Patents
Literature
122results about "Computations using pulse rate multipliers/dividers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
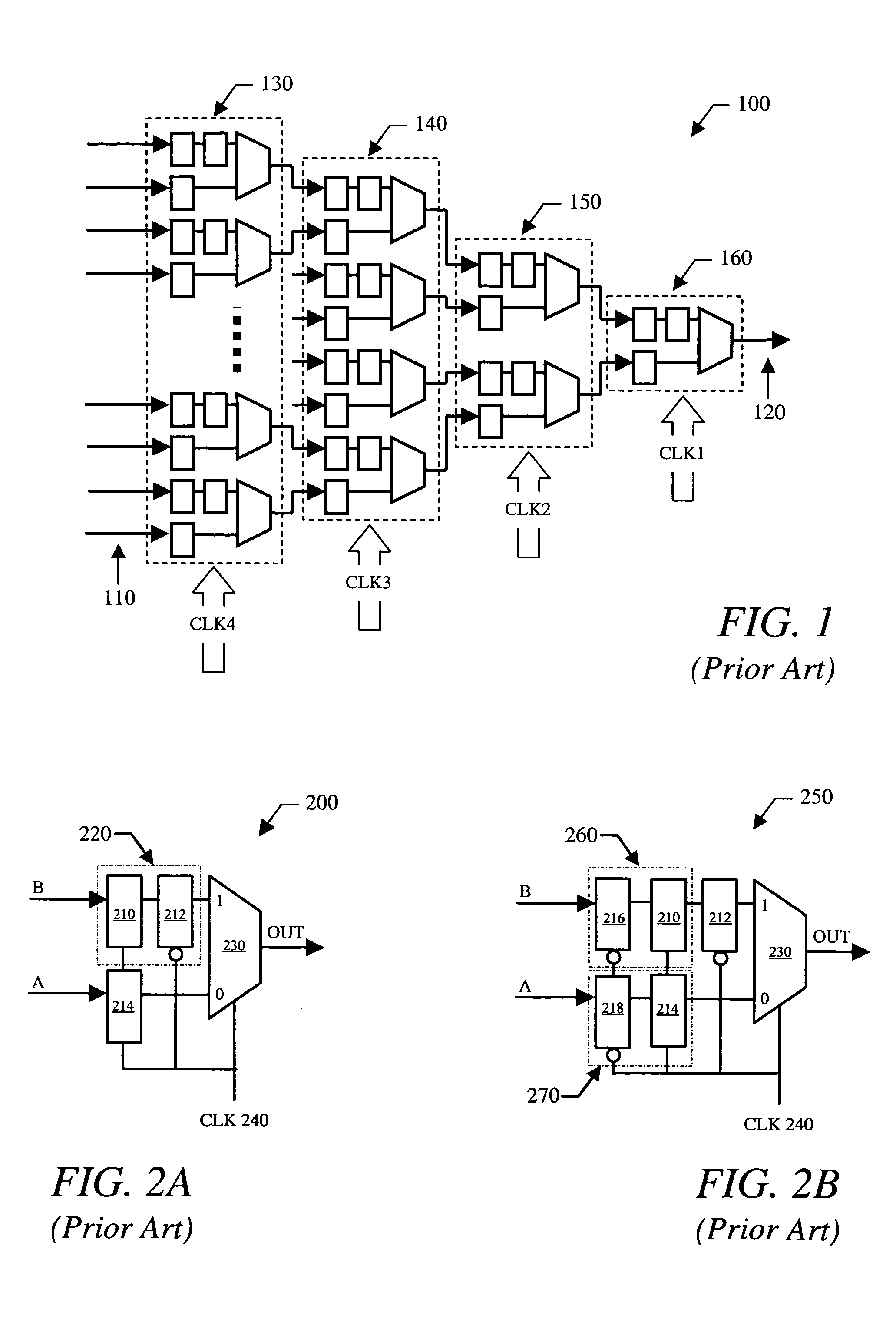
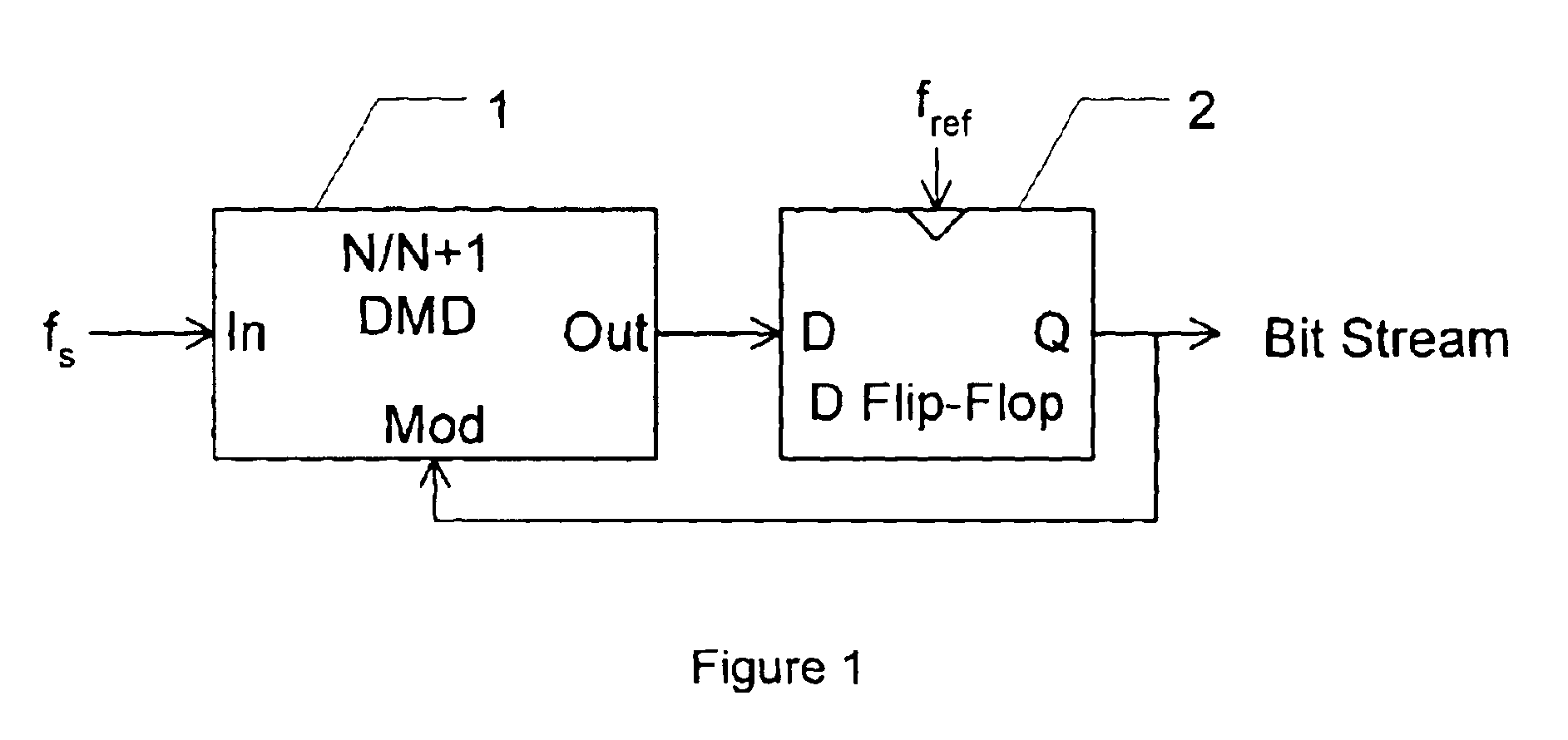
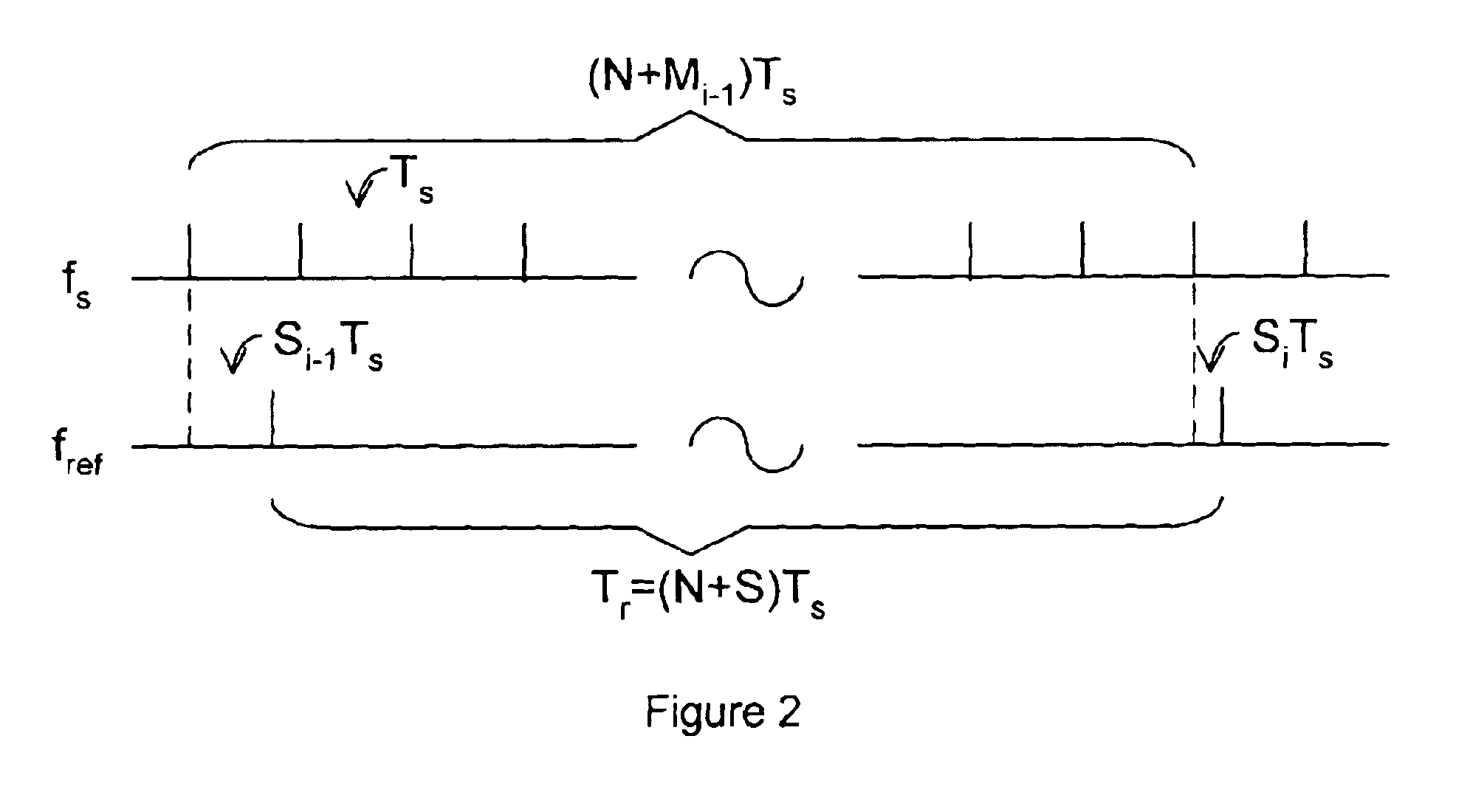
Small scale clock multiplier circuit for fixed speed testing
InactiveUS20080224742A1Counting chain pulse countersComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersRolloverClock rate
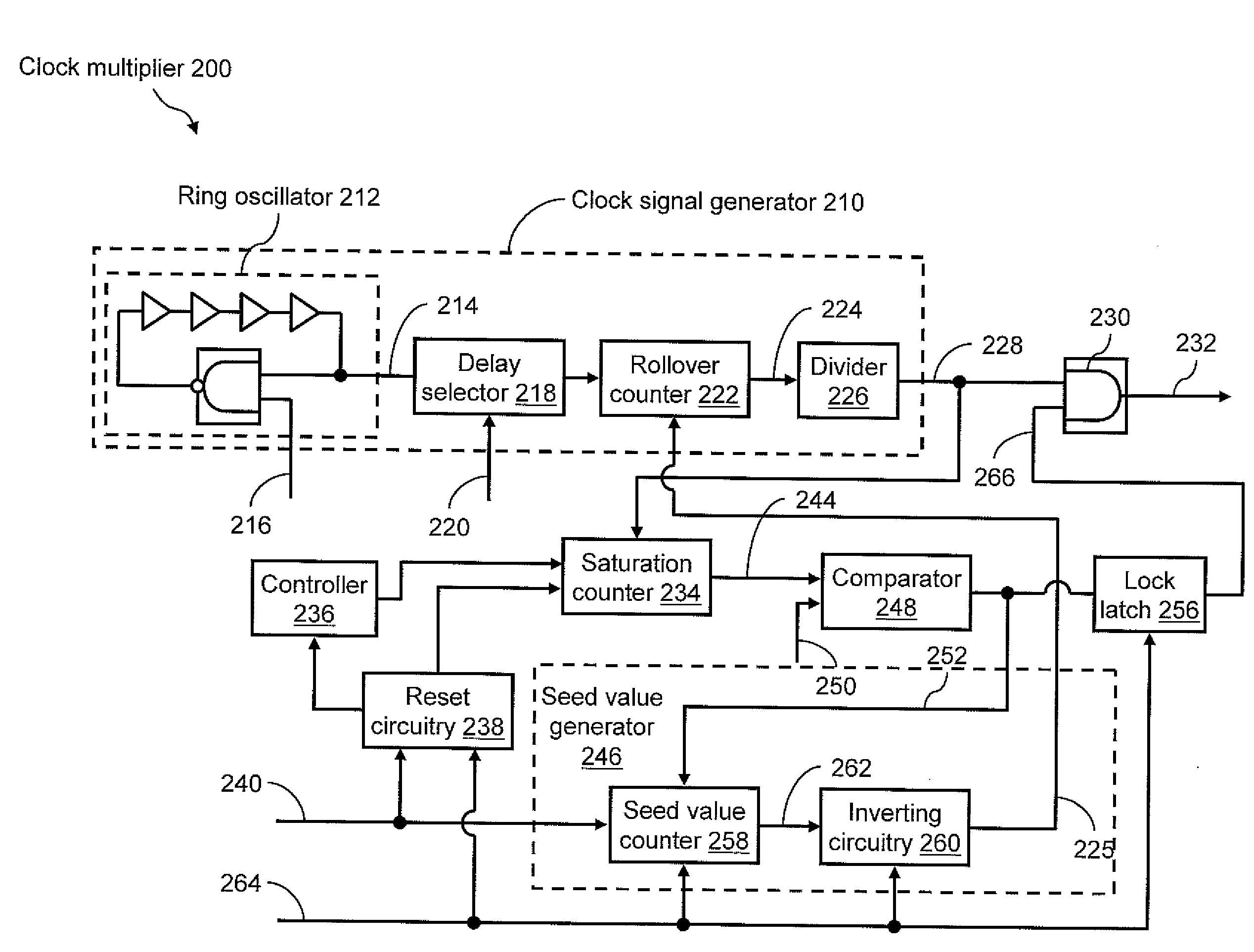
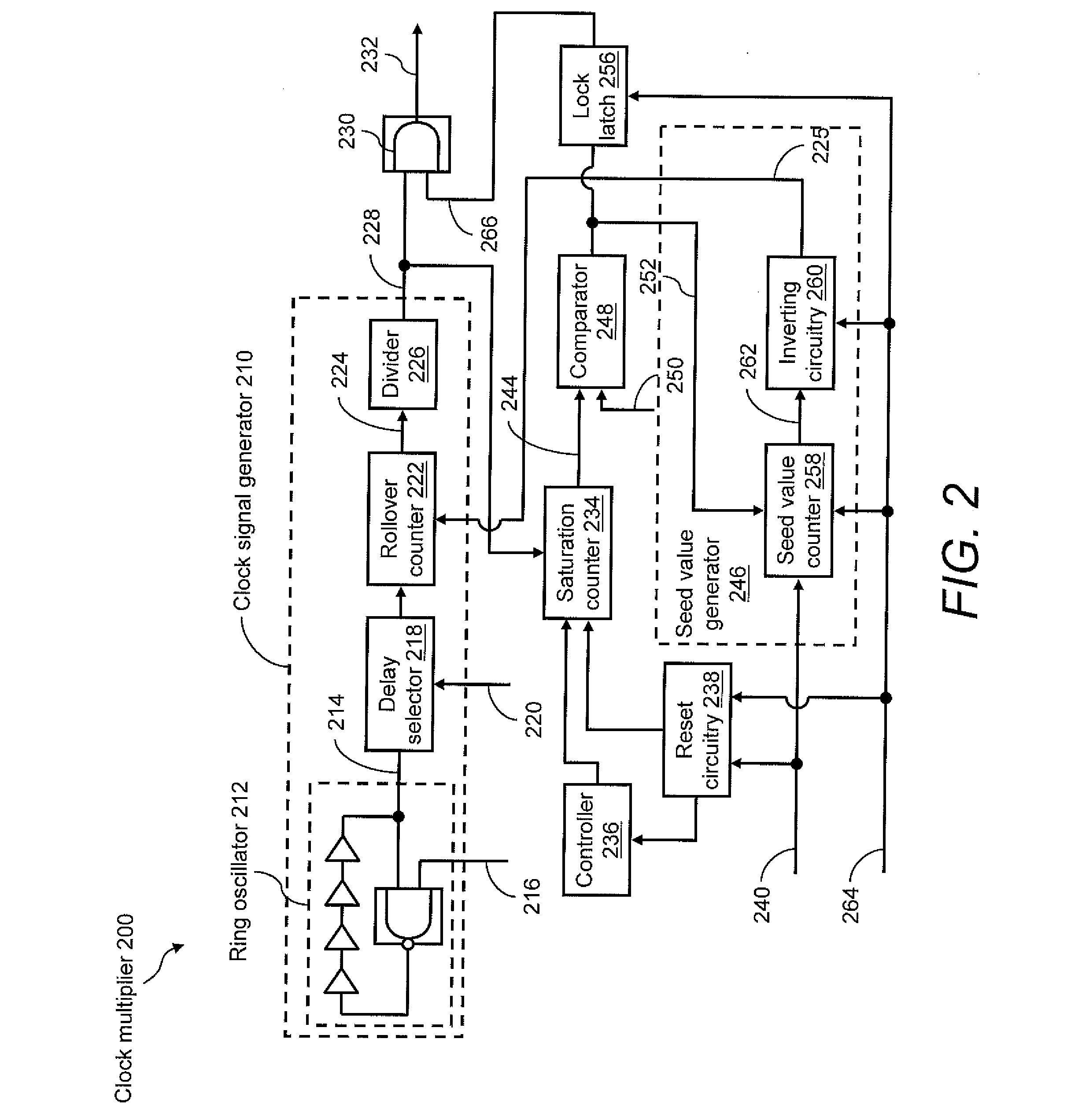
An on-chip clock multiplier for outputting a fast clock that is approximately a predetermined multiple n of a slow clock. The multiplier utilizing a high-speed oscillator to generate a high-frequency base signal. A lower frequency signal is generated using the high-frequency base signal as a function of the output of a rollover counter that counts from a seed value to a terminal value. A saturation counter is used to determine whether no more than n pulses of the lower frequency signal occur within a single cycle of the slow clock. If not, the lower frequency signal is iteratively slowed by changing the seed value until no more than n pulses of the lower frequency signal occur within a single cycle of the slow clock. When this iteration is done, the fast clock having a frequency that is approximately n times the frequency of the slow clock is output.
Owner:IBM CORP
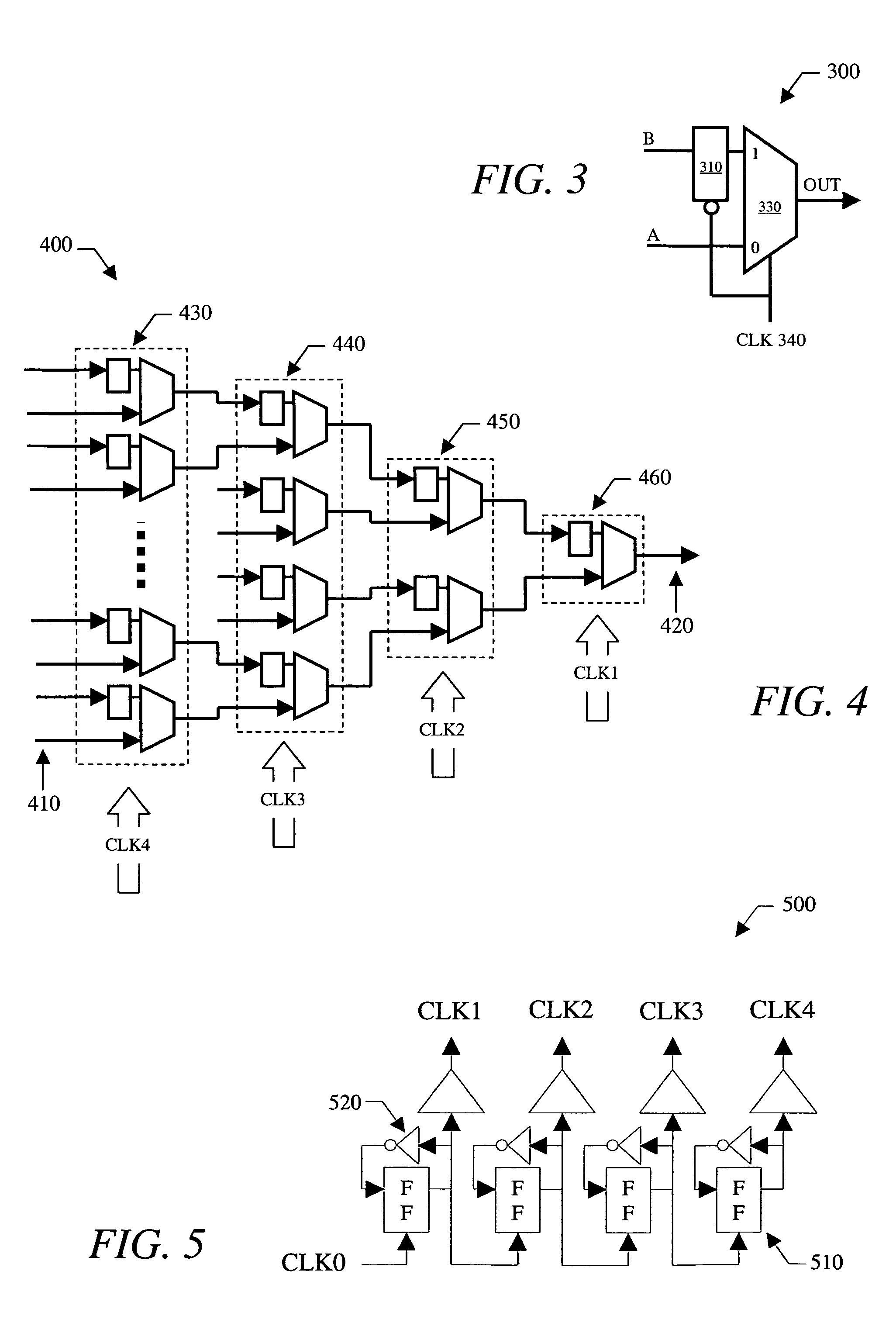
Low power serializer circuit and method
InactiveUS7006021B1Avoid operation failureReduce power consumptionParallel/series conversionComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersMultiplexingTransceiver
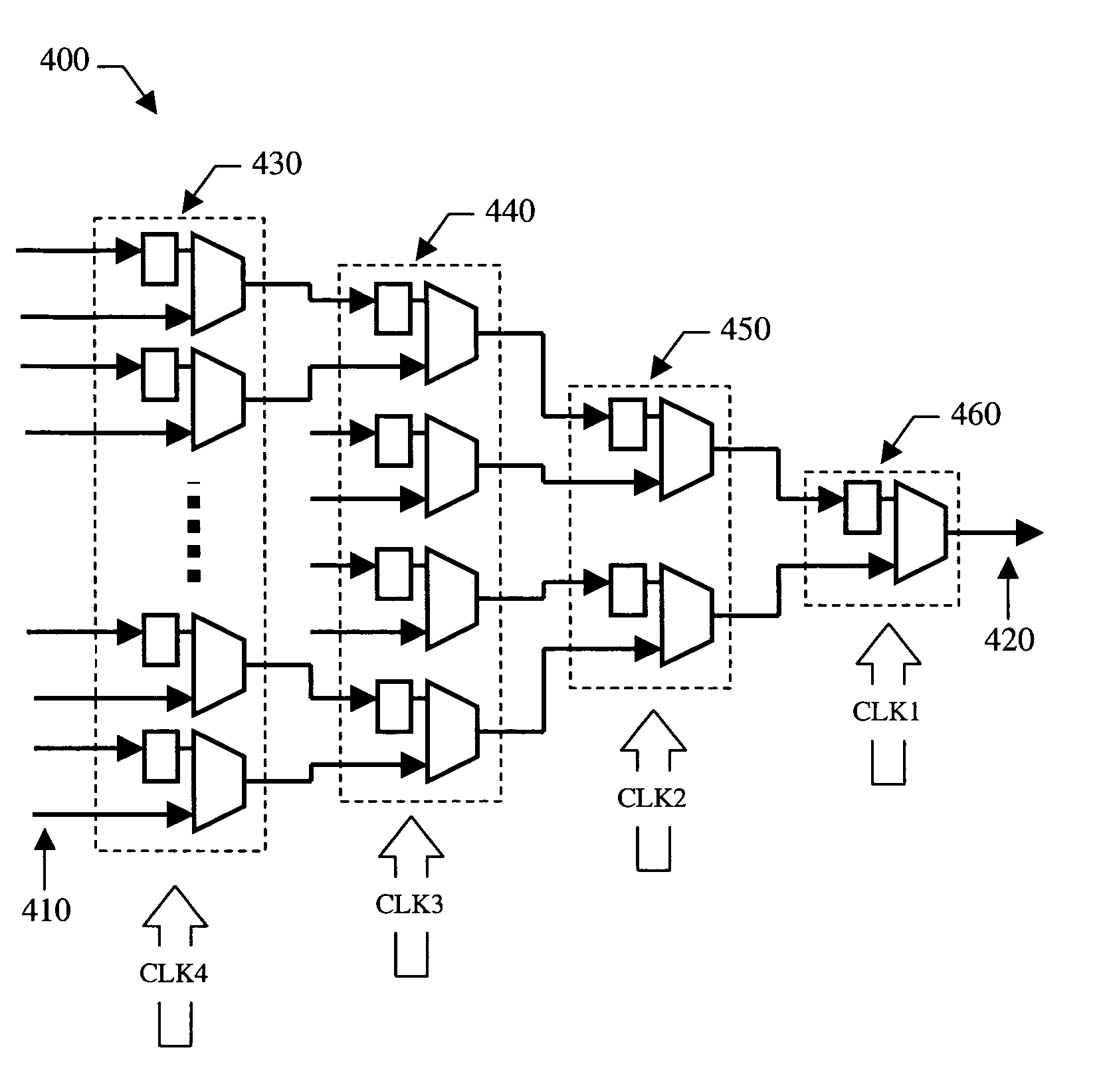
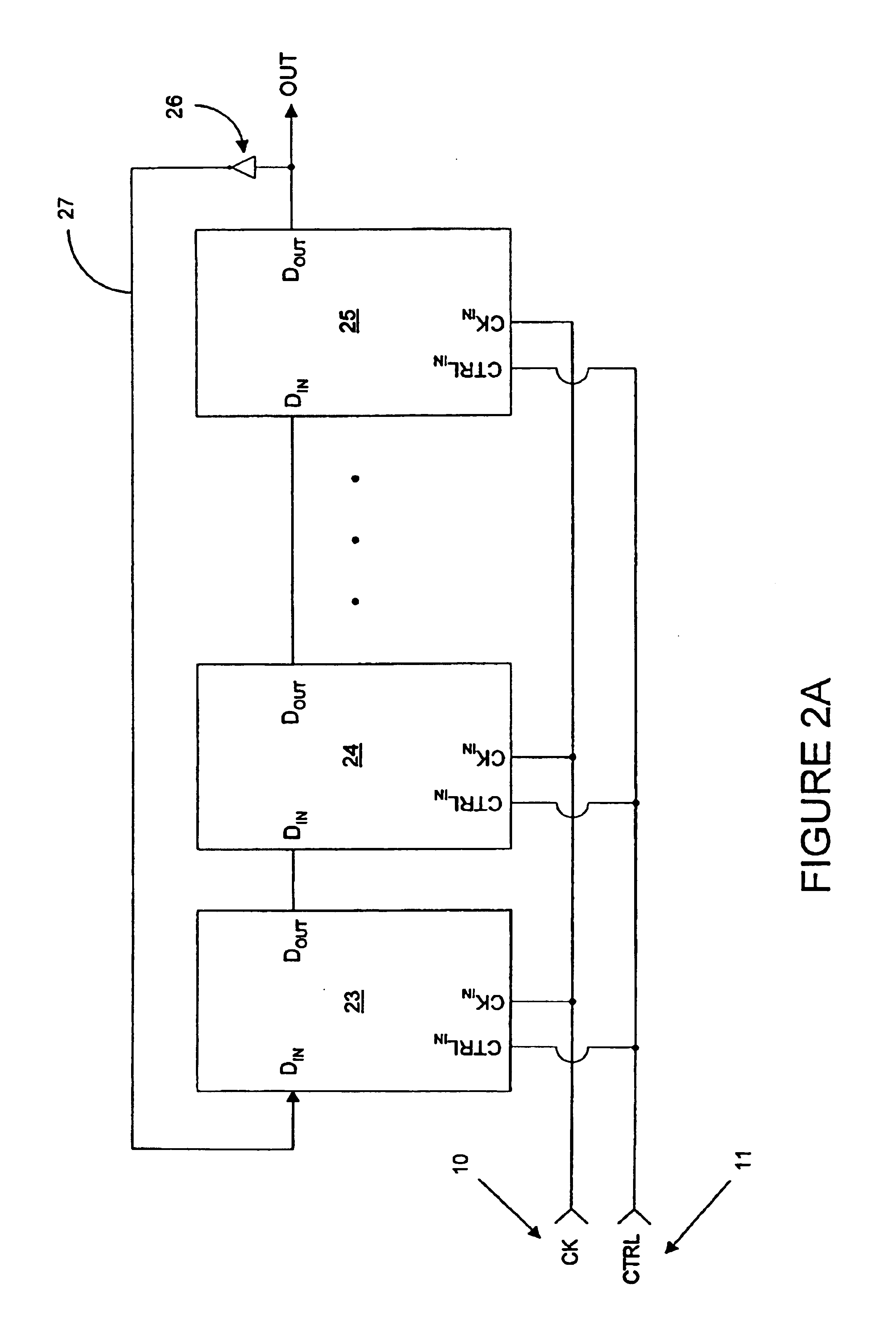
A serializer within, for example, a transceiver is provided having multiple stages of pipelined multiplexing cells. Each multiplexing cell may be substantially the same and each comprises no more than one latch. In some embodiments, each multiplexing cell includes a multiplexer comprising a pair of inputs and a single latch, which is coupled to one input of the multiplexer. No latches are coupled to the other input of the multiplexer. The serializer generally includes a plurality of stages. Each successive stage includes one-half the number of multiplexing cells included in the previous stage, and each successive stage is clocked by a clocking signal that transitions at twice the frequency of the previous stage clock signal.
Owner:RPX CORP
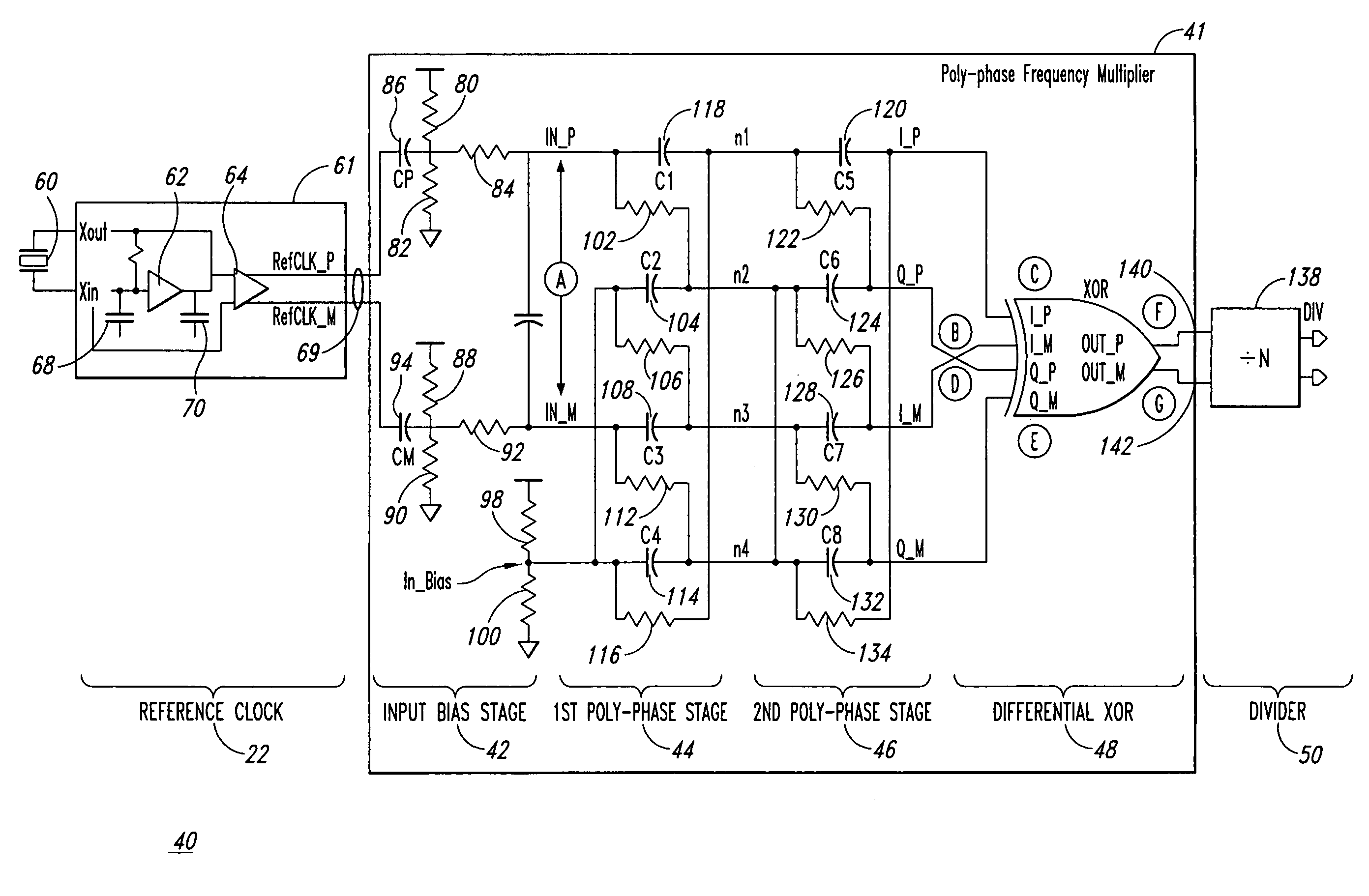
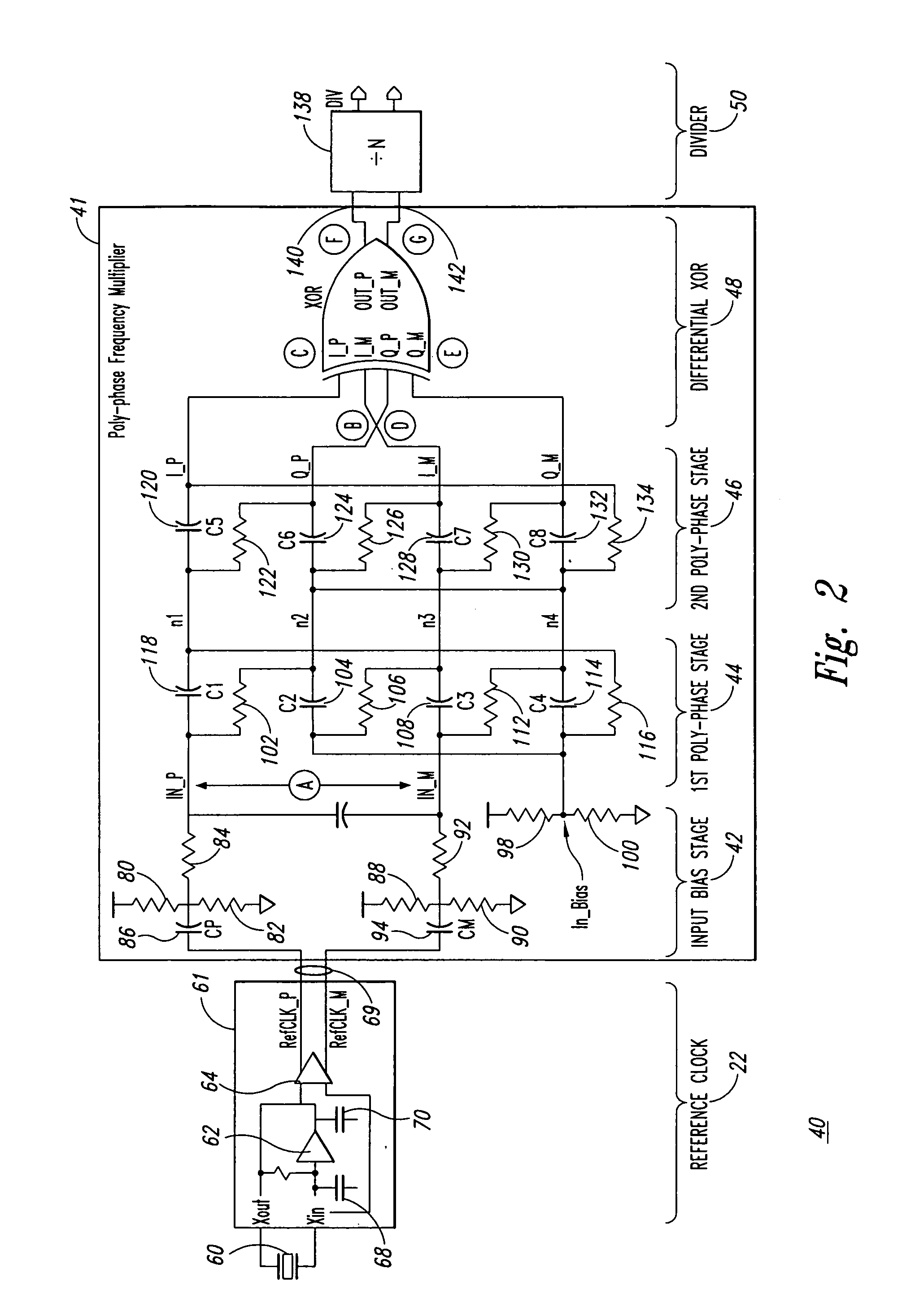
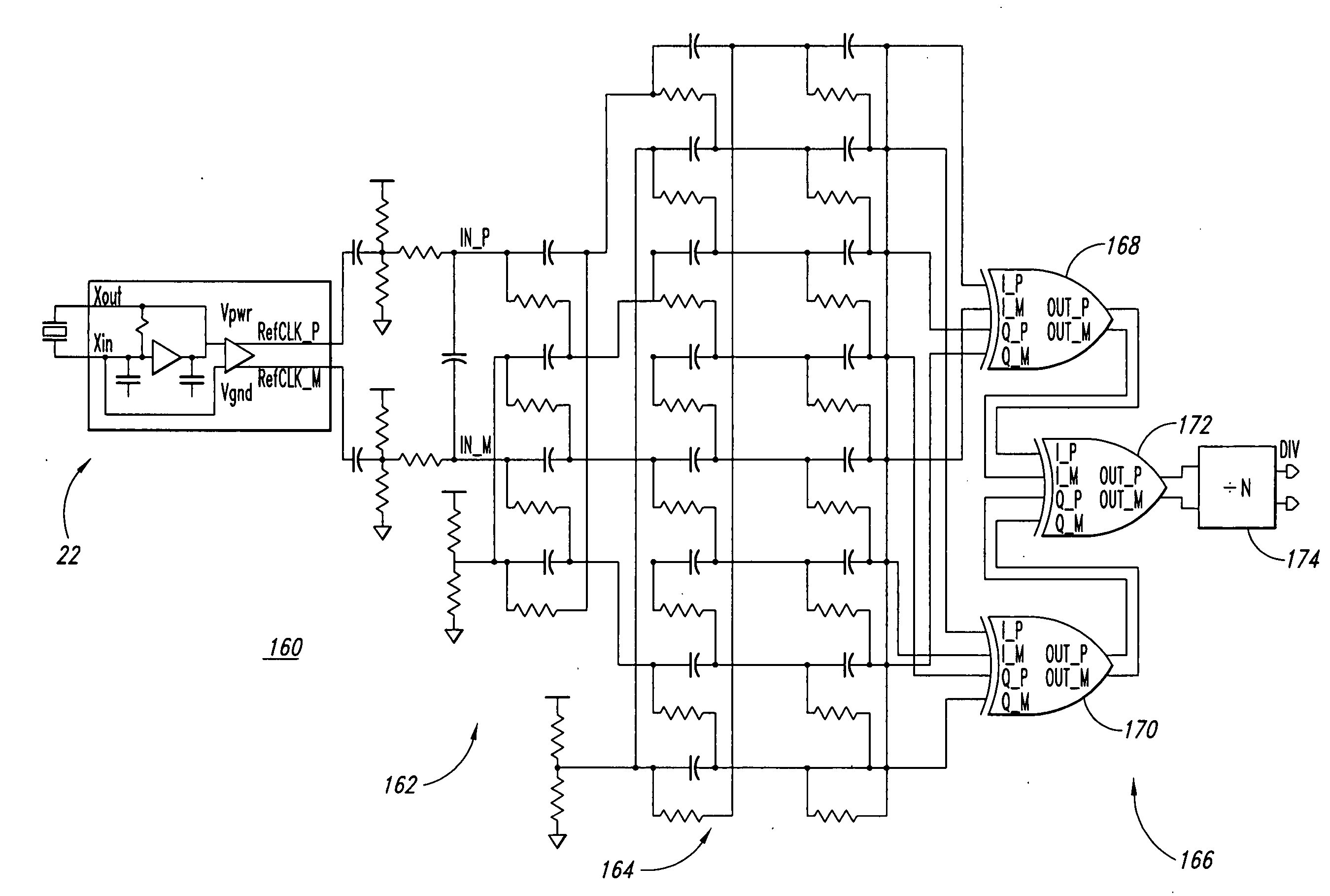
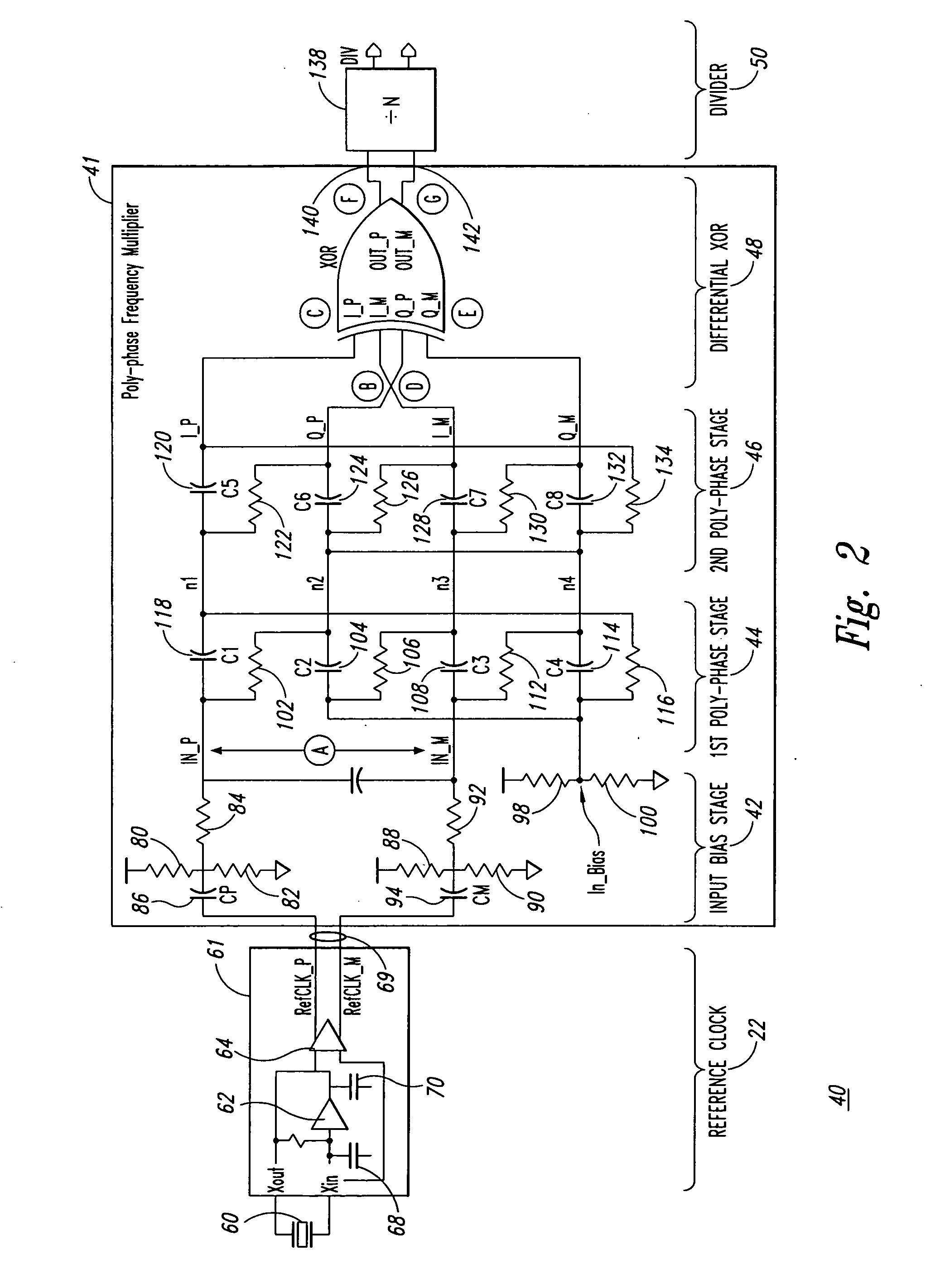
Poly-phase frequency synthesis oscillator
ActiveUS7332976B1Multiple-port networksComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersFrequency synthesisMultiple version
A frequency synthesis / multiplication circuit and method for multiplying the frequency of a reference signal. In one embodiment, multiple versions of the reference signal are generated having different phases relative to one another, and these multiple versions are combined to form an output signal having a frequency that is a multiple of the frequency of the reference signal.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
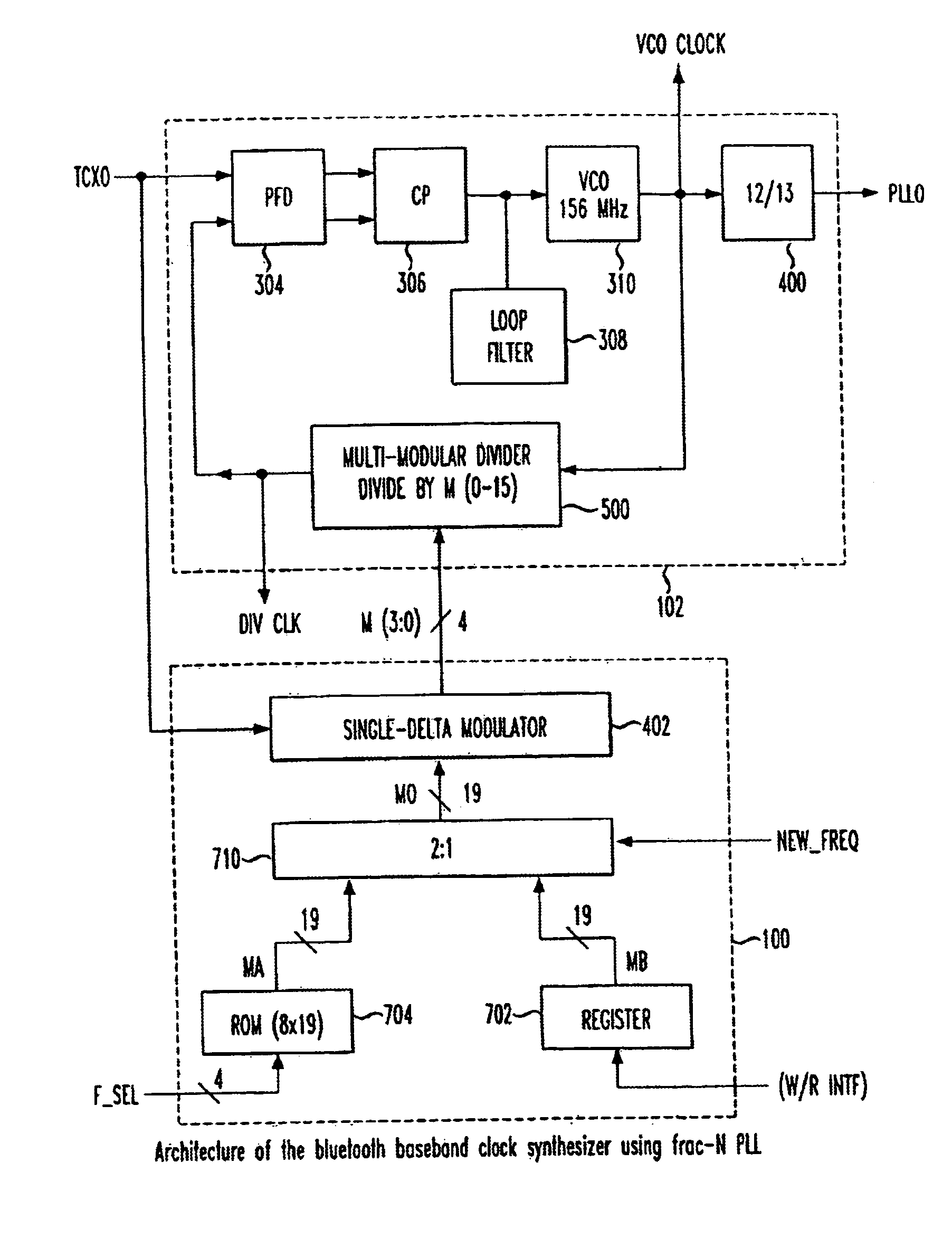
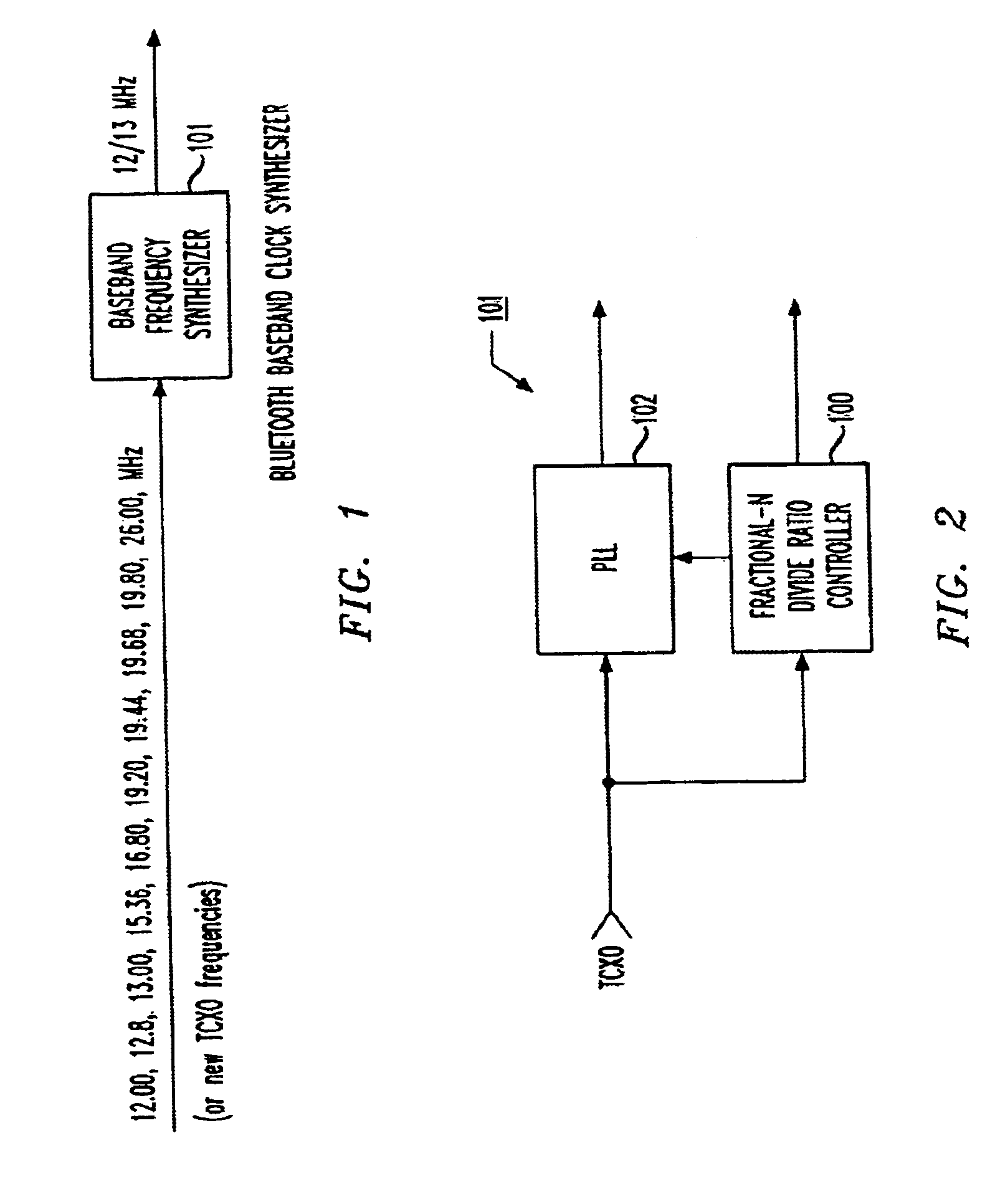
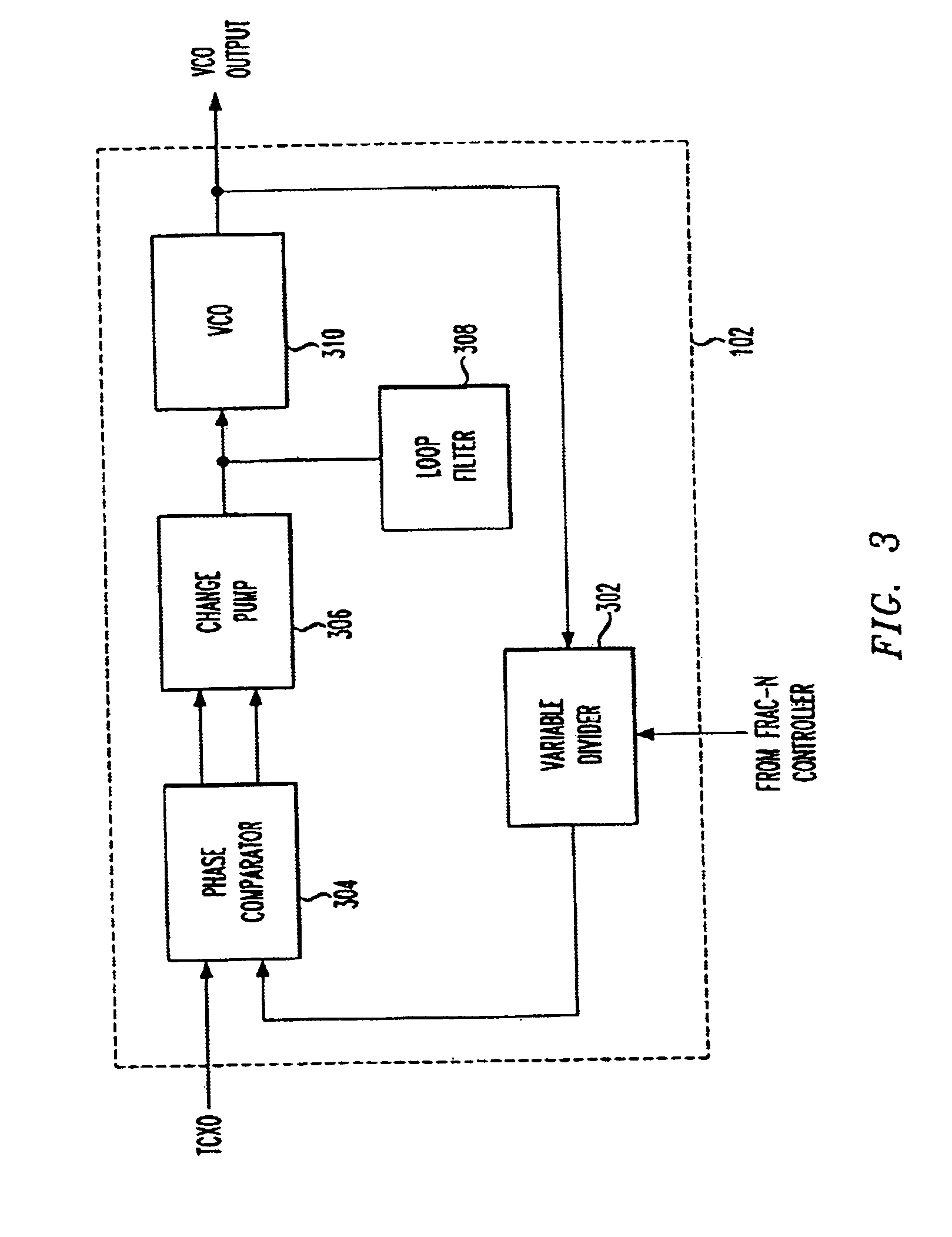
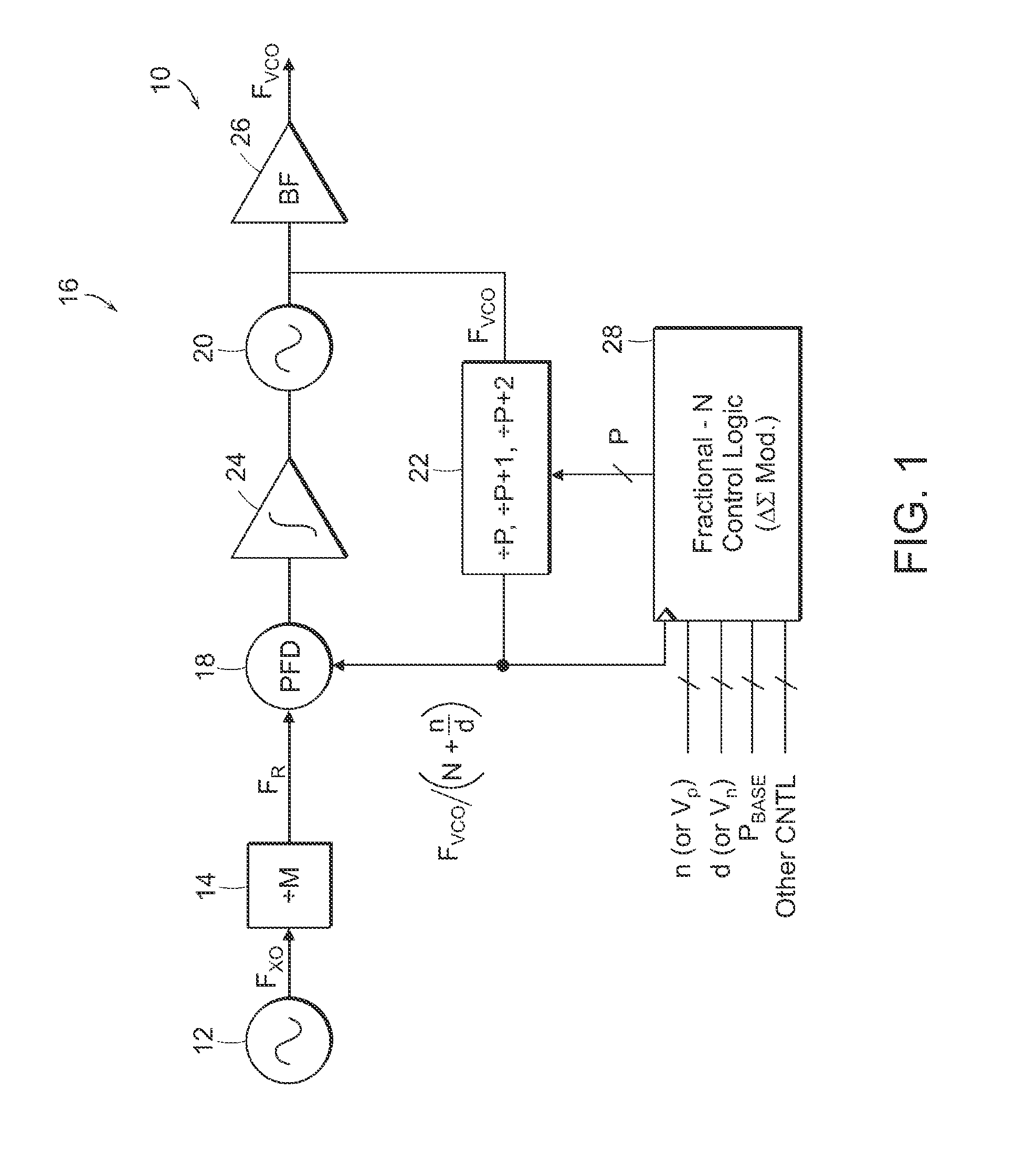
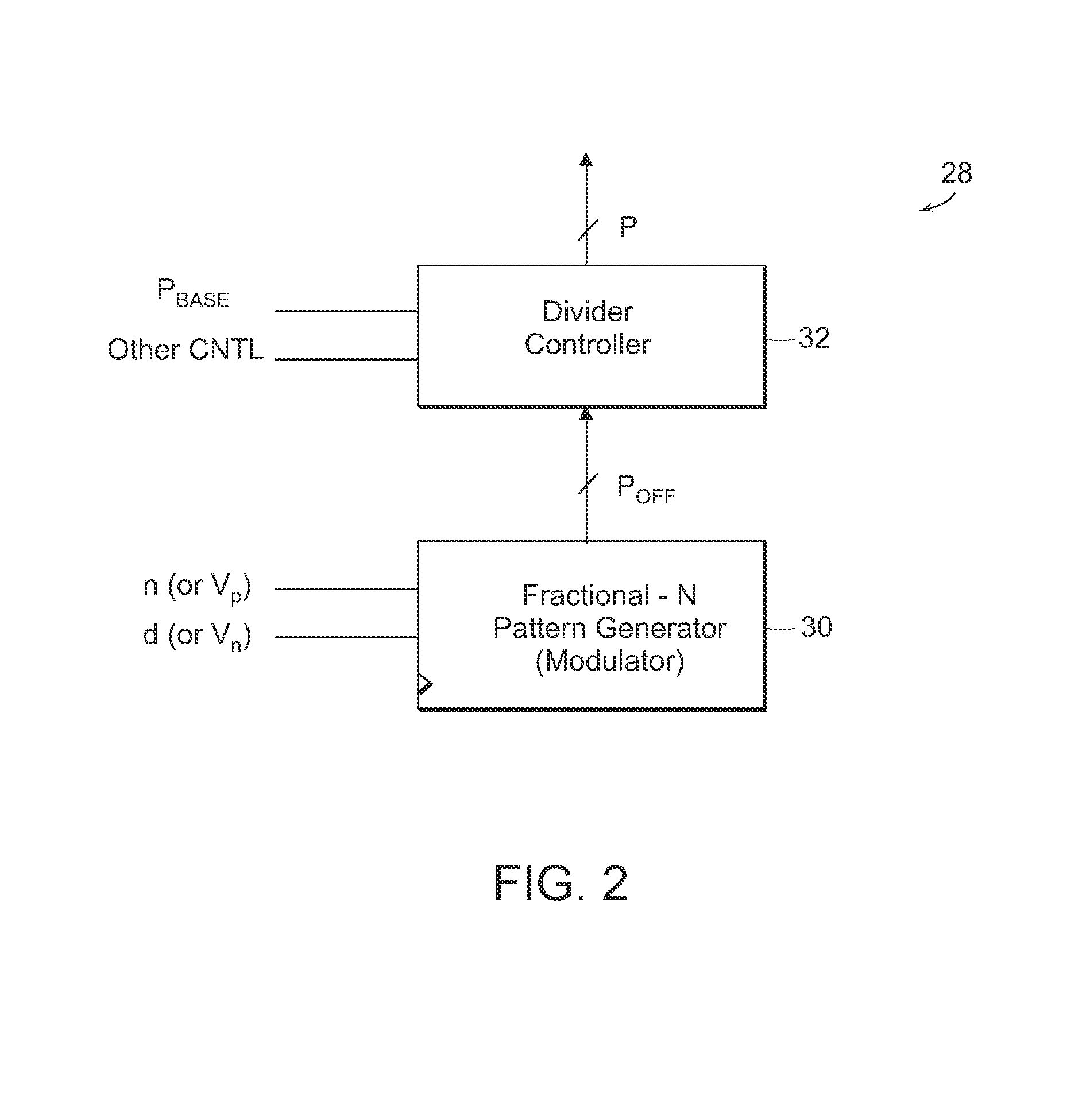
Fractional-N baseband frequency synthesizer in bluetooth applications
InactiveUS6946884B2Pulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersBluetooth piconetsFrequency synthesizer
A baseband clock synthesizer having particular use in a BLUETOOTH piconet device, having the capability of generating either 12 MHz or 13 MHz clock signals generated from any reference clock signal, e.g., 12.00, 12.80, 13.00, 15.36, 16.80, 19.20, 19.44, 19.68, 19.80, and 26.00 MHz. A fractional-N frequency divider is implemented with a PLL including a variable divider allowing the use of virtually any reference frequency input to generate a locked 156 MHz clock signal used as a basis for a 12 MHz or 13 MHz baseband clock signal. A residue feedback sigma-delta modulator provides a varying integer sequence to an integer divider in a feedback path of the PLL, effectively allowing division by non-integer numbers in the PLL. Thus, the PLL can be referenced to virtually any reference clock and still provide a fixed output clock signal (e.g., 12 or 13 MHz).
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Poly-phase frequency synthesis oscillator
ActiveUS20090066427A1Multiple-port networksComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersFrequency synthesisMultiple version
A frequency synthesis / multiplication circuit and method for multiplying the frequency of a reference signal. In one embodiment, multiple versions of the reference signal are generated having different phases relative to one another, and these multiple versions are combined to form an output signal having a frequency that is a multiple of the frequency of the reference signal.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Programmable frequency divider
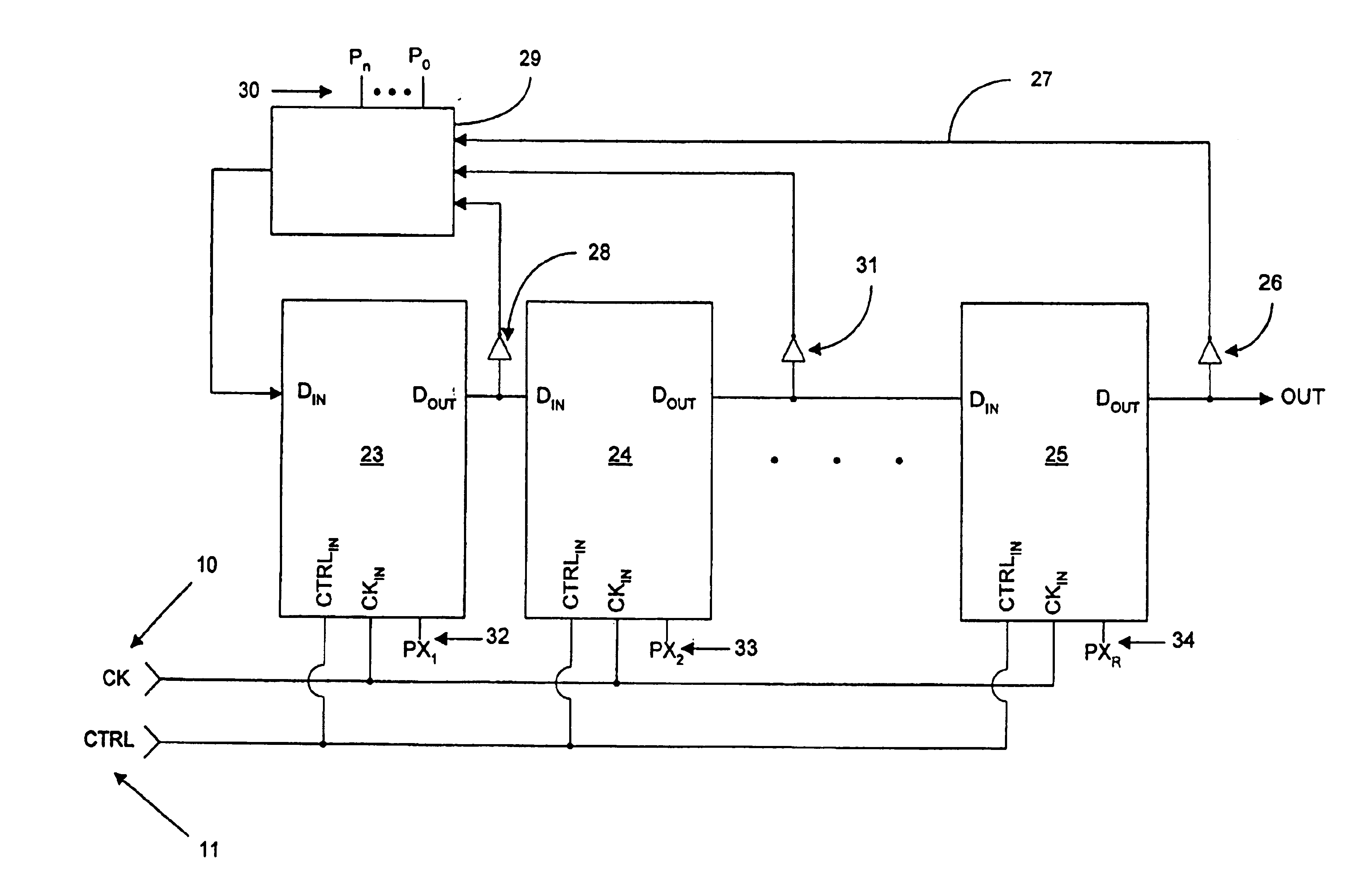
InactiveUS6970025B2Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageLoop inversionPower control
Various apparatus and method embodiments are disclosed. One apparatus embodiment, among others, comprises a frequency divider configured to provide an output signal having a period equal to a period of a clock signal multiplied by a programming division ratio, the frequency divider comprising a plurality of edge-triggered storage elements arranged in at least one loop, wherein each of the storage elements has a state, and a clock input, and wherein the state of each storage element is determined responsive to a transition of the clock input, the state, or the inverse thereof, of one or more previous storage elements in the loop, a characteristic of the division ratio, and the previous state, or the inverse thereof, of the storage element, and the output signal is derived from the state, or the inverse thereof, of at least one of the storage elements in the loop, a circuit for determining the number of storage elements in the loop responsive to the desired division ratio, and wherein the loop is configured such that there are odd number loop inversions within the loop, the loop inversions are implemented through inverters, and each of the storage elements is configured to enter a power save mode responsive to assertion of a power control signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
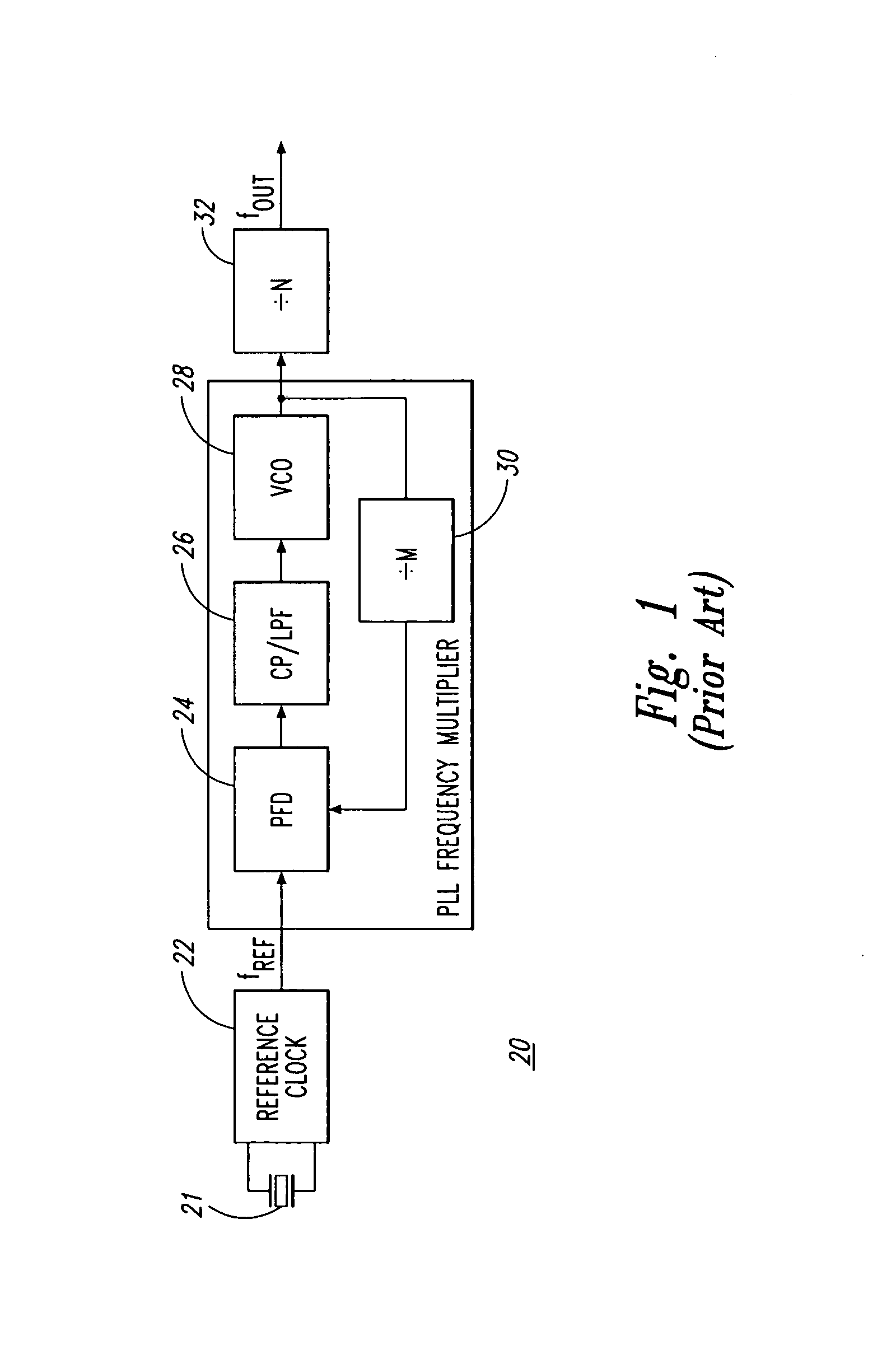
Clock control method, frequency dividing circuit and PLL circuit
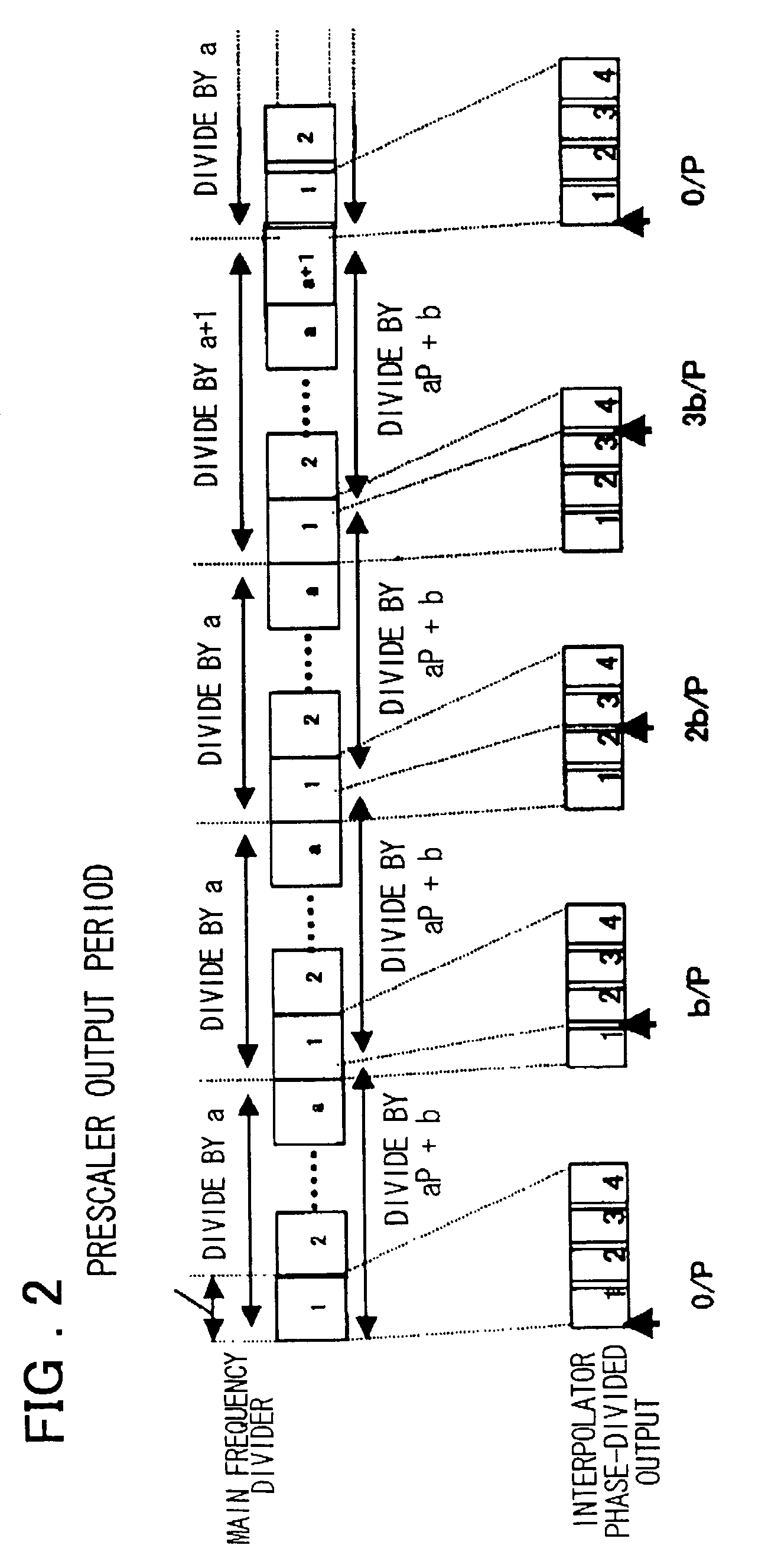
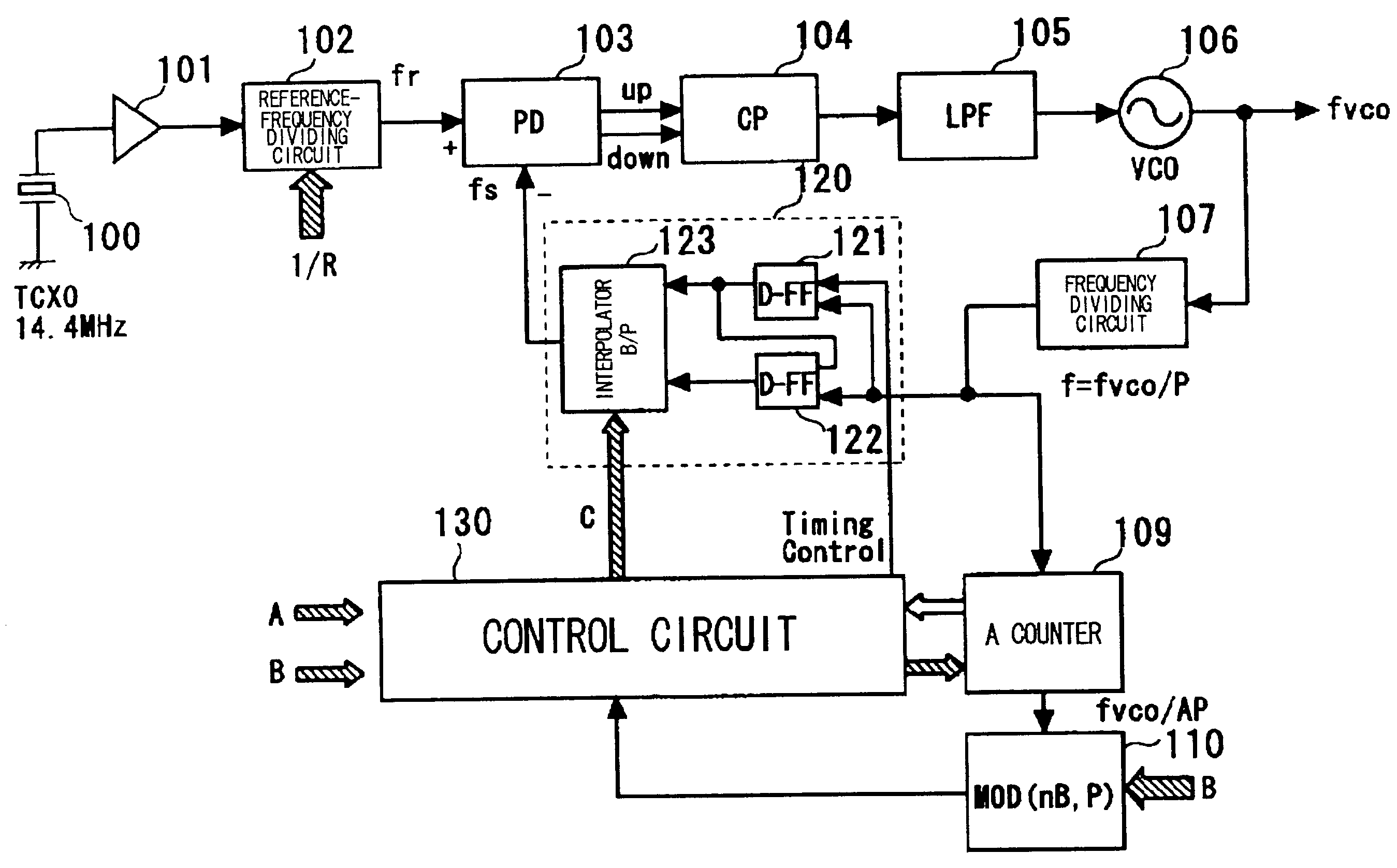
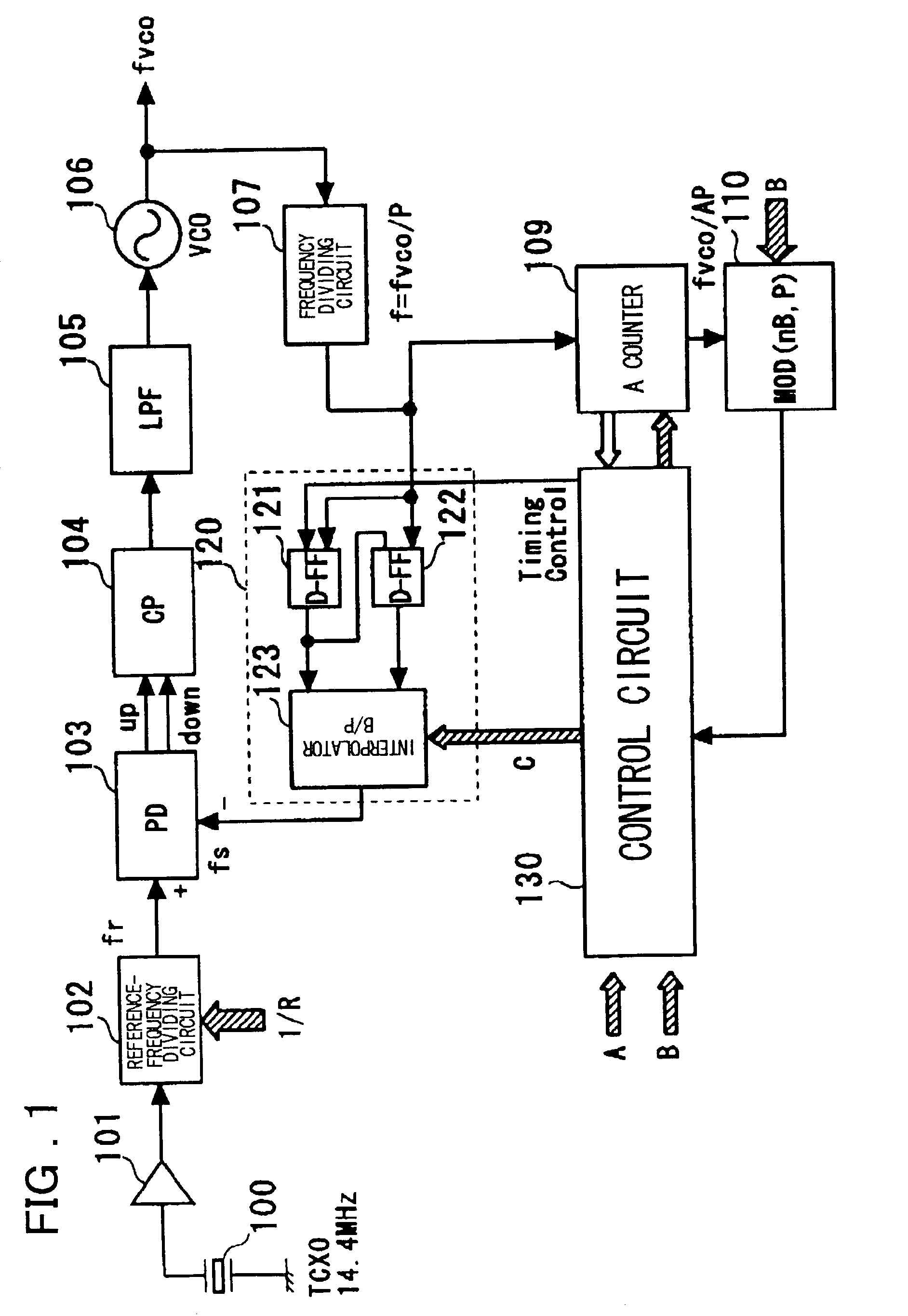
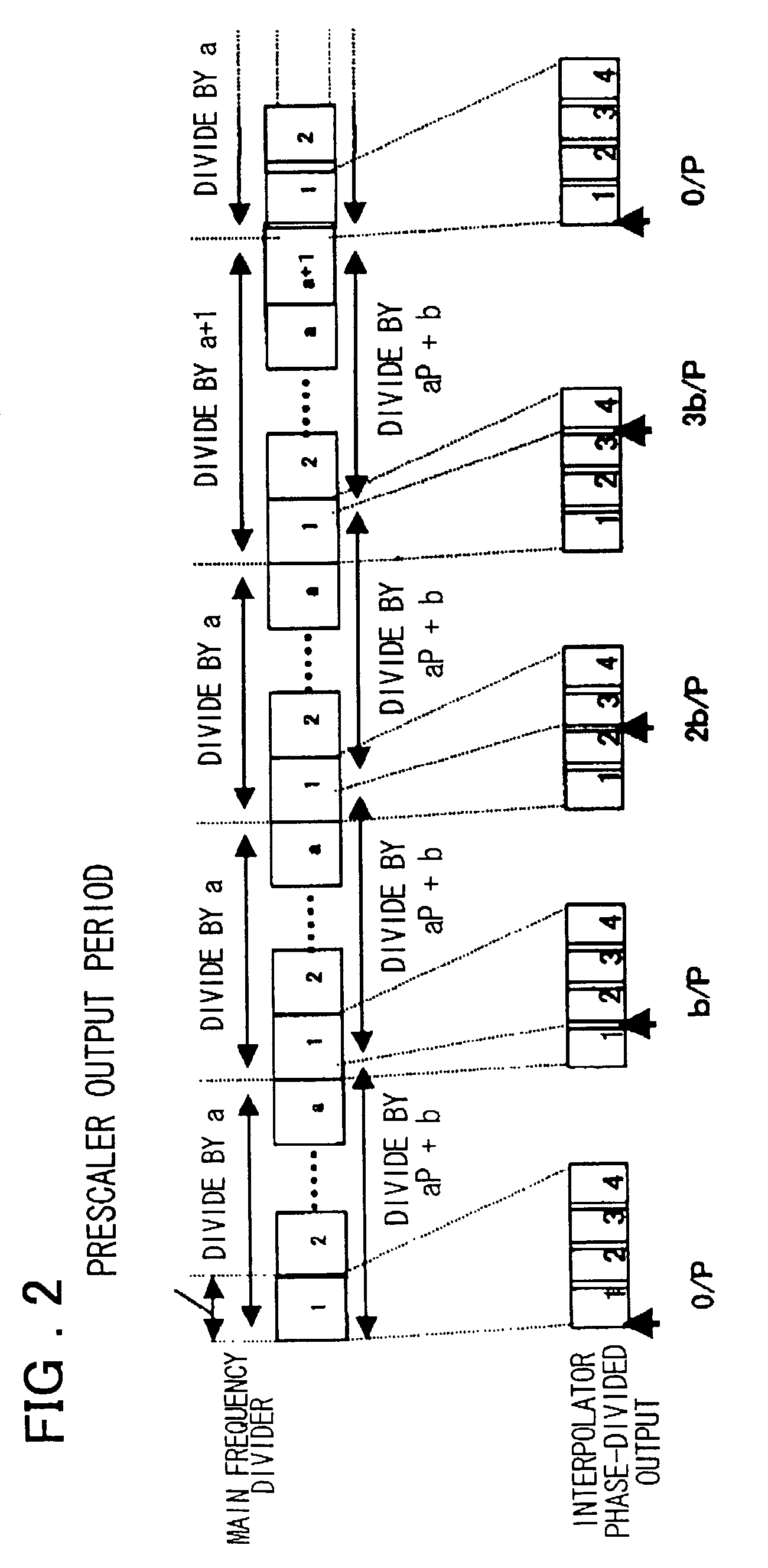
InactiveUS20030048863A1Reduce power consumptionTiming design is facilitatedPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersLoop filterDividing circuits
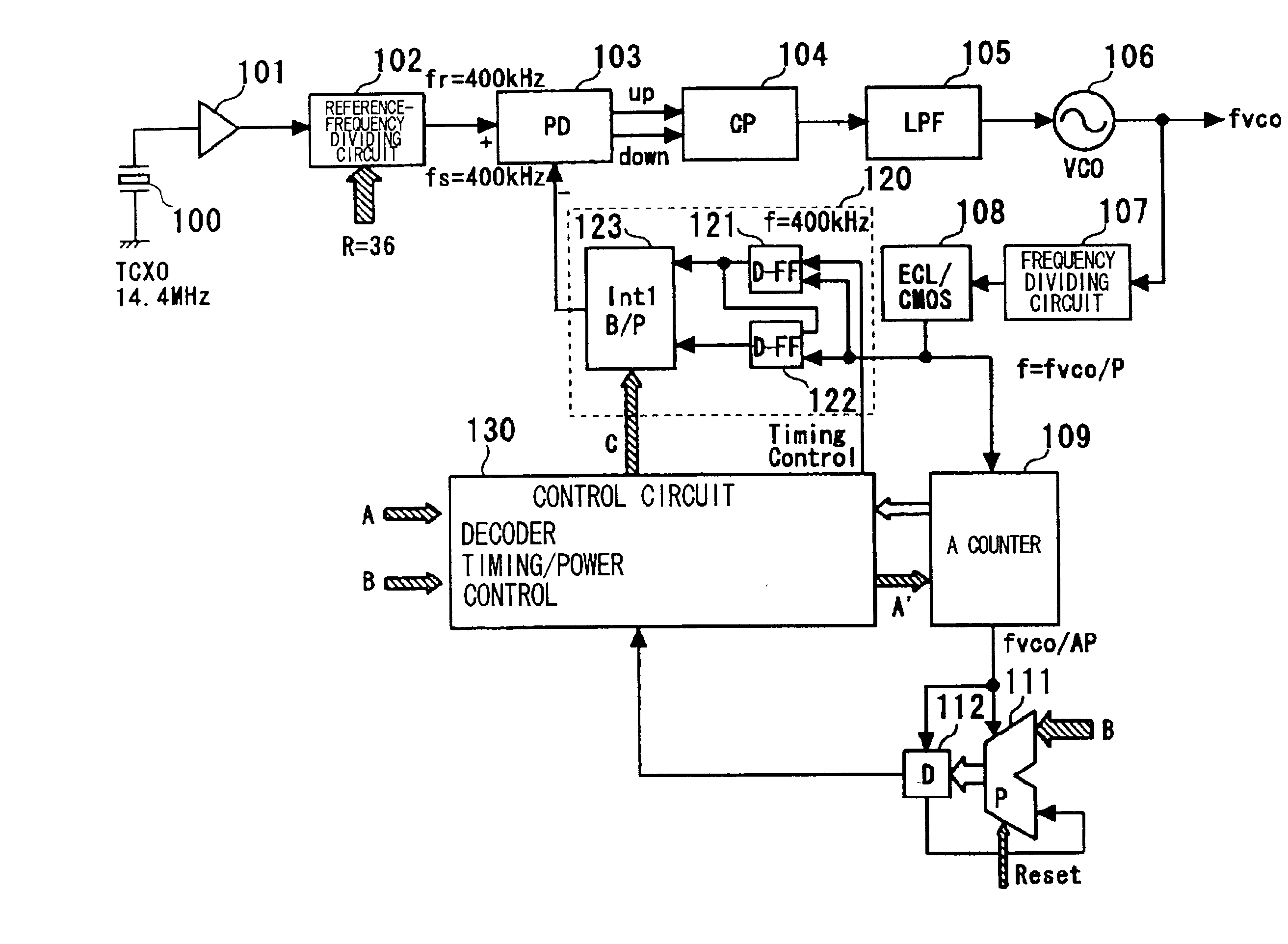
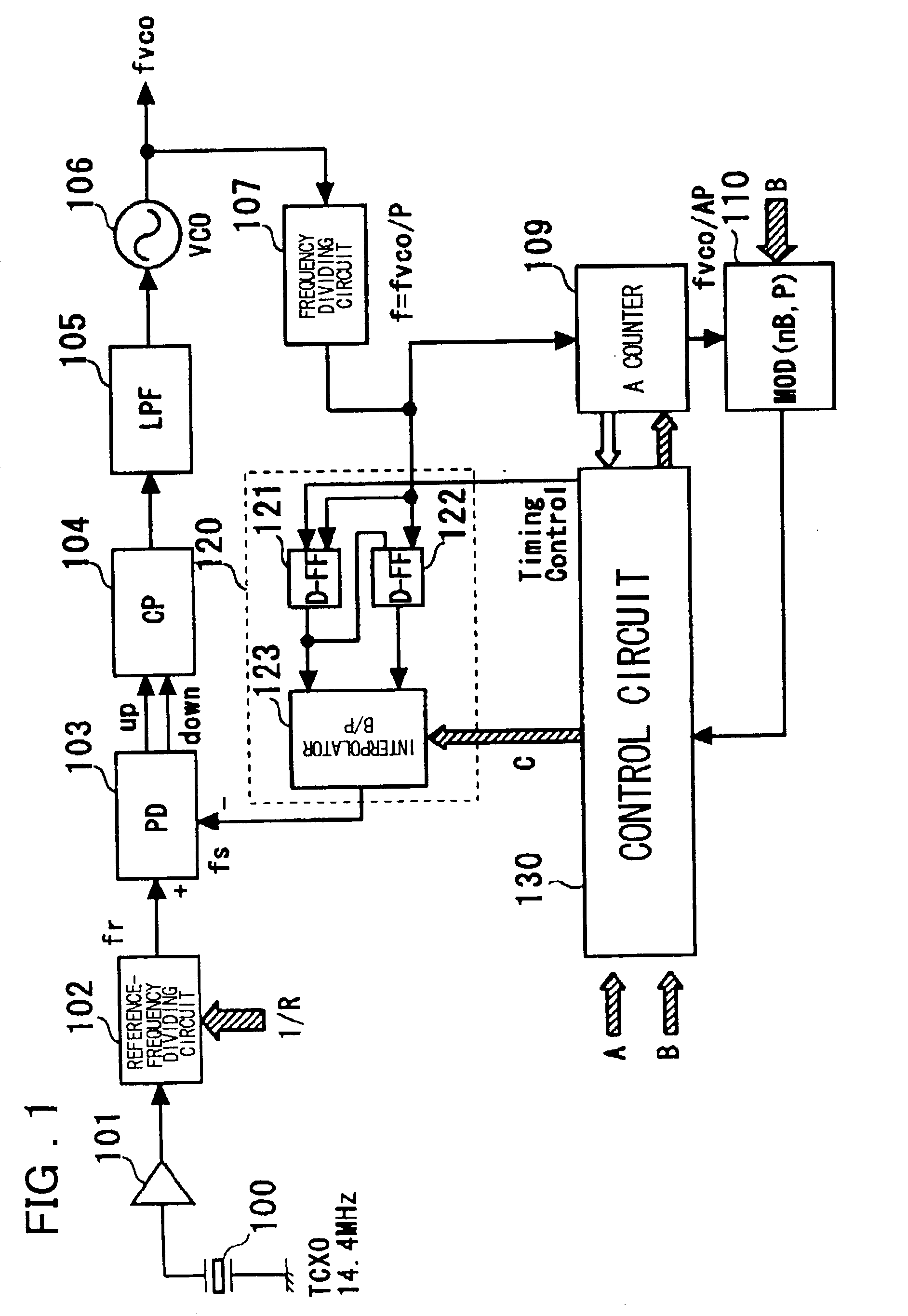
A PLL circuit includes a phase comparator; a charge pump; a loop filter; a voltage-controlled oscillator; a frequency dividing circuit; an A counter for dividing the P-frequency-divided output; circuits for generating two signals, which have a phase difference equivalent to one period of the P-frequency-divided output of the frequency dividing circuit; and an interpolator for producing an output signal obtained by interpolating the phase difference between the two signals in accordance with an interior division ratio. The interpolator interpolates in steps of a value obtained by dividing the phase difference by P and incrementing or decrementing a value B, which decides an interior division ratio B:P-B, by B whenever frequency-division by A is performed, and a control circuit. The phase of the output of the interpolator is fed to the phase comparator and compared with the phase of a reference clock, and divides by a frequency-dividing factor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Clock control method, frequency dividing circuit and PLL circuit
InactiveUS7054404B2Timing design is facilitatedReduce power consumptionPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersLoop filterPhase difference
A PLL circuit includes a phase comparator; a charge pump; a loop filter; a voltage-controlled oscillator; a frequency dividing circuit; an A counter for dividing the P-frequency-divided output; circuits for generating two signals, which have a phase difference equivalent to one period of the P-frequency-divided output of the frequency dividing circuit; and an interpolator for producing an output signal obtained by interpolating the phase difference between the two signals in accordance with an interior division ratio. The interpolator interpolates in steps of a value obtained by dividing the phase difference by P and incrementing or decrementing a value B, which decides an interior division ratio B:P−B, by B whenever frequency-division by A is performed, and a control circuit. The phase of the output of the interpolator is fed to the phase comparator and compared with the phase of a reference clock, and divides by a frequency-dividing factor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Clock controlling method and clock control circuit
InactiveUS6742133B2Simple structureComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersPulse duration/width modulationStart timePhase difference
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Clock controlling method and clock control circuit
InactiveUS20020059536A1Simple structurePulse automatic controlError detection/correctionStart timePhase difference
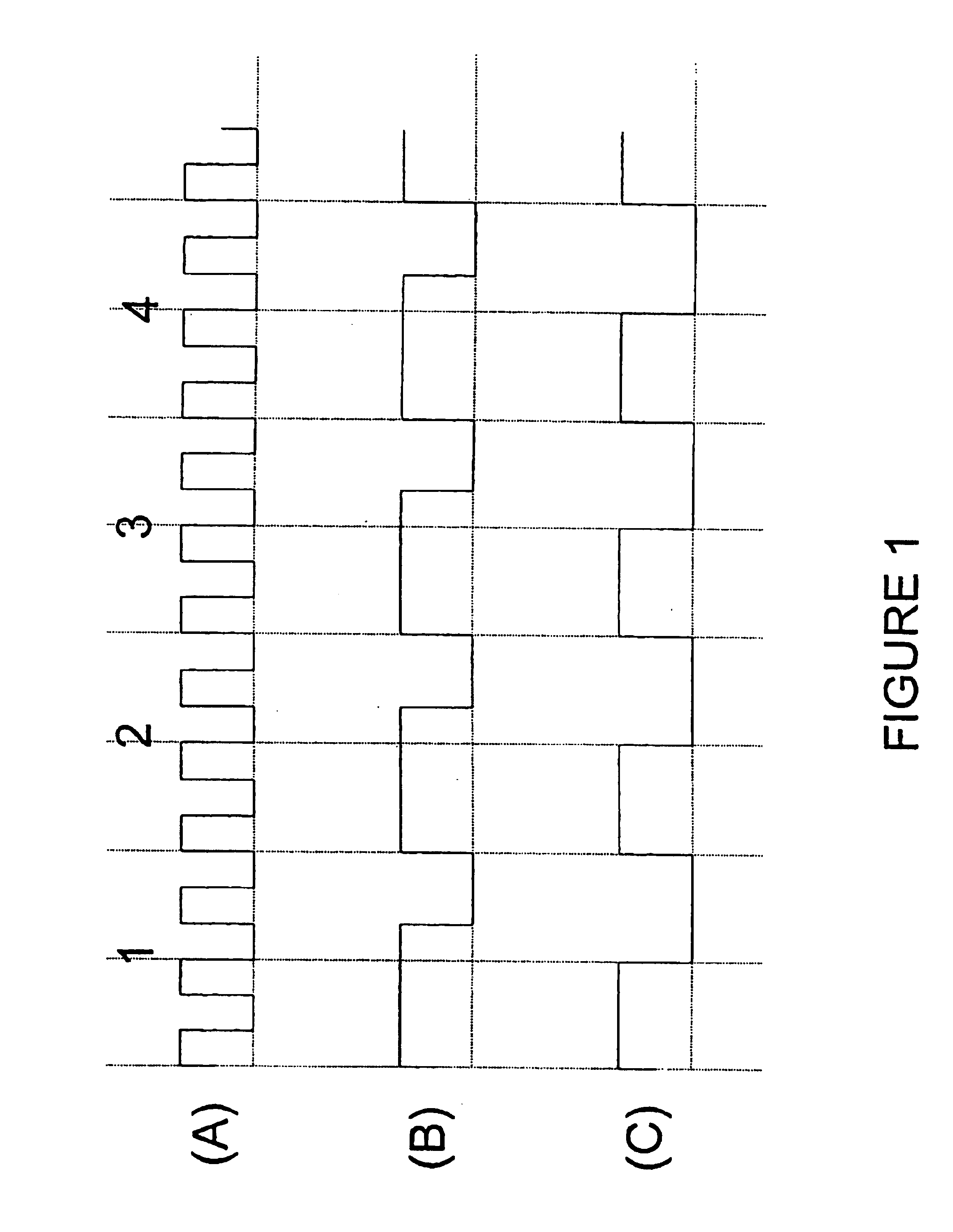
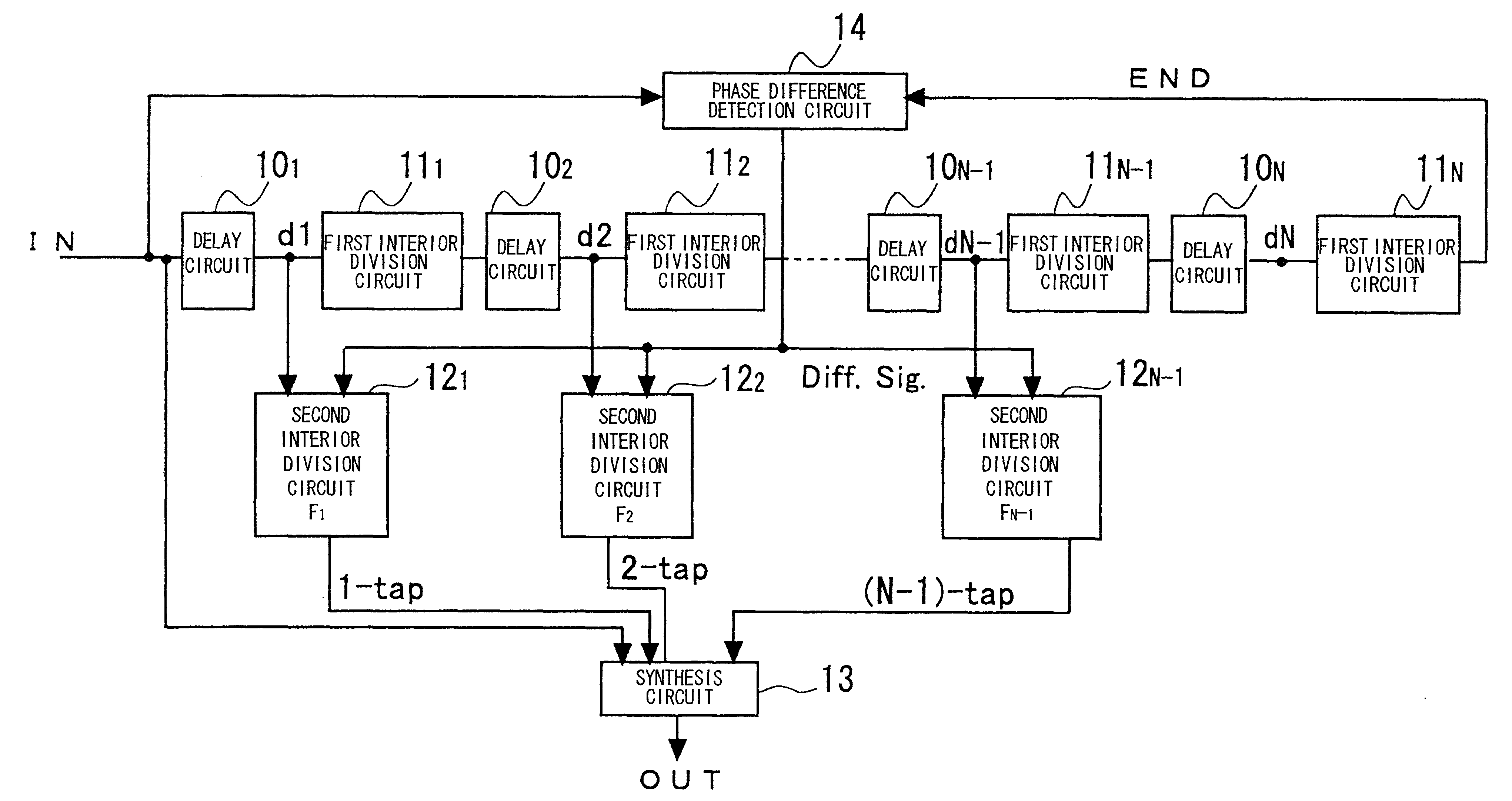
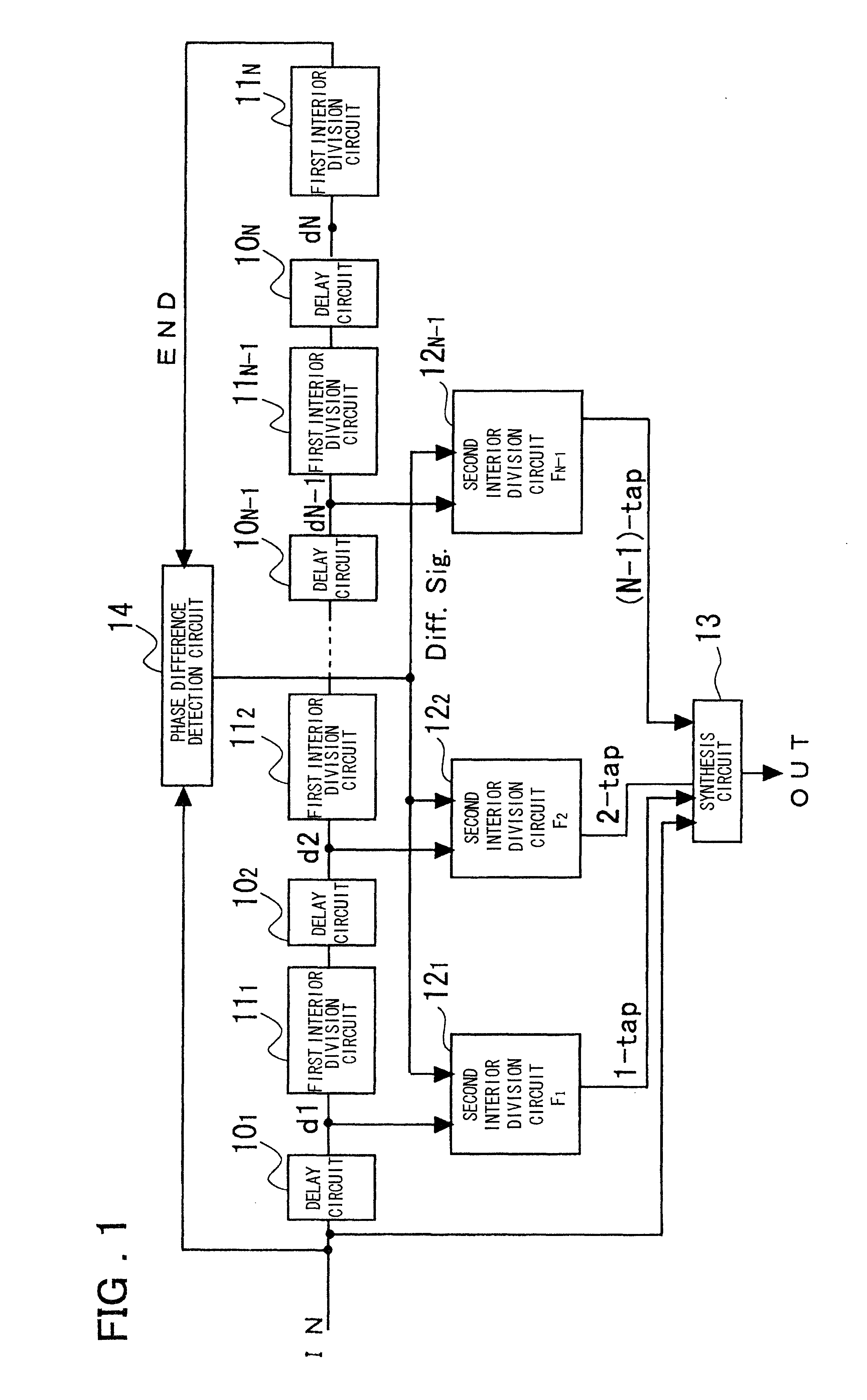
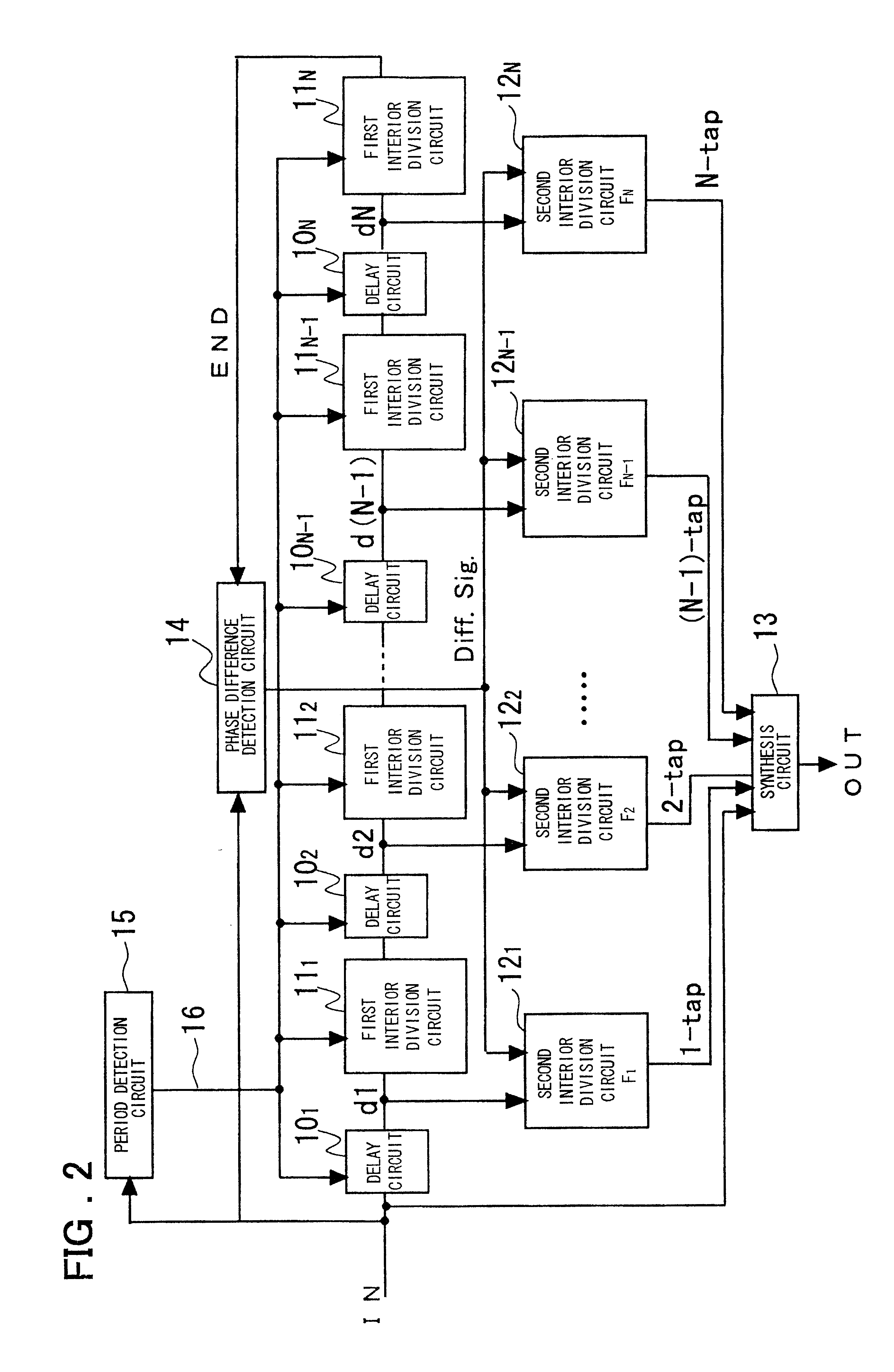
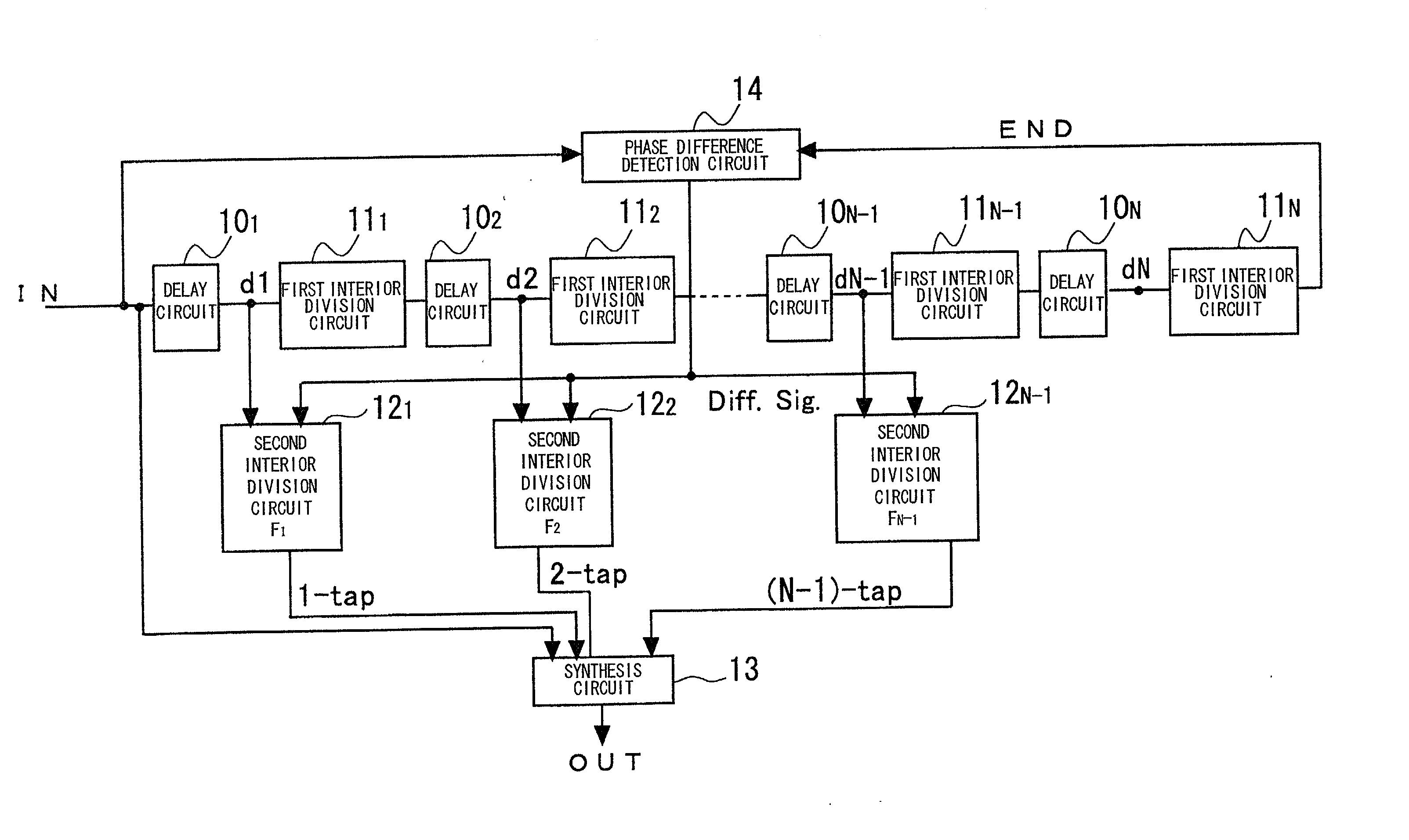
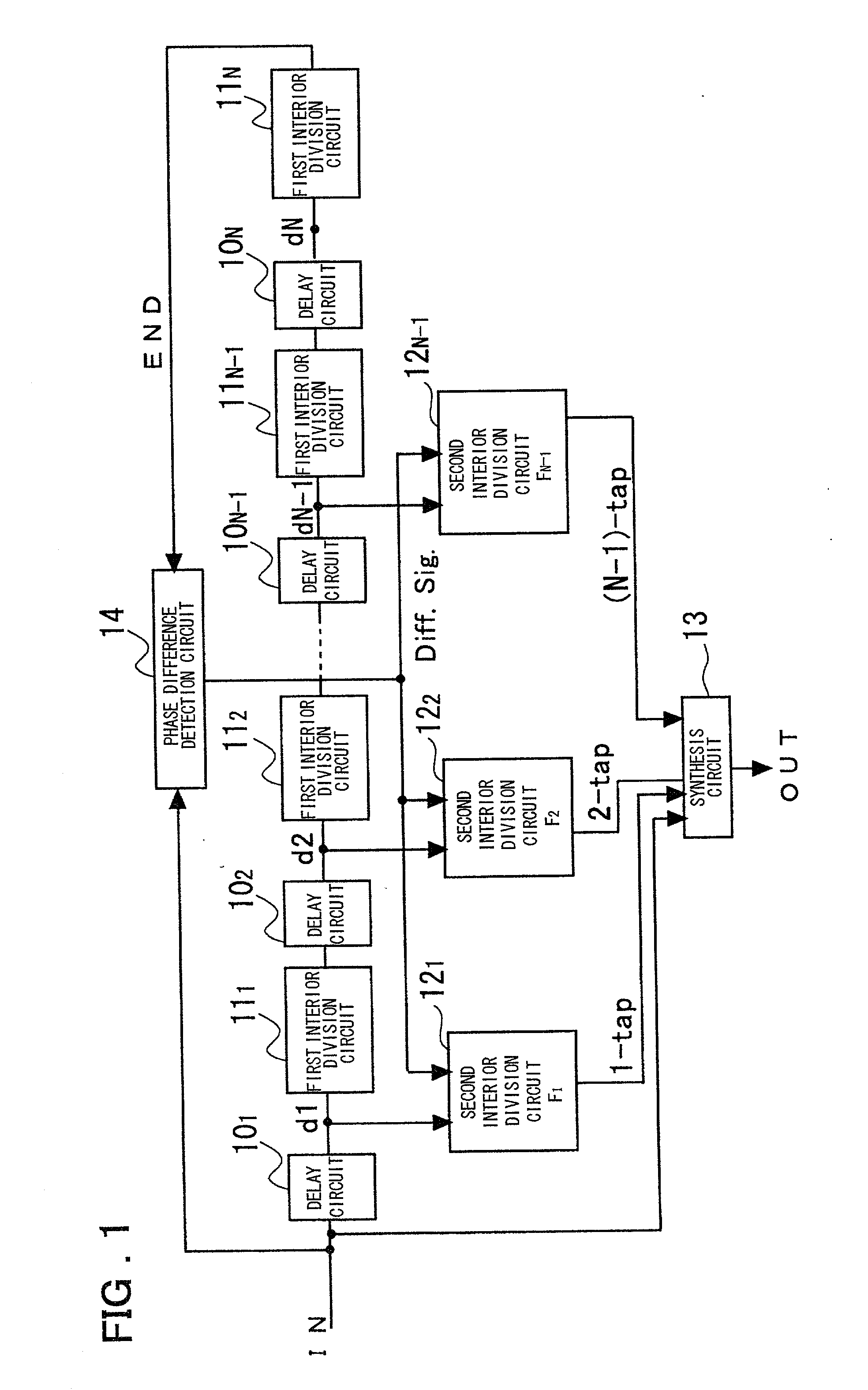
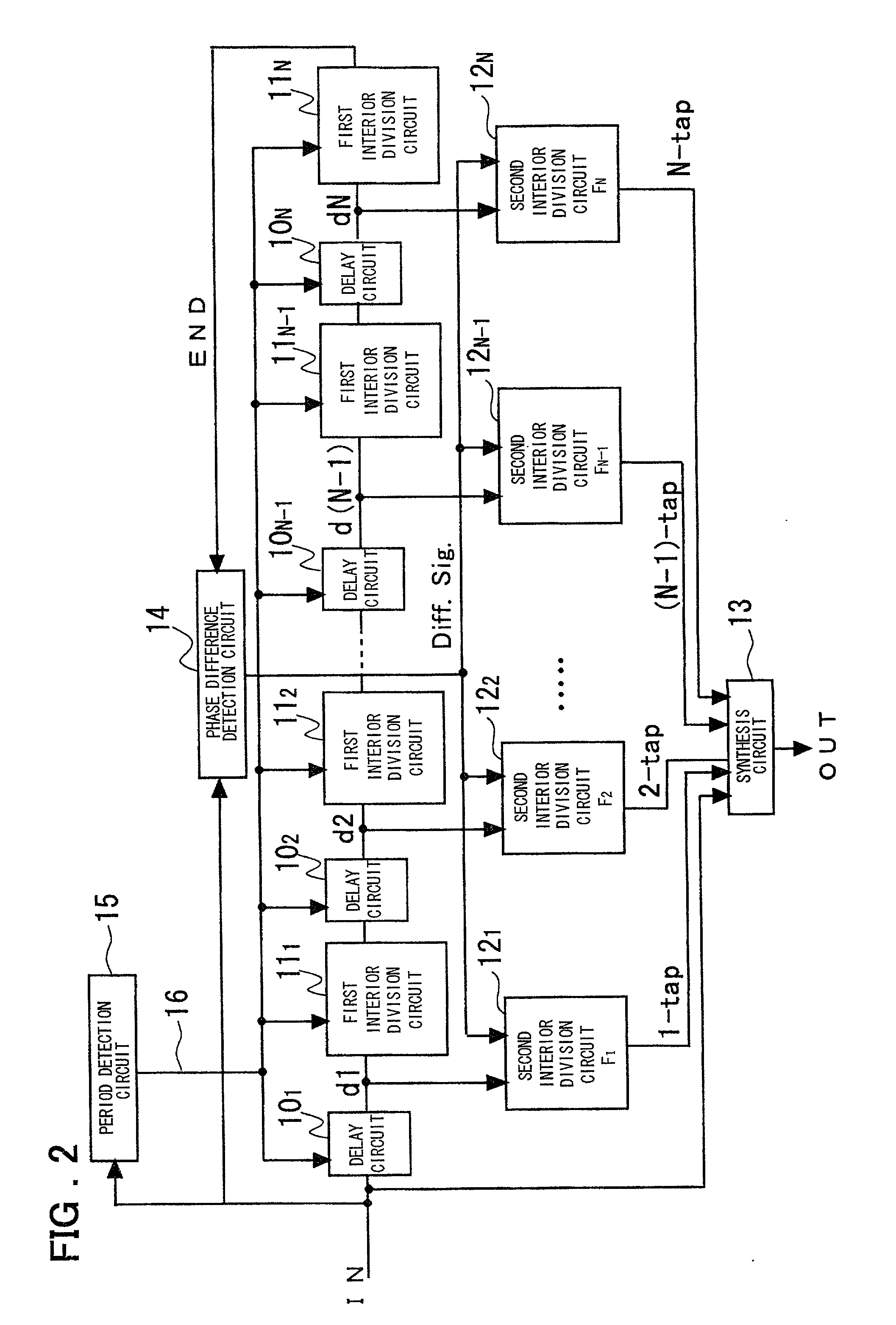
A novel clock control circuit and method in which phase synchronization with respect to an external clock can be realized without recourse to the external clocks. A clock controlling circuit includes a delay circuit sequence comprised of N stages of units each made up of a first delay circuit 10 and a first interior division circuit 11 for delaying the output signal of the first delay circuit, and a phase difference detection circuit 14 for detecting the clock period and the delay time difference of the delay circuit sequence from the input clock IN and a clock END output by the delay circuit sequence as a phase difference of the two signals. A plural number of second interior division circuits 12, fed with an output signal of the first delay circuit, delays a transition edge of an output signal of the first delay circuit by t2-nxT / N to output the delayed signal. The second interior division circuit outputs a signal which makes transition at a timing delayed nxtCK / N as from the start time point of the clock cycle. A synthesis circuit 13 generates a frequency multiplied clock signal which is obtained on equal division of the clock period tCK of the input clock from the input clock IN and the number 1 to numberN-1 third delays circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus and method for generating a distributed clock signal
InactiveUS7263149B2Minimize transfer latencyMaximize timePulse automatic controlComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersControl signalWaiting time
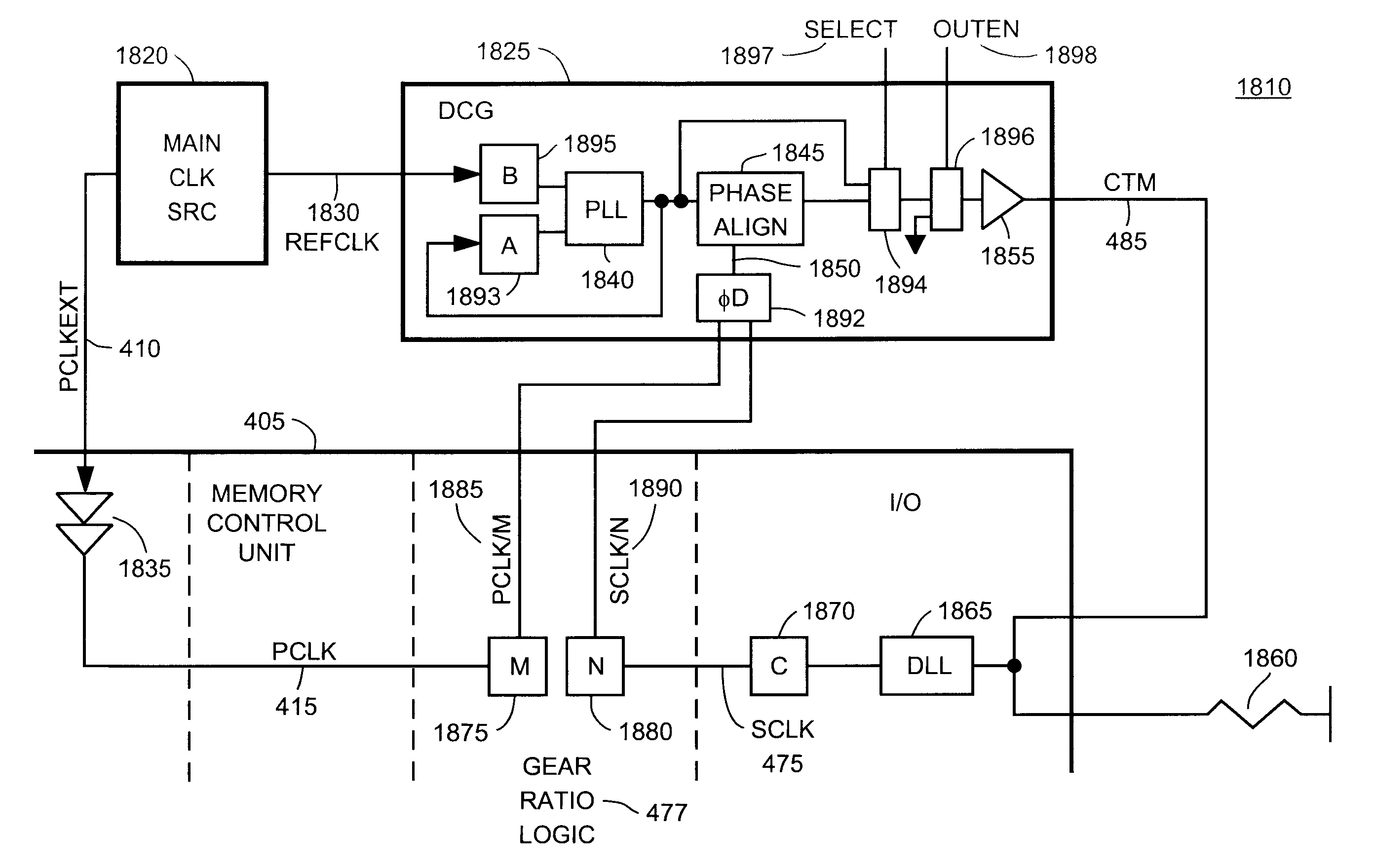
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for synchronizing signal transfers between two clock domains, where the clock domains have a gear ratio relationship. A gear ratio means that the clocks are related by a ratio, such that each clock has a different integer number of clock cycles in a common period. Also, in addition to a gear ratio relationship, the clocks may have a synchronized edge at the end of the common period. For each clock, the cycles in the common period are “colored”, i.e., identified by a number (1st, 2nd, etc.). By using the coloring technique, the appropriate clock edge to perform a data or control signal transfer can be identified. The edges are preferably chosen to minimize the latency of the transfer.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Frequency synthesizer, coupled divide-by-N circuit, current-reuse multiply-by-M circuit
InactiveUS7671635B2Reduce a mismatch generatedPulse automatic controlCounting chain synchronous pulse countersFrequency mixerFrequency synthesizer
A frequency synthesizer is provided in the present invention. The frequency synthesizer includes a single phase-locked loop having a reference frequency signal input, a first output, a second output and a pair of divide-by-N circuits coupled with each other and electrically connected to the second output; a multiply-by-M circuit having a first input electrically connected to the first output and a third output; and a combination of a buffer and a mixer having a second input electrically connected to the second output and a third input electrically connected to the third output generating a frequency signal output.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Frequency Multiplying Transceiver
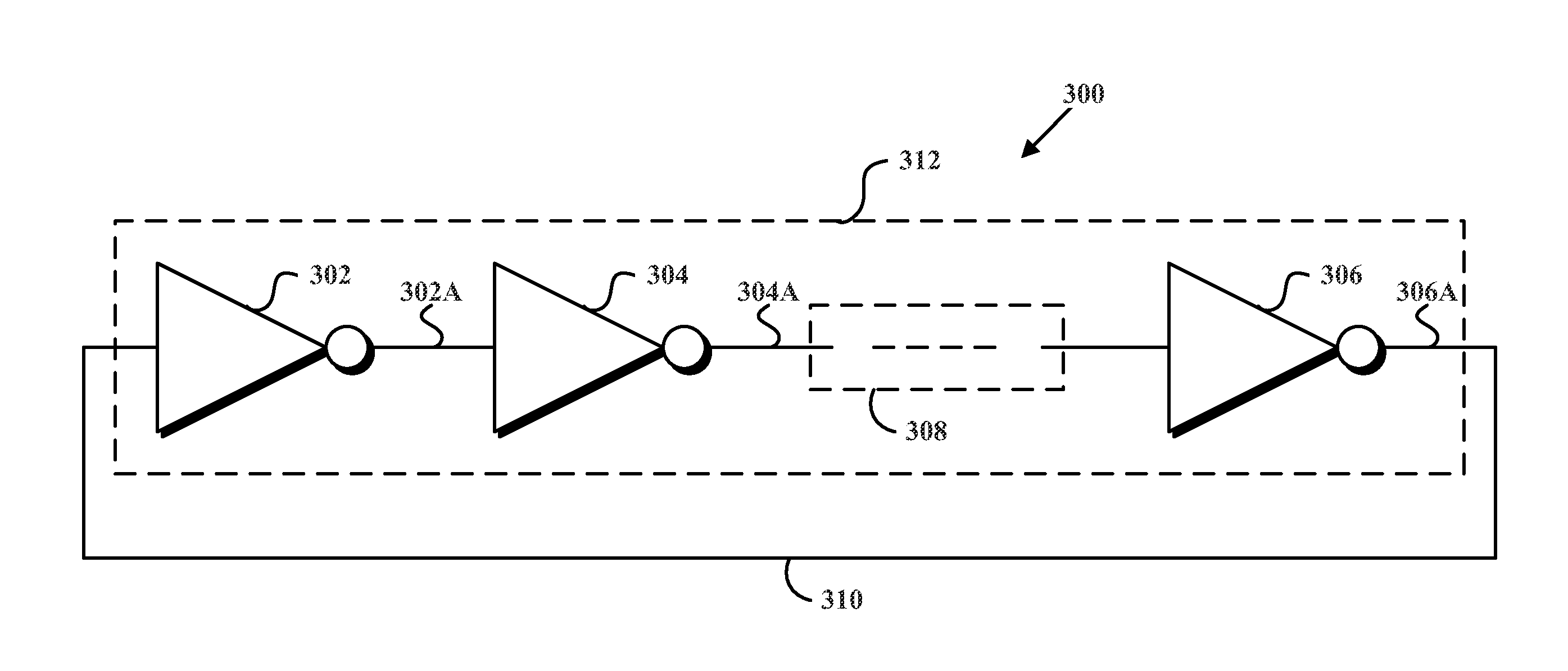
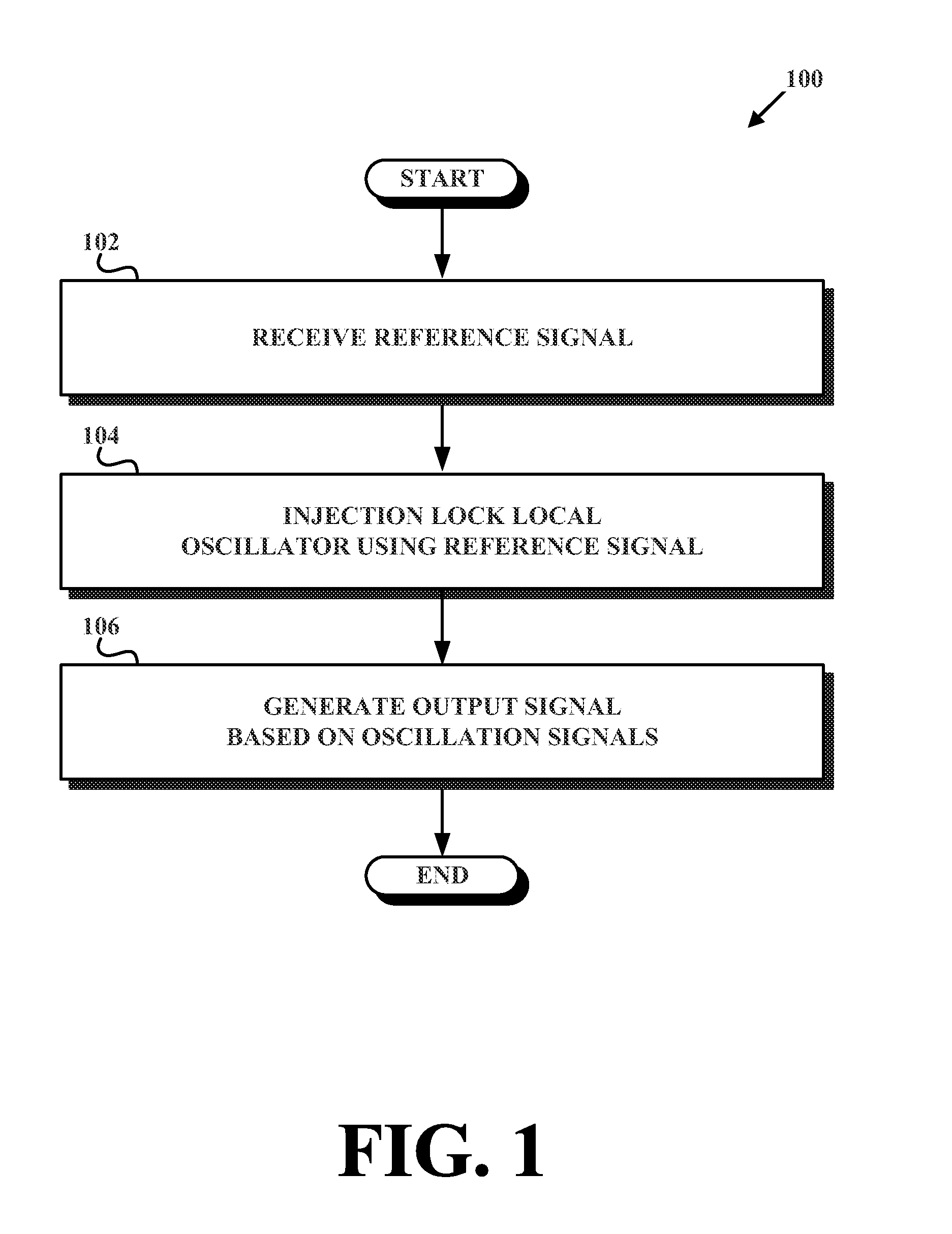
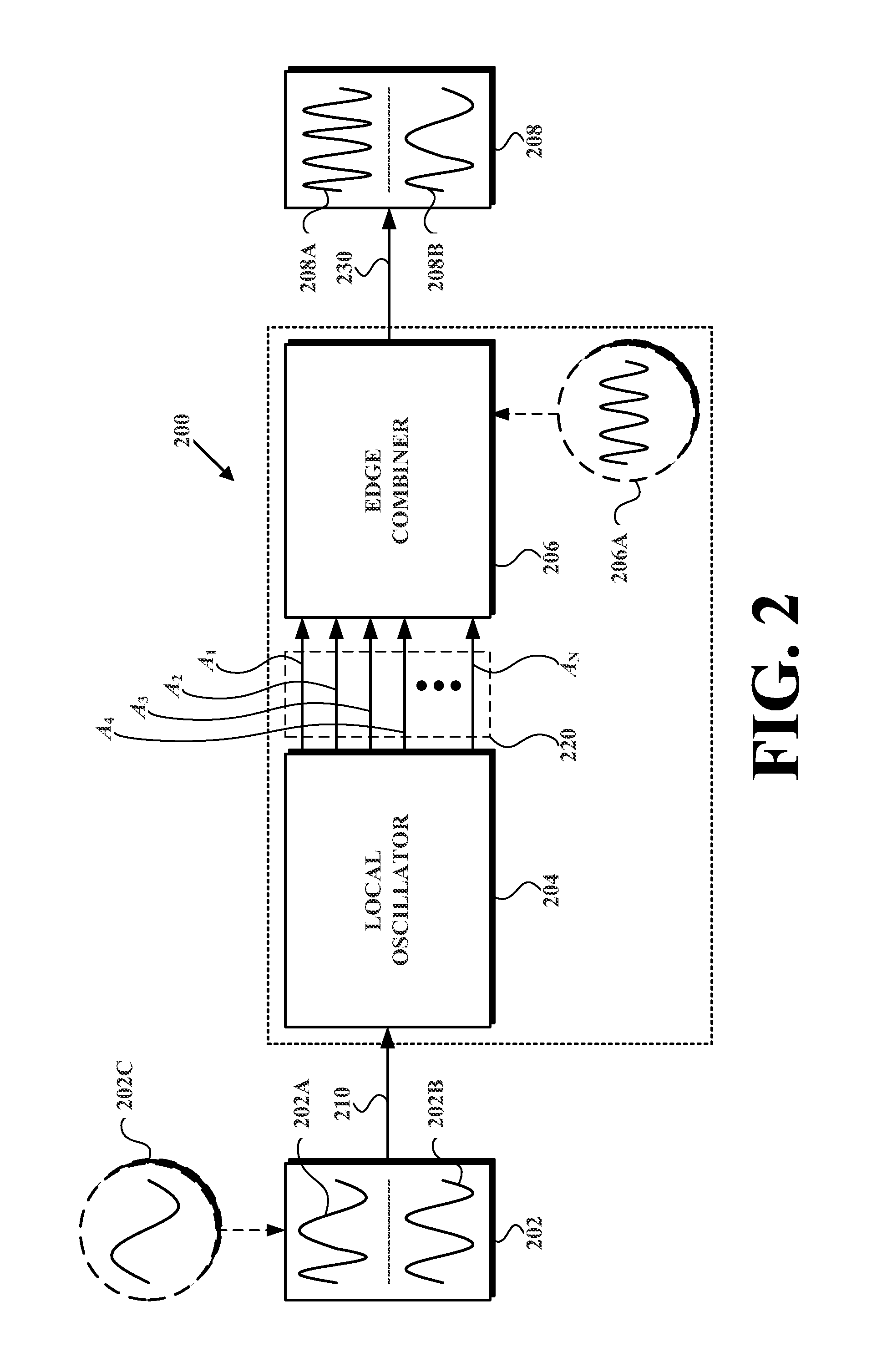
InactiveUS20130058384A1Low Power TransmissionSmall sizePulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInjection lockedElectric power transmission
Described herein is a wireless transceiver and related method that enables ultra low power transmission and reception of wireless communications. In an example embodiment of the wireless transceiver, the wireless transceiver receives a first-reference signal having a first-reference frequency. The wireless transceiver then uses the first-reference signal to injection lock a local oscillator, which provides a set of oscillation signals each having an oscillation frequency that is equal to the first-reference frequency, and each having equally spaced phases. Then the wireless transceiver combines the set of oscillation signals into an output signal having an output frequency that is one of (i) a multiple of the first-reference frequency (in accordance with a transmitter implementation) or (ii) a difference of (a) a second-reference frequency of a second-reference signal and (b) a multiple of the first- reference frequency (in accordance with a receiver implementation).
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
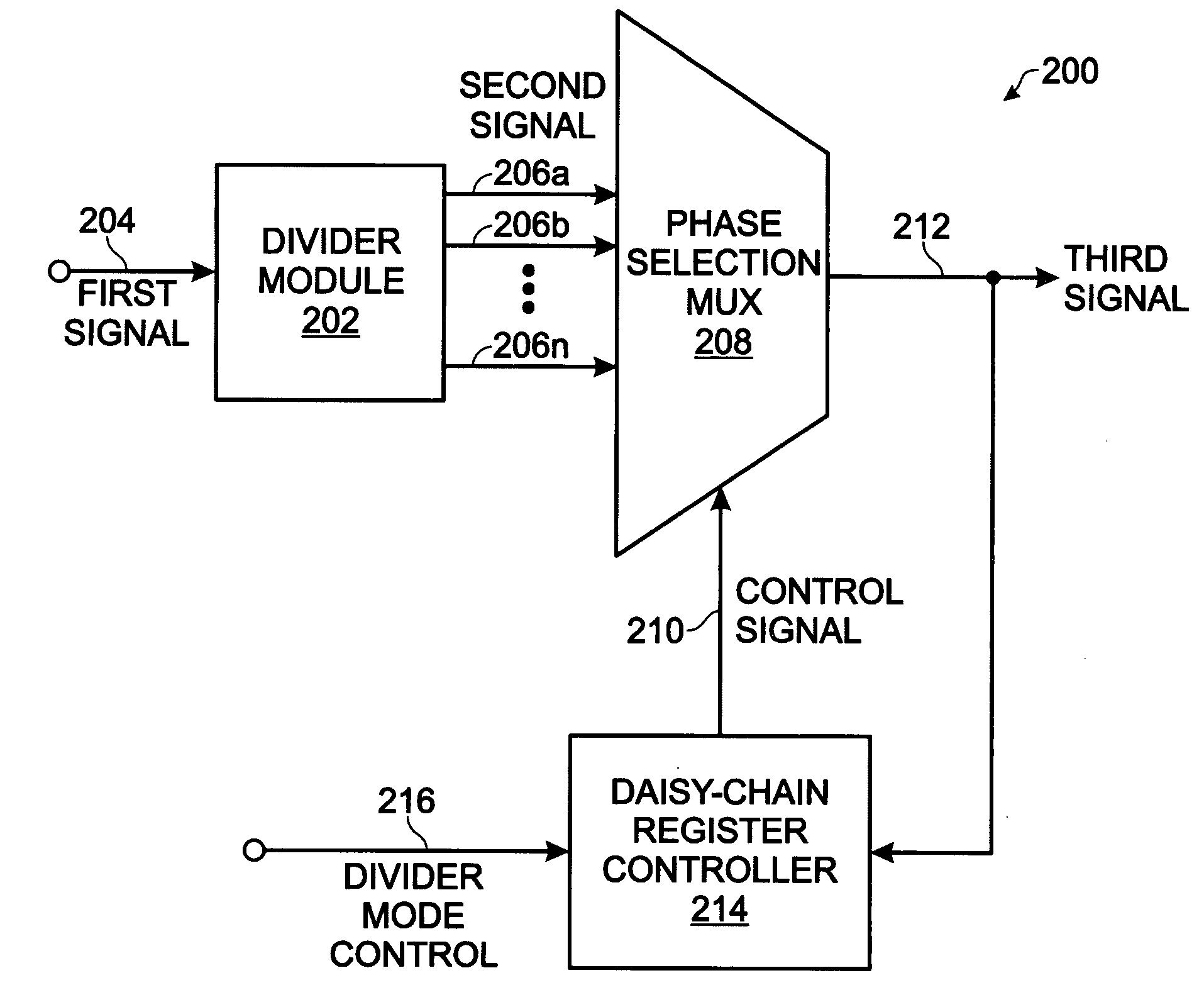
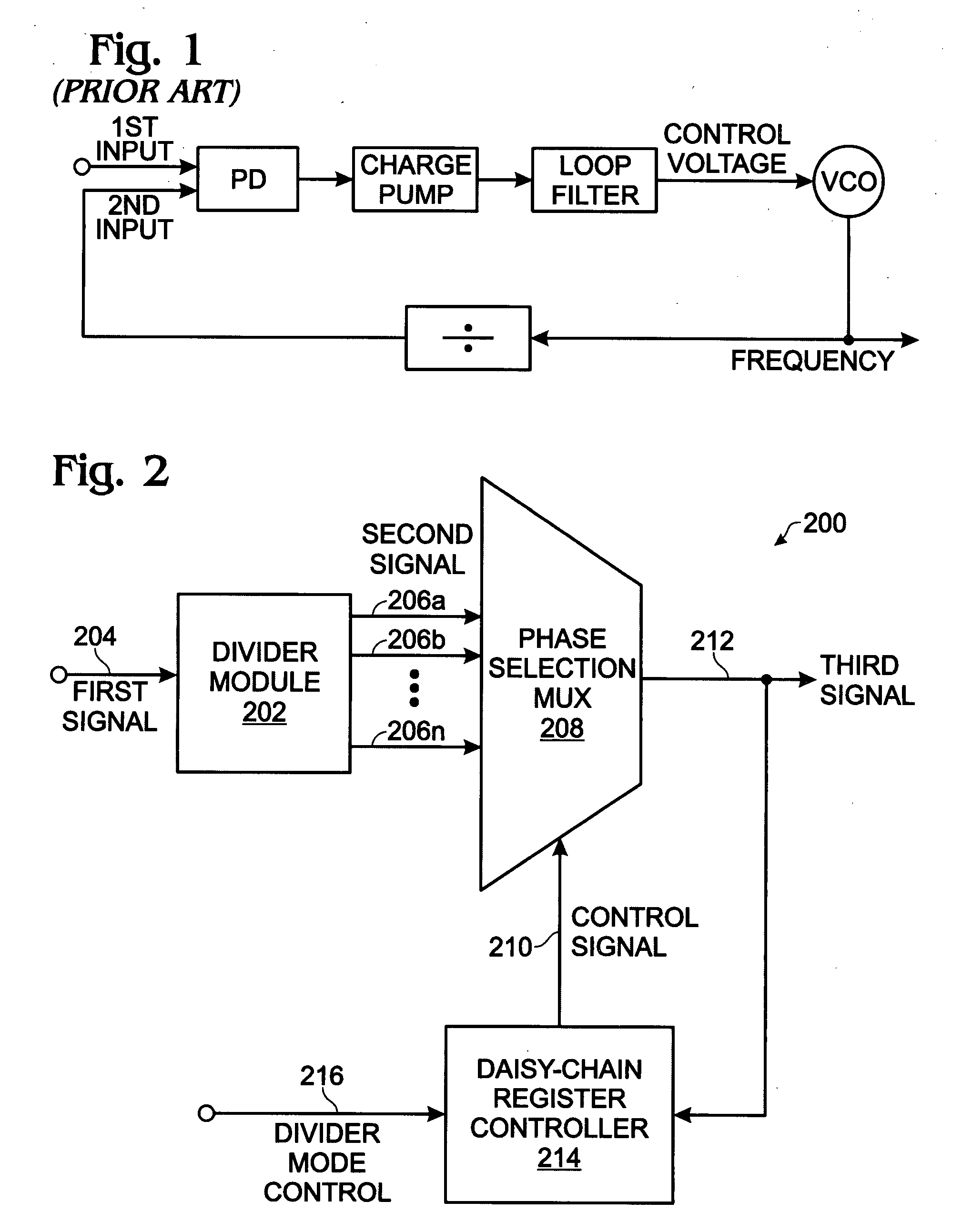
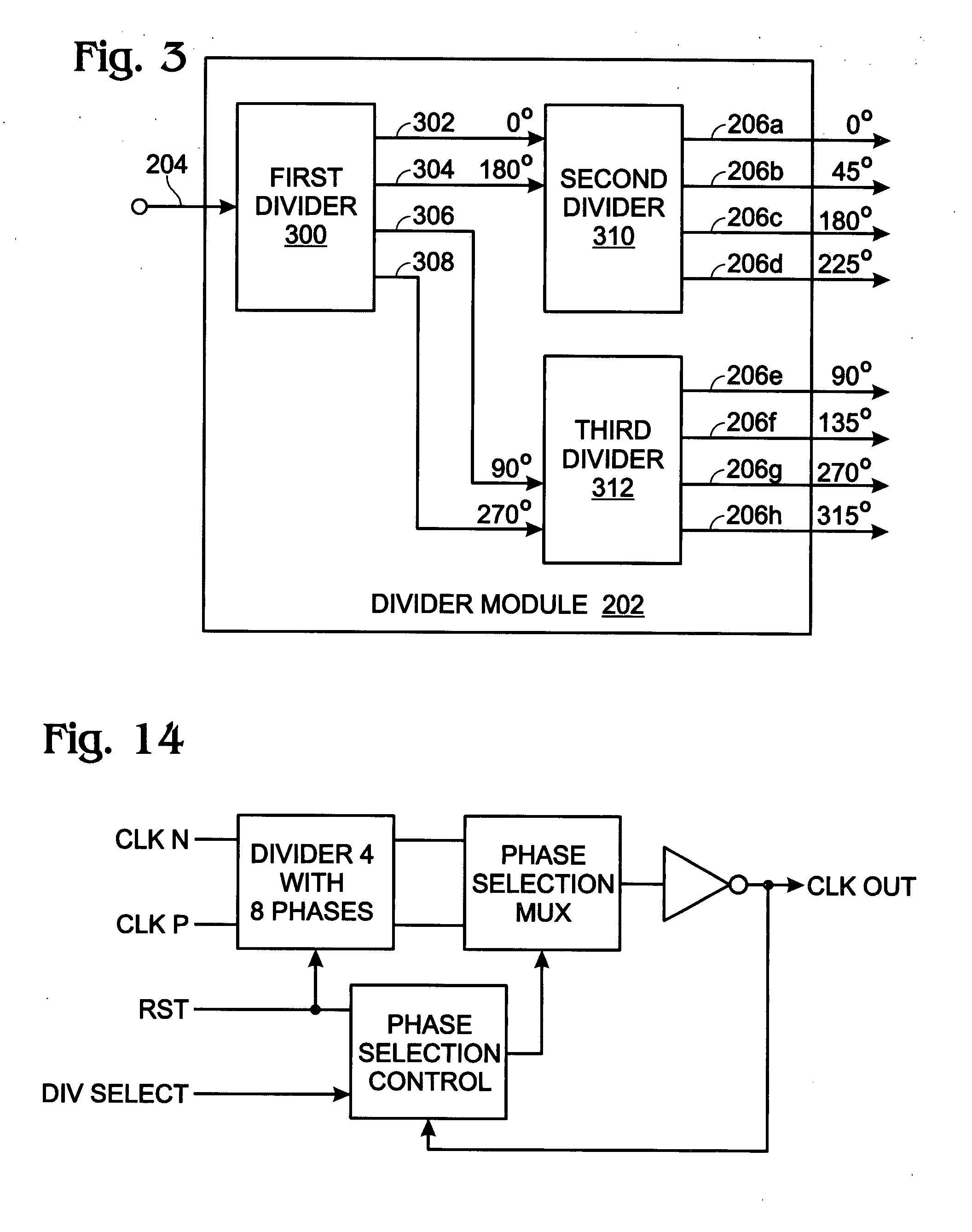
High speed multi-modulus prescalar divider
ActiveUS20080225989A1Reduce the amount of powerHigh input signalPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersProcessor registerClock signal
A system and method are provided for multi-modulus division. The method accepts an input first signal having a first frequency and divides the first frequency by an integral number. A second signal is generated with a plurality of phase outputs, each having a second frequency. Using a daisy-chain register controller, phase outputs are selected and supplied as a third signal with a frequency. Selecting phase outputs using the daisy-chain register controller includes supplying the third signal as a clock signal to registers having outputs connected in a daisy-chain. Then, a sequence of register output pulses is generated in response to the clock signals, and register output pulses are chosen from the sequence to select second signal phase outputs. By using 8-second signal phase outputs, a third signal is obtained with a frequency equal to the second frequency multiplied by one of the following numbers: 0.75, 0.875, 1, 1.125, or 1.25.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
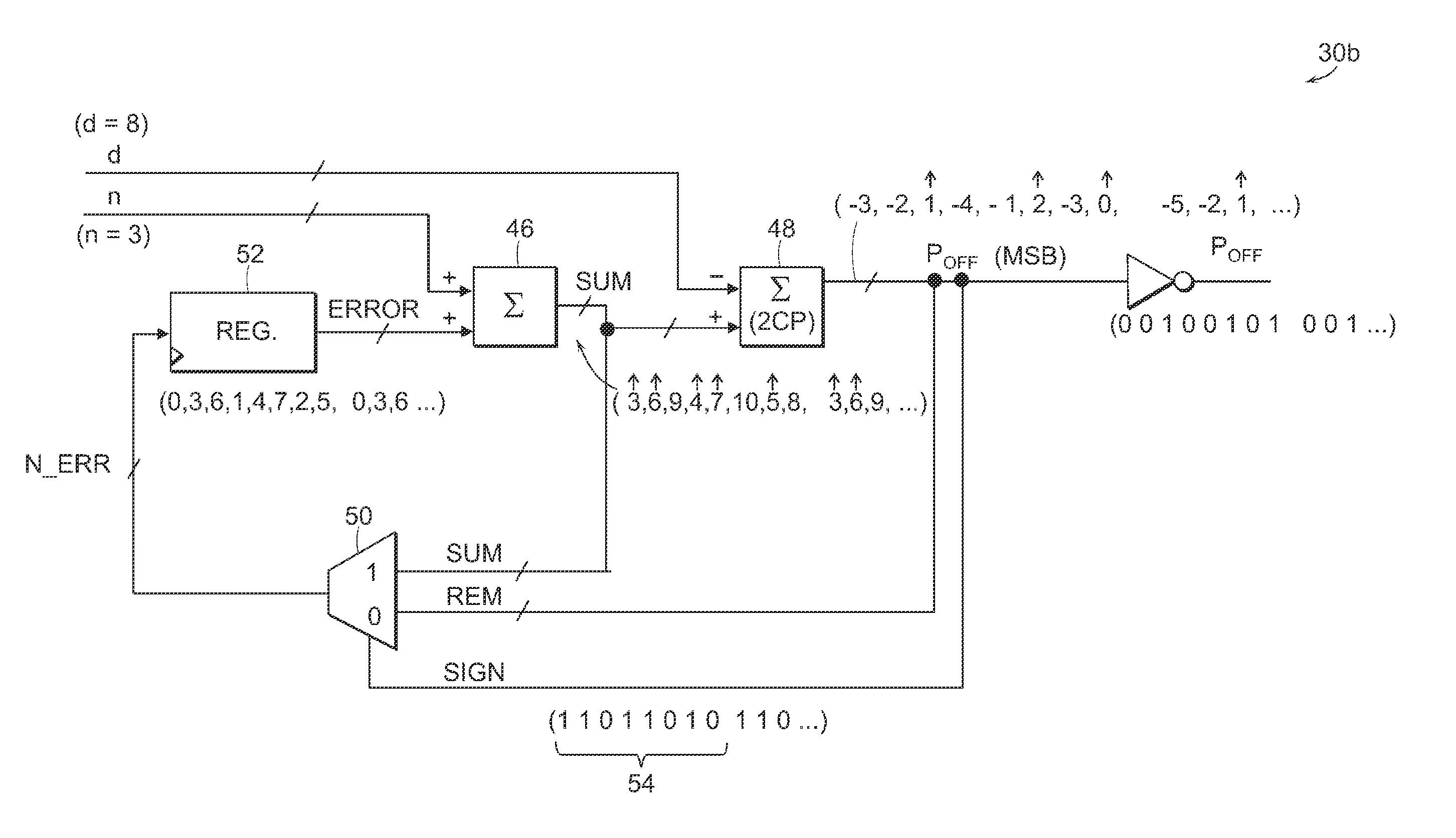
Frequency synthesizer having a more versatile and efficient fractional-N control circuit and method
ActiveUS7126436B1Faster throughputEasy to controlPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsImage resolutionFrequency synthesizer
A frequency synthesizer is provided having a fractional-N control circuit and method that can selectively apply any fractional ratio to a frequency divider within the feedback loop of a PLL. A special digital delta-sigma modulator can be implemented as the control circuit and can receive any arbitrary numerator and denominator value, or their arithmetic combination, or a positive and negative vector values used by the modulator to achieve an average fractional division. Both the numerator and denominator (or the positive and negative vectors) can be chosen based on any integer value to achieve a more optimal, higher frequency resolution and efficient fractional-N control circuit and methodology thereof.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
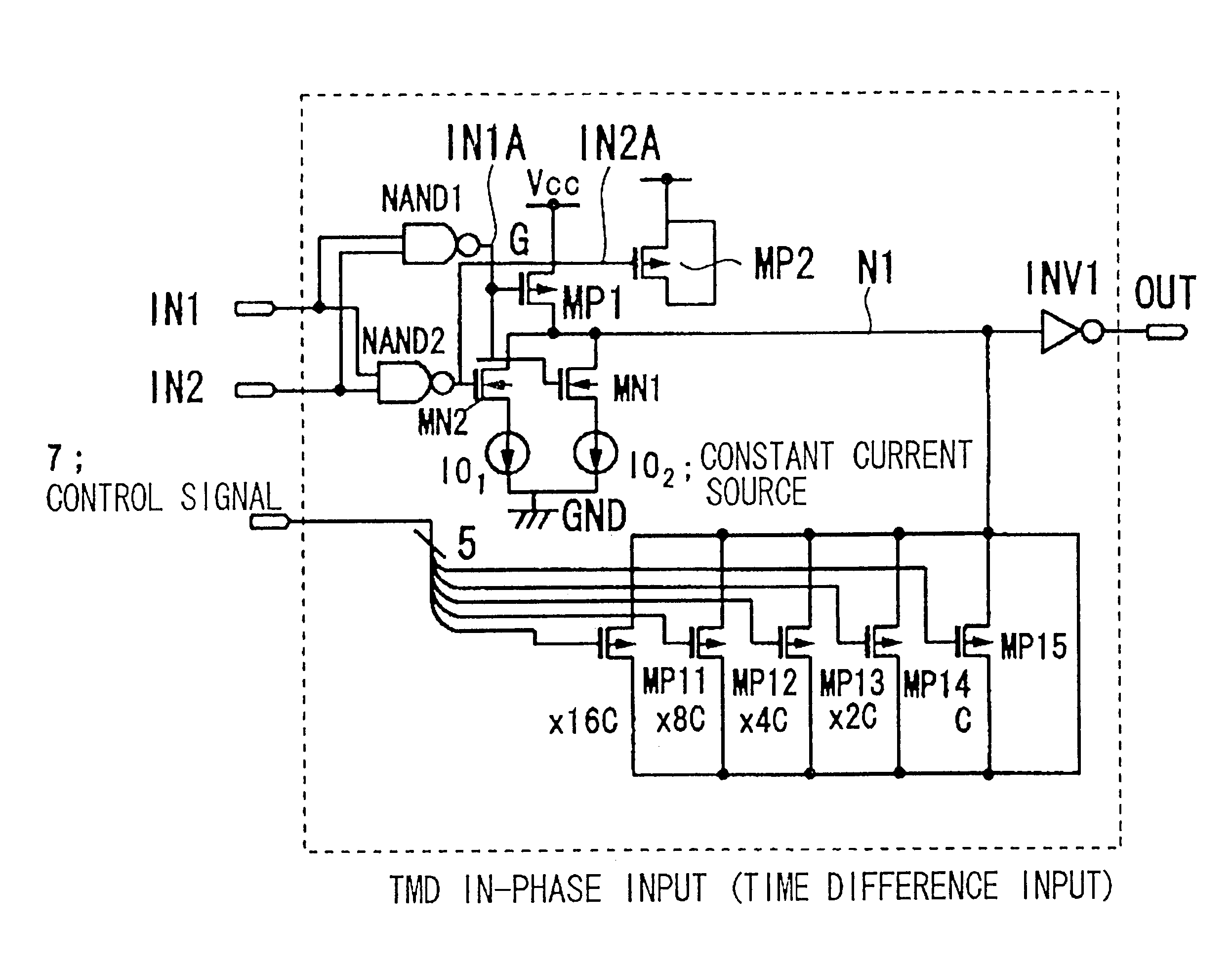
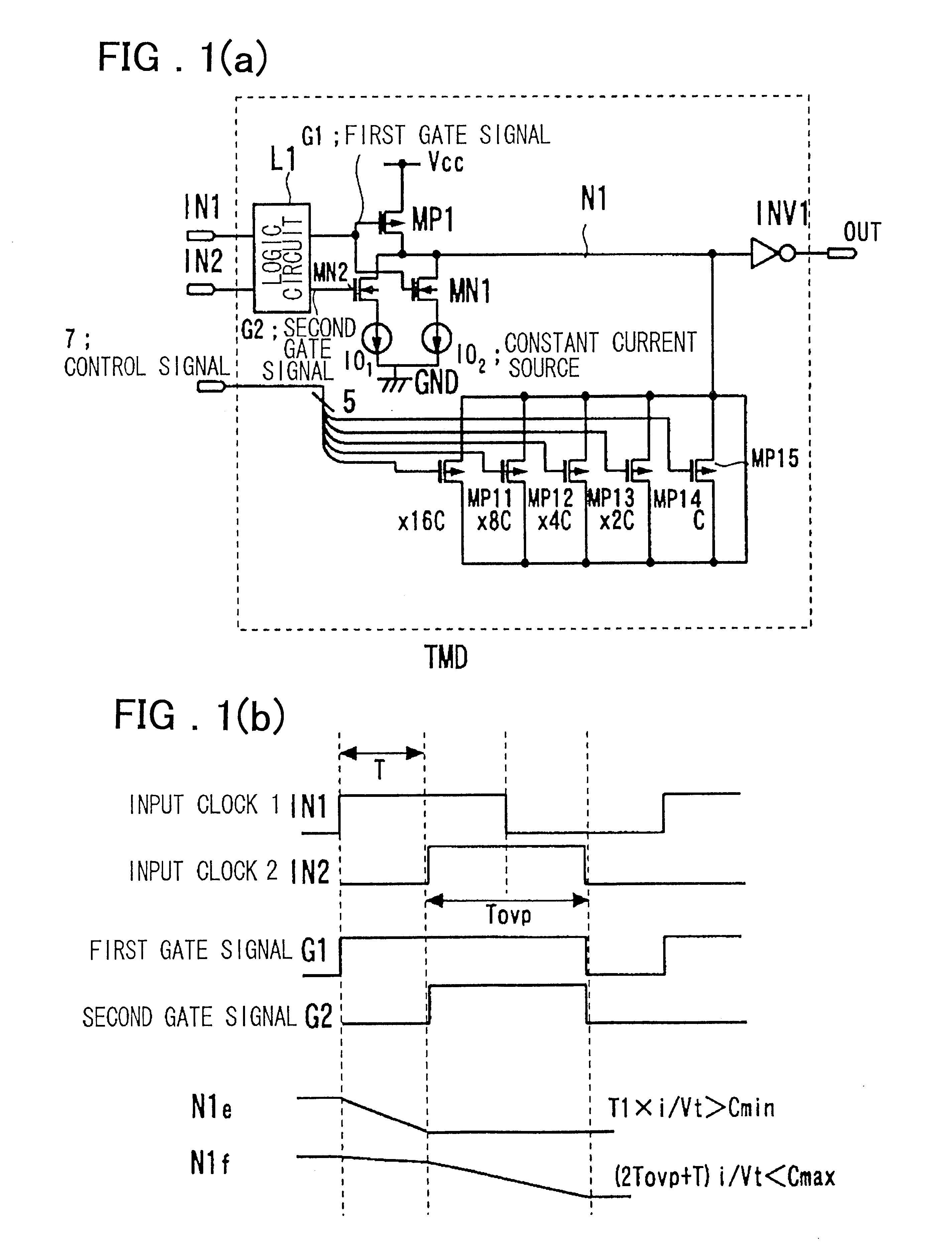
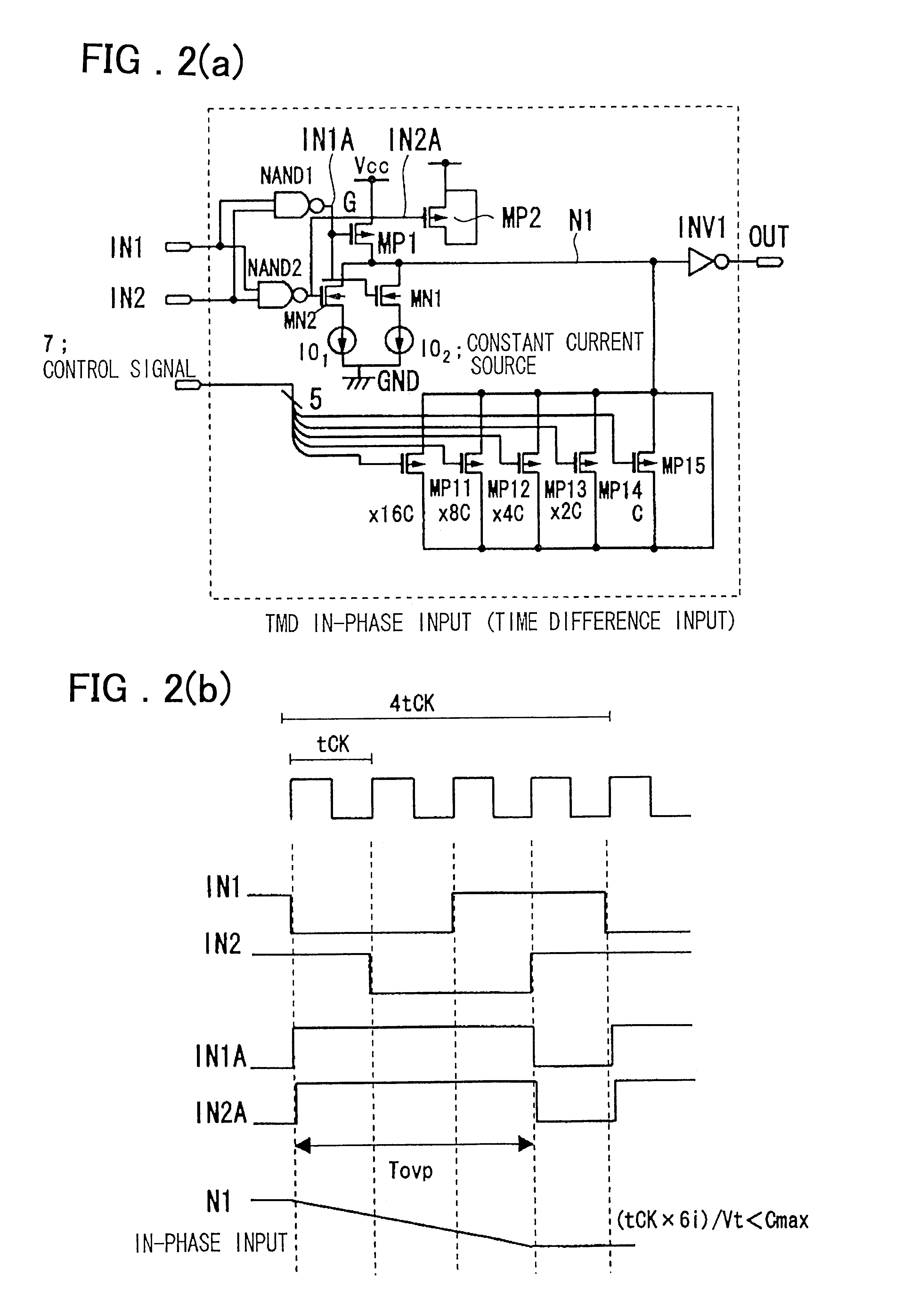
Timing difference division circuit and signal controlling method and apparatus
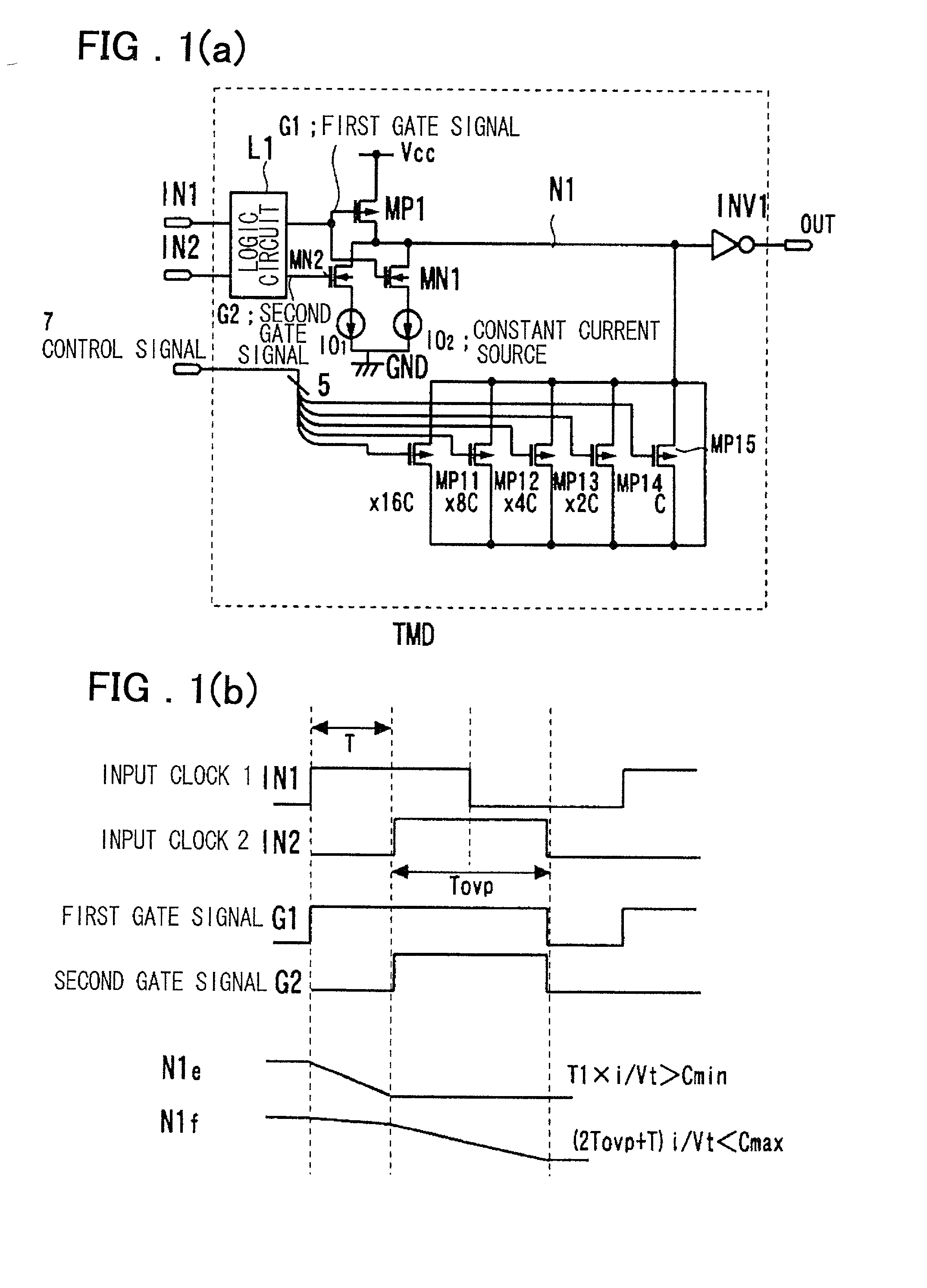
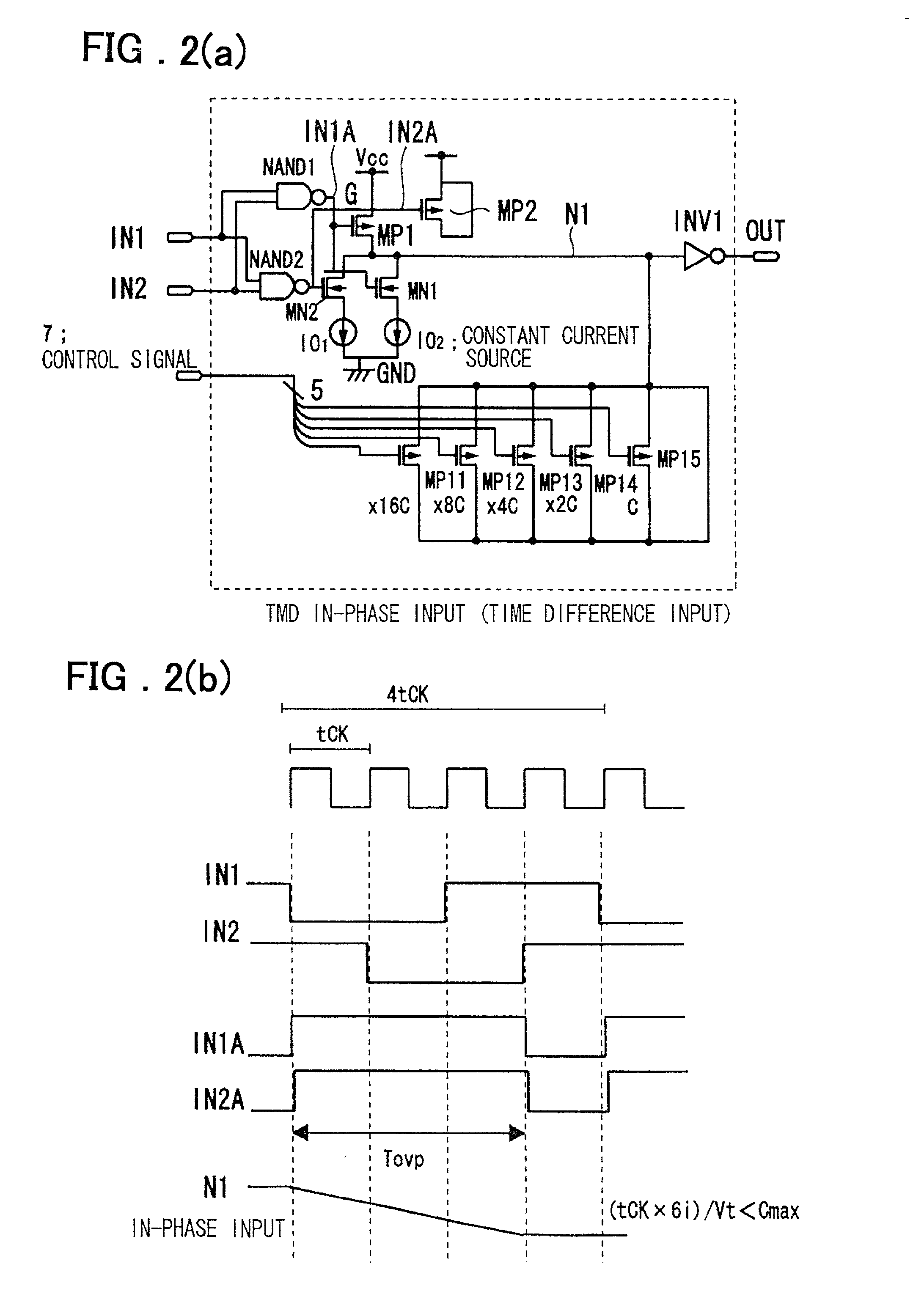
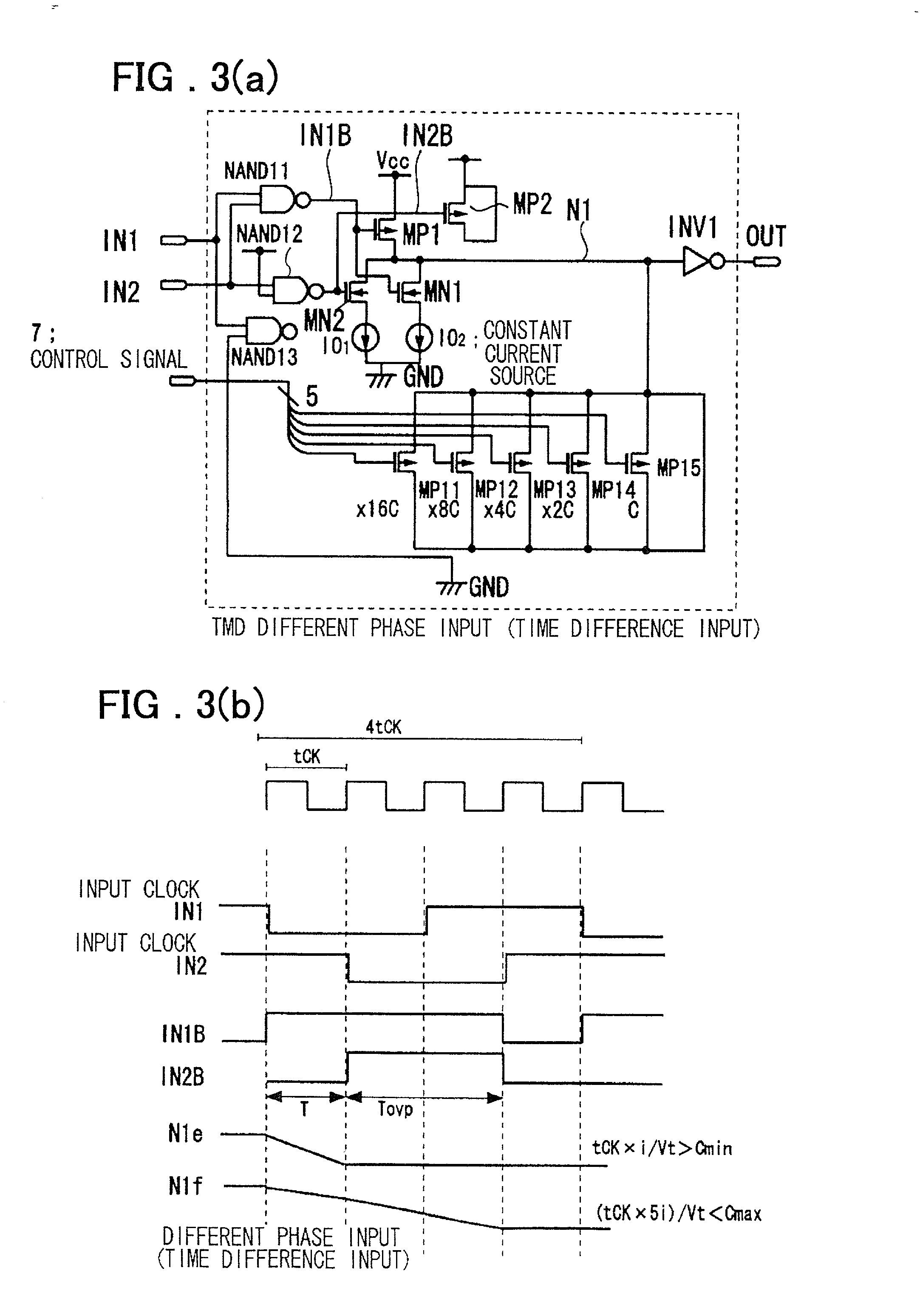
InactiveUS6545518B2Increase the areaHigh speedElectronic switchingSingle output arrangementsRelative magnitudeControl signal
Timing difference division circuit with a high operating speed and a small area, assuring broadband operation. The circuit includes a logic circuit L1 generating a first gate signal and a second gate signal based on a first input signal and a second input signal, a first switch element connected across a first power source and an inner node and having a control terminal to which is fed the first gate signal, a first series circuit made up of a second switch element and a first constant current source and a second series circuit made up of a third switch element and a second constant current source. The first and second series circuits are connected in parallel across the inner node and the second power source. The first and second gate signals are connected to control terminals of the second and third switches, respectively. The circuit also includes a plurality of MOS capacitors, connection of which to the inner node is separately controlled by a control signal, and a buffer circuit an input end of which is connected to the inner node and the value of an output signal of which is determined based on the relative magnitude of the potential of the inner node and a threshold voltage. An overlap period during which the first and second gate signals output from the logic circuit are both activated to turn on the second and third switch elements is set to an optional value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Glitchless pulse generator
InactiveUS6879201B1Reduce errorsOccupies spaceContinuously circulated pulse countersCounting chain synchronous pulse countersGlitchDuration time
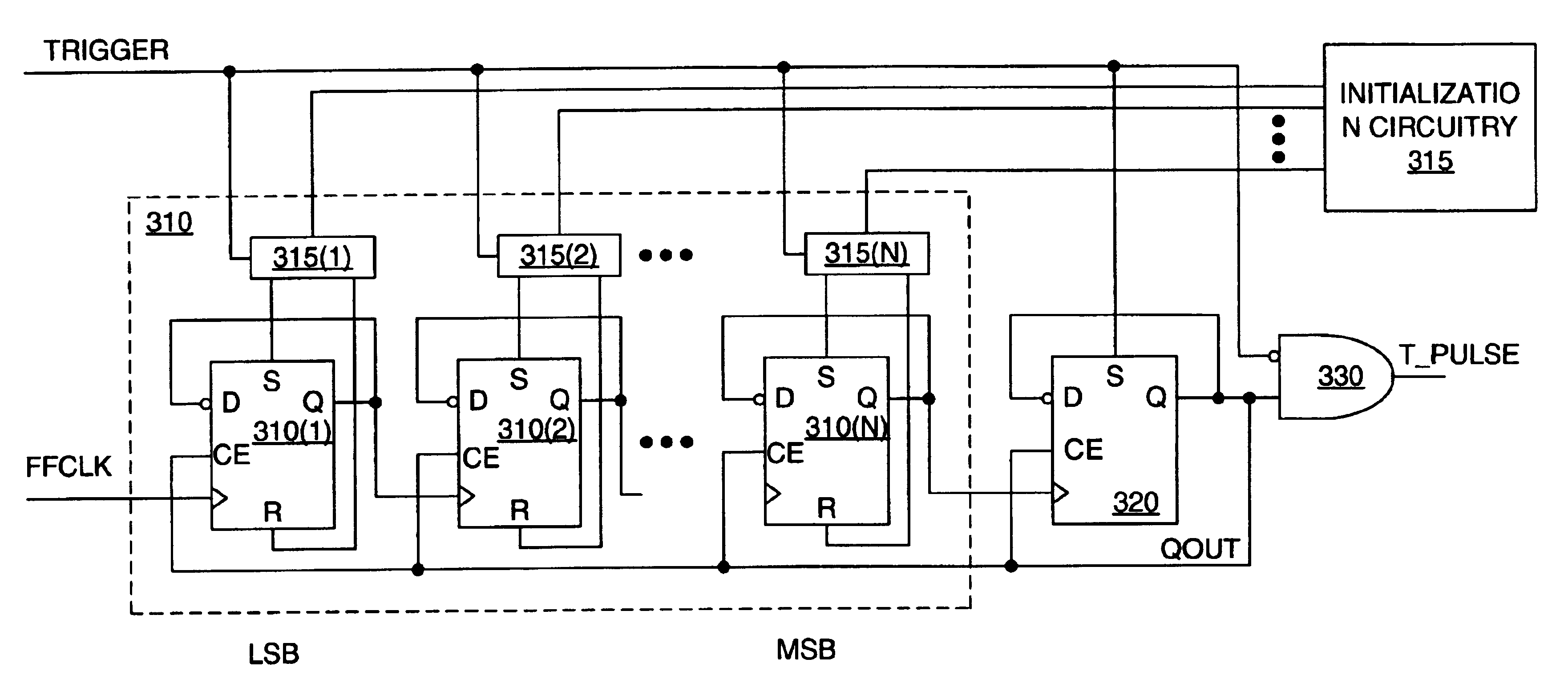
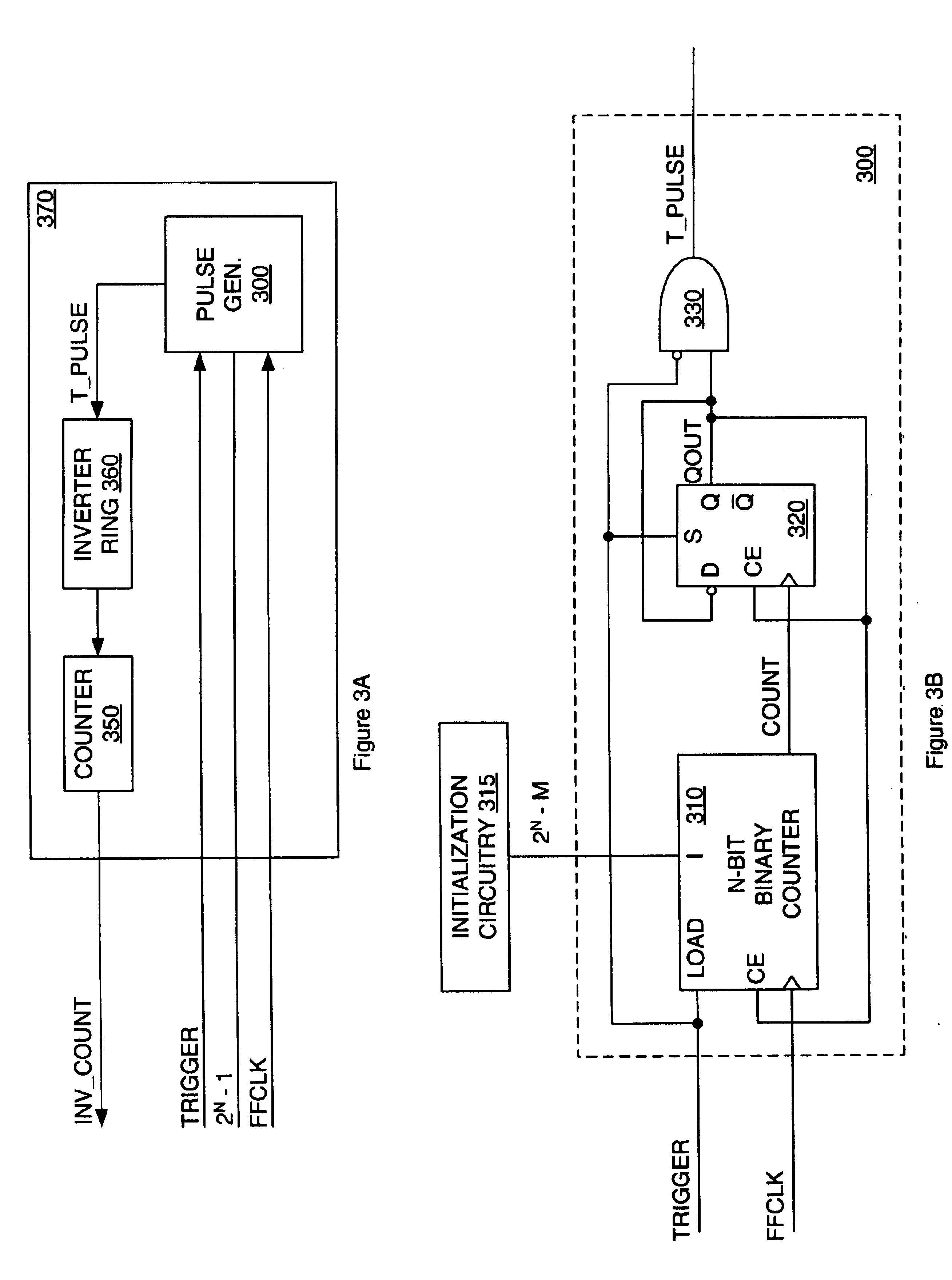
A glitchless T length pulse is generated by coupling a trigger signal and the latched output of a counter. The trigger signal initiates the start of the T length pulse, and the latched output of the counter initiates the end of the T length pulse after counting up a duration of T from a number of clock cycles of a clock signal. Latching the output of the counter prior to terminating the T length pulse eliminates glitches. Accuracy of the count determining the length of the T length pulse may be increased by latching the trigger signal with the clock signal to generated a synchronized trigger signal, and using the synchronized trigger signal to initiate the T length pulse.
Owner:XILINX INC
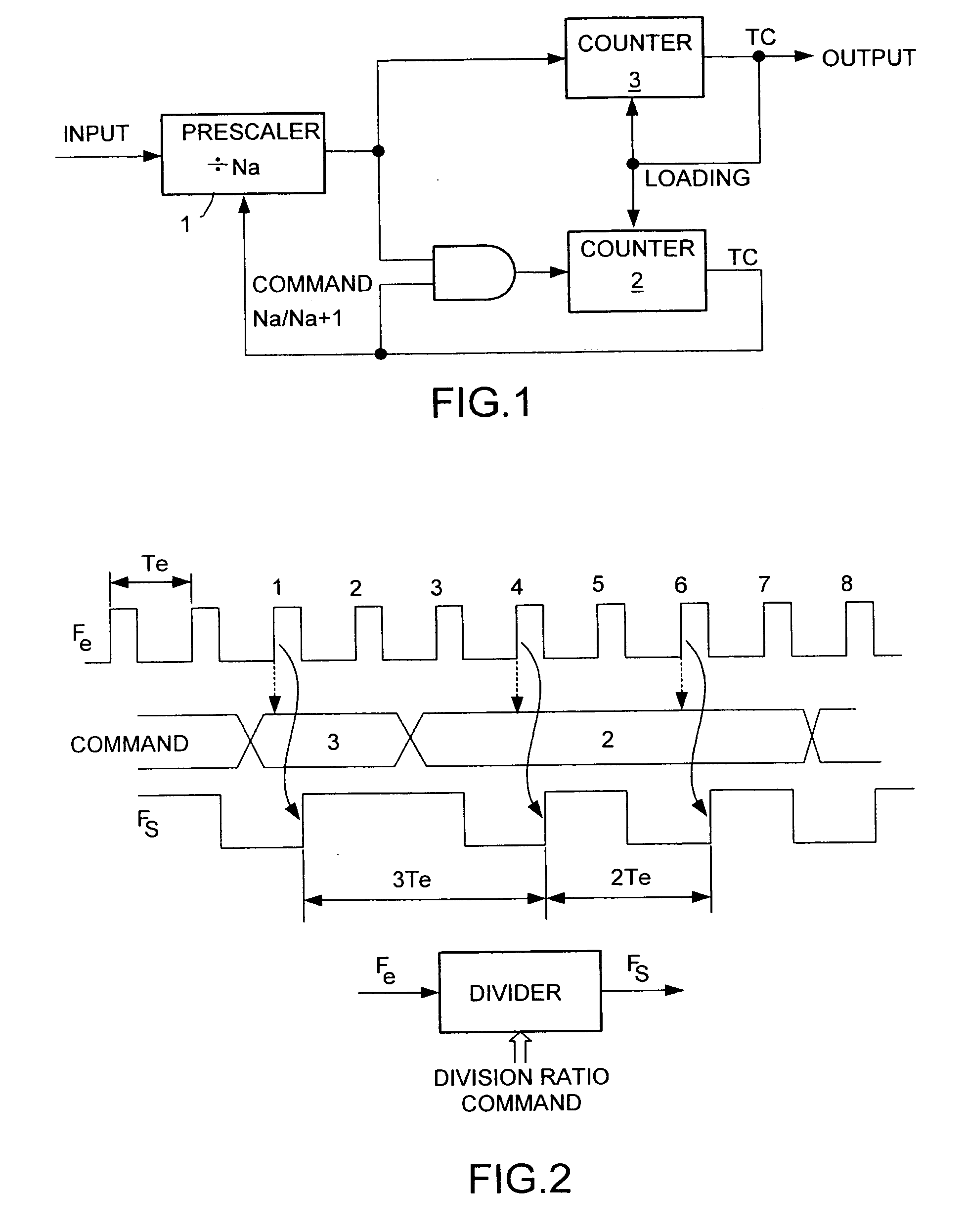
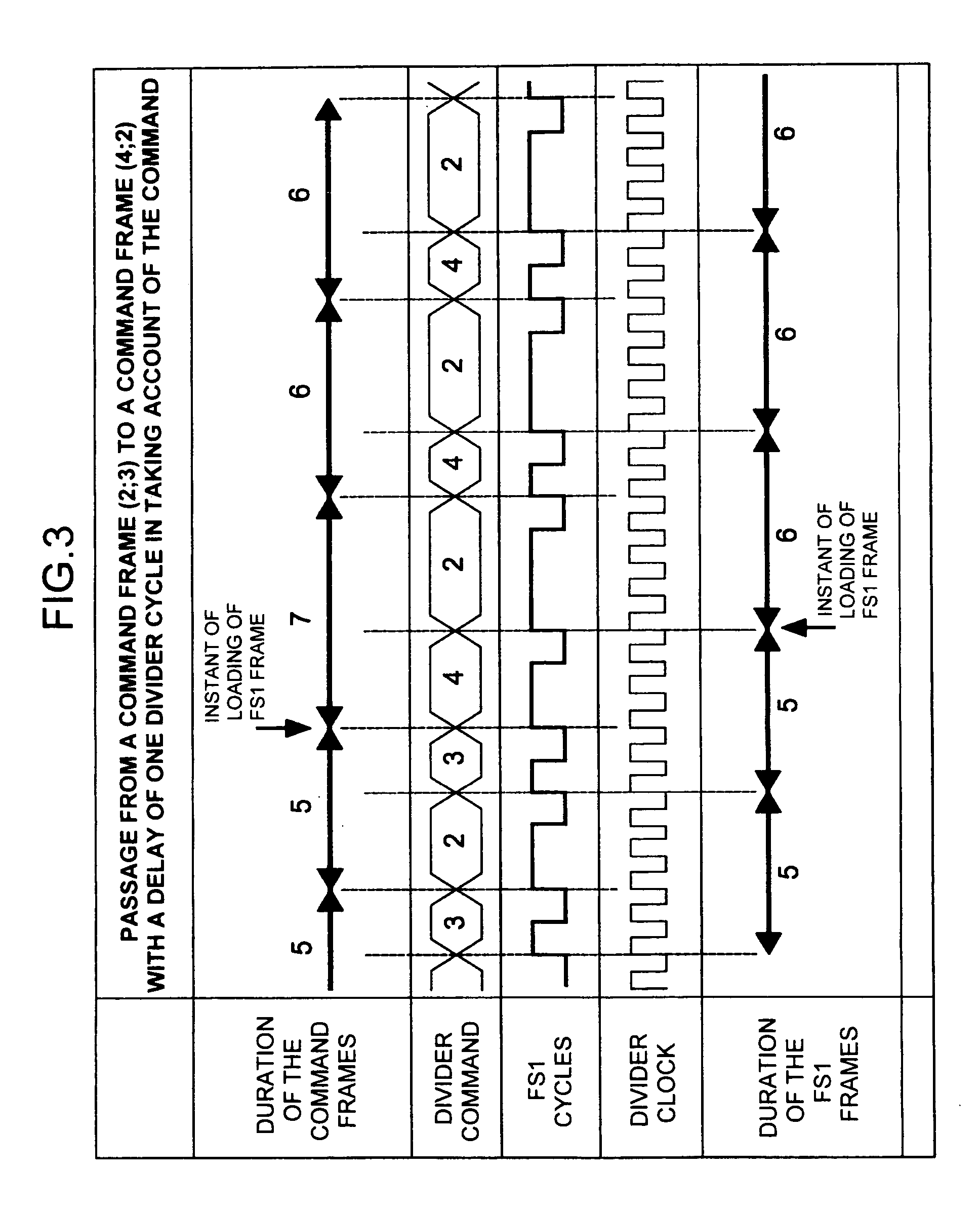
Frequency division method and device
InactiveUS20050180539A1Counting chain synchronous pulse countersComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersEngineeringFrequency divider
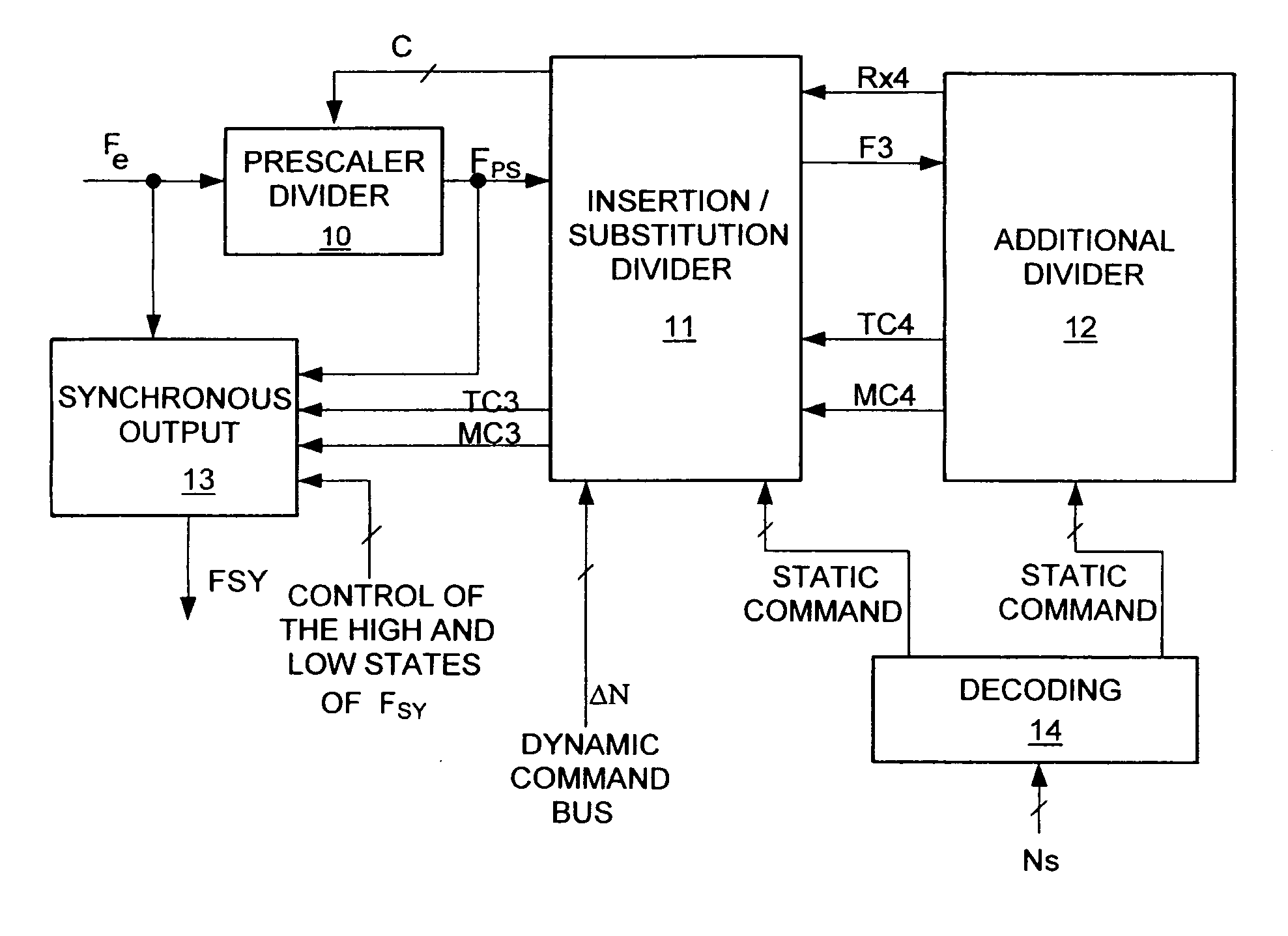
A method and device of frequency division with a division ratio: comprising: an input divider with a division ratio NPs receiving the frequency Fe at input and delivering a signal to an insertion / substitution divider, the insertion / substitution divider having an input of variation of the division ratio, delivering a command frame to the input divider and generating an end-of-count signal, the insertion / substitution divider being adapted to the insertion of one or more input divider cycles and / or the substitution of an input divider cycle in the command frame.
Owner:THALES SA
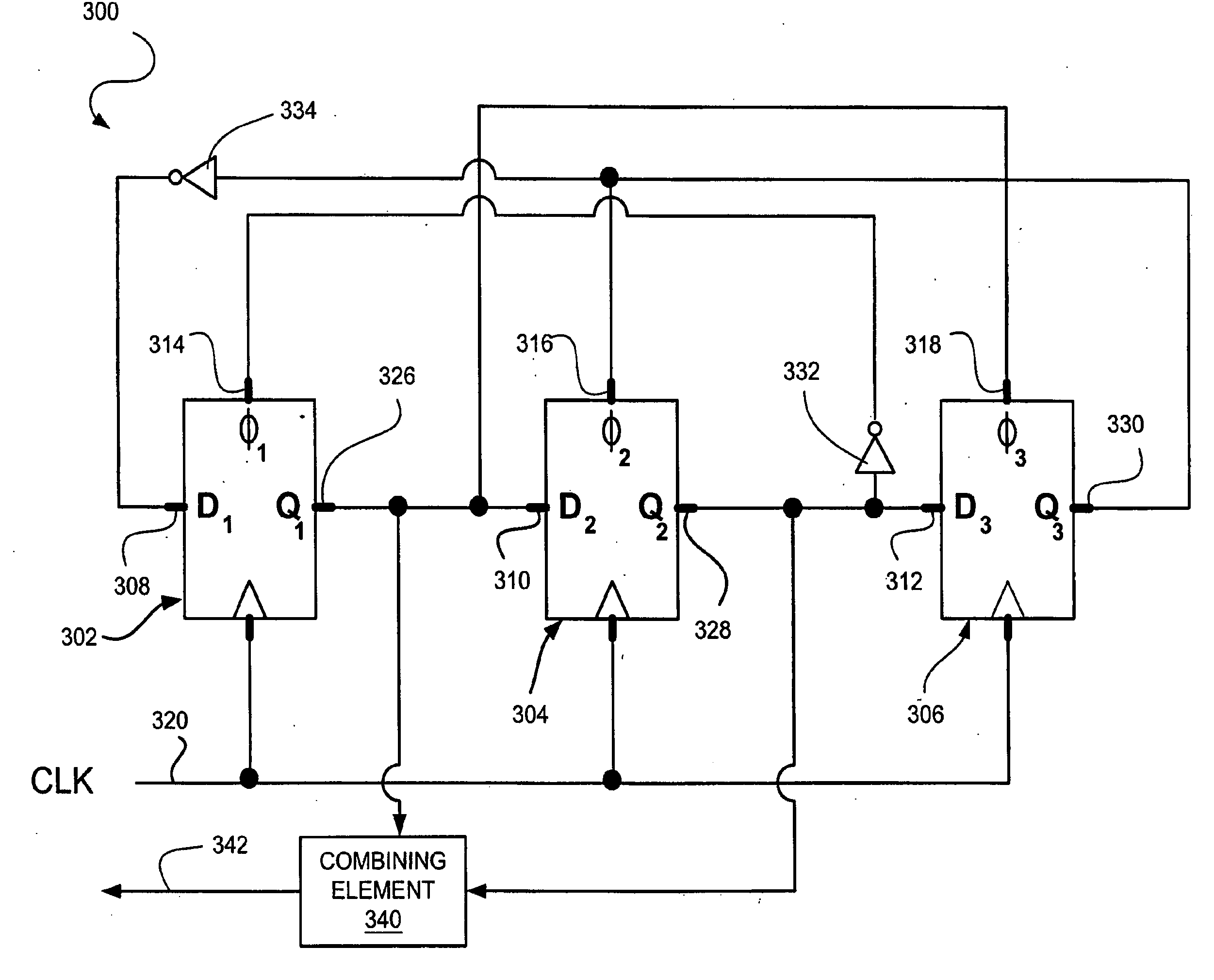
Frequency Dividing Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20070286328A1Counting chain pulse countersComputation using non-contact making devicesPhase differenceFrequency divider
Systems and methods for producing a frequency divider output signal having a period substantially equal to three times a period of a reference input signal, comprising configuring each of three storage elements to receive a first input, a second input, and a reference input signal, and to provide a storage element output, obtaining a frequency divider output signal from at least one storage element output, and using the storage element output from each of the three storage elements as an input to another one of the three storage elements, where a phase difference between the output of the first storage element and the output of the second storage element is substantially equal to 60°.
Owner:CONEXANT SYST INC +1
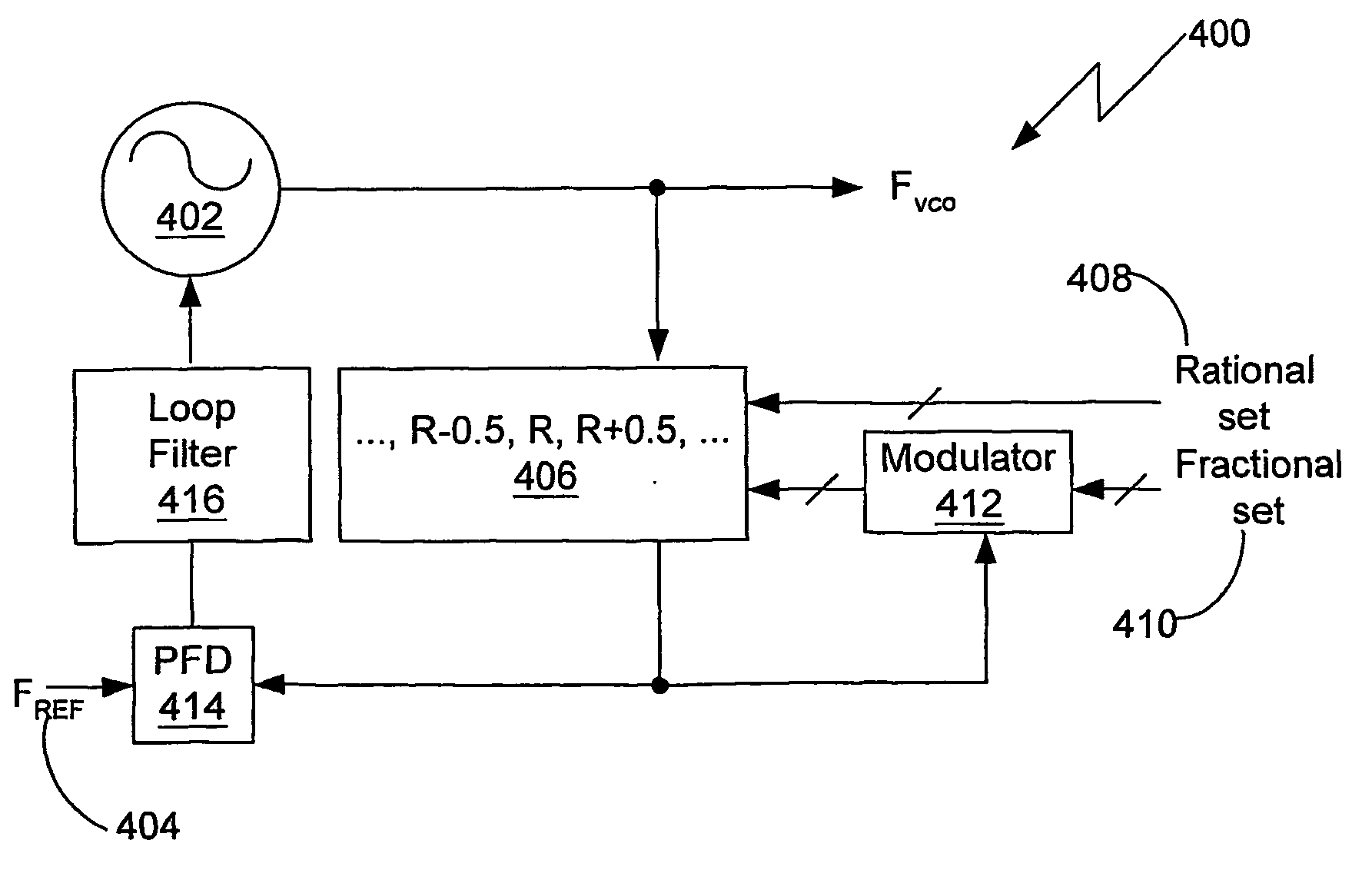
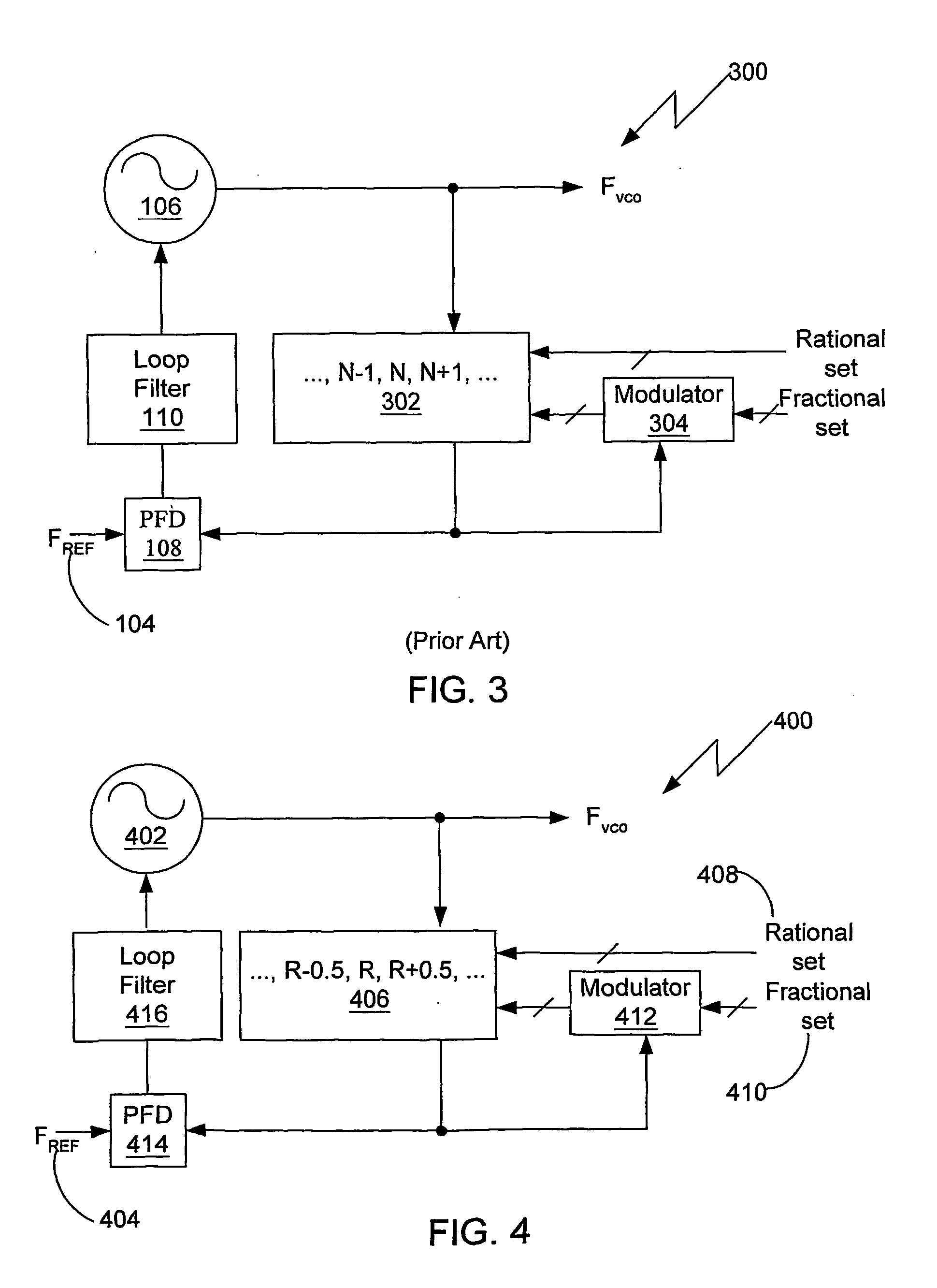
Fractional-r frequency synthesizer
InactiveUS20050063505A1Reduce phase noiseAvoid excessive perturbationPulse automatic controlComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersFrequency synthesizerEngineering
A fractional-R synthesizer having a divider (406) with rational increments and configurable in rational steps able to generate a plurality of frequencies in rational increments from a reference frequency. The fractional-R synthesizer is included in the feedback loop of a PLL. Preferably a Delta-Sigma modulator (412) is responsive to an input representing a fractional value and clocked by the output of said divider (406) to produce an output signal that modulates the divide ratio of the variable rational divider (406).
Owner:CSR TECH INC
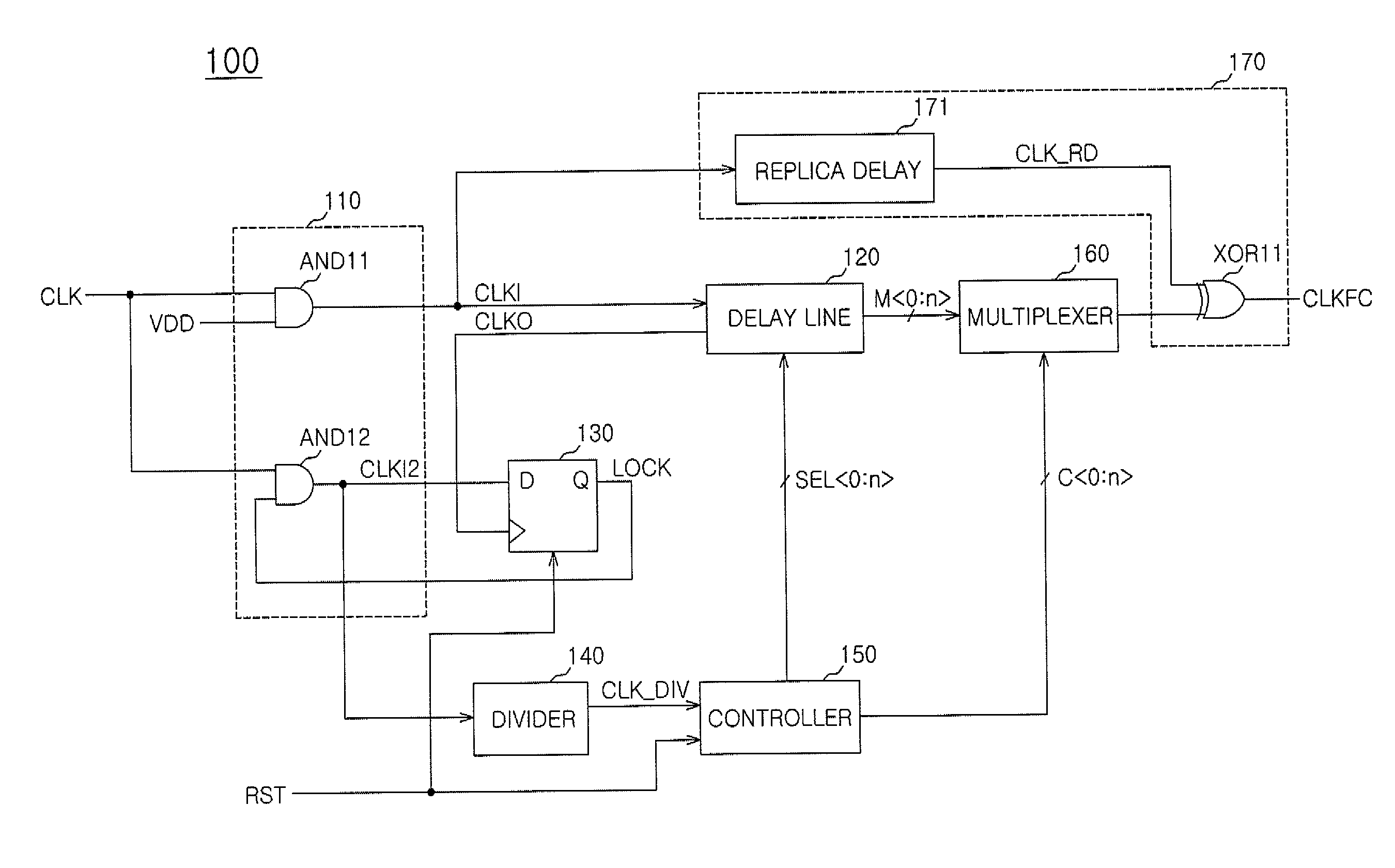
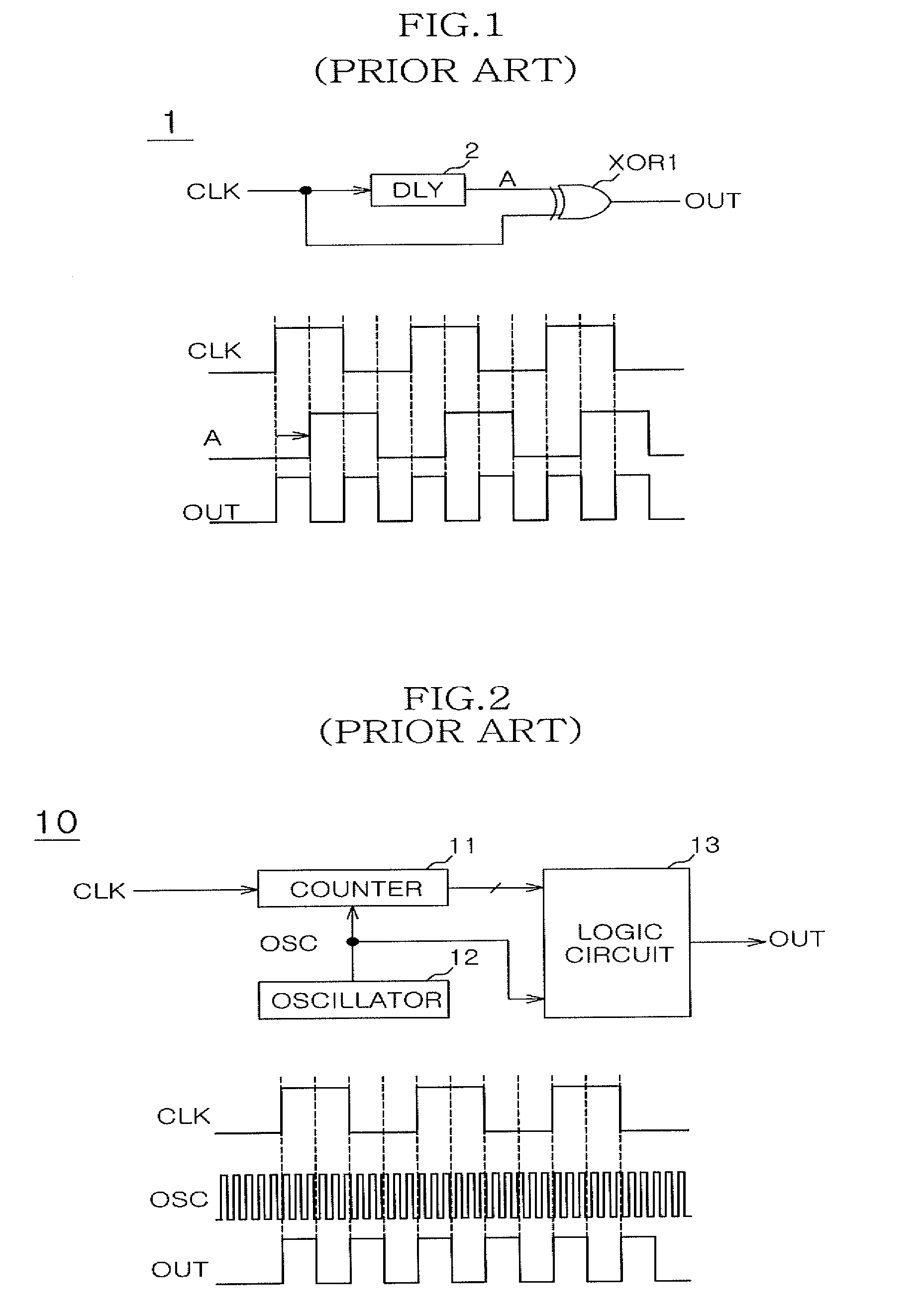
Digital clock frequency multiplier
ActiveUS20070080724A1Lock time is very highIncrease the areaCounting chain pulse countersComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersDigital clockFrequency multiplier
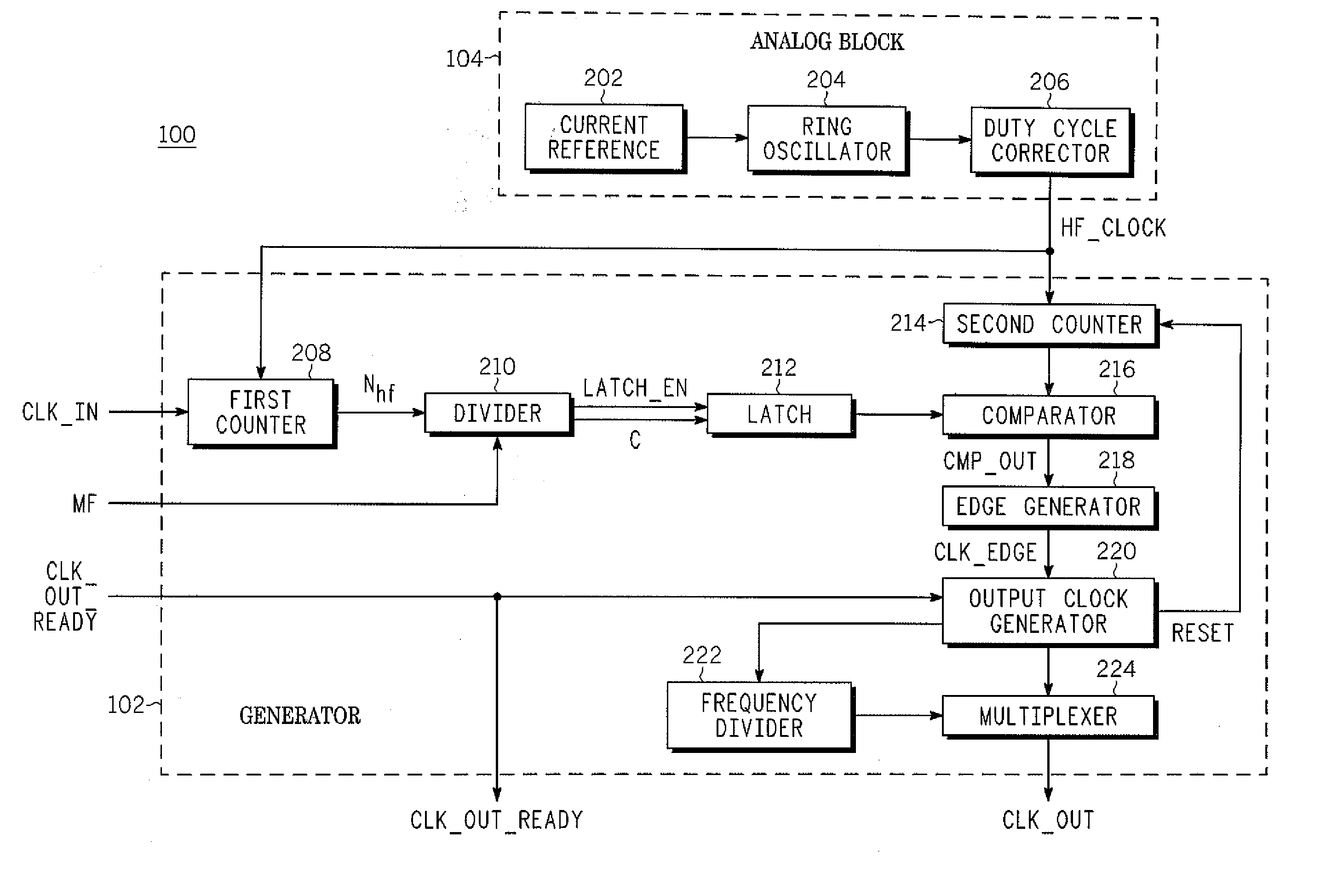
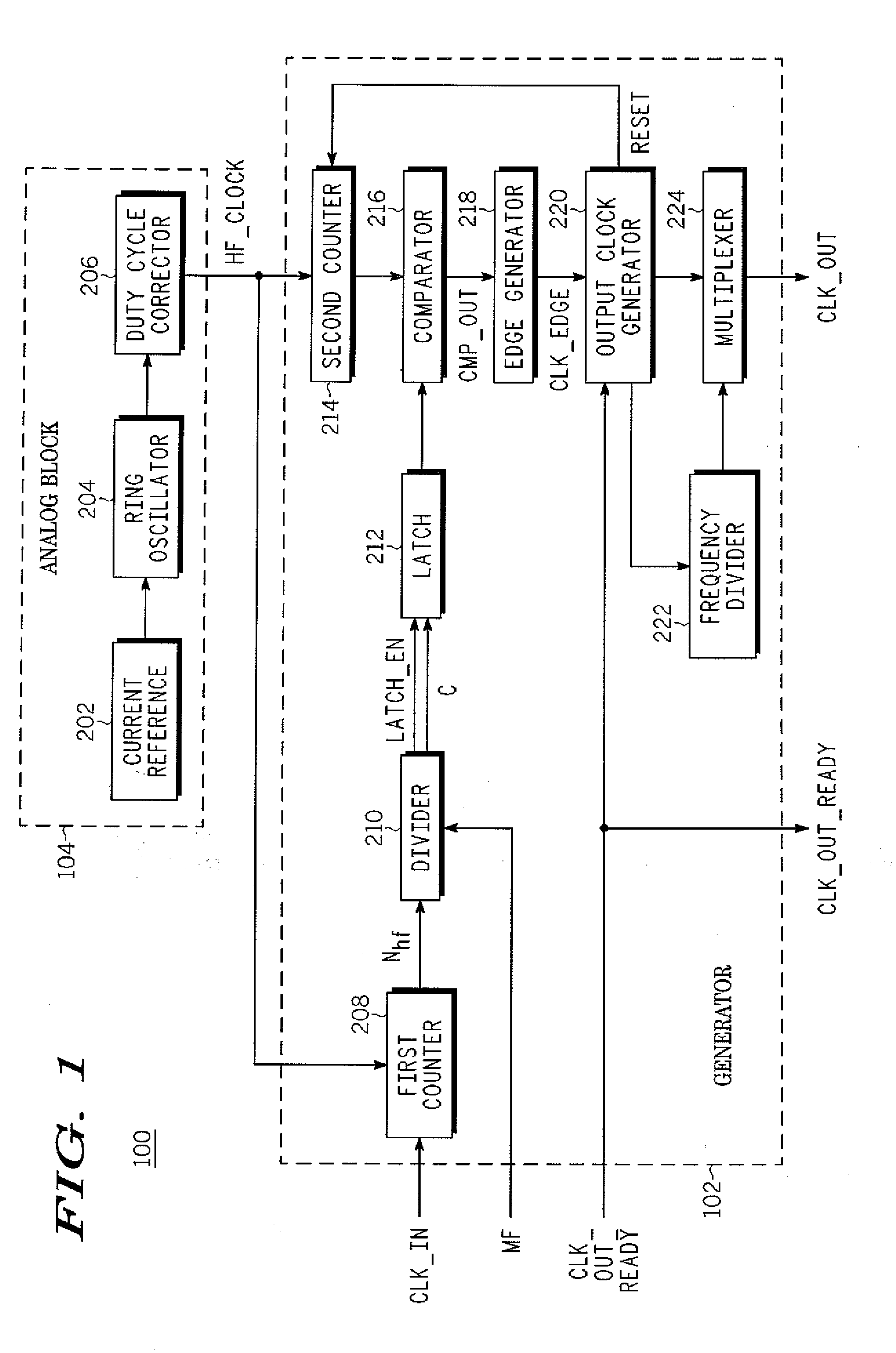
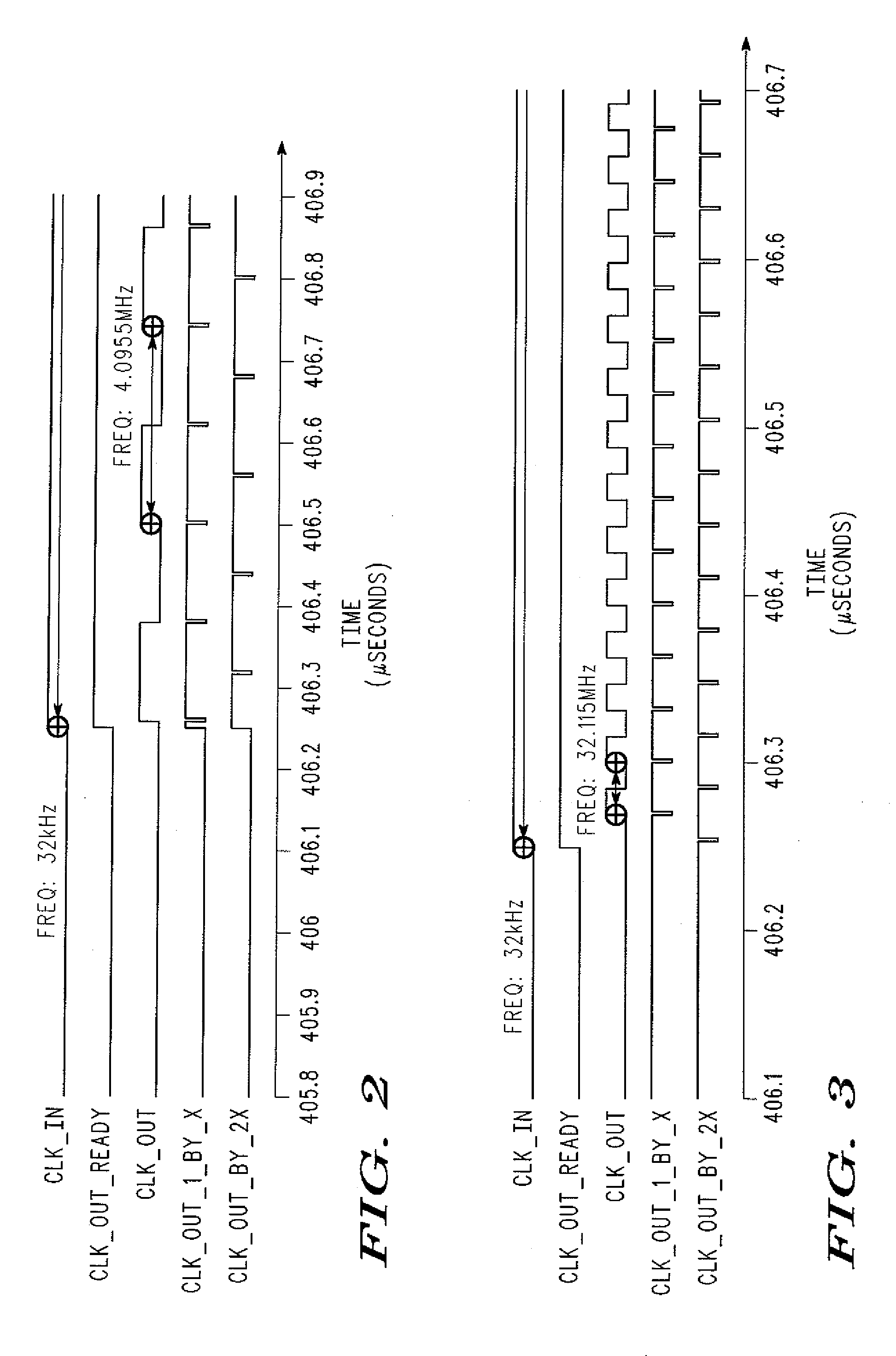
A digital clock frequency multiplier (100) for increasing an input frequency of an input clock signal includes a generator (102) that receives the input clock signal and a high frequency digital signal. The generator (102) divides a count (Nhf) of a number of cycles of the high frequency digital signal in one period of the input clock signal by a predetermined multiplication factor (MF) for generating an output clock signal. The output clock signal has a predetermined output frequency.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Timing difference division circuit and signal controlling method and apparatus
InactiveUS20010045853A1Increase chip areaHigh speedElectronic switchingSingle output arrangementsCapacitanceControl signal
Timing difference division circuit with a high operating speed and a small area, assuring broadband operation. The circuit includes a logic circuit L1 generating a first gate signal and a second gate signal based on a first input signal and a second input signal, a first switch element connected across a first power source and an inner node and having a control terminal to which is fed the first gate signal, a first series circuit made up of a second switch element and a first constant current source and a second series circuit made up of a third switch element and a second constant current source. The first and second series circuits are connected in parallel across the inner node and the second power source. The first and second gate signals are connected to control terminals of the second and third switches, respectively. The circuit also includes a plurality of MOS capacitors, connection of which to the inner node is separately controlled by a control signal, and a buffer circuit an input end of which is connected to the inner node and the value of an output signal of which is determined based on the relative magnitude of the potential of the inner node and a threshold voltage. An overlap period during which the first and second gate signals output from the logic circuit are both activated to turn on the second and third switch elements is set to an optional value.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Clock signal generation circuit and semiconductor device
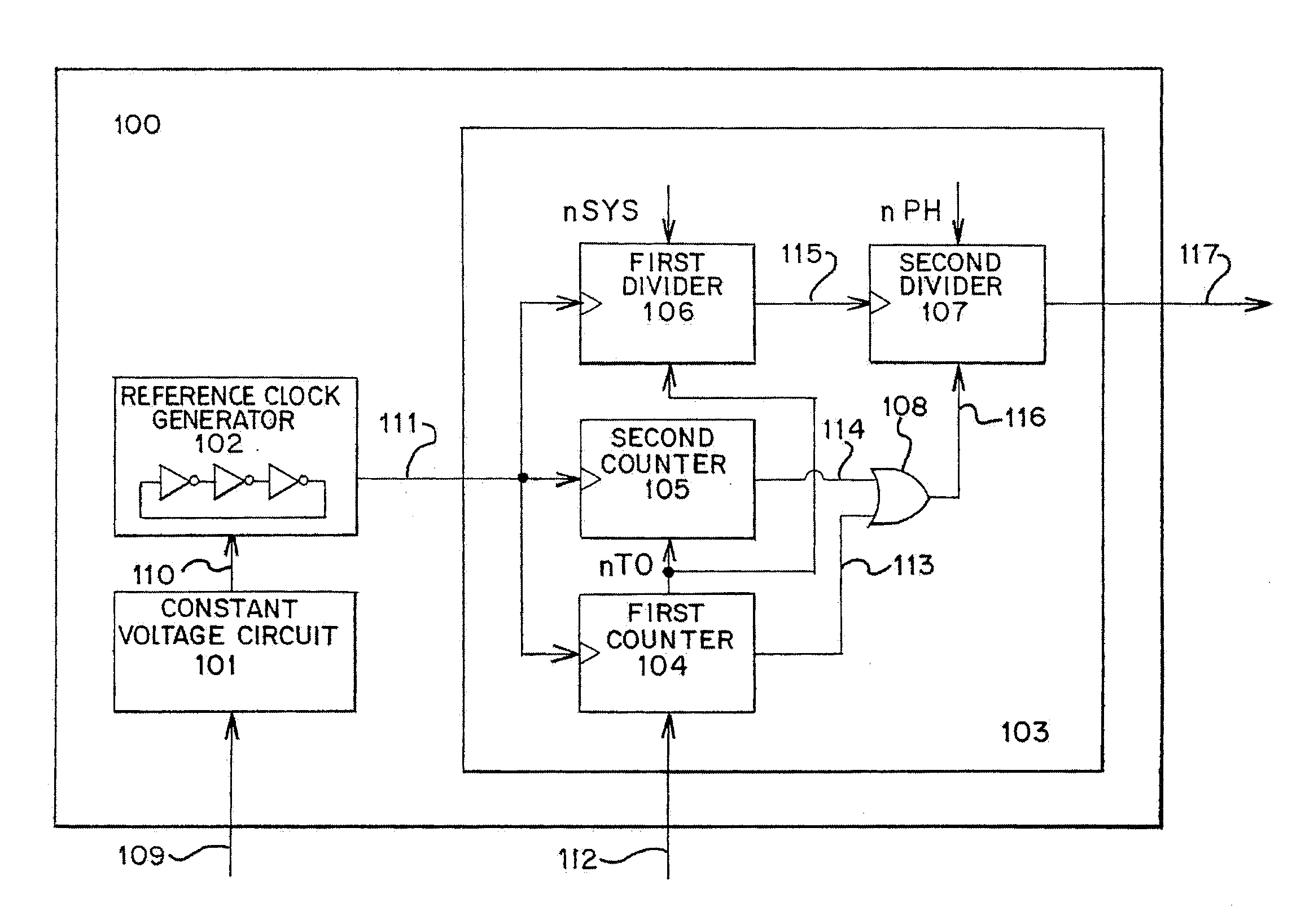
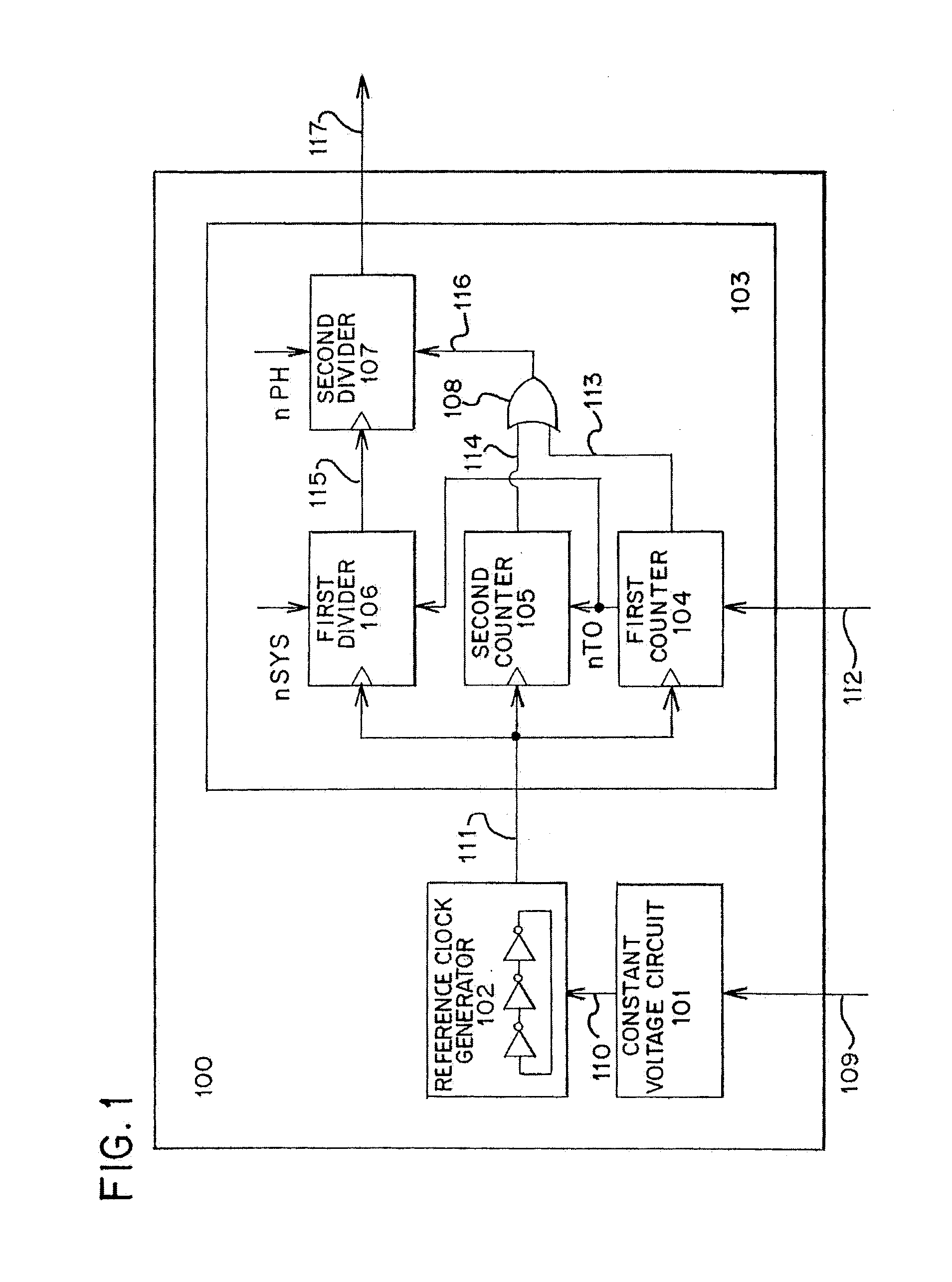
InactiveUS7639058B2Improve performanceImprove communication distancePulse automatic controlDigital storageComputer scienceSemiconductor
The semiconductor device is provided with a clock signal generation circuit that includes a reference clock signal generation circuit which generates a first reference clock signal, a first counter circuit which counts the number of rising edges of the first reference clock signal by using the first reference clock signal and a synchronizing signal, a second counter circuit which counts the number of rising edges of the first reference clock signal by using an enumerated value of the first counter circuit, a first divider circuit which divides a frequency of the first reference clock signal by using the enumerated value of the first counter circuit and generates a second reference clock signal, and a second divider circuit which divides a frequency of the second reference clock signal and generates a clock signal.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
High-speed, high granularity baud clock generation
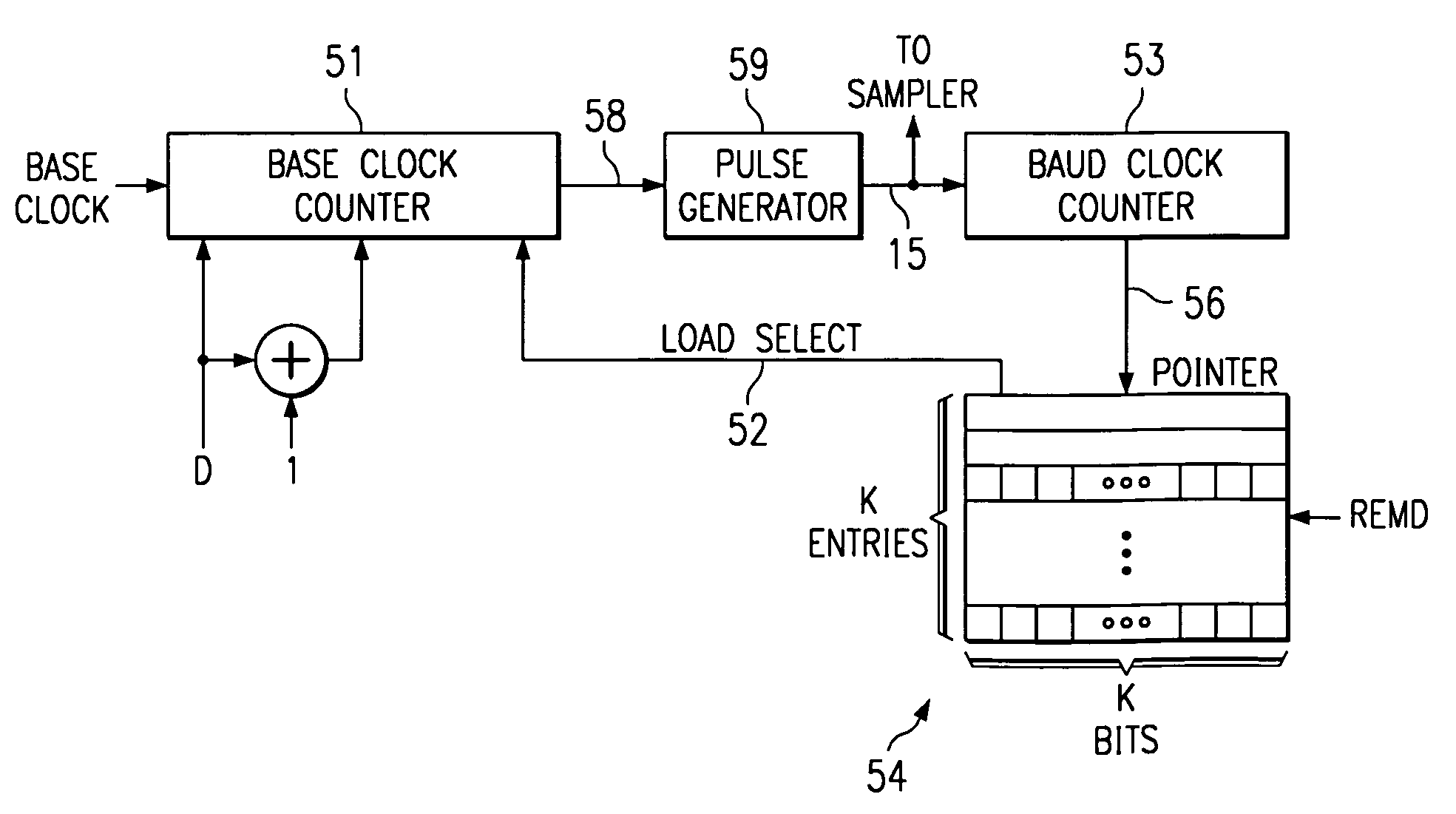
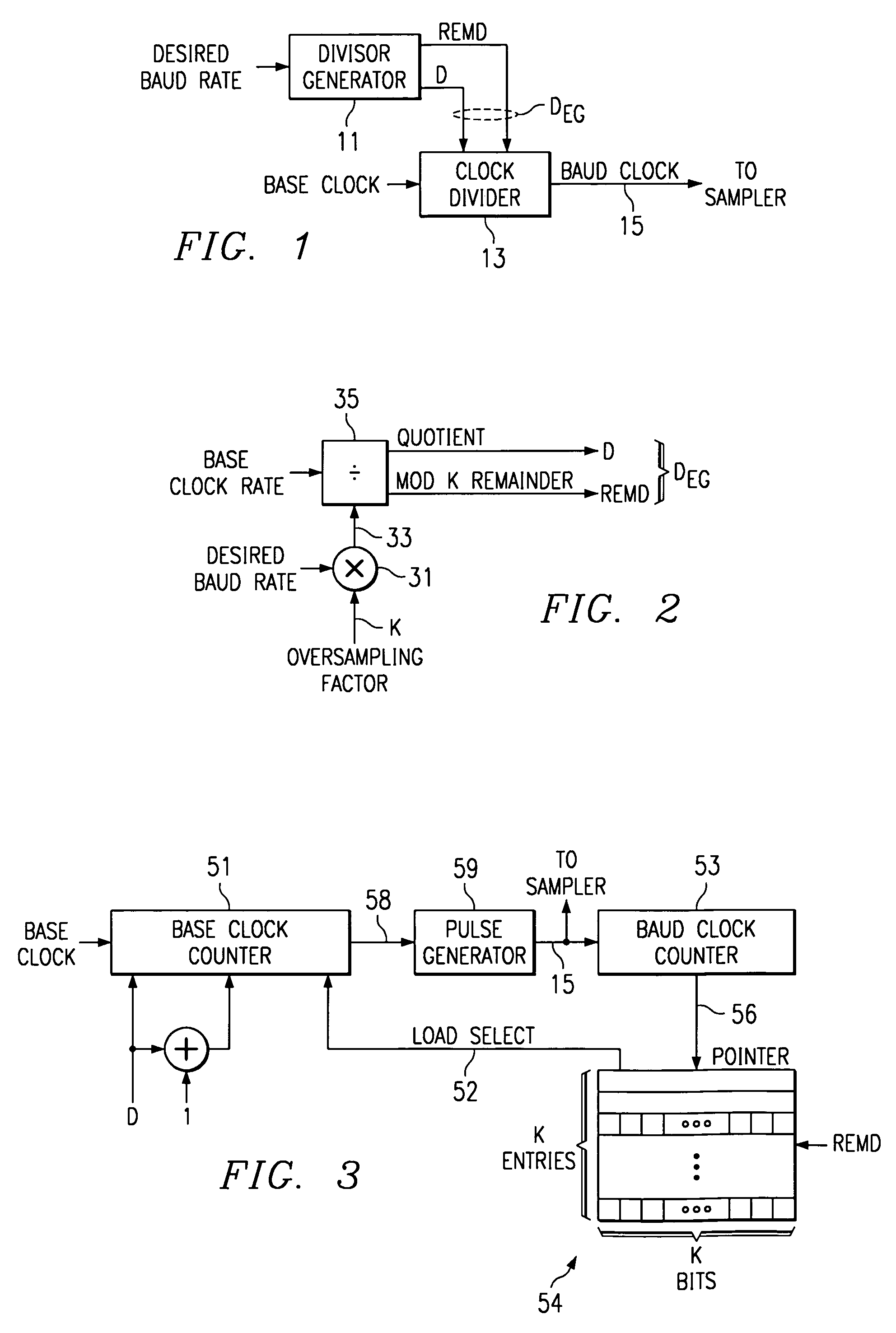
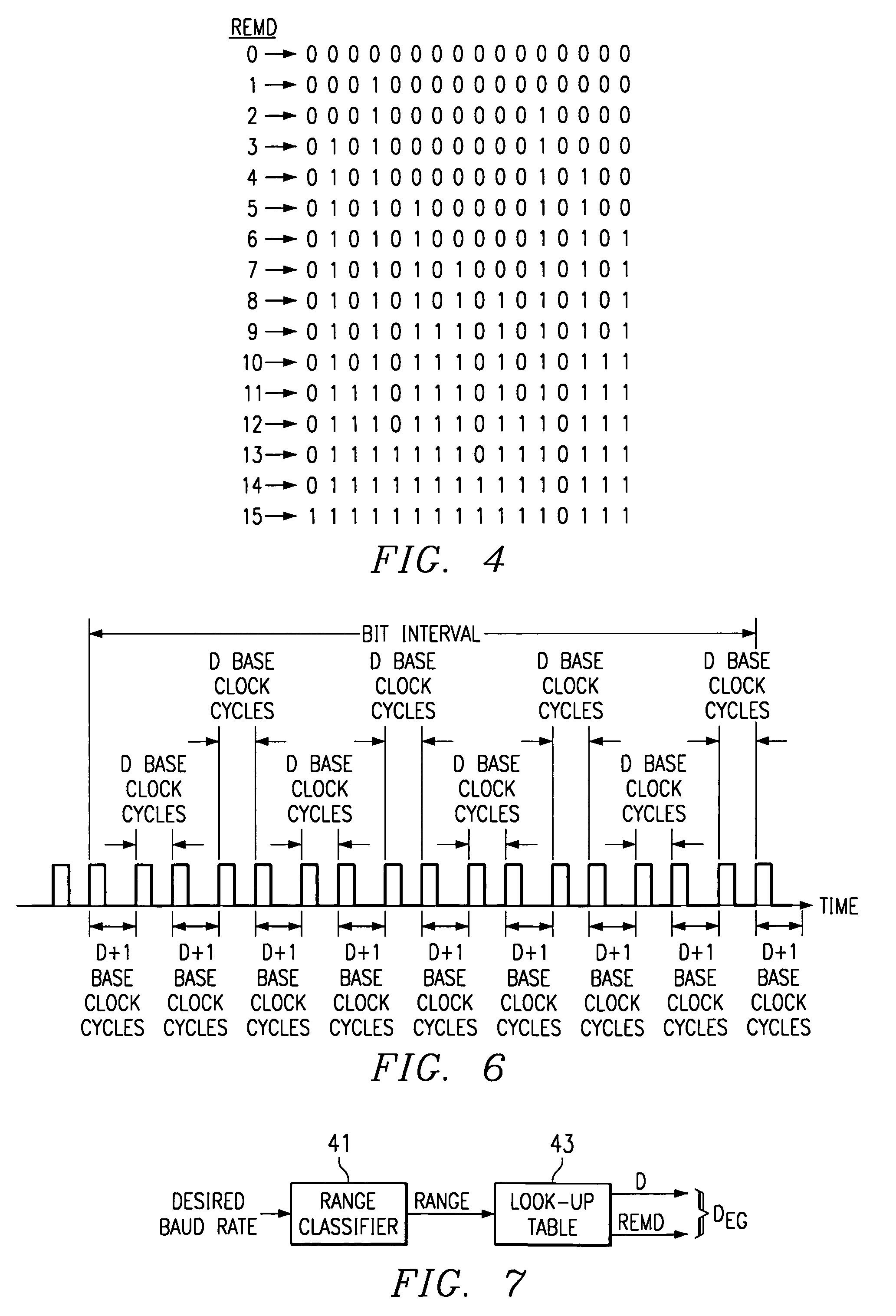
InactiveUS6970525B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesMinimum timeGranularity
A baud clock (15) for use by a serial communication interface (67) is generated by dividing a base clock of the serial communication interface by one of a plurality of possible composite divisors (DEG). Each composite divisor is indicative of a minimum time interval by which adjacent pulses of the baud clock are to be separated, and further indicates that at least one pair of adjacent pulses within each symbol interval of the baud clock are to be separated by an extended time interval which is longer than the minimum time interval.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Maximally digitized fractional-N frequency synthesizer and modulator with maximal fractional spurs removing
InactiveUS6946915B2Cancel almost all the quantization noise in the bit streamEnhanced inhibitory effectPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsLow noiseDiscriminator
A fractional-N frequency synthesizer using the first order Delta-Sigma frequency discriminator which is composed of only a dual modulus frequency divider and a D flip-flop is used to replace the function of phase detector is disclosed. The invented structure is characterized by generating the feedback error signal indirectly from the output bit stream of said discriminator in such a way that the quantization noise contained in the bit stream is maximally canceled by comparing it with another bit stream generated by an accumulator digitally performing the first order Delta-Sigma modulation to the required fractional number, so that there is almost no discrete fractional spurs in the output spectrum of the synthesizer. Most other circuit of the synthesizer could be formed digitally so that high integration level and low noise performance could be achieved. Narrow or wideband phase or frequency modulation could also be conveniently added digitally with good accuracy.
Owner:ZHANG XIAOPIN
Circuit for changing frequency of a signal and frequency change method thereof
ActiveUS20100264960A1Error minimizationReduce current consumptionElectrical testingComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersSignal frequencyEngineering
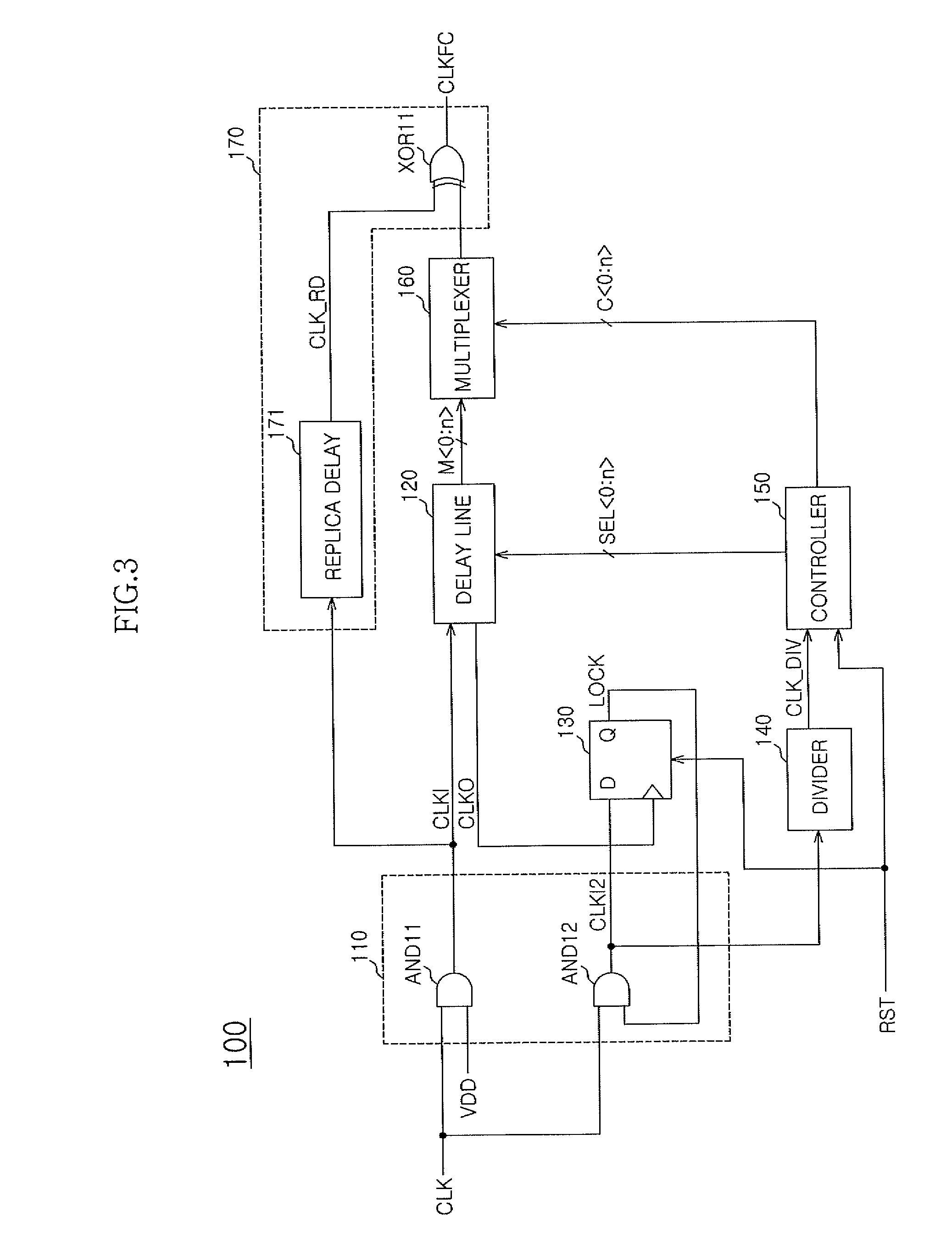
A signal frequency change circuit is presented. The signal frequency change circuit includes a delay line, a detector, a controller, a multiplexer, and an output unit. The delay line delays a clock signal by a first delay time corresponding to a delay control signal to generate a delay signal and delays the clock signal by a second delay time shorter than a first delay time to generate a pre-frequency change clock signal. The detector generates a phase locked completion signal. The controller sequentially shifts the delay control signal and a multiplexing control signal. The multiplexer selects and outputs one of the pre-frequency change clock signals. The output unit generates a frequency change clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method and device for generating a clock signal with predetermined clock signal properties
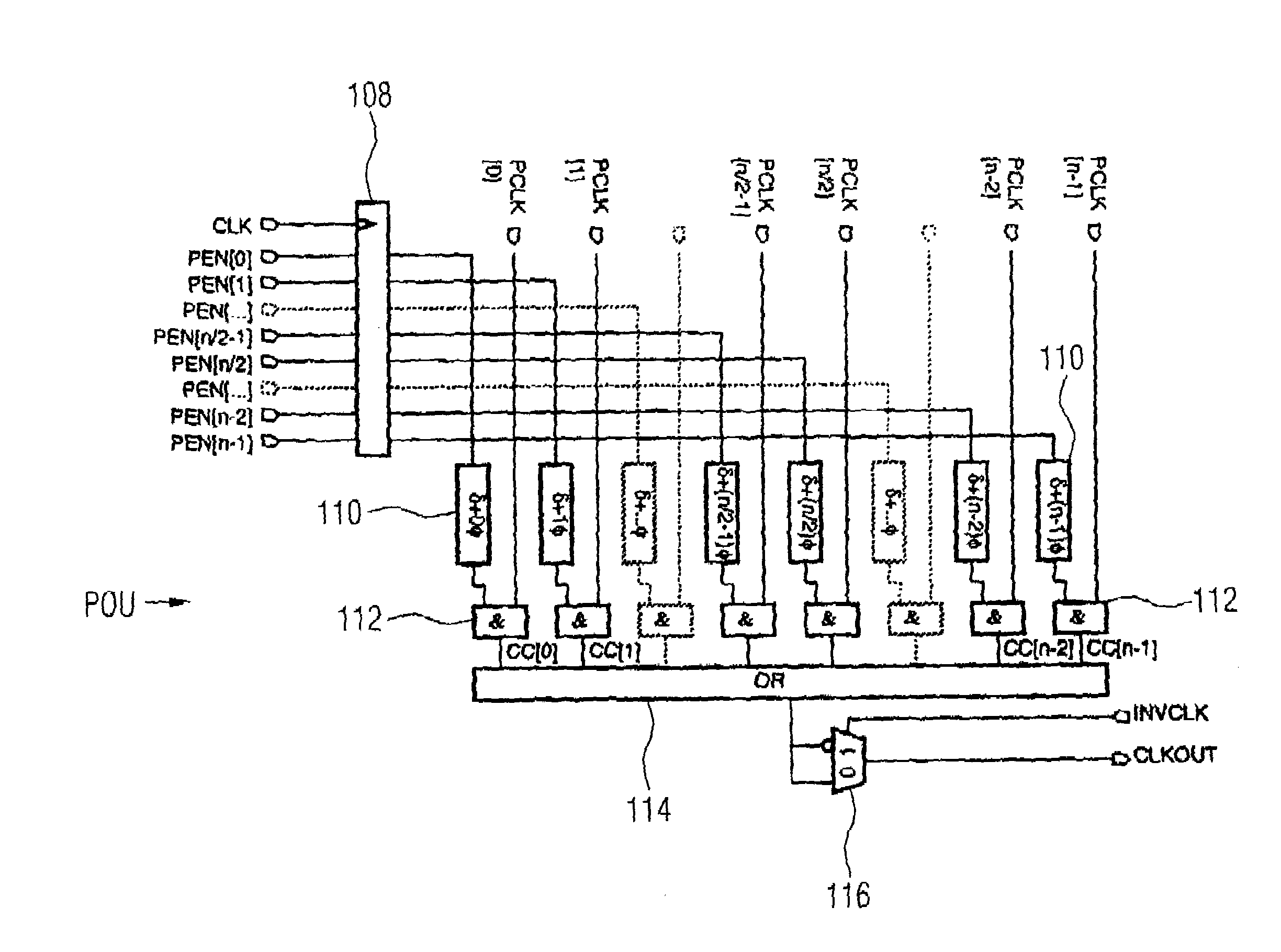
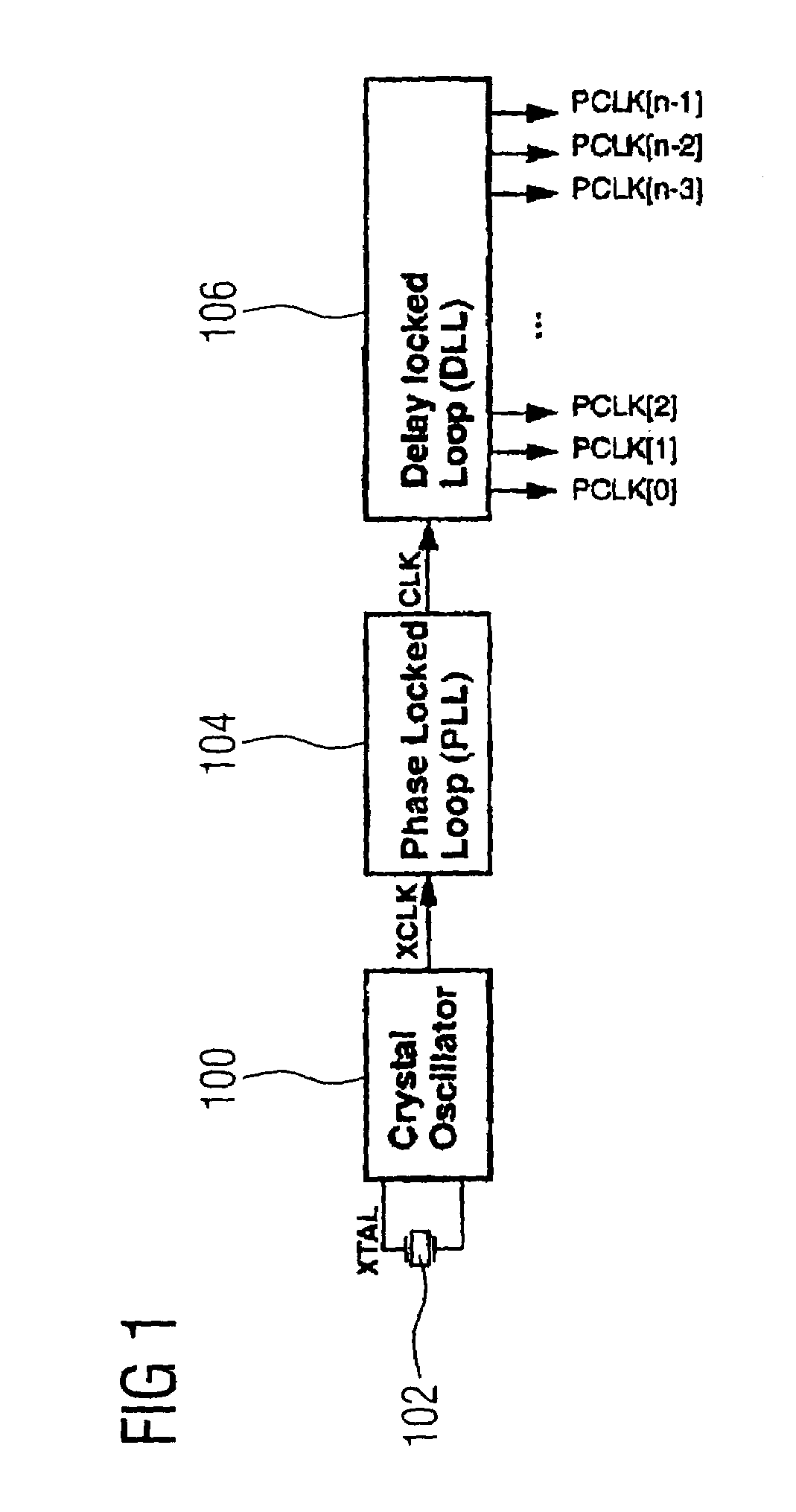
ActiveUS7126407B2High degreeImprove performancePulse automatic controlElectronic switchingControl signalEngineering
A method and device for generating a clock signal with predetermined clock signal properties firstly prepare a number of clock signals with an essentially identical frequency and with a respectively different phase relation with regard to a master clock signal in order to subsequently (on the basis of a control signal, which is prepared according to the clock signal to be generated), select predetermined clock signals from the number of prepared clock signals and to combine the selected clock signals in order to generate the desired clock signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
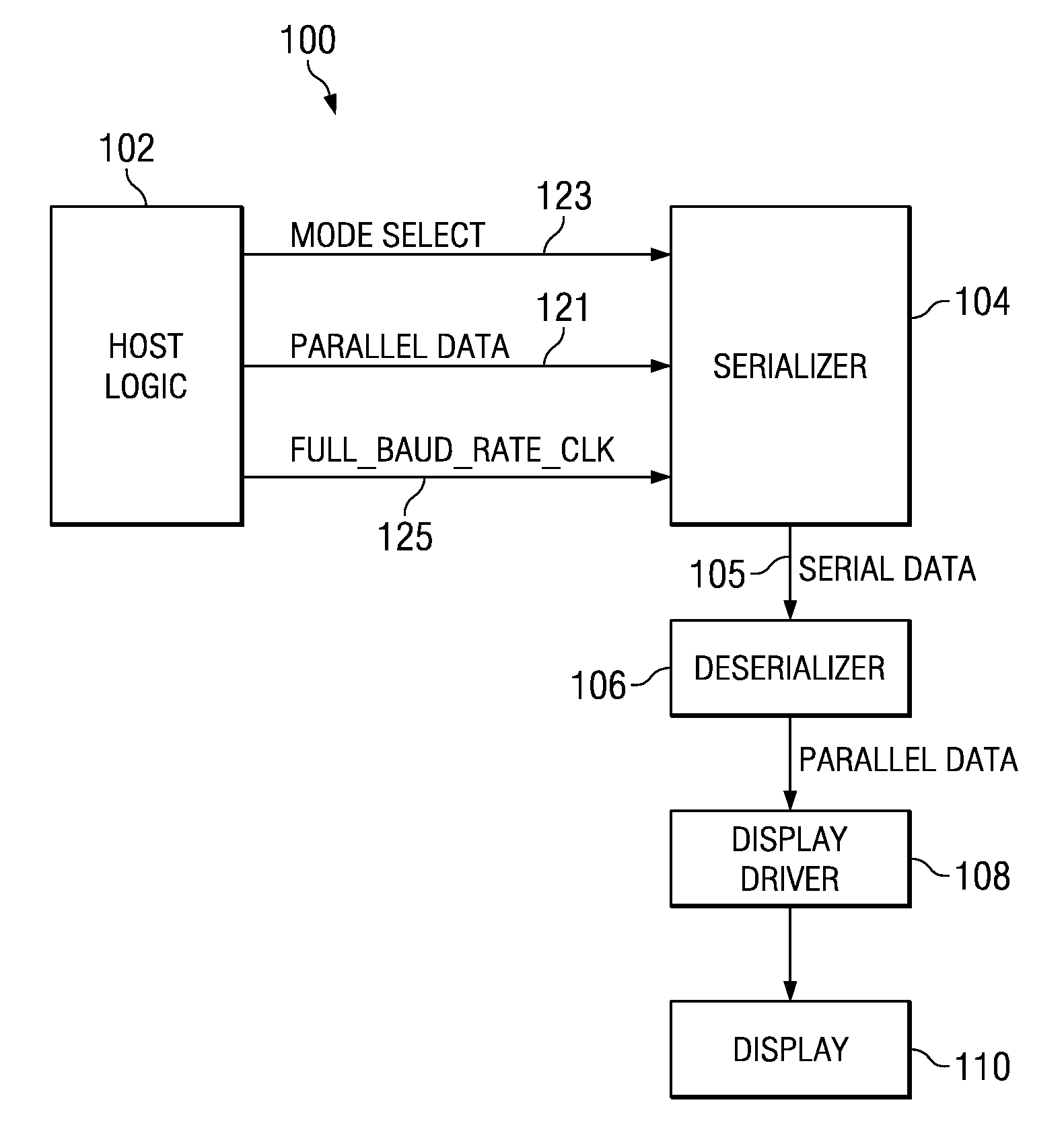
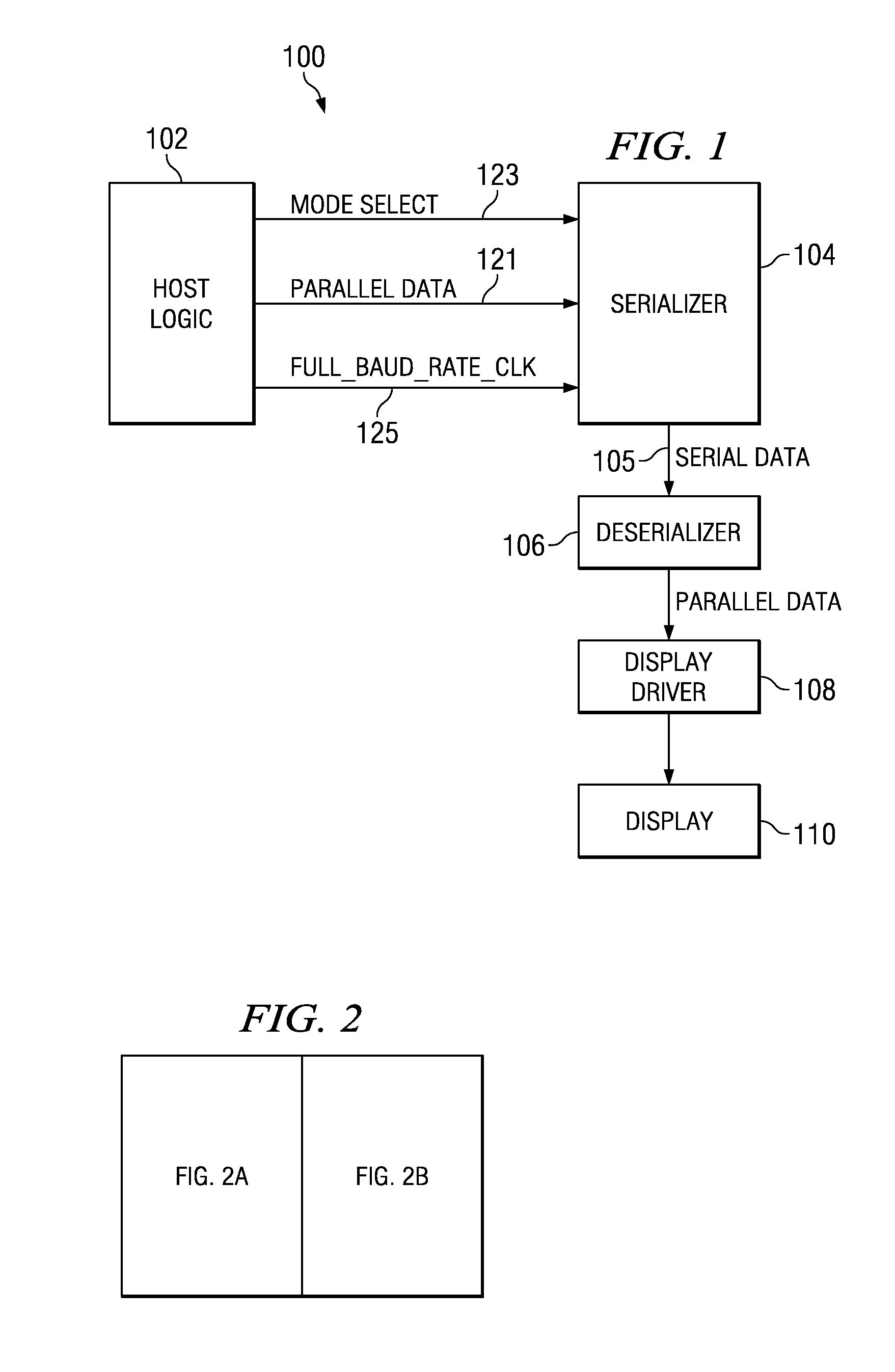
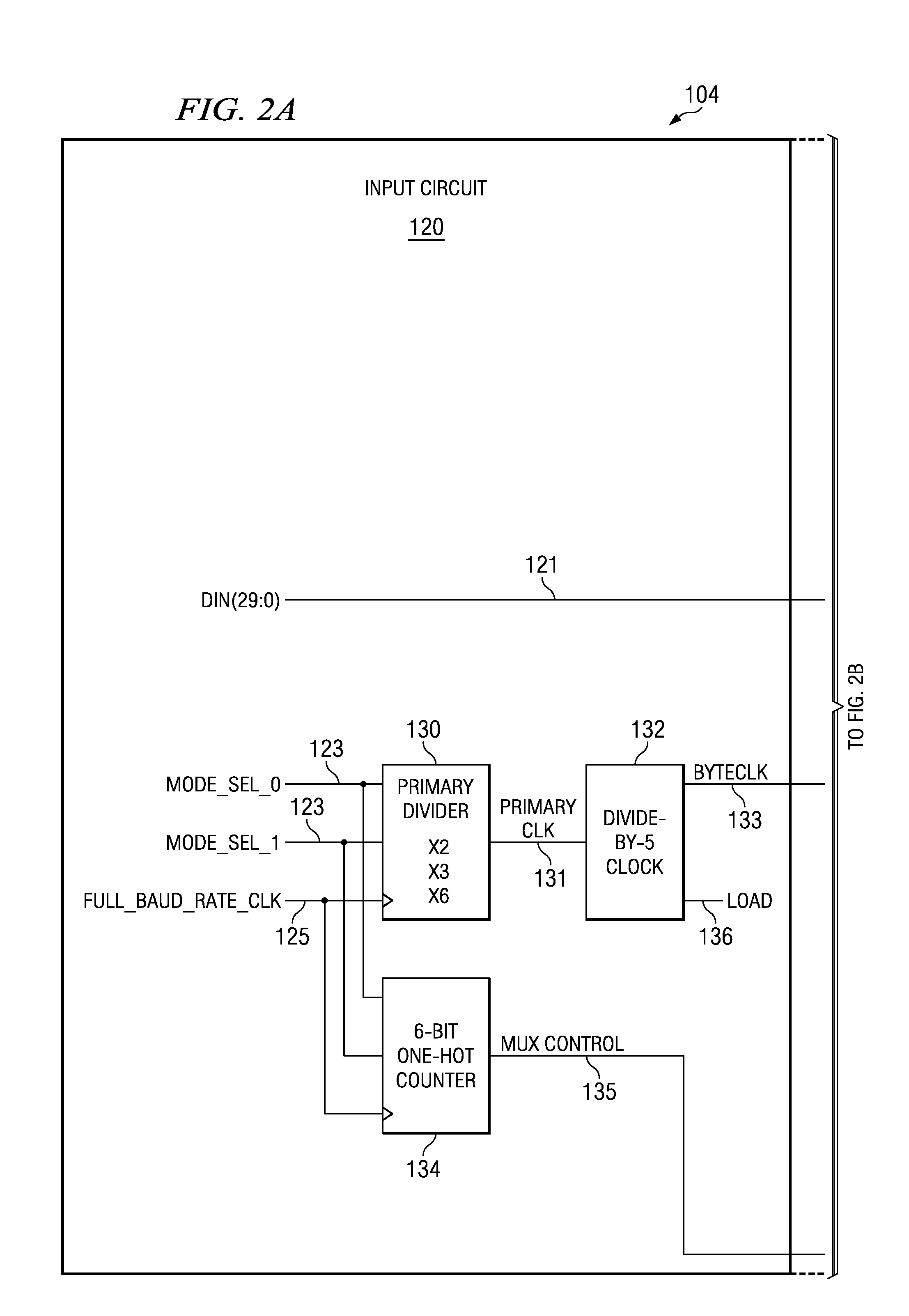
Programmable serializer for a video display
A serializer receives parallel data and a control signal. The serializer splits the parallel data into multiple subportions of data and, based on the control signal, sequentially outputs each of said subportions as serial output data in one or more serial output channels. The number of serial output channels is dictated by the control signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
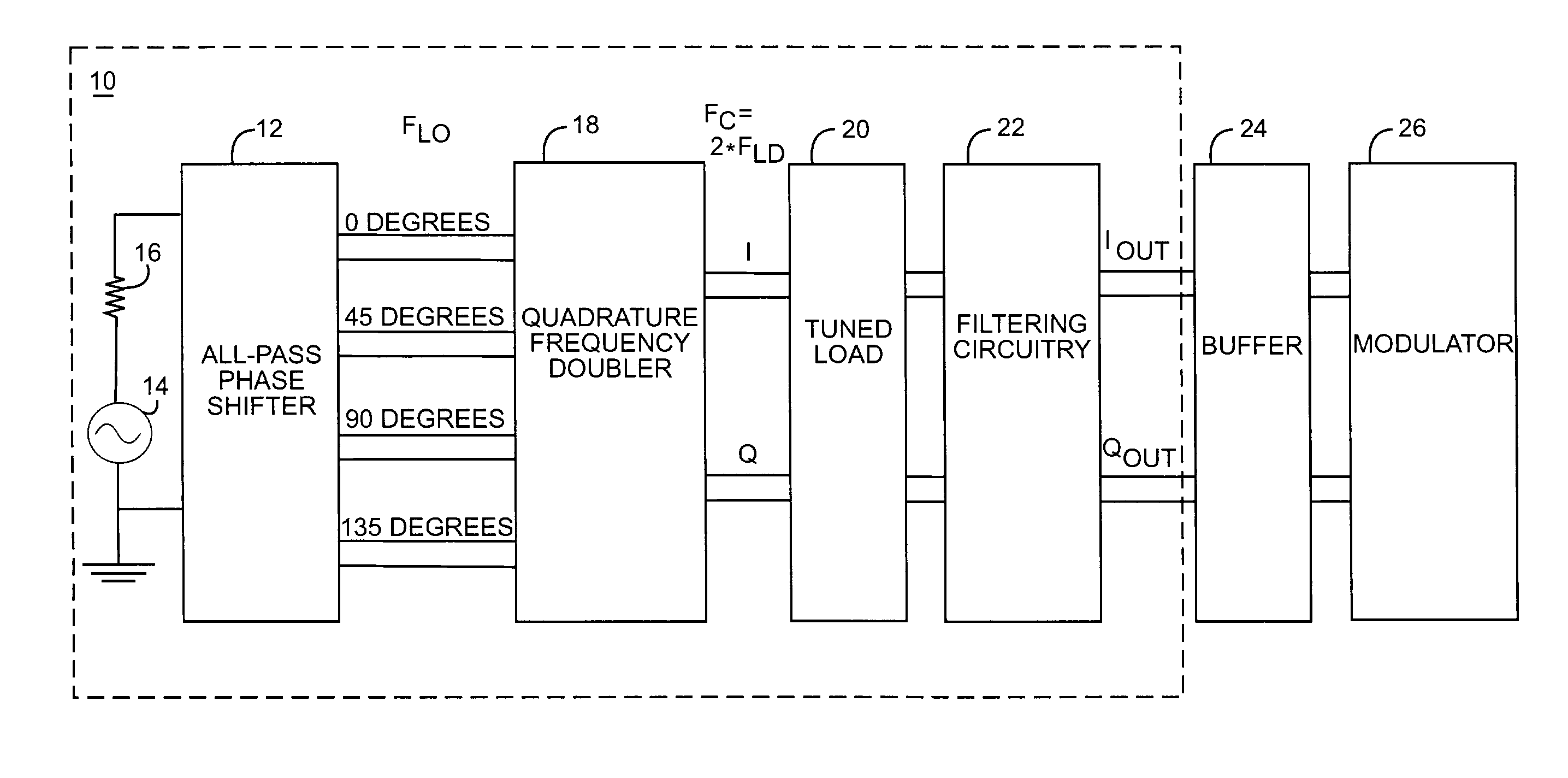
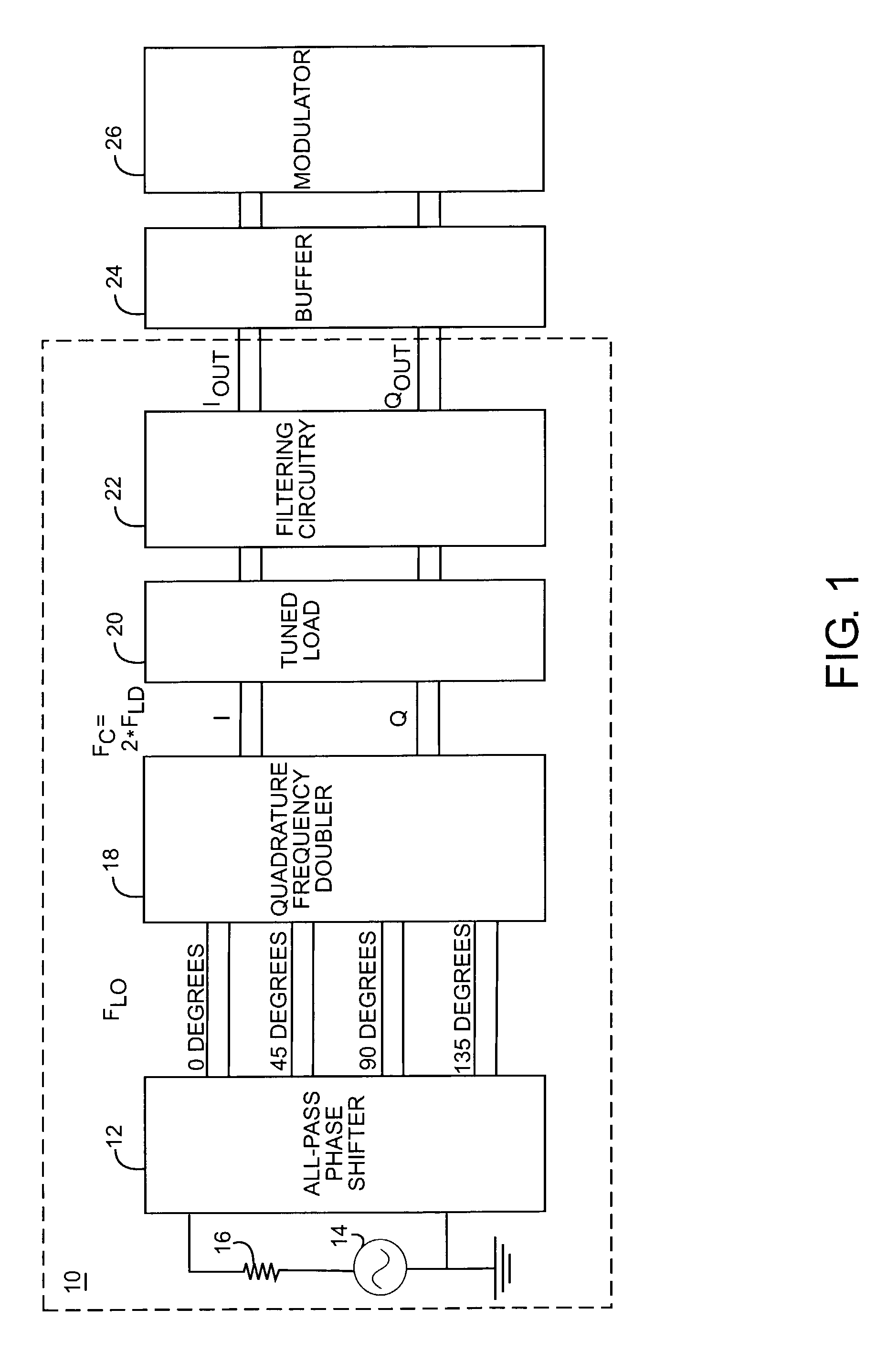
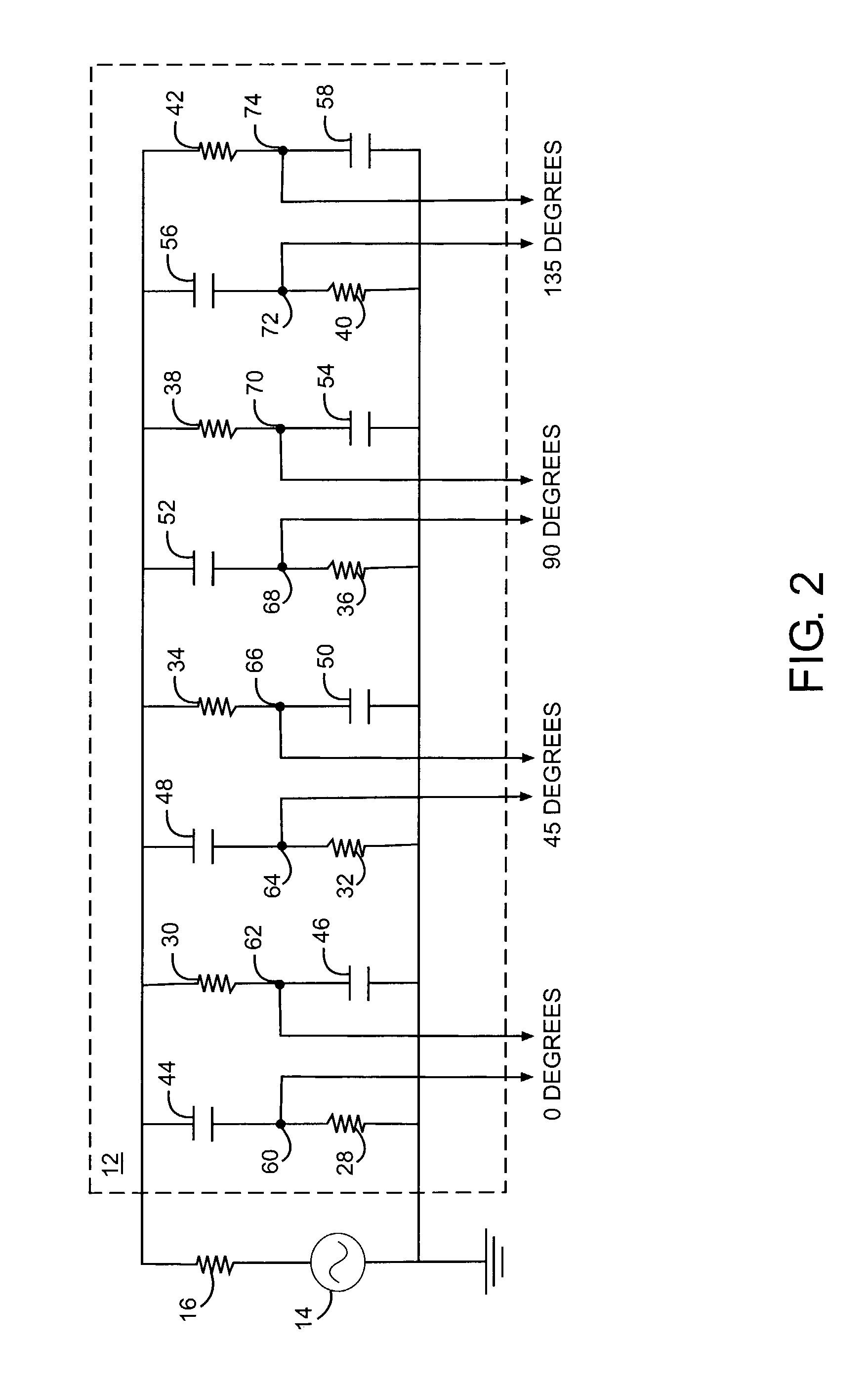
Quadrature frequency doubling system
ActiveUS7302011B1Improve accuracyImprove signal-to-noise ratioBroadcast circuit arrangementsAngle modulationQuadrature signalPhysics
The frequency doubler of the present invention operates to provide an in-phase signal and a quadrature signal, each having a frequency equal to twice the frequency of a reference signal. The in-phase and quadrature signals are based on signals that are 0 degrees, 45 degrees, 90 degrees, and 135 degrees out of phase with the reference signal. The in-phase signal is provided by multiplying the signals that are 0 degrees and 90 degrees out of phase with the reference signal, and the quadrature signal is provided by multiplying the signals that are 45 degrees and 135 degrees out of phase with the reference signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
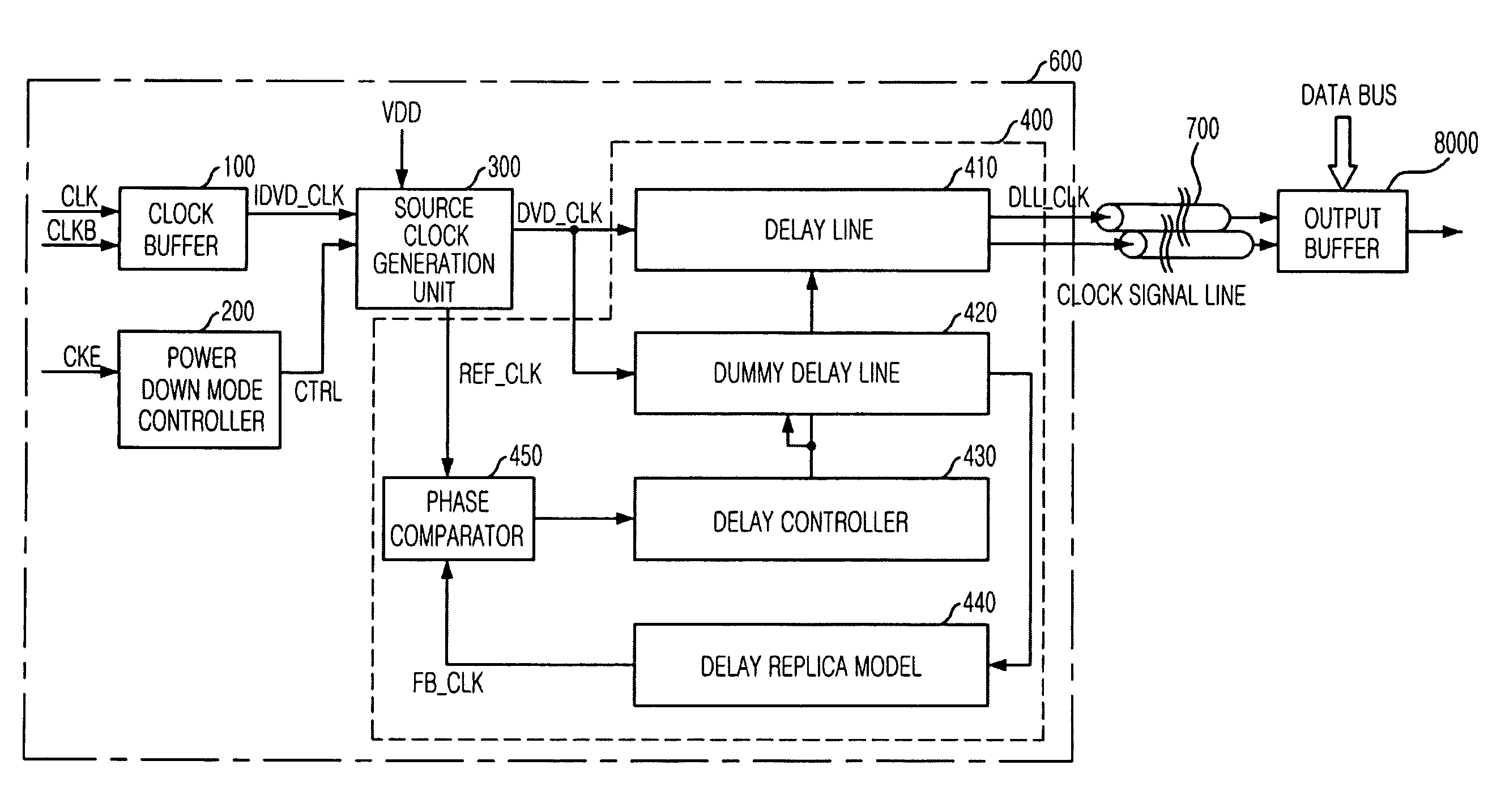
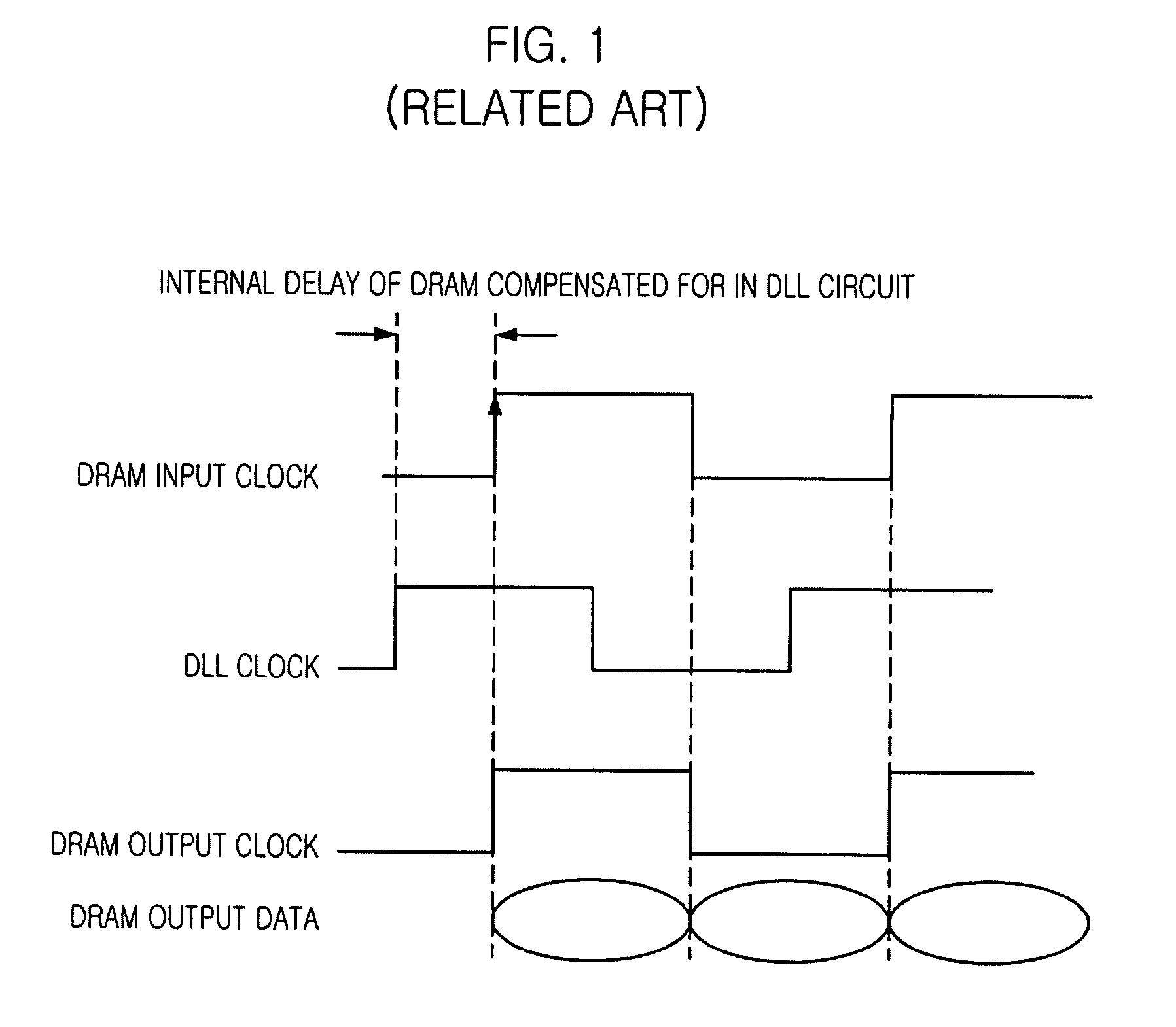
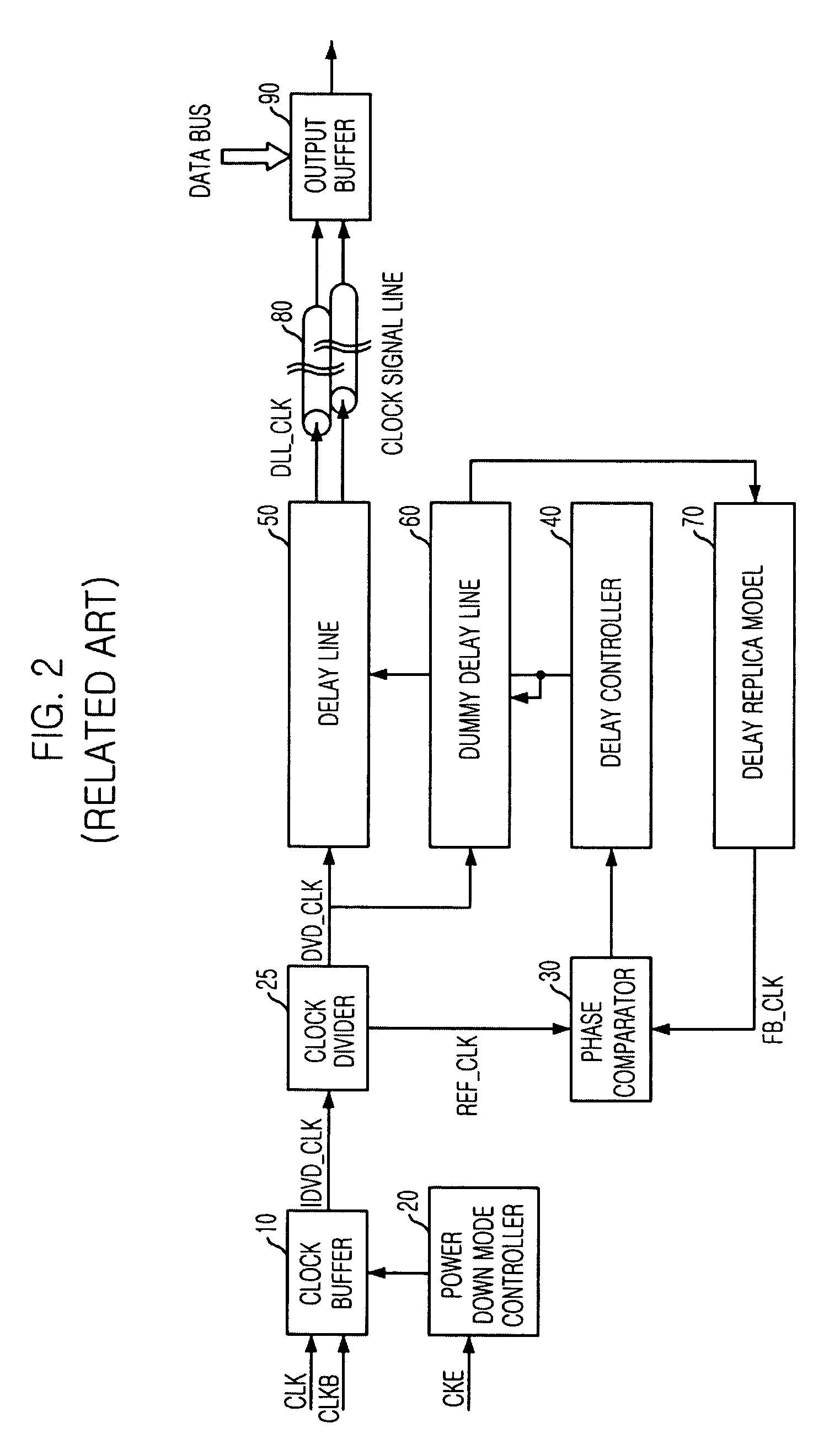
Delay locked loop circuit
ActiveUS7605622B2Avoid failurePulse automatic controlComputations using pulse rate multipliers/dividersControl signalMode control
A DLL of a memory device having a normal mode and a power down mode includes a clock buffer for buffering an external clock signal to output an internal clock signal. A power down mode controller generates a power down mode control signal to define the normal mode or the power down mode in response to a clock enable signal. A source clock generation unit receives the internal clock signal to generate a DLL source clock signal under the control of the power down mode control signal. A phase update unit performs a phase update operation based on the DLL source clock signal to output a DLL clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com