Patents
Literature
49 results about "Laser noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
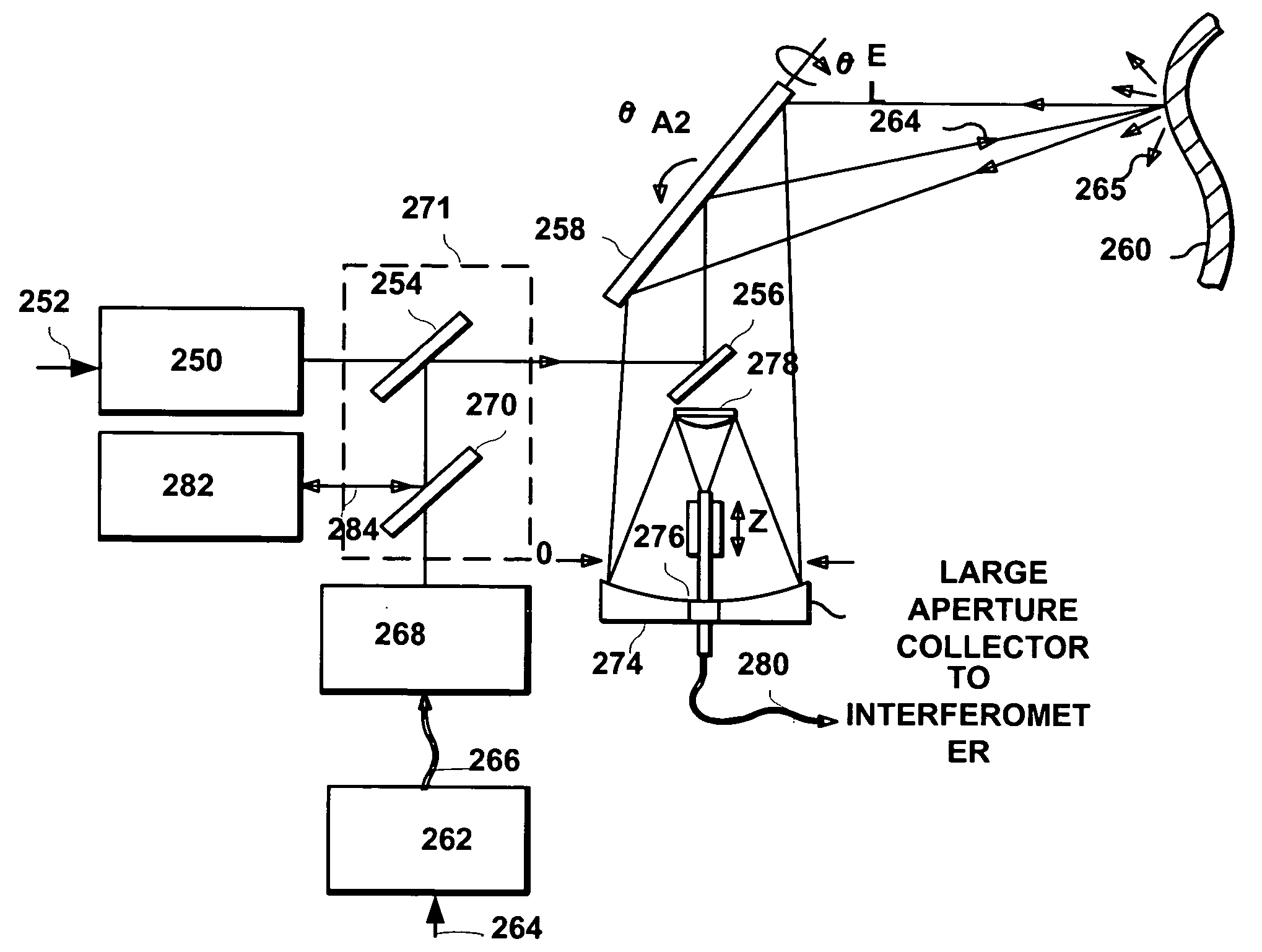
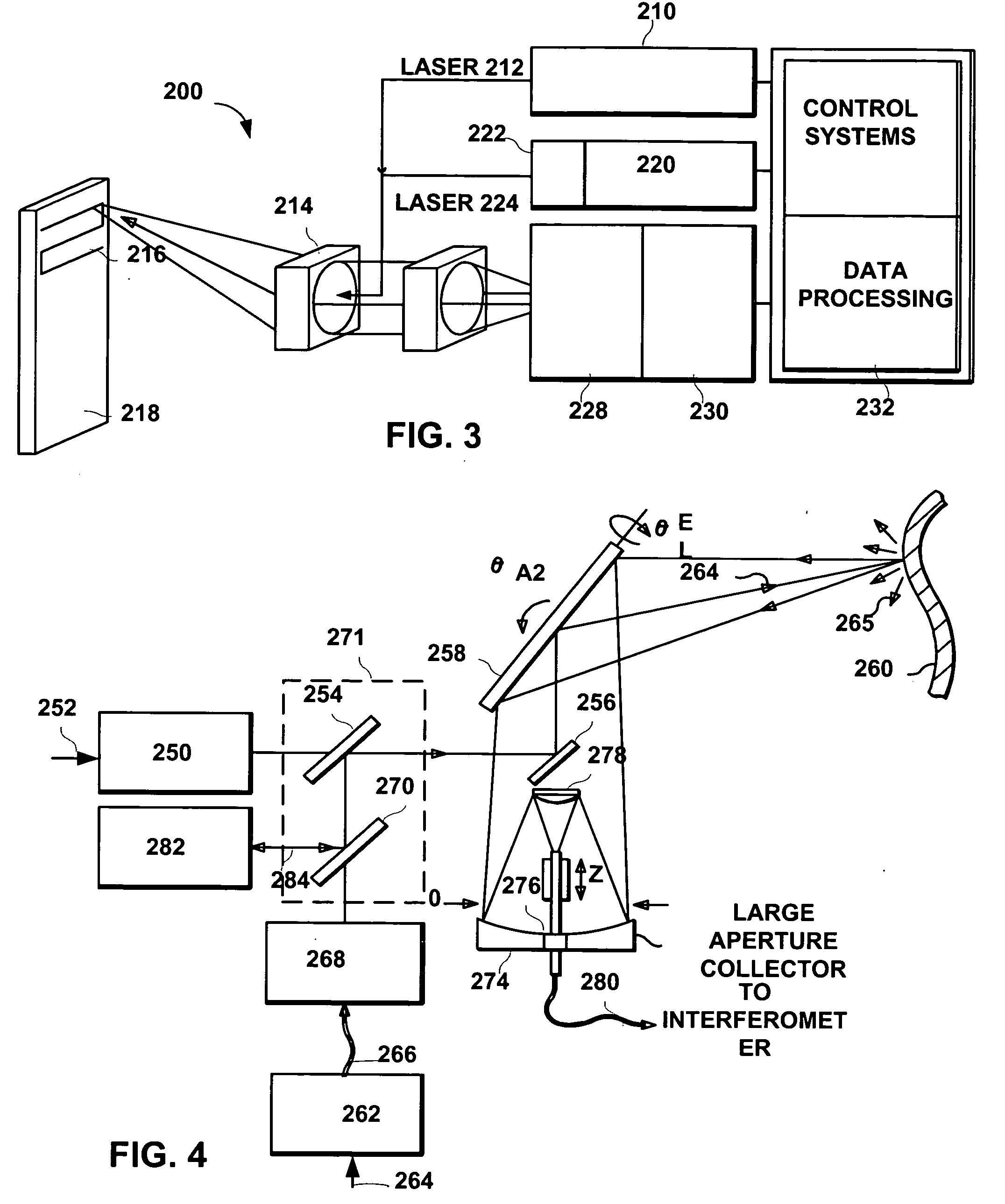
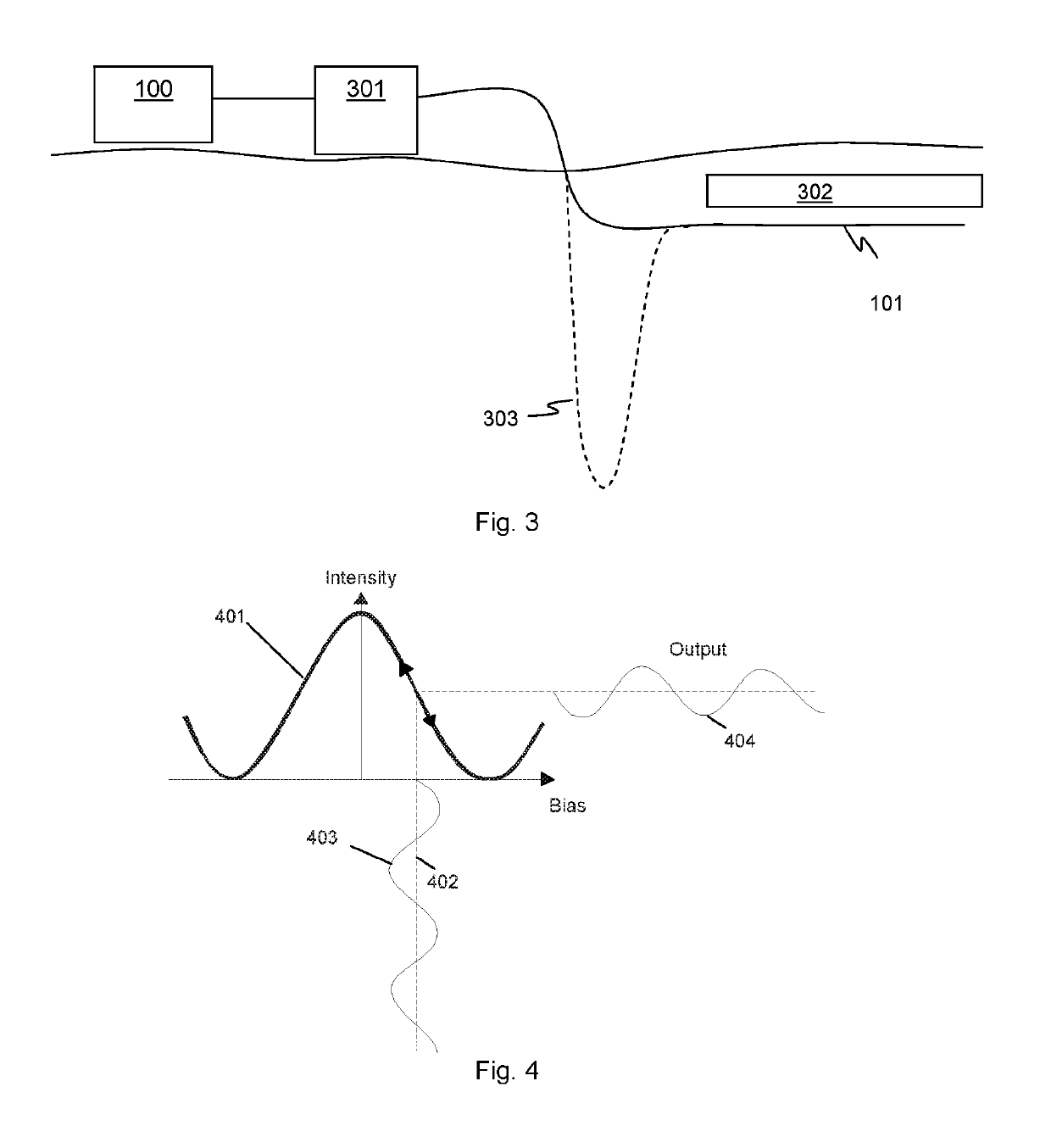
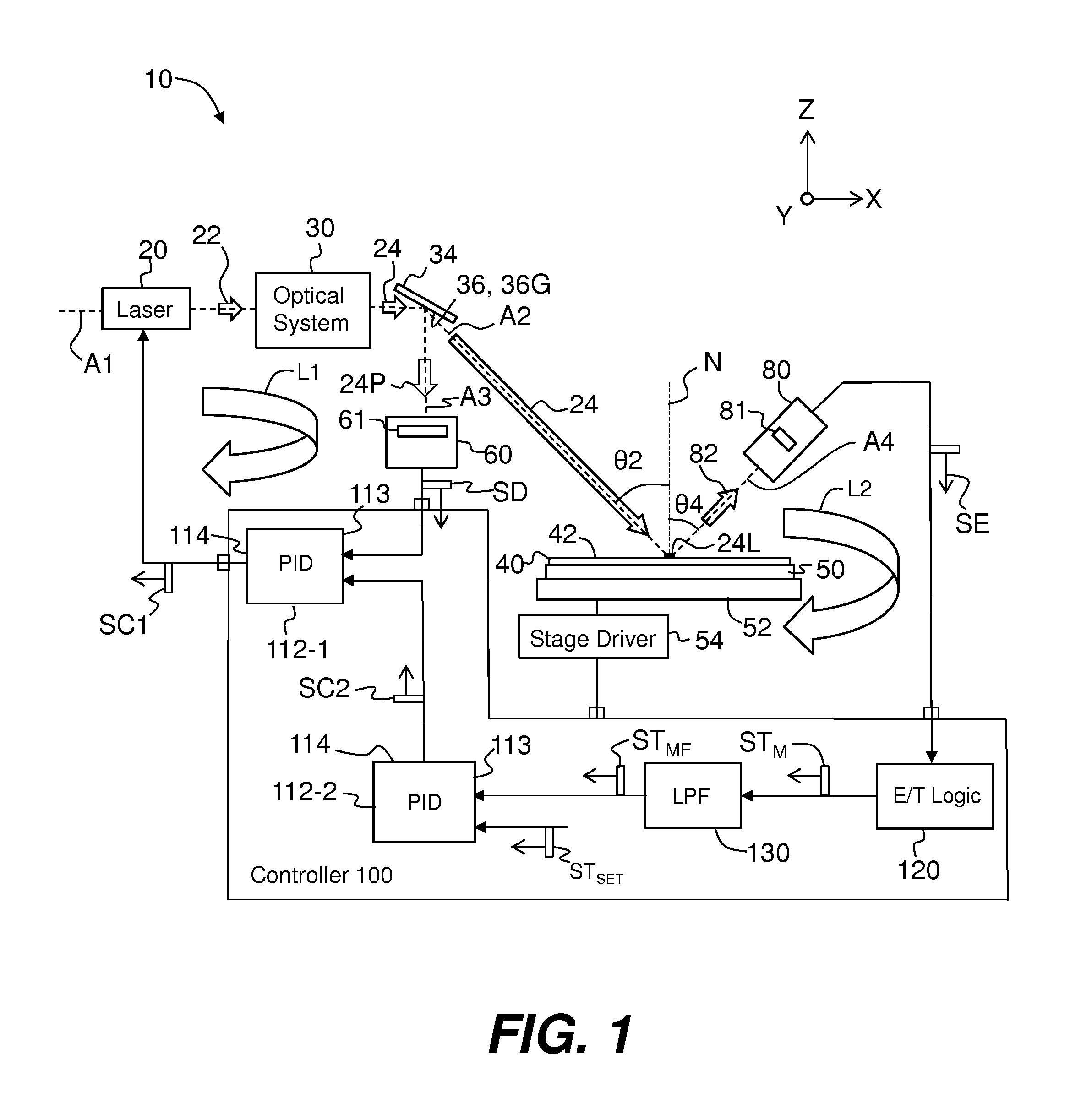
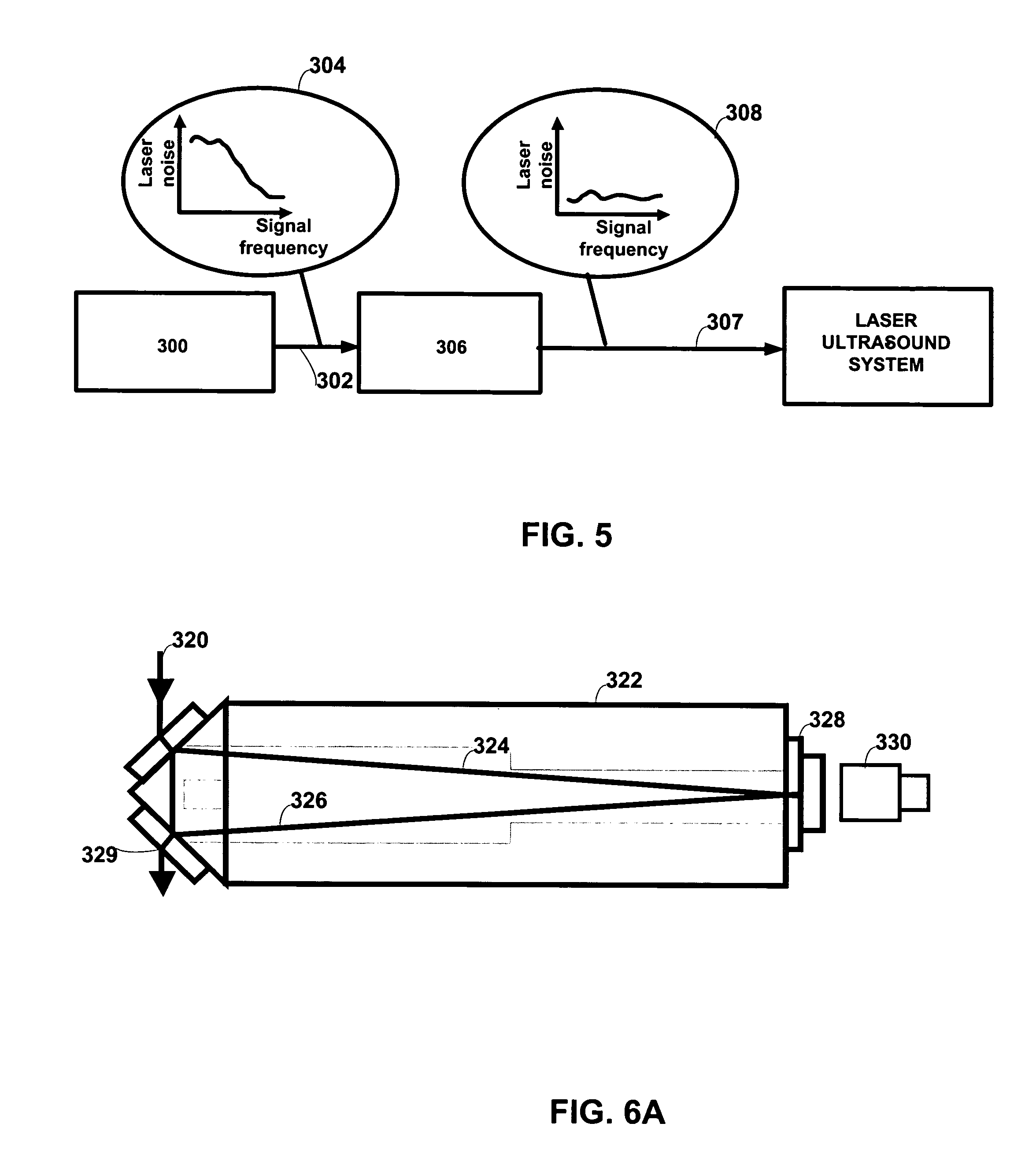
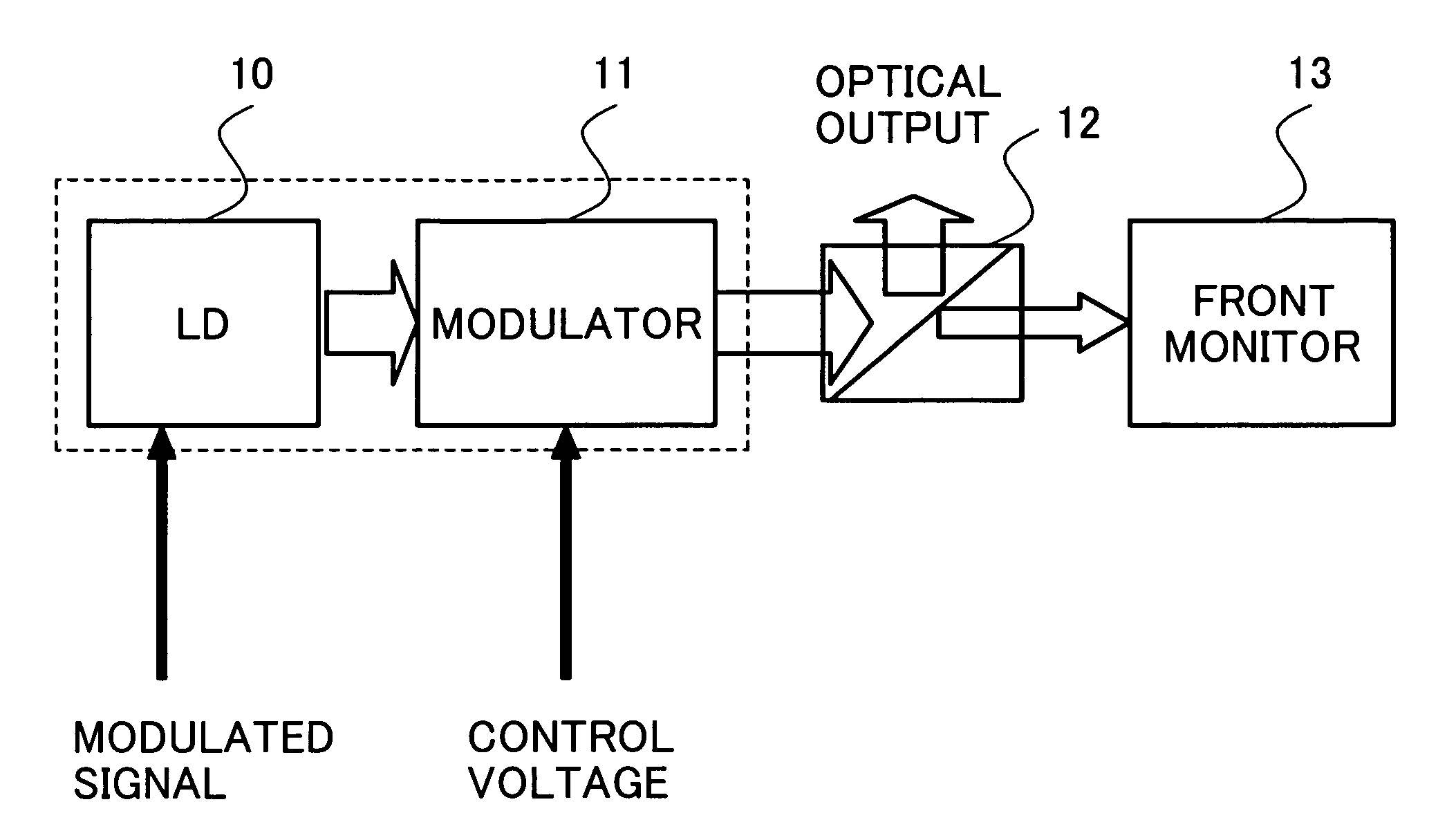
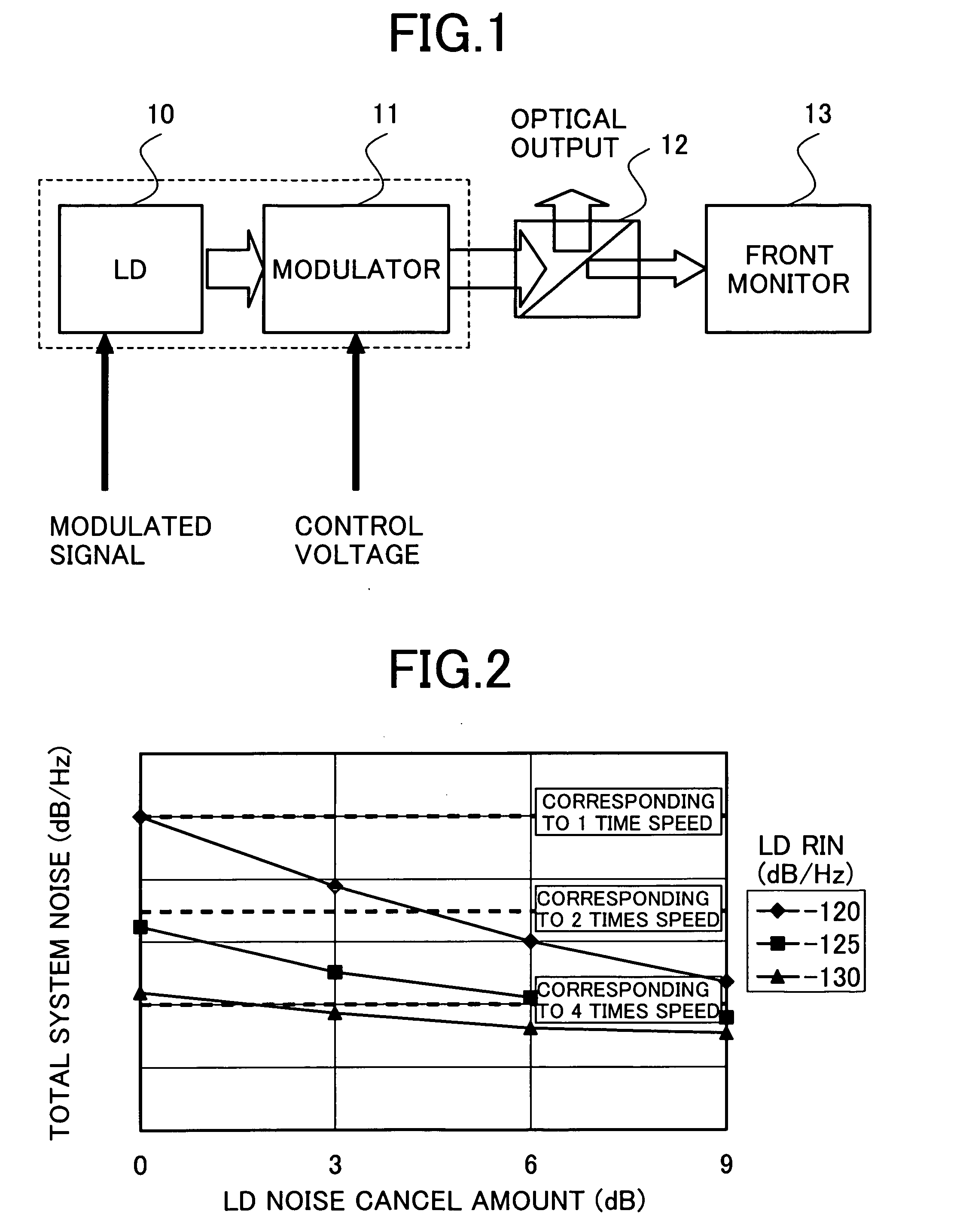
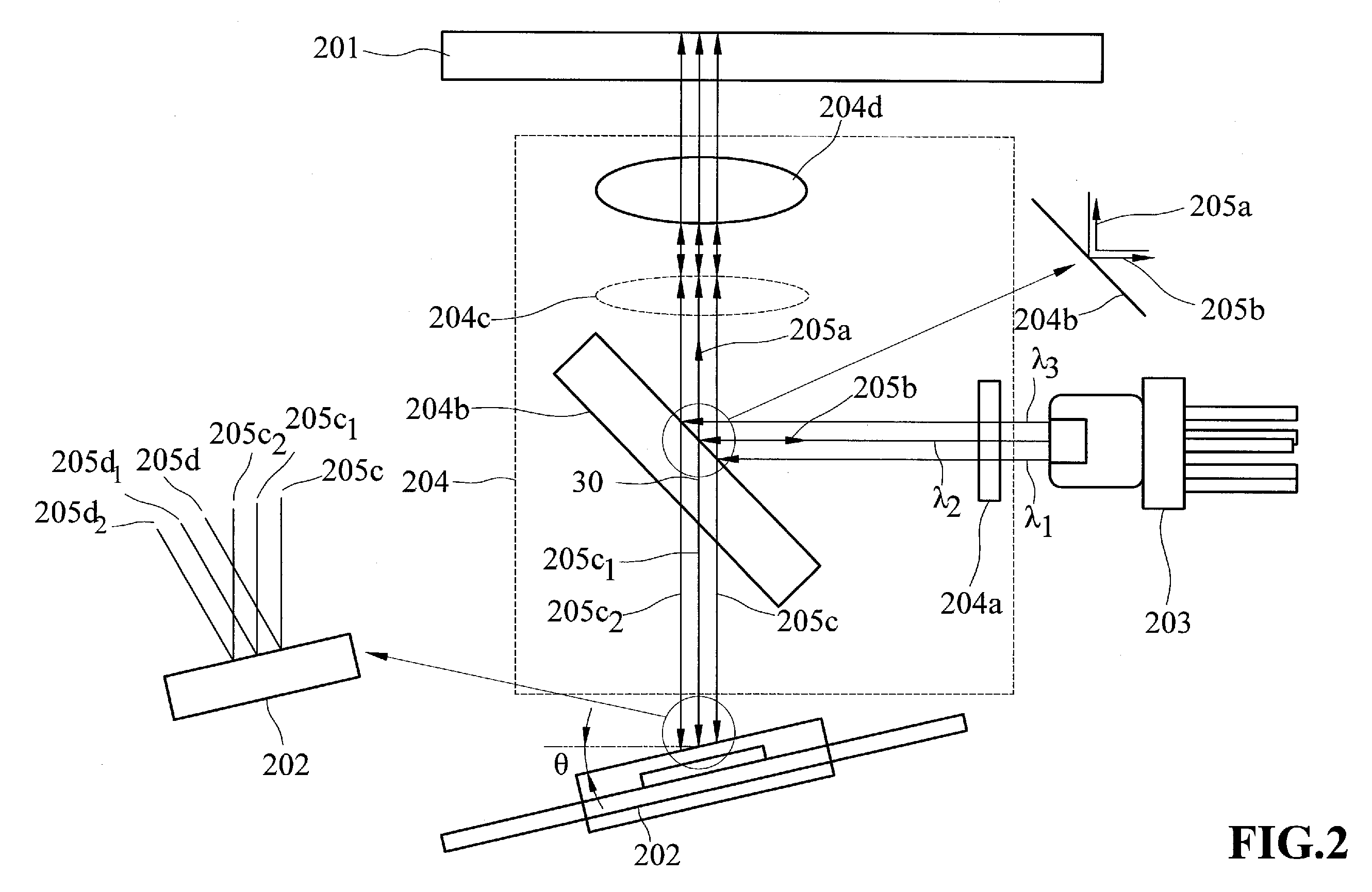
System and method to reduce laser noise for improved interferometric laser ultrasound detection
ActiveUS20050099634A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantage and problemReduce noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansSonificationLaser noise
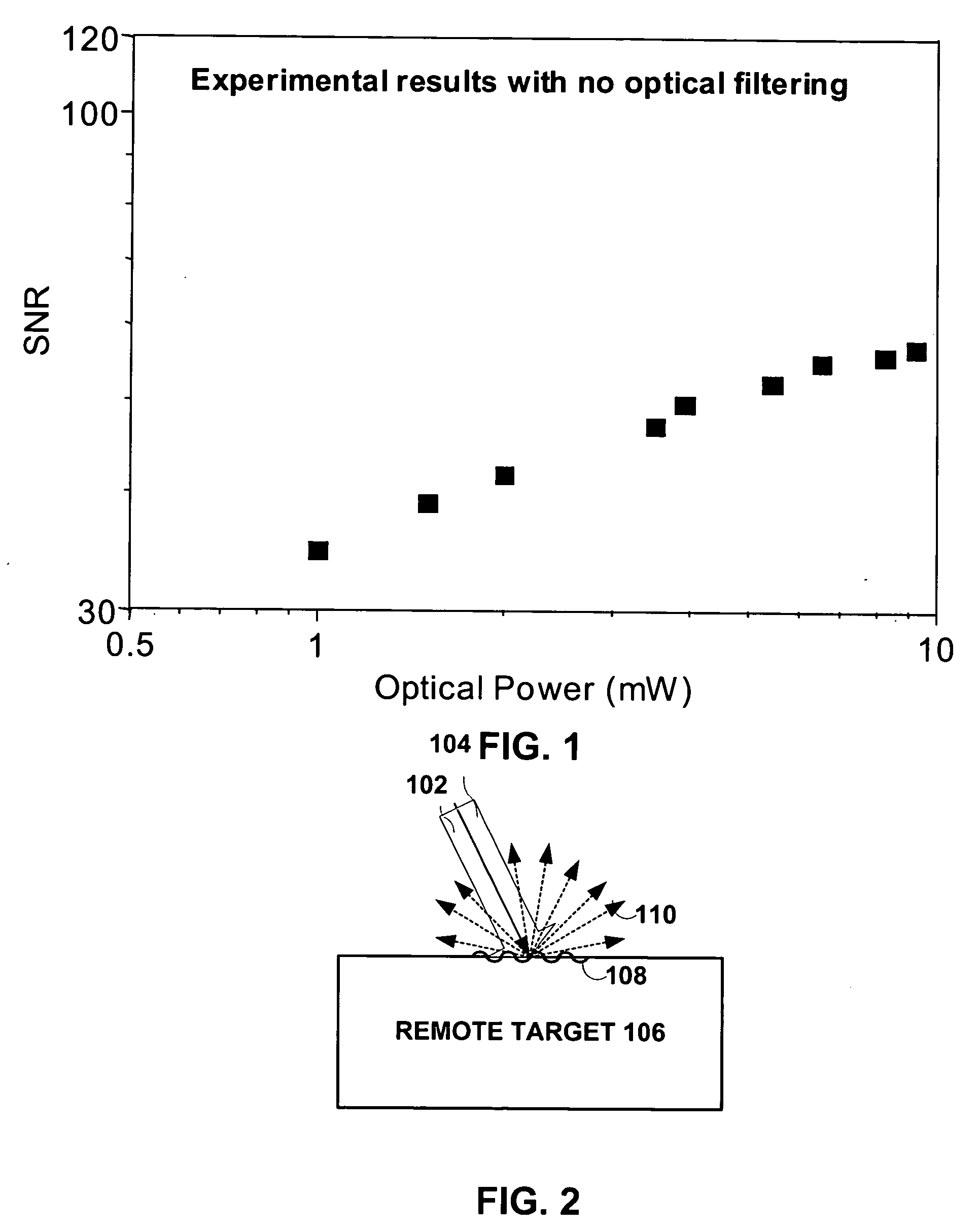
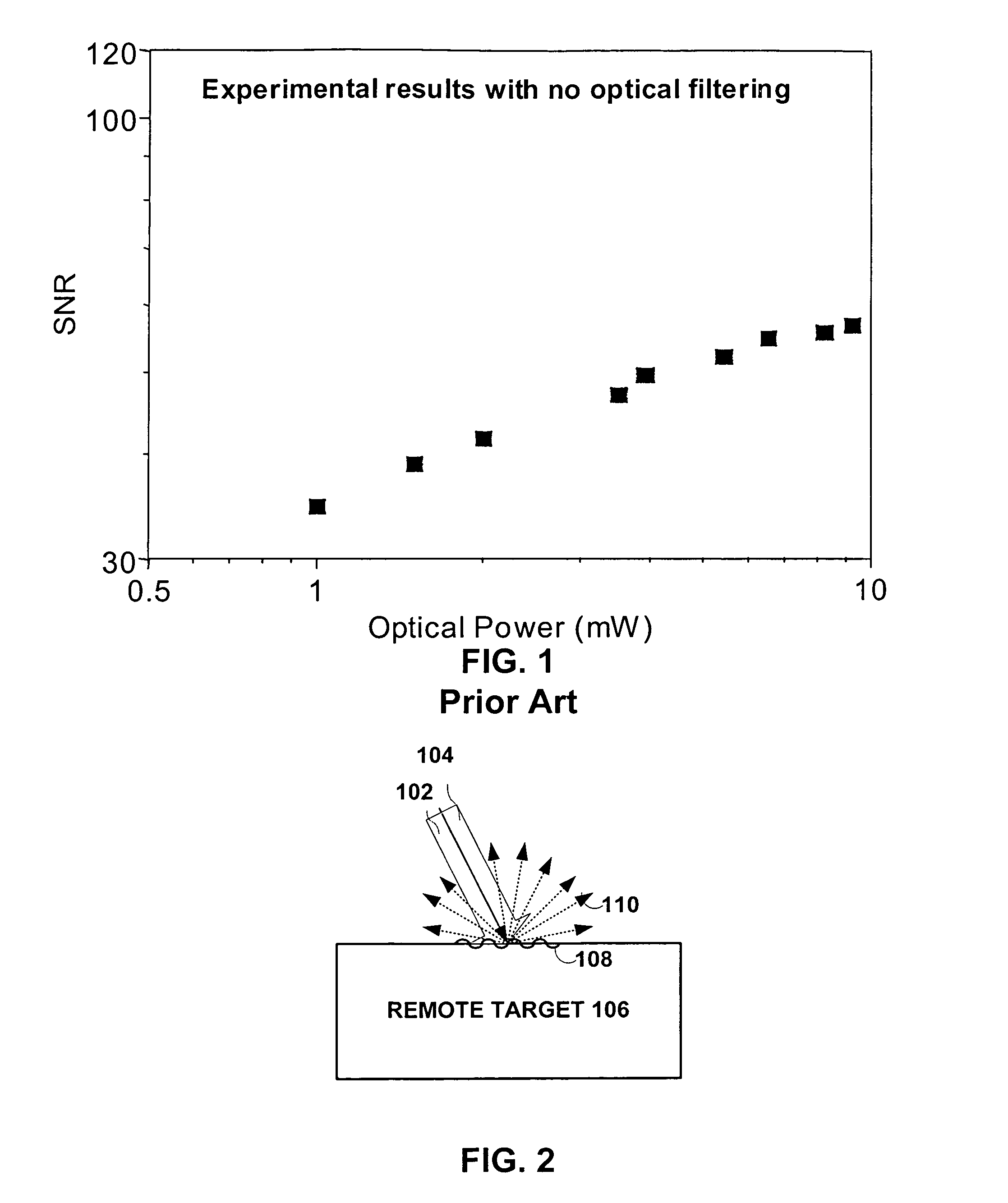
The present invention provides an optical filter assembly that reduces the phase and amplitude noise of a detection laser used to detect ultrasonic displacements. The filtered detection laser is directed to the surface of a remote target. Ultrasonic displacements at the surface scatter the filtered detection laser. Collection optics then gather phase modulated light scattered by the surface and direct the phase modulated light to an optical processor to produce a signal representative of the ultrasonic displacements with an improved SNR. Additional processors may determine the structure of the remote target.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
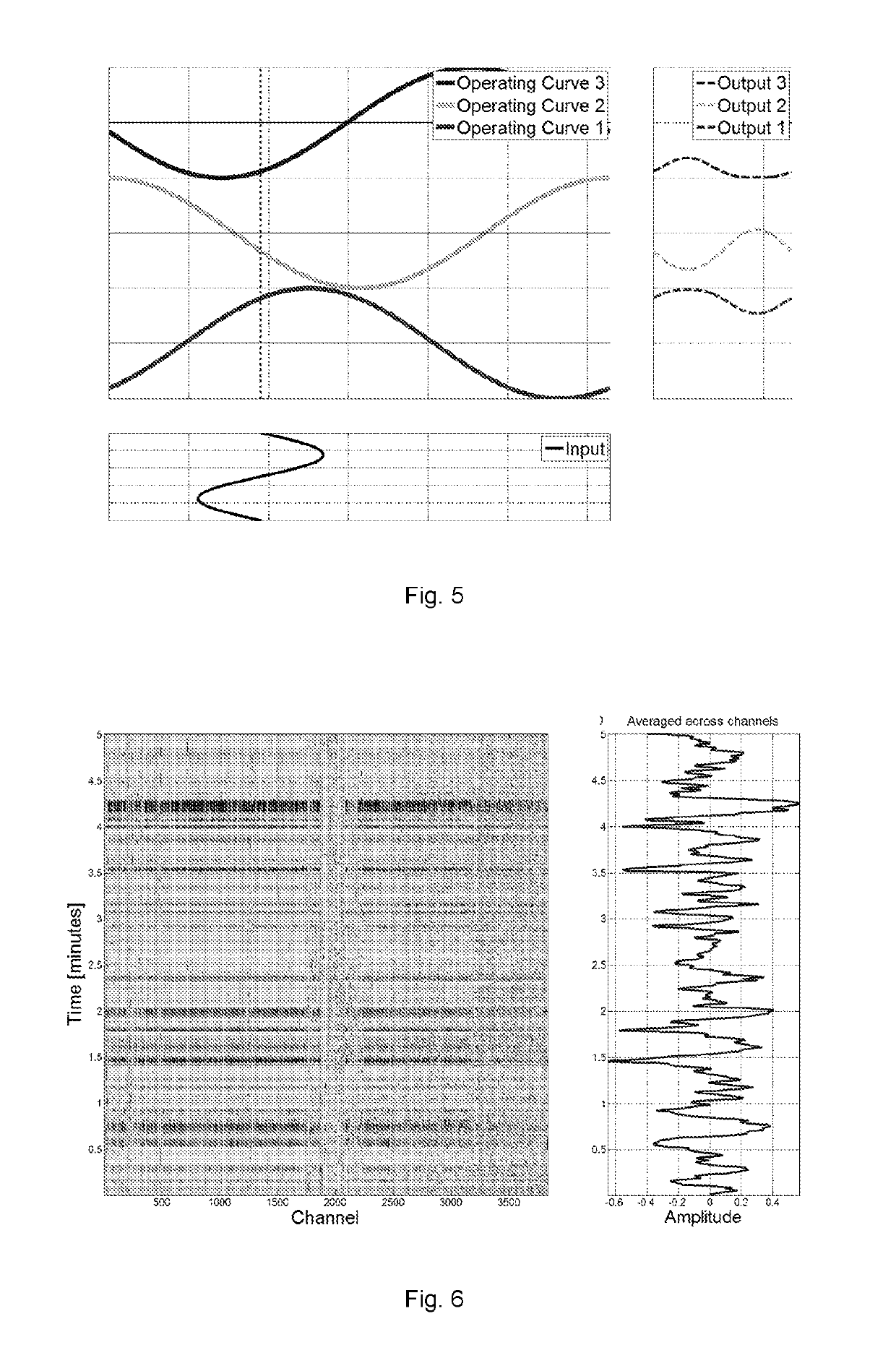
Fibre optic distributed sensing
ActiveUS10247584B2Reduce disadvantagesError minimizationForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesOptical radiationFiber
This application describes methods and apparatus for distributed fiber optic sensing that reduce or compensate for the effects of laser phase noise. The method involves repeatedly interrogating an optical fiber (101), where each interrogation involves launching at least one interrogating pulse into the optical fiber; detecting optical radiation which is backscattered from within the fiber, and forming a measurement signal from a plurality of sensing portions of the fiber. The method involves forming a laser noise template based on the measurement signals within a frequency band of interest from a first set of said sensing portions; and applying a correction to the measurement signals from said plurality of sensing portions based on said laser noise template. The first set of sensing portions may be temperature and / or strain stable portion from an isolated section of fiber (301, 303) or may comprise a selected set of sensing portions, which may include substantially all the sensing portions, which are averaged to form the laser phase noise template. For a phase based DAS type sensor the laser phase noise template may simply be subtracted from the measurement signals. For an intensity based sensor it may be necessary to polarity align and normalize the signals of the first set before averaging and then determine a gain-time profile for each sensing portion prior to applying the correction.
Owner:OPTASENSE HLDG LTD
Dual-loop control for laser annealing of semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS8691598B1Reduce noiseReduce variationLaser detailsAfter-treatment detailsEmissivityControl signal
Owner:VEECO INSTR
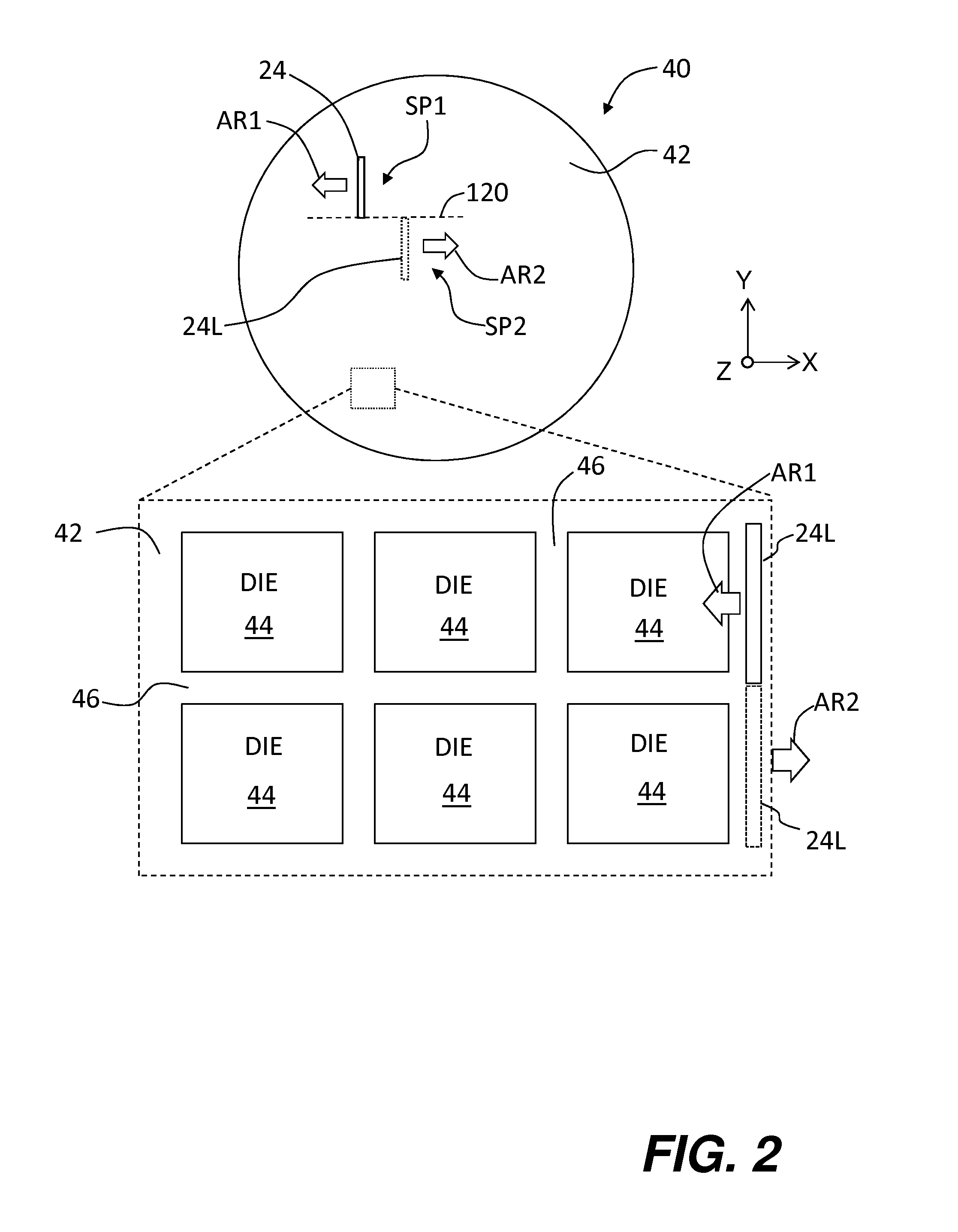
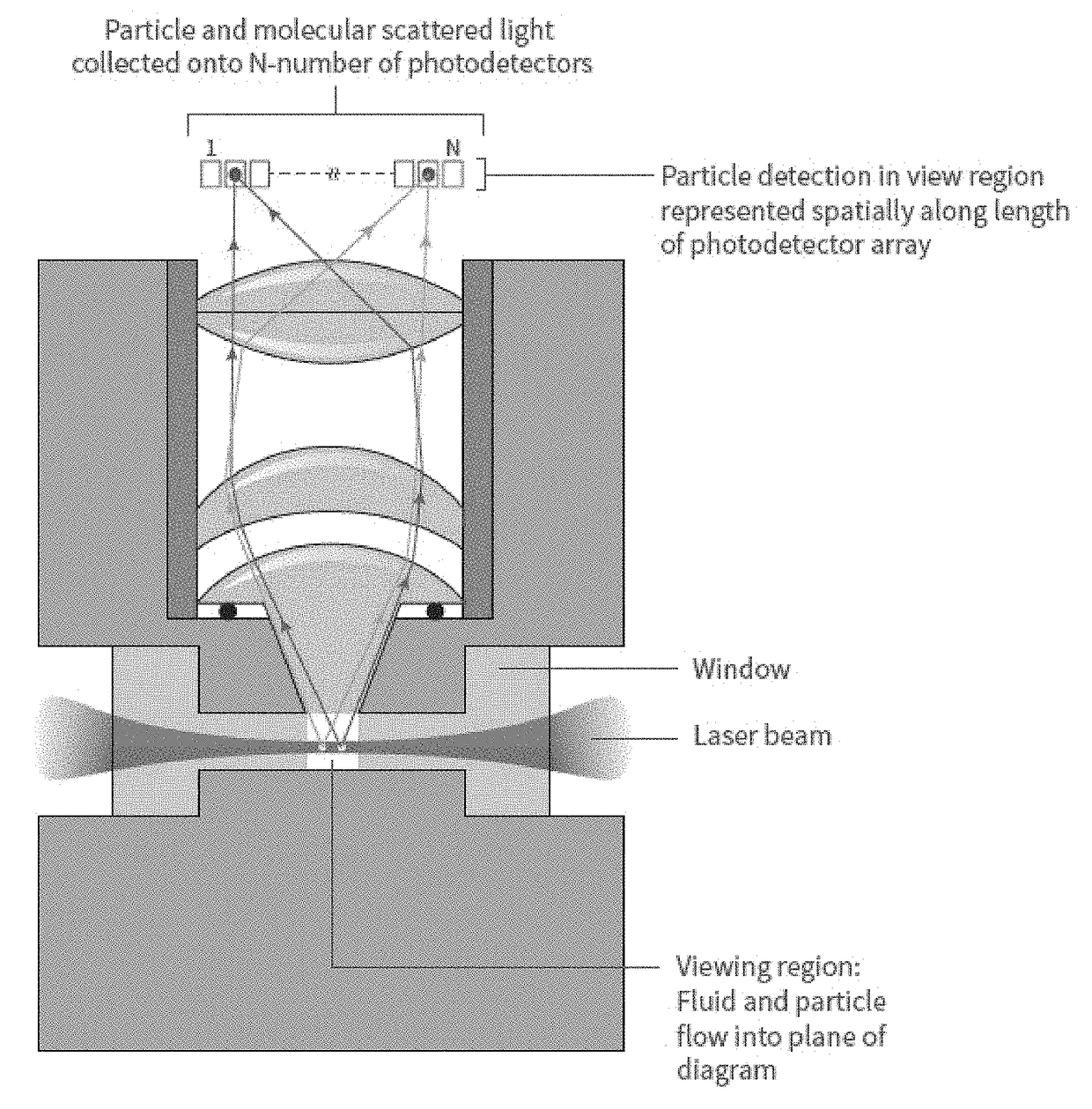
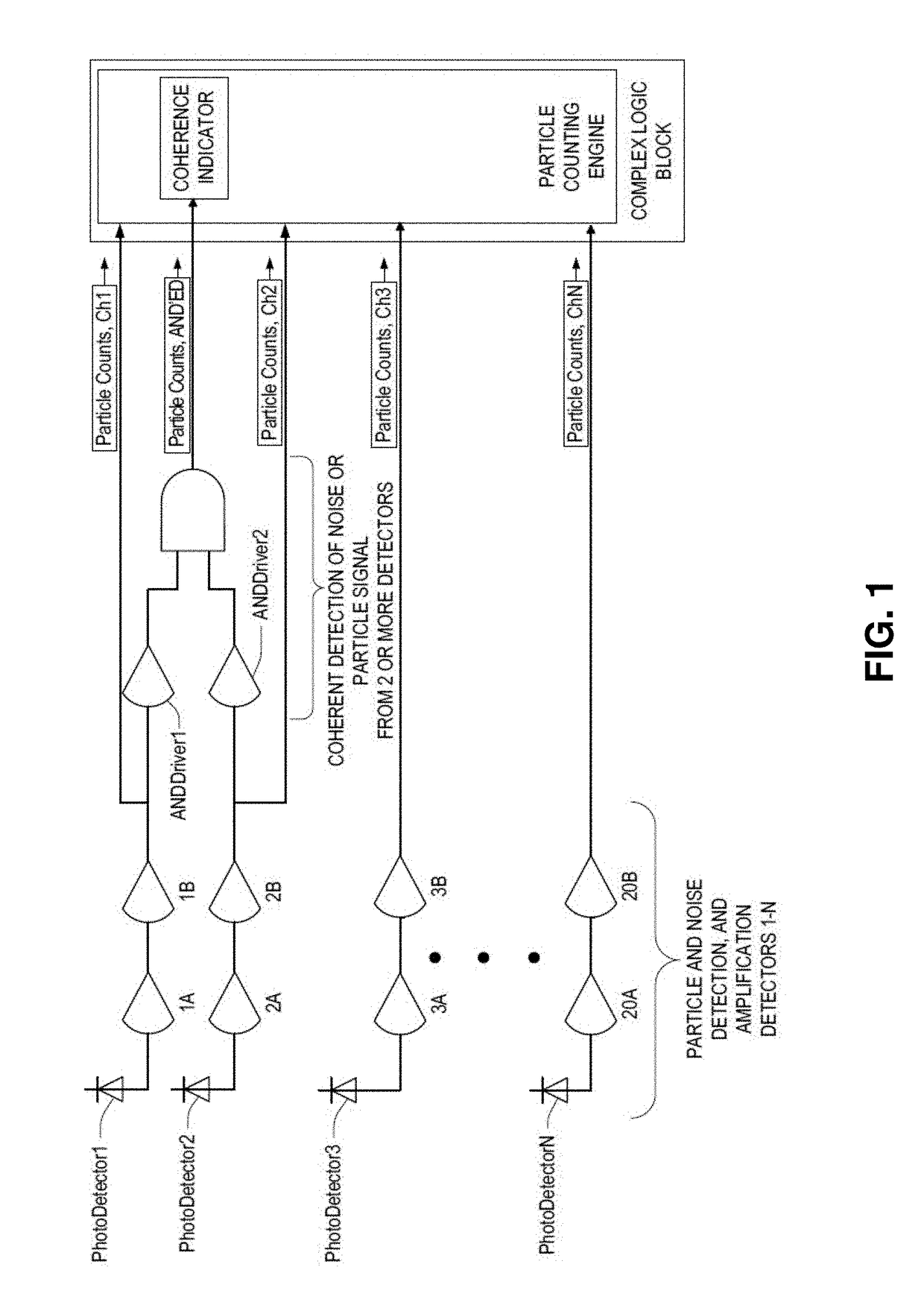
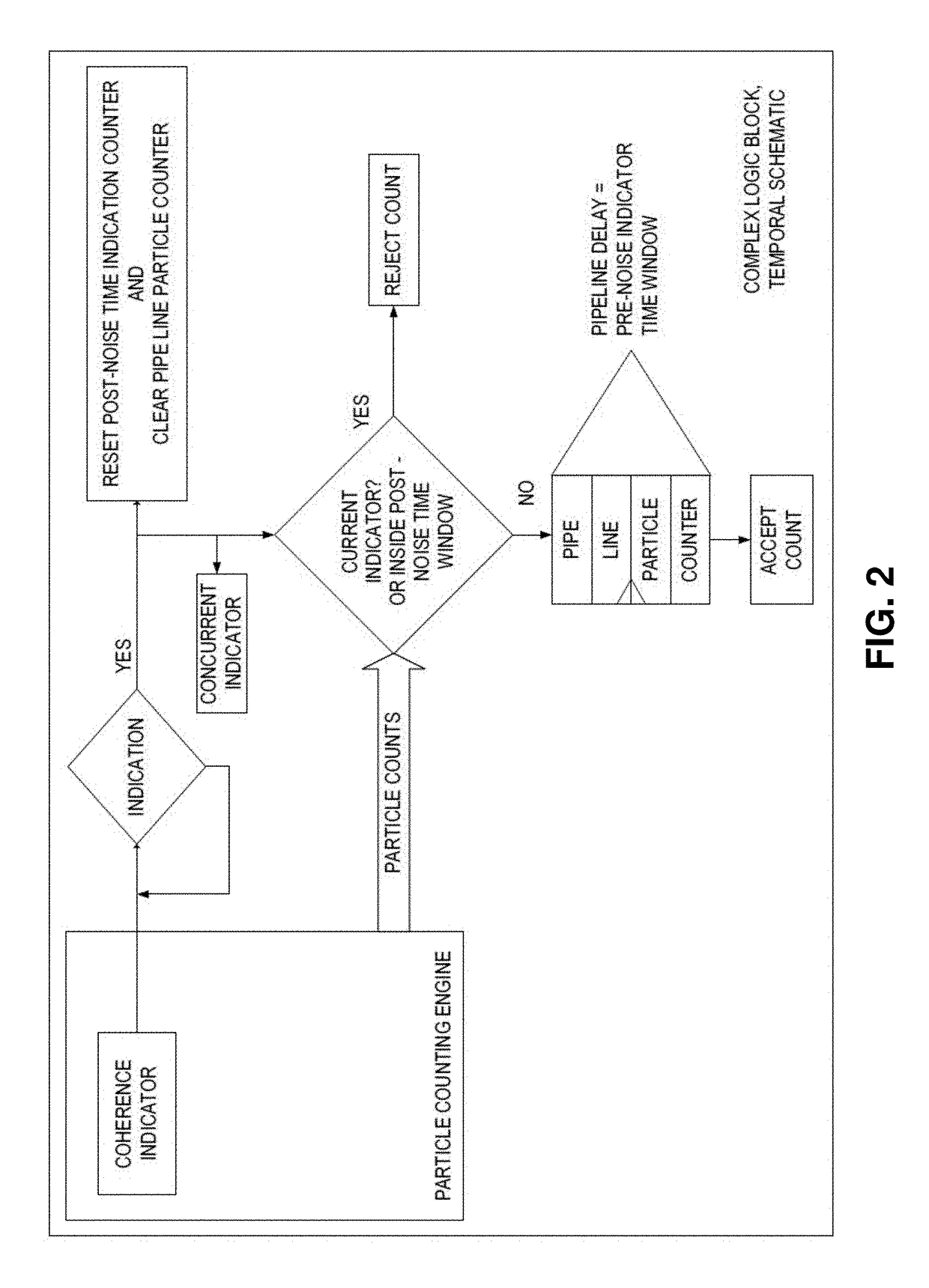
Laser noise detection and mitigation in particle counting instruments
ActiveUS9989462B2Effective distinctionReducing false positivesNanoparticle analysisScattering properties measurementsInstabilityLaser noise
This invention relates to optical particle counters and methods capable of effectively distinguishing signals generated from particle light scattering from sources of noise. Embodiments of the invention, for example, use multisensory detector configurations for identifying and distinguishing signals corresponding to fluctuations in laser intensity from signals corresponding to particle light scattering for the detection and characterization of submicron particles. In an embodiment, for example, methods and systems of the invention compare signals from different detector elements of a detector array to identify and characterize noise events, such as noise generated from laser intensity instability, thereby allow for the detection and characterization of smaller particles. The system and methods of the present invention, thus, provide an effective means of reducing false positives caused by noise or interference while allowing for very sensitive particle detection.
Owner:PARTICLE MEASURING SYST
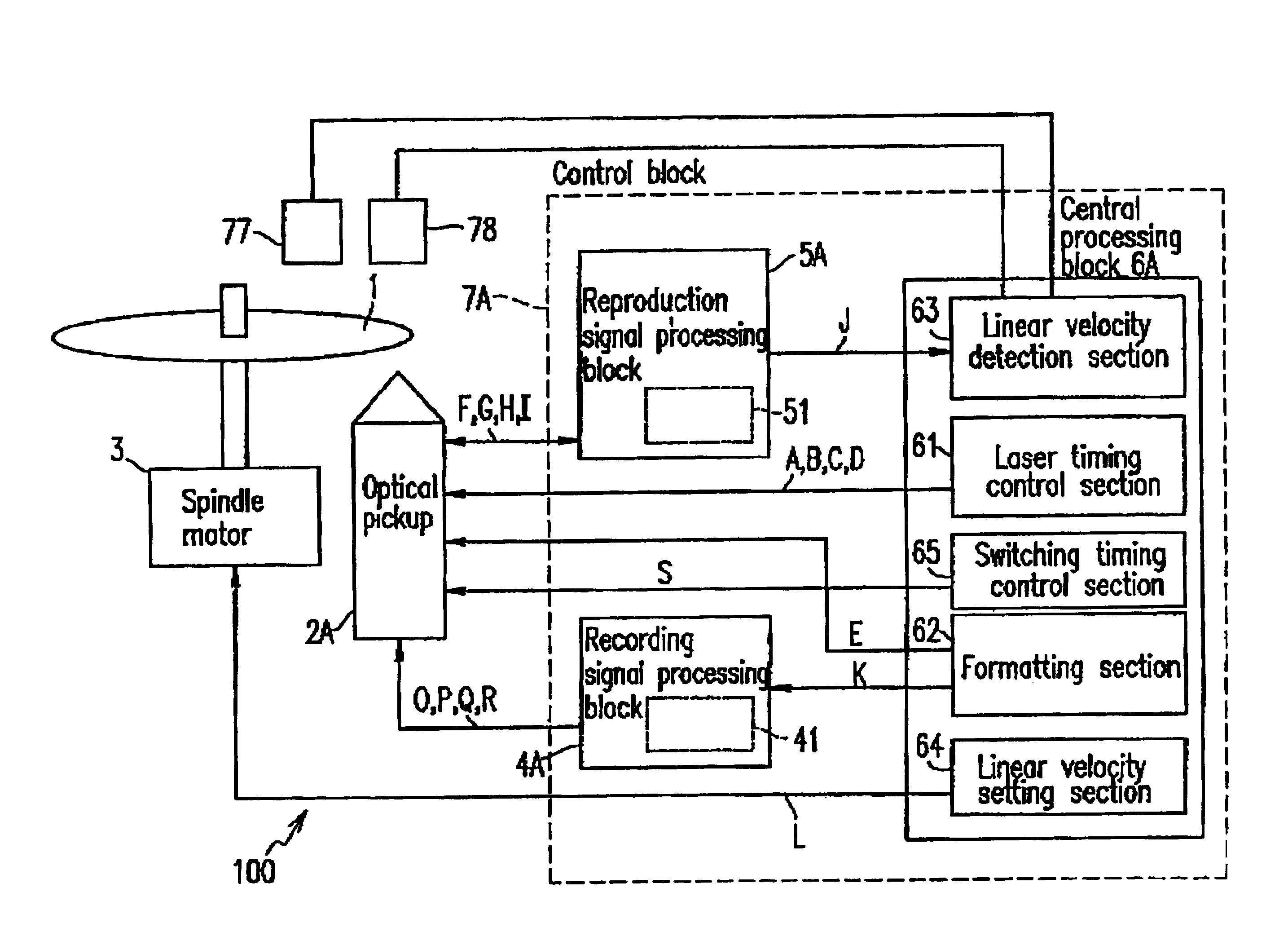
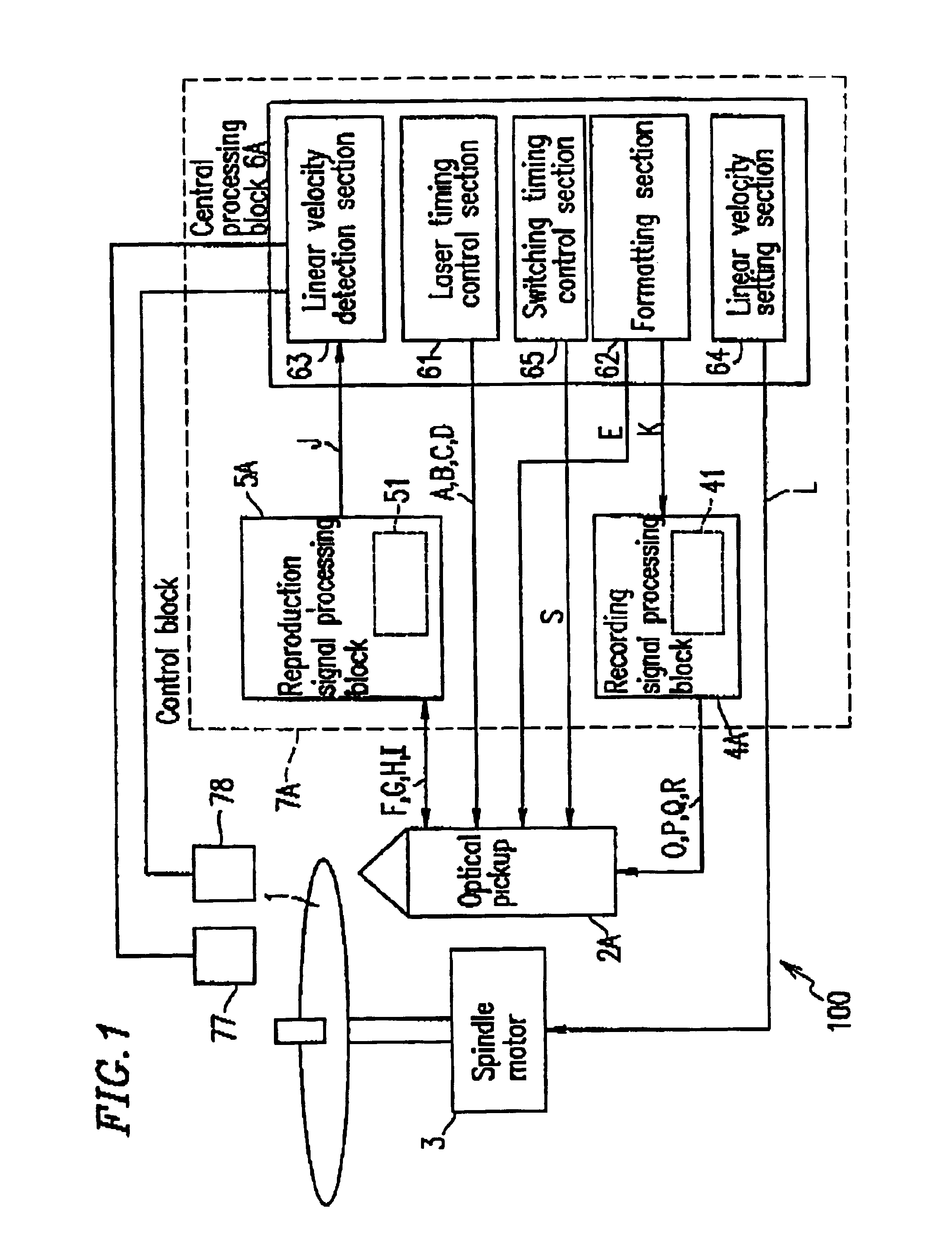
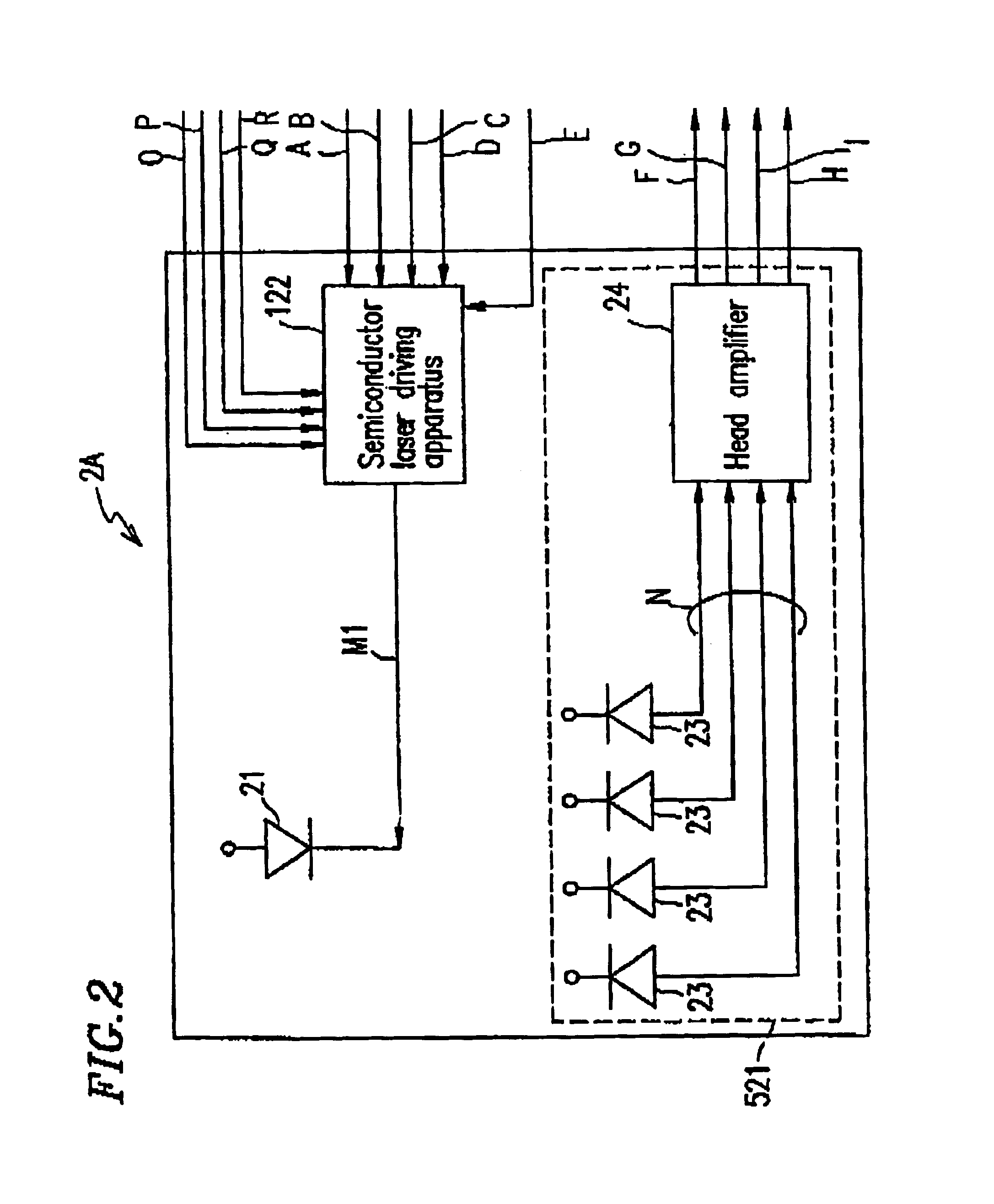
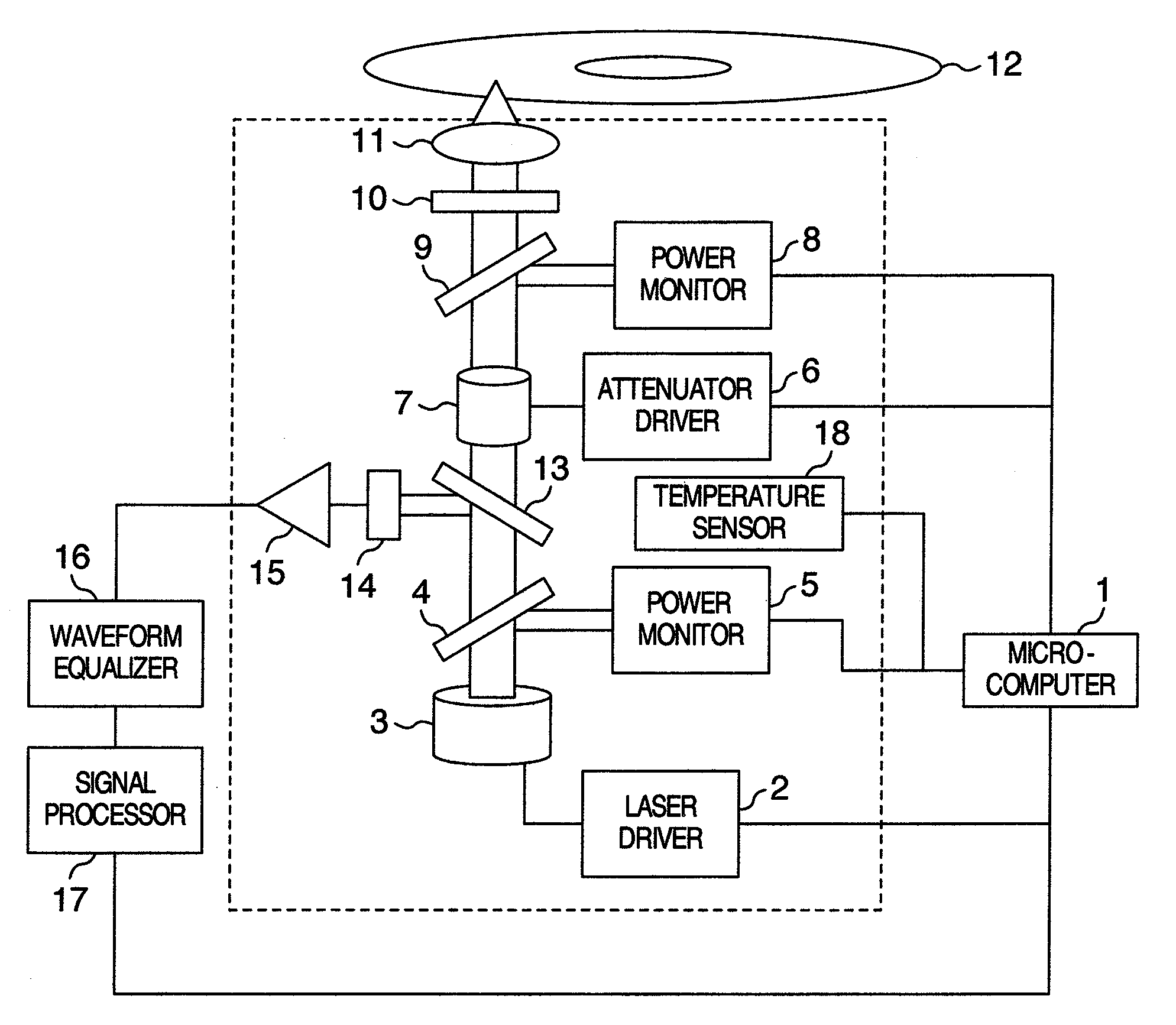
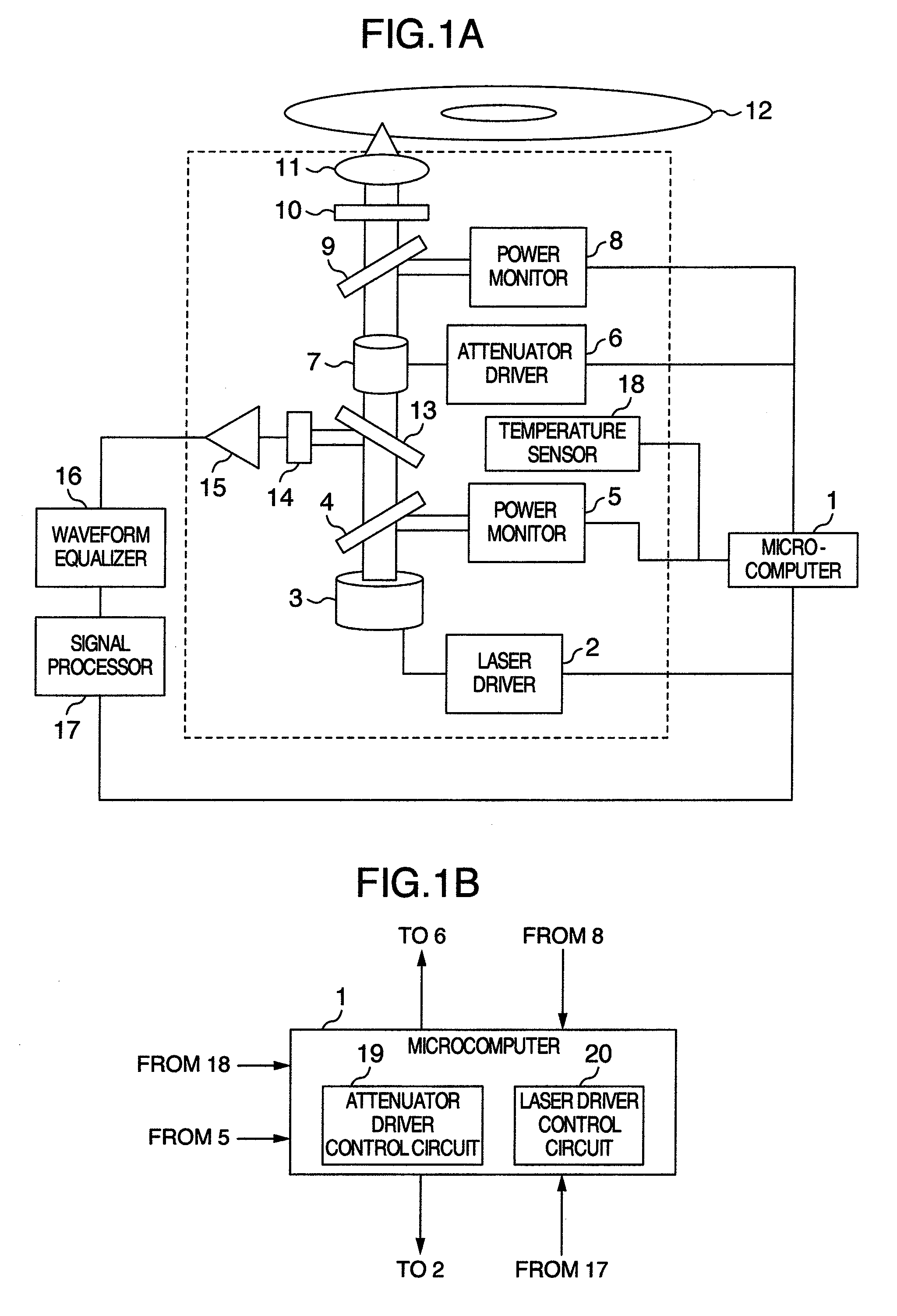
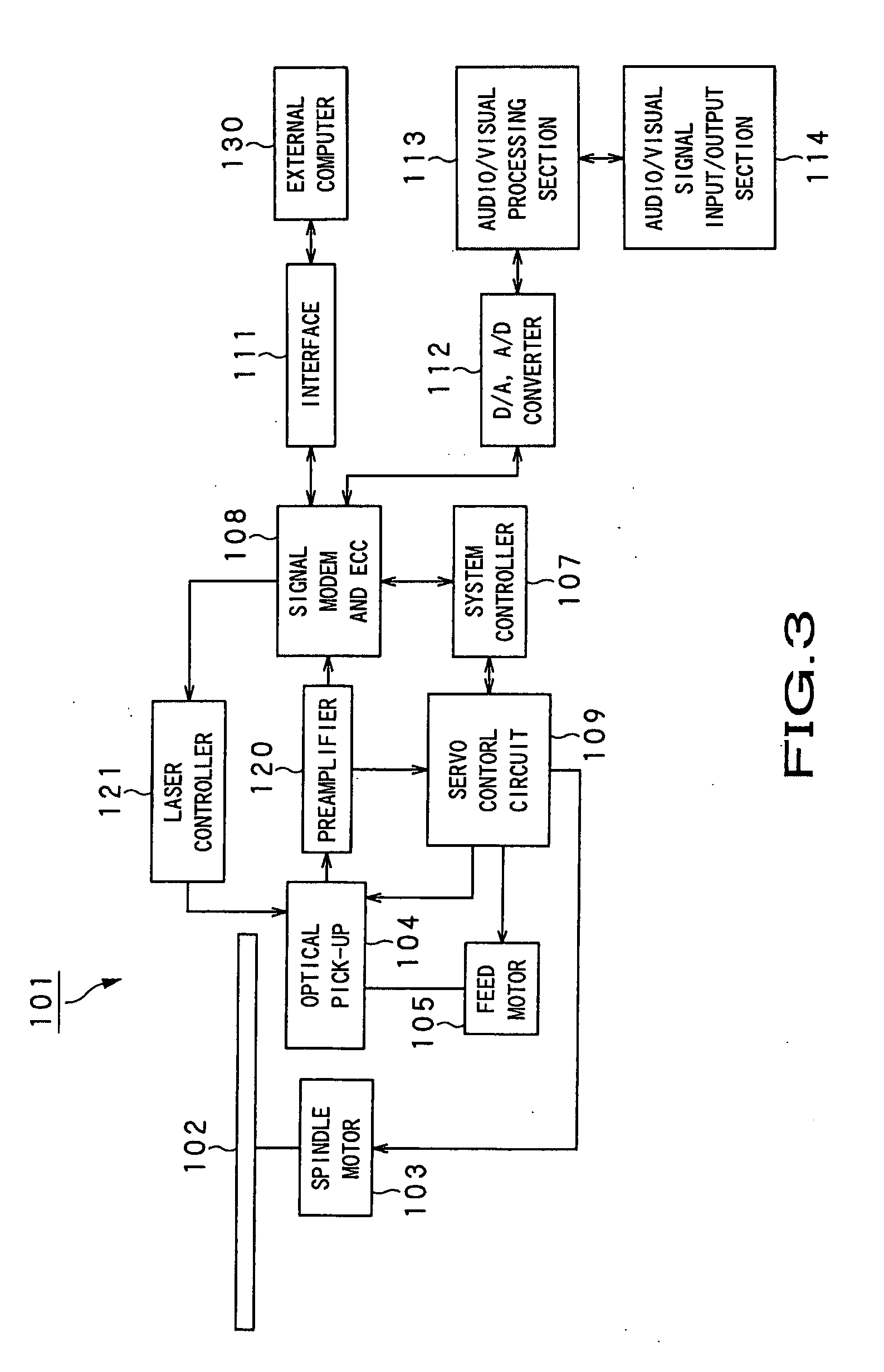
Semiconductor laser driving apparatus with filter to attenuate enhanced frequency component and optical disk apparatus including the same
InactiveUS6930968B2Stable recording characteristicHigh density recordingCombination recordingTelevision system detailsLaser noiseCurrent generation
A semiconductor laser driving apparatus for directing light to an optical disc for recording a recording mark based on a recording current and reproducing the recording mark to generate a reproduction signal. The apparatus includes a reproduction current generation section; a high frequency current generation section for generating a current including a high frequency component for reducing semiconductor laser noise in the reproduction; a recording current generation section, the recording current including a pulse corresponding to the recording mark and including a plurality of multi-pulses; and a current driving section for amplification. The apparatus further includes a filter to attenuate the enhanced high frequency components in the high frequency current and in the enhanced high frequency component; and a switching section for switching the filter so that the enhanced component in the recording current is superposed on at least one of the multi-pulses.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Dual-loop control for laser annealing of semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS20140166632A1Reduce variationReduce noiseContainers to prevent mechanical damagePackaging bottlesEmissivityControl signal
Systems and methods for performing semiconductor laser annealing using dual loop control are disclosed. The first control loop operates at a first frequency and controls the output of the laser and controls the 1 / f laser noise. The second control loop also controls the amount of output power in the laser and operates at second frequency lower than the first frequency. The second control loop measures the thermal emission of the wafer over an area the size of one or more die so that within-die emissivity variations are average out when determining the measured annealing temperature. The measured annealing temperature and an annealing temperature set point are used to generate the control signal for the second control loop.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
System and method to reduce laser noise for improved interferometric laser ultrasound detection
ActiveUS7474411B2Eliminates and reduces disadvantage and problemReduce noiseSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansSonificationLaser noise
The present invention provides an optical filter assembly that reduces the phase and amplitude noise of a detection laser used to detect ultrasonic displacements. The filtered detection laser is directed to the surface of a remote target. Ultrasonic displacements at the surface scatter the filtered detection laser. Collection optics then gather phase modulated light scattered by the surface and direct the phase modulated light to an optical processor to produce a signal representative of the ultrasonic displacements with an improved SNR. Additional processors may determine the structure of the remote target.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Detecting device for laser noise-signal ratio
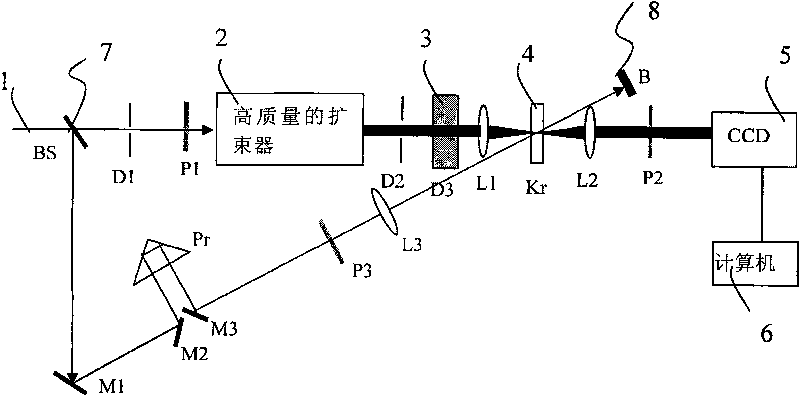
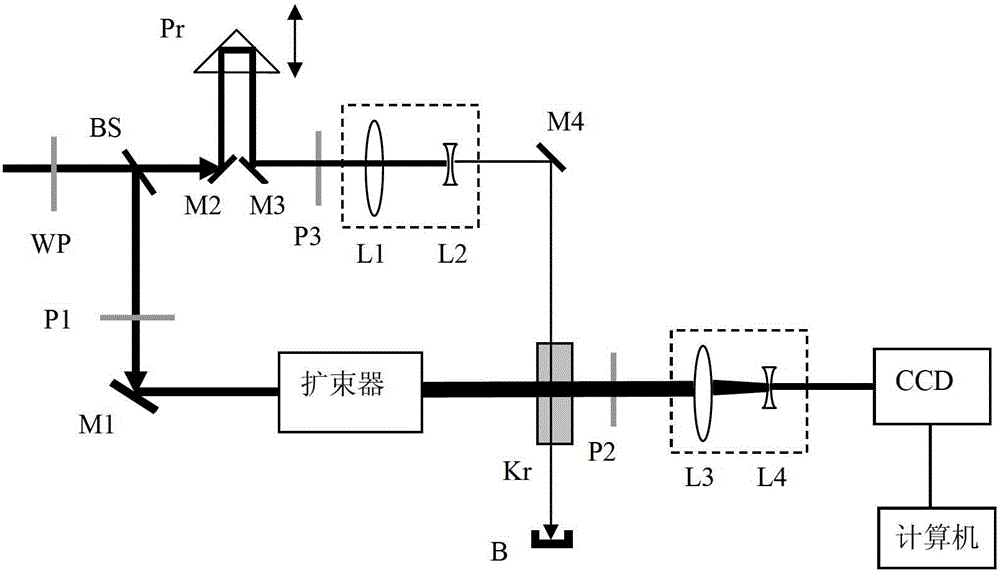
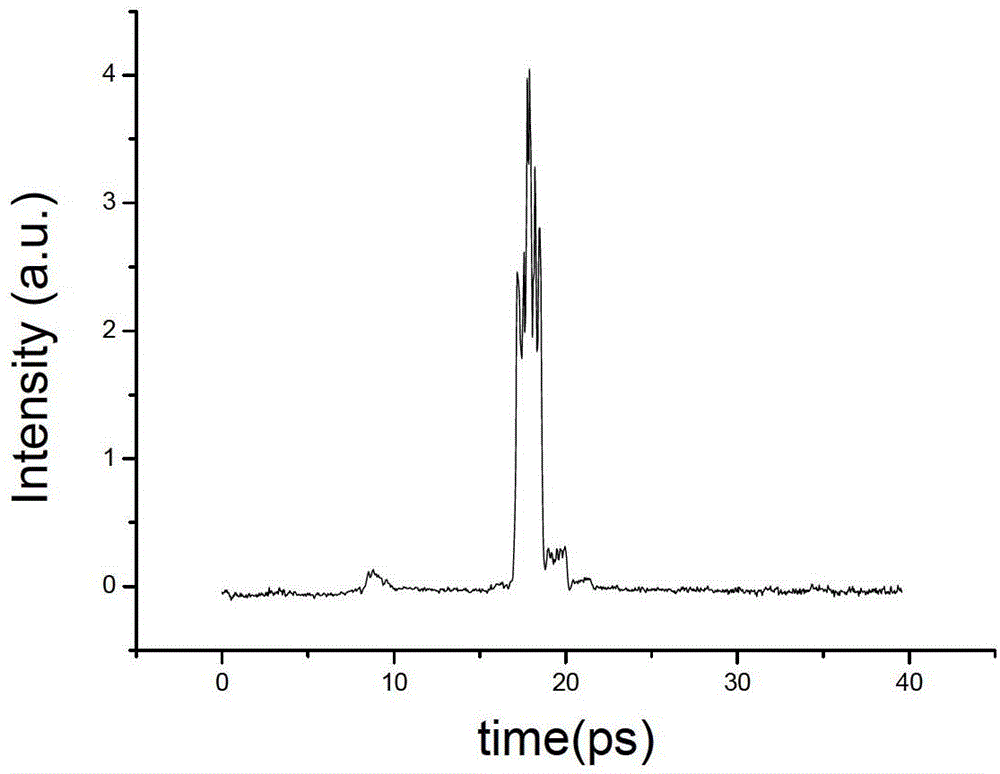
The invention relates to a detecting device for laser noise-signal ratio, comprising a light source, a beam splitter, a beam expander, a single-pulse optical delayer, an optical Kerr-like medium and a detector; the beam splitter is arranged at the output light path of the light source, and divides the light source into shutter light and signal light; the beam expander is arranged at the output light path of the signal light which is divided by the beam splitter; the single-pulse optical delayer is arranged at the output light path of the beam expander; the optical Kerr-like medium is arranged at the cross location in space of the output light path of the single-pulse optical delayer and the output light path of the shutter light divided by the beam splitter; the detector is connected with the optical Kerr-like medium. The invention provides the detecting device for laser noise-signal ratio which can detect the noise-signal ratio for hundreds of picoseconds before and after the laser main pulse, and can detect the single-pulse laser noise-signal ratio, and can measure the laser-pulse noise-signal ratio of repeated frequency.
Owner:XIAN MICROMACH TECH CO LTD
Optical recording and reading equipment
InactiveUS20060114777A1Short response timeLarge laser noiseCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsUltrasound attenuationLaser noise
Disclosed herewith is a data recording and reading equipment capable of reducing laser noise easily. At first, a laser beam source that can reduce the laser noise when reading data from a subject optical disk is obtained. A modulator capable of varying laser attenuation with a voltage is disposed so as to precede the laser, thereby the laser noise when reading data from the optical disk can be reduced without lowering the laser power when in writing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
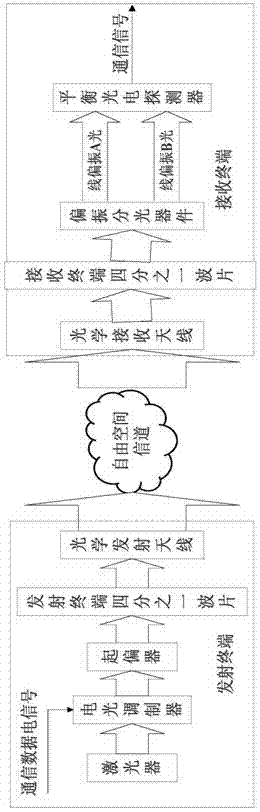
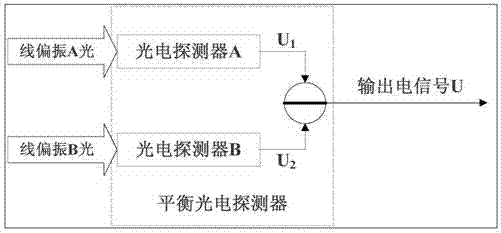
Polarization labeling-based free space laser communication optical denoising method
The invention provides a polarization labeling-based free space laser communication optical denoising method. According to the method, polarization labeling is firstly carried out on laser communication signals at a communication transmitting terminal to enable the polarization state to be left-handed circular polarization and a right-handed circular polarization, laser signals with polarization labeling are recognized at a communication receiving terminal, and background laser noise in the receiving signals are removed. The background laser noise in free space laser communication signals can be effectively removed, the device is mature, the structure is simple, and the promotion difficulty is reduced.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical disk apparatus
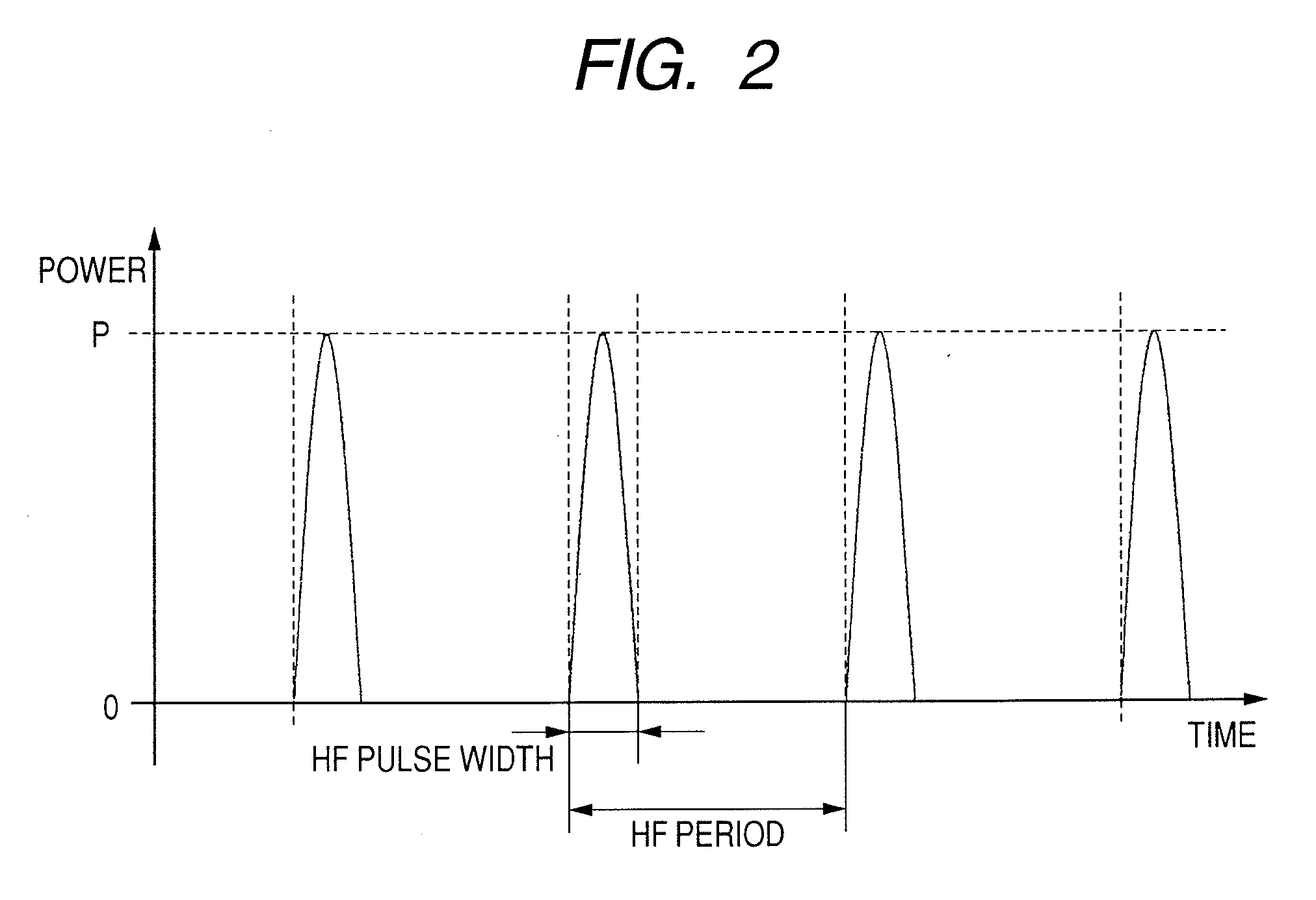
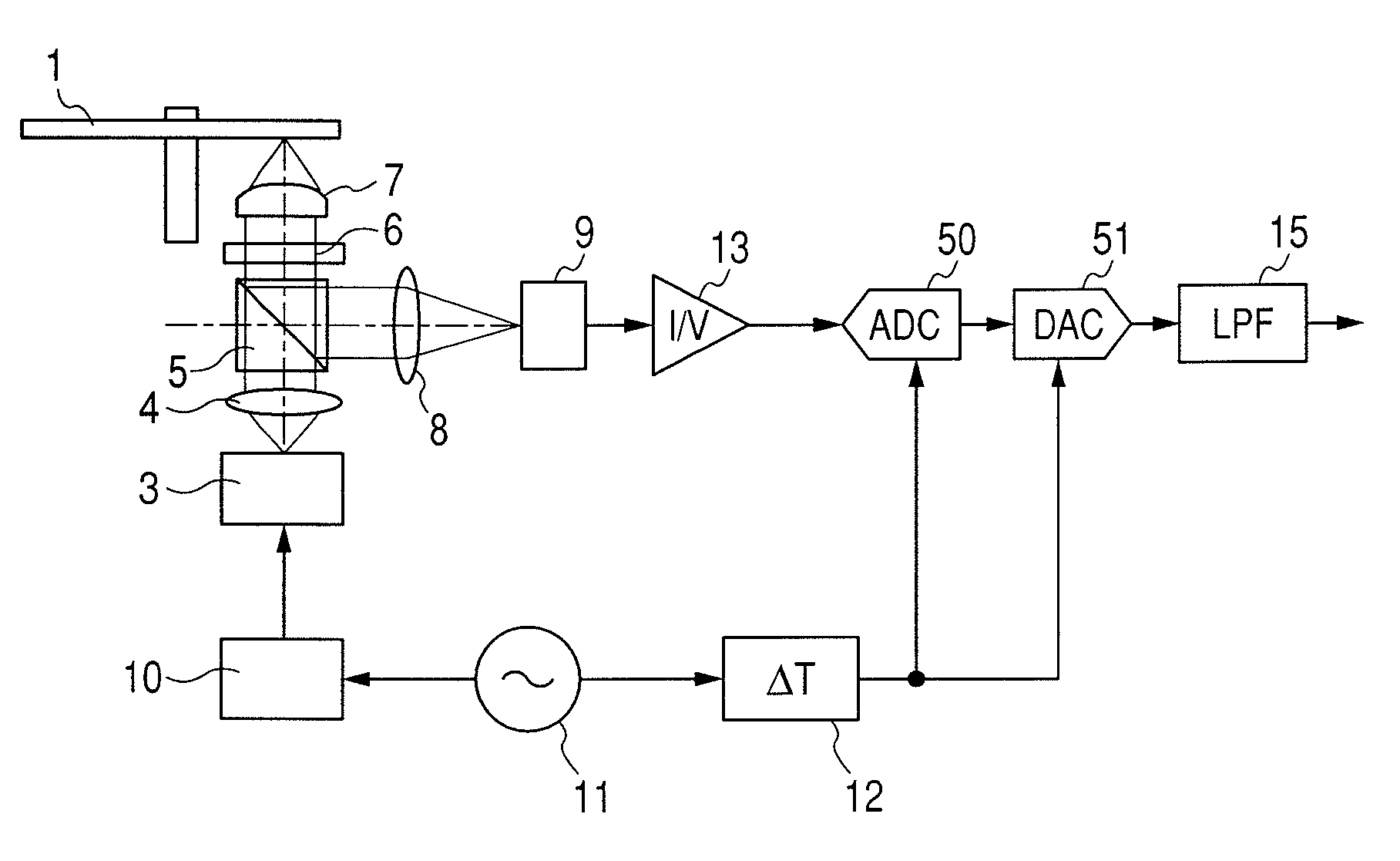
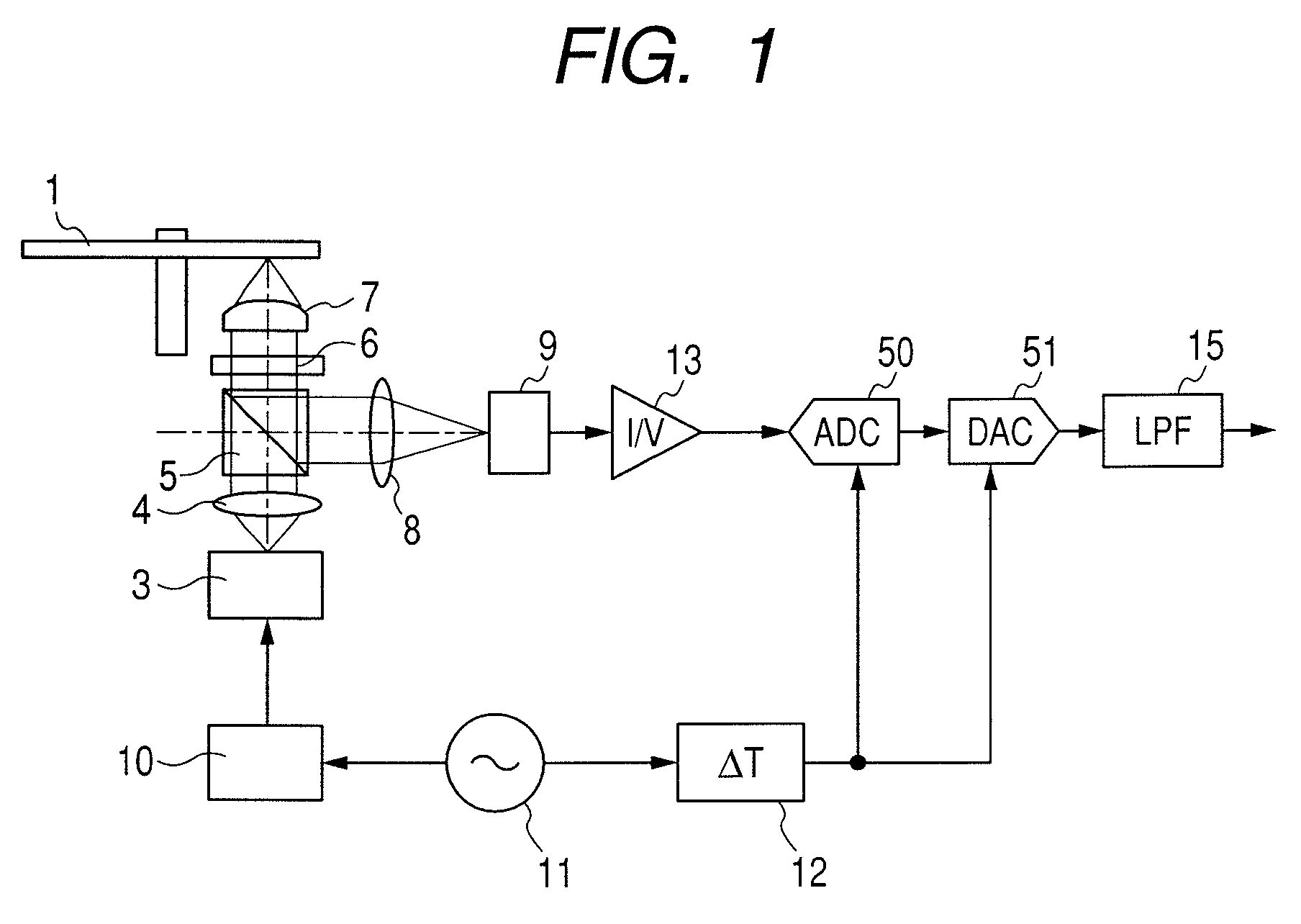
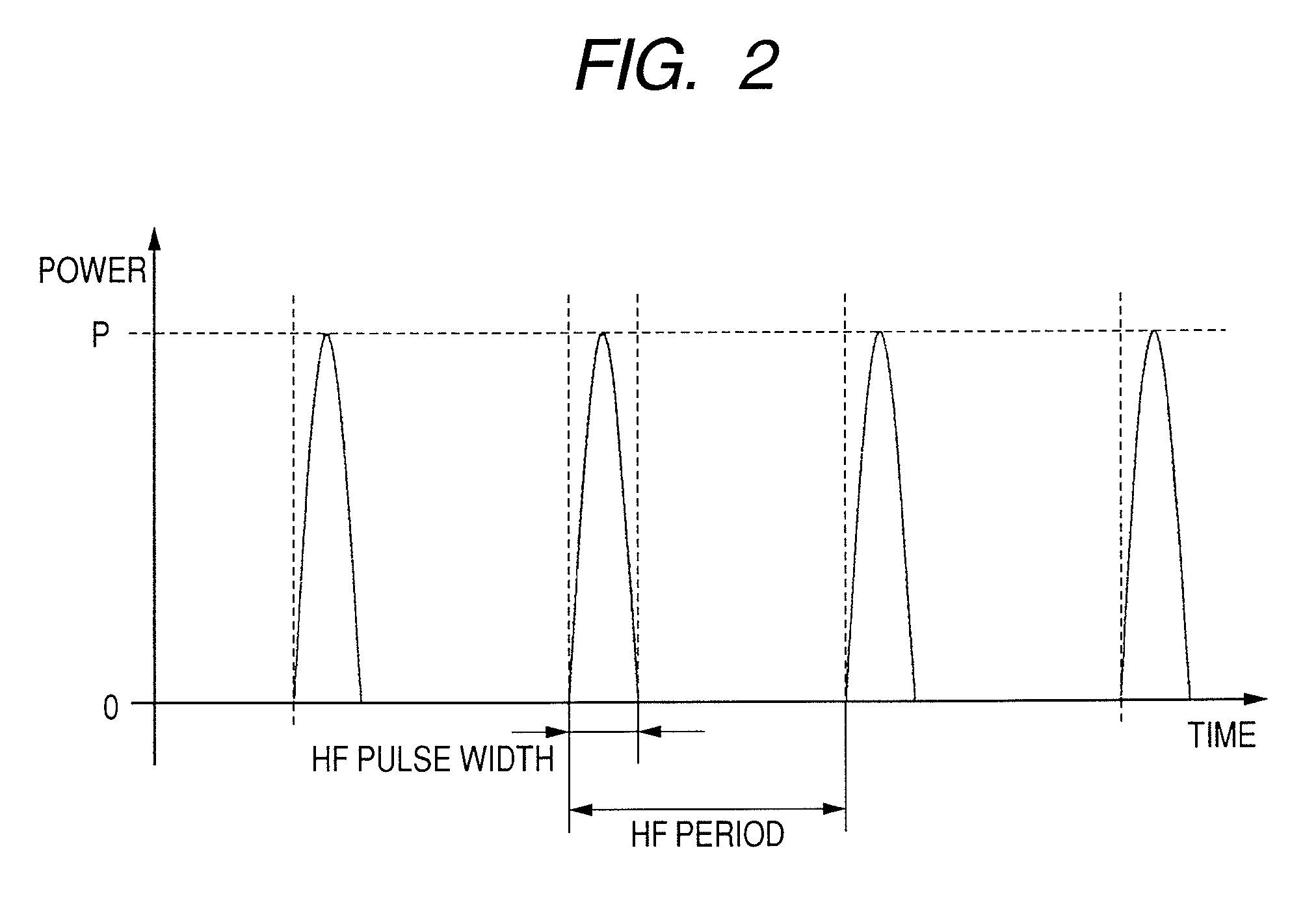
InactiveUS20080219132A1Reduce Laser NoiseImprove reading speedFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesLaser noiseElectrical impulse
An optical disk apparatus is provided which can: prevent an SNR deterioration attributable to an increase in read speed; overcome difficulty in separating a read signal and HF signal components; reduce laser noise; and maintain high reliability even during a high-speed read operation. An optical disk is irradiated with laser light pulsed by a high-frequency signal generated by a HF oscillator. The output of an optical detector which receives laser light reflected from the optical disk is converted into an electric pulse read signal using a current amplifier. The pulse read signal is converted into a temporally continuous read signal using a combination of an AD converter and a DA converter.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus for correcting for the effects of laser noise
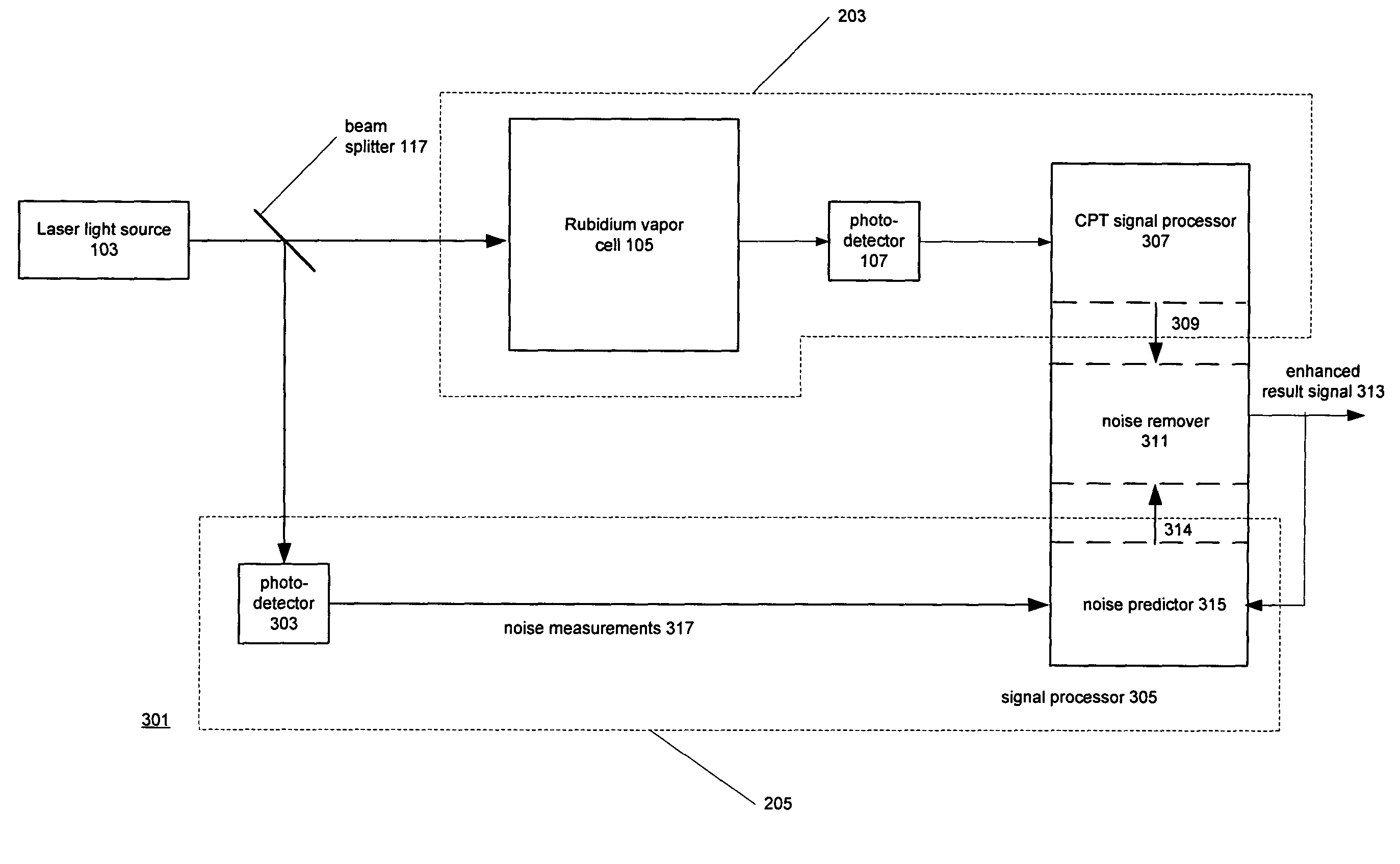
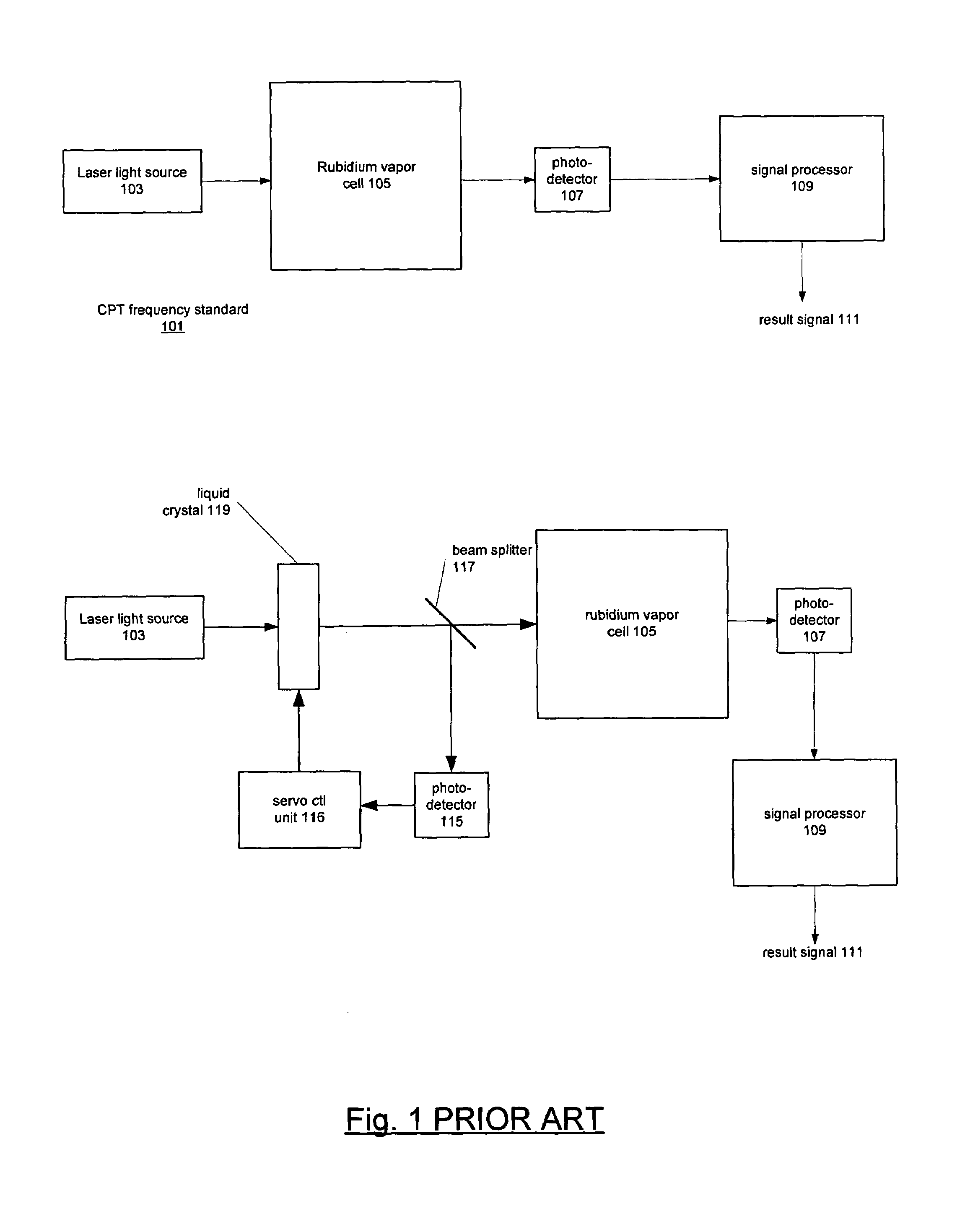
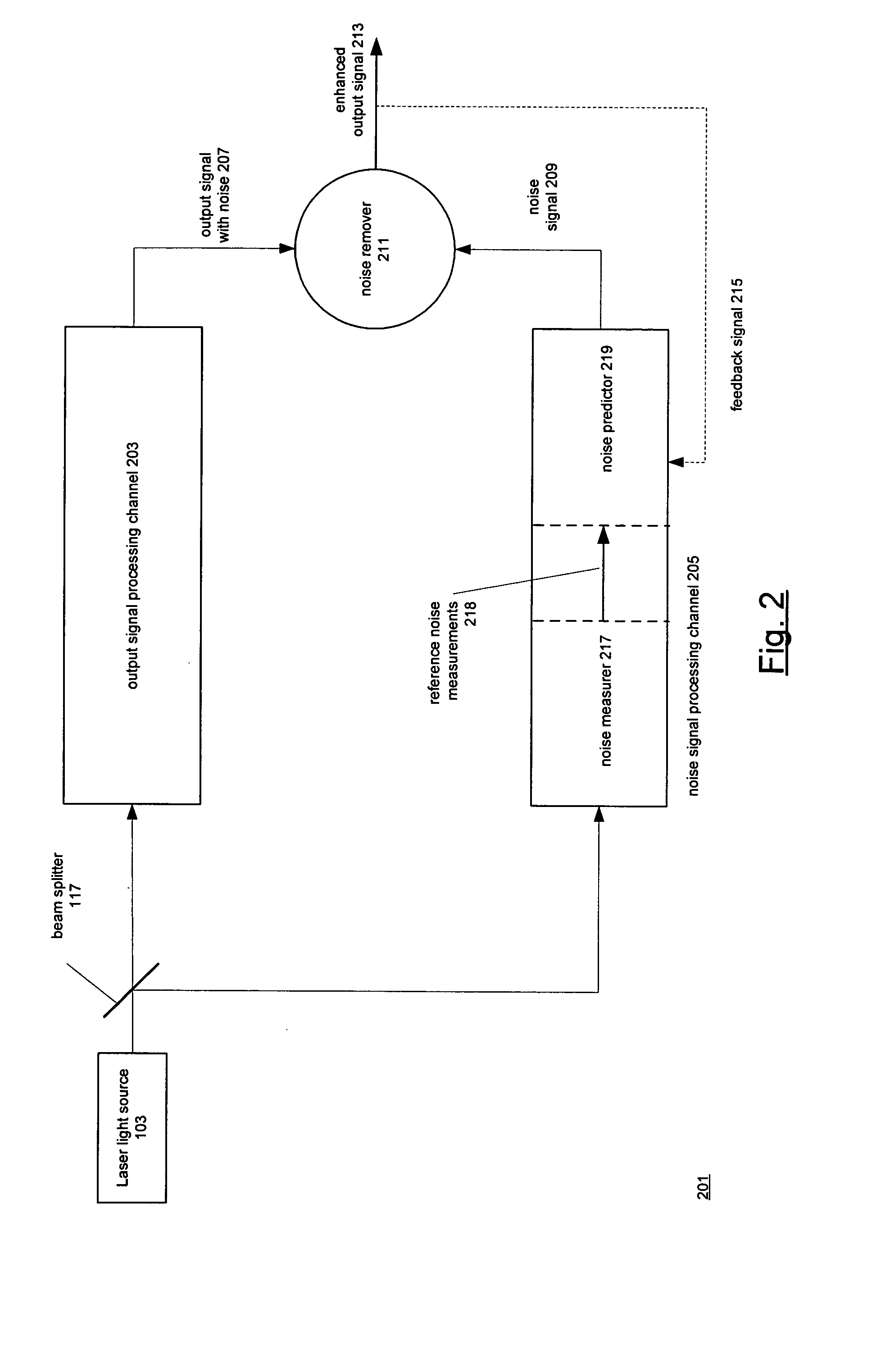
InactiveUS7003438B1Enhanced output signalReduce componentsLaser detailsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePhase noisePhotovoltaic detectors
Adaptive noise reduction techniques used in devices that pass light from a laser through a quantum medium such as a rubidium vapor cell. A CPT frequency standard that employs the techniques has a first channel in which the laser light passes through the quantum medium and to a photodetector to produce a first signal and a second channel in which the light passes to a second photodetector without passing through the quantum medium to produce a second signal. The first and second signals are processed in a signal processor to produce an enhanced output signal in which the noise has been reduced. The signal processor implements noise predictor and noise remover. In a preferred embodiment, the noise predictor employs a FIR filter in which the coefficients are set in response to feedback from the enhanced output signal.
Owner:MICROSEMI FREQUENCY & TIME +1
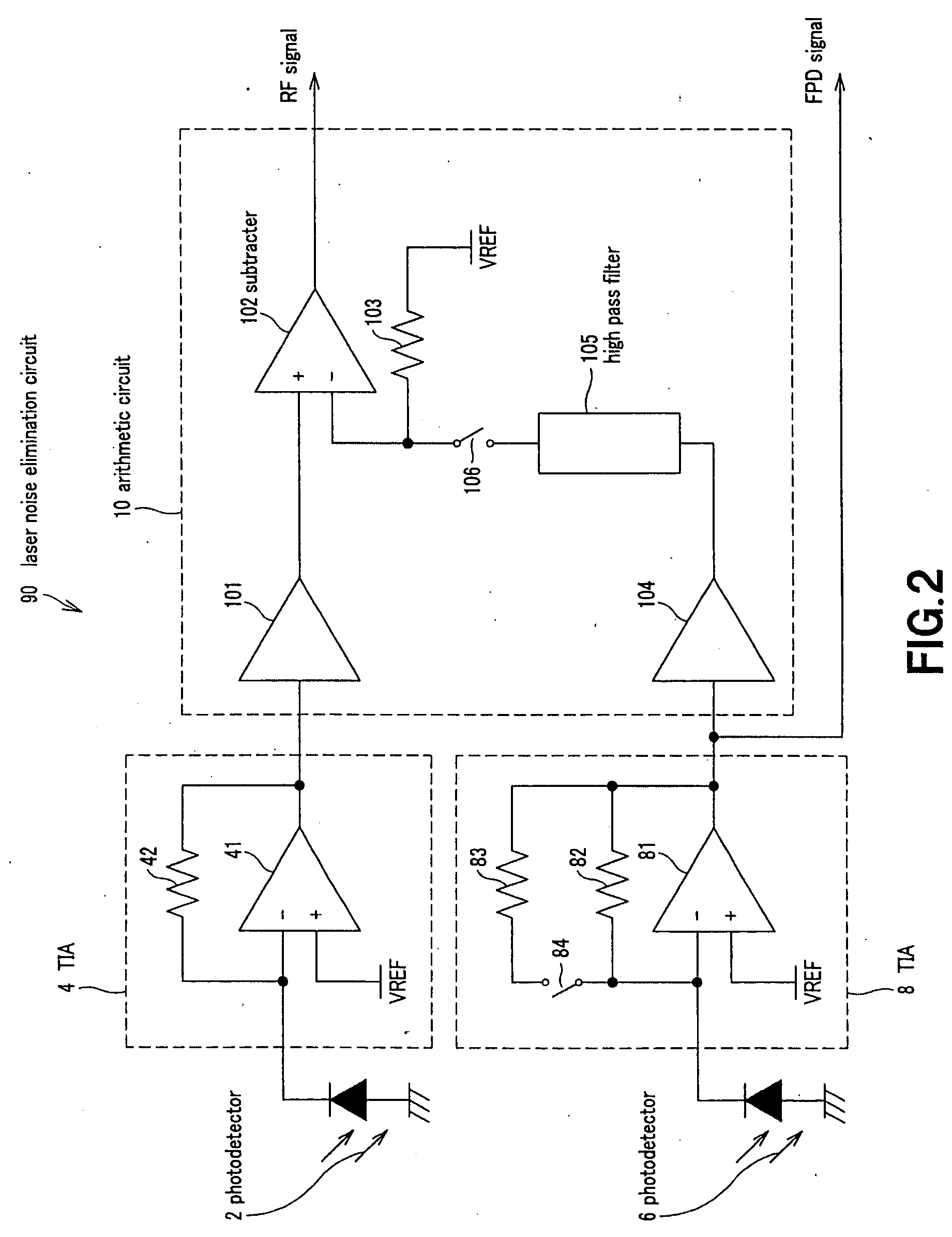
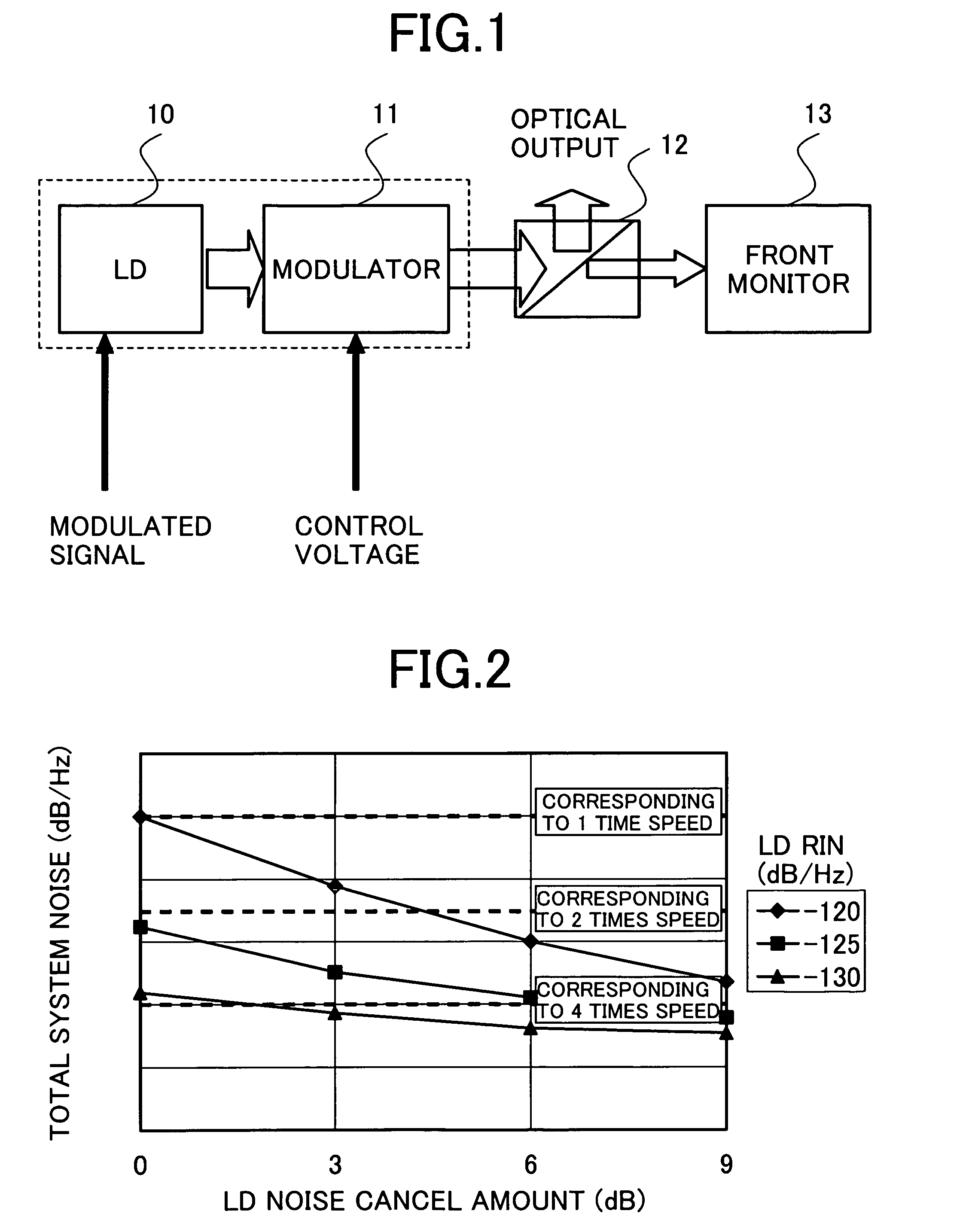
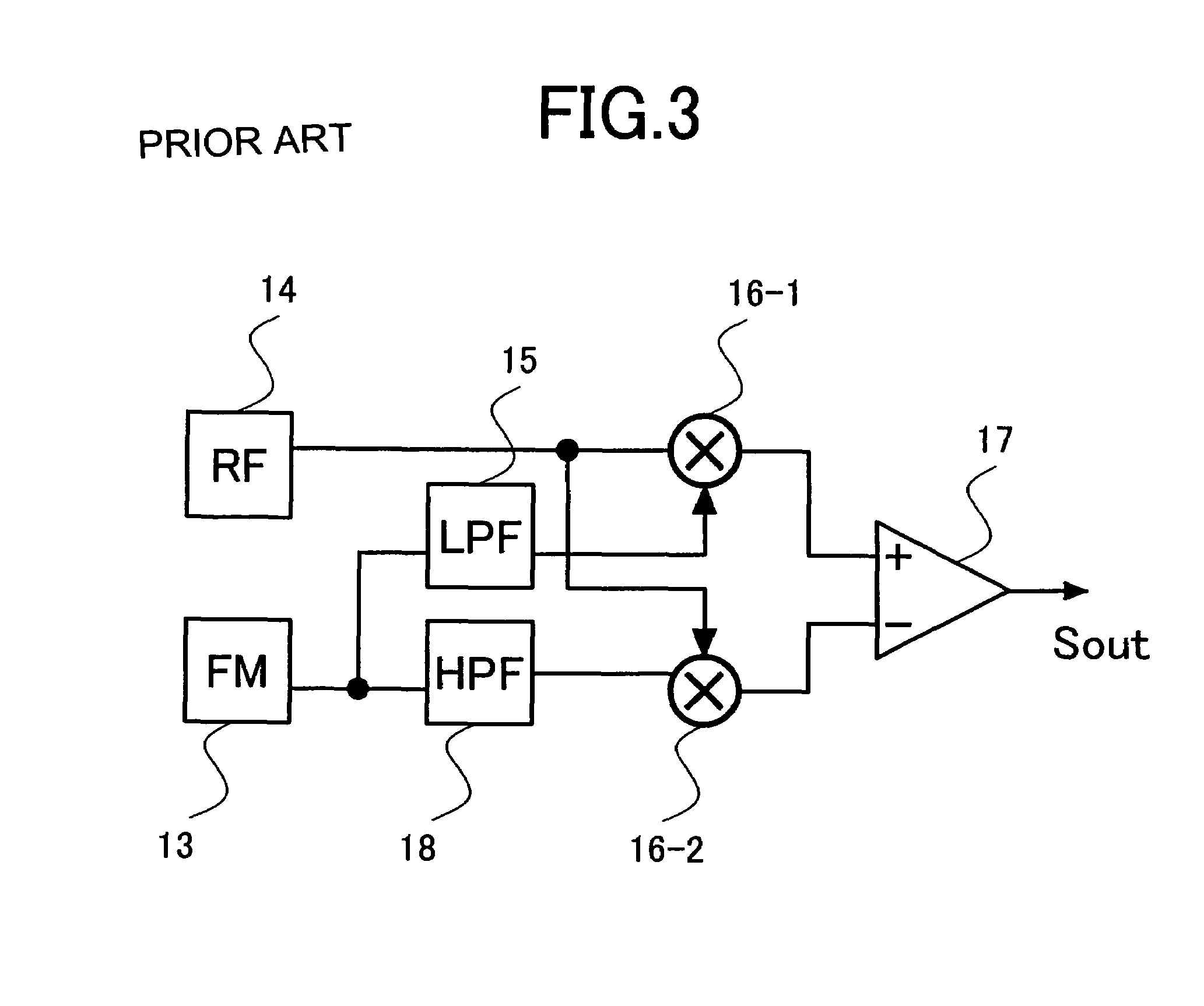
Laser noise cancel circuit and optical disk device
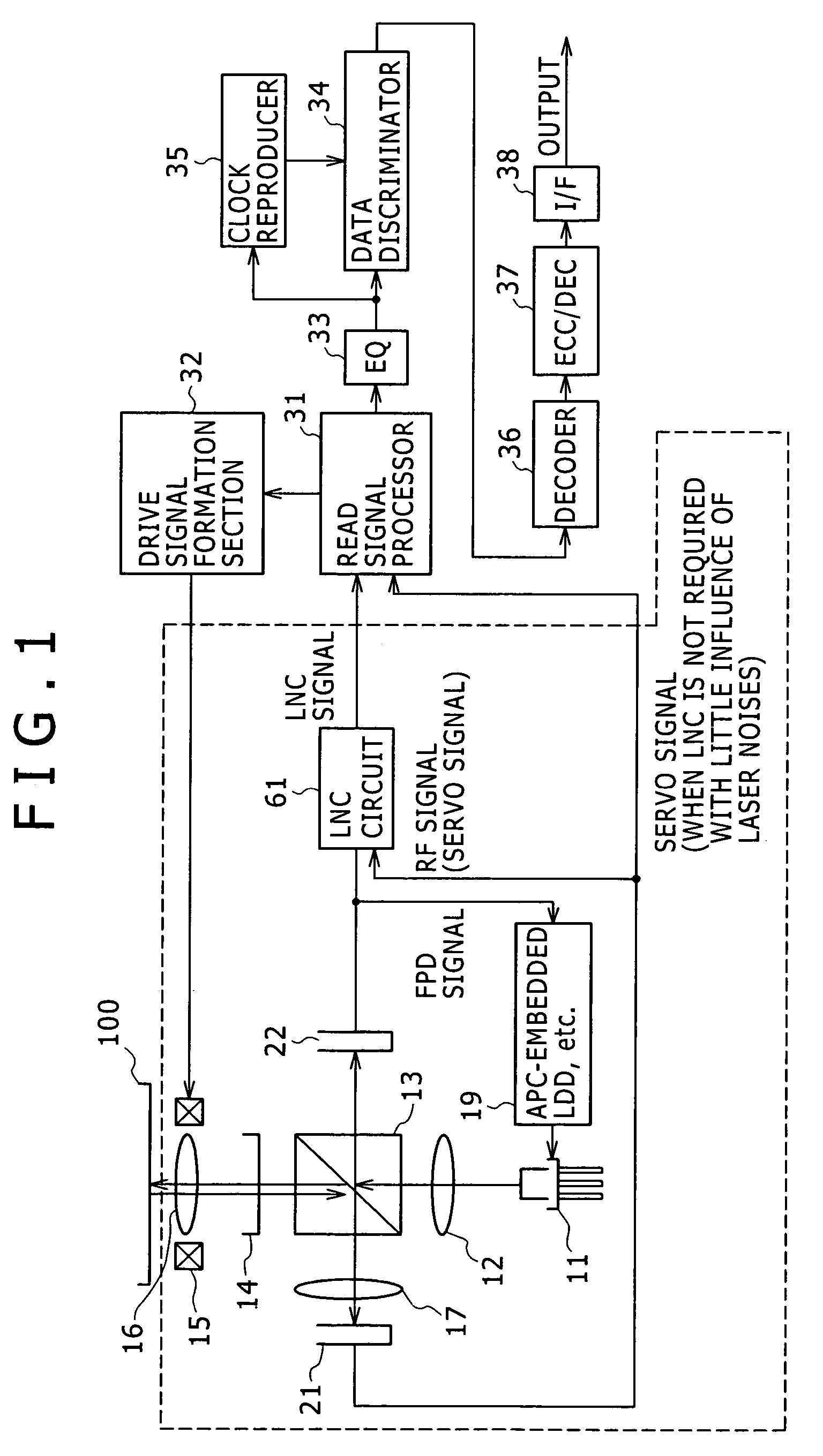
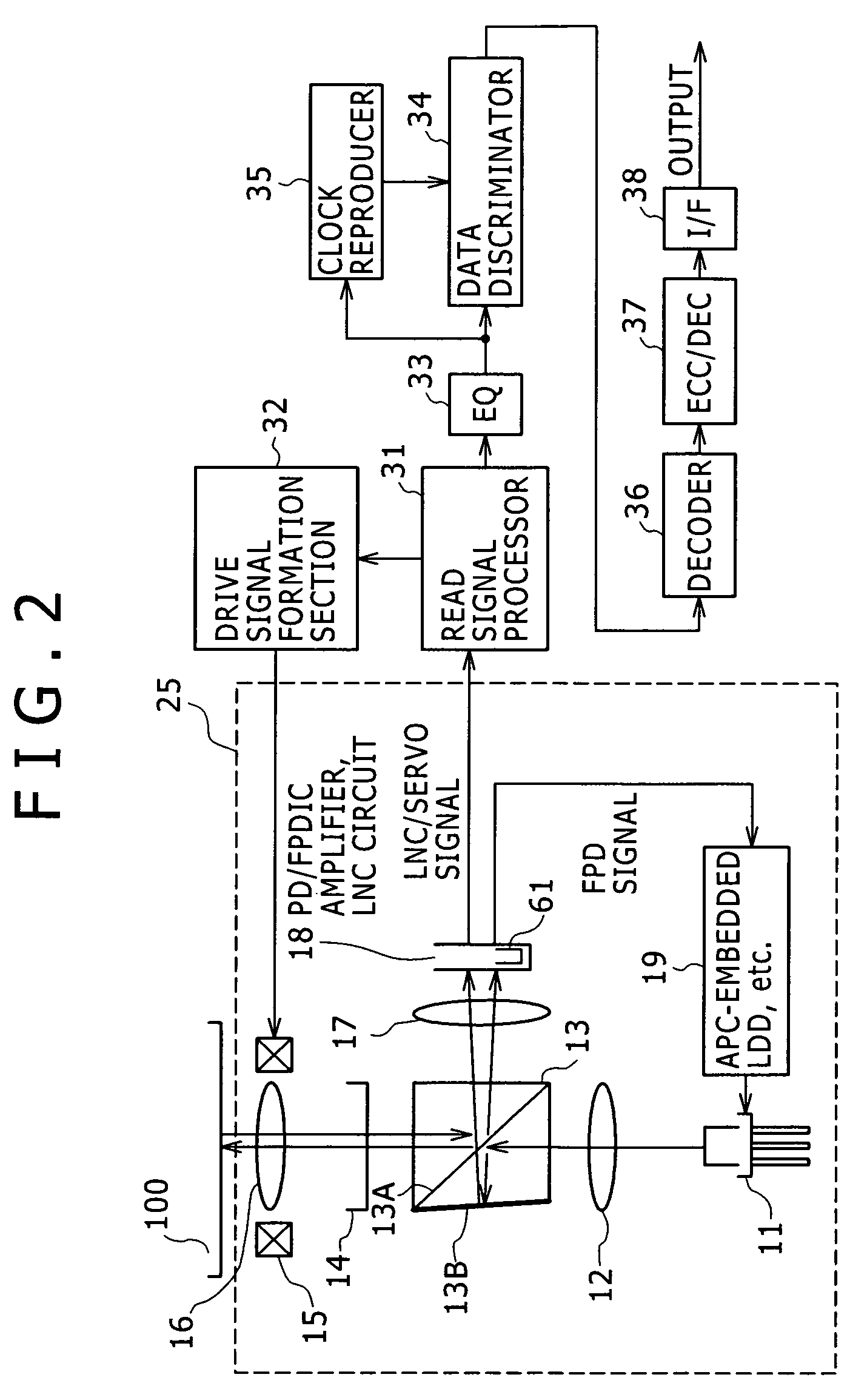
InactiveUS20050265200A1Improve noise reductionWay accurateSignal processing for reducing noiseOptical beam sourcesPhase noiseLow-pass filter
Disclosed herein is a laser noise cancel circuit for reducing laser noises in a reproduction system for an optical disk device including, a gain-variable amplifying noise cancel circuit for amplifying a monitor output signal for laser light, a first low-pass filter for extracting low frequency signal components of a monitor output signal for noise canceling, a second low-pass filter for extracting low frequency signal components, a negative return loop circuit for controlling a gain in the amplifying noise cancel circuit based on the low frequency signal components of the monitor output signal for noise canceling extracted as well as on the low frequency signal components of the reproduced high frequency signal extracted, to determine the low frequency signal component rate of the monitor output signal for noise canceling as identical to the low frequency signal component rate of the reproduced high frequency signal, and an arithmetic circuit for generating the reproduced high frequency signal with the laser noise components cancelled by canceling the laser noise components extracted from the monitor output signal for noise canceling with a low frequency signal component rate determined as identical to the low frequency signal component rate of the reproduced high frequency signal with the laser noise components of the reproduced high frequency signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
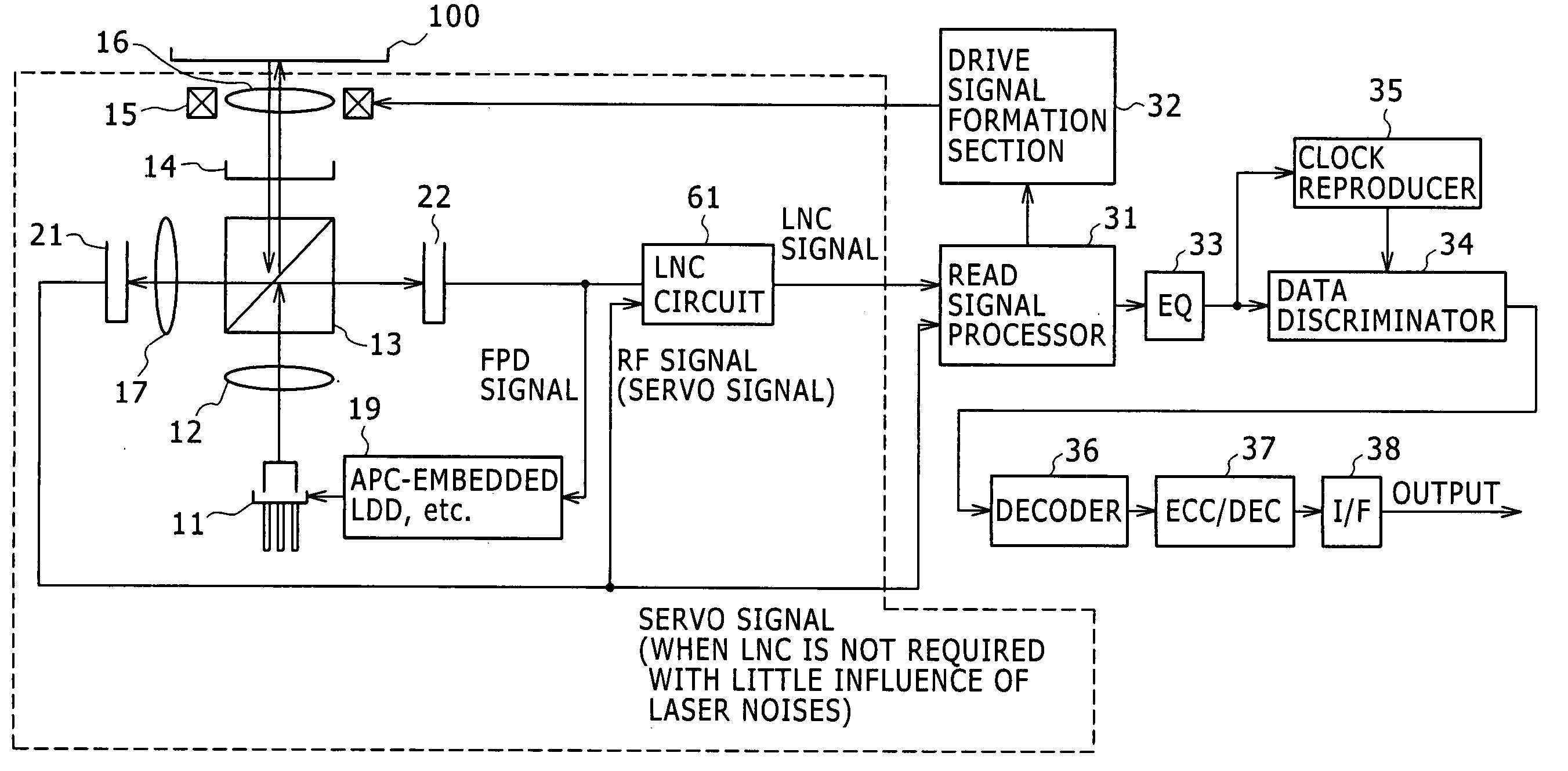
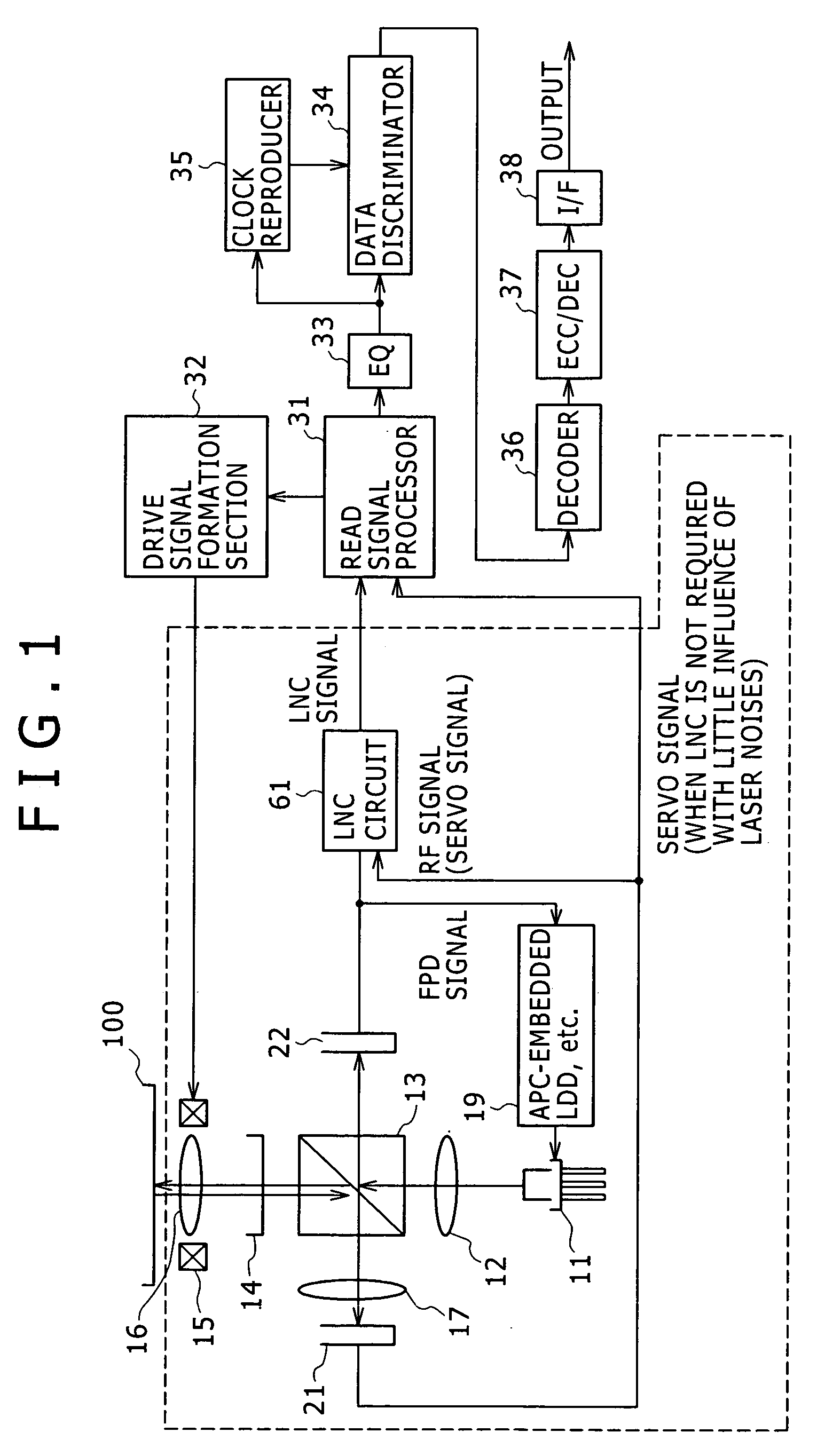
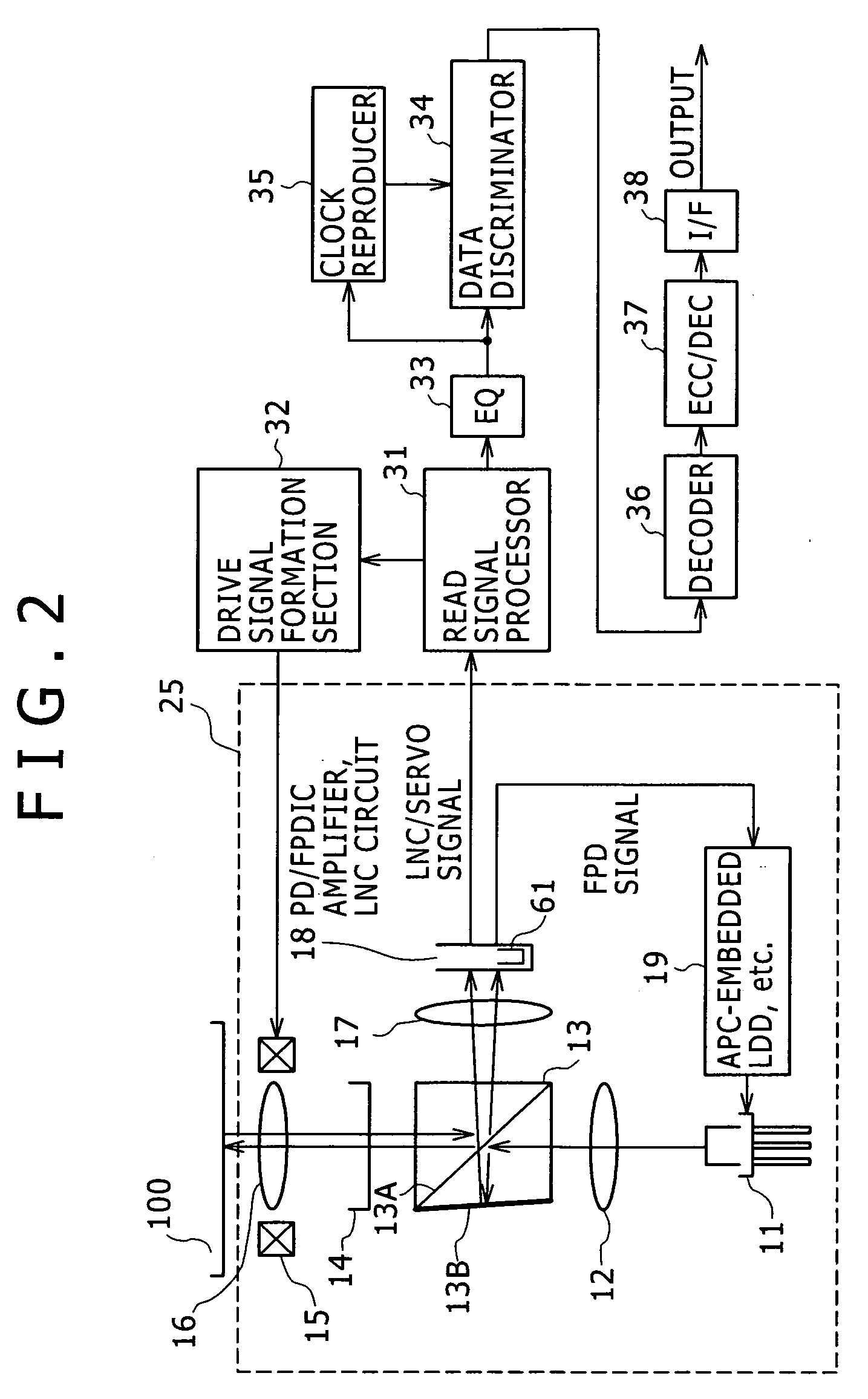
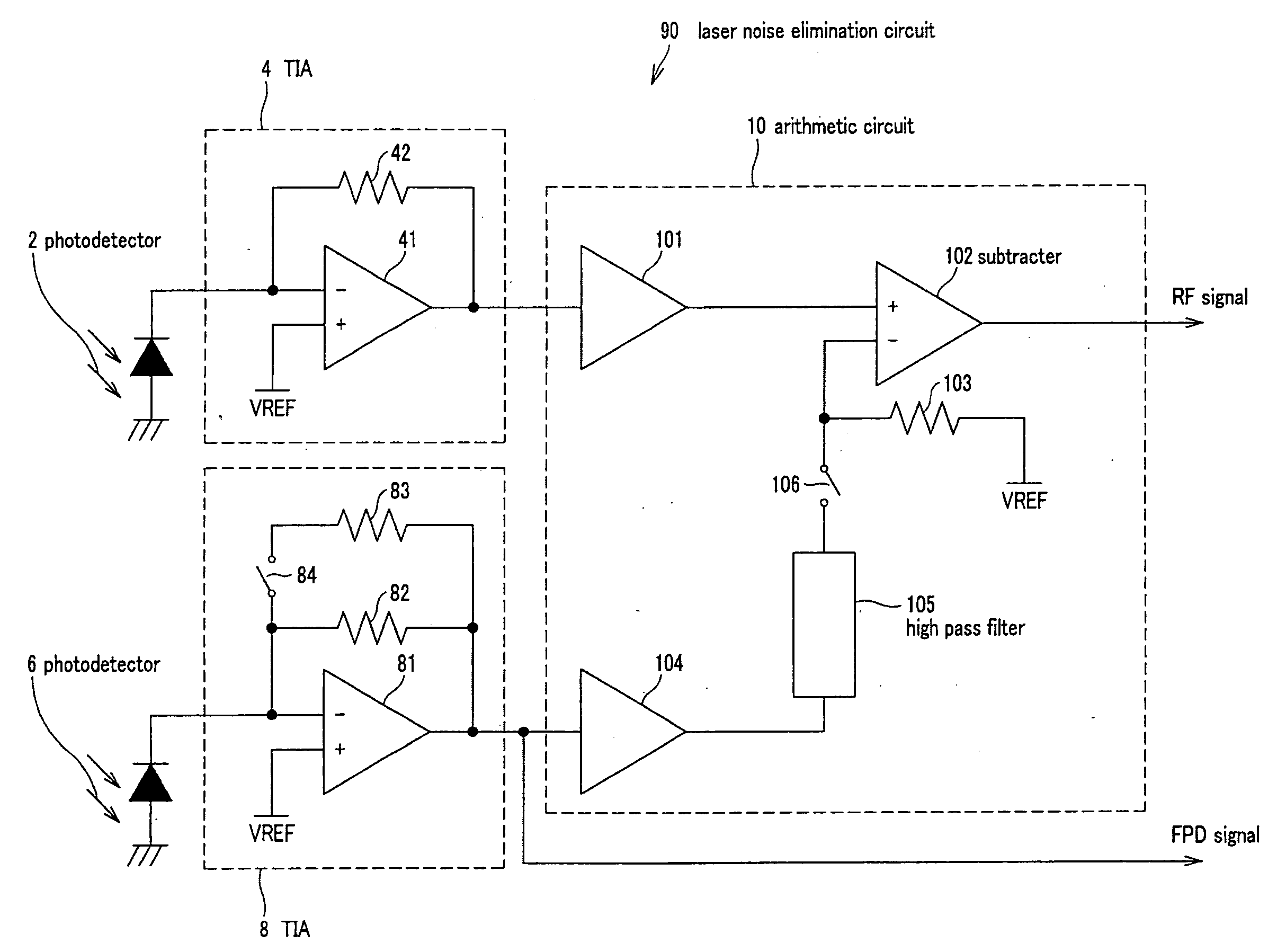
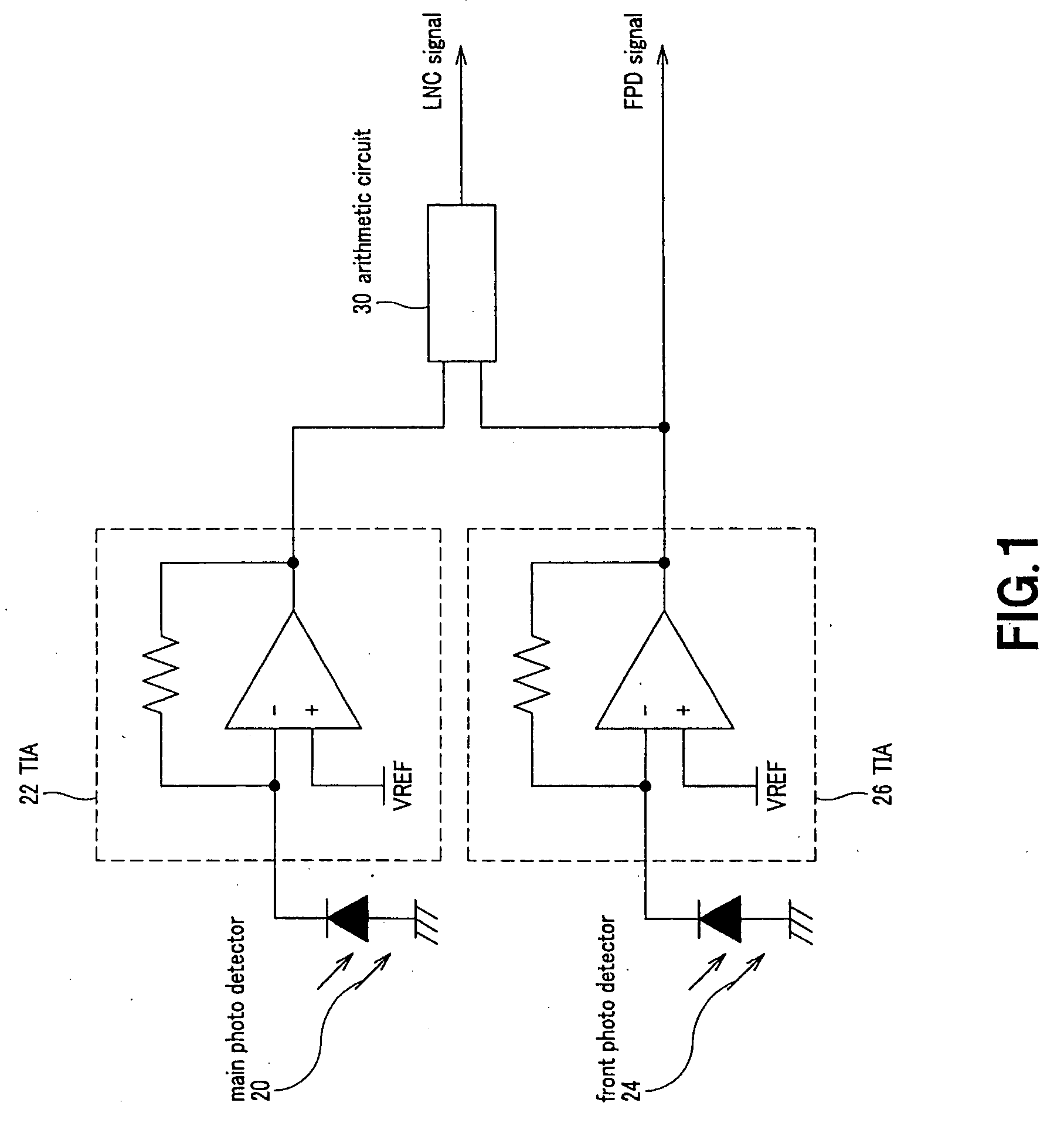
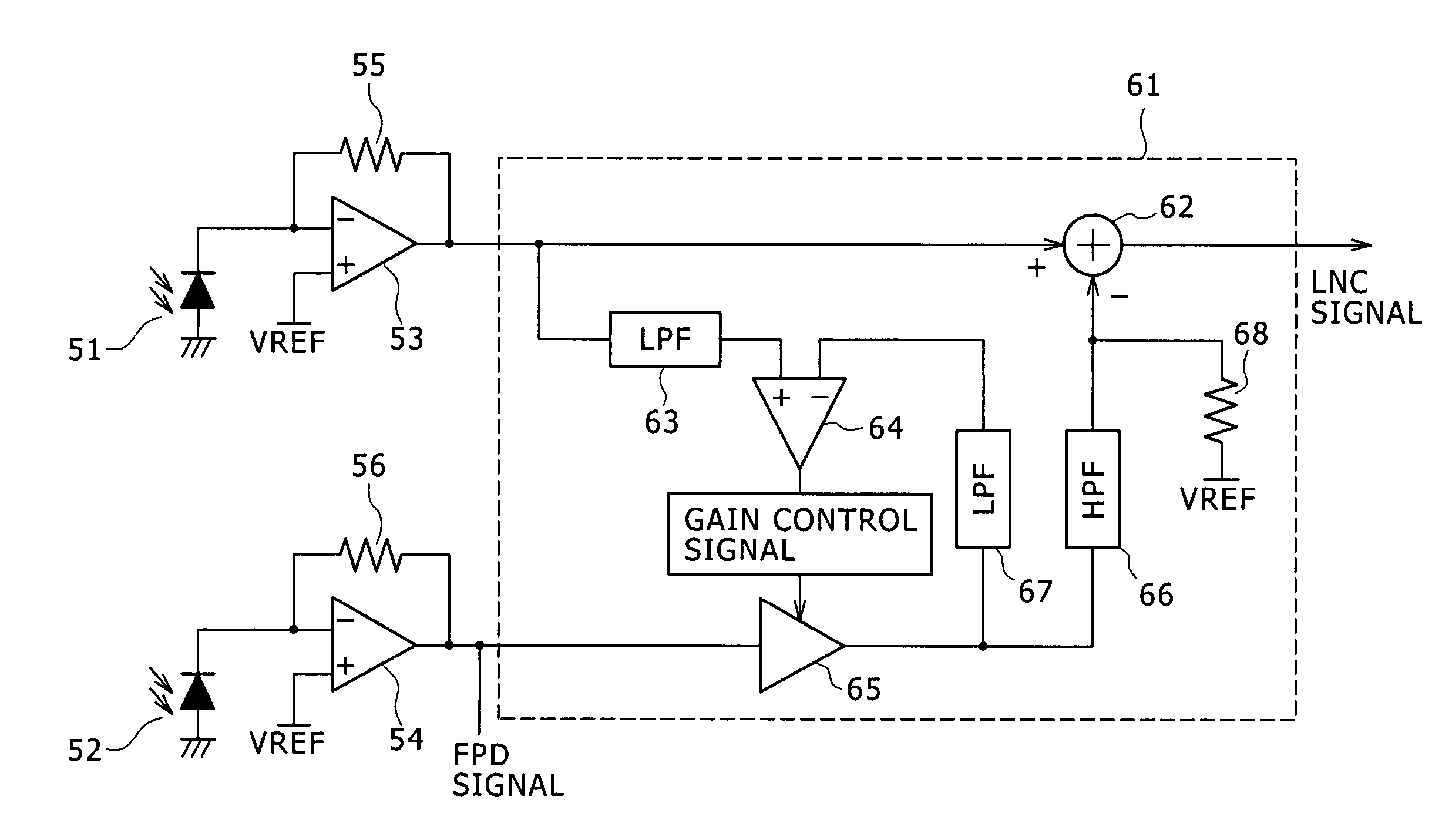
Laser noise elimination circuit and optical disc device
InactiveUS20050135222A1Improved laser levelSmooth APC operationAnalogue recording/reproducingOptical beam sourcesPhotovoltaic detectorsHemt circuits
A laser noise elimination circuit raises the gain of a first TIA and at the same time reflected light from an optical disc of a laser beam is subjected to photoelectric conversion by means of a photo detector and a second TIA to obtain an RF signal. Then, the direct current component of the FPD signal obtained by photoelectric conversion of part of the laser beam by means of another photo detector and the first TIA is cut out by a high pass filter and then subtracted by a subtracter. The gain of the first TIA is raised in a read mode of operation for reading data from the optical disc and lowered in a write mode of operation for writing data onto the optical disc so as to always effectively eliminate only the laser noise from the RF signal and prevent the circuit from being saturated in a write mode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Low noise all solid-state blue laser resonant cavity
InactiveCN101060229ASimple structureLow noise long-term stable output requirementsOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialLow noiseFull wave
The disclosed low-noise full-solid blue laser resonant cavity for I-type phase matching multiple frequency crystal comprises: a semi-conductor laser; on the pumping light direction, a coupling lens, a laser crystal with a standard tool and quartz crystal full-wave sheet between the crystal and an I-type phase matching multiple frequency crystal, and an output lens. This invention improves output stability and reduces laser noise efficiently.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Array type wide-temperature laser module
The invention relates to the field of laser application, in particular to an array type wide-temperature laser module capable of adjusting the laser power and the stability. The array type wide-temperature laser module is characterized in that by combined application of a plurality of laser modules 1, a beam shaping lens groups are added into different positions, so that the power and the stability of the wide-temperature laser module under the extreme temperature are improved, the temperature width of the module is improved in a disguised manner, and simultaneously the noise frequency of the output beam is improved; and when the array type wide-temperature laser module is used on specific equipment and instruments, the perception of the visual system of a person for the problems of fluctuation and line breaking and the like caused by the laser noise is not sensitive. The array type wide-temperature laser module comprises a laser module array, wherein the laser module array at least comprises two laser modules with different temperature bandwidth; and laser beams emitted by the laser module array form a bundle of synthetic beam after being shaped by a beam shaping system and an afocal optical system.
Owner:QINGDAO LASENCE
Optical disc apparatus and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS8000211B2Increase powerRaise the ratioOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageLaser noiseLaser beams
An optical disc apparatus capable of obtaining an effect to reduce the laser noise without shortening the laser diode service life or increasing the power consumption. The optical disc apparatus includes a laser diode for emitting a laser beam, a laser driver for driving the laser diode, a detector for monitoring a first power emitted from the laser diode, a detector for monitoring a second power applied to an optical disc, and an attenuator for attenuating the first power. The light attenuation factor of the attenuator is changed by the ratio between the first power and the second power.
Owner:HITACHI-LG DATA STORAGE +1
Single-shot laser signal-to-noise ratio detection device
ActiveCN103048053BImprove time resolutionHigh strengthLaser detailsInstrumentsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise detection
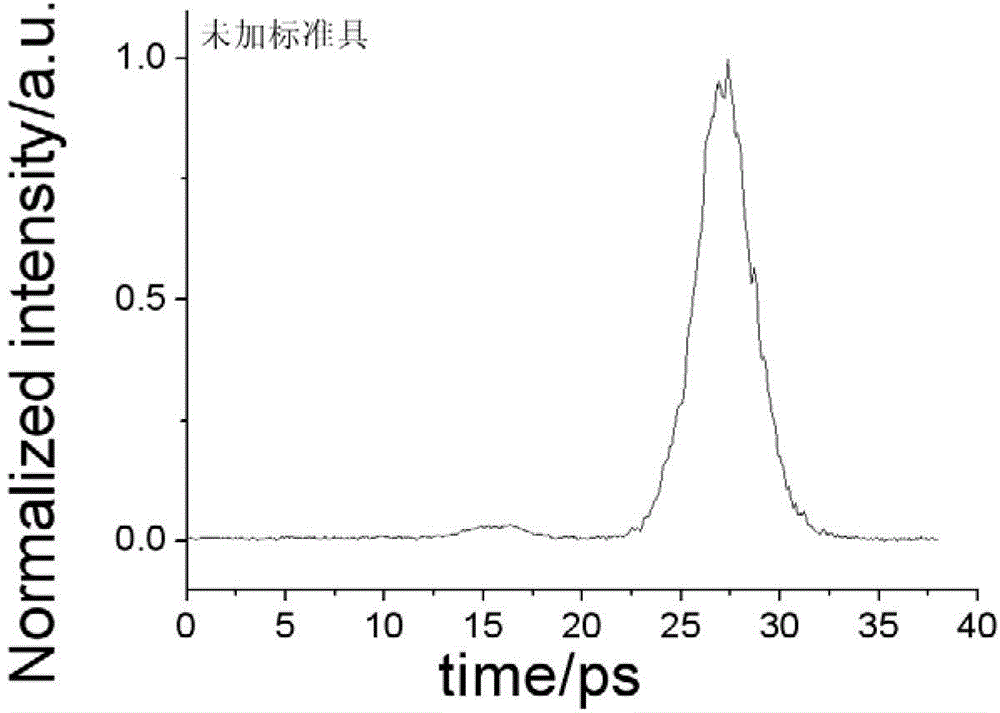
The invention relates to a single laser signal-to-noise detection device. A single pulse delay unit on a light path of signal light is saved, a beam contractor is arranged on a light path of shutter light, the shutter light is transmitted from one side of the beam-expanded signal light to the other side, and only when the shutter light exists, the signal light can reach the detector through an optical Kerr shutter, and then the signal light is subjected to space scanning and sampling by the shutter light, with continuous time. The time resolution is mainly determined by the optical Kerr response and relaxation time of the material, the optical Kerr response and relaxation time of same material can be only several dozens of femtoseconds, and the time resolution is higher in comparison with the prior signal-to-noise detection device,.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical pick-up and optical recording medium recording/reproduction apparatus
InactiveUS20050226126A1Small sizeReduce thicknessLaser detailsOptical beam sourcesRefractive indexLaser noise
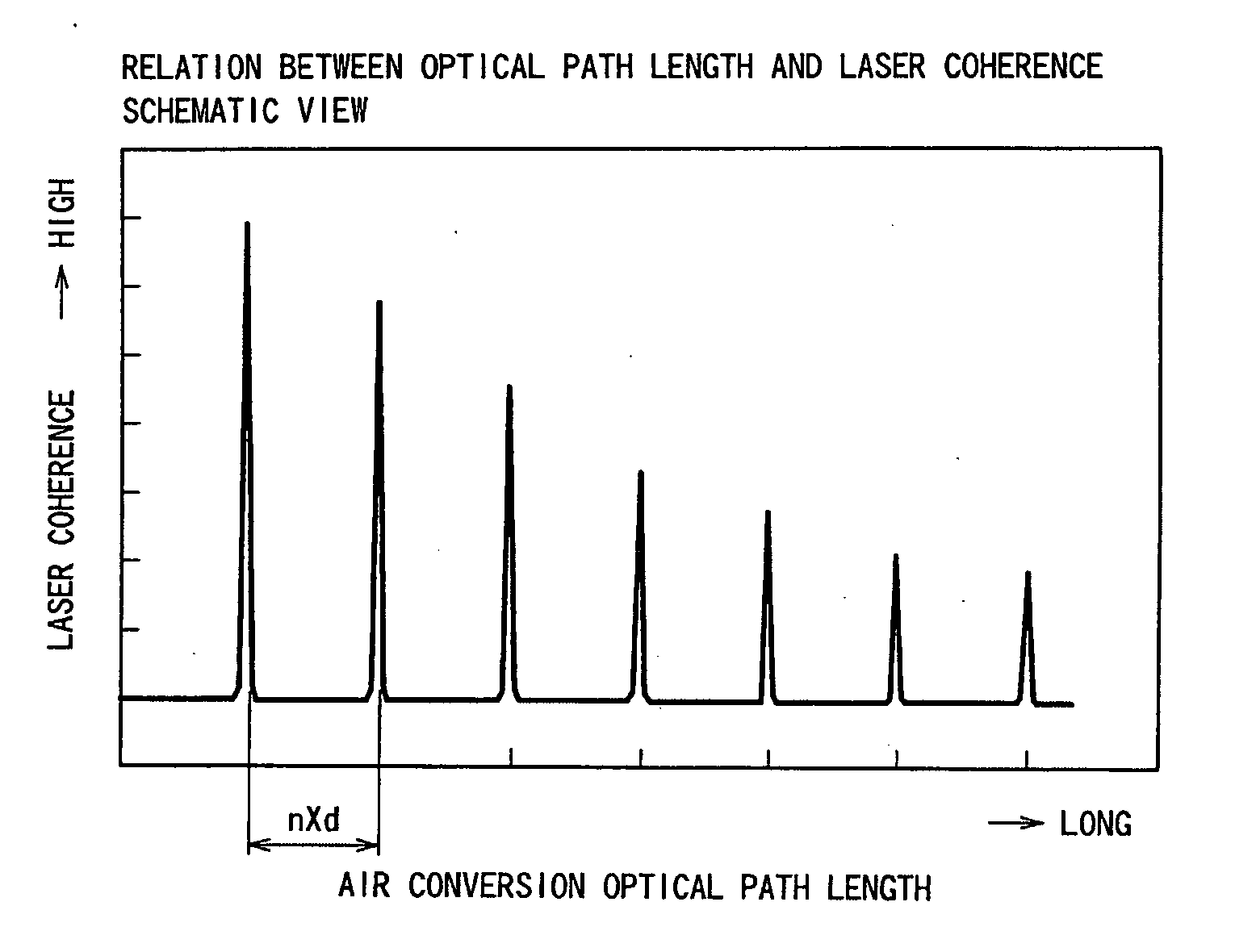
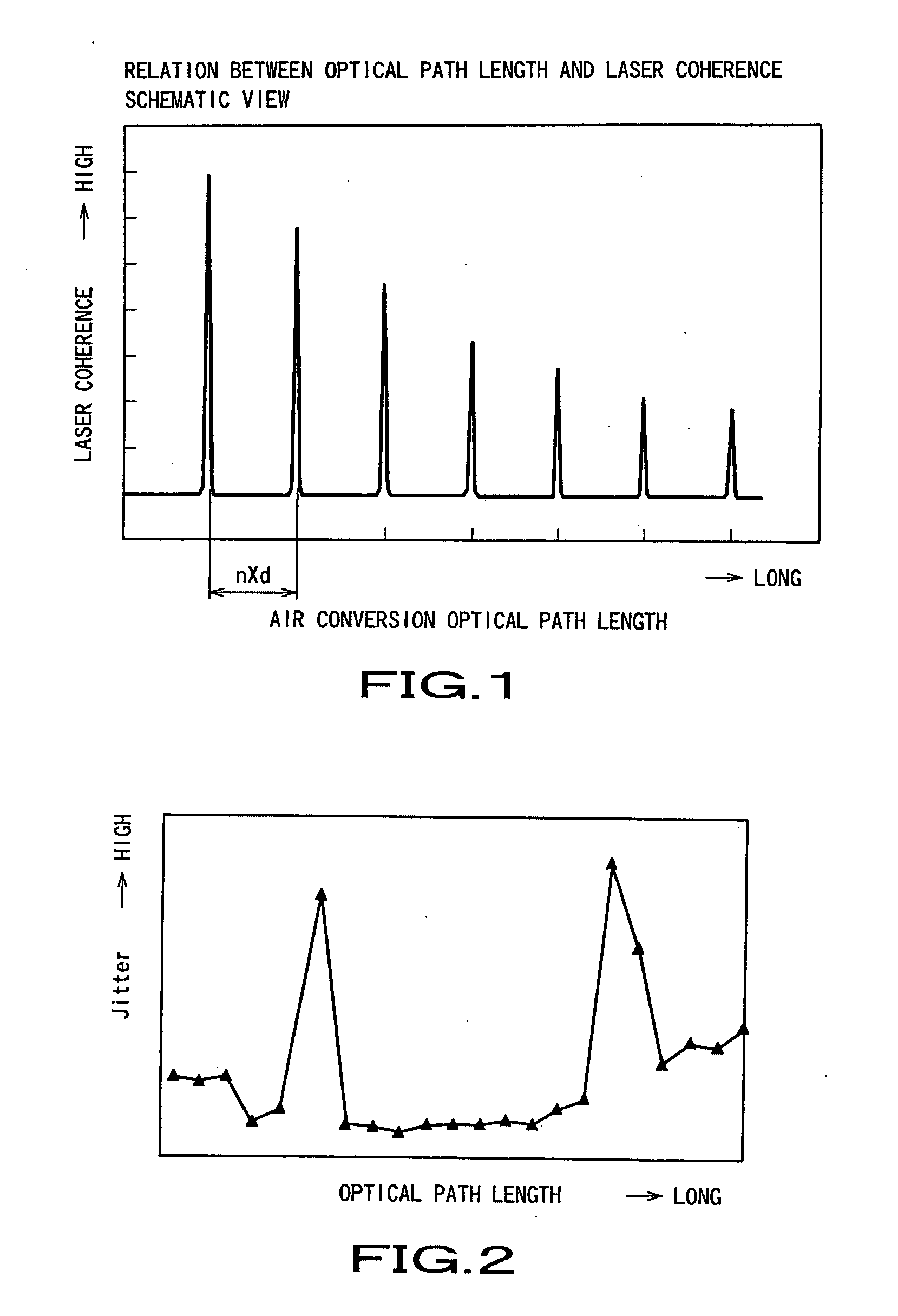
The range of air conversion optical path length L of all optical components in the forward passage of an optical system between a laser emission point and the surface of a disc-shaped recording medium is determined by: i(n0×d)+ΔL / 2<L<(i+1)(n0×d)−ΔL / 2(i is an arbitrary integer) where d is resonator length of a laser diode, n0 is active layer refractive index of the laser diode, and ΔL is acceptable surface blurring in the specification of the disc-shaped recording medium, thereby reducing laser noise (optical feedback noise) that is generated when emitted laser beam from a laser diode is interfered with the optical feedback, which is a part of laser beam that has been focused on the recording surface of the disc and has moved back through the forward passage of the optical system to return to the laser diode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Random fiber laser generating method and system
PendingCN110176712AIncrease powerReduce noiseActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseRayleigh scattering
The invention provides a random fiber laser generating method and system. The random fiber laser generating system comprises an excitation light generation subsystem and a random fiber laser resonantcavity, wherein the excitation light generation subsystem generates two paths of excitation light with stable time domain; the two paths of excitation light with stable time domain are injected into the random fiber laser resonant cavity from the forward direction to the backward direction separately; and the random fiber laser resonant cavity performs random fiber laser generation depending on distributed raman gain and random rayleigh scattering feedback under the pumping of excitation light. The excitation source with the stable time domain is adopted for pumping a random raman fiber laserto inhibit high-order raman stokes random fiber laser and output laser noise, high-power and low-noise random fiber laser output is achieved, and a new idea is provided for the design of optical fibersources in the fields of multi-point detection, optical fiber sensing, optical imaging and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Optical disk apparatus
InactiveUS7969838B2Prevent an SNR deteriorationImprove reading speedFilamentary/web record carriersOptical beam sourcesLaser noiseElectrical impulse
An optical disk apparatus is provided which can: prevent an SNR deterioration attributable to an increase in read speed; overcome difficulty in separating a read signal and HF signal components; reduce laser noise; and maintain high reliability even during a high-speed read operation. An optical disk is irradiated with laser light pulsed by a high-frequency signal generated by a HF oscillator. The output of an optical detector which receives laser light reflected from the optical disk is converted into an electric pulse read signal using a current amplifier. The pulse read signal is converted into a temporally continuous read signal using a combination of an AD converter and a DA converter.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Optical recording and reading equipment
InactiveUS7502302B2Transmissivity decreaseImprove efficiencyCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsUltrasound attenuationPhase noise
Disclosed herewith is a data recording and reading equipment capable of reducing laser noise easily. At first, a laser beam source that can reduce the laser noise when reading data from a subject optical disk is obtained. A modulator capable of varying laser attenuation with a voltage is disposed so as to precede the laser, thereby the laser noise when reading data from the optical disk can be reduced without lowering the laser power when in writing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
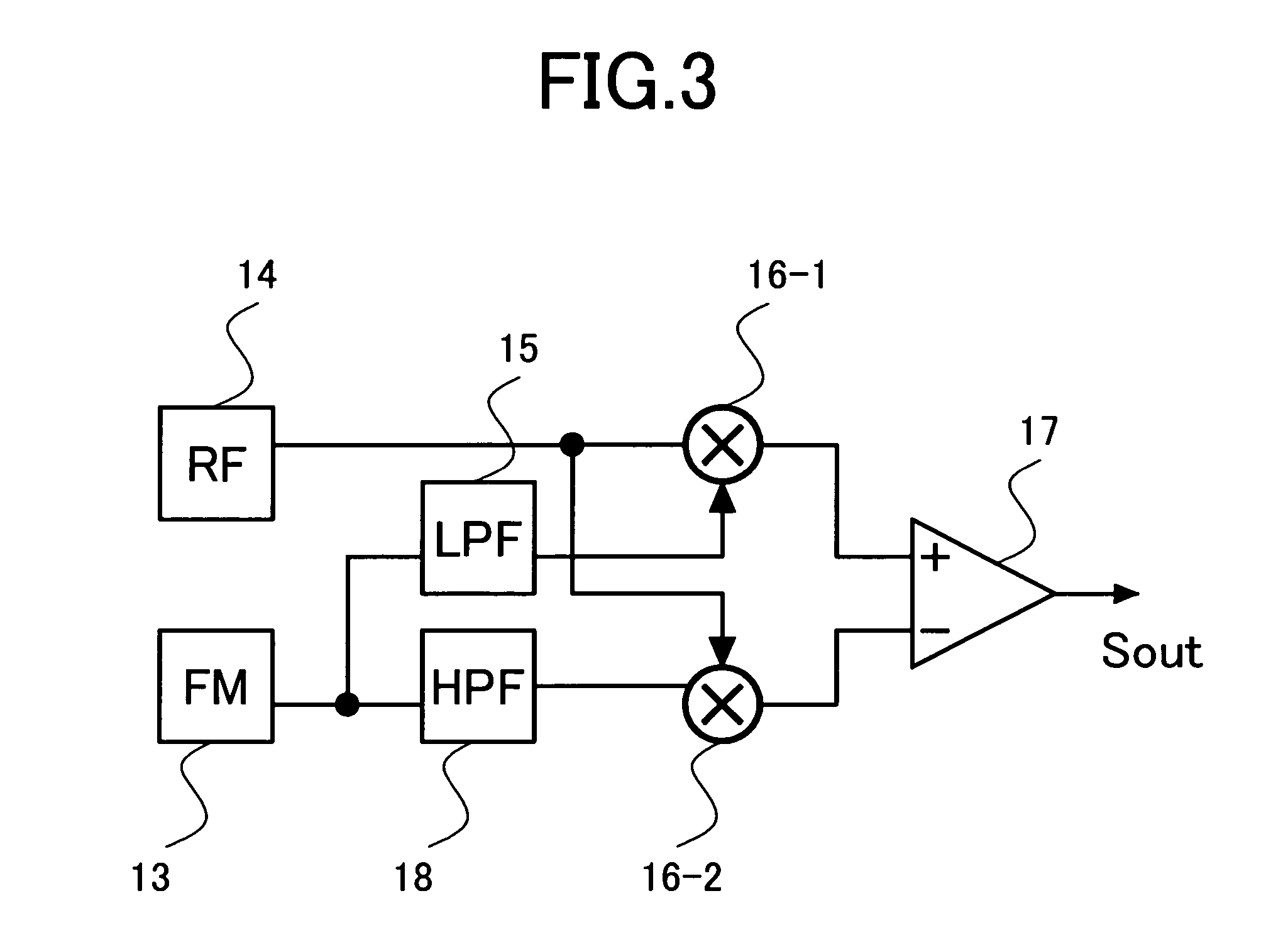
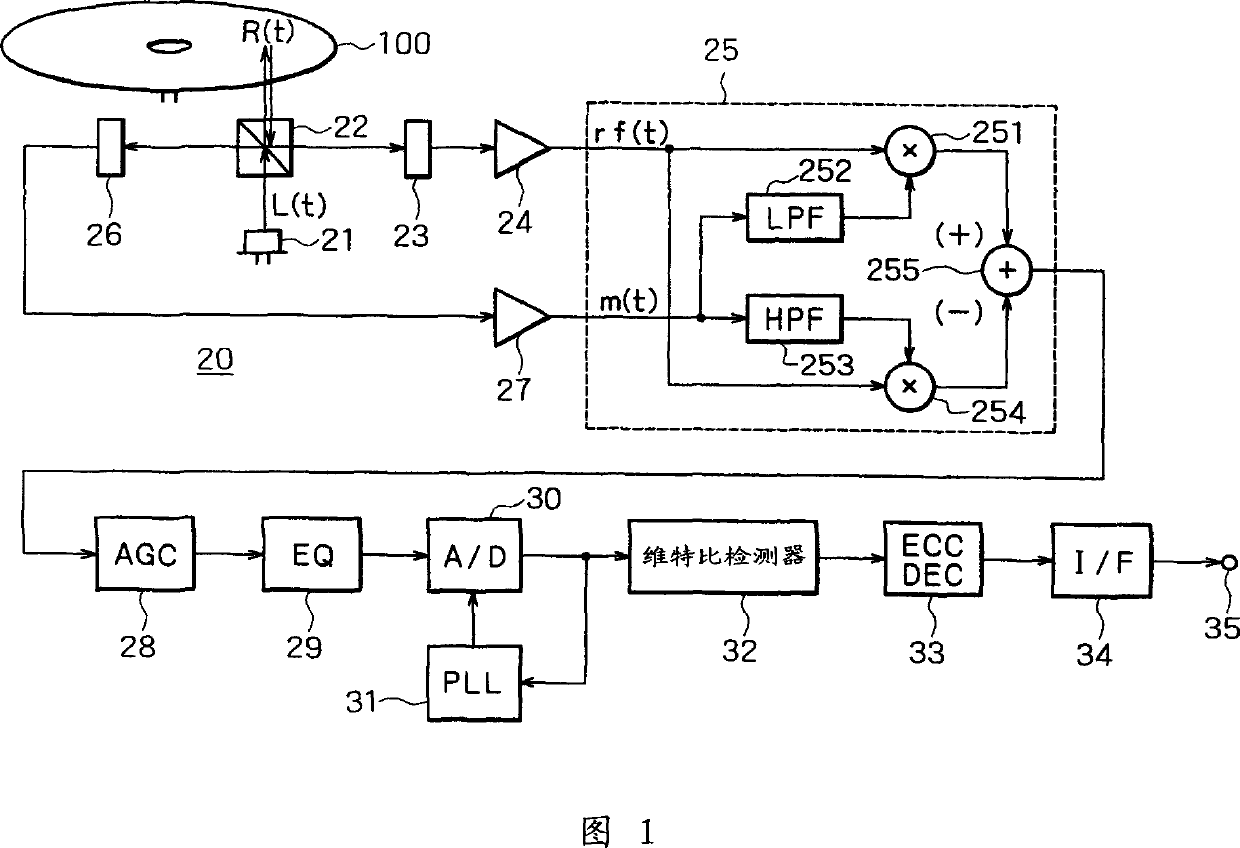
Optic disc replaying device, optic disc recording and replaying device and laser noise clearing circuit
InactiveCN1365105AEasy to removeModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseLaser noiseRadio frequency
A first multiplier 251 multiplies a reproduced RF signal rf(t) by a DC component of an APC monitoring output signal m(t), which component is an output signal from an LPF 252, and then supplies a signal resulting from the multiplication to an arithmetic unit 255. A second multiplier 254 multiplies the reproduced RF signal rf(t) by a laser noise component of the APC monitoring output signal m(t), which component is an output signal from an HPF 253, and then supplies a signal resulting from the multiplication to the arithmetic unit 255. The arithmetic unit 255 subtracts the signal from the multiplier 254 from the signal from the multiplier 251 to thereby remove both an additive noise component and a modulated noise component of laser noise.
Owner:SONY CORP
Laser noise cancel circuit and optical disk device
InactiveUS7149232B2Improve noise reductionWay accurateLaser detailsSignal processing for reducing noisePhase noiseLow-pass filter
Owner:SONY CORP
Structure For Optical Pickup Head
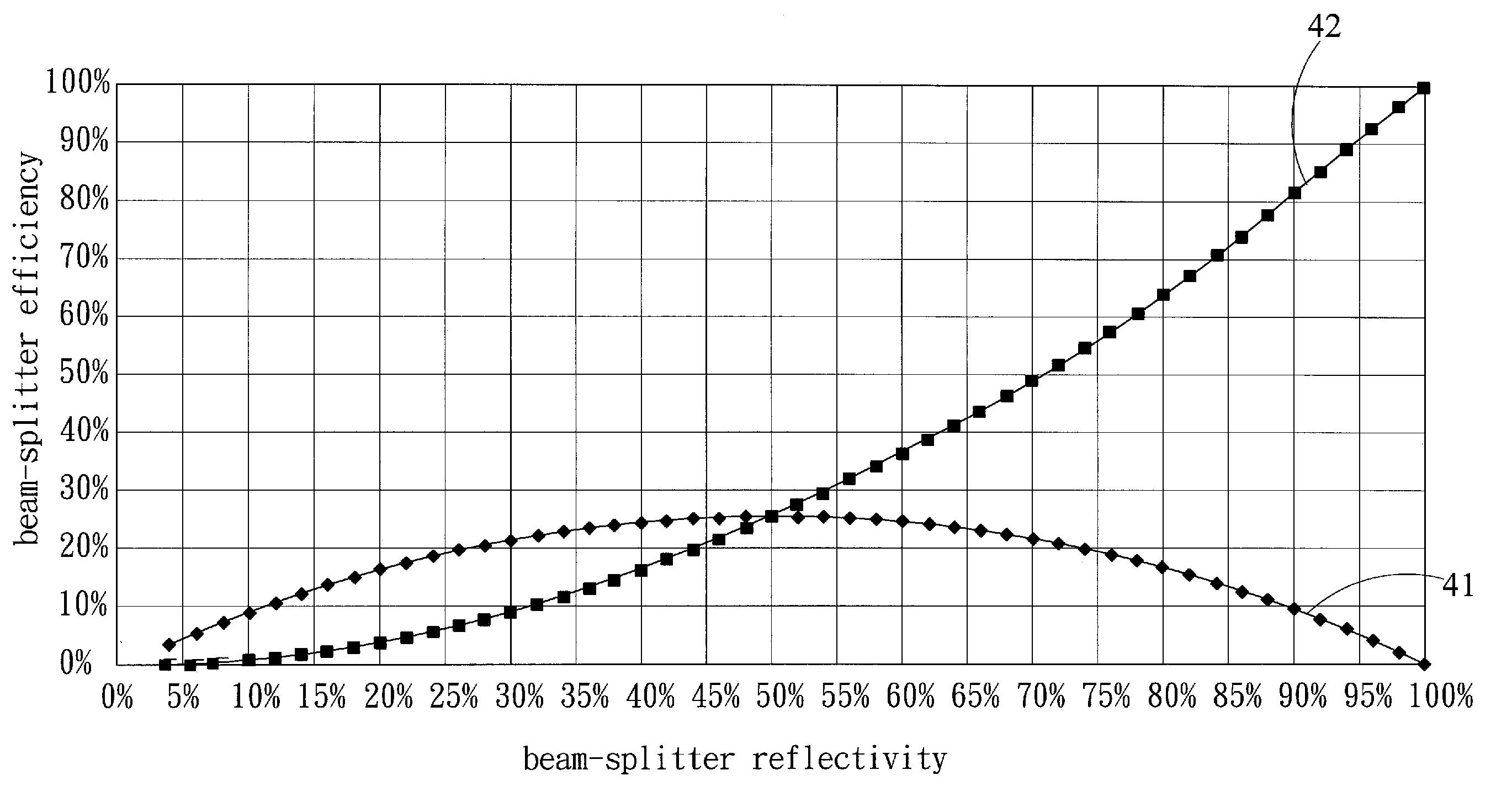
InactiveUS20110051587A1Reduce noiseImprove optical efficiencyRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansOptical pickupBeam splitter
An optical pickup head is provided, including a laser diode set, an optical element set and an optical signal detector. The laser diode set is a laser light source capable of emitting single wavelength, two wavelengths or three wavelengths laser lights. Optical element set includes a low reflectivity beam-splitter and an objective lens. The low reflectivity beam-splitter has an average reflectivity ranging from 10% to 30%. After reflected twice by low reflectivity beam-splitter, the light fed back from recording medium to the laser diode set is reduced to avoid laser noise problem. Moreover, with the optical signal detector having a tilt θ ranging from 3° to 15° to optical axis, the optical signal detector can directly reflect the incident laser light into a different direction so that the reflected light will reduce the feedback light to the laser diode set.
Owner:TOPRAY MEMS
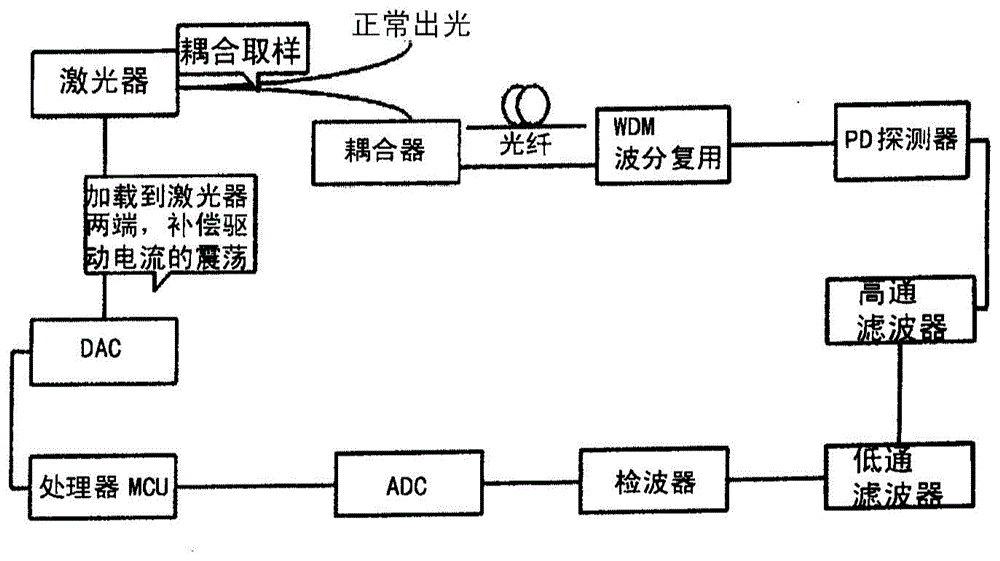
Laser noise reduction device and method for noise reduction by using same
ActiveCN104934852AAvoid noiseThe principle of the method is simpleLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhotovoltaic detectorsWorking environment
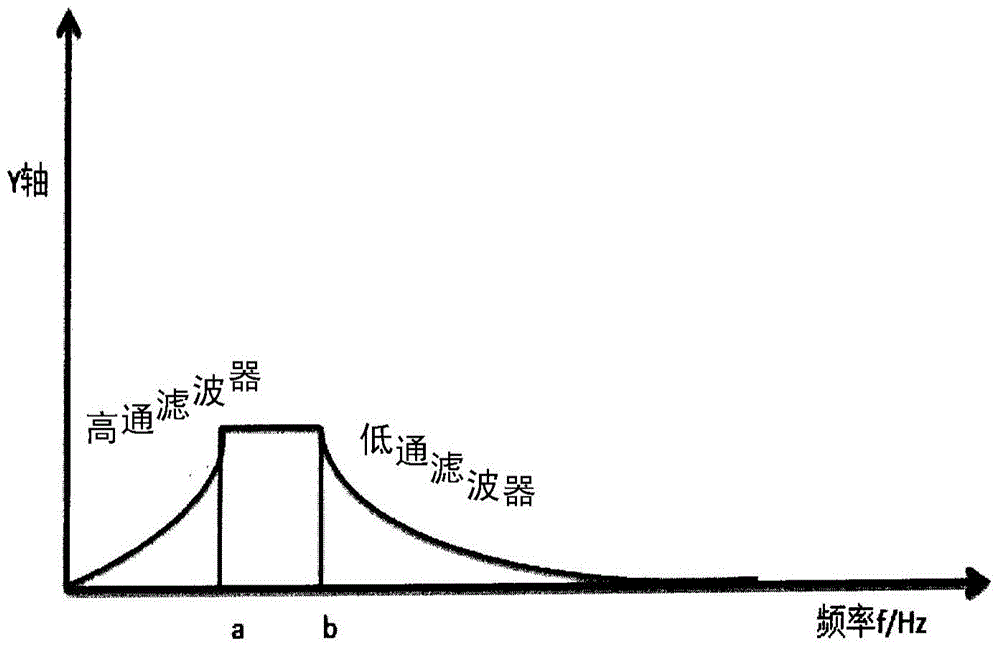
The invention relates to a laser noise reduction device and a method for noise reduction by using the same. The device comprises a laser, two couplers, a wavelength division multiplex (WDM), a plurality of optical fibers, an optical fiber delay line, a photoelectric detector (PD), a high-pass filter, a low-pass filter, a detector, an analog-to-digital conversion chip (ADC), a main control unit (MCU) and a digital-to-analog conversion chip (DAC). By the method, the noise problem of the laser caused by unstable current is effectively prohibited, laser stability is enhanced, the high-pass filter, the low-pass filter, the detector, the ADC, the DAC and the MCU all can be integrated onto a circuit board, the laser noise reduction device is compact and convenient, the integration of all components needed by the method on the laser is promoted, convenience and stability are achieved, and particular working environment is not needed. The laser noise reduction method is applicable for all noise problems caused by unstable current.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three dimensional sensor laser noise reduction method
InactiveUS6930763B2Reduce speckle noiseEliminating mechanical motion errorsOptical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementLaser noiseLaser light
A method for improving the accuracy of measurements made in non-contact gauging an object utilizing a detector to observe a laser line projected onto a surface of the object. A combination of detector lens f-number adjustments, surface scatter statistics, and laser coherence control are utilized to reduce speckle noise in the structured light gauge measurement system without the use of moving mechanical parts. This eliminates added mechanical motion errors and maximizes detectable laser light.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Noise suppression device of a fiber laser based on a double fiber ring filter
InactiveCN109256663ASuppress noiseAvoid mode hoppingActive medium shape and constructionLow noiseGrating
The invention discloses a fiber laser noise suppression device based on a double fiber ring filter, which comprises a constant temperature vibration isolation shell, a fiber laser arranged in the constant temperature vibration isolation shell, a double fiber ring filter, a Bragg grating and a grating coupler. The double optical fiber ring filter is coupled into a double optical fiber ring structure by a first optical fiber ring and a second optical fiber ring through a grating coupler, The first optical fiber ring of the double optical fiber ring filter comprises a first port and a second port, wherein the first port is connected with the optical fiber laser, and the second port is an output port of the low-noise laser processed by the device; The Bragg grating consists of a Bragg gratingwhich is photolithographically etched on an optical fiber and is welded to a second optical fiber ring of the dual optical fiber ring filter. The invention realizes the laser noise suppression throughthe slow light effect of the double optical fiber ring filter to increase the photon lifetime in the cavity, the whole structure is simple and there is no photoelectric conversion module, and the whole suppression bandwidth is greatly improved.
Owner:南京聚科光电技术有限公司
Three-dimensional laser noise reduction method and device, medium and robot
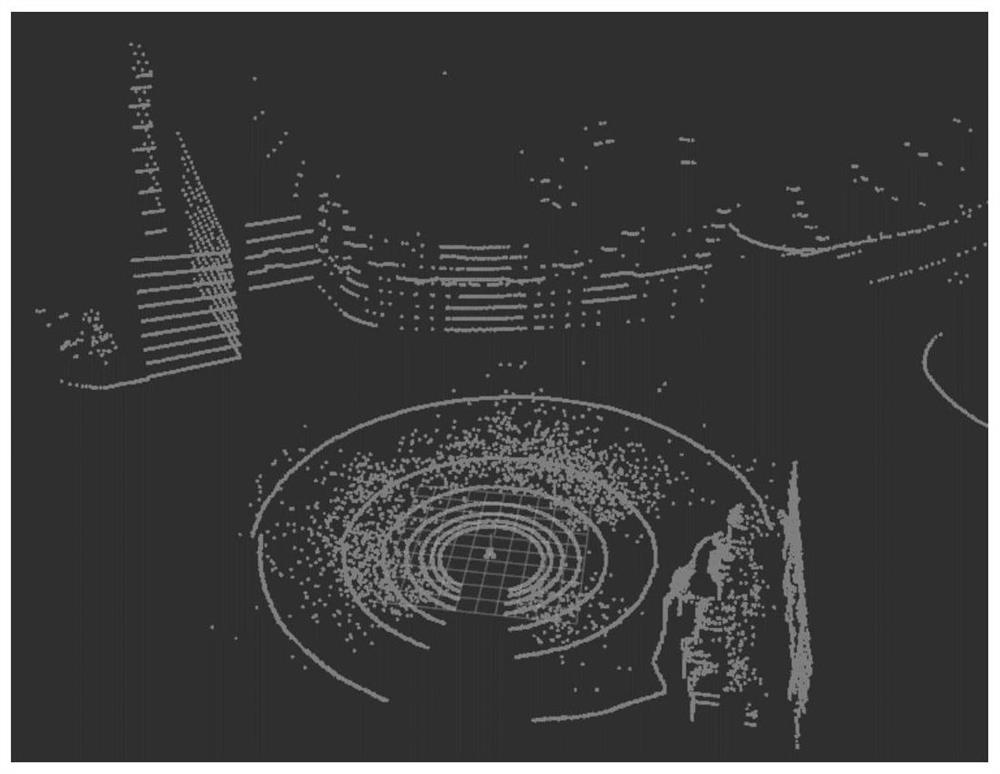
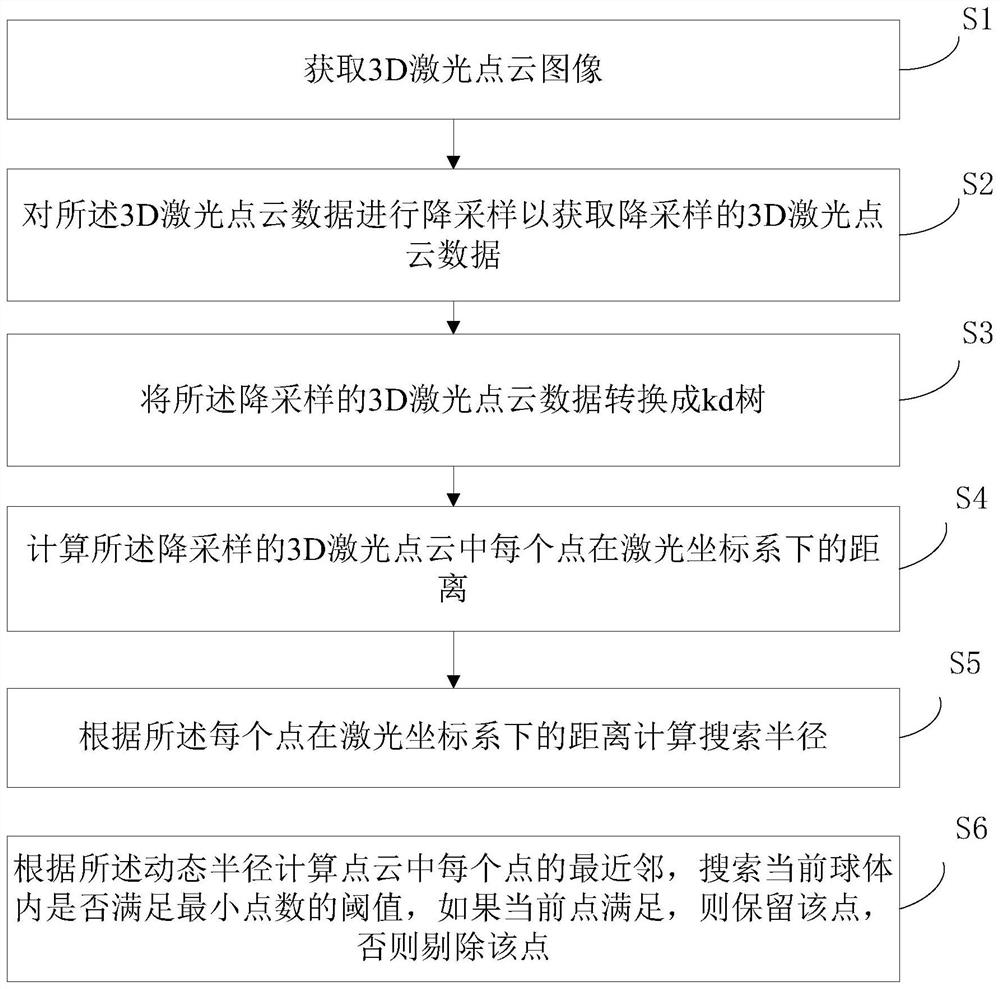
PendingCN114708400AImplement automatic settingsGood removal effectImage enhancementImage analysisSnow removalPoint cloud
The invention provides a three-dimensional laser noise reduction method and device, a medium and a robot. The three-dimensional laser noise reduction method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a 3D laser point cloud image; s2, carrying out downsampling on the 3D laser point cloud data to obtain downsampled 3D laser point cloud data; s3, converting the down-sampled 3D laser point cloud data into a kd tree; s4, calculating the distance of each point in the down-sampled 3D laser point cloud under the laser coordinate system; s5, calculating a search radius ri according to the distance of each point in the laser coordinate system; and S6, calculating the nearest neighbor of each point in the point cloud according to the dynamic radius, searching whether the threshold value of the minimum point in the current sphere is satisfied, if the current point is satisfied, retaining the point, and otherwise, rejecting the point. According to the three-dimensional laser noise reduction method provided by the embodiment of the invention, noise in snow removal weather can be effectively removed.
Owner:广州高新兴机器人有限公司
Laser module
PendingCN109413981AAvoid electromagnetic interferenceMeet miniaturization needsLaser detailsMagnetic/electric field screeningLaser noiseMiniaturization
The invention is suitable to be used in the technical field of electronics, and provides a laser module. The laser module comprises a circuit board, a box for preventing electromagnetic interference and a cover for preventing electromagnetic interference. The cover is disposed on a box body, and the circuit board comprises a plurality of circuit modules. A plurality of mounting slots for placing the circuit modules are formed on the box body, and the mounting slots are disposed in one-to-one correspondence with the circuit modules. The cover has a protruding structure for sealing each mountingslots. In the embodiment, through sealing each circuit module in each mounting slot of the box body, electromagnetic interference on other parts is prevented, thereby satisfying miniaturization requirements of equipment while ensuring output laser noise of a product to reach the standard.
Owner:深圳市大族锐波传感科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com