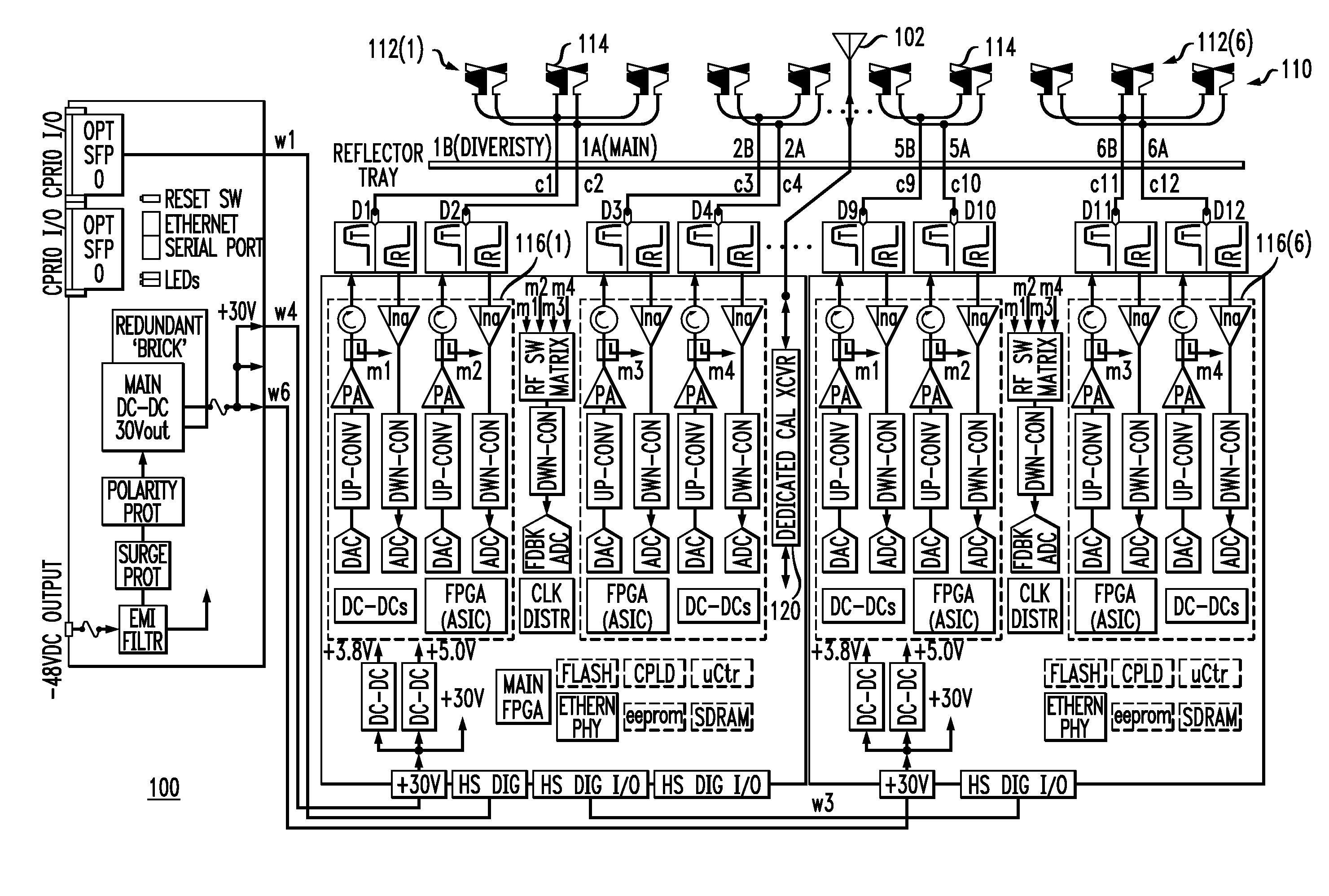
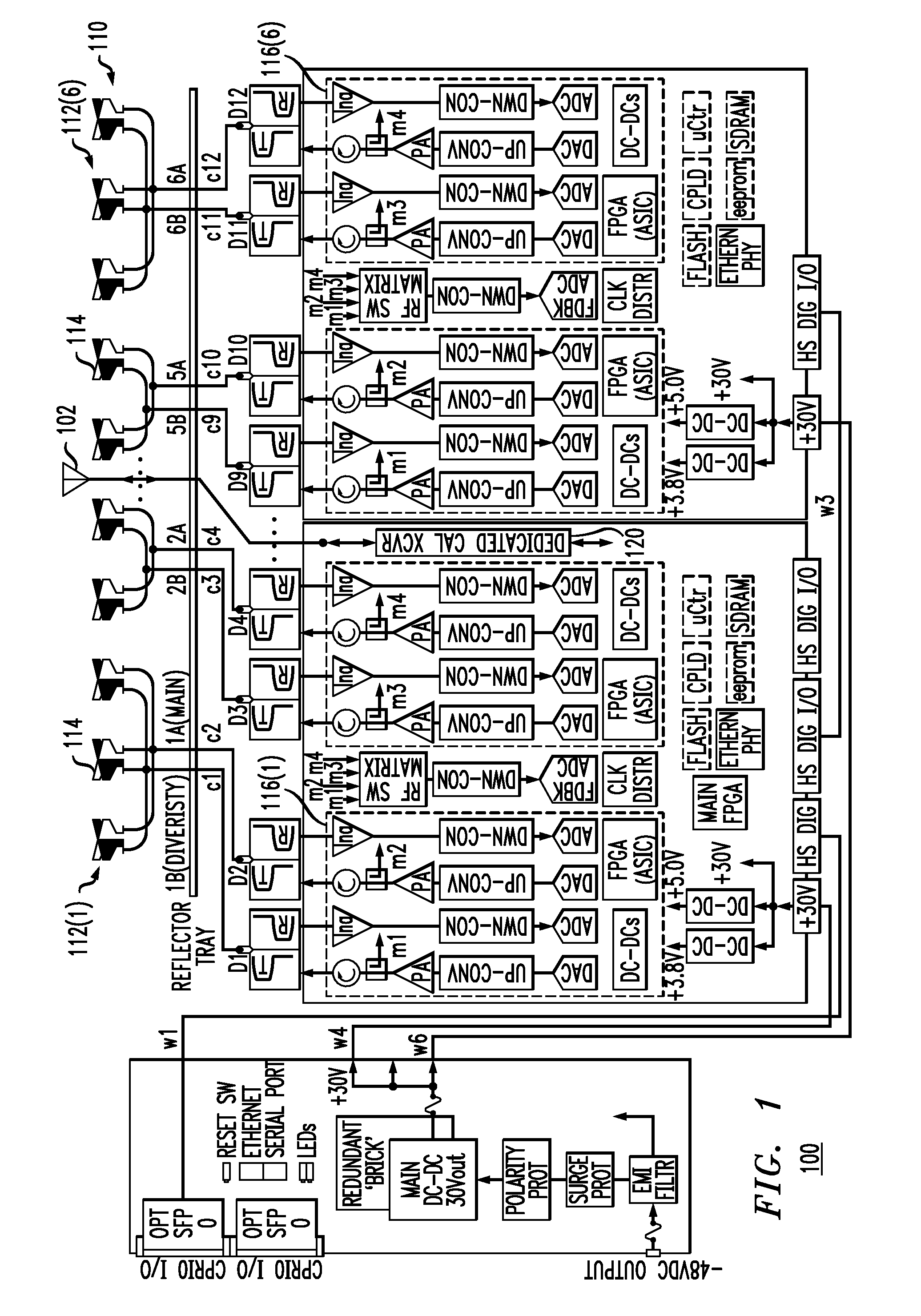
Multi-Element antenna Calibration Technique
Antenna system having an antenna array with multiple sub-arrays, each having one or more antenna elements, is calibrated using a distributed calibration antenna element, such as a leaky coaxial cable, that spans across at least two and possibly all of the sub-arrays. To calibrate the transmit (TX) paths of the sub-arrays, TX calibration test signals are transmitted by the sub-arrays, captured by the distributed calibration element, and processed by a corresponding calibration radio. To calibrate the receive (RX) paths of the sub-arrays, an RX calibration test signal is generated by the calibration radio, transmitted by the distributed calibration element, captured by the sub-arrays, and processed by their corresponding radios. Cross-correlation between the calibration and captured signals is performed to derive the complex gain of each sub-array transmitter and receiver, which provides information for aligning the gain, phase, and delay of the different TX and RX paths of the antenna array.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
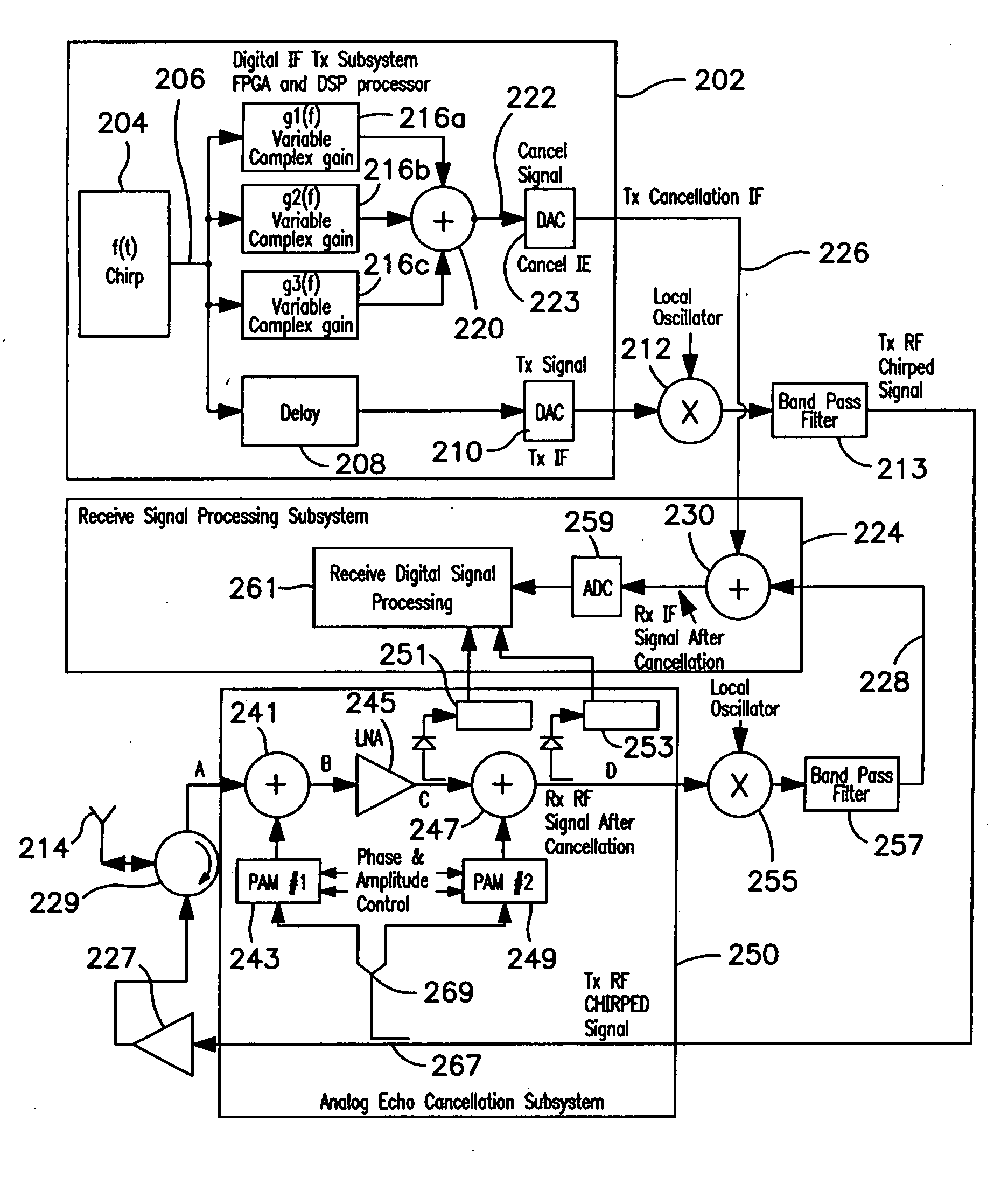
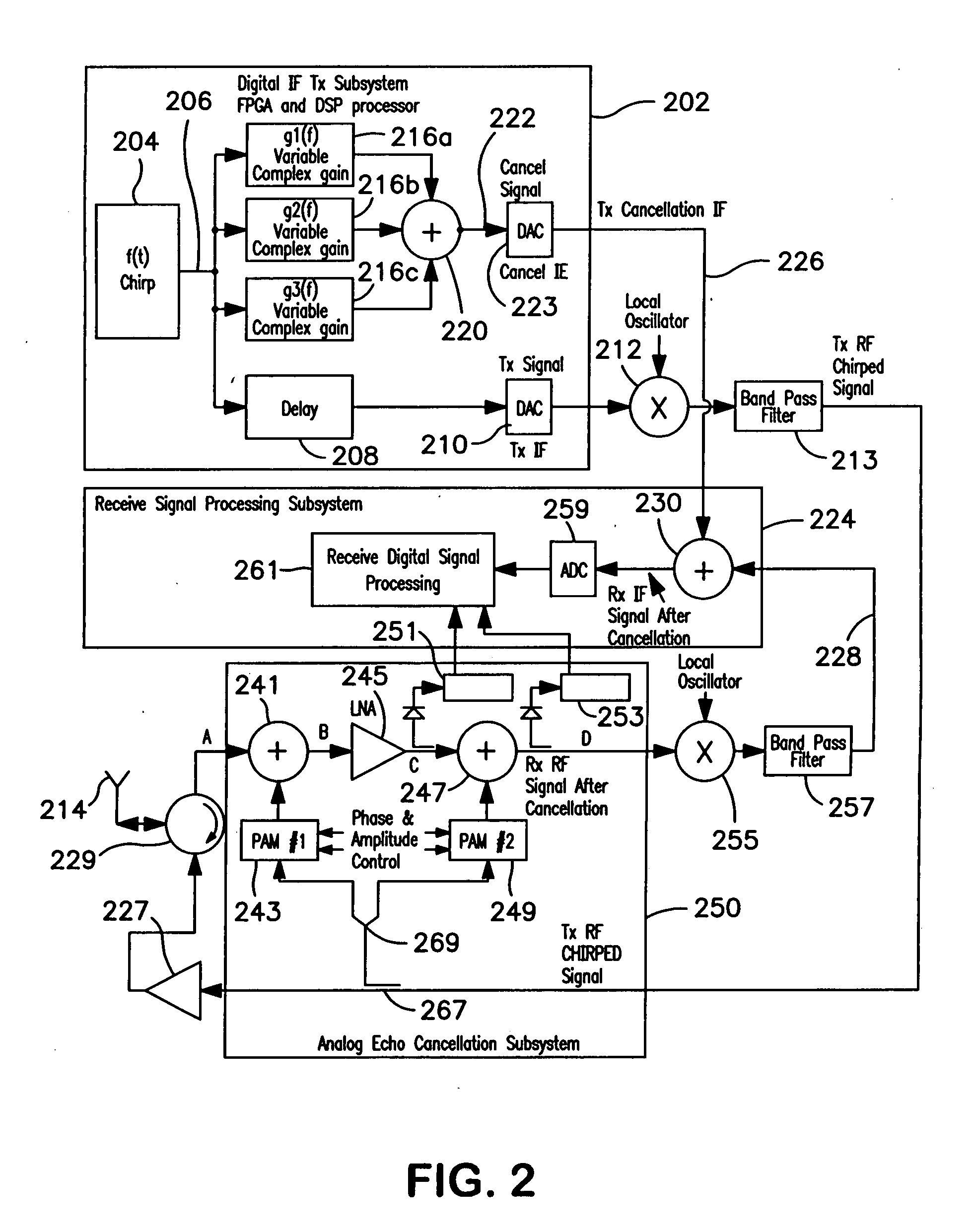
Method and apparatus for equalizing broadband chirped signal
InactiveUS20070279278A1Multiple-port networksRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEngineeringFrequency function
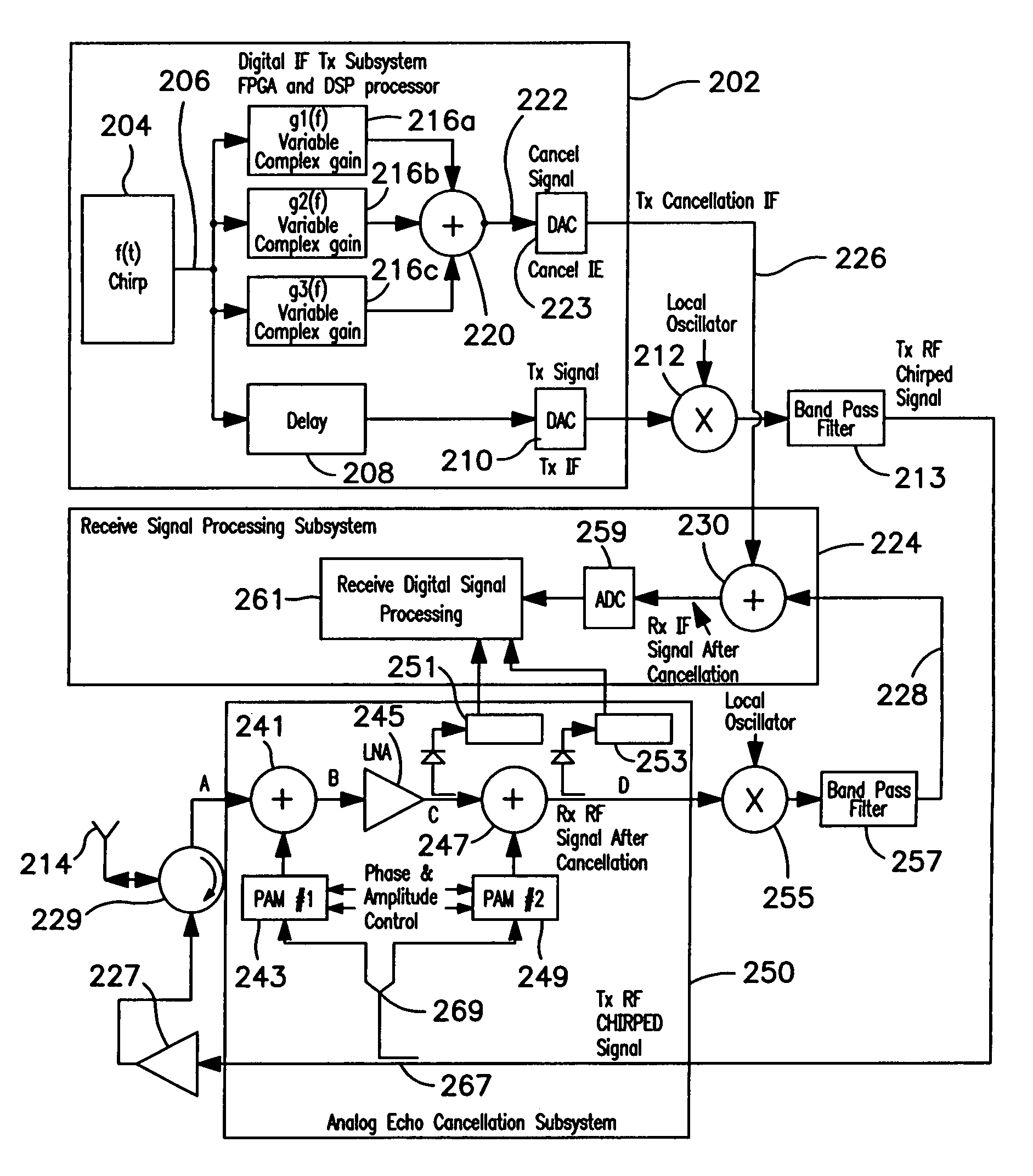
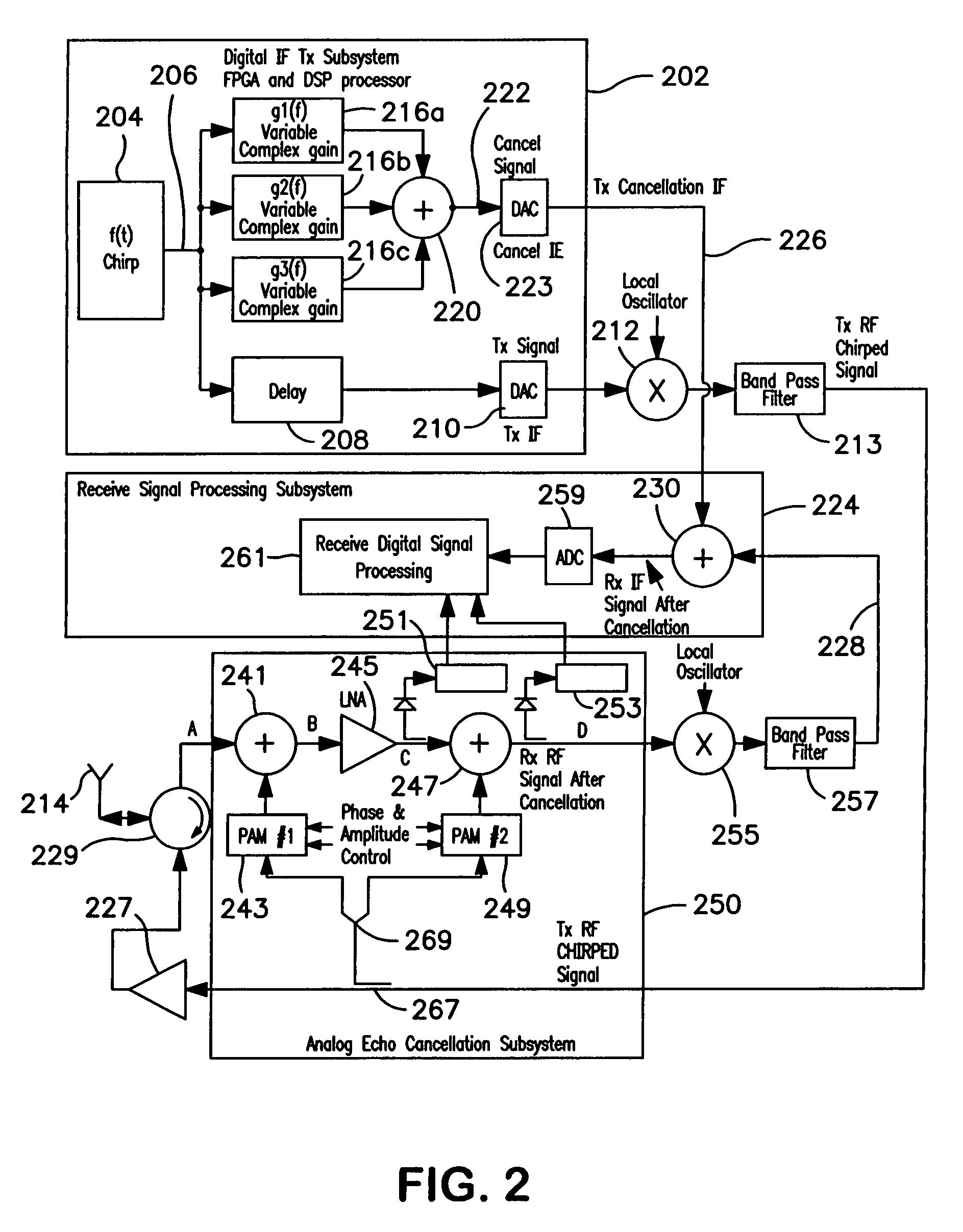
In order to generate a signal for canceling a chirped signal, a transmitter generates a cancellation signal along with the transmitted signal, using a single term variable complex gain multiplier adapted to cancel the chirped signal only at its instantaneous frequency, rather than attempting to cancel it with a complex FIR filter that works over the entire bandwidth of the chirped signal. The cancellation signal is varied in amplitude and phase as a function of the frequency of the chirped transmit signal for which it is intended to compensate. Since the signal that is to be cancelled is essentially sinusoidal but swept through a frequency range, the cancellation signal for the instantaneous transmit signal needs to be swept in both amplitude and phase in unison with the change in frequency of the transmit signal in order to accommodate gain and phase changes in the transmitted signal as a function of frequency. Particularly, the gain as well as the phase of the transmit signal generally will vary as a function of frequency due to limitations of the signal generation circuitry. Therefore, the cancellation signal must be varied in both amplitude and phase as a function of frequency. The necessary algorithm for changing the amplitude and / or phase of the cancellation signal as a function of frequency of the transmit signal can be readily determined by conventional techniques during a training session.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Channel estimation in CDMA communications systems using both lower power pilot channel and higher power date channel
InactiveUS7379513B2Improving estimated complex gain of communication channelAccurate estimateMultiple-port networksError preventionKaiman filterCommunications system
An iterative arrangement of channel estimator (12), a Kalman filter unit (14), and a soft demodulator (16) is provided for producing an estimate of complex gain of a CDMA communications channel carrying data and pilot channels, and demodulated data of the data channel. An initial channel estimate is produced by the estimator (12) using only the low-power pilot channel. This later is improved by the iterative process using the data channel. The complex gains is represented by a sum of sinusoidal signals with different frequencies and randomly variable amplitude and phase.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
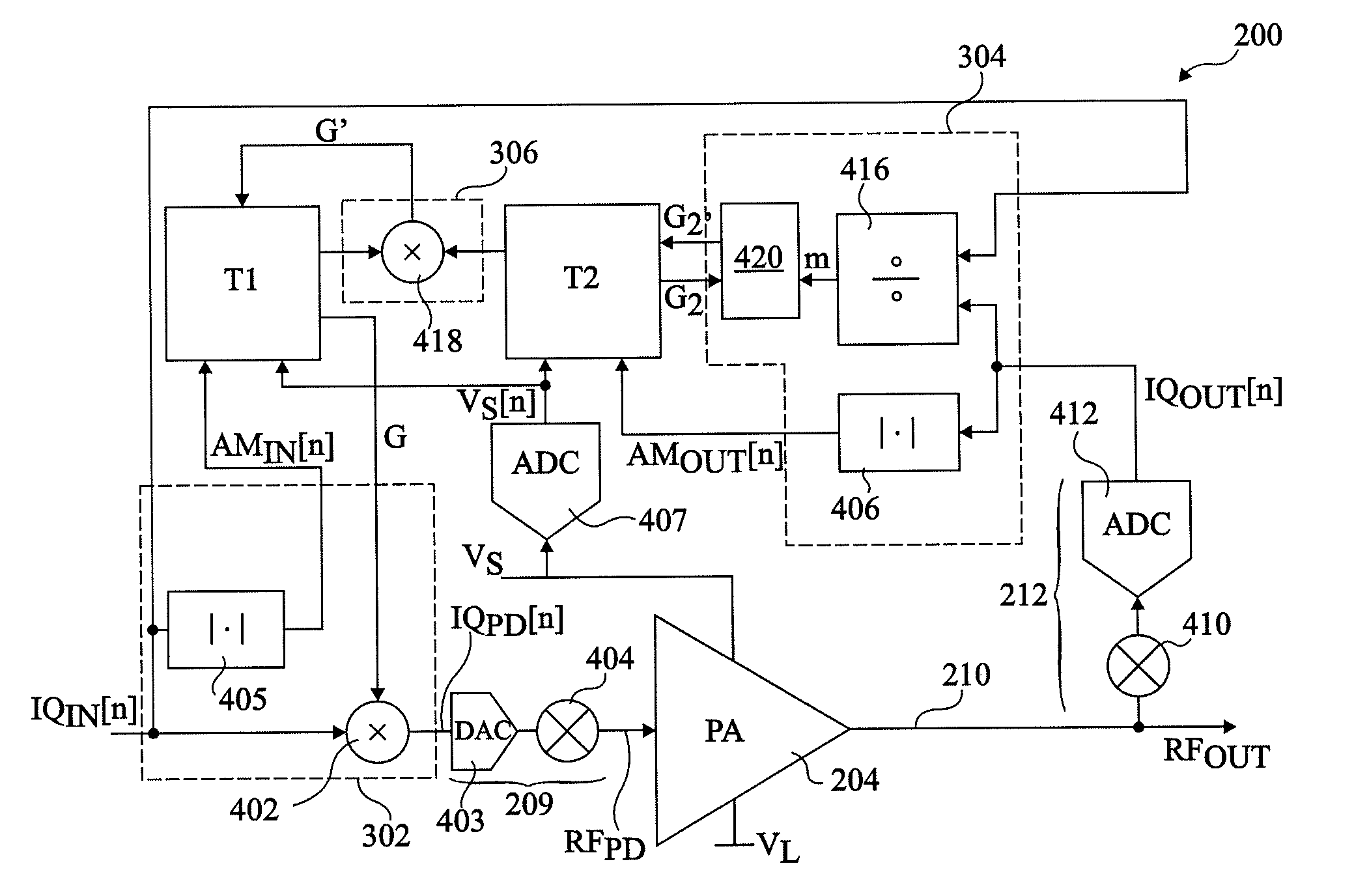
Digital predistorter for variable supply amplifier
ActiveUS20110032032A1Problem be addressAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierEngineering
An adaptive predistorter for applying a predistortion gain to an input signal to be amplified by a power amplifier having a variable supply voltage, the predistorter including: a predistortion gain block adapted to apply a complex gain to a complex input signal; a first table implemented in a first memory and comprising a 2-dimensional array of cells storing complex gain values, the first table adapted to output the complex gain values based on an amplitude of the input signal and the value of the variable supply voltage of the power amplifier; and a second table implemented in a second memory and including a 2-dimensional array of cells storing gain update values for updating the complex gain values of the first table, the gain update values being generated based on an output signal of said power amplifier.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Light-emitting material and preparation method thereof
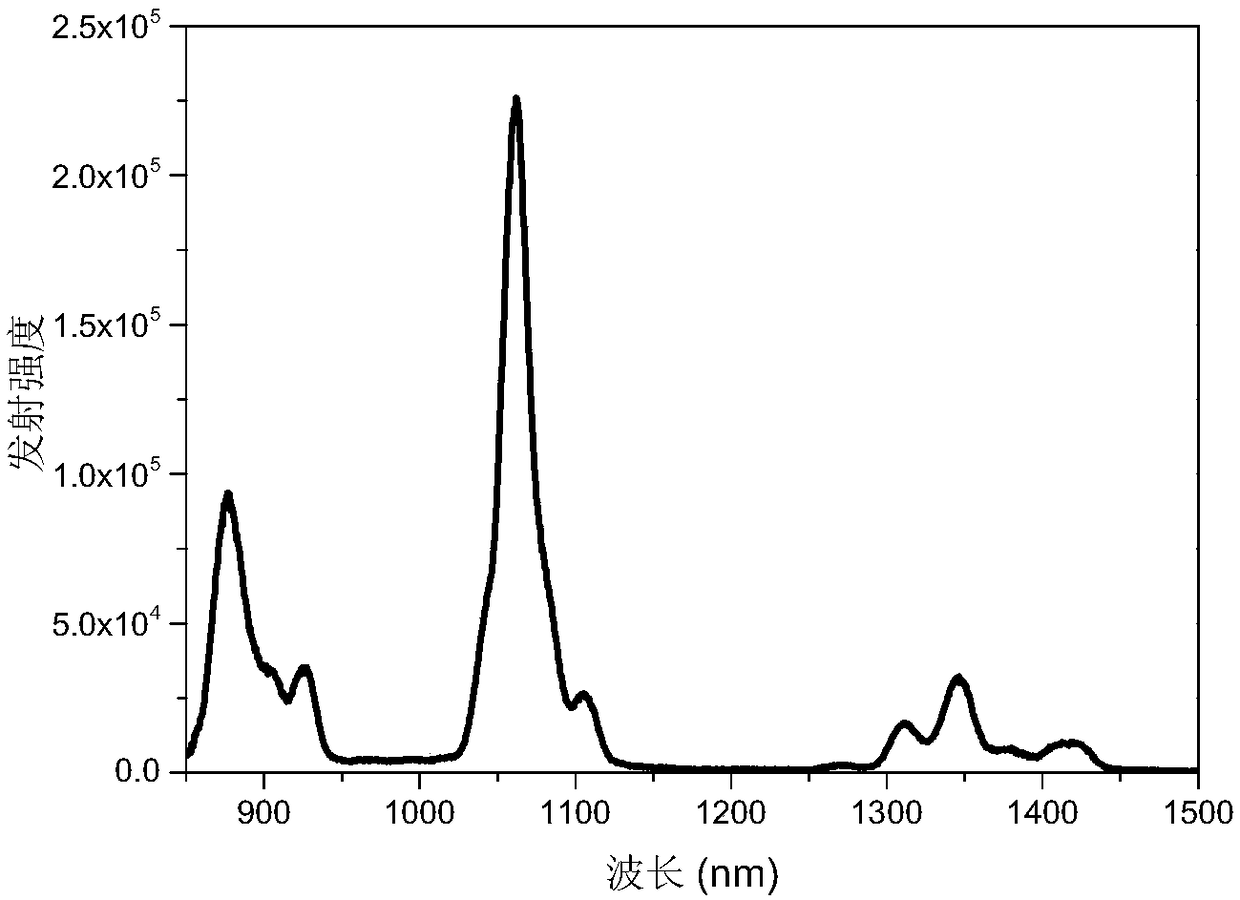
ActiveCN108264896AImprove efficiencyImprove stabilityCobalt organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsBiological imagingComplex gain
The invention provides a light-emitting material and a preparation method thereof. The light-emitting material includes an organic complex; the organic complex is composed of tetrapyrrole macrocyclicligand A, rare-earth ion Ln and deuterated or halogenated tripodal ligand B. The organic complex gains increased external quantum dot efficiency and improved light emergence stability; near-infrared light (800-1600 nm) can be emitted efficiently under purple and blue light excitation; external quantum efficiency is high, light emission life is long, wherein the external quantum efficiency may reach 0.63 and above. In addition, emitting peak position and width can be regulated and controlled through different rare-earth ion or rear-earth ion combinations so as to improve the light-emitting performance of the light-emitting material. The light-emitting material has a promising application prospect in fiber-optic communication, biological imaging, signal conversion and amplification and component analysis fields.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Calibration method
A method for calibration of a magnetic resonance imaging system having a bore, a body coil mounted in the bore, a patient mat, a number of local coils mounted in the patient mat, an upconversion stage having a number of upconverters, and a processing stage, includes the steps of generating a calibration signal in the body coil; receiving the calibration signal at the local coils, upconverting the signal from the local coils in the upconversion stage, transmitting the upconverted signal to the processing stage, synchronously downconverting the signal in the processing stage using the calibration signal generated in the body coil, and processing the downconverted signal to generate an overall path complex gain.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for estimating a pointing error of a satellite antenna
ActiveUS20200313757A1High precisionImprove the level ofCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSatellite antennasAntenna gain
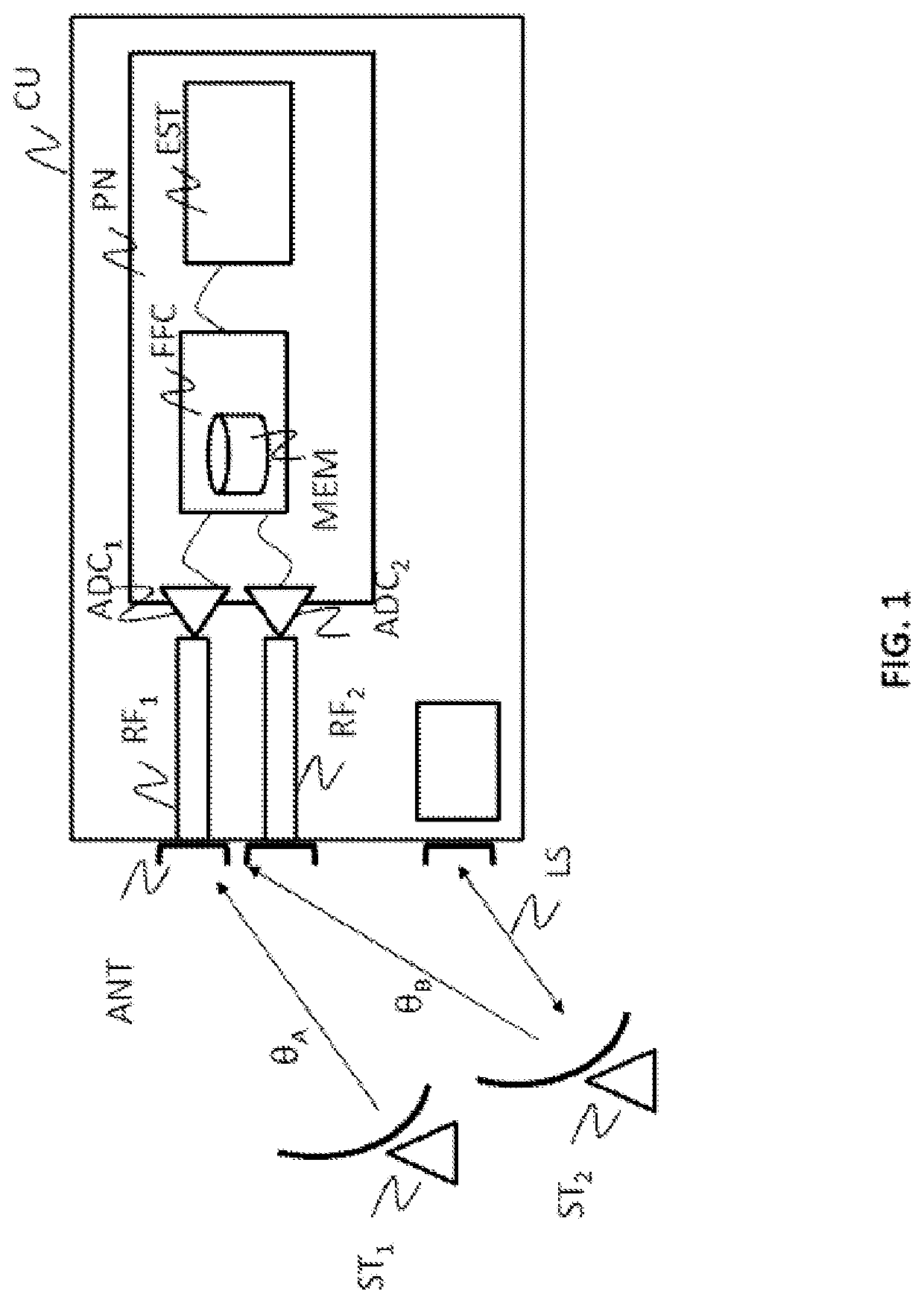
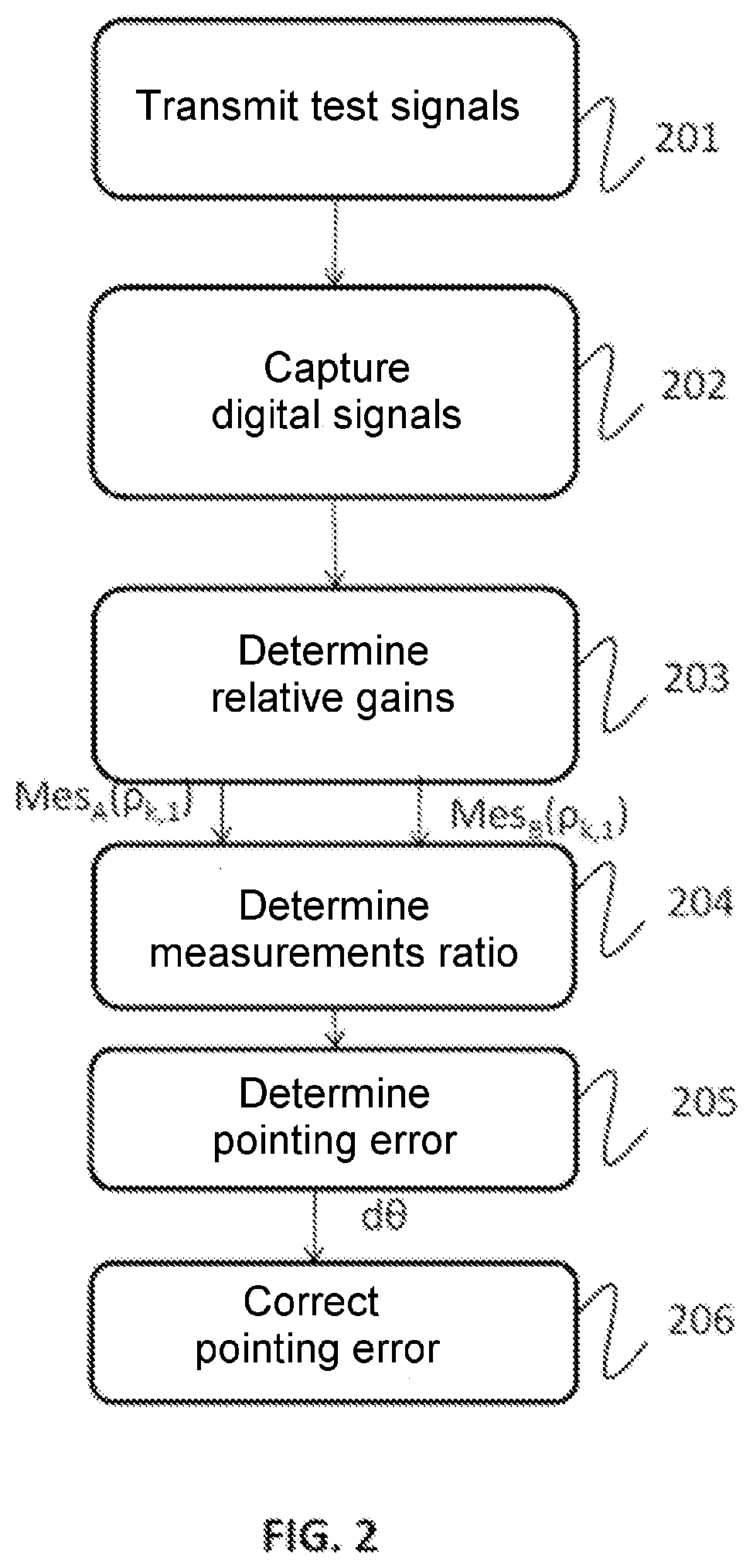
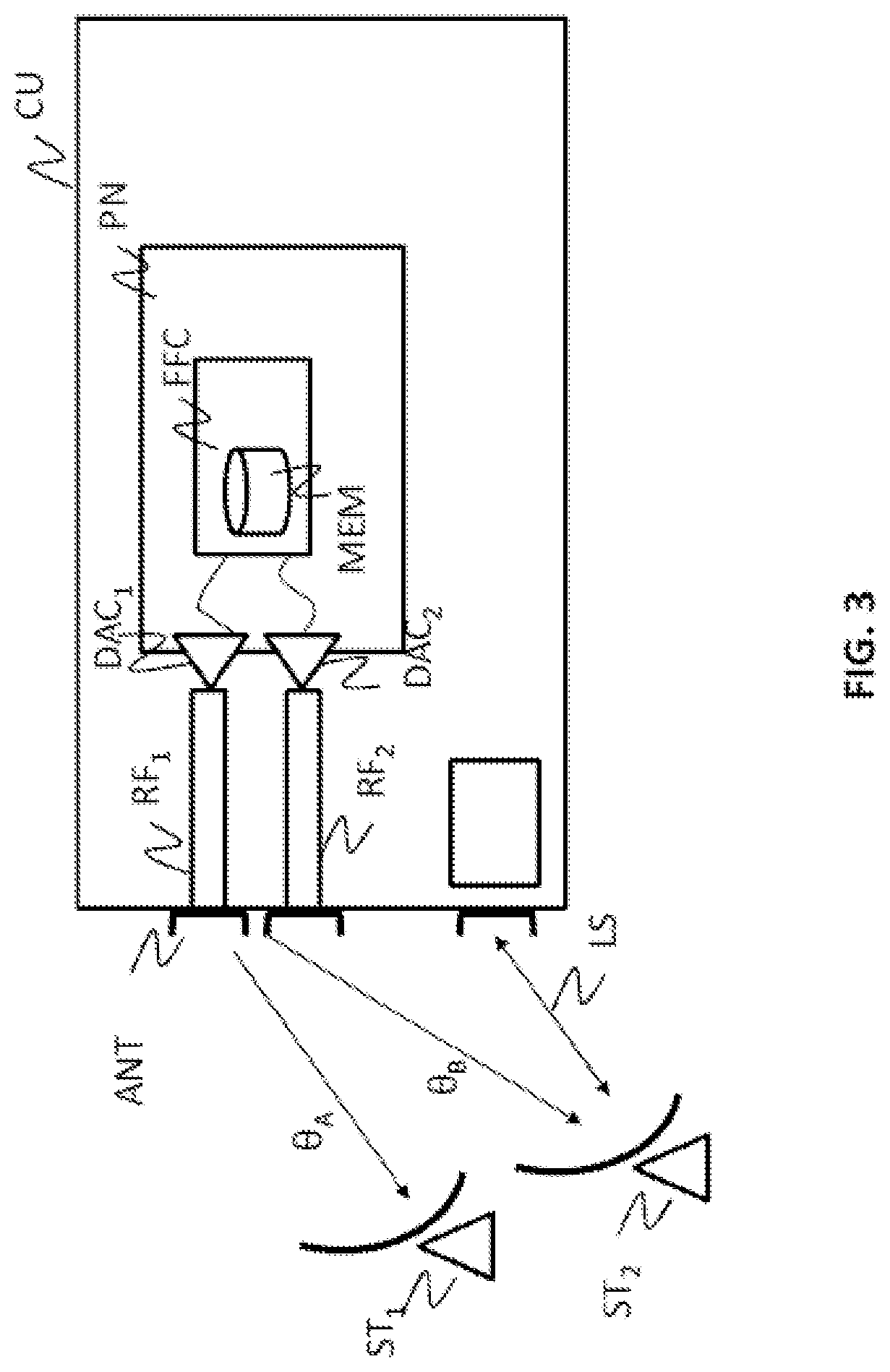
A system for estimating a pointing error of an antenna (ANT) of a satellite, the satellite includes a payload (CU) comprising a multichannel transmitter or receiver comprising a multichannel antenna (ANT), one analogue processing chain per channel and a set of digital integrated circuits (PN), the system comprising an estimation device (EST), implemented aboard the satellite or in a ground station, for estimating a pointing error of the antenna, the device for estimating a pointing error being configured to: acquire, for at least two channels of the transmitter or of the receiver, at least two test signals, each test signal having been transmitted or received by the antenna along a different direction (θA, θB), for at least one pair of acquired test signals, determine, for each test signal, a relative complex gain between the test signal received or transmitted respectively on two distinct channels, determine a comparative measurement between the two test signals from either the ratio between the two relative complex gains and / or the difference between the phases of the two relative complex gains, determine a pointing error (dθ) of the antenna on the basis of the comparative measurement, of the expected directions of transmission or of reception of the test signals (θA, θB) and of a model of the gain of the antenna for each channel and in a plurality of directions.
Owner:THALES SA
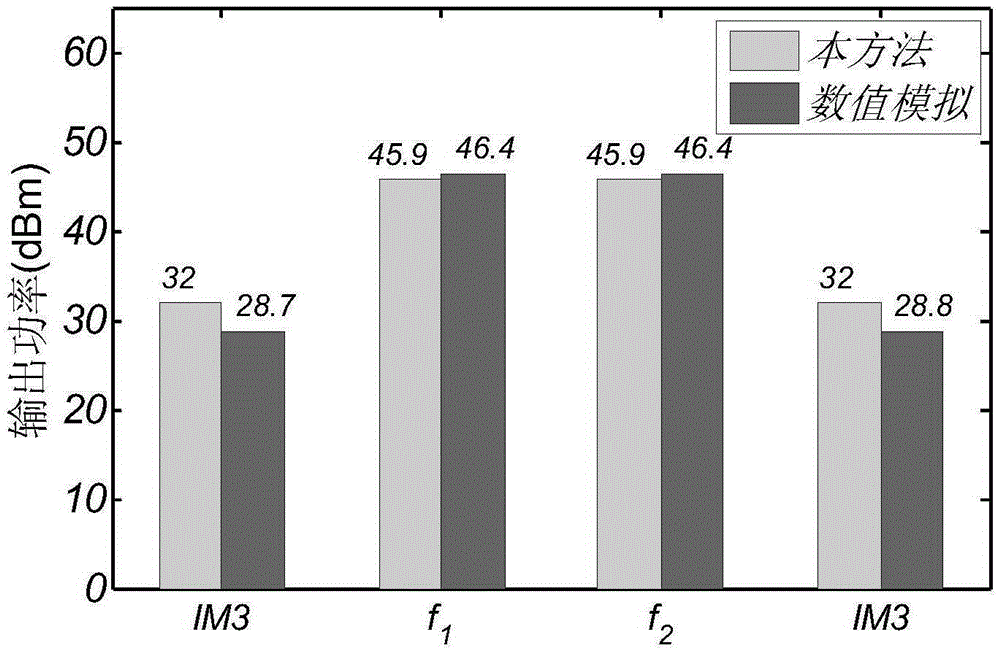
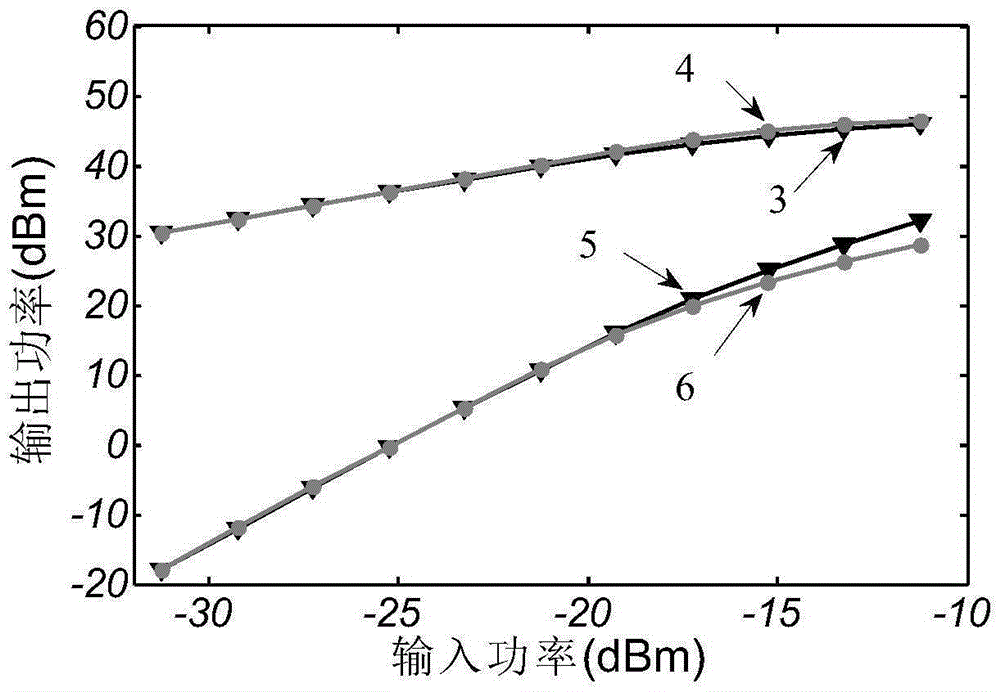
Fast three-order intermodulation calculation method of traveling-wave tube
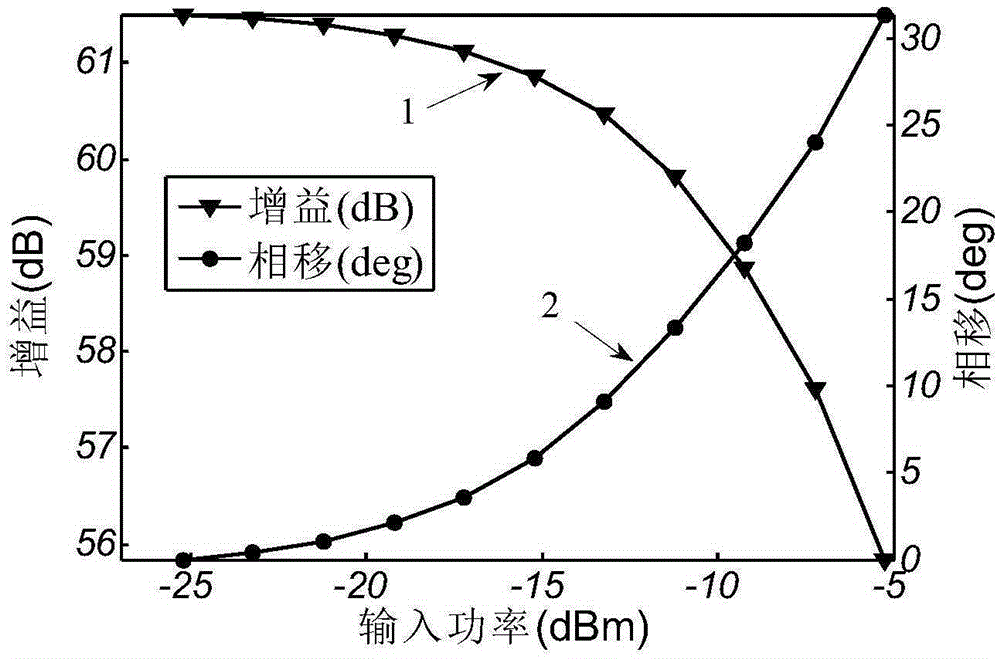
ActiveCN105335585AImprove the calculation efficiency of third-order intermodulation optimizationDesign optimisation/simulationSystems intergating technologiesNonlinear distortionPhase shifted
The invention belongs to the technical field of non-linear distortion of traveling-wave tubes, particularly relates to a fast three-order intermodulation calculation method of a traveling-wave tube and is used for overcoming the defect that three-order intermodulation calculation of an existing traveling-wave tube is low. The method includes the steps that firstly, the center frequency of two input frequencies serves as input signal frequency, input power scanning is conducted, gain curve and phase shift curve data are obtained, and thereby complex gain curve data are obtained; then, the data are introduced into a calculation formula, rapid calculation is conducted, and output power of the two input frequencies and the three-order intermodulation output power are obtained under a specific field magnitude value; finally, the field magnitude value is scanned, and the fundamental wave output power under all input power and the three-order intermodulation output power can be obtained. According to the fast three-order intermodulation calculation method, power scanning needs to be conducted once under a single frequency, then, the three-order intermodulation under all input power can be fast solved through the formula, a one-dimension model only needs several seconds, and a three-dimension model only needs several minutes; three-order intermodulation optimization calculation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Equalizer circuit
In an equalizer circuit of one aspect, a first Fourier transform circuit Fourier-transforms an input signal and outputs a corresponding first Fourier-transformed signal, and a first extracting circuit extracts a plurality of pilot symbols from the first Fourier-transformed signal. An inverse Fourier transform circuit calculates a complex gain of each path of the input signal by inverse-transforming the plurality of pilot symbols extracted by the first extracting circuit. A detecting circuit detects at least one of a power value and a mean amplitude of the input signal, and a coefficient determining circuit determines a coefficient corresponding to the at least one of the power value and the mean amplitude detected by the detecting circuit. A second extracting circuit extracts complex gains having a power larger than a threshold obtained by multiplying the coefficient determined by the coefficient determining circuit by a value obtained by integrating the power for a period of time, wherein the power is obtained from the complex gains of each path of the input signal calculated by the inverse Fourier transform circuit. A second Fourier transform circuit Fourier-transforms the extracted complex gains from the second extracting circuit to obtain a corresponding second Fourier-transformed signal, and an equalizing calculation circuit equalizes the input signal using the second Fourier-transformed signal.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Equalizer and equalizing method
InactiveCN1937600AEqualisersMulti-frequency code systemsFourier transform on finite groupsEqualization
Provided are an equalizer and an equalization method. There is provided an equalizer that includes: a first extracting circuit extracting a plurality of pilot symbols from an inputted signal; an inverse Fourier transform circuit inversely Fourier transforming the extracted plurality of pilot symbols, and computing a complex gain per path; a second extracting circuit extracting a plurality of paths by using the complex gains; a Fourier transform circuit Fourier transforming the extracted paths; and an equalization computing circuit extracting phase components of the Fourier-transformed paths, and carrying out multiplication by using the inputted signal and the extracted phase components.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method and apparatus for equalizing broadband chirped signal
InactiveUS7336220B2Multiple-port networksRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency functionSingle measure
In order to generate a signal for canceling a chirped signal, a transmitter generates a cancellation signal along with the transmitted signal, using a single term variable complex gain multiplier adapted to cancel the chirped signal only at its instantaneous frequency, rather than attempting to cancel it with a complex FIR filter that works over the entire bandwidth of the chirped signal. The cancellation signal is varied in amplitude and phase as a function of the frequency of the chirped transmit signal for which it is intended to compensate. Since the signal that is to be cancelled is essentially sinusoidal but swept through a frequency range, the cancellation signal for the instantaneous transmit signal needs to be swept in both amplitude and phase in unison with the change in frequency of the transmit signal in order to accommodate gain and phase changes in the transmitted signal as a function of frequency. Particularly, the gain as well as the phase of the transmit signal generally will vary as a function of frequency due to limitations of the signal generation circuitry. Therefore, the cancellation signal must be varied in both amplitude and phase as a function of frequency. The necessary algorithm for changing the amplitude and / or phase of the cancellation signal as a function of frequency of the transmit signal can be readily determined by conventional techniques during a training session.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
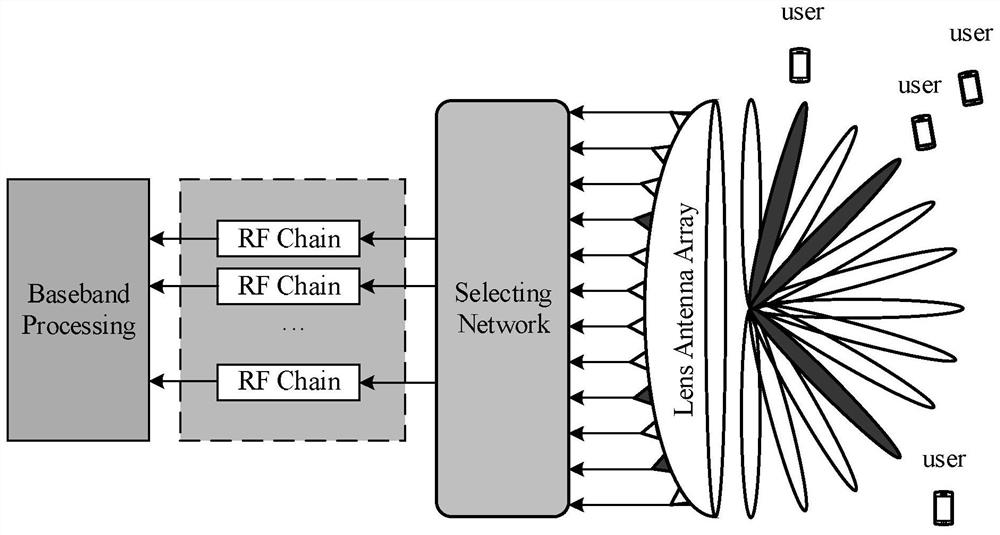
Millimeter wave lens antenna array communication system channel estimation method
ActiveCN112565118AImprove estimation accuracyReduce complexityChannel estimationCommunications systemInterference elimination
The invention discloses a millimeter wave lens antenna array communication system channel estimation method, relates to the technical field of information and communication, and aims to solve the problems of low channel estimation precision, high complexity, poor scene adaptability and difficulty in performance evaluation due to the fact that the number of radio frequency chains in the millimeterwave lens antenna array communication system is far less than that of antennas. The method mainly comprises a beam space channel vector support acquisition method, a DOA and complex gain estimation method according to a preliminary recovery result of a sparse beam space channel, a multipath inter-component interference elimination method based on orthogonalization processing, and a system performance evaluation and parameter design method. Simulation results show that compared with an existing method, the method is higher in estimation precision, lower in complexity, less in environment priorhypothesis and higher in method performance predictability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
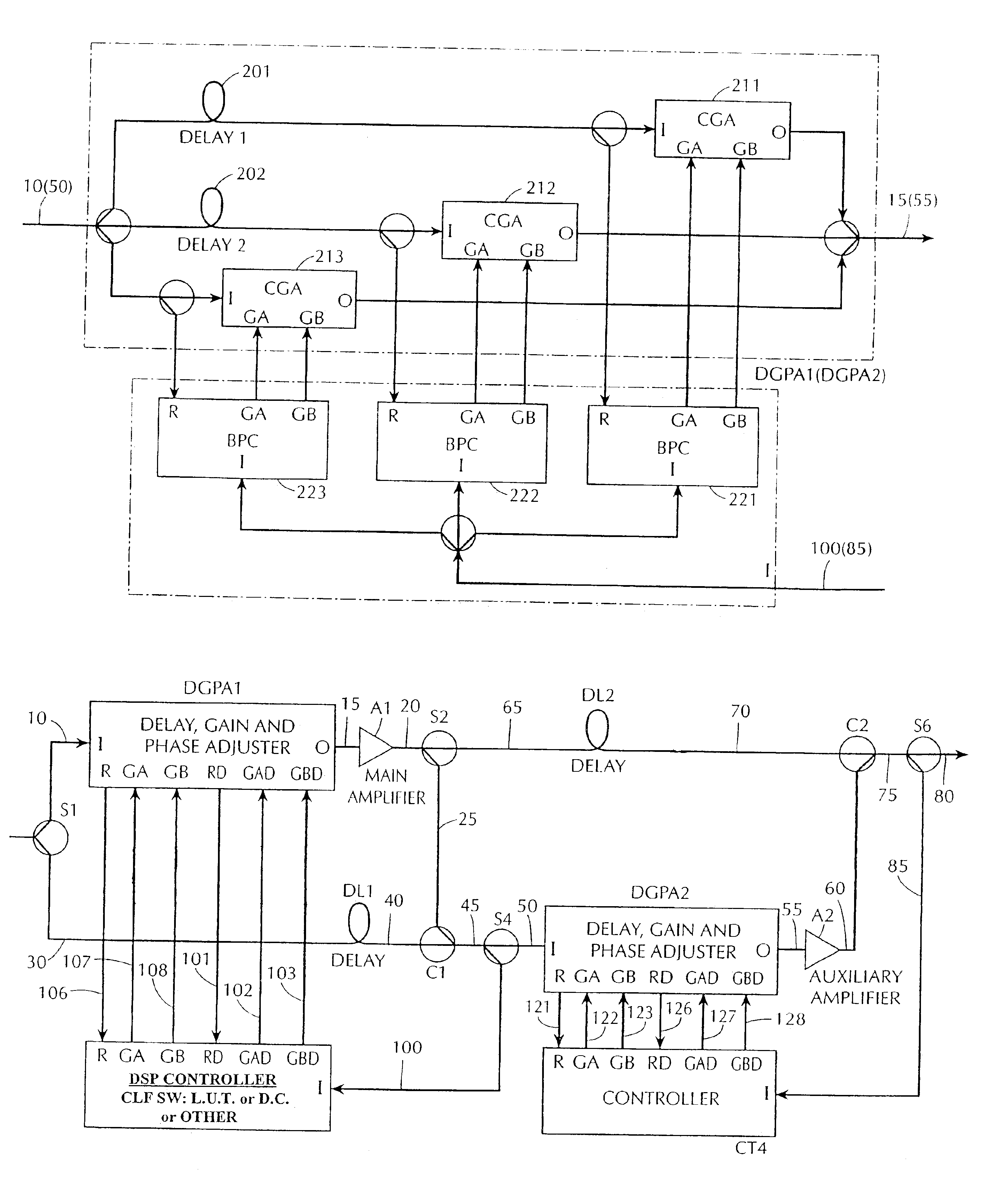
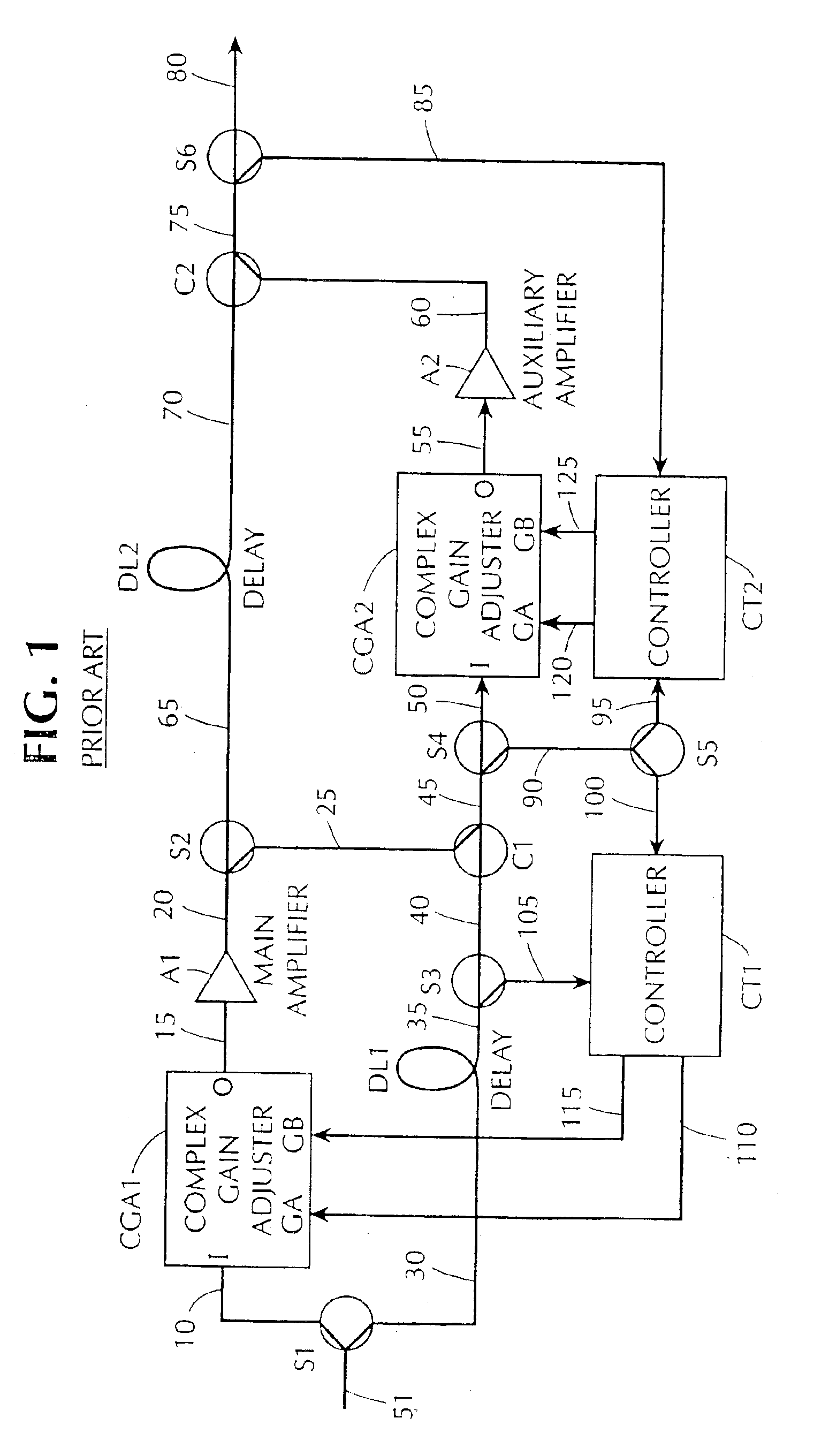
Adaptive linearizer for RF power amplifiers
InactiveUS6897722B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
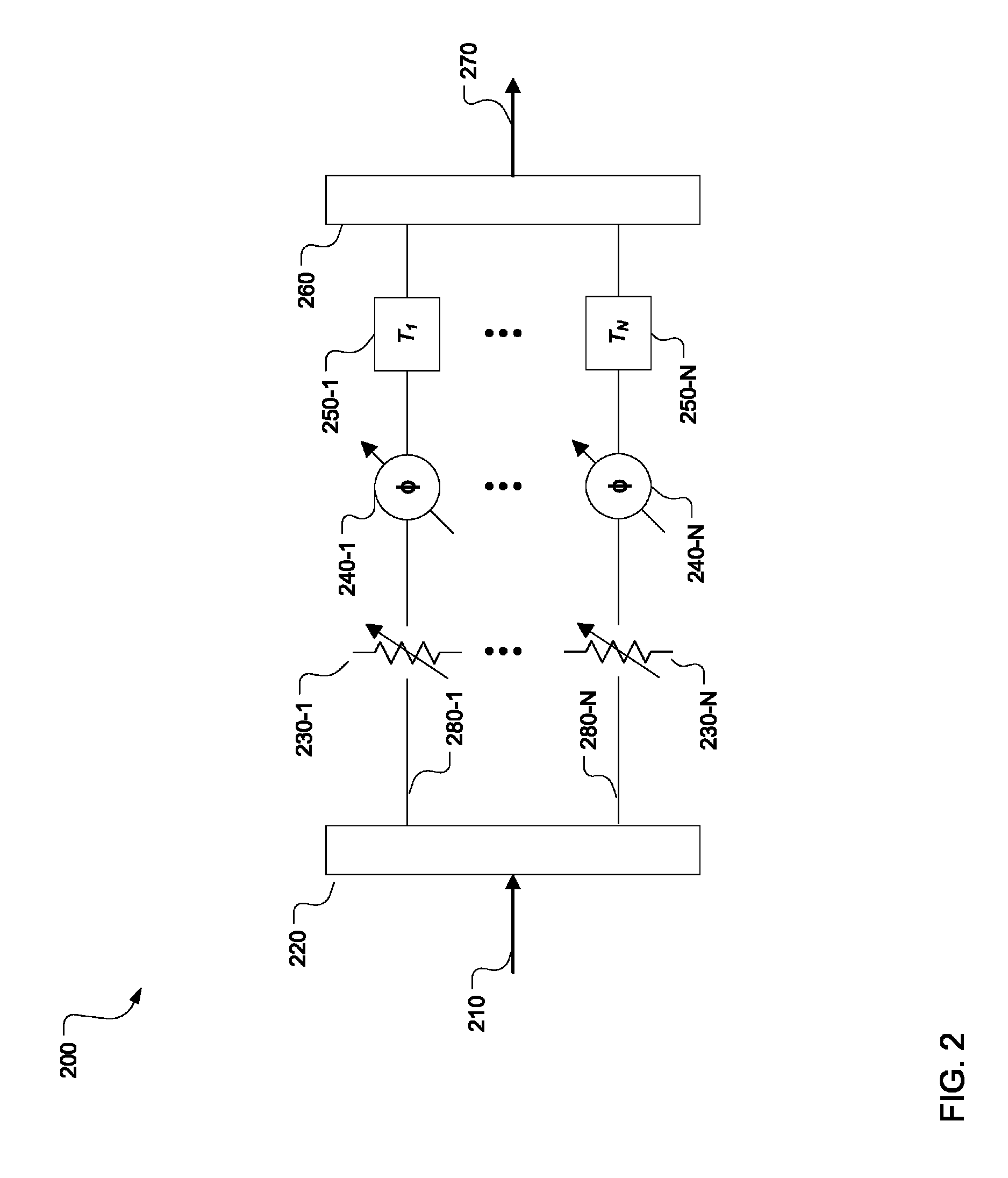
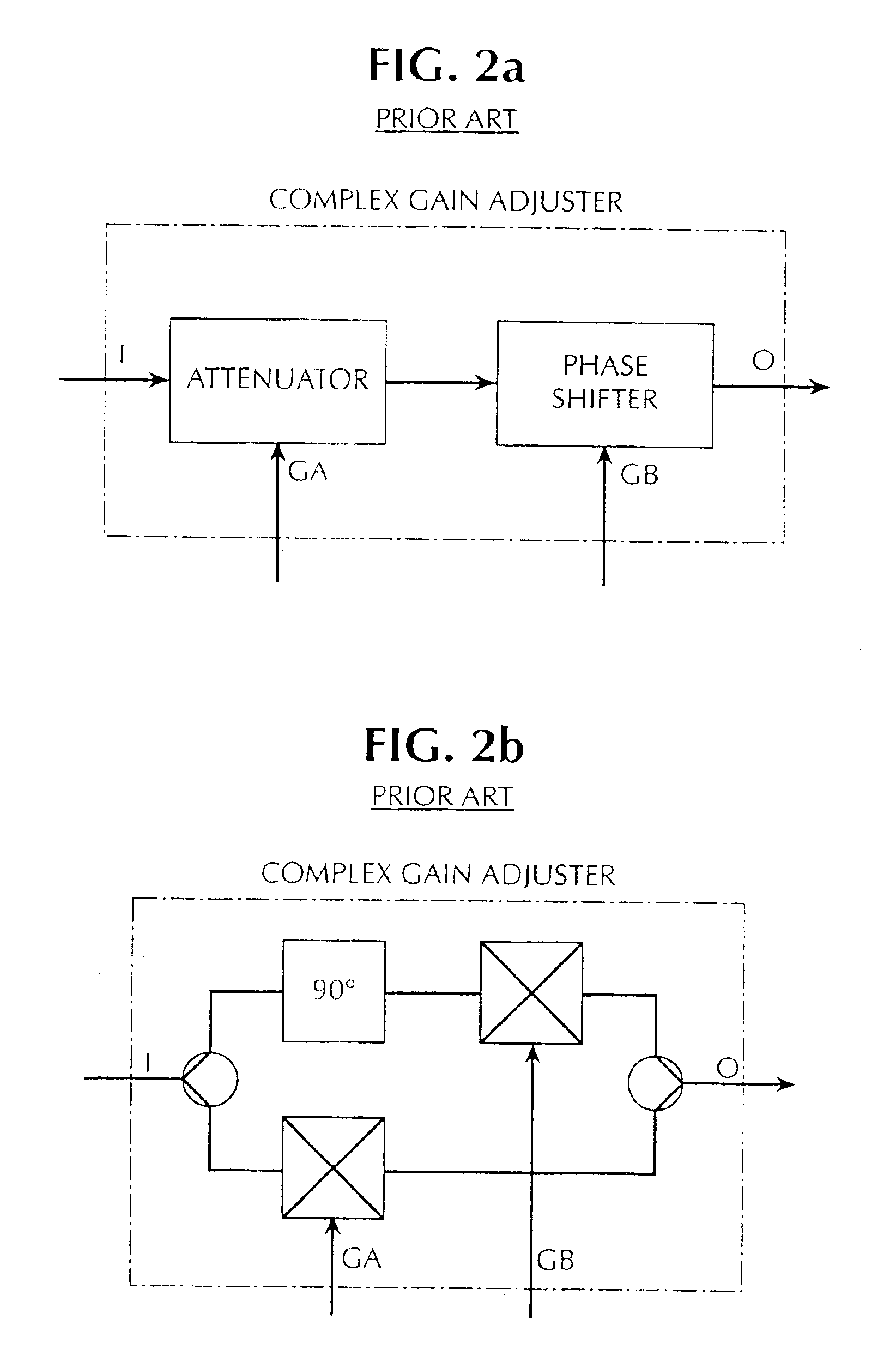
A feedforward amplifier is disclosed in which either the main amplifier or the auxiliary amplifier includes at least three parallel signal paths. Each of the signal paths includes a complex gain adjuster. In addition, a feedforward amplifier is disclosed in which a plurality of control linearizers compensate for nonlinearities in the response of signal adjusters to control inputs.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com