Patents
Literature
105 results about "Feedforward amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
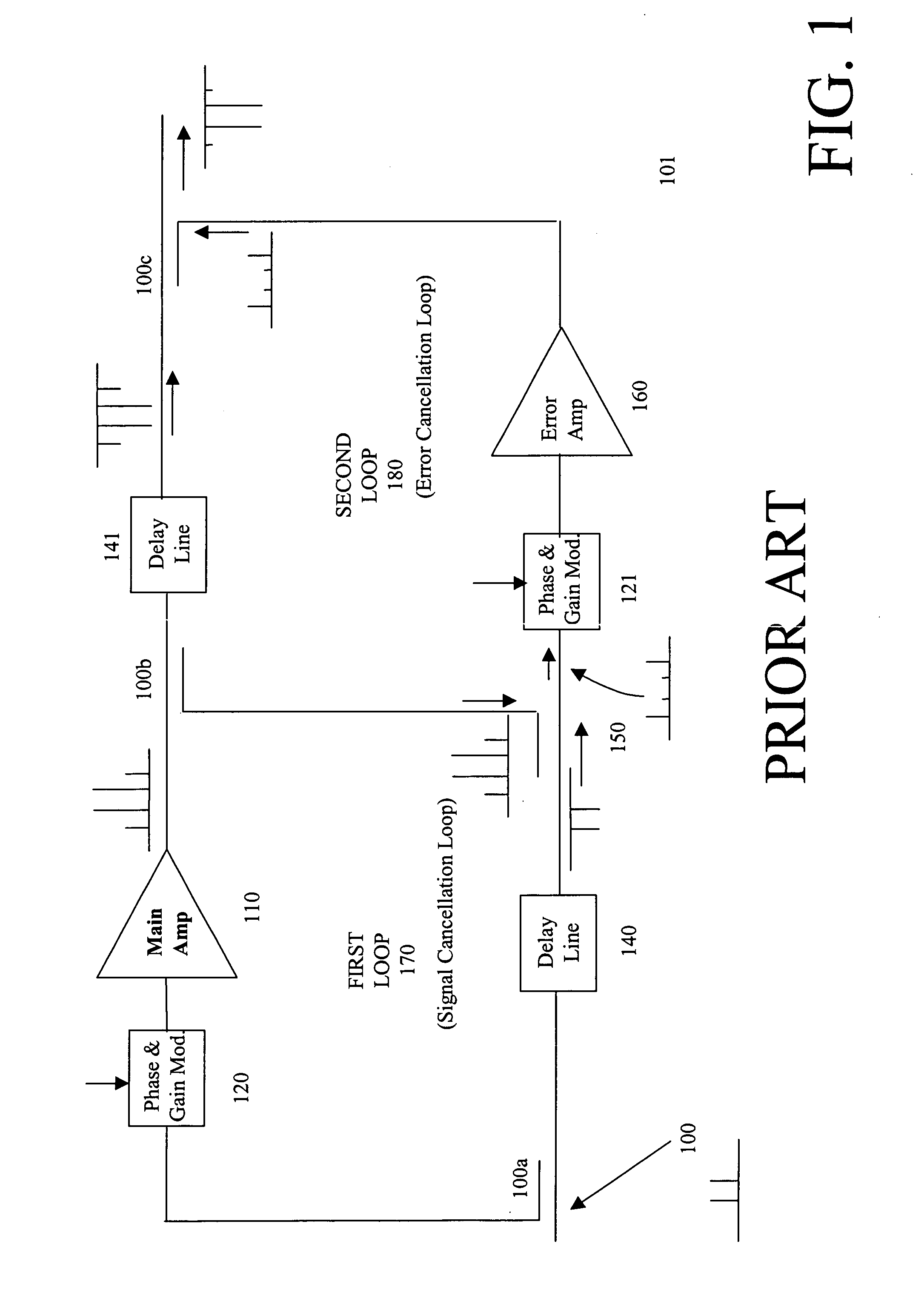
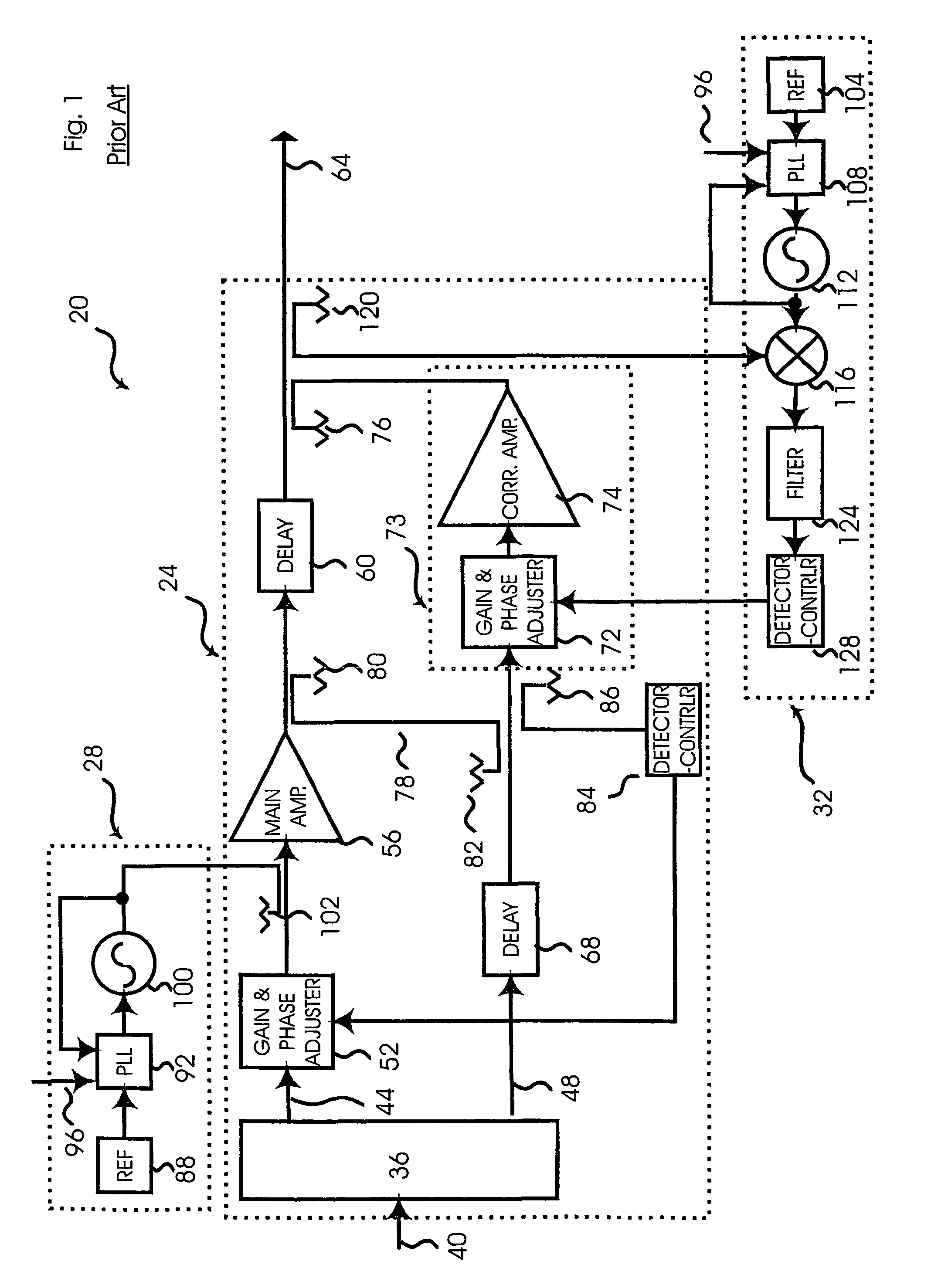
Feedforward amplifier
InactiveUS6326845B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower combinerAudio power amplifier
A feedforward amplifier includes a power divider for dividing the input signal into first and second signals. The first signal is processed in a first path that includes, in sequence, a first vector adjuster, a main amplifier, a directional coupler and a delay circuit. The second signal is delayed in a second path that includes, in sequence, another delay circuit, a first power combiner and an auxiliary amplifier block. The first power combiner combines the first signal, by way of a coupling port from the directional coupler, with the second signal to provide a combined signal into the auxiliary amplifier block. The auxiliary amplifier block further divides the second signal into two divided signals, each having a respective non-overlapping frequency band. The two divided signals are respectively vector adjusted, amplified, and then recombined. The recombined signal is then recombined with the processed signal in the first path to provide the desired output signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
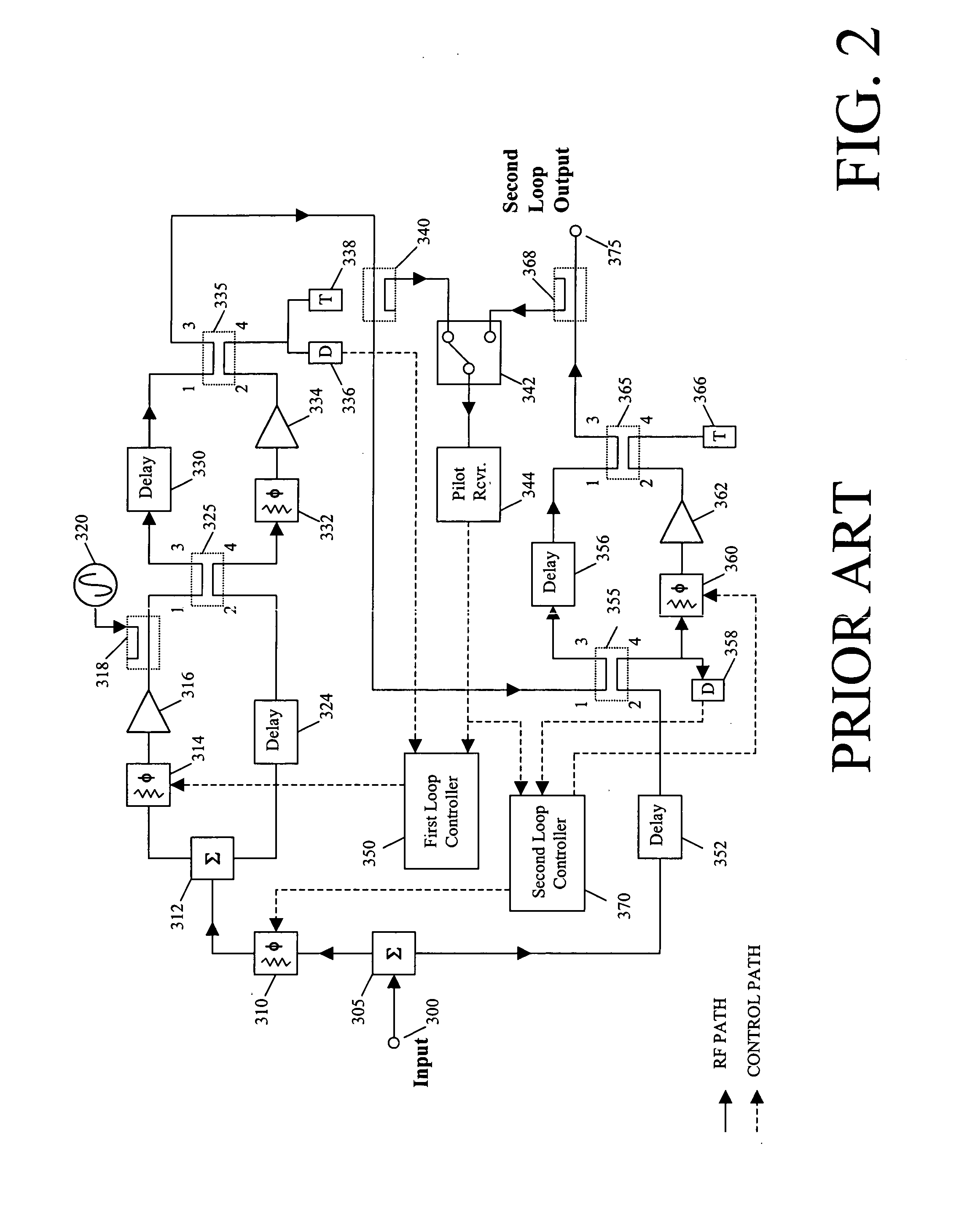
System and method of carrier reinjection in a feedforward amplifier
InactiveUS20050113052A1Signal distortion is smallAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
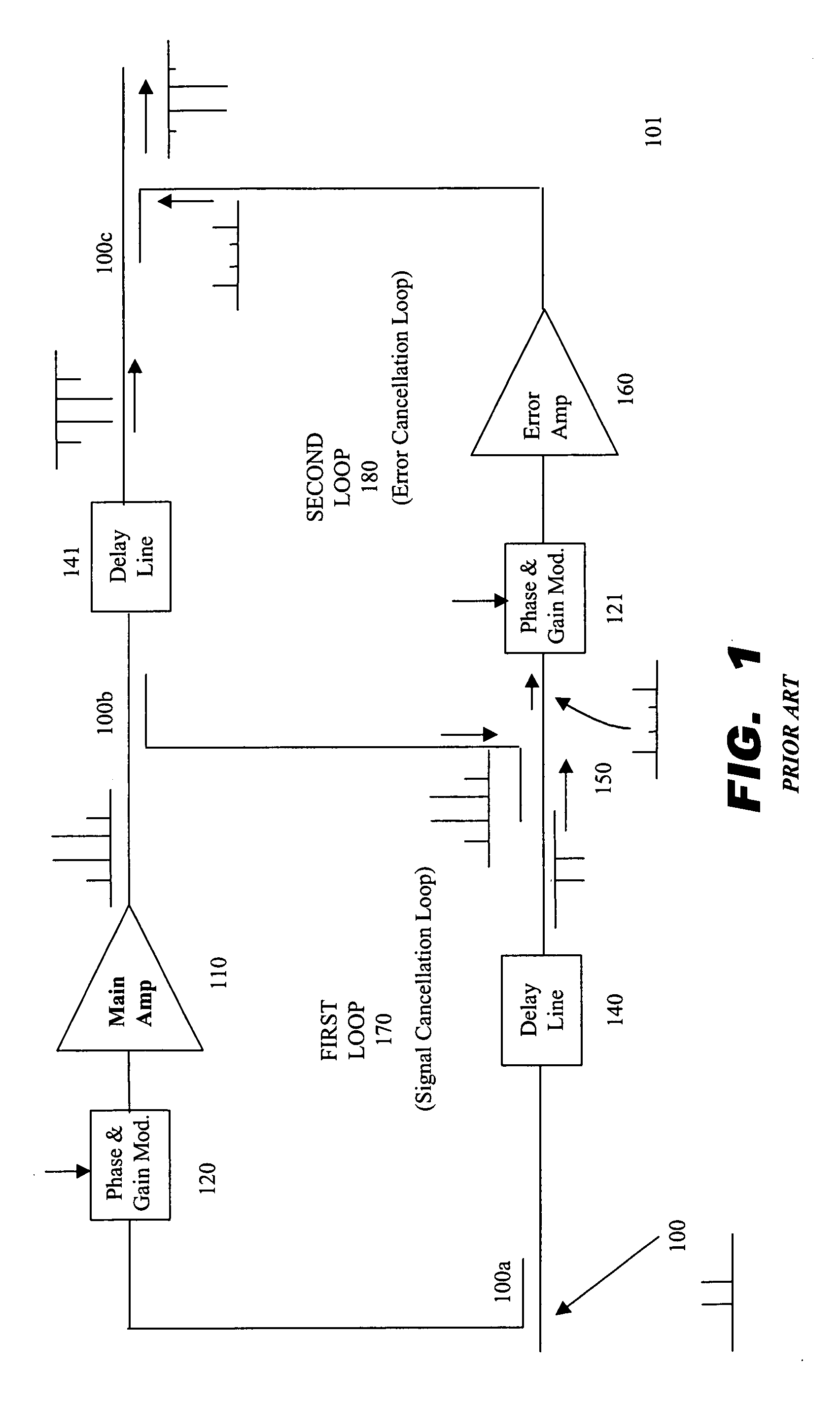
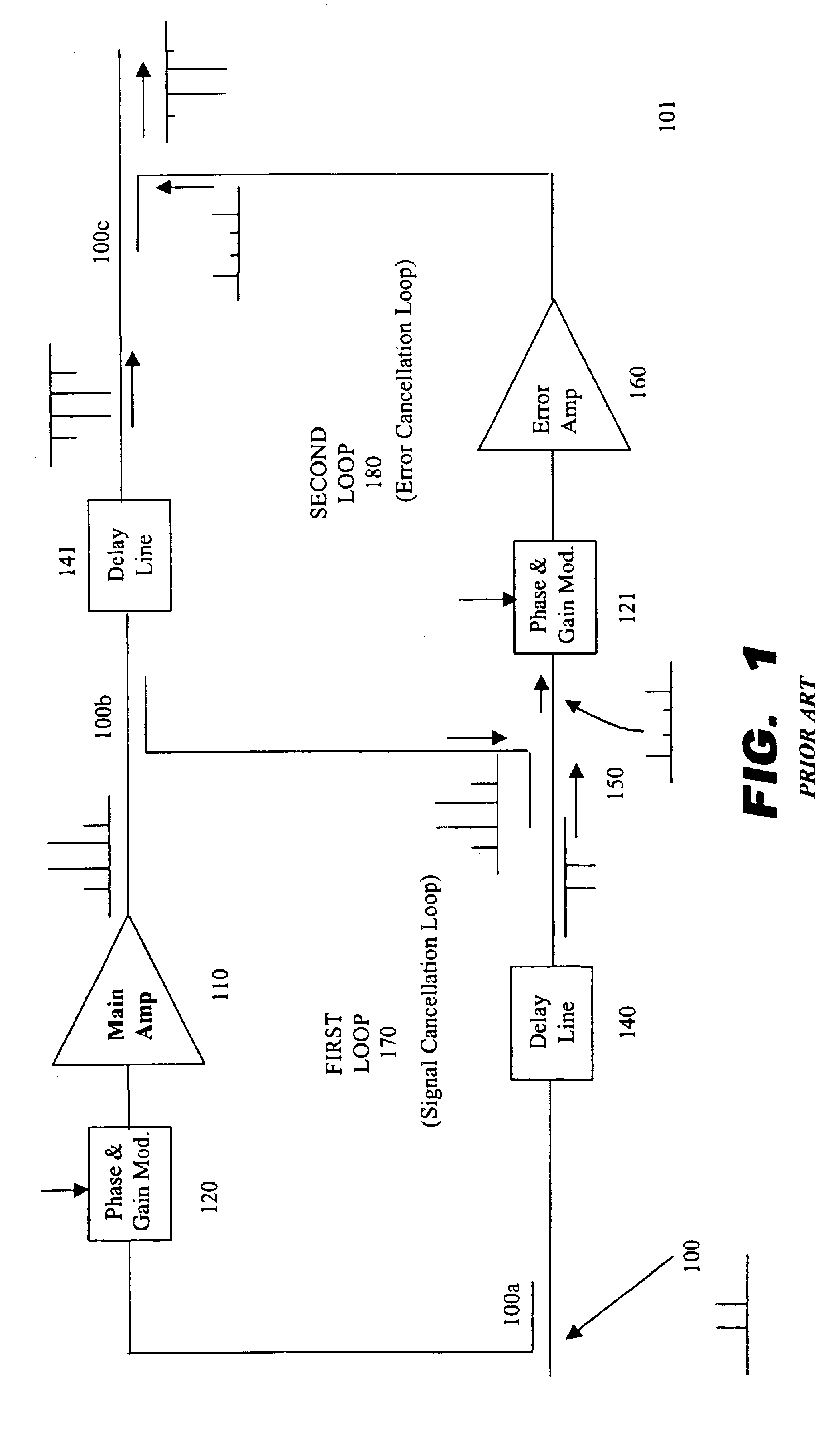
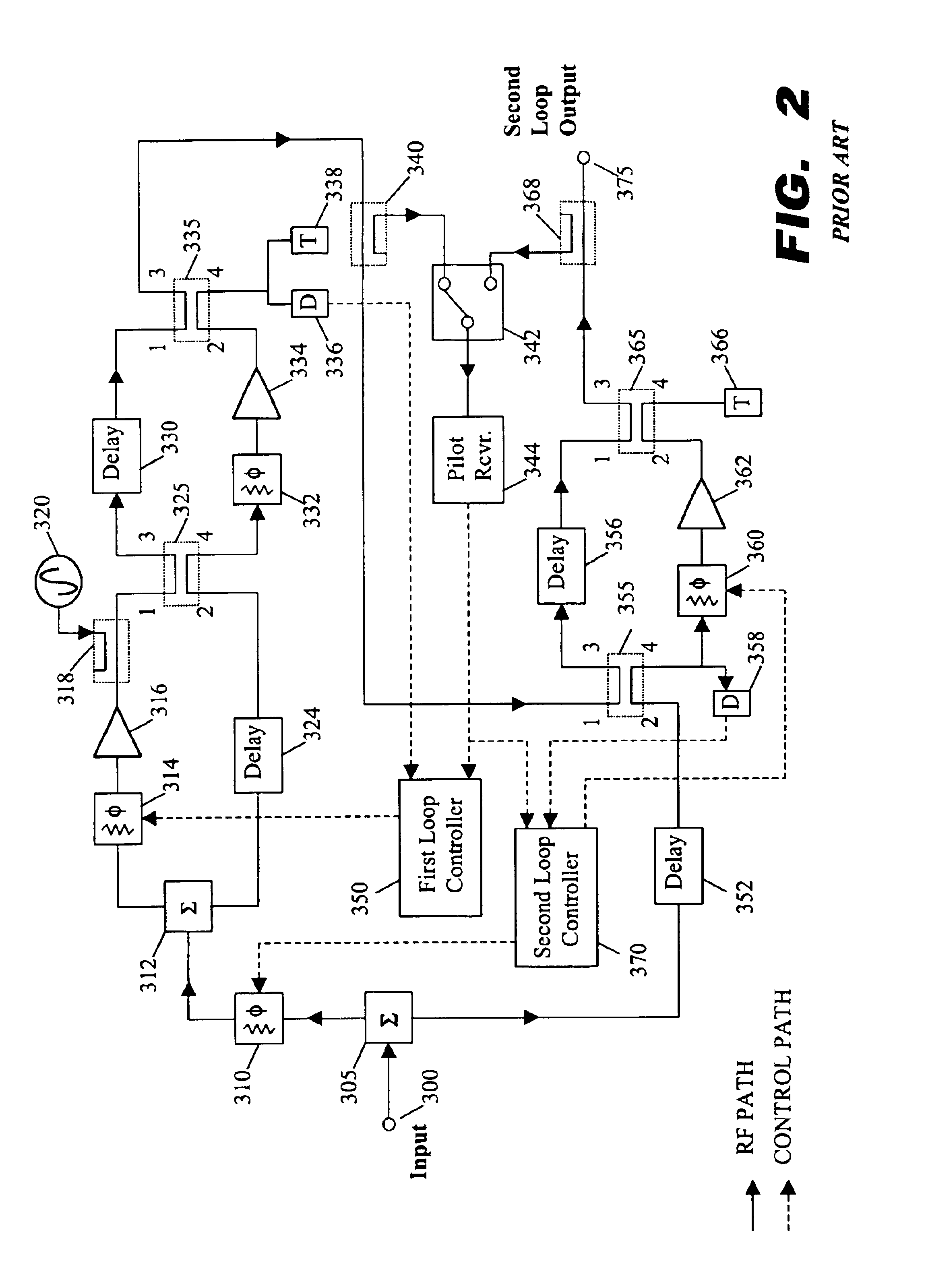
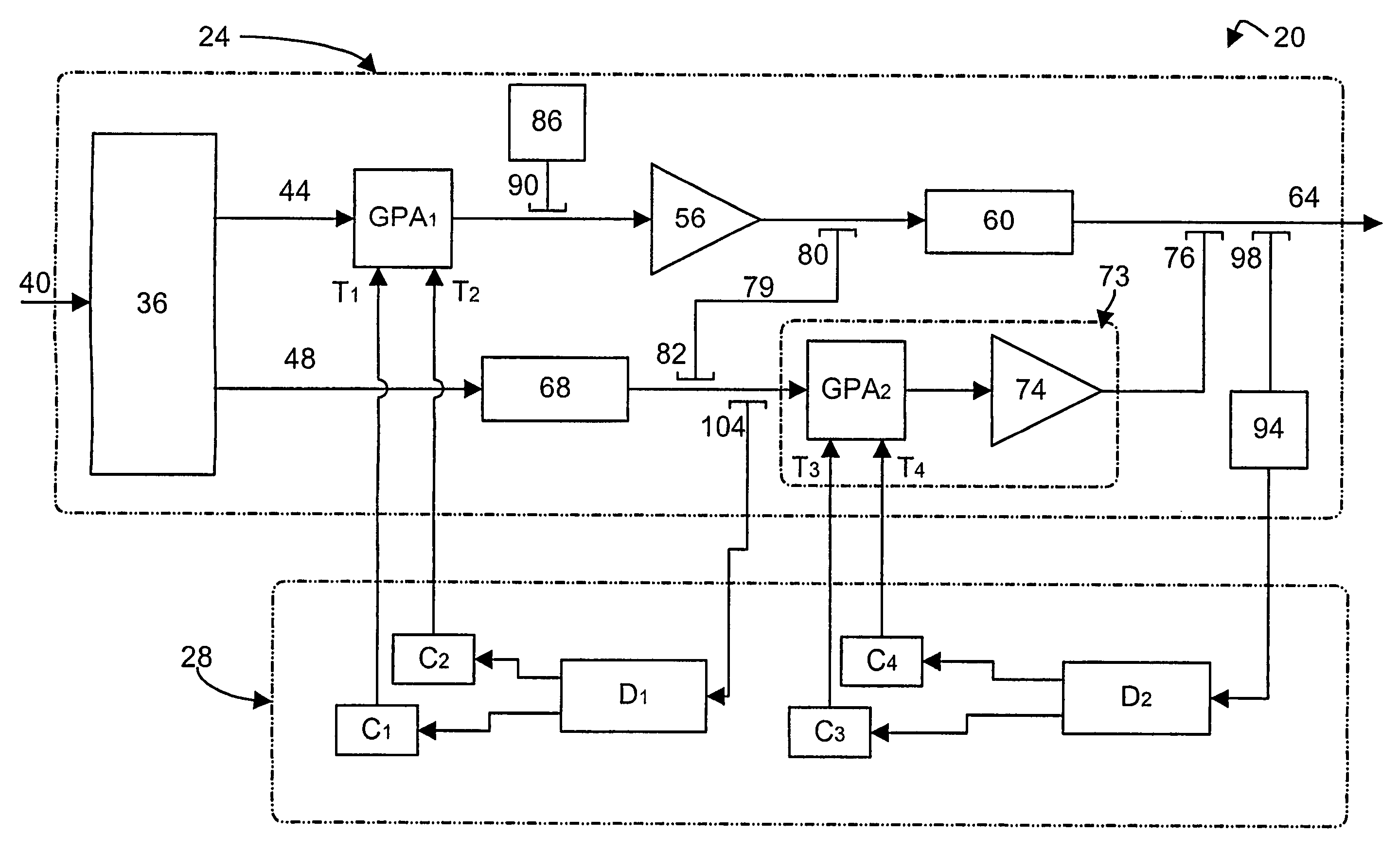
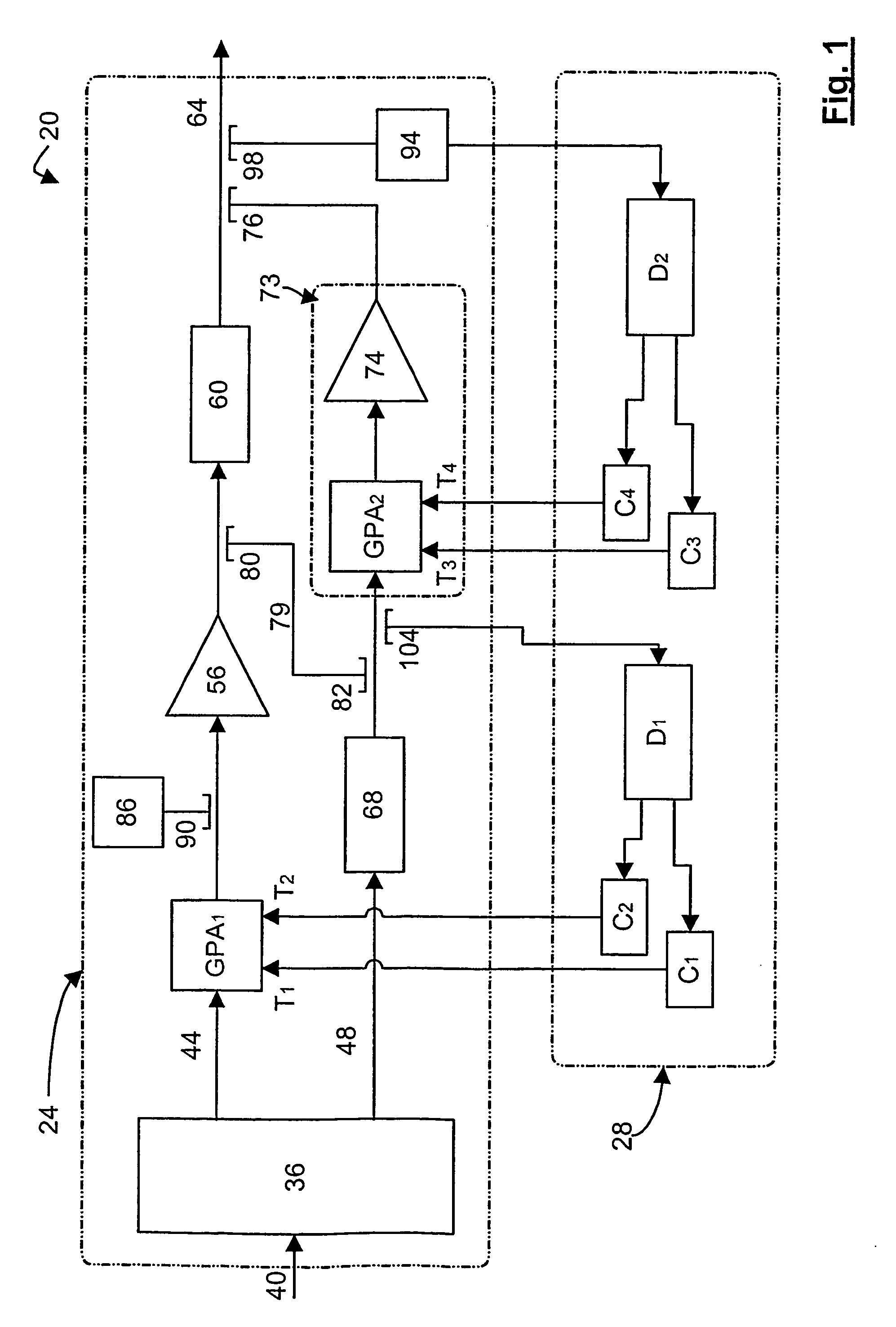
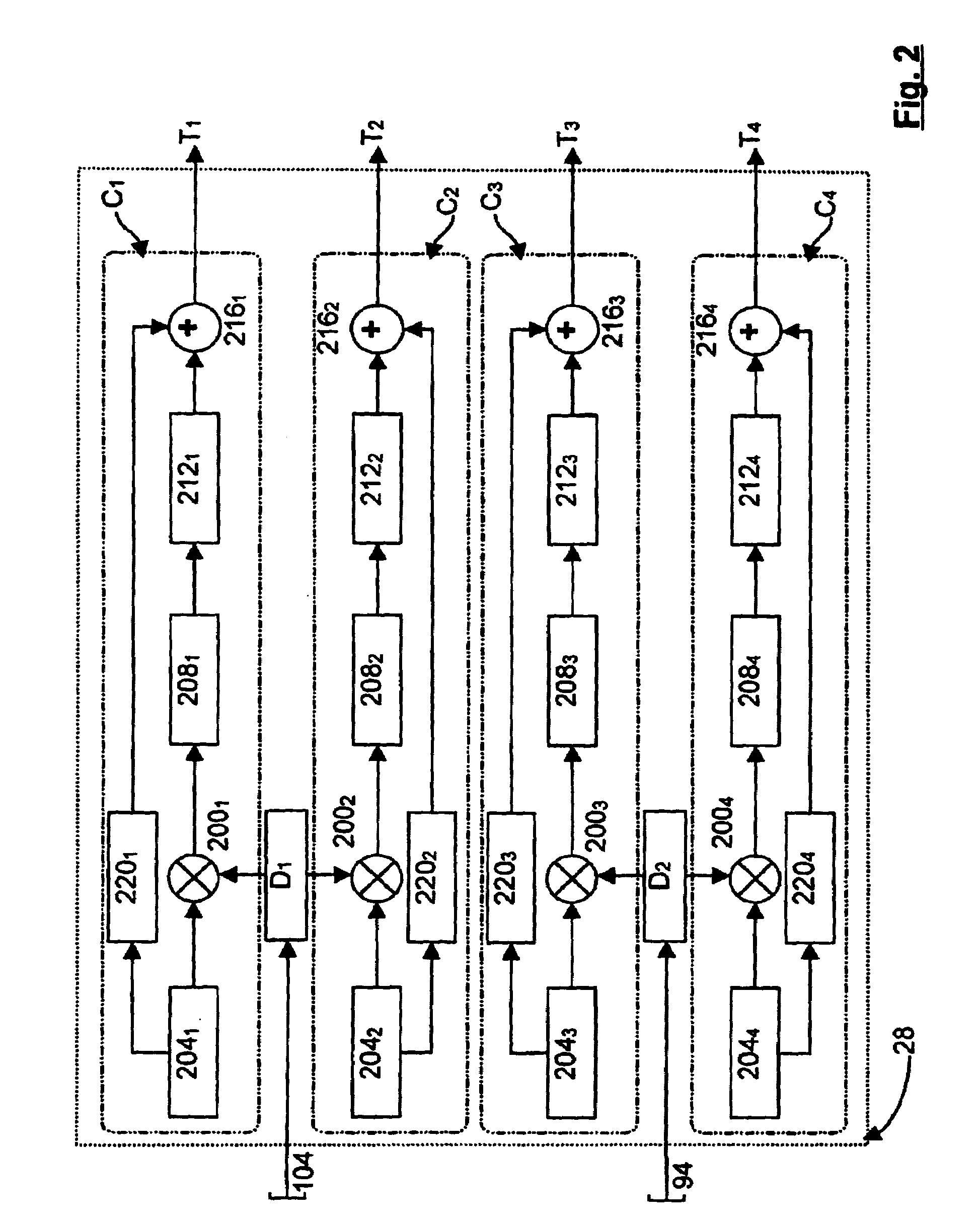
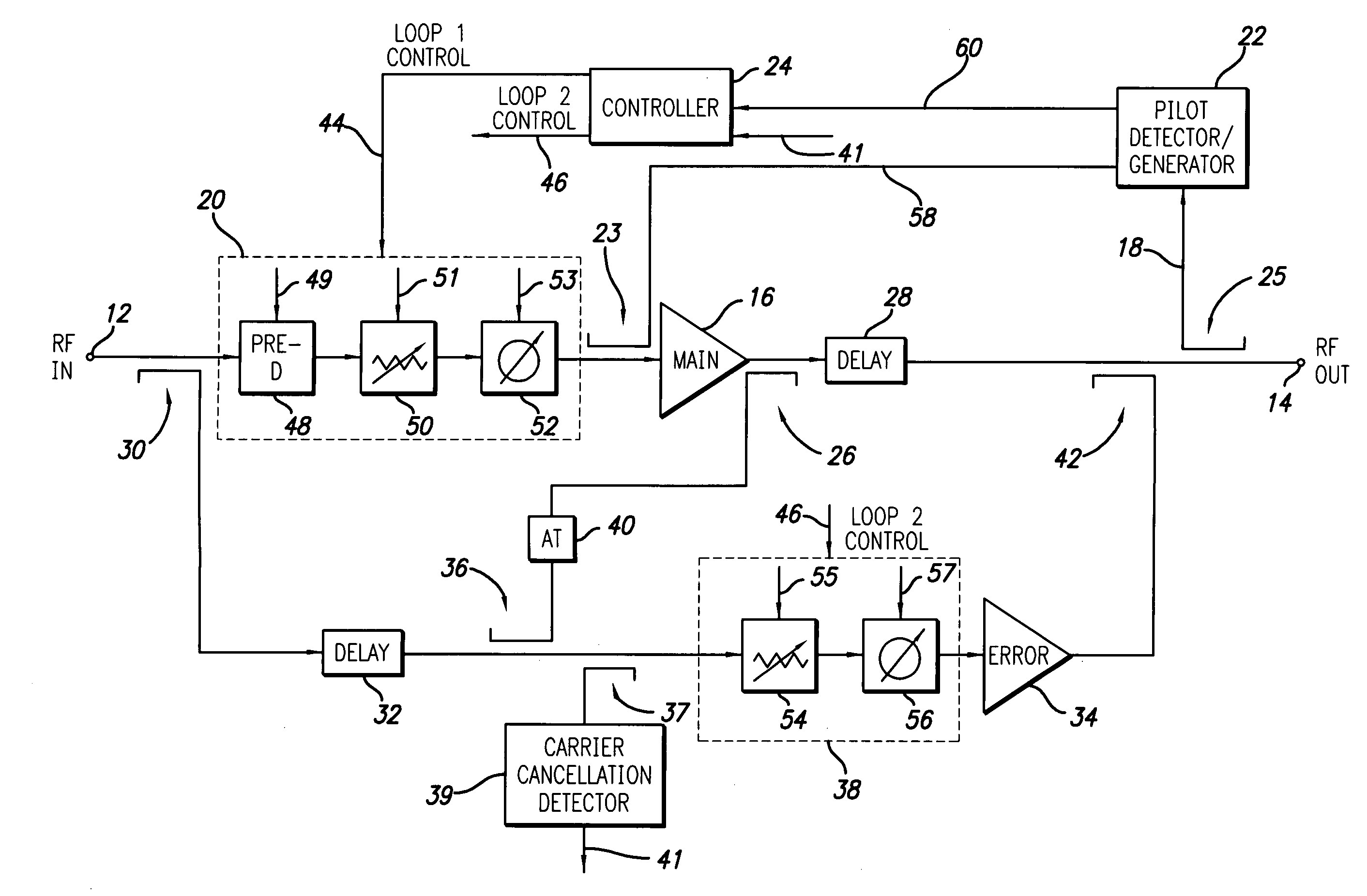
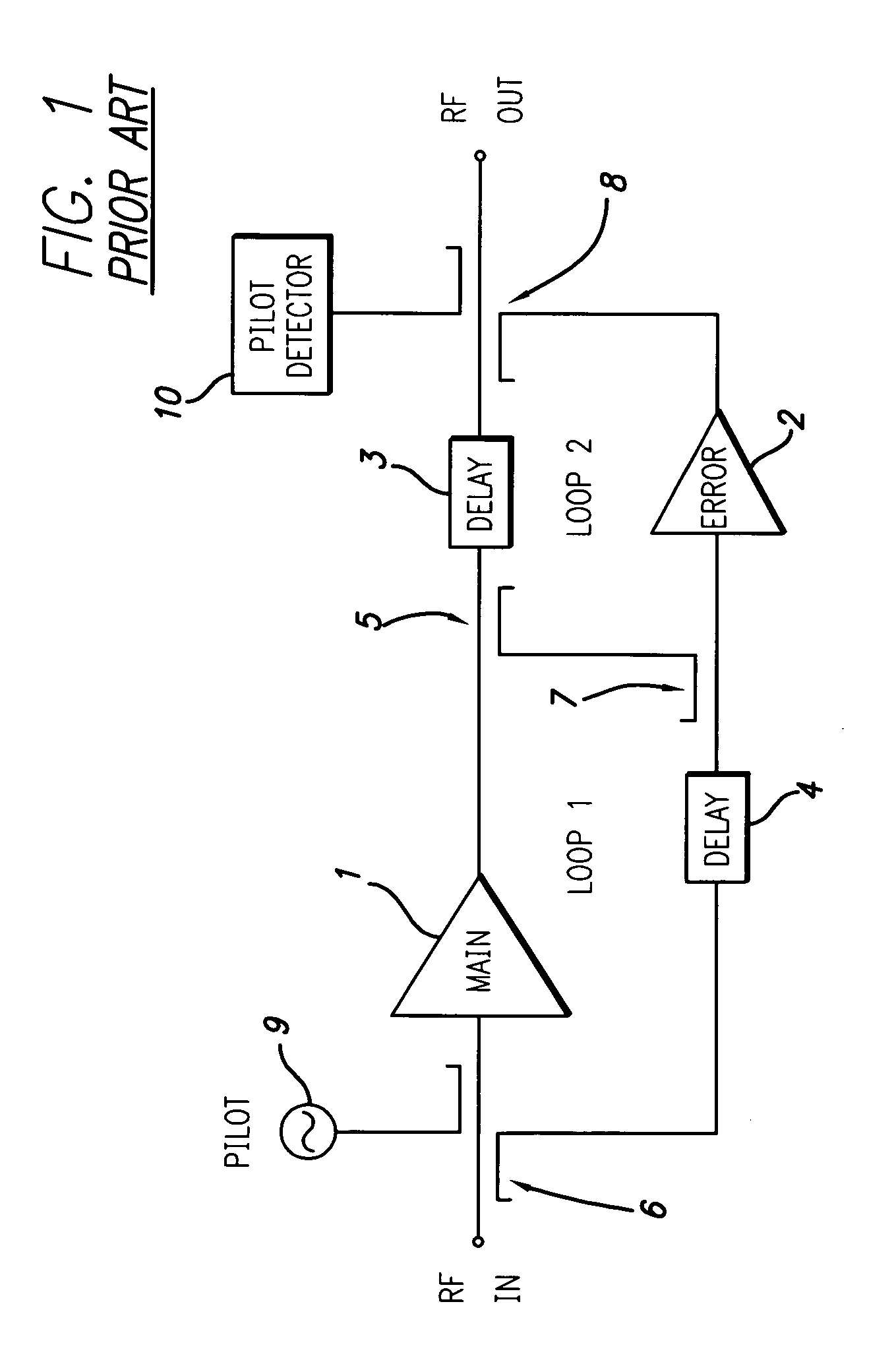
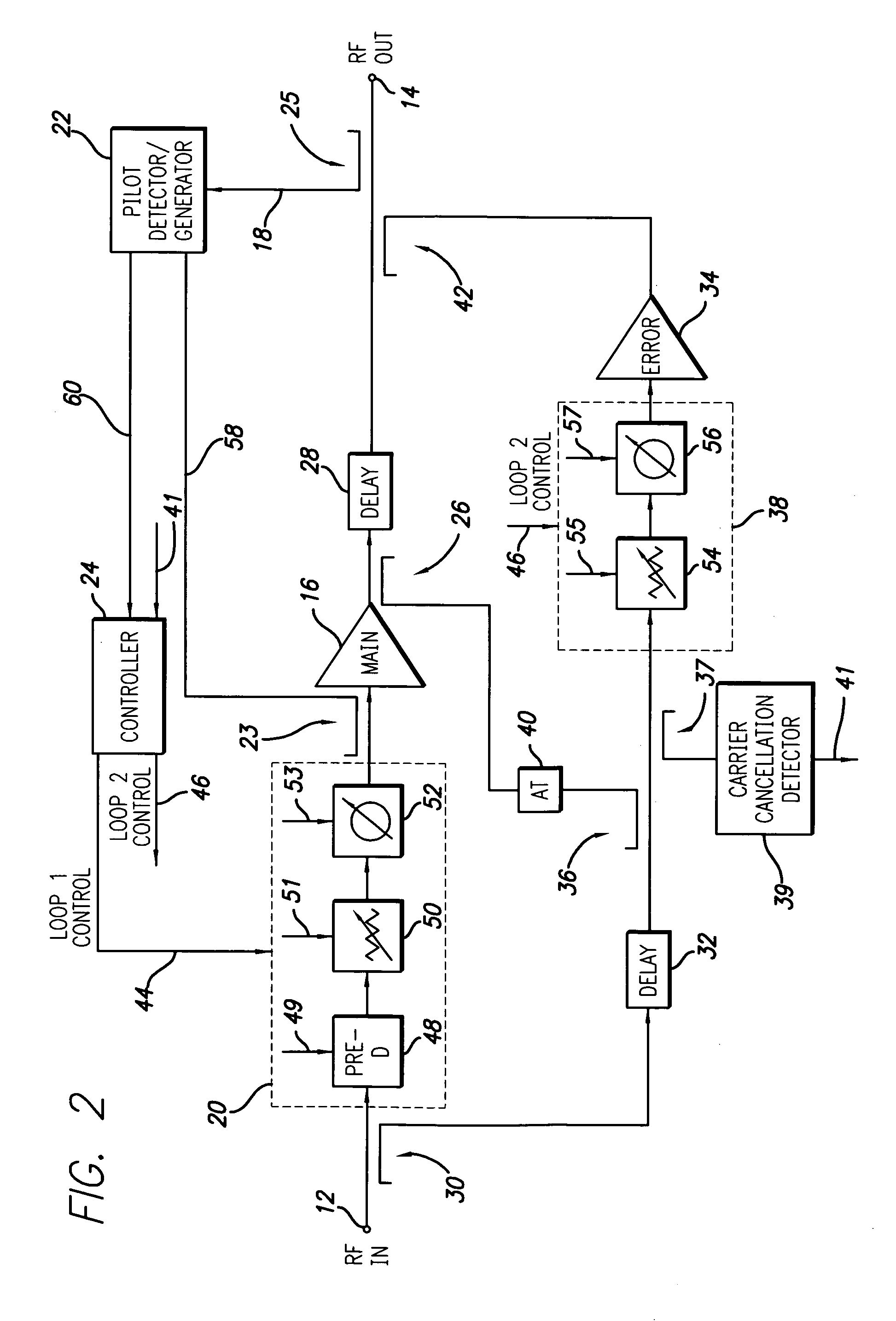
A dual loop feedforward power amplifier. A dual loop feedforward power amplifier, comprising an input that provides a multicarrier signal; a first feedforward power amplifier; and a second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier serves as a main amplifier gain block in the second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier comprises a carrier cancellation loop and a first error amplifier loop, and wherein the second feedforward power amplifier comprises a third loop and a fourth loop that cancel small signal distortions that are not reduced by the first feedforward amplifier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
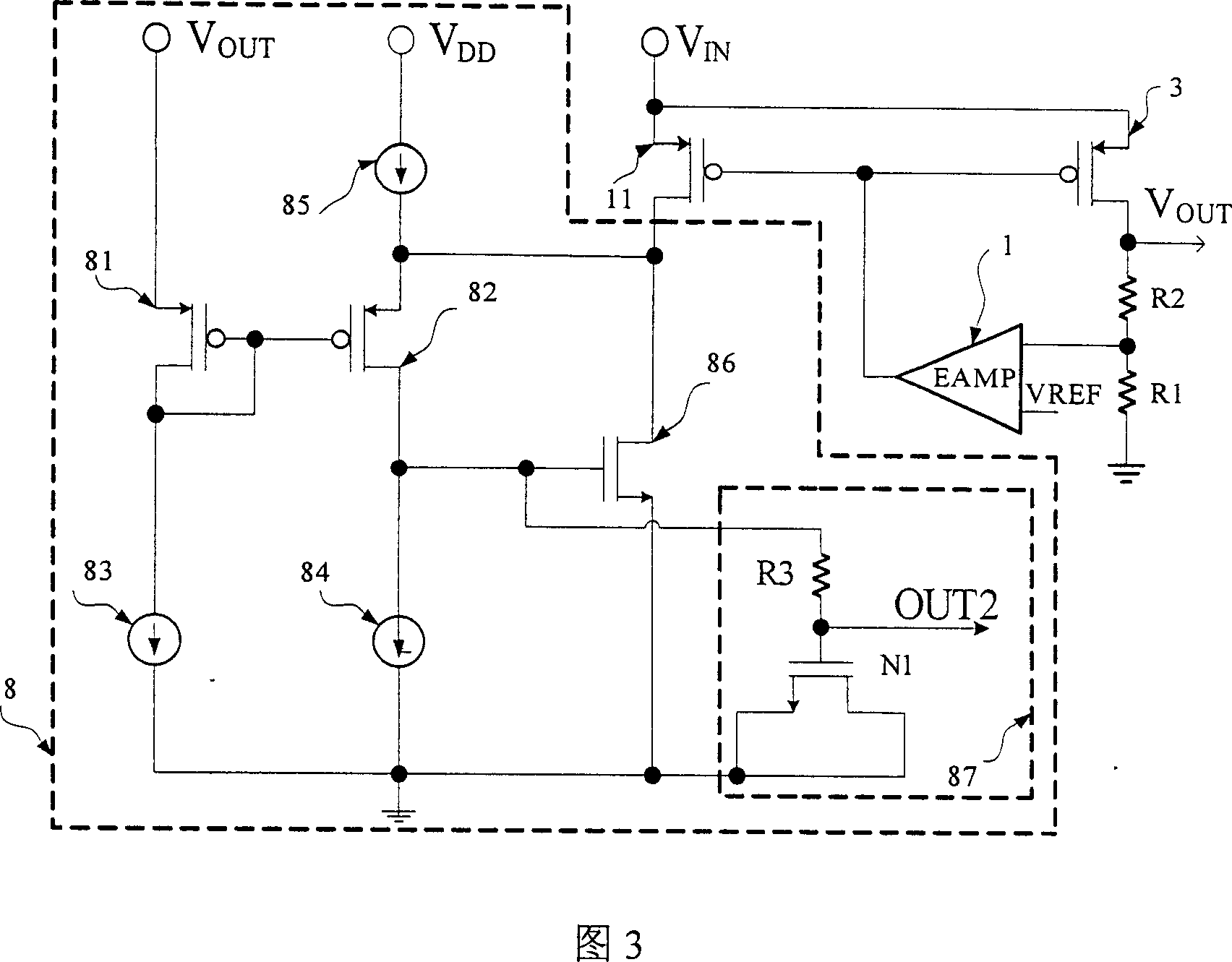
Double ring low differential voltage linear voltage stabilizer circuit
InactiveCN1949121AImproved Load Transient ResponseImprove dynamic performanceElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLoad circuit
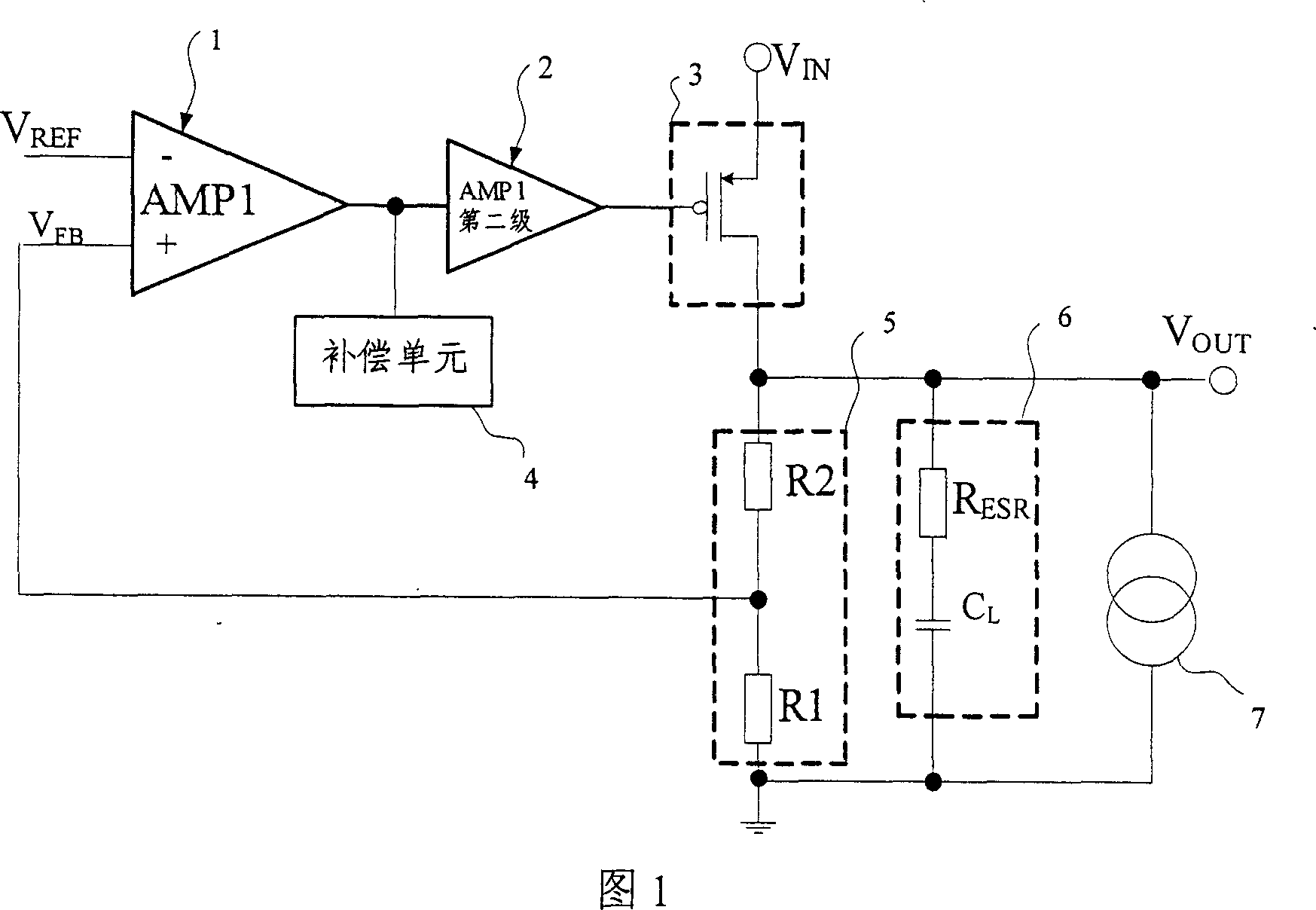
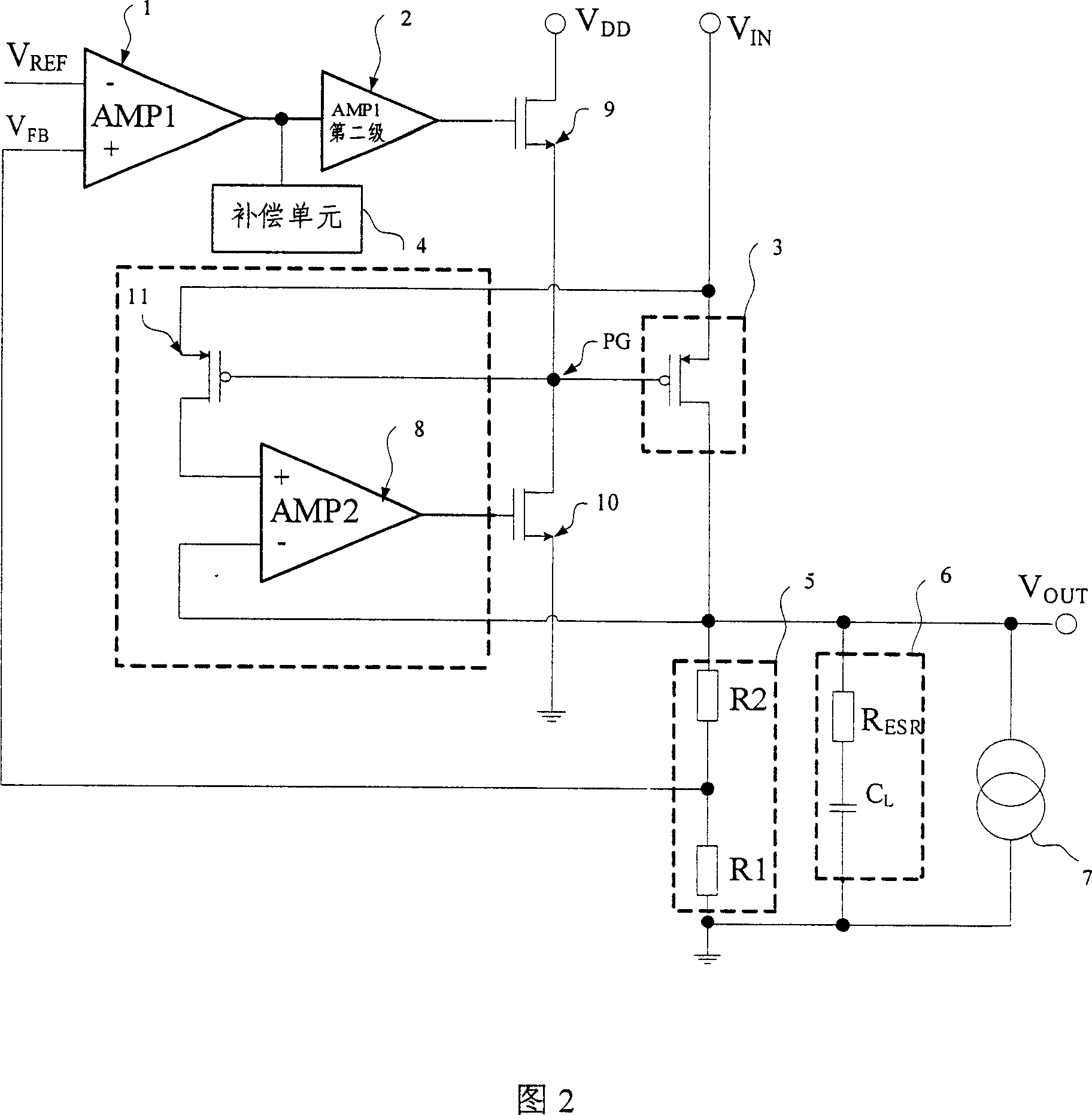
The invention discloses double ring low voltage difference linear voltage regulator circuit. It includes error amplifier, secondary amplifier, power tube, compensating unit, output sampling network, load capacitance and load circuit, feed-forward amplifier, pull-up driving tube, pull-down driving tube, and sampling tube. It includes two loop circuits that the main one includes the error amplifier, secondary amplifier, pull-up driving tube, power tube, and output sampling network which form negative feedback loop to stably output voltage VOUT; the additional one includes feed-forward amplifier, sampling tube, pull-down driving tube, and power tube which refer to output voltage, form feed back loop to dynamically compensate circuit and further stably output voltage VOUT, and refer to load current, form positive feedback loop to increase load step change for the response circuit. The invention can supply better transient response, periphery circuit selecting, and phase margin for the circuit.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
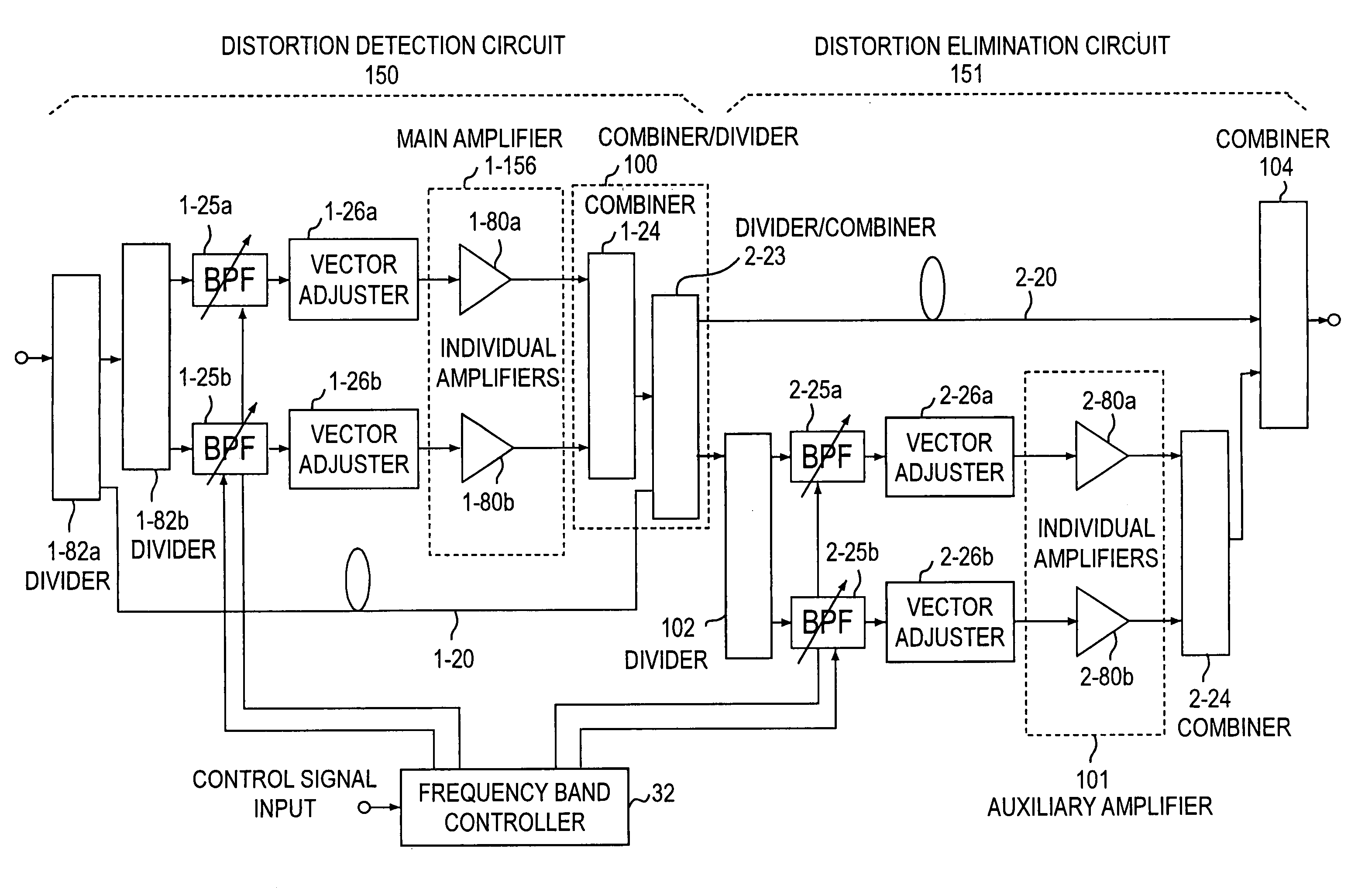
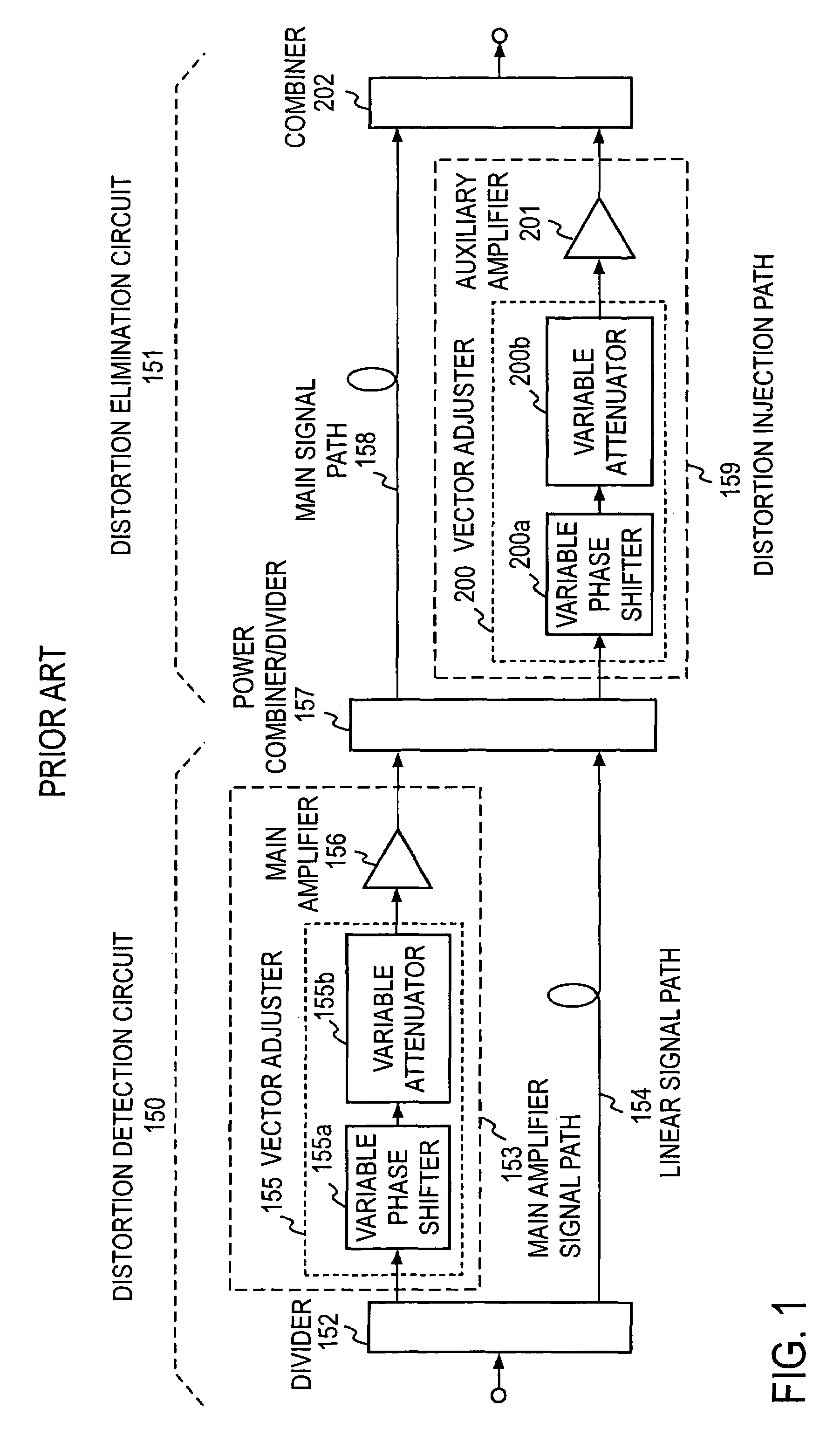
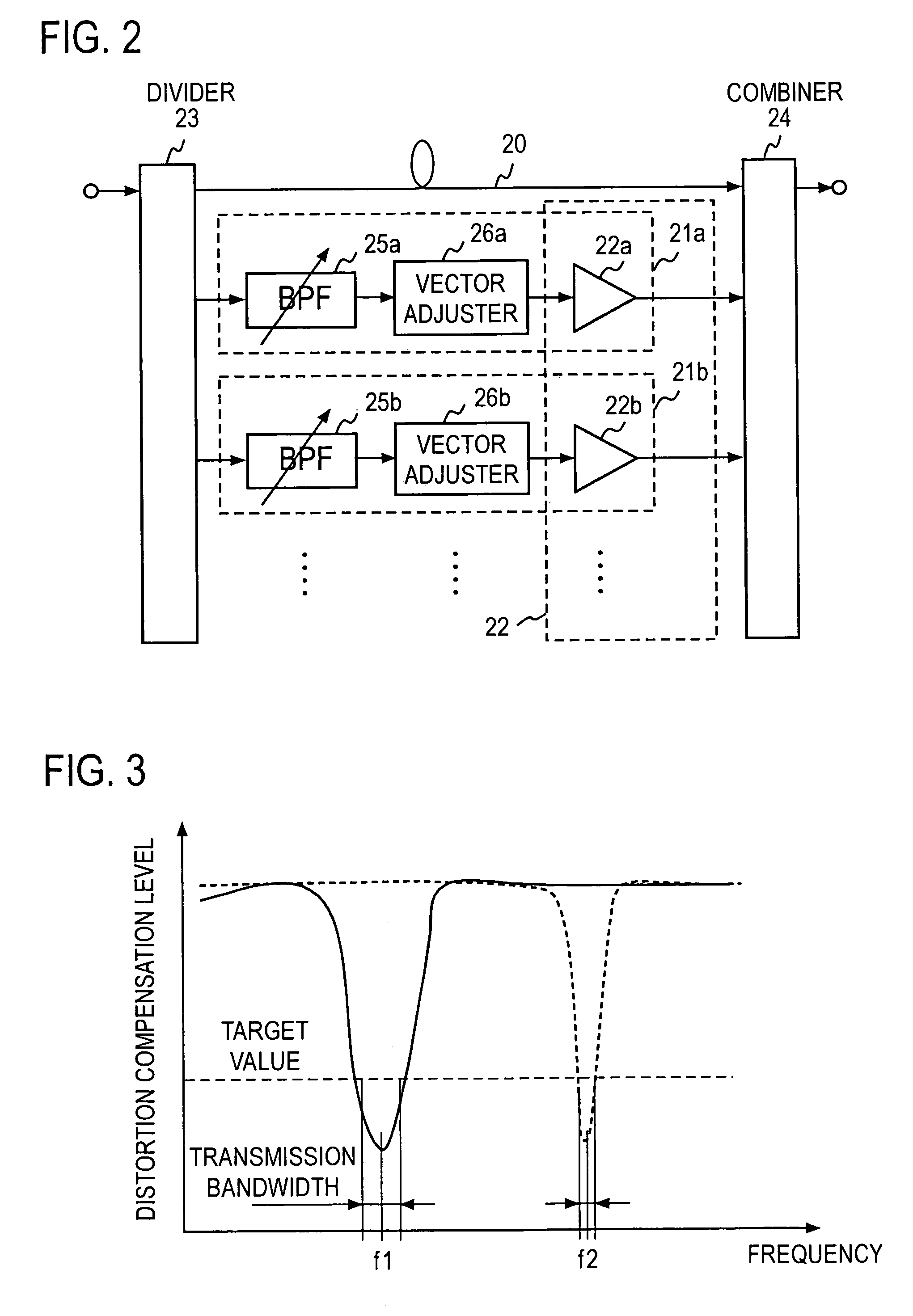
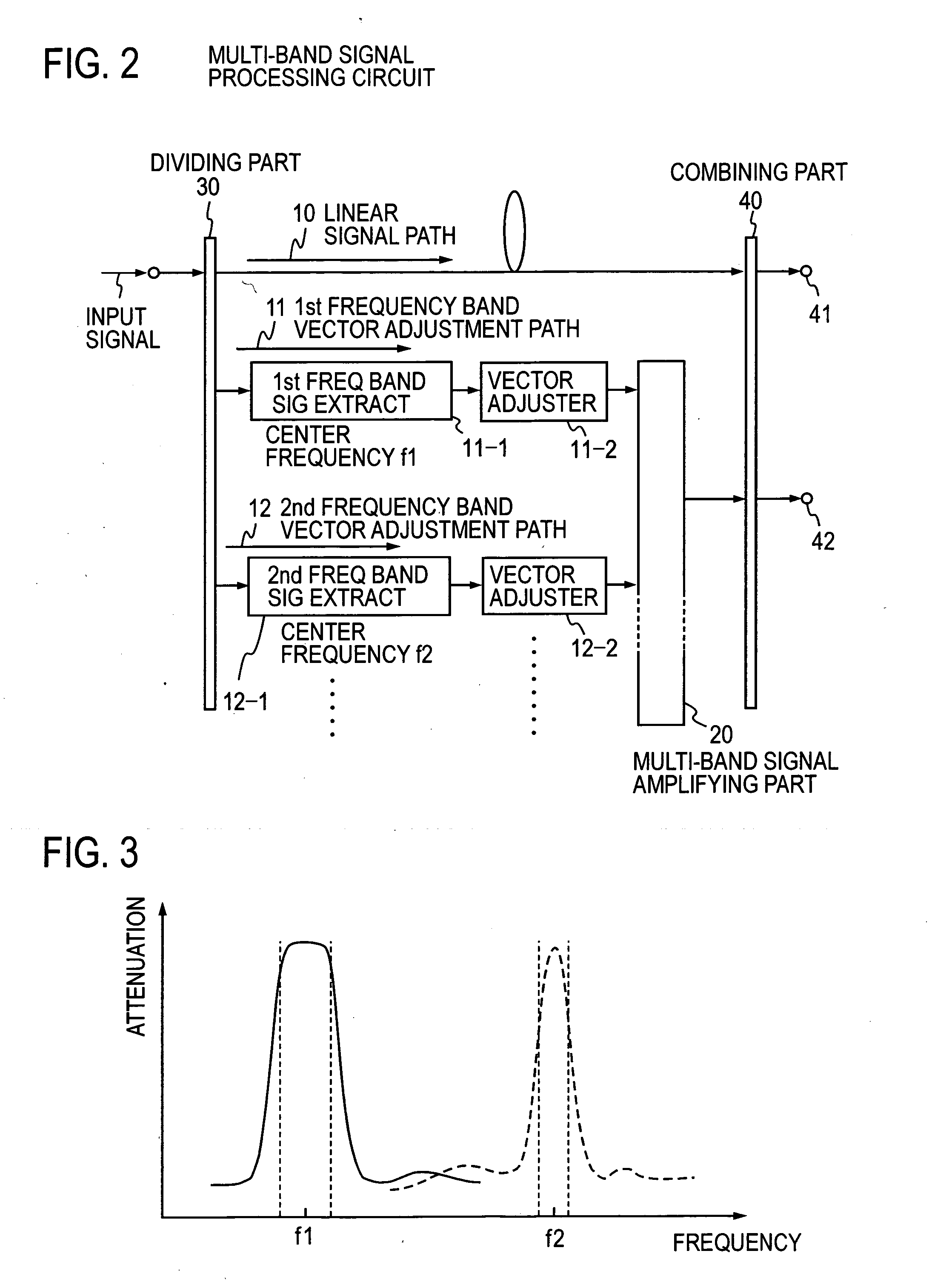
Feed forward amplifier for multiple frequency bands
InactiveUS7336128B2Increase diversityReduce power consumptionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierResponse Frequency
The present invention has for its object to provide, in an environment where plural radio systems coexist, a feed forward amplifier for multiple frequency bands, capable of adaptively selecting the frequency band which is used.The feed forward amplifier of the present invention comprises a distortion detection circuit and a distortion elimination circuit and has first and second variable frequency band extractors 25a and 25b provided in series with respective vector adjustment paths 21a and 21b. Also, the feed forward amplifier comprises a frequency band controller which varies the frequency band of variable frequency band extractors 25a and 25b and has been designed, by changing the frequency band of first and second variable frequency band extractors 25a and 25b in response to a frequency switching request from the outside, to be able to adaptively control the frequency band in which distortion is compensated.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
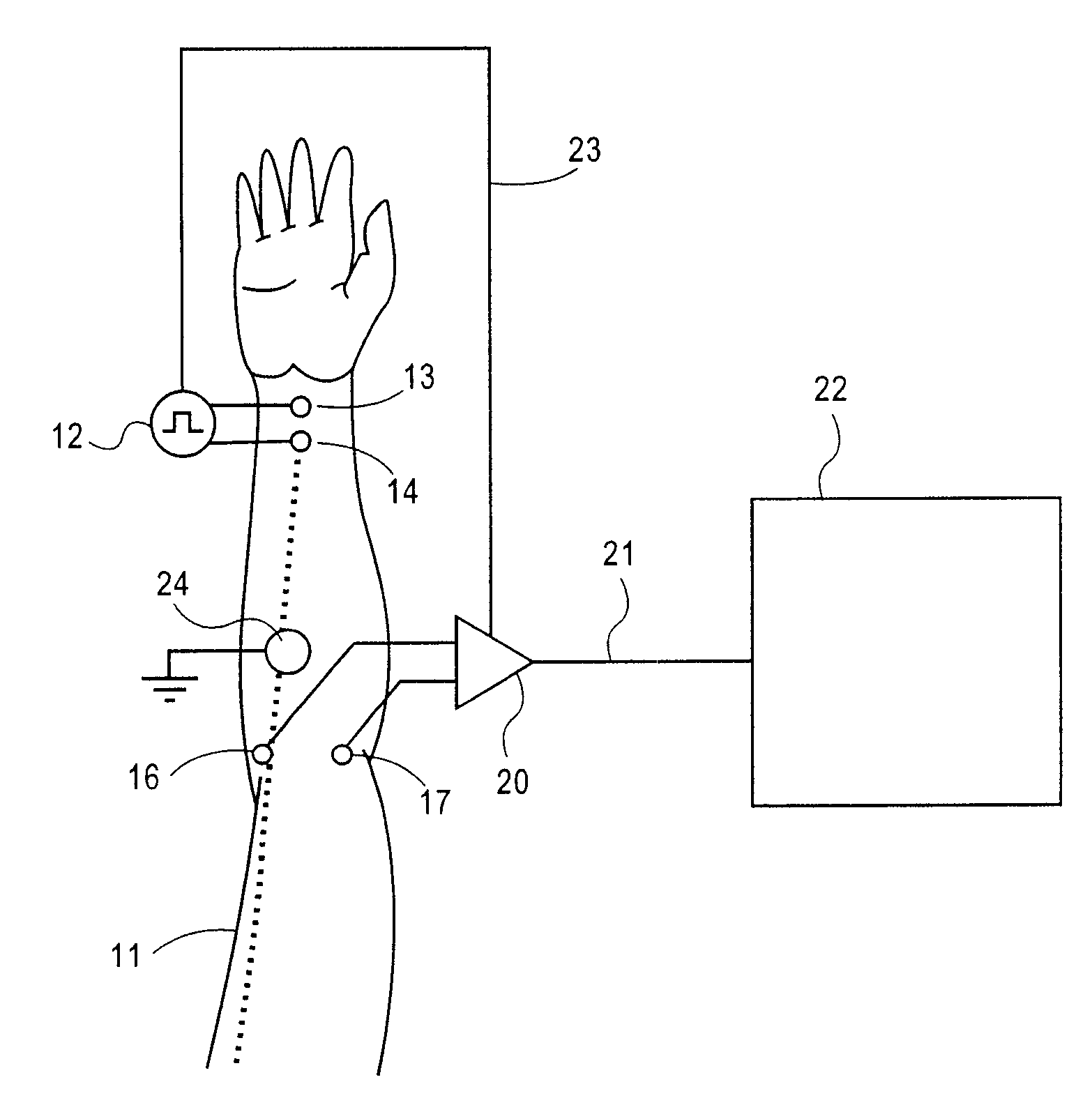
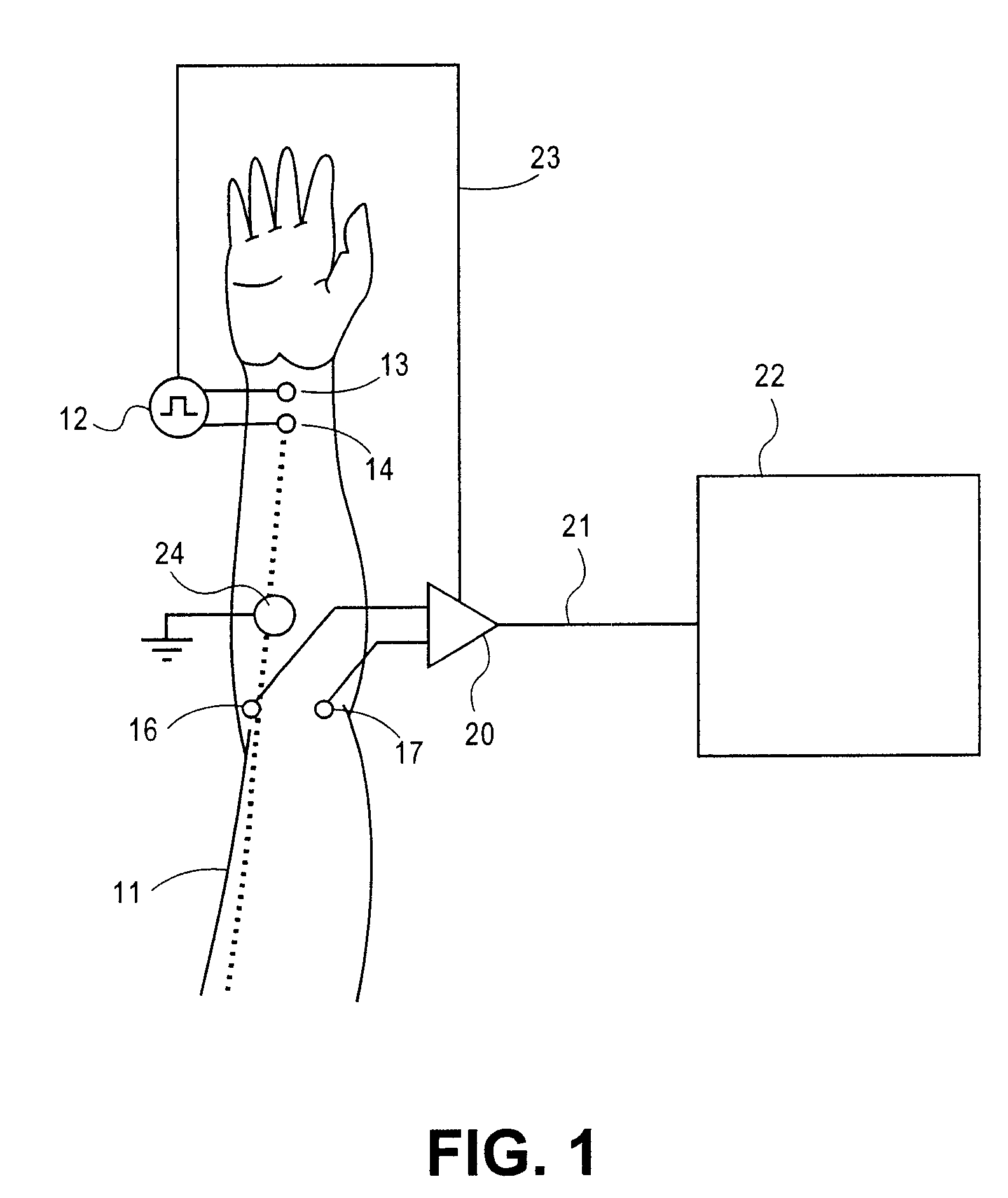
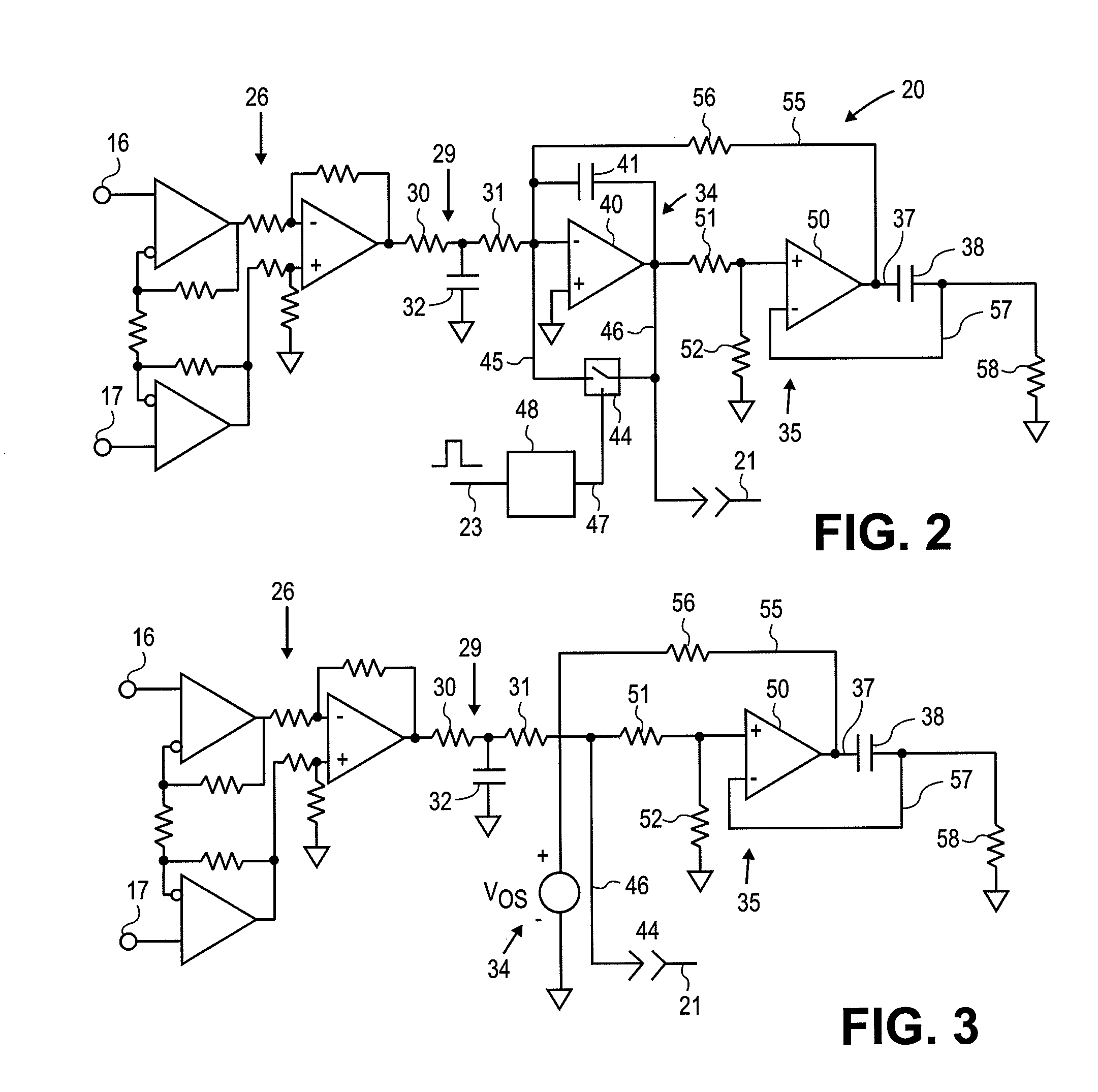
Method and apparatus for stimulus artifact suppression
Amplification of an evoked potential signal is carried out utilizing a high pass filter implemented as an integrator in a feedback loop which drives the DC offset voltage to zero. As a result, the feed-forward amplifier circuit has almost zero volts at its output since the only voltage remaining is the offset voltage of the operational amplifier, which is selected so as to maintain this parameter as low as possible. Because the voltage impressed across the feed-forward amplifier section is close to zero, the gain of this section can be set to zero during the time that the electrical stimulus pulse is present without introducing any additional artifacts and subsequent amplifier stages are not driven into saturation. When the electrical stimulus potential is no longer present or is significantly reduced in amplitude and before the time of receipt of the response signal, the feed-forward amplifier is brought back into the circuit to provide the high gain required to amplify the response signal, which can be measured without interference from saturation of any of the amplifier stages as they recover to baseline.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
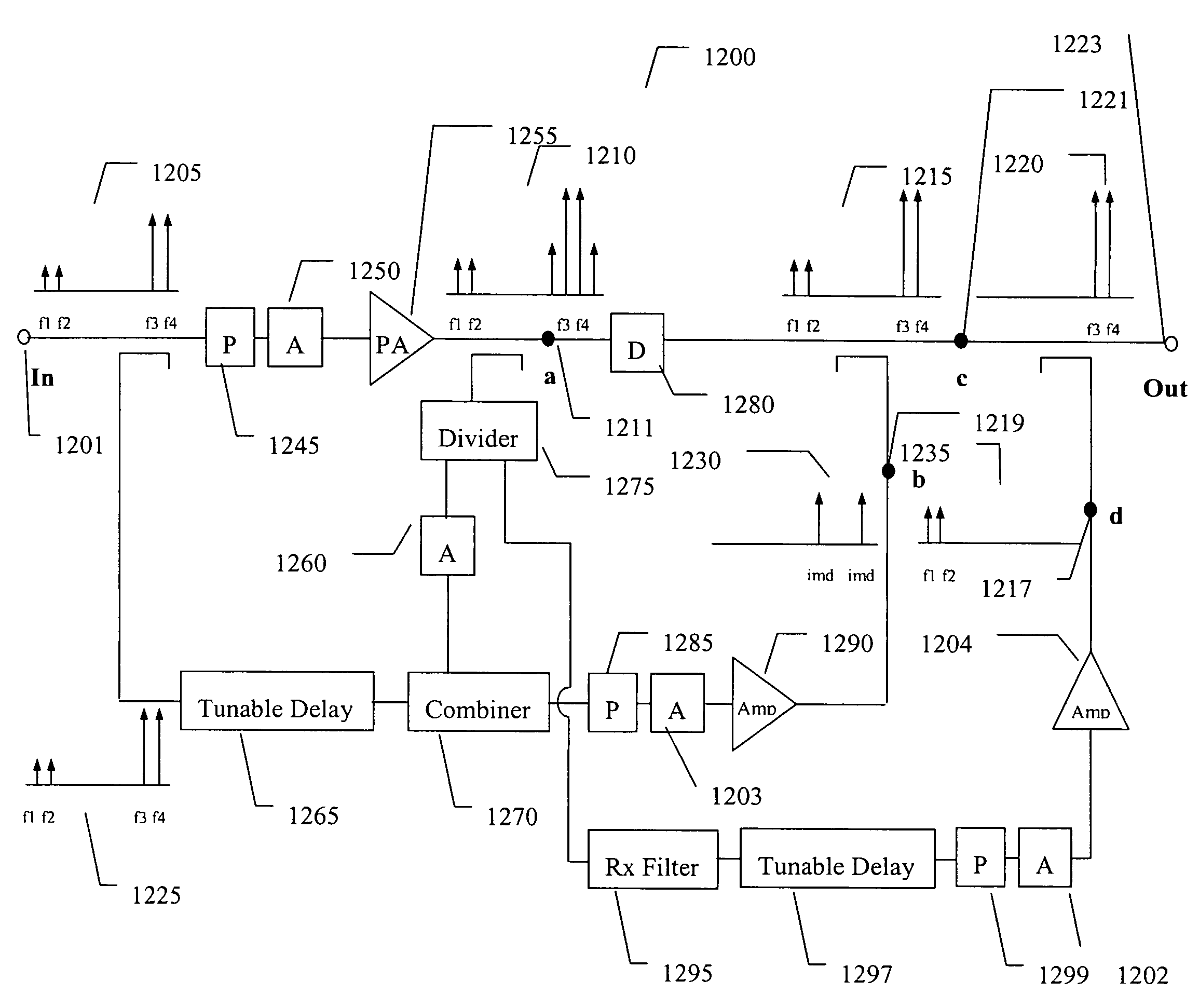
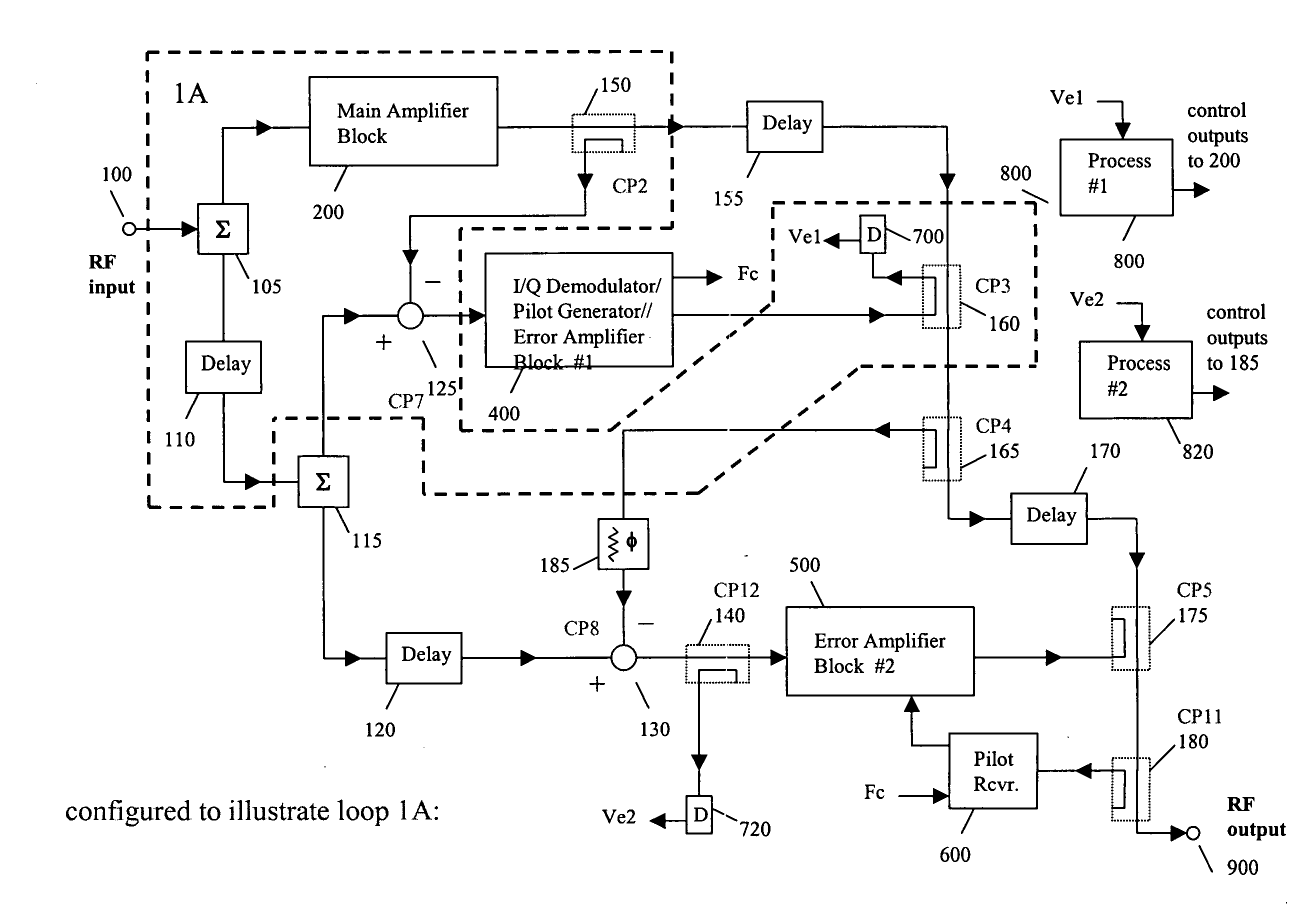
Feed forward amplifier with multiple cancellation loops capable of reducing intermodulation distortion and receive band noise
InactiveUS20060009172A1Reduce distortionReducing receive band noiseSecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksAudio power amplifierDielectric substrate
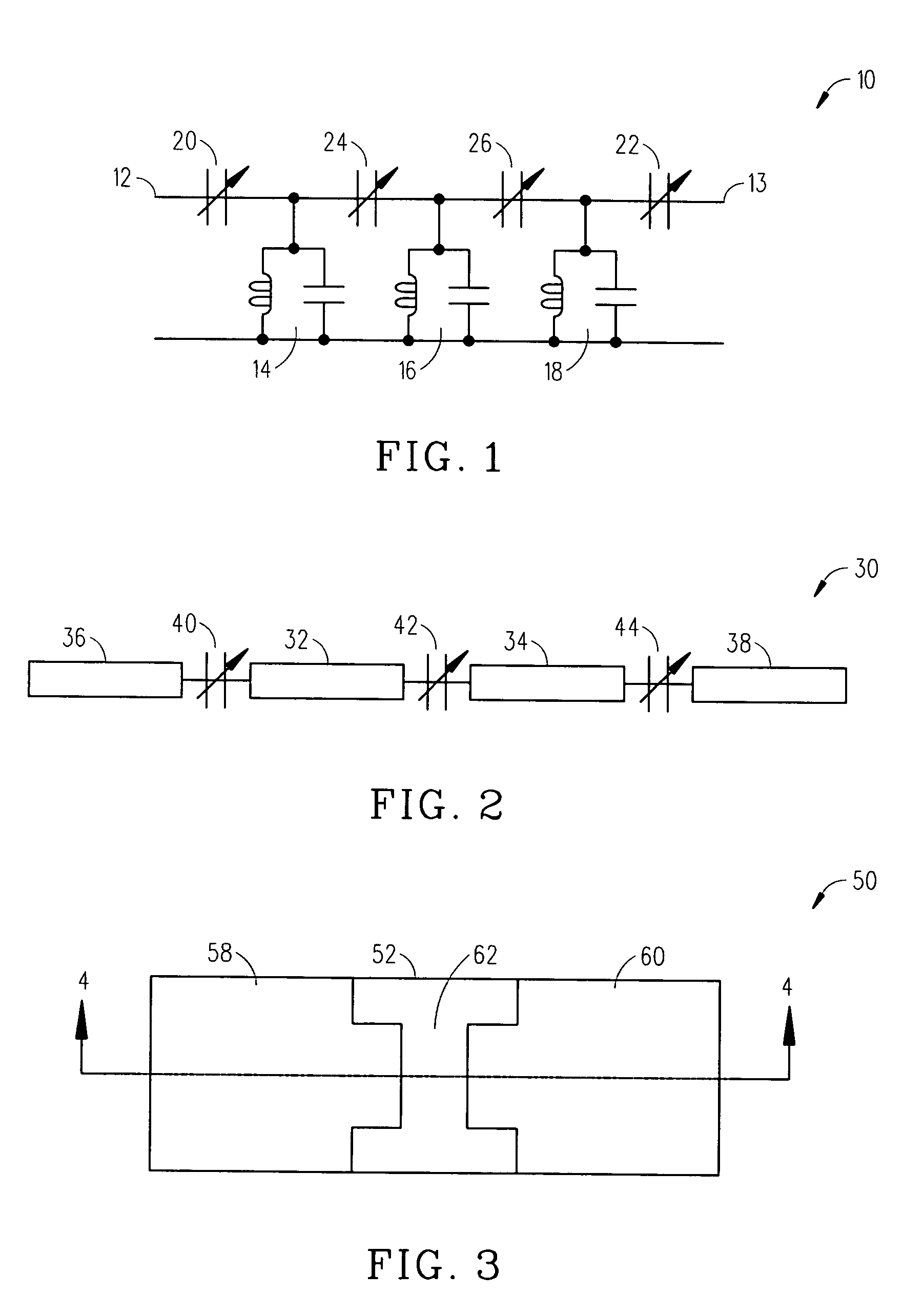
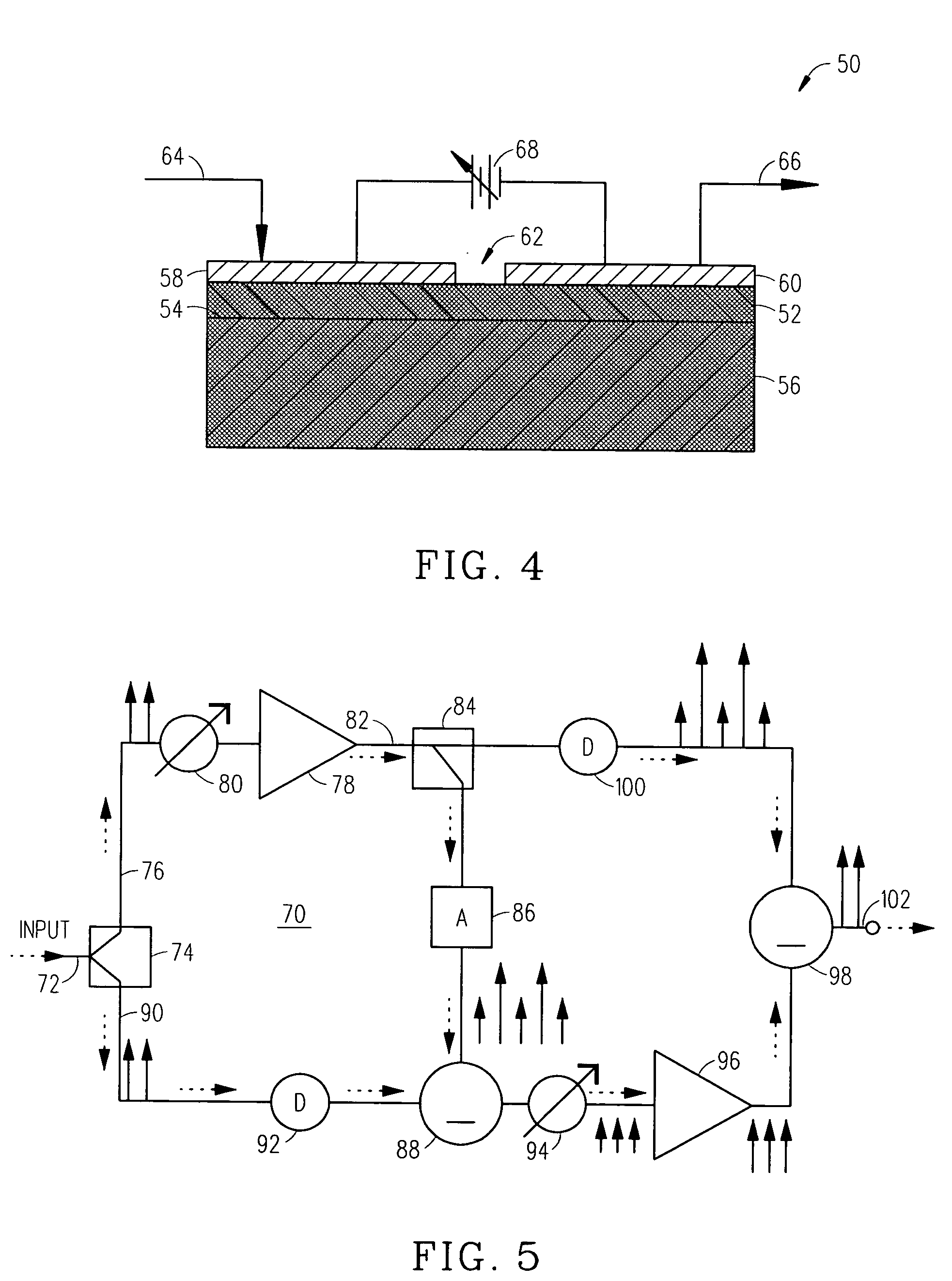
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising a feed forward amplifier capable of receiving an input signal and including a plurality of cancellation loops, wherein at least one of the cancellation loops includes a tunable delay line enabling the reduction of intermodulation distortion and receive band noise when outputs from the plurality of cancellation loops are combined with the input signal to the feed forward amplifier. In an embodiment of the present invention the plurality of cancellation loops may be two cancellations loops and a tunable delay line may be included in both of the cancellation loops. Further, the tunable delay line may be a voltage tunable delay line that includes a voltage tunable dielectric capacitor to facilitate the control of the tunable delay and the voltage tunable dielectric capacitor may include a layer of voltage tunable dielectric material positioned on a surface of a low loss, low dielectric substrate.
Owner:PARATEK MICROWAVE INC
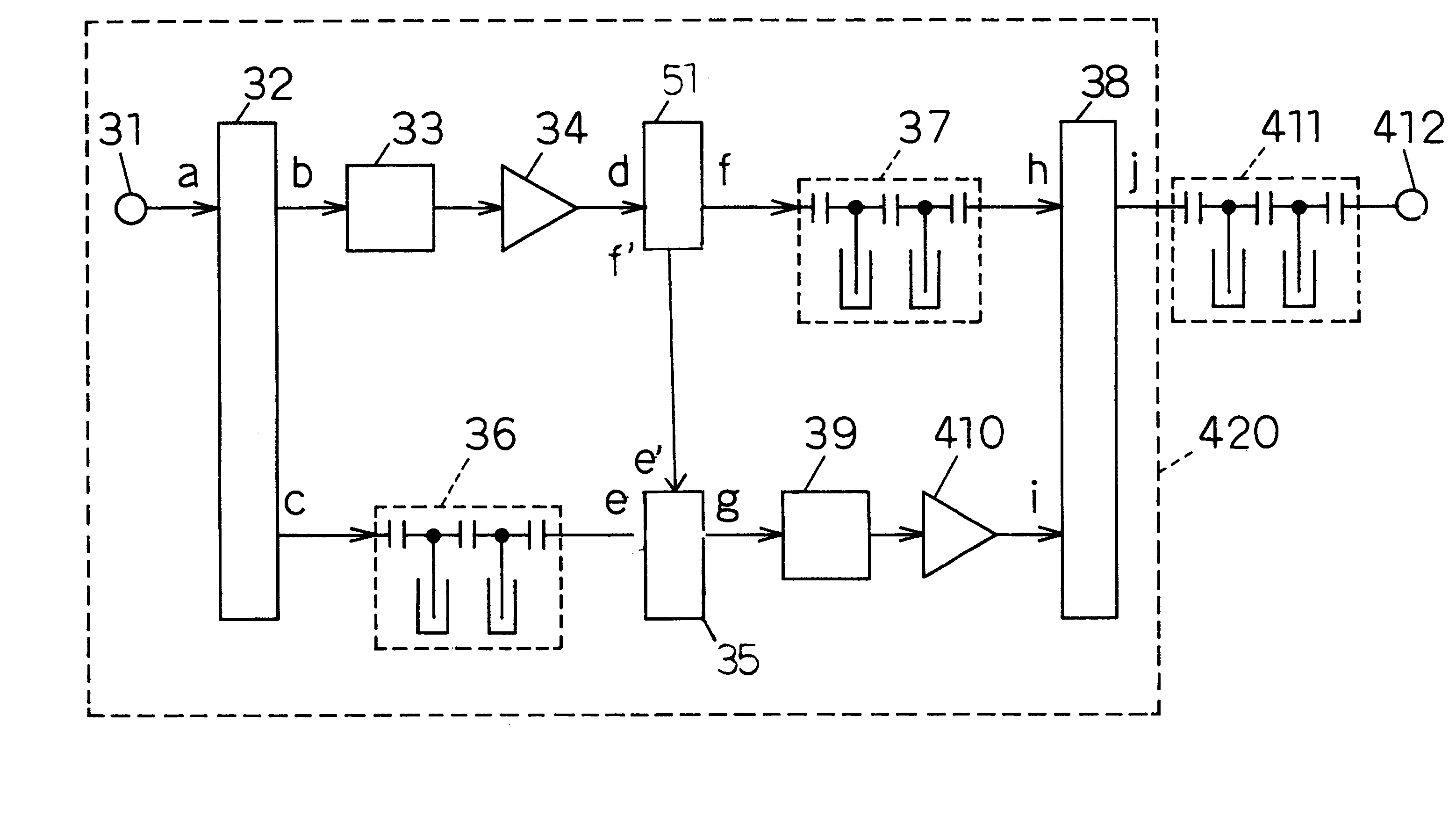
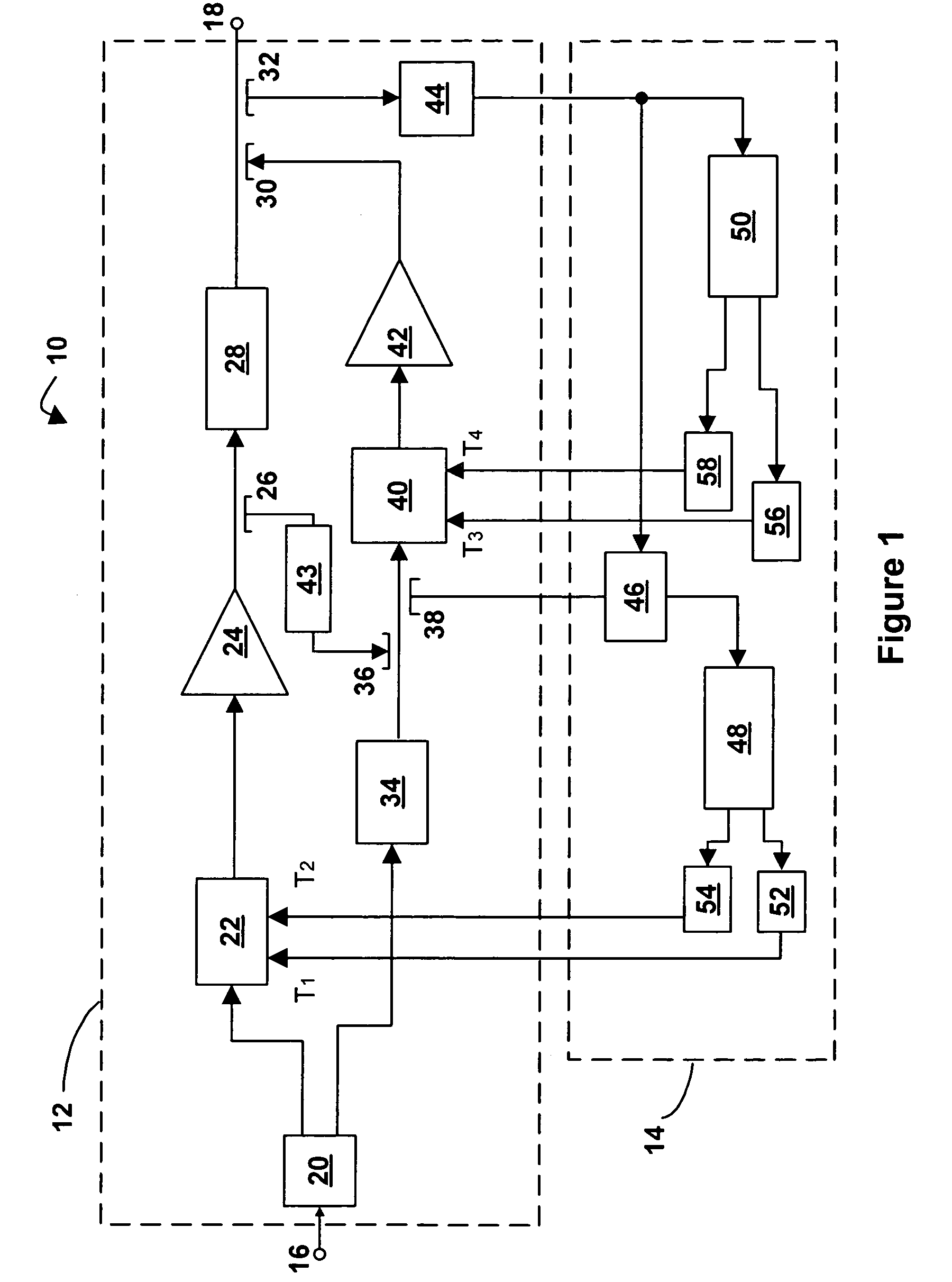
Dual loop feedforward power amplifier
InactiveUS6958647B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
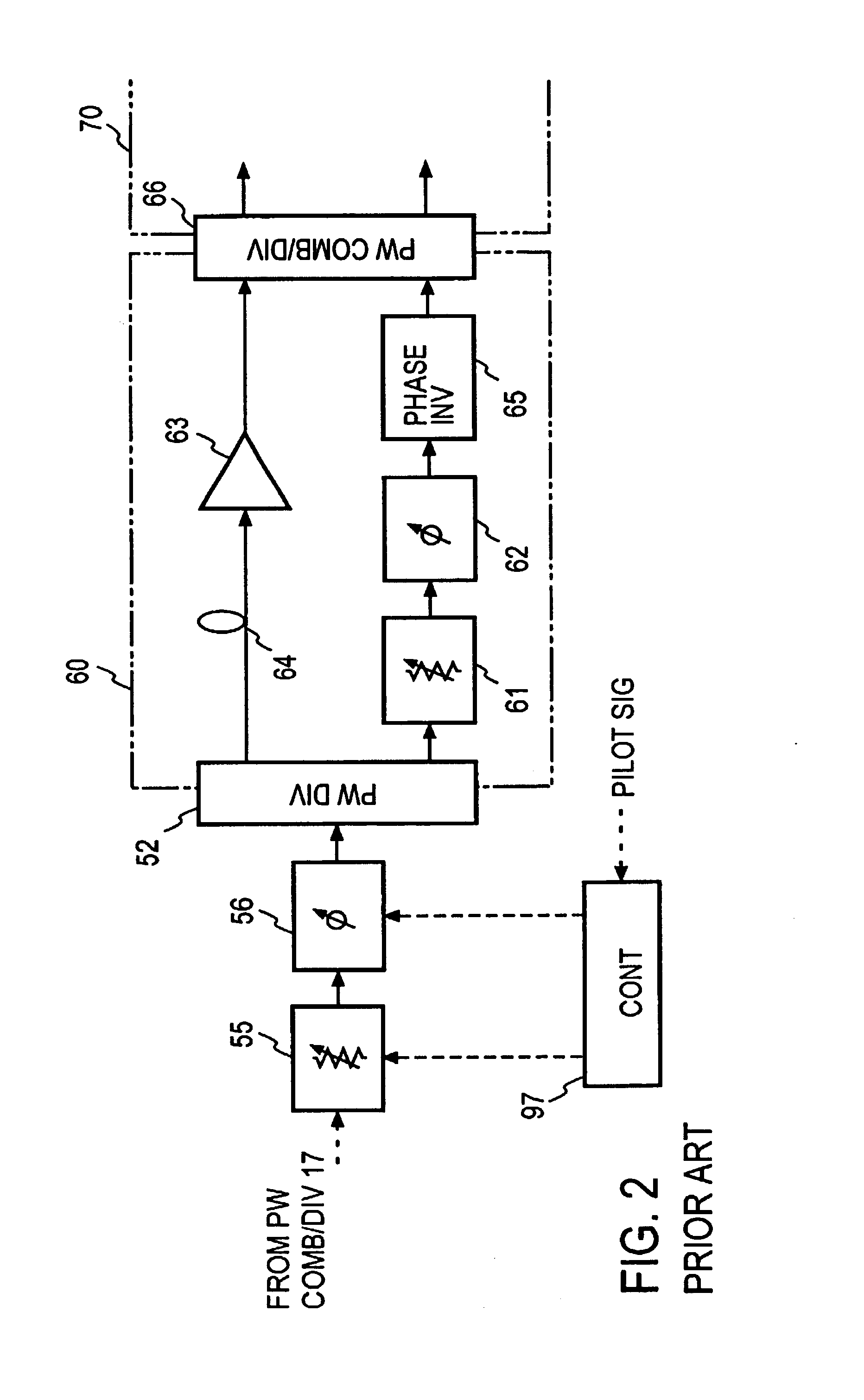
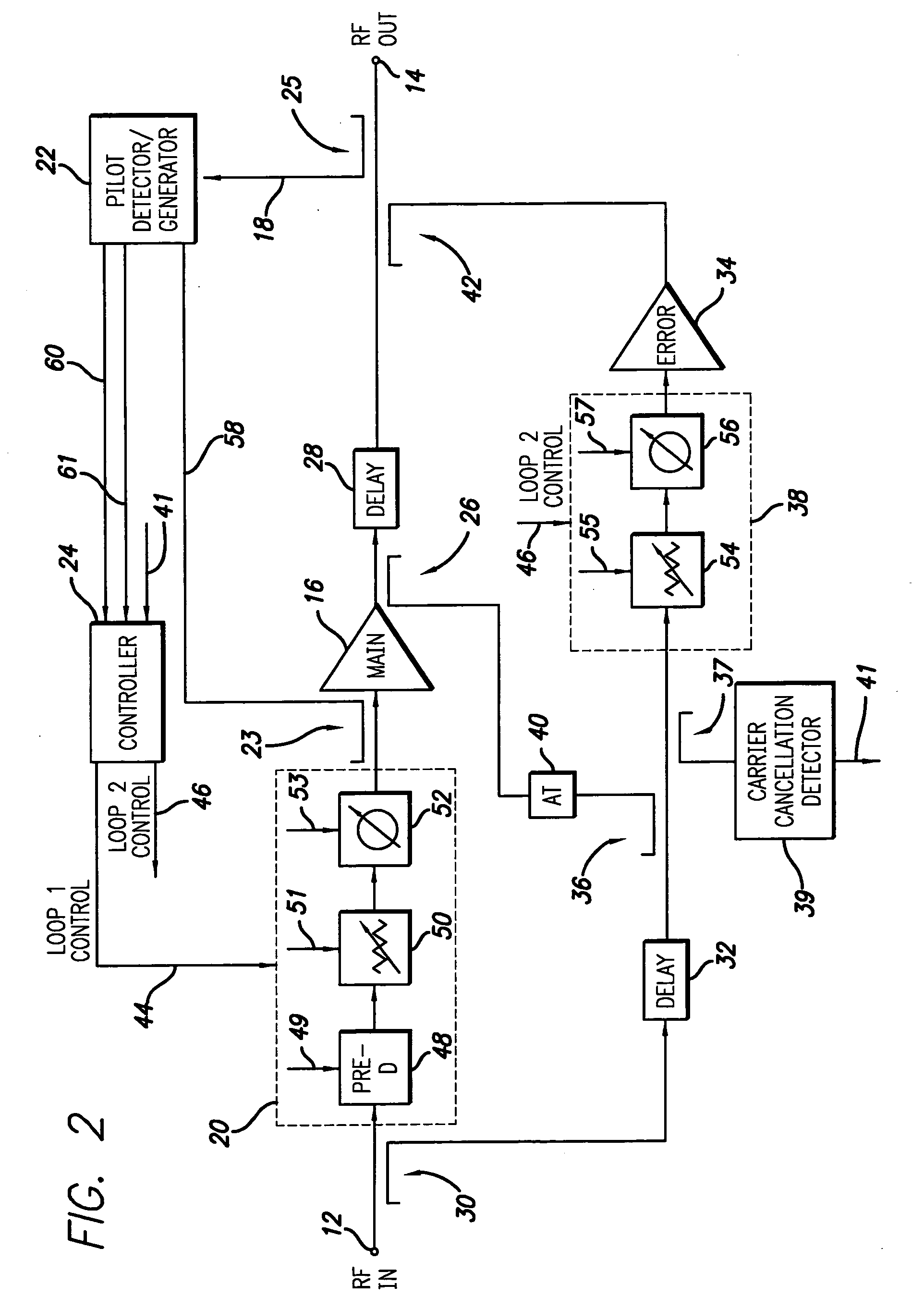
A feedforward amplifier. The present invention therefore provides a feedforward amplifier, comprising: a pilot reference generator that generates a pilot signal; a first carrier cancellation loop; a first error amplifier loop including a first error amplifier, wherein the pilot signal is utilized to provide gain stabilization in the first error amplifier a third loop; a second carrier cancellation loop that includes a first phase and amplitude adjuster in module and a second amplitude and phase adjuster disposed between module and module, wherein the pilot signal is utilized to control the adjustment of the second carrier cancellation loop.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method for controlling adaptive circuits
InactiveUS7218172B2Fast convergenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier with control circuitsPhase shift controlAudio power amplifier
A feed-forward amplifier having a signal cancellation loop including a cancellation node that includes a gain controller and a phase controller. Each controller provides a discrete tap steering signal and modulates the corresponding tap steering signal with a discrete tracer signal that takes on a preselected sequence of values. The sequence chosen so that the tracer signal is mutually orthogonal to each other tracer signal over a preselected period. A gain and phase adjuster connected to the outputs of the controllers provides a controlled gain change and phase shift in the signal cancellation loop, the magnitude of the gain change and phase shift controlled by the corresponding tap steering signals presented to the gain and phase adjuster by the controllers. A detector, the input of which is connected to the cancellation node and the output of which is connected to the controllers, outputs a measure of the envelope of the signal at the cancellation node. After the preselected period new values for the tap steering signals presented to the gain and phase adjuster by the controllers are obtained by multiplying detector output by the respective tracer signal, each over the respective preselected period, summing each resulting series of values, and changing the tap steering signals to be modulated and presented to the gain and phase adjuster in accordance with the values of the respective sums.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
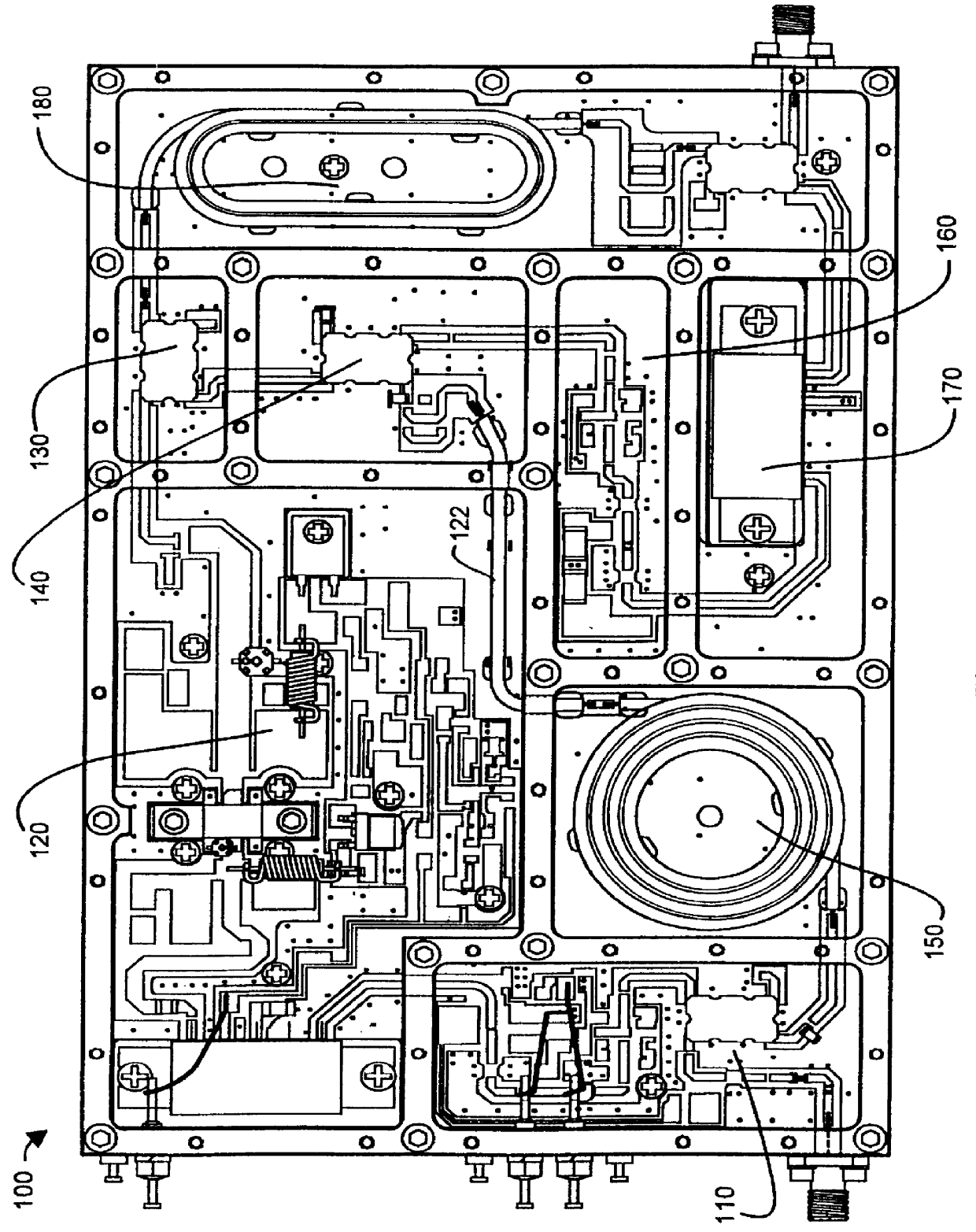
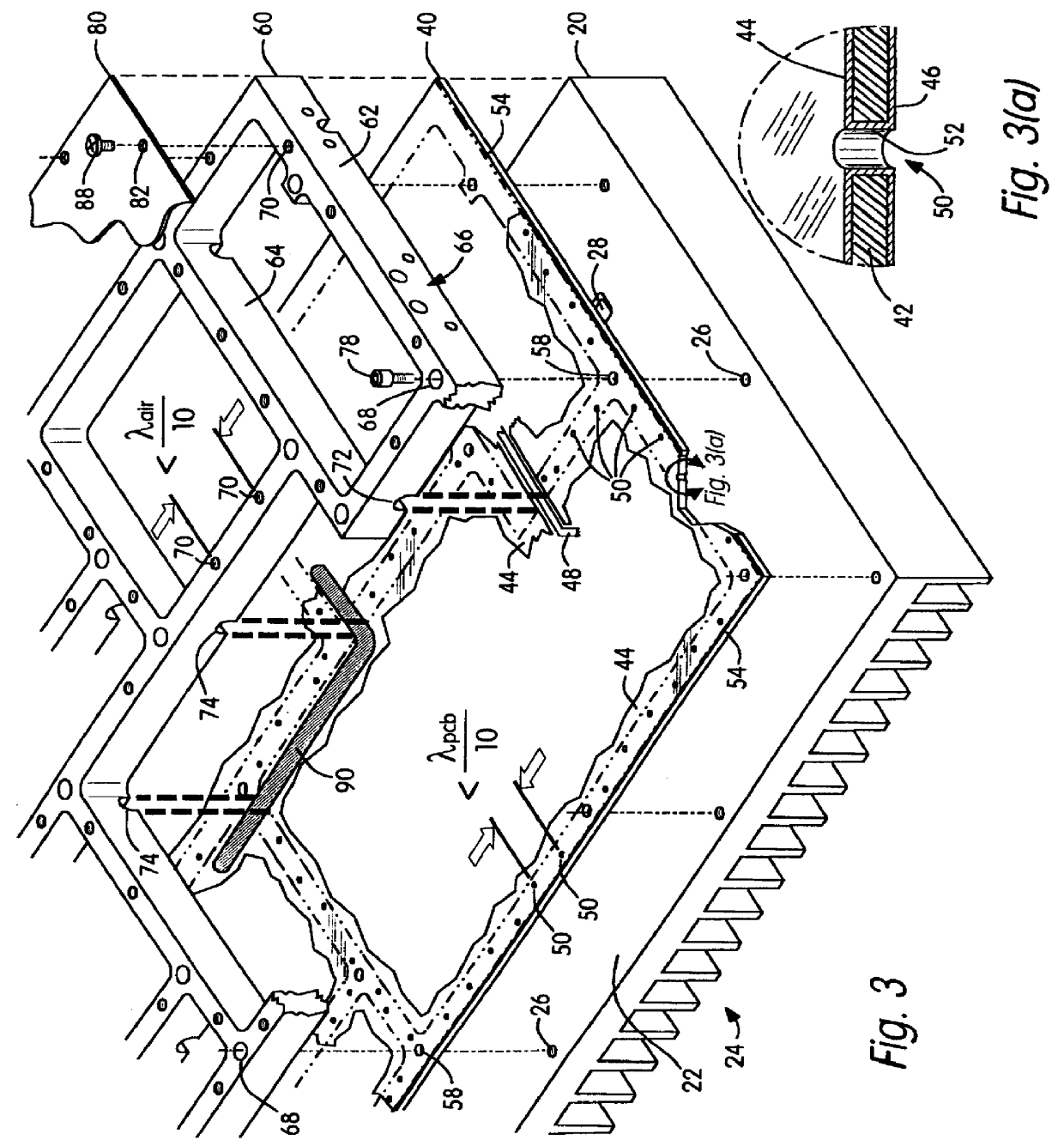
Feedforward amplifier manufacturing module
InactiveUS6094350ASimple and cost-effective assemblyReduce RF LeakageSubstation/switching arrangement detailsDetails with feedforward amplifierAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
A manufacturing module for an RF feed-forward amplifier subsystem that allows for simple and cost-effective assembly, yet provides separate compartments for the different stages of the subsystem, with low RF leakage between the compartments is disclosed. The manufacturing module comprises a printed circuit board having one or more circuit trace layers, and ground planes covering a substantial portion of the top and bottom surfaces. The printed circuited board also has numerous plated-through holes electrically connecting the top and bottom ground planes. The circuit board is sandwiched between a heatsink having a flat upper surface and a machined enclosure having an outer wall and inner divider walls. The plated-through holes, space less than +E,fra 1 / 10+EE wavelength of module's highest carrier frequency apart, serve to electrically connect the heatsink to the machined enclosure, thus creating separate compartments with low RF leakage.
Owner:AML COMM
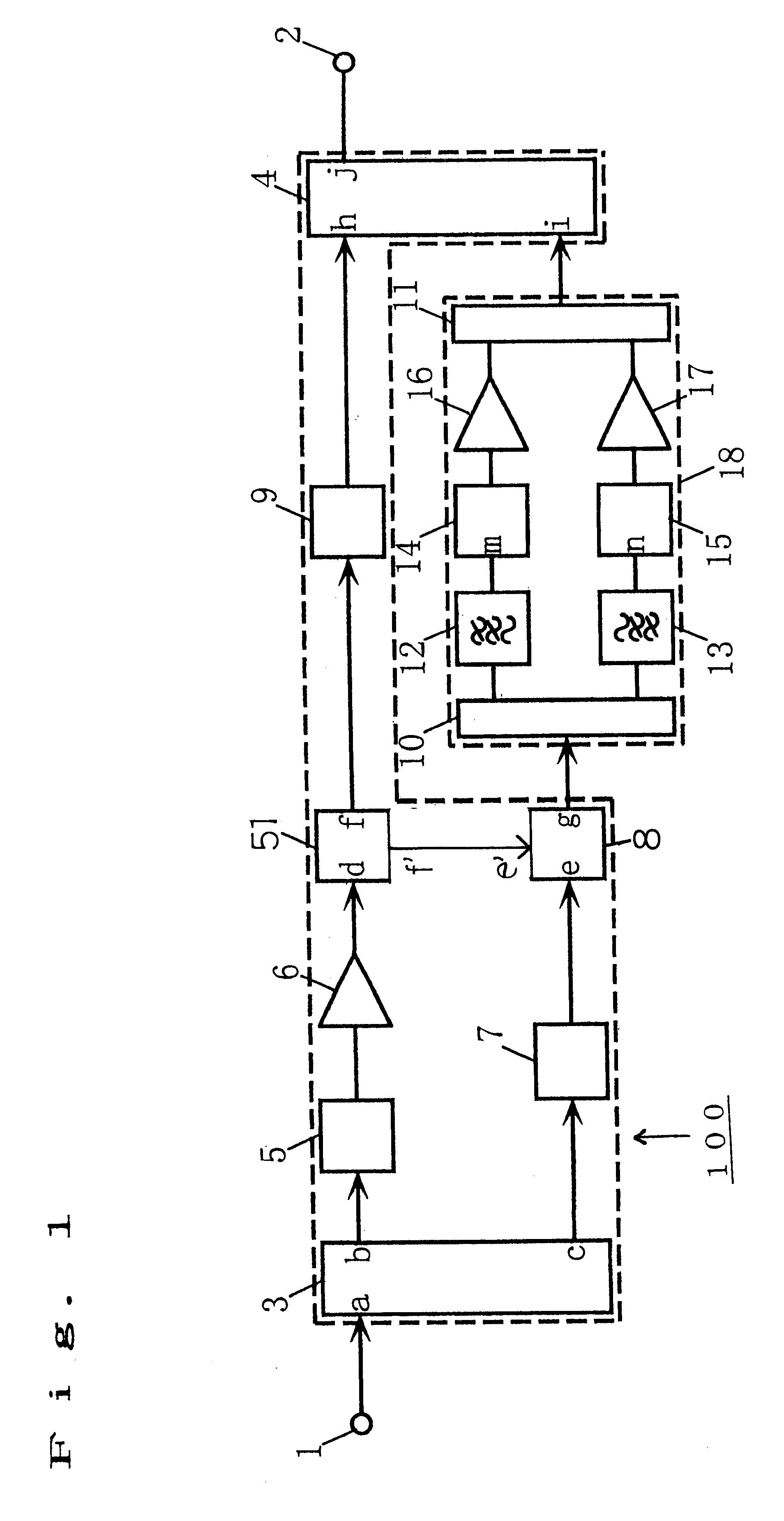
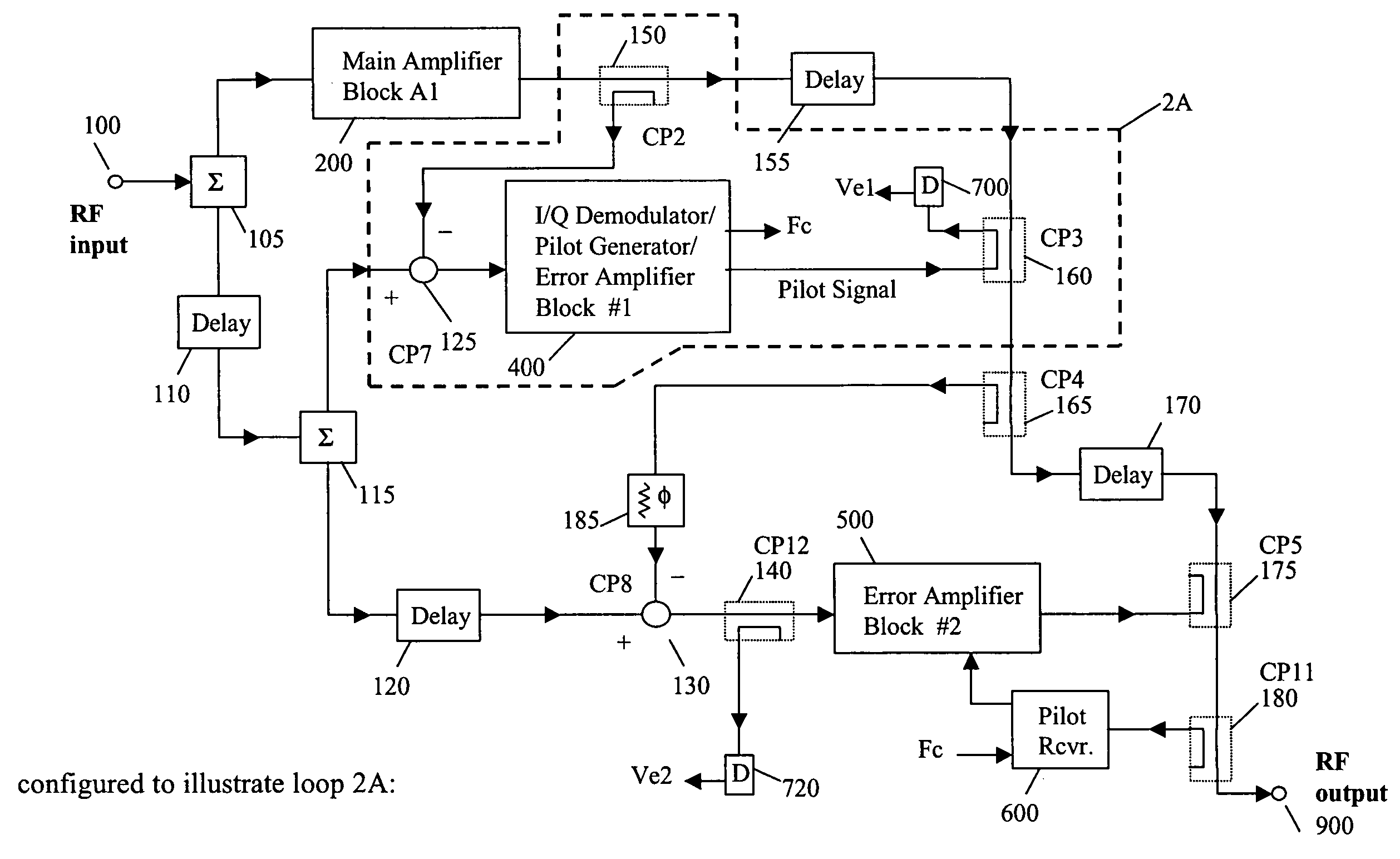
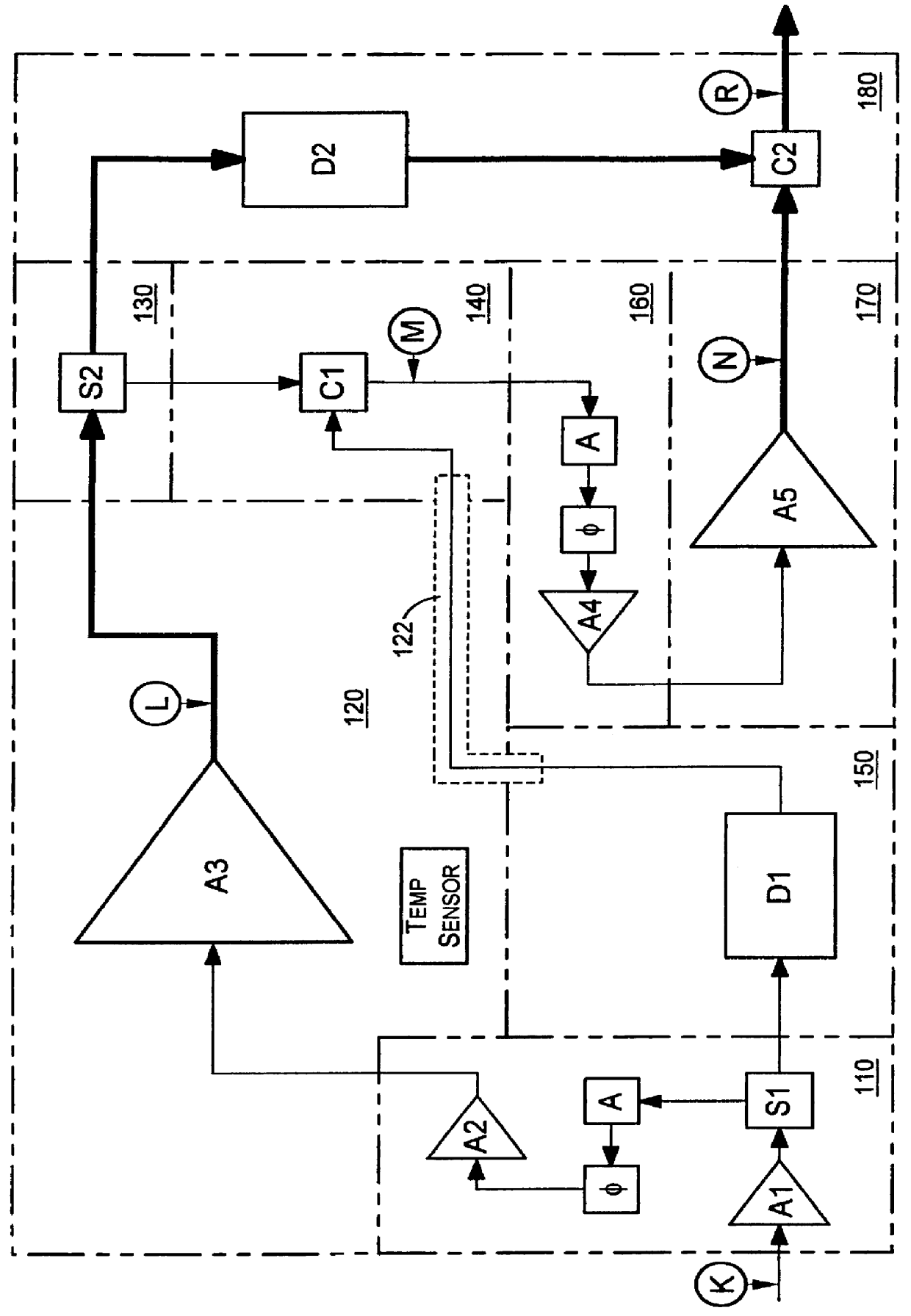
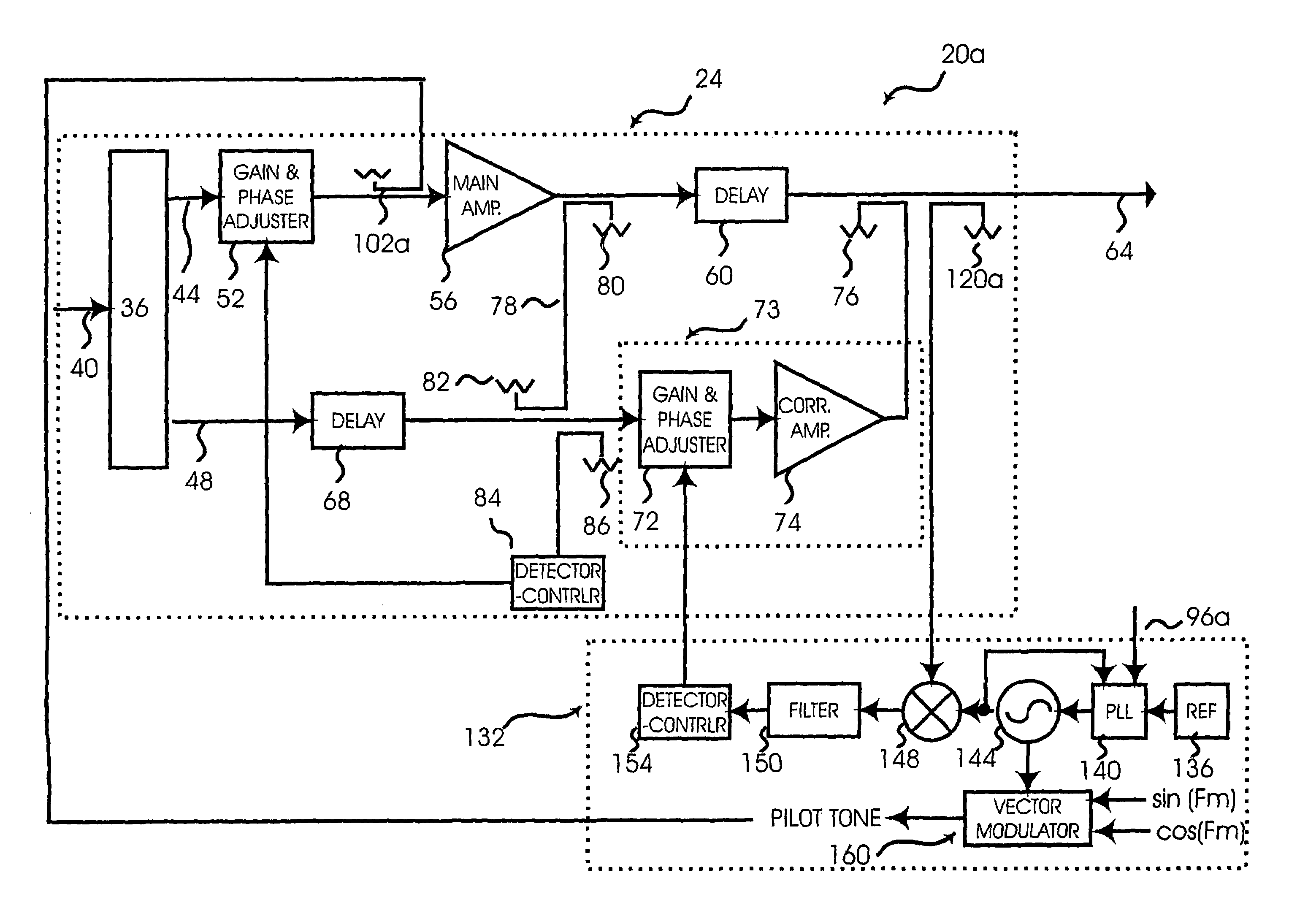
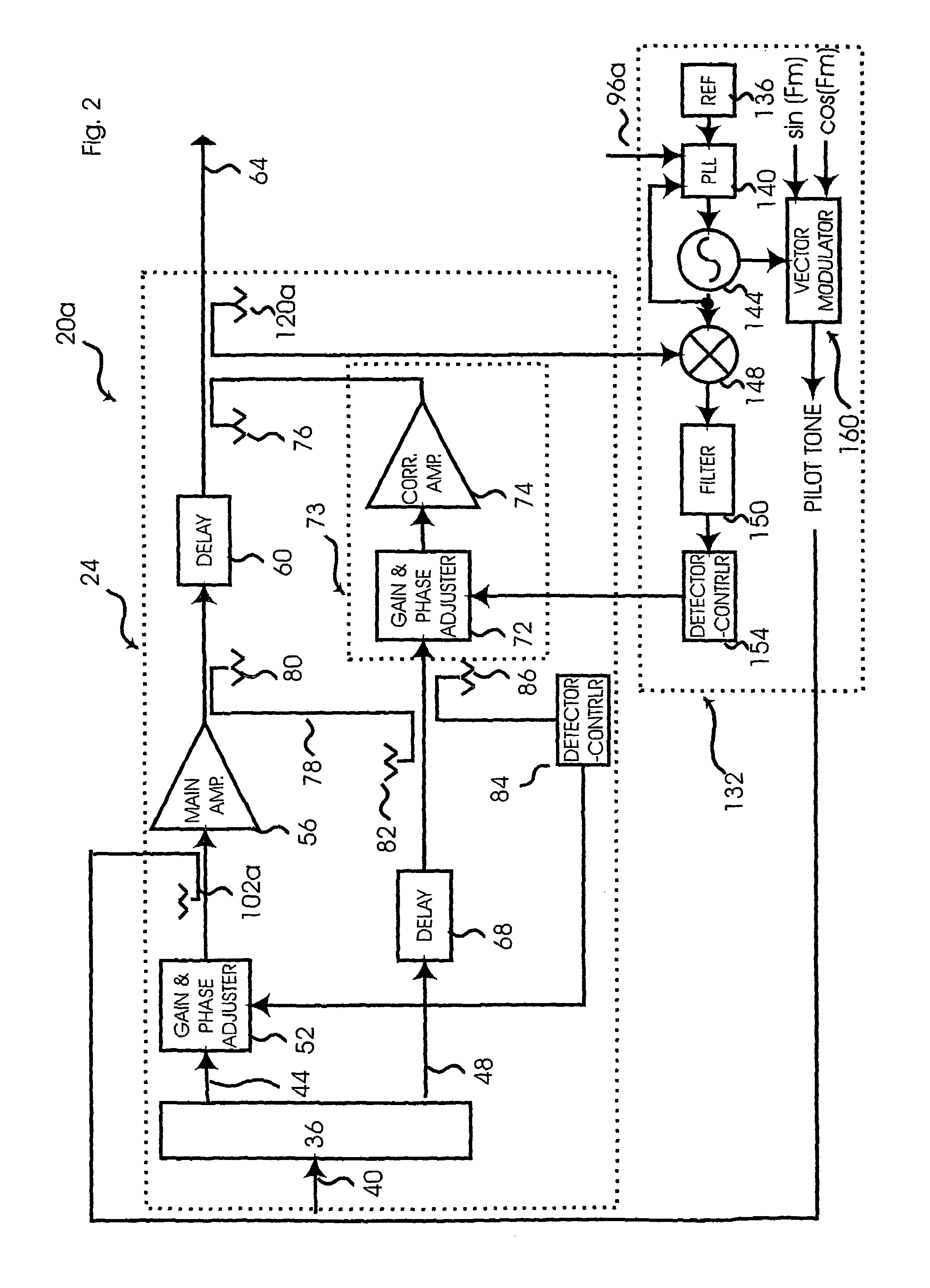
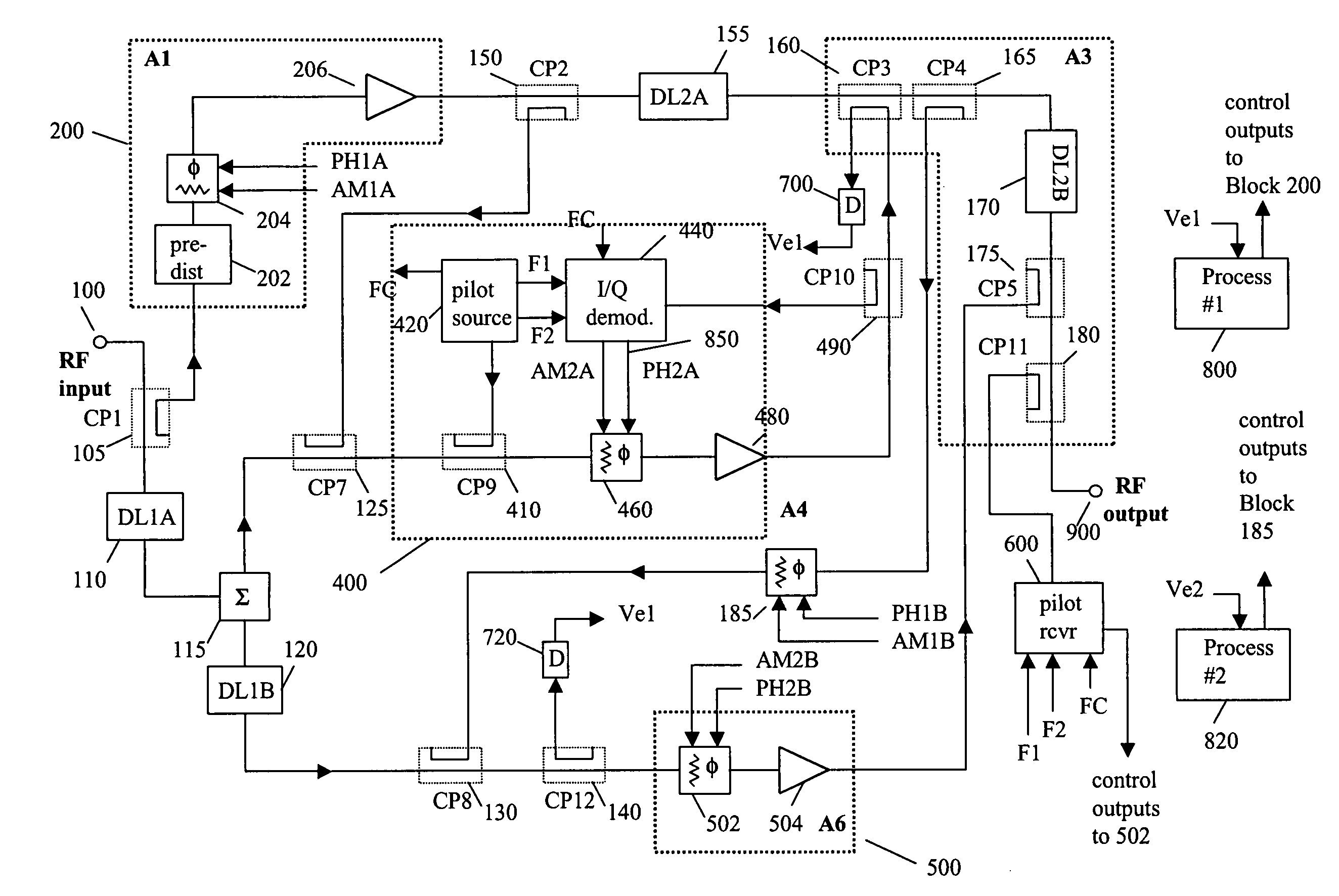
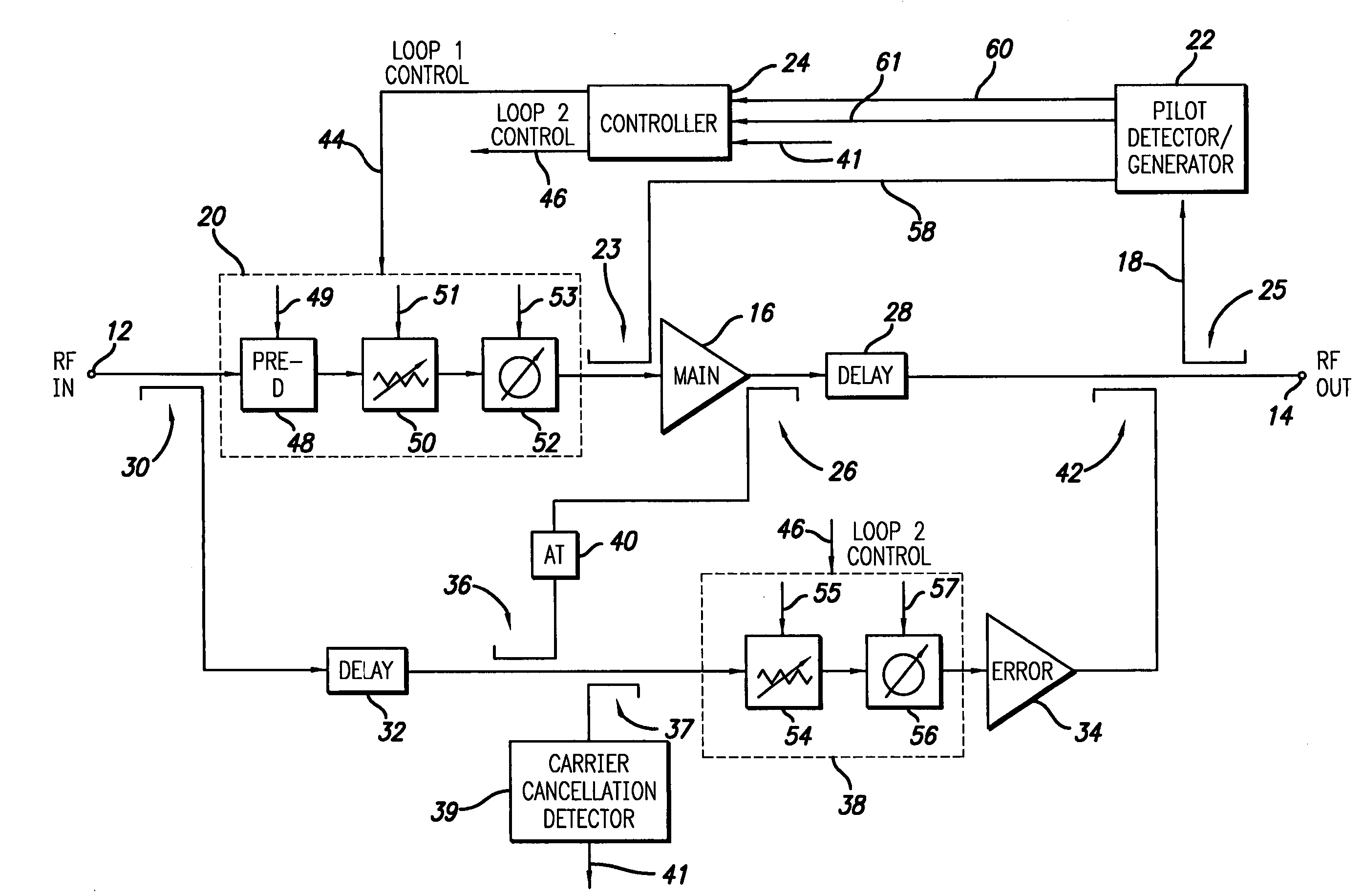
System and method of pilot tone reuse in a feedforward amplifier
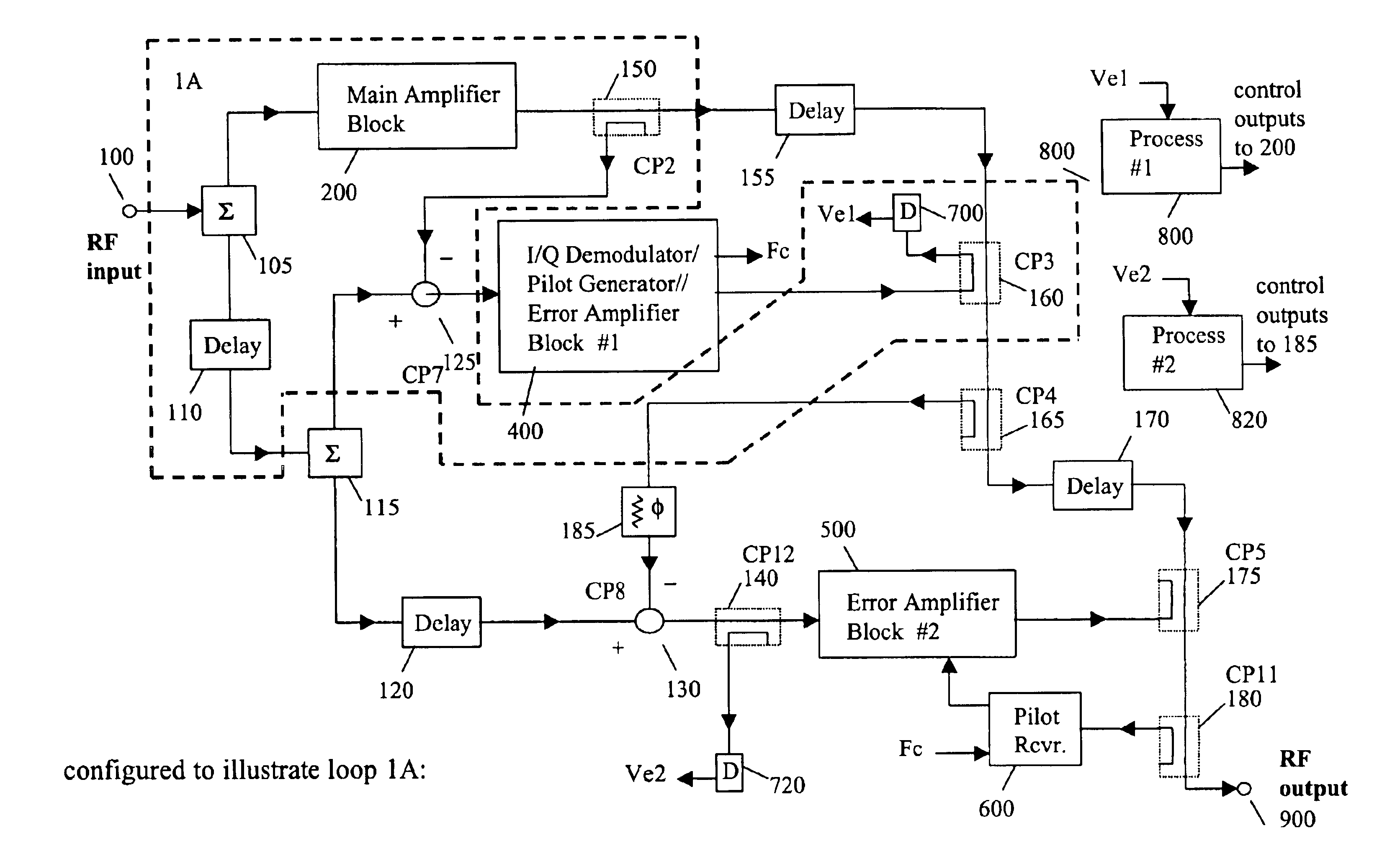
ActiveUS20050110567A1Cancel intermodulation distortionReduce distortion problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierRadio frequency signal
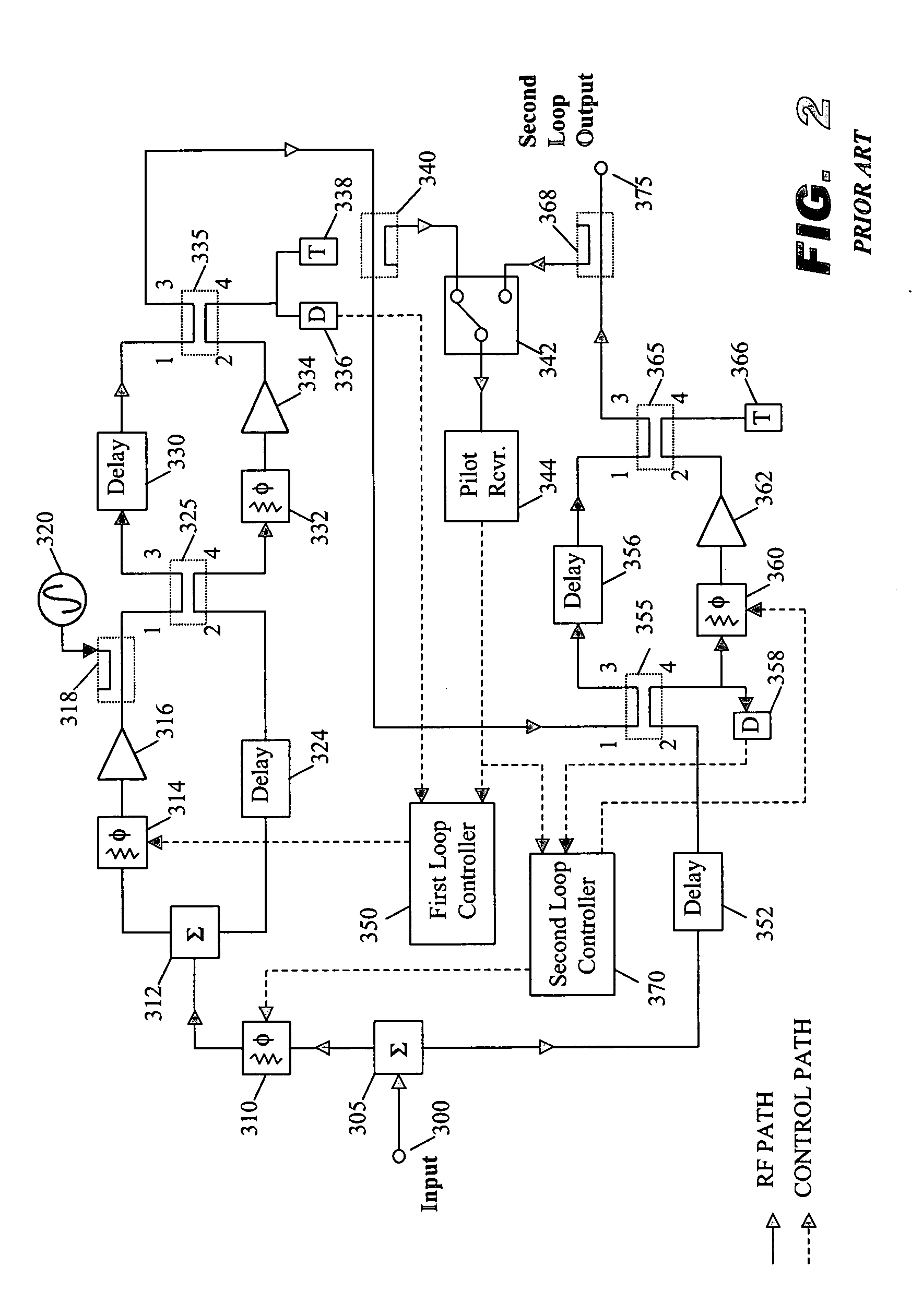
A system and method of pilot tone reuse. The present invention therefore provides a feedforward amplifier, comprising: an input that accepts a radio frequency signal having multiple carriers; a first control loop including a main amplifier block and a detector, wherein the first control loop generates a first carrier cancelled signal; a second control loop including a pilot generator, I / Q demodulator, vector modulator and first error amplifier block, wherein the pilot generator, I / Q demodulator and first error amplifier block amplify the first carrier cancelled signal and generates a pilot signal; a third control loop comprising a vector modulator and a second carrier cancellation detector; and a fourth control loop comprising of vector modulator, a second error amplifier block, and a pilot signal receiver for receiving the pilot signal generated by the pilot generator in the second error amplifier block such that the pilot signal is reused by the fourth control loop to thereby further cancel intermodulation distortion in the output of the main amplifier block.
Owner:INTEL CORP
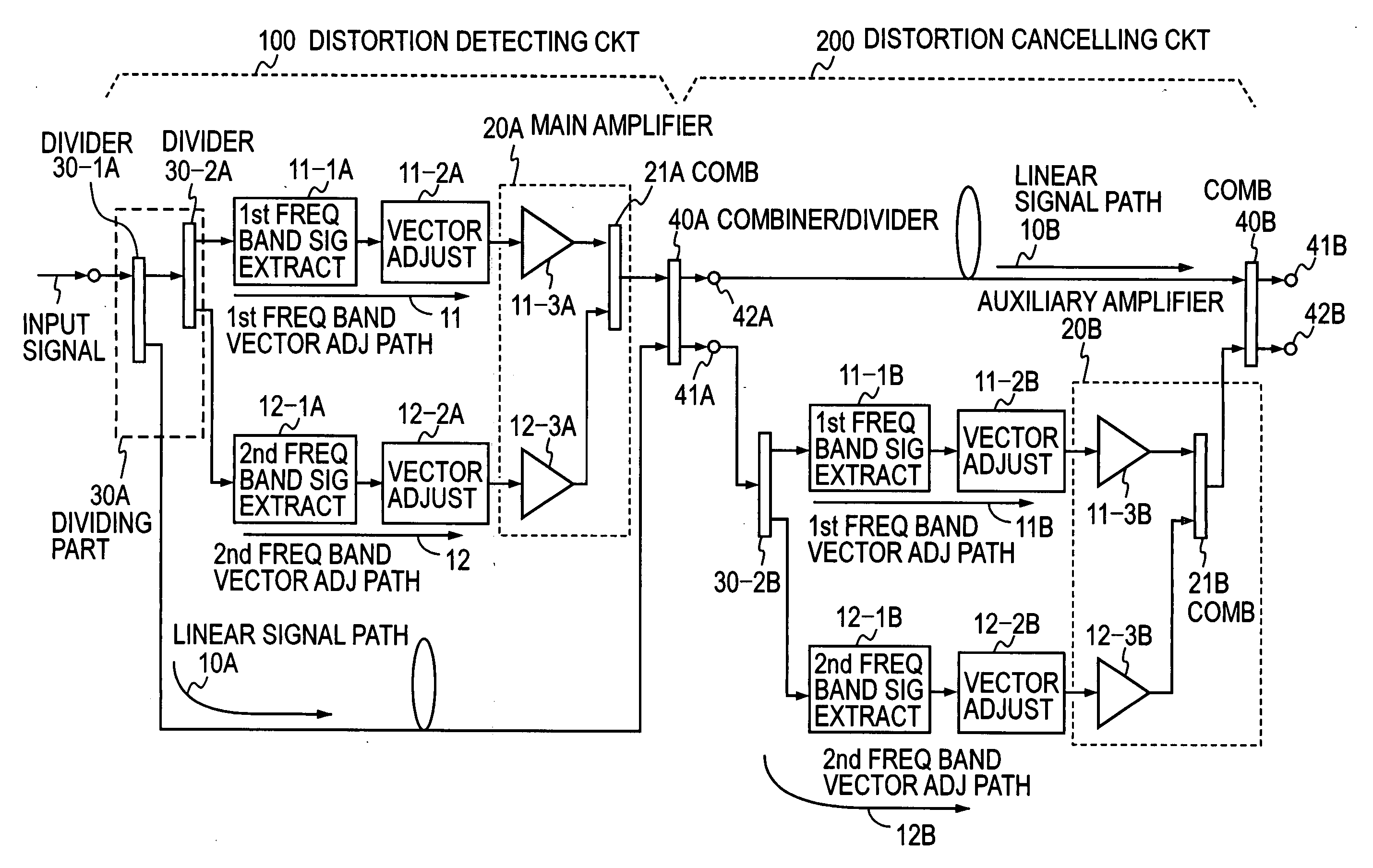
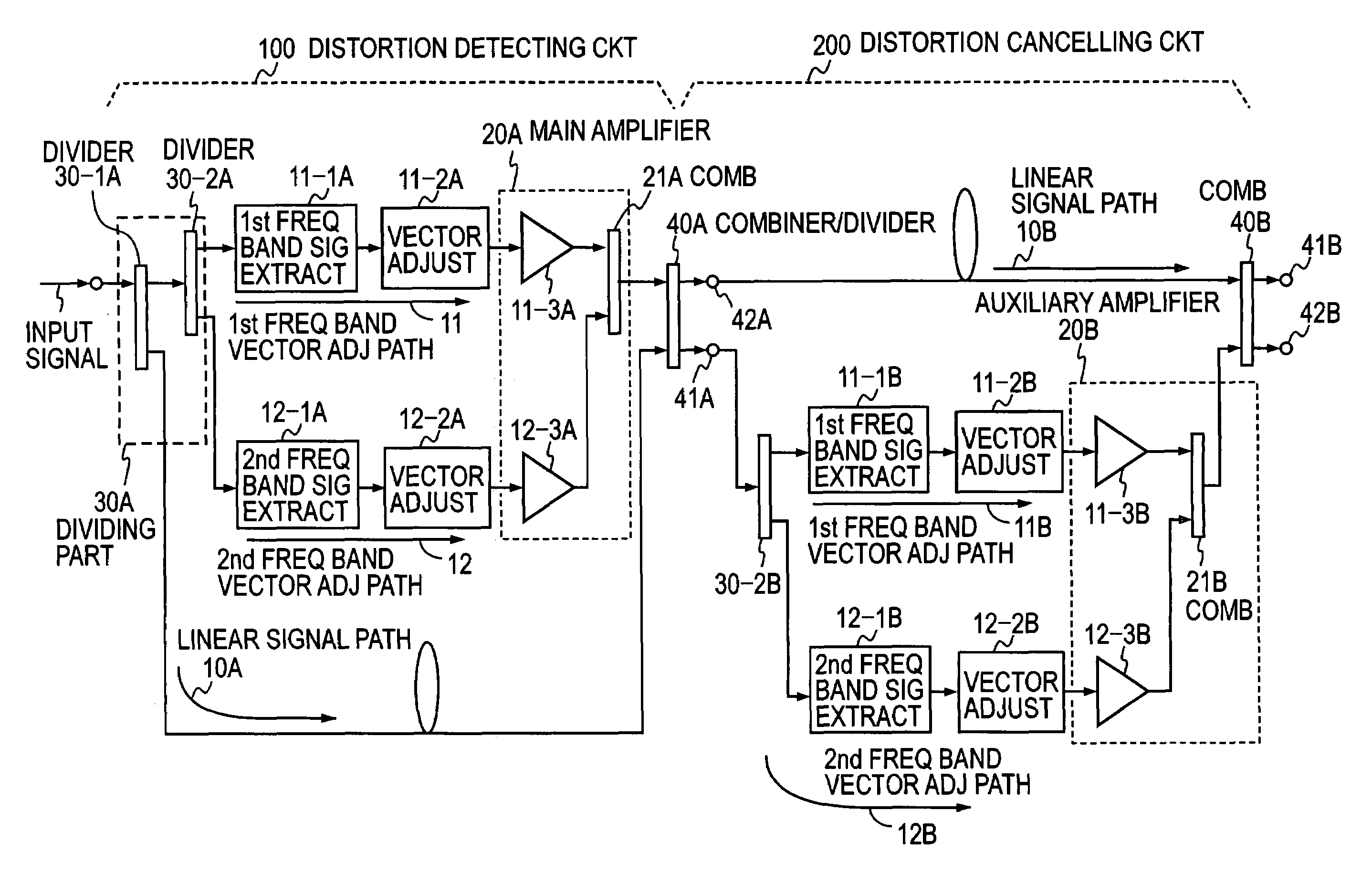
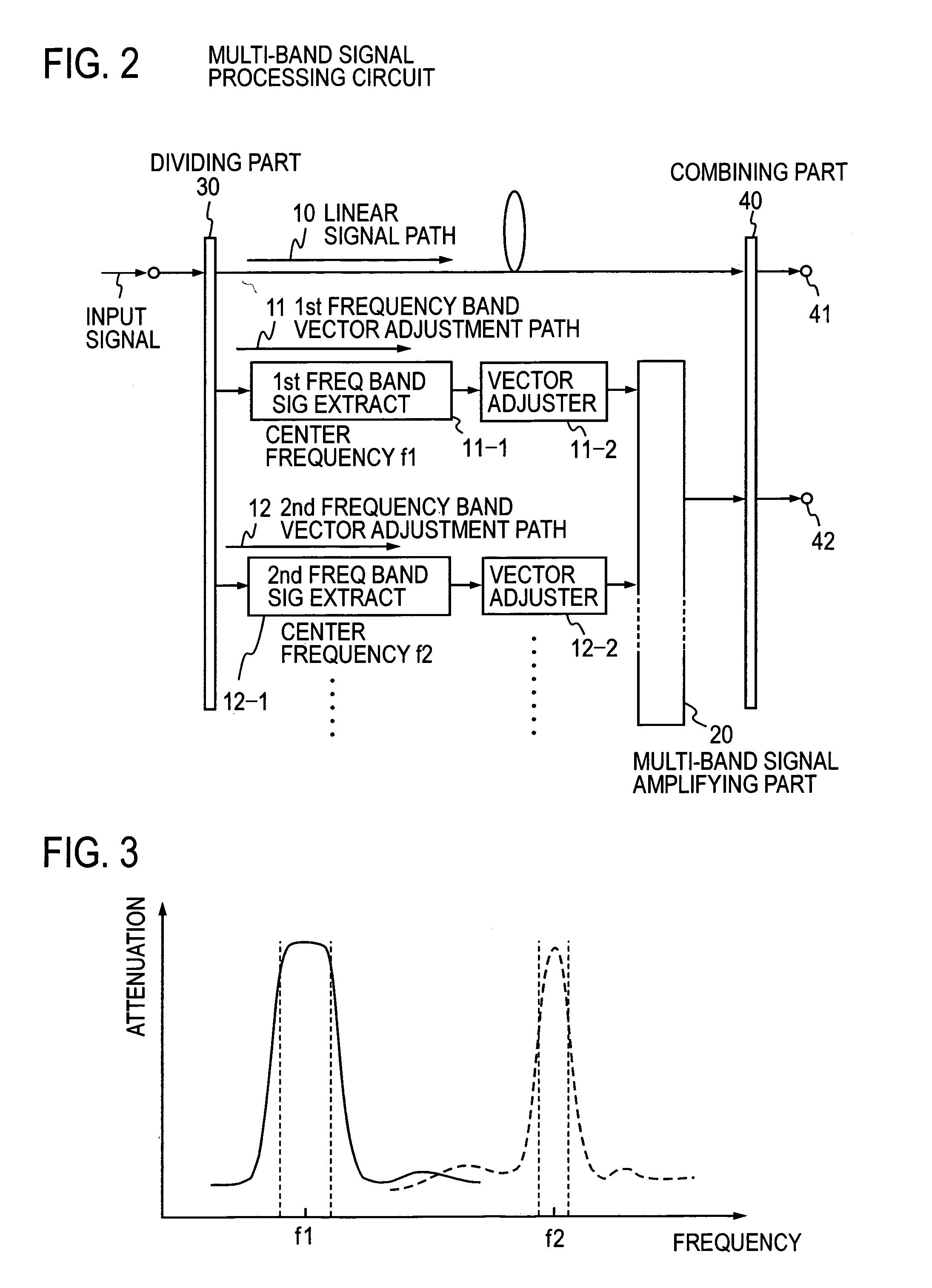
Multi-band feed-forward amplifier and adjustment method therefor
InactiveUS20050163254A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A multi-band feed-forward amplifier is formed by: a dividing part for dividing and applying an input signal containing signals of multiple frequency bands to a linear signal path and N vector adjustment paths of a distortion detecting circuit; frequency band signal extractors provided in the N vector adjustment paths, respectively, for extracting signals of N frequency bands; N vector adjusters for adjusting the vectors of the output signals from the respective frequency band signal extractors; a main amplifier for amplifying the output signals from the N vector adjusters; a combining / dividing part for combining the amplified signals and the signal from the linear signal path of the distortion detecting circuit and for dividing and applying the combined output to a linear signal path and N distortion injection paths of a distortion cancelling circuit; frequency band signal extractors provided in the N distortion injection paths, respectively, for extracting the signals of the N frequency bands; vector adjusters for adjusting the vectors of signals separated into the N frequency bands; an auxiliary amplifying part for amplifying the vector-adjusted N signals; and a combining part for combining the amplified signals and the signal from the linear signal path of the distortion cancelling circuit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
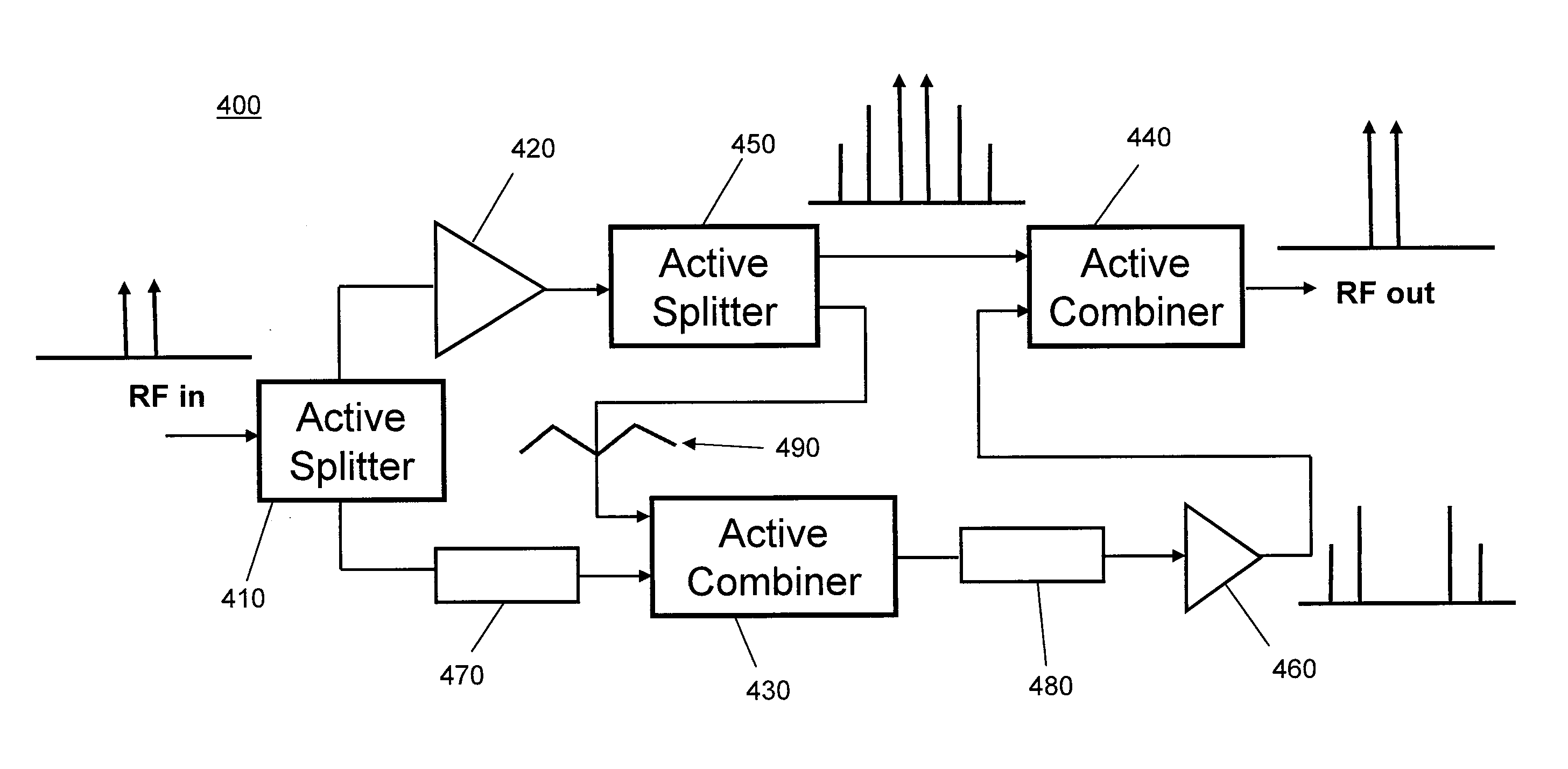
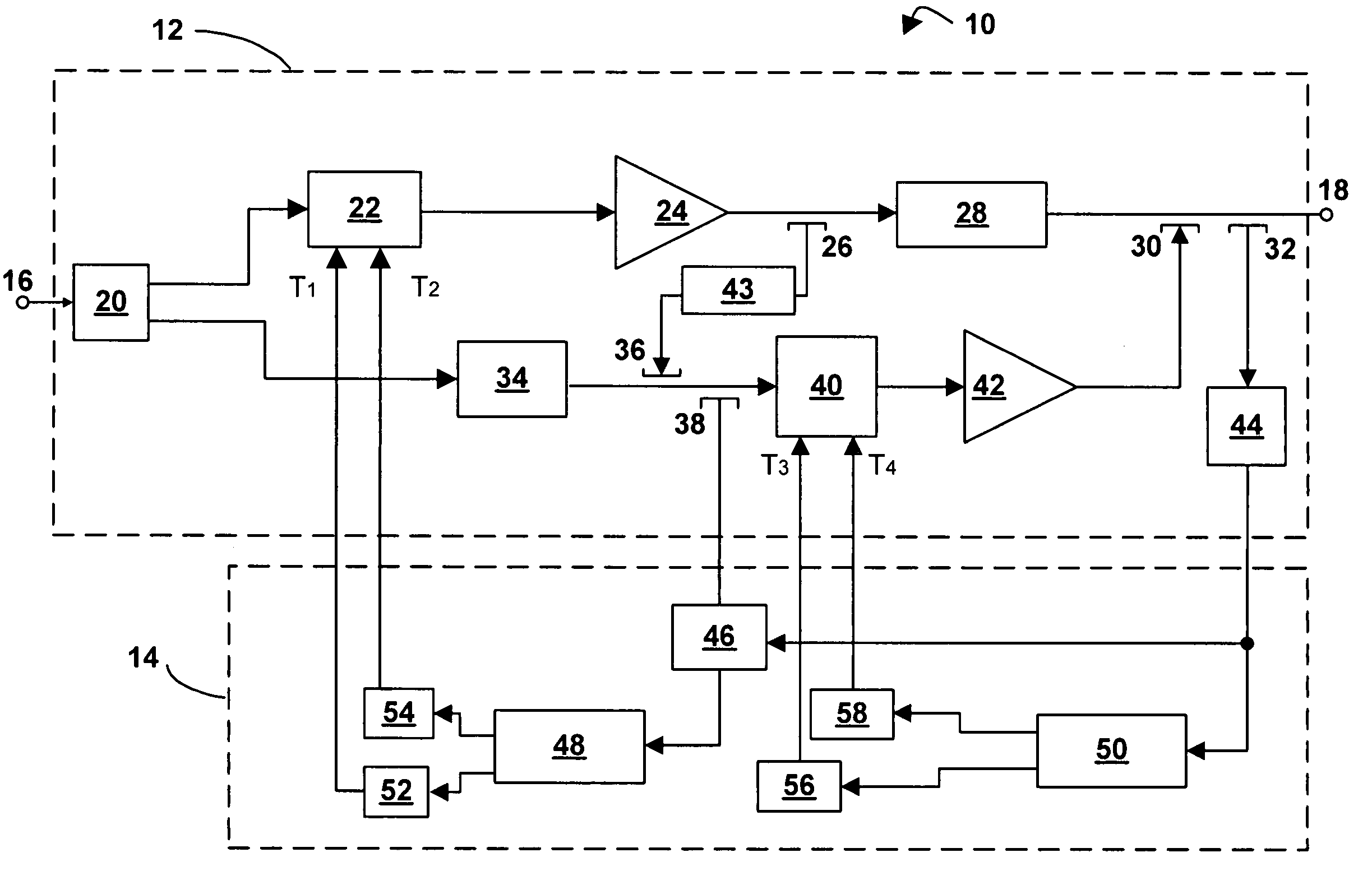
Active feed forward amplifier
ActiveUS8030998B2PerformanceSize andAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierTime delays
An exemplary embodiment of the feed forward amplifier replaces traditional distributed directional couplers, splitters, and delay lines. Moreover, an exemplary feed forward amplifier architecture combines active implementations of RF couplers, power splitters, and / or time delay elements in a novel fashion allowing for ultra-compact size and broadband performance. In an exemplary embodiment, a feed forward amplifier has a main amplifier path and an error amplifier path. The feed forward amplifier comprises a main amplifier in the main amplifier path, and at least one active vector generator in the error amplifier path. The at least one active vector generator is configured to adjust the phase and amplitude of an error amplifier path signal and an error amplifier is configured to receive the adjusted error amplifier path signal. Furthermore, the adjusted error amplifier path signal and an amplified signal are combined to form the output signal of the feed forward amplifier.
Owner:VIASAT INC
High-frequency amplifier, feed-forward amplifier and distortion compensating amplifier
InactiveUS6894562B2Reduce distortion problemsImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
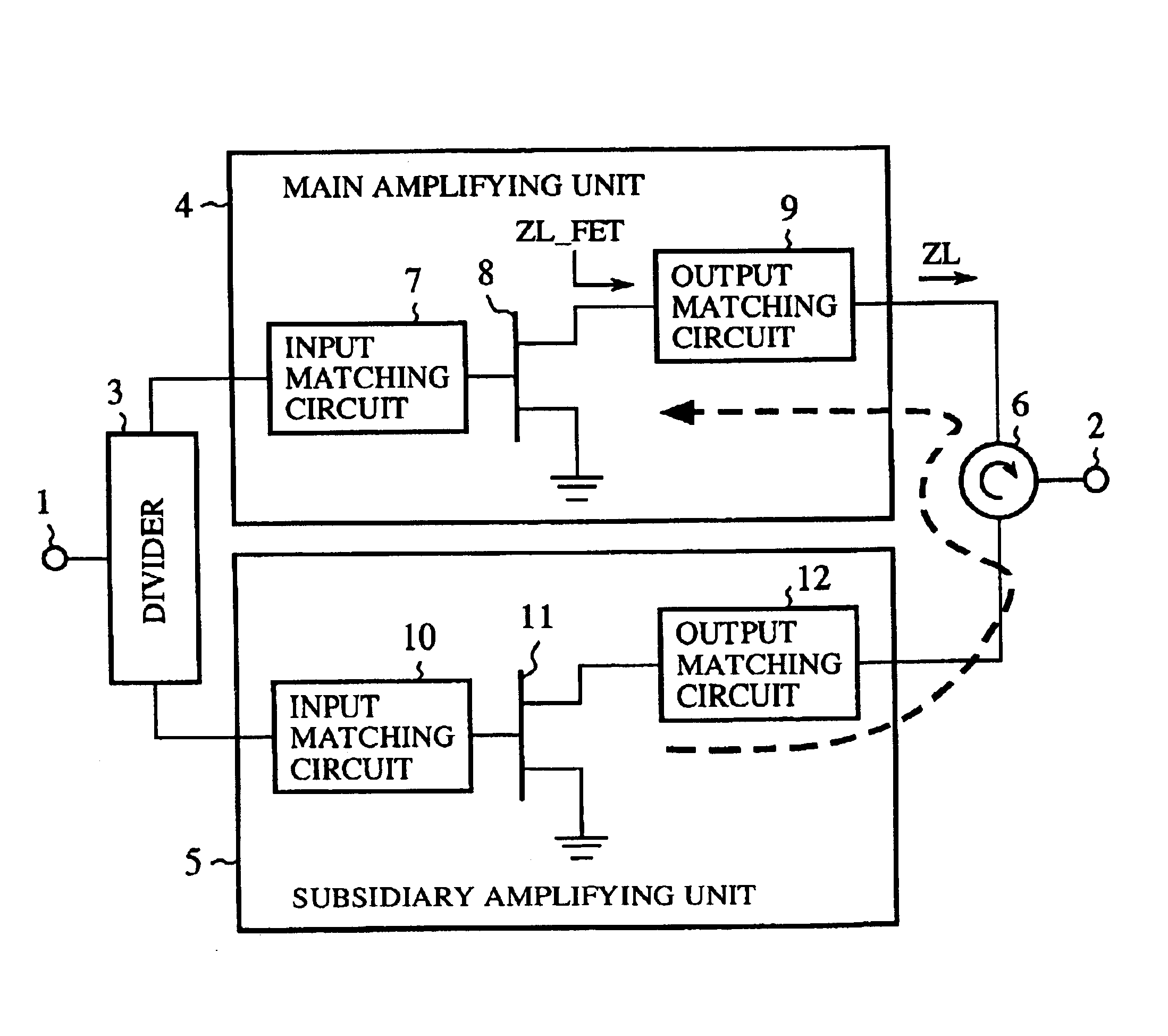
A divider 3 for dividing and distributing a high-frequency signal input from an input terminal 1 to two output sides, a main amplifying unit 4, connected to one output side of the divider 3, for amplifying one high-frequency signal output from the divider 3, a subsidiary amplifying unit 5, connected to the other output side of the divider 3, for performing no operation in case of a low instantaneous electric power of the other high-frequency signal output from the divider 3 and amplifying the other high-frequency signal in case of a high instantaneous electric power of the other high-frequency signal and a circulator 6 for injecting the high-frequency signal amplified in the subsidiary amplifying unit 5 into the output side of the main amplifying unit 4 and injecting the high-frequency signal amplified in the main amplifying unit 4 into an output terminal 2 are arranged.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Feedforward amplifier circuitry
InactiveUS6774716B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
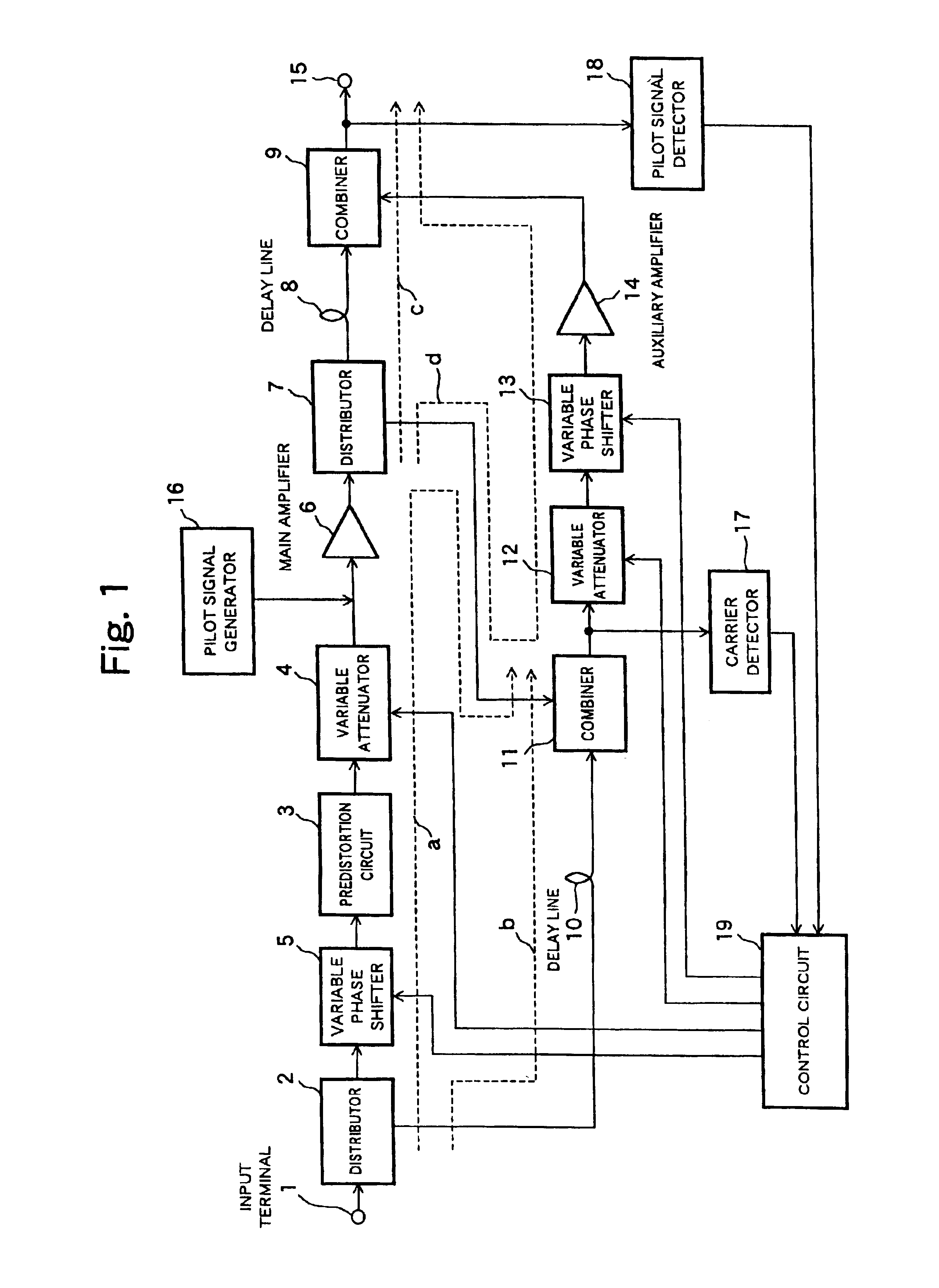
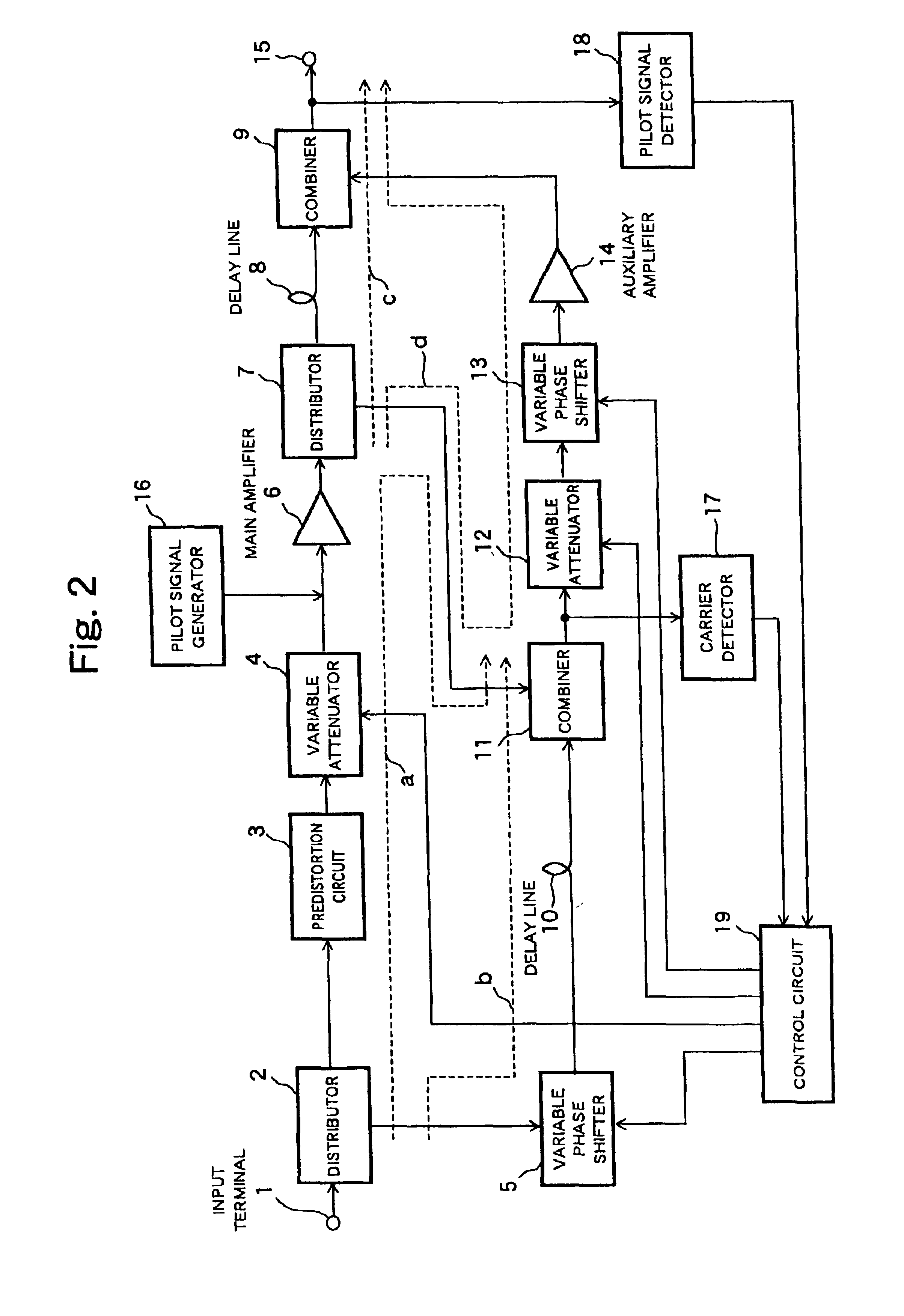
The present invention is intended to provide a feedforward amplifier circuitry which is capable of changing a location or placement of each section constituting the feedforward circuitry, in particular a feedforward amplifier circuitry which is capable of changing an interposing location of a variable phase shifter. In the feedforward amplifier circuitry, a variable phase shifters (5, 12) can be disposed on a location other than a post-stage of a predistortion circuits (3, 20), as a result of which it is advantageously possible to provide a designer with more flexibility in changing the locations of variable shifters, regardless of the conventional arrangement of the variable phase shifters disposed on the post-stages of the distortion circuits, when the feedforward amplifier is actually designed.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
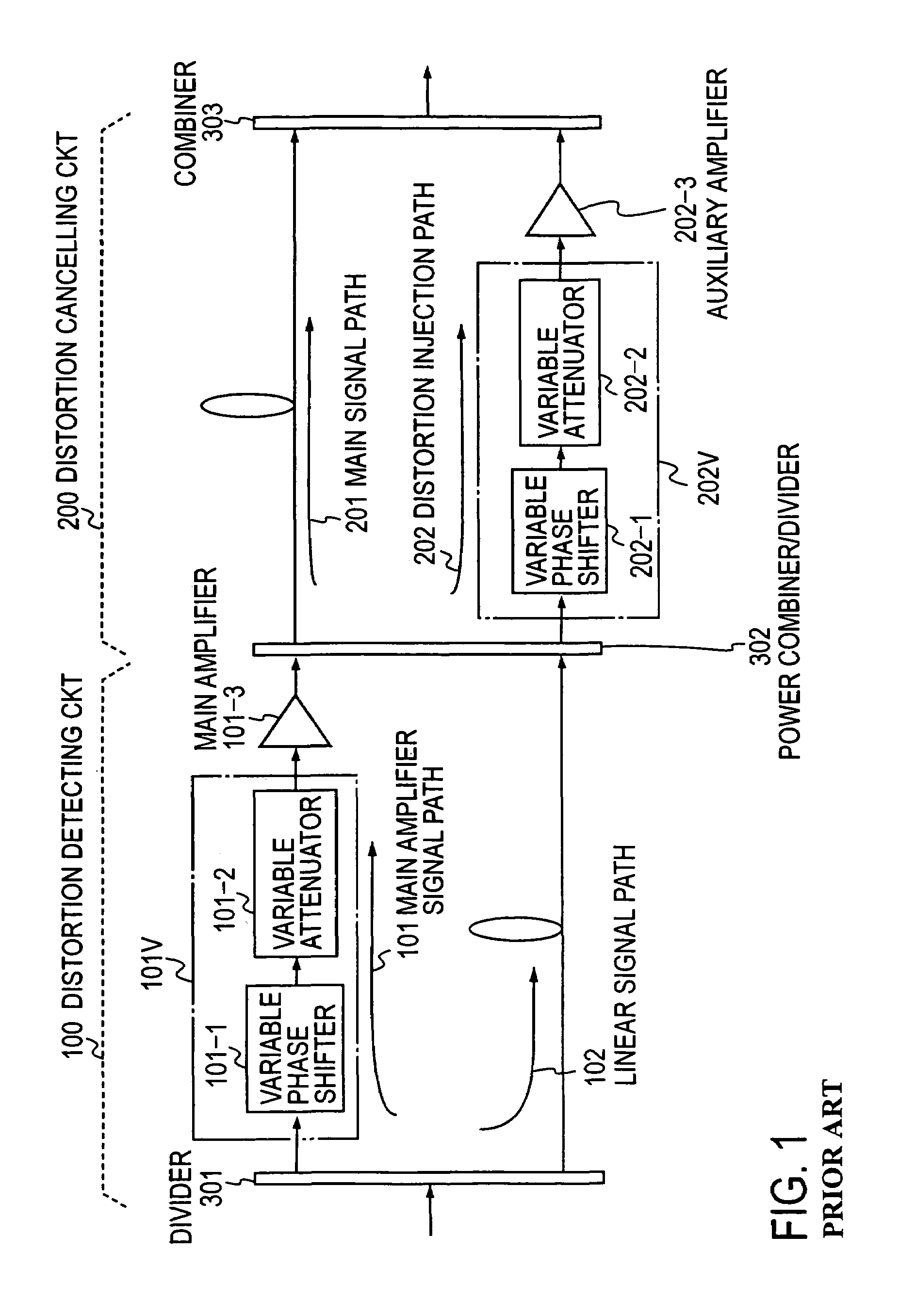
Feedforward amplifier
InactiveUS6710652B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierPower combiner
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Feed forward amplifier employing bias circuit topologies for minimization of RF amplifier memory effects
InactiveUS7106134B2Minimize memory effectHigh impedanceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationConstant impedanceLinearization
An RF power amplifier having reduced memory effects is disclosed. This is achieved by a novel design of the DC supply feed network to achieve low impedance across video frequencies, whilst maintaining the correct RF output matching. One or more transmission zeros are provided in the bias circuit transfer function, which are positioned in the video bandwidth so as to provide low and relatively constant impedance across the video bandwidth. Also, a parallel DC feed line may be employed to reduce impedance across the video bandwidth. The reduction in memory effects allows improved performance of predistortion linearization techniques and an implementation in a feed forward amplifier employing predistortion linearization is also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
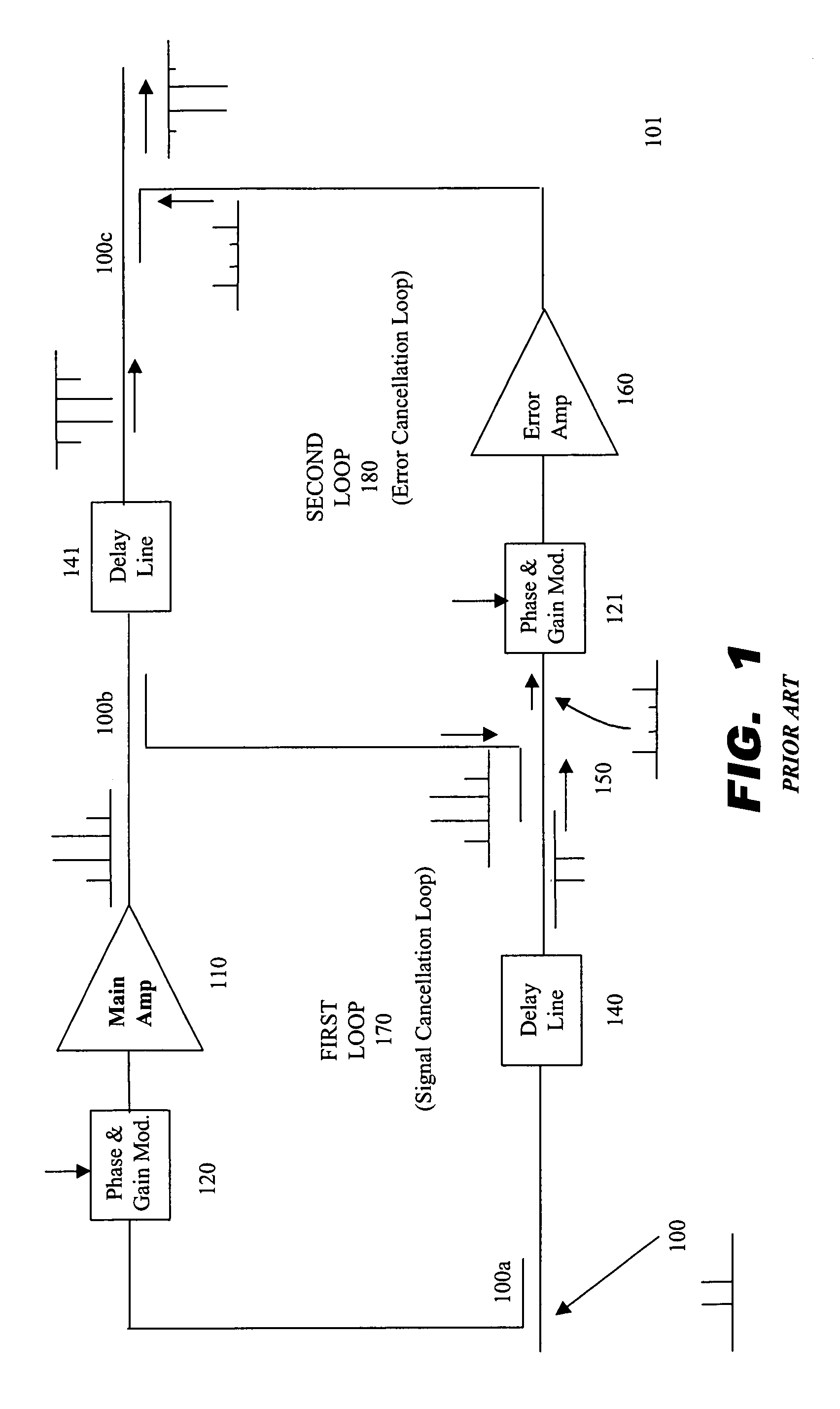
Feedforward linear amplifier
InactiveUS6885242B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierControl signal
A control circuit for a feed forward amplifier provides for pausing control and continuous adjustment of a control signal, provides for the control signal to start at any point, provides for rapid convergence, and that does not perturb the system up or down one step to confirm the convergence of the system. The control circuit receives a sampled version of a feed forward amplifier output signal, generates a non-offset control signal based on the sampled output signal, separately generates an offset voltage by reference to voltages stored in a table or based on the non-offset control signal, and combines the non-offset control signal with the offset voltage to produce a control signal. The feed forward amplifier may then adjust an error signal based on the control signal to produce an adjusted error signal that is capable of reducing distortion in the feed forward amplifier.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
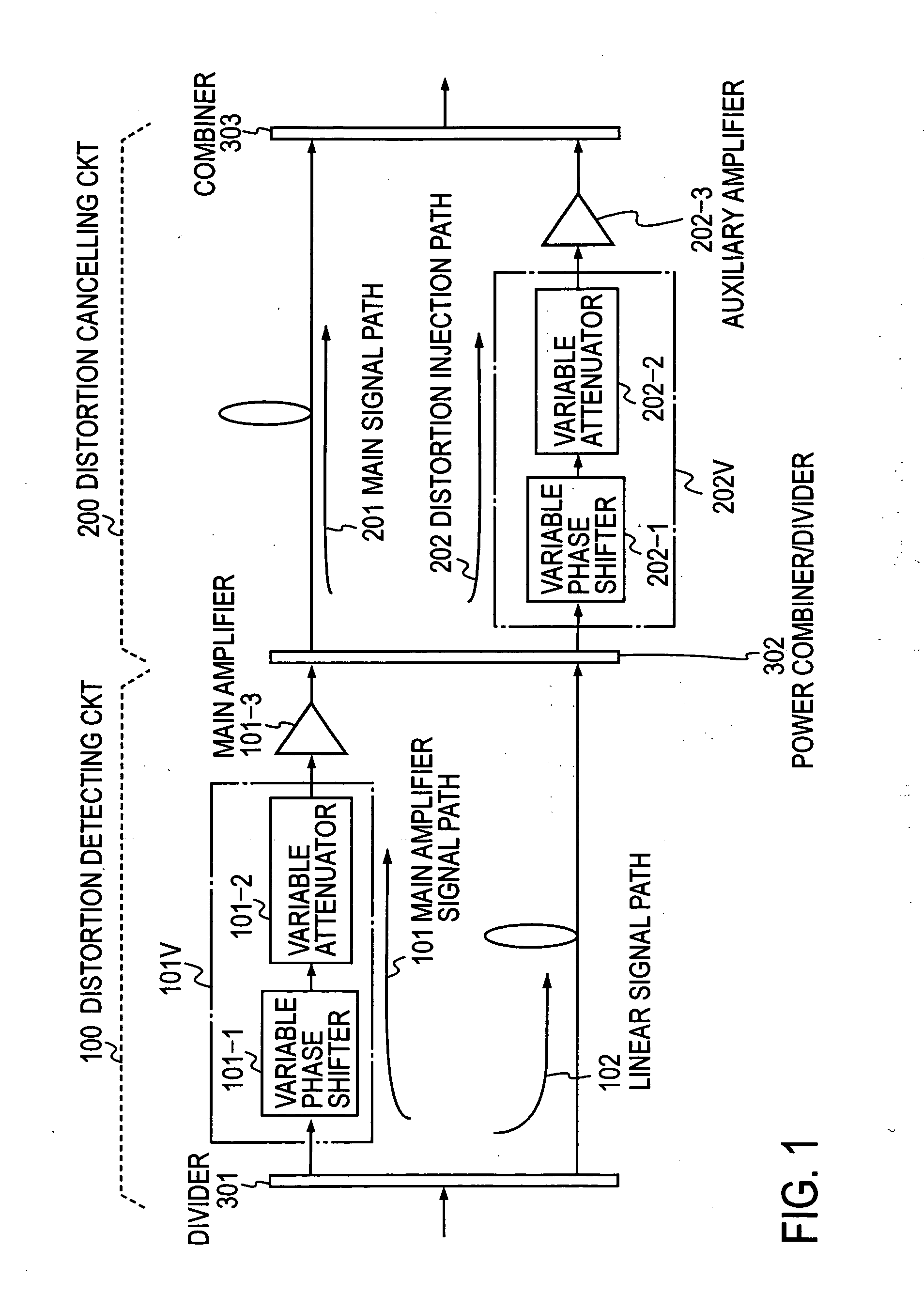
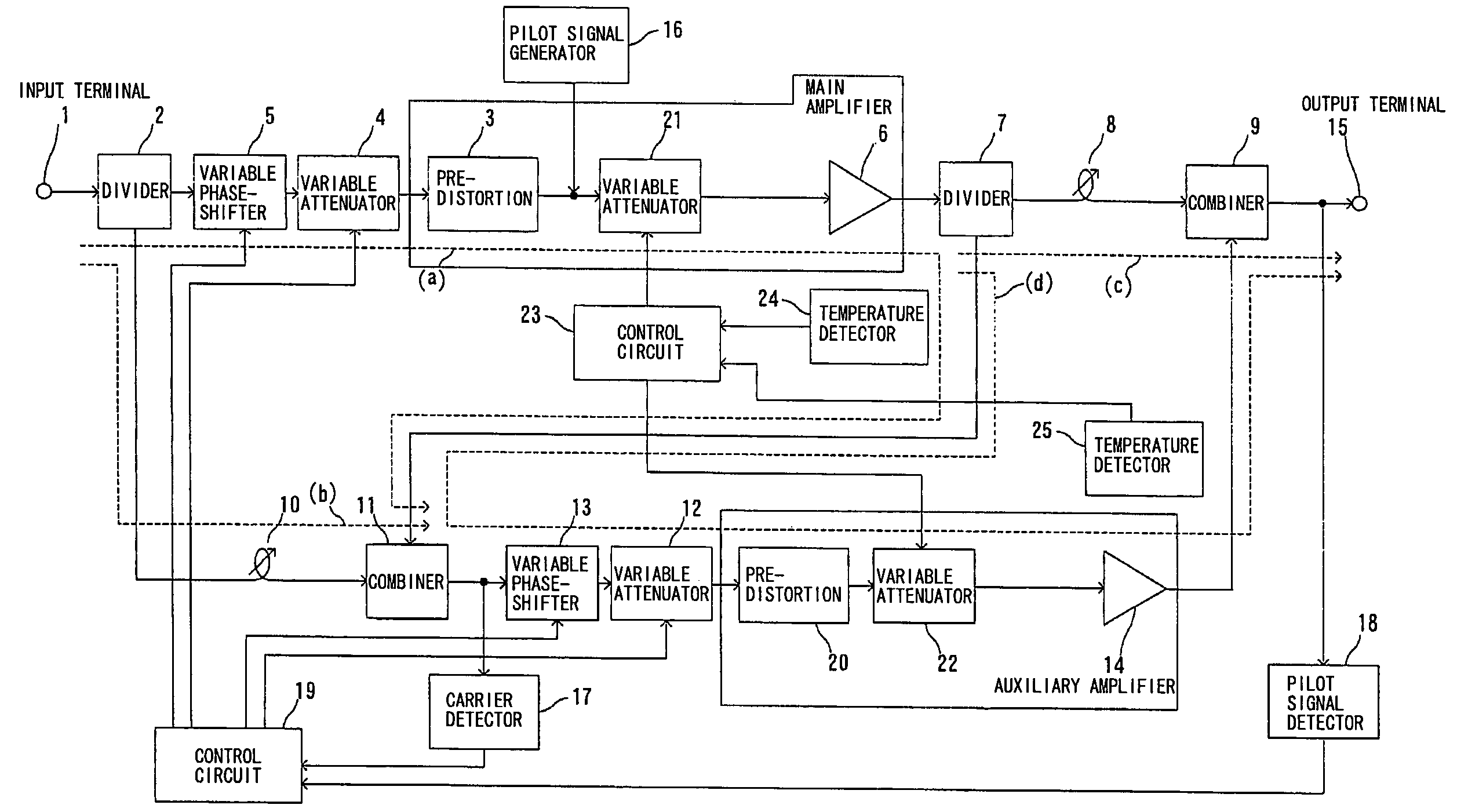
Feed-forward amplifier
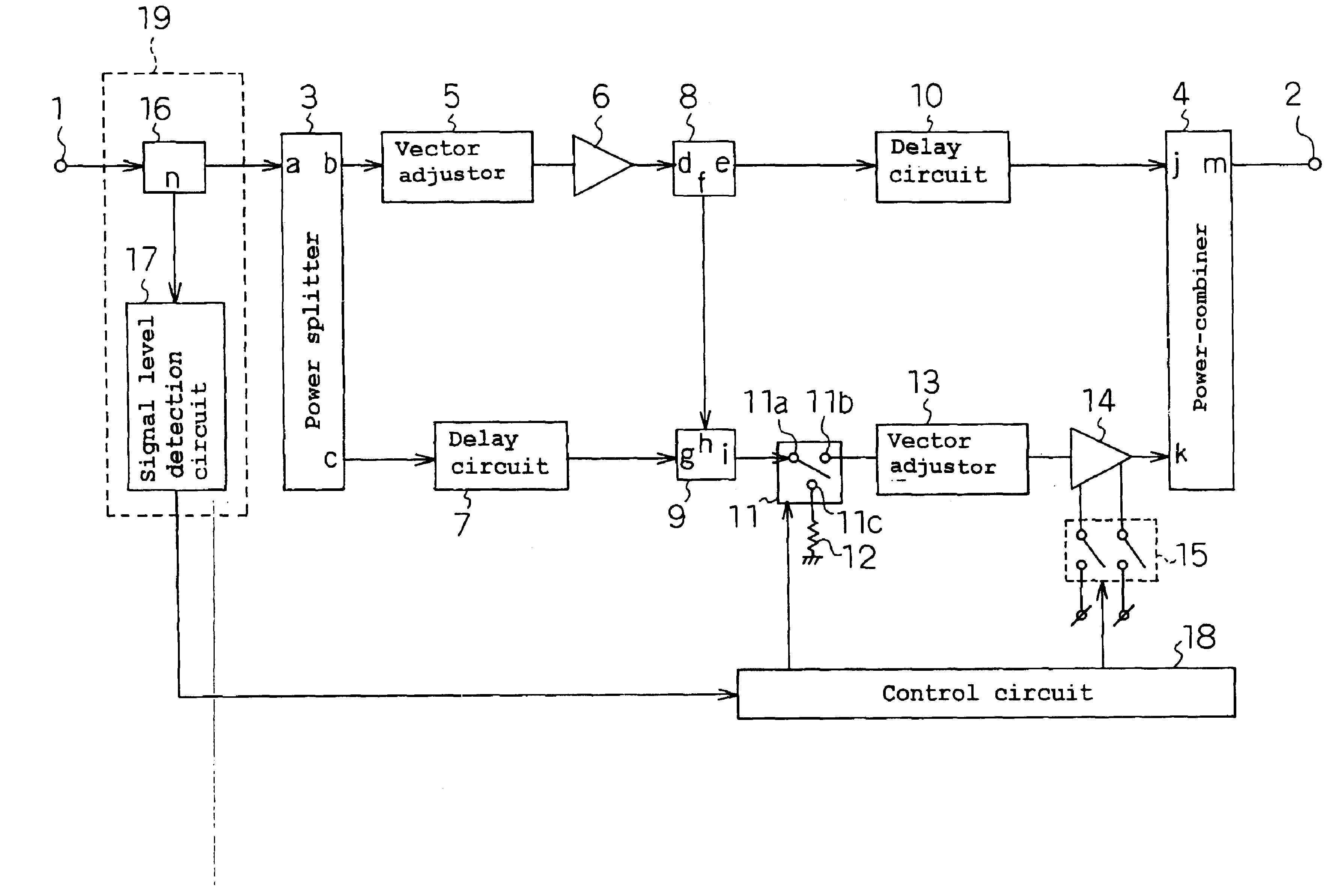
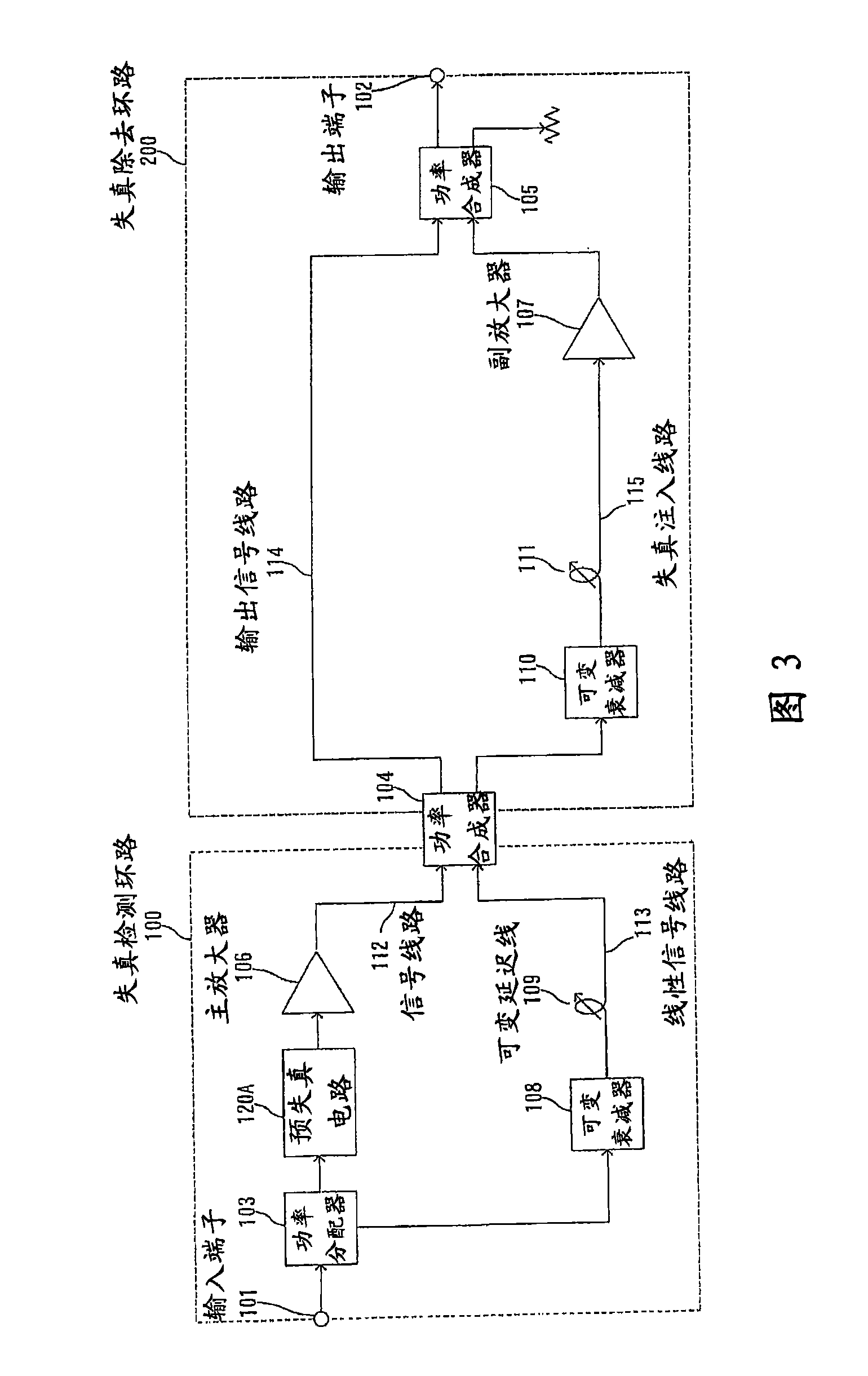
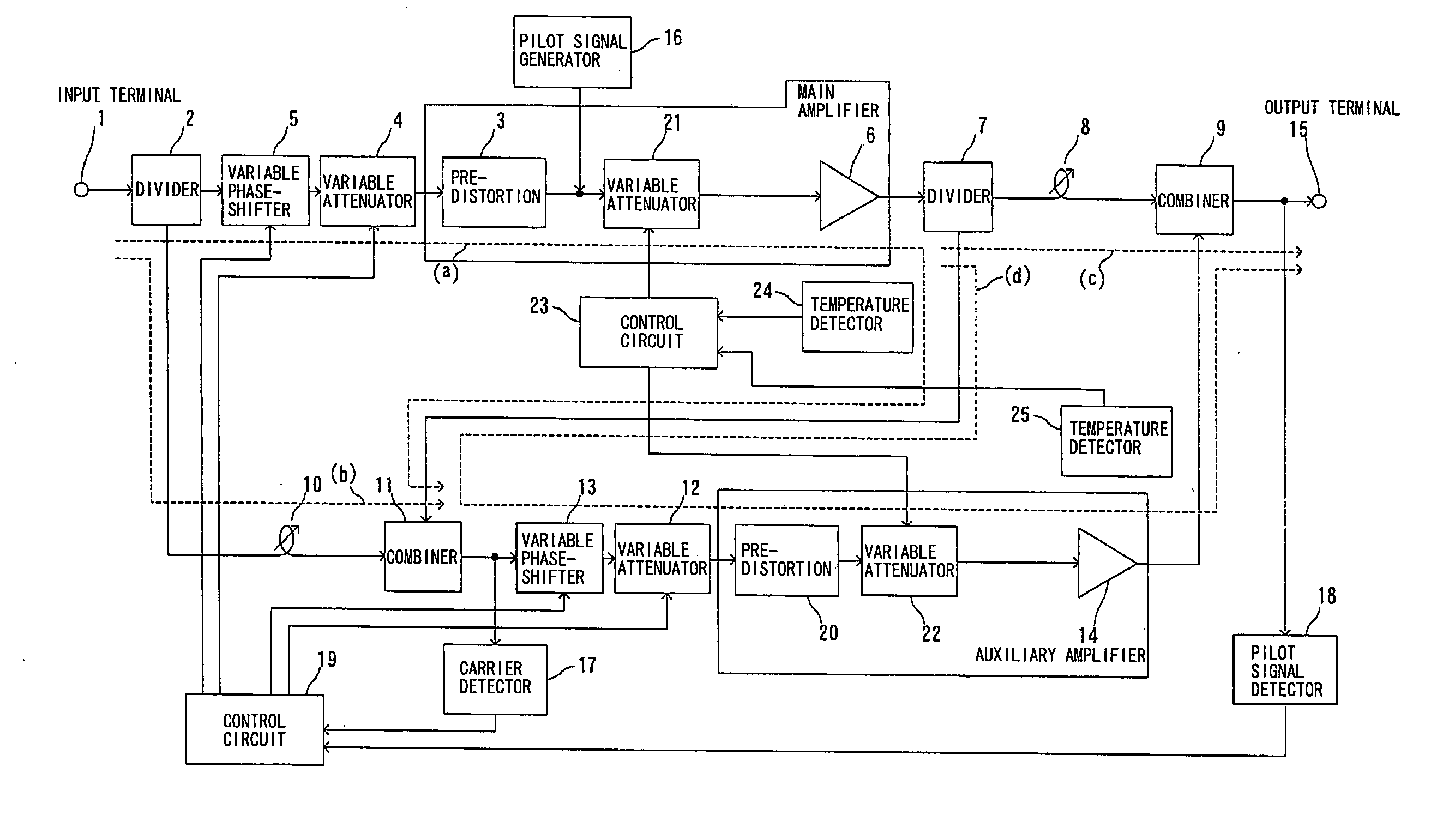
InactiveCN101197558AFull Distortion Compensation EffectAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
The present invention provides a feedforward amplifier capable of obtaining a sufficient distortion compensation effect by a predistortion circuit even when the ambient temperature changes. This feed-forward amplifier is provided with a variable attenuator (4) to control the attenuation of the signal input to the main amplifier (6), and the attenuation is controlled in order to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to changes in the ambient temperature of the main amplifier (6). A variable attenuator (21), a variable attenuator (12) for controlling the attenuation of the signal input to the sub-amplifier (14), in order to prevent distortion compensation caused by changes in the ambient temperature of the sub-amplifier (14) The variable attenuator (22) that degrades and controls the attenuation, controls the variable attenuator (4,12) with the control circuit (19) so that the gain drop with the main amplifier (6) and the gain of the auxiliary amplifier (14) The amount of drop decreases the attenuation accordingly, and the control circuit (23) controls the variable attenuators (21, 22) so as to become the optimum temperature corresponding to the ambient temperature of the main amplifier (6) and the ambient temperature of the sub-amplifier (14). good attenuation.
Owner:ITACHI KOKUSAI ELECTRIC INC
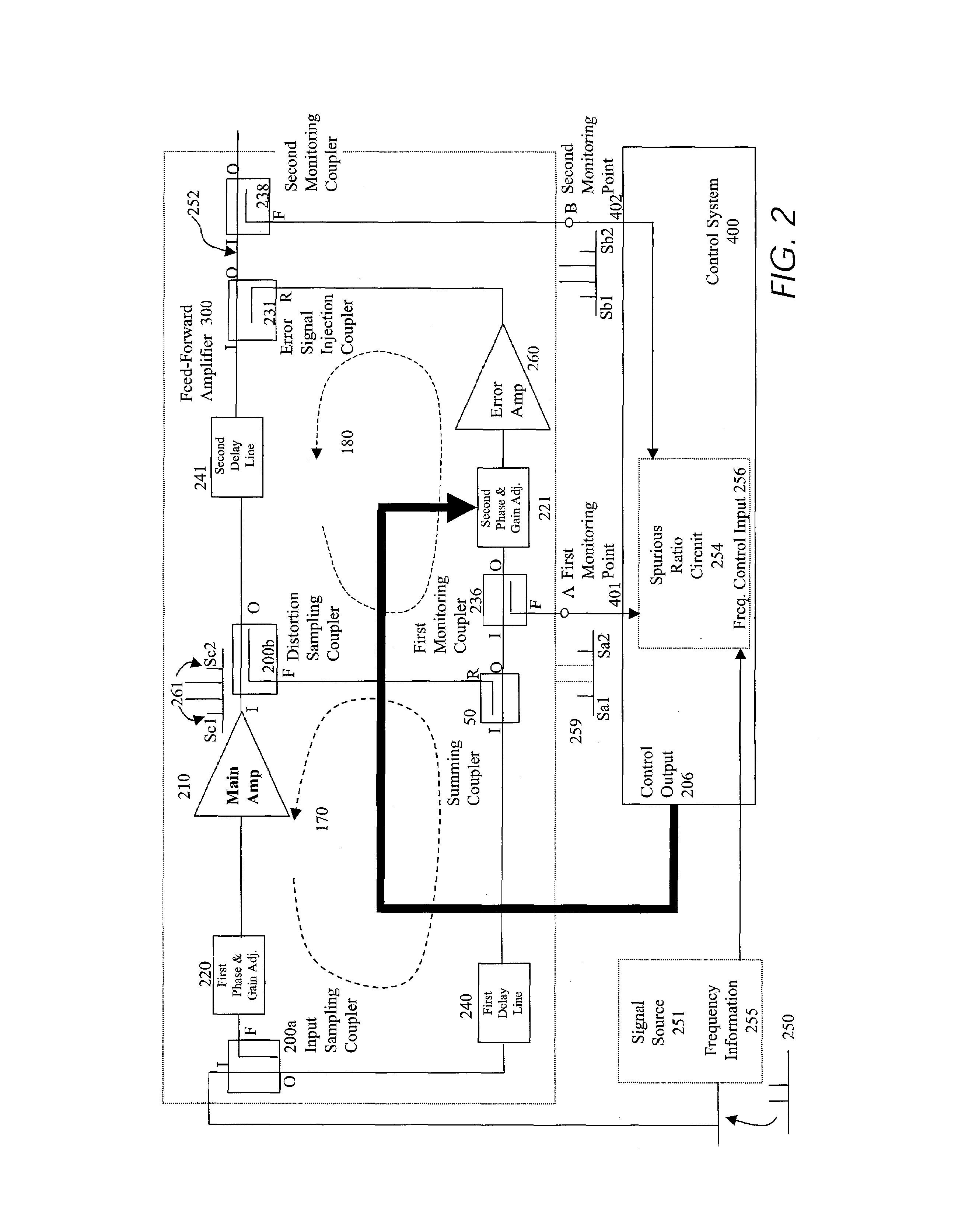
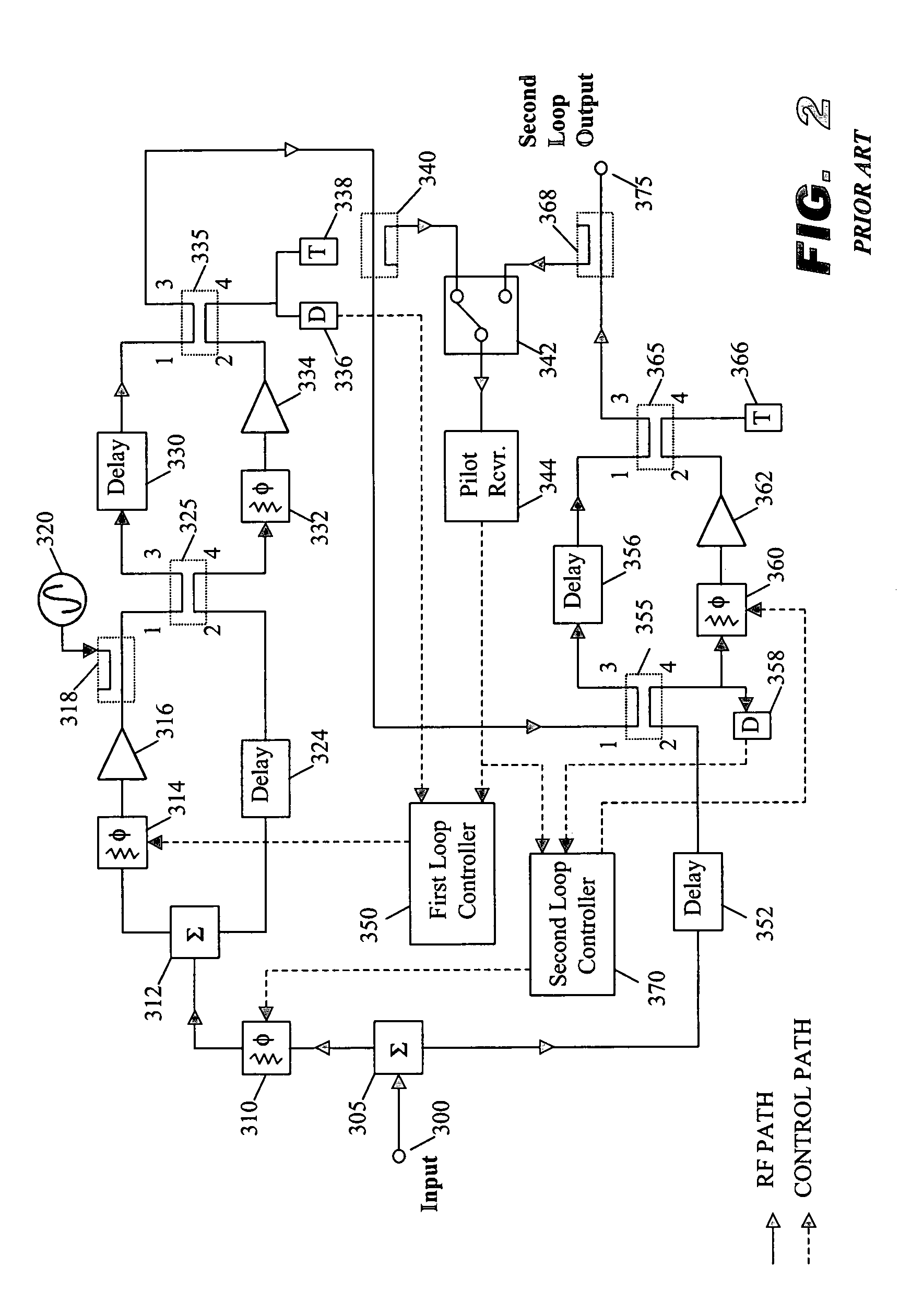
Spurious ratio control circuit for use with feed-forward linear amplifiers
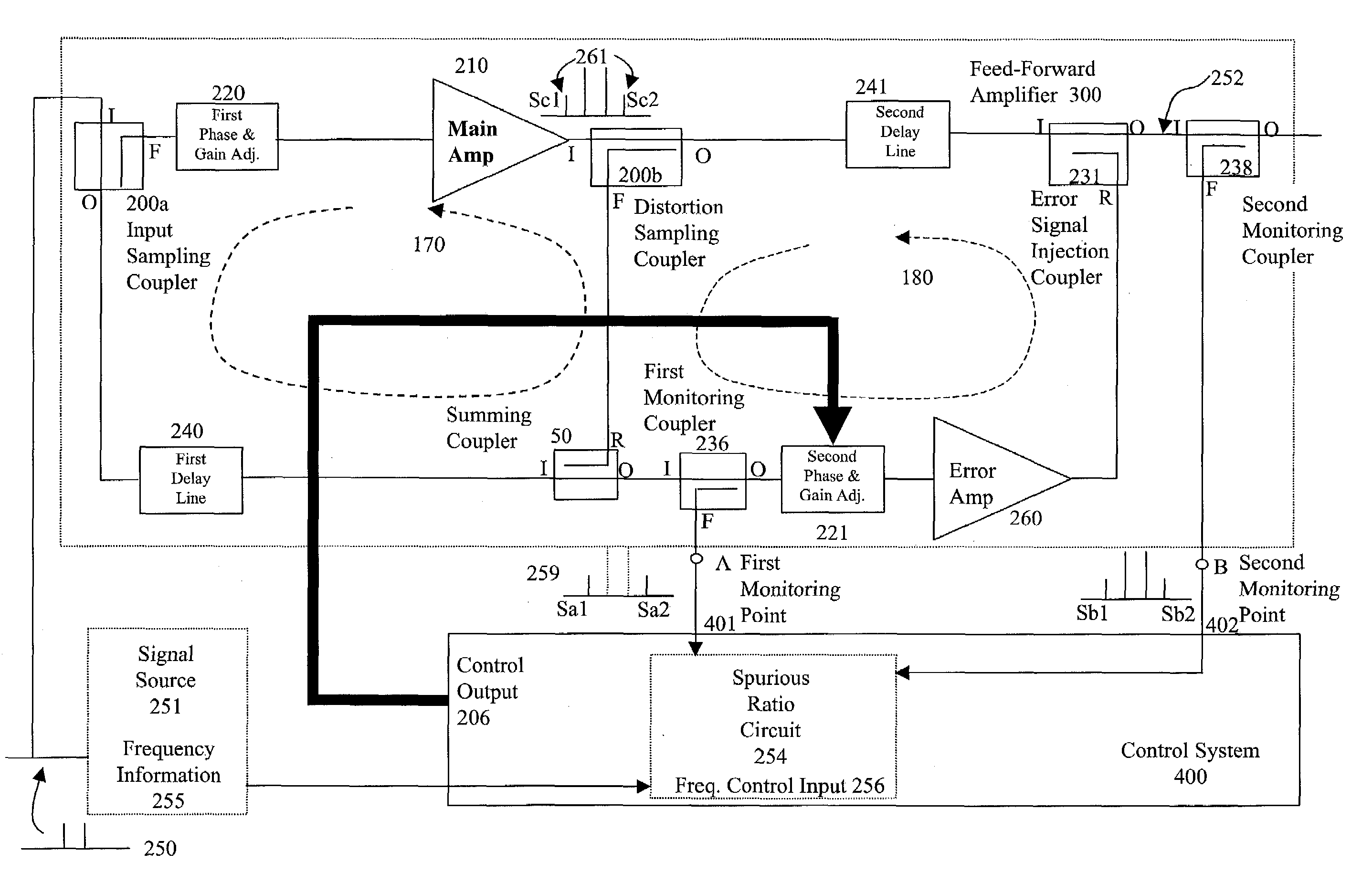
InactiveUS7231191B2Easy to adjustMinimizing ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionRadio transmissionObservational errorAudio power amplifier
A control system for a linear feed-forward amplifier, using the ratio of measured spurious energy. Measuring receivers are coupled to two monitoring points to measure the spurious energy content in the error signal and at the main output of a feed-forward amplifier. The control system measures the ratio of these detected spurious, and uses this to optimize the settings of the second loop distortion cancellation. With the addition of an extra monitoring point, the same technique may also be used to control an adaptive predistorter prior to the main amplifier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
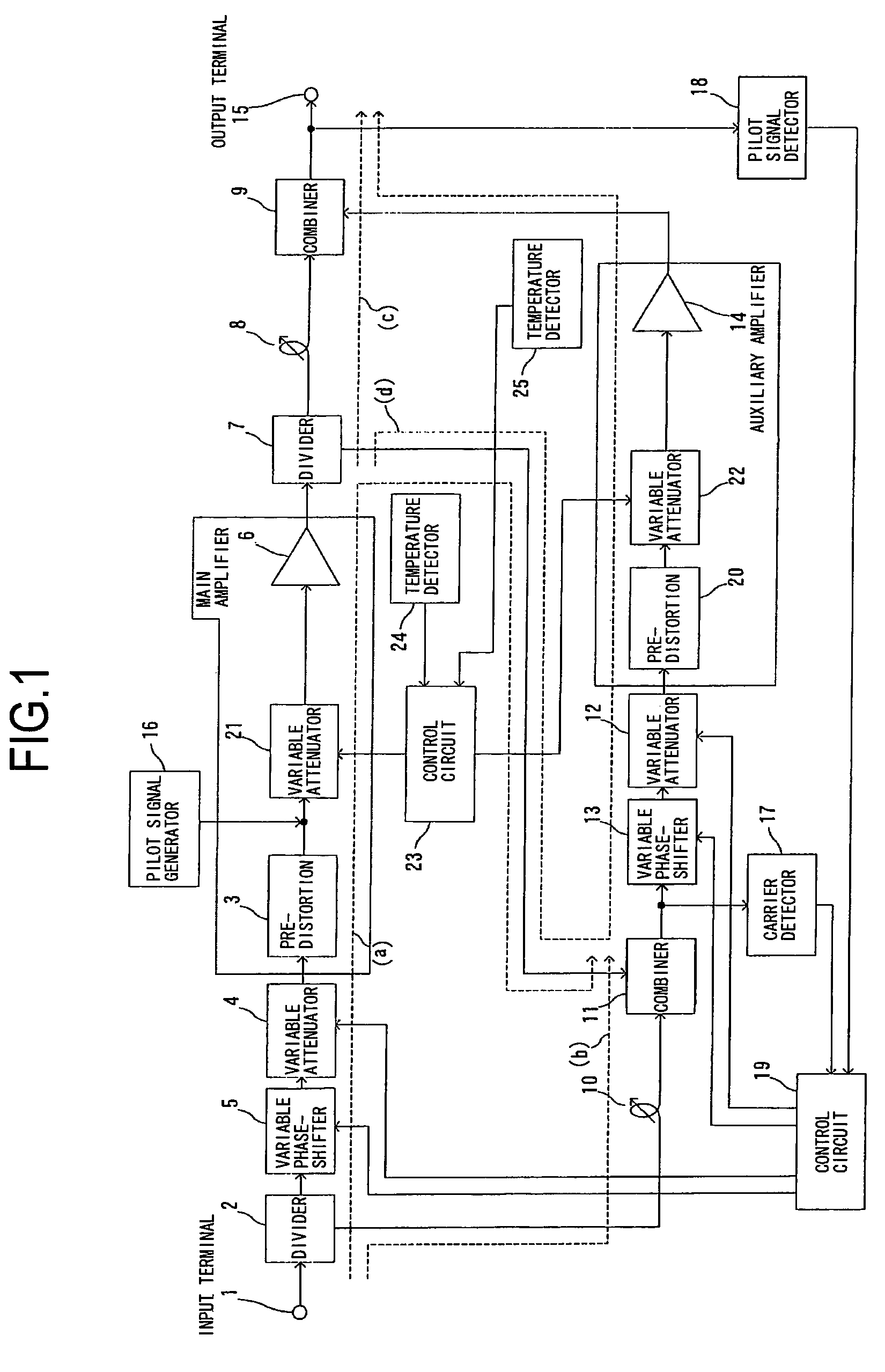
Feed-forward amplifier
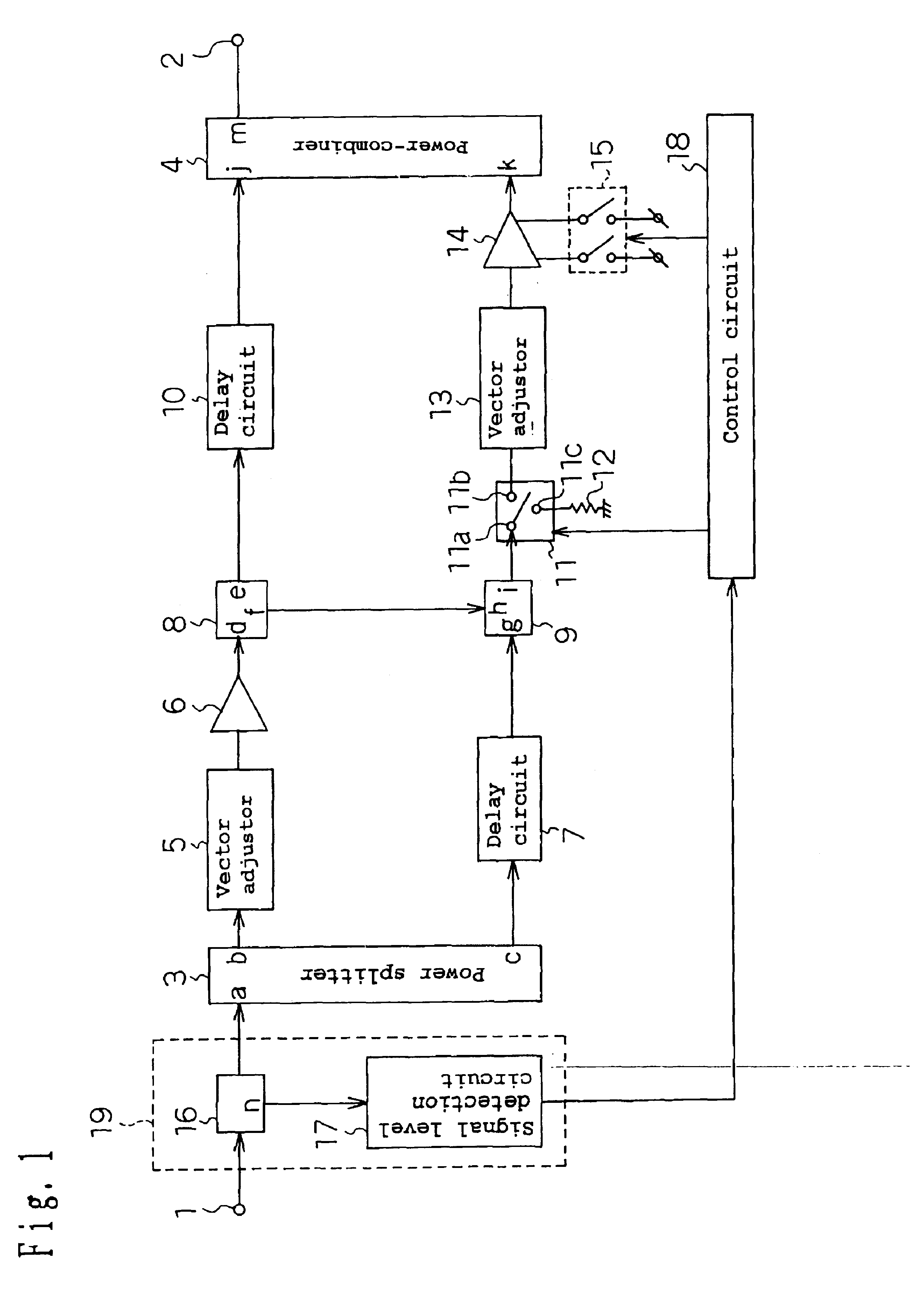
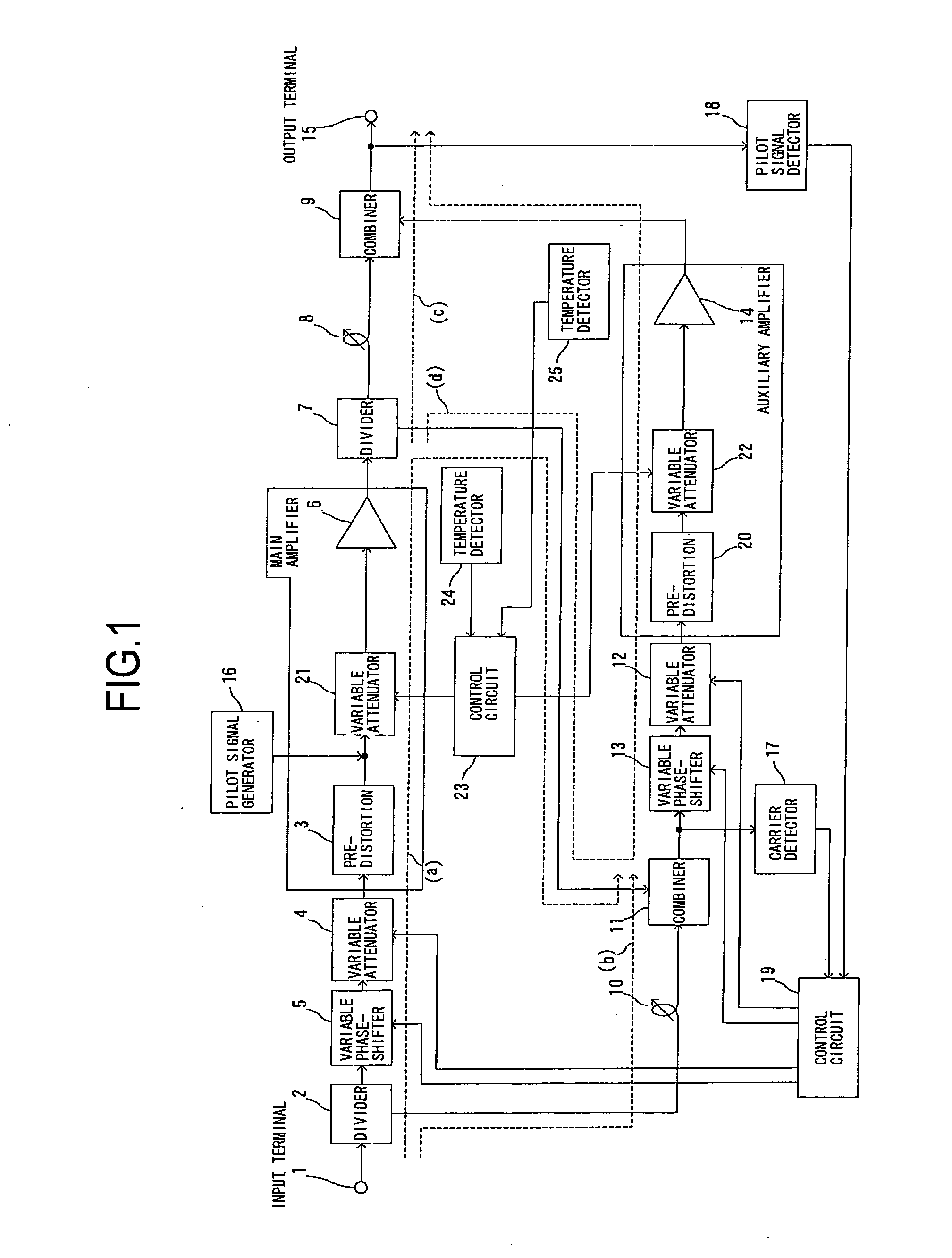
InactiveUS7646239B2Sufficient distortion compensation effectMinimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
There is provided a feed-forward amplifier which enables a predistortion circuit to obtain sufficient distortion compensation effects even if ambient temperature or the like changes. The feed-forward amplifier includes a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to a main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to an auxiliary amplifier, and a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier, wherein a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to reduce the amount of attenuation according to the reduced gain of the main amplifier and the reduced gain of the auxiliary amplifier, and a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to optimize the amount of attenuation according to the ambient temperature of the main amplifier and the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Feed forward amplifier
InactiveUS7053702B2Reduce expensesReduce complexityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyTelecommunicationsAudio power amplifier
The present invention provides a novel feed forward amplifier (“FFA”) and a pilot tone generator-receiver therefor. In an embodiment of the invention, the feed forward amplifier only requires a single oscillator to operate both the pilot tone generator and pilot tone receiver used in conjunction with the amplifier circuitry of the FFA. In another embodiment of the invention, a method is provided of generating and detecting a pilot tone from a single oscillating signal.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Active forward feed amplifier
ActiveUS20100259326A1Optimal spurious signal cancellationPerformanceActive element networkAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierTime delays
An exemplary embodiment of the feed forward amplifier replaces traditional distributed directional couplers, splitters, and delay lines. Moreover, an exemplary feed forward amplifier architecture combines active implementations of RF couplers, power splitters, and / or time delay elements in a novel fashion allowing for ultra-compact size and broadband performance. In an exemplary embodiment, a feed forward amplifier has a main amplifier path and an error amplifier path. The feed forward amplifier comprises a main amplifier in the main amplifier path, and at least one active vector generator in the error amplifier path. The at least one active vector generator is configured to adjust the phase and amplitude of an error amplifier path signal and an error amplifier is configured to receive the adjusted error amplifier path signal. Furthermore, the adjusted error amplifier path signal and an amplified signal are combined to form the output signal of the feed forward amplifier.
Owner:VIASAT INC
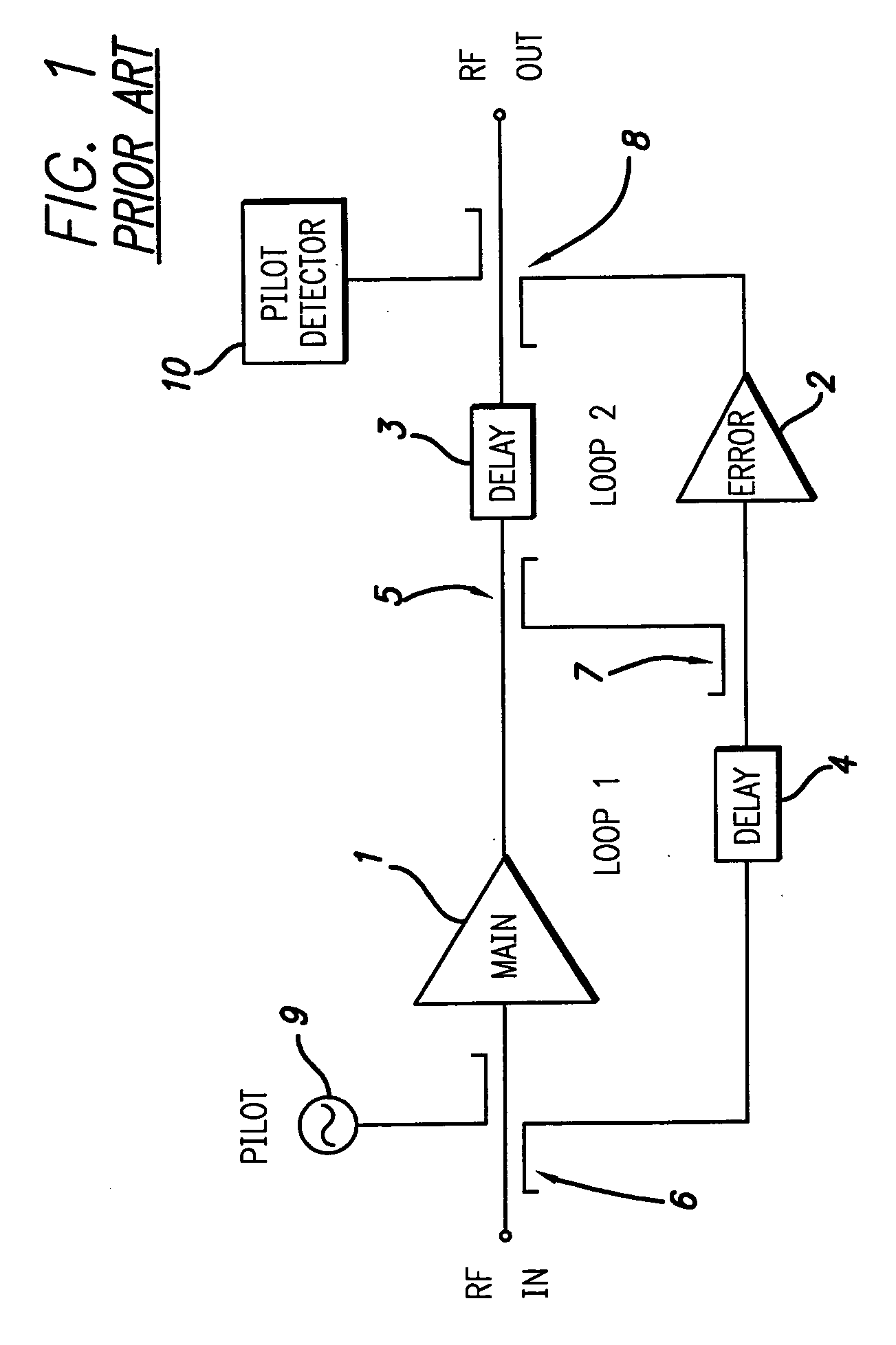
Feedforward amplifier with dual loop
InactiveUS6838934B2Easy balance controlAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
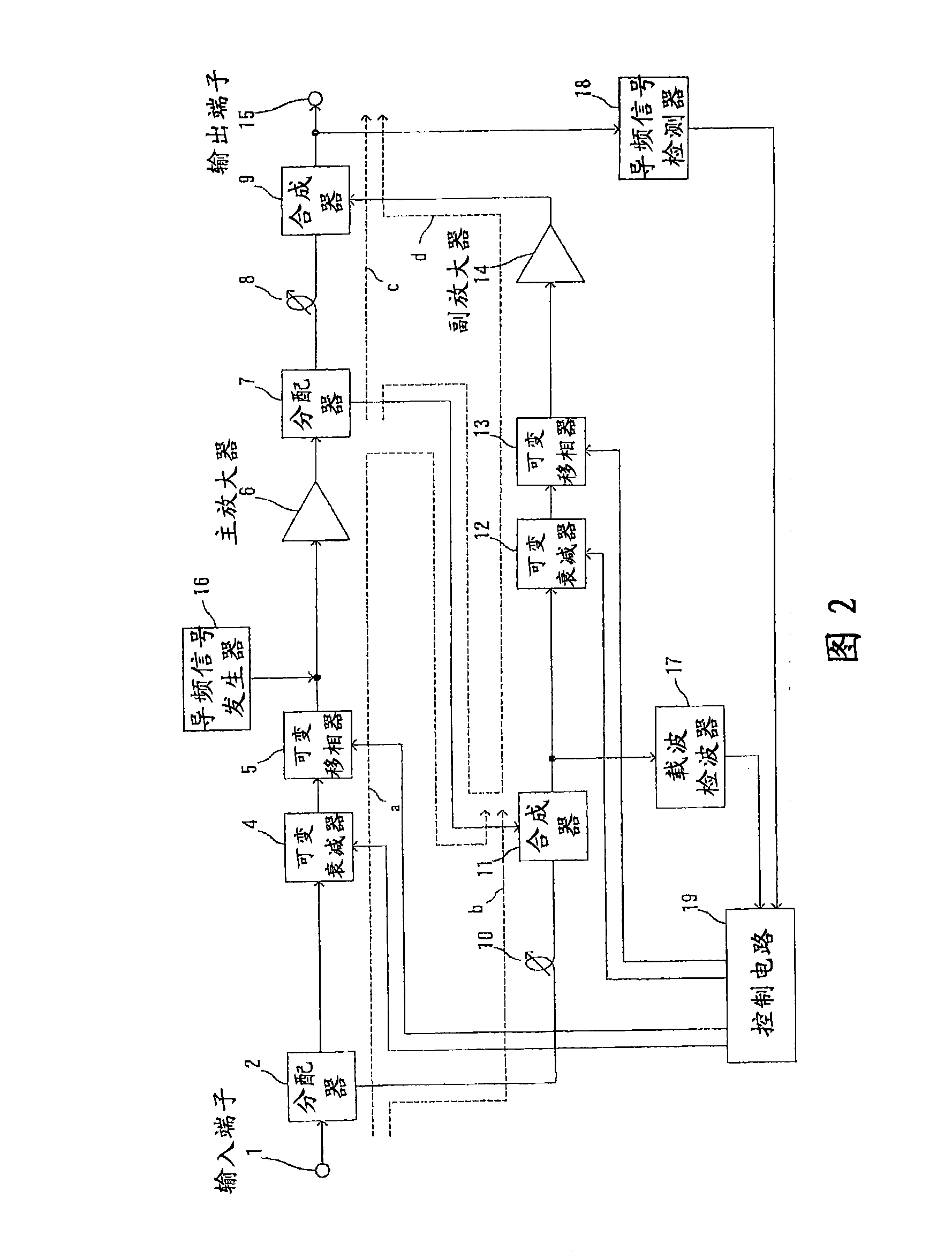
In a feedforward amplifier with a dual loop in which a distortion injection path of a distortion elimination circuit 50 is provided as a feedforward configuration composed of a first auxiliary amplifier distortion elimination circuit 60 and a first auxiliary amplifier distortion elimination circuit, a second variable attenuator 55 and a second variable phase shifter 56 are provided preceding the distortion detection circuit 60, a second pilot signal injected between stages of a main amplifier 14 is detected by a directional coupler 85, and the second variable attenuator 55 and the second variable phase shifter 56 are controlled by a second controller 97 to minimize the level of the detected second pilot signal, thereby bringing the distortion elimination circuit and the first auxiliary distortion detection circuit into balance at the same time.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Feed forward amplifier employing positive feedback pilot generation with automatic level control
InactiveUS20060176113A1Lower Level RequirementsLarge levelAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifiers amplifying and generating simultaneouslyAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
A feed forward amplifier and method of amplification are disclosed. The amplifier output is used to generate a pilot signal via feedback using uncancelled noise in the amplifier output. An automatic level control circuit maintains the pilot signal at a substantially constant level when the detected uncancelled noise in the amplifier output is above a threshold level. The generated pilot signal strength is allowed to vary when the detected uncancelled noise in the amplifier output is below the threshold and disappears automatically when the amplifier is aligned.
Owner:INTEL CORP
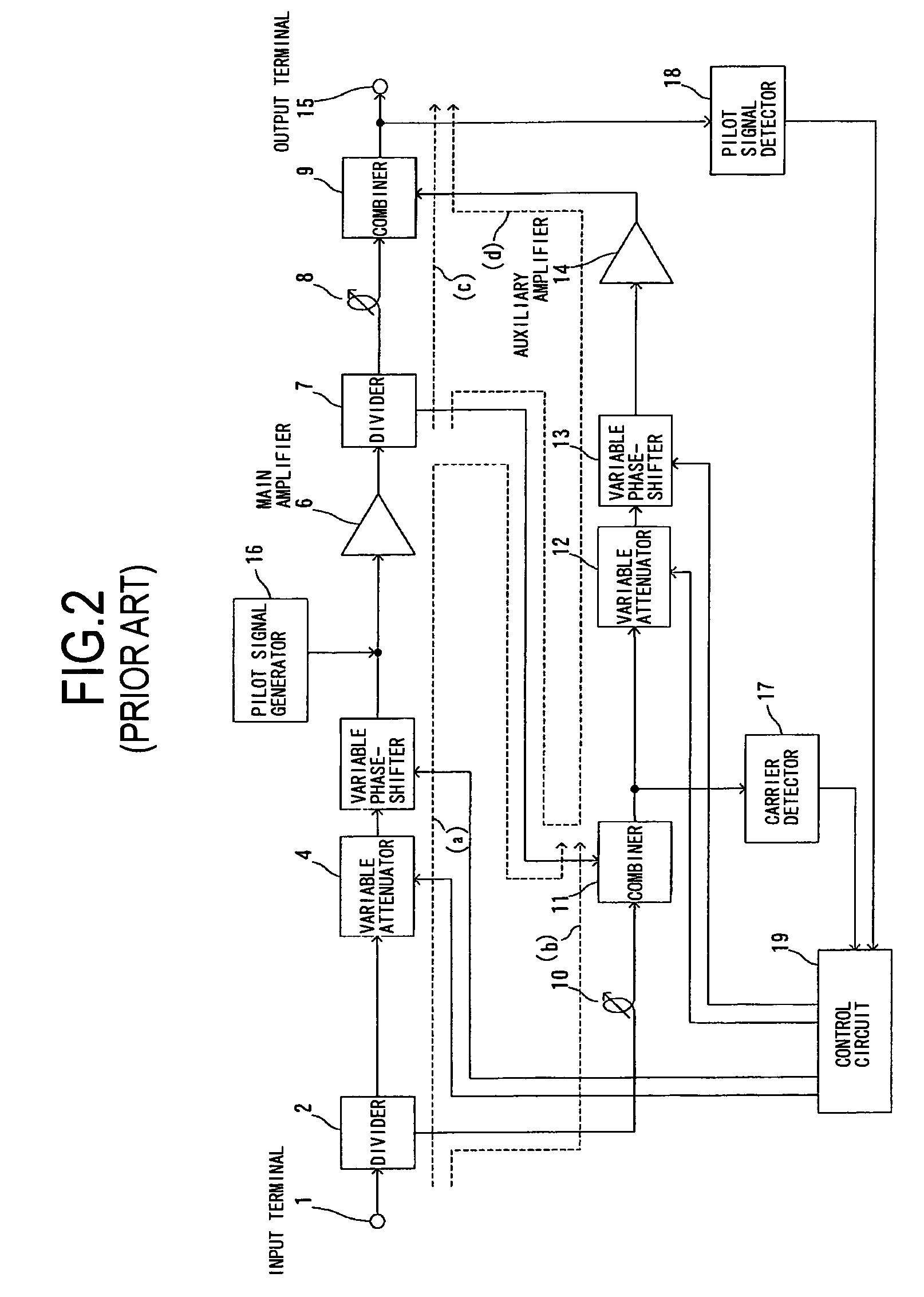
Feed-forward amplifier
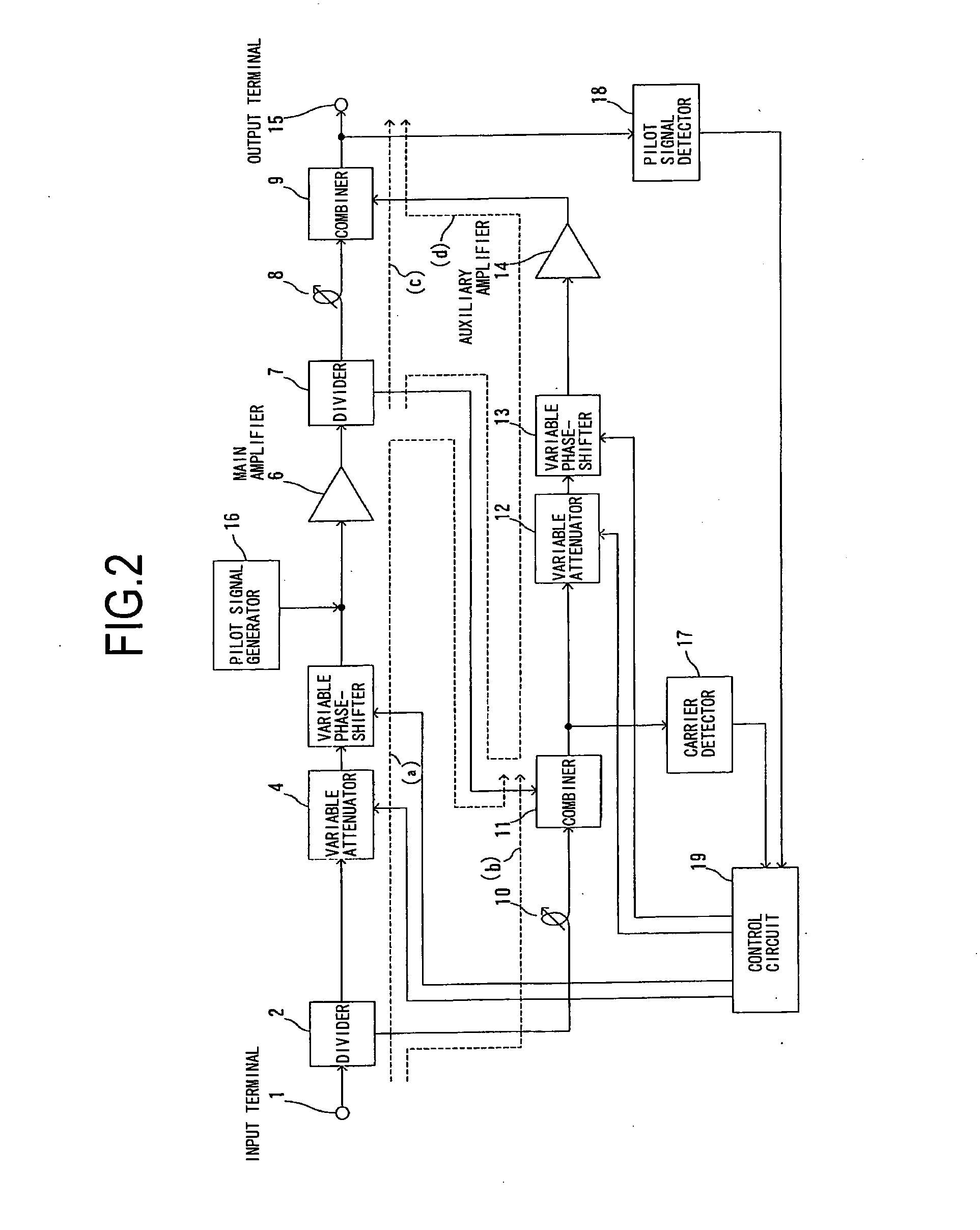
InactiveUS20080136518A1Sufficient distortion compensation effectMinimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
There is provided a feed-forward amplifier which enables a predistortion circuit to obtain sufficient distortion compensation effects even if ambient temperature or the like changes. The feed-forward amplifier includes a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to a main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the main amplifier, a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation of a signal input to an auxiliary amplifier, and a variable attenuator for controlling the amount of attenuation to prevent deterioration of distortion compensation due to a change in the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier, wherein a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to reduce the amount of attenuation according to the reduced gain of the main amplifier and the reduced gain of the auxiliary amplifier, and a control circuit controls the variable attenuators to optimize the amount of attenuation according to the ambient temperature of the main amplifier and the ambient temperature of the auxiliary amplifier.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Forward amplifiers
InactiveUS20050174173A1Improve performanceMaximal cancellationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierSignal cancellation
An apparatus and method for operating a feed-forward amplifier in which, after the signal-cancellation and intermodulation-cancellation loops have initially been nulled, the feed-forward amplifier is operated so that both loops are controlled so as to minimize intermodulation at the output of the feed-forward amplifier.
Owner:WI LAN INC
System and method of carrier reinjection in a feedforward amplifier
InactiveUS7173484B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
A dual loop feedforward power amplifier. A dual loop feedforward power amplifier, comprising an input that provides a multicarrier signal; a first feedforward power amplifier; and a second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier serves as a main amplifier gain block in the second feedforward power amplifier, wherein the first feedforward power amplifier comprises a carrier cancellation loop and a first error amplifier loop, and wherein the second feedforward power amplifier comprises a third loop and a fourth loop that cancel small signal distortions that are not reduced by the first feedforward amplifier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
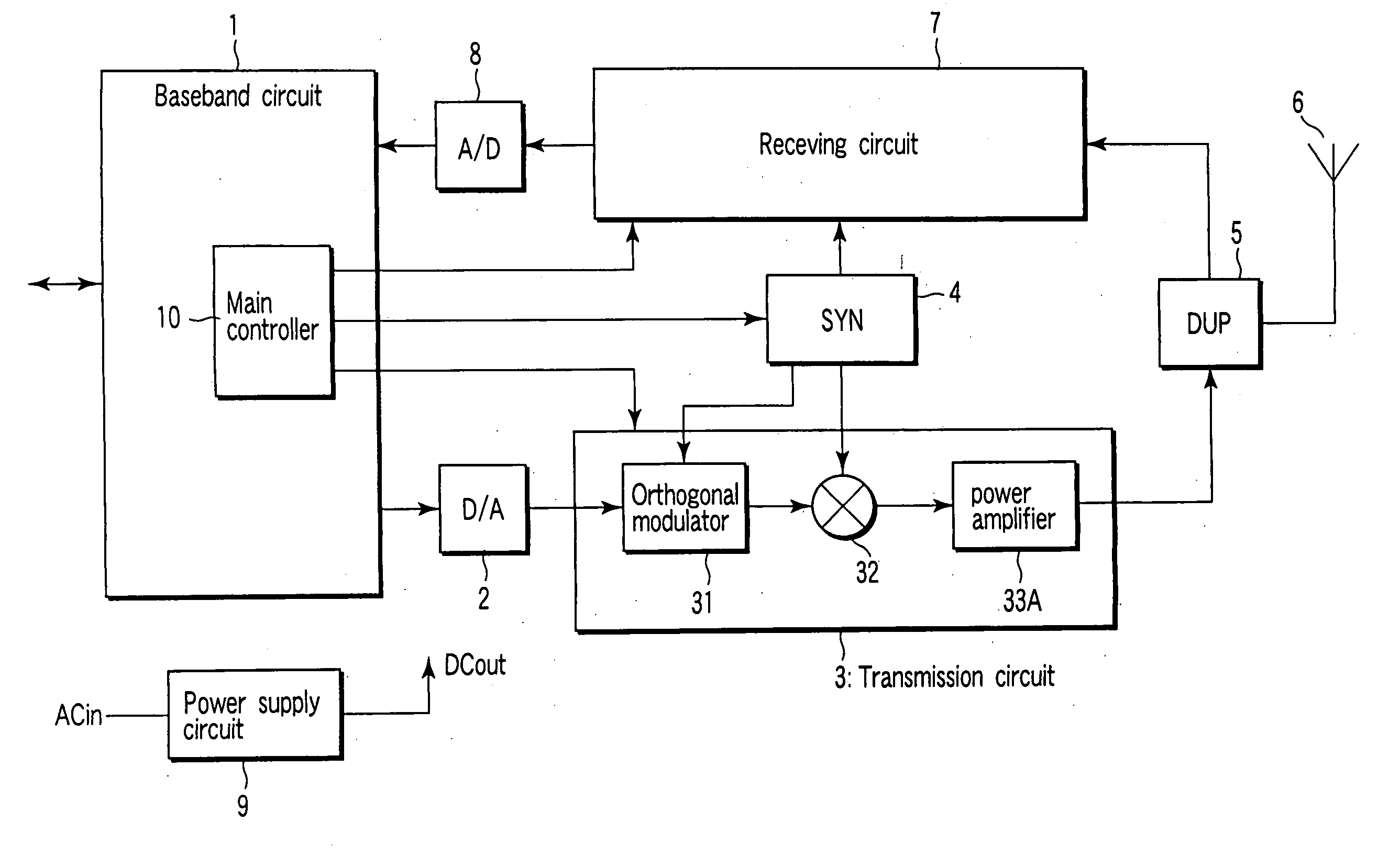
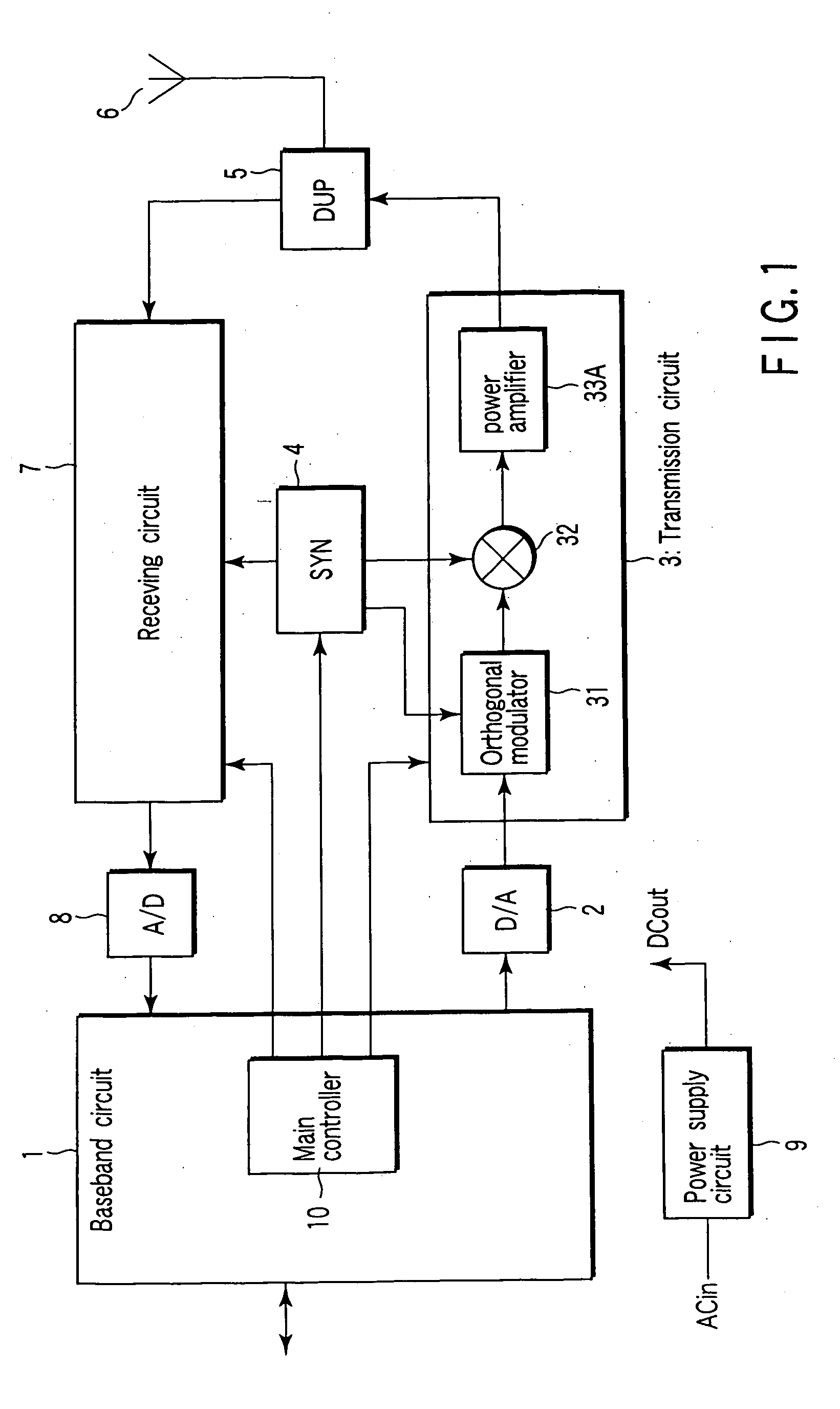
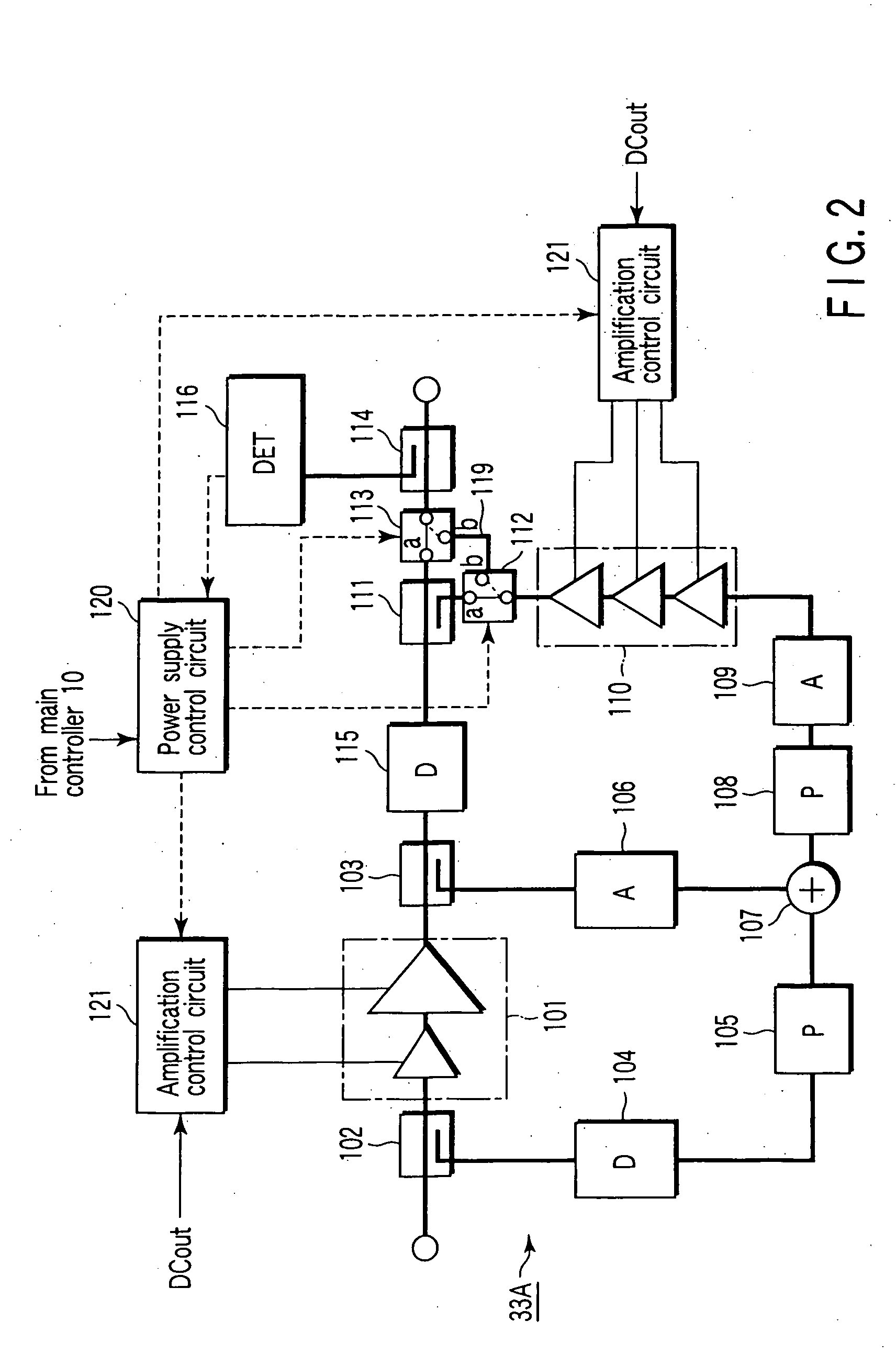
Feedforward amplifier and radio communication apparatus with the amplifier
InactiveUS20040192237A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierFeedforward amplifiers
An amplifier comprises a first amplifier circuit which amplifies a first signal to output an amplified first signal, a circuit which outputs a second signal corresponding to a difference between the first signal and the amplified first signal, a second amplifier circuit which amplifies the second signal to output an amplified second signal, a combine circuit which outputs an amplified signal by combining the amplified second signal with the amplified first signal, and a controller which controls a supply of a power to the first amplifier circuit and the second amplifier circuit and has a first mode to supply the power to the second amplifier circuit without supplying the power to the first amplifier circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi-band feed-forward amplifier and adjustment method therefor
InactiveUS7126422B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A multi-band feed-forward amplifier is formed by: a dividing part for dividing and applying an input signal containing signals of multiple frequency bands to a linear signal path and N vector adjustment paths of a distortion detecting circuit; frequency band signal extractors provided in the N vector adjustment paths, respectively, for extracting signals of N frequency bands; N vector adjusters for adjusting the vectors of the output signals from the respective frequency band signal extractors; a main amplifier for amplifying the output signals from the N vector adjusters; a combining / dividing part for combining the amplified signals and the signal from the linear signal path of the distortion detecting circuit and for dividing and applying the combined output to a linear signal path and N distortion injection paths of a distortion cancelling circuit; frequency band signal extractors provided in the N distortion injection paths, respectively, for extracting the signals of the N frequency bands; vector adjusters for adjusting the vectors of signals separated into the N frequency bands; an auxiliary amplifying part for amplifying the vector-adjusted N signals; and a combining part for combining the amplified signals and the signal from the linear signal path of the distortion cancelling circuit.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Feed forward amplifier system and method using the pilot frequency from a positive feedback pilot generation and detection circuit to improve second loop convergence
InactiveUS20060222104A1Resonant long antennasAmplifier with control circuitsPilot systemAudio power amplifier
A pilot system and method is disclosed that increases the rate of convergence of the second loop alignment control in a feed forward amplifier. Both a pilot generation and detection system and search algorithm controlling the alignment are disclosed. By measuring the frequency of the generated pilot, phase information regarding the second loop cancellation transfer function can be inferred. Changes in the pilot frequency as the search algorithm makes steps in the second loop alignment indicate errors in the direction of the search. Using this pilot frequency measurement along with the existing log-power measurement of the residual pilot power improves the convergence speed because fewer steps will be made to reach the optimal alignment setting.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com