Patents
Literature
225results about "Manipulation where pulse delivered at different times" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
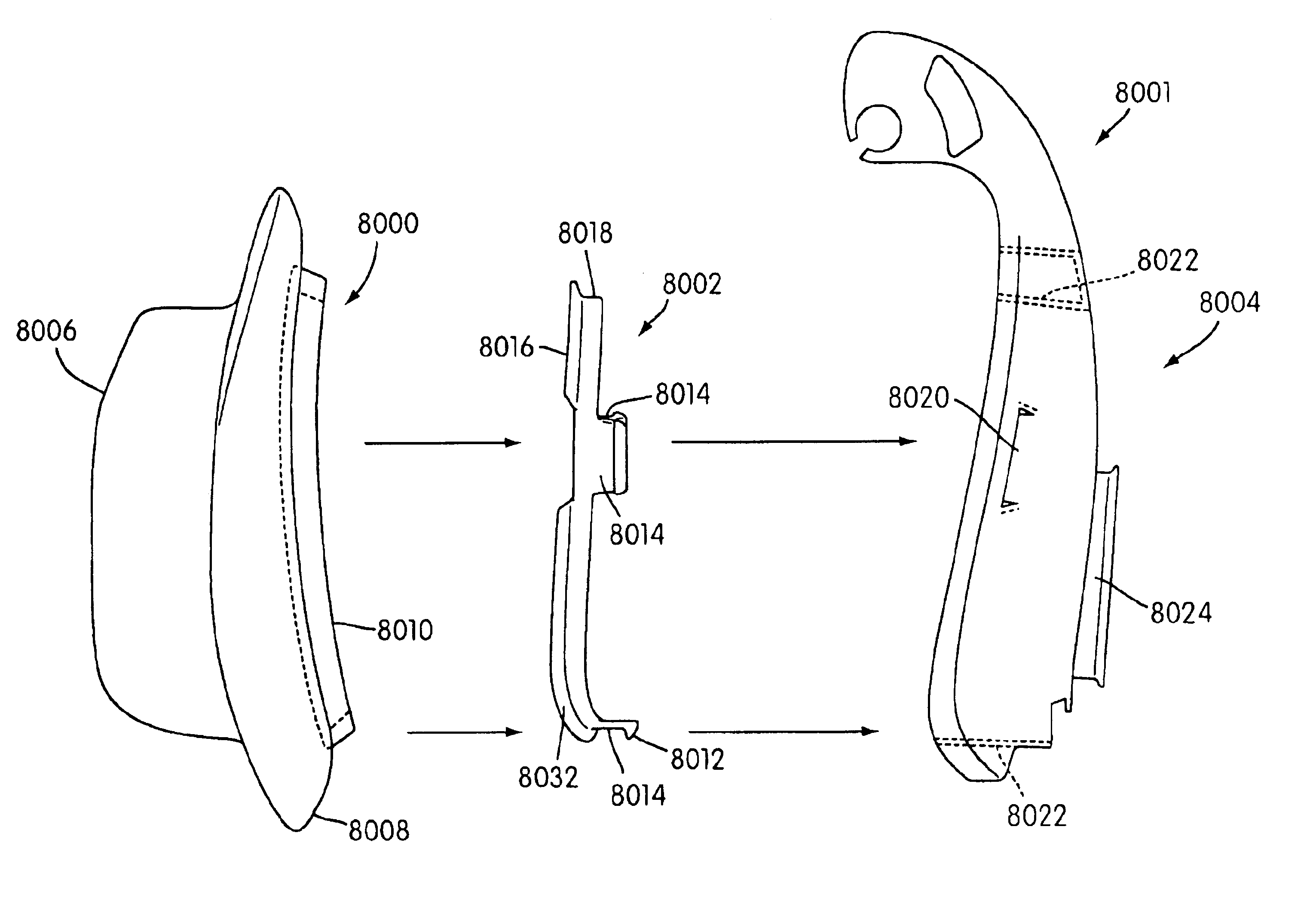
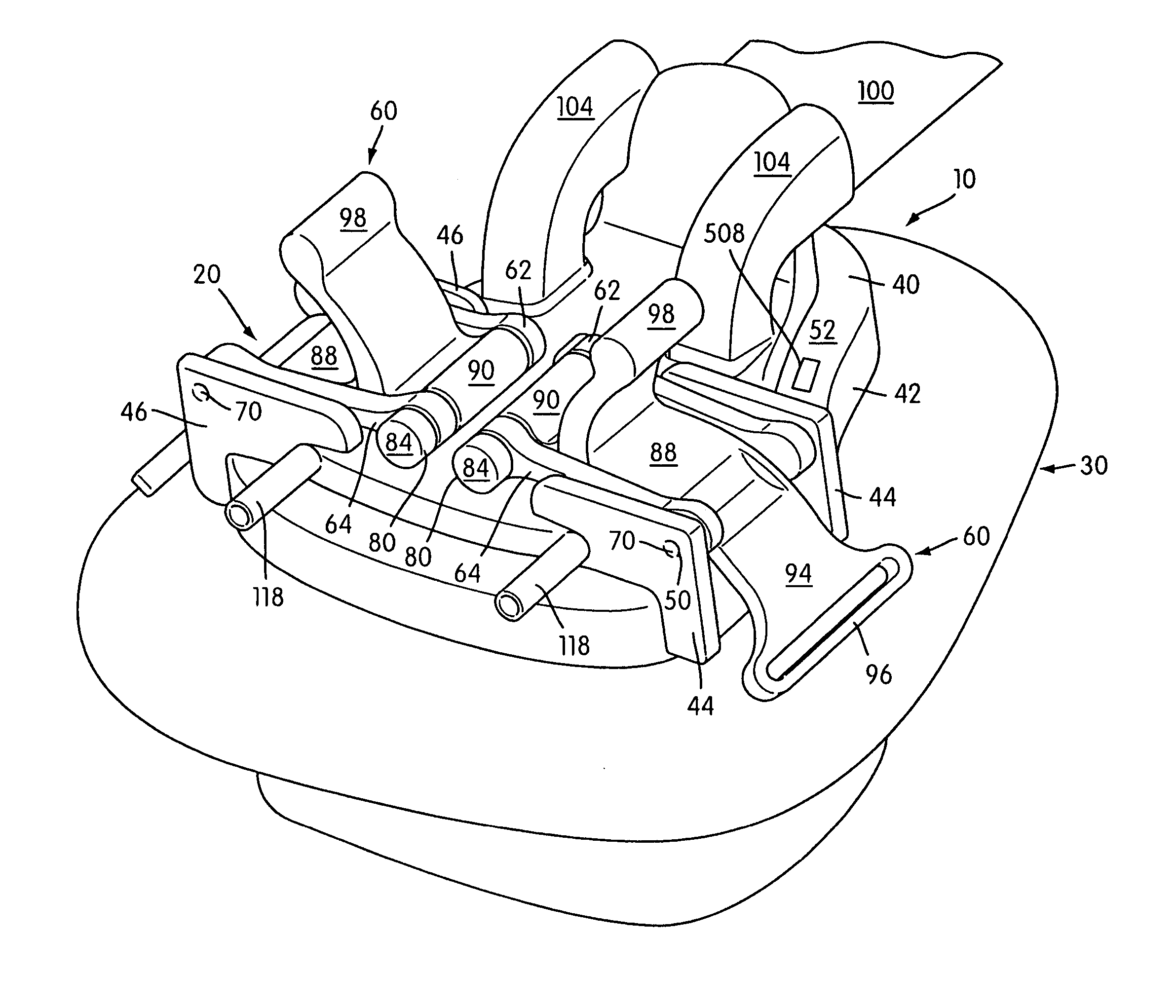
Mask assembly
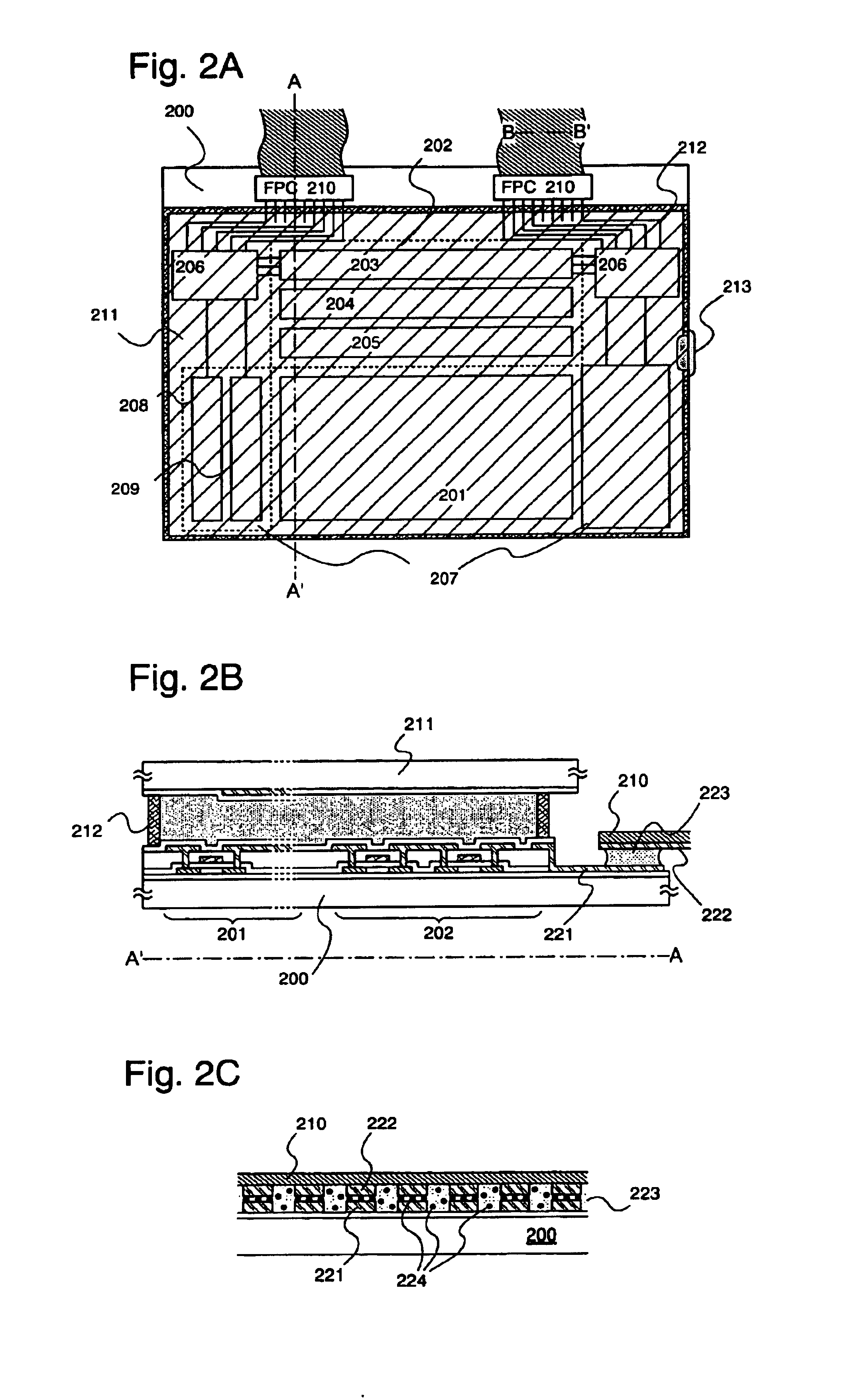
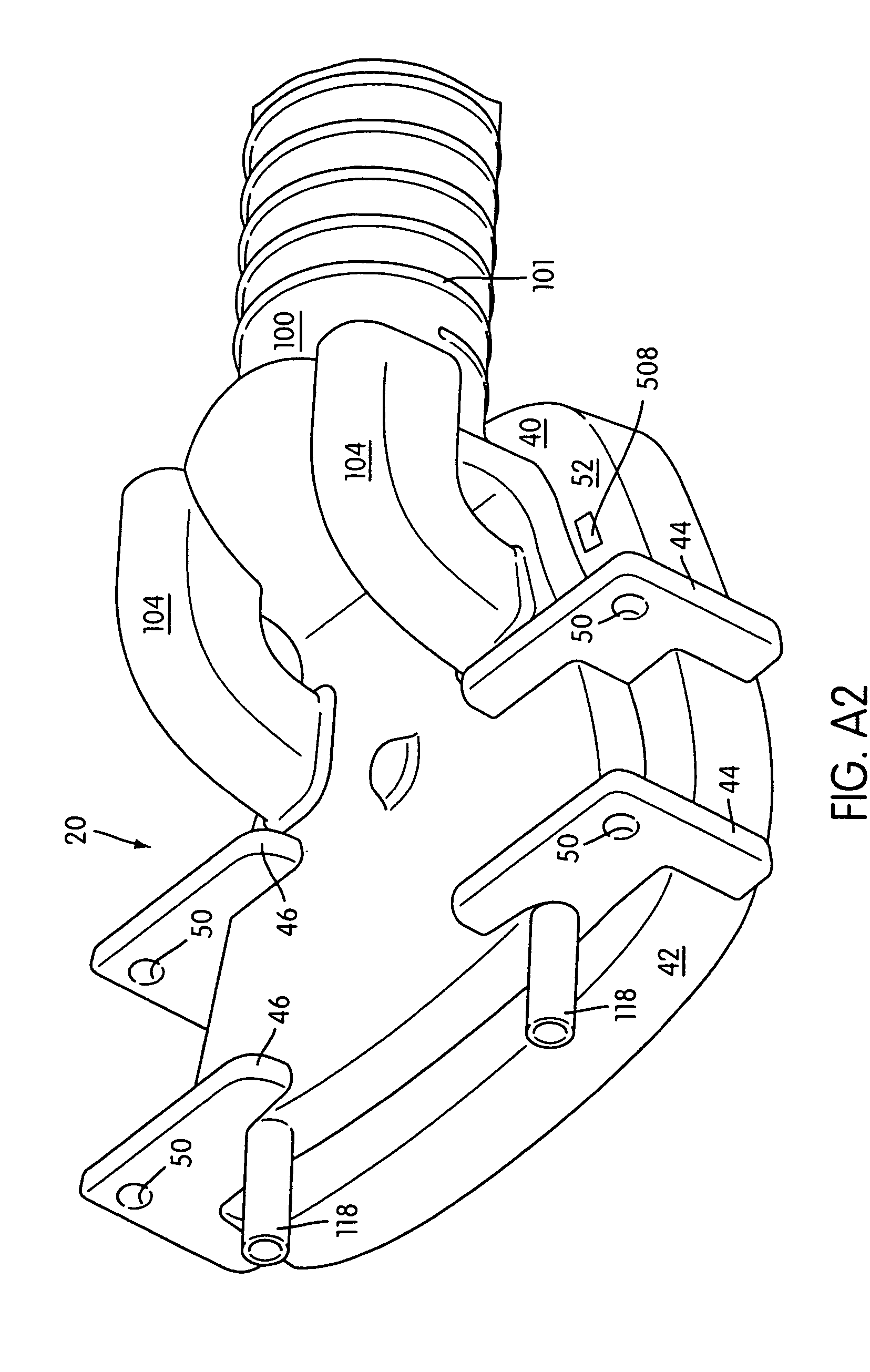
A respiratory mask assembly for use in the delivery of non-invasive positive airway pressure to a user. The assembly includes a rigid shell having a channel portion defined by an inner wall, an outer wall and a channel floor, a face-contacting cushion acting to space the shell away from the user's face and a sealing tab extending from the cushion to engage a portion of the shell to provide a continuous airtight seal between the cushion and the shell. A retaining ring within the mask assembly is configured to secure the cushion to the shell. The retaining ring has a first portion including at least one clip configured to pass through at least one slot portion such that an underside surface of the at least one clip engages a section of the shell when the retaining ring is positioned within the channel.
Owner:RESMED LTD
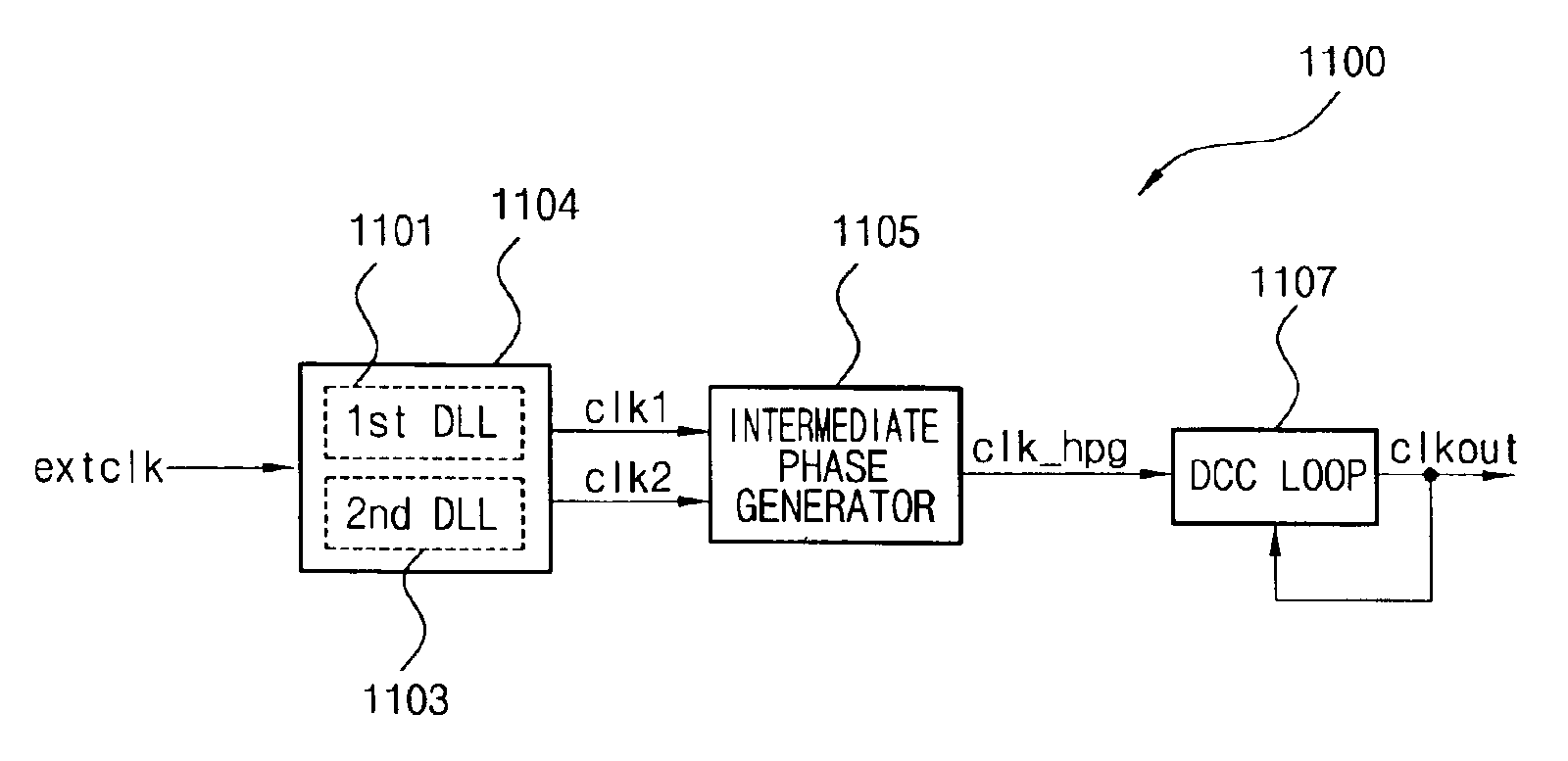
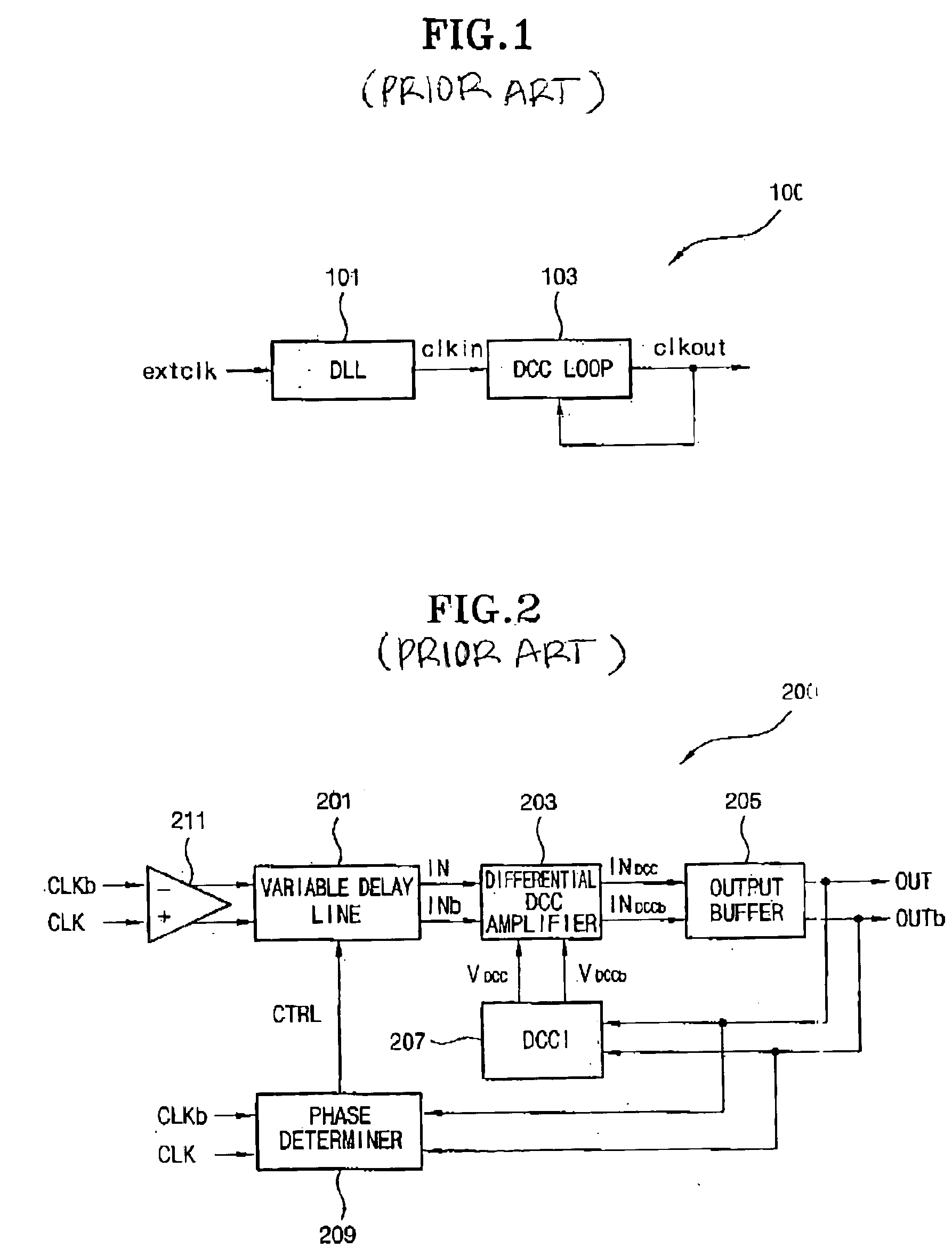
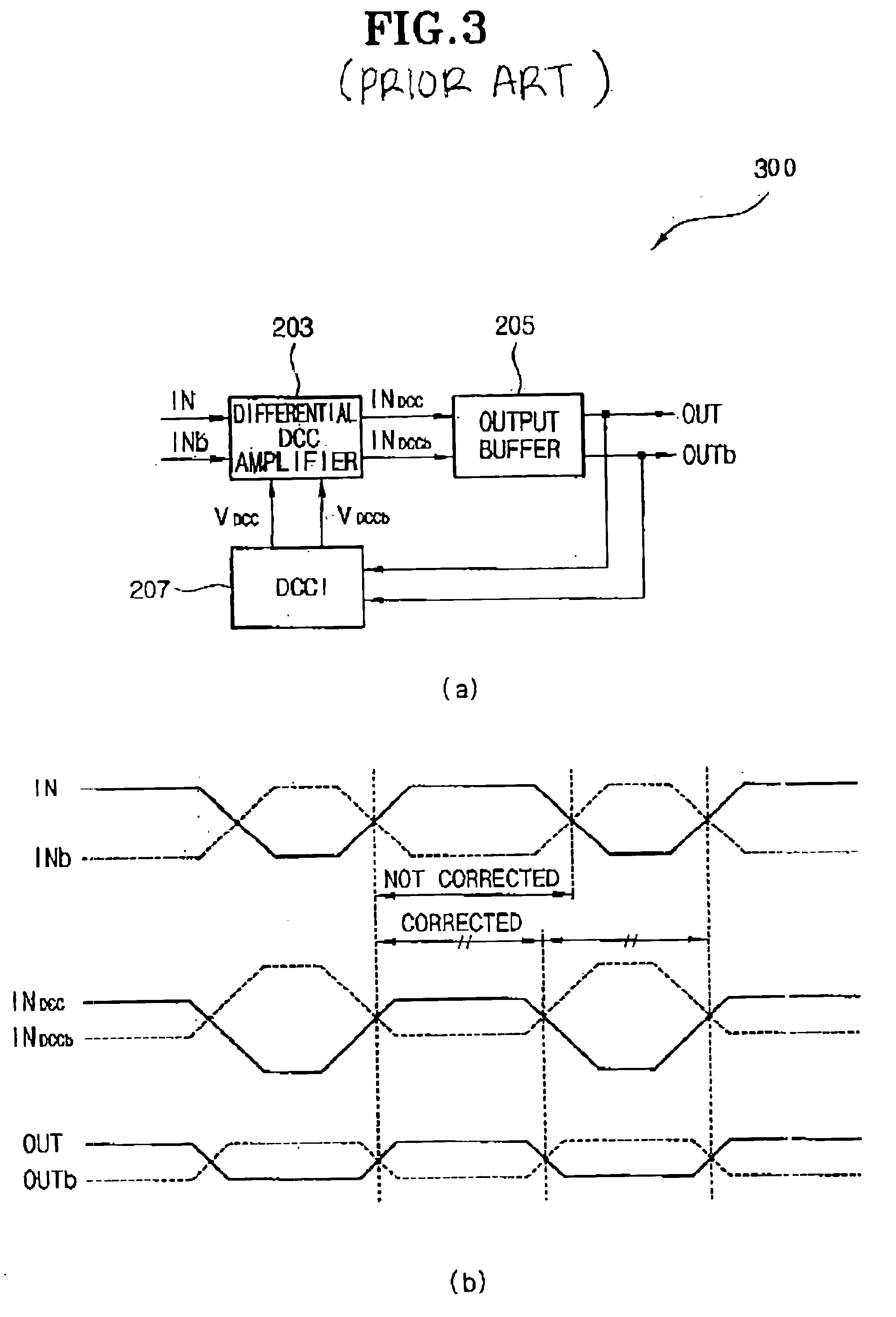
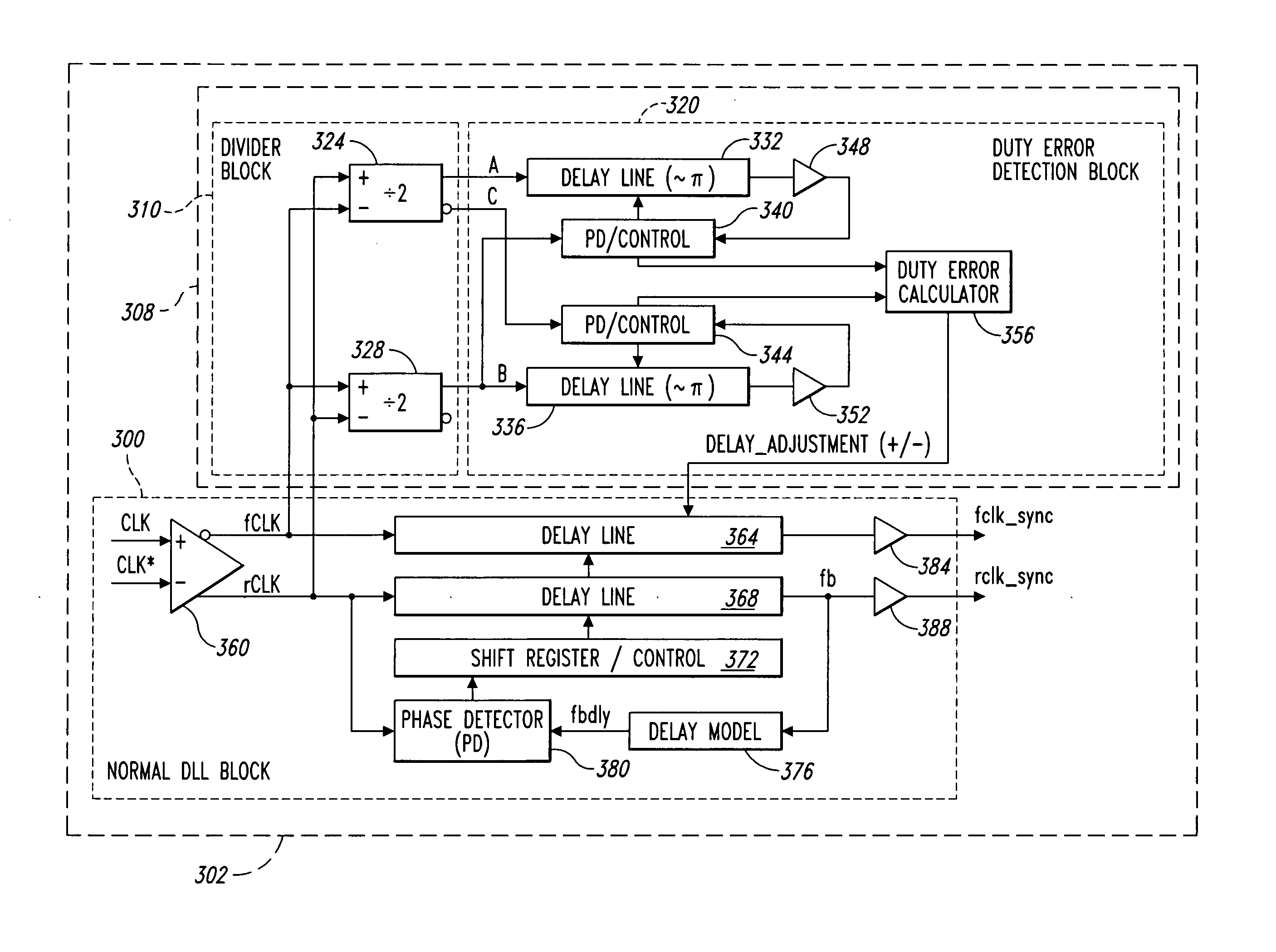
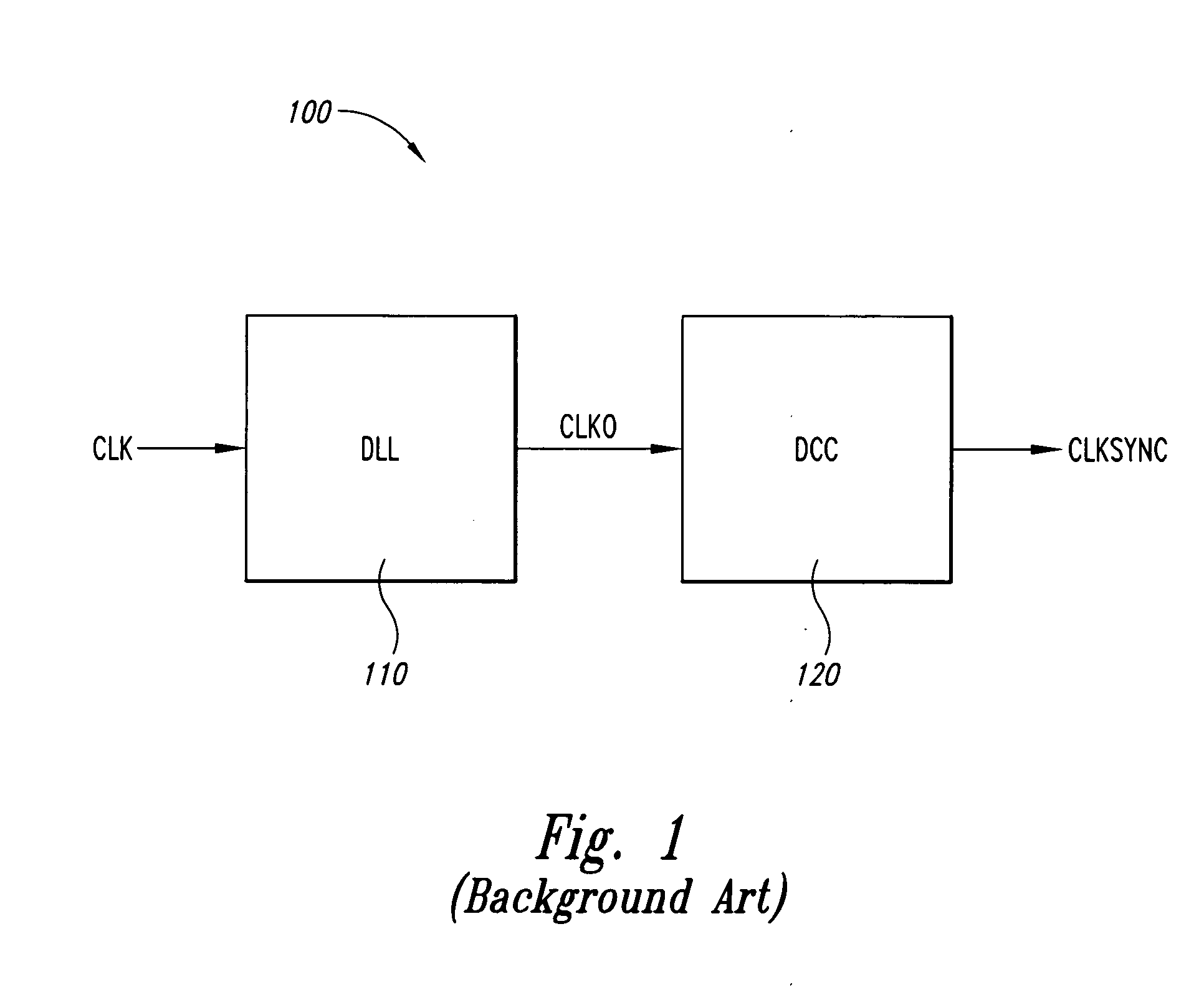
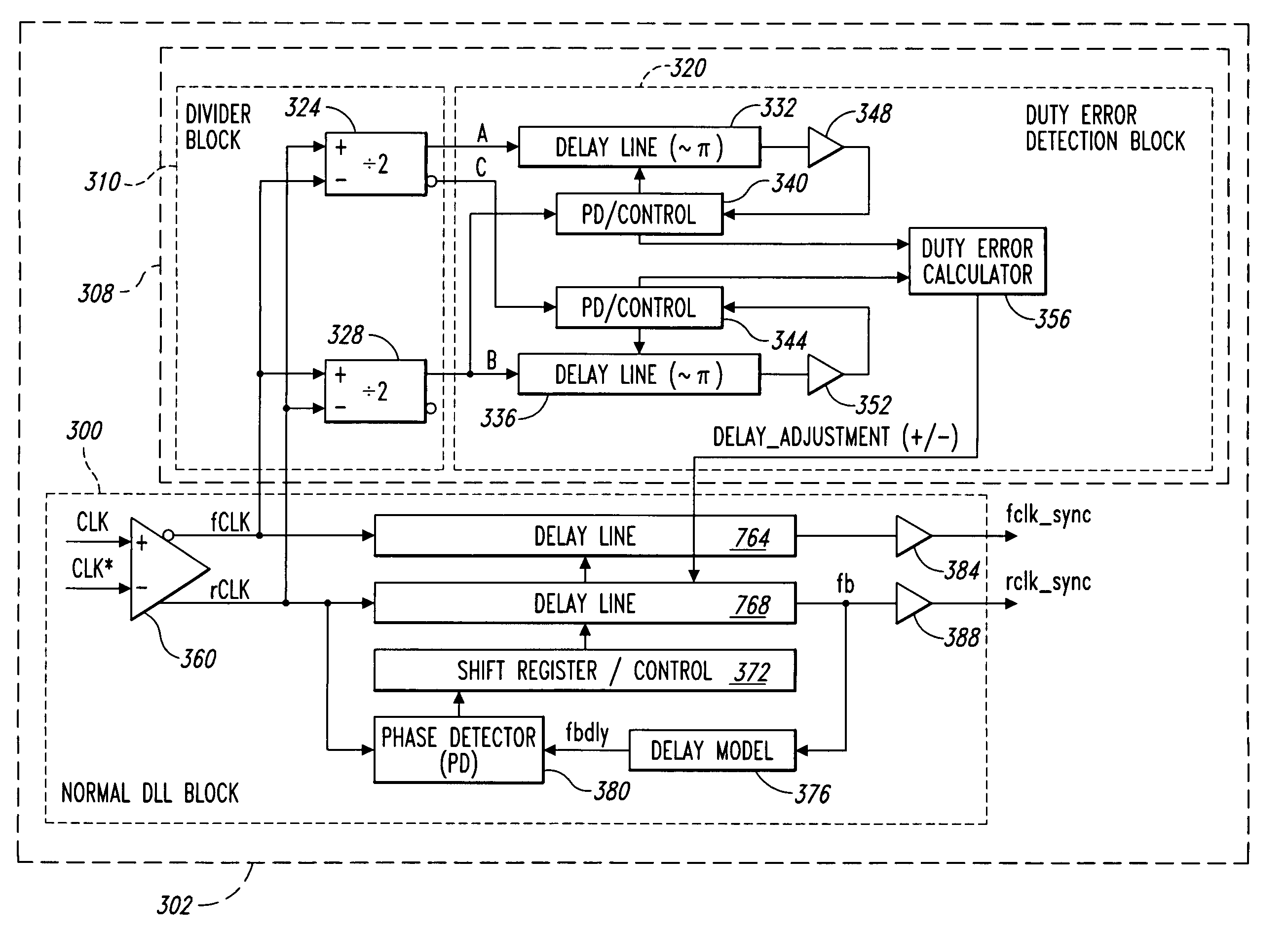
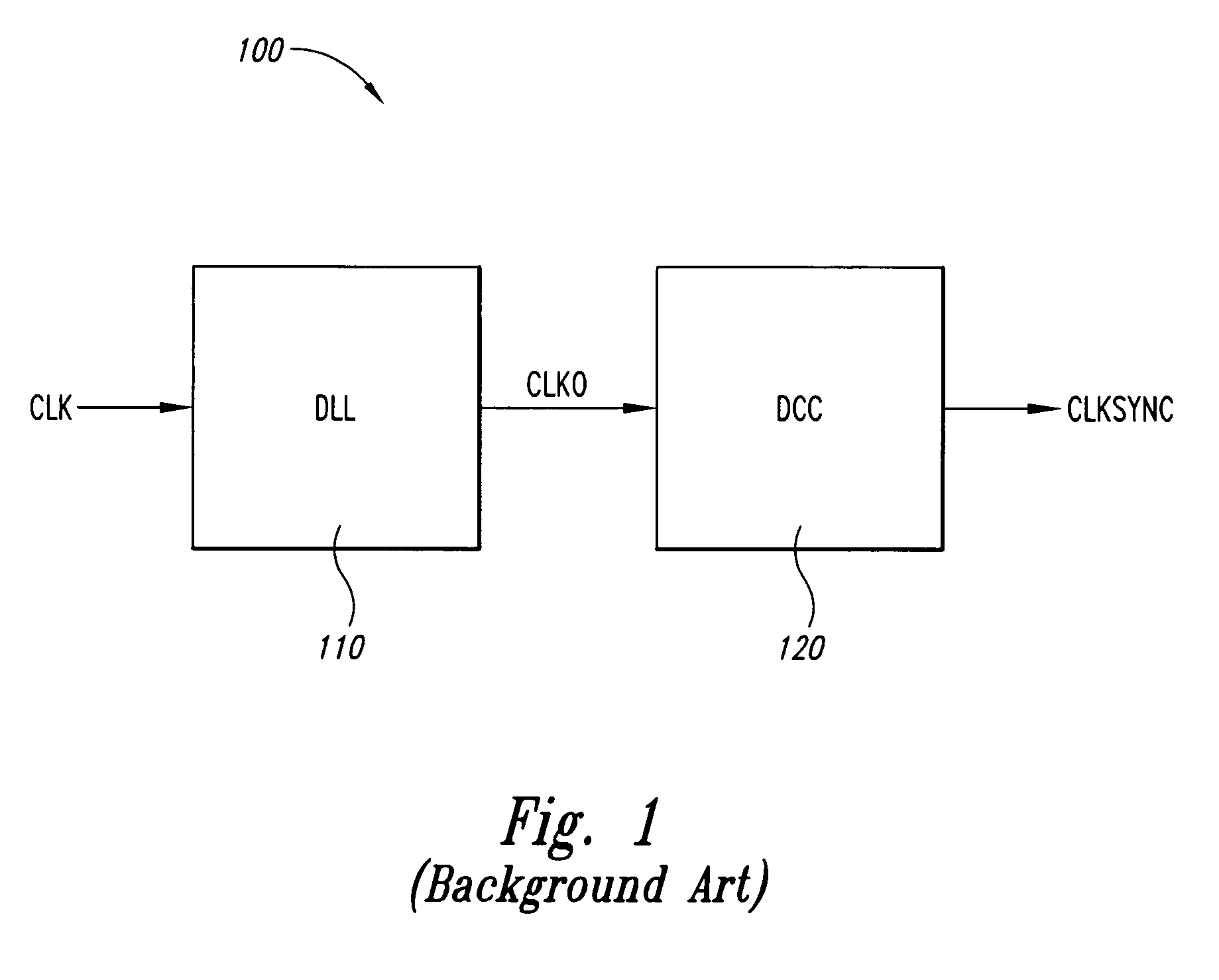
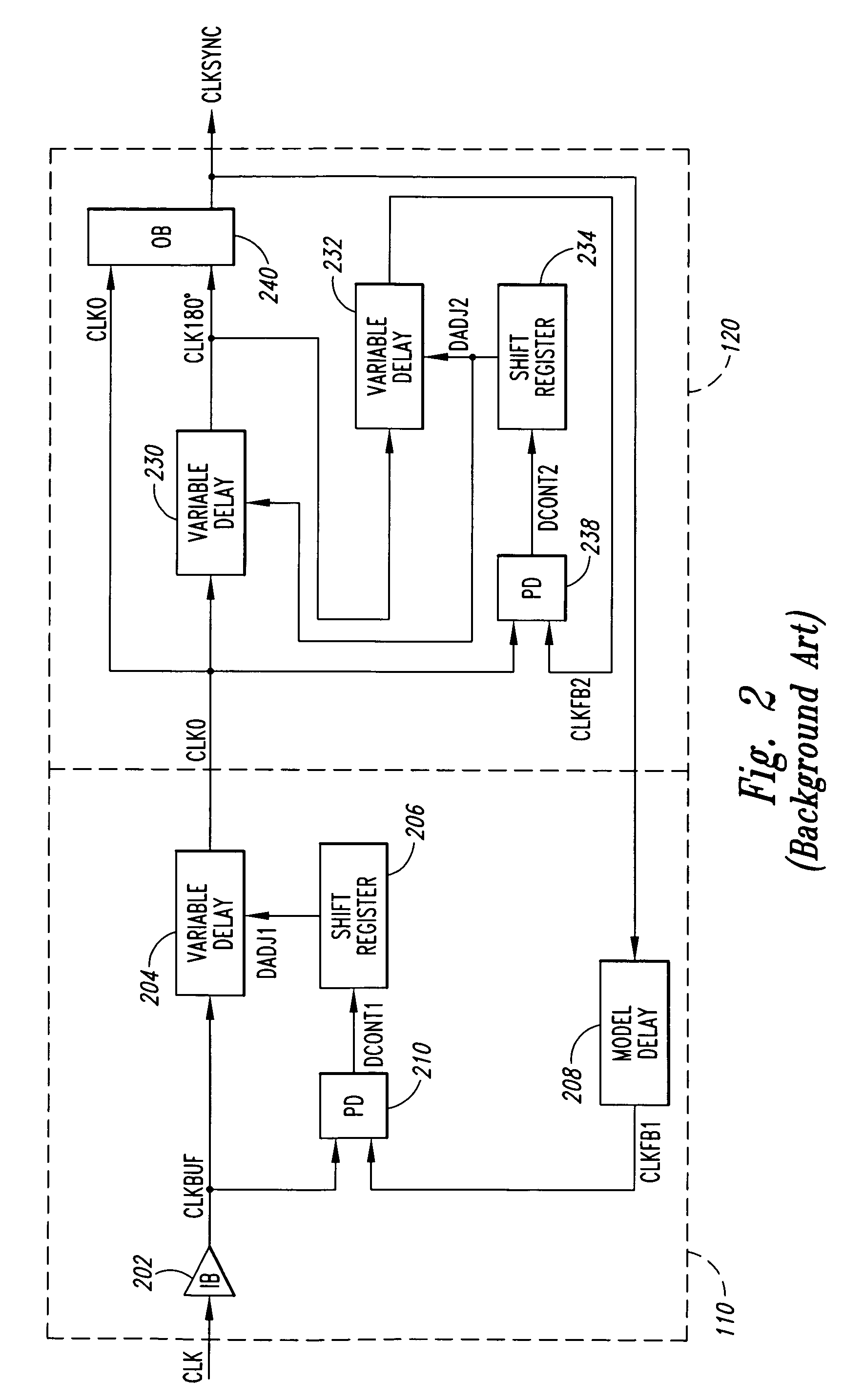
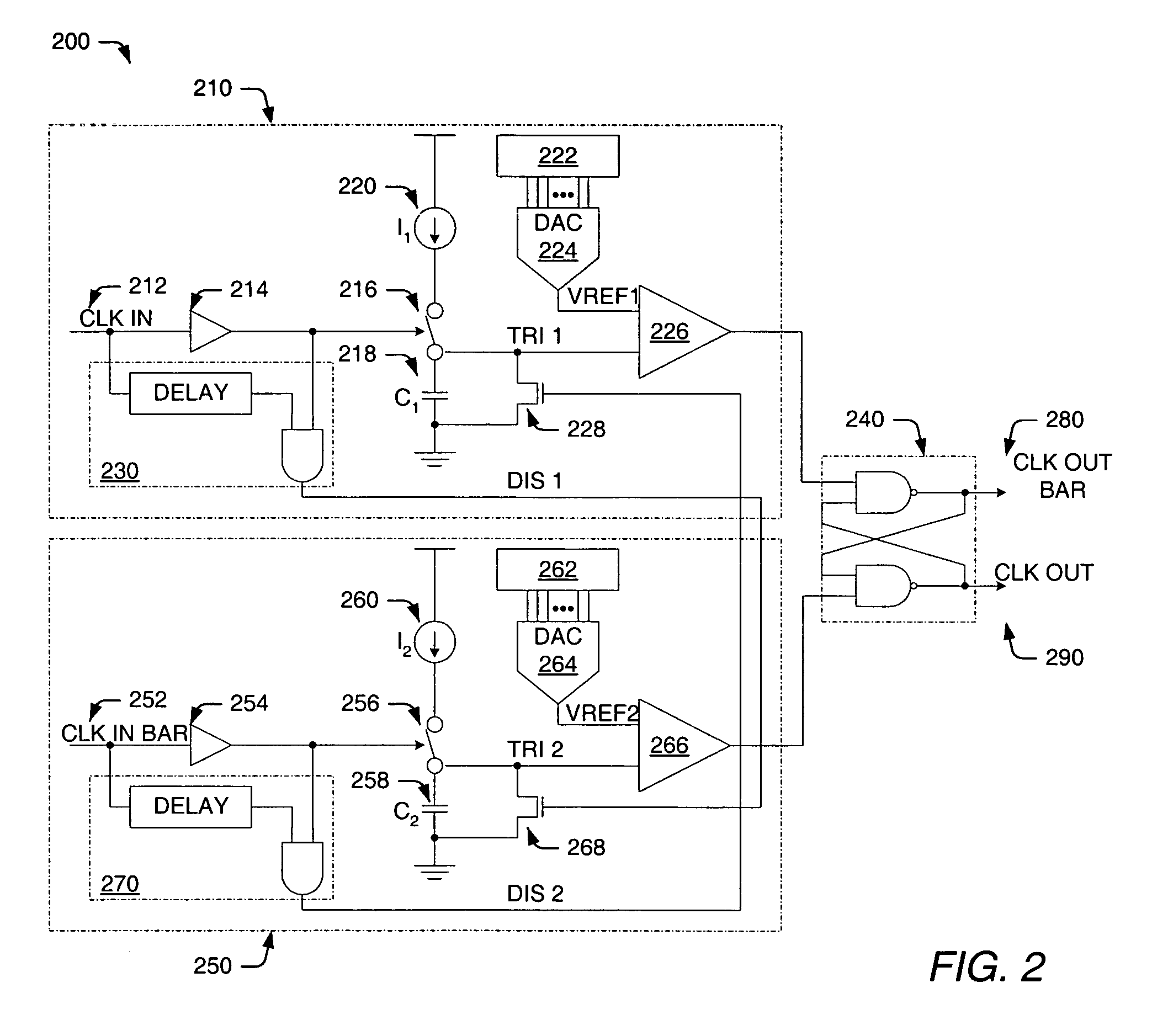
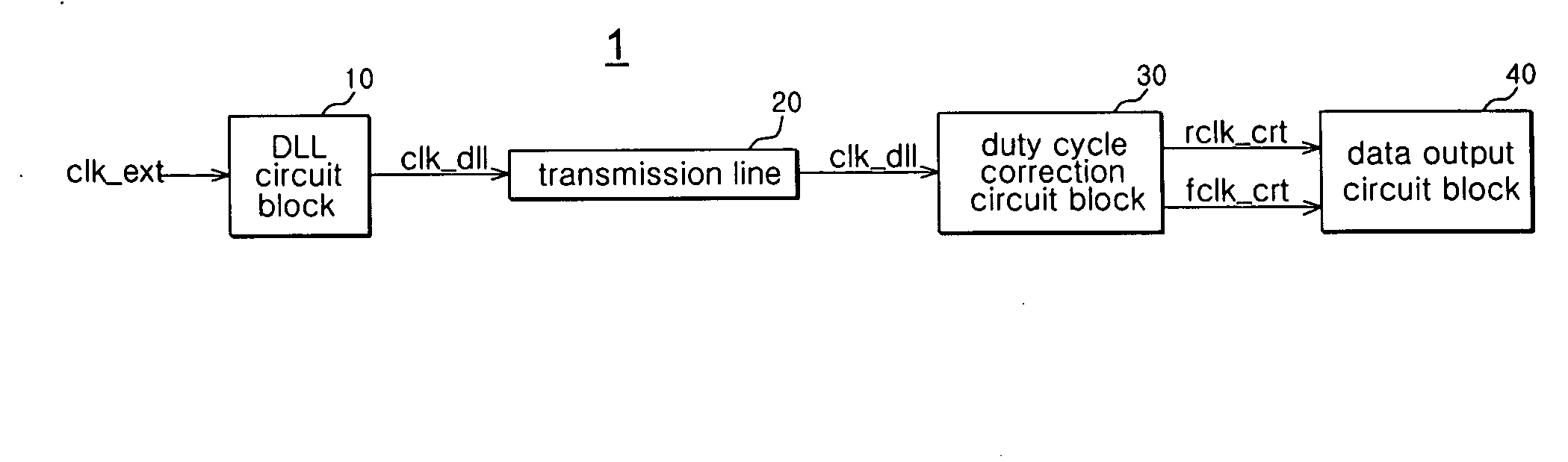
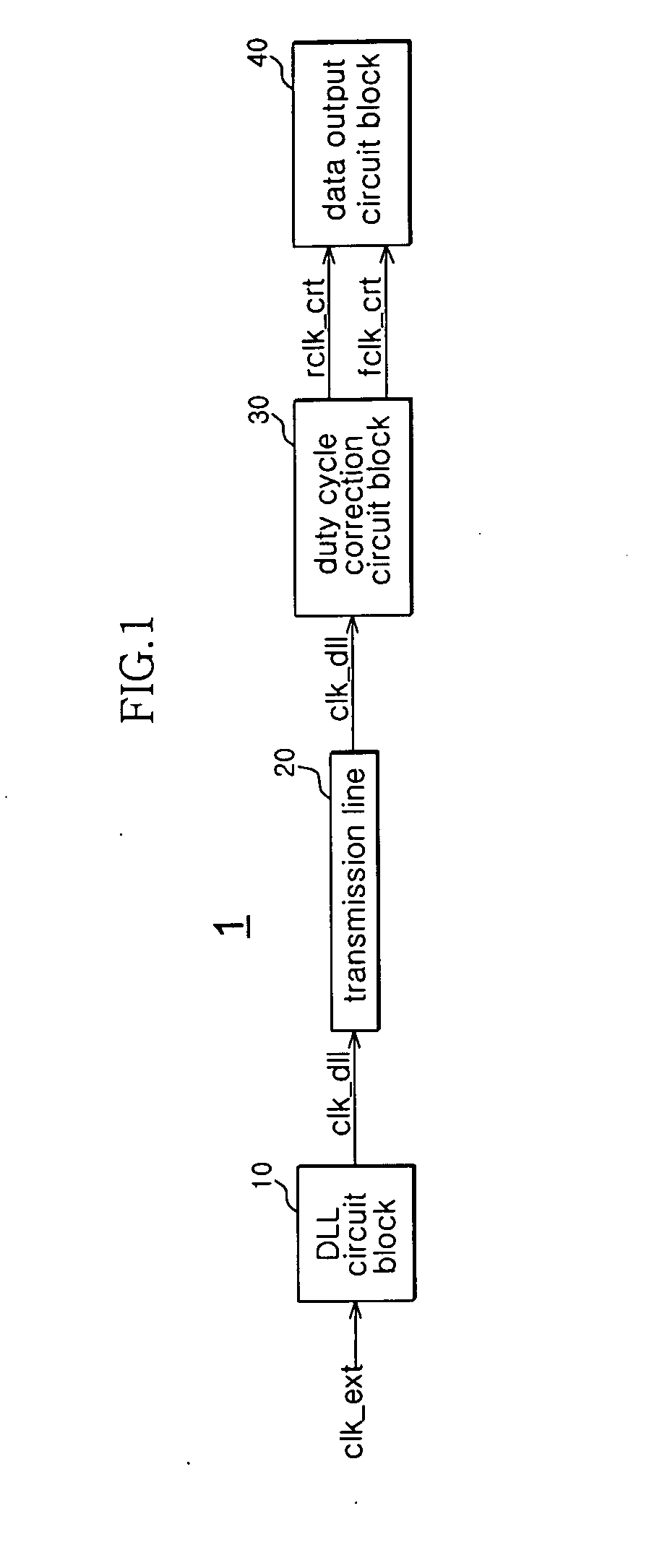
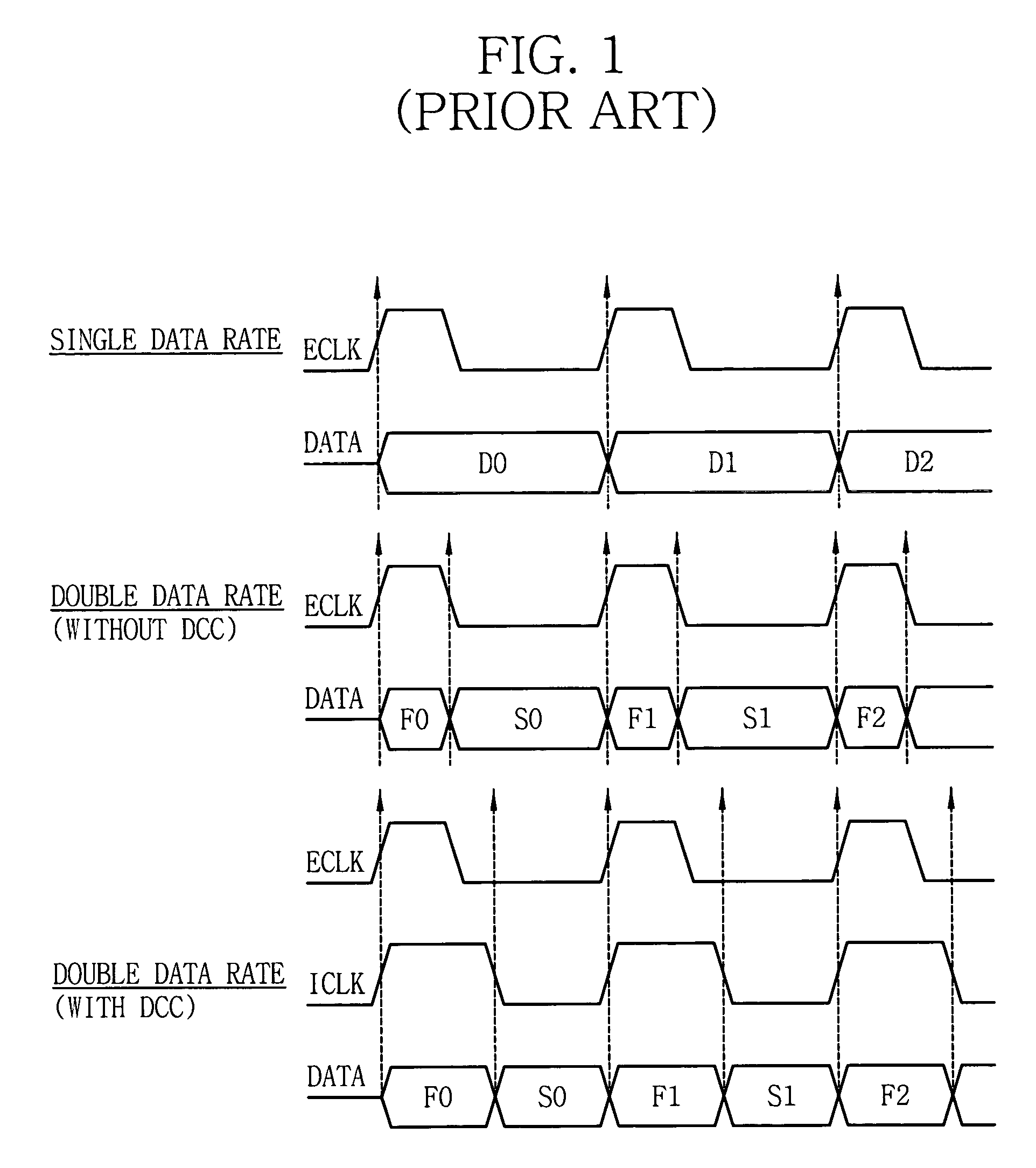
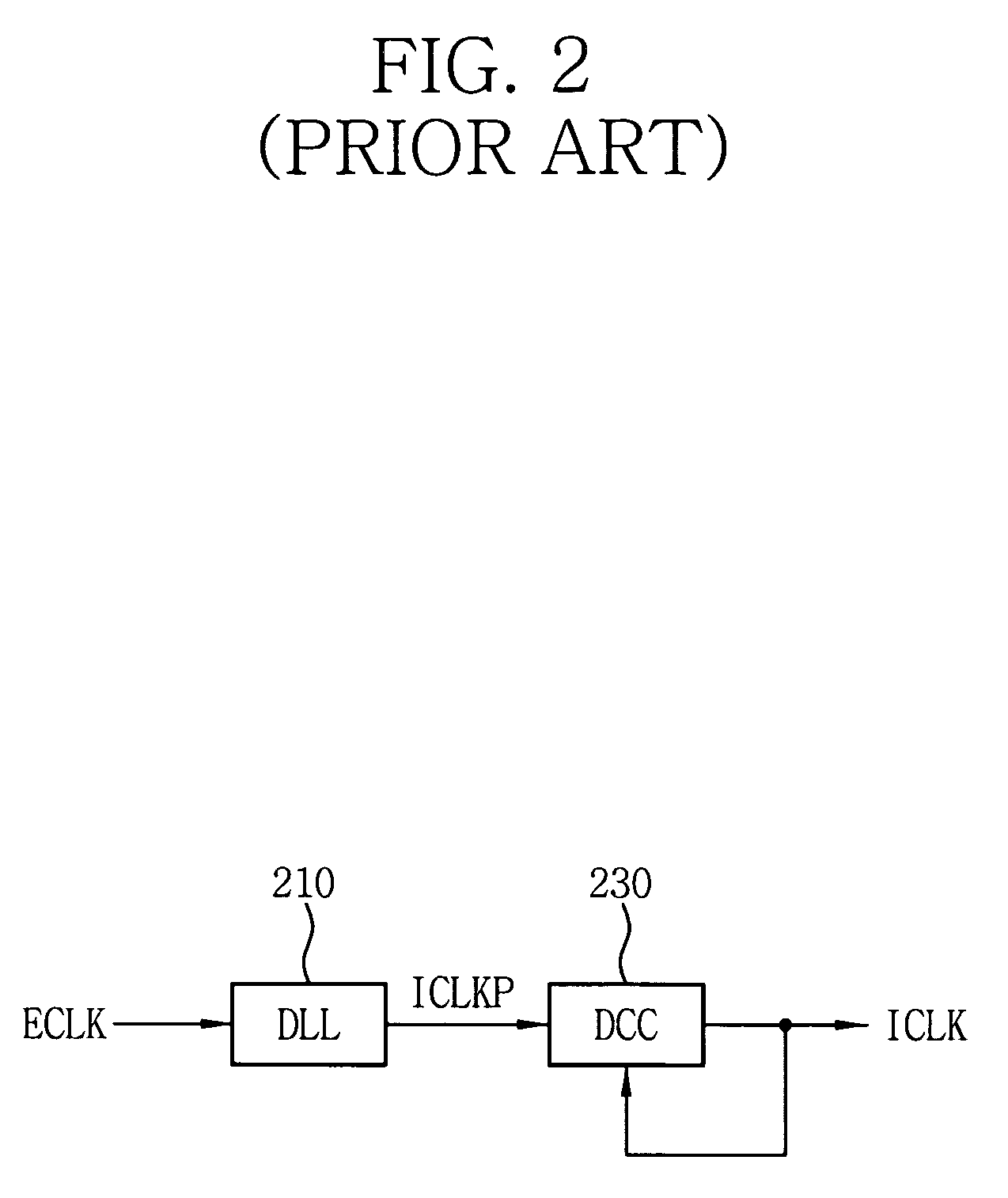
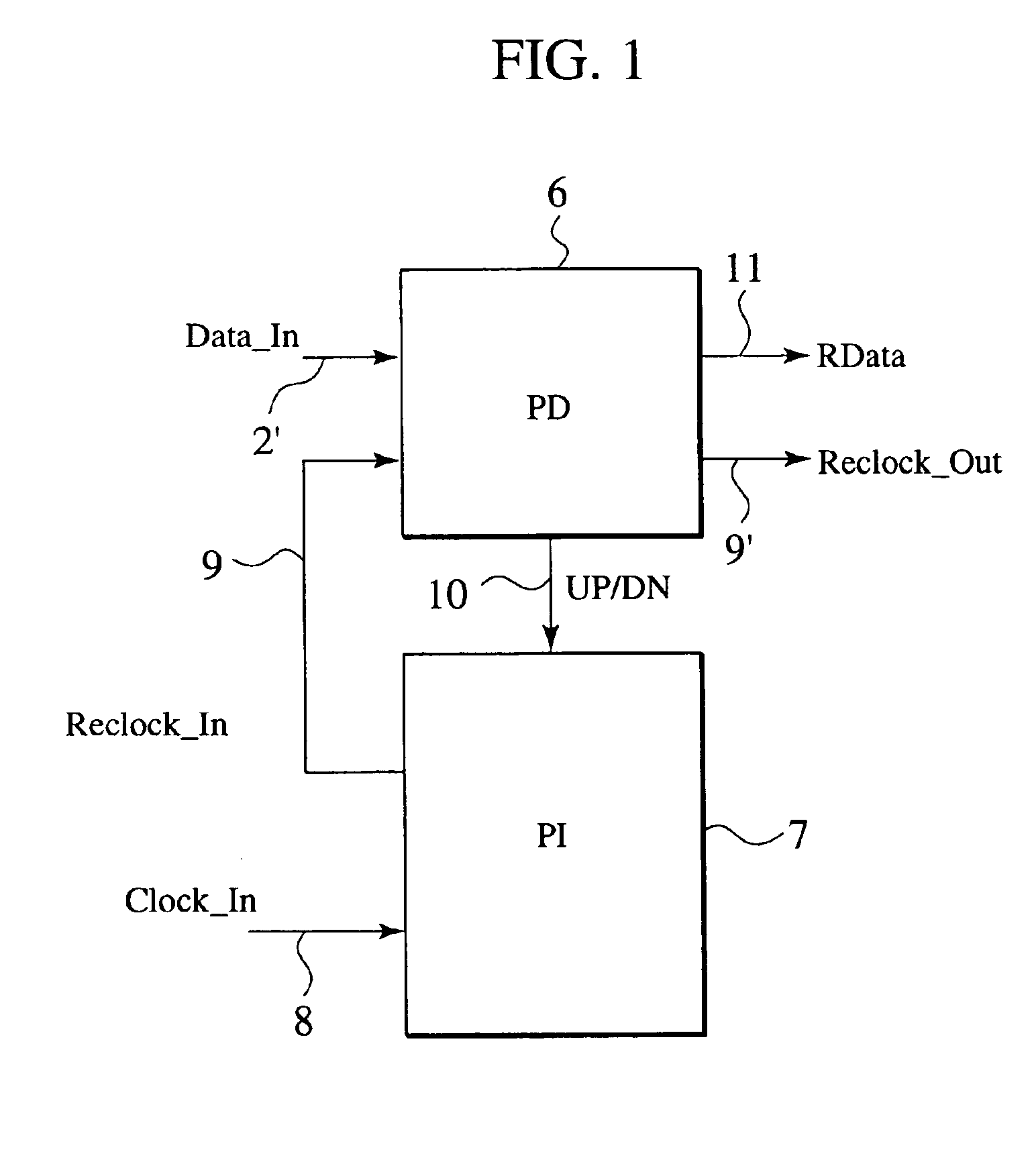
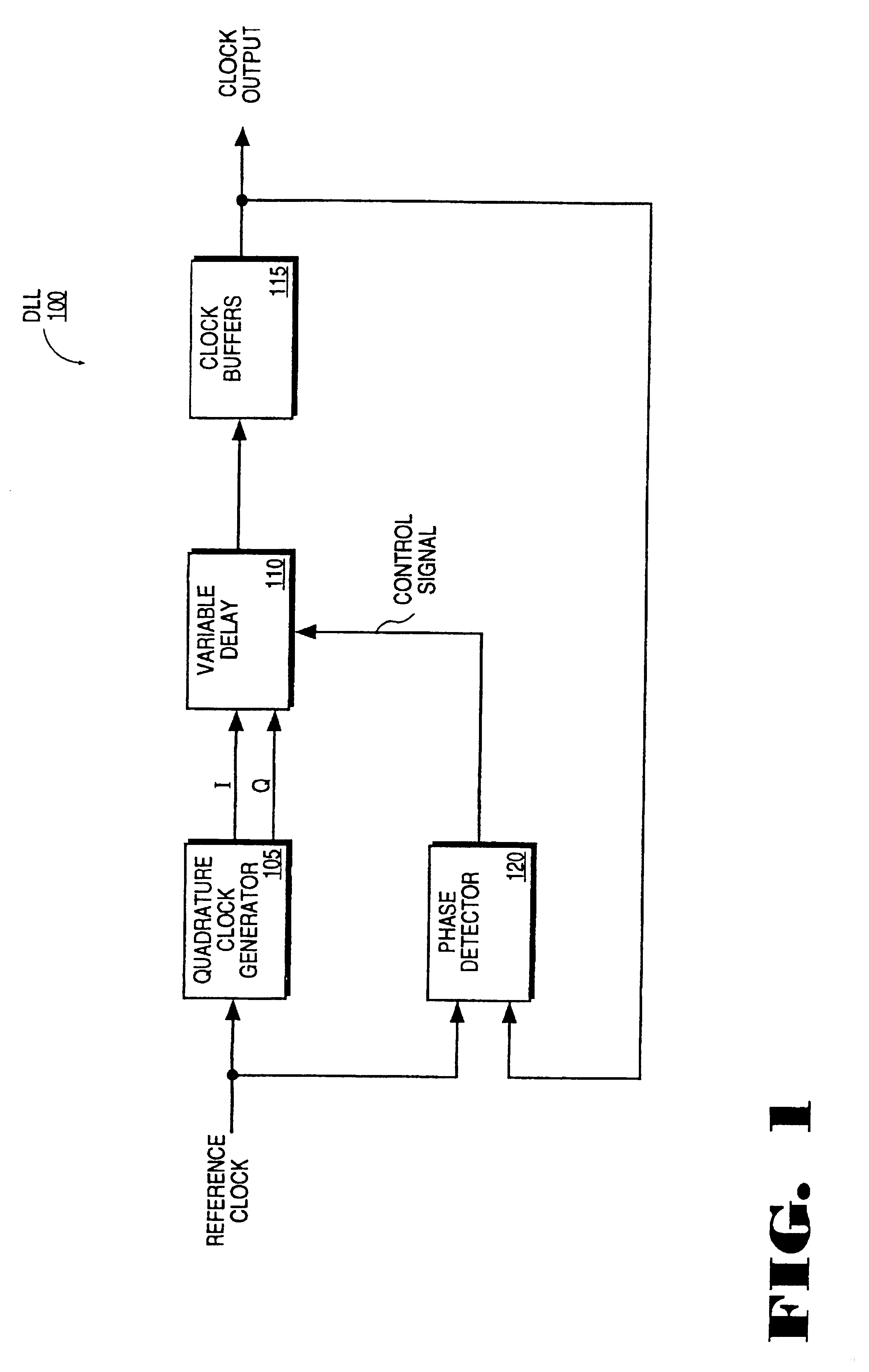
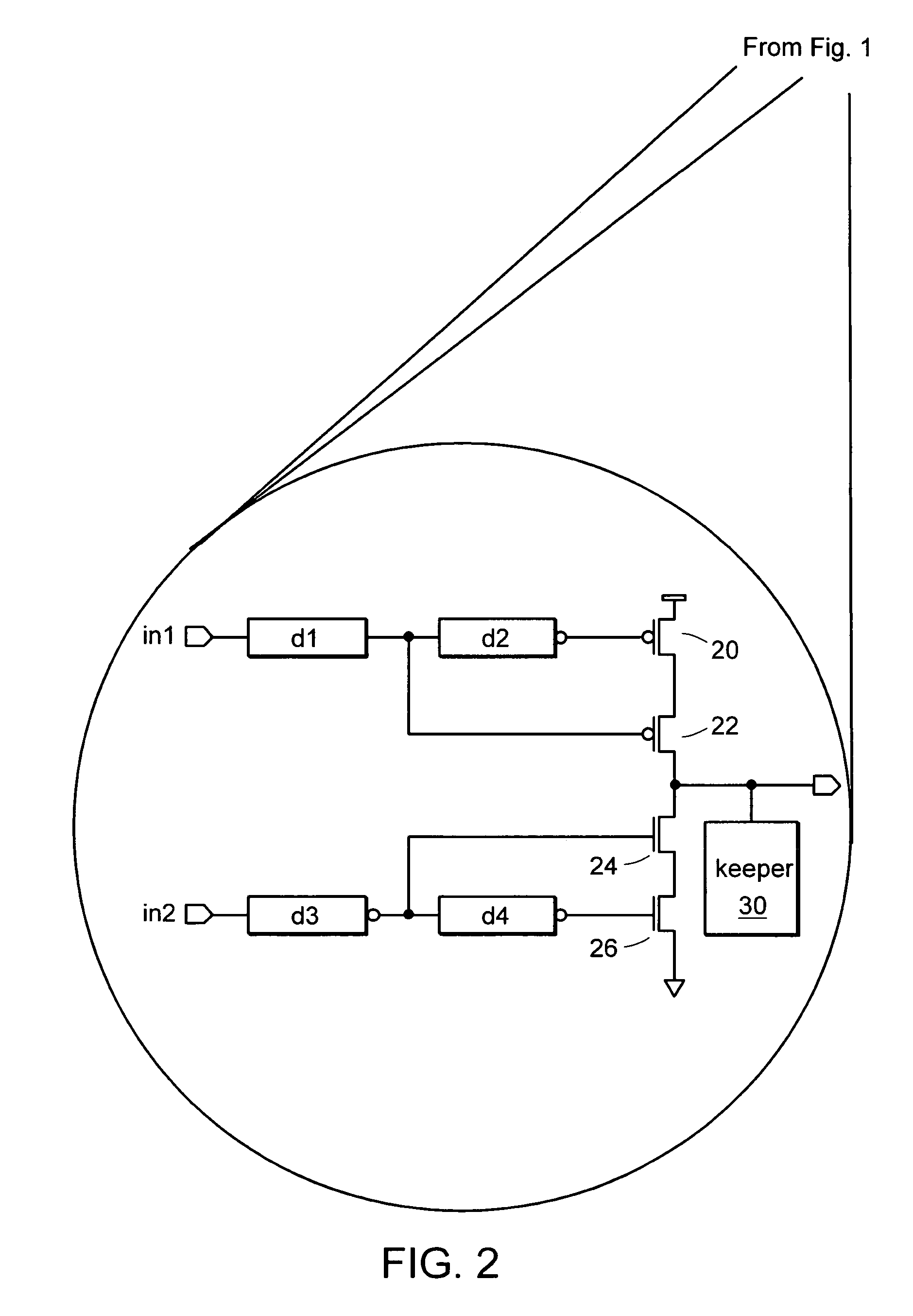
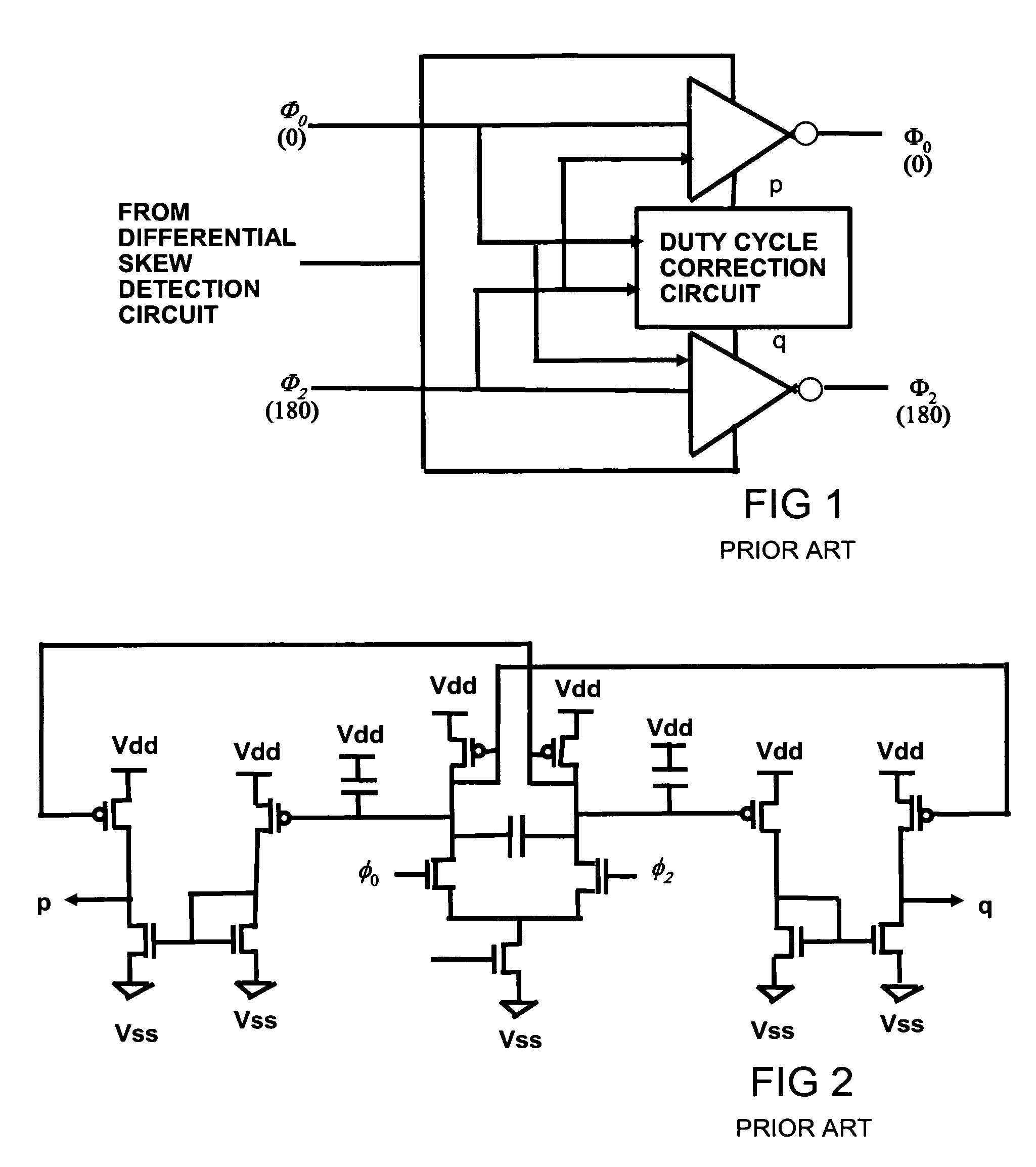
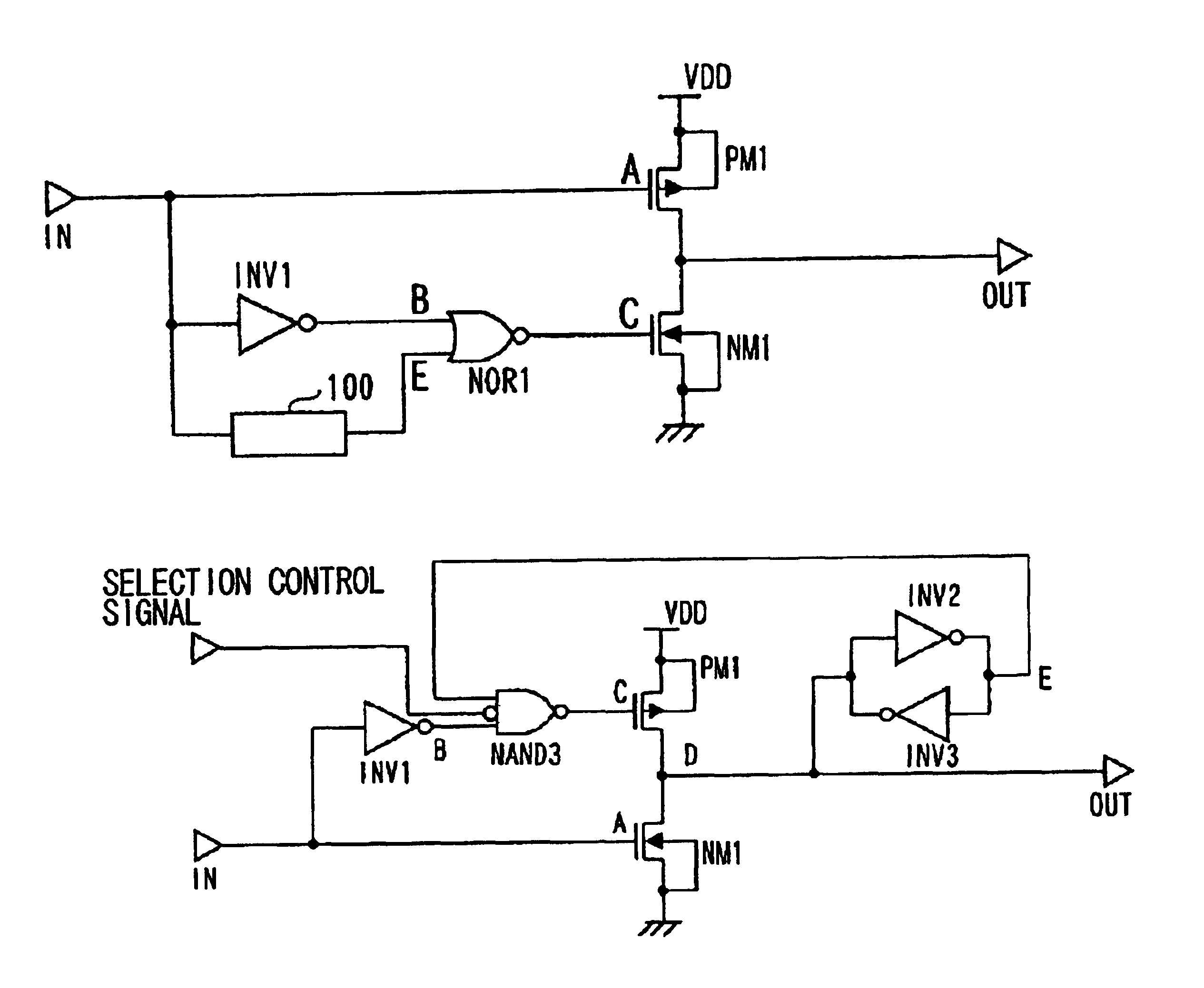
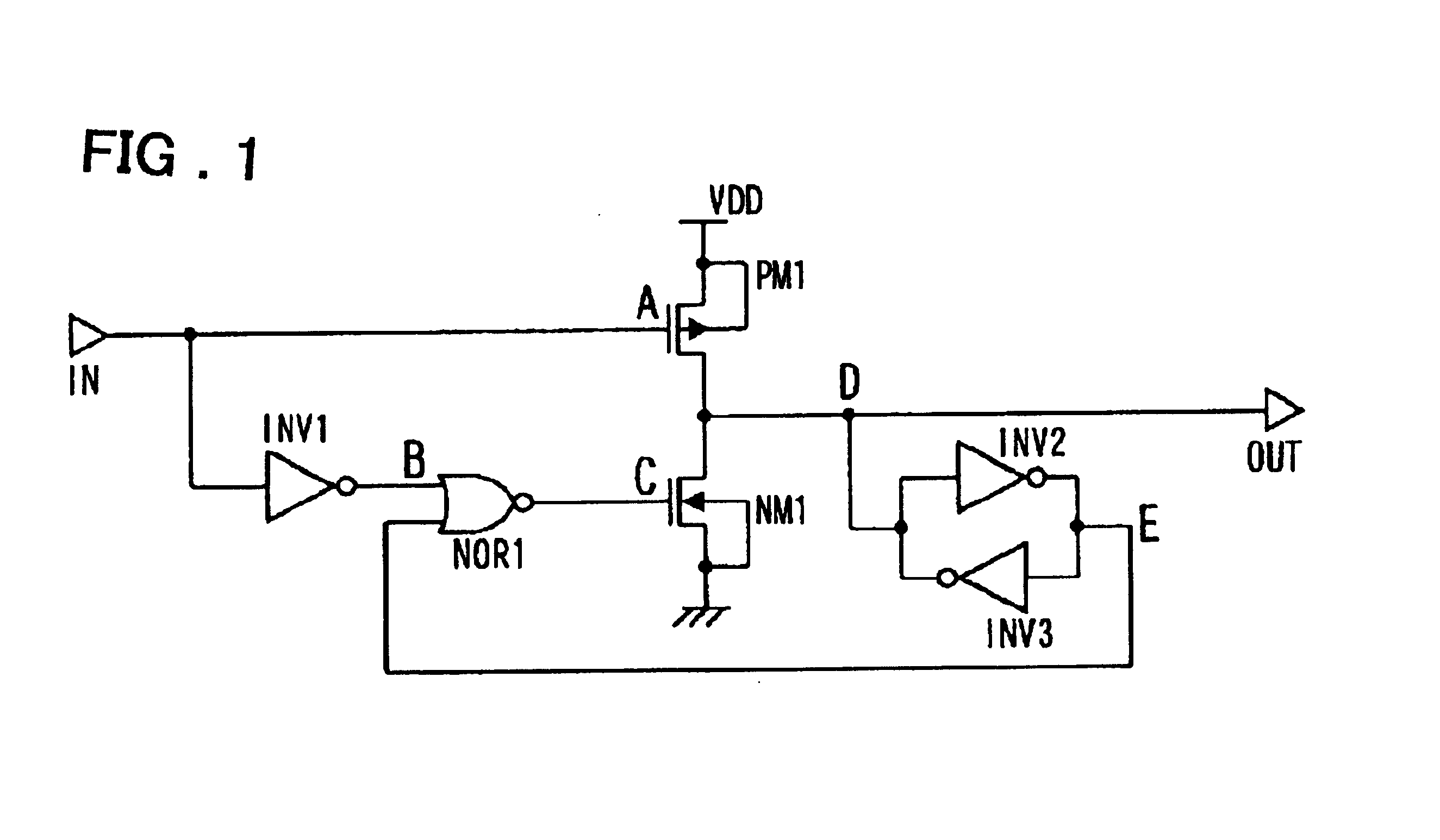
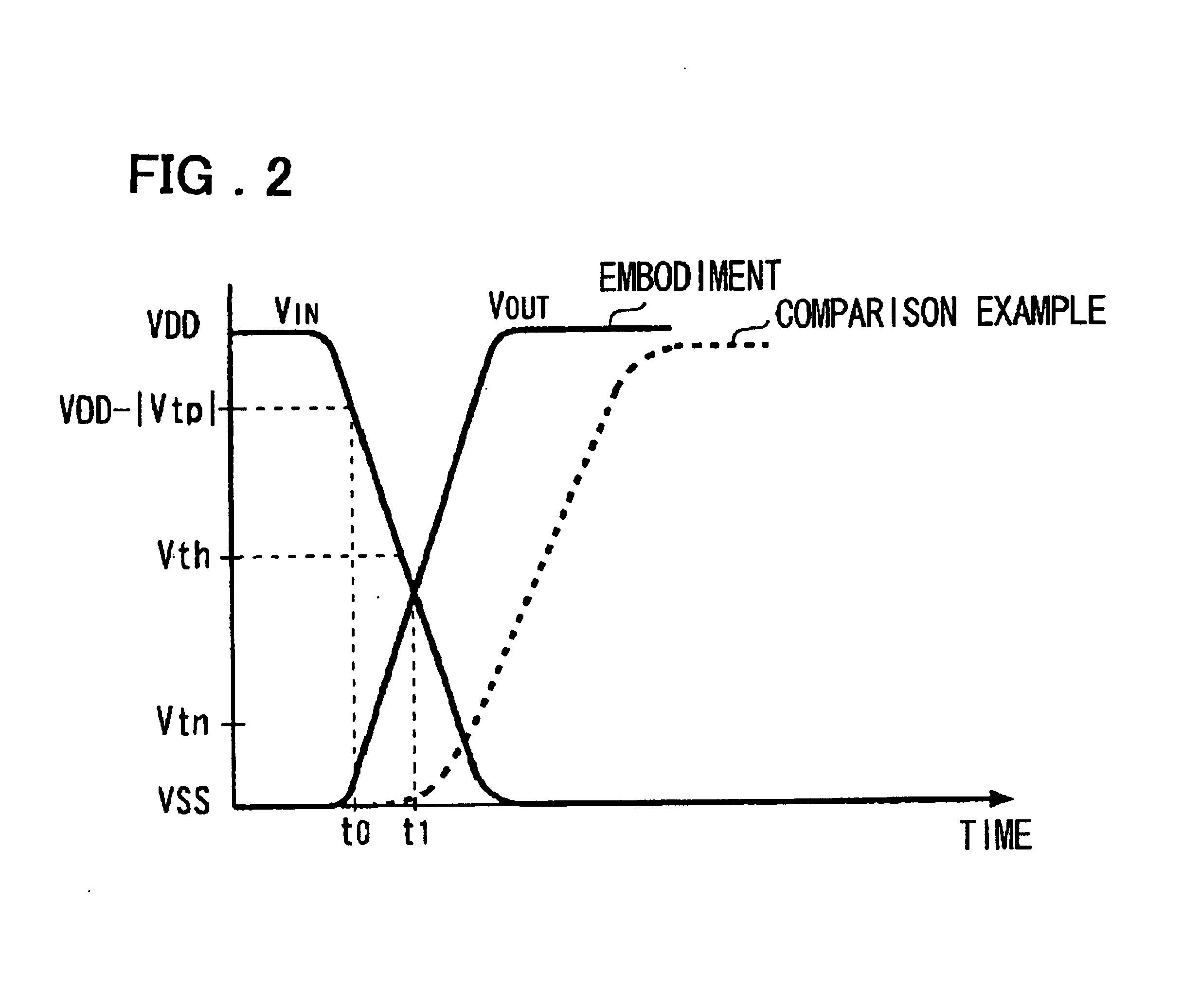
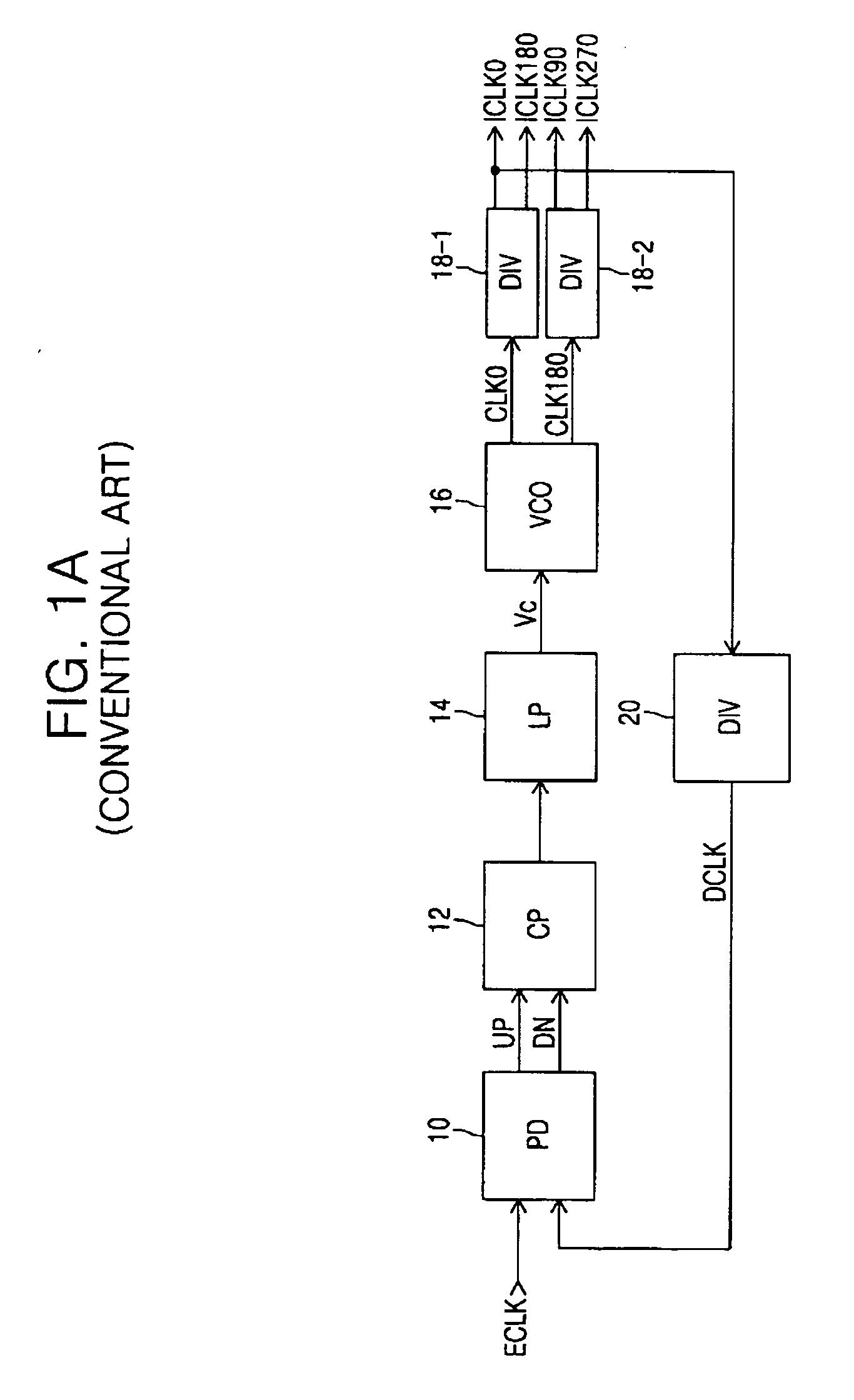
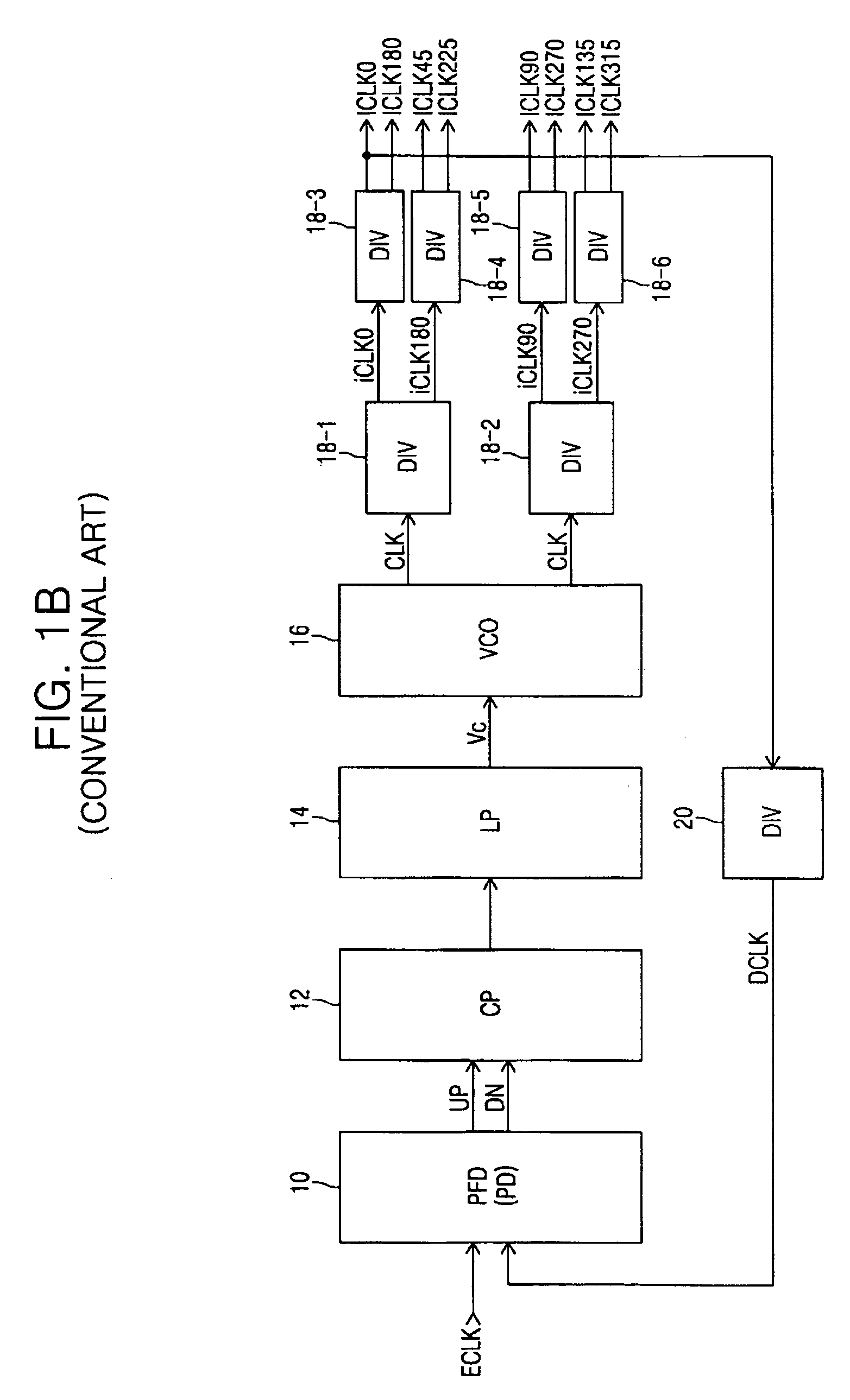
Delay locked loop circuit with duty cycle correction function
InactiveUS6853225B2Improve accuracyShort lock timePulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationNegative feedbackDelay-locked loop
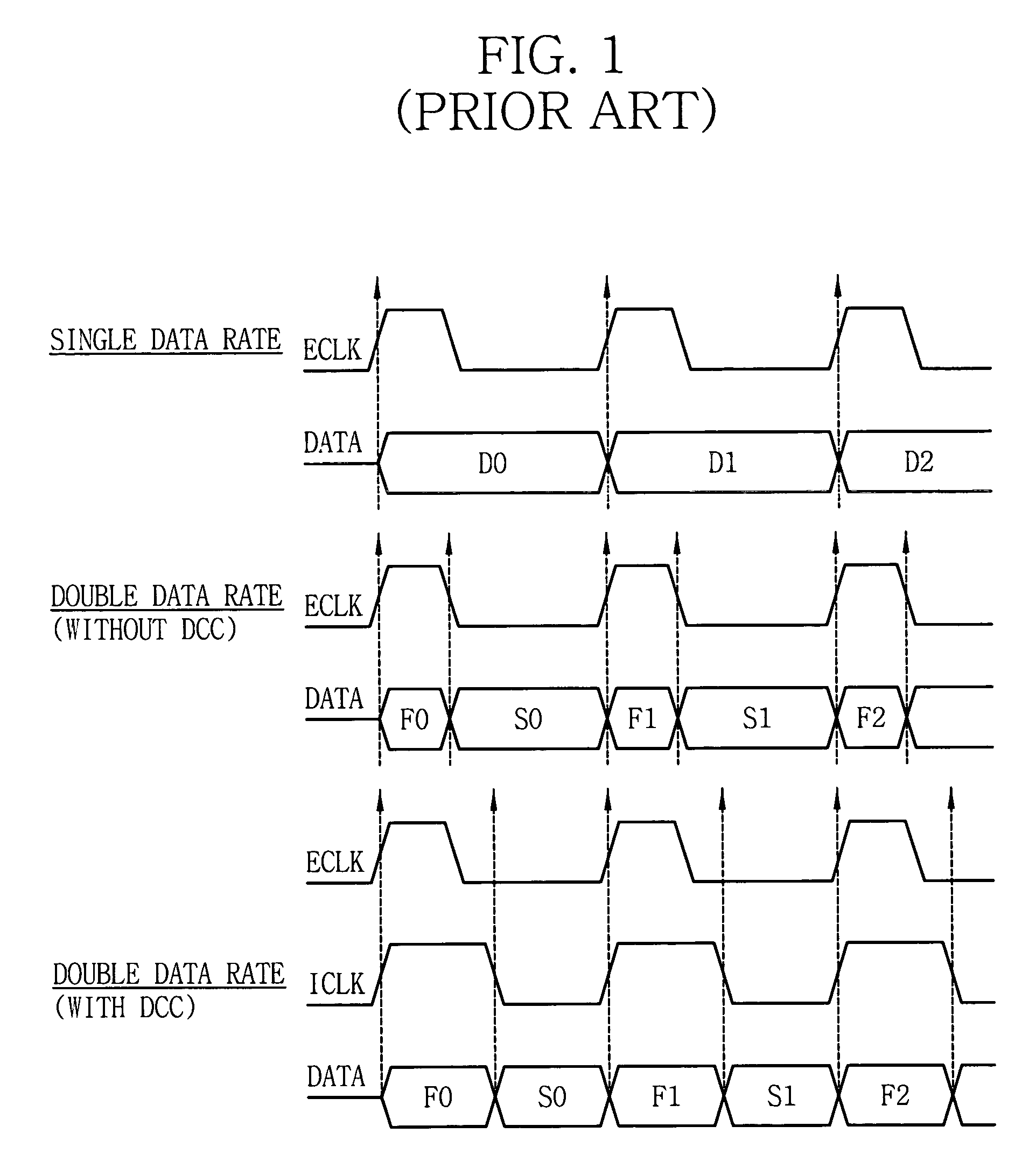
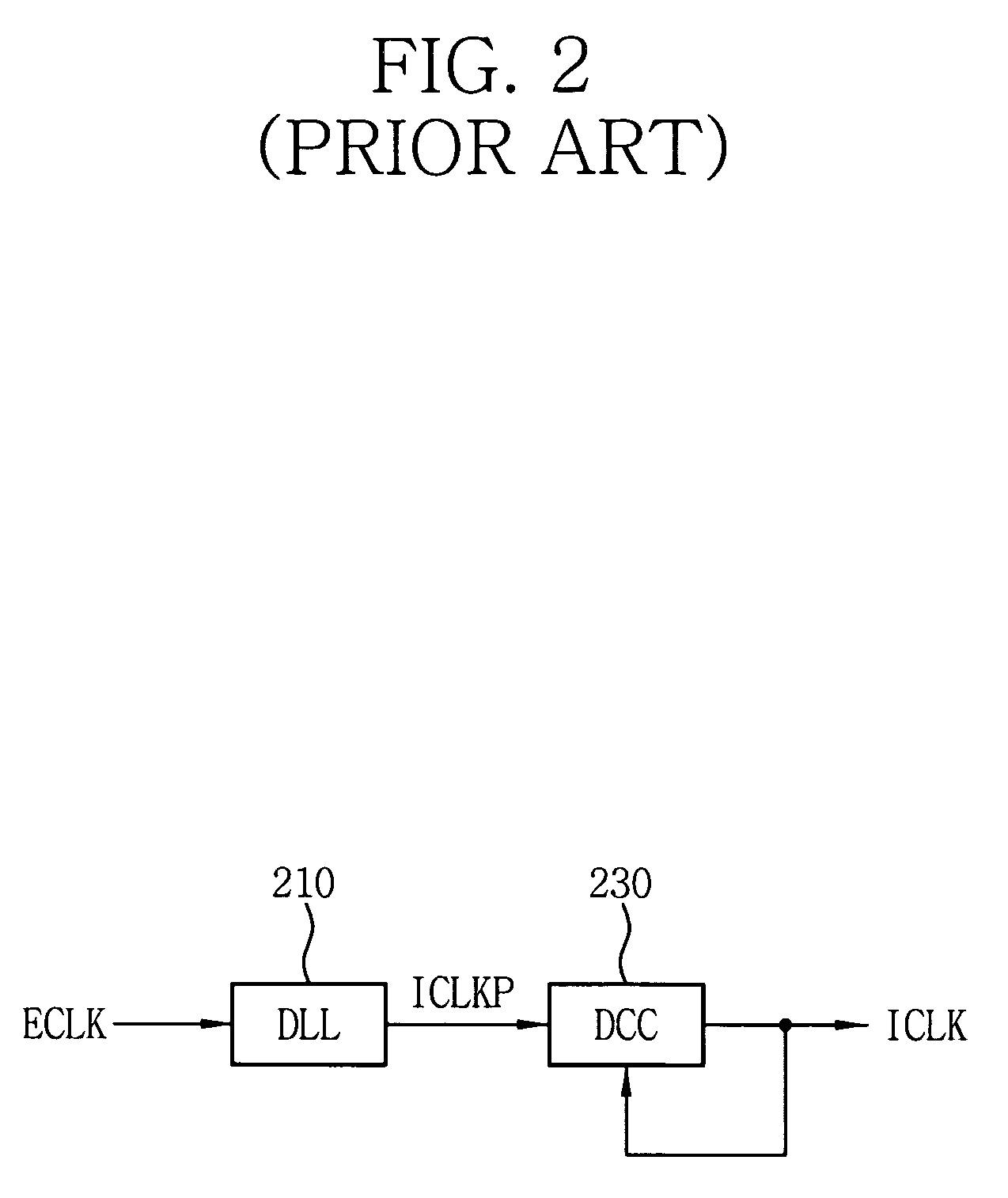
A delay locked loop (DLL) circuit having a structure in which a method of performing duty cycle correction (DCC) using two DLLs and an intermediate phase composer and a method of performing DCC by forming a closed loop using a negative feedback are combined with each other is provided. The DLL circuit includes a first DLL for receiving an external clock signal and generating a first clock signal and a second DLL for receiving an external clock signal and generating a second clock signal. The first clock signal and the second clock signal are synchronized with an external clock signal. The DLL circuit further includes an intermediate phase generation circuit for receiving the first and second clock signals and generating an intermediate phase clock signal and a DCC loop for receiving the intermediate phase clock signal and generating an output clock signal. The intermediate phase clock signal has an intermediate phase between the phases of the first and second clock signals. The output clock signal is generated through correction of the duty cycle of the intermediate phase clock signal using a value obtained by integrating the output clock signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor device and display device
InactiveUS7068076B2Obstruction is producedPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital videoDevice material
A circuit capable of reducing a consumption current is provided for a digital display device composed of unipolar TFTs. There is provided a latch circuit for holding a digital video signal. According to the latch circuit, when the digital video signal is inputted to an input electrode of a TFT (101), a non-inverting output signal is outputted from an output electrode of the TFT (101) and an inverting output signal is outputted from output electrodes of TFTs (102 and 103). Two line outputs of non-inversion and inversion are obtained. Thus, when a buffer located in a subsequent stage is operated, a period for which a direct current path is produced between a high potential and a low potential of a power source can be shortened, thereby contributing to reduction in a consumption current.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Clock generator having a delay locked loop and duty cycle correction circuit in a parallel configuration
ActiveUS20070086267A1Pulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesDelay-locked loopClock generator
A clock generator having a delay locked loop and a duty cycle correction circuit. The delay locked loop adjusts a first adjustable delay circuit to generate a first output clock signal that is synchronized with a first input clock signal and adjusts a second adjustable delay circuit to provide a delay that is equal to the first adjustable delay circuit. A duty cycle correction circuit is coupled to the first and second inputs of the delay locked loop and further coupled to the second adjustable delay circuit. The duty cycle correction circuit is configured to determine a duty cycle error of at least one of the first and second input clock signals and adjust the second adjustable delay circuit to provide a corrected delay compensating for the duty cycle error.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
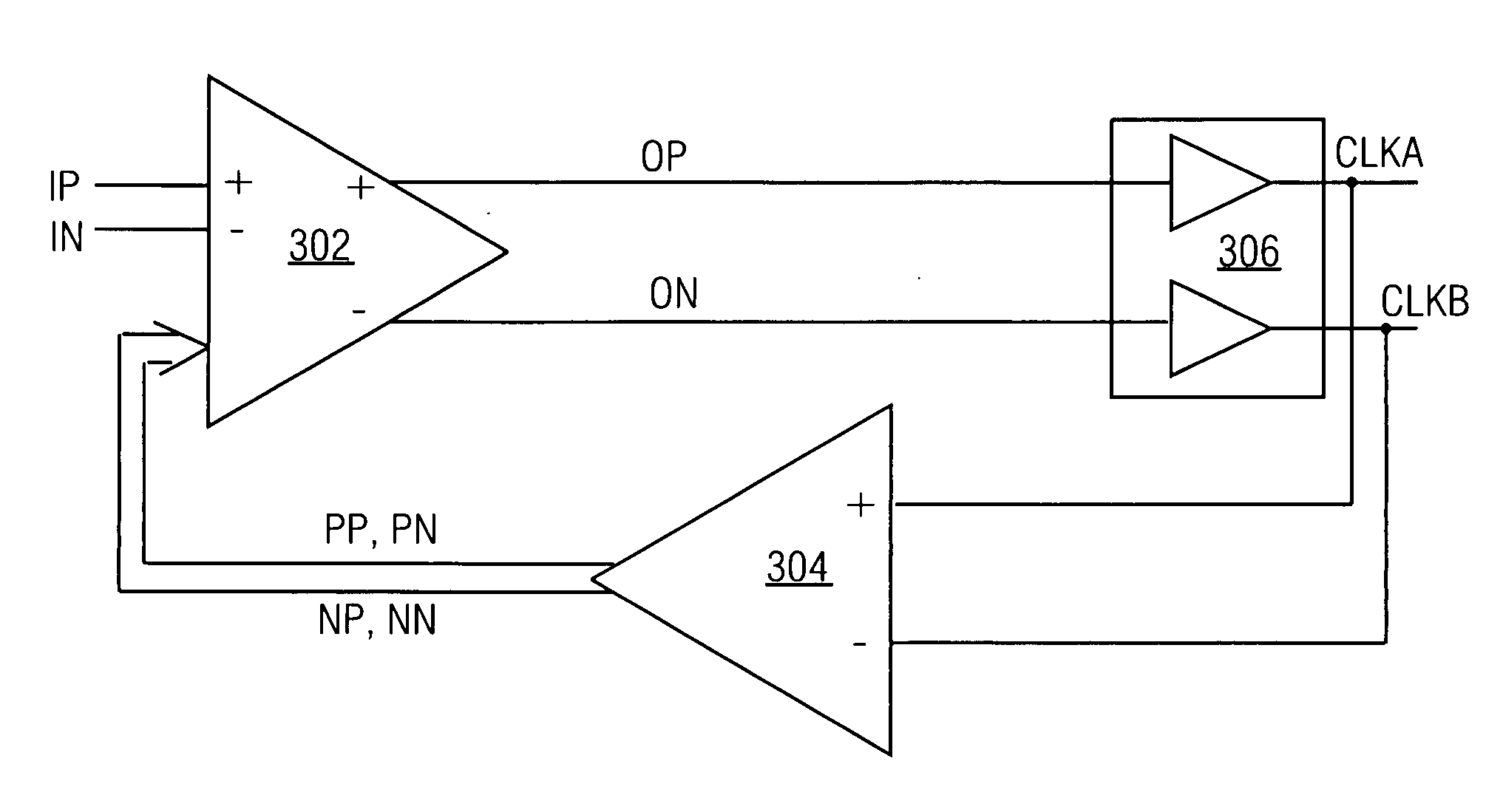
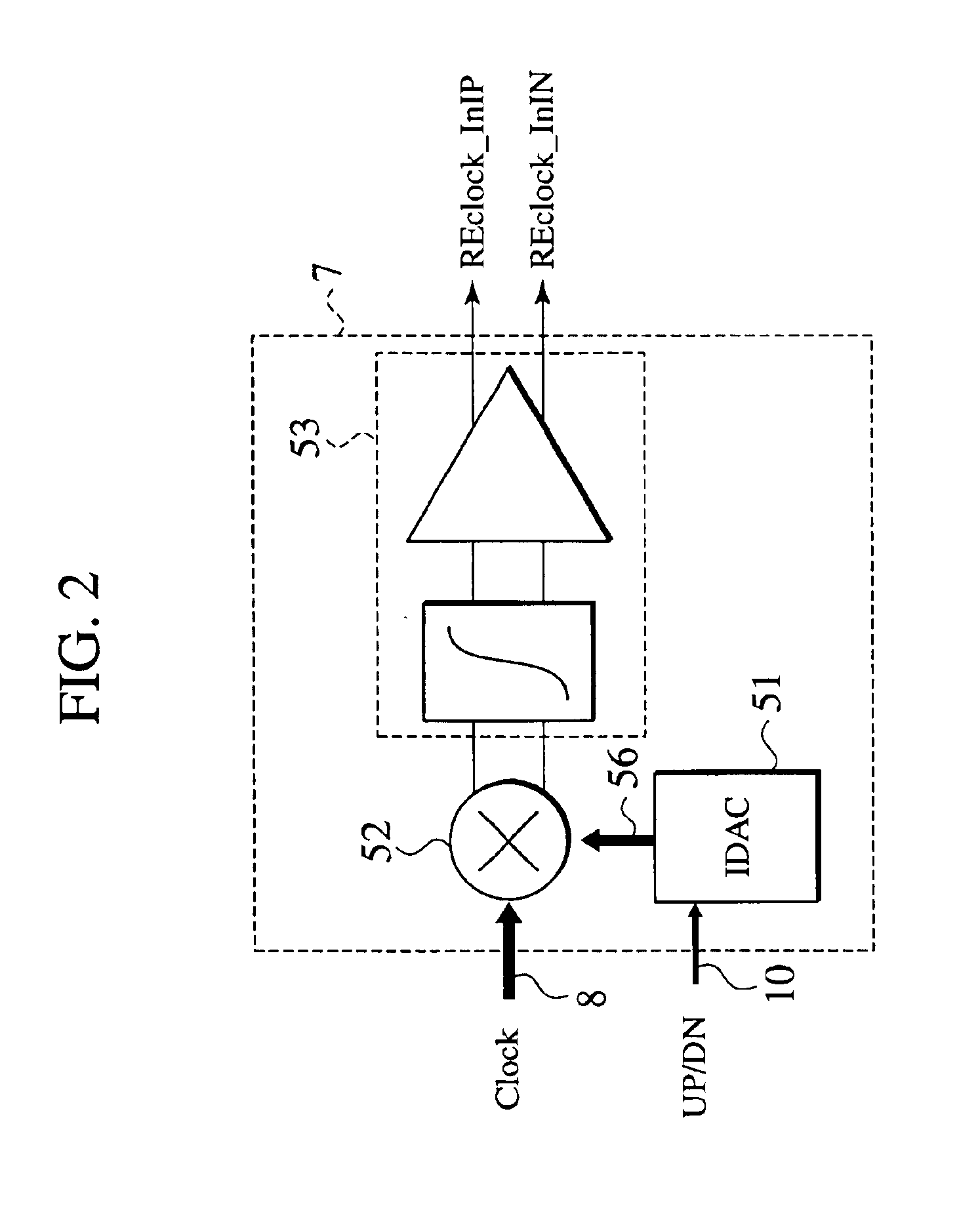
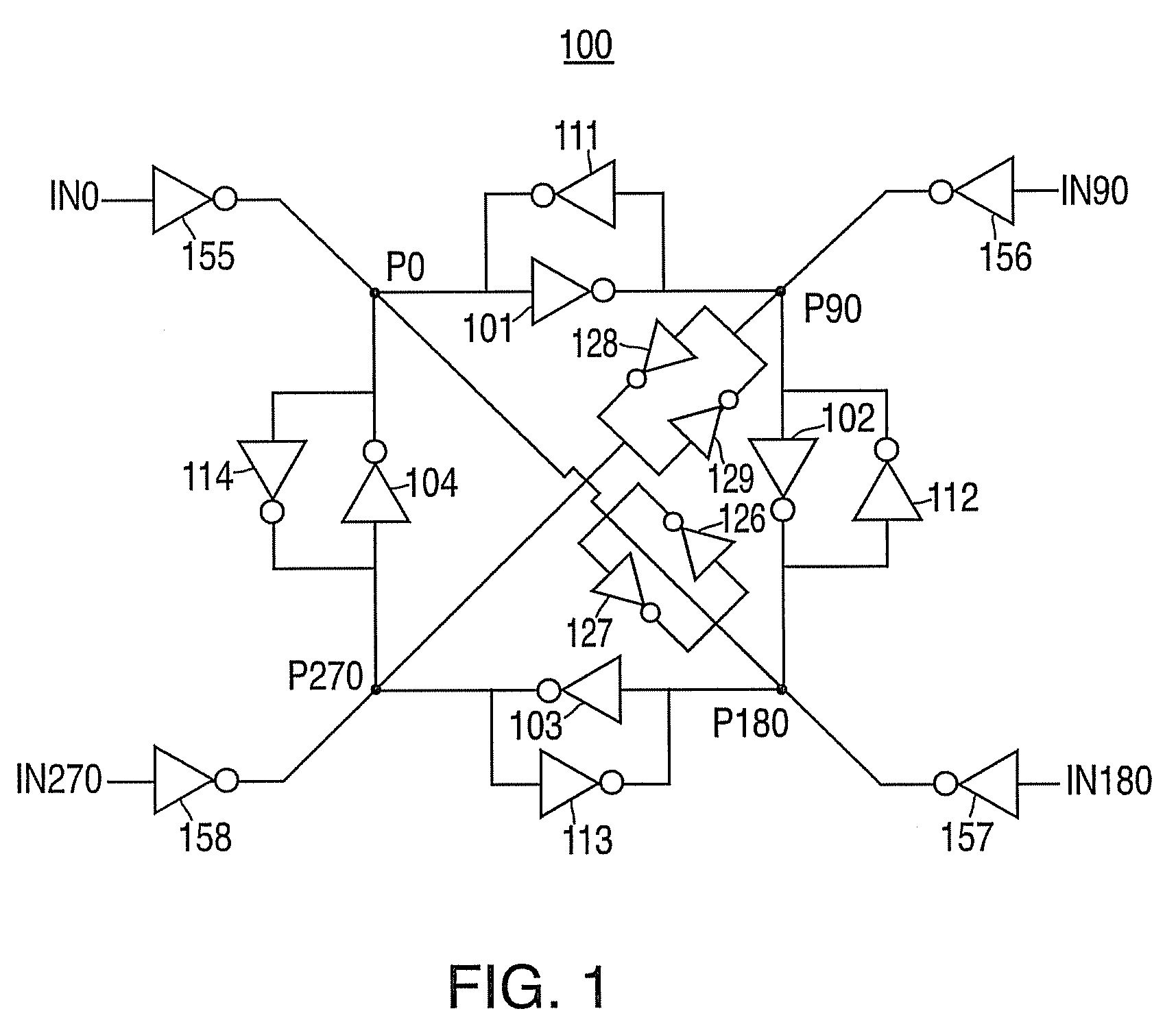
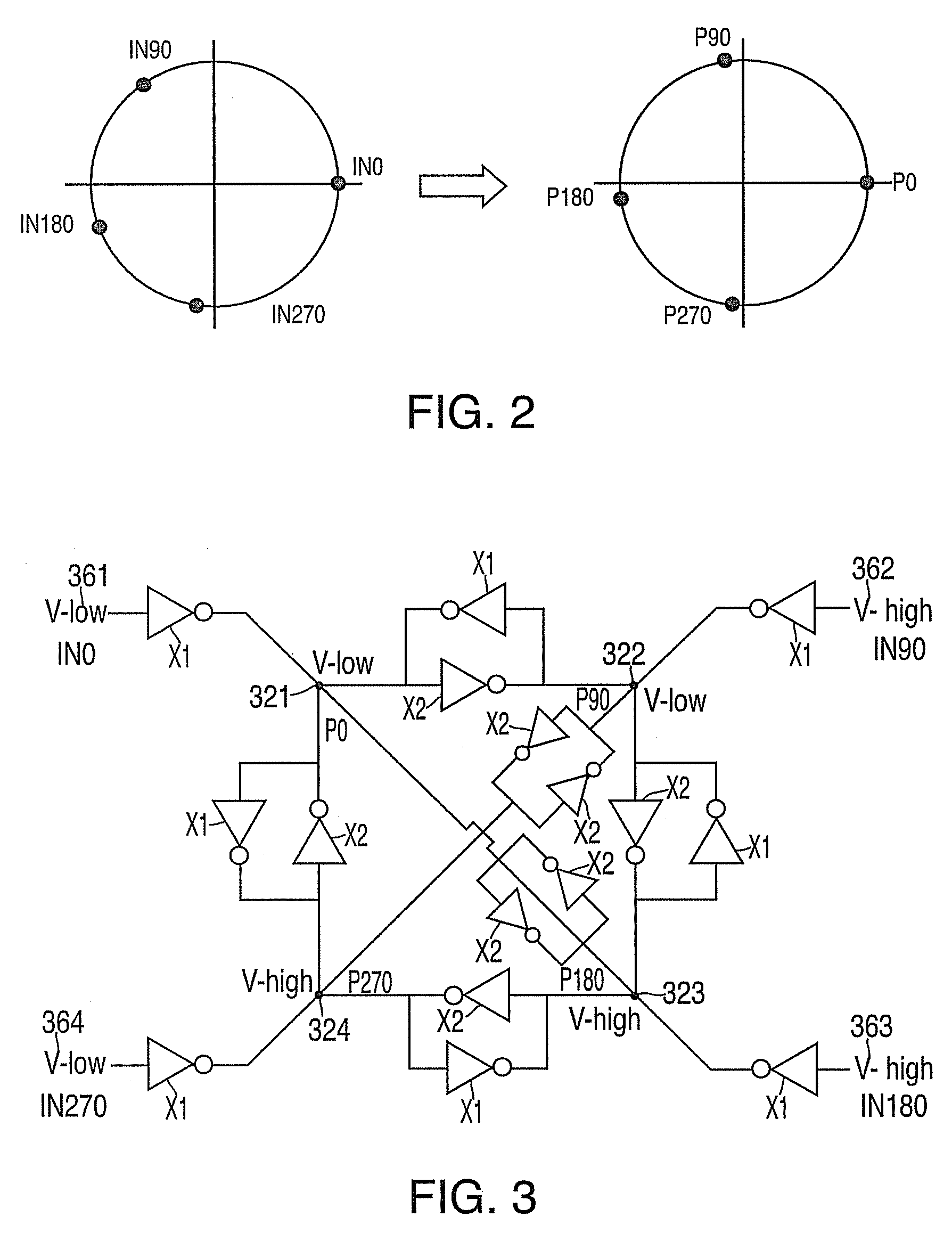
Phase interpolator and receiver
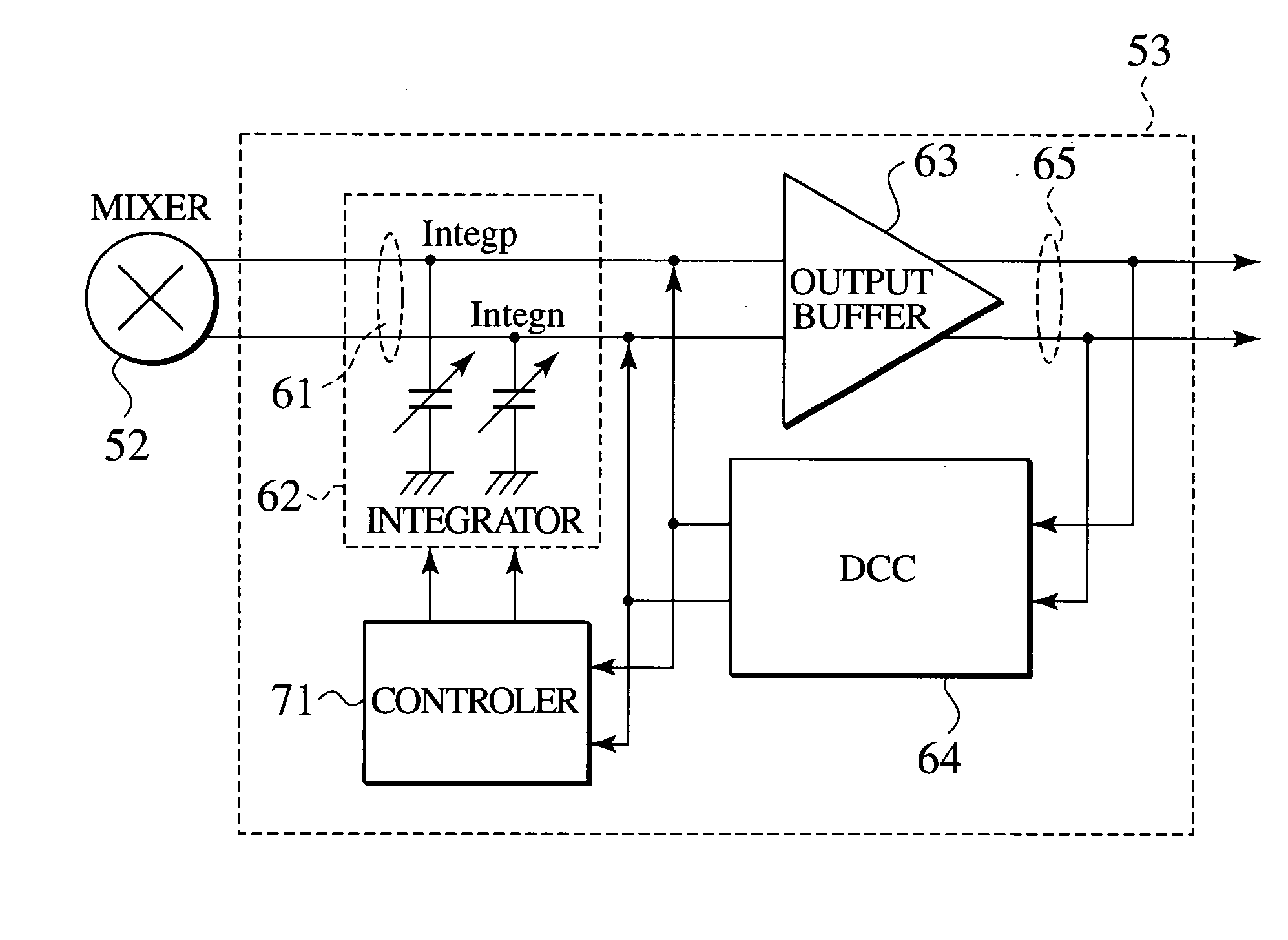
InactiveUS20040189363A1Pulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationIntegratorEngineering
An aspect of the present invention provides a phase interpolator for adjusting a phase of differential clock signals of a receiver to a phase of a data from a transmitter that includes, an integrator configured to slew edges of differential clock signals adjusted to the phase of the data from the transmitter, a output buffer configured to amplify an output of the integrator, a duty cycle correction circuit configured to feed duty correction signals back to the adjusted differential clock signals, and a controller configured to ensure operations of an amplitude of the output buffer and a data read circuit to adjust the swings and duties of the adjusted differential clock signals.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Clock generator having a delay locked loop and duty cycle correction circuit in a parallel configuration
ActiveUS7227809B2Pulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesDelay-locked loopClock generator
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Programmable phase shift and duty cycle correction circuit and method
ActiveUS7138841B1Manipulation where pulse delivered at different timesElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitPhase shifted
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
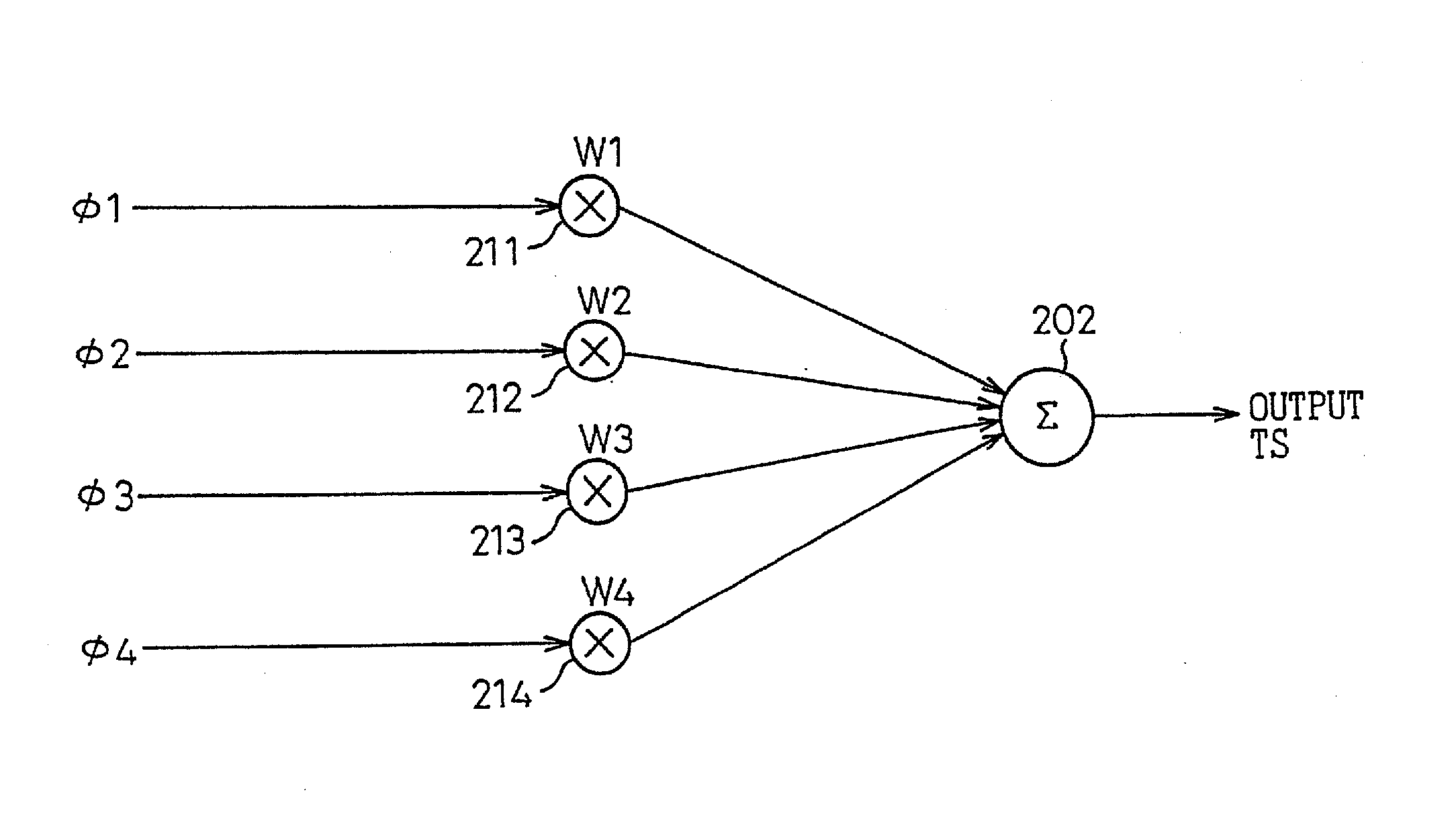
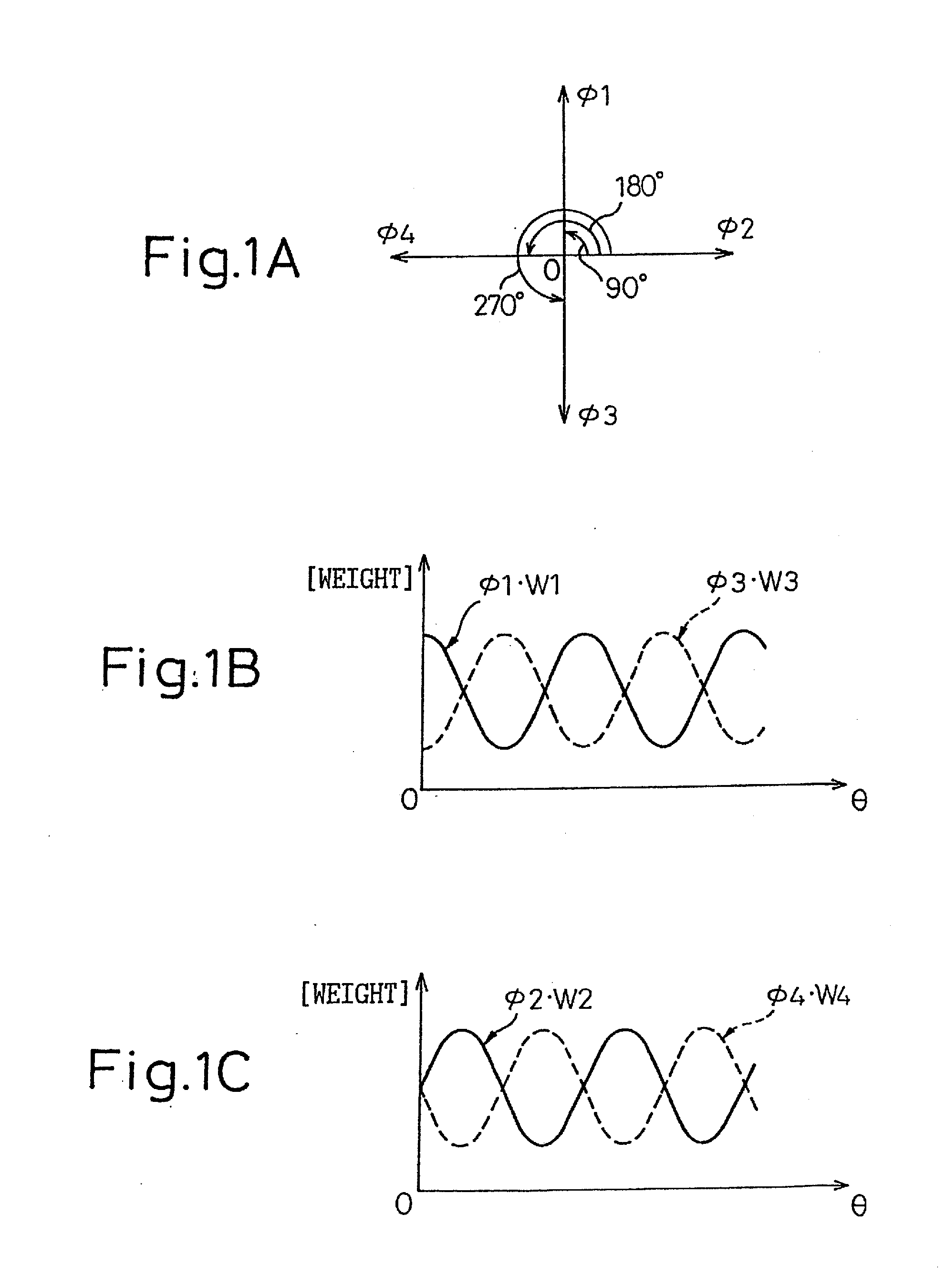
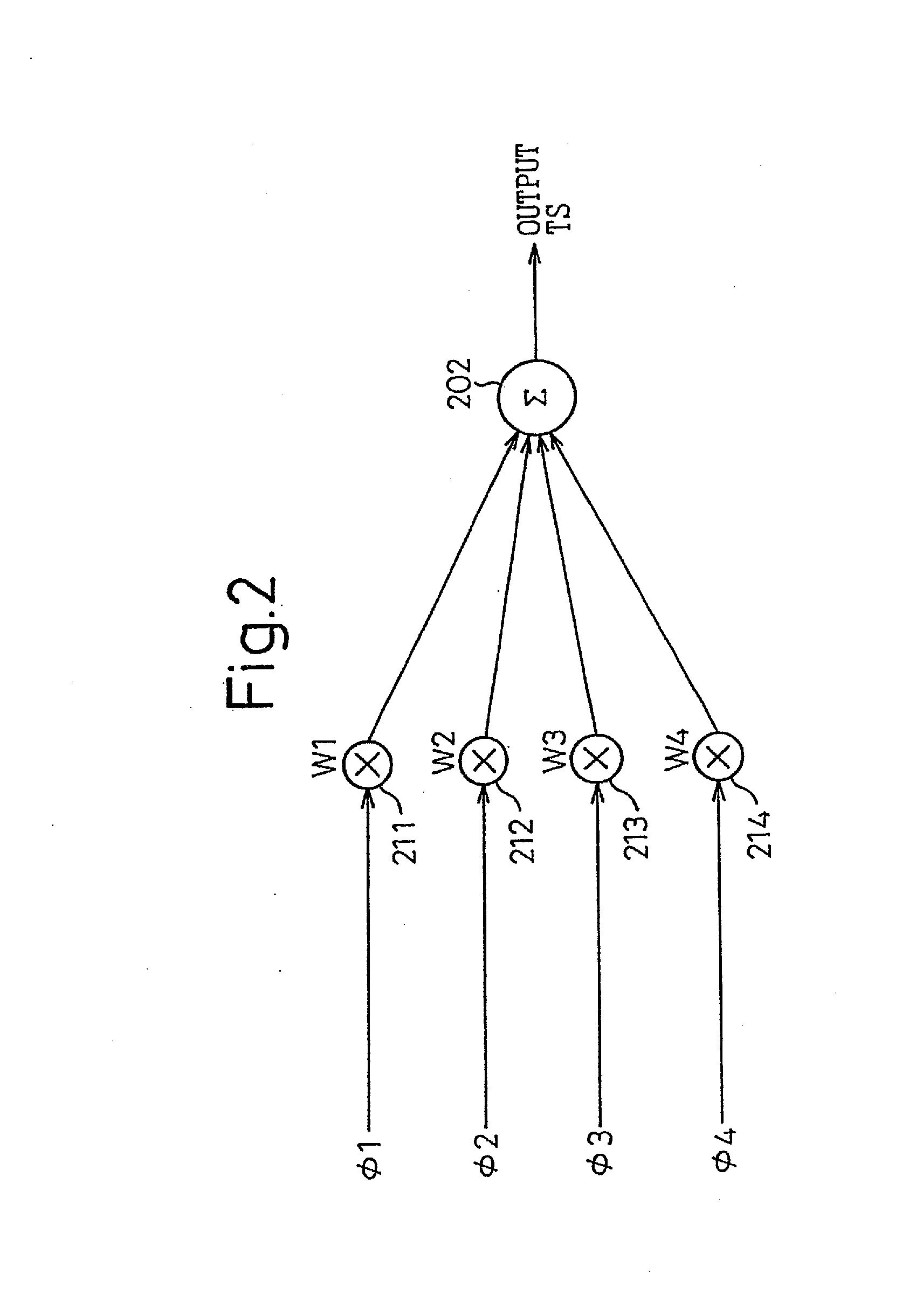
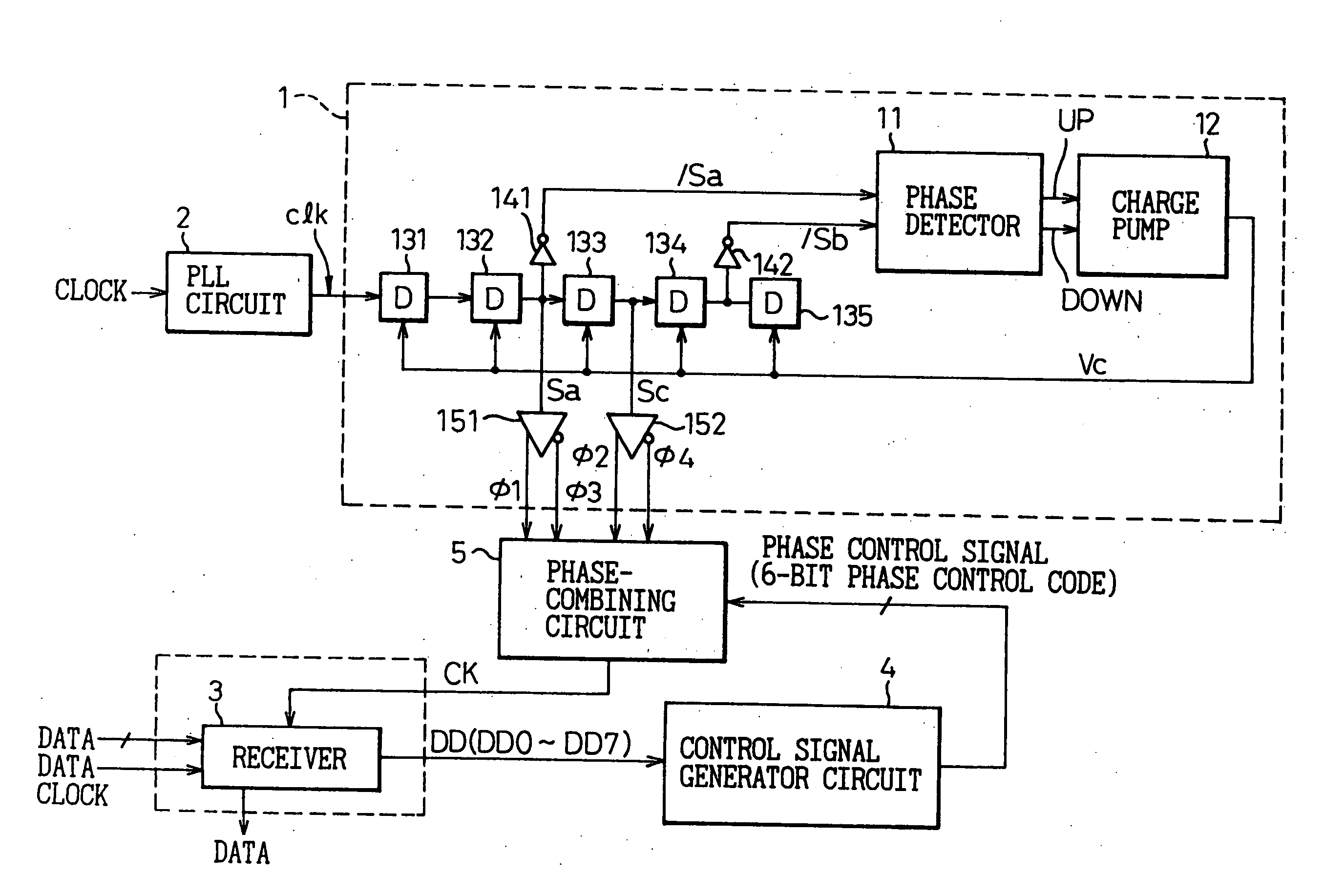
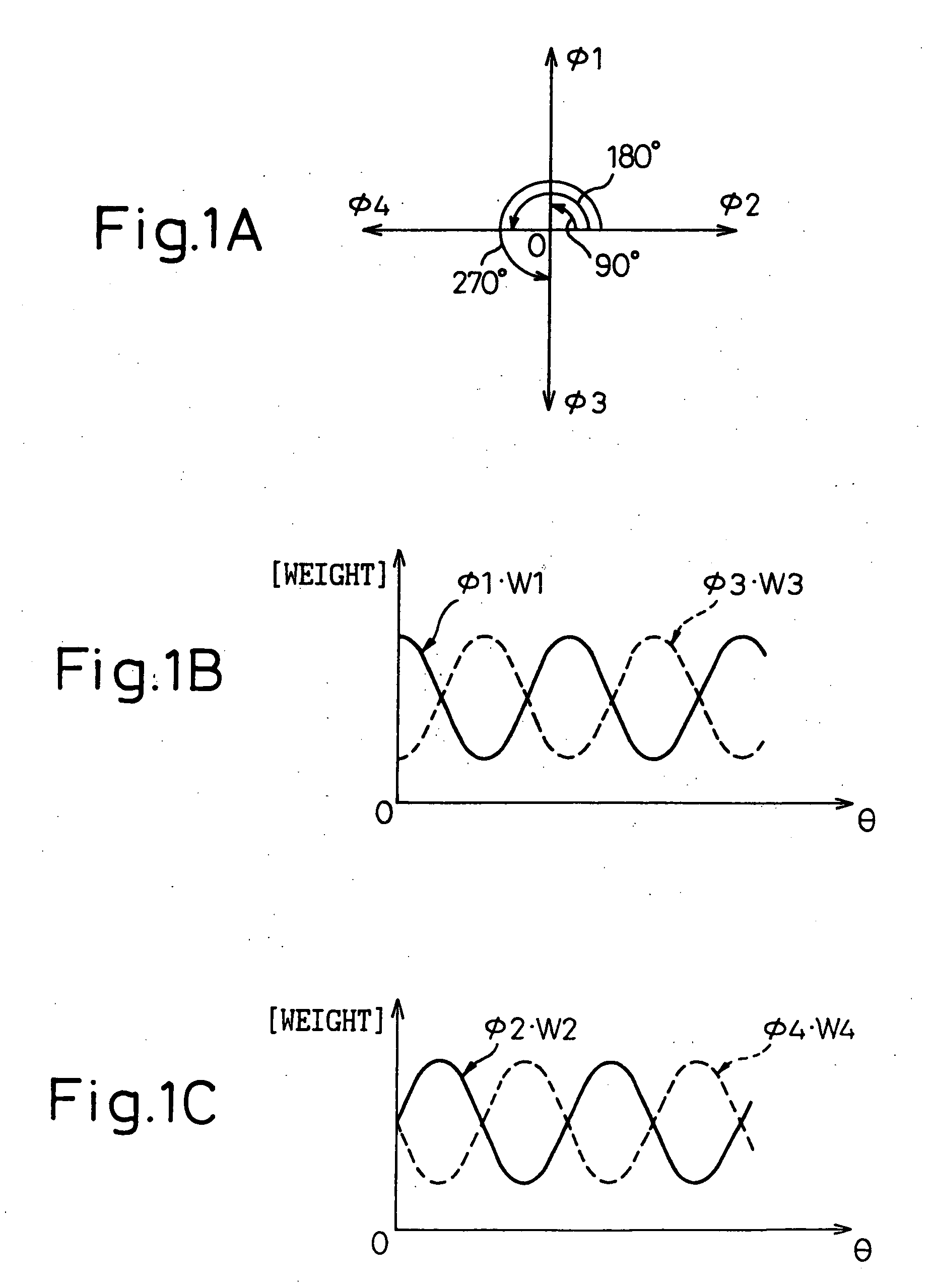
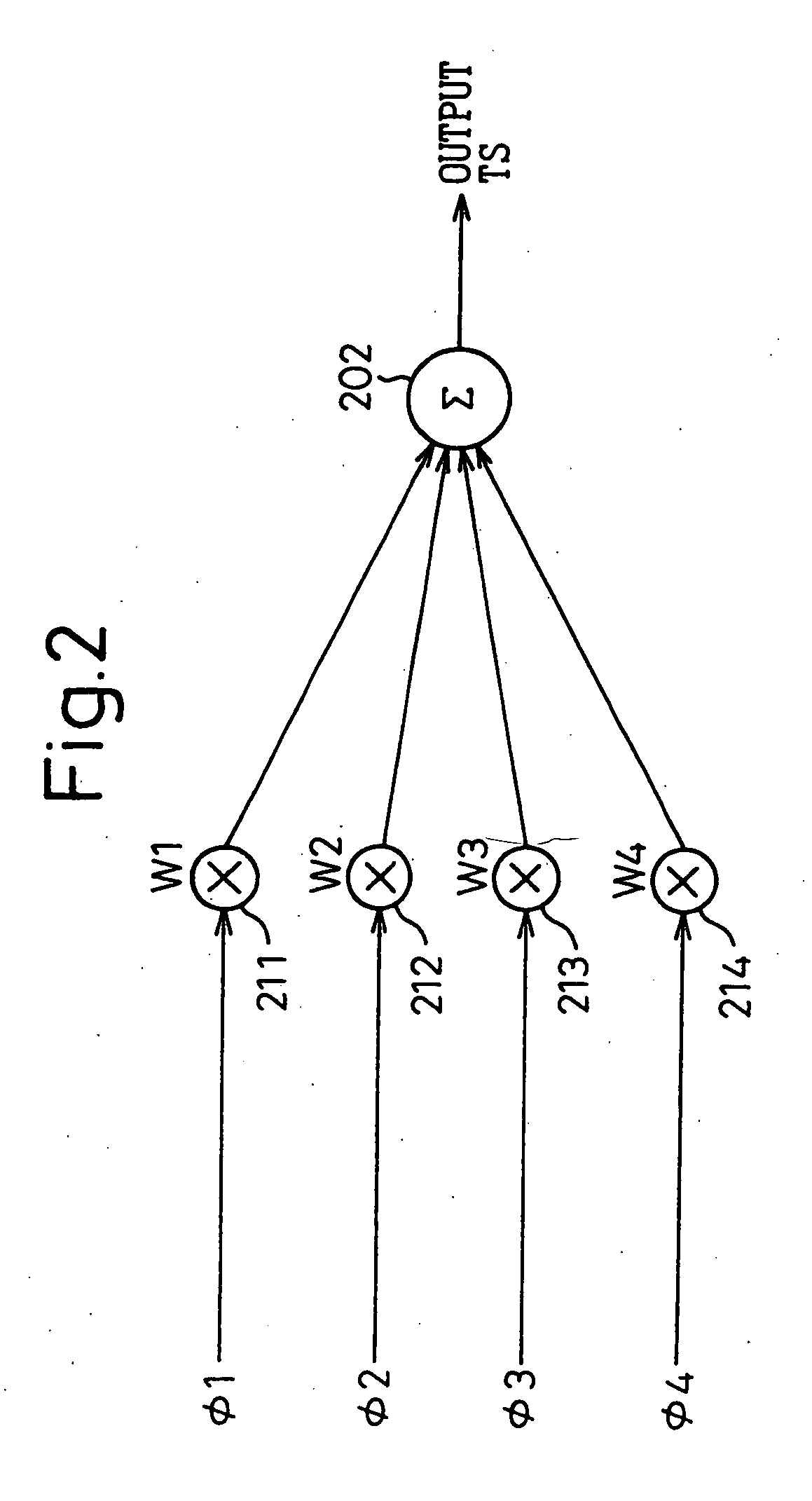
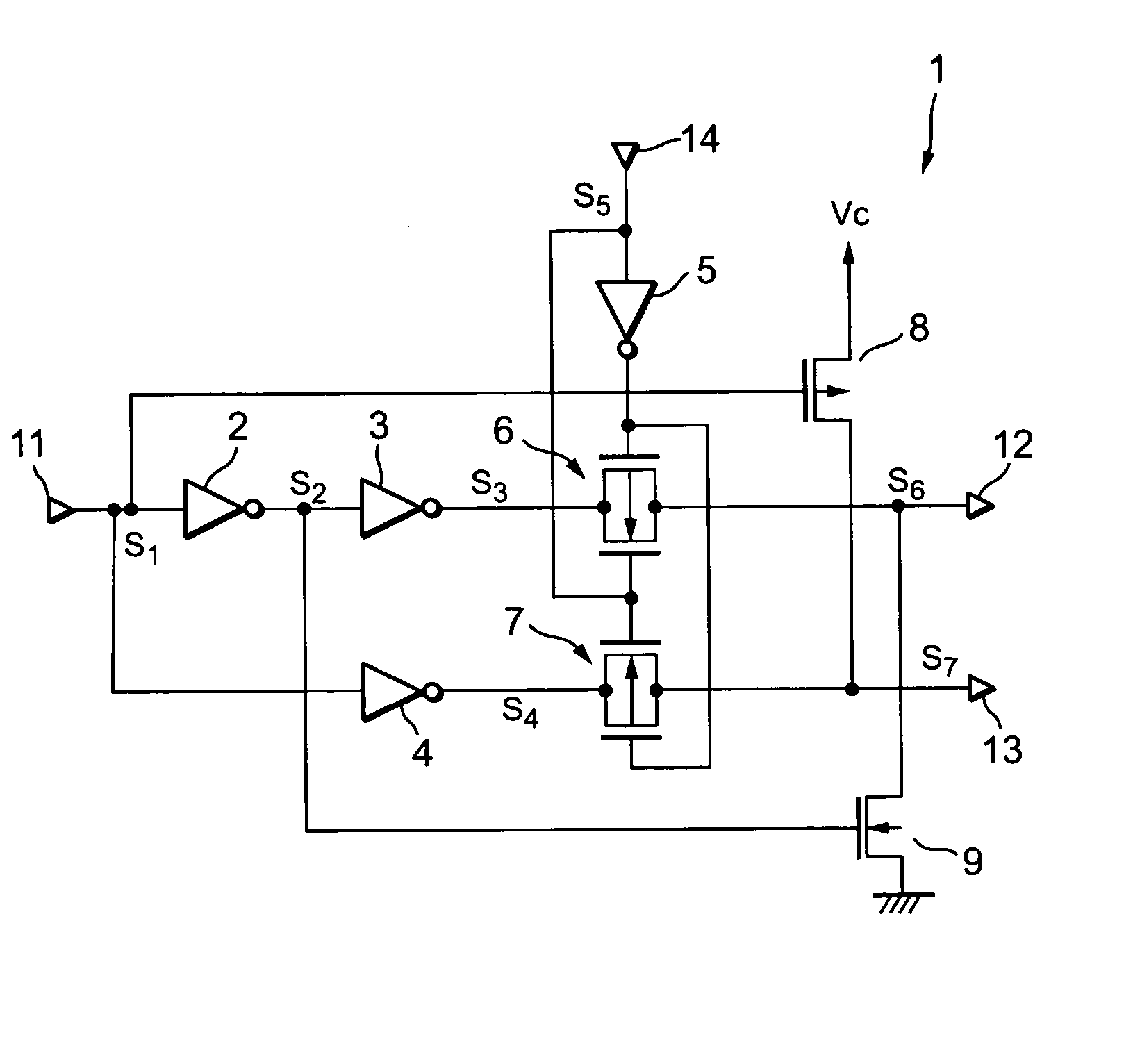
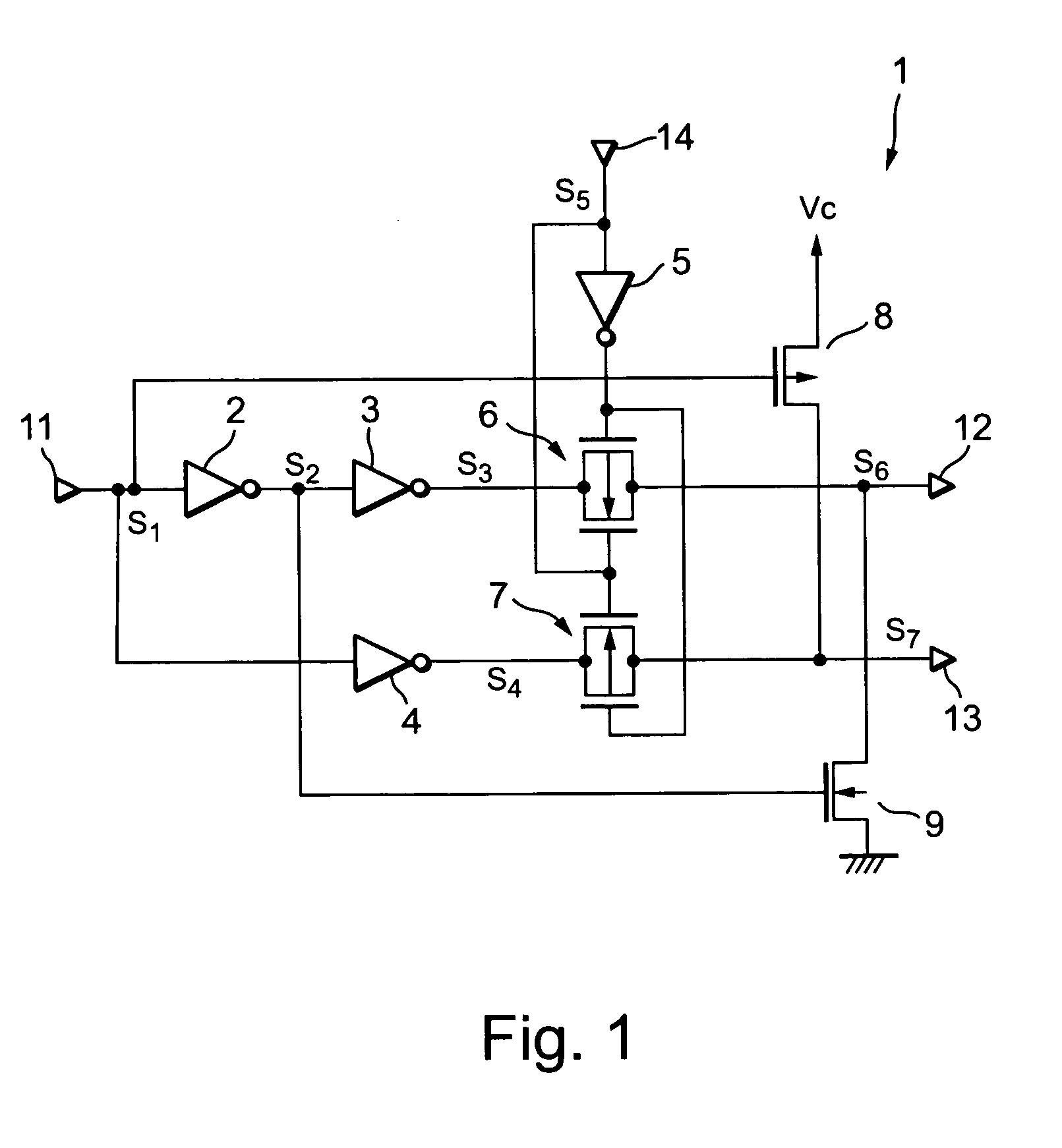
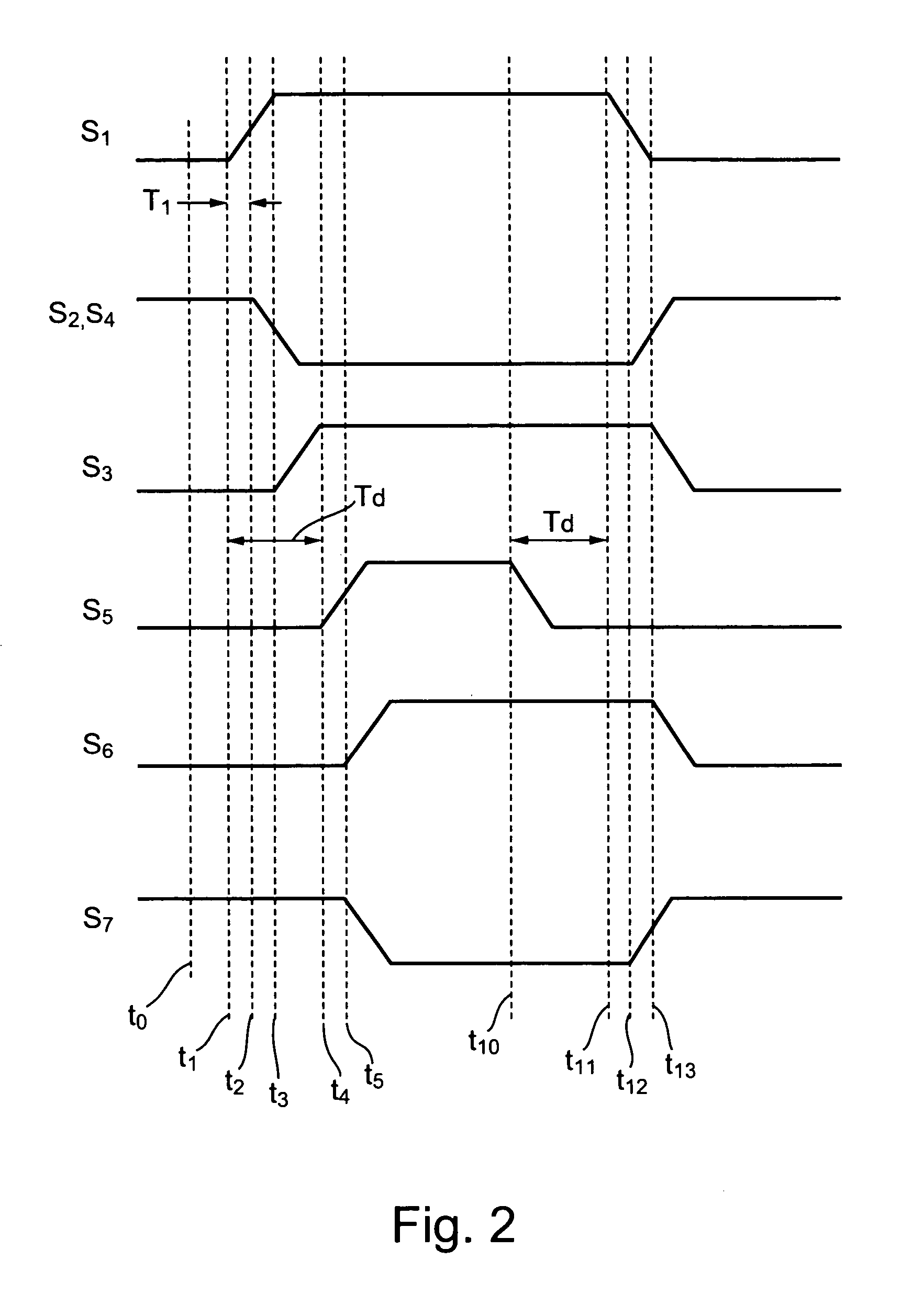
Phase-combining circuit and timing signal generator circuit for carrying out a high-speed signal transmission
InactiveUS20130314142A1Simple structureError minimizationPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsControl signalPhase control
A phase-combining circuit for combining cyclic timing waveforms that have been phase-controlled by control signals based on three or more input signals of different phases, has a weight signal generating circuit and a weighting circuit. The weight signal generating circuit generates weights according to the control signals, and the weighting circuit gives the weights to the respective input signals, with a positive or negative polarity for each one signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
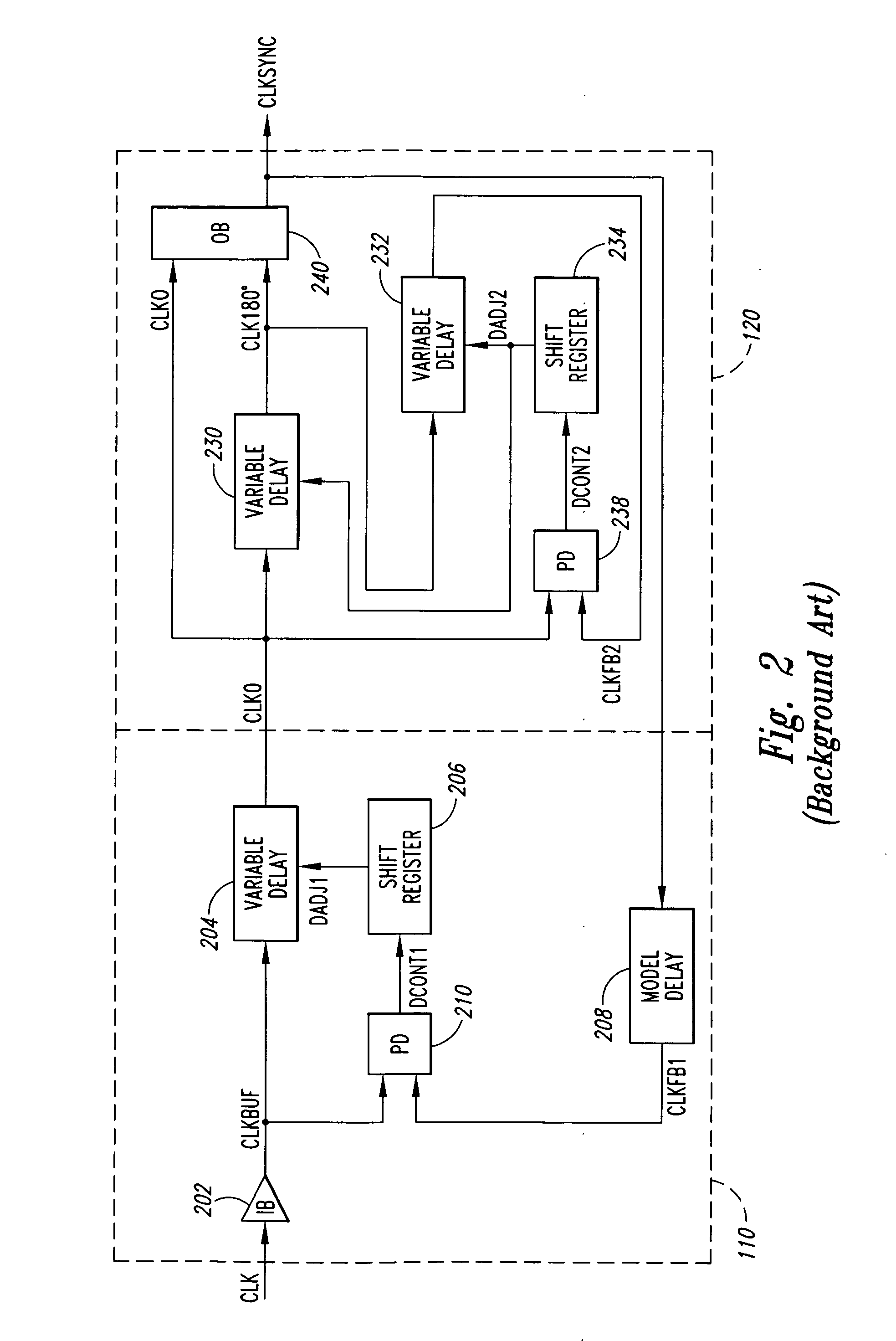
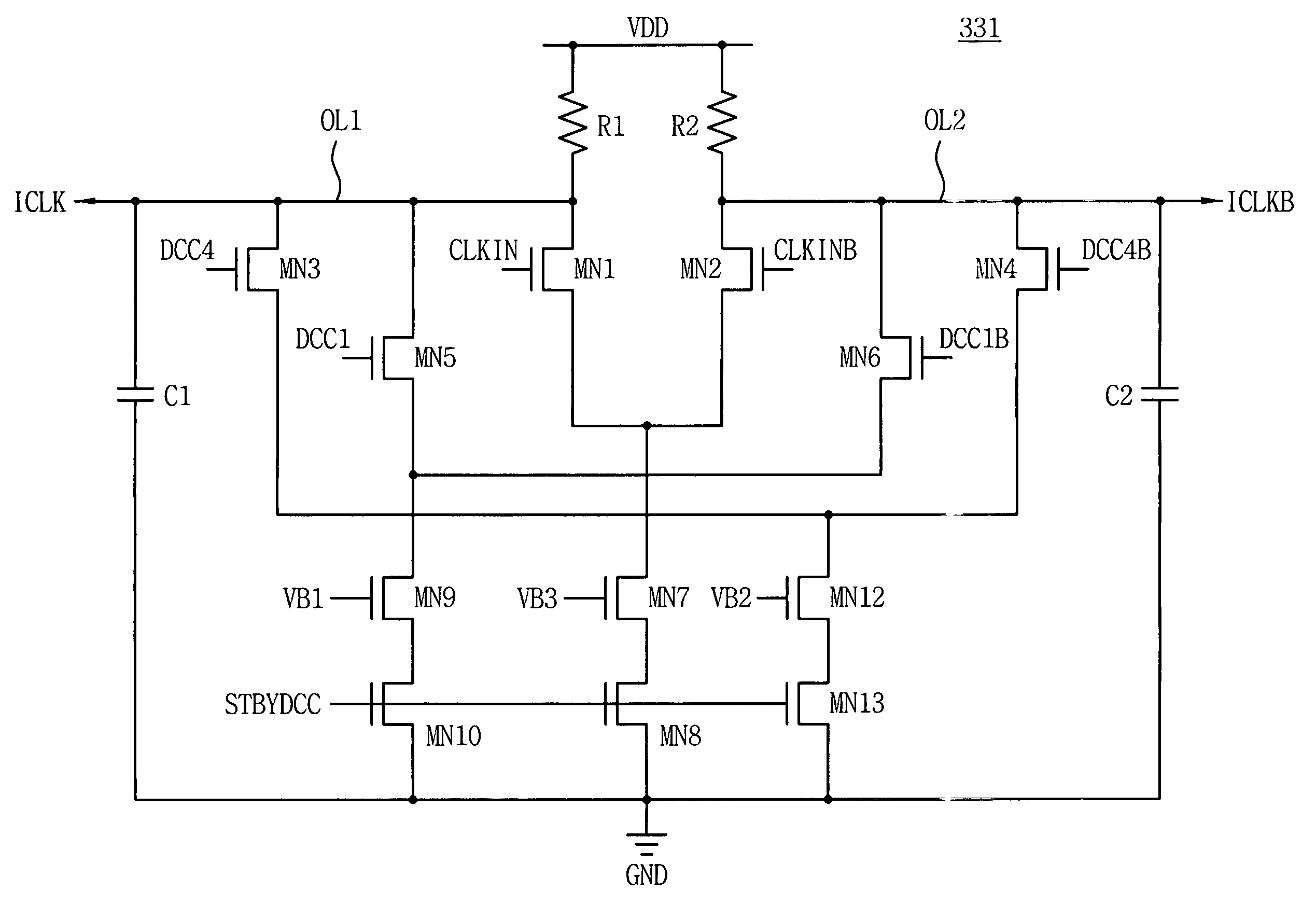
Duty cycle correction circuits suitable for use in delay-locked loops and methods of correcting duty cycles of periodic signals
InactiveUS7199634B2Pulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationControl signalDelay-locked loop
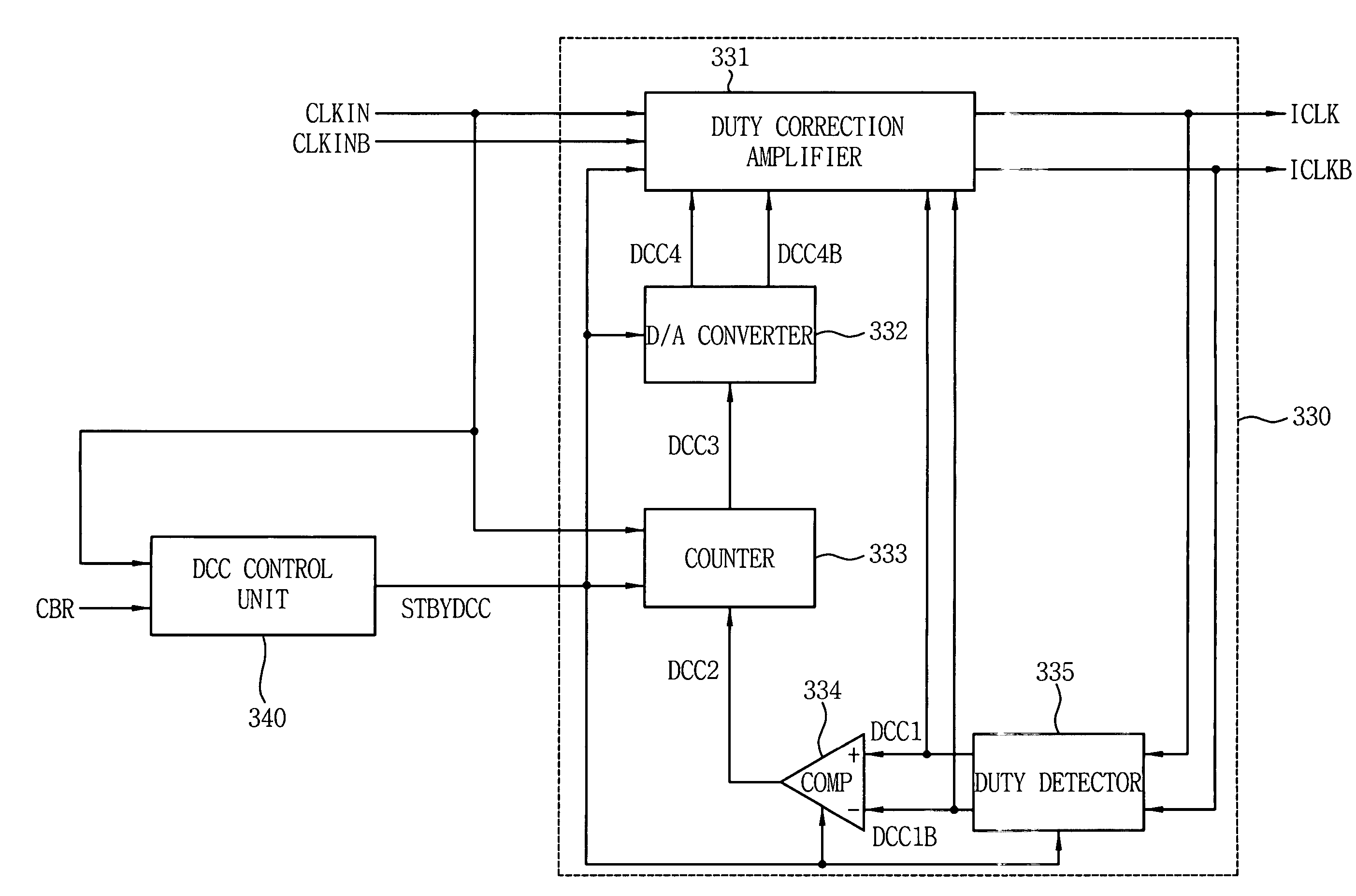
Delay-locked loop integrated circuits include a duty cycle correction circuit. This duty cycle correction circuit generates at least one output clock signal having a substantially uniform duty cycle in response to at least one input clock signal having a non-uniform duty cycle. The duty cycle correction circuit is also responsive to a standby control signal that synchronizes timing of power-saving duty cycle update operations within the duty cycle correction circuit. These update operations reset the set point of the correction circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
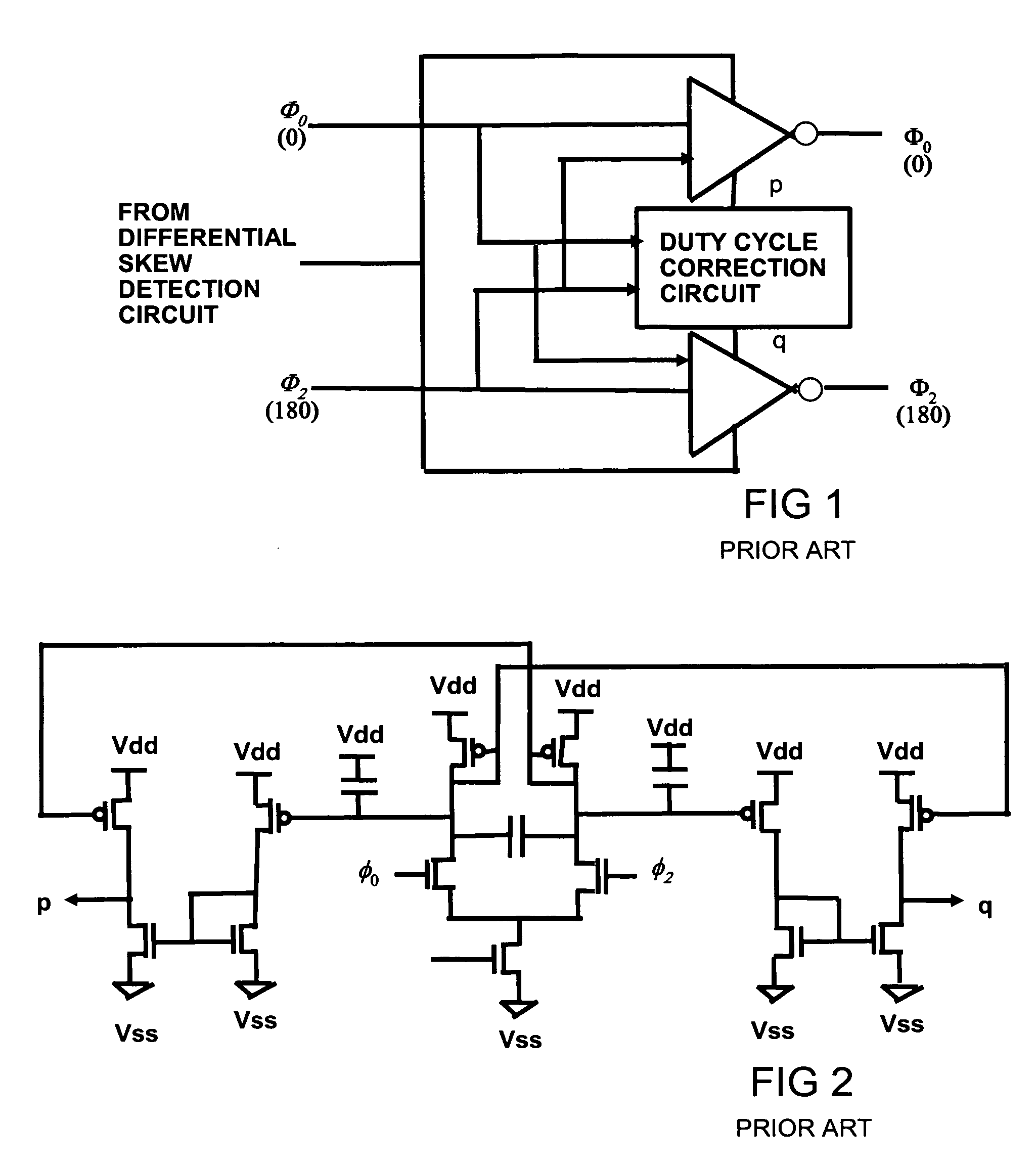
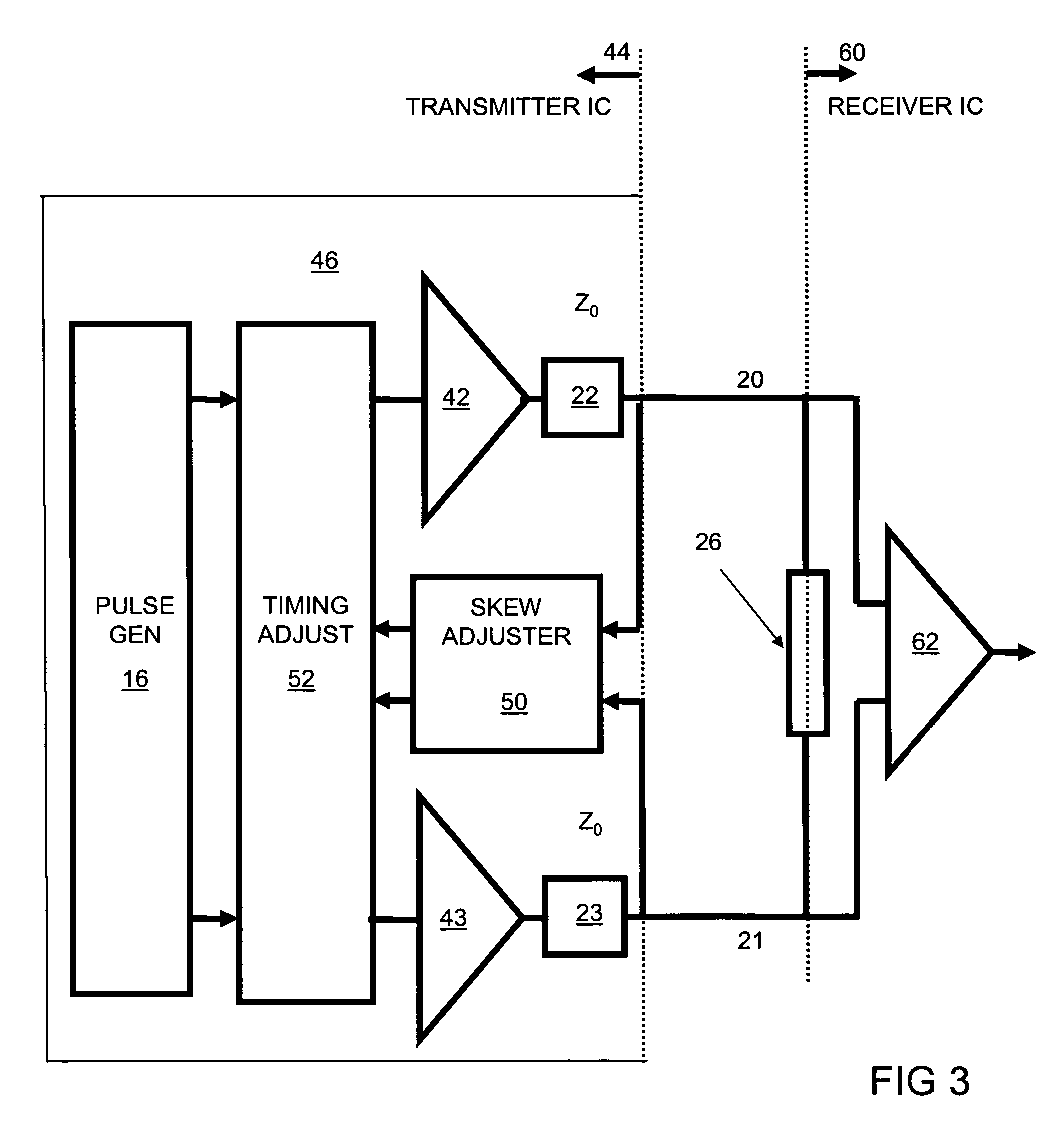
Intra-pair differential skew compensation method and apparatus for high-speed cable data transmission systems
ActiveUS20060244505A1Pulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesTraining periodTelecommunications link
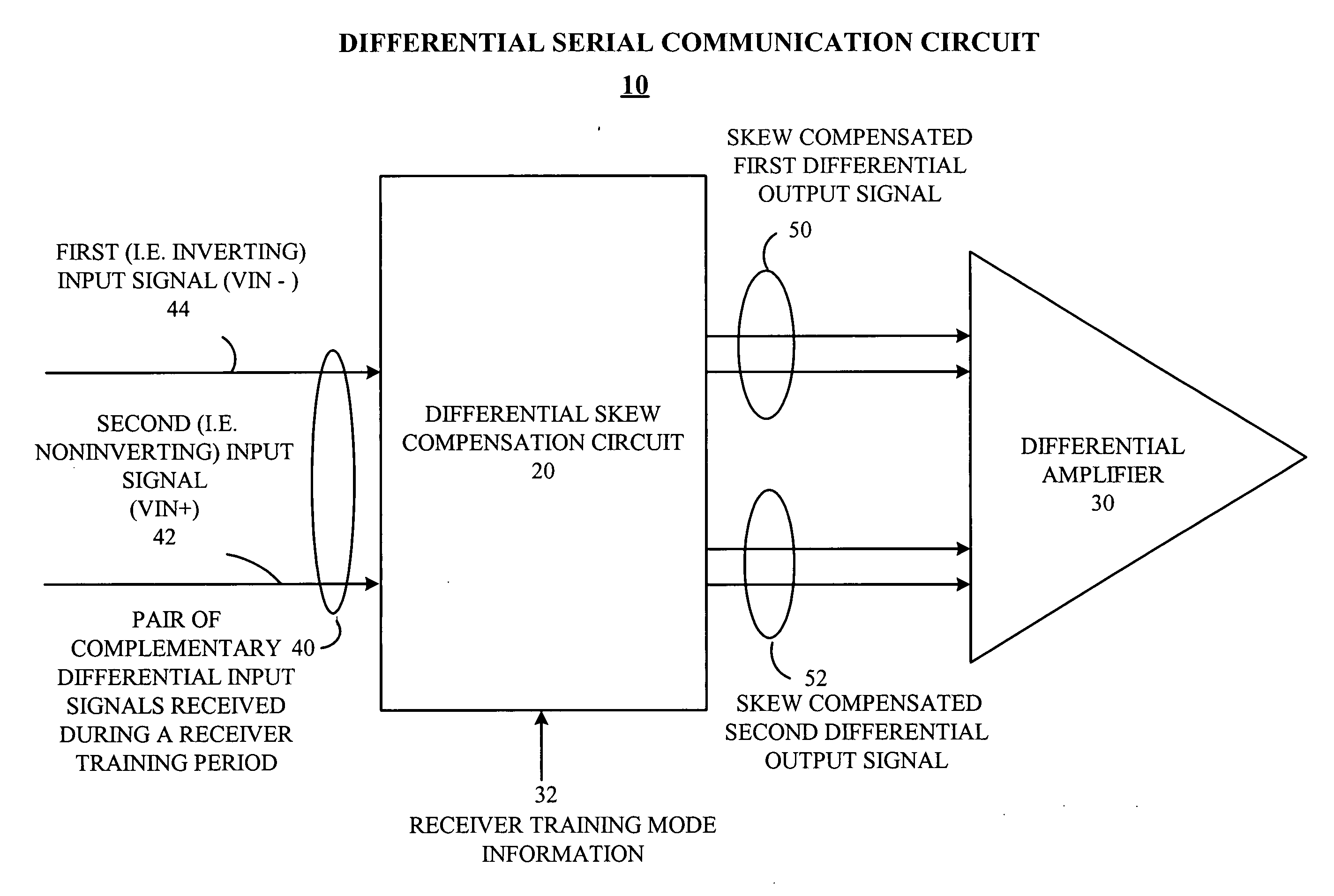
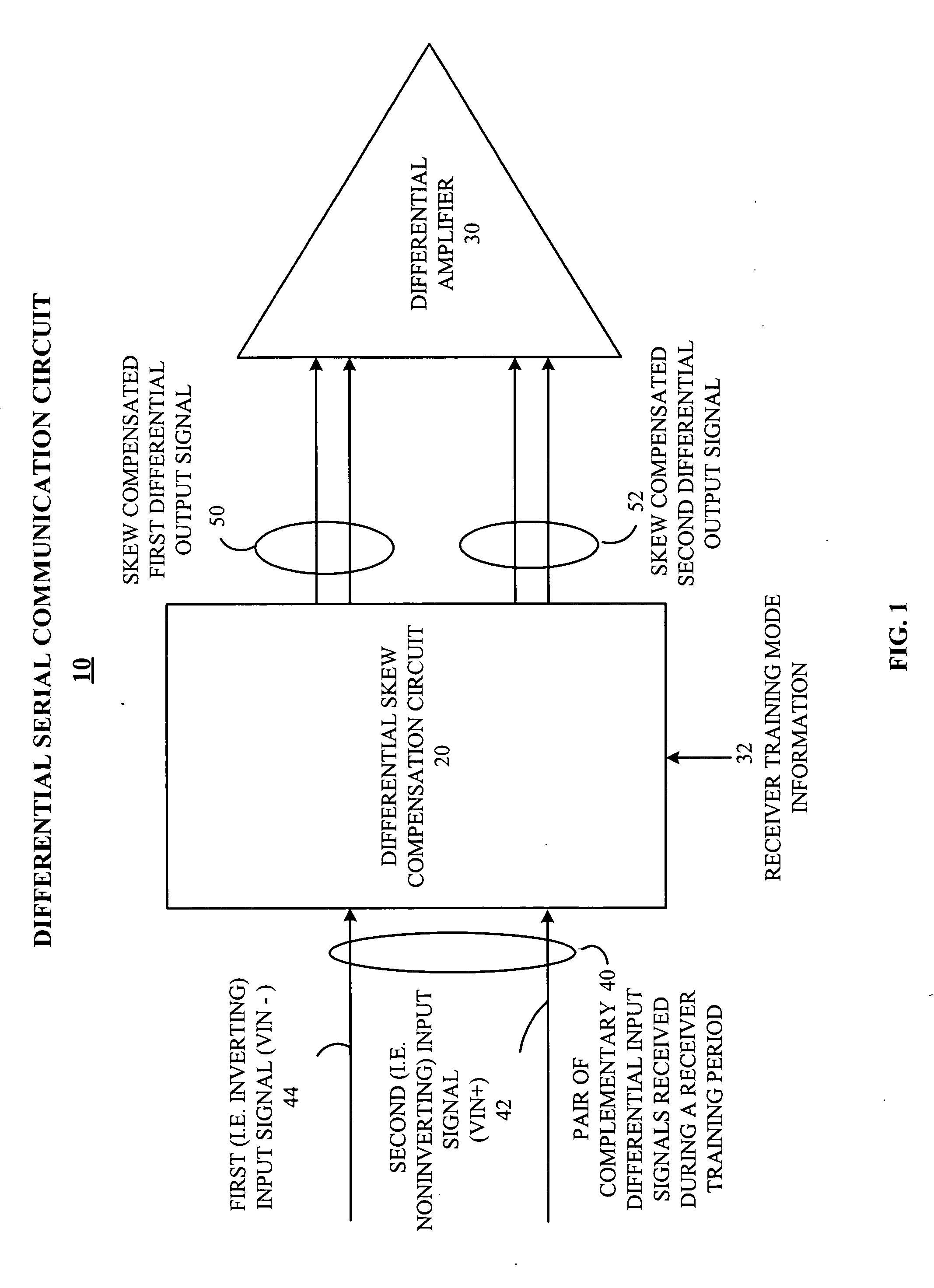
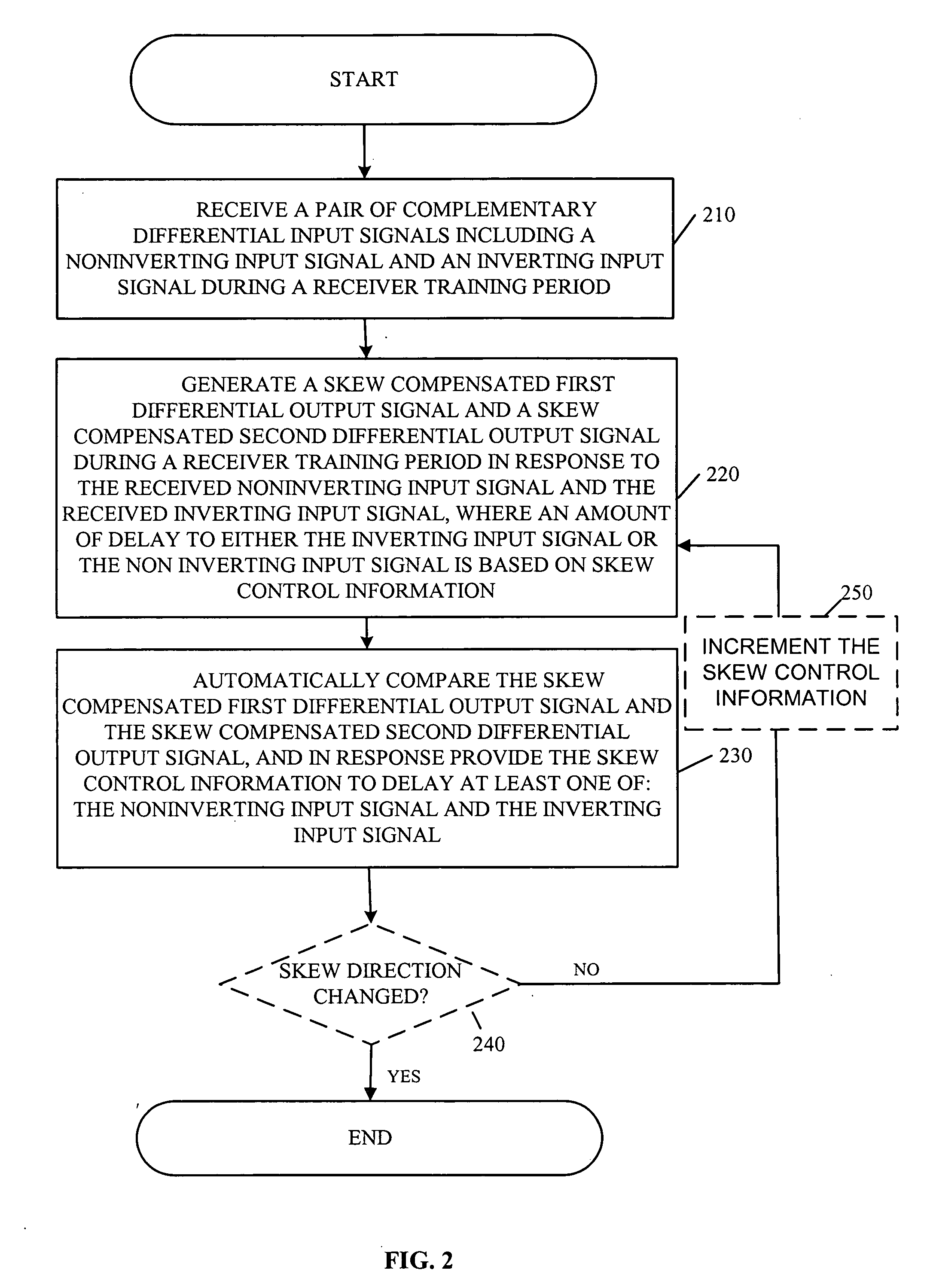
A differential serial communication receiver circuit automatically compensates for intrapair skew between received differential signals on a serial differential communication link, with deterministic skew adjustment set during a receiver training period. Intrapair skew refers to the skew within a pair of differential signals, and is hence interchangeable with the term differential skew in the context of this document. During the receiver training period, a training data pattern is received, such as alternating ones and zeros (e.g., a D10.2 pattern as is known in the art), rather than an actual data payload. The differential serial communication receiver circuit includes a differential skew compensation circuit to compensate for intrapair skew. The differential skew compensation circuit receives a pair of complementary differential input signals including a noninverting input signal and an inverting input signal, and in response generates a skew compensated first differential output signal and a skew compensated second differential output signal. The differential skew compensation circuit compares the relative delay of the skew compensated first differential output signal and the skew compensated second differential output signal, and in response delays at least one of the noninverting input signal or the inverting input signal to reduce intrapair skew.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
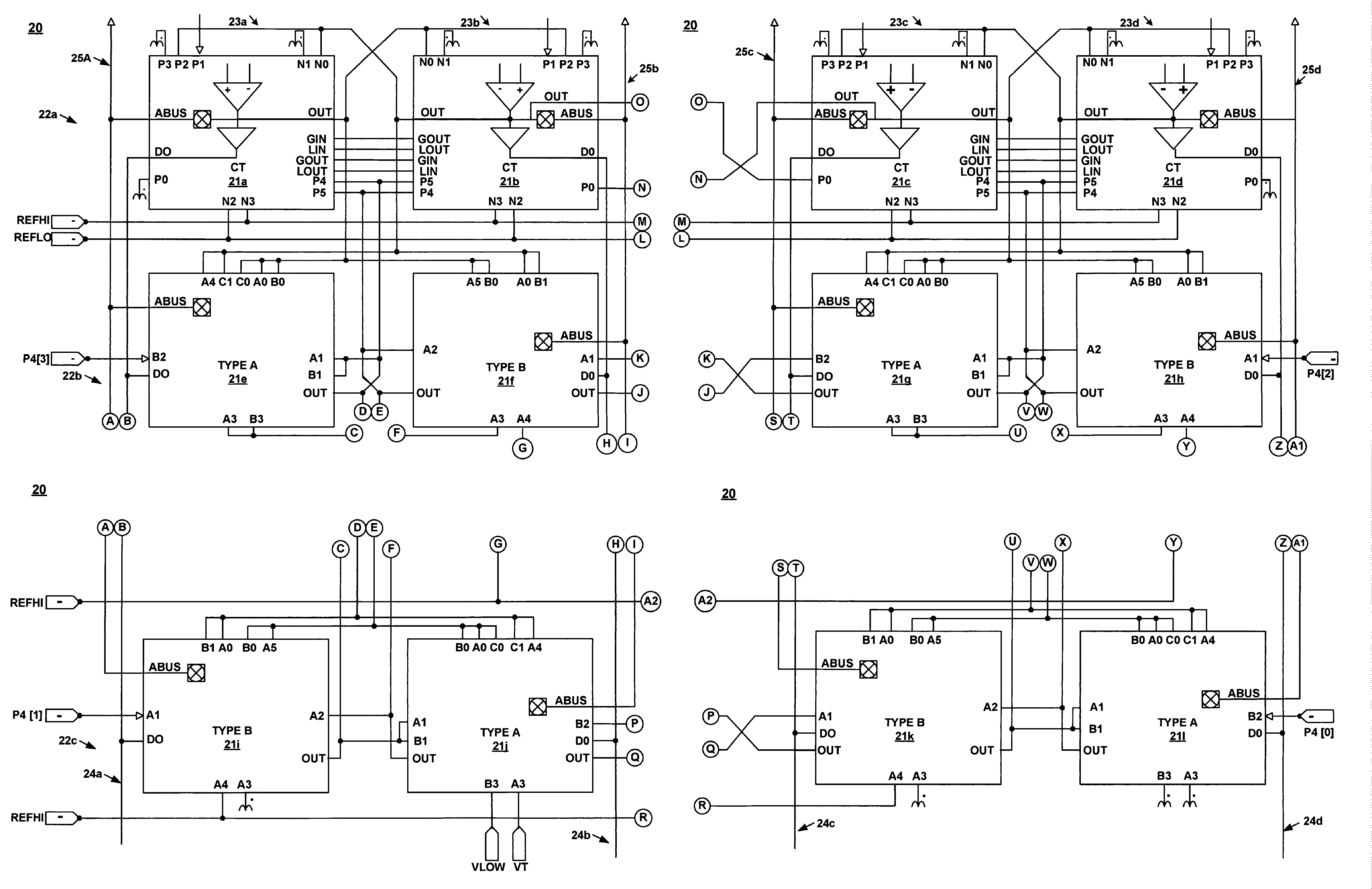
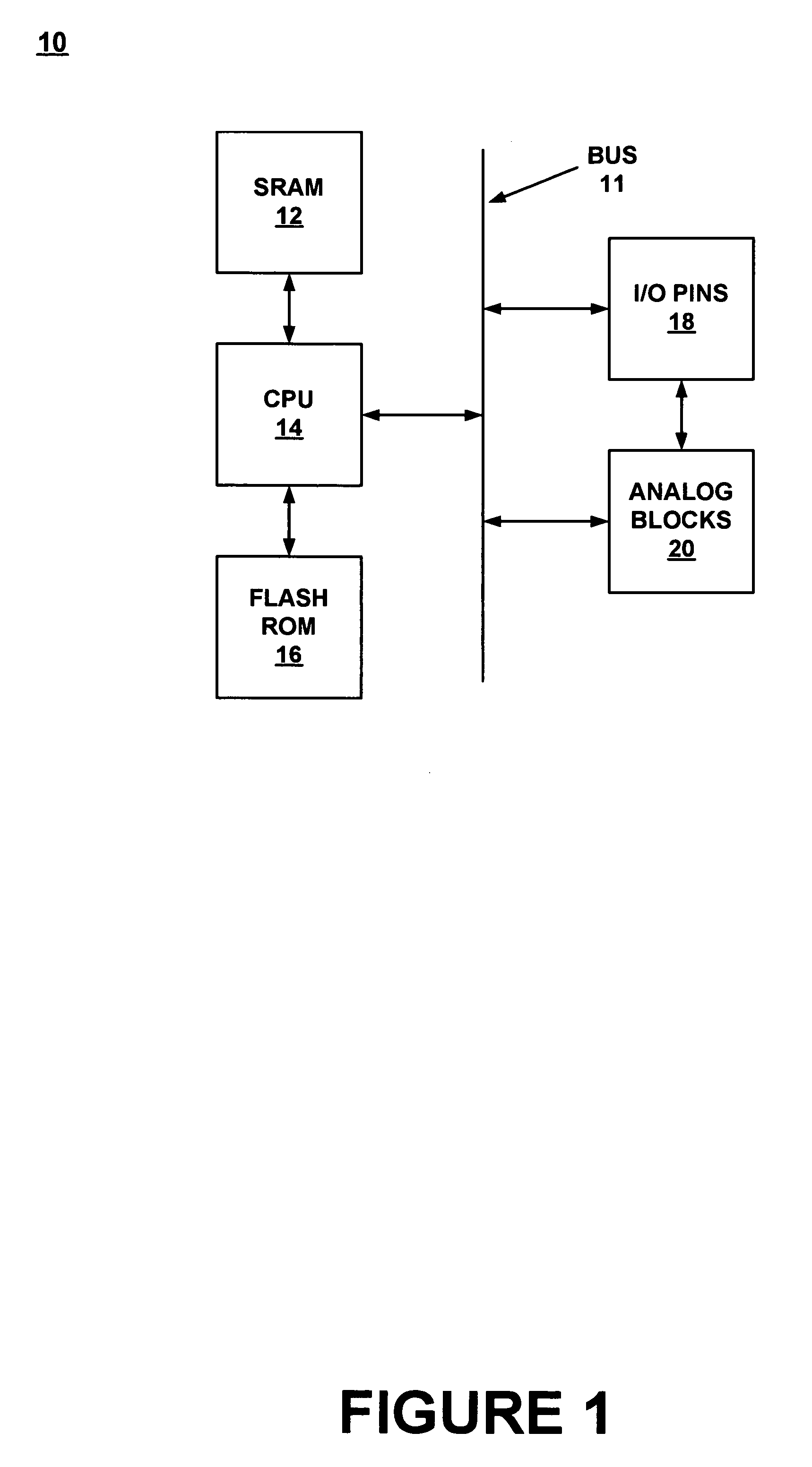
Method for synchronizing and resetting clock signals supplied to multiple programmable analog blocks
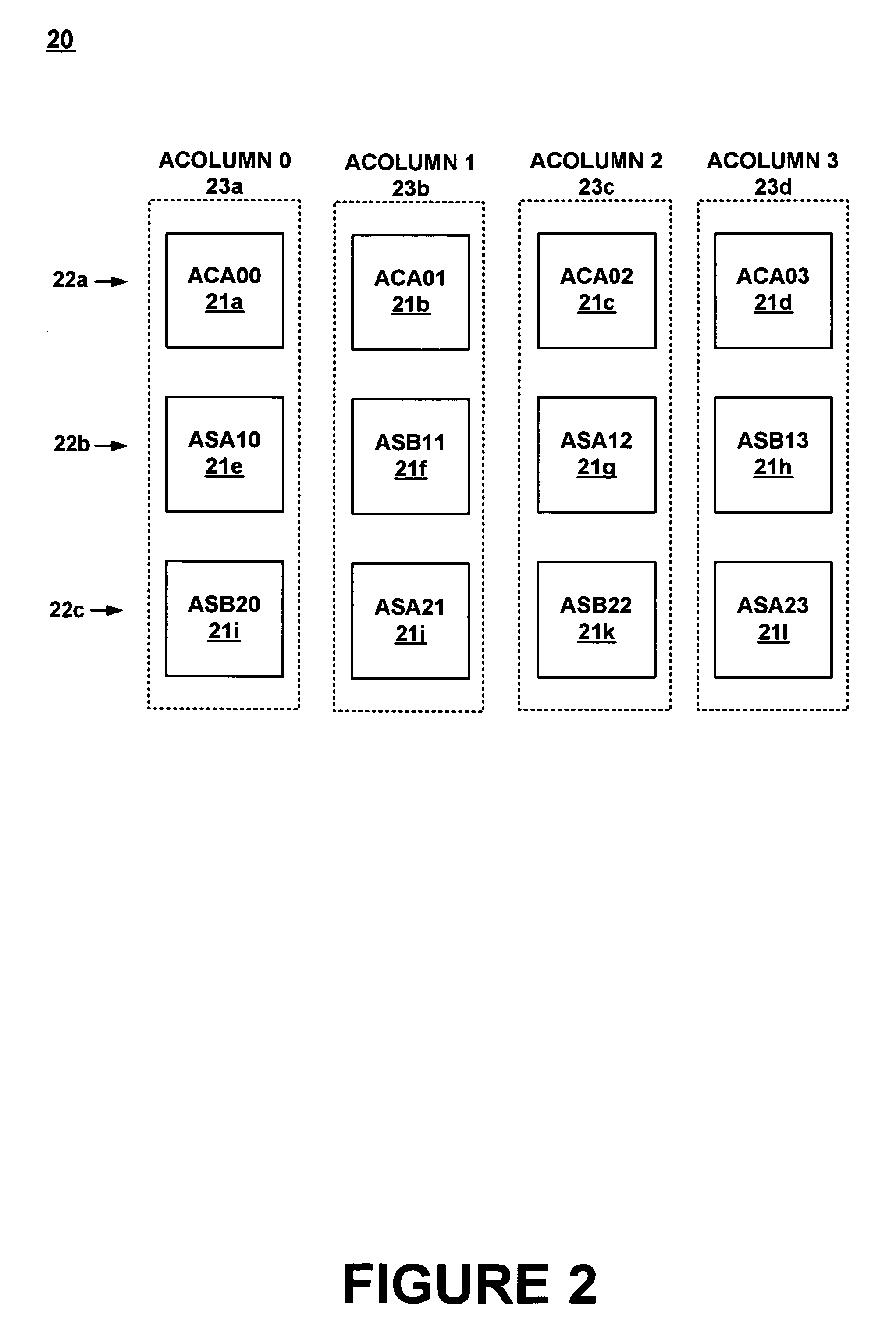
InactiveUS6967511B1Efficiently usLow costComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationA domainComputer science
A method for establishing frequency and phase alignment of clock signals across a domain of analog blocks coupled in a single integrated circuit. Different analog functions are implemented by selectively and electrically coupling different combinations of analog blocks. The analog blocks may be arrayed in a number of columns. A synchronized clock signal is supplied to all of the analog blocks in a combination of blocks, even when the blocks are in different columns. The frequency of the clock signal can be changed dynamically depending on the analog function to be achieved.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
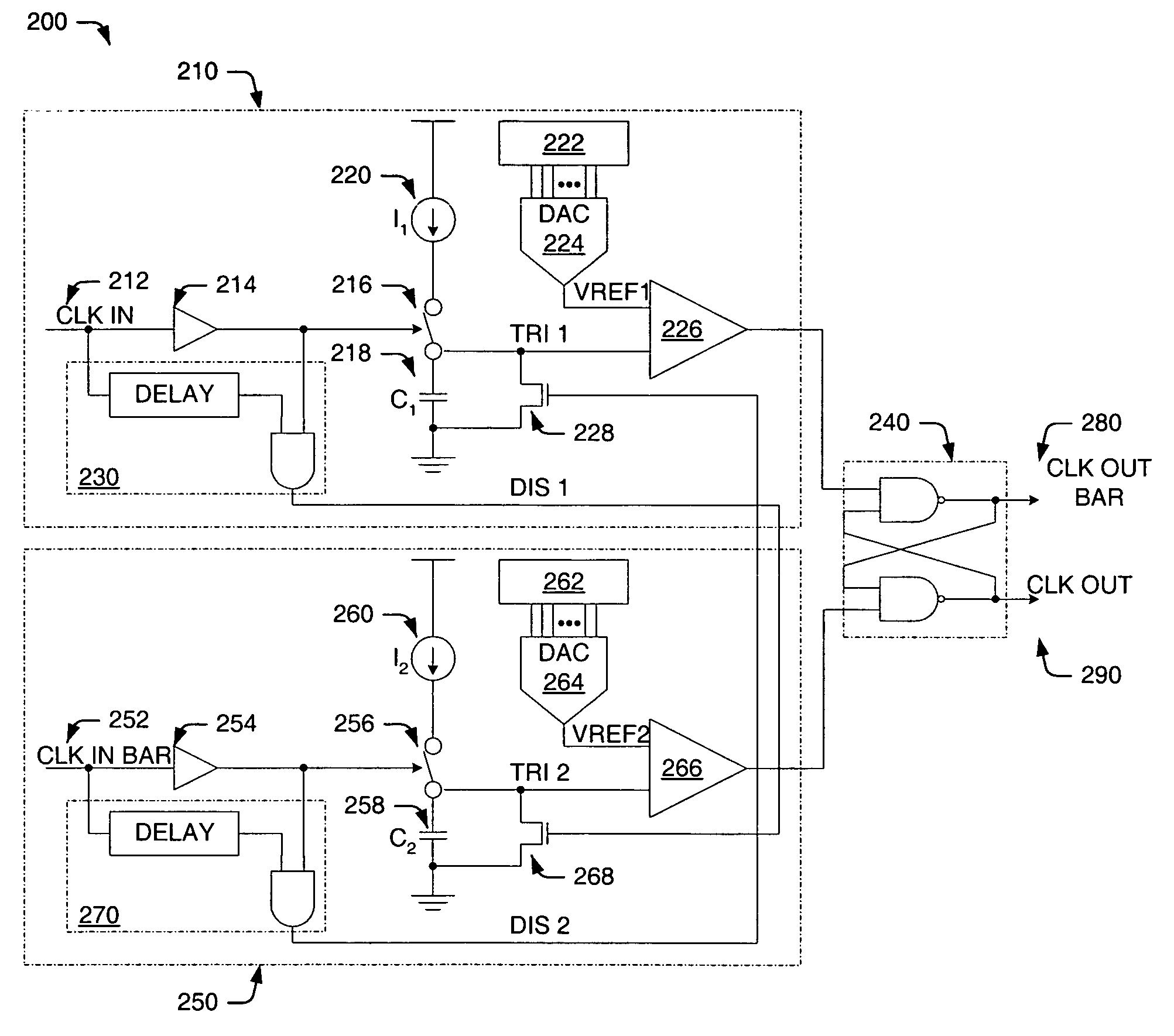
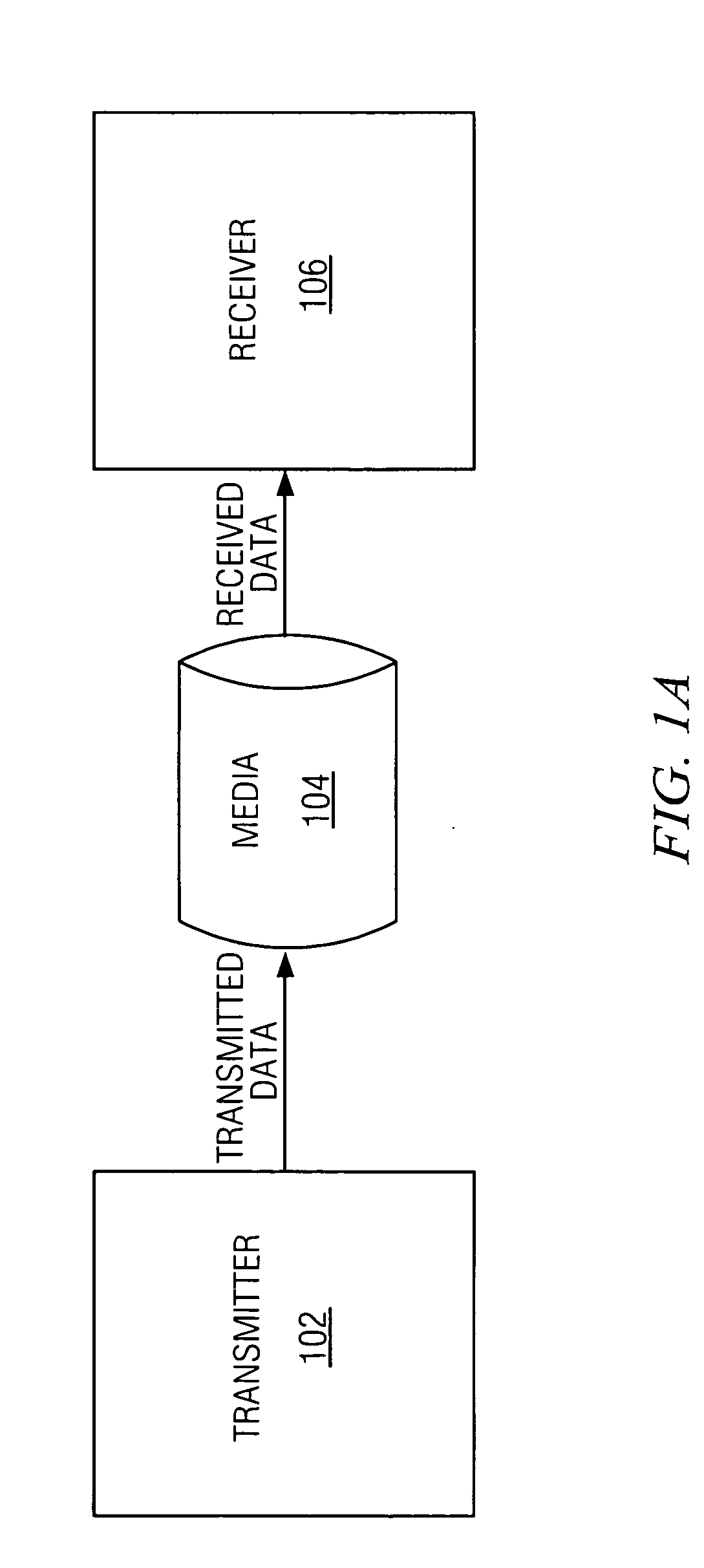
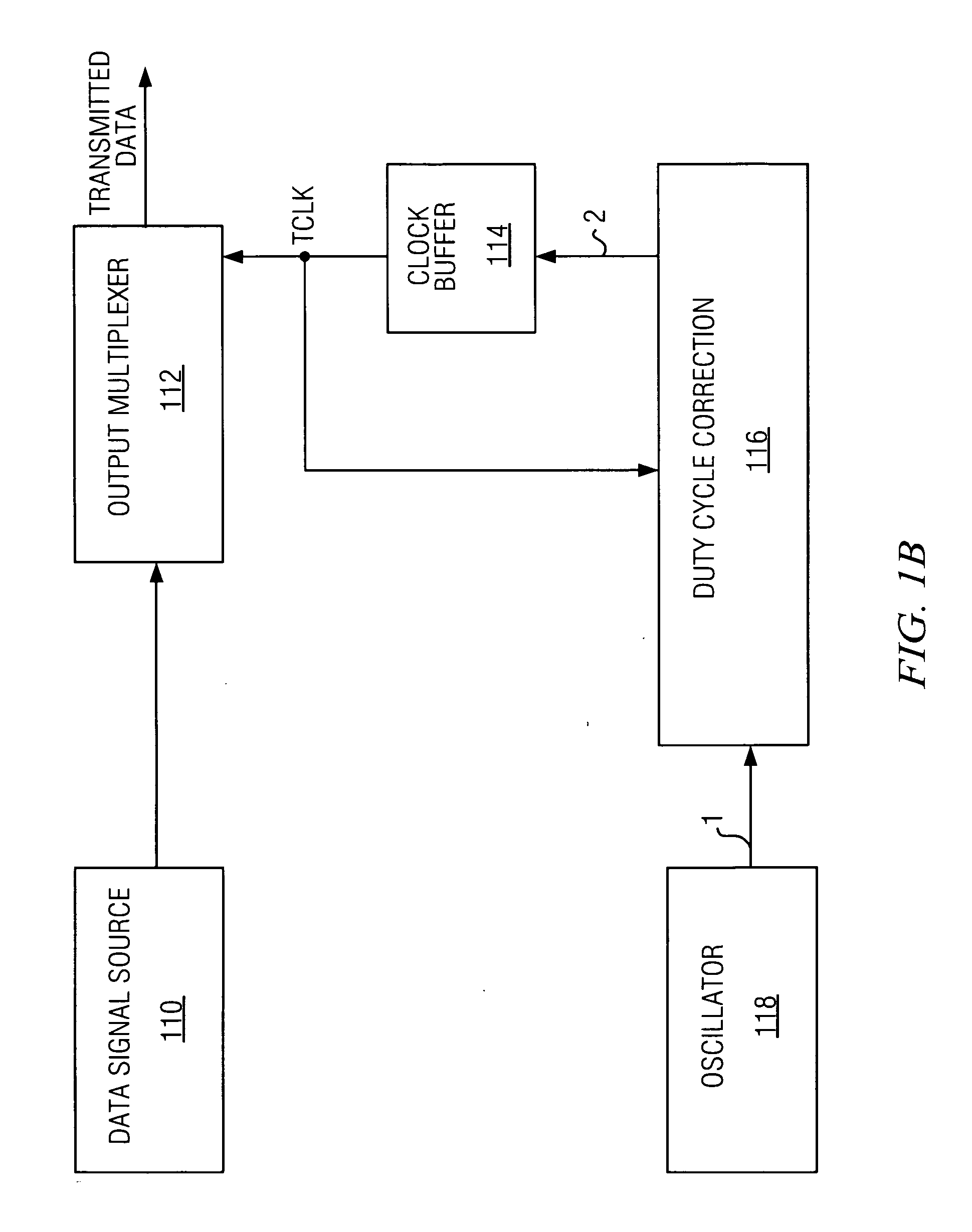
Systems and methods of performing duty cycle control
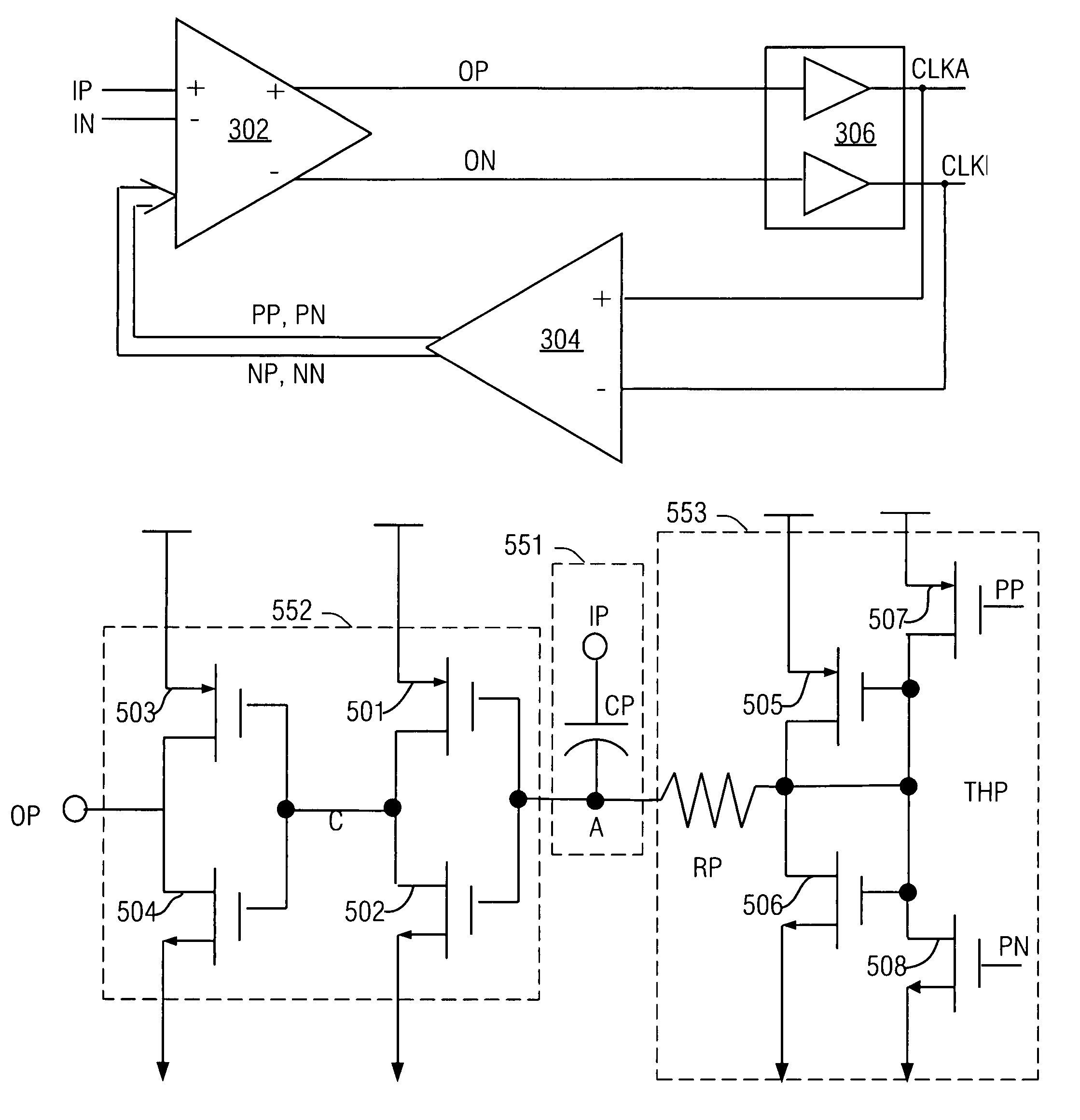
ActiveUS6933759B1Reduce error rateFacilitate communicationContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesMultiplexingCycle control
The present invention facilitates serial communication by performing duty cycle correction. A duty cycle correction component 302 performs duty cycle corrections on a pair of differential sinusoidal signals according to a pair of adjustment signals and, as a result, generates a differential pair of square wave signals. A cross coupled buffer 306 buffers the differential pair of square wave signals and provides the buffered signals to a feedback circuit 304 that measures duty cycles of the signals and generates the pair of adjustment signals accordingly. The buffer 306 can also remove skew from the signals. In a transmitter 102, the buffered signals are also generally provided to a multiplexer 112 or encoder and in a receiver 106, the buffered signals are also generally provided to a sampling component 122.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
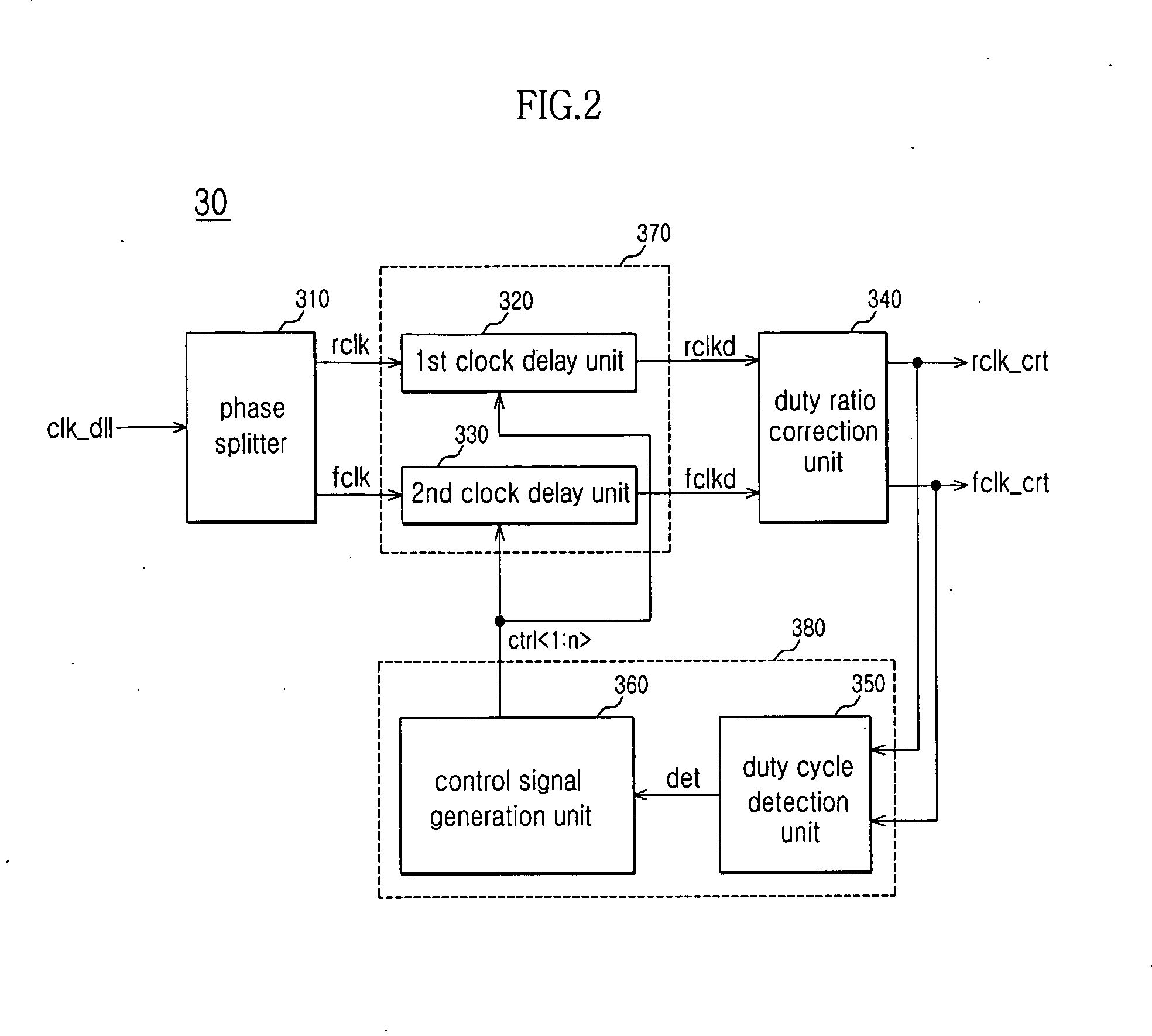
Duty cycle correction circuit and semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus including the same
ActiveUS20090231006A1Improved duty ratio characteristicEasy to integratePulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesIntegrated circuitPhase splitter
A duty cycle correction circuit includes a phase splitter configured to control a phase of a DLL clock signal to generate a rising clock signal and a falling clock signal, a clock delay unit configured to delay the rising clock signal and the falling clock signal in response to control signals to generate a delayed rising clock signal and a delayed falling clock signal, a duty ratio correction unit configured to generate a correction rising clock signal and a correction falling clock signal that toggle in response to an edge timing of the delayed rising clock signal and the delayed falling clock signal, and a delay control unit configured to detect duty cycles of the correction rising clock signal and the correction falling clock signal to generate the control signals.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
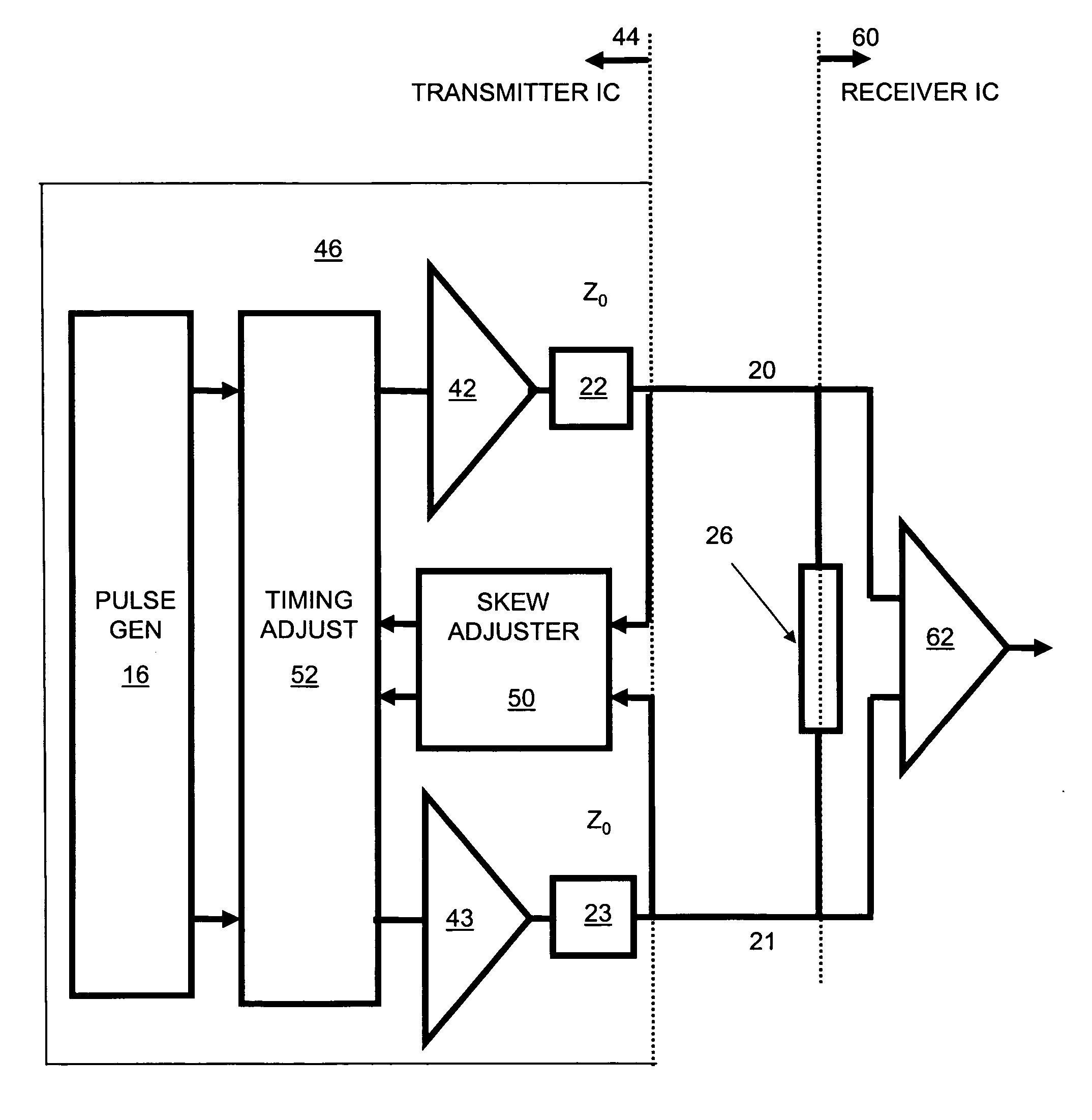
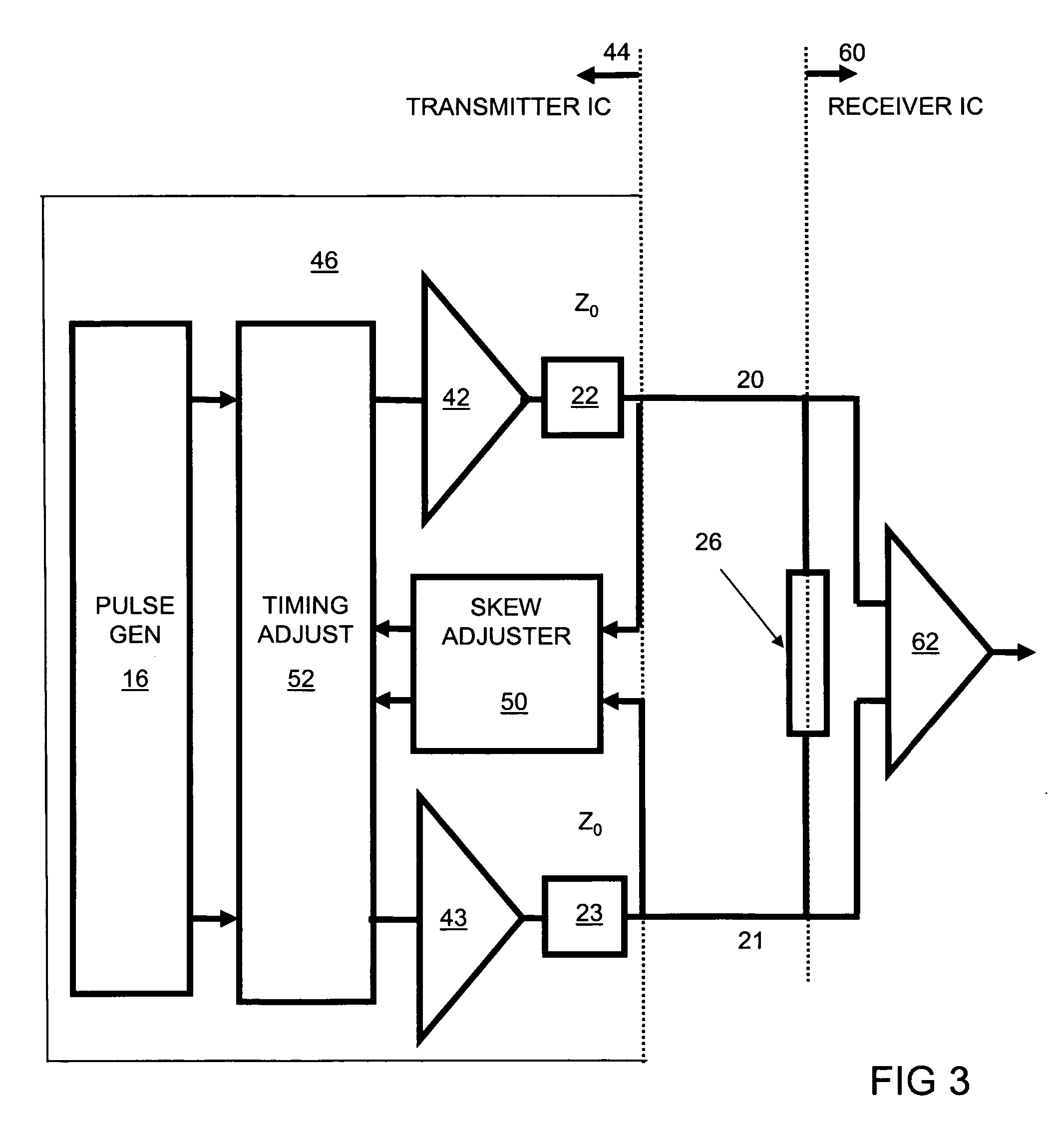
Automatic skew correction for differential signals
InactiveUS20060256880A1Reduce skewReliability increasing modificationsElectrical testingSignal onSignal monitoring
A skew correction system incorporated into a transmitter forwarding a differential signal on a differential lane monitors returning signal reflections when the receiving end of the differential lane is appropriately terminated. Based on an analysis of the reflections, the skew correction system adjusts the relative timing of complementary edges of the differential signal departing the transmitter so as to substantially eliminate skew at the receiving end of the differential lane.
Owner:WARPSPEED CHIPS
Ring oscillator using current mirror inverter stages
InactiveUSRE37124E1Limit maximum frequencyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsLow voltageEngineering
A ring oscillator having an odd number of single ended stages, each stage including two transistors connected as a current mirror. The stage provides for low-voltage performance and improved process tolerance characteristics.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Duty cycle correction circuits suitable for use in delay-locked loops and methods of correcting duty cycles of periodic signals
InactiveUS20050122149A1Pulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationControl signalDelay-locked loop
Delay-locked loop integrated circuits include a duty cycle correction circuit. This duty cycle correction circuit generates at least one output clock signal having a substantially uniform duty cycle in response to at least one input clock signal having a non-uniform duty cycle. The duty cycle correction circuit is also responsive to a standby control signal that synchronizes timing of power-saving duty cycle update operations within the duty cycle correction circuit. These update operations reset the set point of the correction circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods of performing duty cycle control
ActiveUS20050174156A1Facilitates serial communicationReduce error rateContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesMultiplexingSquare waveform
The present invention facilitates serial communication by performing duty cycle correction. A duty cycle correction component 302 performs duty cycle corrections on a pair of differential sinusoidal signals according to a pair of adjustment signals and, as a result, generates a differential pair of square wave signals. A cross coupled buffer 306 buffers the differential pair of square wave signals and provides the buffered signals to a feedback circuit 304 that measures duty cycles of the signals and generates the pair of adjustment signals accordingly. The buffer 306 can also remove skew from the signals. In a transmitter 102, the buffered signals are also generally provided to a multiplexer 112 or encoder and in a receiver 106, the buffered signals are also generally provided to a sampling component 122.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Phase interpolator and receiver for adjusting clock phases into data phases
InactiveUS6900681B2Pulse automatic controlContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationIntegratorEngineering
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
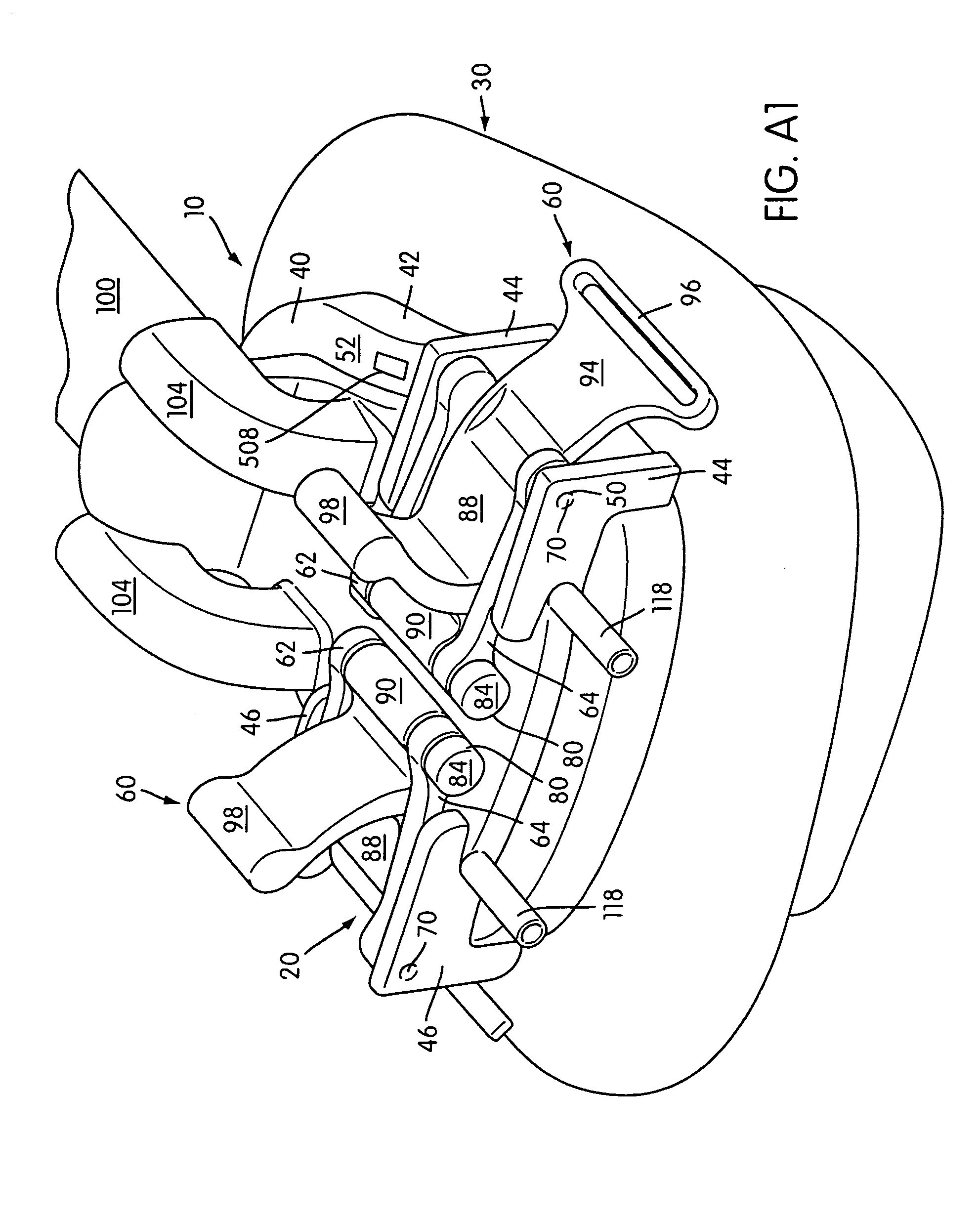
Mask assembly
InactiveUS20050081858A1Not create excessive forceRespiratory masksBreathing masksPositive airway pressureHermetic seal
A respiratory mask assembly for use in the delivery of non-invasive positive airway pressure to a user. The assembly includes a rigid shell having a channel portion defined by an inner wall, an outer wall and a channel floor, a face-contacting cushion acting to space the shell away from the user's face and a sealing tab extending from the cushion to engage a portion of the shell to provide a continuous airtight seal between the cushion and the shell. A retaining ring within the mask assembly is configured to secure the cushion to the shell. The retaining ring has a first portion including at least one clip configured to pass through at least one slot portion such that an underside surface of the at least one clip engages a section of the shell when the retaining ring is positioned within the channel.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Phase-combining circuit and timing signal generator circuit for carrying out a high-speed signal transmission
InactiveUS20090179674A1Simple structureError minimizationAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsControl signalEngineering
A phase-combining circuit for combining cyclic timing waveforms that have been phase-controlled by control signals based on three or more input signals of different phases, has a weight signal generating circuit and a weighting circuit. The weight signal generating circuit generates weights according to the control signals, and the weighting circuit gives the weights to the respective input signals, with a positive or negative polarity for each one signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
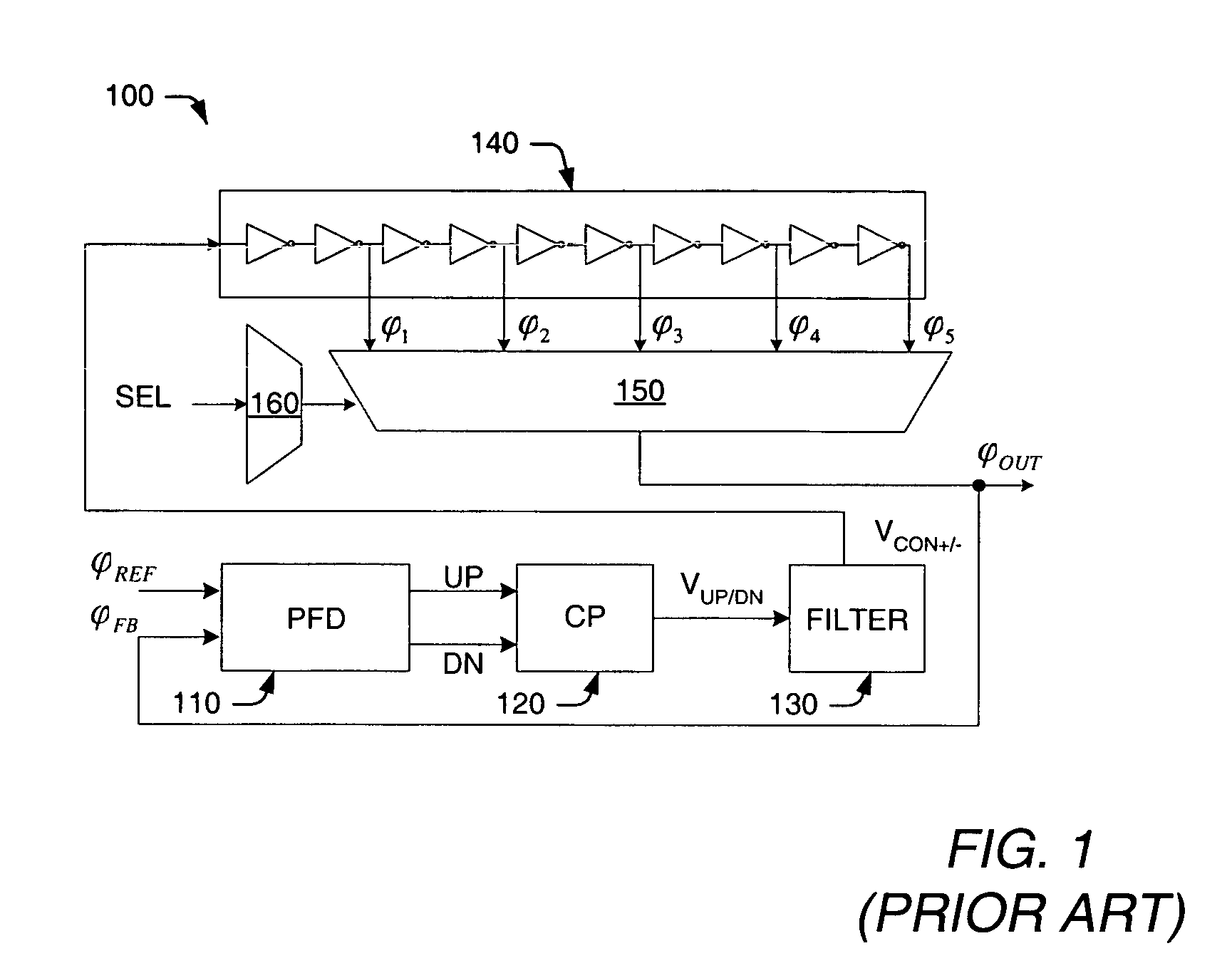
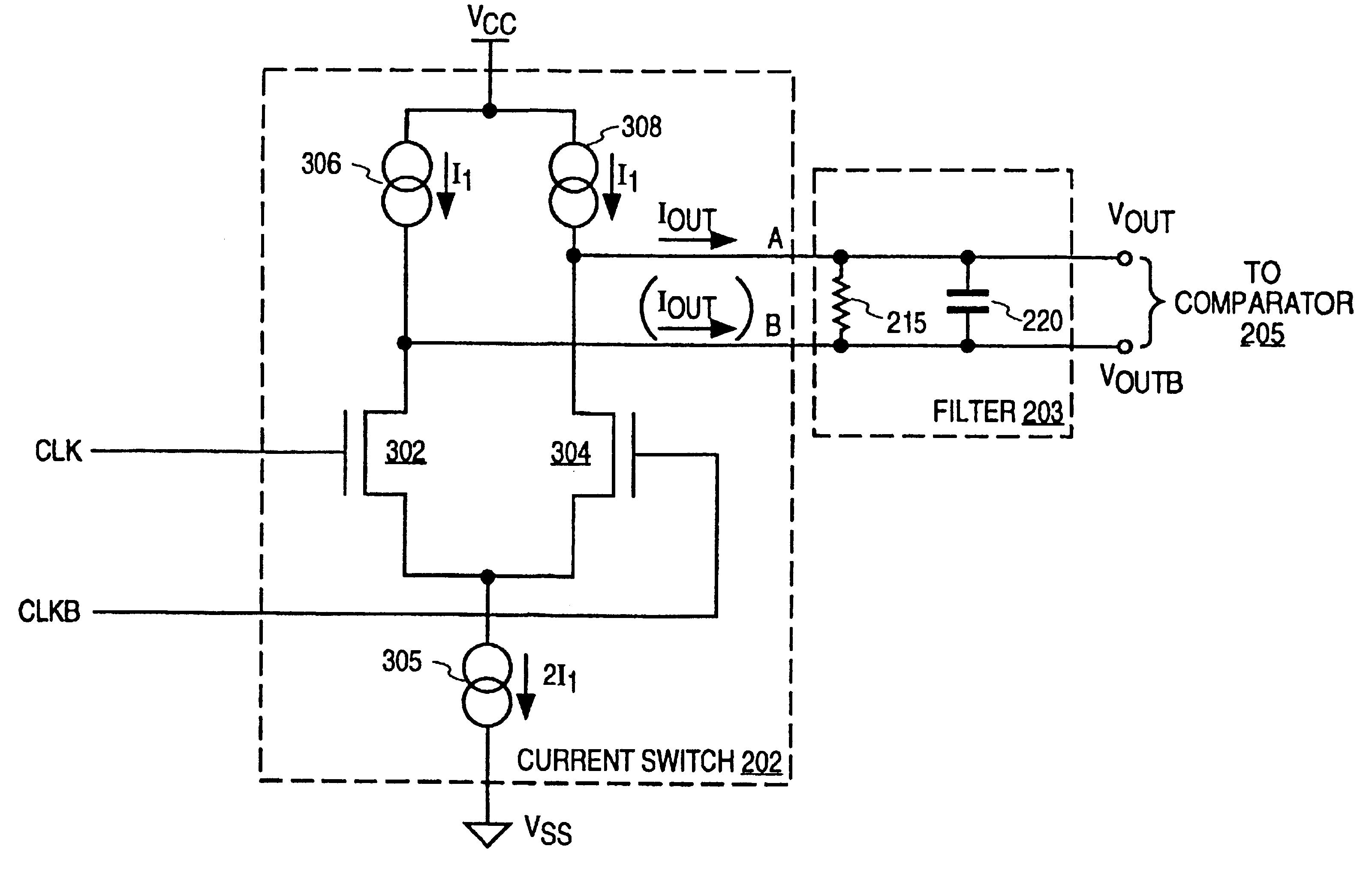
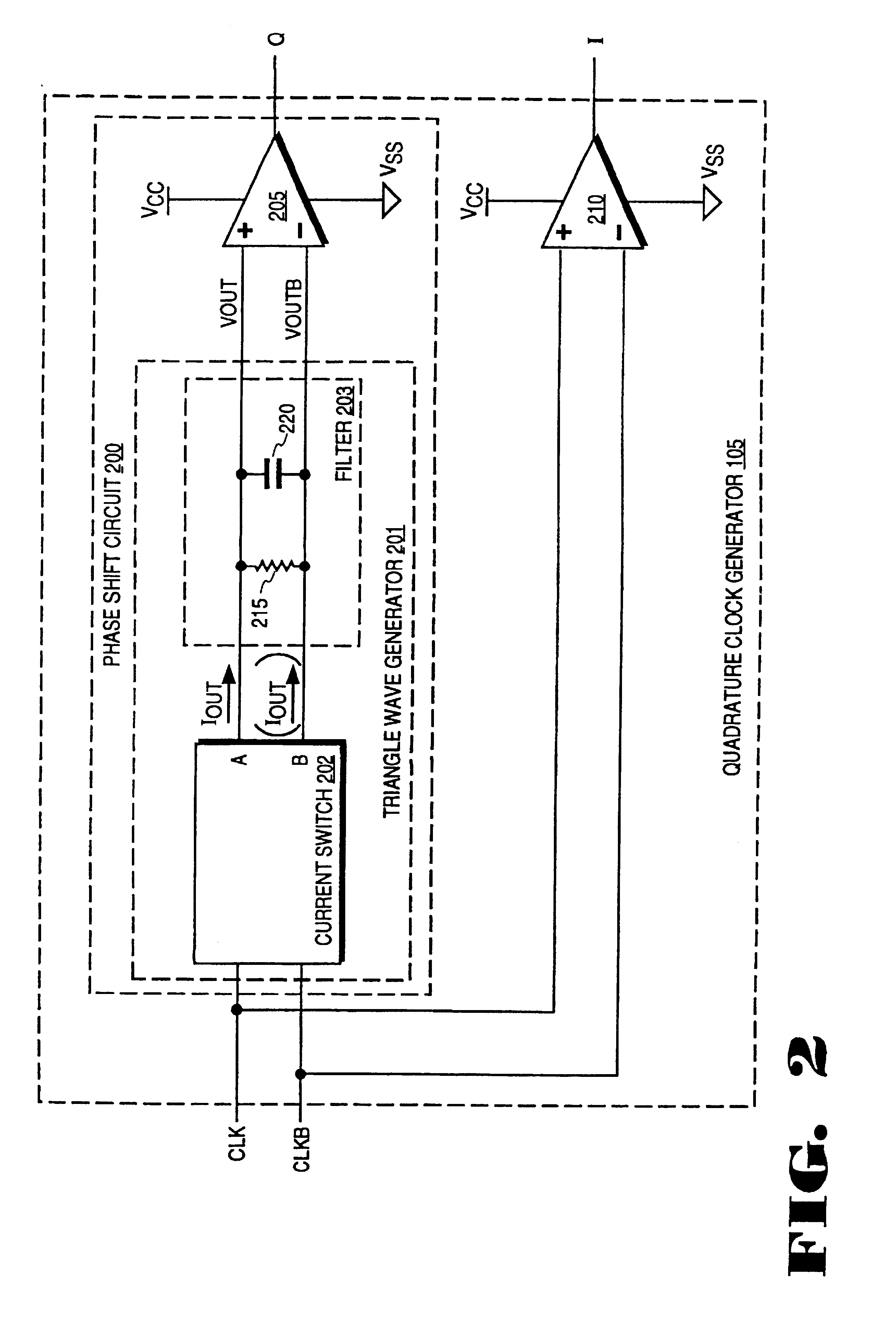
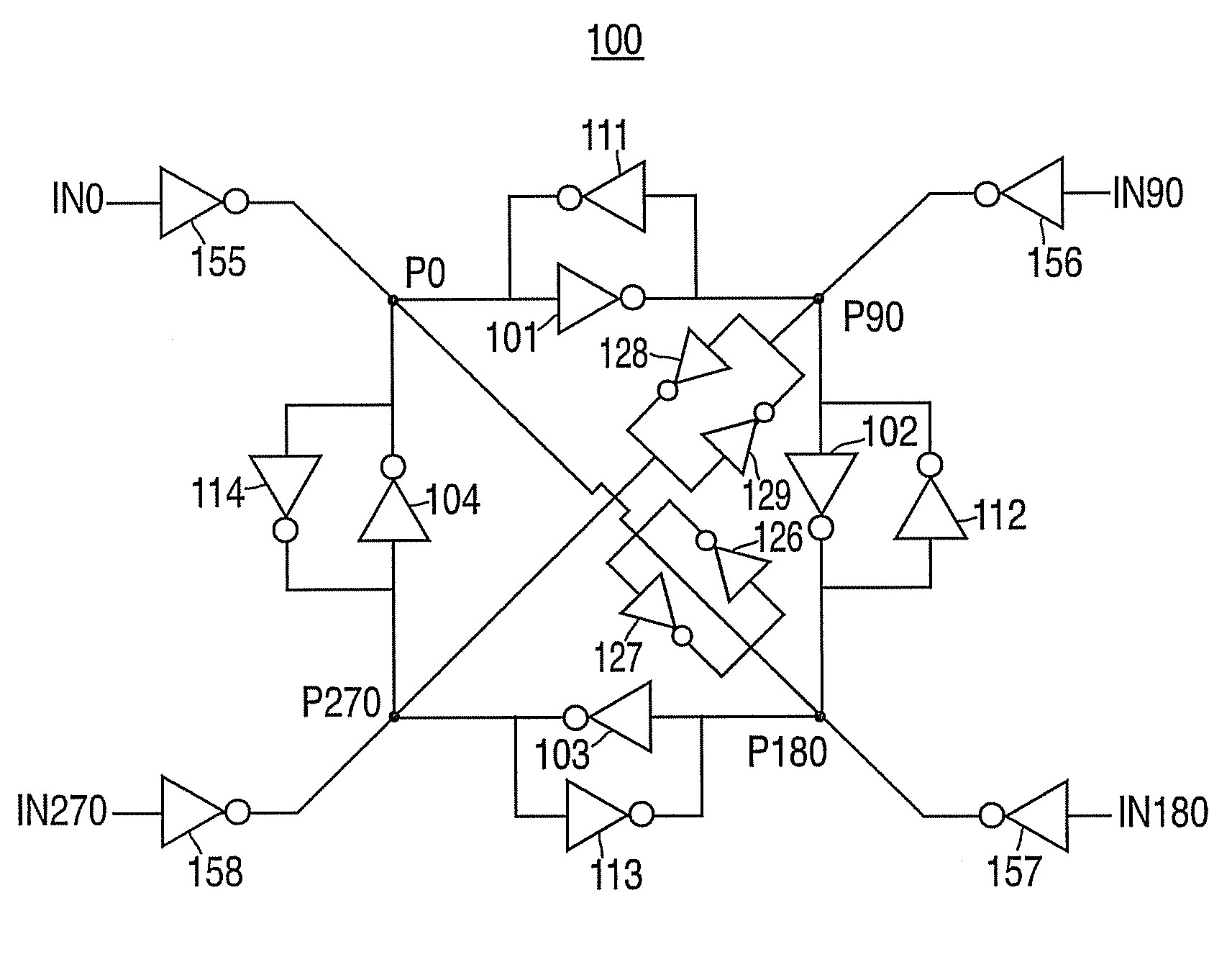
At frequency phase shifting circuit for use in a quadrature clock generator
InactiveUSRE37452E1Enhance the shake effectComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationPhase shiftedClock generator
A phase shifting circuit that may be used as part of a quadrature clock generator. The phase shifting circuit comprises a triangle wave generator coupled to receive an input reference signal. The triangle wave generator outputs a pair of complementary triangle wave signals in response to the input reference signal. A comparator having a pair of inputs is coupled to receive the pair of complementary triangle wave signals. The comparator outputs an output signal having a predetermined phase relationship with the input reference signal in response to a comparison between the pair of complementary triangle wave signals.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
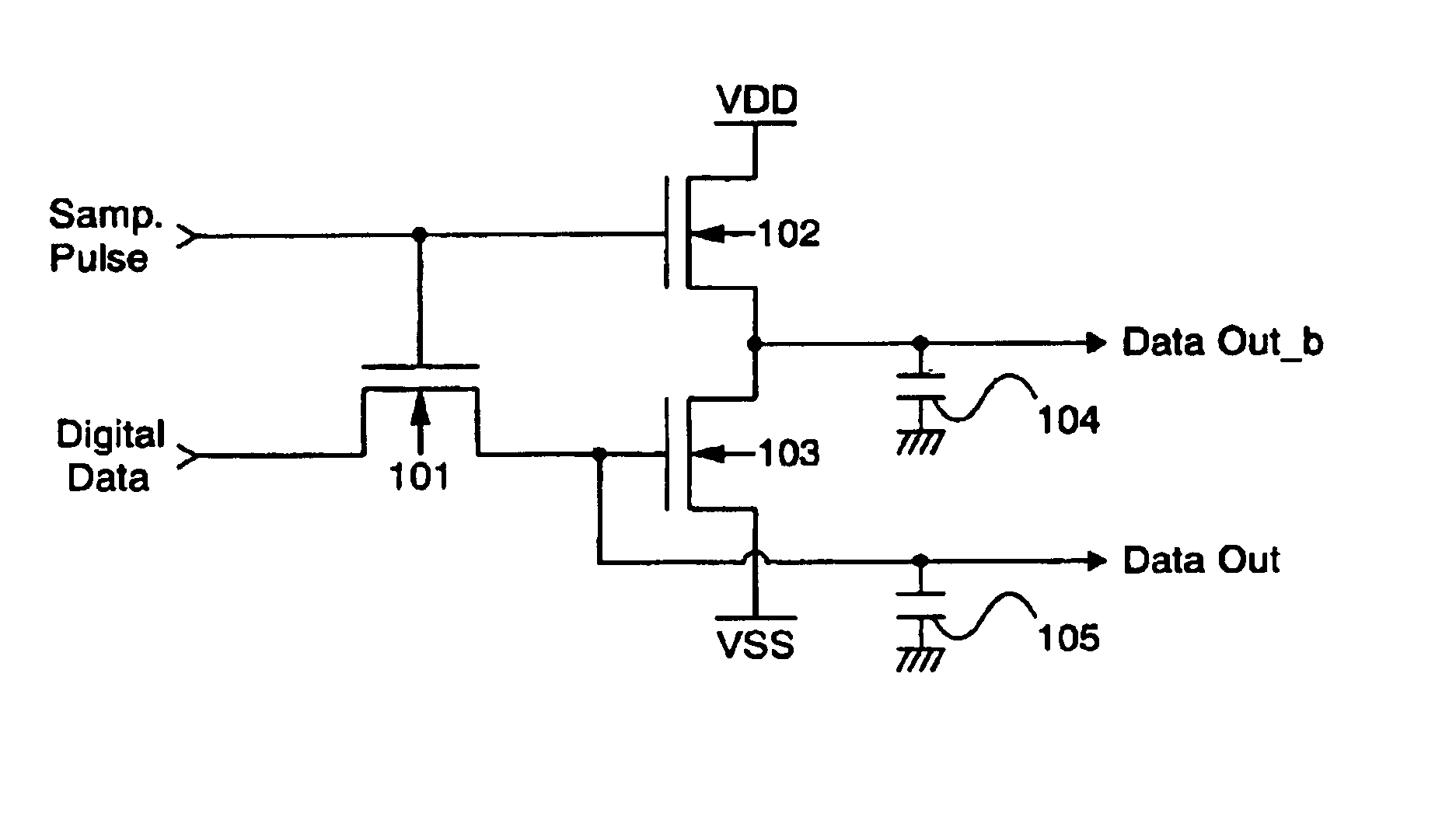
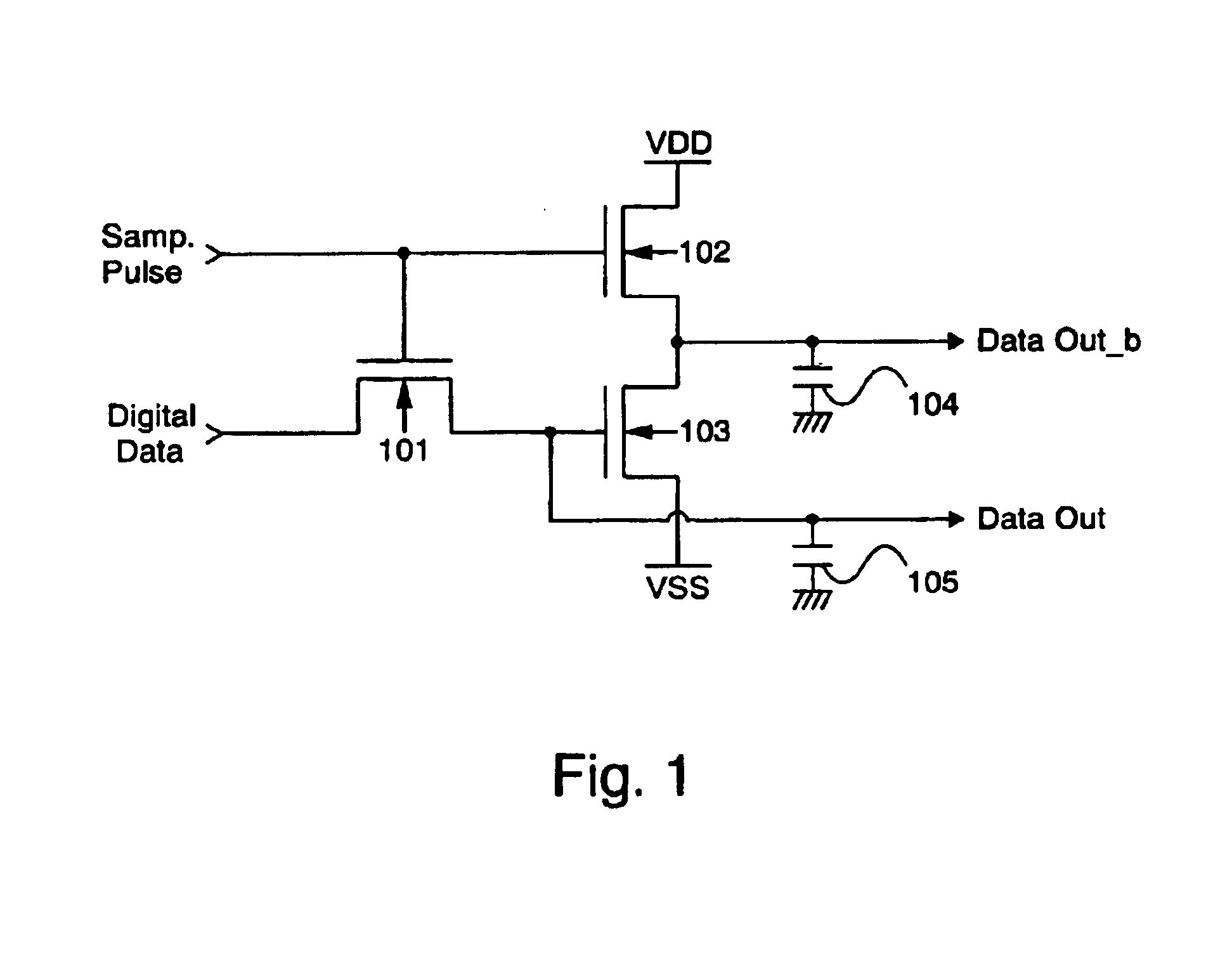
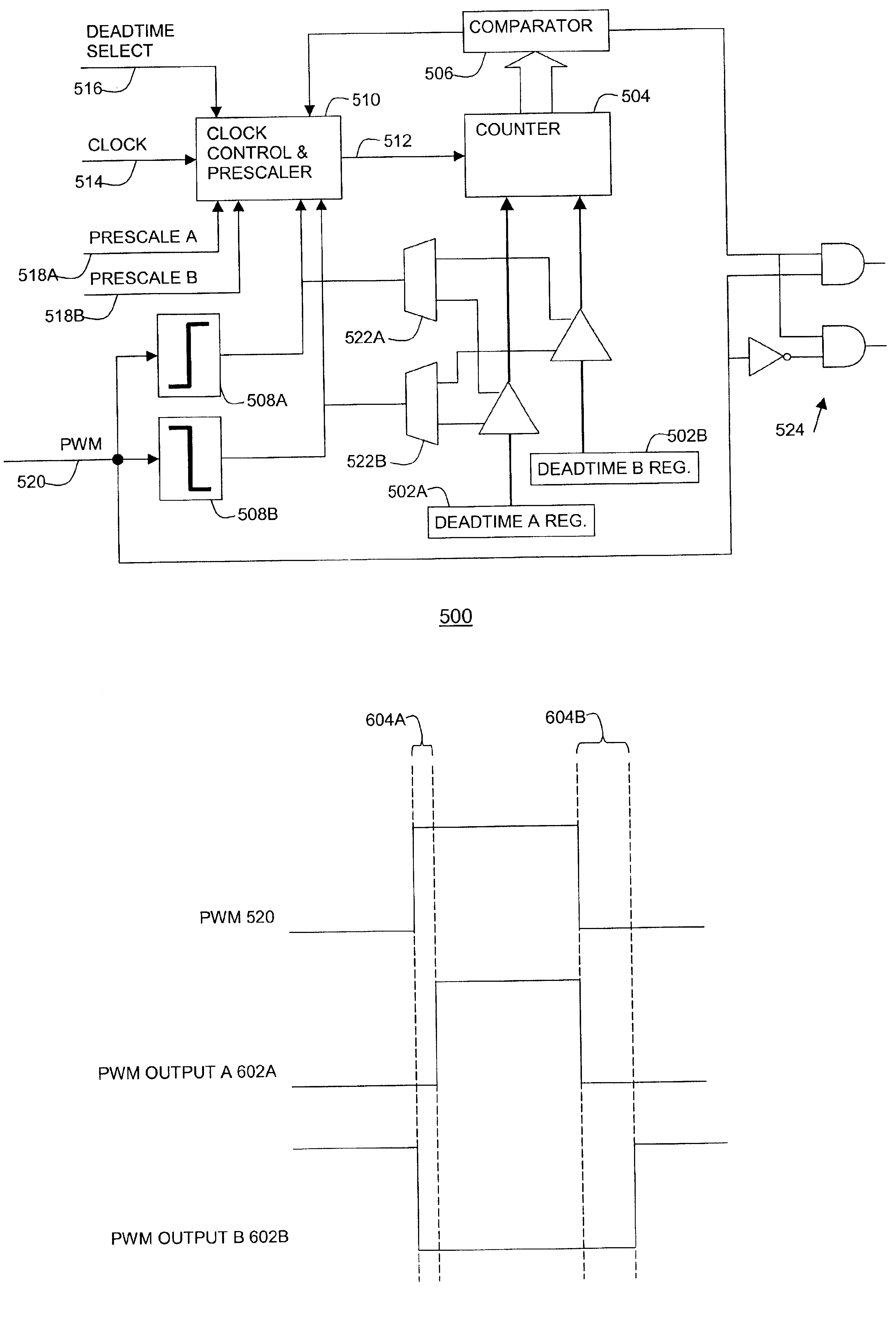
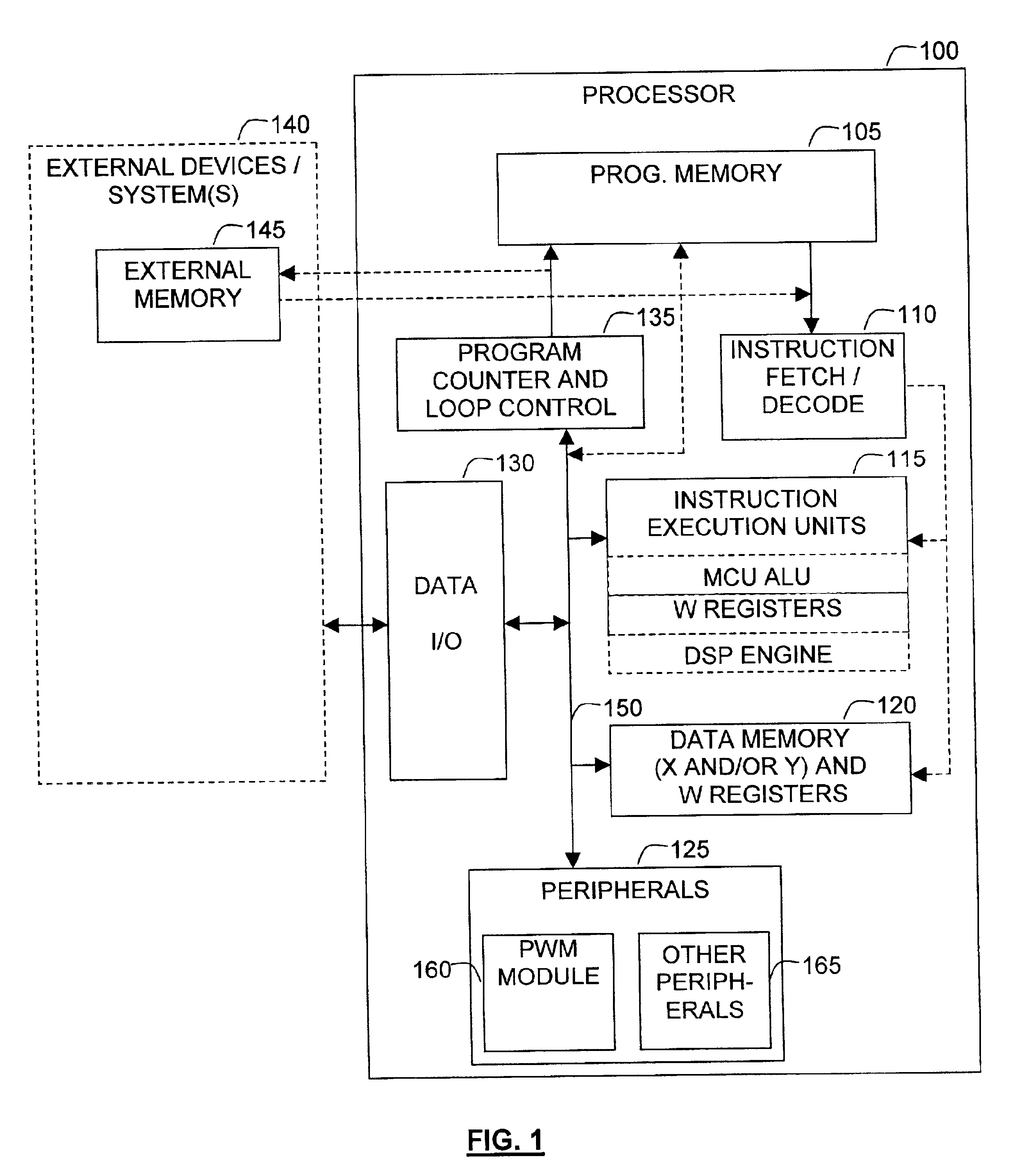
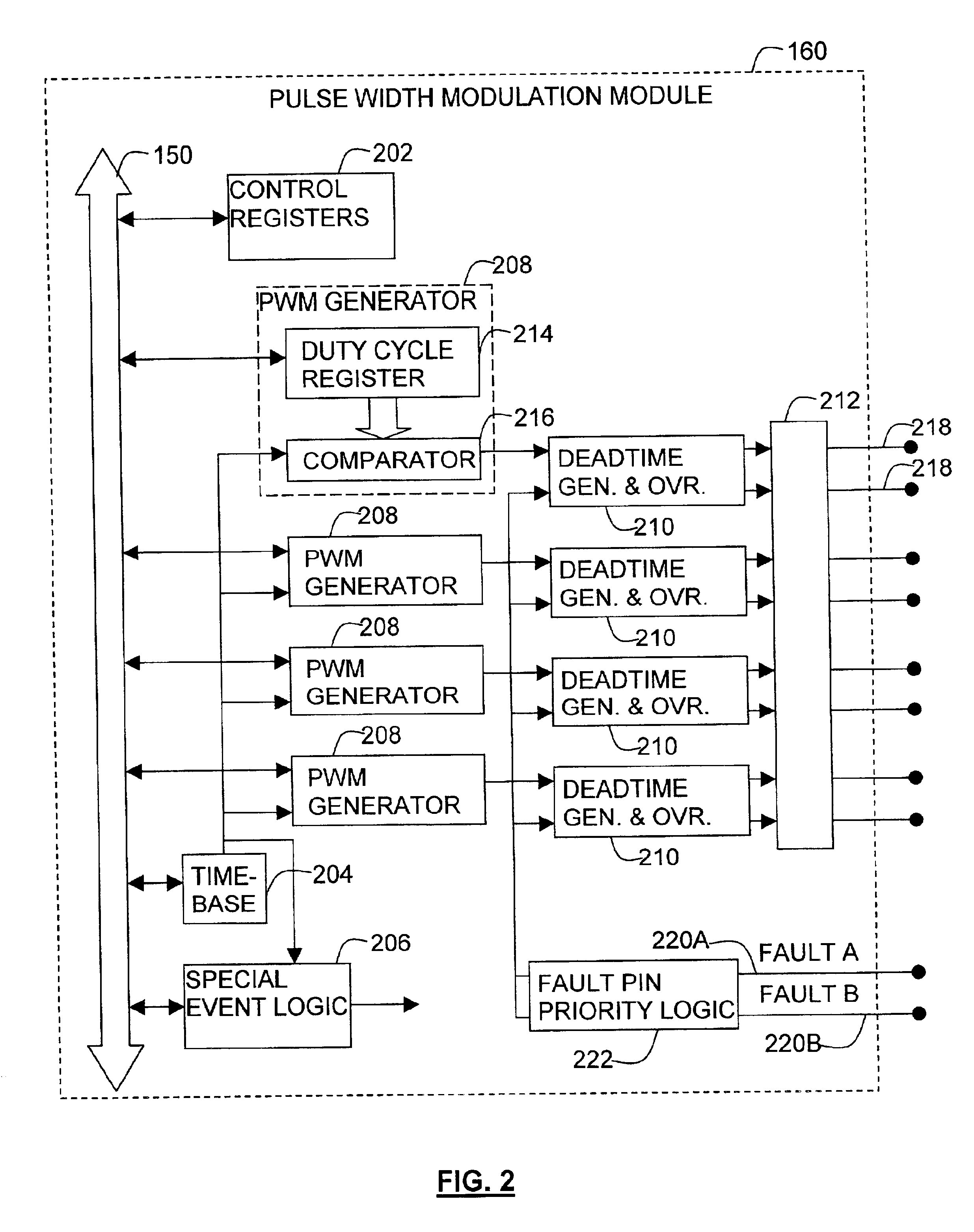
Processor with dual-deadtime pulse width modulation generator
ActiveUS6937084B2Easy to handleGeneral purpose stored program computerElectronic switchingNon symmetricEngineering
A processor that has pulse width modulation generation circuitry that provides an improved ability to deal with the less than perfect switching characteristics of external switching devices that are connected to PWM hardware included in a processor. Complementary PWM output signals have dual deadtime delay in which the delay between the inactivation of the first signal and the activation of the second signal may be different than the delay between the inactivation of the second signal and the activation of the first signal. This provides an improved capability to deal with non-symmetric switching characteristics of the external switching devices, and the circuitry to which they are connected. The dual deadtime pulse width modulation generator for a processor includes deadtime generation circuitry operable to generate a first pulse width modulated signal and a second pulse width modulated signal complementary to the first pulse width modulated signal, wherein there is a first delay between inactivation of the first pulse width modulated signal and activation of the second pulse width modulated signal, a second delay between inactivation of the second pulse width modulated signal and activation of the first pulse width modulated signal, and the first and second delays are not equal. The first delay and the second delay may be independently settable.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
System and method for reducing skew in complementary signals that can be used to synchronously clock a double data rate output
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Complementary signal generator
InactiveUS20050017781A1Single output arrangementsManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesState variationSignal generator
A complementary signal generator, for outputting complementary positive-phase and antiphase signals that vary between a first logical value and a second logical value, which includes a signal forming unit for outputting a positive-phase intermediate signal being in phase with an input signal varying between the first logical value and the second logical value, and an antiphase intermediate signal antiphase to the input signal. The generator also includes a first connecting means for simultaneously transferring the second logical value of the positive-phase intermediate signal and the first logical value of the antiphase intermediate signal to a positive-phase signal output part and an antiphase signal output part in synchronism with a state change of the input signal from the first logical value to the second logical value.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
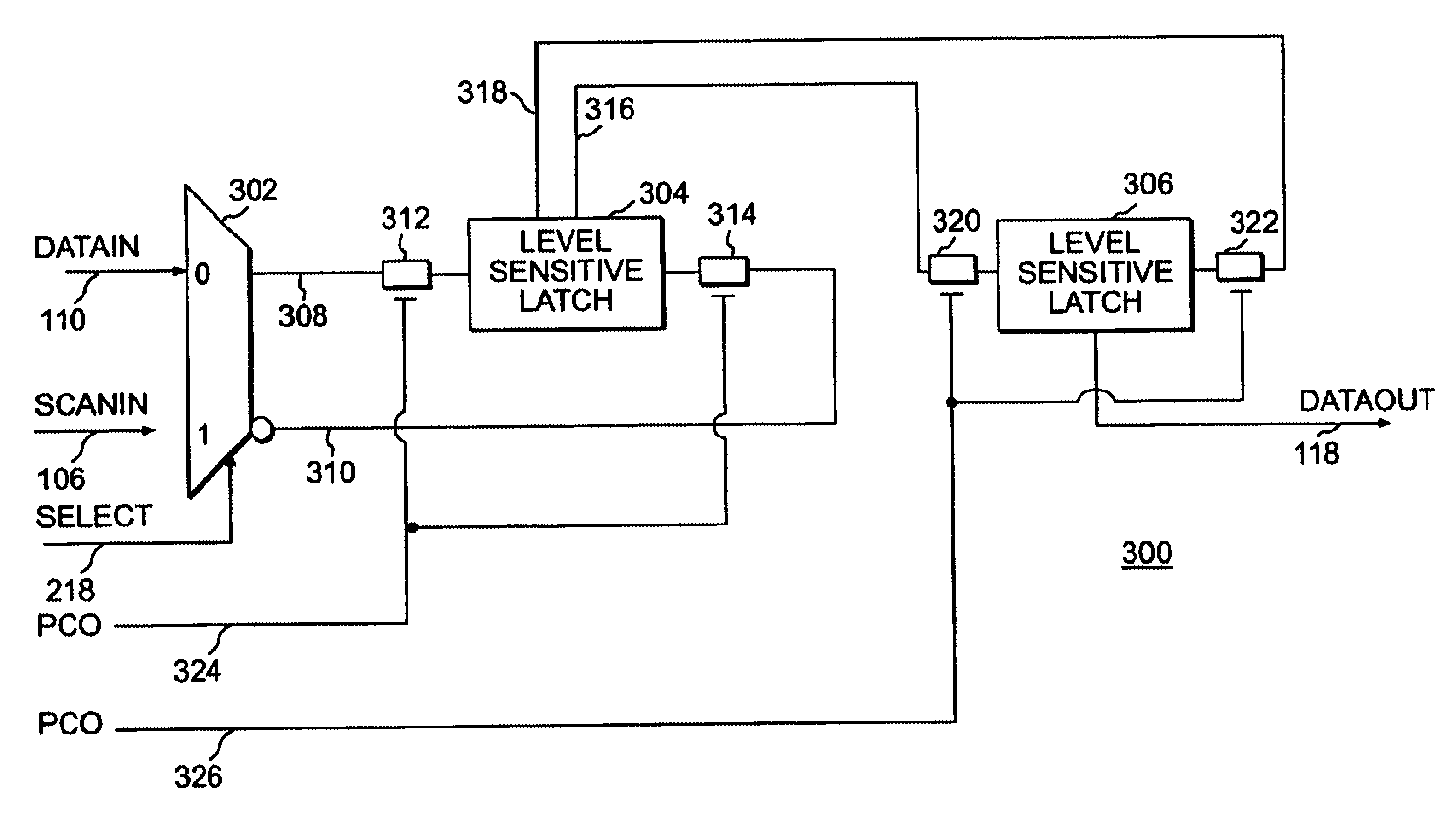
Method and apparatus for a scannable hybrid flip flop
InactiveUS6629276B1Reliability increasing modificationsPulse automatic controlMultiplexerProcessor register
A scannable flip flop for space-based LSSD testable integrated circuits. A scannable register can be formed from the scannable flip flops. The scannable flip flops can be radiation hardened. Each scannable flip flop can include a 2:1 input multiplexer, a first latch and a second latch. The input multiplexer is coupled to the first latch by a pair of pass gates. The pass gates are gated by a first clock input signal. A second pass gate pair couples the first latch to the second latch. A second clock input signal gates the second pass gate pair. The first and second clock input signals are non-overlapping. The latch can be employed in edge triggered logic ECAD tools for designing IC. The resulting IC logic can be tested using LSSD test testing techniques and patterns.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
System for providing open-loop quadrature clock generation
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Automatic skew correction for differential signals
A skew correction system incorporated into a transmitter forwarding a differential signal on a differential lane monitors returning signal reflections when the receiving end of the differential lane is appropriately terminated. Based on an analysis of the reflections, the skew correction system adjusts the relative timing of complementary edges of the differential signal departing the transmitter so as to substantially eliminate skew at the receiving end of the differential lane.
Owner:WARPSPEED CHIPS
Buffer circuit, buffer tree, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS6933750B2Reduce latencyPower reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceControl circuit
A buffer circuit includes first and second transistors which are connected in series between first and second power supplies and which are controlled to be on / off based on values of signals at their control terminals are provided, in which a connection point between the two transistors is connected to an output terminal (OUT) and a control terminal of the first transistor is connected to an input terminal (IN), and a control circuit for performing on / off control over the second transistor based on an input signal from the input terminal (IN). The control circuit performs control so that when the input signal is at a second logic level corresponding to the second power supply, the second transistor is turned off, when the input signal goes to a first logic level corresponding to the first power supply, the second transistor is turned on to cause the output terminal (OUT) to a second power supply voltage, next, when the second transistor is turned off and then the input signal undergoes a transition from the first logic level to the second logic level and the first transistor switches from off to on, with the second transistor being kept off. A flip-flop is connected to the output terminal (OUT).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
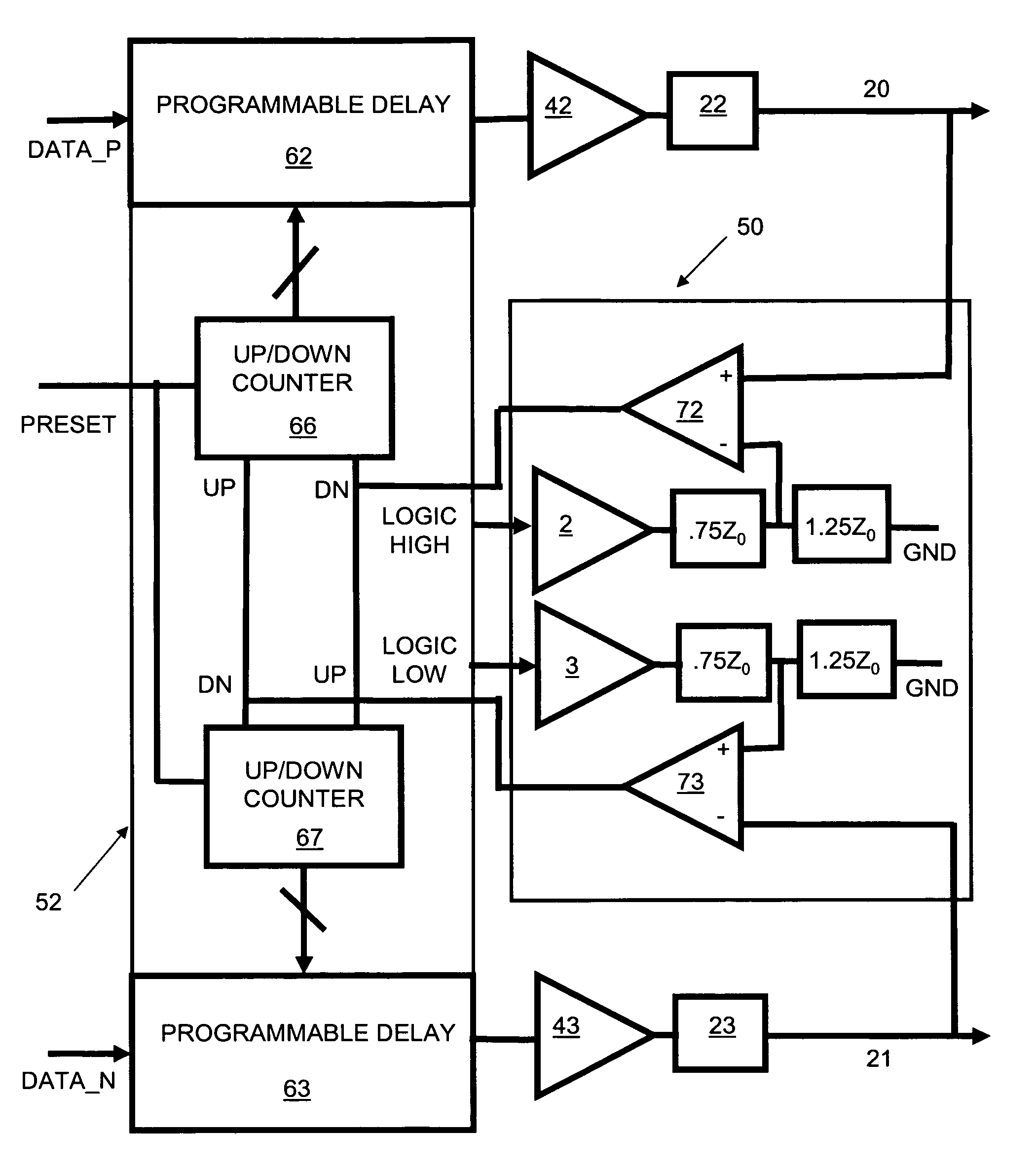
Pulse-width control loop for clock with pulse-width ratio within wide range
InactiveUS20070146025A1Accelerating modulating speedSimple designPulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesInput controlWidth ratio
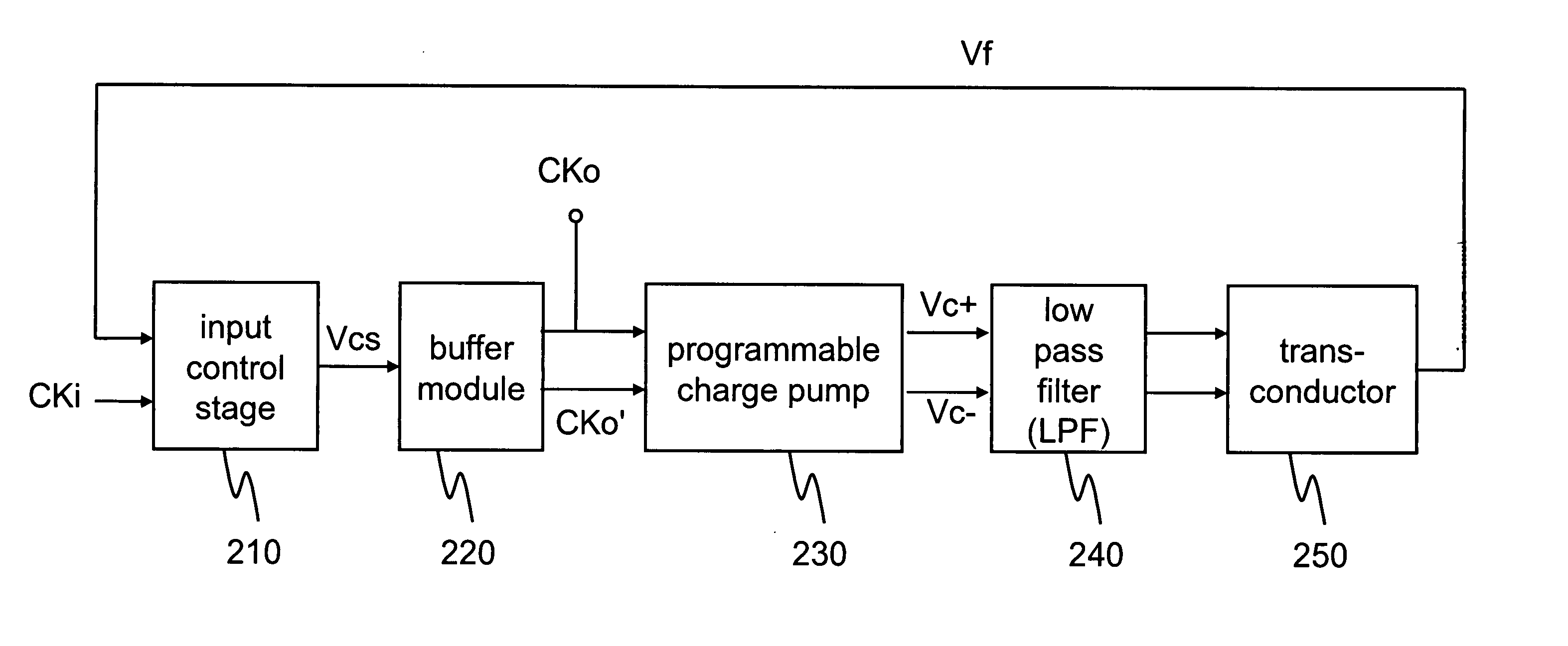
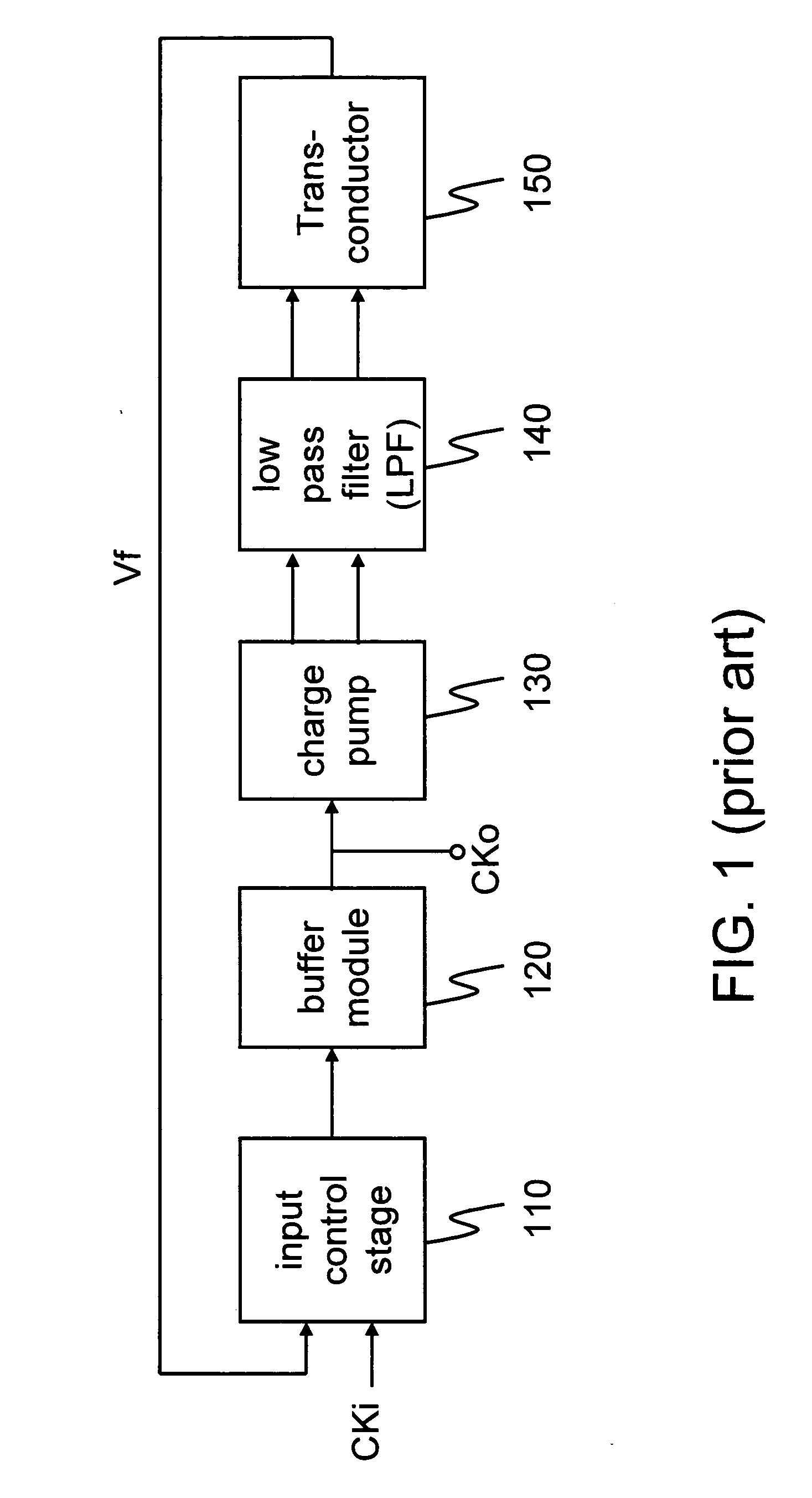
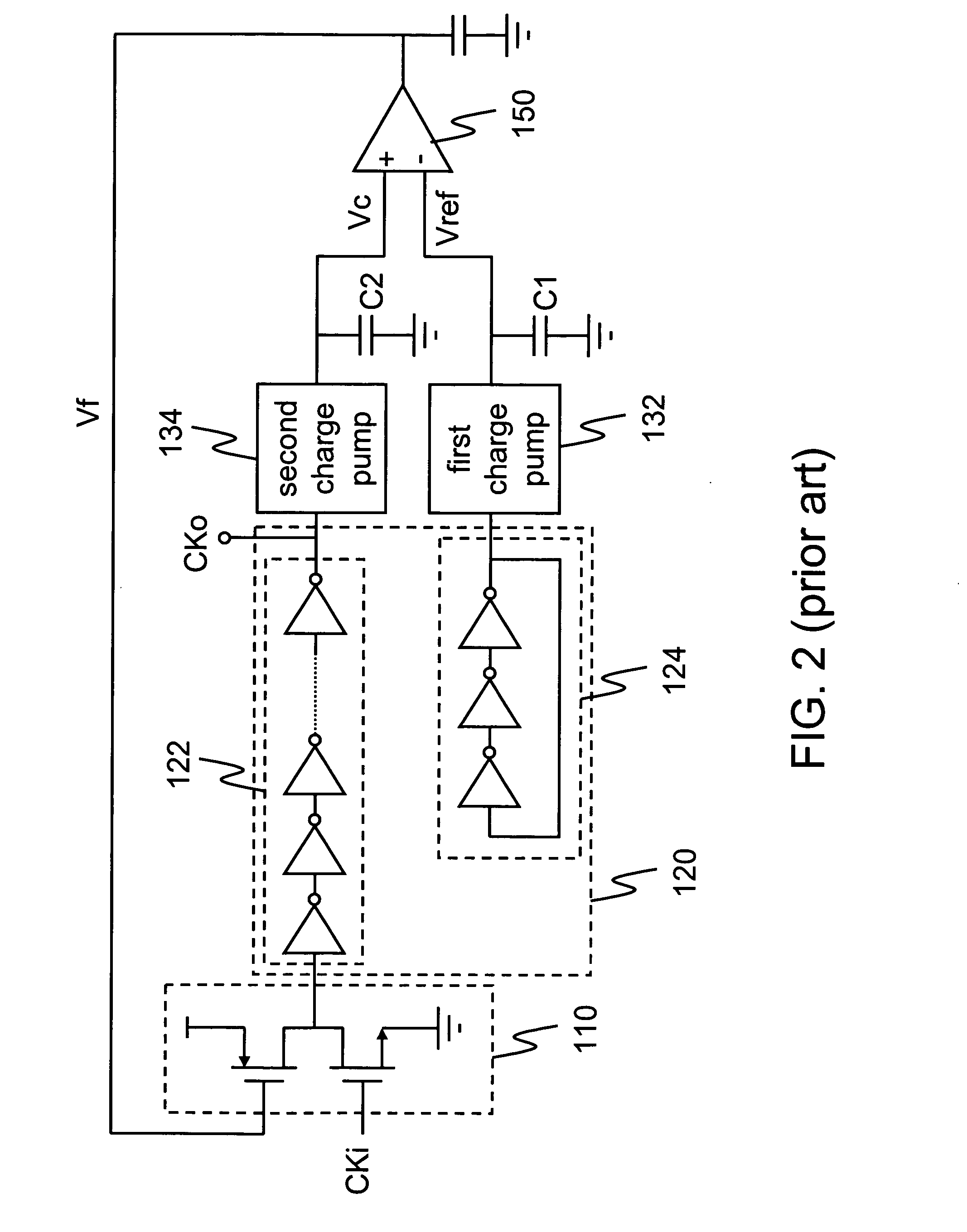
A pulse-width control loop (PWCL) for clock with any pulse-width ratio within a wide range is provided. A differential programmable charge pump is employed to stabilize the current source by complementary connection. The differential programmable charge pump has a pair of differential charge pumps and a current source module to adjust the ratio of charge to discharge, so as to accelerate the range of the adjustable pulse-width ratio of the output clock and increase the output resolution. Further, a ratioless input control stage is employed to simplify the circuit design and avoid static power consumption. Moreover, the control stage adjusts rising pulse width and dropping pulse width at one period, thereby accelerating the lock speed and the range of the adjustable pulse-width ratio (i.e., duty cycle) of the input clock.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
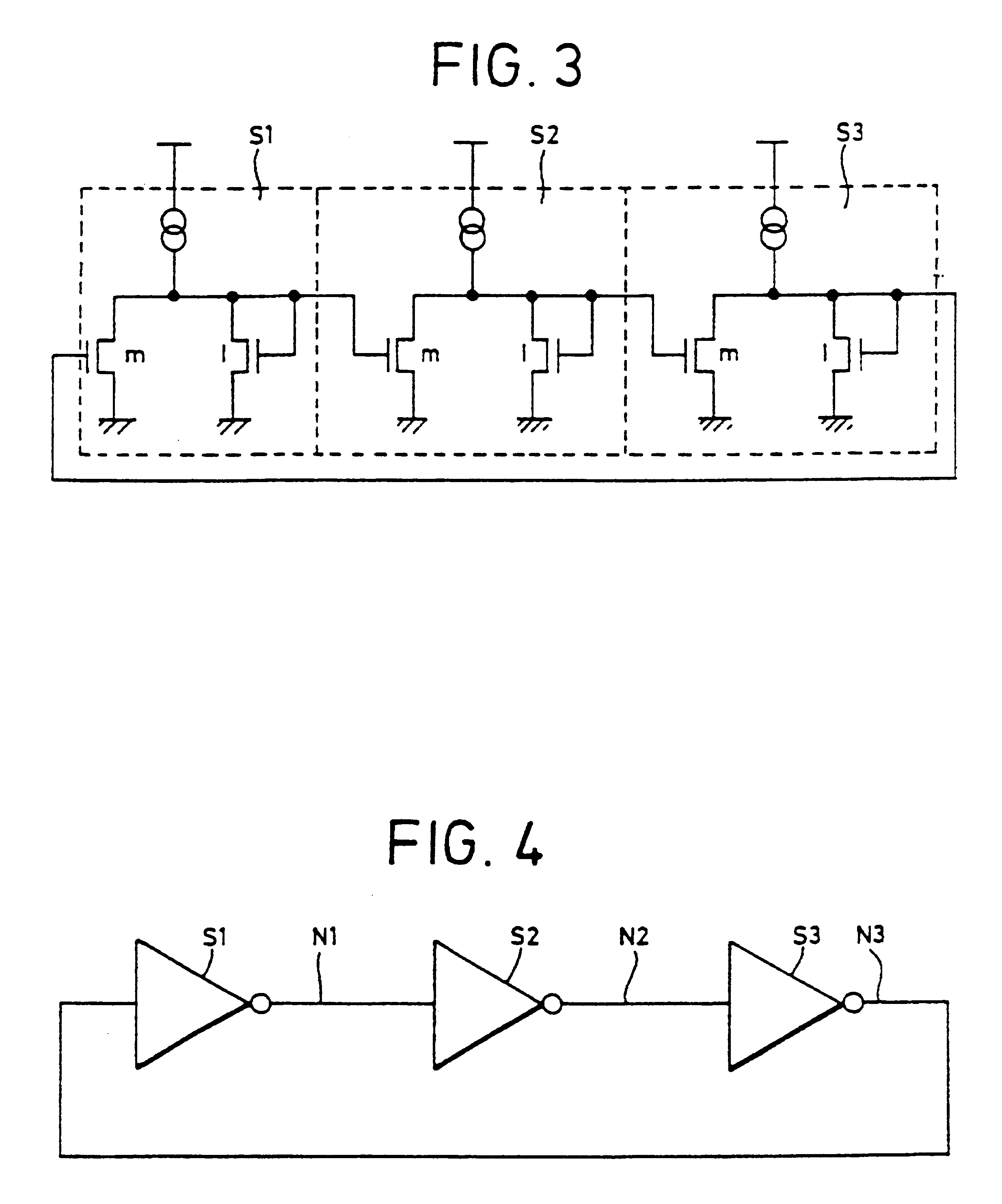
Clock generation circuit and method of generating clock signals
InactiveUS20070090867A1Shorten the timePulse automatic controlManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesInverterHemt circuits
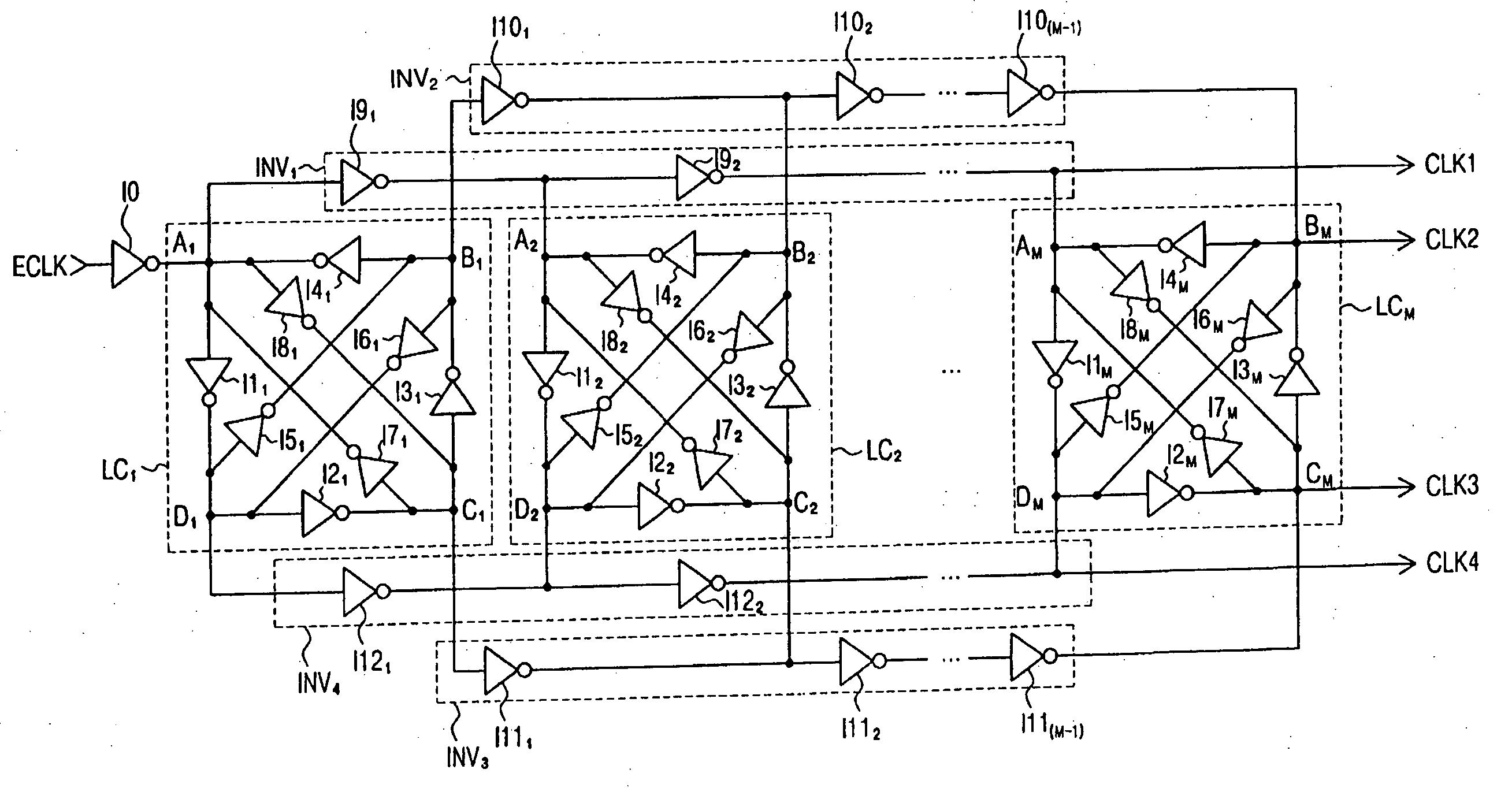
Clock generation circuit and method of generating clock signals. The clock generation circuit includes an inverter directly receiving an external clock signal and outputting an inverted external clock signal, M (where M is an integer ≧1) loop circuits arranged in series, the first loop circuit receiving the inverted external clock signal, each of the N loop circuits having n (where n is an integer ≧2) nodes, each of the M−1 loop circuits generating n intermediate internal clock signals, each at a corresponding one of the n nodes, wherein a frequency of the n intermediate internal clock signals is a multiple of a frequency of the external clock signal and the inverted external clock signal; and n sets of inverters, each including M−1 inverters connected in series, each of the M−1 inverters receiving a corresponding intermediate internal clock signal from a previous loop circuit and outputting a corresponding intermediate internal clock signal to a next loop circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com