Patents
Literature
126results about "Pulse generation by super conductive devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
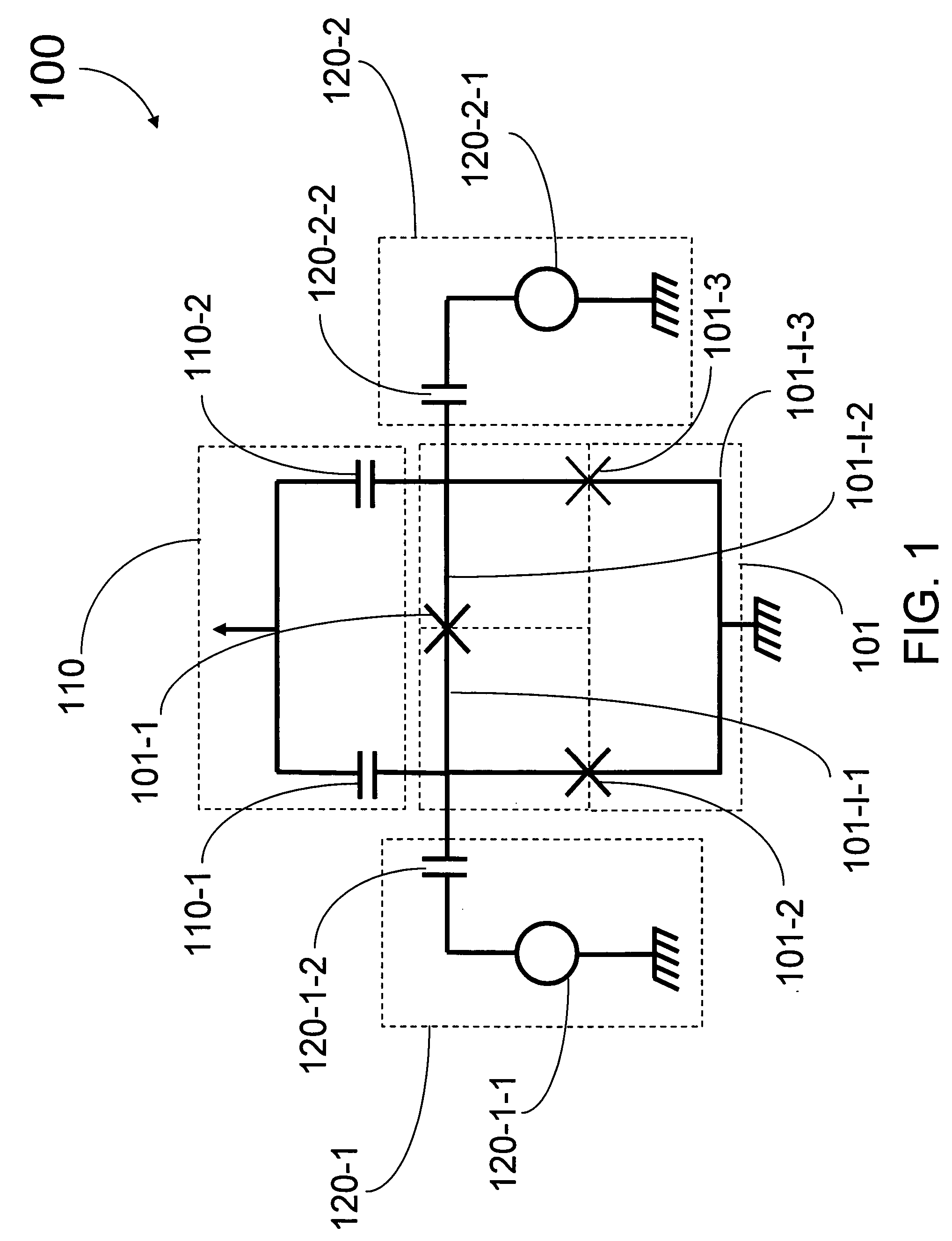
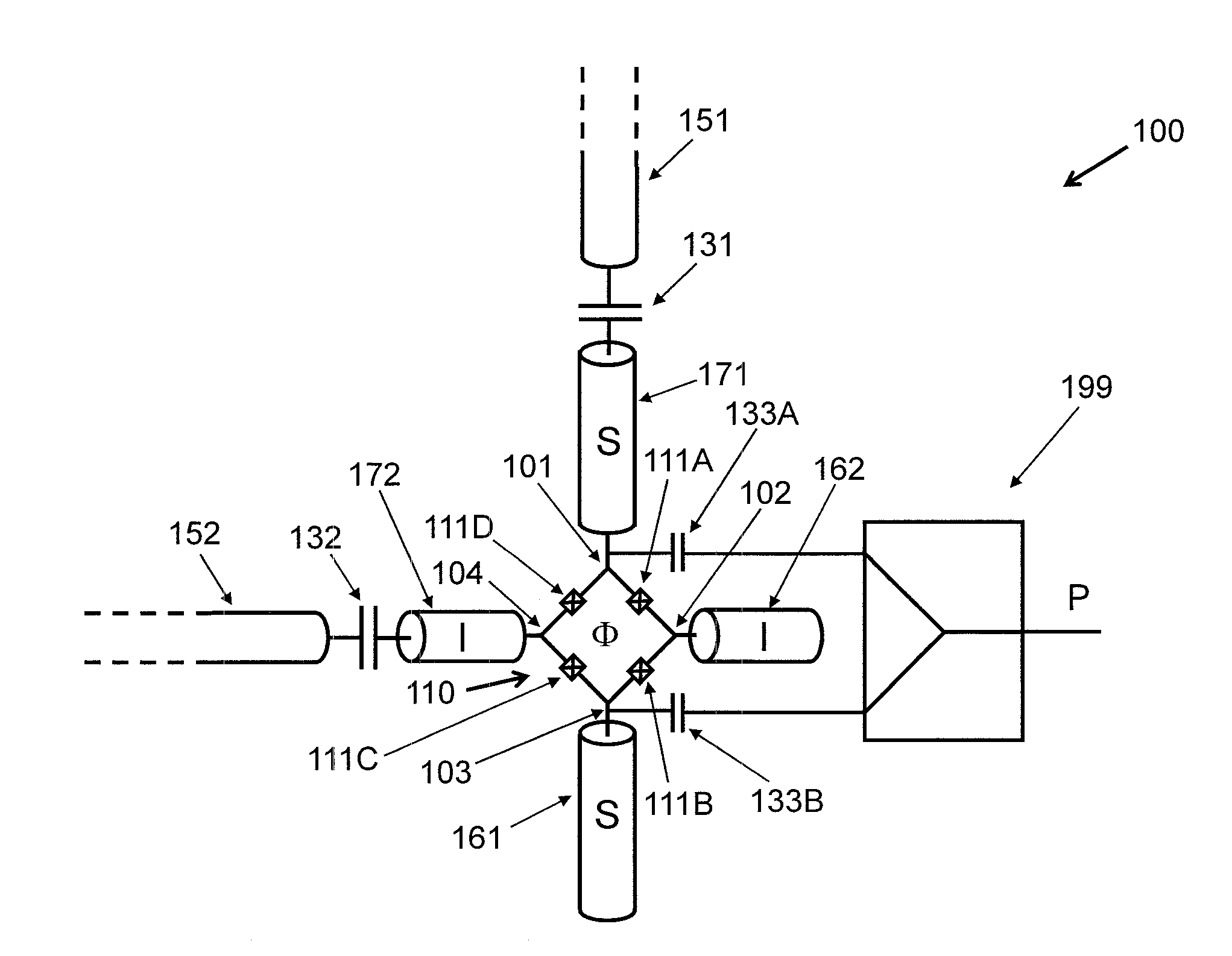
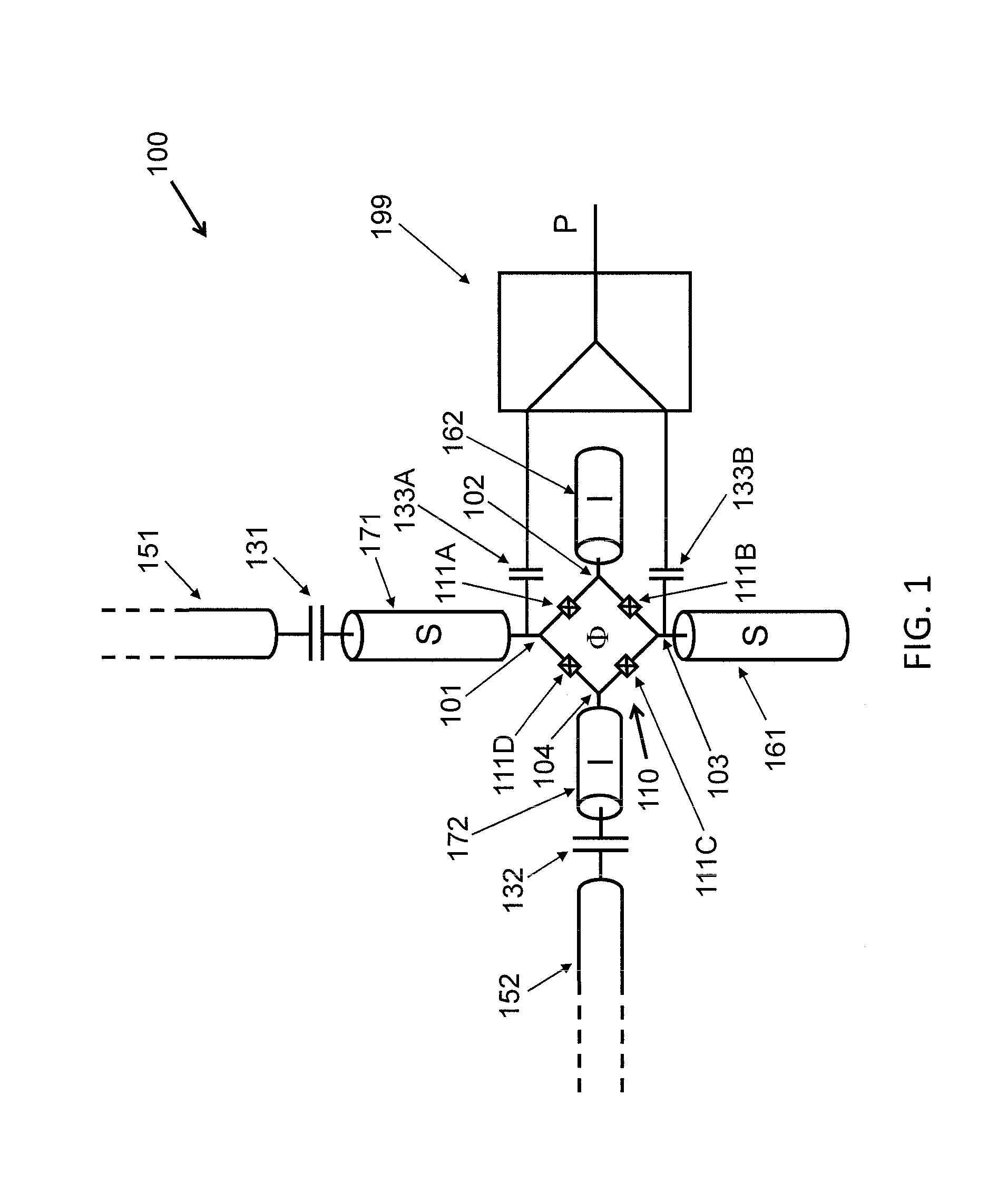
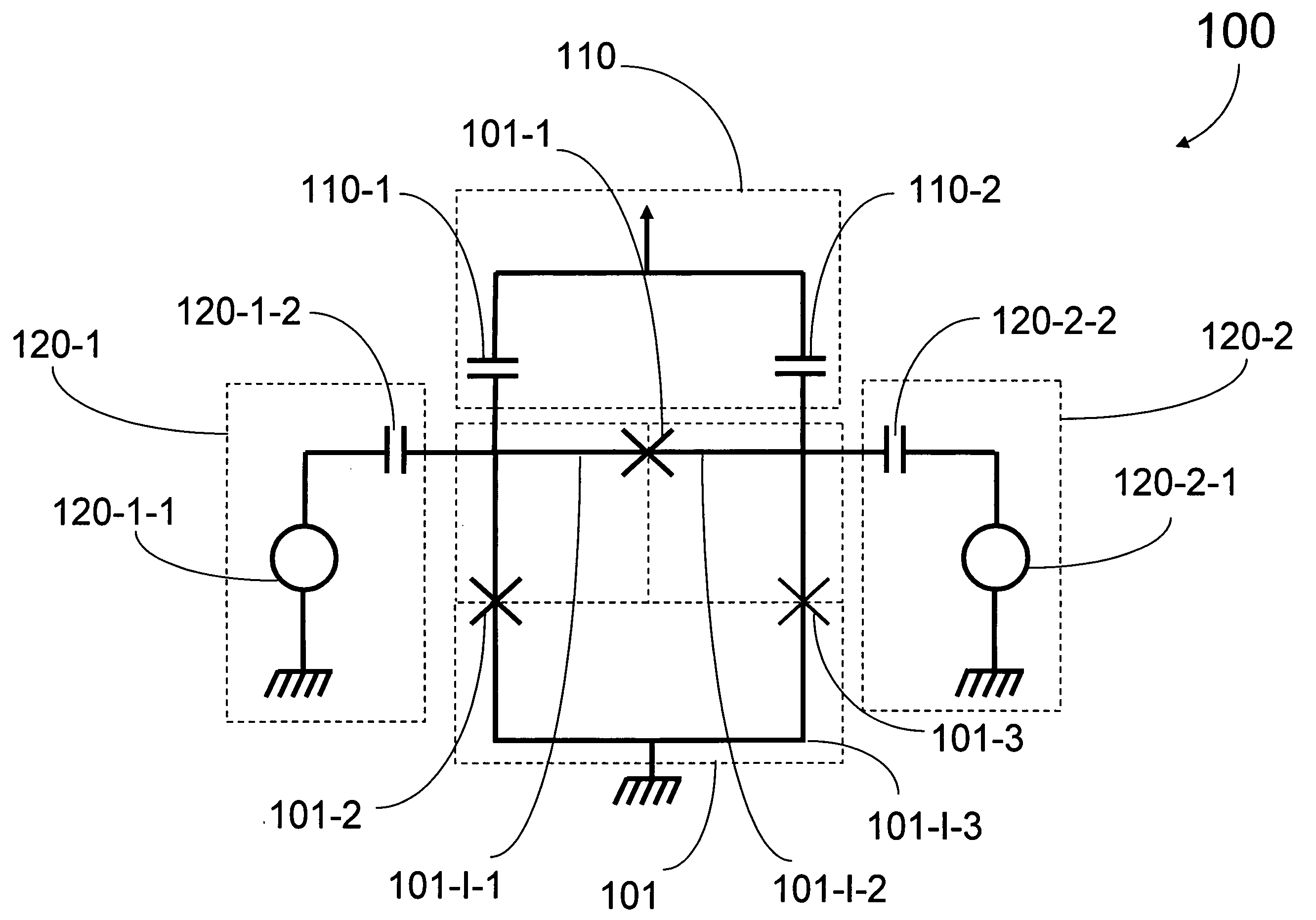
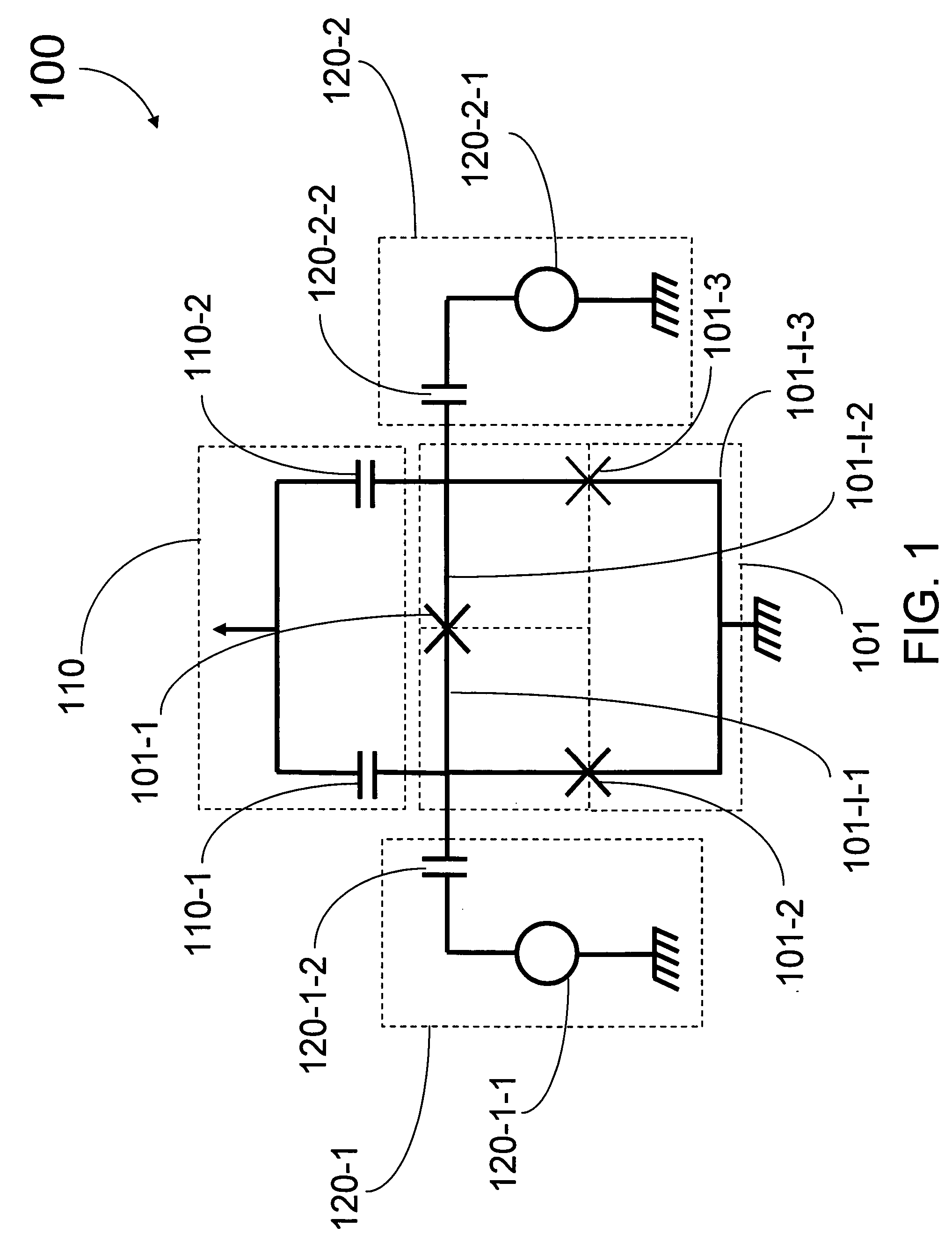
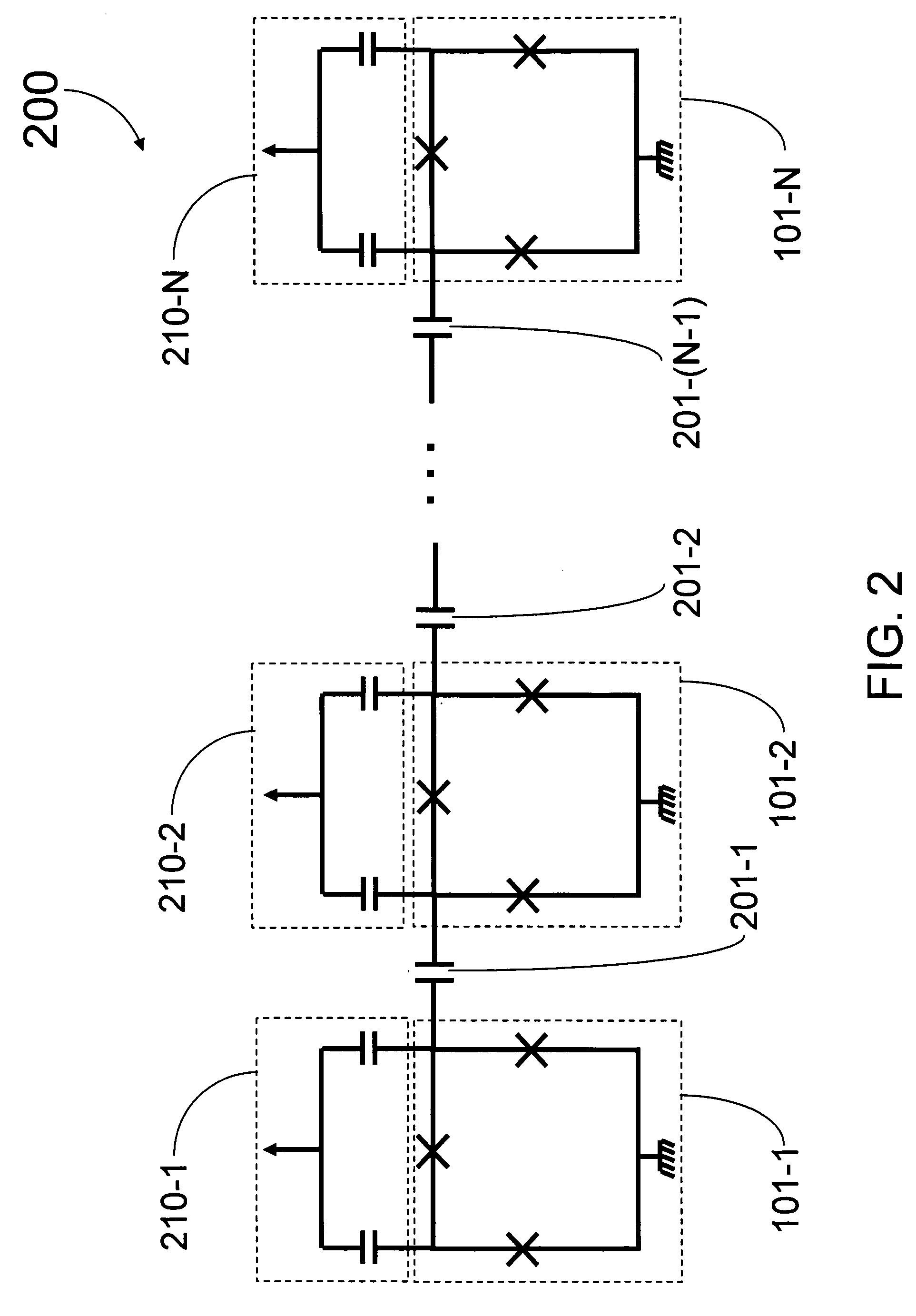
Analog processor comprising quantum devices
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
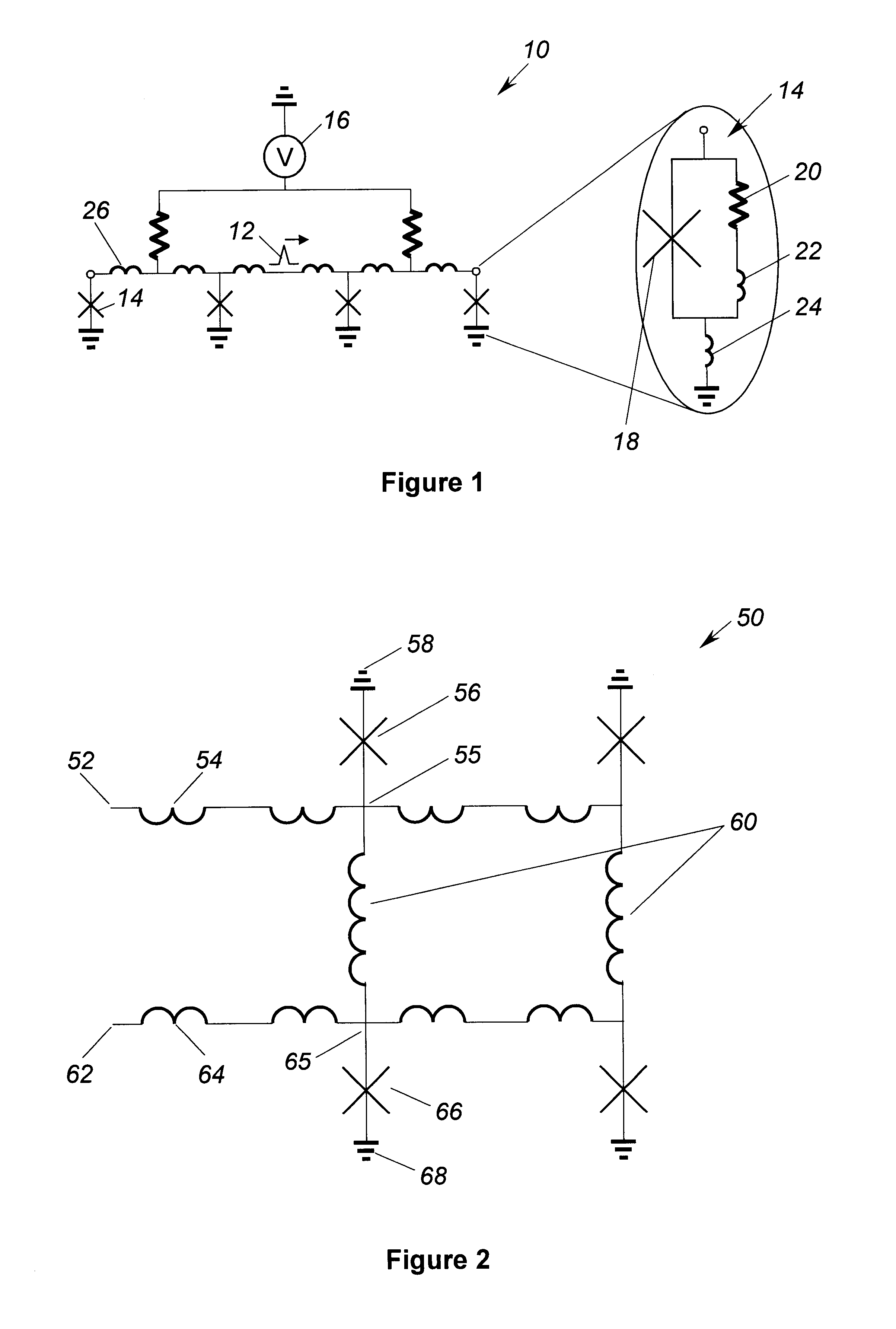
Analog processor comprising quantum devices
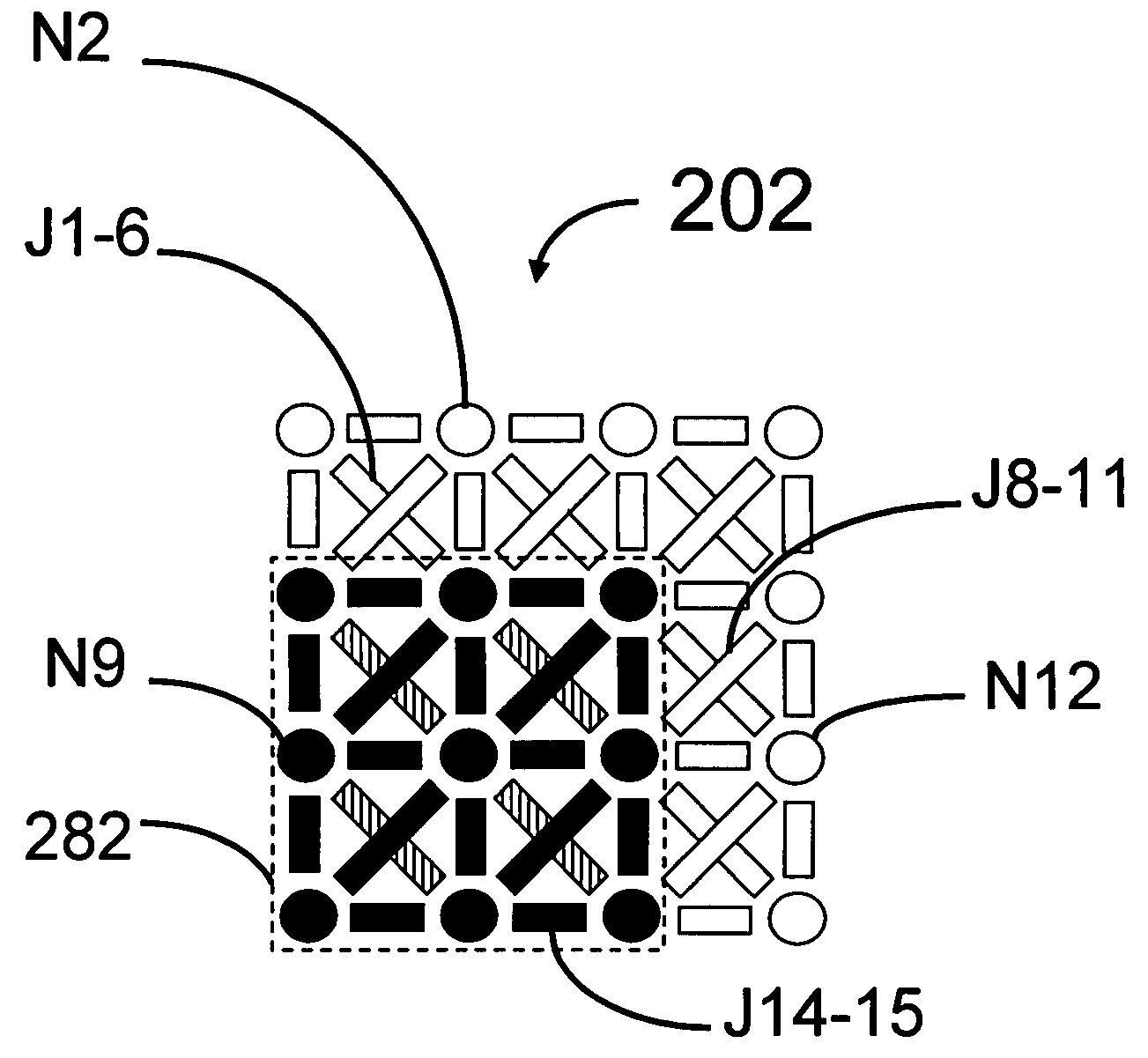
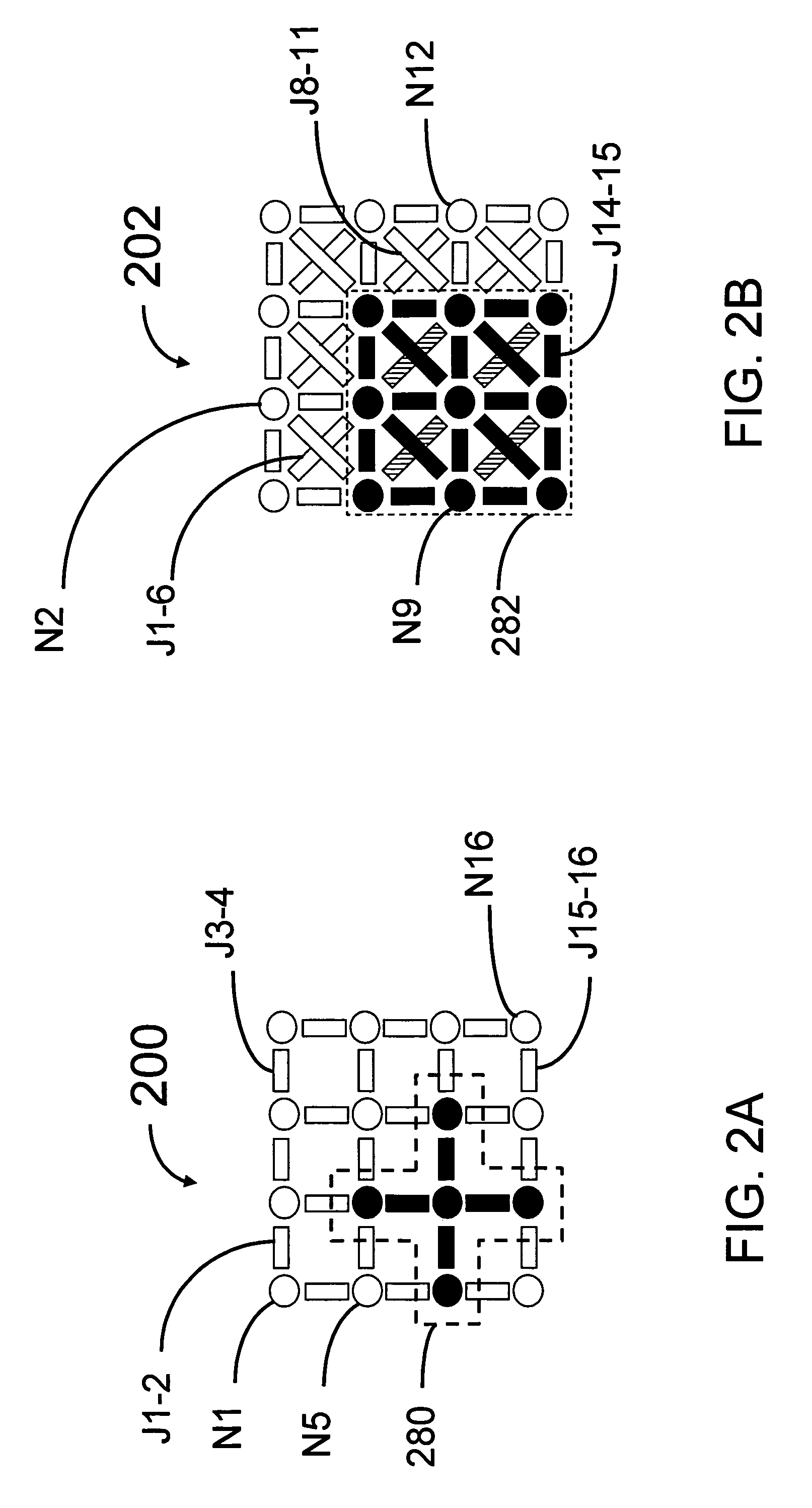
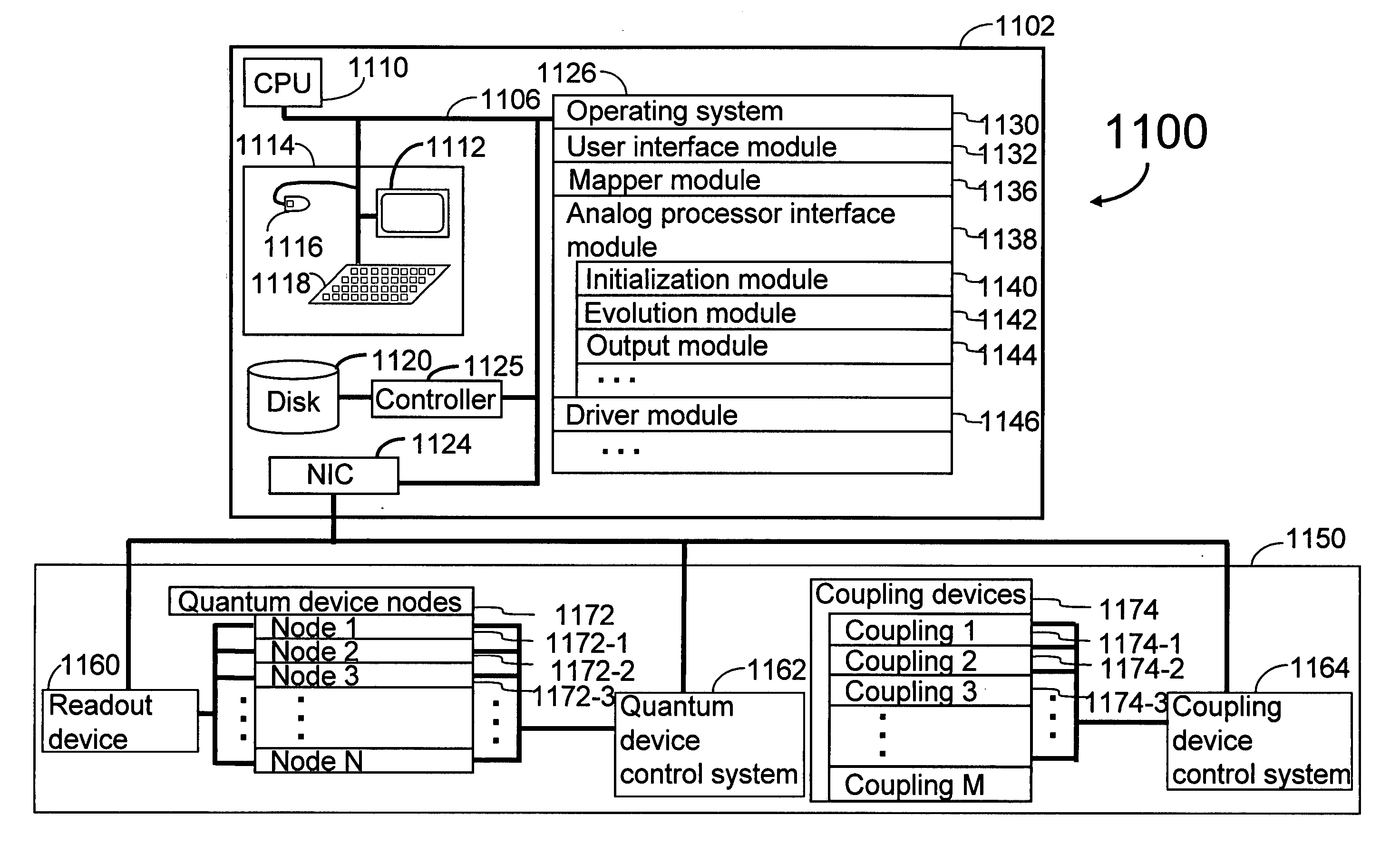
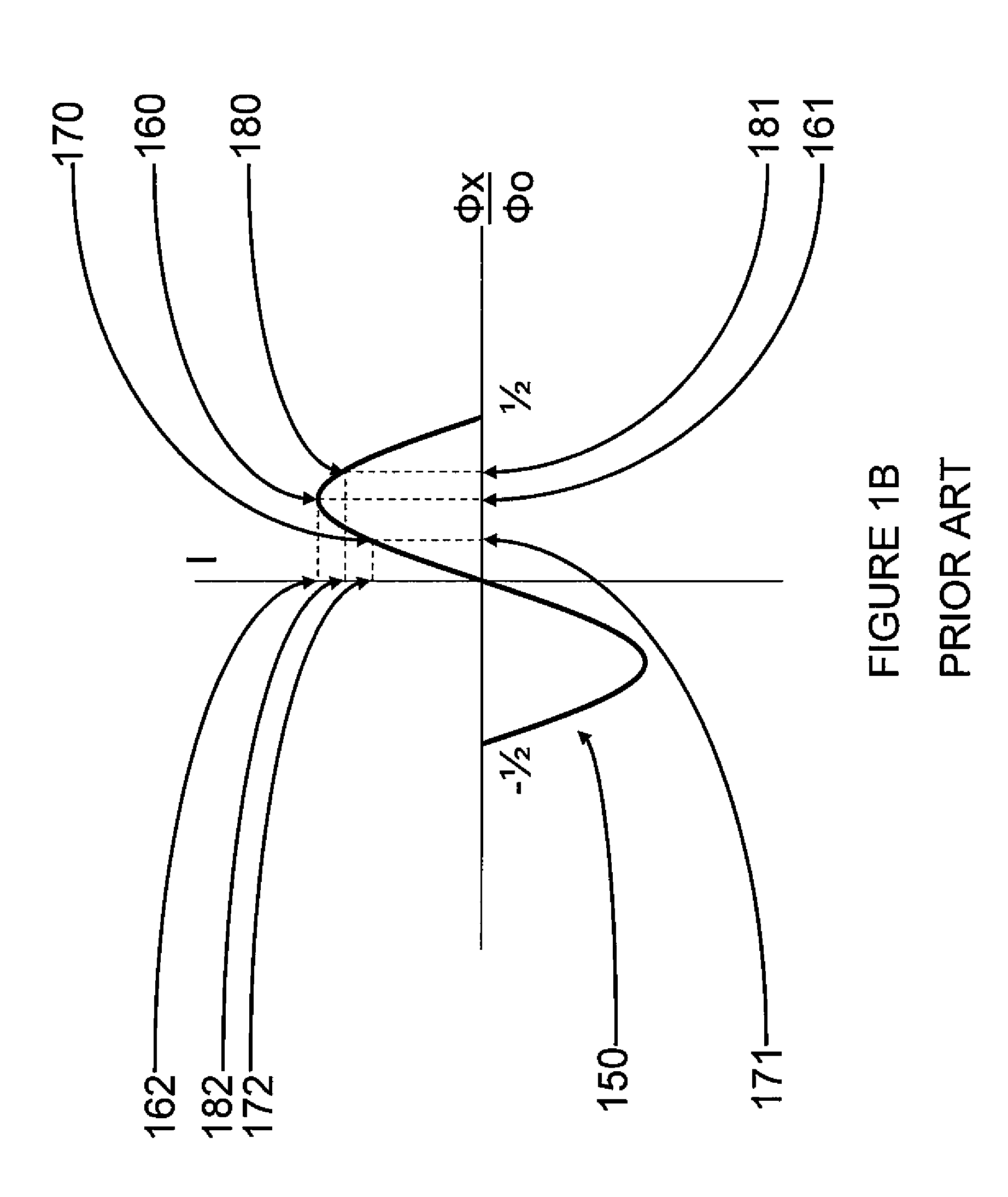
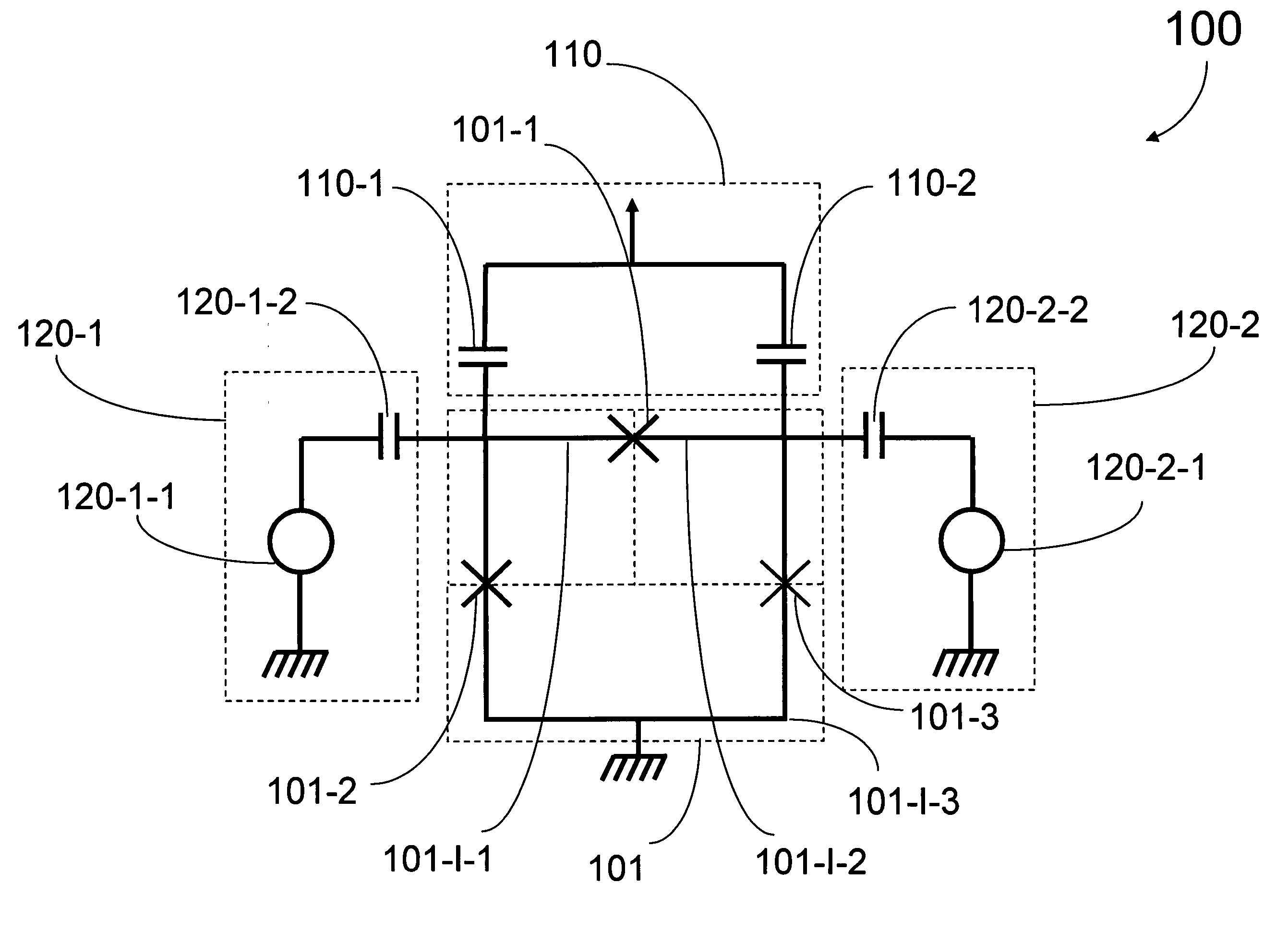
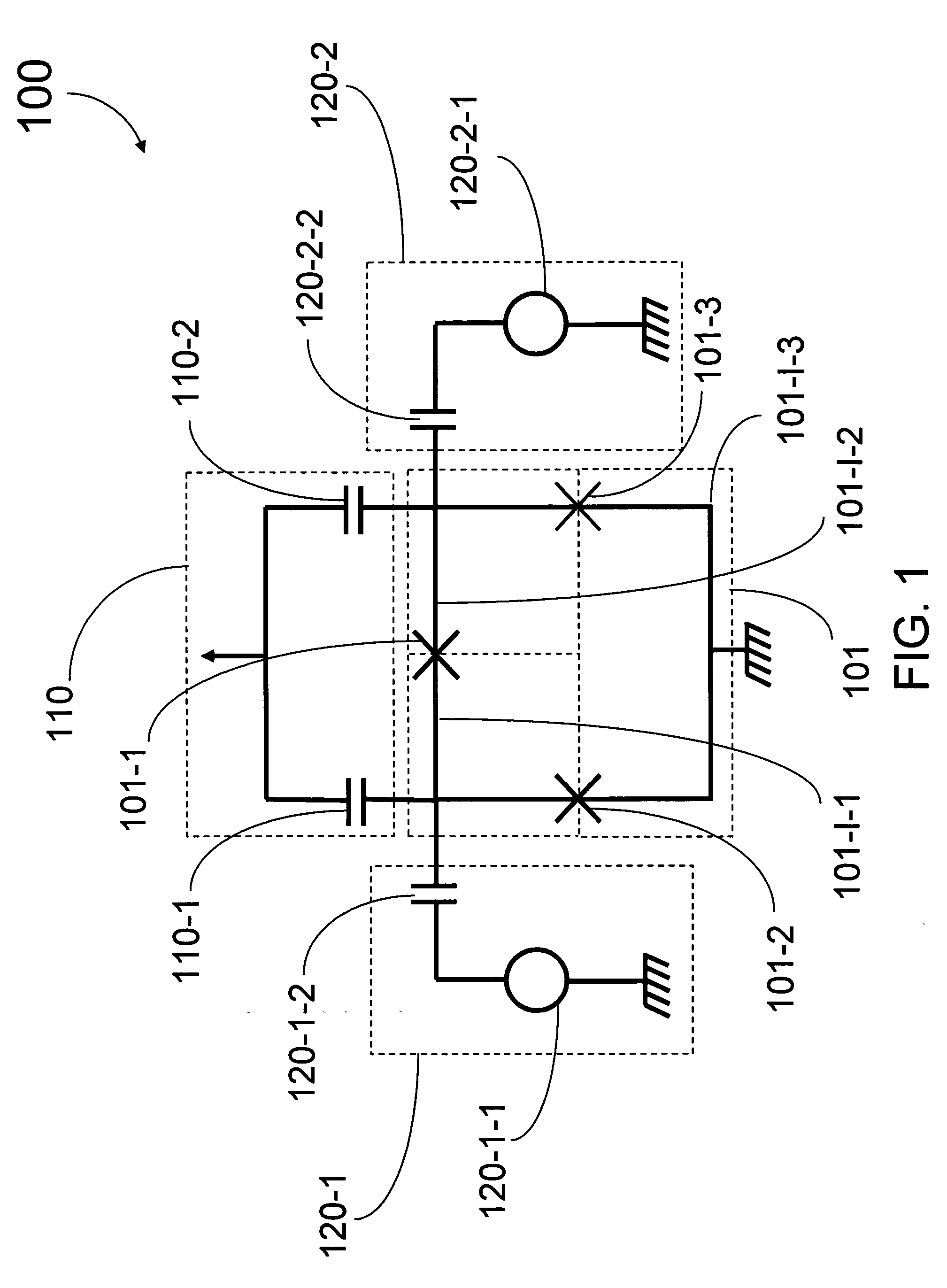
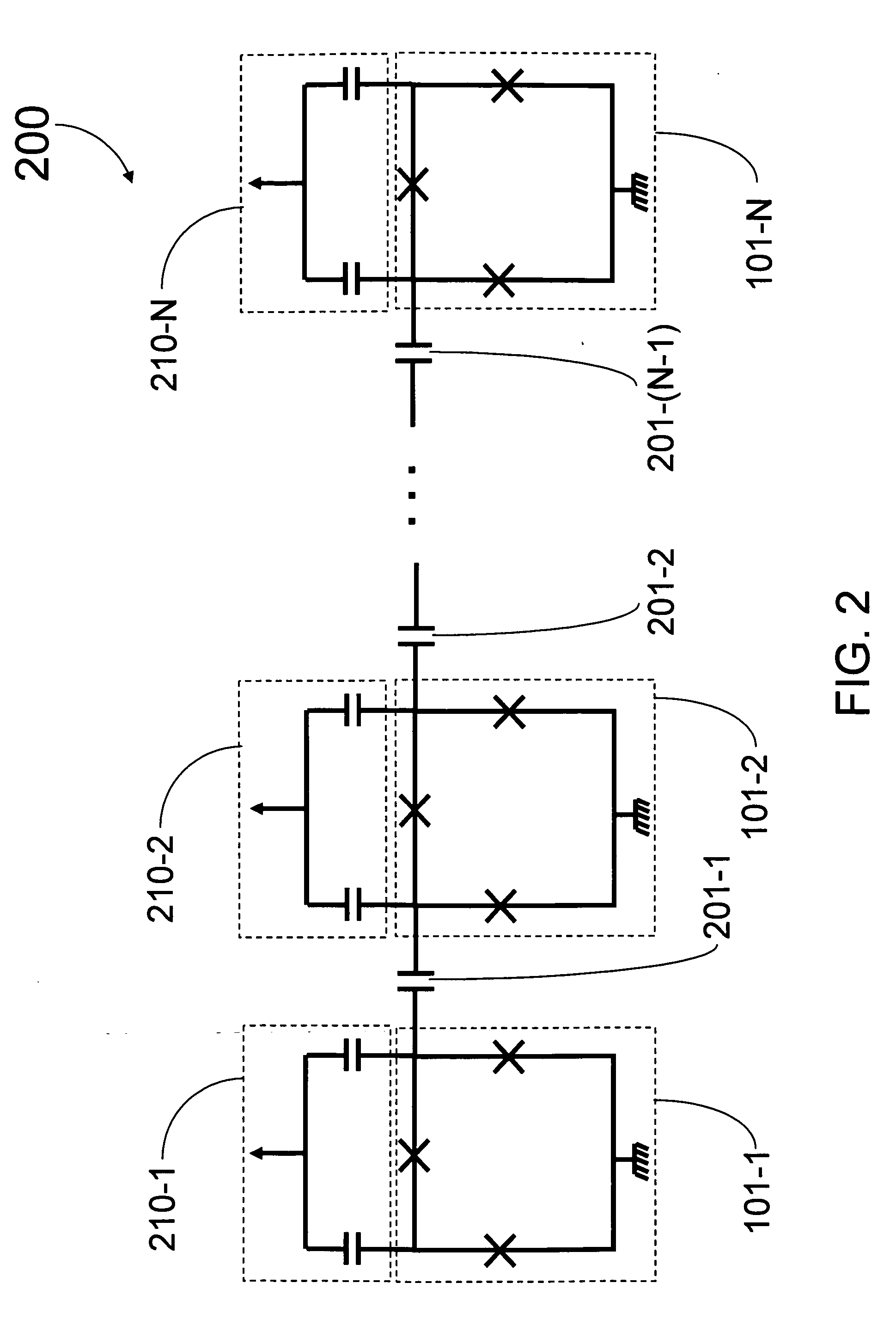
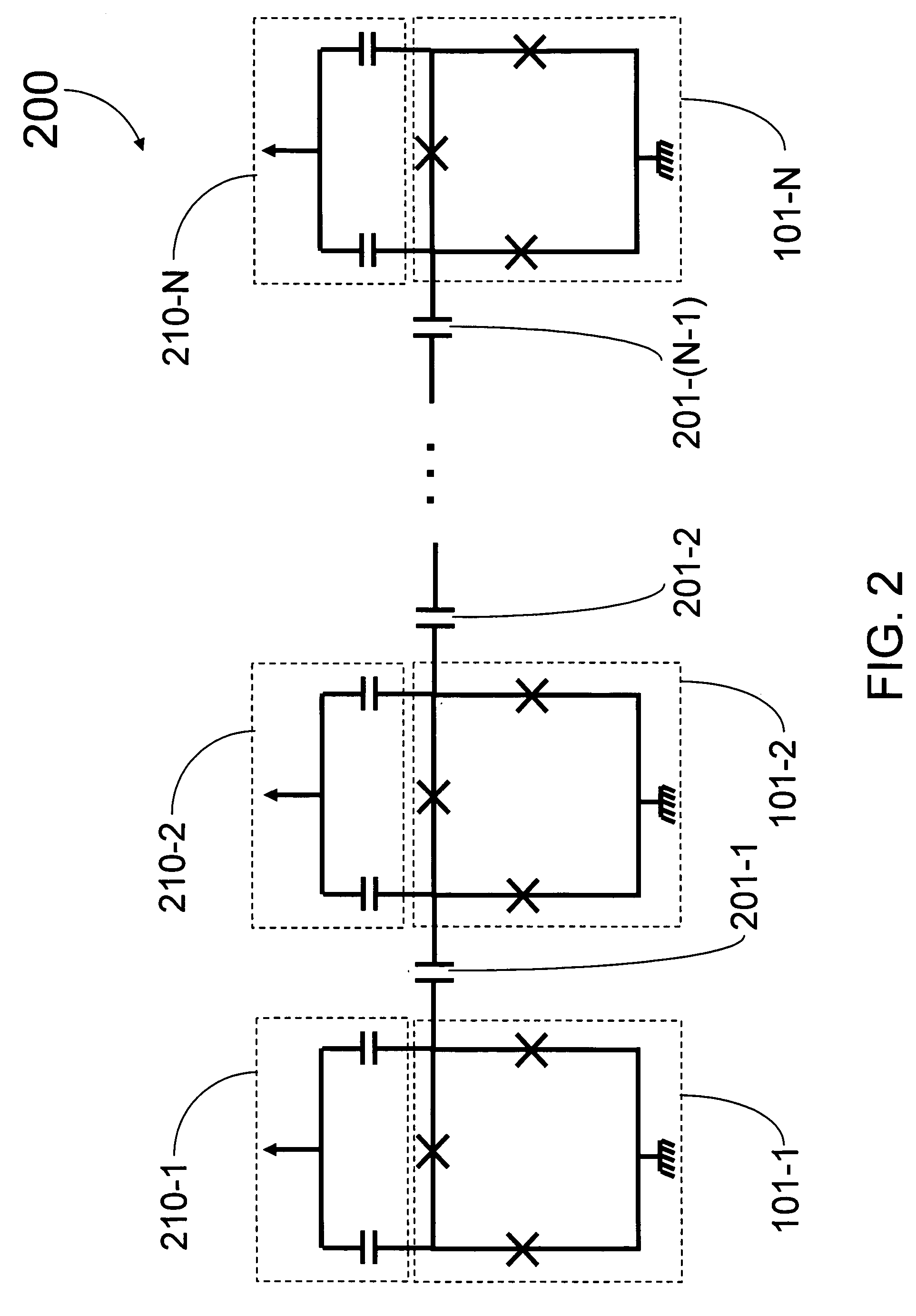
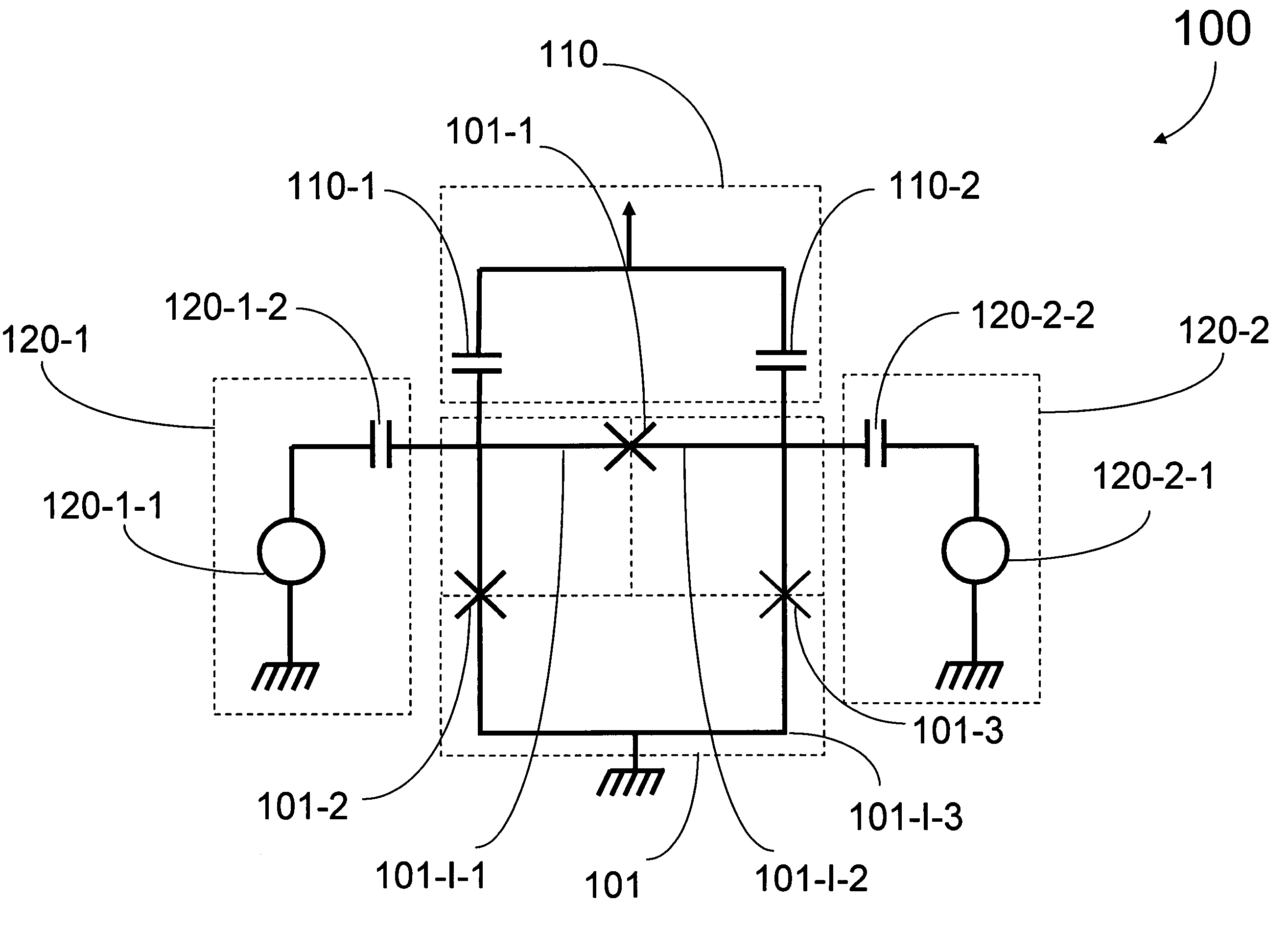
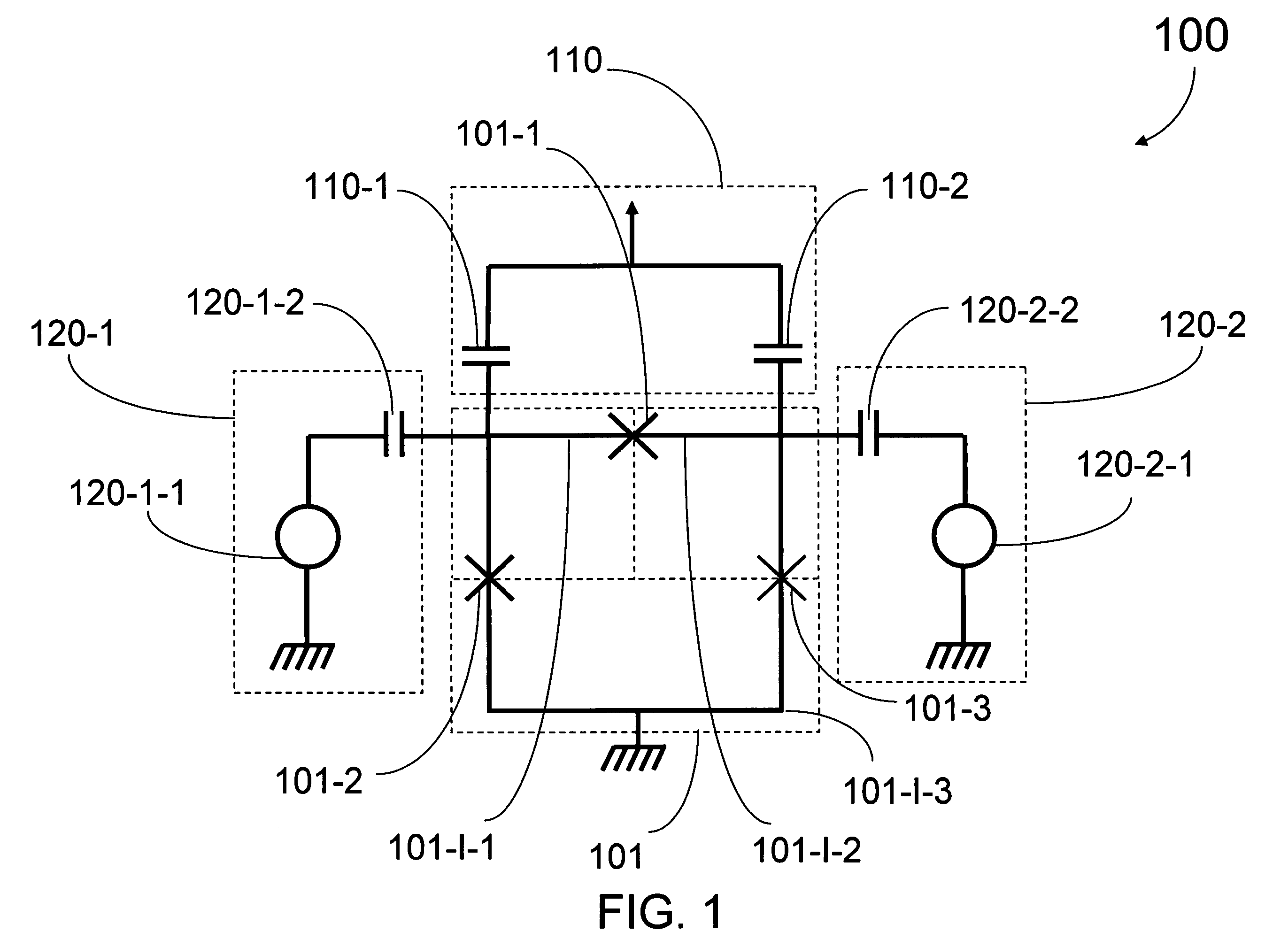
Analog processors for solving various computational problems are provided. Such analog processors comprise a plurality of quantum devices, arranged in a lattice, together with a plurality of coupling devices. The analog processors further comprise bias control systems each configured to apply a local effective bias on a corresponding quantum device. A set of coupling devices in the plurality of coupling devices is configured to couple nearest-neighbor quantum devices in the lattice. Another set of coupling devices is configured to couple next-nearest neighbor quantum devices. The analog processors further comprise a plurality of coupling control systems each configured to tune the coupling value of a corresponding coupling device in the plurality of coupling devices to a coupling. Such quantum processors further comprise a set of readout devices each configured to measure the information from a corresponding quantum device in the plurality of quantum devices.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
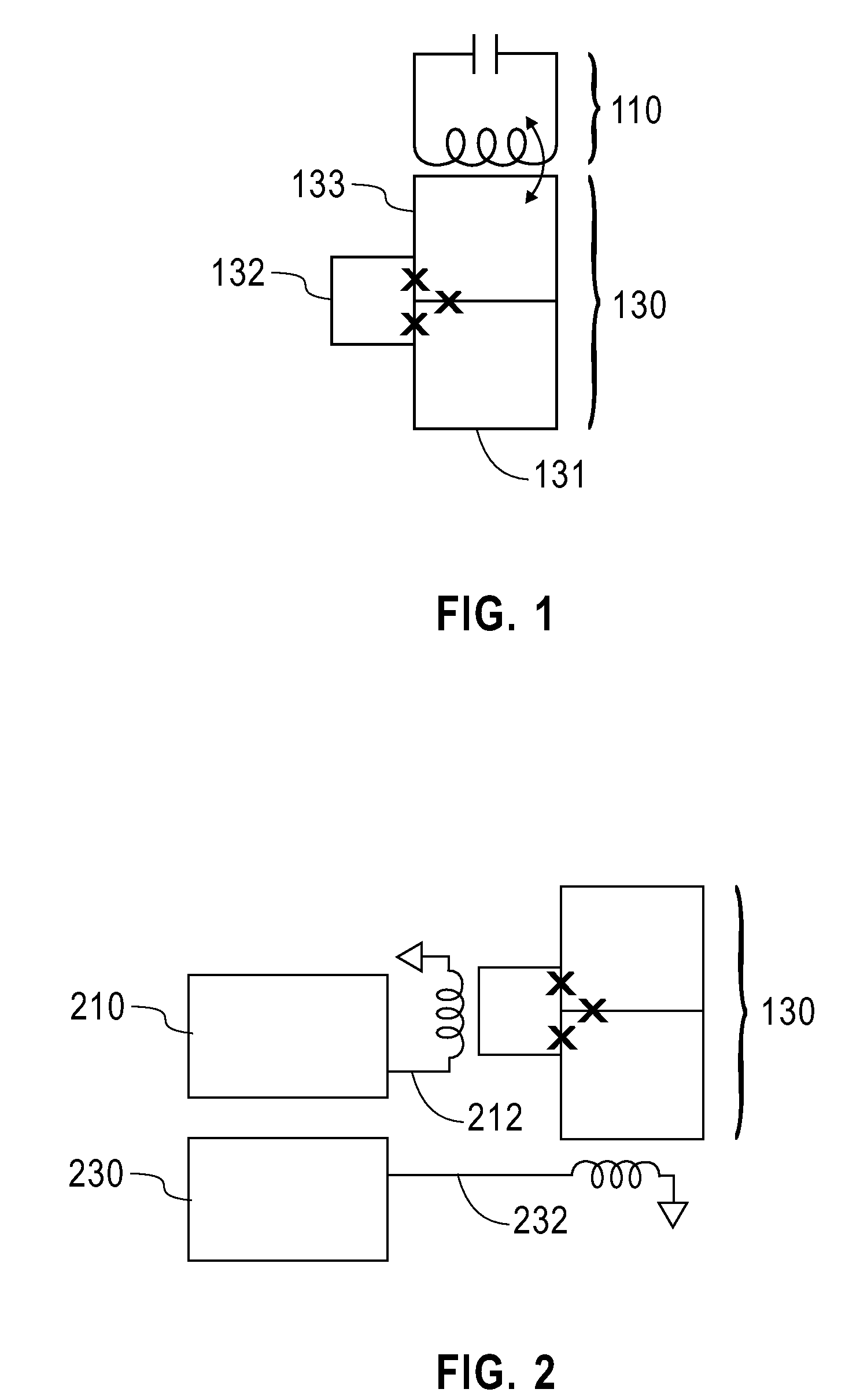
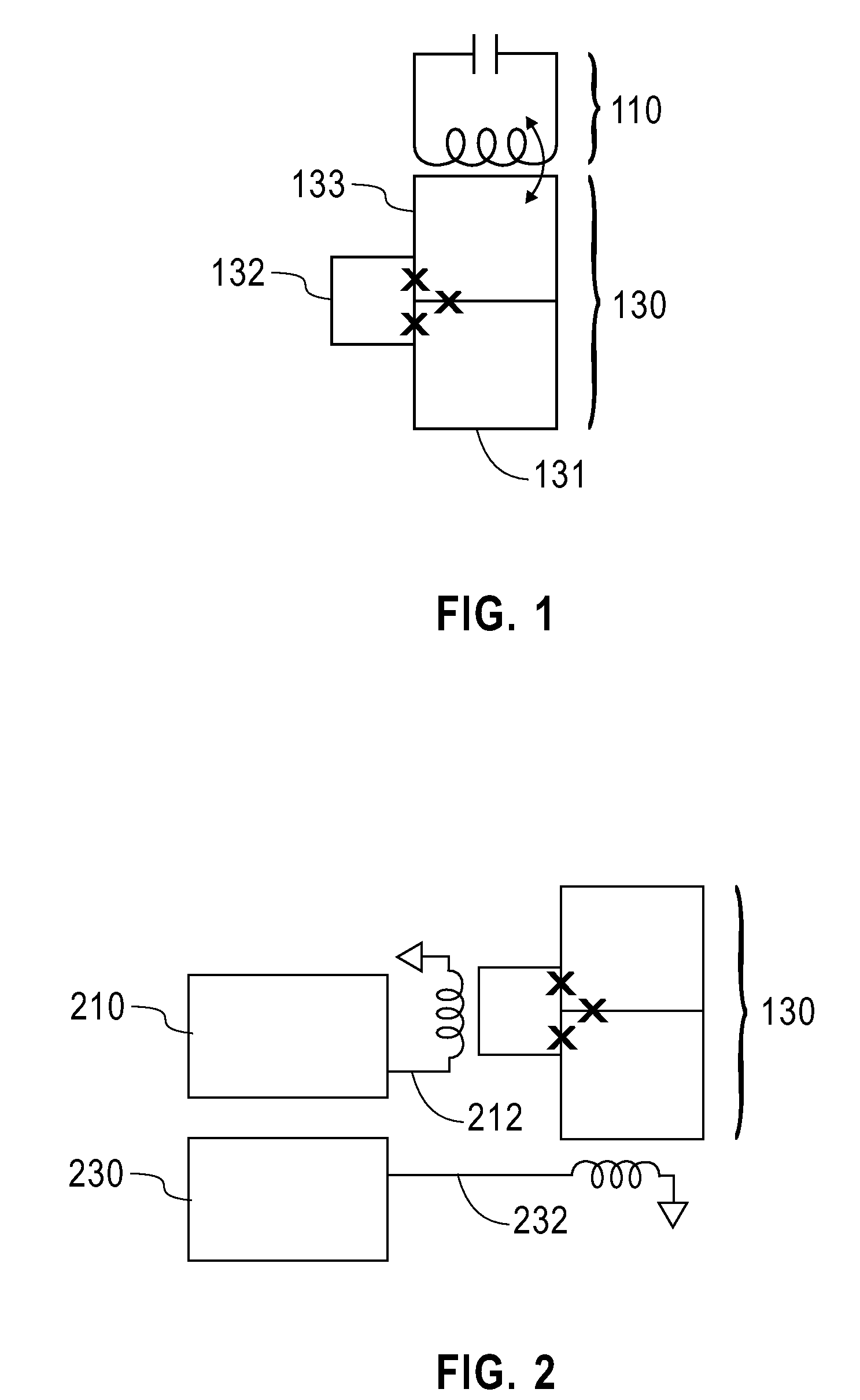
Systems, devices, and methods for controllably coupling qubits
InactiveUS20080238531A1Improve drawing legibilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCoupling systemInductor
A coupling system may include an rf-SQUID having a loop of superconducting material interrupted by a compound Josephson junction; and a first magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a mutual inductance coupling the first magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction, wherein the loop of superconducting material positioned with respect to a first and second qubits to provide respective mutual inductance coupling therebetween. The coupling system may further include a second magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a second magnetic flux inductor mutual inductance coupling the second magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction. A superconducting processor may include the coupling system and two or more qubits. A method may include providing the first, the second and the third mutual inductances.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Superconducting qubit with a plurality of capacitive couplings
A first qubit having a superconducting loop interrupted by a plurality of Josephson junctions is provided. Each junction interrupts a different portion of the superconducting loop and each different adjacent pair of junctions in the plurality of Josephson junctions defines a different island. An ancillary device is coupled to the first qubit. In a first example, the ancillary device is a readout mechanism respectively capacitively coupled to a first and second island in the plurality of islands of the first qubit by a first and second capacitance. Quantum nondemolition measurement of the first qubit's state may be performed. In a second example, the ancillary device is a second qubit. The second qubit's first and second islands are respectively capacitively coupled to the first and second islands of the first qubit by a capacitance. In this second example, the coupling is diagonal in the physical basis of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
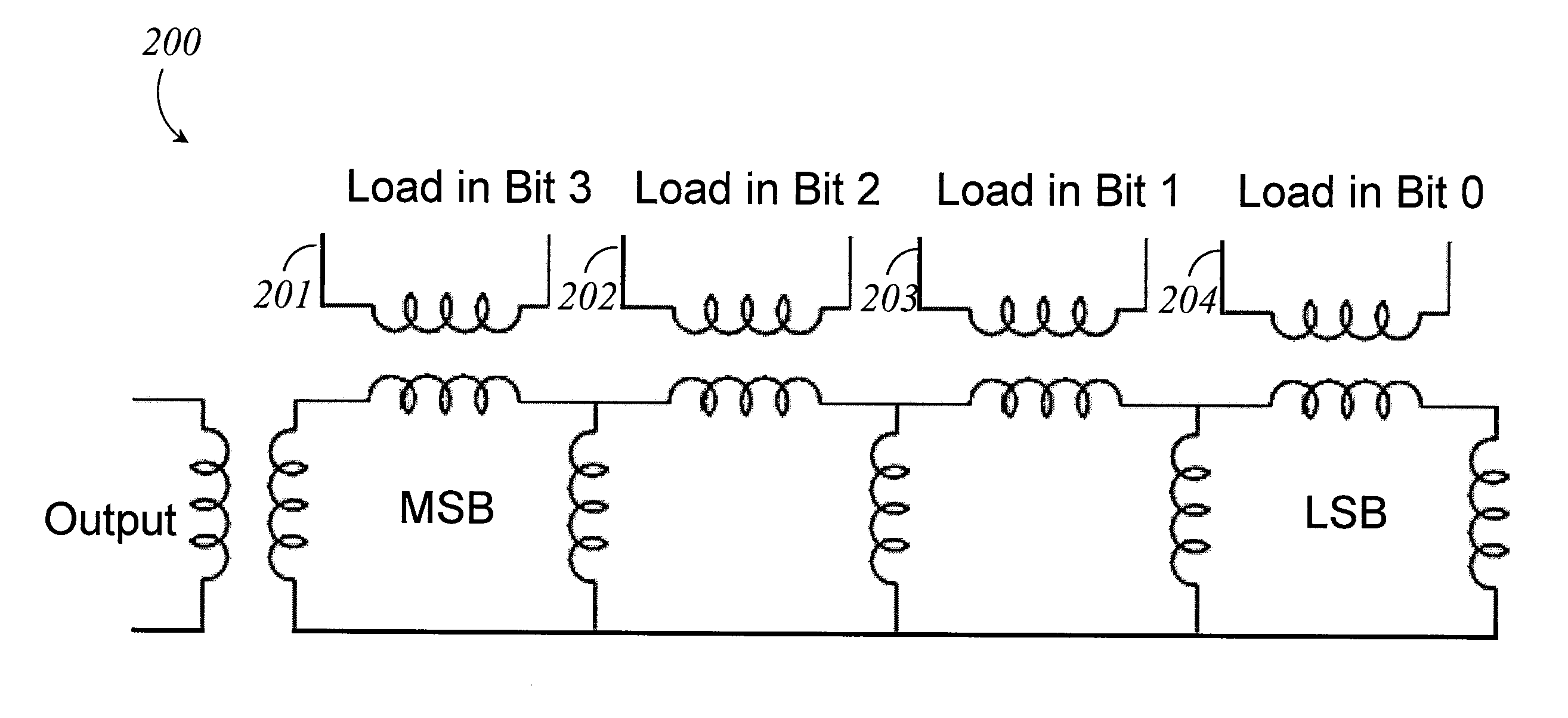
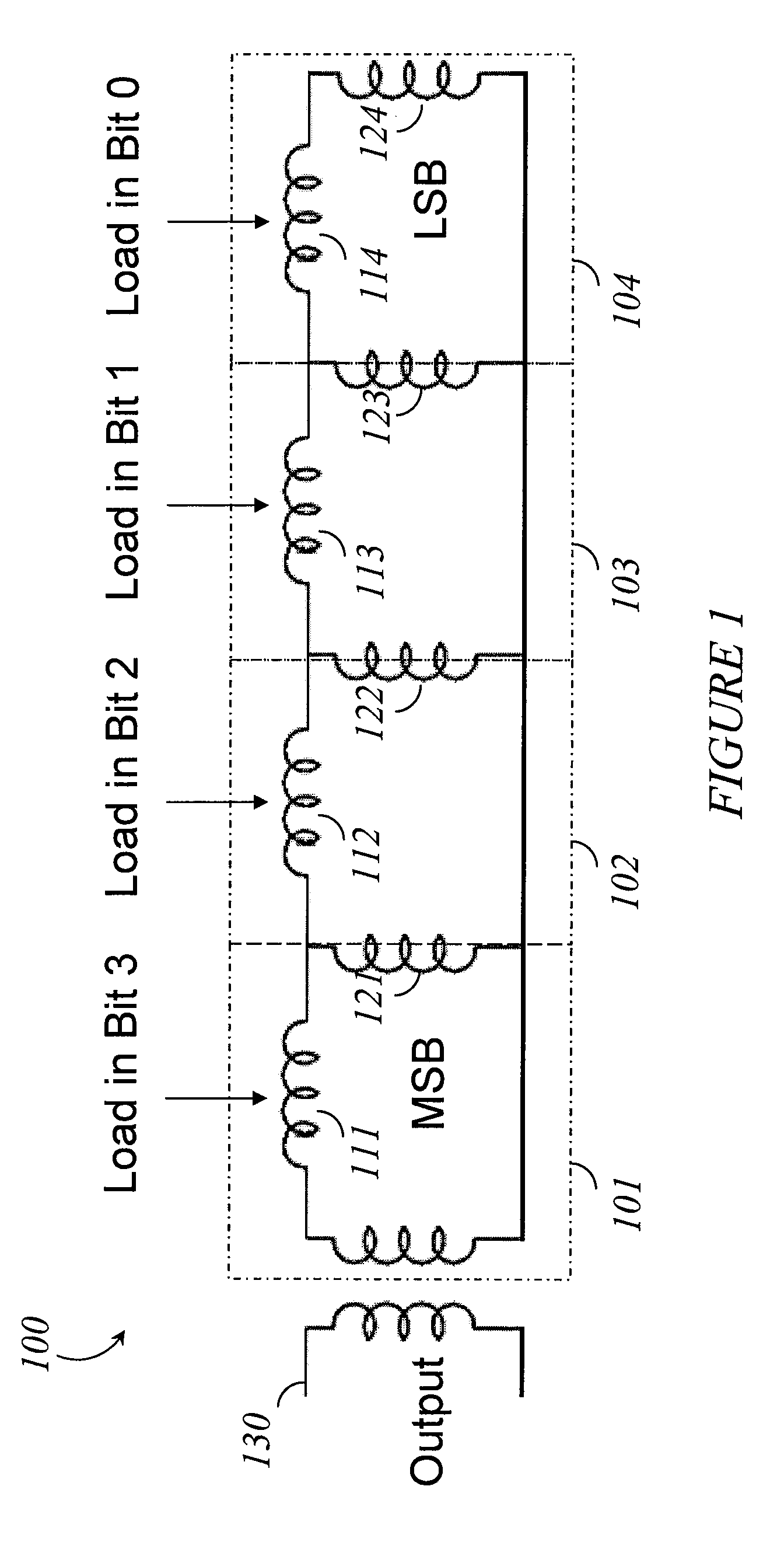
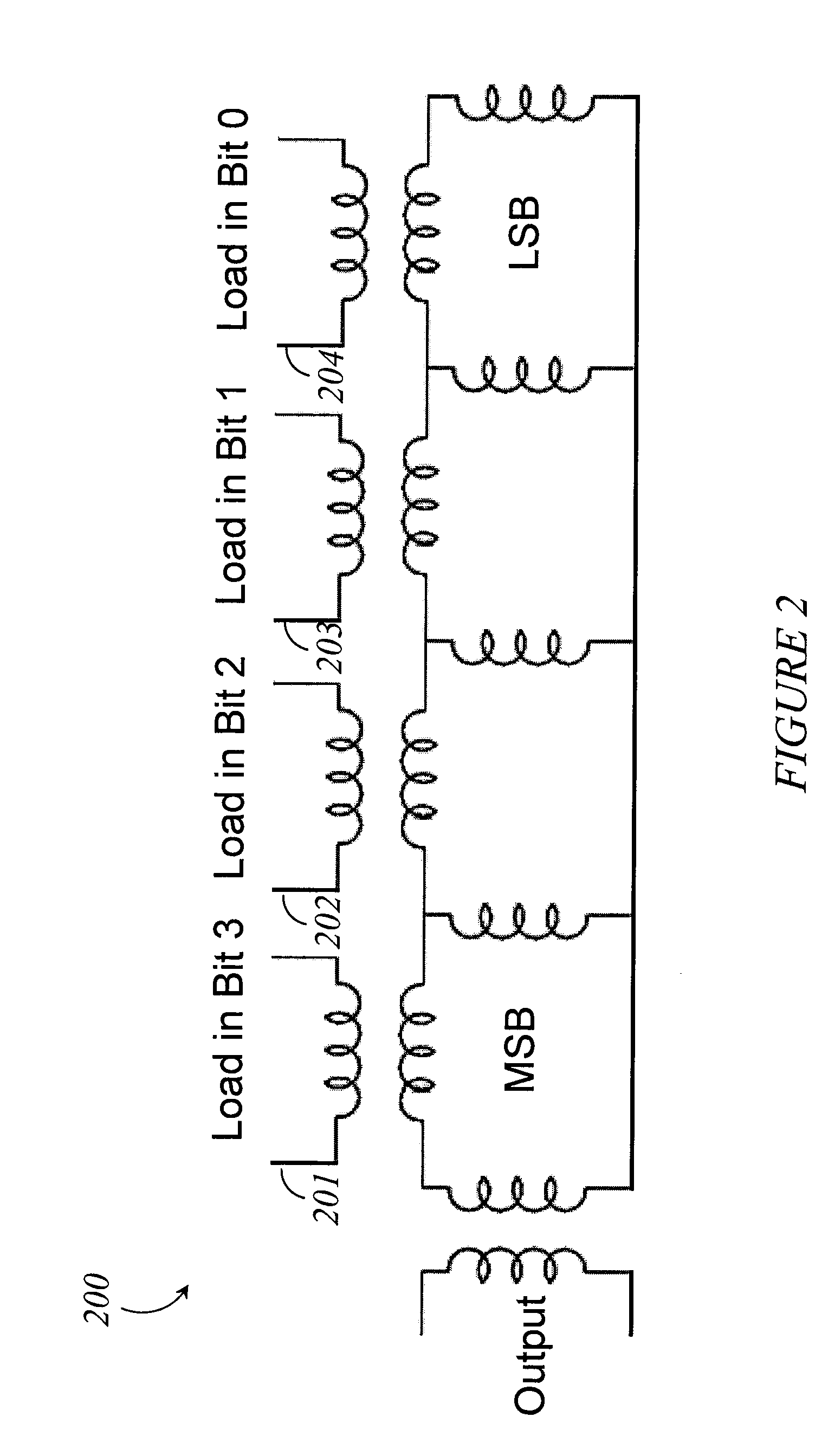
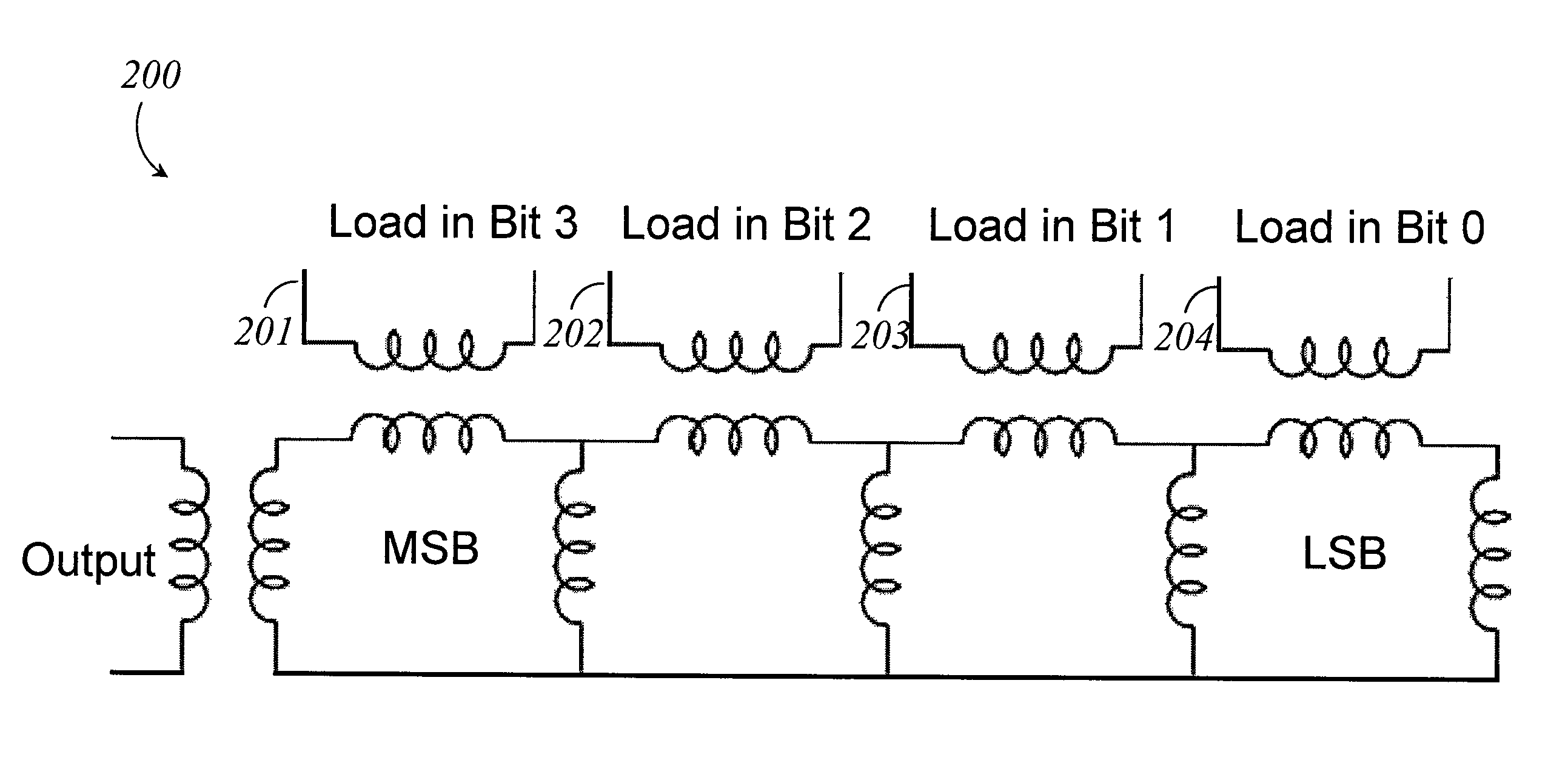
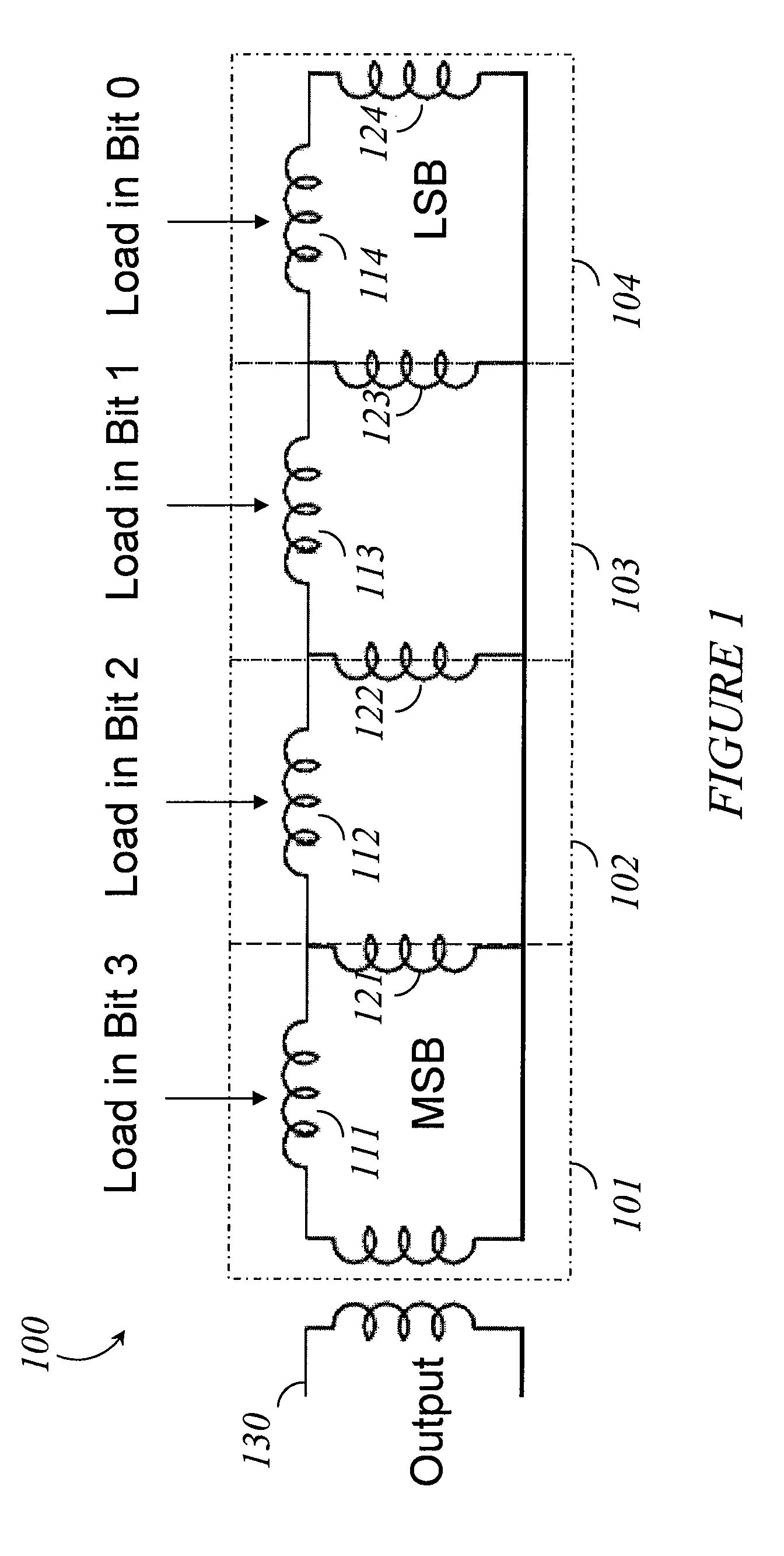
Systems, methods and apparatus for digital-to-analog conversion of superconducting magnetic flux signals
ActiveUS20090082209A1Fast switching speedShort calculation timeElectric signal transmission systemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShift registerData signal
A superconducting flux digital-to-analog converter includes a superconducting inductor ladder circuit. The ladder circuit includes a plurality of closed superconducting current paths that each includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series to form a respective superconducting loop, successively adjacent or neighboring superconducting loops are connected in parallel with each other and share at least one of the superconducting inductors to form a flux divider network. A data signal input structure provides a respective bit of a multiple bit signal to each of the superconducting loops. The data signal input structure may include a set of superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). The data signal input structure may include a superconducting shift register, for example a single-flux quantum (SFQ) shift register or a flux-based superconducting shift register comprising a number of latching qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
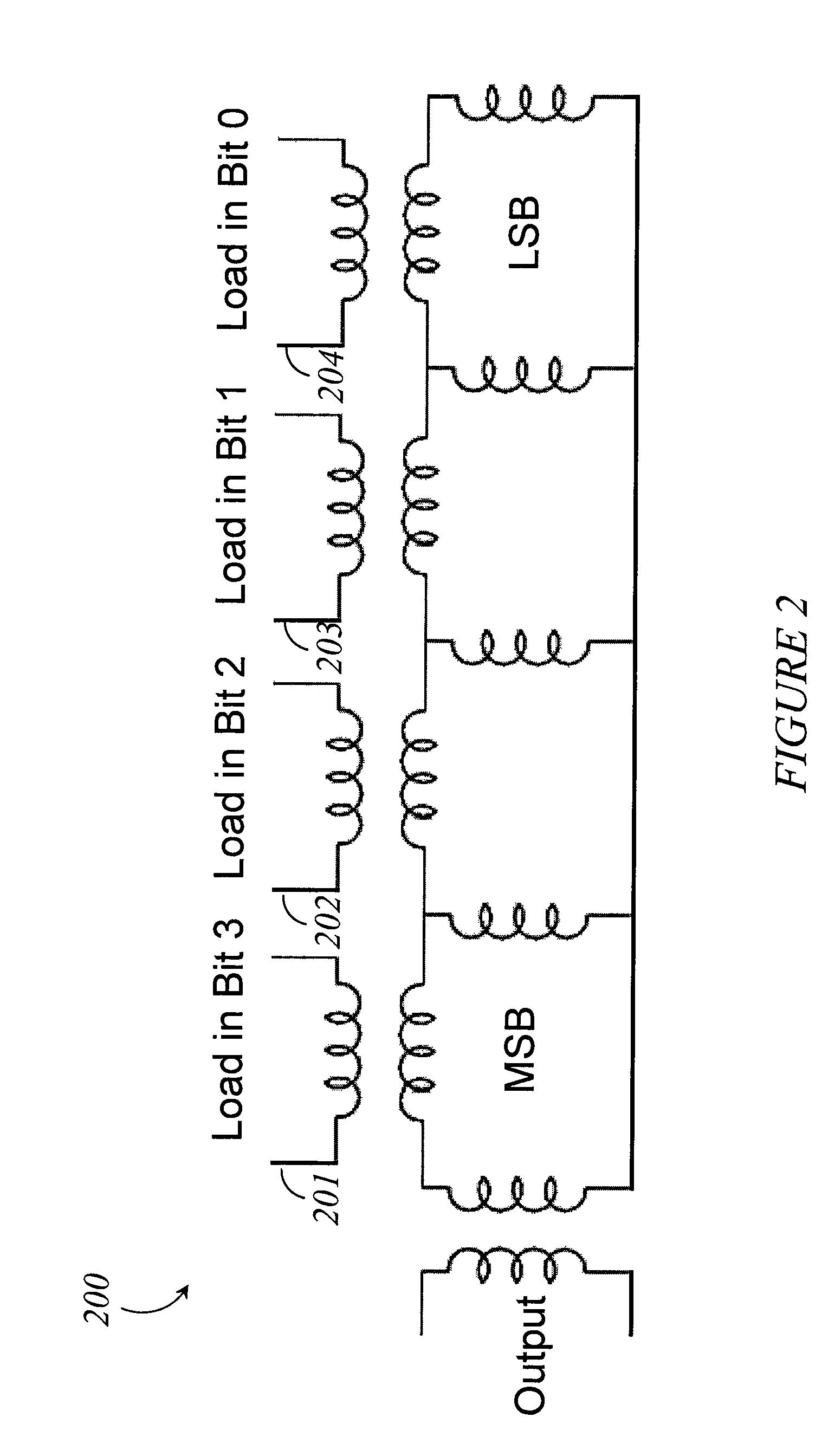
Systems, methods and apparatus for digital-to-analog conversion of superconducting magnetic flux signals
A superconducting flux digital-to-analog converter includes a superconducting inductor ladder circuit. The ladder circuit includes a plurality of closed superconducting current paths that each includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series to form a respective superconducting loop, successively adjacent or neighboring superconducting loops are connected in parallel with each other and share at least one of the superconducting inductors to form a flux divider network. A data signal input structure provides a respective bit of a multiple bit signal to each of the superconducting loops. The data signal input structure may include a set of superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). The data signal input structure may include a superconducting shift register, for example a single-flux quantum (SFQ) shift register or a flux-based superconducting shift register comprising a number of latching qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Superconducting qubits having a plurality of capacitive couplings
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
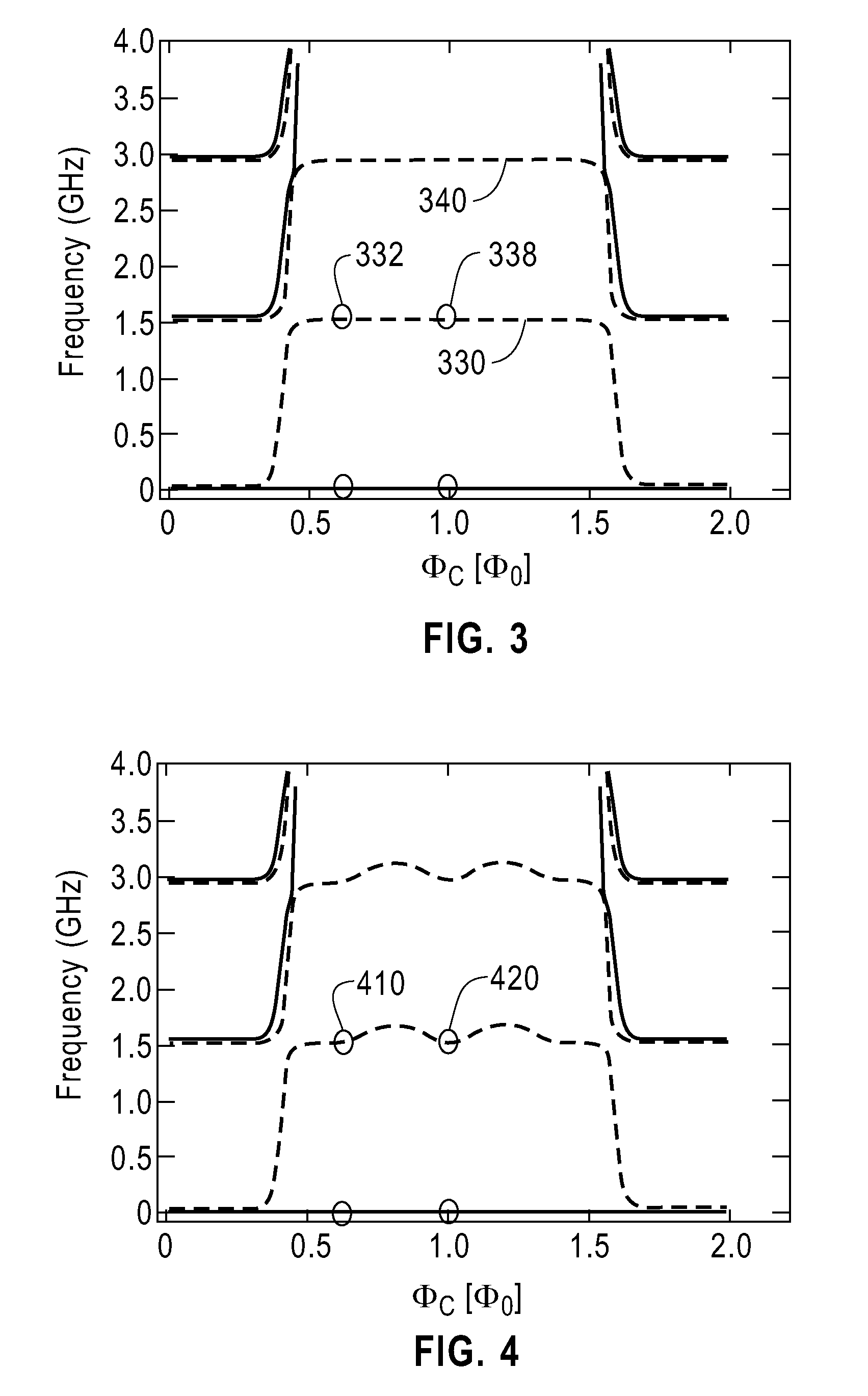
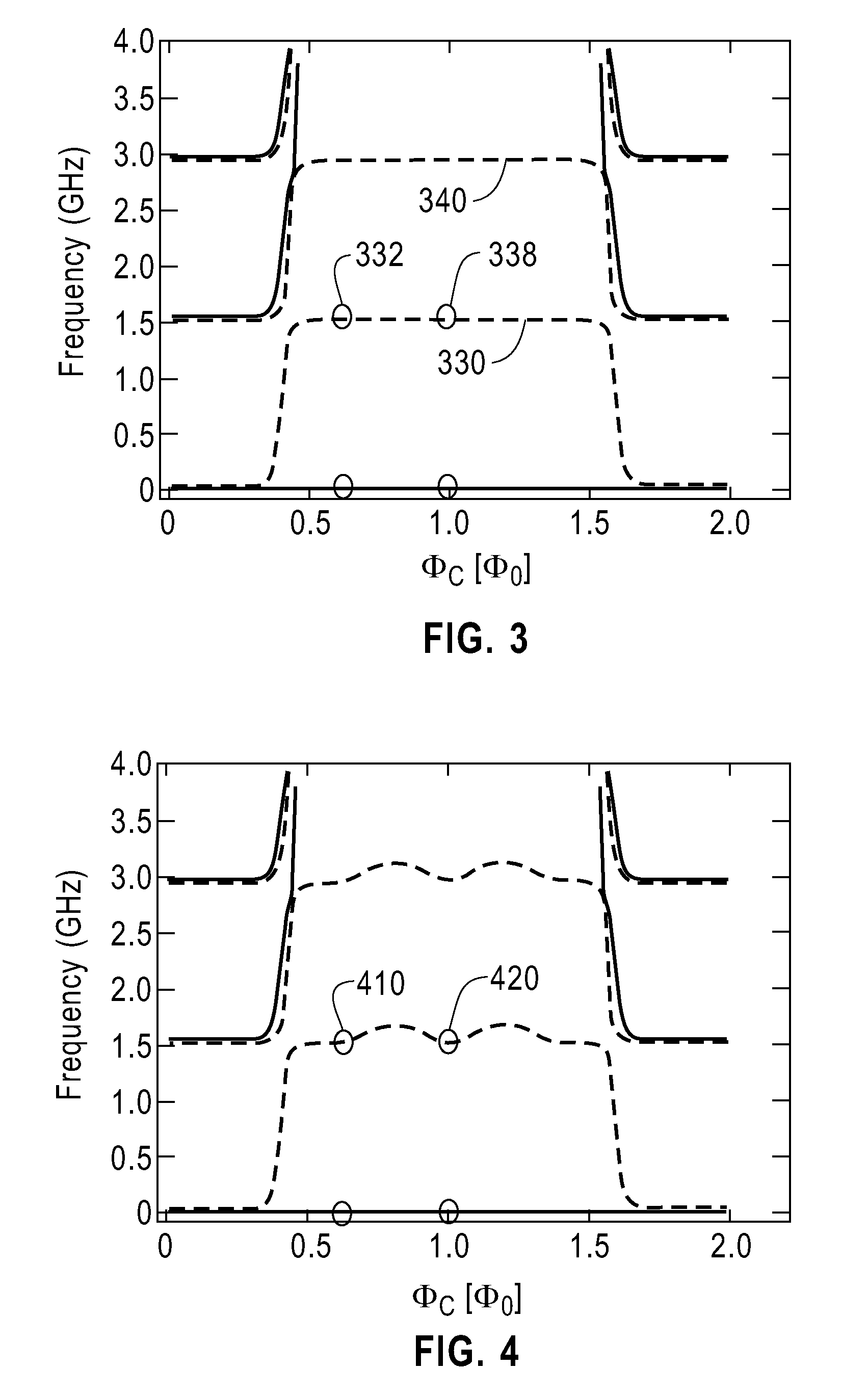
Universal adiabatic quantum computing with superconducting qubits
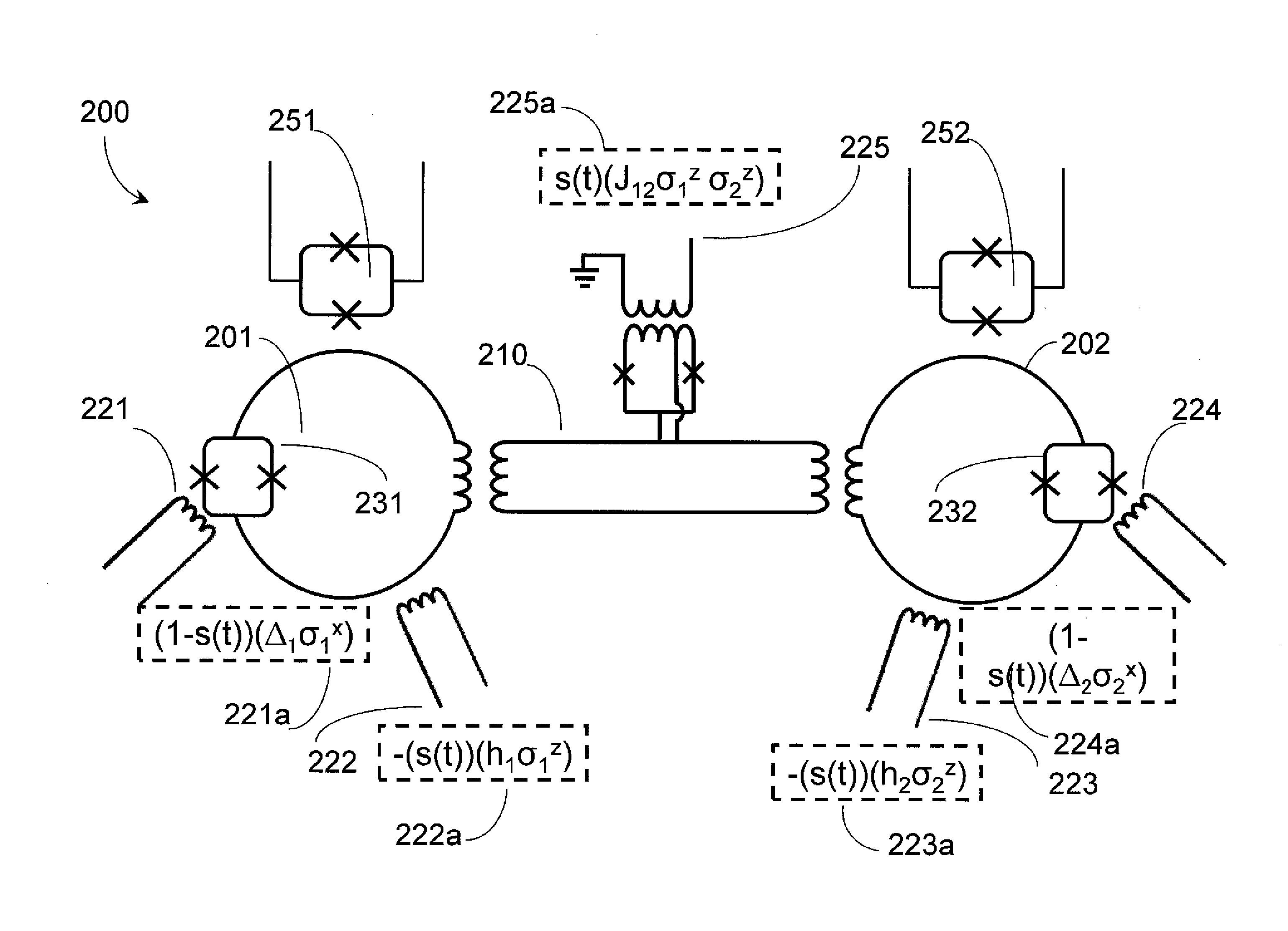
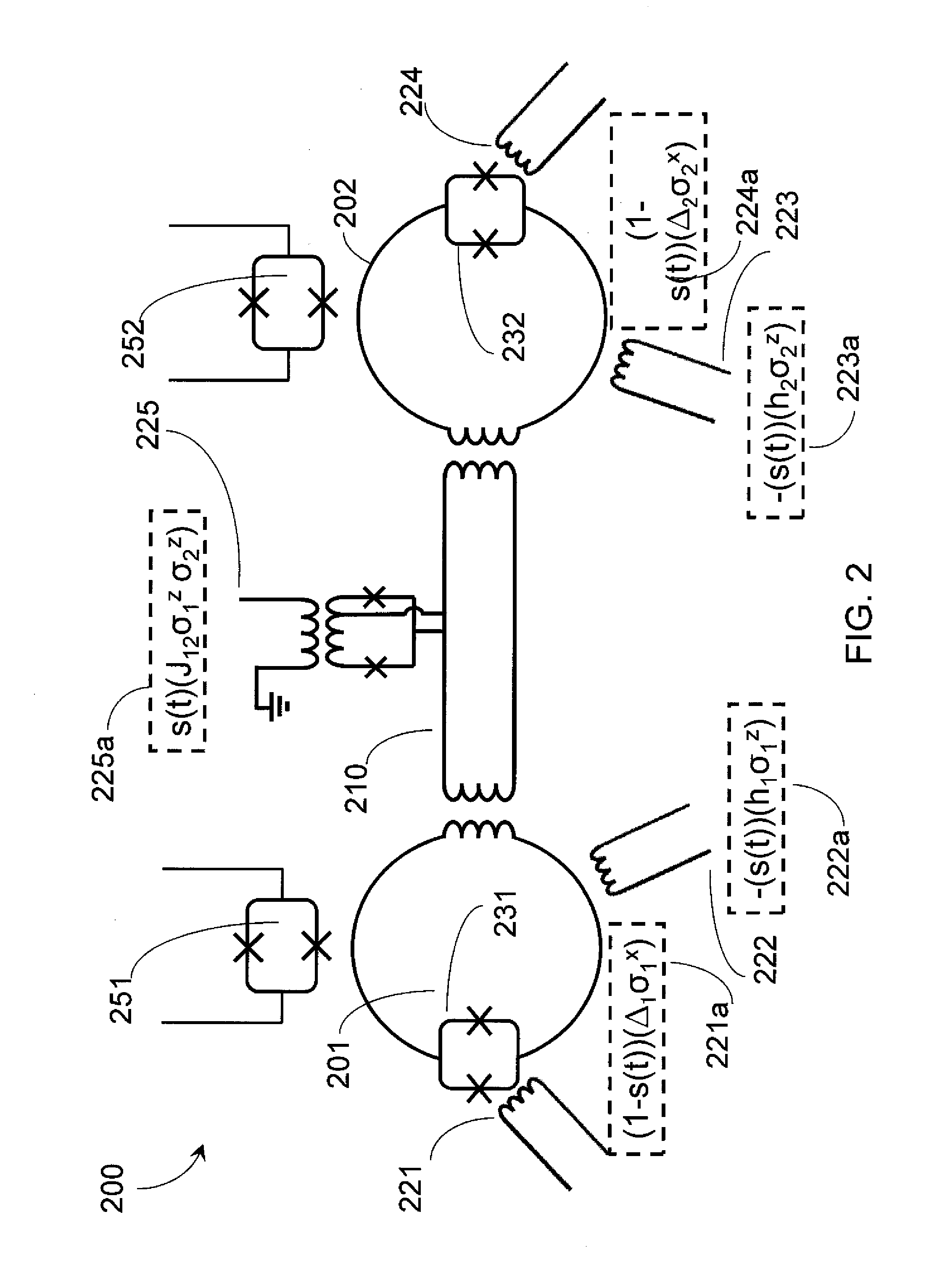
A quantum processor is operable as a universal adiabatic quantum computing system. The quantum processor includes physical qubits, with at least a first and second communicative coupling available between pairs of qubits via an in-situ tunable superconducting capacitive coupler and an in-situ tunable superconducting inductive coupler, respectively. Tunable couplers provide diagonal and off-diagonal coupling. Compound Josephson junctions (CJJs) of the tunable couplers are responsive to a flux bias to tune a sign and magnitude of a sum of a capacitance of a fixed capacitor and a tunable capacitance which is mediated across a pair of coupling capacitors. The qubits may be hybrid qubits, operable in a flux regime or a charge regime. Qubits may include a pair of CJJs that interrupt a loop of material and which are separated by an island of superconducting material which is voltage biased with respect to a qubit body.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
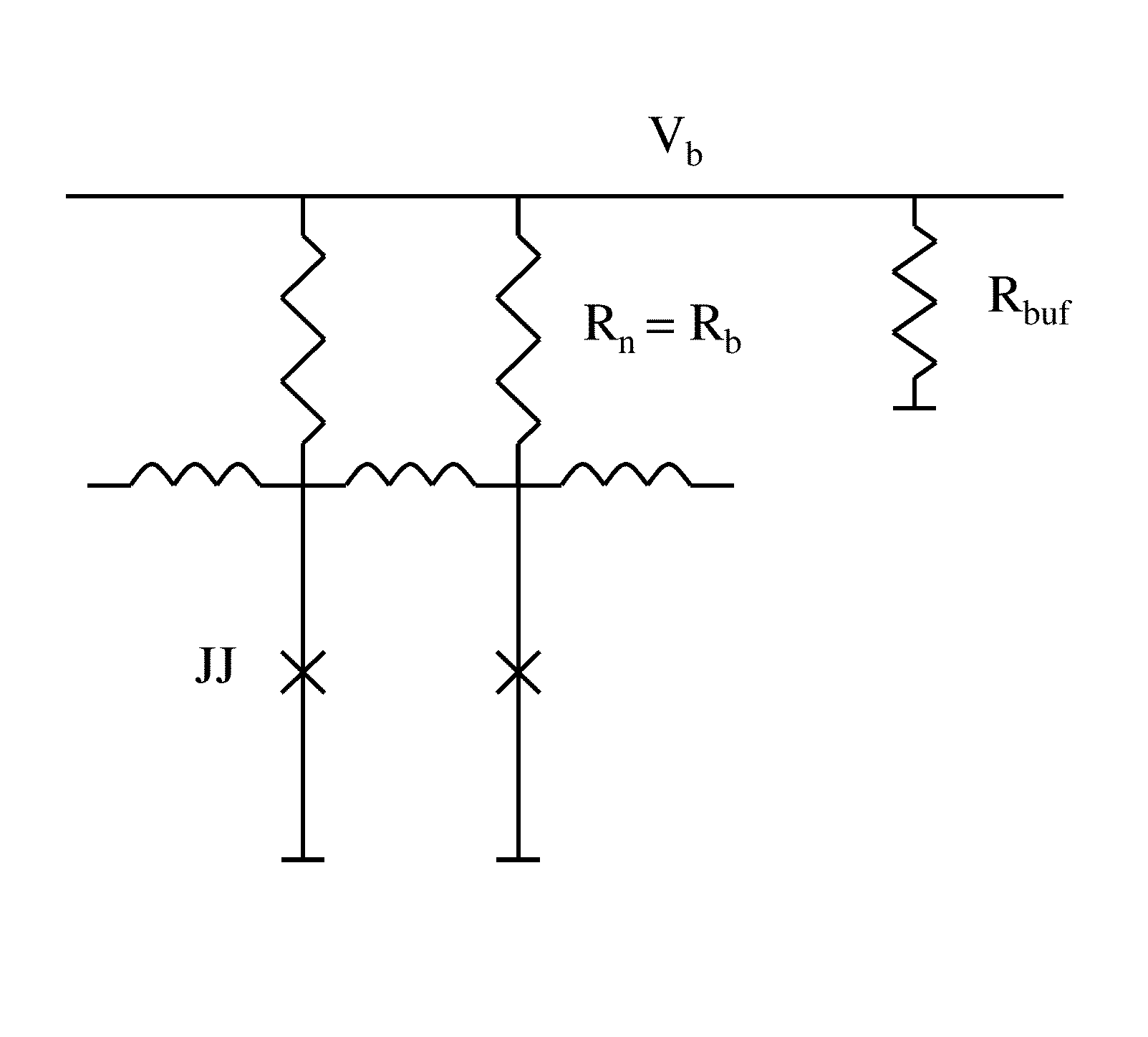
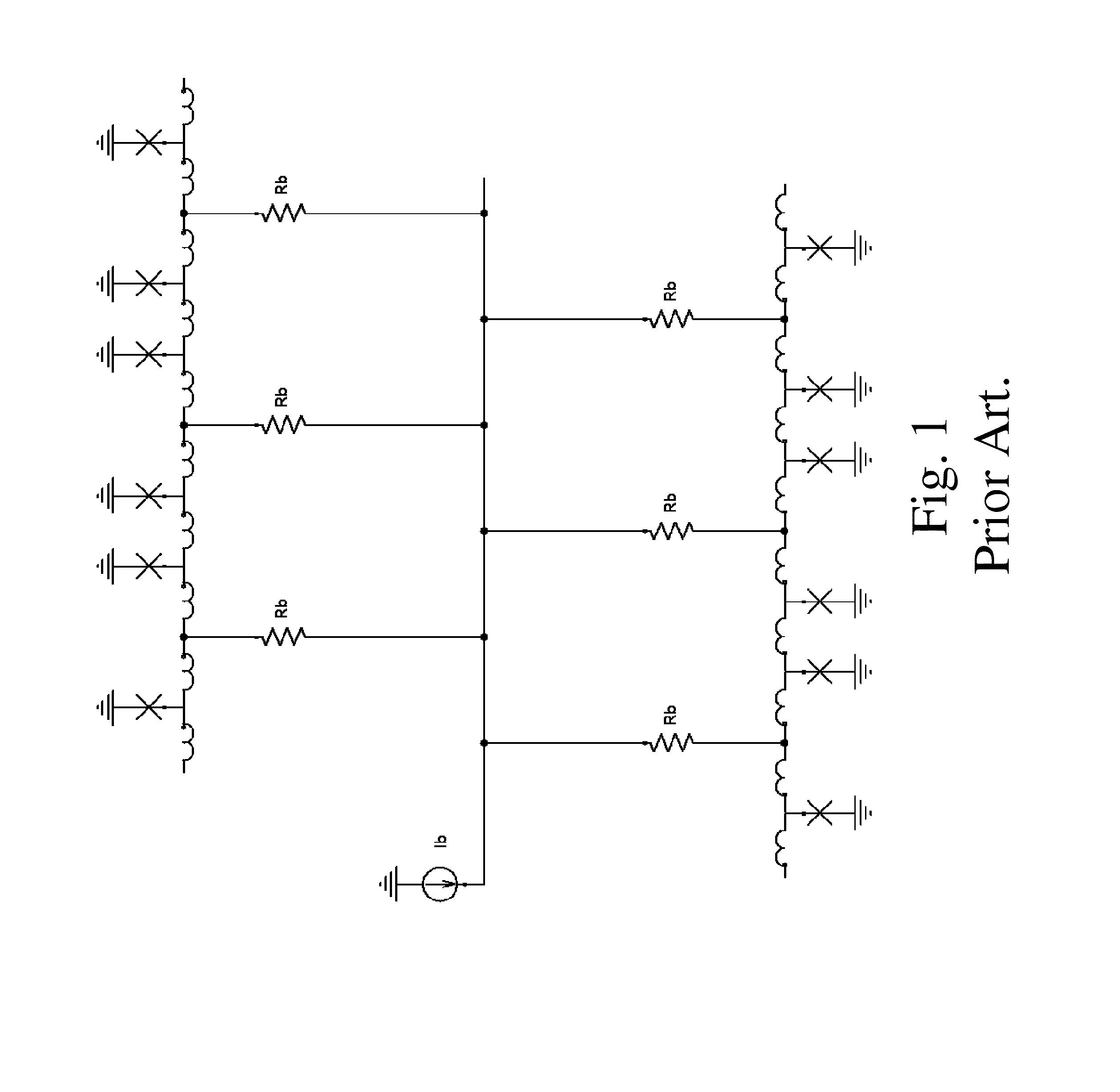
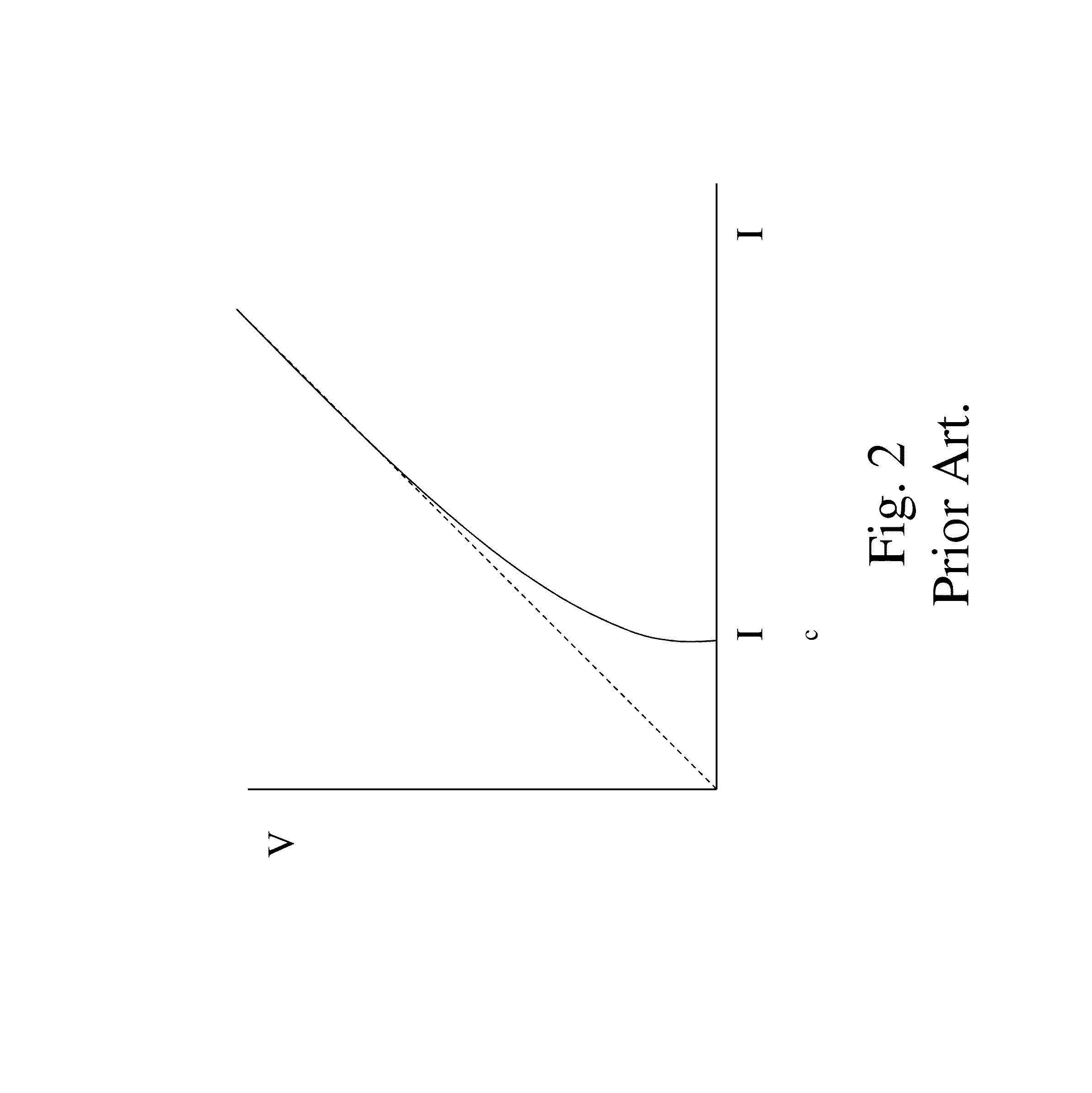
Low-power biasing networks for superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS8571614B1Maintain stabilityHigh dynamic impedanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSuperconducting integrated circuits
A superconducting integrated circuit, comprising a plurality of superconducting circuit elements, each having a variation in operating voltage over time; a common power line; and a plurality of bias circuits, each connected to the common power line, and to a respective superconducting circuit element, wherein each respective bias circuit is superconducting during at least one time portion of the operation of a respective superconducting circuit element, and is configured to supply the variation in operating voltage over time to the respective superconducting circuit element.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Systems and methods for superconducting flux qubit readout
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
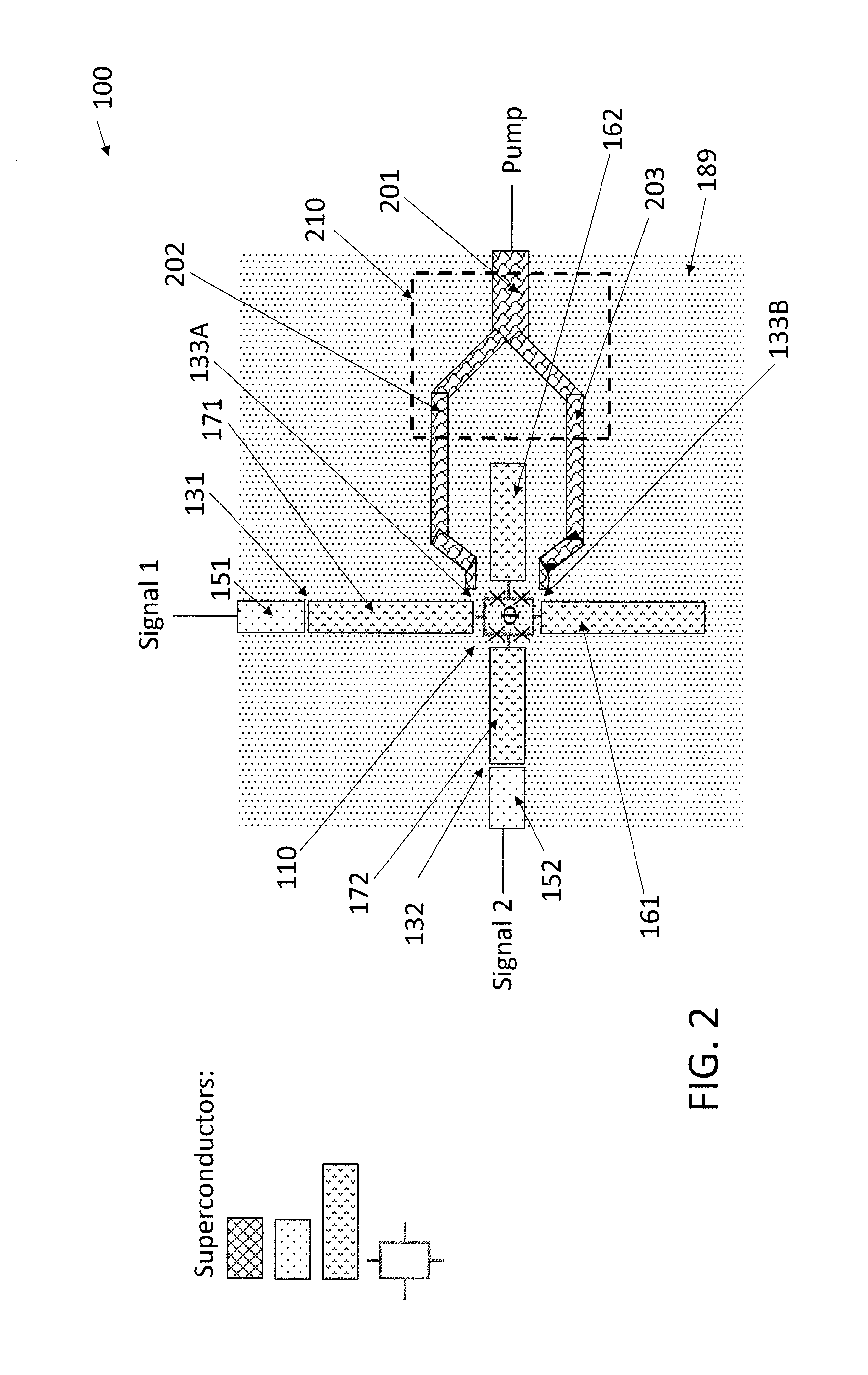
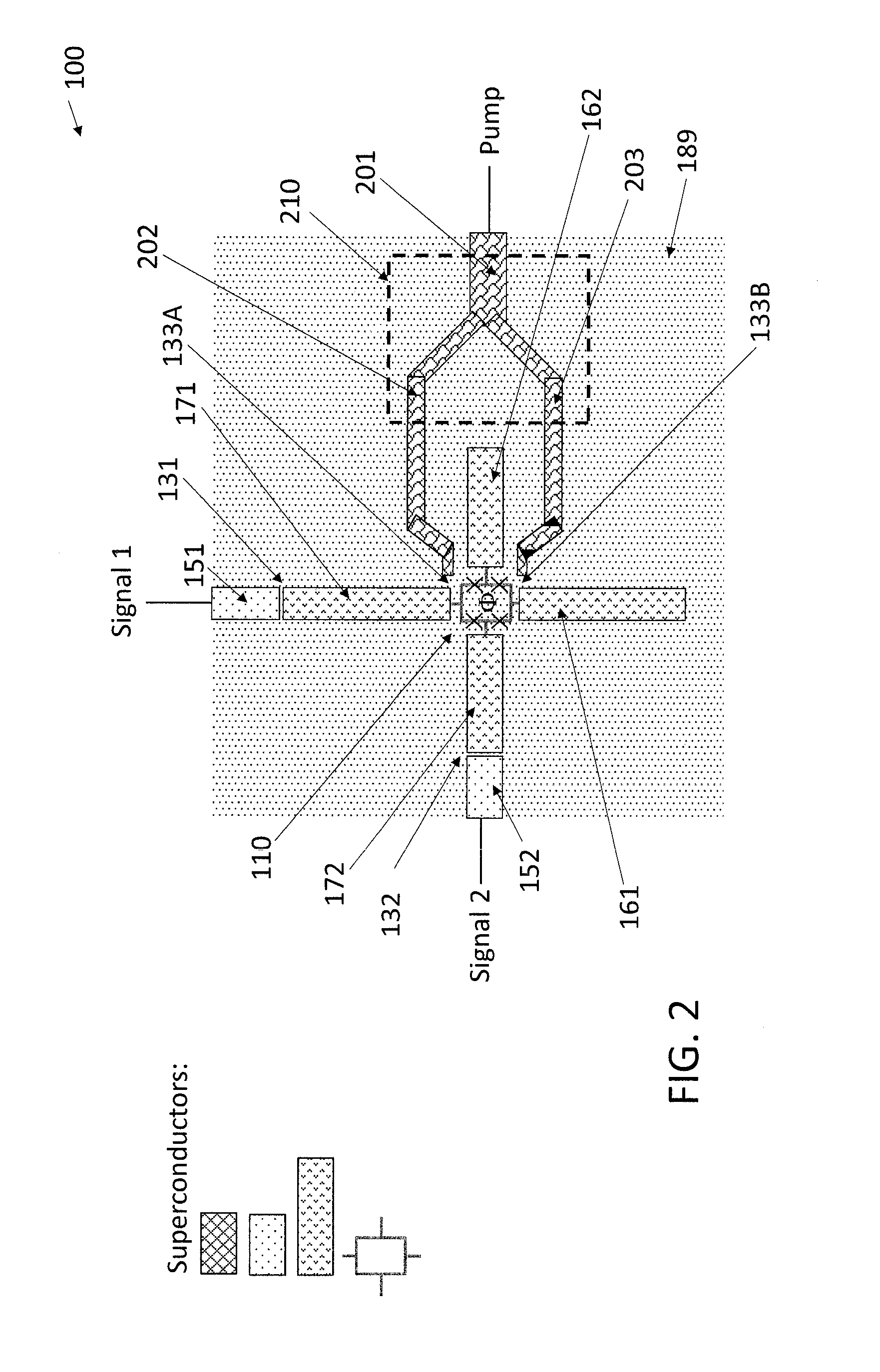
ActiveUS20160380636A1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:IBM CORP
Active timing arbitration in superconductor digital circuits
InactiveUS6507234B1Electronic switchingDissimilar materials junction devicesInductorSuperconducting transmission lines
A superconductor circuit (50) for providing active timing arbitration between SFQ pulses. The superconductor circuit (50) includes a first superconducting transmission line (52) having at least one inductor (54) for transmitting first input pulses, and a second superconducting transmission line (62) having at least one inductor (64) for transmitting second input pulses that are correlated to the first input pulses. The first and second superconducting transmission lines (52, 62) are coupled together in order to generate a flux attraction between the first and second input pulses for reducing relative timing uncertainty.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
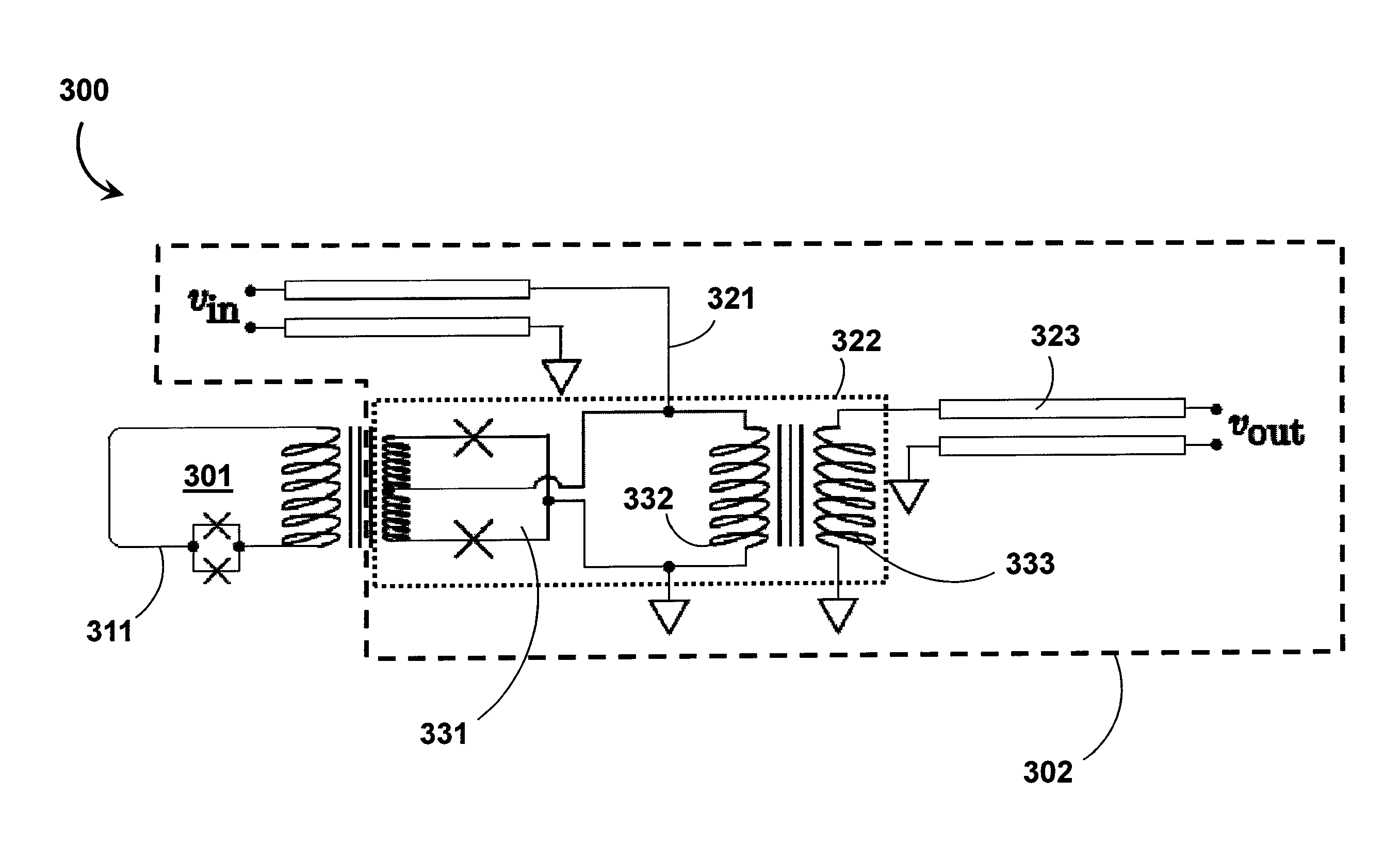
Superconducting quantum logic and applications of same
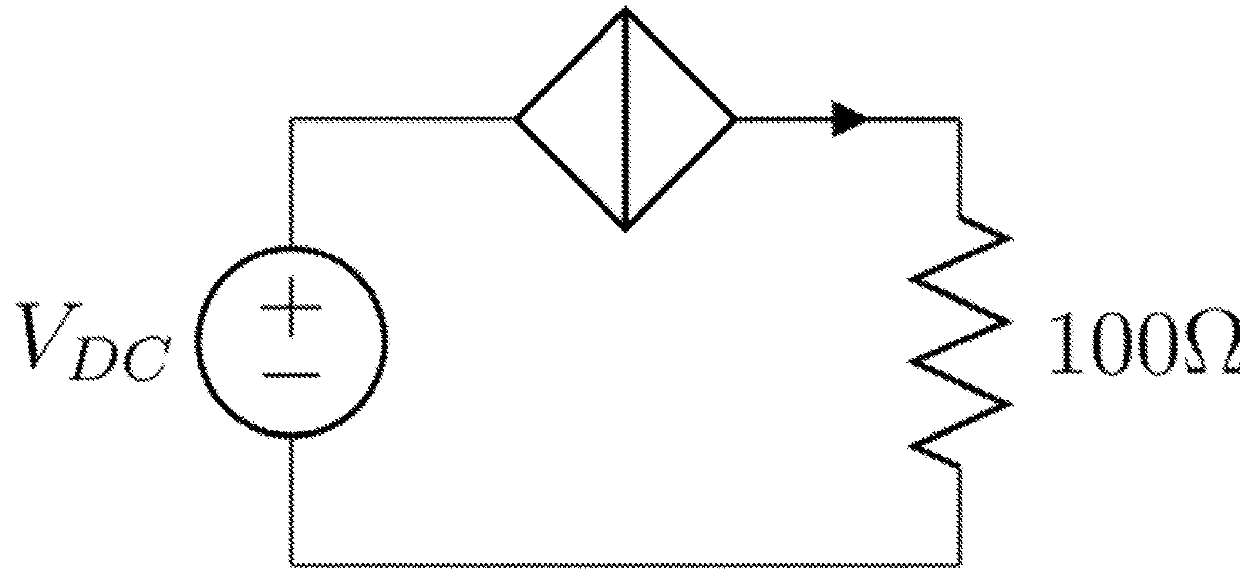
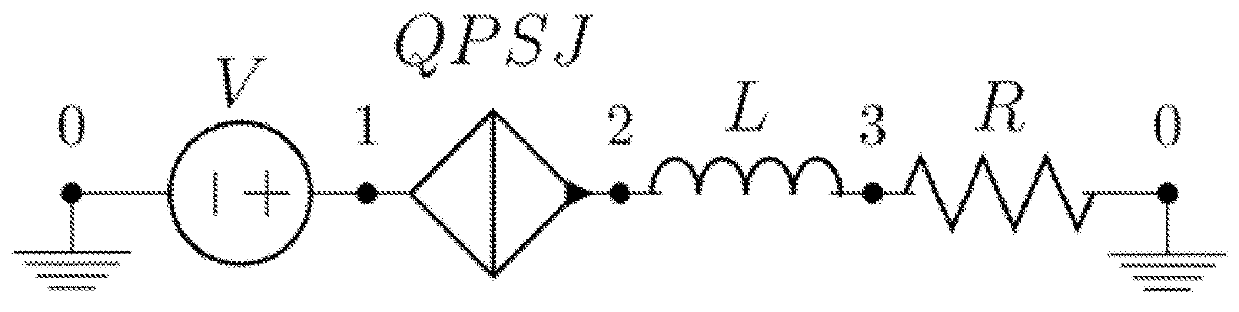
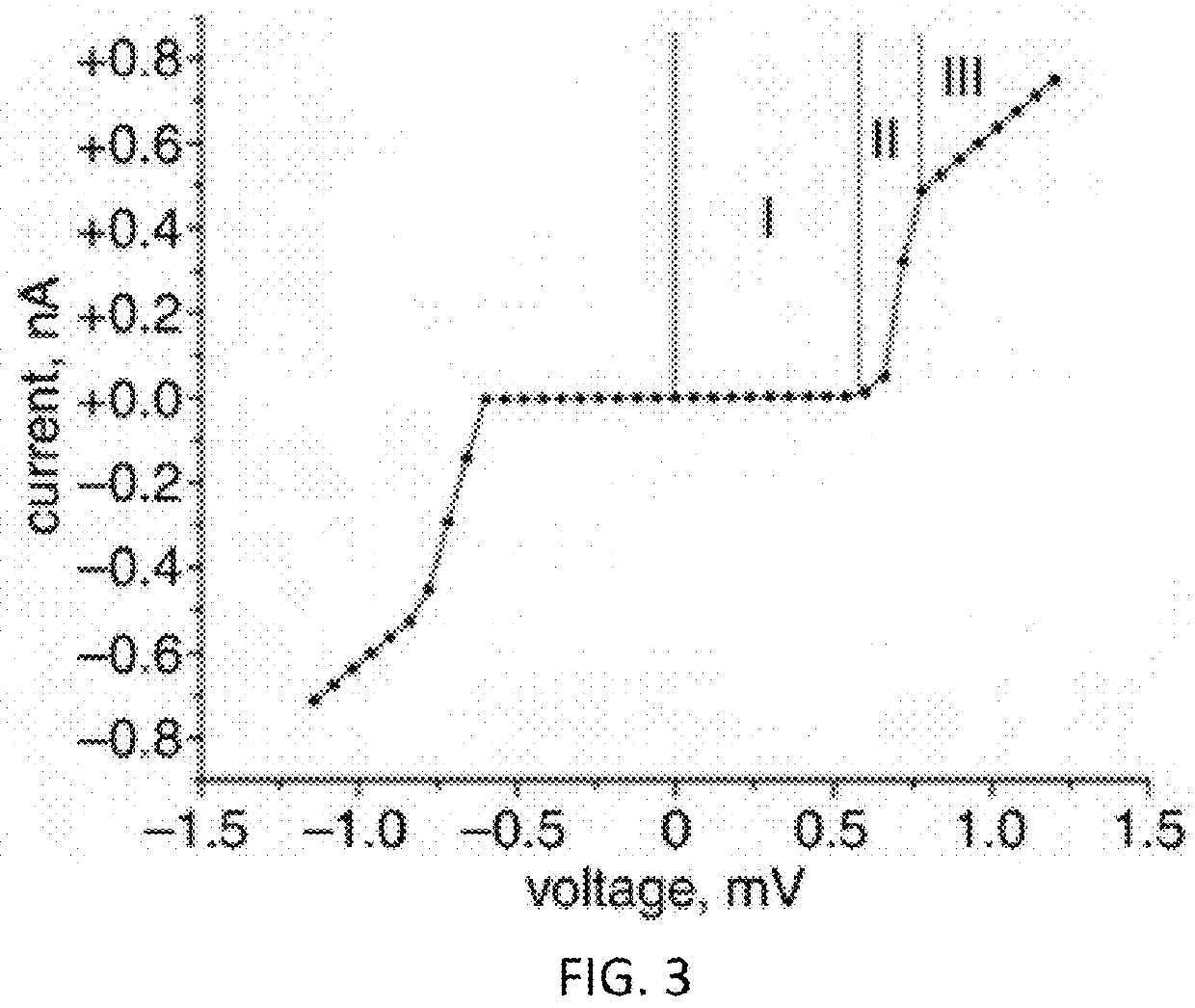
ActiveUS9998122B2Avoid flowExclusive-OR circuitsPulse generation by super conductive devicesVoltage pulseLogic cell
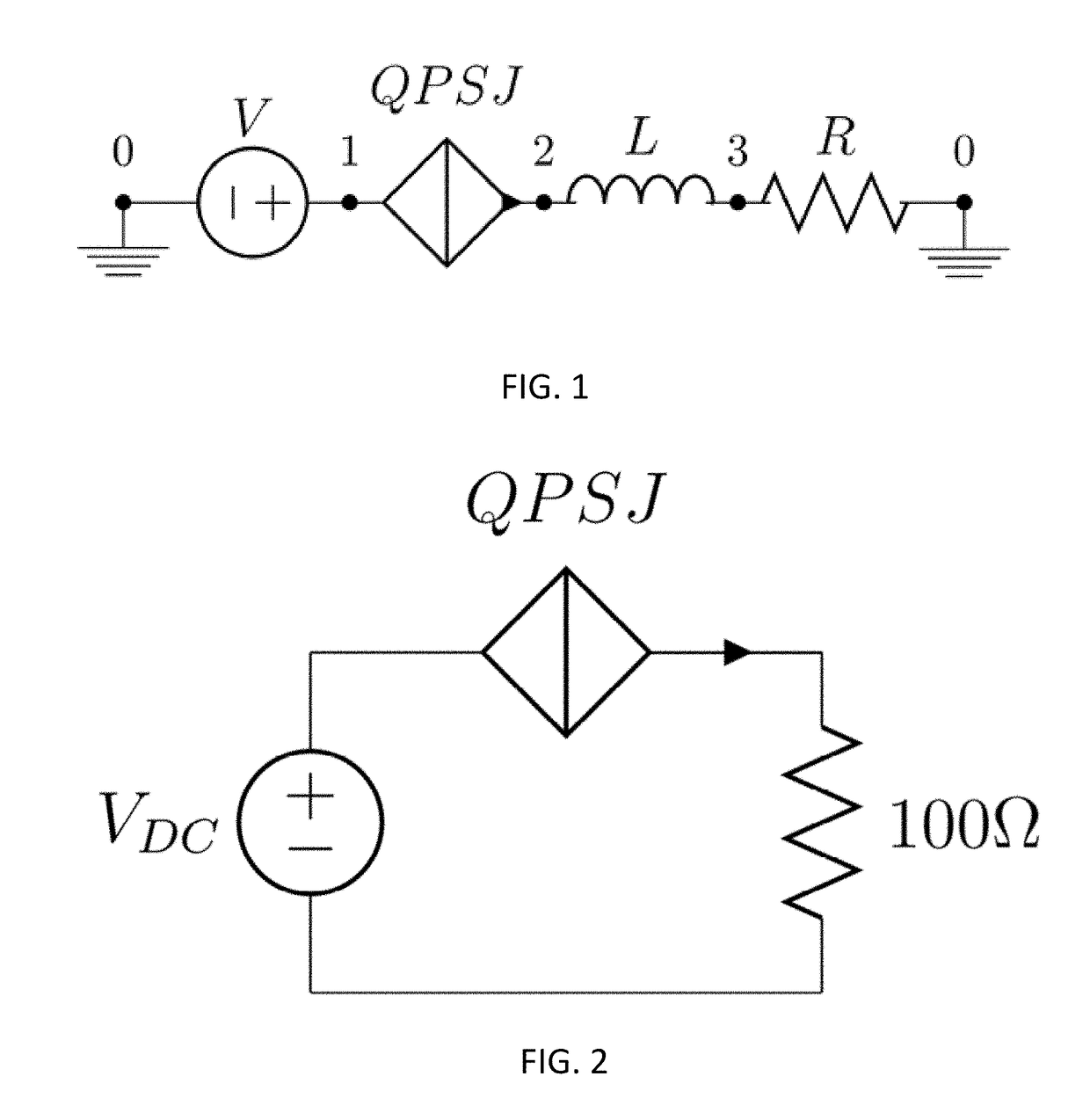
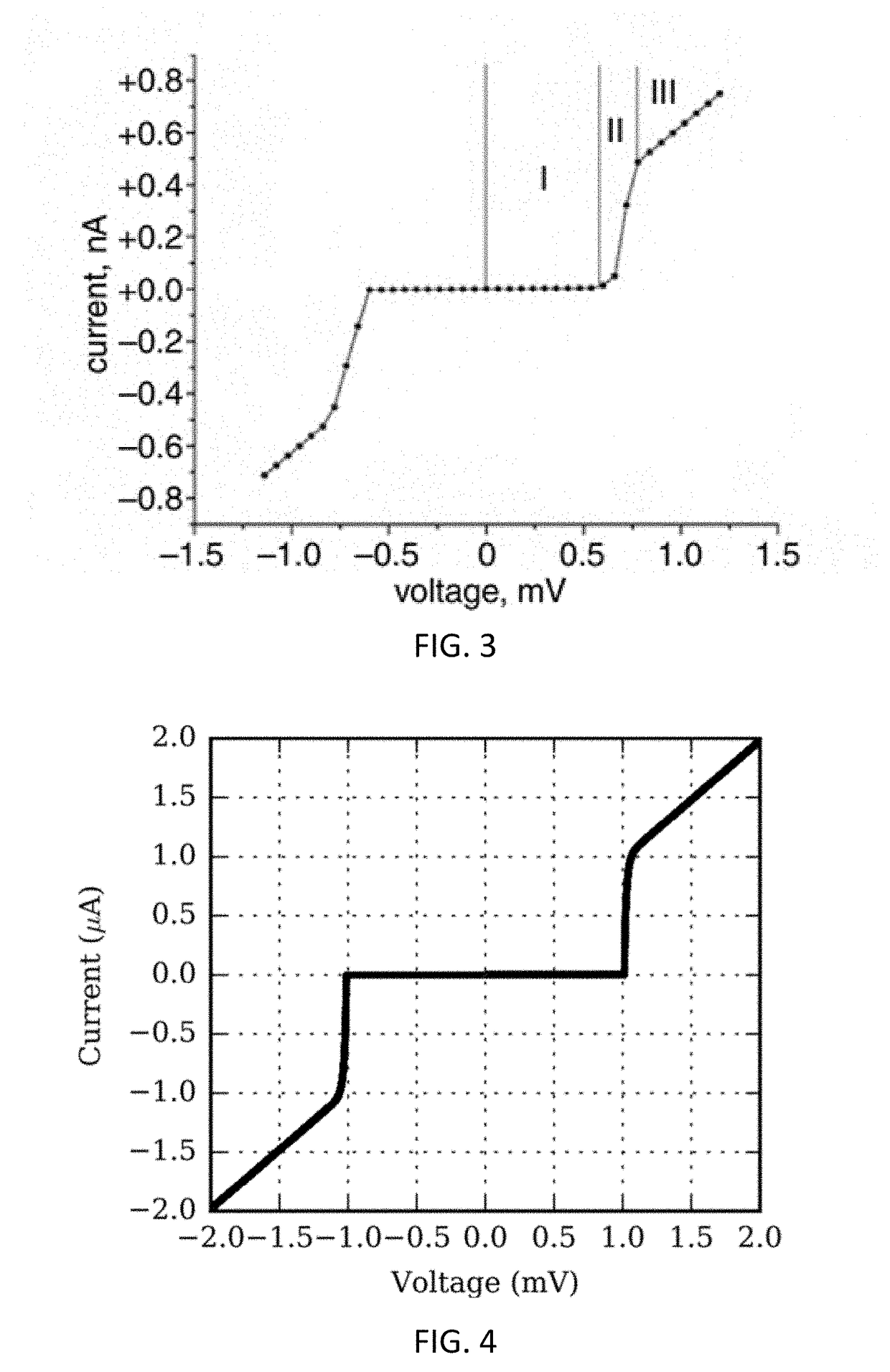
A superconducting logic cell includes at least one quantum phase-slip junction (QPSJ) for receiving at least one input and responsively providing at least one output, each QPSJ being configured such that when an input voltage of an input voltage pulse exceeds a critical value, a quantized charge of a Cooper electron pair tunnels across said QPSJ as an output, when the input voltage is less than the critical value, no quantized charge of the Cooper electron pair tunnels across said QPSJ as the output, where the presence and absence of the quantized charge in the form of a constant area current pulse in the output form two logic states, and the at least one QPSJ is biased with a bias voltage. The superconducting logic cell further includes at least one Josephson junction (JJ) coupled with the at least one QPSJ to perform one or more logic operations.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
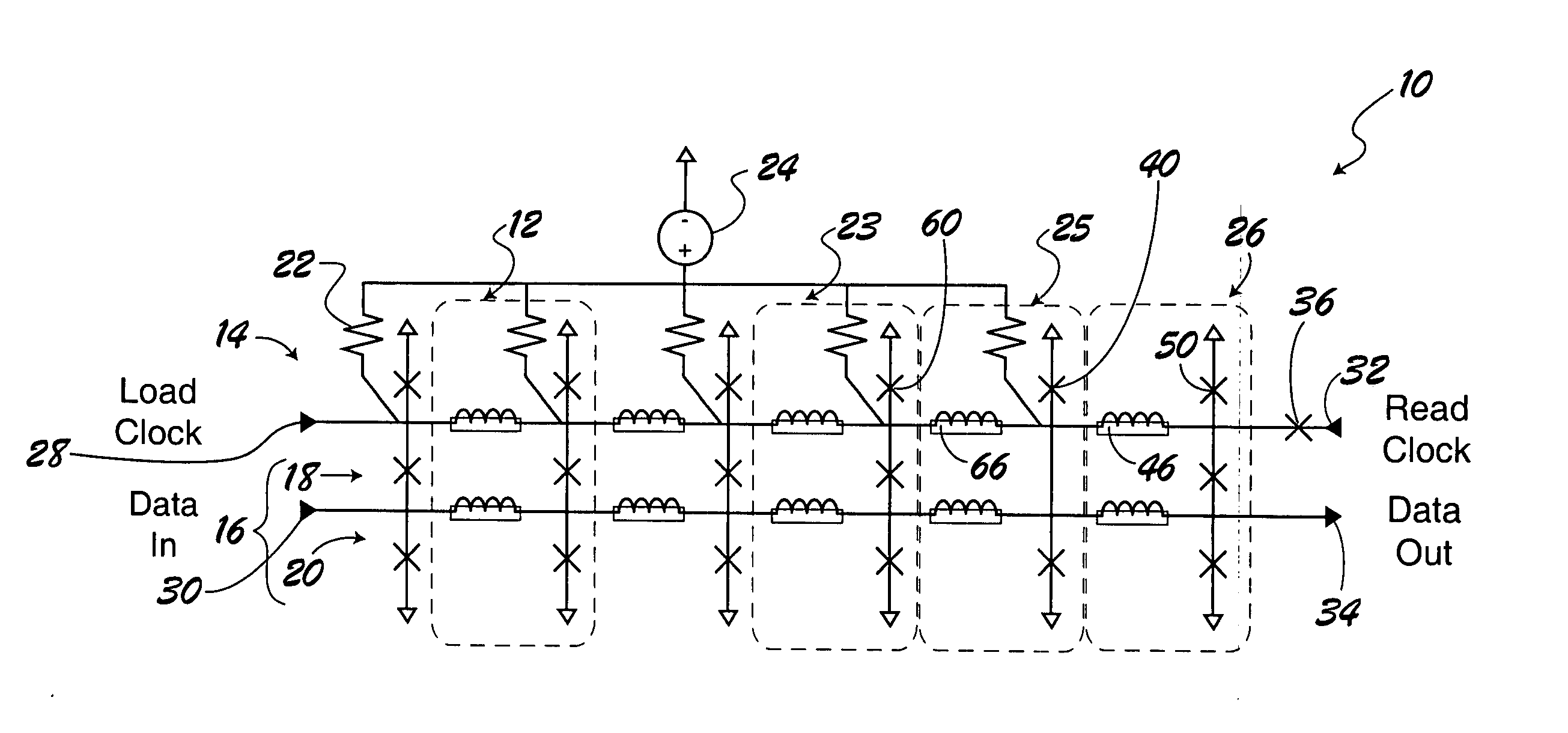
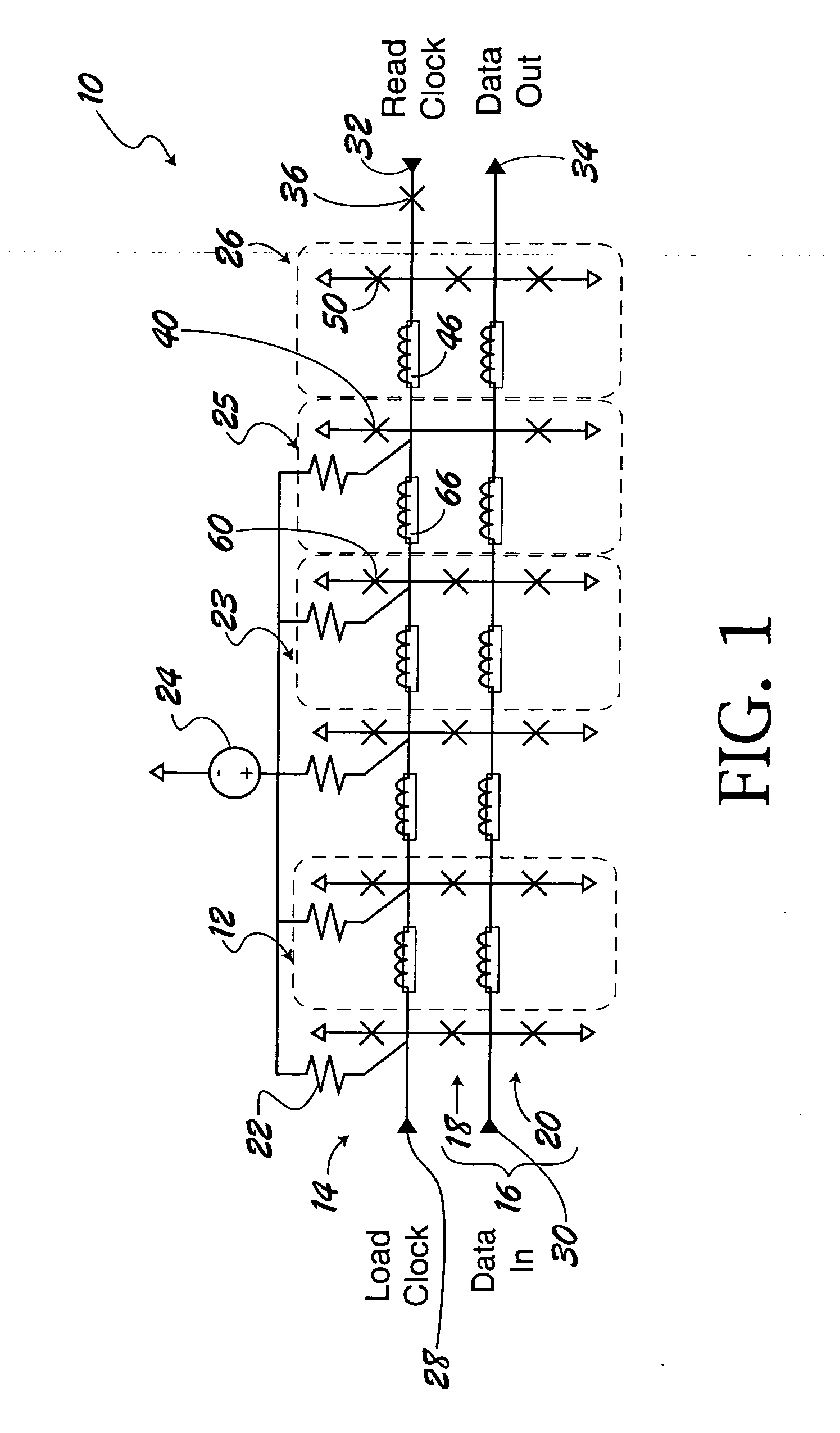
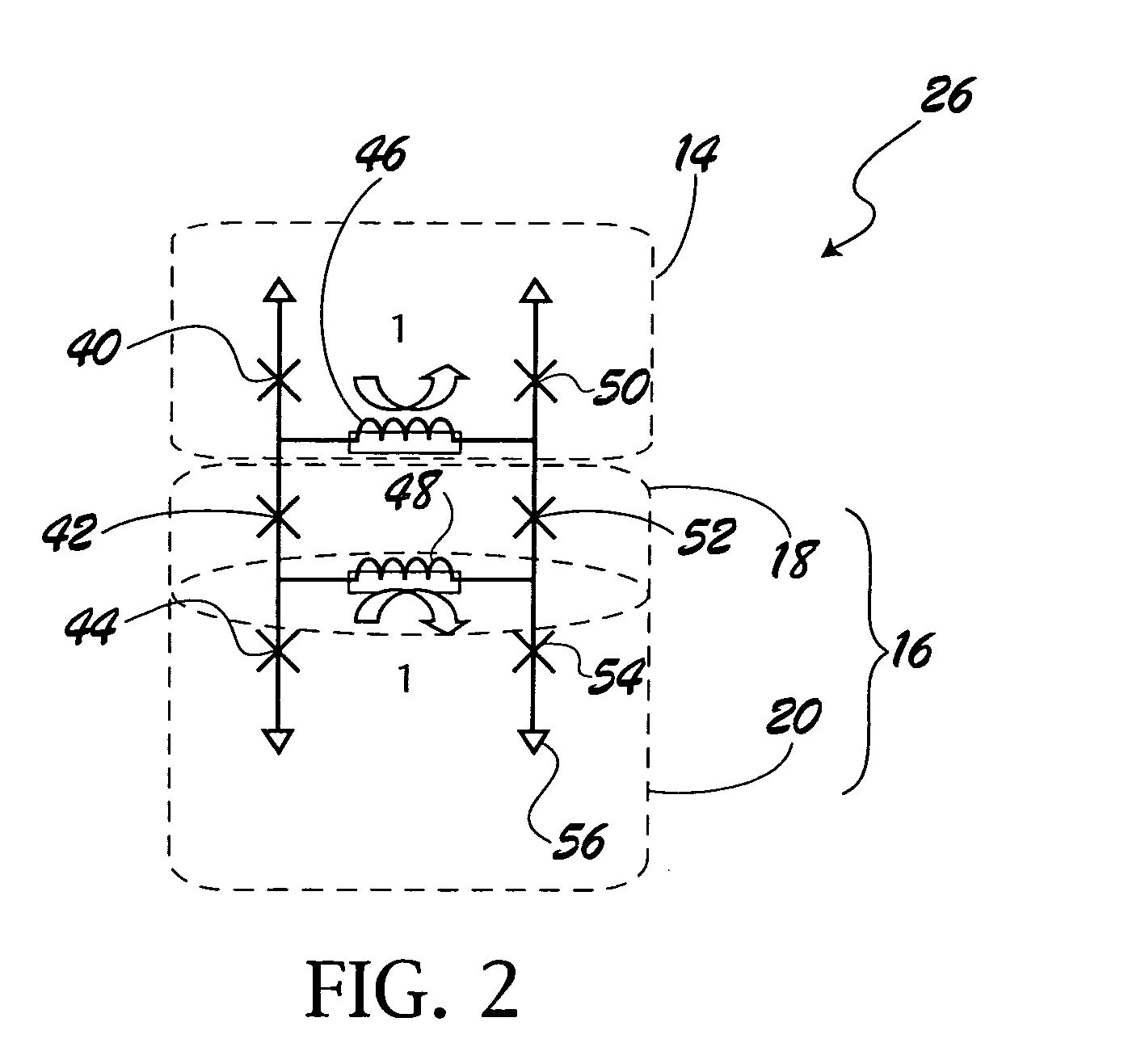
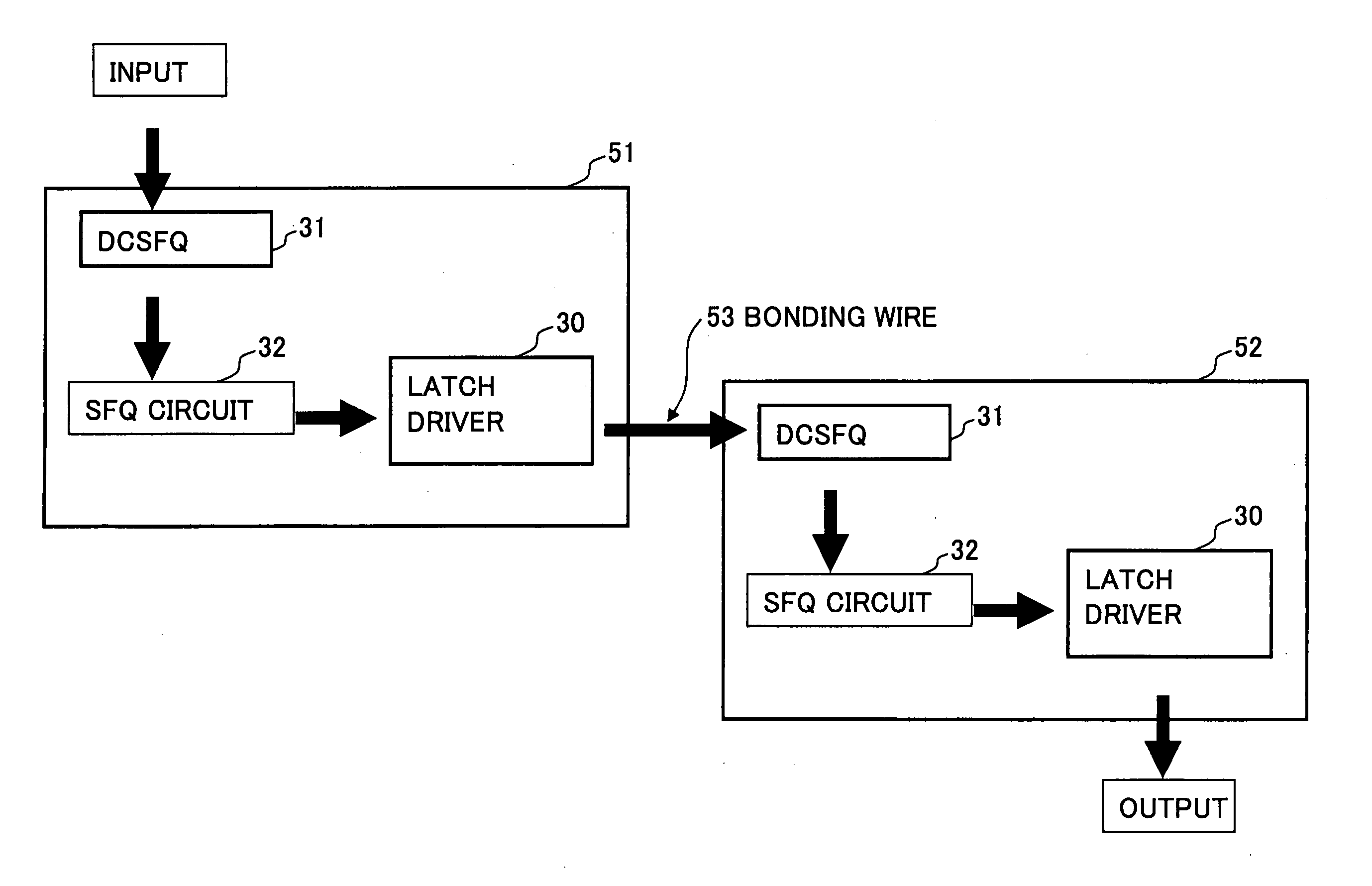
Superconducting digital first-in first-out buffer using physical back pressure mechanism
InactiveUS20050023518A1Digital storageDissimilar materials junction devicesData signalComputer science
A digital first-in first-out (FIFO) buffer (10) for use with Single Flux Quantum (SFQ) superconductive integrated circuits. The digital FIFO buffer (10) includes a clock-storage circuit (14) for receiving and storing load and read clock signals (100, 104) and a data-storage circuit (16) connected to the clock-storage circuit (14) for receiving and storing data signal pulses (102) in the order which the data signal pulses (102) are received relative to the load clock signal (100). The data-storage circuit (16) outputs the SFQ pulse signal independent of the load clock signal (100). The previously stored clock and data signal pulses (100, 102) provide physical back pressure to their subsequent signal pulses.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
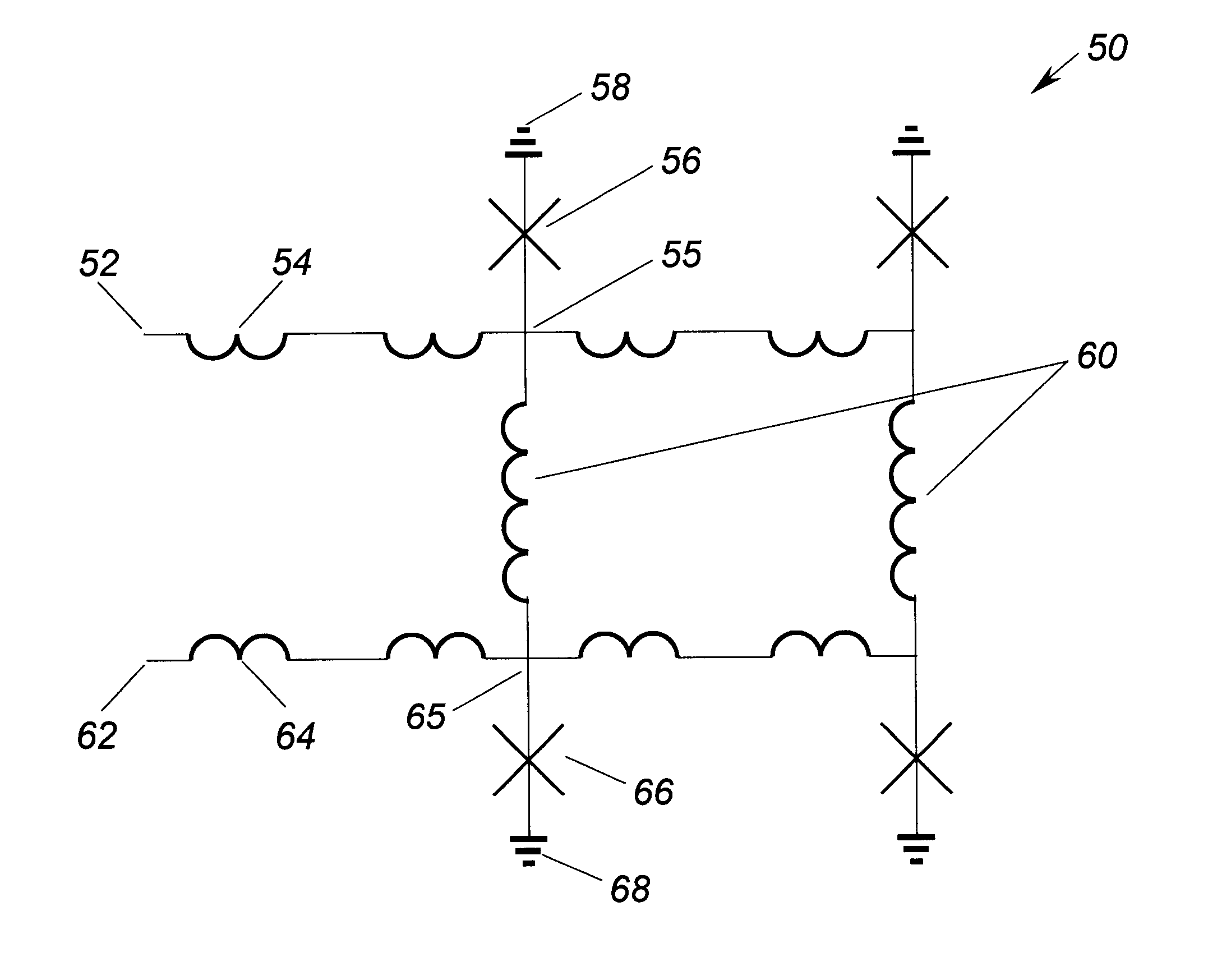
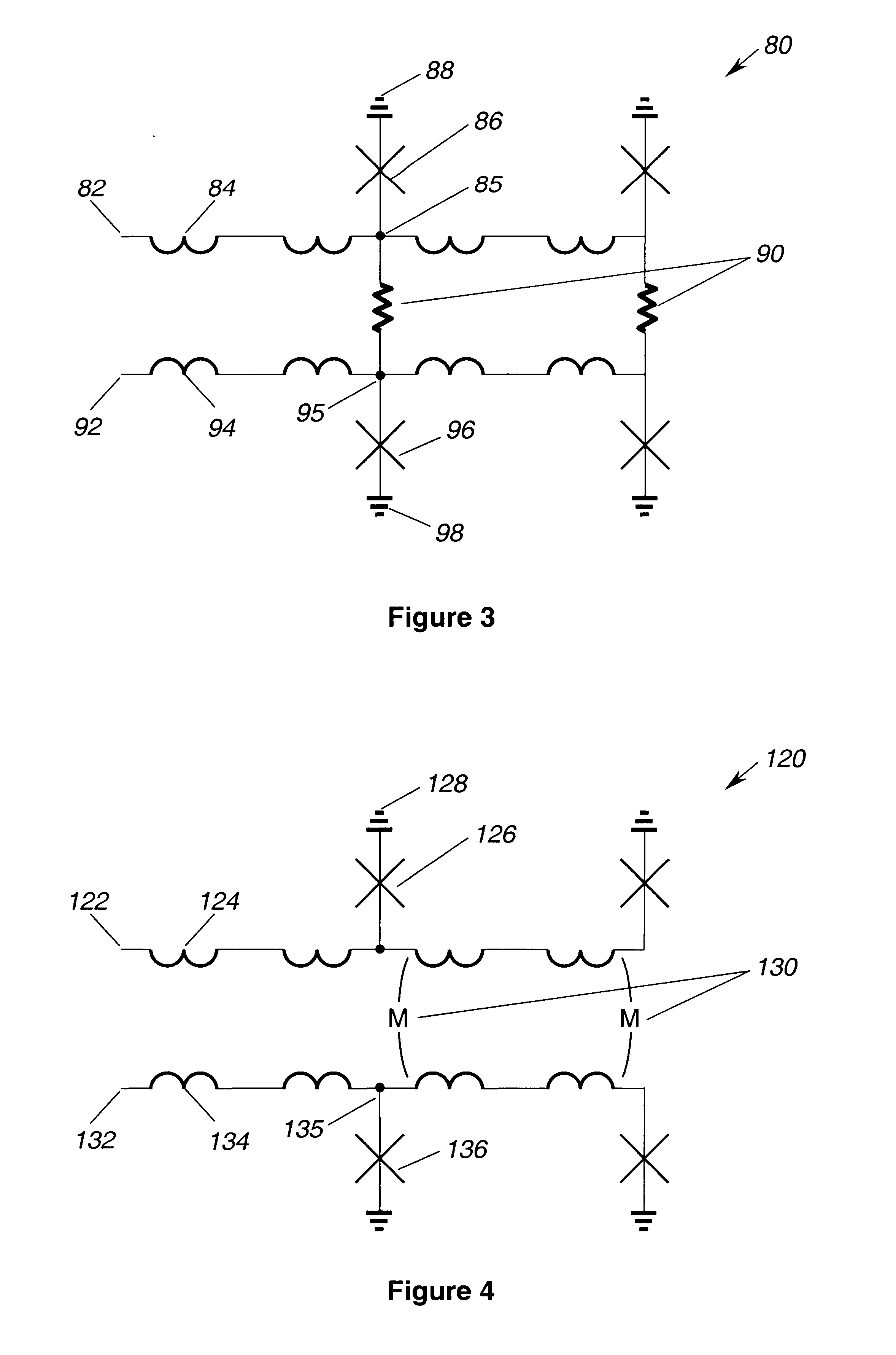
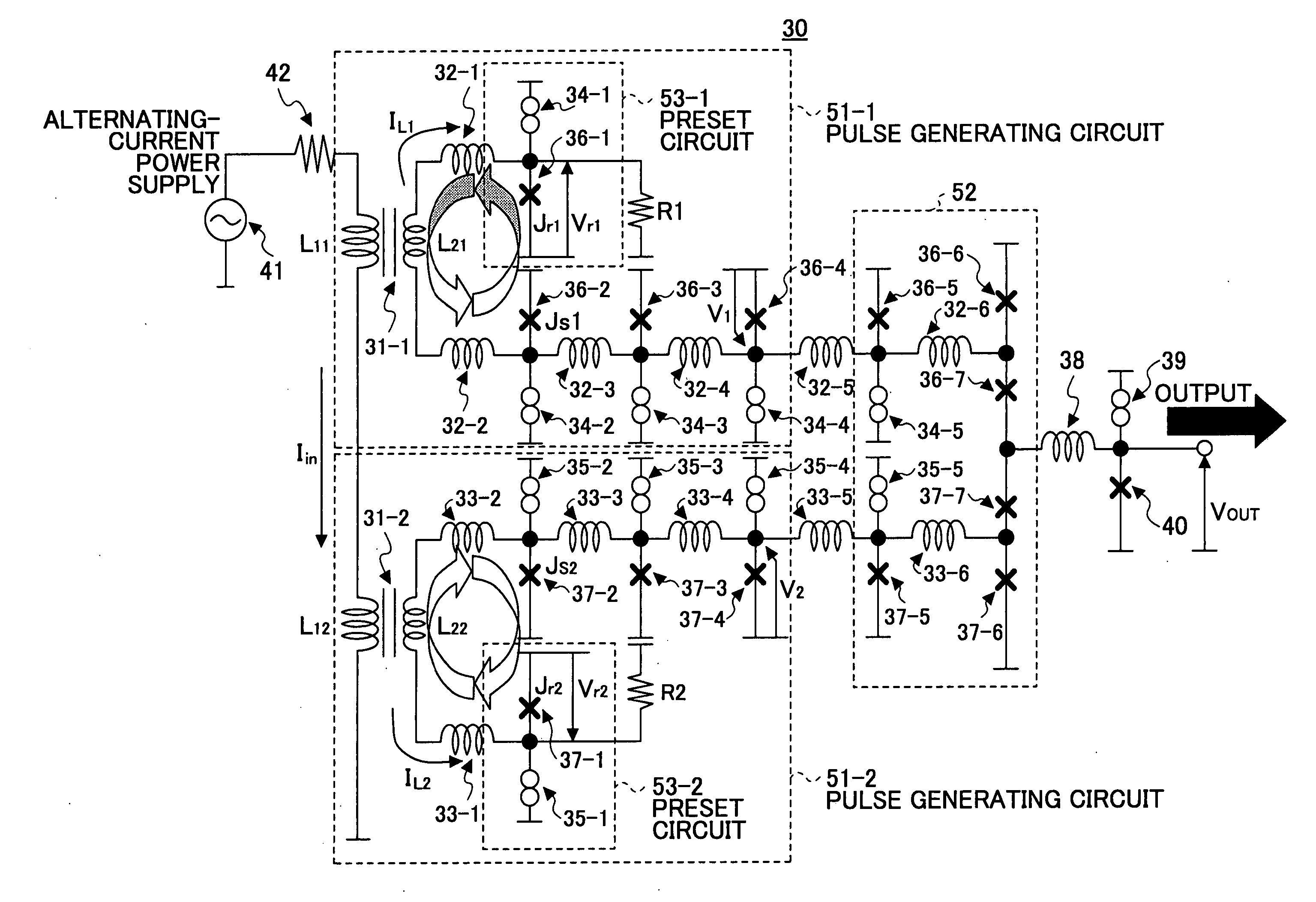
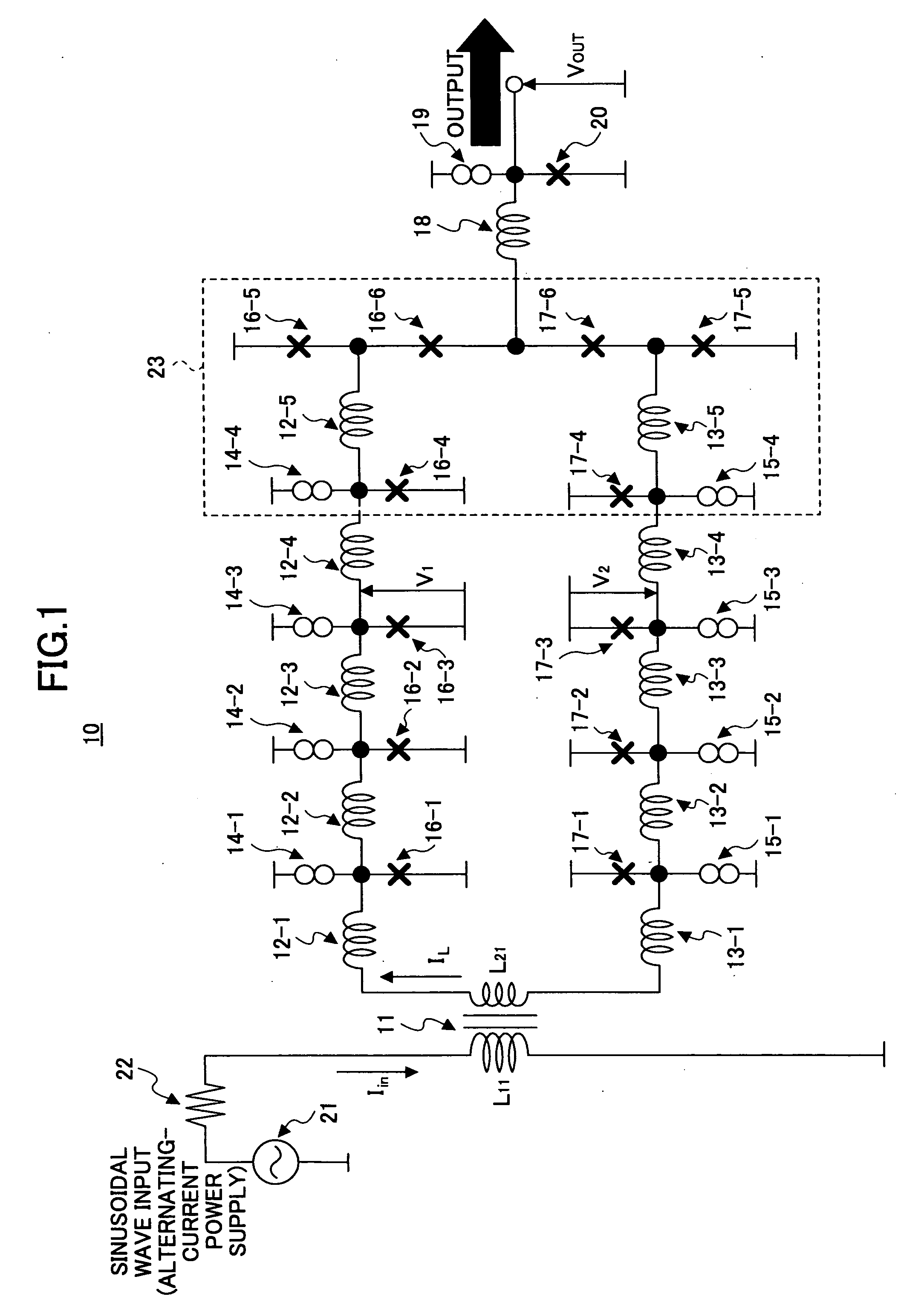
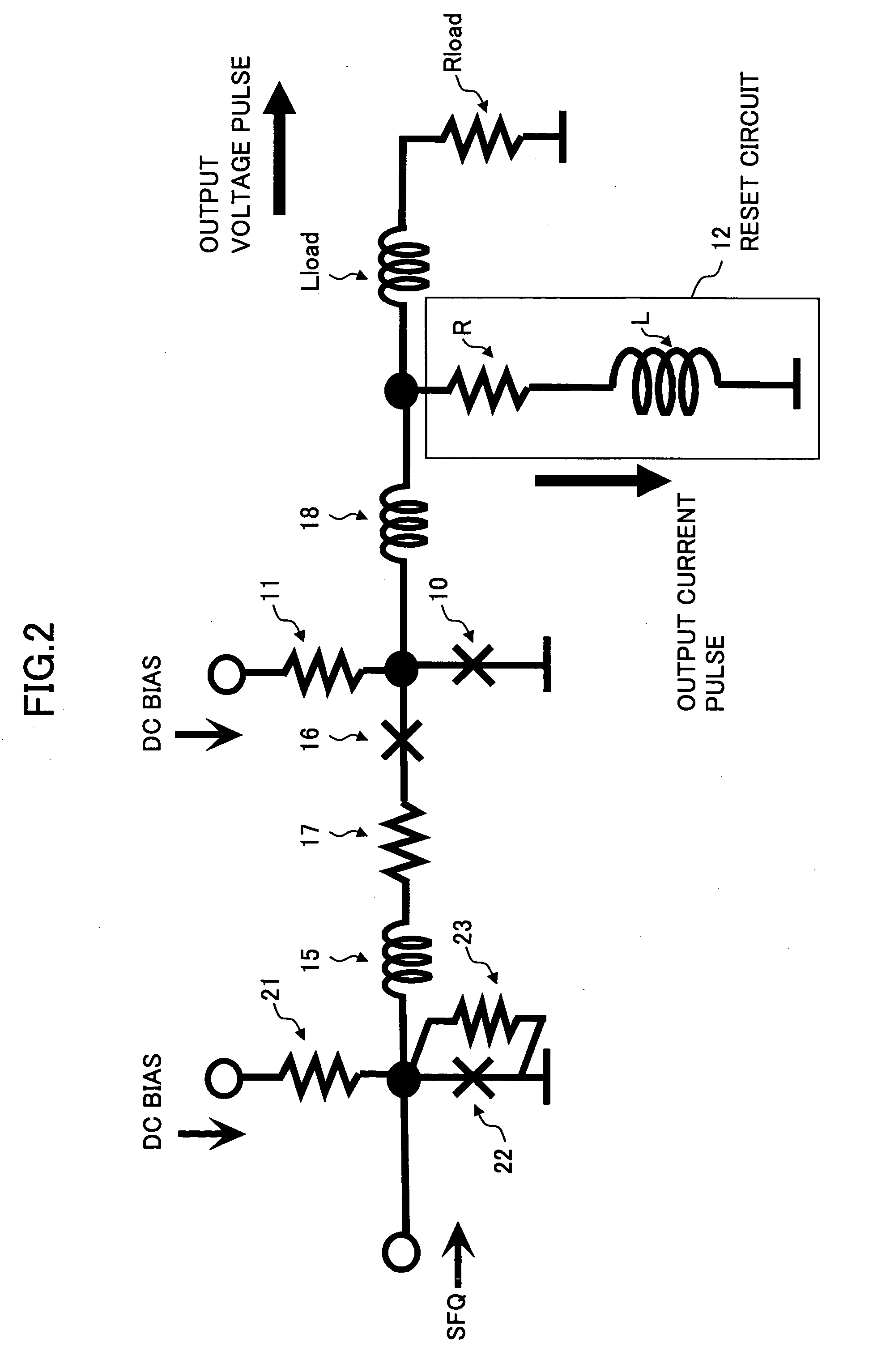
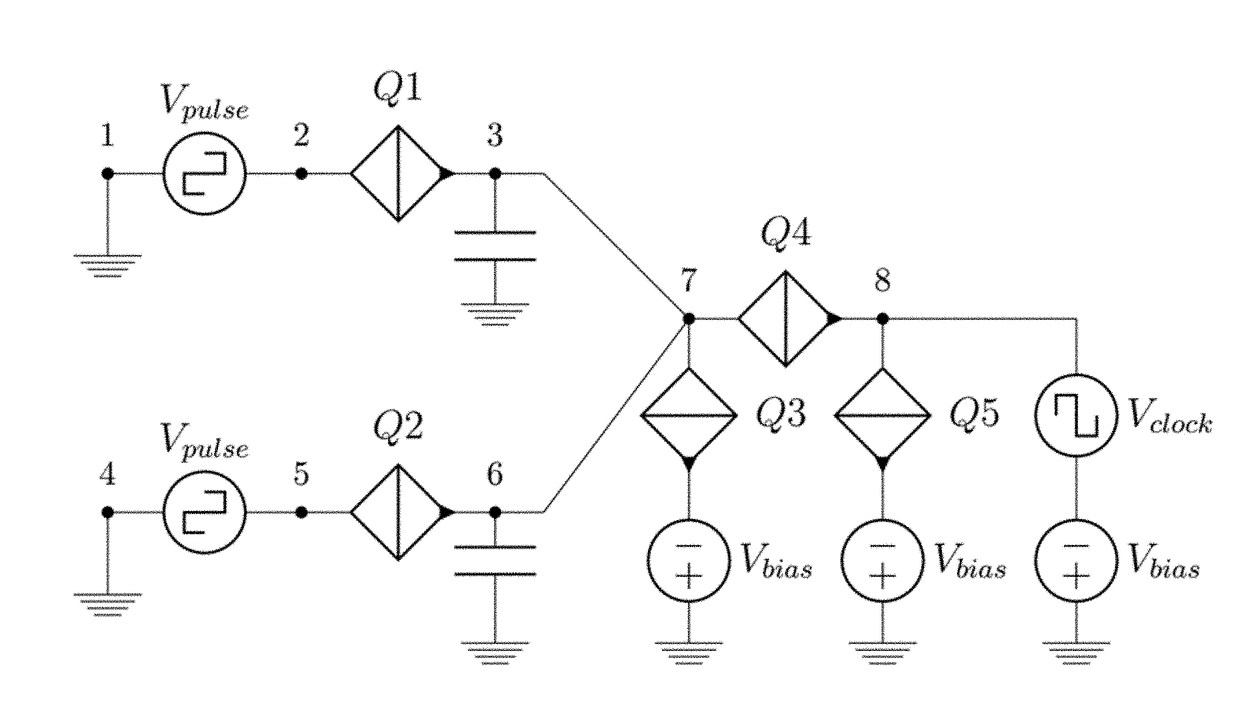
Superconducting circuit for generating pulse signal
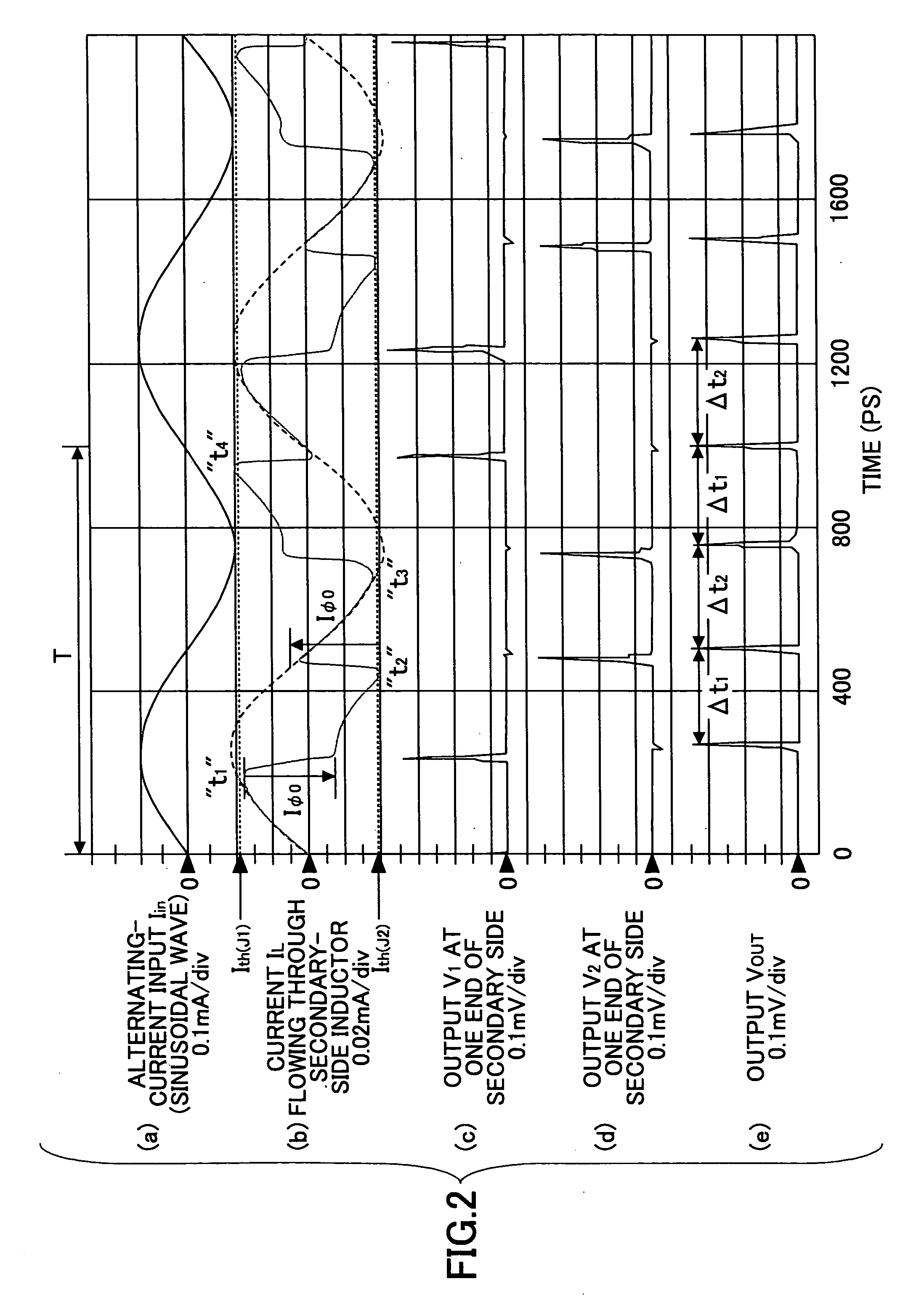
InactiveUS20070052441A1Small jitterImprove accuracyPulse generation by super conductive devicesManipulation for frequency changeInductorAlternating current
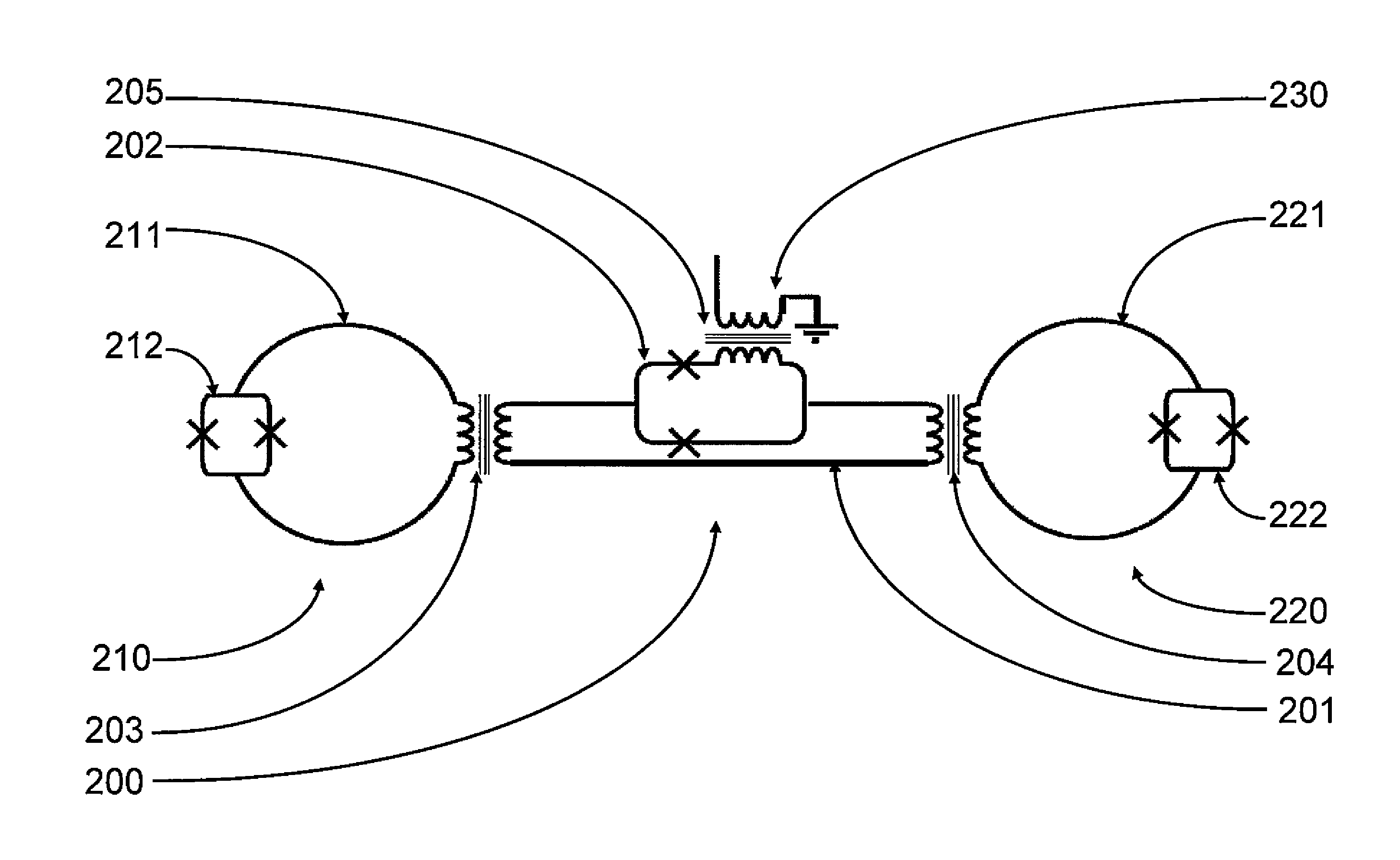
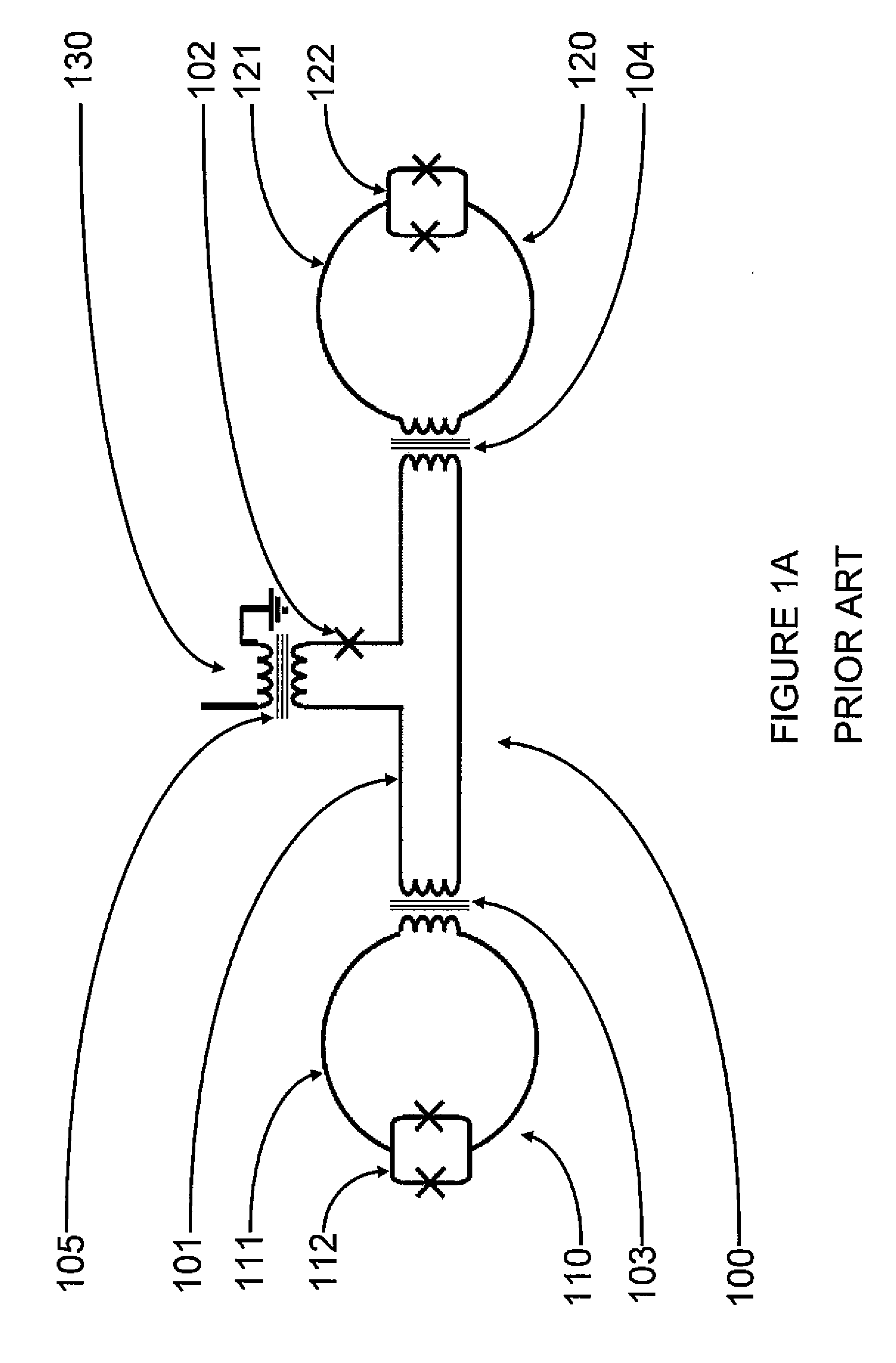
A superconducting circuit includes a first transformer to produce a first alternating-current output at a secondary-side inductor, a second transformer to produce a second alternating-current output at a secondary-side inductor, a first pulse generating circuit to produce a single flux quantum pulse responsive to the first alternating-current output, a second pulse generating circuit to produce a single flux quantum pulse responsive to the second alternating-current output, and a confluence buffer circuit to merge the single flux quantum pulses from the pulse generating circuits, wherein each of the pulse generating circuits includes a superconducting loop including the secondary-side inductor, a first Josephson junction situated in the superconducting loop to generate the single flux quantum pulse, and a second Josephson junction situated in the superconducting loop, a threshold value of the second Josephson junction for an electric current flowing through the secondary-side inductor being different from that of the first Josephson junction.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Superconductive crossbar switch
ActiveUS6960929B2Low powerDetects and resolve conflictMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectronic switchingCrossbar switchGigabit
Owner:BEDARD FERNAND D
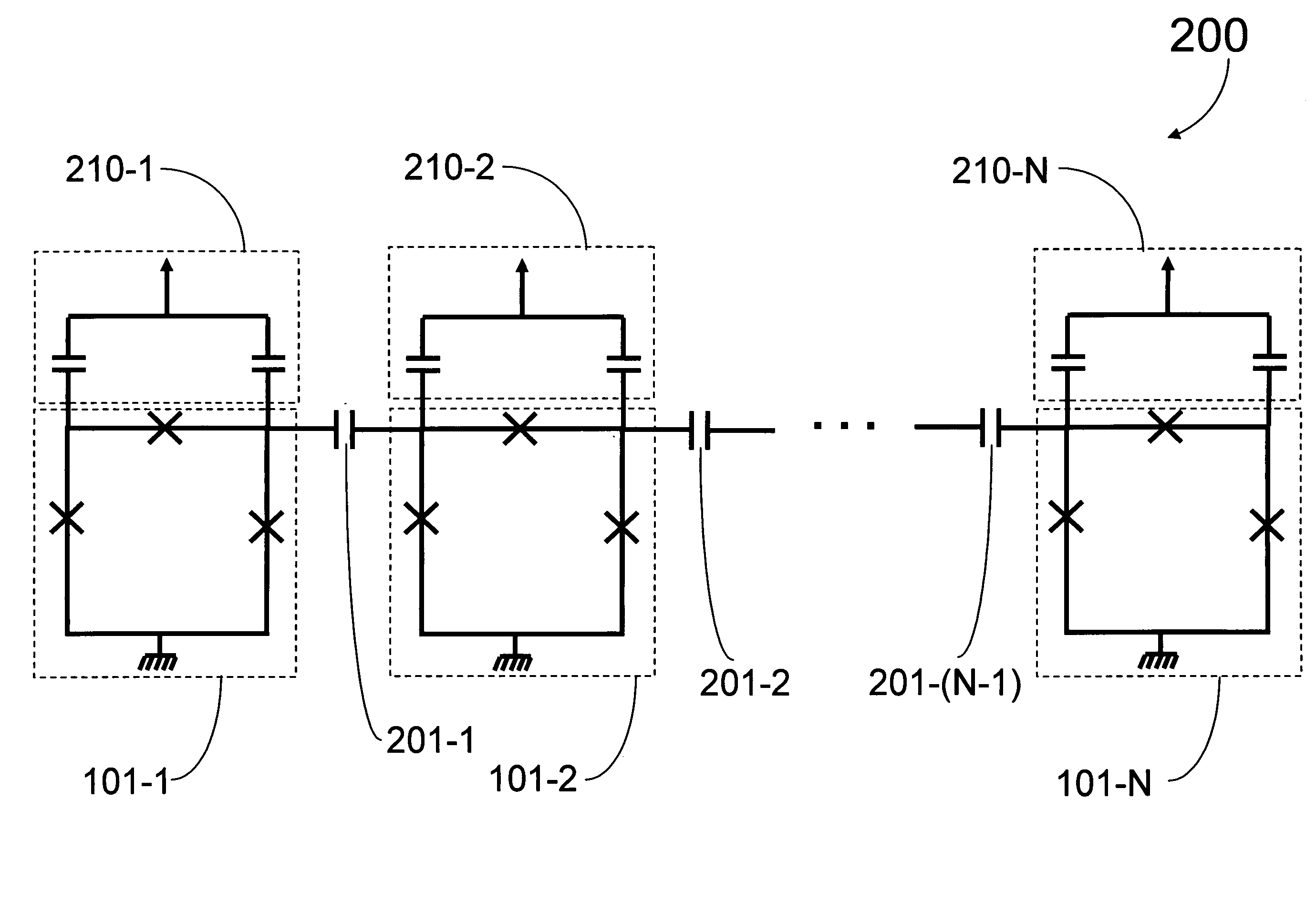
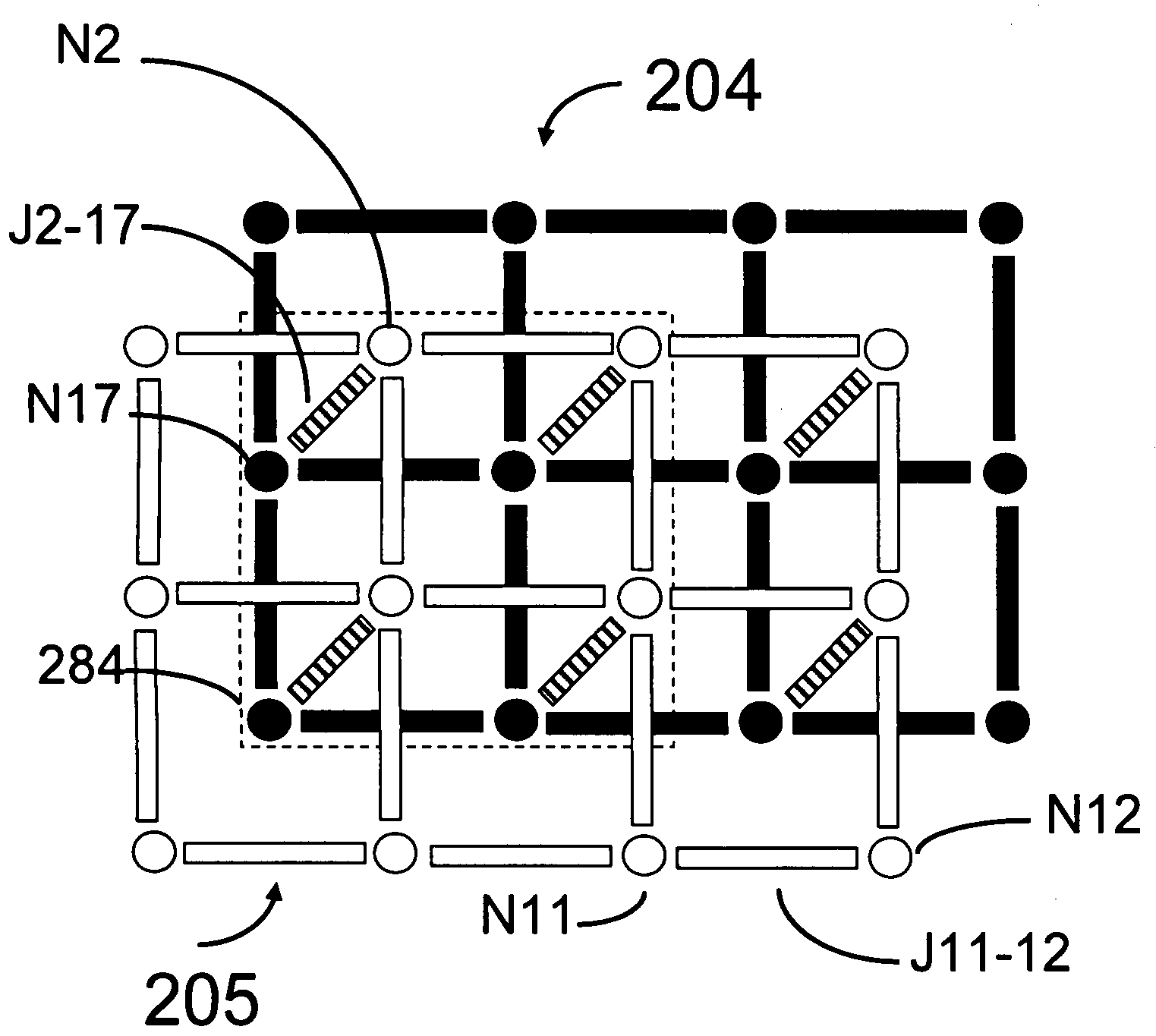
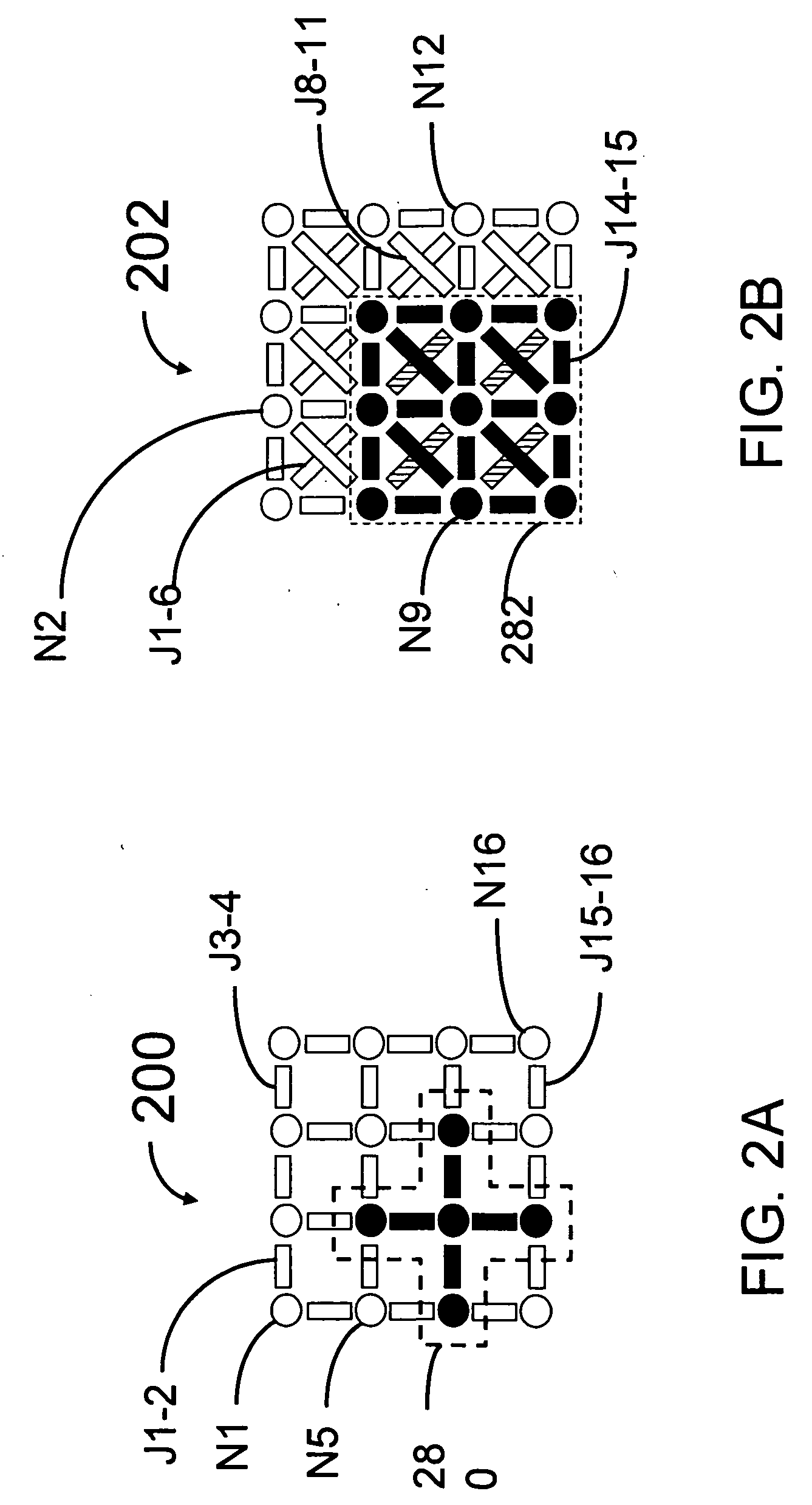
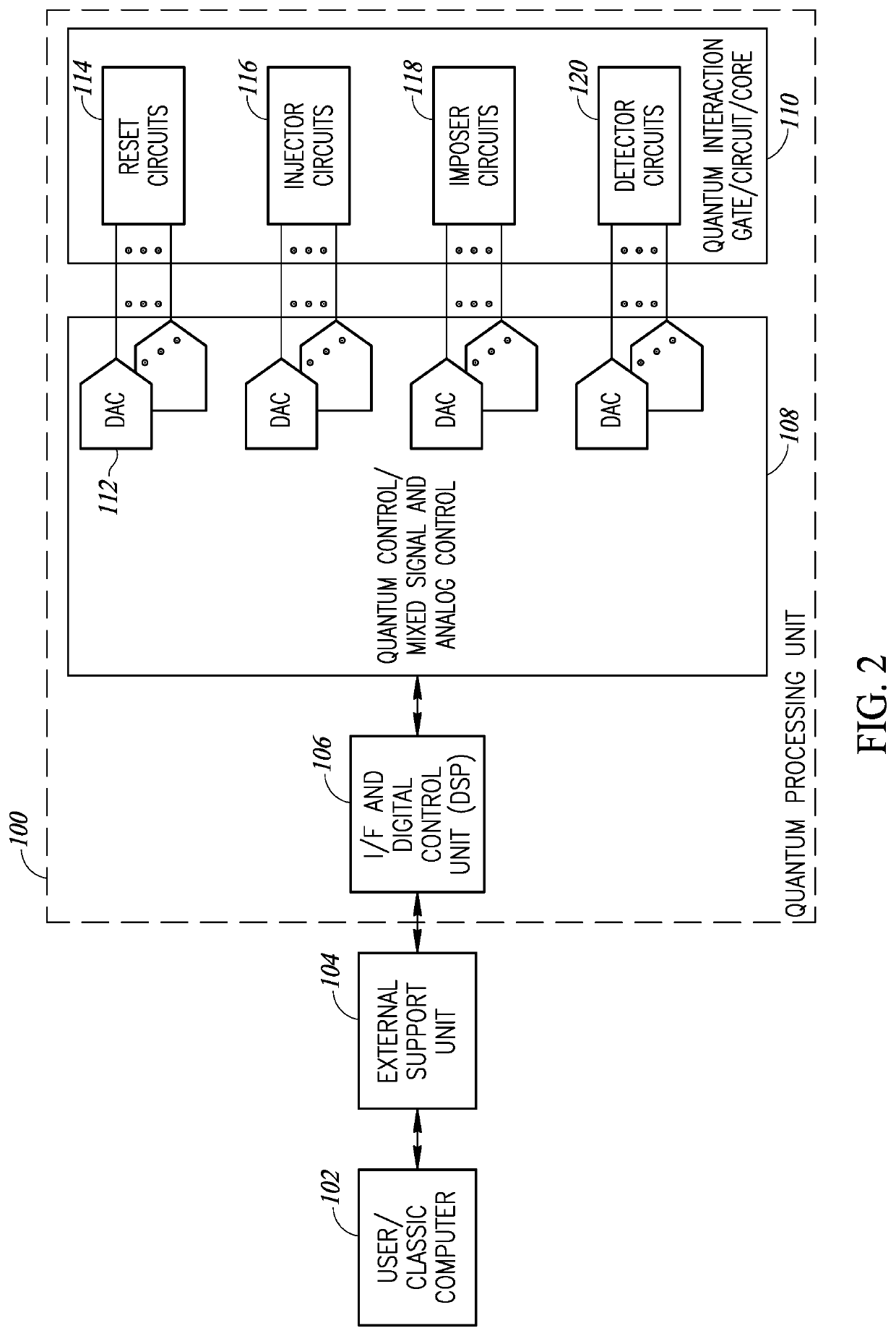
Analog processor comprising quantum devices
ActiveUS20090167342A1Quantum computersLogic circuits characterised by logic functionComputational problemAnalog processor
Analog processors for solving various computational problems are provided. Such analog processors comprise a plurality of quantum devices, arranged in a lattice, together with a plurality of coupling devices. The analog processors further comprise bias control systems each configured to apply a local effective bias on a corresponding quantum device. A set of coupling devices in the plurality of coupling devices is configured to couple nearest-neighbor quantum devices in the lattice. Another set of coupling devices is configured to couple next-nearest neighbor quantum devices. The analog processors further comprise a plurality of coupling control systems each configured to tune the coupling value of a corresponding coupling device in the plurality of coupling devices to a coupling. Such quantum processors further comprise a set of readout devices each configured to measure the information from a corresponding quantum device in the plurality of quantum devices.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
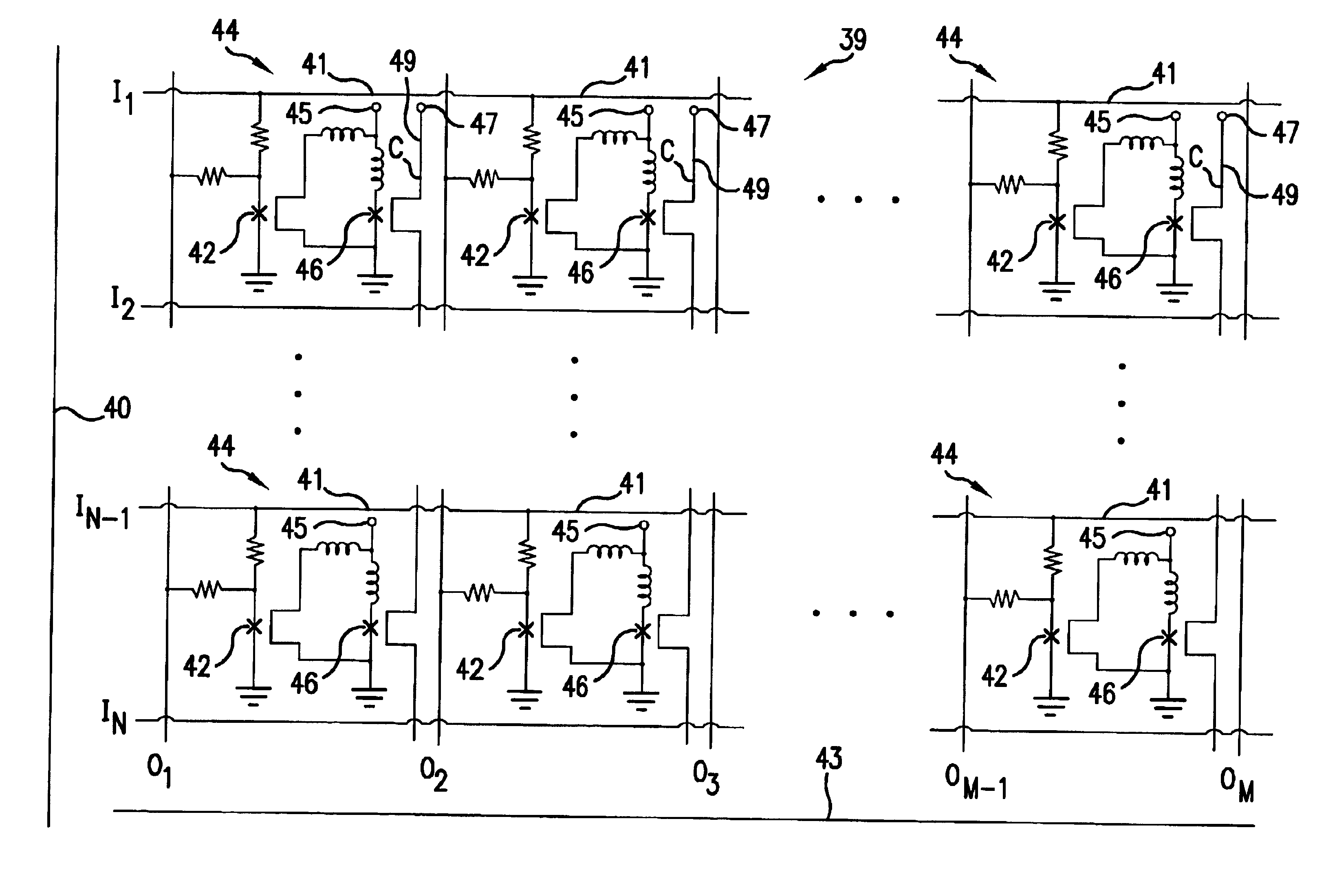
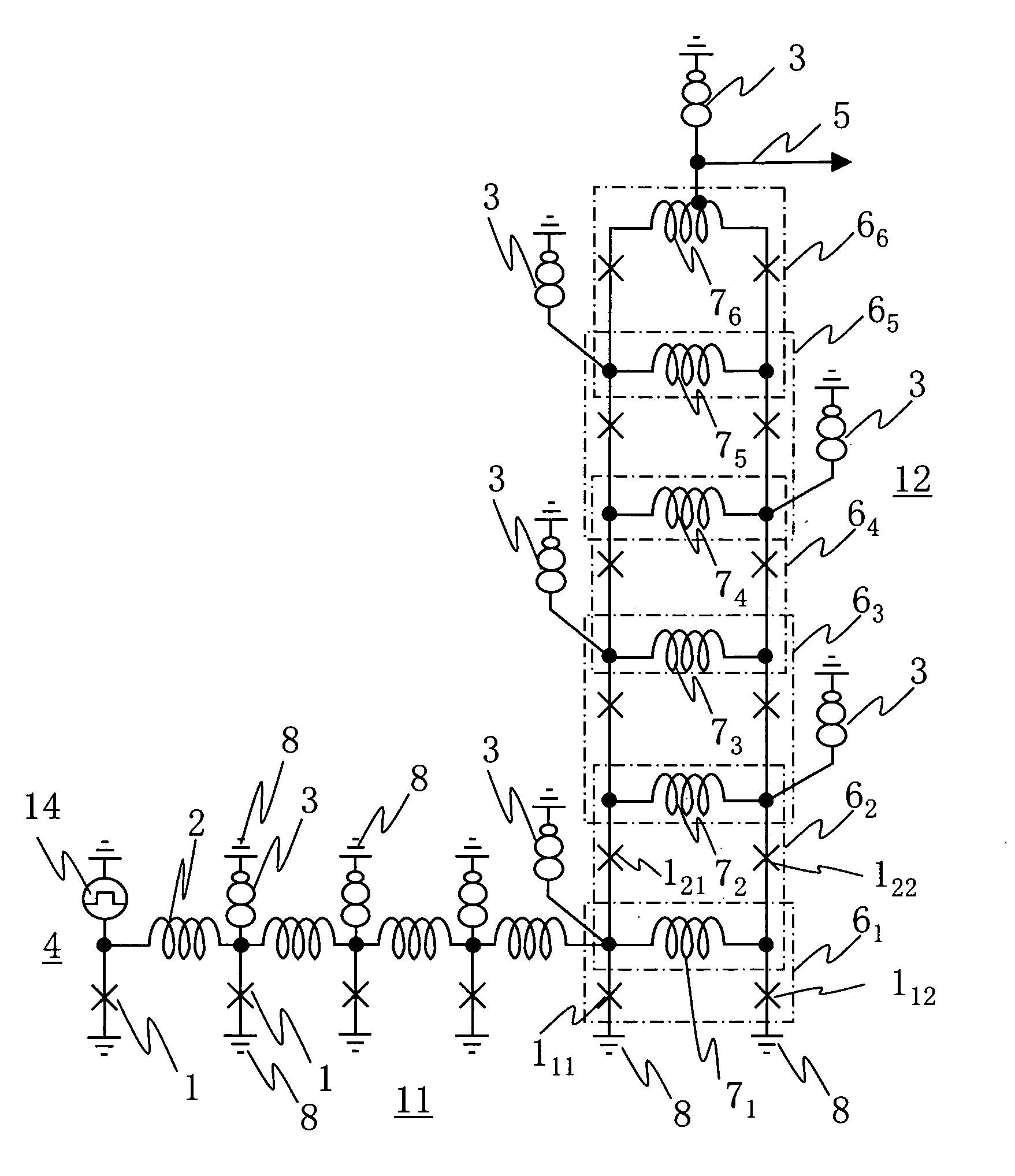
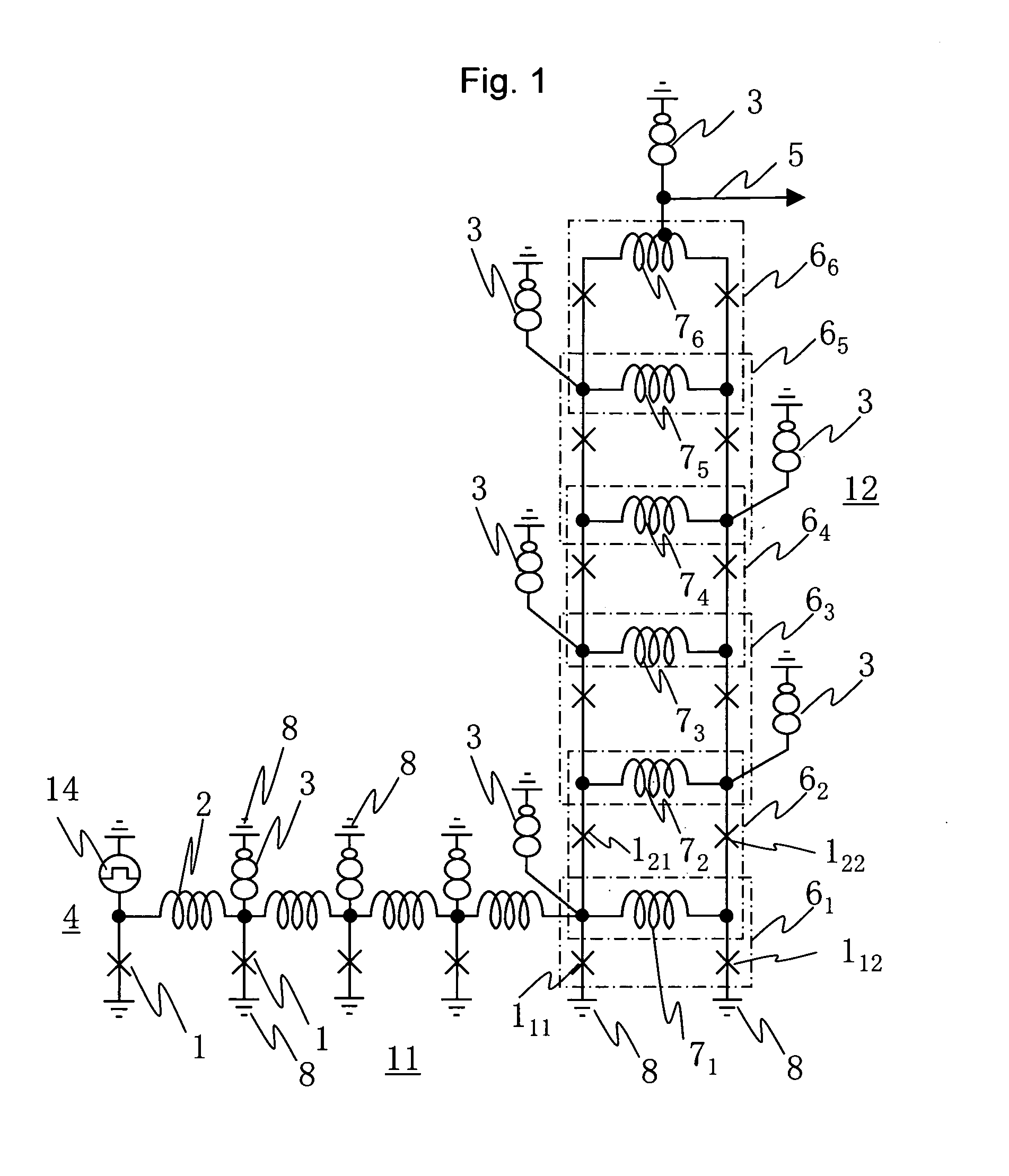
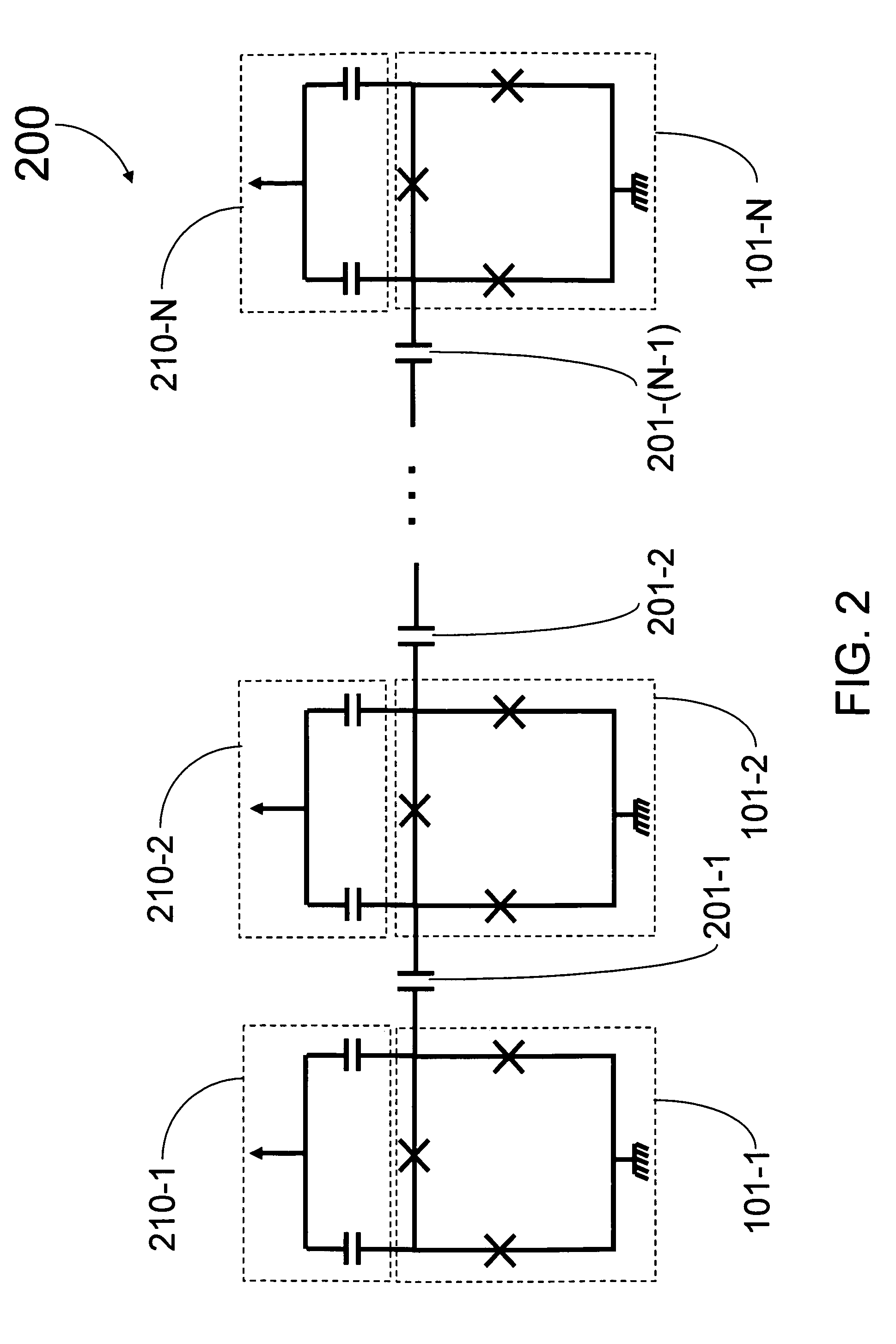
Control system architecture for qubits
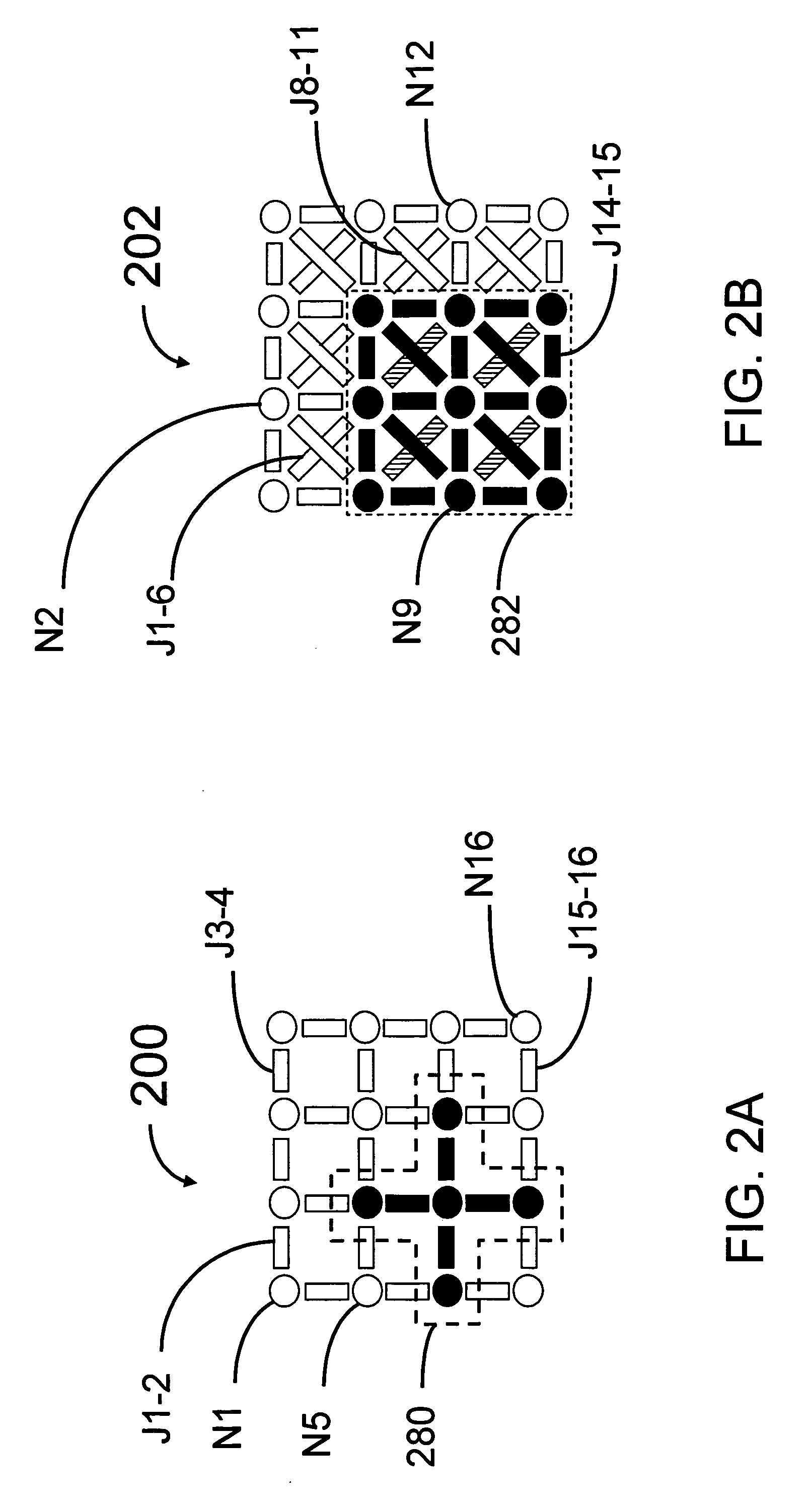
A control system architecture for quantum computing includes an array of qubits, which is divided into a plurality of sub-arrays based on a first direction and a second direction, the second direction intersecting the first direction, a plurality of control lines each coupled to a corresponding sub-array of qubits in the first directions a plurality of enable / unenable lines each coupled to a corresponding sub-array of qubits in the second direction, a controls signal source that generates a control signal, wherein the control lines are used to apply the control signal commonly to one or more sub-arrays of qubits in the first direction, an enable / unenable signal source that generates a enable signal, wherein the enable / unenable lines are used to apply the enable signal independently to the corresponding sub-array of qubits in the second direction to set a bias point of each qubit of the corresponding sub-array of qubits in the second direction between a first position, in which the qubit is unenabled and not responsive to the control signal, and a second position, in which the qubit is enabled and responsive to the control signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
ActiveUS9548742B1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Superconducting switching amplifier
InactiveUS20080048762A1Selectively raised and loweredAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
A superconducting switching amplifier embodying the invention includes superconductive devices responsive to input / control signals for clamping the output of the amplifier to a first voltage or to a second voltage. The amplifier includes a first set of superconducting devices serially connected between a first voltage line and an output terminal and a second set of superconducting devices serially connected between the output terminal and a second voltage line. The first set and the second set of devices are operated in a complementary fashion in response to control signals. When one of the first and second sets is driven to a superconducting (zero resistance) state the other set is driven to a resistive state. In accordance with the invention, the devices of each set are laid out in a pattern and driven in a manner to enable all the devices of each set to be driven to a selected state at substantially the same time. In one embodiment, the devices in each set are superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs). Four sets of superconductive devices may be interconnected to function as a differential switching amplifier. The operating voltage applied to an amplifier may be varied to provide additional shaping of the output signal.
Owner:HYPRES
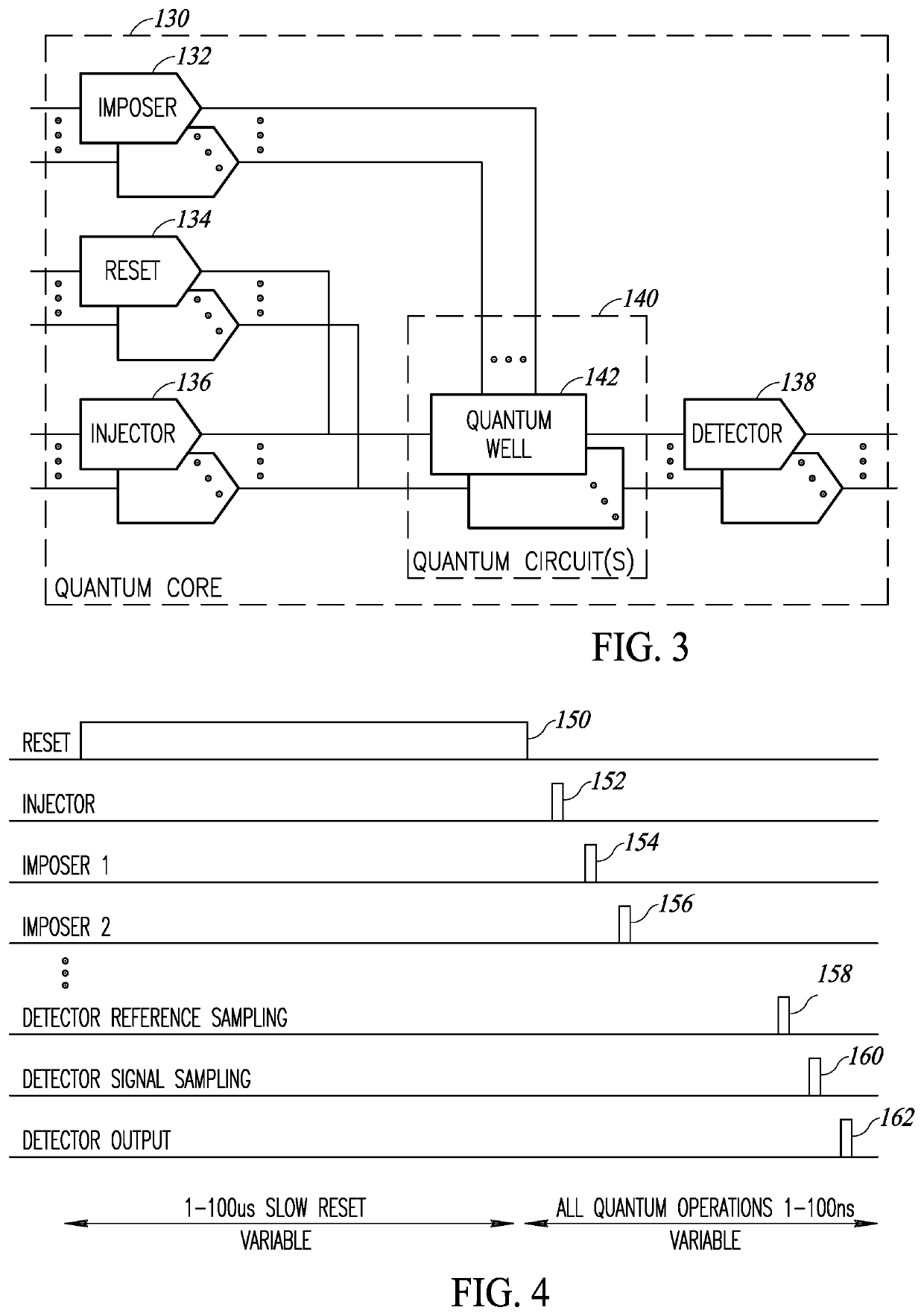
Quantum shift register based ancillary quantum interaction gates
A novel and useful controlled quantum shift register for transporting particles from one quantum dot to another in a quantum structure. The shift register incorporates a succession of qdots with tunneling paths and control gates. Applying appropriate control signals to the control gates, a particle or a split quantum state is made to travel along the shift register. The shift register also includes ancillary double interaction where two pairs of quantum dots provide an ancillary function where the quantum state of one pair is replicated in the second pair. The shift register also provides bifurcation where an access path is split into two or more paths. Depending on the control pulse signals applied, quantum dots are extended into multiple paths. Control of the shift register is provided by electric control pulses. An optional auxiliary magnetic field provides additional control of the shift register.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
Quantum shift register incorporating bifurcation
A novel and useful controlled quantum shift register for transporting particles from one quantum dot to another in a quantum structure. The shift register incorporates a succession of qdots with tunneling paths and control gates. Applying appropriate control signals to the control gates, a particle or a split quantum state is made to travel along the shift register. The shift register also includes ancillary double interaction where two pairs of quantum dots provide an ancillary function where the quantum state of one pair is replicated in the second pair. The shift register also provides bifurcation where an access path is split into two or more paths. Depending on the control pulse signals applied, quantum dots are extended into multiple paths. Control of the shift register is provided by electric control pulses. An optional auxiliary magnetic field provides additional control of the shift register.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
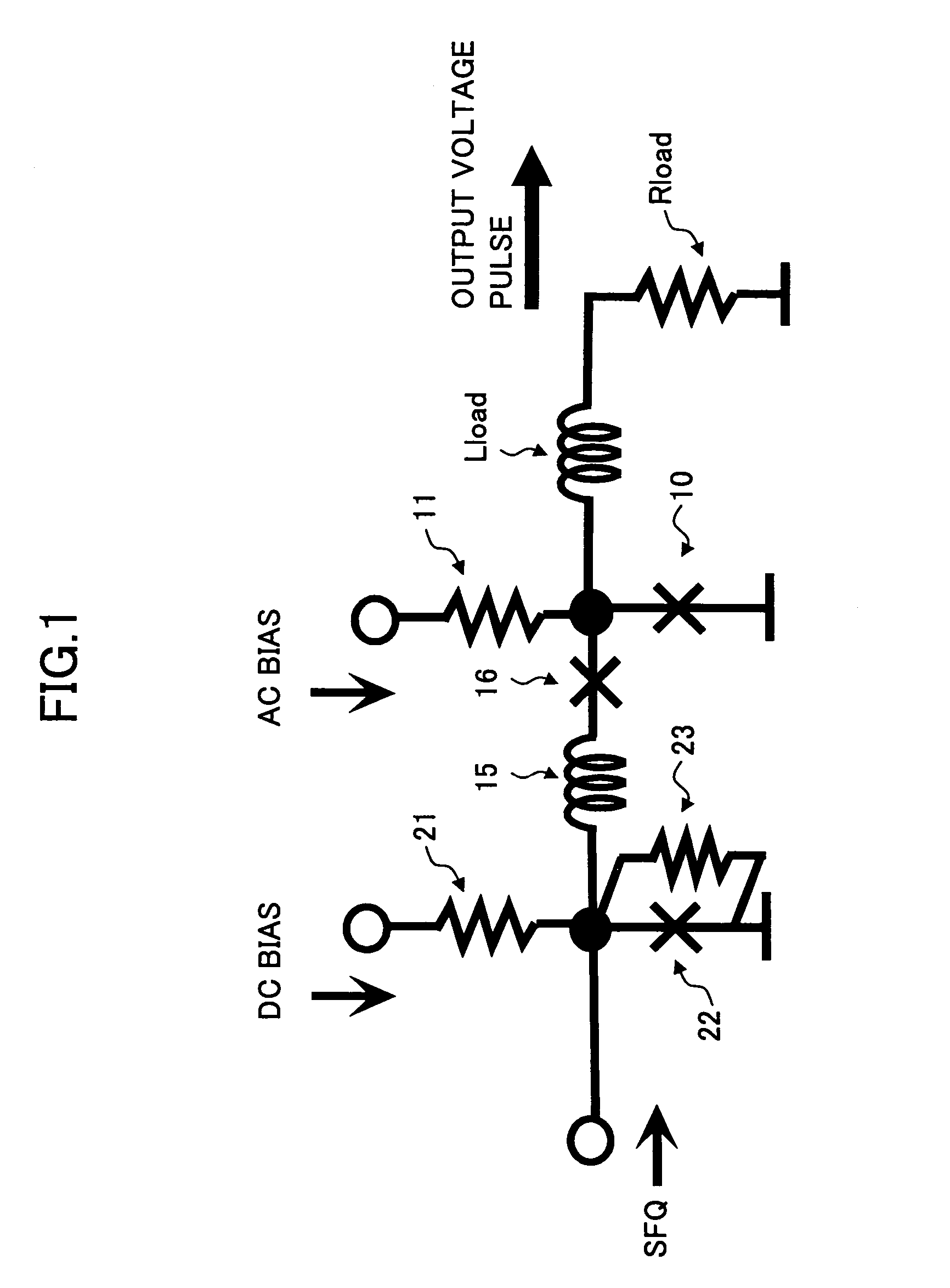
Superconducting circuit
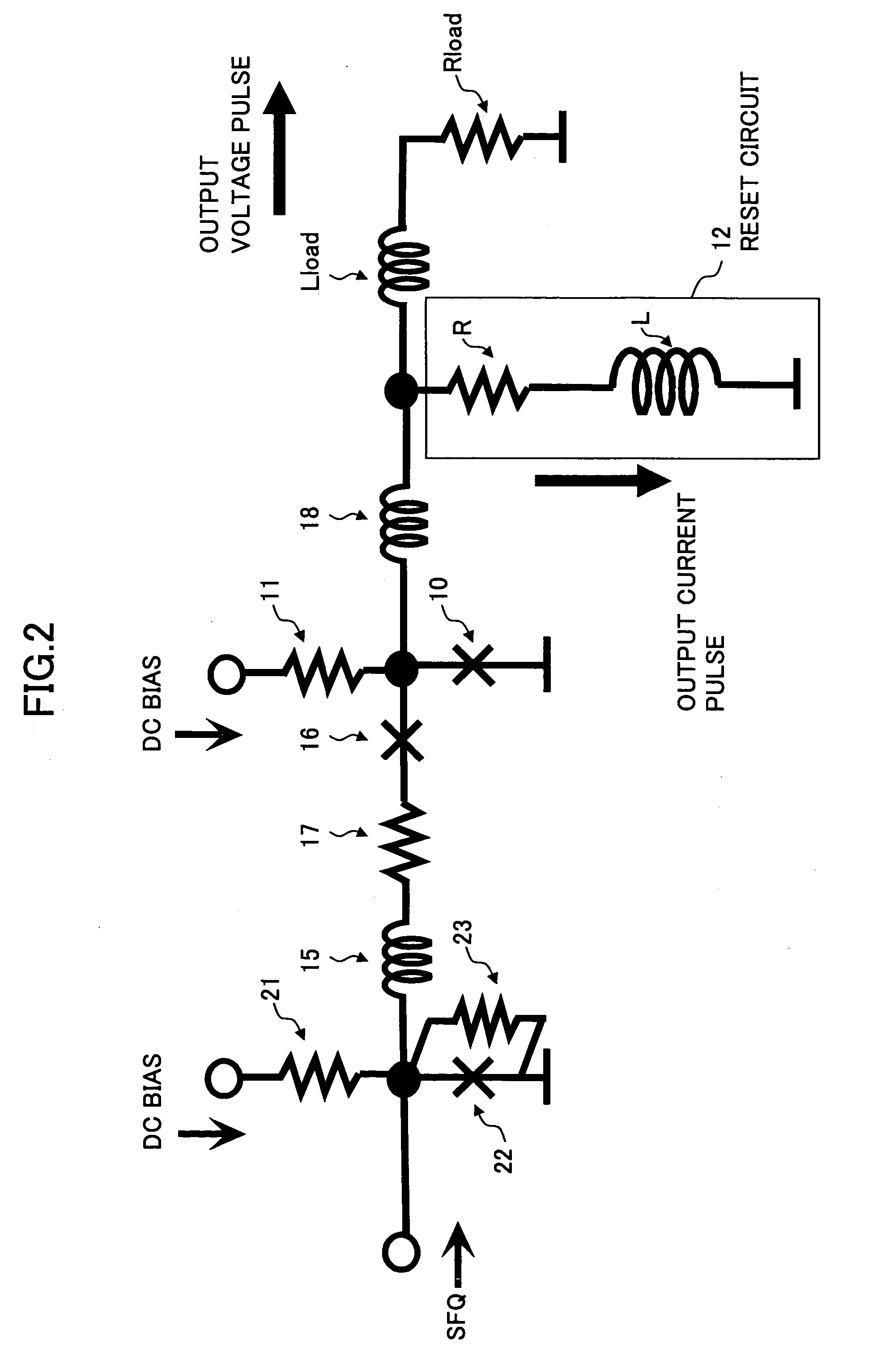
InactiveUS20050078022A1High outputReduce ground ripplesAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsLoad circuitHysteresis
A circuit includes a latch circuit including a Josephson junction and configured to perform a latch operation based on a hysteresis characteristic in response to a single flux quantum, a load circuit including load inductance and load resistance and coupled to an output of the latch circuit, and a reset circuit provided between the output of the latch circuit and the load circuit and configured to reset the latch circuit a predetermined time after the latch operation by the latch circuit, wherein the Josephson junction is driven by a direct current.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Superconducting qubits having a plurality of capacitive couplings
A first qubit having a superconducting loop interrupted by a plurality of Josephson junctions is provided. Each junction interrupts a different portion of the superconducting loop and each different adjacent pair of junctions in the plurality of Josephson junctions defines a different island. An ancillary device is coupled to the first qubit. In a first example, the ancillary device is a readout mechanism respectively capacitively coupled to a first and second island in the plurality of islands of the first qubit by a first and second capacitance. Quantum nondemolition measurement of the first qubit's state may be performed. In a second example, the ancillary device is a second qubit. The second qubit's first and second islands are respectively capacitively coupled to the first and second islands of the first qubit by a capacitance. In this second example, the coupling is diagonal in the physical basis of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Fast flux locked loop
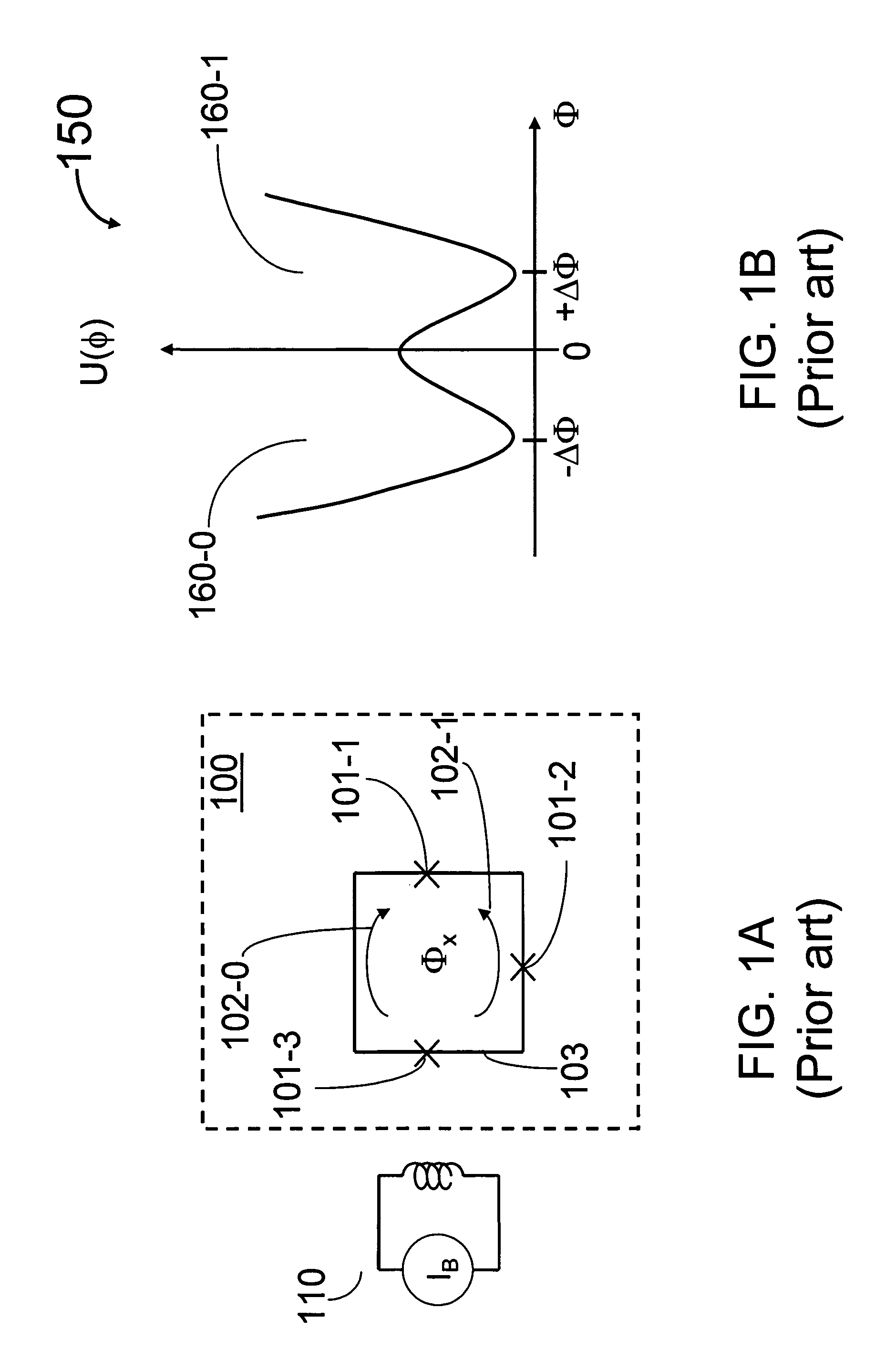
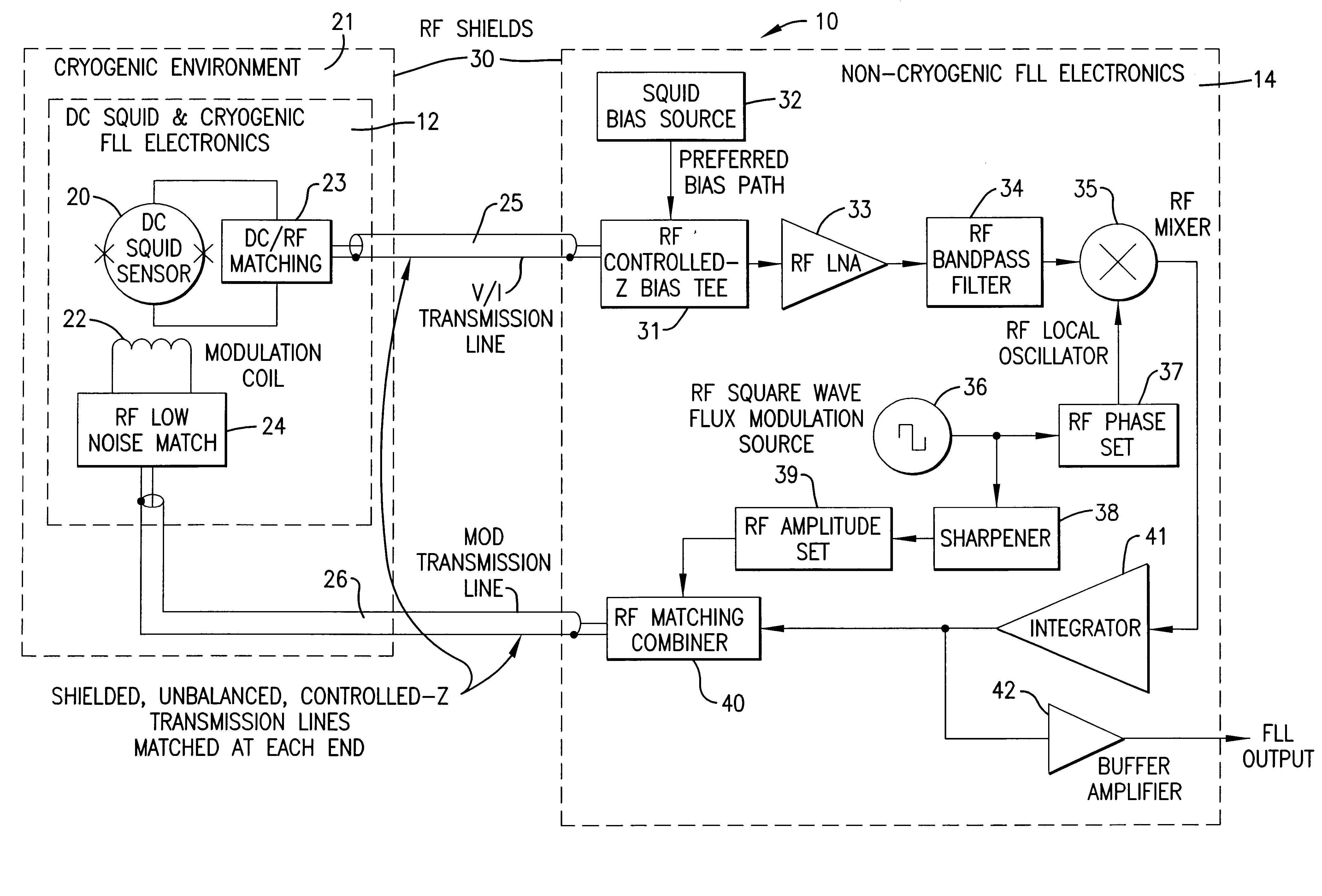
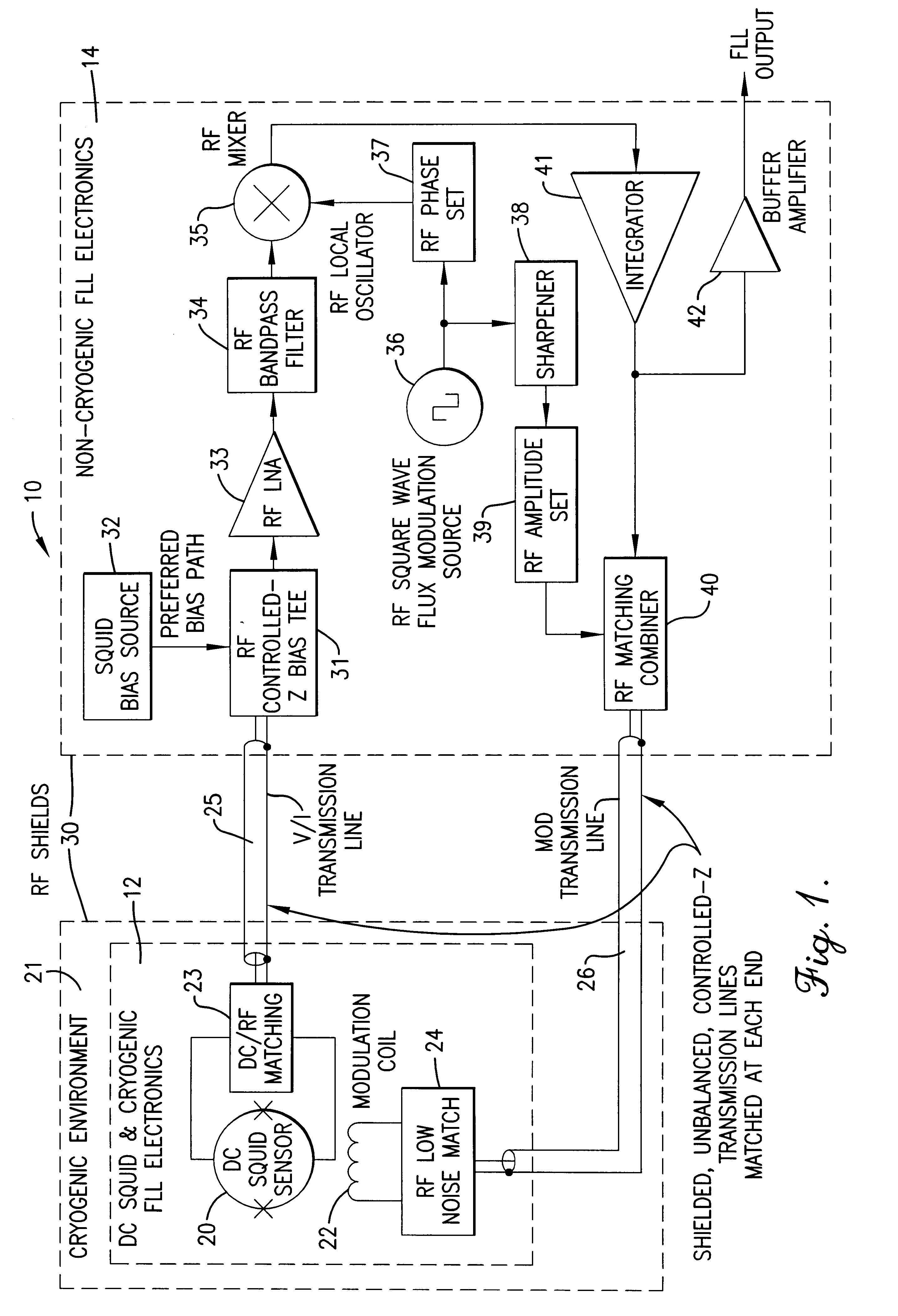
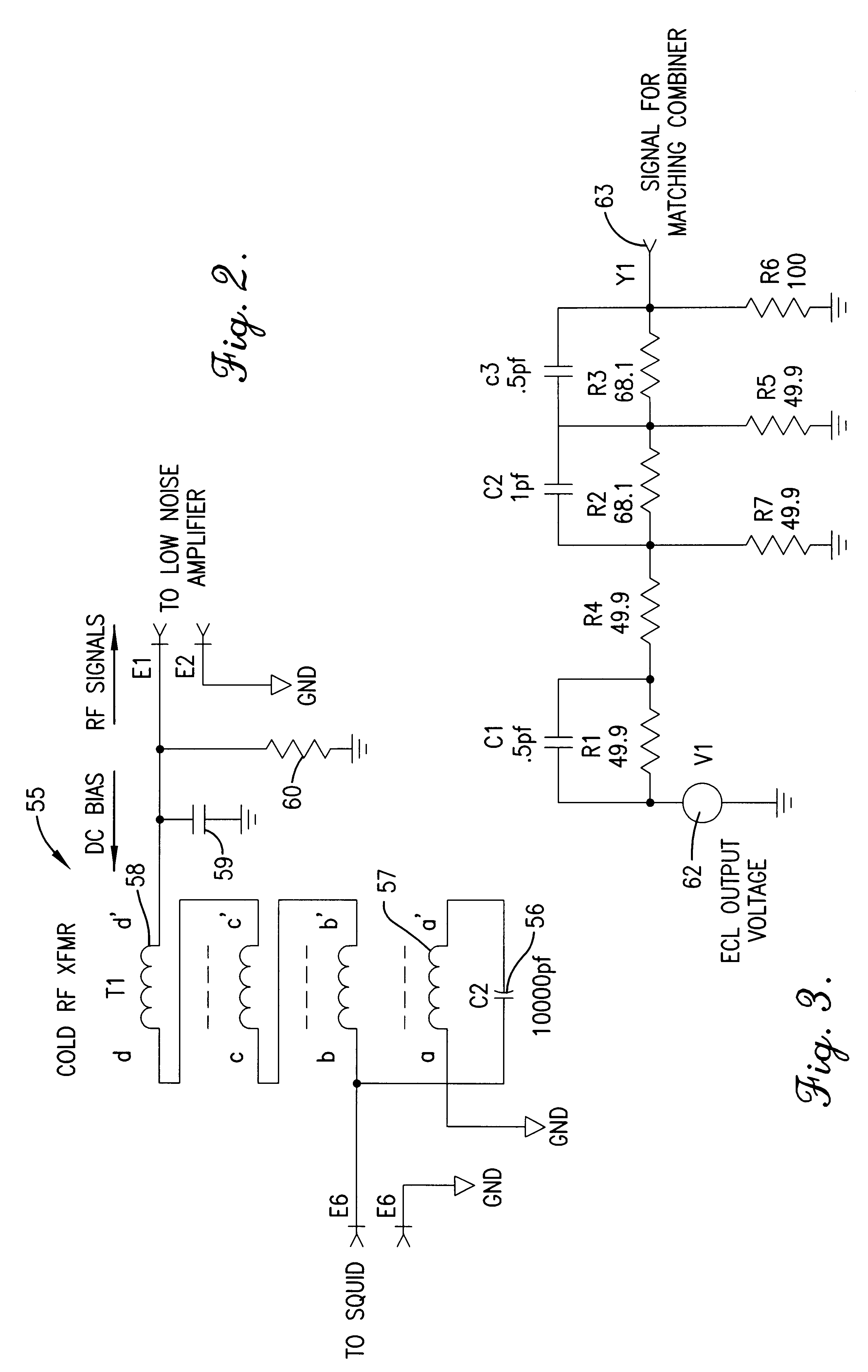
InactiveUS6448767B1Benefit control loop DC stabilityReduce effective amplifier input noiseMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesPulse generation by super conductive devicesElectricityMagnetic measurements
A flux locked loop for providing an electrical feedback signal, the flux locked loop employing radio-frequency components and technology to extend the flux modulation frequency and tracking loop bandwidth. The flux locked loop of the present invention has particularly useful application in read-out electronics for DC SQUID magnetic measurement systems, in which case the electrical signal output by the flux locked loop represents an unknown magnetic flux applied to the DC SQUID.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Control system architecture for qubits
A control system architecture for quantum computing includes an array of qubits, which is divided into a plurality of sub-arrays based on a first direction and a second direction, the second direction intersecting the first direction, a plurality of control lines each coupled to a corresponding sub-array of qubits in the first direction, a plurality of enable / unenable lines each coupled to a corresponding sub-array of qubits in the second direction, a controls signal source that generates a control signal, wherein the control lines are used to apply the control signal commonly to one or more sub-arrays of qubits in the first direction, an enable / unenable signal source that generates a enable signal, wherein the enable / unenable lines are used to apply the enable signal independently to the corresponding sub-array of qubits in the second direction to set a bias point of each qubit of the corresponding sub-array of qubits in the second direction between a first position, in which the qubit is unenabled and not responsive to the control signal, and a second position, in which the qubit is enabled and responsive to the control signal.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
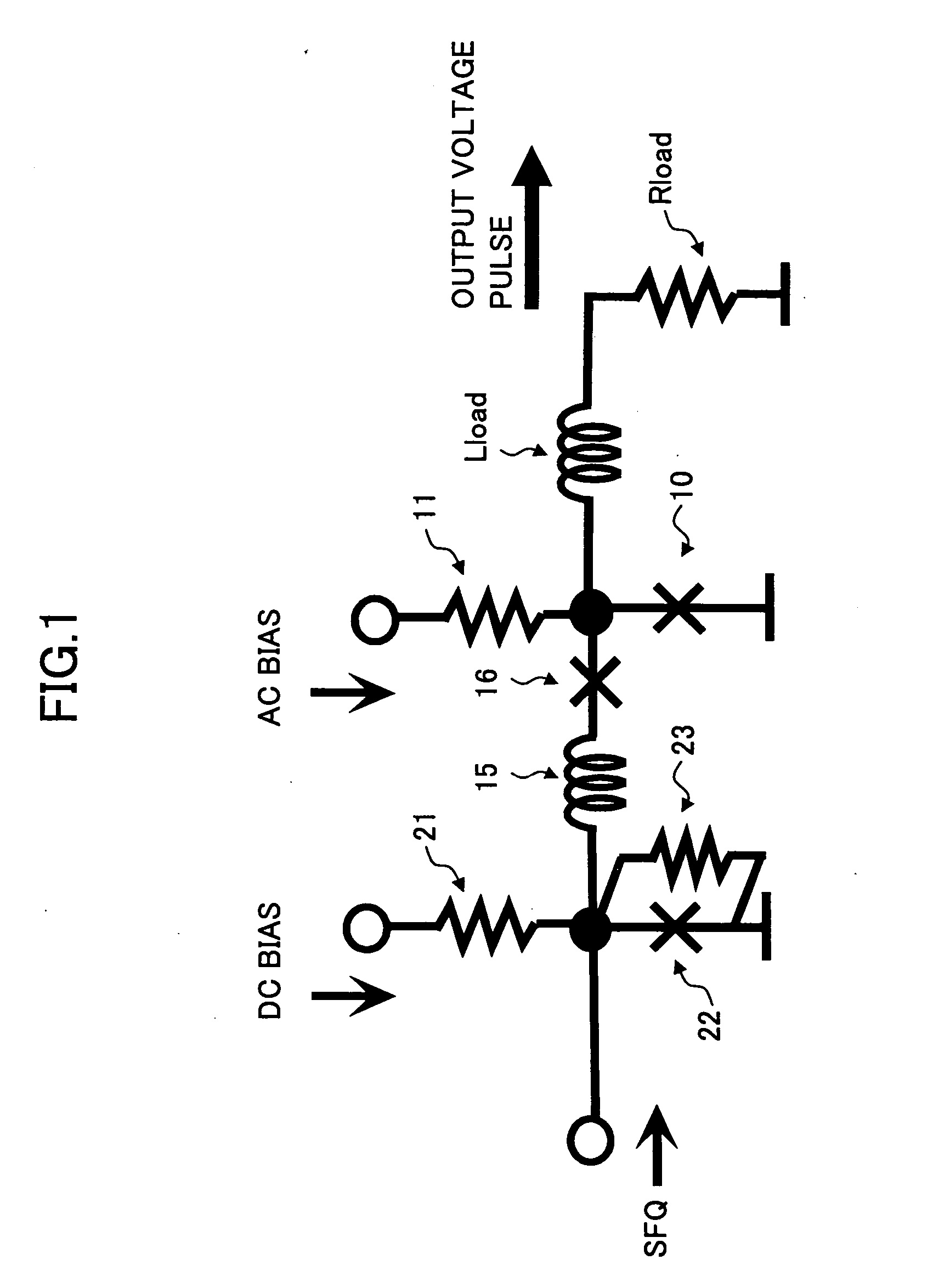
Superconducting latch driver circuit generating sufficient output voltage and pulse-width
InactiveUS7129870B2High outputReduce ground ripplesAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsHysteresisLoad circuit
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Superconducting driver circuit
InactiveUS7095227B2Discharge longerSuperconductors/hyperconductorsElectronic switchingCapacitanceDriver circuit
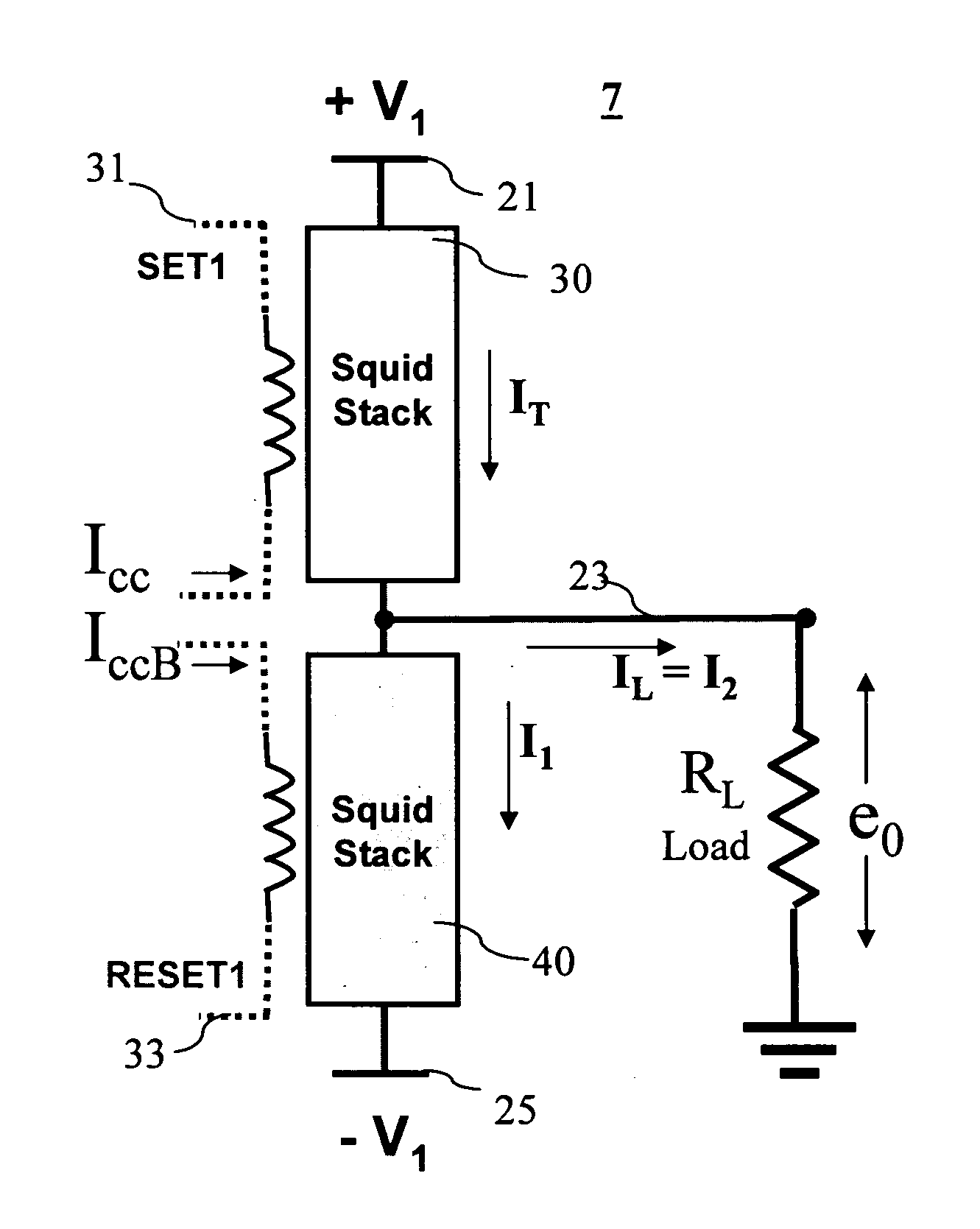
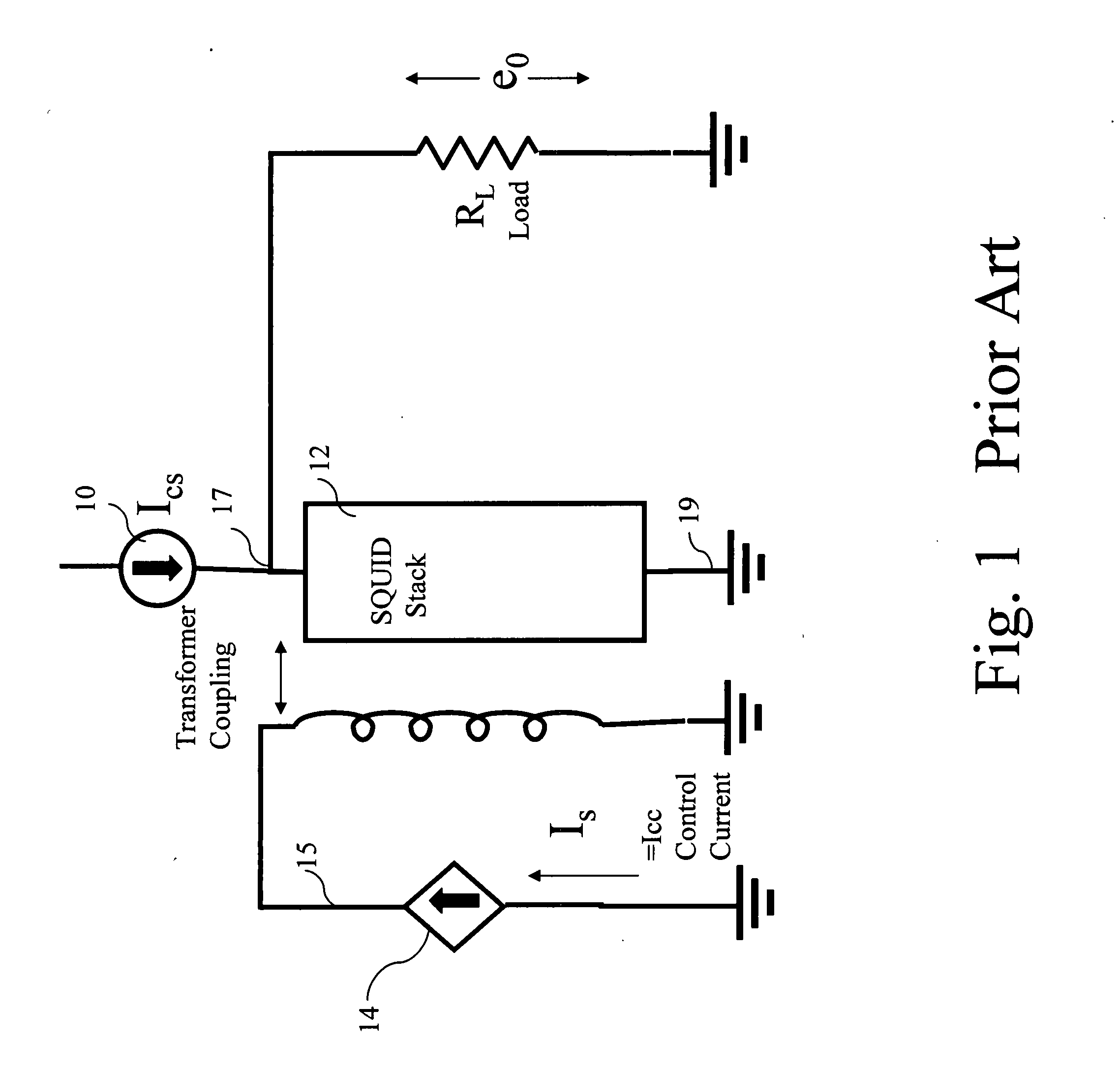
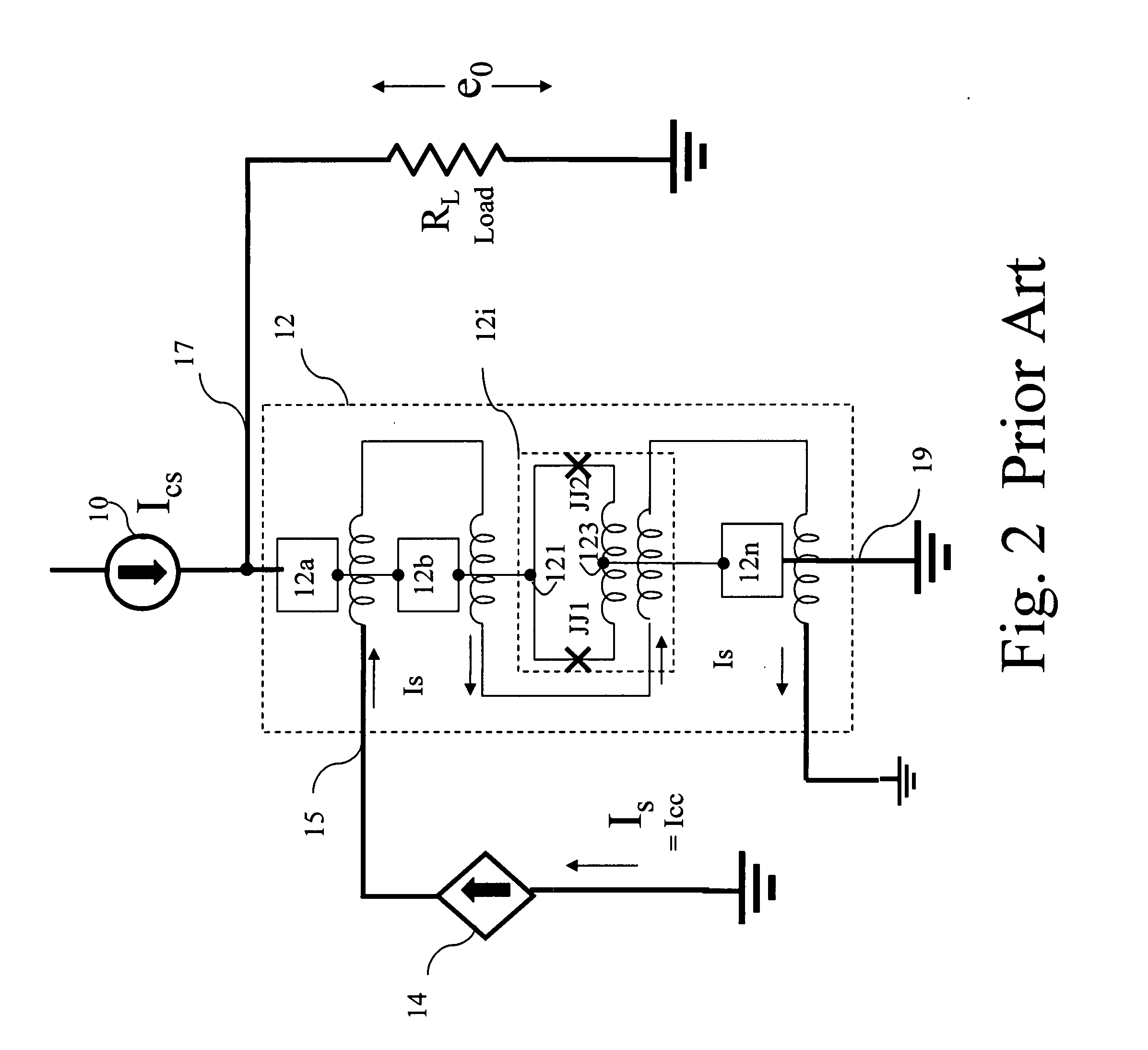
To obtain a superconducting driver circuit which can obtain an output voltage of several millvolts or above, can use a DC power source as a driving power source, can form no capacitance between it and a ground plane, and has a small occupation area, the superconducting driver circuit is constructed by superconducting flux quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) each constructing a closed loop having as components two superconducting junctions and an inductor. The SQUIDs share the inductors and are connected in series in three or more stages.
Owner:INT SUPERCONDUCTIVITY TECH CENT
Superconducting qubit with a plurality of capacitive couplings
A first qubit having a superconducting loop interrupted by a plurality of Josephson junctions is provided. Each junction interrupts a different portion of the superconducting loop and each different adjacent pair of junctions in the plurality of Josephson junctions defines a different island. An ancillary device is coupled to the first qubit. In a first example, the ancillary device is a readout mechanism respectively capacitively coupled to a first and second island in the plurality of islands of the first qubit by a first and second capacitance. Quantum nondemolition measurement of the first qubit's state may be performed. In a second example, the ancillary device is a second qubit. The second qubit's first and second islands are respectively capacitively coupled to the first and second islands of the first qubit by a capacitance. In this second example, the coupling is diagonal in the physical basis of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Superconducting quantum logic and applications of same
ActiveUS20170359072A1Avoid flowExclusive-OR circuitsPulse generation by super conductive devicesVoltage pulseLogic state
A superconducting logic cell includes at least one quantum phase-slip junction (QPSJ) for receiving at least one input and responsively providing at least one output, each QPSJ being configured such that when an input voltage of an input voltage pulse exceeds a critical value, a quantized charge of a Cooper electron pair tunnels across said QPSJ as an output, when the input voltage is less than the critical value, no quantized charge of the Cooper electron pair tunnels across said QPSJ as the output, where the presence and absence of the quantized charge in the form of a constant area current pulse in the output form two logic states, and the at least one QPSJ is biased with a bias voltage. The superconducting logic cell further includes at least one Josephson junction (JJ) coupled with the at least one QPSJ to perform one or more logic operations.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com