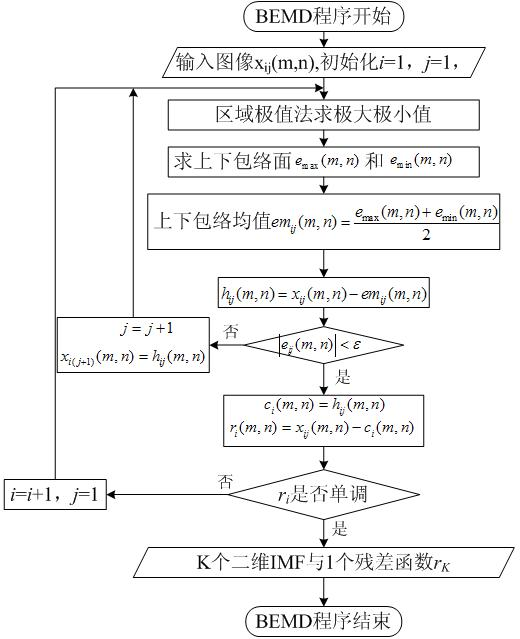
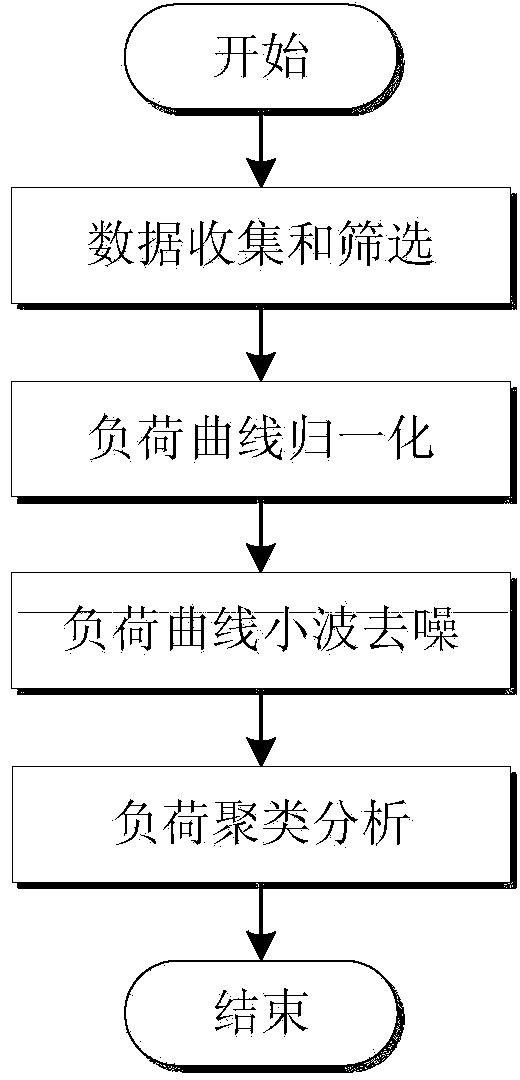
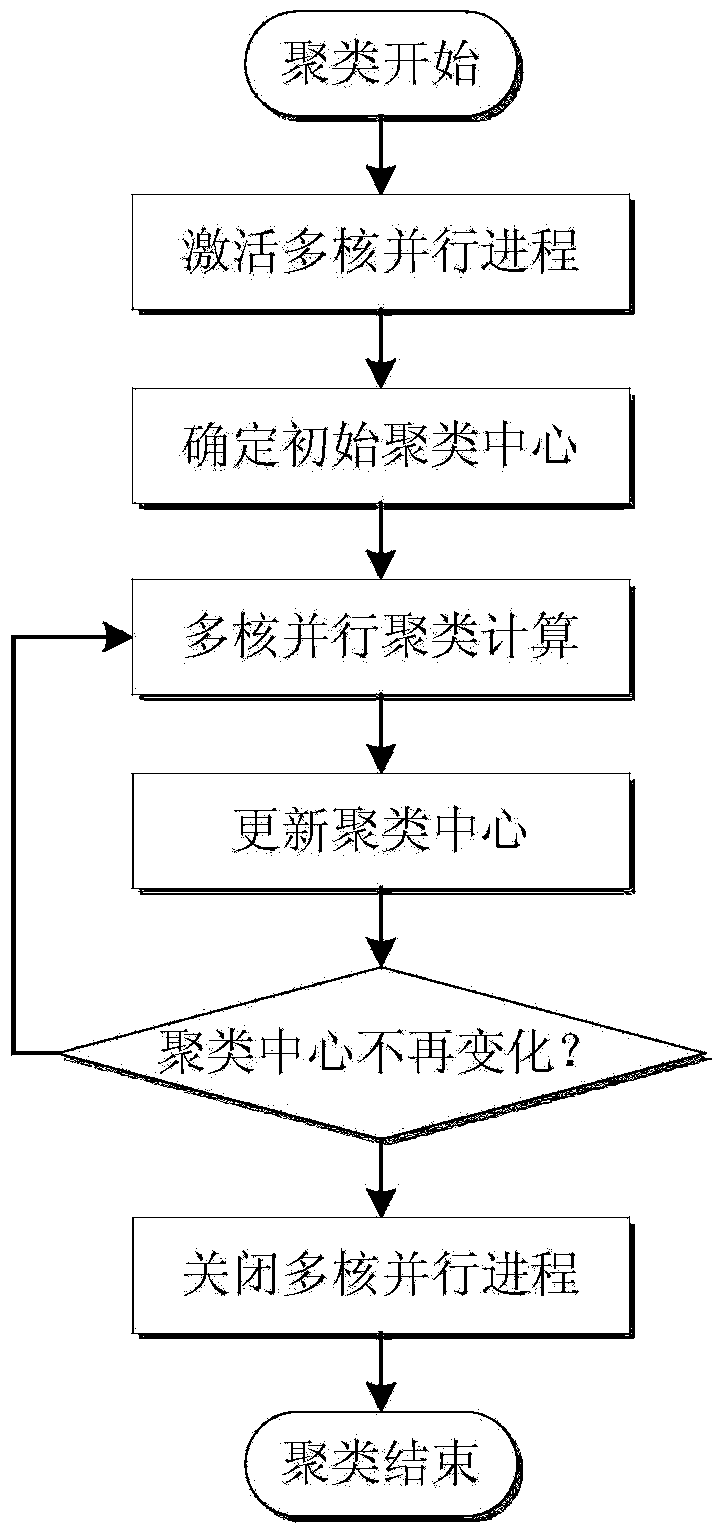
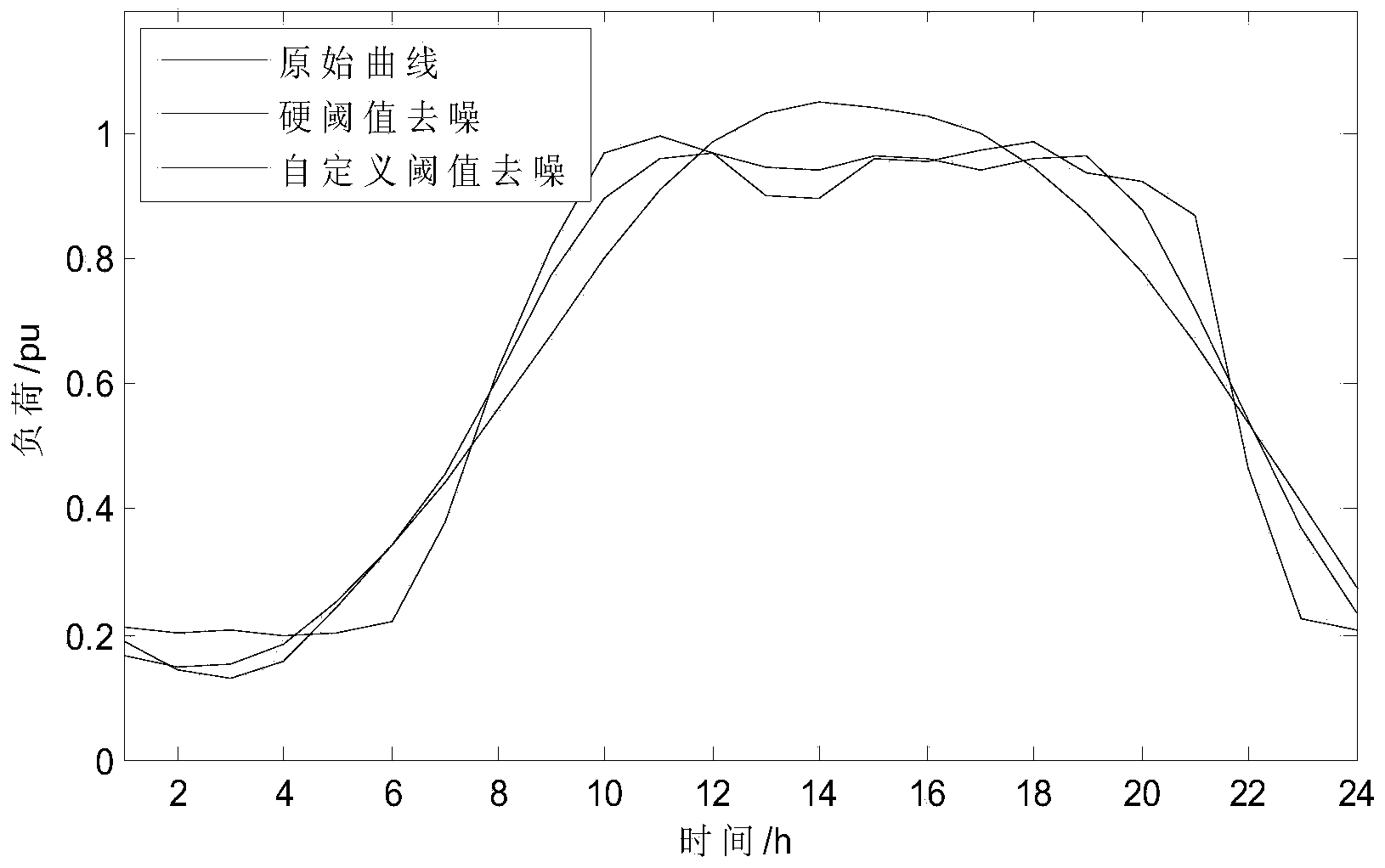
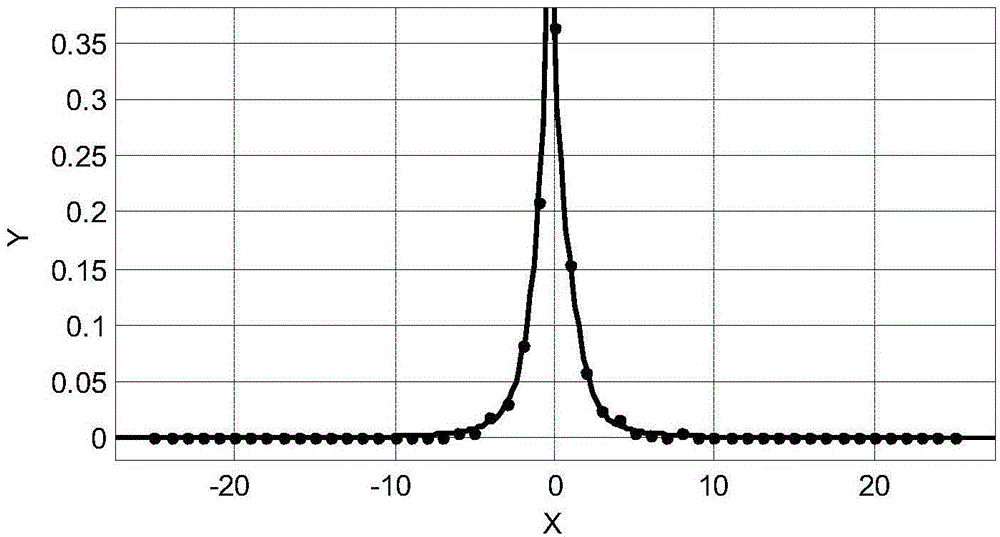
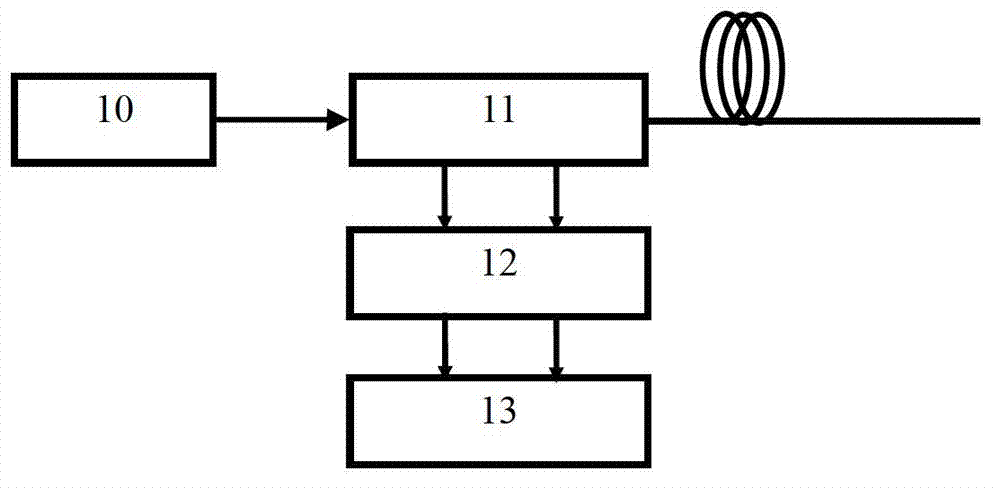
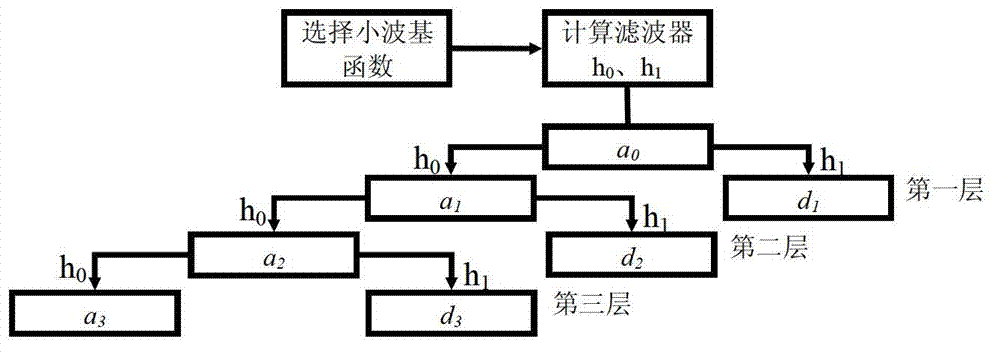
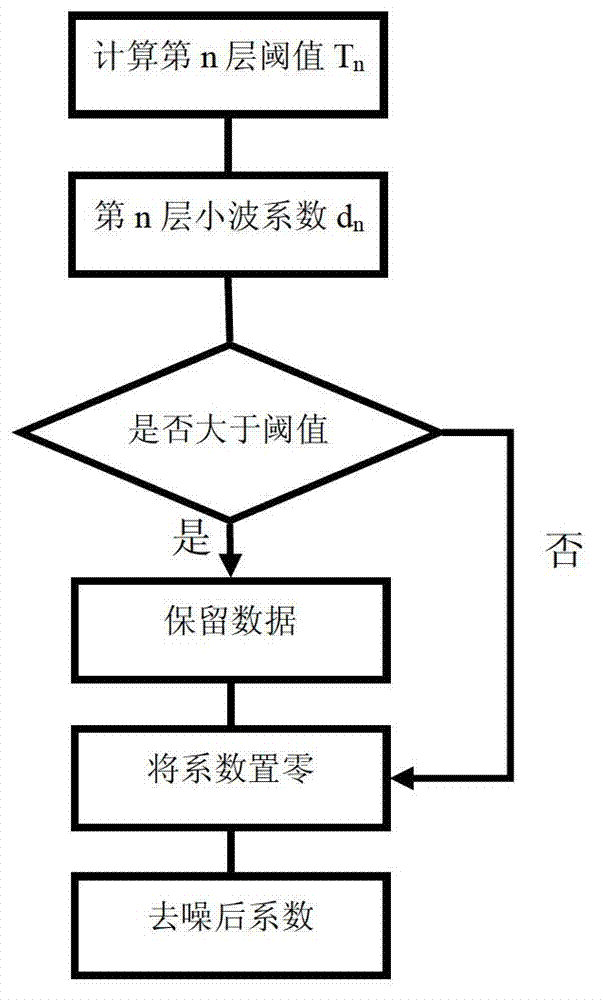
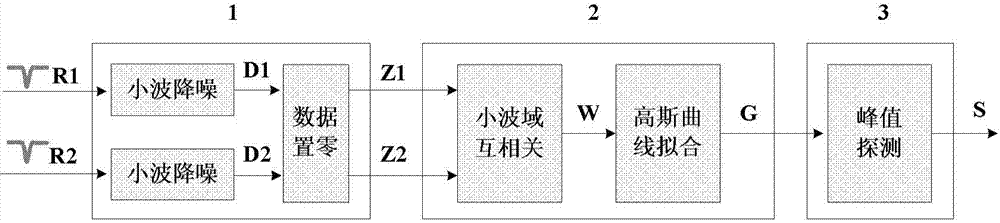
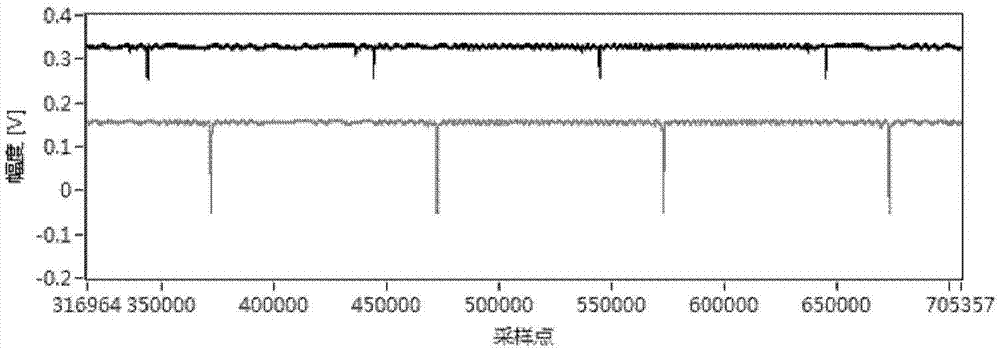
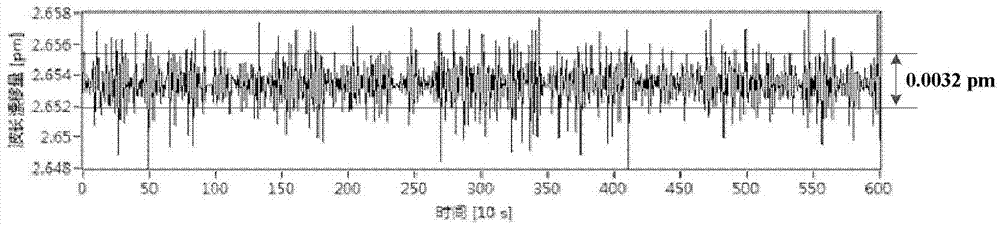
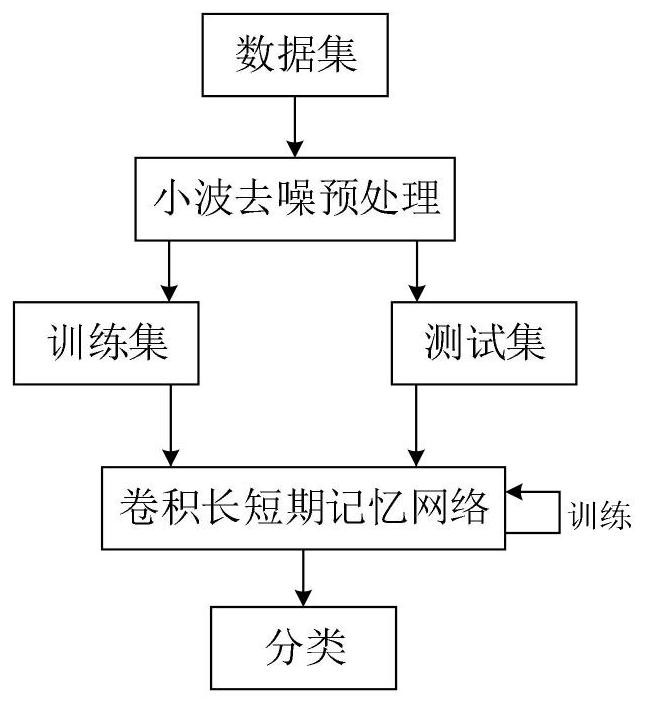
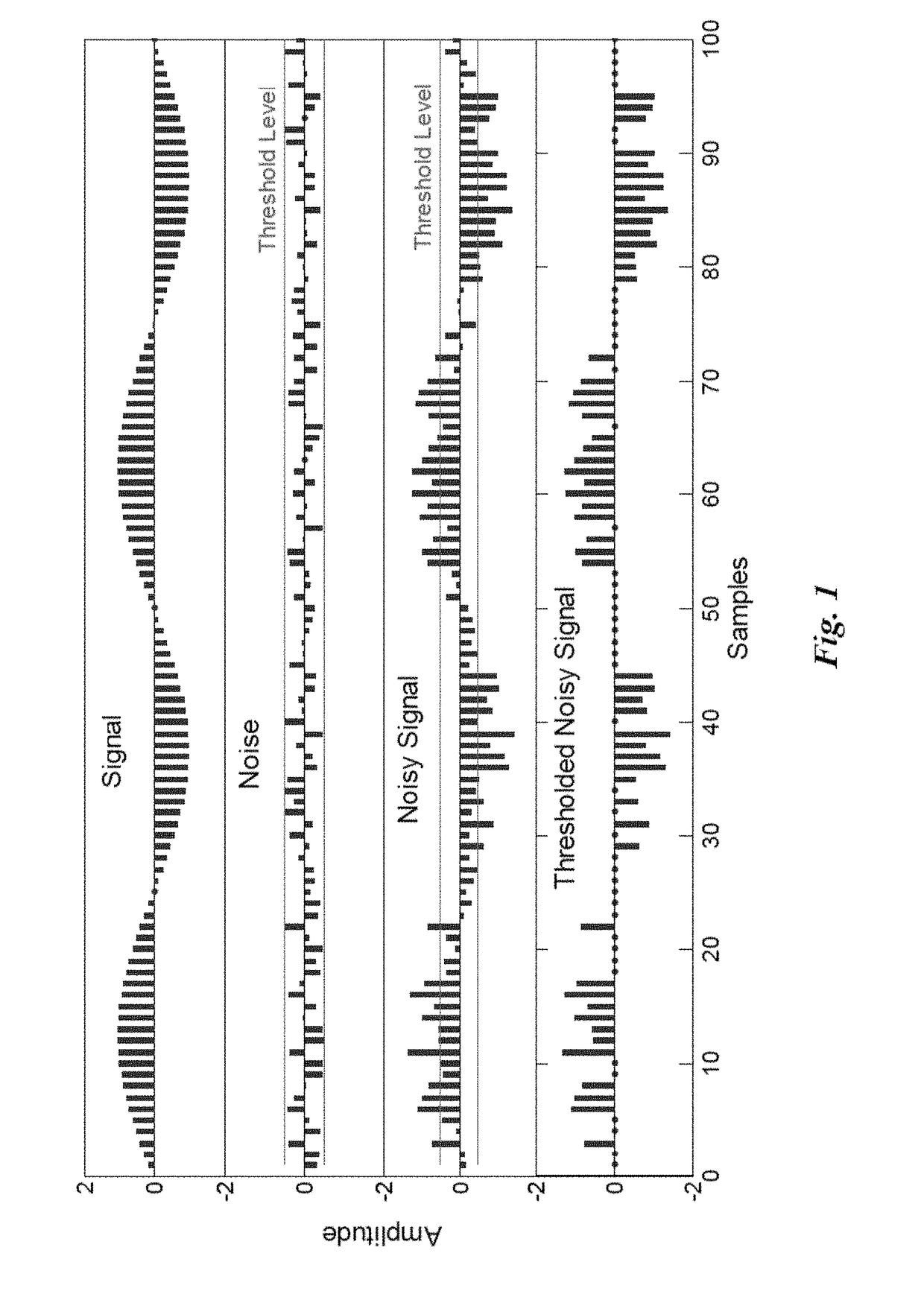
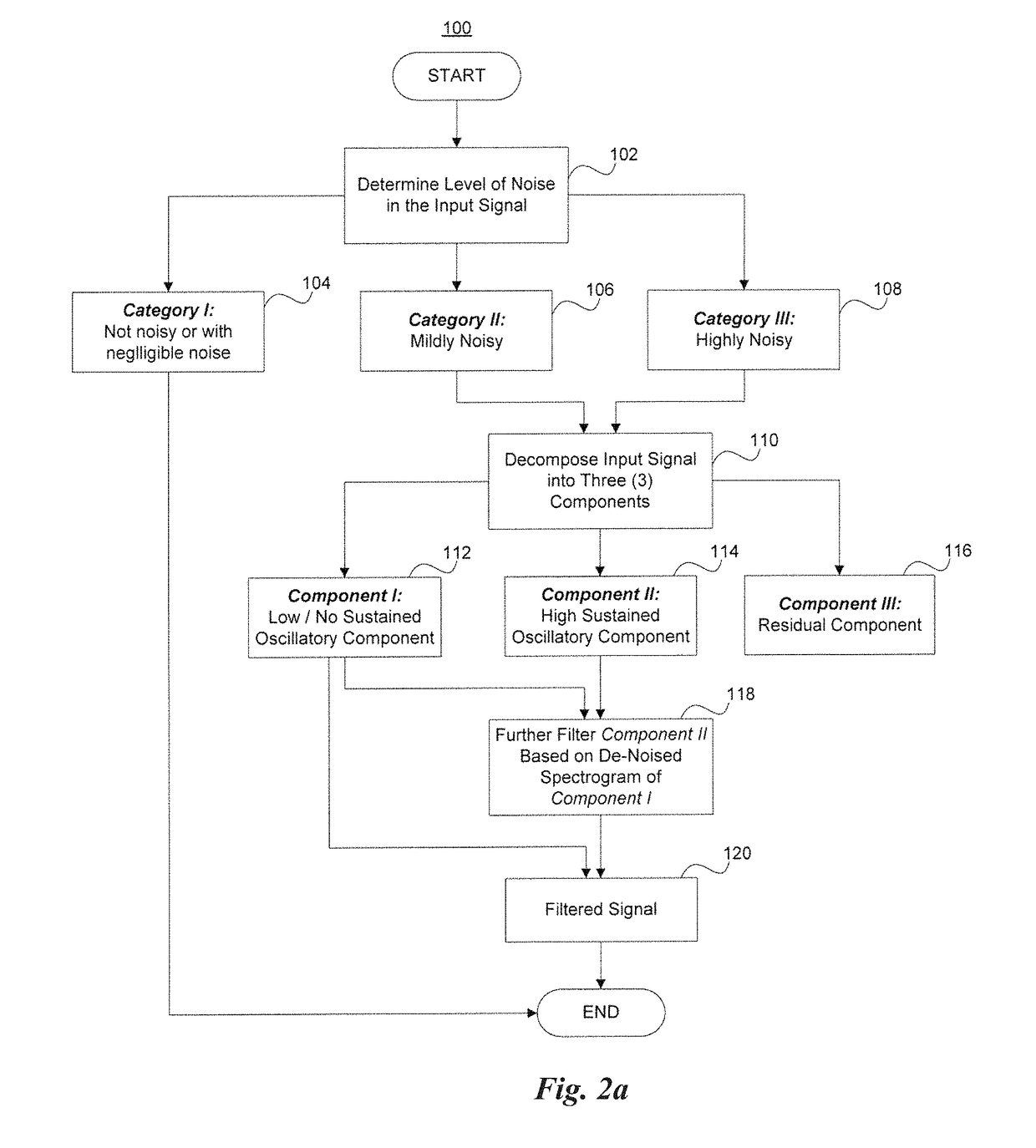
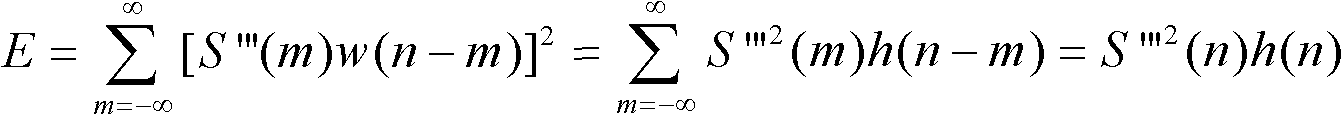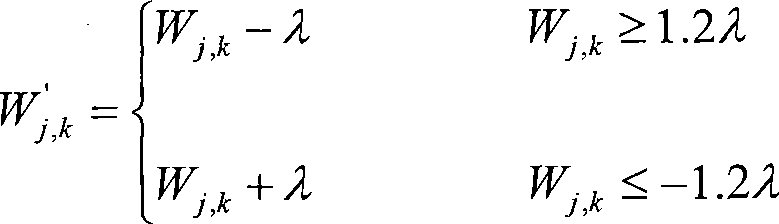Patents
Literature
398 results about "Wavelet denoising" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
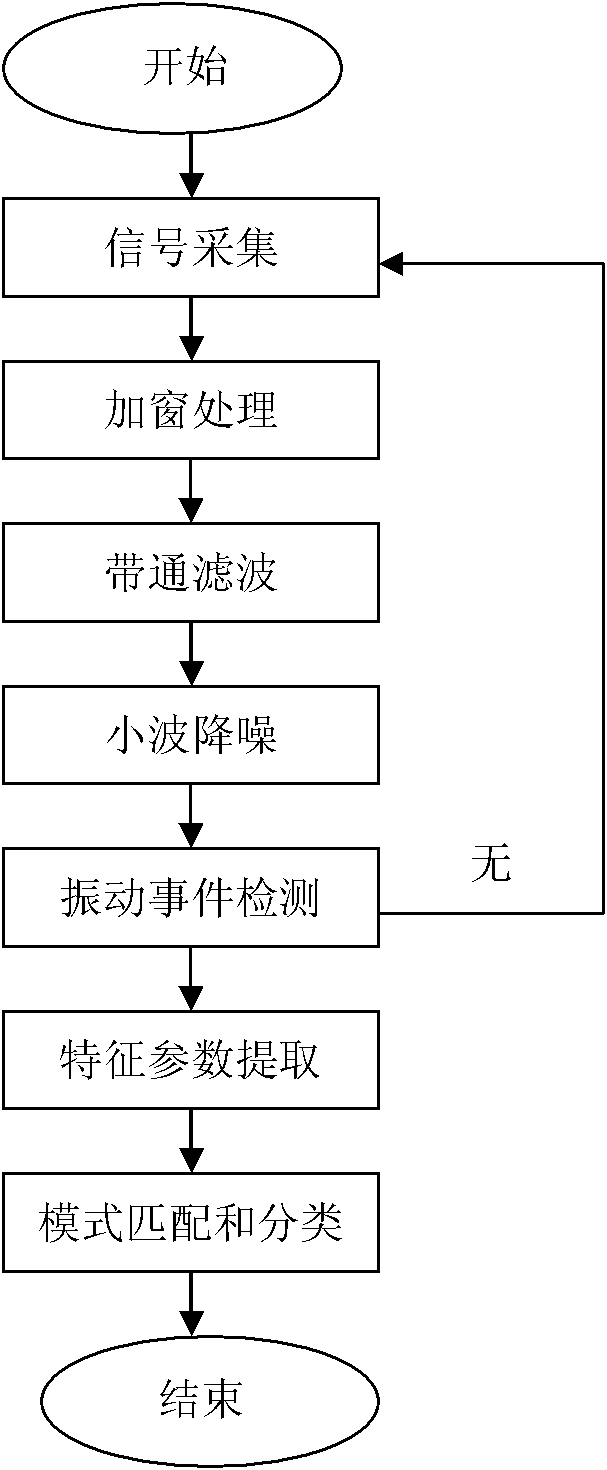
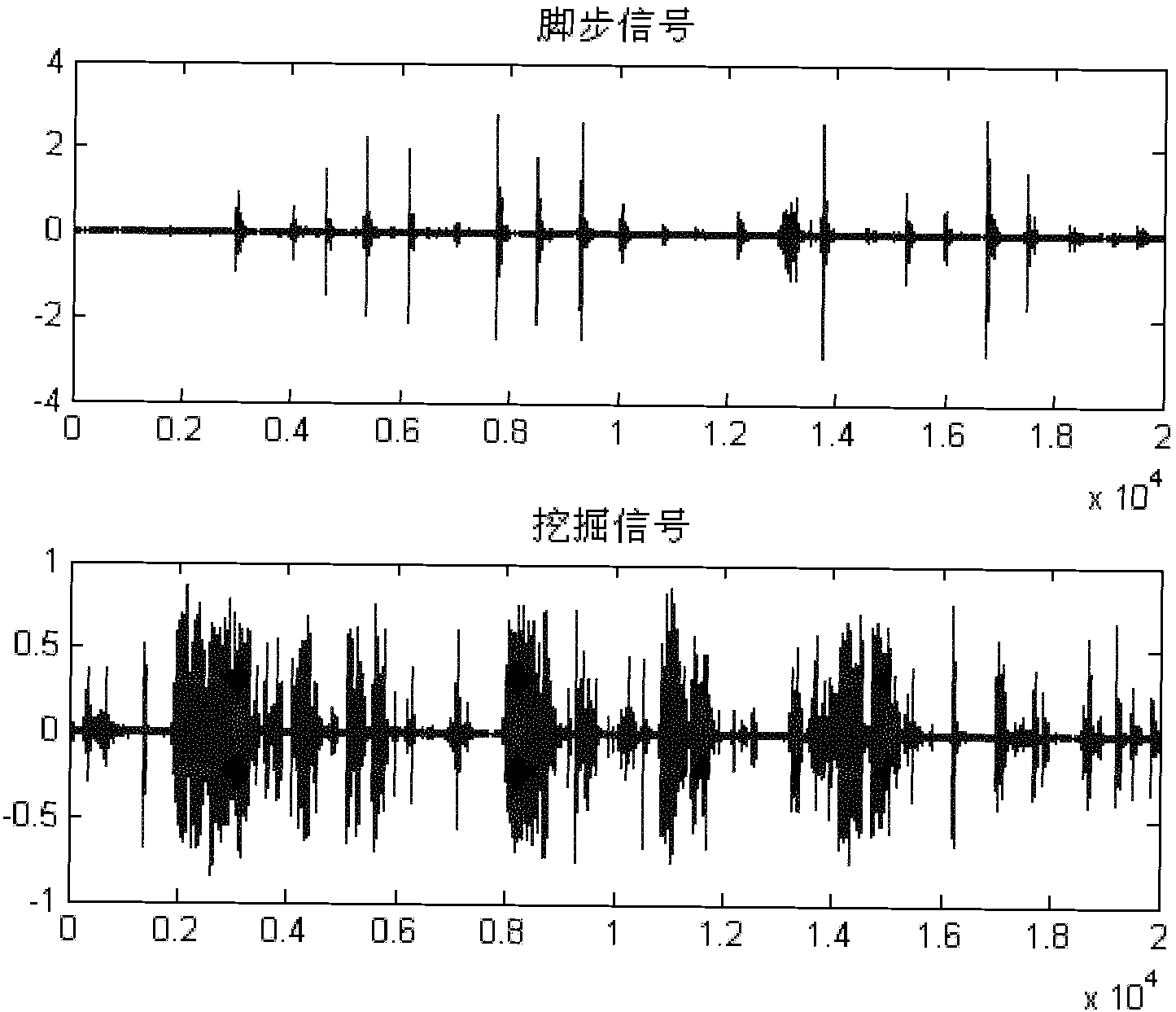
Vibration signal identification method for optical fiber perimeter system
ActiveCN102045120AAccurate judgmentReduce false alarm rateFibre transmissionTransmission monitoringBandpass filteringWavelet denoising
The invention relates to a vibration signal identification method for an optical fiber perimeter system, which comprises the following steps of: (1) signal acquisition; (2) windowing treatment; (3) bandpass filtering; (4) wavelet denoising; (5) vibration event detection; (6) characteristic parameter extraction; and (7) pattern matching and classification. The invention has the advantages that the method introduces more characteristic parameters such as short-term energy E, short-time average magnitude M, short-term average zero-crossing rate Z, each wavelet decomposition scale detail signal energy Ew and vibration signal power spectrum P in comparison with the prior art, accurately judges the classification of external vibration signals, and reduces the probability of false alarm.
Owner:CHENGDU JIUZHOU ELECTRONIC INFORMATION SYSTEM CO LTD
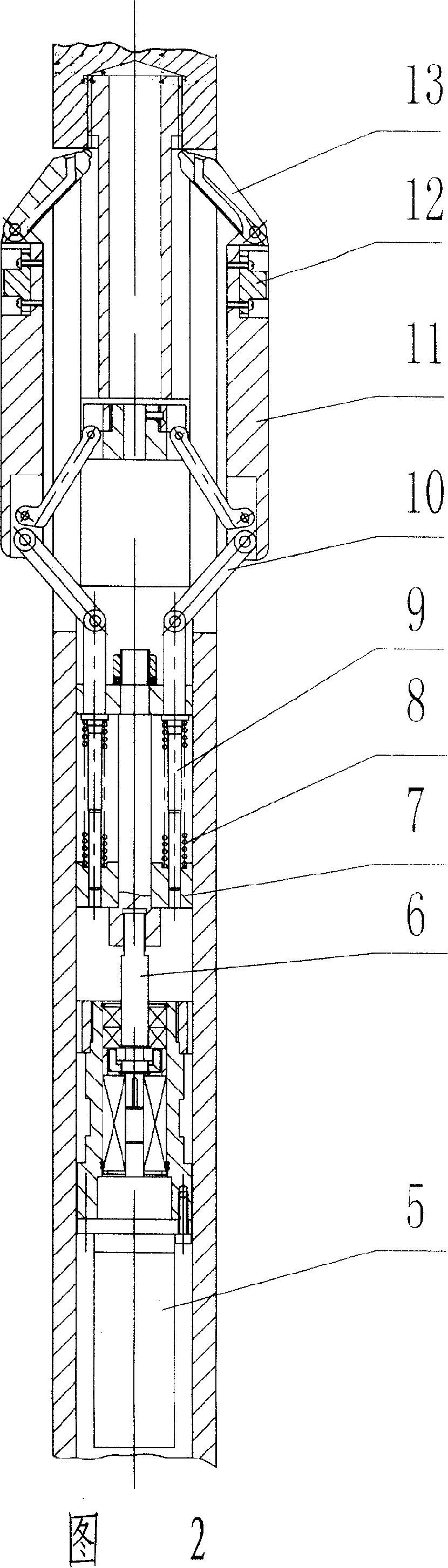
Method for prediction of oil well annular tube damage and detecting instrument for implementing the method
ActiveCN101012746AAvoid casing damage and economic lossBorehole/well accessoriesMaterial magnetic variablesWavelet denoisingMagnetic memory
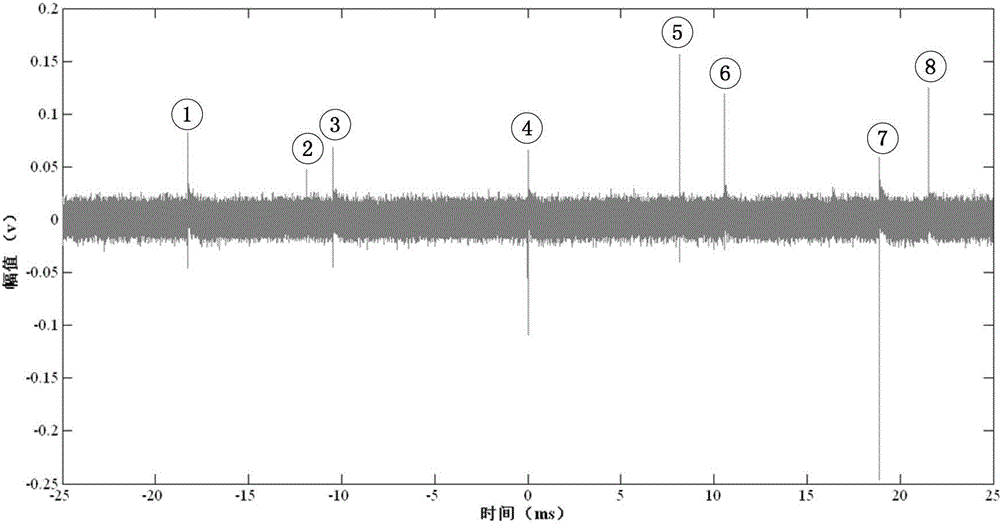
The invention relates to a method of forecasting casing pipe damage by exploring casing pipe inner stress and the metal magnetic memory testing instrument designed specially for the method, which mainly solves the problem that prior casing damage testing technology only estimates the existed casing damage and can not forecast the possible casing damage. It is characterized in that the metal magnetic memory testing instrument is set to the objective measuring well segment; it moving along the underground casing pipe takes the normal component of leakage magnetic field Hy; The ground treatment system makes sampling data sequence x(n) is filtered in data by hanning filter; index wavelet denoising is carried out by Db4 wavelet function and four decomposed layers; denoising signal f(ti) is used to draw the magnetic memory data and grads curve; according to the curve the peak value of magnetic memory signal is taken out; the value is controlled with the four-grade semi-quantity evaluation underground casing stress distribution state table to forecast the criticality of casing damage. It has the early forecasting casing damage and can avoid huge economical loss of casing damage in oil field.
Owner:DAQING OILFIELD CO LTD +1
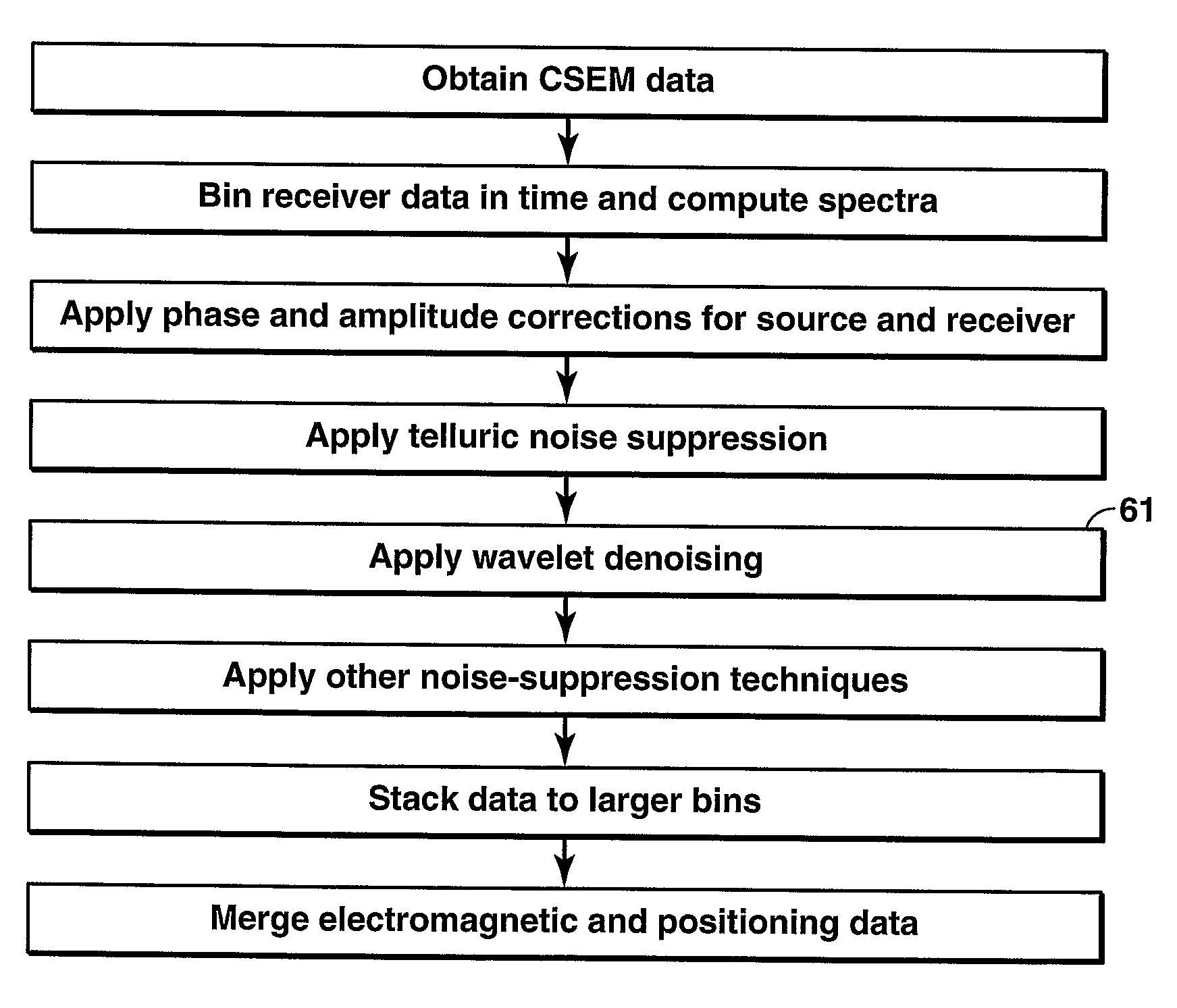
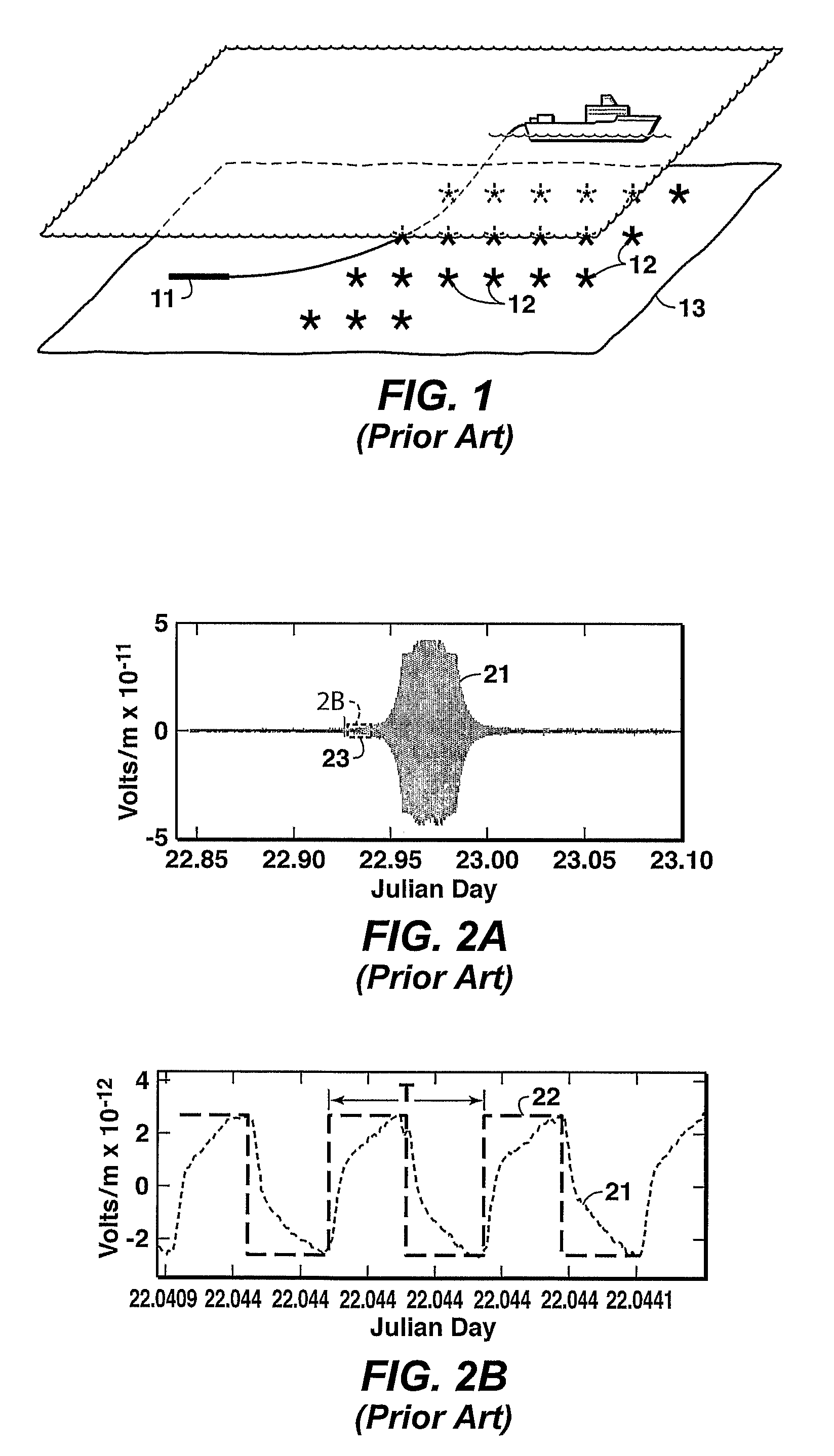
Method for Wavelet Denoising of Controlled Source Electromagnetic Survey Data
InactiveUS20090103395A1Weakening rangeSeismology for water-covered areasDetection using electromagnetic wavesWavelet denoisingControlled source electro-magnetic
Method for denoising a receiver signal from a controlled source electromagnetic survey. A discrete wavelet transform is performed on the signal, and the resulting detail coefficients are truncated using a selected threshold value, which may be zero. Further levels of decomposition may be performed on the approximation coefficients from the preceding level. After the final level of decomposition, a denoised signal is restructured by performing the inverse wavelet transformation on the last set of approximation coefficients combined with the thresholded detail coefficients accumulated from all levels of decomposition.
Owner:WILLEN DENNIS W
Voice secret communication system design method based on compressive sensing and information hiding
ActiveCN102034478AQuality improvementImprove sparsitySpeech analysisSecret communicationWavelet denoisingVoice communication
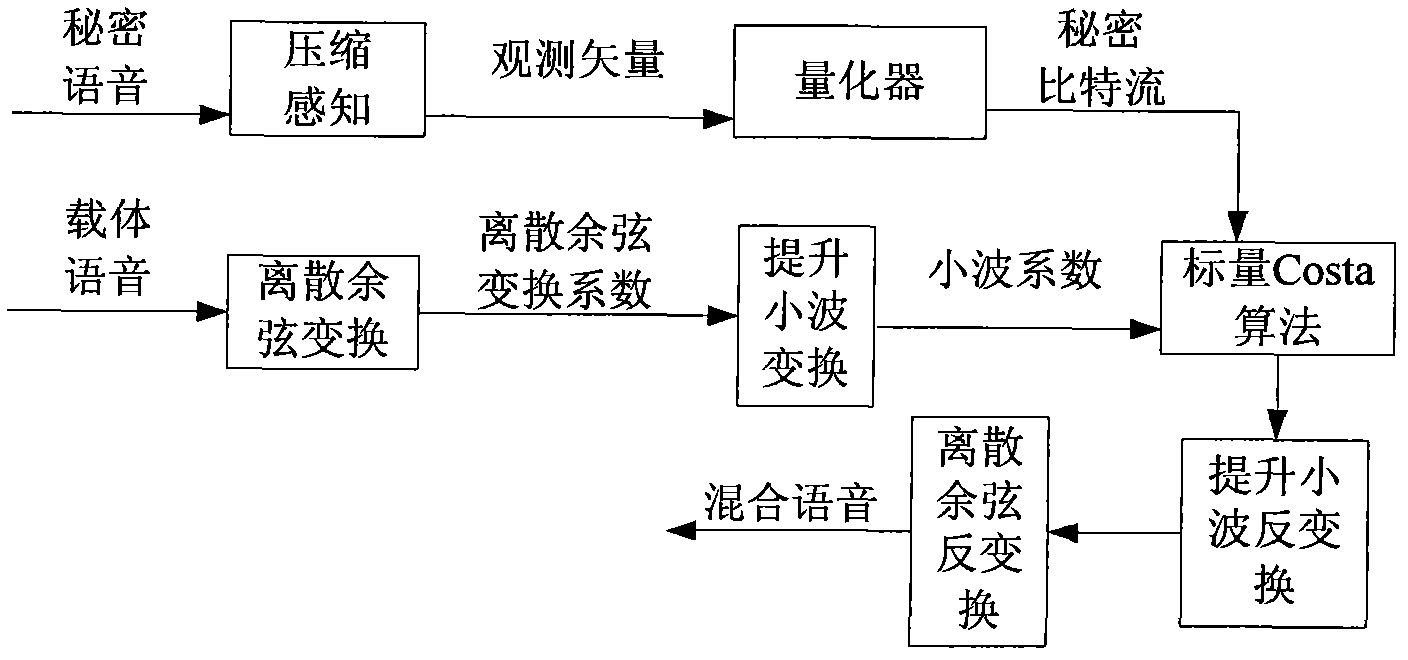
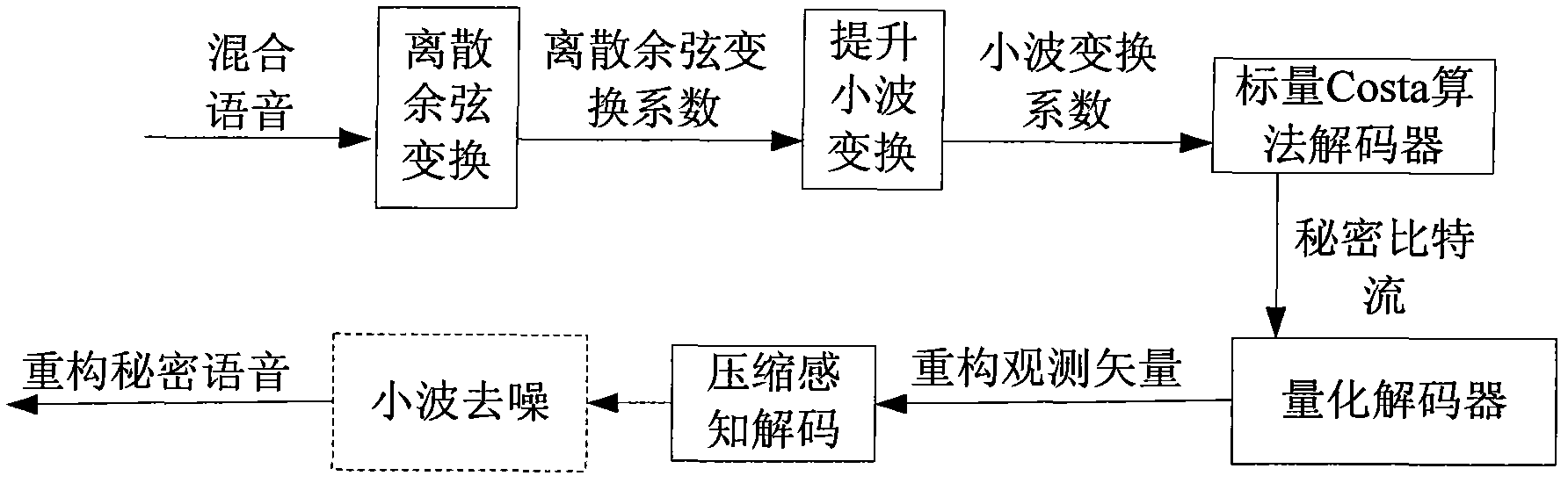
The invention discloses a voice secret communication system design method based on compressive sensing and information hiding, comprising the following steps: embedding secret voice into carrier voice by an embedded system to obtain mixed voice; designing a compressive sensing overcomplete dictionary aiming at the voice signal; sampling the secret voice by a compressive sensing self-adaption observation matrix to obtain a observation vector for reducing dimensions; quantizing the observation vector by an LBG (Linde-Buzo-Gray algorithm) vector, taking the quantized observation vector to serve as secret information to embed into the carrier voice, and carrying out two-stage transform on the carrier voice to obtain mixed voice; extracting the secret voice from the mixed voice by an extraction system; carrying out discrete cosine transform on mixed voice, and improving wavelet transform two-stage transform to obtain a wavelet transform coefficient; obtaining a secret bit stream by a scalar Costa decoding algorithm; obtaining a reconstructing observation vector by an LBG vector quantization decoder; reconstructing the secret voice by a compressive sensing orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm; and improving the quality of the reconstructed secret voice with a wavelet denoising method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
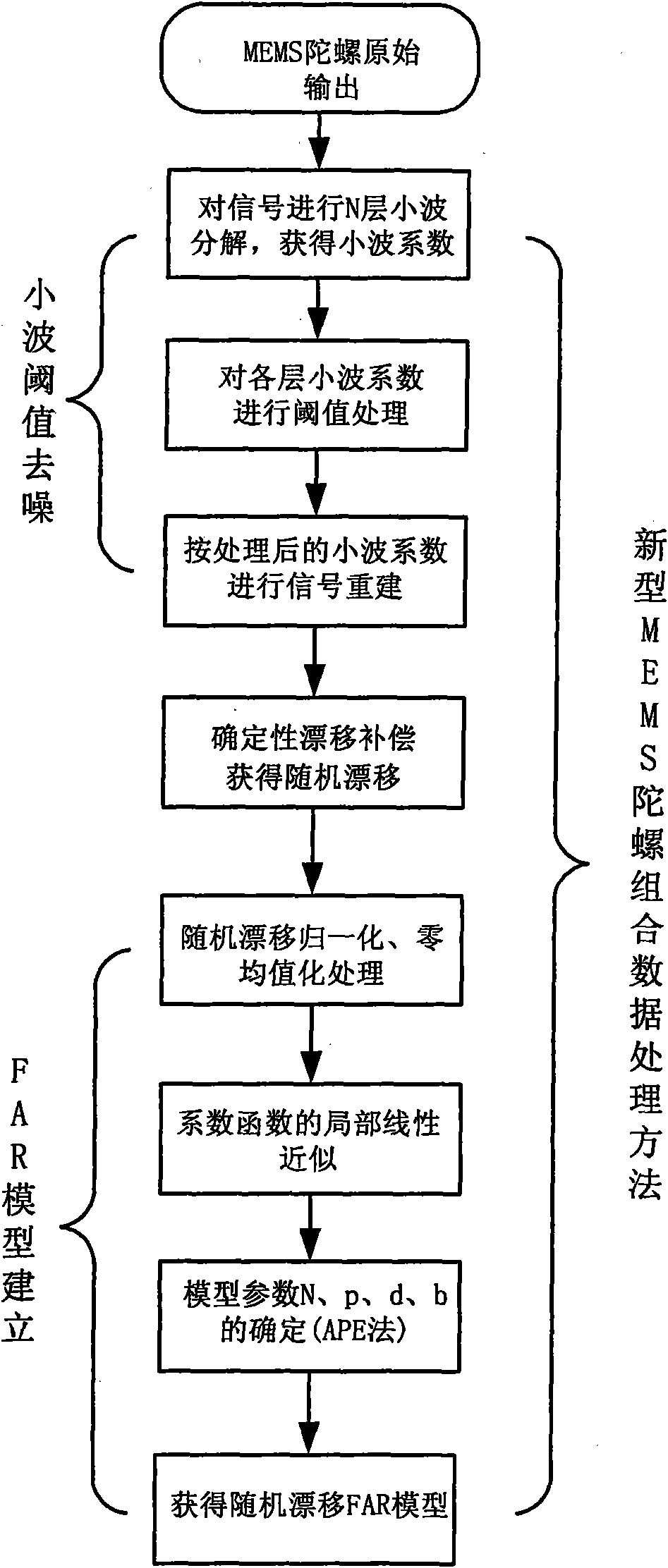
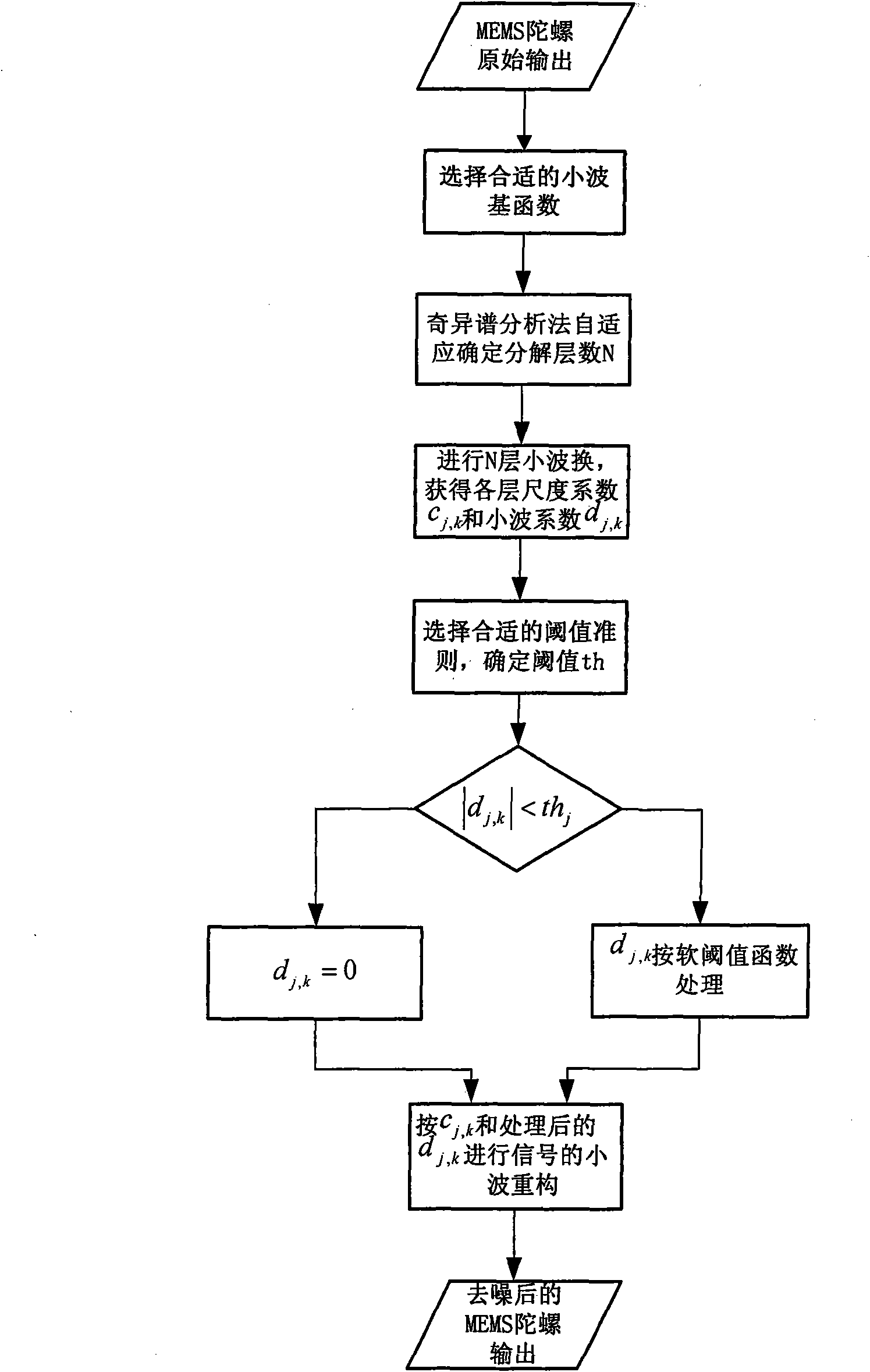
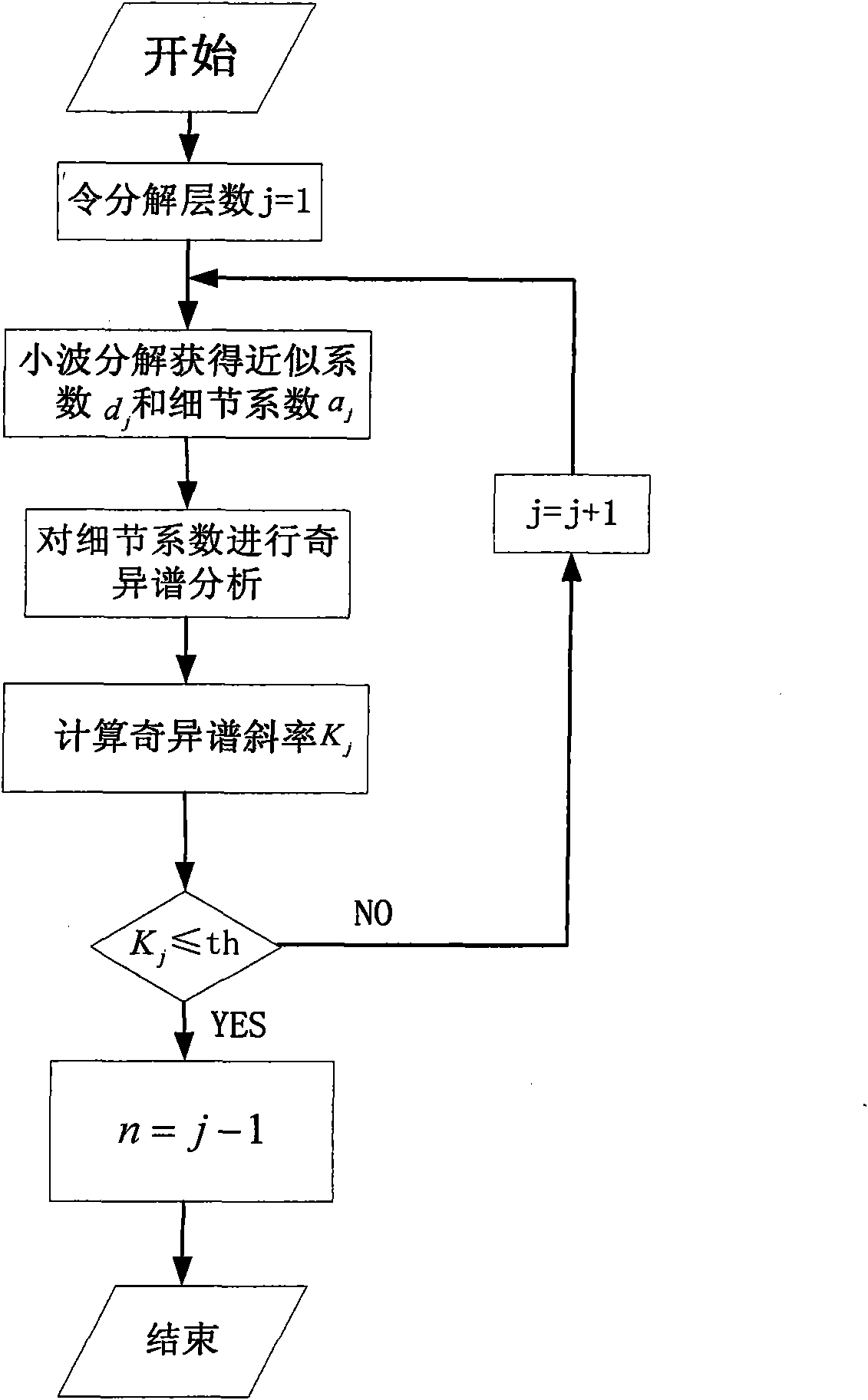
MEMS (Micro Electronic Mechanical System) gyro data processing method based on wavelet threshold de-noising and FAR (Finite Automaton Recognizable) model
InactiveCN101876546ASolve the problem of large output noiseSolve the problem of random drift modelingSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsComplex mathematical operationsSample sequenceAutomaton
The invention discloses an MEMS (Micro Electronic Mechanical System) gyro data processing method based on wavelet threshold de-noising and an FAR (Finite Automaton Recognizable) model. For solving the problem that large amount of noise exists in the MEMS gyro output signal, the wavelet threshold de-noising method is used to process the gyro output signal to filter the noise and improve the signal-noise ratio; aiming at a static signal formed by de-noising gyro wavelet, a polynomial fitting method is used for the compensation to the gyro deterministic drift, wherein a residual error after the compensation is a random drift of the gyro, that is to say, a sample sequence required by modeling the random drift of the gyro is obtained; and aiming at modeling the random drift of the MEMS gyro at higher precision, the FAR model is used for modeling the random drift. The invention solves the problem of high output noise of the MEMS gyro, improves the signal-noise ratio and can accurately model the random drift of the gyro, thereby improving the output precision of the MEMS gyro.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
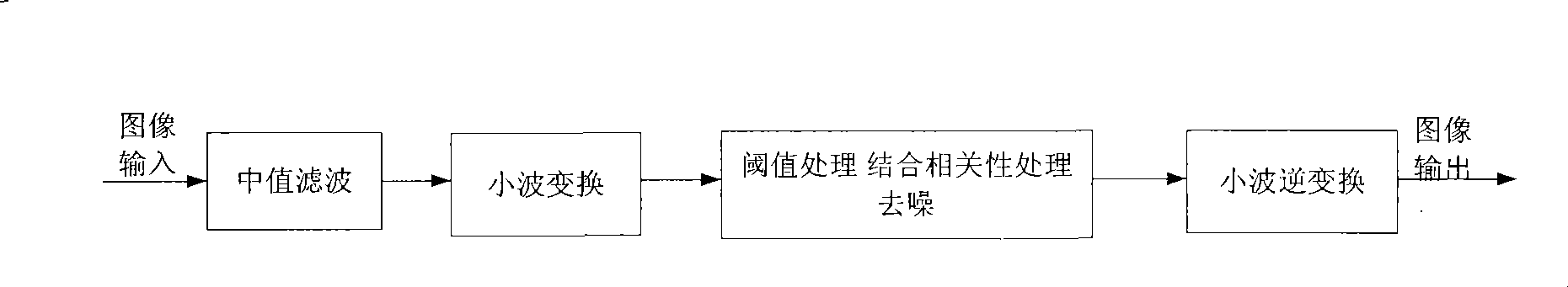
Image wavelet de-noising method based on median filter
InactiveCN101425176AAvoid confusionAvoid the influence of high frequency partImage enhancementWavelet denoisingScale dependent
The invention provides an image wavelet denoising method based on median filtering, which belongs to the field of digital remote sensing image processing. In the method, median pre-filtering is firstly performed on images containing noise, wavelet conversion, threshold value treatment and denoising treatment are then carried out, wavelet reverse conversion is finally carried out, and filtered images are output. The invention has the advantages that the median filtering method is used for the pre-filtering of images containing noise, much noise of pepper salt type is removed, and influence on the high-frequency part of images is avoided; the wavelet threshold value method is then combined with the denoising method of the relativity of wavelet coefficient size, and the mixture of signal coefficient and noise coefficient caused by using the wavelet threshold value method singly is avoided; and meanwhile, a large amount of computation required by using the denoising method of the relativity of wavelet coefficient size singly is reduced. The experiments prove that the method has stable denoising effect and moderate computation amount.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
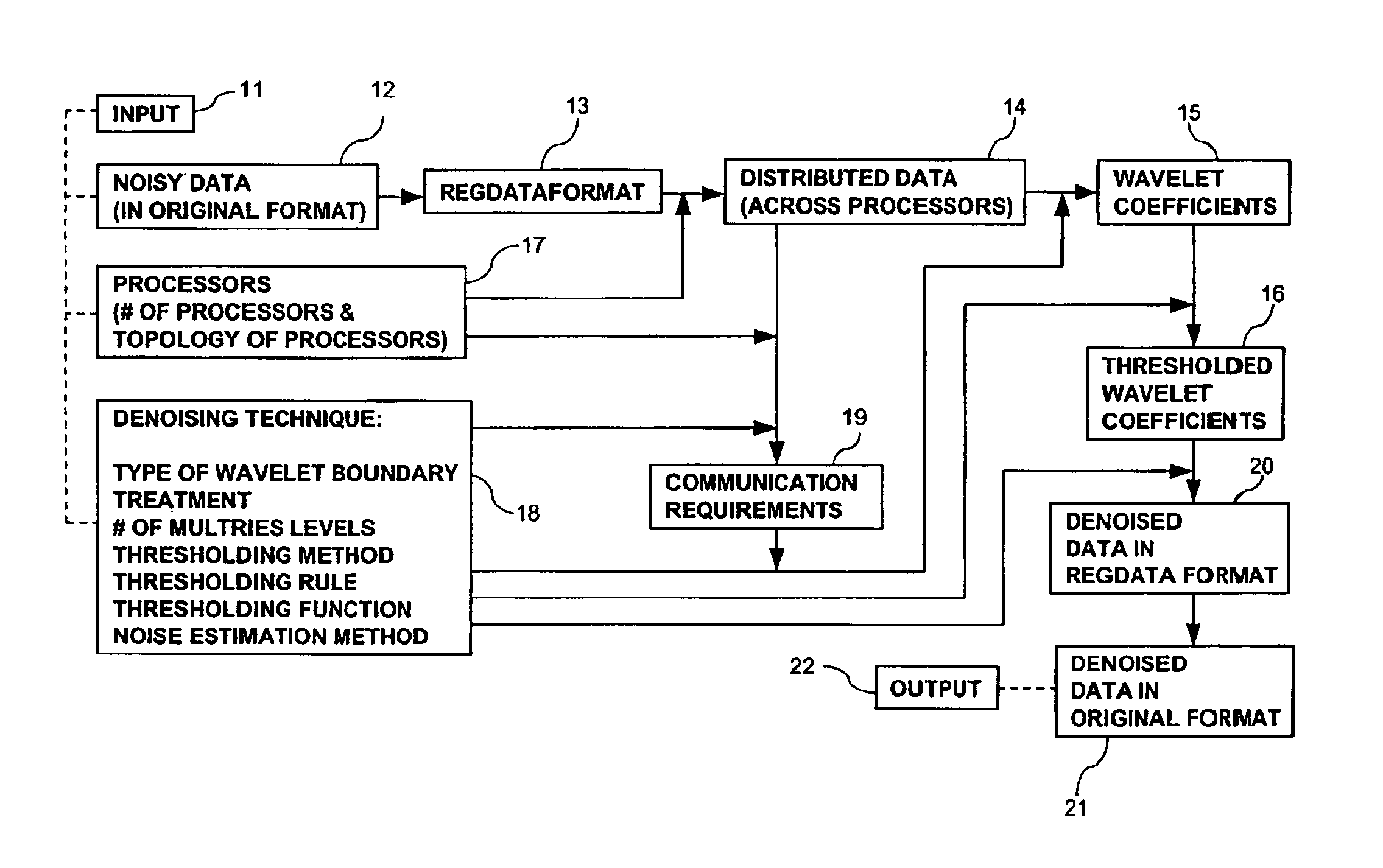
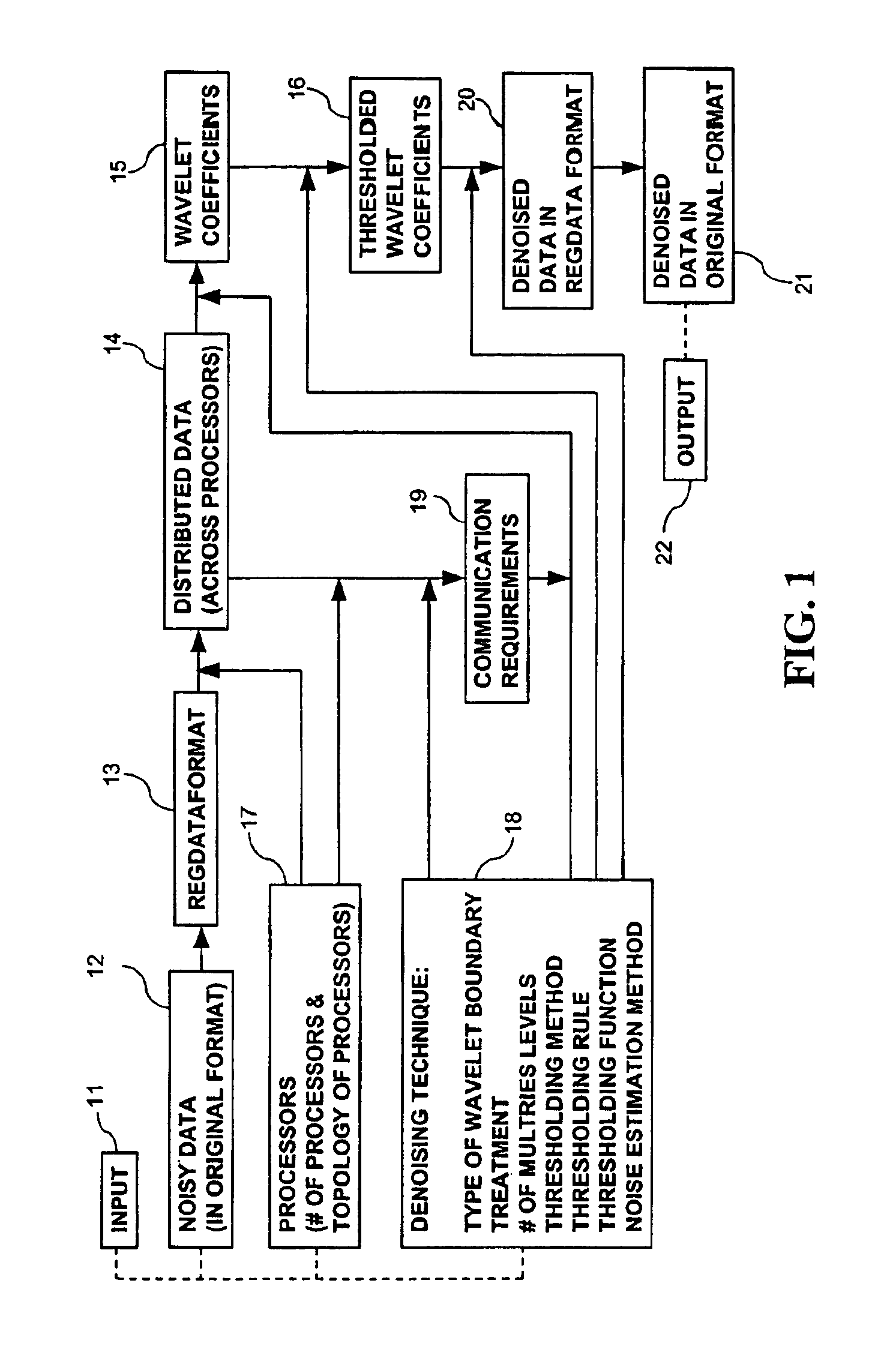
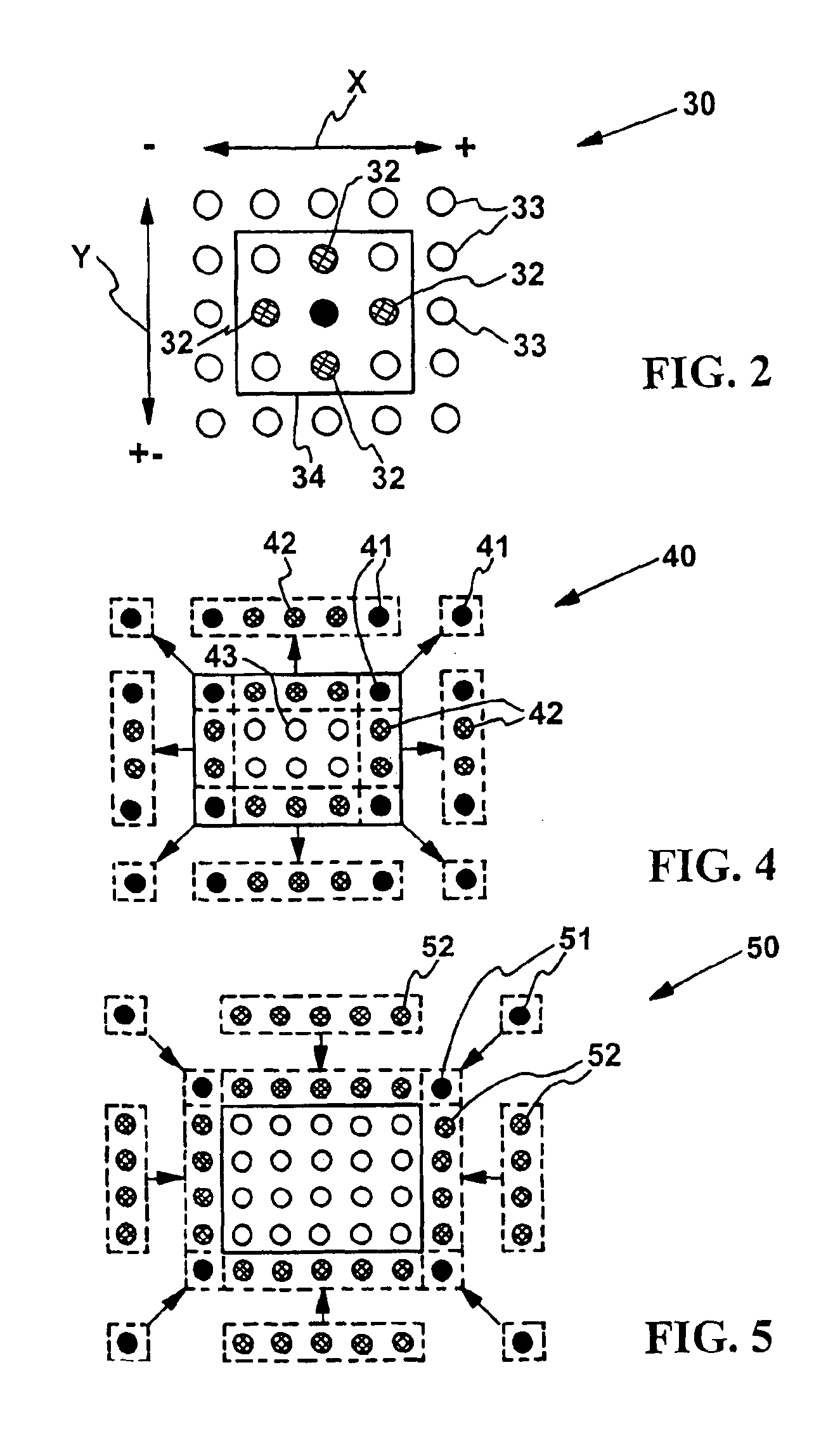
Parallel object-oriented, denoising system using wavelet multiresolution analysis
The present invention provides a data de-noising system utilizing processors and wavelet denoising techniques. Data is read and displayed in different formats. The data is partitioned into regions and the regions are distributed onto the processors. Communication requirements are determined among the processors according to the wavelet denoising technique and the partitioning of the data. The data is transforming onto different multiresolution levels with the wavelet transform according to the wavelet denoising technique, the communication requirements, and the transformed data containing wavelet coefficients. The denoised data is then transformed into its original reading and displaying data format.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
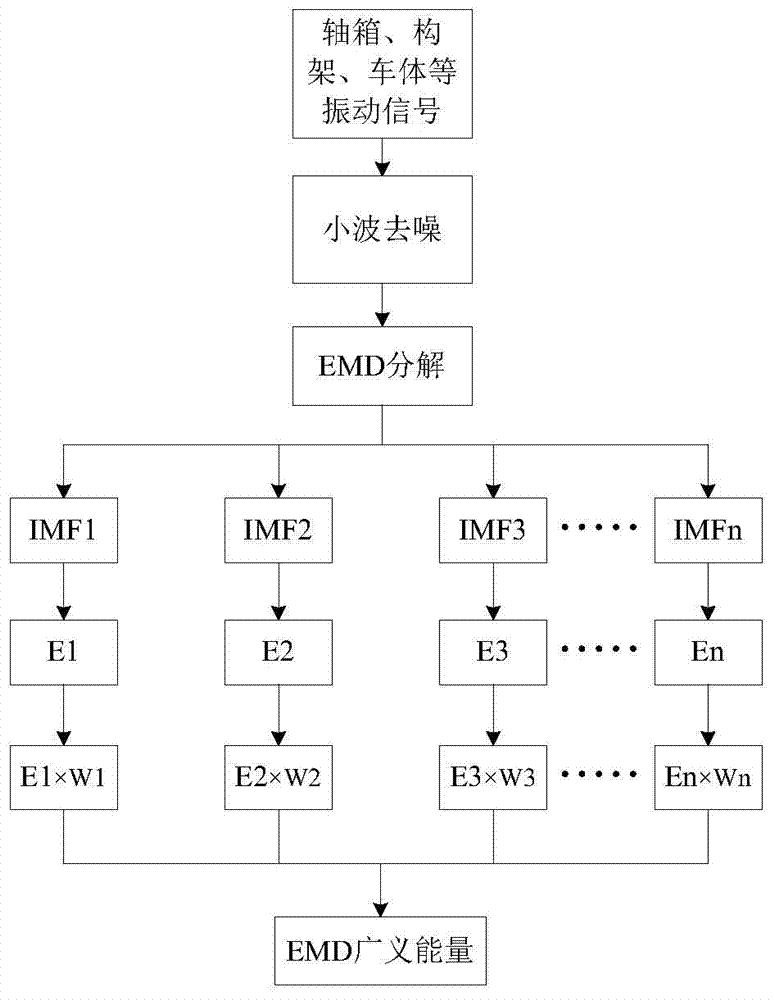
EMD generalized energy-based wheeltrack vibration signal fault feature extraction method
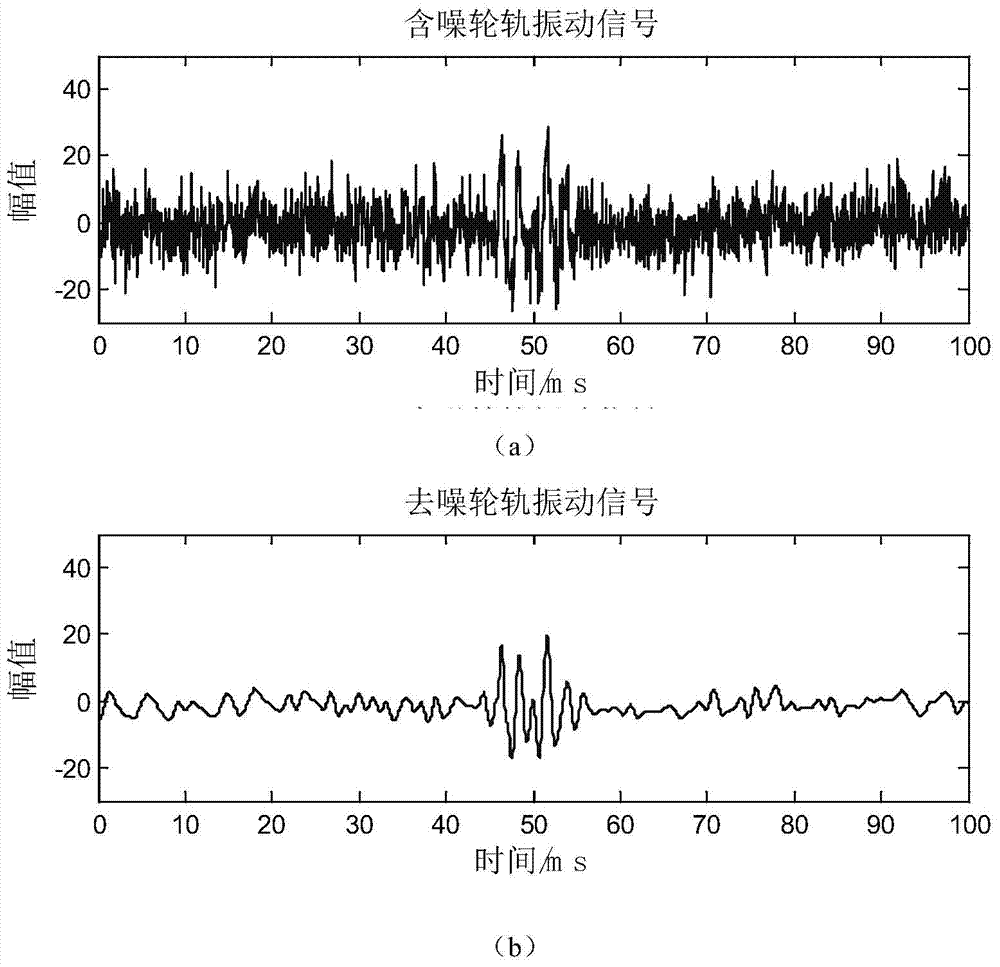
InactiveCN104776908ALow costGeneralized energy calculation is smallSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementComplex mathematical operationsWavelet denoisingVibration acceleration
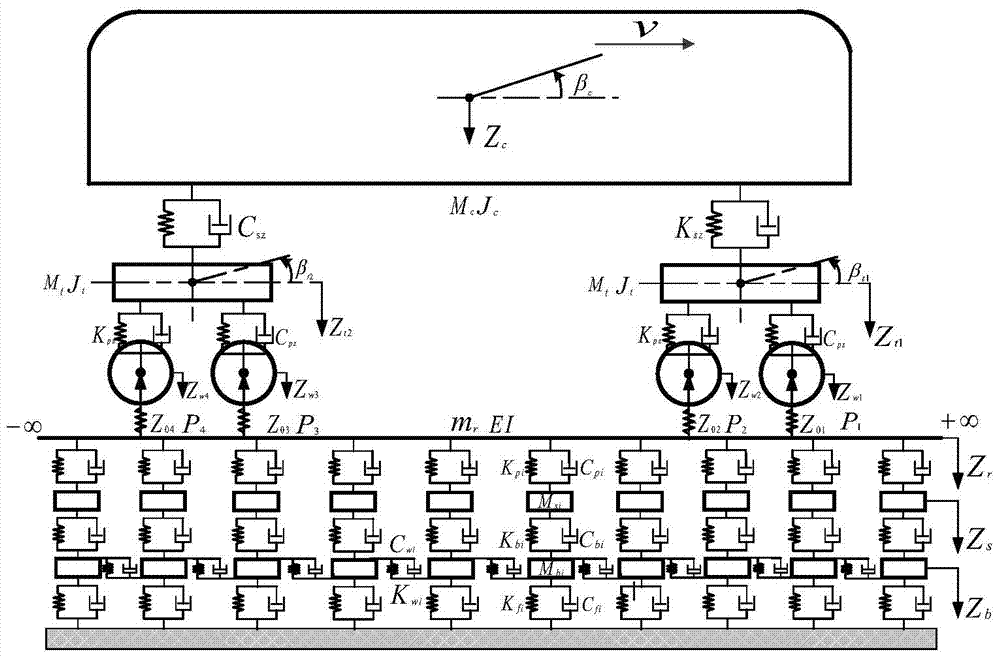
The invention discloses an EMD generalized energy-based wheeltrack vibration signal fault feature extraction method which comprises the following steps: collecting a vibration acceleration signal of a real-time running train, integrating the train speed to determine the starting and stopping moments corresponding to one revolution of the wheel, and intercepting the acceleration signal of corresponding time history by using the starting and stopping moments; carrying out wavelet decomposition, threshold processing of each layer of wavelet coefficient and wavelet reconstruction on the collected vibration acceleration signal to realize wavelet denoising; carrying out empirical mode decomposition on the obtained axle box vibration acceleration signal to obtain a series of intrinsic mode functions; finally determining the energy weight coefficient by combining the vibration acceleration signal under fault excitation simulated by a vehicle track coupling kinetic model, calculating the empirical mode decomposition generalized energy and determining the fault feature according to the value. The EMD generalized energy-based wheeltrack vibration signal fault feature extraction method has the advantages of being low in cost, and high in feature extraction resolution ratio and real-time performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
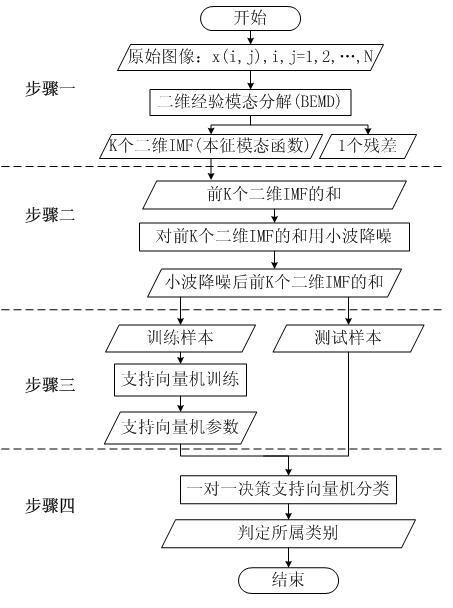
Multi-group image classification method based on two-dimensional empirical modal decomposition and wavelet denoising
ActiveCN101847210AEliminate noise interferenceImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionWavelet denoisingImaging processing
The invention relates to a multi-group image classification method based on two-dimensional empirical modal decomposition and wavelet denoising, belonging to the filed of image processing. The invention aims at solving the problems of insufficient utilization of image essential characteristics and low classification precision of the traditional classification method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, respectively carrying out two-dimensional empirical modal decomposition on each wave band in multi-group images to obtain the former K two-dimensional components and one residual error; secondly, summarizing the former K two-dimensional components as a characteristic value, and obtaining a denoised characteristic value after wavelet denoising; thirdly, randomly and proportionally selecting the denoised characteristic values of a plurality of multi-group images as training samples and test samples of a support vector machine, carrying out parameter training of the support vector machine on the training samples, and then carrying out attribution judgment to form a plurality of sub-classifiers of the support vector machine; and fourthly, constructing multiple classifiers based on a one-to-one strategy by utilizing the sub-classifiers of the support vector machine, and determining the attribution classes of the test samples according to a strategy function to complete the classification of the multi-group images.
Owner:哈尔滨工大正元信息技术有限公司
Load curve parallel clustering method based on big data of electric power
ActiveCN104063480AImprove the speed of clusteringImprove load clustering efficiencyRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmElectricity
The invention discloses a load curve parallel clustering method based on big data of electric power. Wavelet denoising is performed on all load curves through a dbN wavelet system in order to reduce effect of small fluctuation in the curves on clustering results, a K means clustering algorithm based on the multi-core parallel technology is adopted to perform load curve clustering, the clustering results with obvious features are screened out, and load curve classification is obtained through confluence analysis. By means of the load curve parallel clustering method based on big data of electric power, the parallel clustering algorithm of a great number of the load curves is achieved, clustering speed of the load curves is increased effectively, and a foundation is laid for load and electricity quantity predication.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method for predicting remaining service life of lithium battery based on wavelet denoising and relevant vector machine
ActiveCN104459560AImprove forecast accuracyMathematical modelsElectrical testingWavelet denoisingHealth condition
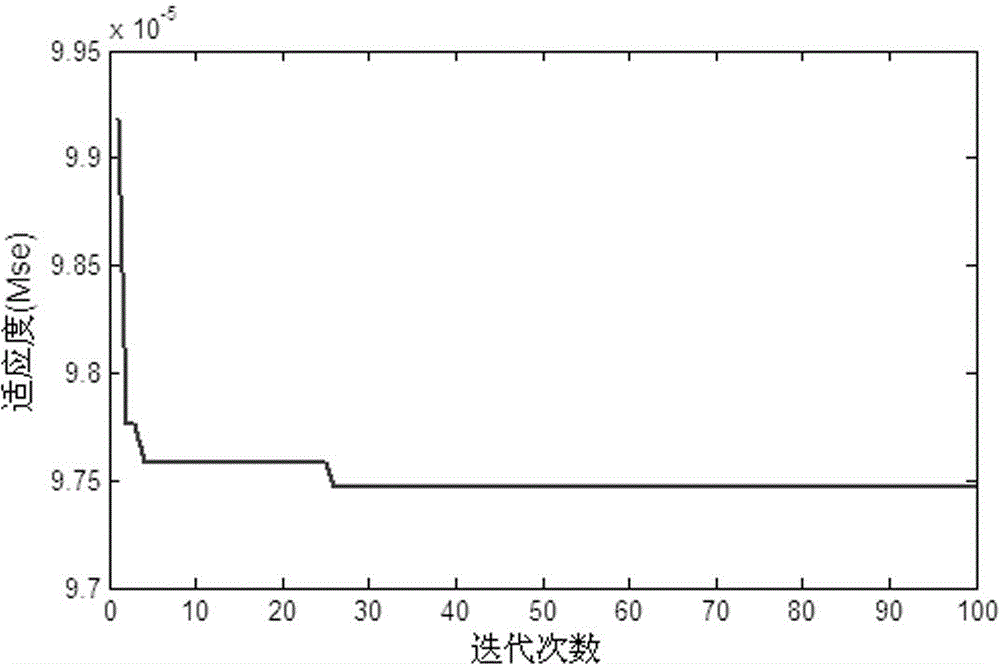
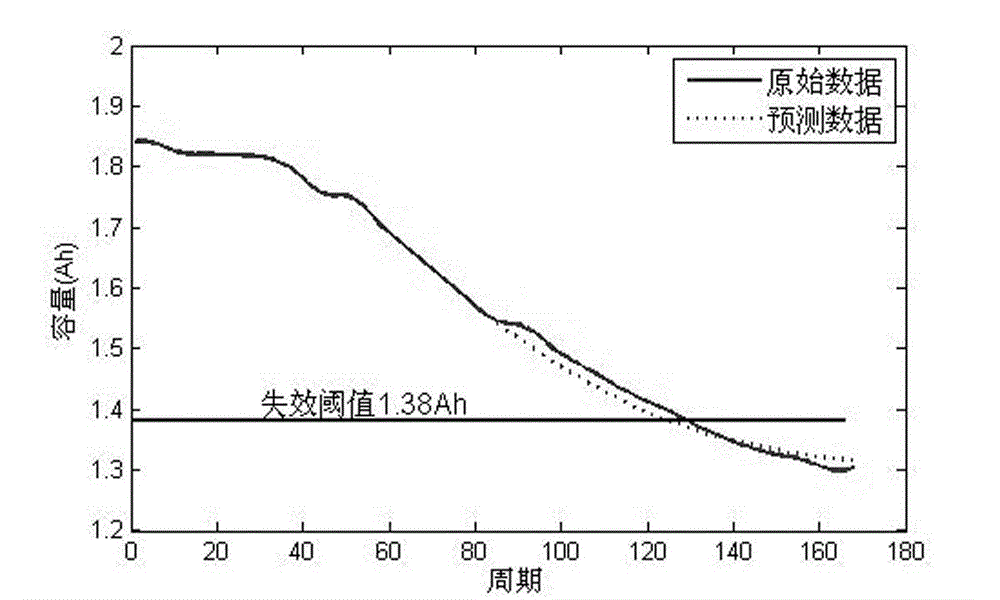
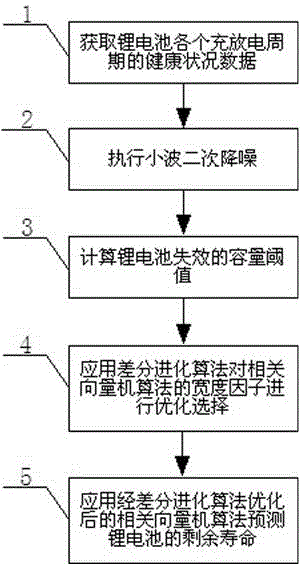
The invention provides a method for predicting the remaining service life of a lithium battery based on wavelet denoising and a relevant vector machine and relates to a method for estimating the health condition of the lithium battery and predicting the remaining service life of the lithium battery. The method comprises the following steps of measuring health condition data of the lithium battery along with charging and discharging periods, carrying out secondary wavelet denoising on measured lithium battery capacity data; calculating a capacity threshold that lithium battery loses effect; carrying out optimization selection on a width factor of a relevant vector machine algorithm through a differential evolutionary algorithm based on a lithium battery capacity data sequence and a charging and discharging period data sequence; predicting the remaining service life of the lithium battery through the relevant vector machine algorithm optimized by the differential evolutionary algorithm. The method for predicting the remaining service life of the lithium battery based on wavelet denoising and the relevant vector machine is easy to operate and effective, and the remaining service life of the lithium battery can be accurately predicted.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on SIFT-KPCA and SVM
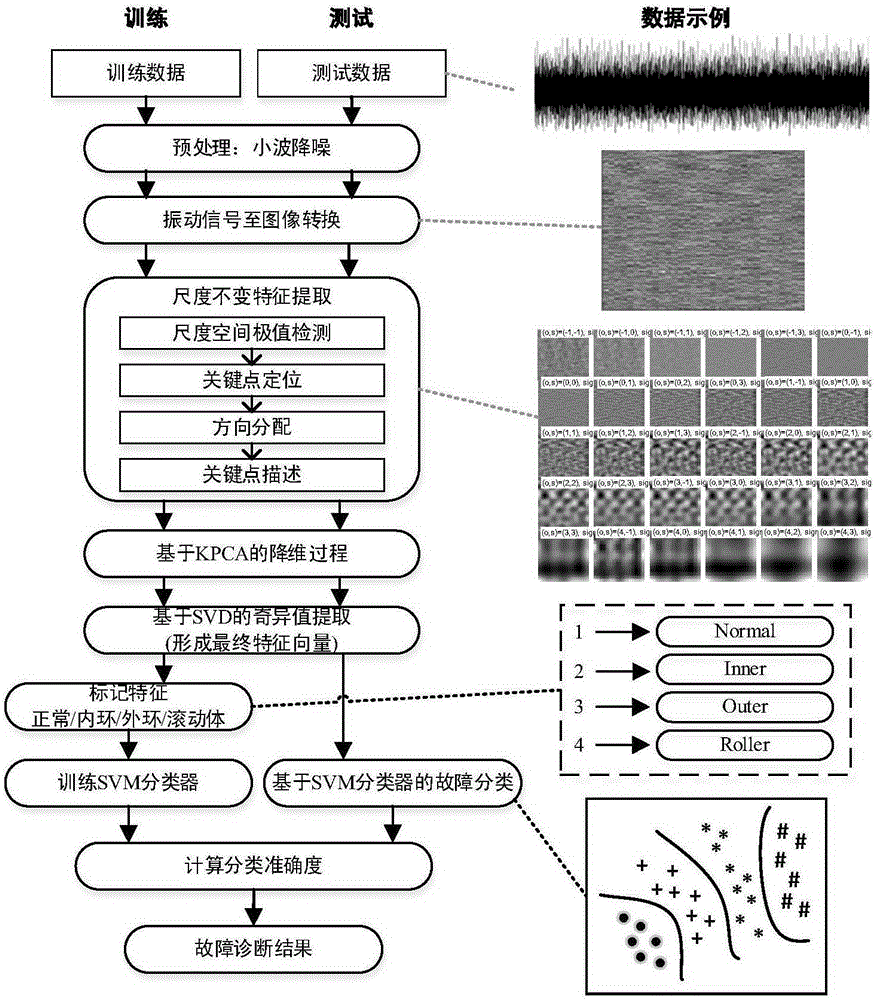
InactiveCN105181110AImprove robustnessSmall amount of calculationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMachine bearings testingFeature vectorWavelet denoising
The invention provides a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on SIFT-KPCA and SVM. The rolling bearing fault diagnosis method comprises the steps of: firstly, converting vibration signals into a two-dimensional image, and utilizing wavelet denoising to reduce interference of noise on feature extraction before the conversion; secondly, extracting scale-invariant feature vectors of the two-dimensional image by adopting an SIFT algorithm to obtain a 128-dimensional feature matrix, and achieving dimension reduction of the feature vectors by adopting a KPCA algorithm; thirdly, and extracting singular values of the simplified feature vectors, and inputting the singular values into an SVM classifier to achieve fault classification finally. The rolling bearing fault diagnosis method has high classification accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
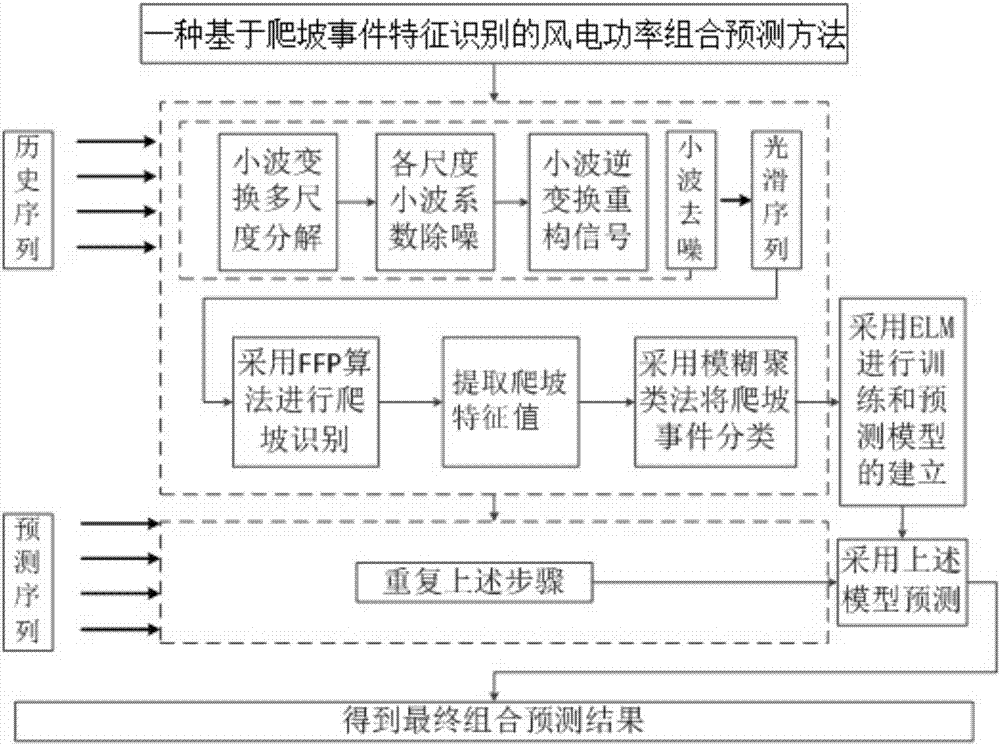
Fluctuation feature identification-based wind power combination prediction method
InactiveCN106933778AImprove forecast accuracyAdaptableForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityPeaking power plant
The invention discloses a fluctuation feature identification-based wind power combination prediction method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, processing historical wind speed and power data of a wind power plant by utilizing a wavelet denoising method to obtain smooth curves; 2, performing fluctuation feature identification and extraction on the obtained curves by adopting a compression algorithm; 3, classifying eigenvalues of fluctuations of wind power obtained in the step 2 by utilizing a fuzzy clustering method; 4, training different fluctuation types by utilizing a statistical method and building a prediction model; 5, performing the steps 1-2 on real-time wind speed test data and real-time power test data of the wind power plant, and extracting eigenvalues of fluctuations of the real-time wind speed and power test data; and 6, classifying the extracted eigenvalues of the fluctuations of the real-time wind speed and power test data by utilizing the prediction model obtained in the step 4, and performing prediction by utilizing the prediction model, thereby obtaining a final combination prediction result finally.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
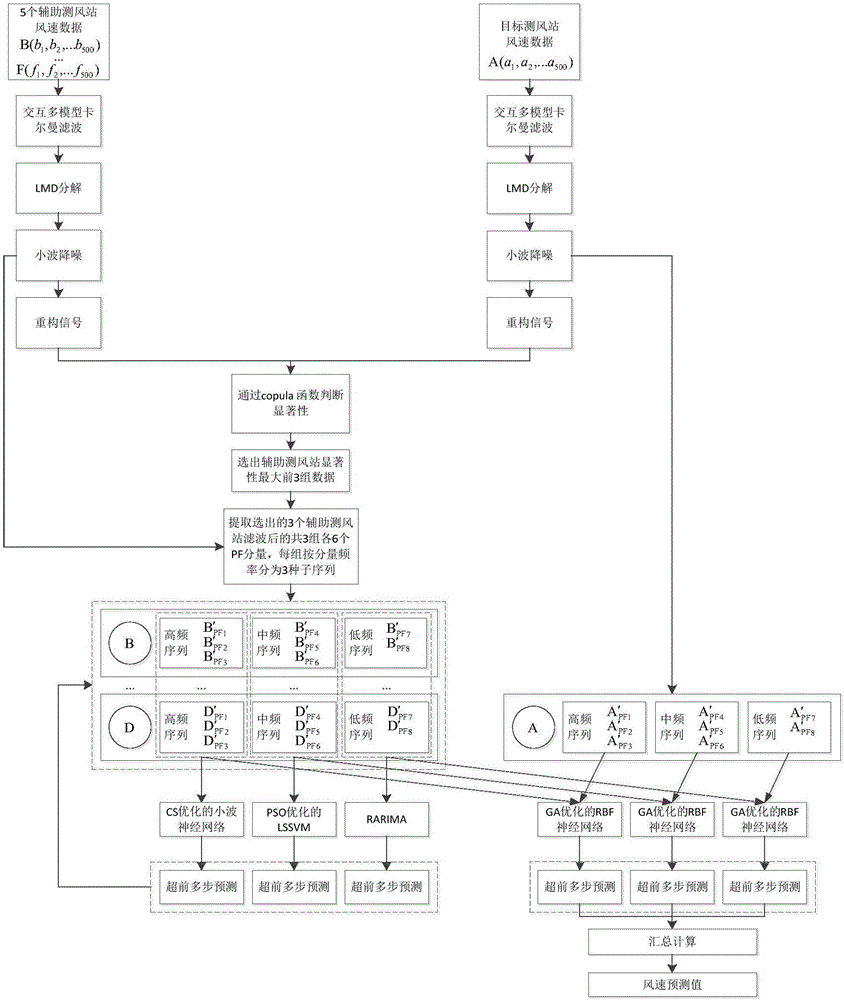
Multipoint multilayer coupling prediction method for wind speed along high-speed railway
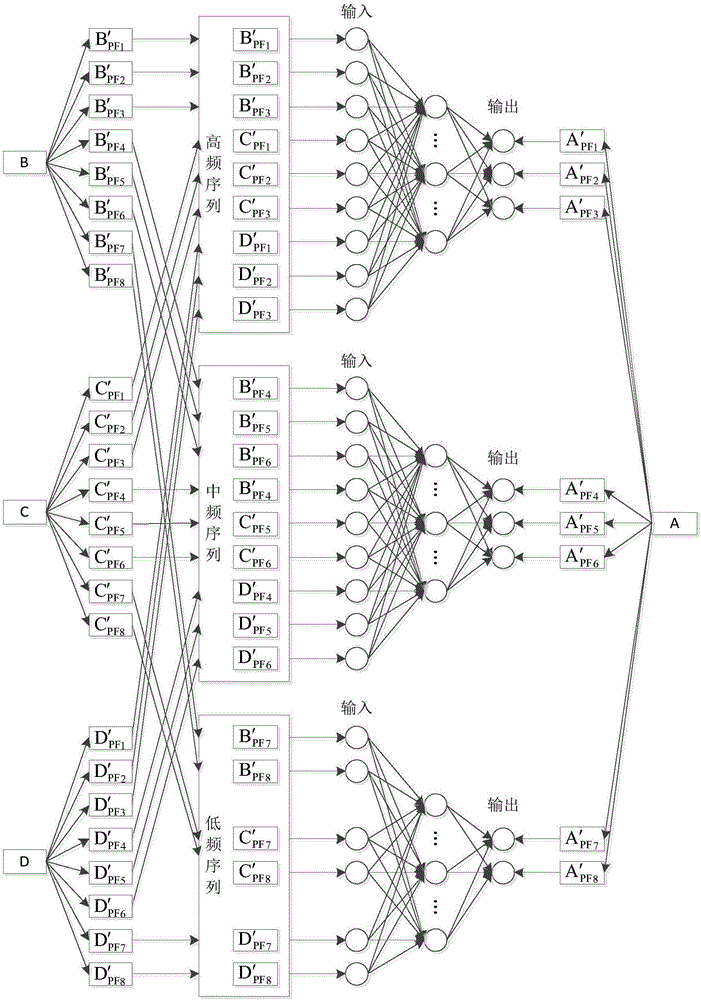
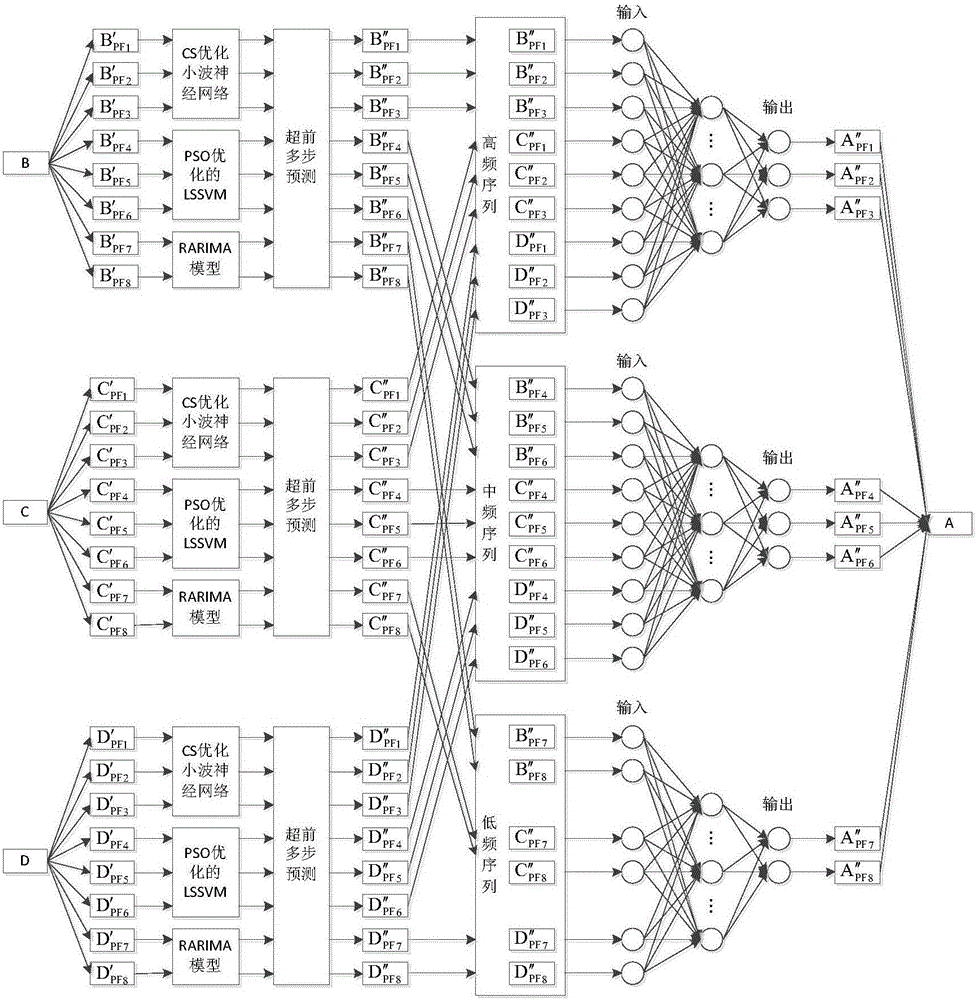
ActiveCN106779151AHigh wind speed signal correlationForecastingNeural learning methodsWavelet denoisingPredictive methods
The invention discloses a multipoint multilayer coupling prediction method for wind speed along a high-speed railway. The method comprises the steps that 1, five auxiliary wind-measuring stations are installed around a target wind-measuring station; 2, after original wind speed data is filtered and disintegrated, wavelet denoising is performed; 3, signals are summated and reconstructed; 4, m auxiliary wind-measuring stations with high significance relative to the target wind-measuring station are selected; 5, prediction models are established for all PF components of subsequences of all frequency layers of the selected auxiliary wind-measuring stations; 6, the PF components of all the frequency layers of the m selected auxiliary wind-measuring stations are used as input, PF components of all frequency layers of the target wind-measuring station are used as output, and a GA-optimized RBF neural network is adopted to perform training; and 7, ahead multistep predicted values of the m auxiliary wind-measuring stations are utilized to obtain an ahead multistep wind speed predicted value of the target wind-measuring station. Through the method, the wind speed along the railway can be subjected to high-precision ahead multistep prediction to be used for effectively dispatching and commanding a train in a strong wind environment of the high-speed railway, and data interruption caused by a hardware fault of a single wind-measuring station can be avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Statistical model based bridge health monitoring data wavelet denoising method
InactiveCN104881567AEasy to handleImprove denoising abilitySpecial data processing applicationsWavelet denoisingAlgorithm
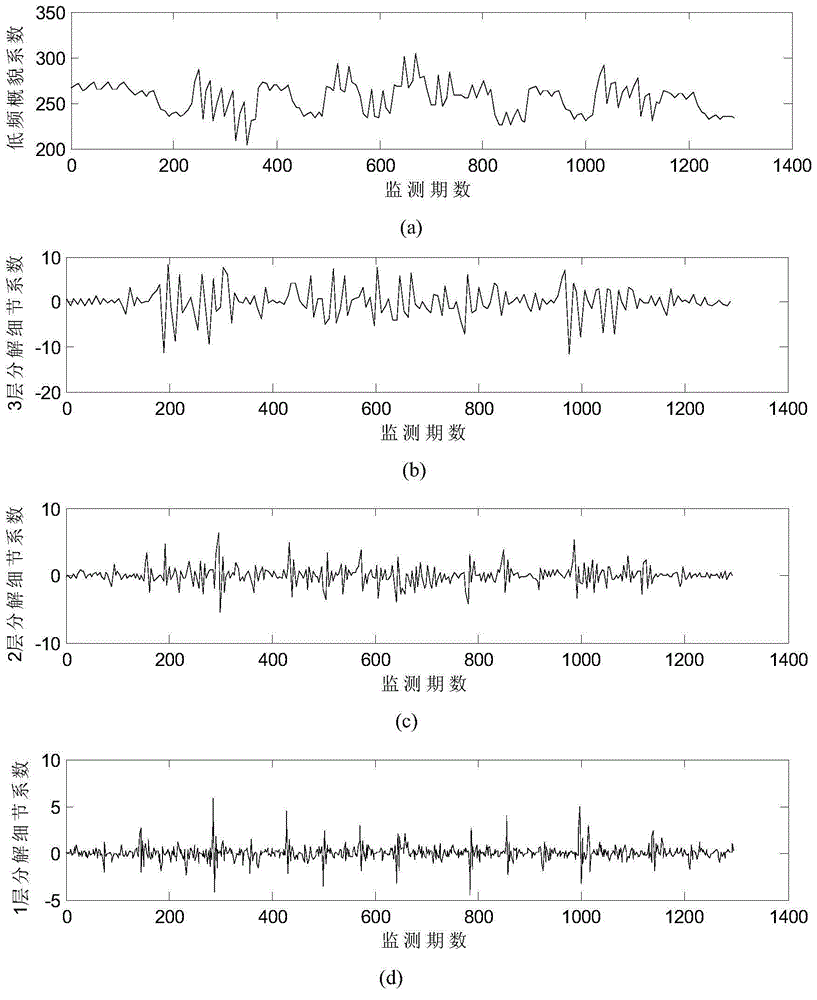
The invention relates to a statistical model based bridge health monitoring data wavelet denoising method. The method includes the following steps: firstly, establishing a bridge monitoring signal model; secondly, subjecting an obtained structure monitoring signal to wavelet decomposition to obtain two frequency domains, namely a low frequency domain A1 and a high frequency domain D1, continuing performing wavelet decomposition on the low frequency domain A1 to obtain two frequency domains, namely a low frequency domain A2 and a high frequency domain D2, and repeating the step till maximum layers are decomposed; thirdly, subjecting the actual monitoring signal to wavelet decomposition and establishing a statistical model of wavelet decomposition coefficients; fourthly, deducing a wavelet threshold contracting function and subjecting the wavelet coefficients of a high-frequency part (Dj,j=1,2,...J) of each layer to thresholding method contracting processing; fifthly, performing wavelet inverse transformation processing to obtain denoised bridge structure monitoring data. Denoising is performed effectively, quality of the monitoring data is improved, and signal smoothness is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Distributed optical fiber Raman temperature measurement system
ActiveCN103115693ARealize wavelet denoisingProcessing speedThermometers using physical/chemical changesWavelet denoisingPulsed laser device
The invention relates to the field of distributed optical fiber temperature measurement systems, and discloses a distributed optical fiber Raman temperature measurement system. The system comprises a pulse laser device, a wavelength division multiplexer, a sensor optical fiber, a double-channel avalanche photodiode, and a digital signal processor (DSP). The whole optical fiber laser device emits pulse lasers, the pulse lasers enter into a to-be-tested sensor optical fiber after passing through the wavelength division multiplexer, the pulse lasers continuously generate backscattering inside the optical fiber in the spreading process, and then backscattering light returns back to the wavelength division multiplexer, after the backscattering light passes through the wavelength division multiplexer, Stokes scattering light and anti-Stokes Raman scattering light are respectively filtered out and enter the double-channel avalanche photodiode to be conducted photovoltaic conversion, and after an electrical signal of the double-channel avalanche photodiode is processes by the DSP, a temperature signal is obtained. The high-speed DSP is used for achieving wavelet denoising, and therefore processing speed is quick, and real time performance of temperature measurement is not influenced on the premise that precision is guaranteed.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Identification method of various partial discharge source types in gas insulated substation (GIS)
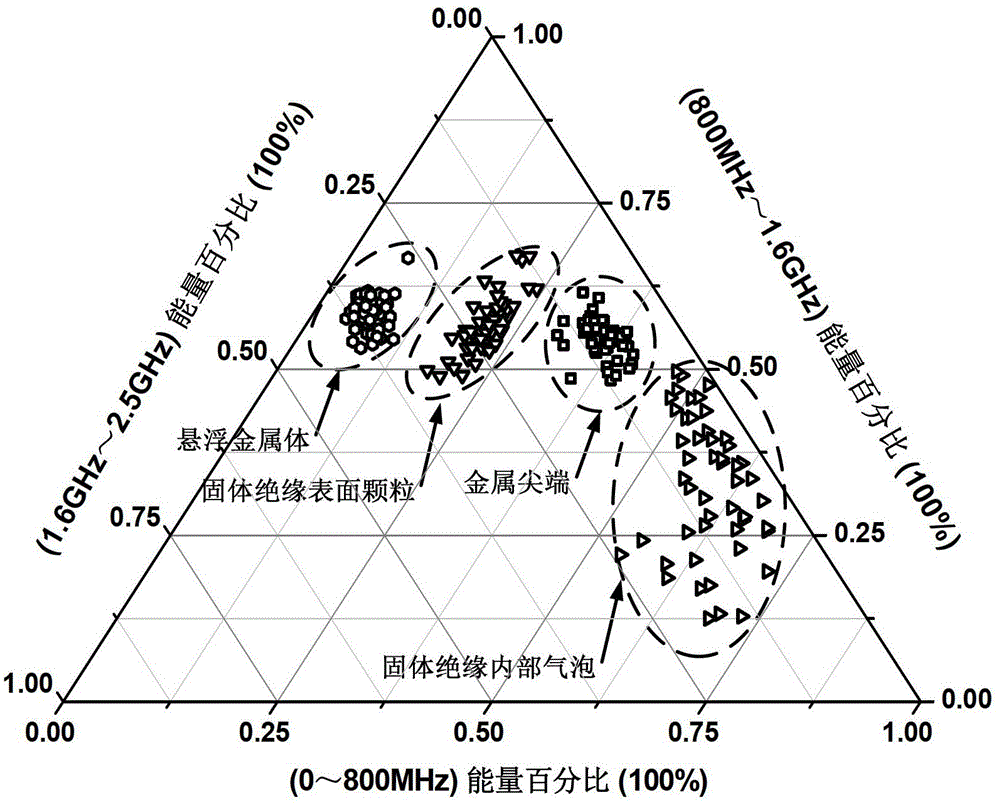
ActiveCN103336226AAccurate extractionShorten the timeTesting dielectric strengthFrequency spectrumWavelet denoising
The invention relates to an identification method of various partial discharge source types in a gas insulated substation (GIS), and belongs to the electrical equipment technology field. In the method, a data acquisition card with a high sampling rate and a long record length is utilized to record long time partial discharge signals; a wavelet denoising method is used for a noise reduction treatment of the partial discharge signals, and then the discharge signals are extracted to obtain a frequency spectrum energy distribution of the discharge signals; and finally, a support vector machine is used to distinguish discharge types to realize the partial discharge source identification in the GIS. The method of the invention utilizes the acquisition card with the long record depth and the high sampling rate, so that the identification time for different discharge sources is reduced; according to an ultrahigh frequency signal energy ratio, a least square support vector machine is trained; according to an ultrahigh frequency signal in the long time record data, various discharge source types are identified; and the accuracy of the discharge source identification is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Image denoising method
InactiveCN105528768AHighlight desired characteristicsGuarantee authenticityImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingWavelet denoising
The present invention discloses an image denoising method. For an image with a pulse noise and a Gaussian noise, through detecting and separating a pulse noise point, a pixel which is polluted by the pulse noise is subjected to median filter processing in a spatial domain, then a processed image is converted into a wavelet domain, and a wavelet denoising method is employed to remove the Gaussian noise in the image. By using the method, the pulse noise and the Gaussian noise in the image can be effectively removed, the authenticity of image transmission is ensured, the signal to noise ratio is raised, and the desired characteristic of the image is highlighted.
Owner:国网四川省电力公司天府新区供电公司 +1
Method for processing fibber Bragg grating (FBG) signals based on translation invariant wavelet
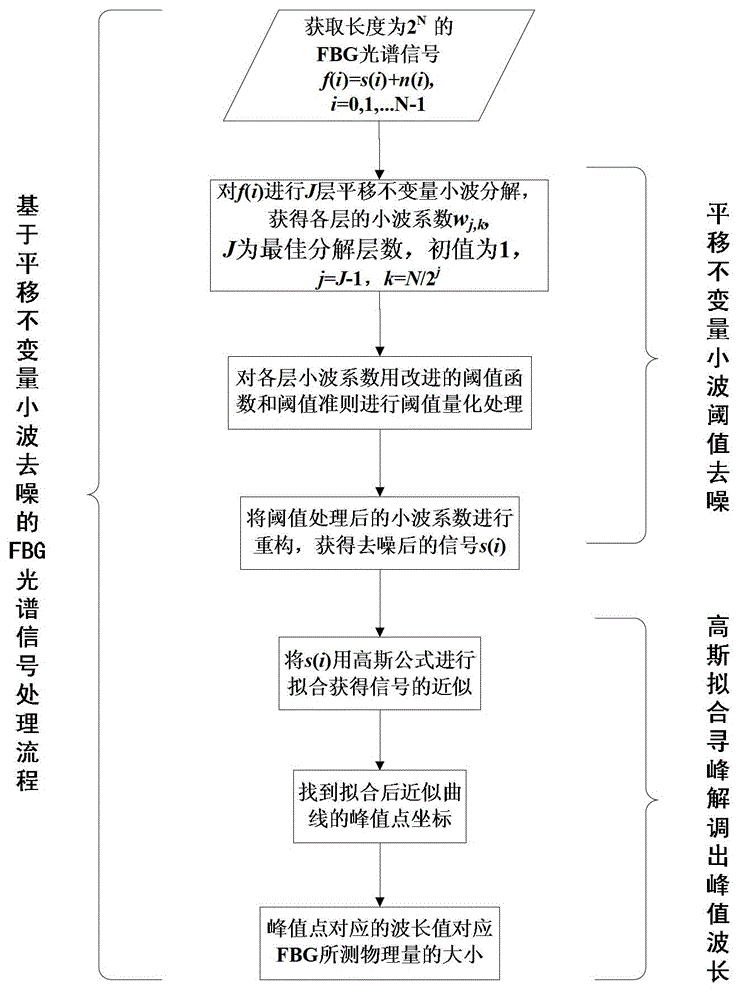
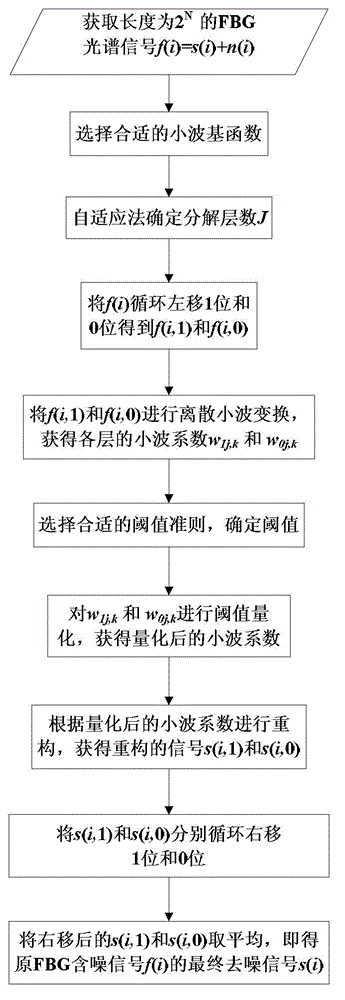
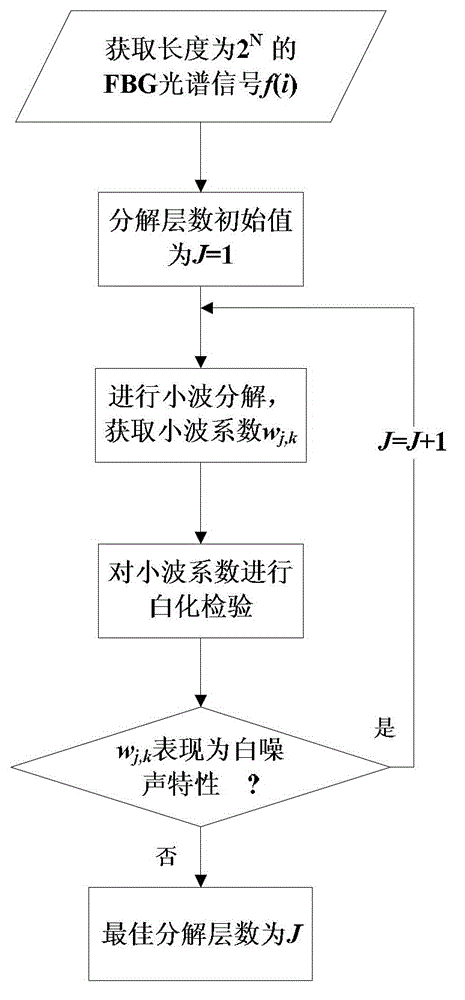
ActiveCN102944252AImprove demodulation accuracyOvercoming constant biasConverting sensor output opticallyGratingWavelet denoising
The invention relates to a method for processing FBG signals based on a translation invariant wavelet of an improved threshold value. The method includes providing an improved threshold function and combining the threshold function with the translation invariant wavelet to denoise the FBG noisy signals; and fitting denoised FBG spectral signals through a Gaussian fitting formula so as to position the peak wavelength. The wavelet denoising portion mainly includes performing cycle spinning on the FBG noisy signals, performing discrete wavelet decomposition on the spun signals to extract the wavelet coefficient in each layer, performing threshold value quantization on the wavelet coefficients by using improved threshold function, reconstructing the wavelet coefficients after the threshold value quantization, performing reverse cycle spinning on the reconstructed signals, and averaging the reconstructed signals at different spinning positions to obtain the final denoised signals. A Gaussian fitting peak searching algorithm mainly includes fitting the denooised signals through the Gaussian formula and obtaining the wavelength corresponding to the peak to finish demodulation of the FBG spectral signals.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Hyper spectral image classification method based on wavelet threshold denoising and empirical mode decomposition
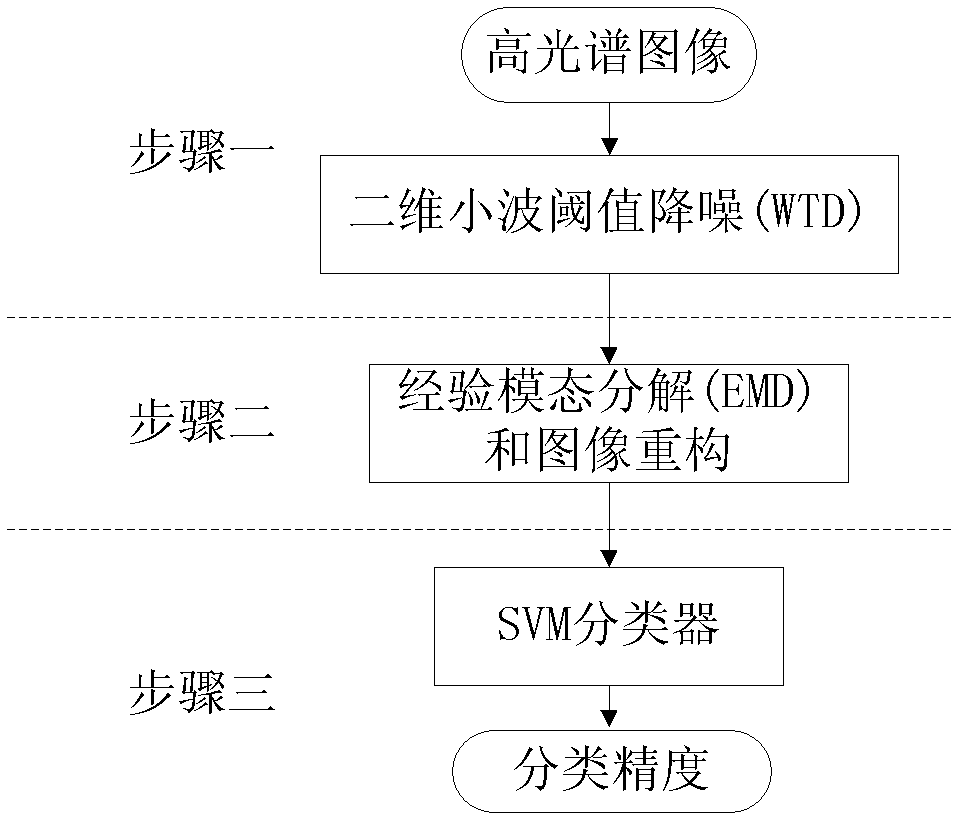
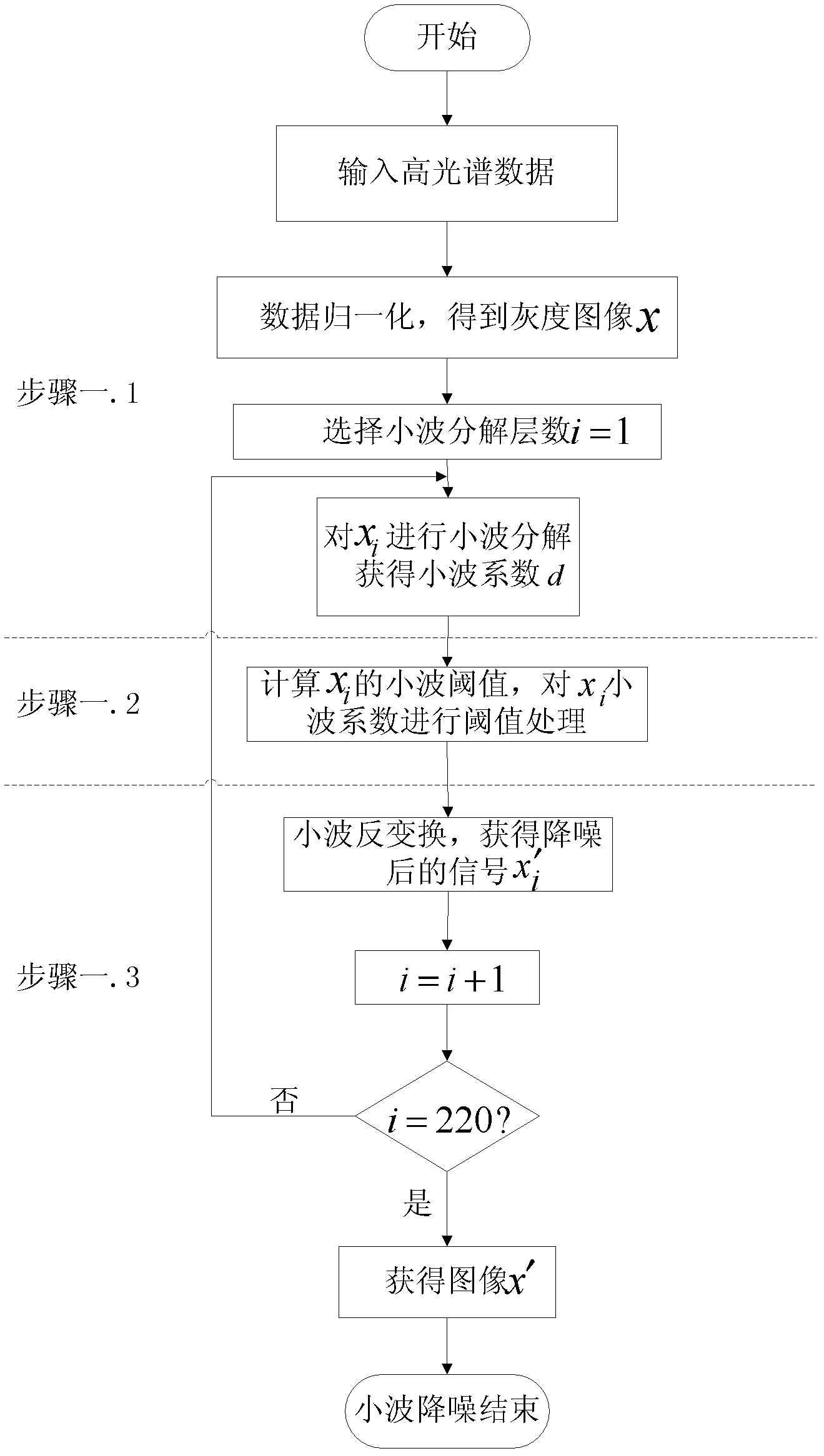
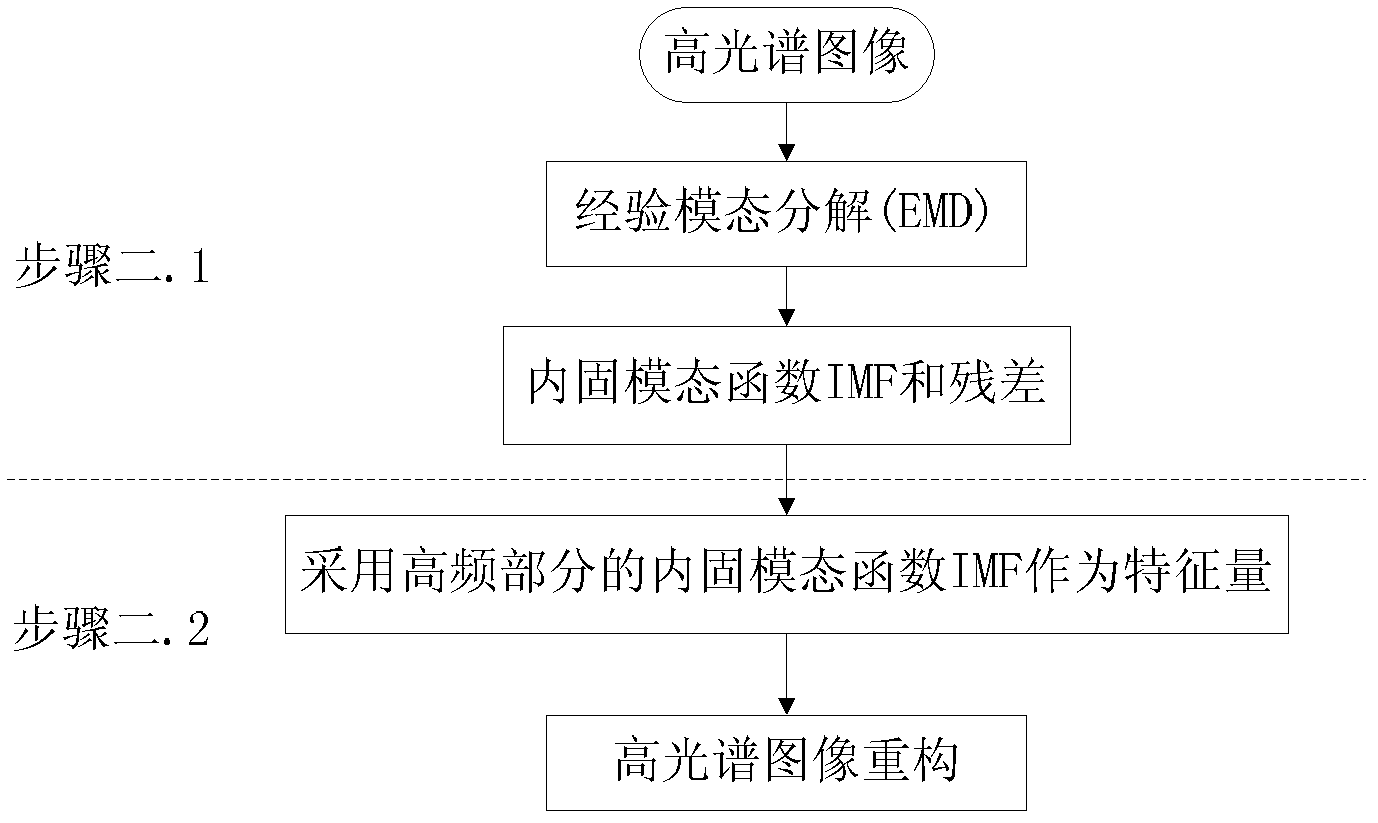
ActiveCN102436586AHigh precisionReduce the amount of redundant informationCharacter and pattern recognitionWavelet denoisingDecomposition
A hyper spectral image classification method based on wavelet threshold denoising and empirical mode decomposition relates to a hyper spectral image classification method in a remote sensing field. In the traditional method, the wavelet is not suitable for a non-linear and non-stationarity hyper spectral image, a first intrinsic mode function decomposed by using an empirical mode decomposition method has a loud noise and acquired classification result precision is not high. By using the method of the invention, the above problems can be solved. The method comprises the following steps: step 1. performing two-dimensional wavelet threshold denoising of the hyper spectral image; step 2. carrying out empirical mode decomposition and image reconstruction to the hyper spectral image which is performed with wavelet denoising; step 3. using a SVW classifier to classify the hyper spectral reconstruction image nIMFs so as to obtain the classification precision. The method can be used in the classification of the hyper spectral image.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
High-precision optical fiber strain low-frequency sensing demodulation method based on wavelet cross-correlation technology
ActiveCN103940363AImprove wavelength demodulation accuracyEliminate non-stationary noiseUsing optical meansWavelet denoisingGrating
The invention discloses a high-precision optical fiber strain low-frequency sensing demodulation method based on a wavelet cross-correlation technology. The high-precision optical fiber strain low-frequency sensing demodulation method comprises the steps data are preprocessed, wherein wavelet denoising processing is conducted on a reference fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum and a sensing fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum, and zero setting processing is conducted on data outside the bandwidth of the denoised reference fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum and the bandwidth of the denoised sensing fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum, so that the preprocessed reference fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum and the preprocessed sensing fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum are obtained; wavelet domain cross-correlation is conducted, wherein a wavelet domain cross-correlation value of the preprocessed reference fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum and the preprocessed sensing fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum is calculated; peak value detection is carried out, wherein the peak value position of the wavelet domain cross-correlation value is obtained, and the external strain value corresponding to the sensing fiber bragg grating reflectance spectrum is obtained according to the peak value position.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modulation signal identification method based on wavelet transform and convolutional long short-term memory neural network
PendingCN112418014ASuppress high frequency noiseEffective classificationModulation type identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionWavelet denoisingData set
The invention discloses a modulation signal identification method based on wavelet transform and a convolutional long short-term memory neural network, and the method comprises the steps: firstly obtaining a wireless continuous time signal in advance through a wireless communication system, and forming a data set; secondly, filtering the noisy signal by selecting a reasonable threshold value, andthen reconstructing a wavelet coefficient obtained after processing by utilizing inverse wavelet transform to recover an effective signal; finally, executing the signal feature extraction capability of the convolutional neural network and combining with the memorability of the long short-term memory network, fully learning global features and effectively classifying signal samples with time sequence. A wavelet denoising preprocessing technology is used for suppressing high-frequency noise of an input signal, a convolutional long-term and short-term memory neural network is constructed, globalfeatures are fully learned, and then signal samples with time sequence are more effectively classified; recognition accuracy under a complex environment is improved. therefore, the invention is a modulation identification method suitable for a real channel environment.
Owner:南京信息工程大学滨江学院
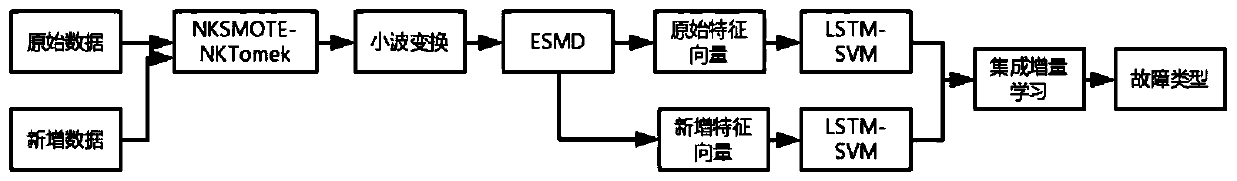
Equipment fault classification method based on dynamic weight combination of integrated increment
PendingCN110334580ASmall sample sizeImprove sampling efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesShort-term memoryWavelet denoising
The invention discloses an equipment fault classification method based on dynamic weight combination of integrated increment, and relates to an equipment fault diagnosis technology. The method is mainly divided into the following parts: performing unbalanced data processing, performing wavelet denoising and reconstruction, performing feature extraction through empirical mode decomposition, building a long-short-term memory neural network, building a support vector machine model, using a support vector machine for dynamically adjusting the weight of each classifier in the long-short-term memoryneural network and support vector machine combined model, and using an integrated incremental model for realizing rapid dynamic incremental learning. Based on the research, the dynamic weight combination classification model based on the integration increment is finally provided and applied to rolling bearing equipment fault diagnosis, and the classification accuracy of equipment fault diagnosisis improved.
Owner:天津开发区精诺瀚海数据科技有限公司
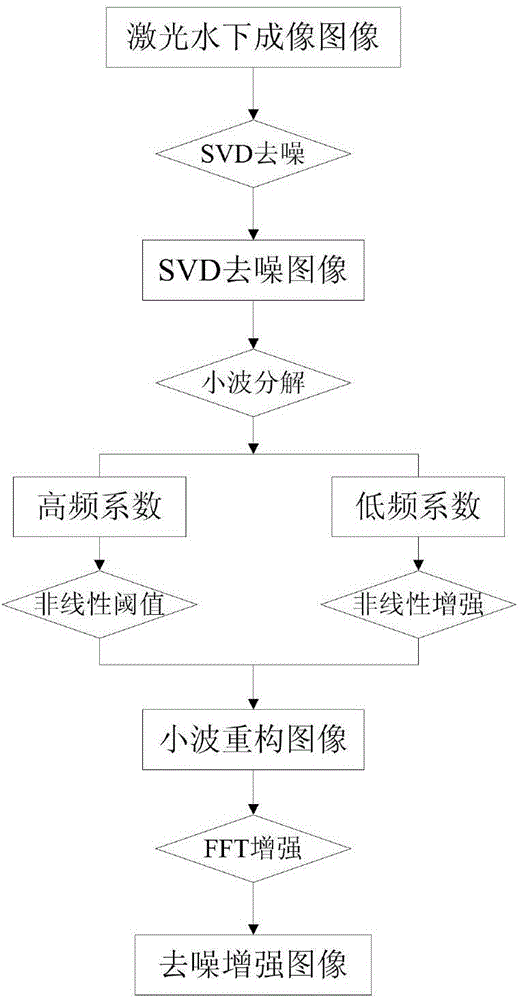
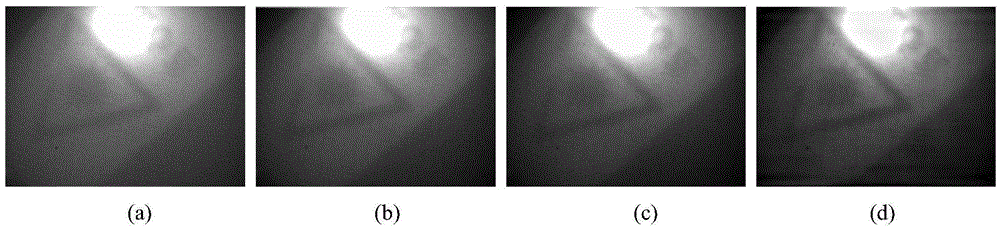
Laser underwater imaged image denoising and enhancing method for ocean exploration
ActiveCN104657948AAvoid block effectIncrease contrastImage enhancementSingular value decompositionWavelet denoising
The invention provides a laser underwater imaged image denoising and enhancing method for ocean exploration, and belongs to the field of image processing and pattern recognition. The core of the method is that at first, noise processing is performed on a laser underwater imaged image by applying SVD (singular value decomposition) and reconstruction in an airspace; then, aiming at the problem that the image has a little noise after SVD processing, wavelet decomposition and reconstruction are performed on the image in a wavelet domain to realize the purpose of wavelet denoising and enhancing; at last, FFT enhancing is performed on the image in a frequency domain to improve the image contrast and effectively keep the image resolution. Experiments show that the method can overcome a blocking effect due to equalization of local histogram equalization, and the image noise is effectively inhibited and the image resolution is kept under the premise that the image enhancement is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and system for multi-talker babble noise reduction
ActiveUS20180012614A1Improve intelligibilityReduce noiseElectrotherapySpeech analysisWavelet denoisingNoise reduction
A system and method for improving intelligibility of speech is provided. The system and method may include obtaining an input audio signal frame, classifying the input audio signal frame into a first category or a second category, wherein the first category corresponds to the noise being stronger than the speech signal, and the second category corresponds to the speech signal being stronger than the noise, decomposing the input audio signal frame into a plurality of sub-band components; de-noising each sub-band component of the input audio signal frame in parallel by applying a first wavelet de-noising method including a first wavelet transform and a predetermined threshold for the sub-band component, and a second wavelet de-noising method including a second wavelet transform and the predetermined threshold for the sub-band component, wherein the predetermined threshold for each sub-band component is based on at least one previous noise-dominant signal frame received by the receiving arrangement.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Non-contact real-time heart rate measurement method based on video image
InactiveCN107506716AReal-timeMaximum optimizationCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePattern recognitionWavelet denoising
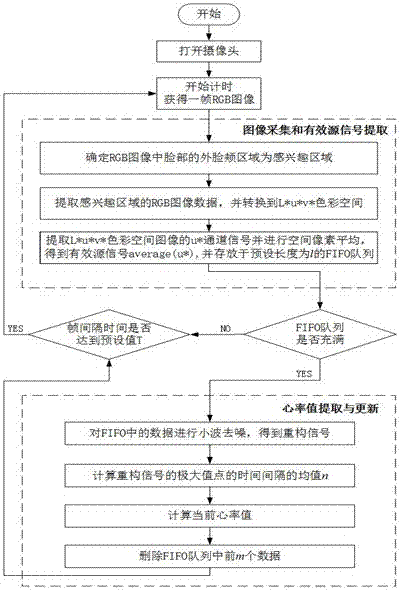
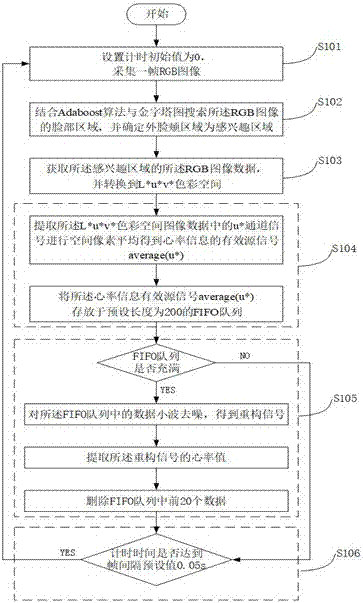
The invention discloses a non-contact real-time heart rate measurement method based on a video image. The method comprises the following steps: starting timing and obtaining a frame of RGB image; determining an outer cheek area of the face portion in the RGB image as an area of interest; extracting RGB image data in the area of interest, and converting the data into an L*u*v *color space; extracting a u* channel signal and carrying out space pixel average to obtain an effective source signal average (u*), and storing the effective source signal to an FIFO queue, the preset length of which is l; judging whether the FIFO queue is full; if so, carrying out wavelet denoising on the data in the FIFO queue to obtain re-constructed signals; calculating a time interval mean value n of maximum value points of the re-constructed signals; calculating a current heart rate value, and deleting the front m data in the FIFO queue; judging whether frame interval time reaches a preset value T; and if so, collecting the next frame of image for the same operation, and if not, keeping waiting till meeting the preset conditions, and then, repeating the steps above till finishing measurement. The method realizes noninvasive and real-time detection of heart rate, and has the advantages of low cost and high precision and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
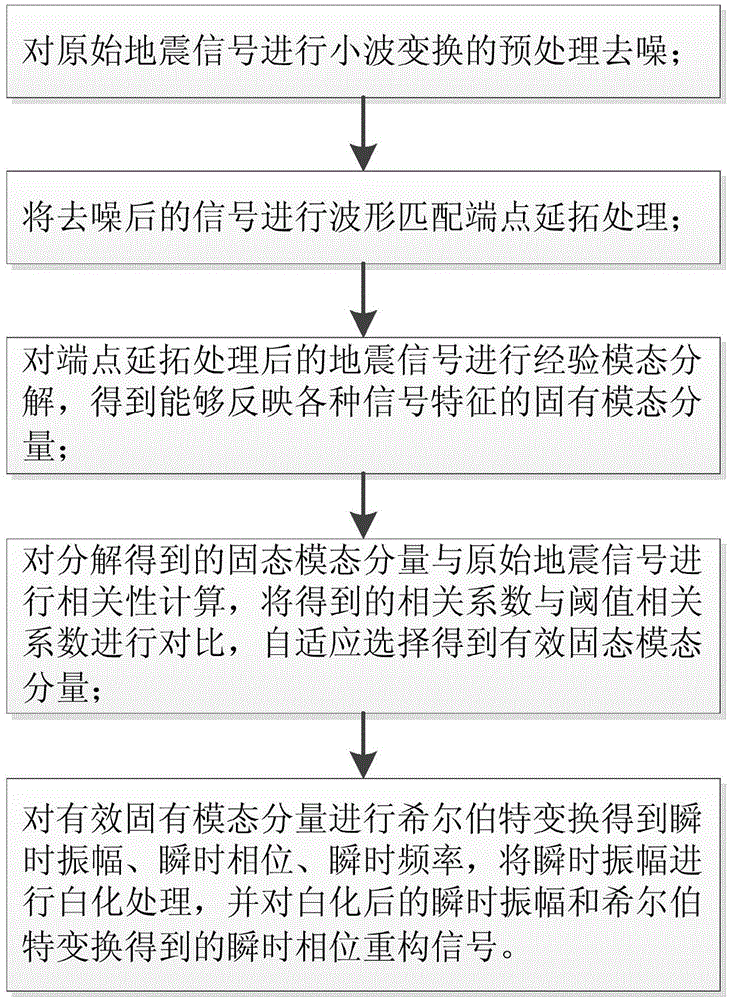
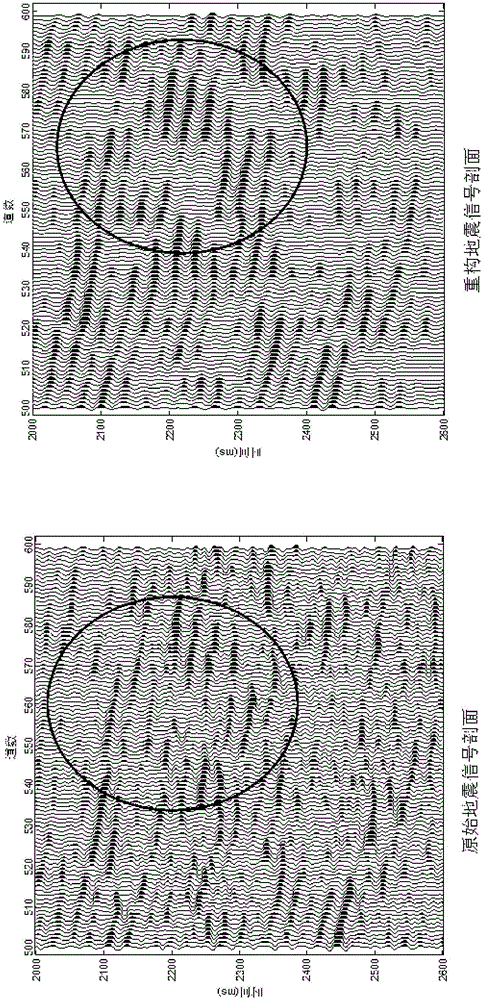
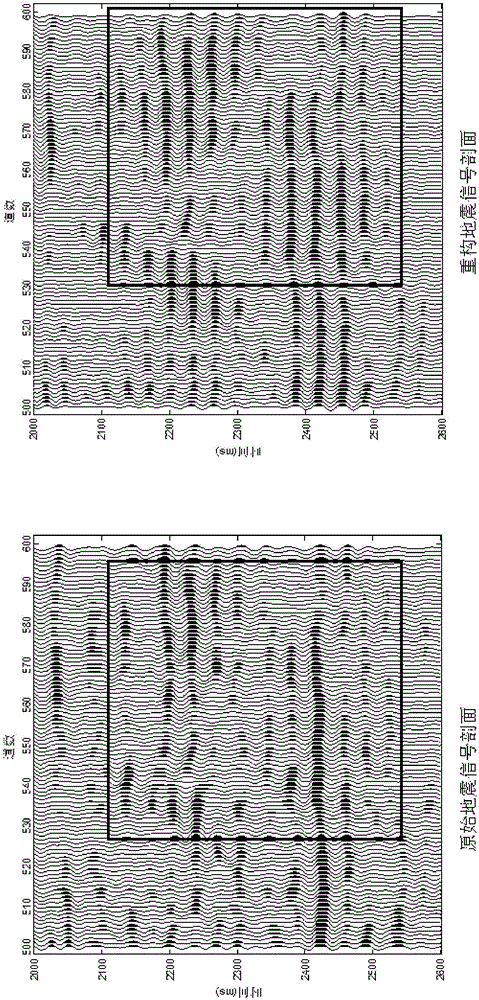
Lithologic oil-gas reservoir weak-reflection seismic signal reconstruction method
InactiveCN105116442AHigh-resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingLow noiseLithology
The invention discloses a lithologic oil-gas reservoir weak-reflection seismic signal reconstruction method. According to the method, intrinsic mode components are obtained through carrying out wavelet denoising and waveform matching endpoint continuation processing on an original seismic signal respectively and decomposing the original seismic signal by adopting empirical mode decomposition, the effective intrinsic mode components are selected in a self-adaptive mode for Hilbert transformation by adopting correlation, an obtained instantaneous amplitude is subjected to self-adaptive spectral whitening processing, and the instantaneous amplitude after spectral whitening and an instantaneous phase obtained through Hilbert transformation are used for reconstructing a signal to obtain a reconstructed seismic signal with low noise and high energy. Compared with the original seismic signal, the reconstructed seismic signal increases the signal-to-noise ratio and the resolution ratio of seismic sections, and is more convenient to detect and identify.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
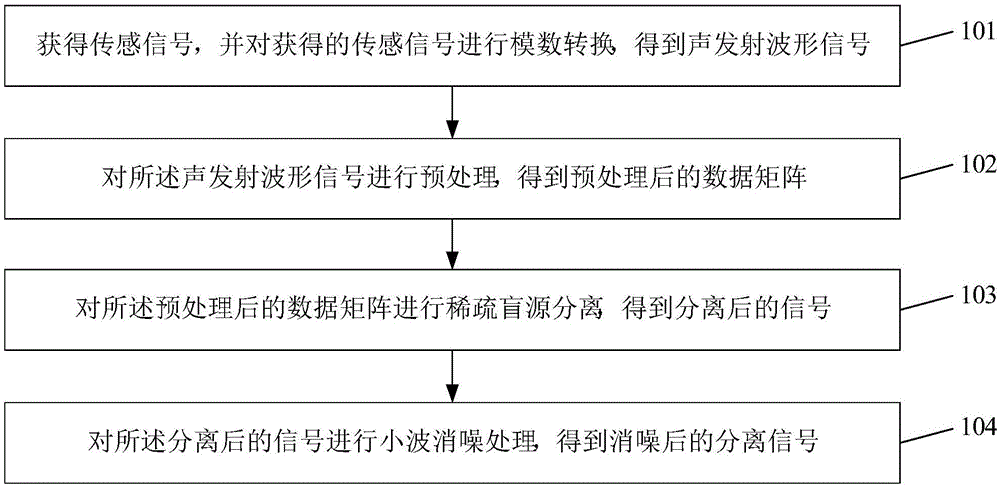
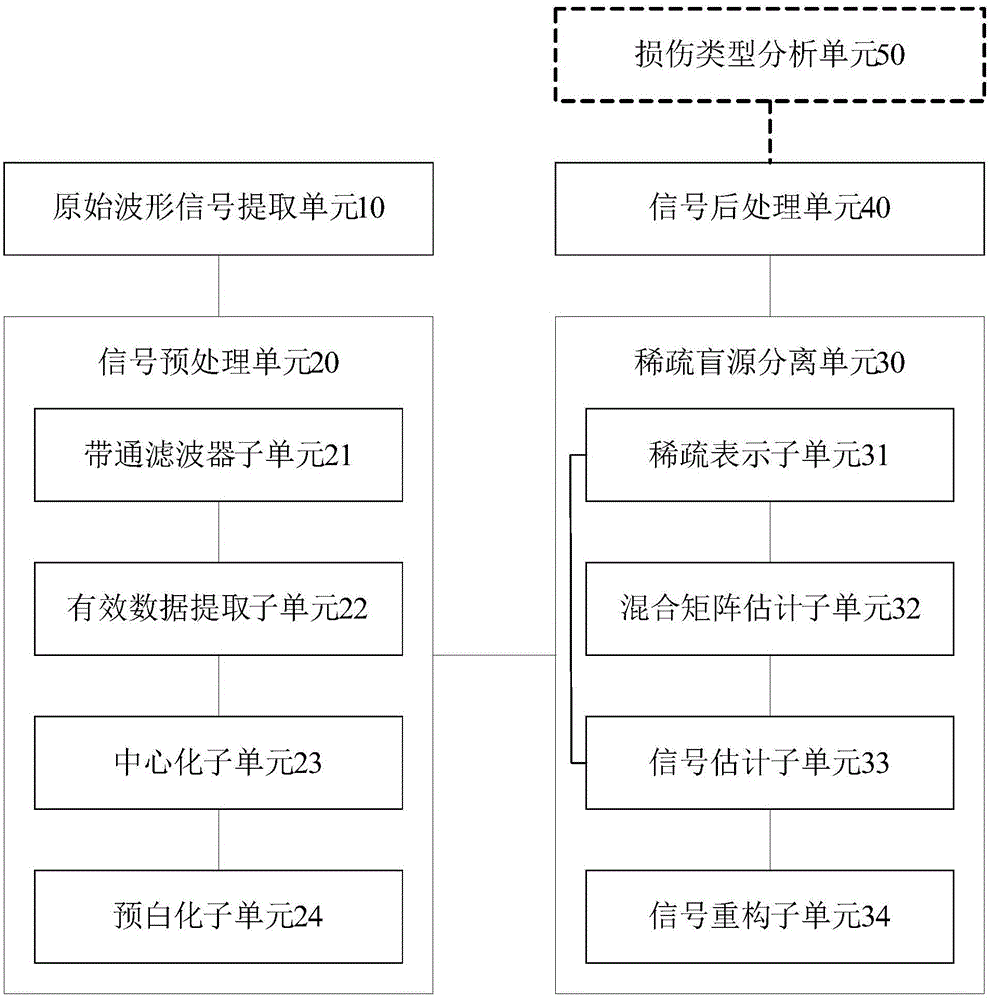
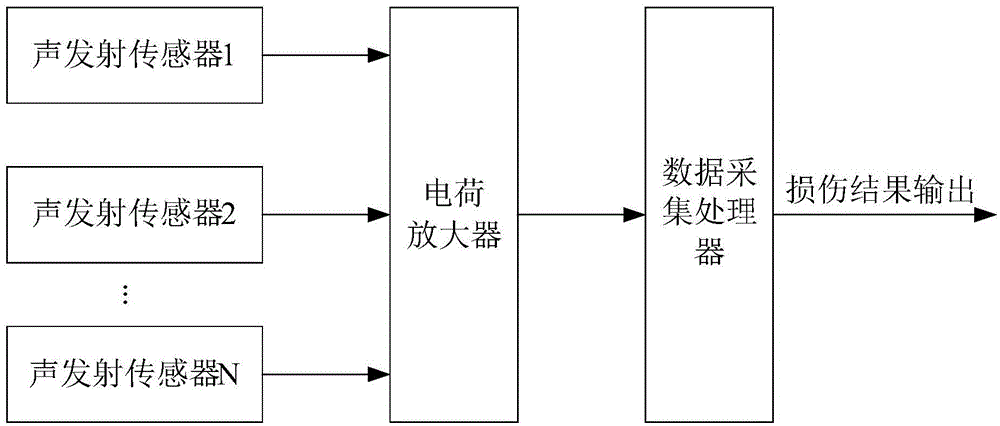
Damage monitoring method of composite material structure, and apparatus and system thereof
ActiveCN105067707AAccurate assessmentQuantifiedMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesProcessing detected response signalWavelet denoisingEngineering
The invention discloses a damage monitoring method of a composite material structure. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a sensing signal, and carrying out analog-to-digital conversion on the acquired sensing signal to obtain a sound emission waveform signal; preprocessing the sound emission waveform signal to obtain a preprocessed data matrix; carrying out sparse blind source separation on the preprocessed data matrix to obtain a separated signal; and carrying out wavelet denoising processing on the separated signal to obtain a denoised separation signal. The invention also discloses a damage monitoring apparatus of the composite material structure, and a system thereof.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method of diagnosing GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear) mechanical defects based on abnormal vibration analysis
ActiveCN105629100AGuaranteed uptimeIdeal signal-to-noise separationVibration measurement in solidsElectrical testingWavelet denoisingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a system and a method of diagnosing GIS (Gas Insulated Switchgear) mechanical defects based on abnormal vibration analysis. An acceleration sensor is fixed at the position of a measurement point on the surface of the GIS shell, and the acceleration sensor, a charge amplifier, a data acquisition unit and a data processing device are serially connected in sequence; after the data processing device carries out wavelet denoising on measured vibration signals, a spectrum for vibration signals at each measurement point is obtained finally; and through analyzing the signal component of each frequency range of the spectrum, the GIS mechanical fault type is determined. The system and the method of the invention have the beneficial effects that the GIS diagnosis technology research based on abnormal vibration analysis provides an important and feasible detection means for discovering GIS mechanical defects or hidden fault, and an important role is played in ensuring reliable operation of the GIS.
Owner:HEFEI POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER +1
Systems and methods for brain activity interpretation
ActiveUS20160235351A1Minimizes valueElectroencephalographyMedical data miningPersonalizationNervous system
The present invention provides a computer-implemented method, including:a. obtaining, in real-time, by a specifically programmed processor, electrical signal data representative of brain activity of a particular individual;b. processing, in real-time the electrical signal data representative of brain activity of a particular individual based upon a pre-determined predictor associated with a particular brain state, selected from a library of predictors containing a plurality of pre-determined predictors, wherein each individual pre-determined predictor is associated with a unique brain state,wherein the pre-determined predictor associated with a particular brain state includes:i. a pre-determined mother wavelet,ii. a pre-determined representative set of wavelet packet atoms, created from the pre-determined mother wavelet,iii. a pre-determined ordering of wavelet packet atoms, andiv. a pre-determined set of normalization factors,wherein the processing includes:i. causing, by the specifically programmed processor, the electrical signal data to be deconstructed into a plurality of pre-determined deconstructed wavelet packet atoms, utilizing the pre-determined representative set of wavelet packet atoms,wherein time windows of the electrical signal data are projected onto the pre-determined representative set of wavelet packet atoms wherein the projection is via convolution or inner product, andwherein each pre-determined representative wavelet packet atom corresponds to a particular pre-determined brain activity feature from a library of a plurality of pre-determined brain activity features;ii. storing the plurality of pre-determined deconstructed wavelet packet atoms in at least one computer data object;iii. causing, by the specifically programmed processor, the stored plurality of pre-determined deconstructed wavelet packet atoms to be re-ordered within the computer data object, based on utilizing a pre-determined order;iv. obtaining a statistical measure of the activity of each of the re-ordered plurality of pre-determined deconstructed wavelet packet atoms; andv. normalizing the re-ordered plurality of pre-determined wavelet packet atoms, based on utilizing a pre-determined normalization factor; andc. outputting, a visual indication of at least one personalized mental state of the particular individual, at least one personalized neurological condition of the particular individual, or both, based on the processing,wherein the individual pre-determined predictor associated with a particular brain state from within the plurality of pre-determined predictors is generated by the steps including:i. obtaining the pre-determined representative set of wavelet packet atoms by:a. obtaining from a plurality of individuals, by the specifically programmed processor, at least one plurality of electrical signal data representative of a brain activity of a particular brain state;b. selecting a mother wavelet from a plurality of mother wavelets, wherein mother wavelet is selected from an wavelet family selected from the group consisting of: Haar, Coiflet Daubehies, and Mayer wavelet families;c. causing, by the specifically programmed processor, the at least one plurality electrical signal data to be deconstructed into a plurality of wavelet packet atoms, using the selected mother wavelet;d. storing the plurality of wavelet packet atoms in at least one computer data object;e. determining, an optimal set of wavelet packet atoms using the pre-determined mother wavelet, and storing the optimal set of wavelet packet atoms in at least one computer data object, wherein the determining is via utilizing analysis Best Basis algorithm; andf. applying, by the specifically programmed processor, wavelet denoising to the number of wavelet packet atoms in the optimal set;ii. obtaining the pre-determined ordering of wavelet packet atoms by:a. projecting, by the specifically programmed processor, the at least one plurality of electrical signal data representative of a brain activity for each 4 second window of the data onto the pre-determined representative set of wavelet packet atoms;b. storing the projections in at least one computer data object;c. determining, by the specifically programmed processor, the wire length for every data point in the projection by determining the mean absolute distance of the statistical measure of the projections of different channels from their adjacent channels;d. storing the wire length data in at least one computer data object; ande. re-ordering the stored projections, by the specifically programmed computer to minimize a statistical value of the wire length value across each time window, and across all individuals within the plurality of individuals, and across the projections; andiii. obtaining the pre-determined set of normalization factors by:a. determining, by the specifically programmed computer, the mean and standard deviation of the values of the stored projections.
Owner:NEUROSTEER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com