Patents
Literature
163results about "Pulse manipulation delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
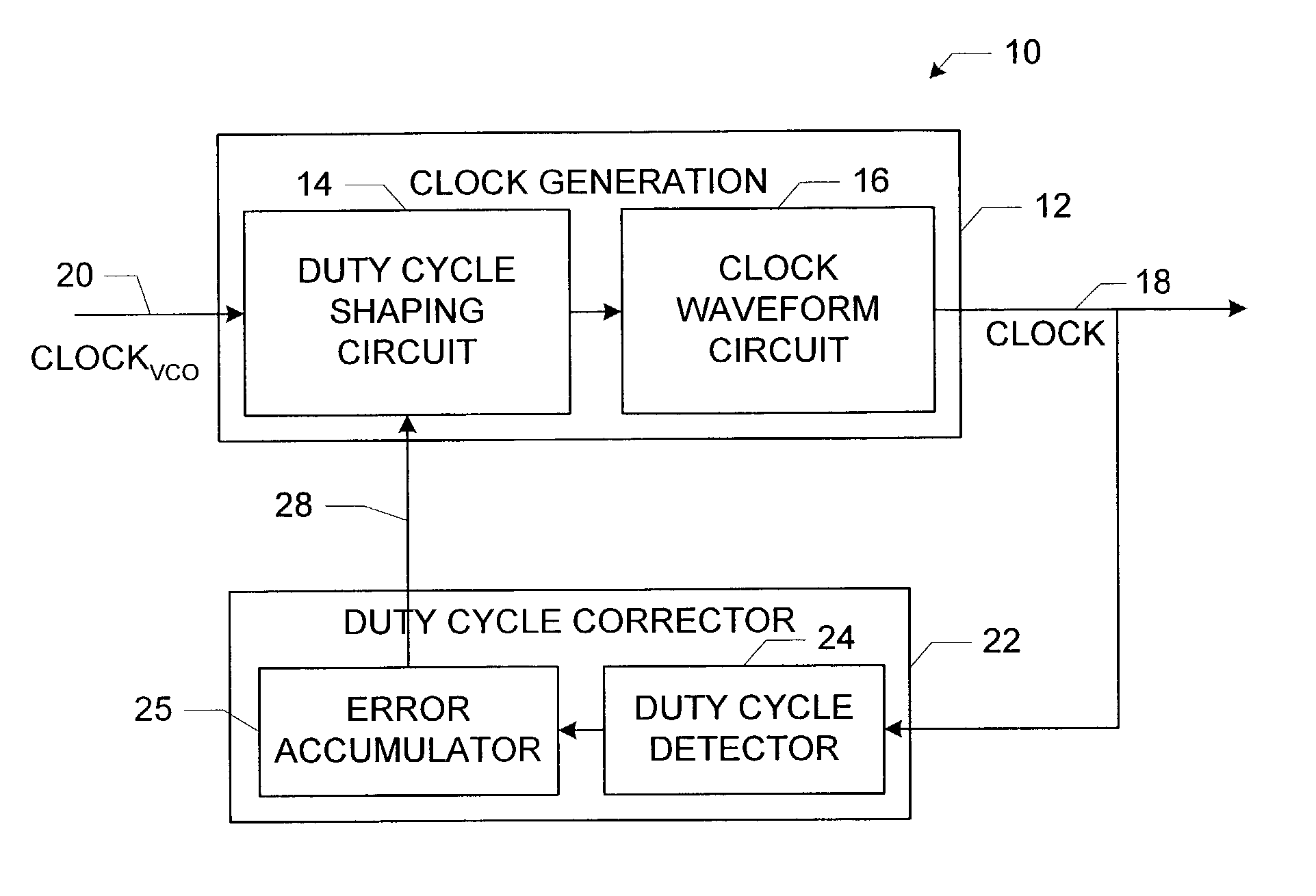
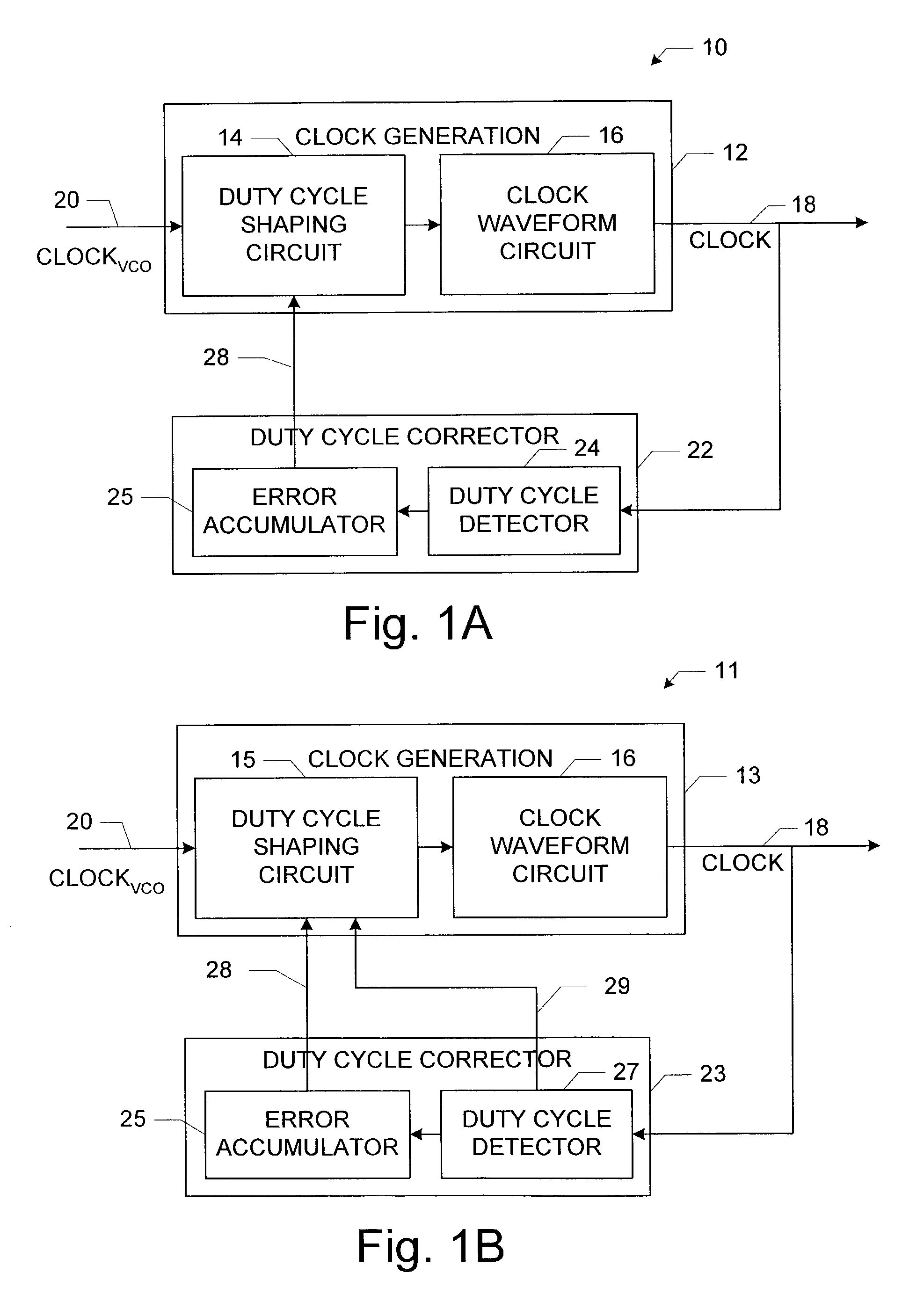
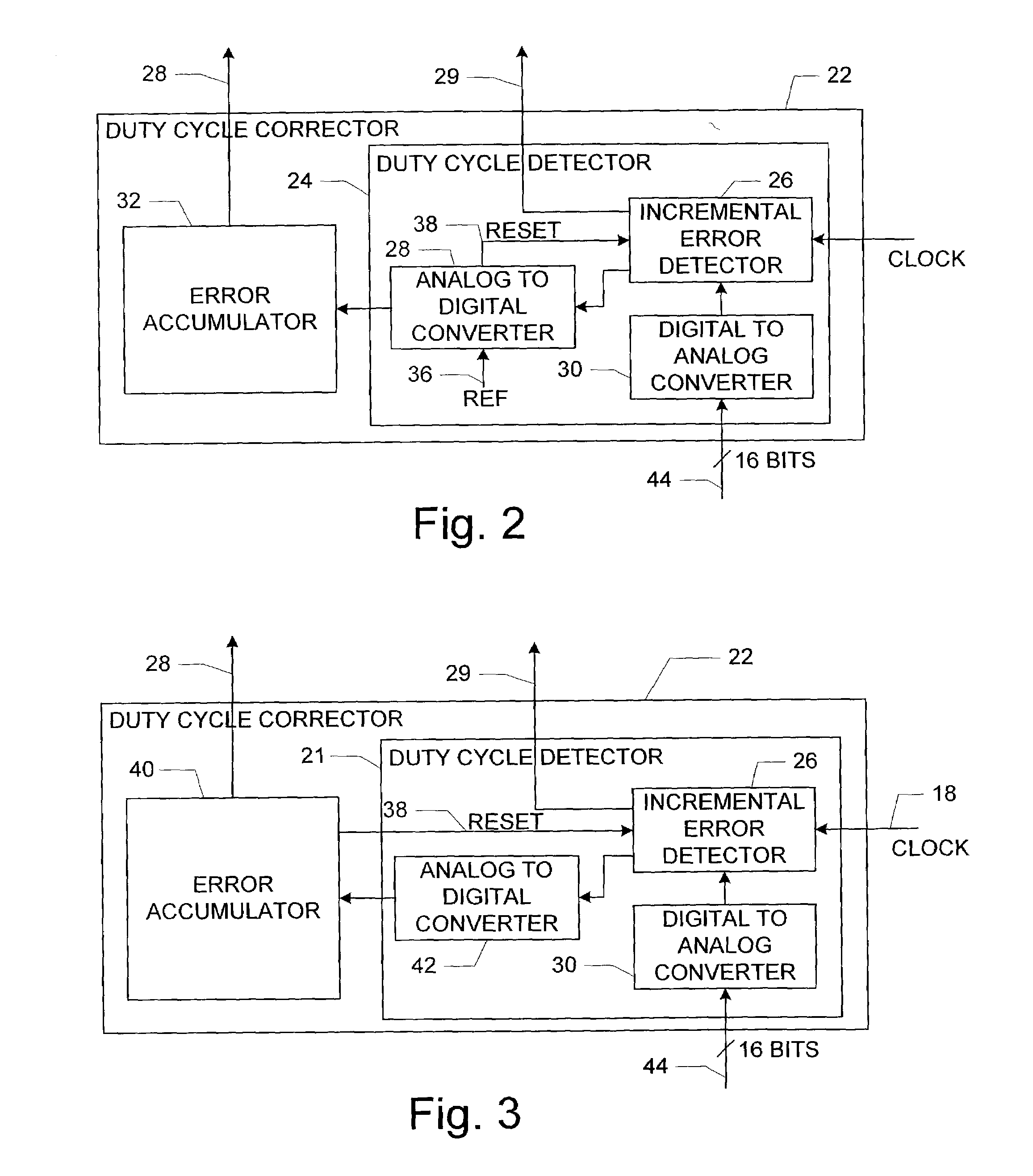
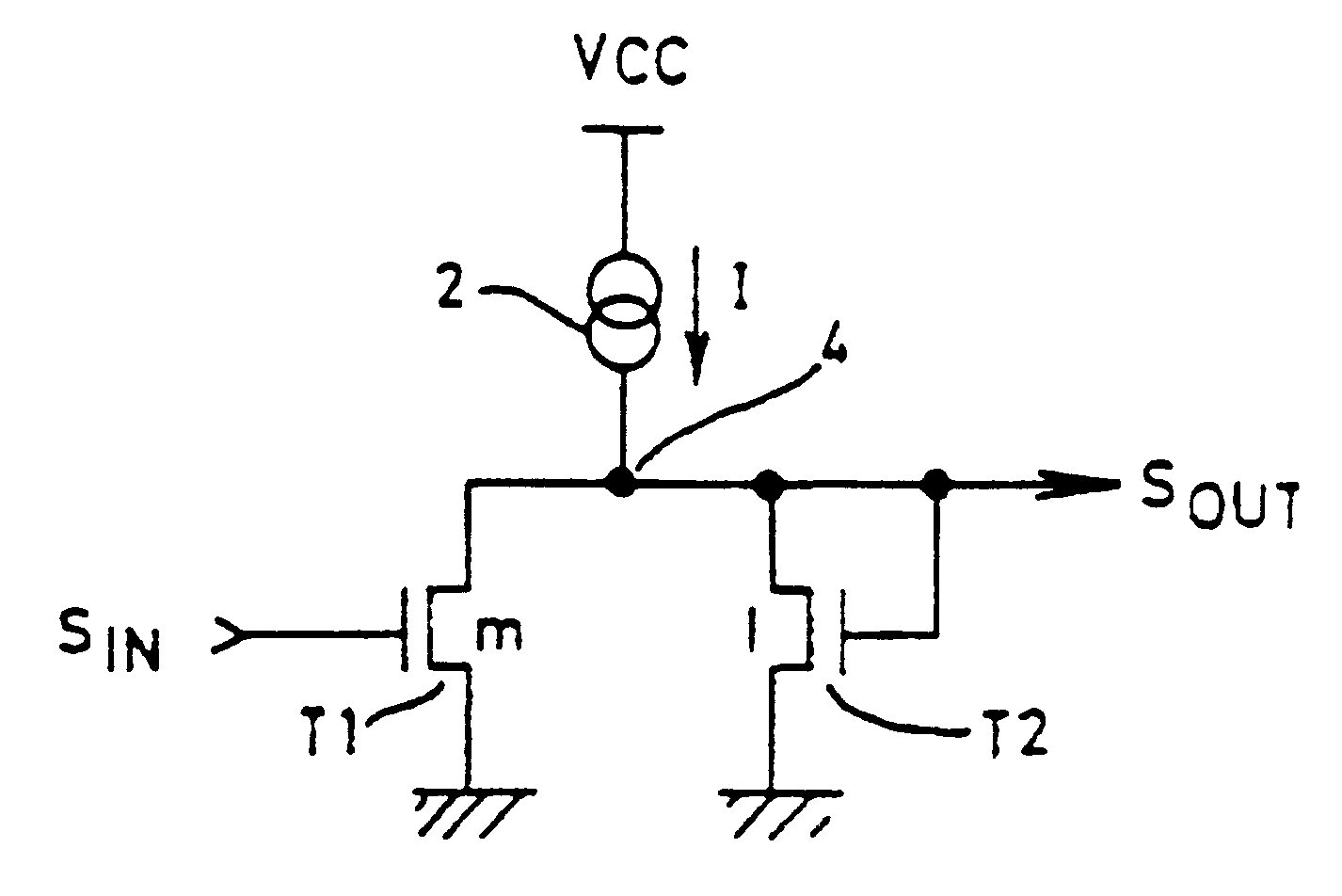
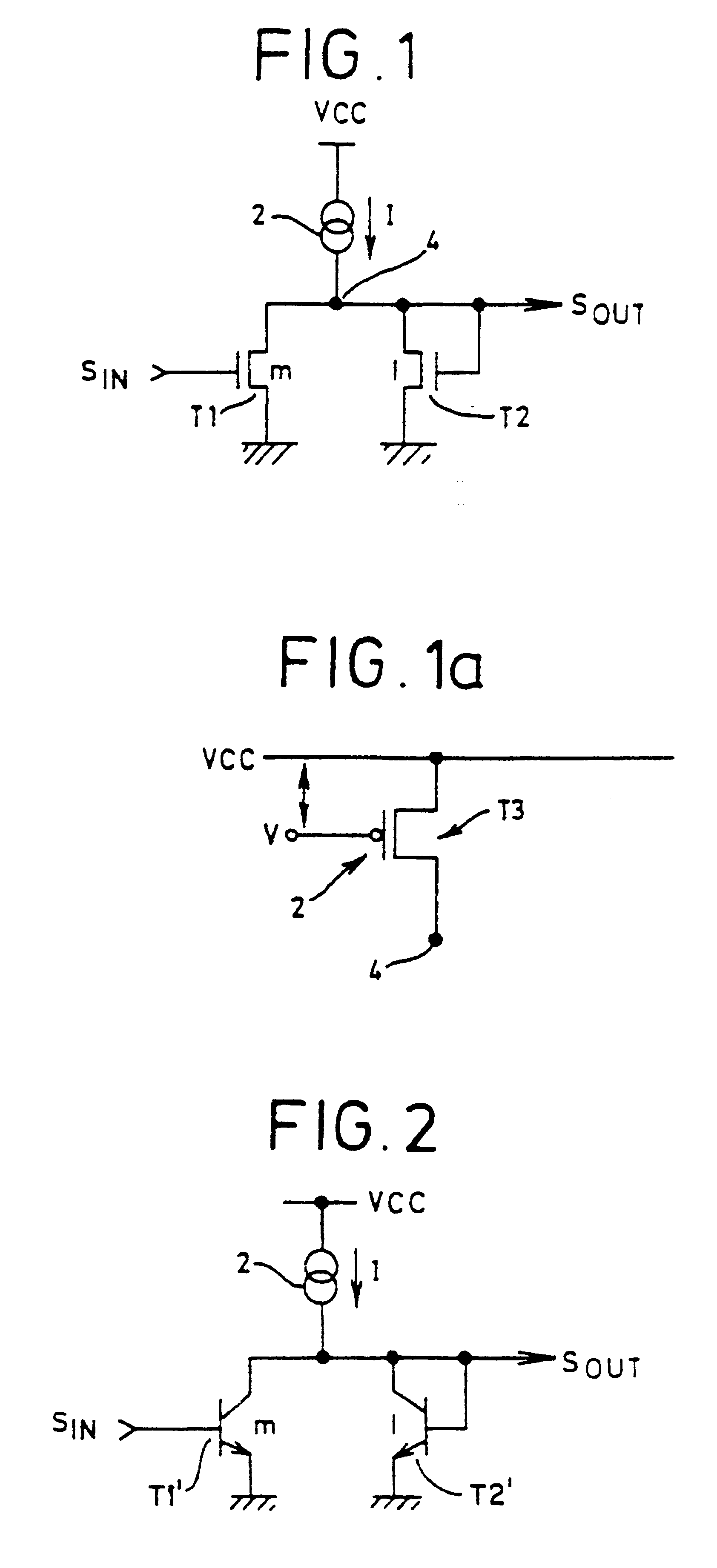
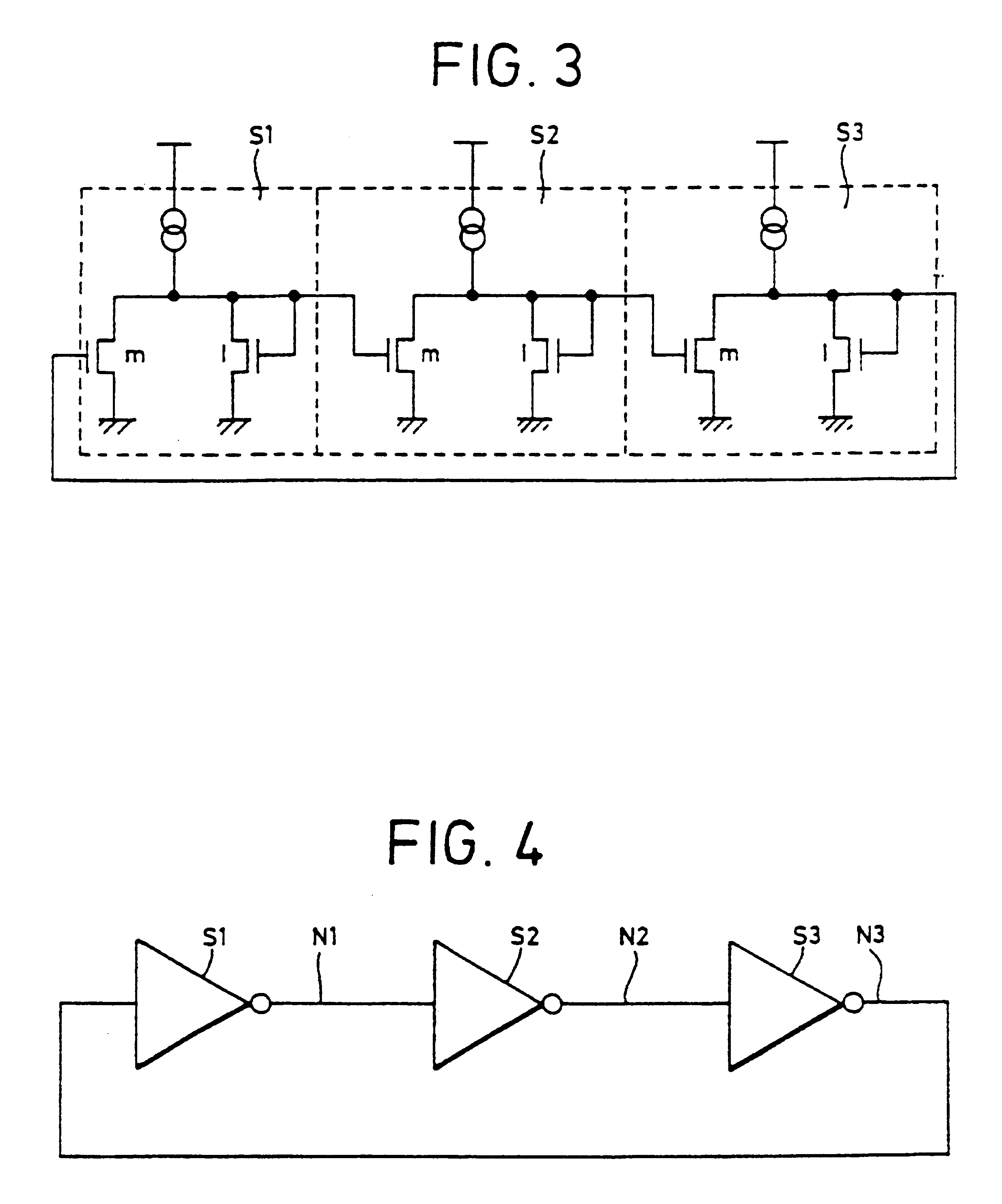
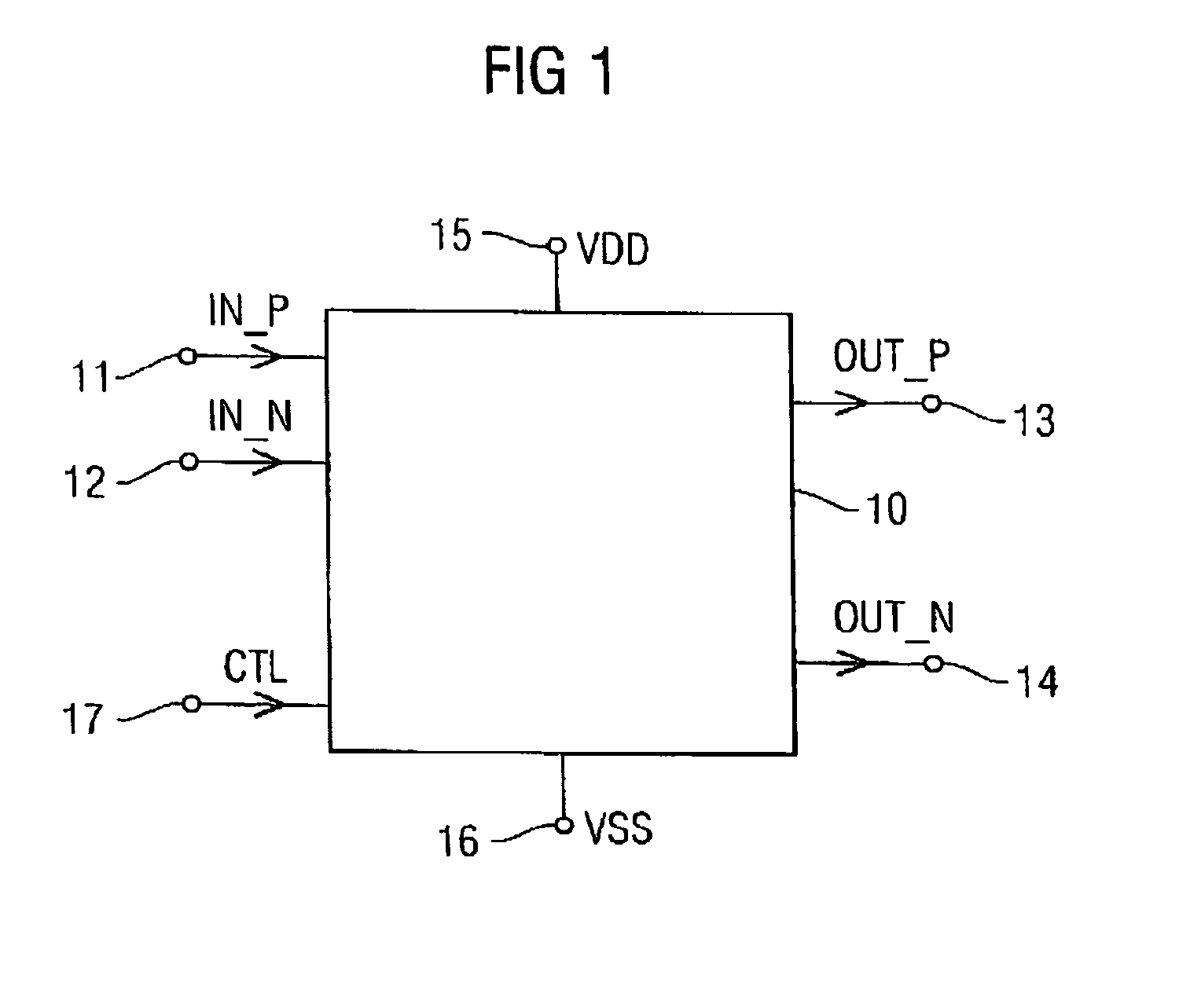
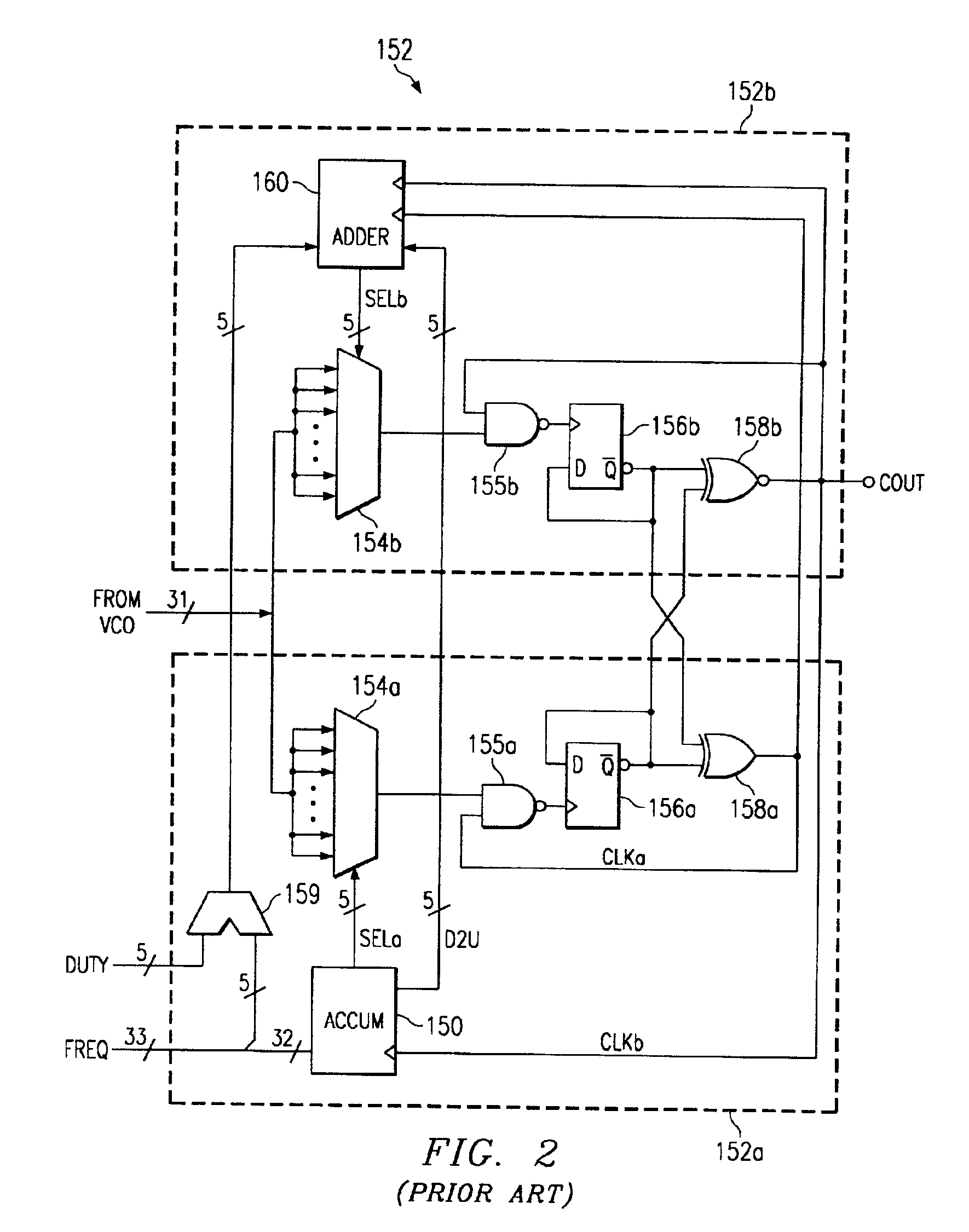
Method and apparatus for digital duty cycle adjustment
InactiveUS6967514B2Reliability increasing modificationsContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationError signalClock signal
Adjusting a clock duty cycle. An incremental error signal is generated in response to the clock signal. A cumulative error signal is generated in response to the incremental error signal. The incremental error signal is reset and the duty cycle of the clock signal is adjusted in response to the cumulative error signal.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
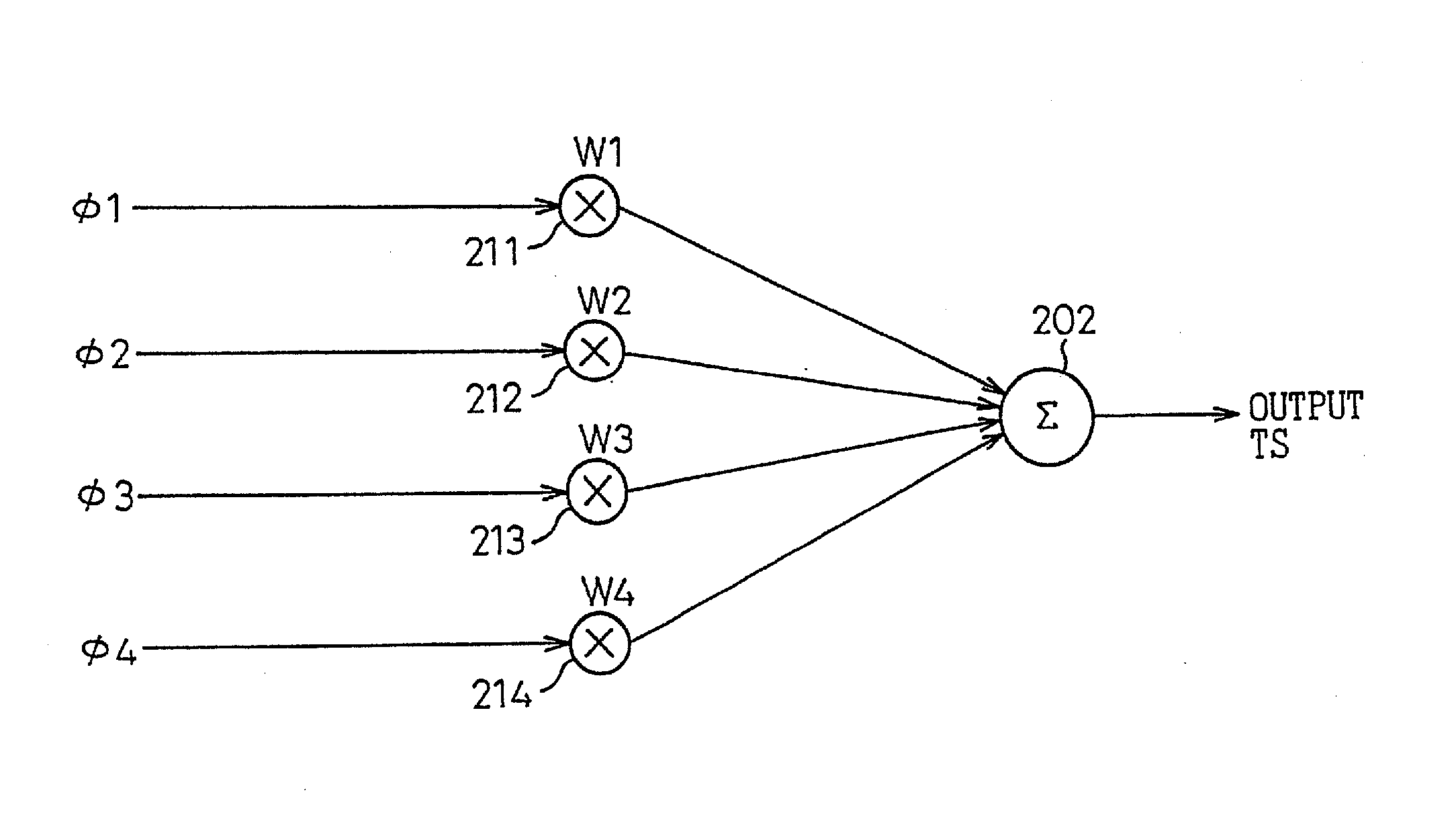
Phase-combining circuit and timing signal generator circuit for carrying out a high-speed signal transmission
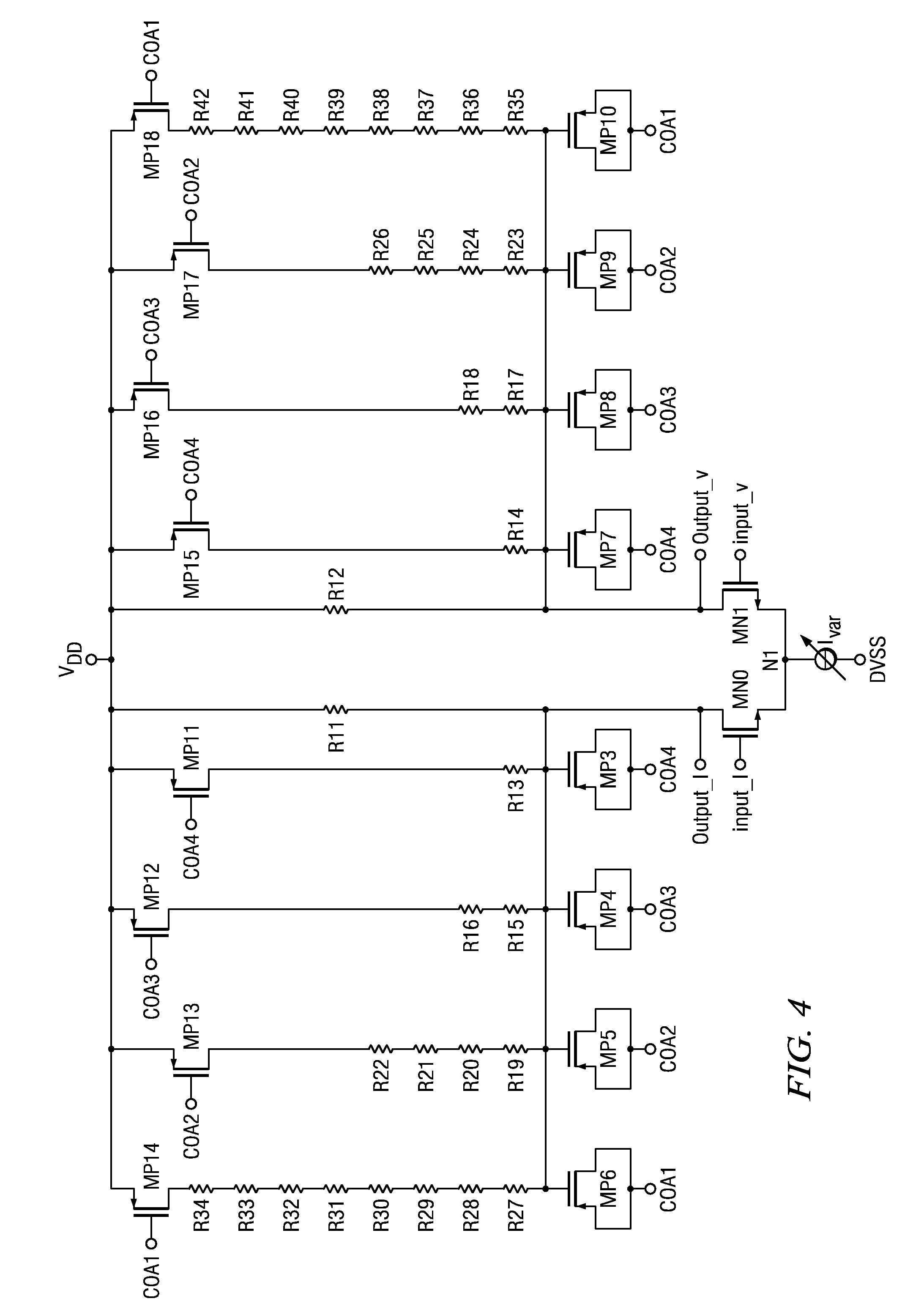
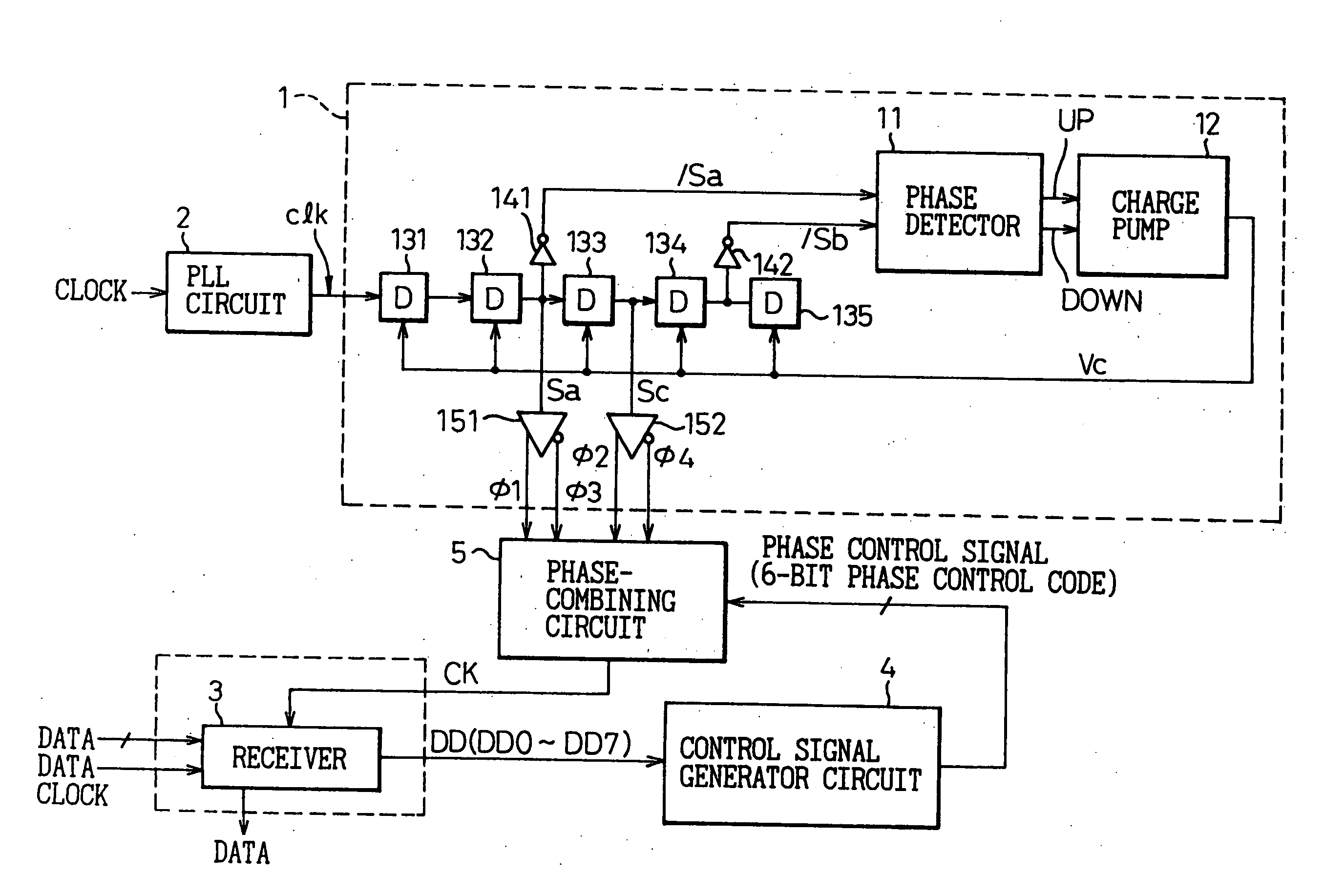
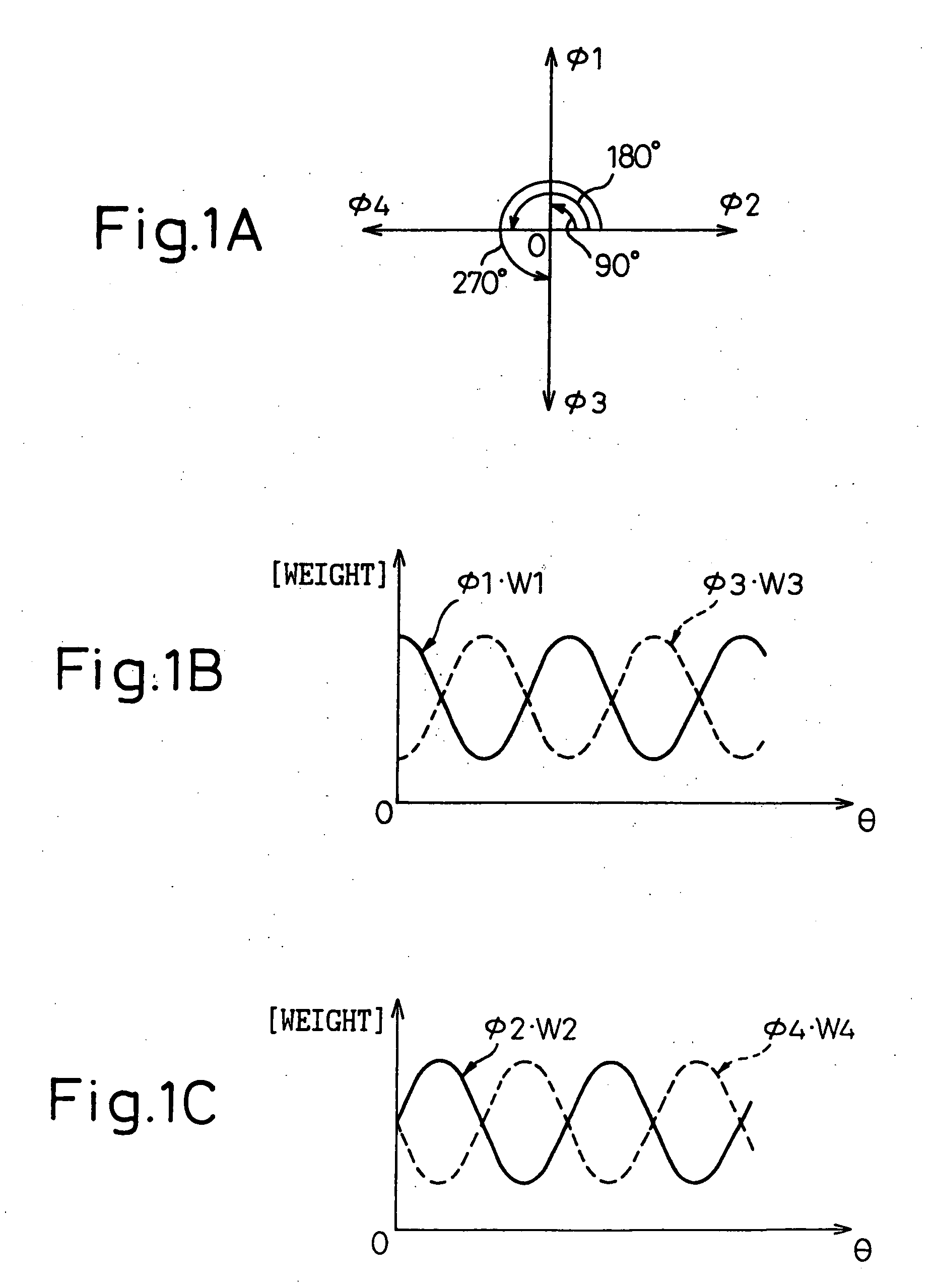
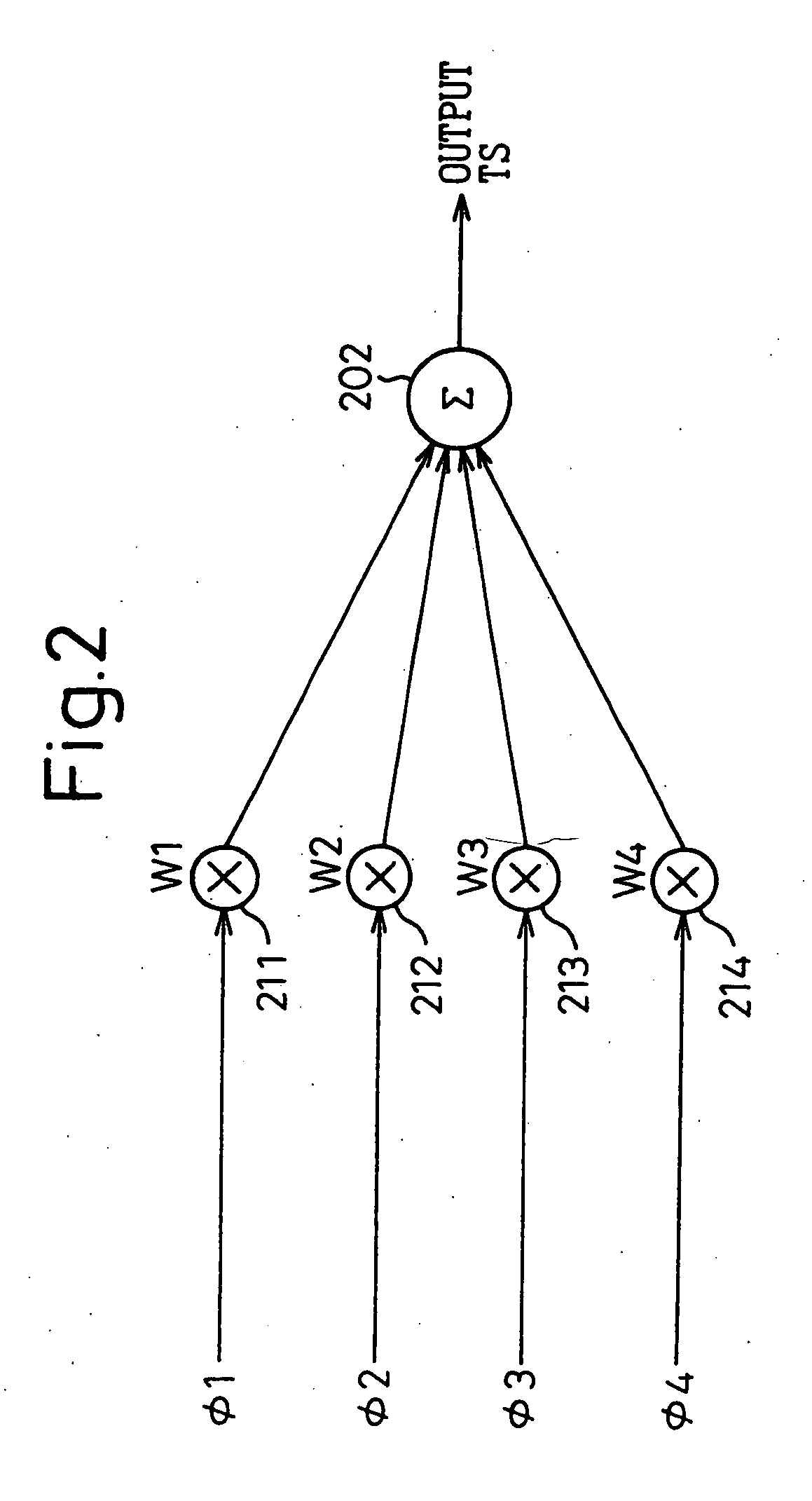
InactiveUS20130314142A1Simple structureError minimizationPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsControl signalPhase control
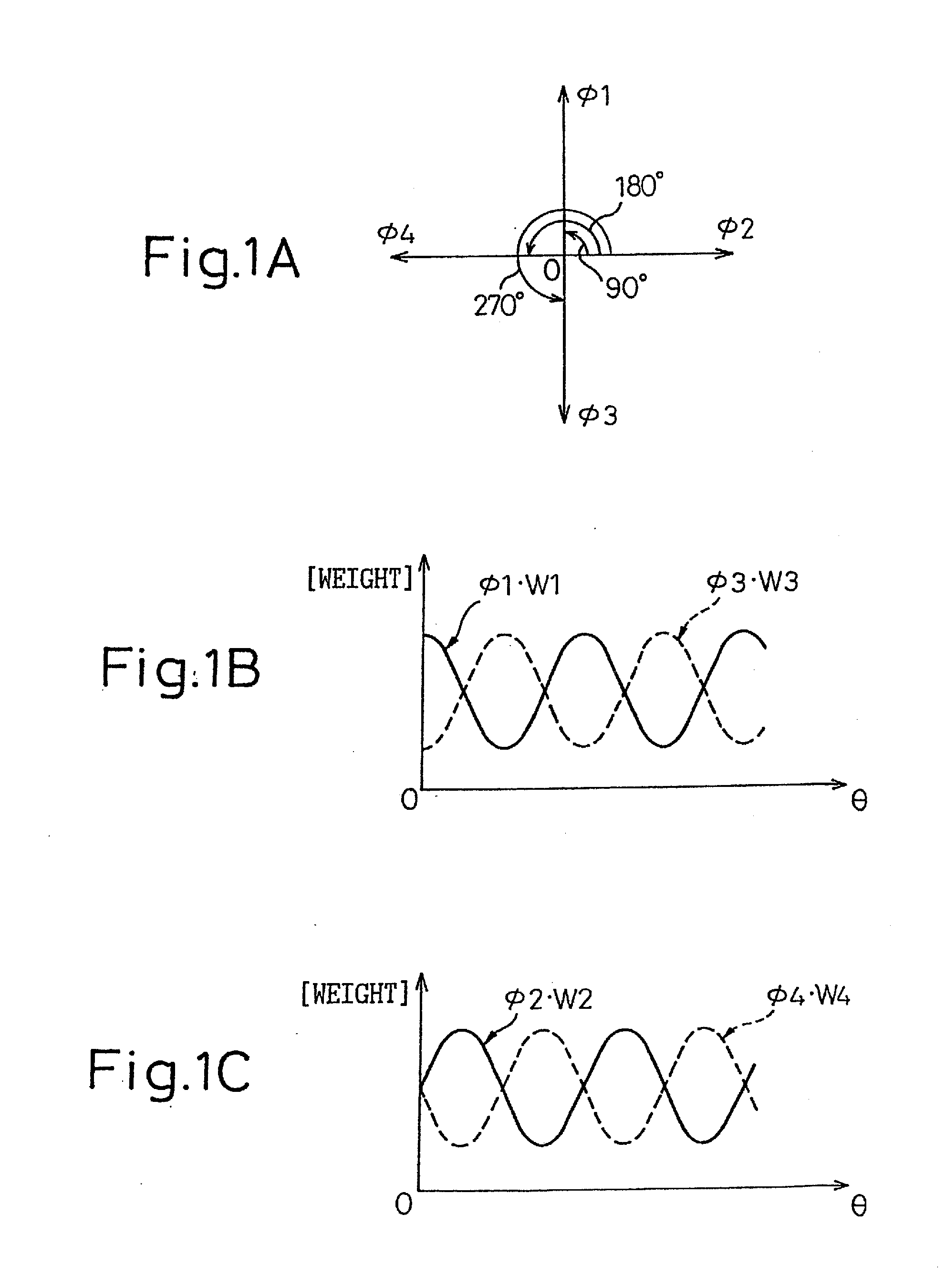
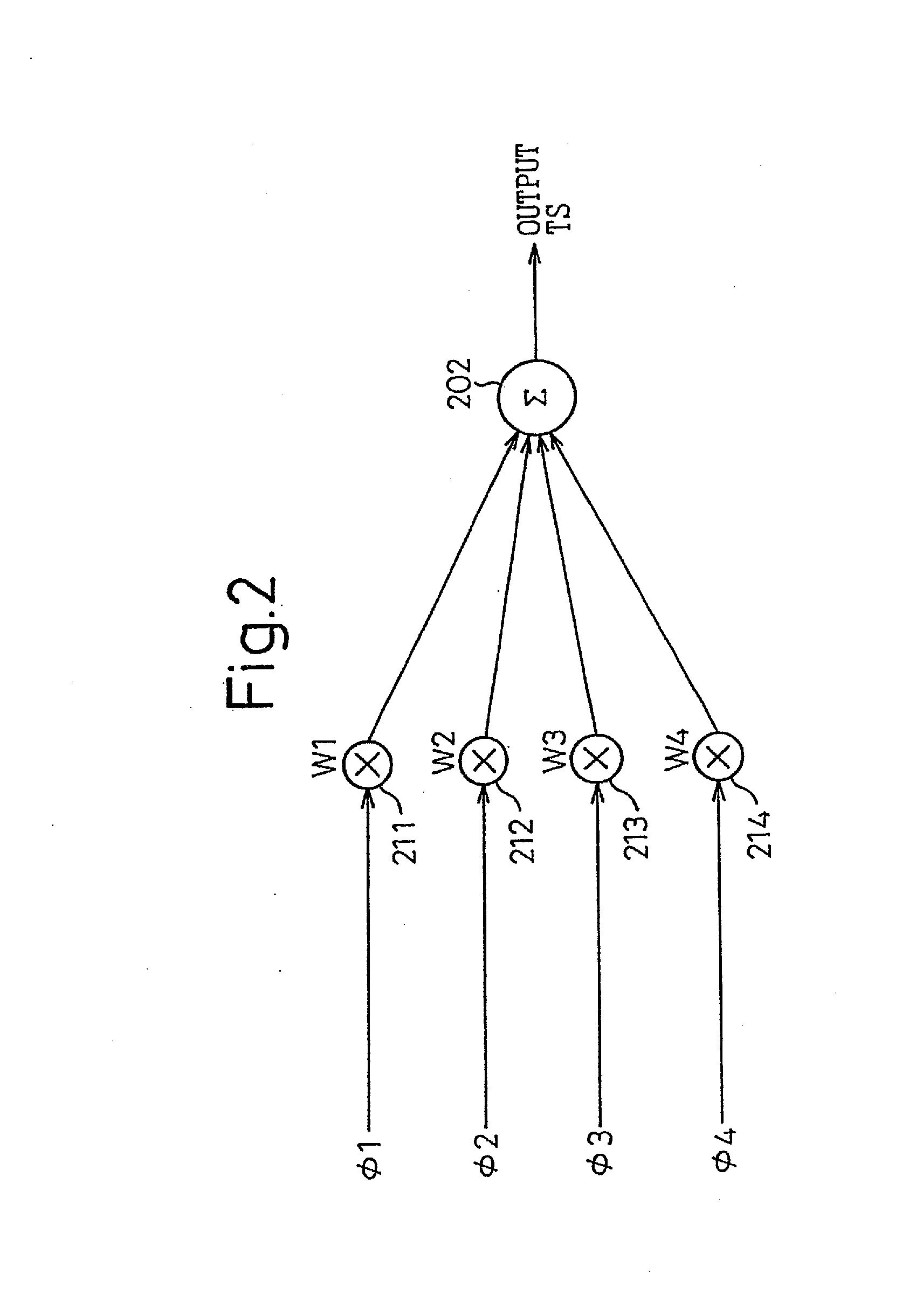
A phase-combining circuit for combining cyclic timing waveforms that have been phase-controlled by control signals based on three or more input signals of different phases, has a weight signal generating circuit and a weighting circuit. The weight signal generating circuit generates weights according to the control signals, and the weighting circuit gives the weights to the respective input signals, with a positive or negative polarity for each one signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
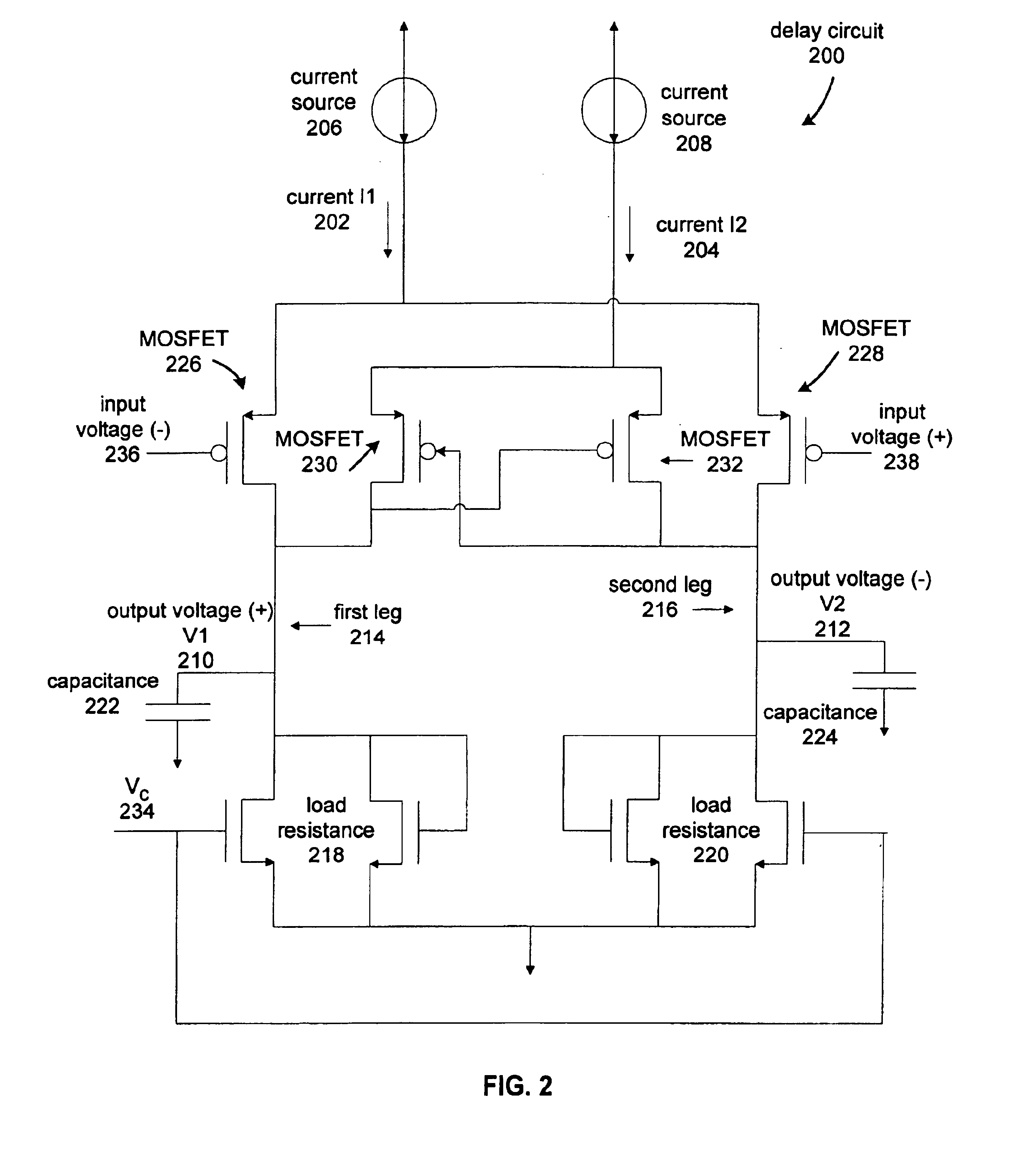
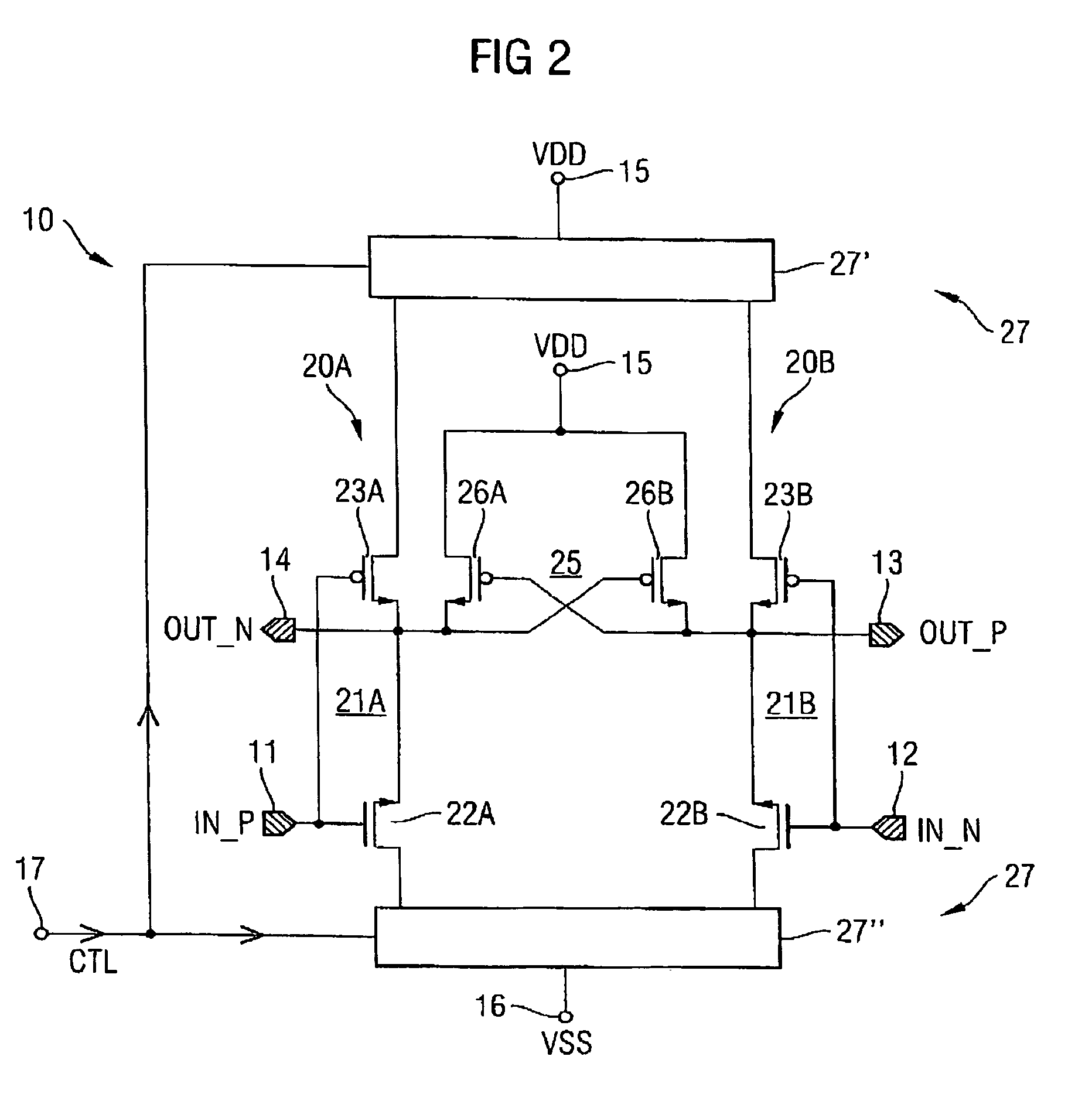
Current controlled delay circuit
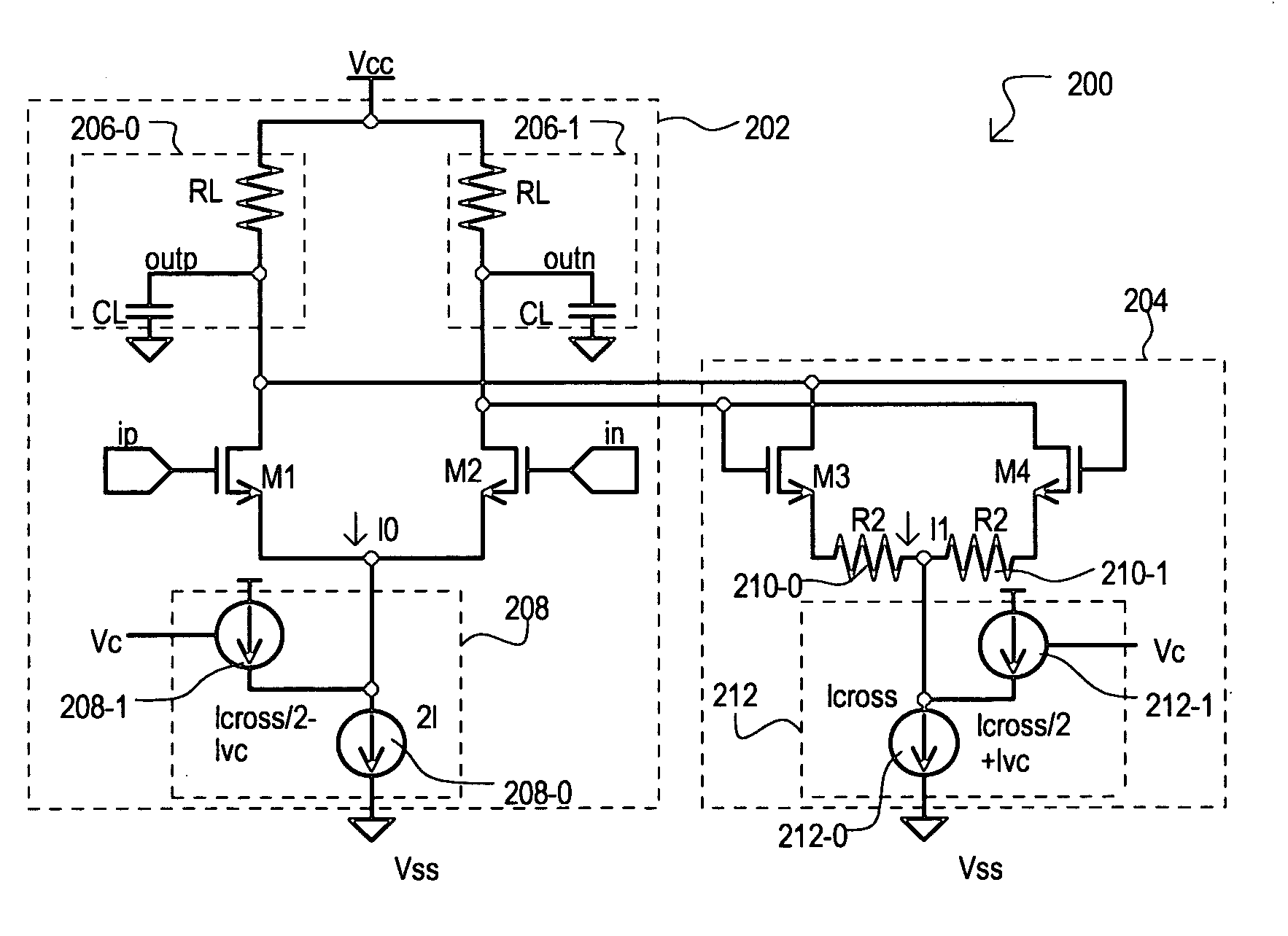
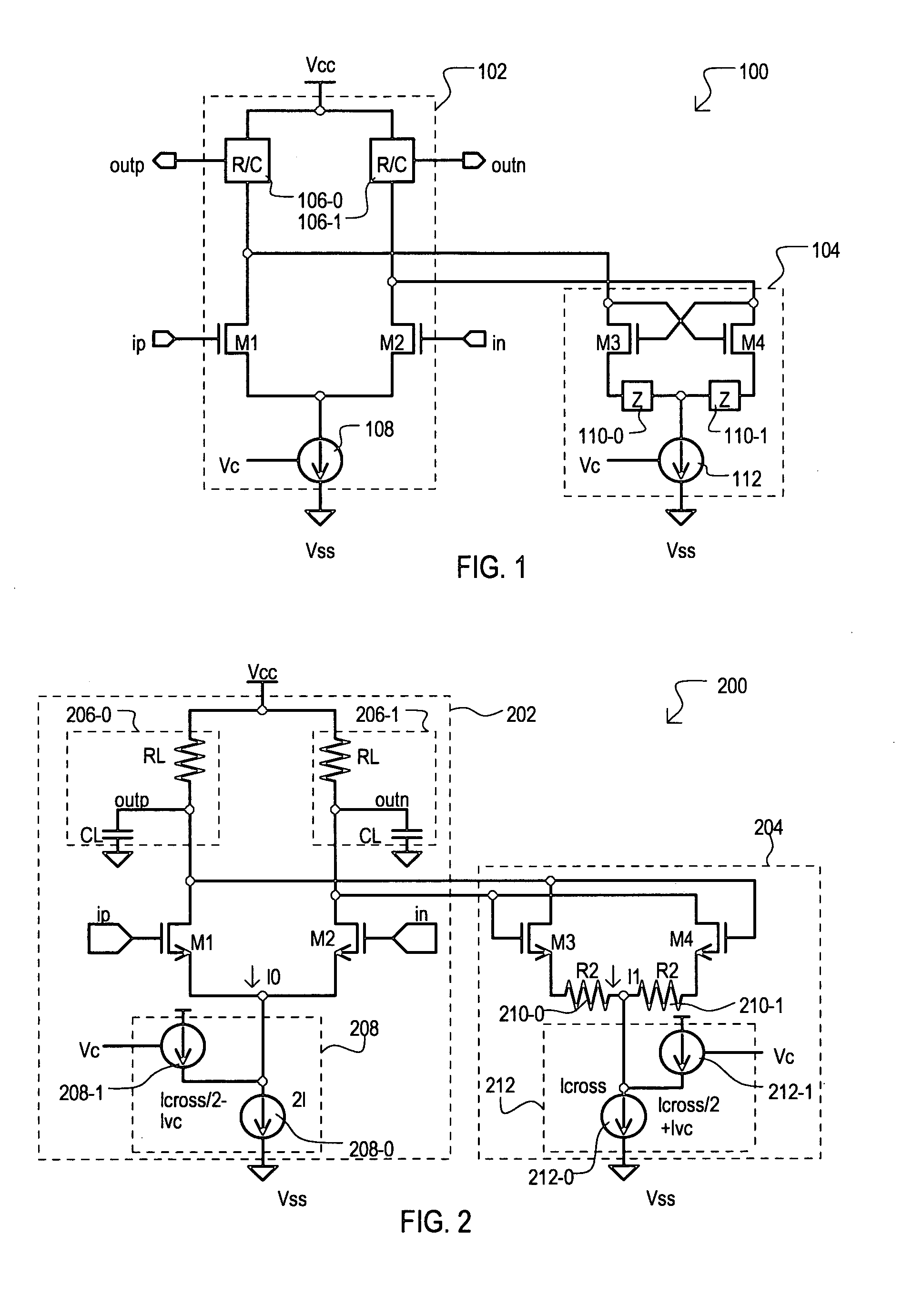
A current controlled delay circuit is disclosed. Two currents of constant sum are generated to control the delay of the circuit. The circuit includes a differential pair to switch one of the two currents from one leg of the circuit to another leg of the circuit. The circuit includes a cross-coupled pair to switch the other of the two currents from one leg of the circuit to another leg of the circuit. The circuit may include a fixed or variable load.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
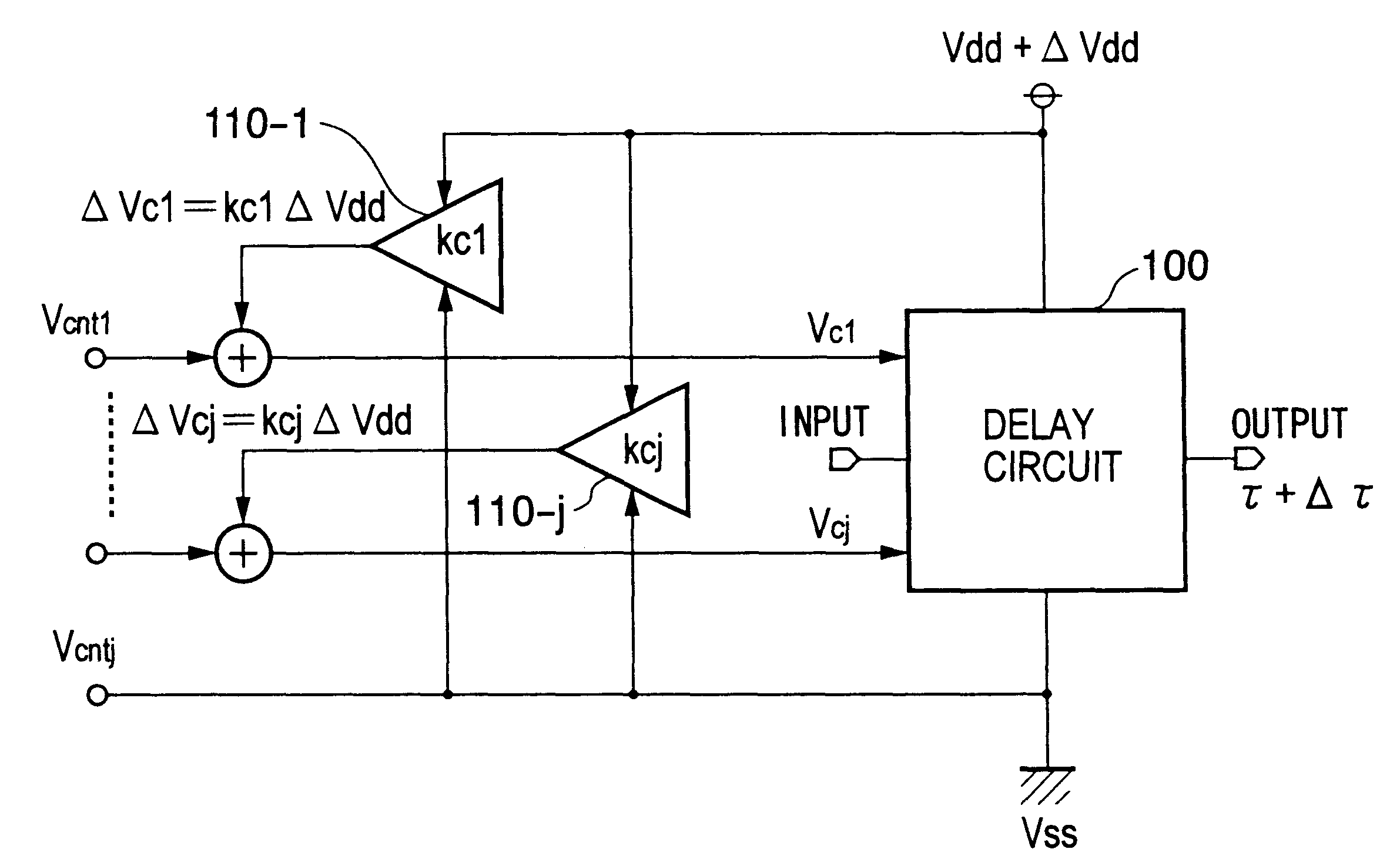
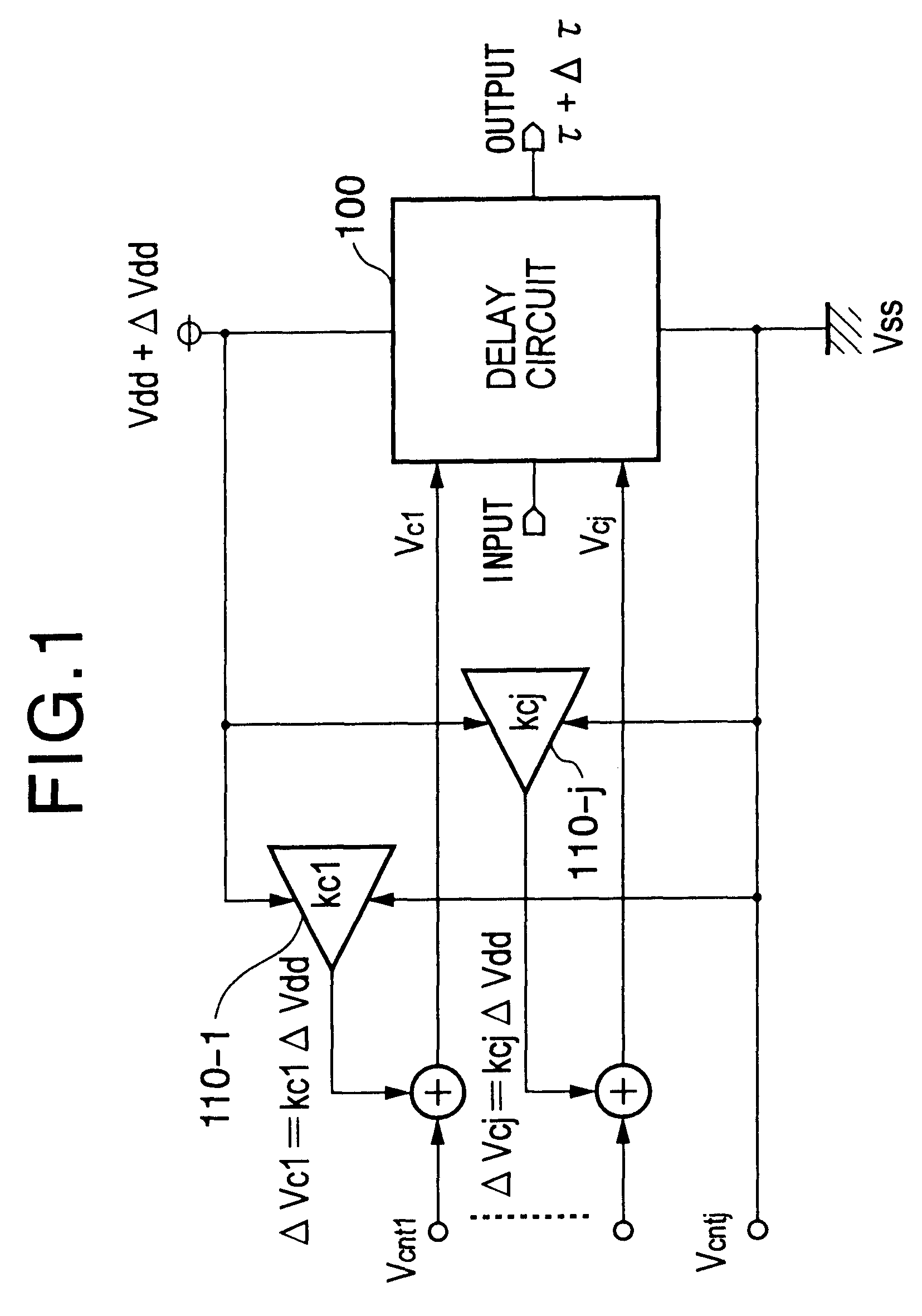
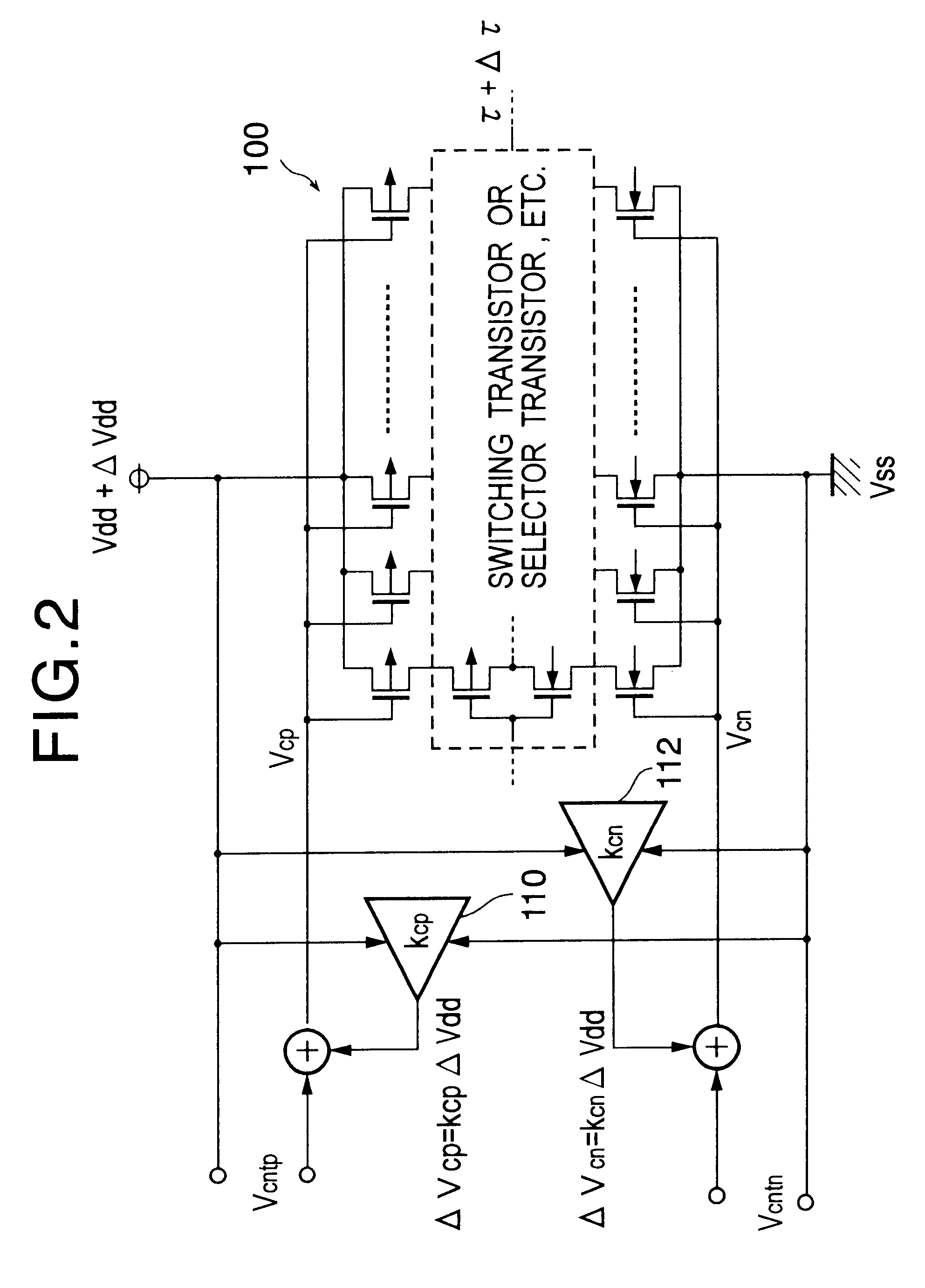
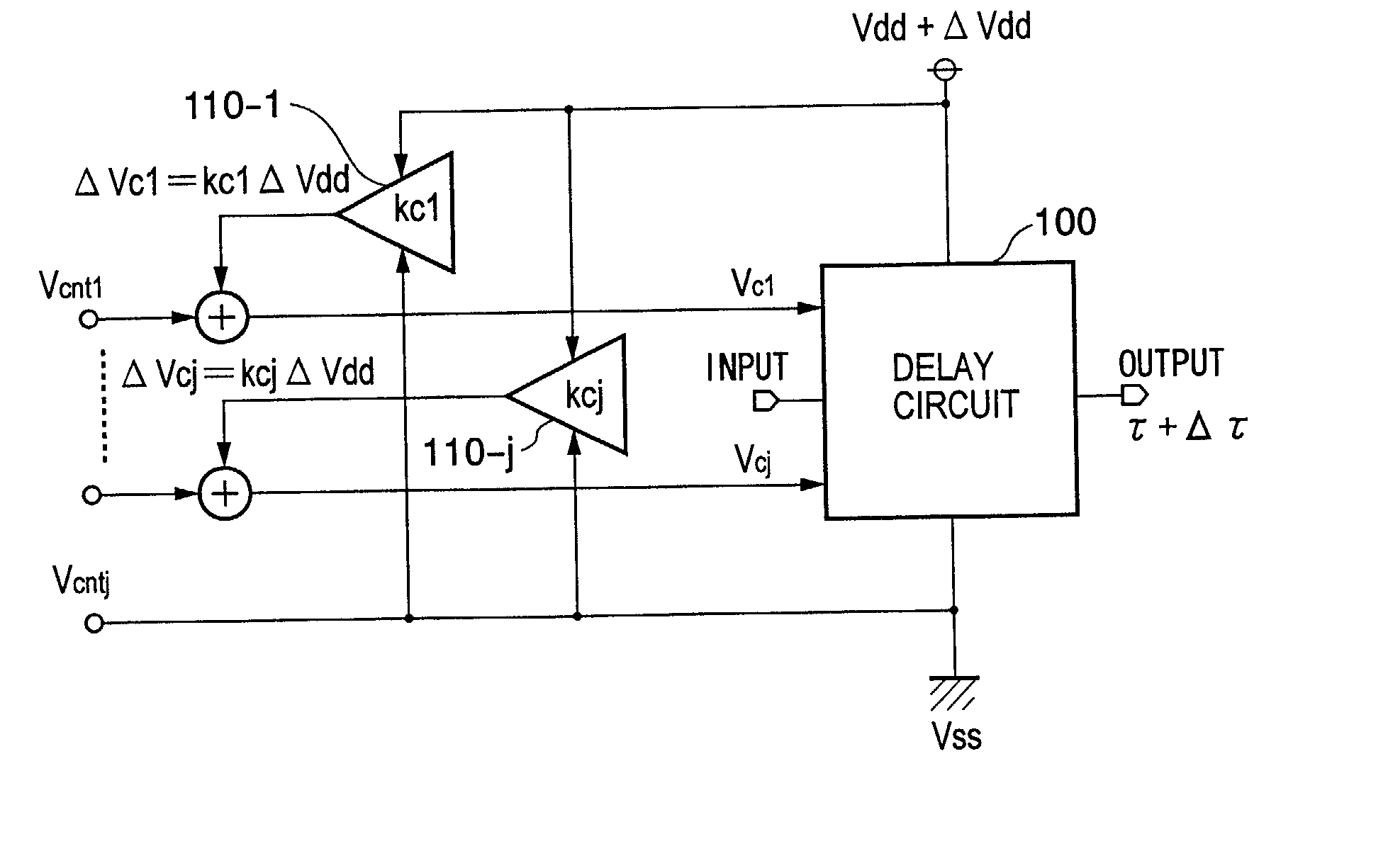
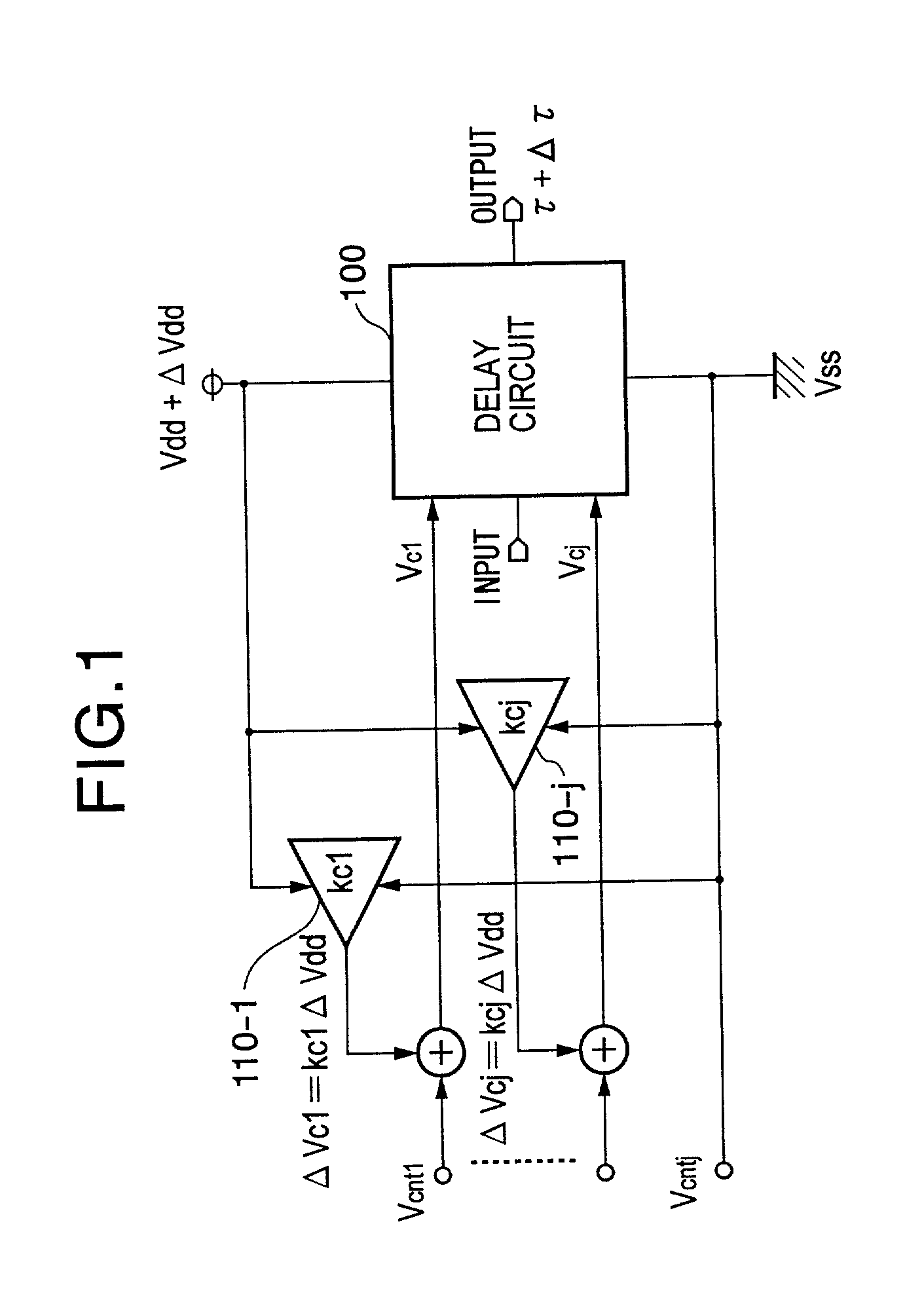
Delay circuit, voltage-controlled delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, delay adjustment circuit, DLL circuit, and PLL circuit
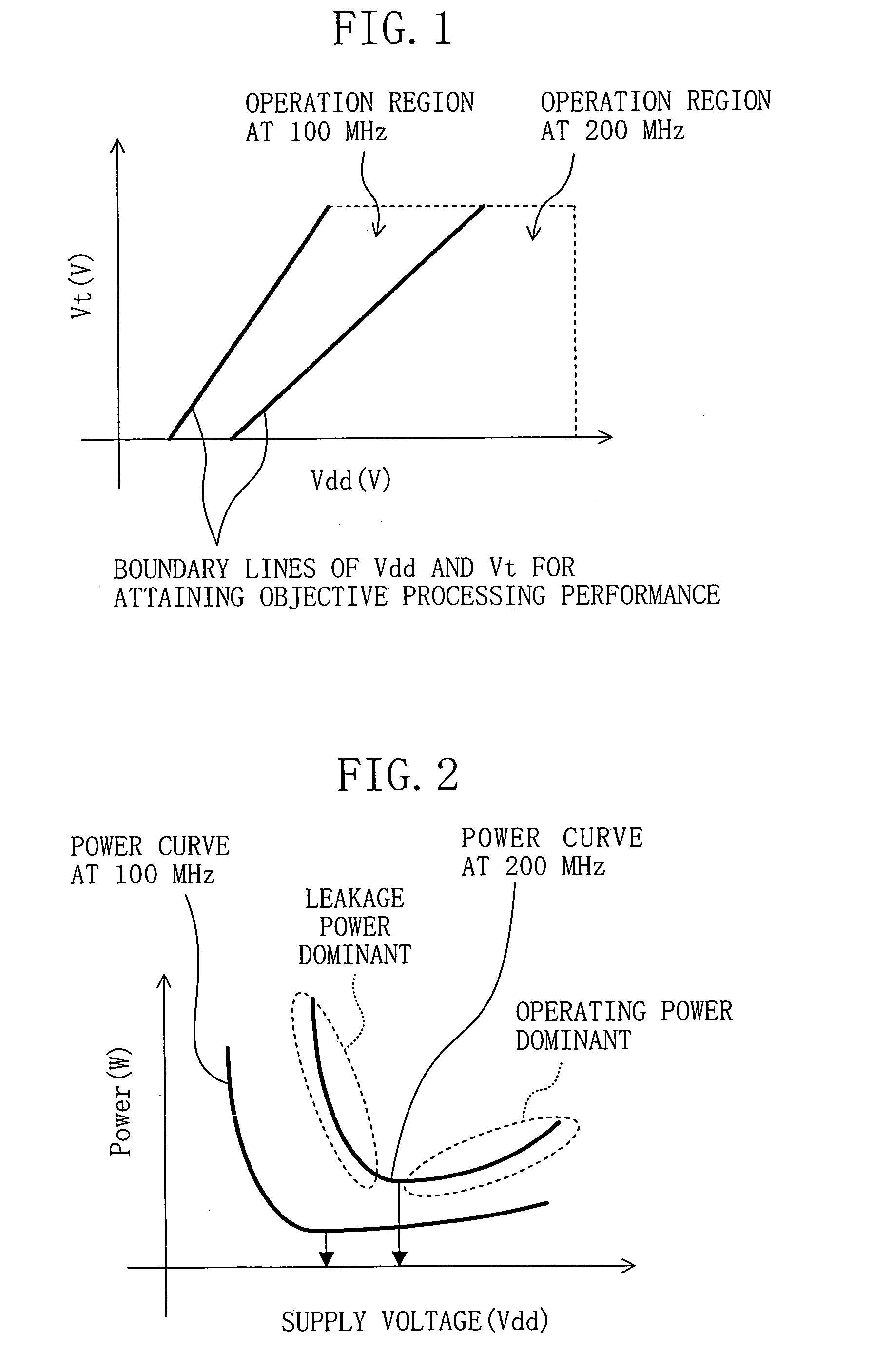
An inverter type delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, and voltage-controlled delay circuit capable of realizing simplification of circuit configuration, reduction of an effect of power source noise, and reduction of jitter, wherein a delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, and voltage-controlled delay circuit comprised of a plurality of delay stages controlled in drive current in accordance with a bias voltage or a control voltage and determined in delay time by the drive current, adding a change of a power source voltage to the above bias voltage or control voltage by a predetermined ratio and supplying a result of the addition to the above delay stages to suppress the power source voltage dependencies of the delay times of the delay stages, or connecting by a predetermined ratio a plurality of delay stages having different power source voltage dependencies, for example, power source voltage dependencies of opposite delay times, to suppress the power source voltage dependencies of delay times of the delay stages are realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
Clock synchronization circuit and operation method thereof
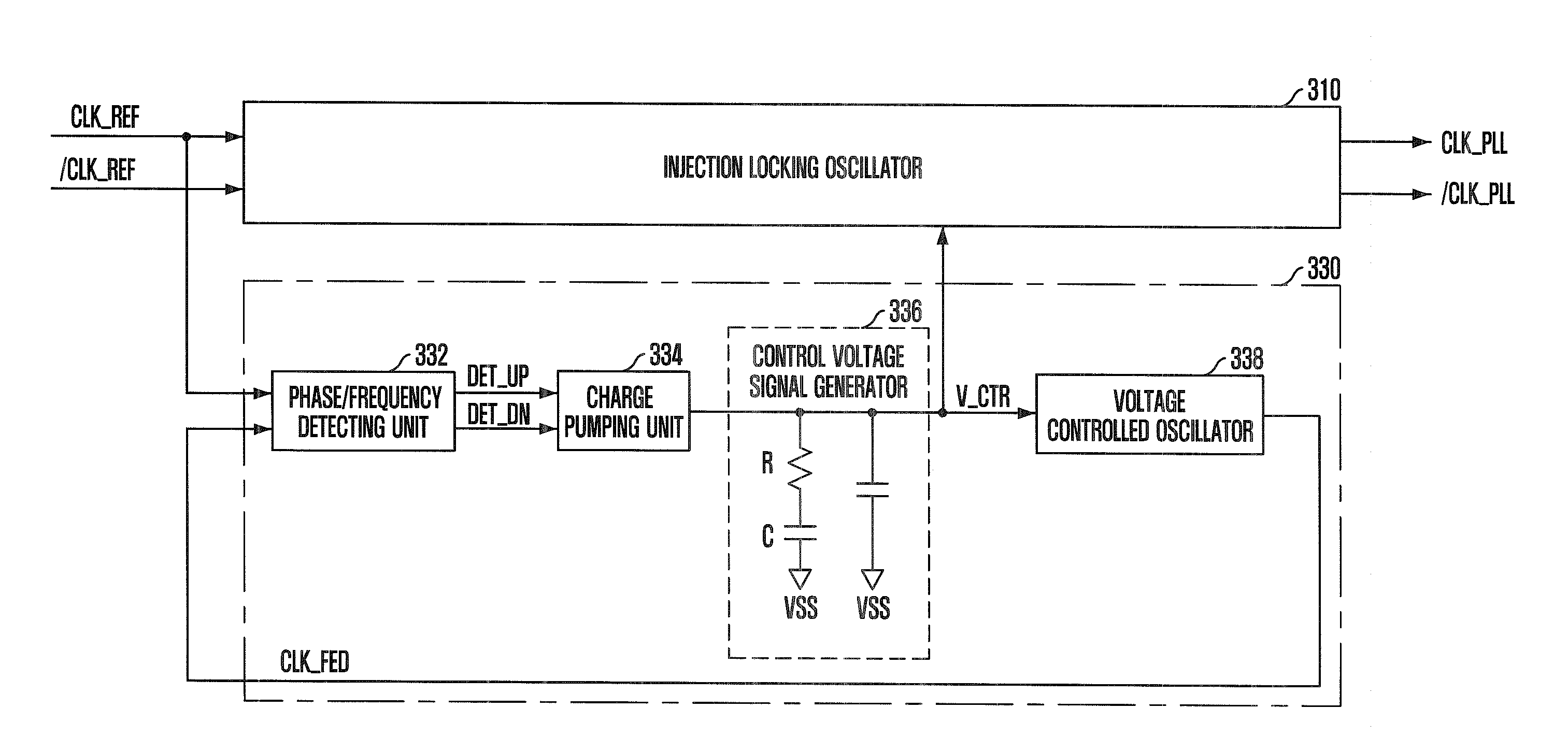
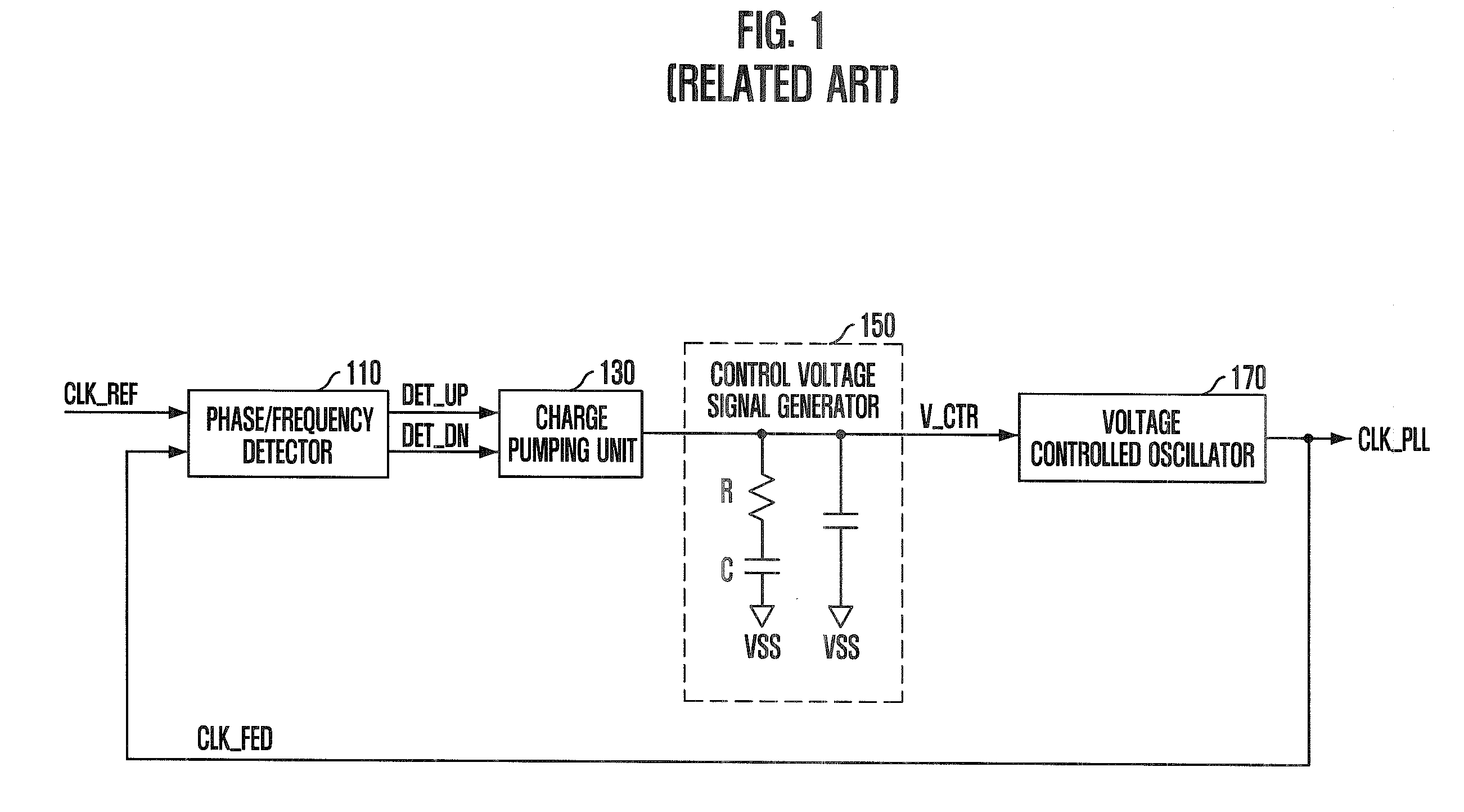
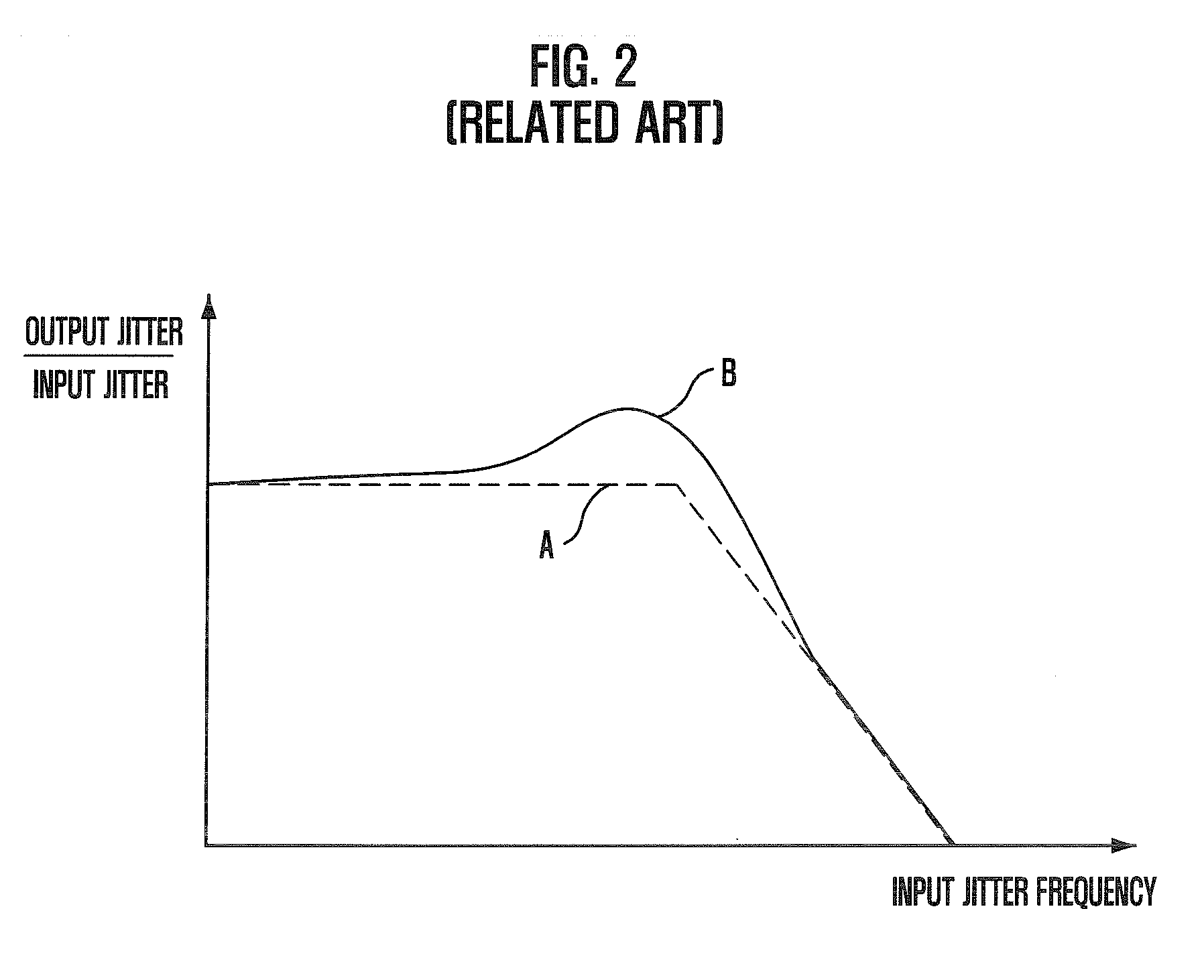
InactiveUS20090175116A1Improve operating characteristicsStable phase/frequency locking operationPulse automatic controlDigital storageInjection lockedPeak value
A semiconductor memory device with a clock synchronization circuit capable of performing a desired phase / frequency locking operation, without the jitter peaking phenomenon and the pattern jitter of an oscillation control voltage signal using injection locking. The device includes a phase-locked loop that detects a phase / frequency difference between a feedback clock signal and a reference clock signal to generate an oscillation control voltage signal corresponding to the detected phase / frequency difference, and generates the feedback clock signal corresponding to the oscillation control voltage signal. An injection locking oscillation unit sets up a free running frequency in response to the oscillation control voltage signal and generates an internal clock signal which is synchronized with the reference clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20050116765A1Increase probabilityReduce power consumptionTransistorPower reduction in field effect transistorsEngineeringControl circuit
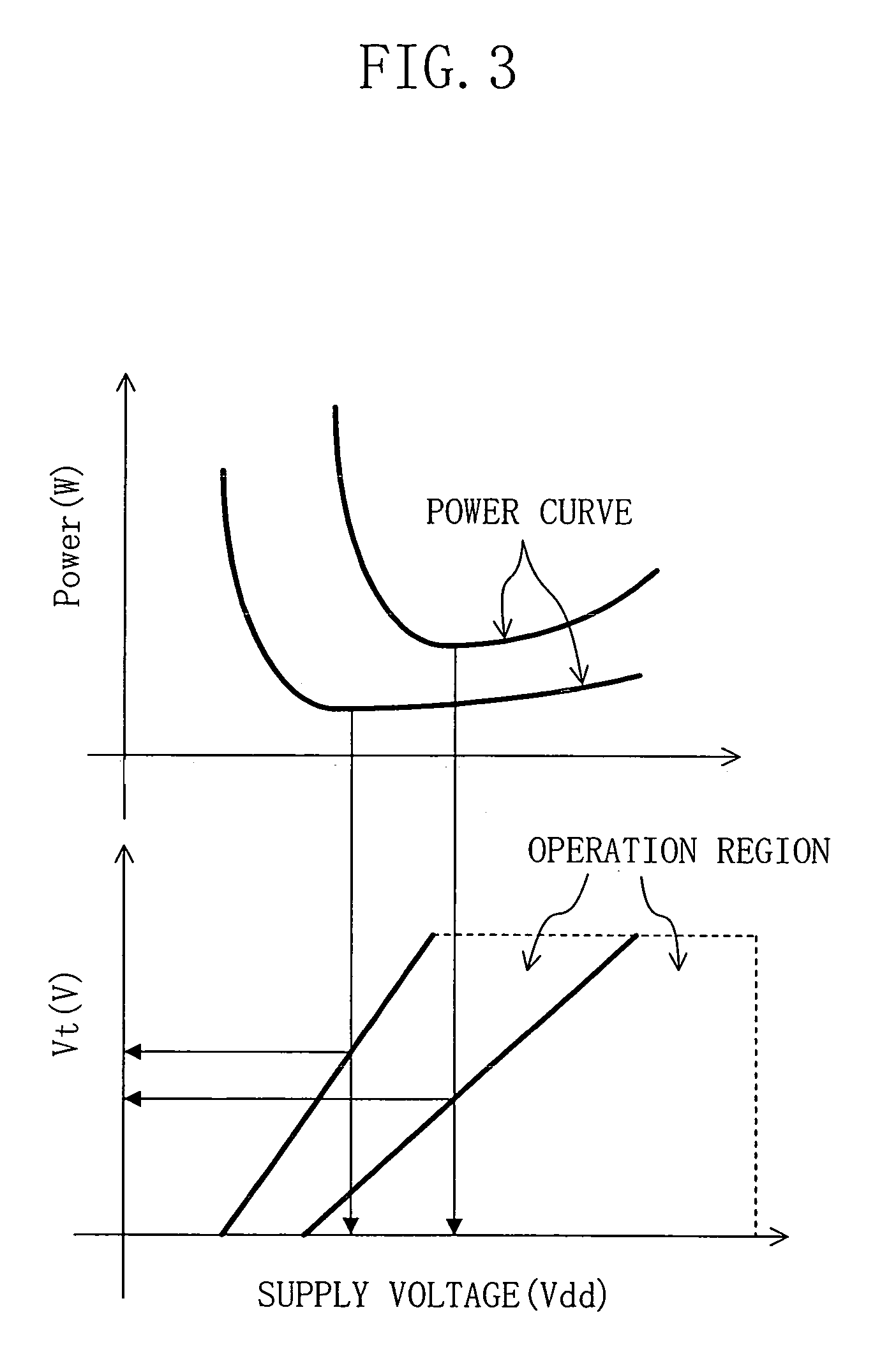
In a semiconductor integrated circuit, respective semiconductor circuits are disposed in different regions partitioned in accordance with their operation probabilities per unit time, and a supply voltage and a threshold voltage are correlatively controlled in each region. A target value for controlling the threshold voltage is determined in accordance with the operation probability of the semiconductor circuit. A threshold voltage control circuit controls substrate voltages of p-type and n-type MOS transistors included in the semiconductor circuit so that the threshold voltage can be constant at the target value regardless of the temperature change occurring in use. Simultaneously, a supply voltage control circuit controls the supply voltage for the semiconductor circuit so that an objective operating frequency can be attained. As a result, a semiconductor integrated circuit with low power consumption can be obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
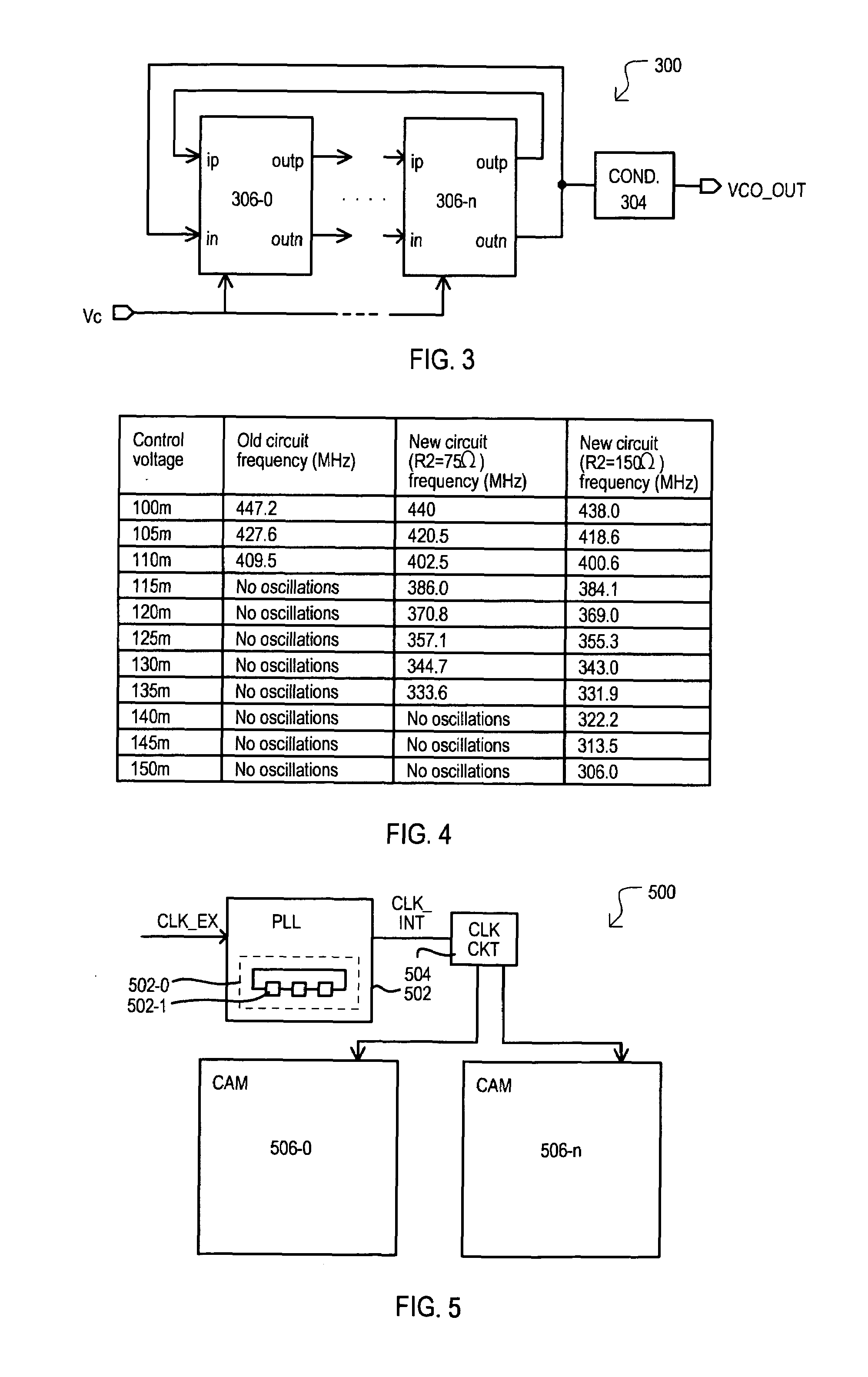
Voltage controlled oscillator delay cell and method
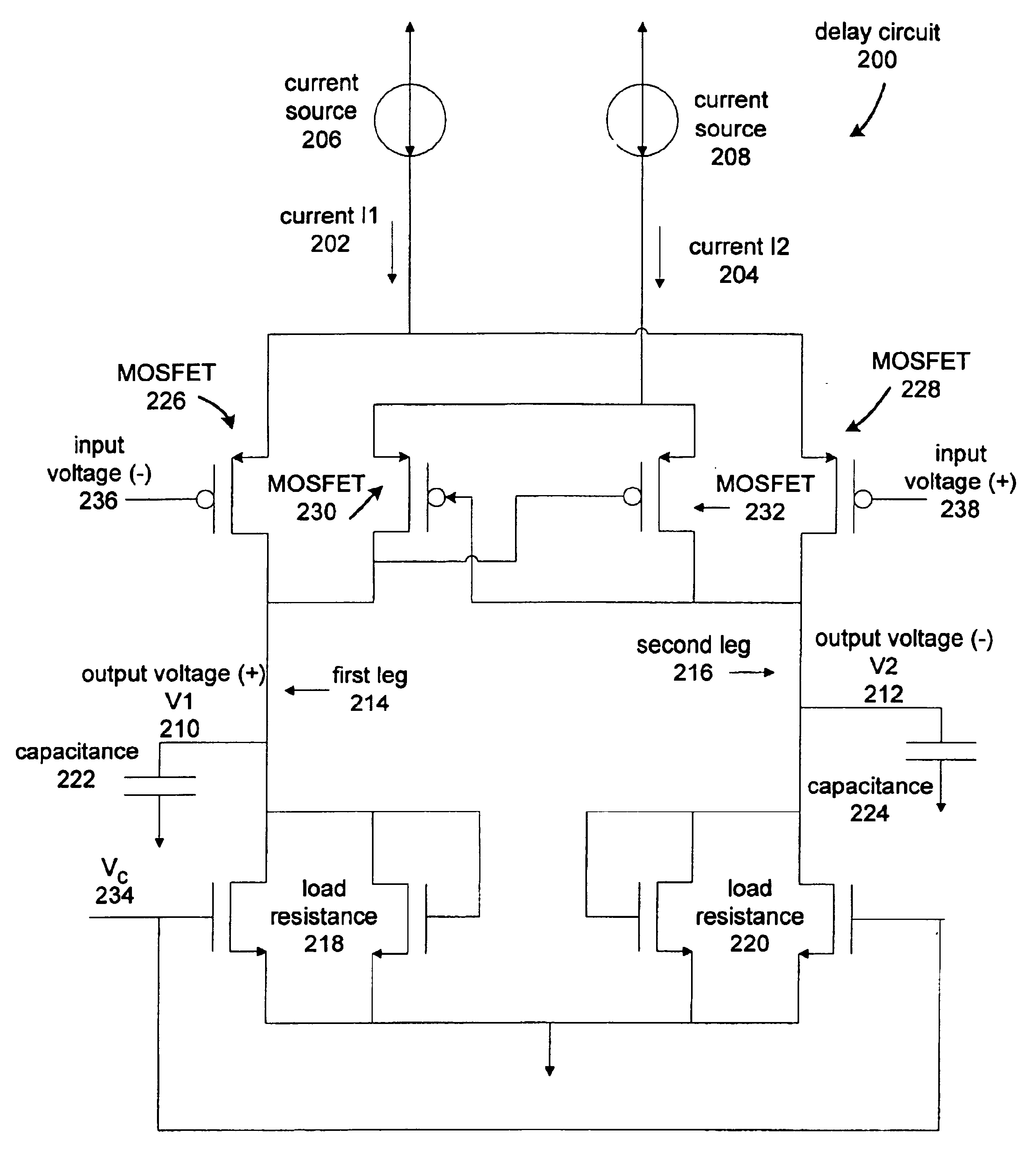
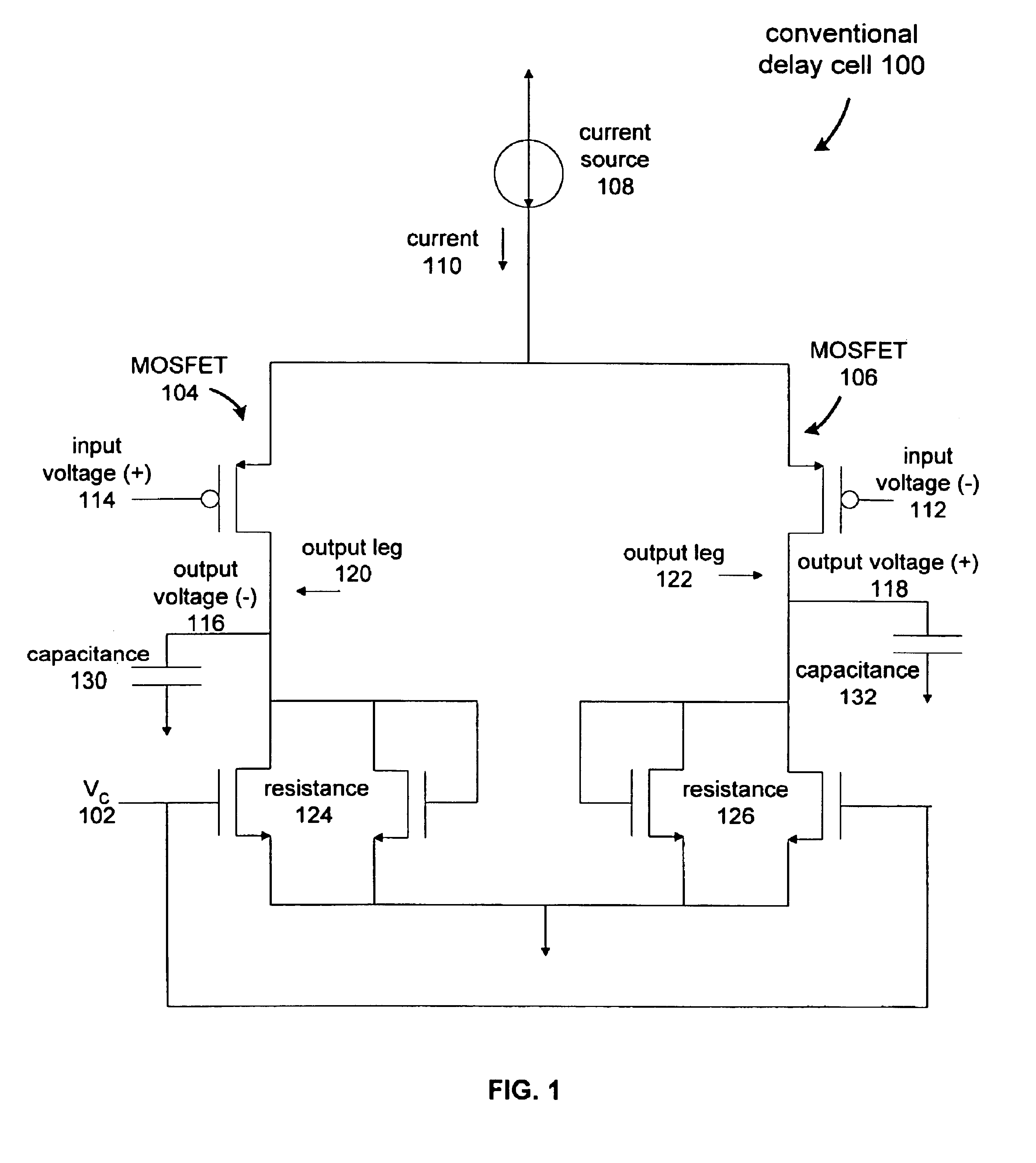
A delay cell circuit (200) is disclosed. The delay cell circuit may include a differential stage (202) and a cross-coupled stage (204). The cross-coupled stage can include resistors (210-0 and 210-1) the function to reduce a gain. The differential stage (202) and cross-coupled stage (204) can include variable currents sources (208 and 212), respectively. As frequency of operation increases, variable current source (208) provides a larger current to the differential stage (202) and variable current source (212) provides a smaller current to cross-coupled stage (204). Delay cell circuit (200) may be used in a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO). By including gain attenuating devices such as resistors (210-0 and 210-1), a frequency tuning range of the VCO may be increased.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
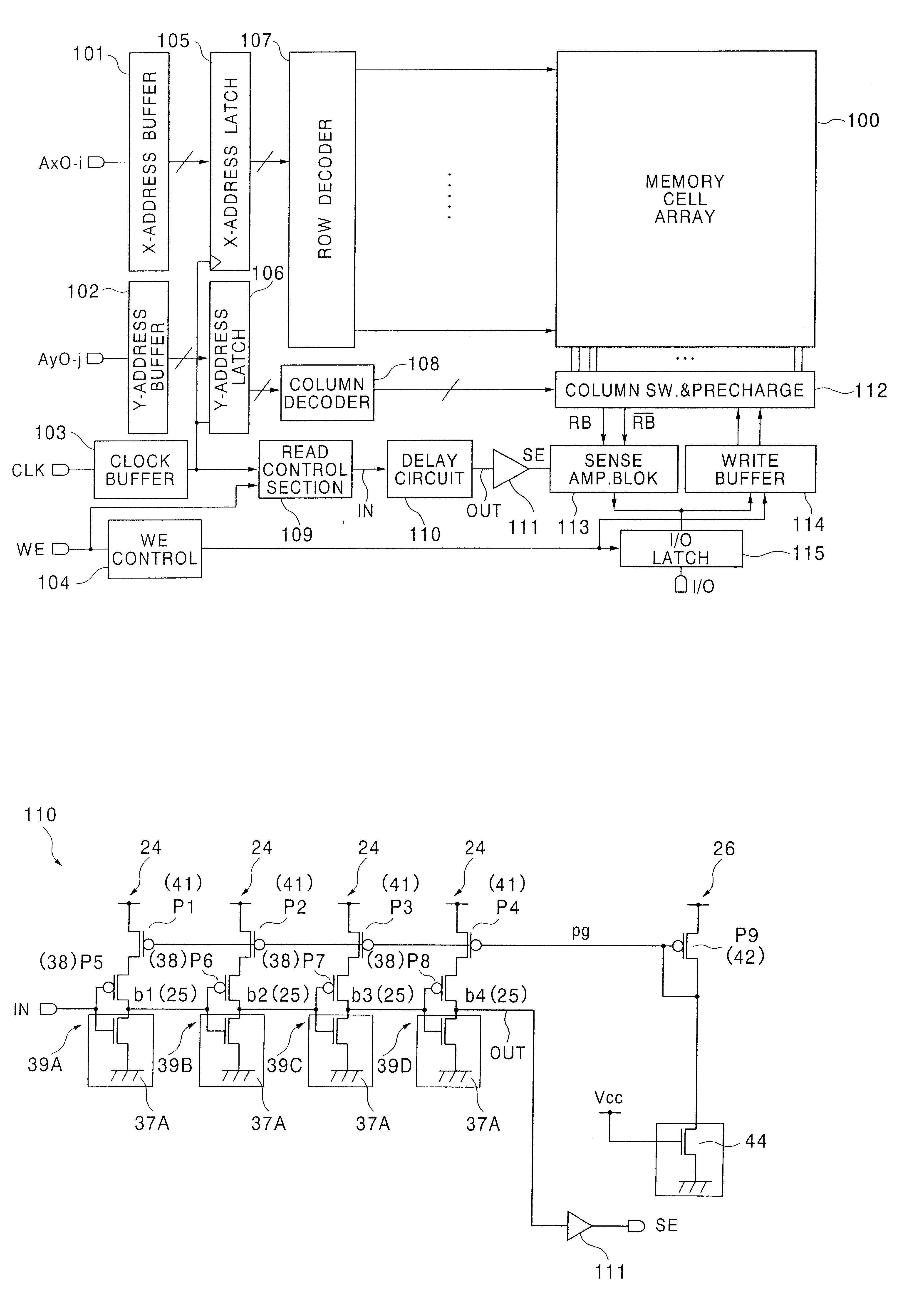
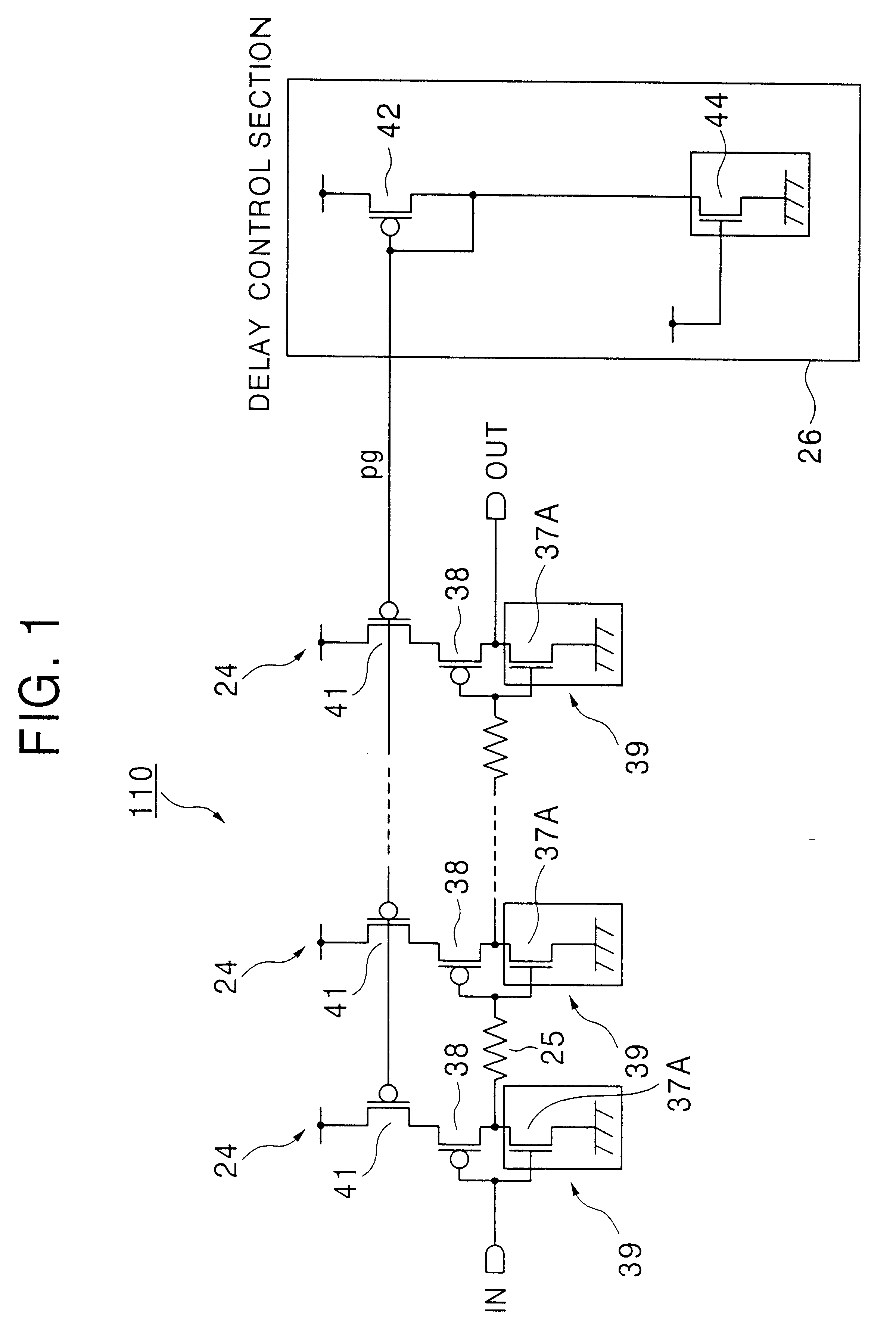
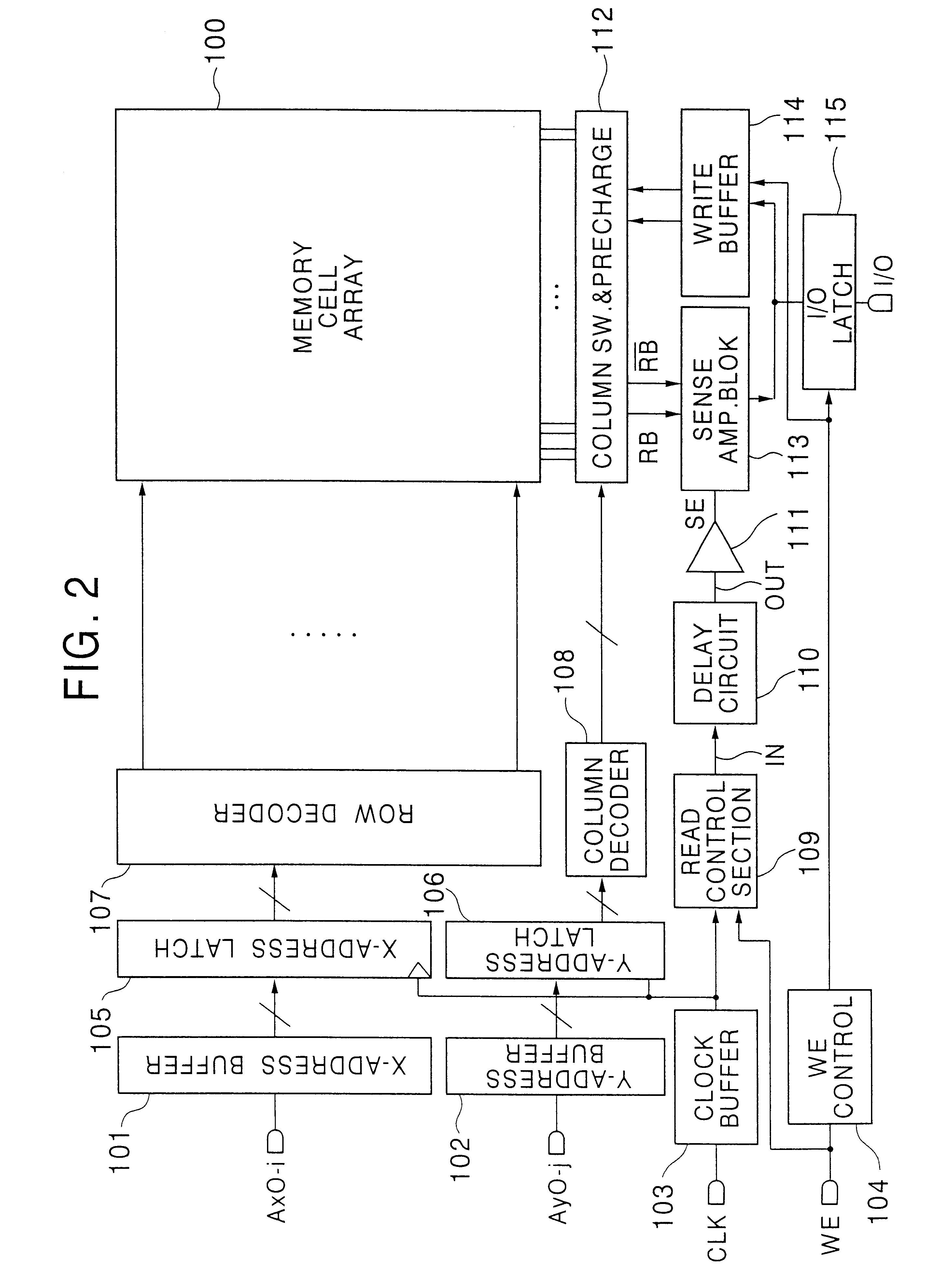
Semiconductor memory device having a delay circuit for generating a read timing
InactiveUS6282133B1Optimize timingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAudio power amplifierComputer science
A delay circuit in a semiconductor memory device generates a sense amplifier enable signal having a delay time with respect to the timing of selection of one of memory cells. The delay time corresponds to the largest read time for the memory cell located at the most distant position and has an irregularity reflecting an irregularity in threshold voltage of nMOSFET transfer gates in each memory cell, which affects the read time. An optimum timing for the sense amplifier enable signal can be obtained by the delay circuit irrespective of the irregularity in the threshold voltage of the nMOSFET transfer gates.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Ring oscillator using current mirror inverter stages
InactiveUSRE37124E1Limit maximum frequencyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsLow voltageEngineering
A ring oscillator having an odd number of single ended stages, each stage including two transistors connected as a current mirror. The stage provides for low-voltage performance and improved process tolerance characteristics.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
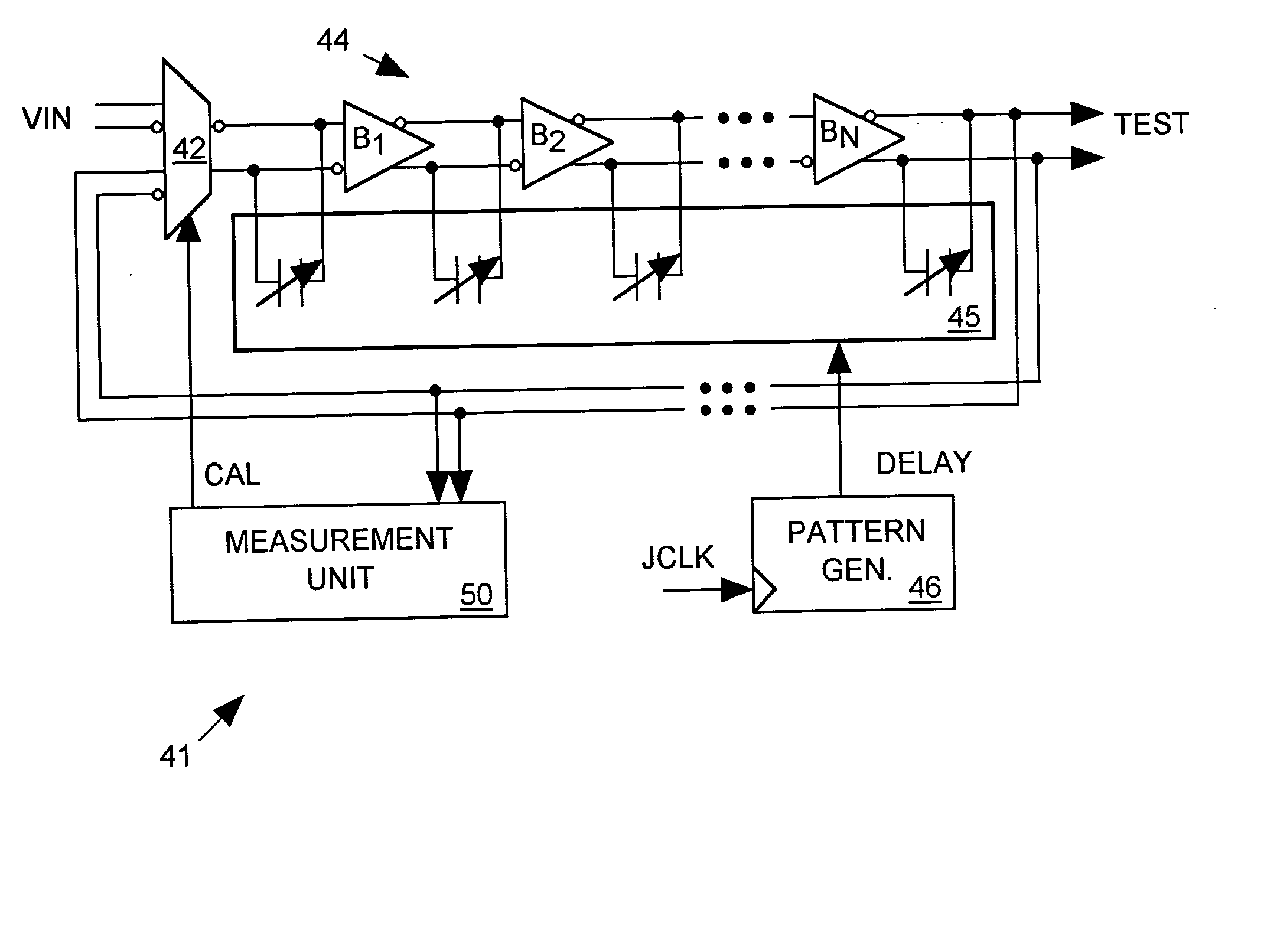
Programmable jitter generator
ActiveUS20050044463A1Reduce manufacturing costDigital circuit testingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementMeasurement testControl data
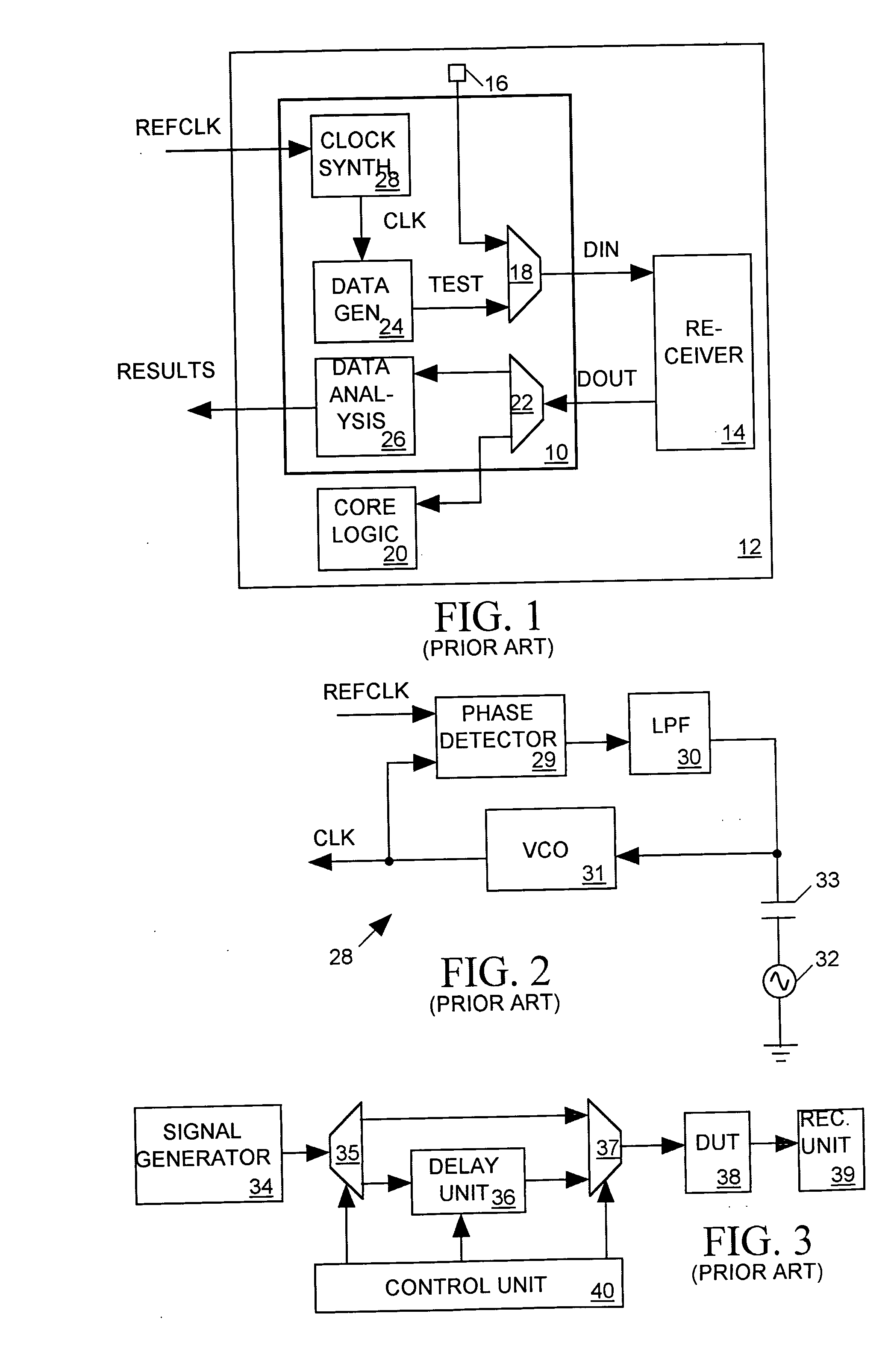
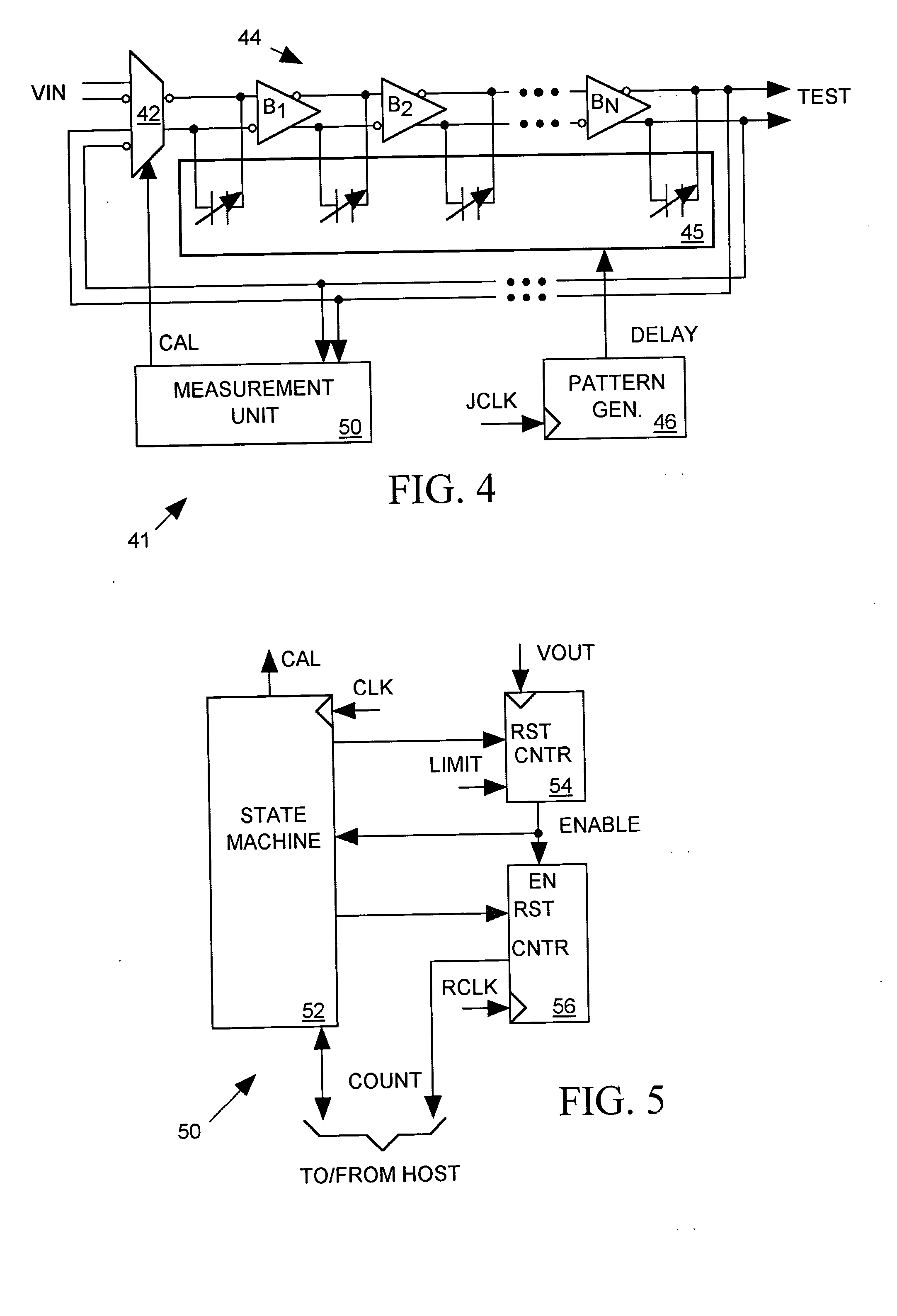
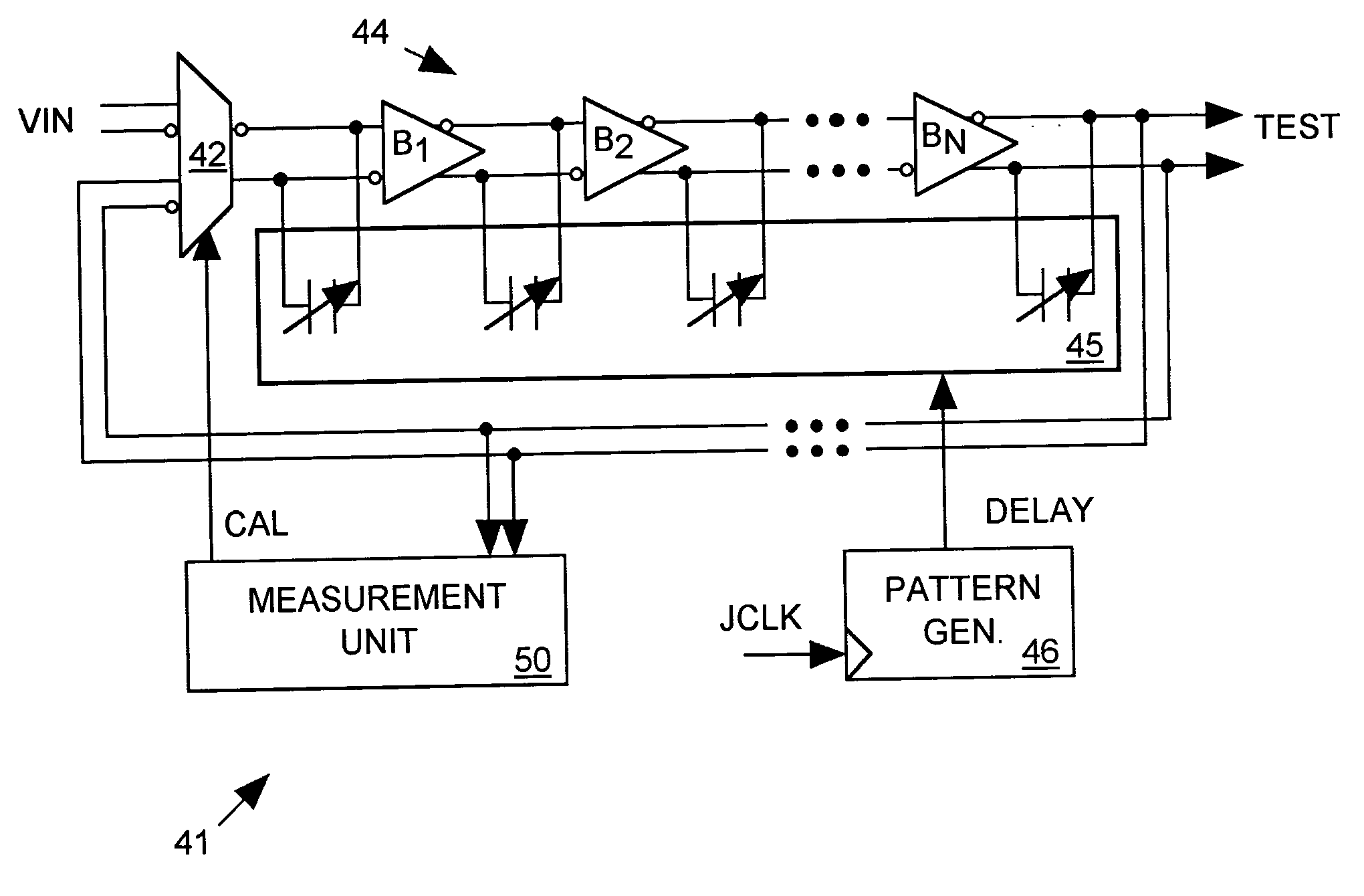
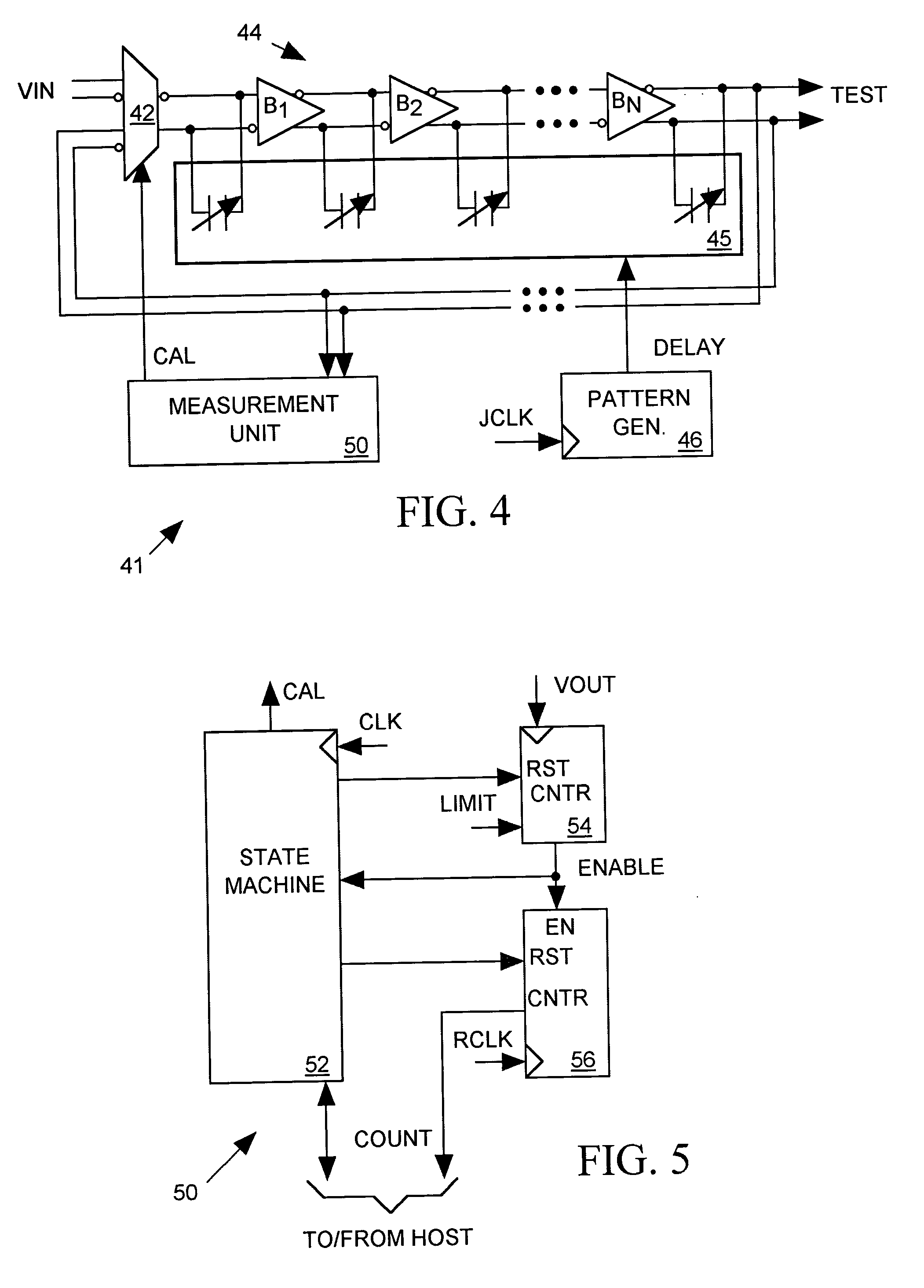
A jitter generator produces a jittery test signal for use in performing a jitter test on an integrated circuit (IC) device under test (DUT). The jitter generator includes a programmable delay circuit for delaying a non-jittery input signal with a varying delay controlled by input digital delay control data to produce the test signal. A pattern generator supplies a sequence of delay control data to the programmable delay circuit causing it to produce a desired jitter pattern in the test signal. During a calibration process, a measurement unit feeds the test signal back to the input of the programmable delay circuit, causing the test signal to oscillate with a period proportional to the delay through the delay circuit. The measurement unit then measures the period of the test signal for various values of delay control data and reports measurement results. Based on the measurement results, host equipment then determines an appropriate sequence of delay control data for producing a desired jitter pattern in the test signal and programs the pattern generator to produce that sequence of delay control data during a jitter test. The jitter generator can form a part of a built-in, self-test (BIST) circuit implemented within the DUT itself.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus of a ring oscillator for phase locked loop (PLL)
InactiveUS20080284529A1Pulse generation by logic circuitsOscillations generatorsResistive loadRC oscillator
The present invention relates to a ring oscillator including a delay stage, the delay stage includes a differential pair of input transistor, a variable resistive load coupled to the transistor, a differential output between the variable resistive load and the corresponding input transistor, a variable current source coupled to the differential pair of transistors for variably setting a bias current through the differential pair of transistors, and an input coupled to the variable resistive load and the variable current source for receiving an configuration signal, wherein the variable resistive load and the variable current source are changed in response to the configuration signal, wherein the bias current of the variable current source increases and the variable resistive load decreases, and vice versa.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Phase-combining circuit and timing signal generator circuit for carrying out a high-speed signal transmission
InactiveUS20090179674A1Simple structureError minimizationAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsControl signalEngineering
A phase-combining circuit for combining cyclic timing waveforms that have been phase-controlled by control signals based on three or more input signals of different phases, has a weight signal generating circuit and a weighting circuit. The weight signal generating circuit generates weights according to the control signals, and the weighting circuit gives the weights to the respective input signals, with a positive or negative polarity for each one signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
At frequency phase shifting circuit for use in a quadrature clock generator
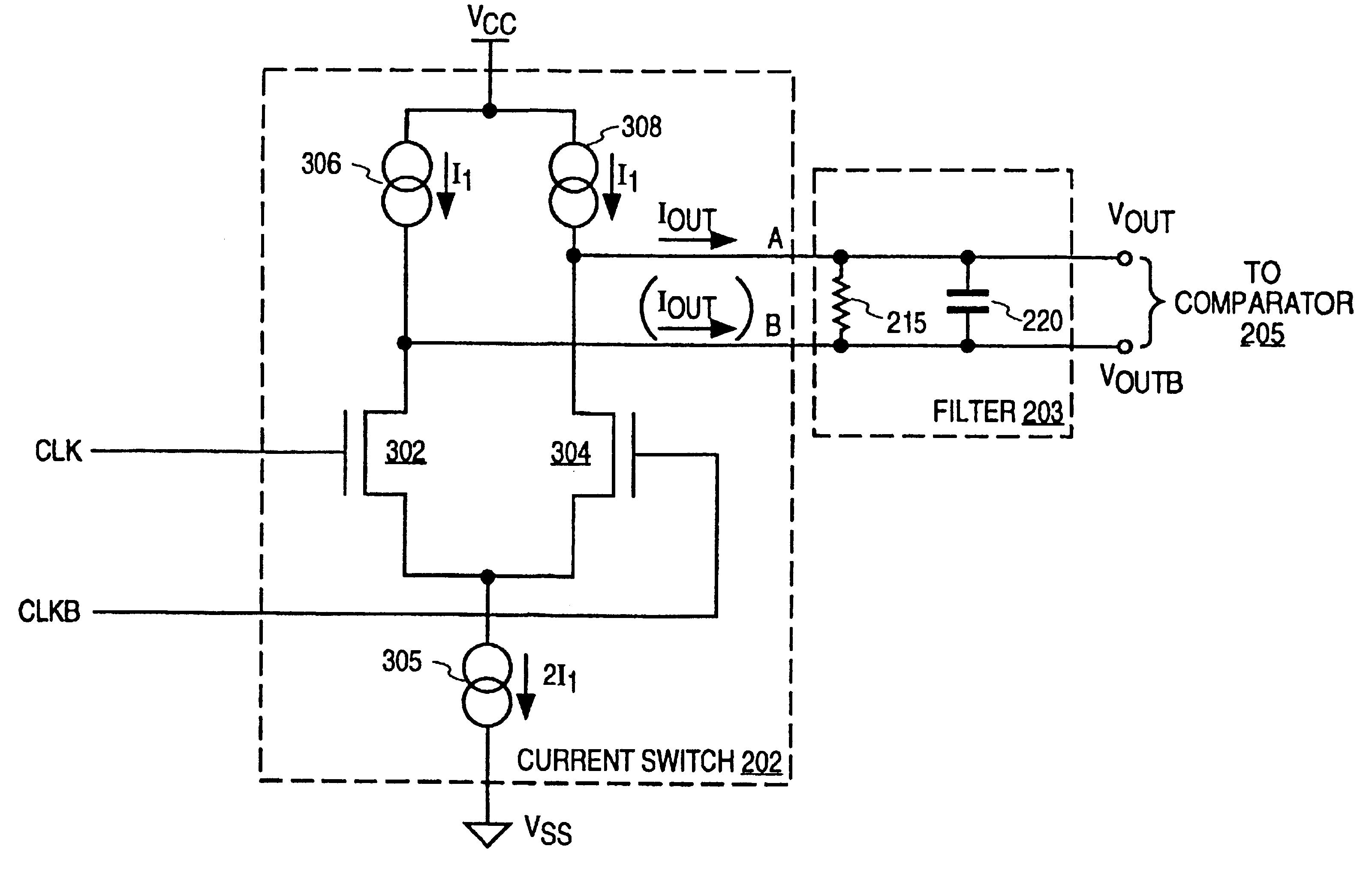
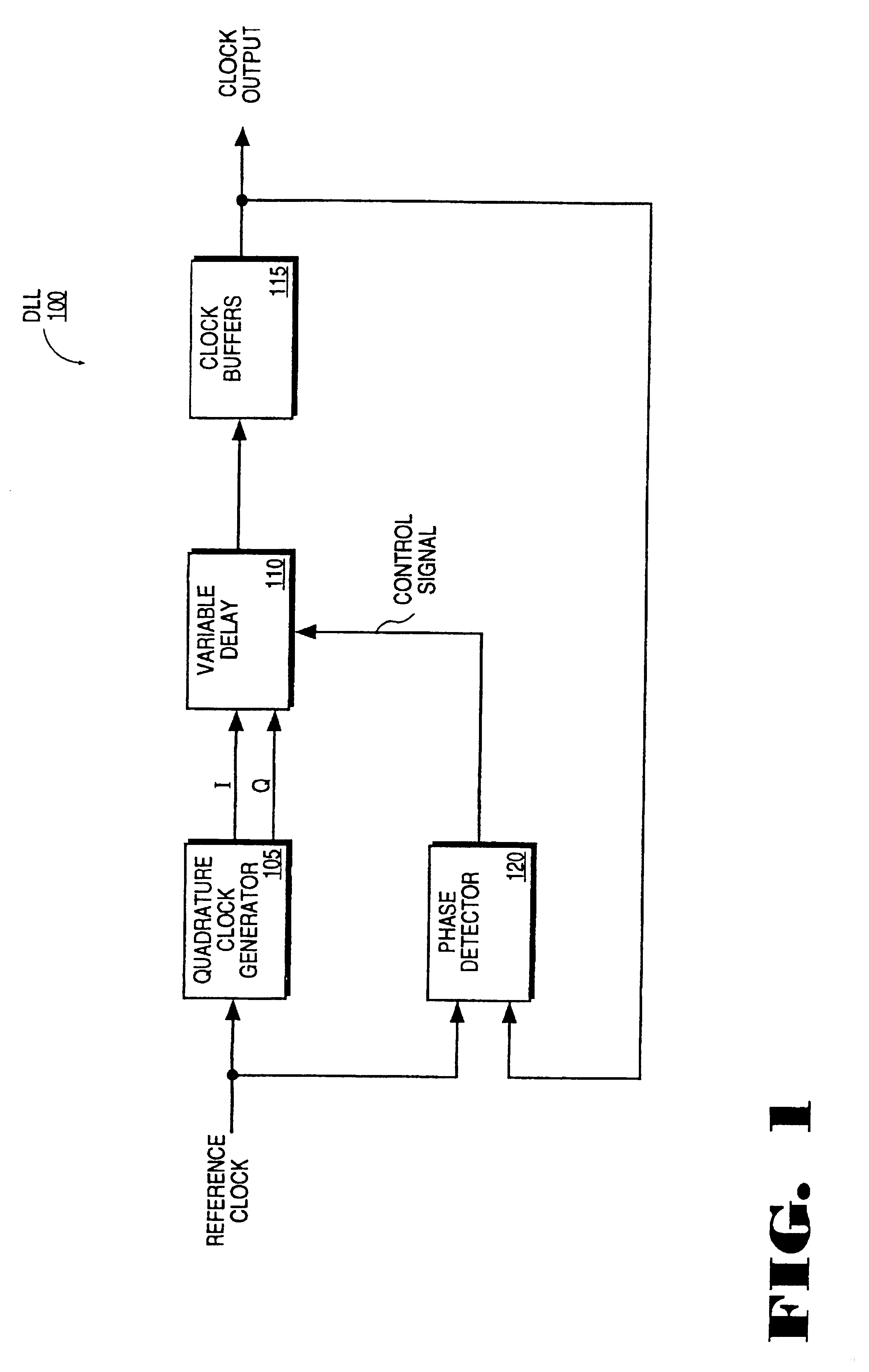
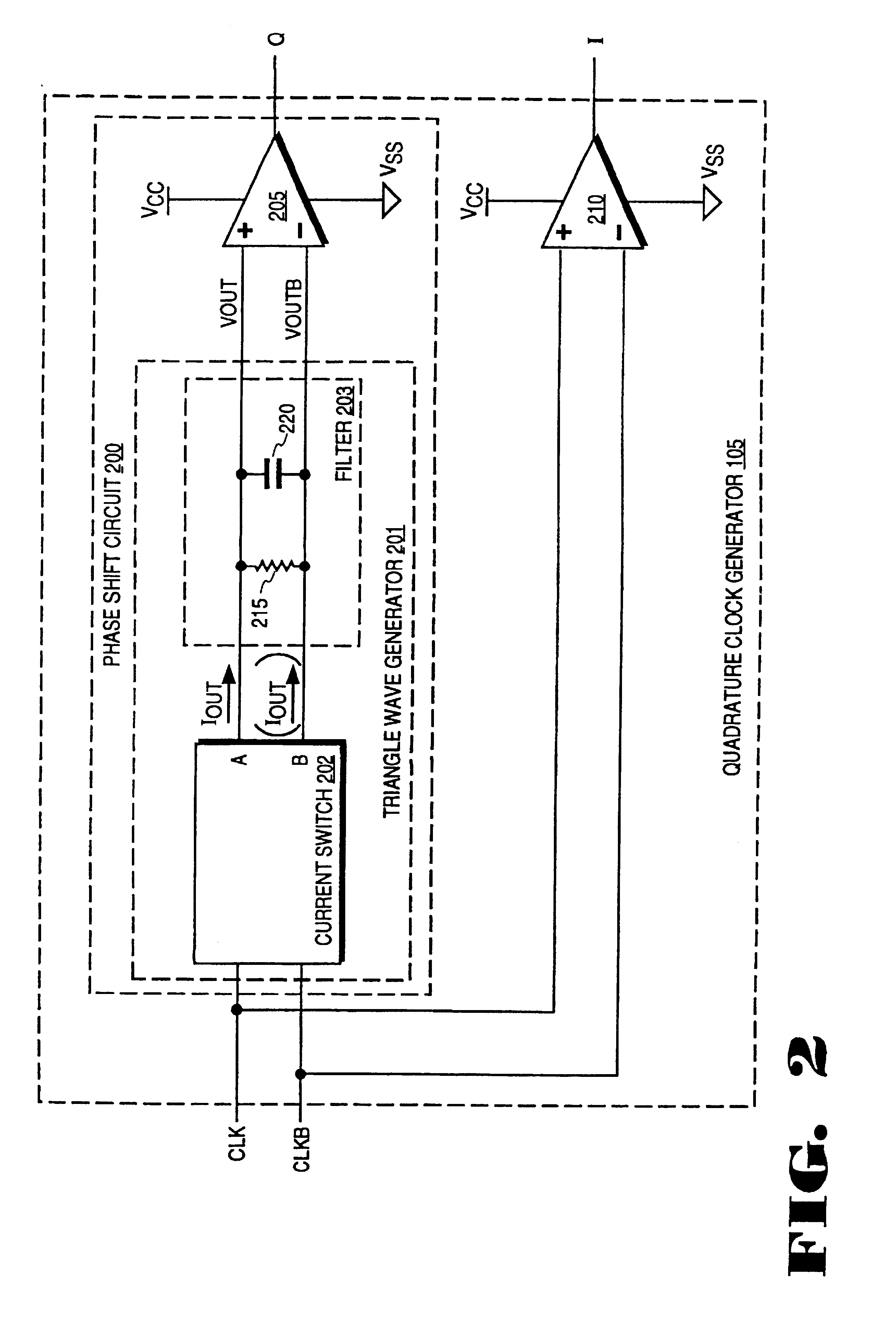
InactiveUSRE37452E1Enhance the shake effectComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationPhase shiftedClock generator
A phase shifting circuit that may be used as part of a quadrature clock generator. The phase shifting circuit comprises a triangle wave generator coupled to receive an input reference signal. The triangle wave generator outputs a pair of complementary triangle wave signals in response to the input reference signal. A comparator having a pair of inputs is coupled to receive the pair of complementary triangle wave signals. The comparator outputs an output signal having a predetermined phase relationship with the input reference signal in response to a comparison between the pair of complementary triangle wave signals.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Variable frequency oscillator and communication circuit with it
InactiveUS7592877B2Shorten the length of timeReduce jitterParallel/series conversionPulse automatic controlPhase noiseDelayed time
In a variable frequency oscillator in a semiconductor device, as the variation of an oscillation frequency caused by the variation of temperature and supply voltage and process variation is large, it is difficult to reduce the conversion ratio of control voltage dependent upon phase noise and the oscillation frequency and therefore, phase noise is large. The variation of the oscillation frequency is suppressed and phase noise is reduced by connecting a voltage-to-current conversion circuit that converts input control voltage to control current of a ring oscillator to the ring oscillator where delay circuits a delay time of which increases and decreases according to the amplitude of input control current are cascade-connected by a plurality of stages in a ring and increasing / decreasing current dependent upon any of temperature, supply voltage and the threshold voltage of a transistor inside the voltage-to-current conversion circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Ring oscillator and semiconductor integrated circuit and electronic device including the same
InactiveUS20080061894A1Increase productionImprove robustnessPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationControl signalEngineering
A differential amplifier circuit includes: a differential transistor pair composed of first and second transistors; a first resistance connected to a junction point of the first and second transistors at one terminal and to a first voltage node at the other terminal; second and third resistances provided between the first and second transistors, respectively, and a second voltage node; and first and second passive circuits respectively connected to the second and third resistances, the load characteristics of the passive circuits changing according to a control signal supplied. A ring oscillator is composed of a plurality of such differential amplifier circuits connected in a loop.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
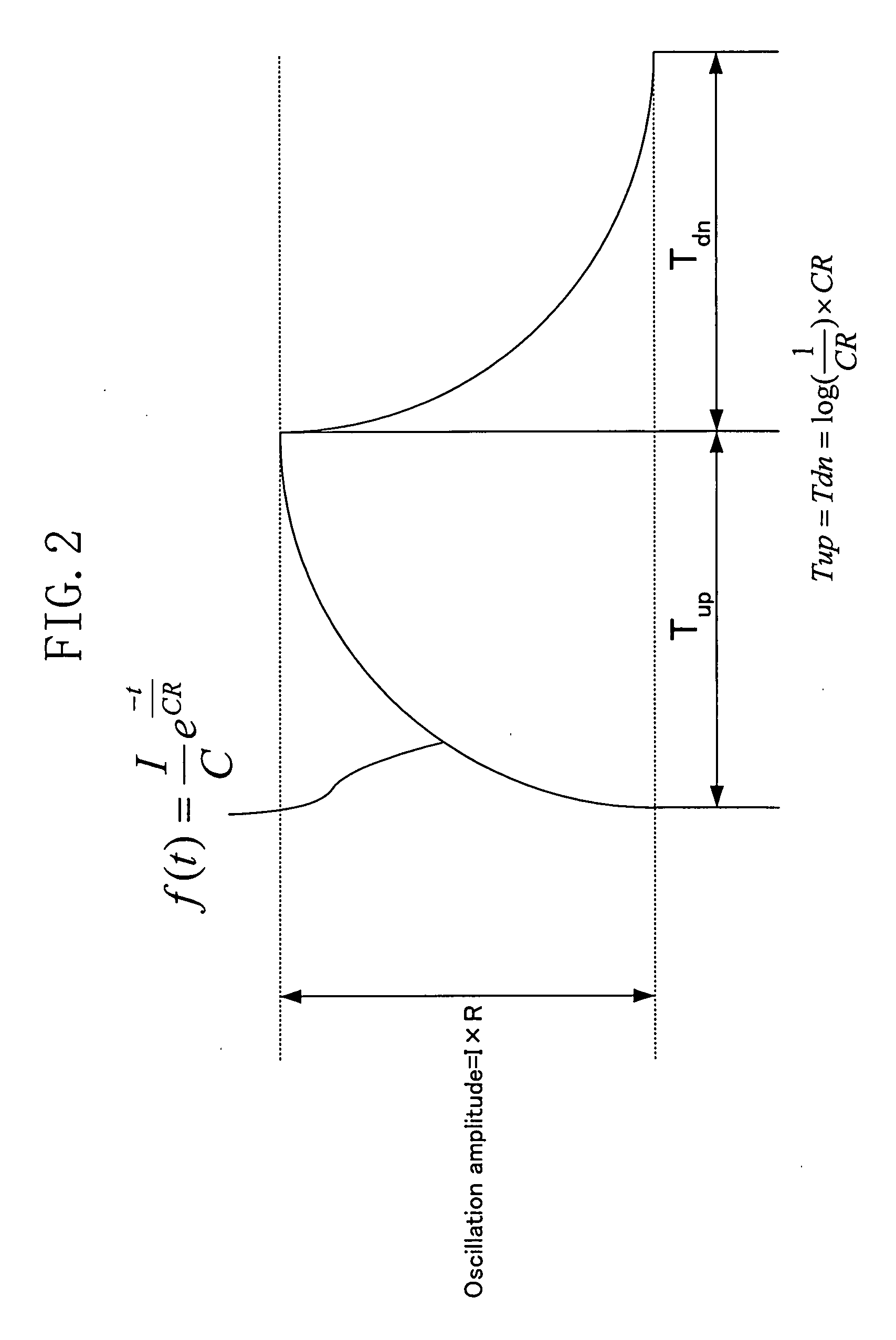
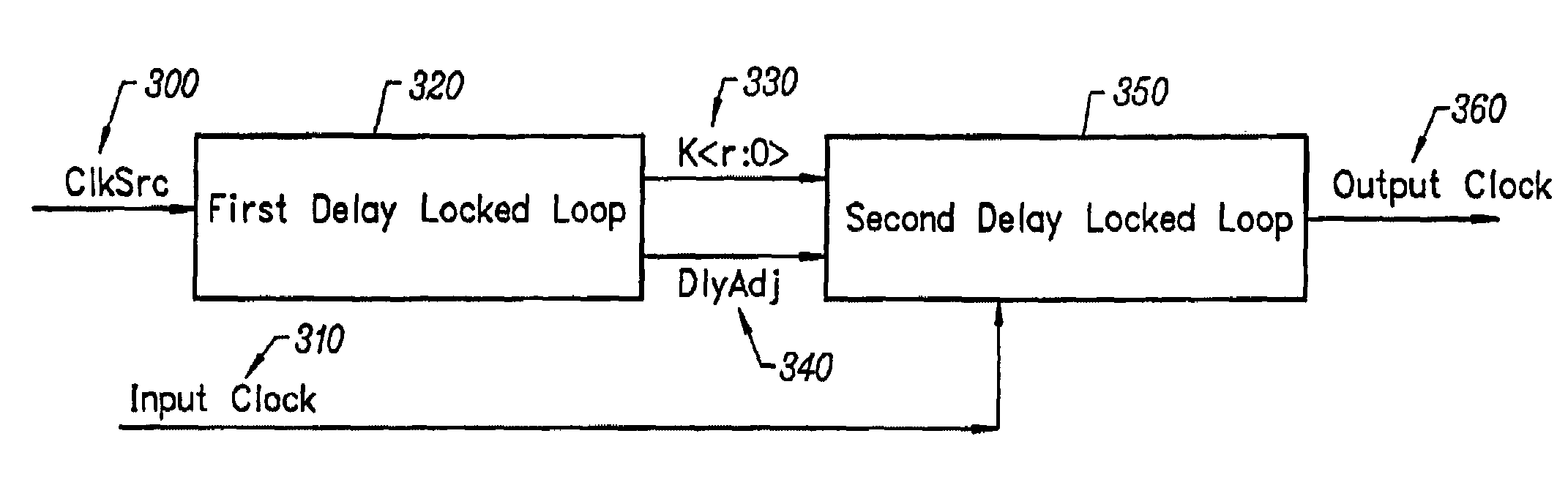
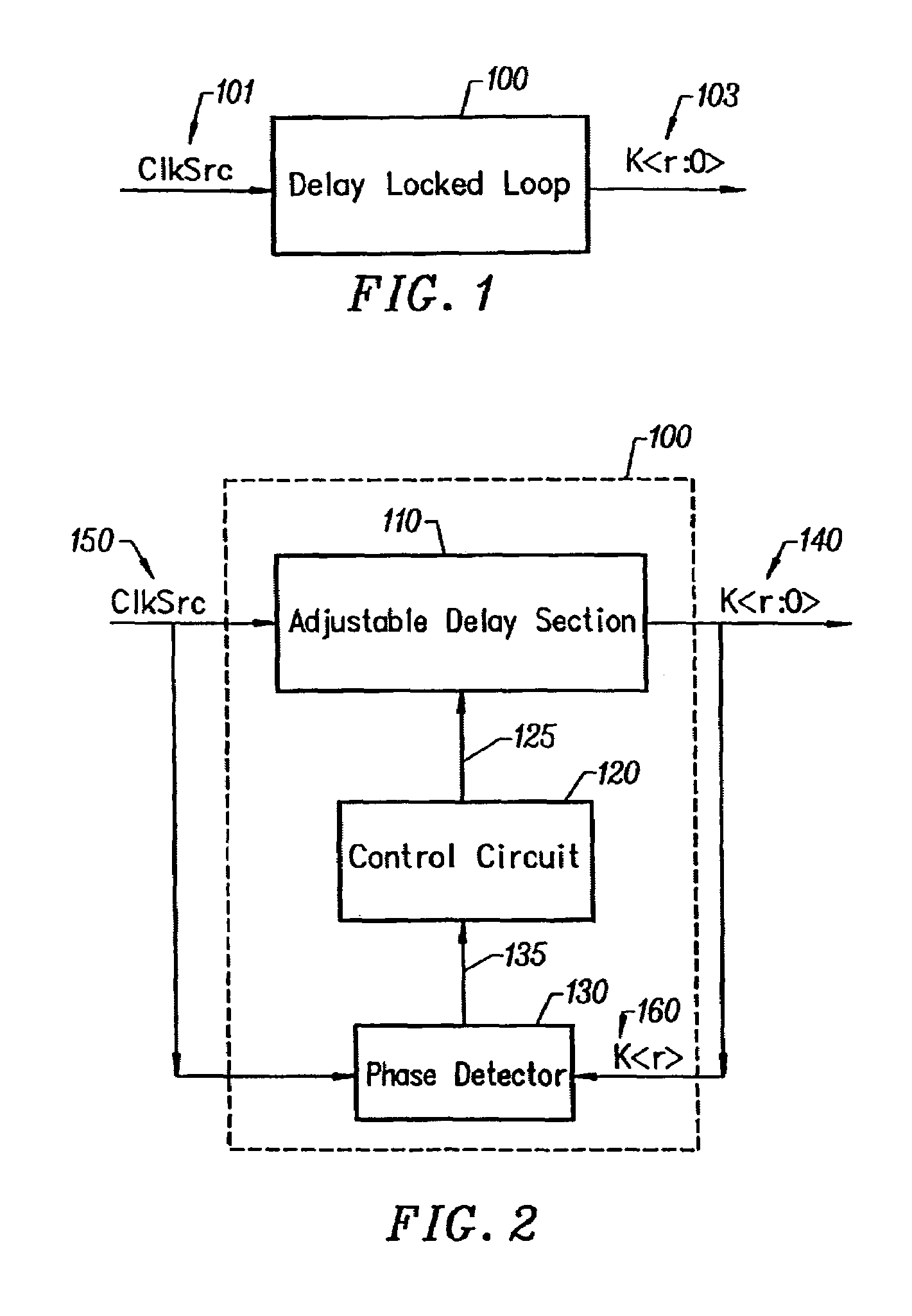
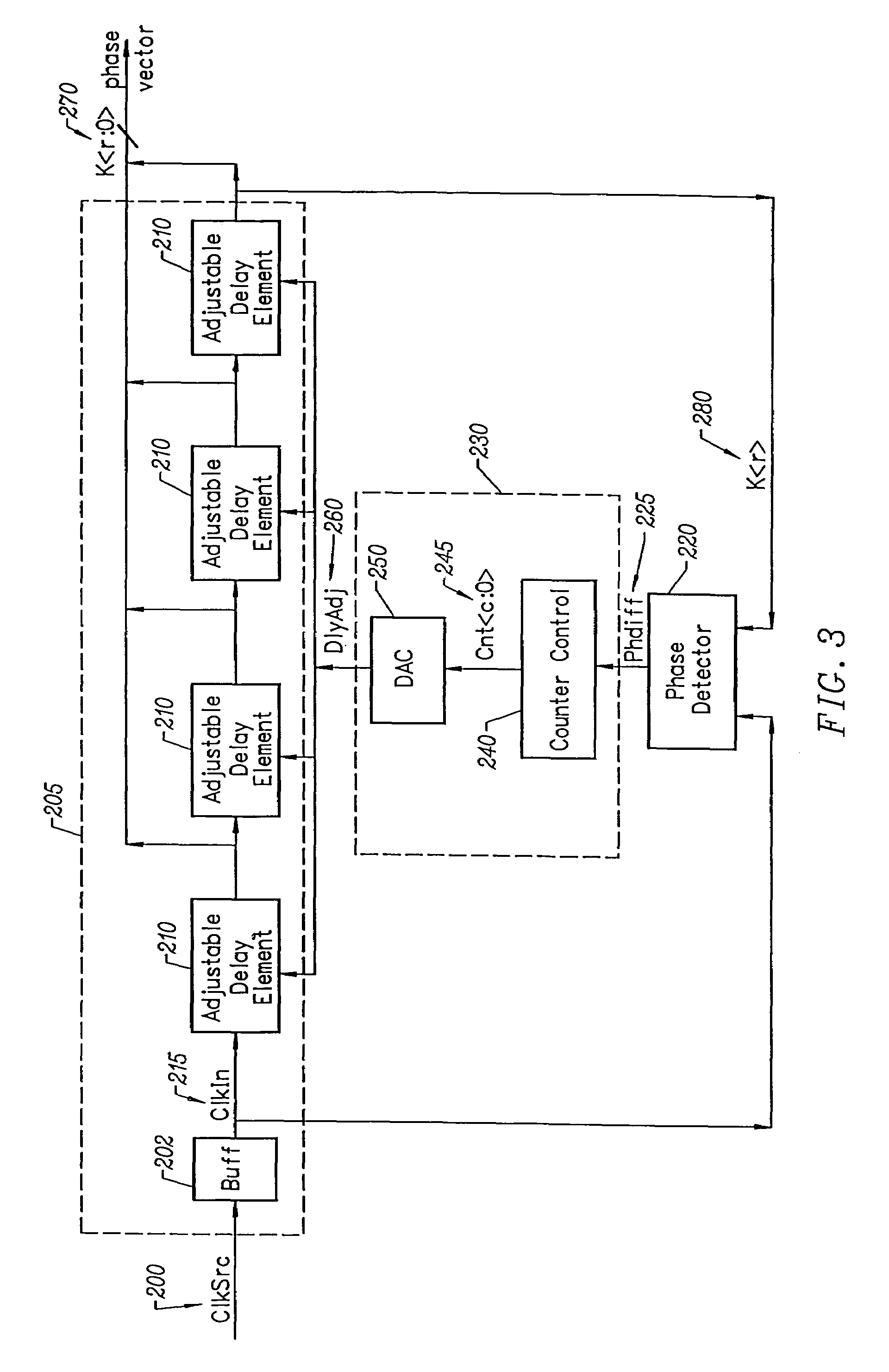
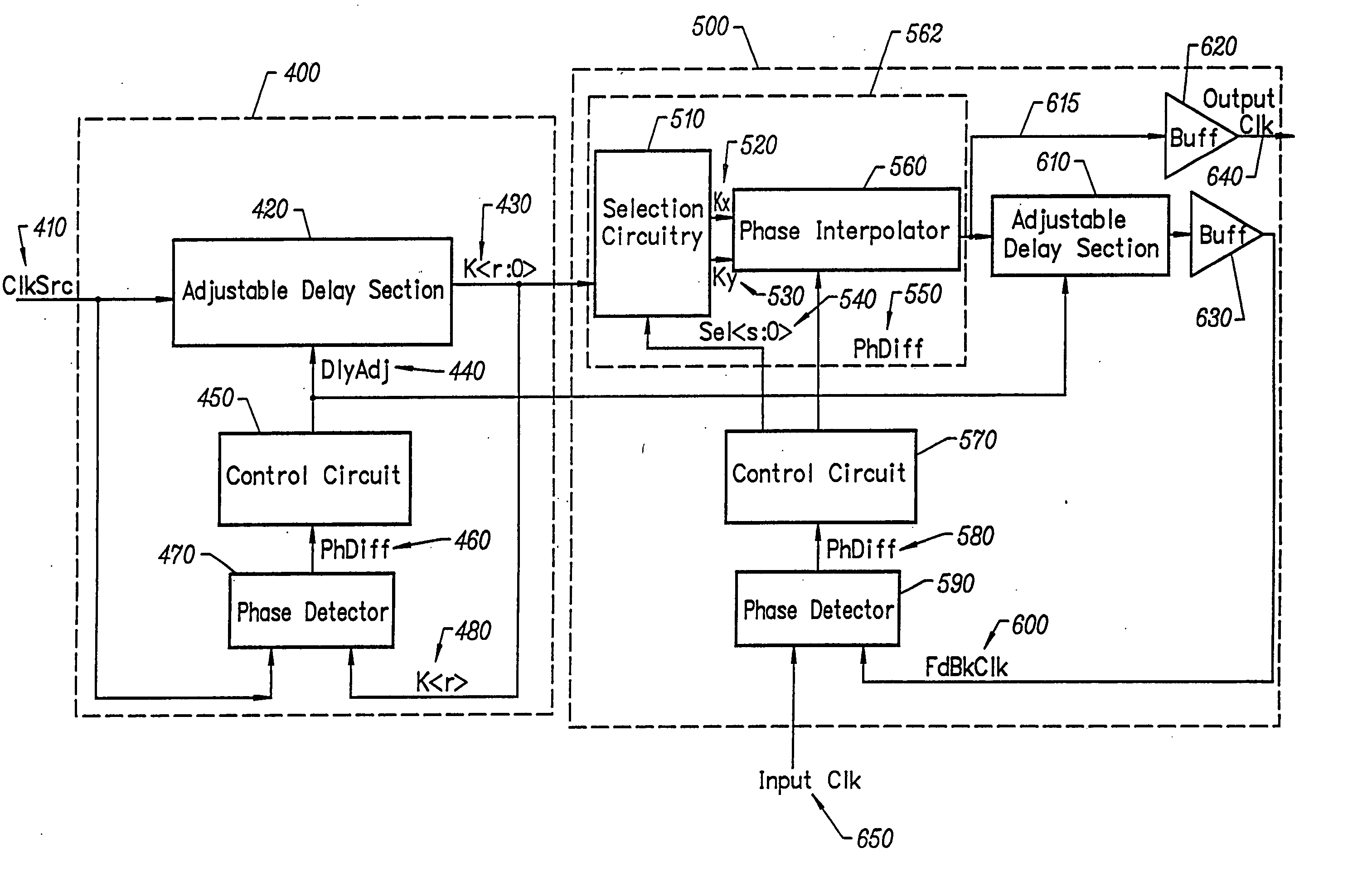
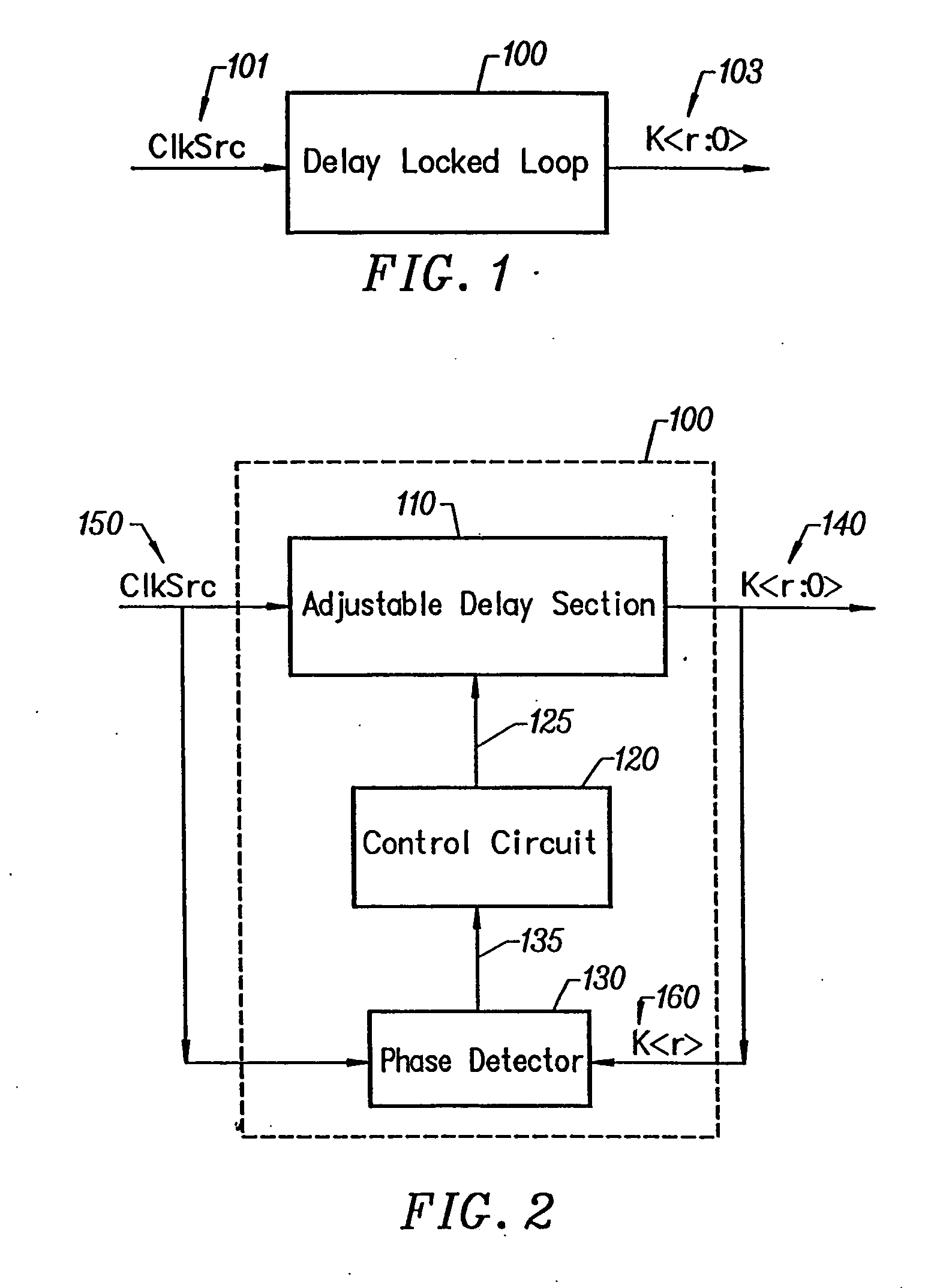
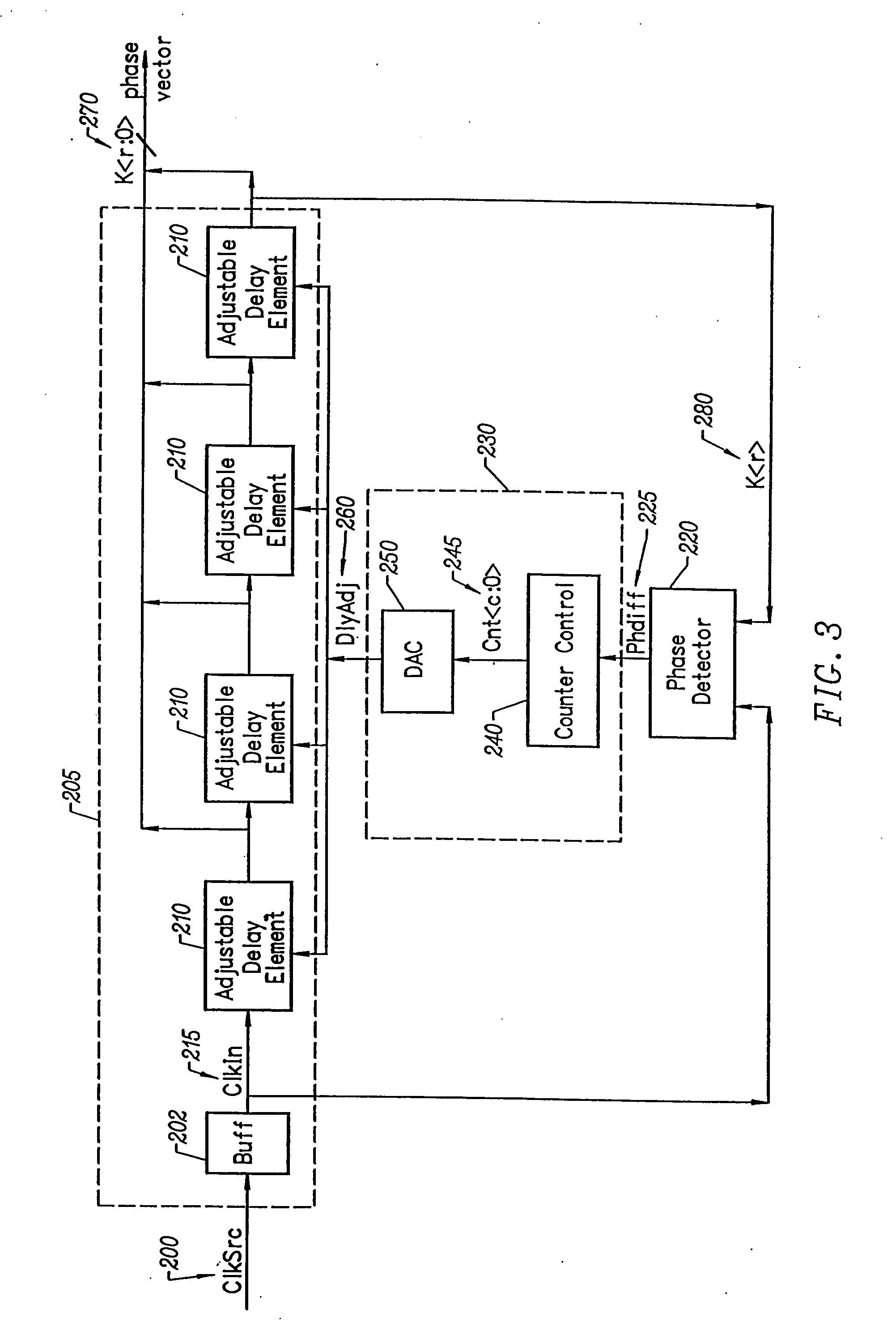
Delay locked loop circuitry for clock delay adjustment
InactiveUS7039147B2Reduce loop jitterMultiple input and output pulse circuitsSynchronisation information channelsPhase detectorPhase shifted
Delay locked loop circuitry for generating a predetermined phase relationship between a pair of clocks. A first delay-locked loop includes a delay elements arranged in a chain, the chain receiving an input clock and generating, from each delay element, a set of phase vectors, each shifted a unit delay from the adjacent vector. The first delay-locked loop adjusts the unit delays in the delay chain using a delay adjustment signal so that the phase vectors span a predetermined phase shift of the input clock. A second delay-locked loop selects, from the first delay-locked loop, a pair of phase vectors which brackets the phase of an input clock. A phase interpolator receives the selected pair of vectors and generates an output clock and a delayed output clock, the amount of the delay being controlled by the delay adjustment signal of the first delay-locked loop circuitry. A phase detector compares the delayed output clock with the input clock and adjusts the phase interpolator, based on the phase comparison, so that the phase of the delayed output clock is in phase with the input clock. As a result, there is a predetermined phase relationship between the output clock and the input clock, the phase relationship being the amount of delay between the output clock and the delayed output clock. Different phase relationships between the input and output clock are possible depending on the number of unit delays used in the path of the, delayed output clock or the output clock.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Delay locked loop circuitry for clock delay adjustment
InactiveUS20060188051A1Reduce loop jitterMultiple input and output pulse circuitsSynchronisation information channelsDelay-locked loopComputer science
A receiver adapted to be coupled to a data bus and configured to receive data in accordance with a receive clock includes first and second delay-locked loops. The first delay-locked loop is configured to generate a plurality of phase vectors from a first reference clock, and the second delay-locked loop is coupled to the first delay-locked loop and configured to generate the receive clock from at least one phase vector selected from the plurality of phase vectors and a second reference clock.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
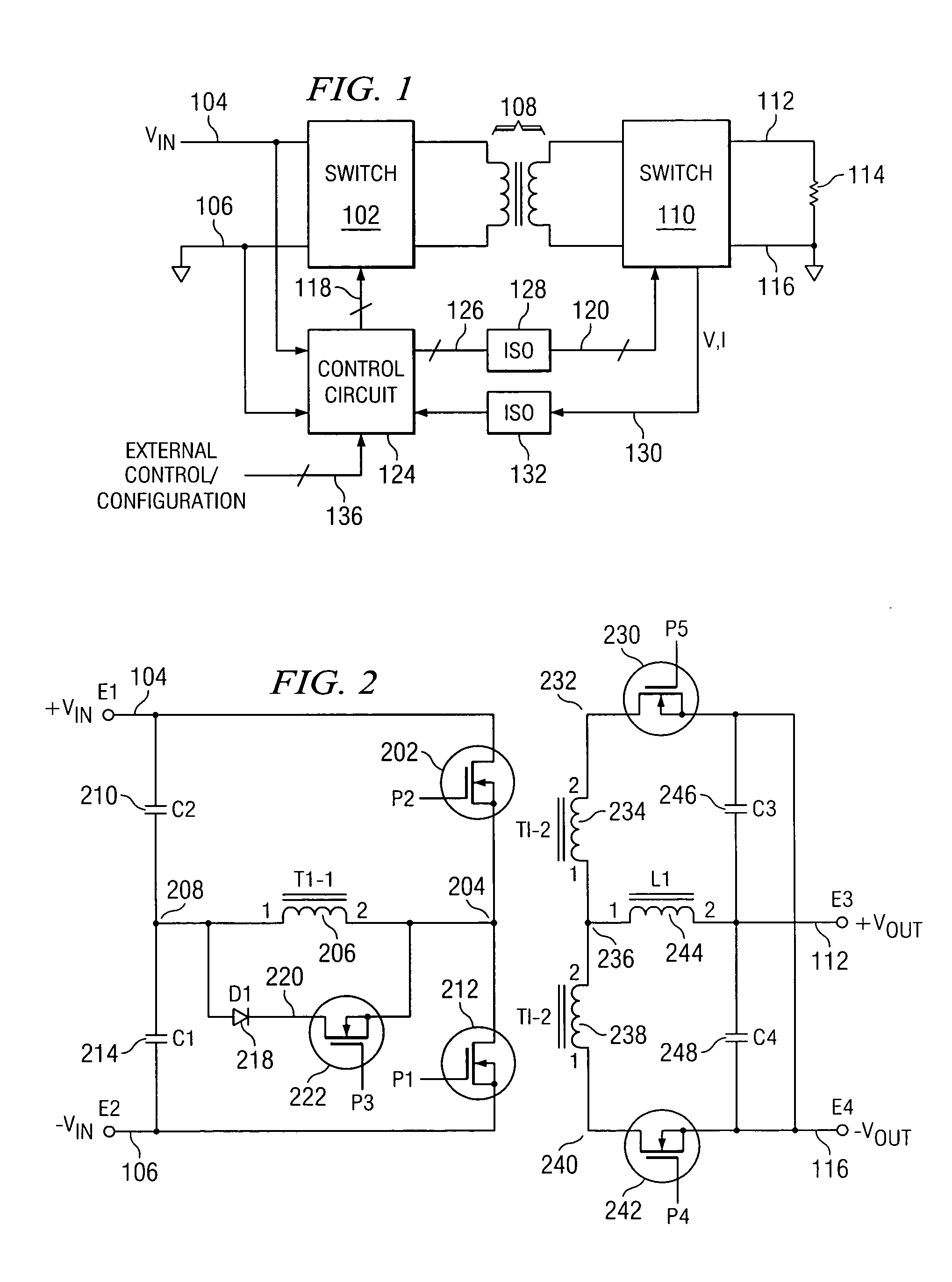
Low power PLL for PWM switching digital control power supply
A timing source for a pulse generator is disclosed, which timing source includes an input for receiving a reference clock output at a reference operating frequency. An edge generator is provided for generating a plurality of clock edges from an edge of the reference clock during one period thereof, with the spacing of the plurality of clock edges being a multiple of a predetermined divisor. As such, the resolution of such spacing emulates a higher clock frequency than the reference operating frequency. A selector then selects one of the plurality of clock edges from a reference one thereof to define the width of a pulse.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Delay circuit, voltage-controlled delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, delay adjustment circuit, DLL circuit, and PLL circuit
An inverter type delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, and voltage-controlled delay circuit capable of realizing simplification of circuit configuration, reduction of an effect of power source noise, and reduction of jitter, wherein a delay circuit, voltage-controlled oscillation circuit, and voltage-controlled delay circuit comprised of a plurality of delay stages controlled in drive current in accordance with a bias voltage or a control voltage and determined in delay time by the drive current, adding a change of a power source voltage to the above bias voltage or control voltage by a predetermined ratio and supplying a result of the addition to the above delay stages to suppress the power source voltage dependencies of the delay times of the delay stages, or connecting by a predetermined ratio a plurality of delay stages having different power source voltage dependencies, for example, power source voltage dependencies of opposite delay times, to suppress the power source voltage dependencies of delay times of the delay stages are realized.
Owner:SONY CORP
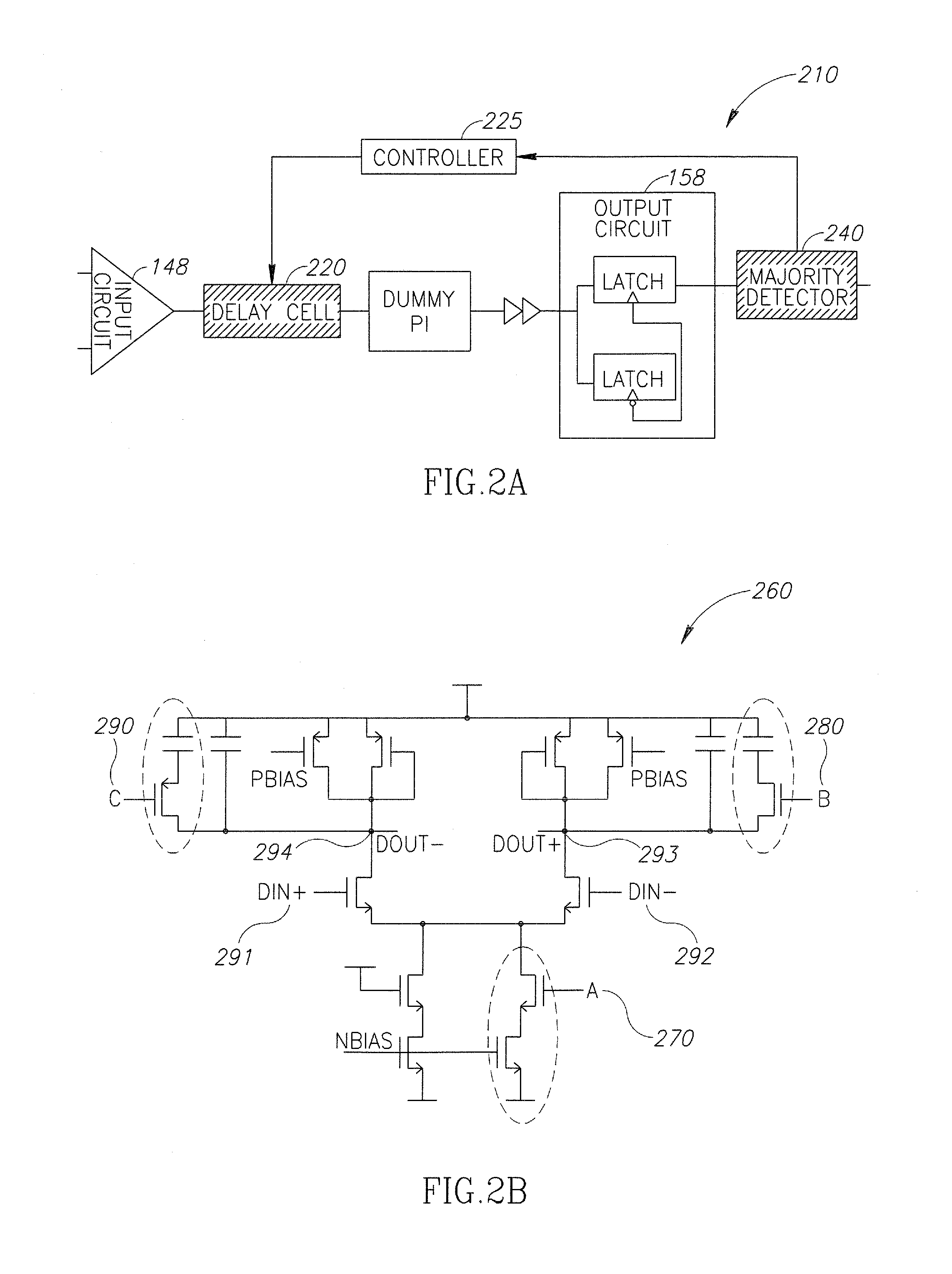
Current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) fully differential integrated delay cell with variable delay and high bandwidth
Current-controlled CMOS (C3MOS) fully differential integrated delay cell with variable delay and high bandwidth. A novel implementation includes a wideband differential transistor pair and a cross-coupled differential transistor pair. The wideband differential transistor pair can be implemented with appropriate input and output impedances to extend its bandwidth for use in broadband applications. These two stages, (1) buffer stage (or data amplifier stage) and (2) cross-coupled differential pair stage, are both very fast operating stages. This design does not incur any increased loading to previous or subsequent stages in a device. In addition, there is no increase in the total amount of current that is required.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Programmable jitter generator
ActiveUS7171601B2Reduce manufacturing costAnalog circuit testingDigital circuit testingData controlControl data
A jitter generator produces a jittery test signal for use in performing a jitter test on an integrated circuit (IC) device under test (DUT). The jitter generator includes a programmable delay circuit for delaying a non-jittery input signal with a varying delay controlled by input digital delay control data to produce the test signal. A pattern generator supplies a sequence of delay control data to the programmable delay circuit causing it to produce a desired jitter pattern in the test signal. During a calibration process, a measurement unit feeds the test signal back to the input of the programmable delay circuit, causing the test signal to oscillate with a period proportional to the delay through the delay circuit. The measurement unit then measures the period of the test signal for various values of delay control data and reports measurement results. Based on the measurement results, host equipment then determines an appropriate sequence of delay control data for producing a desired jitter pattern in the test signal and programs the pattern generator to produce that sequence of delay control data during a jitter test. The jitter generator can form a part of a built-in, self-test (BIST) circuit implemented within the DUT itself.
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Bandpass filter circuit, band-elimination filter circuit, infrared signal processing circuit
ActiveUS20080112712A1Reduce light noiseDistortion in outputGain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesBandpass filteringSignal processing circuits
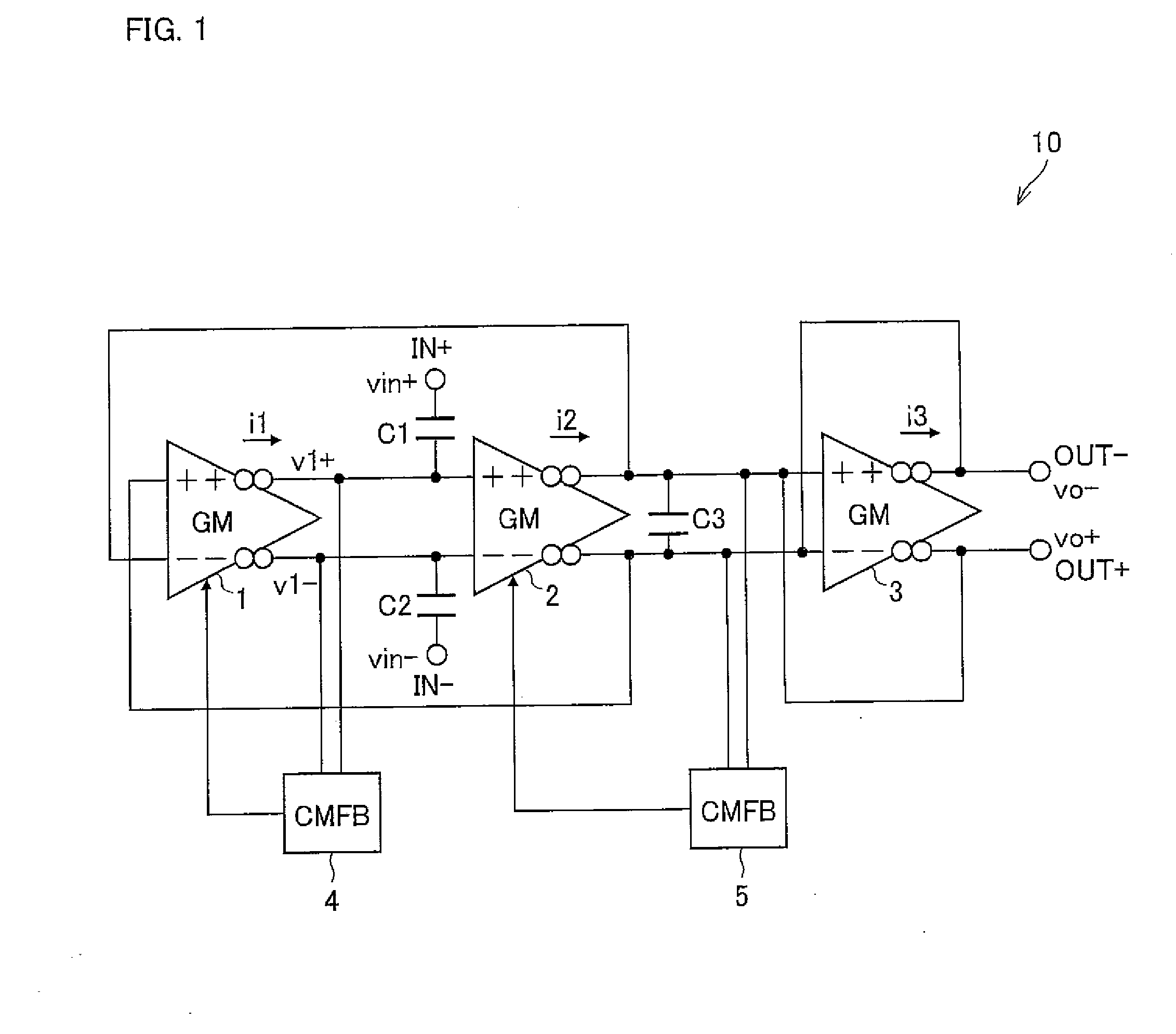
A bandpass filter circuit 10 of the present invention includes: transconductance amplifier circuits 1 to 3; a common-mode feedback circuit 4 which outputs a first control signal to the transconductance amplifier circuit 1 so that a D.C. voltage level of a differential output of the transconductance amplifier circuit 1 is at a predetermined level; a common-mode feedback circuit 5 which outputs a second control signal to the transconductance amplifier circuit 2 so that a D.C. voltage level of a differential output of the transconductance amplifier circuit 2 is at a predetermined level; and capacitors C1 to C3. Each of the members are connected as shown in FIG. 1. With the configuration, a bandpass filter circuit capable of adjusting constants such as a Q-value is realized.
Owner:SHARP KK
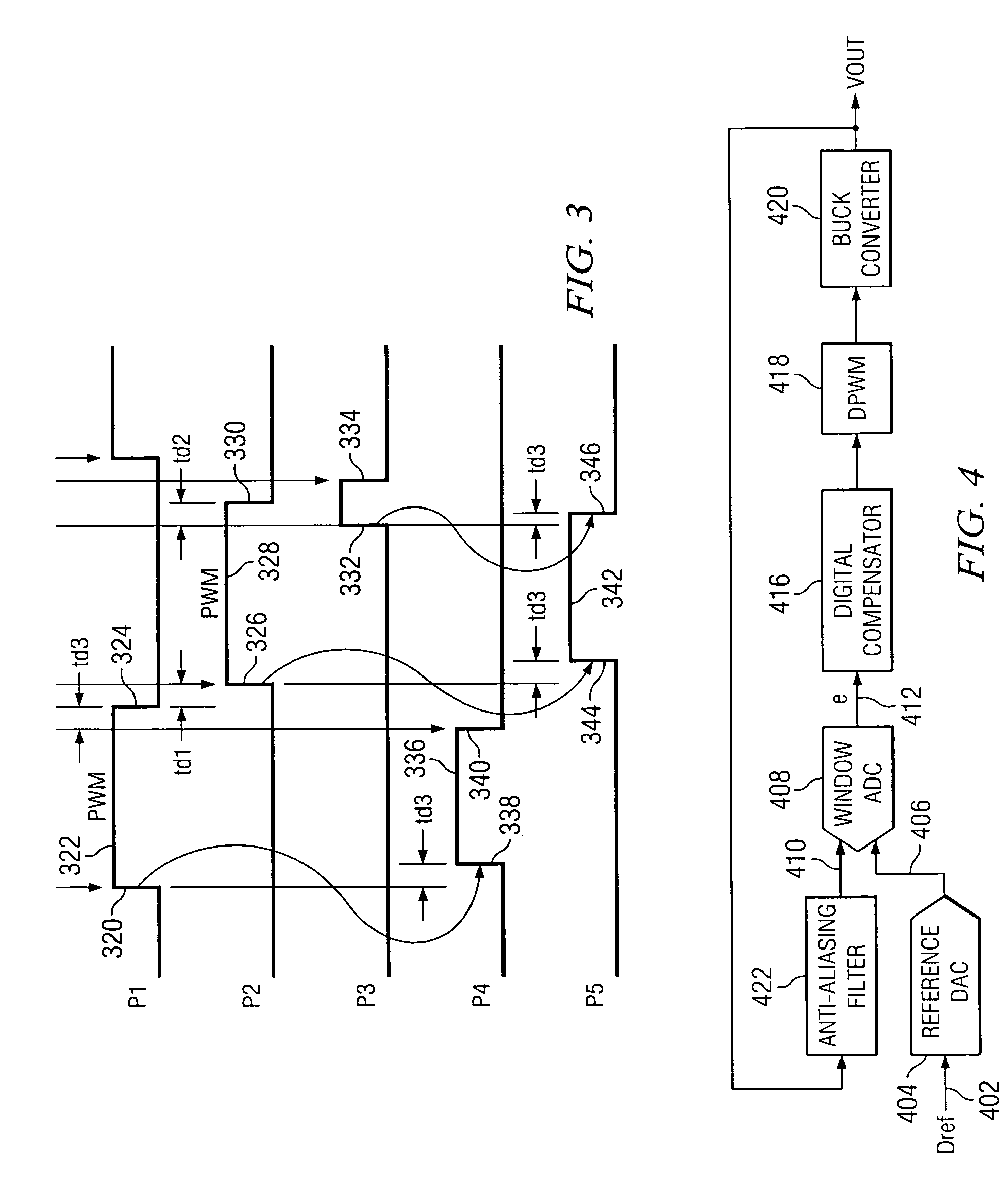
Duty cycle correction circuit with small duty error and wide frequency range
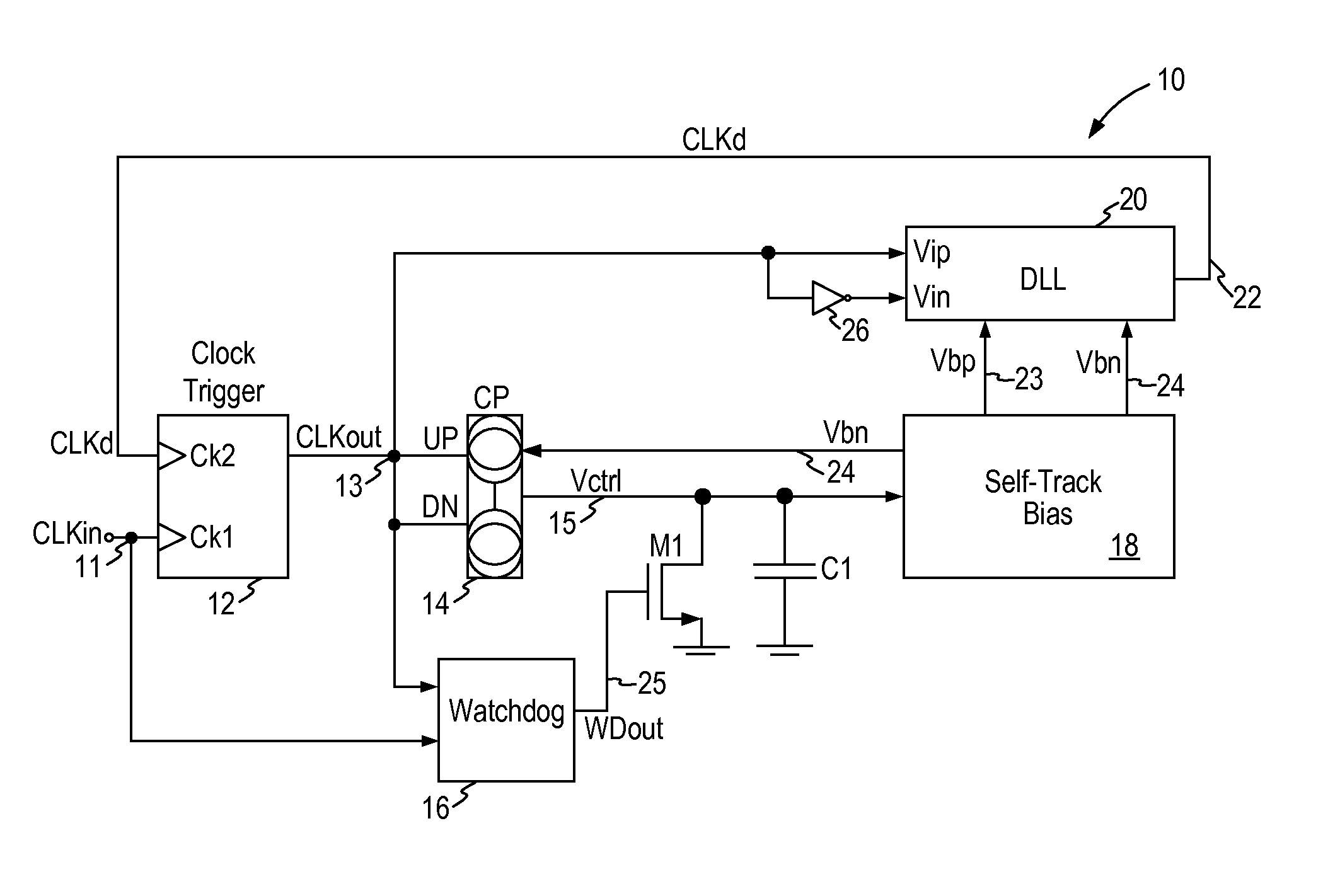
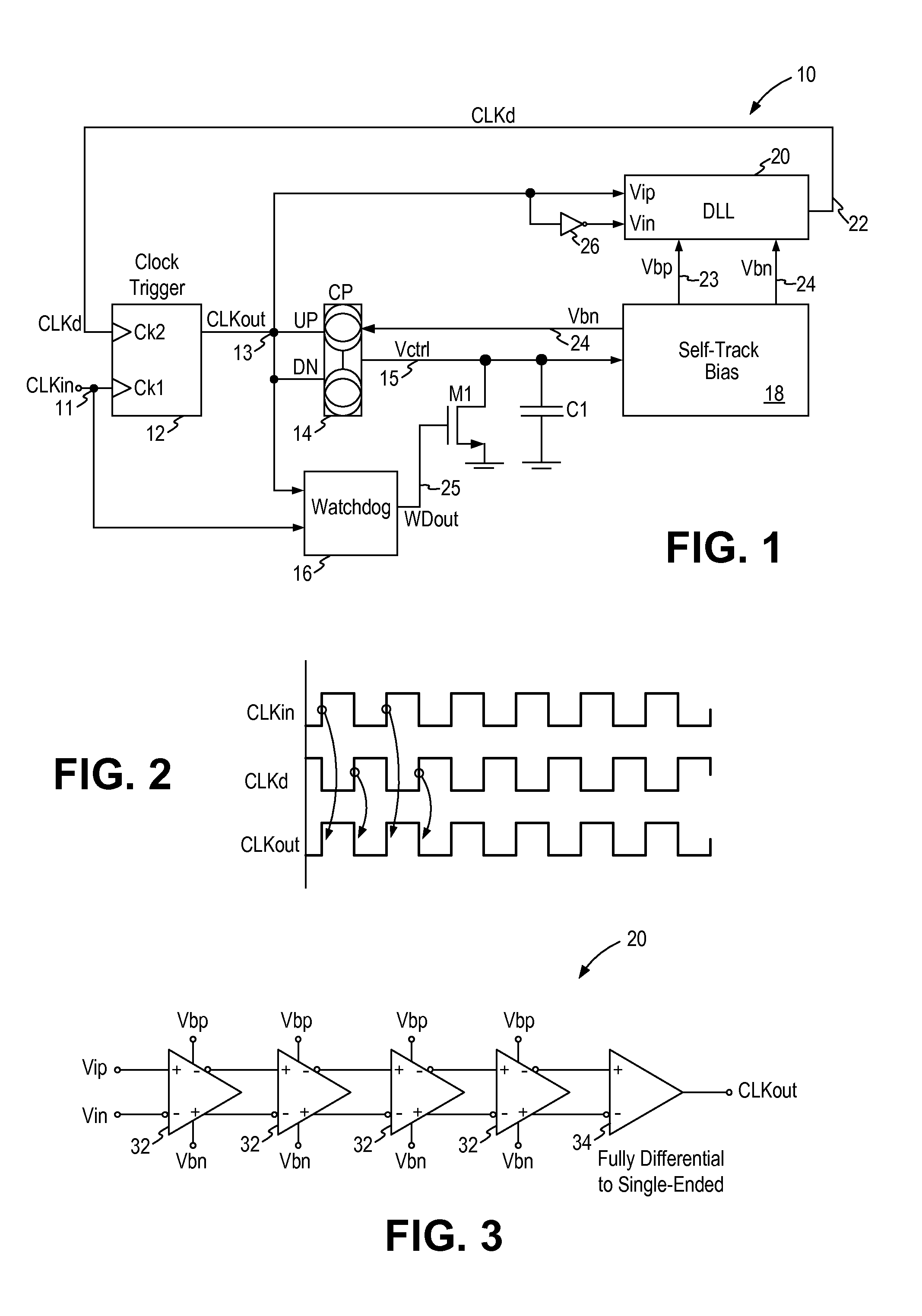
A duty cycle correction circuit (10) for receiving an input clock signal (11) and generating an output clock signal (13) having a predetermined duty cycle includes a clock trigger circuit (12) generating the output clock signal (13) having a first clock edge triggered from the input clock signal and a second clock edge triggered from a delayed clock signal (22); a charge pump circuit (14) receiving the output clock signal and generating charging and discharging currents for a capacitor (C1) where a control voltage develops on the capacitor indicative of the duty cycle error of the output clock signal; a self-track bias circuit (18) receiving the control voltage and generating first and second bias voltages (23, 24) in response to the control voltage; and a delay-locked loop circuit (20) receiving the output clock signal and the first and second bias voltages and generating the delayed clock signal.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Clock generating apparatus
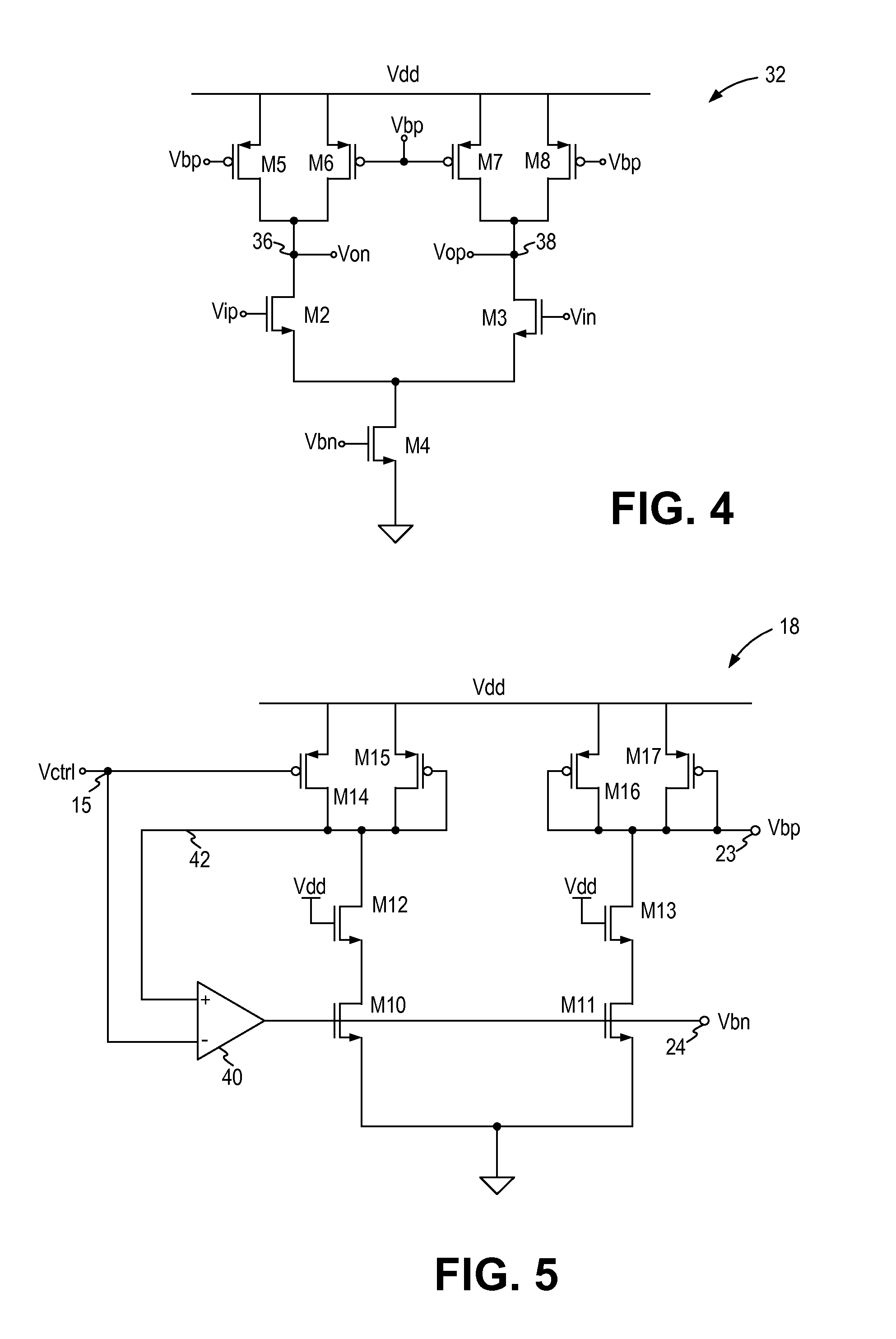
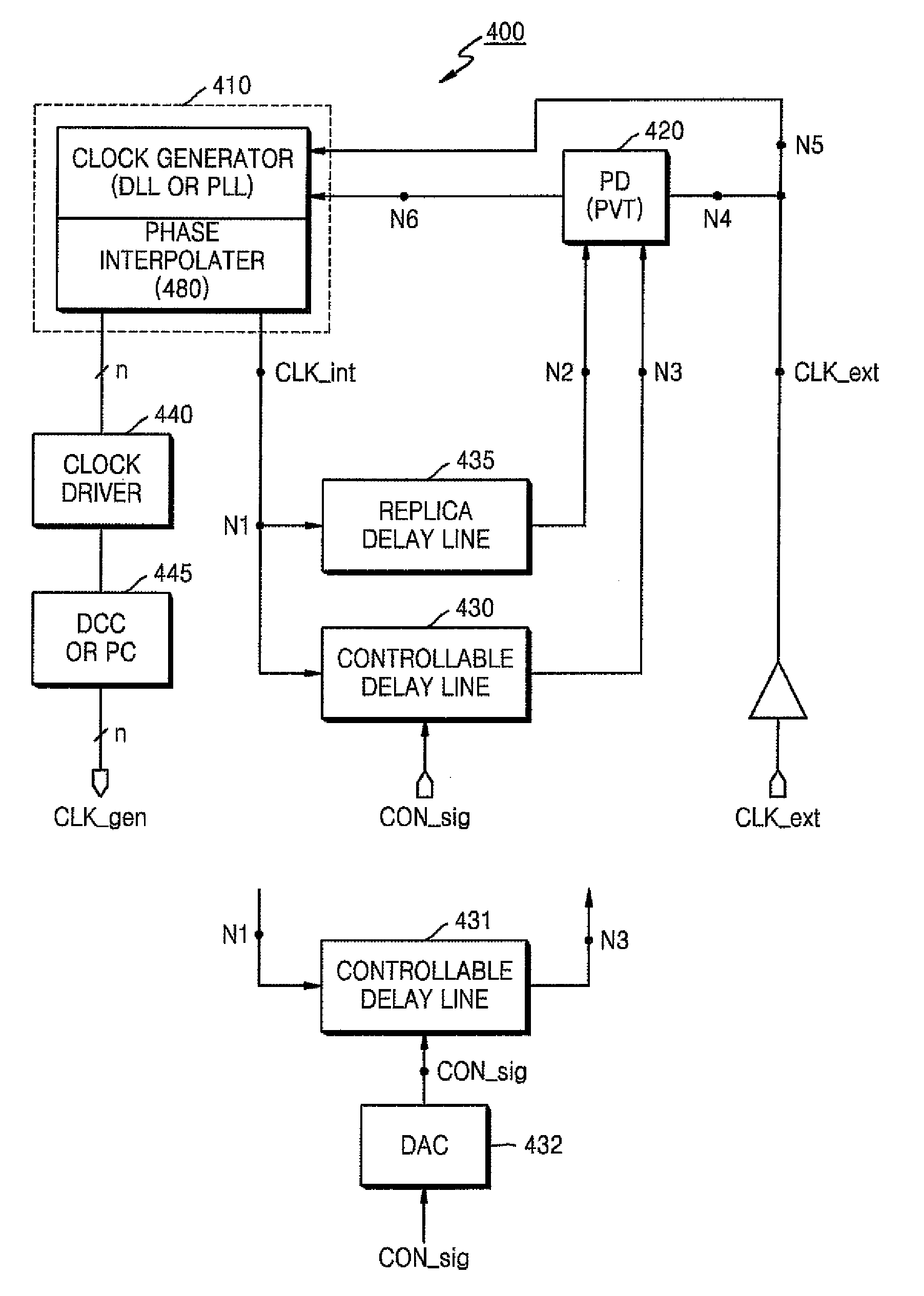
A clock generating apparatus includes a clock generator and a controllable delay line. The clock generator receives an external clock signal and generates multiple clock signals having different phases by delaying the external clock signal. The controllable delay line receives one of the multiple clock signals as a first clock signal and delays the first clock signal by a first interval in response to an externally applied control signal. The delayed first clock signal is input to the clock generator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Clock recovery circuit
InactiveUS7242733B2Optimize phaseClock frequency is easedPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsData signalClock recovery
The clock recovery circuit includes a first oscillator and an edge detector. The first oscillator generates a plurality of clocks having different phases and a predetermined frequency. The edge detector detects two clocks, among the plurality of clocks, between edges of which an input data signal has made a transition. The first oscillator includes a plurality of delay cells connected in a ring, and outputs of the plurality of delay cells are output as the plurality of clocks. Each of the plurality of delay cells selectively delays a first-delay added input data signal or the signal output from the preceding delay cell, and outputs the selected delayed signal. The edge detector controls one delay cell among the plurality of delay cells corresponding to the result of the detection, to delay and output the first-delay added input data signal.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Delay stage, ring oscillator, PLL-circuit and method
ActiveUS7629856B2Pulse automatic controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesRC oscillatorSemiconductor
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
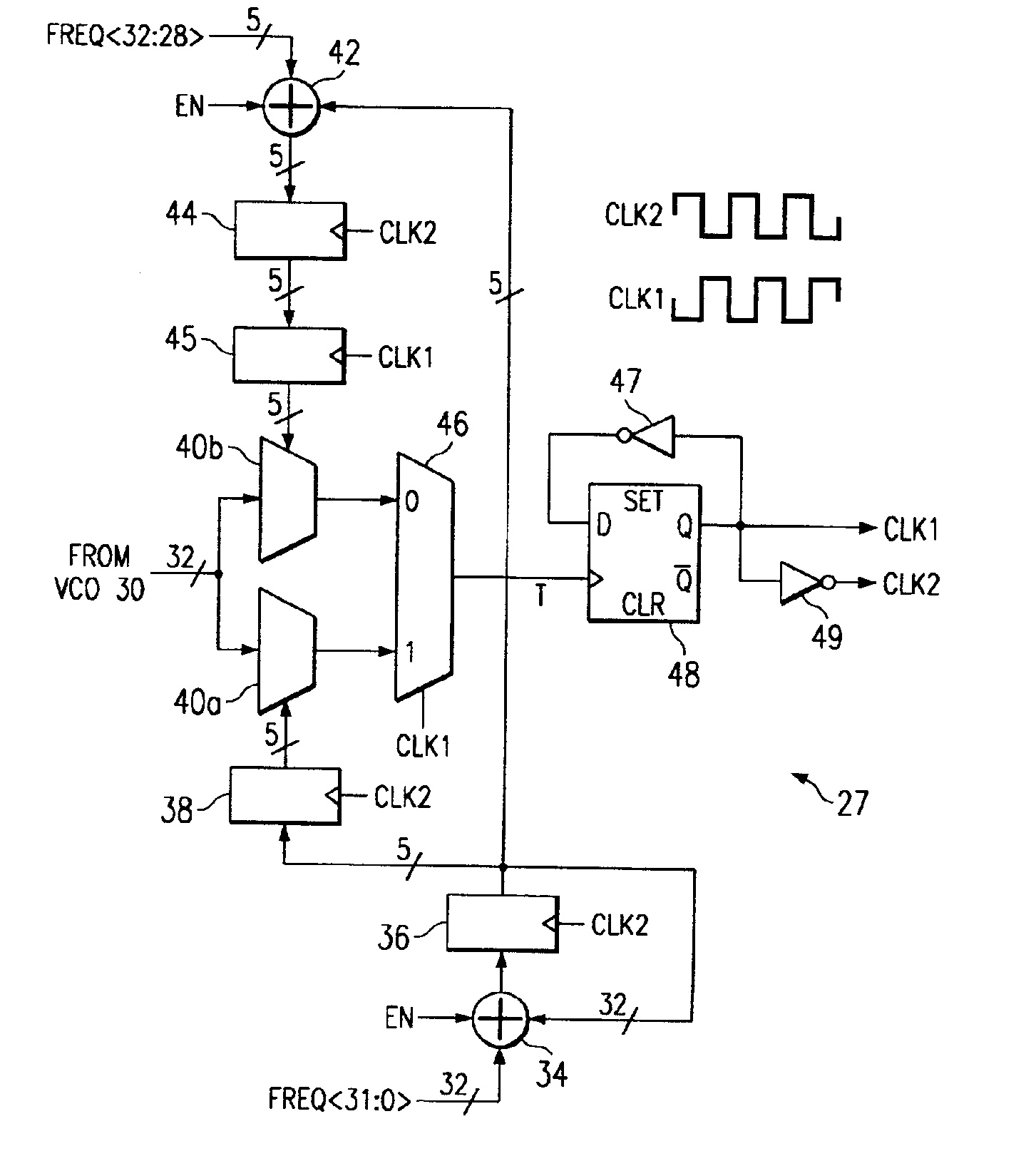
Scalable high-speed precision frequency and phase synthesis
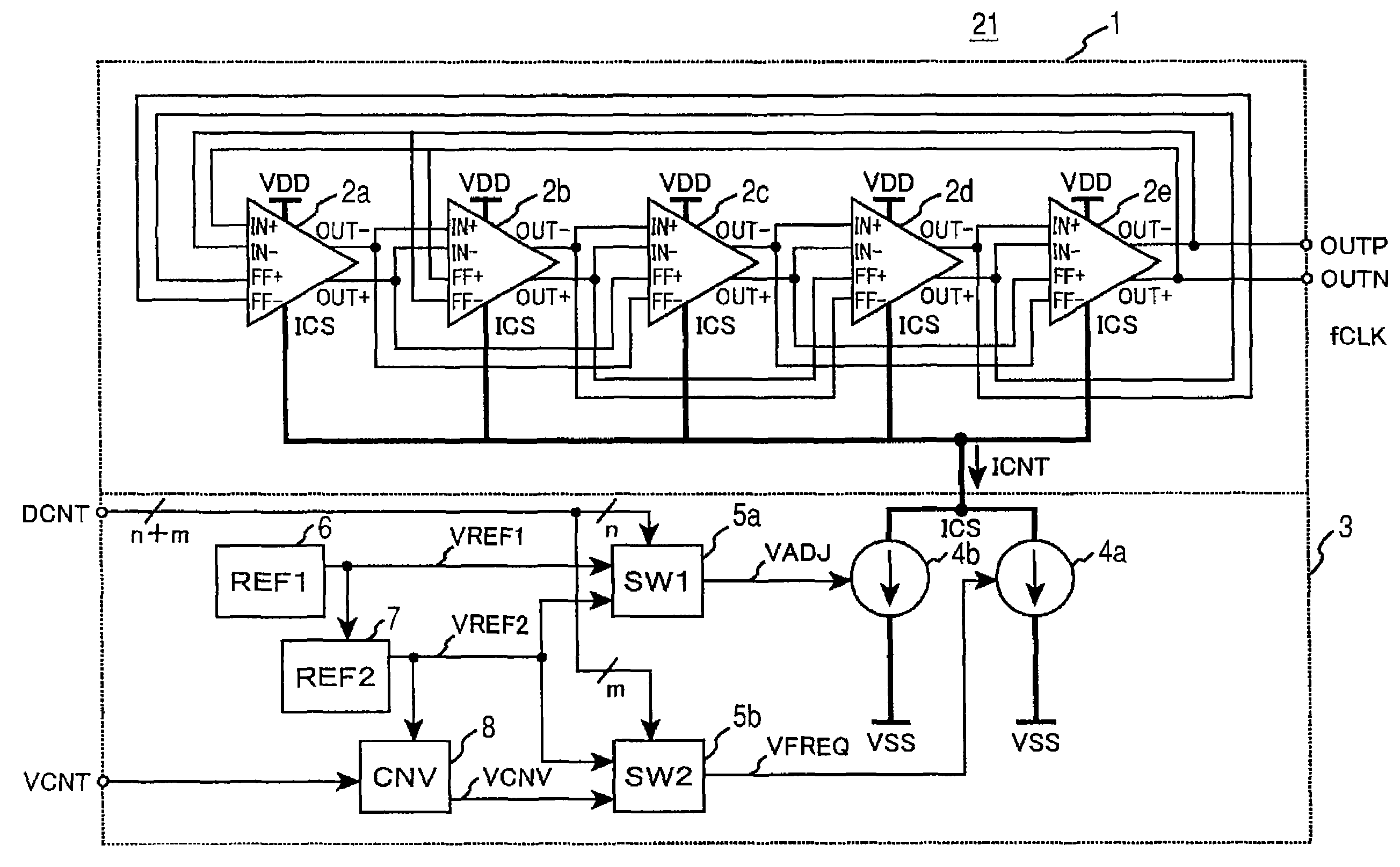
ActiveUS6940937B2Increase the output frequencyIncrease the number ofPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionPhase shiftedPhase difference
A clock synthesis circuit (22) including a phase-locked loop (25) and one or more frequency synthesis circuits (27; 77; 227; 237) is disclosed. A disclosed implementation of the phase-locked loop (25) includes a voltage-controlled oscillator (30) having an even number of differential stages (31) to produce an even number of equally spaced clock phases. In one arrangement, the frequency synthesis circuit (27) includes two adder legs that generate select signals applied to first and second multiplexers (40a, 40b), for selecting among the clock phases from the voltage-controlled oscillator (30). The outputs of the first and second multiplexers (40a, 40b) are applied to a two-to-one multiplexer (46) which is controlled by the output clock signal (CLK1), to drive clock edges to a T flip-flop (48) to produce the output clock signals (CLK1, CLK2). In another embodiment, more than two adder and register units (55) control corresponding multiplexers (56) for selecting clock phases from the voltage-controlled oscillator (30) for application to an output multiplexer (58), which is controlled by a clock control circuit (60) to apply the selected clock phases to the T flip-flop (62). In another embodiment, primary and phase-shifted frequency synthesis circuits (227, 327) receive initialization values (INIT1, INIT2) that establish the phase differential and ensure proper initialization.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
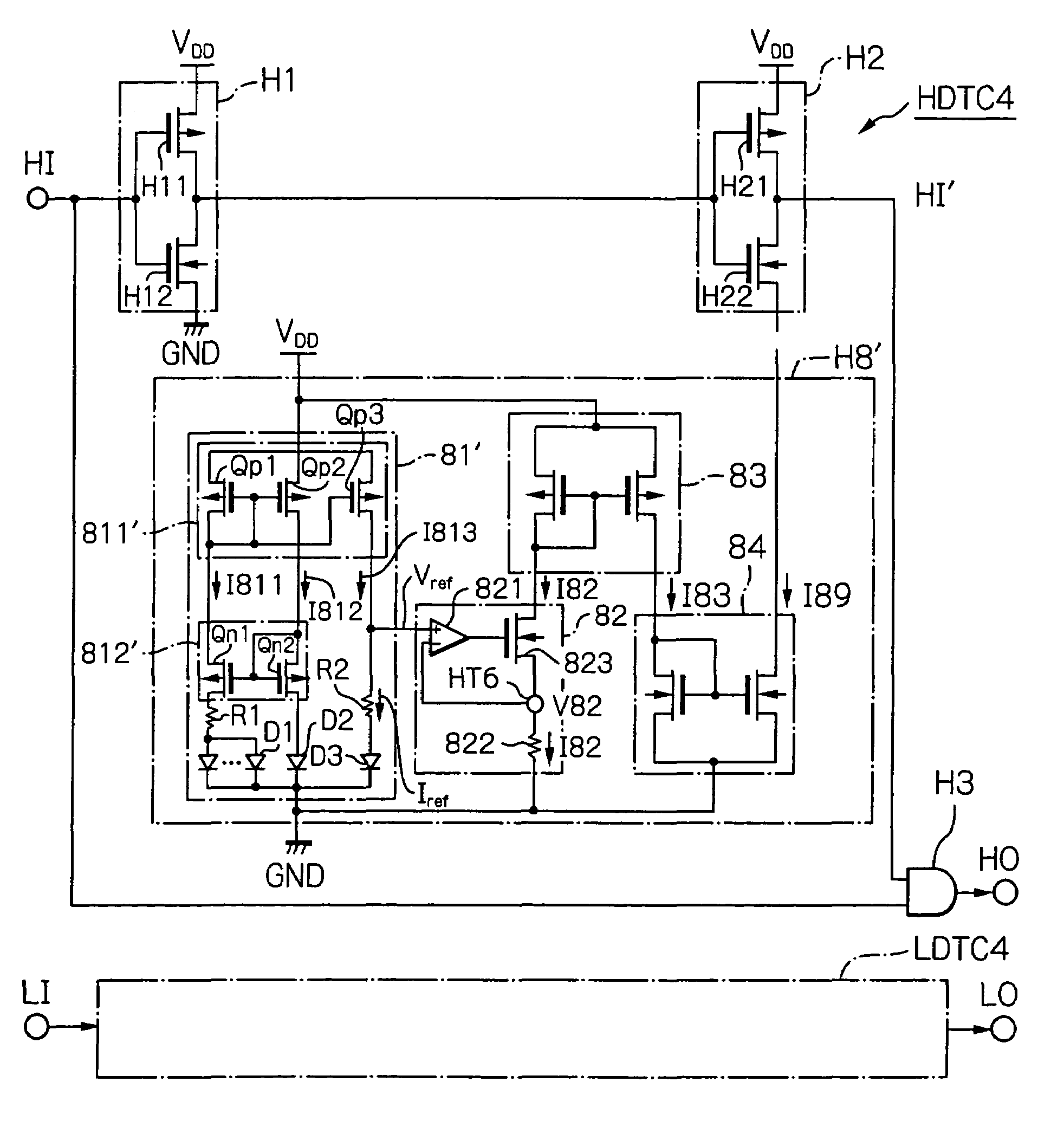
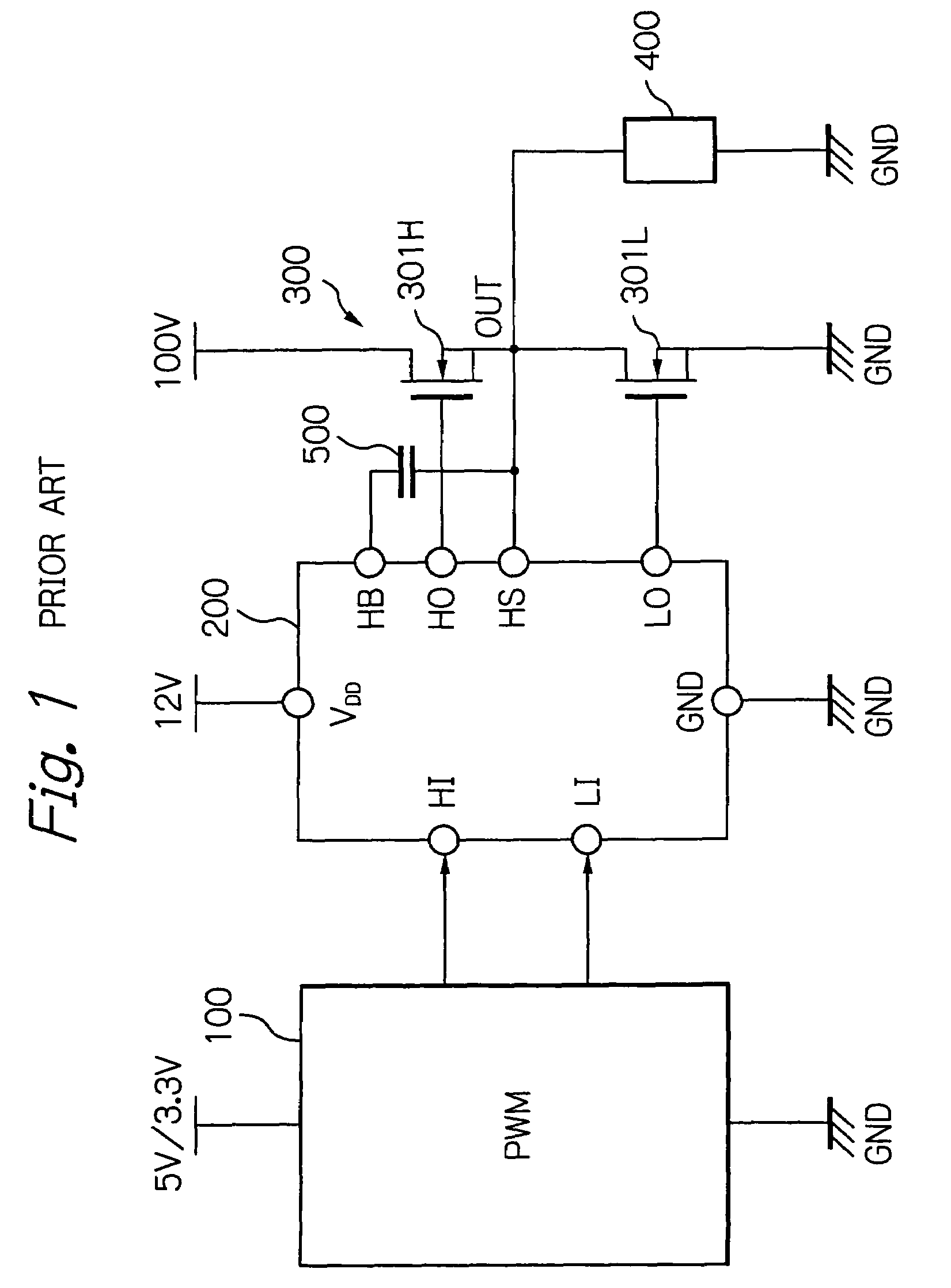
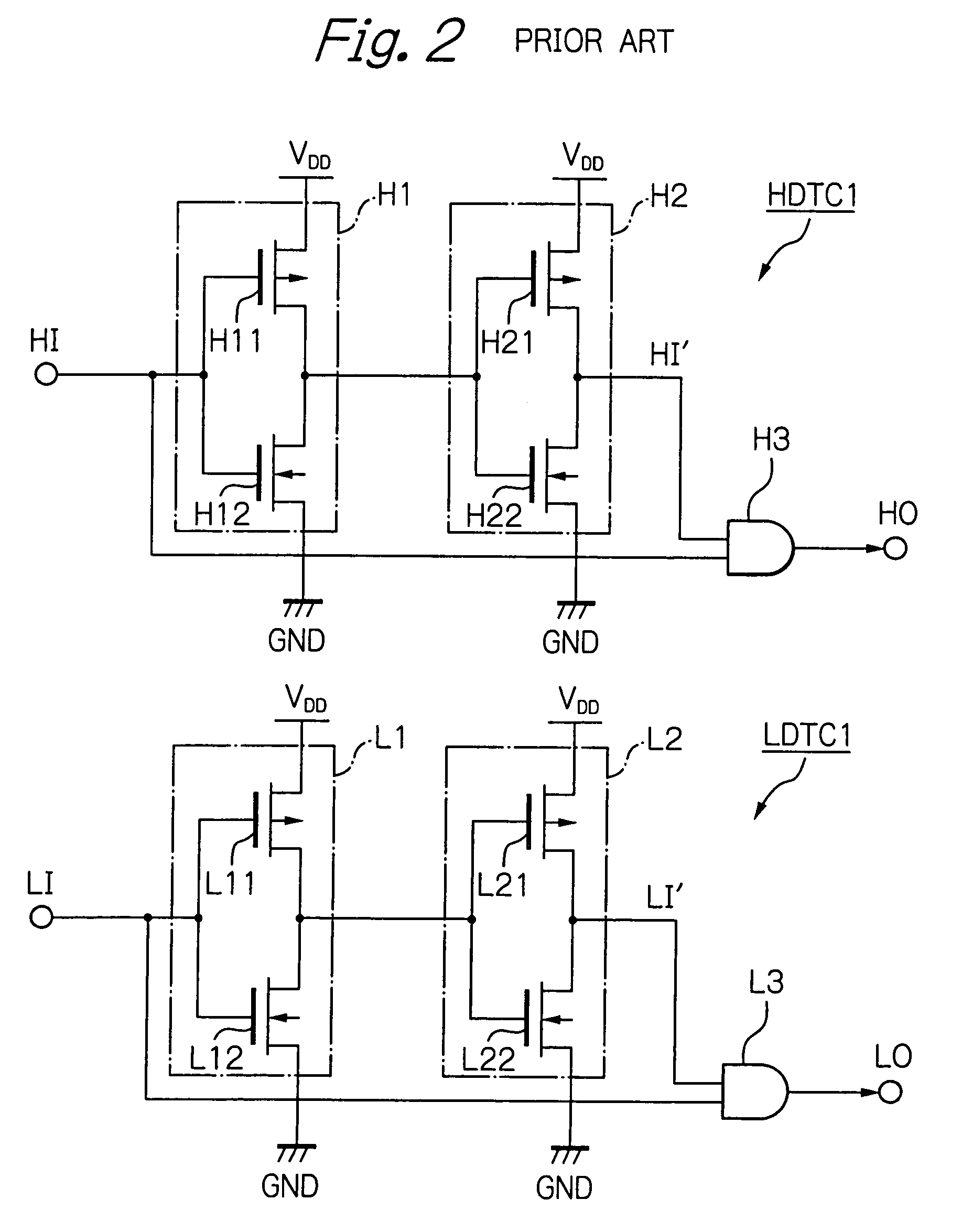
Dead time control circuit capable of adjusting temperature characteristics of dead time
In a dead time control circuit, a delay circuit is connected to an input terminal and adapted to delay signals therethrough by a delay time corresponding to a dead time. A logic circuit has a first input connected via the delay circuit to the input terminal, a second input connected directly to the input terminal, and an output connected to an output terminal. The dead time having adjustable temperature characteristics.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated circuit devices having high precision digital delay lines therein
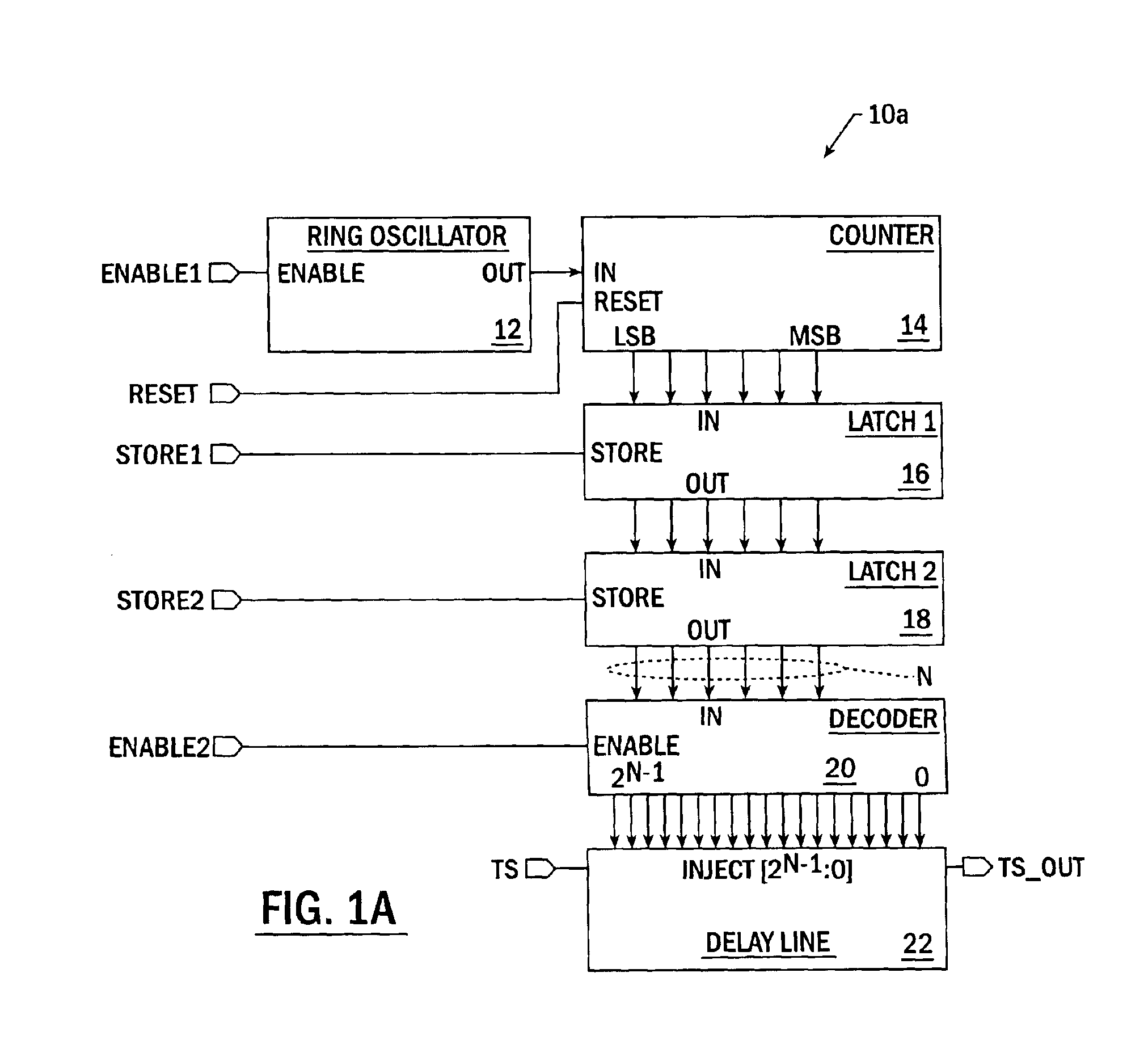
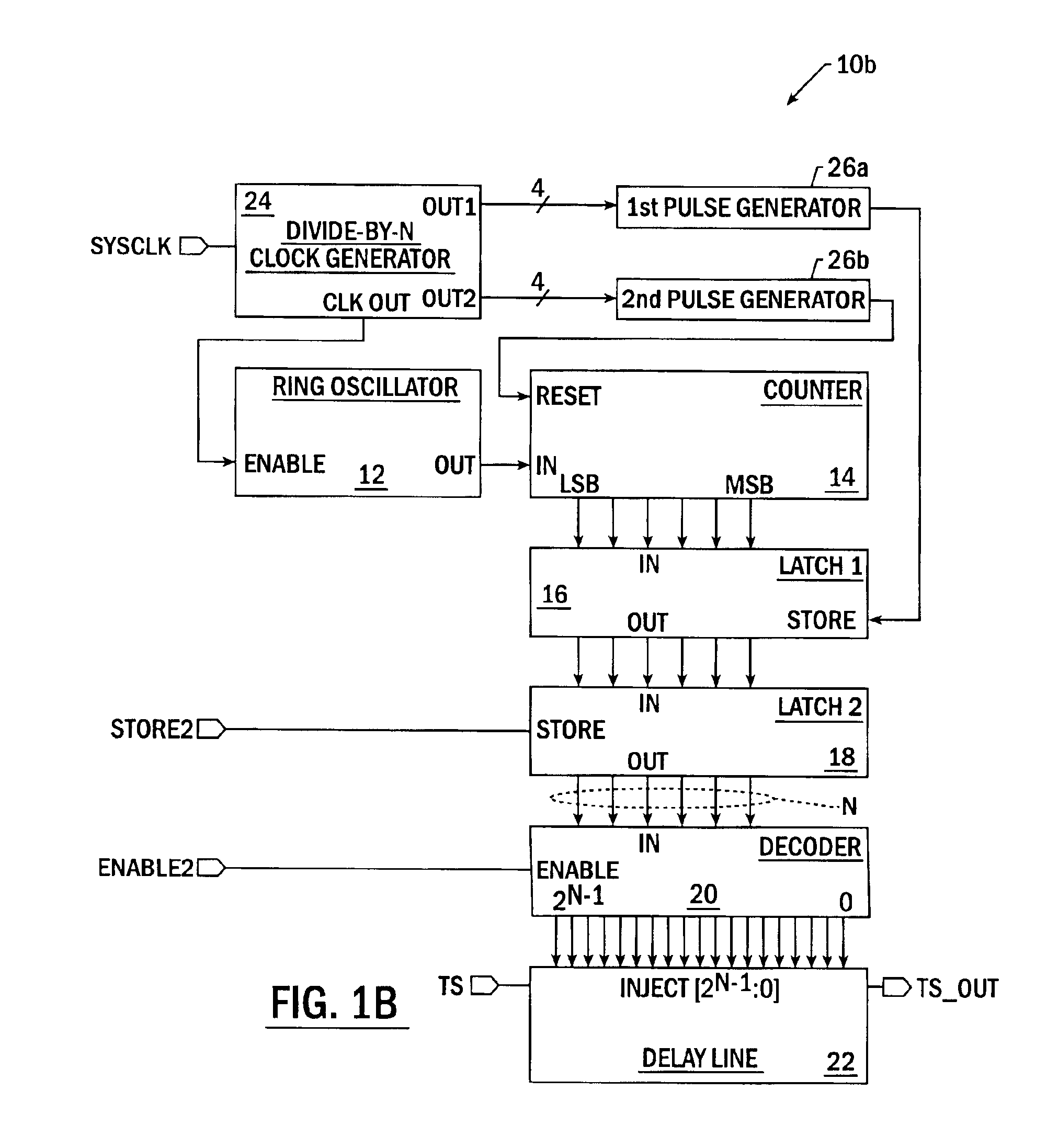
InactiveUS6856558B1High resolutionConvenient power supplyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsInjection portControl signal
Integrated circuit delay devices include a digital delay line that is configured to provide a percent-of-clock period delay to a timing signal accepted at an enabled one of a plurality of injection ports thereof. The digital delay line may be responsive to an injection control signal having a value that sets a length of the delay by specifying a location of the enabled one of the plurality of injection ports, with the end of the delay line being a fixed output port. A delay line control circuit is also provided that is responsive to a clock signal having a period from which the percent-of-clock period delay is preferably measured. The delay line control circuit is configured to generate the injection control signal by counting multiple cycles of a high frequency ring oscillator signal having a period less than, and typically substantially less than, the clock period, over a time interval having a duration greater than, and typically substantially greater than, the clock period. The ring oscillator signal may be generated by a ring oscillator having a relatively small number of stages and the time interval may be sufficiently long so that a large number of cycles of the ring oscillator signal may be counted over many periods of the clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
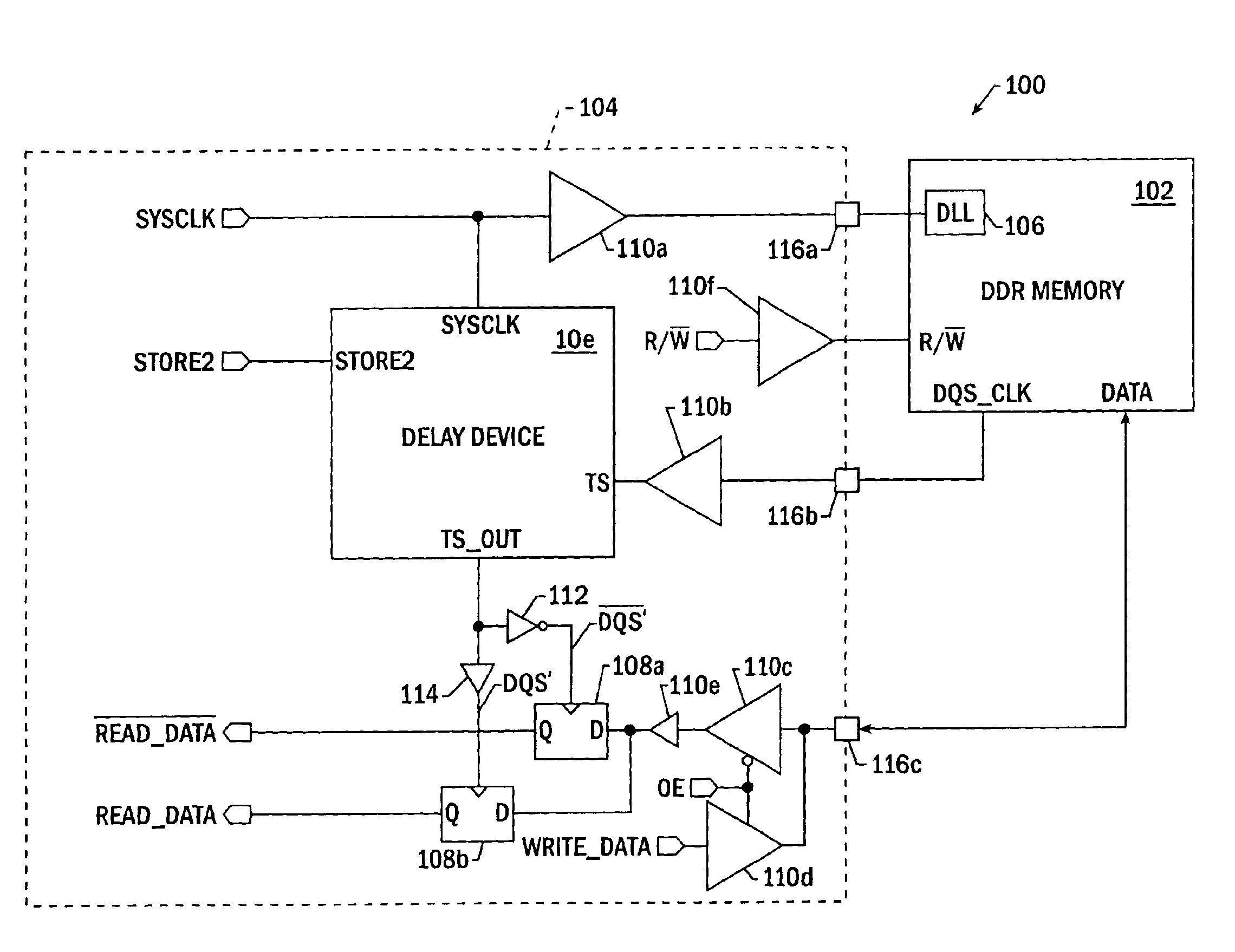
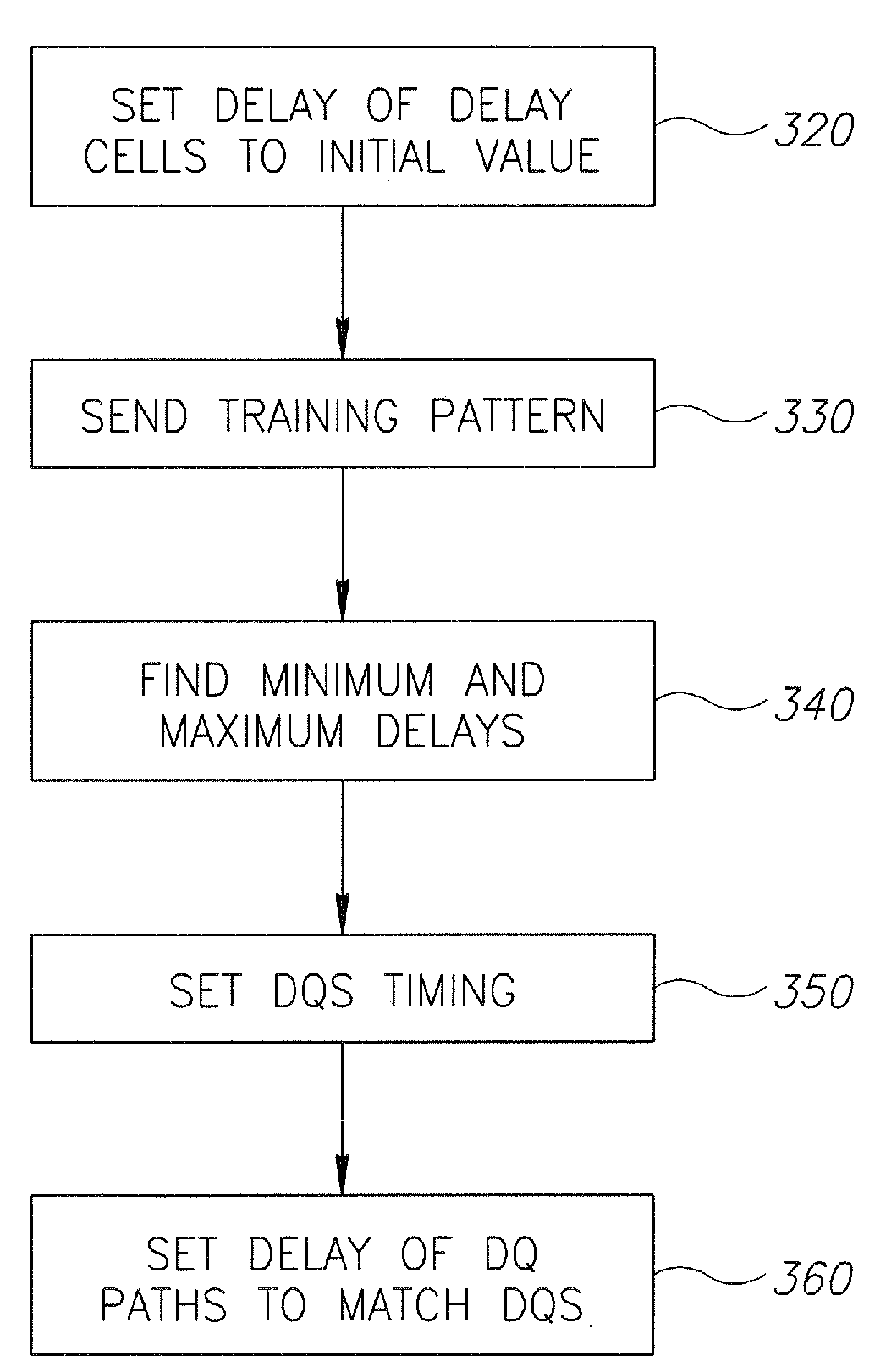
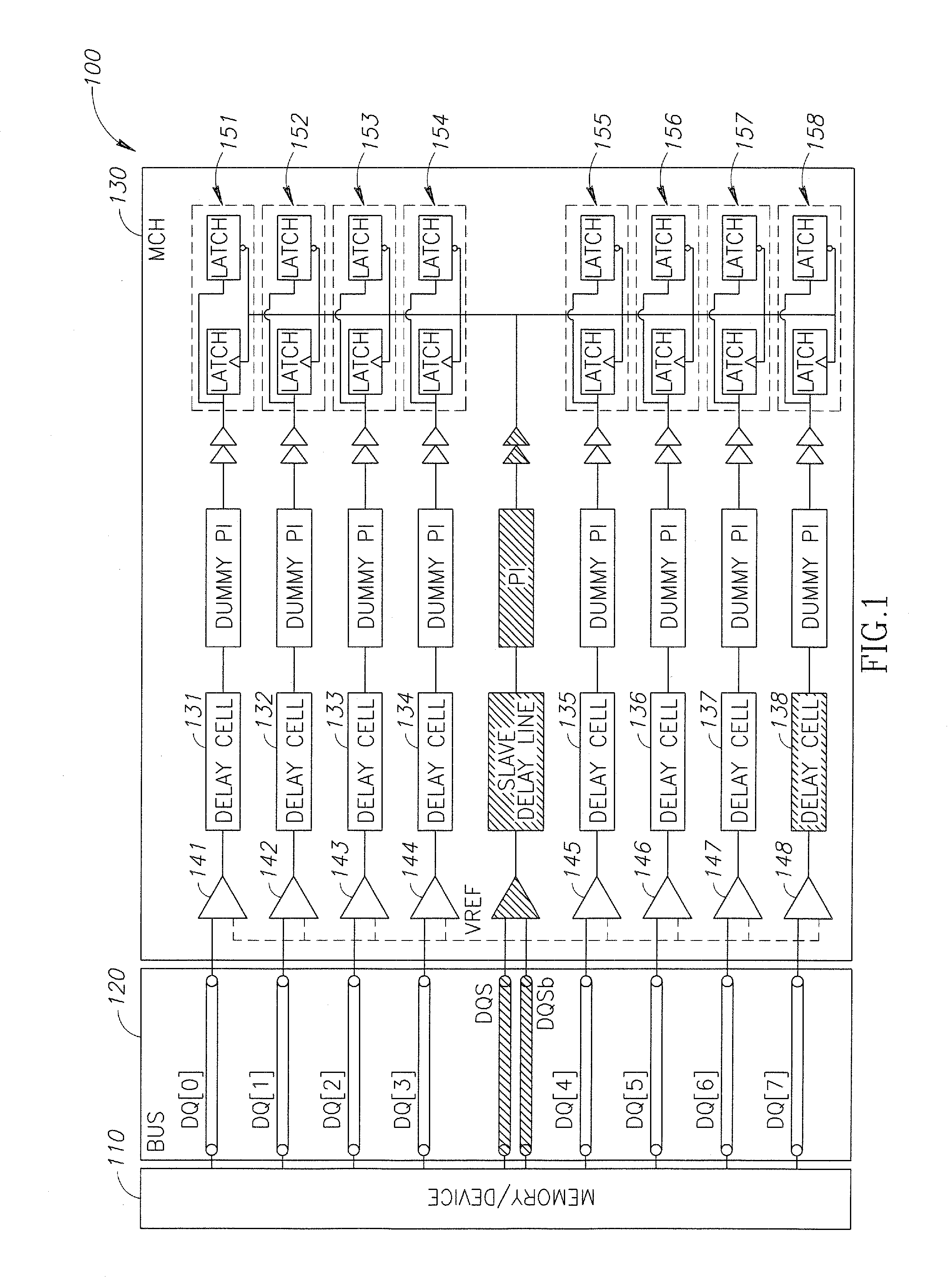
Apparatus, system, and method for bitwise deskewing
InactiveUS20090168563A1Channel dividing arrangementsPulse automatic controlEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A system and method for bitwise deskew. A DQS timing is used as reference, the delays of a plurality of transmission wires are calibrated with reference to a DQS line timing. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com