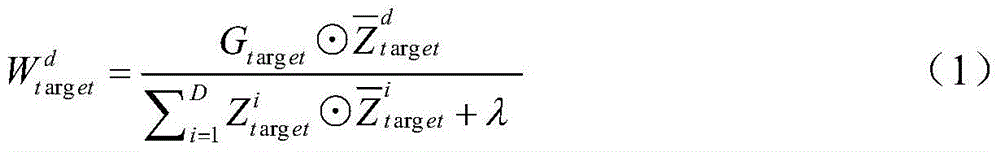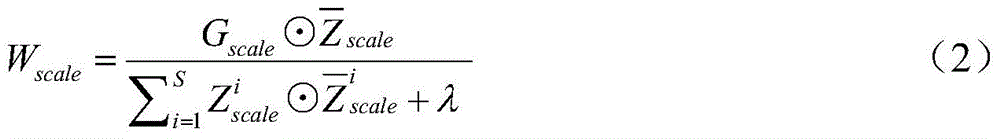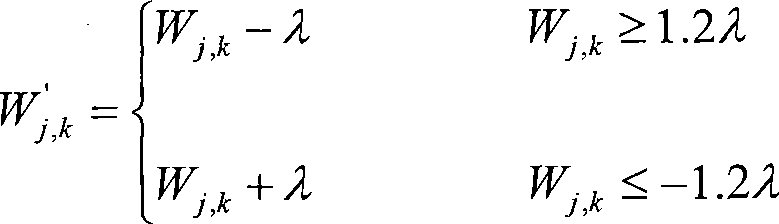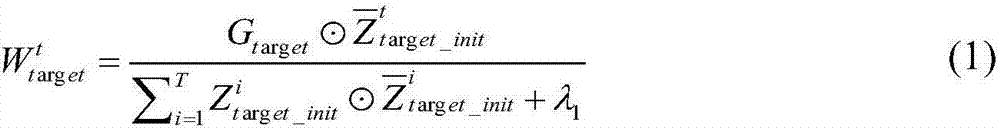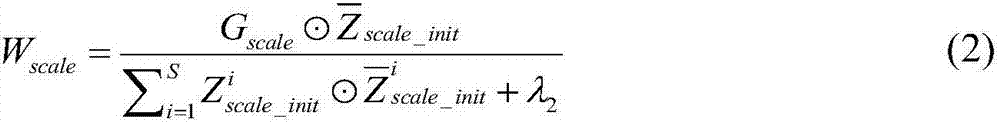Patents
Literature
42 results about "Scale dependent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The scale of measurement of the dependent variable helps us to choose the broad category of statistical procedures appropriate for our hypothesis (nonparametric vs. parametric). The scale of measurement of the independent variable helps us to determine which statistical procedure within the broad category is appropriate. Type of Statistic.
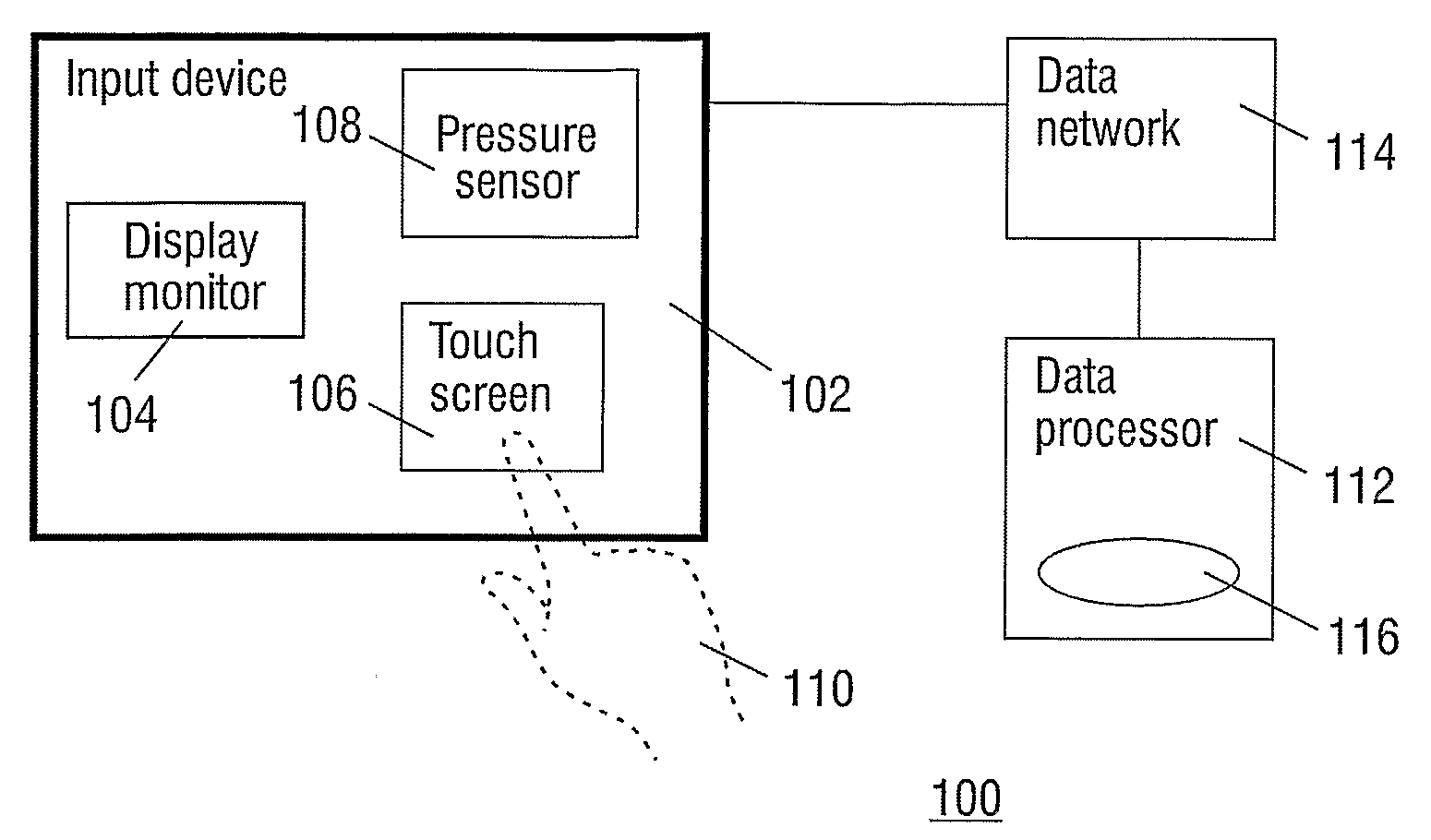
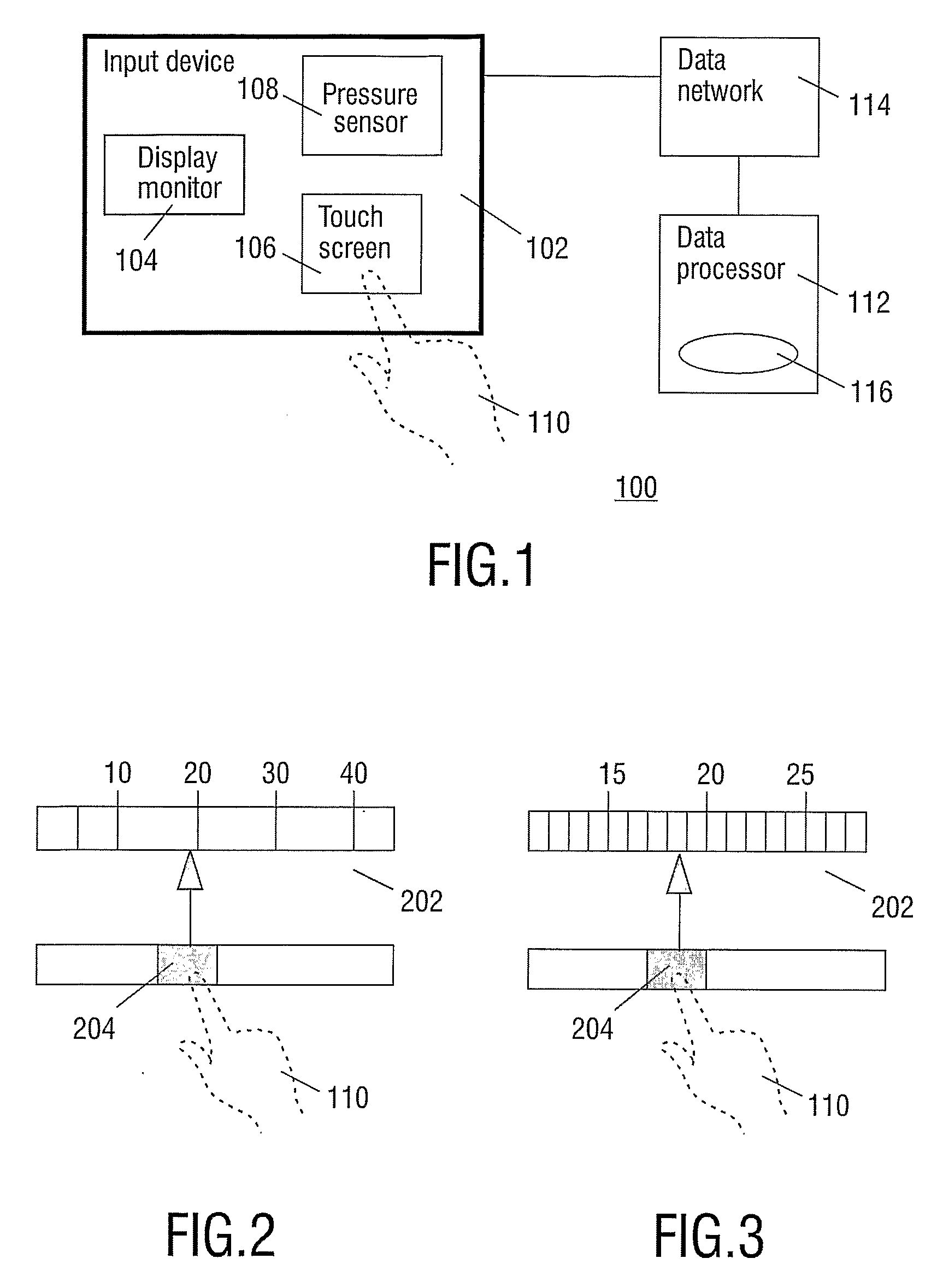
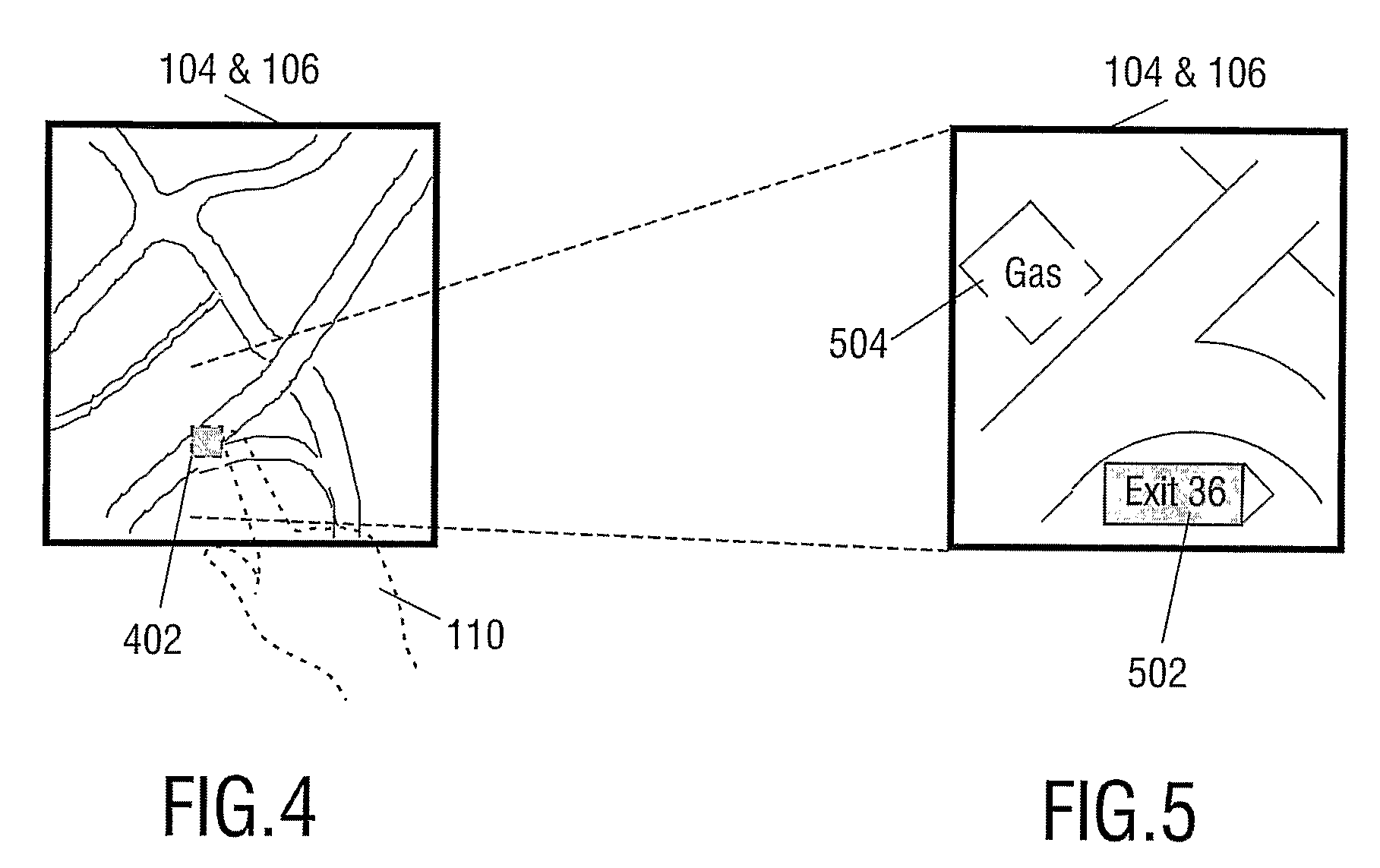
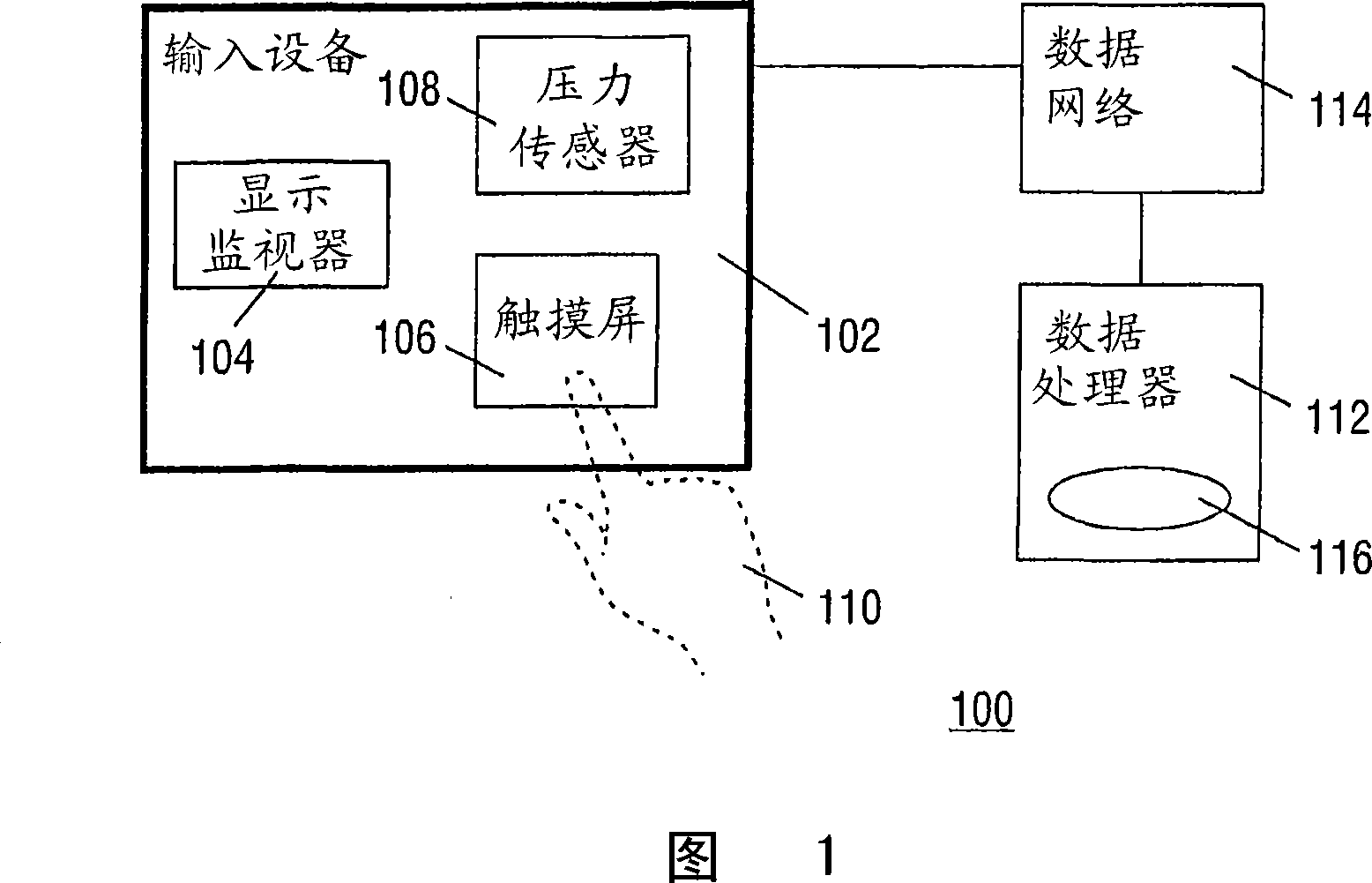
Pressure-Controlled Navigating in a Touch Screen
InactiveUS20080094367A1Improve user friendlinessUser-friendliness of the known systems can be further increasedInput/output processes for data processingRemote controlOperation mode
A remote control device has a display monitor for rendering an image and a touch screen for user interaction. The touch screen is pressure-sensitive. The device has an operational mode wherein the image is being scaled dependent on a value of the pressure registered by the touch screen.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
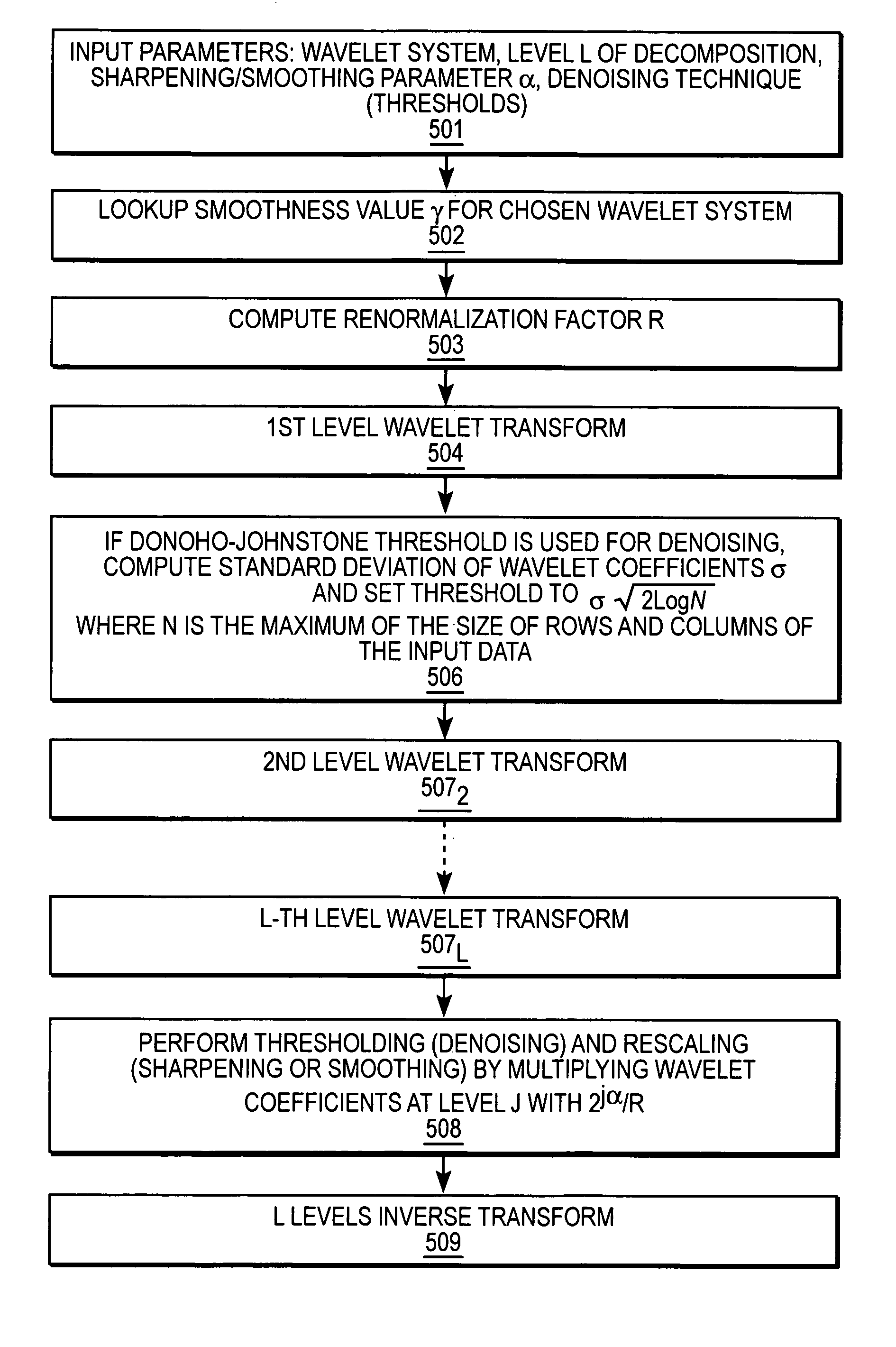
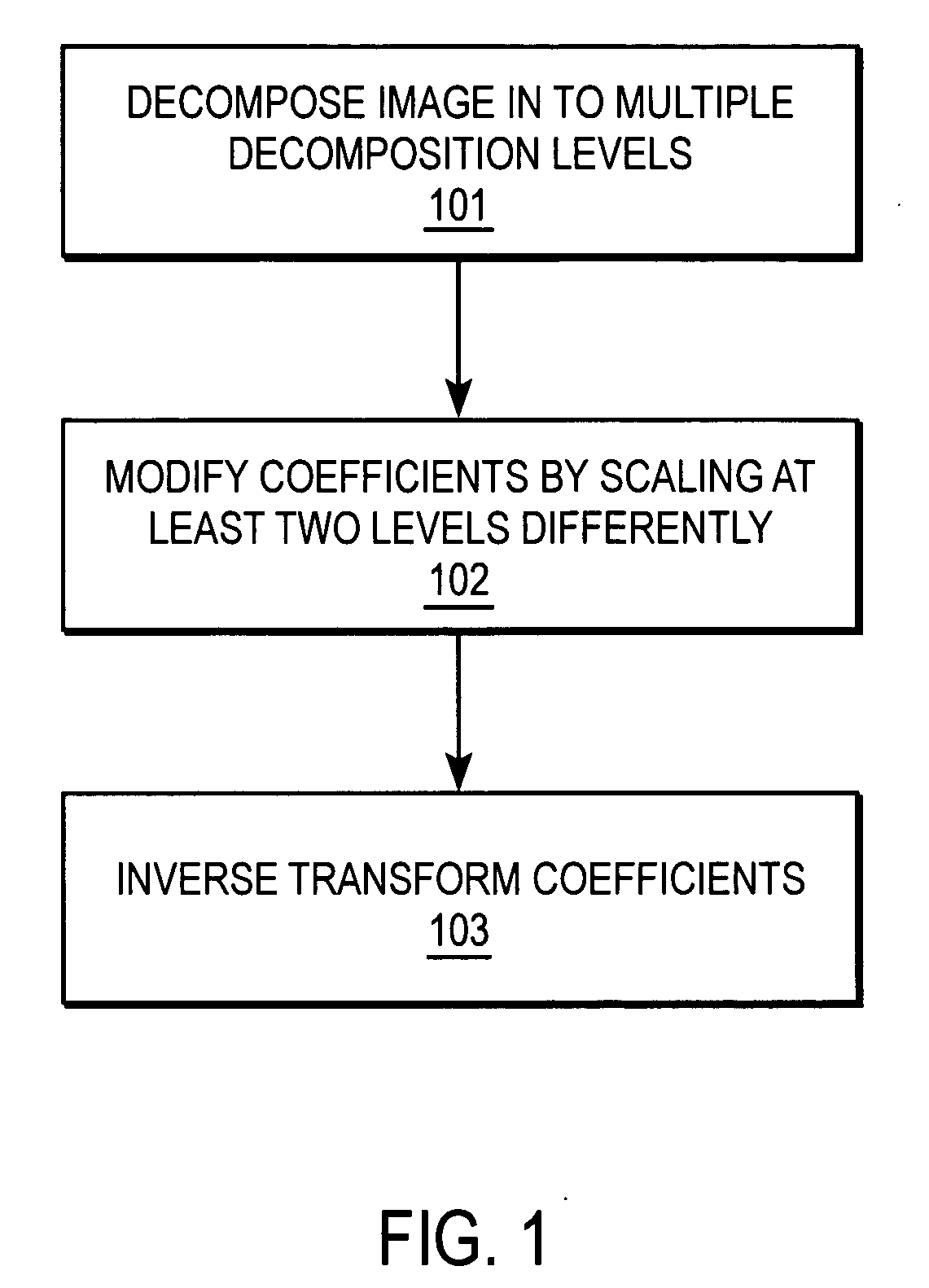
Multiscale sharpening and smoothing with wavelets
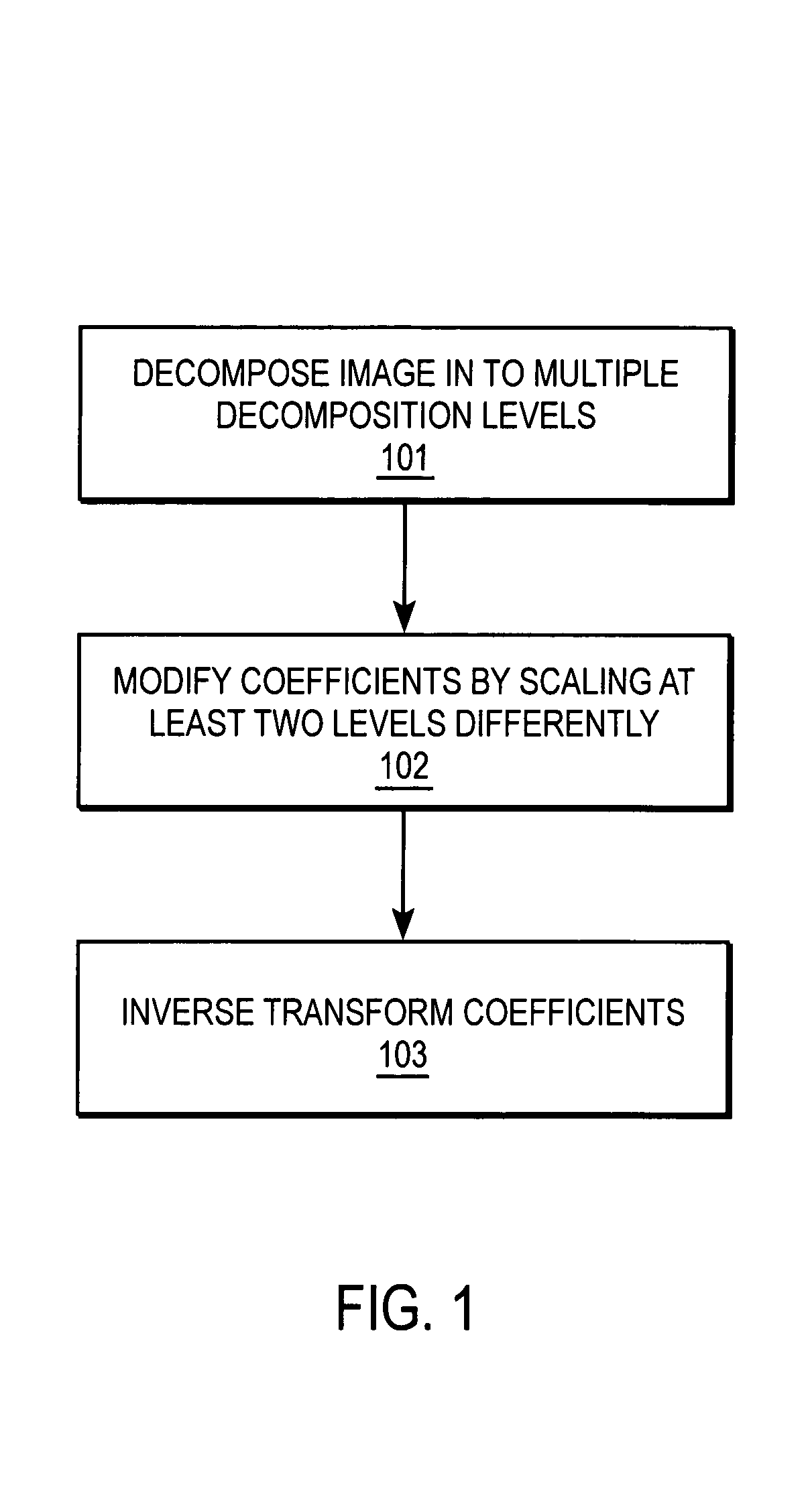
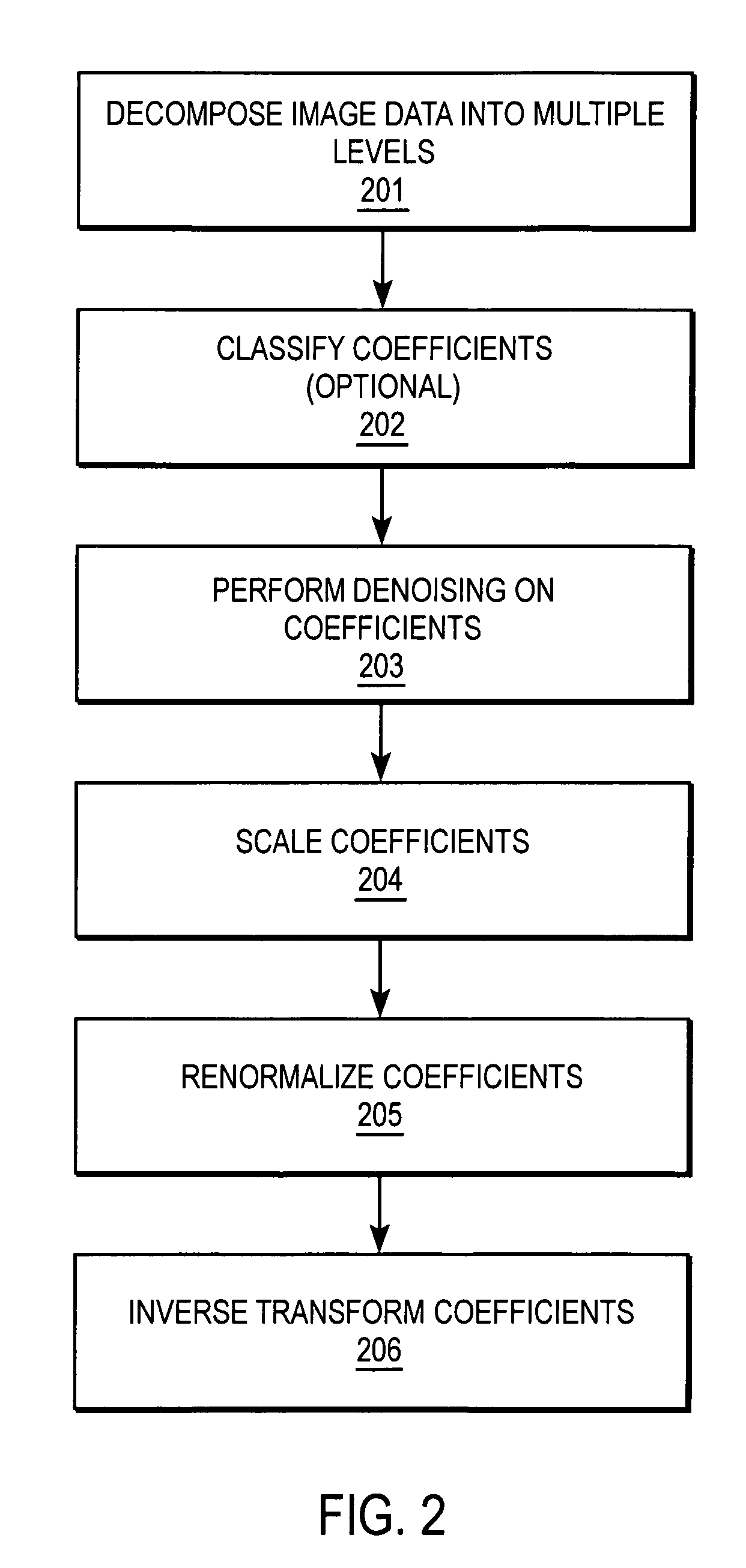
A method and apparatus for processing image data are described. In one embodiment, a method of processing image data comprises decomposing the image data into multiple decomposition levels by applying a wavelet transform to the image data, and modifying coefficients in at least two of the decomposition levels by scaling coefficients in theses decomposition levels using different scale dependent parameters for each of the decomposition levels.
Owner:RICOH KK
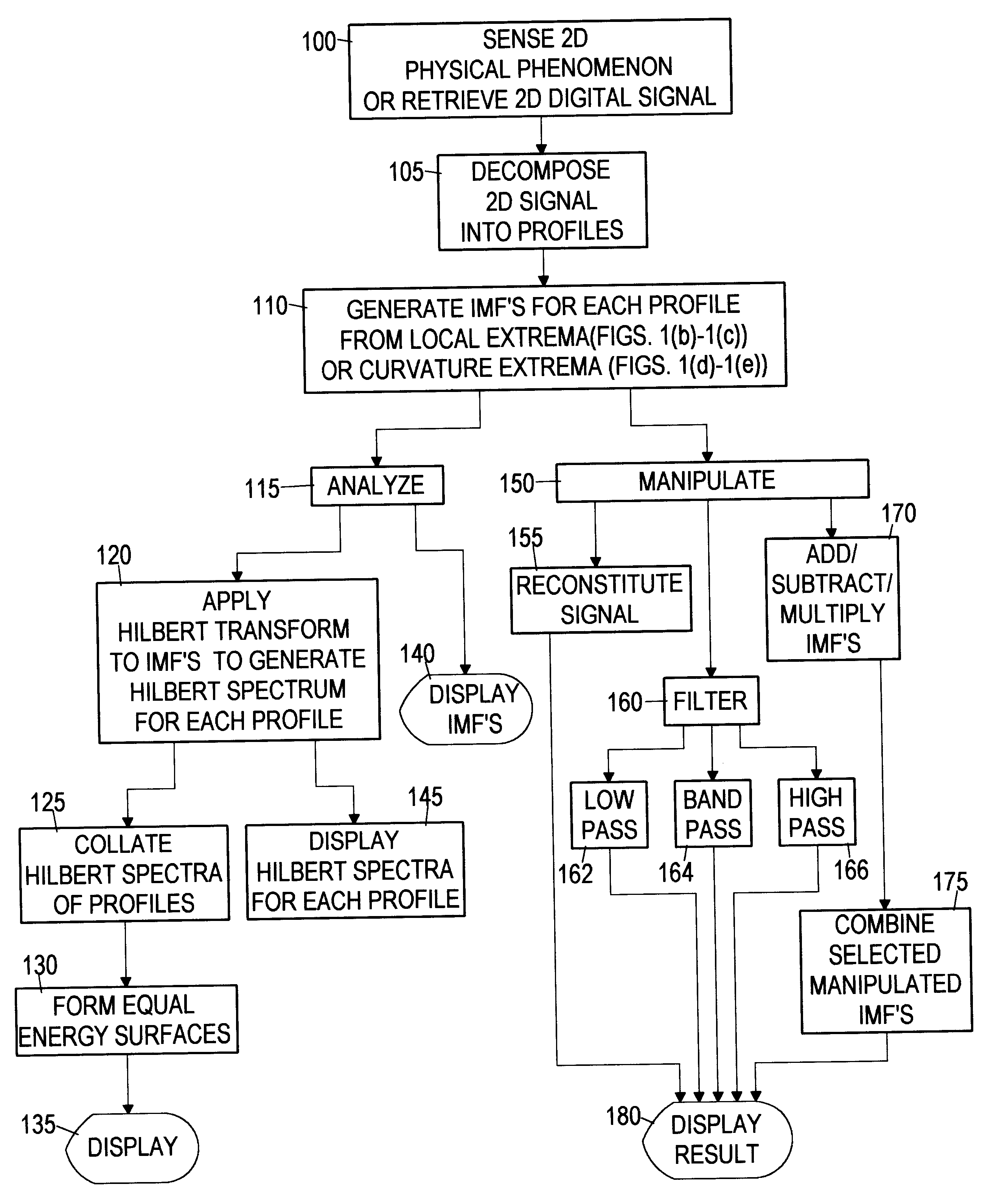
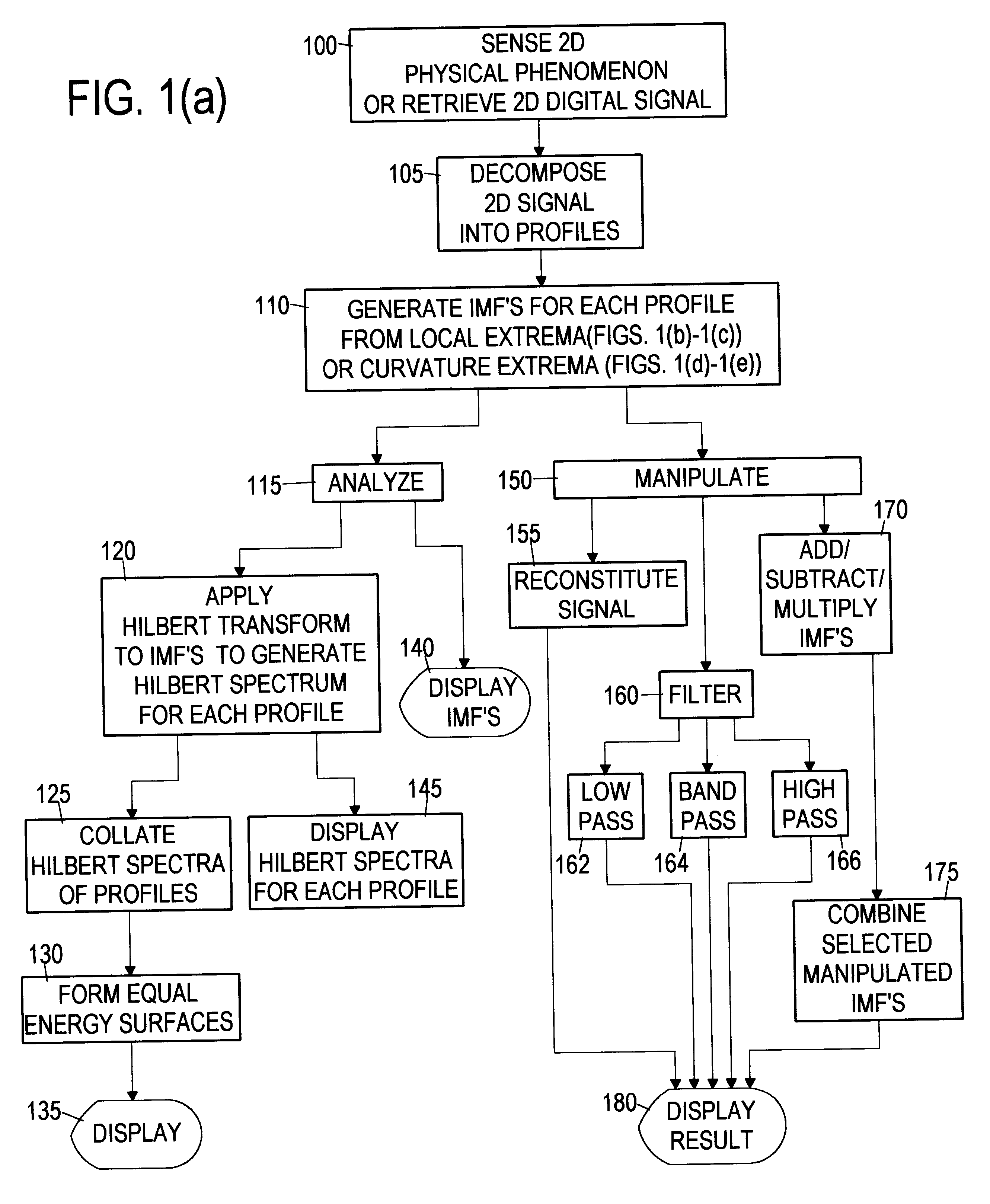
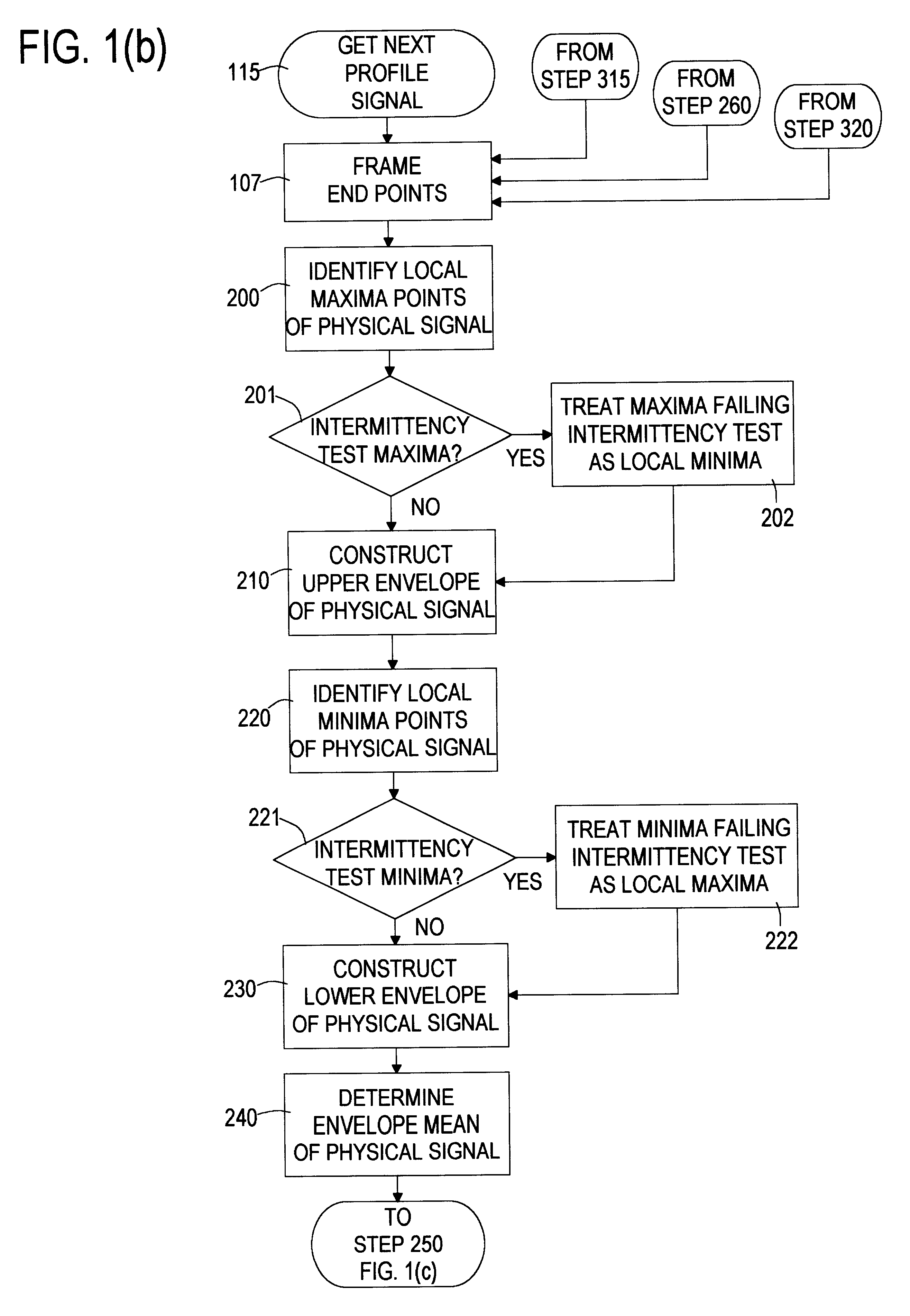
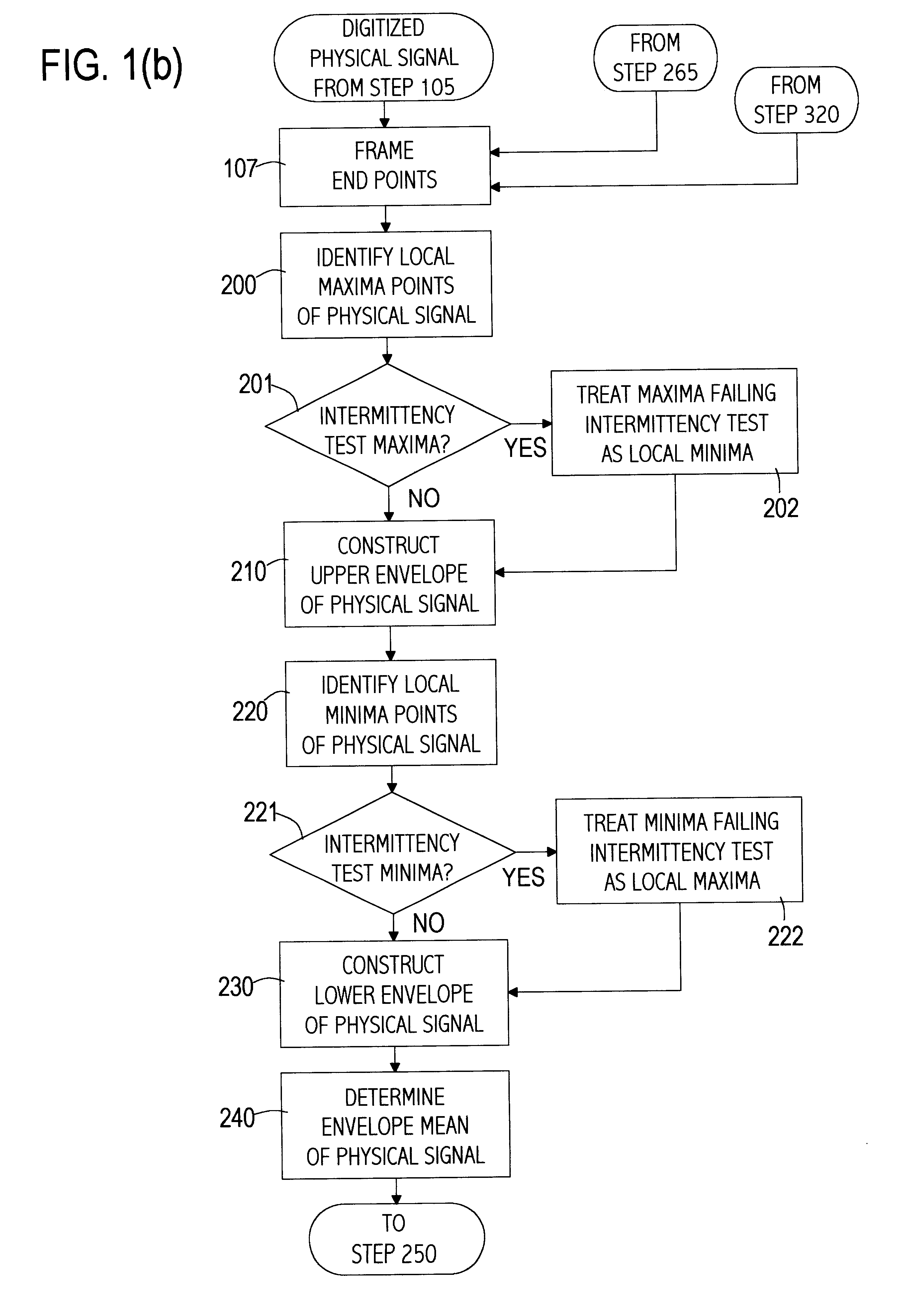
Computer implemented empirical mode decomposition method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for two-dimensional signals
InactiveUS6311130B1Easy to useSeismic signal processingElectric/magnetic detectionDecompositionHilbert spectrum
A computer implemented method of processing two-dimensional physical signals includes five basic components and the associated presentation techniques of the results. The first component decomposes the two-dimensional signal into one-dimensional profiles. The second component is a computer implemented Empirical Mode Decomposition that extracts a collection of Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMF's) from each profile based on local extrema and / or curvature extrema. The decomposition is based on the direct extraction of the energy associated with various intrinsic time scales in the profiles. In the third component, the IMF's of each profile are then subjected to a Hilbert Transform. The fourth component collates the Hilbert transformed IMF's of the profiles to form a two-dimensional Hilbert Spectrum. A fifth component manipulates the IMF's by, for example, filtering the two-dimensional signal by reconstructing the two-dimensional signal from selected IMF(s).
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMISTRATOR OF THE
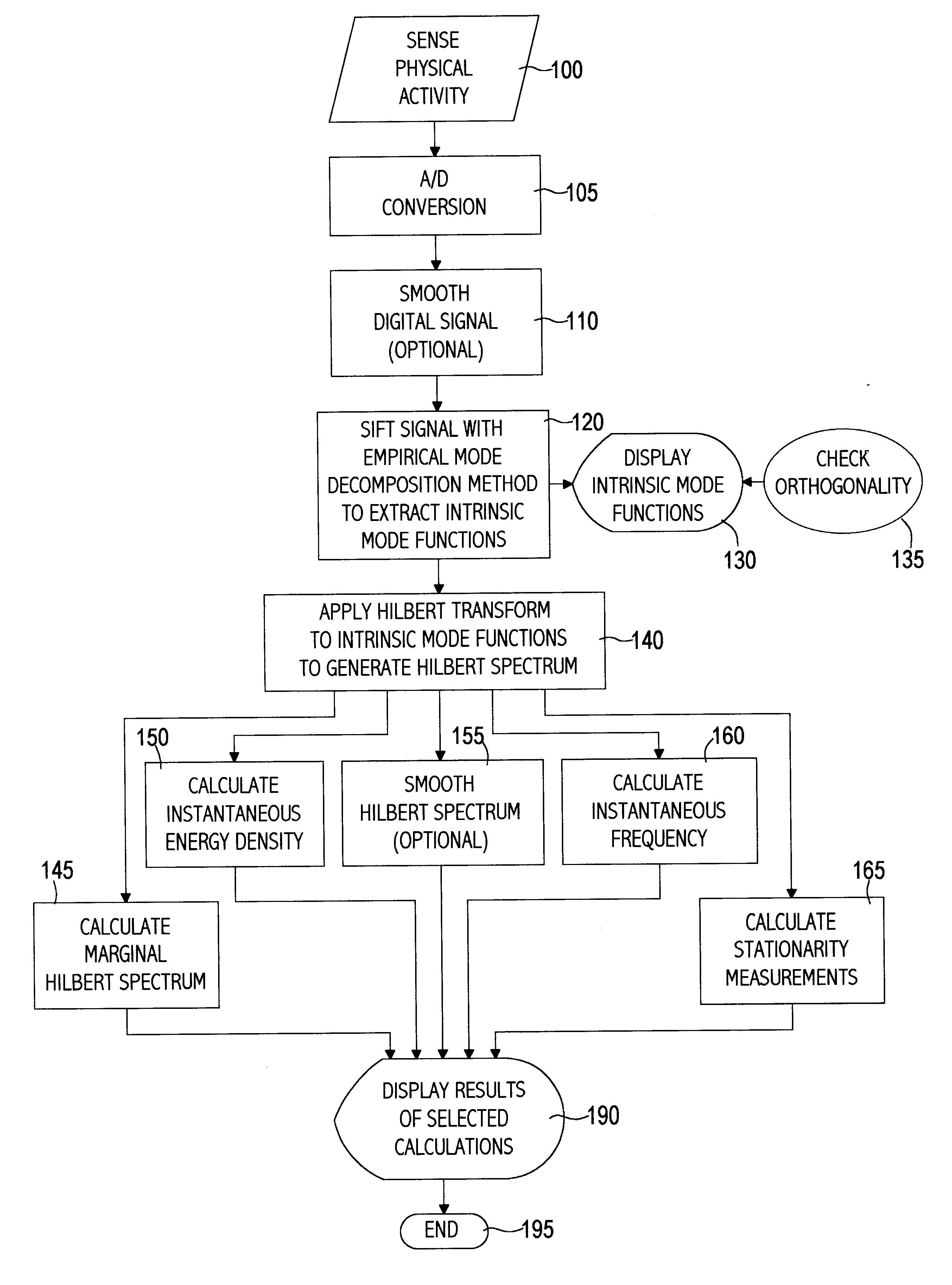
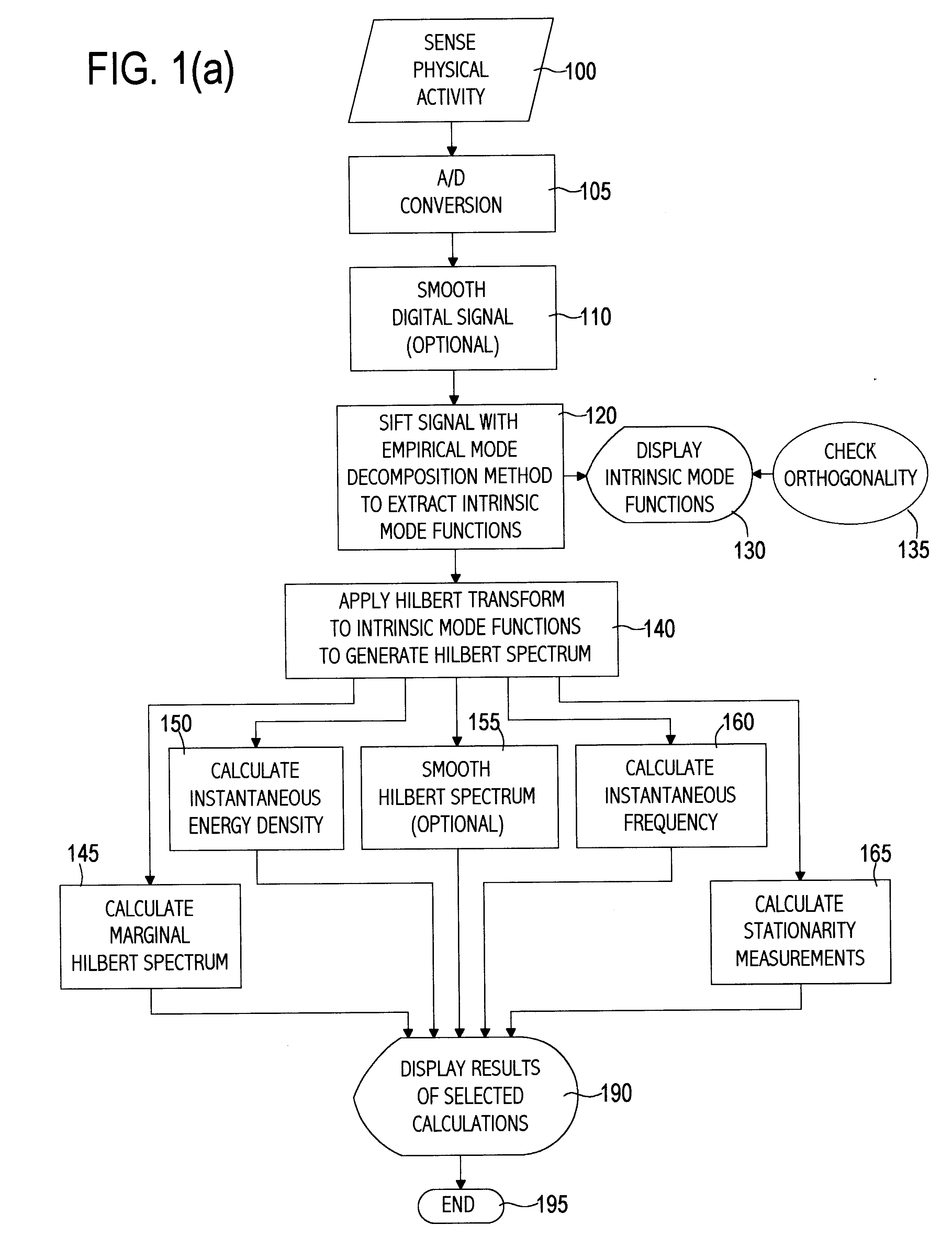
Empirical mode decomposition apparatus, method and article of manufacture for analyzing biological signals and performing curve fitting
InactiveUS6738734B1Easy to useAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDecompositionCurve fitting
A computer implemented physical signal analysis method includes four basic steps and the associated presentation techniques of the results. The first step is a computer implemented Empirical Mode Decomposition that extracts a collection of Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMF) from nonlinear, nonstationary physical signals. The decomposition is based on the direct extraction of the energy associated with various intrinsic time scales in the physical signal. Expressed in the IMF's, they have well-behaved Hilbert Transforms from which instantaneous frequencies can be calculated. The second step is the Hilbert Transform which produces a Hilbert Spectrum. Thus, the invention can localize any event on the time as well as the frequency axis. The decomposition can also be viewed as an expansion of the data in terms of the IMF's. Then, these IMF's, based on and derived from the data, can serve as the basis of that expansion. The local energy and the instantaneous frequency derived from the IMF's through the Hilbert transform give a full energy-frequency-time distribution of the data which is designated as the Hilbert Spectrum. The third step filters the physical signal by combining a subset of the IMFs. In the fourth step, a curve may be fitted to the filtered signal which may not have been possible with the original, unfiltered signal.
Owner:NASA
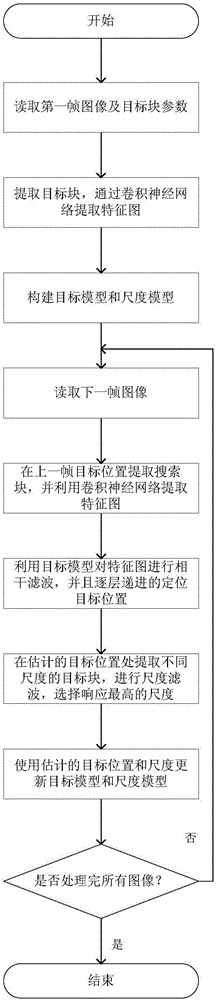
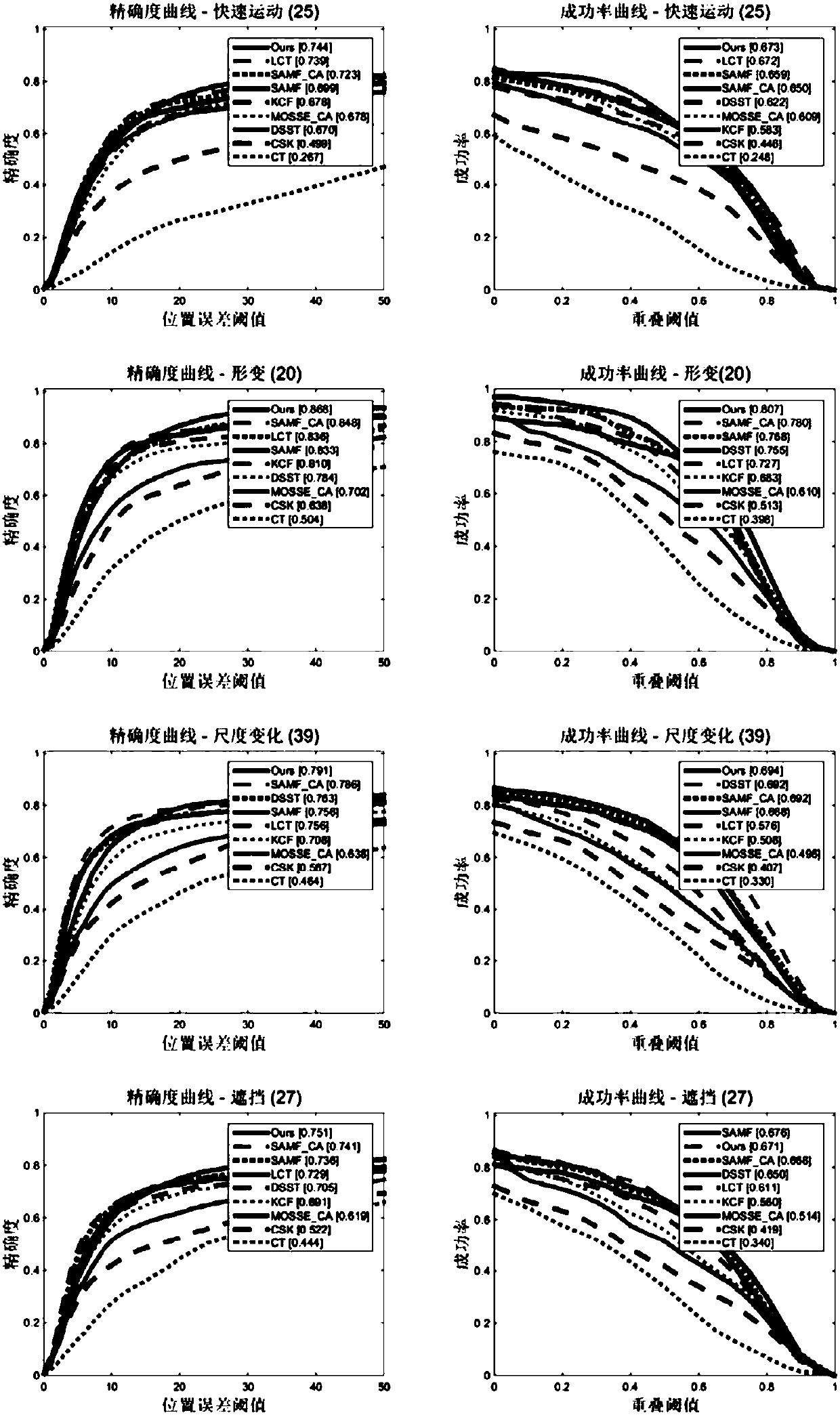
Robust target tracking method based on deep learning and multi-scale correlation filtering
ActiveCN105741316APrevent extractionRun fastImage enhancementImage analysisCorrelation filterScale dependent
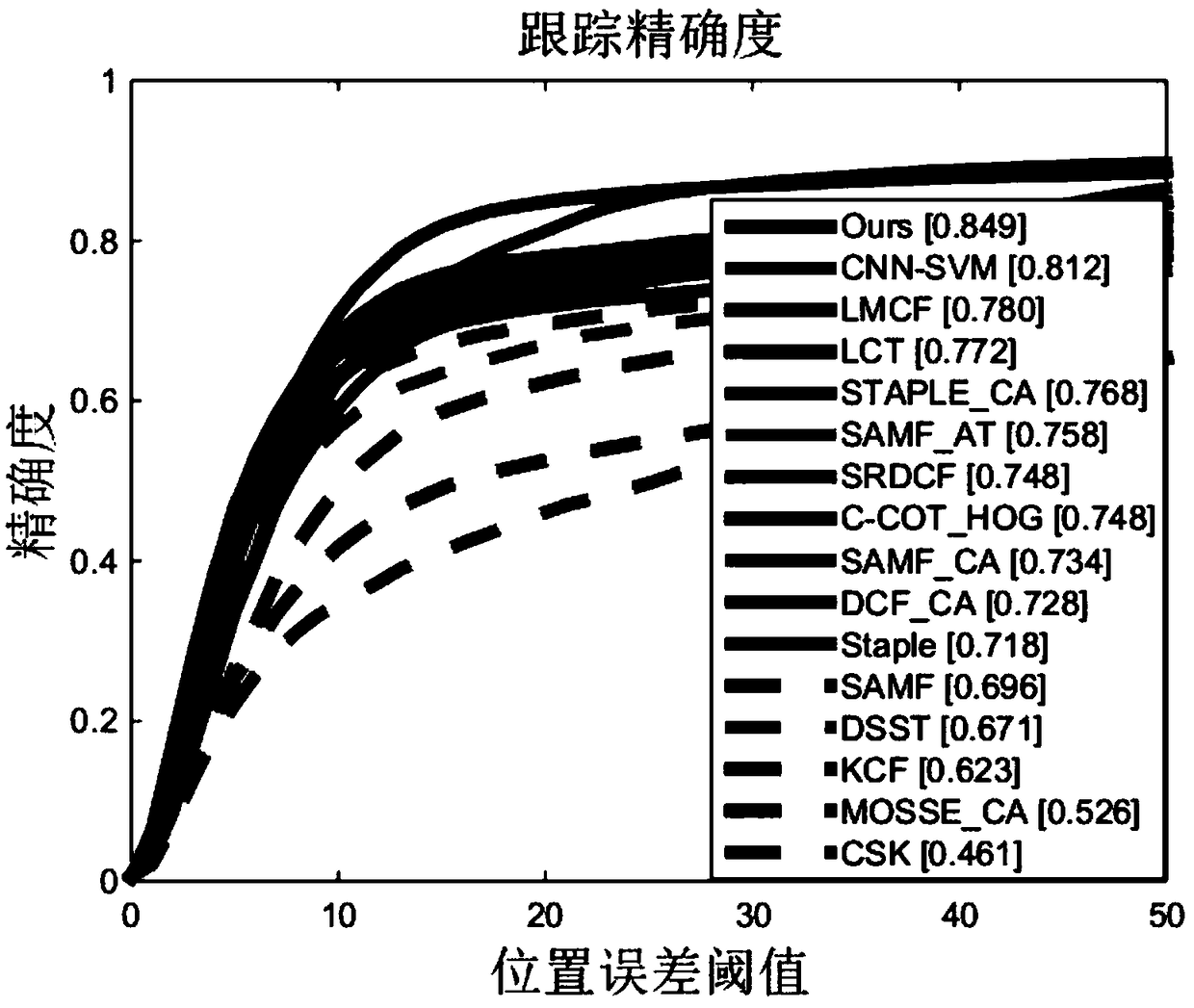
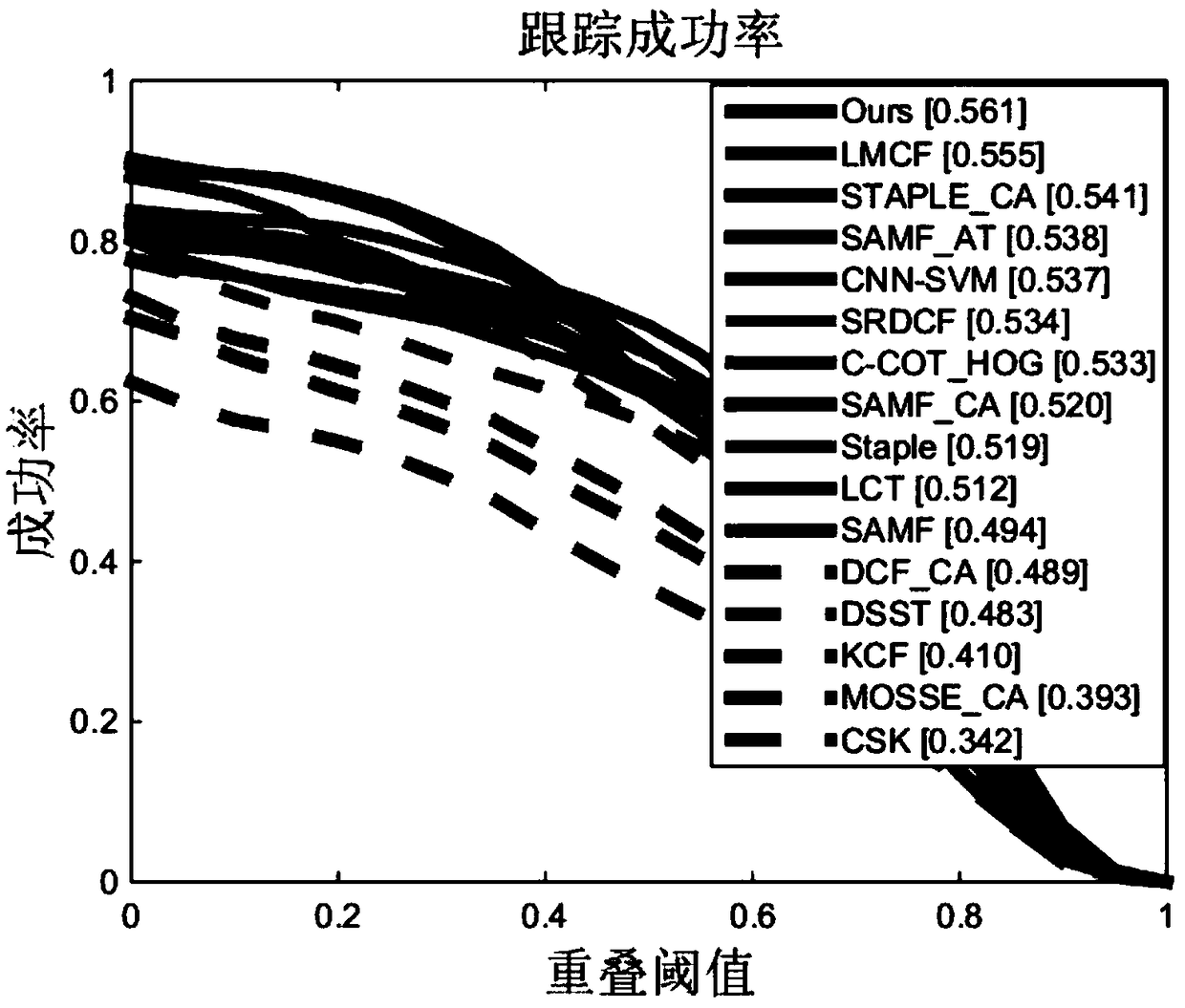
The invention relates to a robust target tracking method based on deep learning and multi-scale correlation filtering. The tracking process is divided into a target location part and a scale selection part. In the target location part, the position of a target is located through a convolutional neural network and correlation filtering. In the scale selection part, a scale pyramid is used, and different scales are selected in a matching manner for targets through scale filtering. The multilayer characteristic of the convolutional neural network is taken as a representation model of targets, so the structural and semantic information of targets can be described robustly. Through use of the characteristics of correlation filtering, there is no need to train a classifier online, and the running speed of the algorithm is increased greatly. The idea of scale pyramid is adopted in scale, and correlation filtering matching is performed on targets of different scales to select the optimal scale. The method is of strong robustness to deformation, shading and scale change of targets.
Owner:XIAN ANMENG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Multiscale sharpening and smoothing with wavelets
A method and apparatus for processing image data are described. In one embodiment, a method of processing image data comprises decomposing the image data into multiple decomposition levels by applying a wavelet transform to the image data, and modifying coefficients in at least two of the decomposition levels by scaling coefficients in theses decomposition levels using different scale dependent parameters for each of the decomposition levels.
Owner:RICOH KK
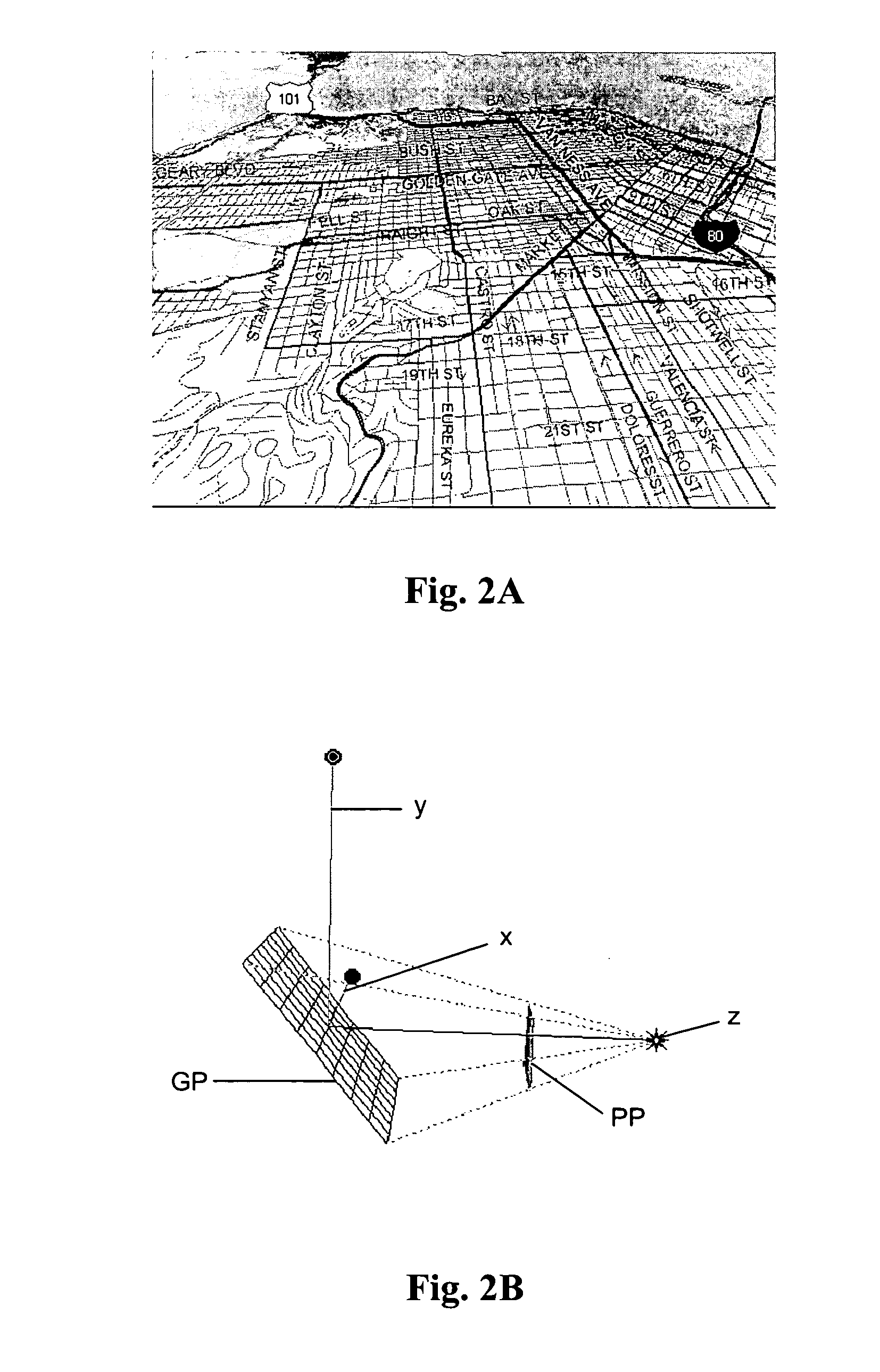
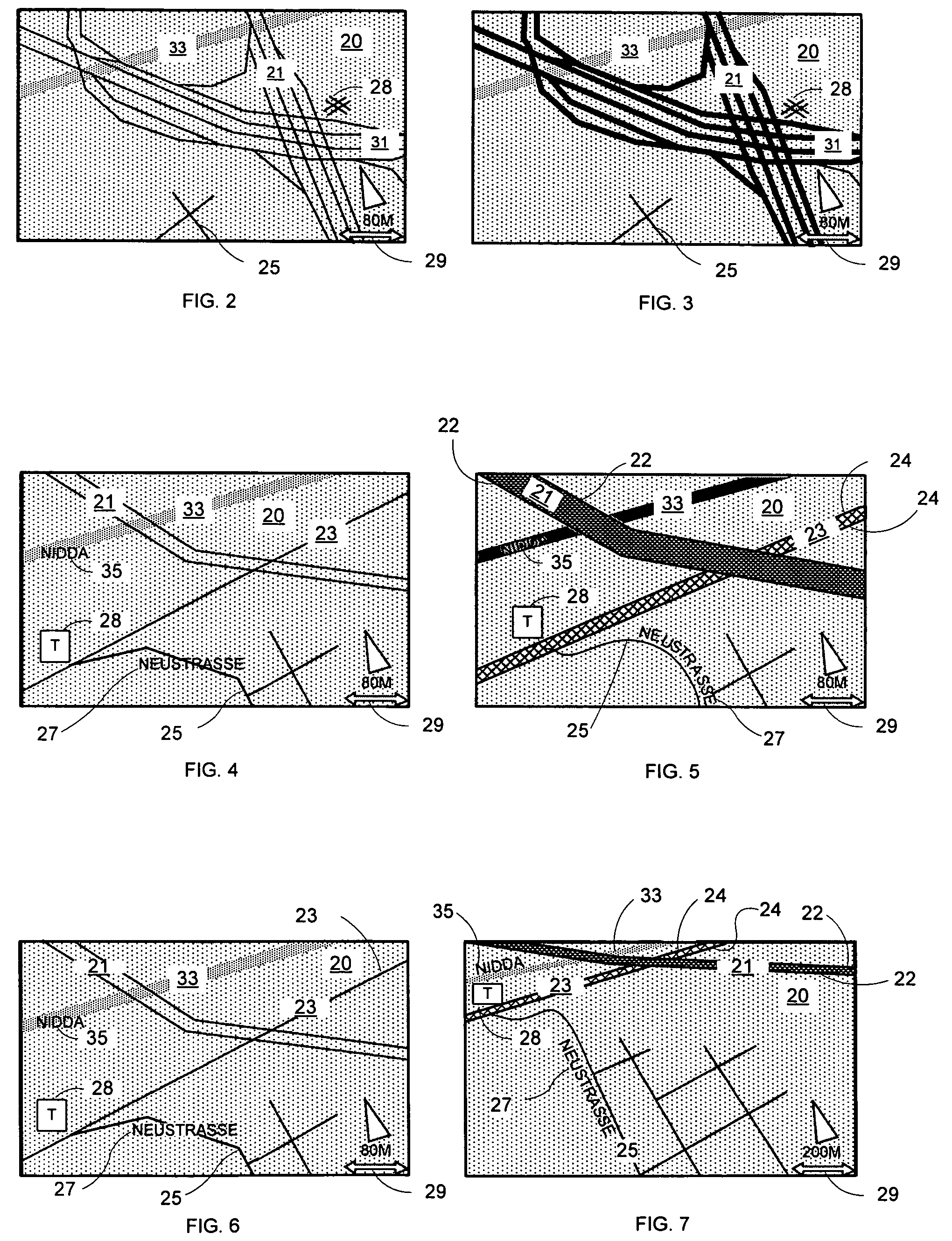
Non-perspective variable-scale map displays
InactiveUS20060267803A1More functionalityImprove usabilityRoad vehicles traffic controlMaps/plans/chartsFeature setModem device
Map displays have been an important element in the feature set of in-car navigation systems. Actually, with modem equipment extending such system functionality to personal digital assistants (PDAs) and cellular telephones, virtually all travelers may use and benefit from the present invention. Early digital displays were monochrome, single-line-vector, planar representations. Color, area fill, scale-dependent attribute selection, labeling, heading-up rotation, line thickness, signs and icons have all been added to make the display more informative and intuitive. Still today, the designer is challenged to provide a more informative, less distracting display to serve the multitasking driver. More recently, perspective view and 3D objects have gained popularity because of their added utility as well as aesthetic appeal. Just as the planar map is a special case of the perspective map, perspective is a special case of the variable-scale map. This disclosure offers some approaches to the use of non-perspective continuous variable-scale maps to solve inherent problems of more conventional navigation map displays.
Owner:TELE ATLAS NORTH AMERICA
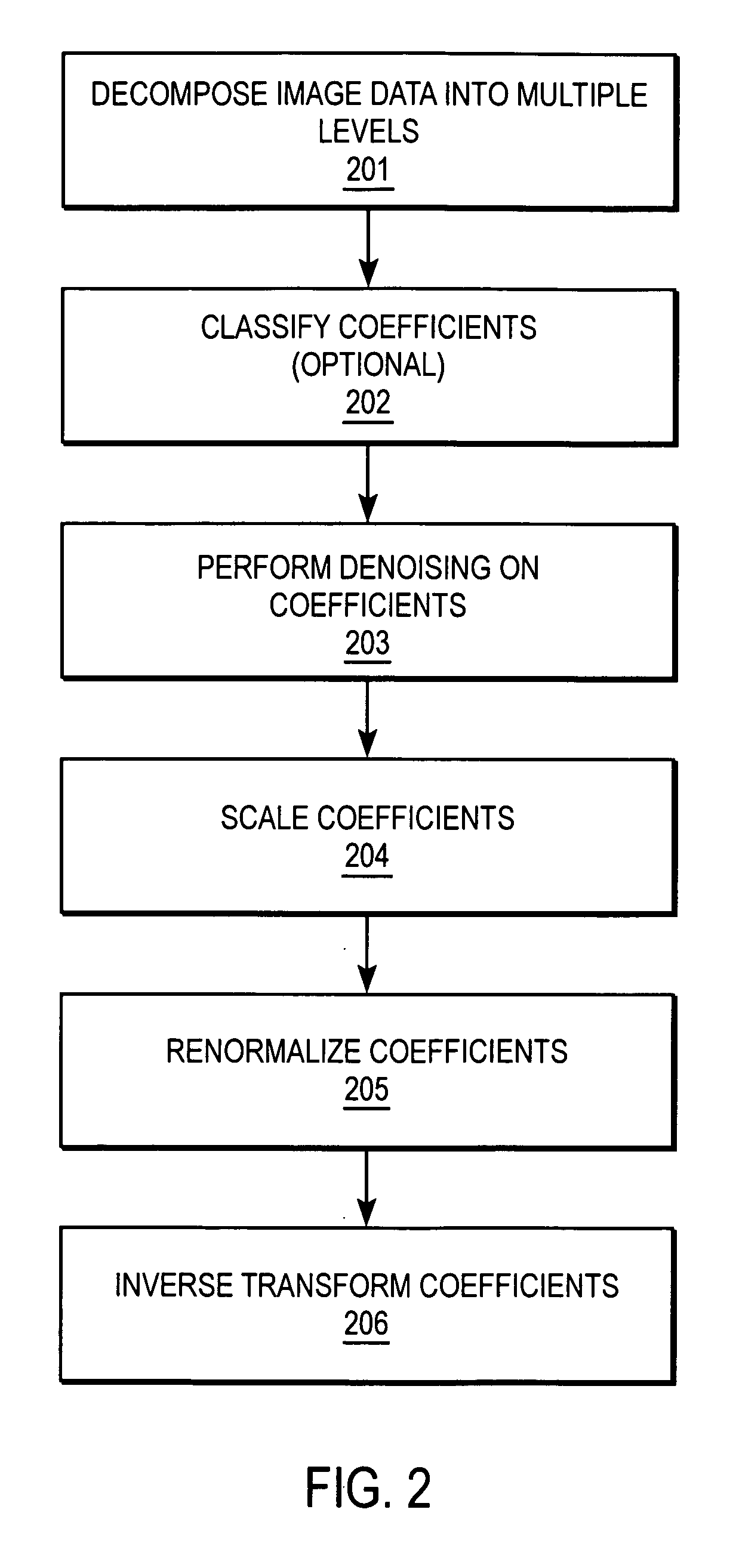
Image wavelet de-noising method based on median filter
InactiveCN101425176AAvoid confusionAvoid the influence of high frequency partImage enhancementWavelet denoisingScale dependent
The invention provides an image wavelet denoising method based on median filtering, which belongs to the field of digital remote sensing image processing. In the method, median pre-filtering is firstly performed on images containing noise, wavelet conversion, threshold value treatment and denoising treatment are then carried out, wavelet reverse conversion is finally carried out, and filtered images are output. The invention has the advantages that the median filtering method is used for the pre-filtering of images containing noise, much noise of pepper salt type is removed, and influence on the high-frequency part of images is avoided; the wavelet threshold value method is then combined with the denoising method of the relativity of wavelet coefficient size, and the mixture of signal coefficient and noise coefficient caused by using the wavelet threshold value method singly is avoided; and meanwhile, a large amount of computation required by using the denoising method of the relativity of wavelet coefficient size singly is reduced. The experiments prove that the method has stable denoising effect and moderate computation amount.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pressure-controlled navigating in a touch screen
A remote control device has a display monitor for rendering an image and a touch screen for user interaction. The touch screen is pressure-sensitive. The device has an operational mode wherein the image is being scaled dependent on a value of the pressure registered by the touch screen.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Self-adaptive feature fusion-based multi-scale correlation filtering visual tracking method
ActiveCN108549839AImprove performanceAvoid the problem of limited expression of a single featureImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionScale estimationPhase correlation
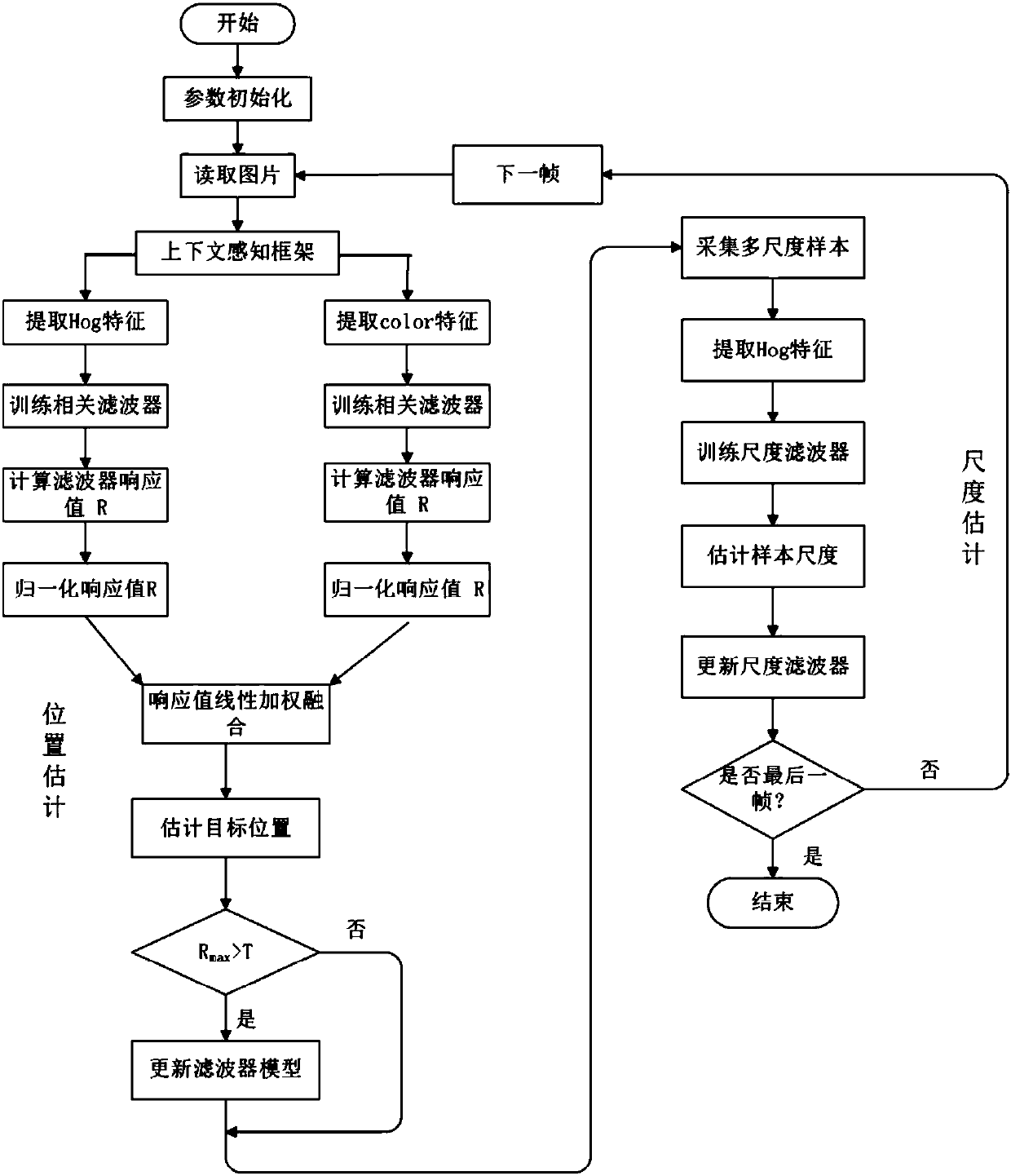
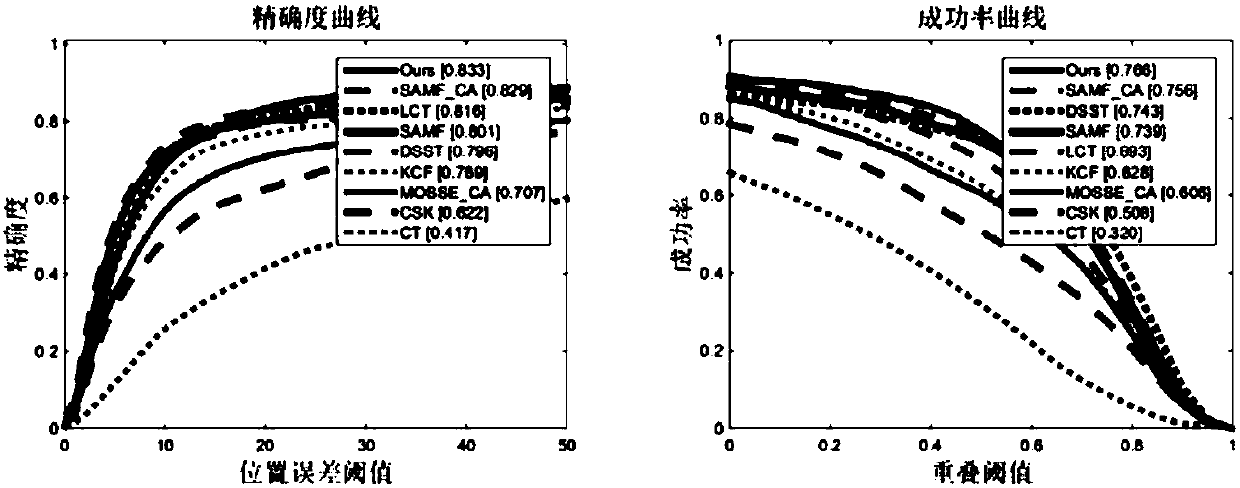
The invention discloses a self-adaptive feature fusion-based multi-scale correlation filtering visual tracking method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the correlation filtering is carried out on a target HOG feature and a target color feature respectively by using a context-aware correlation filtering framework; the response values under the two features are normalized; weightsare distributed according to the proportion of the response values and then are subjected to linear weighted fusion, so that a final response graph after fusion is obtained; the final response graph is compared with a pre-defined response threshold value to judge whether the filtering model is updated or not; finally, a scale correlation filter is introduced in the tracking process, so that the scale adaptability of the algorithm is improved. The method can be used for tracking various features. The performance advantages of the features are brought into play, and a model self-adaptive updating method is designed. In addition, a precise scale estimation mechanism is further introduced. According to the invention, the updating quality and the tracking precision of the model can be effectively improved, and the model can be changed in scale. The method is good in robustness under complex scenes such as rapid movement, deformation, shielding and the like.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY +1
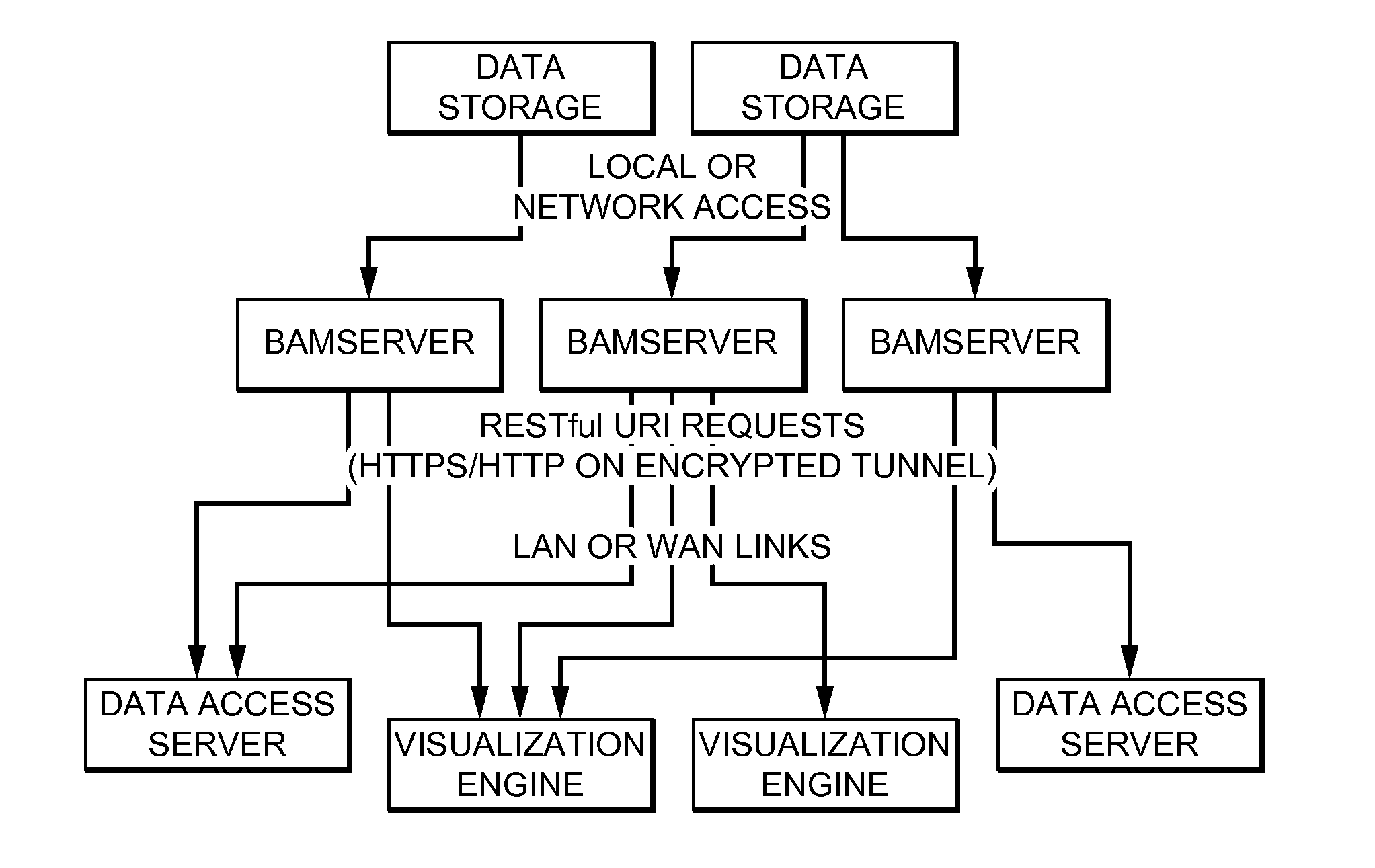
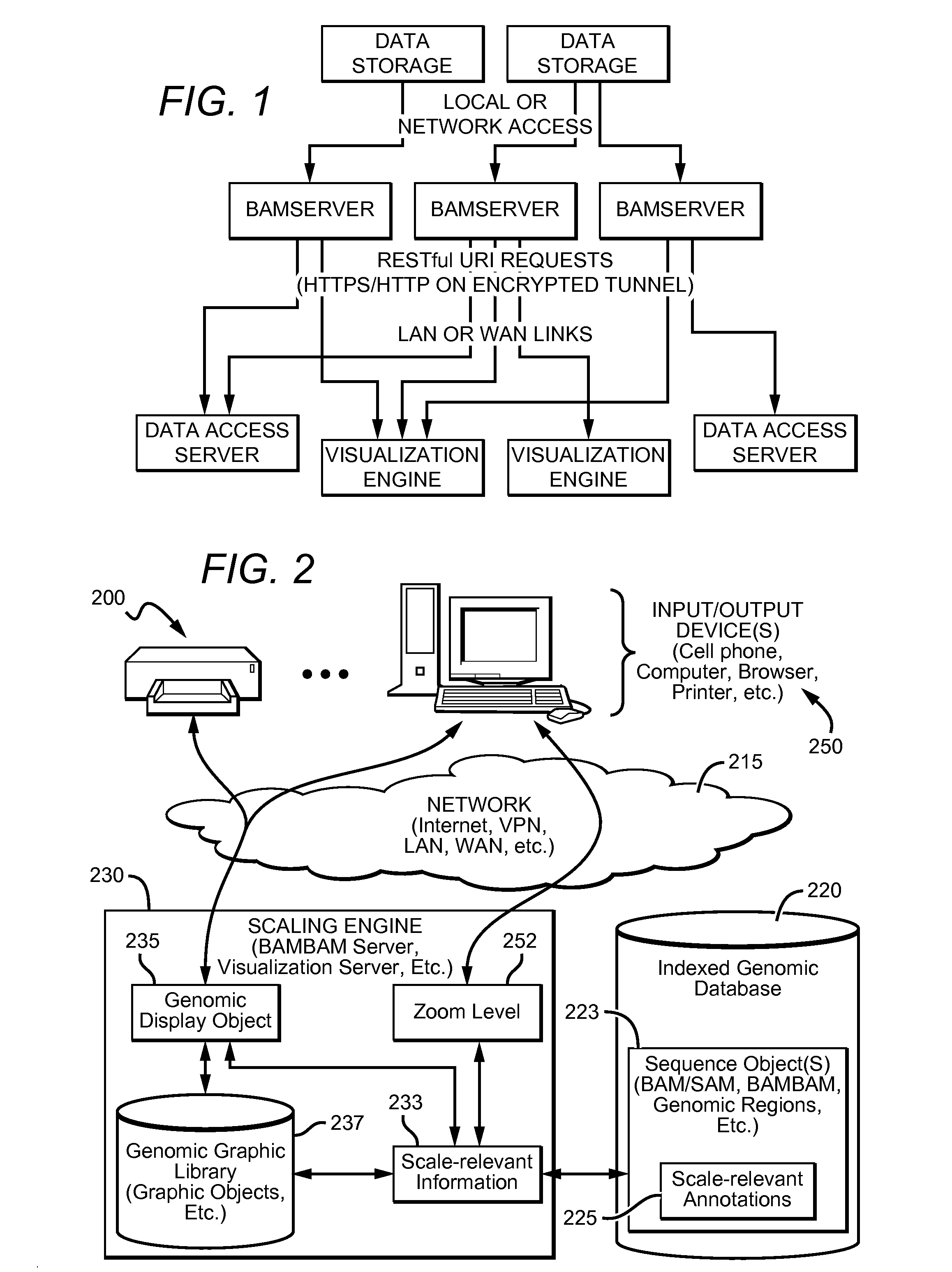
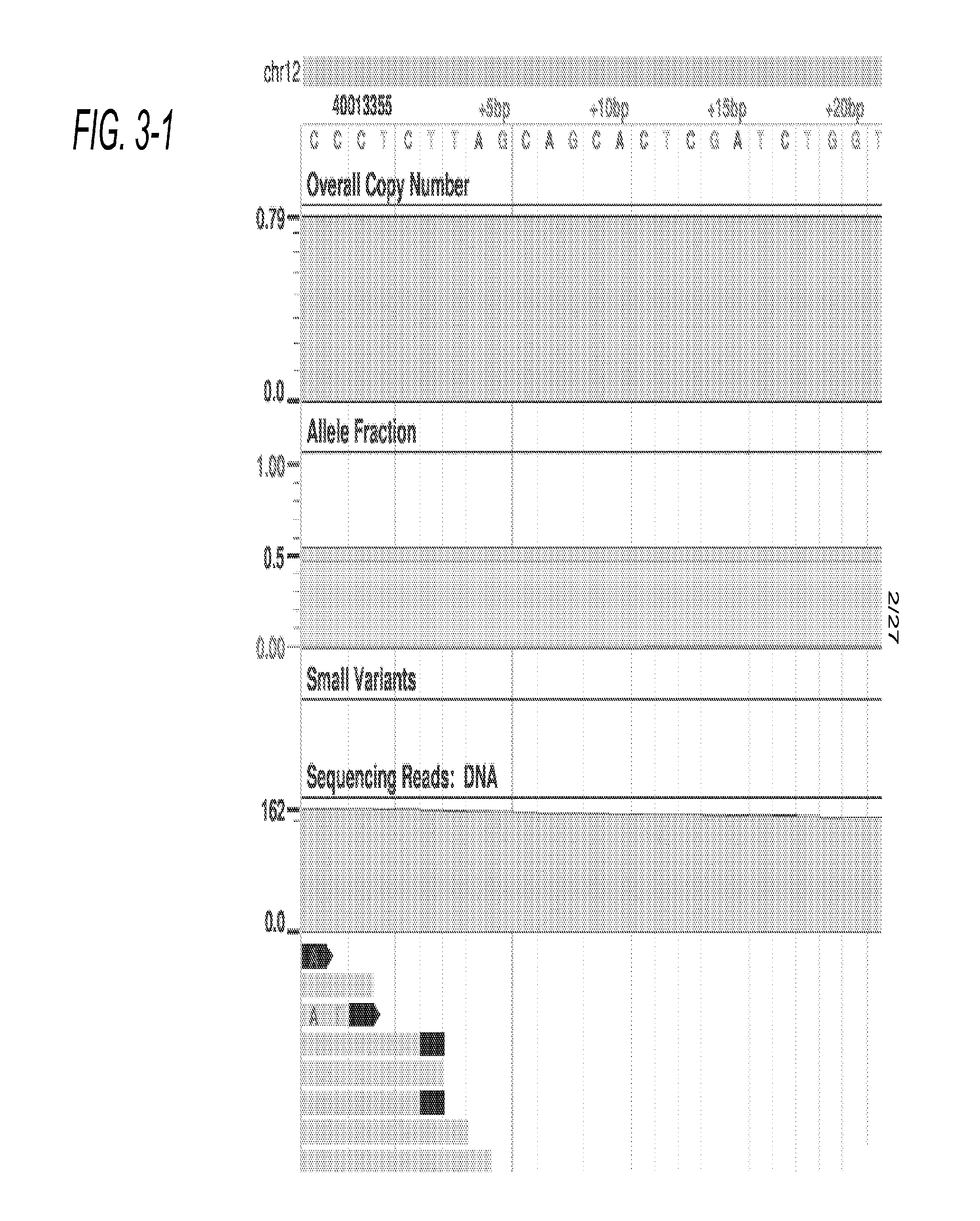
Distributed System Providing Dynamic Indexing And Visualization Of Genomic Data
ActiveUS20140368550A1Reduced data analysisReduce transferGeometric image transformationData visualisationGenomic dataData system
Systems and methods for dynamic visualization of genomic data are provided in which a genomic visualization system adapts presentation of information content according to scale-relevant annotations within a sequence object.
Owner:FIVE3 GENOMICS
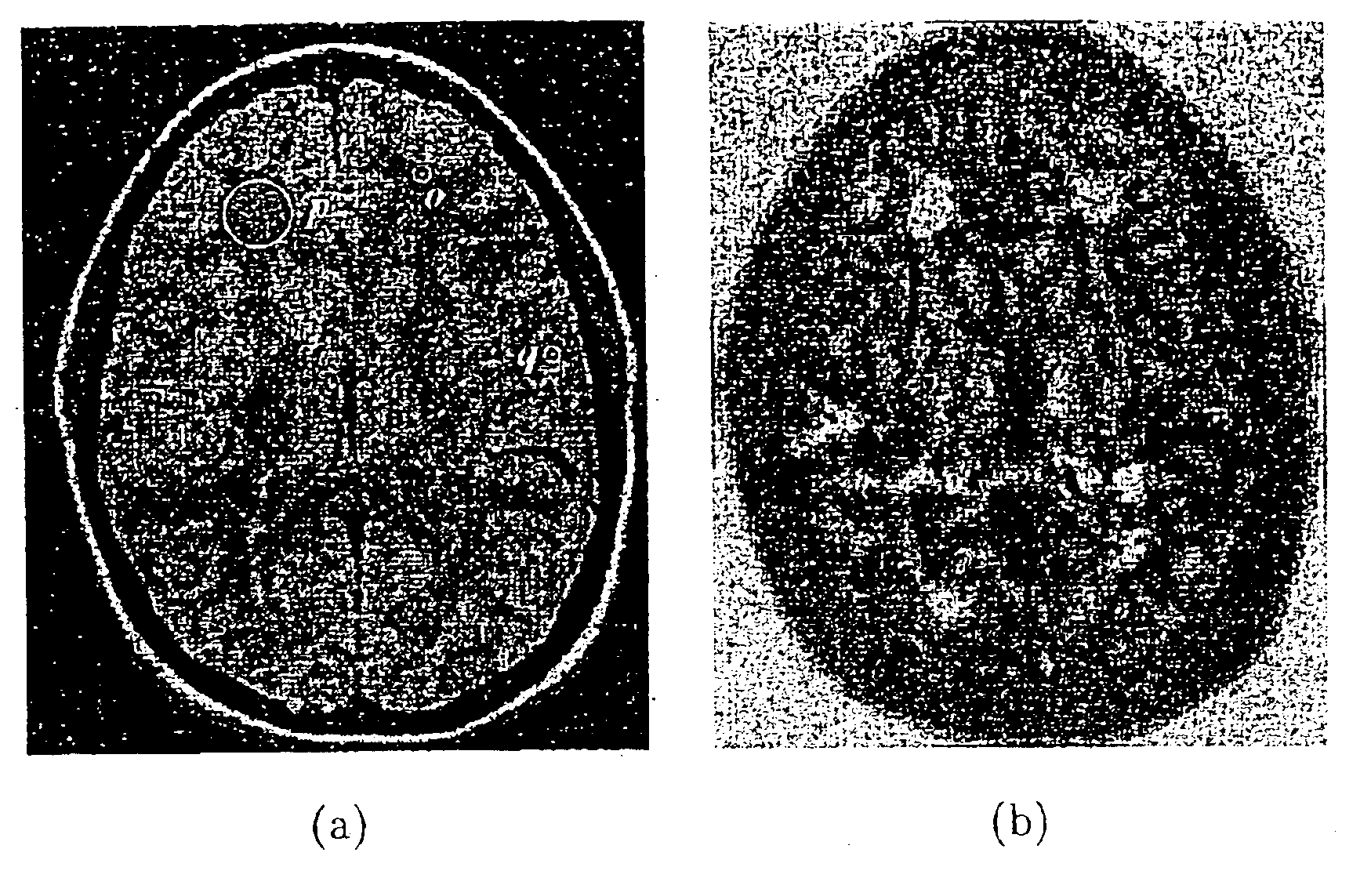
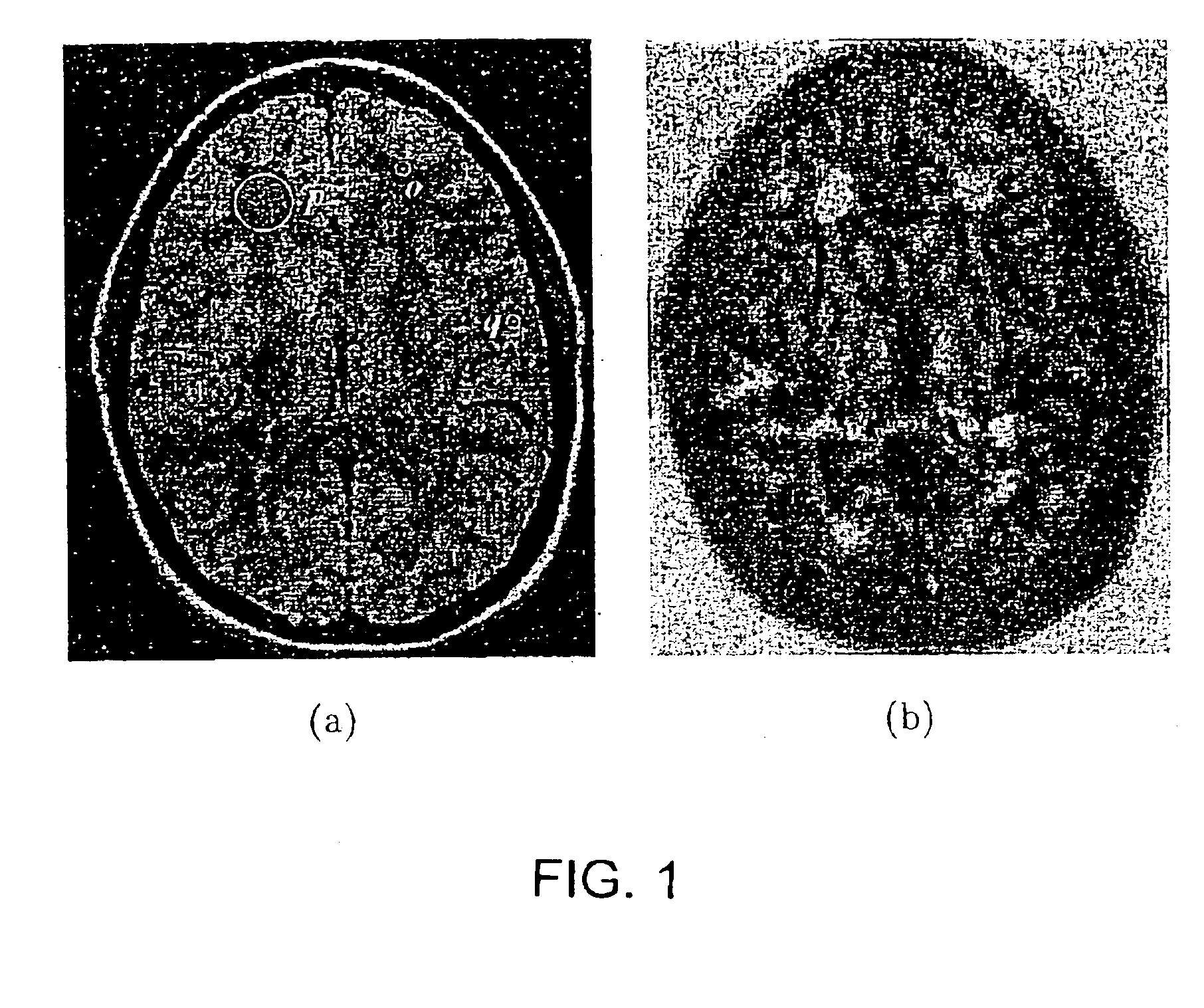
Scale-based image filtering of magnetic resonance data
InactiveUS6885762B2Efficient use ofImprove segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDiffusion
The invention provides novel scale-based filtering methods that use local structure size or “object scale” information to arrest smoothing around fine structures and across even low-gradient boundaries. One method teaches a weighted average over a scale-dependent neighborhood; while another employs scale-dependent diffusion conductance to perform filtering. Both methods adaptively modify the degree of filtering at any image location depending on local object scale. This permits a restricted homogeneity parameter to be accurately used for filtering in regions with fine details and in the vicinity of boundaries, while at the same time, a generous filtering parameter is used in the interiors of homogeneous regions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
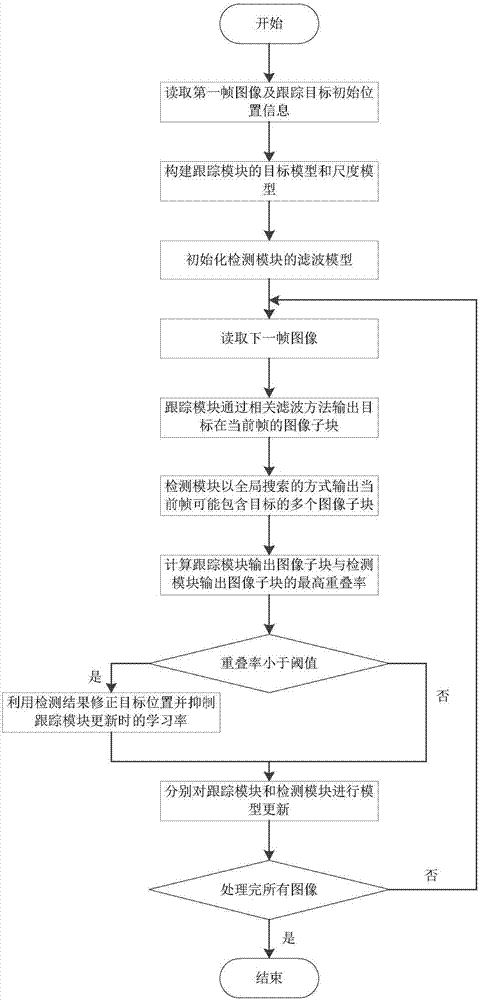
Long-time sheltering robust tracking method based on convolutional features and global search detection
The invention relates to a long-time sheltering robust tracking method based on convolutional features and global search detection. Through adopting a convolutional feature and multi-scale relative filtering method in a tracking module, the feature representation capacity of a tracking object appearance model is enhanced, so that a tracking result is very robust to factors such as illumination variation, object scale variation and object rotation. In addition, through the introduced global search detection mechanism, a detection module can detect the object again when the tracking fails because the object is sheltered for a long time, thus the tracking module can recover from error, and the object can be continuously tracked for a long time even in the case of object appearance changes.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
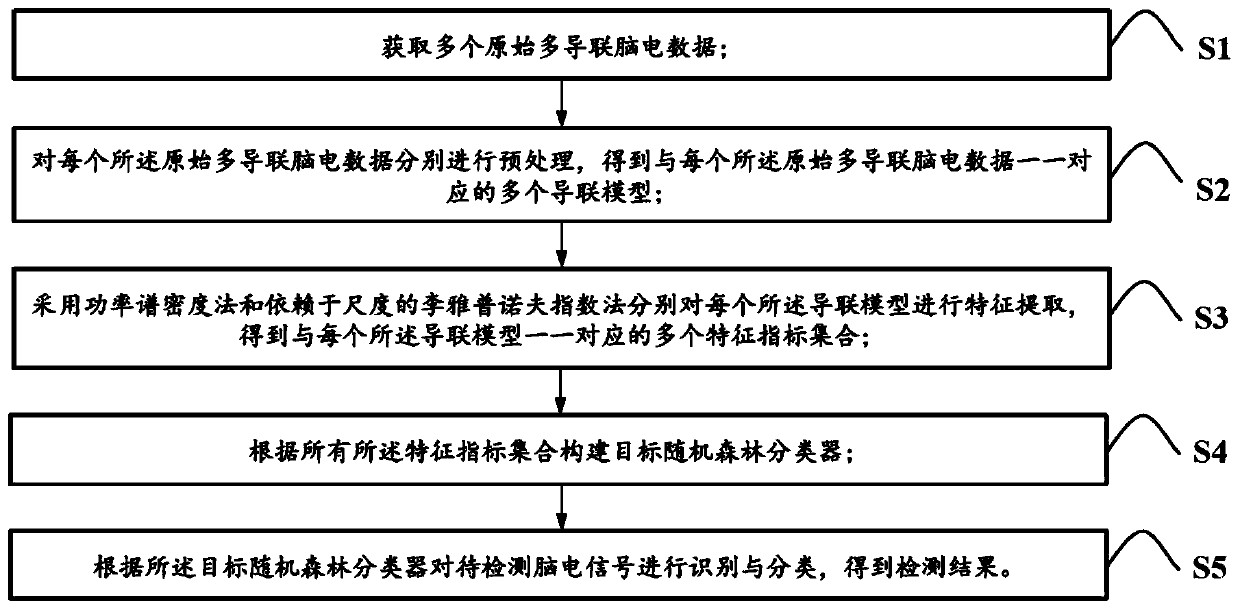
Method for identifying and classifying epileptiform discharges, system, device thereof and medium
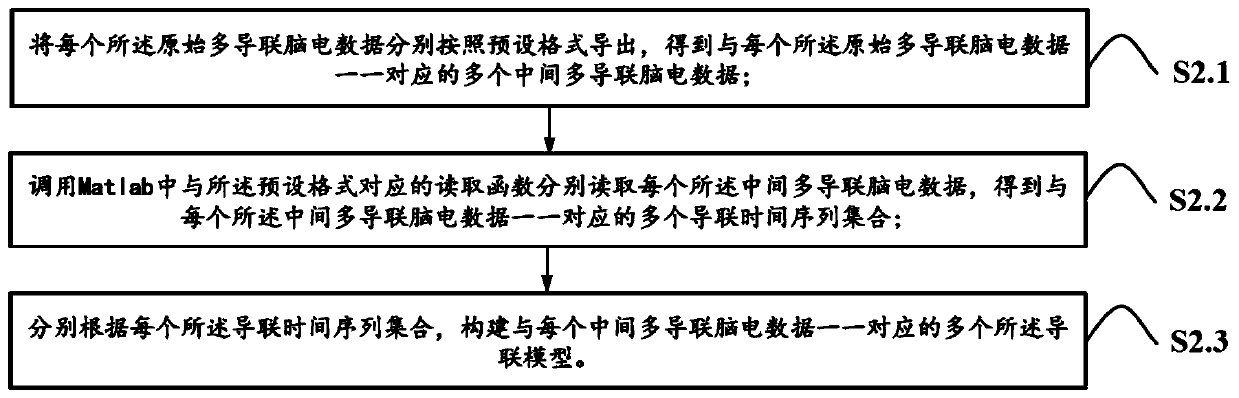
ActiveCN110338786AEasy to identifyEasy to classifyDiagnostic signal processingSensorsEeg dataFeature extraction
The invention relates to a method for identifying and classifying epileptiform discharges, a ystem, a device thereof and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a plurality of original multi-lead EEG data; respectively pre-processing each original multi-lead EEG data to obtain a plurality of lead models corresponding to each original multi-lead EEG data; employing a power spectral density method and a scale-dependent Lyapunov exponential method to extract features of each lead model respectively, and obtaining a plurality of feature index sets corresponding to each of thelead models one by one; constructing a target random forest classifier according to all the feature index sets; and perofmirng identification and classification on the EEG signals to-be-detected according to the target random forest classifier, and obtaining the test results. The method can make up for the deficiency of a traditional nonlinear signal processing method in the digitized EEG signalanalysis, realizes the classification of the normal human brain electrical signal and the epileptiform discharges, and has high recognition and classification accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
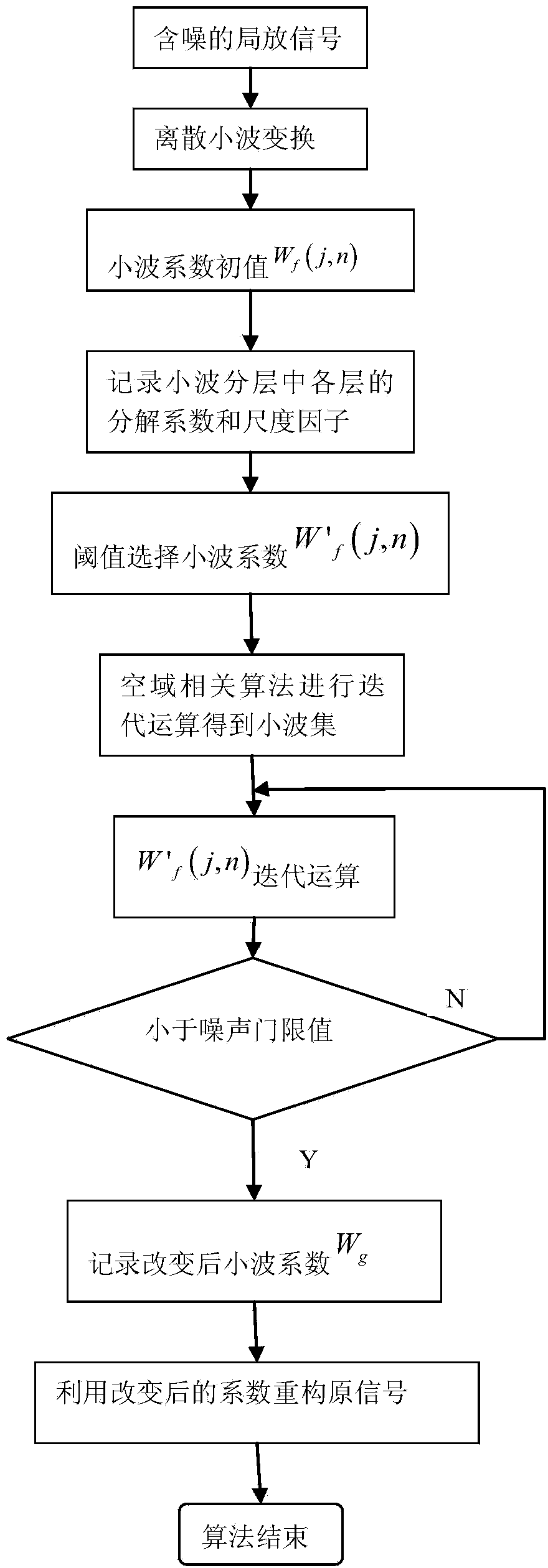
Wavelet coefficient partial discharge signal noise elimination method based on related space domain correction threshold values
InactiveCN103995950AReduce the impactHigh speedSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientAlgorithm convergence
The invention belongs to the field of industrial signal processing, and particularly relates to a wavelet coefficient partial discharge signal noise elimination method based on related space domain correction threshold values. The method includes the steps that wavelet transformation is carried out on partial discharge signals containing white noise; an initial value and an estimated value of a wavelet coefficient are extracted; size correlation coefficients are solved; correlation values are obtained after normalization; discrete wavelet transform is recorded and signals after noise elimination are obtained. A wavelet threshold value selection method is improved, a space domain related optimizing partial reestablishment weight matrix is introduced, and therefore, influences of noise points on sample data are reduced, the algorithm convergence rate is improved, and the noise elimination speed and precision of the partial discharge signals are improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV +2
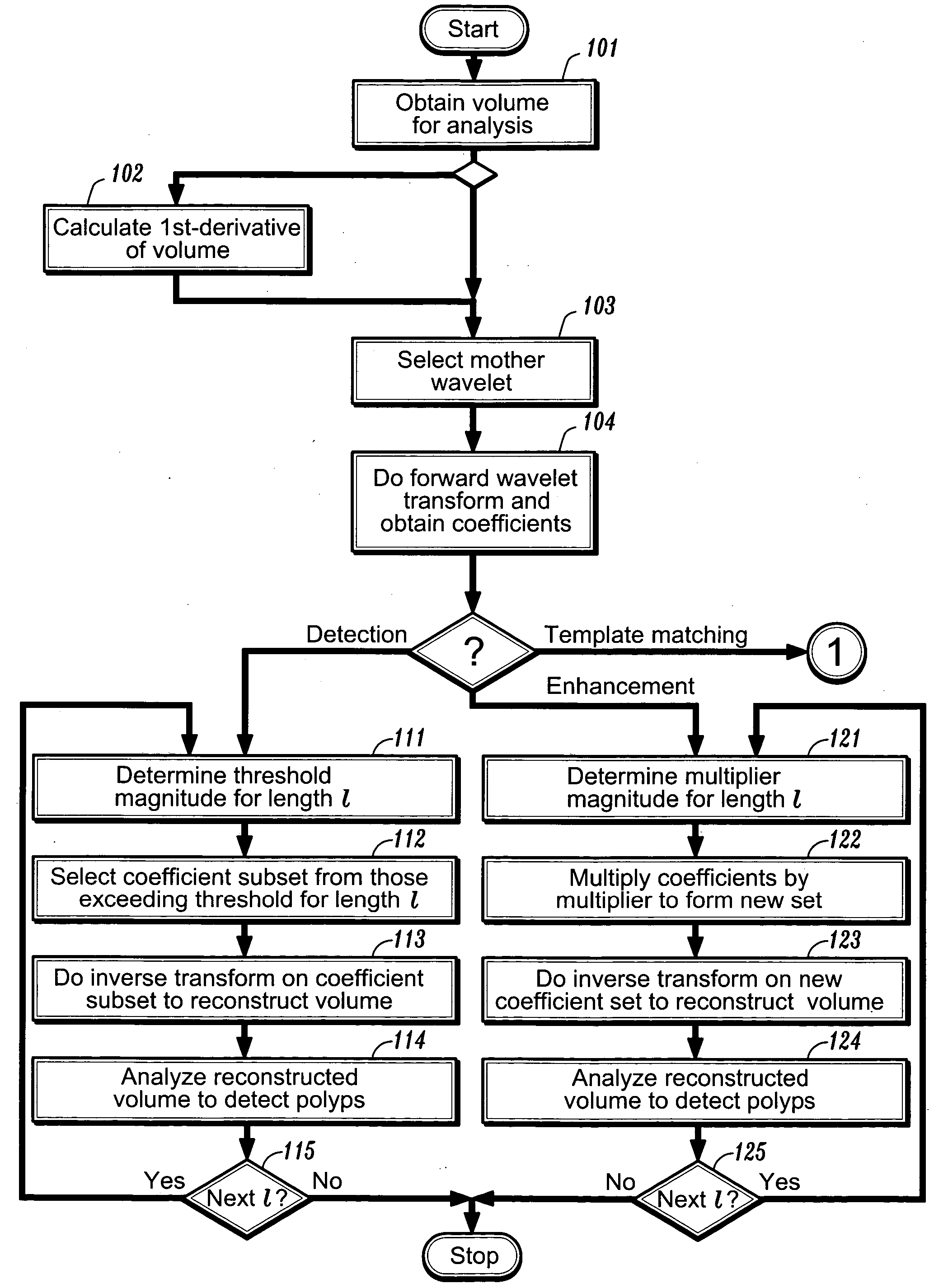
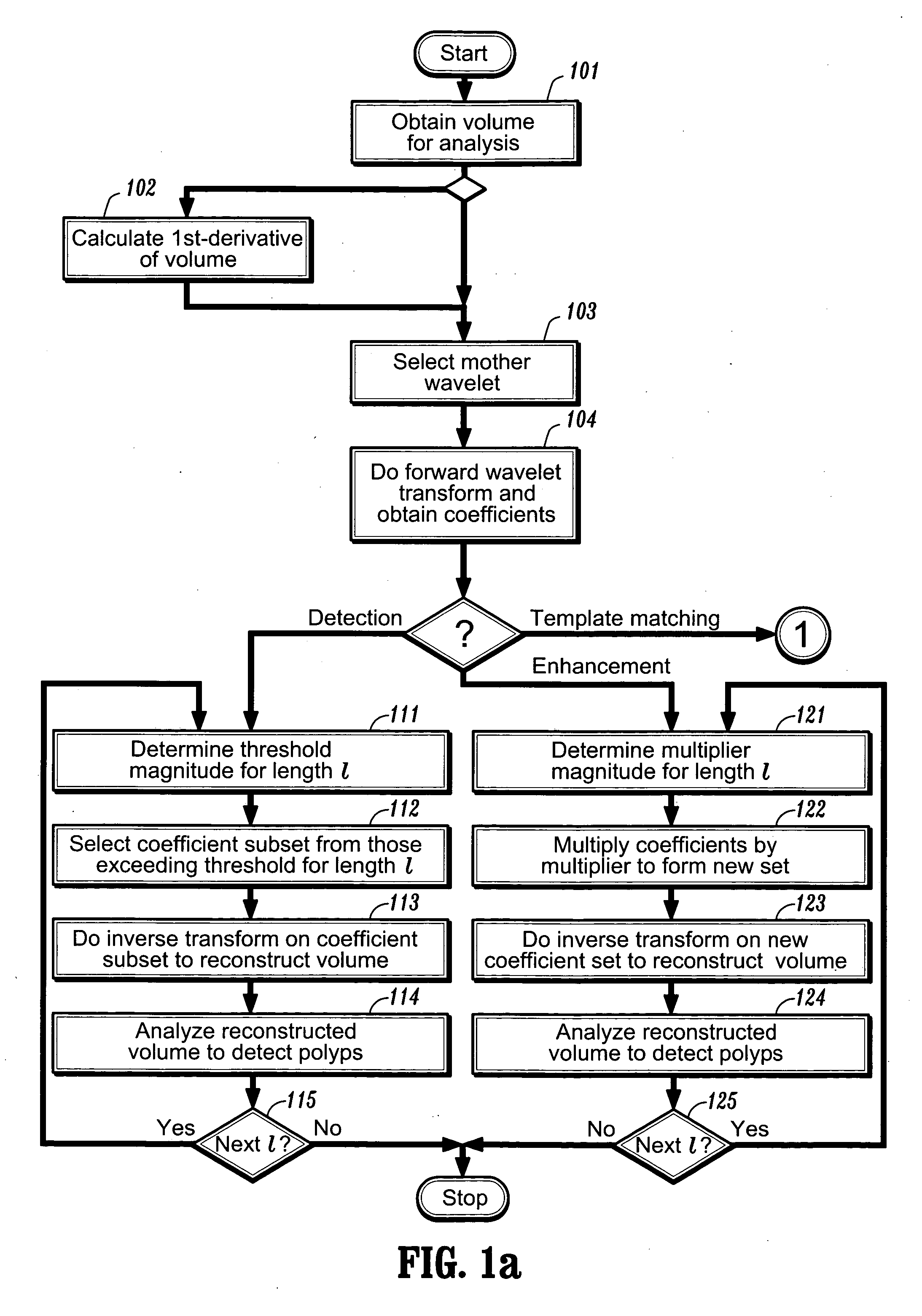
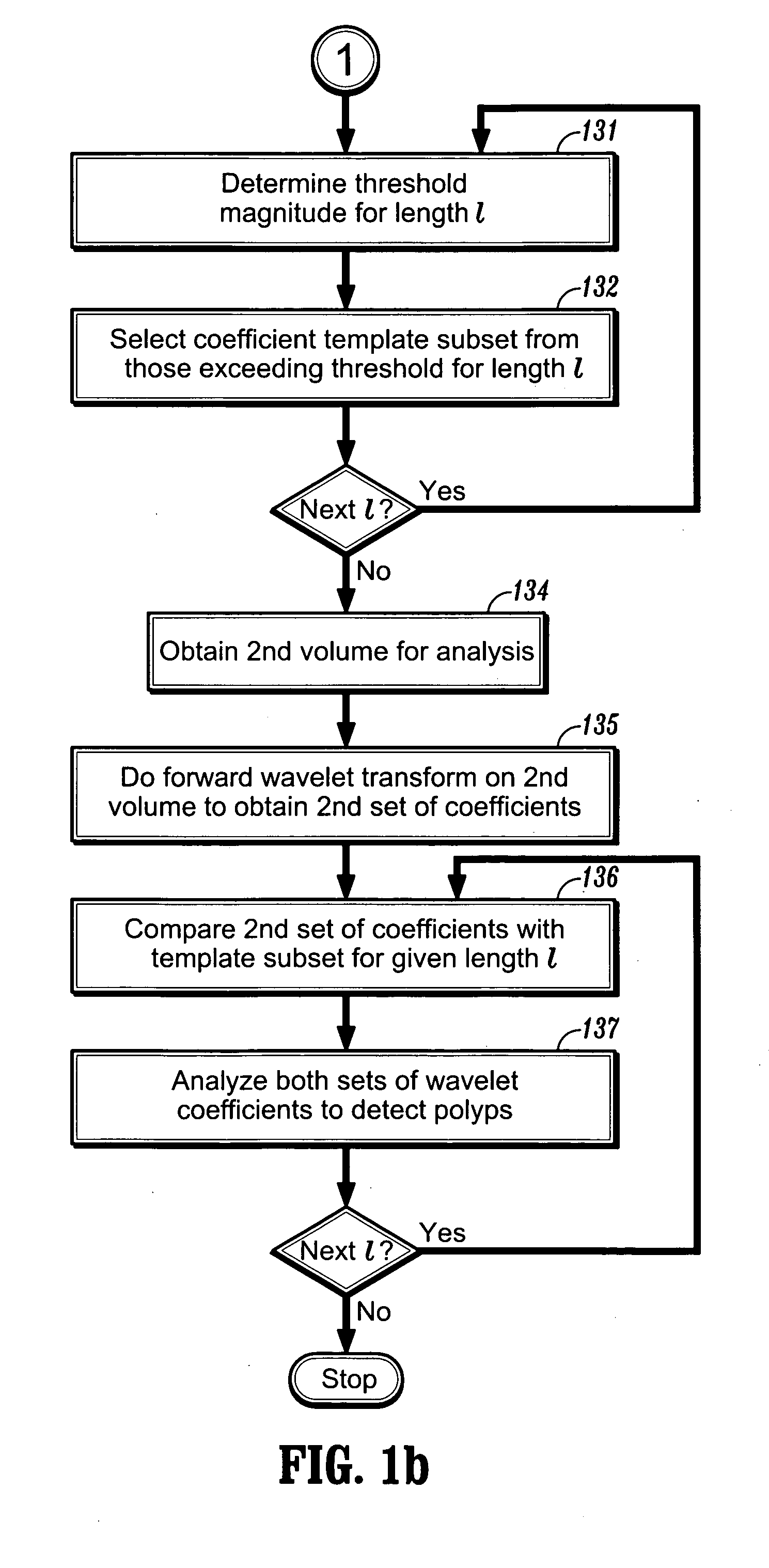
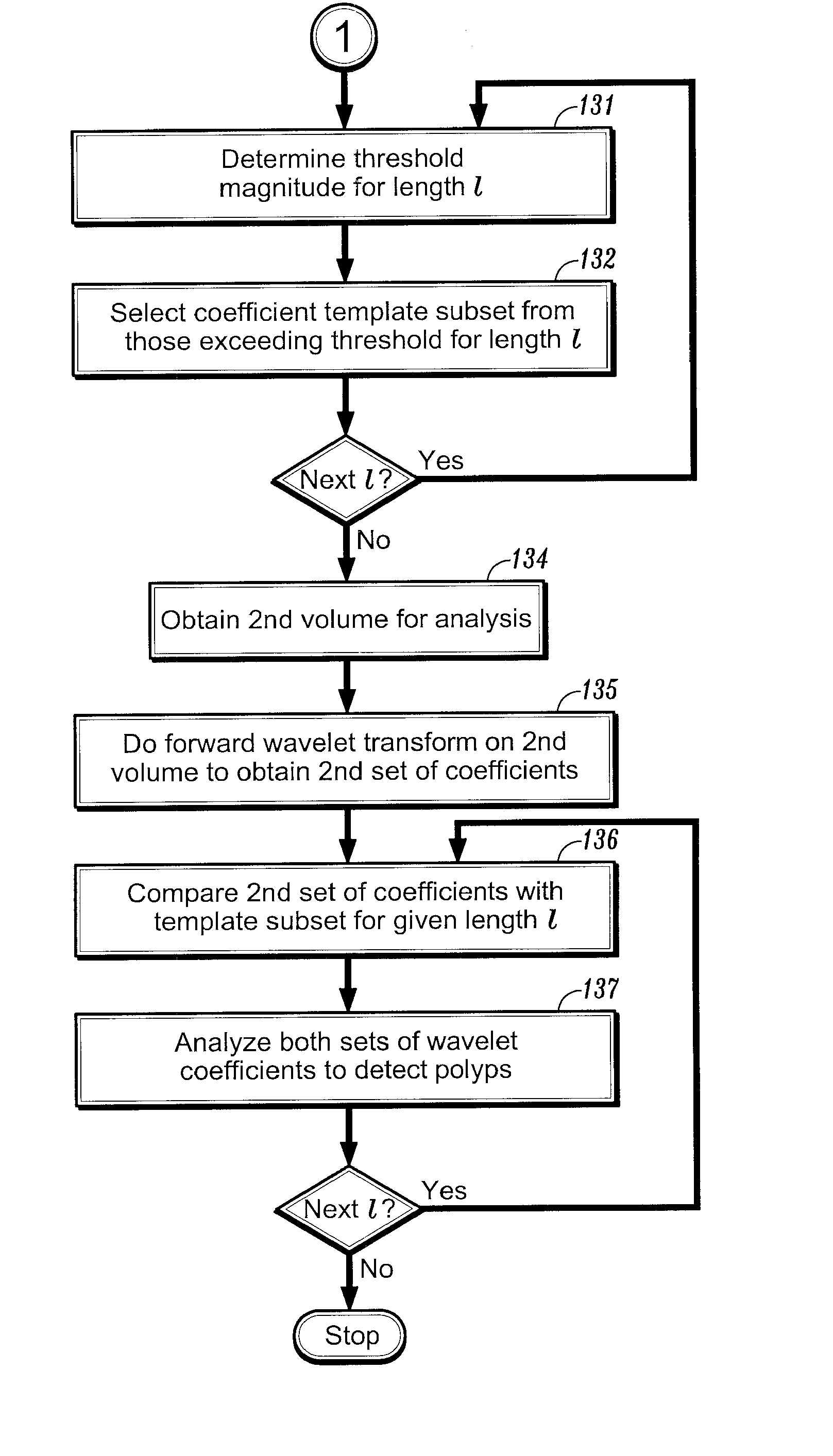
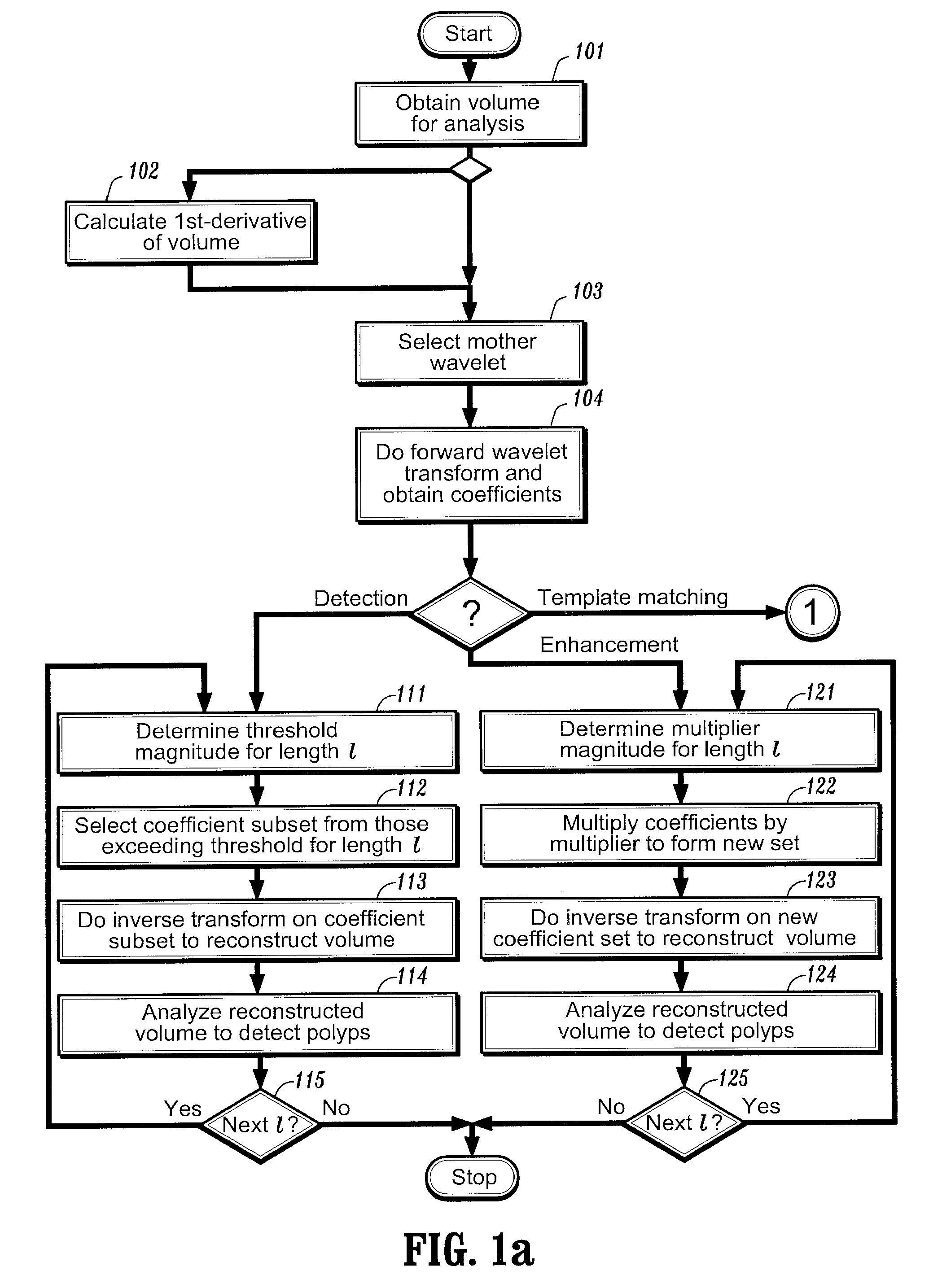
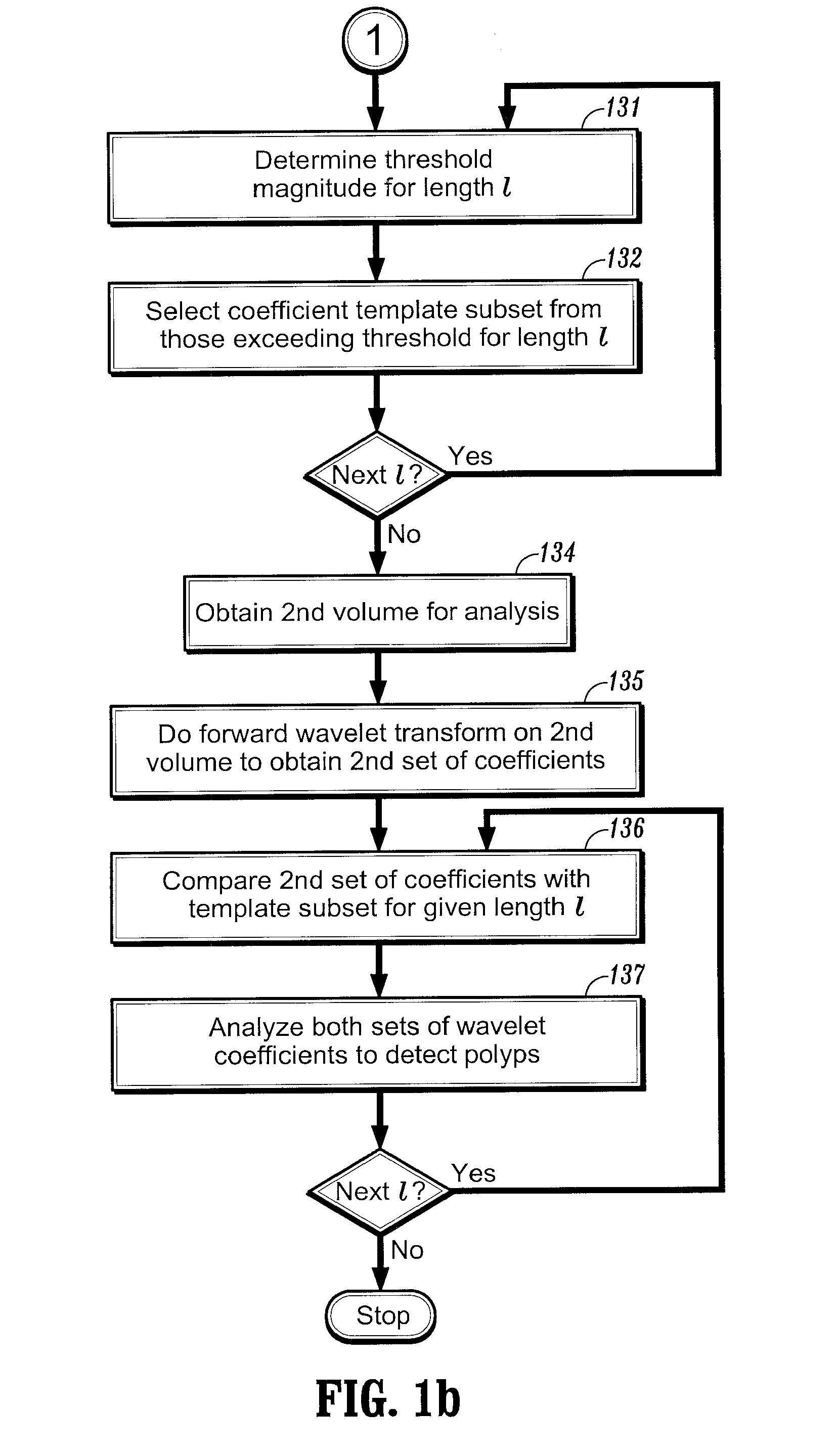
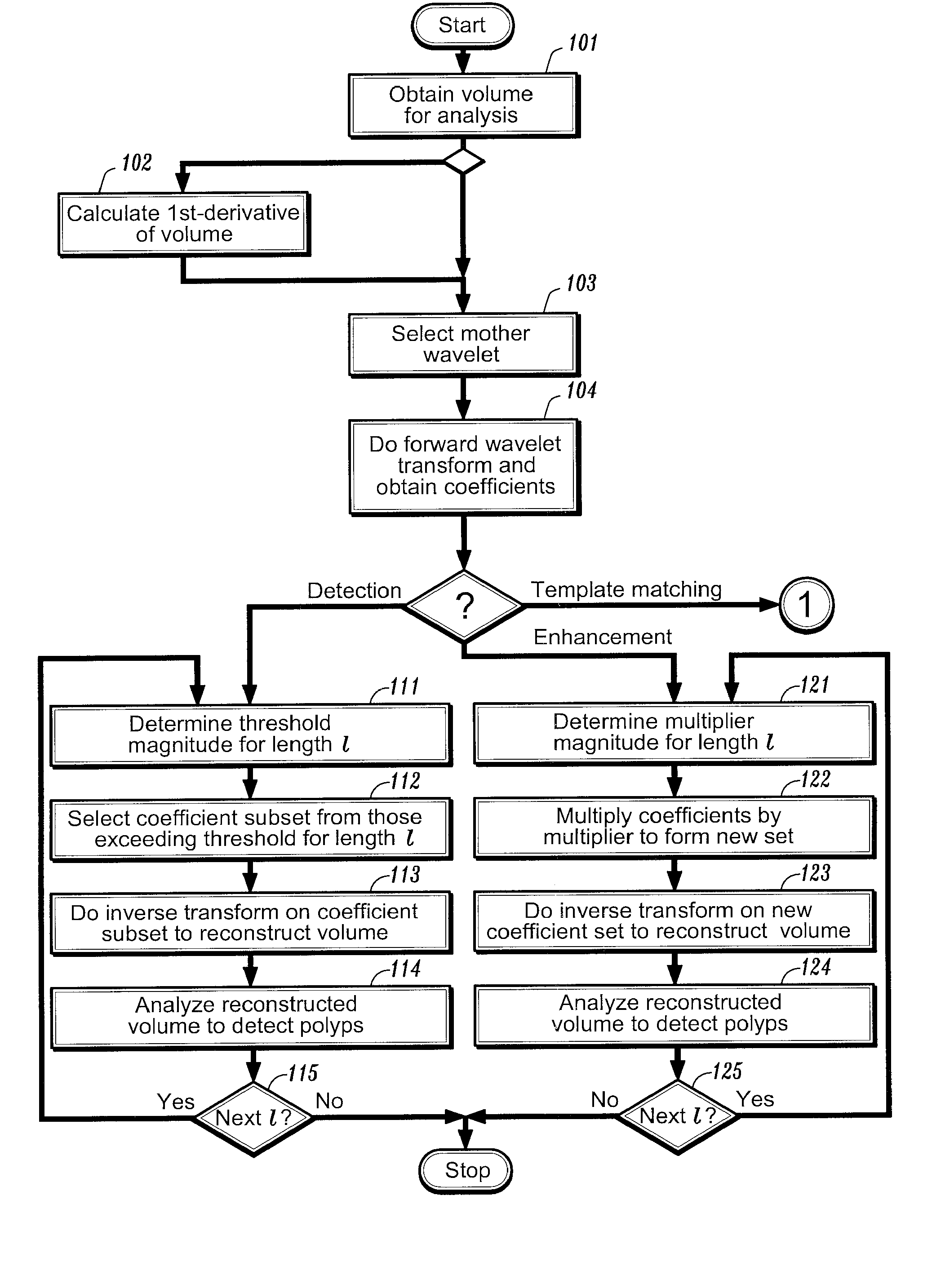
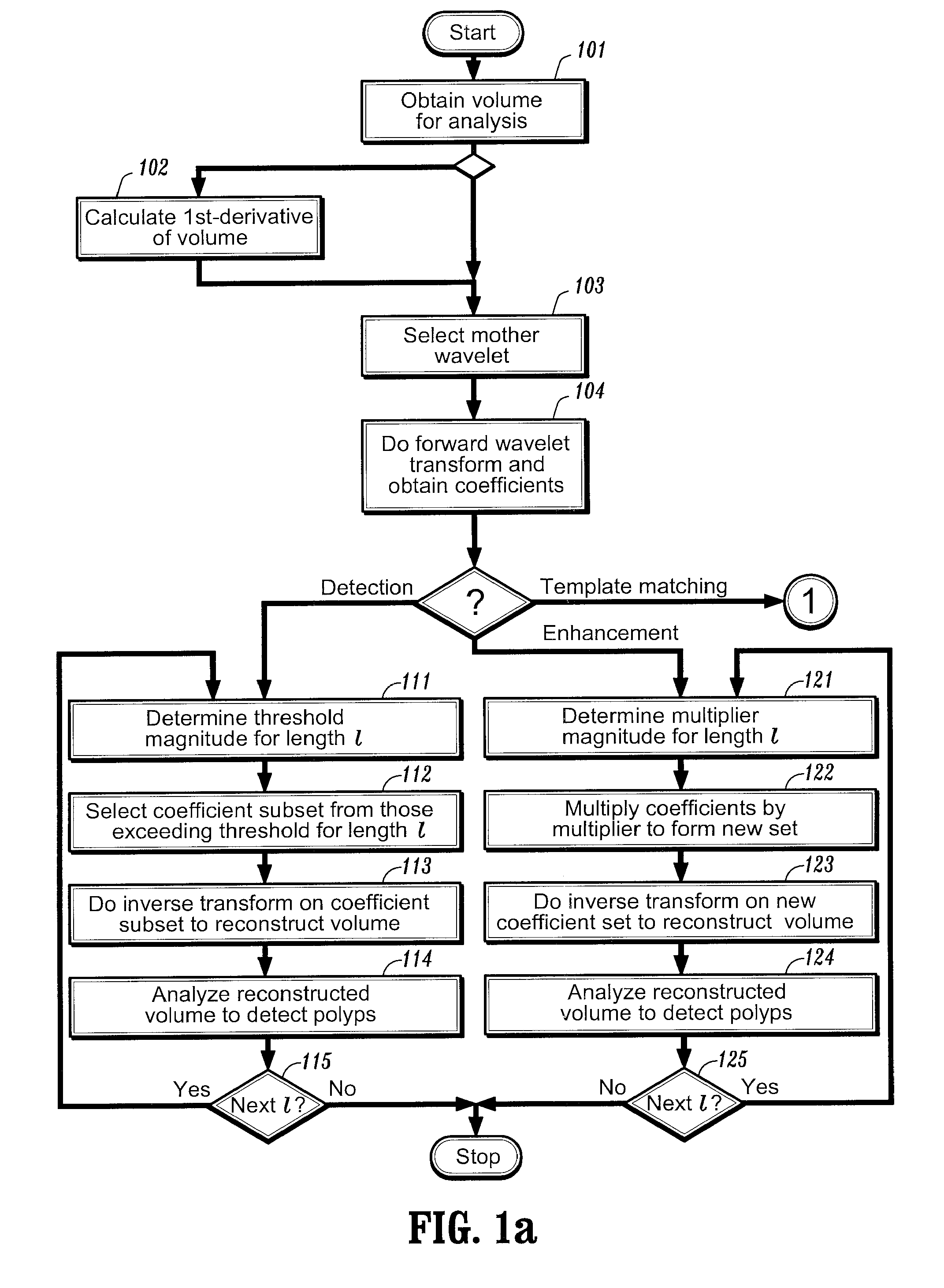
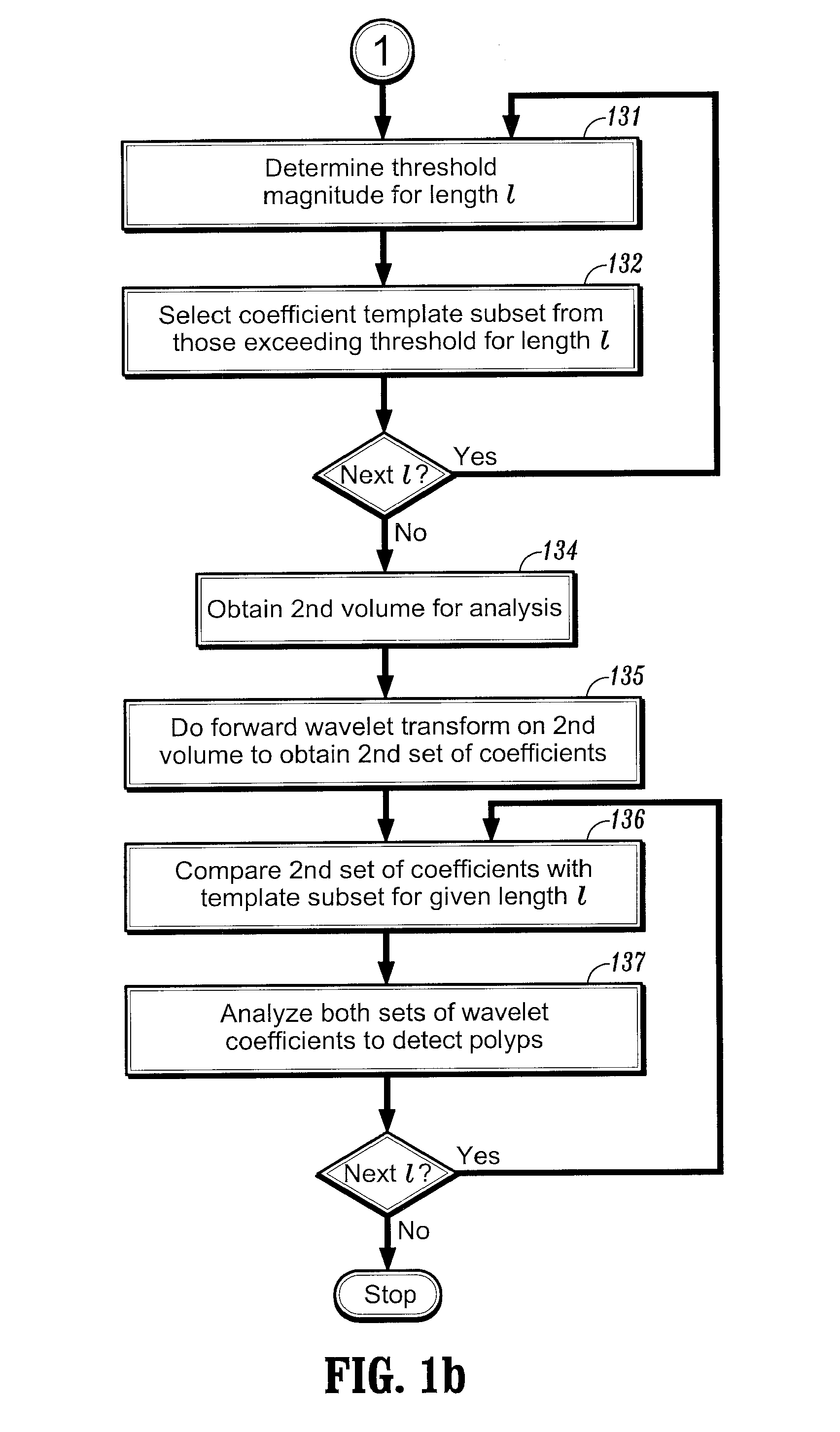
Method and system for wavelet based detection of colon polyps
A method of identifying colon polyps in a digital volume, wherein the volume includes a plurality of values corresponding to a domain of points in a 3D space, is provided. The method includes selecting a mother wavelet scaling function that corresponds to a polyp; performing a forward wavelet transformation on the volume to obtain a set of wavelet coefficients, wherein each wavelet coefficient is associated with a length scale; determining, for each length scale, a transformation magnitude; and forming, for each length scale, a transformed set of wavelet coefficients associated with the length scale. An inverse wavelet transform is performed on the transformed wavelet coefficients for each length scale to obtain a reconstructed volume, and the reconstructed volume is analyzed for the existence of polyps.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
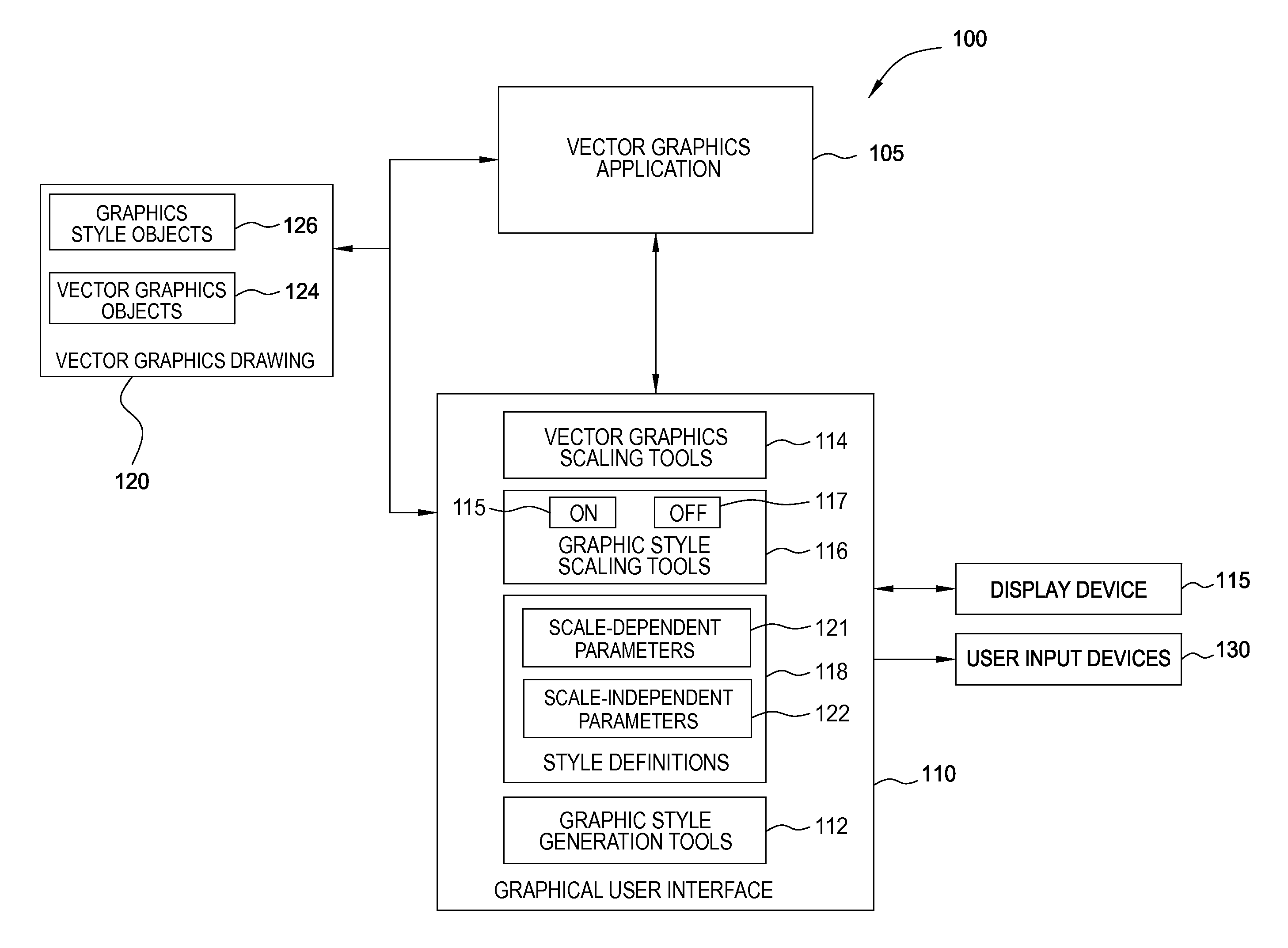
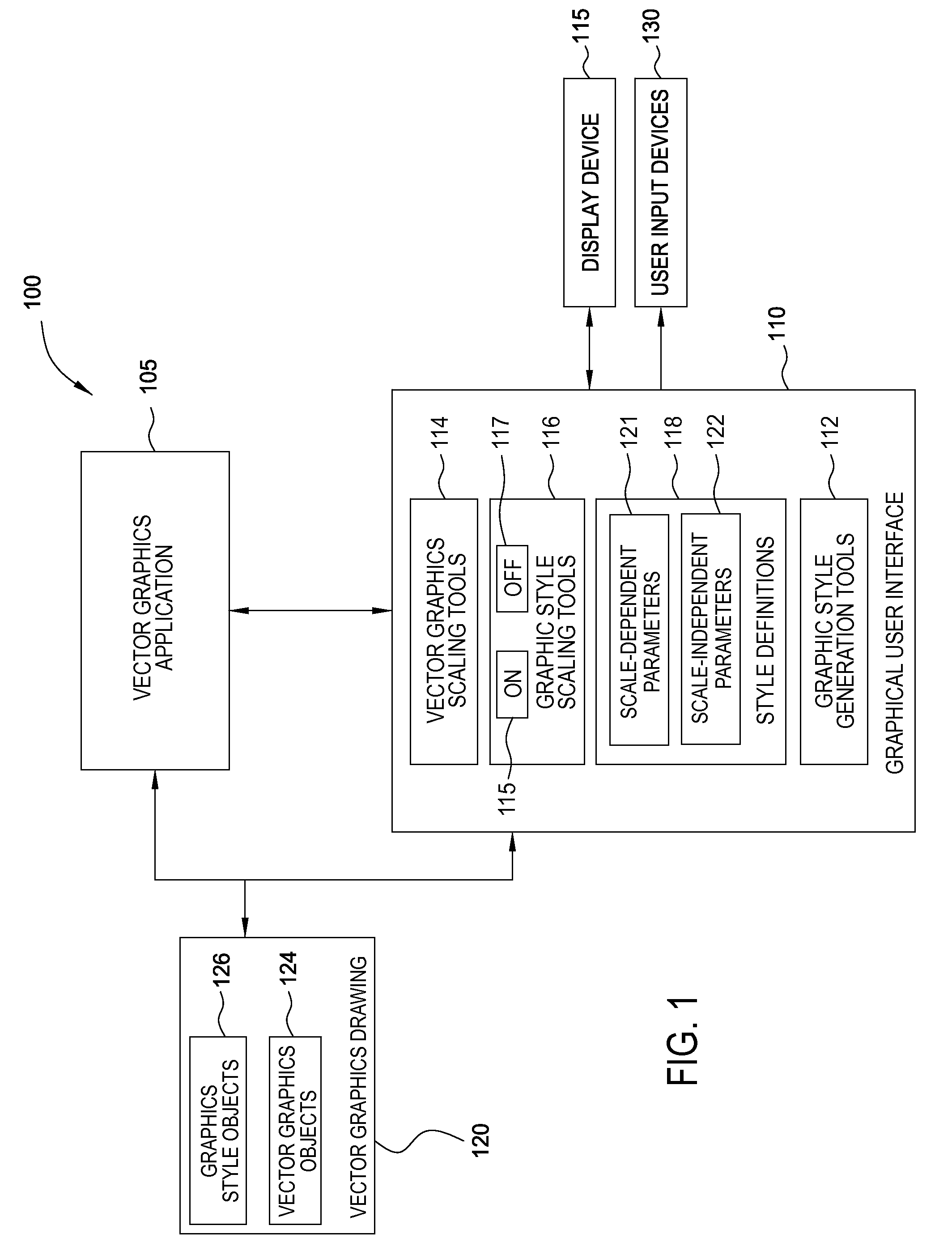
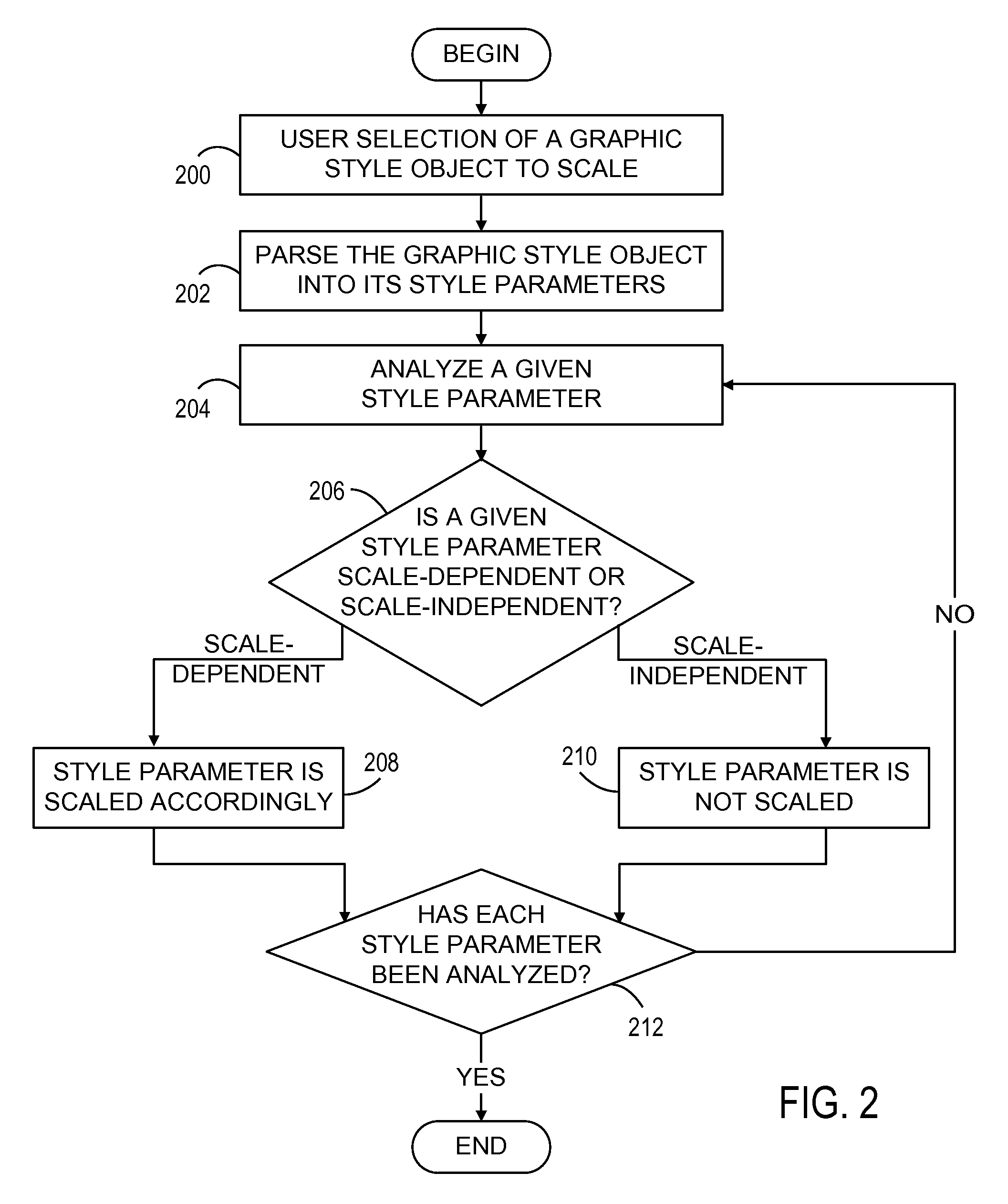
Scale-dependent rendering of natural media styles
ActiveUS20090009534A1Simplify amountSimple processDrawing from basic elementsGeometric image transformationGraphicsIndependent parameter
A method for generating a scale-dependent rendering of natural media styles in a vector-based graphics application is disclosed. A vector-based graphics drawing may be resized such that certain scale-dependent parameters are scaled proportionately, while other scale-independent parameters are not scaled. The result of such resizing is a scaled rendering of the vector-based graphics drawing that closely resemble hand drawn images created using natural media materials.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
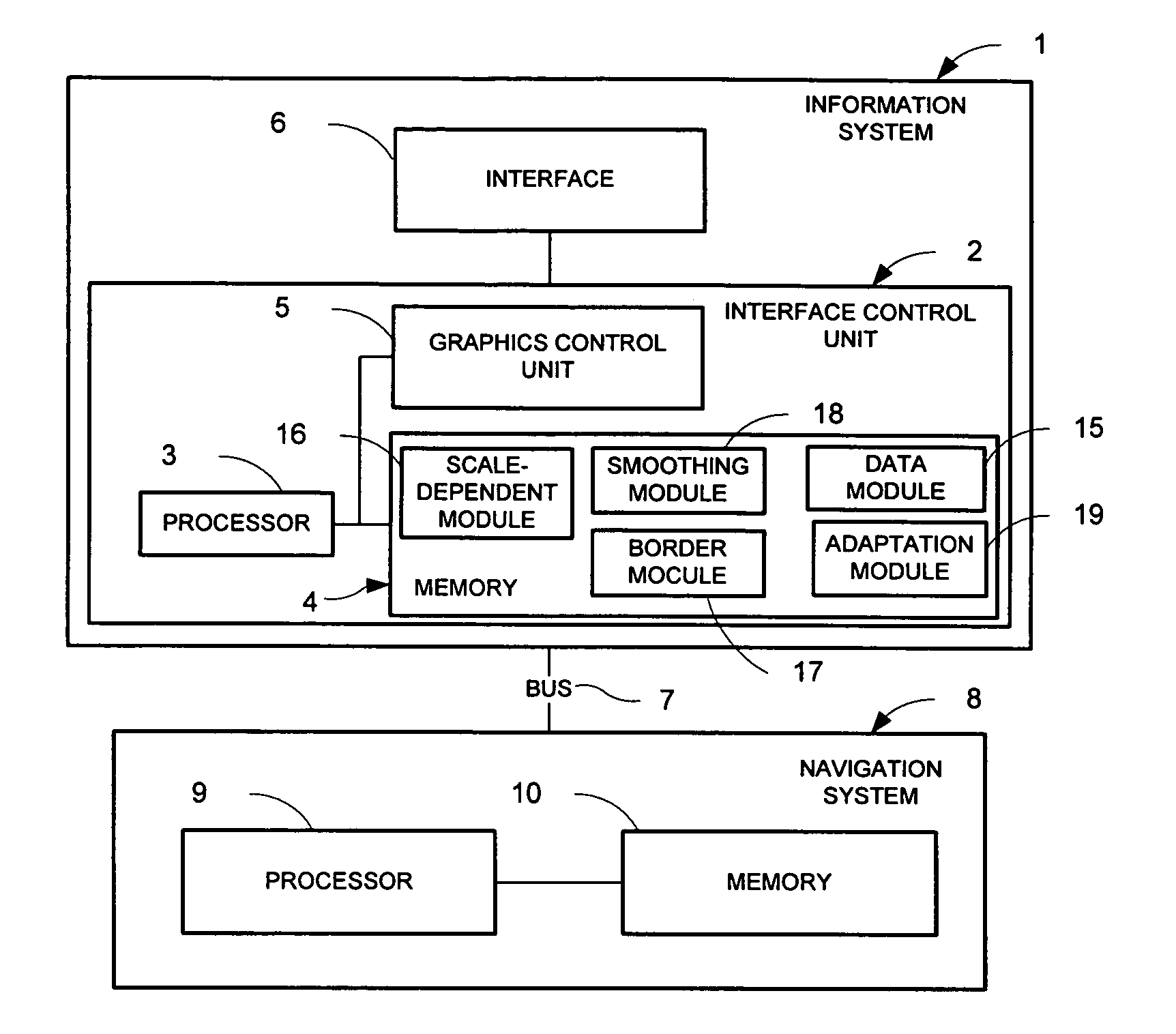
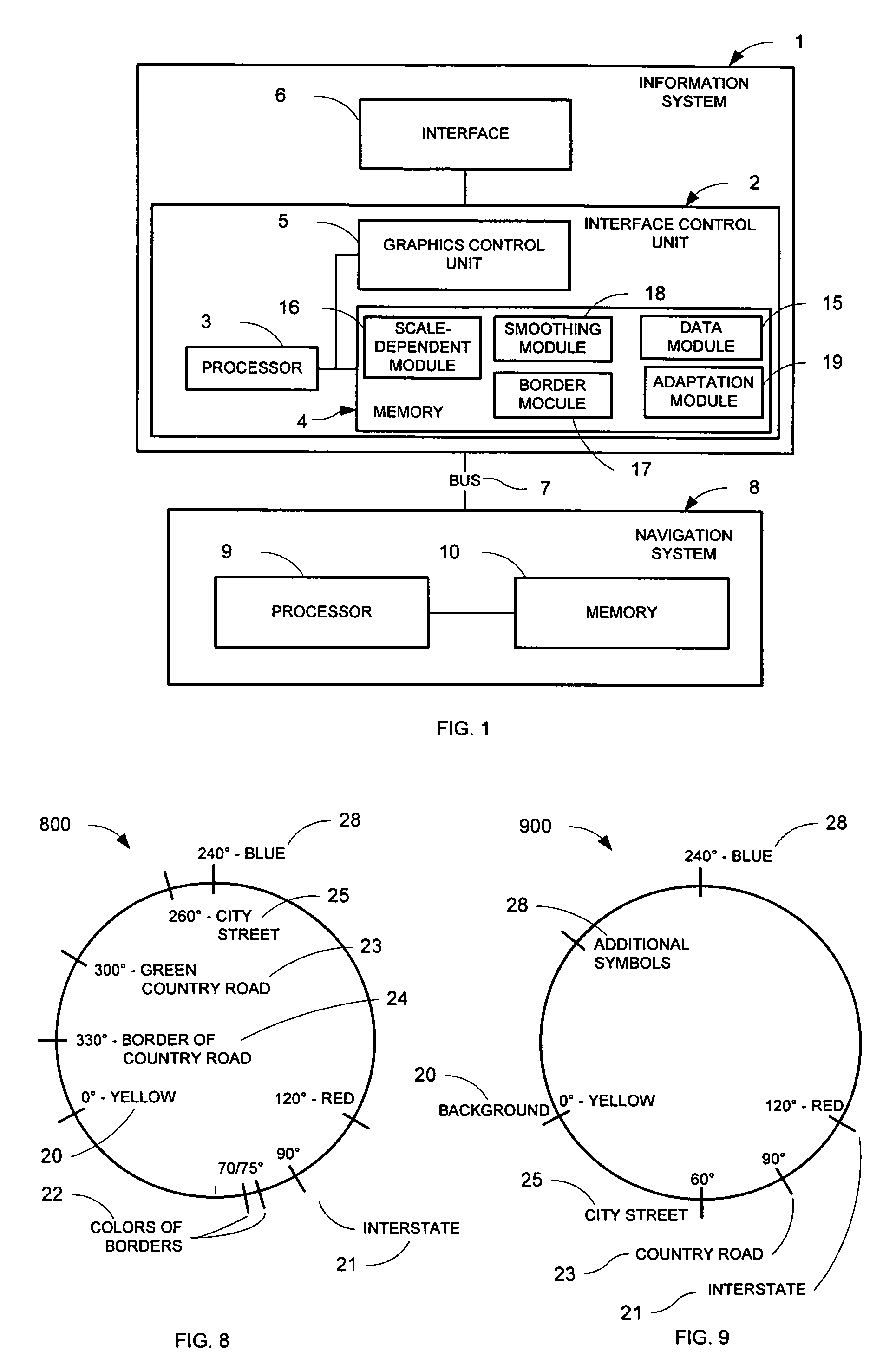
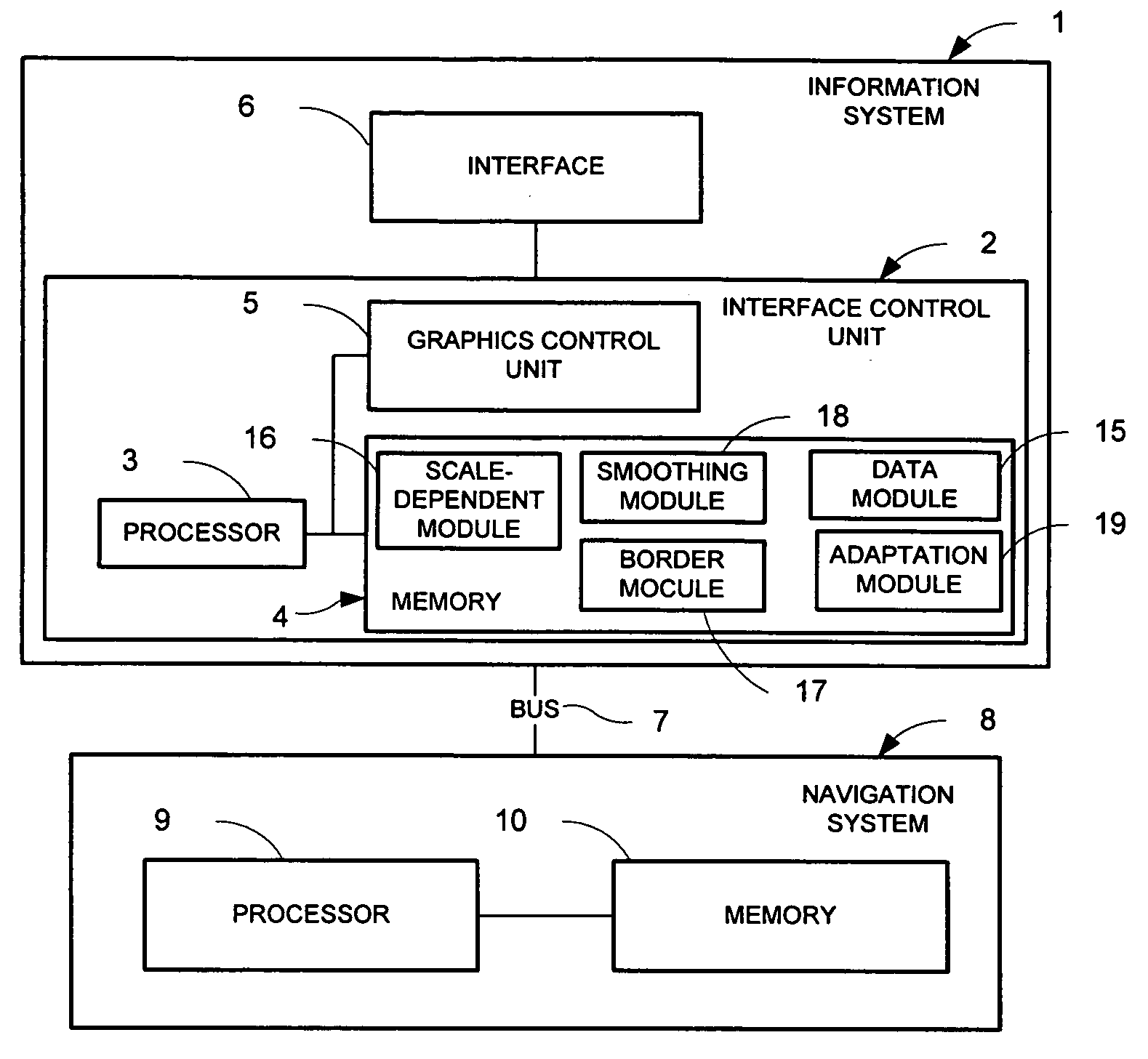
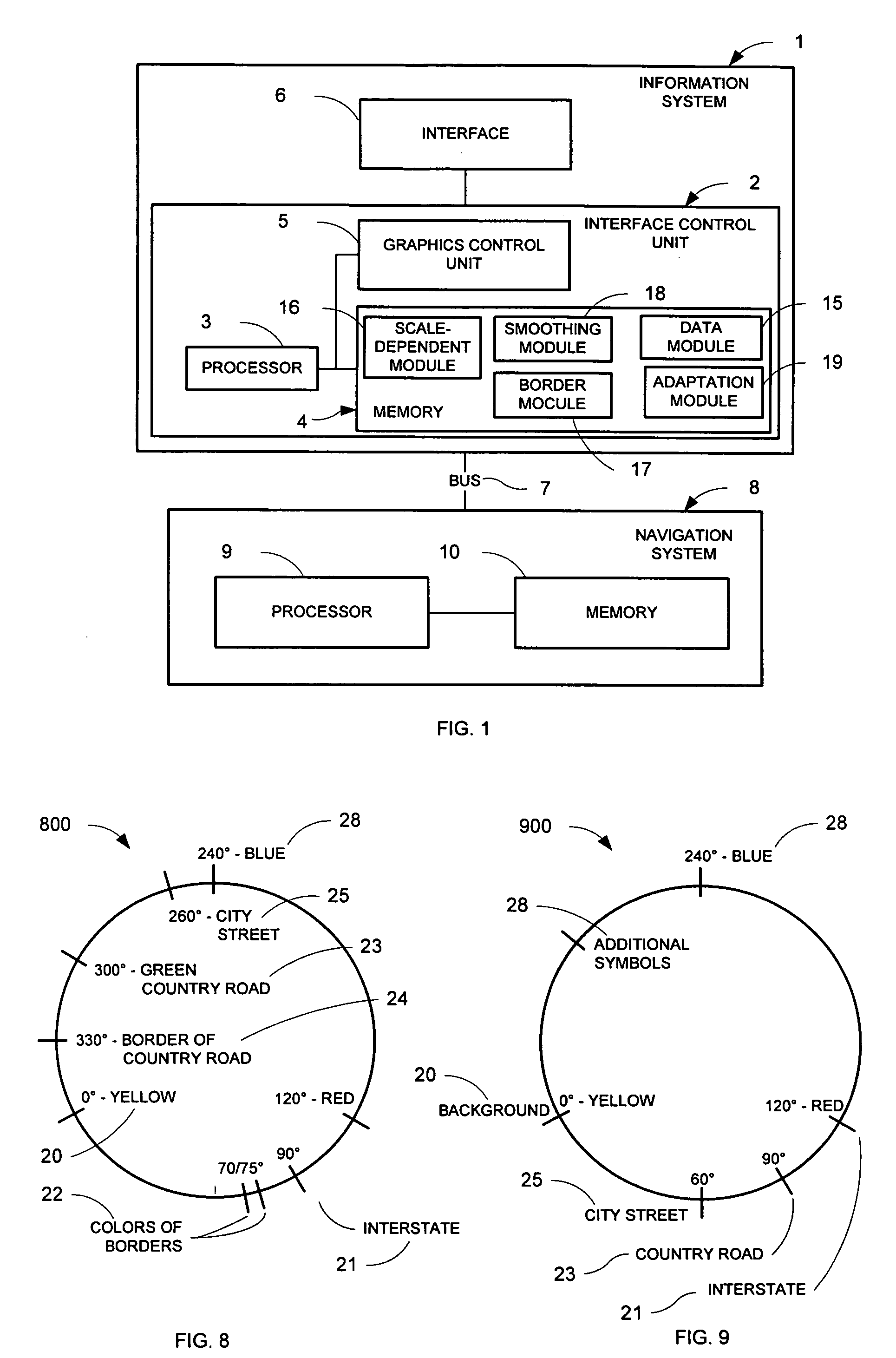
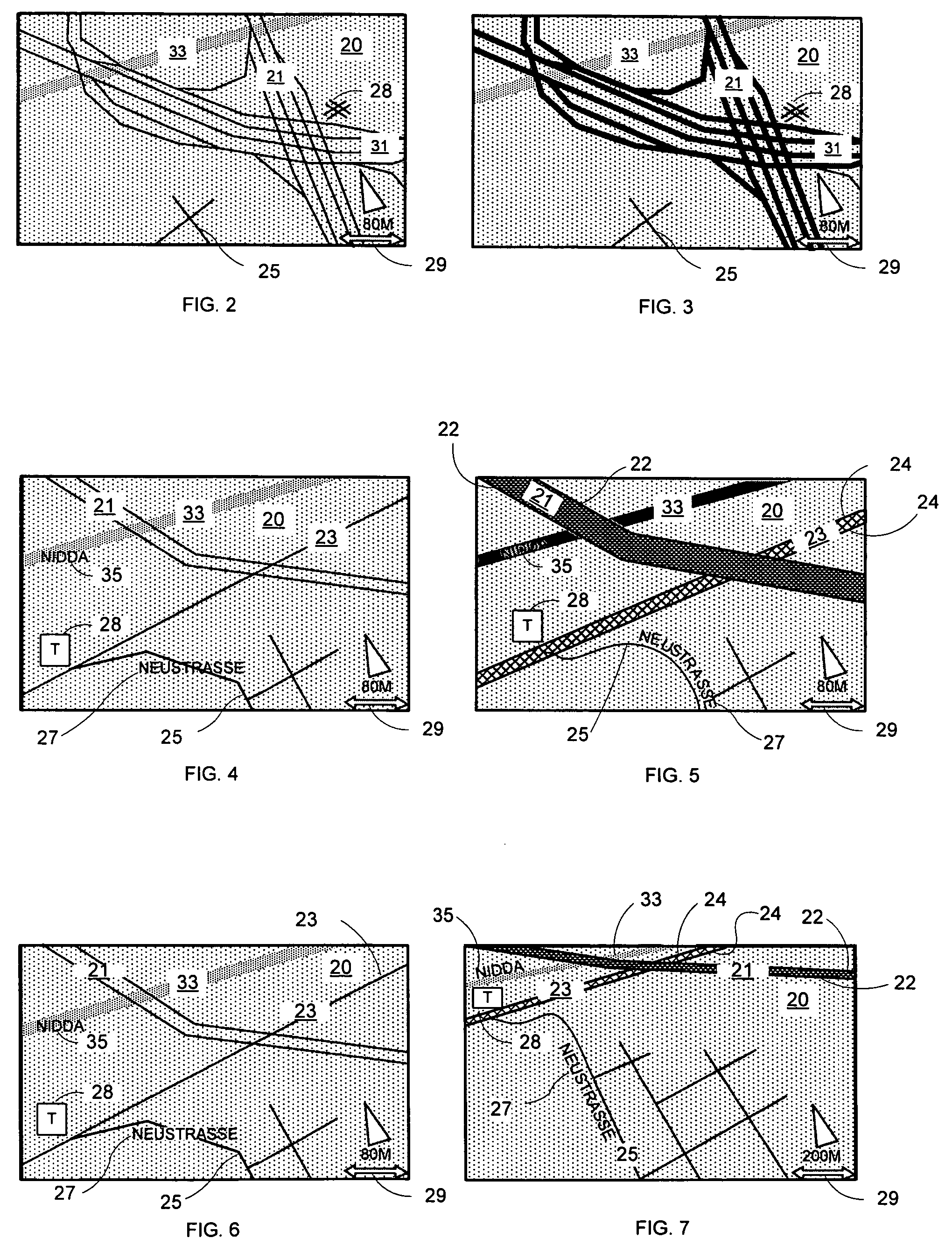
Ergonomic map information system
InactiveUS7096118B2Easy to handleHigh strengthImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationGraphicsColor intensity
A system for the ergonomic communication of a map portion is presented. The map portion may include map information, map background, and additional information. The system includes an interface control unit that may include a graphics control unit, a processor and a memory. The system may include one or more modules for creating an ergonomic presentation including: a border module that may add the additional information to the representation; an adaptation module for adapting the map information and map background and / or additional information with one another, such as within a maximum color contrast; a scale-dependent module that may adapt the color intensity and width of map information as a function of scale and type; and a smoothing module to increase the quality of the map portion representation. The system may include a method for controlling the representation of a map portion.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
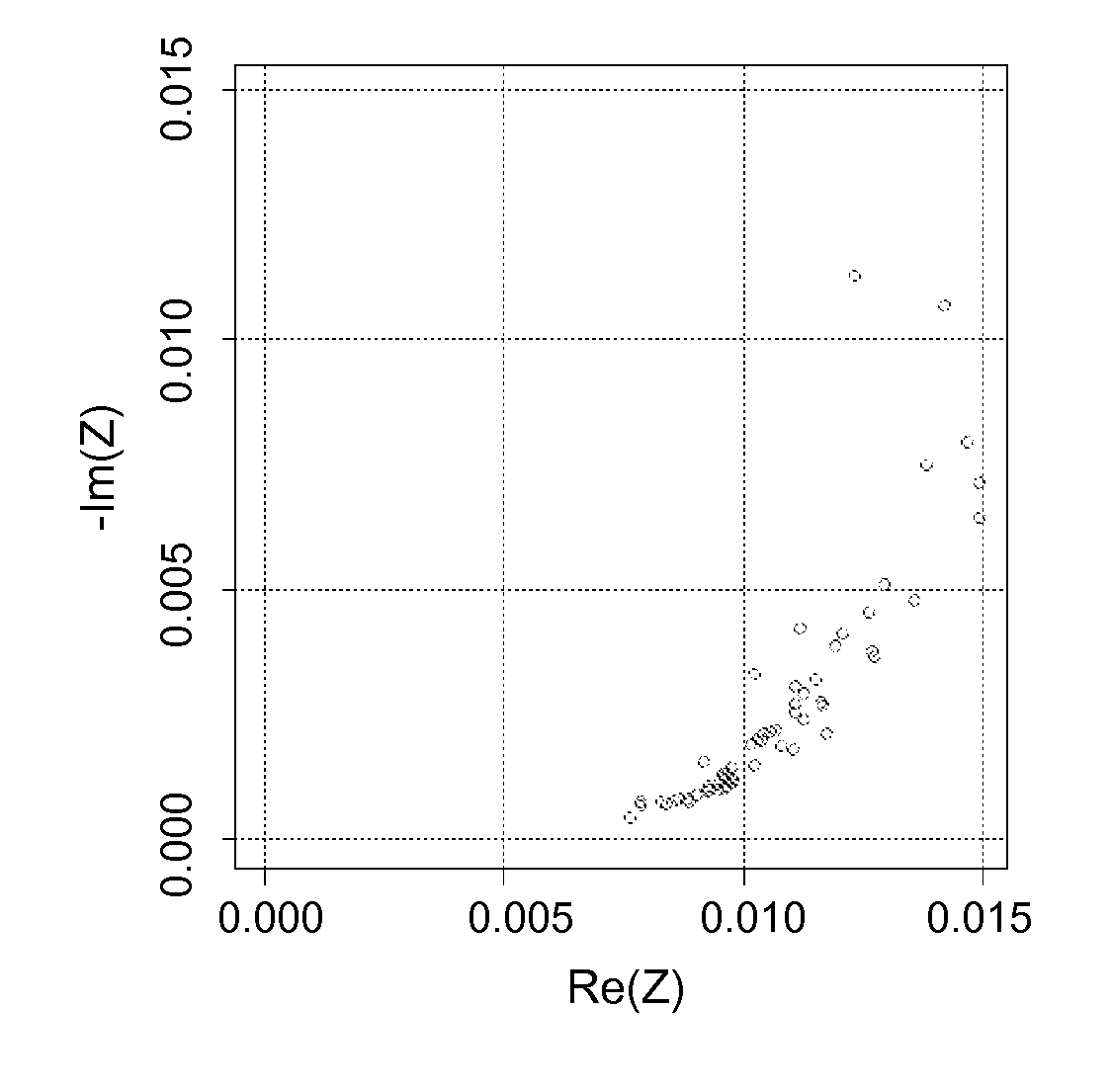
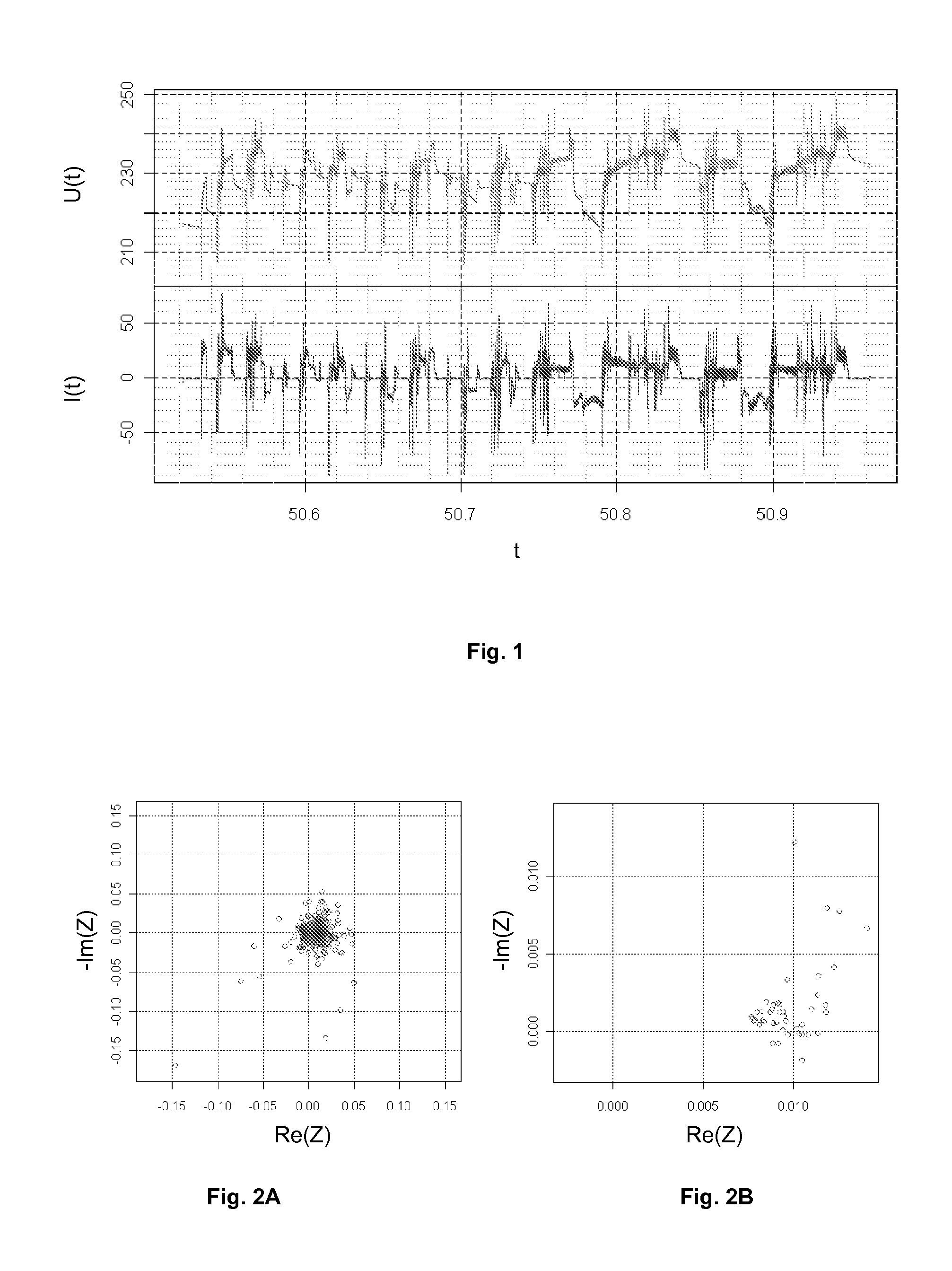
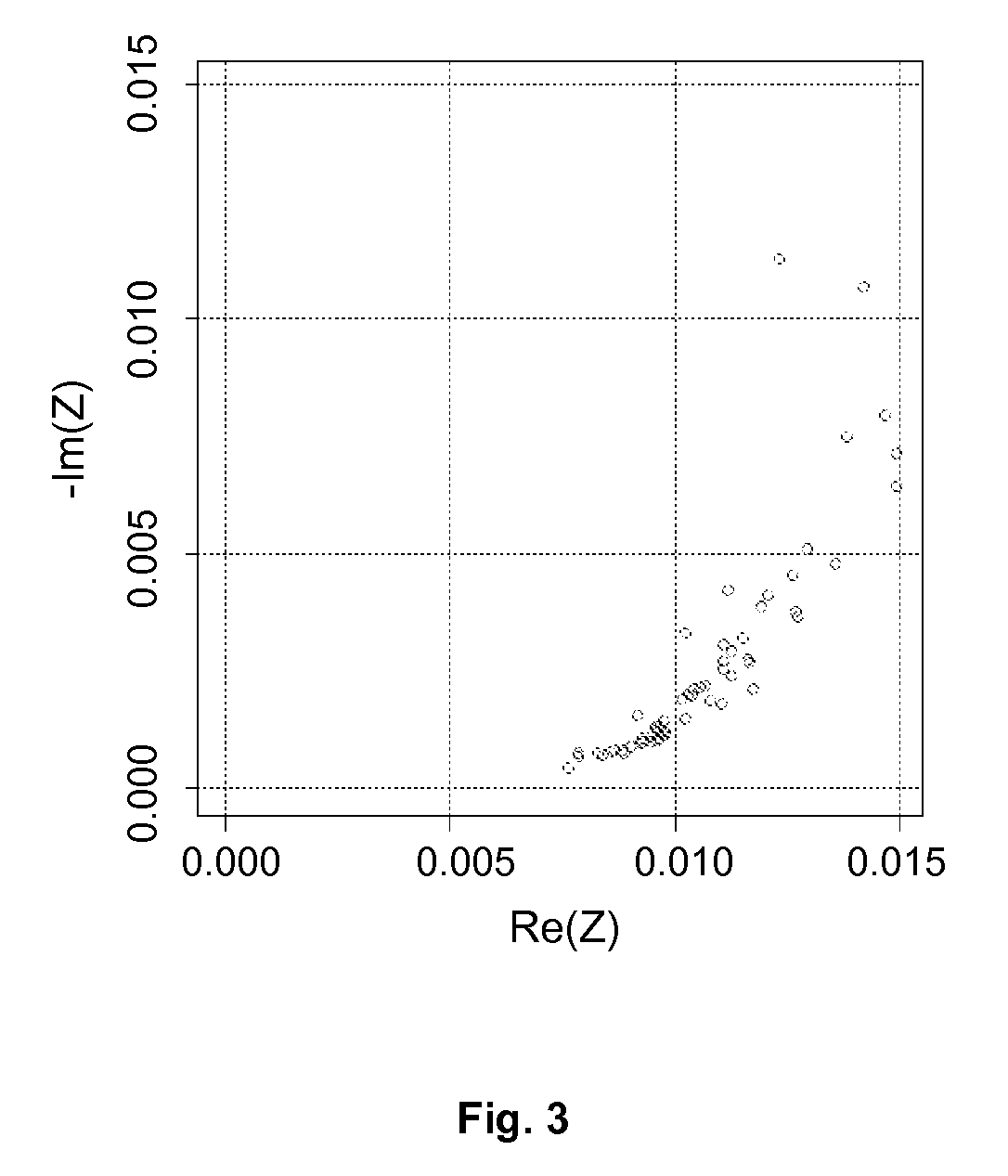
Non-invasive method of determining the electrical impedance of a battery
InactiveUS20110208452A1Easy to implementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingElectrical batteryEngineering
A non-invasive method and device for determining the electrical impedance of an electrochemical system for electric power is disclosed. The voltage and current are measured at terminals as a function of time, and these measurements are converted to signals dependent on frequency. The signals dependent on frequency are subjected to at least one segmentation. For each segment, a power spectral density of the current signal ΨI dependent on frequency and the cross power spectral density of the voltage and current signals ΨIV dependent on frequency are determined for each segment. The electrical impedance of the electrochemical system is determined by calculating a ratio dependent on frequency of a mean of the power spectral densities ΨI dependent on frequency to a mean of the cross power spectral densities ΨIV dependent on frequency.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
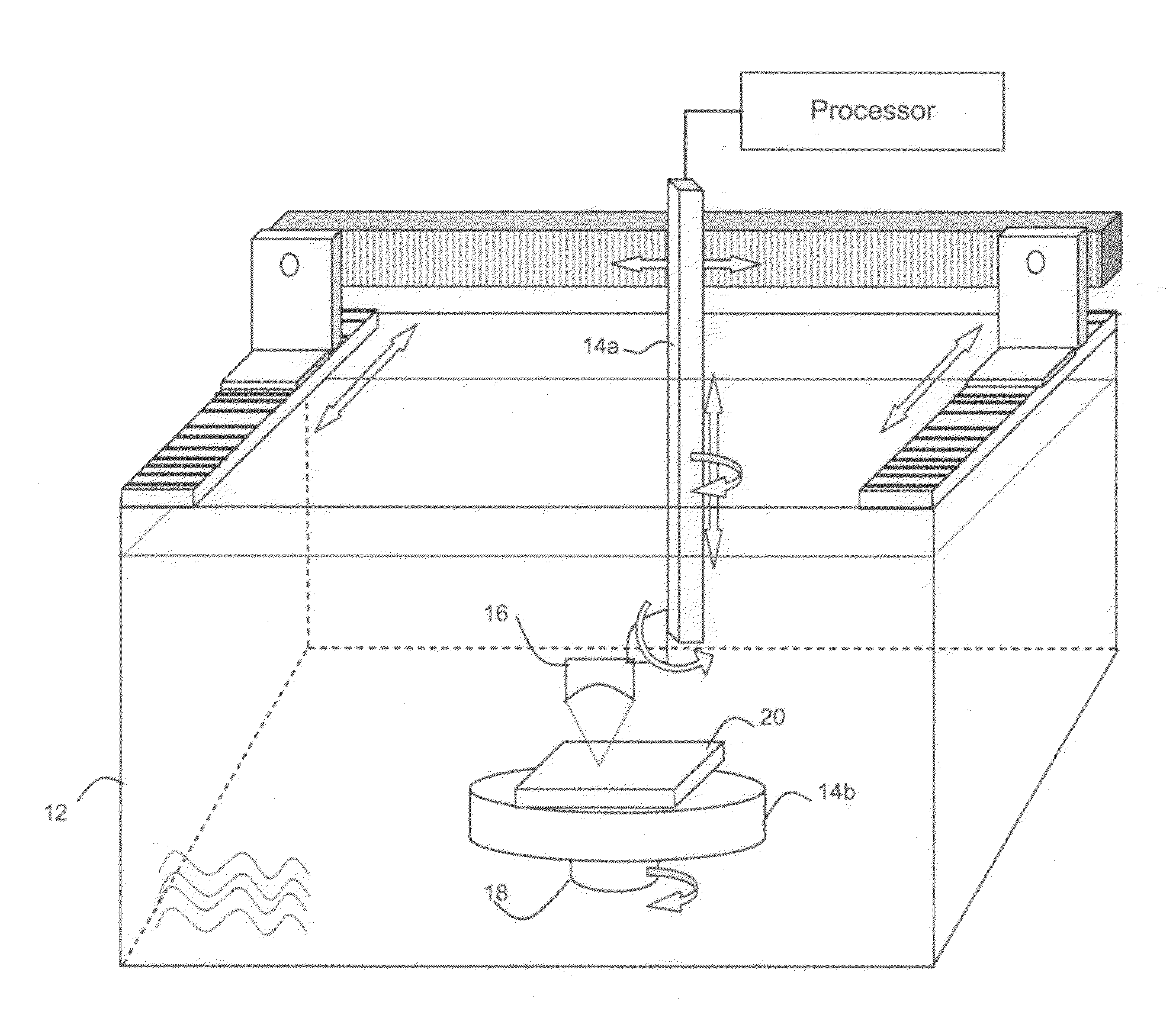
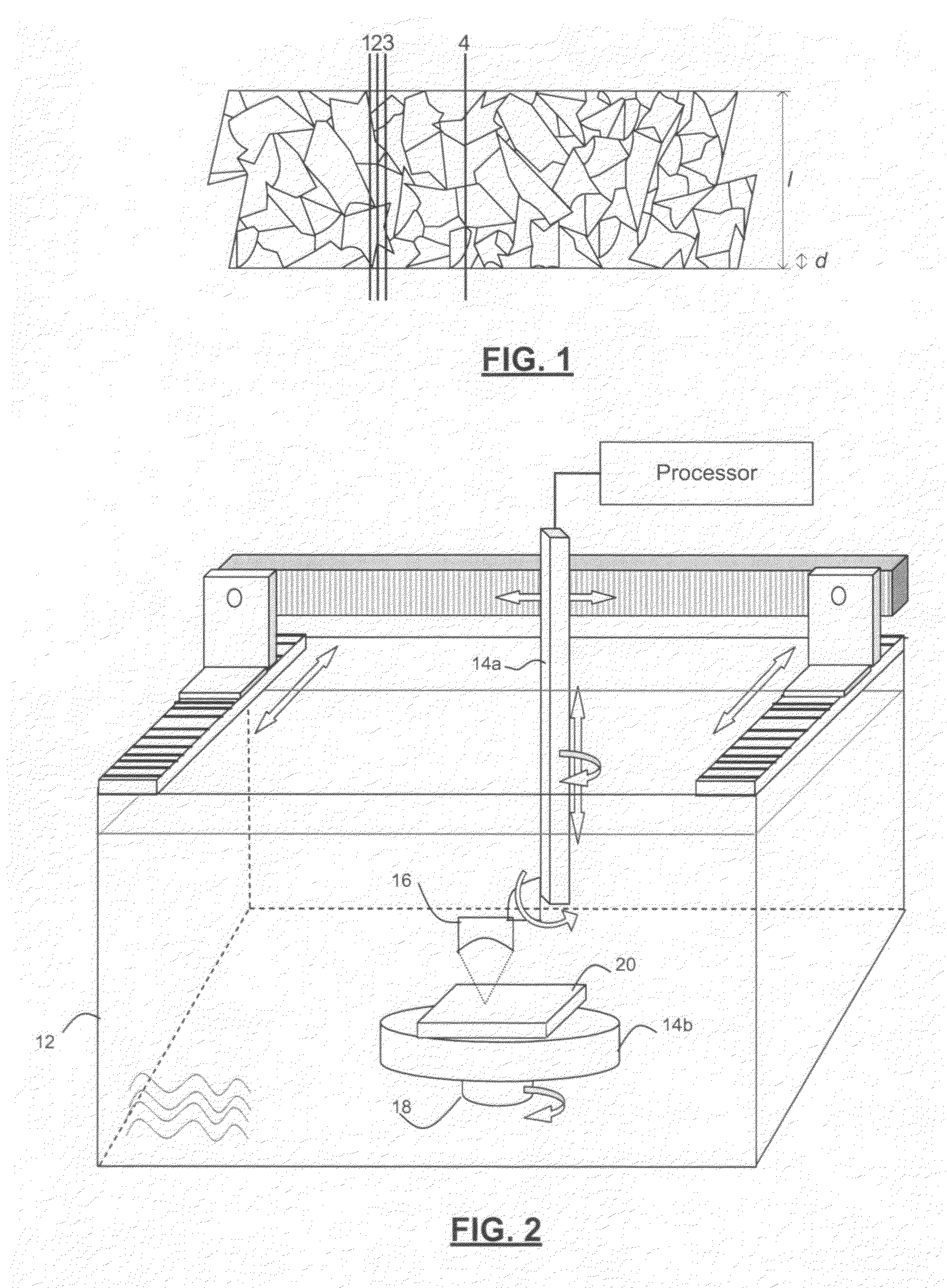
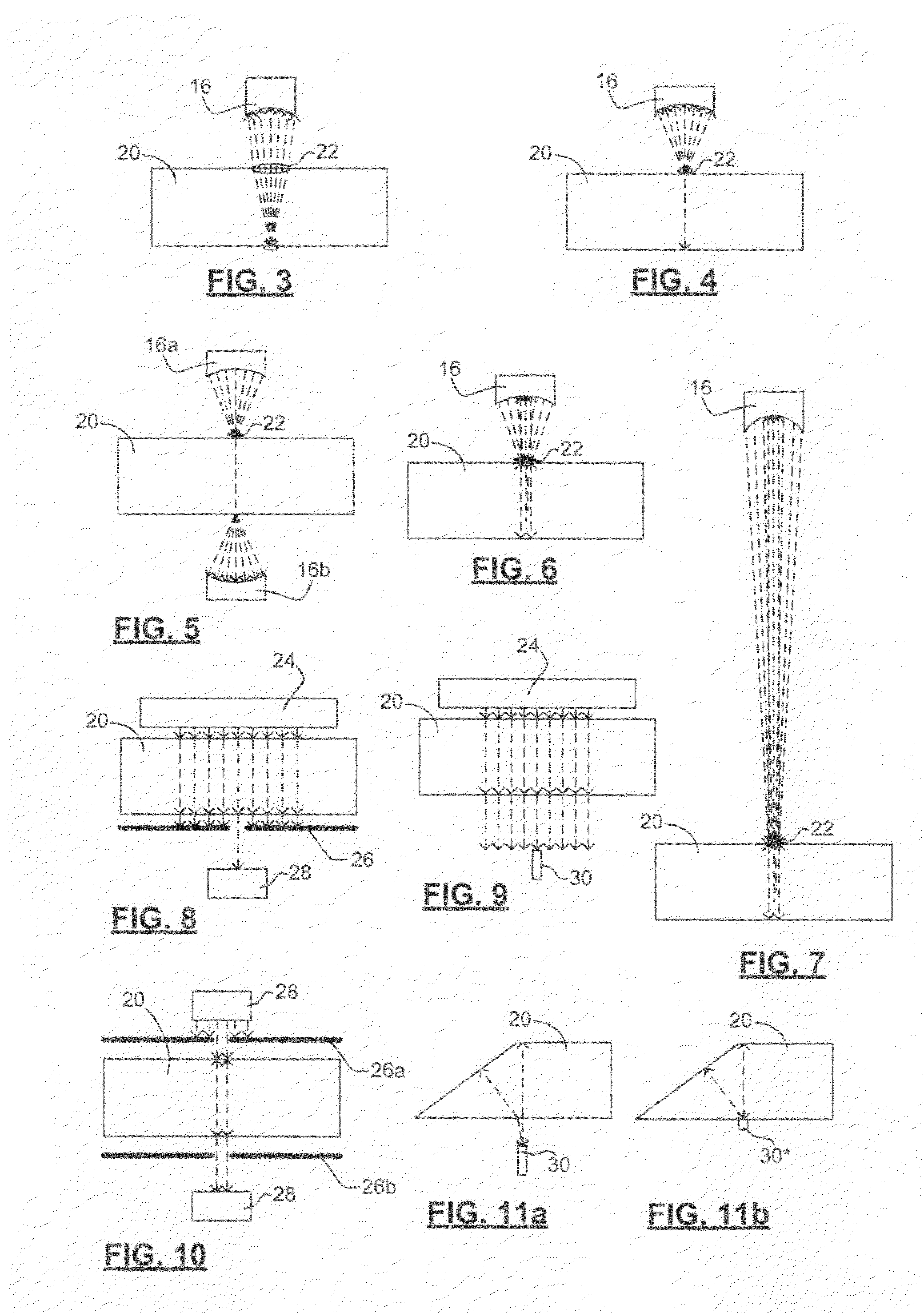
Method and apparatus for ultrasonic characterization of scale-dependent bulk material heterogeneities
InactiveUS20100121584A1Small wavelengthFlow propertiesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansSonificationCrystal structure
Methods and apparatuses are provided for detecting and characterizing heterogeneities within a bulk material that exhibit scale-dependent uniformity represented by locally representative volume elements (LRVEs). The invention is particularly useful in the characterization of local variations of crystallographic texture of metals and alloys, including metallurgical Ti alloys. The invention consists of generating ultrasonic waves through different paths in the object, and detecting differences in time, amplitude and / or phase of the detected frequency components traveling the different paths to characterize a statistical mean dimensions of the LRVEs, for example, by autocorrelation. Mean sizes of the LRVEs in the scan directions can be computed by autocorrelation, and mean sizes in the direction of the propagation can also be approximated.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Ergonomic map information system
InactiveUS20050182560A1Easy to handleHigh strengthImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationGraphicsColor intensity
A system for the ergonomic communication of a map portion is presented. The map portion may include map information, map background, and additional information. The system includes an interface control unit that may include a graphics control unit, a processor and a memory. The system may include one or more modules for creating an ergonomic presentation including: a border module that may add the additional information to the representation; an adaptation module for adapting the map information and map background and / or additional information with one another, such as within a maximum color contrast; a scale-dependent module that may adapt the color intensity and width of map information as a function of scale and type; and a smoothing module to increase the quality of the map portion representation. The system may include a method for controlling the representation of a map portion.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
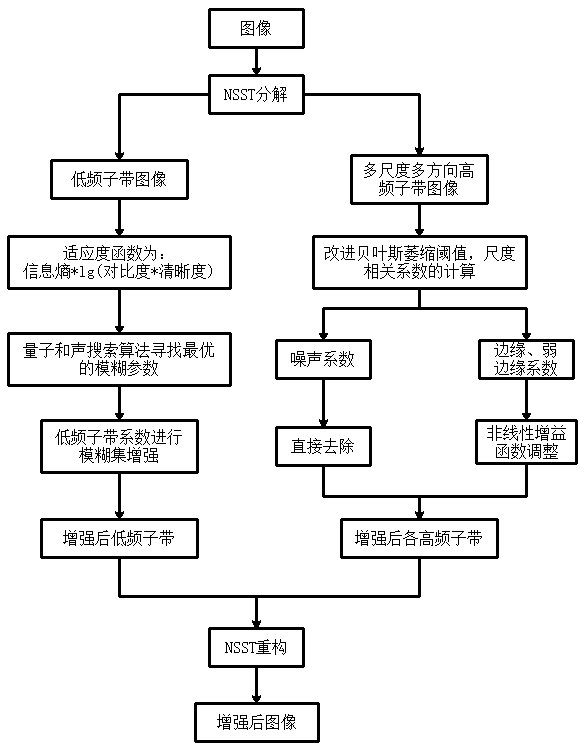
NSST domain flotation froth image enhancement and denoising method based on quantum harmony search fuzzy set
ActiveCN110246106AIncrease brightnessIncrease contrastImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDecomposition
The invention relates to an NSST domain flotation froth image enhancement and denoising method based on a quantum harmony search fuzzy set. The NSST domain flotation froth image enhancement and denoising method comprises the steps: carrying out NSST decomposition on a flotation froth image, and obtaining a low-frequency sub-band image and multi-scale high-frequency sub-bands; performing quantum harmony search fuzzy set enhancement on the low-frequency sub-band image; secondly, for the multi-scale high-frequency sub-bands, removing a noise coefficient by combining an improved BayesShrink thresholding and scale correlation, and enhancing an edge coefficient and a texture coefficient through a nonlinear gain function; and finally, performing NSST reconstruction on coefficients of the processed low-frequency sub-band and each high-frequency sub-band to obtain an enhanced de-noised image. According to the NSST domain flotation froth image enhancement and denoising method, the brightness, the contrast and the definition of the froth image can be improved, and the froth edge is obviously enhanced while noise is effectively inhibited, and more texture details are reserved, and subsequent processing such as froth segmentation and edge detection is facilitated.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
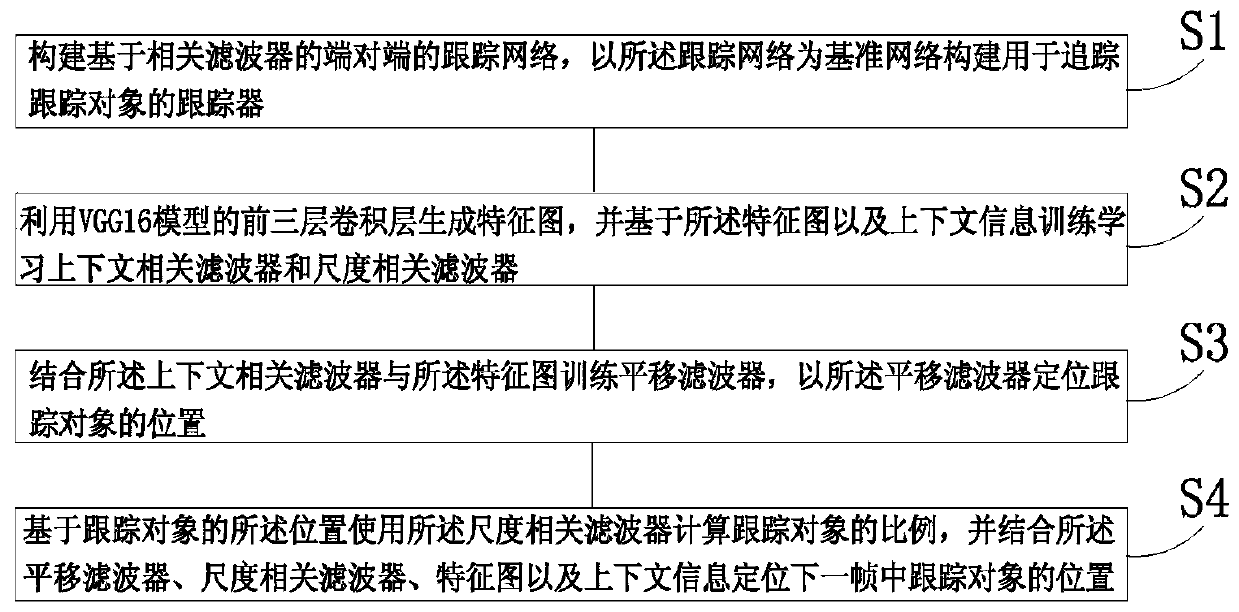
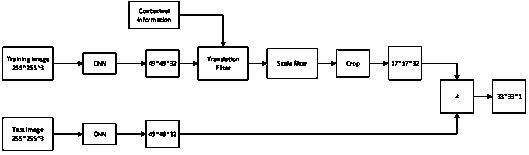
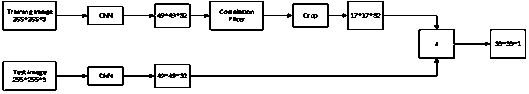
A target tracking method based on context correlation and a discriminant correlation filter
InactiveCN109544600AImprove tracking accuracyRobustImage enhancementImage analysisObject basedCorrelation filter
The invention discloses a target tracking method based on context correlation and a discriminant correlation filter. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing an end-to-end tracking network based on correlation filter, and constructing a tracker for tracking an object with the tracking network as a reference networkS2, generating a feature map by using the first three convolutionlayers of the VGG16 model, and training and learning a context-related filter and a scale-related filter based on the feature map and the context information; 3, training a translation filter in combination with that context-related filt and the feature map, and locating a position of a tracking object with the translation filter; S4, using the scale correlation filter to calculate the proportionof the tracking object based on the position of the tracking object, and locating the position of the tracking object in the next frame in combination with the translation filter, the scale correlation filter, the feature map and the context information; The invention can effectively improve the accuracy and robustness of target tracking.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and System for Wavelet Based Detection of Colon Polyps
A method of identifying colon polyps in a digital volume, wherein the volume includes a plurality of values corresponding to a domain of points in a 3D space, is provided. The method includes selecting a mother wavelet scaling function that corresponds to a polyp; performing a forward wavelet transformation on the volume to obtain a set of wavelet coefficients, wherein each wavelet coefficient is associated with a length scale; determining, for each length scale, a transformation magnitude; and forming, for each length scale, a transformed set of wavelet coefficients associated with the length scale. An inverse wavelet transform is performed on the transformed wavelet coefficients for each length scale to obtain a reconstructed volume, and the reconstructed volume is analyzed for the existence of polyps.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System for Wavelet Based Detection of Colon Polyps
A method of identifying colon polyps in a digital volume, wherein the volume includes a plurality of values corresponding to a domain of points in a 3D space, is provided. The method includes selecting a mother wavelet scaling function that corresponds to a polyp; performing a forward wavelet transformation on the volume to obtain a set of wavelet coefficients, wherein each wavelet coefficient is associated with a length scale; determining, for each length scale, a transformation magnitude; and forming, for each length scale, a transformed set of wavelet coefficients associated with the length scale. An inverse wavelet transform is performed on the transformed wavelet coefficients for each length scale to obtain a reconstructed volume, and the reconstructed volume is analyzed for the existence of polyps.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
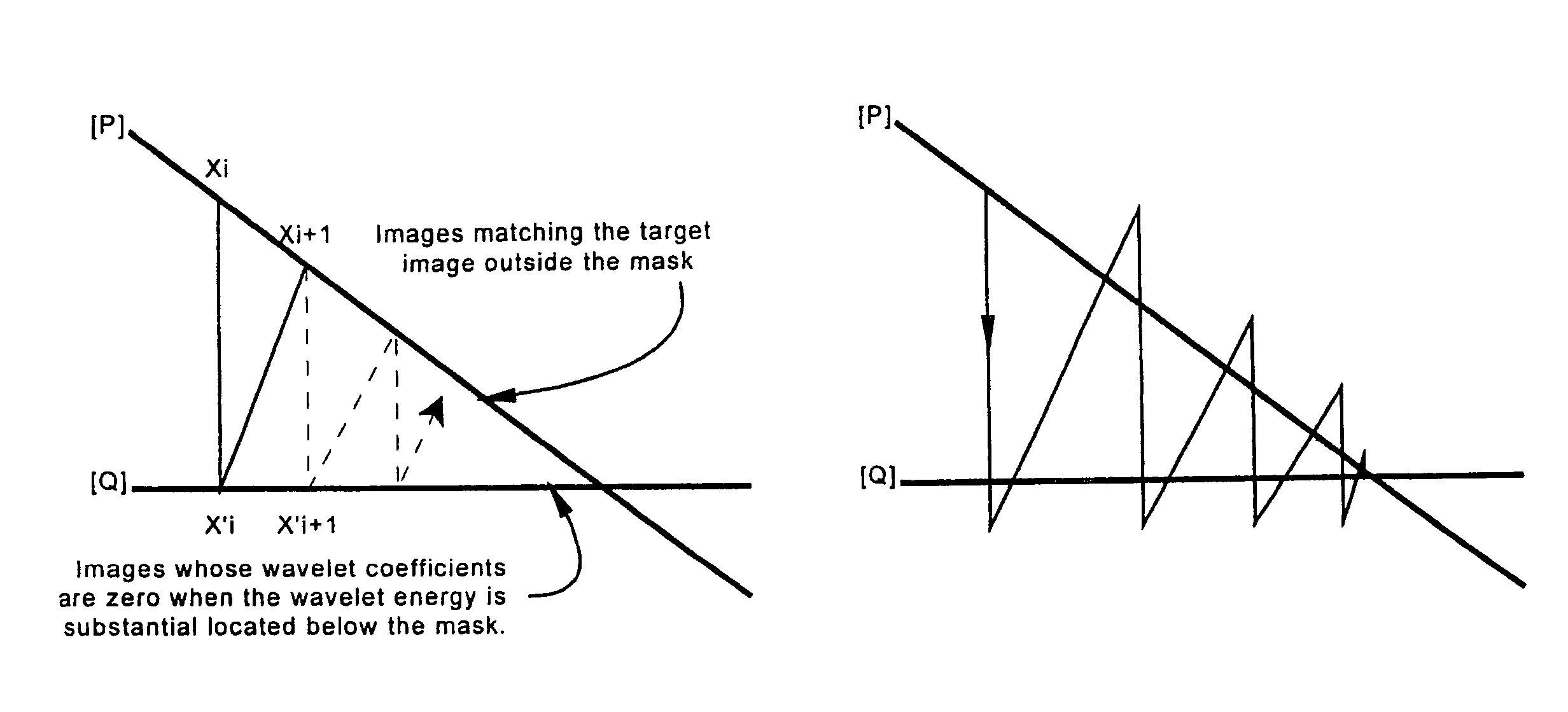
Compression of partially-masked image data
InactiveUS7286711B2Fast convergenceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingWavelet codingScale dependent
Wavelet coding of partially-masked image information may be made faster by either of two embodiments of the present invention. In a first embodiment, quick convergence is obtained by performing wavelet encoding in stages, each stage associated with a predetermined wavelet scale. By advancing the stages from finest scale to coarsest scale, coefficients of masked wavelets are identifies early in the coding process. In a second embodiment, quick convergence is obtained by introducing overshoot techniques when masked coefficients are identified, modified and image data is reconstructed therefrom.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
A method for carrying out visual tracking through a spatio-temporal context
ActiveCN109325966ASolve Tracking DriftAlleviating the noisy sample problemImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionScale model
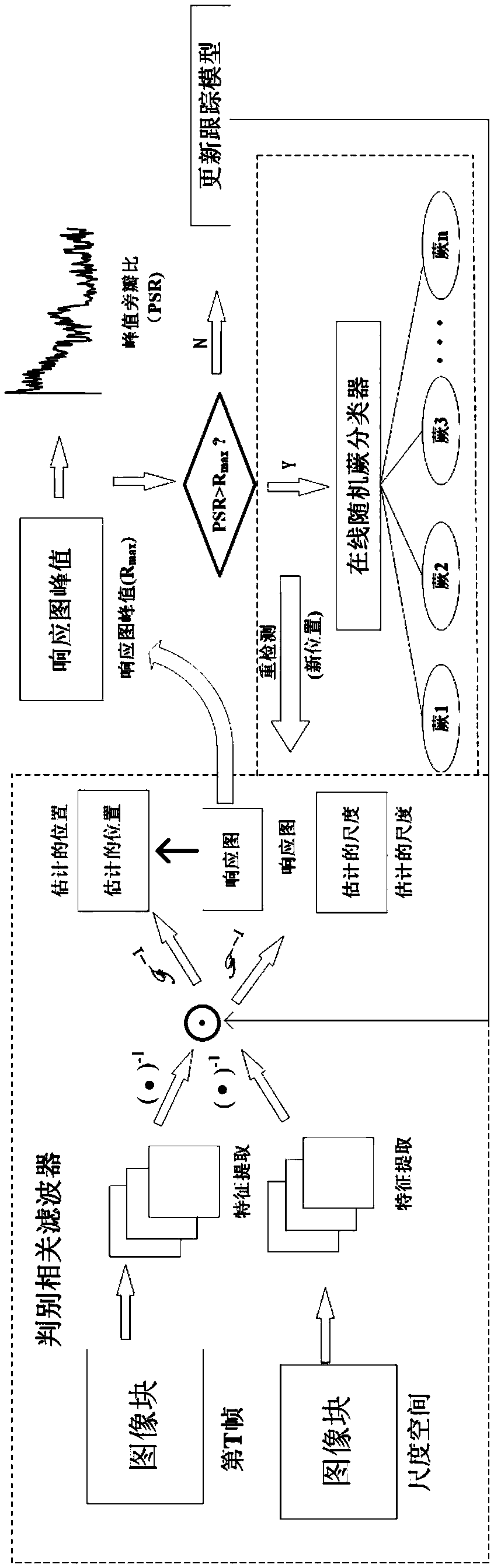
The invention provides a method for carrying out visual tracking through a spatio-temporal context, comprising the following steps of step 1, initializing parameters; 2, training a context-aware filter to obtain a position model; 3, training the maximum scale response value of a scale correlation filter to obtain a scale model; 4, outputting a response diagram by the classifier; discriminating thepeak sidelobe ratio corresponding to the peak value of the response map generated by the correlation filter; 5, comparing the peak-to-peak sidelobe ratio of the response map, and if the peak-to-peaksidelobe ratio of the response map is greater than the peak-to-peak sidelobe ratio, introducing an on-line random fern classifier for re-detection; if the peak value of the response map is less than the peak sidelobe ratio, updating the position model of the step 2 and the scale model of the step 3; if the peak value of the response map is equal to the peak sidelobe ratio, continuing to maintain the current visual tracking state; 6, applying the updated position model and the scale model to the next frame tracking; returning to the step 4.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY +1
Automatic depth correction method based on dual-scale correlation contrast
ActiveCN104832161ASolve the problem of accurate depth correctionAdd depthSurveyScale dependentComputer science
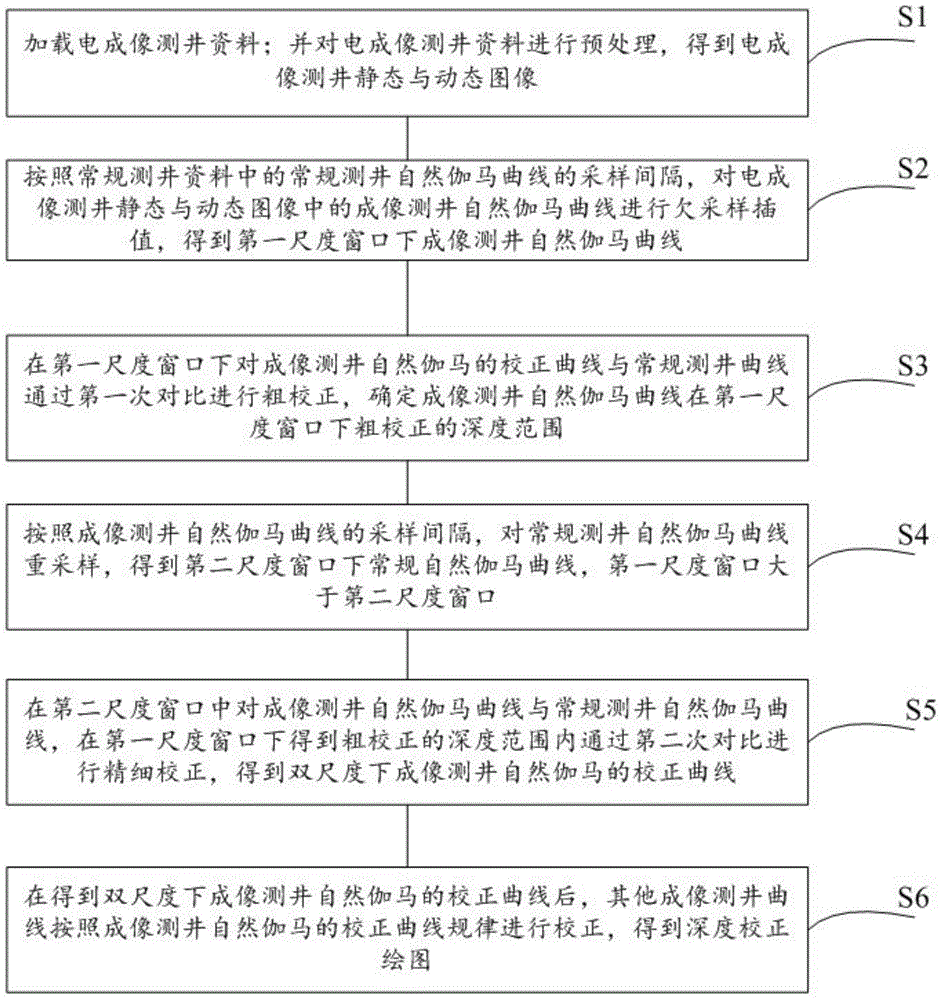
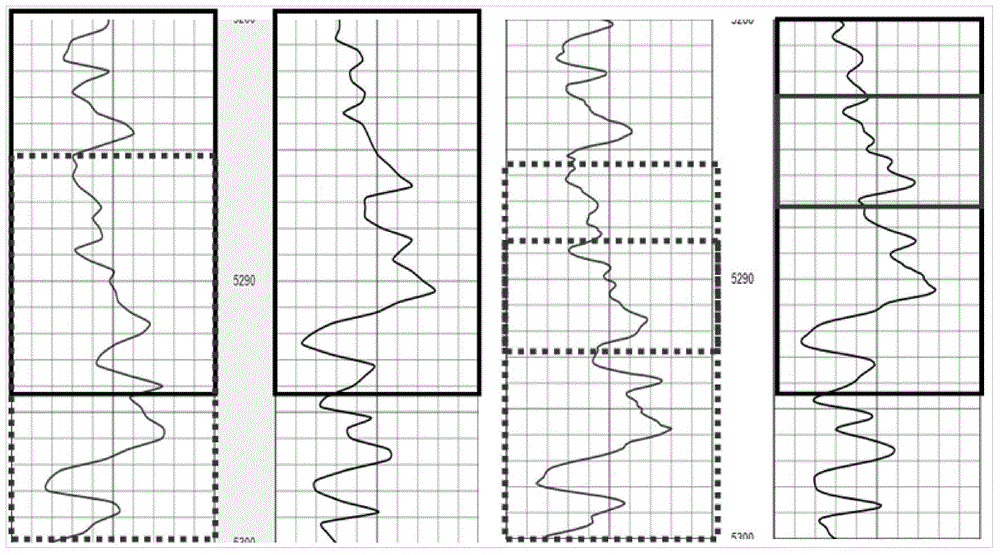
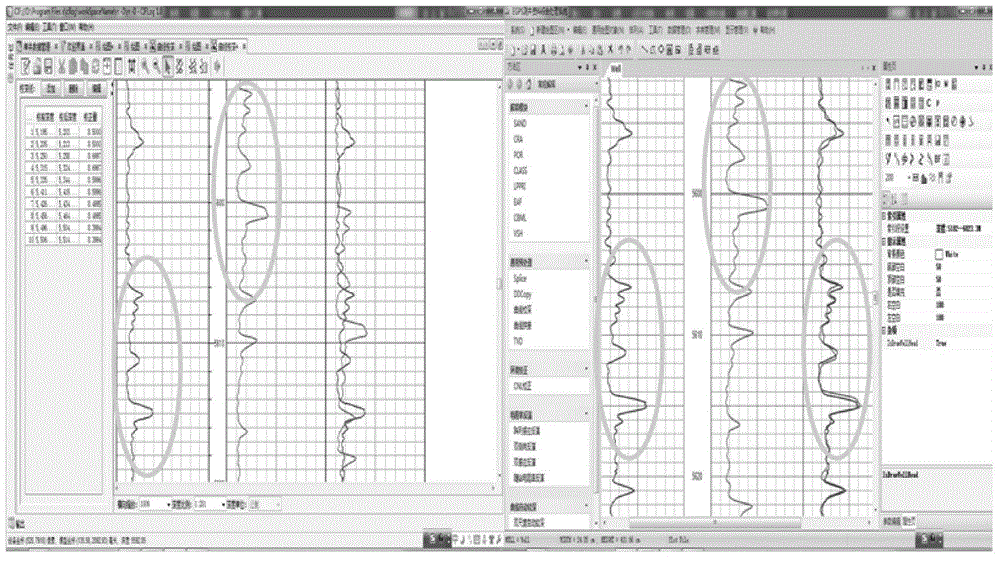
The invention provides an automatic depth correction method based on dual-scale correlation contrast. The method comprises the steps that S1. electric imaging logging data are loaded and the electric imaging logging data are preprocessed; S2. undersampling interpolation is performed on an imaging logging natural gamma curve GR<0><image> according to the sampling interval of a conventional logging natural gamma curve GR<0><log> in conventional logging data; S3. rough correction is performed on an imaging logging natural gamma correction curve GR<1><image> and the conventional logging curve GR<0><log> through first time of contrast under a first scale window; S4. resampling is performed on the conventional logging natural gamma curve GR<0><log> according to the sampling interval of the imaging logging natural gamma curve GR<0><image>; S5. fine correction is performed on the imaging logging natural gamma curve GR<0><image> and the conventional logging natural gamma curve GR<1><log> within depth range of rough correction obtained under the first scale window through the second time of contrast in a second scale window; and S6. an imaging logging natural gamma correction curve GR<2><image> under dual scales is obtained, and then other imaging logging curves are corrected according to the rule of the imaging logging natural gamma correction curve GR<2><image>.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Road extraction method using non-subsampled contourlet direction field
InactiveCN101976443AIncrease the differenceImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisContourletScale dependent
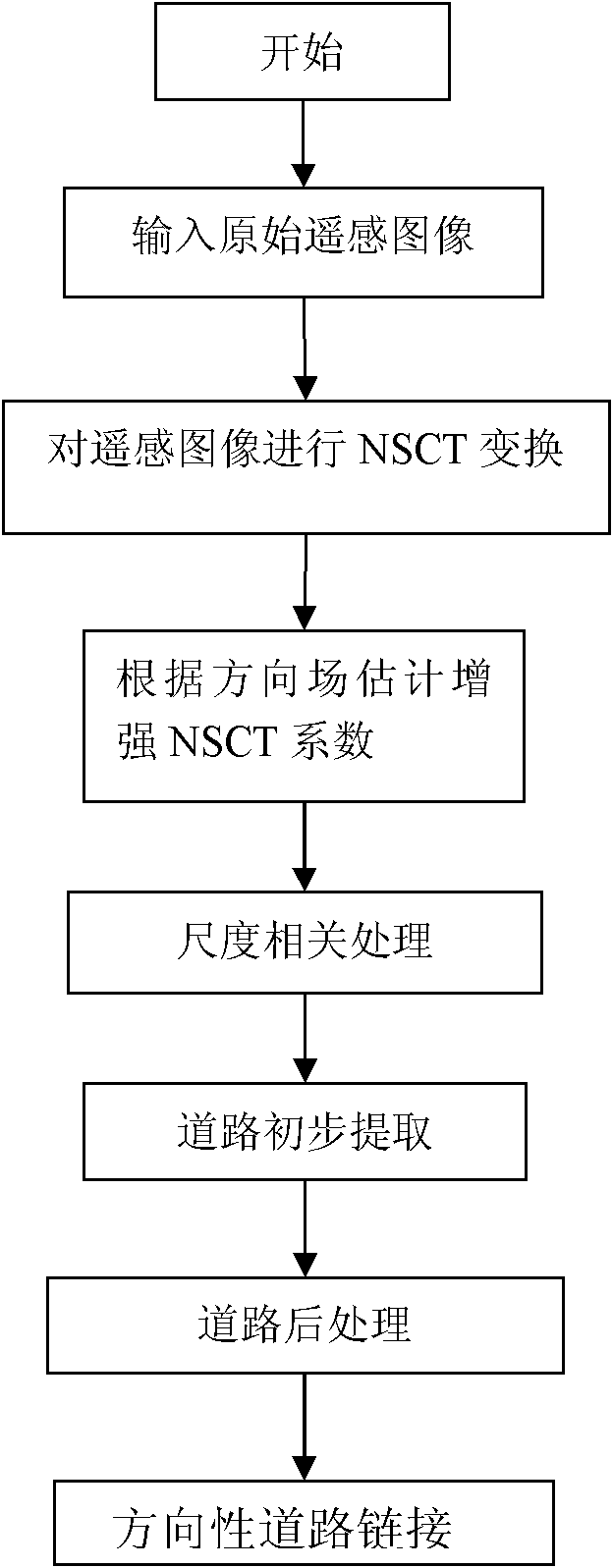
The invention discloses a road extraction method using a non-subsampled contourlet direction field, which mainly overcomes the shortcomings that the road extraction is incomplete and the road is wrongly linked or incompletely linked in the original road extraction method for remote sensing images. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) on an input remote sensing image to obtain a direct sub-band needing to be processed; (2) estimating the direction field of a direction sub-band and performing directional sub-band correction; (3) performing scale correlation processing on the processed direction sub-band; (4) primarily extracting the road; (5) post-processing the primary road extraction result according to the characteristics of length, direction and shape of road segments; and (6) linking the road segments according to the characteristics of the road segment direction field and the road mutual characteristics. The method can perfectly extract relatively fuzzy road characteristics of the remote sensing images and eliminate interference of the non-road information, ensures relatively accurate extraction result and is applicable to the road extraction application for the remote sensing images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A physical action attribute analysis and recognition method for intelligent teaching space-time correlation
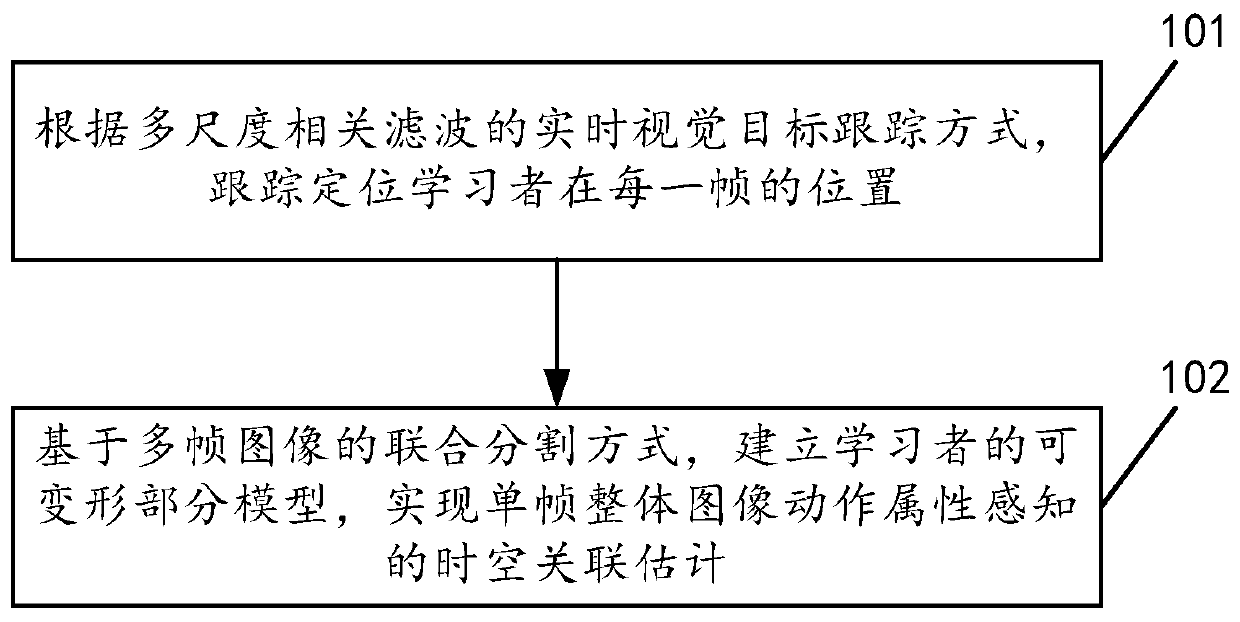
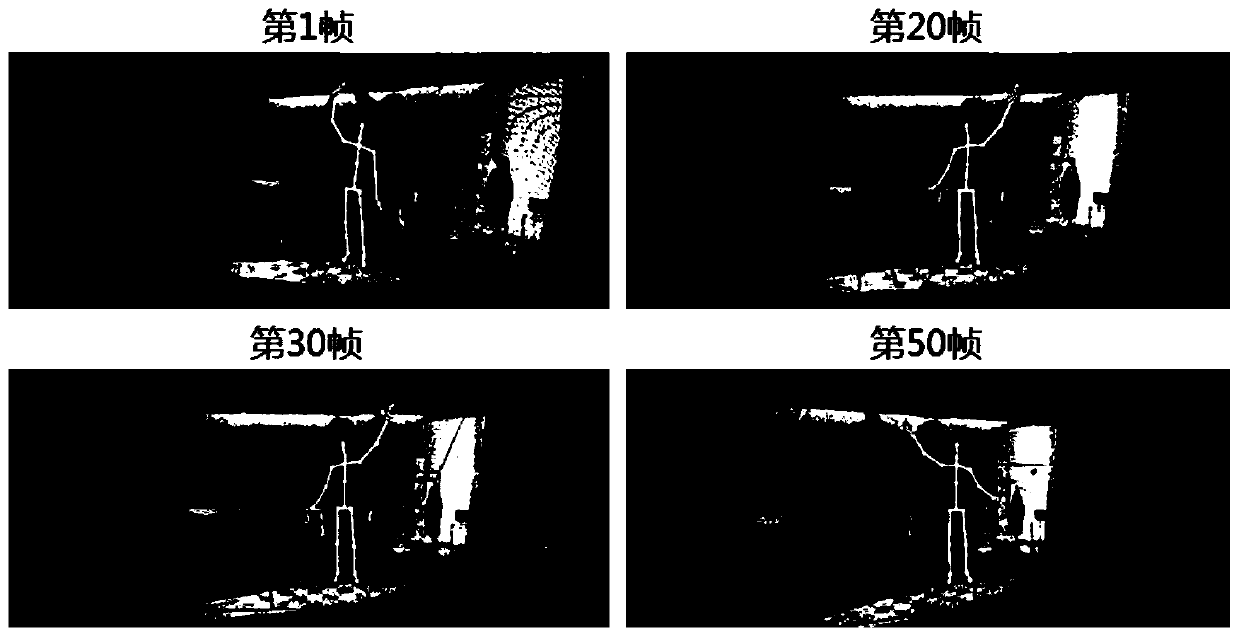
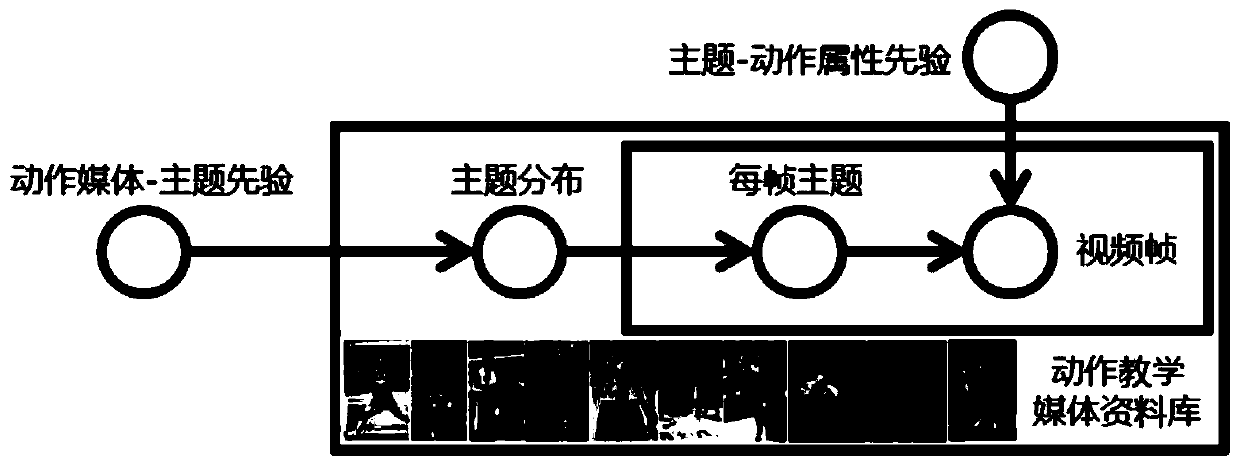
InactiveCN109919024ARealize analysisAchieving identifiabilityData processing applicationsImage analysisPattern recognitionTemporal consistency
The invention discloses a physical action attribute analysis and recognition method for intelligent teaching space-time correlation. The method comprises the following steps: tracking and positioningthe position of a learner in each frame according to a real-time visual target tracking mode of multi-scale correlation filtering; And based on a multi-frame image joint segmentation mode, establishing a deformable part model of the learner, and realizing space-time correlation estimation of single-frame overall image action attribute perception. The scheme provided by the invention can improve the spatial-temporal structure prediction and recognition capability of the high-quality physical action education resource visual media of the education resource public service platform, and the structural, continuous and spatial-temporal consistency of physical actions and the like are analyzed to realize the analysis and recognition of the physical actions and the accurate prediction of the change trend of the physical actions.
Owner:陈强 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com