Room temperature magnetic cooling material
A magnetic refrigeration material and room temperature technology, applied in the field of magnetic refrigeration materials, can solve the problems of large thermal hysteresis, inappropriate Curie point, and large magnetic hysteresis of magnetic refrigeration materials, and achieve small thermal hysteresis and appropriate Curie point , the effect of small hysteresis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Mix the raw materials Mn, P, and B uniformly according to the proportion, then crush them, press the mixture into a block with a pressure higher than 500 atmospheres, place it in a quartz tube filled with argon, and sinter it at 200°C for 2 days, and then heated to 950 ° C, sintered for 7 days. Then cool it to room temperature, grind it, press it into blocks, place it in a quartz tube filled with argon, heat it to 950°C, and sinter it for 7 days. Finally, it is cooled to room temperature by water quenching to obtain a magnetic cold material (see figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
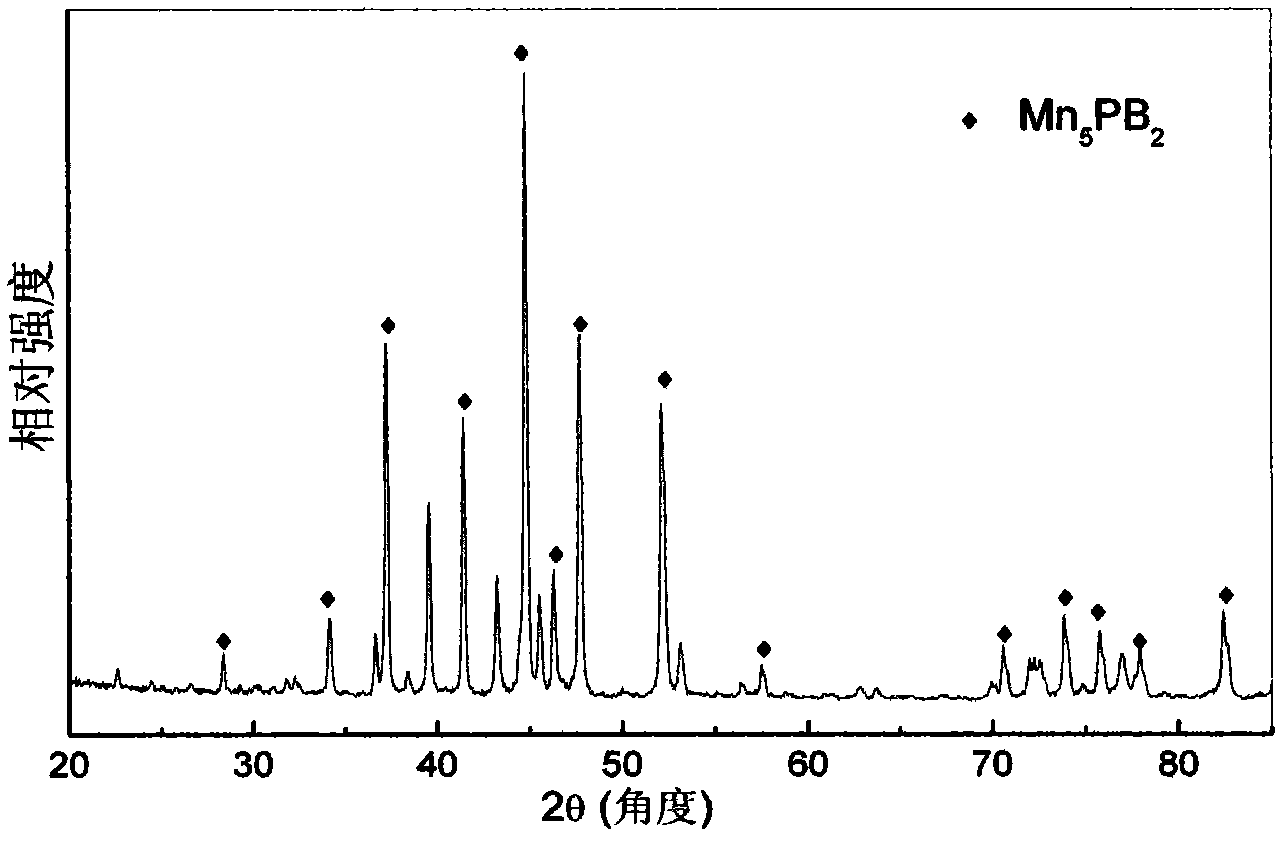
[0035] Prepare magnetic refrigeration material A according to the above method, wherein the atomic percentages of each component are: Mn: 62.3%, P: 12.8%, B remainder, the main phase Mn of gained magnetic refrigeration material A 5 PB 2 Accounting for 95% of the total weight, the X-ray diffraction pattern analysis is carried out to the magnetic refrigeration material A (see figure 2 ). Such as figure 2 Shown in: the main phase is Mn with tetragonal structure 5 PB 2 , the space group is I4 / mcm.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Prepare magnetic refrigeration material B according to the above method, wherein the atomic percentages of each component are respectively: Mn: 62%, P: 13%, B surplus, the main phase Mn of the gained magnetic refrigeration material B 5 PB 2 70% of the total weight,
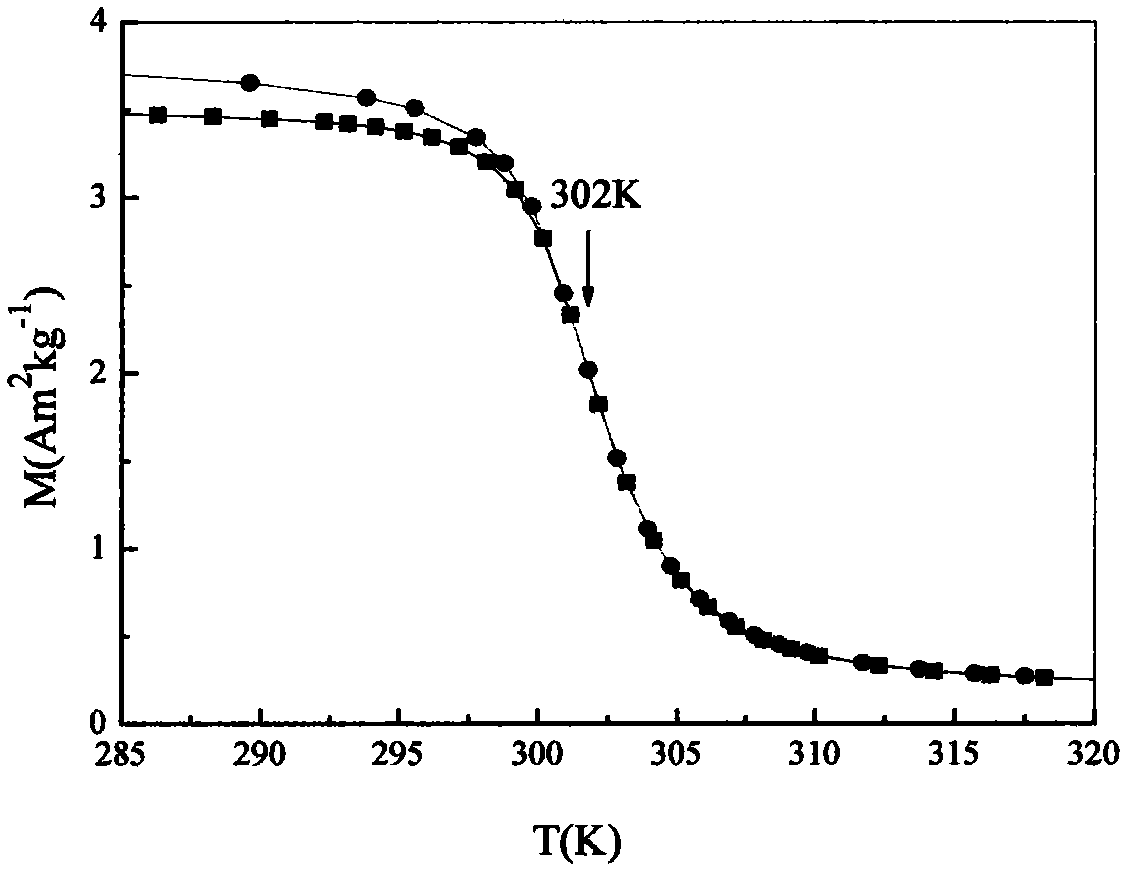
[0038] Place the magnetic refrigeration material B in the magnetic field, and observe its magnetization curve (see image 3 ). Among them, the squares in the figure represent the magnetization curve when the temperature drops to 12°C without applying a magnetic field, and then the temperature rises to 47°C with a 100Oe magnetic field; the circle represents that the temperature drops from 47°C with a 100Oe magnetic field Magnetization curve up to 12°C;
[0039] therefore, image 3 It shows that the magnetic transition point of the magnetic refrigeration material B is about 302K (29°C), there is no hysteresis above 302K, and it is a second-order phase transition.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com