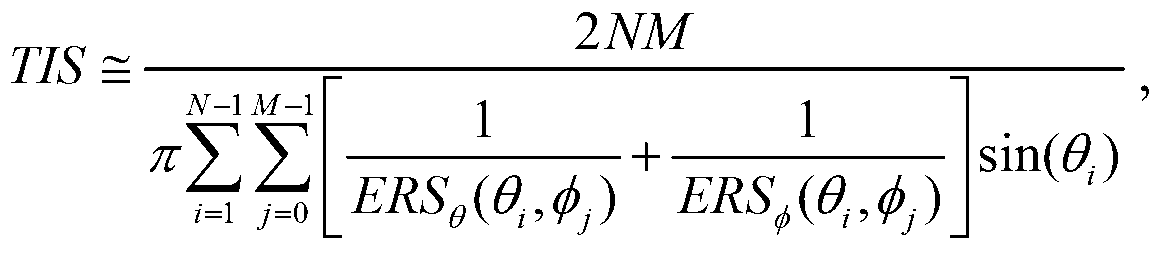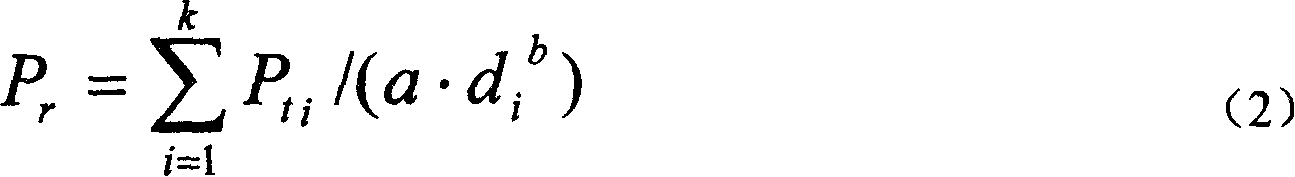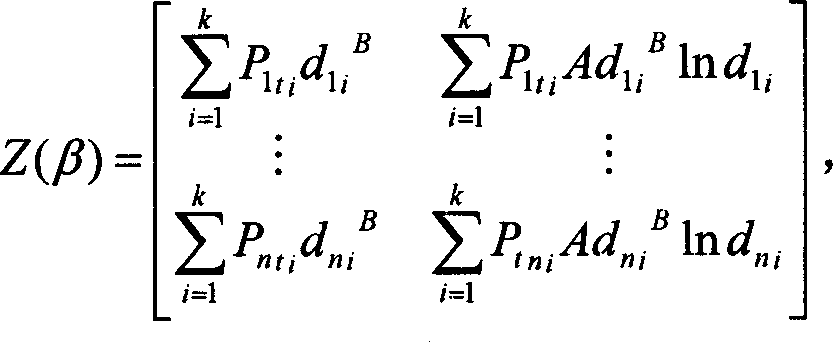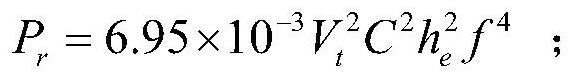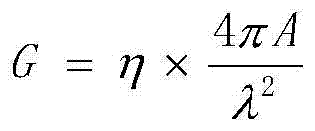Patents
Literature
32 results about "Effective radiated power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Effective radiated power (ERP), synonymous with equivalent radiated power, is an IEEE standardized definition of directional radio frequency (RF) power, such as that emitted by a radio transmitter. It is the total power in watts that would have to be radiated by a half-wave dipole antenna to give the same radiation intensity (signal strength in watts per square meter) as the actual source at a distant receiver located in the direction of the antenna's strongest beam (main lobe).
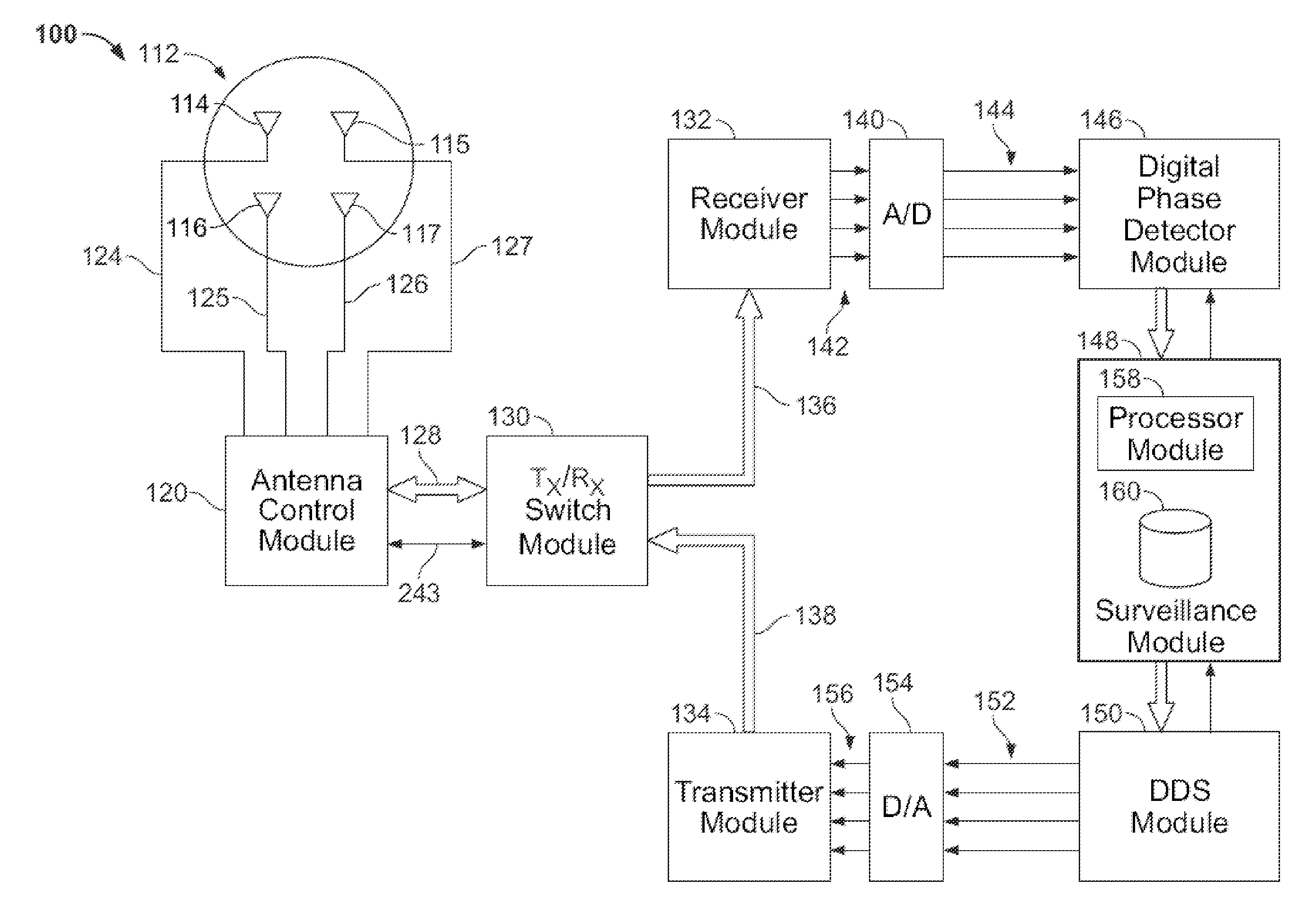
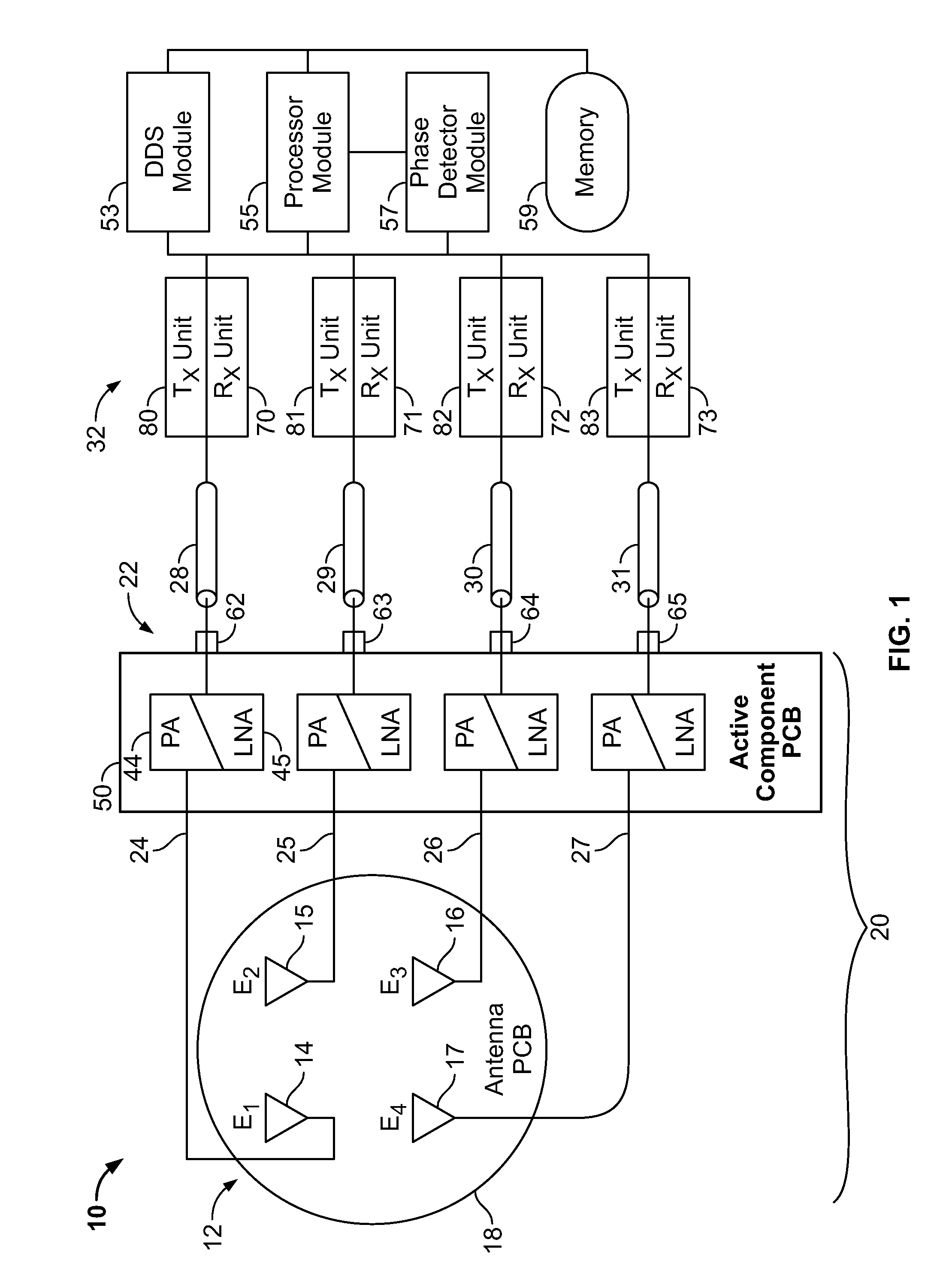
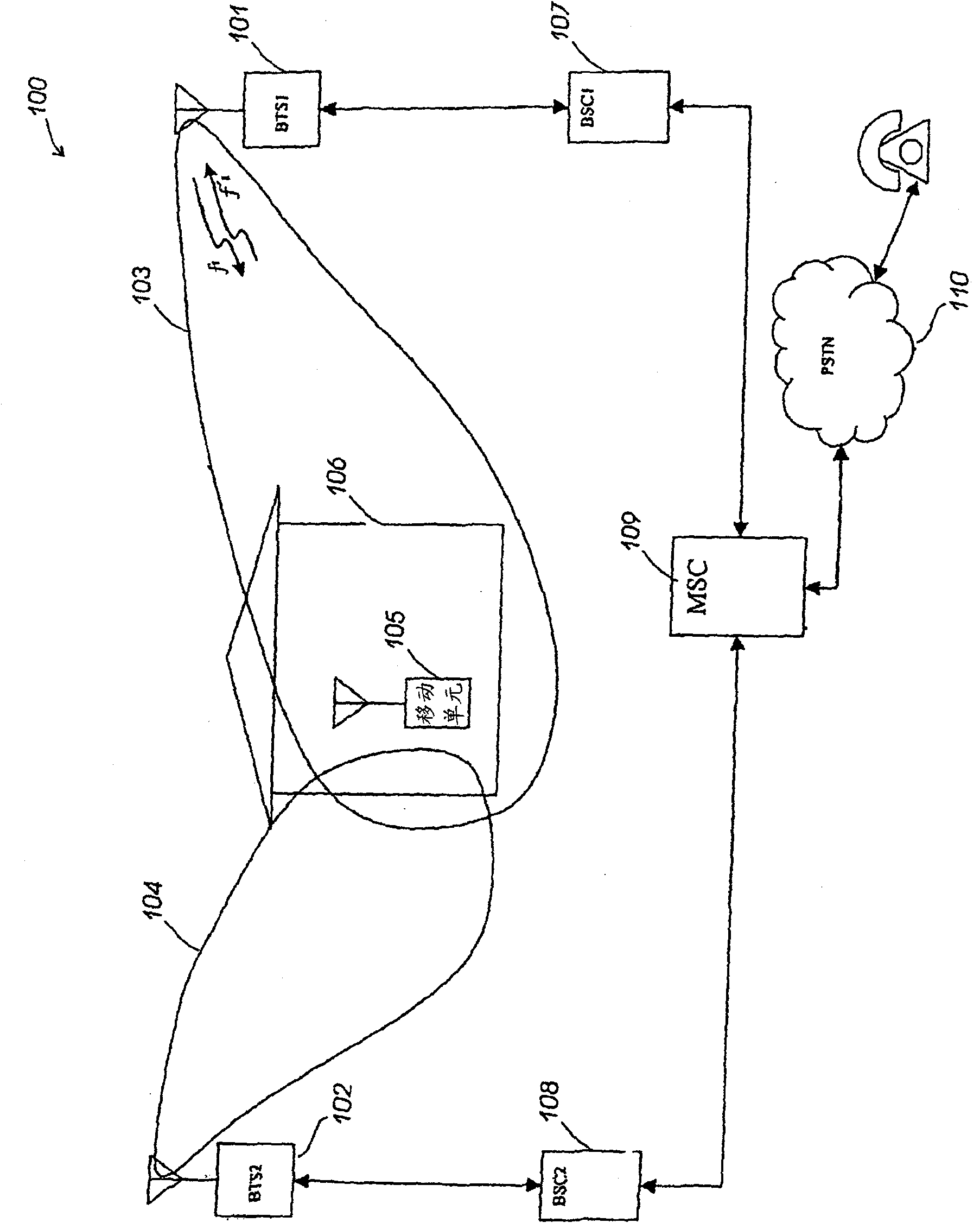
Active phased array antenna for aircraft surveillance systems
ActiveUS7439901B2Increase power levelAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionElectricityTelecommunications link
An active antenna is provided that includes an antenna element for transmitting RF transmit signals at a predetermined effective radiated power (ERP). An antenna module is configured to be mounted to an aircraft, with the antenna element being mounted to the antenna module. A connector module is provided at the antenna module and is configured to be coupled to a communications link and receive electrical transmit signals from the communications link. A transmit path is provided within the antenna module and extends between the antenna element and the connector module. A power amplifier is provided on the antenna module along the transmit path. The power amplifier increases a power level of the electrical transmit signals, received from the communications link, by a predetermined amount sufficient to drive the antenna element to transmit the RF transmit signals at the predetermined ERP.
Owner:GARMIN INT
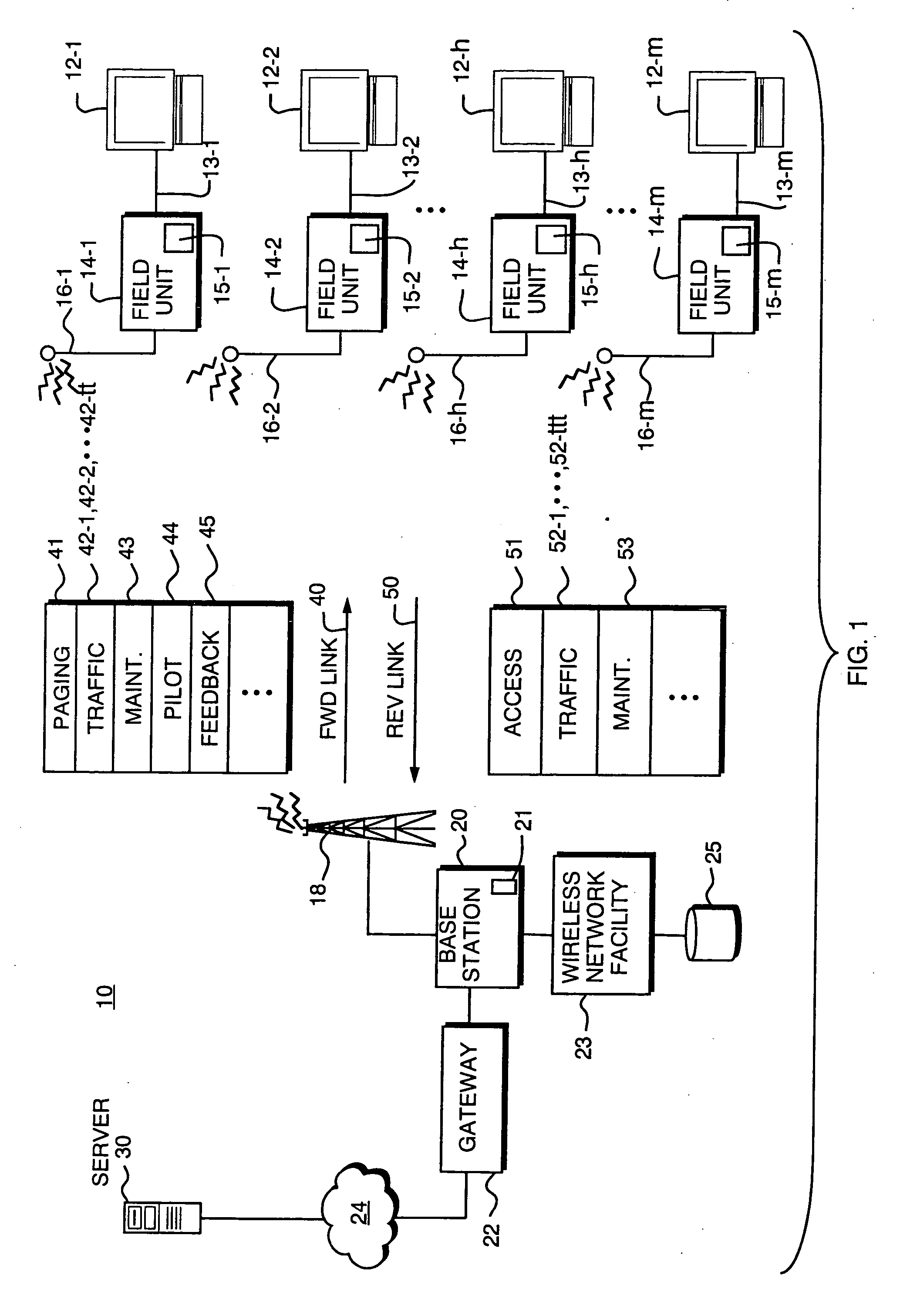
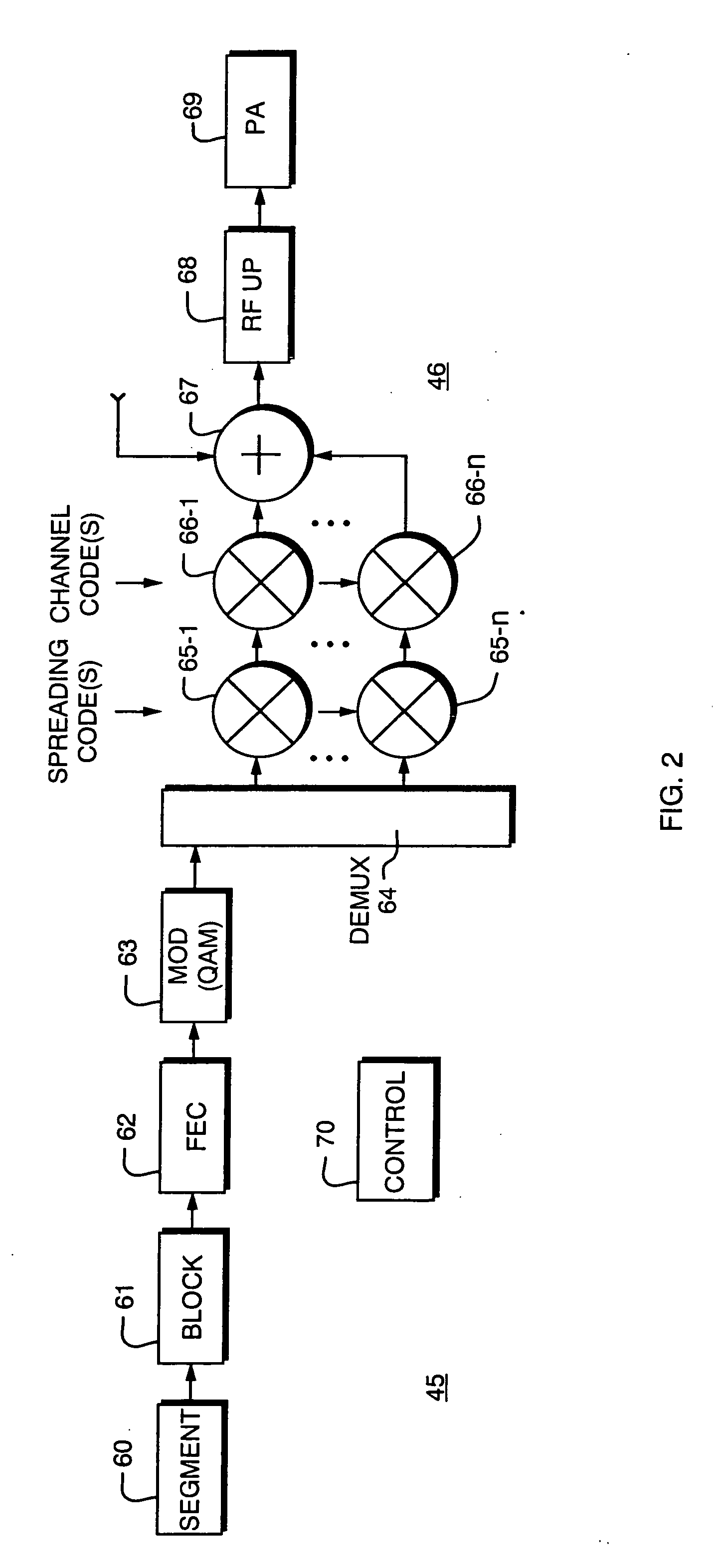
Qualifying available reverse link coding rates from access channel power setting
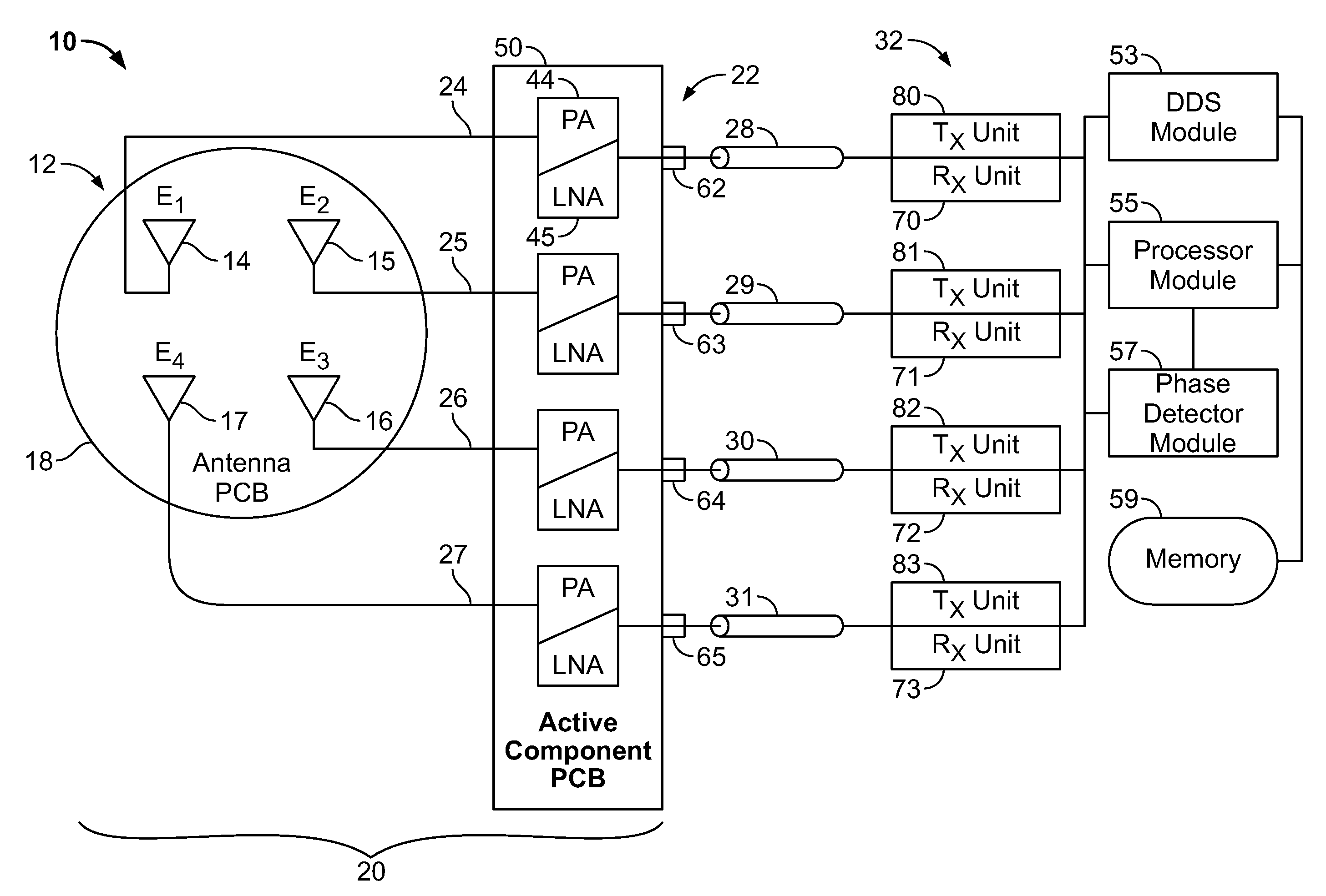
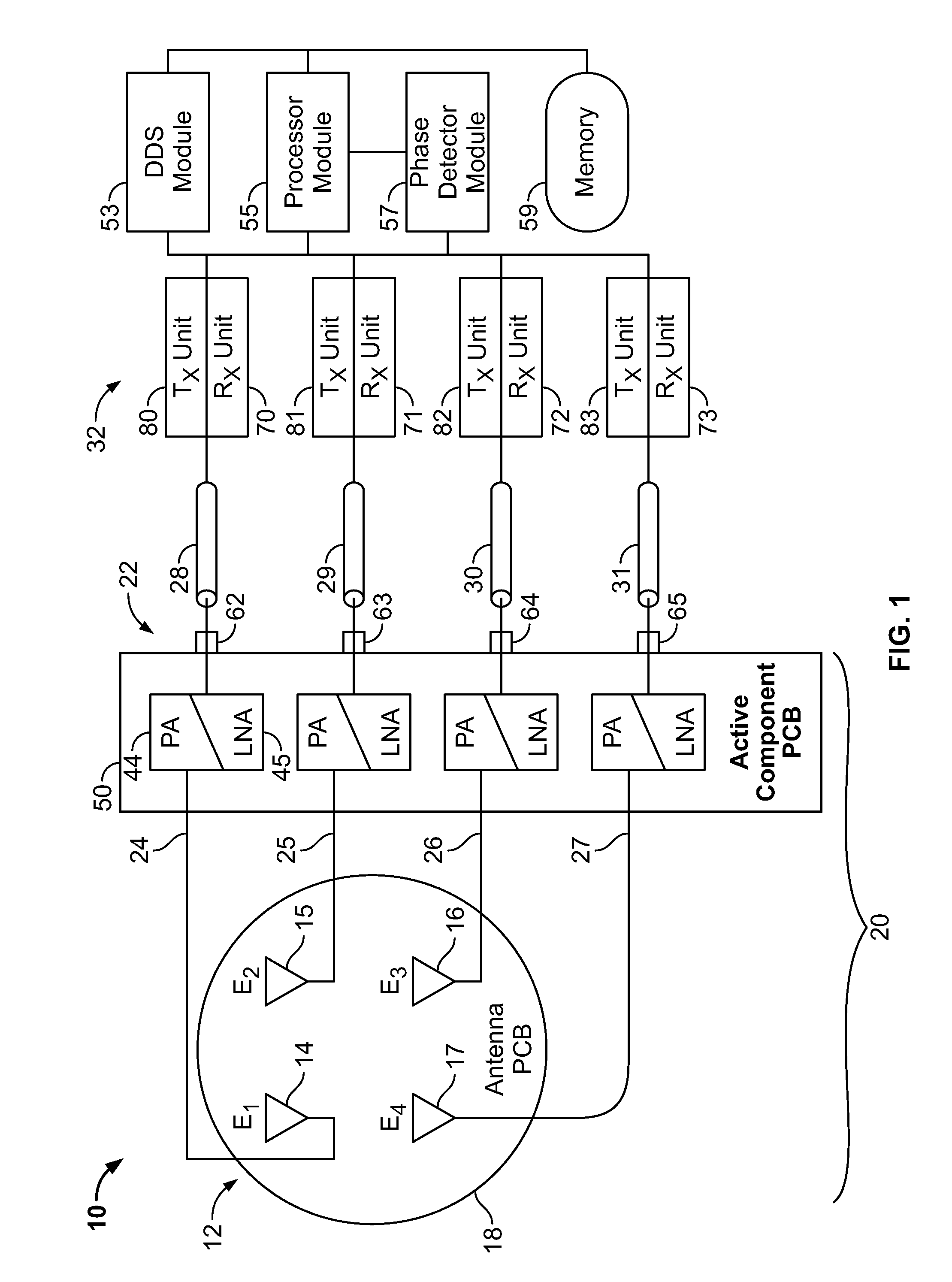
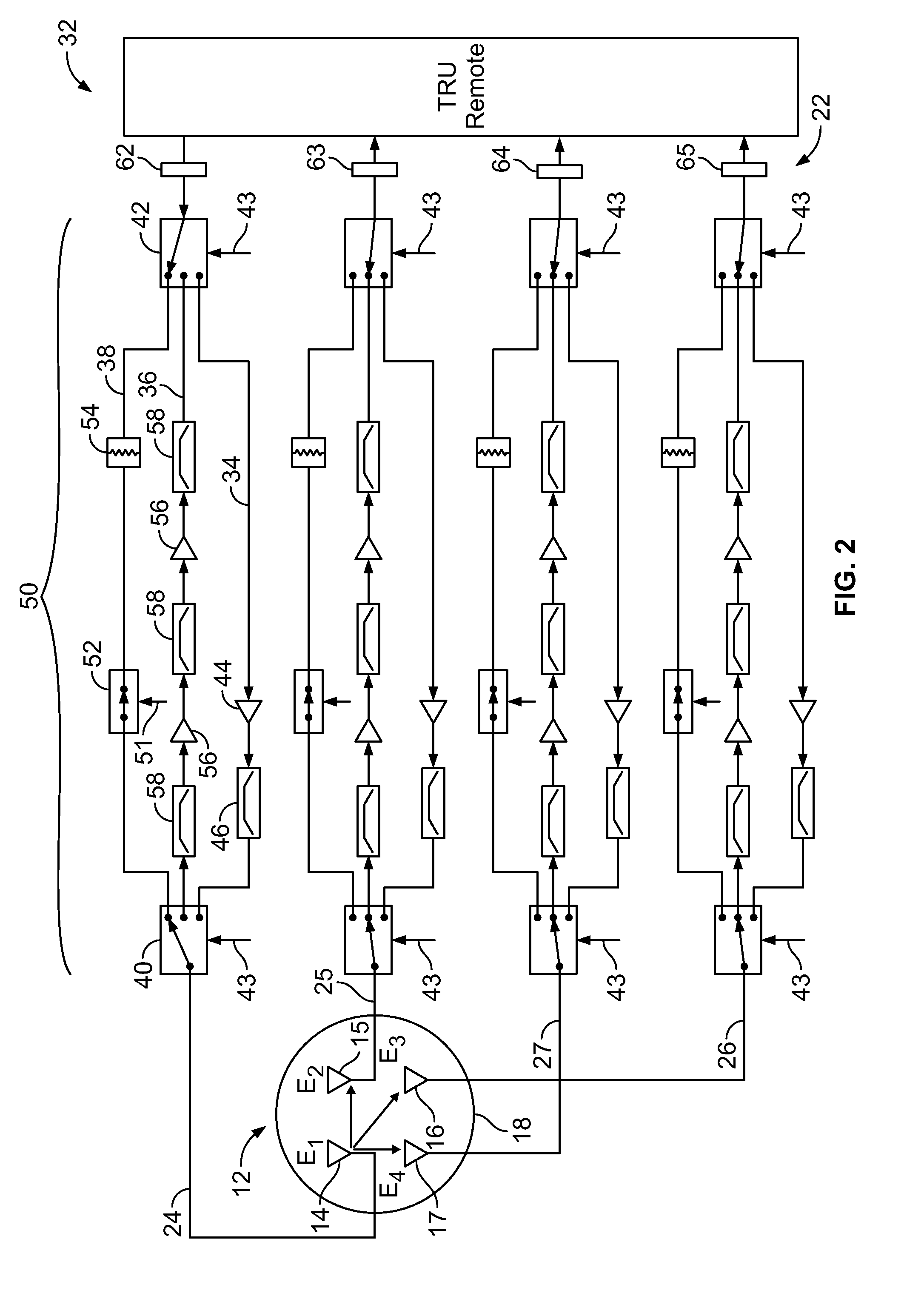
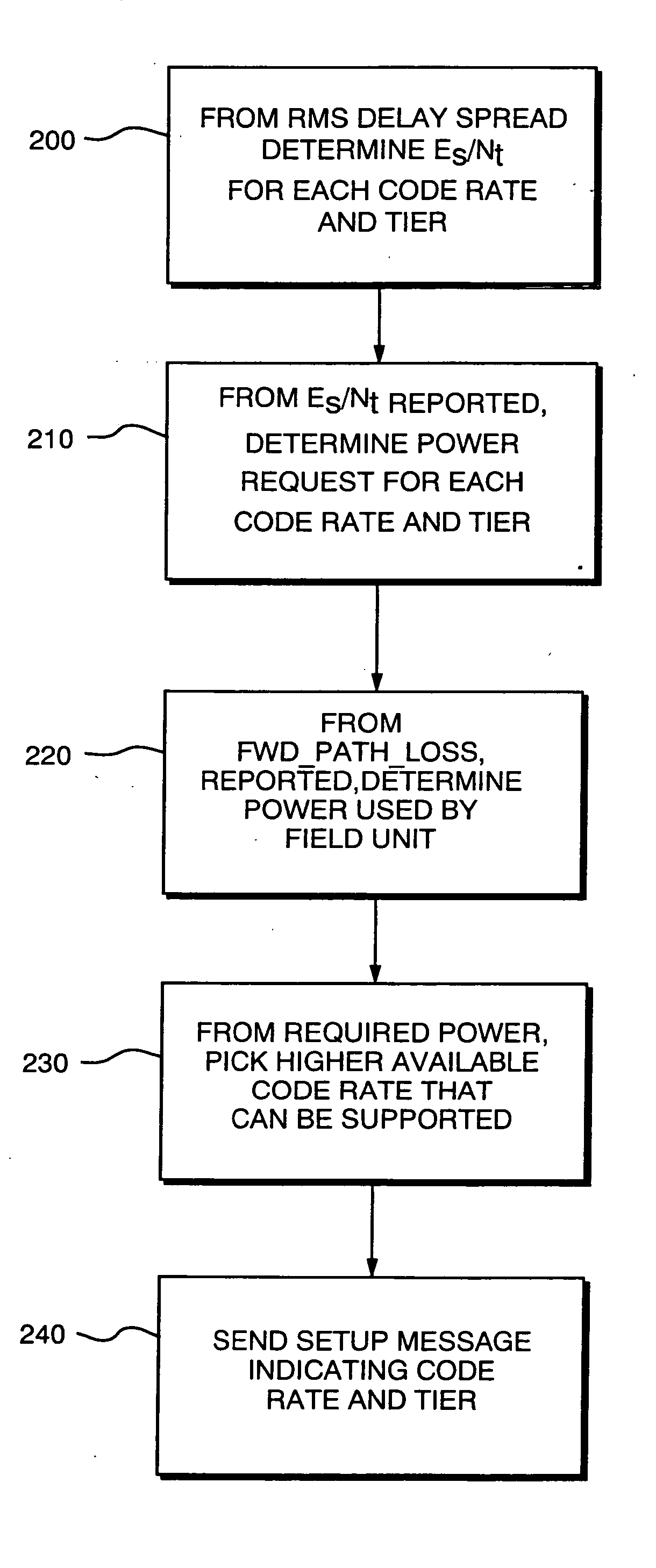
Data rate allocation decisions are made for a communications channel, such as a wireless reverse link connection. A first parameter used in this determination is a path loss, which is determined by the following process. First, a message is sent from a first station to a second station, such as on a paging channel. The message indicates a forward Effective Radiated Power (ERP) of a pilot signal transmitted by the first station. The second station then determines the received signal strength of this pilot signal, taking into account receiver gains. The path loss can then be estimated by the second station as the difference between the forward ERP data value that it received and the detected received pilot power. The second station also then preferably determines a transmit power level when transmitting a message back to the first station. This transmit power level information is encoded as a digital data word together with the forward path loss information as calculated by the first station. Upon receipt of these two pieces of information by the first station, the forward path loss estimate as calculated by the second station, and the output power value of the second station, the first station can then determine the amount of excess power available at the field unit. This excess power difference is indicative of the amount of dynamic range available in the transmit power amplifier in the particular second station. With this information, the first station can then make a determination as to whether coding rates which require a higher dynamic range will be acceptable for use by the particular second station.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
Active phased array antenna for aircraft surveillance systems
ActiveUS20080122693A1Increase power levelAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTelecommunications linkAudio power amplifier
An active antenna is provided that includes an antenna element for transmitting RF transmit signals at a predetermined effective radiated power (ERP). An antenna module is configured to be mounted to an aircraft, with the antenna element being mounted to the antenna module. A connector module is provided at the antenna module and is configured to be coupled to a communications link and receive electrical transmit signals from the communications link. A transmit path is provided within the antenna module and extends between the antenna element and the connector module. A power amplifier is provided on the antenna module along the transmit path. The power amplifier increases a power level of the electrical transmit signals, received from the communications link, by a predetermined amount sufficient to drive the antenna element to transmit the RF transmit signals at the predetermined ERP.
Owner:GARMIN INT
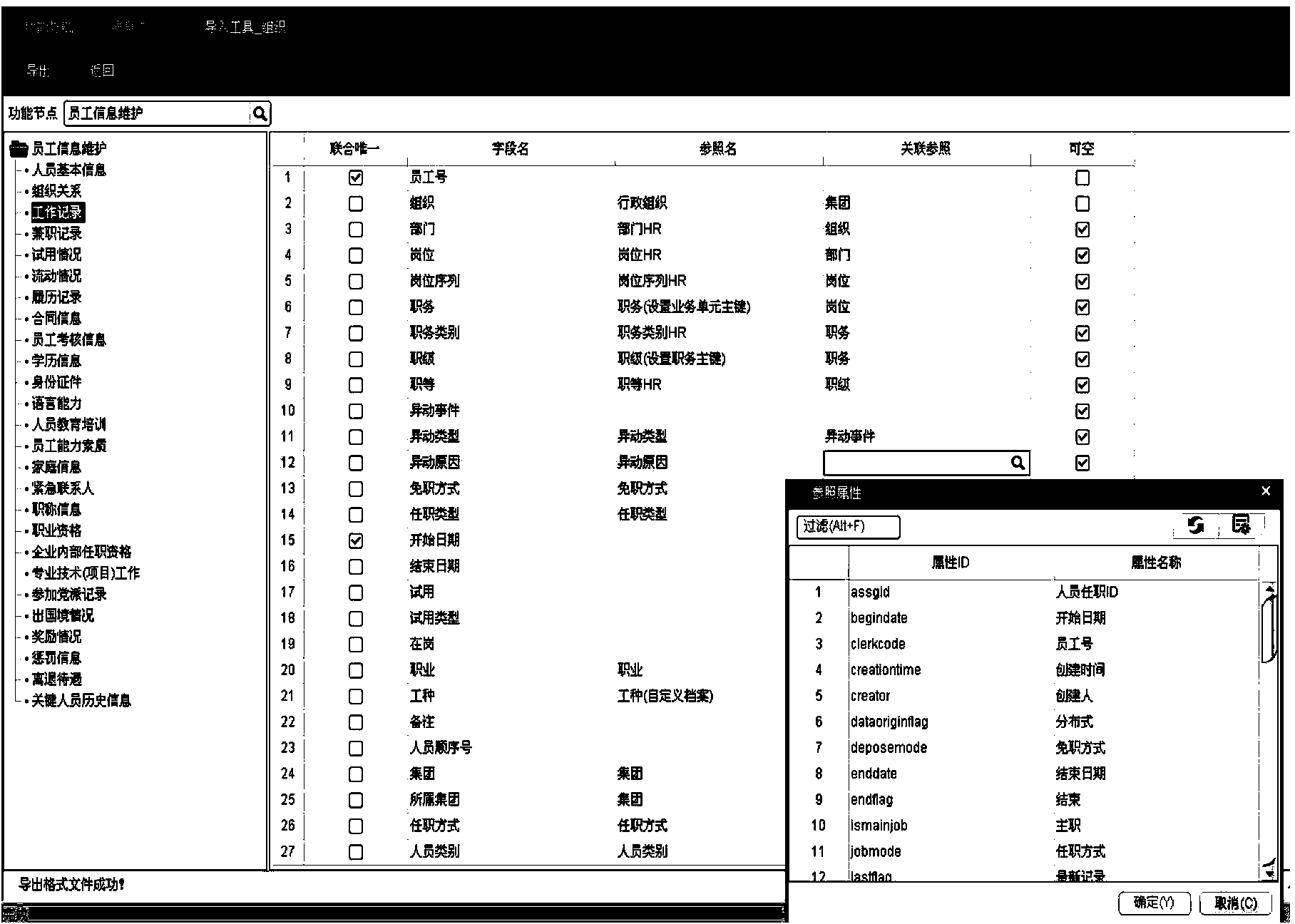
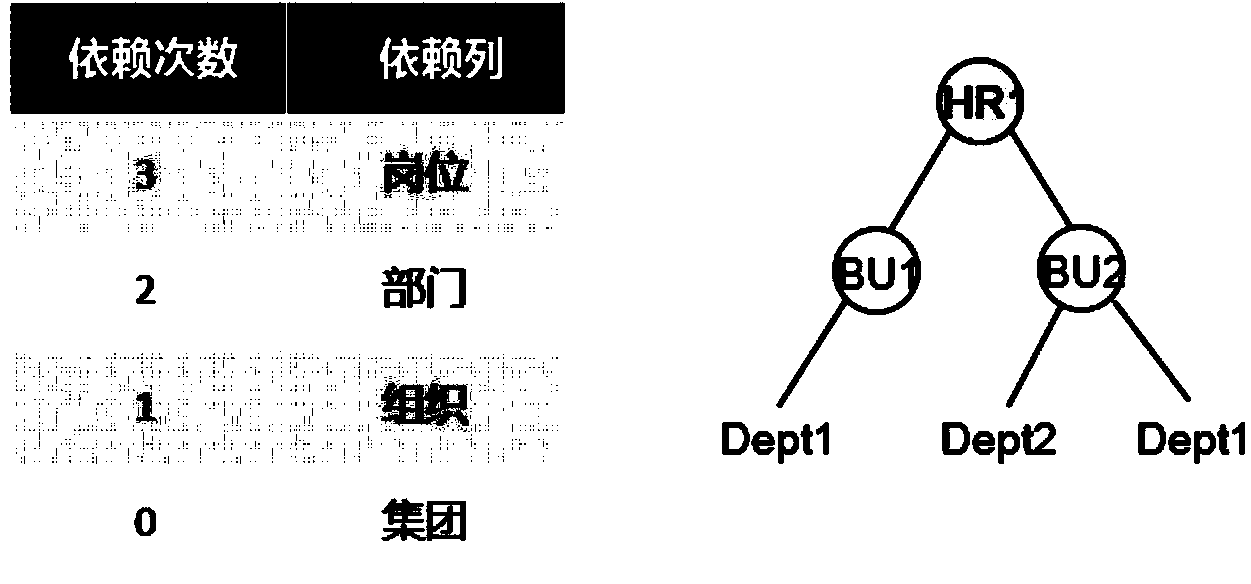
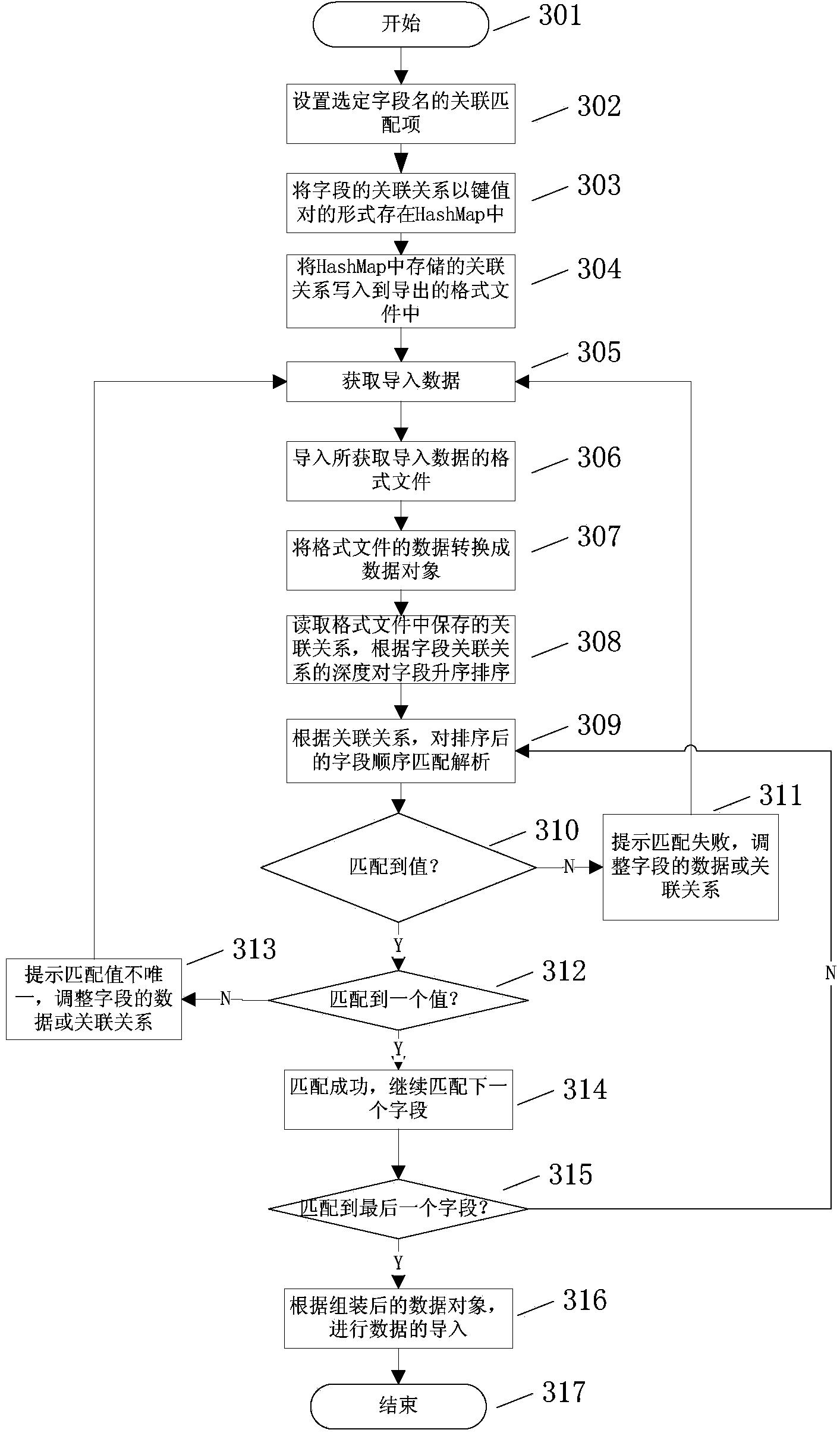
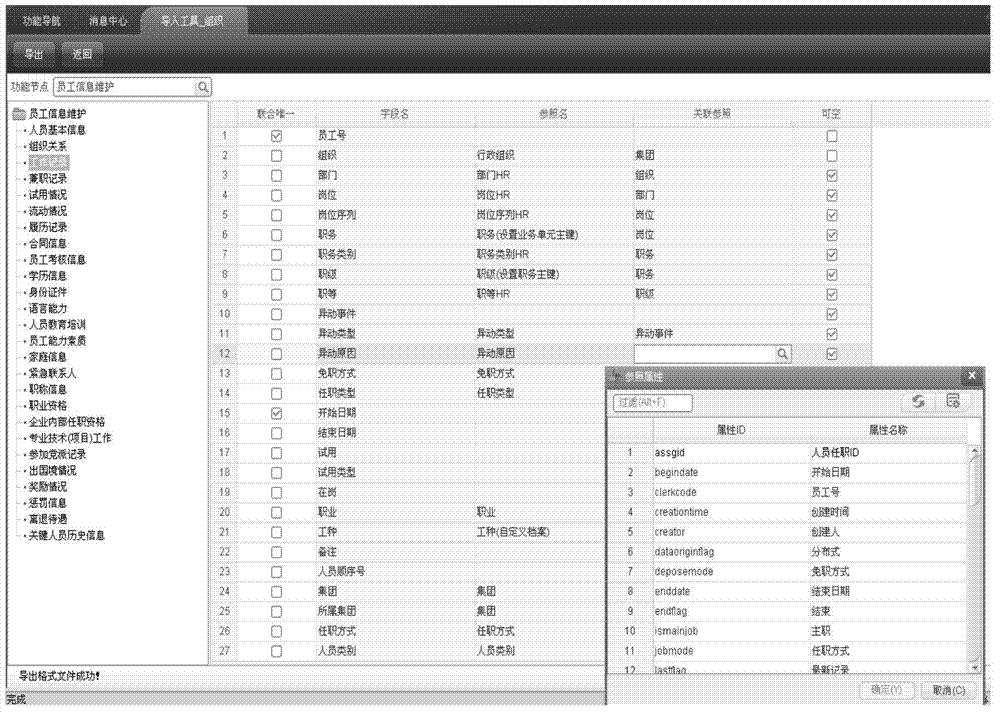
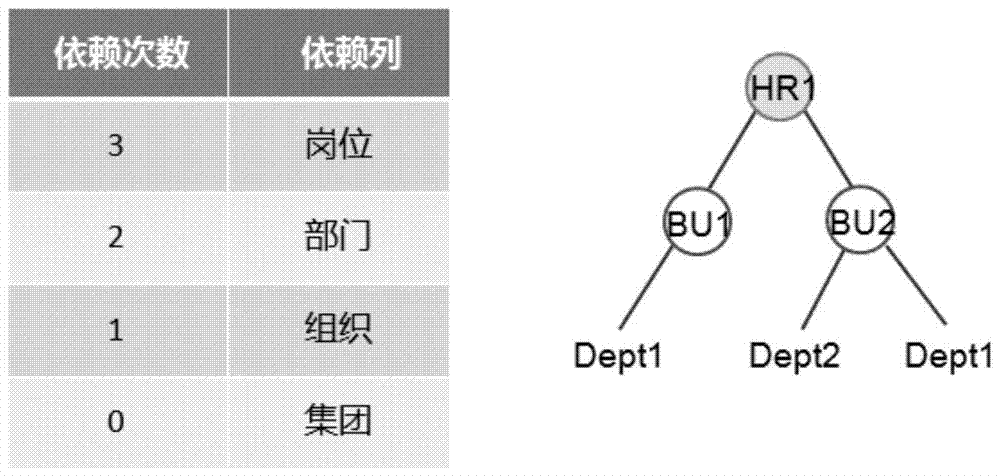
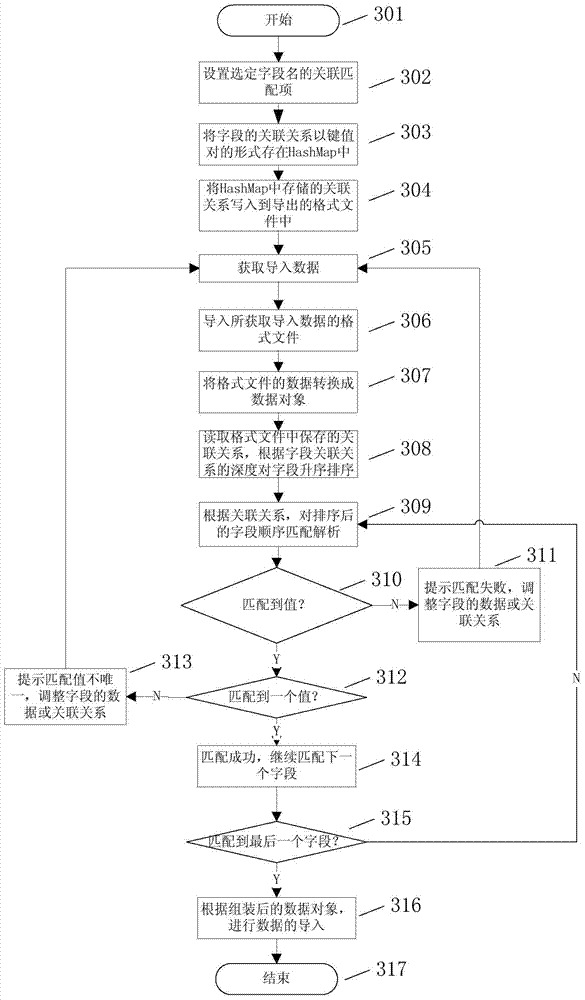
Configurable multiple-valued matching field analysis method
The invention provides a configurable multiple-valued matching field analysis method. According to the method, field association rules can be flexibly set; according to the set field association rules, the data is automatically checked when being imported, and whether the input data has error or not can be checked; if the data has error, prompt is carried out, so that the data wanted by a user can be accurately imported. The configurable multiple-valued matching field analysis method can be applied to an import facility of an effective radiated power (ERP) product, and is suitable for importing some special fields having multiple-valued matching conditions. After the special rules are set, the unique value can be determined when the multiple-valued matching field is imported, so that the accuracy of the imported data can be guaranteed.
Owner:YONYOU NETWORK TECH
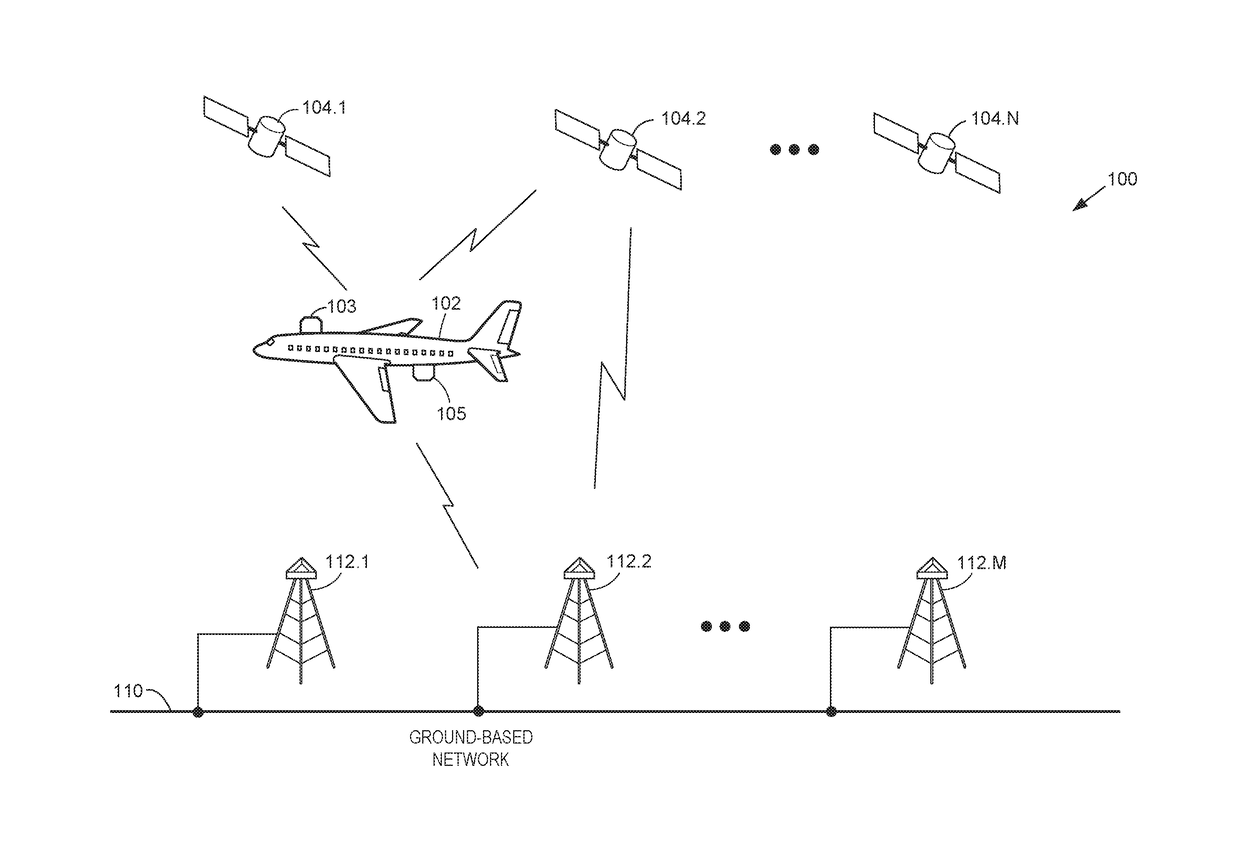
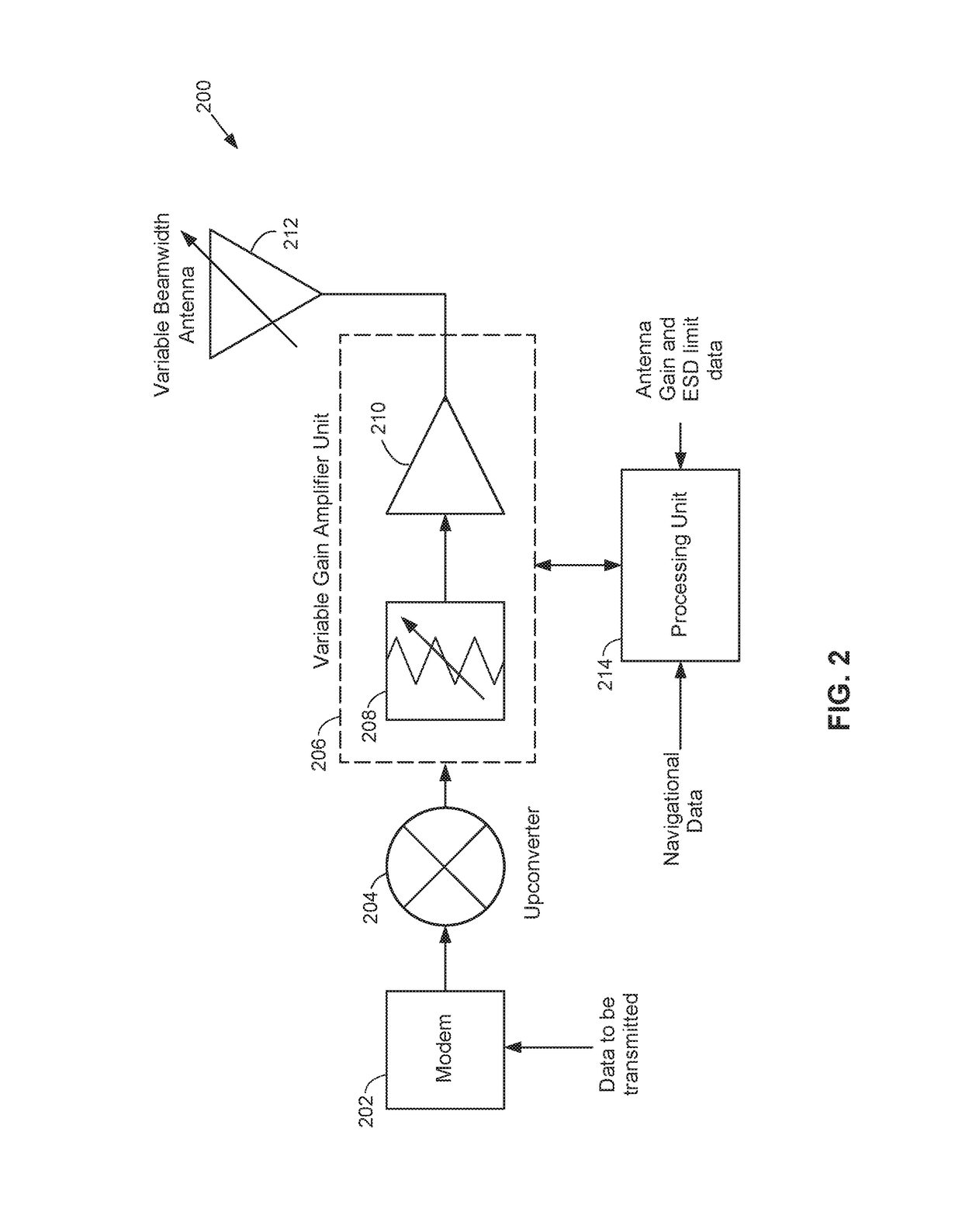
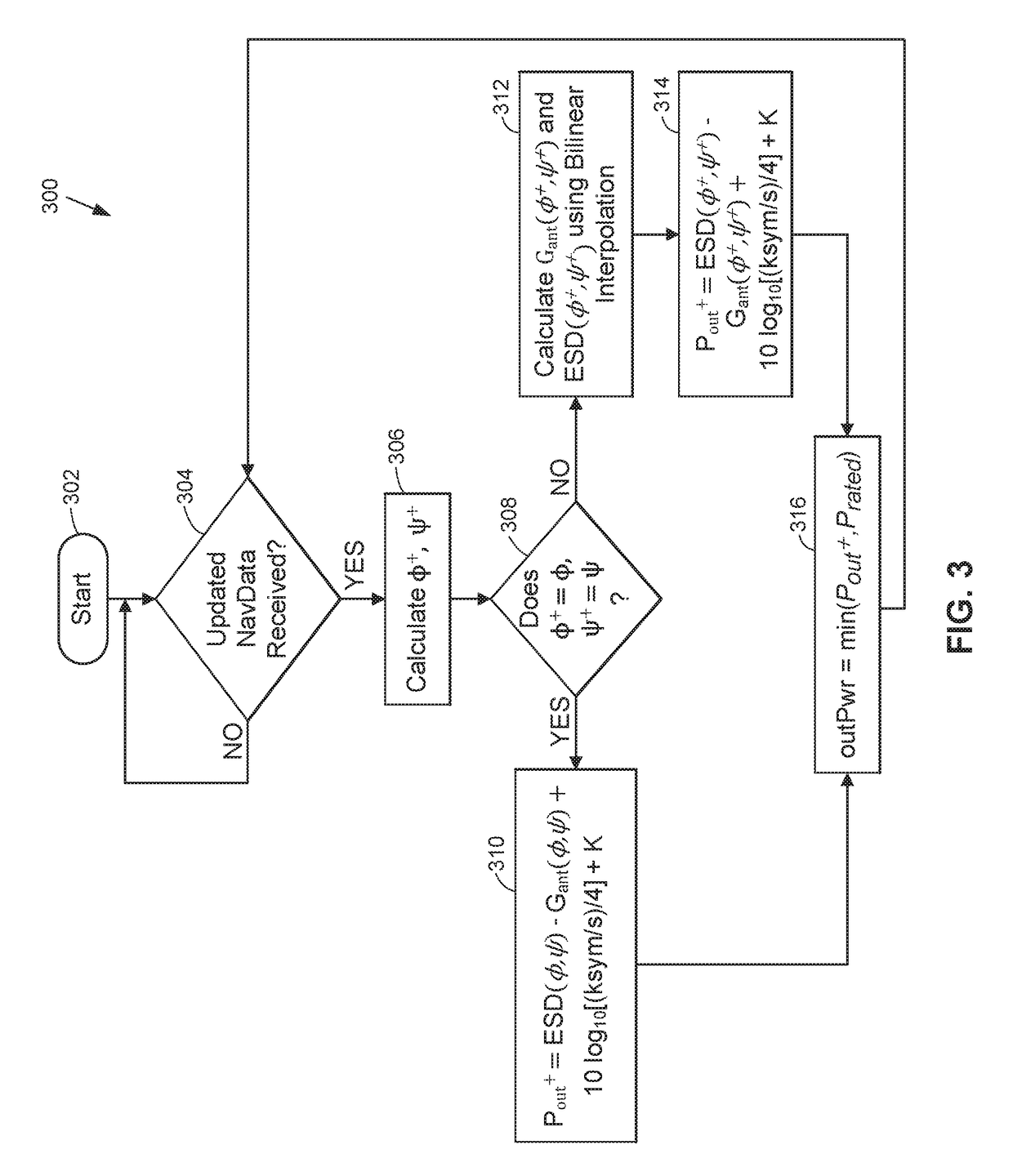
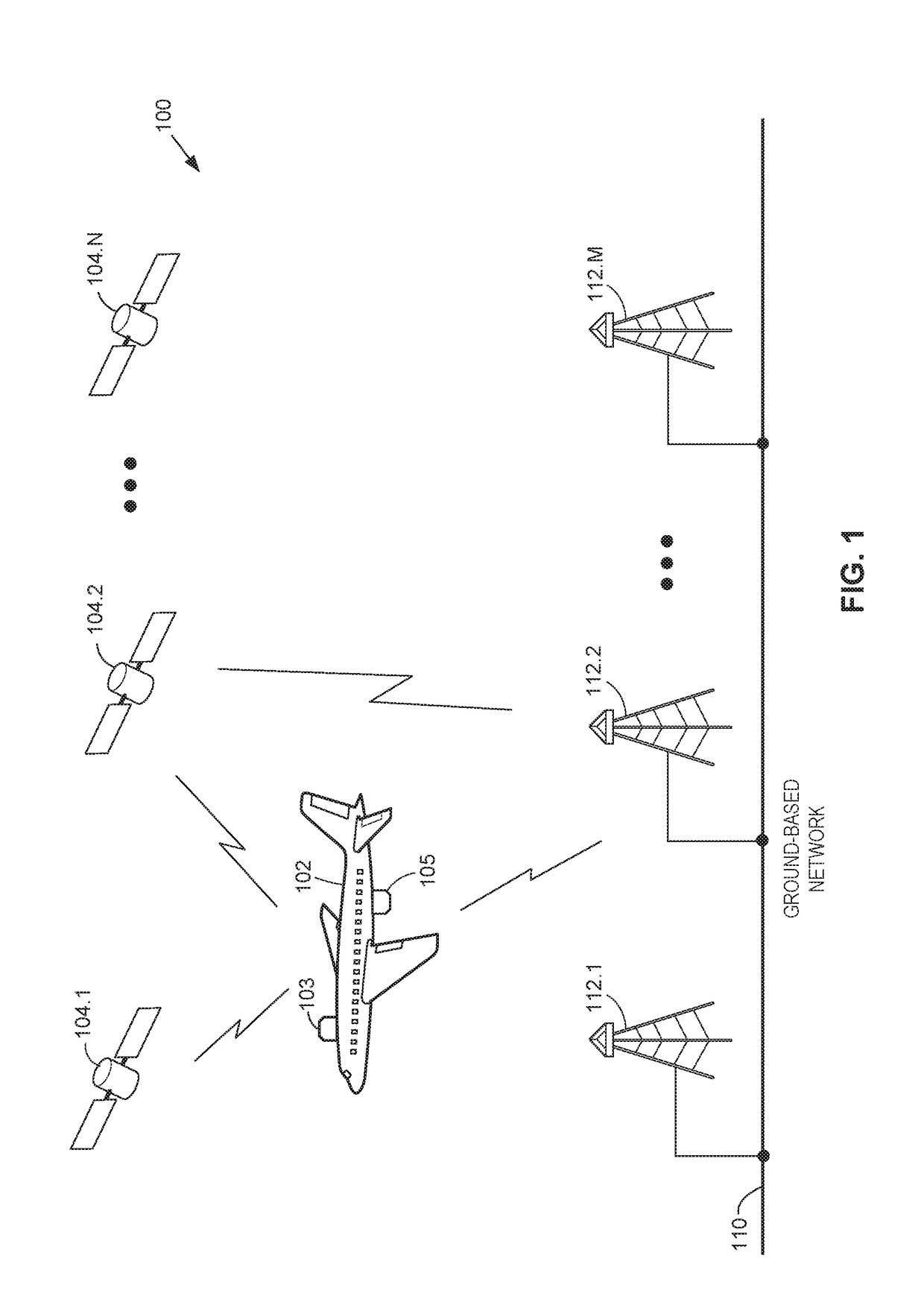
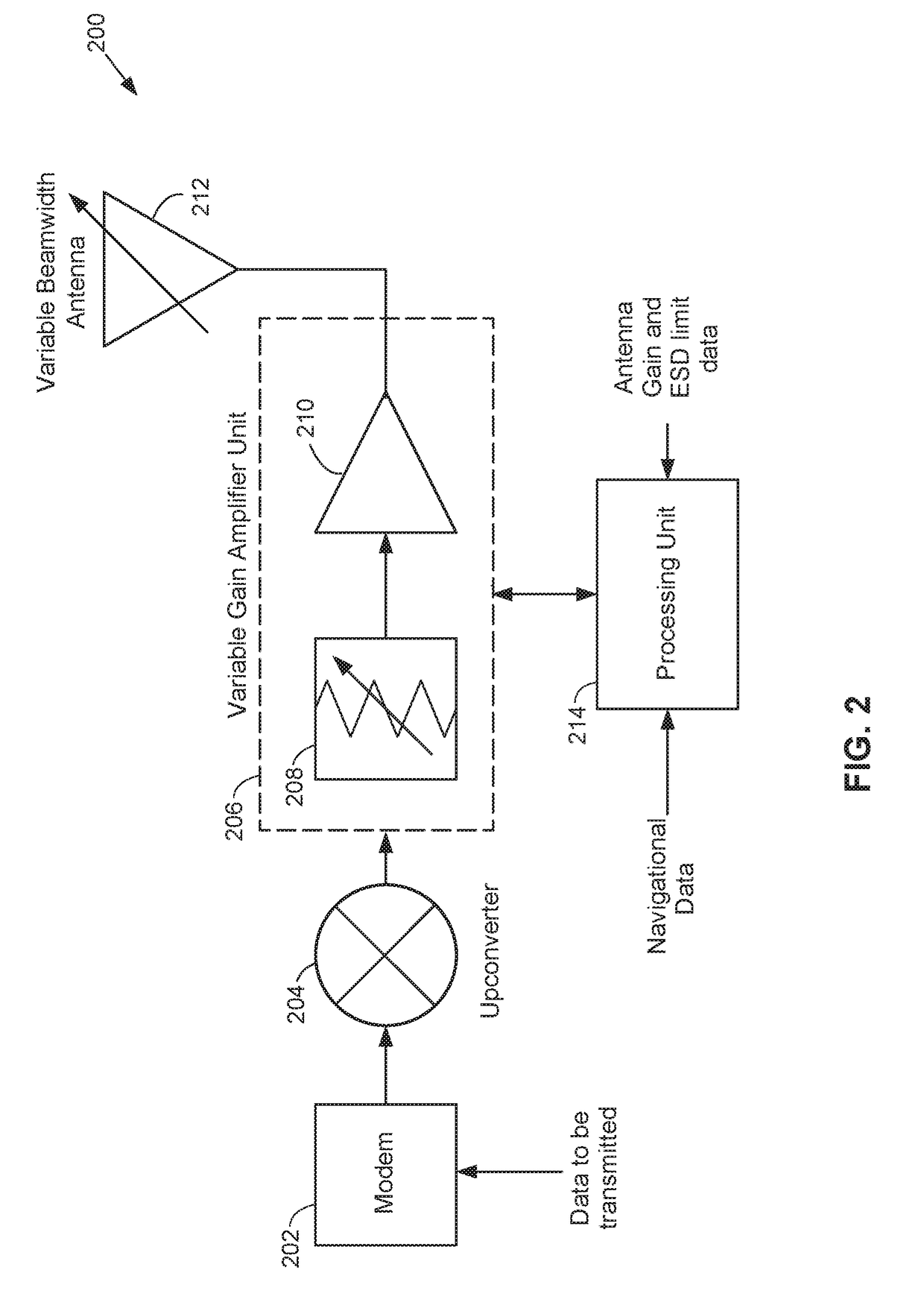
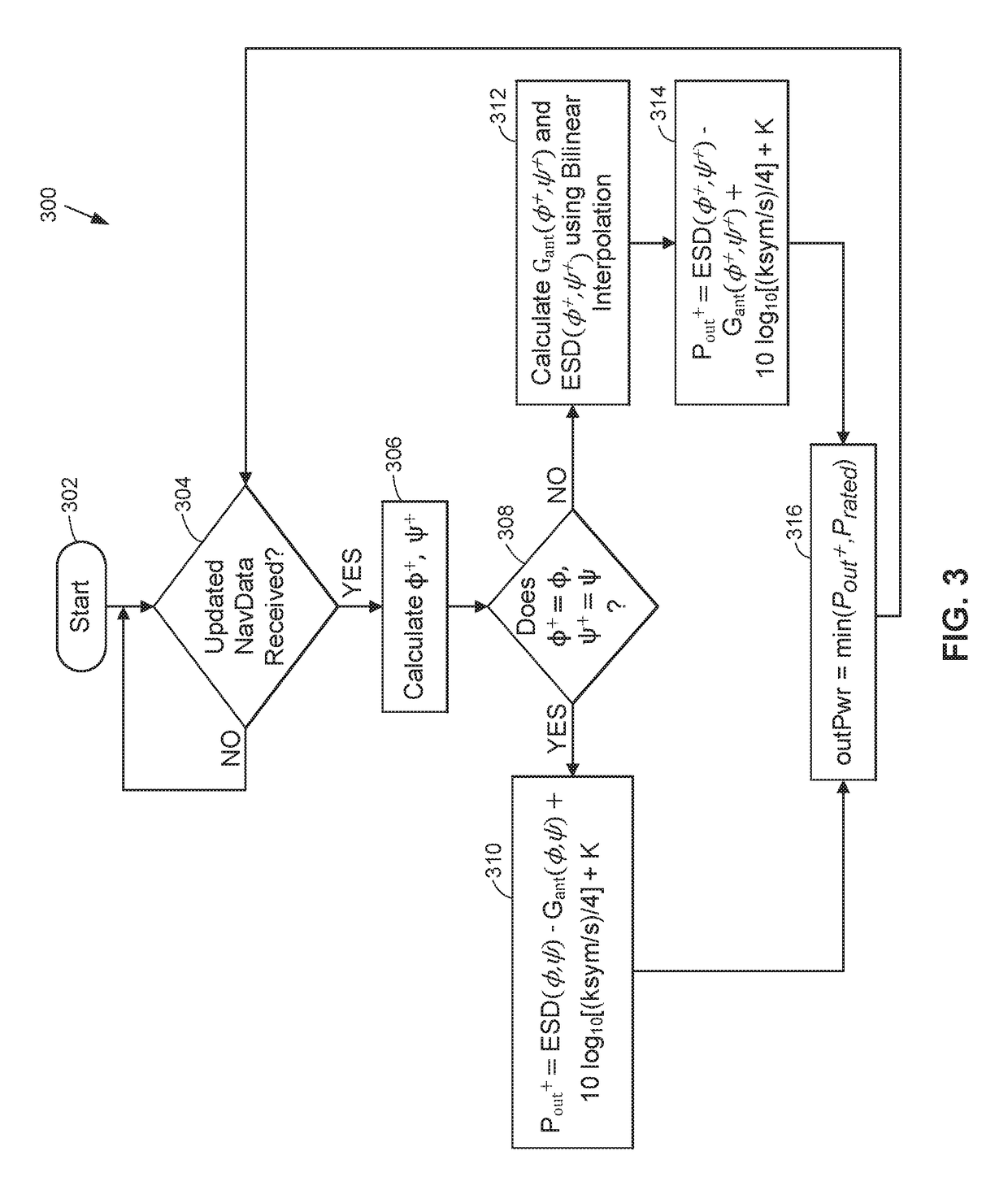
Dynamic effective radiated power (ERP) adjustment
ActiveUS20180006371A1Reduce outputNavigational calculation instrumentsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesOn boardSkew angle
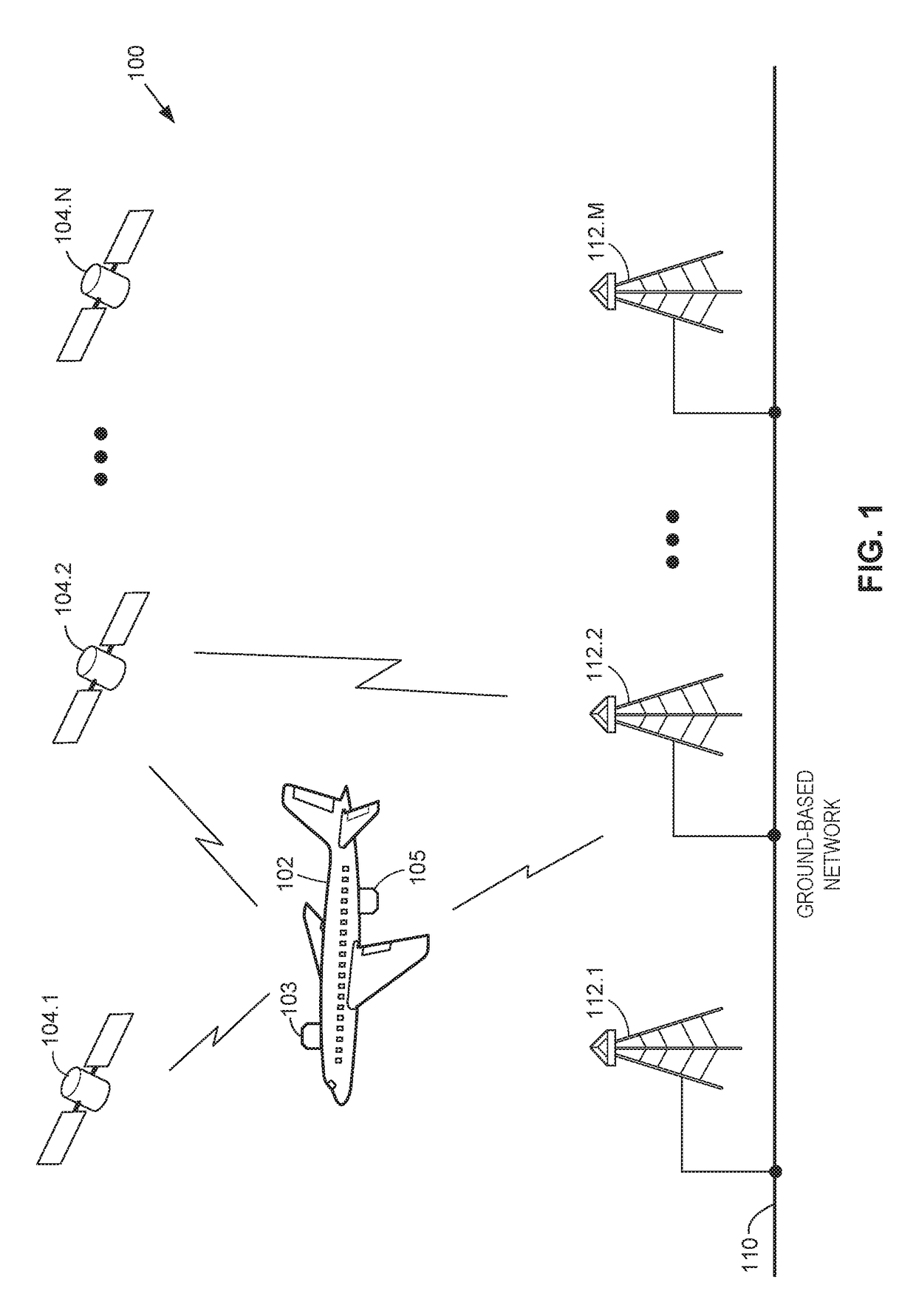
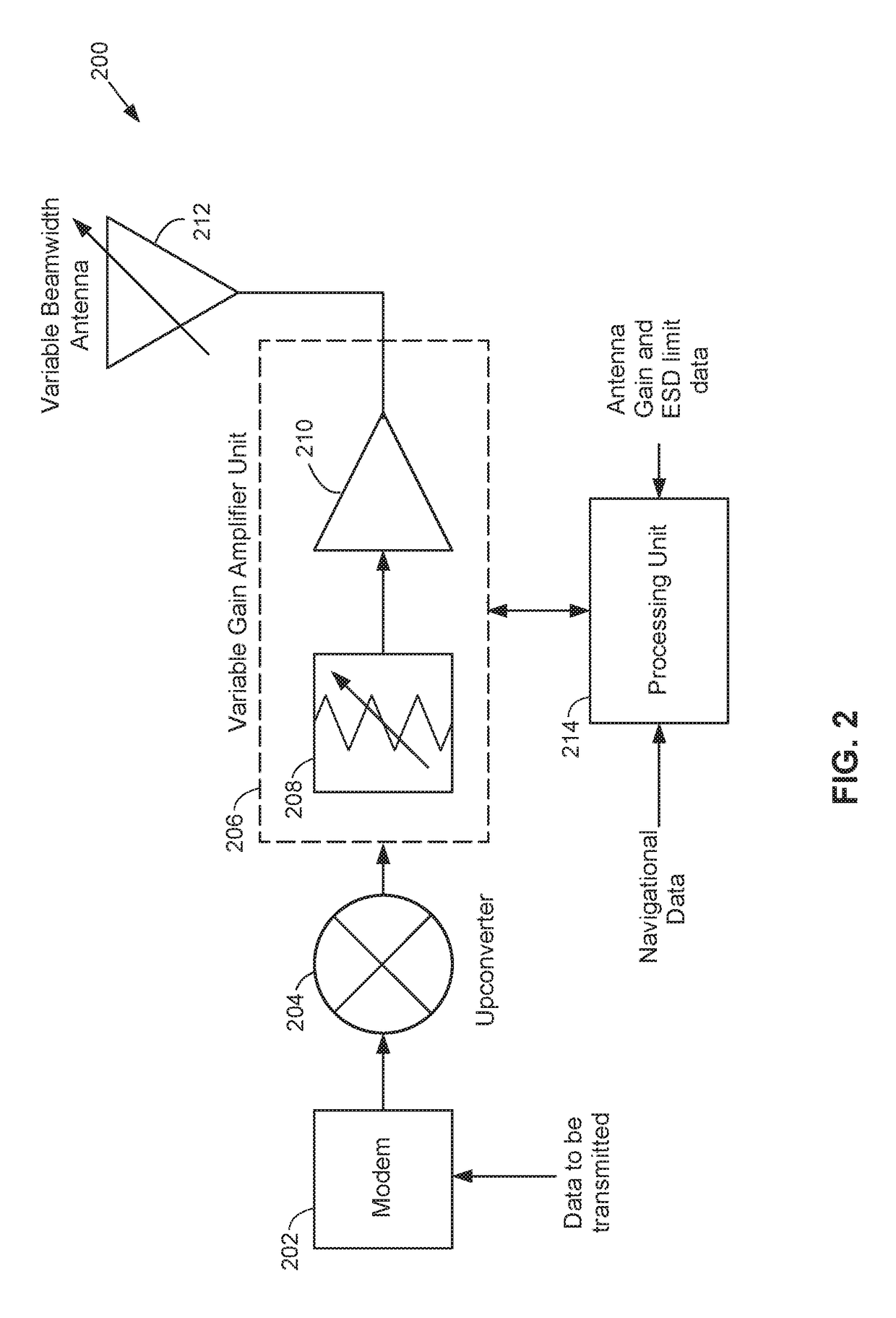
Antennas used aboard aircraft to communicate with satellites or ground stations may have complex antenna patterns, which may vary as the aircraft moves throughout a given coverage area. Techniques are disclosed for dynamically adjusting the instantaneous power fed to an antenna system to ensure that the antenna transmits at the regulatory or coordinated effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) spectral limit. The antenna may transmit, in accordance with aircraft location and attitude, steerable beam patterns at different scan and skew angle combinations, causing variations in antenna gain and fluctuations in the transmitted EIRP. Using on-board navigational data, an antenna gain and ESD limit may be calculated for a particular scan and skew angle, which may be used to adjust power fed to the antenna such that the antenna transmits substantially at maximum allowable EIRP as the steerable beam pattern is adjusted.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
WIFI OTA (wireless fidelity over the air) testing method and system of mobile terminal
ActiveCN103298020AImprove test efficiencyShorten test timeReceivers monitoringWireless communicationTest efficiencyComputer terminal
The invention discloses a WIFI OTA (wireless fidelity over the air) testing method and system of a mobile terminal. The WIFI OTA (wireless fidelity over the air) testing method includes measuring effective radiated power of the mobile terminal at each position, and forming a directional diagram of the effective radiated power according to the same; determining a first position corresponding to the effective radiated power when being the strongest according to the directional diagram of the effective radiated power, and measuring a primary ERSbest (effective radiated sensitivity) of the mobile terminal at the first position; calculating a secondary ERSbest of the rest at a second position according to the following relation: ERS: ERS= ERSbest+( ERPbest-ERP (effective radiated power)), wherein the ERSbest is the effective radiated power at the first position, and the ERP is the effective radiated power of every other second positions; summing integration of the primary ERSbest measured and the secondary ERS acquired by calculating to acquire receive sensitivity of an antenna of the mobile terminal. According to the arrangement, testing effect can be improved.
Owner:威海高新园区运营管理有限公司
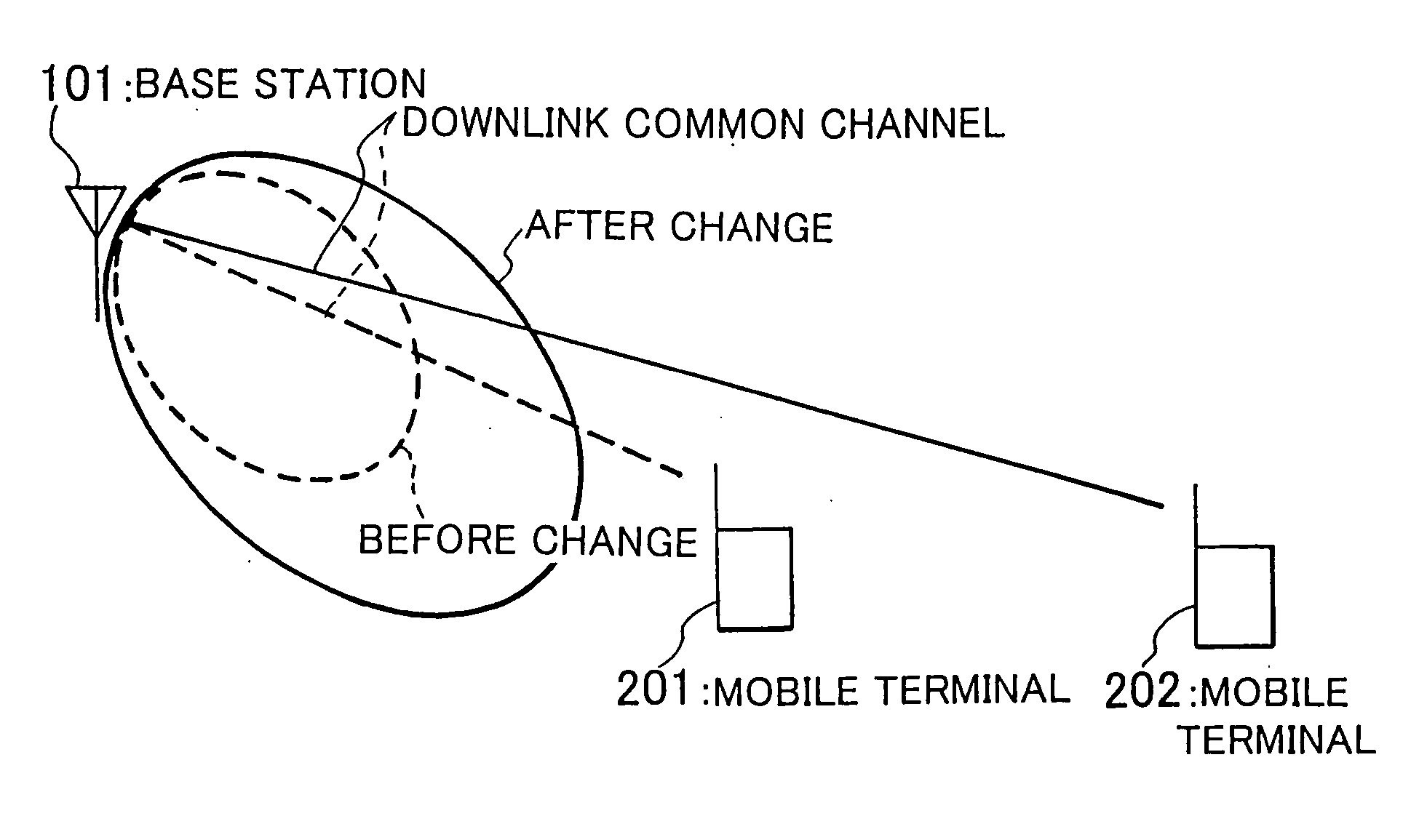
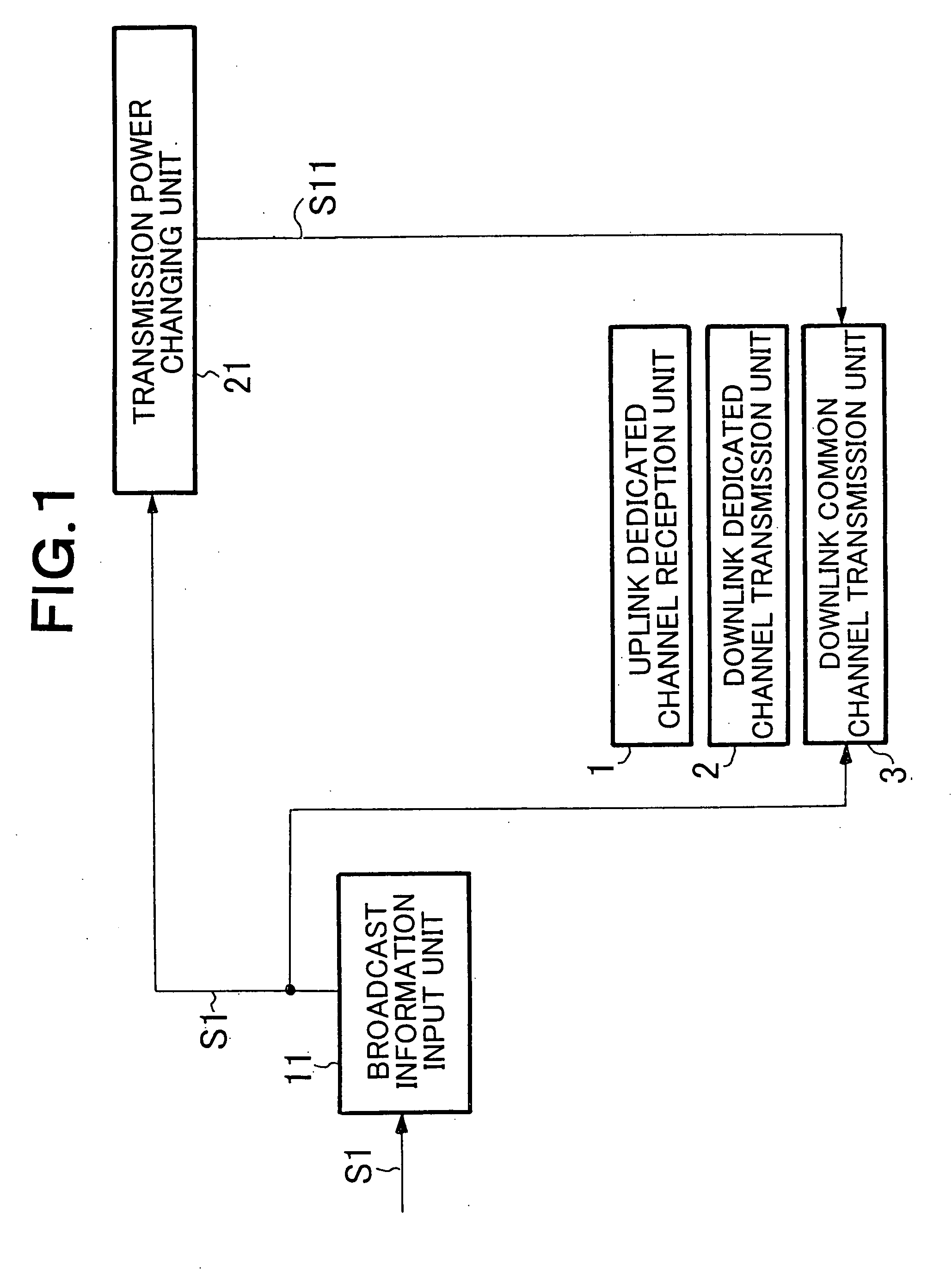
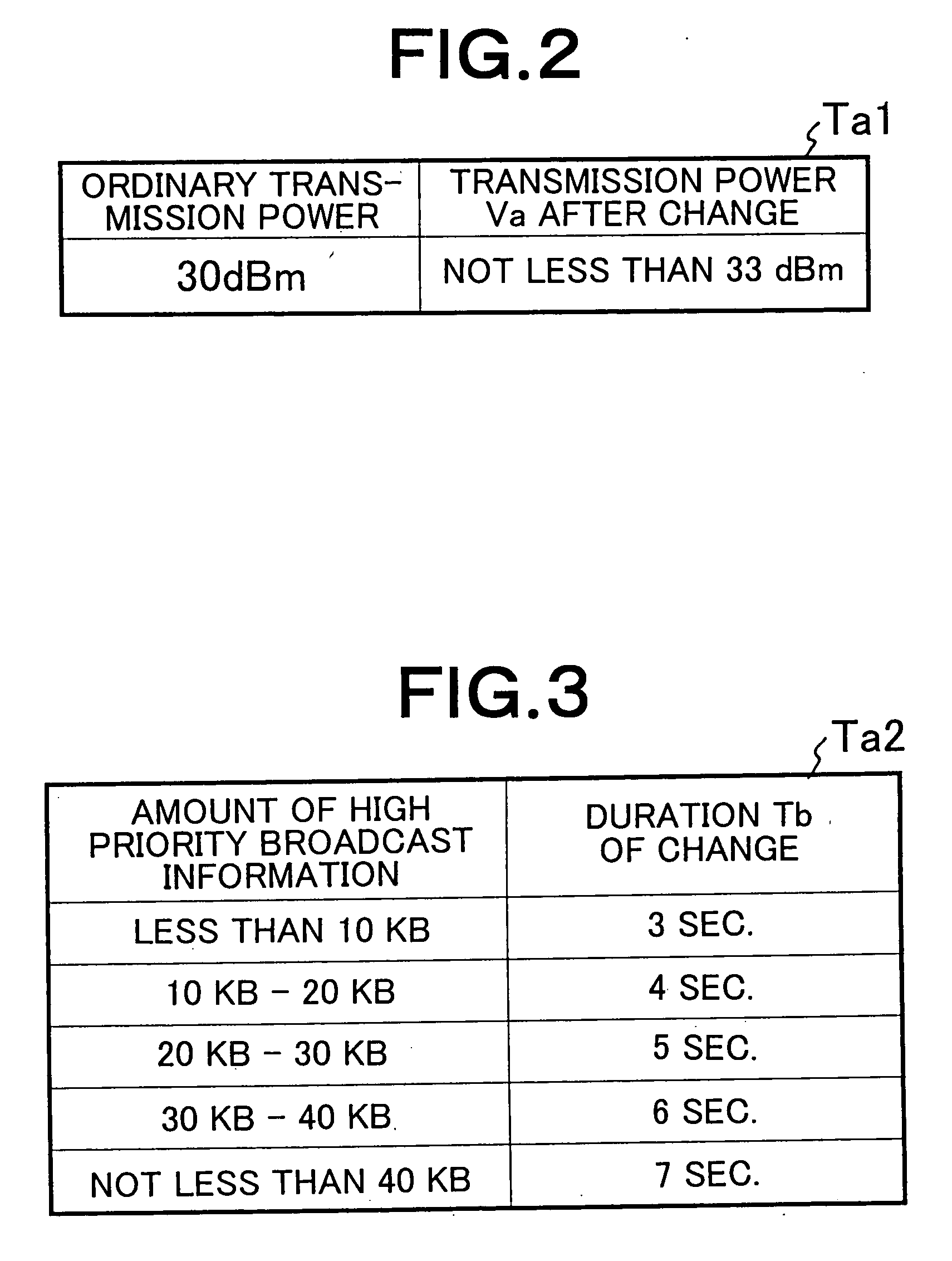
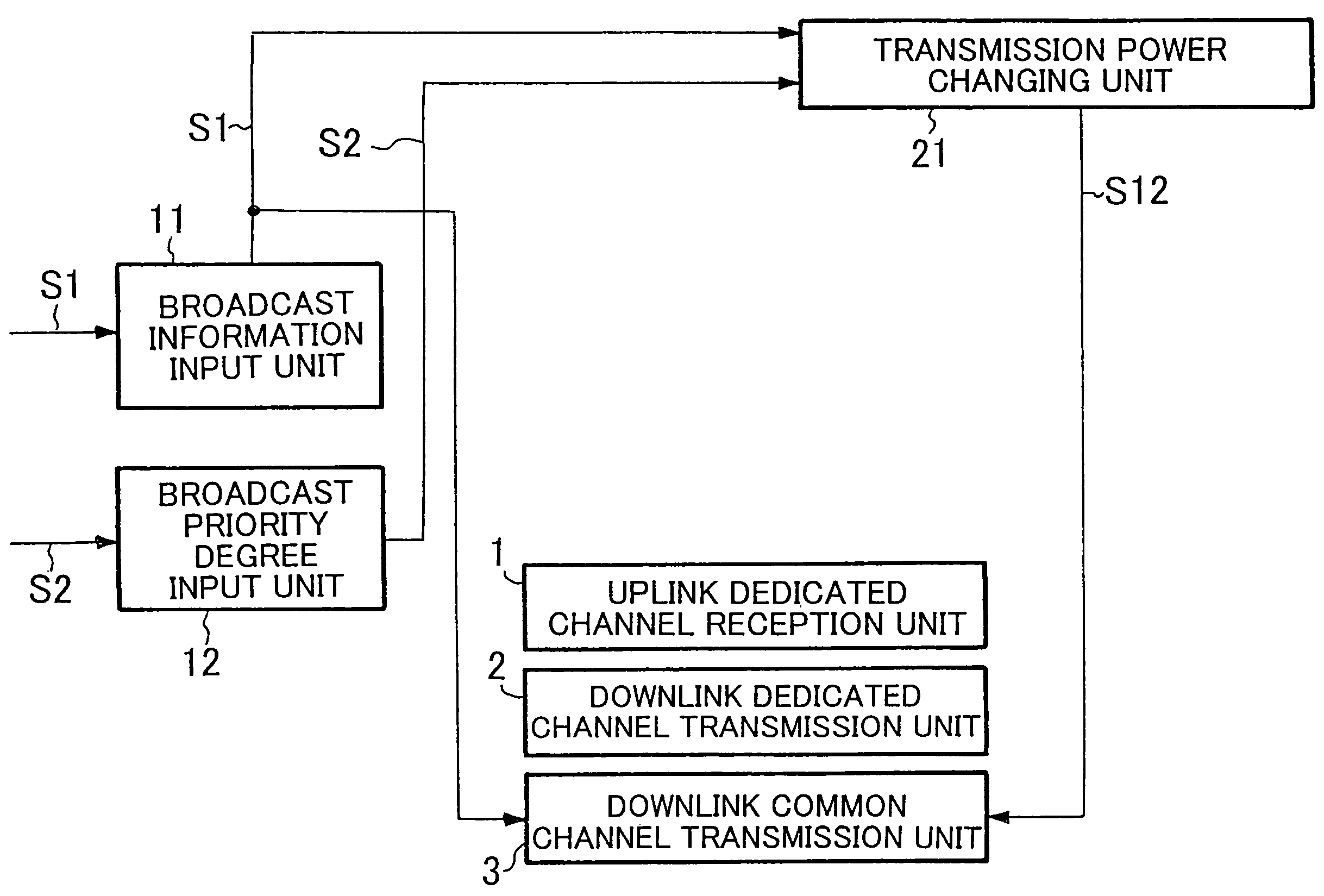
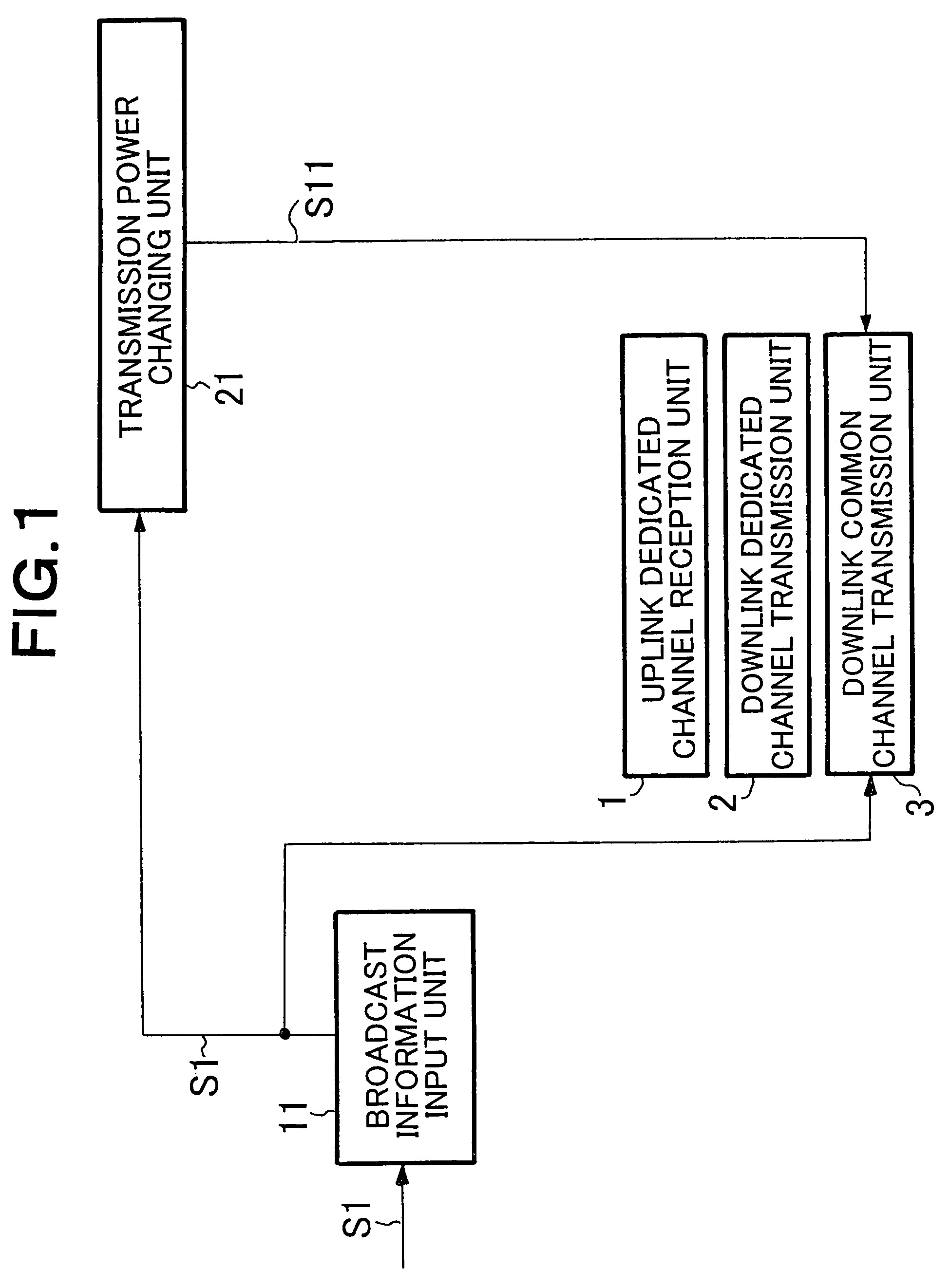
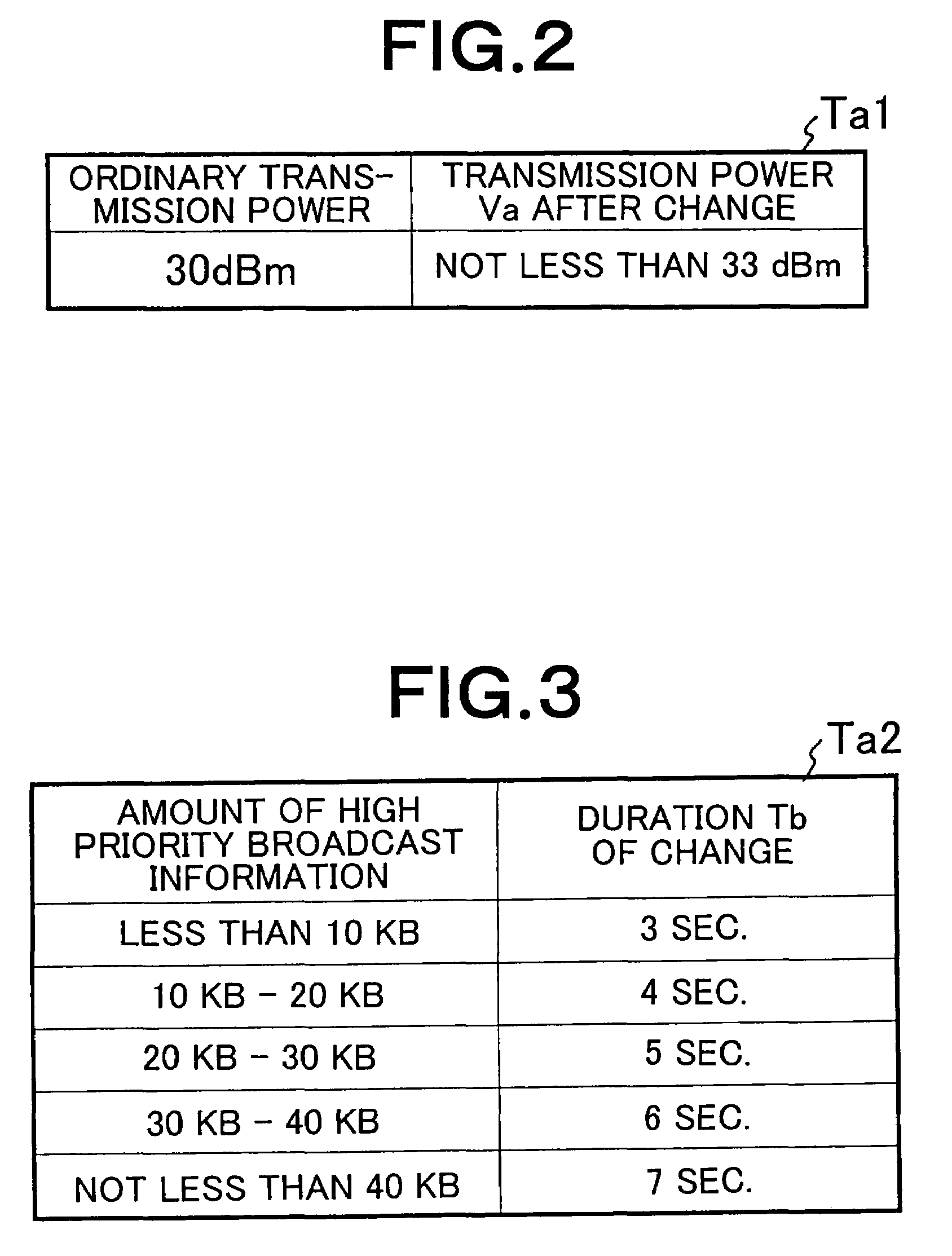
Wireless communication network and method for broadcasting high priority information using downlink common channels
InactiveUS20060293043A1Raise priorityReliable deliveryPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPopulated areaEffective radiated power
A wireless communication network can reliably deliver high priority broadcast information from base stations to mobile terminals located deep in building and those located in scarcely populated areas that are remote from the base stations. Each of the base stations of the wireless communication network comprises a broadcast information input unit for receiving high priority broadcast information and a transmission power changing unit for changing the transmission power of the downlink common channel when high priority broadcast information is input to it. As broadcast information is input, the transmission power changing unit changes the transmission power of the downlink common channel so as to boost the effective radiation power used by the downlink common channel of the base station at places in the coverage of the base station that are subjected to a propagation loss. The effective radiation power to the mobile terminals located at places in the coverage of the base station that are subjected to propagation loss is boosted to raise the reception level of the mobile terminals located at such places.
Owner:NEC CORP
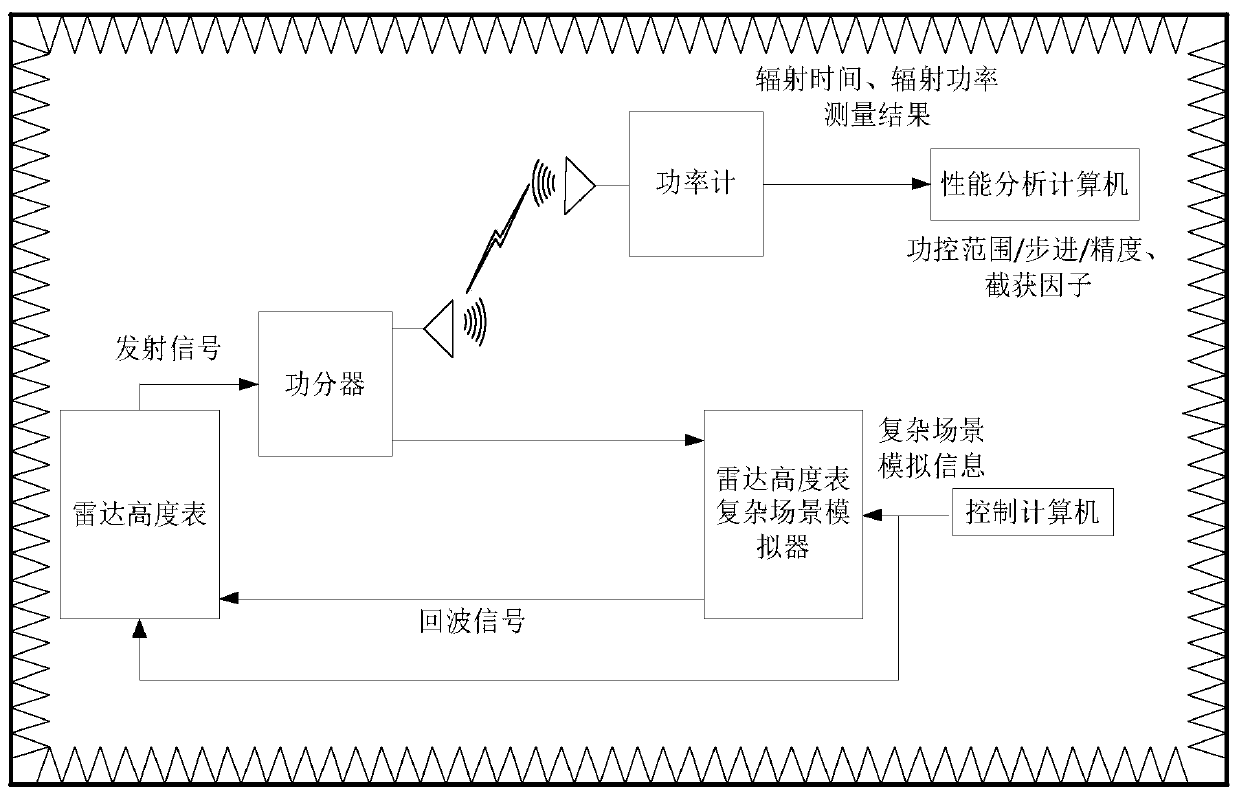
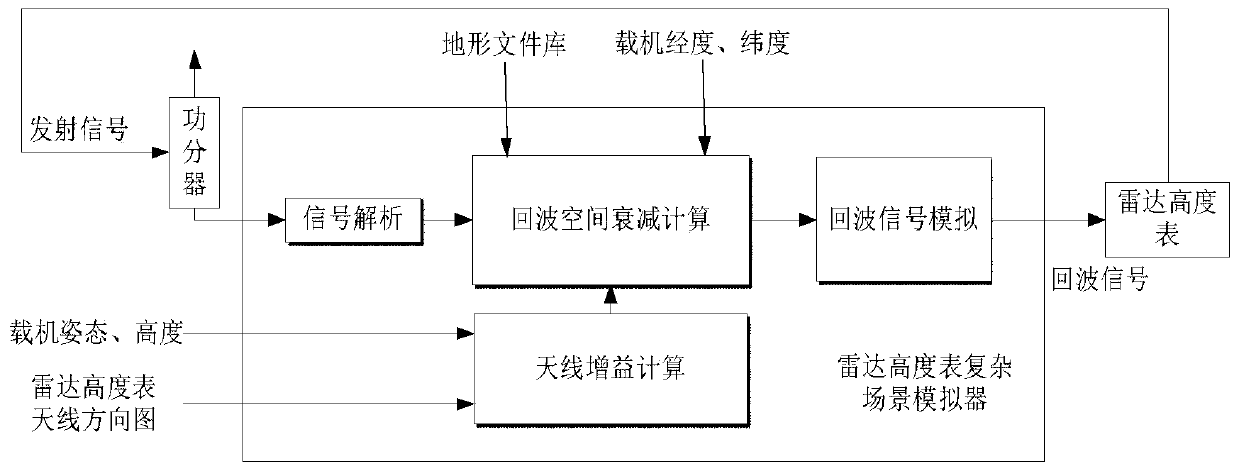
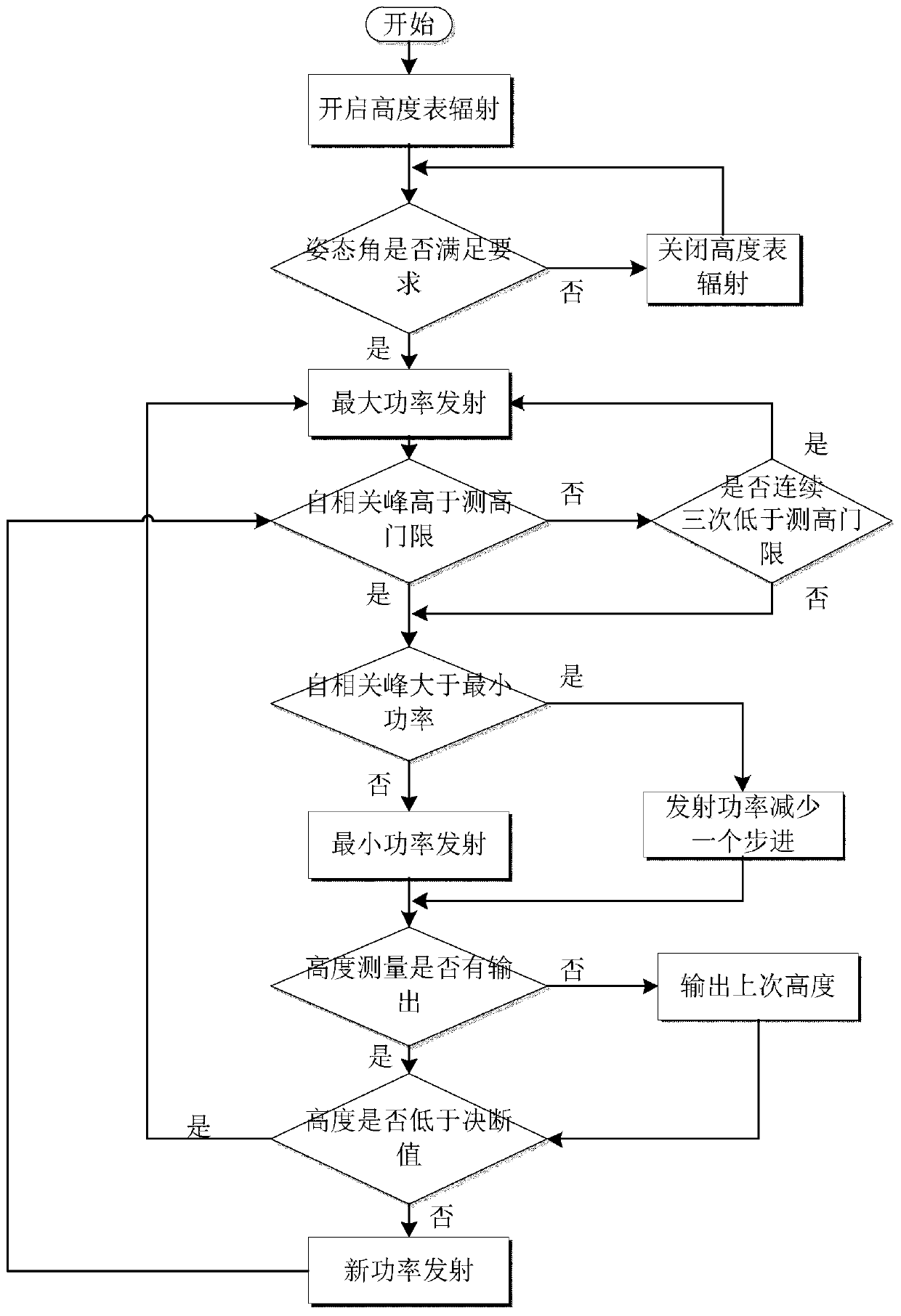
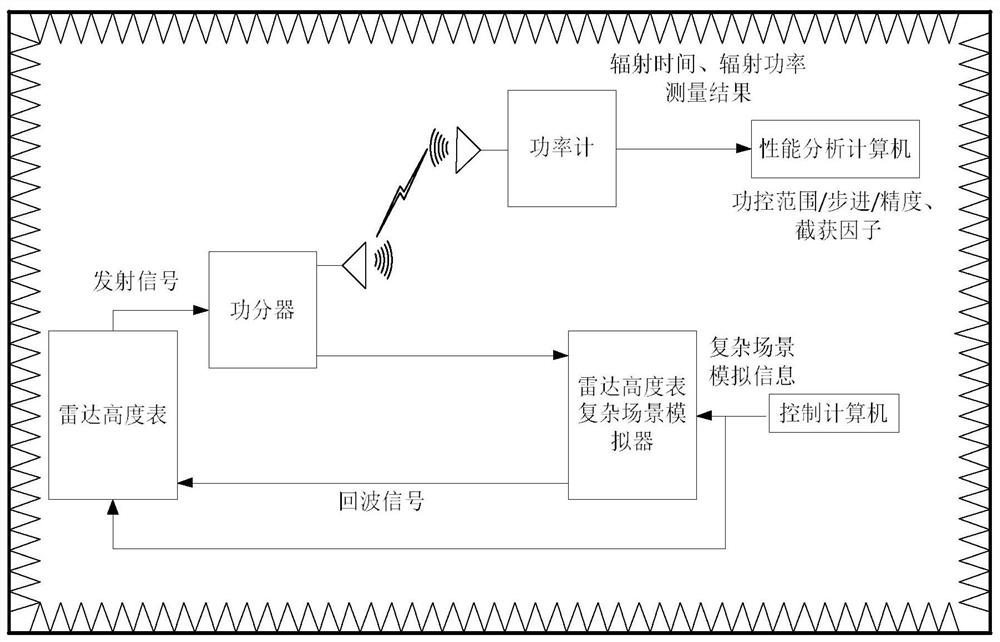
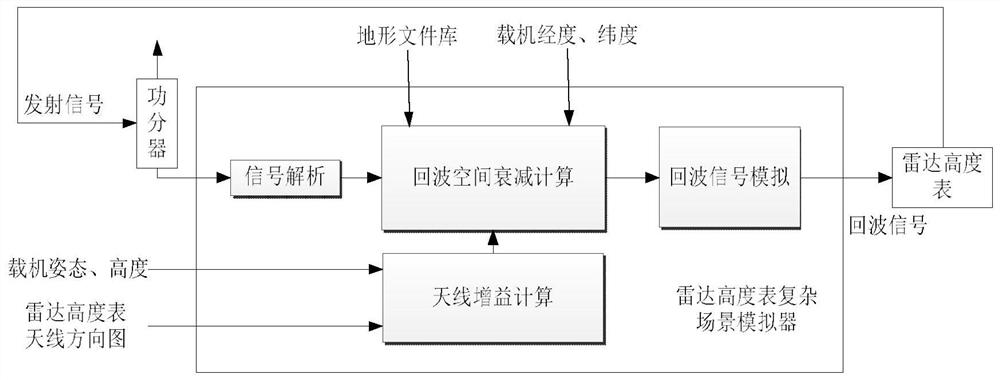
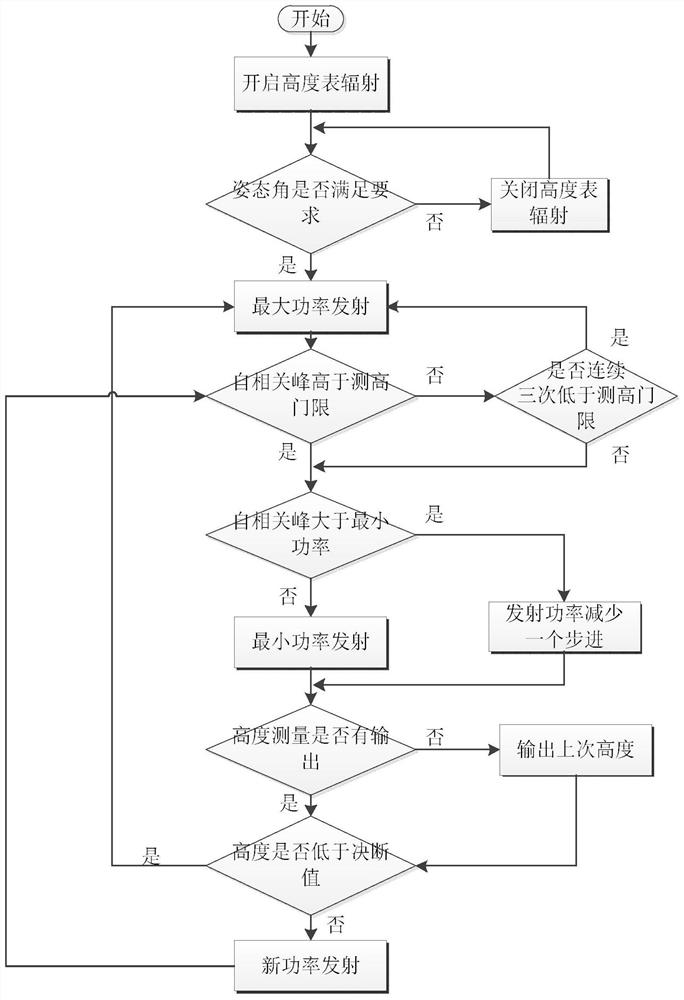
Radar altimeter low interception performance test method
The invention discloses a radar altimeter low interception performance test method, aiming to provide a radar altimeter low interception performance test method with full test index, high test precision and low test cost. The invention is realized through the following technical scheme: sending complex scene simulation information to a radar altimeter complex scene simulator by using a control computer; outputting a generated echo signal to the radar altimeter to start the radio frequency control software; managing the radiation switch status of the radar altimeter in real time; analyzing theneed for effective radiant power when the radar altimeter is operating normally at anyone height in the altimetry range; determining the minimum radiant power under the premise of meeting the altimetry performance; sending a transmitting signal to a power meter through an antenna connected to a power divider; testing the transmitting signal of the radar altimeter; transmitting the radiant time andradiant power to a performance analysis computer; and performing analysis according to the radiation parameter measurement results of the power meter, and calculating to obtain the power control range, the step, the accuracy and an interception factor.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
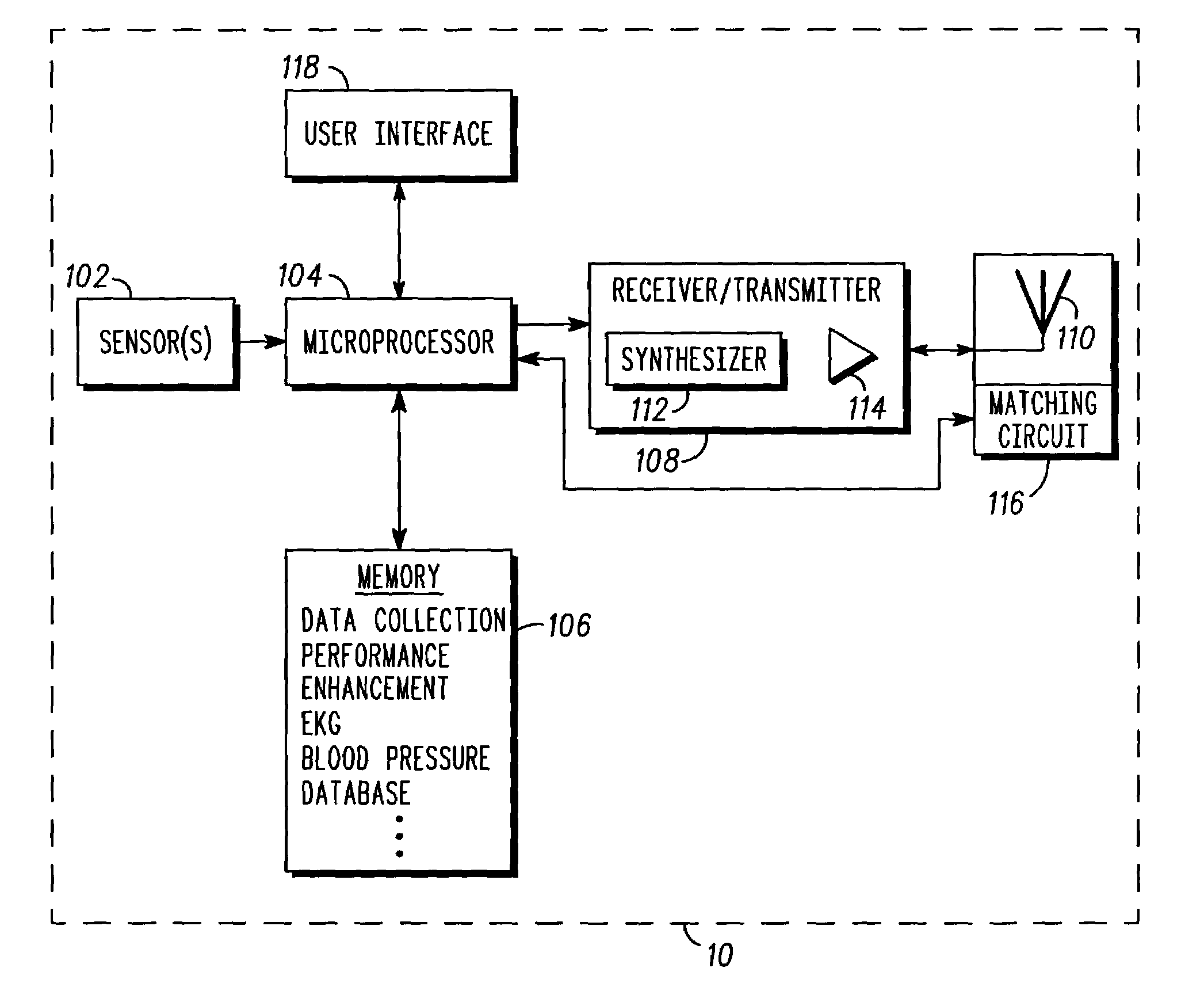
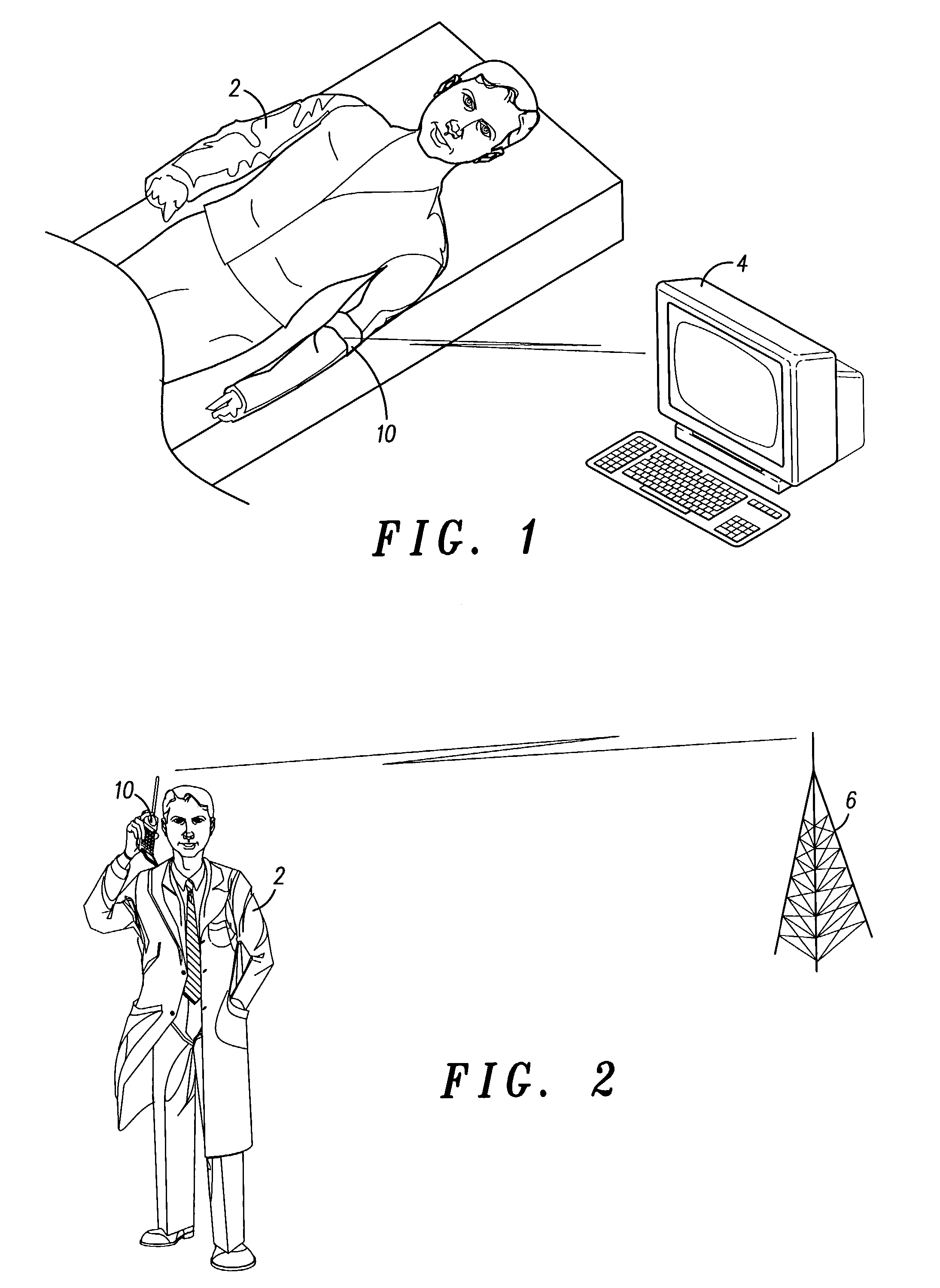
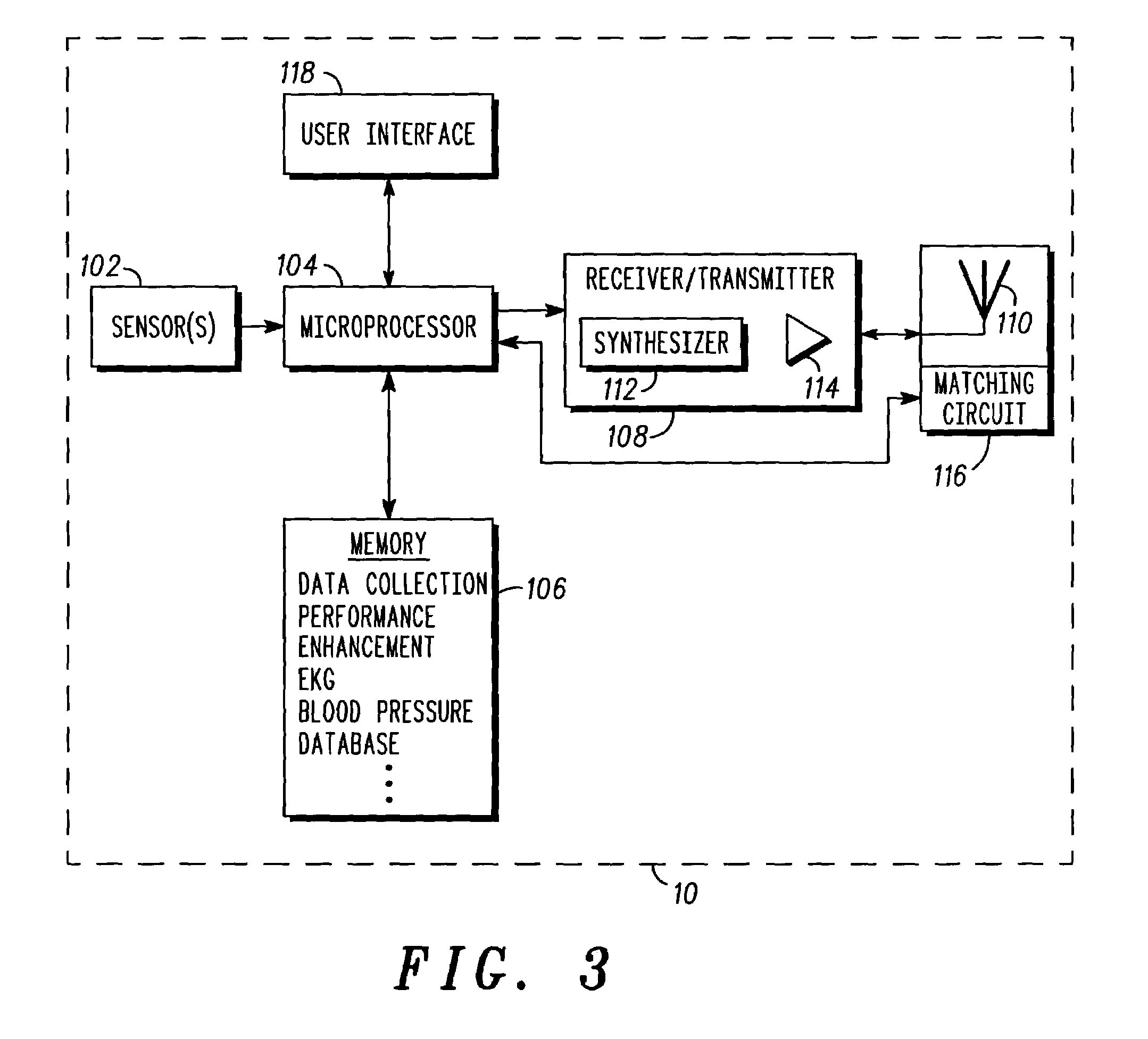
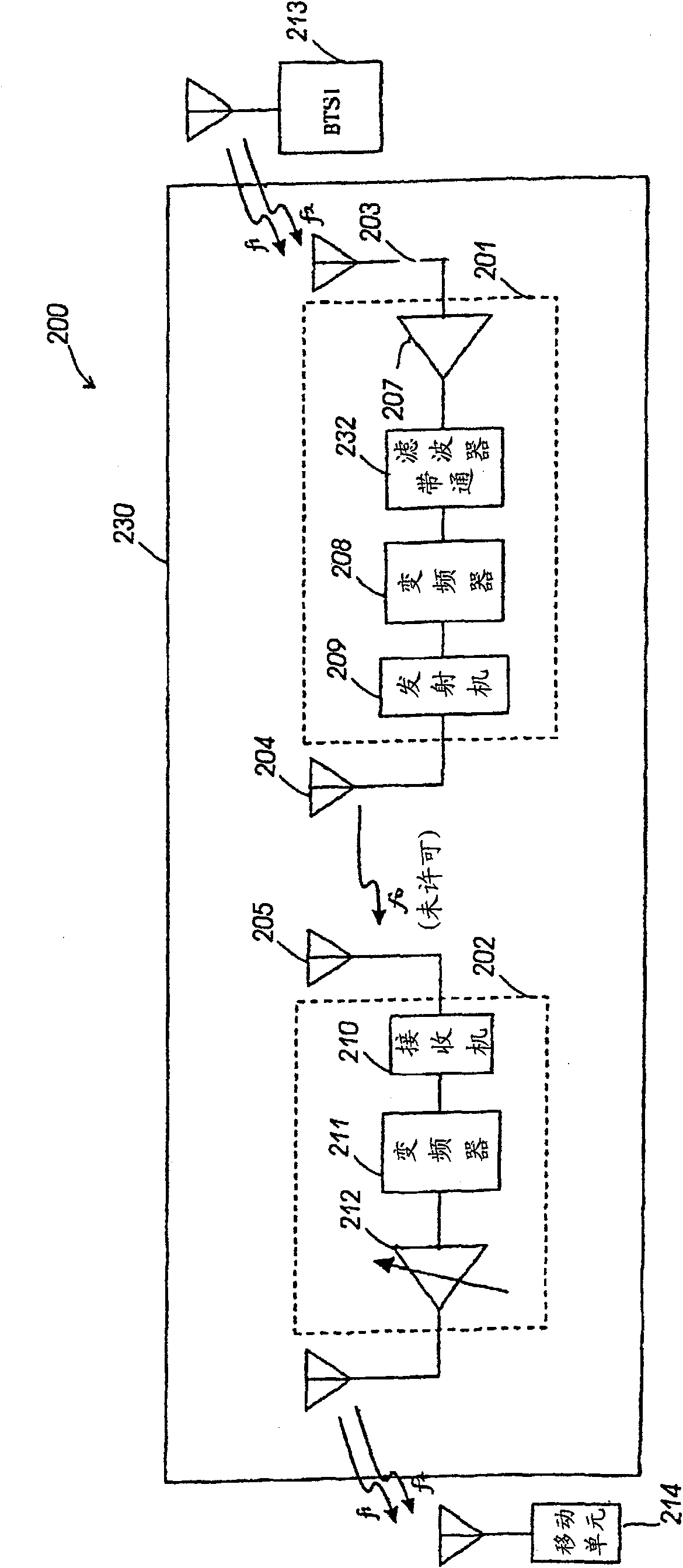
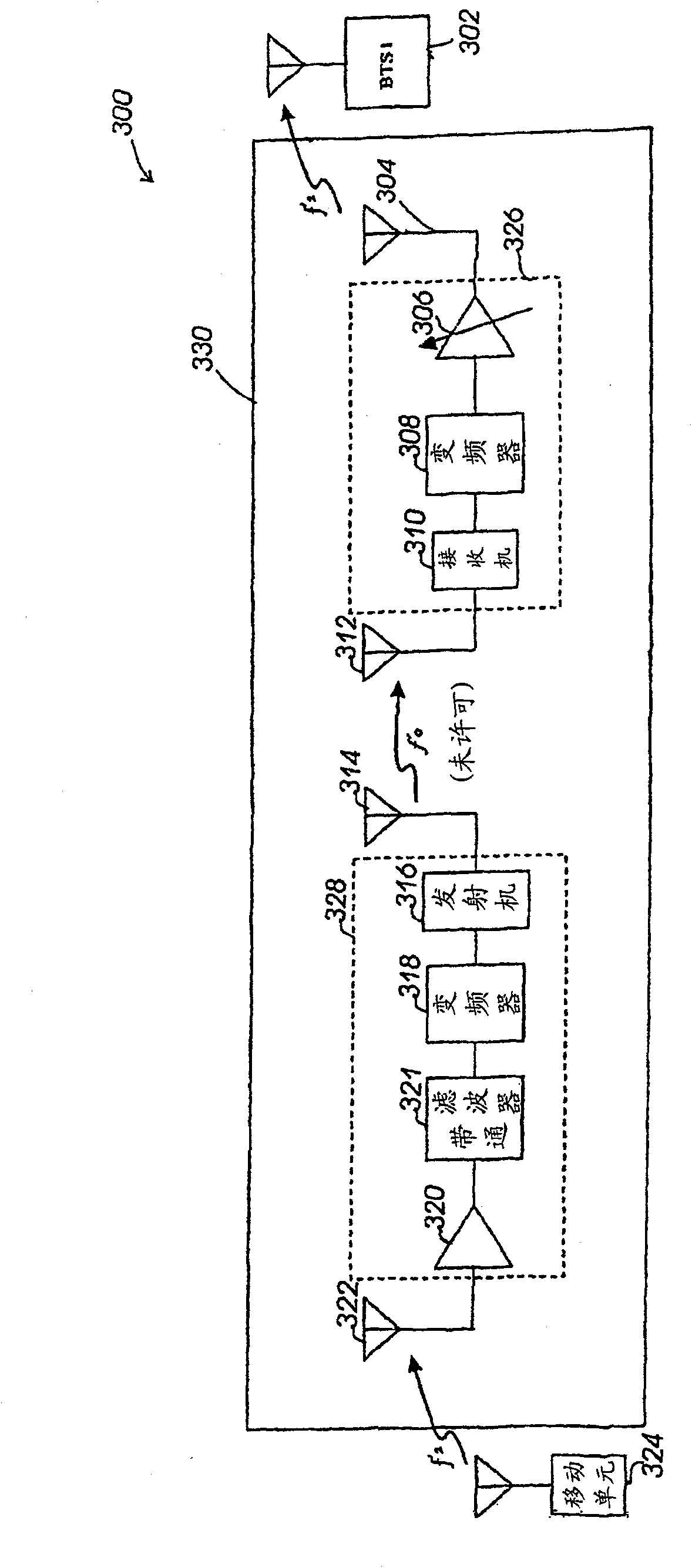
Method and device for increasing effective radiated power from a subscriber device
ActiveUS6972692B2Electric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsUser deviceAudio power amplifier
A subscriber device (10) includes one or more sensors (102) for measuring a object electromagnetic characteristic, such as conductivity, permittivity or permeability. A controller (104) stores the object electromagnetic parameter in memory (106) and, operating in accordance with a performance enhancement routine stored in the memory (106), enhances operation of the subscriber device (10) in accordance with the electromagnetic parameter. The controller (104) may do this by adjusting the power of an amplifier (112), the frequency of a synthesizer (114) or the impedance of an antenna (110). A software program controlling the subscriber device and a corresponding method are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
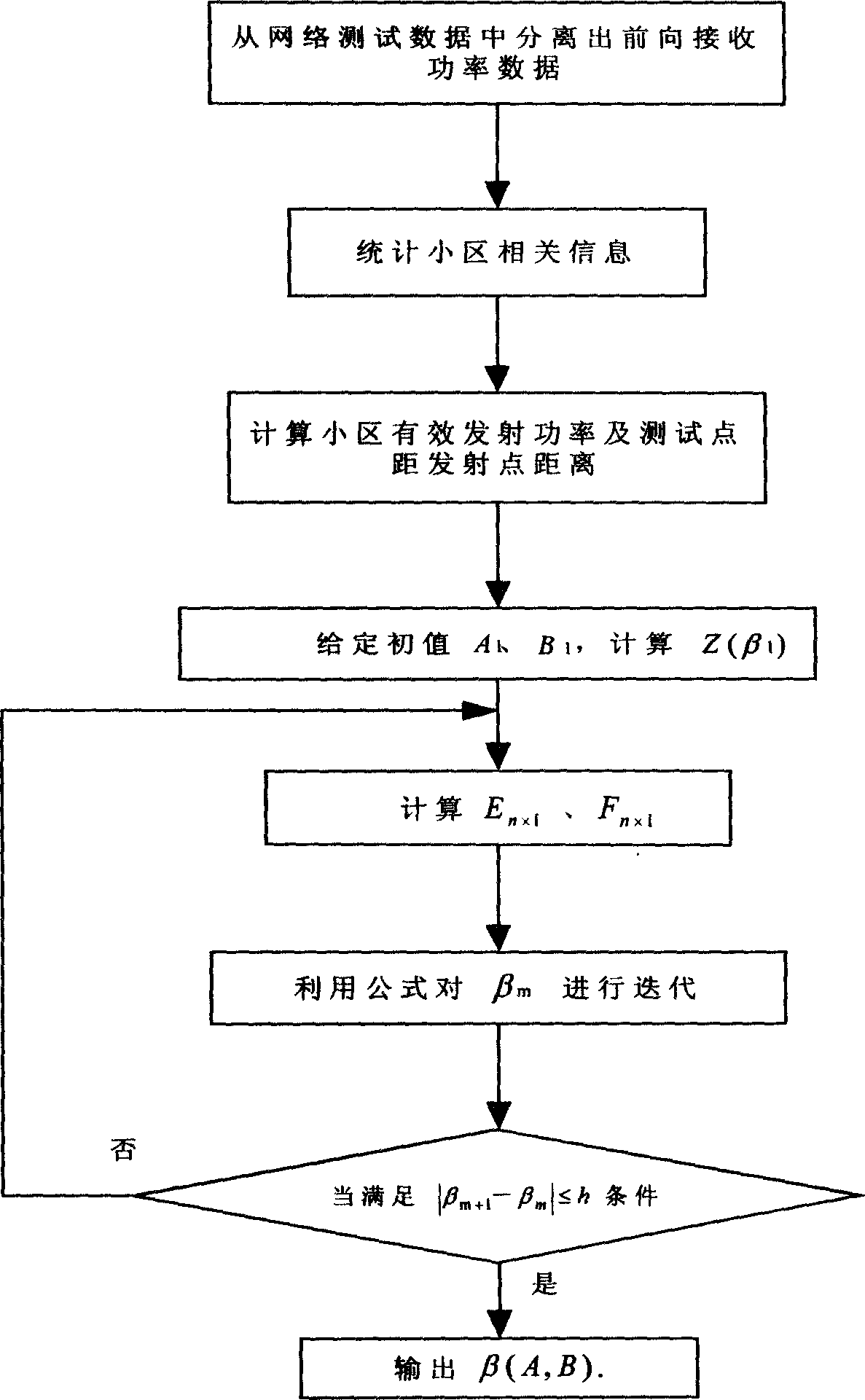
Method for correcting wireless transmission model in CDMA system
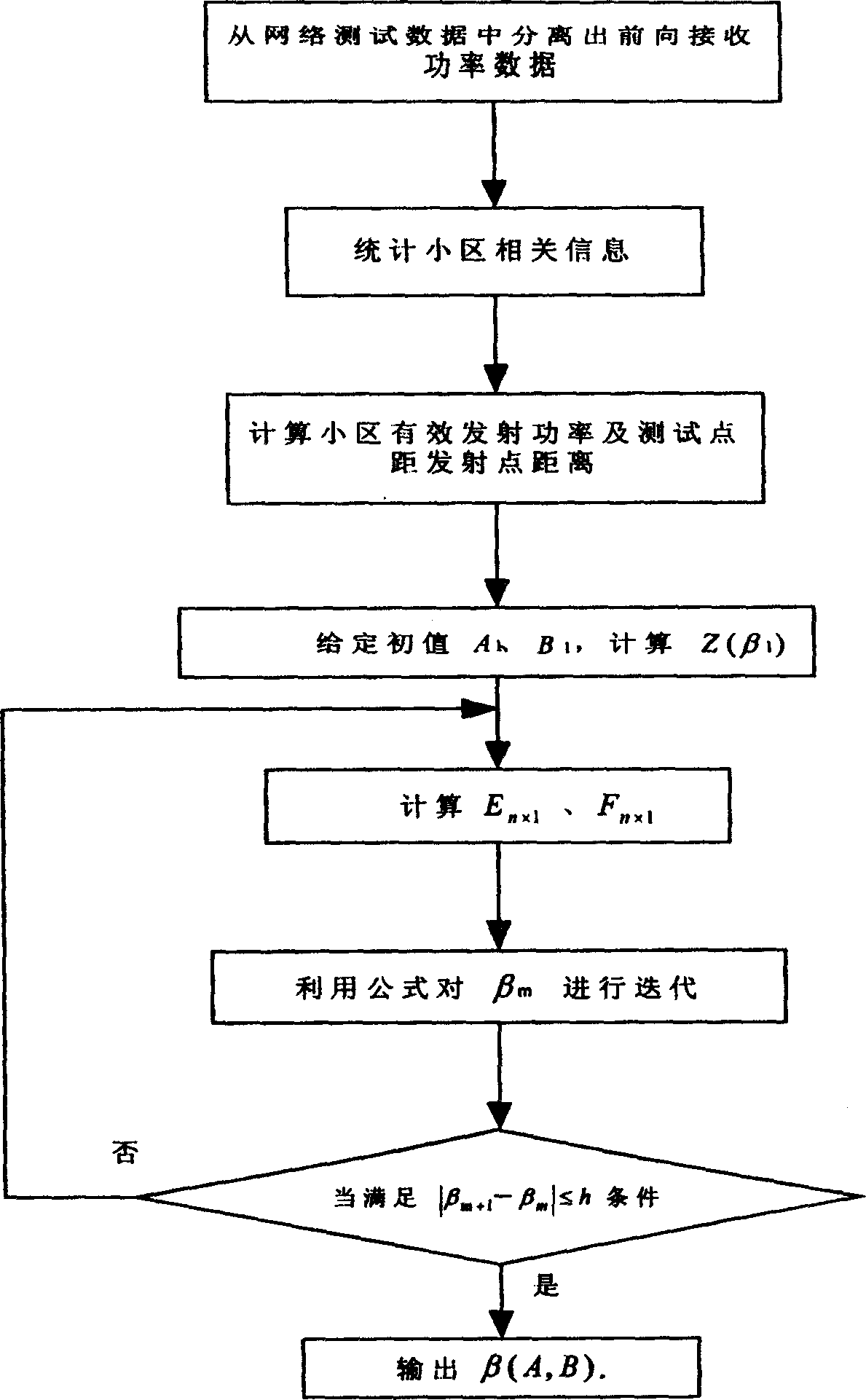
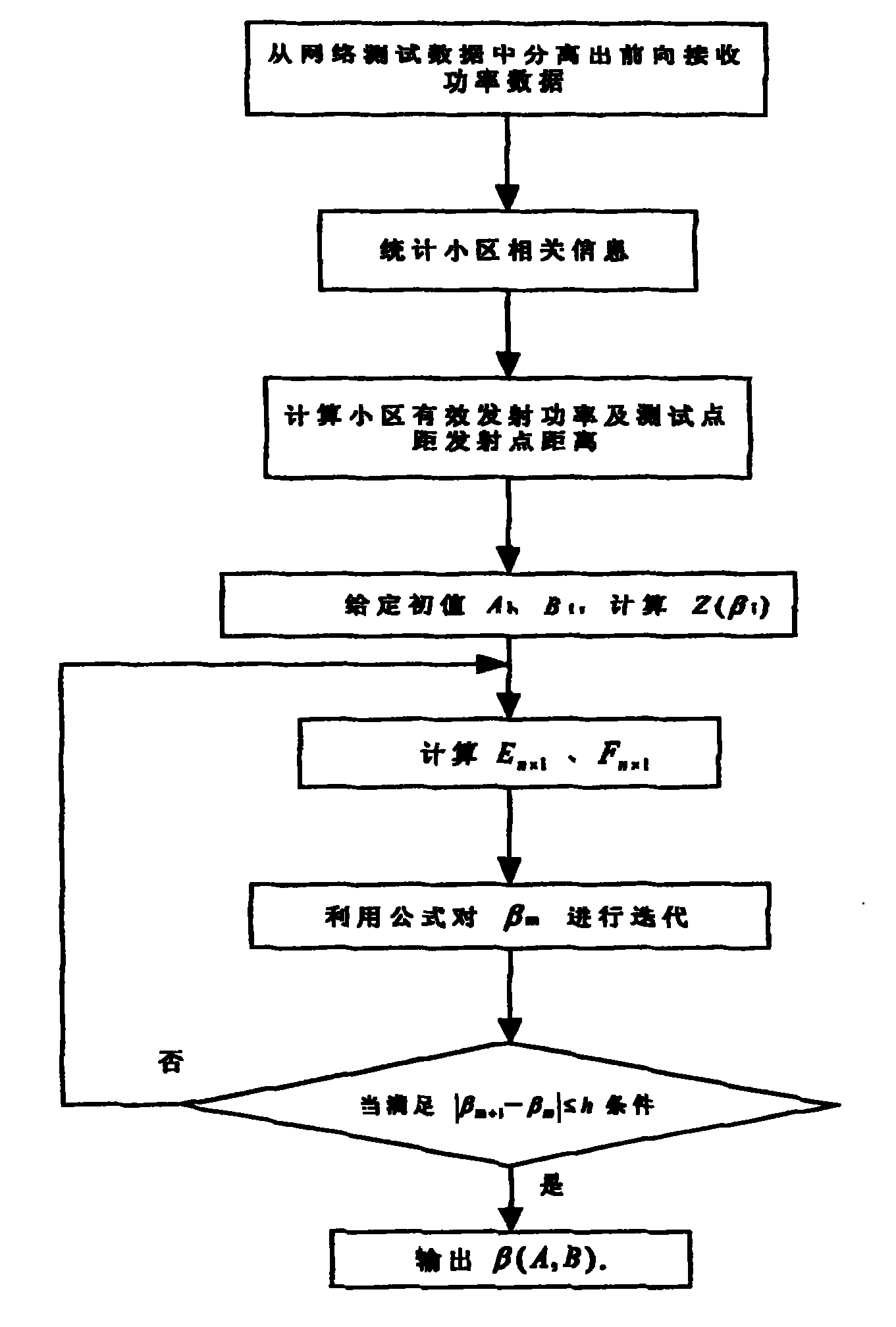
InactiveCN1529445AImprove work efficiencyImprove portabilitySupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsCode division multiplexTransmitted powerLongitude
The method picks up data needed for correcting model by using data of tested forward received power in test data of actual network. Treating data includes following steps: accounting information of latitude and longitude of transmitting site in each subzone within network, transmitting power and antenna parameter of each subzone; calculating effective radiated power in each direction for each subzone, and distance between test point and transmitting site in each subzone; fitting of multielement non-linear regression method is utilized so as to obtain parameters of propagation model. Comparing with prior art, the invention uses tested data to correct model, omitting a series of works such as selecting station site, erecting antenna, driving cars for testing etc. The invention saves time, raises work efficiency providing model with high precision, and good portability.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Wireless communication network and method for broadcasting high priority information using downlink common channels
InactiveUS7519352B2Raise priorityReliable deliveryPower managementEnergy efficient ICTPopulated areaChannel use
Owner:NEC CORP
Terminal antenna total radiated power (TRP) fast testing method
ActiveCN103257282ASimplify the build processImprove measurement efficiencyPower managementTransmitters monitoringDarkroom testAntenna polarization
A terminal antenna total radiated power (TRP) fast testing method is used for testing radiation performance of a terminal antenna in an over-the-air (OTA) darkroom test. A terminal placed on a darkroom turntable takes every antenna polarization direction with a certain theta angle and a certain phi angle as a testing point to test the power of a certain channel so as to obtain the effective radiated power (ERP) of a corresponding point and then generates a transmitting power strength directional diagram. The antenna polarization direction at the best theta angle and the best phi angle is sought according to the transmitting power strength directional diagram and the ERP<CH1> of a channel to be tested is measured. All the ERP<CH1> values are subjected to integrated computation and the TRP of the terminal antenna is obtained. The method simplifies the generating process of the ERP in two antenna polarization directions at each theta angle and each phi angle of the turntable, corrects the test result to enable the test result to be more accurate, promotes the measuring efficiency of the TRP due to simplifying of the algorithm and reduces testing cost.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Effective radiated power (ERP) system based on radio frequency identify technology (FTID)
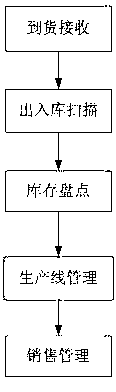
InactiveCN103136649ARealize intelligent managementGuarantee product qualitySensing record carriersLogisticsSystems managementManagement efficiency
The invention discloses an effective radiated power (ERP) system based on a radio frequency identify technology (FTID). The system comprises five function modules of arrival of the goods receiving, goods storage scanning, inventory verification, production line management and sale management. All links of the system all adopt the FTID as unique product identifications to perform tracking, scanning, statistics and management operations. The system can achieve management and tracking of all the links of purchasing, producing, processing, selling, finance, quality guaranteeing, and the like of product processing, information sharing is achieved, and enterprise efficiency is improved. Automatic reading and writing of product data and system management are achieved, scientific analysis and processing of data are achieved, human power is saved, and management efficiency is improved. Tracking of production process and selling process of products is achieved, and therefore product quality is ensured, selling condition is known, and problems are found and solved timely.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOLU INFORMATION TECH
Dynamic effective radiated power (ERP) adjustment
ActiveUS10211530B2Reduce outputNavigational calculation instrumentsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesFrequency spectrumOn board
Antennas used aboard aircraft to communicate with satellites or ground stations may have complex antenna patterns, which may vary as the aircraft moves throughout a given coverage area. Techniques are disclosed for dynamically adjusting the instantaneous power fed to an antenna system to ensure that the antenna transmits at the regulatory or coordinated effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) spectral limit. The antenna may transmit, in accordance with aircraft location and attitude, steerable beam patterns at different scan and skew angle combinations, causing variations in antenna gain and fluctuations in the transmitted EIRP. Using on-board navigational data, an antenna gain and ESD limit may be calculated for a particular scan and skew angle, which may be used to adjust power fed to the antenna such that the antenna transmits substantially at maximum allowable EIRP as the steerable beam pattern is adjusted.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
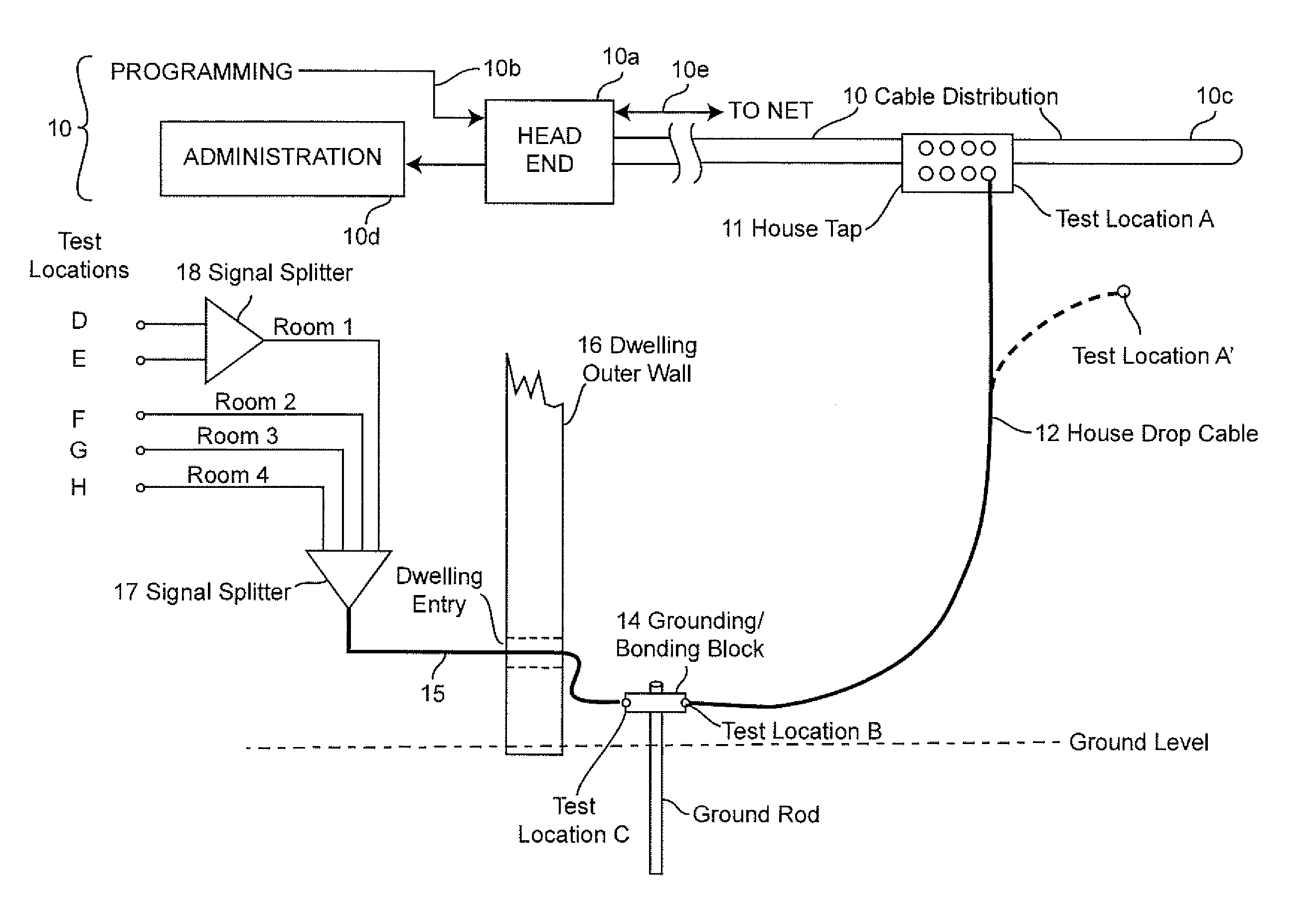
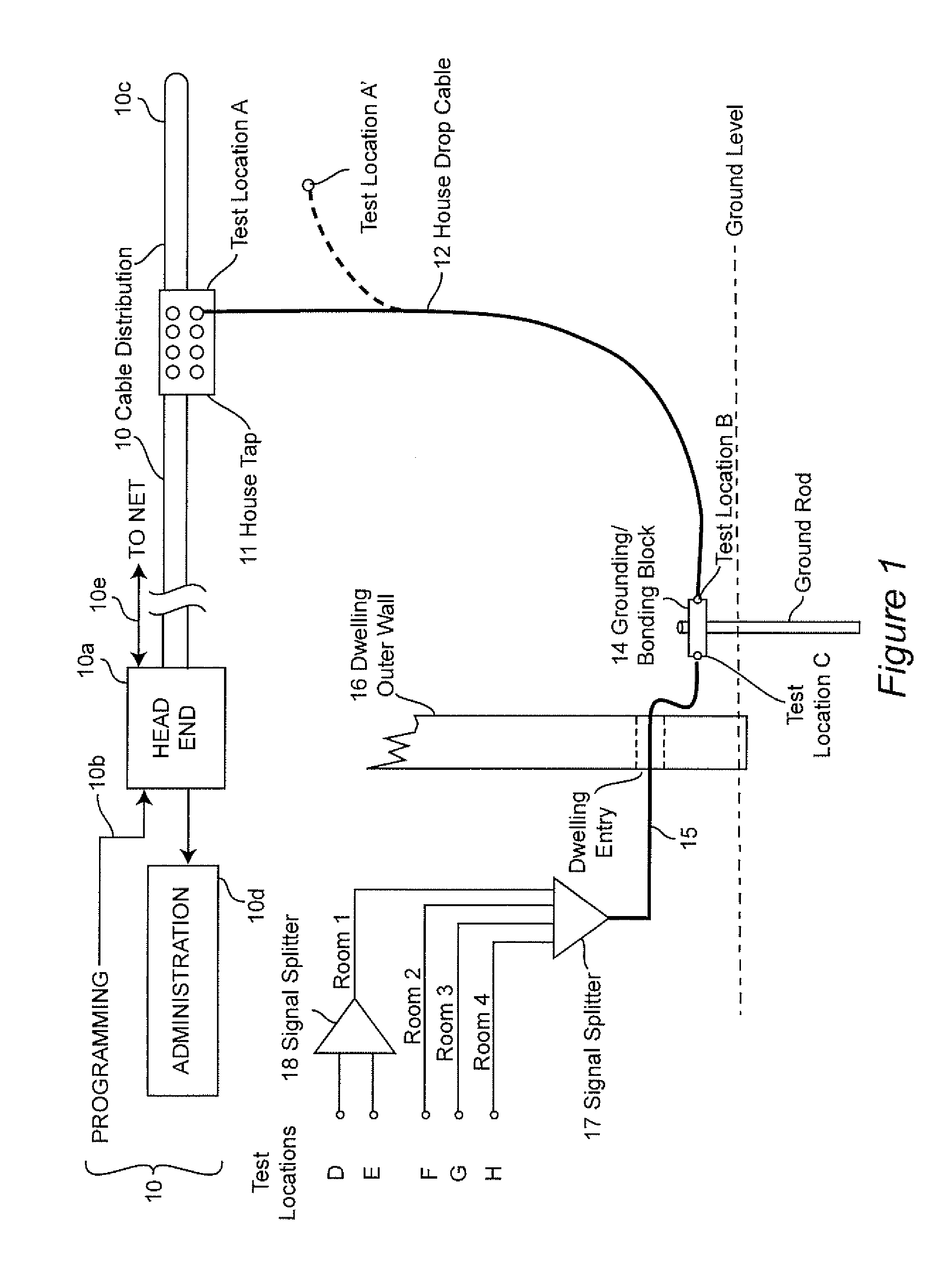
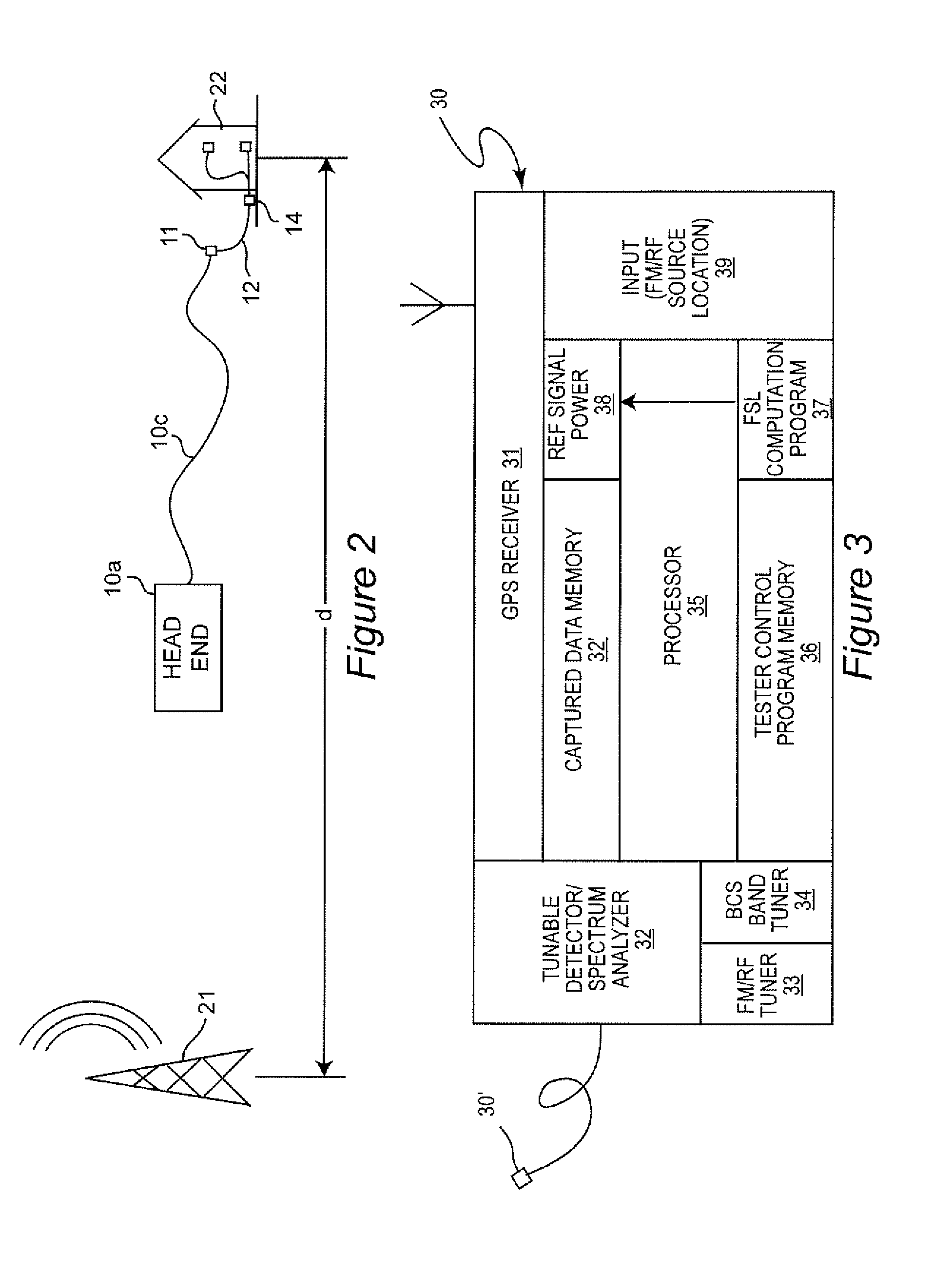
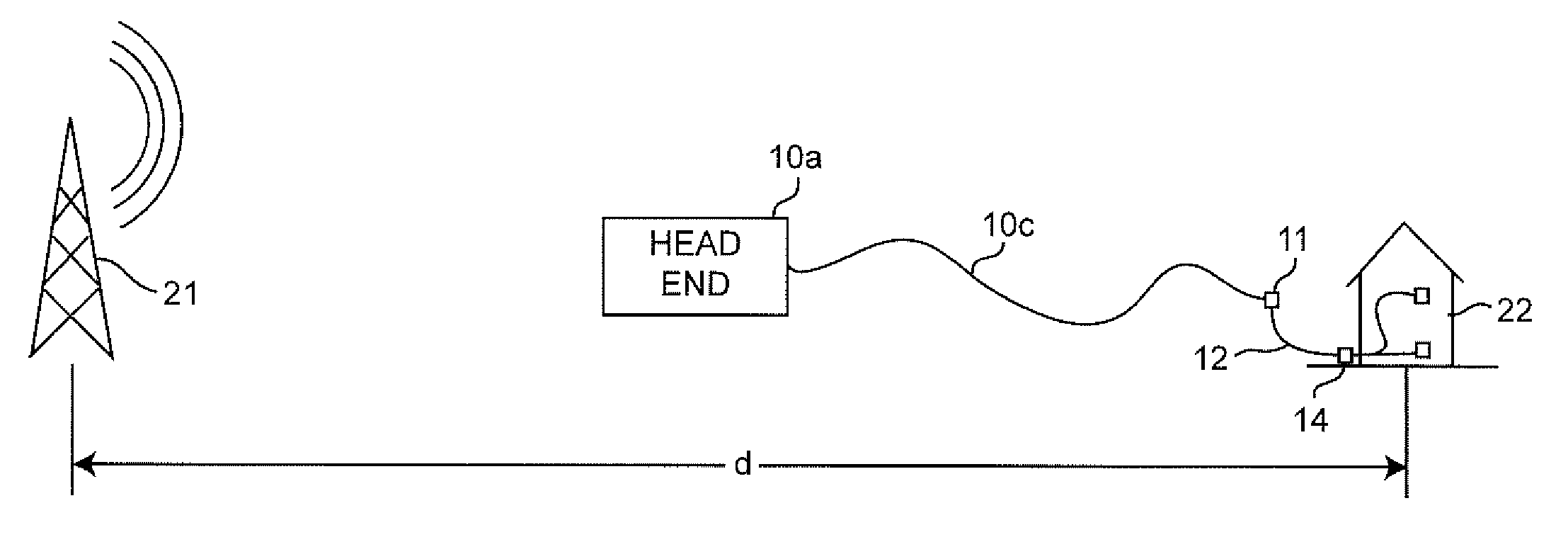
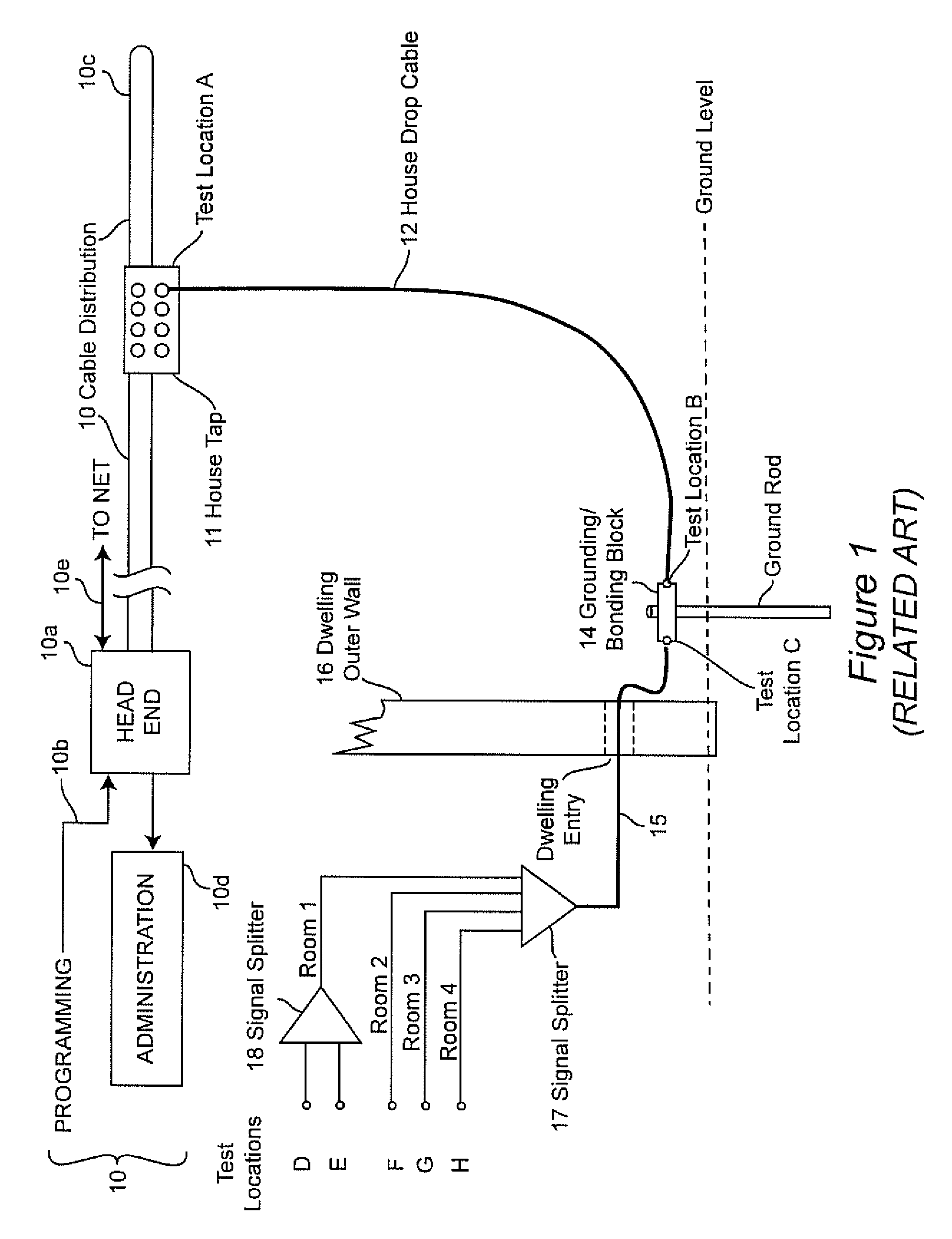
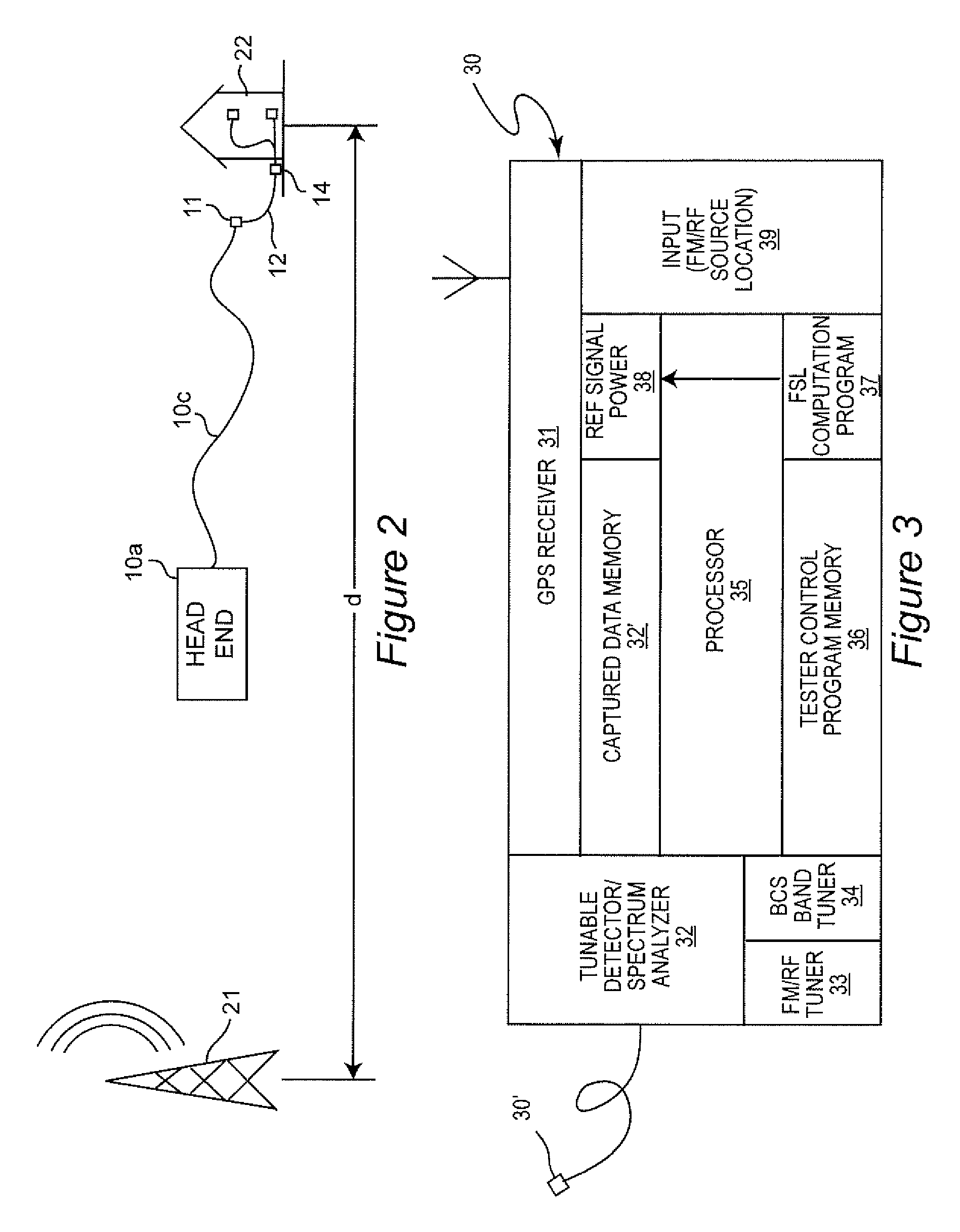
Shielding integrity testing for cable drop
InactiveUS20130110466A1Increase expensesWeight increaseReceivers monitoringAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceShielded cableCommunications system
Signal ingress at an installations site forming a part of a broadband communication system is quantitatively evaluated for resistance to signal ingress using a computed ambient broadcast signal level based on a known location and effective radiated power of one or more transmitters. Anomalies due to signal path obstruction and / or multi-path reception are compensated by performing computations for a plurality of broadcast transmitters located in different directions from the installation site.
Owner:COMSONICS
Hemispherical multilayer dielectric lens, antenna module, high-frequency wireless module and equipment
PendingCN111600135AGood radiation characteristicsLow output power requirementParallel-plate/lens fed arraysEngineeringBeam scanning
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, and provides a hemispherical multilayer dielectric lens, an antenna module, a high-frequency wireless module and equipment. According to the invention, gradient change of dielectric constants of different dielectric layers in the hemispherical multilayer dielectric lens is utilized; high-frequency electromagnetic waves pass through the multilayer dielectric lens. According to the invention, a high-focusing directional radiation wave beam is formed, the radiation characteristic of a millimeter wave or terahertz active module can be remarkably improved, the effective radiation power of a high-frequency wireless signal can be improved on the premise of reducing the number of array antenna units, the requirement on the output power of the active module is reduced, and the wave beam scanning range is expanded. Meanwhile, the multilayer dielectric stack is low in cost and easy to be integrated with an active module. Themethod is very suitable for a millimeter wave radar system and a terahertz high-resolution imaging system.
Owner:深圳市前海派速科技有限公司
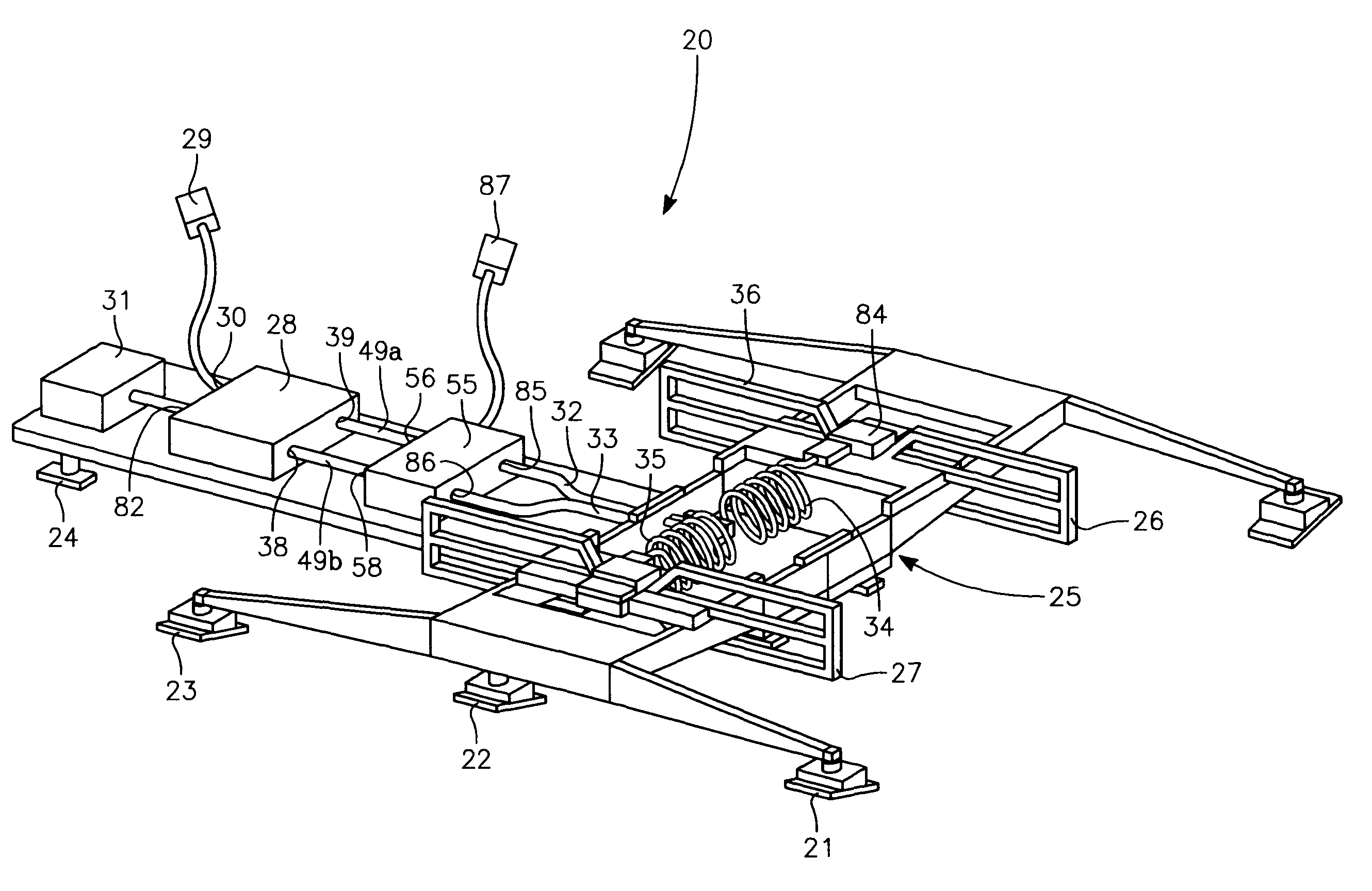
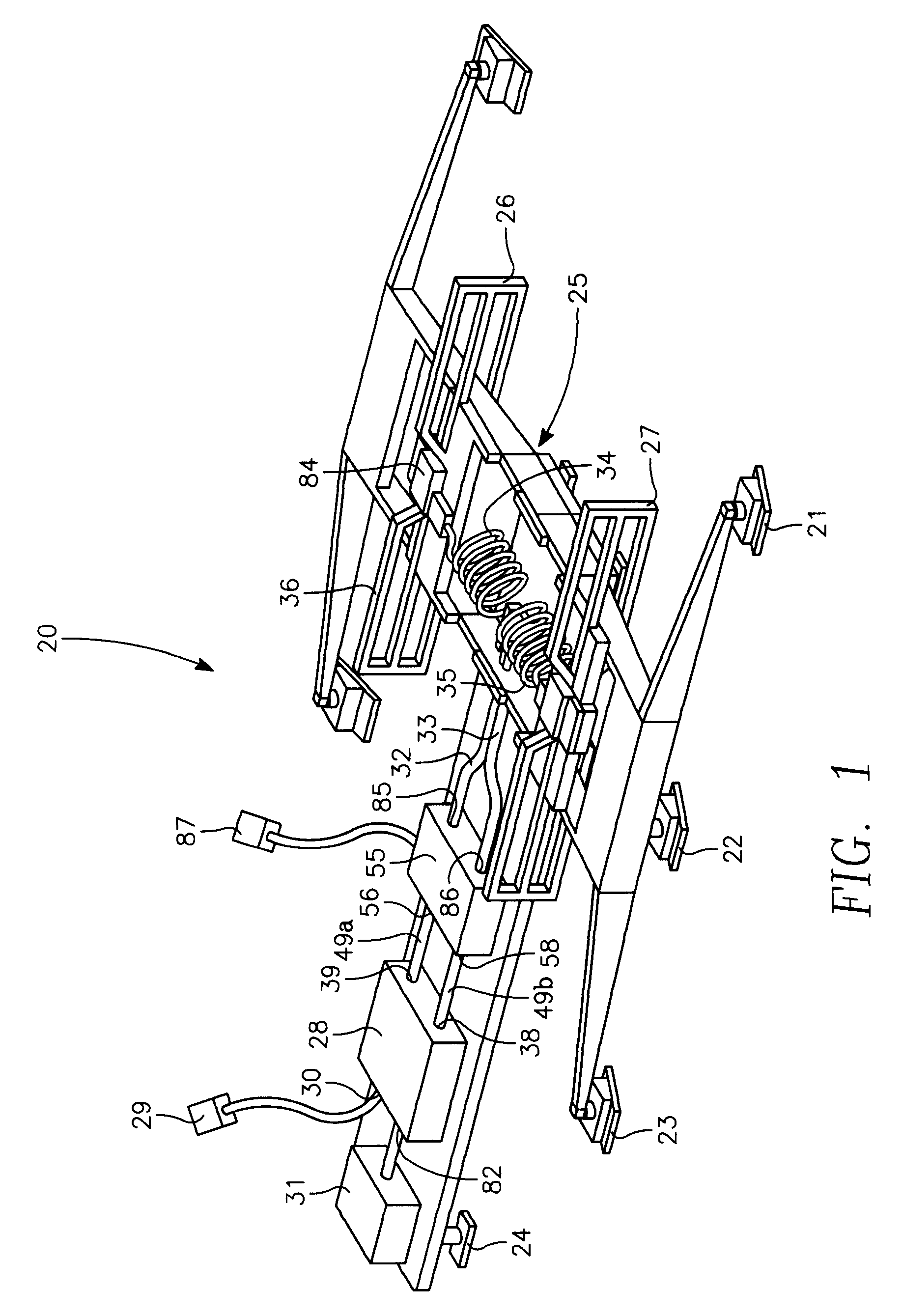
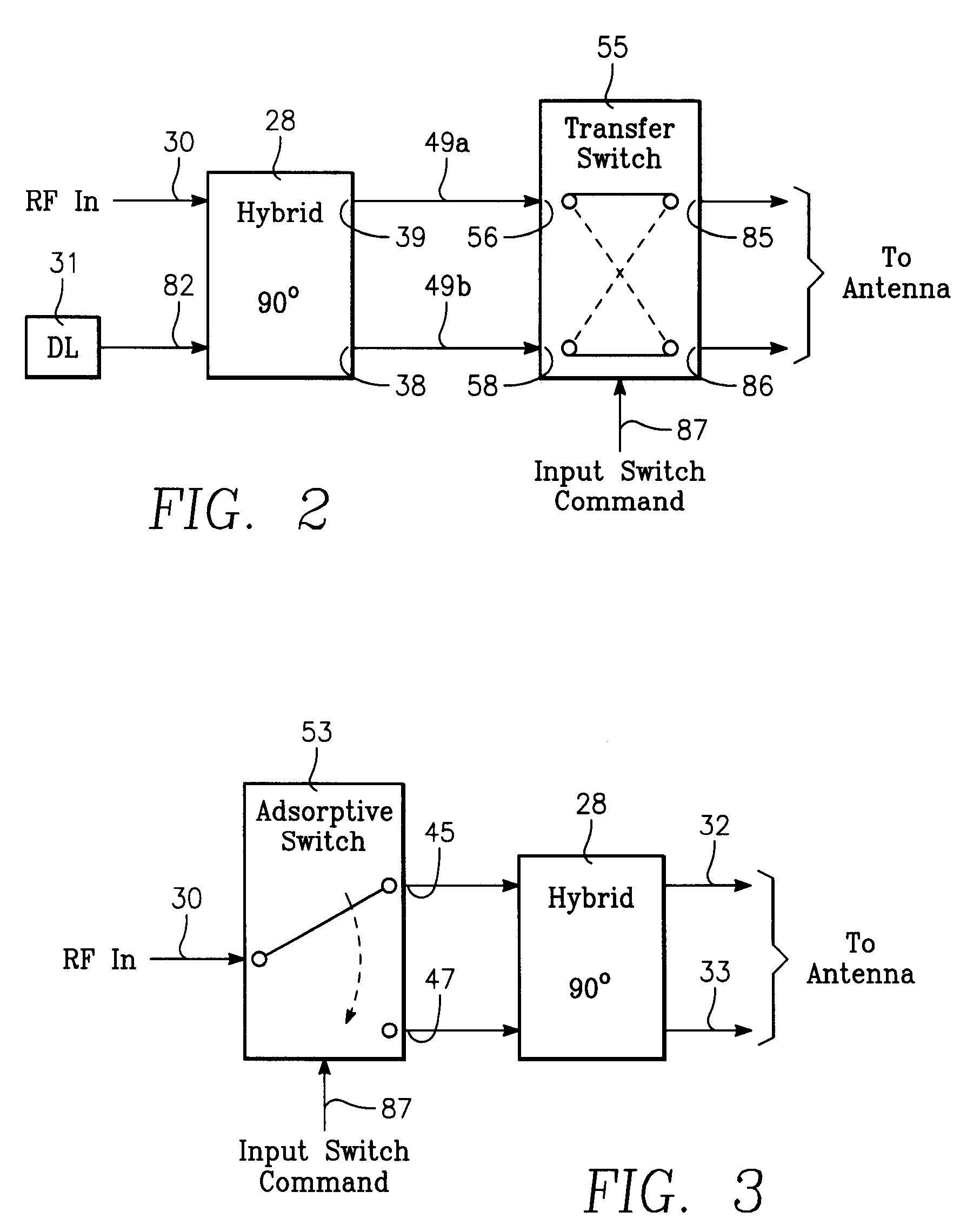
Phased array blade antenna assembly
ActiveUS7280083B1Improved lateral target coverageIncrease effective radiated powerAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesIndividually energised antenna arraysAntenna designDirectional antenna
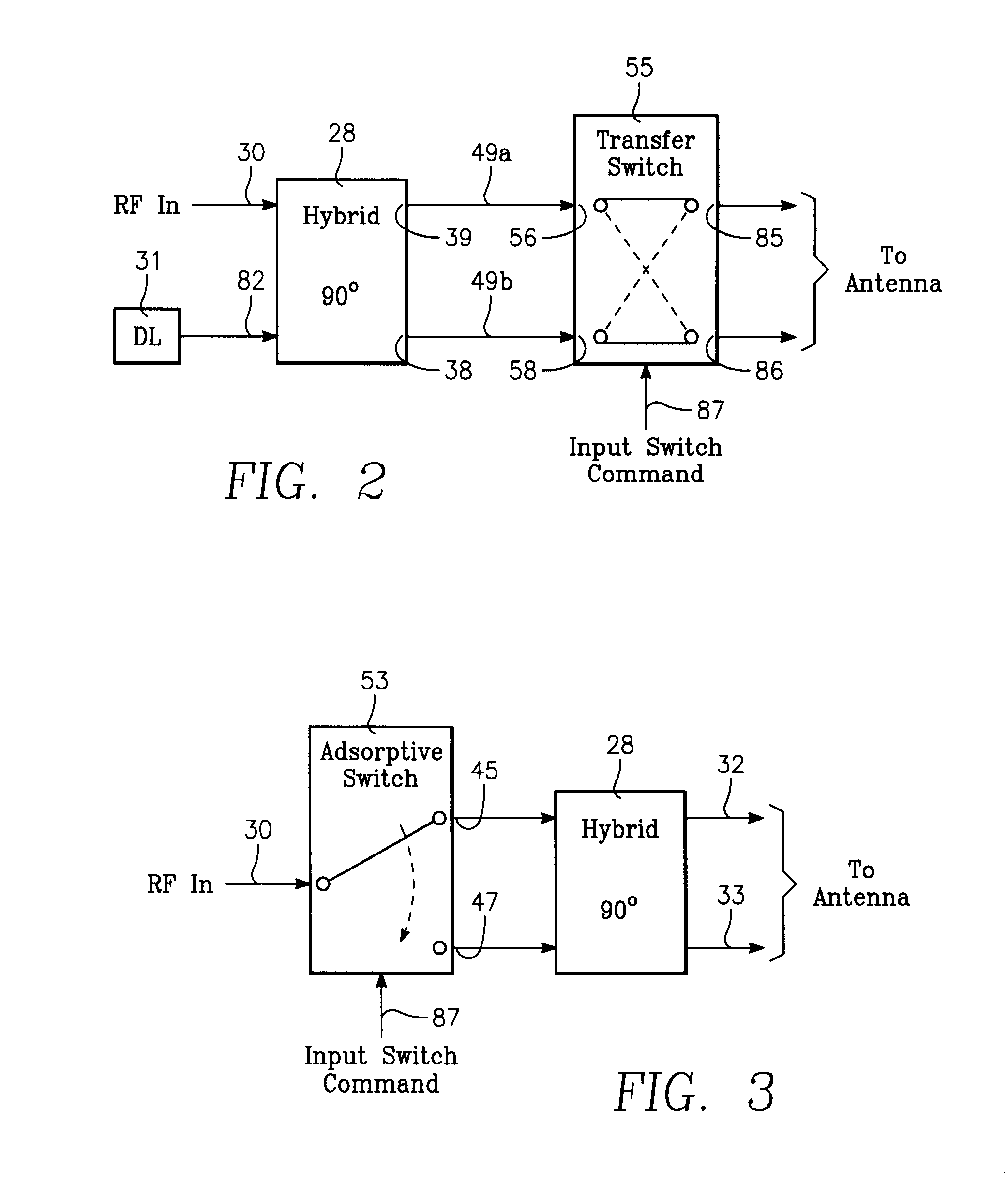
An antenna design, having two symmetrical phased array blade antenna elements which provide improved lateral target coverage with an increased effective radiated power and exhibits smooth null-free bi-directional antenna patterns. Each blade antenna element is coupled to a 180 degrees hybrid divider / combiner by a semi-rigid RF cable. Each blade antenna element is also connected to a sub-resonant choke balun for improved impedance matching and resultant distortion-less antenna patterns.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Electronically Steered Phased Array Blade Antenna Assembly
InactiveUS20090189823A1Improved lateral target coverageIncrease effective radiated powerIndividually energised antenna arraysElongated active element feedAntenna designHybrid coupler
An antenna design, having two symmetrical phased array blade antenna elements which provide improved lateral target coverage with an increased effective radiated power and exhibits smooth null-free unidirectional antenna patterns. The direction of the unidirectional antenna pattern is dictated by a switching command under control of a user. Each blade antenna element is coupled to a 90-degree hybrid coupler and an RF switching device by a semi-rigid RF cable. Each blade antenna element is also connected to a sub-resonant choke balun for improved impedance matching and resultant distortion-less antenna patterns.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Real-time dynamic checking system of medical shop and working process thereof
InactiveCN103268582AGuaranteed accuracyRealize seamless dockingData processing applicationsNetwork topologiesWireless routerData acquisition
The invention discloses a real-time dynamic checking system of a medical shop. The real-time dynamic checking system is characterized by comprising a data acquisition part, a wireless base station and a server part, wherein the data acquisition part comprises a plurality of data acquirers; the wireless base station is a wireless fidelity (WIFI) wireless base station or a WIFI wireless router; and the server part comprises a server provided with a client effective radiated power) (ERP) system and a plurality of personal computers connected with the server. As improvement, the data acquirers are handheld data acquisition terminals; and the handheld data acquisition terminals are connected with the wireless base station through wireless signals. According to the real-time dynamic checking system, paper-free operation is realized; furthermore, medicine information of which the paper inventory amount is different from an actual checking amount and overdue medicine information can be displayed timely on site, so that the checking efficiency is improved, and the cost is saved; furthermore, medicines in the shop can be checked; the checking accuracy and the information promptness are guaranteed; and the whole efficiency of an enterprise is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN ESCAN INFORMATION TECH
Apparatus and method for detecting effective radiated power
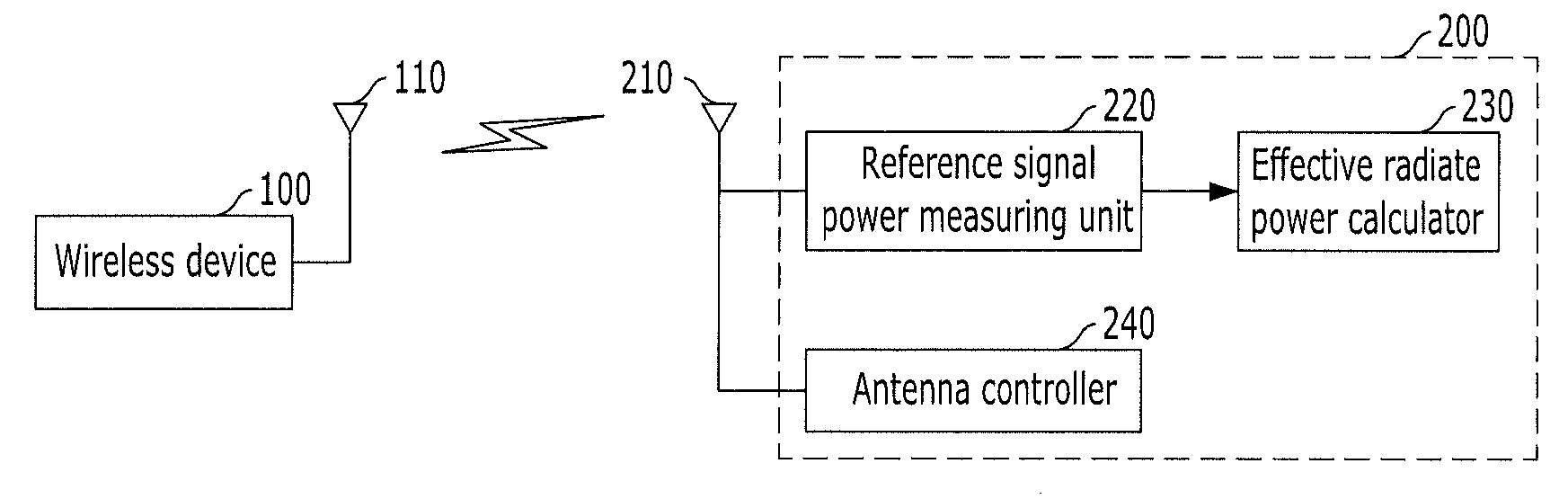
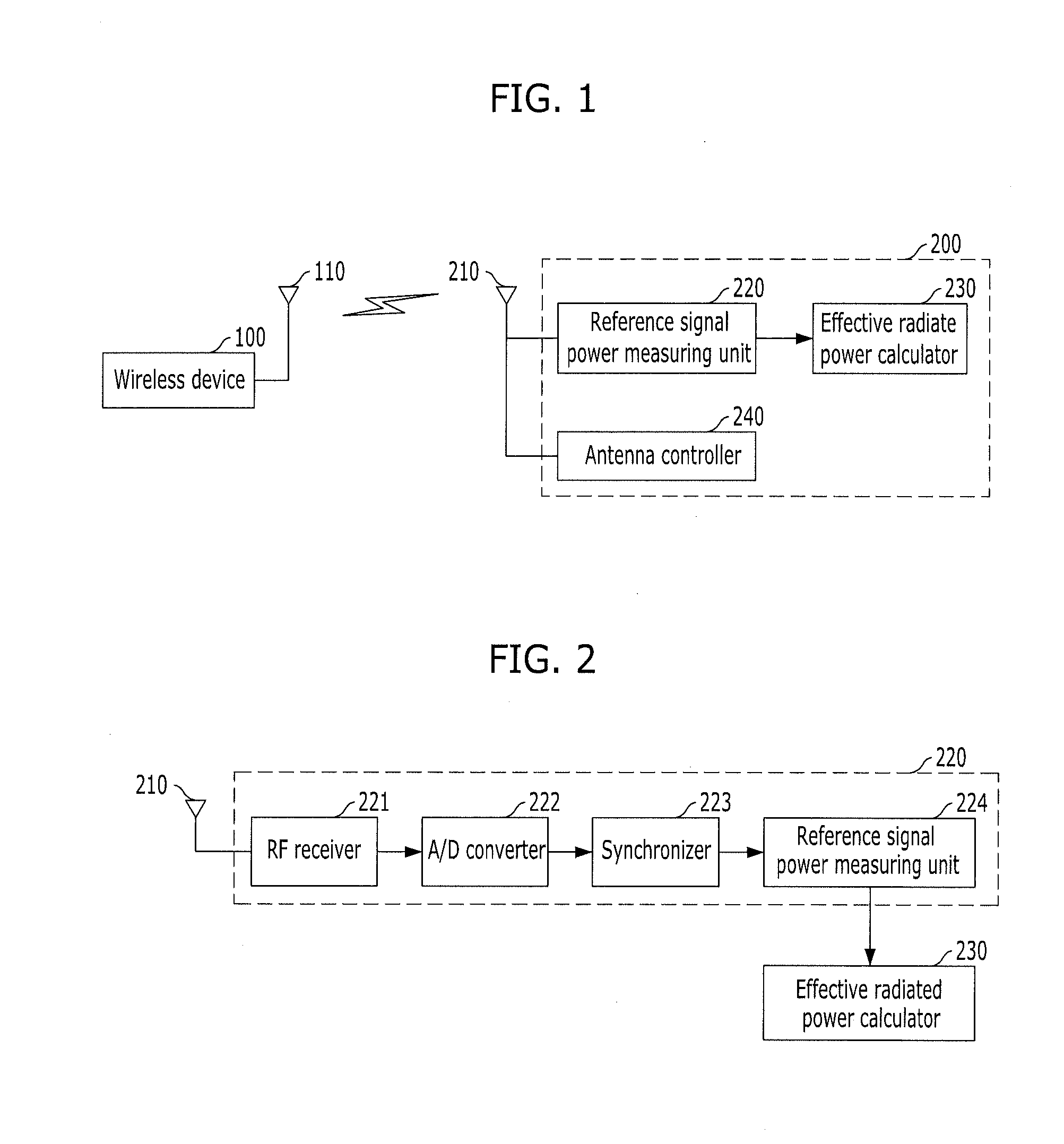
InactiveUS20120142290A1Reduced measurement timeImprove accuracyTransmission monitoringAmplitude modulationEngineeringEffective radiated power
Provided is an apparatus and method for measuring effective radiated power. The apparatus includes a reference signal power measuring unit configured to measure power of a reference signal from a wireless signal transmitted from a wireless device, and an effective radiated power calculating unit configured to calculate effective radiated power according to an allocation ratio of a reference signal in an entire signal domain using the measured reference signal power from the reference signal power measuring unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for correcting wireless transmission model in CDMA system
InactiveCN1277360CImprove work efficiencyImprove portabilitySupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsCode division multiplexTransmitted powerLongitude
Owner:ZTE CORP
Shielding integrity testing for cable drop
InactiveUS9091712B2Increase expensesWeight increaseTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringShielded cableCommunications system
Signal ingress at an installations site forming a part of a broadband communication system is quantitatively evaluated for resistance to signal ingress using a computed ambient broadcast signal level based on a known location and effective radiated power of one or more transmitters. Anomalies due to signal path obstruction and / or multi-path reception are compensated by performing computations for a plurality of broadcast transmitters located in different directions from the installation site.
Owner:COMSONICS
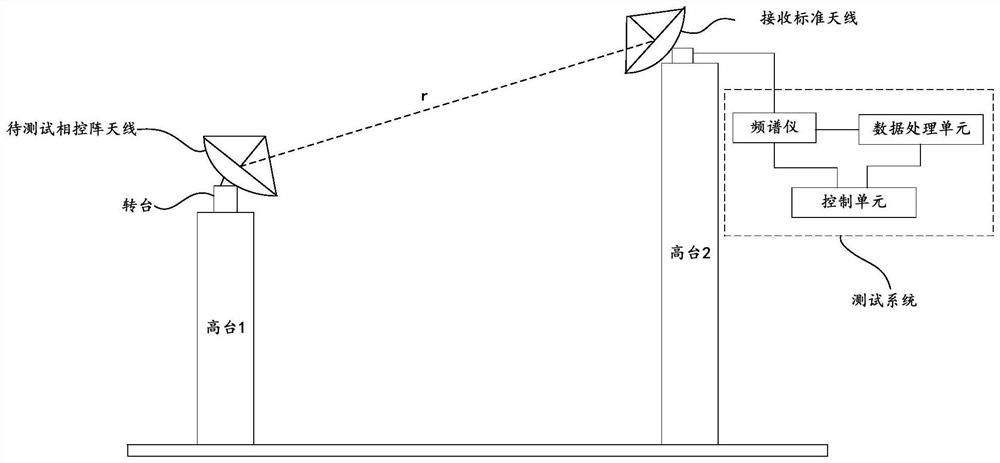
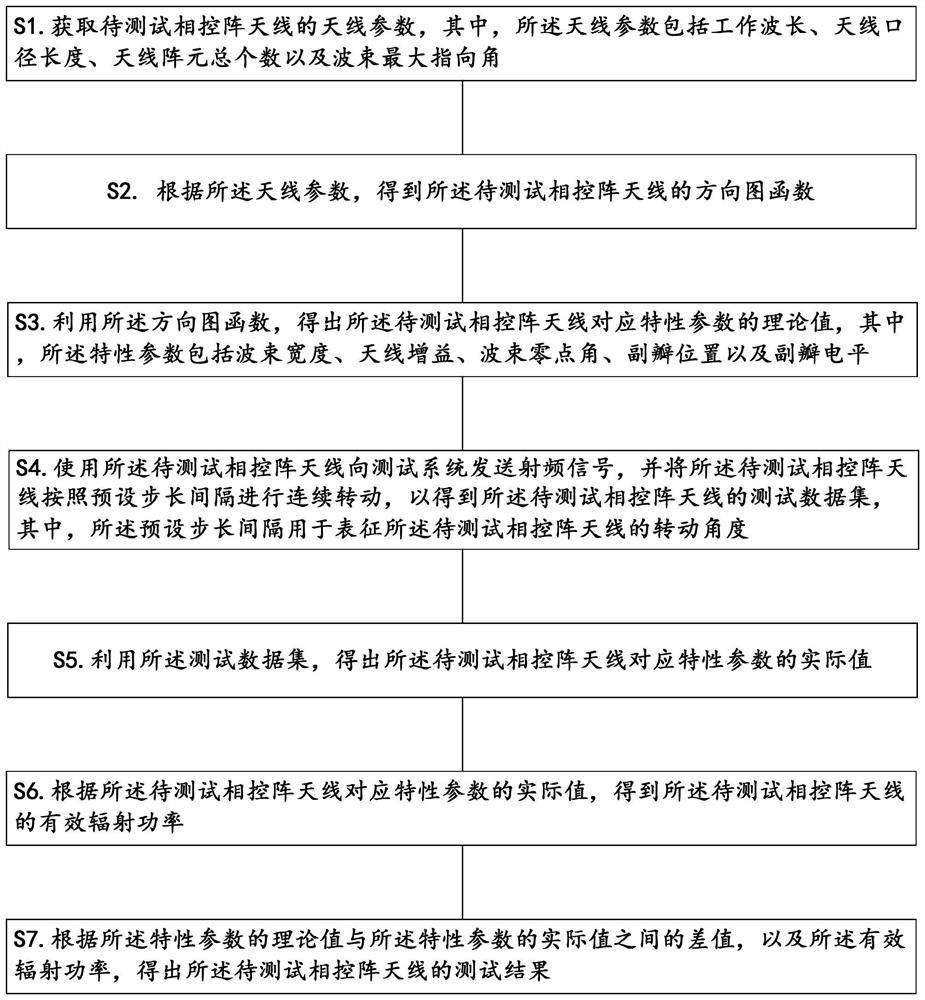
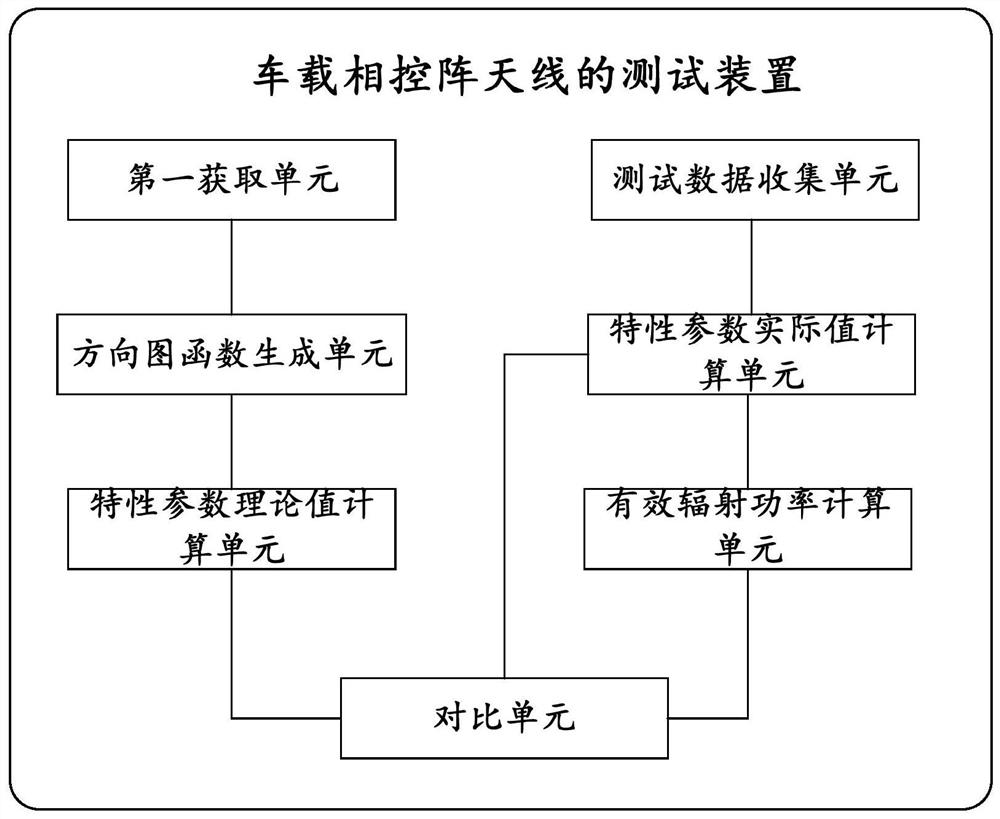
Test method and device of vehicle-mounted phased-array antenna and electronic equipment
The invention discloses a test method and device of a vehicle-mounted phased-array antenna and electronic equipment. On one hand, whether a test result of an antenna is reliable or not is obtained according to a difference value between a theoretical value and an actual value of each characteristic parameter, and on the other hand, the performance of the antenna is further obtained through the size of effective radiation power. Therefore, the antenna can be tested from the two aspects of the characteristic parameters of the antenna pattern and the effective radiation power of the antenna, and compared with traditional manual testing, the testing method provided by the embodiment of the invention is higher in precision, smaller in error and more suitable for testing the vehicle-mounted phased-array antenna.
Owner:浩泰智能(成都)科技有限公司
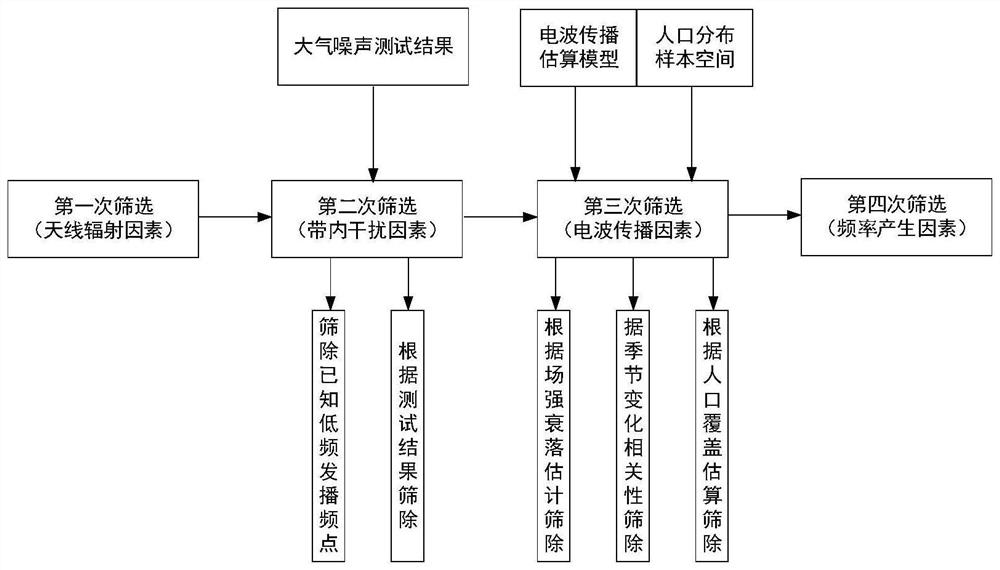
Low-frequency time code time service signal carrier frequency optimization method and system
PendingCN113992287AMeet the carrier frequencyComprehensiveTransmission monitoringCarrier signalFrequency generation
The invention discloses a low-frequency time code time service signal carrier frequency optimization method and system, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the first screening of frequency points based on a preset antenna effective radiation power threshold value, and obtaining a first screening result; carrying out the second screening of the frequency points based on the in-band interference factors, and obtaining a second screening result; carrying out the third screening of the frequency points based on the sky-ground wave interference characteristic factors, and obtaining a third screening result; based on the first screening result, the second screening result and the third screening result, carrying out screening according to frequency generation factors to obtain a final screening result, and completing the low-frequency time code time service signal carrier frequency optimization. According to the method provided by the invention, the low-frequency time code time service signal carrier frequency meeting the preset requirement can be selected.
Owner:封开低频时码授时台 +1
Dynamic effective radiated power (ERP) adjustment
ActiveUS20190089051A1Reduce outputNavigational calculation instrumentsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesFrequency spectrumSkew angle
Antennas used aboard aircraft to communicate with satellites or ground stations may have complex antenna patterns, which may vary as the aircraft moves throughout a given coverage area. Techniques are disclosed for dynamically adjusting the instantaneous power fed to an antenna system to ensure that the antenna transmits at the regulatory or coordinated effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) spectral limit. The antenna may transmit, in accordance with aircraft location and attitude, steerable beam patterns at different scan and skew angle combinations, causing variations in antenna gain and fluctuations in the transmitted EIRP. Using on-board navigational data, an antenna gain and ESD limit may be calculated for a particular scan and skew angle, which may be used to adjust power fed to the antenna such that the antenna transmits substantially at maximum allowable EIRP as the steerable beam pattern is adjusted.
Owner:GOGO BUSINESS AVIATION LLC
A configurable way to parse multi-valued match fields
ActiveCN103631966BGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringEngineering
Owner:YONYOU NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Electronically steered phased array blade antenna assembly
InactiveUS7737906B2Improve targeting coverageIncrease effective radiated powerIndividually energised antenna arraysElongated active element feedAntenna designHybrid coupler
An antenna design, having two symmetrical phased array blade antenna elements which provide improved lateral target coverage with an increased effective radiated power and exhibits smooth null-free unidirectional antenna patterns. The direction of the unidirectional antenna pattern is dictated by a switching command under control of a user. Each blade antenna element is coupled to a 90-degree hybrid coupler and an RF switching device by a semi-rigid RF cable. Each blade antenna element is also connected to a sub-resonant choke balun for improved impedance matching and resultant distortion-less antenna patterns.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
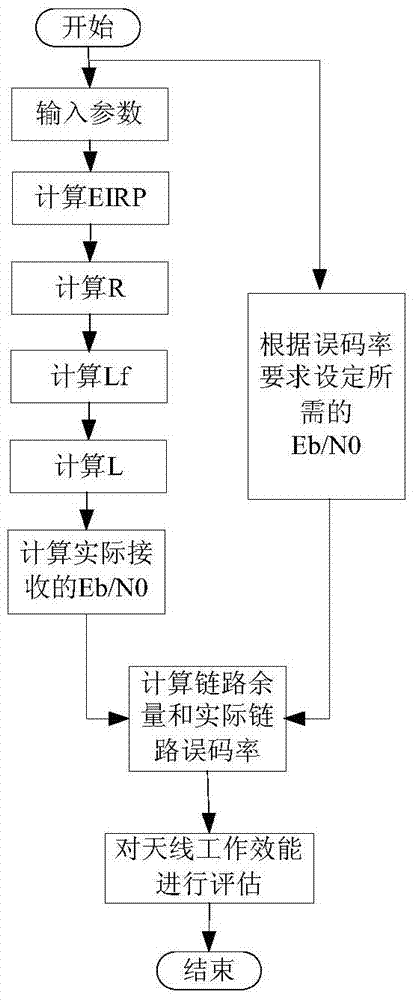
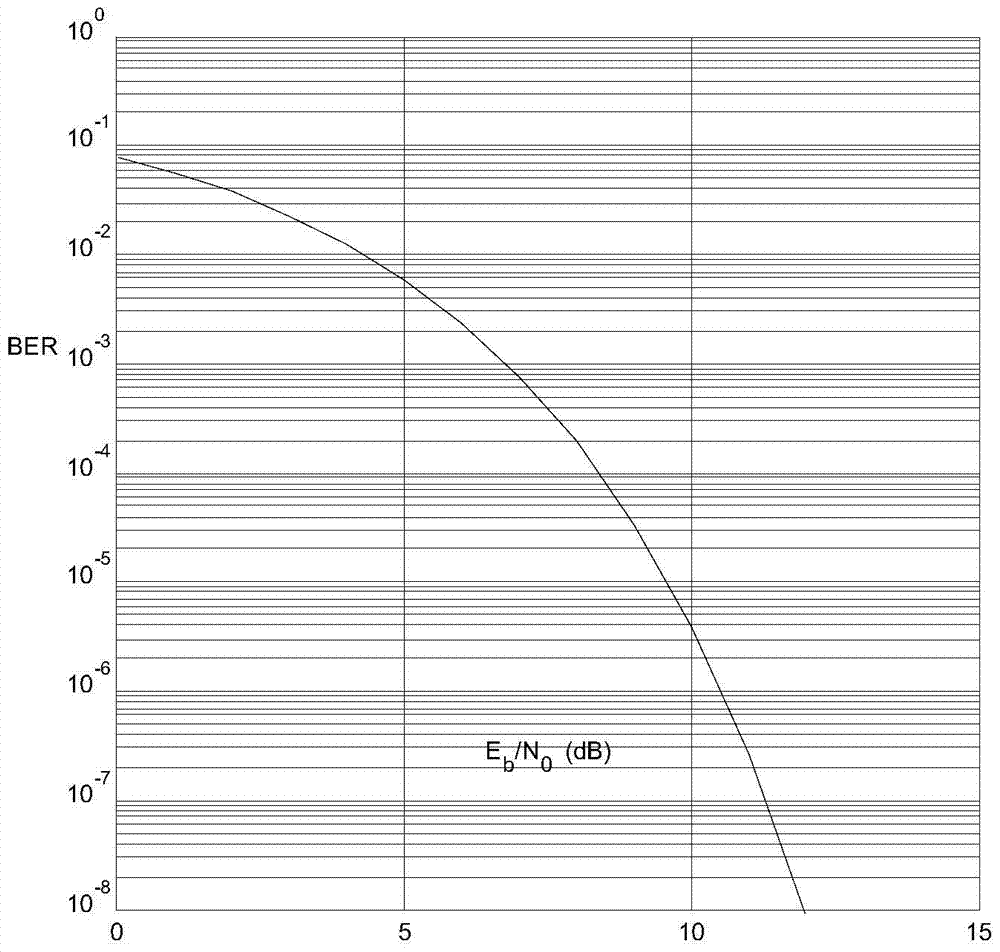
A Method for Analyzing Work Efficiency of a Damaged Satellite-to-Earth Digital Transmission Antenna
ActiveCN104467987BComprehensive assessment of work performance impactEase of evaluationTransmitters monitoringAntenna polarizationLink margin
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Short-range cellular booster
InactiveCN100557658CEnergy efficient ICTArrangements for variable traffic instructionsTransceiverCommunications system
A repeater that passes traffic between network transceivers and user transceivers in a wireless communication system. The transponder contains: a network unit, which maintains a network link with the network transceiver; a subscriber unit, which maintains a subscriber link with the subscriber transceiver; a bidirectional communication path between the network unit and the subscriber unit, which facilitates self-government Signal communication between network transceivers and user transceivers in transponder hops between network transceivers and network elements, between user transceivers and user elements, and between network elements and between the subscriber units; and beamformers coupled to the network unit and the subscriber unit respectively and adapted to convey signals in the frequency bands of operation of the network and subscriber transceivers and to control the effective radiated power.
Owner:贝扎德·B·莫赫比
Radar altimeter low intercept performance test method
ActiveCN110045341BReduce precisionFull indexRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringRadar altimeter
The invention discloses a radar altimeter low intercept performance testing method, aiming to provide a radar altimeter low intercept performance test method with complete test indicators, high test accuracy and low test cost. The present invention is realized through the following technical solutions: the control computer sends the complex scene simulation information to the radar altimeter complex scene simulator, outputs the generated echo signal to the radar altimeter to start the radio frequency control software, and manages the radiation switch of the radar altimeter in real time State, analyze the demand for effective radiation power when the radar altimeter works normally at any height within the altimetry range, determine the minimum radiation power under the premise of meeting the high performance, and send the transmitted signal to The power meter is used to test the transmission signal of the radar altimeter, and the radiation time and radiation power are transmitted to the performance analysis computer. According to the measurement results of the radiation parameters of the power meter, the power control range, step, accuracy and interception factor are calculated.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com