Patents
Literature
483results about "Pulse counters with static storage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
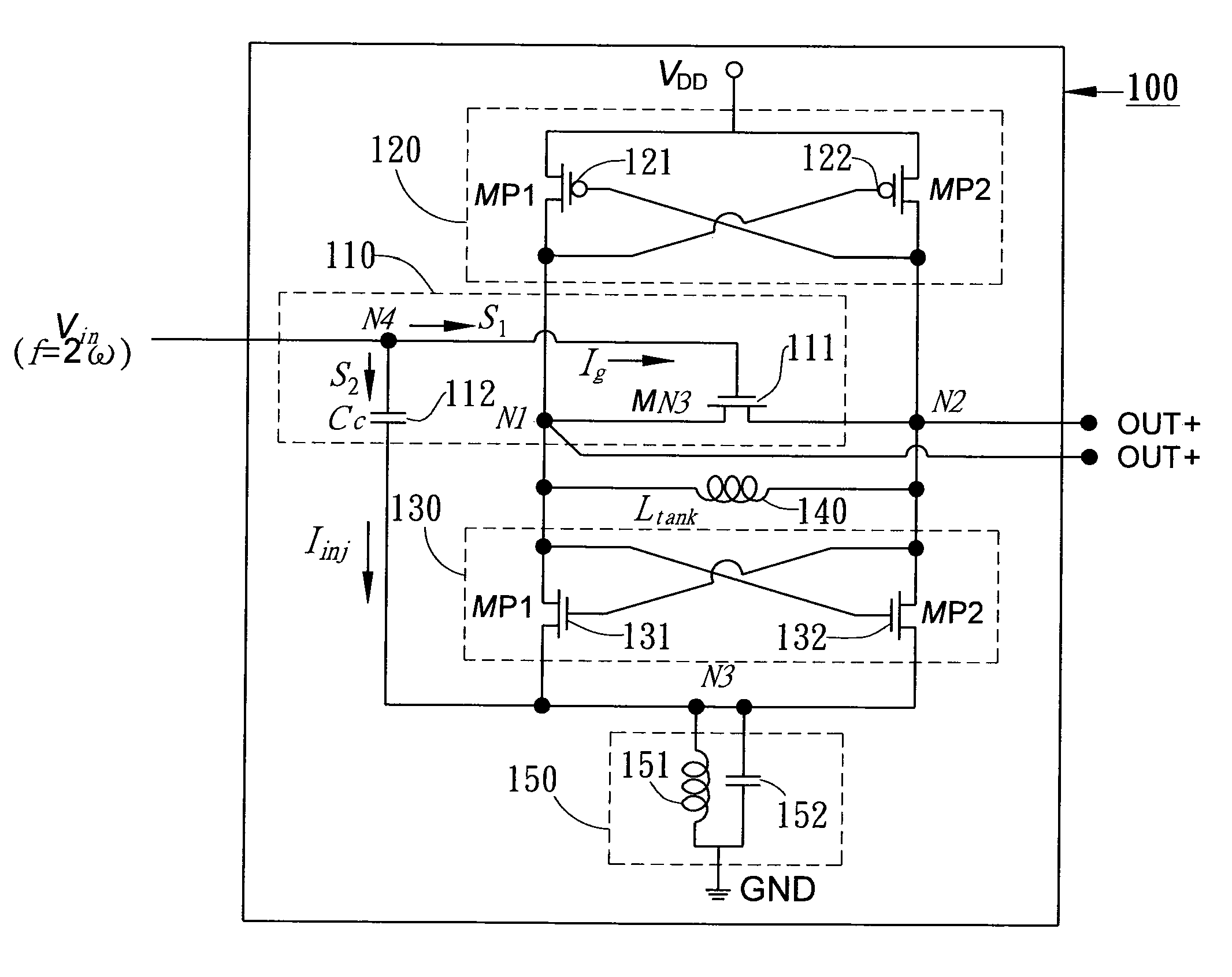
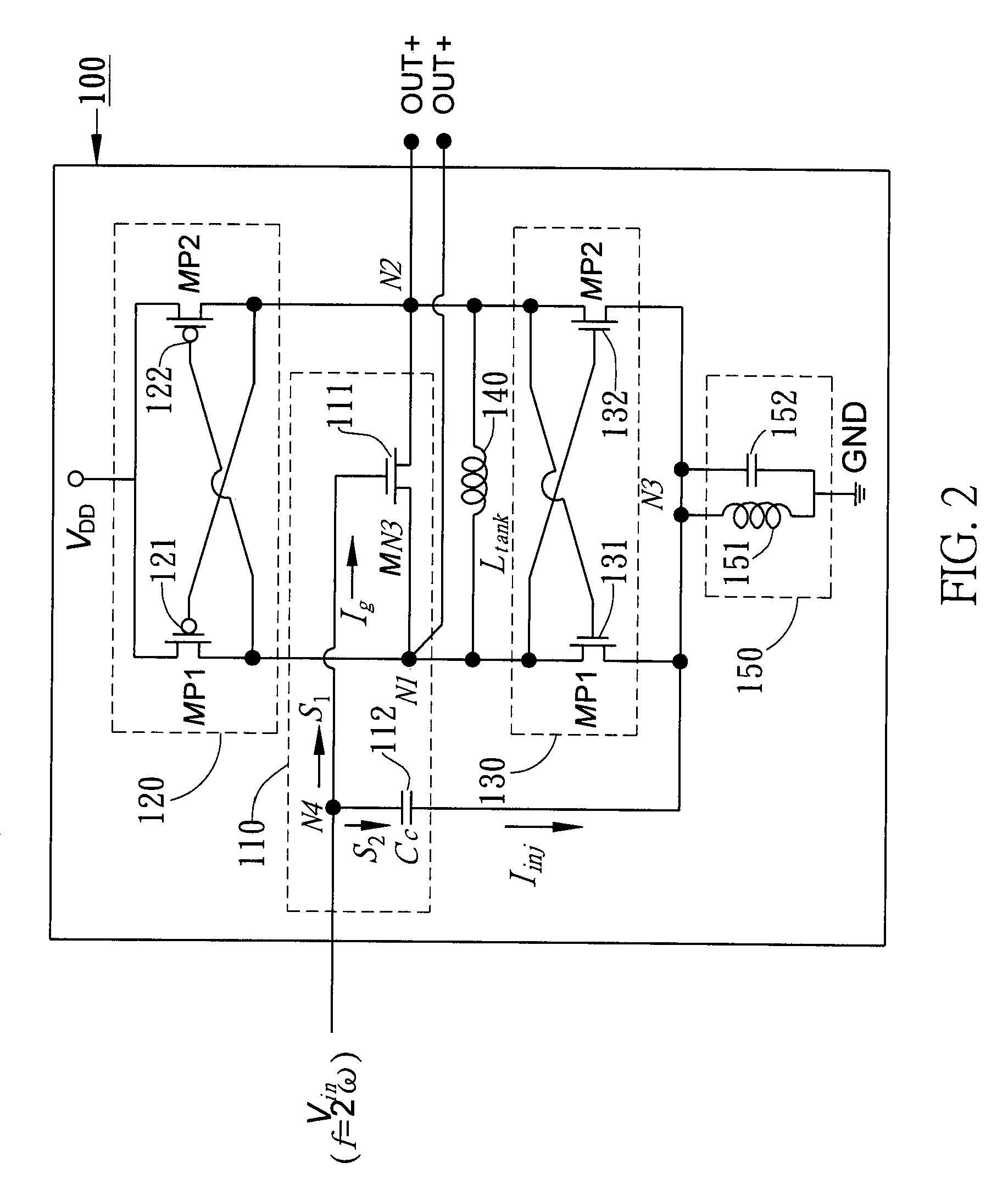
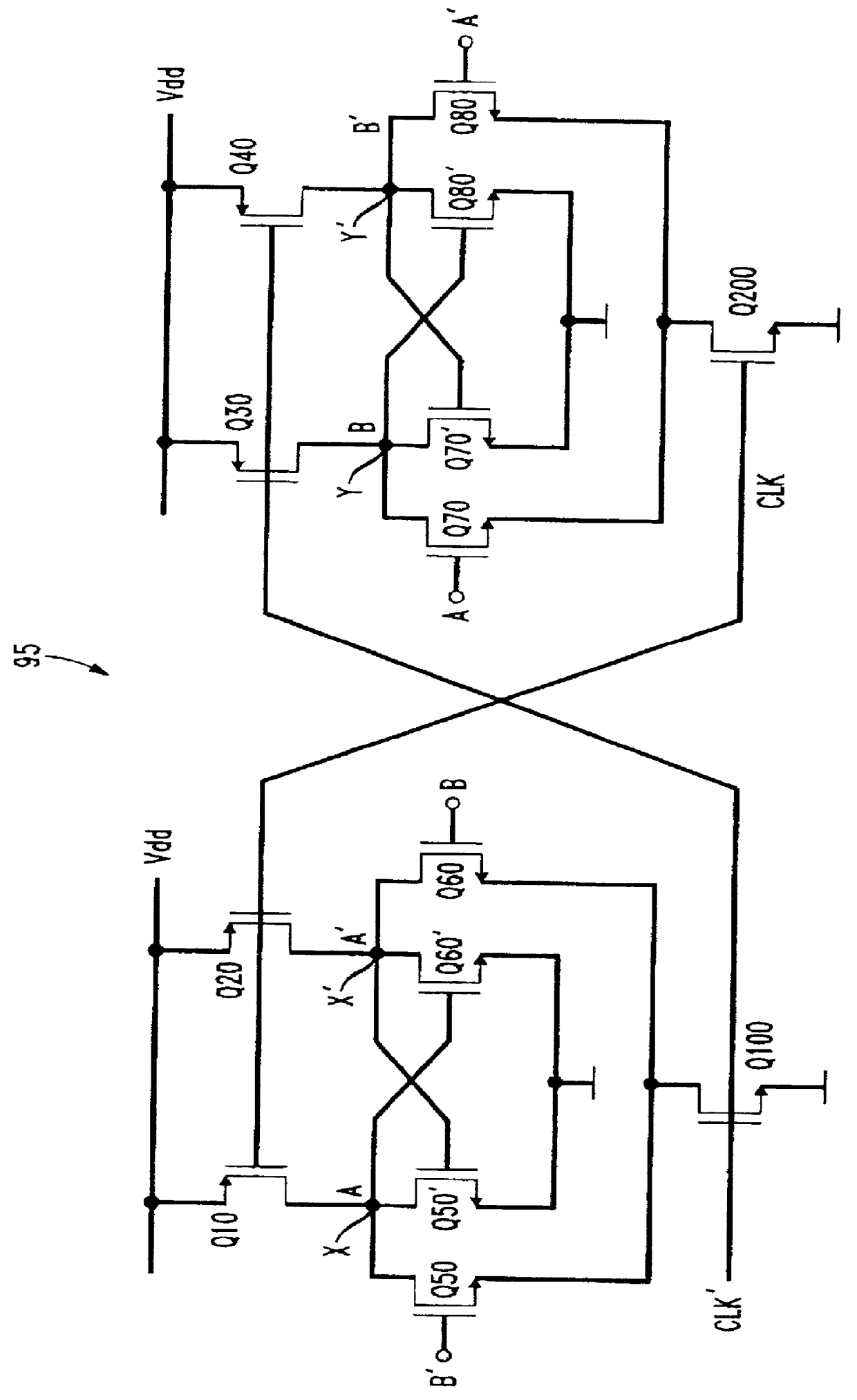
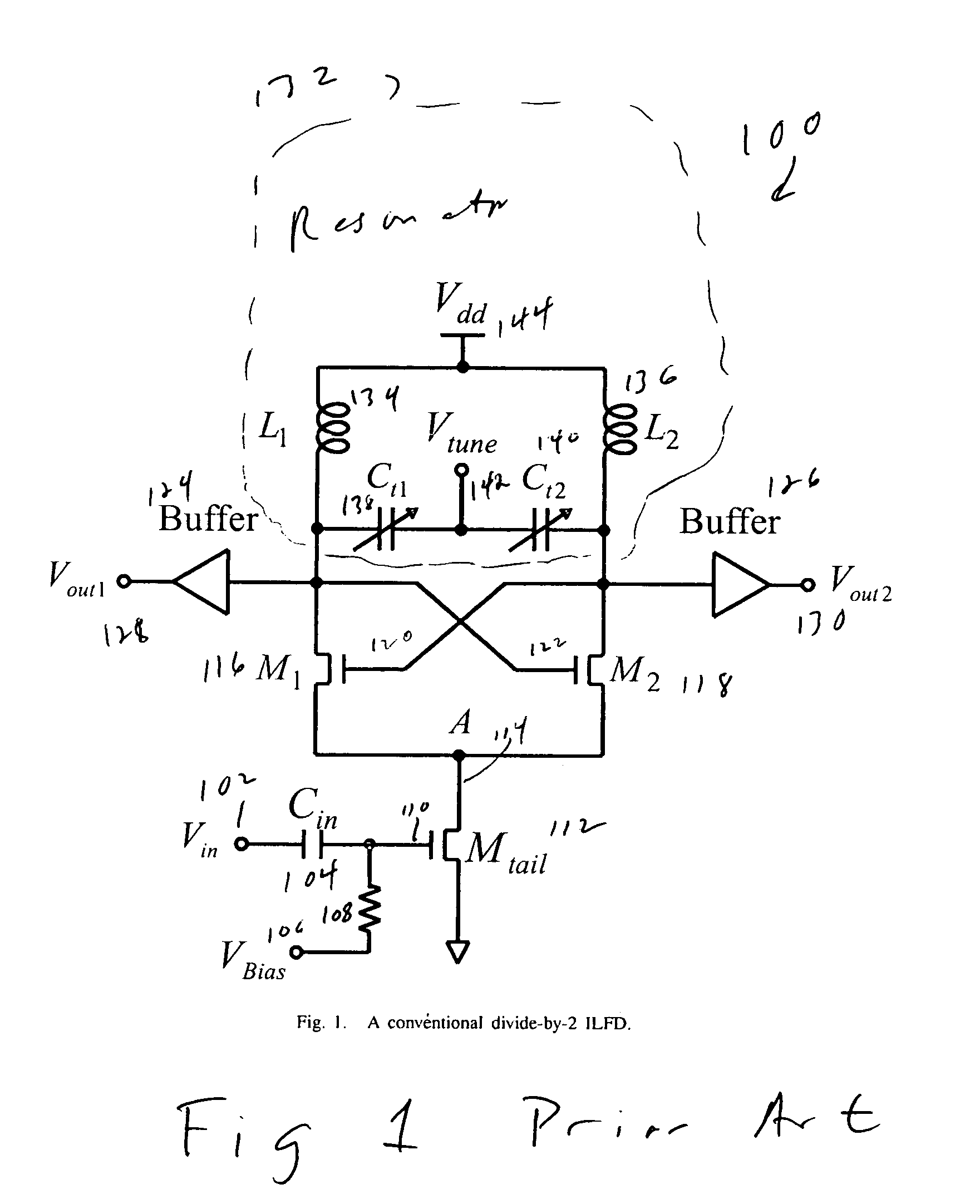
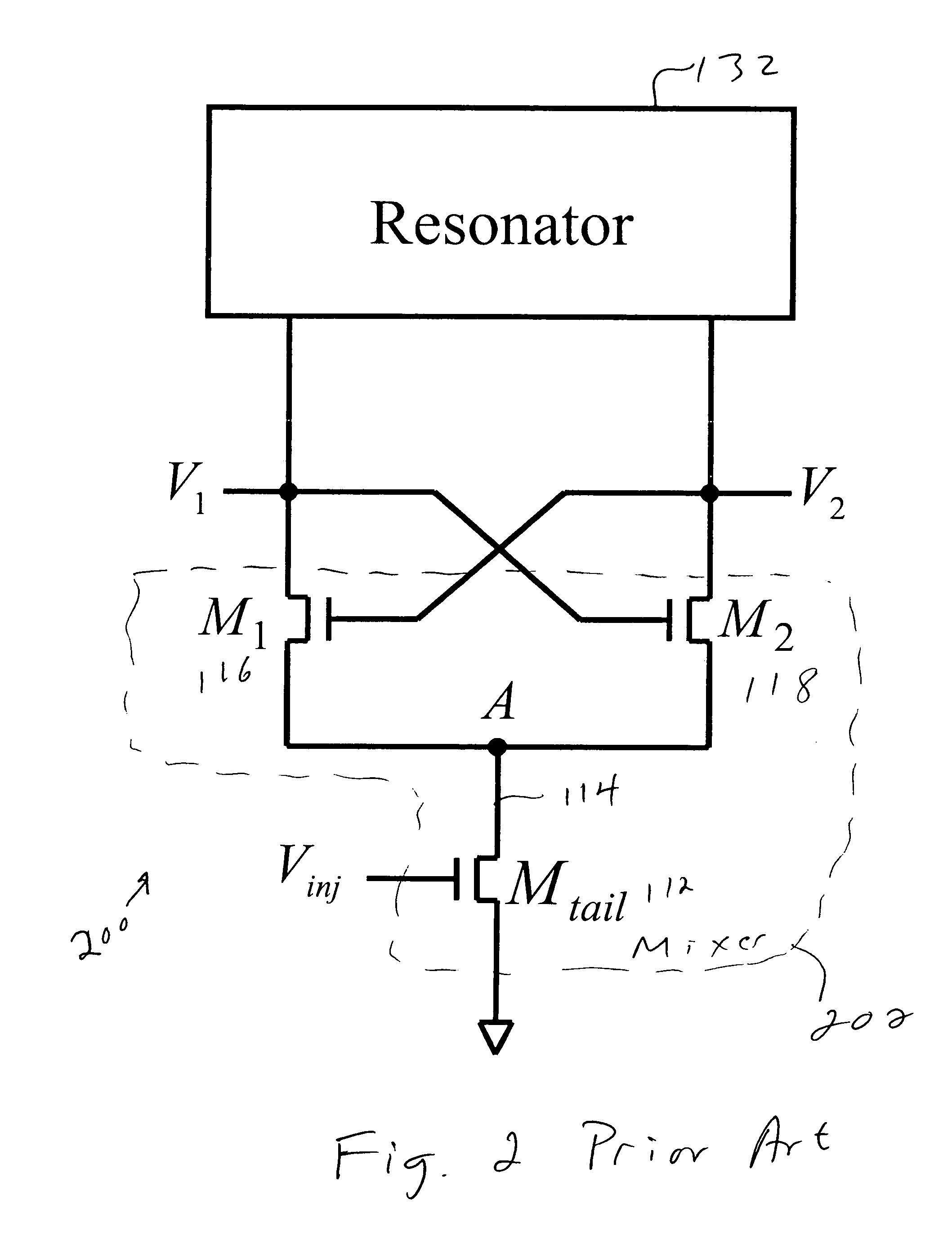
Dual-injection locked frequency dividing circuit
InactiveUS7656205B2Reduce power consumptionCounting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageDual injectionSignal processing circuits
A dual-injection locked frequency dividing circuit is proposed, which is designed for integration to a gigahertz signal processing circuit system for providing a frequency dividing function to gigahertz signals. The proposed circuit architecture is characterized by the provision of a dual-injection interface module on the input end for dividing the input signal into two parts for use as two injection signals, wherein the first injection signal is rendered in the form of a voltage signal and injected through a direct injection manner to the internal oscillation circuitry, while the second injection signal is rendered in the form of an electrical current and injected through a resonant circuit to the internal oscillation circuitry. This feature allow the proposed frequency dividing circuit to have broad frequency locking range and low power consumption.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
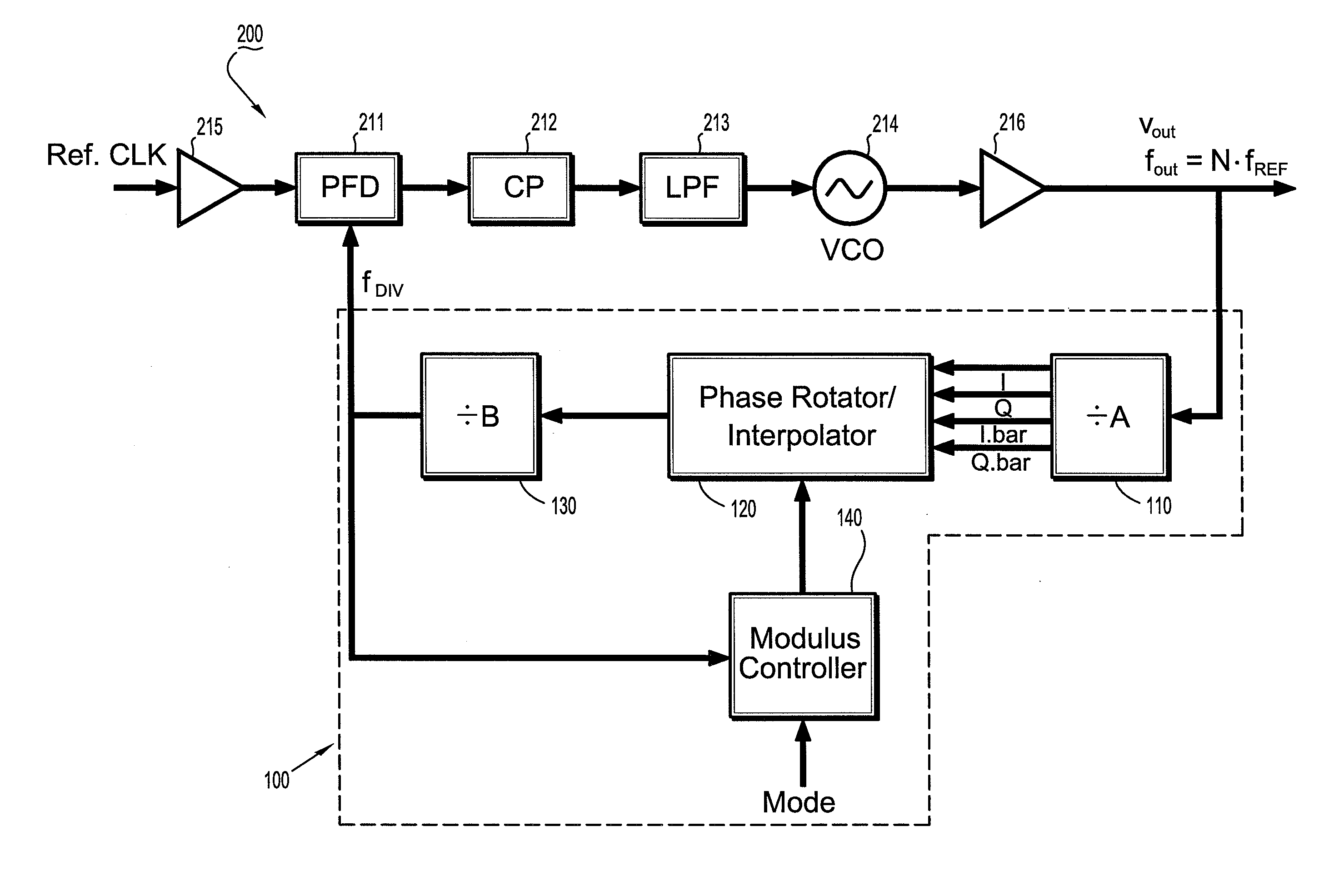
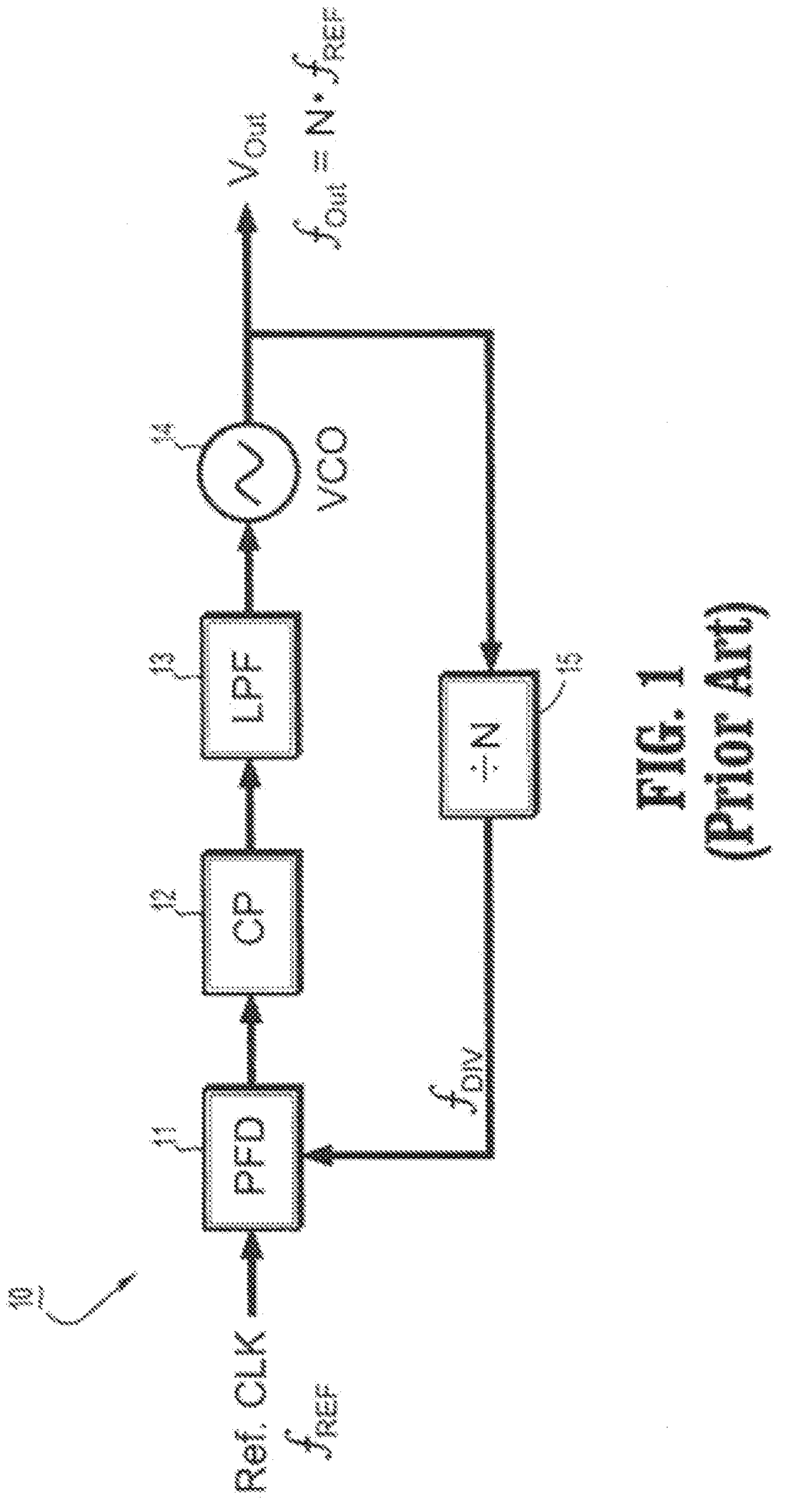
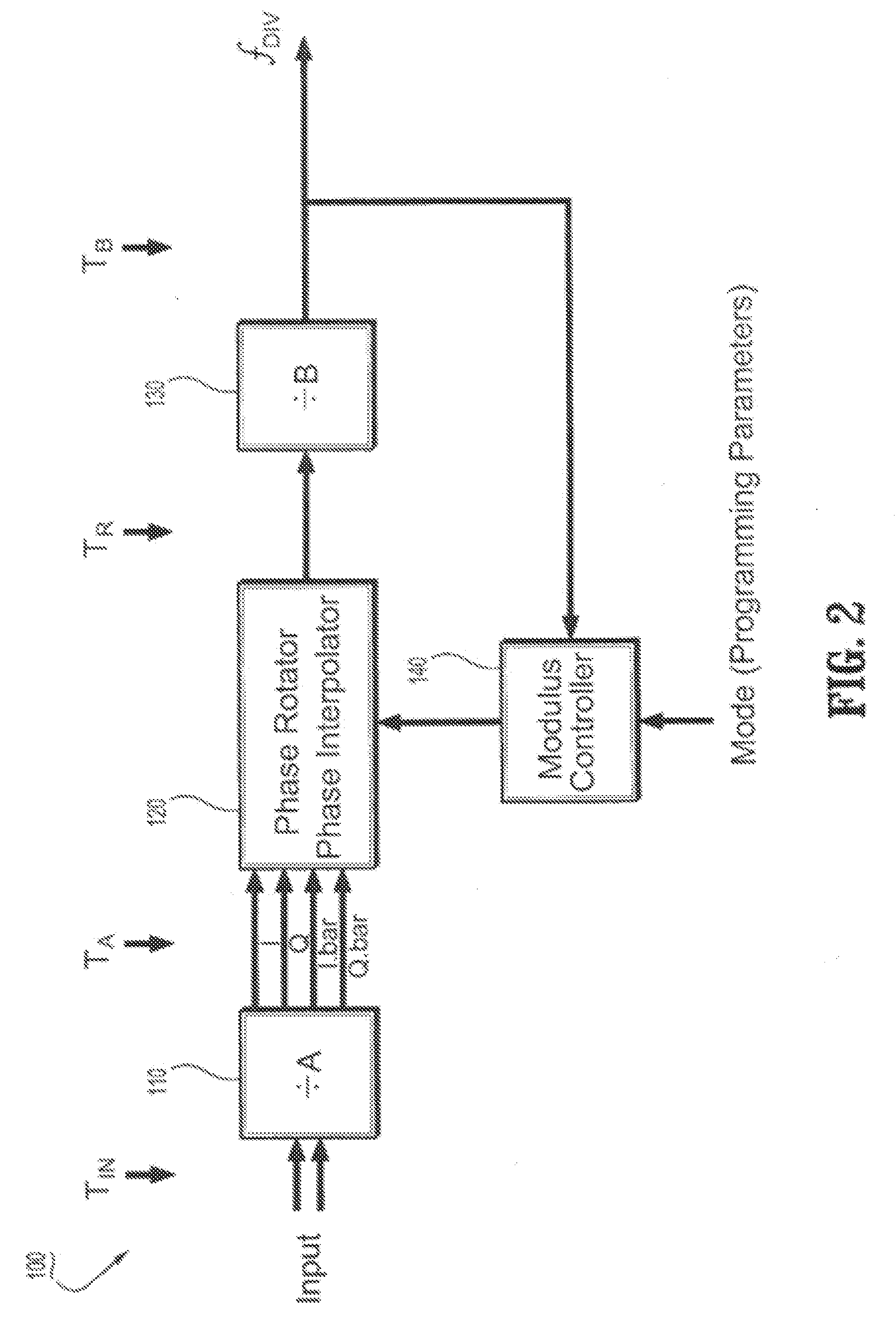
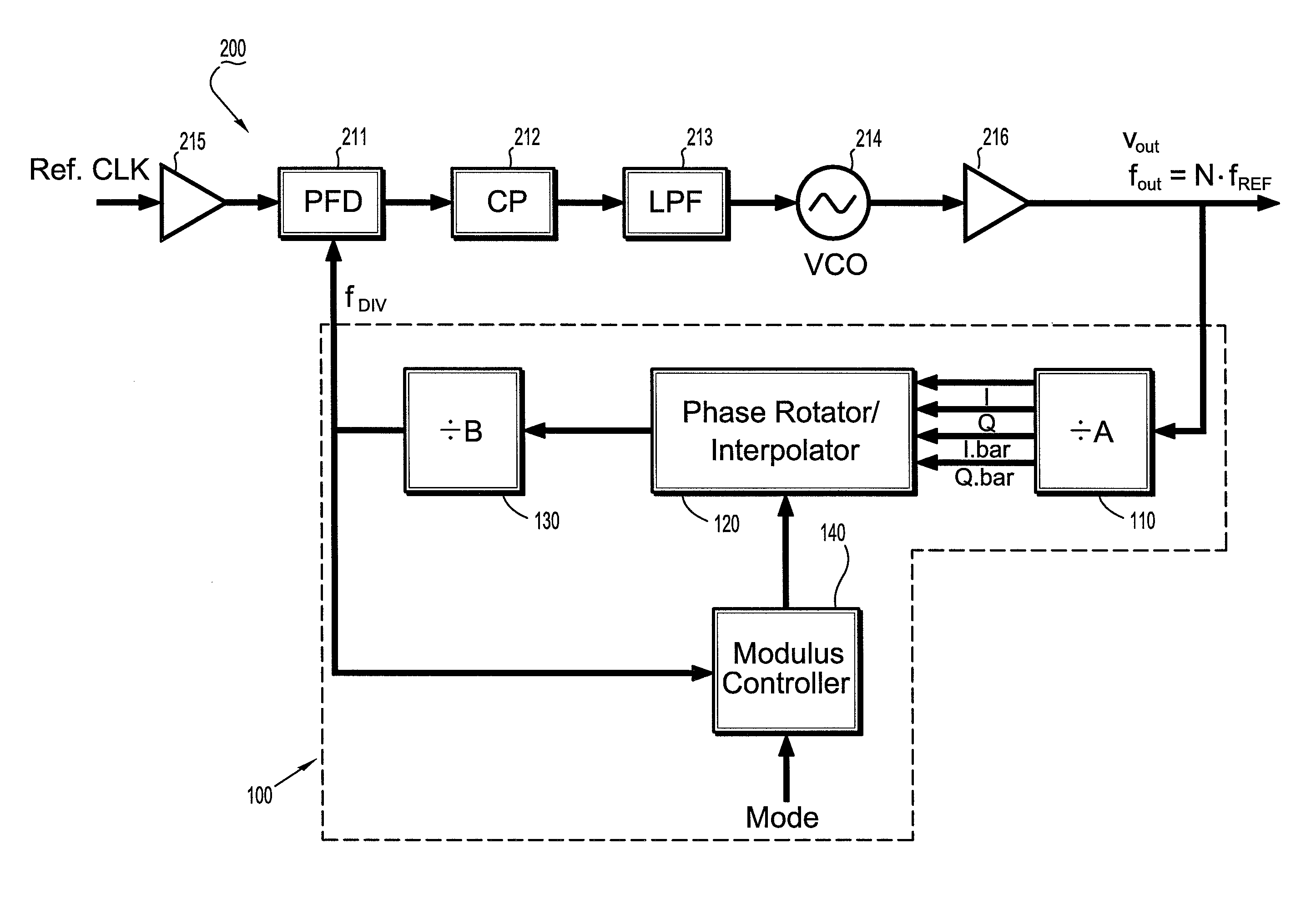
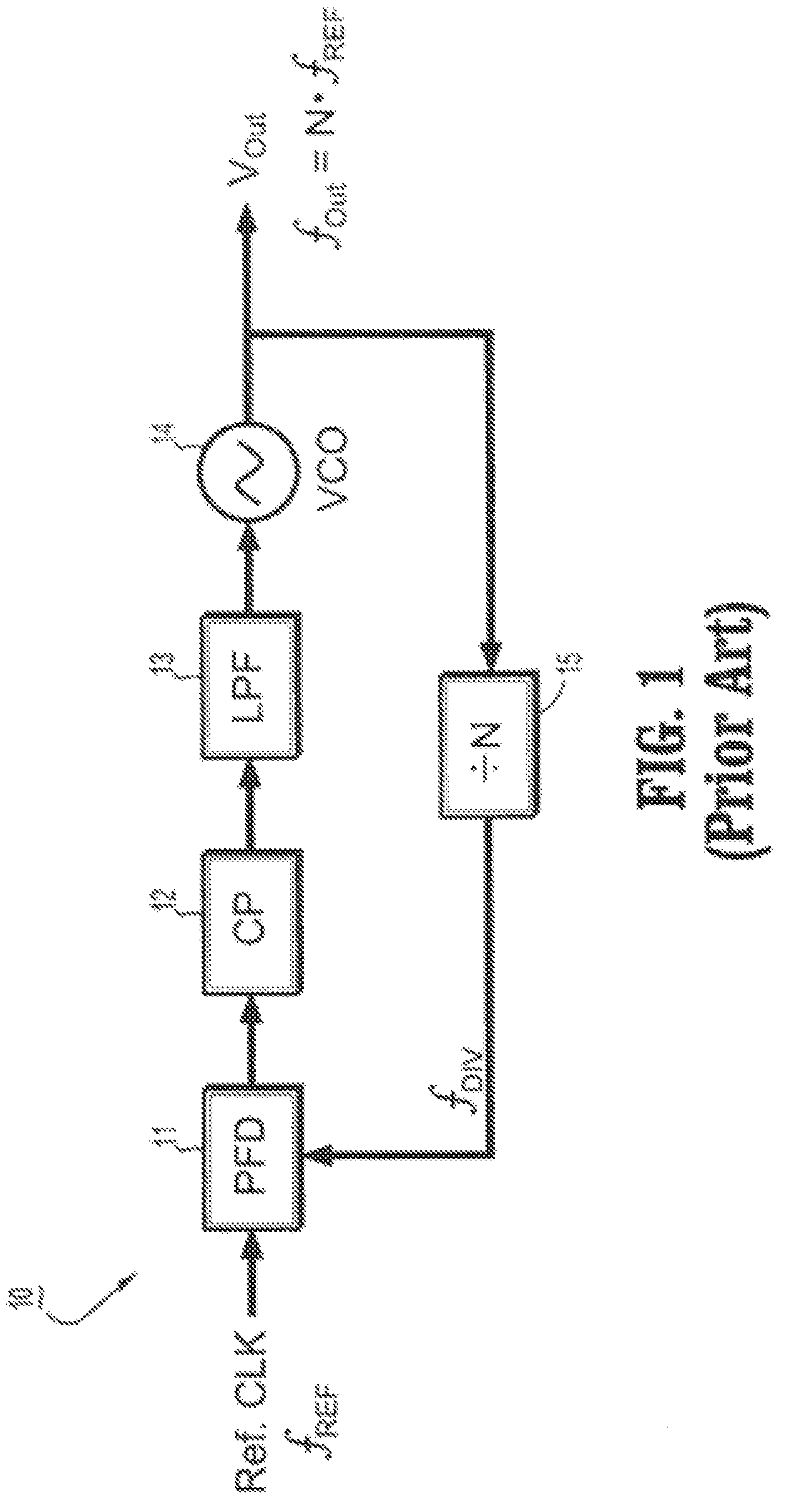
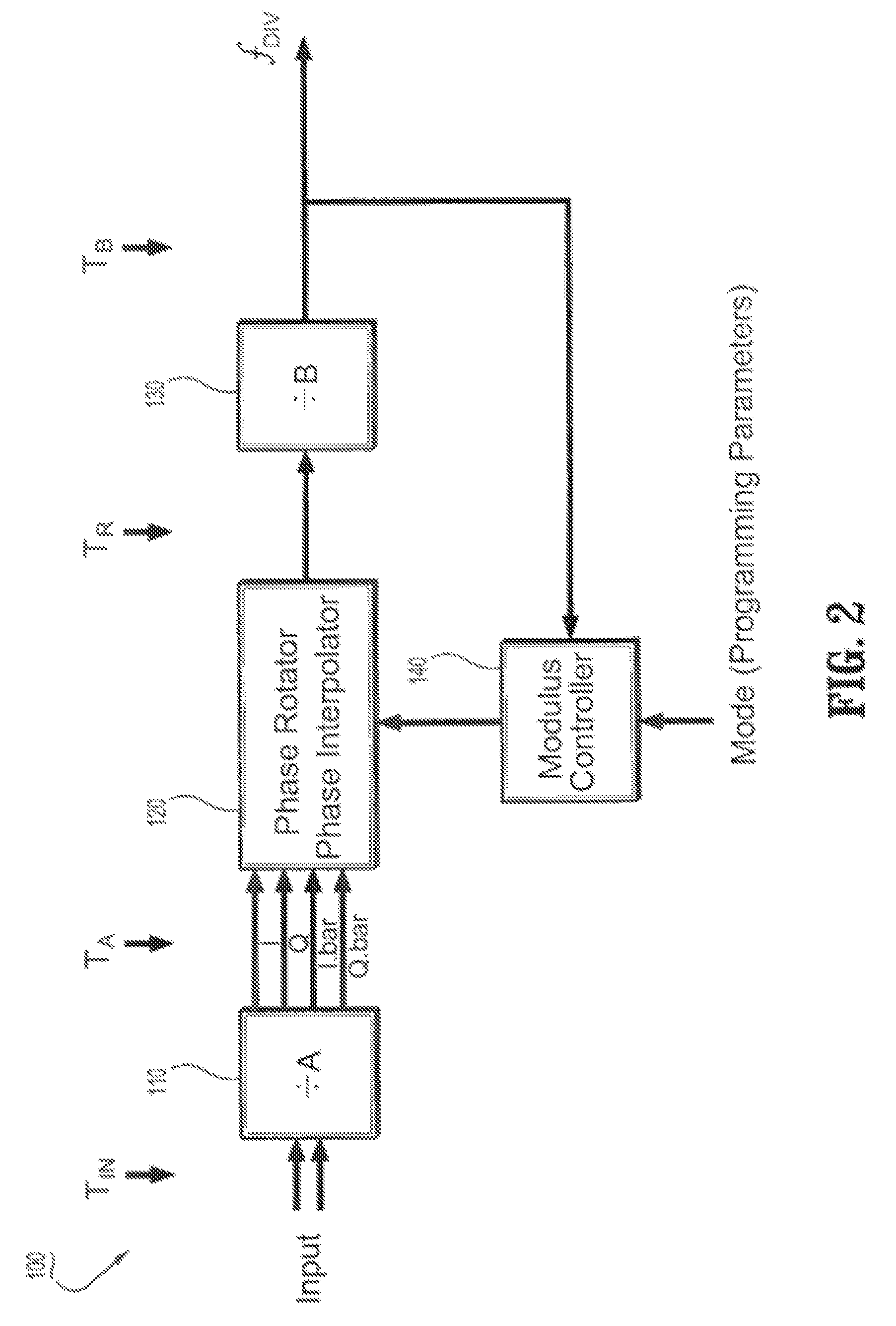
Circuits and methods for implementing sub-integer-n frequency dividers using phase rotators
ActiveUS20080164917A1Reduce and eliminate glitch in output signalPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency synthesizerFrequency divider
Circuits and methods are provided for implementing programmable sub-integer N frequency dividers for use in, e.g., frequency synthesizer applications, providing glitch free outputs signals with minimal fractional spurs. Phase-rotating sub-integer N frequency dividers are programmable to provide multi-modulus division with a wide range of arbitrary sub-integer division ratios.
Owner:IBM CORP
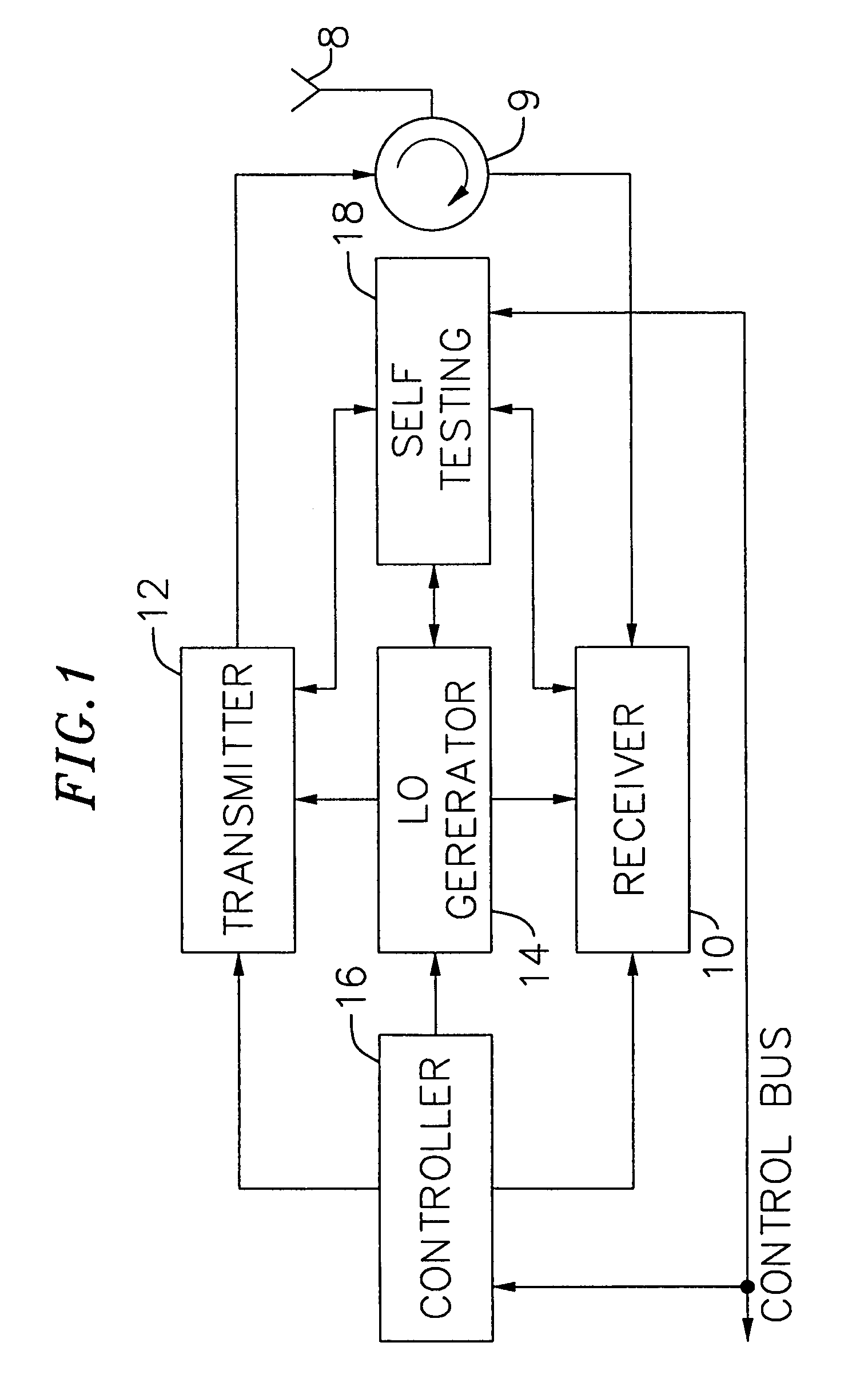
Adaptive radio transceiver with CMOS offset PLL
InactiveUS7082293B1Minimize adverse effectsReduce power consumptionTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCMOSAdaptive programming
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
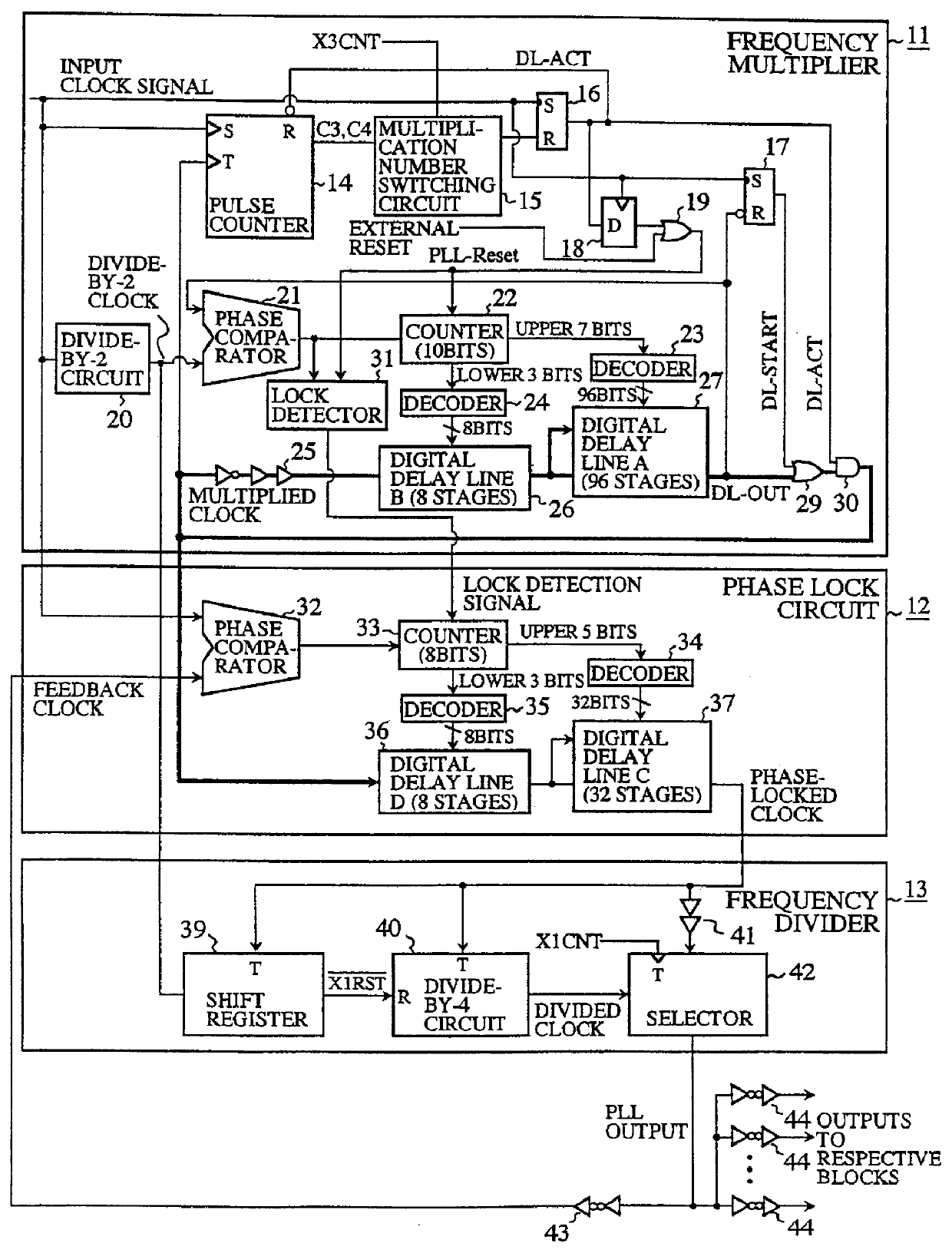
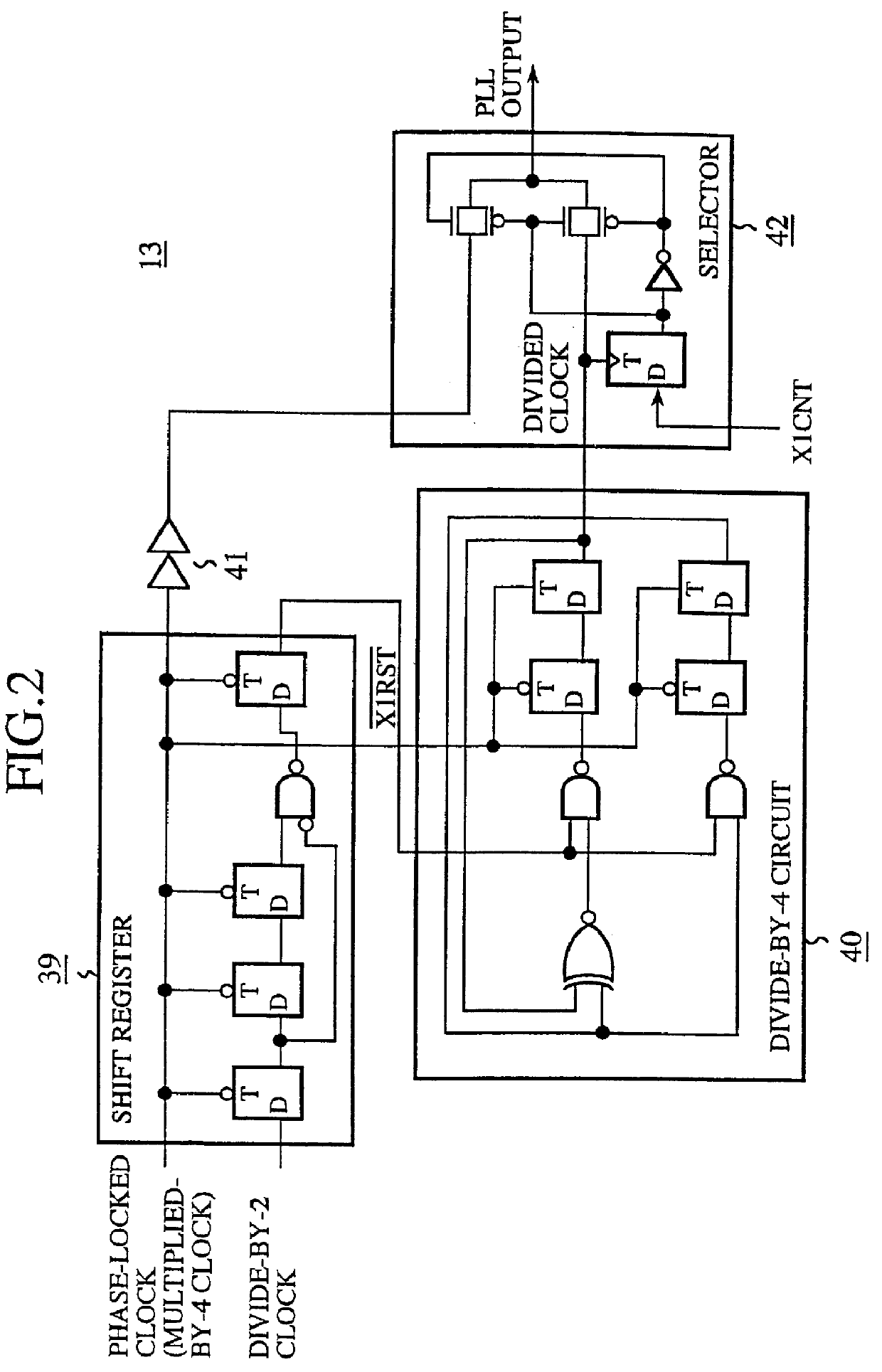
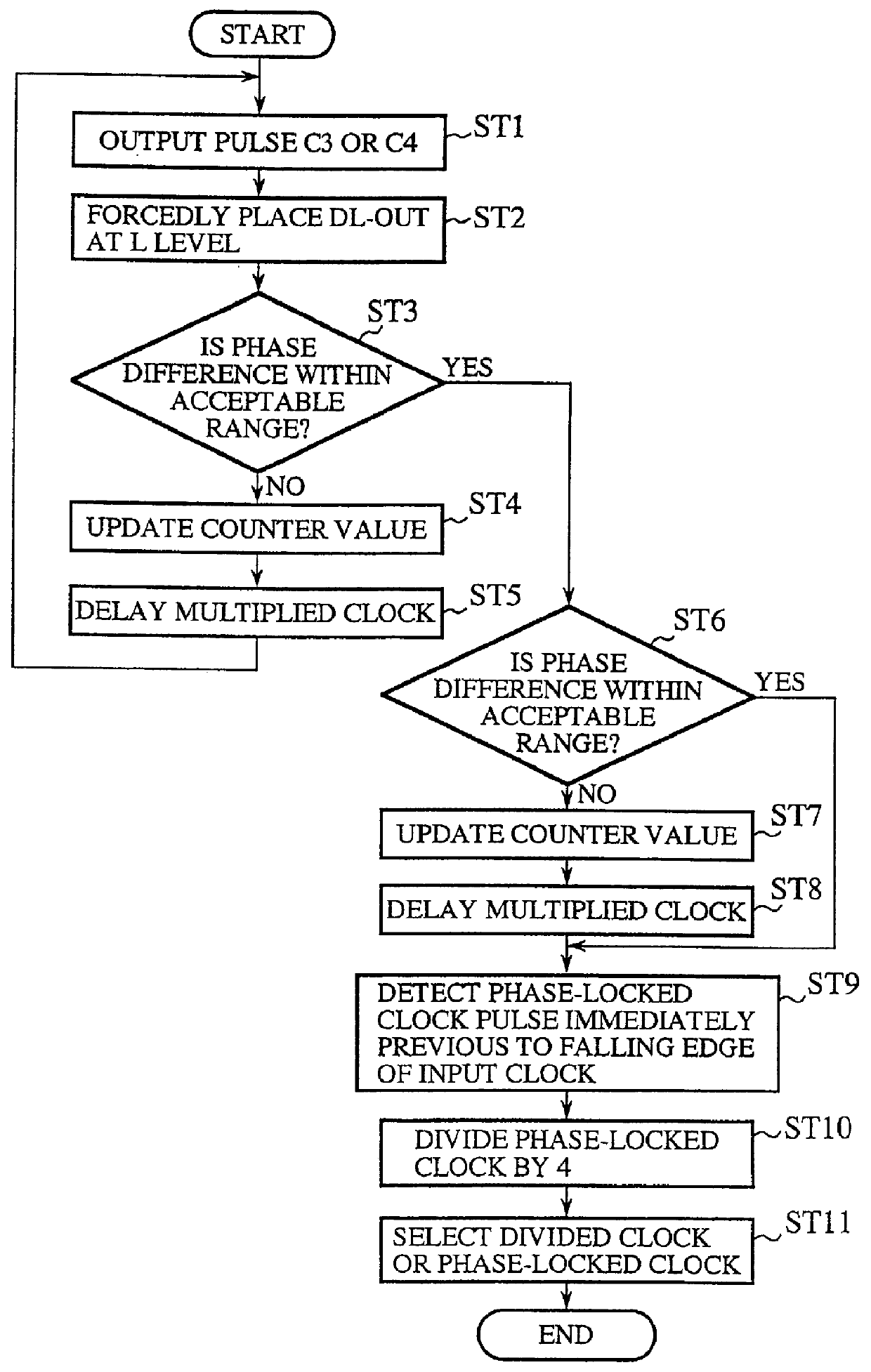
Clock generator and clock generating method capable of varying clock frequency without increasing the number of delay elements
InactiveUS6049238AReduce frequencyDelay lines pulse generationPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDelayed time
A clock generator including a frequency multiplier, a phase lock circuit and a frequency divider. The frequency multiplier generates a frequency multiplied clock by multiplying the frequency of an input clock. The phase lock circuit detects a phase difference between the input clock and a frequency divided clock, and generates, by delaying the frequency multiplied clock by an amount corresponding to the phase difference, a phase-locked clock with its phase locked with the input clock. The frequency divider detects in every fixed cycle a particular pulse of the phase-locked clock, and generates the frequency divided clock by dividing the phase-locked clock with reference to the particular pulse of the phase-locked clock. In particular, the frequency divider detects the particular pulse immediately previous to a falling edge of the input clock. This can reduce the phase difference between the input clock and the phase-locked clock, and hence to solve a problem of a conventional clock generator in that a delay time of a digital delay line in a phase lock circuit must be lengthened with a reduction in the multiplication number of the frequency multiplied clock, which requires a greater number of delay elements because of a large occupying area of the delay elements and a decoder, thereby increasing the circuit scale and cost of a chip to reduce the multiplication number of the frequency multiplied clock.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
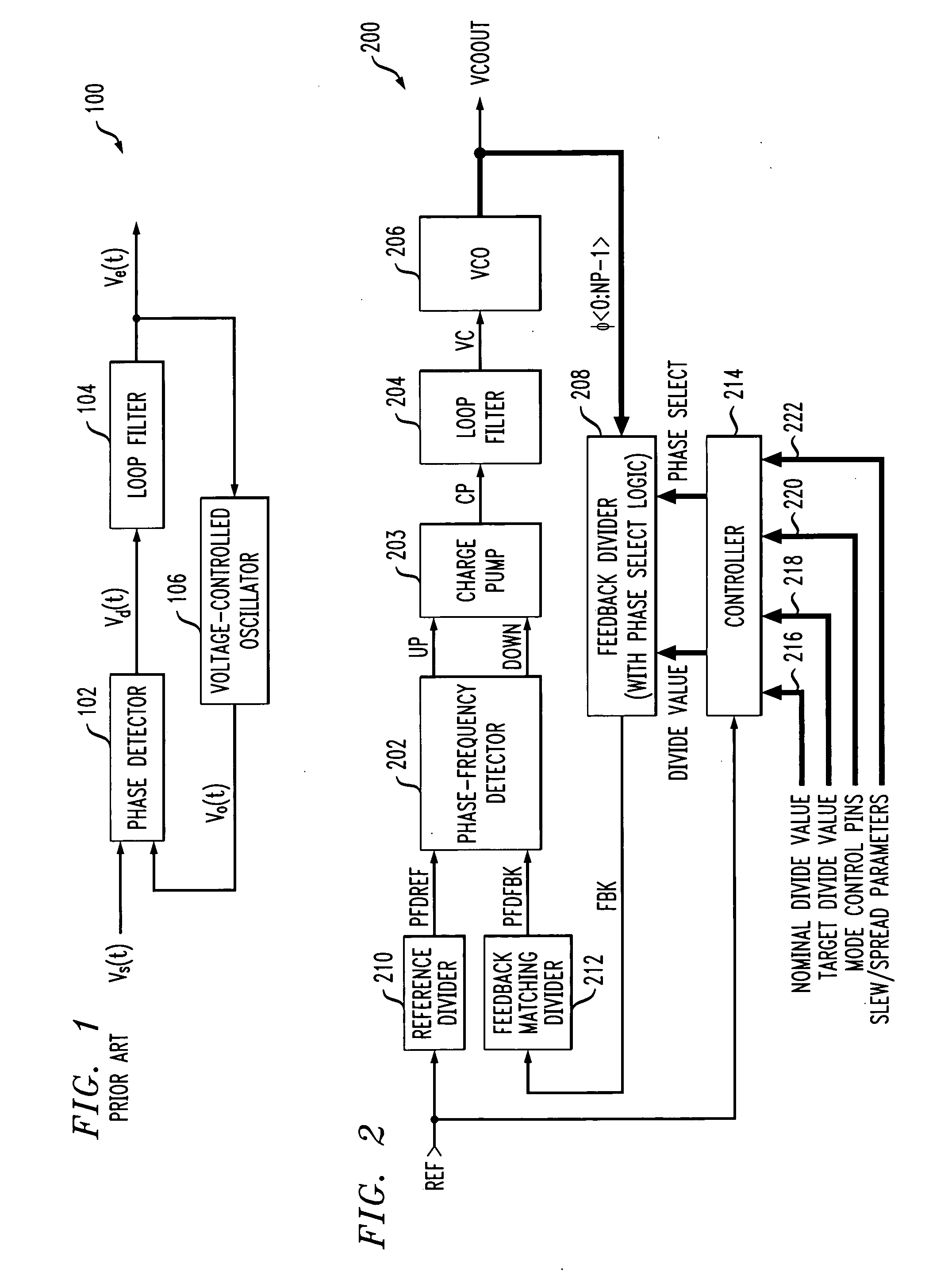
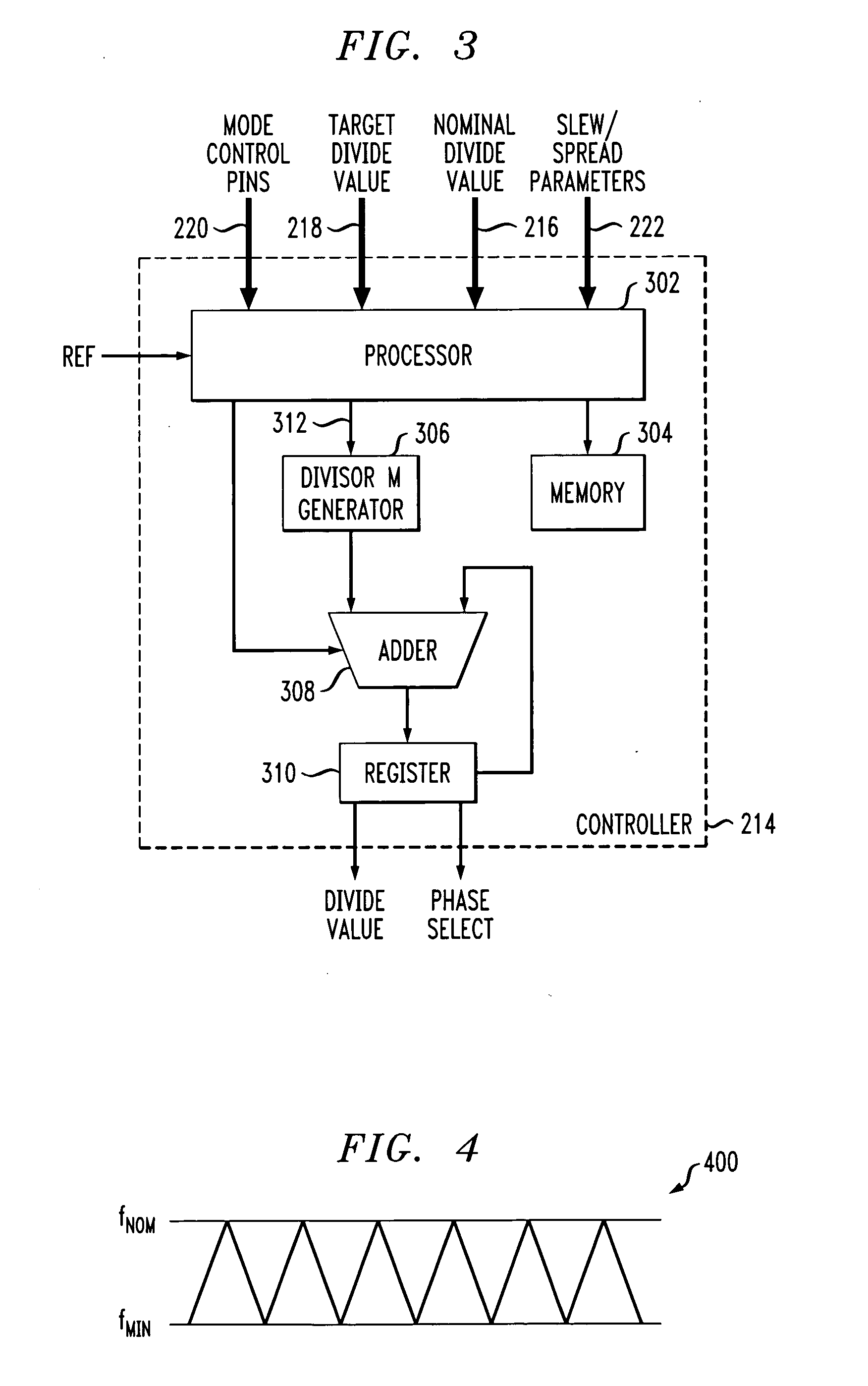
Signal generator with selectable mode control
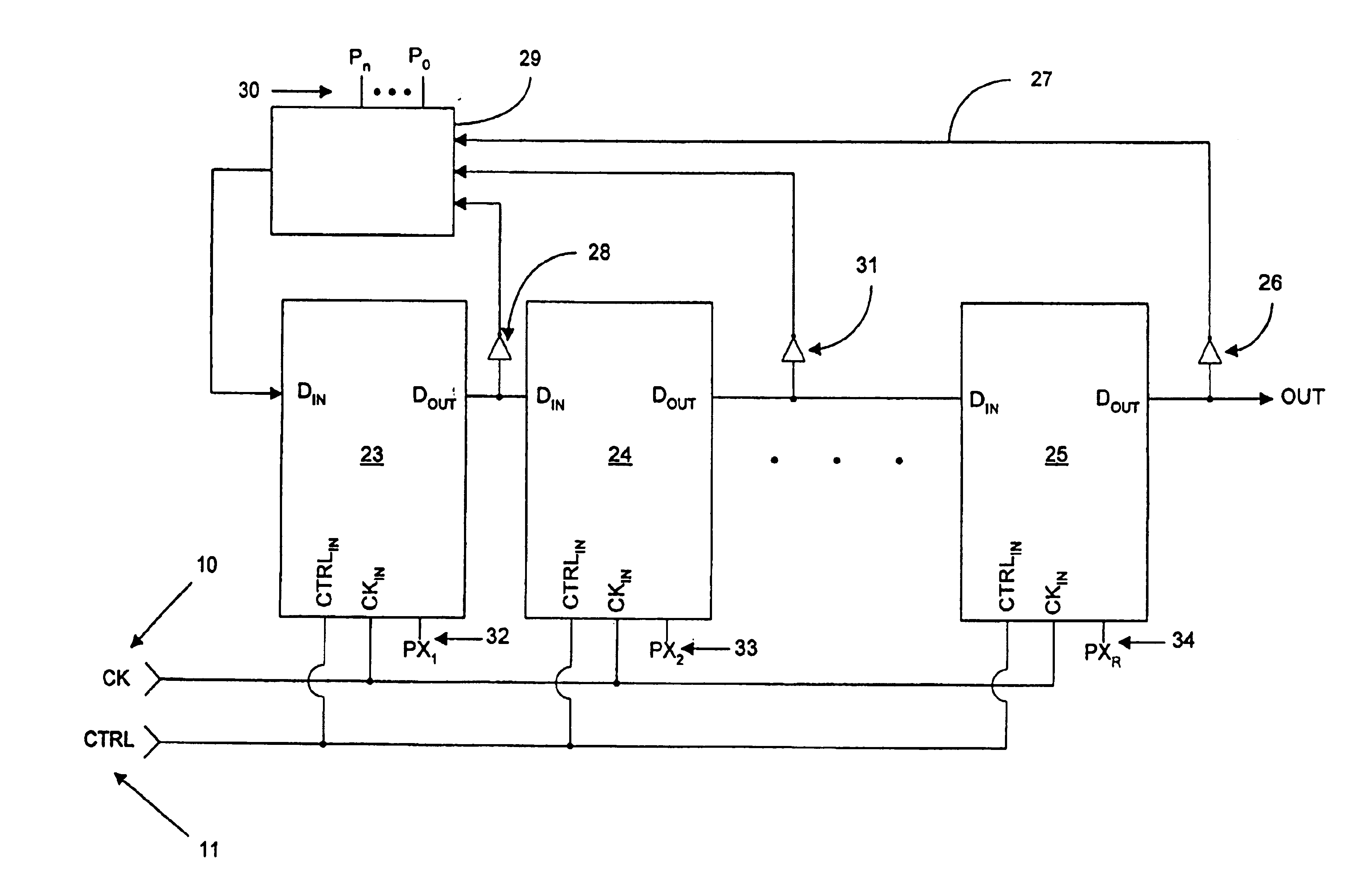
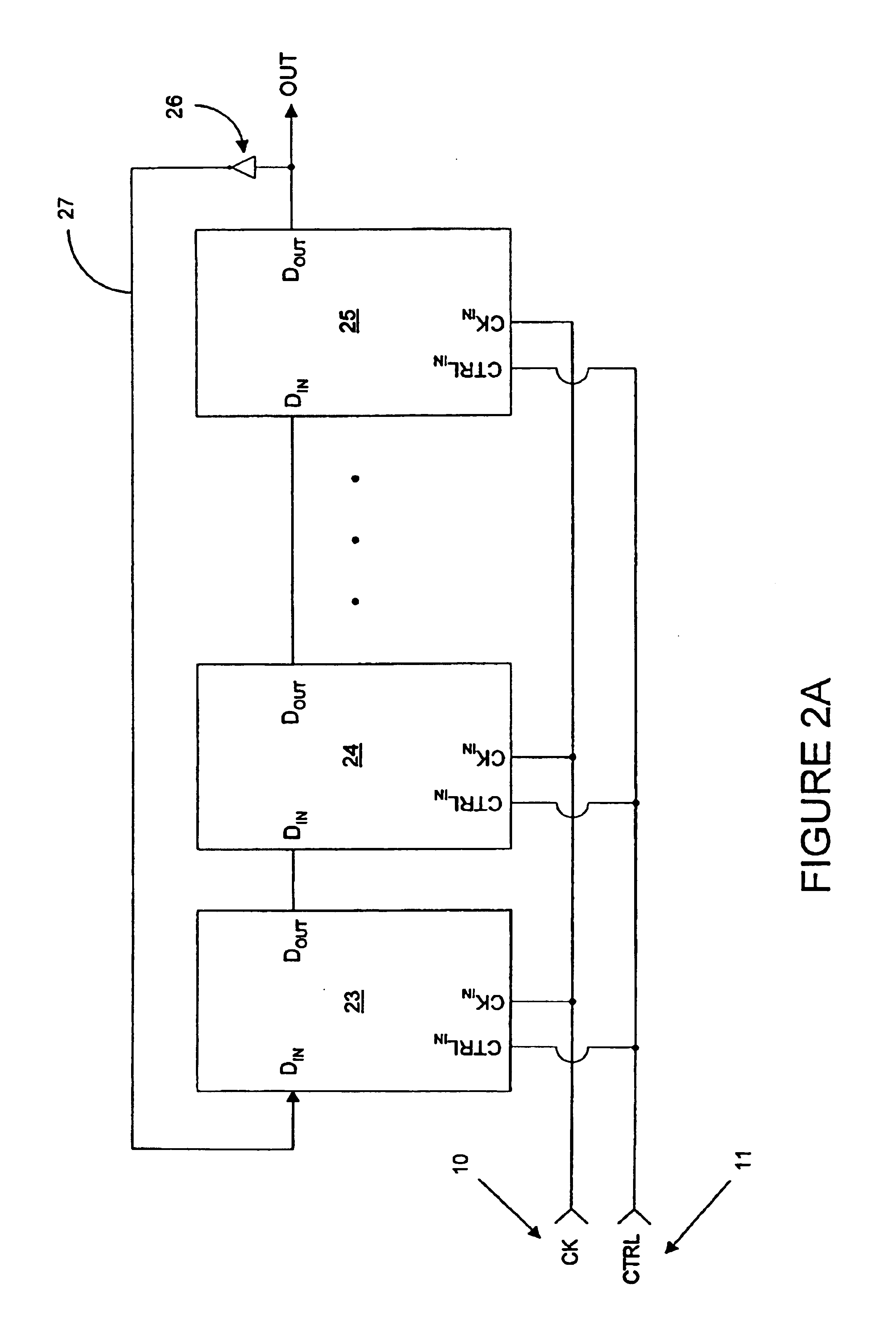
InactiveUS7042258B2Smooth switchingReduce discontinuityPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersControl signalMode control
A signal generator circuit includes a controller adapted to generate a divide value in accordance with at least a first control signal, and a divider adapted to divide an output signal of the signal generator circuit by the divisor value. The controller is selectively operable in at least one of a plurality of modes in accordance with at least a second control signal. The controller is configured to calculate each of one or more new divide values so as to vary a frequency of the output signal in accordance with at least one of the first and second control signals. The controller is configured to switch between operational modes and / or switch between divide values, the switching between operational modes and / or divide values being performed in such a manner so as to substantially eliminate discontinuities in the frequency of the output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
High speed frequency divider circuit
InactiveUS6166571ACounting chain synchronous pulse countersPulse counters with static storageRC time constantEngineering
A high frequency divider circuit for producing output signals of half the frequency of an input clock signal includes two identical circuit sections, each producing an output signal and its complement. The circuit sections are connected to each other so that the output signals of one circuit section serve as input signals to the other circuit section. Each circuit section contains a load transistor which is controlled by one of the clock signal and the clock signal complement, and a switch transistor which is controlled by the other of the clock signal and the clock signal complement. The inventive circuit exhibits a reduced RC time constant for each circuit section and an increased output signal swing between the output signals and their respective complements, as contrasted with prior art frequency dividers, thereby increasing the overall circuit response time and its ability to operate at high frequencies.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for reducing power consumption
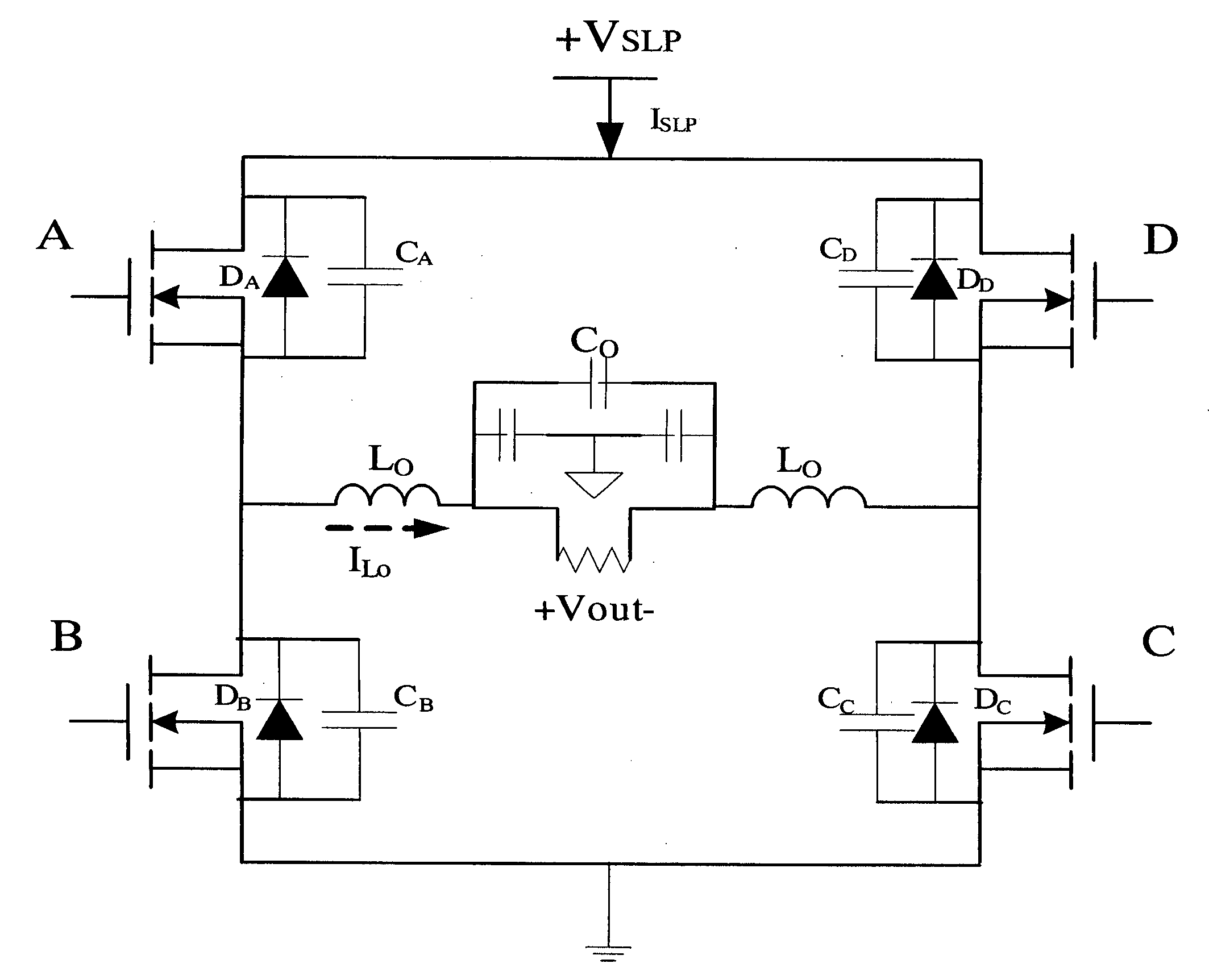
A power supply is provided. The power supply is comprised of a first power module, a second power module, and a controller. The first power module is capable of delivering a first preselected amount of power. The second power module is capable of delivering a second preselected amount of power. The first and second power modules are coupled together to be capable of delivering an aggregate amount of power related to the first and second preselected amounts of power. The controller is adapted to selectively enable the first and second power modules to make power available in one of the first preselected amount, the second preselected amount, and the aggregate amount.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Peak Power Reduction Methods in Distributed Charge Pump Systems
InactiveUS20090174441A1Reduces peak power usagePulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersEngineeringVoltage reference
A distributed charge pump system uses a delay element and frequency dividers to generate out of phase pump clock signals that drive different charge pumps, to offset peak current clock edges for each charge pump and thereby reduce overall peak power. Clock signal division and phase offset may be extended to multiple levels for further smoothing of the pump clock signal transitions. A dual frequency divider may be used which receives the clock signal and its complement, and generates two divided signals that are 90° out of phase. In an illustrative embodiment the clock generator comprises a variable-frequency clock source, and a voltage regulator senses an output voltage of the charge pumps, generates a reference voltage based on a currently selected frequency of the variable-frequency clock source, and temporarily disables the charge pumps (by turning off local pump clocks) when the output voltage is greater than the reference voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Injection-locked frequency divider
InactiveUS7557664B1Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageInjection lockedPhase difference
An injection-locked frequency divider (ILFD) can go beyond simple frequency division by an even number. In one embodiment, another differential pair of transistors is added to convert the injection signal into differential currents, which are mixed in the original transistor pair such as that of the conventional ILFD shown above. In another, a double-balanced ILFD structure includes multiple ILFD's which are independently tunable to allow phase differences other than quadrature.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Circuits and methods for implementing sub-integer-N frequency dividers using phase rotators
ActiveUS7486145B2Reduce and eliminate glitch in output signalPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency synthesizerEngineering
Circuits and methods are provided for implementing programmable sub-integer N frequency dividers for use in, e.g., frequency synthesizer applications, providing glitch free outputs signals with minimal fractional spurs. Phase-rotating sub-integer N frequency dividers are programmable to provide multi-modulus division with a wide range of arbitrary sub-integer division ratios.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
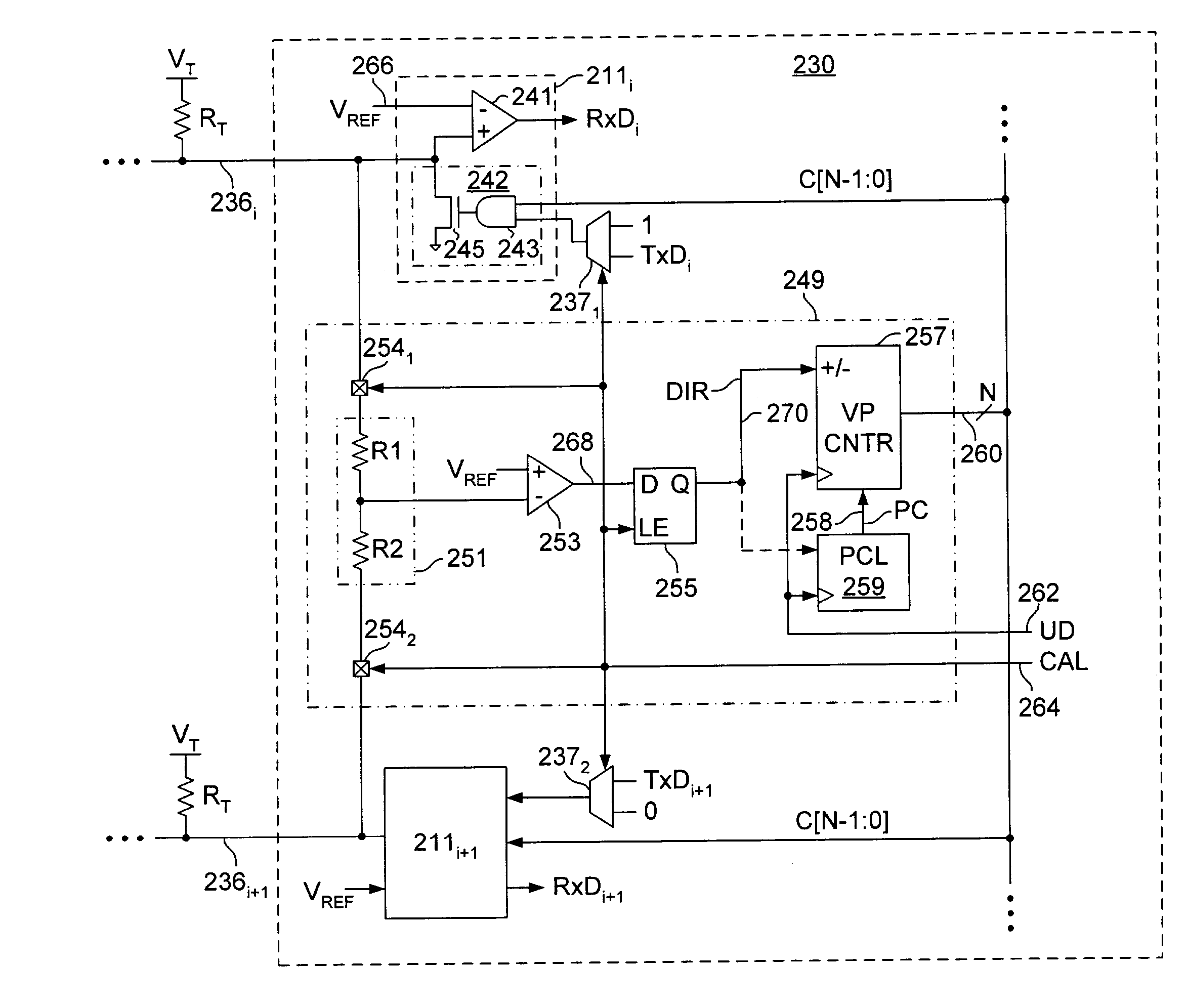
Output calibrator with dynamic precision
InactiveUS7119549B2Reliability increasing modificationsResistance/reactance/impedenceDriver circuitControl circuit
An integrated circuit device having an output driver circuit and a control circuit. The output driver circuit outputs a first signal having a signal level according to a control value. The control circuit is coupled to receive the first signal from the output driver and adjusts the control value by a first increment until a transition event is detected. After the transition event is detected, the control circuit adjusts the control value by a second increment, the second increment being smaller than the first increment.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
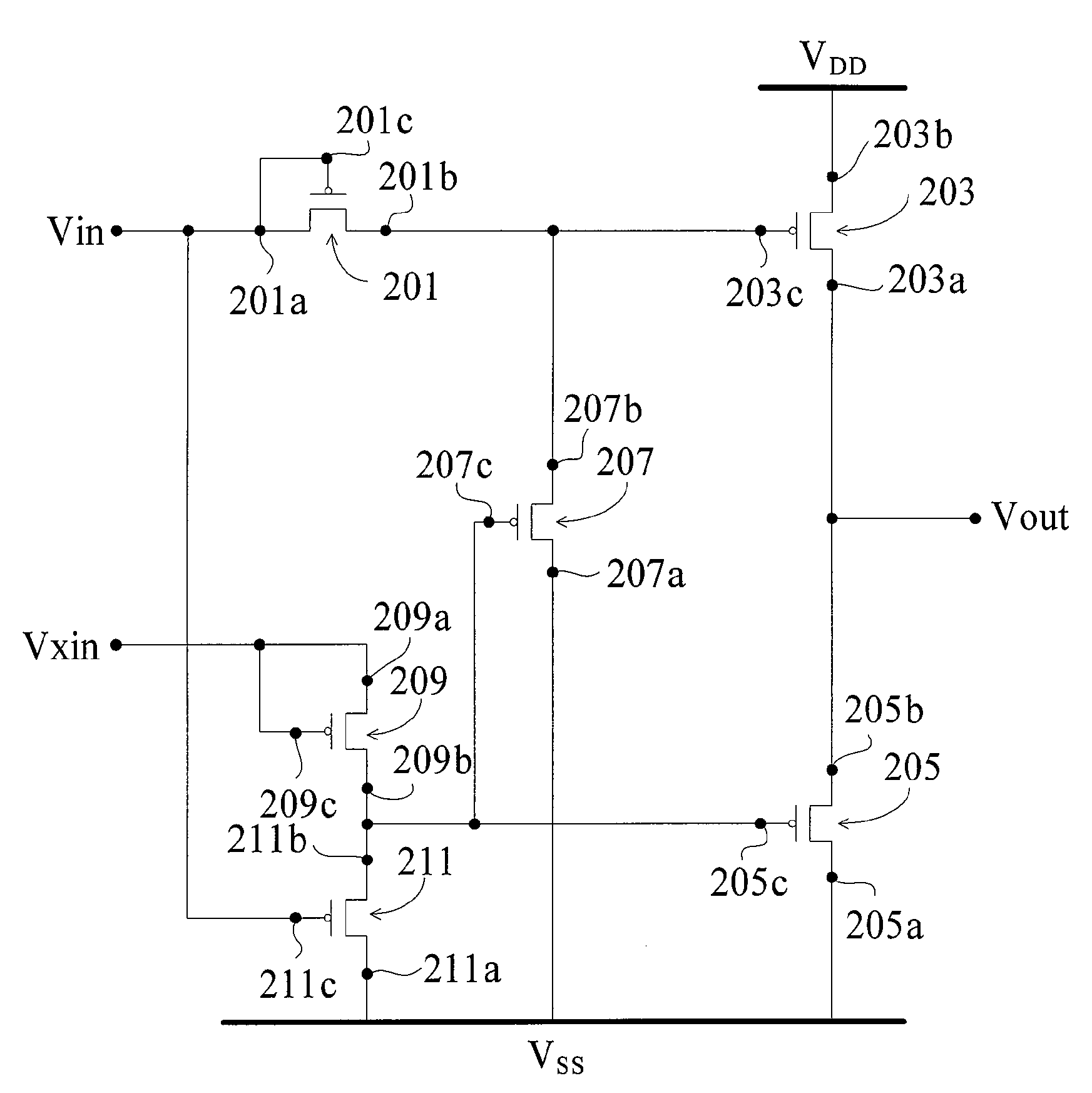
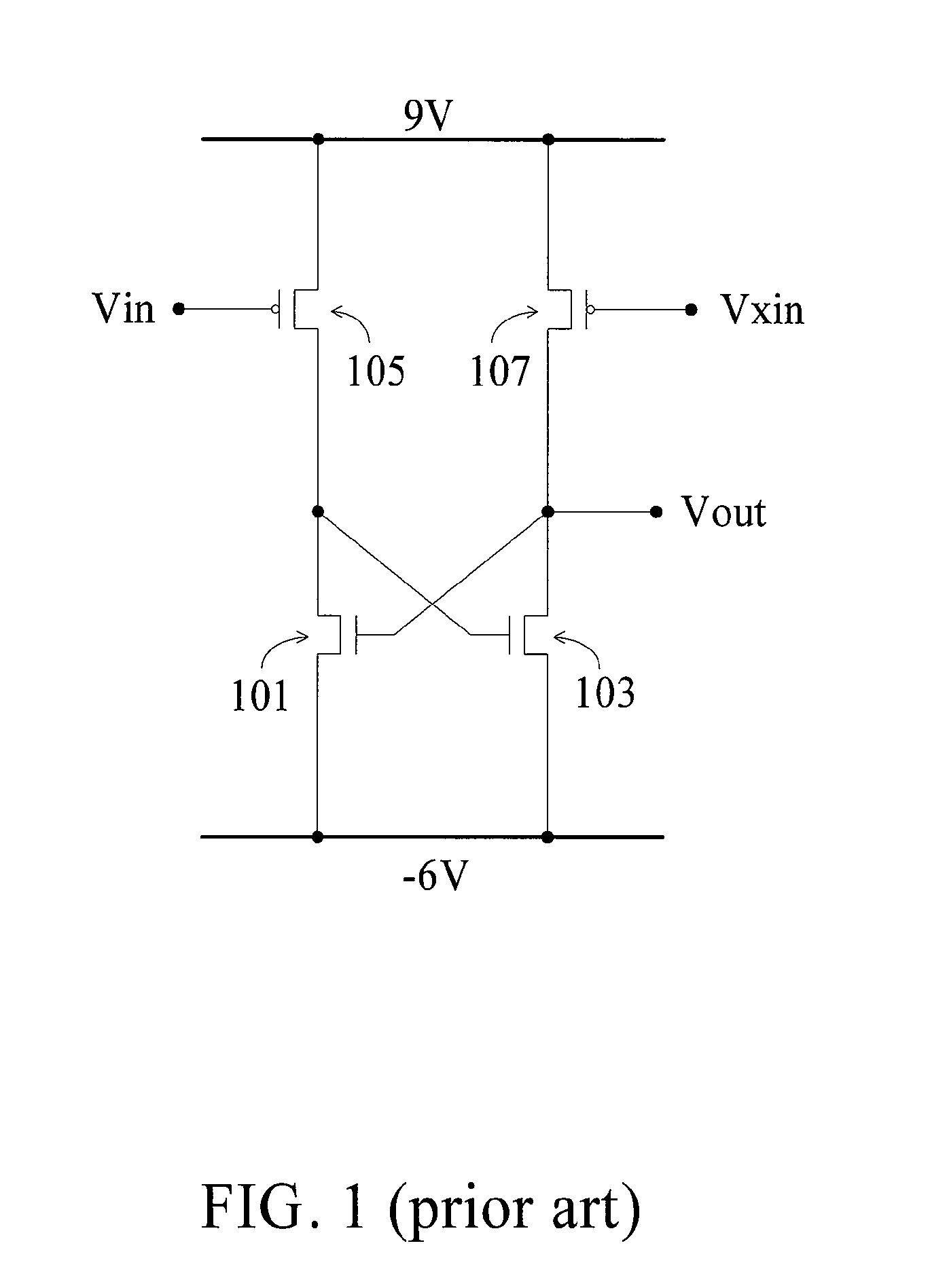
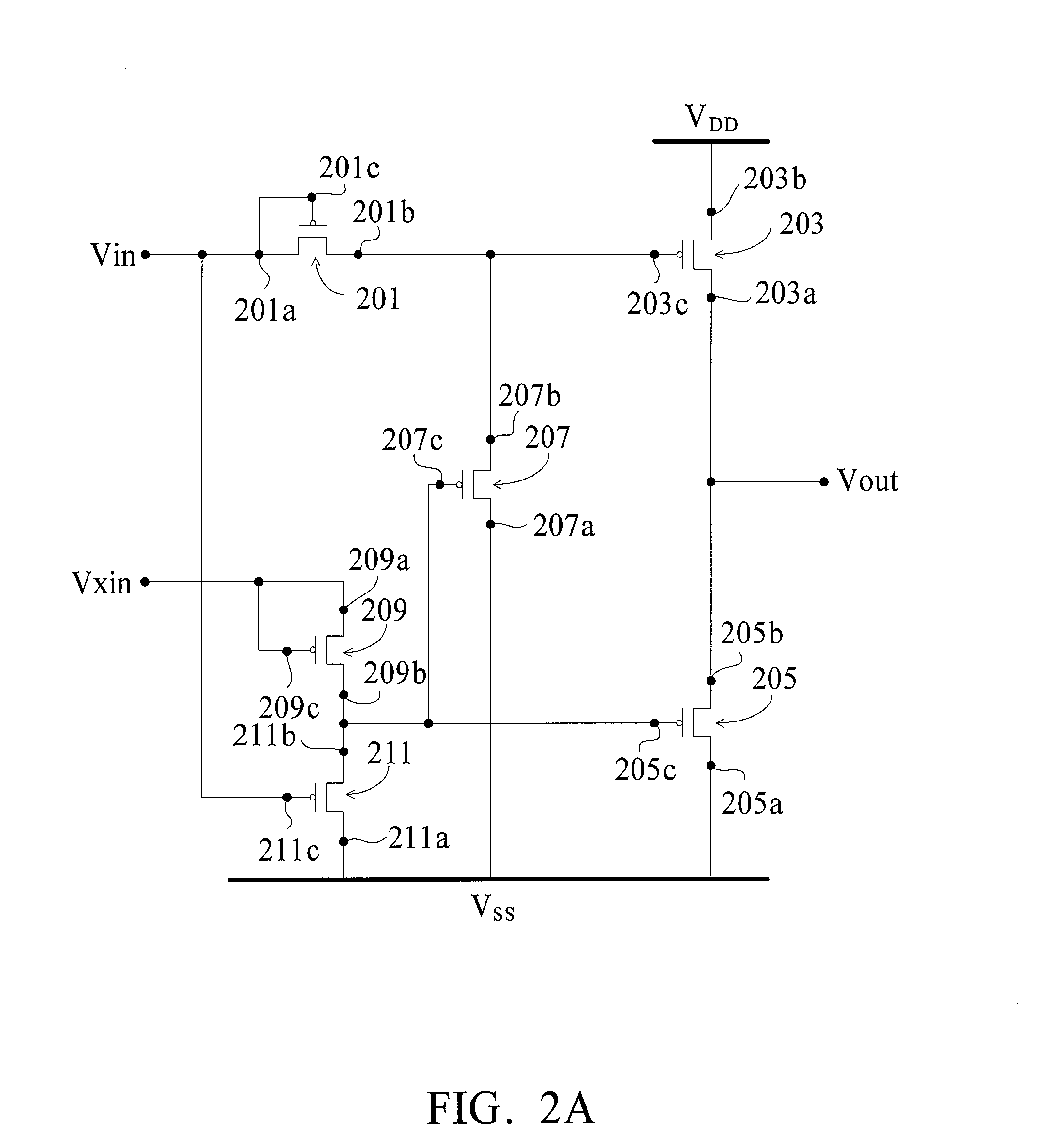
Voltage Level Shifter
ActiveUS20070247412A1Simple manufacturing processSave powerPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersSingle typeLevel converter
A voltage level shifter formed by single-typed transistors comprises two input terminals, two power supply terminals, a plurality of thin-film transistors, and an output terminal. Another voltage level shifter formed by single-typed transistors comprises two input terminals, an output terminal, two power supply terminals, two input units, a first thin-film transistor, a disable unit, a feedback unit, and a second thin-film transistor. The voltage level shifters are formed by single-typed TFTs. When integrating the voltage level shifters into a substrate of a TFT display, the manufacturing processes are simplified. Besides, power is saved.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
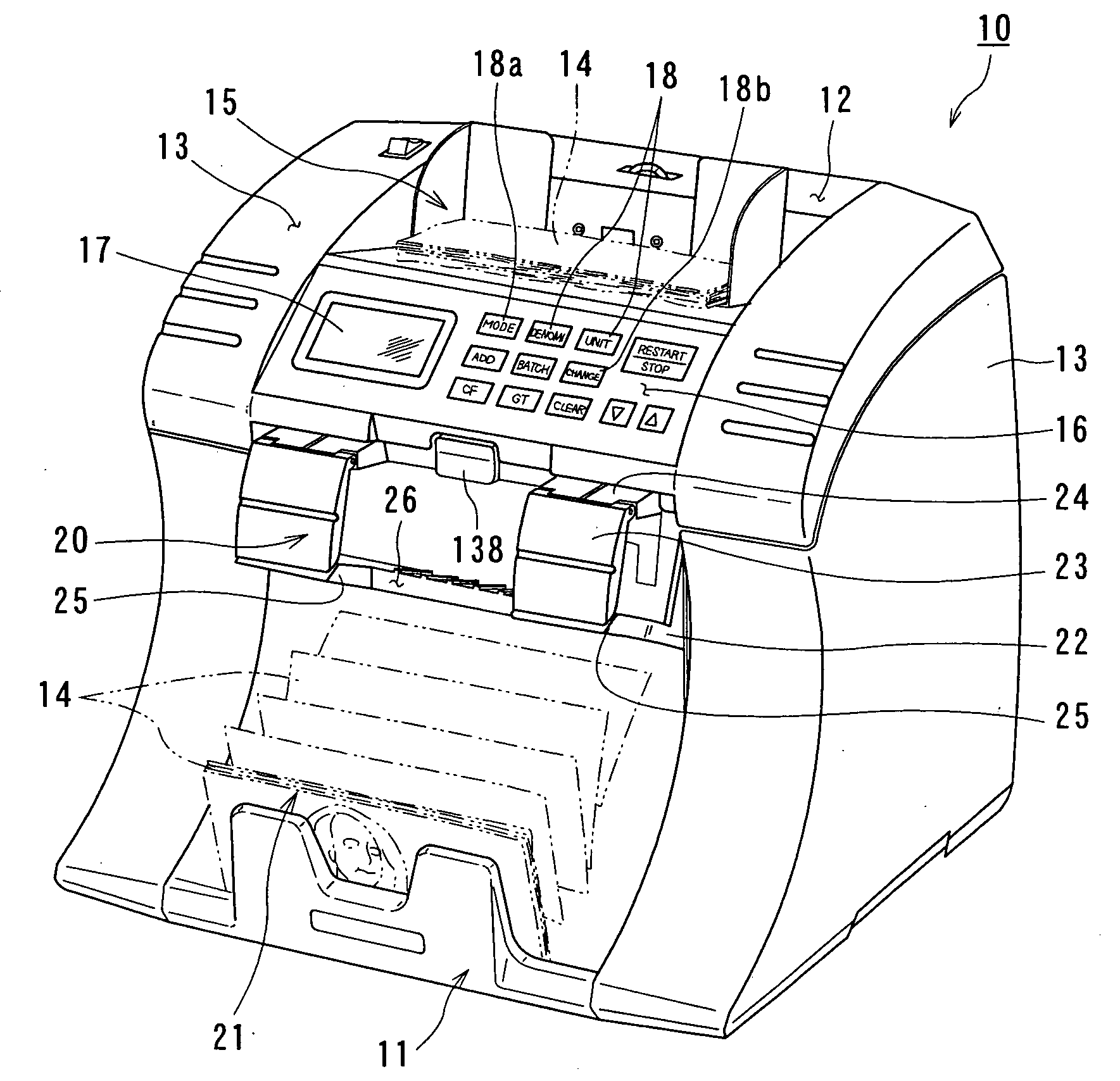
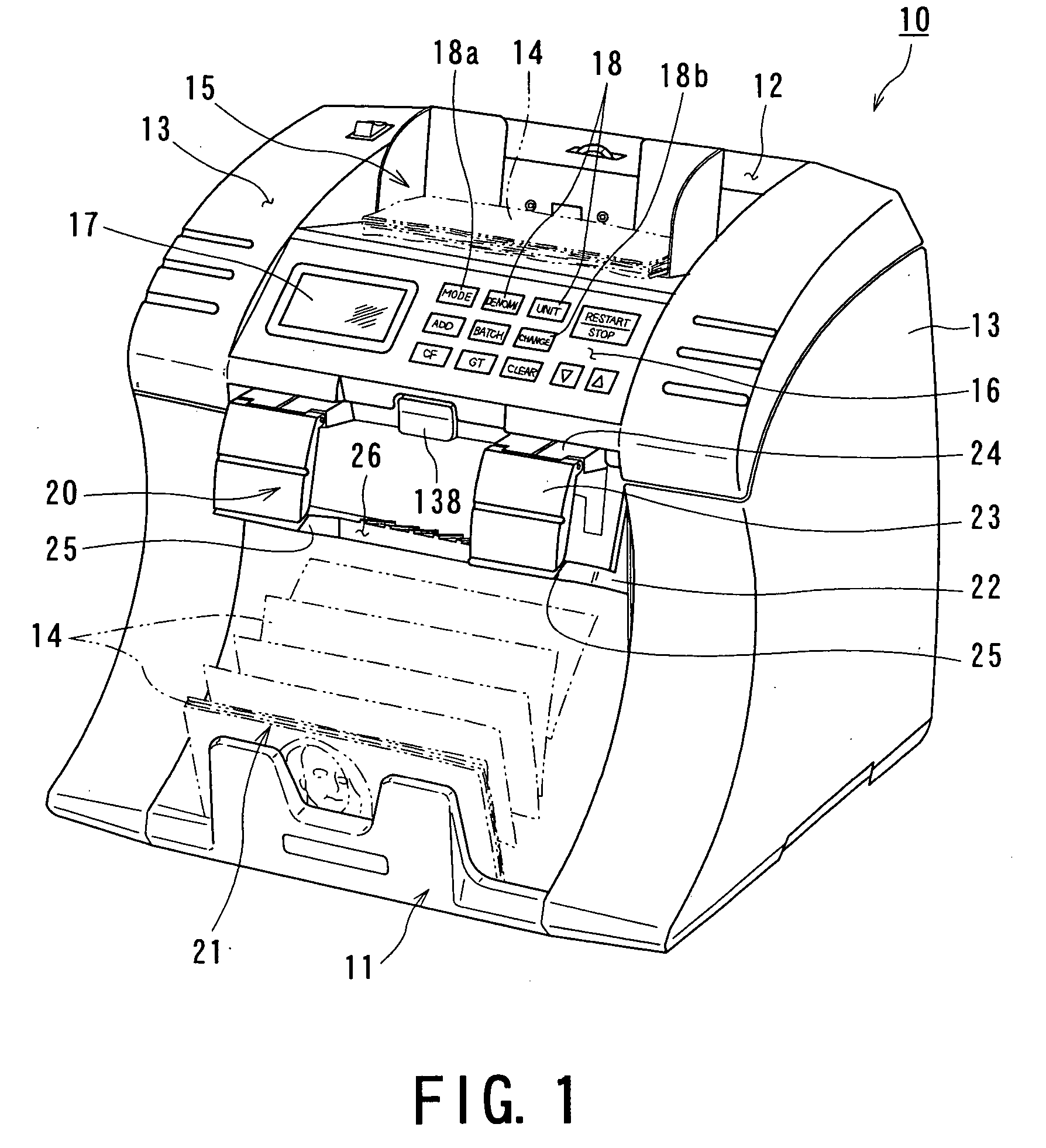
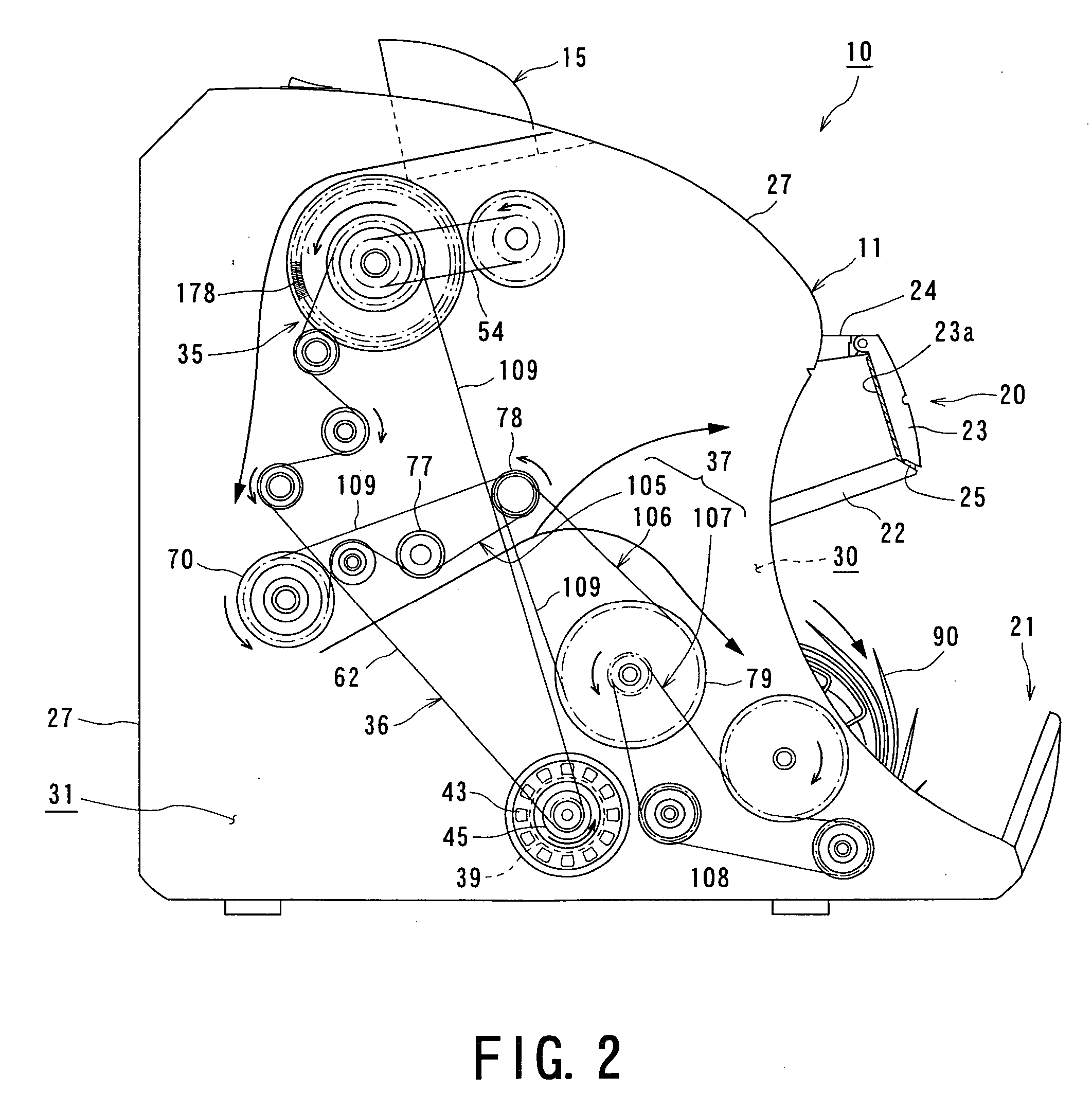
Paper sheet identifying and counting machine and method for identifying and counting paper sheet
InactiveUS20050053183A1Long processIncrease speedImage analysisPaper-money testing devicesPaper sheetStacker
A sheet discriminating / counting machine selects sheets to be discriminated of a predetermined country or region by discrimination object selecting means, transports the sheets to be discriminated at high speed along a transporting path, and performs sheet discriminating / counting processing at a sheet discriminating / counting unit disposed along the transporting path. The sheet discriminating / counting machine comprises: a hopper to which sheets to be discriminated are supplied; a sheet transporting device for transporting sheets supplied to the hopper one by one along a transporting path with the shorter side of each sheet parallel to the transporting direction; a sheet discriminating unit disposed along the transporting path for discriminating / counting sheets; and a stacker upon which sheets fed out from the transporting path are stacked. The transporting path is provided with a curved transporting region which is curved in a U-shape partway and has a reject transport path connected to a pocket from a the subsequent downstream side transporting path. The sheet discriminating / counting machine performs discrimination processing of 1200 sheets or more per minute and has one stacker and one pocket.
Owner:BILLCON
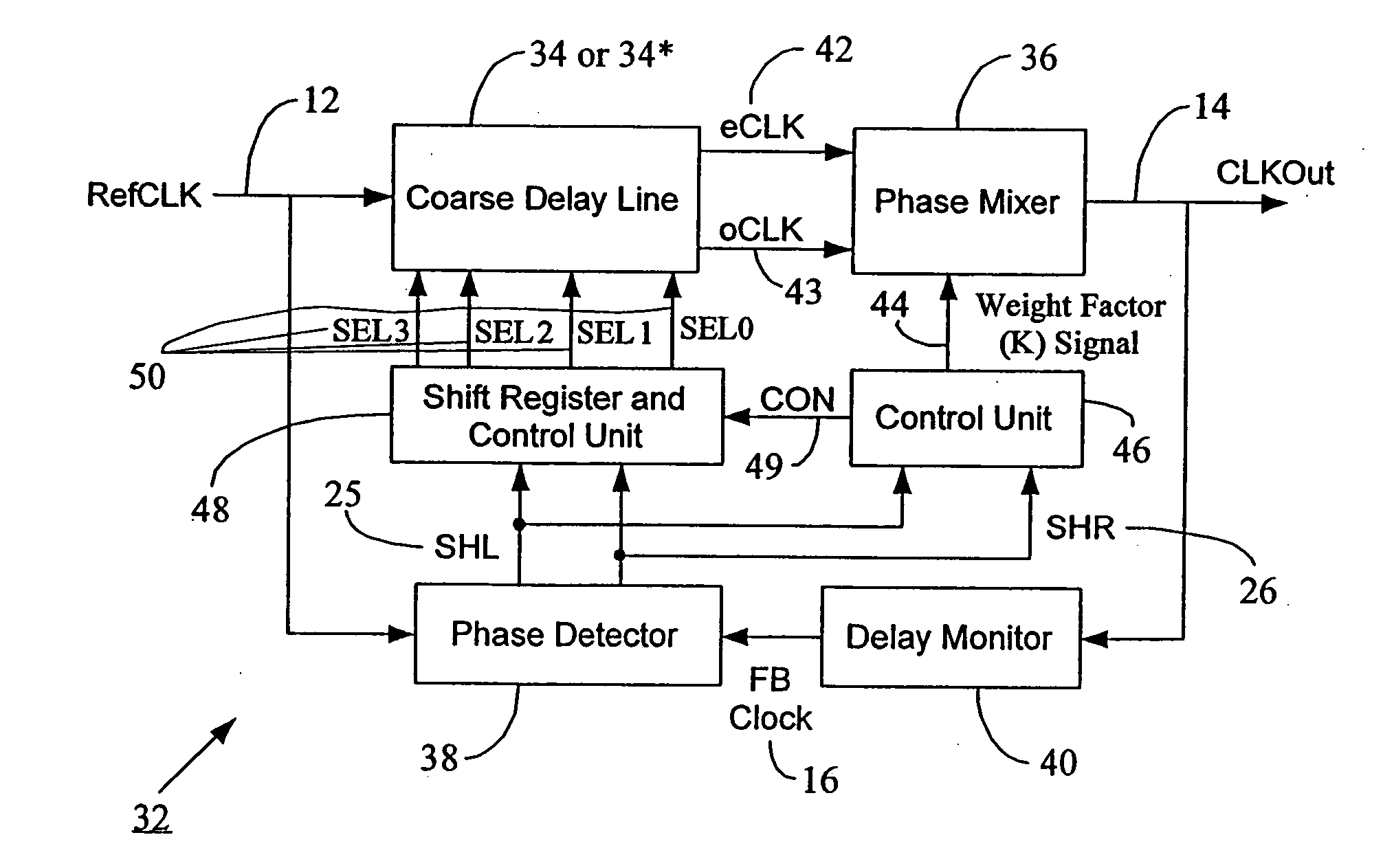
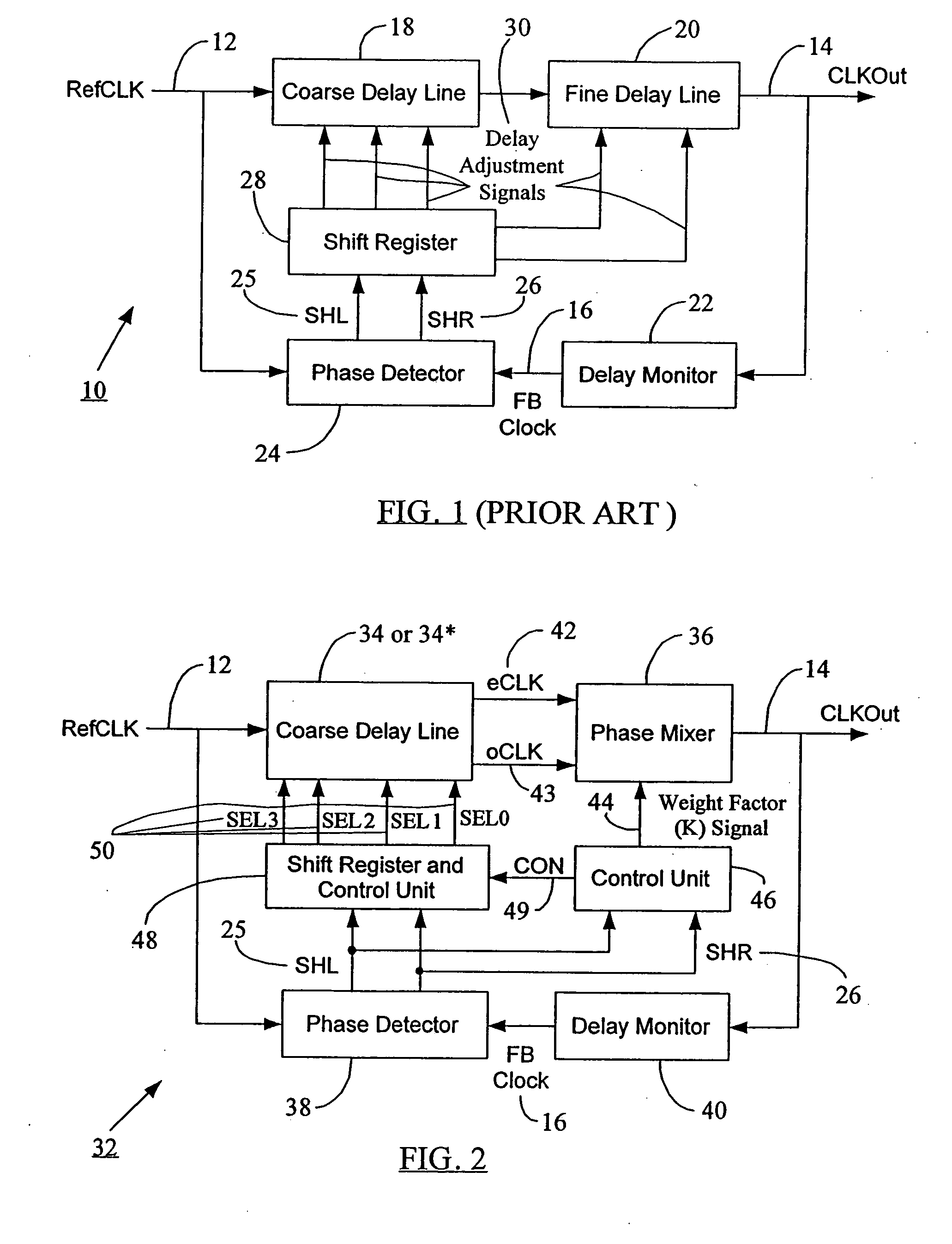
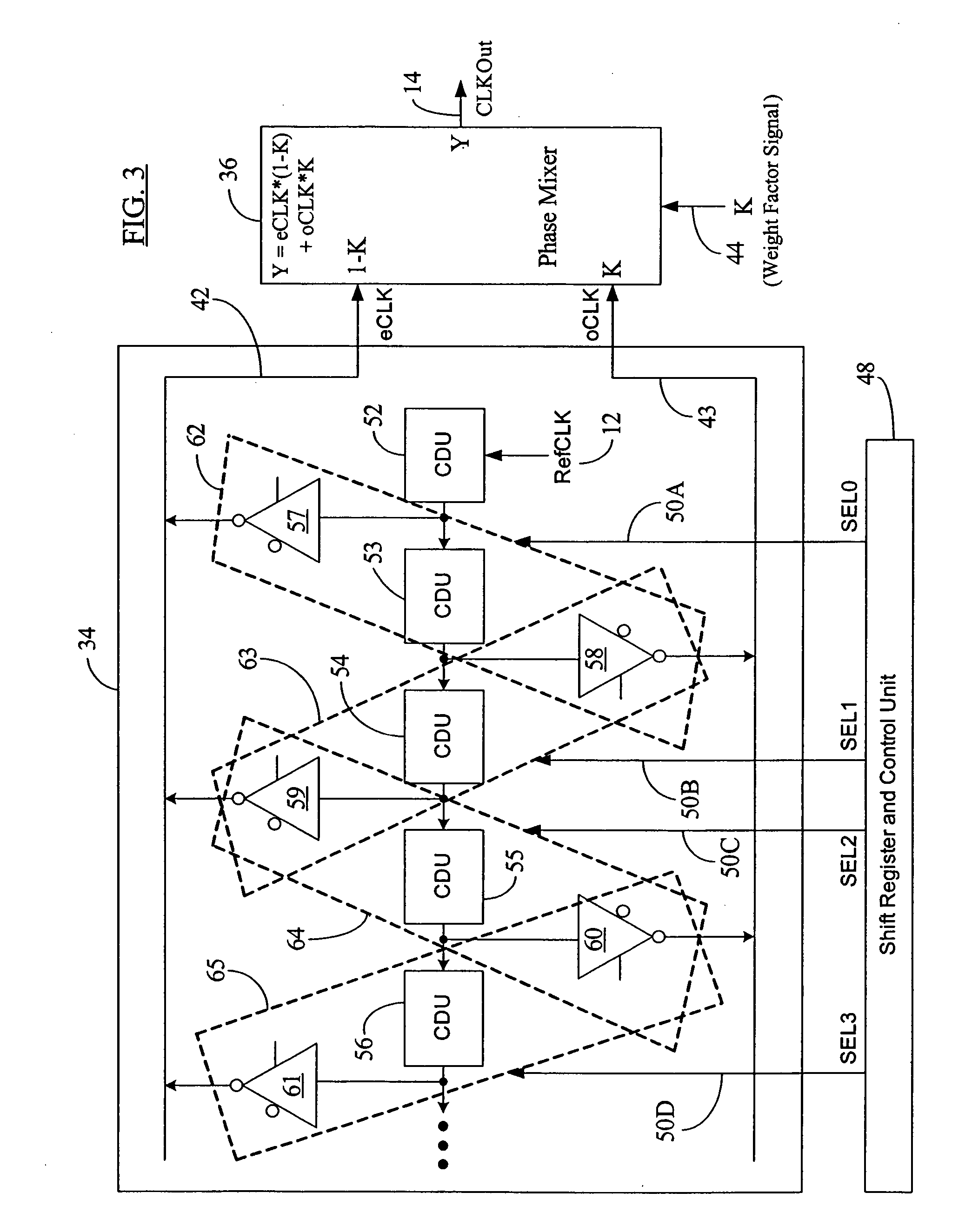
Seamless coarse and fine delay structure for high performance DLL
ActiveUS20070030753A1Smooth phase transitionDelay problemPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersClock timePhase difference
A clock synchronization system and method avoids output clock jitter at high frequencies and also achieves a smooth phase transition at the boundary of the coarse and fine delays. The system may use a single coarse delay line configured to generate two intermediate clocks from the input reference clock and having a fixed phase difference therebetween. The coarse delay line may have a hierarchical or a non-hierarchical structure. A phase mixer receives these two intermediate clocks and generates the final output clock having a phase between the phases of the intermediate clocks. The coarse shifting in the delay line at high clock frequencies does not affect the phase relationship between the intermediate clocks fed into the phase mixer. The output clock from the phase mixer is time synchronized with the input reference clock and does not exhibit any jitter or noise even at high clock frequency inputs. Because of the rules governing abstracts, this abstract should not be used to construe the claims.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
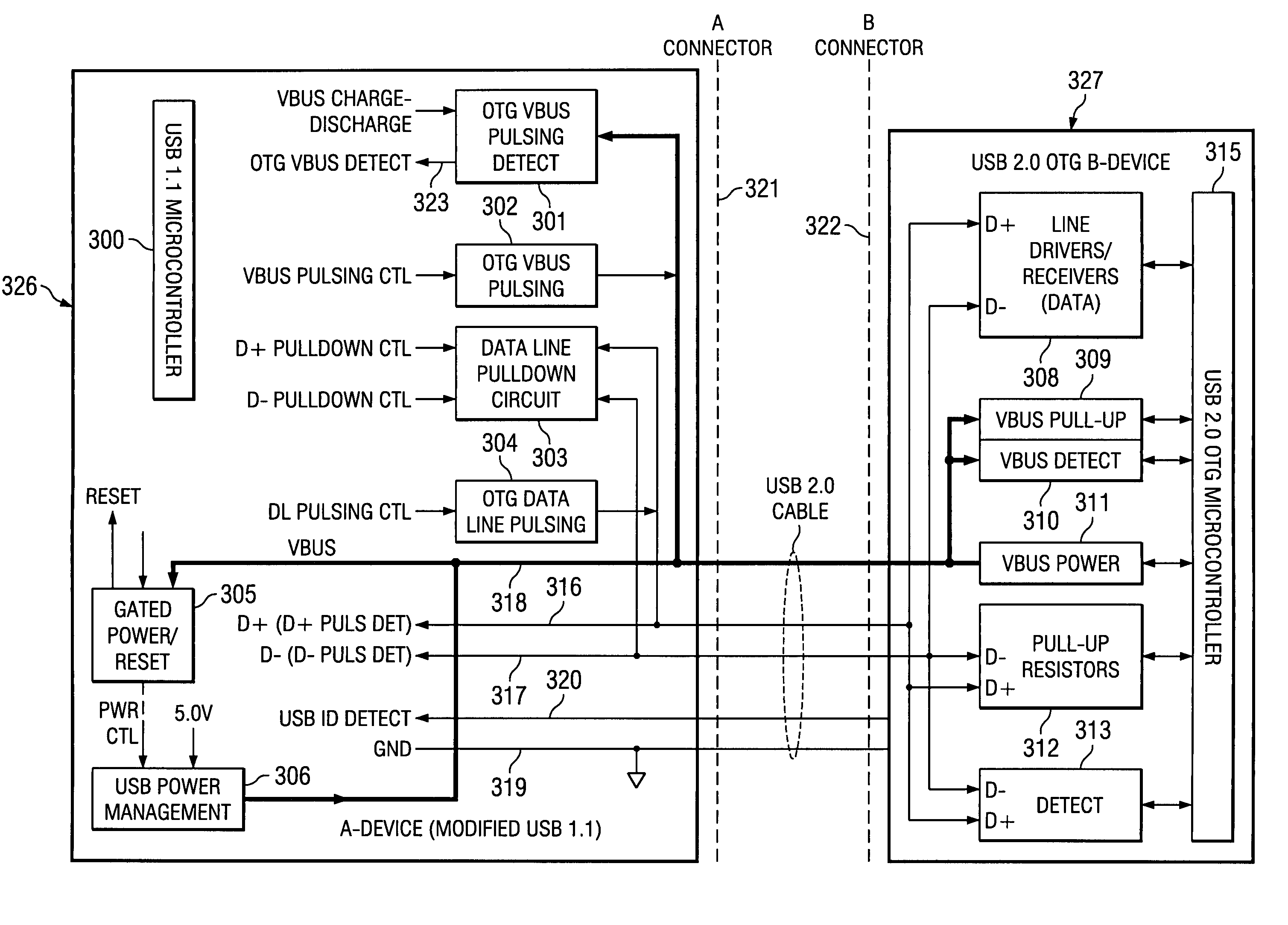
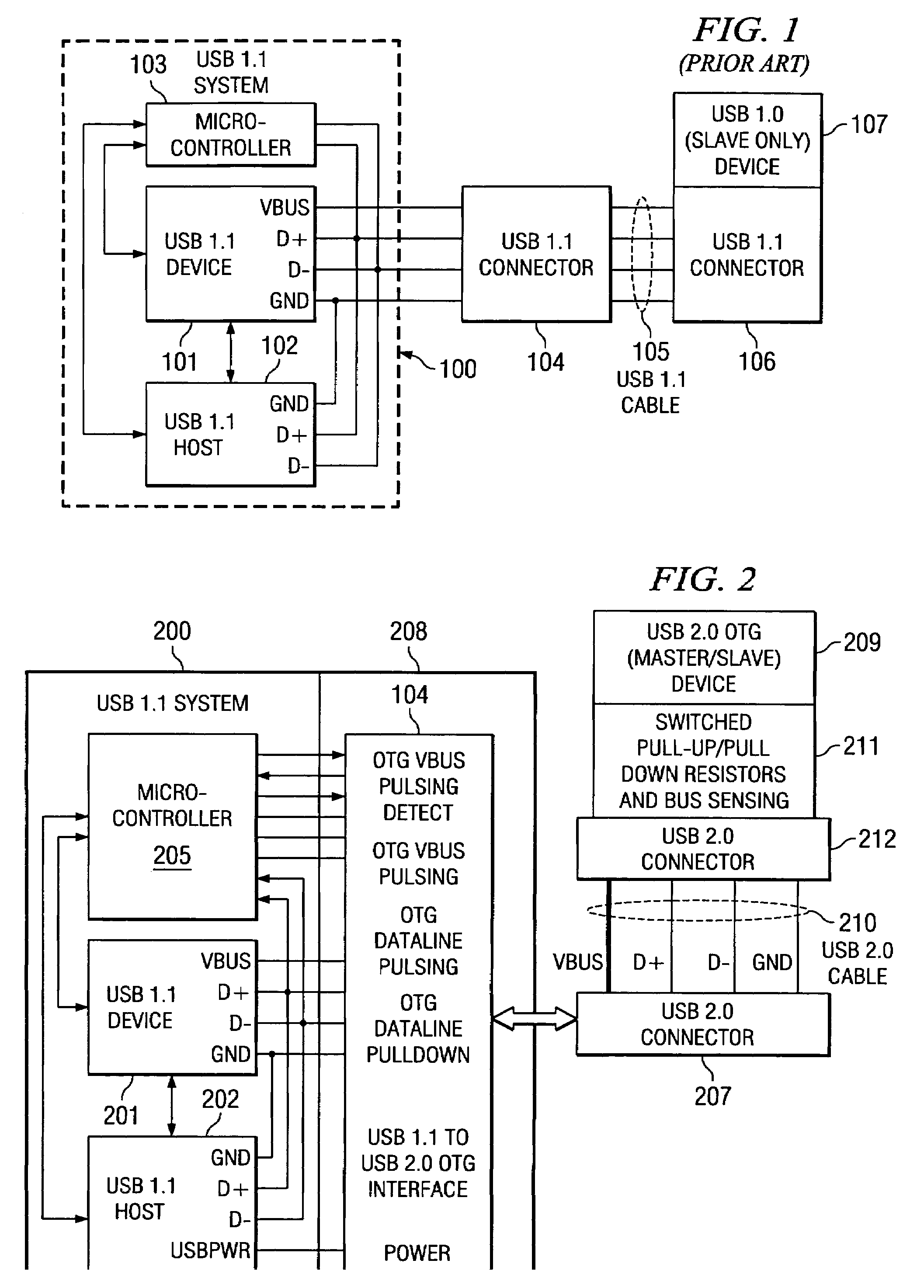
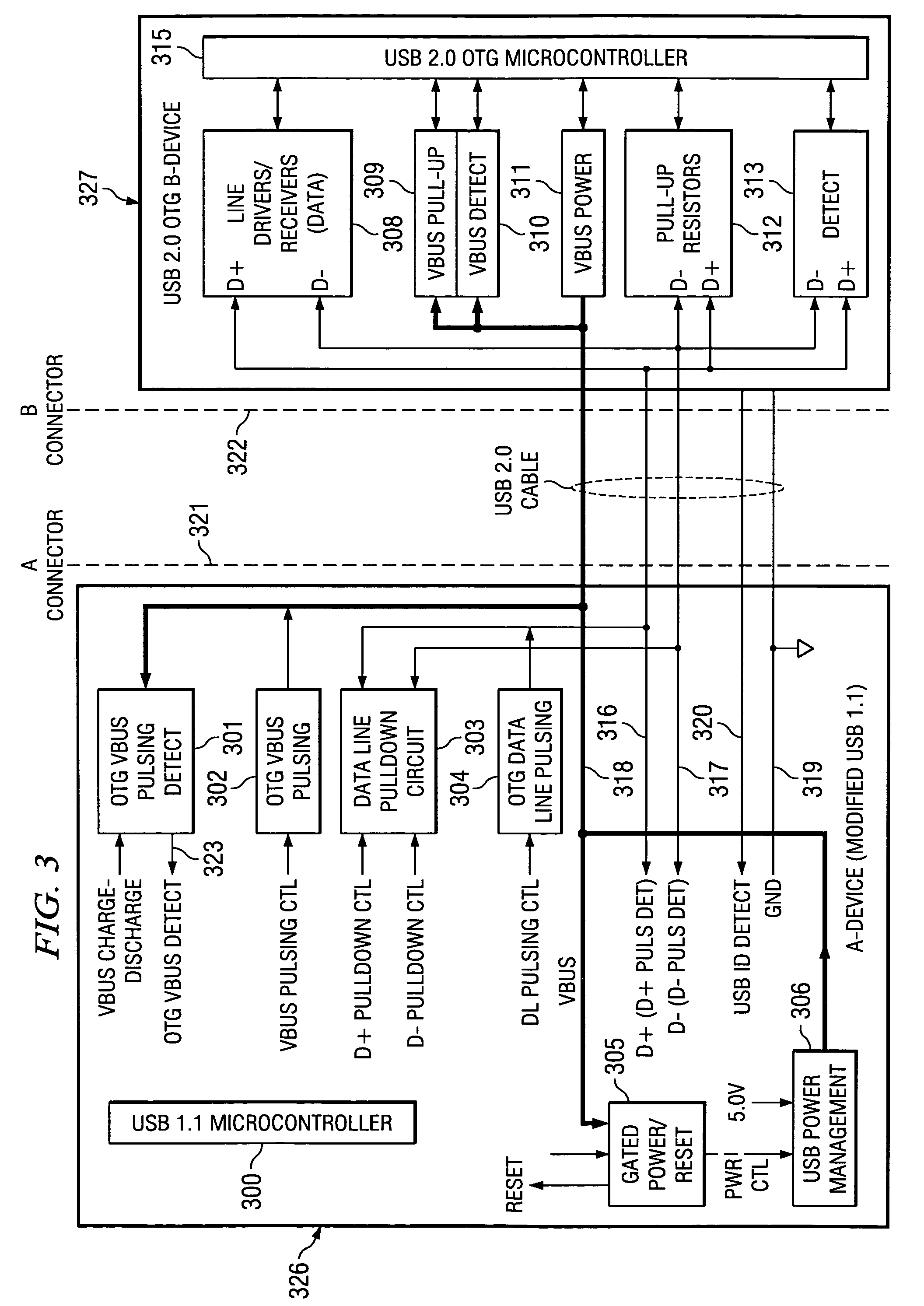
USB 1.1 for USB OTG implementation
This invention enables a USB 1.1 device and a USB 1.1 host to communicate seamlessly with a USB OTG device. The invention complies with both USB 1.1 and OTG specifications. The invention includes the USB 1.1 host, USB 1.1 device and mixed signal circuits to implement USB OTG functions. The mixed signal components are controlled by the USB 1.1 device microcontroller. The invention is a cost effective implementation compared to a custom ASIC design for USB OTG implementation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Receiver circuit and receiving method
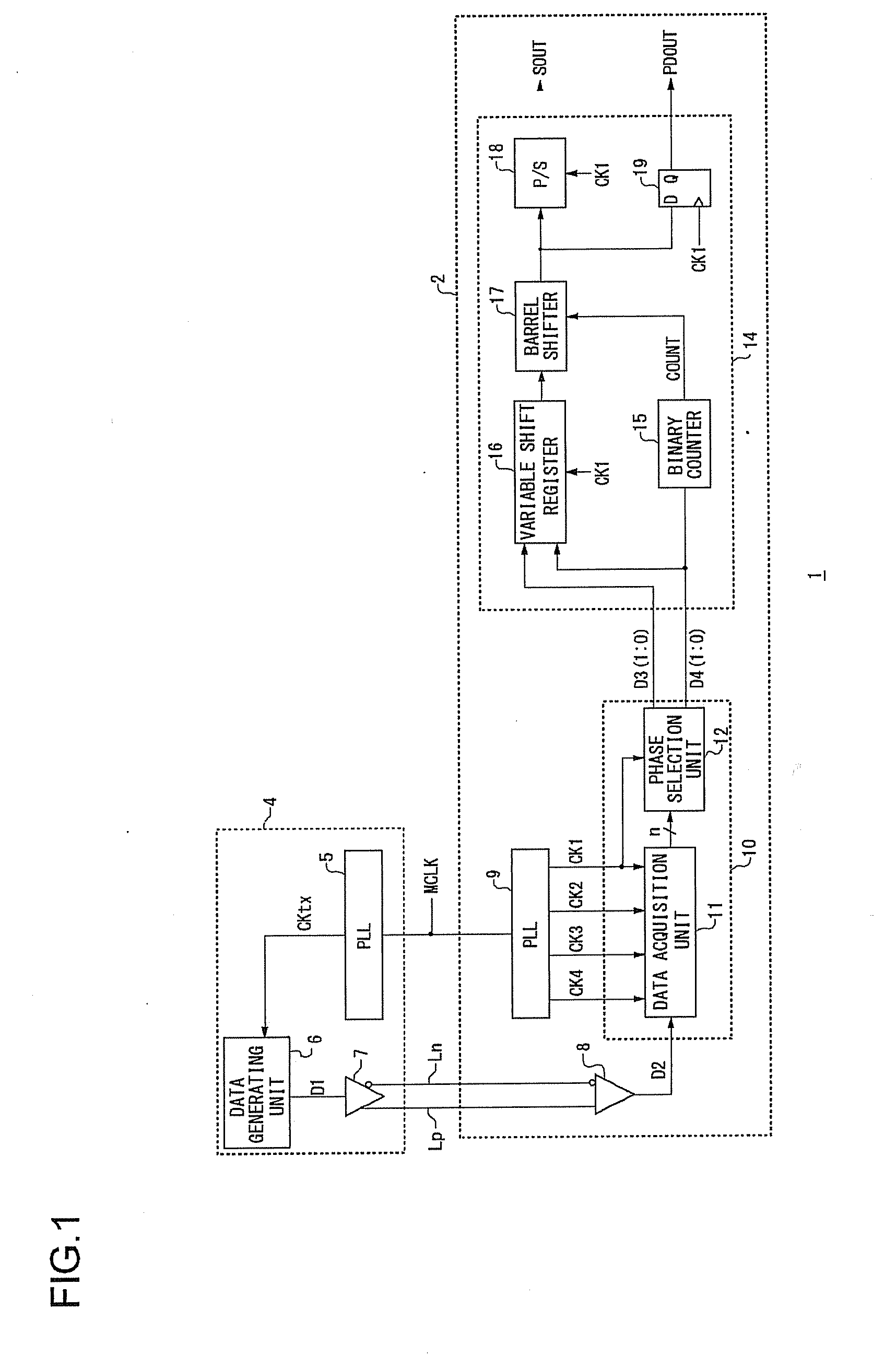
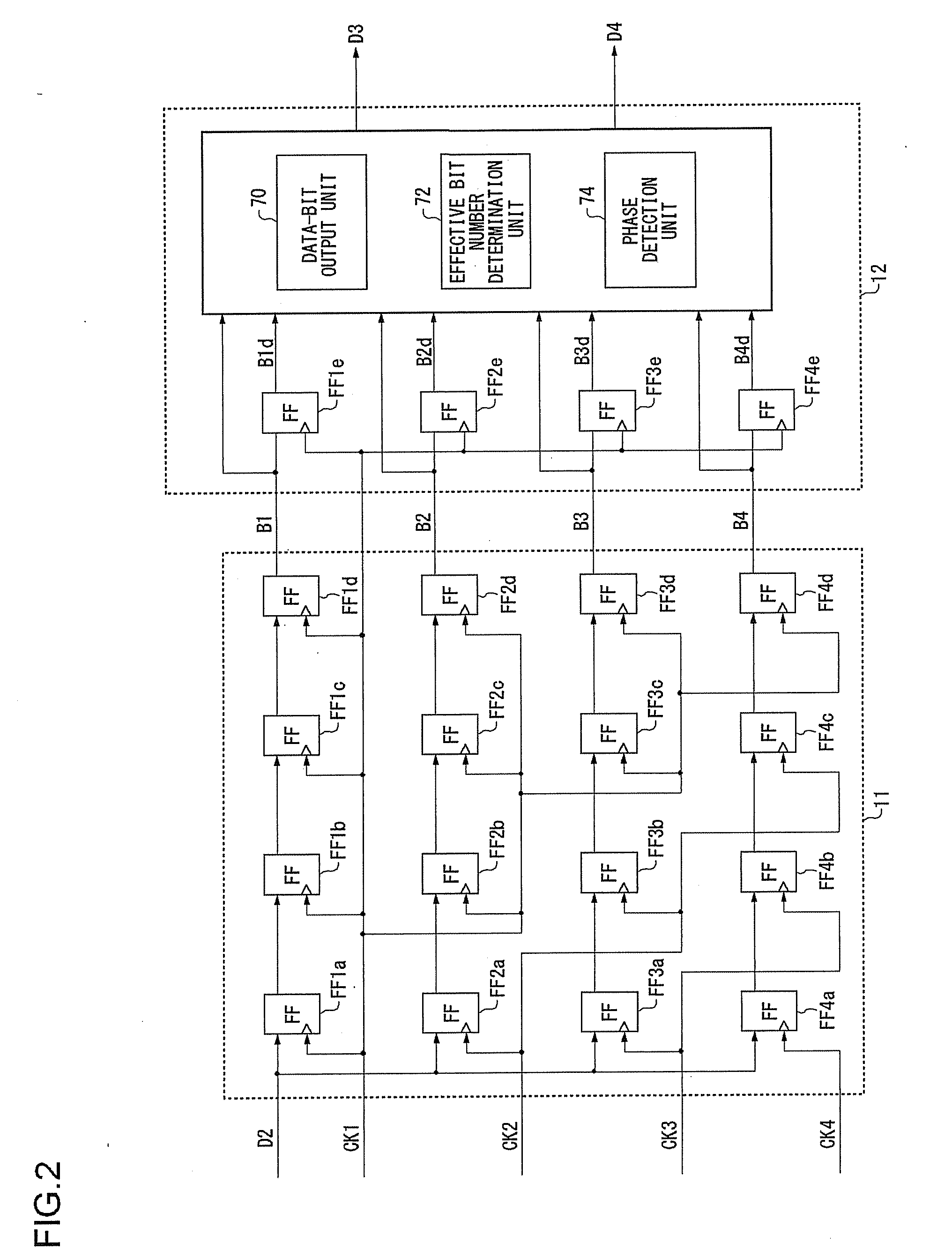
InactiveUS20080159444A1Parallel/series conversionPulse automatic controlPhase shiftedTransition edge
Clock signals are supplied, with a phase shift of 1 / n cycles between adjacent clock signals. A data acquisition unit acquires serial data at a timing of each of the clock signals. A phase detection unit detects the phase of the transition edge of the serial data using n bits of data. An effective bit number determination unit determines the effective bit number, which is the number of bits to be acquired, based upon the phase of the transition edge of the serial data in the current data-bit acquisition step and the phase of the transition edge of the serial data in the previous data-bit acquisition step. A data-bit output unit outputs the effective bit number of the bits of data acquired at a timing of each clock signal having a predetermined phase relation with the transition edge of the serial data.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Modified high-efficiency phase shift modulation method
InactiveUS20060221648A1Reduce power lossSpeed up the conversion processEfficient power electronics conversionCounting chain pulse countersPhase shiftedFull bridge
Disclosed is a high-efficiency phase shift modulation method suitable for use in a traditional DC / AC single-phase full-bridge inverter. In this method, phase-shifted signal timing is used to modulate a duty cycle so that a power transistor is operated in a zero voltage switching state. As such, noises and switching loss of a switching device when turned on or off, may be reduced and thus efficiency of the inverter may be promoted. With this high-efficiency phase shift modulation method, at least the following advantages may be achieved: lower switching stresses, lower switching losses and thus increased conversion efficiency, lower electromagnetic interferences (EMIs) and no additional circuit required and thus easier realization of a controller for the inverter.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
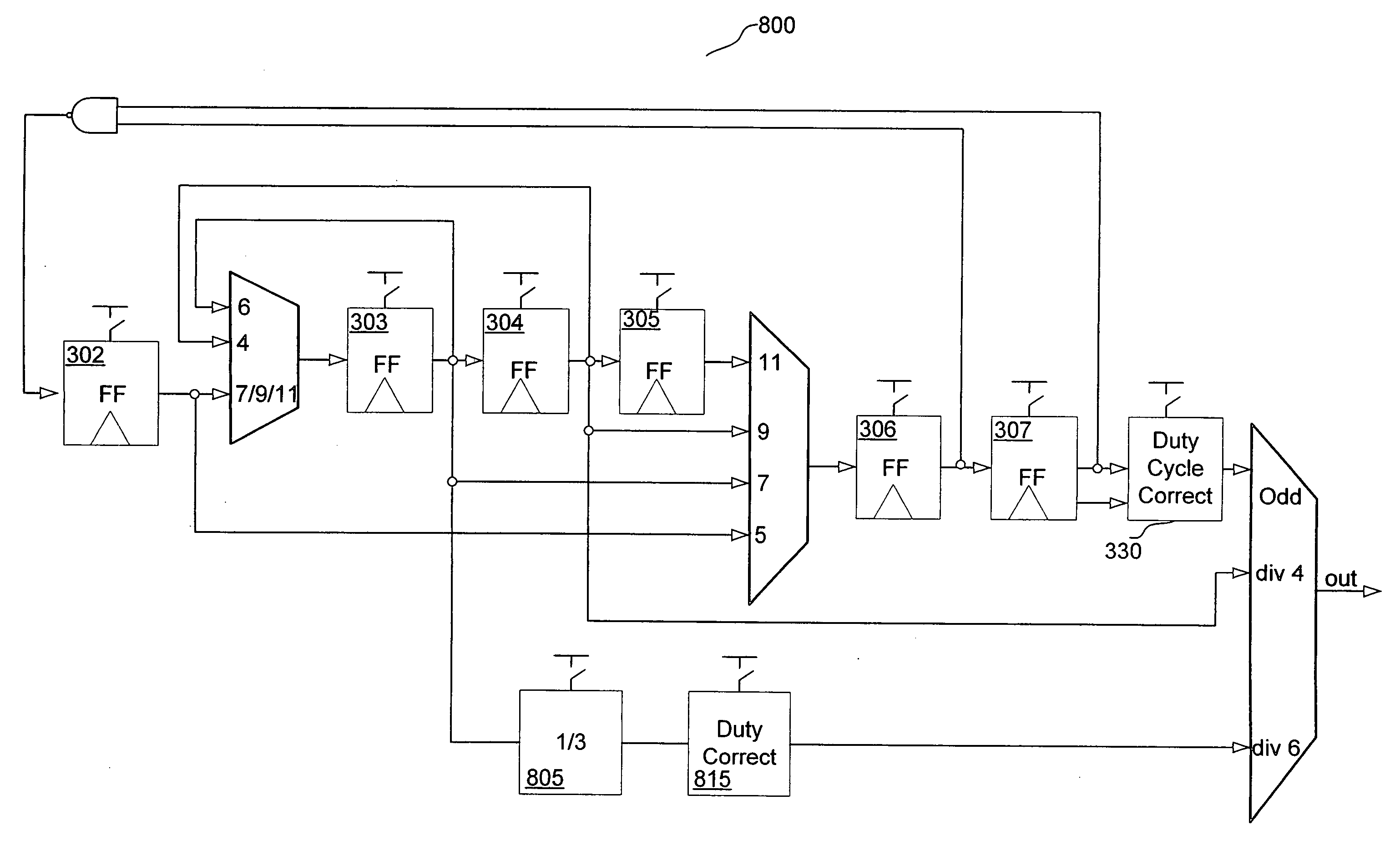
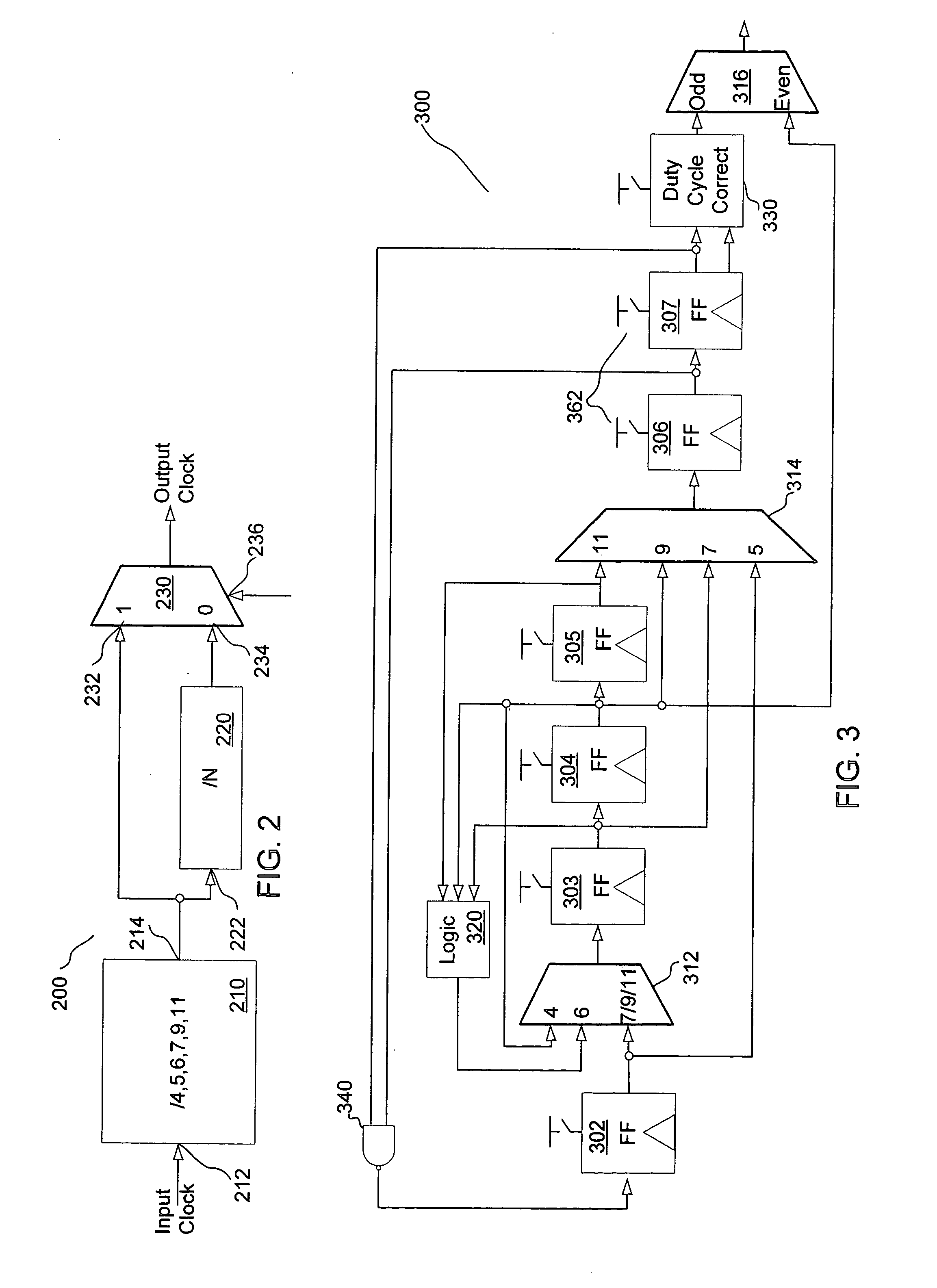
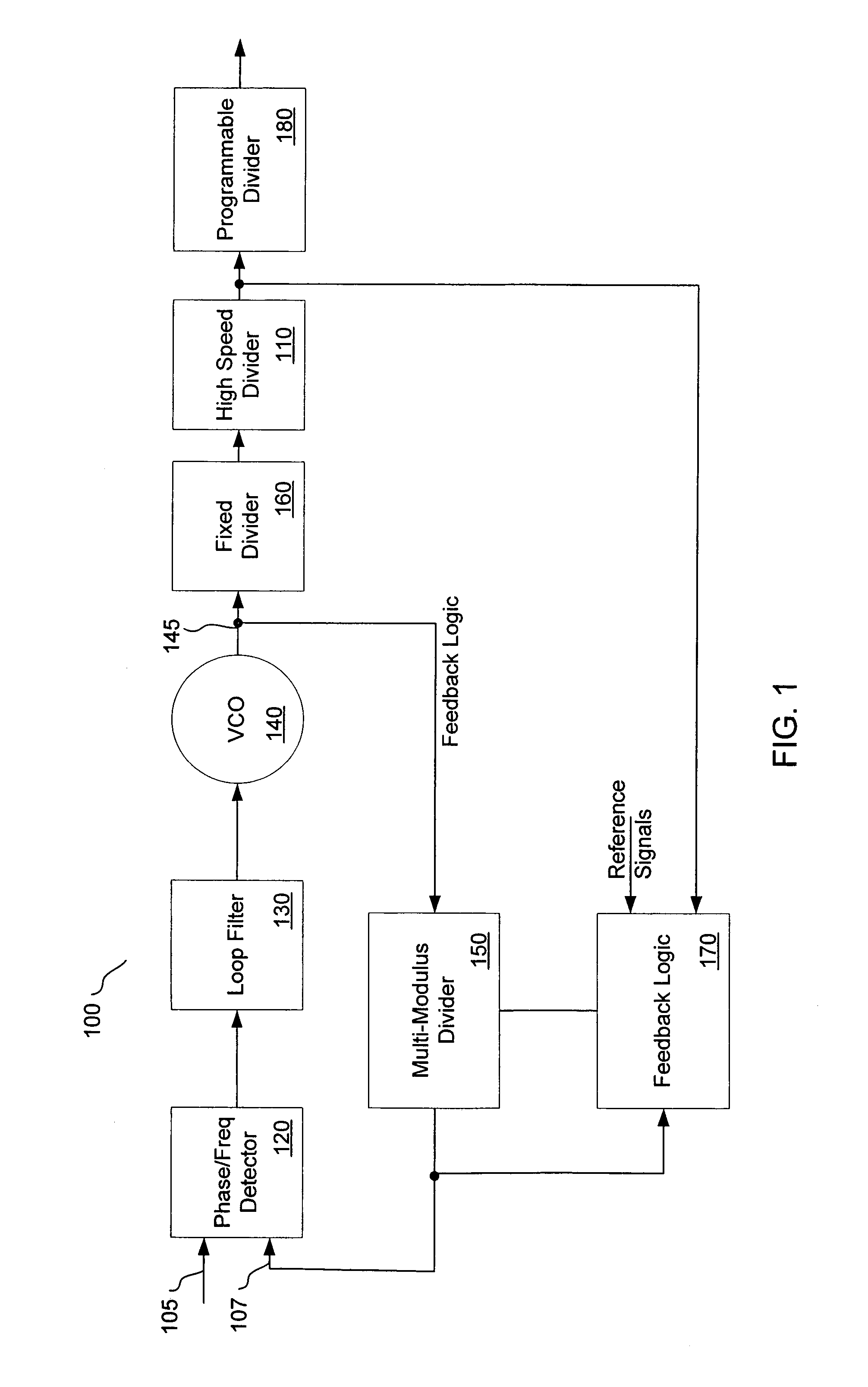
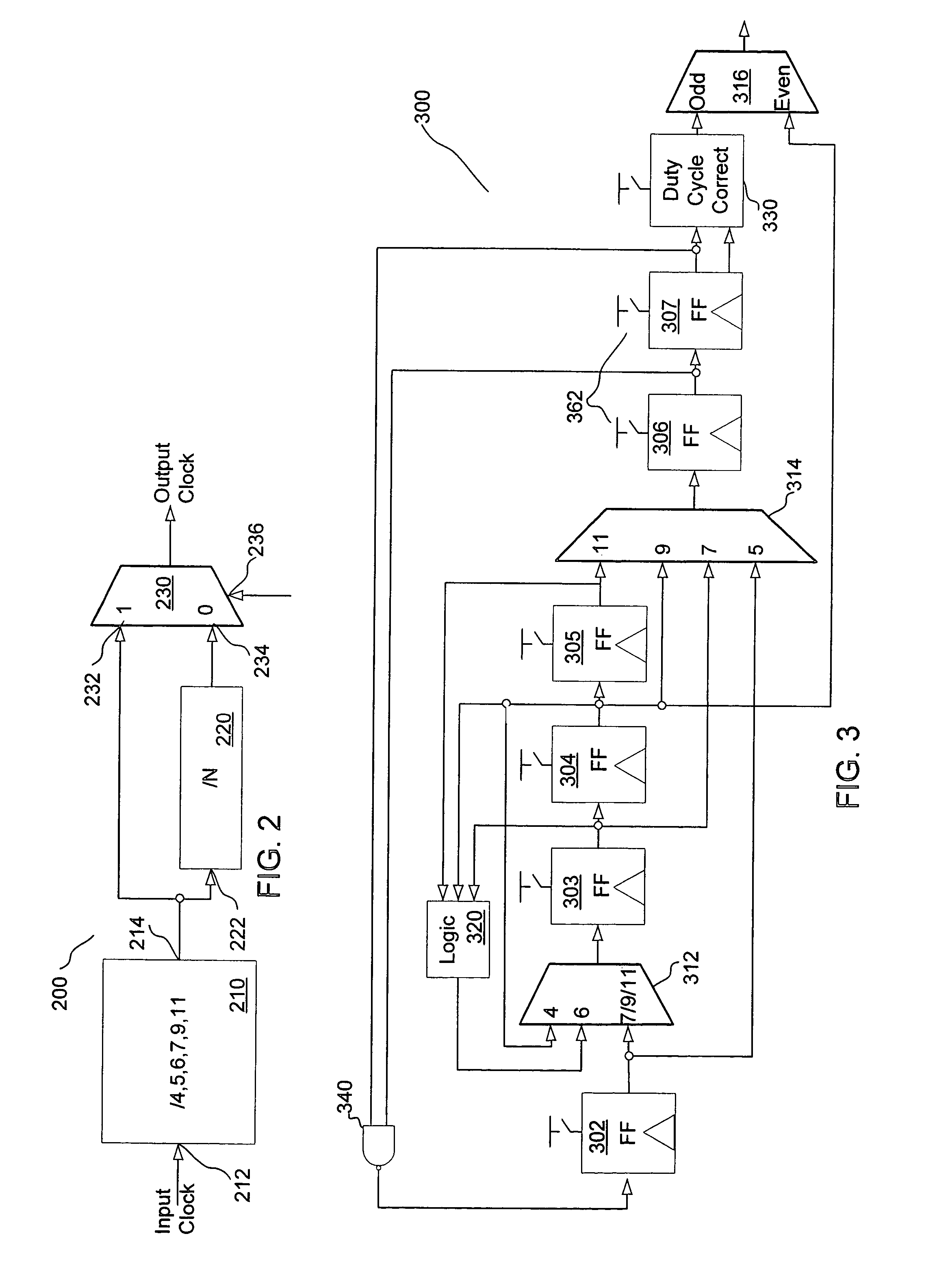
Programmable frequency divider
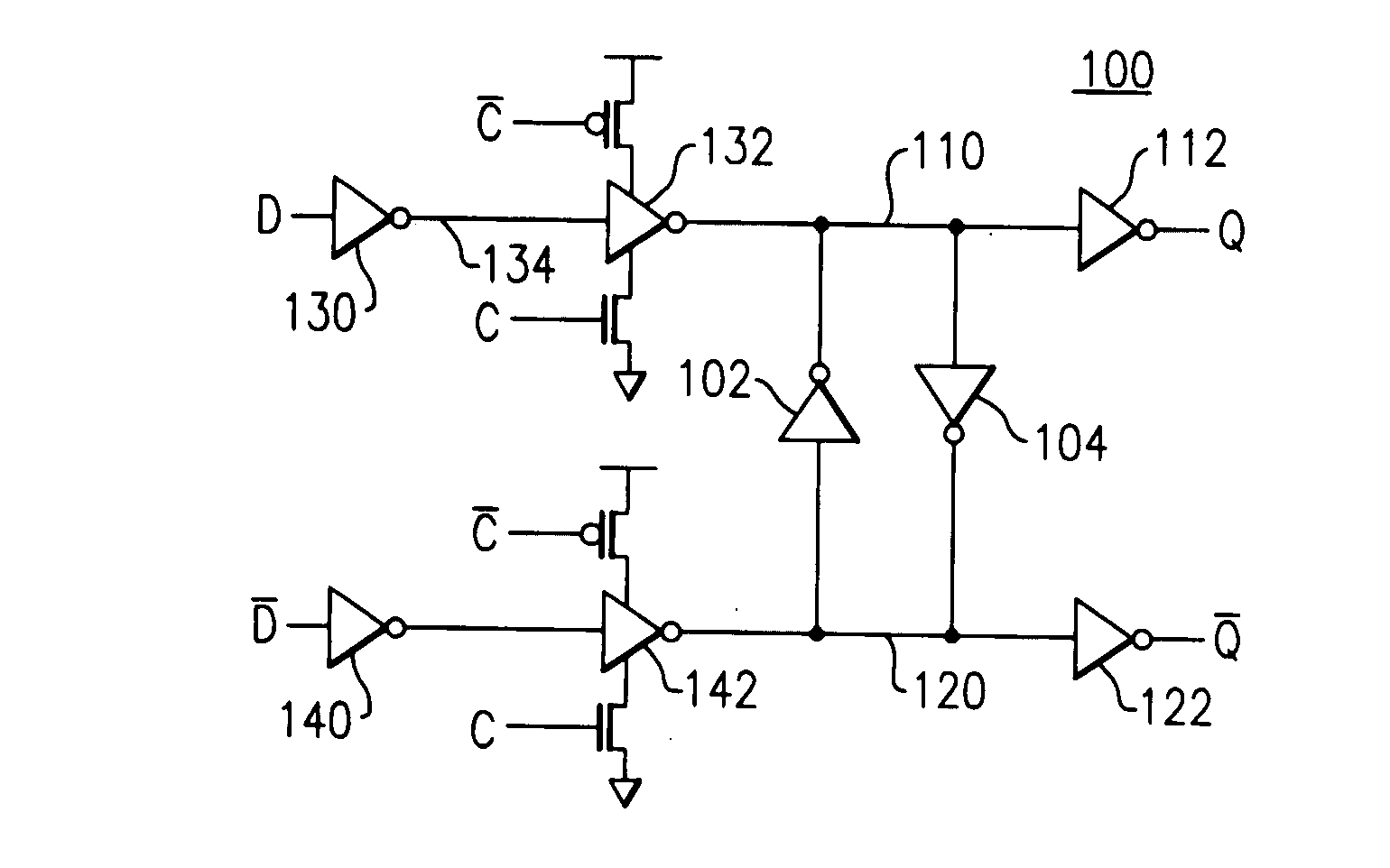
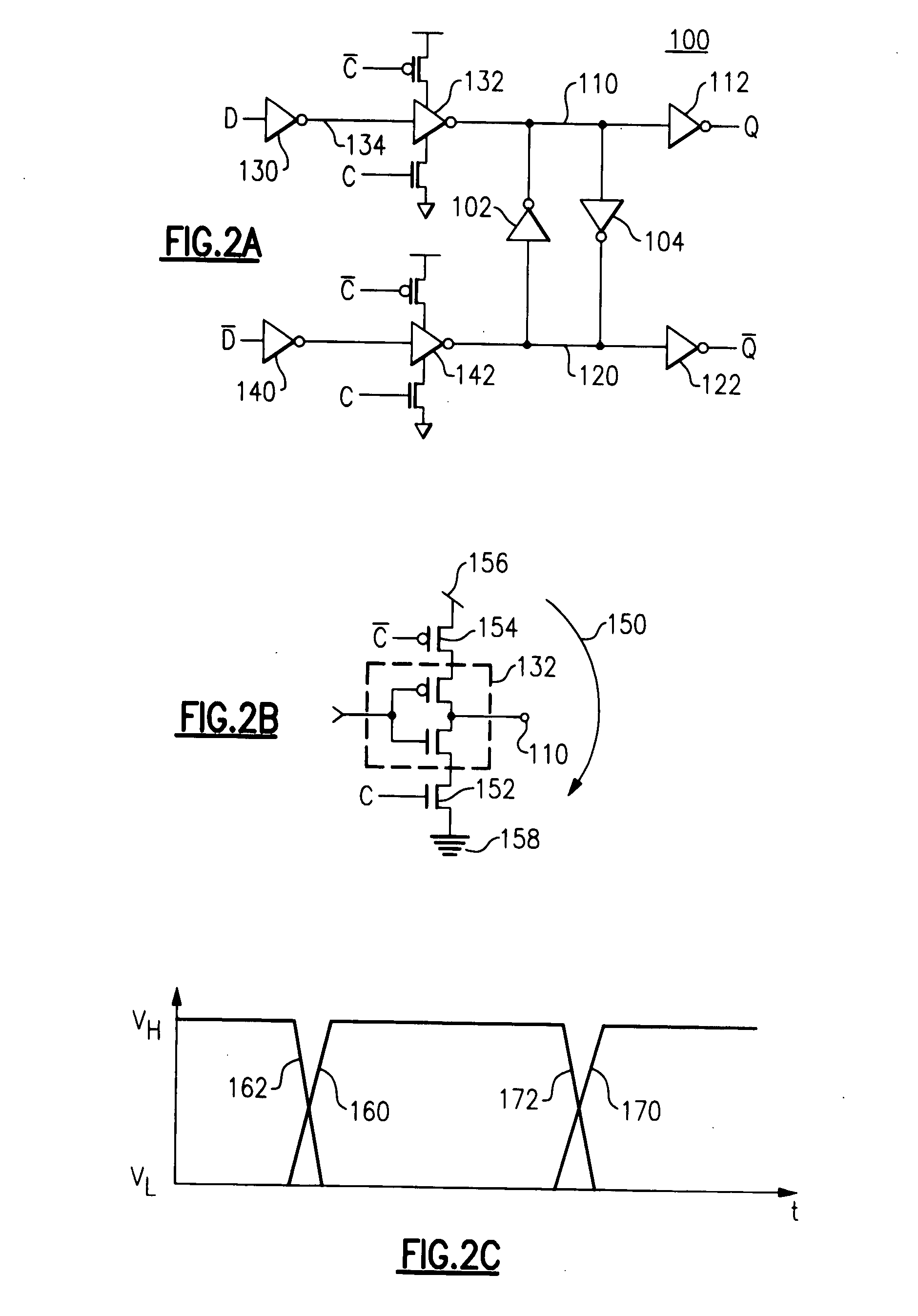
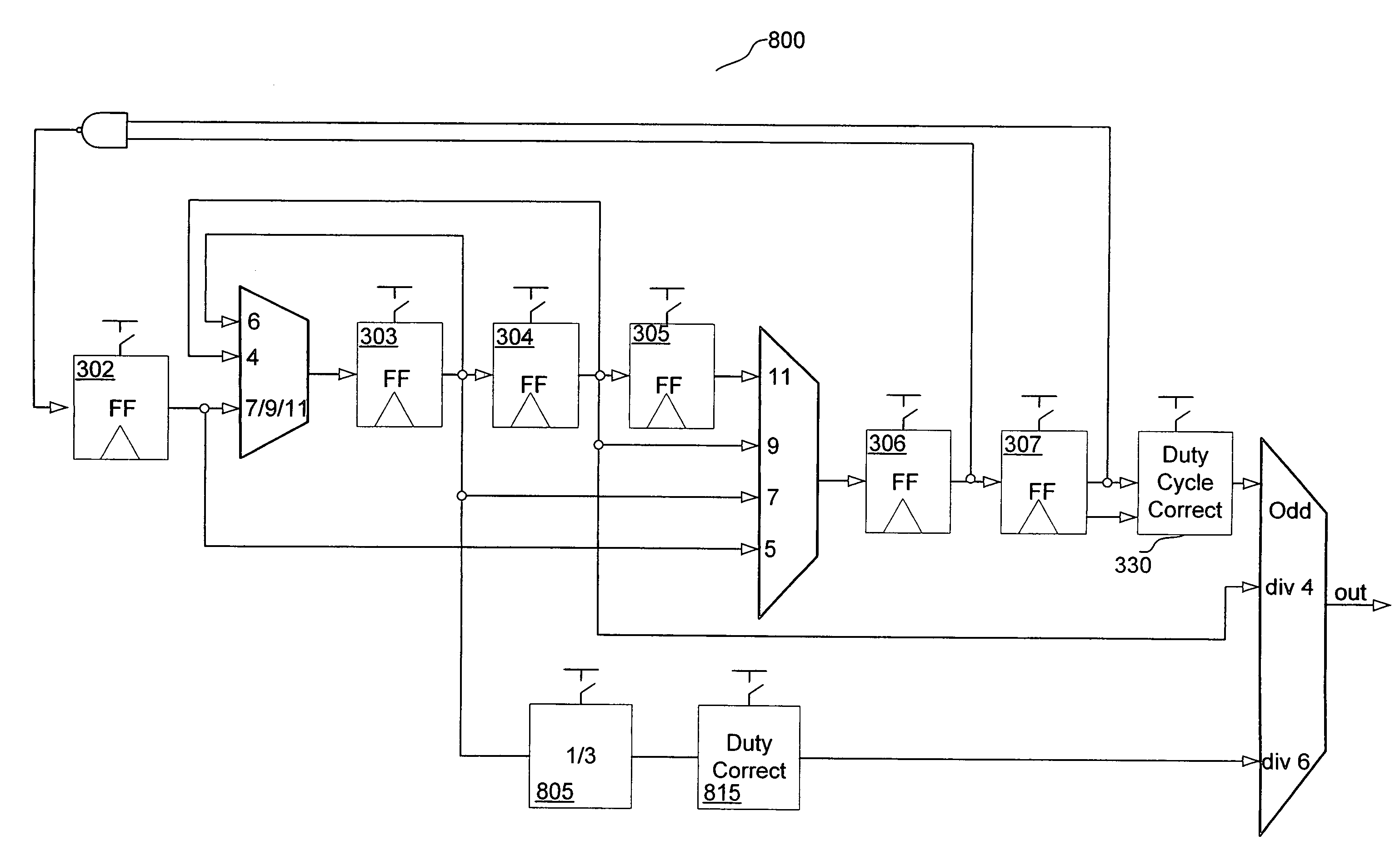
ActiveUS20050212570A1Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageMultiplexerEngineering
A divider is disclosed herein. The divider includes a sequence of divide stages programmably coupled to provide a variety of divide ratios. The divider also includes one or more multiplexers to feedback the output of a divide stage to the input of a divide stage earlier in the sequence of divide stages. The divider may also include duty cycle correction circuitry and self correction logic to correct abnormal logic states. The divide stages can operate in synchronism with each other. Multiplexer functionality, self correction circuitry functionality, and divide stage functionality may be implemented in a combination latch circuit.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
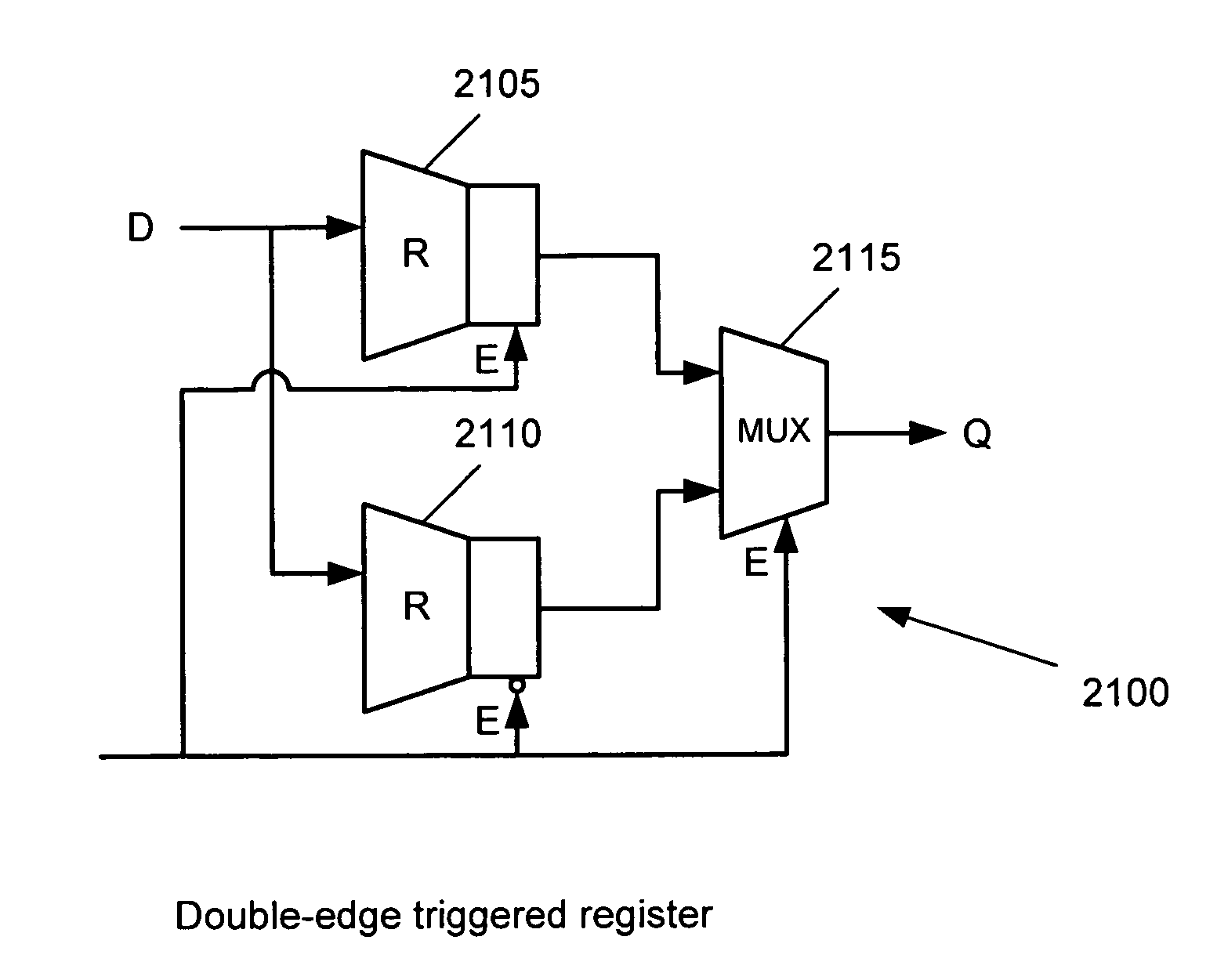
User registers implemented with routing circuits in a configurable IC
Some embodiments of the invention provide a configurable integrated circuit (“IC”). The configurable IC includes a set of configurable logic circuits for configurably performing a set of functions. The configurable IC also includes a set of configurable routing circuits for routing signals to and from the configurable circuits. During several operational cycles of the configurable IC, a set of data registers are defined by the configurable routing circuits. These data registers may be used wherever a flip-flop can be used.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Direct digital synthesizer for reference frequency generation
InactiveUS20110095830A1Reduce power consumptionLow frequency signalPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersFrequency generationRandom noise
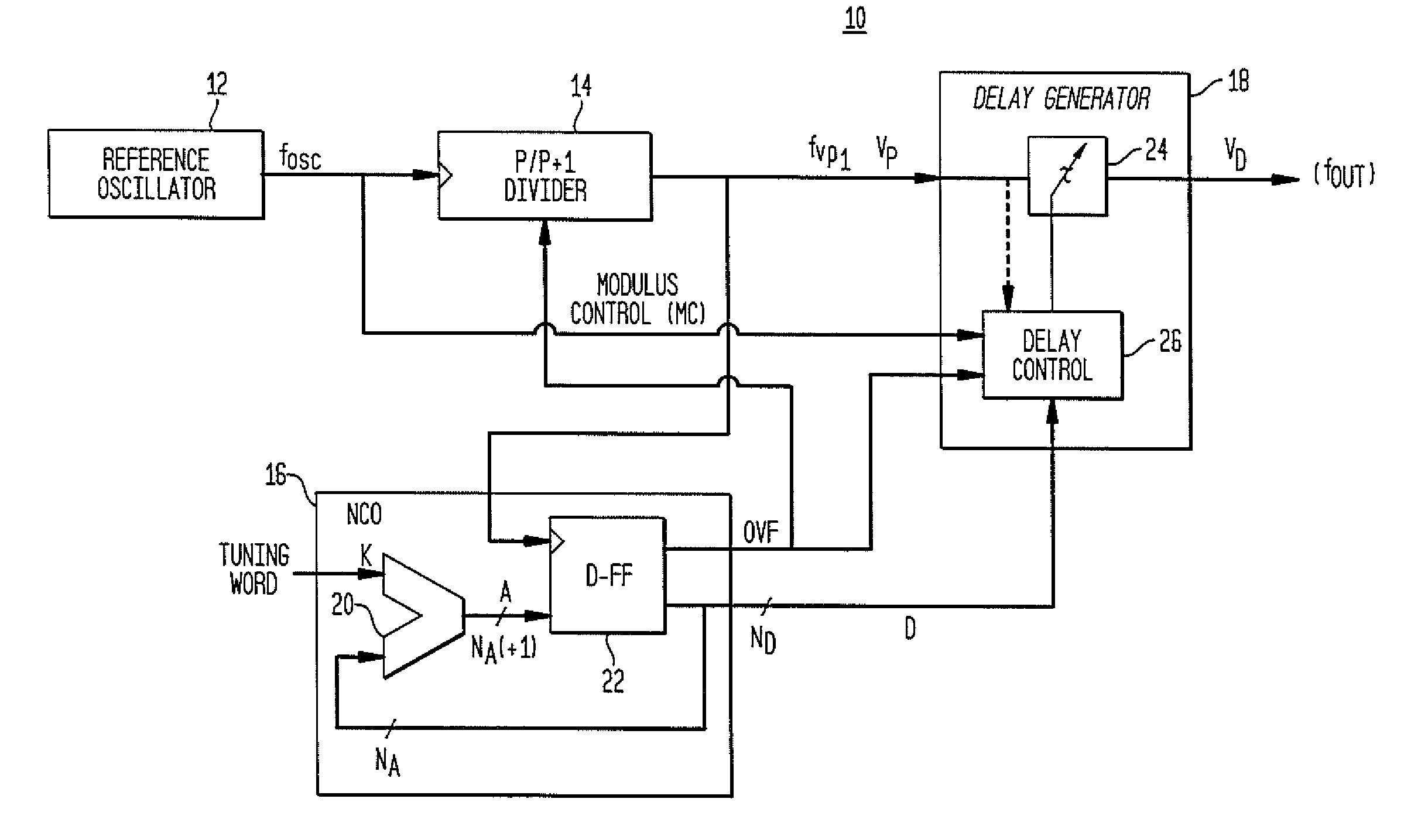
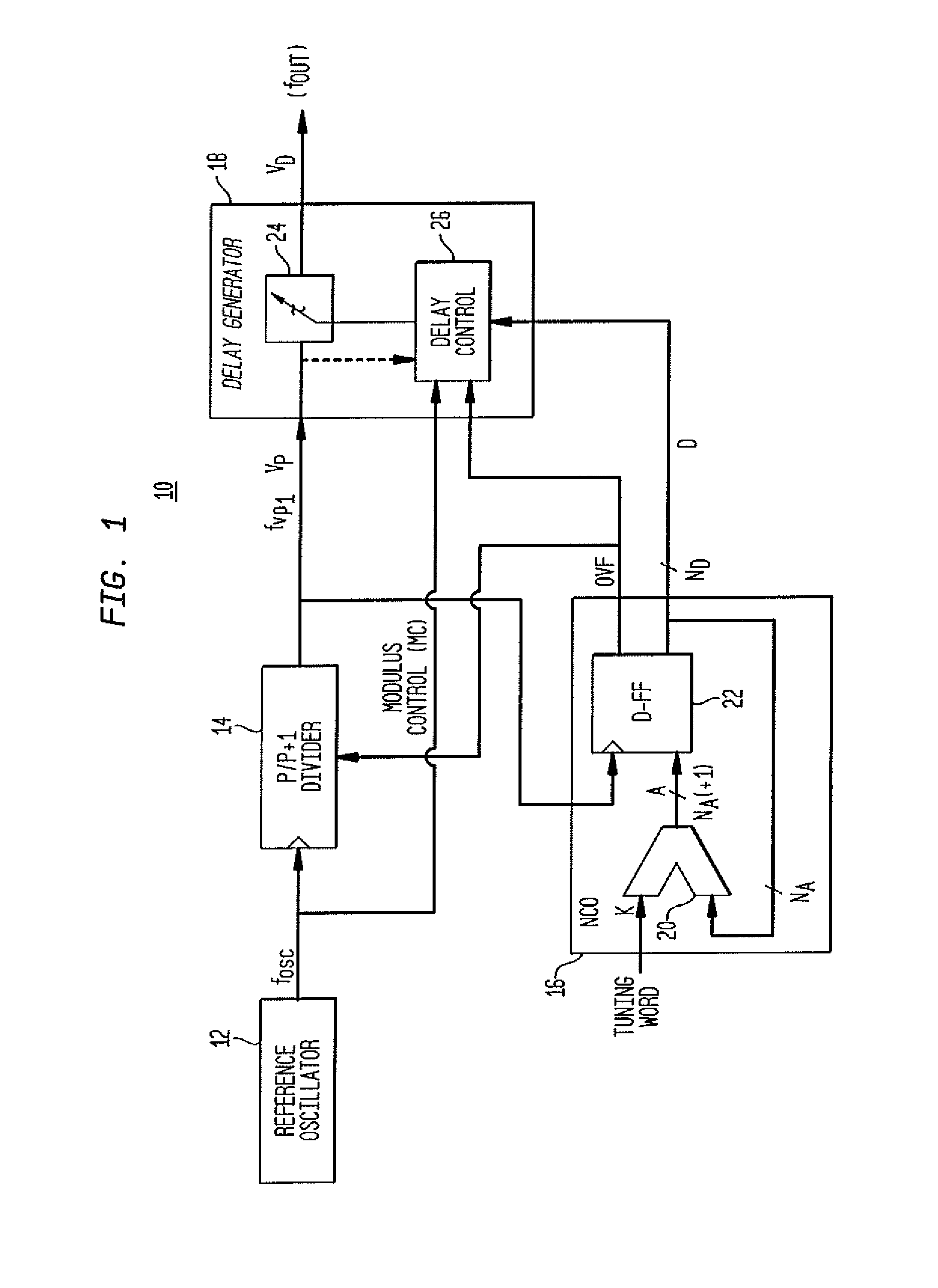
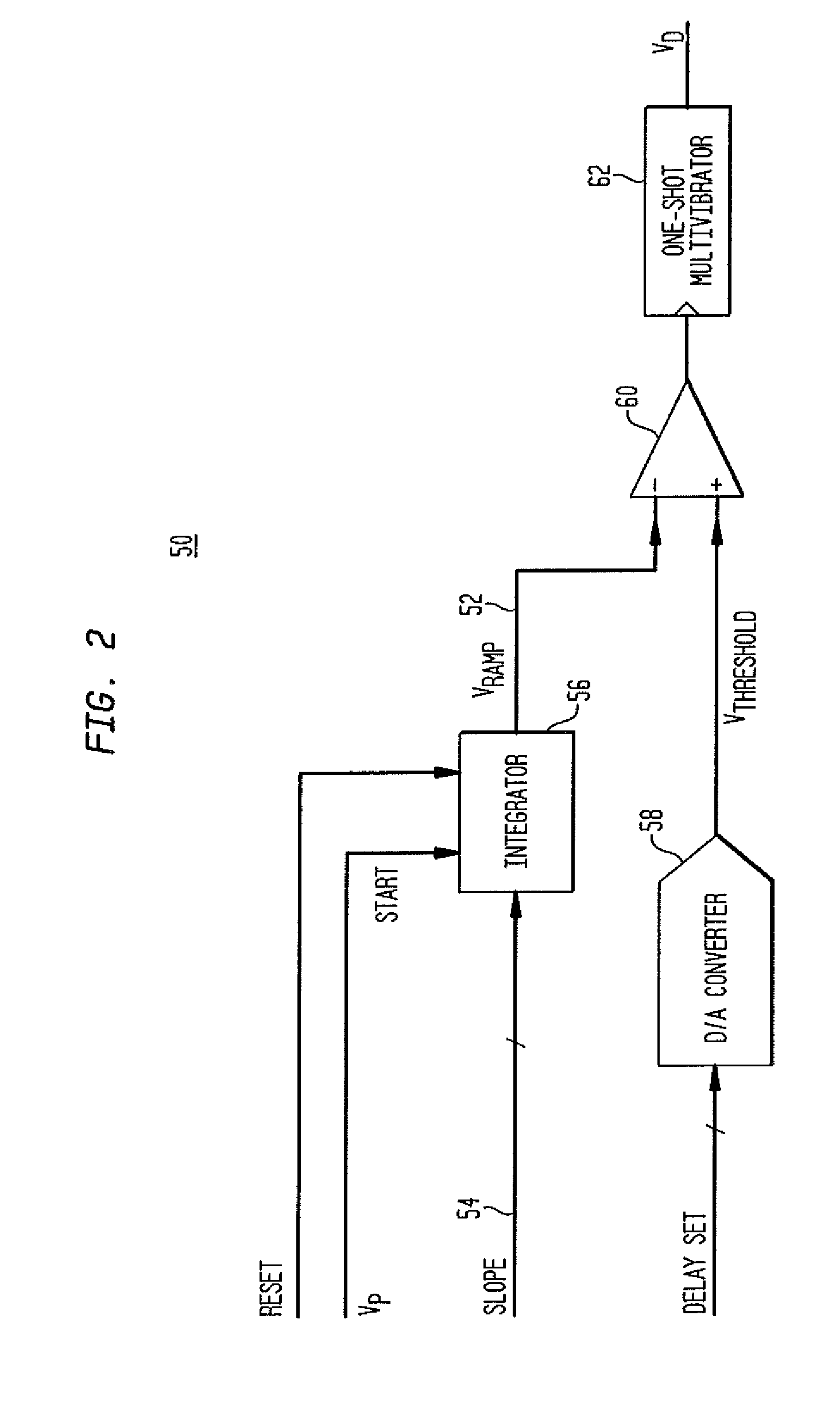
A direct digital frequency synthesizer having a multi-modulus divider, a numerically controlled oscillator and a programmable delay generator. The multi-modulus divider receives an input clock having an input pulse frequency fosc and outputs some integer fraction of those pulses at an instantaneous frequency fVp that is some integer fraction (1 / P) of the input frequency. The multi-modulus divider selects between at least two ratios of P (1 / P or 1 / P+1) in response to a signal from the numerically controlled oscillator. The numerically controlled oscillator receives a value which is the accumulator increment (i.e. the number of divided pulse edges) required before an overflow occurs that causes the multi-modulus divider to change divider ratios in response to receiving an overflow signal. The numerically controlled oscillator also outputs both the overflow signal and a delay signal to the delay generator. The delay signal contains phase-dithering noise that is induced by input into the accumulator of an increment generated from a pseudo-random noise generator. The delay signal further controls the frequency of the multi-modulus divider output signal (Vp) to provide an output signal (VD) with an fOUT that has improved phase and timing jitter performance over prior art direct digital frequency synthesizer architectures.
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
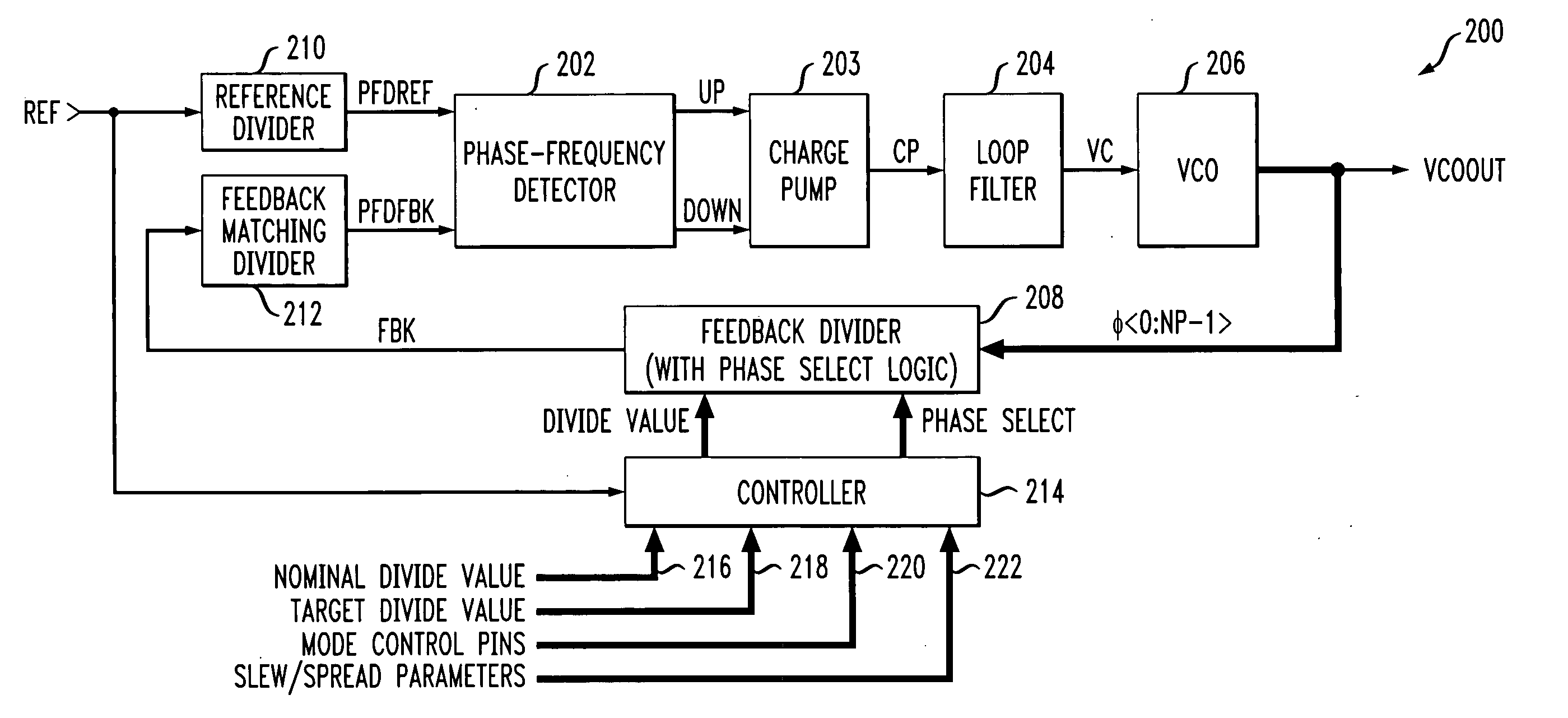
Wide-band multimode frequency synthesizer and variable frequency divider
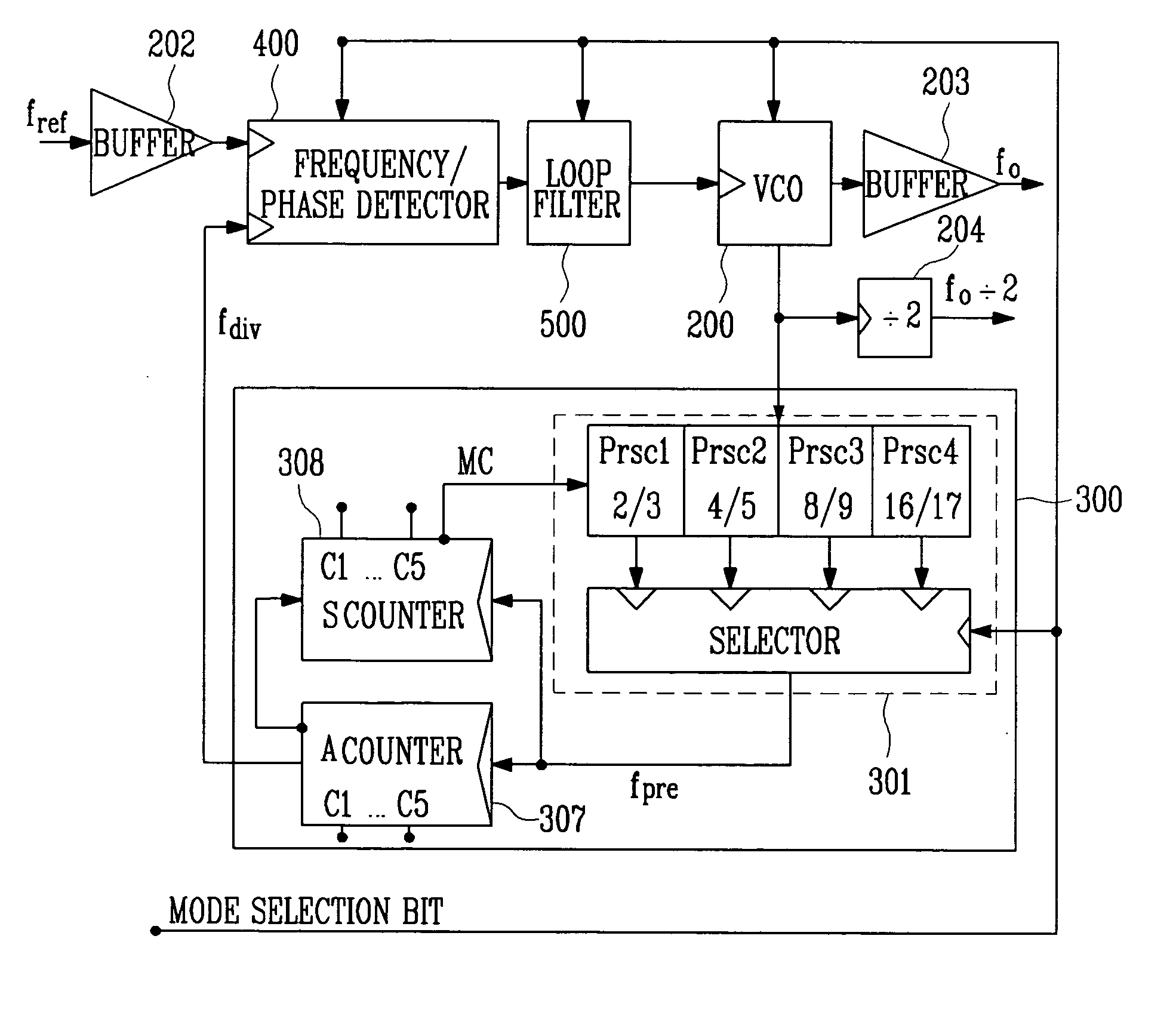
InactiveUS20070132515A1Reducing area consumptionReduce electrical power consumptionPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersPhase noiseCharge pump
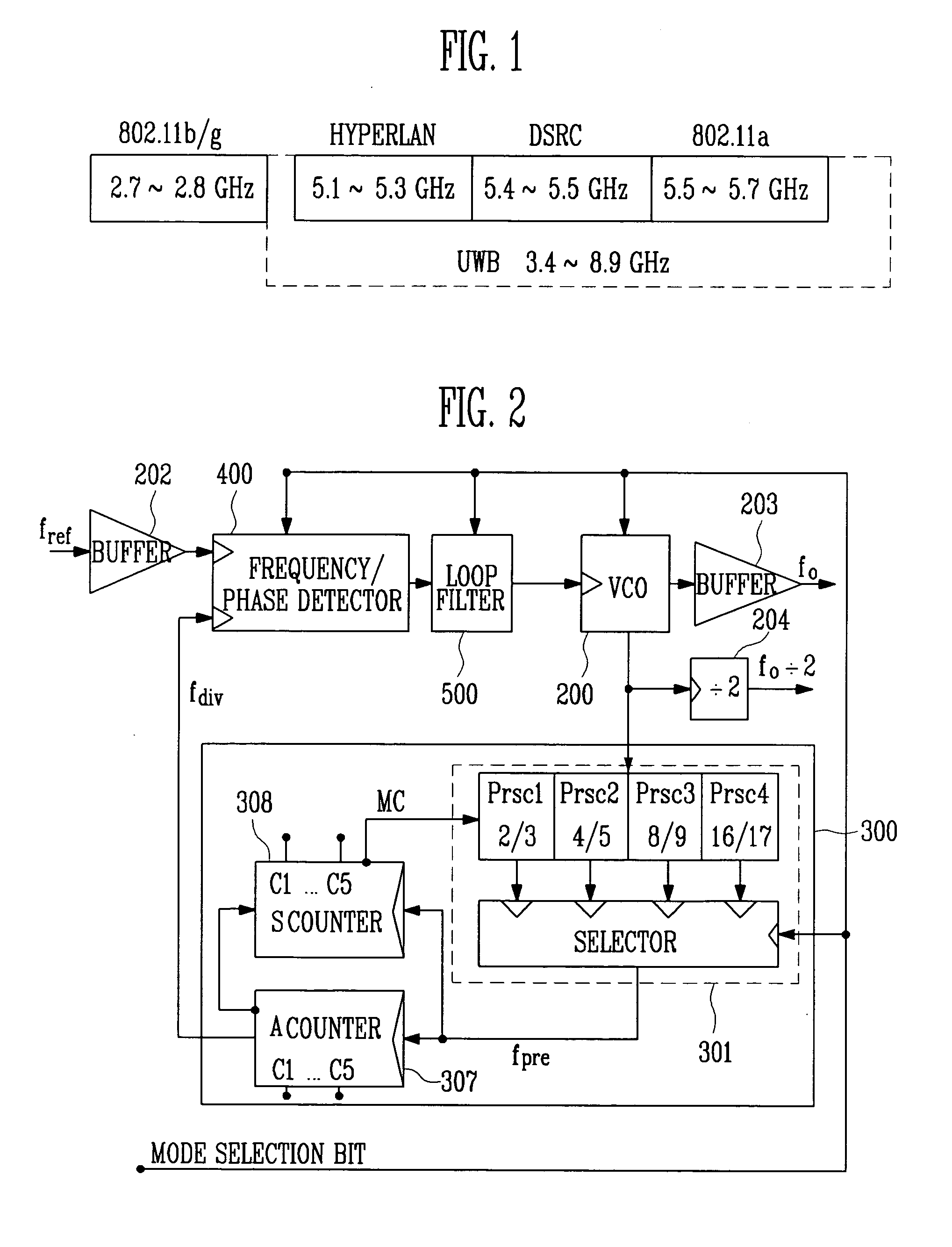
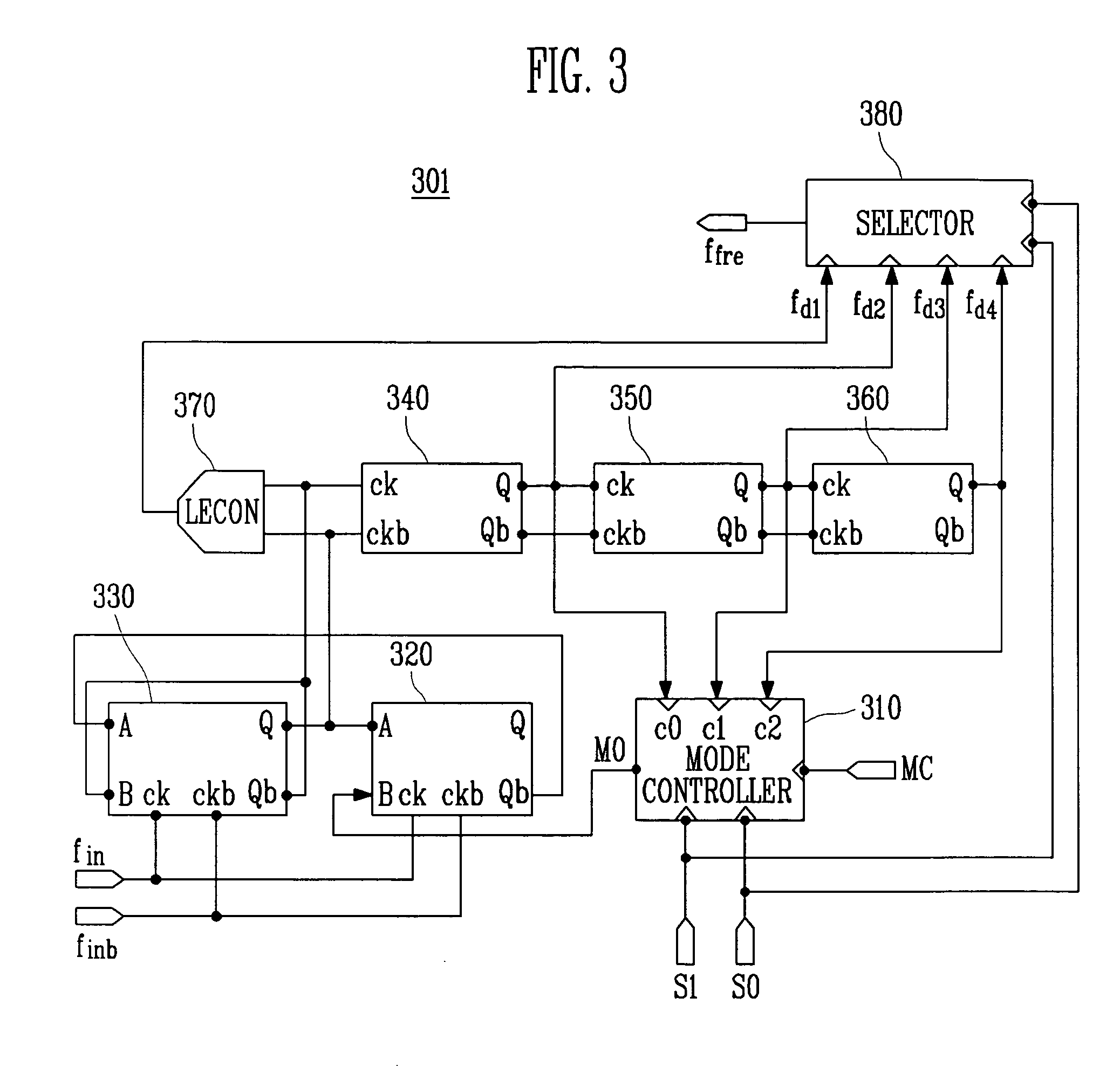
A wide-band multimode frequency synthesizer using a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) is provided. The multiband frequency synthesizer includes a multimode prescaler, a phase detector / a charge pump, a swallow type frequency divider, and a switching bank LC tuning voltage-controlled oscillator having wide-band and low phase noise characteristics. The multimode prescaler operates in five modes and divides a signal up to 12 GHz. The wide-band frequency synthesizer can be used in various fields such as WLAN / HYPERLAN / DSRC / UWB systems that operate in the frequency range from 2 GHz to 9 GHz. The wide-band multimode frequency synthesizer includes a frequency / phase detector for comparing a frequency and phase of a reference high-frequency signal with a frequency and phase of a feedback high-frequency signal; a charge pump for producing an output current corresponding to the result of the comparison performed by the frequency / phase detector; a loop filter for producing an output voltage corresponding to an accumulated value of the output current of the charge pump; a voltage-controlled oscillator for generating an oscillation signal having a frequency corresponding to the output voltage of the loop filter; and a variable frequency divider for dividing an output signal of the voltage-controlled oscillator by a designated integer value, and outputting the result as a feedback signal, wherein at lease two of an amount of unit pumping charges of the charge pump, an RLC value of the loop filter, an RLC value of the voltage-controlled oscillator, and a divisor value of the variable frequency divider are controlled according to a band.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Fractional-N baseband frequency synthesizer in bluetooth applications
InactiveUS6946884B2Pulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersBluetooth piconetsFrequency synthesizer
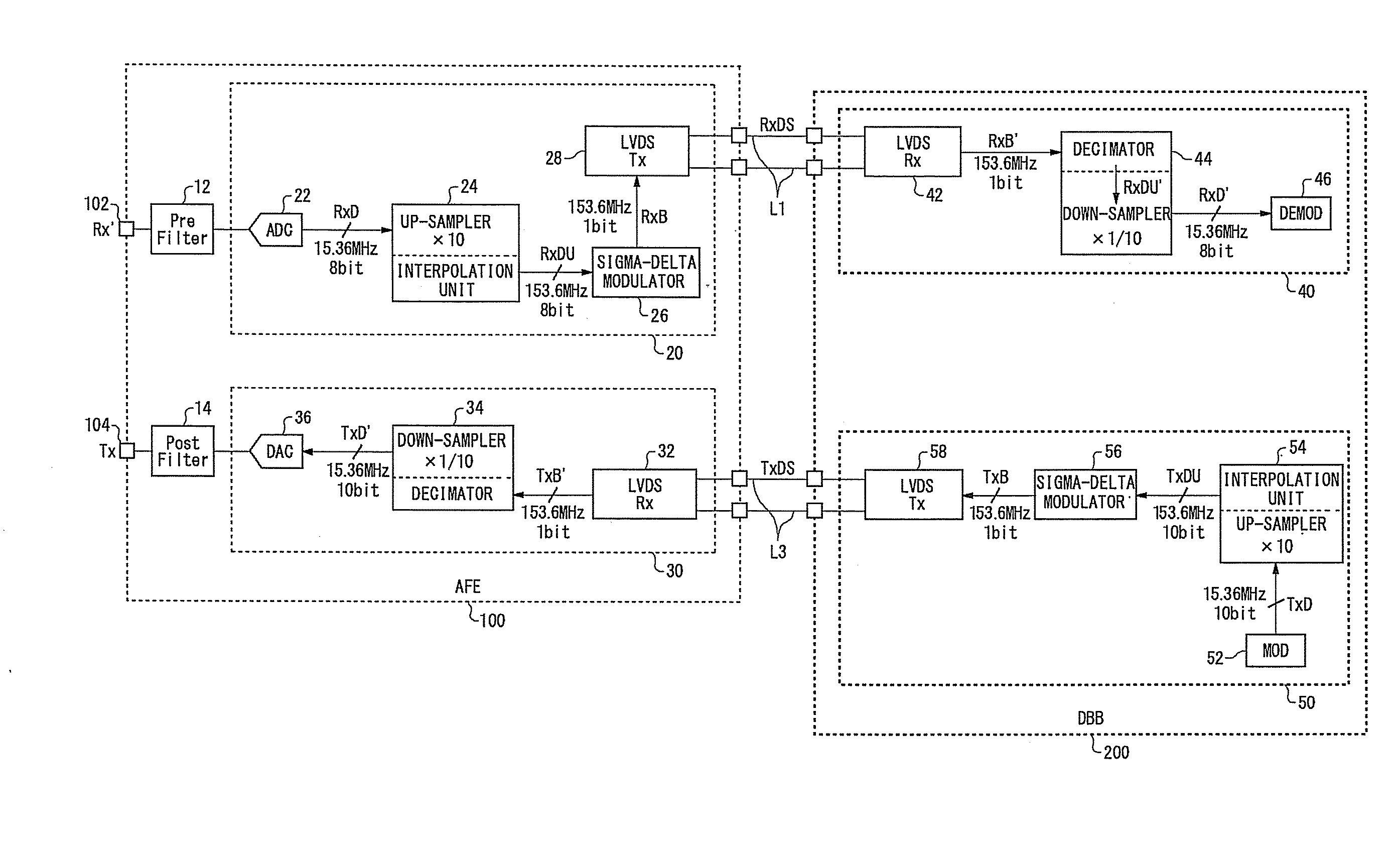
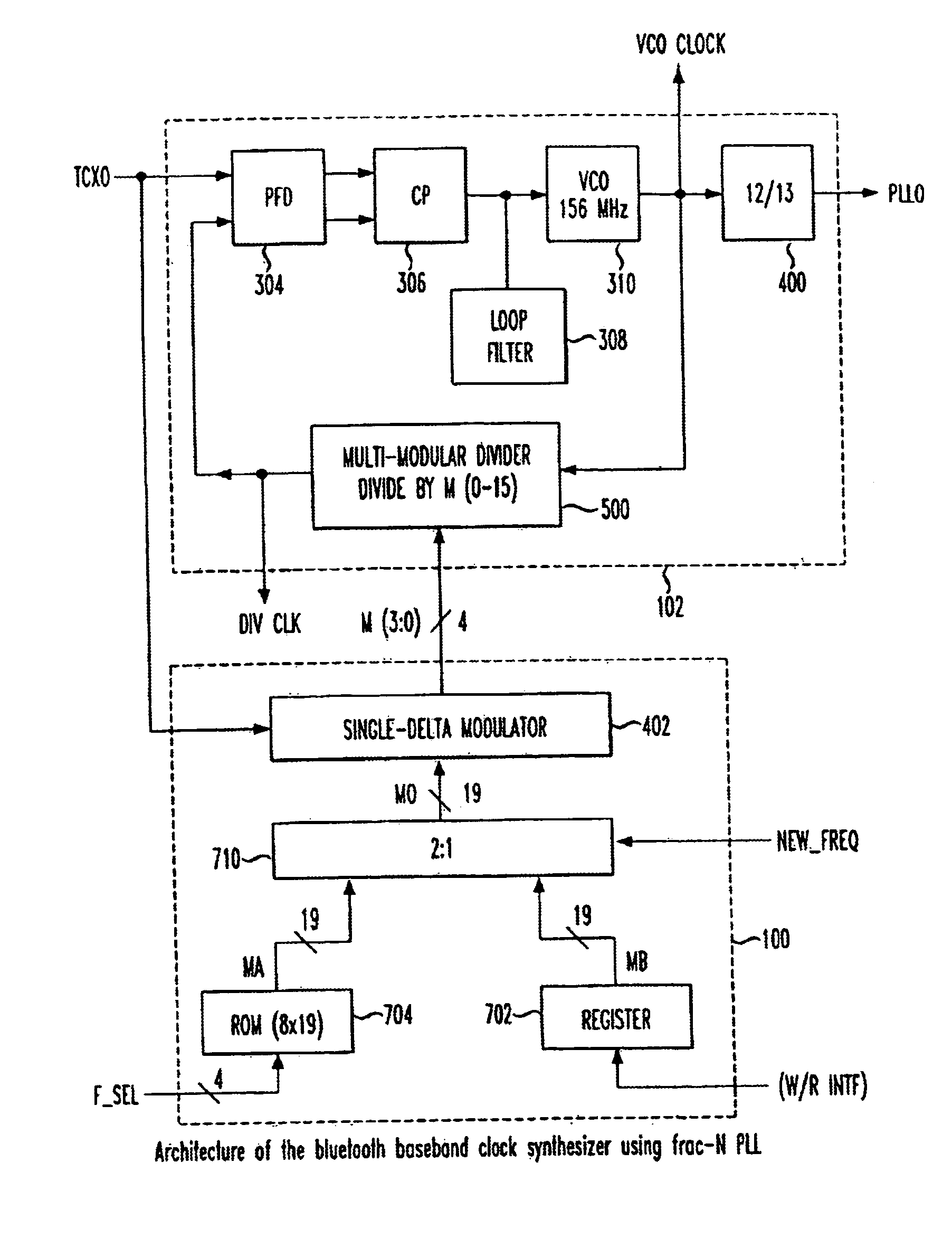
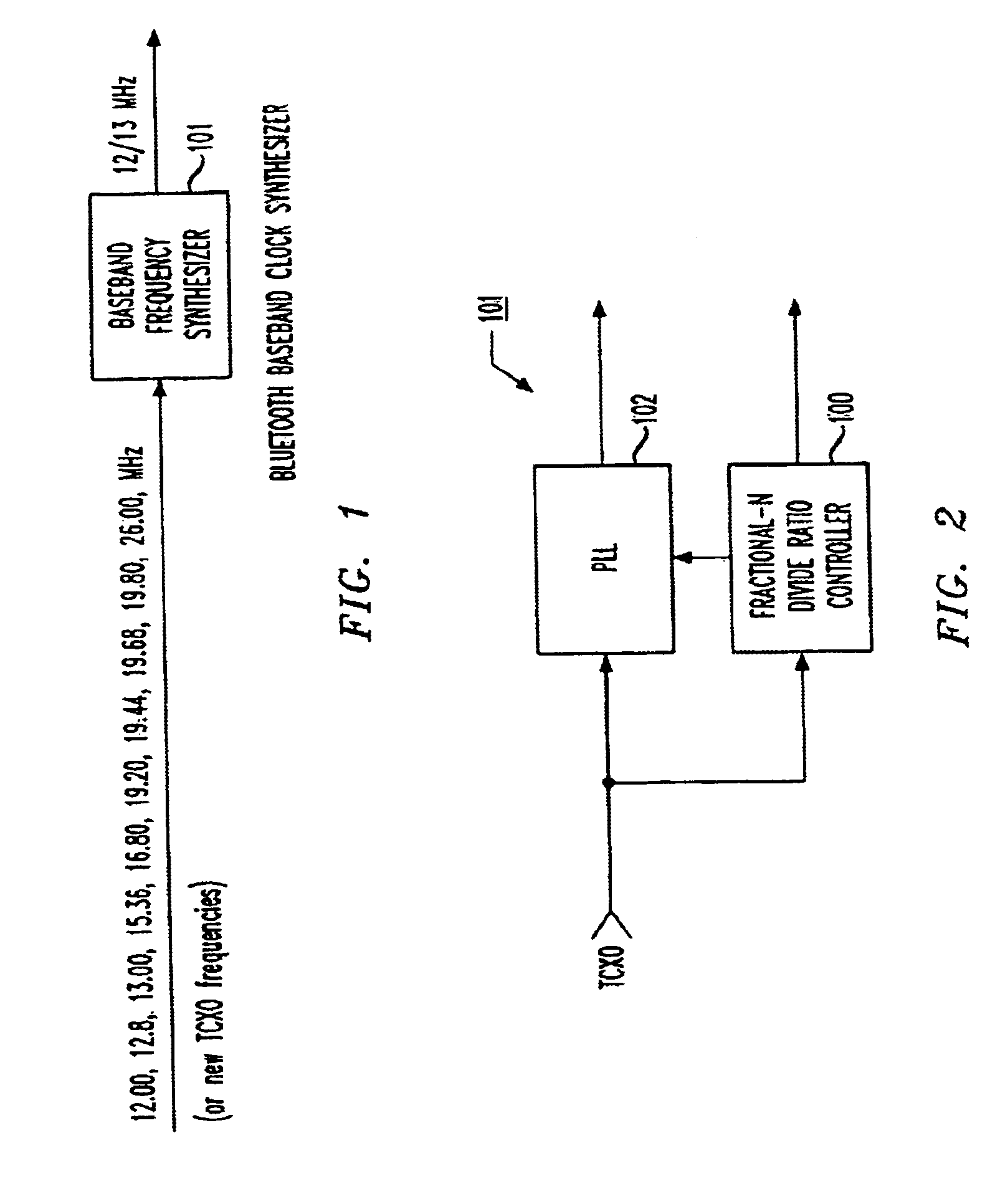
A baseband clock synthesizer having particular use in a BLUETOOTH piconet device, having the capability of generating either 12 MHz or 13 MHz clock signals generated from any reference clock signal, e.g., 12.00, 12.80, 13.00, 15.36, 16.80, 19.20, 19.44, 19.68, 19.80, and 26.00 MHz. A fractional-N frequency divider is implemented with a PLL including a variable divider allowing the use of virtually any reference frequency input to generate a locked 156 MHz clock signal used as a basis for a 12 MHz or 13 MHz baseband clock signal. A residue feedback sigma-delta modulator provides a varying integer sequence to an integer divider in a feedback path of the PLL, effectively allowing division by non-integer numbers in the PLL. Thus, the PLL can be referenced to virtually any reference clock and still provide a fixed output clock signal (e.g., 12 or 13 MHz).
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
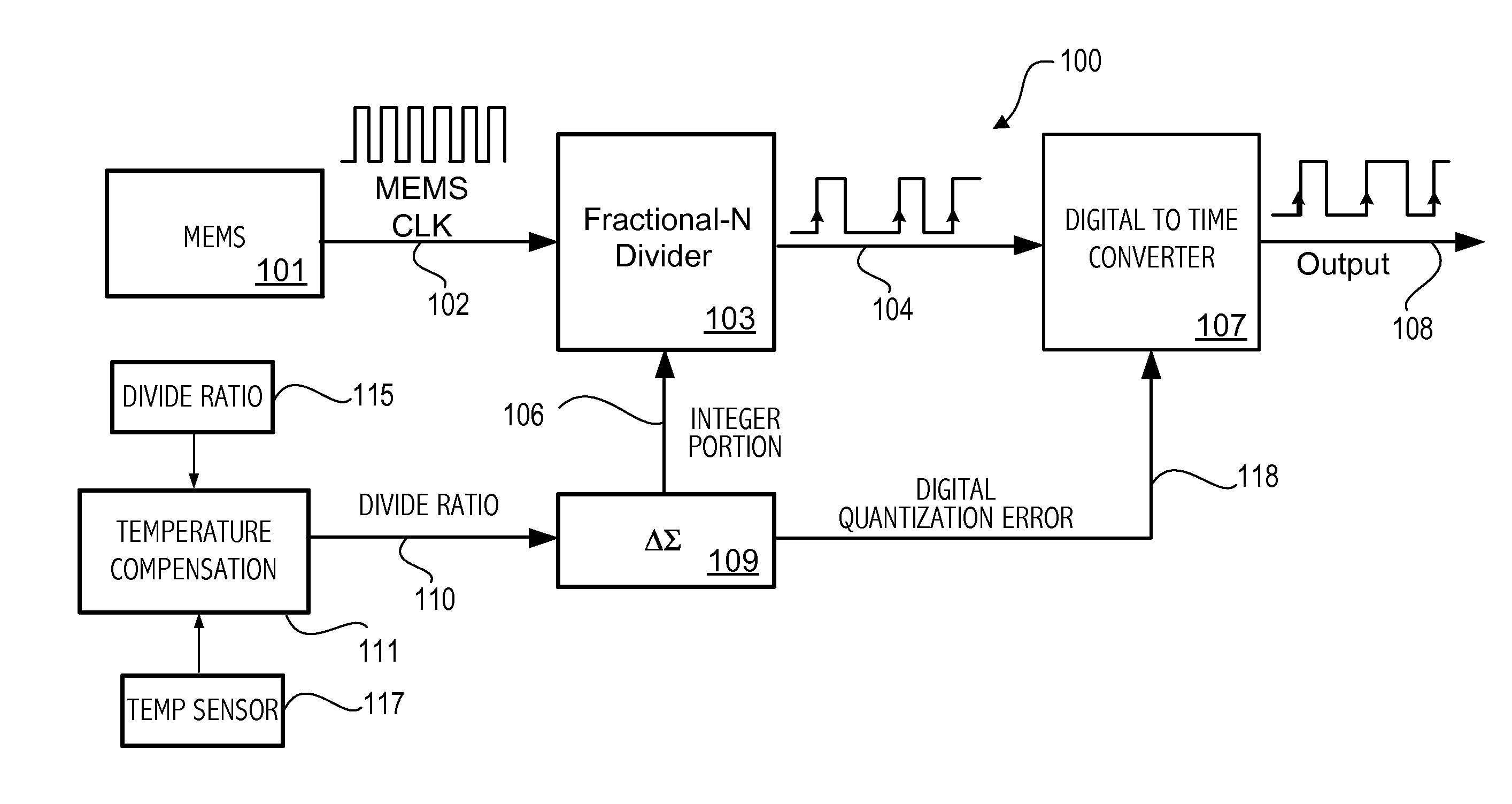
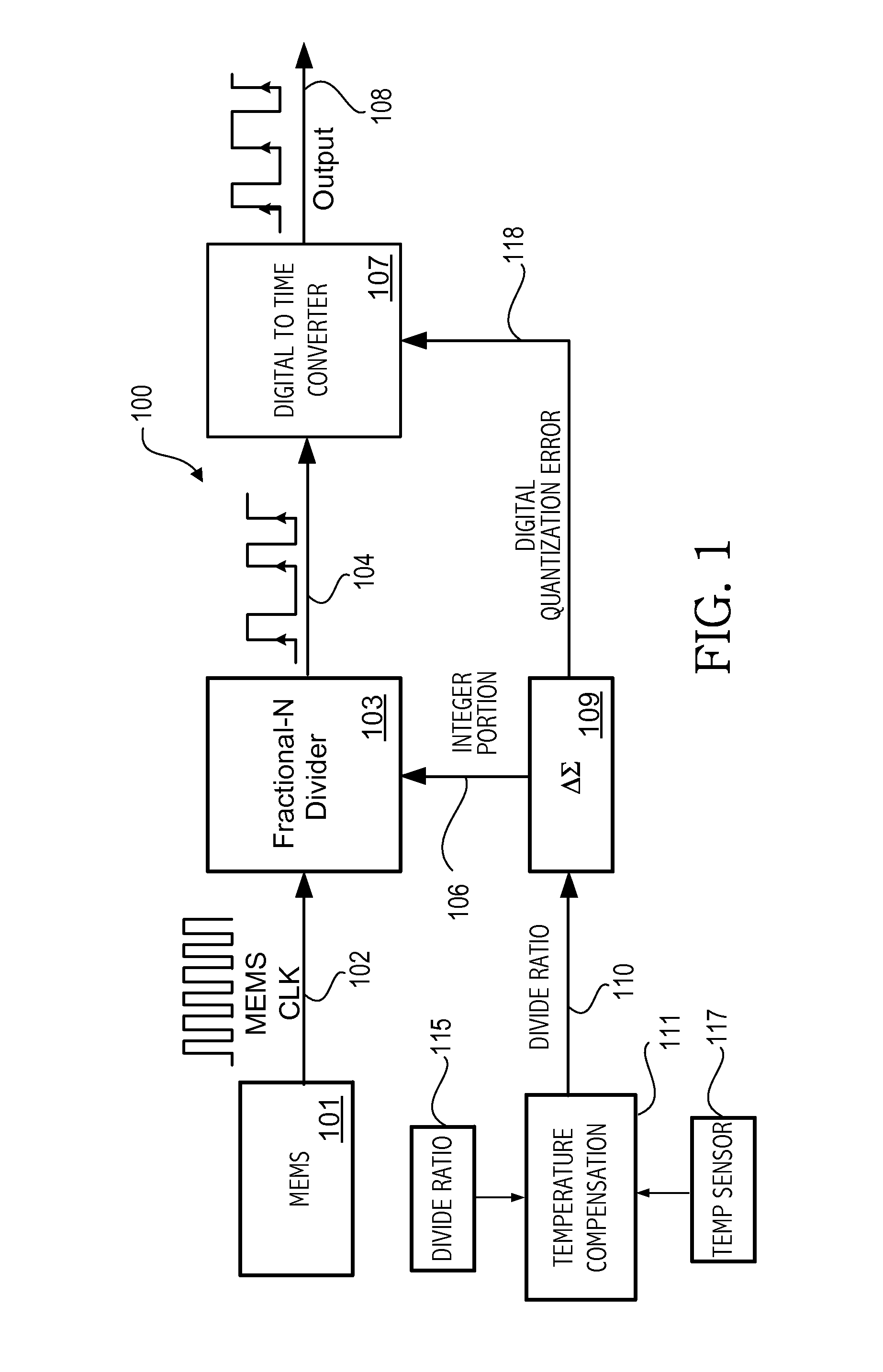
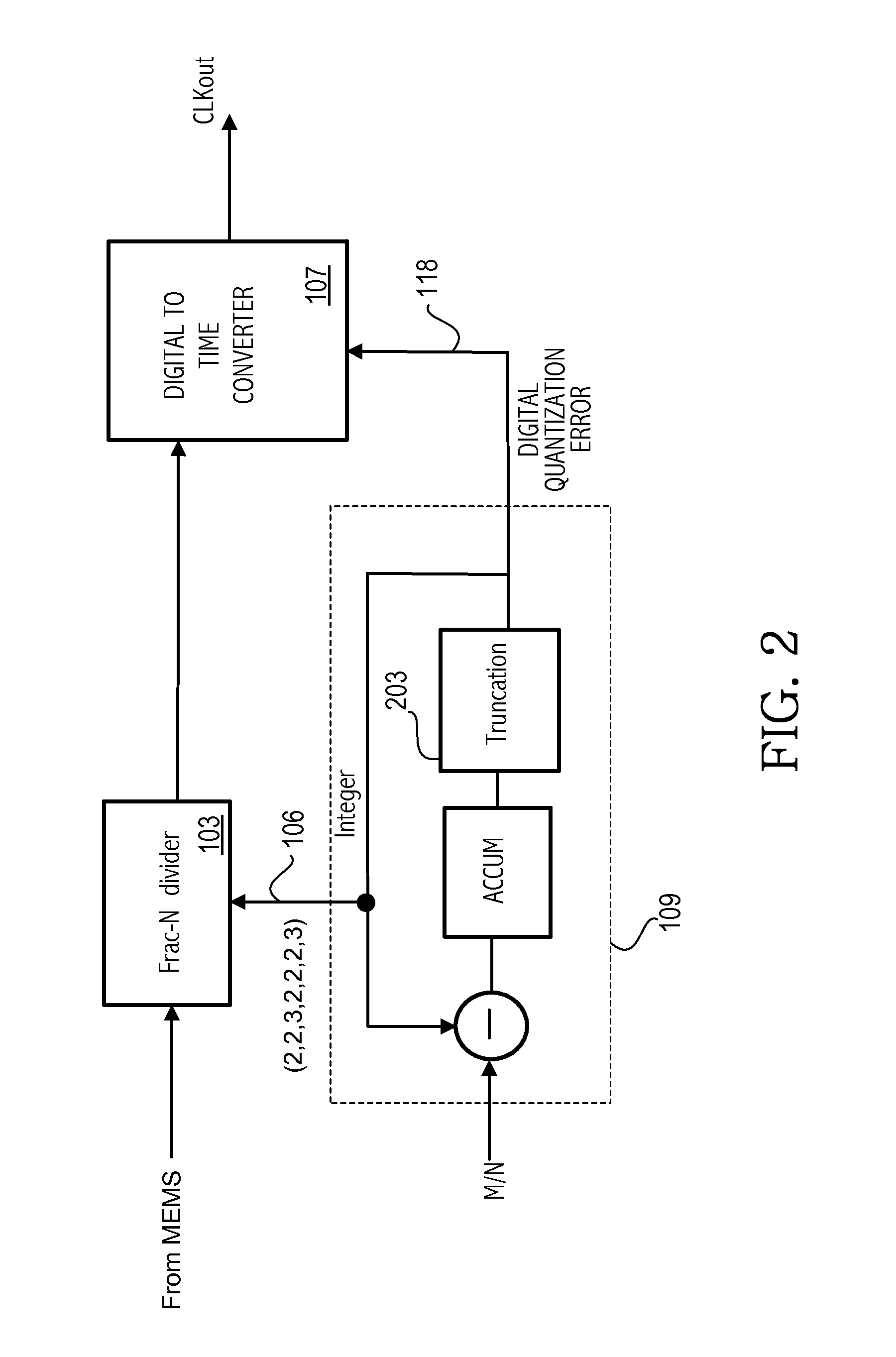
Time-interleaved digital-to-time converter
ActiveUS20140176201A1Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageEngineeringTime interleaved
A fractional-N divider supplies a divided clock signal. An adjusted divided clock signal is generated in a digital-to-time converter circuit having a delay linearly proportional to digital quantization errors of the fractional-N divider. The adjusted divided clock signal is generated based on first and second capacitors charging to a predetermined level. The charging of the first and second capacitors is interleaved in alternate periods of the divided clock. The charging of each capacitor with a current corresponding to respective digital quantization errors is interleaved with charging with a fixed current. A first edge of a first pulse of the adjusted divided clock signal is generated in response to the first capacitor charging to a predetermined voltage and a first edge of a next pulse of the adjusted divided clock signal is generated in response to the second capacitor charging to the predetermined voltage.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Programmable frequency divider
InactiveUS6970025B2Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageLoop inversionPower control
Various apparatus and method embodiments are disclosed. One apparatus embodiment, among others, comprises a frequency divider configured to provide an output signal having a period equal to a period of a clock signal multiplied by a programming division ratio, the frequency divider comprising a plurality of edge-triggered storage elements arranged in at least one loop, wherein each of the storage elements has a state, and a clock input, and wherein the state of each storage element is determined responsive to a transition of the clock input, the state, or the inverse thereof, of one or more previous storage elements in the loop, a characteristic of the division ratio, and the previous state, or the inverse thereof, of the storage element, and the output signal is derived from the state, or the inverse thereof, of at least one of the storage elements in the loop, a circuit for determining the number of storage elements in the loop responsive to the desired division ratio, and wherein the loop is configured such that there are odd number loop inversions within the loop, the loop inversions are implemented through inverters, and each of the storage elements is configured to enter a power save mode responsive to assertion of a power control signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Signal generator with selectable mode control
InactiveUS20050242851A1Smooth switchingReduce discontinuityPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersMode controlControl signal
A signal generator circuit includes a controller adapted to generate a divide value in accordance with at least a first control signal, and a divider adapted to divide an output signal of the signal generator circuit by the divisor value. The controller is selectively operable in at least one of a plurality of modes in accordance with at least a second control signal. The controller is configured to calculate each of one or more new divide values so as to vary a frequency of the output signal in accordance with at least one of the first and second control signals. The controller is configured to switch between operational modes and / or switch between divide values, the switching between operational modes and / or divide values being performed in such a manner so as to substantially eliminate discontinuities in the frequency of the output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
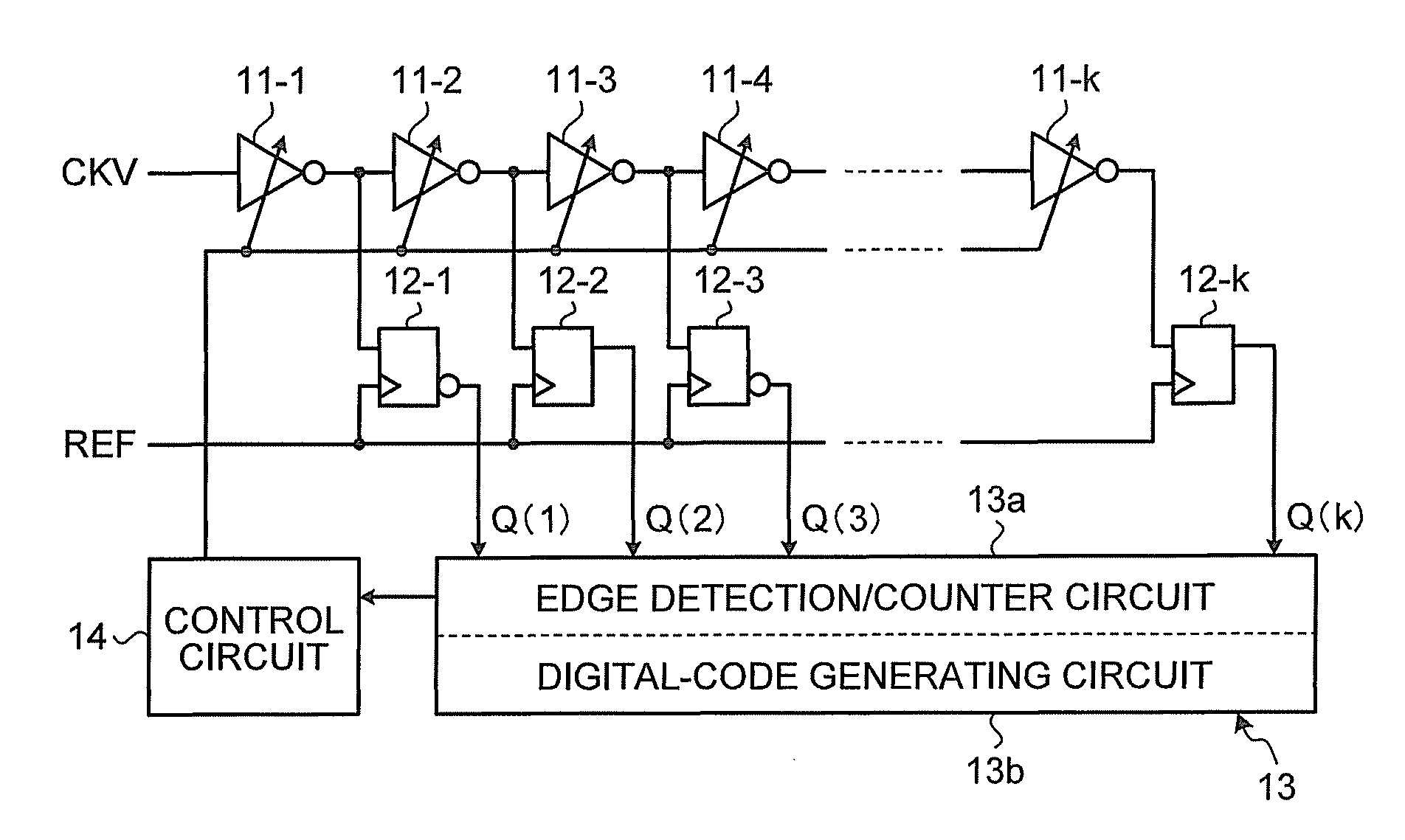
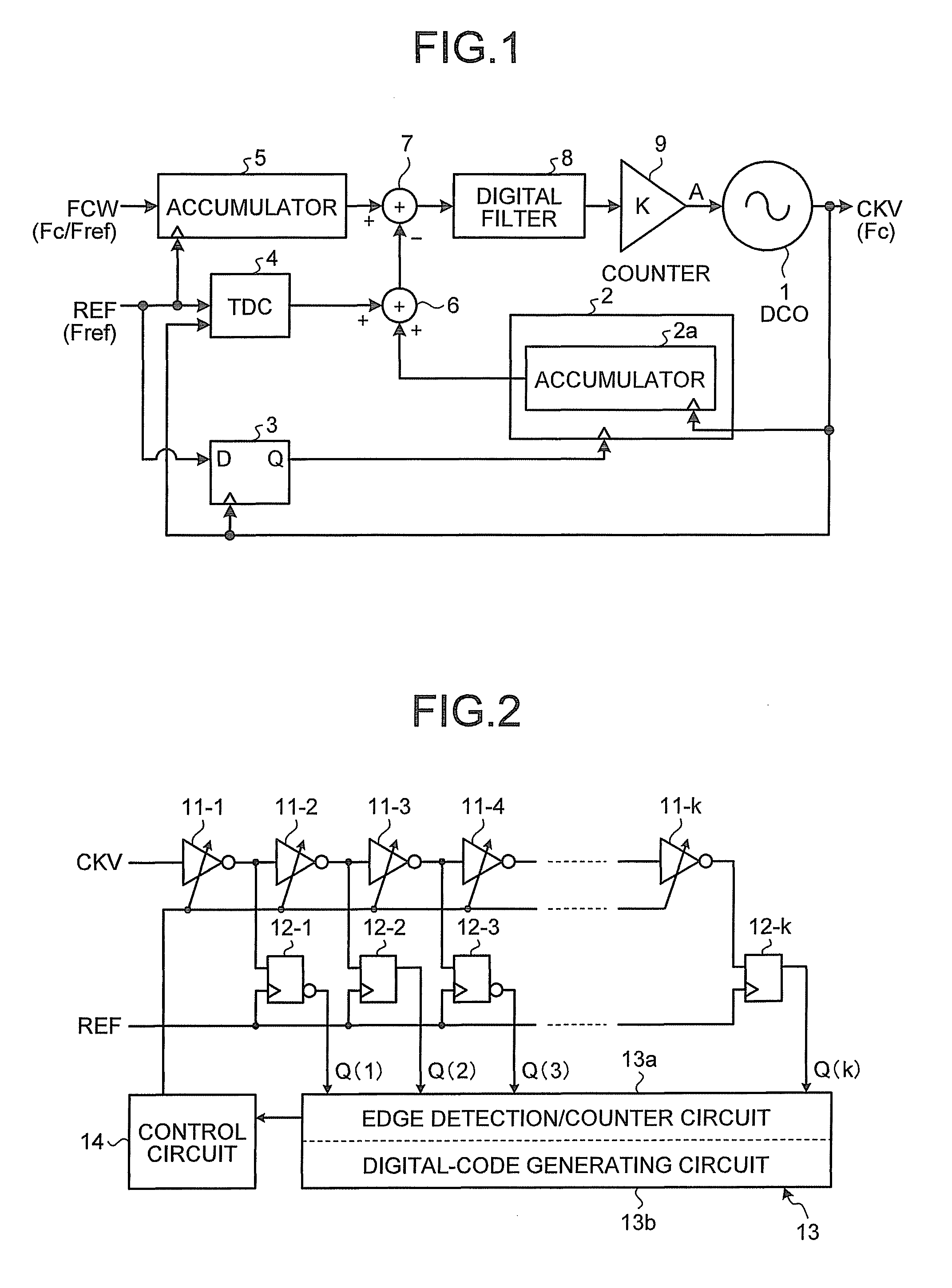
Time to digital converter
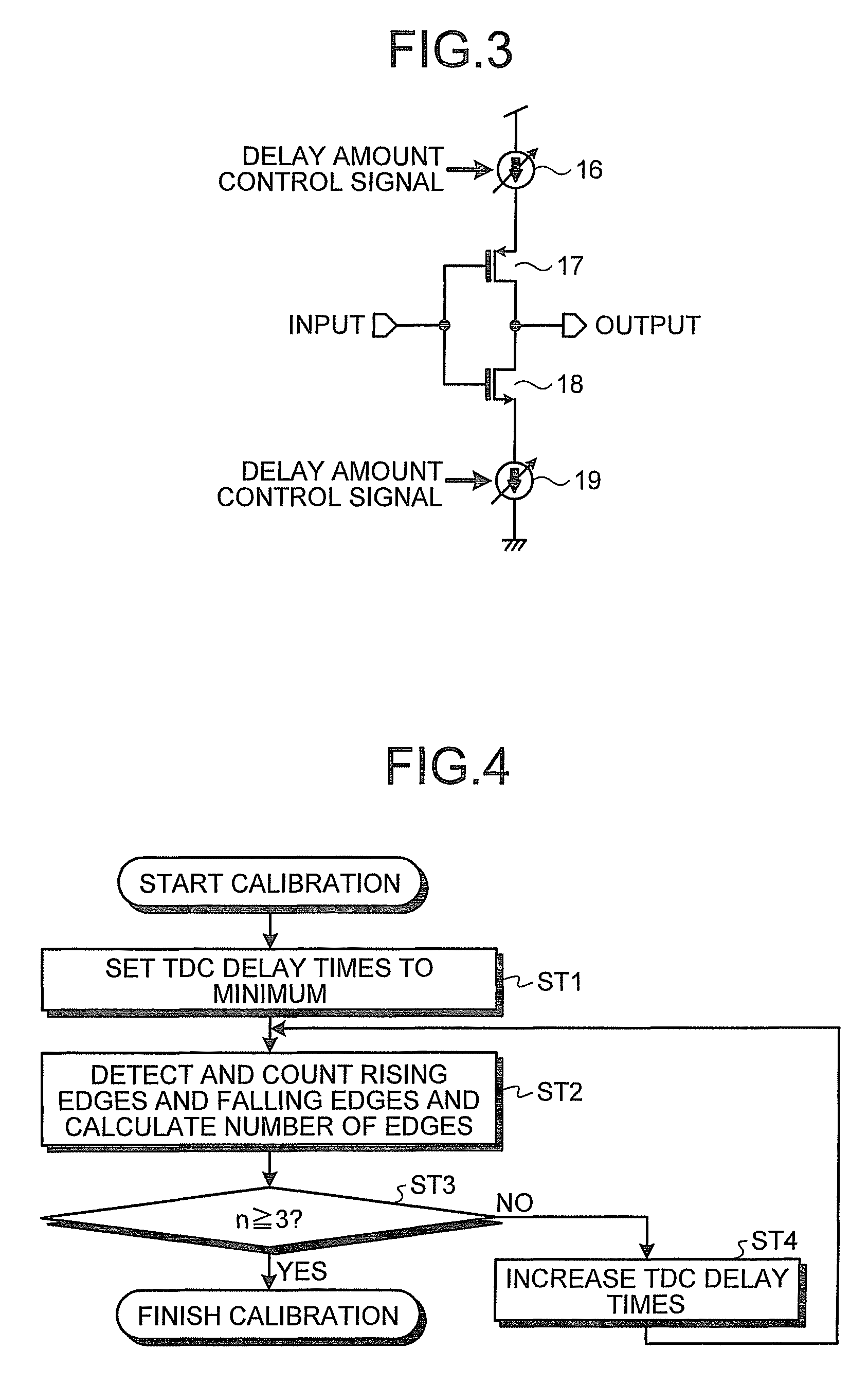
InactiveUS8174293B2Multiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlDigital down converterEngineering
A time to digital converter includes: a delay circuit having a plurality of delay stages that delay an input clock signal in multiple stages, at least one of the delay stages being a variable delay stage; a plurality of flip flops that capture outputs of the delay stages corresponding thereto in a one-to-one relation in response to input of a reference signal; an edge detecting circuit that detects changing edges of respective outputs of the flip flops; a counter circuit that counts a number of edges detected by the edge detecting circuit; and a control circuit that controls a delay amount of the variable delay stage according to the number of edges counted by the counter circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Device and control method of device
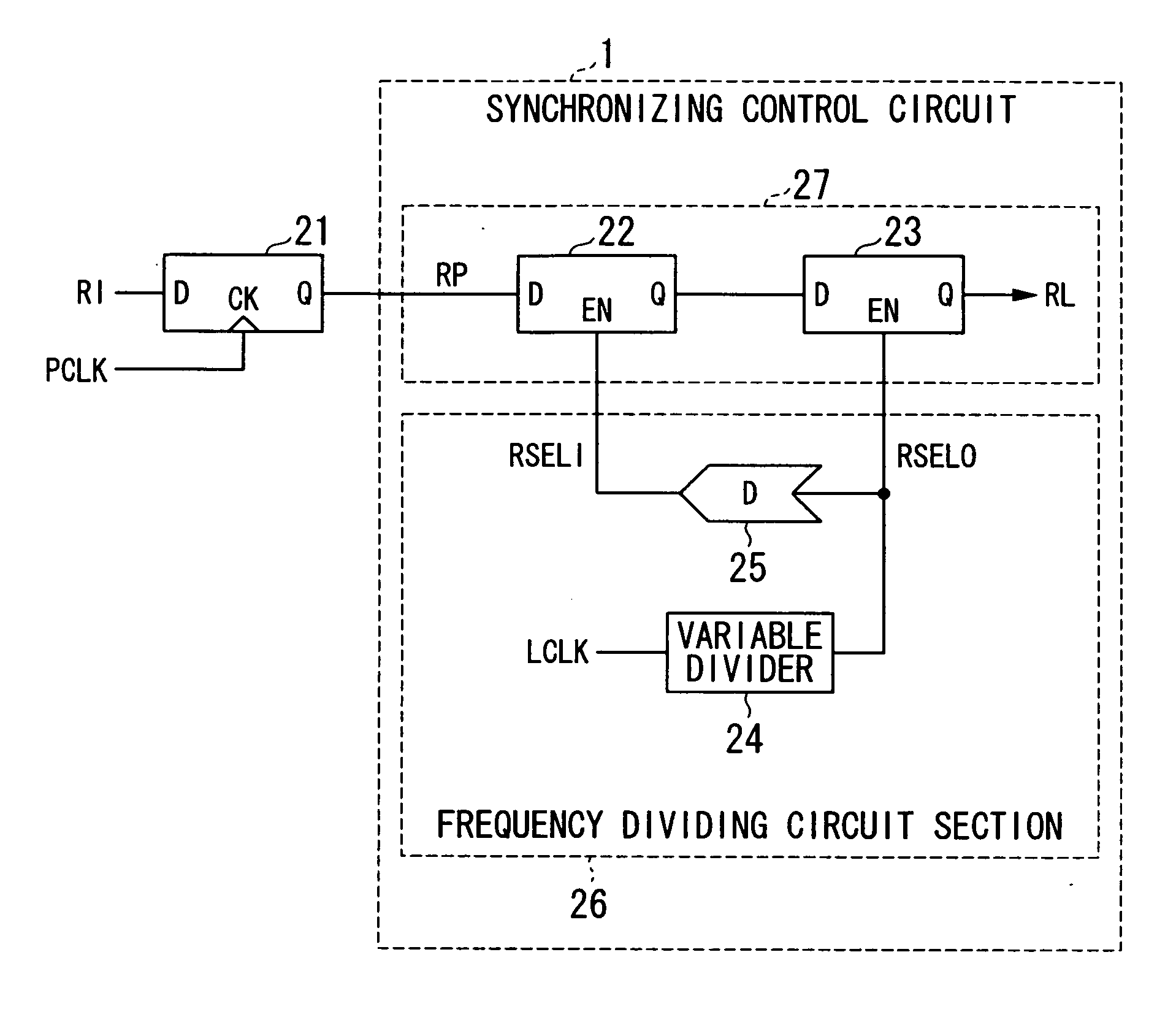
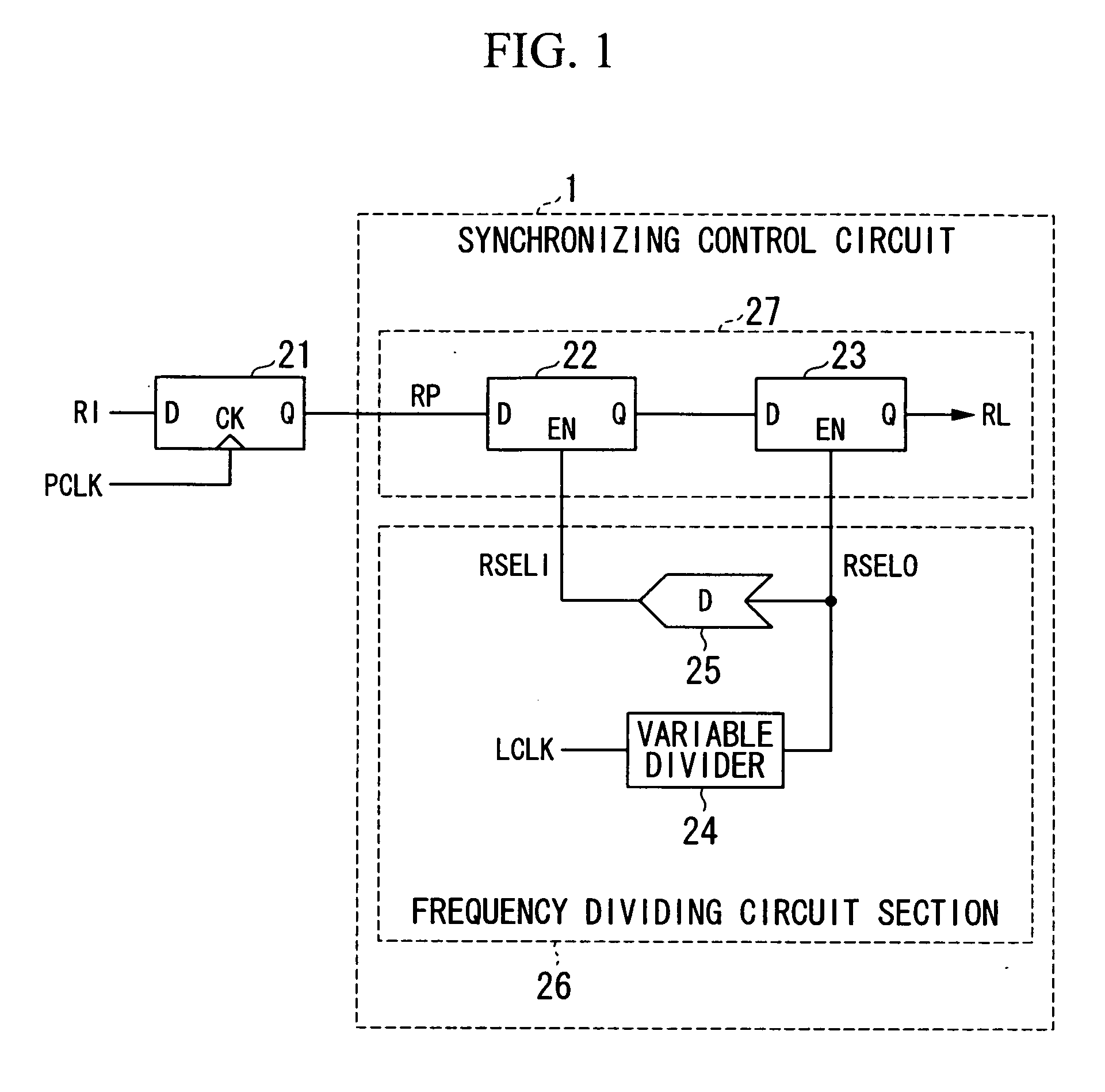
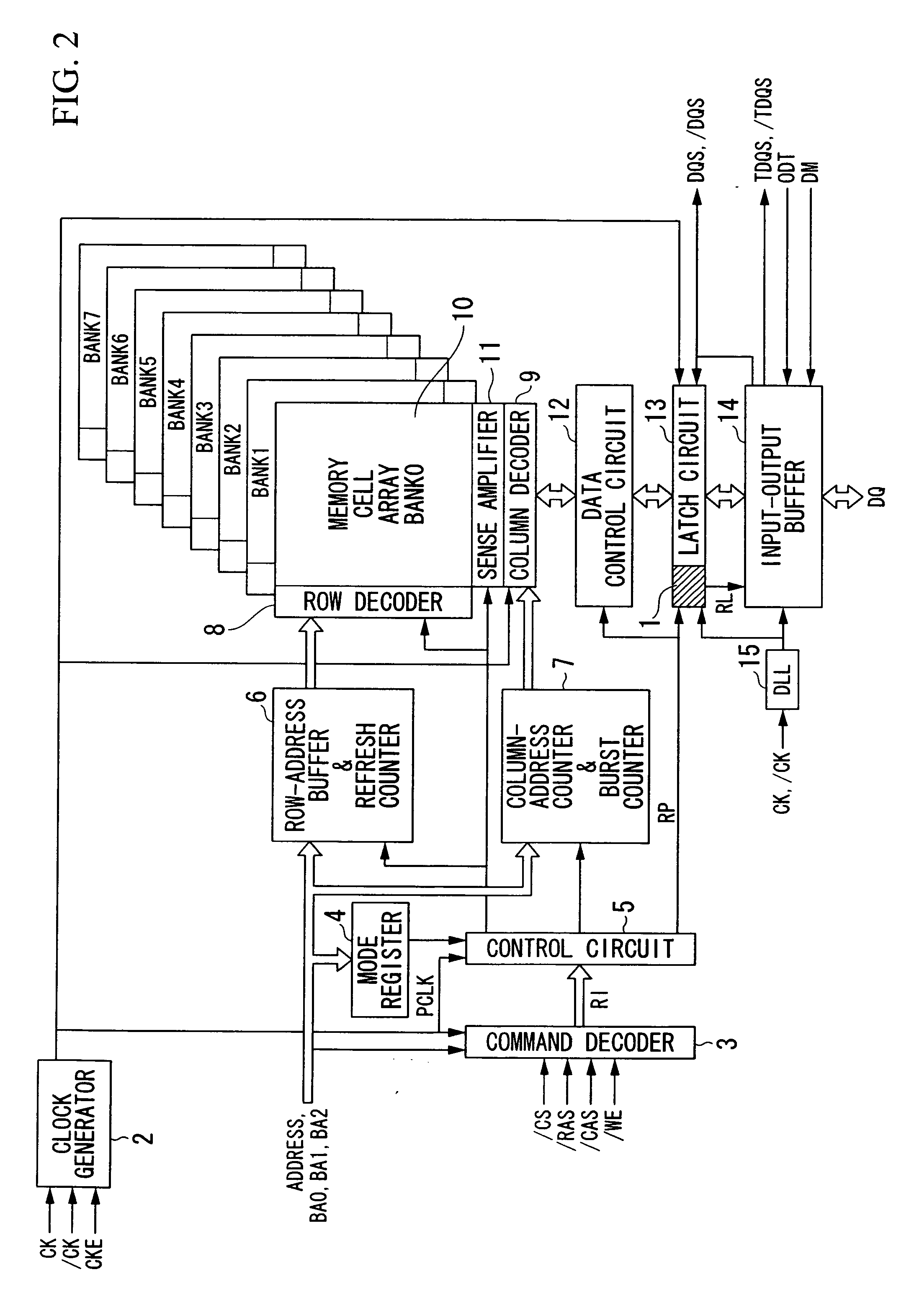
ActiveUS20100052739A1Pulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersEngineeringFrequency divider
A frequency divider section generates a frequency-divided clock RSELO by dividing the frequency of an internal clock LCLK, which lags behind an external clock in phase, and generates a delayed frequency-divided clock RSELI by delaying the frequency-divided clock RSELO. A signal input from the outside in synchronization with an internal clock PCLK which lags behind the external clock in phase is held in a latch circuit in synchronization with the delayed frequency-divided clock RSELI. Then, an output signal of the latch circuit is read into a latch circuit in synchronization with the frequency-divided clock RSELO and is output as a signal which is synchronized with the internal clock LCLK. In addition, a frequency divider section includes a variable divider which divides the frequency of the internal clock LCLK by a predetermined divide ratio which can be changed.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Design structure for CMOS differential rail-to-rail latch circuits
InactiveUS20090108885A1Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageCMOSEngineering
A design structure including a CMOS rail-to-rail differential latch is provided in which a plurality of cross-coupled devices pull first and second nodes of the latch to opposite rail-to-rail voltages. Desirably, first and second output isolating elements have inputs coupled to the first and second nodes, the output isolating elements being operable to output versions of the opposite rail-to-rail voltages as a true and a complementary output of the latch. In this way, the true output has a rising edge occurring simultaneously with a falling edge of the complementary output. The complementary output has a rising edge occurring simultaneously with a falling edge of the true output. First and second input isolating elements of the latch have outputs coupled to the first and second nodes, the first and second input isolating elements being operable to apply versions of input signals to the first and second nodes.
Owner:IBM CORP
Programmable frequency divider
ActiveUS7113009B2Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageMultiplexerLogic state
A divider is disclosed herein. The divider includes a sequence of divide stages programmably coupled to provide a variety of divide ratios. The divider also includes one or more multiplexers to feedback the output of a divide stage to the input of a divide stage earlier in the sequence of divide stages. The divider may also include duty cycle correction circuitry and self correction logic to correct abnormal logic states. The divide stages can operate in synchronism with each other. Multiplexer functionality, self correction circuitry functionality, and divide stage functionality may be implemented in a combination latch circuit.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Power Switch Ramp Rate Control Using Daisy-Chained Flops
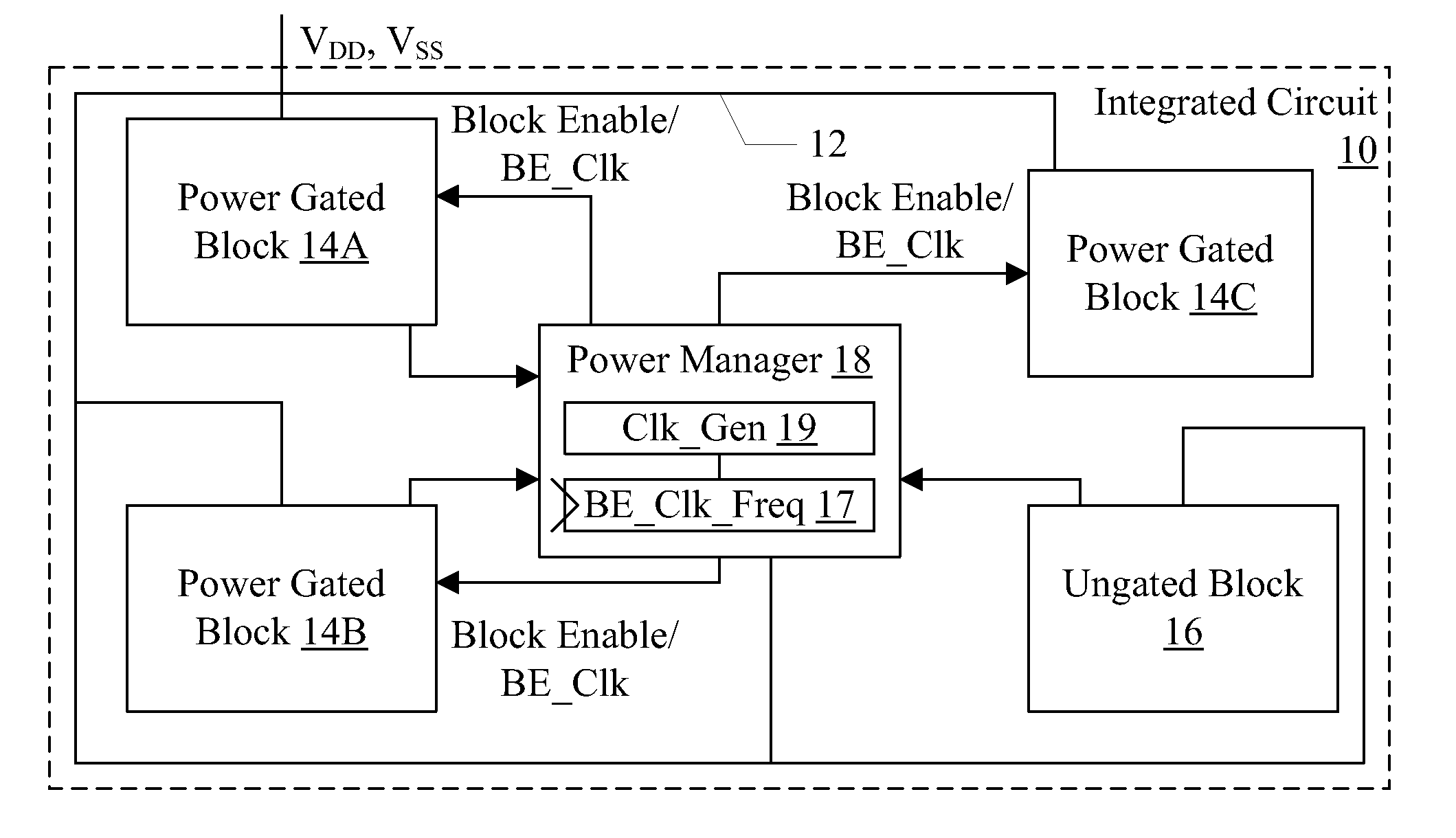
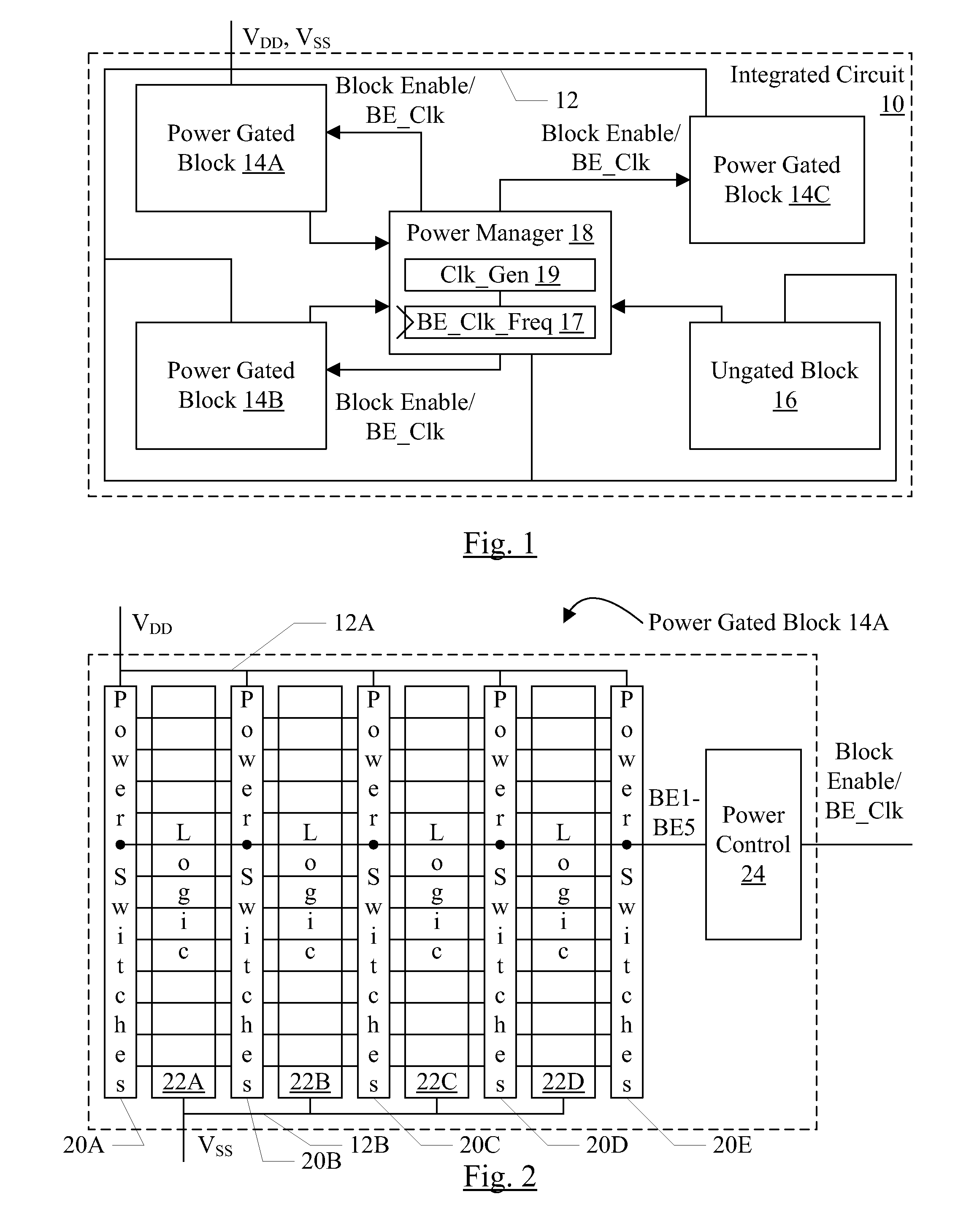
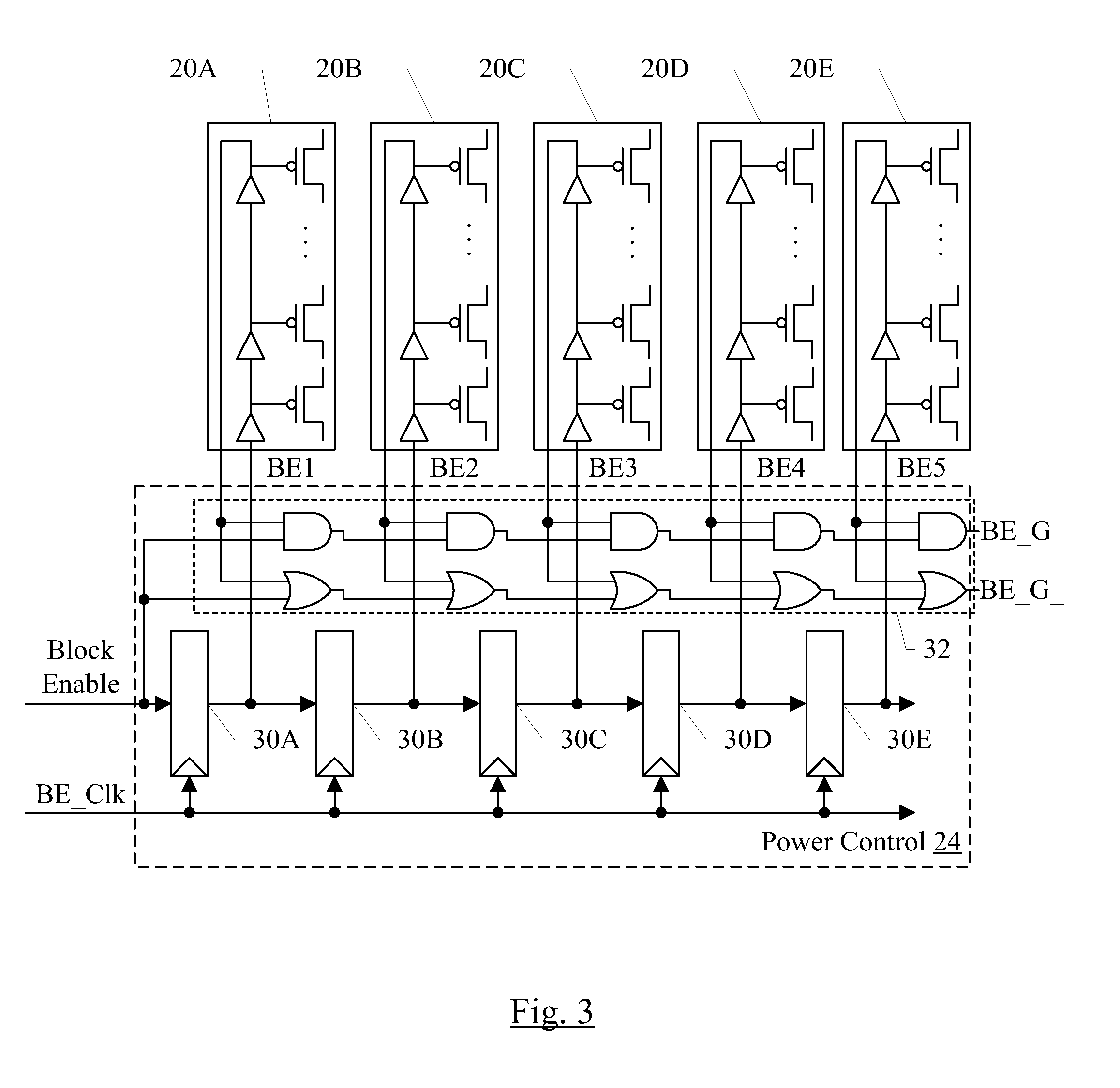
ActiveUS20110198941A1Control changesReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalIntegrated circuitVoltage
In an embodiment, an integrated circuit may include one or more power managed blocks and a power manager circuit. The power manager circuit may be configured to generate a block enable for each power managed block and a block enable clock. The power managed block may generate local block enables to various power switches in the power managed block, staggering the block enables over two or more block enable clock cycles. In particular, the power managed block may include a set of series-connected flops that receive the block enable from the power manager circuit. The output of each flop may be coupled to a respective set of power switches and may enabled those switches. The change in current flow due to enabling and / or disabling the power managed block may thus be controlled. In an embodiment, the frequency of the block enable clock may be set to a defined value independent of process, voltage, and temperature conditions in the integrated circuit.
Owner:APPLE INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com