Patents
Literature
333results about "Manipulation for frequency change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
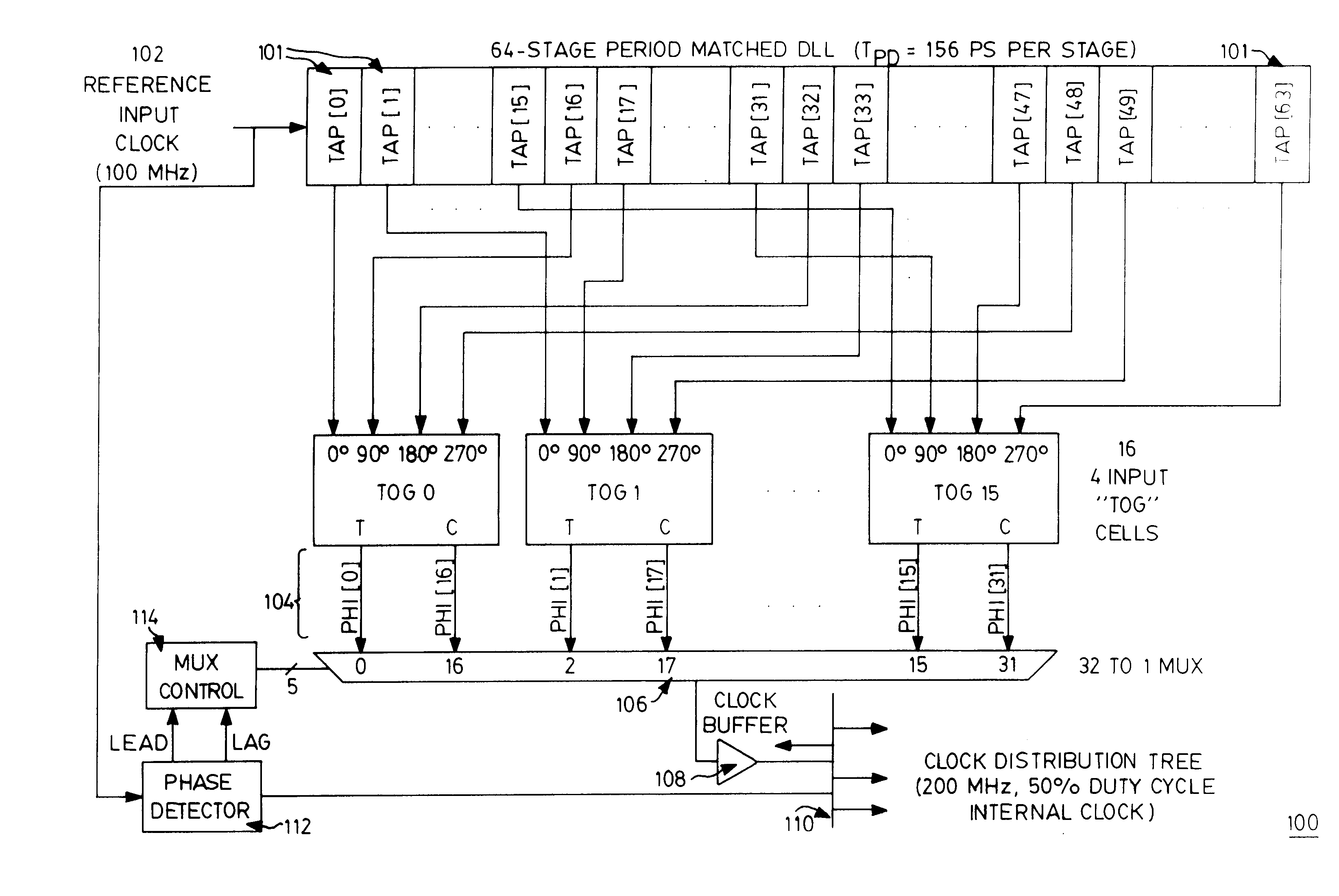
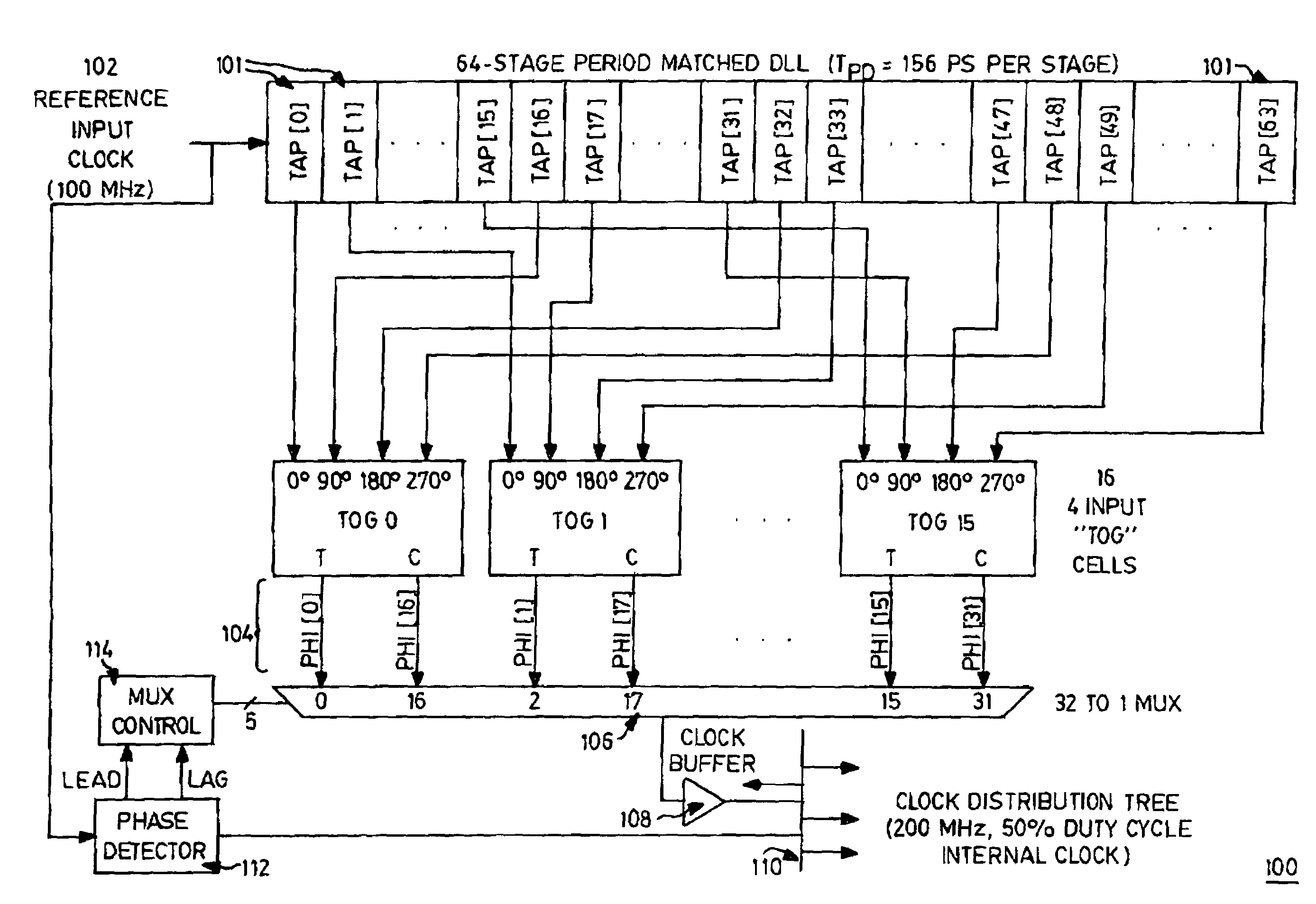
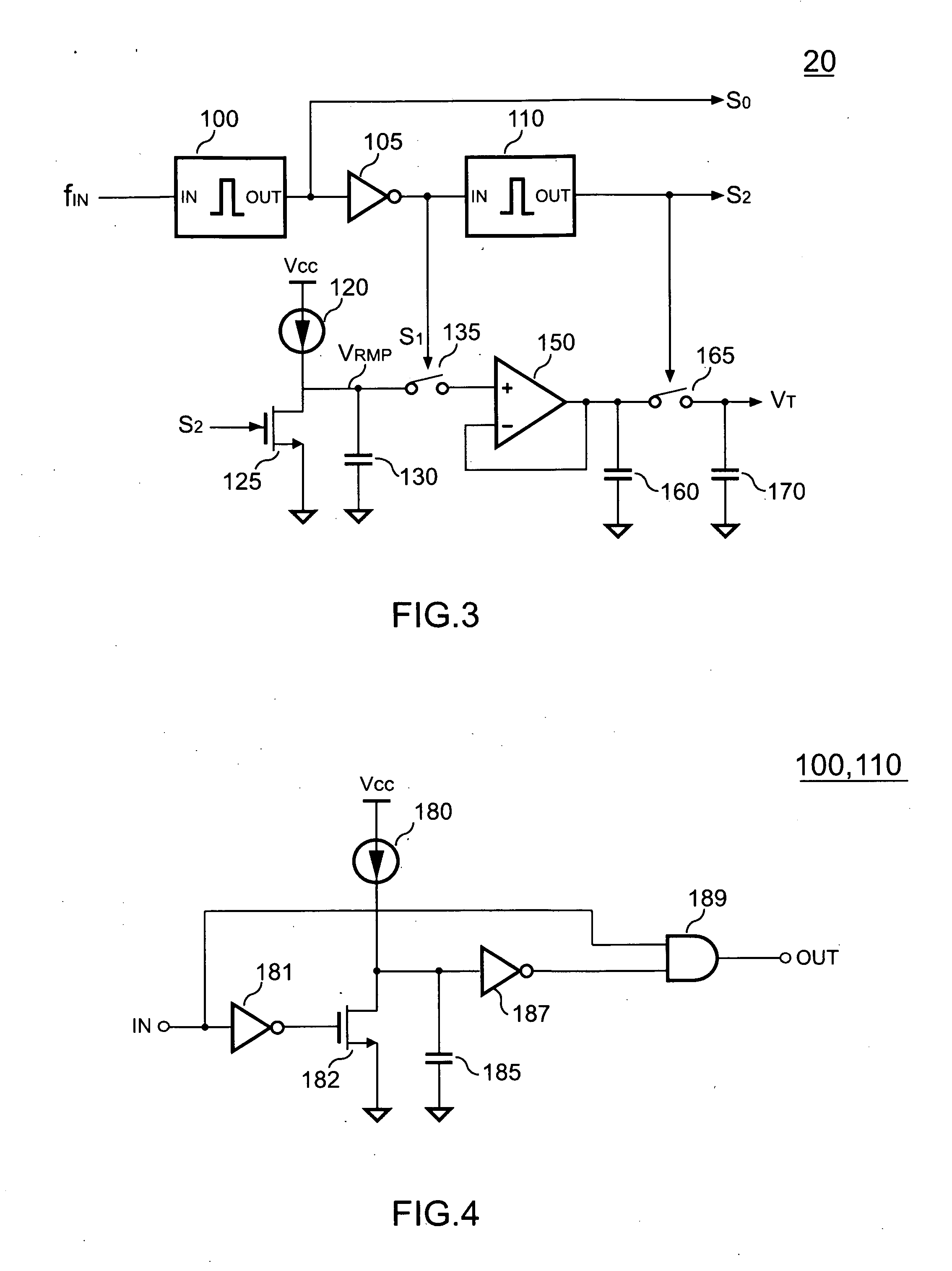
Frequency-doubling delay locked loop
A frequency multiplier circuit comprising a delay line receiving at one end thereof a reference clock for generating clock tap outputs from respective ones of a plurality of period matched delay elements; a clock combining circuit responsive to pairs of tap outputs for generating a rising and falling edge of an output clock pulse from respective ones of the pairs whereby the output clock period is less than the input clock period.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
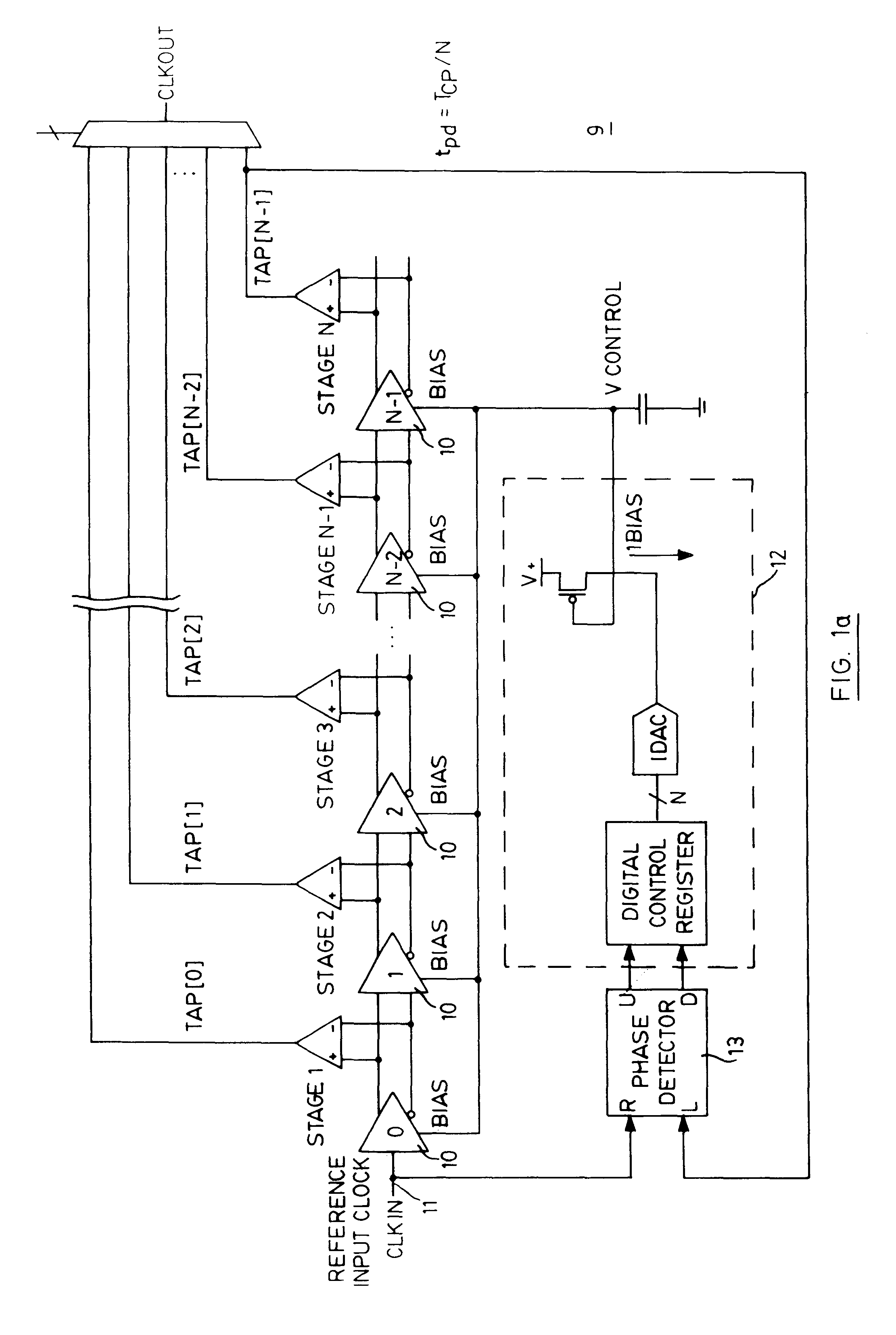
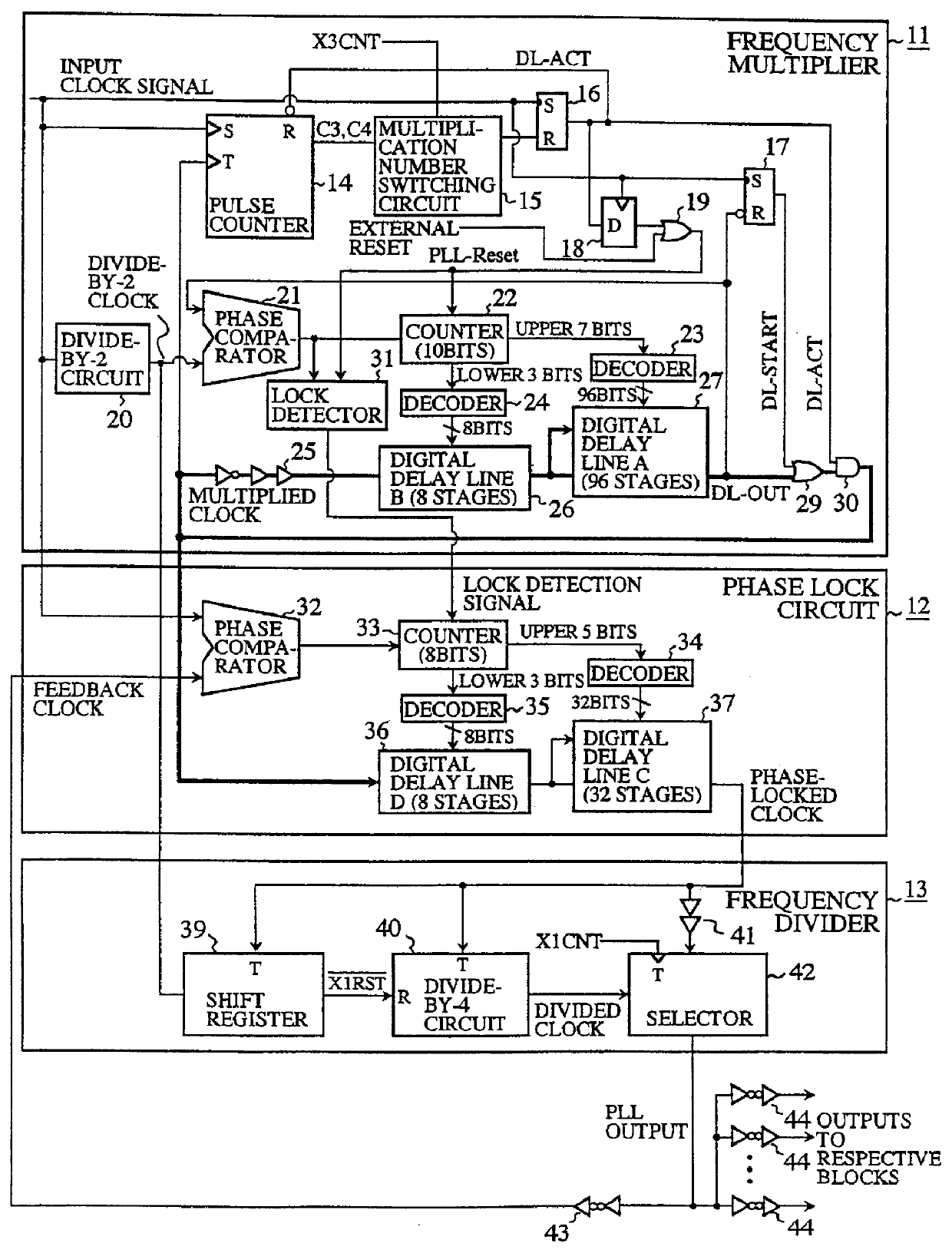
Clock generator and clock generating method capable of varying clock frequency without increasing the number of delay elements
InactiveUS6049238AReduce frequencyDelay lines pulse generationPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDelayed time
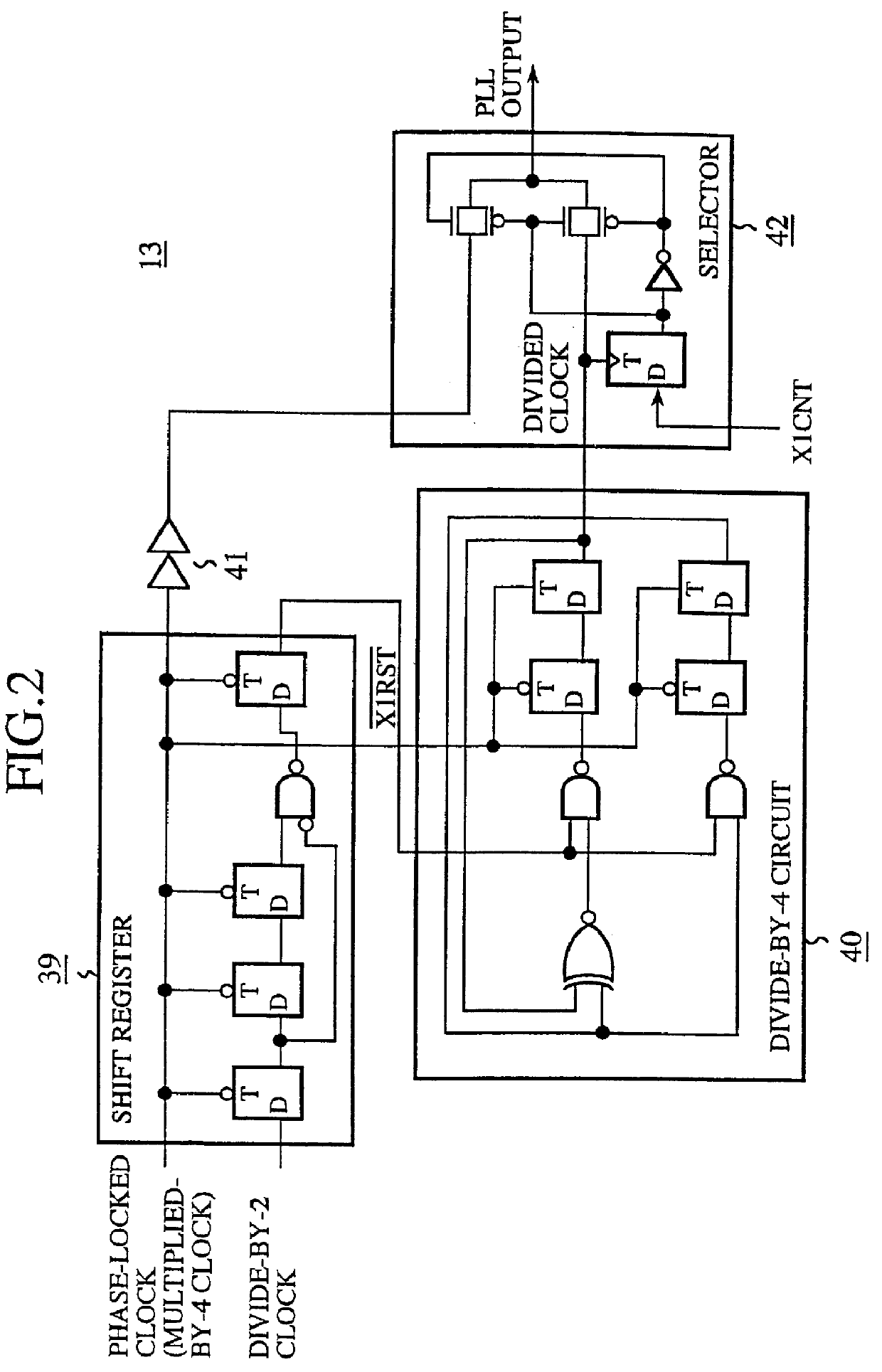
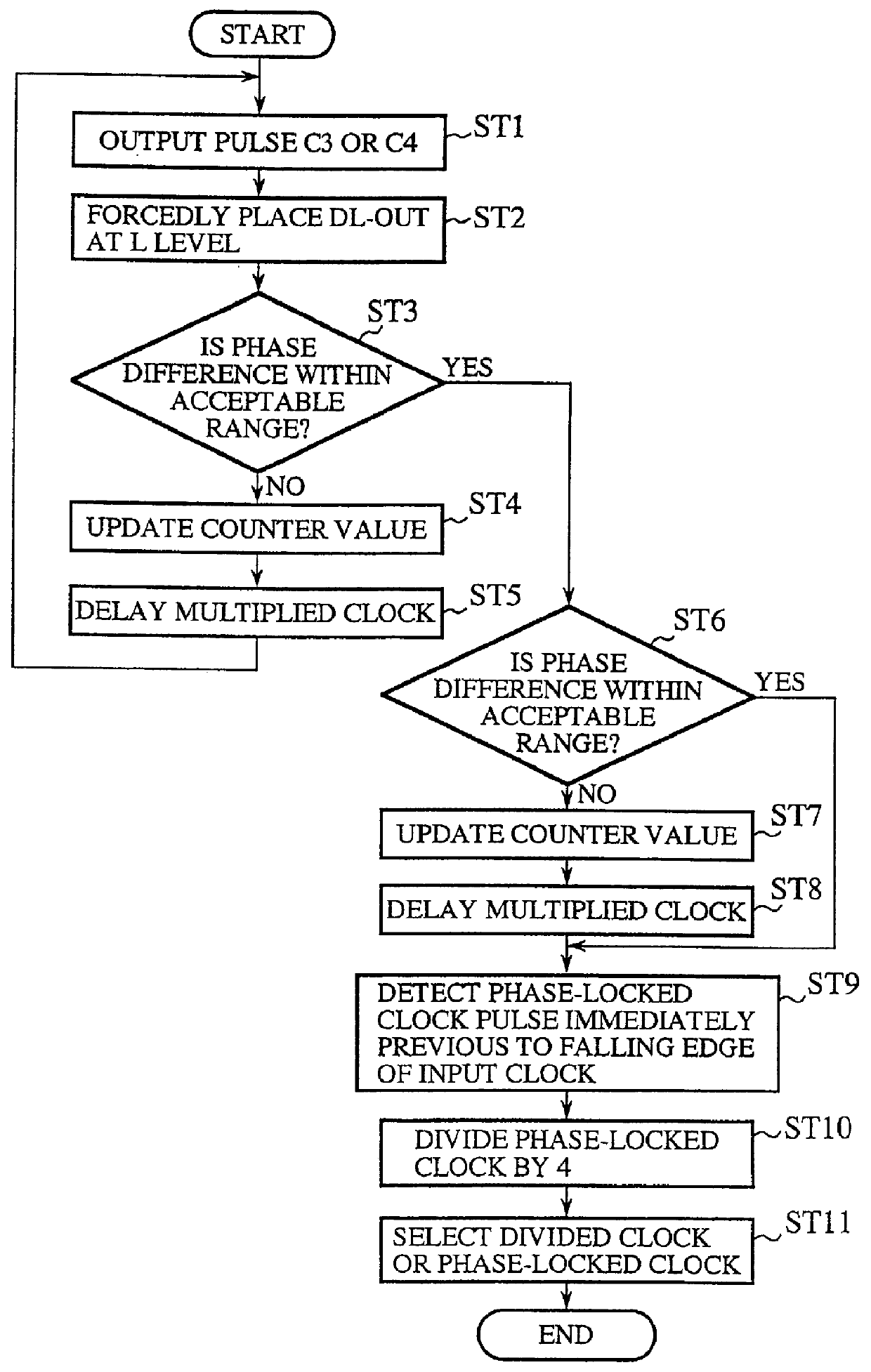
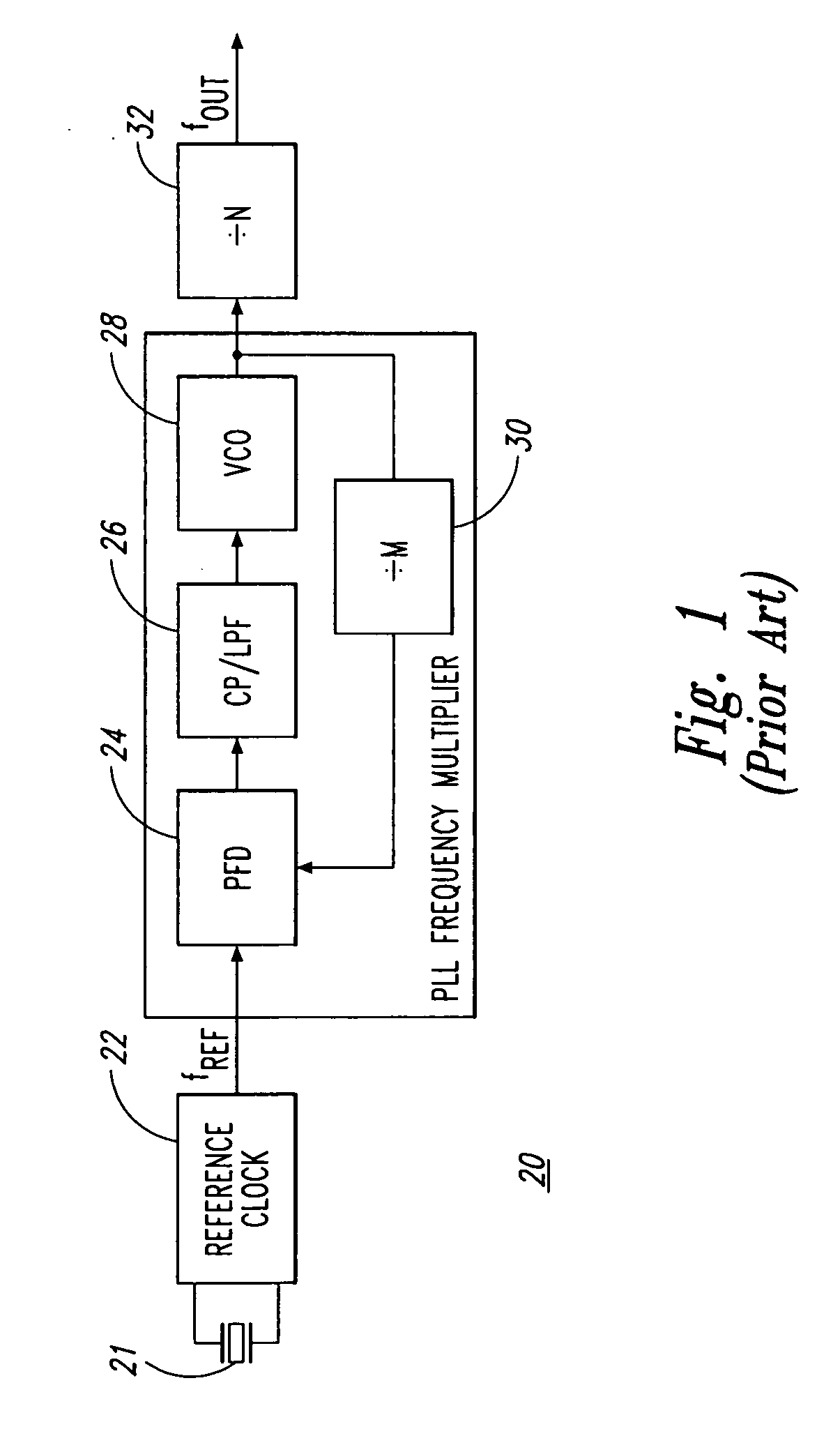
A clock generator including a frequency multiplier, a phase lock circuit and a frequency divider. The frequency multiplier generates a frequency multiplied clock by multiplying the frequency of an input clock. The phase lock circuit detects a phase difference between the input clock and a frequency divided clock, and generates, by delaying the frequency multiplied clock by an amount corresponding to the phase difference, a phase-locked clock with its phase locked with the input clock. The frequency divider detects in every fixed cycle a particular pulse of the phase-locked clock, and generates the frequency divided clock by dividing the phase-locked clock with reference to the particular pulse of the phase-locked clock. In particular, the frequency divider detects the particular pulse immediately previous to a falling edge of the input clock. This can reduce the phase difference between the input clock and the phase-locked clock, and hence to solve a problem of a conventional clock generator in that a delay time of a digital delay line in a phase lock circuit must be lengthened with a reduction in the multiplication number of the frequency multiplied clock, which requires a greater number of delay elements because of a large occupying area of the delay elements and a decoder, thereby increasing the circuit scale and cost of a chip to reduce the multiplication number of the frequency multiplied clock.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Ring oscillator using current mirror inverter stages
InactiveUSRE37124E1Limit maximum frequencyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsLow voltageEngineering
A ring oscillator having an odd number of single ended stages, each stage including two transistors connected as a current mirror. The stage provides for low-voltage performance and improved process tolerance characteristics.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Differential serial interface for supporting a plurality of differential serial interface standards
An active capacitor multiplying circuit that in one embodiment comprises (i) a clock synthesis loop filter of at least second order comprising a series combination of a first resistor and a first capacitor, wherein the series combination is coupled between a first charge pump interface and ground, wherein the clock synthesis loop filter further comprises a second capacitor coupled between the first charge pump interface and the ground; (ii) a capacitor multiplying loop filter comprising a second capacitor coupled between a second charge pump interface and the ground, wherein the capacitor multiplying loop filter further comprises a second resistor coupled to the second charge pump interface and the second charge pump interface is coupled to the first charge pump interface; and (iii) an operational amplifier, driven by the first capacitor, for driving the second resistor, wherein a voltage presented at the first charge pump interface drives a voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
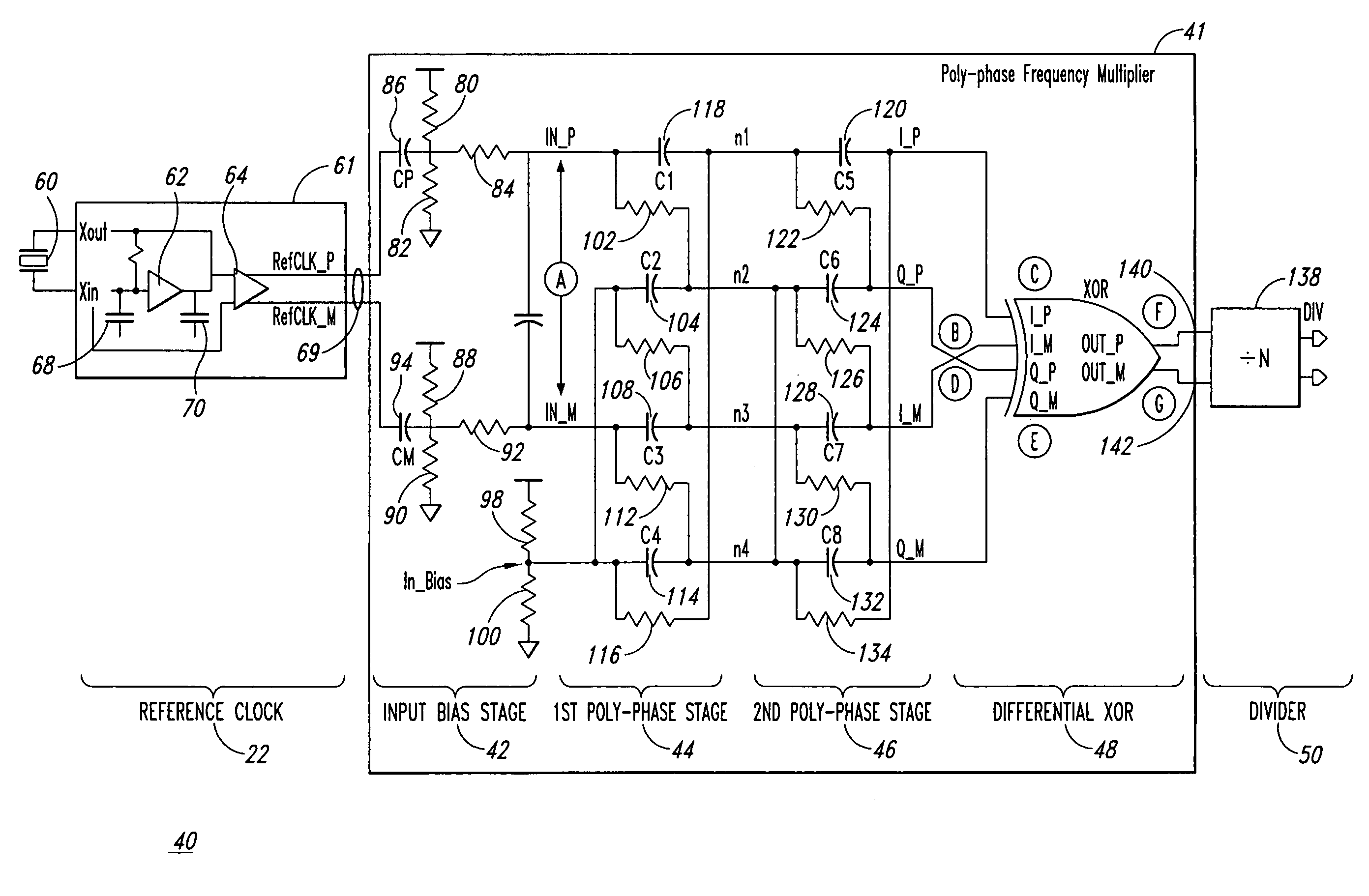
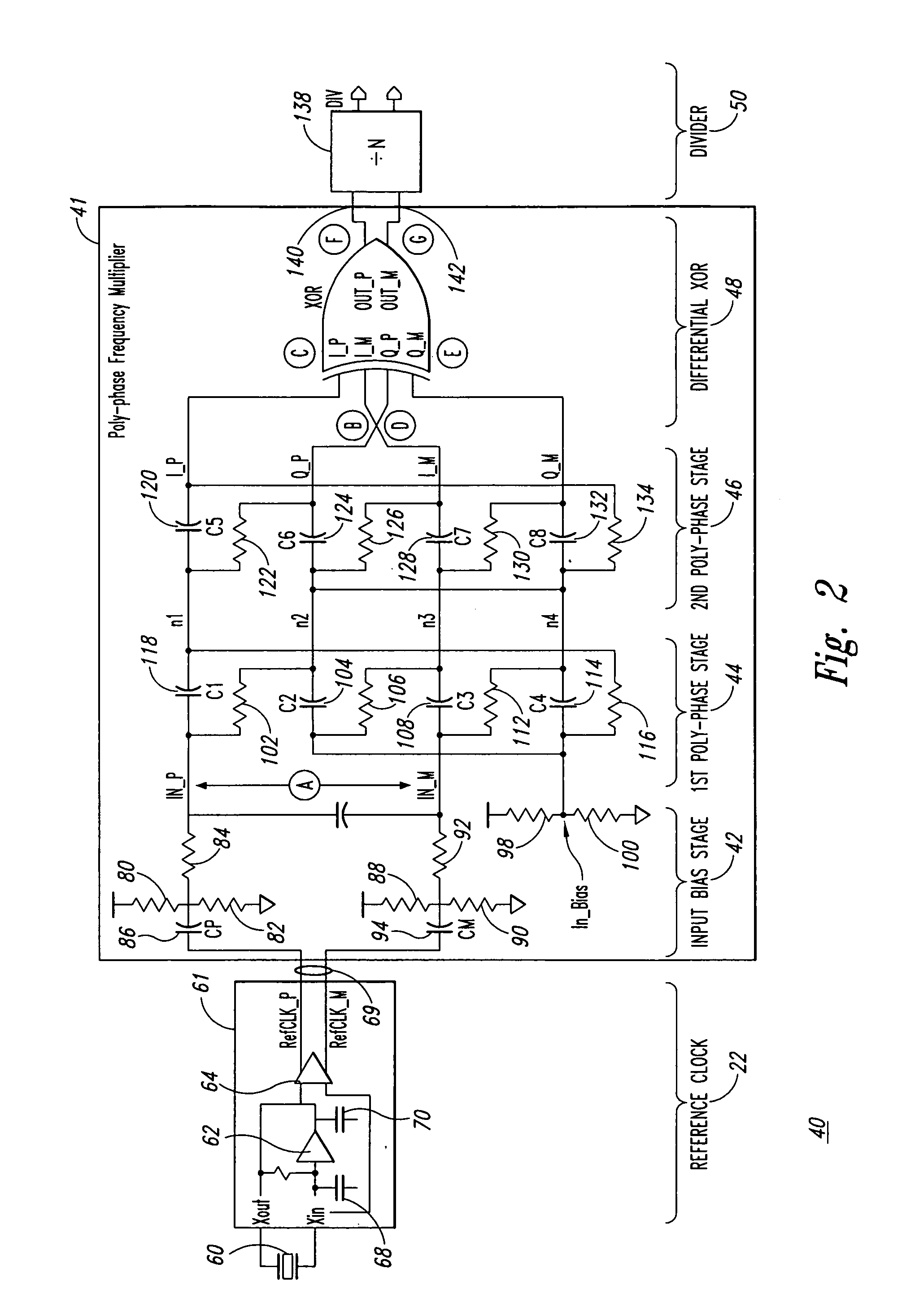
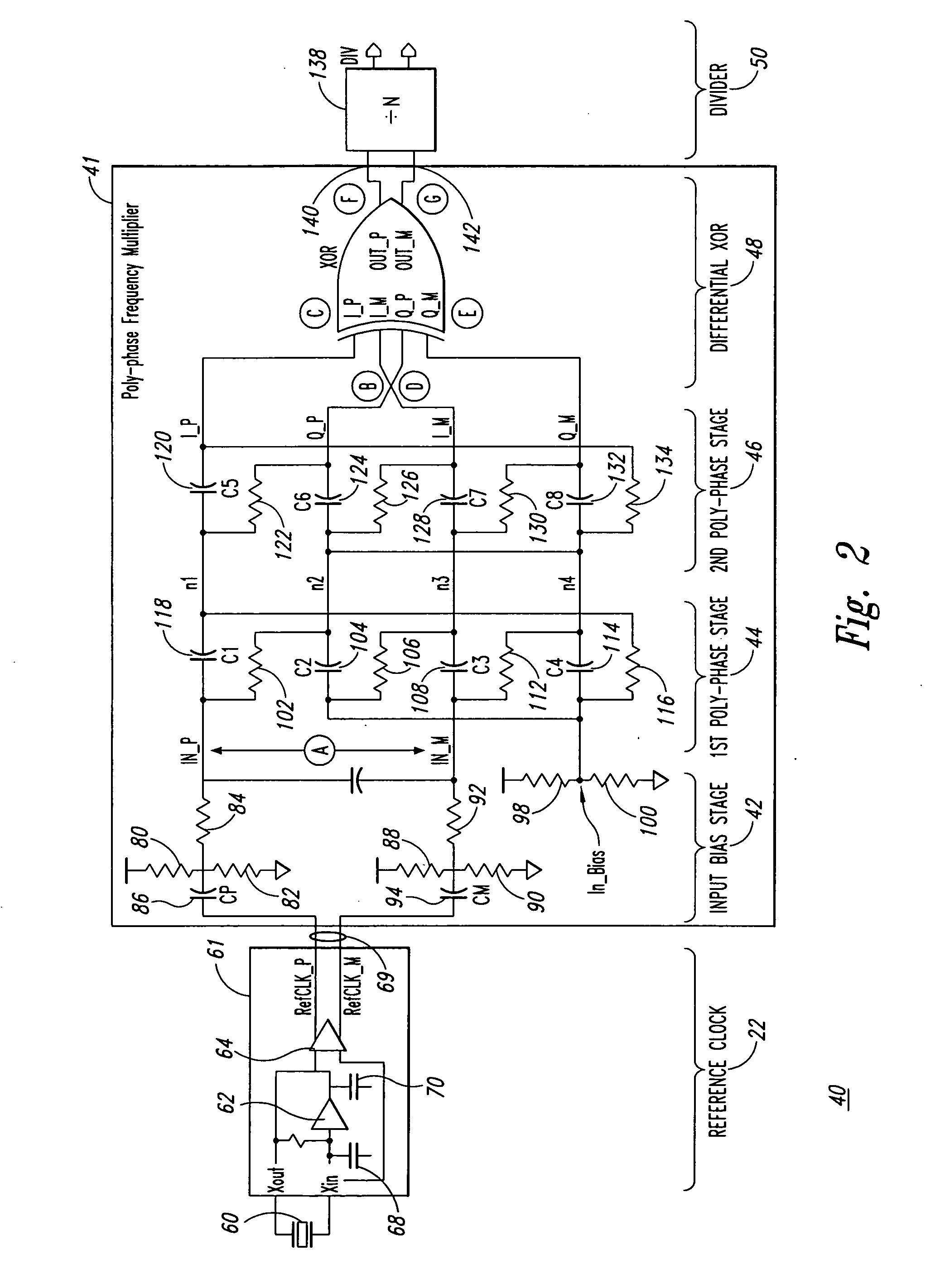
Poly-phase frequency synthesis oscillator
ActiveUS7332976B1Multiple-port networksComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersFrequency synthesisMultiple version
A frequency synthesis / multiplication circuit and method for multiplying the frequency of a reference signal. In one embodiment, multiple versions of the reference signal are generated having different phases relative to one another, and these multiple versions are combined to form an output signal having a frequency that is a multiple of the frequency of the reference signal.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
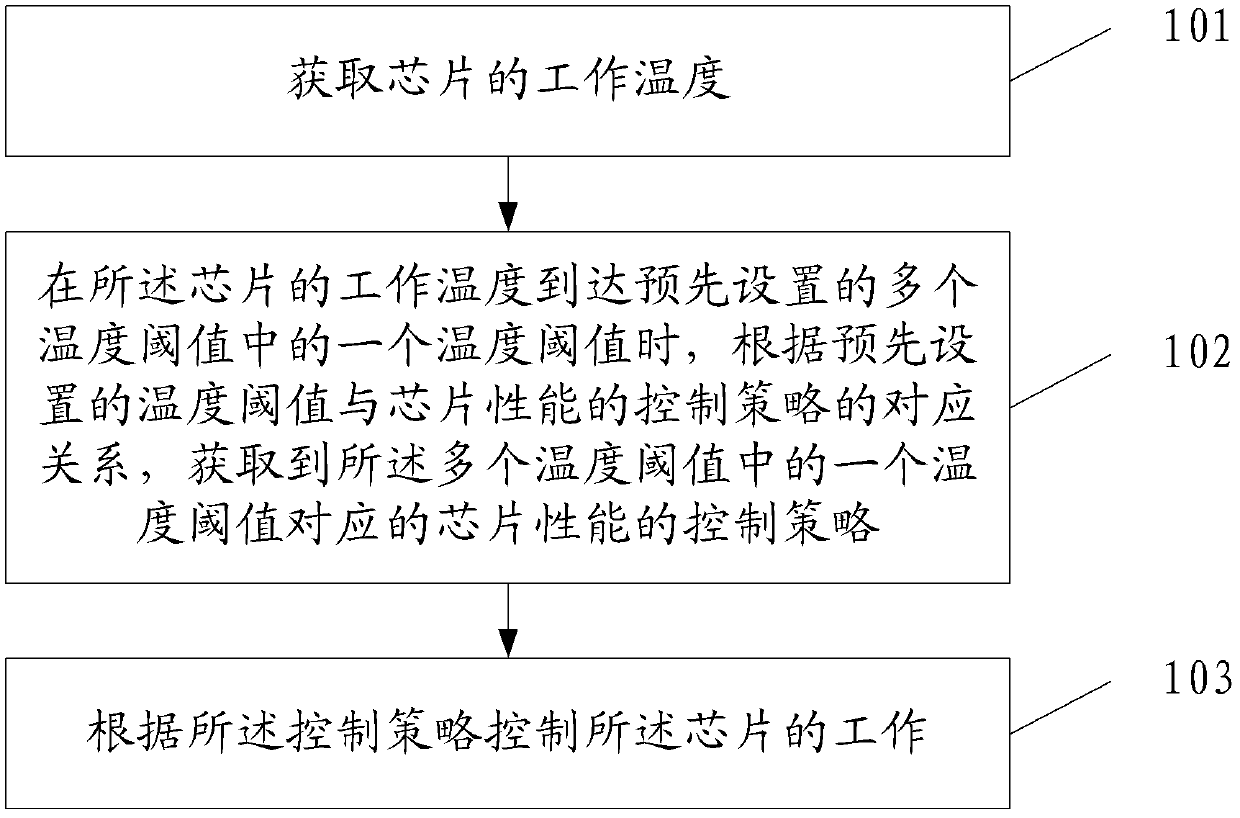
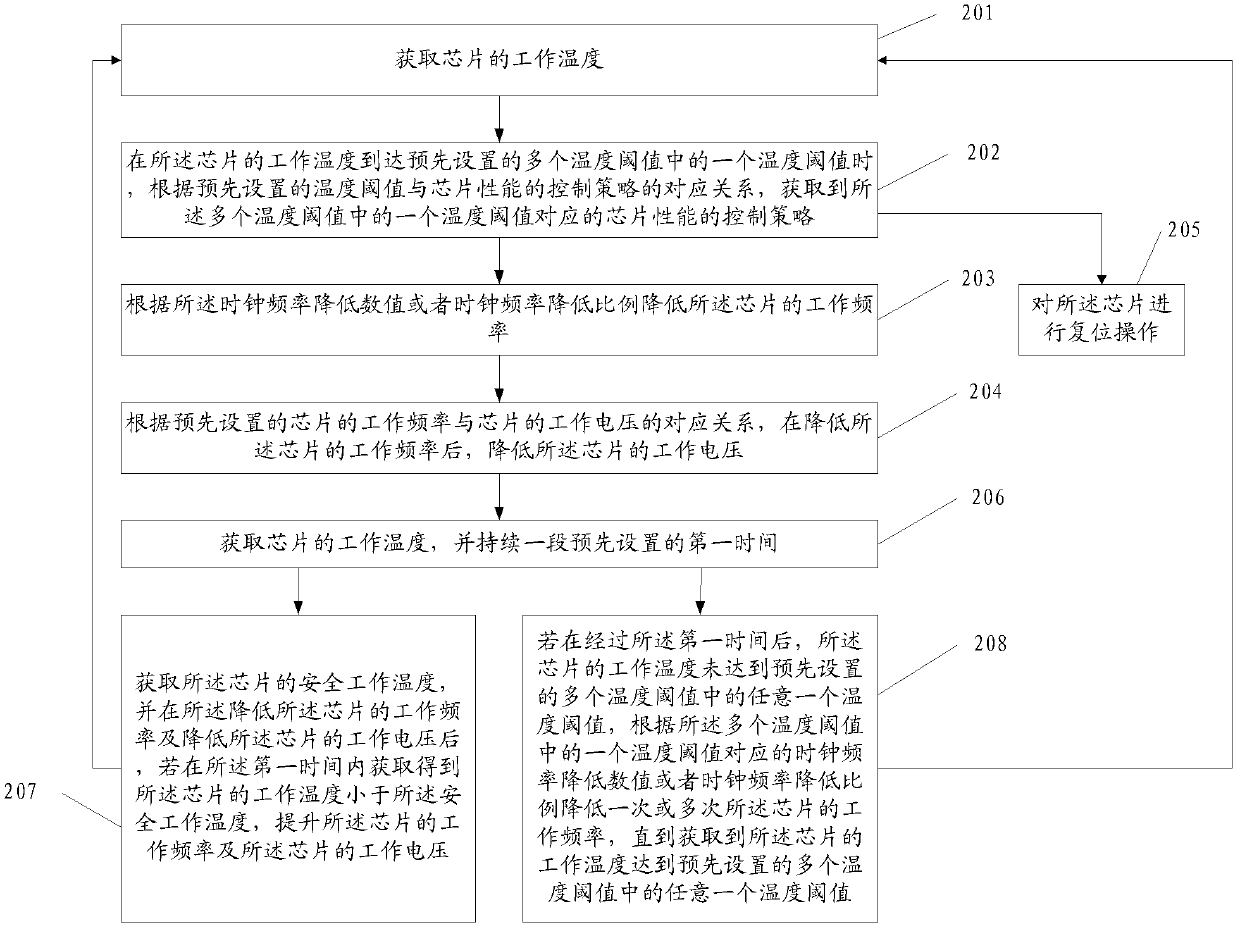
Chip performance control method and device
ActiveCN103376859AAvoid the problem of large performance degradationDigital data processing detailsEnergy efficient computingWorking temperatureThermal threshold
Embodiments of the present invention disclose a method and an apparatus for controlling chip performance, and relate to the field of communications technologies, which solves a problem in the prior art that a chip is reset or performance is greatly decreased as long as a temperature of the chip is higher than a preset threshold. The method includes: obtaining a working temperature of a chip; when the working temperature of the chip reaches one of multiple preset temperature thresholds, obtaining, according to preset correspondence between a temperature threshold and a chip performance control policy, a chip performance control policy that corresponds to the one of the multiple temperature thresholds; and controlling working of the chip according to the control policy. The present invention is applicable to an electronic device to which a chip is applied, such as a desktop computer or a notebook computer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
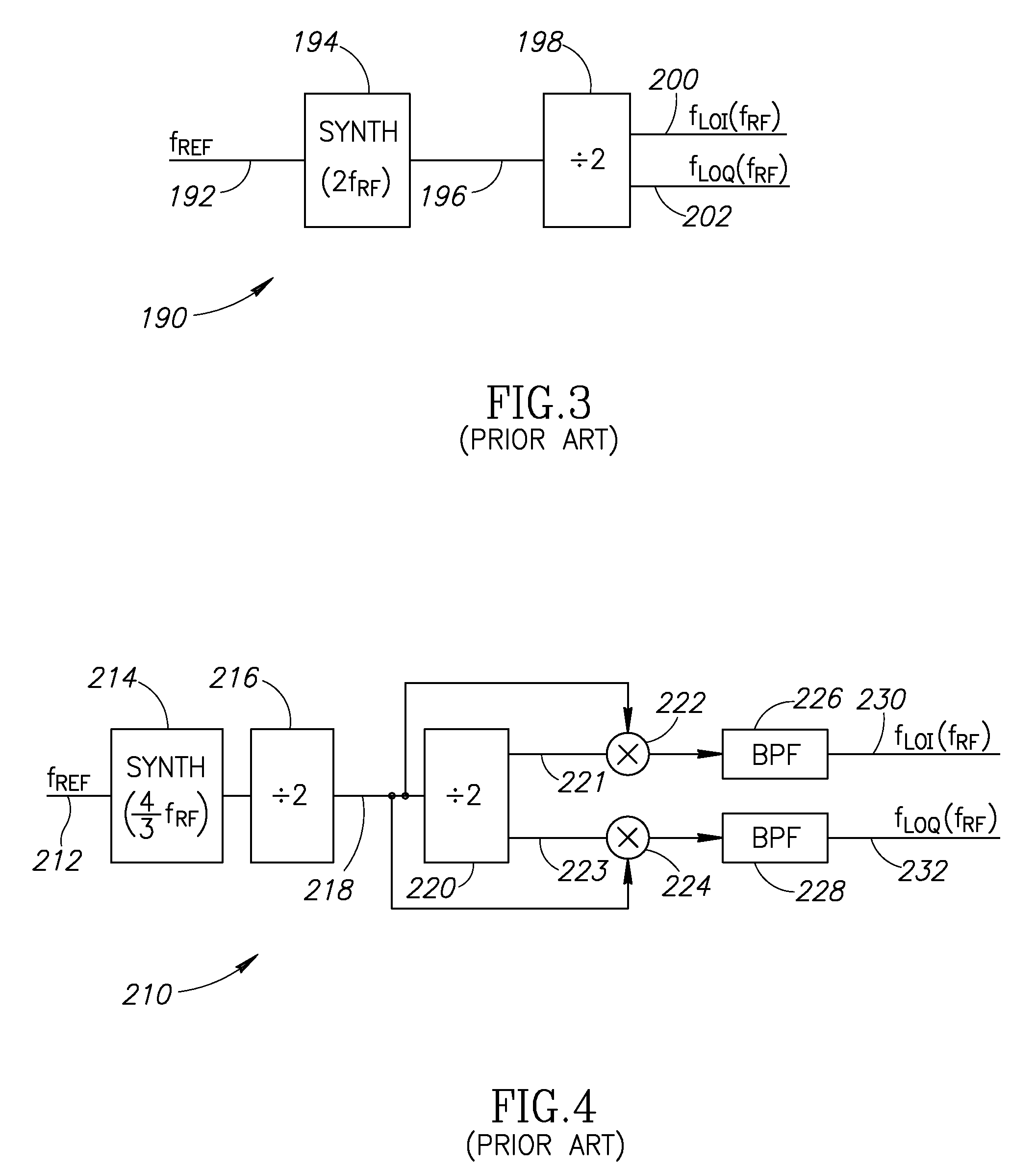
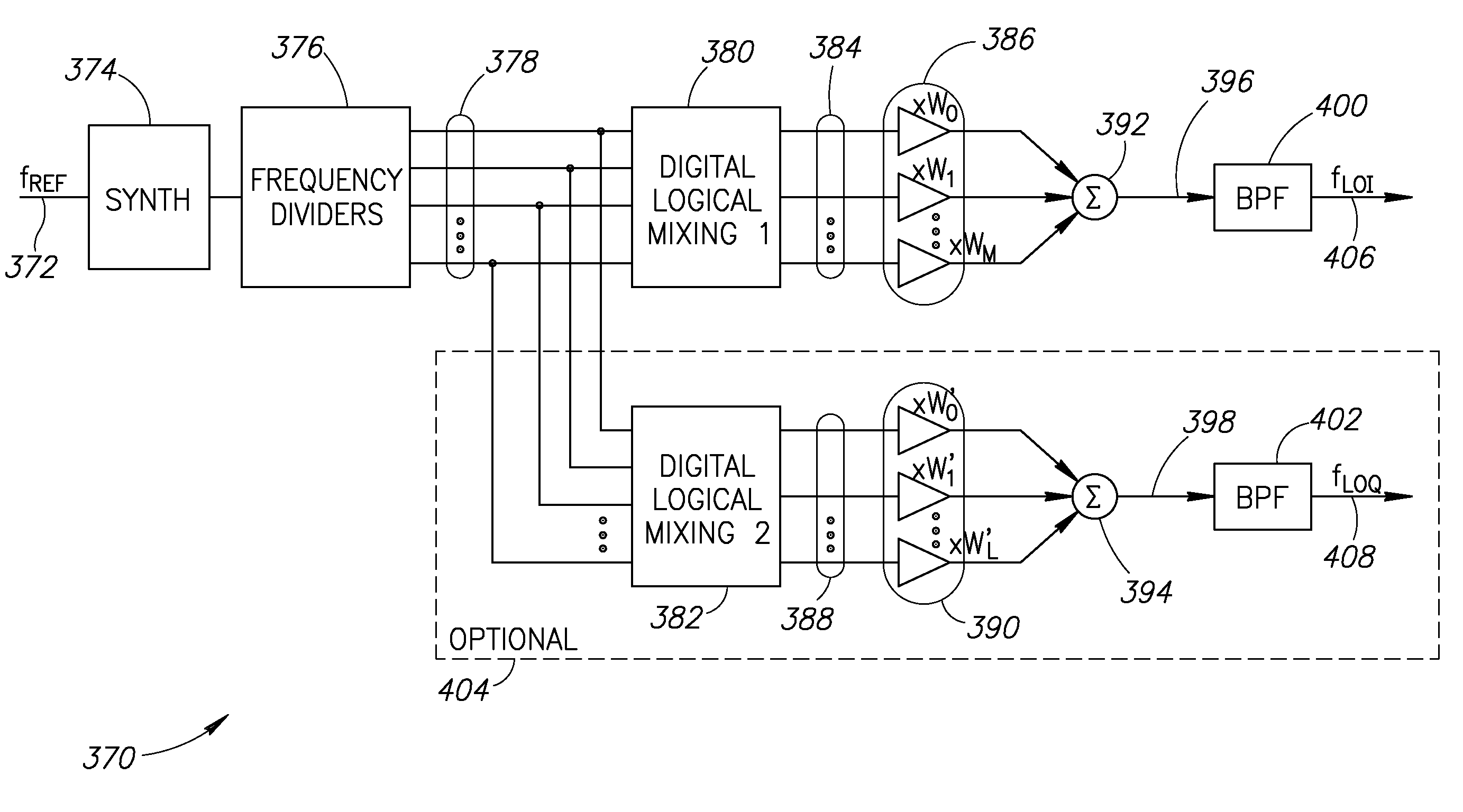
Local oscillator with non-harmonic ratio between oscillator and RF frequencies using pulse generation and selection
ActiveUS20080055010A1Avoid serious problemsEasy to implementModulated-carrier systemsElectrical testingHarmonicLocal oscillator
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of local oscillator (LO) generation with non-integer multiplication ratio between the local oscillator and RF frequencies. The LO generation schemes presented are operative to generate I and Q square waves at a designated frequency while avoiding the well known issue of harmonic pulling. The input signal is fed to a synthesizer timed to a rational multiplier of the RF frequency L / N fRF. The clock signal generated is divided by a factor Q to form 2Q phases of the clock at a frequency of L(N*Q) fRF, wherein each phase undergoes division by L. The phase signals are input to a pulse generator which outputs a plurality of pulses. The pulses are input to a selector which selects which signal to output at any point in time. By controlling the selector, the output clock is generated as a TDM based signal. Any spurs are removed by an optional filter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
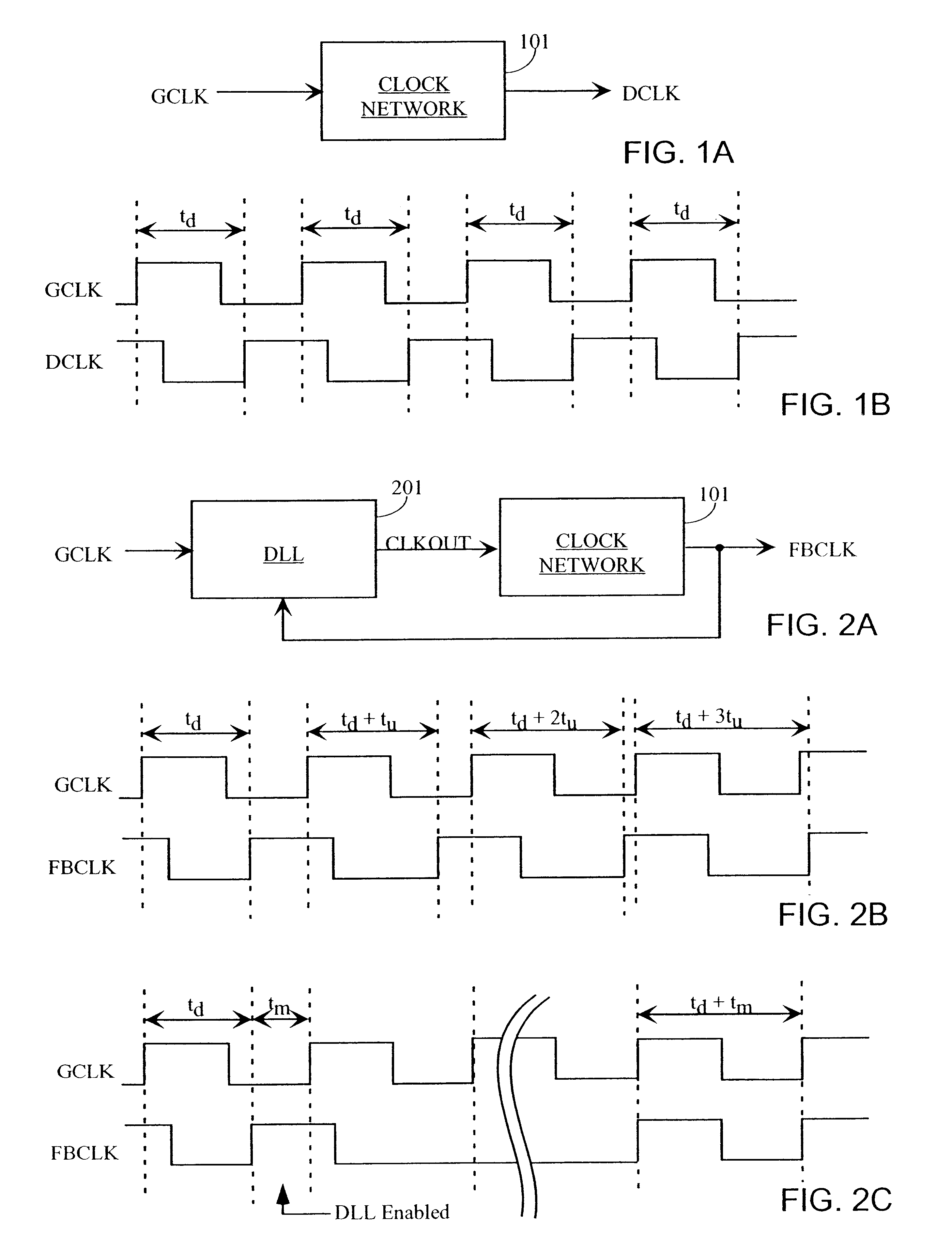
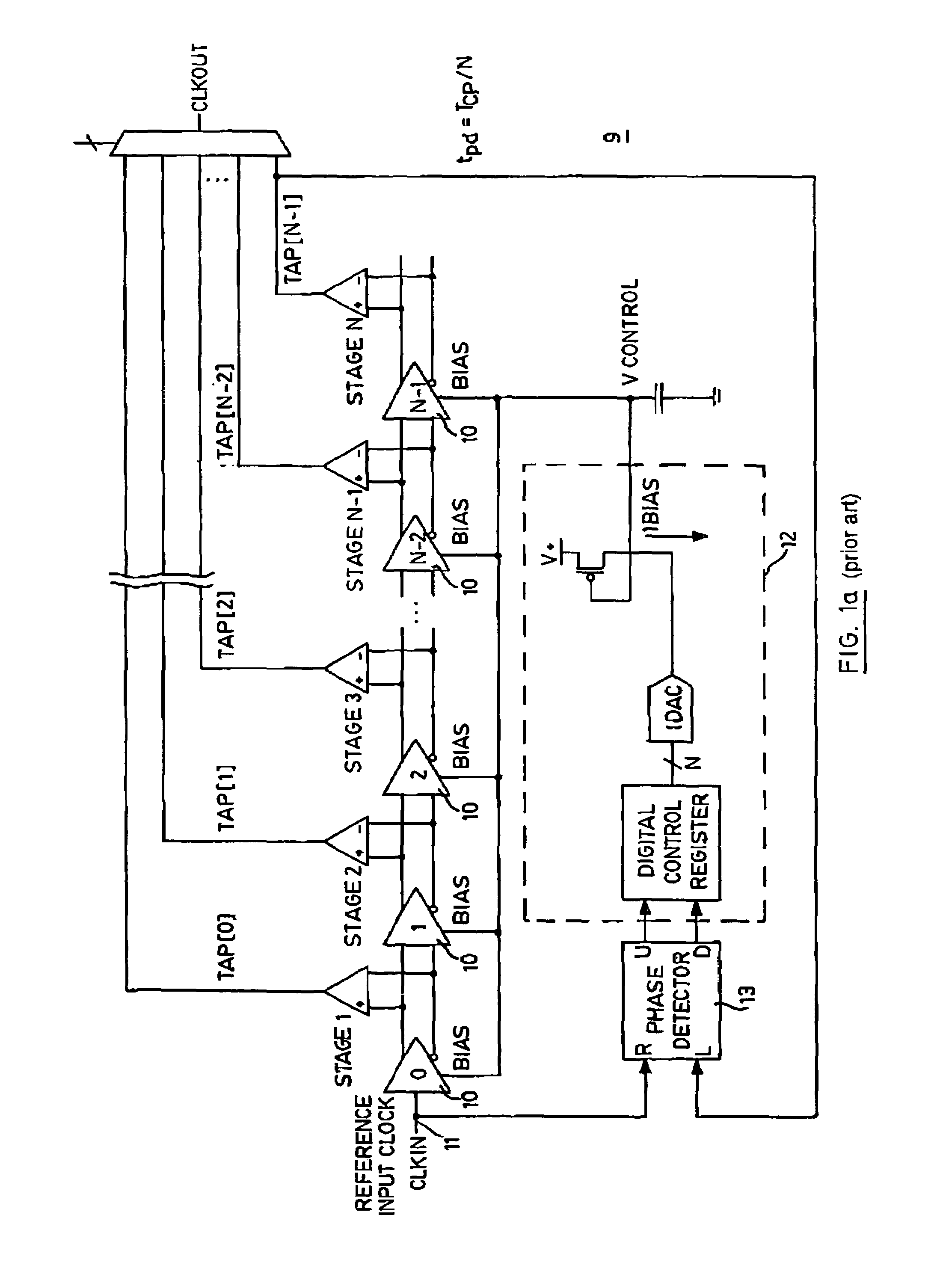
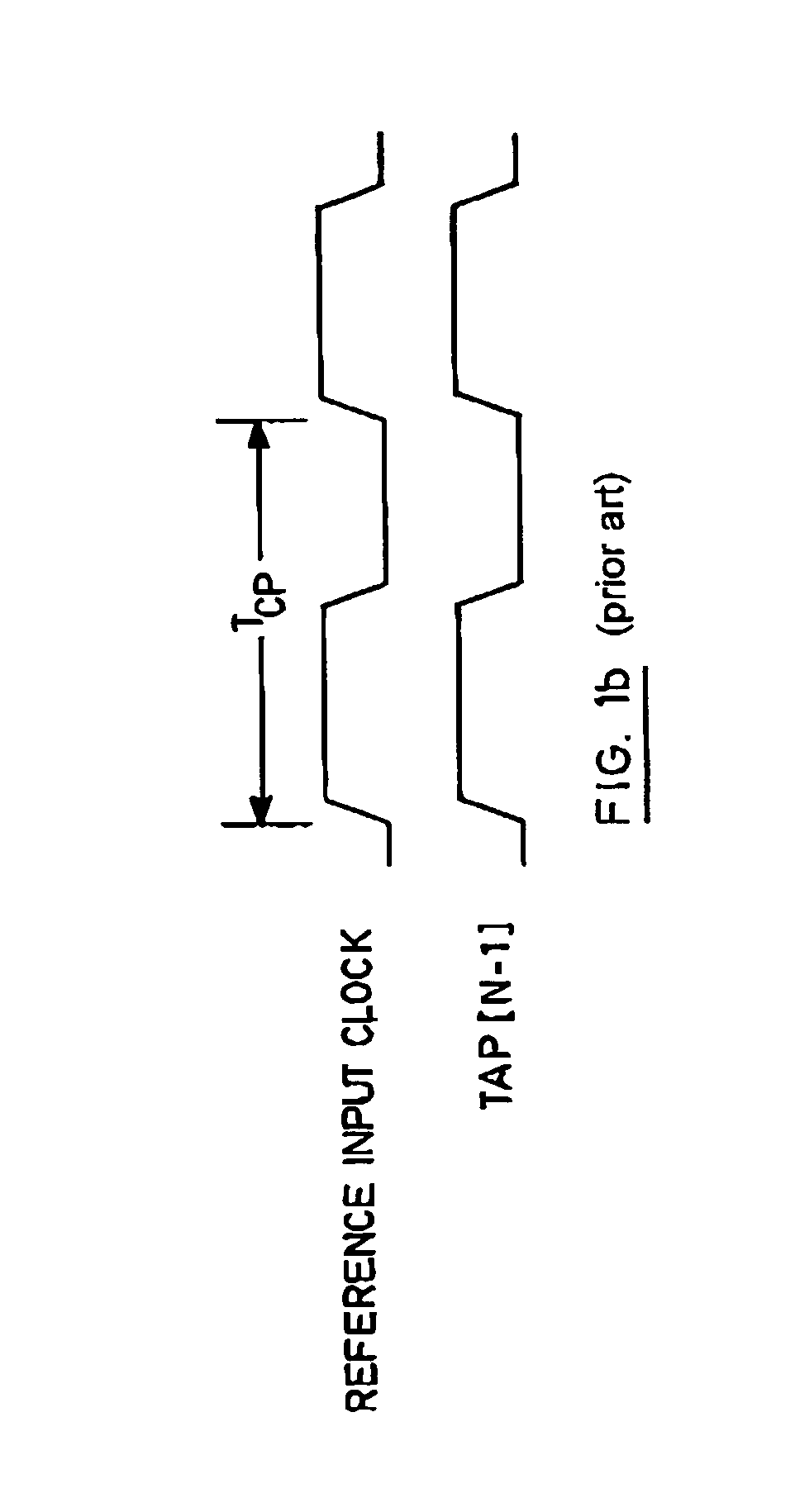
Direct-measured DLL circuit and method
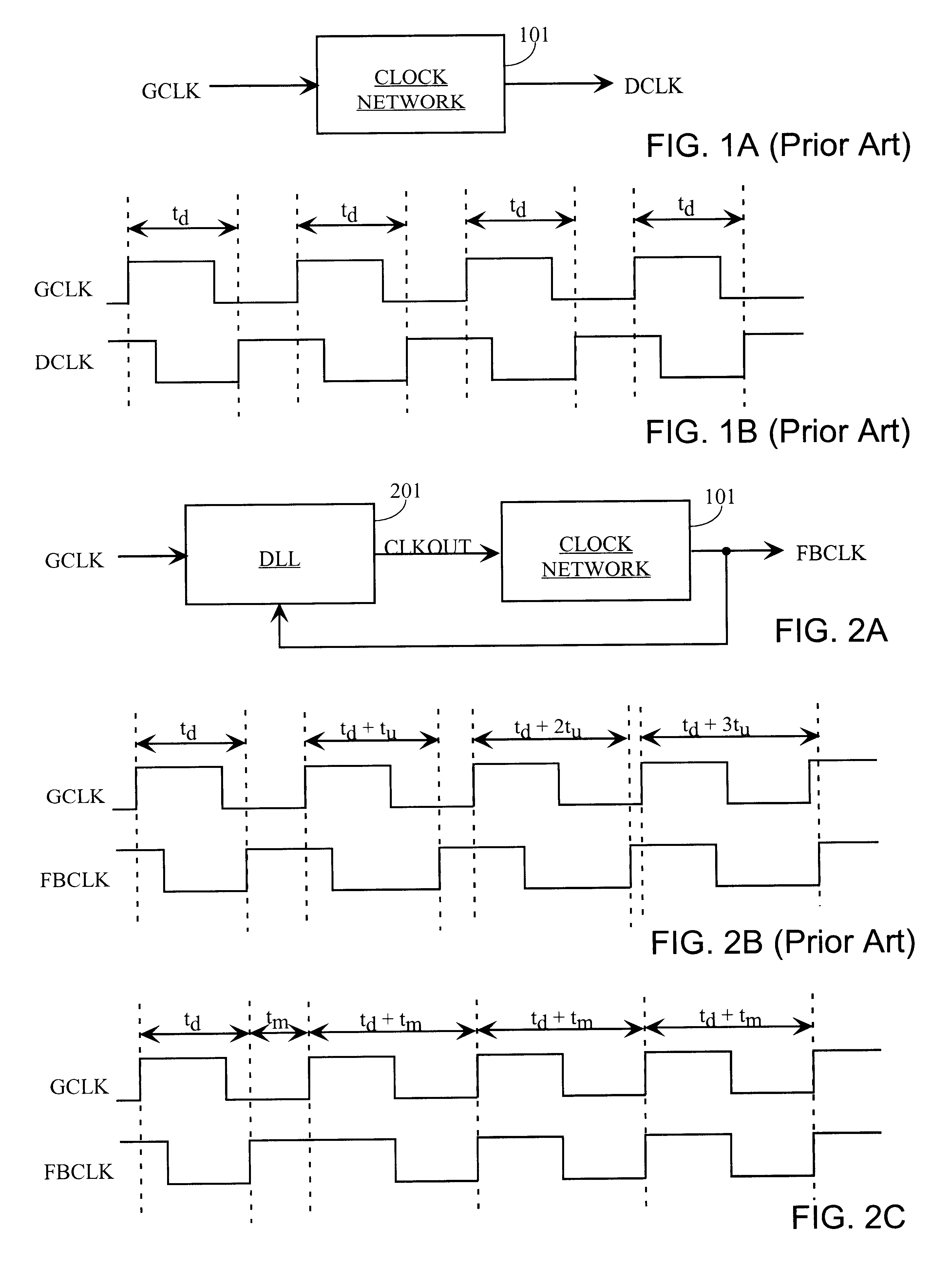
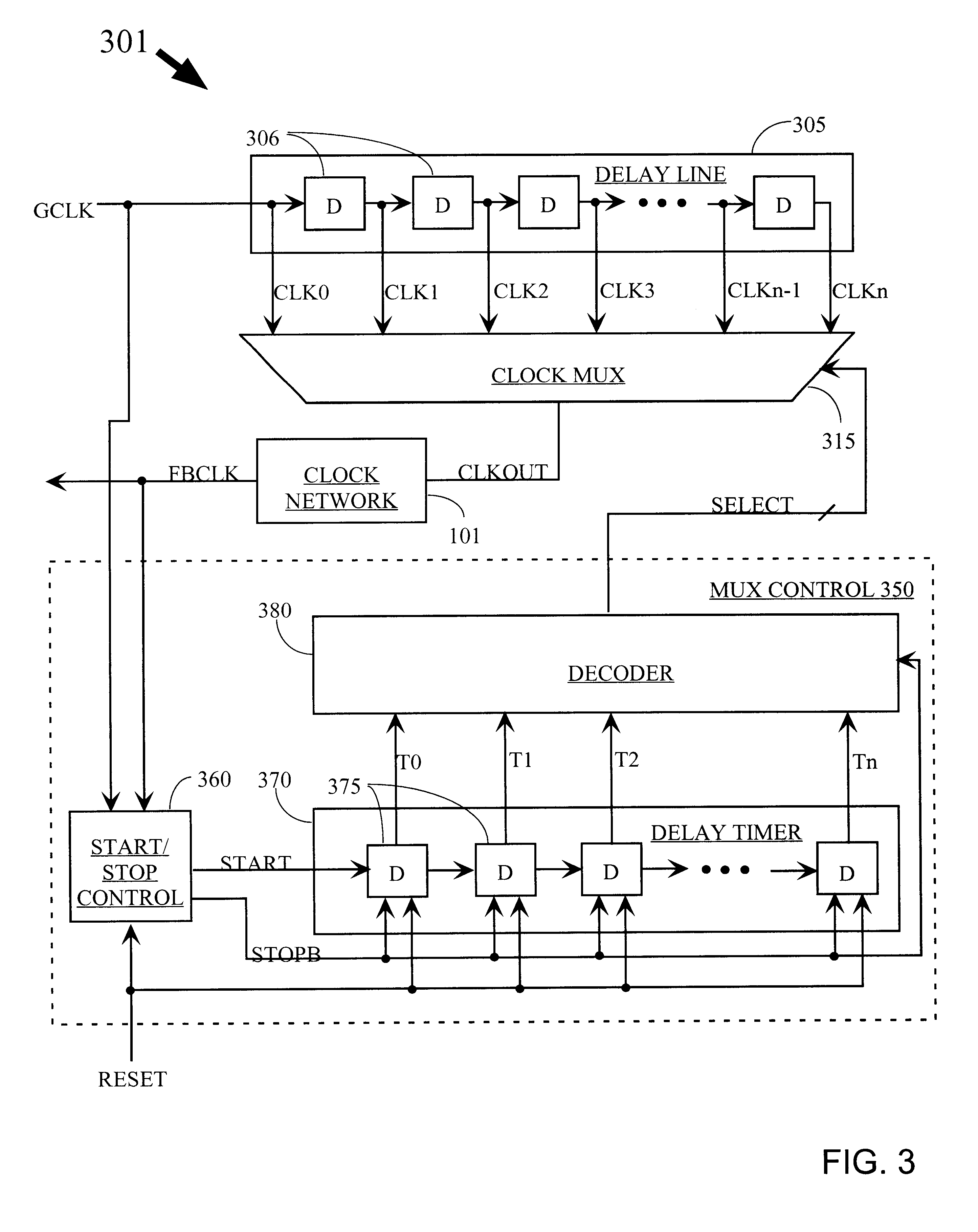
A delay-lock loop (DLL) circuit and method that accept an input clock signal and a feedback clock signal, and provide the necessary additional delay to synchronize the feedback clock signal to the input clock signal. A single synchronization step is sufficient, provided that the frequency of the input clock signal is stable. Further, only one delay line is required to implement the DLL circuit. Therefore, the DLL of the present invention is both quick to "lock in" a clock signal and efficient in the use of hardware resources. Further, the present DLL is very accurate, because the same delay line is used to calculate the necessary additional delay and to generate the output clock signal.
Owner:XILINX INC
Superconducting circuit for generating pulse signal
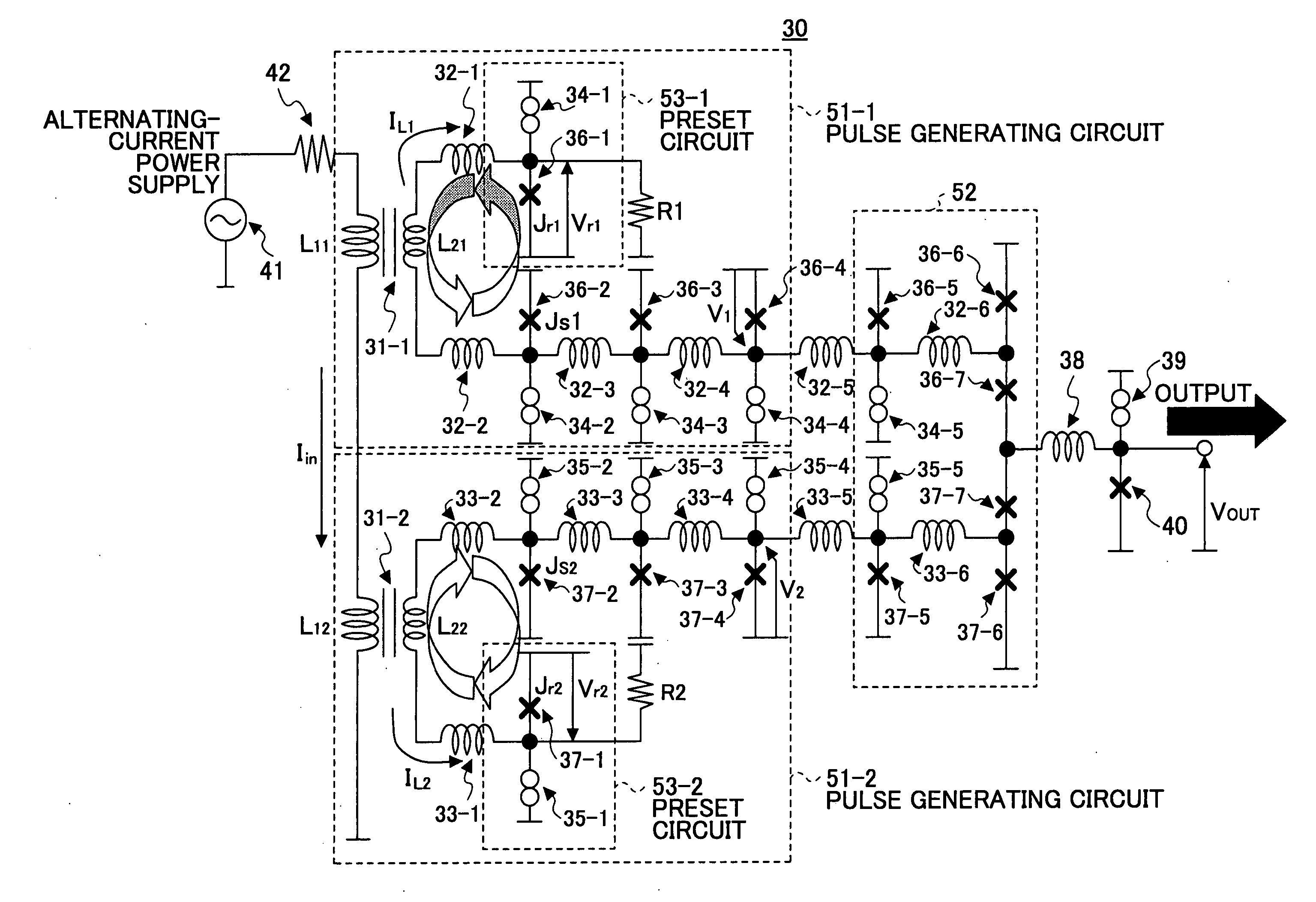
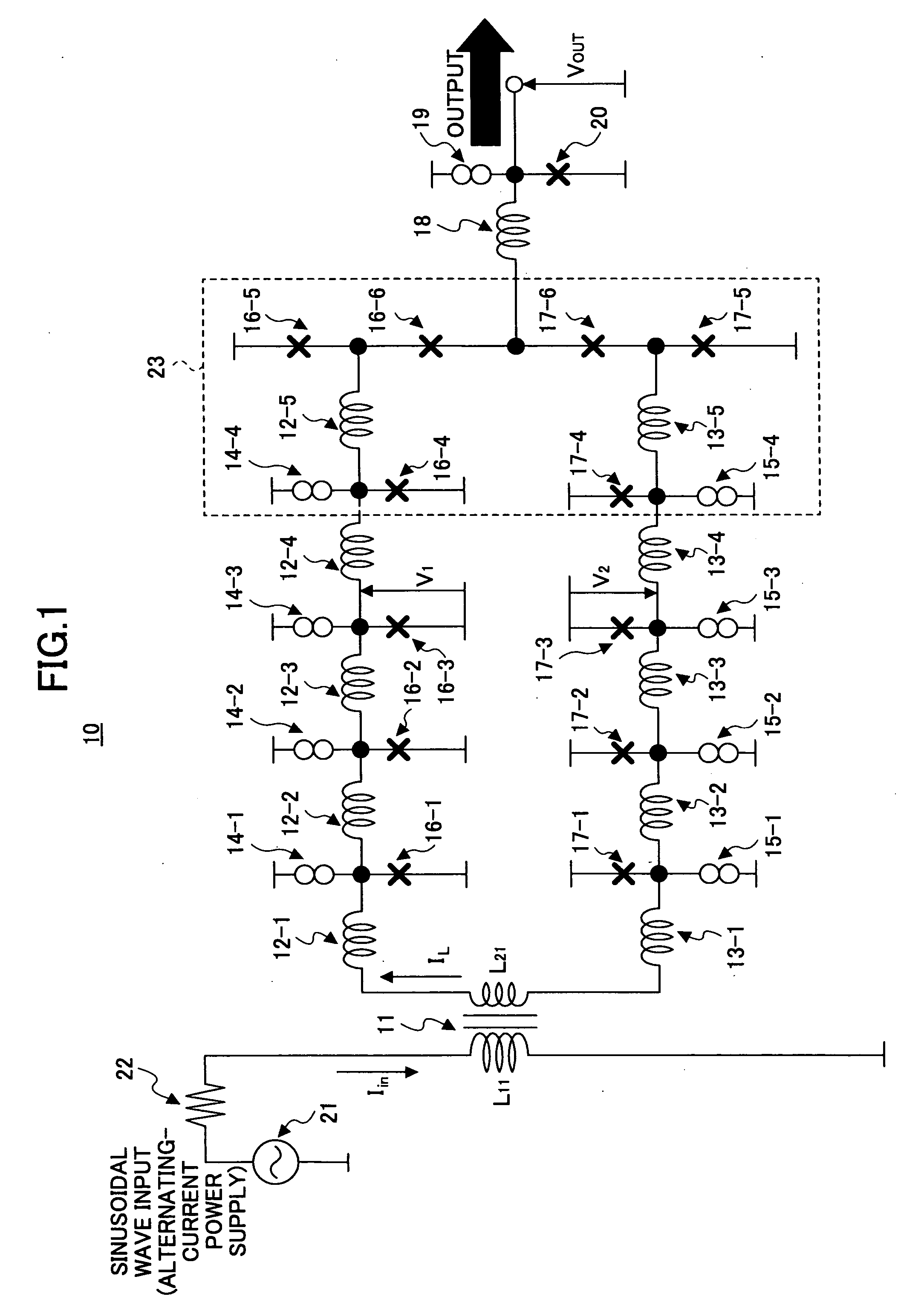
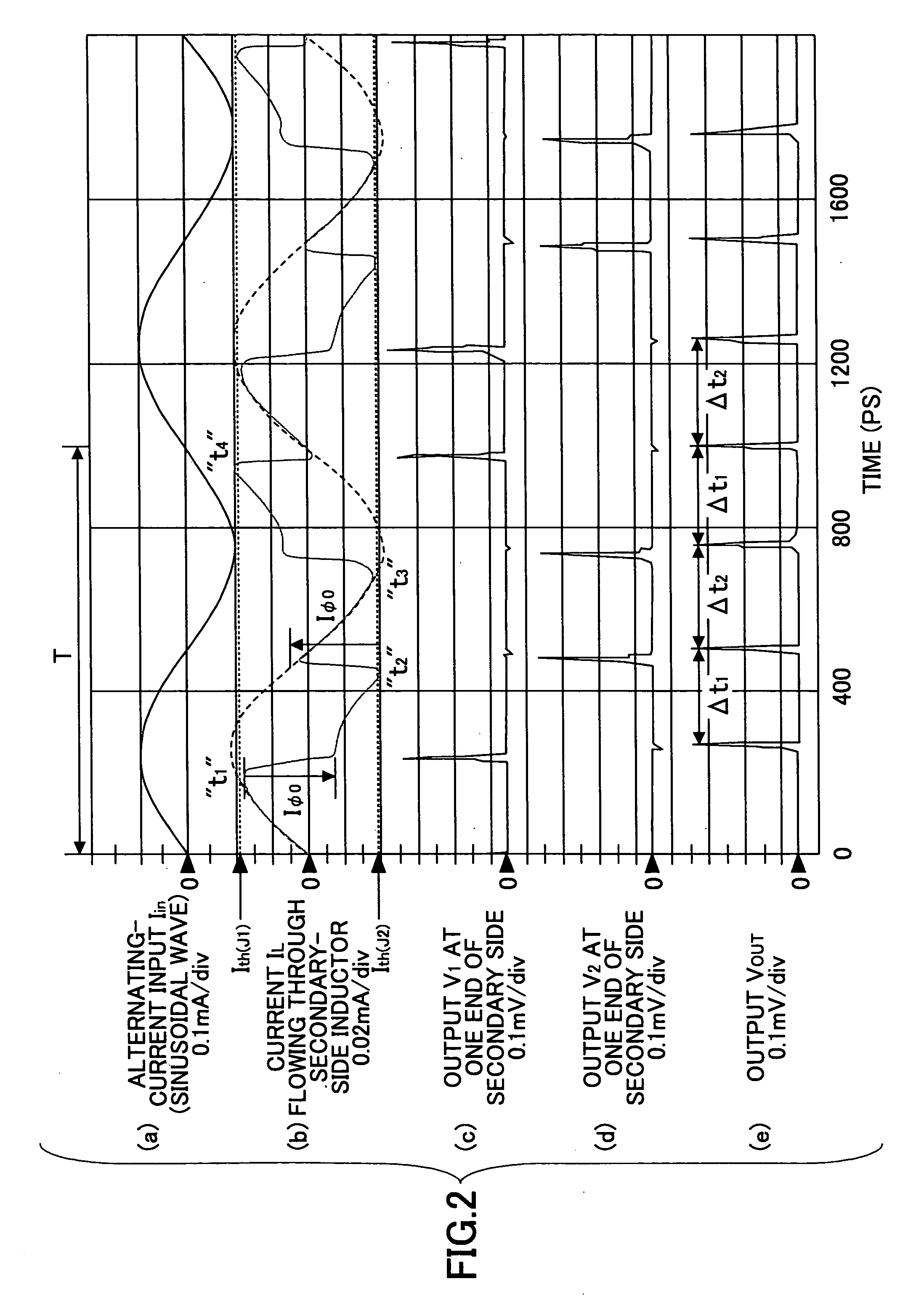
InactiveUS20070052441A1Small jitterImprove accuracyPulse generation by super conductive devicesManipulation for frequency changeInductorAlternating current
A superconducting circuit includes a first transformer to produce a first alternating-current output at a secondary-side inductor, a second transformer to produce a second alternating-current output at a secondary-side inductor, a first pulse generating circuit to produce a single flux quantum pulse responsive to the first alternating-current output, a second pulse generating circuit to produce a single flux quantum pulse responsive to the second alternating-current output, and a confluence buffer circuit to merge the single flux quantum pulses from the pulse generating circuits, wherein each of the pulse generating circuits includes a superconducting loop including the secondary-side inductor, a first Josephson junction situated in the superconducting loop to generate the single flux quantum pulse, and a second Josephson junction situated in the superconducting loop, a threshold value of the second Josephson junction for an electric current flowing through the secondary-side inductor being different from that of the first Josephson junction.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
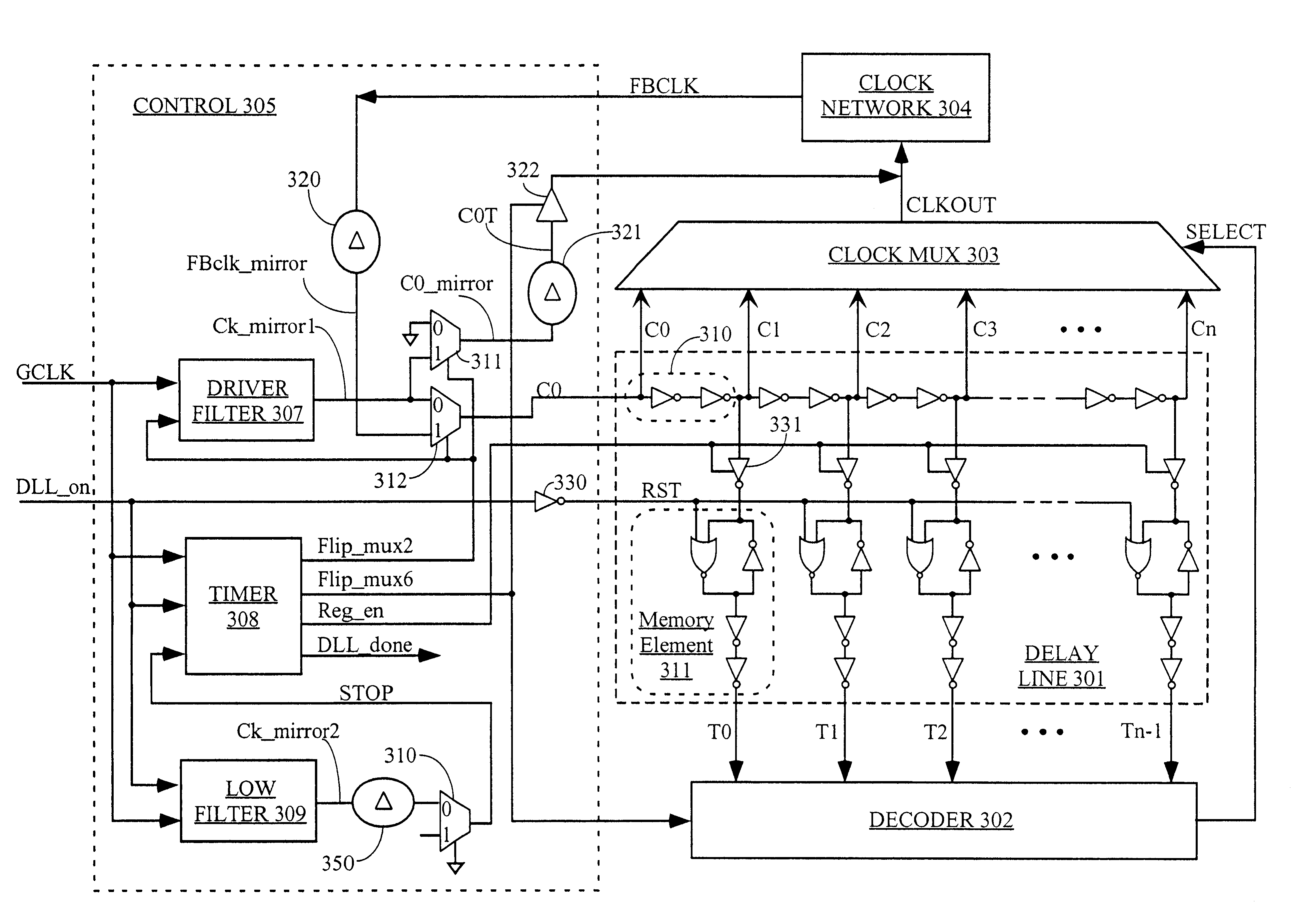
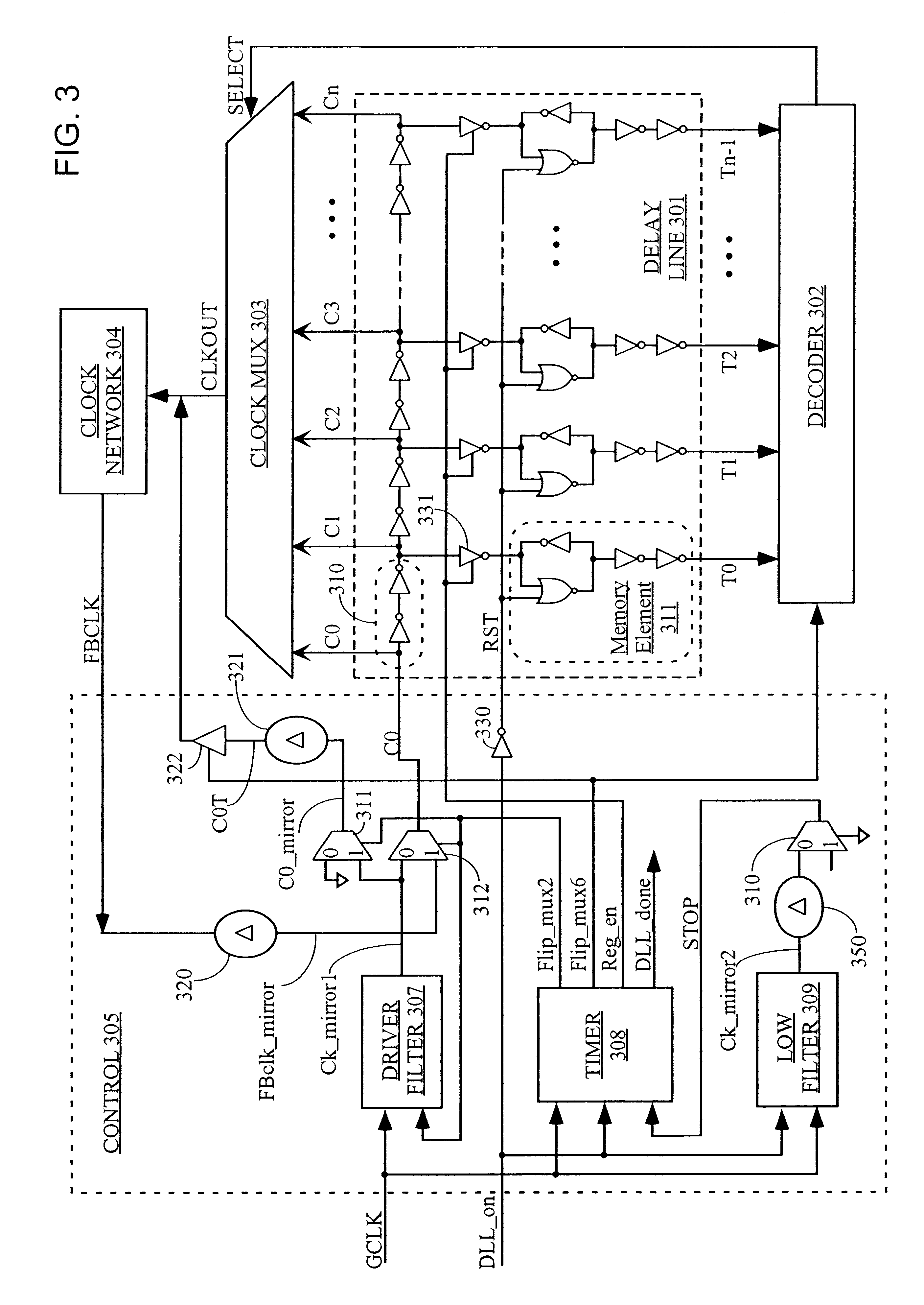
One-shot DLL circuit and method
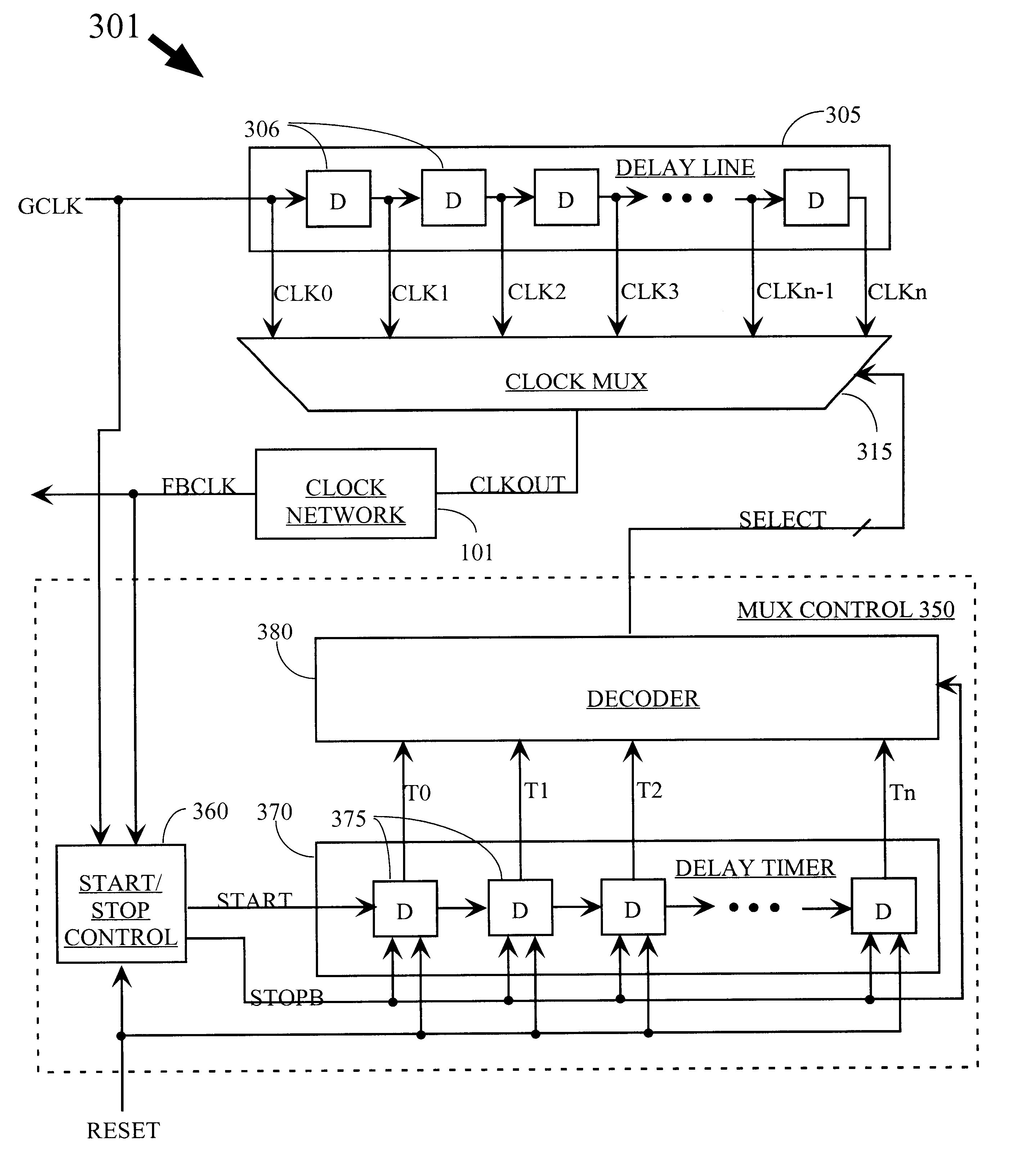
InactiveUS6255880B1Reduce noiseHigh simulationPulse automatic controlTime-division multiplexMultiplexerDelay-locked loop
A delay-lock loop (DLL) circuit and method that accept an input clock signal and a feedback clock signal, and provide the necessary additional delay to synchronize the feedback clock signal to the input clock signal. Unlike previous circuits and methods, a single synchronization step is sufficient, provided that the frequency of the input clock signal is stable. A circuit according to the invention includes an input clock terminal supplying an input clock signal, and a delay line driven by the input clock signal and supplying a plurality of intermediate clock signals delayed from the input clock signal by incremental unit delays. A clock multiplexer selects from among these intermediate clock signals, under control of a multiplexer control circuit, the clock signal that provides the necessary additional delay to synchronize the feedback clock signal to the input clock signal. The output clock signal from the clock multiplexer is distributed through the clock network to provide the distributed clock signal as well as the feedback clock signal.
Owner:XILINX INC
Poly-phase frequency synthesis oscillator
ActiveUS20090066427A1Multiple-port networksComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersFrequency synthesisMultiple version
A frequency synthesis / multiplication circuit and method for multiplying the frequency of a reference signal. In one embodiment, multiple versions of the reference signal are generated having different phases relative to one another, and these multiple versions are combined to form an output signal having a frequency that is a multiple of the frequency of the reference signal.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Local oscillator with non-harmonic ratio between oscillator and RF frequencies using pulse generation and selection
ActiveUS7756487B2Avoid serious problemsEasy to implementModulated-carrier systemsElectrical testingHarmonicLocal oscillator
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of local oscillator (LO) generation with non-integer multiplication ratio between the local oscillator and RF frequencies. The LO generation schemes presented are operative to generate I and Q square waves at a designated frequency while avoiding the well known issue of harmonic pulling. The input signal is fed to a synthesizer timed to a rational multiplier of the RF frequency L / N fRF. The clock signal generated is divided by a factor Q to form 2Q phases of the clock at a frequency of L(N*Q)fRF, wherein each phase undergoes division by L. The phase signals are input to a pulse generator which outputs a plurality of pulses. The pulses are input to a selector which selects which signal to output at any point in time. By controlling the selector, the output clock is generated as a TDM based signal. Any spurs are removed by an optional filter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Local oscillator with non-harmonic ratio between oscillator and RF frequencies using wideband modulation spectral replicas
ActiveUS20080055014A1Easy to implementAvoid serious problemsModulation transferencePulse automatic controlBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
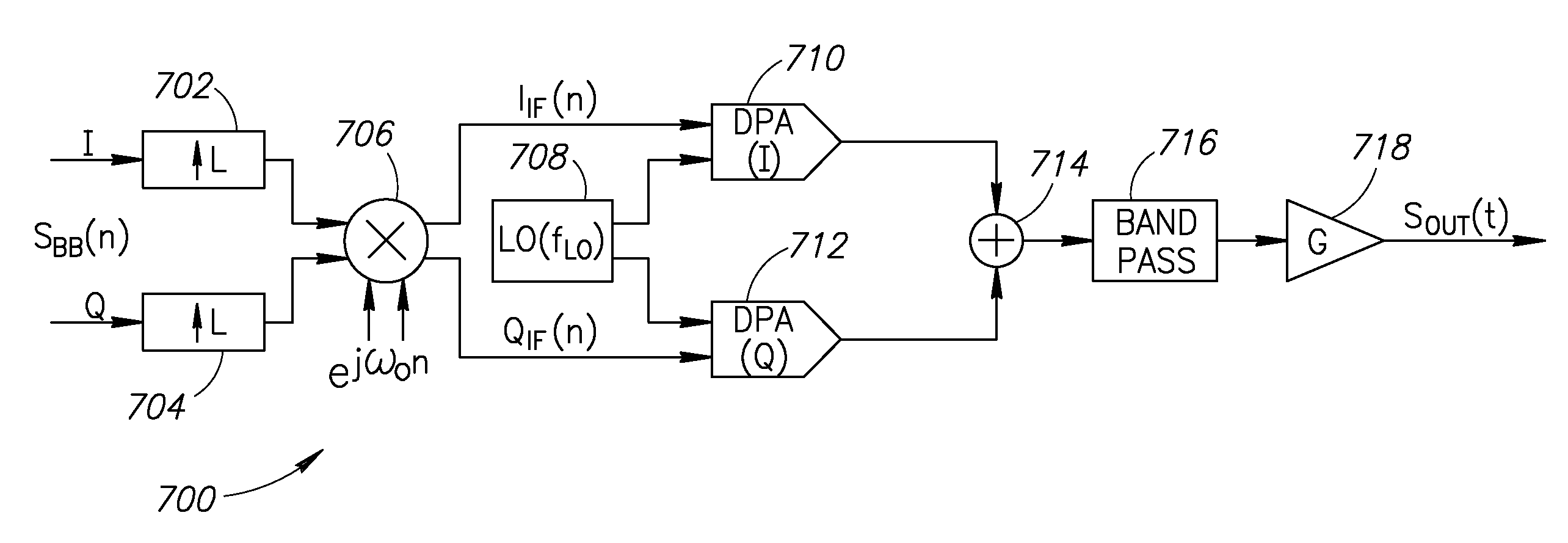
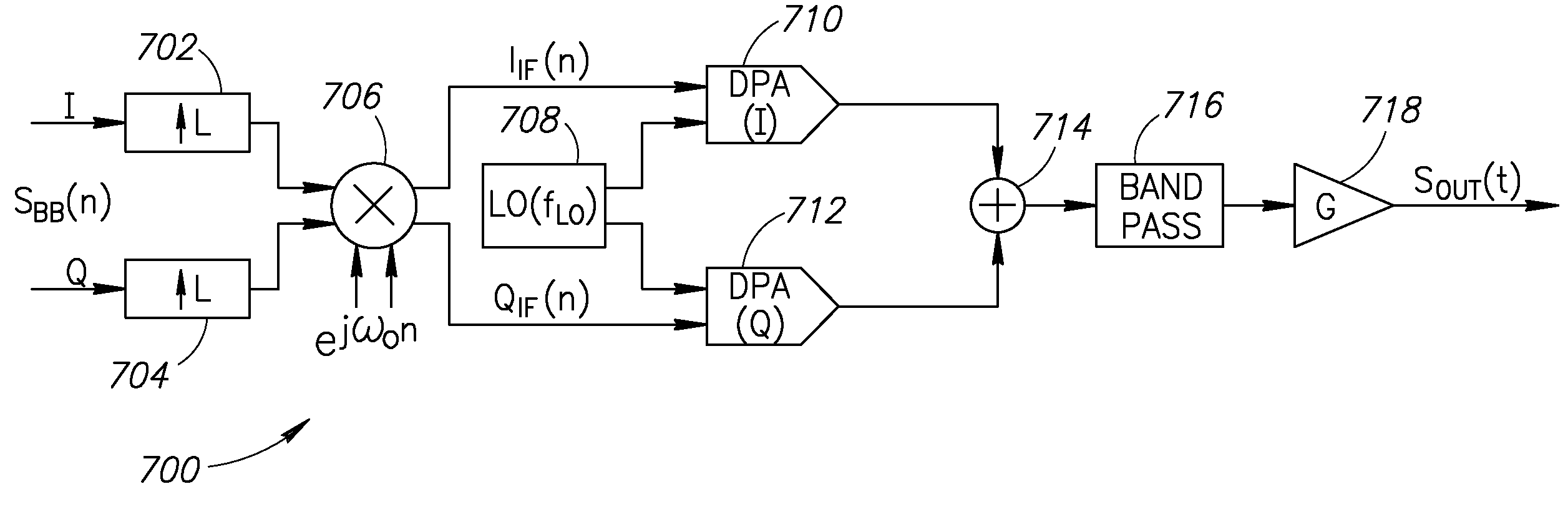
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of local oscillator (LO) generation with non-integer multiplication ratio between the local oscillator and RF frequencies. The LO generation schemes presented are operative to generate I and Q square waves at a designated frequency while avoiding the well known issue of harmonic pulling. An input baseband signal is interpolated and upconverted in the digital domain to an IF. The LO operates at a frequency which is a n / m division of the target RF frequency fRF. The IF frequency is configured to ½ of the LO frequency. The upconverted IF signal is then converted to the analog domain via digital power amplifiers followed by voltage combiners. The output of the combiners is band pass filtered to extract the desired replica.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Local oscillator with non-harmonic ratio between oscillator and RF frequencies using wideband modulation spectral replicas
ActiveUS7809338B2Avoid serious problemsEasy to implementModulation transferencePulse automatic controlBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of local oscillator (LO) generation with non-integer multiplication ratio between the local oscillator and RF frequencies. The LO generation schemes presented are operative to generate I and Q square waves at a designated frequency while avoiding the well known issue of harmonic pulling. An input baseband signal is interpolated and upconverted in the digital domain to an IF. The LO operates at a frequency which is a n / m division of the target RF frequency fRF. The IF frequency is configured to ½ of the LO frequency. The upconverted IF signal is then converted to the analog domain via digital power amplifiers followed by voltage combiners. The output of the combiners is band pass filtered to extract the desired replica.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
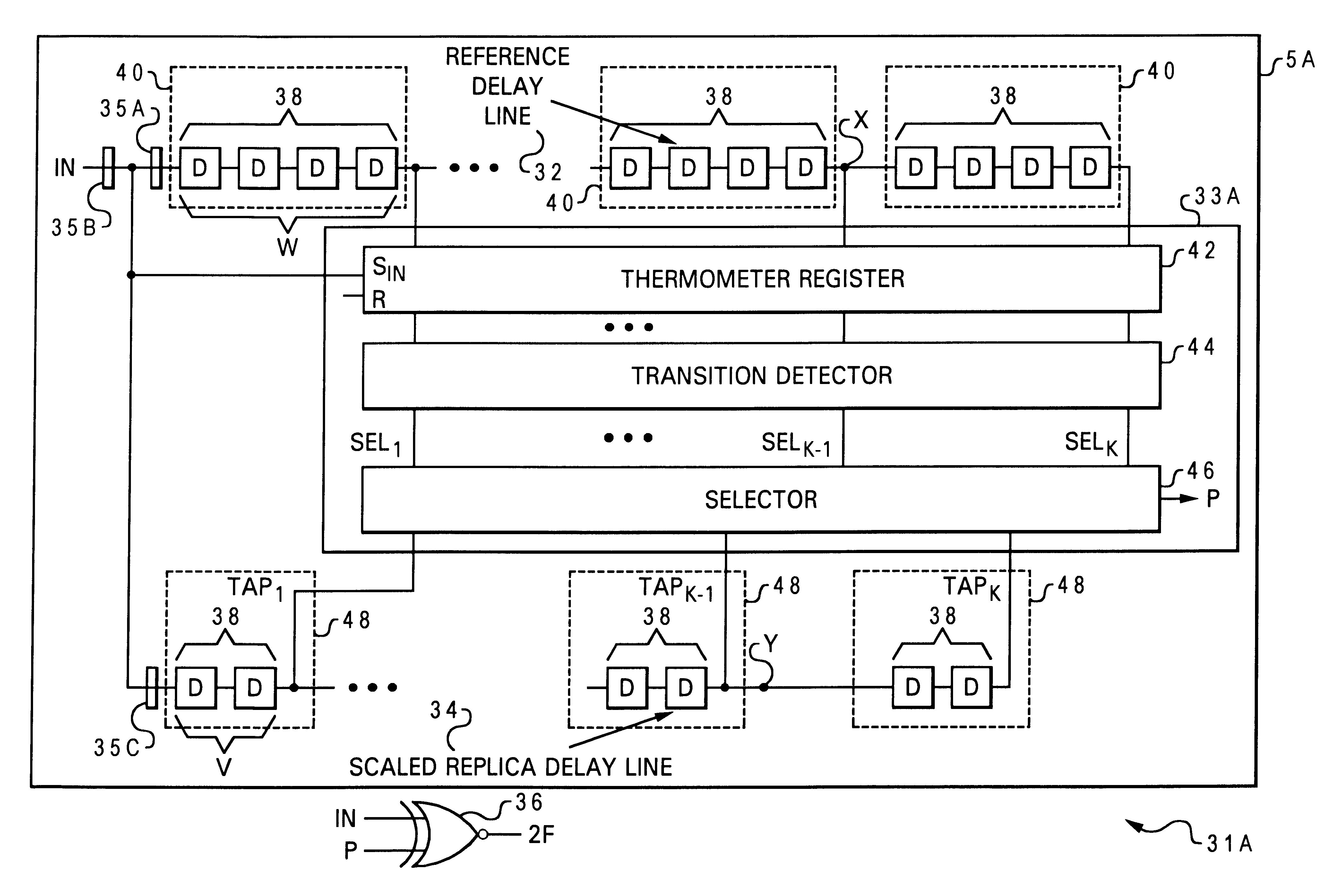
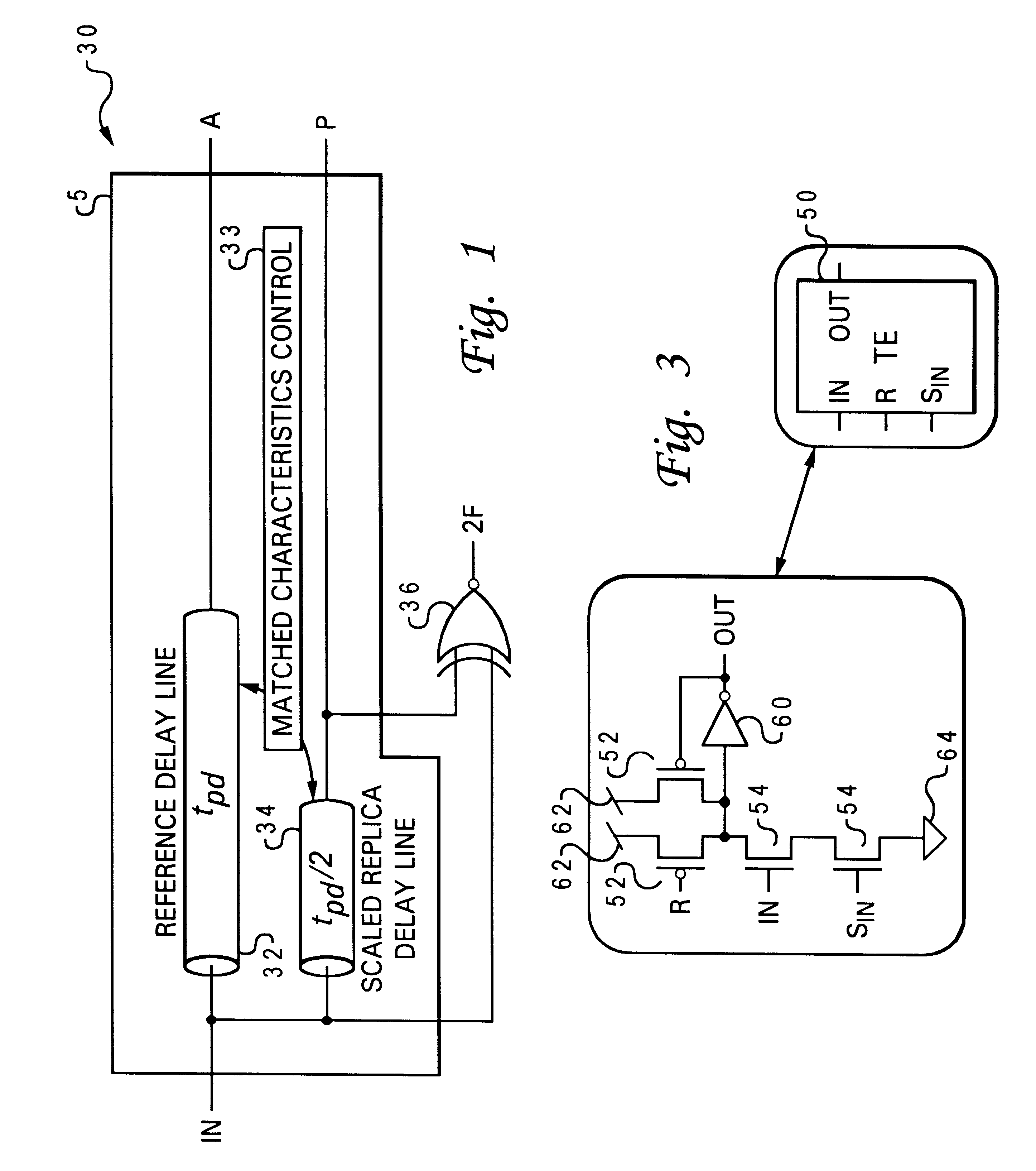
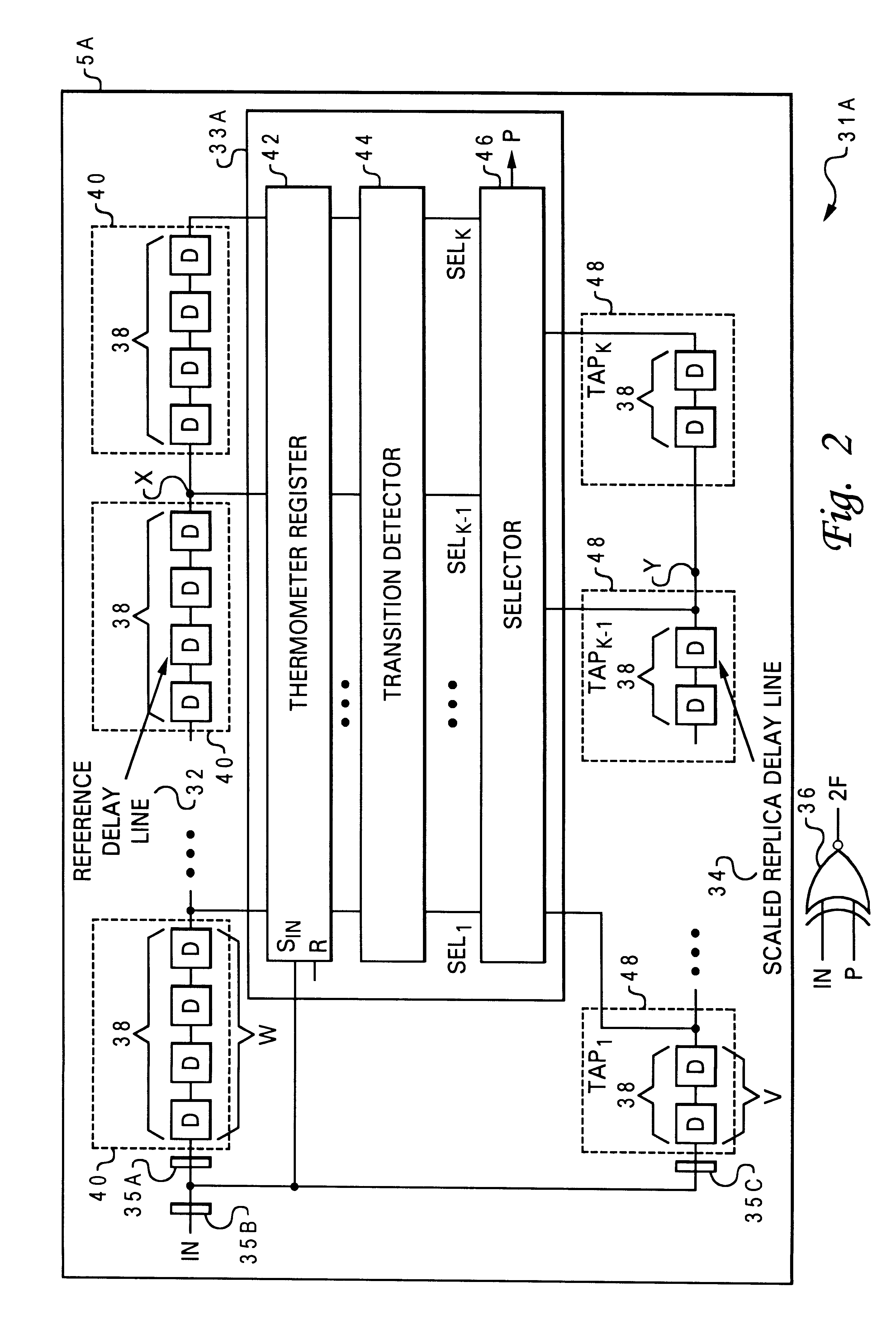
Delayed matching signal generator and frequency multiplier using scaled delay networks
A delayed matching signal generator and frequency multiplier using scaled delay networks for providing precisely delayed matching signals and multiplied frequency signals is provided. The system and method of phase shifting a periodic input digital signal comprises a reference delay line, a replica delay line, and a matched characteristics control system. The reference delay line is composed of multiple reference delay stages through which the input signal is propagated, and the replica delay line is composed of replica delay stages scaled in proportion to the multiple reference delay stages by a scaled delay factor wherein the input signal is propagated. The matched characteristics control system is coupled to the reference delay line and the replica delay line for extracting a phase shifted signal from the replica delay line based upon the scaled delay factor and a scaled propagation of the input signal through the reference delay line. The matched characteristics control system further comprises a capture and detect system for detecting transitions of the input signal and through which the input signal is propagated and a selector for halting propagation and capturing the input signal equivalent to the on-time period. A frequency multiplier converter is coupled to the replica delay line for logically combining the input signal with the phase shifted signal to generate an output signal that has a frequency that is a frequency multiplication factor of the reference frequency of the input signal IN.
Owner:IBM CORP
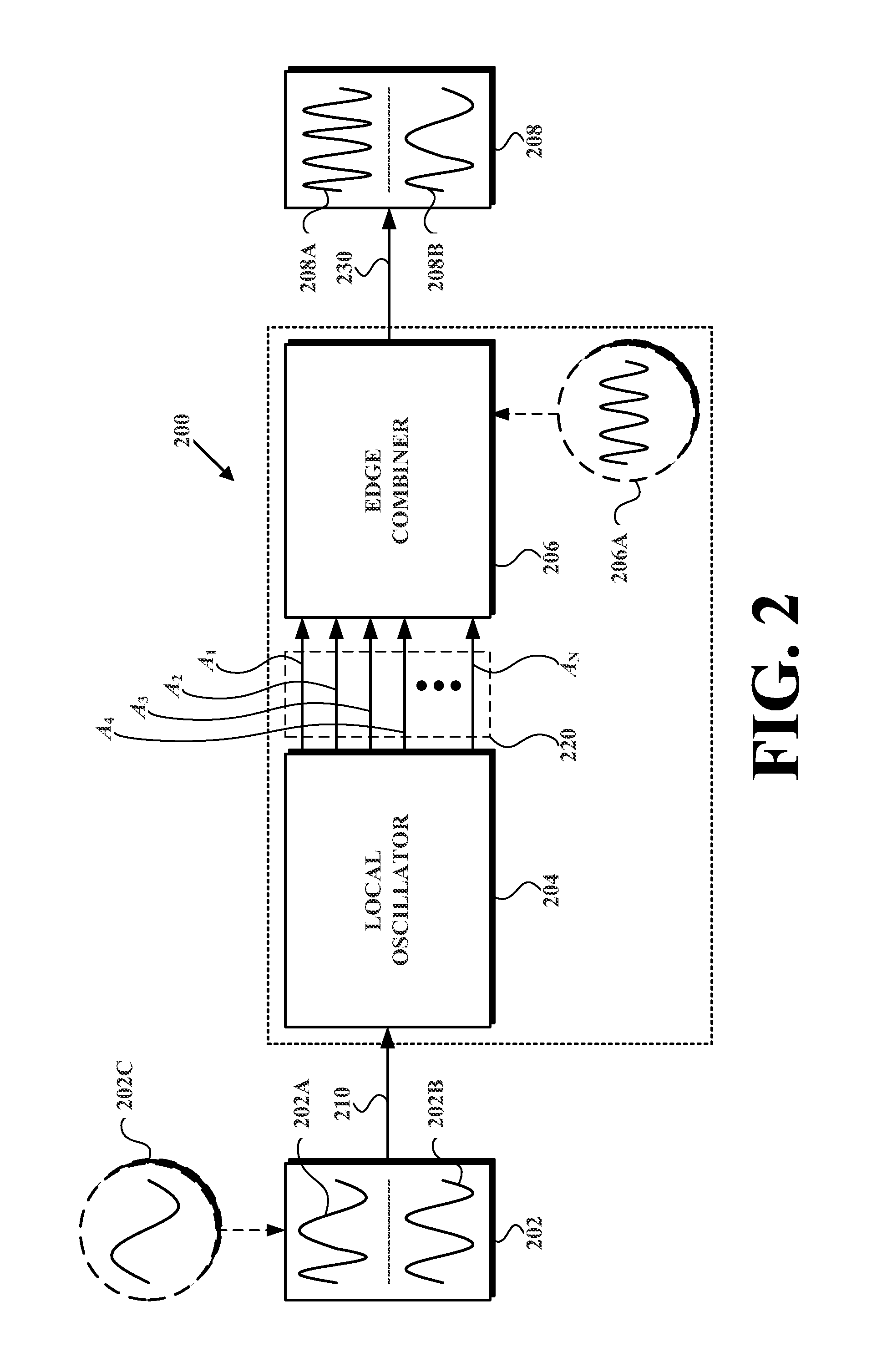
Frequency Multiplying Transceiver
InactiveUS20130058384A1Low Power TransmissionSmall sizePulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInjection lockedElectric power transmission
Described herein is a wireless transceiver and related method that enables ultra low power transmission and reception of wireless communications. In an example embodiment of the wireless transceiver, the wireless transceiver receives a first-reference signal having a first-reference frequency. The wireless transceiver then uses the first-reference signal to injection lock a local oscillator, which provides a set of oscillation signals each having an oscillation frequency that is equal to the first-reference frequency, and each having equally spaced phases. Then the wireless transceiver combines the set of oscillation signals into an output signal having an output frequency that is one of (i) a multiple of the first-reference frequency (in accordance with a transmitter implementation) or (ii) a difference of (a) a second-reference frequency of a second-reference signal and (b) a multiple of the first- reference frequency (in accordance with a receiver implementation).
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
Frequency-doubling delay locked loop
A frequency multiplier circuit comprising a delay line receiving at one end thereof a reference clock for generating clock tap outputs from respective ones of a plurality of period matched delay elements; a clock combining circuit responsive to pairs of tap outputs for generating a rising and falling edge of an output clock pulse from respective ones of the pairs whereby the output clock period is less than the input clock period.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
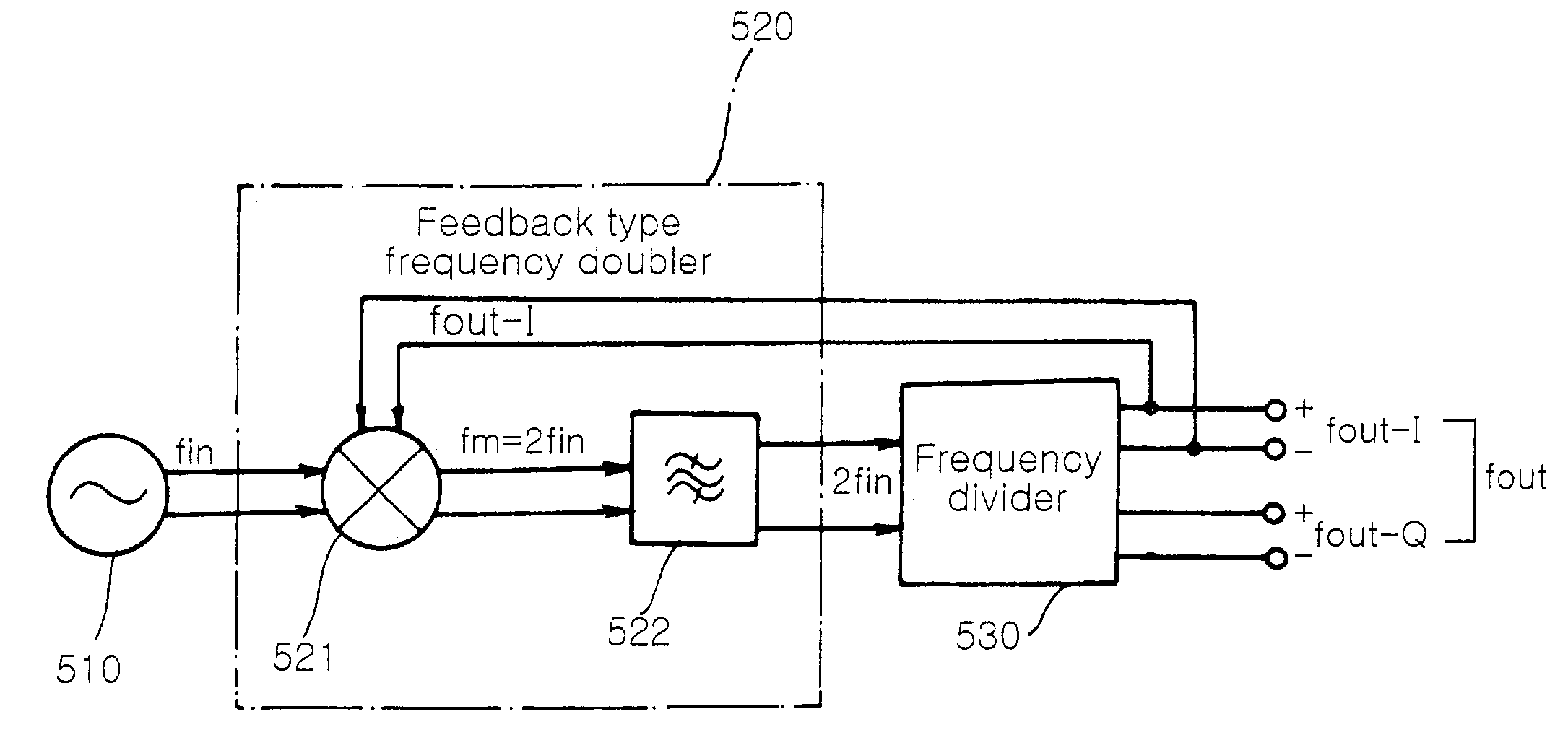
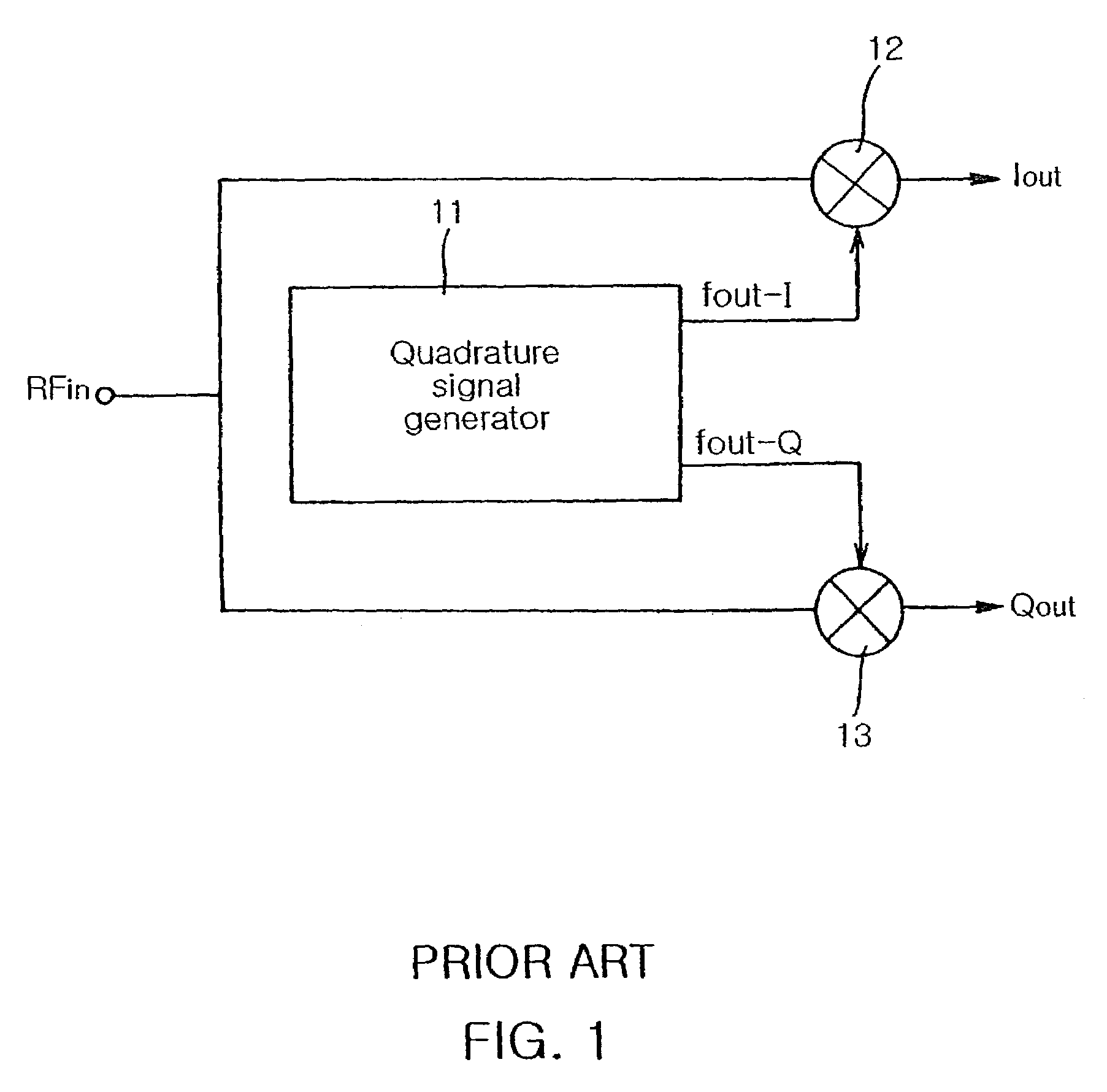
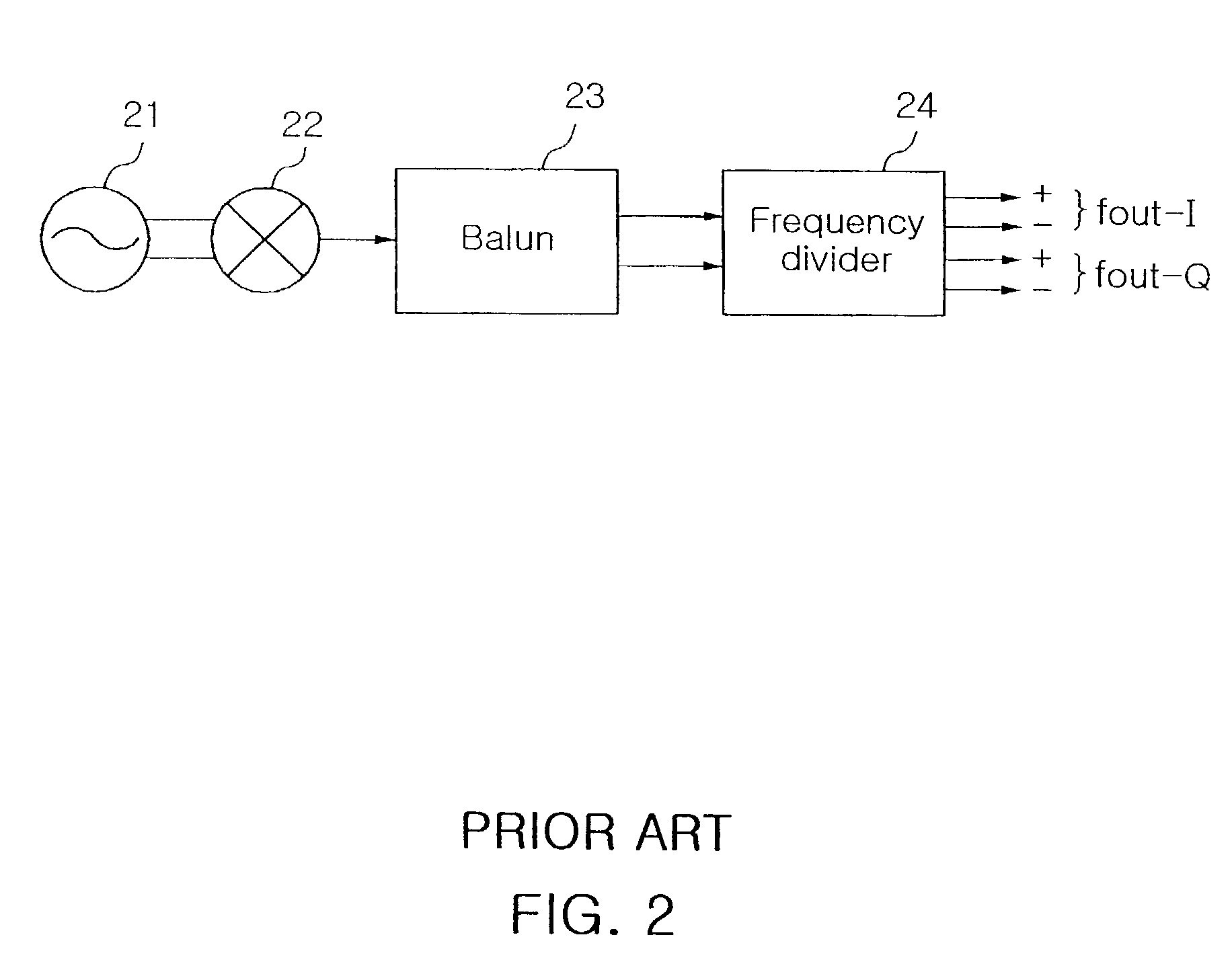
Quadrature signal generator with feedback type frequency doubler
InactiveUS7010287B2Reliable characteristicVessel manufacturingPulse automatic controlType frequencyControl system
Disclosed is a quadrature signal generator for generating an in-phase signal and a quadrature-phase signal, which is capable of generating a quadrature signal having the same frequency as a differential oscillating frequency, using a feedback control system. The quadrature signal generator includes an oscillator for generating a differential oscillation frequency signal having predetermined differential oscillation frequencies; a feedback type frequency doubler for generating a differential frequency signal having differential frequency components corresponding to differential frequency components of a frequency sum signal obtained by summing the differential oscillation frequency signal received from the oscillator and a differential feedback signal received at the differential feedback terminal; and a frequency divider for dividing the differential frequency signal received at the differential input terminal thereof by 2, thereby generating a quadrature signal consisting of two differential output frequency signals to supply at least one differential output frequency signal of the quadrature signal to the feedback type frequency doubler as the differential feedback signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
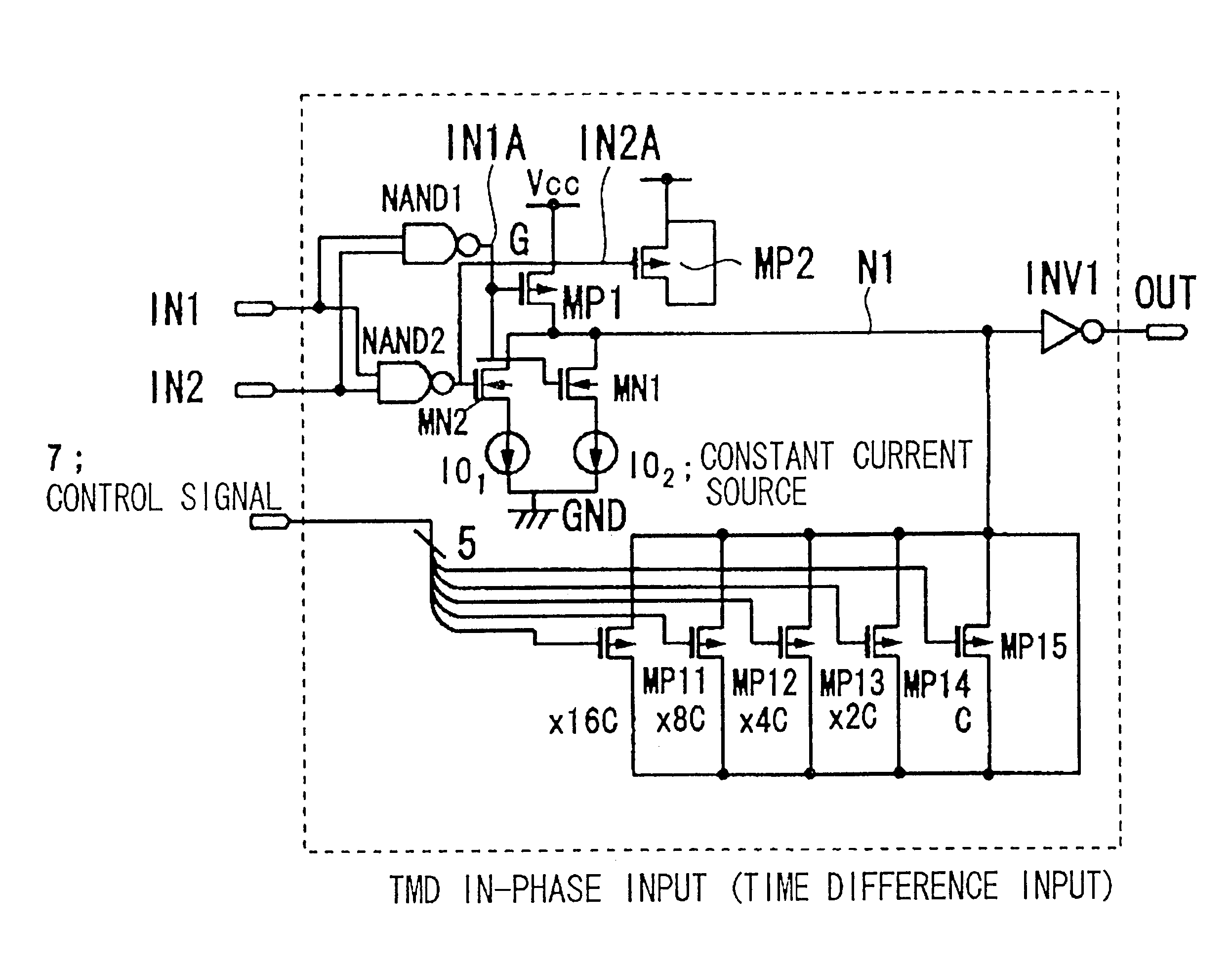
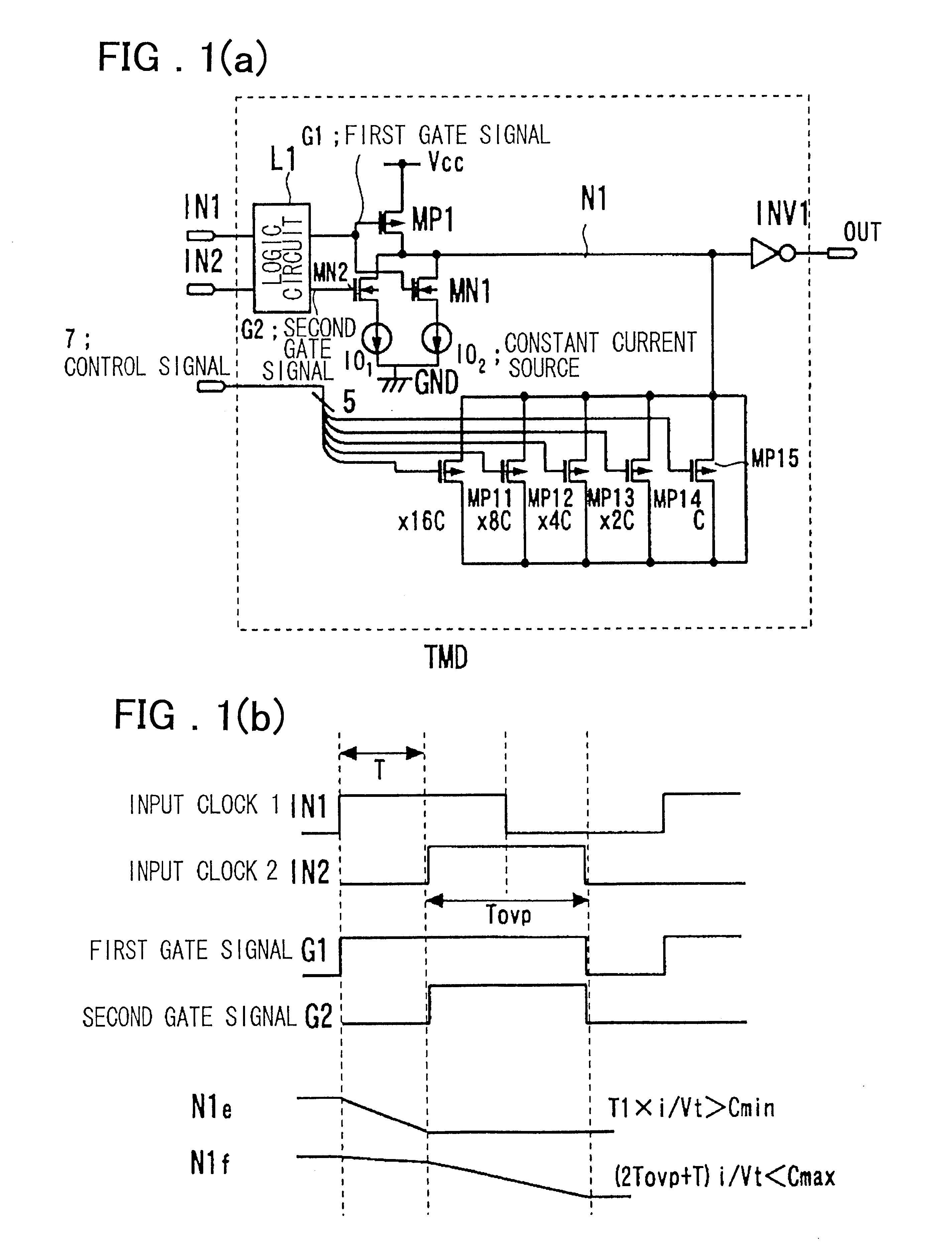
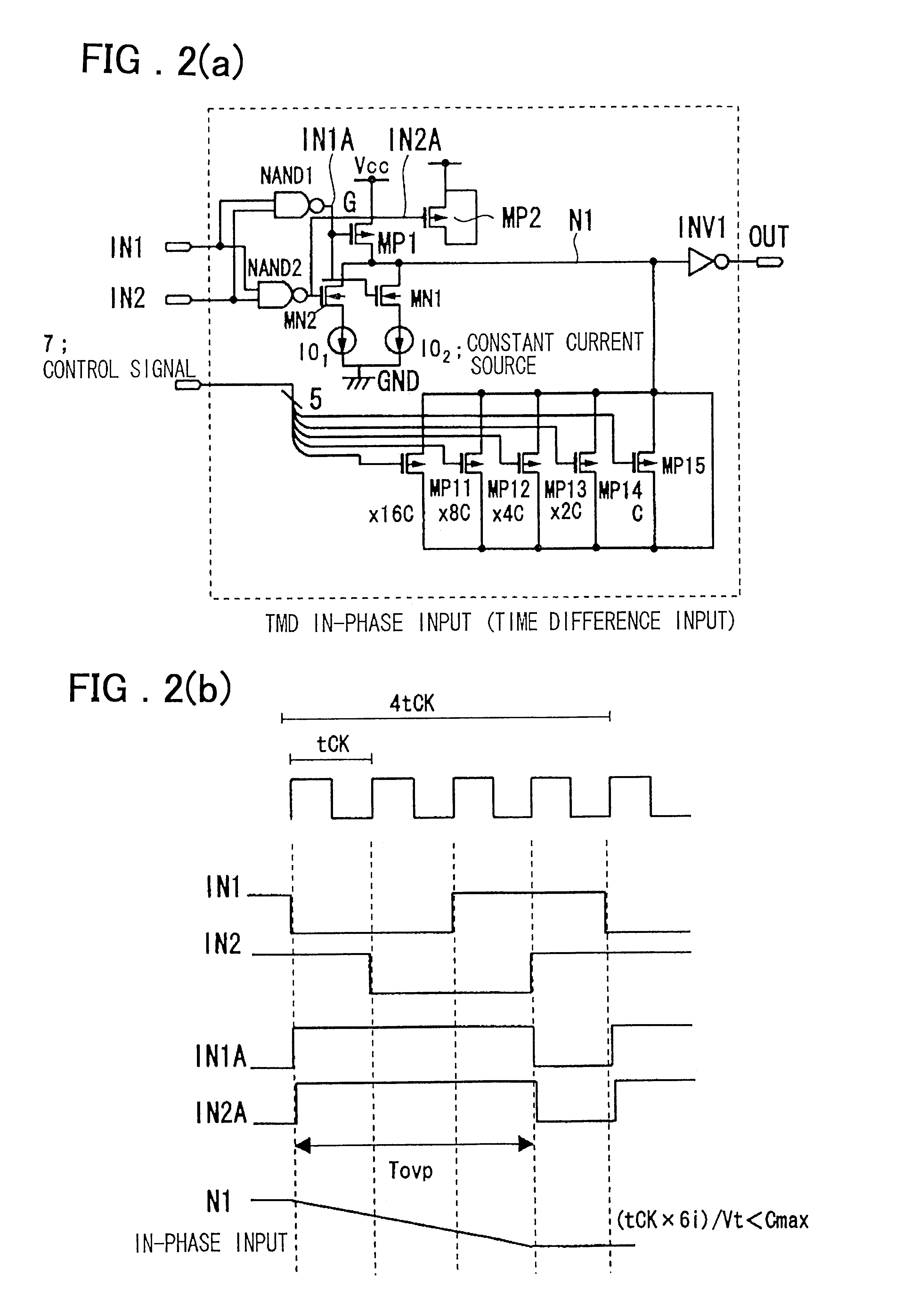
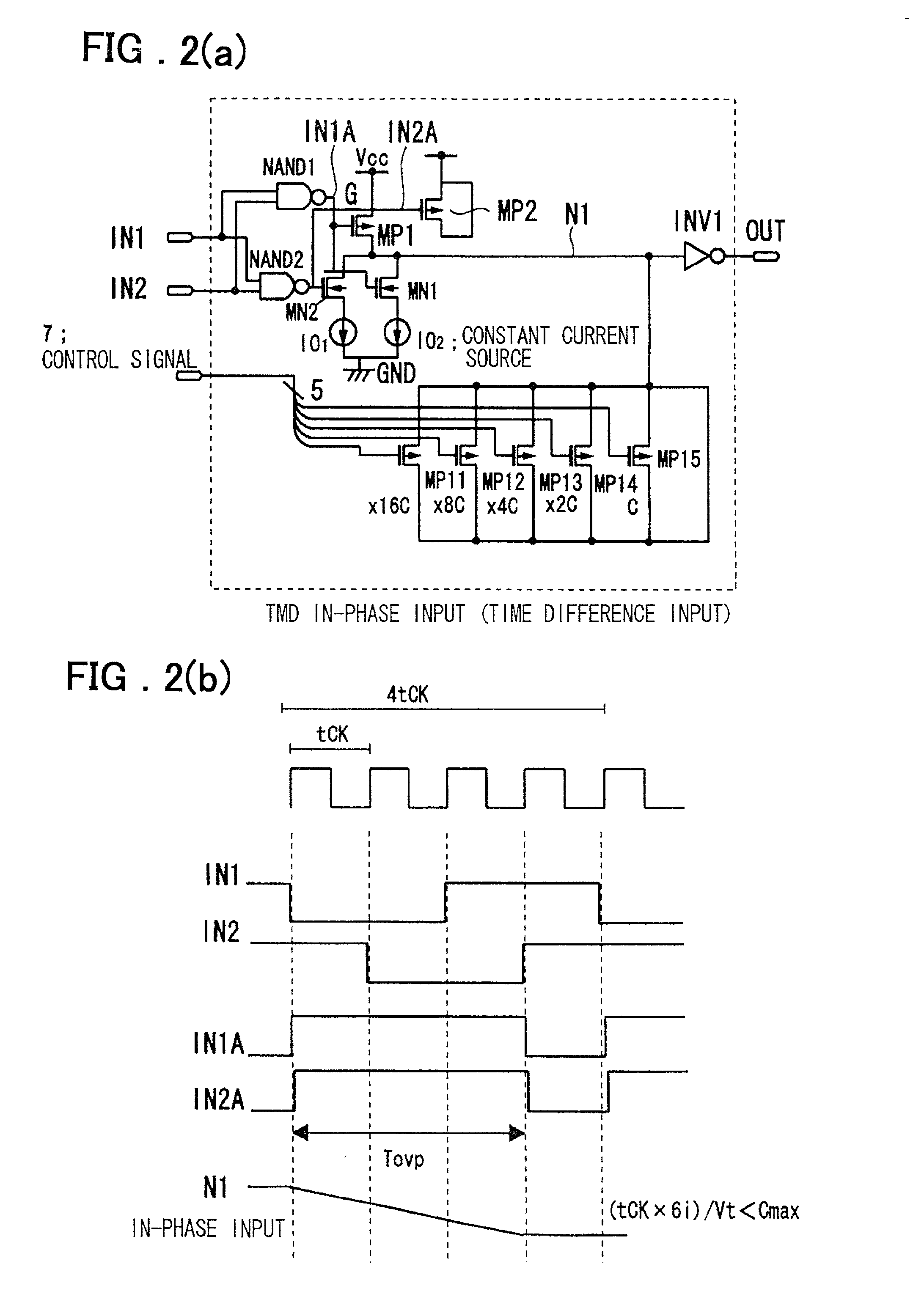
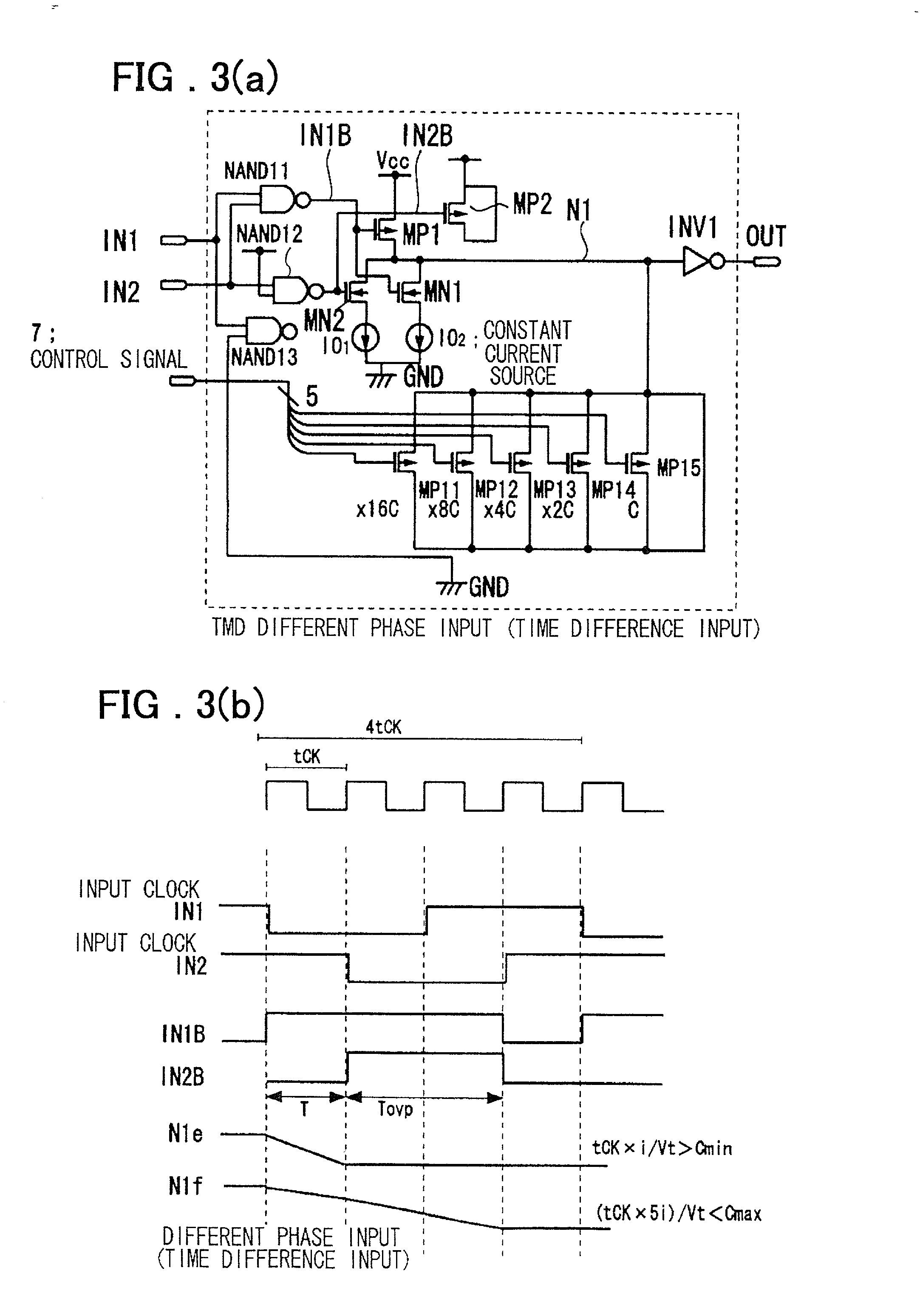
Timing difference division circuit and signal controlling method and apparatus
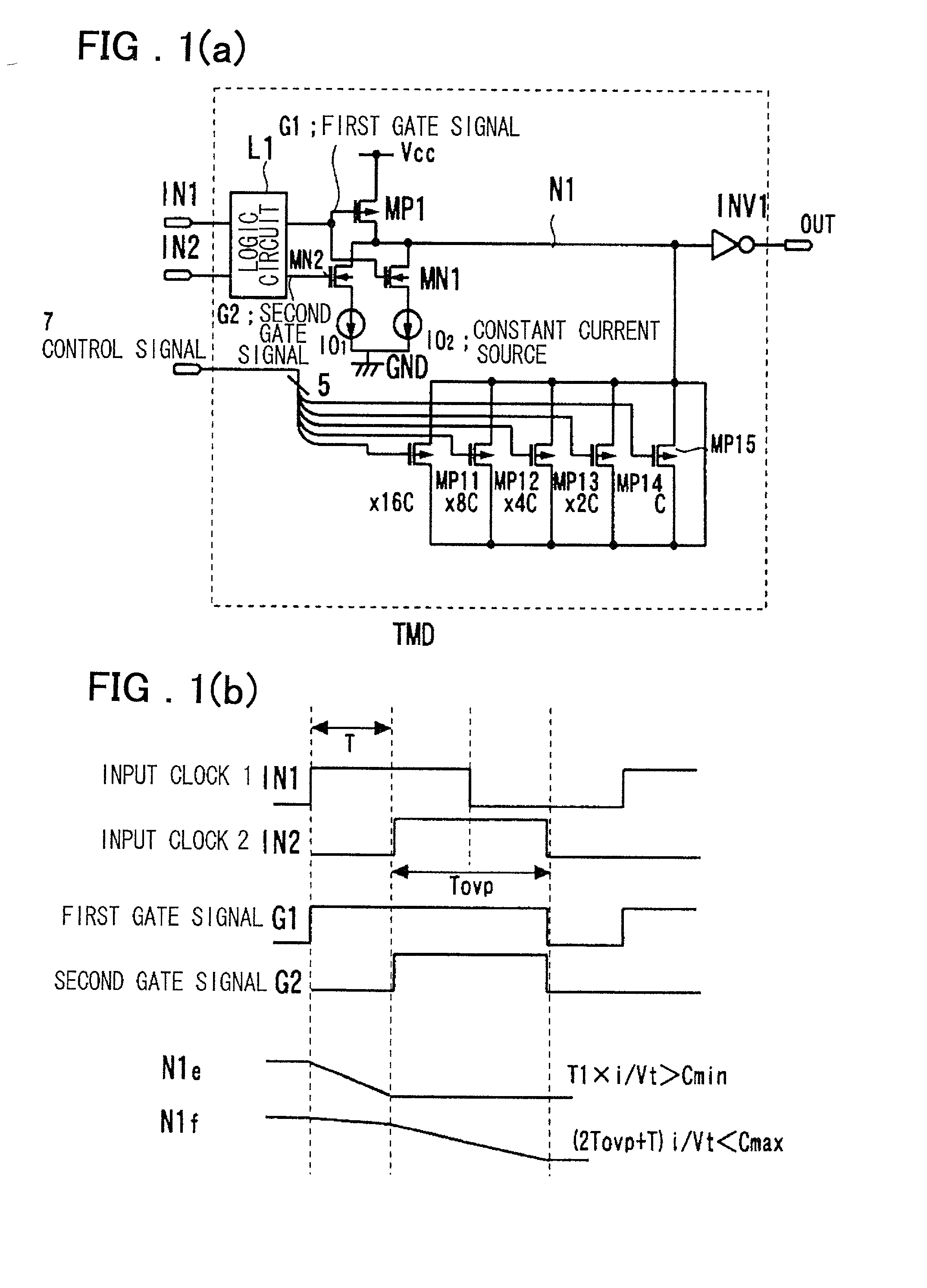
InactiveUS6545518B2Increase the areaHigh speedElectronic switchingSingle output arrangementsRelative magnitudeControl signal
Timing difference division circuit with a high operating speed and a small area, assuring broadband operation. The circuit includes a logic circuit L1 generating a first gate signal and a second gate signal based on a first input signal and a second input signal, a first switch element connected across a first power source and an inner node and having a control terminal to which is fed the first gate signal, a first series circuit made up of a second switch element and a first constant current source and a second series circuit made up of a third switch element and a second constant current source. The first and second series circuits are connected in parallel across the inner node and the second power source. The first and second gate signals are connected to control terminals of the second and third switches, respectively. The circuit also includes a plurality of MOS capacitors, connection of which to the inner node is separately controlled by a control signal, and a buffer circuit an input end of which is connected to the inner node and the value of an output signal of which is determined based on the relative magnitude of the potential of the inner node and a threshold voltage. An overlap period during which the first and second gate signals output from the logic circuit are both activated to turn on the second and third switch elements is set to an optional value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
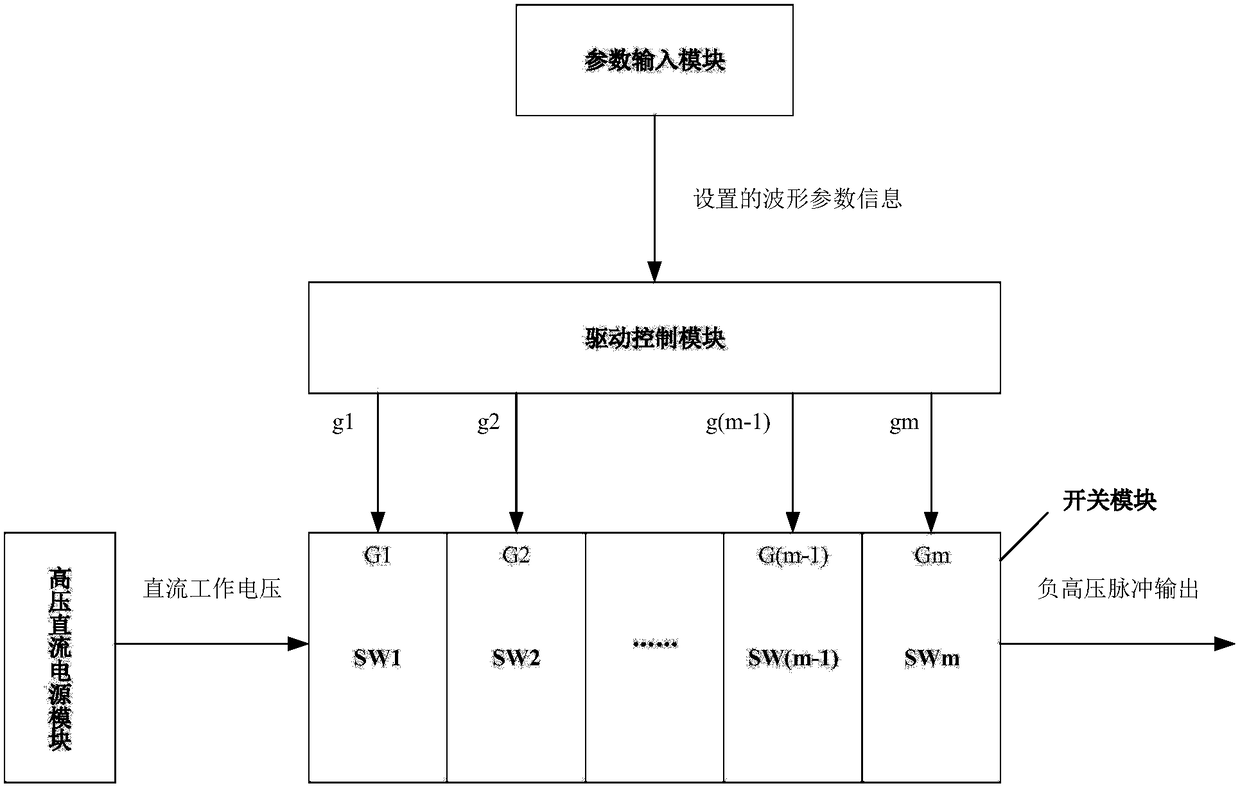
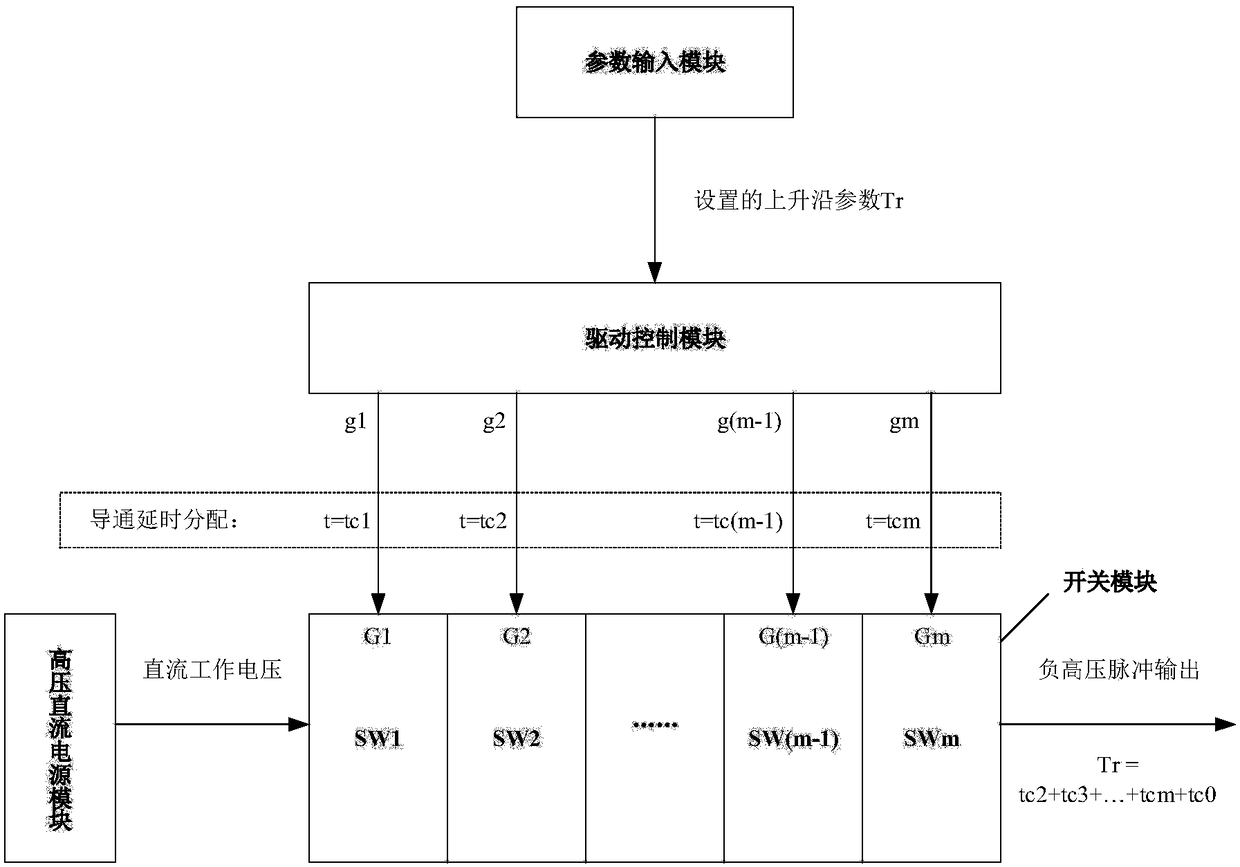
Negative high-voltage pulse power supply device with adjustable parameters and parameterized adjustment method
The invention discloses a negative high-voltage pulse power supply device with adjustable parameters and a parameterized adjustment method, belonging to the field of high-voltage pulse power supply structure design. The device comprises a parameter input module, a driving control module, a high-voltage direct current power supply module and a switch module, wherein the parameter input module is used to set the required negative high-voltage pulse waveform parameters and send the parameters to the driving control module; the driving control module is used to process and convert the set negativehigh-voltage pulse waveform parameters into control signals of the switch module and send the control signals to the switch module; the high-voltage direct current power supply module is used to provide a direct current working voltage for the switch module; and the switch module is used to respond to the received control signals correspondingly and output a negative high-voltage pulse that meetsthe set negative high-voltage pulse waveform parameters.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
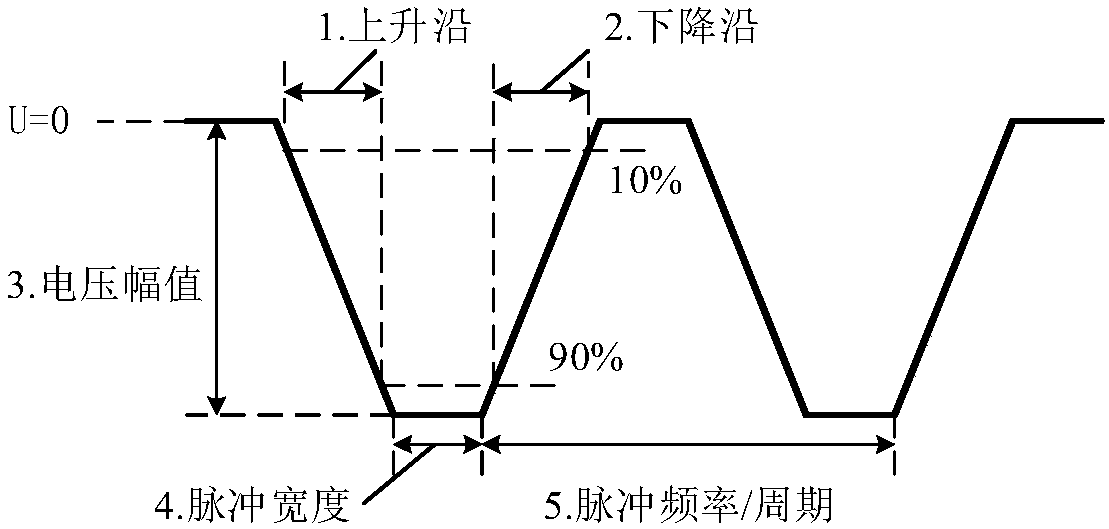
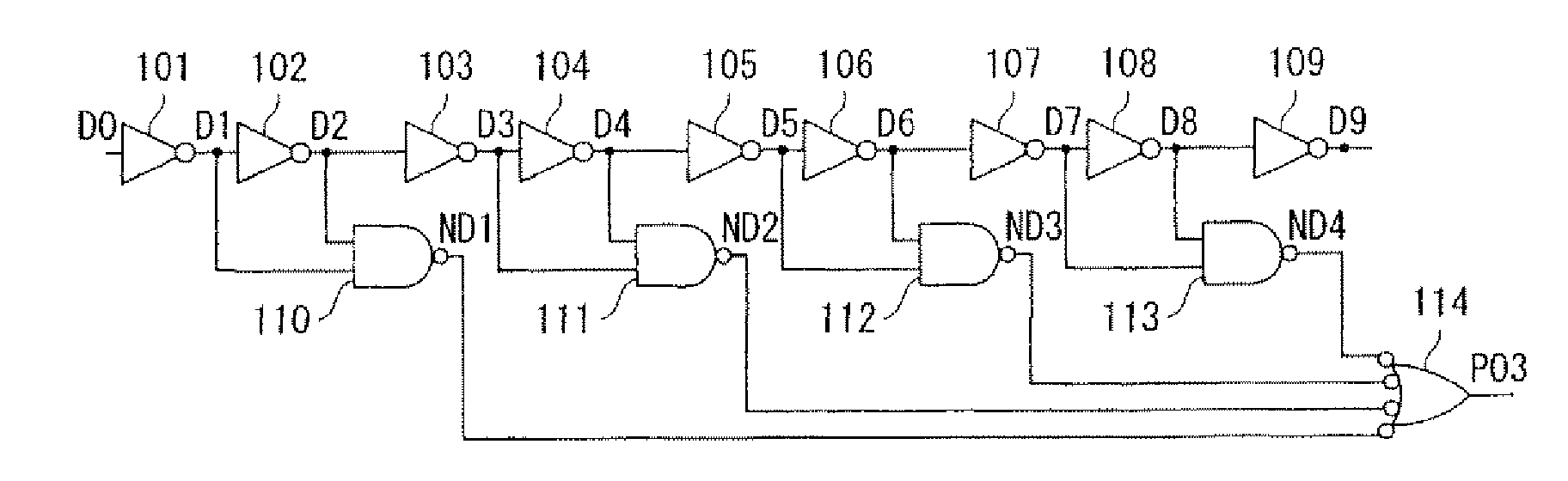
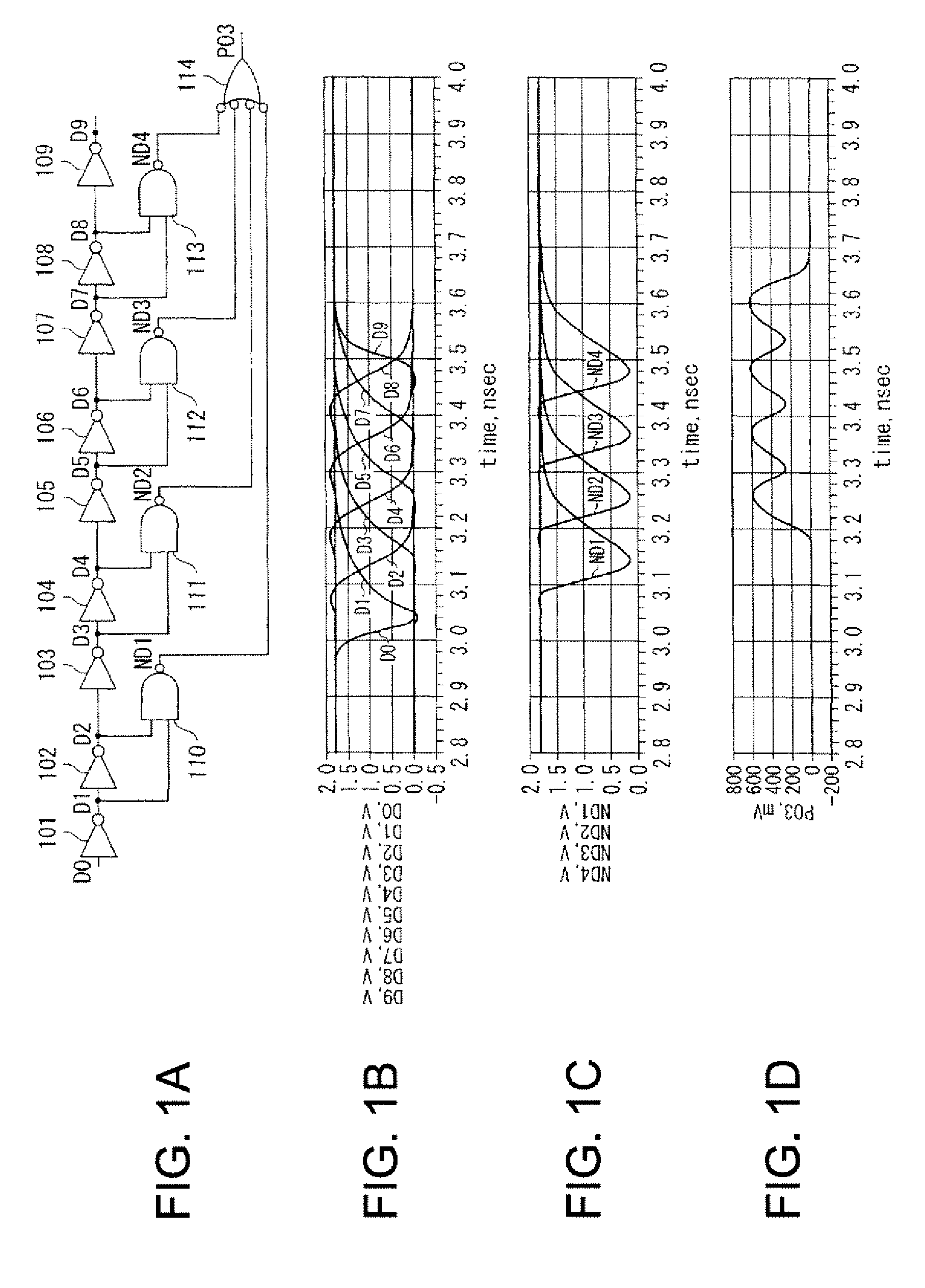
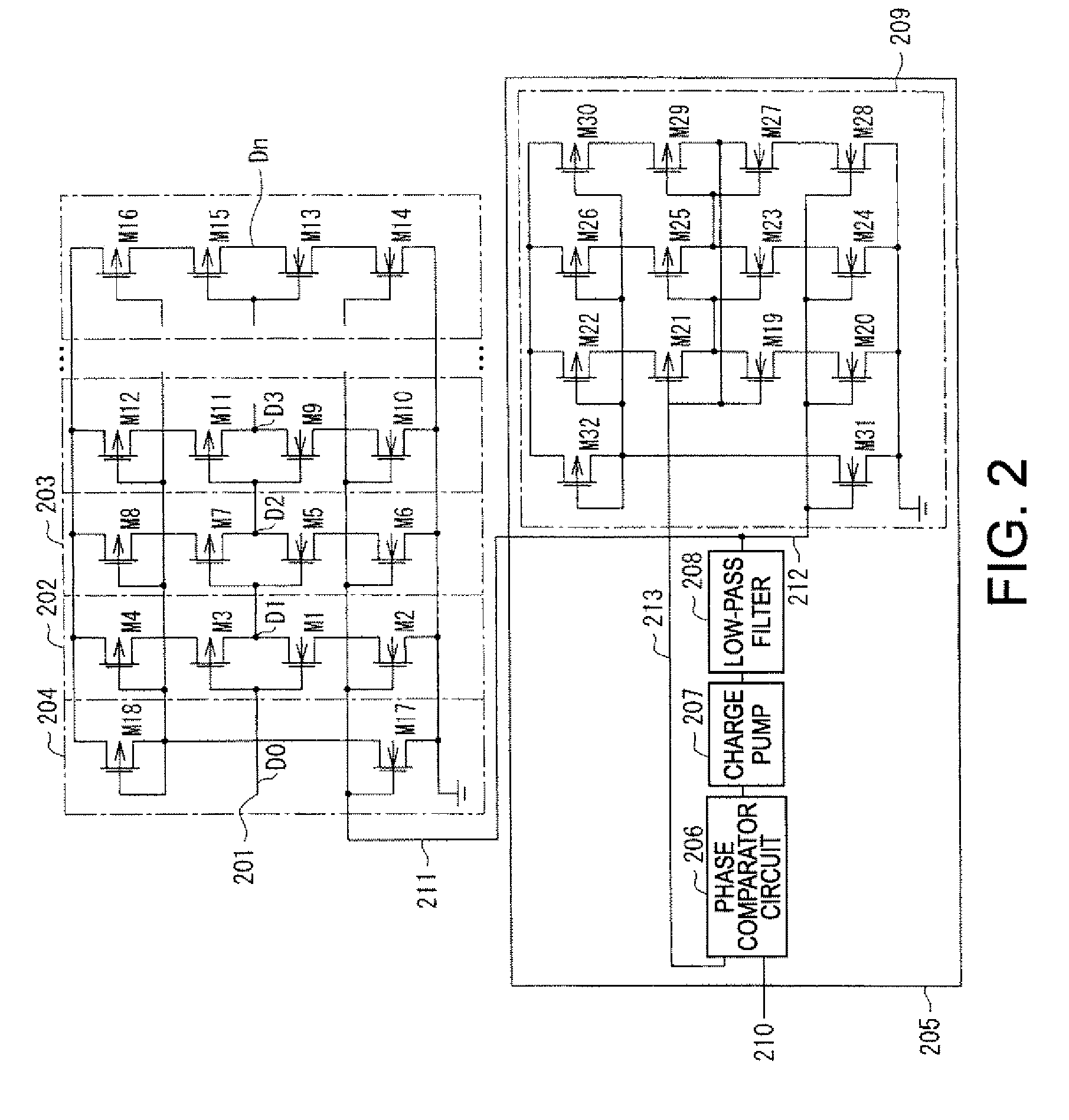
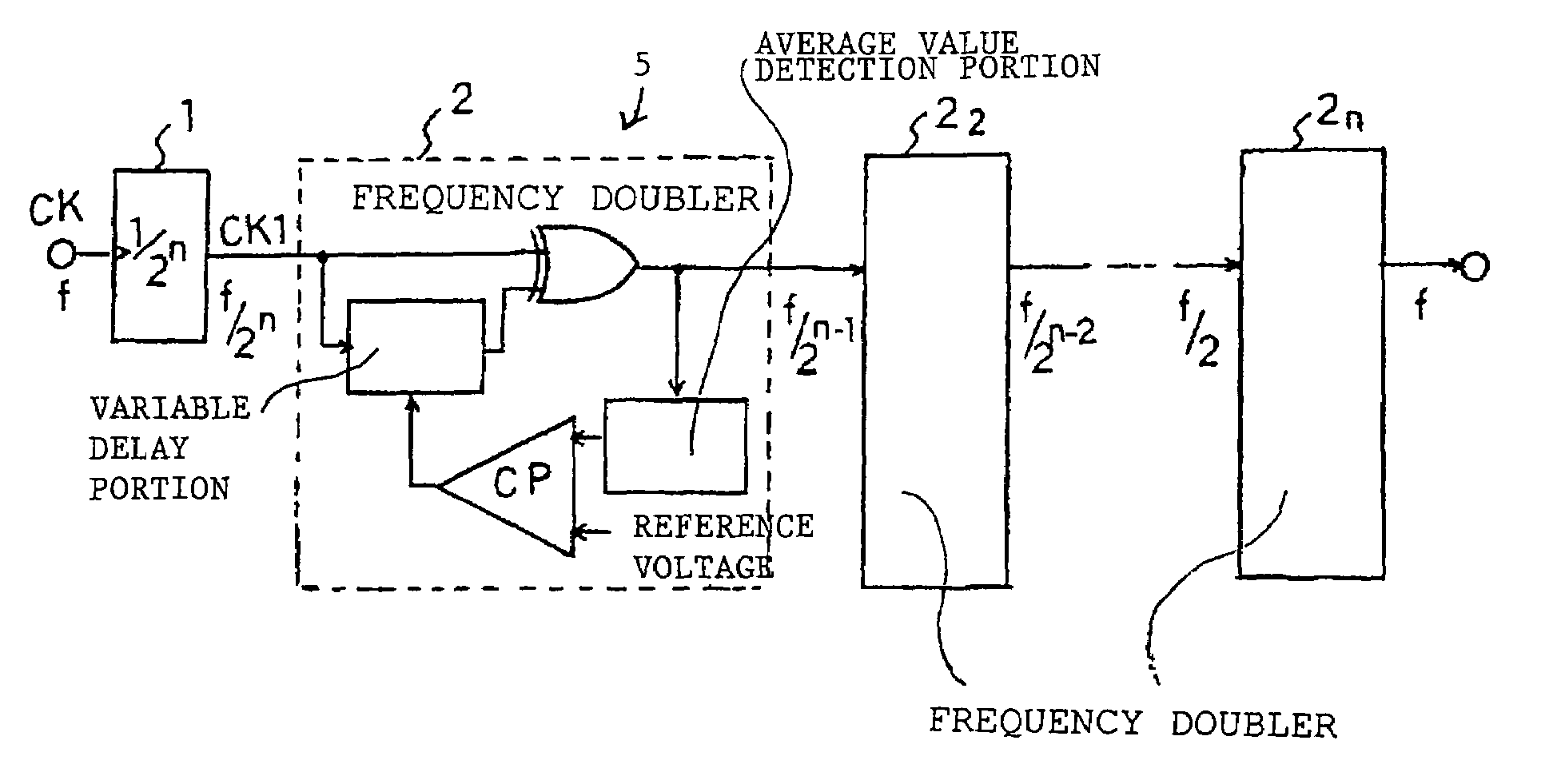
Duty adjustment circuit
InactiveUS20050184781A1Reduce adverse effectsInfluences of high-level instantaneous noise can be suppressedContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationElectric pulse generatorControl signalFrequency multiplier
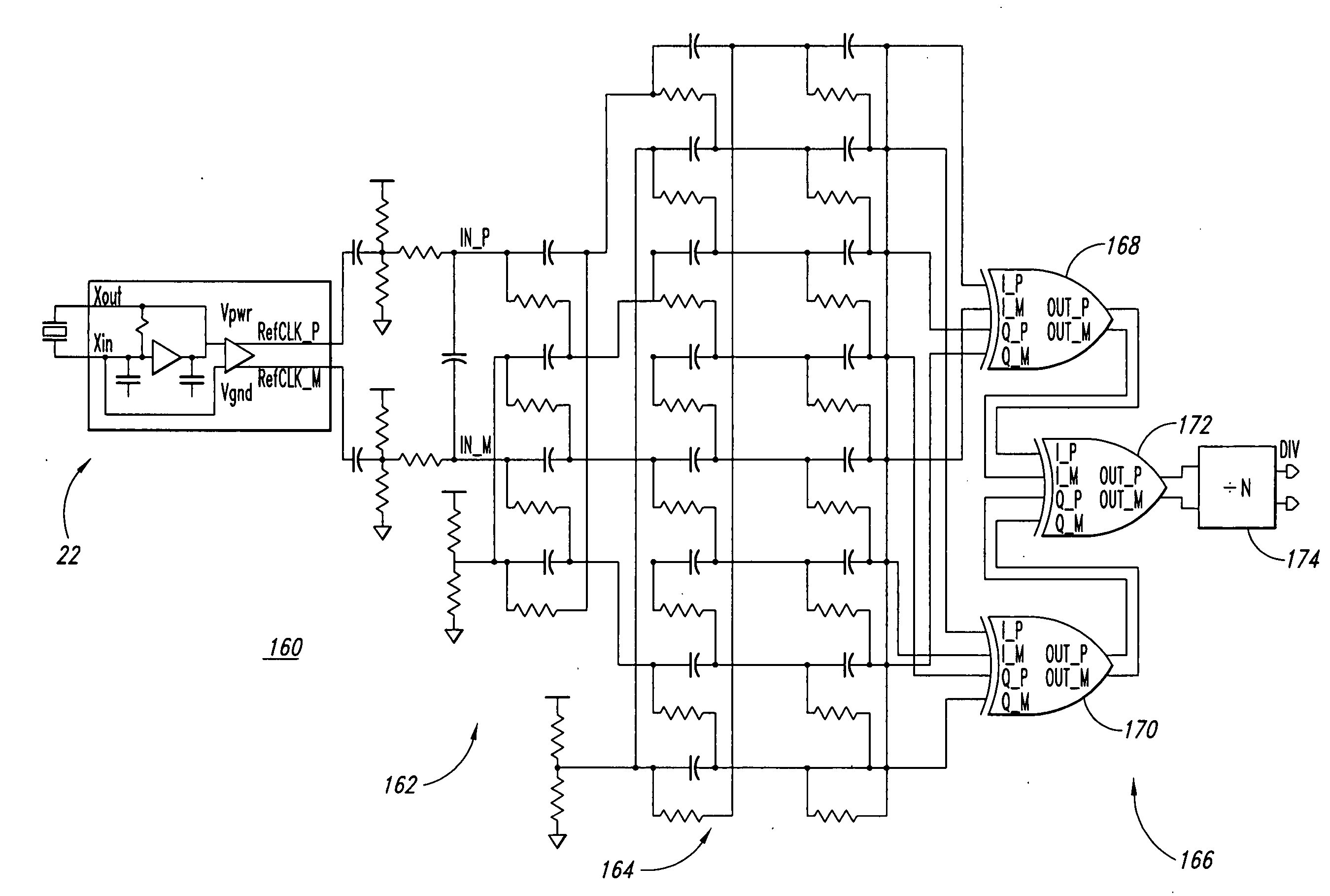
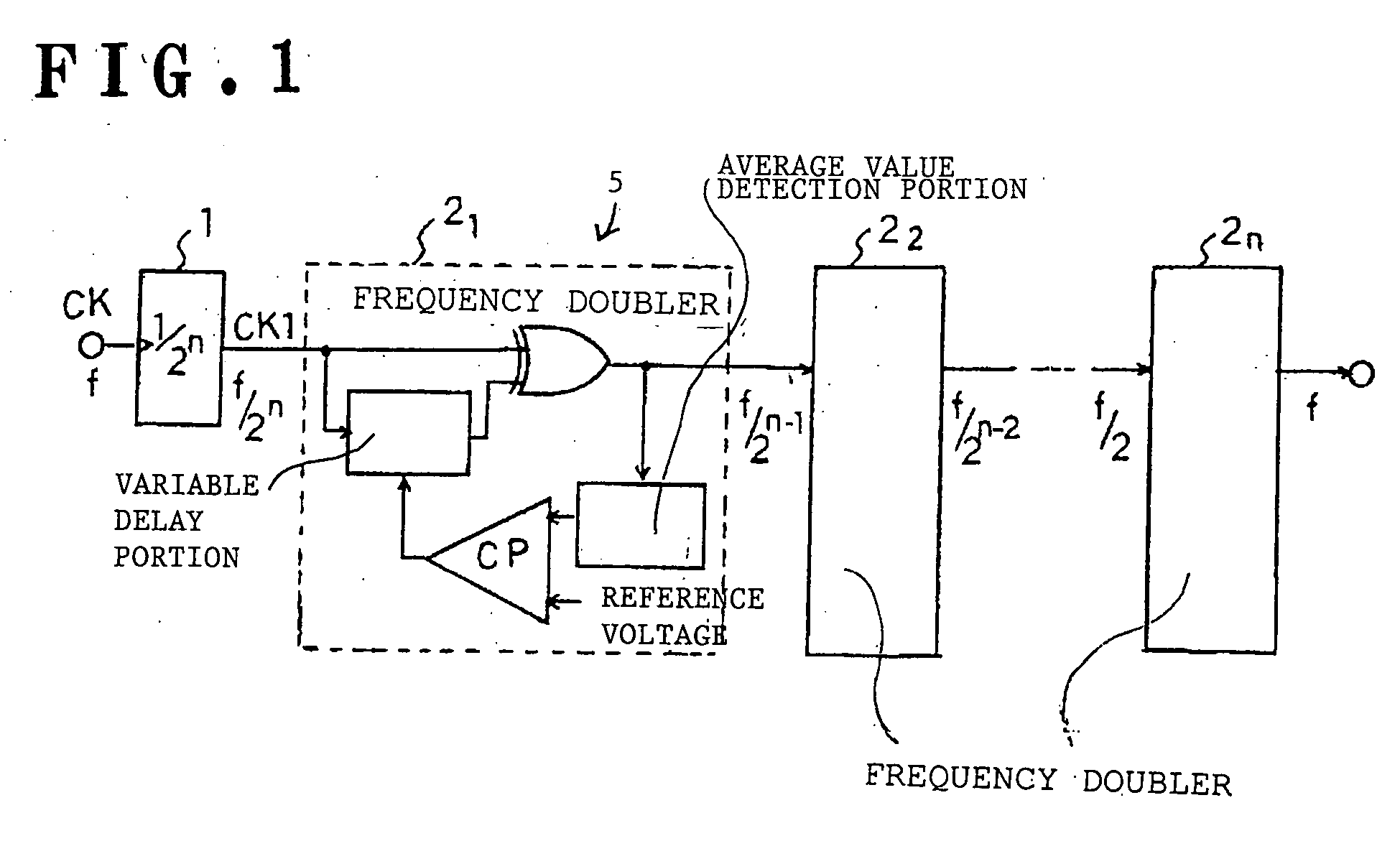
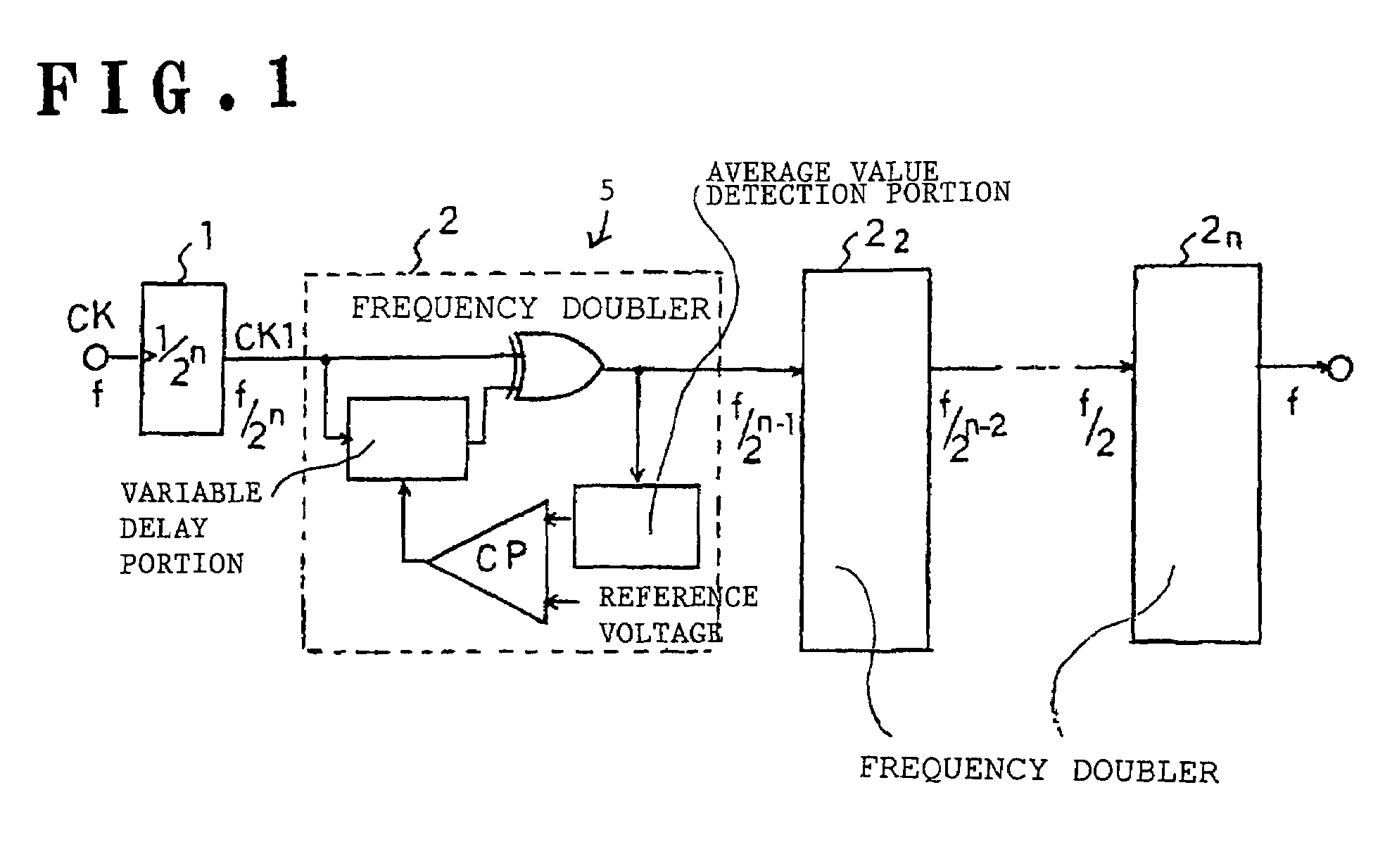
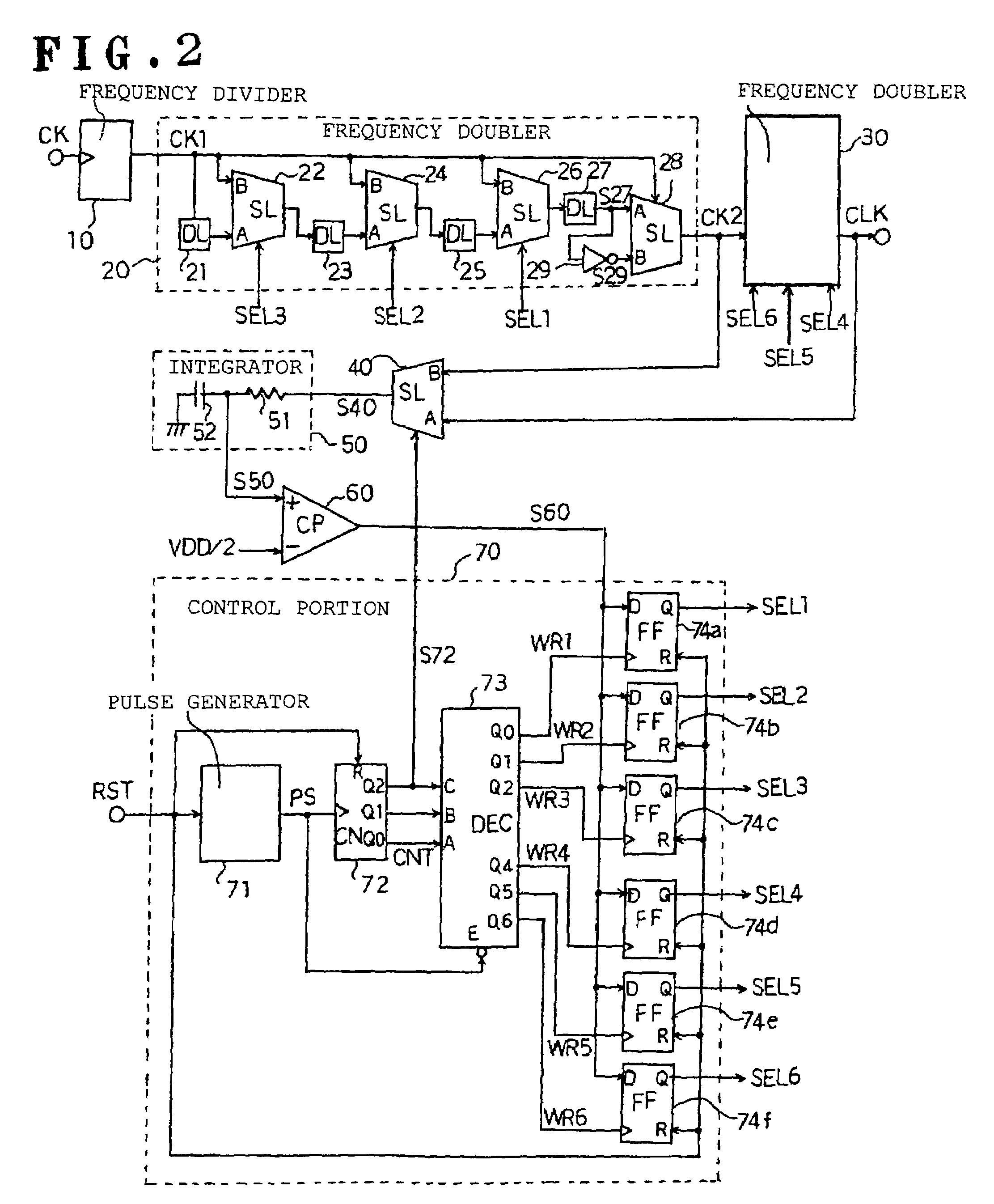
In a duty adjustment circuit, a clock signal is frequency-divided to ½n by a frequency divider, and then provided to the first frequency doubler among n cascade-connected frequency doublers. In the first frequency doubler, the input clock signal is delayed by a variable delay portion according to a control signal, and the exclusive logical sum of the delayed signal and of the clock signal is taken by a frequency-doubling portion to double the frequency. The average voltage of the frequency-doubled signal is detected by an average value detection portion, this average voltage is compared with a reference voltage by a comparison control portion, and a control signal is fed back to the variable delay portion so as to cause the average voltage to become equal to the reference voltage. In this manner, a clock signal is generated from the last frequency doubler with frequency equal to that of the original clock signal, and with duty ratio adjusted to a desired value.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Apparatus and method for driving liquid crystal display device
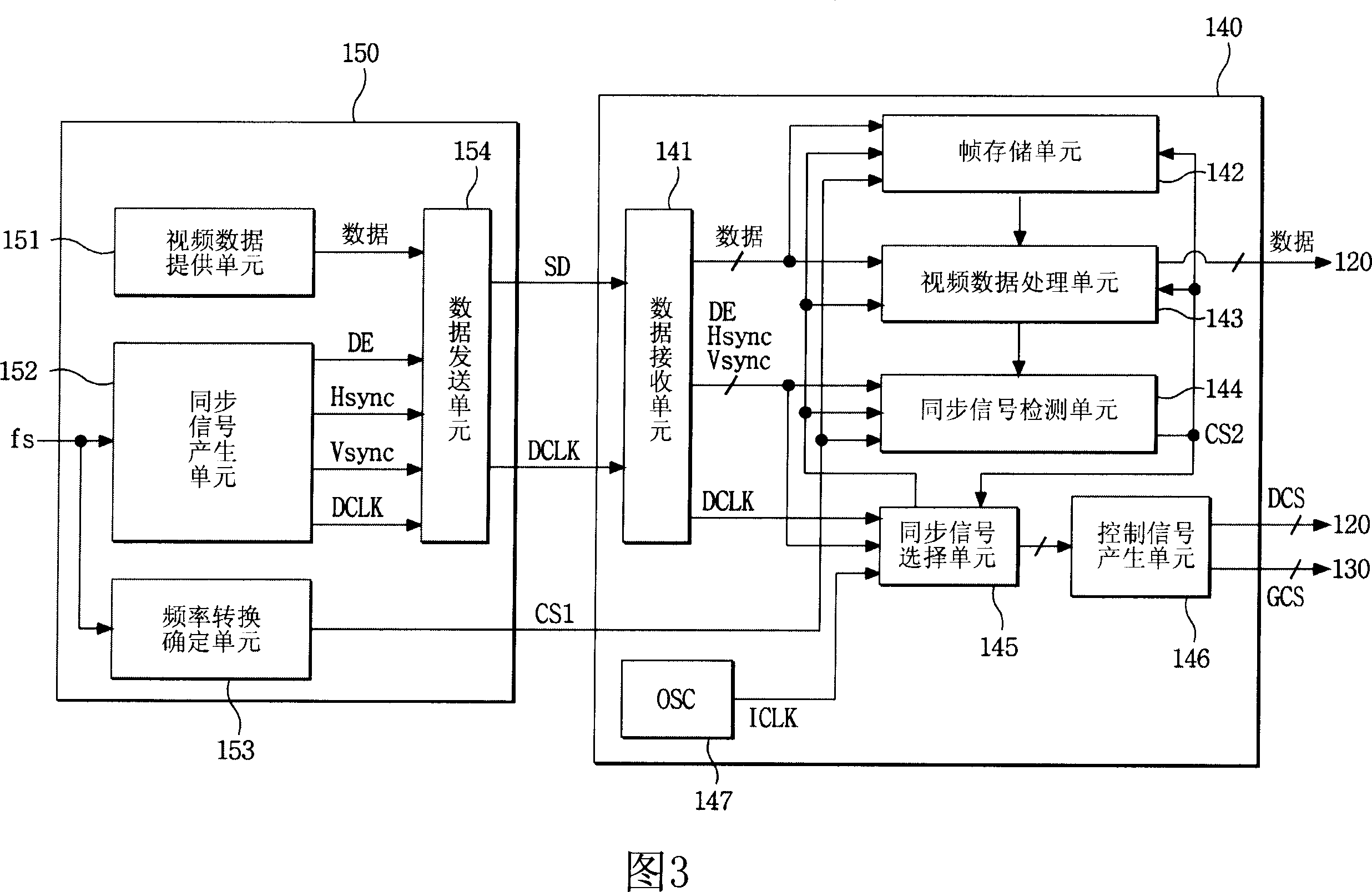
InactiveCN101046941ACathode-ray tube indicatorsManipulation for frequency changeGraphicsLiquid-crystal display
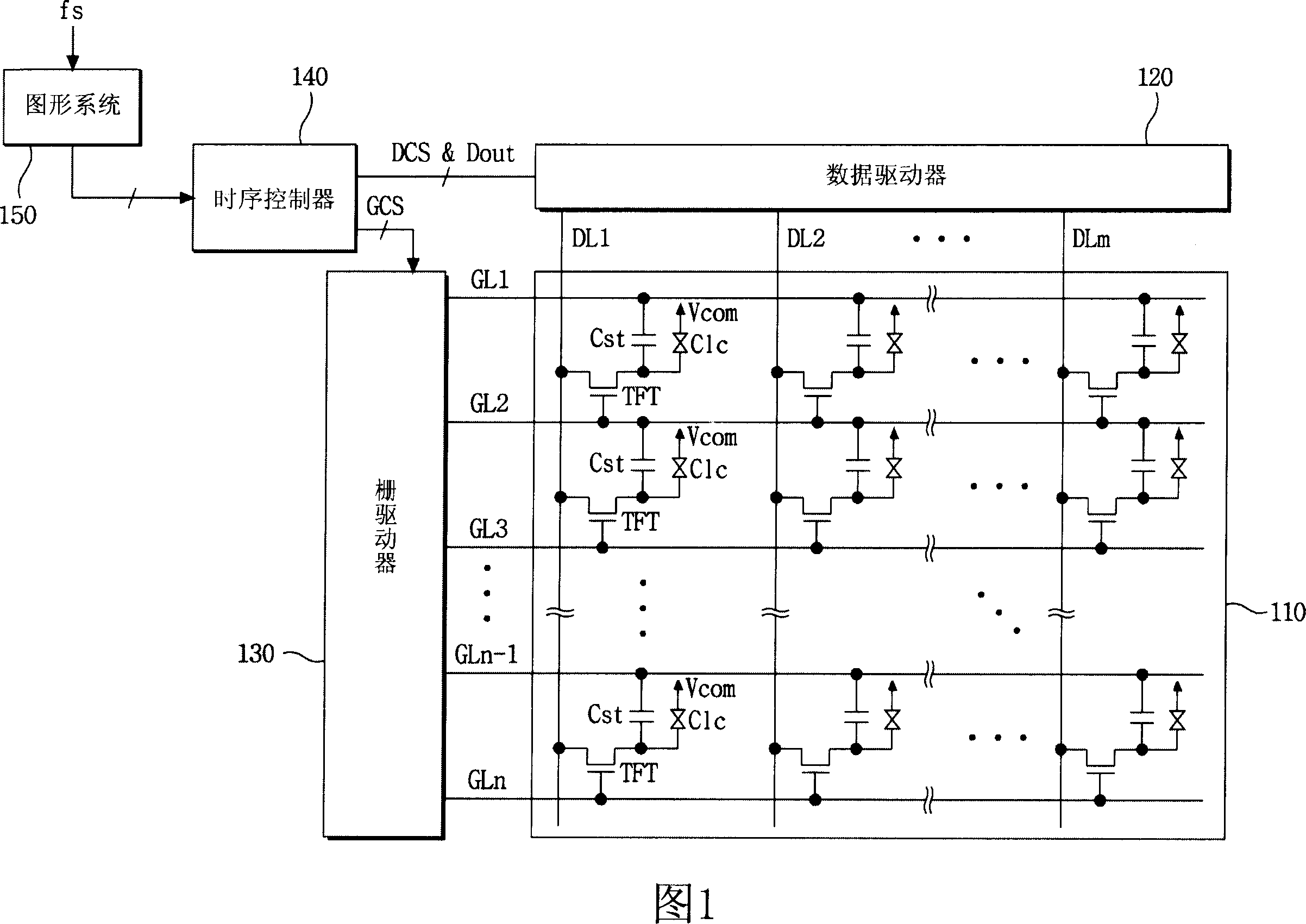
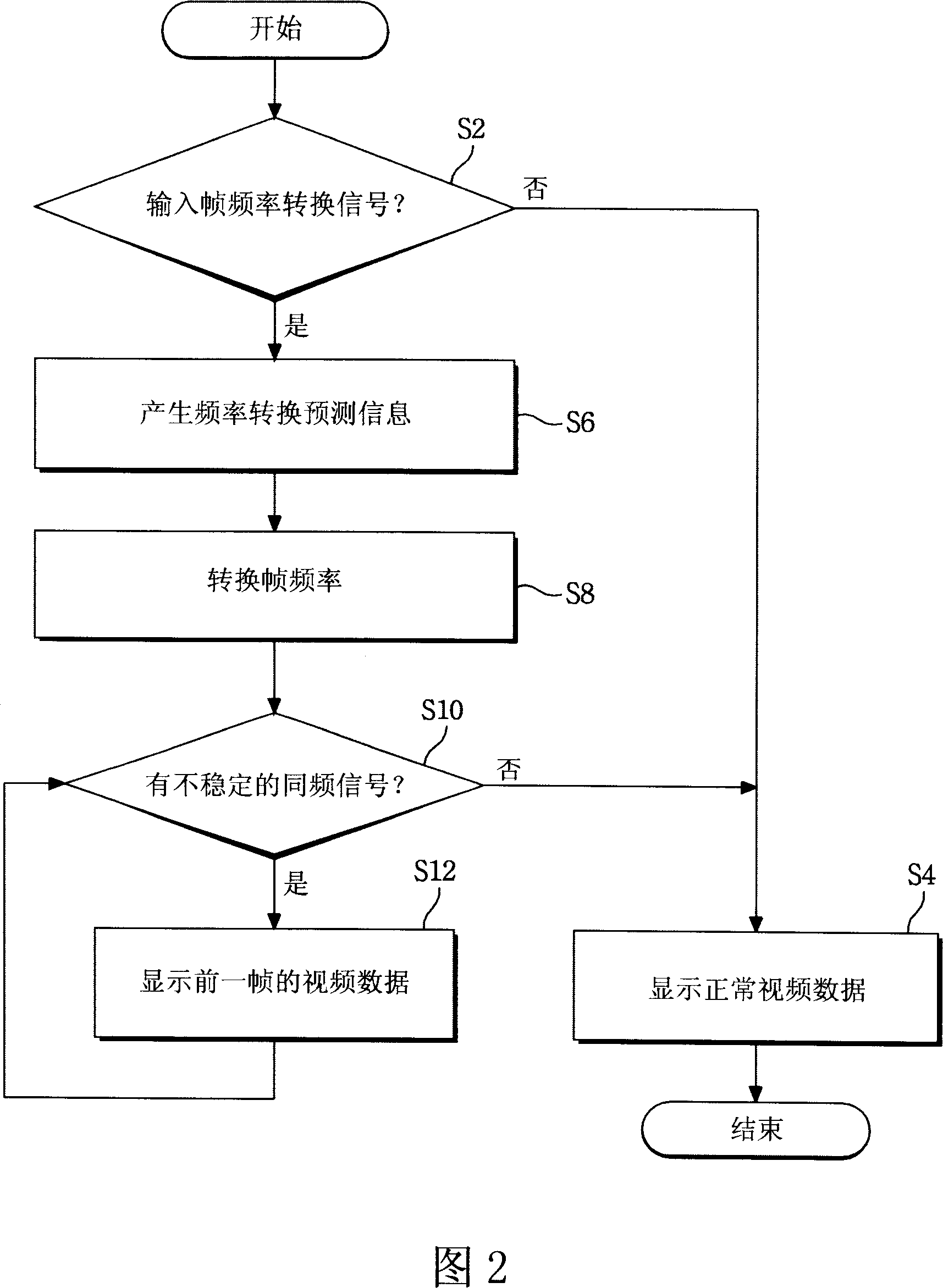
An apparatus and method for driving a liquid crystal display (LCD) device is disclosed, to prevent error of a timing controller and to prevent the defective image on a frequency conversion, the apparatus comprising a liquid crystal display part to display images, a driver to drive the liquid crystal display part, a graphic system to output frequency-conversion prediction information in accordance with a frequency-conversion signal, and perform frequency conversion of a plurality of synchronizing signals, and a timing controller to control the driver to display video data according to a previous frame during the frequency conversion, in response to the frequency-conversion prediction information.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
System and method for reduced power open-loop synthesis of output clock signals having a selected phase relative to an input clock signal
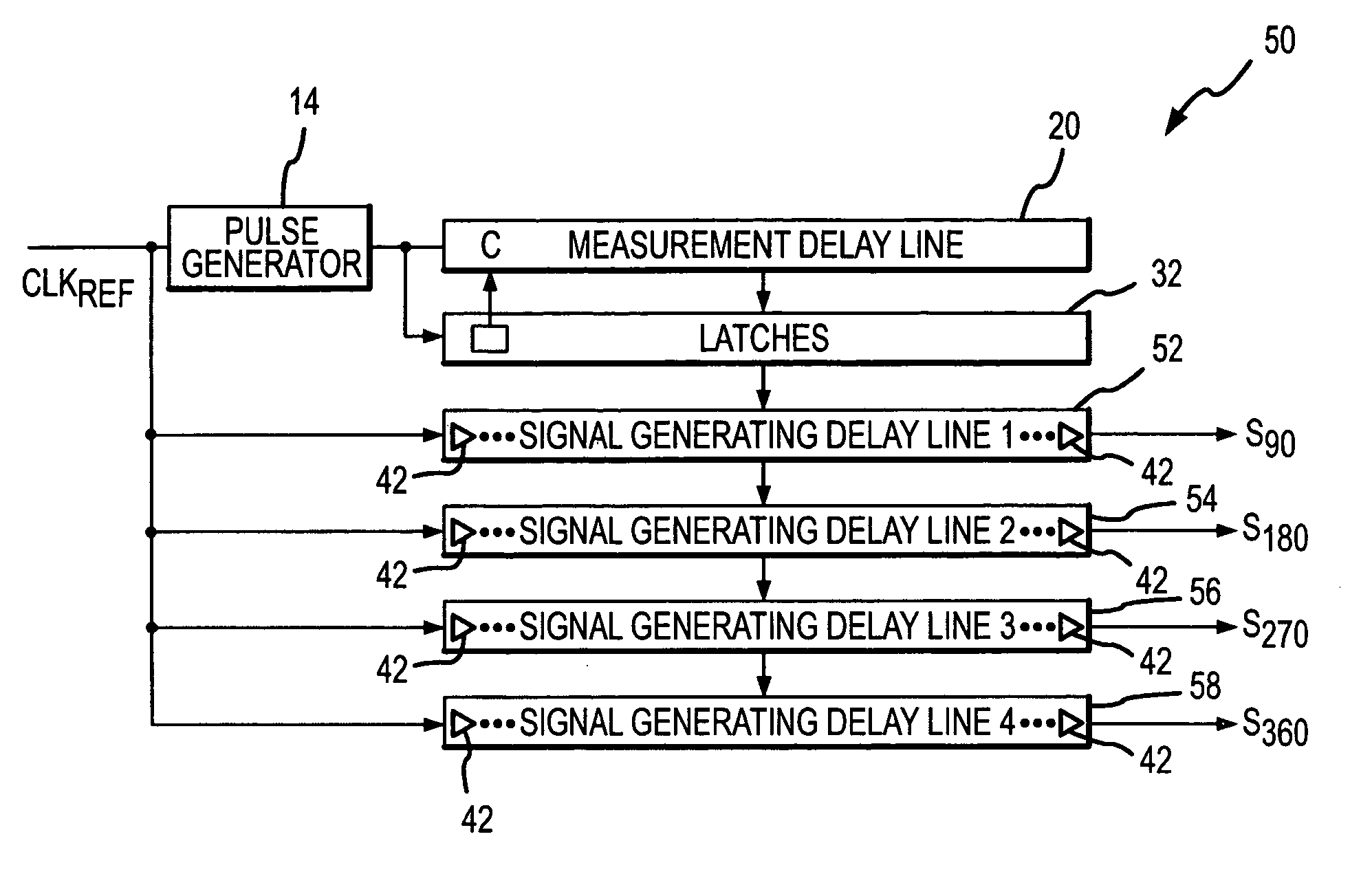
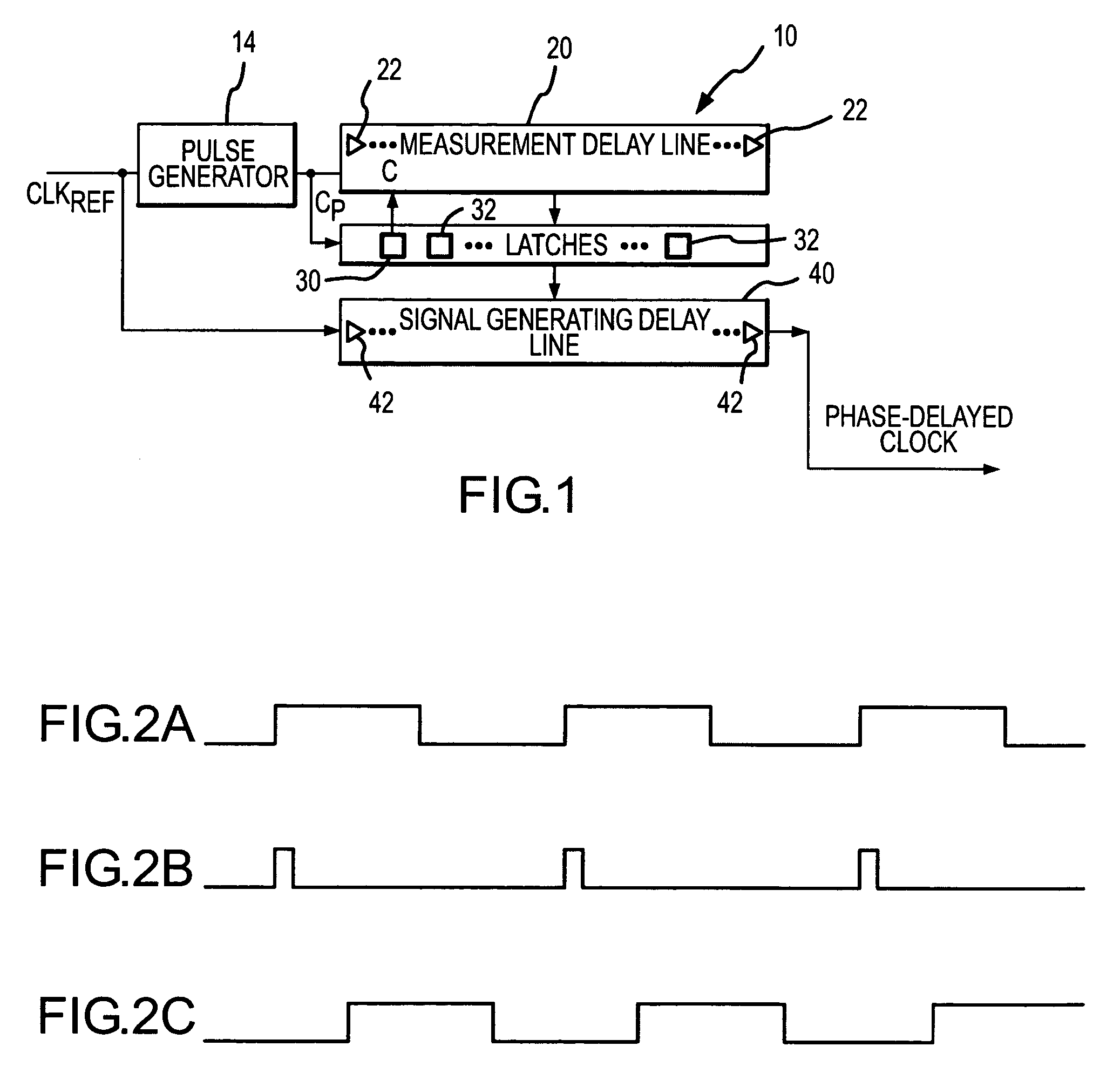
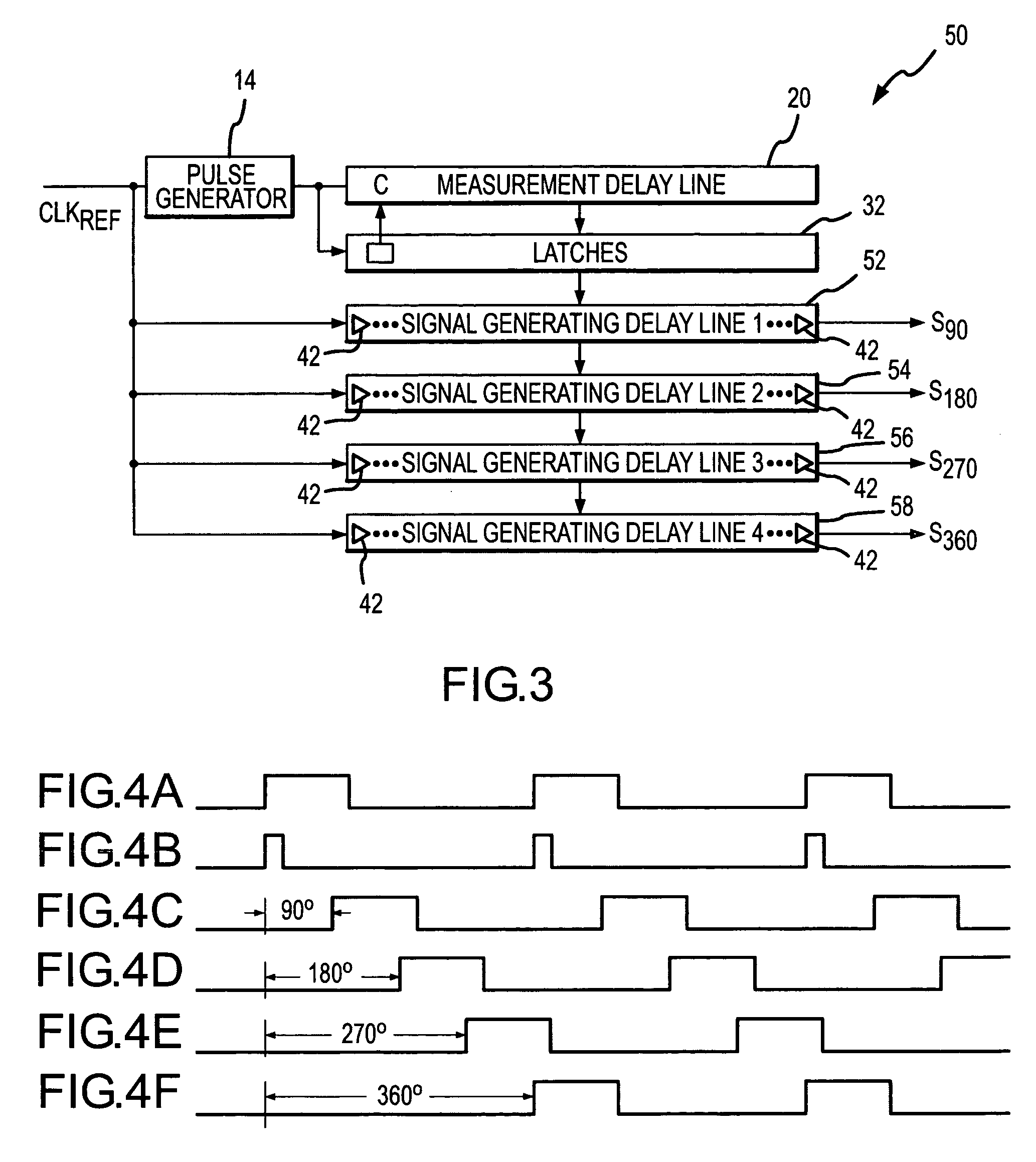
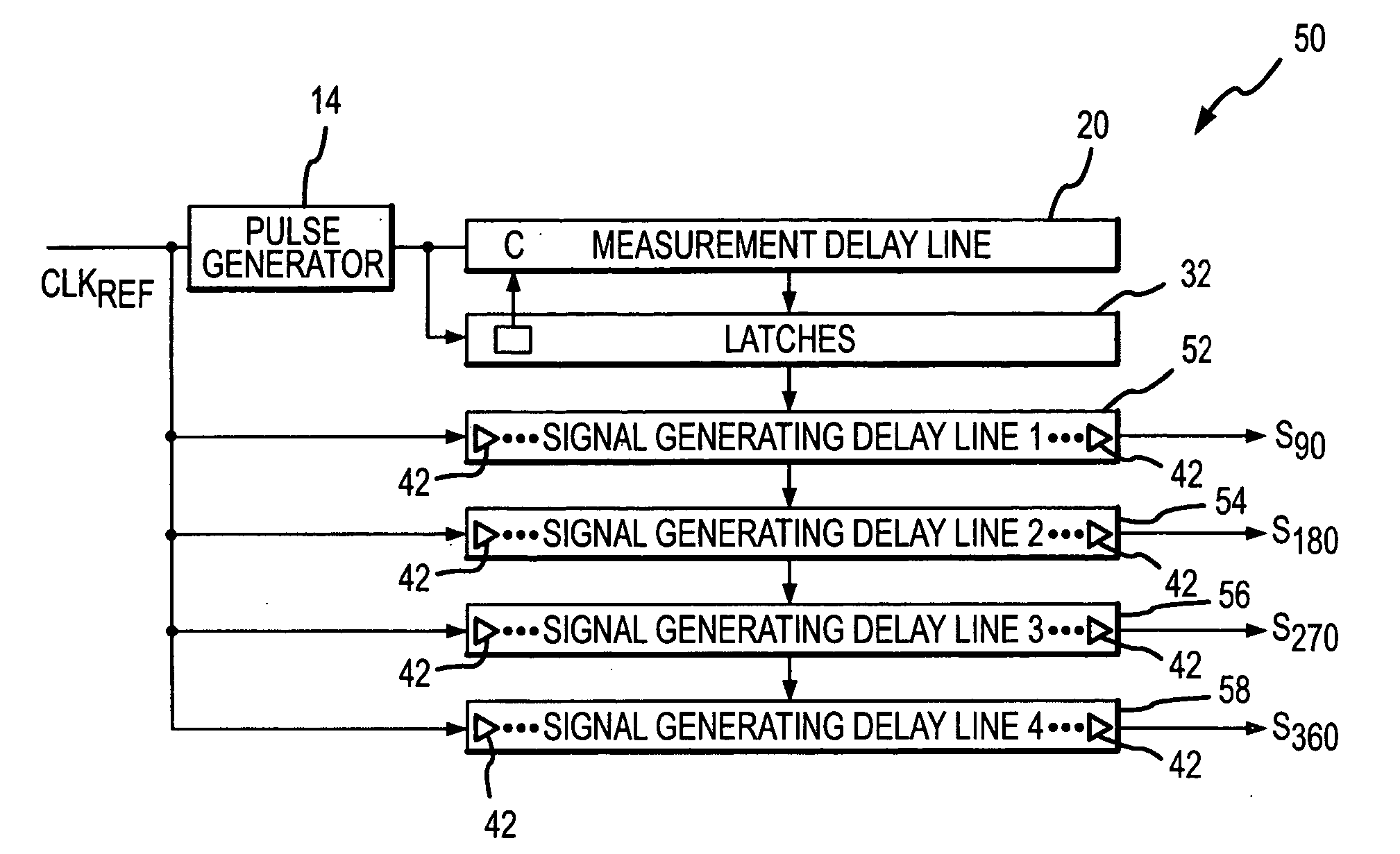
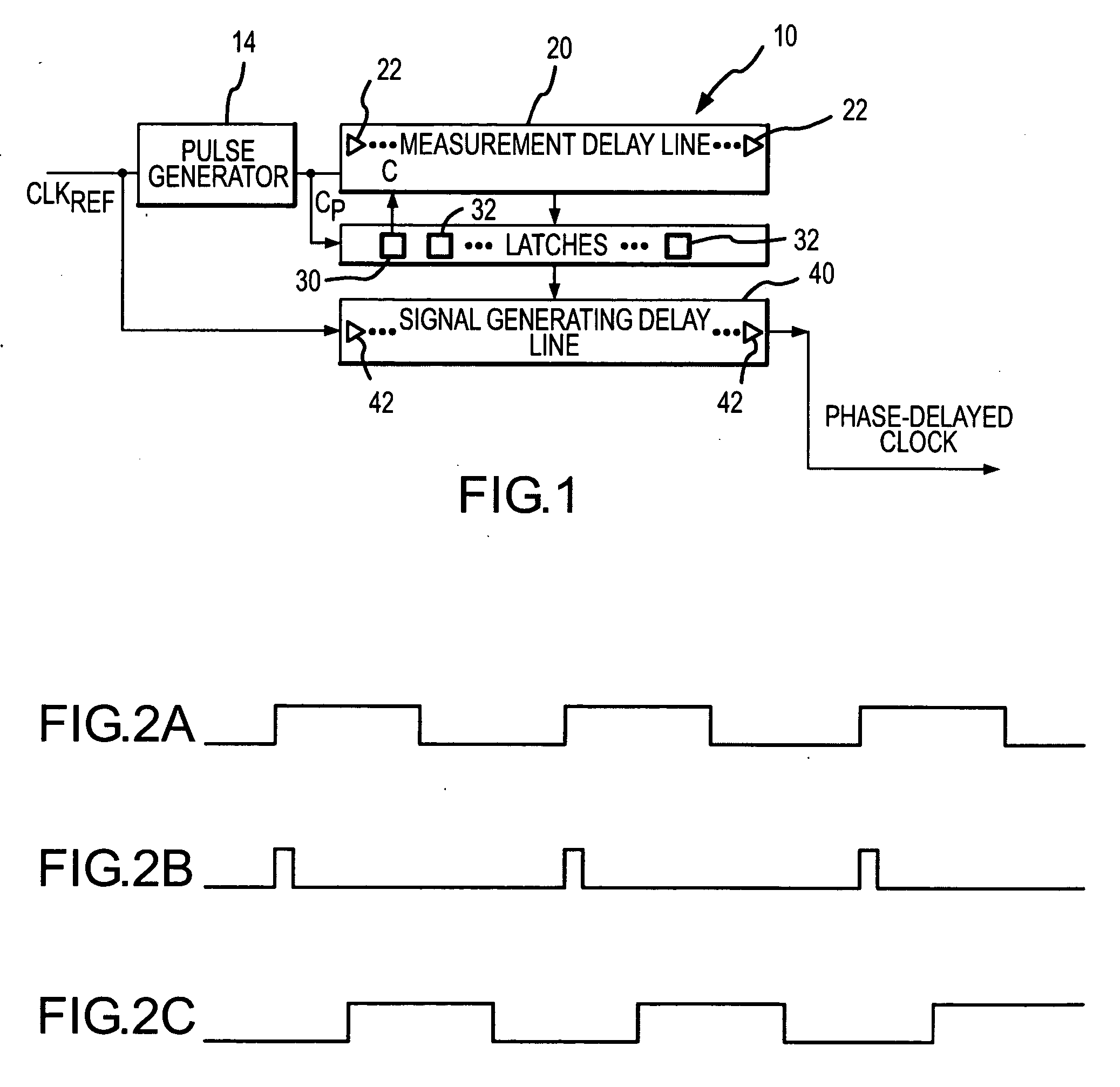
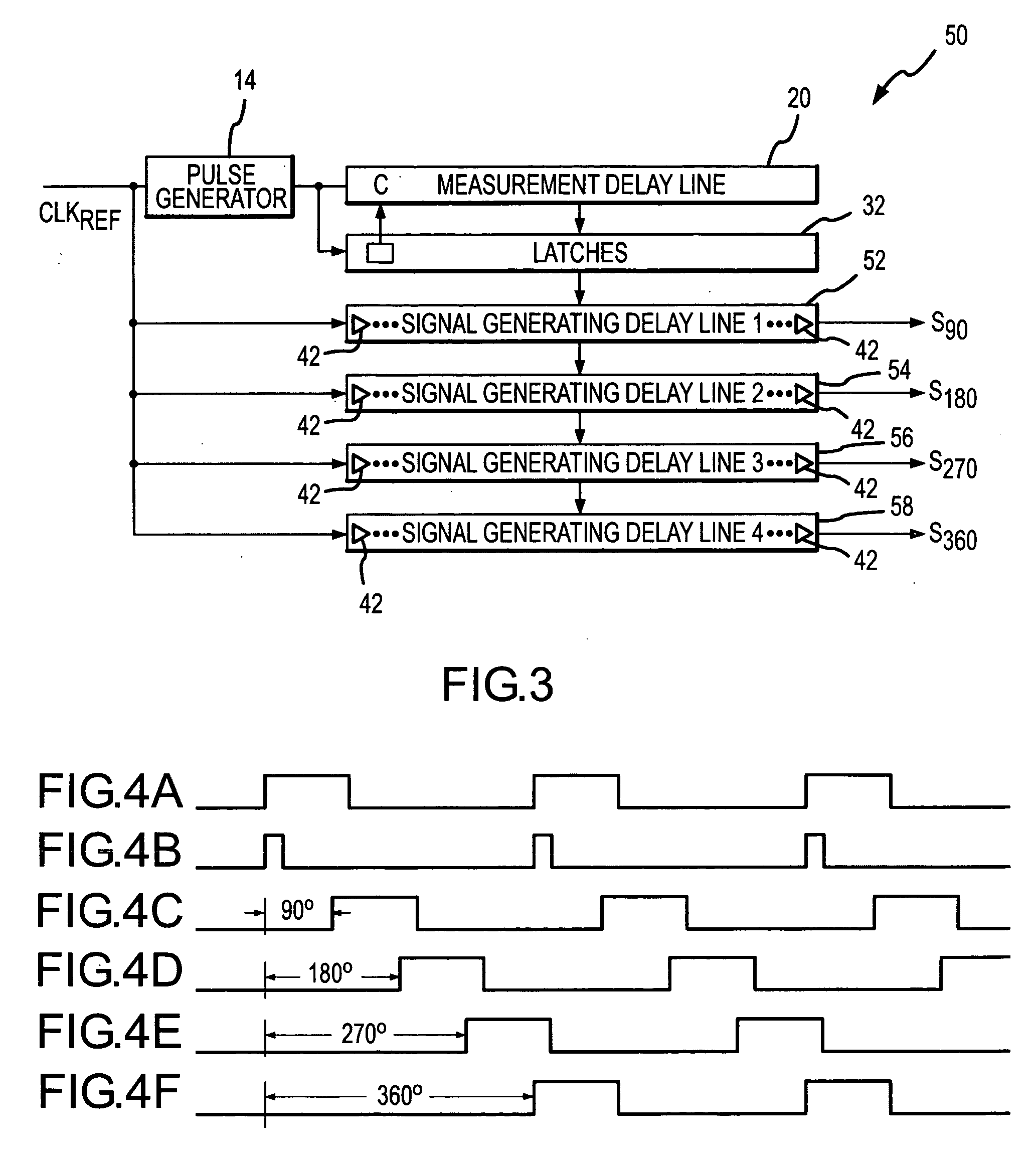
InactiveUS7078951B2Reduce degradationReduce power consumptionDigital storagePhase shifterEngineeringMeasurement delay
A signal generating circuit includes a pulse generator generating a pulse responsive to a periodic clock reference signal. The pulse propagates through a plurality of series-connected delay elements in a measurement delay line. The measurement delay line is coupled to a series of latches that correspond to respective groups of delay elements in the measurement delay line. The delay element to which the pulse has propagated when the next pulse is received causes a corresponding latch to be set. The clock reference signal propagates through a signal generating delay line, which contains a sub-multiple of the number of delay elements in the measurement delay line, starting at a location corresponding to the set latch. The latch may remain set for a large number of periods of the clock reference signal so that it is not necessary for the clock reference signal to propagate through the measurement delay line each cycle.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
System and method for reduced power open-loop synthesis of output clock signals having a selected phase relative to an input clock signal
InactiveUS20060044037A1Reduce delay of delay lineReduce power consumptionDigital storagePhase shifterEngineeringMeasurement delay
A signal generating circuit includes a pulse generator generating a pulse responsive to a periodic clock reference signal. The pulse propagates through a plurality of series-connected delay elements in a measurement delay line. The measurement delay line is coupled to a series of latches that correspond to respective groups of delay elements in the measurement delay line. The delay element to which the pulse has propagated when the next pulse is received causes a corresponding latch to be set. The clock reference signal propagates through a signal generating delay line, which contains a sub-multiple of the number of delay elements in the measurement delay line, starting at a location corresponding to the set latch. The latch may remain set for a large number of periods of the clock reference signal so that it is not necessary for the clock reference signal to propagate through the measurement delay line each cycle.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Timing difference division circuit and signal controlling method and apparatus
InactiveUS20010045853A1Increase chip areaHigh speedElectronic switchingSingle output arrangementsCapacitanceControl signal
Timing difference division circuit with a high operating speed and a small area, assuring broadband operation. The circuit includes a logic circuit L1 generating a first gate signal and a second gate signal based on a first input signal and a second input signal, a first switch element connected across a first power source and an inner node and having a control terminal to which is fed the first gate signal, a first series circuit made up of a second switch element and a first constant current source and a second series circuit made up of a third switch element and a second constant current source. The first and second series circuits are connected in parallel across the inner node and the second power source. The first and second gate signals are connected to control terminals of the second and third switches, respectively. The circuit also includes a plurality of MOS capacitors, connection of which to the inner node is separately controlled by a control signal, and a buffer circuit an input end of which is connected to the inner node and the value of an output signal of which is determined based on the relative magnitude of the potential of the inner node and a threshold voltage. An overlap period during which the first and second gate signals output from the logic circuit are both activated to turn on the second and third switch elements is set to an optional value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
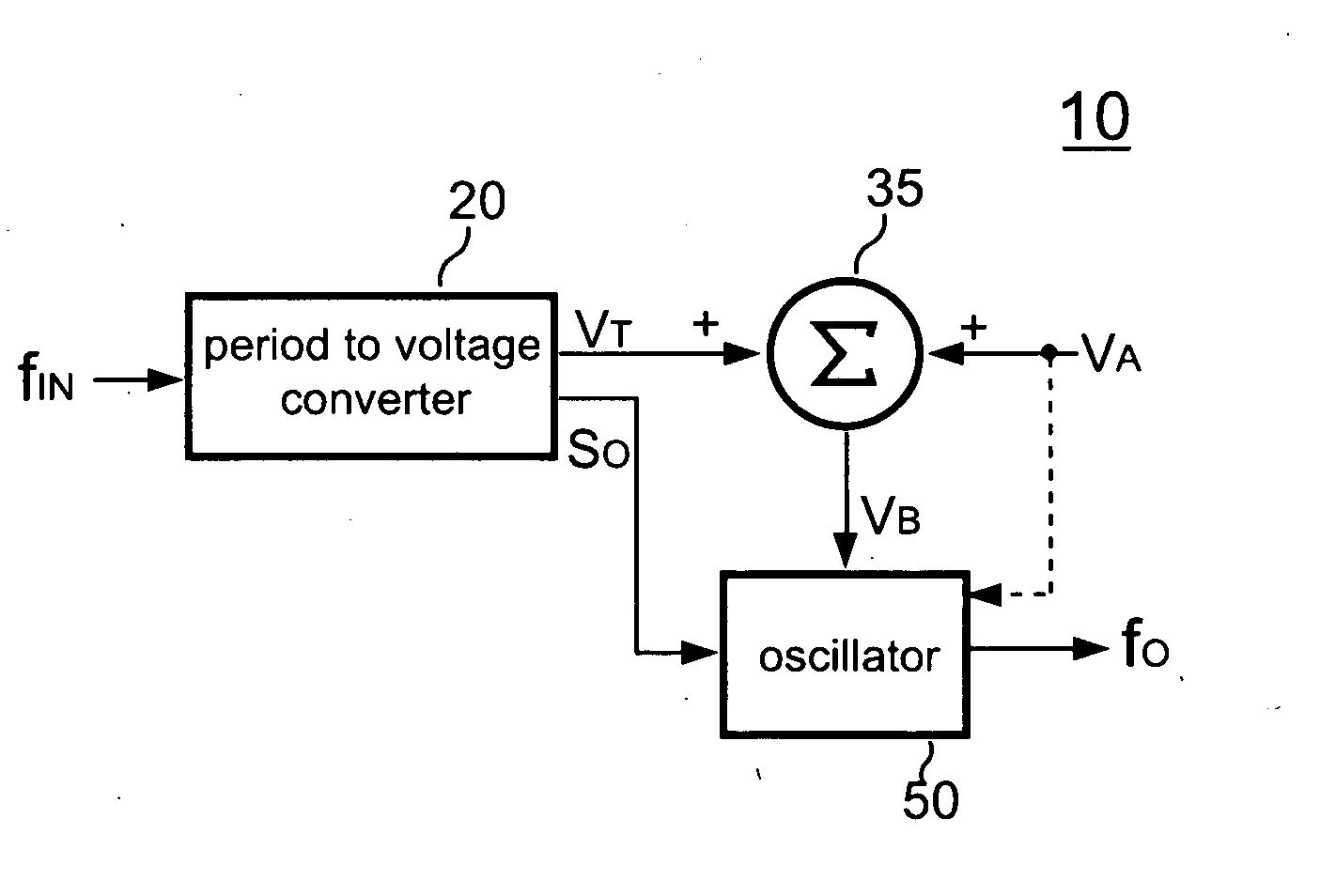
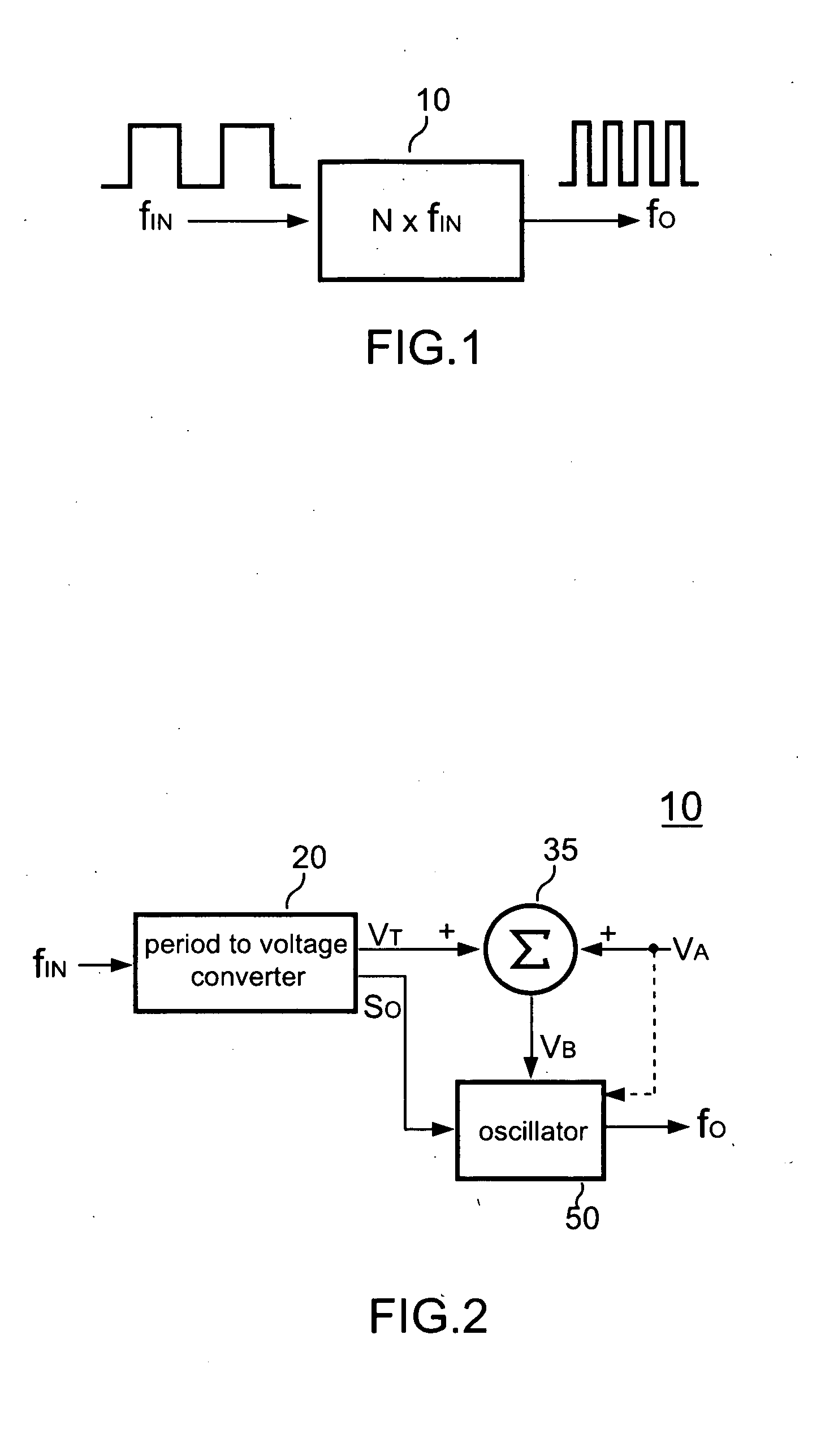
Frequency multiplier and method for frequency multiplying
InactiveUS20100141307A1Low costOscillations generatorsManipulation for frequency changeVoltage converterControl signal
A frequency multiplier according to the present invention comprises a period-to-voltage converter that generates a control signal in response to the period of an input signal. An oscillator generates an output signal in accordance with the control signal. The level of the control signal is corrected to the frequency of the input signal. The control signal is coupled to determine the frequency of the output signal.
Owner:FAIRCHILD TAIWAN
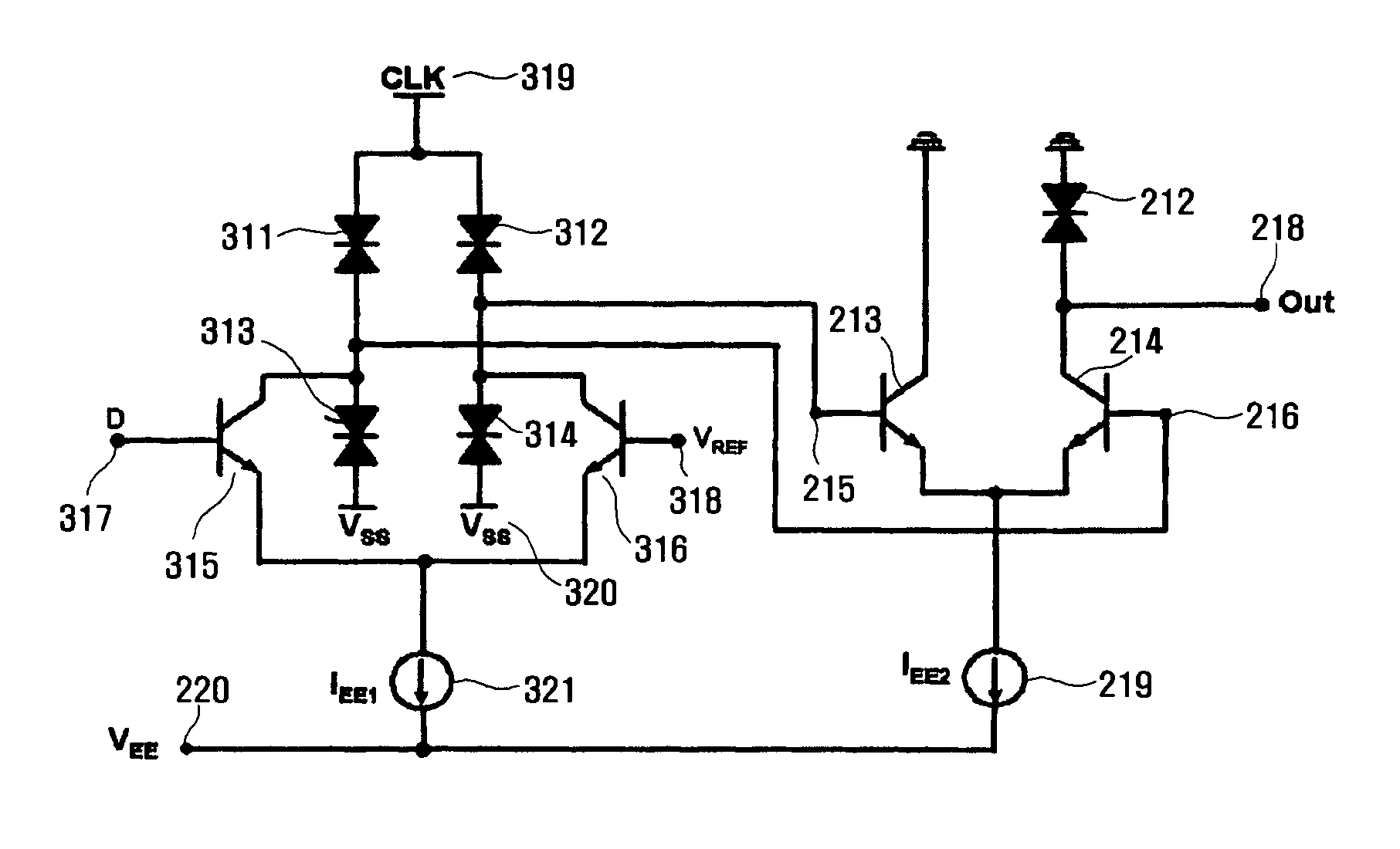
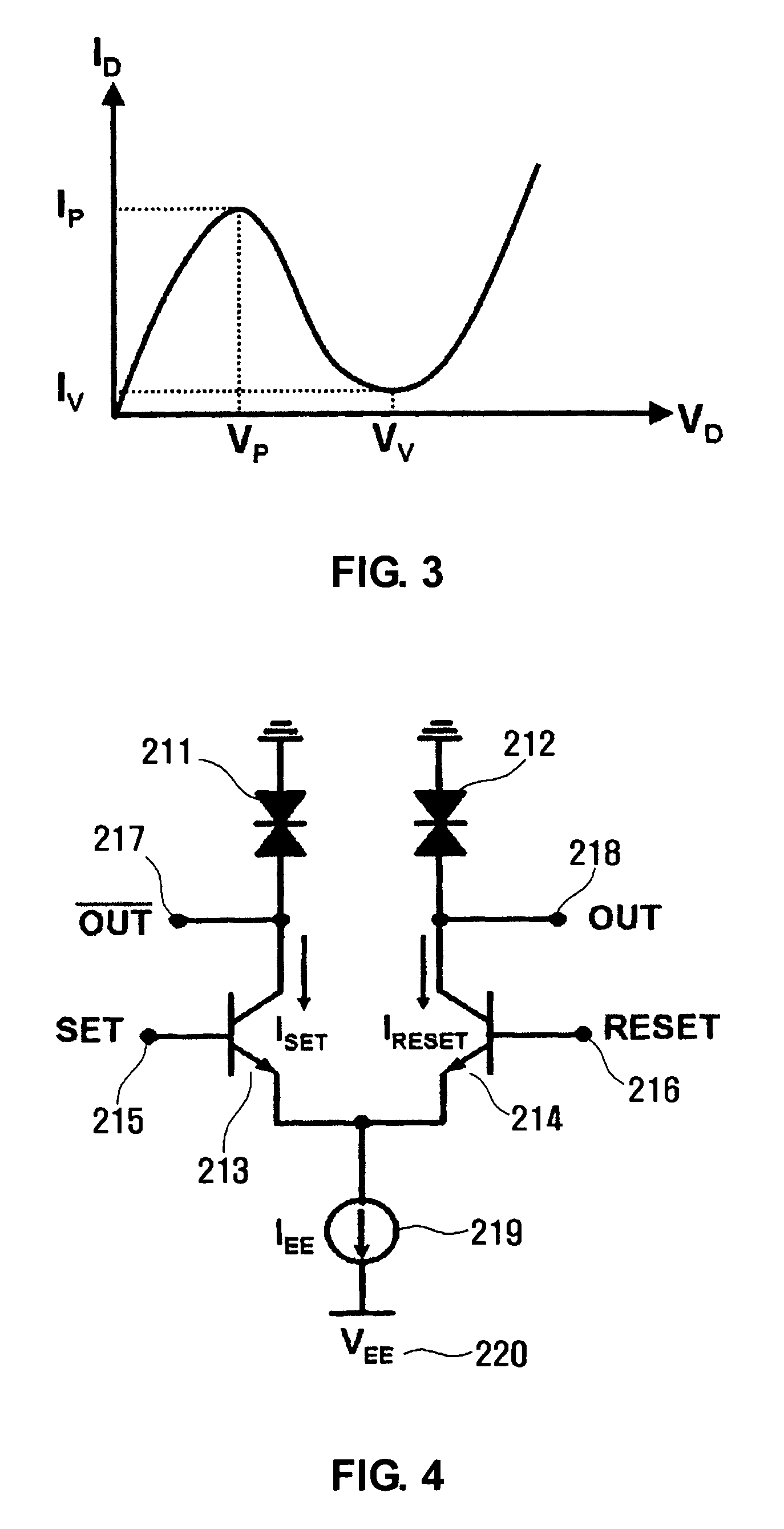
SET/RESET latch circuit, Schmitt trigger circuit, and MOBILE based D-type flip flop circuit and frequency divider circuit thereof
InactiveUS7573310B2Easy to useHigh speedLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDiodeSchmitt triggerEngineering
The present invention relates to a SET / RESET latch circuit a Schmitt trigger circuit, and a MOBILE based D-type flip flop circuit and frequency divider circuit using the SET / RESET latch circuit and Schmitt trigger circuit. The SET / RESET latch circuit is configured with CML-type transistors and negative differential resistance diodes. The SET / RESET latch circuit can be applied to very high speed digital circuits.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Pulse generating circuit, electronic device using this pulse generating circuit, cellular phone set, personal computer, and information transmitting method using this circuit
ActiveUS7449932B2Easily generating high-frequency band pulseSimple structurePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorPersonal computerEngineering
A pulse generating circuit includes a plurality of delay elements cascaded so as to constitute a predetermined loop, wherein when a predetermined input pulse is supplied to a leading end of the series connection, an effective frequency multiplication is applied to signals which appear at a plurality of portions out of the node portions among the plurality of delay elements and the terminal end portion of the series connection by a logical circuit to obtain an output pulse having a higher frequency than the input pulse.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
Duty adjustment circuit
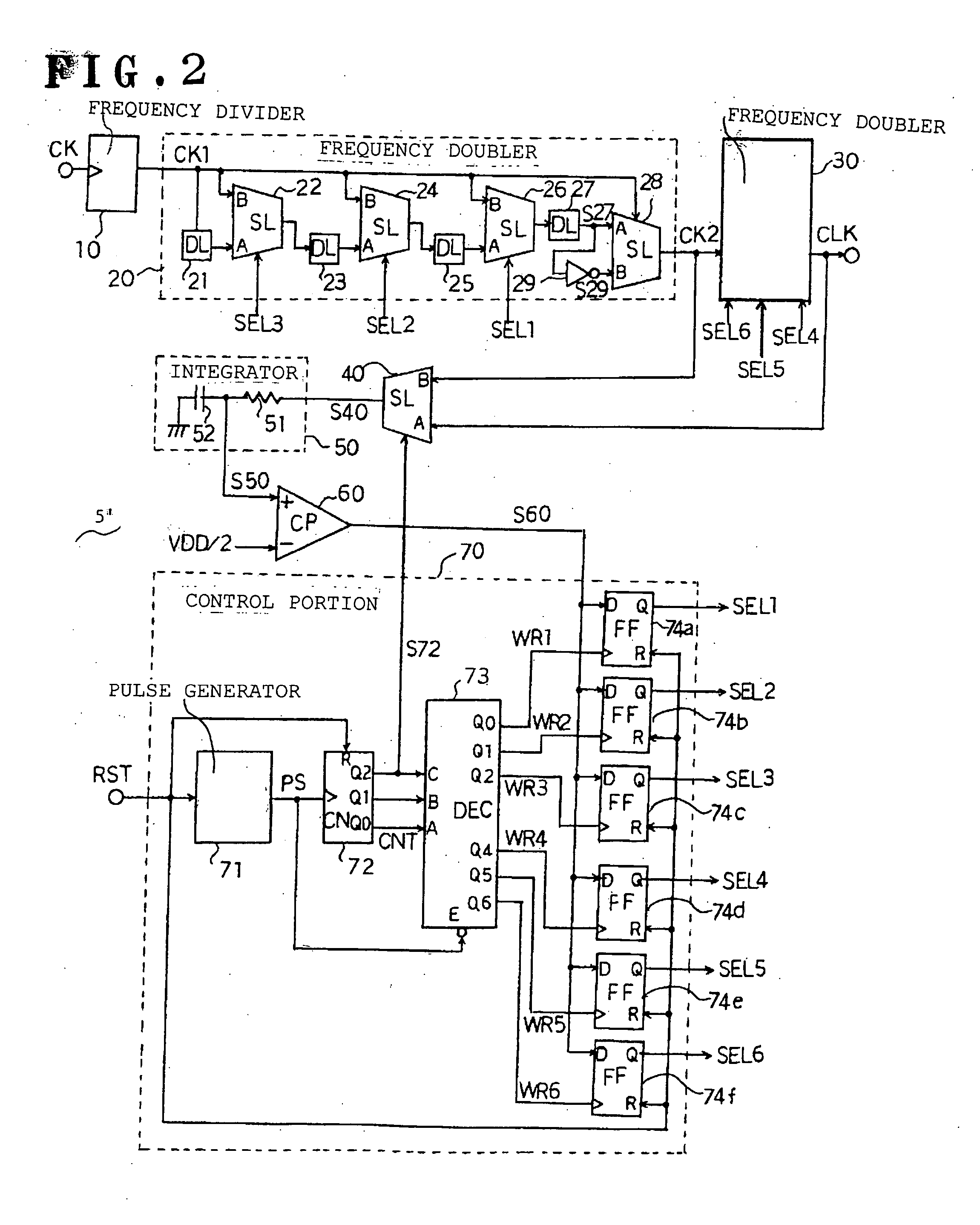
InactiveUS7173464B2Reduce adverse effectsInfluences of high-level instantaneous noise can be suppressedContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationElectric pulse generatorControl signalFrequency multiplier
In a duty adjustment circuit, a clock signal is frequency-divided to ½n by a frequency divider. In a first frequency doubler among n cascade-connected frequency doublers, the divided clock signal is delayed by a variable delay portion according to a control signal. The exclusive logical sum of the delayed signal and the divided clock signal in the frequency-doubling portion doubles the frequency. The average voltage of the frequency-doubled signal is detected by an average value detection portion, and is compared with a reference voltage by a comparison control portion. A control signal is fed back to the variable delay portion to cause the average voltage to become equal to the reference voltage. In this manner, a clock signal is generated from the last frequency doubler with frequency equal to that of the original clock signal, and with duty ratio adjusted to a desired value.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Popular searches
Generating/distributing signals Counting chain pulse counters Pulse counters with static storage Manipulation where pulse delivered at different times Oscillator tubes Electrial characteristics varying frequency control Pulse manipulation delay Time-delay networks Baseband systems Duplex signal operation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com