Patents
Literature
113 results about "Pilot power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
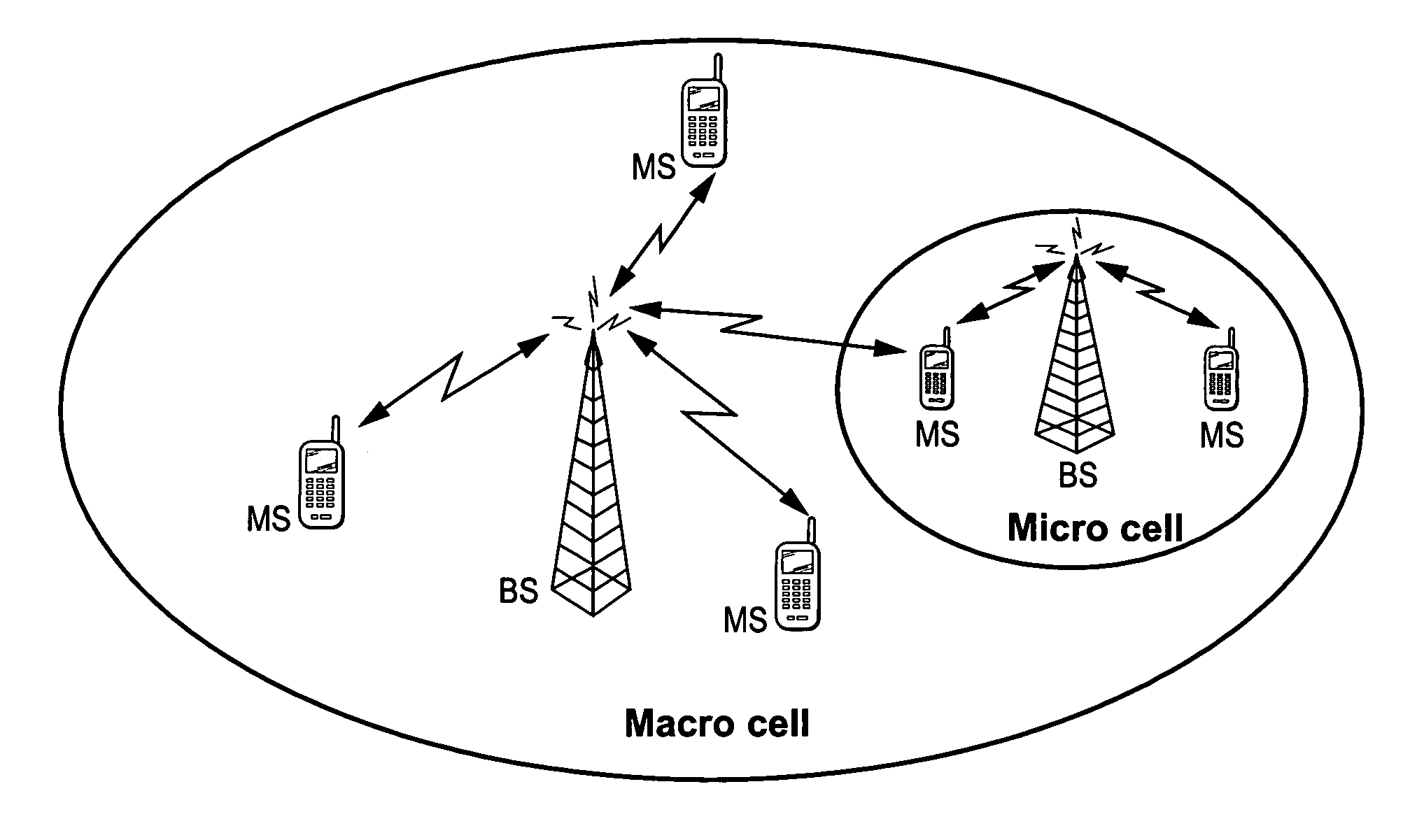
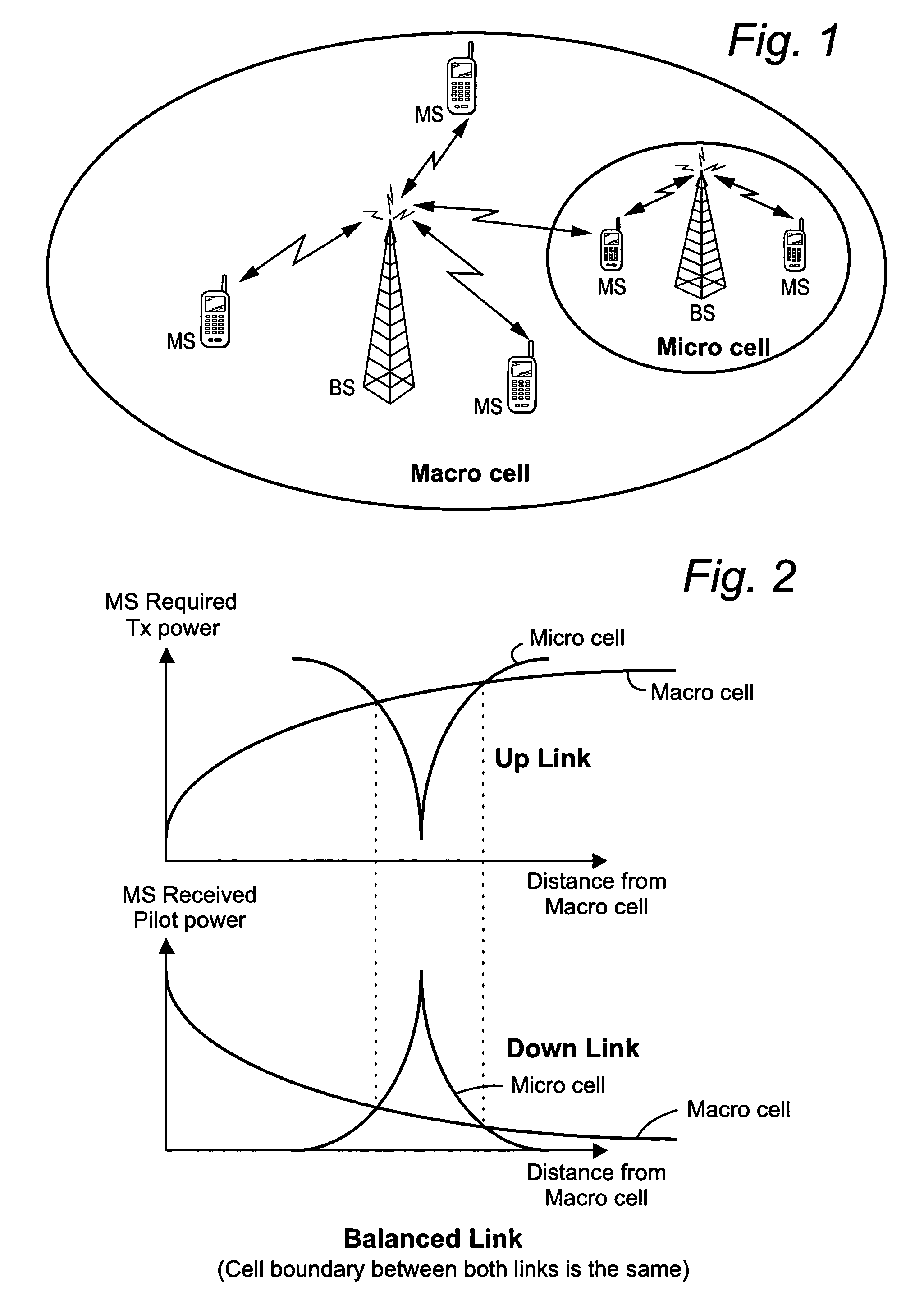
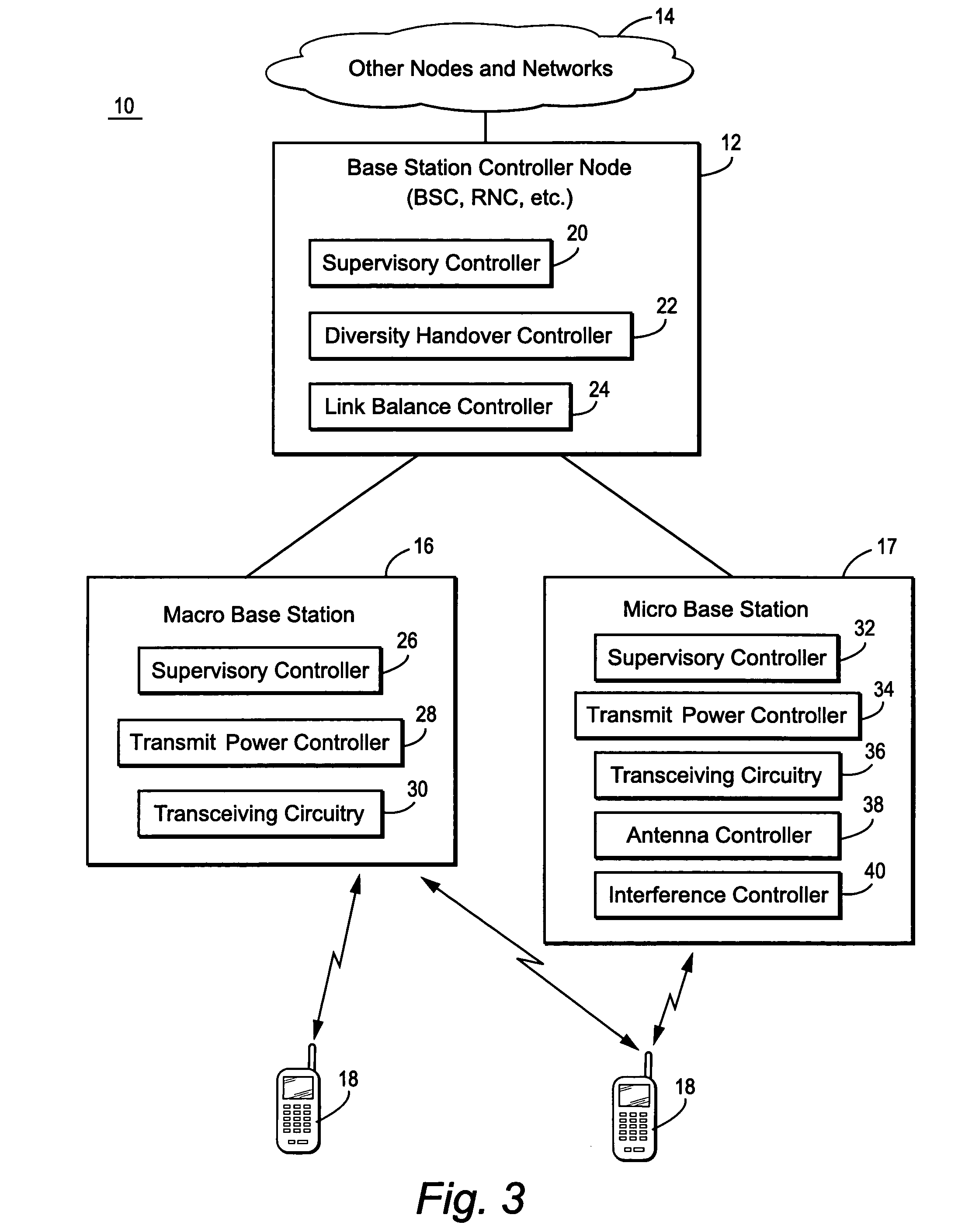
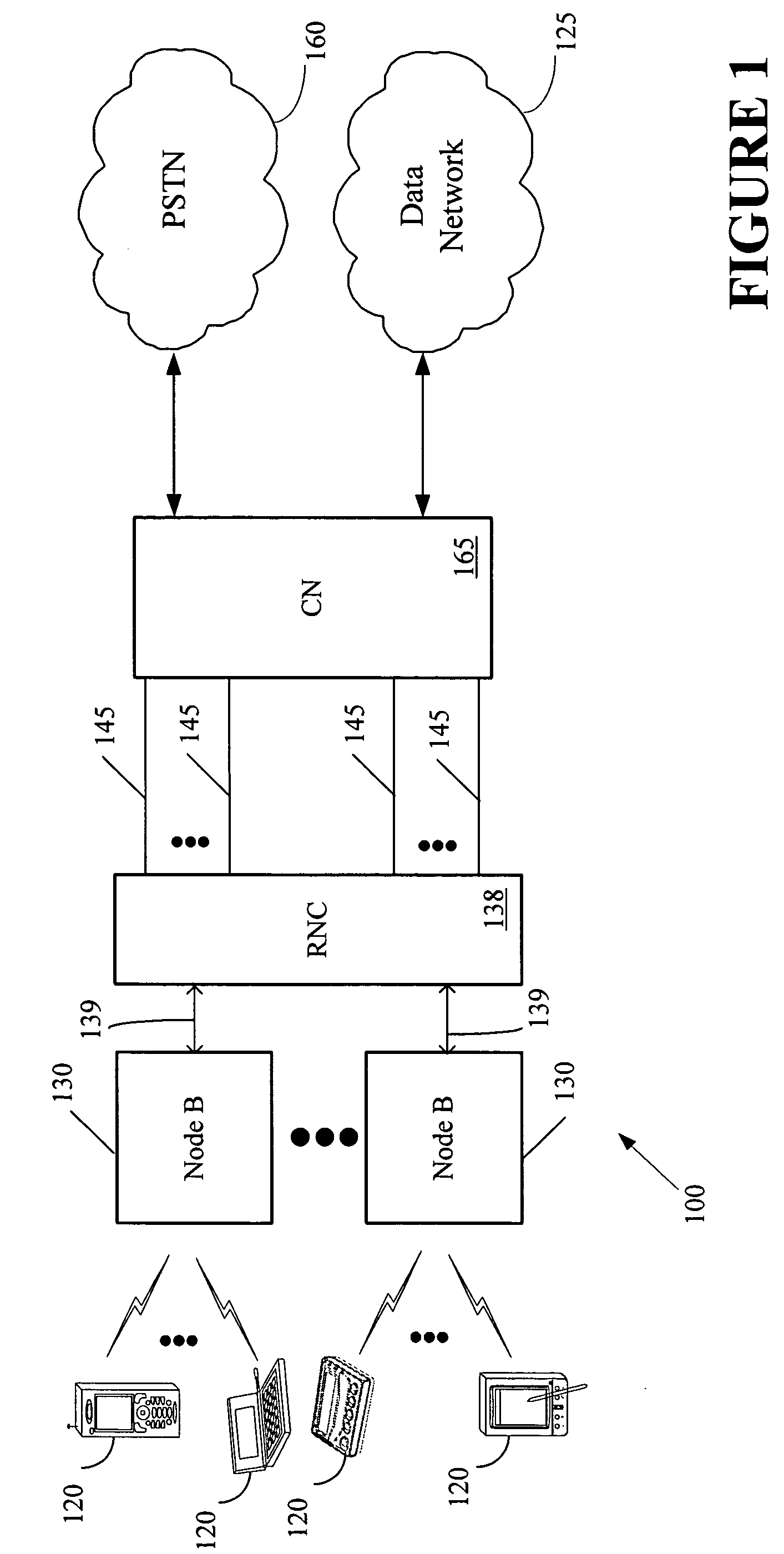
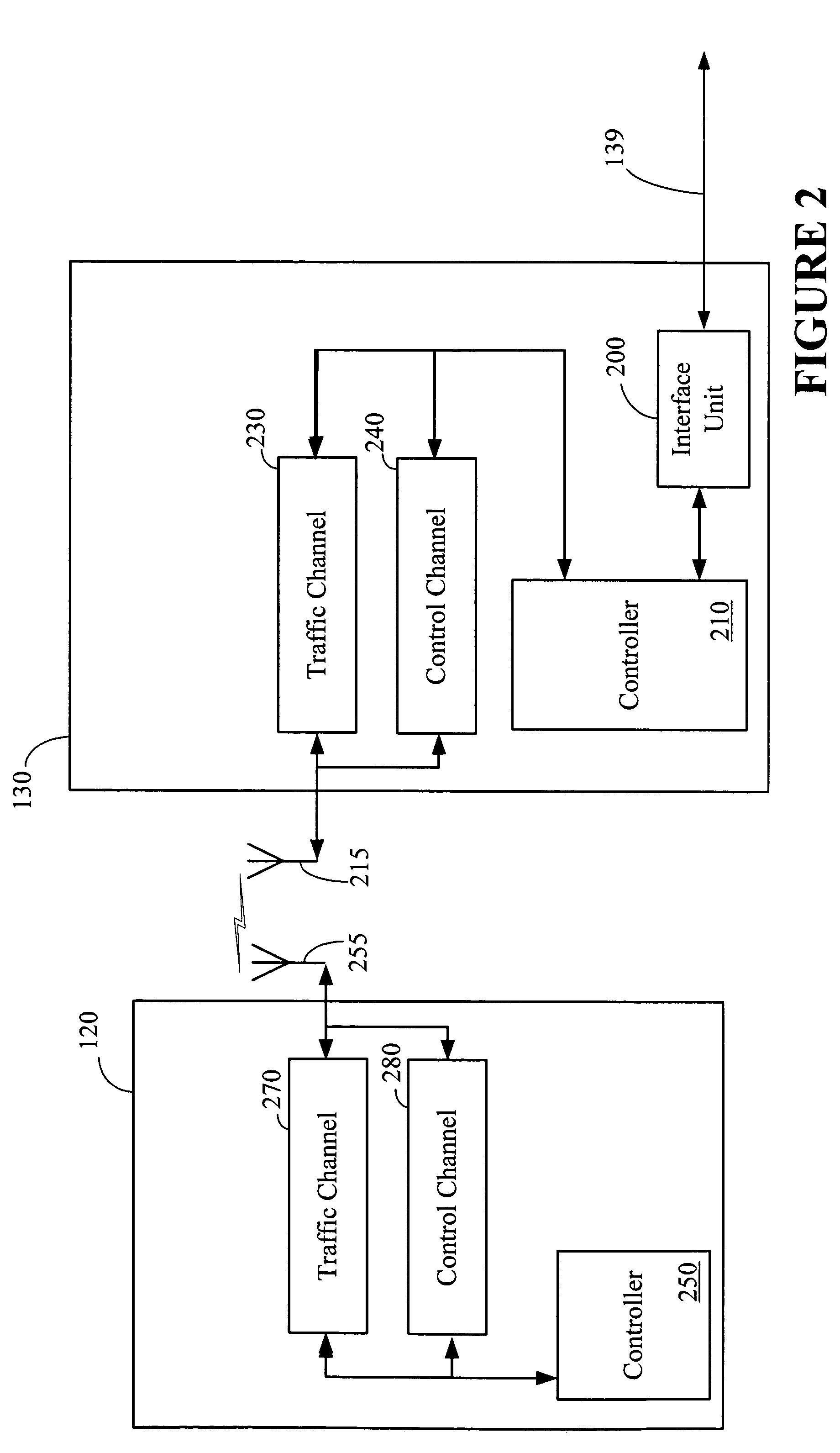
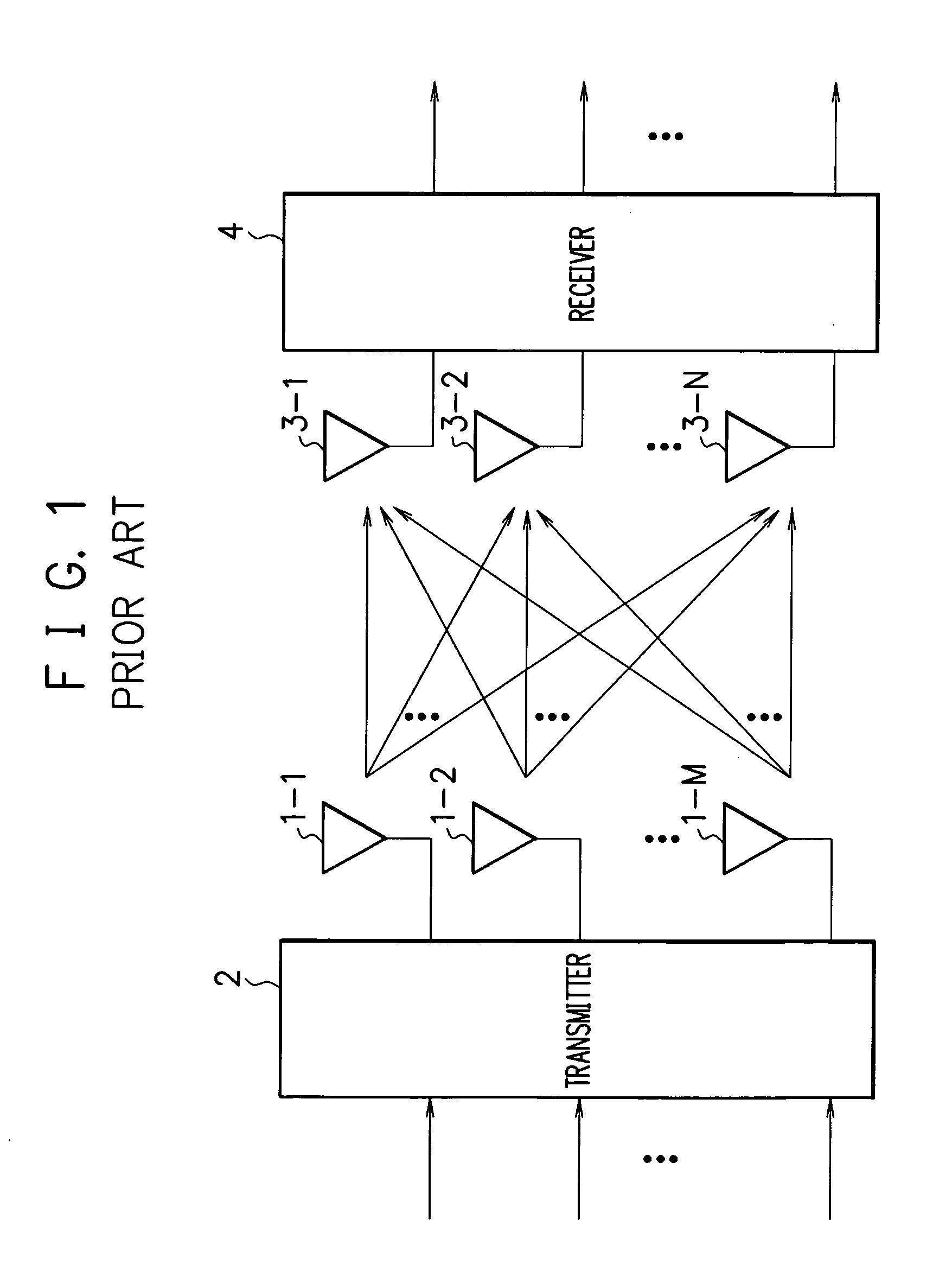
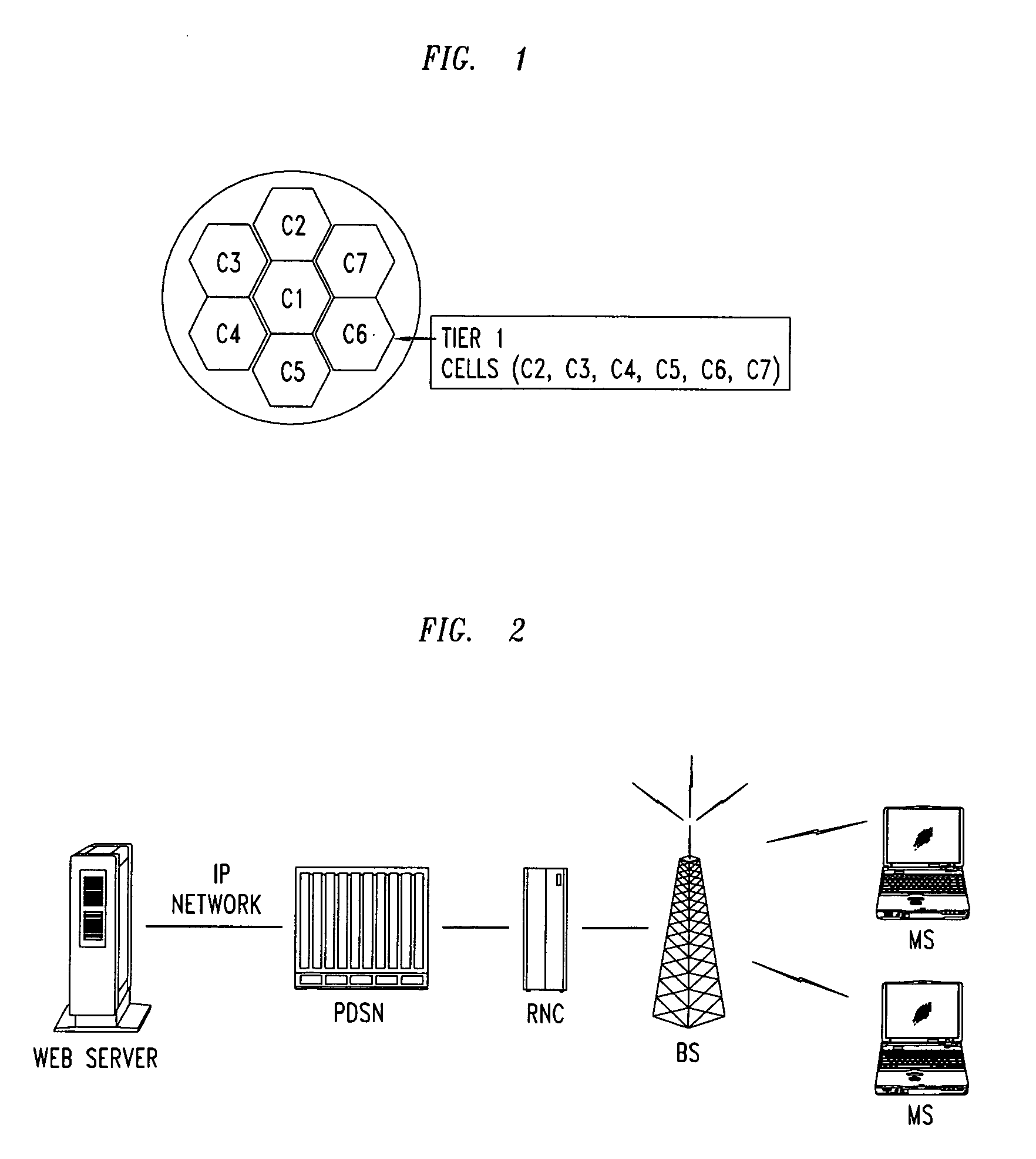
Mobile communications in a hierarchical cell structure
InactiveUS7142861B2Long talk timeIncrease capacityCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio networksCommunications system
A hierarchical cell structure (HCS) cellular communications system includes a macro cell encompassing a smaller micro cell that employ the same frequency band. The macro cell includes a macro cell base station, and the micro cell includes a micro cell base station. An uplink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established, and a downlink communication cell boundary between the macro cell and the micro cell is established. A radio network controller determines whether a condition exists in the HCS system which indicates that the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries should be unbalanced. If the condition is met or exists, the power and / or antenna beam tilt of a downlink transmission from the micro cell base station is reduced to unbalance the uplink and downlink micro cell boundaries. Alternatively, the radio network controller may employ an offset value to mathematically reduce mobile detected pilot power levels associated with the micro base station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
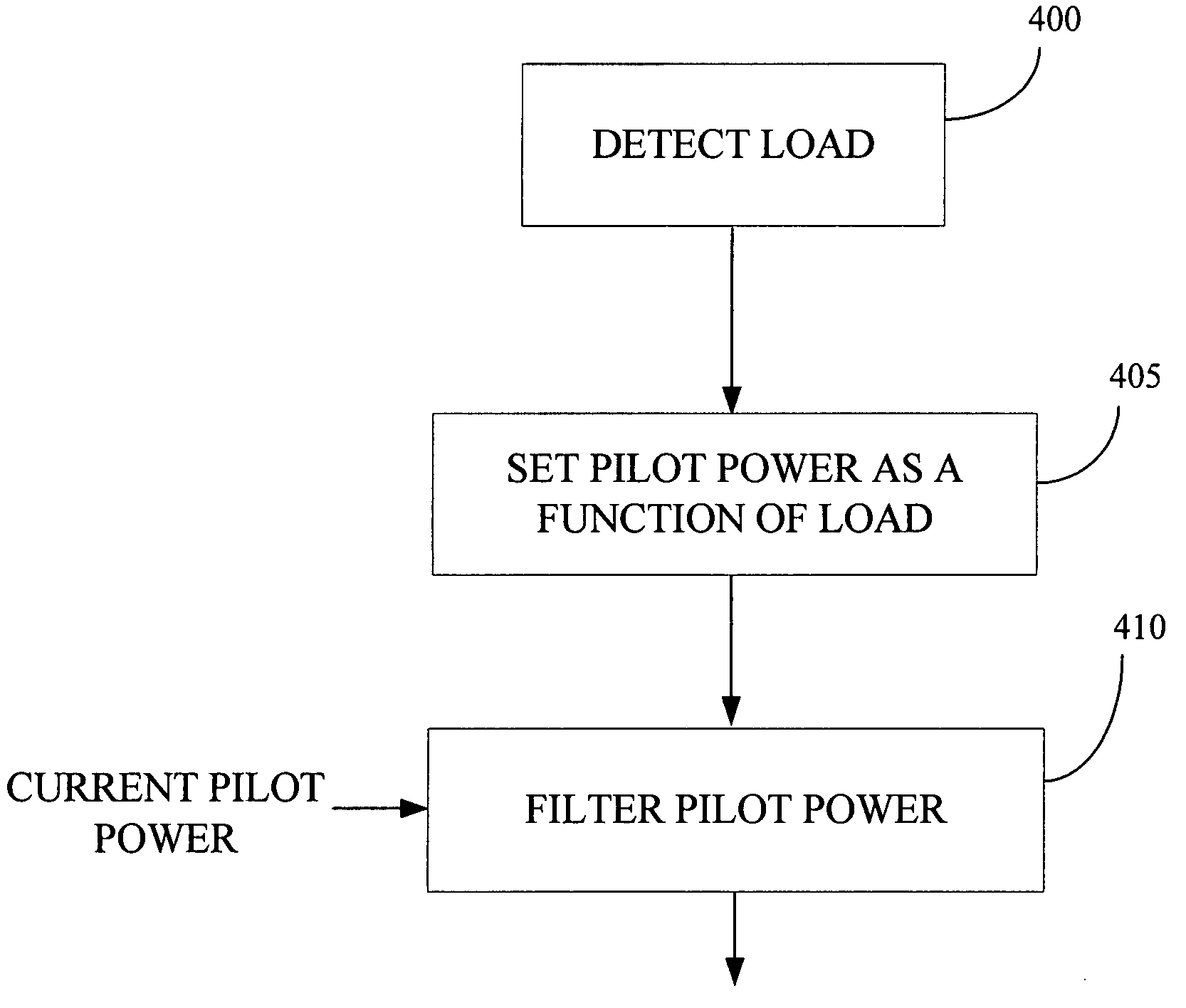
Dynamic pilot power in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS20050250527A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionControl communicationsEngineering
A method is provided for controlling pilot power in a communications system. The method comprises determining a load associated with a cell in the communications system, and setting pilot power at a level associated with the determined load. In one exemplary embodiment, pilot power is set at a first low level in response to the determined load being less than a preselected setpoint and at a second, higher level in response to the determined load being greater than the preselected setpoint.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method, Apparatus and Computer Program Product to Provide Enhanced Reverse Link Medium Access Control in a Multi-Carrier Wireless Communications System
InactiveUS20090103507A1Modulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method determines whether information corresponding to one of a number of carriers indicates the one carrier is loaded or unloaded, wherein the carriers are used for transmission of a MAC flow by the access terminal over a reverse link. Responsively, the transmission resource allocation corresponding to the MAC flow for the one carrier is adjusted based on information corresponding to carrier loading for each of the carriers and on information corresponding to reverse link pilot power for each of the carriers. An access terminal includes a function that determines whether the one is loaded or unloaded. Responsively, the function adjusts transmission resource allocation for the MAC flow for the one carrier based on information of carrier loading for each of the carriers and on information of reverse link pilot power for each of the carriers.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Apparatus and method for transceiving high speed packet data in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050094615A1Avoid problemsError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer hardwareMobile communication systems
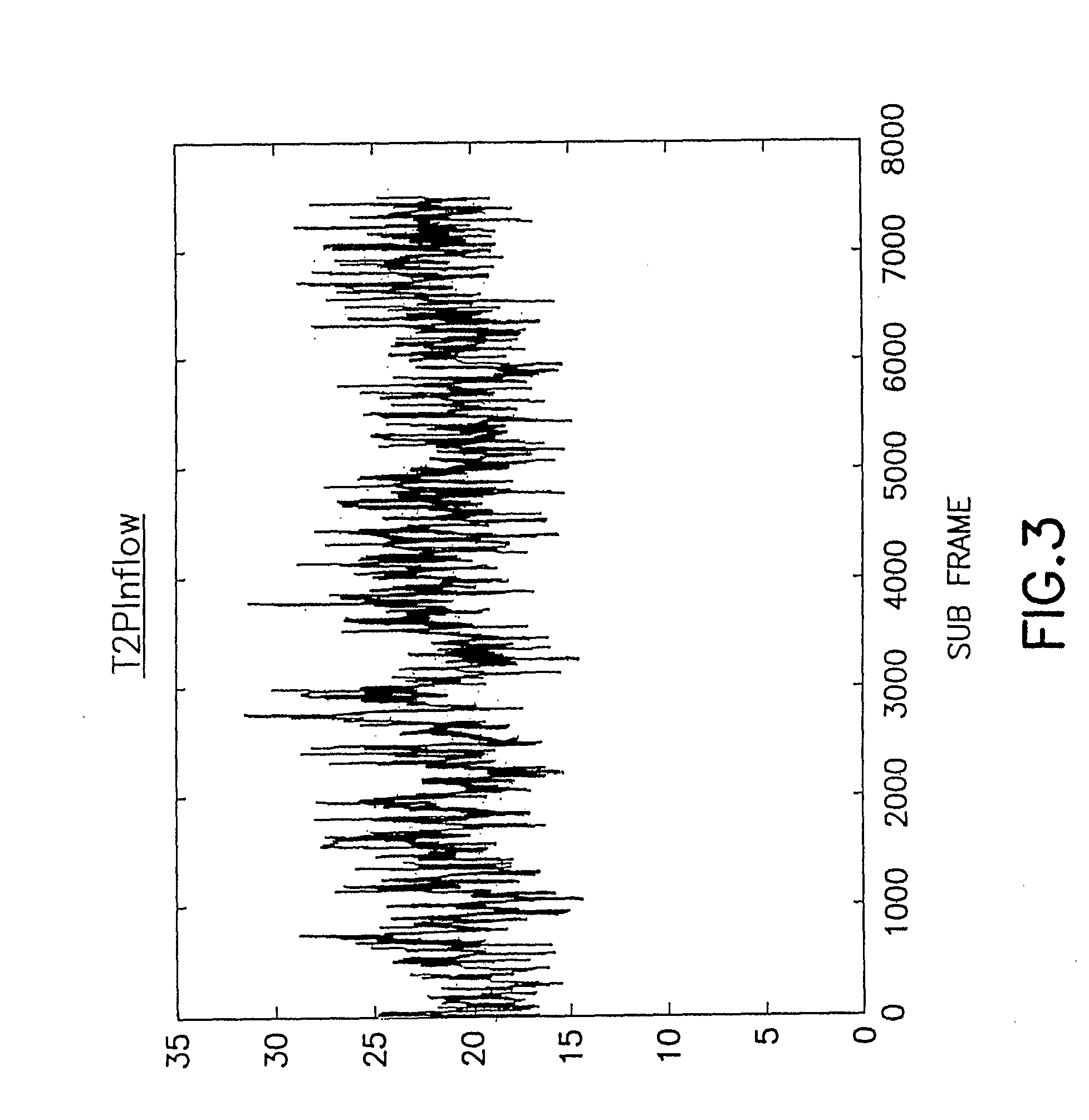
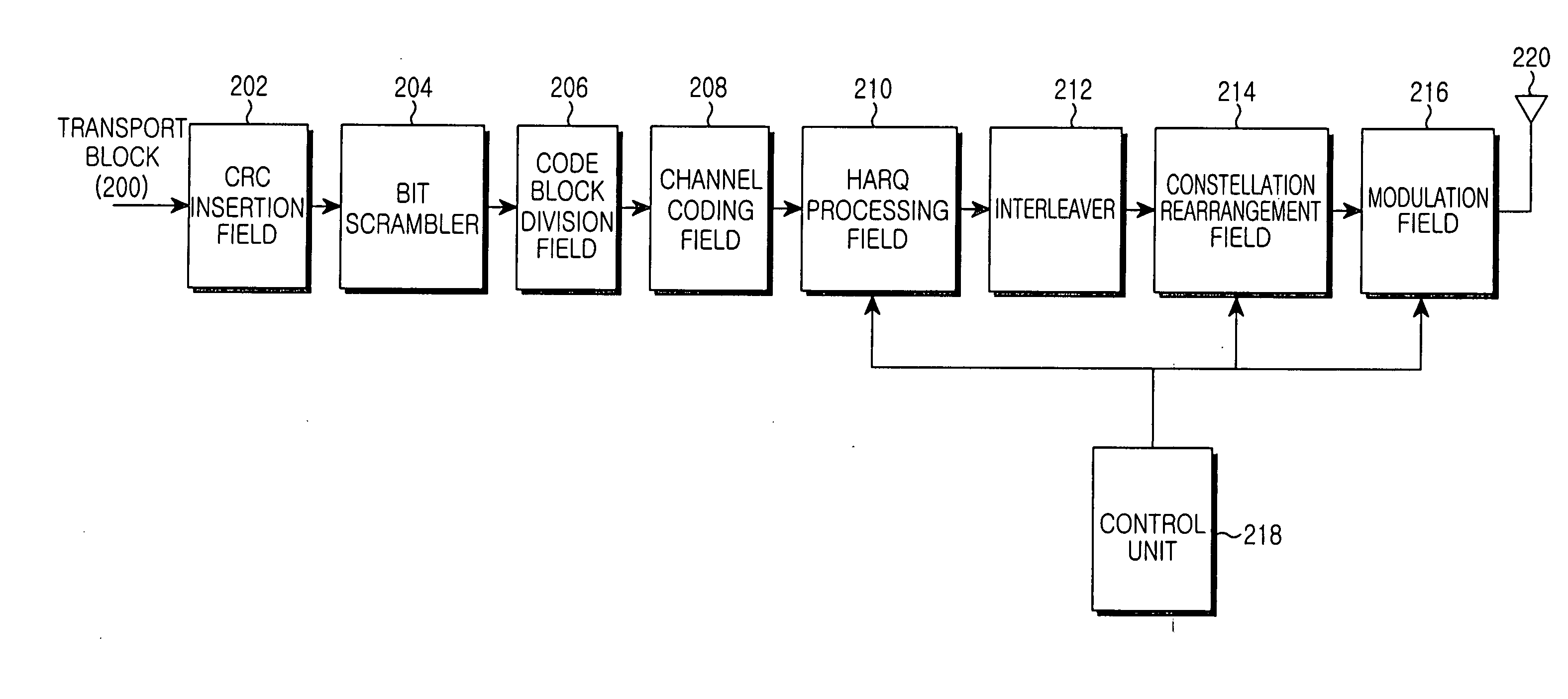
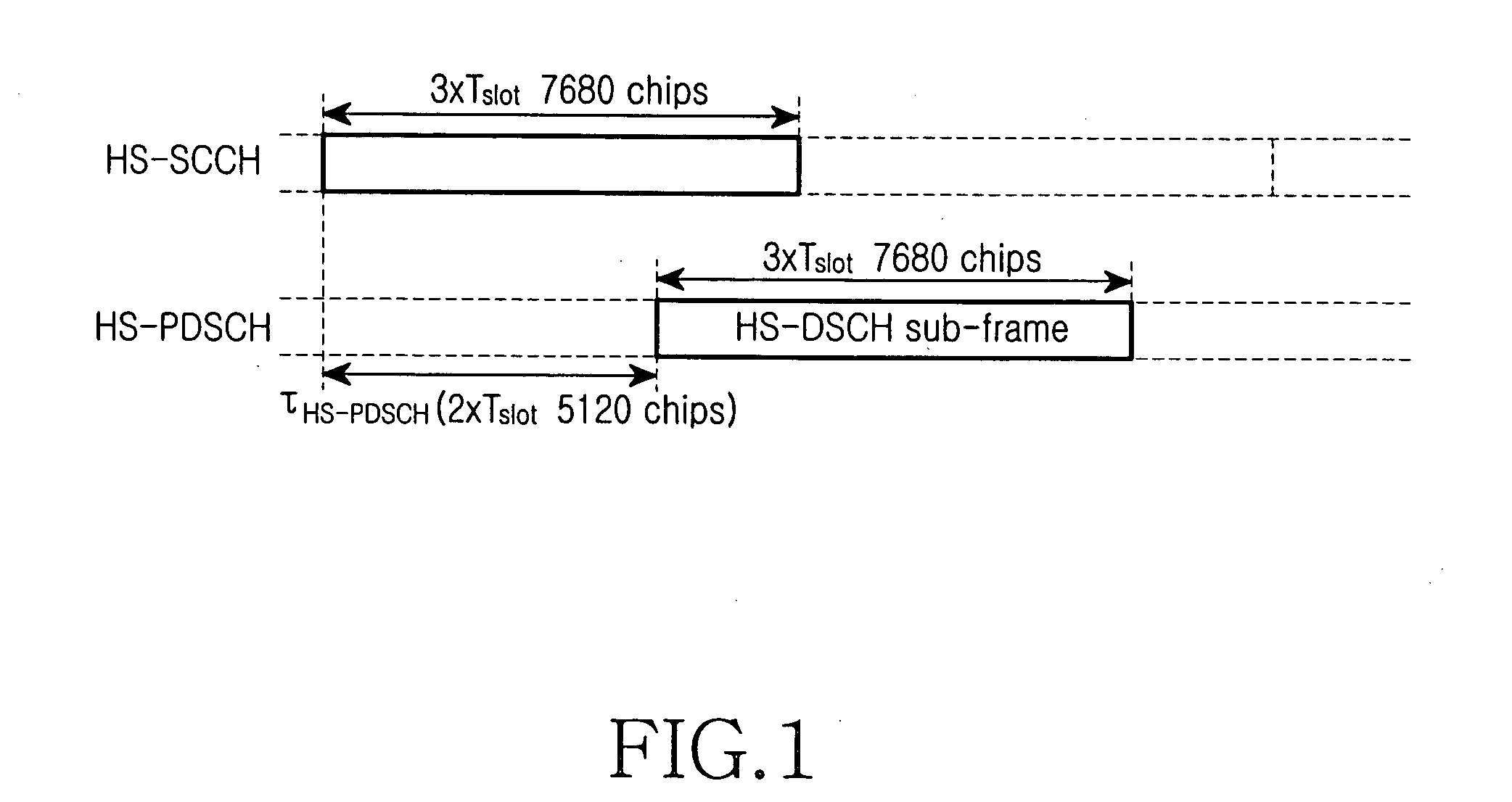
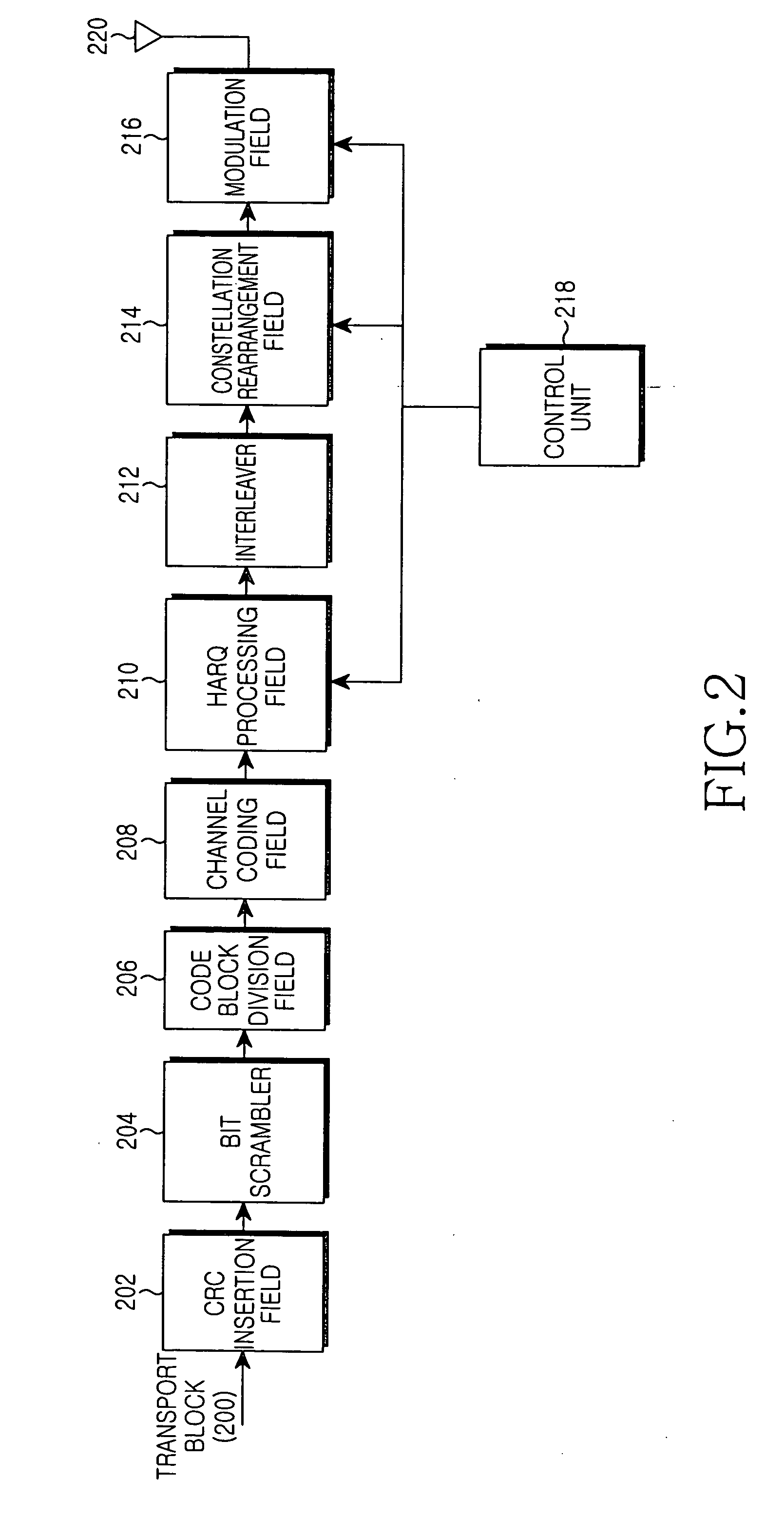
Disclosed is an apparatus and a method for transceiving high speed packet data, in which the high speed packet data are scrambled by using a scrambling code at a transmitter and the high speed packet data are de-scrambled by using a scrambling code at a receiver. When estimating a ratio of pilot power to traffic power, a problem caused by an unevenness of the power ratio is prevented. In addition, data is prevented from being transferred to an upper layer even if an HS-PDSCH is demodulated without UE data due to a detection error in an HS-SCCH during transmission of the HS-PDSCH.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
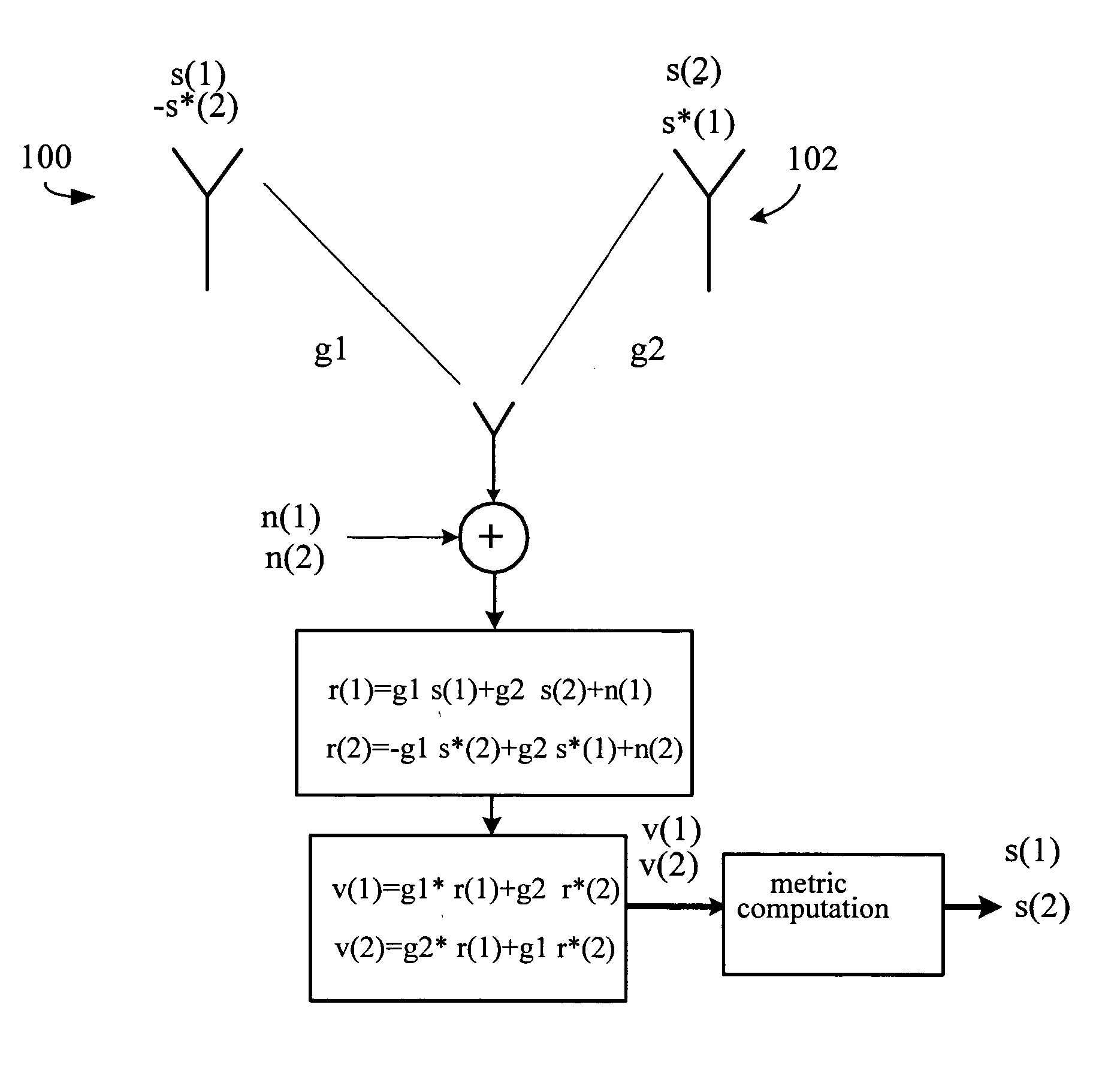
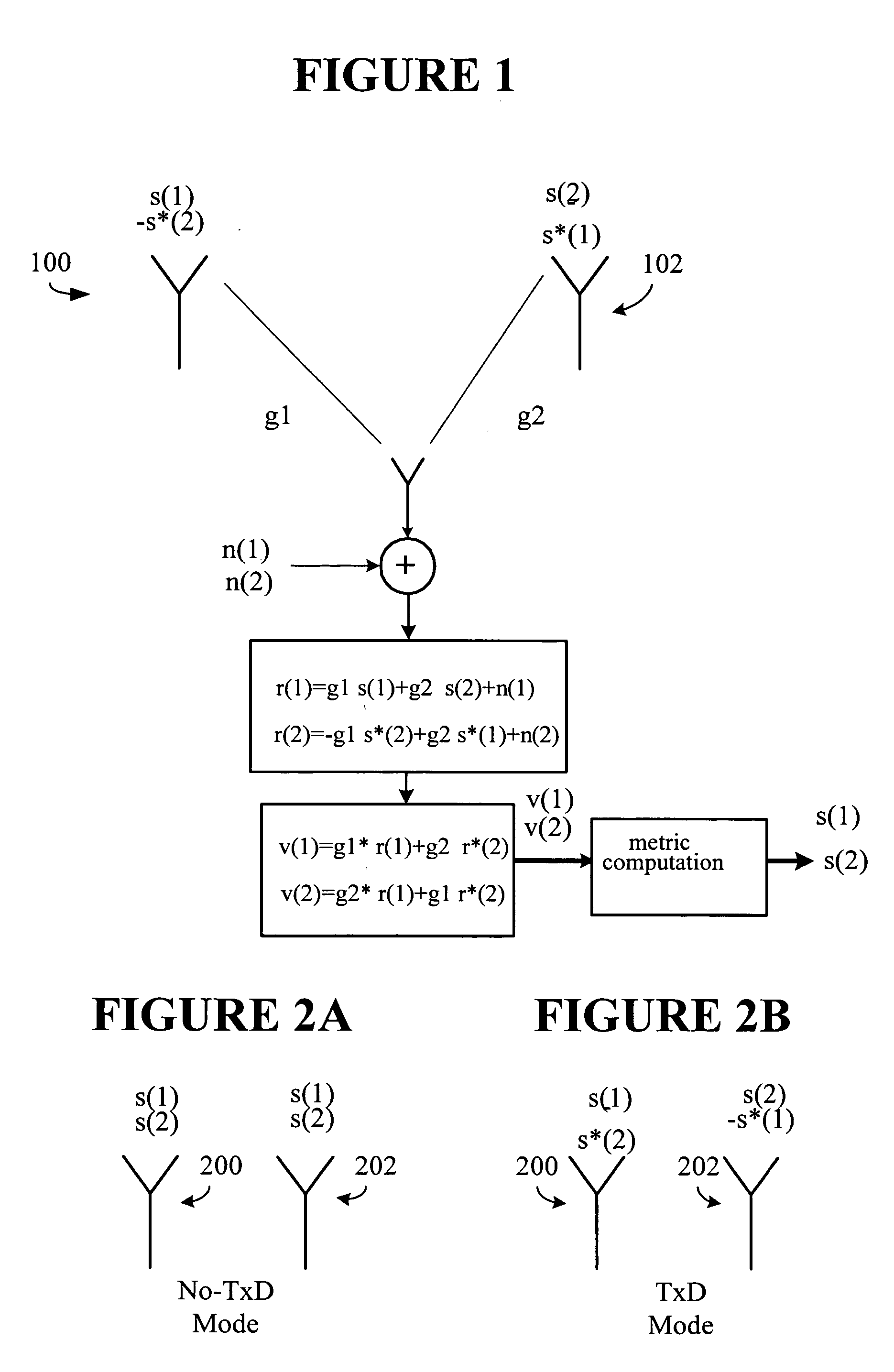
Method for controlling transmissions using both diversity and nondiversity transmission schemes
InactiveUS20060009168A1Power managementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A wireless communications system is provided in which transmissions may be made in either a diversity mode or a non-diversity mode on a slot by slot basis. When transmitting in the diversity mode, separate pilot signals are delivered over a first and second antenna. When transmitting in the non-diversity mode, substantially identical pilot signals are delivered over the first and second antennas with available pilot power substantially equally distributed therebetween.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Adaptive Femto Cell pilot power adjustment method and device
InactiveCN101674600AReduce distractionsReduce noise levelEnergy efficient ICTPower managementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
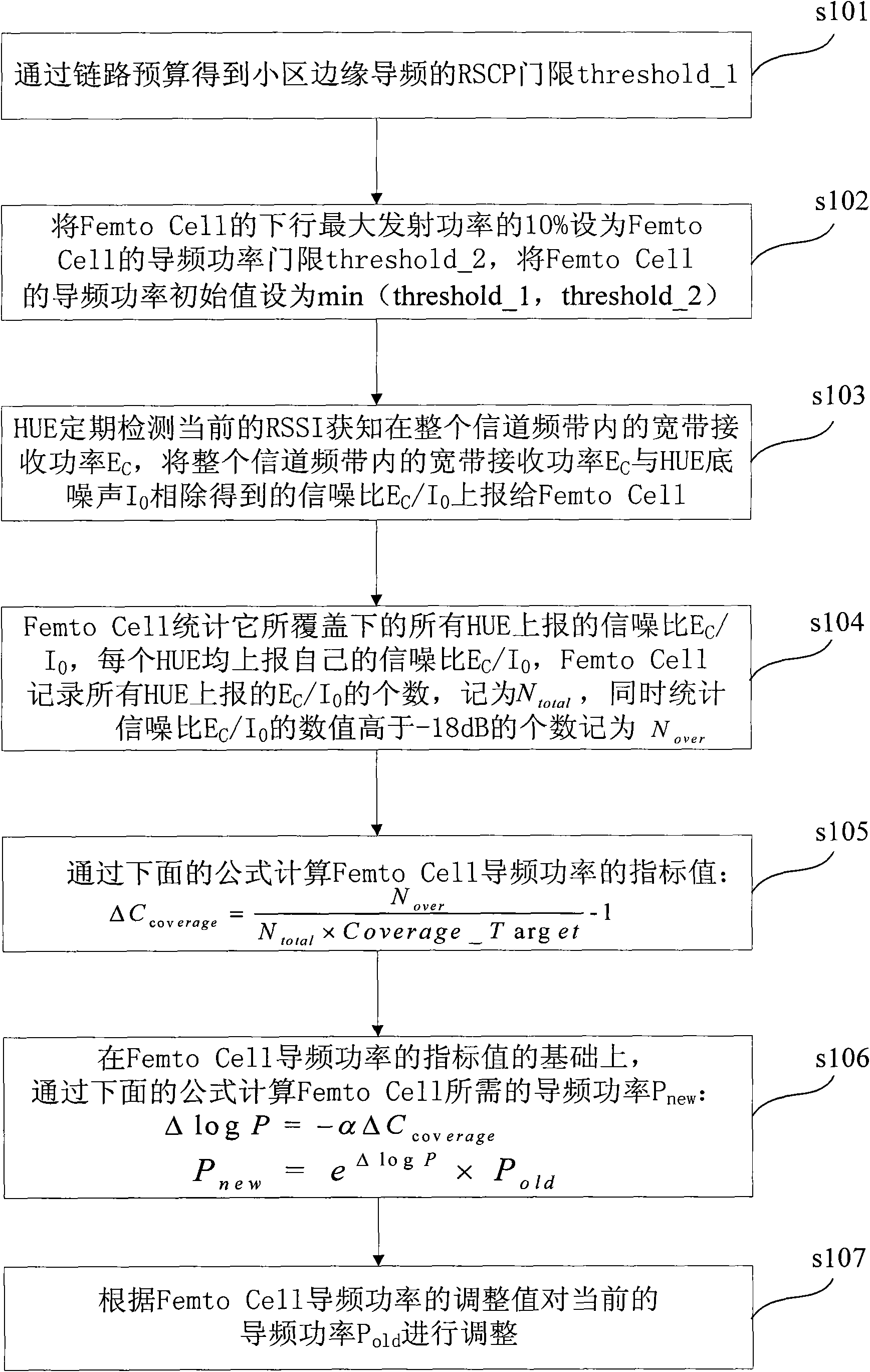
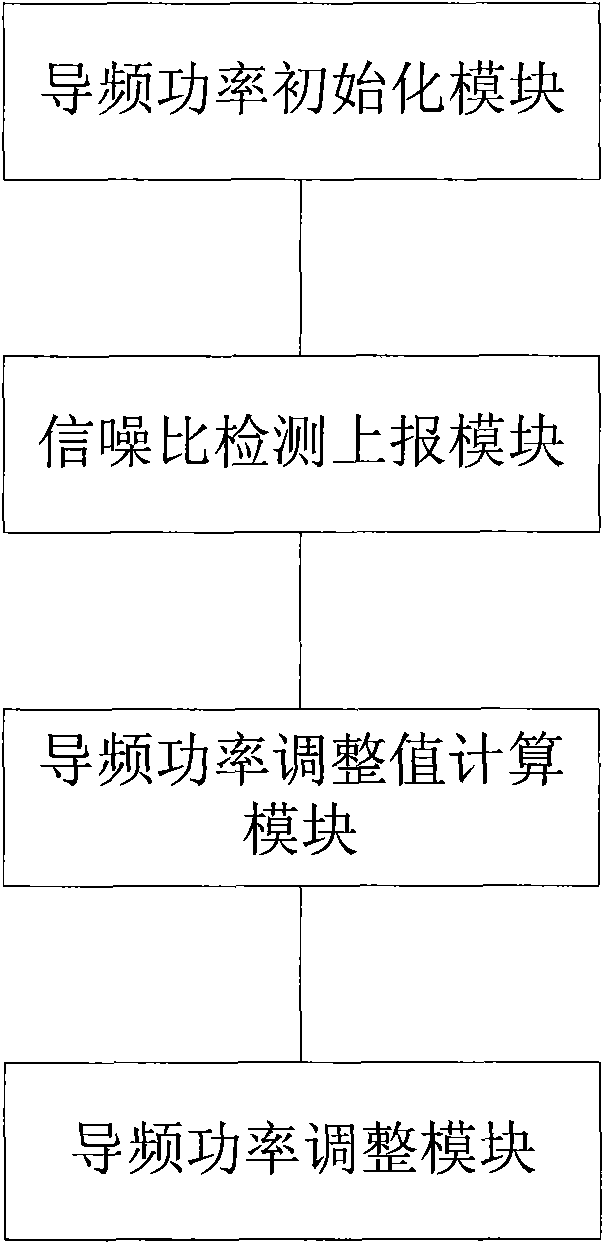
The invention discloses an adaptive Femto Cell pilot power adjustment method and a device, which is characterized in that a new power control mechanism is adopted, after the pilot power of the femto cell is initialized, the femto cell determines the adjustment value of the pilot power according to the signal-to-noise ratio reported by home user equipment in real time and accordingly controls the pilot power, accessed to each home user equipment, of the femto cell to enable the current pilot power of the femto cell to exactly satisfy the lowest power emission signal required by the signal target of the home user equipment in the coverage area of the pilot power. The invention can realize exact power control, effectively access the home user equipment to the network besides reducing the interference level of the system, thereby increasing the capacity of the system, and farthest reduce the interference of the pilot power of the femto cell in the users in the macrocell and the interference among the femto cells under the condition of ensuring the minimum emission power required by the home users.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for adaptively controlling other cell interference
InactiveUS20080051096A1Power managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsTransmitted power
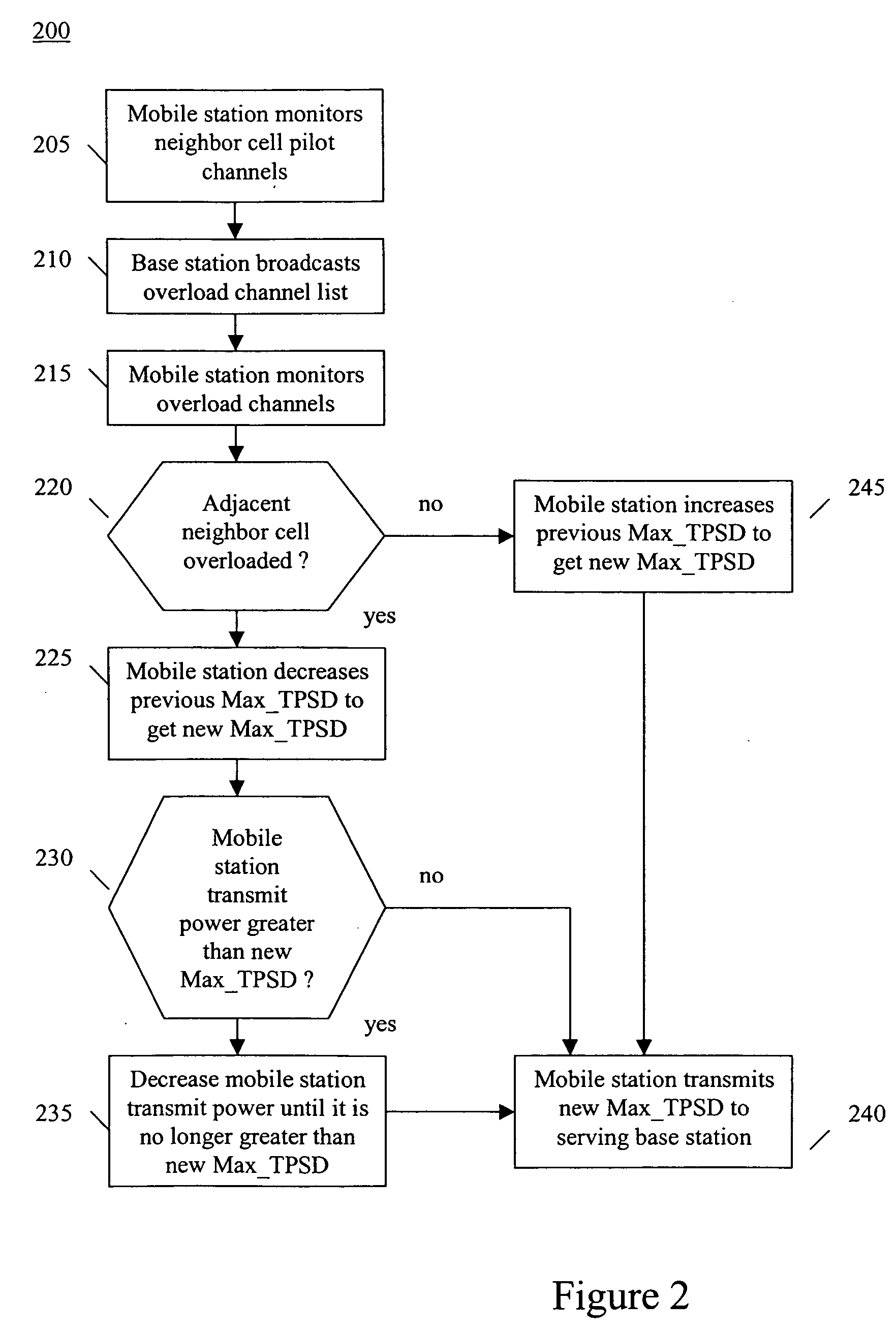
Disclosed is a method of controlling a transmit power constraint at a mobile station using a pilot power ratio (PPR) or other measurement of relative received powers (or signal strengths) between a neighbor cell transmission and a serving cell transmission such that other-cell interference produced by the mobile station may be managed. The transmit power constraint may, for example, correspond to a total or per sub-carrier maximum allowable mobile station transmit power. The transmit power constraint may be decreased if an adjacent neighbor cell, or an adjacent neighbor cell with a strongest pilot signal strength at the mobile station, is interference overloaded, i.e., interference levels in the adjacent neighbor cell is above a threshold interference level. Such decrease may be based on a pilot power ratio between a received pilot power of the overloaded adjacent neighbor cell at the mobile station and a received pilot power of the serving cell at the mobile station. Conversely, the transmit power constraint may be decreased if at least one adjacent neighbor cell, or the adjacent neighbor cell with the strongest pilot signal strength at the mobile station, is not interference overloaded. Such increase may be based on a pilot power ratio between a received pilot power of the adjacent neighbor cell with the strongest pilot signal strength at the mobile station and a received pilot power of the serving cell at the mobile station.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and apparatus for wireless communication
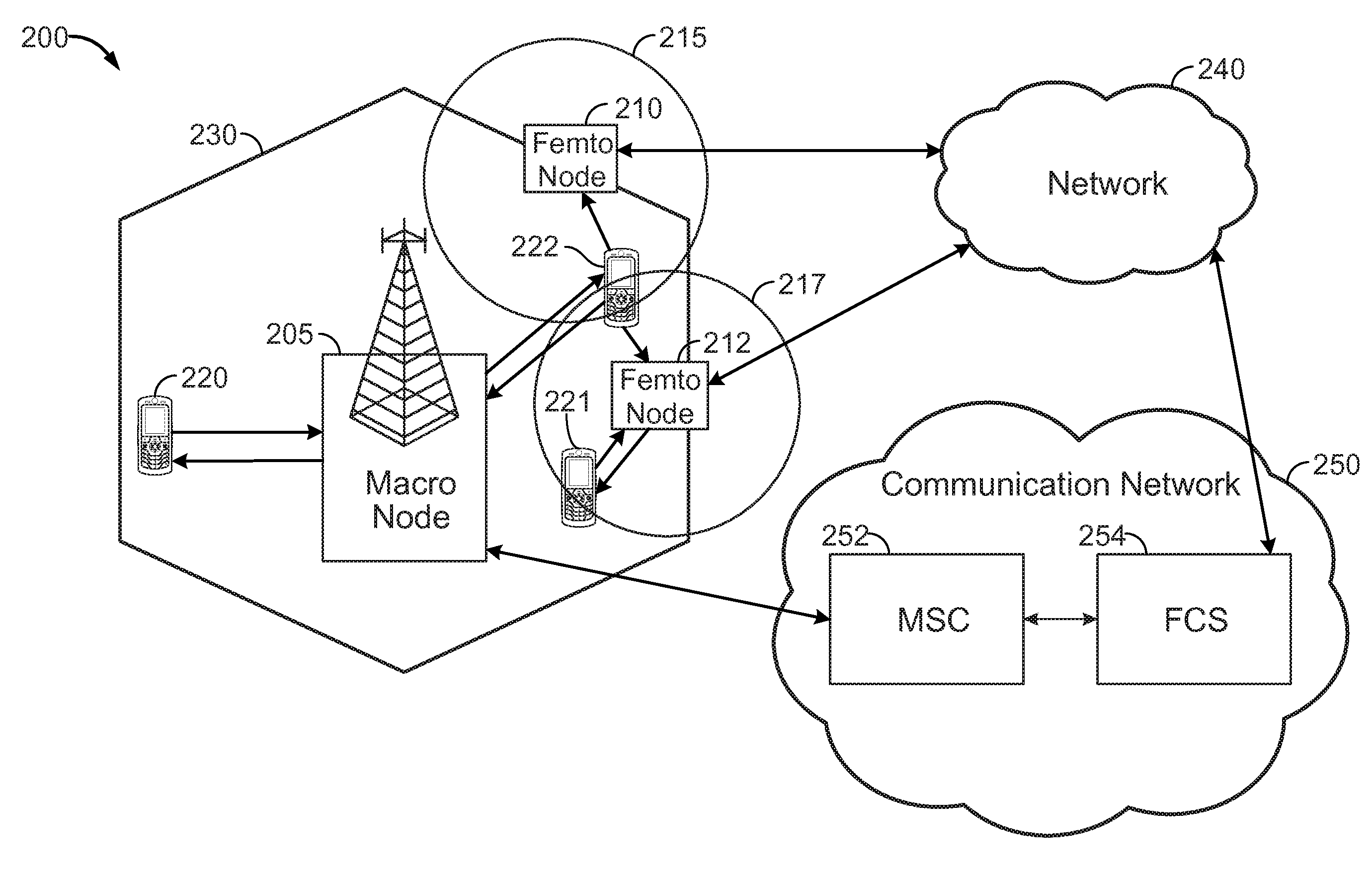
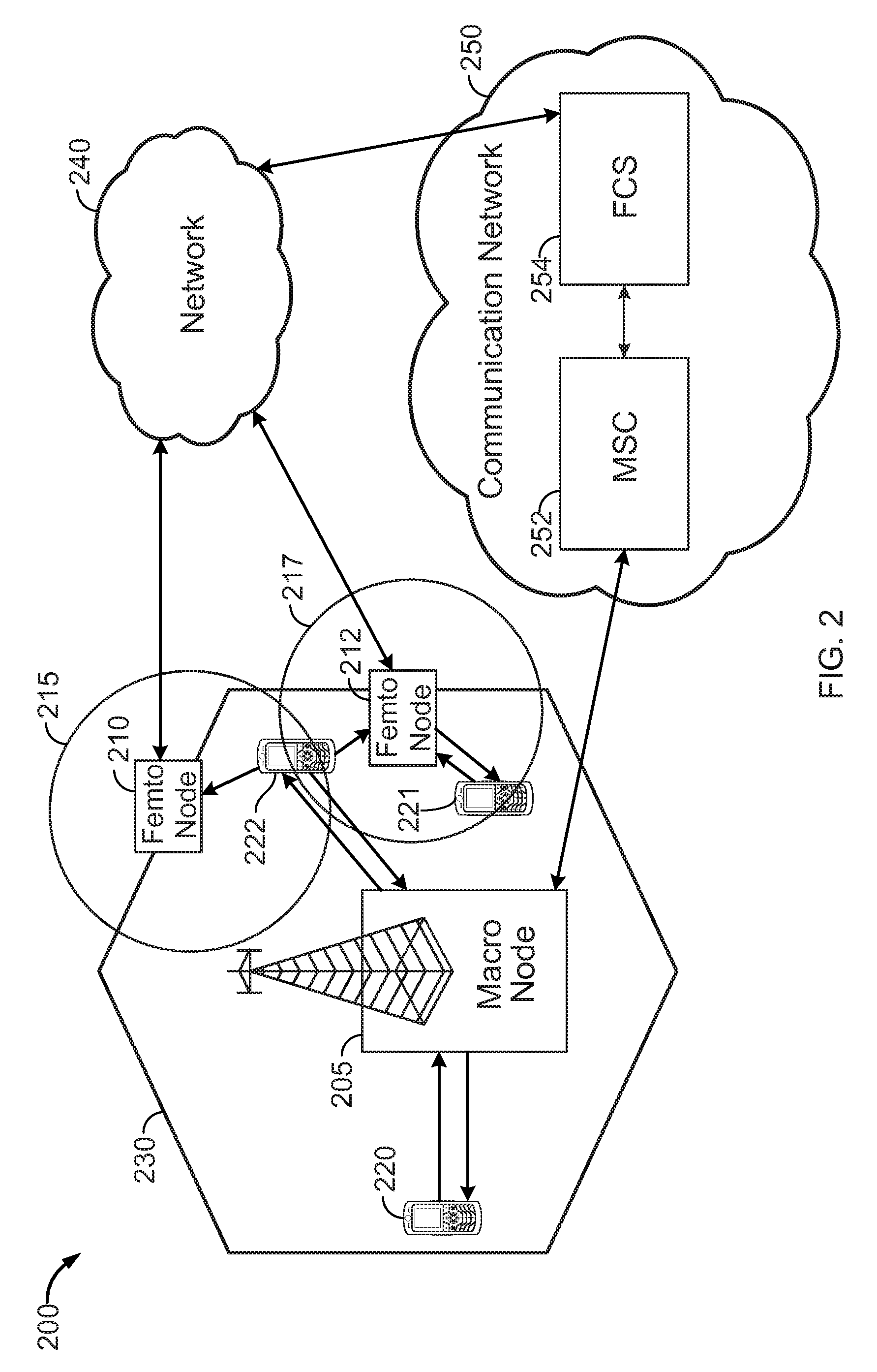
Systems and methods for performing a handoff of an access terminal from a macro node to a femto node are disclosed. In one embodiment, a femto convergence server may select a target femto node based on, at least in part, signal strengths of the reverse links between femto nodes with a specific identifier and an access terminal, and the transmit pilot powers of the femto nodes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Qualifying available reverse link coding rates from access channel power setting
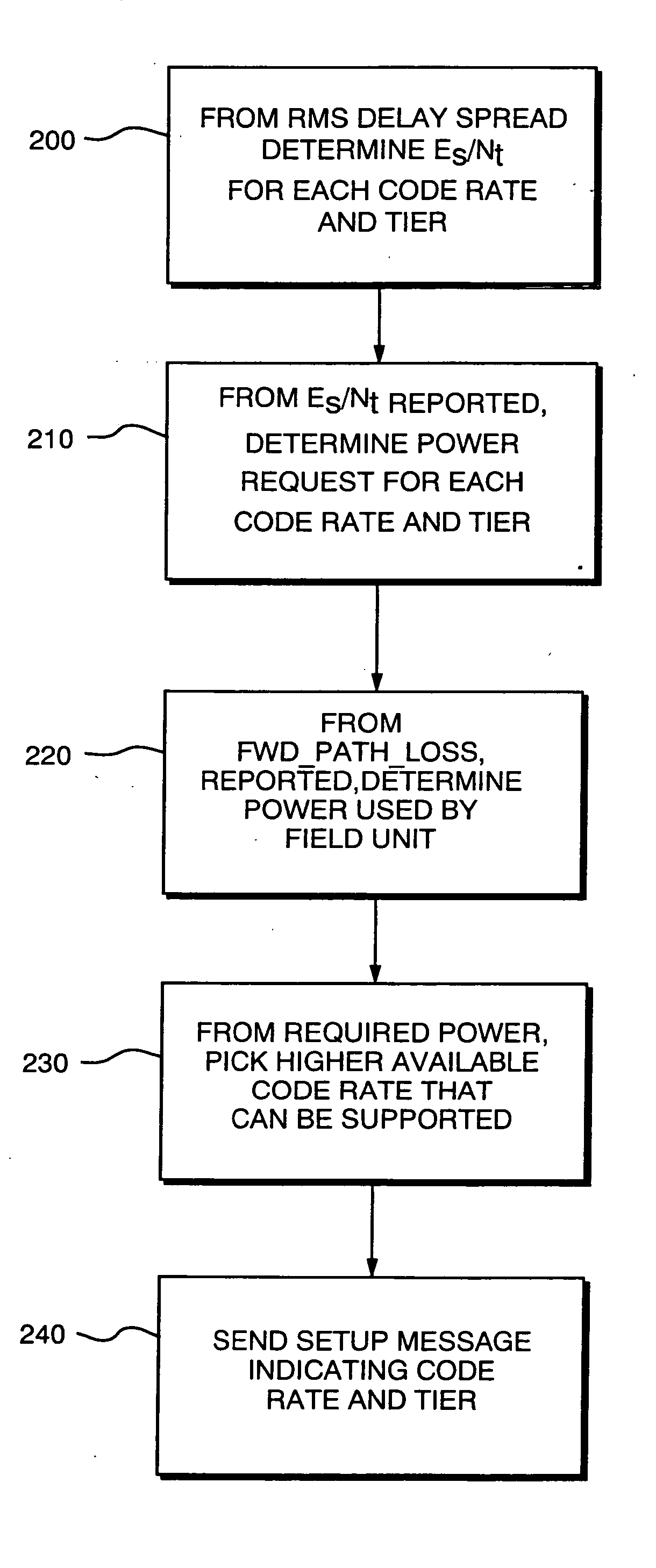
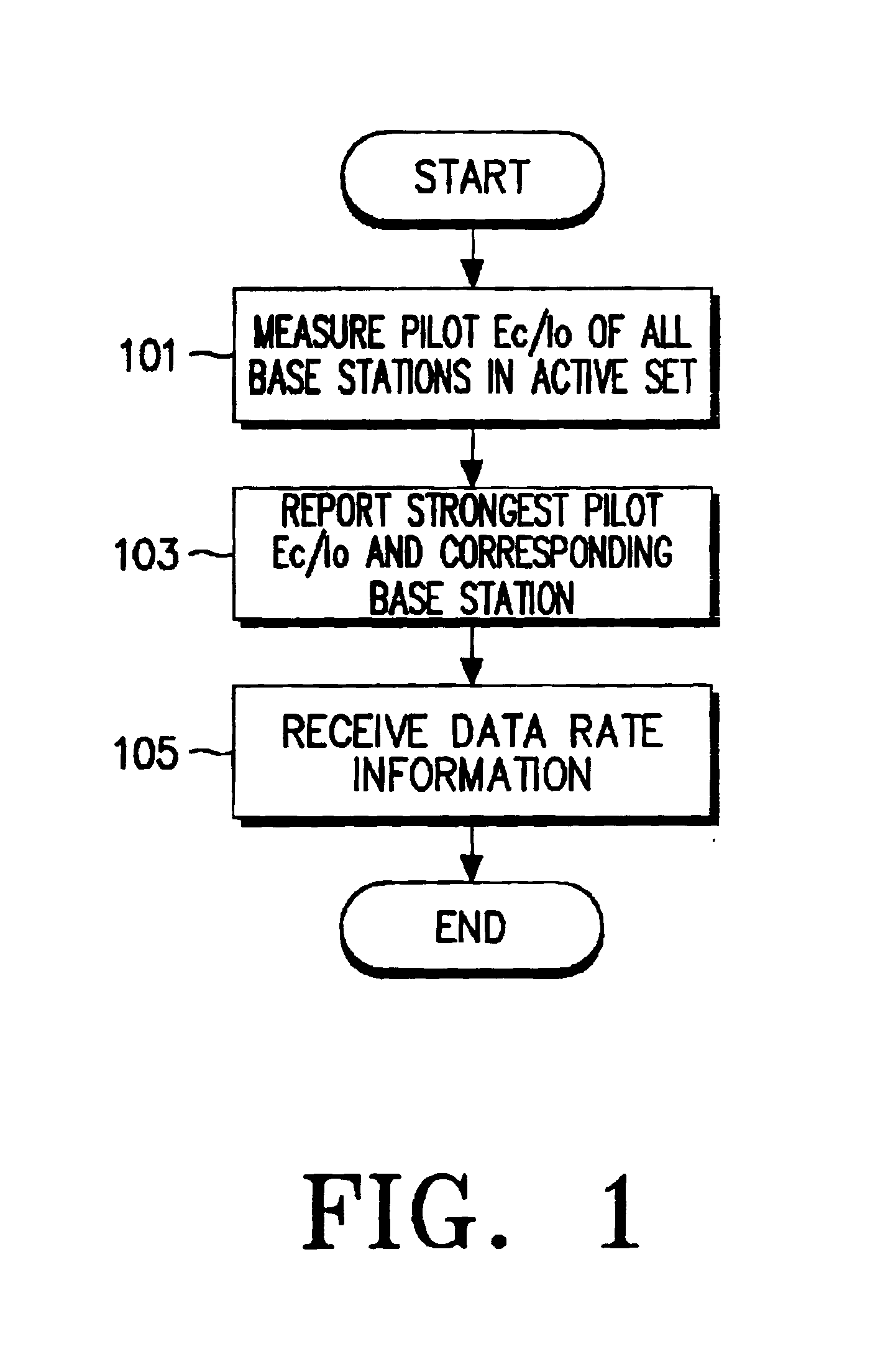
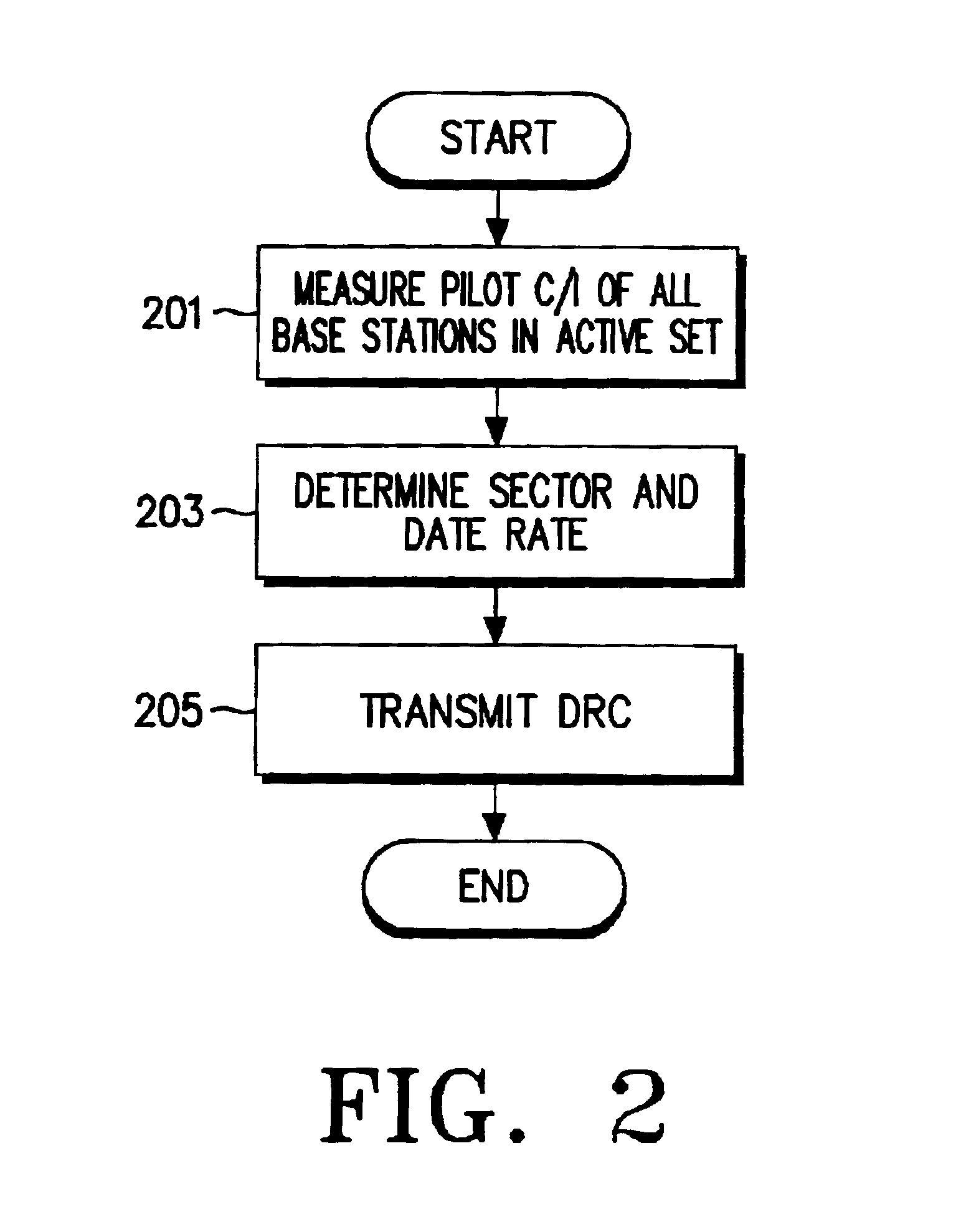
Data rate allocation decisions are made for a communications channel, such as a wireless reverse link connection. A first parameter used in this determination is a path loss, which is determined by the following process. First, a message is sent from a first station to a second station, such as on a paging channel. The message indicates a forward Effective Radiated Power (ERP) of a pilot signal transmitted by the first station. The second station then determines the received signal strength of this pilot signal, taking into account receiver gains. The path loss can then be estimated by the second station as the difference between the forward ERP data value that it received and the detected received pilot power. The second station also then preferably determines a transmit power level when transmitting a message back to the first station. This transmit power level information is encoded as a digital data word together with the forward path loss information as calculated by the first station. Upon receipt of these two pieces of information by the first station, the forward path loss estimate as calculated by the second station, and the output power value of the second station, the first station can then determine the amount of excess power available at the field unit. This excess power difference is indicative of the amount of dynamic range available in the transmit power amplifier in the particular second station. With this information, the first station can then make a determination as to whether coding rates which require a higher dynamic range will be acceptable for use by the particular second station.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
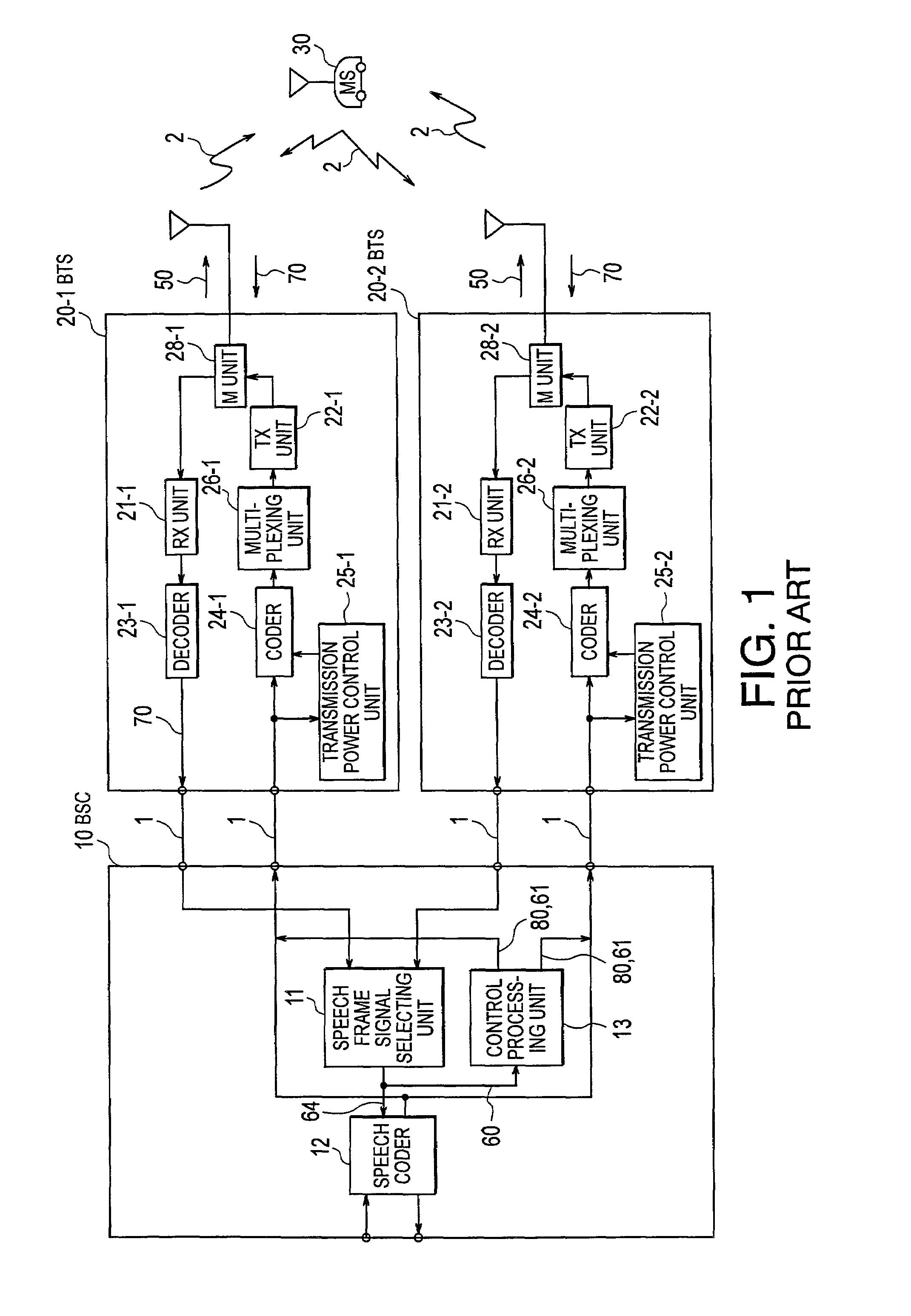
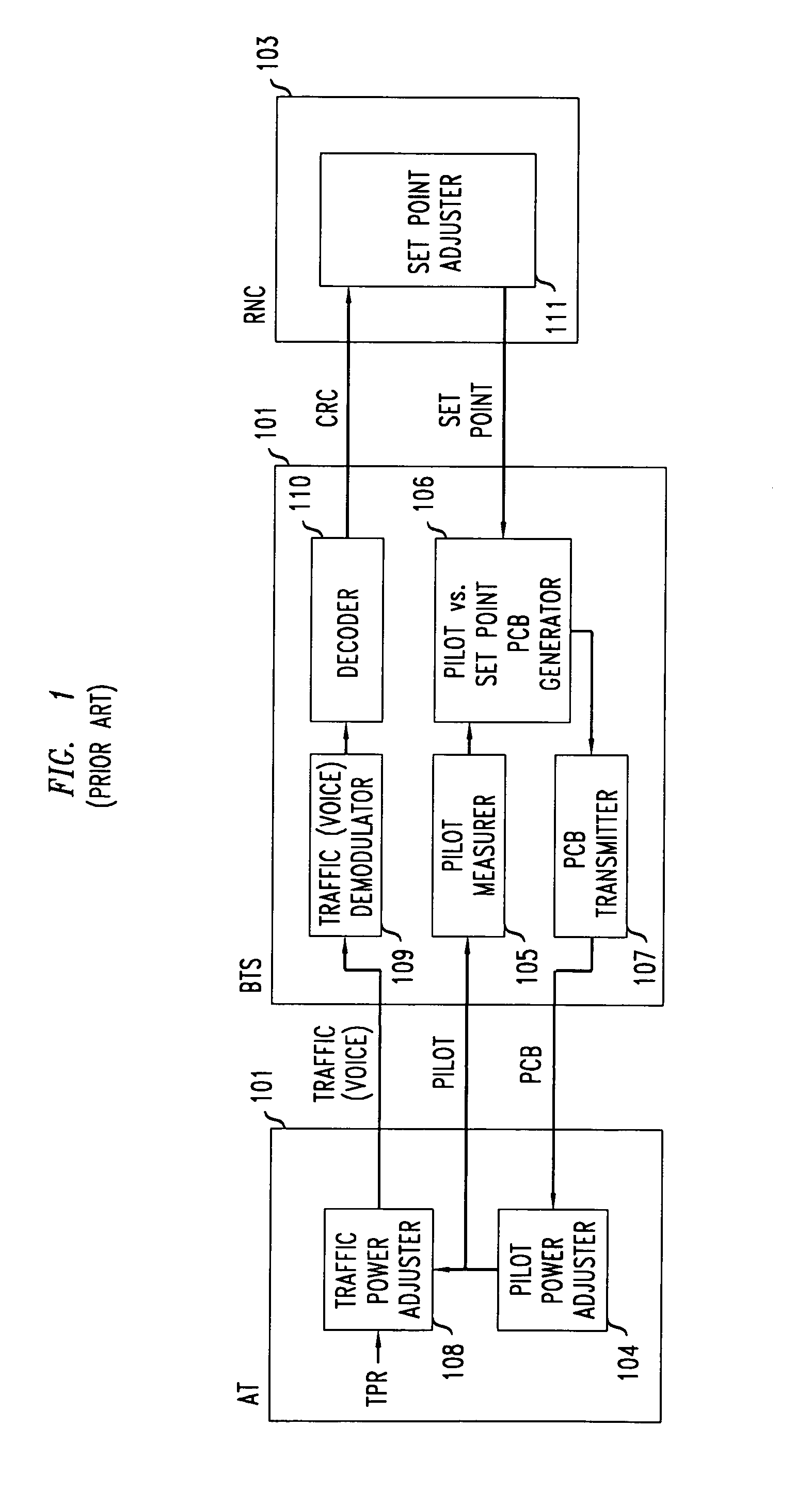
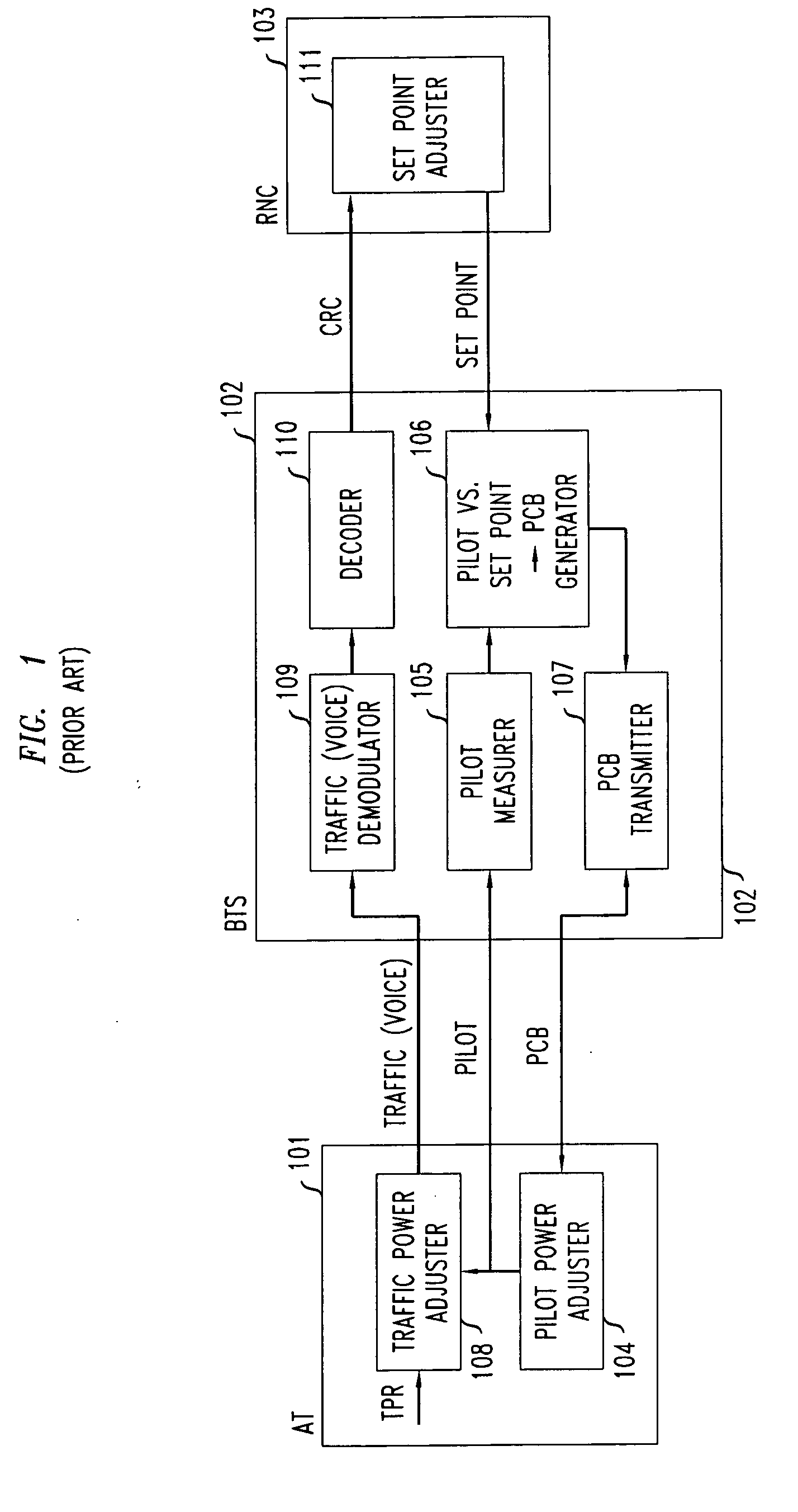
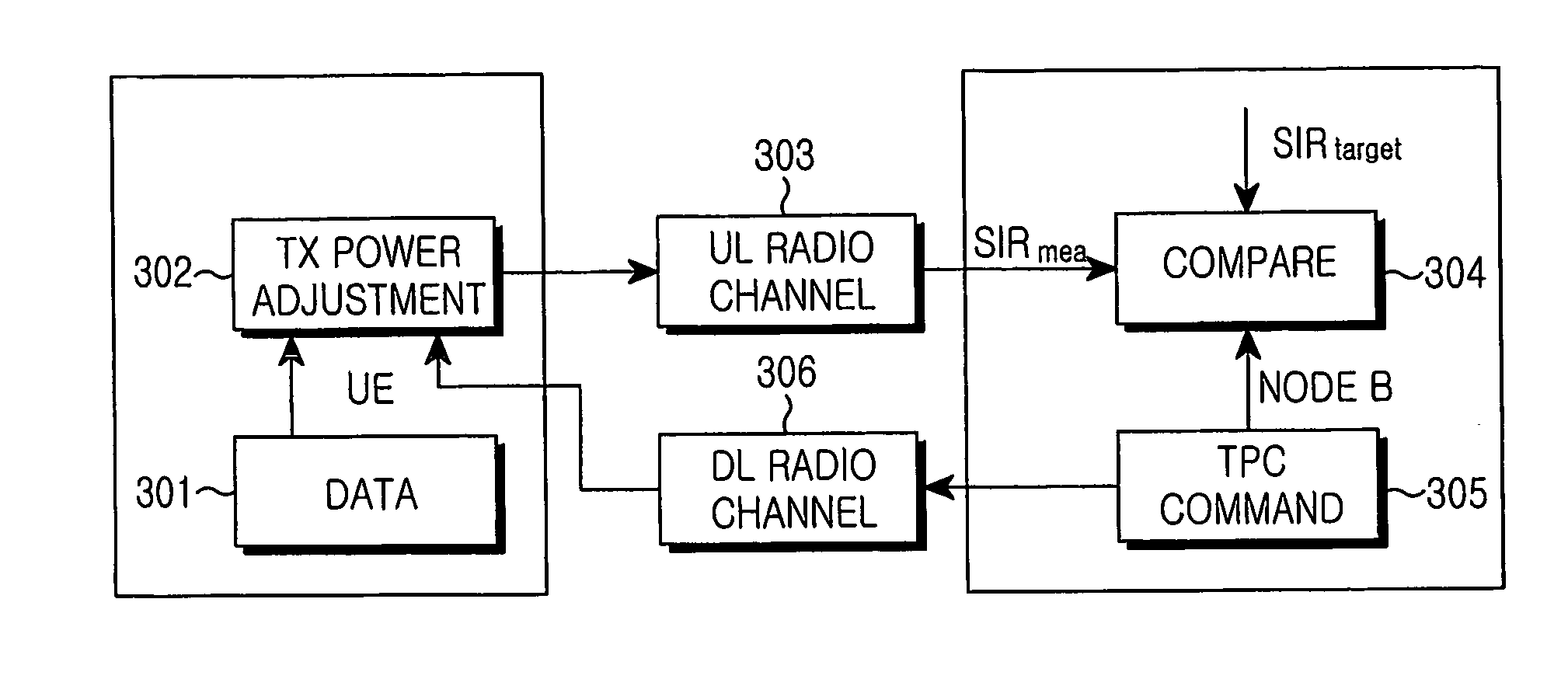
CDMA communication system with pilot power control unit
InactiveUS7236467B2Increase power valueSatisfactory reception environmentPower managementTransmission control/equalisingMultiplexingTraffic intensity
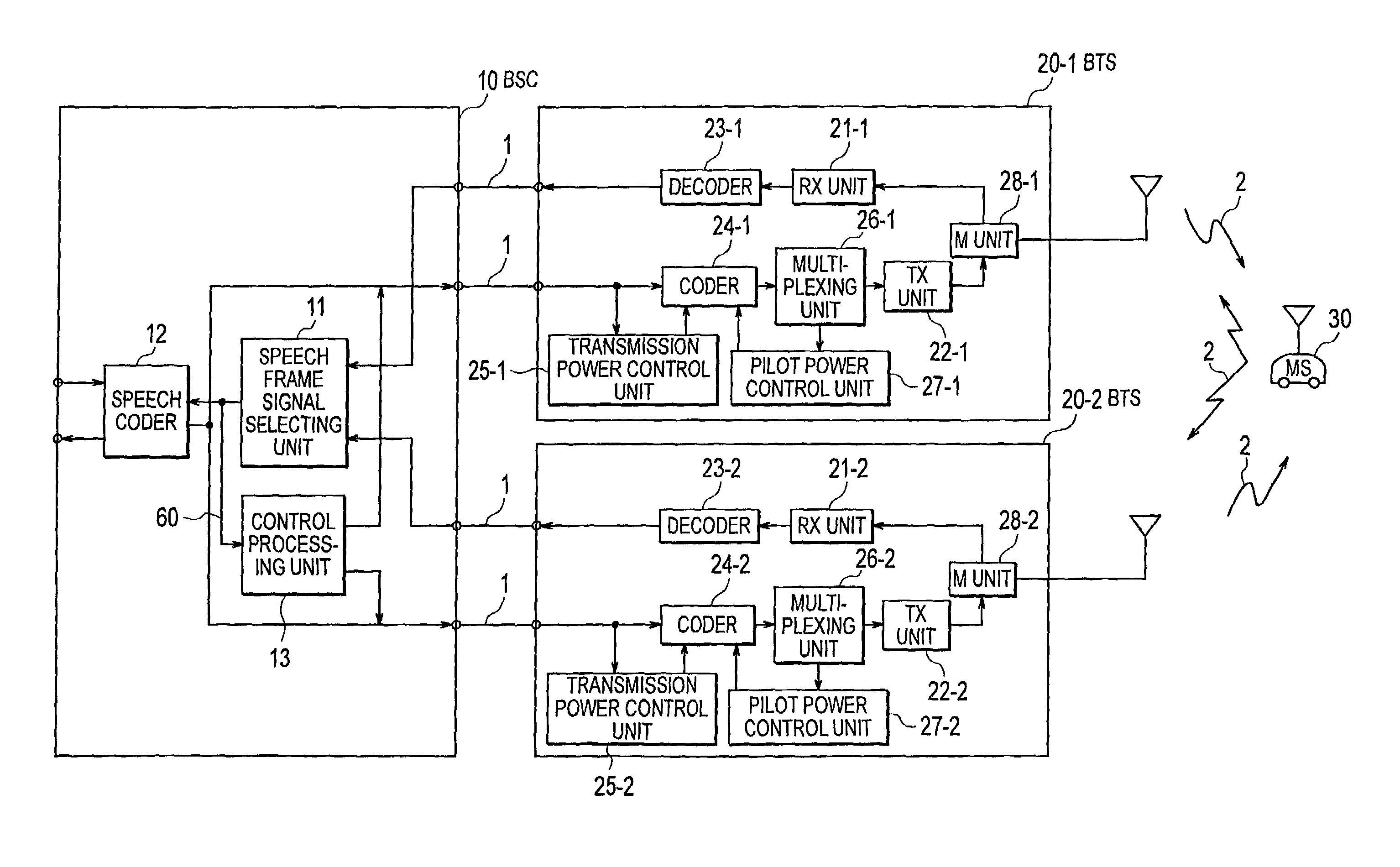
A satisfactory reception environment is secured efficiently regardless of a degree of the traffic intensity. A pilot power control unit is provided to a base station radio unit. The pilot power control unit controls a desired wave power-to-interference wave power ratio of a pilot signal to stay at a preset value. More specifically, upon receipt of a multiplex wave from a multiplexing unit, the pilot power control unit computes a desired wave power-to-interference wave power ratio of a pilot signal. Then, the pilot power control unit transmits a command signal to a coder to change a transmission power value of the pilot signal in an amount corresponding to a difference between the computed desired wave power-to-interference wave power ratio and a set desired wave power-to-interference wave power ratio.
Owner:NEC CORP
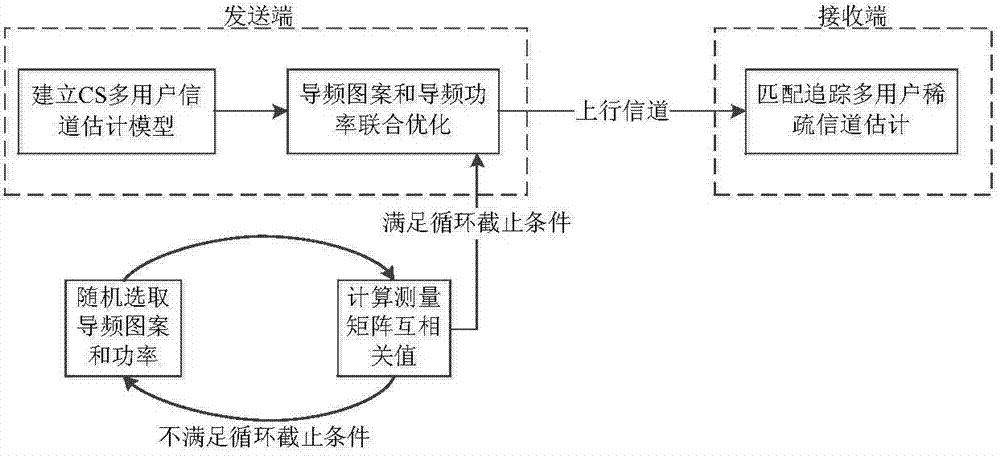
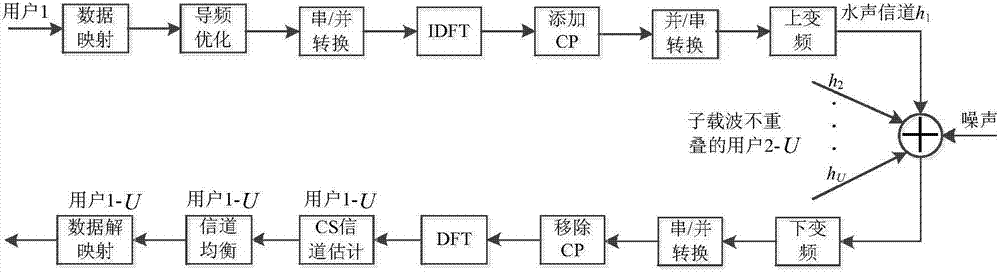
Sparse channel estimation and pilot optimization method for underwater sound OFDMA uplink communication
ActiveCN104780128AOvercoming the Error Floor PhenomenonImprove performanceBaseband system detailsTransmission path multiple useAlgorithmMatching pursuit algorithms
The invention discloses a sparse channel estimation and pilot optimization method for underwater sound OFDMA uplink communication. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a comb-pilot-based multi-user CS sparse channel estimation model at a sending end to obtain a measurement matrix cross-correlation expression; performing joint optimization on pilot patterns and pilot power at the sending end according to the measurement matrix cross-correlation expression to reduce measurement matrix cross-correlation under a CS channel estimation model; performing multi-user sparse channel estimation through a matching pursuit algorithm under a CS frame at a receiving end by utilizing the multi-user CS sparse channel estimation model and the pilot information about the joint optimization on the pilot patterns and the pilot power. The sparse channel estimation and pilot optimization method for the underwater sound OFDMA uplink communication has the advantage that estimation errors can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
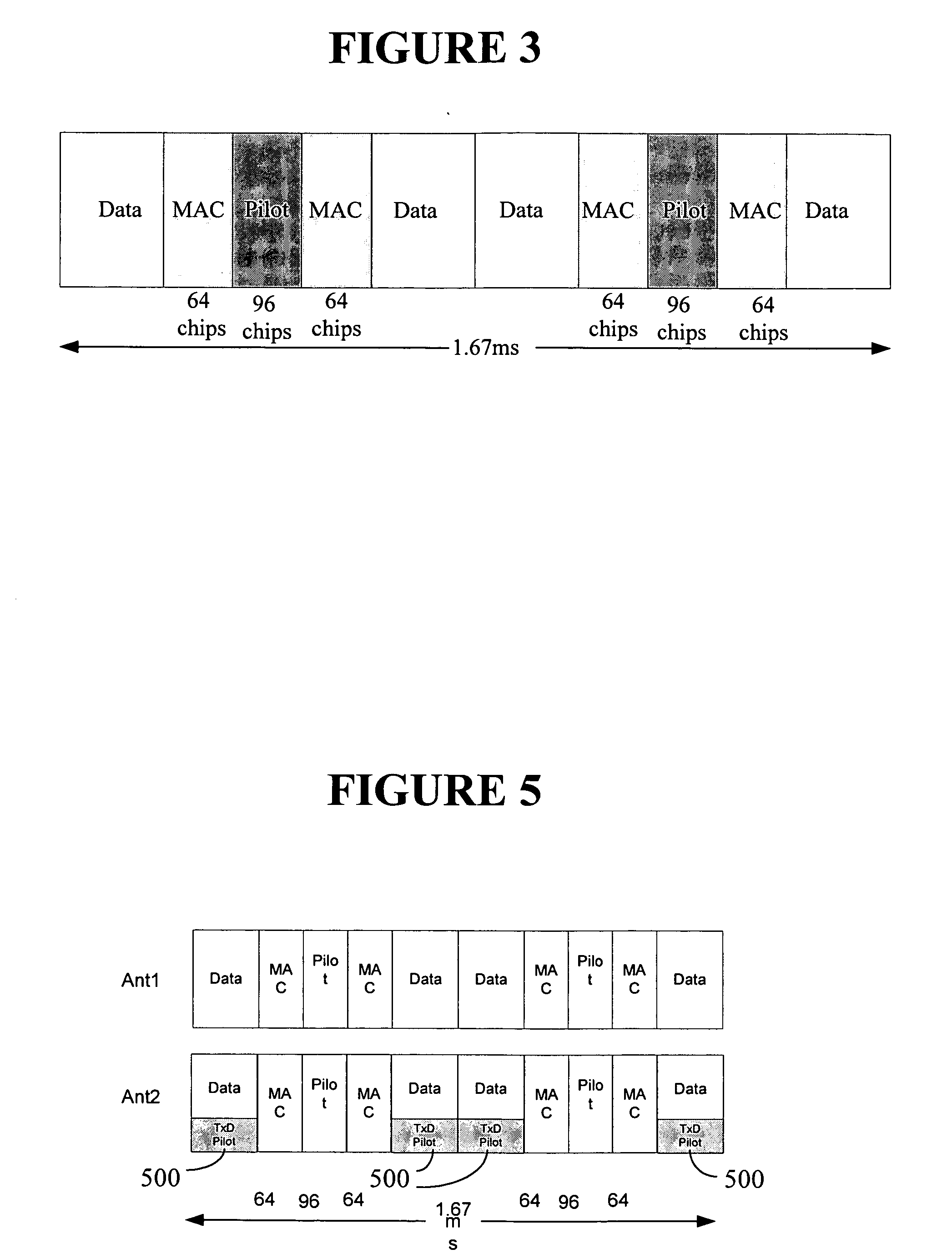
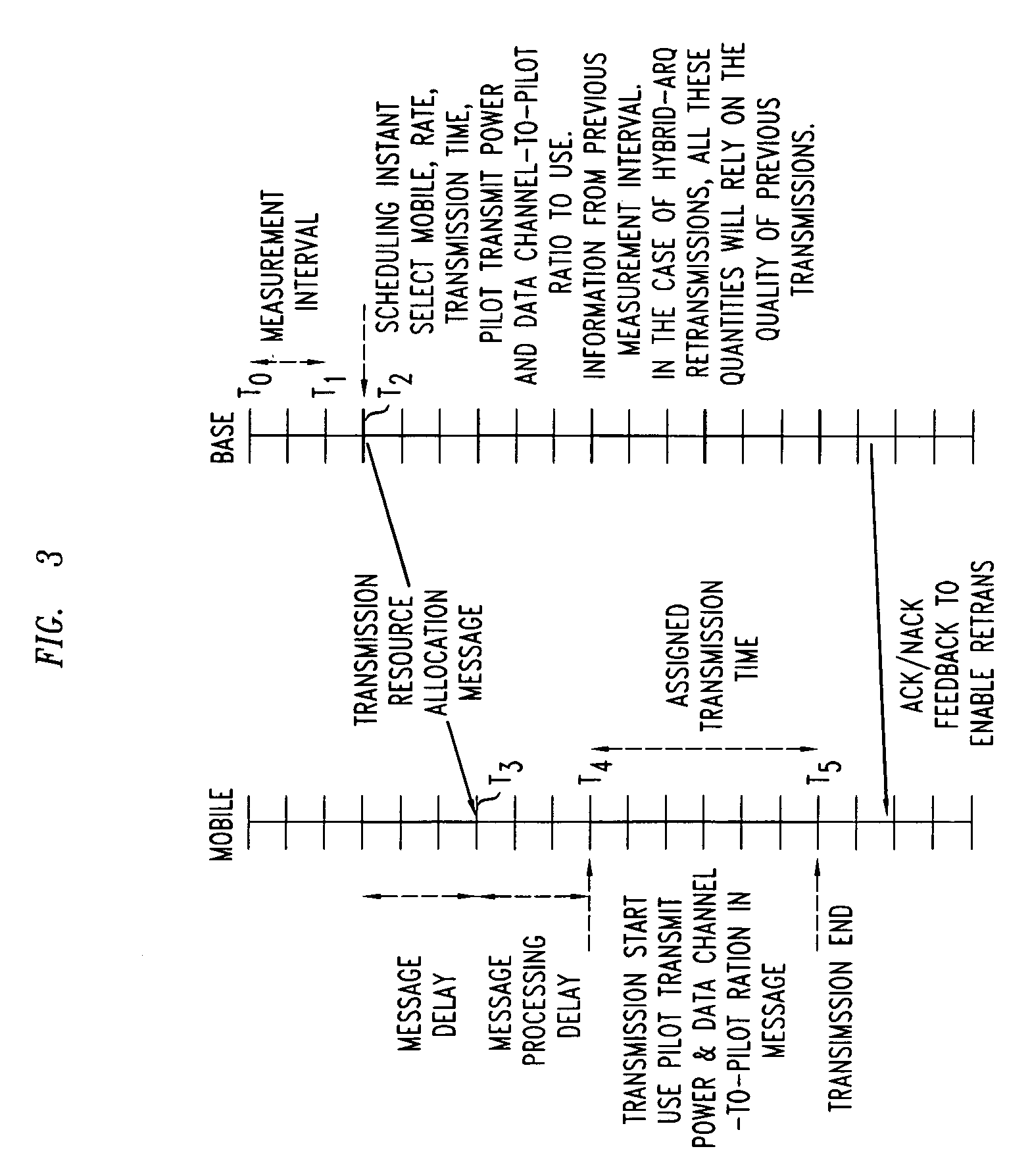
Method for improving capacity of a reverse link channel in a wireless network
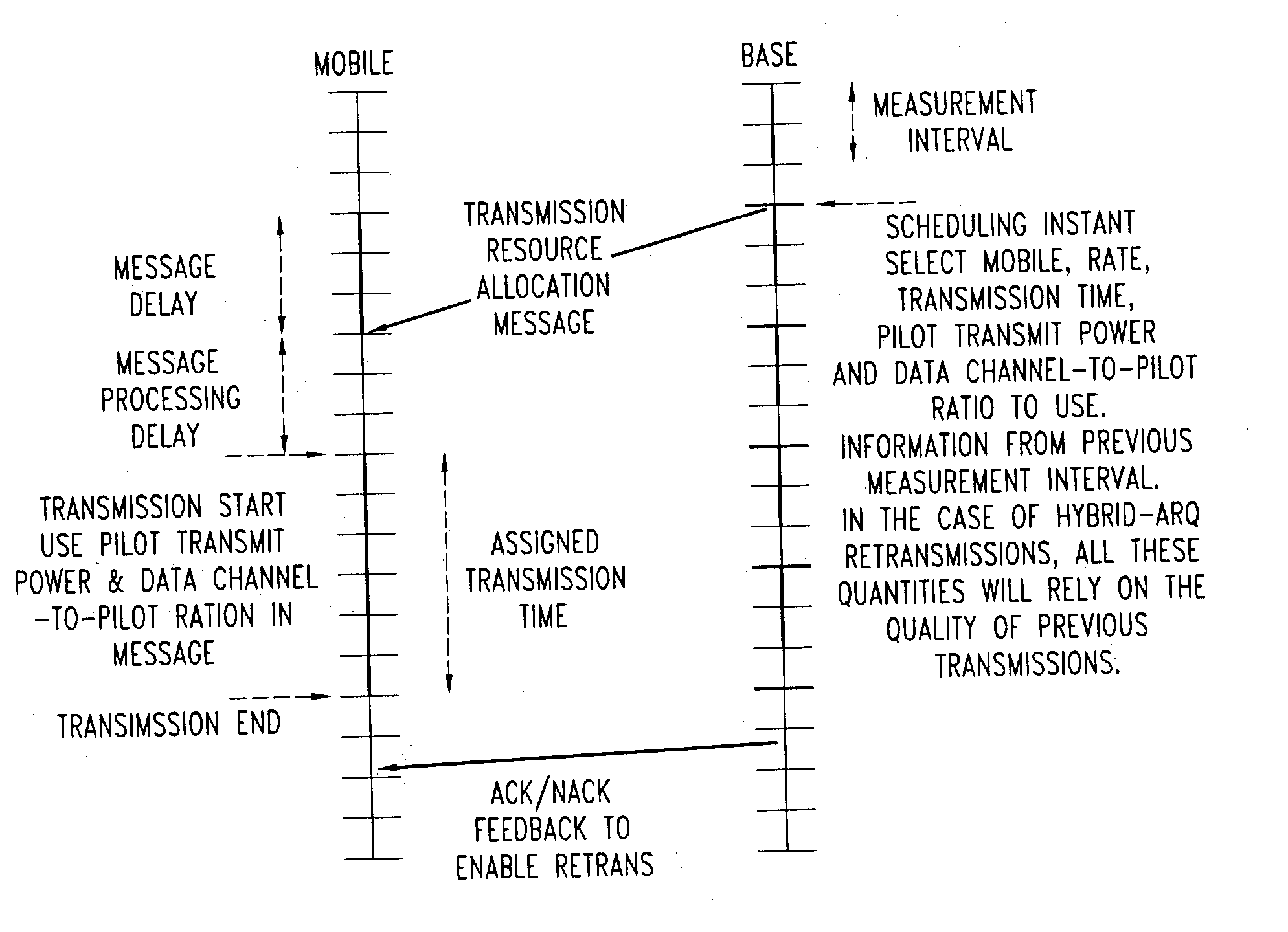
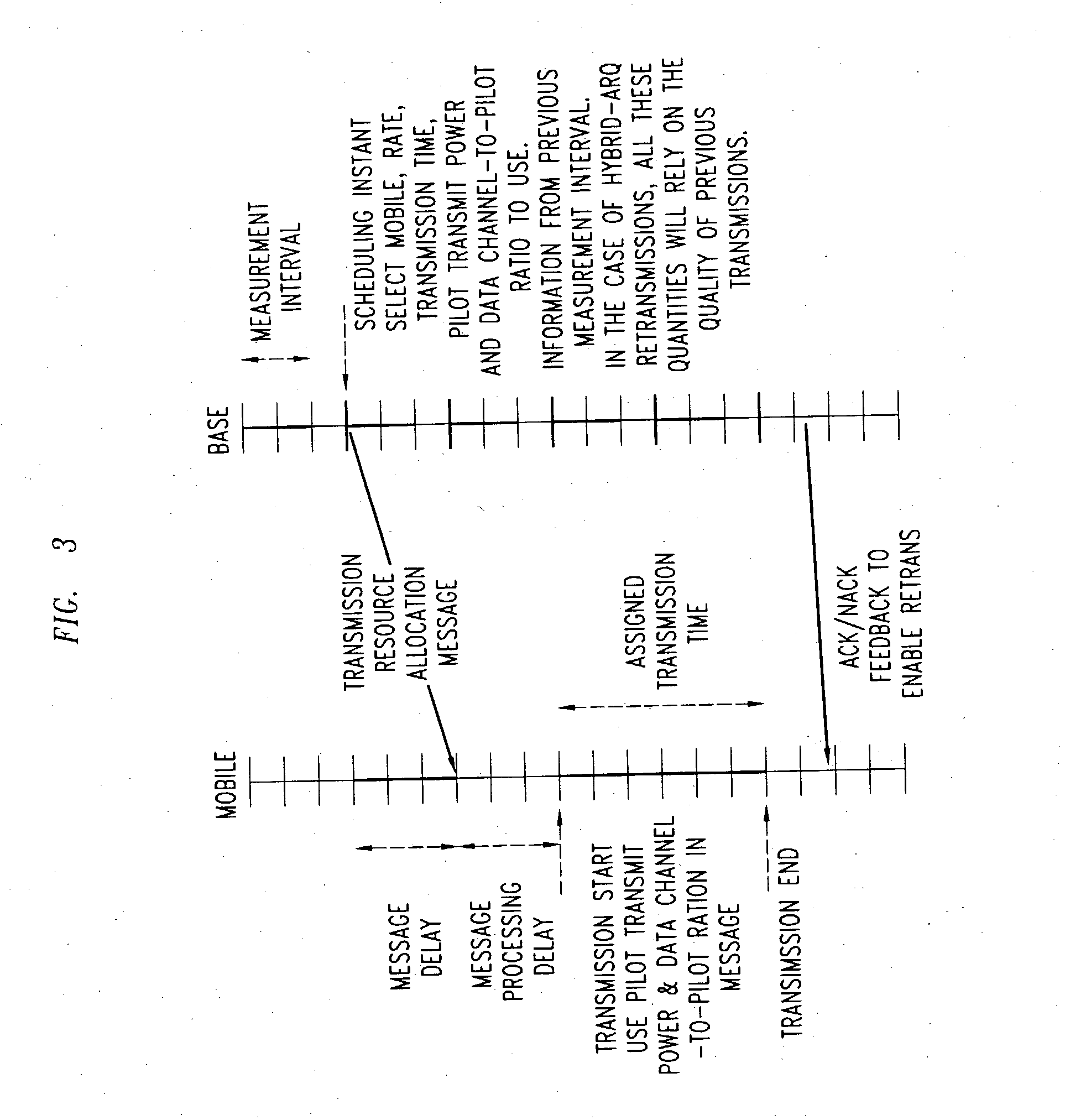
An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for improving the capacity of a reverse link by realizing a scheme to effect sharp changes in pilot channel transmit power (PCTP) and data channel to pilot power ratio (DCPR), coordinated with the start of the data channel transmission. The change in pilot power and data channel to pilot power ratio is also applicable to mobiles that use multiple pilots and / or multiple antennas at the transmitter and / or receiver.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
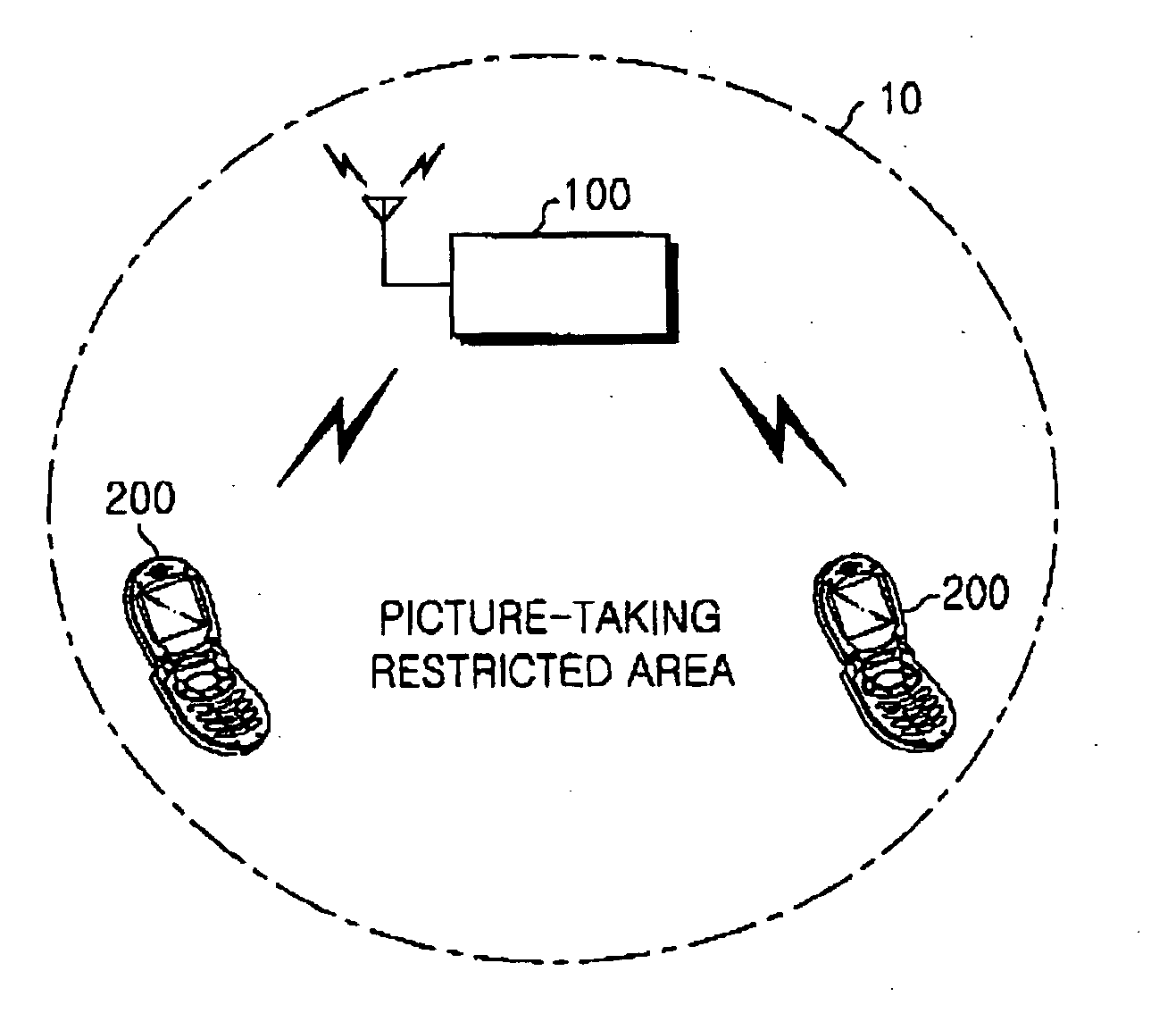
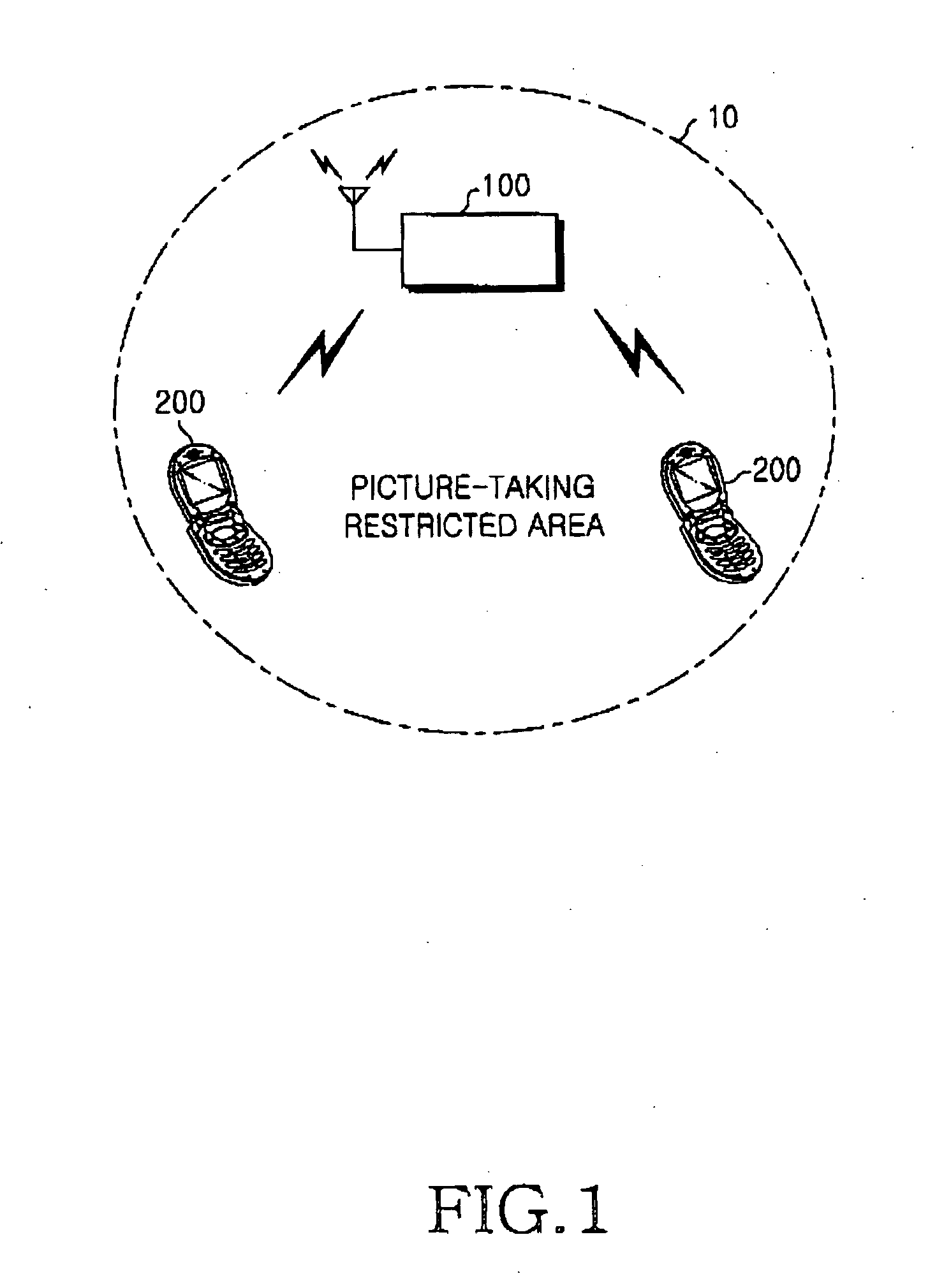
Camera-equipped mobile terminal and method for controlling picture-taking function of the same
InactiveUS20050192038A1Ensure safetyHigh Received Signal Strength IndicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionTransmission monitoringTelecommunicationsReceived signal strength indication
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
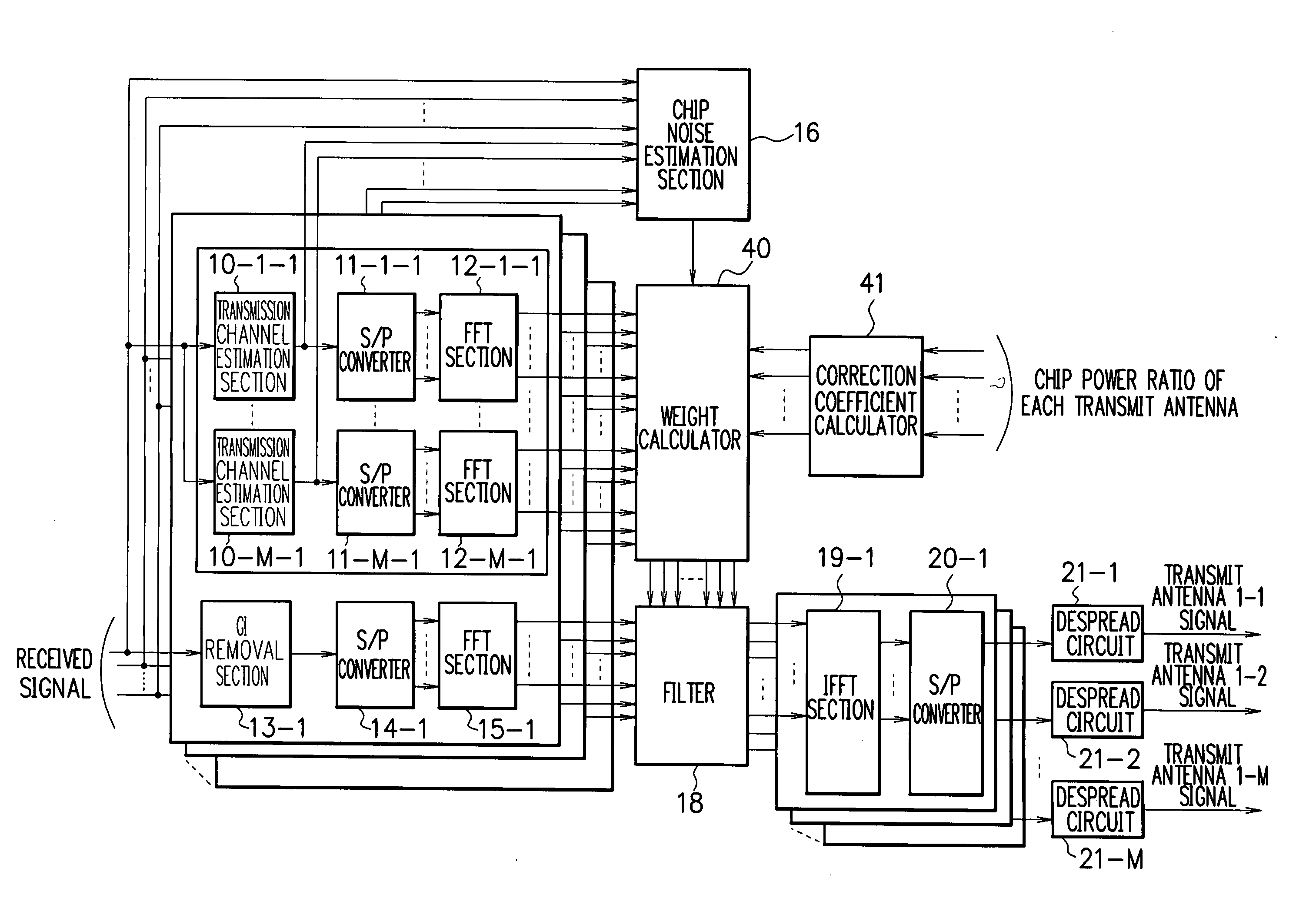
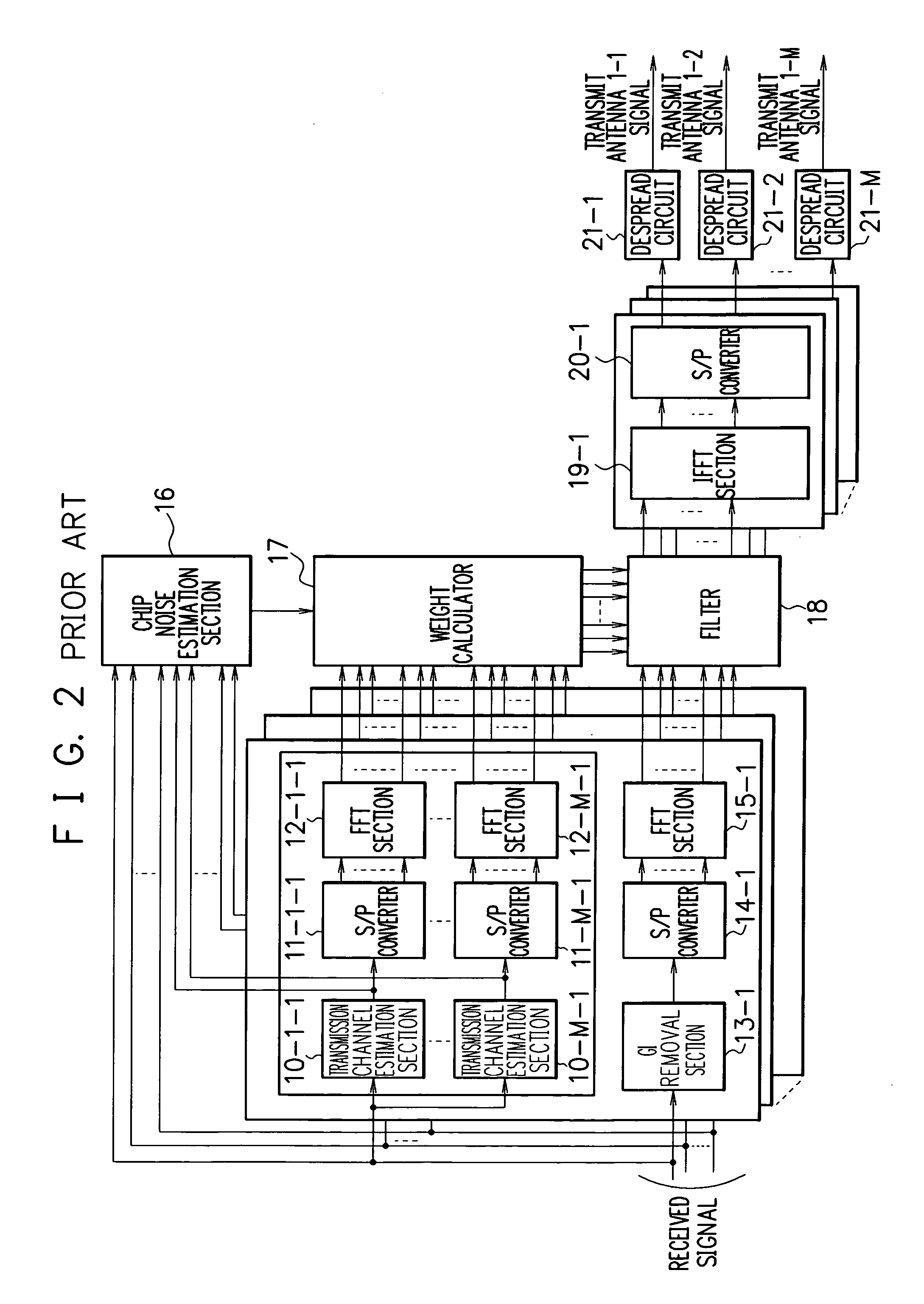
MIMO receiver, MIMO reception method and wireless communication system
ActiveUS20060199557A1Improve featuresPower managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemTransmission channel
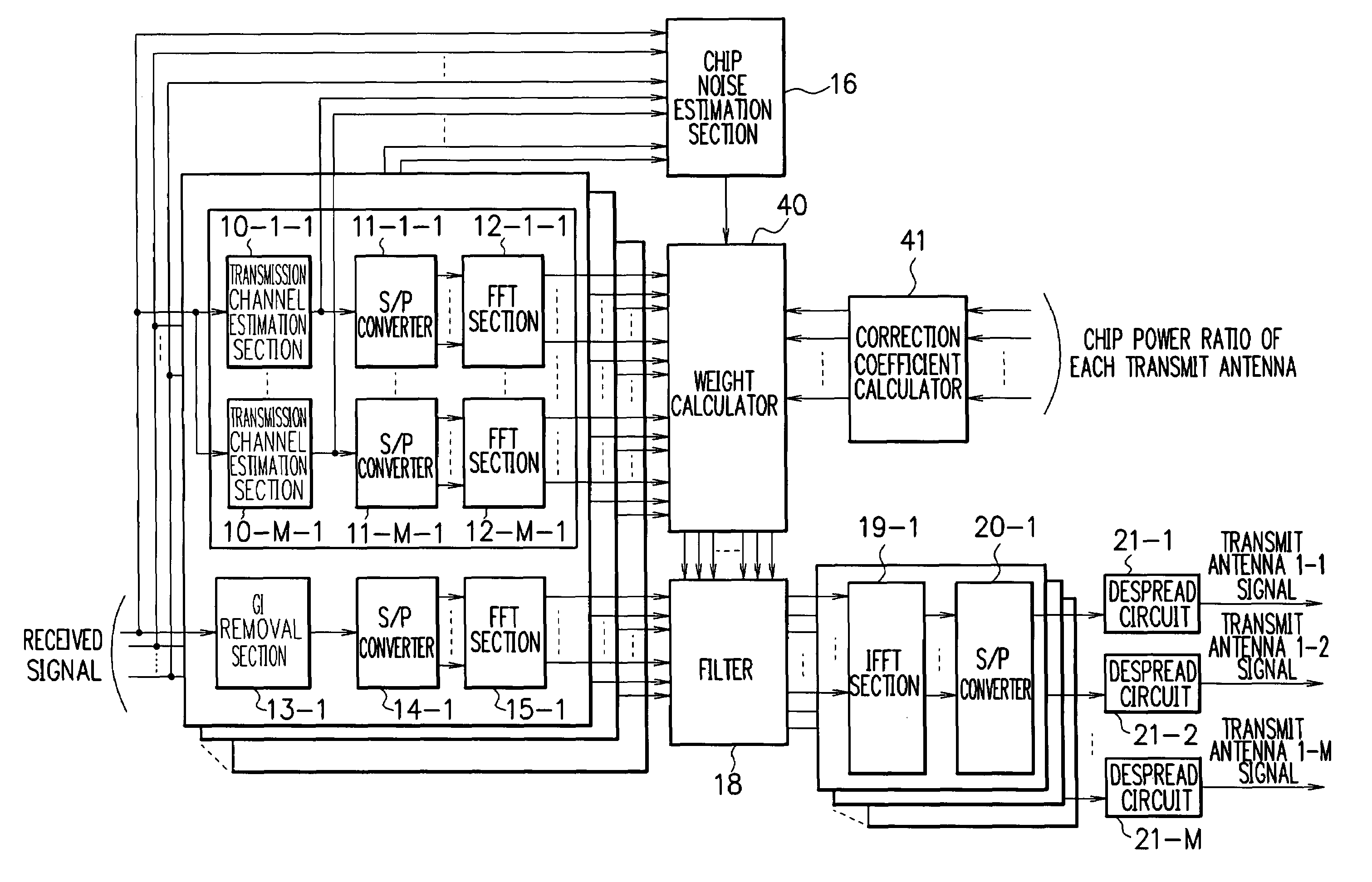
A MIMO receiver, a MIMO reception method and a wireless communication system capable of accurate MMSE control even when each transmit antenna uses a different chip power ratio in MIMO filter reception. A correction coefficient calculator receives as input the chip power ratio of each transmit antenna, and estimates such pilot power that renders the chip power ratio of each transmit antenna equal to that of a reference transmit antenna. Thereby, the correction coefficient calculator calculates a correction coefficient βm to correct the actual pilot power of each transmit antenna. A weight calculator receives as input transmission channel impulse responses transferred into frequency domain by FFT sections, chip noise power estimated by a chip noise estimation section, and the correction coefficient βm obtained by the correction coefficient calculator. The weight calculator calculates filter weights according to the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion.
Owner:NEC CORP
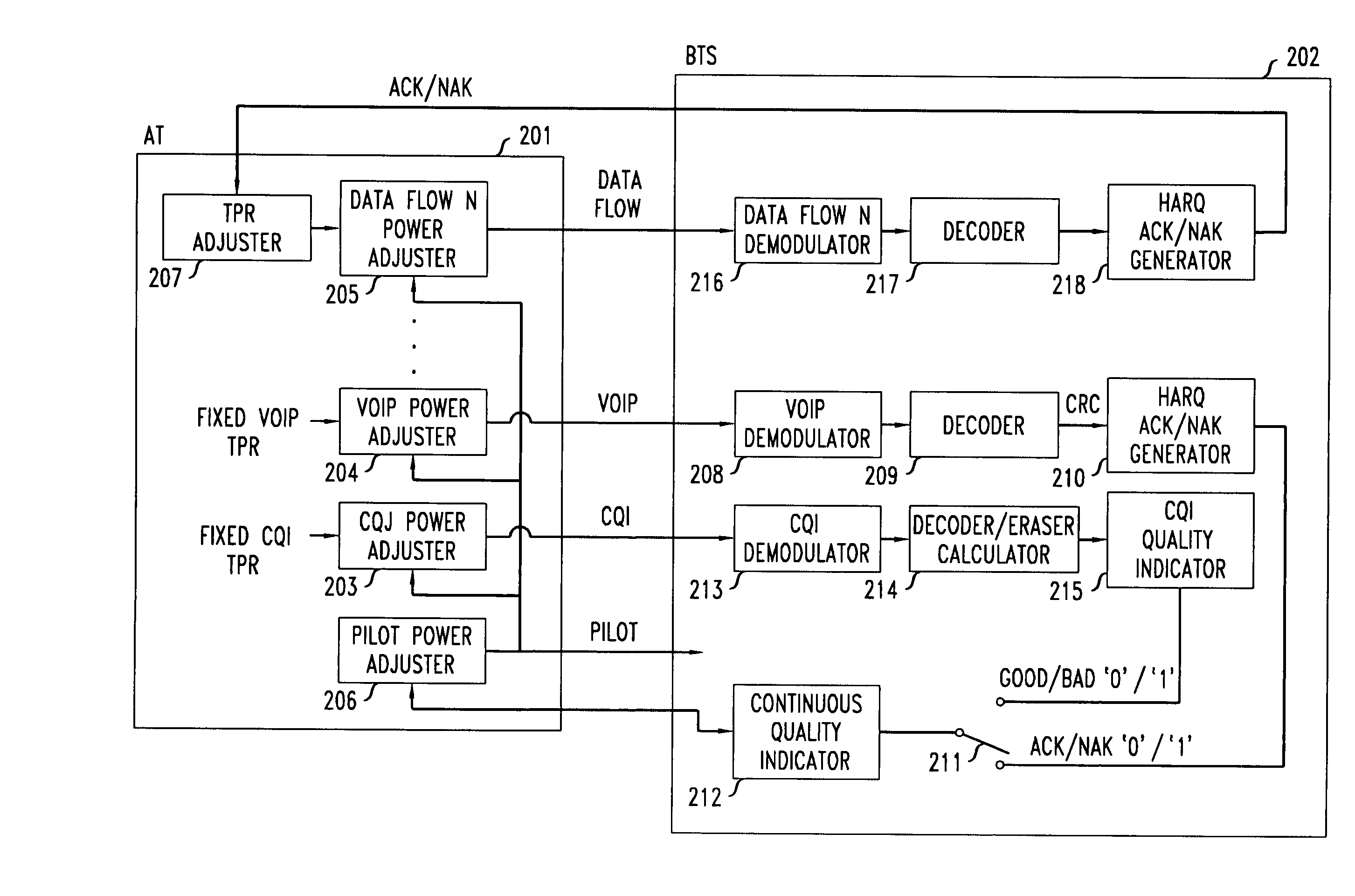
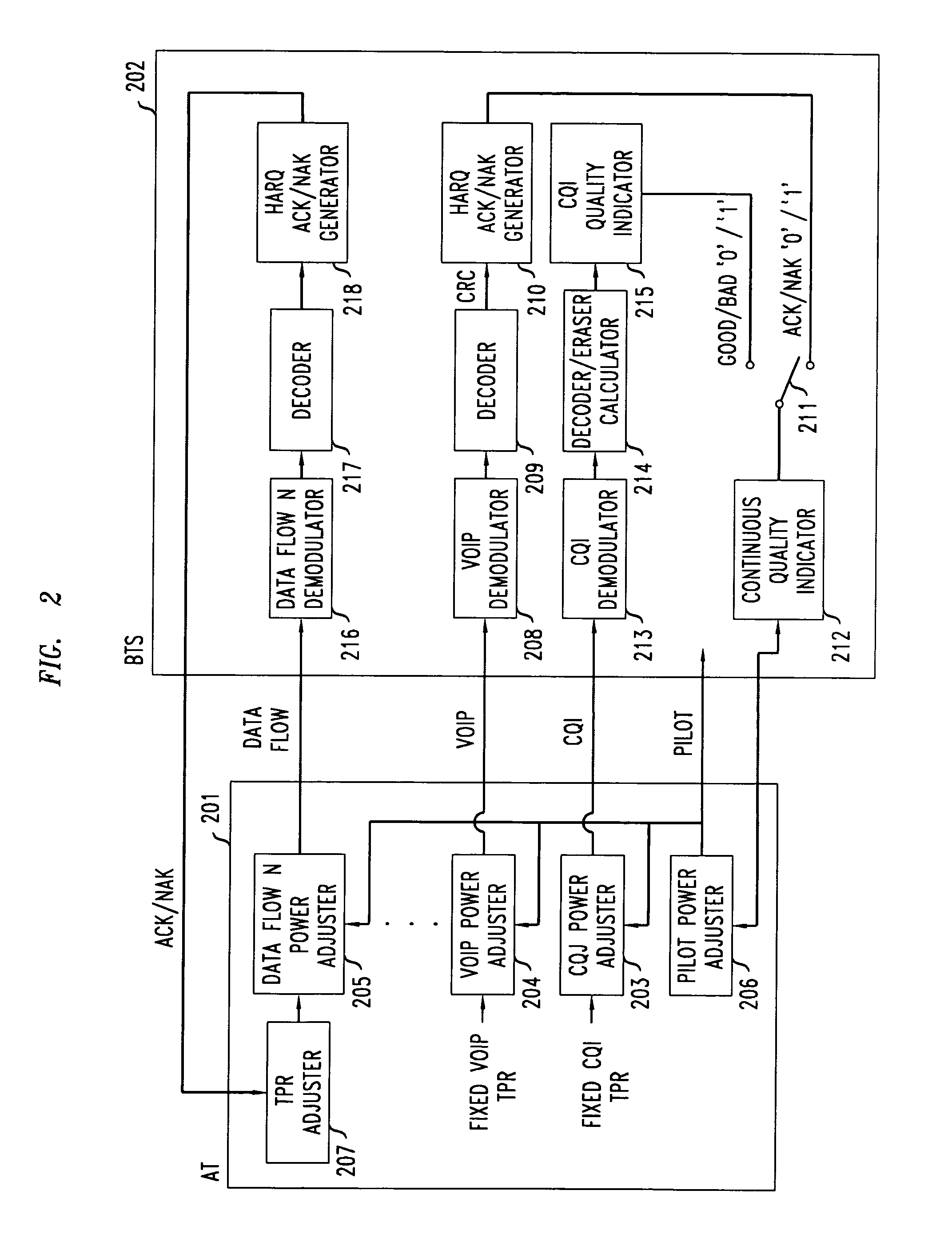
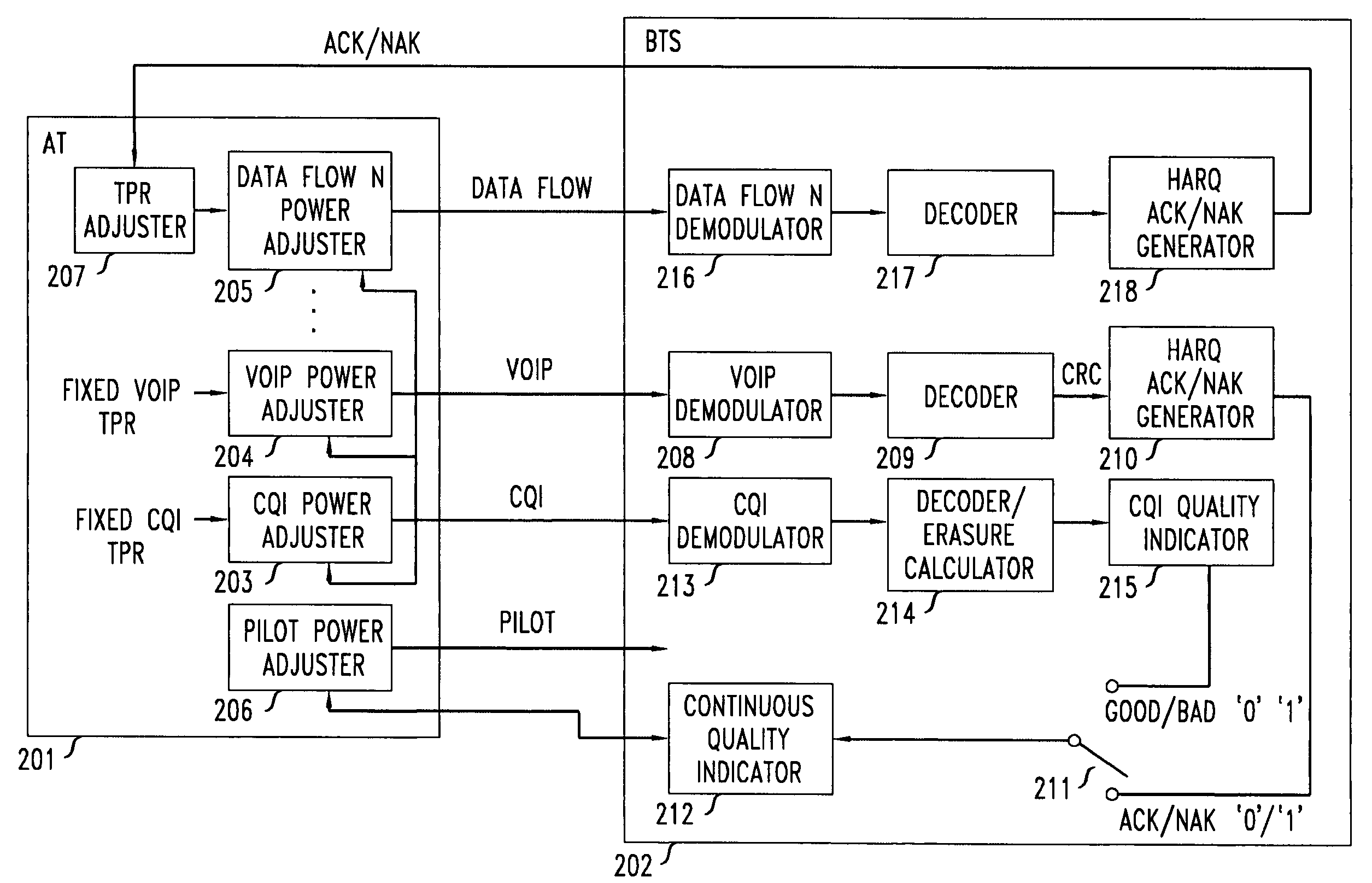
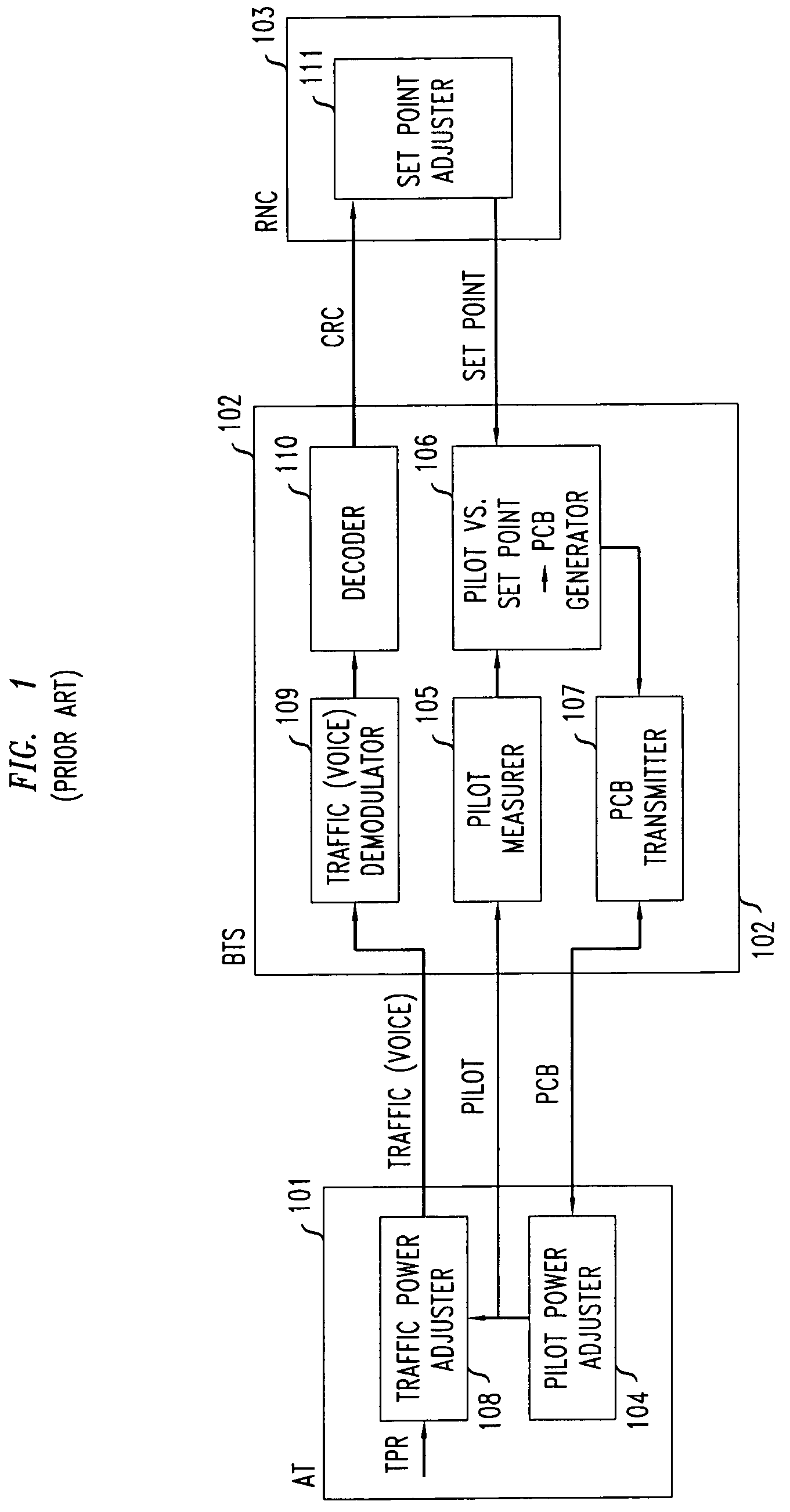
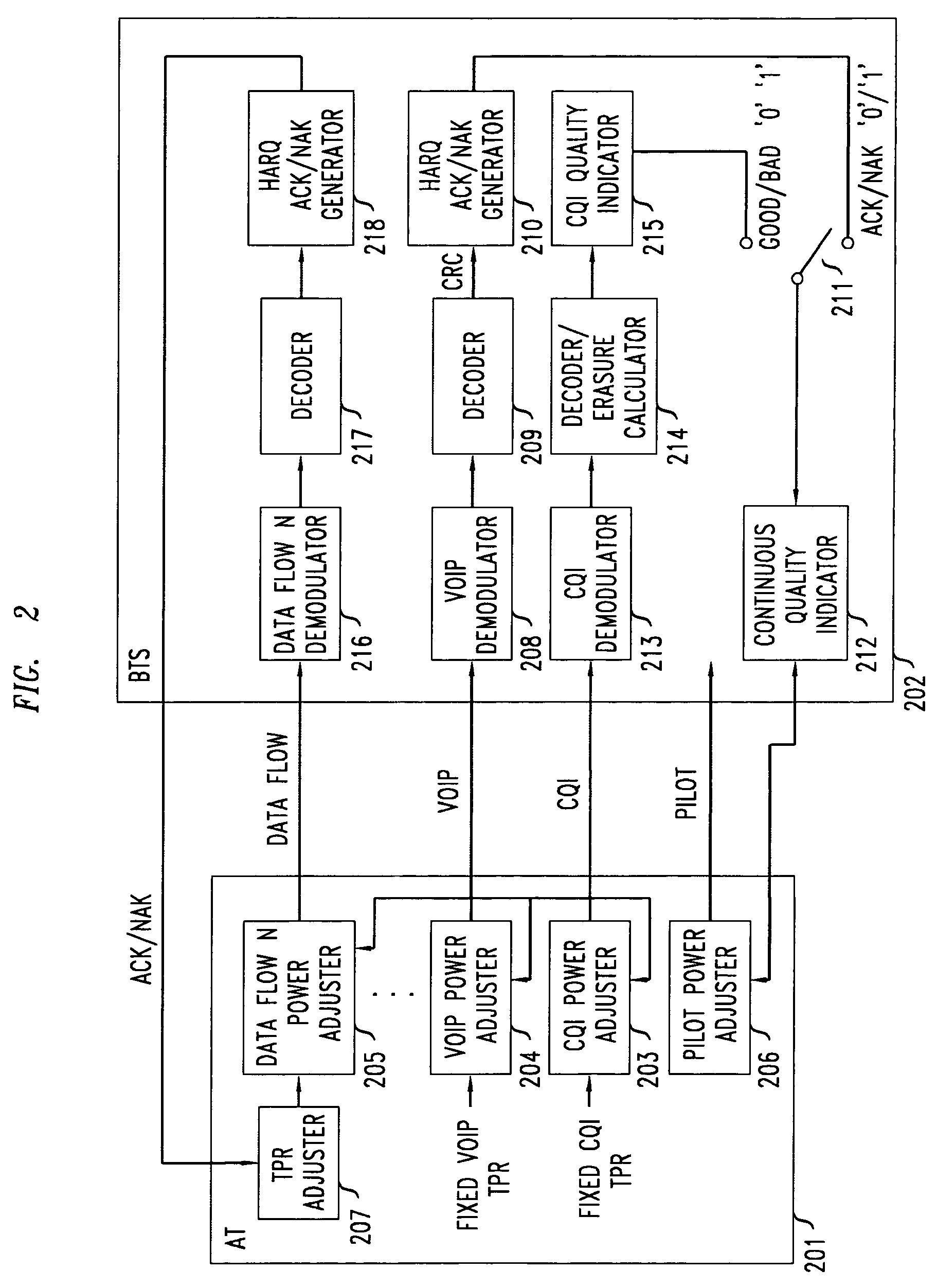
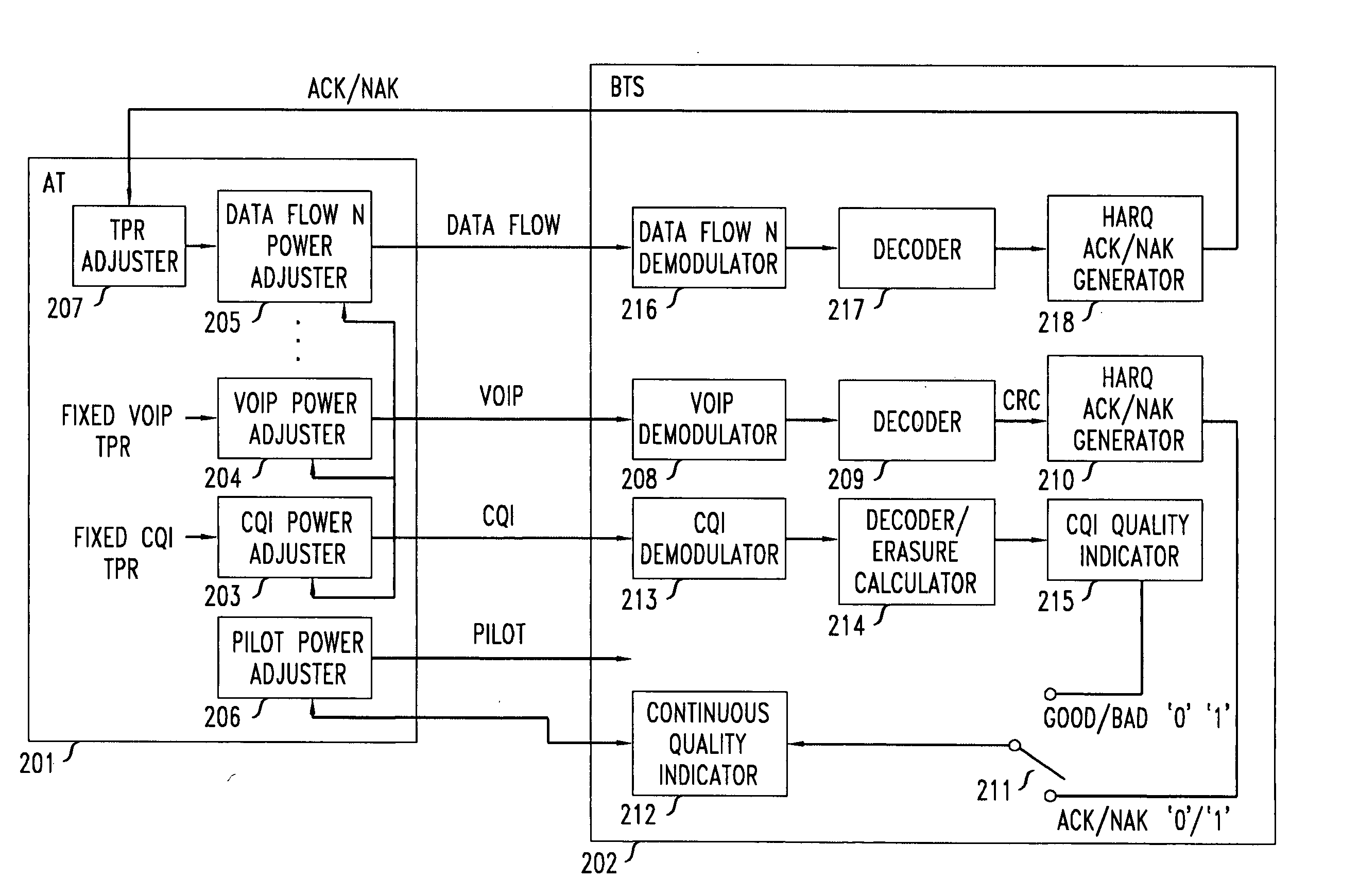
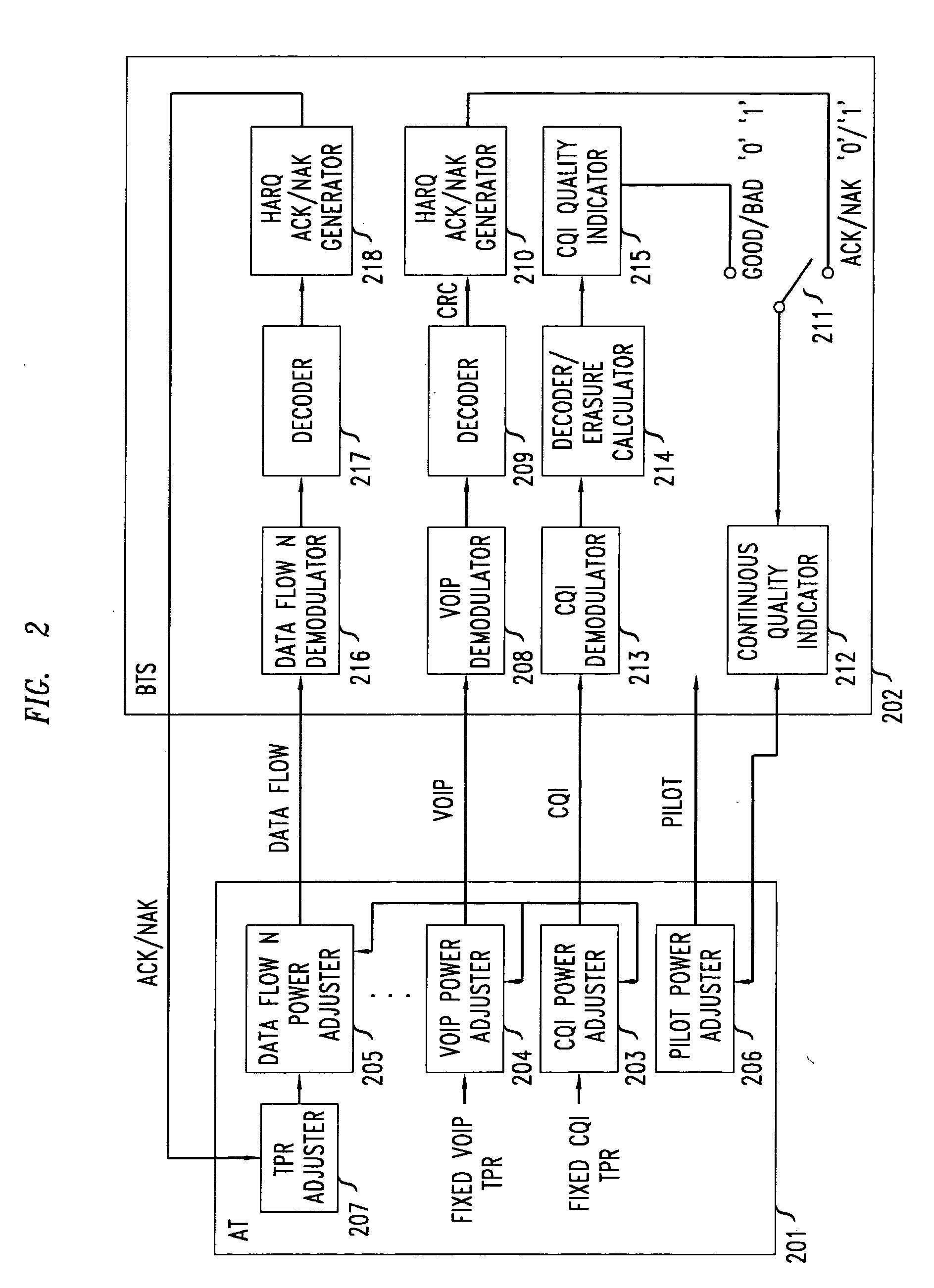
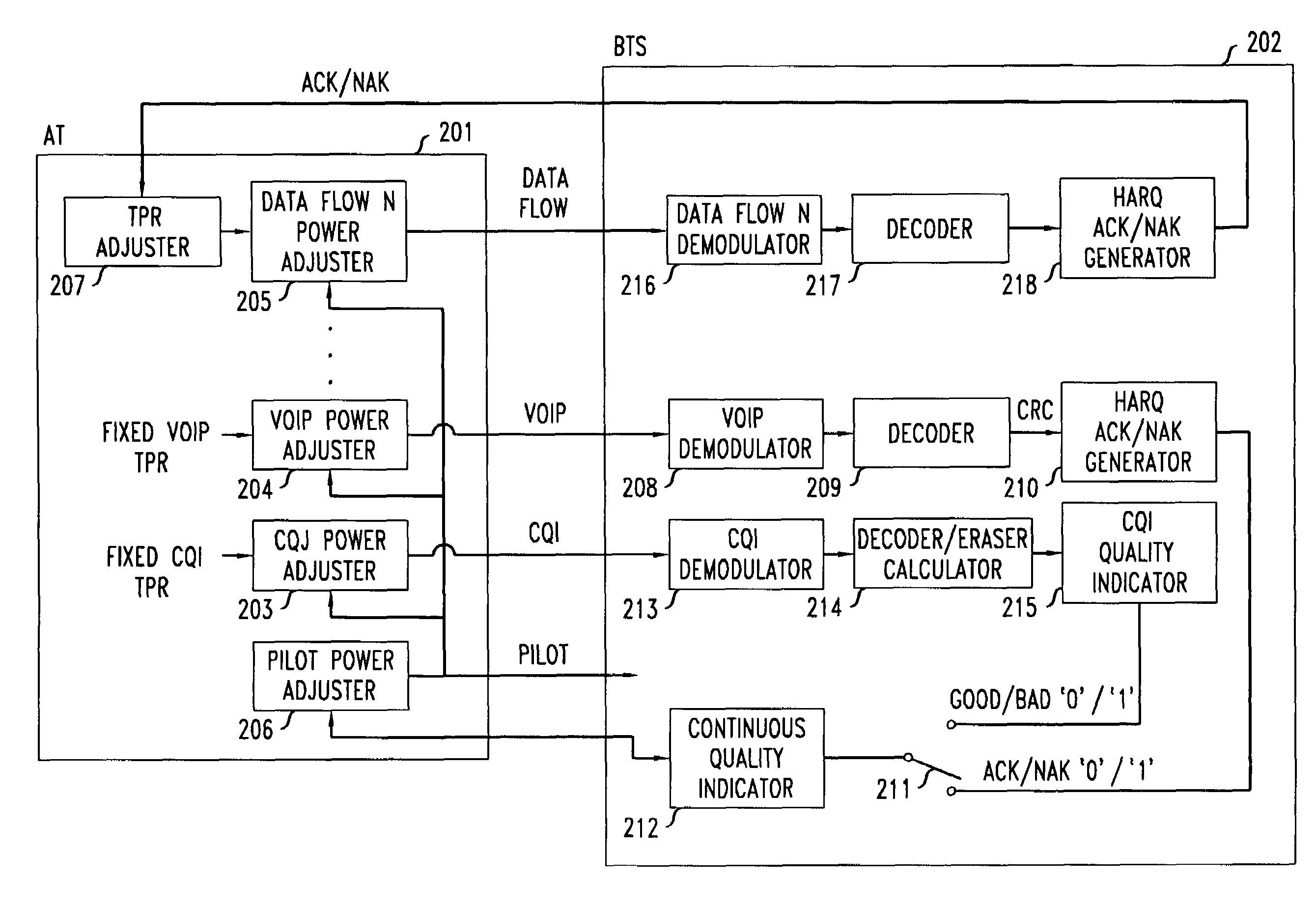
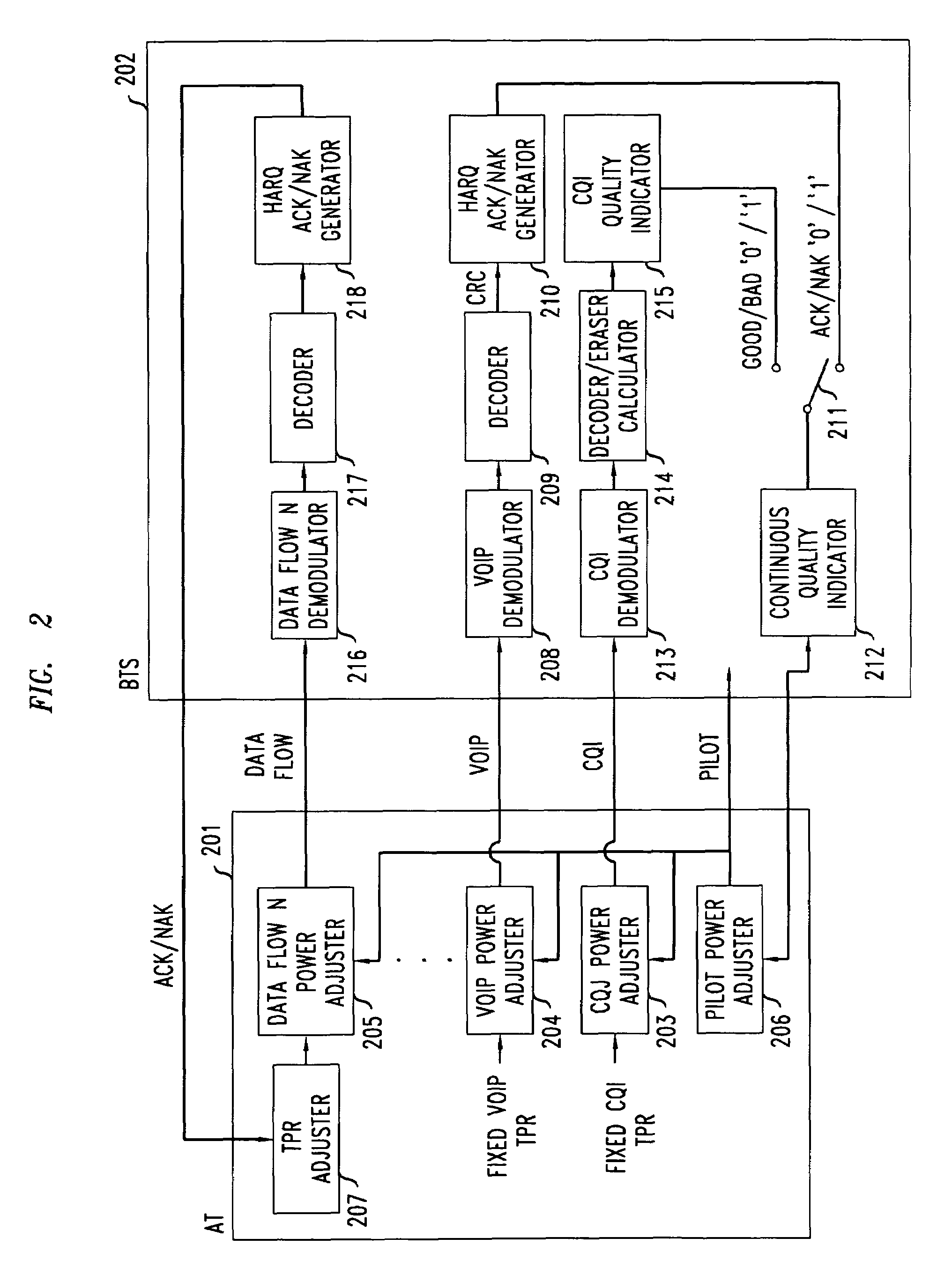
Method of reverse link dynamic power control in a wireless communication system using per-flow quality feedback for multi-flow data traffic
InactiveUS20070173275A1Reduce complexityReduce overheadPower managementError preventionCommunications systemData stream
A closed loop power control based on receiving a continuous quality feedback is described. A main reverse link (RL) pilot is controlled by the quality feedback of a substantially continuous delay sensitive traffic stream, such as Voice-over-IP (VoIP), when such a stream is enabled. When such a stream is not enabled, the quality of a continuous RL overhead channel is used to control the pilot power. At the same time, the Traffic-to-Pilot Ratios (TPR) of contemporaneously transmitted delay sensitive data streams are independently adjusted based on a quality feedback associated with each such data stream.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method of reverse link dynamic power control in a wireless communication system using quality feedback from a delay-sensitive traffic stream or overhead channel
InactiveUS7548760B2Reduce complexityReduce overheadPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemData stream
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
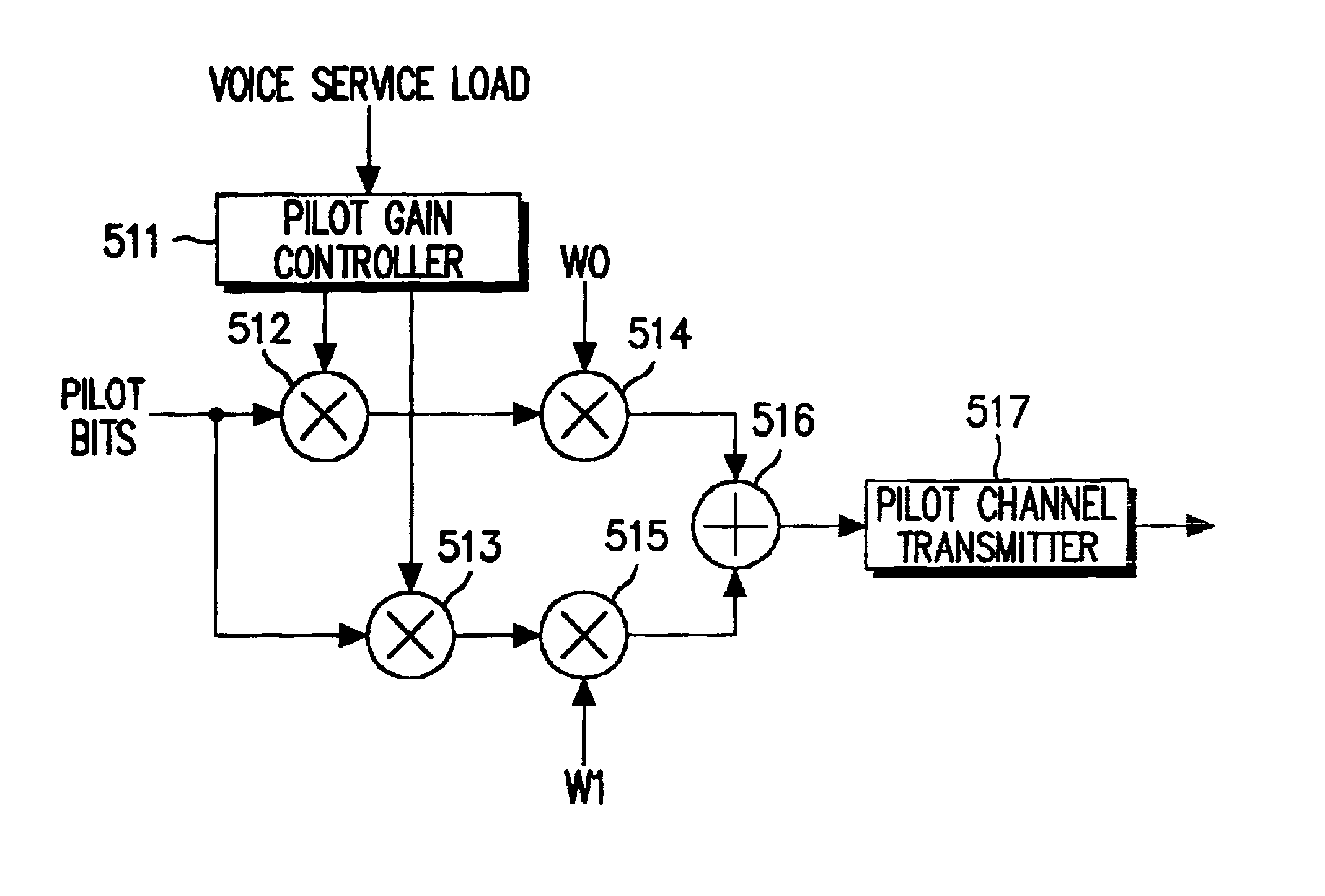
Apparatus and method for reporting service load to mobile station in mobile telecommunication system
InactiveUS6937640B2Increase ratingsGood servicePower managementTransmission control/equlisationData rateMobile station
There is provided a method and apparatus for selecting an appropriate base station and an optimal data rate to provide a voice service and a data service based on a voice service load in a CDMA system. A base station transmits two pilot signals orthogonally spread with different orthogonal codes in association with its voice service load, and a mobile station estimates the voice service load based on a pilot power ratio.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for user access and switching in wireless network with unbalance load
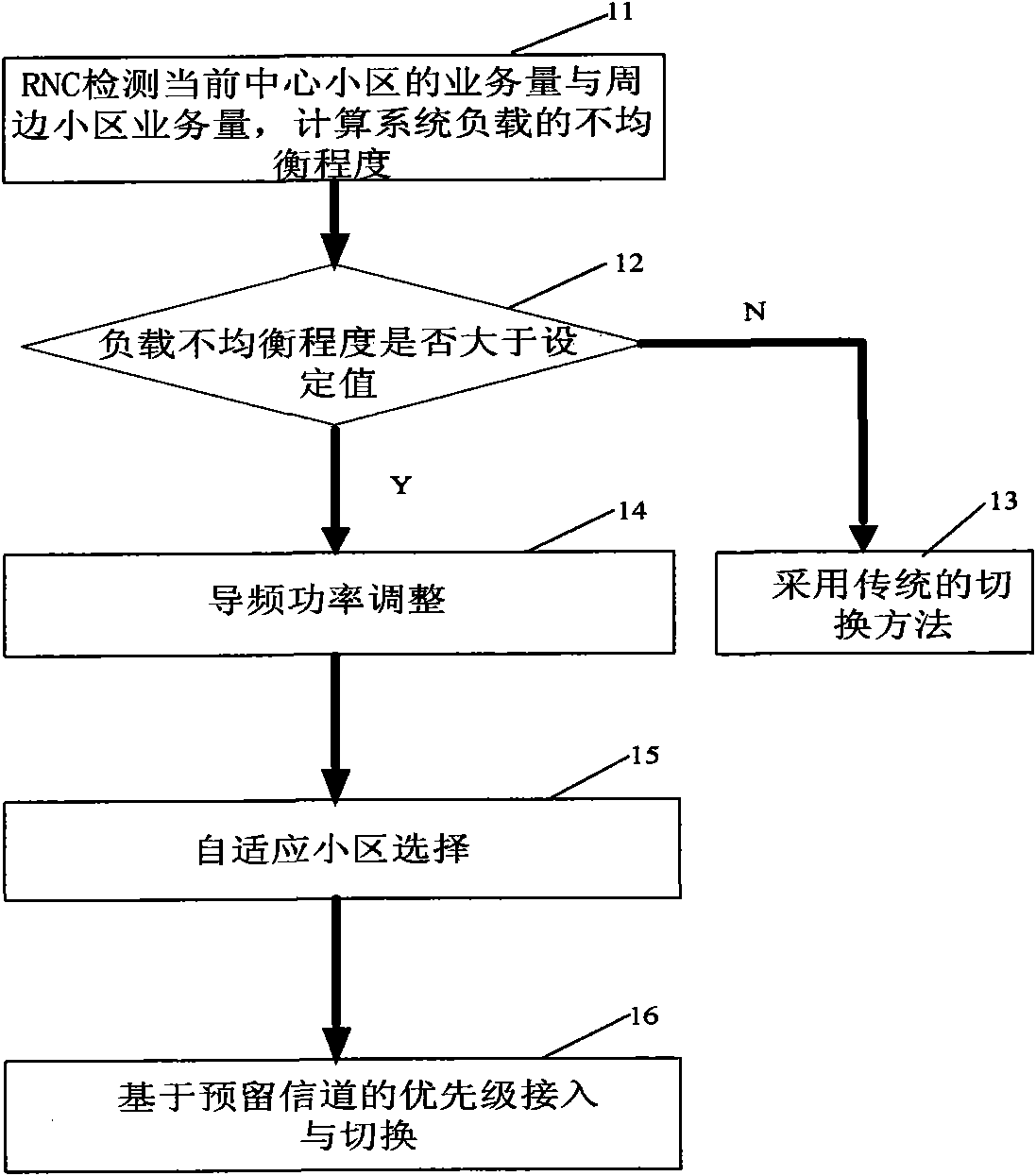
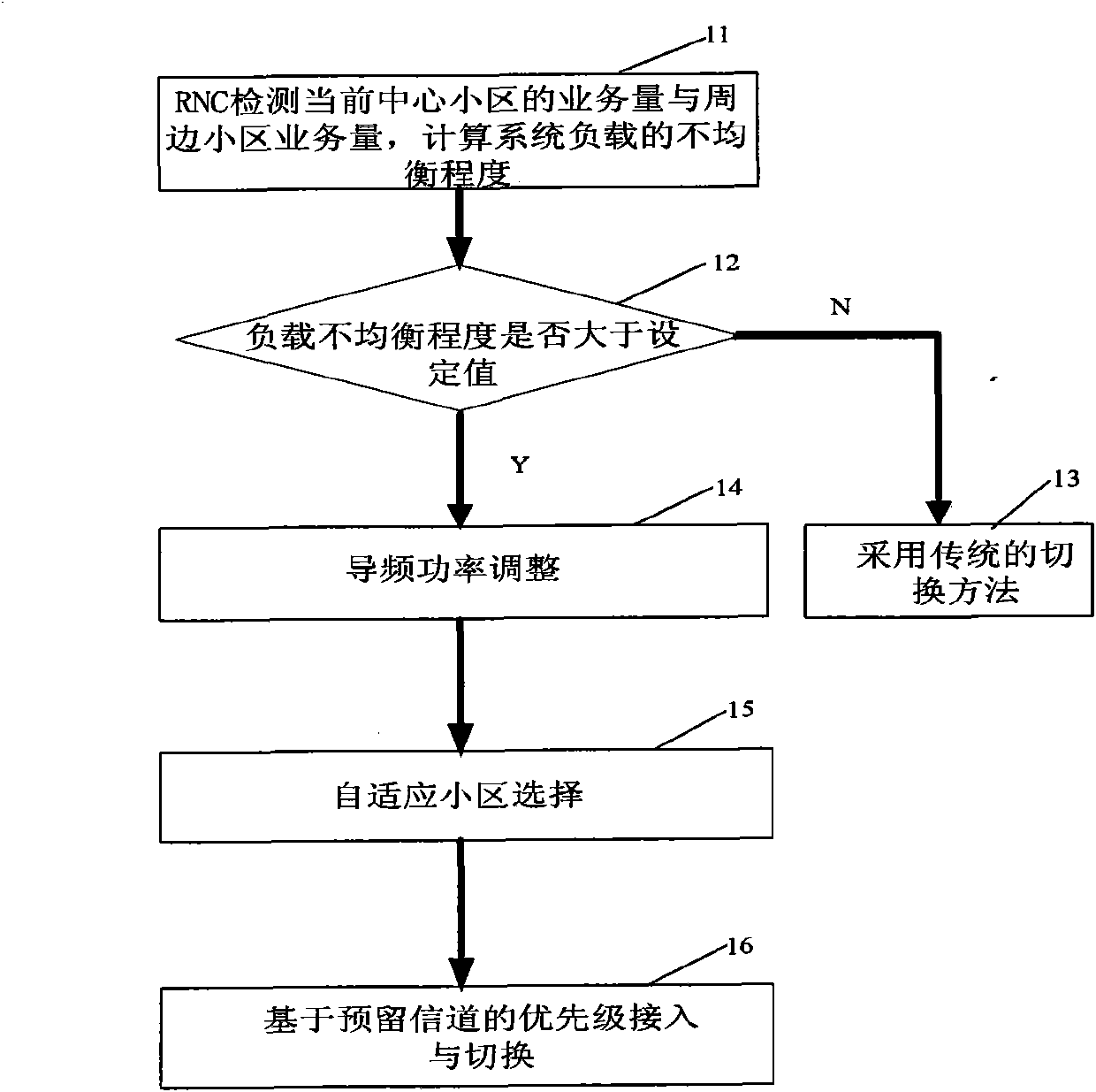
InactiveCN101951664ALoad balancingAlleviate high blocking ratesAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for user access and switching in a wireless network with an unbalance load, which is particularly suitable for use in networks with unbalance loads, such as railway stations and department stores. The method comprises: 1, judging if a current network is in an unbalance load state through a wireless network controller; 2, if the system is in an unbalance load state, regulating the coverage of each cell by dynamically regulating the pilot power of the cell according to an load condition of cells to balance the load of the cells, or if the system is in a balance load state, adopting the conventional switching method; 3, if the load of the system is balanced, allowing a mobile stations to select an optimal main cell for enabling the system to obtain an optimal transmission rate; and 4, allowing the mobile station to perform access and switching in queue on the basis of the priority of preserved channels. The method can balance the loads of neighboring cells and therefore relieve the serious switching queuing condition of cells of large service loads and a high system blockage rate condition and improve resource utilization rate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method of reverse link dynamic power control in a wireless communication system using quality feedback from a delay-sensitive traffic stream or overhead channel
InactiveUS20070167183A1Reduce complexityReduce overheadPower managementTransmission systemsCommunications systemData stream
A closed loop power control based on receiving a continuous quality feedback is described. A main reverse link (RL) pilot is controlled by the quality feedback of a substantially continuous delay-sensitive traffic stream, such as Voice-over-IP (VoIP), when such a stream is enabled. When such a stream is not enabled, the quality of a continuous RL overhead channel is used to control the pilot power. At the same time, the Traffic-to-Pilot Ratios (TPR) of contemporaneously transmitted delay-sensitive data streams are independently adjusted based on a quality feedback associated with each such data stream.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
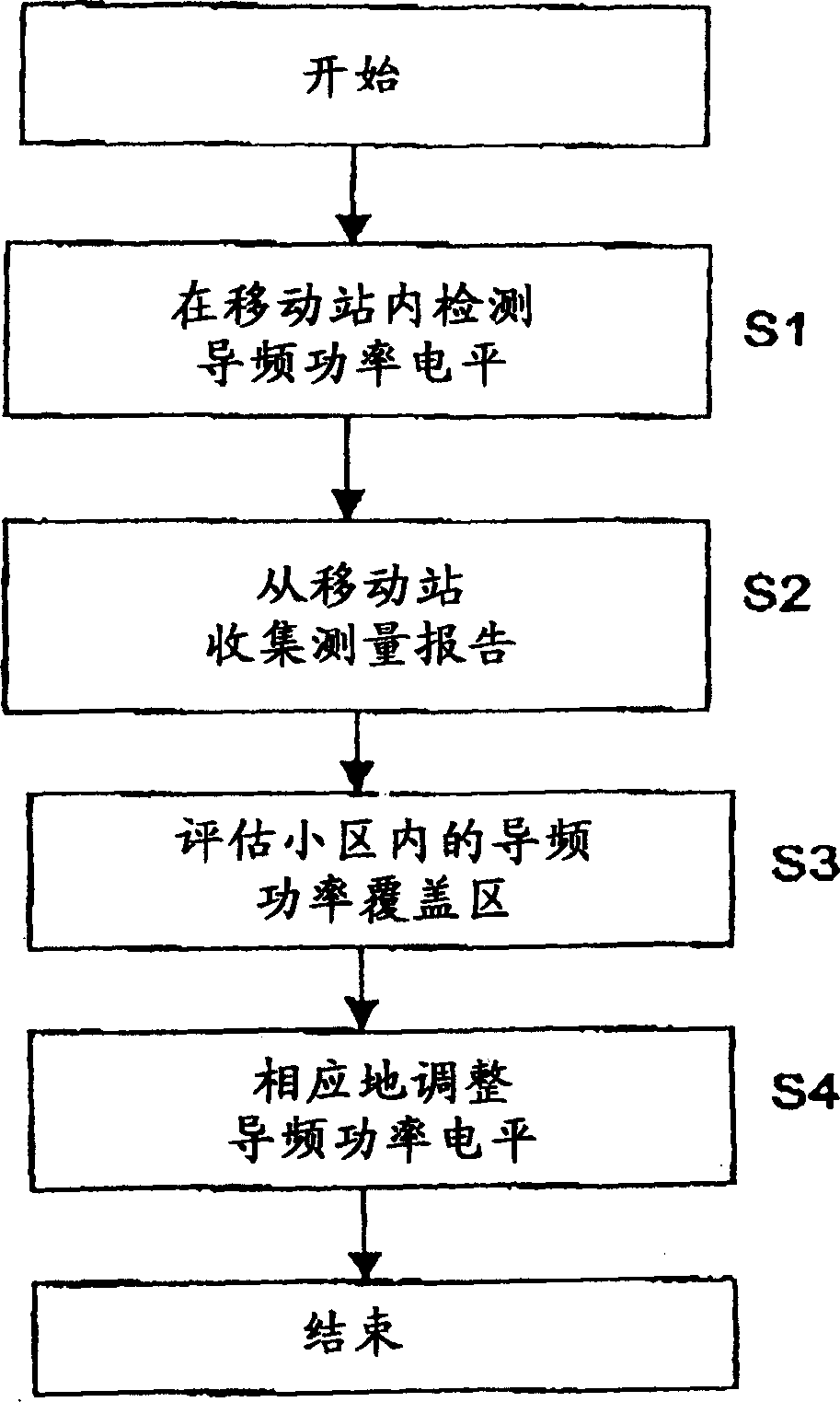
Pilot channel power autotuning
The invention proposes a method for controlling a network, comprising at least one cell served by a first type network device, wherein the first type network device is adapted to serve second type network devices, wherein the emission of the first type network device includes an individual pilot signal to the second type network devices, and the emission of the second type network devices includes measurement reports including information on the status and the situation of the respective device, the method comprising the steps of detecting information (S1) in the second type network devices, said information indicating the power level of the pilot signals received, collecting (S2) measurement reports (MR) from the second type network devices, said measurement reports (MR) including the pilot power information gained in the detecting step (S1), evaluating (S3) the pilot signal power coverage in that cell on the basis of a pre-given number of measurement reports (MR), automatically adjusting (S4) the pilot signal power coverage in that cell on the basis of the result of the evaluation step. The invention proposes also a device for controlling a network.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
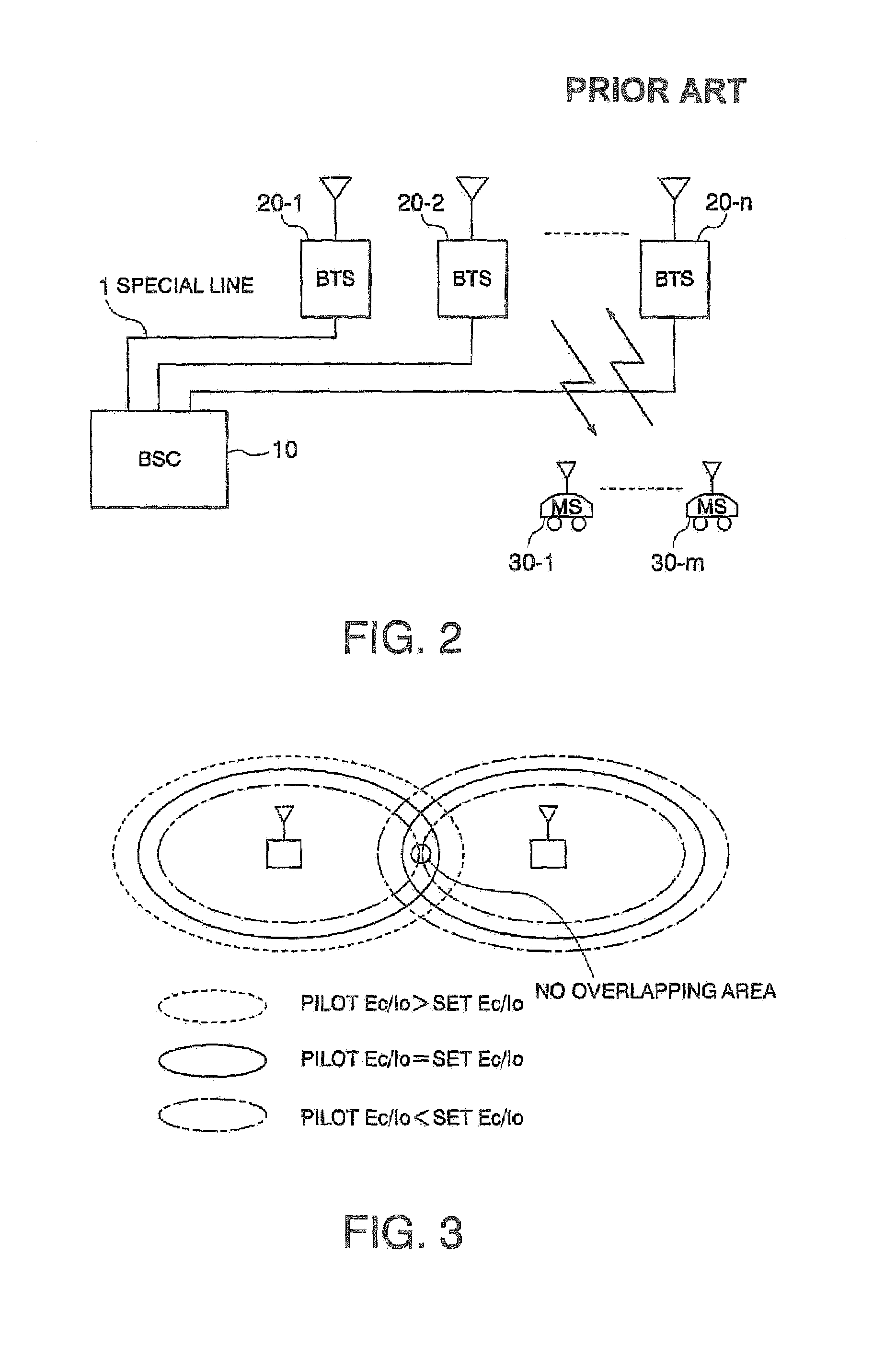
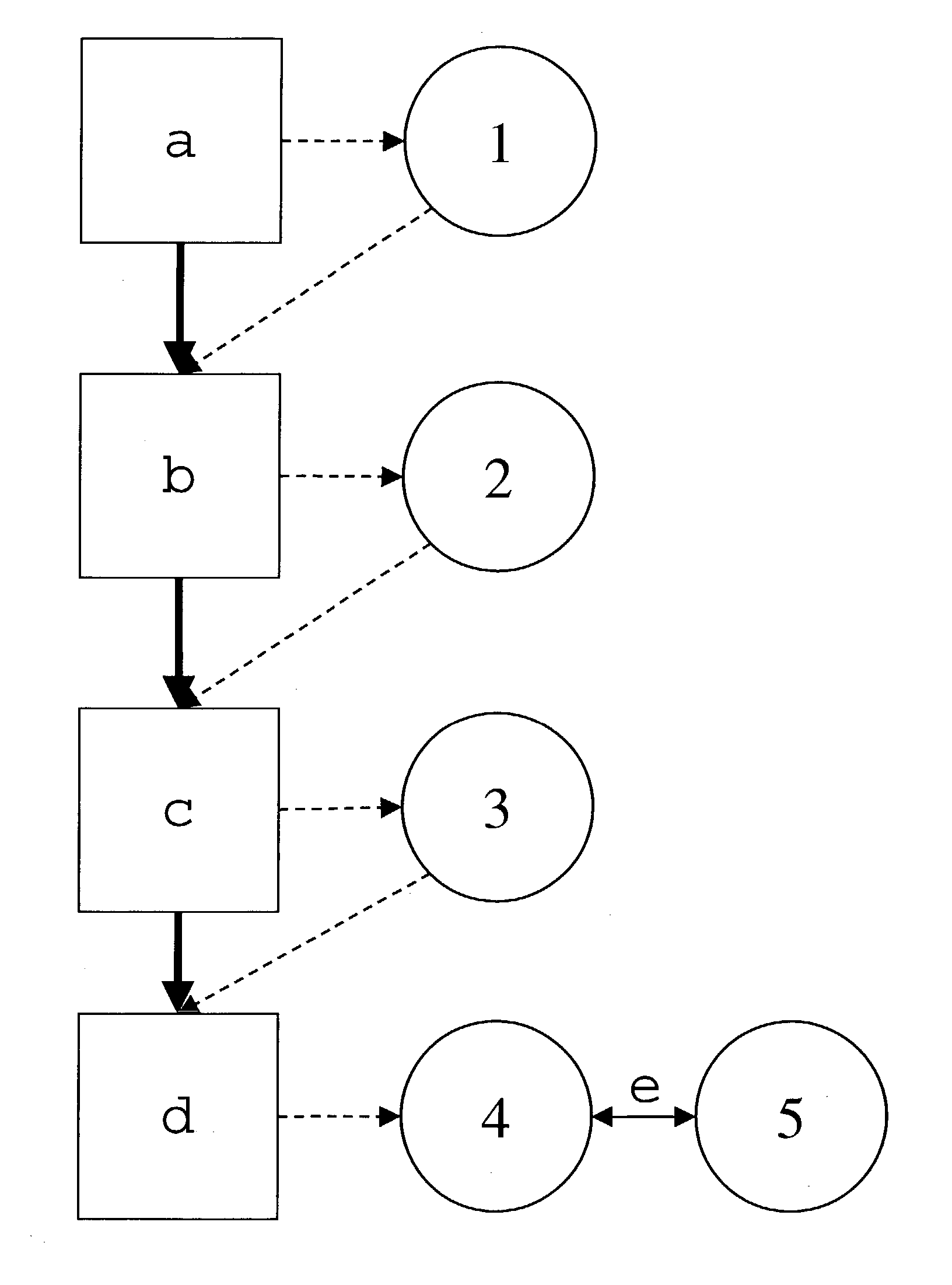
Method and system for planning and/or evaluation of downlink coverage in (CDMA) radio networks
InactiveUS20030148782A1Fast and reliable planningCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio networksEngineering
Method and system for the planning and / or evaluation of downlink coverage in a (CDMA) radio network. The service area of the radio network can be divided into pixels defined (a) by the grid (1), and cells (2) can be assigned (b) to the pixels. After assigning (c) the pilot power (3), the desired downlink transmission power (4) can be estimated (d) for the cell (2), which can be compared (e) to the maximum transmission power (5) of the base station. If needed changes in the radio network can be made and the planning and / or evaluation is restarted.
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
Method of reverse link dynamic power control in a wireless communication system using per-flow quality feedback for multi-flow data traffic
InactiveUS7515927B2Reduce complexityReduce overheadPower managementError preventionData streamCommunications system
A closed loop power control based on receiving a continuous quality feedback is described. A main reverse link (RL) pilot is controlled by the quality feedback of a substantially continuous delay sensitive traffic stream, such as Voice-over-IP (VoIP), when such a stream is enabled. When such a stream is not enabled, the quality of a continuous RL overhead channel is used to control the pilot power. At the same time, the Traffic-to-Pilot Ratios (TPR) of contemporaneously transmitted delay sensitive data streams are independently adjusted based on a quality feedback associated with each such data stream.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
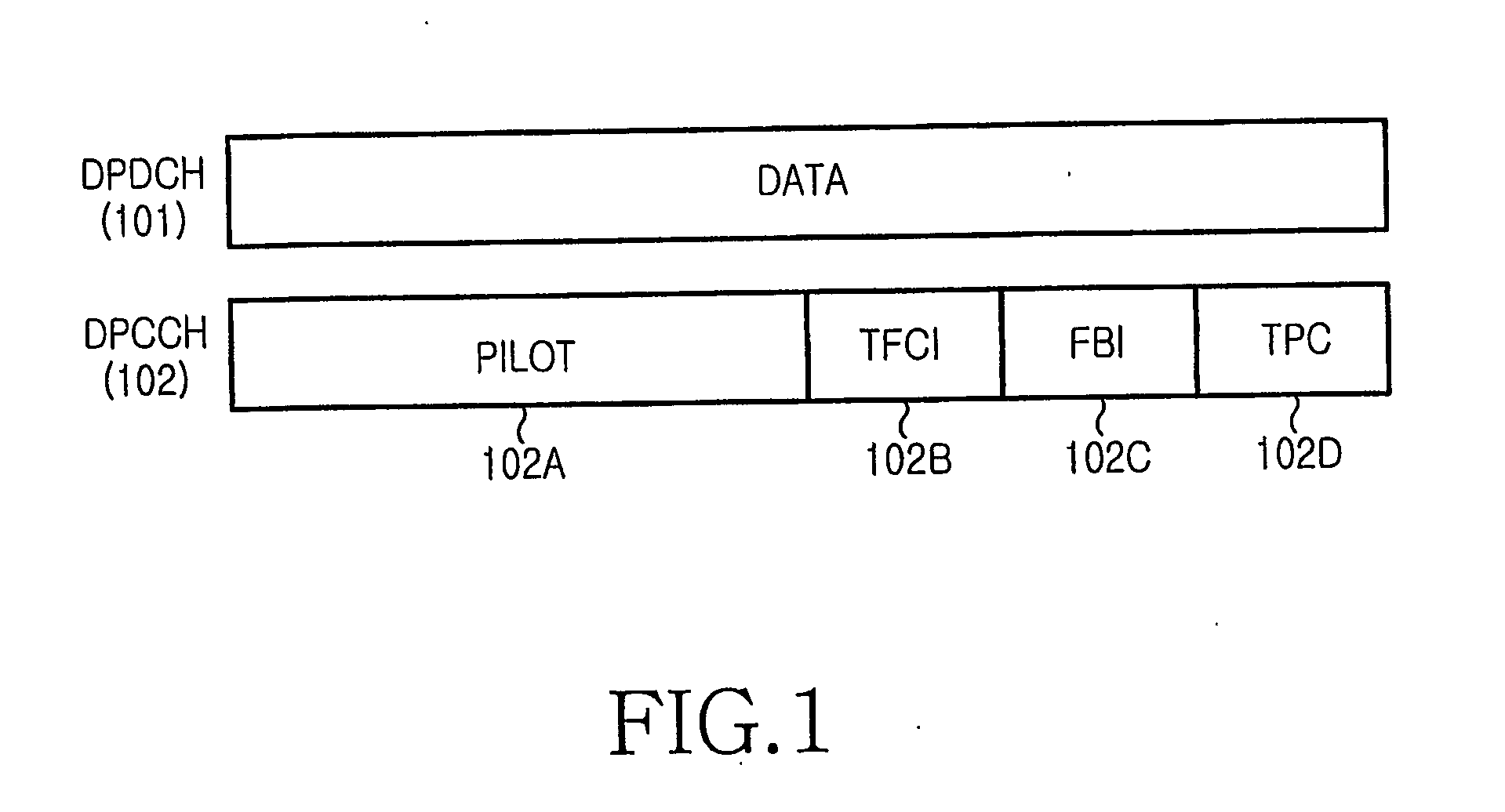
Method For Supporting Pilot Boost In E-Dch Of Wcdma
InactiveUS20070211684A1Increase capacityPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemInner loop
The method for supporting pilot boost to the uplink dedicated channels in the WCDMA system comprising steps of: transmitting E-TFCI to a Node B by a UE; adjusting an uplink pilot power boosting amplitude by the UE according to the E-TFCI; and performing a uplink inner loop power control by the Node B according to a measured SIR, a target preset by the inner loop power control and a pilot boost amplitude resulted from the E-TFCI. The object of supporting pilot boost is achieved by transmitting E-TFCI in advance by the UE, adjusting the power of pilot according to the E-TFCI properly, and considering the pilot power boosting amplitude when the Node B performs inner loop power control in the invention. Thus, the object of improving the capacity of the wireless communication system can be accomplished through supporting the pilot boost in the invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
MIMO receiver, MIMO reception method and wireless communication system
ActiveUS7466969B2Improve featuresPower managementSpatial transmit diversityEngineeringTransmitter antenna
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for improving capacity of a reverse link channel in a wireless network
The capacity of a reverse link is improved by realizing a scheme to effect sharp changes in pilot channel transmit power (PCTP) and data channel to pilot power ratio (DCPR), coordinated with the start of the data channel transmission. The change in pilot power and data channel to pilot power ratio is also applicable to mobiles that use multiple pilots and / or multiple antennas at the transmitter and / or receiver.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
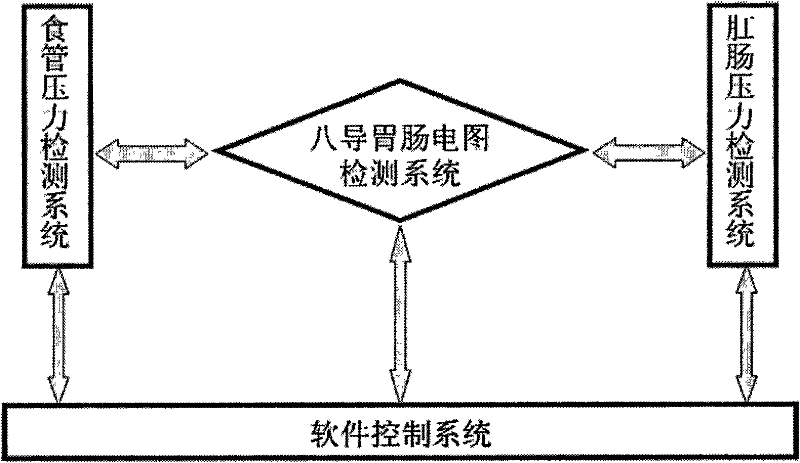
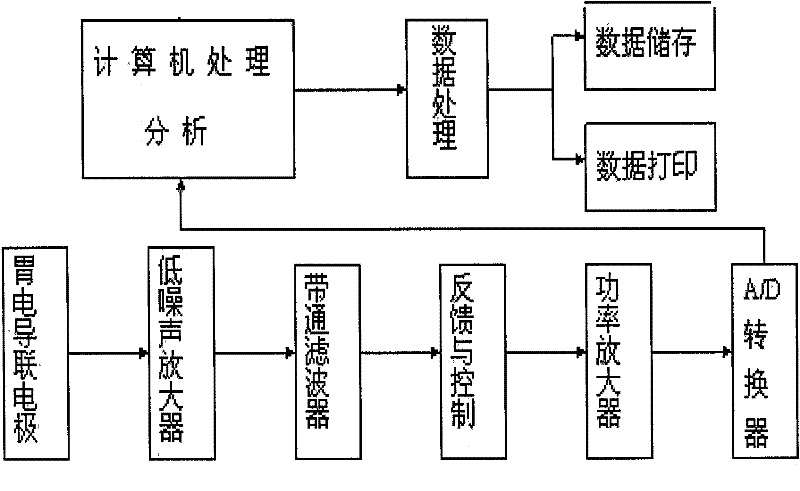
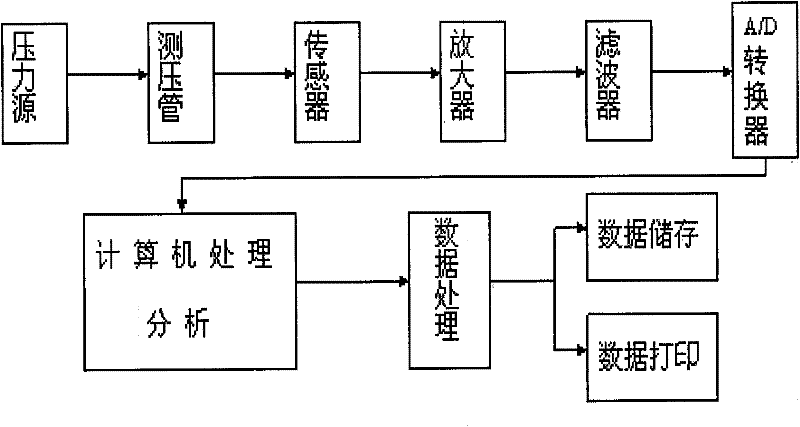
A digestive tract power detection system
A digestive tract power detection system relates to the field of digestive tract power detection, including an eight-lead gastrointestinal electrogram detection system, a pressure detection system and a software control system. The pressure detection system includes an esophageal pressure detection system and anorectal pressure detection system. Through the software control system, the instrument conducts two-way data transmission between the eight-lead gastrointestinal electrogram detection system, esophageal pressure detection system and anorectal pressure detection system, and realizes the collection of esophageal dynamic detection, anorectal dynamic detection and eight-lead gastrointestinal electrogram detection Digestive tract motility detection system with three functions in one. The best effect is that the digestive tract dynamic detection system embodies the highly integrated circuit technology of the gastrointestinal electrogram detection system and pressure detection system, and integrates signal processing circuits such as signal amplification, active filtering, feedback and control, power amplification and A / A series of circuits such as D conversion are integrated on a computer-specific detection card; and many information processing and automatic control technologies such as electrophysiological signal processing technology, pressure source constant pressure control technology of pressure detection system, automatic control software and data analysis are adopted. Processing technology and database management technology bring great convenience to the diagnosis and research of digestive tract motility diseases, and more accurate and comprehensive diagnosis and research of digestive tract motility diseases.
Owner:HEFEI KAILI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Joint dynamic pilot and data power allocation method for time division duplex large-scale MIMO systems
A joint dynamic pilot and data power allocation method for time division duplex large-scale MIMO systems belongs to the technical field of time division duplex large-scale MIMO, and is provided to adaptively reduce pilot pollution and balance mutual interference. Because the real-time channel state information before pilot is unknown, the Gauss-Markov process of a time-dependent channel is used, and a Kalman filter is used not only to filter pilot pollution, but also to provide a priori estimate. Then, the deterministic approximation of rate is derived as a function of prior channel estimationand prior estimation error, and rate maximization for maximum-minimization is formulated. In order to solve the optimization of pilot power and data power as well as the coupling between users, an iterative alternation rate optimization algorithm consisting of two sub-problems is presented, and successive convex approximation (SCA) and relaxation variables are introduced. The numerical results ofsimulation confirm the improvement rate provided by the scheme.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method of self-adoptive regulating high-speed share control channel power
InactiveCN1852041AFast convergenceTelevision system scanning detailsModulated-carrier systemsChannel powerInit
This invention discloses a method for adaptively regulating HS-SCCH power including A, designing a power offset Poffset of the HS-SCCH channel emission power corresponding to the DPCCH pilot domain power when a mobile user HSDPA link is changed, B, obtaining the pilot power PDPCCH, Pilot, on the down DPCCH channel of said mobile user and designing the initial emission power of said mobile user HS-SCCH: P HS-SCCH, Init=P DPCCH, Pilot +P offset, C, designing the regulation volume of the HS-SCCH channel power when dispatching said mobile user for the Nth time based on the ACK / NACK / DTX information fed back by HS-DPCCH, D, adding the regulation volume of the HS-SCCH channel power to its emission power to get the emission power when dispatching said mobile user for the Nth time.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
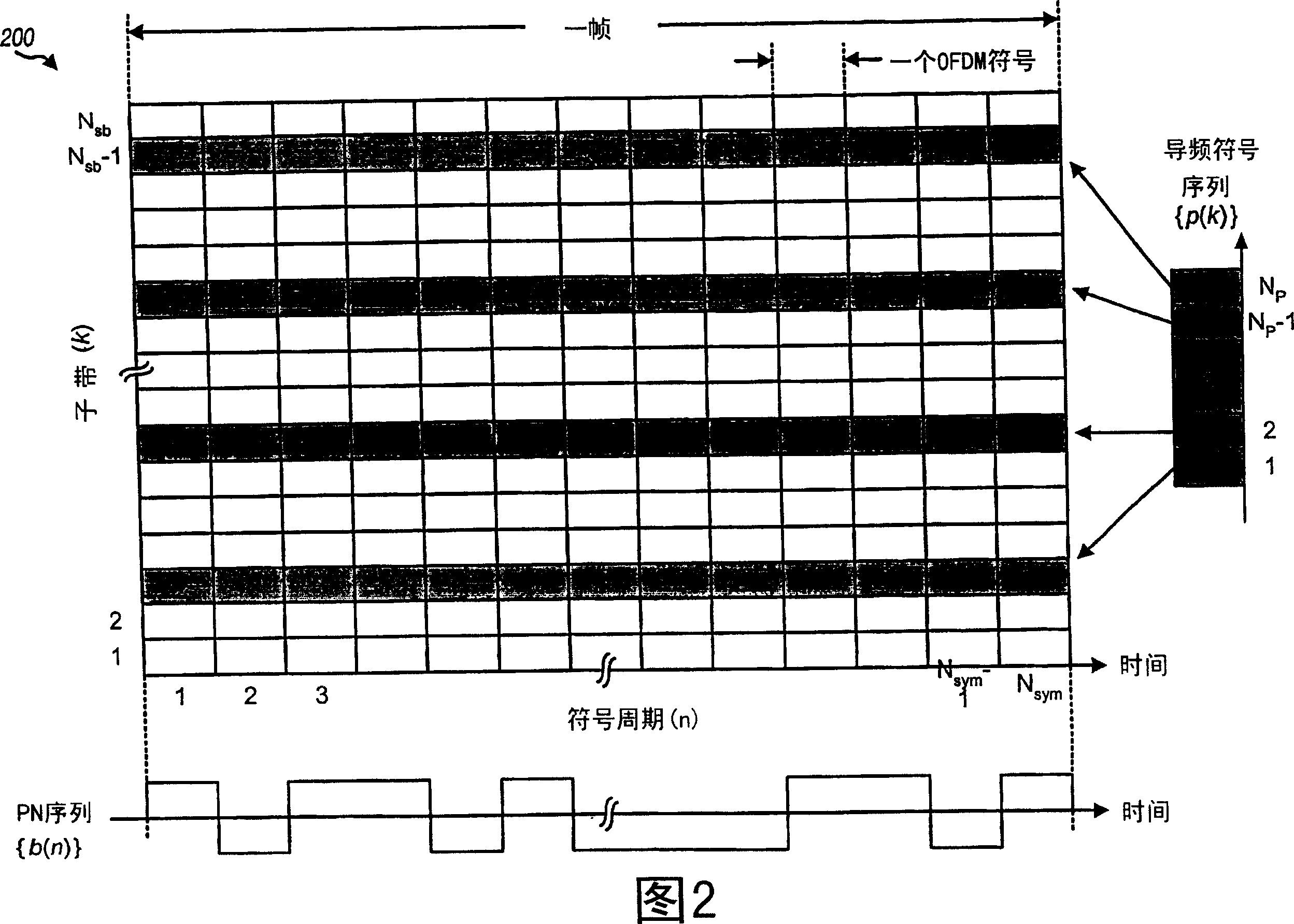
Frequency error estimation and frame synchronization in an OFDM system
Frequency error estimation and frame synchronization are performed at a receiver in an OFDM system based on a metric that is indicative of detected pilot power. The metric may be defined based on cross-correlation between two received symbols obtained in two OFDM symbol periods. For frequency error estimation, a metric value is computed for each of multiple hypothesized frequency errors. The hypothesized frequency error for the metric value with the largest magnitude is provided as the estimated frequency error. For frame synchronization, a correlation value is obtained for each OFDM symbol period by correlating metric values obtained for NC (e.g., most recent) OFDM symbol periods with NC expected values. The expected values are computed in a manner consistent with the manner in which the metric values are computed. Peak detection is performed on the correlation values obtained for different OFDM symbol periods to determine frame synchronization.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for planning and/or evaluation of downlink coverage in (CDMA) radio networks
InactiveUS7076250B2Fast and reliable planningError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio networksDownlink transmission
Method and system for planning and / or evaluation of downlink coverage in a (CDMA) radio network. A service area of the radio network can be divided into pixels defined by a grid, and cells can be assigned to the pixels. After assigning pilot power, desired downlink transmission power can be estimated for the cell, which can then be compared to maximum transmission power of the base station. If needed changes in the radio network are to be made, the planning and / or evaluation is restarted.
Owner:KONINK KPN NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com