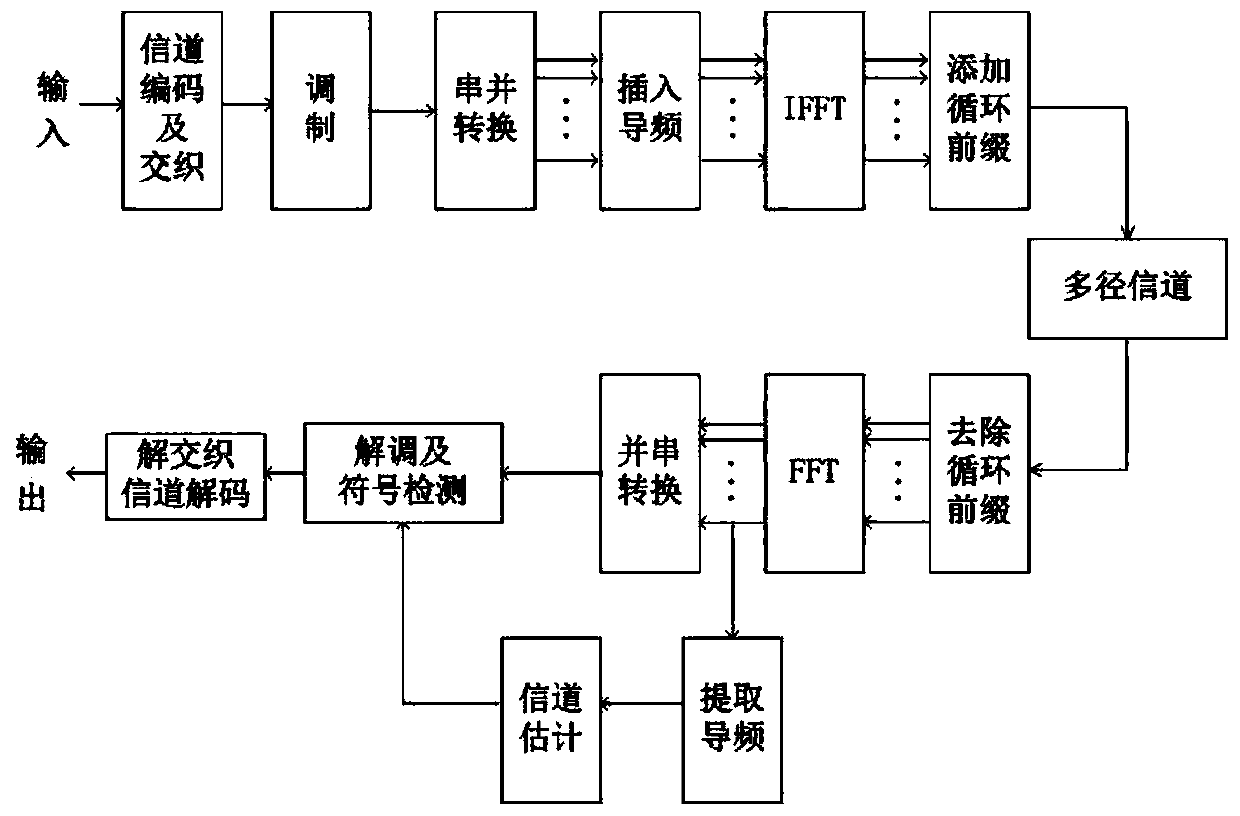
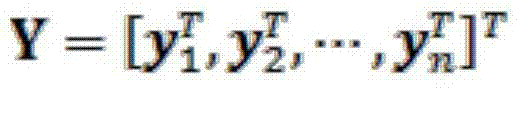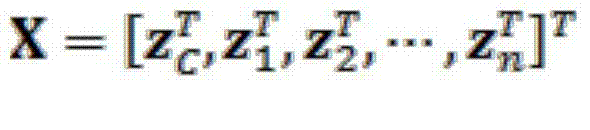Patents
Literature
154 results about "Matching pursuit algorithms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
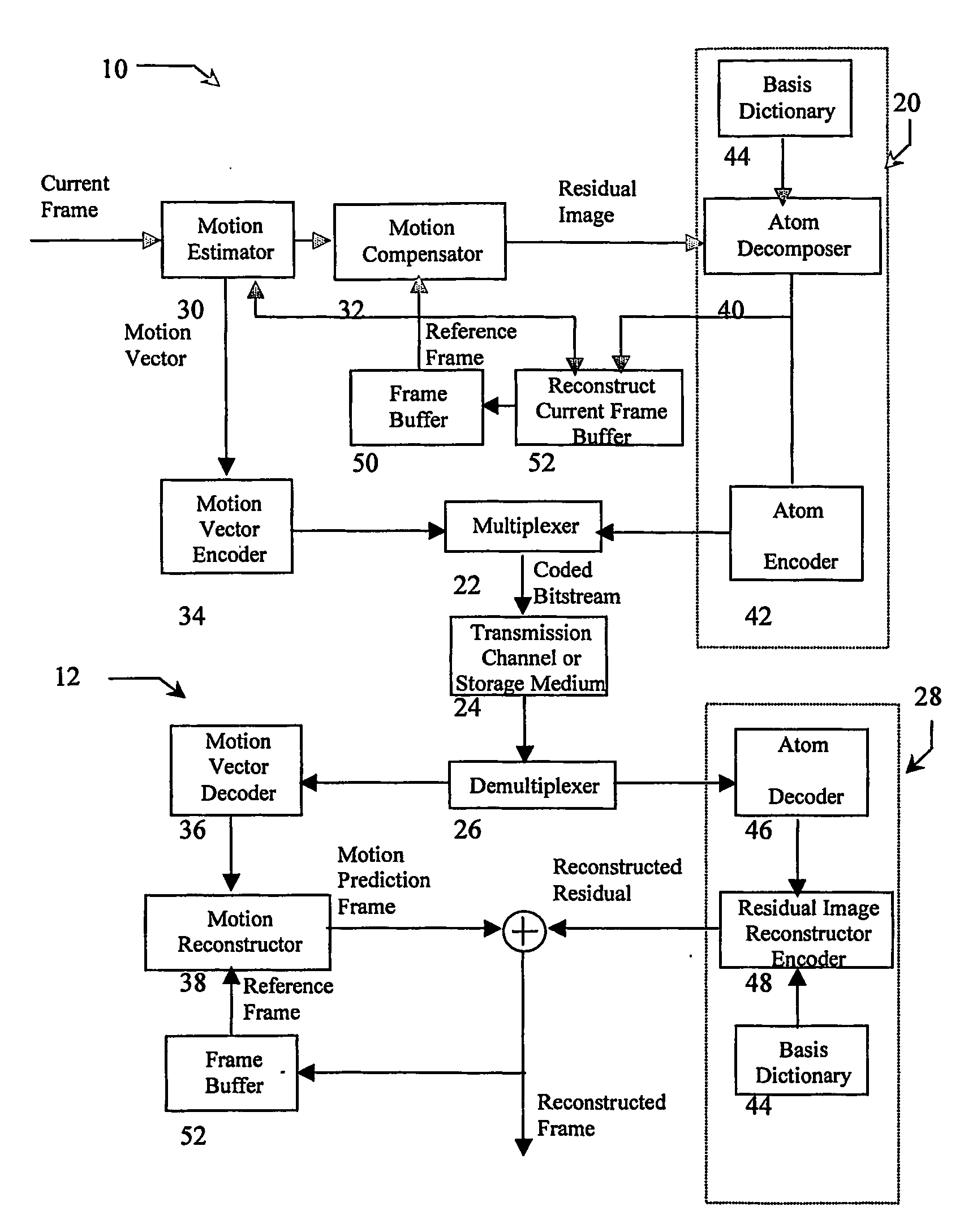
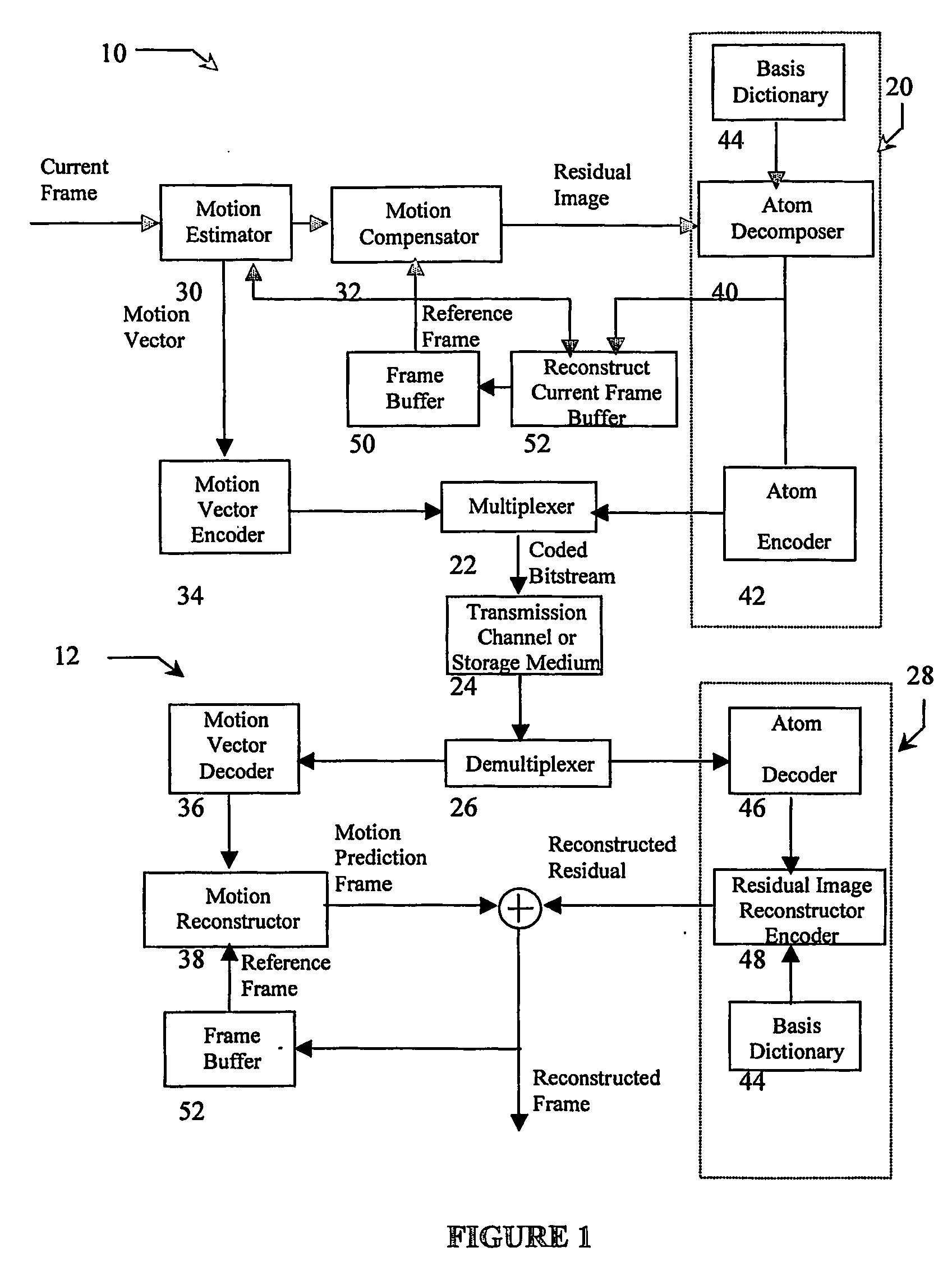
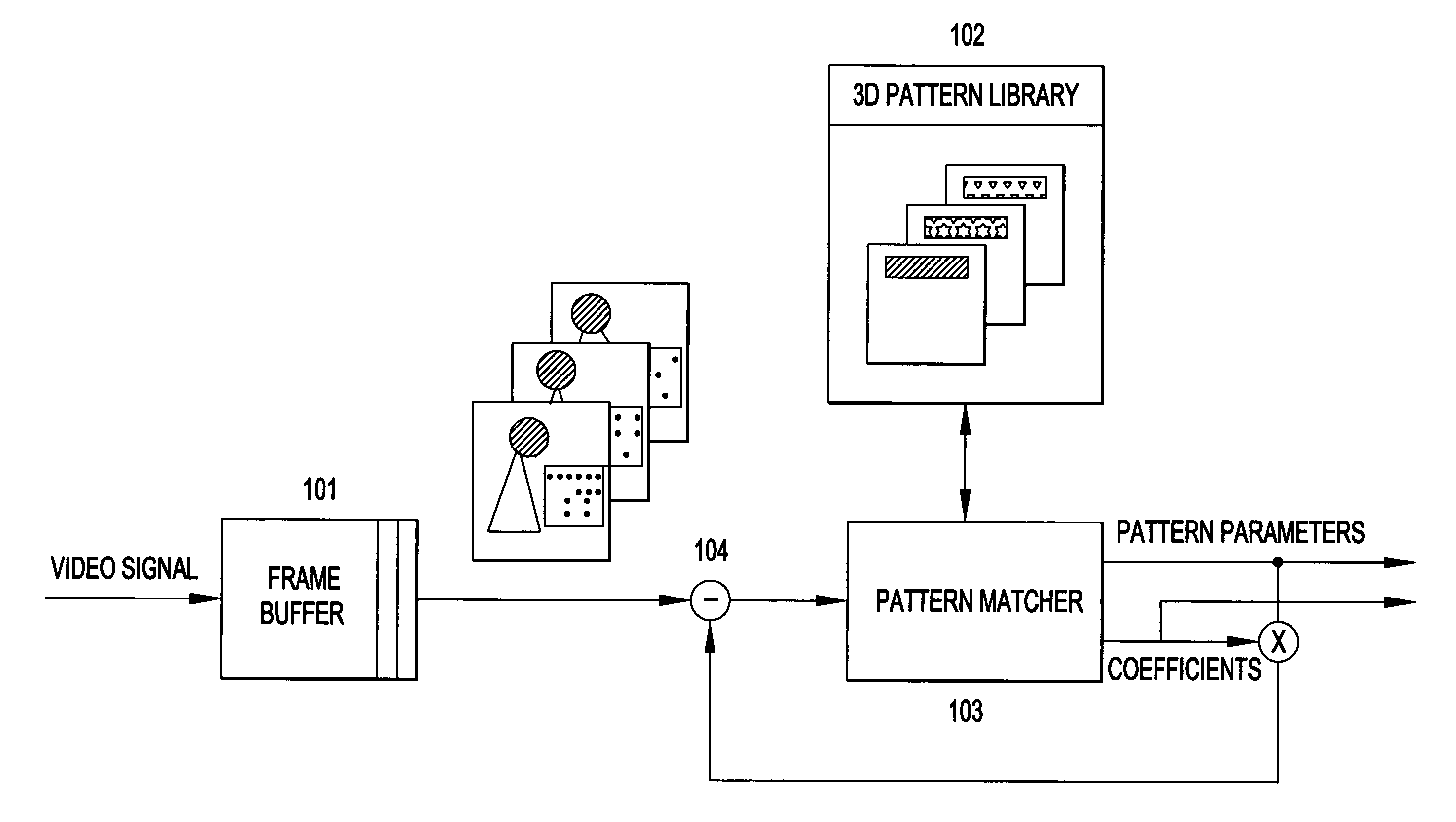
Overcomplete basis transform-based motion residual frame coding method and apparatus for video compression
ActiveUS20090103602A1Weaken energySmall sizeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionHigh energy
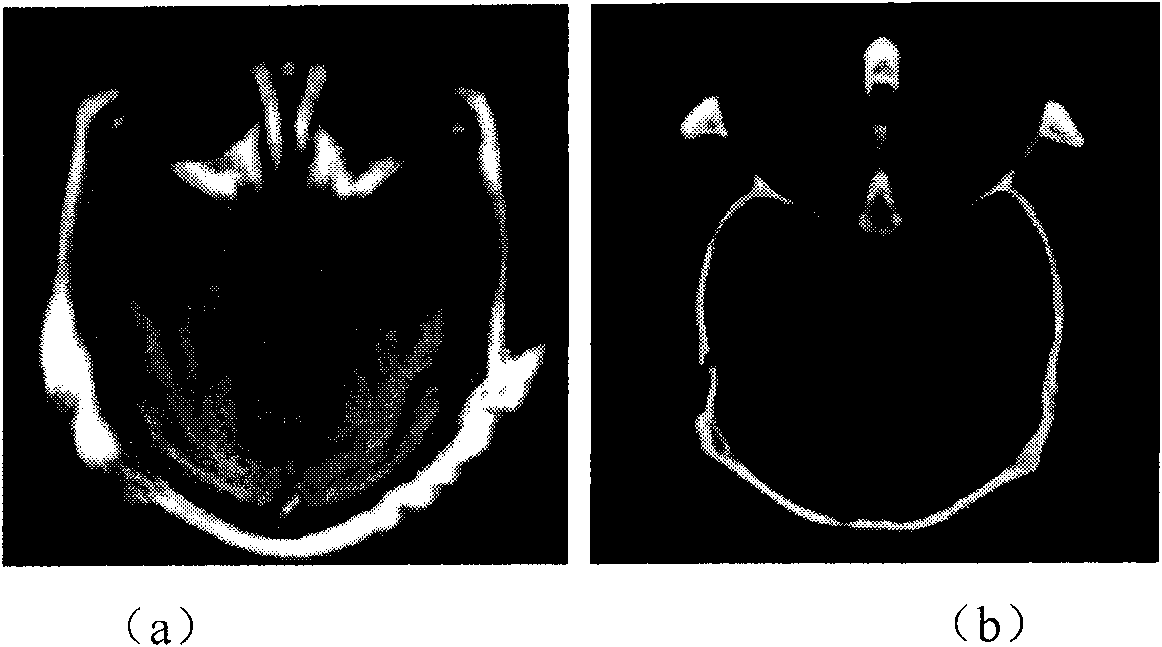
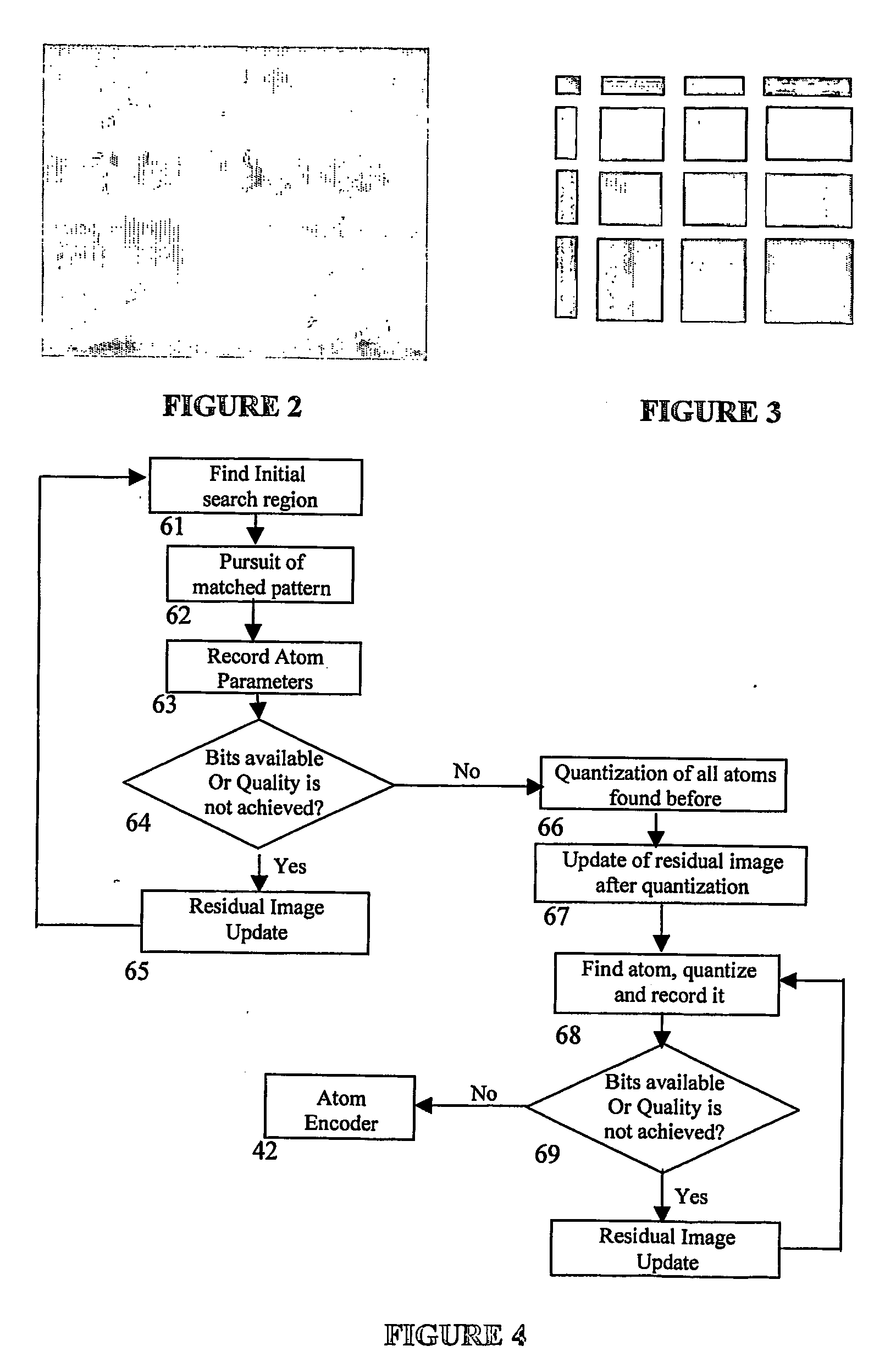
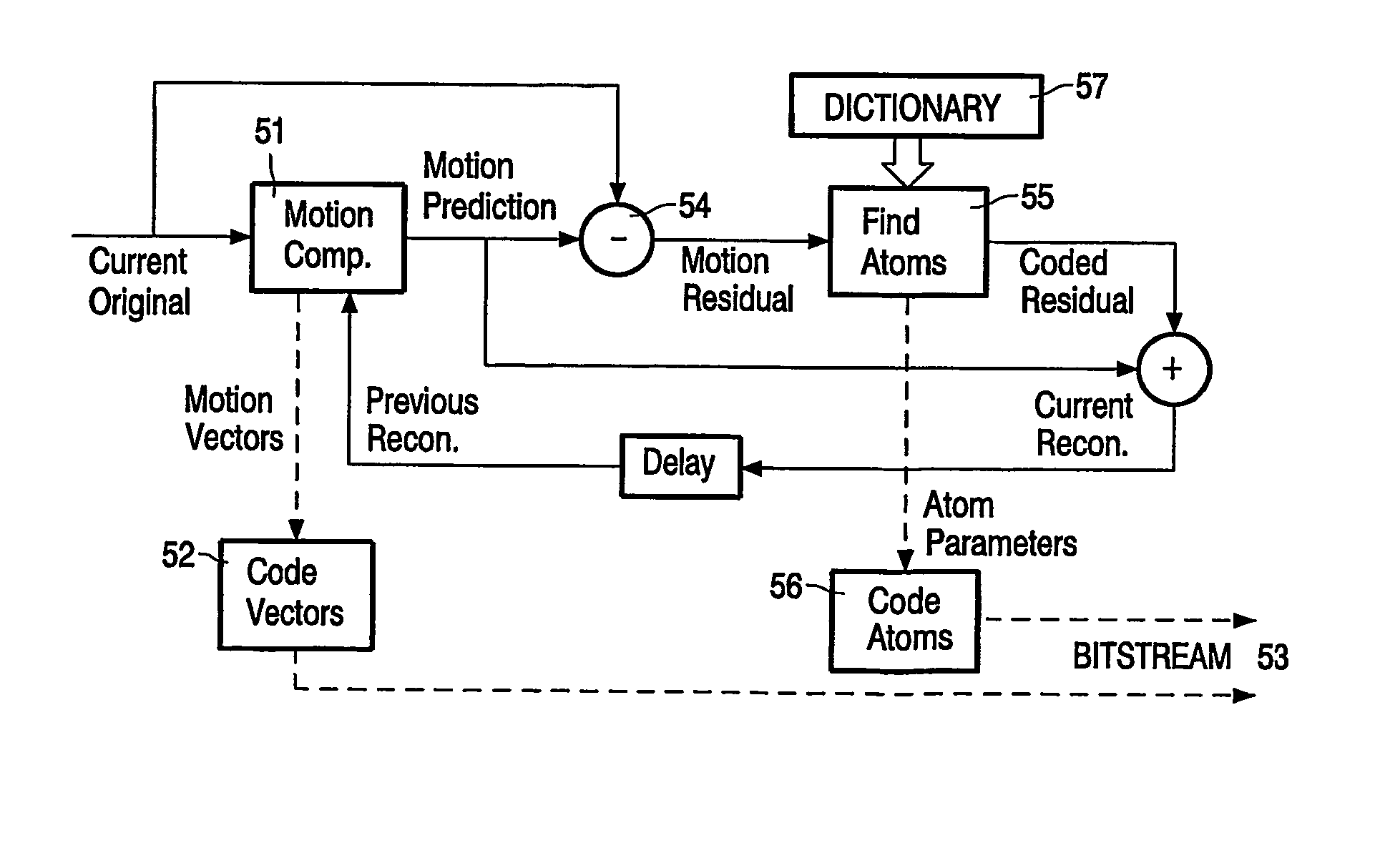
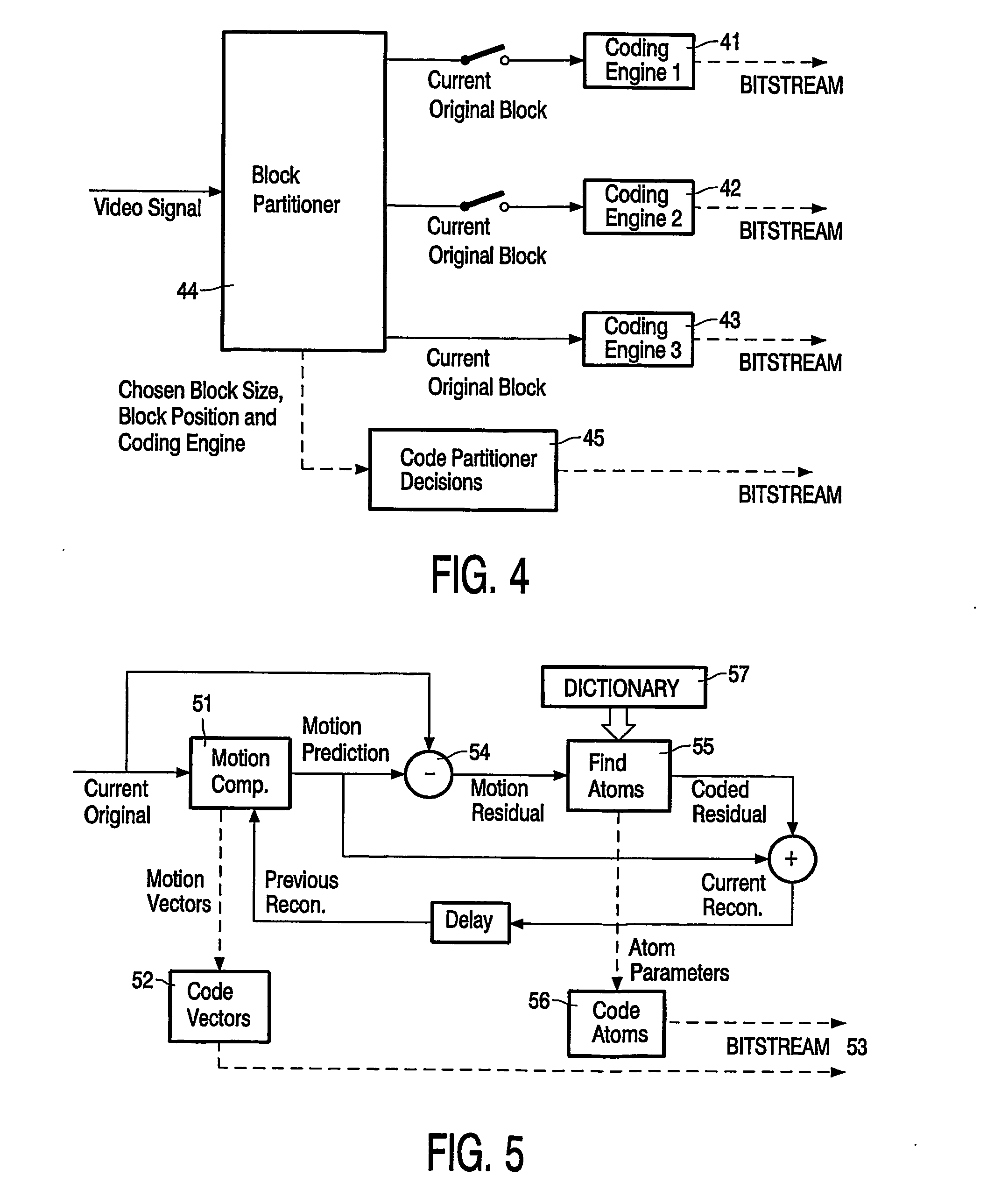
The present invention provides a method to compress digital moving pictures or video signals based on an overcomplete basis transform using a modified Matching Pursuit algorithm. More particularly, this invention focuses on the efficient coding of the motion residual image, which is generated by the process of motion estimation and compensation. A residual energy segmentation algorithm (RESA) can be used to obtain an initial estimate of the shape and position of high-energy regions in the residual image. A progressive elimination algorithm (PEA) can be used to reduce the number of matching evaluations in the matching pursuits process. RESA and PEA can speed up the encoder by many times for finding the matched basis from the pre-specified overcomplete basis dictionary. Three parameters of the matched pattern form an atom, which defines the index into the dictionary and the position of the selected basis, as well as the inner product between the chosen basis pattern and the residual signal. The present invention provides a new atom position coding method using quad tree like techniques and a new atom modulus quantization scheme. A simple and efficient adaptive mechanism is provided for the quantization and position coding design to allow a system according to the present invention to operate properly in low, medium and high bit rate situations. These new algorithm components can result in a faster encoding process and improved compression performance over previous matching pursuit based video coders.
Owner:ETIIP HLDG
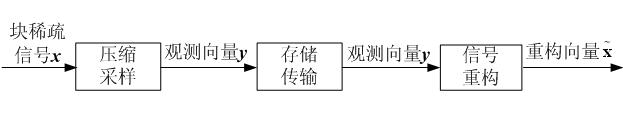
Compressed sensing-oriented block-sparse signal reconfiguring method
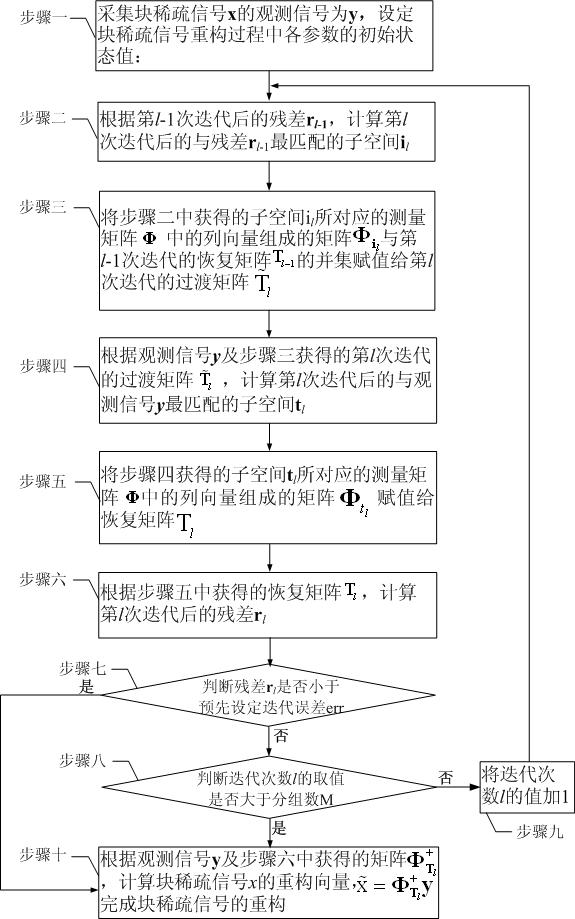
The invention discloses a compressed sensing-oriented block-sparse signal reconfiguring method, and particularly relates to a block-sparse signal reconfiguring algorithm, which aims to solve the problems that the optimization complexity of a mixed l2 / l1 optimization algorithm in the conventional block-sparse signal reconfiguring algorithm is relatively higher and that overmatching phenomenon is easily caused by a block-sparse matching pursuit algorithm or a block-sparse orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of: correcting labels, in ameasurement matrix, of column vectors of a recovery matrix calculated in the iteration operation of the (l-1)th time by performing the iteration of the lth time, and for a block-sparse signal x with the block sparsity of K, reconfiguring the block-sparse signal x by performing the iteration for not more than K times. The method is applied to the reconfiguration of the block-sparse signal, particularly to the reconfiguration of a binary block-sparse signal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
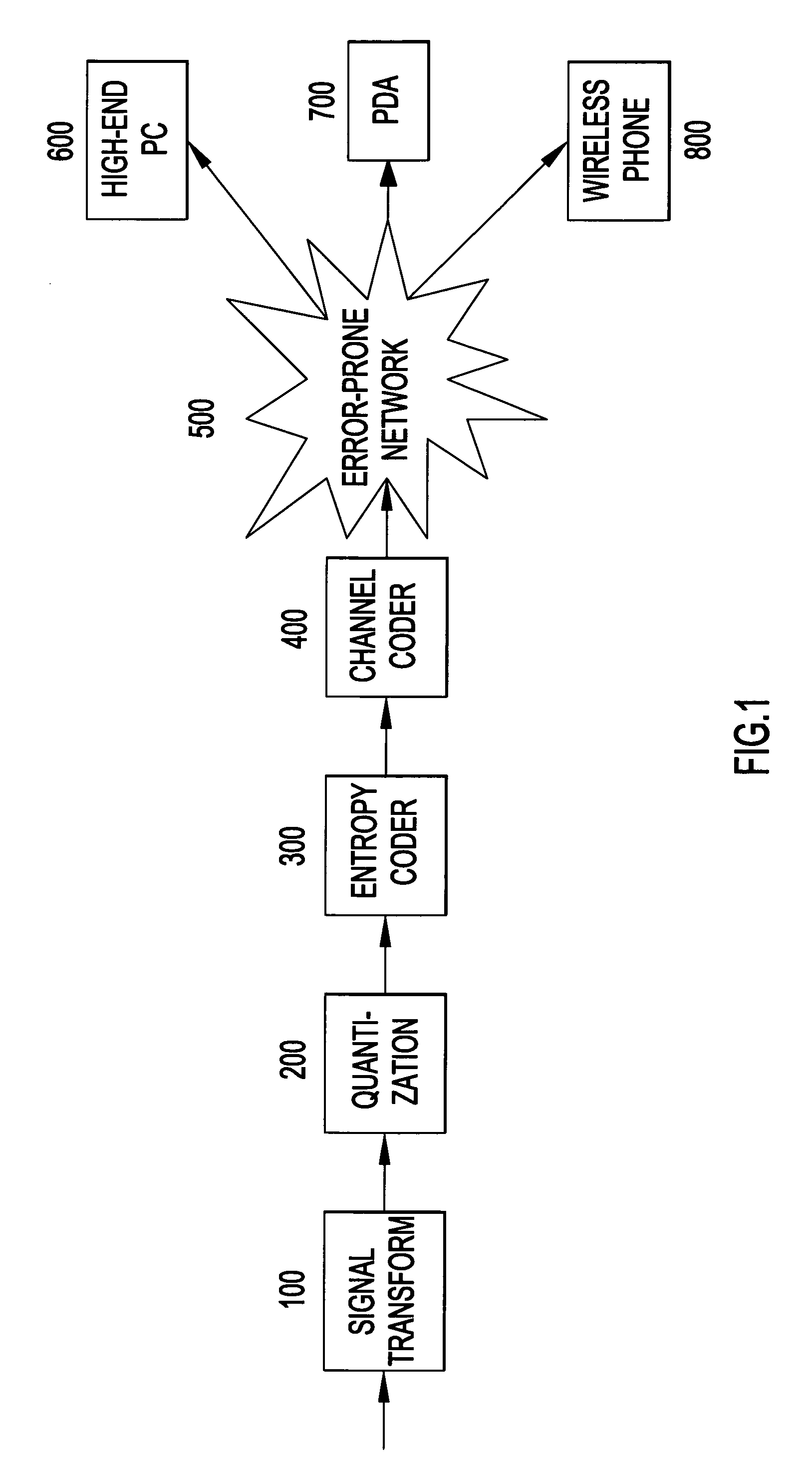
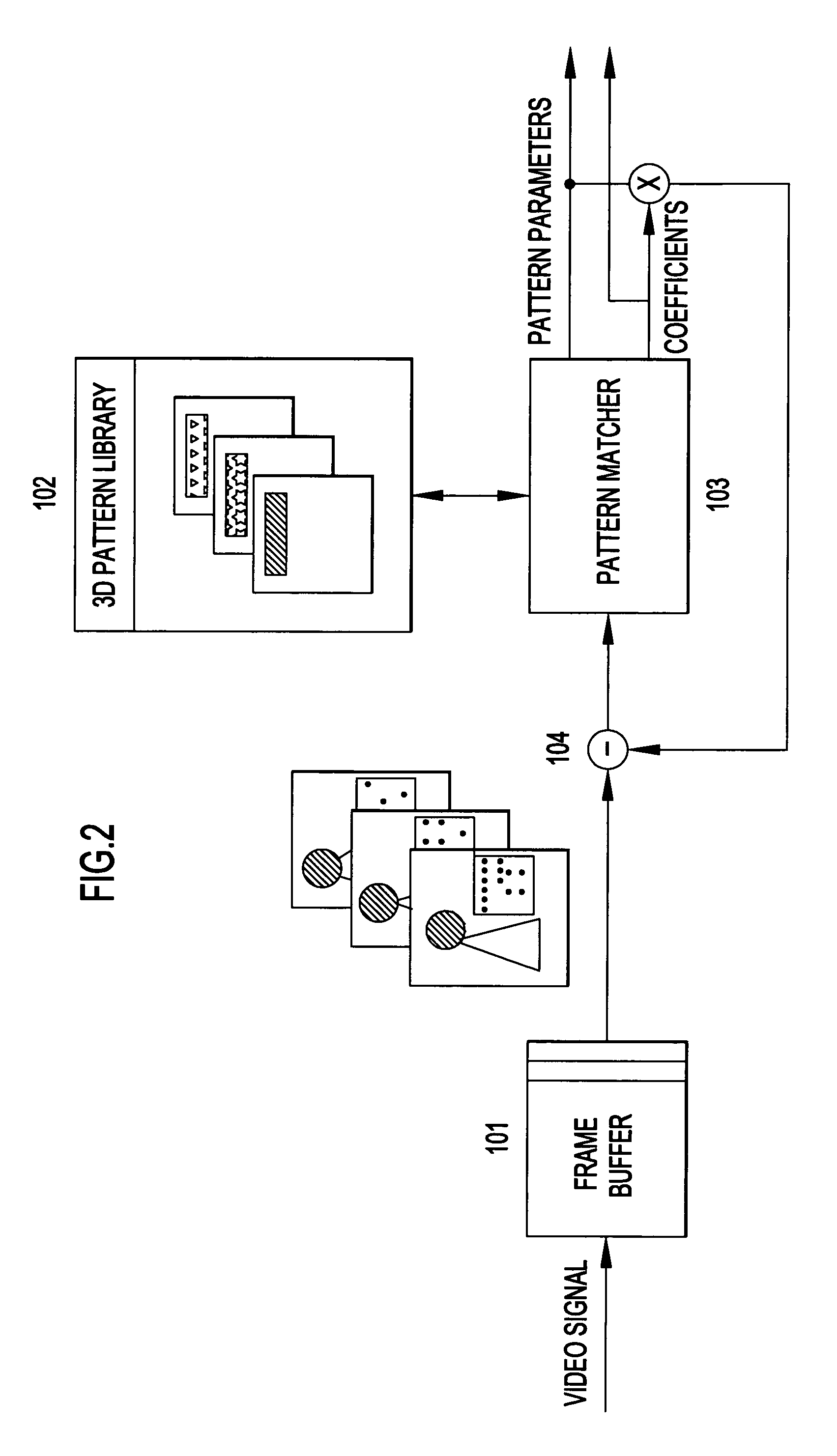
System and method for encoding three-dimensional signals using a matching pursuit algorithm
InactiveUS7006567B2Resistant to data lossImproves source coding qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionTime space
An apparatus and method to represent a video signal for improved source quality versus decoding complexity for a given compression rate and improved resistance against data loss when delivered over an error-prone network. The method comprises a 3-D matching pursuit algorithm with an improved 3-D dictionary. The 3-D MP encoder transforms blocks of frames into a set of spatio-temporal functions from the improved dictionary. The 3-D coder outputs a video stream that is highly resistant to data loss. Also, the proposed dictionary is optimized for source quality versus decoding complexity for a given compression rate.
Owner:IBM CORP
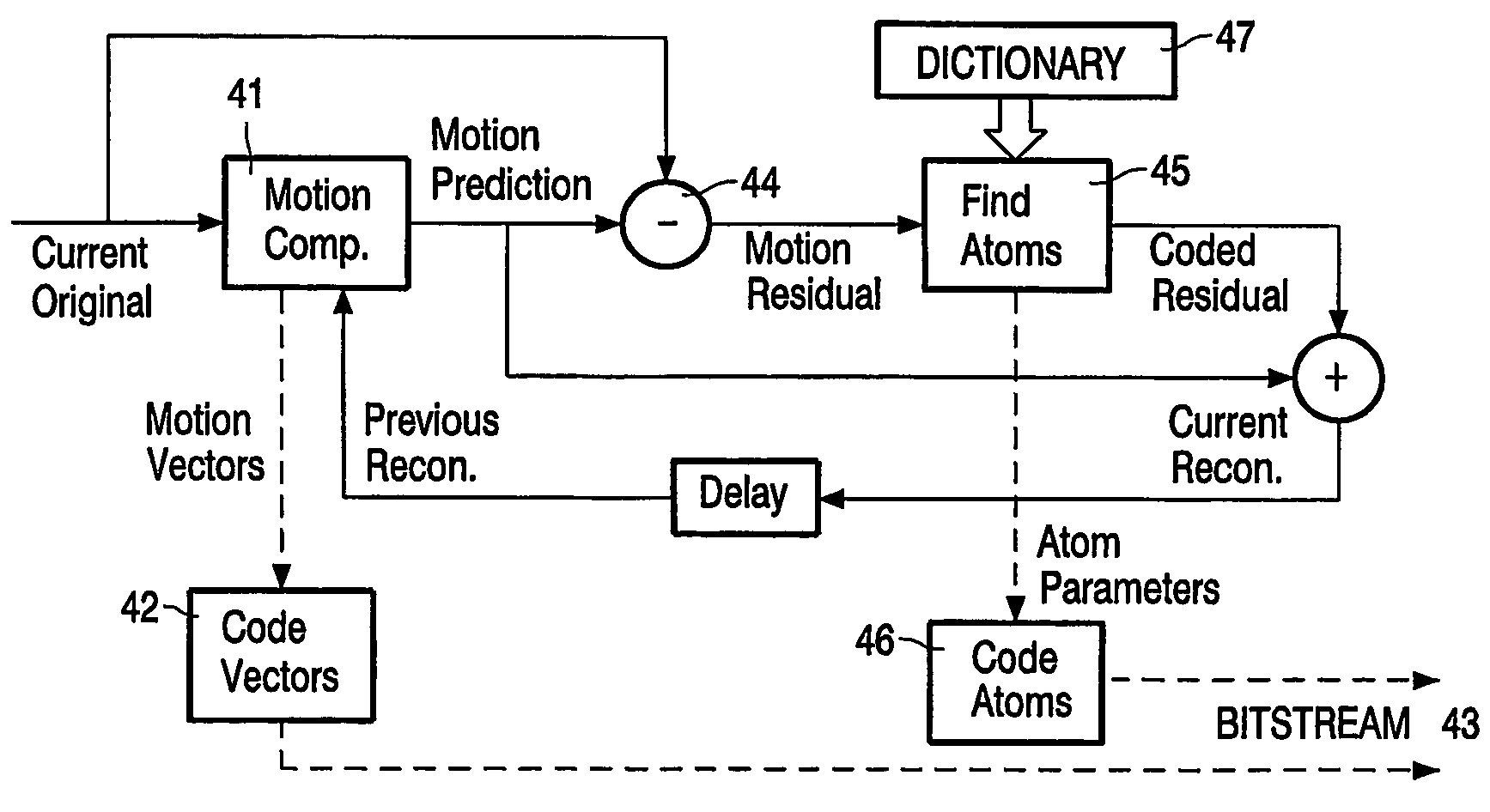
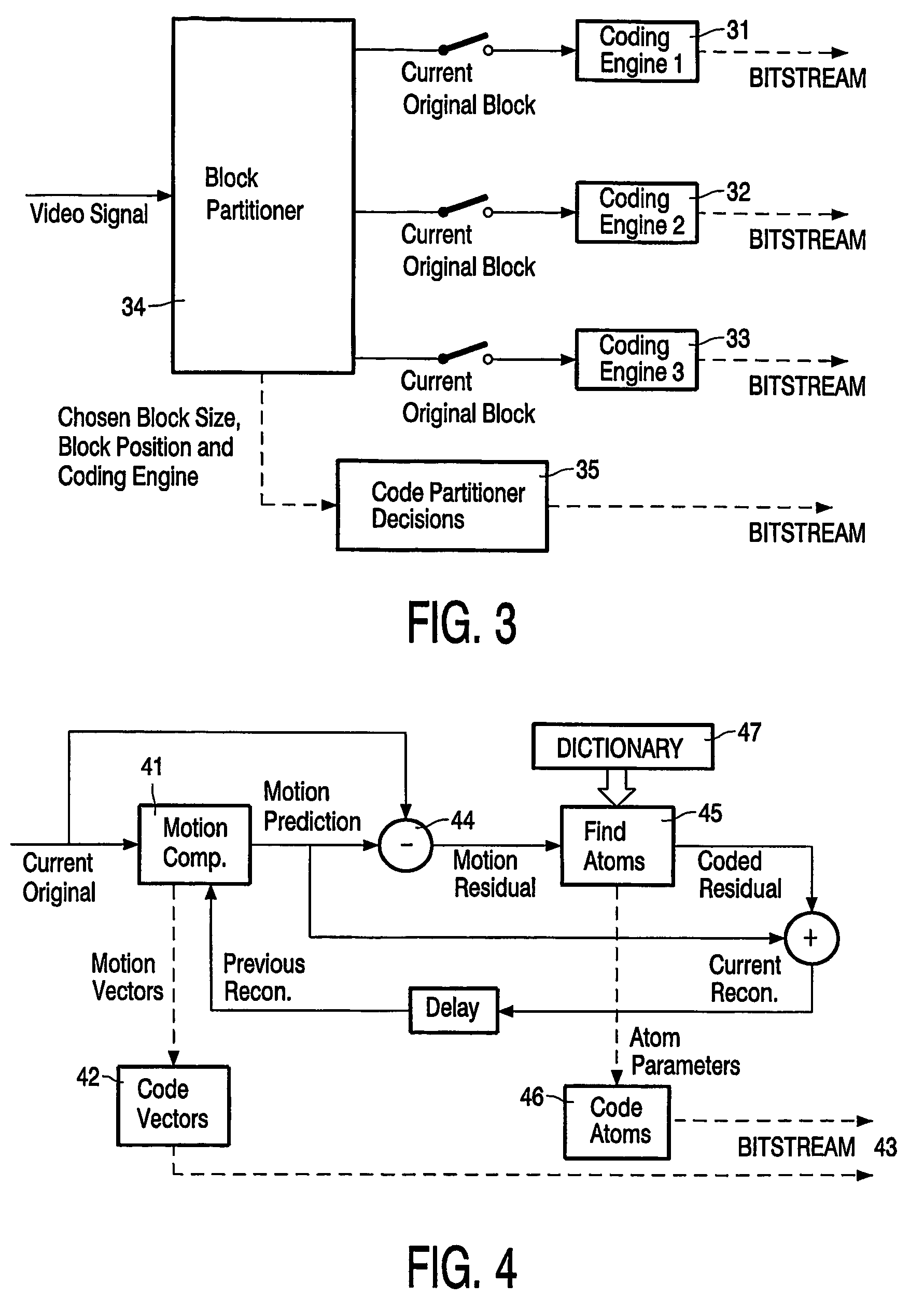
Video encoding and decoding methods and corresponding devices
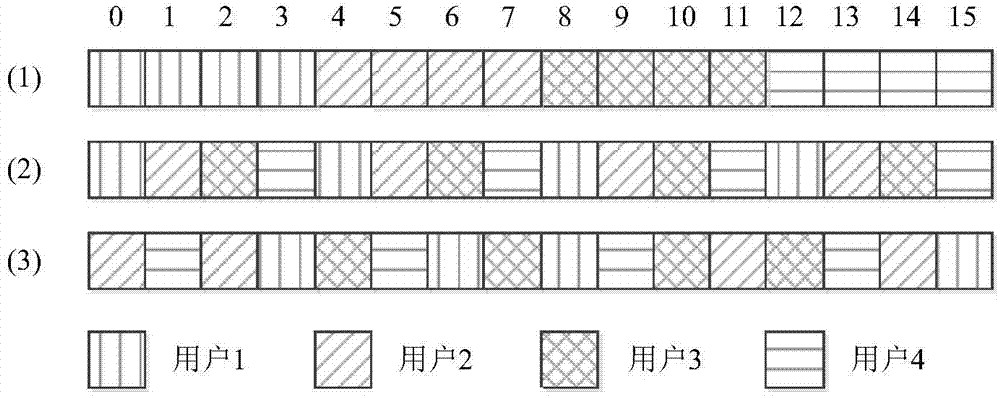
InactiveUS7746929B2Model blocky structureAugments the dictionary diversityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningMotion vectorVideo encoding
The invention relates to the field of video compression and, more specifically, to a video encoding method applied to an input sequence of frames in which each frame is subdivided into blocks of arbitrary size. This method comprises, for at least a part of the blocks of the current frame, the steps of: generating on a block basis motion-compensated frames obtained from each current original frame and a previous reconstructed frame; generating the said motion-compensated frames residual signals; using a matching pursuit algorithm for decomposing each of the generated residual signals into coded dictionary functions called atoms, the other blocks of the current frame being processed by means of other coding techniques; coding said atoms and the motion vectors determined during the motion compensation step, for generating an output coded bitstream; said method being such that any atom acts only on one block B at a time, said block-restriction leading to the fact that the reconstruction of a residual signal f is obtained from a dictionary that is composed of basis functions gγnæBrestricted to the block B corresponding to the indexing parameter γn, according to the following 2D spatial domain operation: gγnæB(i,j)=gγn(i,j) if pixel (i,j)εB; gγnæB(i,j)=0 otherwise (i.e. (i,j)∉B).
Owner:DYNAMIC DATA TECH LLC
Rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on signal sparse representation theory
InactiveCN105241666AWide versatilityReduce pointsMachine bearings testingDamping ratioAdaptive method
The invention discloses a rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on the signal sparse representation theory, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing an over-complete dictionary representing local damages of a rolling bearing through employing a multi-stage inherent frequency unit impulse response function; recognizing the multi-stage inherent frequency and damping ratio of the rolling bearing and a sensor system from a vibration response signal through a related filtering method, and obtaining an optimized dictionary; solving a sparse coefficient through employing a matching tracking algorithm, and improving the solving speed and precision through reasonable segmentation; reconstructing an impact response signal of each segment, and obtaining the sparse representation of a fault feature signal; carrying out time domain index statistic characteristic analysis of time intervals of adjacent impact response components in a sparse signal, and diagnosing the type of a fault through combining a mean value and a mean square deviation value. The method has the advantages of an analytical method and an adaptive method, improves the precision of waveform features, and can iron out the defects that a conventional method based on Fourier transform is not suitable for rotating speed fluctuation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Voice secret communication system design method based on compressive sensing and information hiding
ActiveCN102034478AQuality improvementImprove sparsitySpeech analysisSecret communicationWavelet denoisingVoice communication
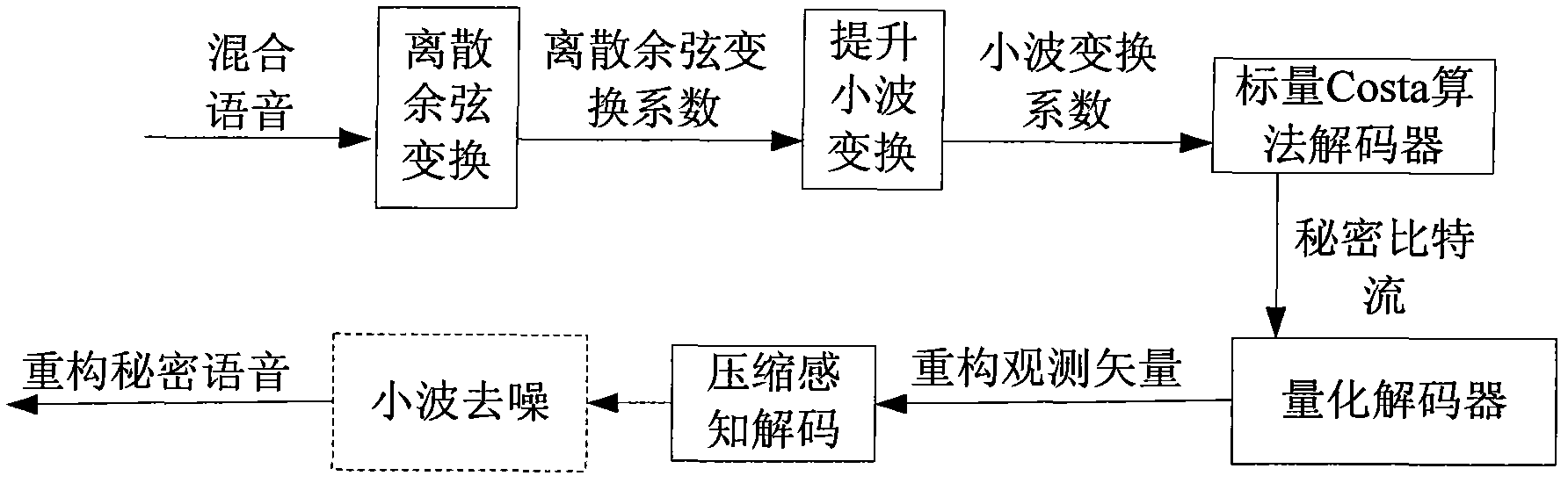
The invention discloses a voice secret communication system design method based on compressive sensing and information hiding, comprising the following steps: embedding secret voice into carrier voice by an embedded system to obtain mixed voice; designing a compressive sensing overcomplete dictionary aiming at the voice signal; sampling the secret voice by a compressive sensing self-adaption observation matrix to obtain a observation vector for reducing dimensions; quantizing the observation vector by an LBG (Linde-Buzo-Gray algorithm) vector, taking the quantized observation vector to serve as secret information to embed into the carrier voice, and carrying out two-stage transform on the carrier voice to obtain mixed voice; extracting the secret voice from the mixed voice by an extraction system; carrying out discrete cosine transform on mixed voice, and improving wavelet transform two-stage transform to obtain a wavelet transform coefficient; obtaining a secret bit stream by a scalar Costa decoding algorithm; obtaining a reconstructing observation vector by an LBG vector quantization decoder; reconstructing the secret voice by a compressive sensing orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm; and improving the quality of the reconstructed secret voice with a wavelet denoising method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-source image fusion method based on synchronous orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm
InactiveCN101540045AConform to visual characteristicsSparse Signal RepresentationImage enhancementPattern recognitionSlide window
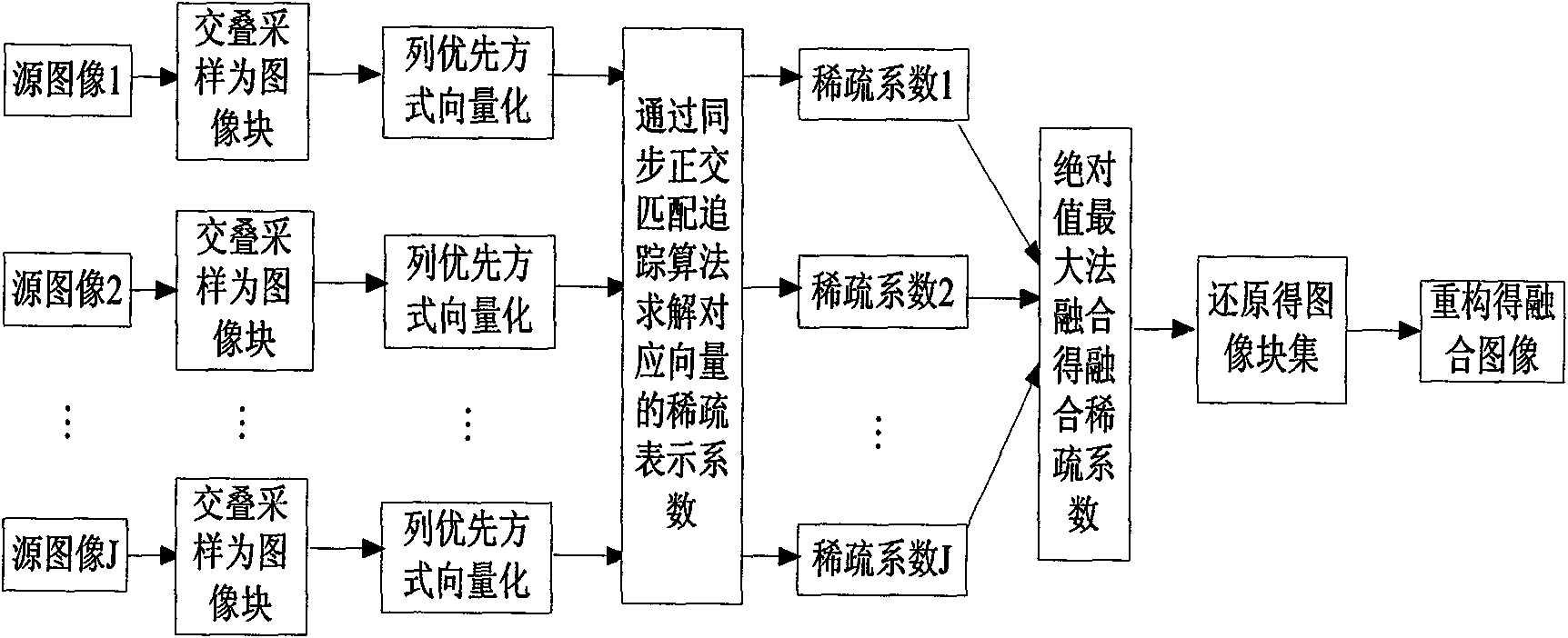
The invention discloses a multi-source image fusion method based on the synchronous orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. The multi-source image fusion method comprises the following steps: sampling a source image pixel by pixel in an overlapping manner into image blocks of the same size by a sliding window of the fixed size and expanding each image block by columns into column vectors; obtaining the sparse representation coefficient corresponding to each vector on the over-complete dictionary by the synchronous orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm; fusing the corresponding coefficient by the maximum absolute value method; inverse-transforming the fused sparse representation coefficient into the fusion result vector of corresponding to the vectors according to the over-complete dictionary; and restoring all the fusion result vectors to image blocks and re-constructing to obtain the fused image. The invention fully considers the intrinsic characteristics of the image sparsity and the method using sparse representation can more effectively present the useful information of each source image and achieve better fusion effect, therefore, the invention is of great significance and practical value to the post-processing and image display of various application systems.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Compressed sensing-based antifriction bearing fault diagnosis method under working condition disturbance condition
InactiveCN105258947AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionOn boardDiagnosis methods
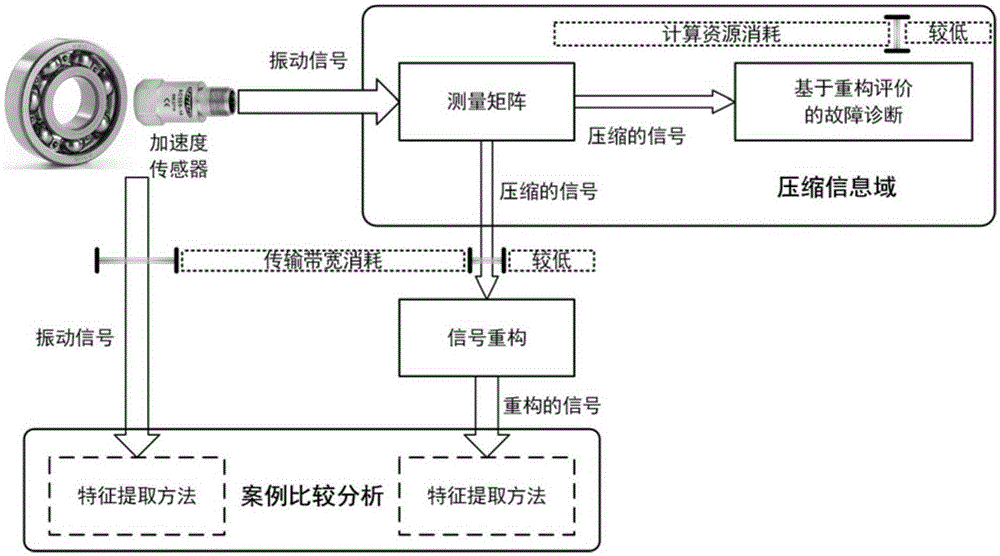
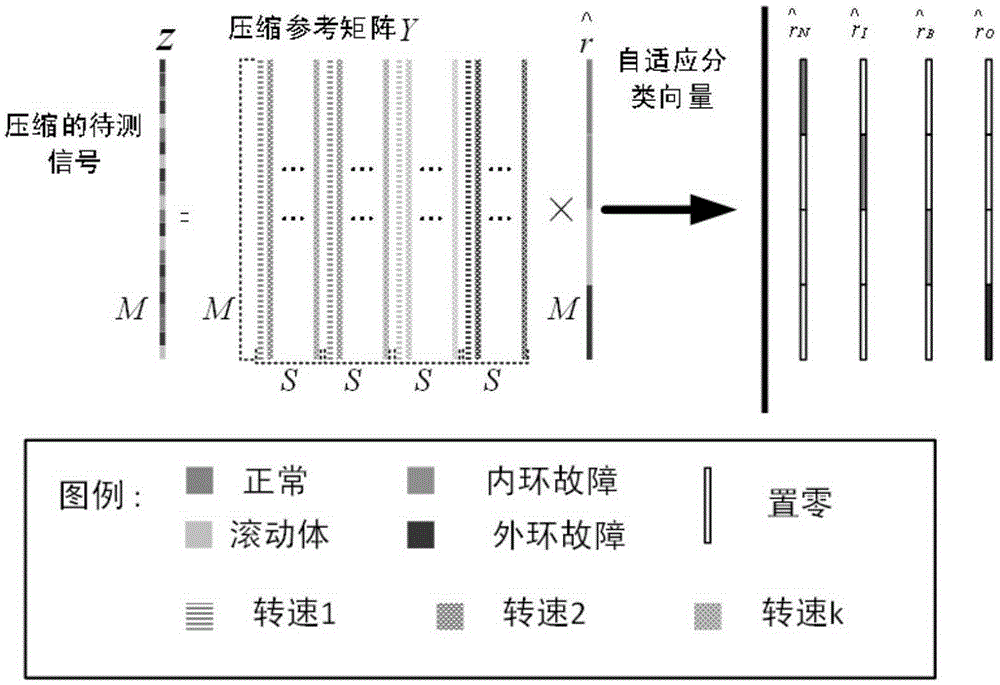
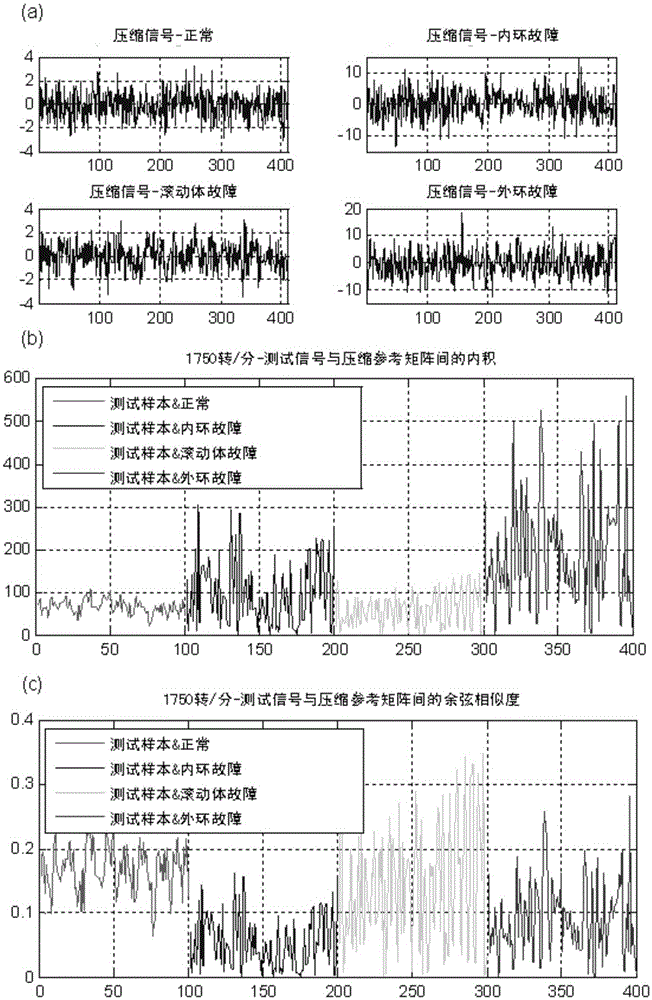
The invention provides a compressed sensing-based antifriction bearing fault diagnosis method based on a working condition disturbance condition. The antifriction bearing fault diagnosis method comprises signal compression, front fault diagnosis and a far-end signal reconstruction algorithm. The method utilizes a vibration signal of a bearing to perform fault diagnosis. Based on the compressed sensing theory, a measuring matrix is constructed and compression of vibration signals is realized so that the transmission bandwidth consumption of the vibration signals of the bearing is effectively reduced. The on-board fault diagnosis part utilizes the compression reference matrix, the matching pursuit algorithm to realize fault diagnosis under the working condition disturbance condition through the reconstruction matching method. Based on the on-board fault diagnosis, the far-end signal reconstruction can be realized through the reconstruction matching method so that fault diagnosis enhancement and performance assessment of the far end can be realized. The method system is complete and is suitable for the working condition disturbance condition, and is high in the accuracy of fault diagnosis and is high in engineering practicality.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Sparse channel estimation and pilot optimization method for underwater sound OFDMA uplink communication
ActiveCN104780128AOvercoming the Error Floor PhenomenonImprove performanceBaseband system detailsTransmission path multiple useAlgorithmMatching pursuit algorithms
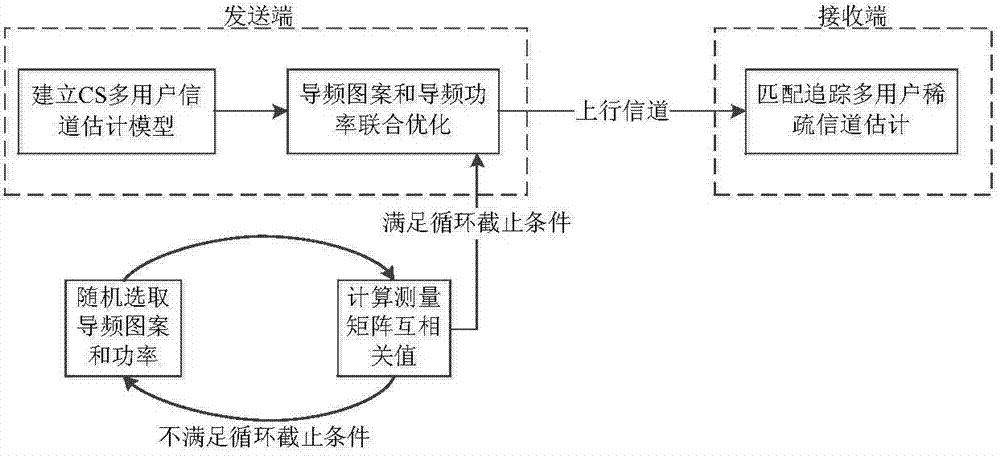
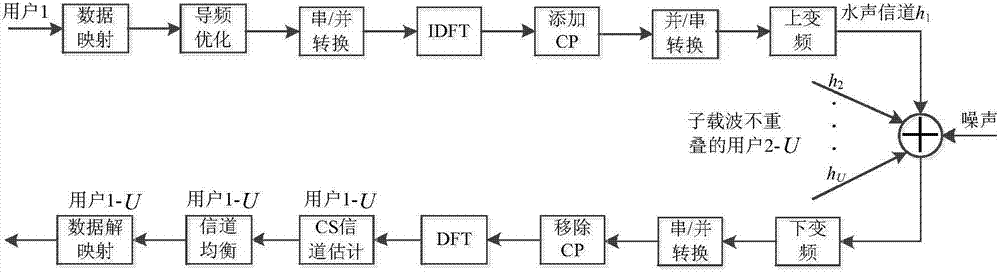
The invention discloses a sparse channel estimation and pilot optimization method for underwater sound OFDMA uplink communication. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a comb-pilot-based multi-user CS sparse channel estimation model at a sending end to obtain a measurement matrix cross-correlation expression; performing joint optimization on pilot patterns and pilot power at the sending end according to the measurement matrix cross-correlation expression to reduce measurement matrix cross-correlation under a CS channel estimation model; performing multi-user sparse channel estimation through a matching pursuit algorithm under a CS frame at a receiving end by utilizing the multi-user CS sparse channel estimation model and the pilot information about the joint optimization on the pilot patterns and the pilot power. The sparse channel estimation and pilot optimization method for the underwater sound OFDMA uplink communication has the advantage that estimation errors can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Video encoding and decoding methods and corresponding devices
InactiveUS20070019723A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingMotion vector
The invention relates to the field of video compression and, more specifically, to a video encoding method applied to an input sequence of frames in which each frame is subdivided into blocks of arbitrary size. This method comprises, for at least a part of said blocks of the current frame, the steps of generating on a block basis motion-compensated frames, each one being obtained from each current original frame and a previous reconstructed frame, generating from said motion-compensated frames residual signals, using a so-called matching pursuit (MP) algorithm for decomposing each of said generated residual signals into coded dictionary functions called atoms, the other blocks of the current frame being processed by means of other coding techniques, and coding said atoms and the motion vectors determined during the motion compensation step, for generating an output coded bitstream. According to the invention, said method is such that, when using said MP algorithm, a specific dictionary is available at the encoding side for each block shape respectively. According to another implementation, it is also possible to use several specific dictionaries. In this second solution, if several dictionaries are available at the encoding side, a bitstream syntax is defined for placing, at a predetermined level, flags provided to indicate which dictionary should be used and placed for example at the atom level, at the block level, at the macroblock level or at the picture level.
Owner:DYNAMIC DATA TECH LLC
Bearing combined failure diagnosis method based on improved impact dictionary matching pursuit
ActiveCN103018044AImplement fault diagnosisImprove search speedMachine bearings testingBearing vibrationEngineering
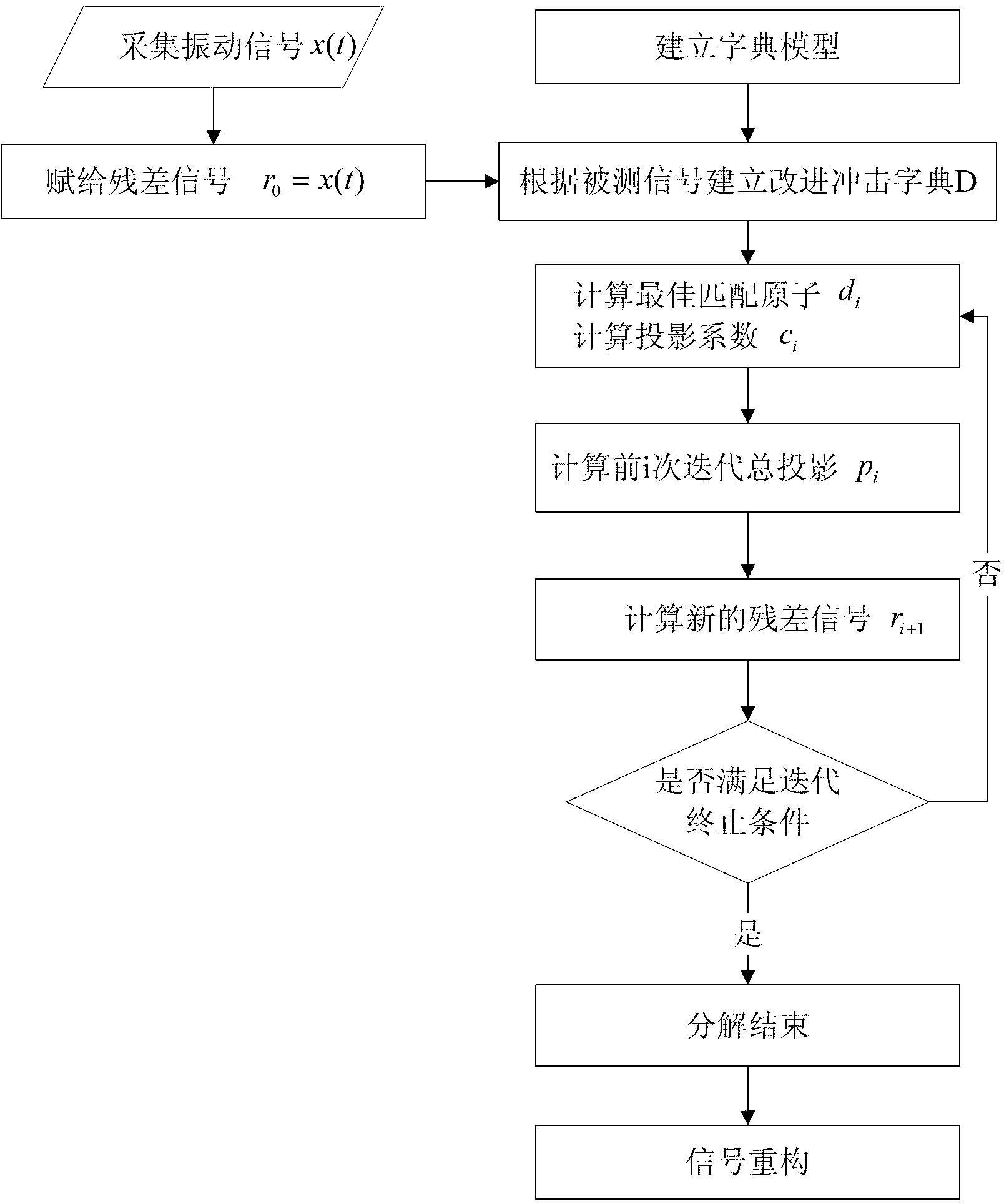
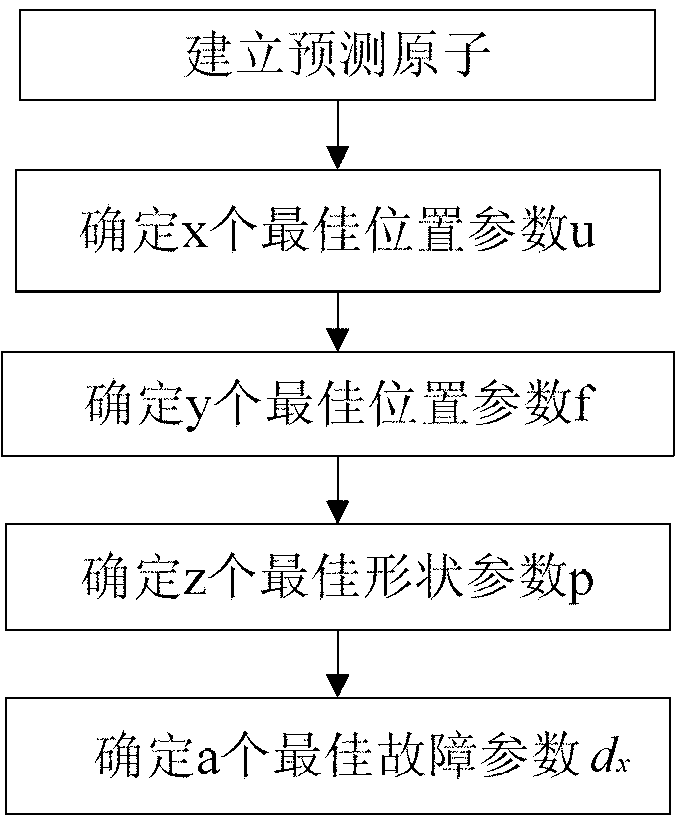
The invention discloses a bearing combined failure diagnosis method based on improved impact dictionary matching pursuit. According to the method, a bearing vibration signal is iterated and decomposed successively to be a linear combination based on an i-item atom of an improved impact model dictionary; an improved model is established according to the type of an analyzed bearing, and can very accurately indicate out an impact signal of a fault bearing in the running process; a position parameter u in the improved model is used as a preferentially changing parameter according to the cycle characteristic of a bearing failure signal, an atom base with relatively low redundancy is established by using a method of gradually changing the parameters, and the search speed of an optimal atom is greatly improved; a analyzed signal is cut in the signal decomposing process, the optimal atom is searched from atoms in the atom base, and a corresponding impact signal component can be obtained by impact component reconfiguration; and then the failure characteristic frequency of a bearing is obtained by time-frequency transform, and thus the failure diagnosis of the bearing is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
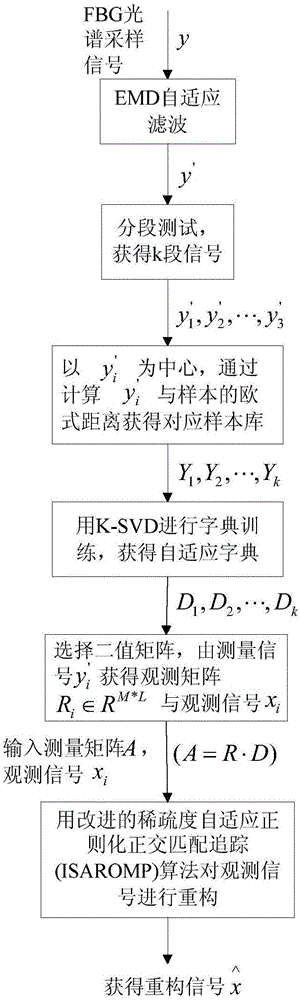
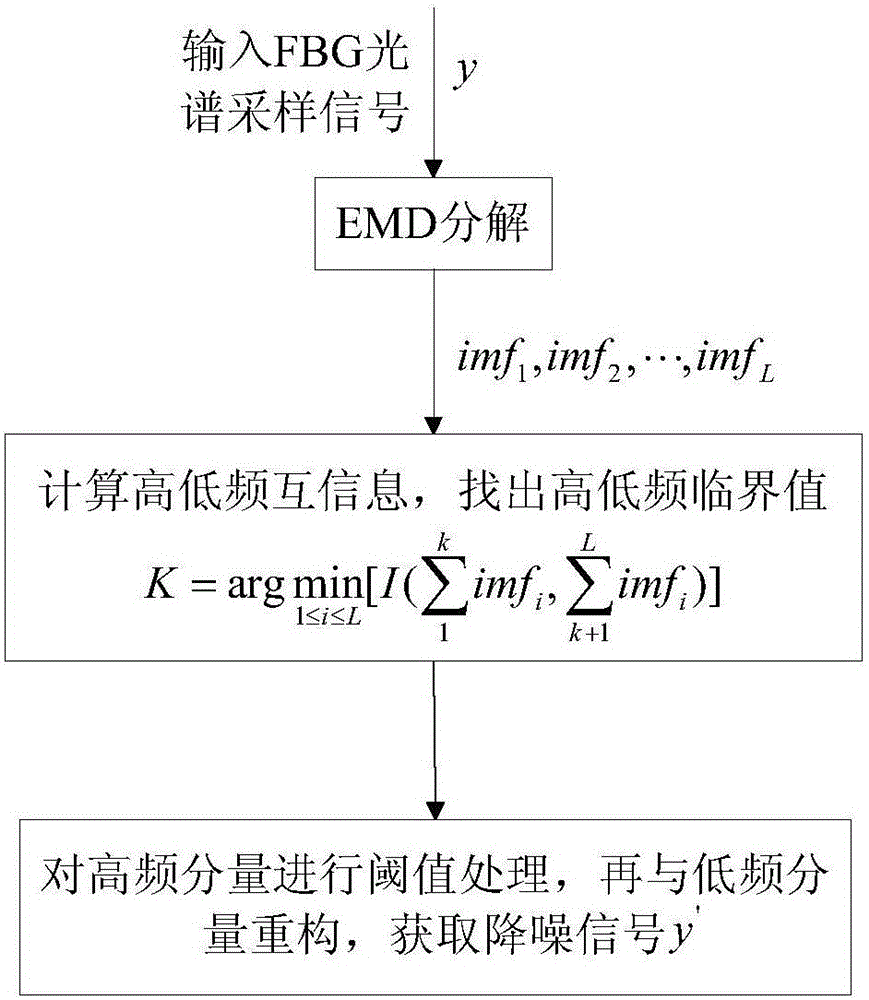
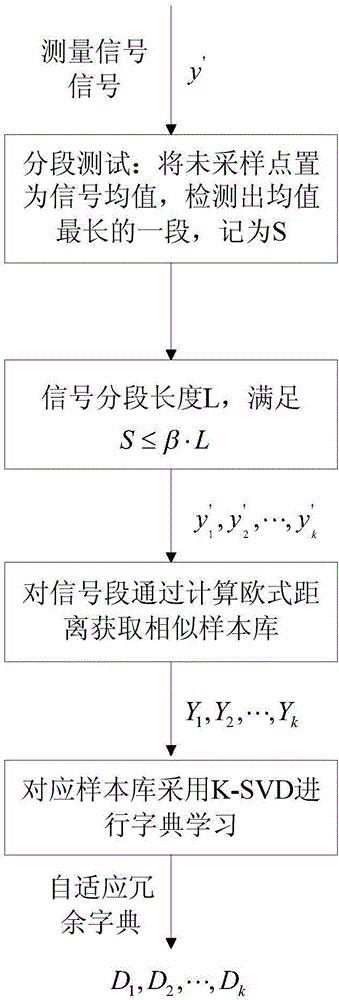
FBG signal self-adapting restoration method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN106500735AImprove reconstruction accuracyExtended run timeSpecial purpose recording/indication apparatusGratingRestoration method
The invention relates to a FiberBragg grating(FBG) signal self-adapting restoration method based on compressed sensing, and belongs to a signal restoration technology field of an optical fiber sensing system. The FBG signal self-adapting restoration method comprises steps that step 1: EMD combination mutual information is used for self-adapting denoising processing of spectral signals; step 2, segmented testing of a denoising signal is carried out, and the signal is divided into k segments, and sample databases corresponding to the signals are acquired by calculating Euclidean distances among various segments of signals and samples, and self-adapting dictionaries D corresponding to the signals are acquired by adopting a K-SVD dictionary learning method; step 3, measured signals are used to acquire observation matrixes R and observation signals xi; step 4, the observation signals are reconstructed by adopting an improved regularized orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm to acquire complete reconstructed signals. The FBG signal self-adapting restoration method is advantageous in that problems such as interferences of noises on the signals, targeted dictionary learning, and the signal self-adapting reconstruction are considered, and each part represents the self-adaptability of the algorithm, and can be flexibly used in practical engineering, and then influences caused by manual misoperation are reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
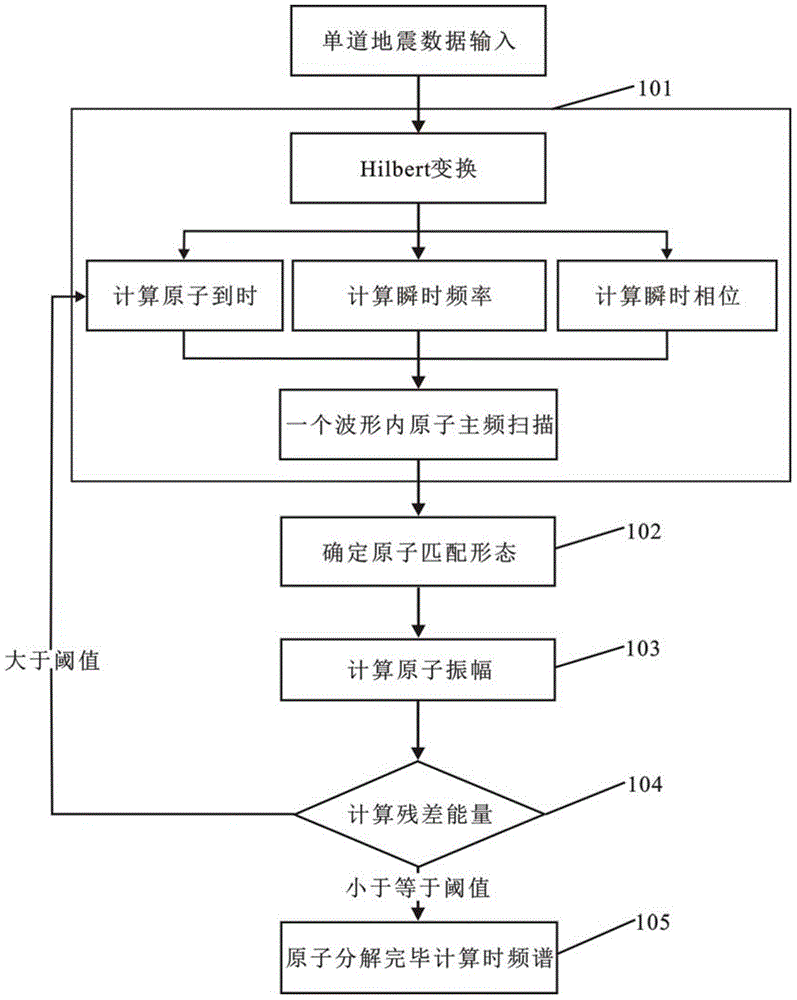
Time-frequency analysis method based on improved matching pursuit algorithm
InactiveCN104570107AImprove computing efficiencySolve matching problemsSeismic signal processingTime frequency spectrumComputer science
The invention relates to a time-frequency analysis method based on an improved matching pursuit algorithm. The time-frequency analysis method comprises the steps of constructing a complex analysis signal of a seismic signal, and determining instantaneous phases and optimal master frequencies at the arrival time and the delayed time; calculating the master frequency and the phase of a time delay position, and determining an atom form according to the master frequency and the phase which are used as Ricker wavelet parameters; calculating an instantaneous amplitude of a wavelet under a wavelet energy normalization condition; matching an atomic amplitude according to a given percentage, and subtracting a matching wavelet which is in maximum correlation with the seismic signal from a seismic channel after four key parameters such as the atom arrival time, the atom master frequency, the atom phase and the atom amplitude are determined to obtain a residual signal, and carrying out recursion iteration on the residual signal within a certain threshold range to finish decomposition of original signal; stacking the time frequencies of all the matching wavelets to obtain a time frequency spectrum of the seismic signal. According to the time-frequency analysis method, the accuracy of atom master frequency matching is guaranteed under the condition that the calculation frequency of matching pursuit time frequency analysis is improved, so that the problem of discontinuity of an inphase axis on the section of a seismic frequency division body is solved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Channel estimation method for large-scale MIMO system based on improved distributed compressed sensing algorithm
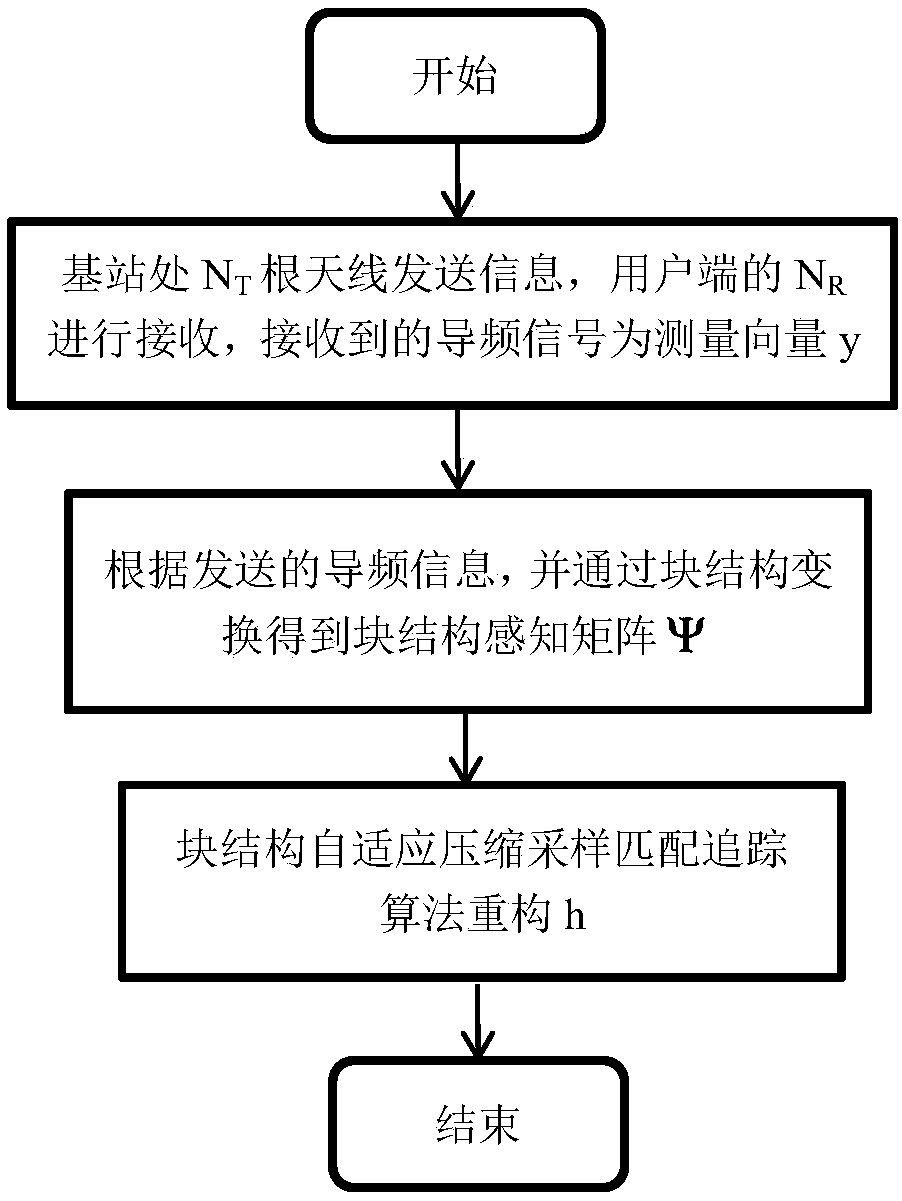
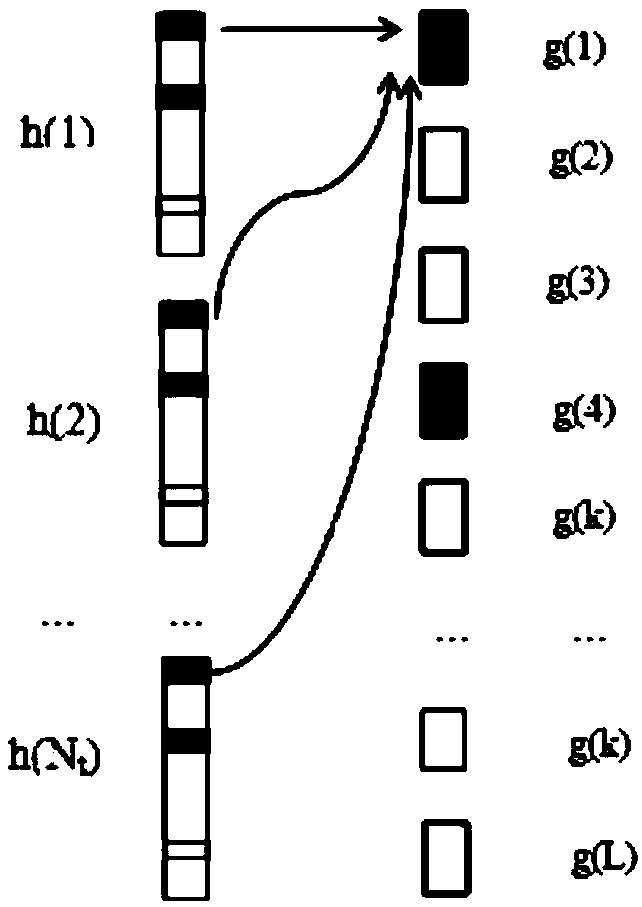
InactiveCN109560841AImprove estimation performanceSolve problems such as low accuracyBaseband system detailsRadio transmissionAdaptive compressionMathematical model
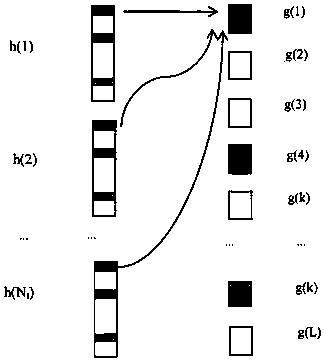
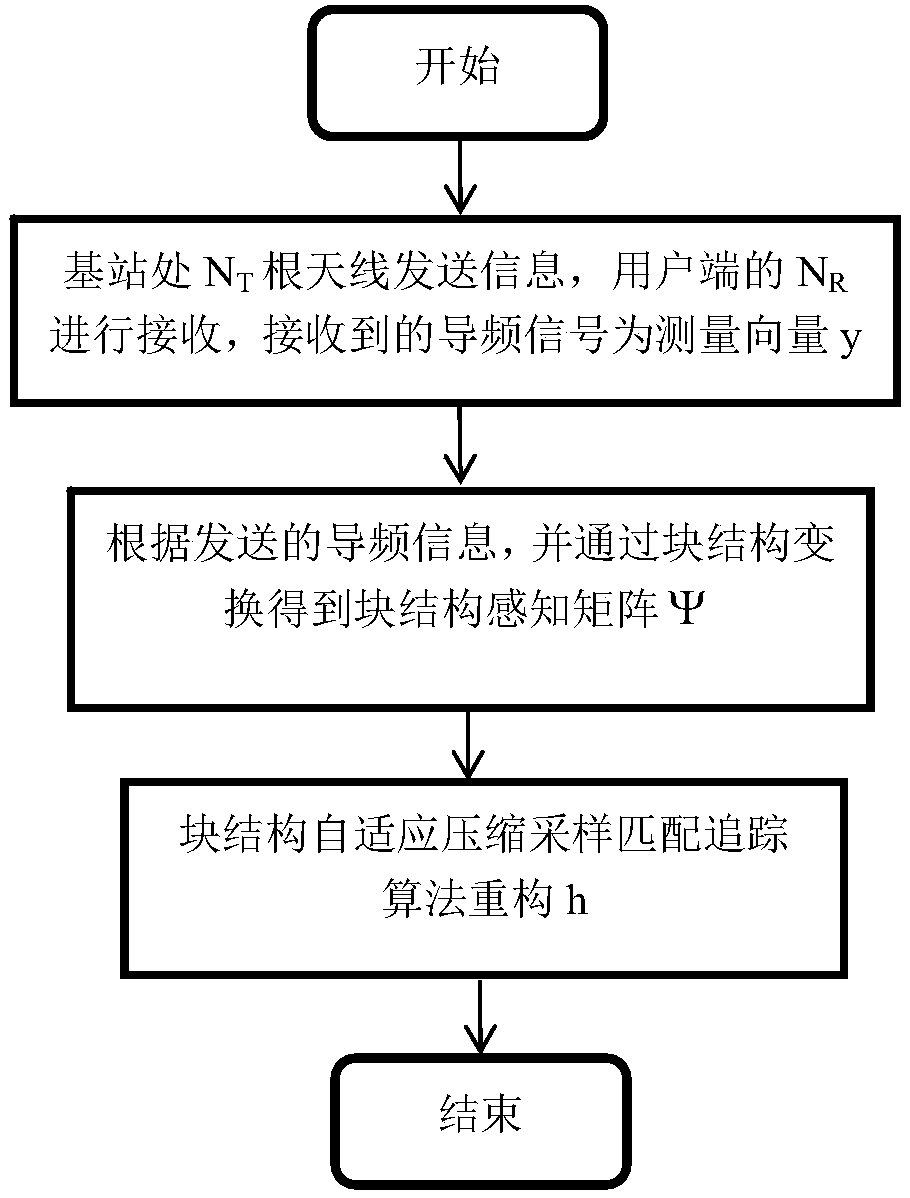
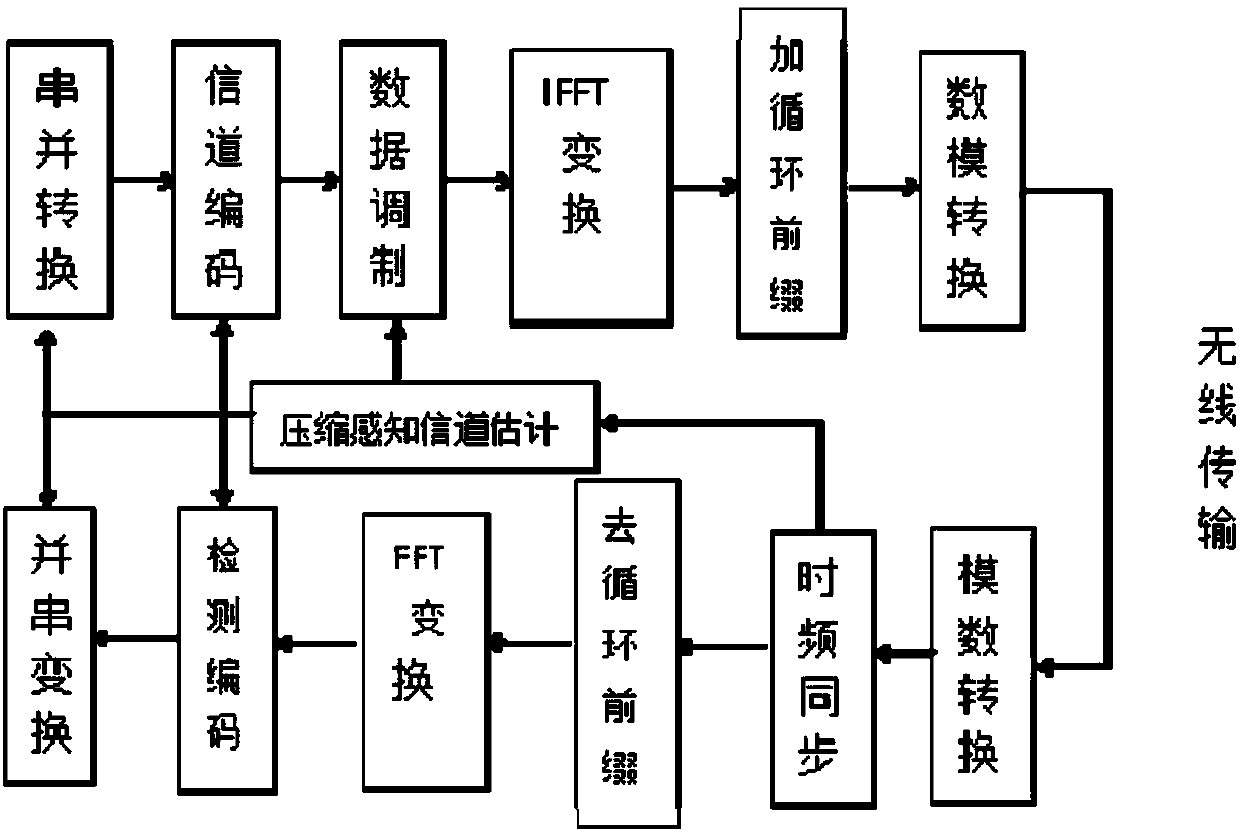
The invention discloses a channel estimation method for a large-scale MIMO system based on an improved distributed compressed sensing algorithm. Pilot information is transmitted through NT antennas ata single cell base station and received at NR single antenna user terminals. The method includes the steps of S1, calculating a measurement vector y of the pilot information received at each user receiving terminal, establishing a compressed sensing mathematical model for the pilot information transmission process according to the sparsity consistency of channels of the large-scale MIMO system, and constructing a sensing matrix [Phi]; S2, obtaining a block structure sensing matrix [Psi] through block structure transformation, and reconstructing a block sparse signal g through a reconstructionalgorithm; and S3, reconstructing a sparse signal h by using a block structure adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit algorithm. According to the invention, the time domain sparsity consistency of the channels of the large-scale MIMO system is utilized, the channel impulse response is reconstructed by using the block structure adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit algorithm, the estimation can be performed when the sparsity is unknown, and the use of the pilot frequency can be reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Signal sparse decomposition method based on set partitioning of over-complete dictionary
ActiveCN103995973AShorten operation timeCode conversionSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a signal sparse decomposition method based on set partitioning of an over-complete dictionary and relates to a signal sparse decomposition method. The method is provided in order to solve the problem that when a classic MP method and an existing improvement method are used for decomposing signals, the operation time is too long. According to the method, the over-complete dictionary is subjected to set partitioning by selecting different factors, a huge redundant dictionary is divided into a plurality of sub-dictionaries, appropriate time frequency is selected from the sub-dictionaries through a matching pursuit algorithm to accurately and rapidly decompose signals, signal residuals are decomposed again according to the standard of actual requirements till reconstructed signals conforming to the standard are obtained, and the reconstructed signals can be shown in the form of the sum of the products of all stages of iteration residuals and corresponding matched atoms. The signal sparse decomposition method is applicable to the field of signal sparse decomposition.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Double-circuit on same tower double-circuit line fault distance measurement method
ActiveCN103116112AImprove fault location accuracyEasy extractionFault locationMeasurement pointEngineering
The invention discloses a double-circuit on the same tower double-circuit line fault distance measurement method which includes the following steps: (S1) using double-circuit three-phase transient currents which are obtained by sampling as original current signals for denoising; (S2) conducting six-phase phase-mode transformation to denoised current processing signals and extracting one mode of components to be used as fault analysis signals; (S3) conducting matching pursuit to the fault analysis signals which are obtained by applying a matching pursuit algorithm by using pulse signal atoms, comparing peak time of three optimum matching pulse atom signals with the largest energy, and taking the time which reaches a peak value at the earliest to be used as the time when a traveling-wave head reaches a measurement point; and (4) calculating and obtaining the distances respectively from measurement points at two ends and a fault point according to the obtained time during which the traveling-wave head can reach the measurement points at the two ends. By means of the double-circuit on the same tower double-circuit line fault distance measurement method, the characteristics of the traveling-wave head can be extracted accurately and reliably, and precision and reliability are achieved in the double-circuit on the same tower double-circuit line fault distance measurement.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
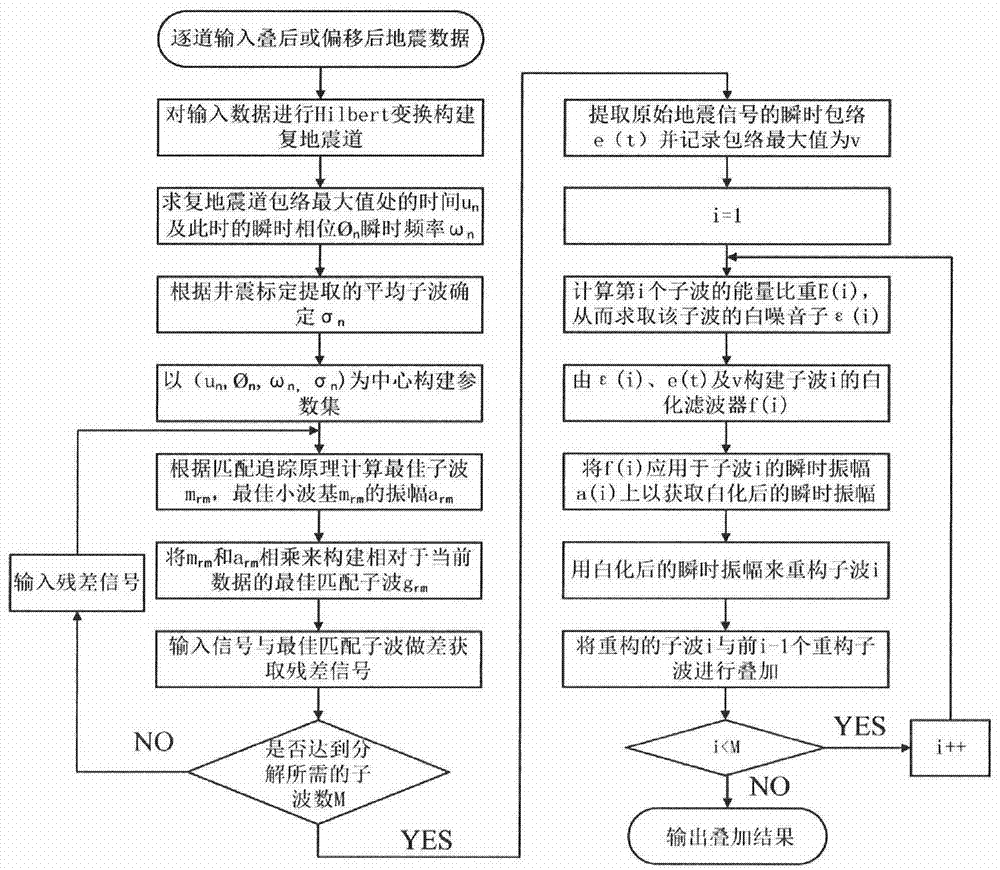
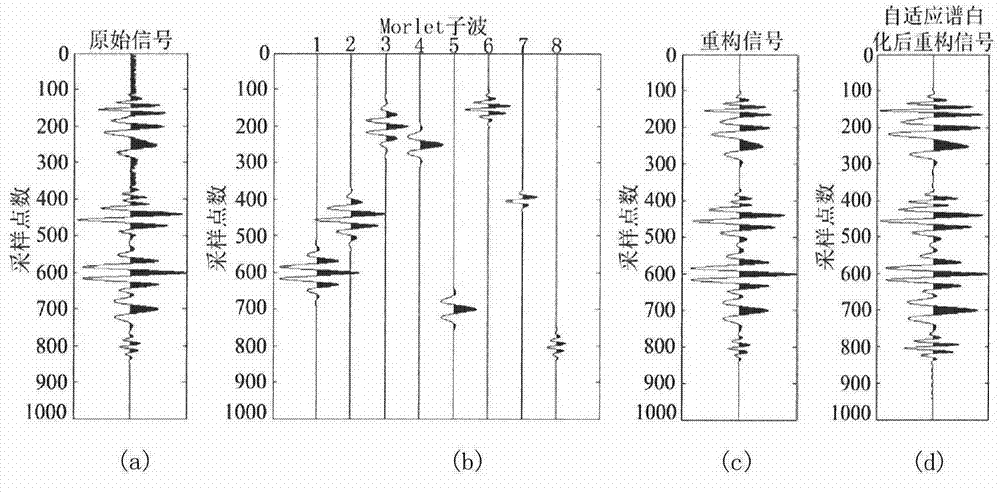
Method for improving resolution ratio of seismic data and enhancing energy of valid weak signals
The invention relates to a method for improving the resolution ratio of seismic data and enhancing energy of valid weak signals. The method needs to process stacked or migrated seismic data channel by channel, and carries out the following steps on single-channel seismic data: 1) Hilbert transformation is performed on the single-channel seismic data, the envelope, the time shift quantity and the instantaneous attribute of the single-channel seismic data are obtained, and combined with an average wavelet extracted by well-seismic calibration, a Morlet wavelet library is built; 2) based on the wavelet library built in the step 1), a matching pursuit algorithm is used to obtain valid wavelets through decomposition which form the single-channel seismic data; 3) a spectrum whitening algorithm is improved, and self-adaptive frequency extension and energy compensation processing are performed on the valid wavelets obtained through decomposition; and 4) valid wavelets after the processing of the step 3) are superposed, thereby obtaining single-channel seismic data with an improved resolution ratio and enhanced energy of valid weak signals. The method integrates logging and seismic data, and combines spectrum whitening algorithm improvement with the matching pursuit algorithm, thereby achieving effects of broadening a data frequency band and enhancing energy of the valid weak signals.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Time division ground-based MIMO landslide radar imaging method based on IFFT and mix-match pursuit
ActiveCN107957574AReduce the numberLow costWave based measurement systemsHigh resolution imagingImaging quality
The invention discloses a time division ground-based MIMO landslide radar imaging method based on IFFT and mix-match pursuit, and aims to solve the problems that an existing mountain landslide monitoring field imaging method is high in data processing complexity and uses too many antennas; aiming at a multi-target imaging pseudo shadow point problem, the method introduces the mix-match pursuit algorithm, thus greatly improving the imaging quality; the method comprises the following steps: building an equivalent random sparse transmit-receive array; building an echo signal acquisition model; range direction compression treatment; azimuth compression treatment; finishing two dimension object high resolution imaging. The advantages are that the method can reduce the array quantity, can reducehardware cost, can reduce the data processing complexity, and can improve the range and azimuth resolutions.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Channel estimation method for large-scale MIMO system based on block structure adaptive compressive sampling matching pursuit algorithm
InactiveCN108599820AAchieve reconstructionReduce mean square errorRadio transmissionChannel estimationAdaptive compressionMathematical model
The invention discloses a channel estimation method for a large-scale MIMO system based on a block structure adaptive compressive sampling matching pursuit algorithm. Pilot information is sent at a single cell base station through NT antennae and received at NR single antenna user terminals. The method includes the following steps: S1, calculating a pilot information measurement vector y receivedat each user receiving end, establishing a compressive sensing mathematical model for a pilot information transmission process according to the sparsity consistency of channels of the large-scale MIMOsystem, and constructing a sensing matrix phi; S2, obtaining a block structure sensing matrix psi through block structure transformation, and reconstructing a block sparse signal g through a reconstruction algorithm; and S3, reconstructing a sparse signal h by using the block structure adaptive compressive sampling matching pursuit algorithm. According to the scheme of the invention, the time domain sparsity consistency of the channels of the large-scale MIMO system is utilized, a channel impulse response is reconstructed by using the block structure adaptive compressive sampling matching pursuit algorithm, and moreover, the estimation can be performed when the sparsity is unknown, and the use of pilots can be reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Fault characteristic extraction method for non-stationary signal of gear box
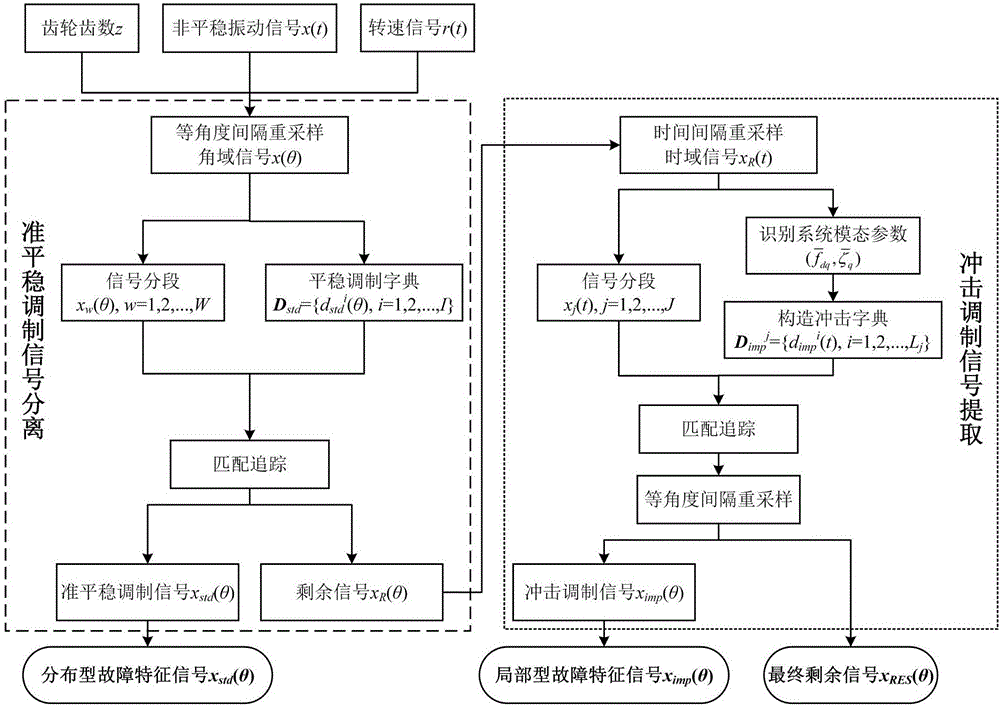
ActiveCN106644467AImprove matching accuracyReduce pointsMachine gearing/transmission testingTime domainVibration acceleration
The invention discloses a fault characteristic extraction method for a non-stationary signal of a gear box. The method comprises the following steps: synchronously gathering a time domain vibration acceleration signal and a rotating speed signal of the gear box in a variable speed working condition; performing order tracking on the vibration acceleration signal to acquire an angular domain vibration acceleration signal; constructing a stationary modulation dictionary and segmenting the signal in complete alternation; performing a matching pursuit algorithm on the signal in each section, and reconstructing a quasi-stationary modulation signal in the signal; converting the residual angular domain signal into a time domain signal; recognizing a multiple-order inhered frequency and a damping ratio of the gear box from the residual signals; segmenting the residual time domain signal to construct an impact modulation dictionary; extracting an impact modulation component in the signal by virtue of the matching pursuit algorithm, and performing order tracking on the impact modulation component; and analyzing the order domain characteristic of the extracted signal for fault diagnosis. By applying a sparse decomposition method to characteristic extraction for the non-stationary signal of the gear box in the variable working condition, the calculating speed and the matching precision of the signal can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
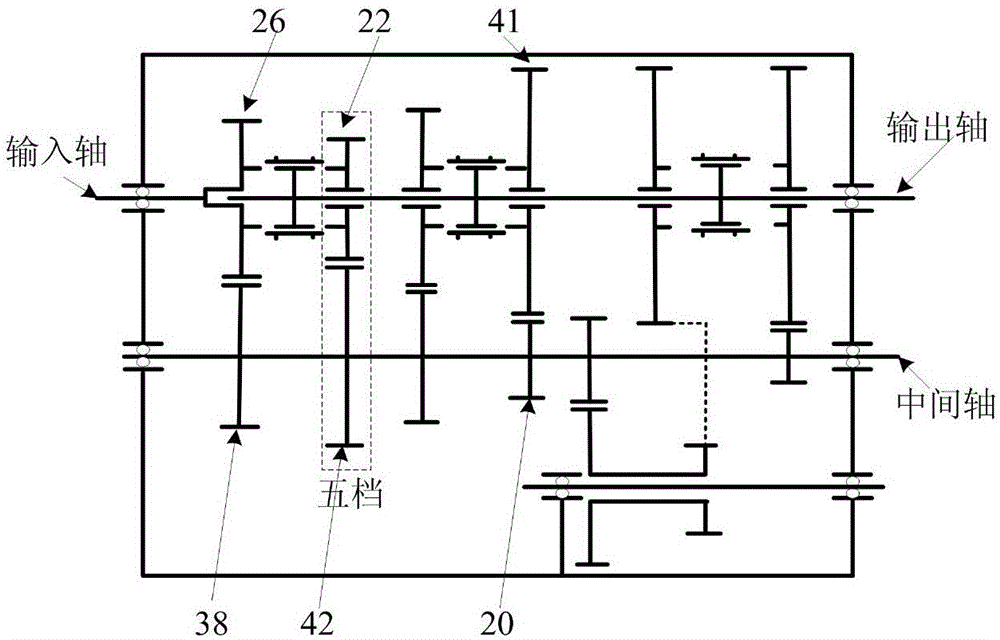
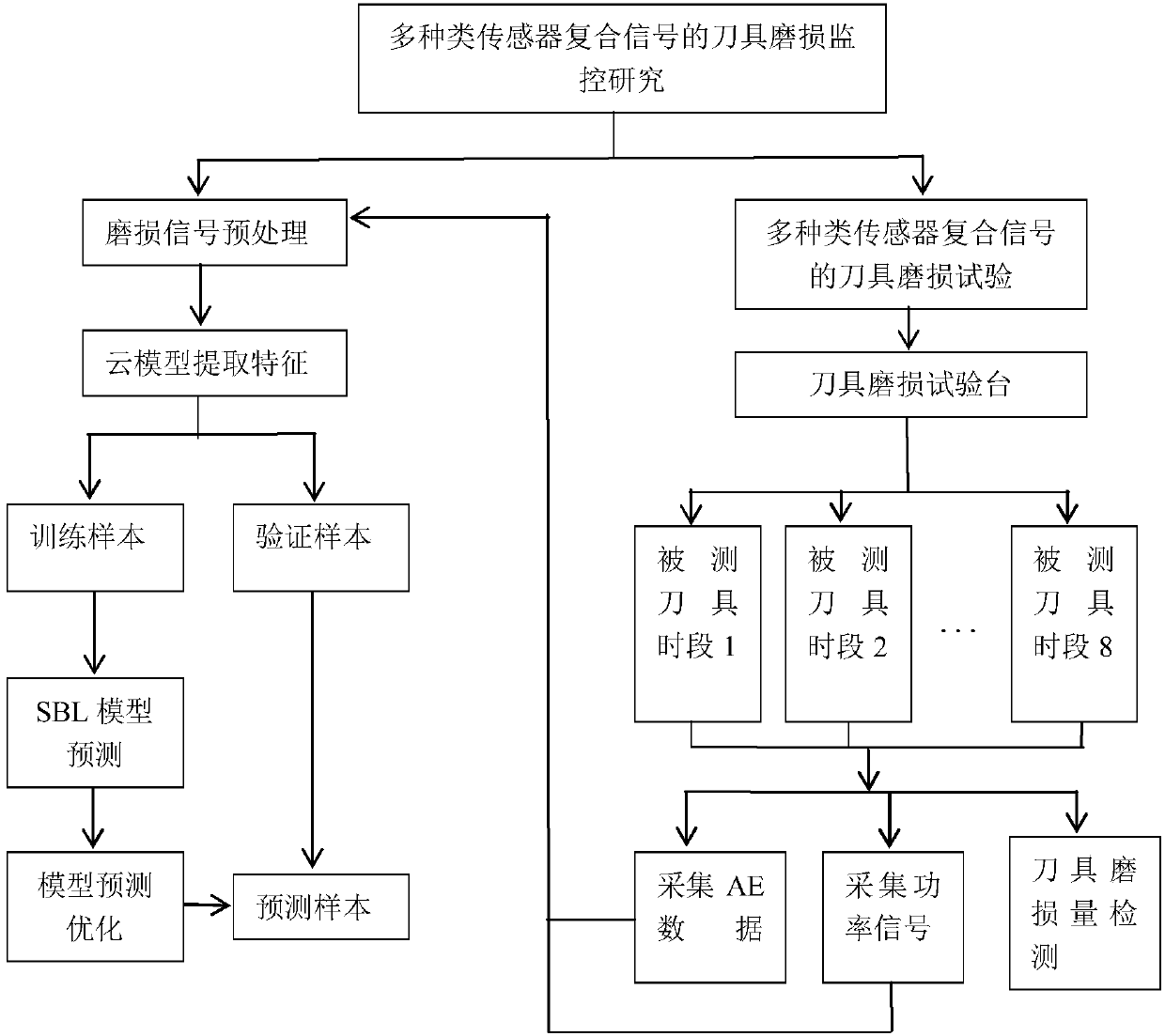
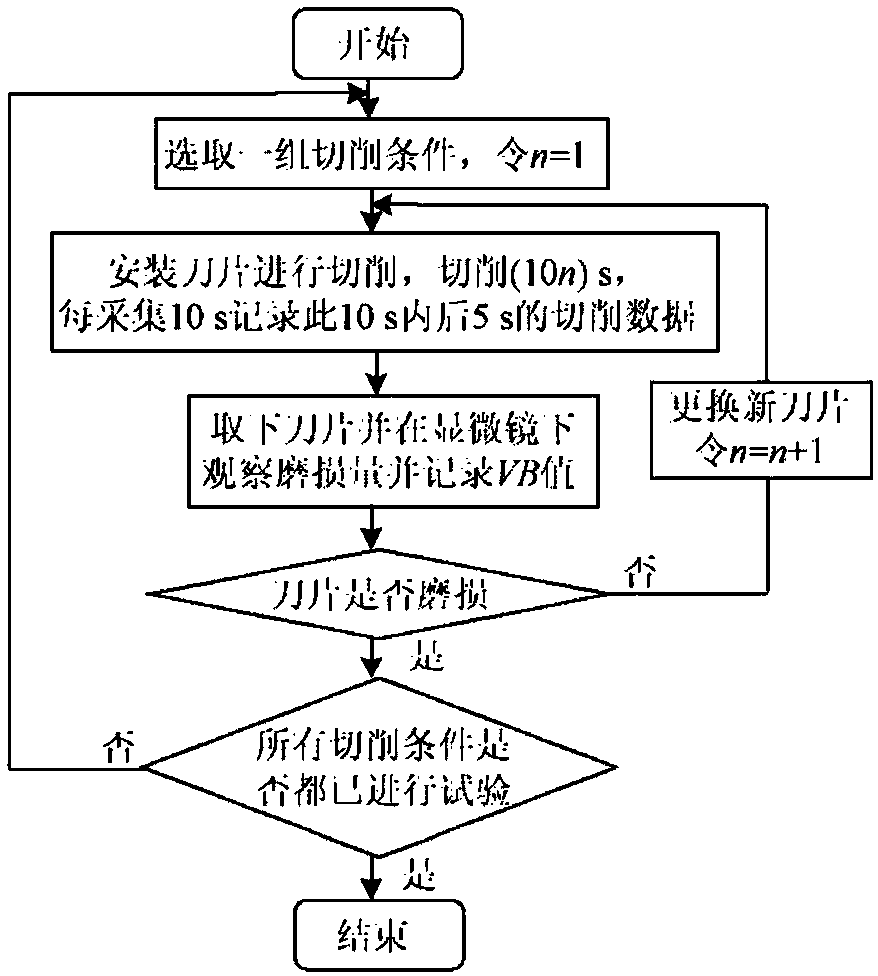
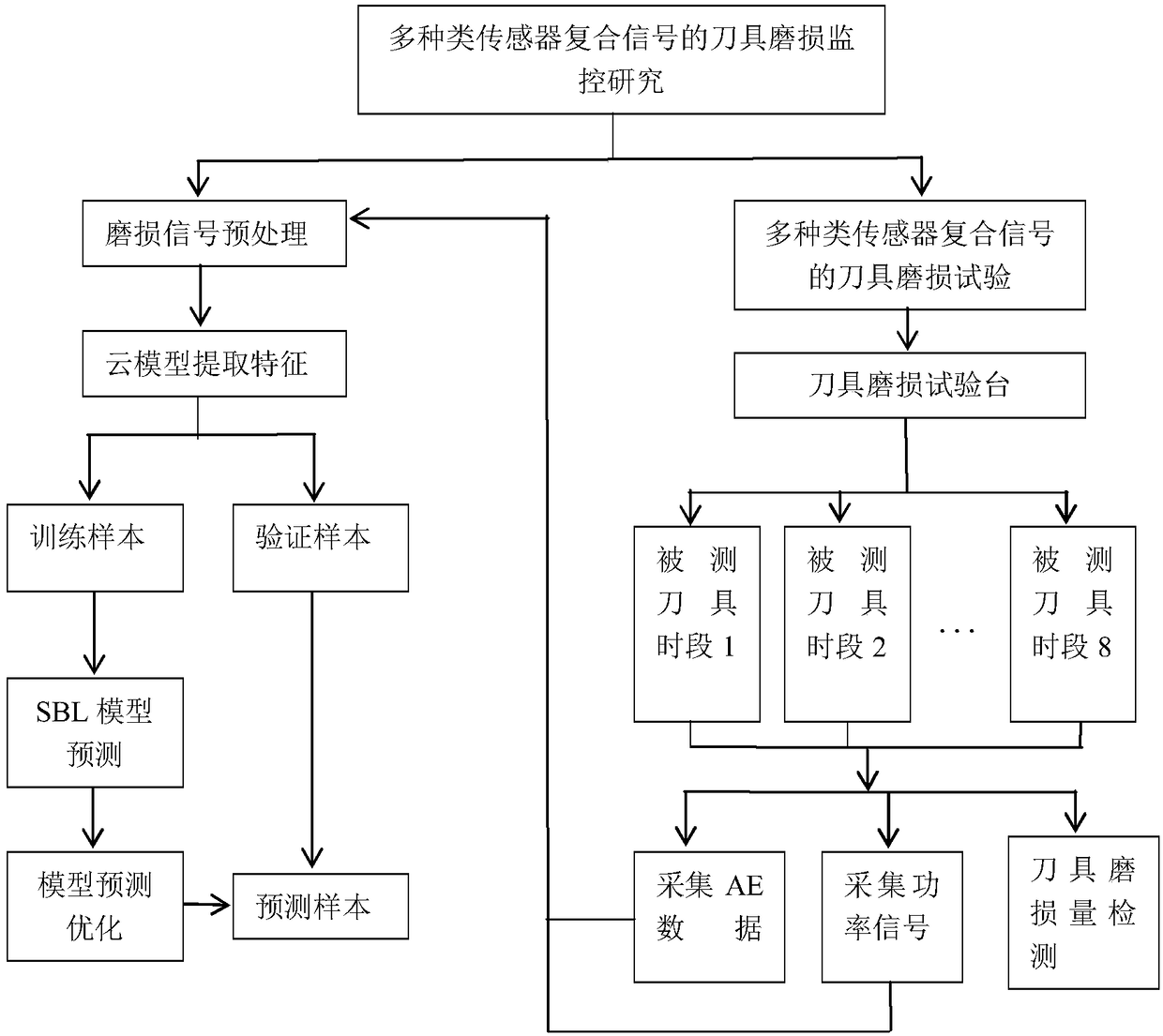
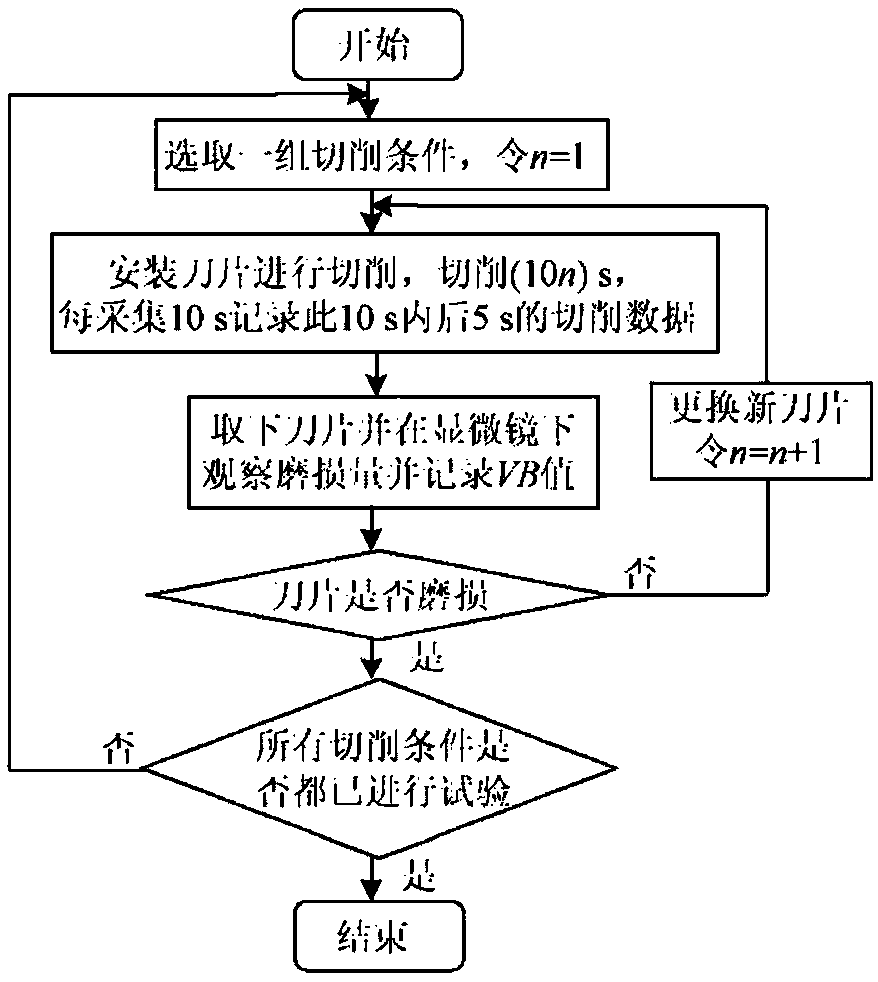
Tool wear monitoring method based on multi-sensor composite signals
InactiveCN107553219ARealize monitoringImprove efficiencyMeasurement/indication equipmentsPower sensorAcoustic emission
The invention relates to a tool wear monitoring method based on multi-sensor composite signals. According to the tool wear monitoring method based on the multi-sensor composite signals, the related signal information of machine-tool tool wear is acquired by the adoption of an acoustic emission sensor and a power sensor, and the defect of the single signal can be overcome by the adoption of the twokinds of signal collection methods. Two kinds of information are scientifically coupled by the adoption of a cloud model algorithm, the characteristic factors of tool wear amount reflected in the signals can be extracted, a model is built through a sparse Bayesian method, and the tool wear amount is forecast; modelling is conducted on data by the adoption of a recognition method based on SBL, andthe width parameters of a SBL model kernel function is optimized by the adoption of a Bayesian matching pursuit algorithm; and the tool wear amount is precisely forecast, and the efficiency and accuracy of tool wear monitoring are improved.
Owner:沈阳百祥机械加工有限公司
Sparse feature extraction method for fault signal of rotating machine
ActiveCN107992843AImprove extraction accuracyReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency spectrumFeature extraction
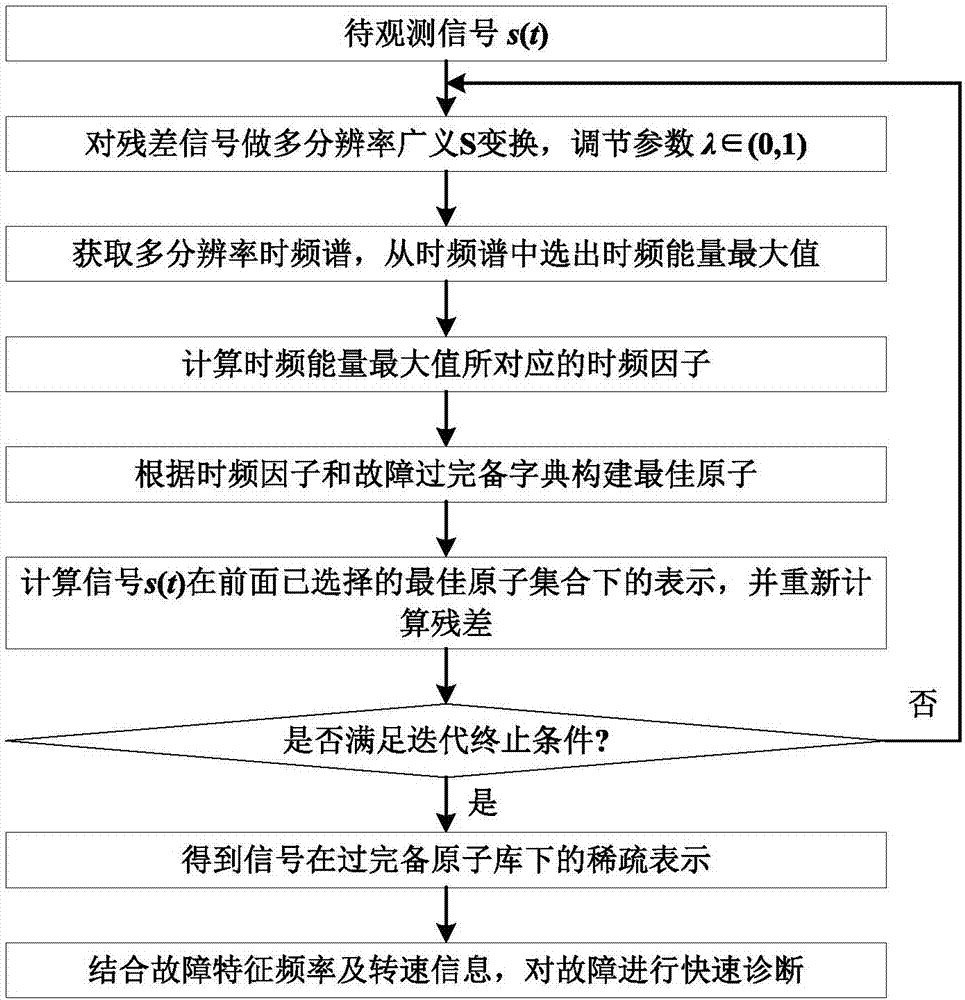
The invention provides a sparse feature extraction method for a fault signal of a rotating machine. The method includes the steps of constructing a fault overcomplete atom library according to a faultgeneration mechanism of an impact fault of the rotating machine; calculating a multi-resolution time-frequency spectrum of a to-be-analyzed signal through multi-resolution generalized S-transform resolution and normalization processing according to a mathematical model of a to-be-observed signal and the fault overcomplete atom library; calculating a maximum value of the normalized multi-resolution time-frequency spectrum, and calculating an atom set capable of best performing sparse representation on the to-be-observed signal by combination with an orthogonal matching tracking algorithm; andaccording to the fault sparse representation signal and fault feature frequency of a device and rotating speed information, determining a fault type, to achieve a rapid fault diagnosis of the mechanical device. The sparse feature extraction method has the advantages that the complexity of the atomic search and the search time are greatly reduced, the efficiency of sparse decomposition is improved,and the efficiency of fault diagnosis of impact faults such as crack, pitting or spalling is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Magnetic resonance image denoising method based on improved multi-path matching pursuit algorithm
ActiveCN109191399AThe principle is simpleImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMatching pursuit algorithms
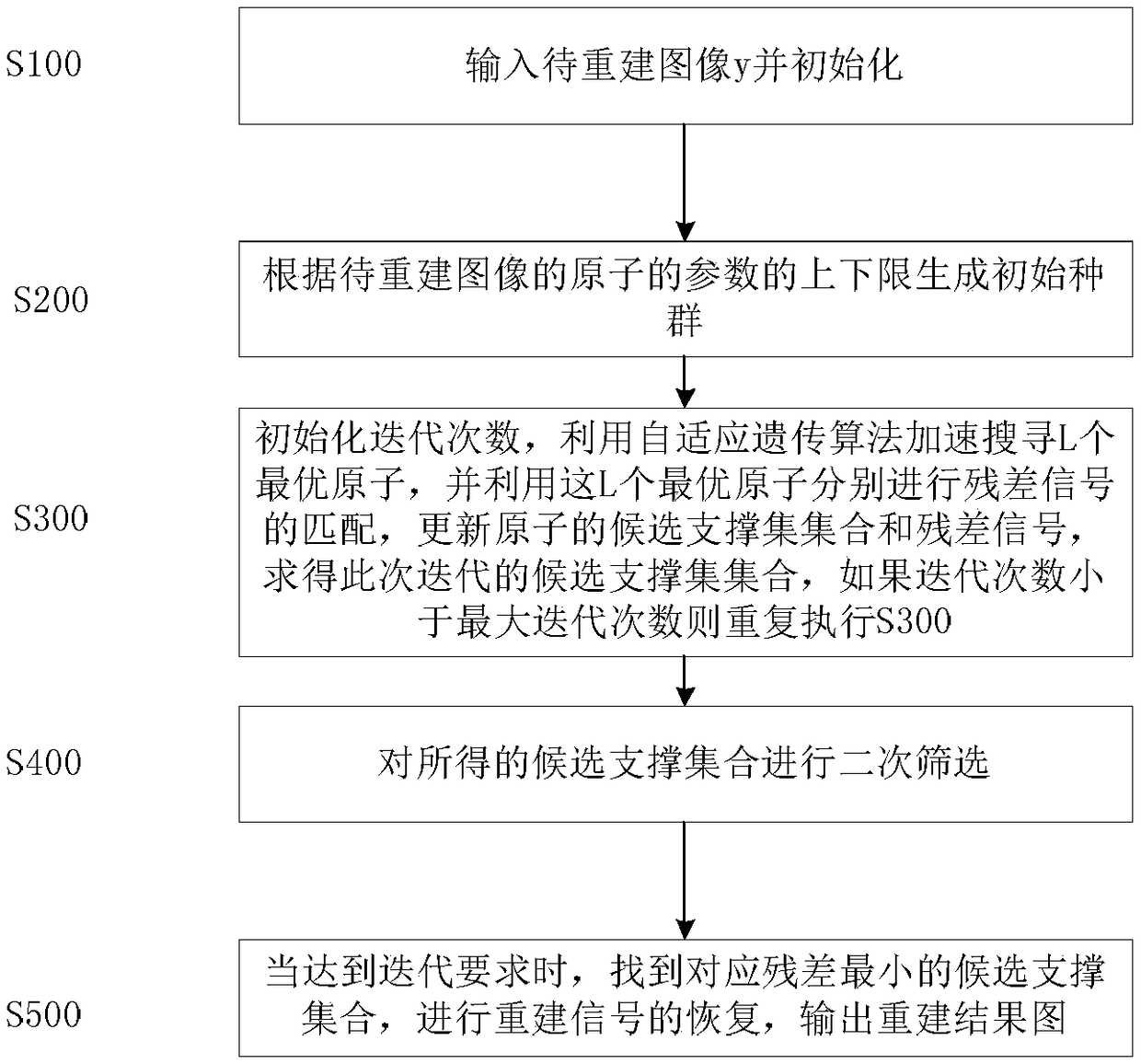
A magnetic resonance image denoising method relates to image processing. In this method, the adaptive genetic algorithm (AGA) is introduced into the iterative search of multiple candidate atoms matched with the local image features in multipath matching pursuit algorithm. The method combines the advantages of adaptive genetic algorithm and multi-path matching pursuit algorithm, thereby avoiding the shortcomings that genetic algorithm is easy to fall into the local optimum and getting the best matching parameters with high precision, reducing the computational load of multi-path matching pursuit algorithm and overcoming the shortcomings that the conventional method cannot be popularized and applied because of too much computational load.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
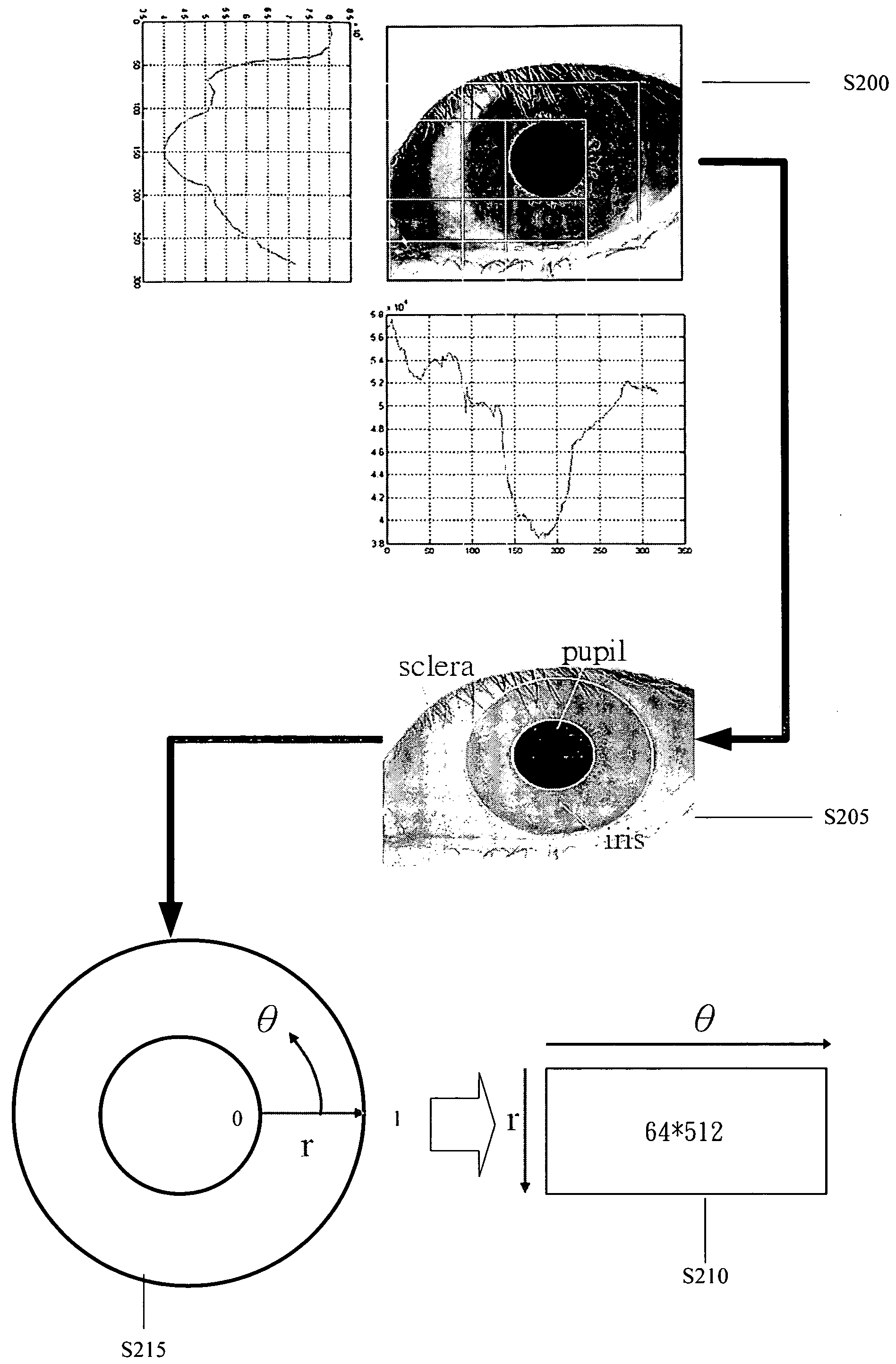
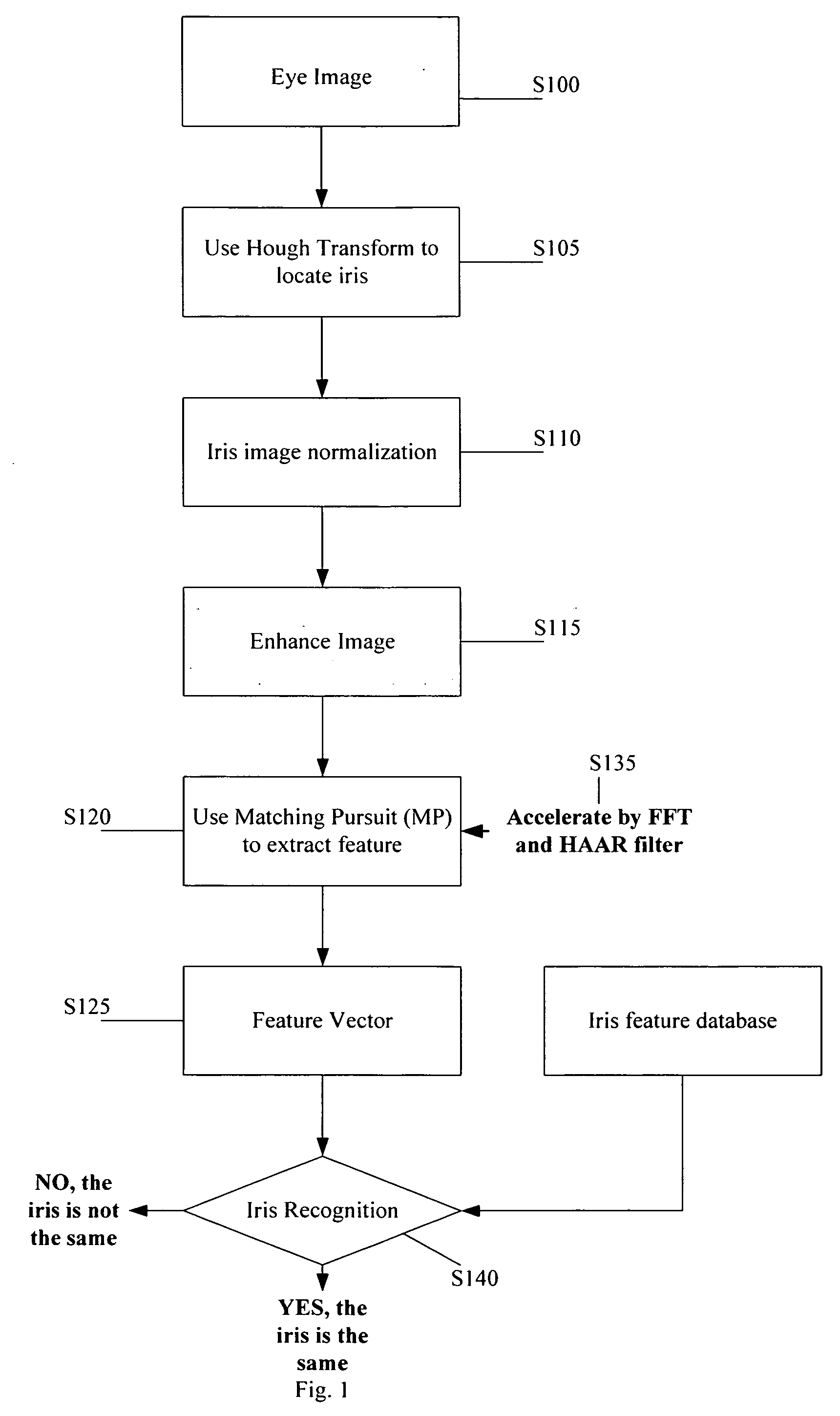
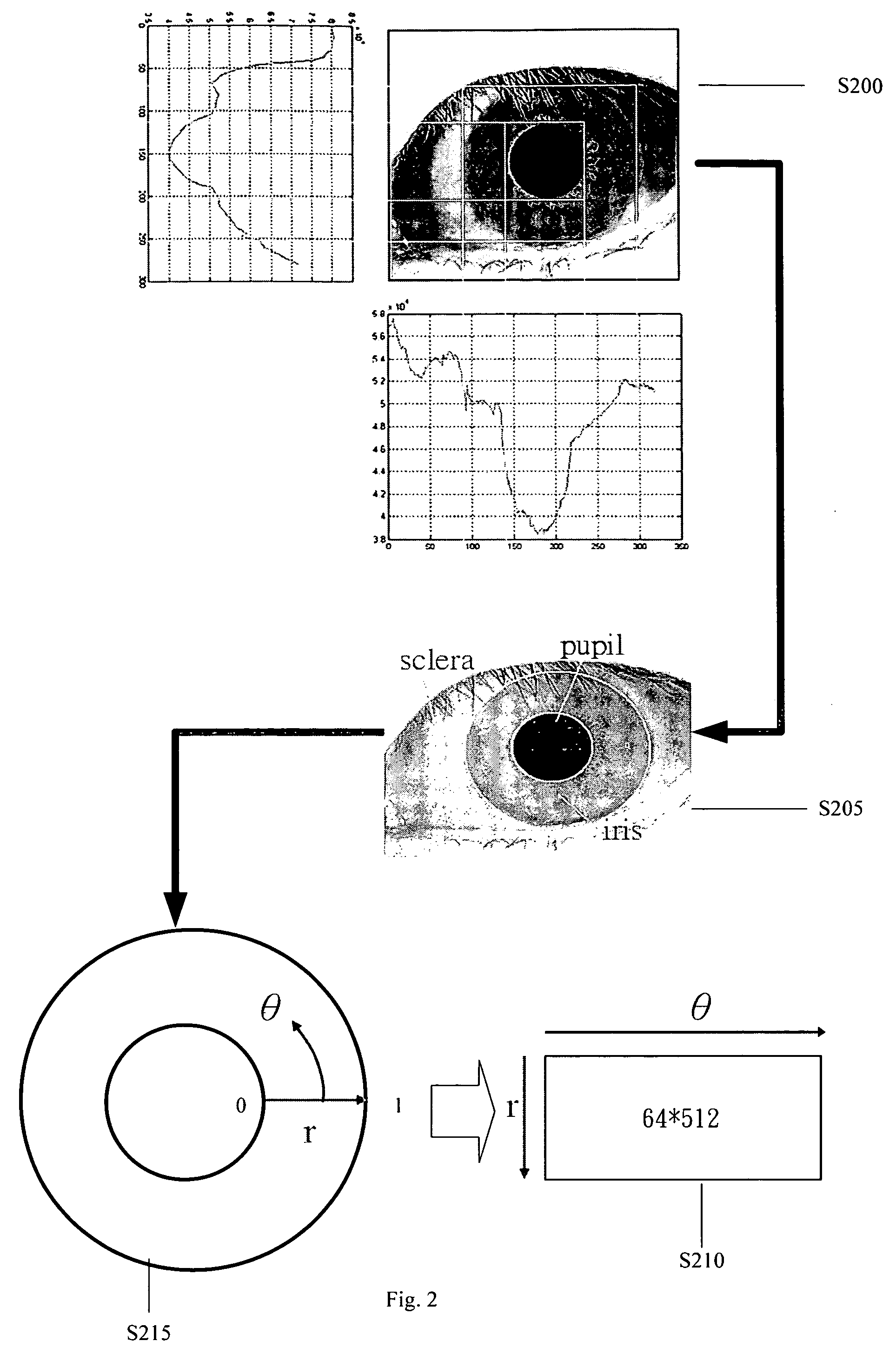
Iris recognition method
InactiveUS20080095411A1Simplify extraction and reconstructionReduce memory spaceAcquiring/recognising eyesFeature vectorPattern matching
The present invention disclose an iris recognition method, which utilizes a matching pursuit algorithm to simplify the extraction and reconstruction of iris features and reduce the memory space required by each iris feature vector without the penalty of recognition accuracy. The iris recognition method of the present invention comprises an iris-localization component and a pattern matching component. The iris-localization component locates the iris region via the color difference between different portions of the eyeball. The primary iris features are extracted from iris information and transformed into a sequence of iris feature vectors by a matching pursuit algorithm. Thus, the iris image can be represented by a sequence of atoms, and each atom contains base, amplitude and location. Then, the comparison between the feature vectors of two irises is performed to determine whether the two irises match.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Tool wear monitor method based on composite signal of multiple kinds of sensors
InactiveCN109318056ARealize monitoringImprove efficiencyMeasurement/indication equipmentsPower sensorAcoustic emission
The invention relates to a tool wear monitor method based on a composite signal of multiple kinds of sensors. An acoustic emission sensor and a power sensor are adopted for collecting signal information relevant to machine tool wear, and the defects of a single signal can be avoided through two signal collection methods. Two kinds of information are scientifically coupled through a cloud model algorithm, and the characteristic factor for reflecting tool wear in the signal can be extracted; a sparse bayes method is used for modeling, and then the tool wear is predicted; an SBL based recognitionmethod is adopted for carrying out modeling on data; a bayes matching pursuit algorithm is adopted for optimizing width parameters of an SBL model kernel function; and the tool wear is accurately predicted, and the efficiency and accuracy of tool wear monitor are improved.
Owner:沈阳百祥机械加工有限公司
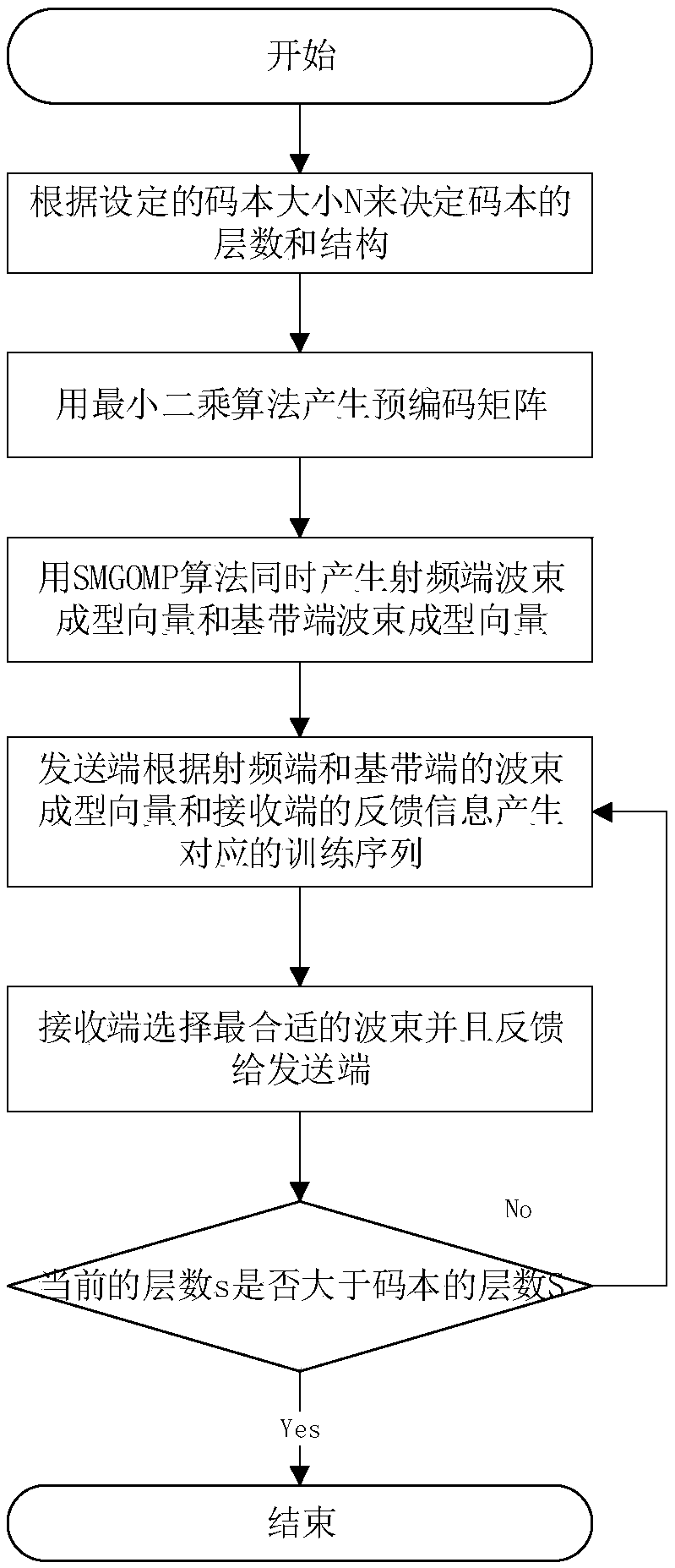
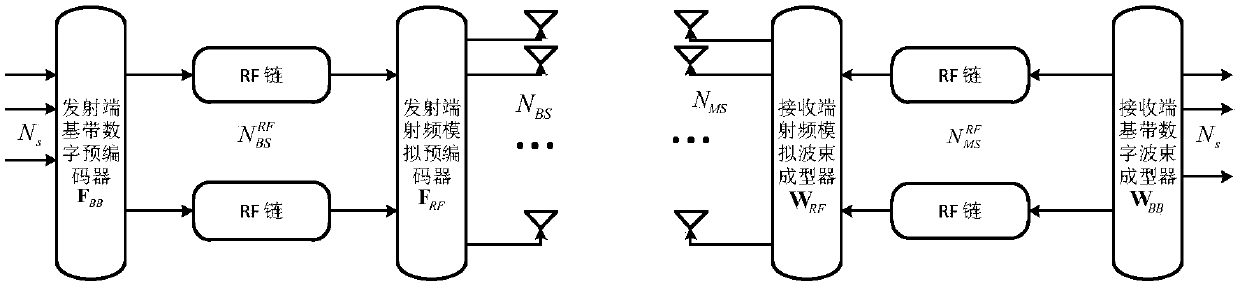
Angle domain channel estimation method based on flexible codebook configuration for millimeter wave system
InactiveCN108111208ASolve the problem of low signal-to-noise ratioReduce complexityRadio transmissionChannel estimationComputation complexityEstimation methods
The invention discloses an angle domain channel estimation method based on flexible codebook configuration for a millimeter wave system. A pre-coded codebook of a corresponding angle is generated before implementation of channel estimation by an adjustable compressed sensing technology, and then a codebook space is traversed to perform beamforming matching, so that a matching operation of optimalprecoding is completed at the end of the channel estimation. The performance of the estimation algorithm depends on the size of the codebook space. Specific to the characteristic, a progressive resolution matching pursuit algorithm is proposed, so that an accuracy-configurable pre-coded codebook vector space can be generated synchronously. Through adoption of the method, the computational complexity of a channel estimation algorithm is lowered effectively without loss of channel estimation performance, so that the method can be effectively applied to angle domain channel estimation of an actual millimeter wave large-scale MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Bearing fault intelligent diagnosis method based on compressed sensing and correlation vector machine
PendingCN112287889AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyMachine part testingCode conversionEngineeringSignal-to-noise ratio
The invention discloses a bearing fault intelligent diagnosis method based on compressed sensing and a correlation vector machine. According to the method, fault diagnosis is achieved through vibration signal analysis. The method comprises the steps of firstly selecting a Gaussian random matrix as a measurement matrix based on a compressed sensing theory to realize compressed sampling of signals,secondly constructing an over-complete redundant dictionary to perform sparse representation on the signals, then utilizing an orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm to realize signal reconstruction, and selecting a time domain index sensitive to fault features as a feature vector for the reconstructed signals; and finally, selecting a Gaussian function as a kernel function, dividing a training sample and a test sample by utilizing a feature vector, importing the training sample into an intelligent recognizer of a relevance vector machine model constructed by a relevance vector machine, and comparing a test result with an actual fault type and degree to obtain the effectiveness of the diagnosis model. According to the invention, the problems of difficult transmission and processing of massdata and low signal-to-noise ratio of bearing vibration signals can be solved, and qualitative and quantitative identification of bearing faults can be realized more accurately.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
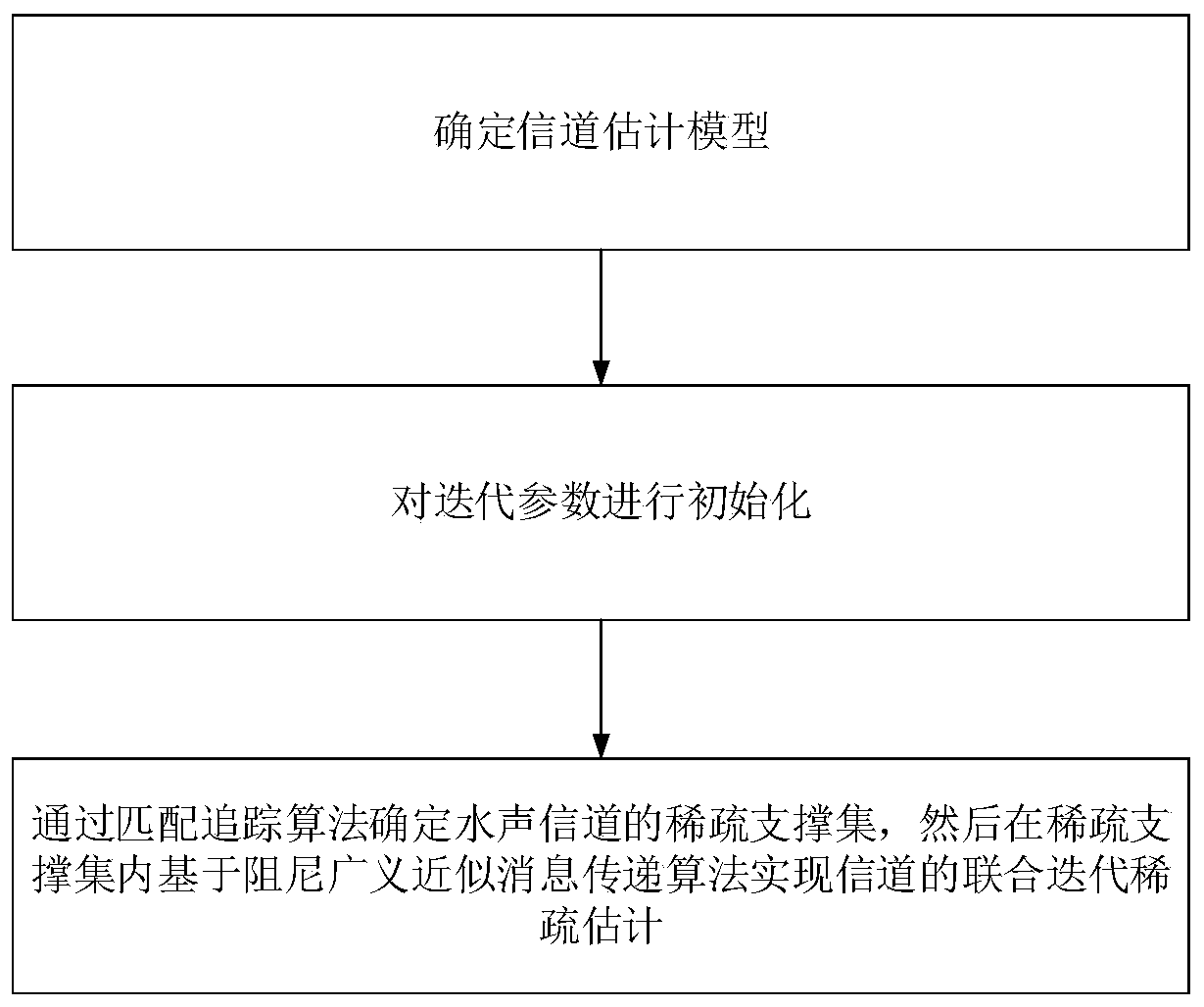
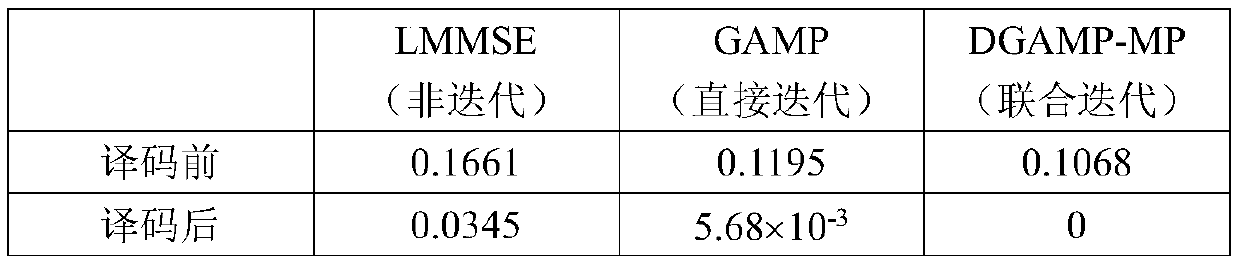
Underwater acoustic sparse channel estimation method, system and device and storage medium
ActiveCN110311872AReduce computational complexityGuaranteed convergenceChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityEstimation methods
The invention provides an underwater acoustic sparse channel estimation method, system and device and a storage medium. The method comprises: establishing an underwater acoustic channel estimation model; and determining a sparse support set of the underwater acoustic channel through a matching pursuit algorithm, and then realizing joint iteration sparse estimation of the channel in the sparse support set based on a damping generalized approximate message transfer algorithm. According to the invention, a matching pursuit MP algorithm and a DGAMP algorithm are organically combined, a sparse channel joint iteration estimation method is provided, on one hand, a support set of sparse points is determined through MP iteration, the number of nodes of a DGAMP factor is reduced, the convergence ofthe DGAMP is ensured, and the robustness of the DGAMP factor is greatly improved; and on the other hand, DGAMP iterative estimation is adopted in the support set to obtain the estimation value of thechannel, and the iteration process only involves scalar operation, so that the calculation complexity is greatly reduced.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Signal reconstruction method of OMP (orthogonal matching pursuit) based on rapid inner product calculation under distributed type CS (compressed sensing) framework
ActiveCN103532567AHigh speedReduce the number of multiply and addCode conversionSignal reconstructionOrthogonal matching pursuit algorithm
The invention provides a signal reconstruction method of the OMP based on rapid inner product calculation under a distributed type CS framework, relates to the technical field of multichannel CS, and aims to solve the problem that the reconstruction speed of a conventional signal reconstruction method is low. According to the signal reconstruction method, after multichannel signals are subjected to compression observation, signal reconstruction is performed with the OMP, rapid calculation of the inner product in the OMP is realized by the aid of the internal sparsity of a joint observation matrix, and signal reconstruction is realized further. The signal reconstruction method is applicable to signal reconstruction of the OMP based on the rapid inner product calculation under the distributed type CS framework.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
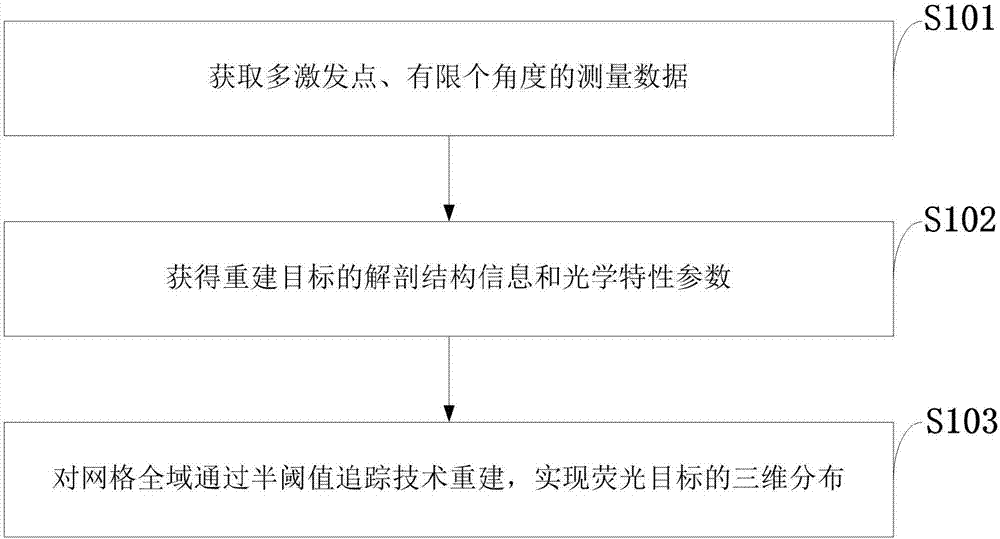
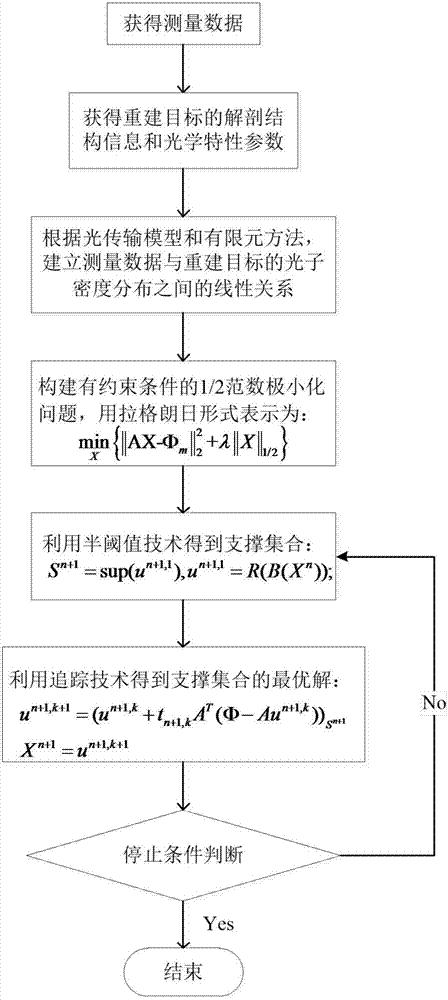
Method for reconstructing fluorescence molecular tomography based on semi-threshold tracking algorithm
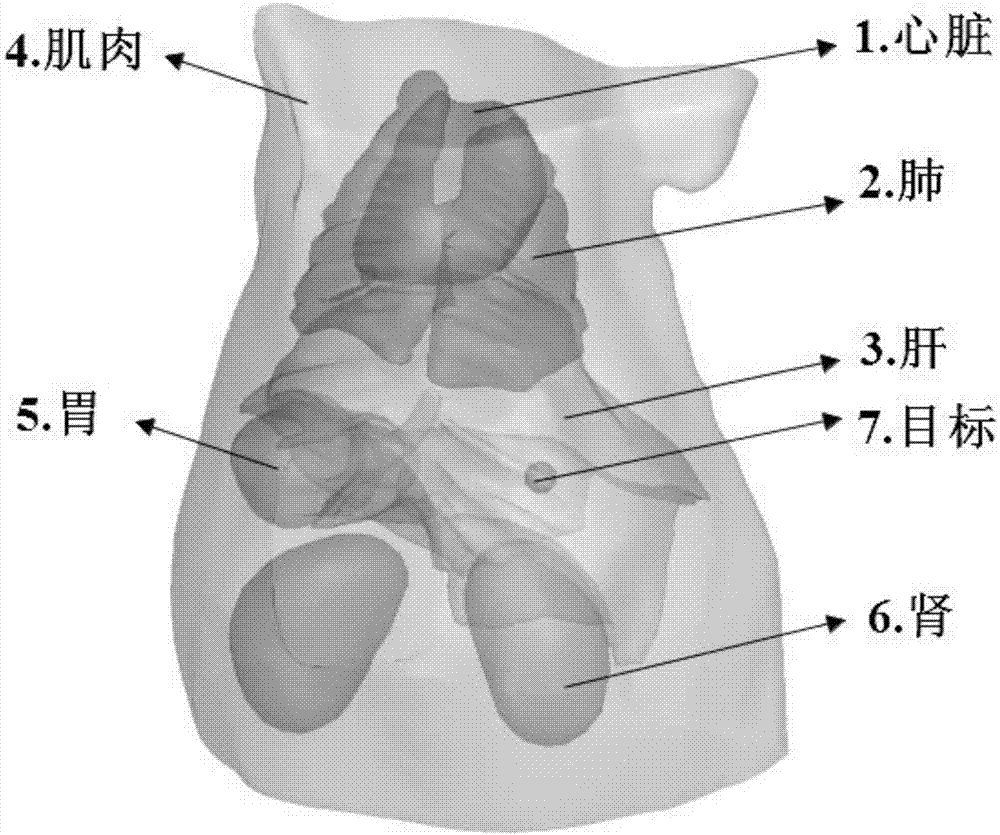
InactiveCN107220961AImprove stabilityThe reconstruction results are accurateImage enhancementDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionAnatomical structuresCanonical model
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular imaging, and discloses a method for reconstructing fluorescence molecular tomography based on semi-threshold tracking algorithm. The multi-point excitation and finite angle measurement are used to construct a sparse canonical model of a non-convex problem, and the linear relationship between the surface measurement data and fluorescence target distribution is established. The linear relationship is transformed into the 1 / 2 norm minimization problem to solve and obtain the three-dimensional distribution and concentration of the fluorescent targets within a reconstructed target. The model is solved by threshold iteration and matching tracing algorithm. The method reduces the morbidity of the problem. Optical characteristic parameters and the anatomical structure information are used as a priori knowledge to improve the accuracy of the reconstruction result and the quality of a reconstructed image. The reconstruction problem is transformed into a 1 / 2-norm minimization problem with constraint conditions and is solved by using the semi-threshold tracing algorithm, which makes the solution satisfy the minimum of 1 / 2- norm and guarantees the robustness of the reconstruction problem to the parameters and the acceleration reconstruction time.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com