Patents
Literature
203results about "Logic circuits using superconductive devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
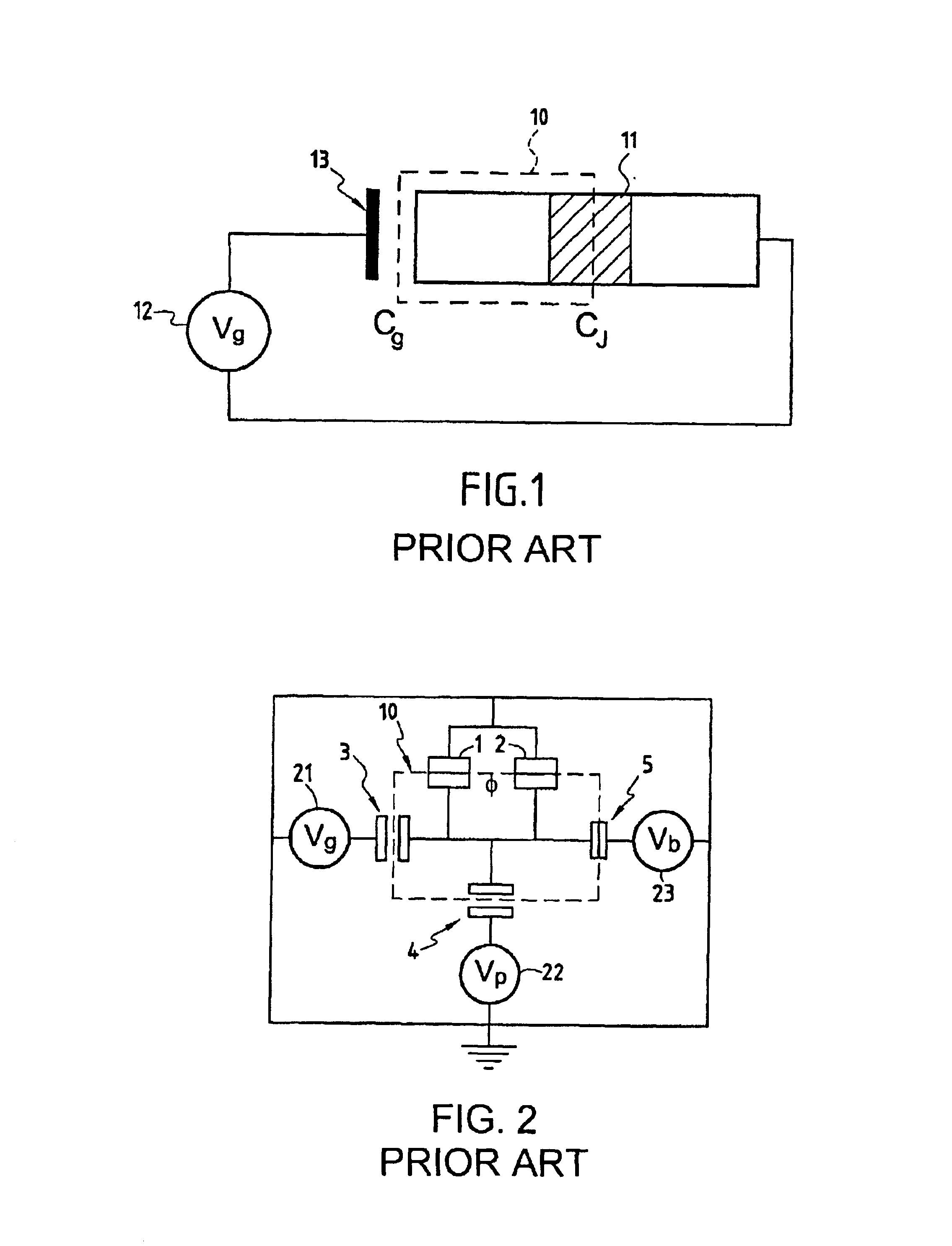
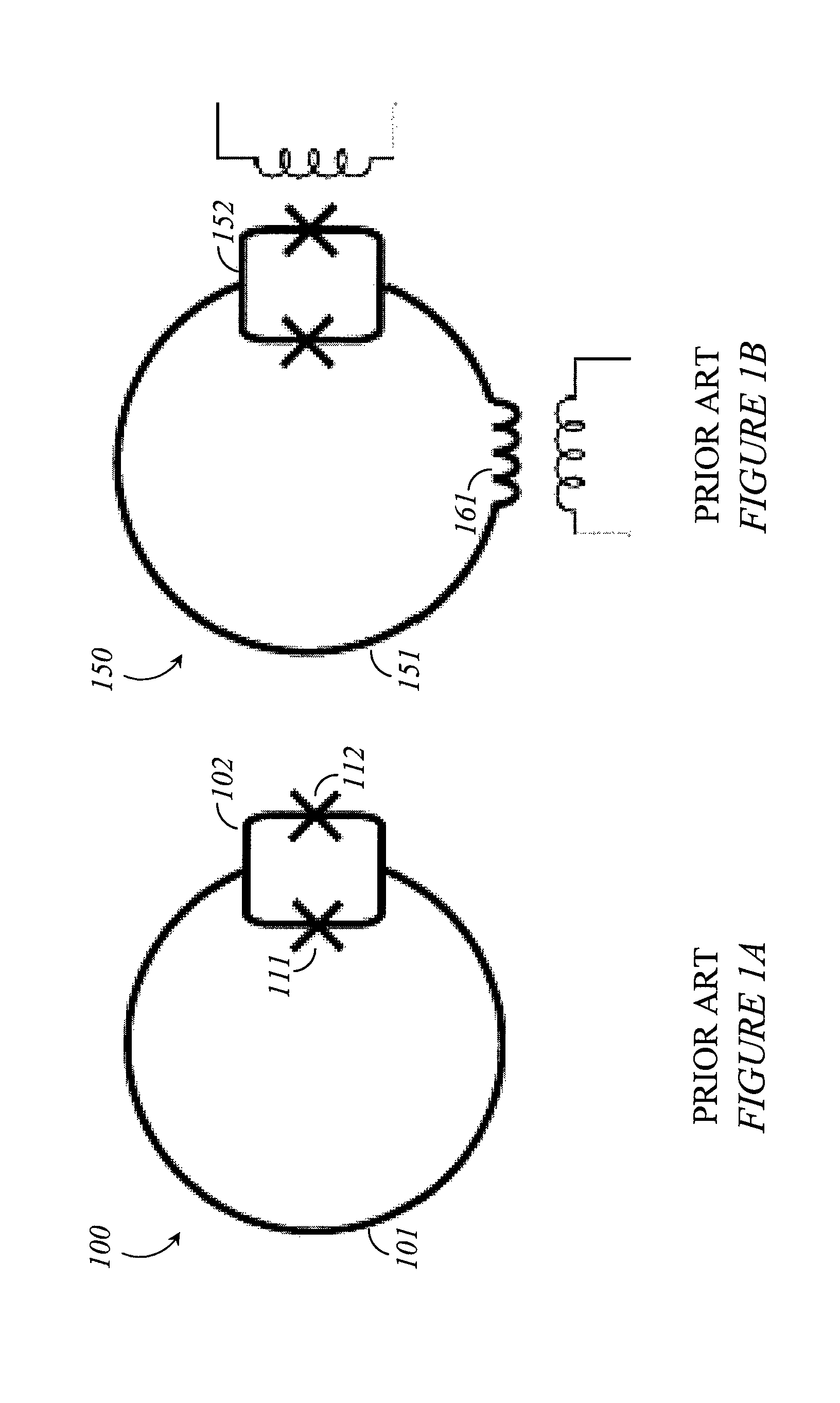
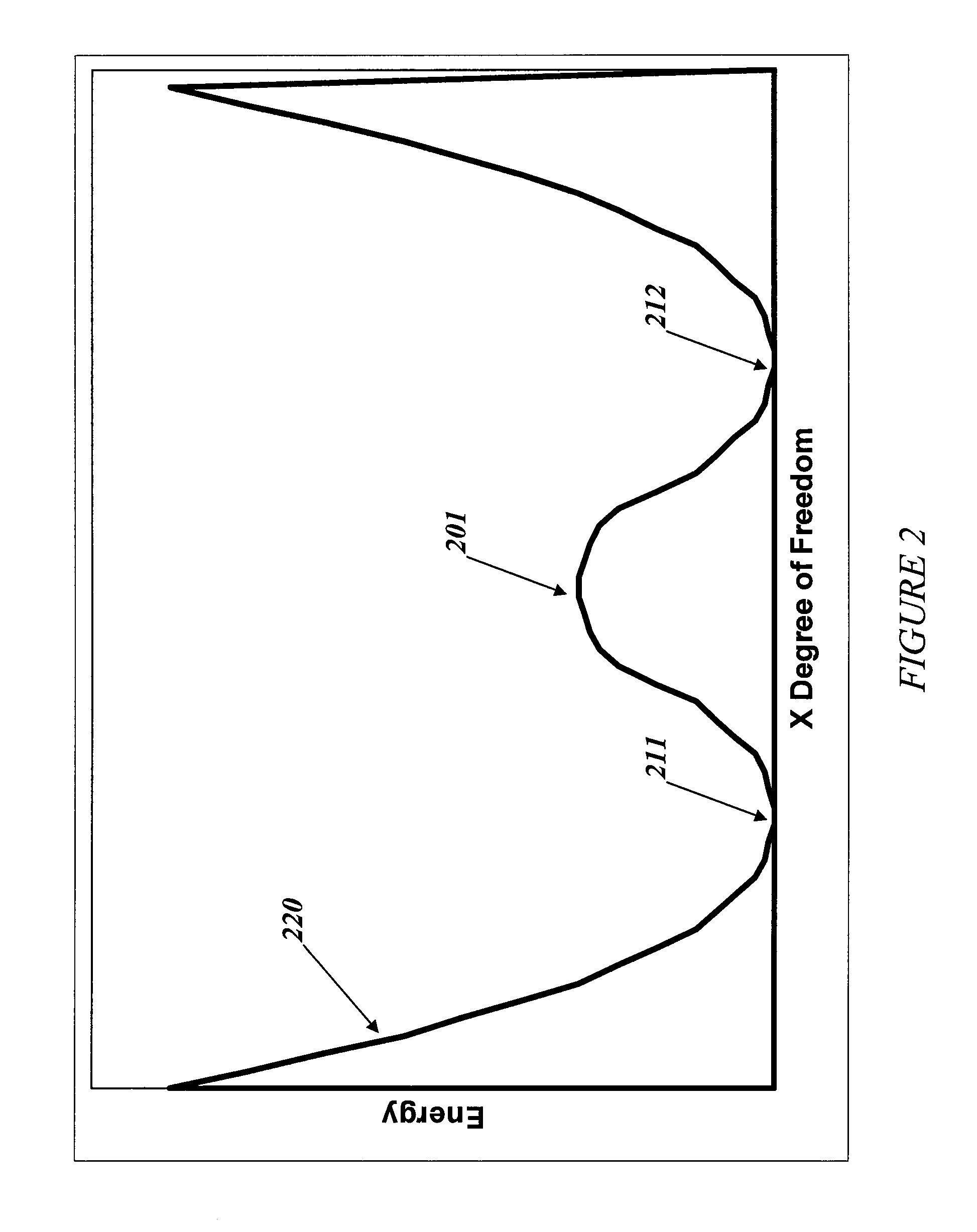
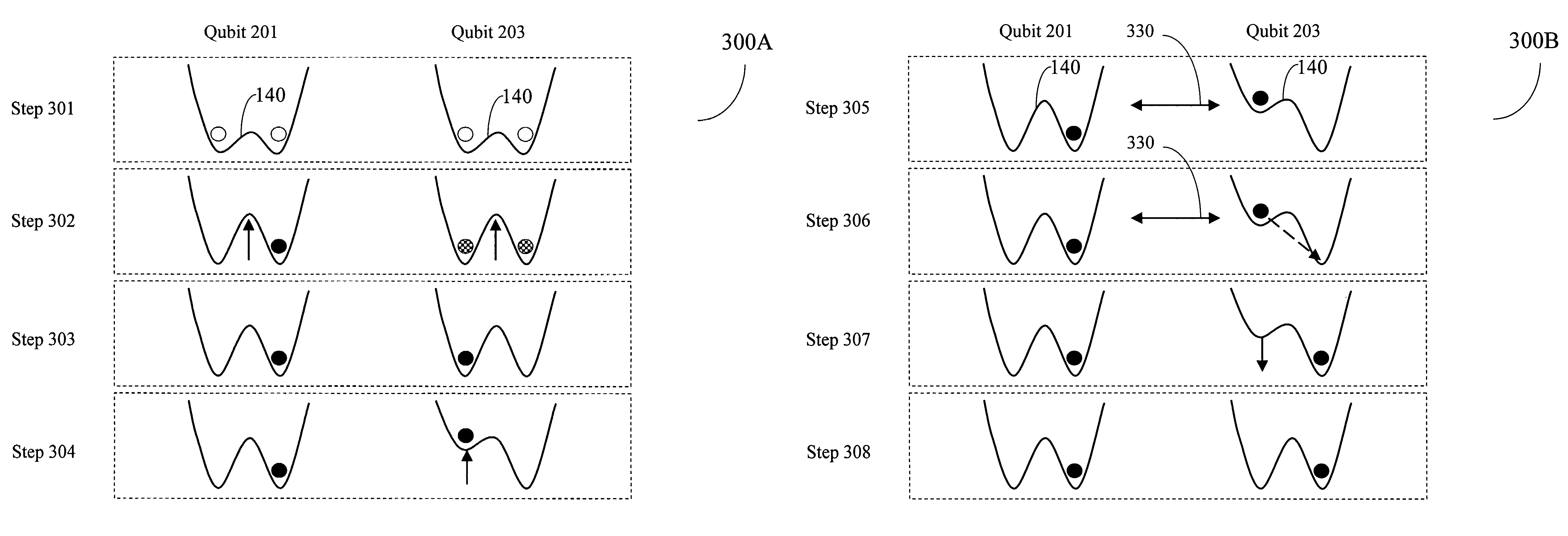
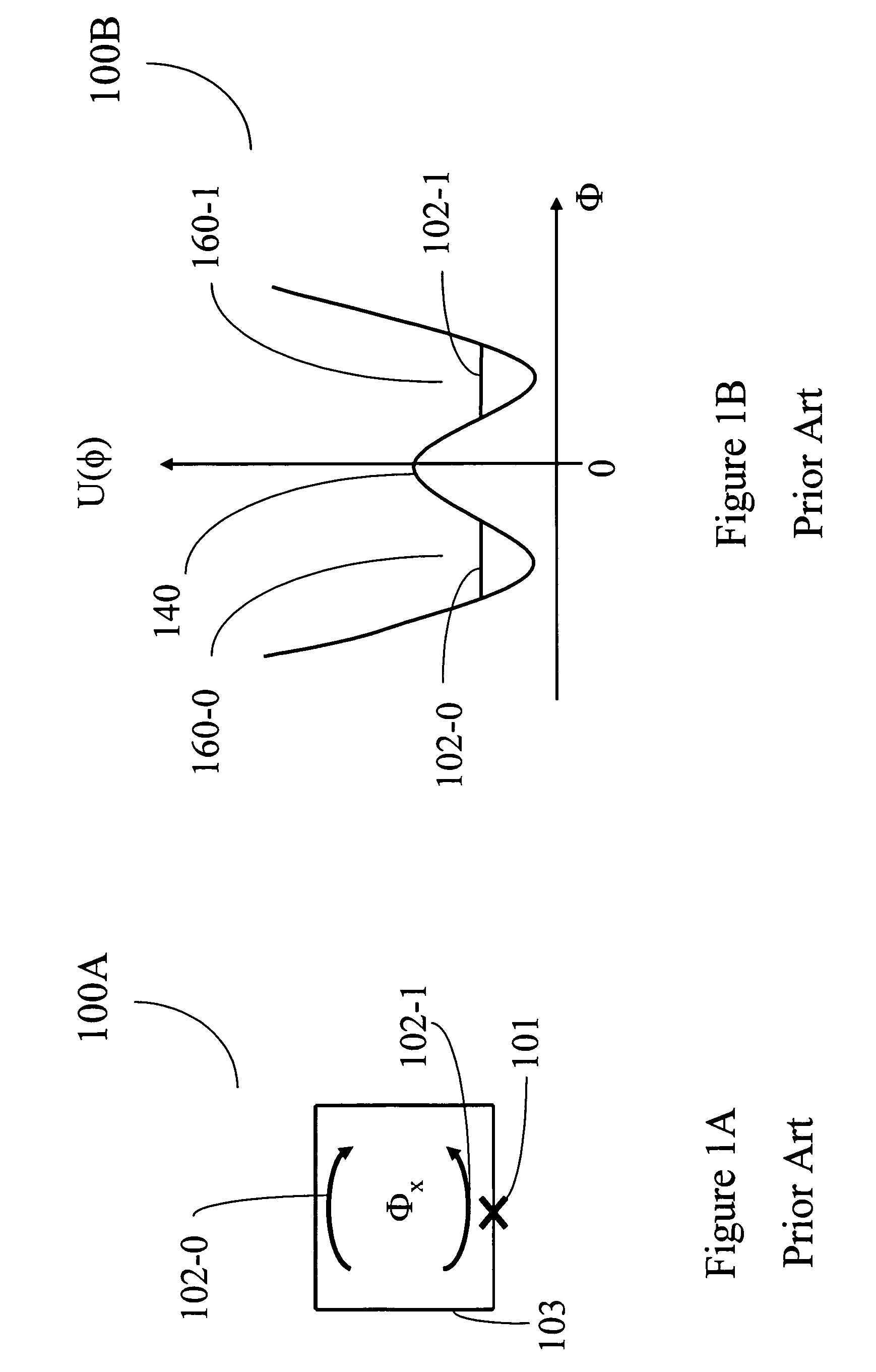
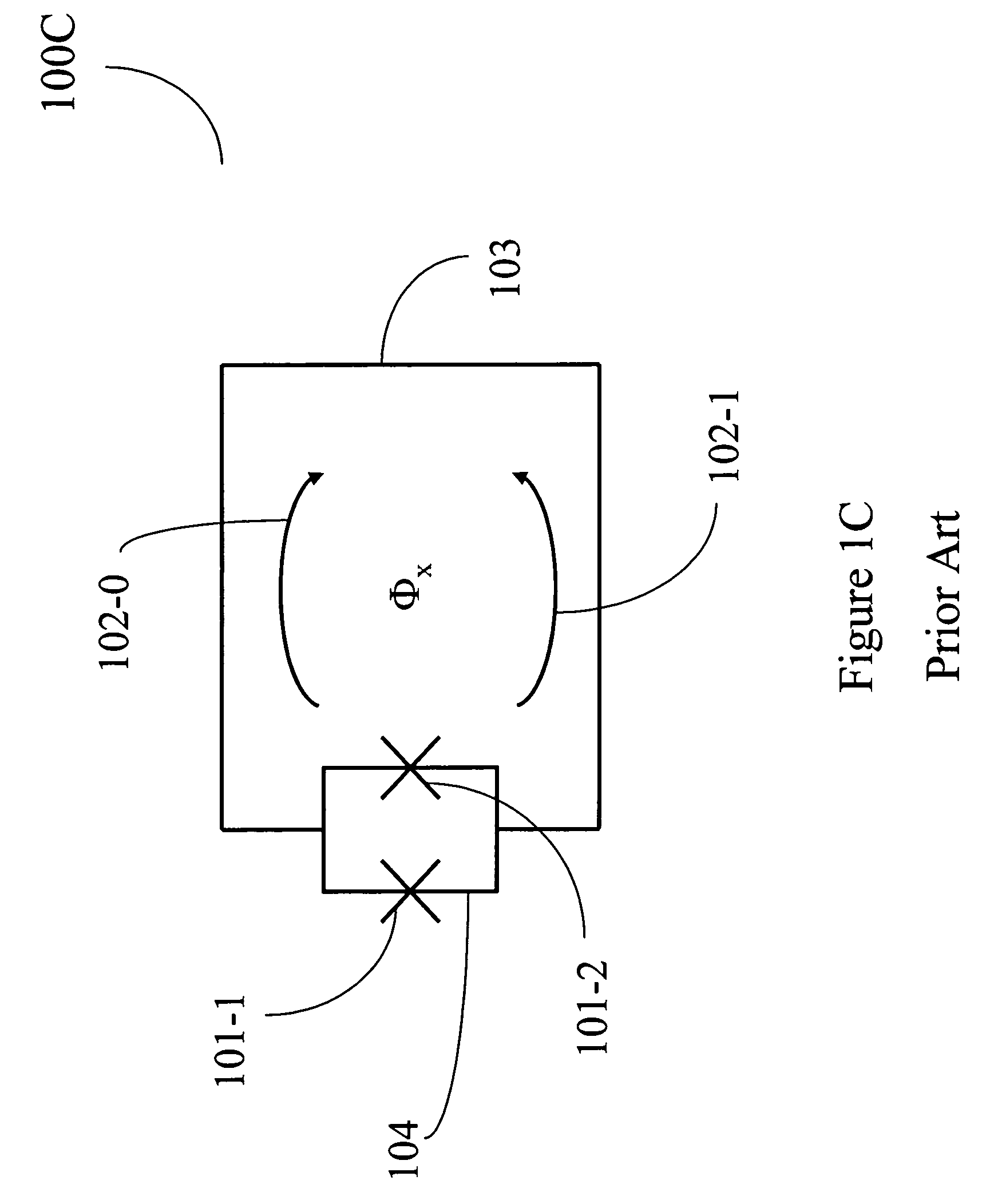
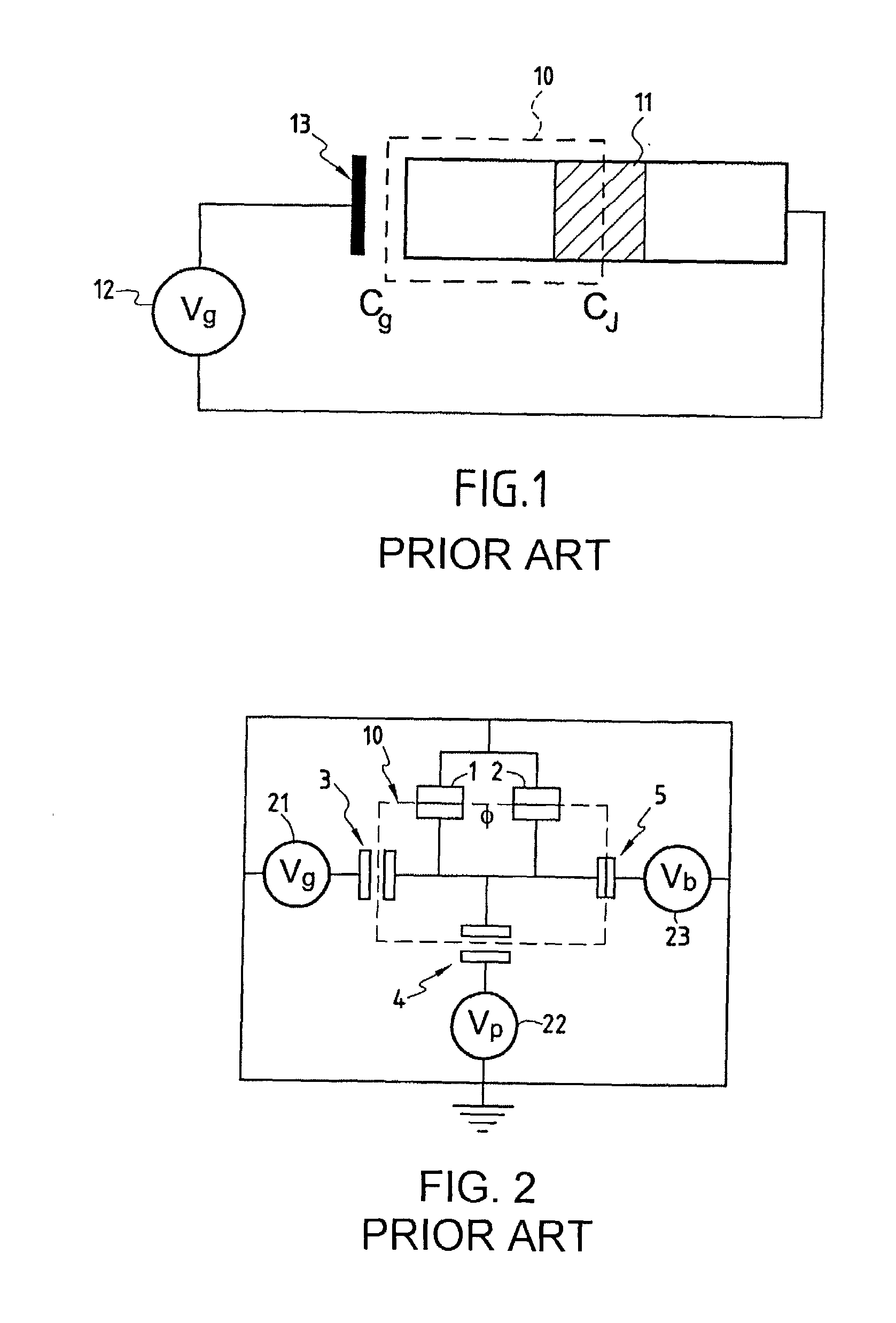
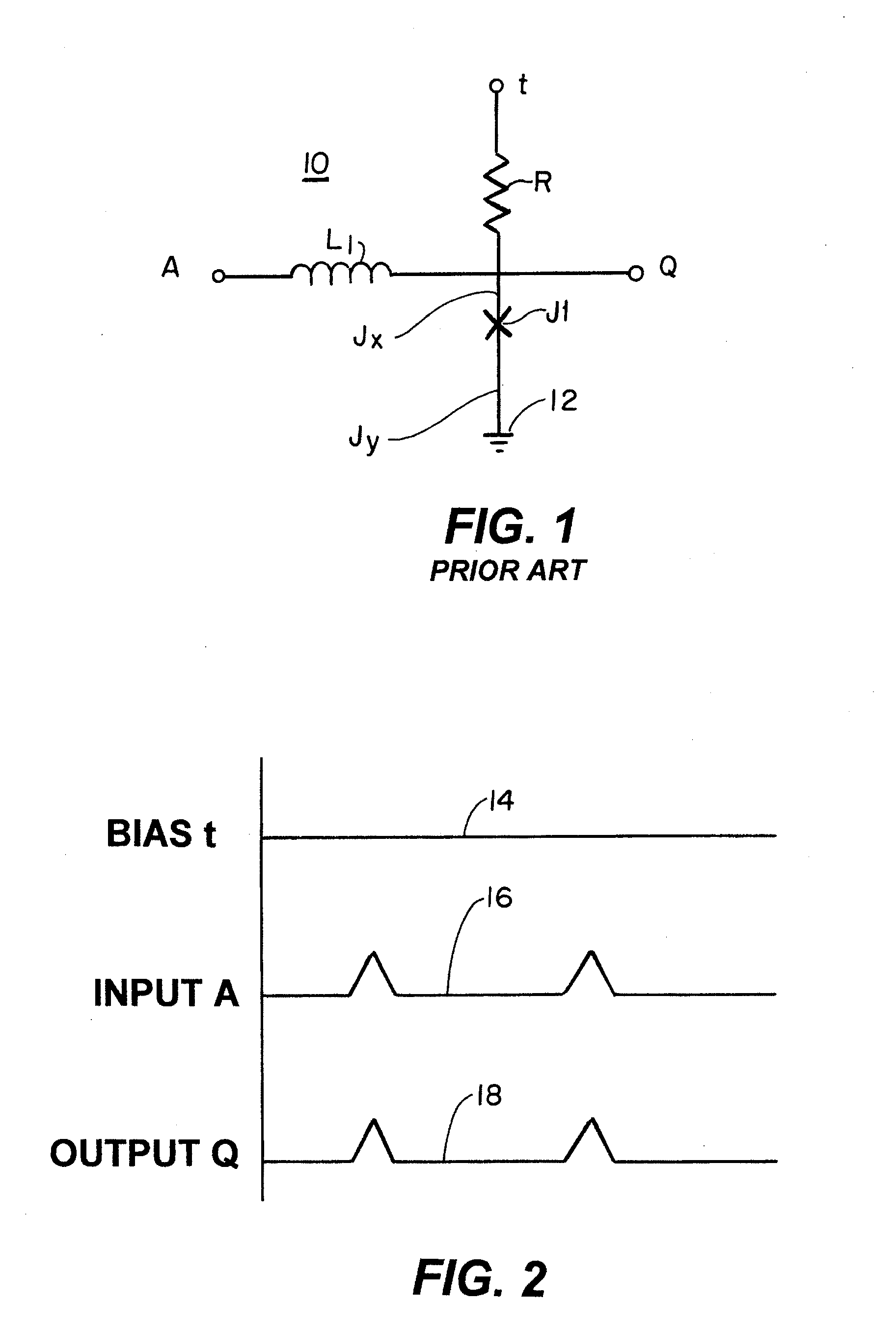
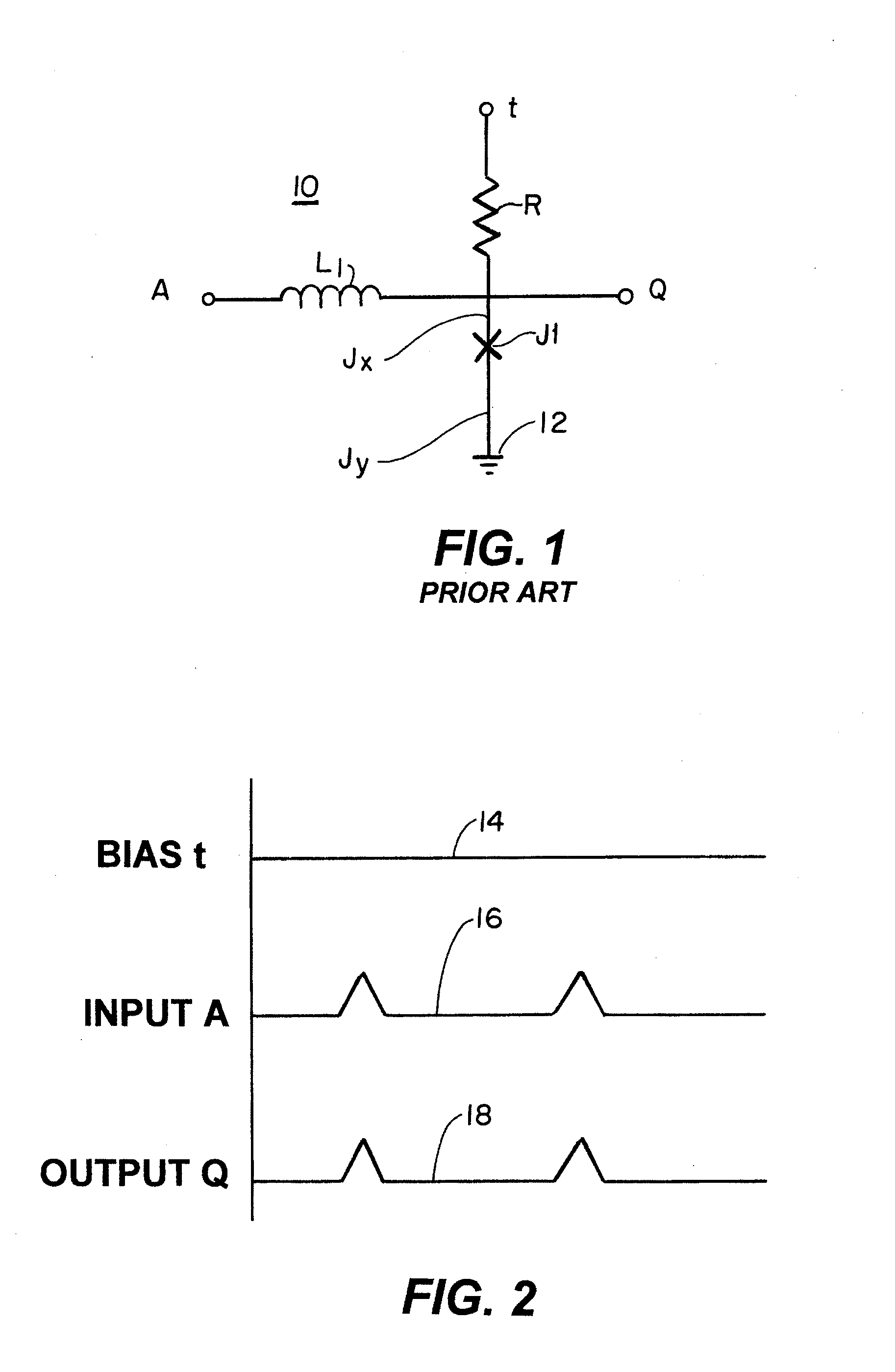
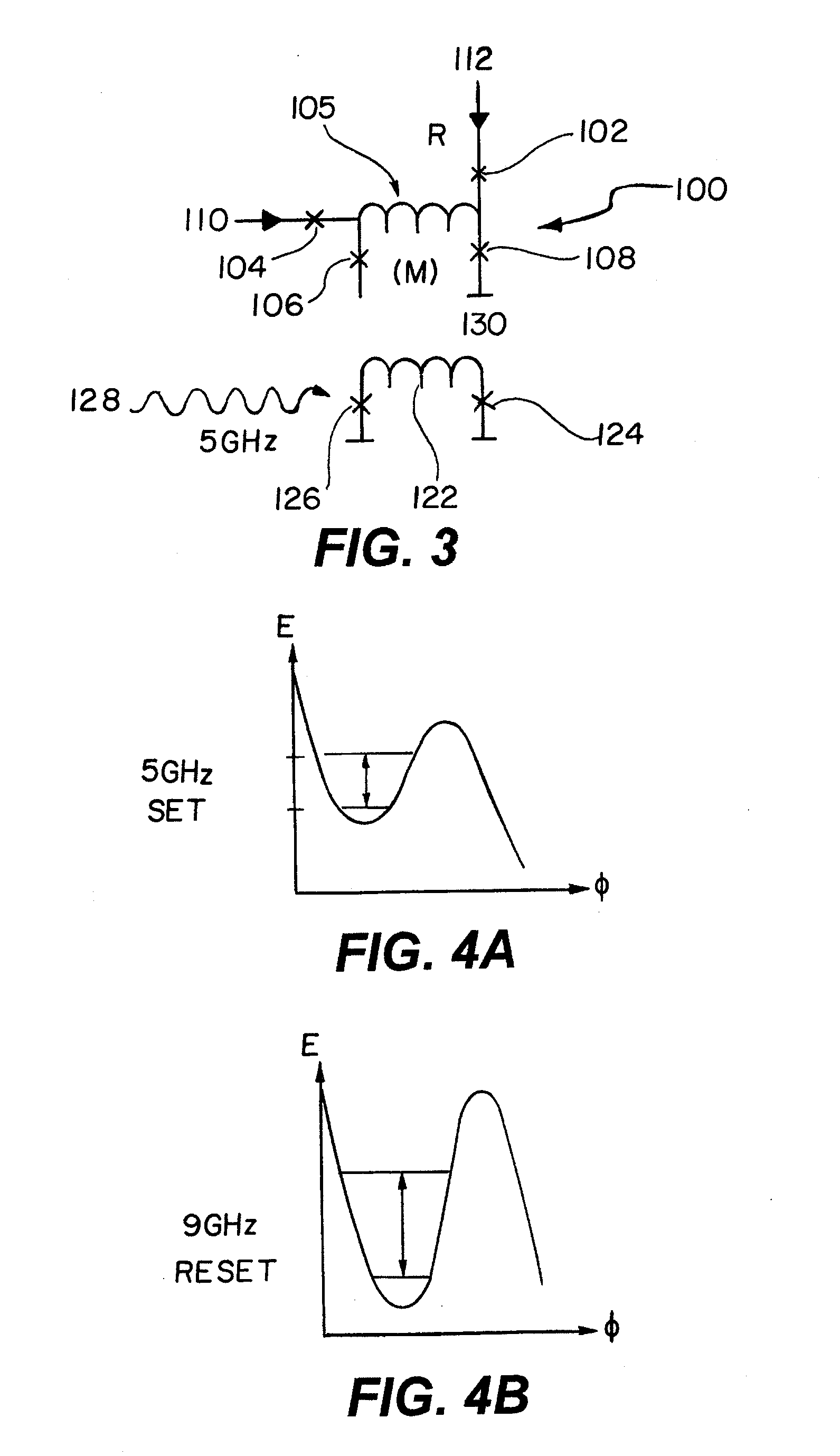
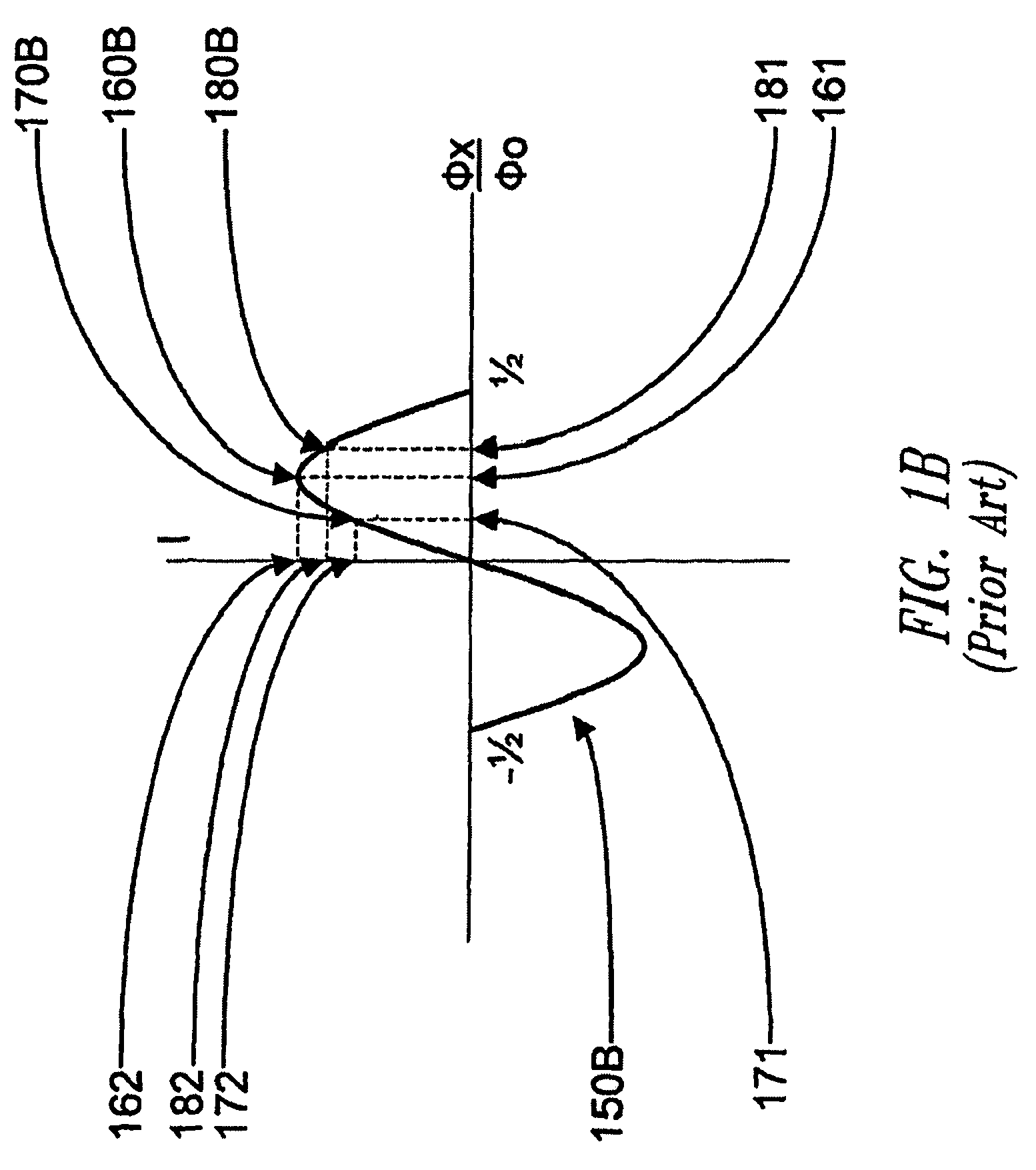
Superconducting quantum-bit device based on Josephson junctions
InactiveUS6838694B2Enhanced couplingShortness of the coherence timeQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCooper pairDegrees of freedom
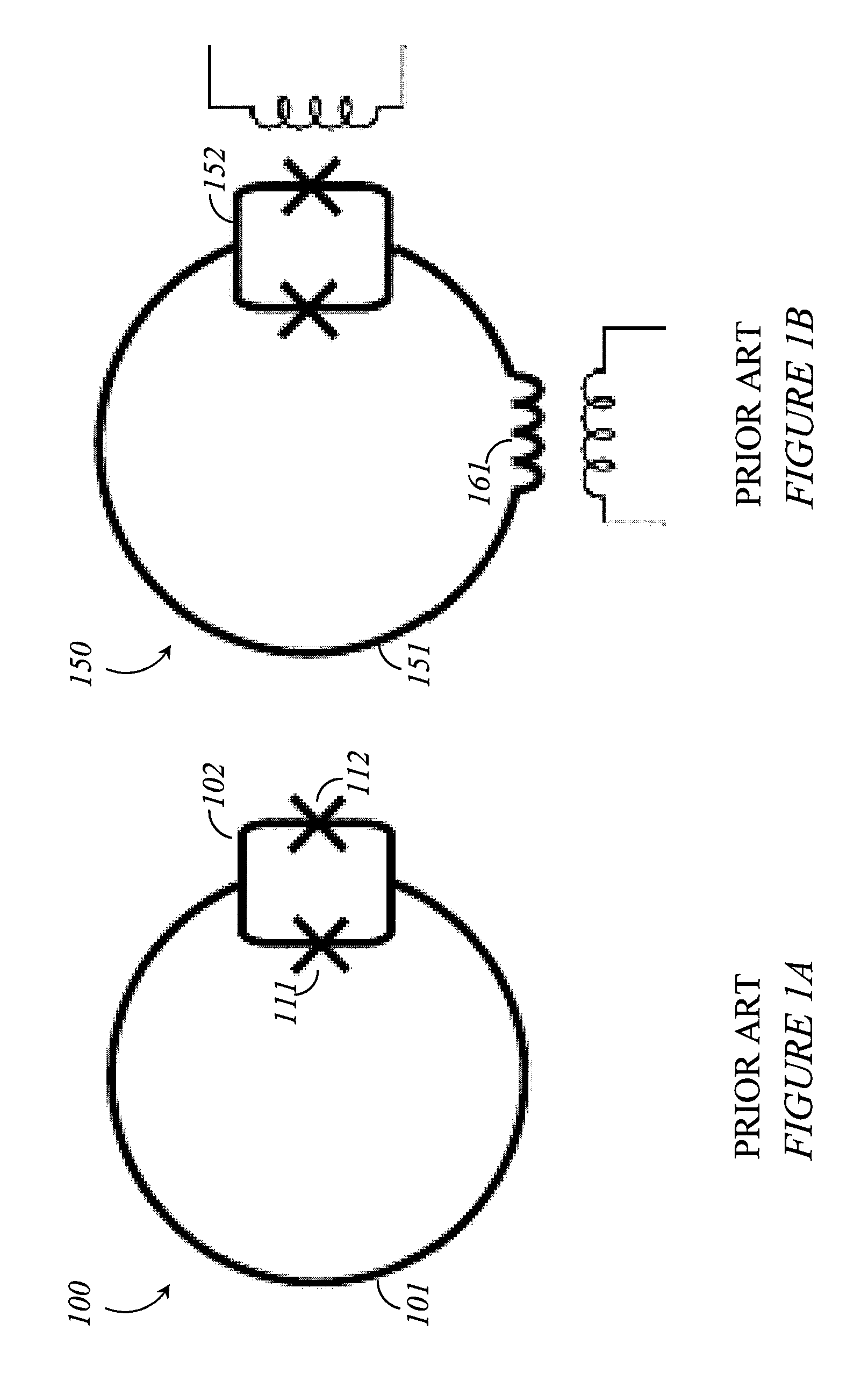
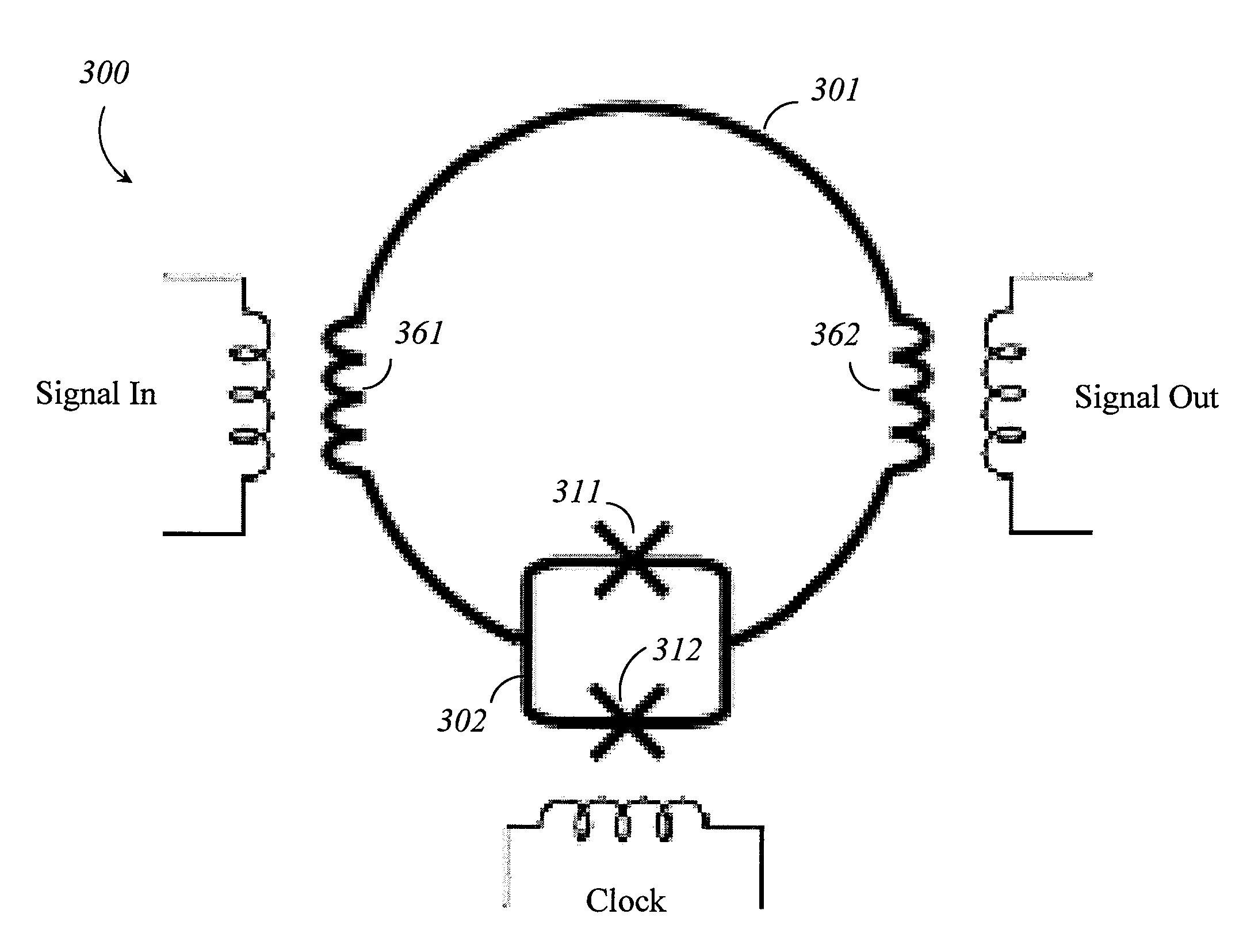
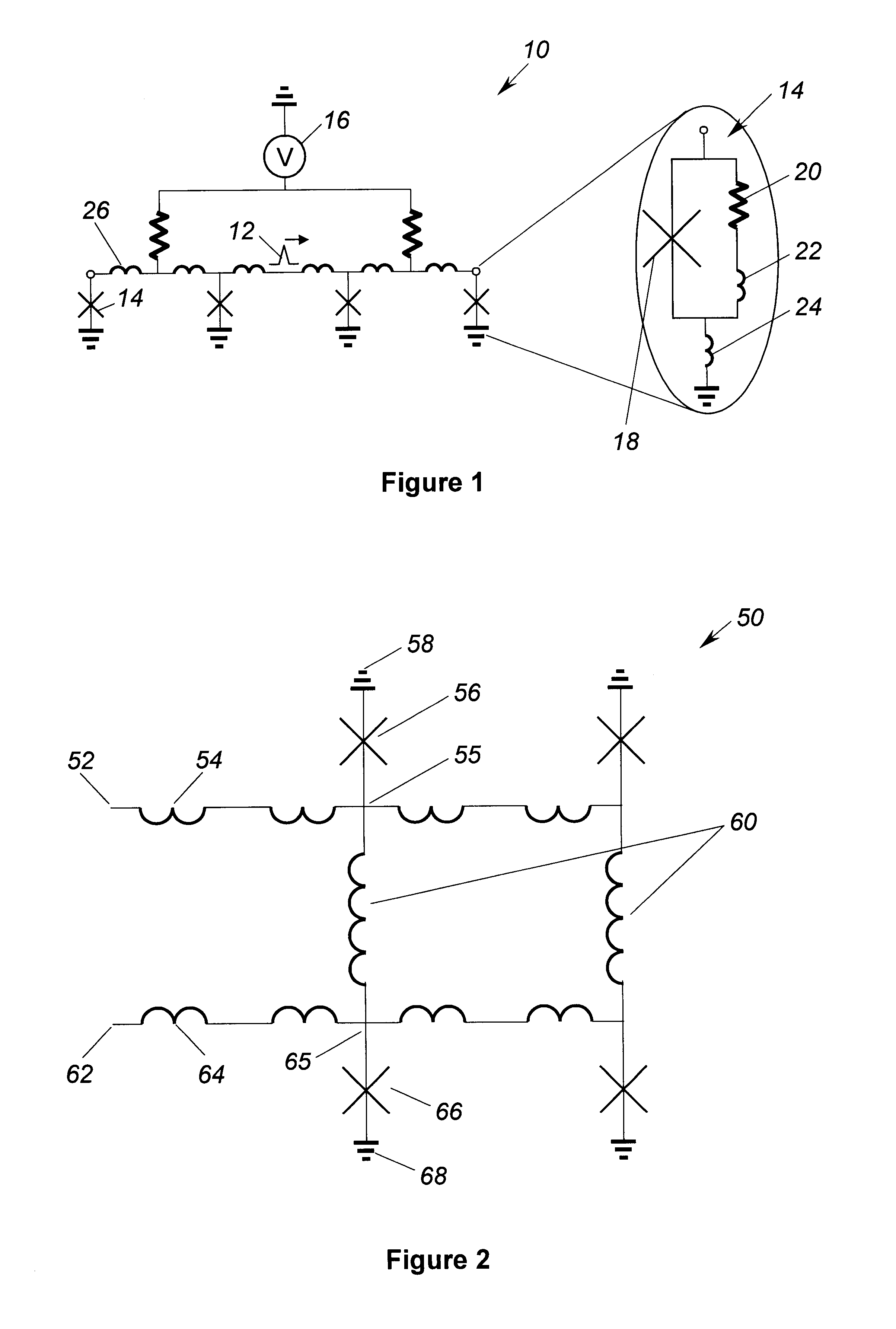
A superconducting quantum-bit device based on Josephson junction has a charge as a first principal degree of freedom assigned to writing and a phase as a second principal degree of freedom assigned to reading. The device comprises a Cooper-pair box comprising first and second Josephson junctions defining a charge island of the Cooper-pair box closing up onto a superconducting loop. A read circuit comprises a read Josephson junction JL inserted into the superconducting loop and having a Josephson energy Ej at least 50 times greater than the Josephson energy of each of the first and second Josephson junctions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
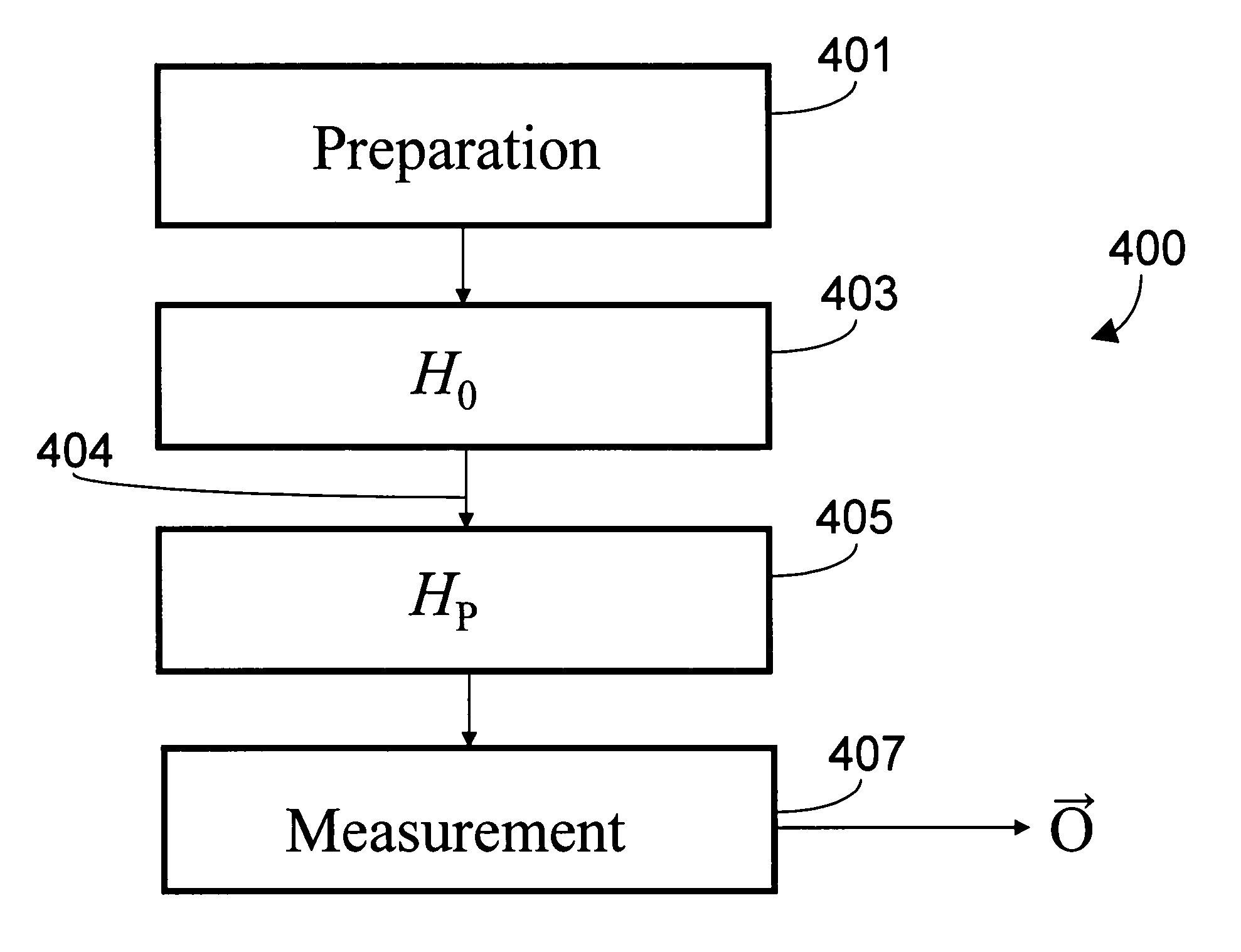
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
ActiveUS20050224784A1Increasing effective charging energyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A method for computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of superconducting qubits is provided. Quantum system can be in any one of at least two configurations including (i) an initialization Hamiltonian H0 and (ii) a problem Hamiltonian HP. The plurality of superconducting qubits are arranged with respect to one another, with a predetermined number of couplings between respective pairs of superconducting qubits in the plurality of qubits, such that the plurality of superconducting qubits, coupled by the predetermined number of couplings, collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, quantum system is initialized to the initialization Hamiltonian HO. Quantum system is then adiabatically changed until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. The quantum state of quantum system is then readout thereby solving the computational problem to be solved.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Adiabatic quantum computation with superconducting qubits
InactiveUS20050250651A1Quantum computersNanoinformaticsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A computer program product with computer program mechanism embedded therein is provided. The mechanism has instructions for initializing a quantum system, which includes a plurality of qubits, to an initialization Hamiltonian HO. The system is capable of being in one of at least two configurations at any give time including HO and a problem Hamiltonian HP. Each respective first qubit in the plurality of qubits is arranged with respect to a respective second qubit in the plurality of qubits such that the first respective qubit and the second respective qubit define a predetermined coupling strength. The predetermined coupling strengths between the qubits in the plurality of qubit collectively define a computational problem to be solved. The mechanism further comprises instructions for adiabatically changing the system until it is described by the ground state of the problem Hamiltonian HP and instructions for reading out the state of the system.
Owner:AMIN MOHAMMAD H S +4
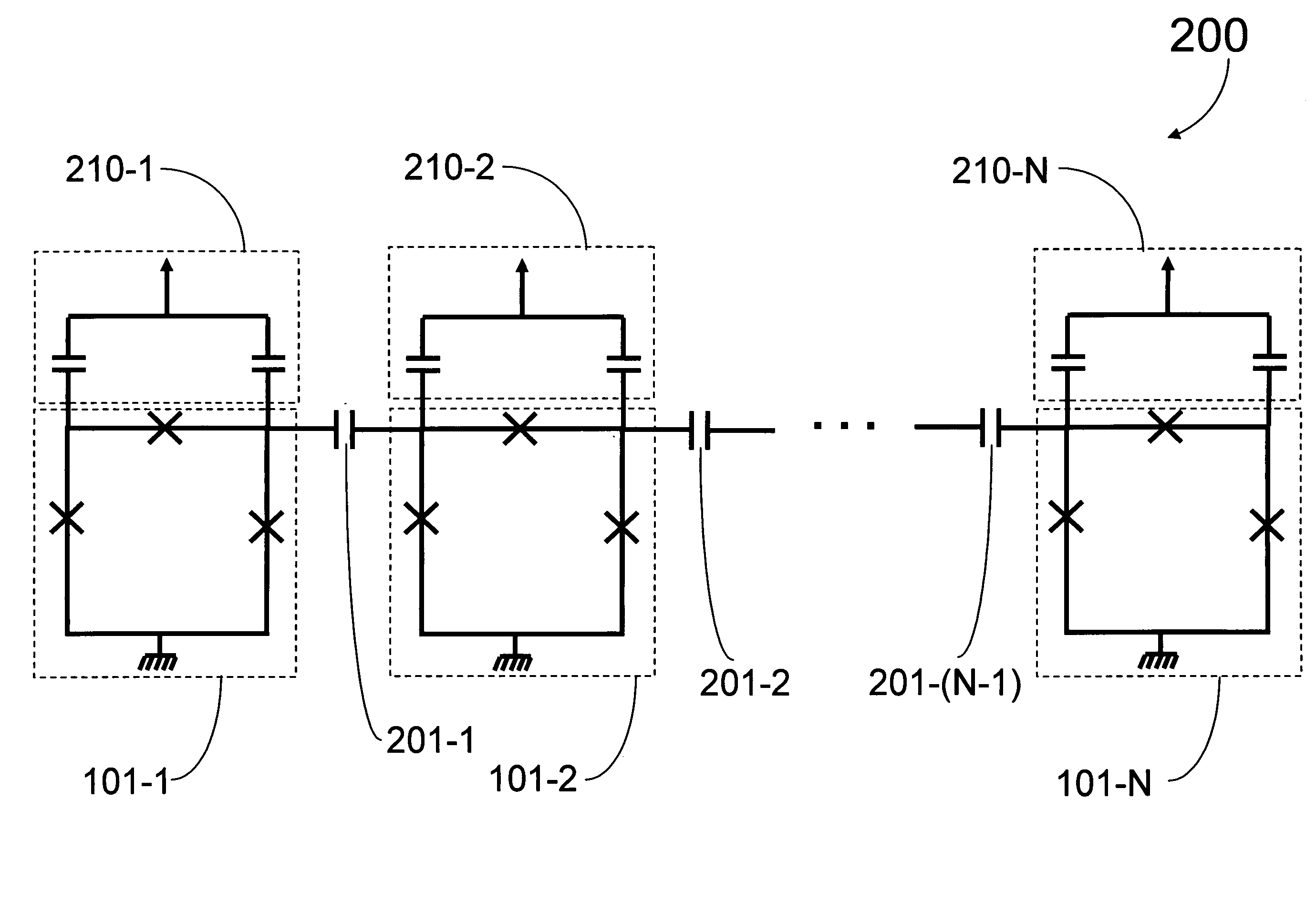
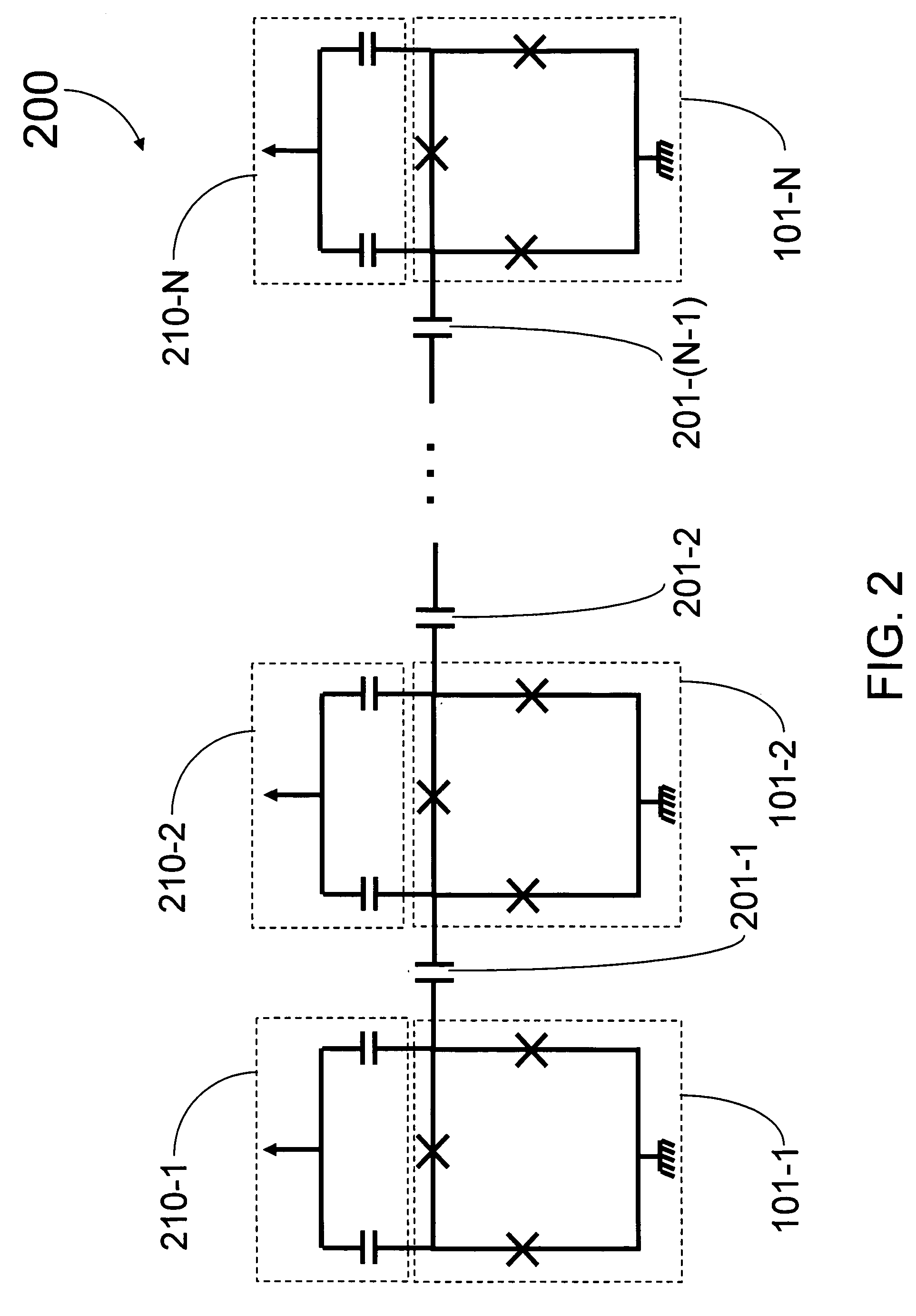
Coupling methods and architectures for information processing
A structure comprising (i) a first information device, (ii) a second information device, (iii) a first coupling element and (iv) a second coupling element is provided. The first information device has at least a first lobe and a second lobe that are in electrical communication with each other. The second information device and has at least a first lobe and a second lobe that are in electrical communication with each other. The first coupling element inductively couples the first lobe of the first information device to the first lobe of the second information device. The second coupling element inductively couples the first lobe of the first information device to the second lobe of the second information device.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, methods, and apparatus for qubit state readout
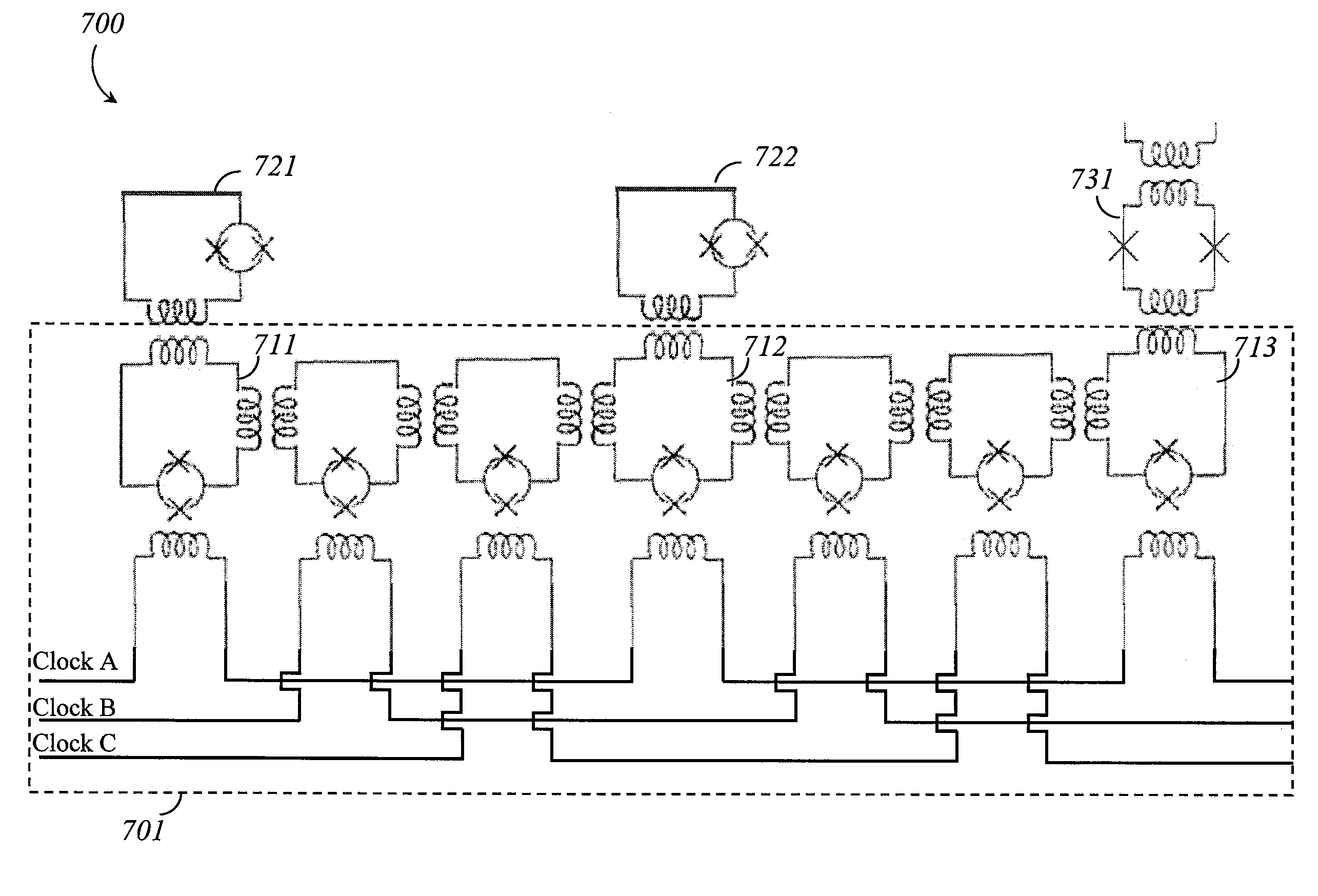
A superconducting readout system includes a computation qubit; a measurement device to measure a state of the computation qubit; and a latch qubit that mediates communicative coupling between the computation qubit and the measurement device. The latch qubit includes a qubit loop that includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series with each other; a compound Josephson junction that interrupts the qubit loop that includes at least two Josephson junctions coupled in series with each other in the compound Josephson junction and coupled in parallel with each other with respect to the qubit loop; and a first clock signal input structure to couple clock signals to the compound Josephson junction.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, methods, and apparatus for qubit state readout
A superconducting readout system includes a computation qubit; a measurement device to measure a state of the computation qubit; and a latch qubit that mediates communicative coupling between the computation qubit and the measurement device. The latch qubit includes a qubit loop that includes at least two superconducting inductors coupled in series with each other; a compound Josephson junction that interrupts the qubit loop that includes at least two Josephson junctions coupled in series with each other in the compound Josephson junction and coupled in parallel with each other with respect to the qubit loop; and a first clock signal input structure to couple clock signals to the compound Josephson junction.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Architecture for local programming of quantum processor elements using latching qubits
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
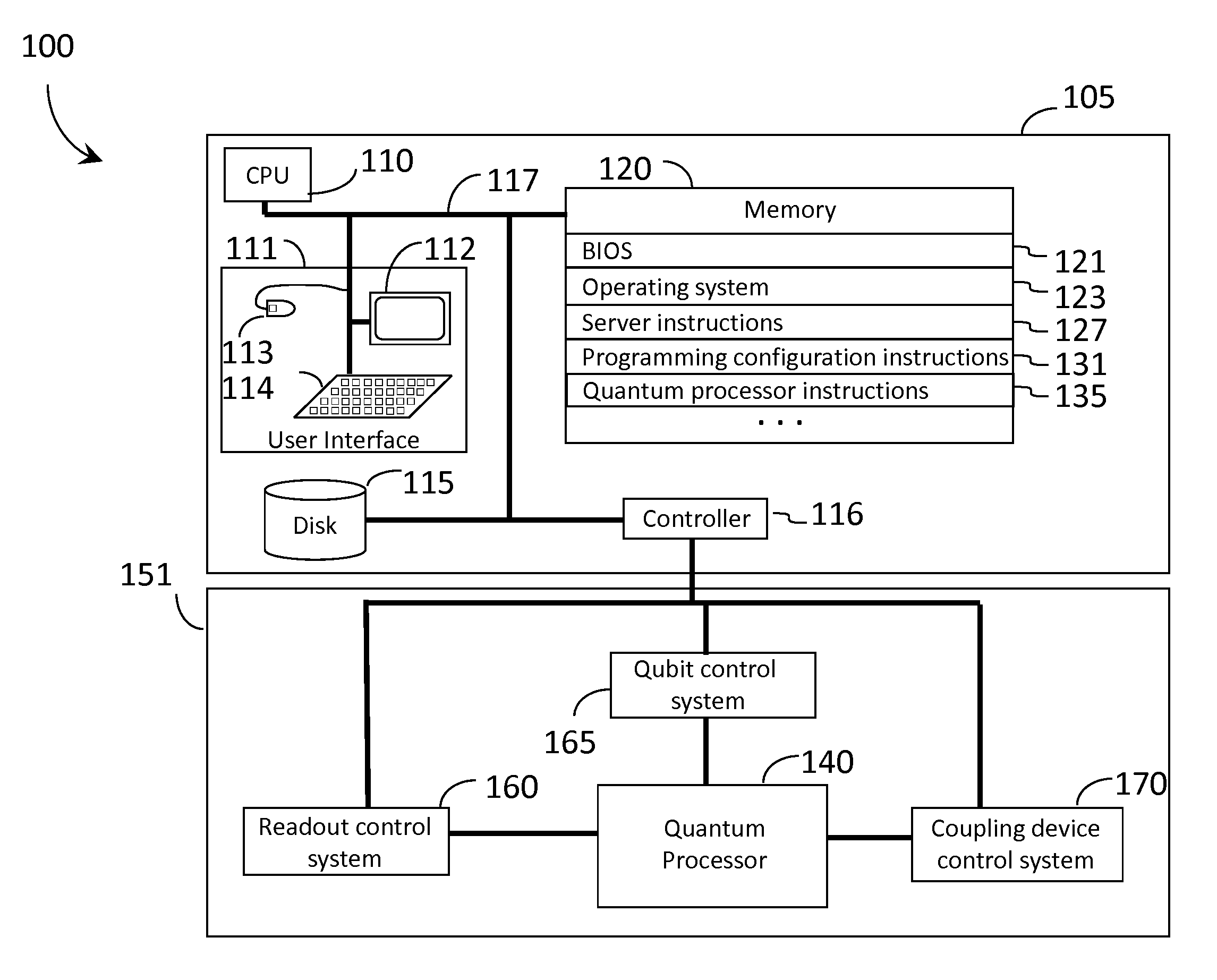
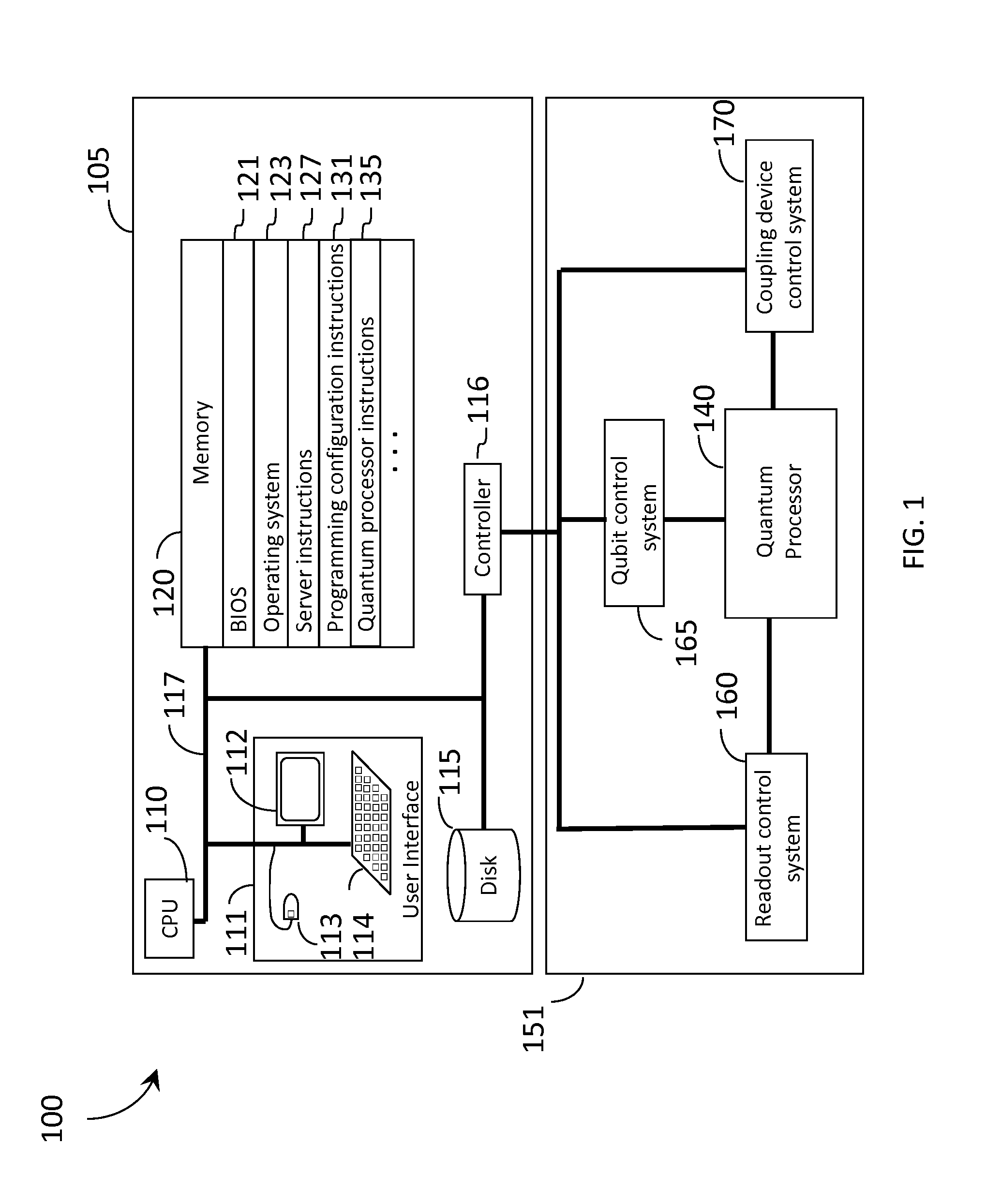
Quantum processor
Multiple substrates that carry quantum devices are coupled to provide quantum mechanical communicators therebetween, for example, using superconducting interconnects, vias, solder and / or magnetic flux. Such may advantageously reduce a footprint of a device such as a quantum processor.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
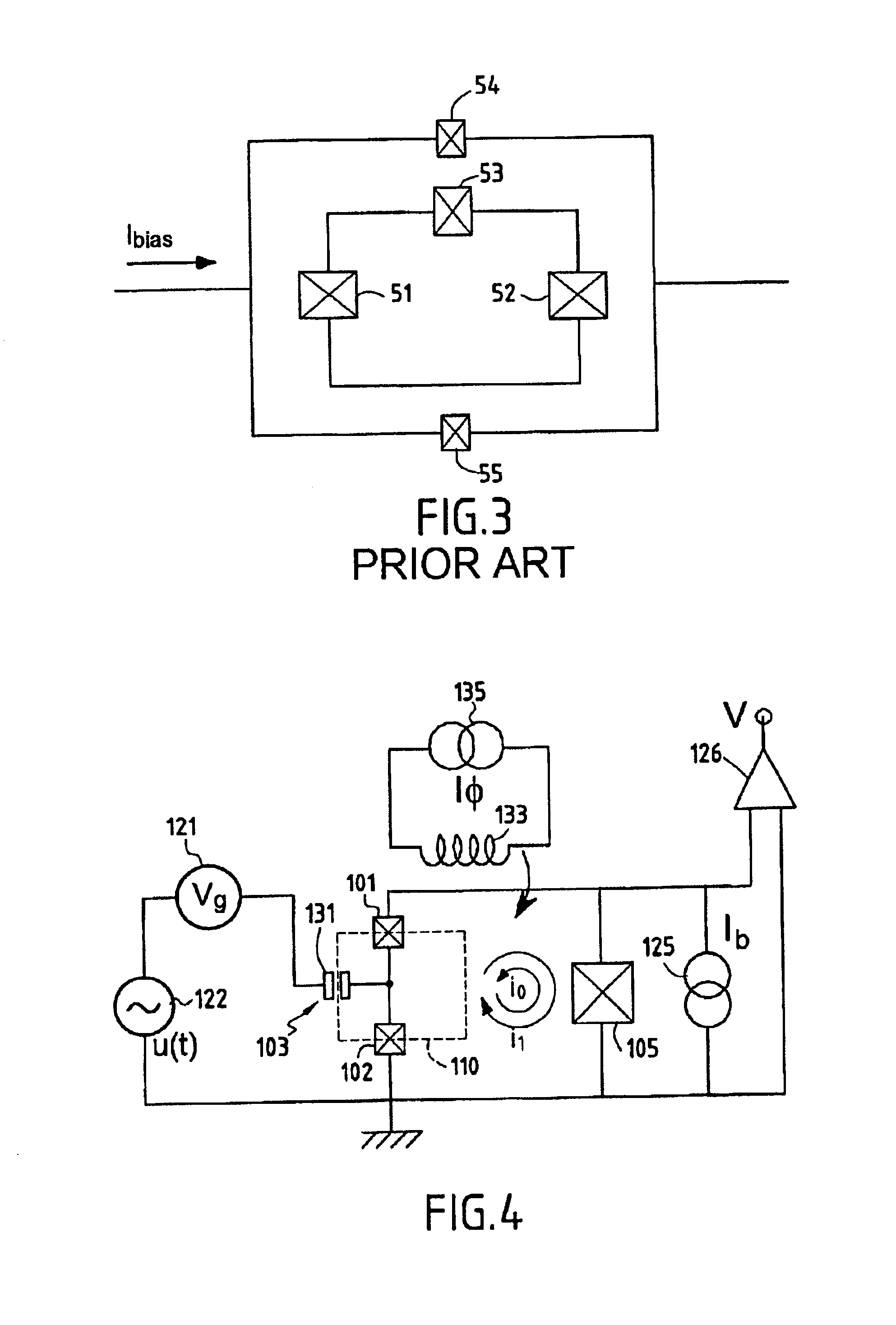
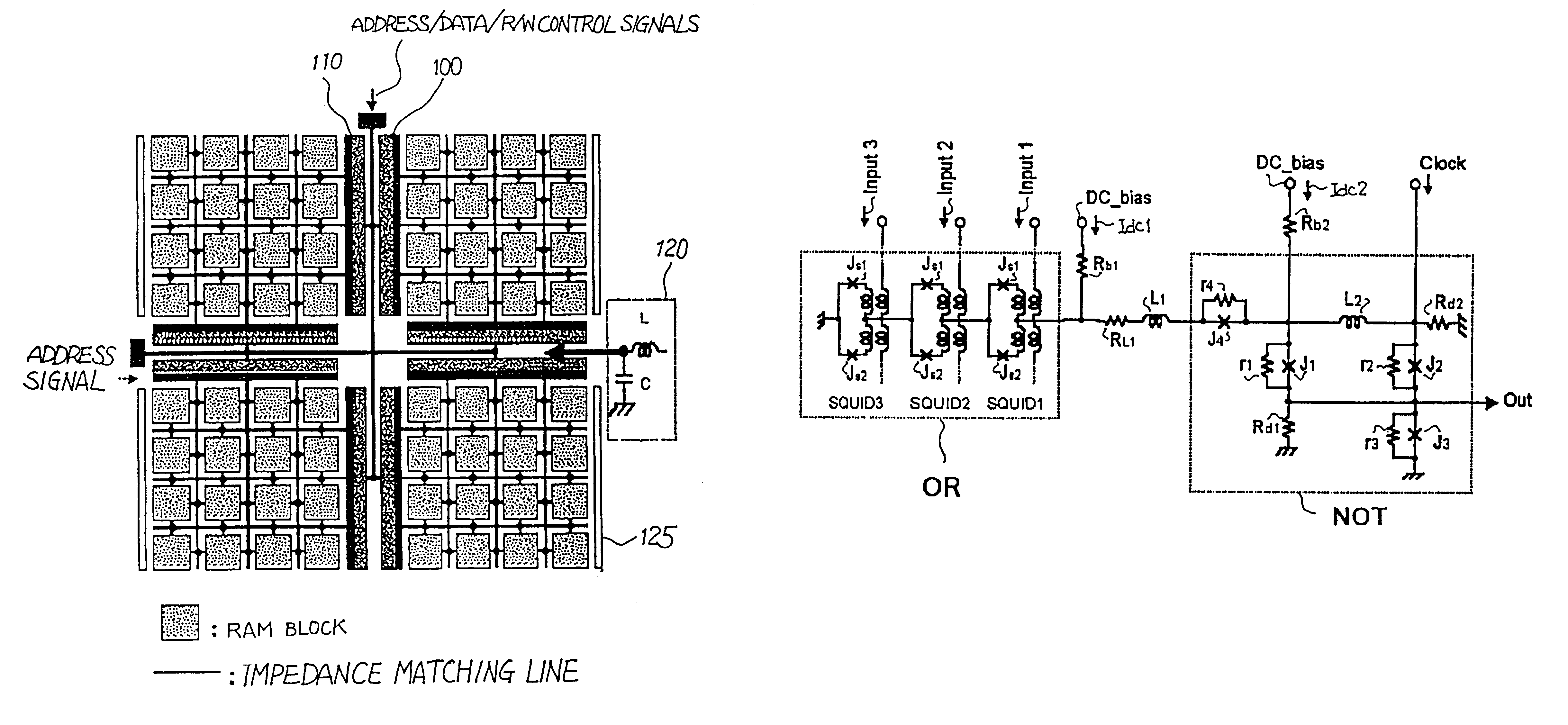
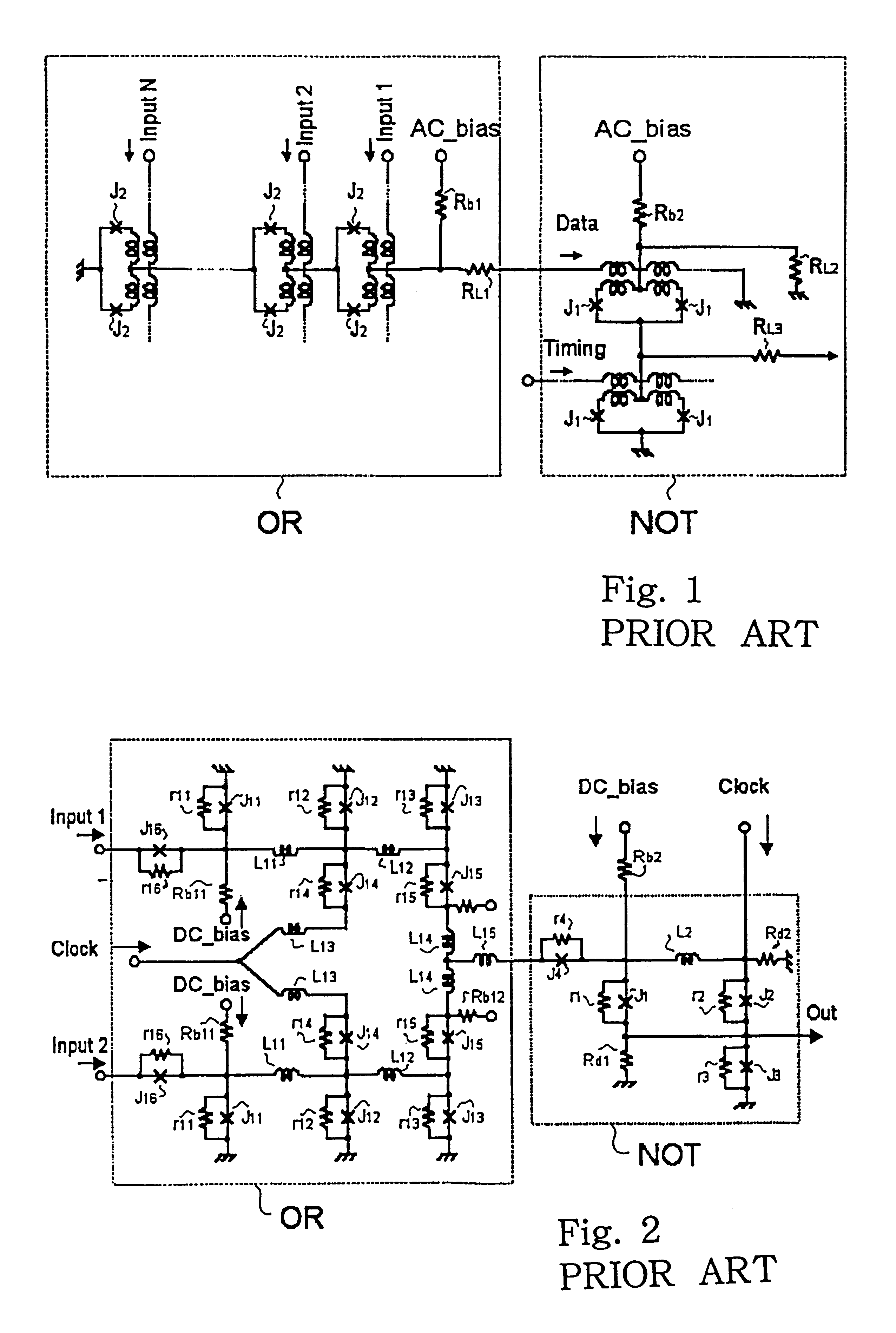
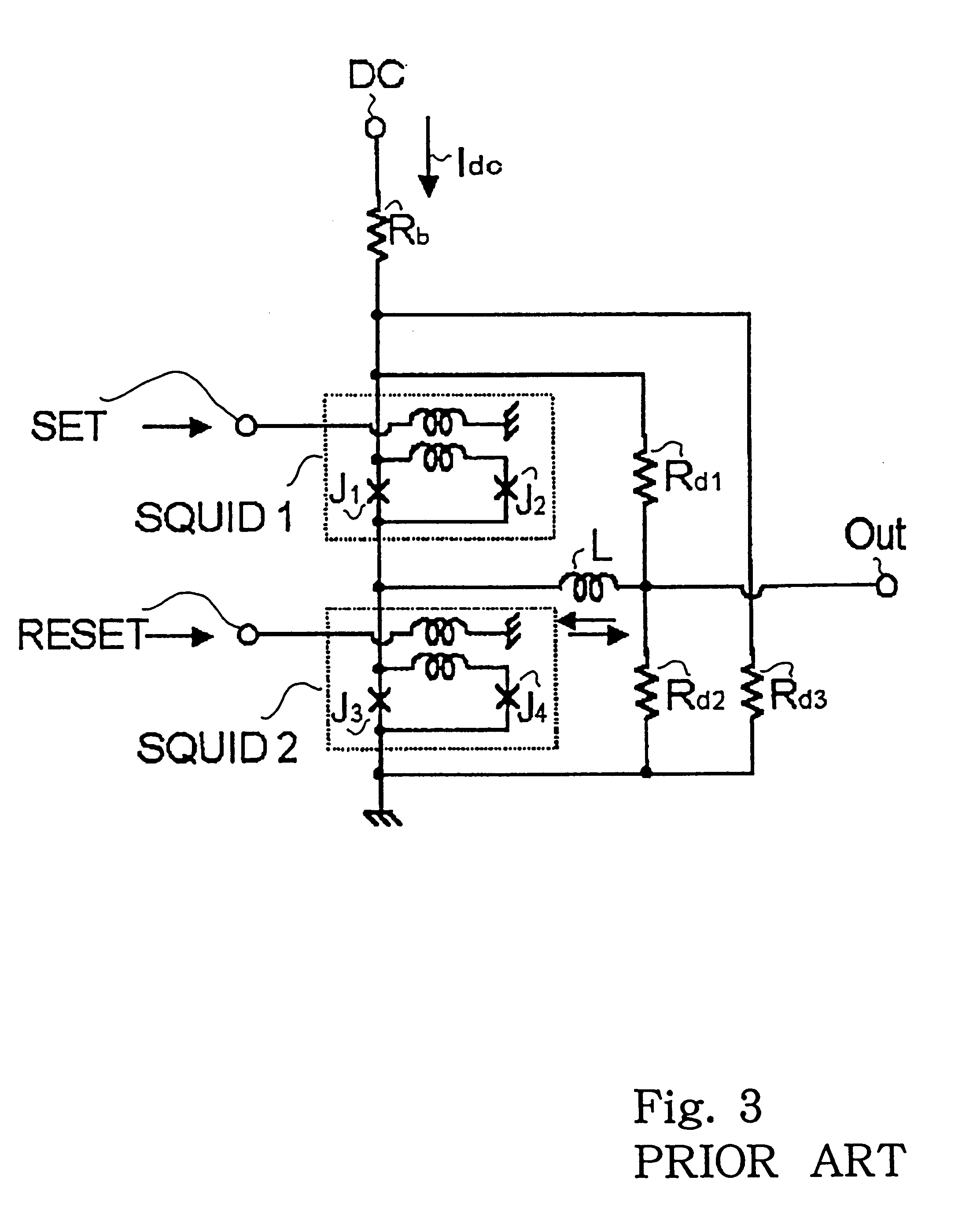
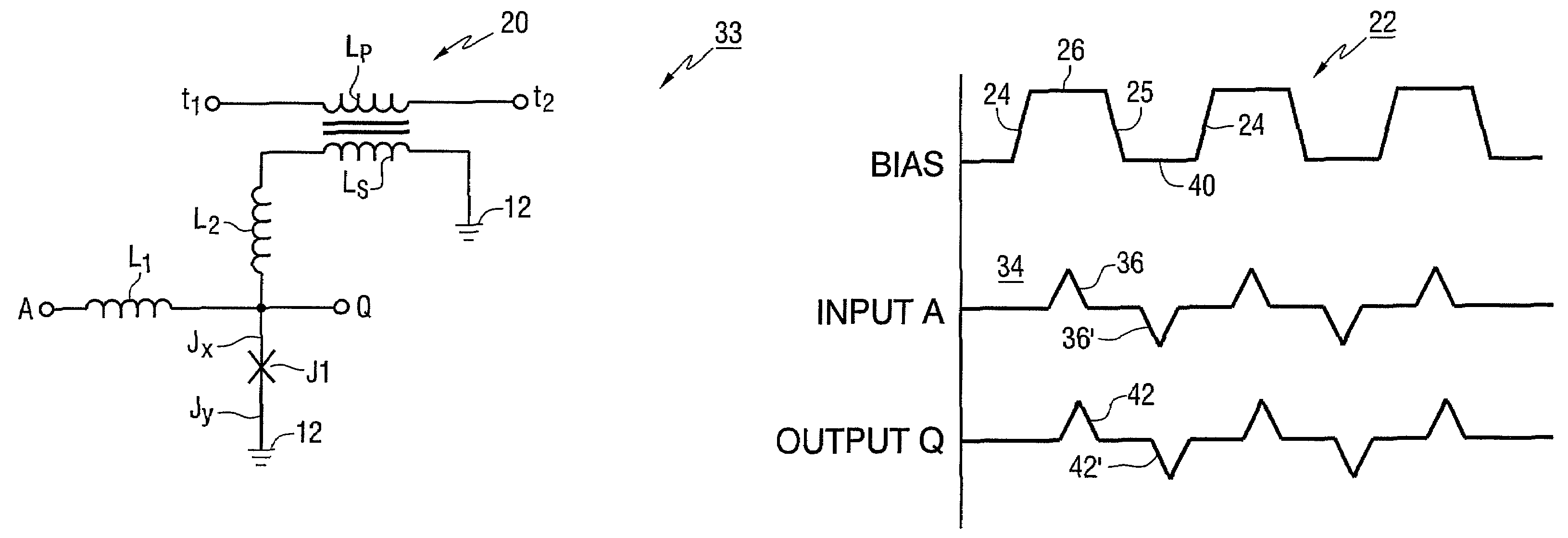
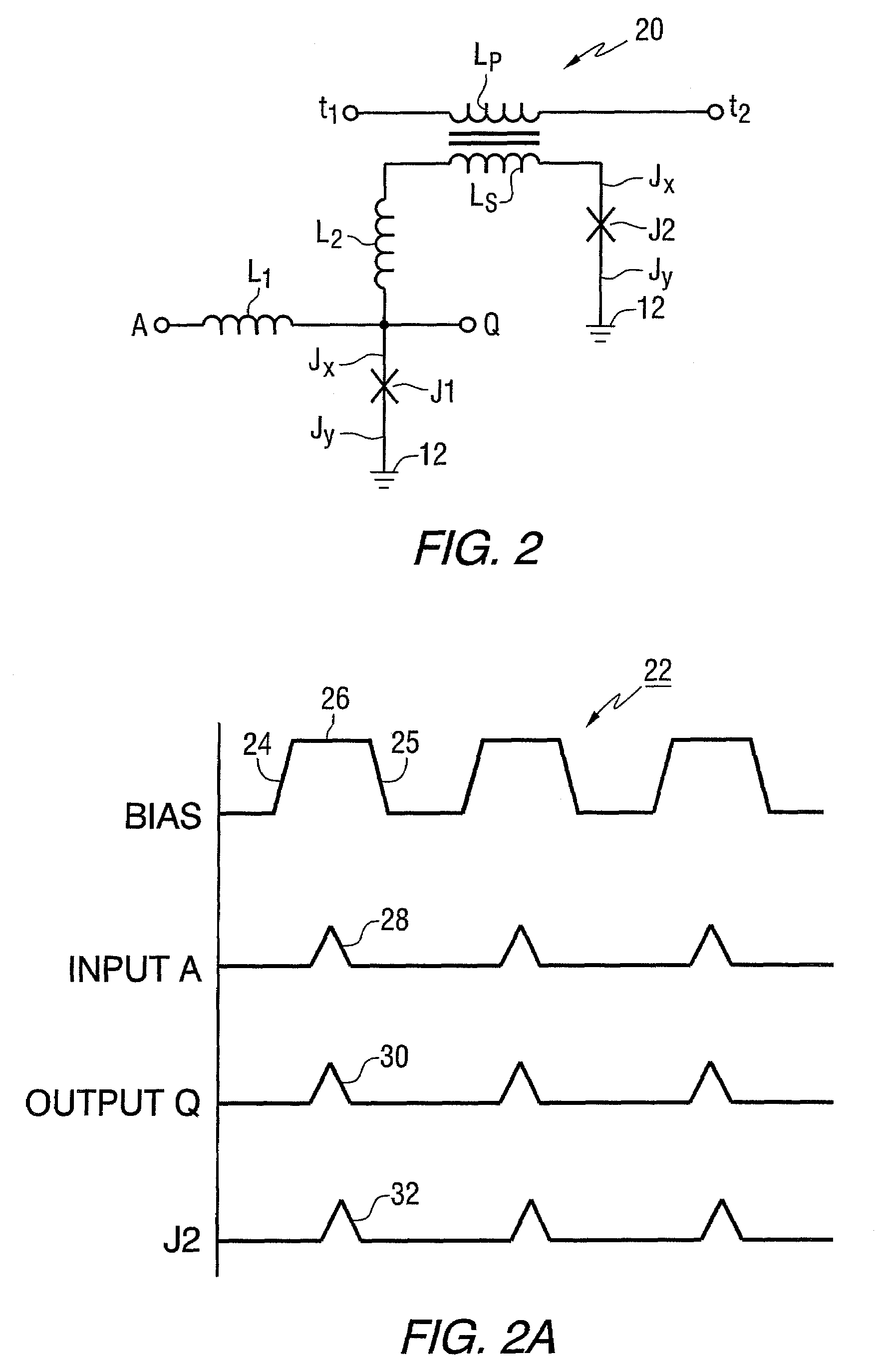
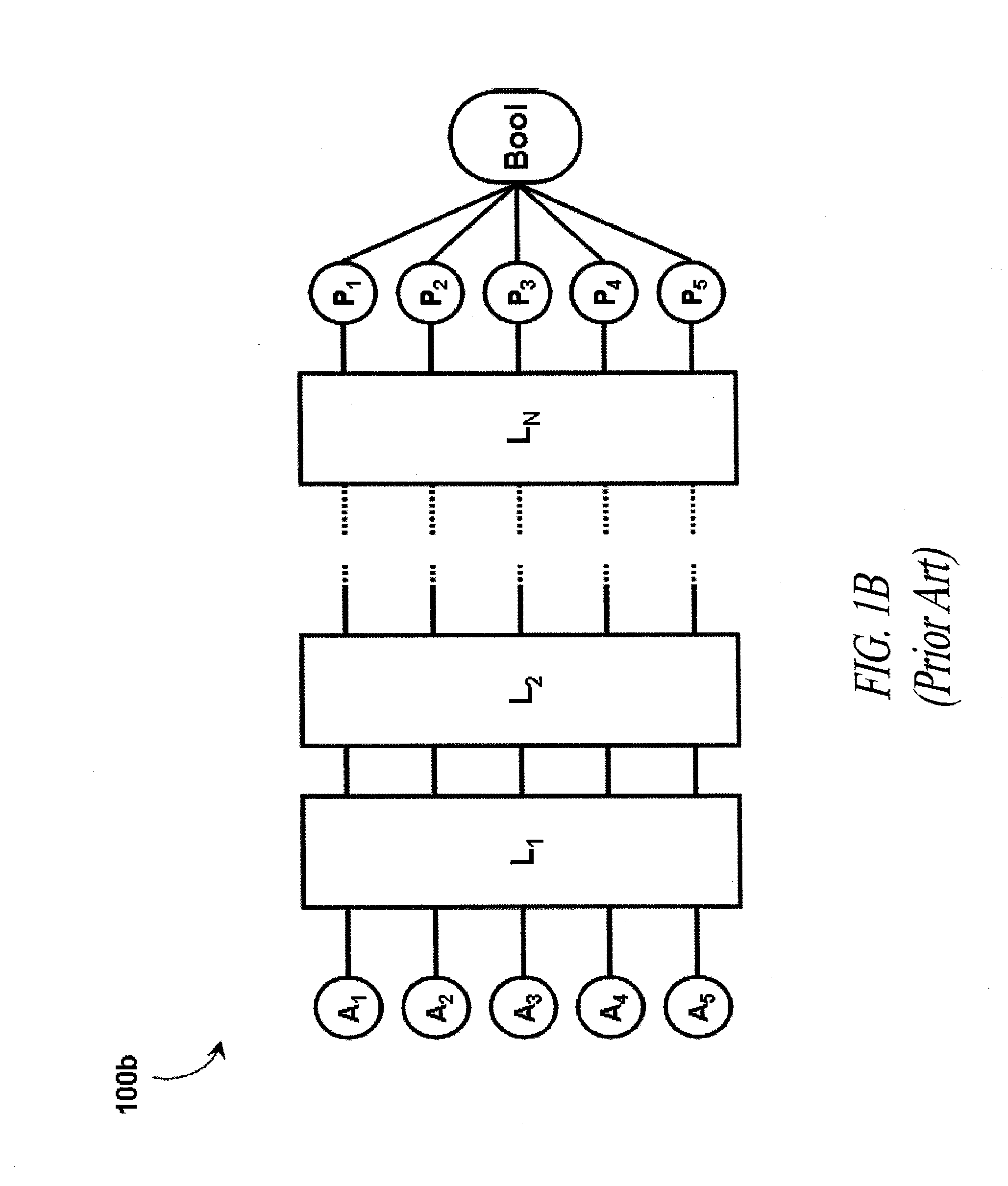
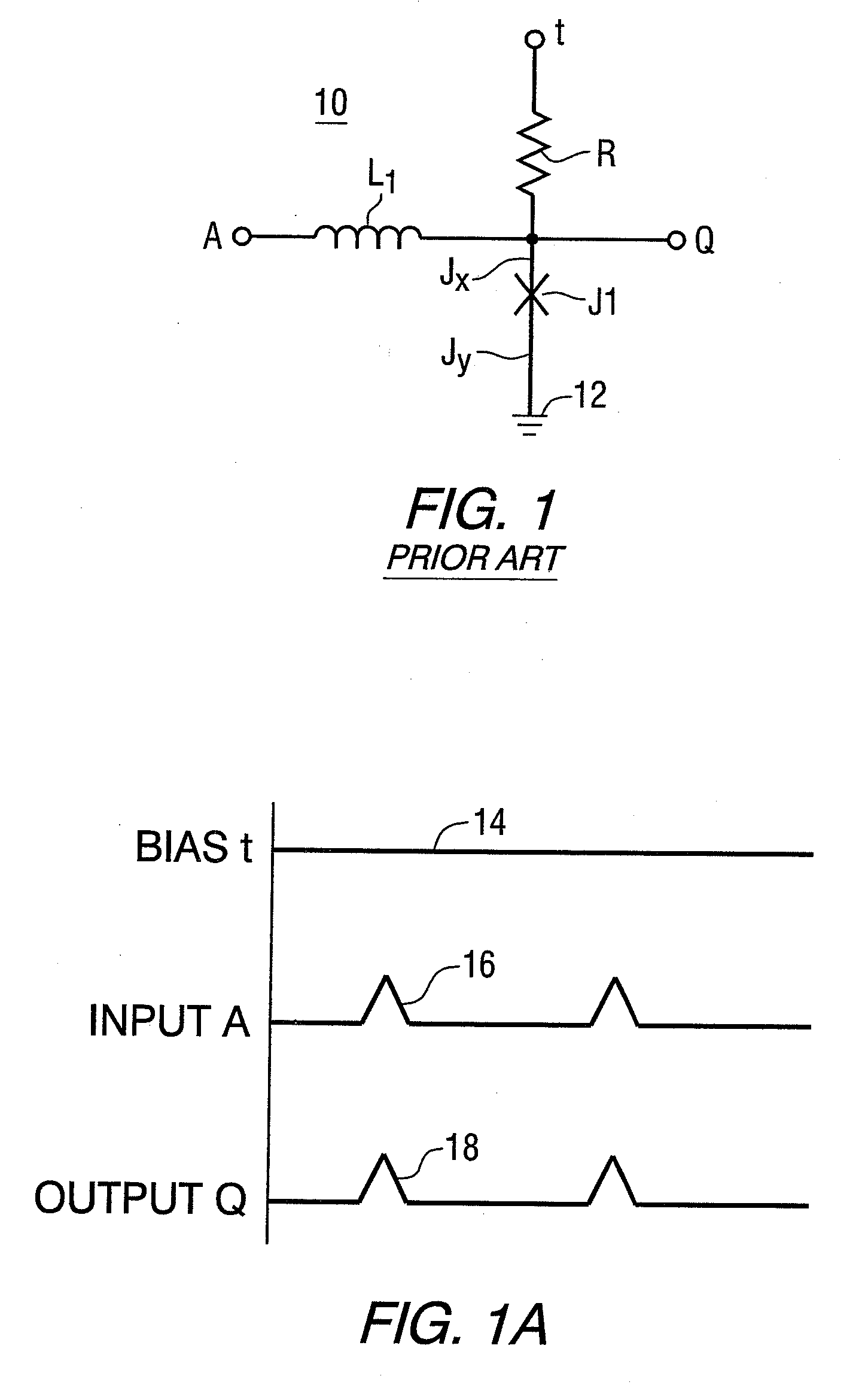
Superconducting circuit having superconductive circuit device of voltage-type logic and superconductive circuit device of fluxoid-type logic device selectively used therein
InactiveUS6242939B1Digital storageLogic circuits using superconductive devicesVoltageSuperconducting circuits
A superconducting circuit device of a voltage-type logic device is large in current driving capability and, accordingly, electric power consumption; however, the switching speed is not so fast, and a superconducting circuit device of a fluxoid-type logic device is small in current driving capability and, accordingly, the electric power consumption; however the switching speed is faster than that of the superconducting circuit device of the voltage-type logic device, wherein the superconducting circuit device of the voltage-type logic device and the superconducting circuit device of the fluxoid-type logic device are selectively used in a superconducting circuit such as a superconducting random access memory, a superconducting NOR circuit and a superconducting signal converting circuit so as to realize small electric power consumption and high-speed switching action.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
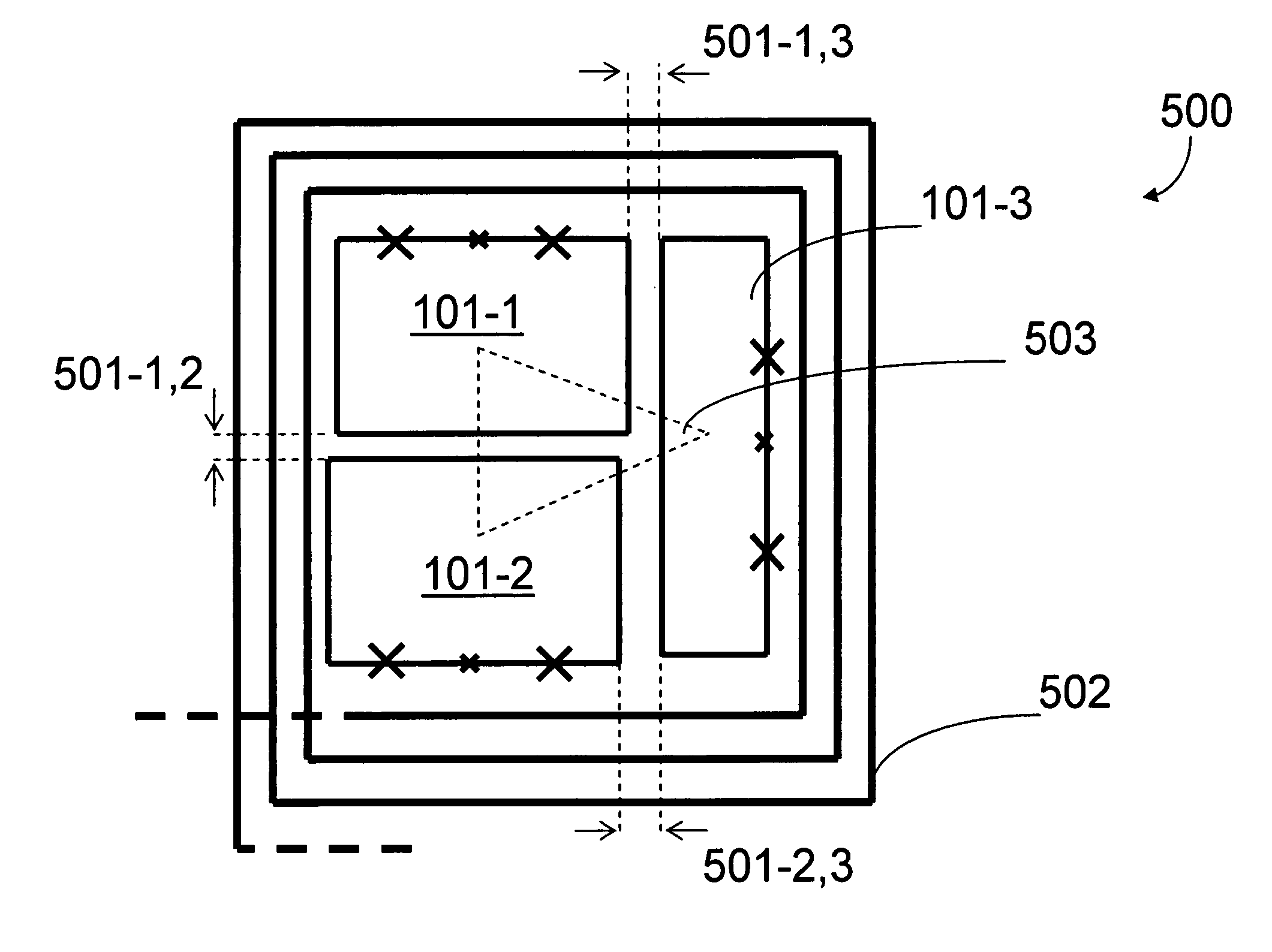
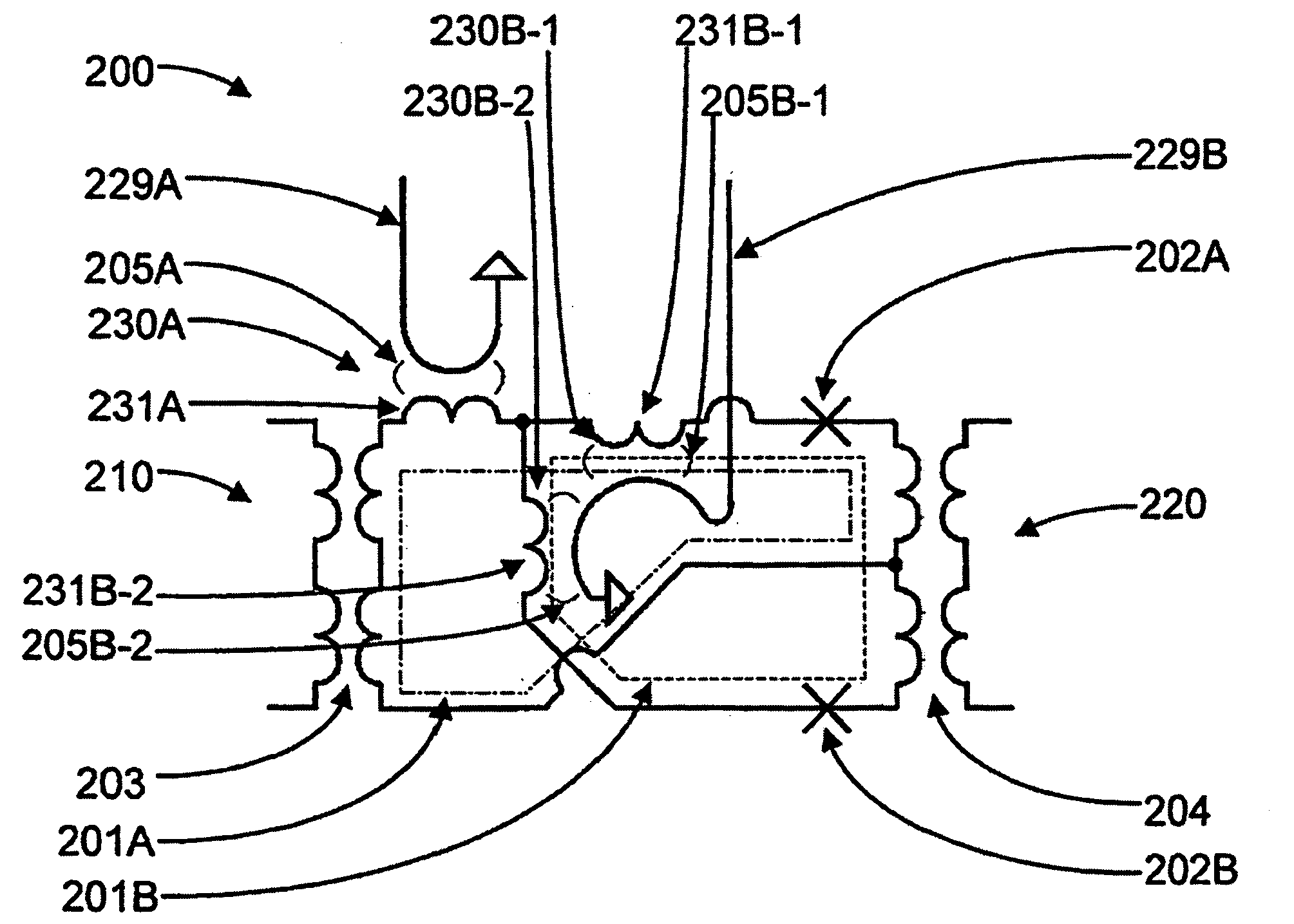
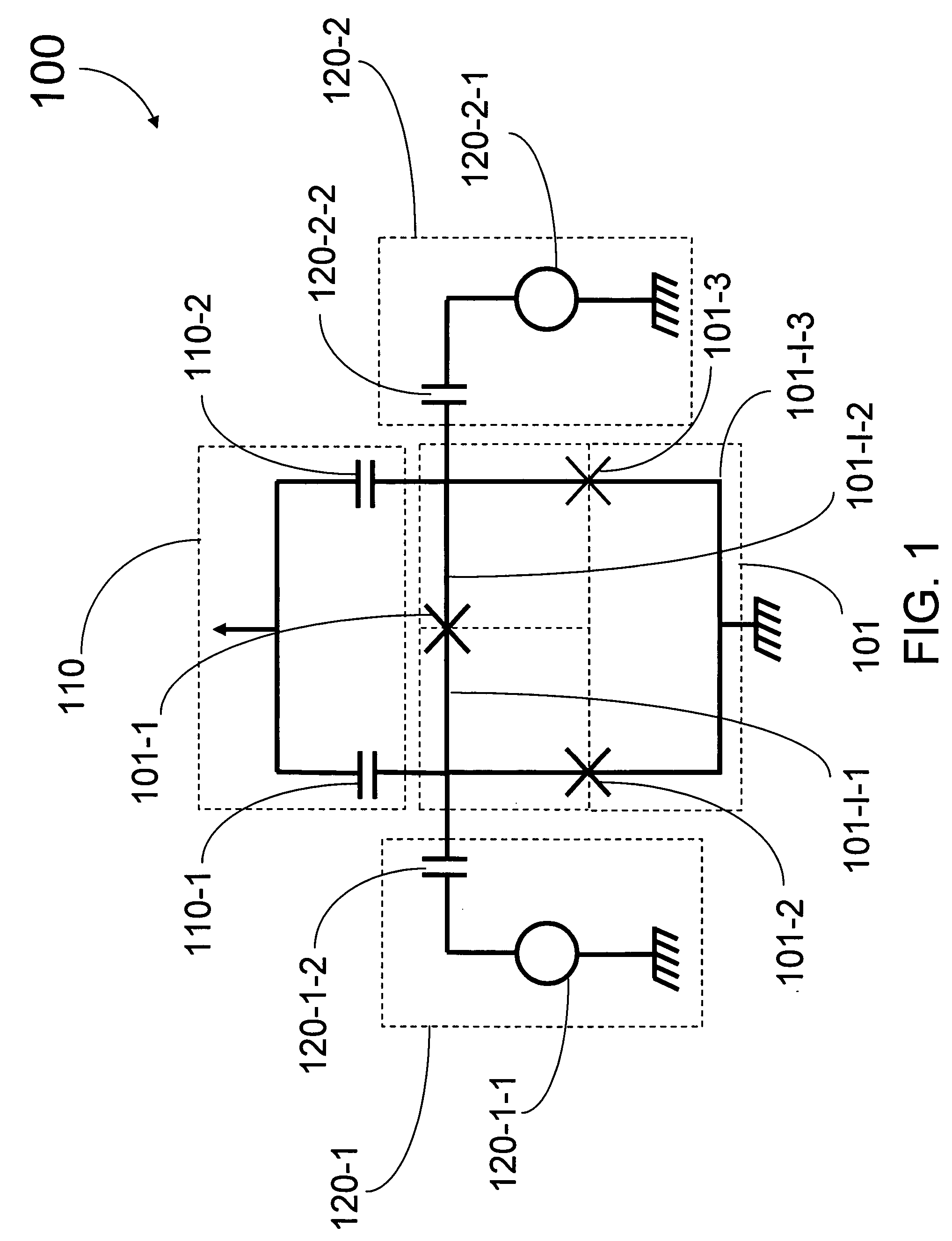
Superconducting qubit with a plurality of capacitive couplings
A first qubit having a superconducting loop interrupted by a plurality of Josephson junctions is provided. Each junction interrupts a different portion of the superconducting loop and each different adjacent pair of junctions in the plurality of Josephson junctions defines a different island. An ancillary device is coupled to the first qubit. In a first example, the ancillary device is a readout mechanism respectively capacitively coupled to a first and second island in the plurality of islands of the first qubit by a first and second capacitance. Quantum nondemolition measurement of the first qubit's state may be performed. In a second example, the ancillary device is a second qubit. The second qubit's first and second islands are respectively capacitively coupled to the first and second islands of the first qubit by a capacitance. In this second example, the coupling is diagonal in the physical basis of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method and apparatus for Josephson distributed output amplifier
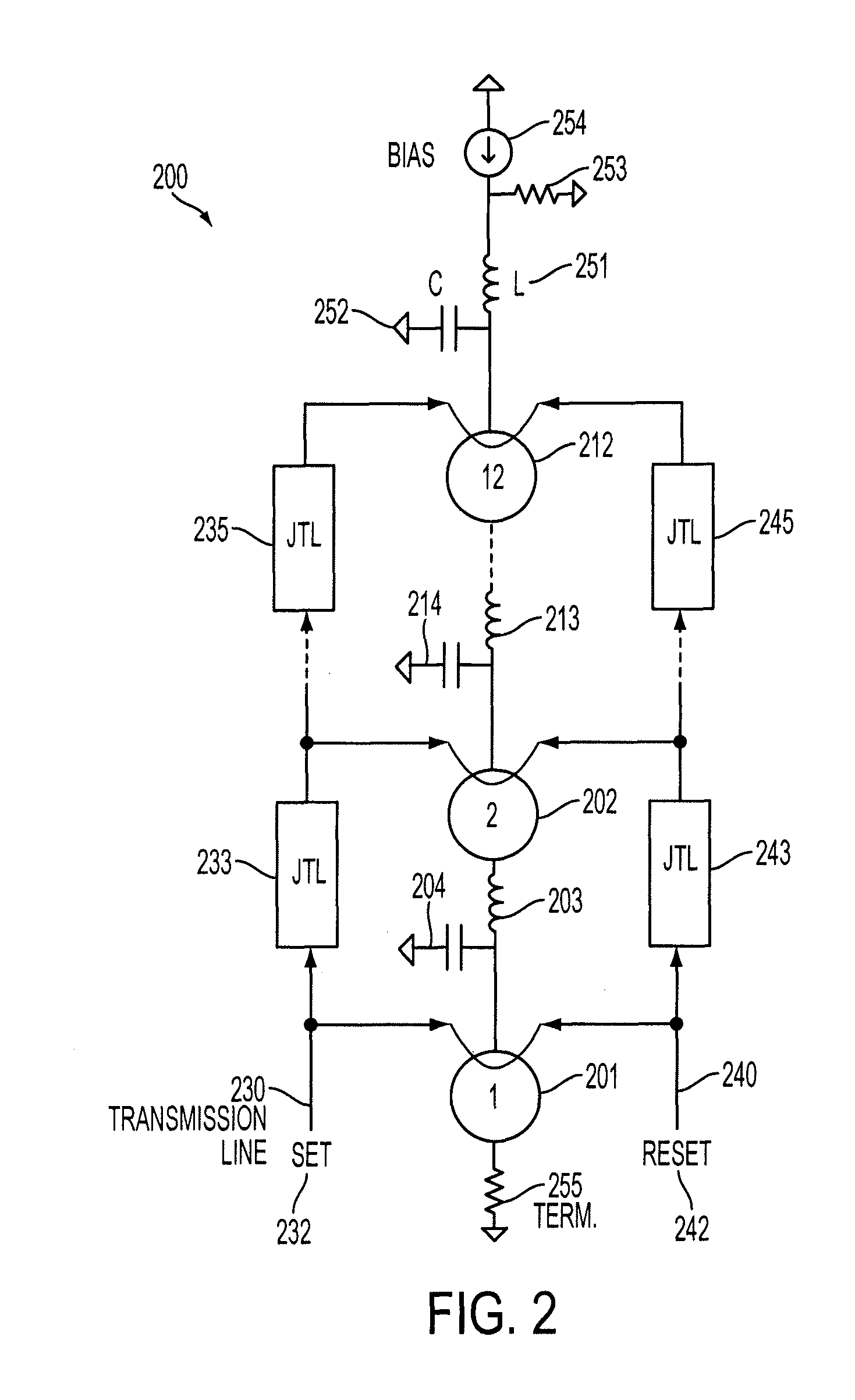
The disclosure generally relates to a method and apparatus for providing high-speed, low signal power amplification. In an exemplary embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method for providing a wideband amplification of a signal by forming a first transmission line in parallel with a second transmission line, each of the first transmission line and the second transmission line having a plurality of superconducting transmission elements, each transmission line having a transmission line delay; interposing a plurality of amplification stages between the first transmission line and the second transmission line, each amplification stage having an resonant circuit with a resonant circuit delay; and substantially matching the resonant circuit delay for at least one of the plurality of amplification stages with the transmission line delay of at least one of the superconducting transmission lines.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Single flux quantum circuits
ActiveUS7724020B2Reduce and eliminate unnecessary power dissipationQuantum computersPower consumption reductionQuantum circuitTransformer
Superconducting single flux quantum circuits are disclosed herein, each having at least one Josephson junction which will flip when the current through it exceeds a critical current. Bias current for the Josephson junction is provided by a biasing transformer instead of a resistor. The lack of any bias resistors ensures that unwanted power dissipation is eliminated.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
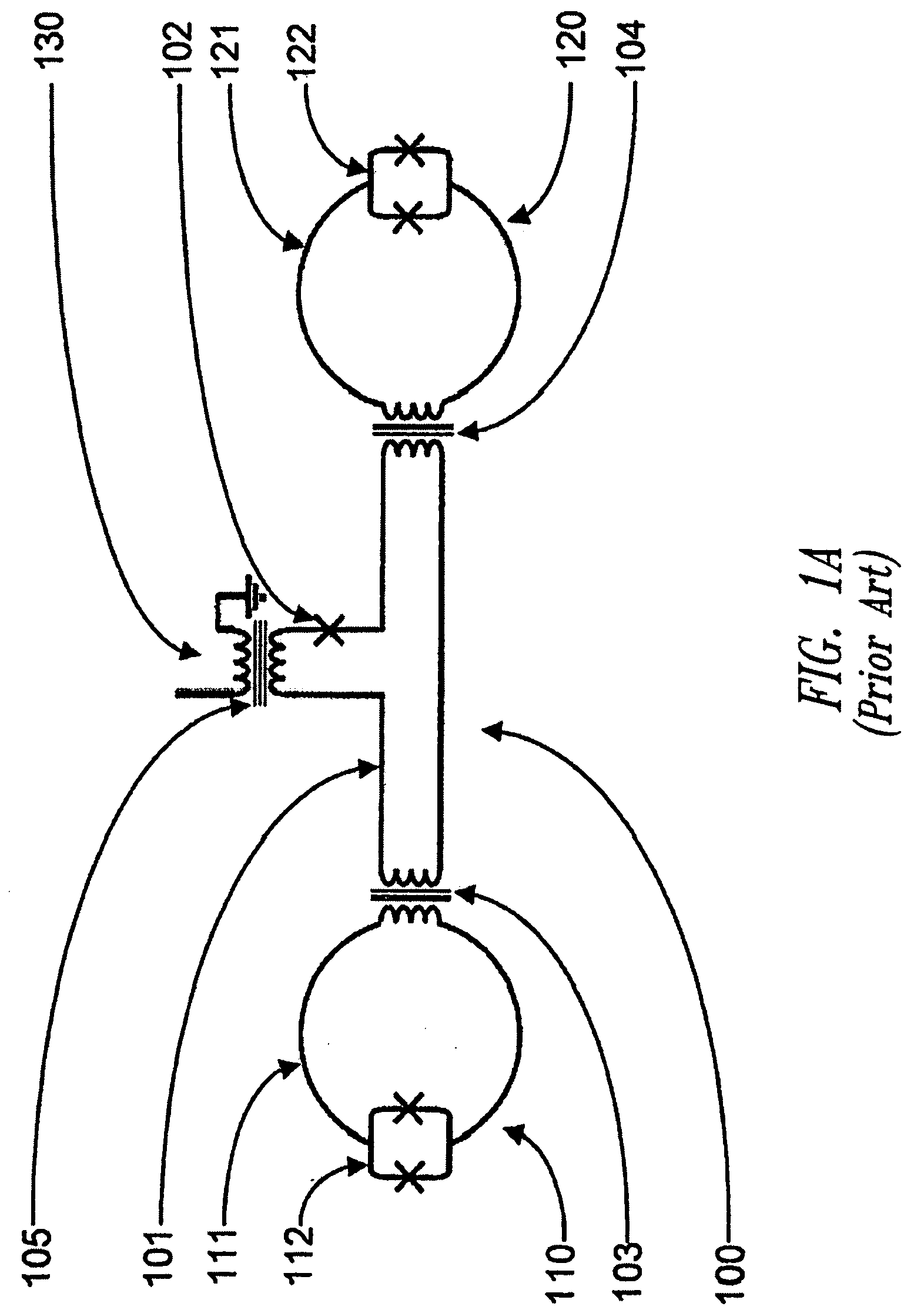
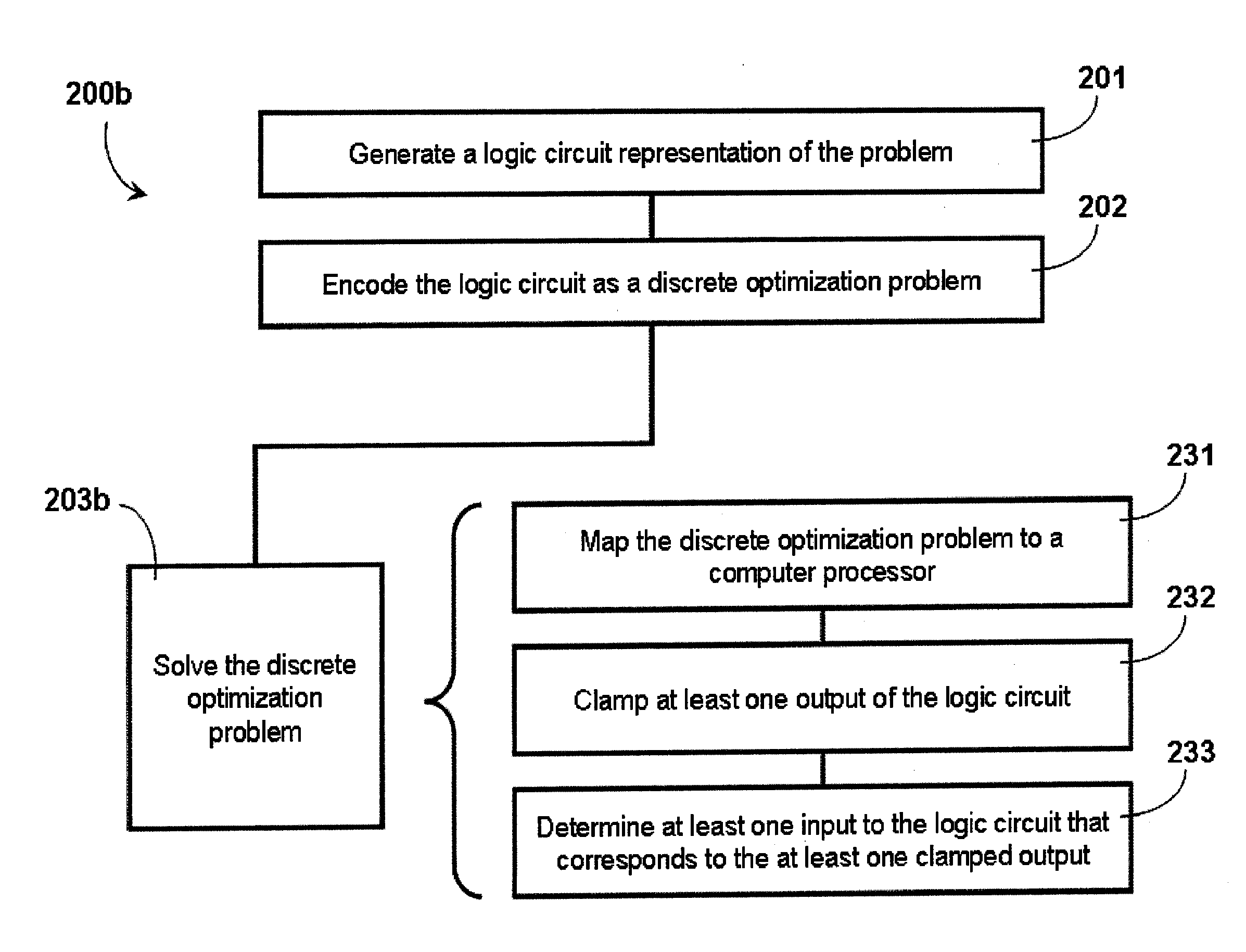
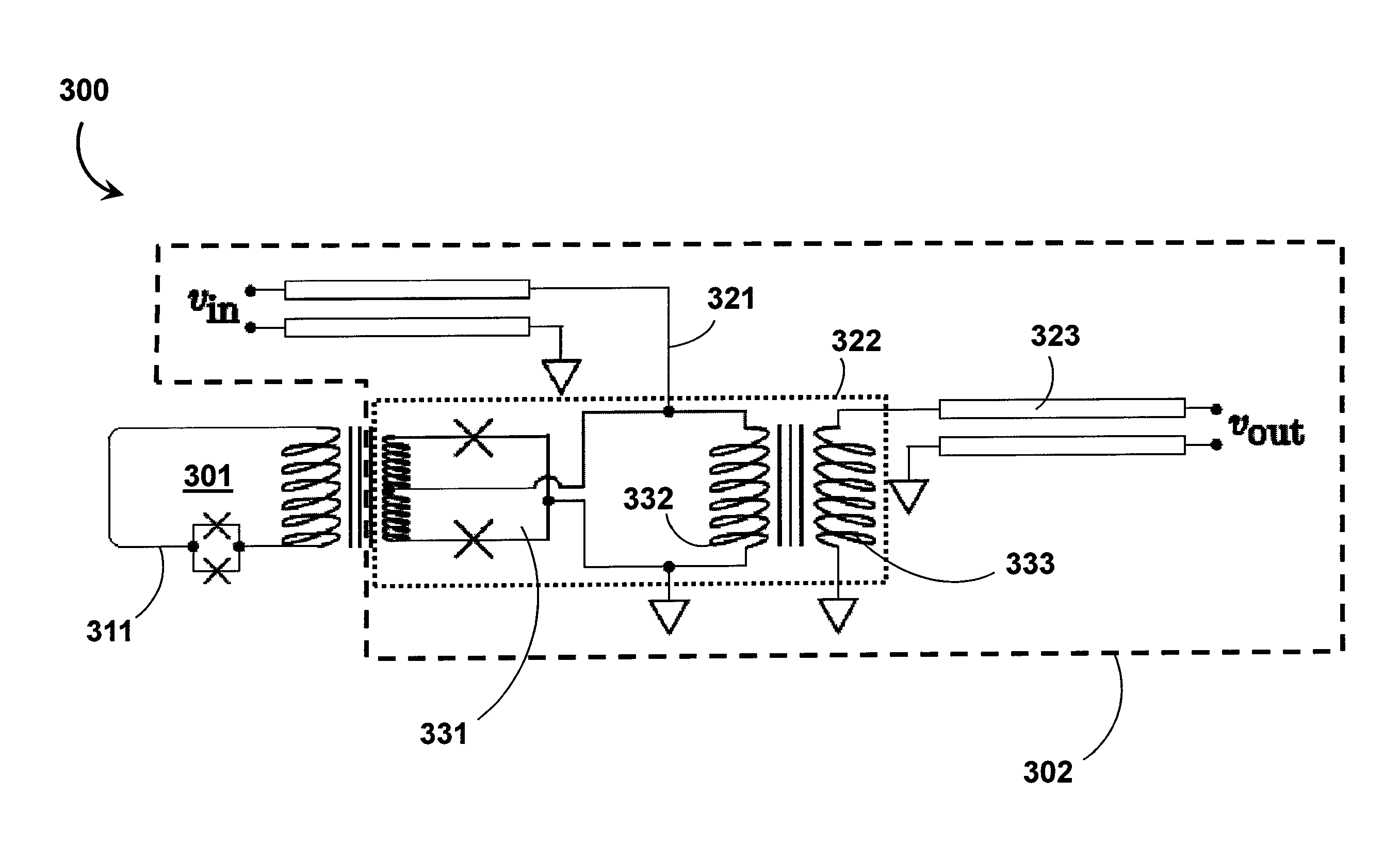
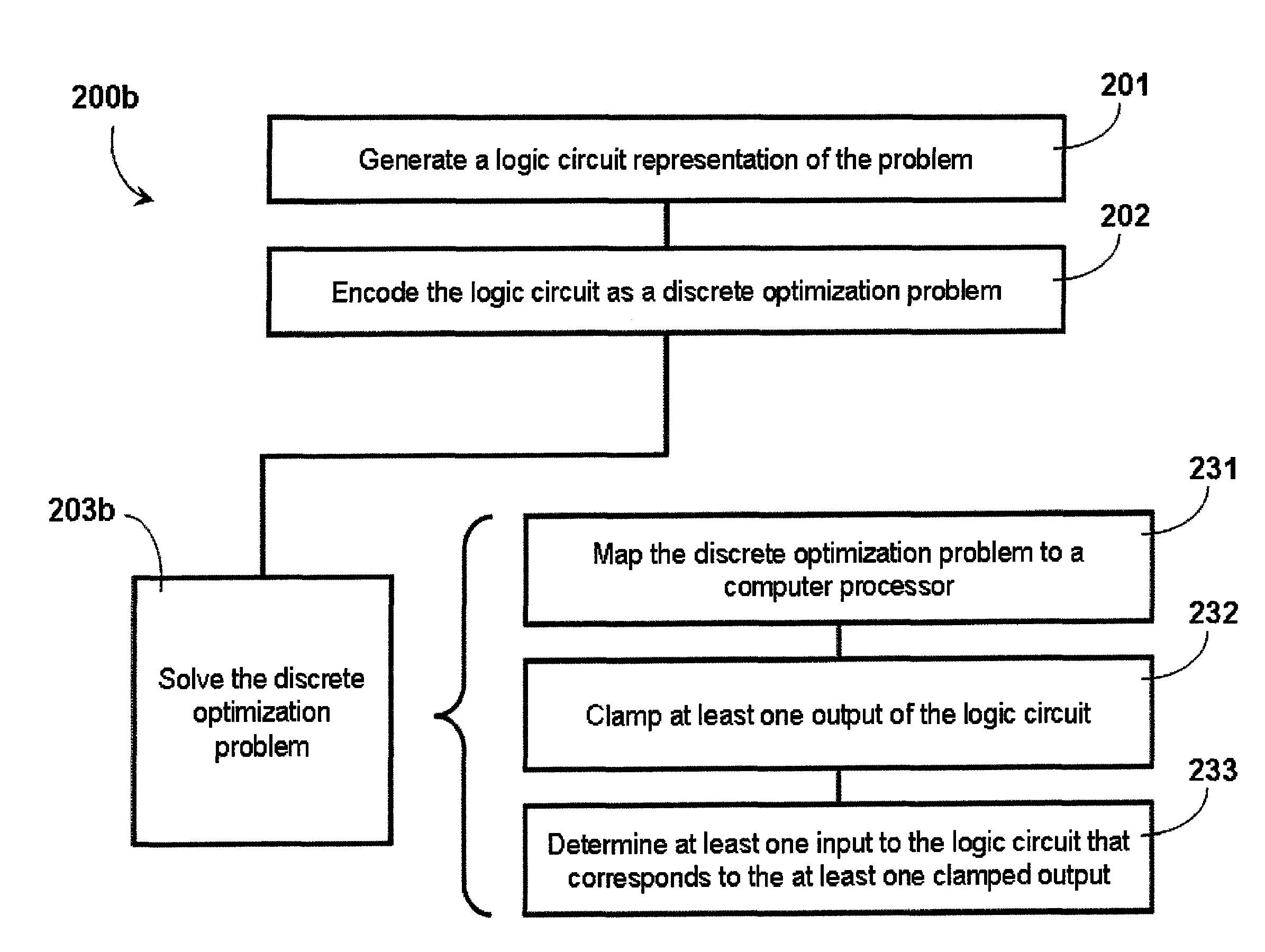
Systems and methods for solving computational problems
ActiveUS20110231462A1Quantum computersNanoinformaticsComputational problemTheoretical computer science
Solving computational problems may include generating a logic circuit representation of the computational problem, encoding the logic circuit representation as a discrete optimization problem, and solving the discrete optimization problem using a quantum processor. Output(s) of the logic circuit representation may be clamped such that the solving involves effectively executing the logic circuit representation in reverse to determine input(s) that corresponds to the clamped output(s). The representation may be of a Boolean logic circuit. The discrete optimization problem may be composed of a set of miniature optimization problems, where each miniature optimization problem encodes a respective logic gate from the logic circuit representation. A quantum processor may include multiple sets of qubits, each set coupled to respective annealing signal lines such that dynamic evolution of each set of qubits is controlled independently from the dynamic evolutions of the other sets of qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
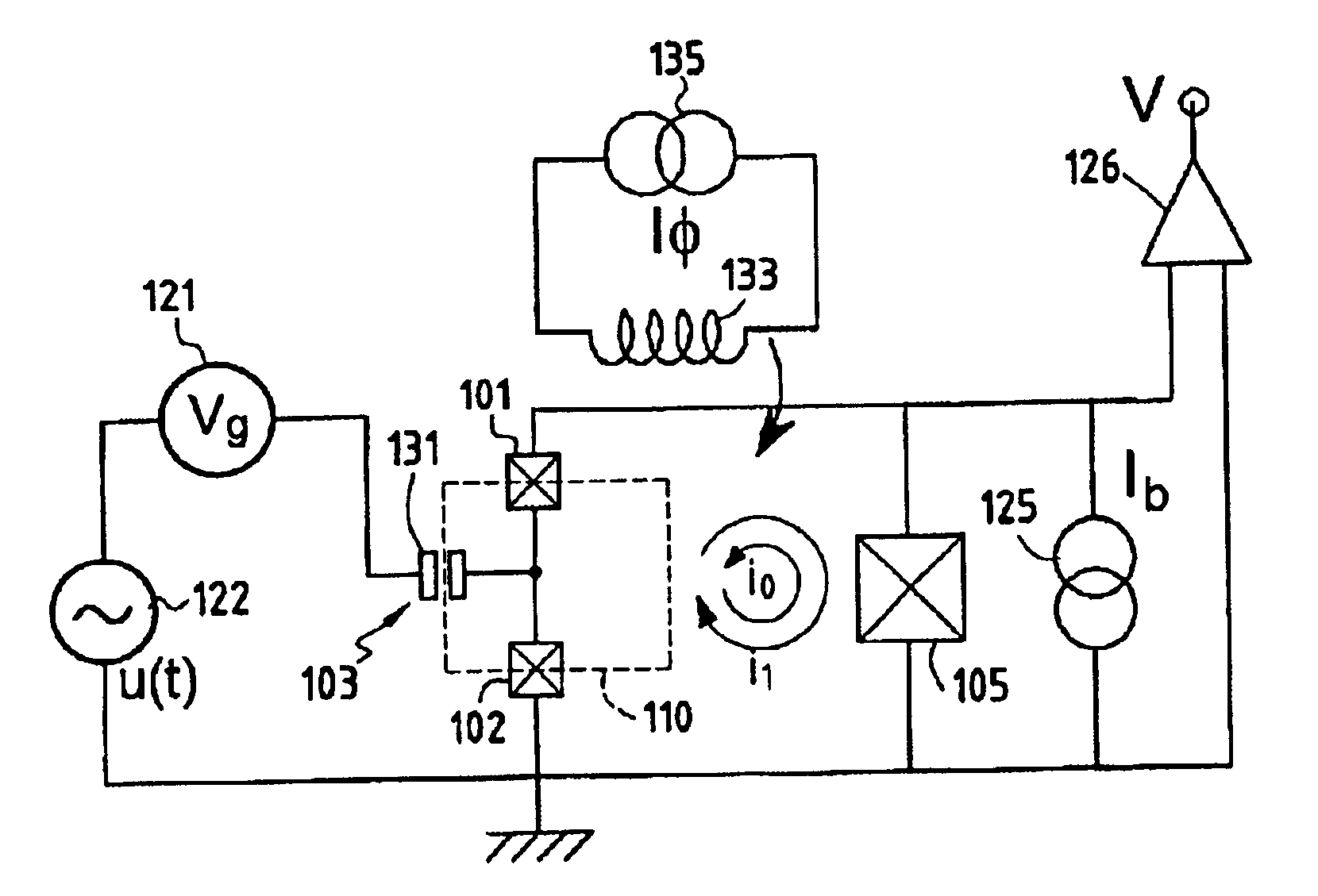
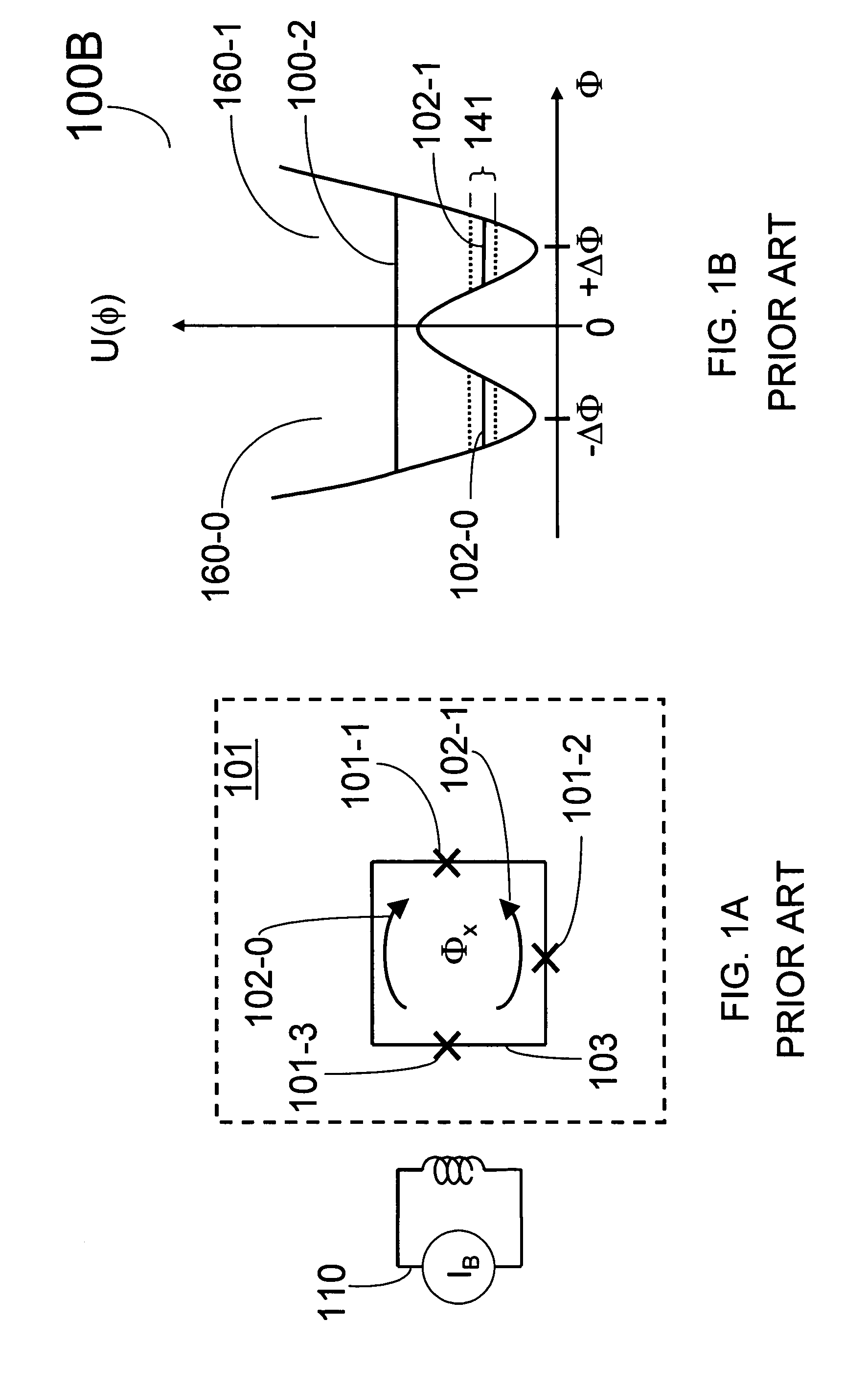
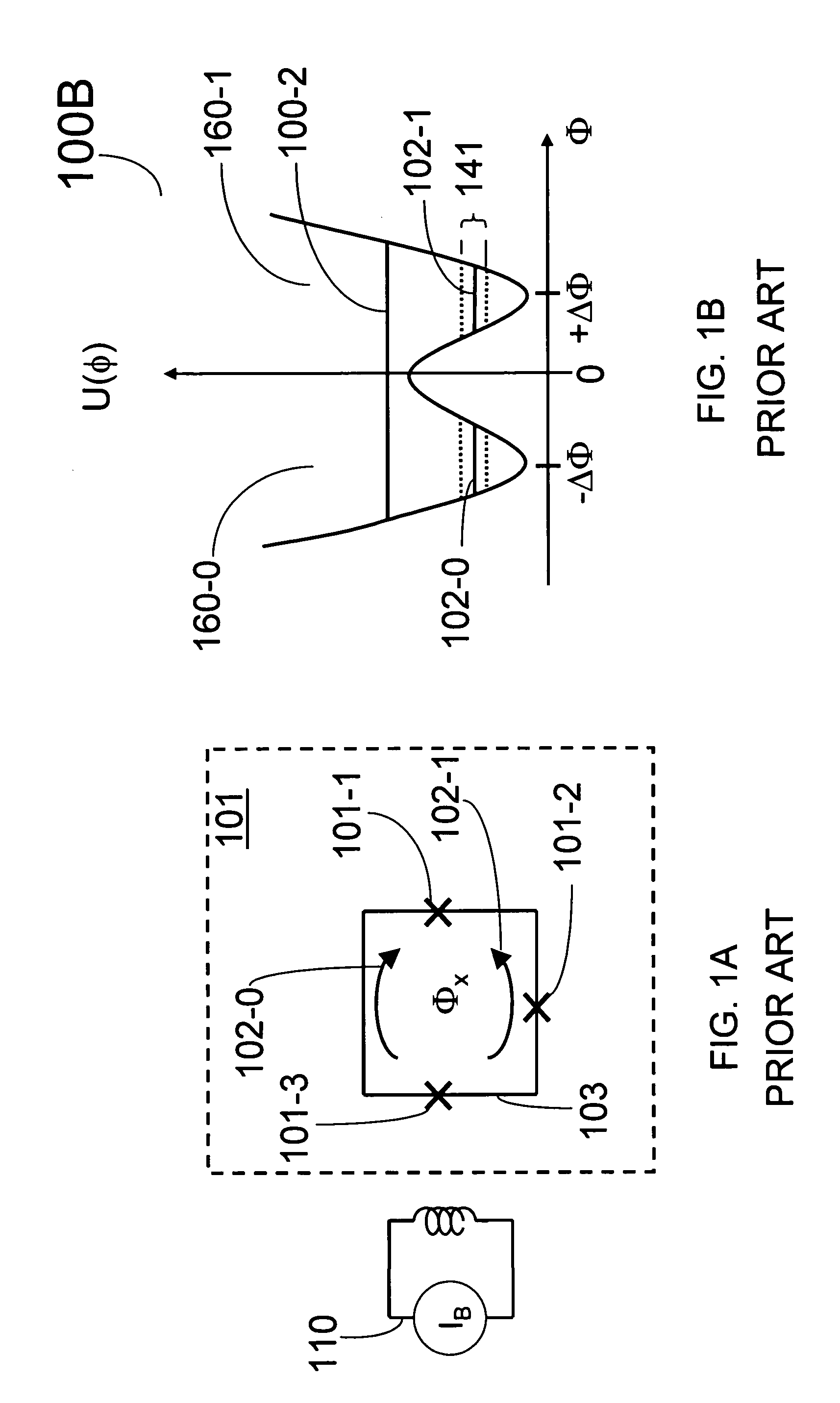
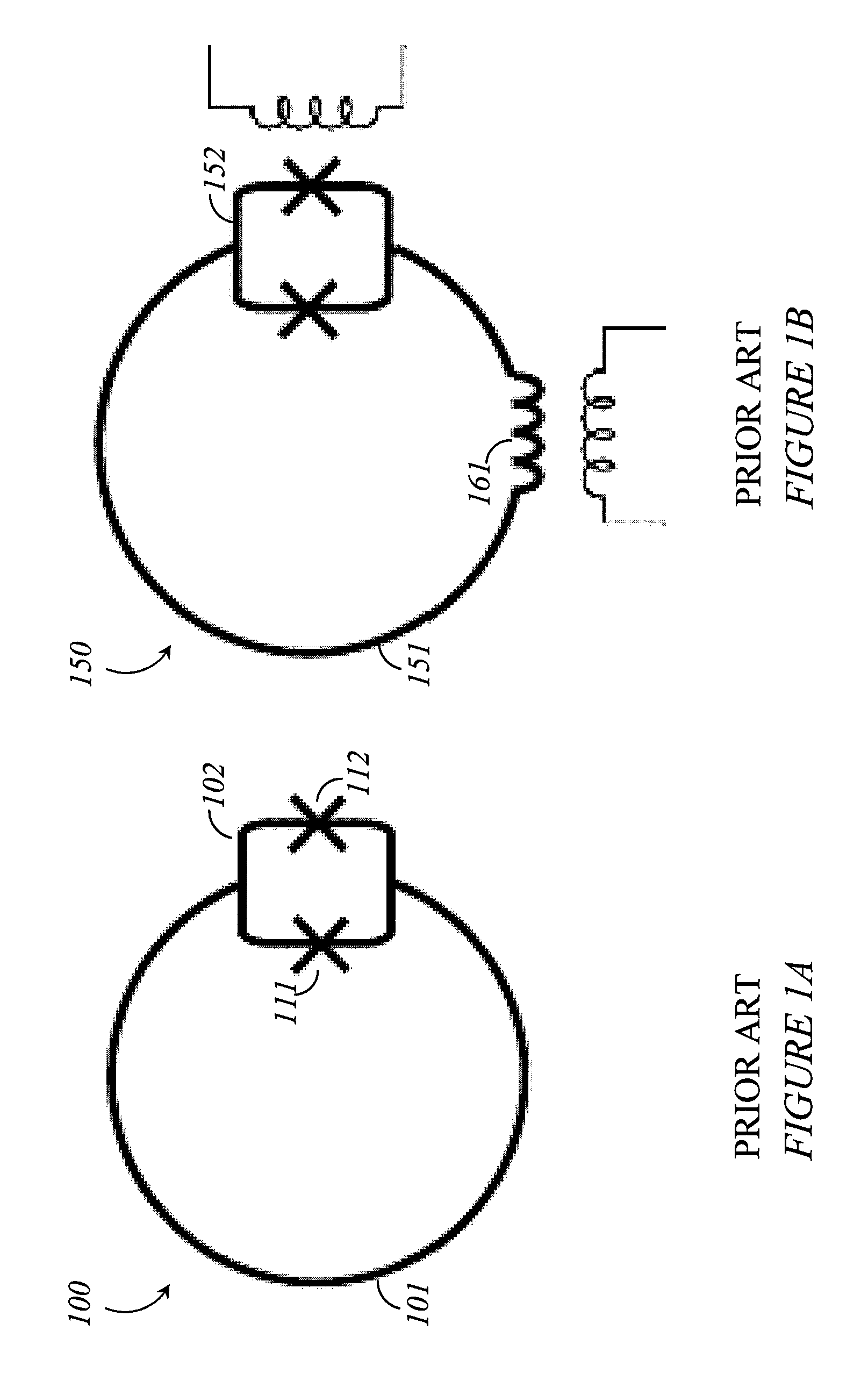
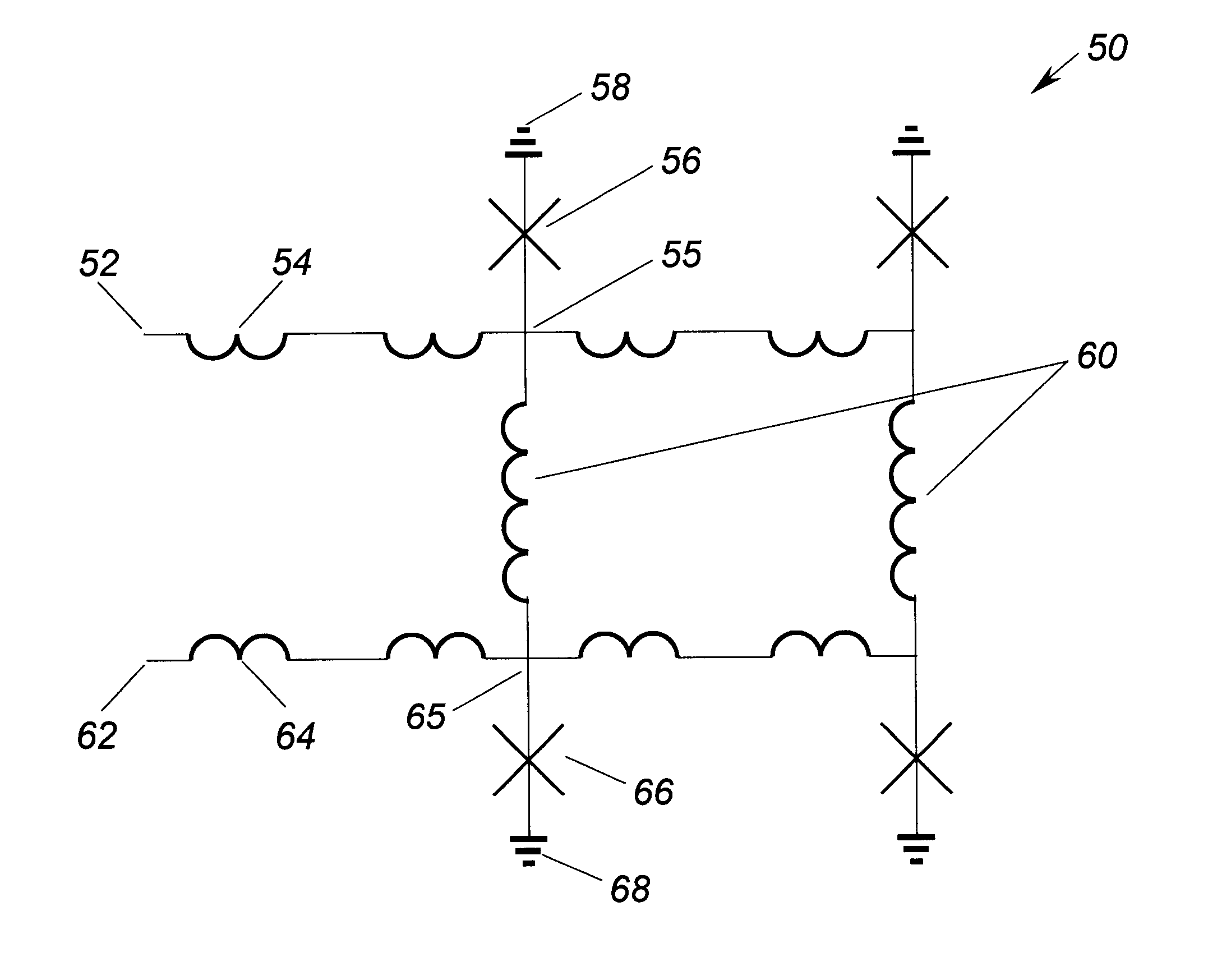
Superconducting quantum-bit device based on josephson junctions
InactiveUS20030207766A1Quantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsCooper pairDegrees of freedom
A superconducting quantum-bit device based on Josephson junction has a charge as a first principal degree of freedom assigned to writing and a phase as a second principal degree of freedom assigned to reading. The device comprises a Cooper-pair box comprising first and second Josephson junctions defining a charge island of the Cooper-pair box closing up onto a superconducting loop. A read circuit comprises a read Josephson junction JL inserted into the superconducting loop and having a Josephson energy Ej at least 50 times greater than the Josephson energy of each of the first and second Josephson junctions.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Superconducting qubits having a plurality of capacitive couplings
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
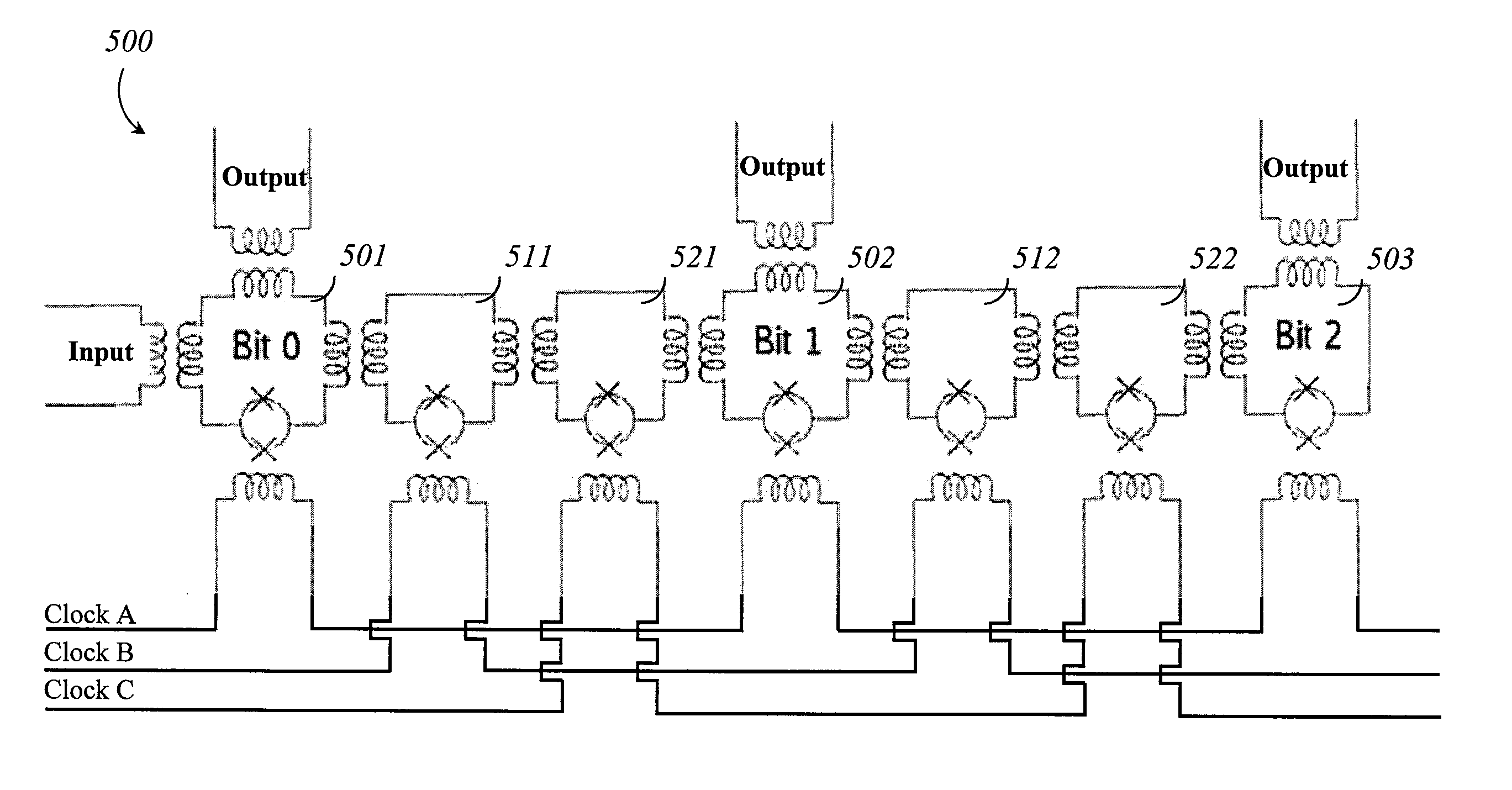
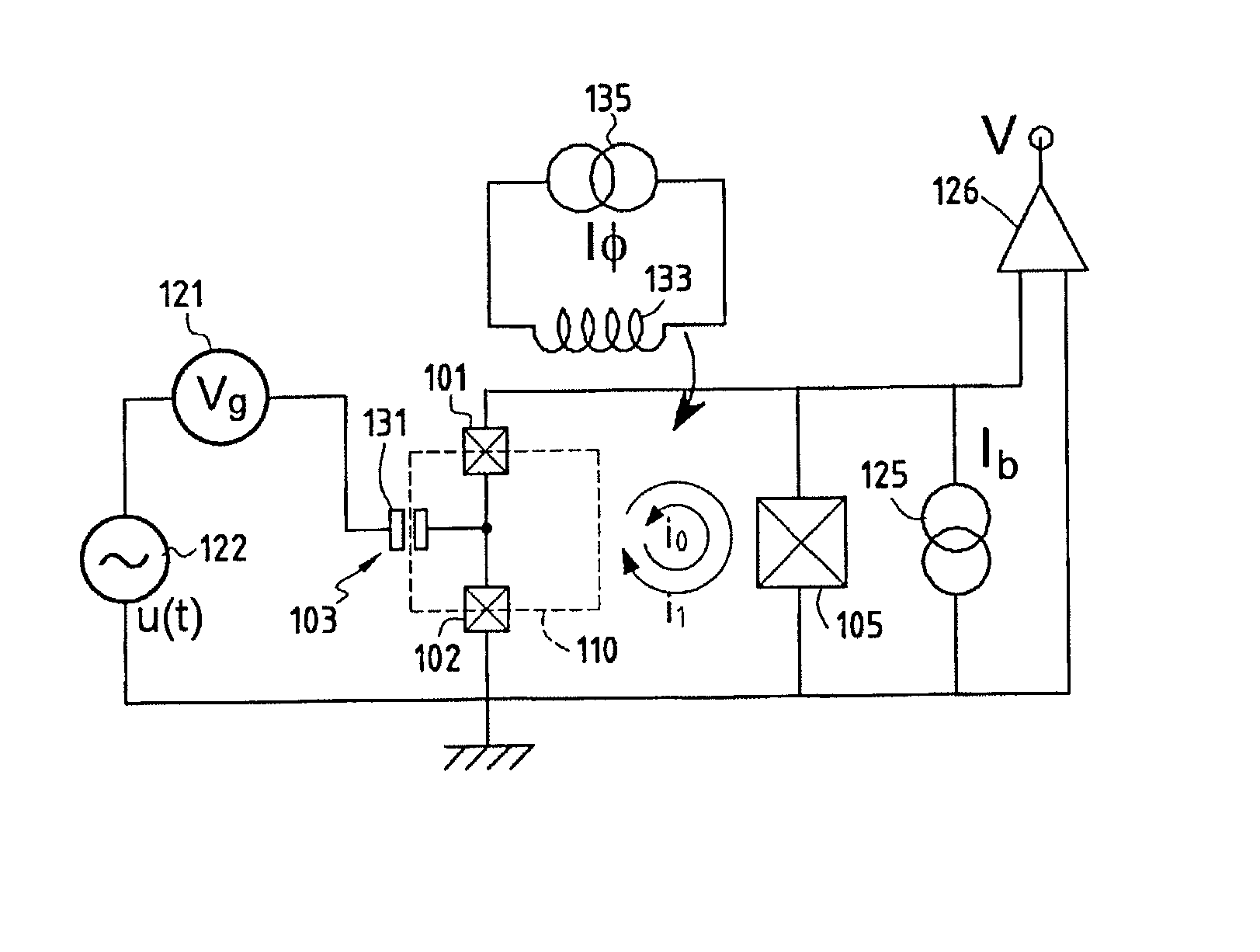
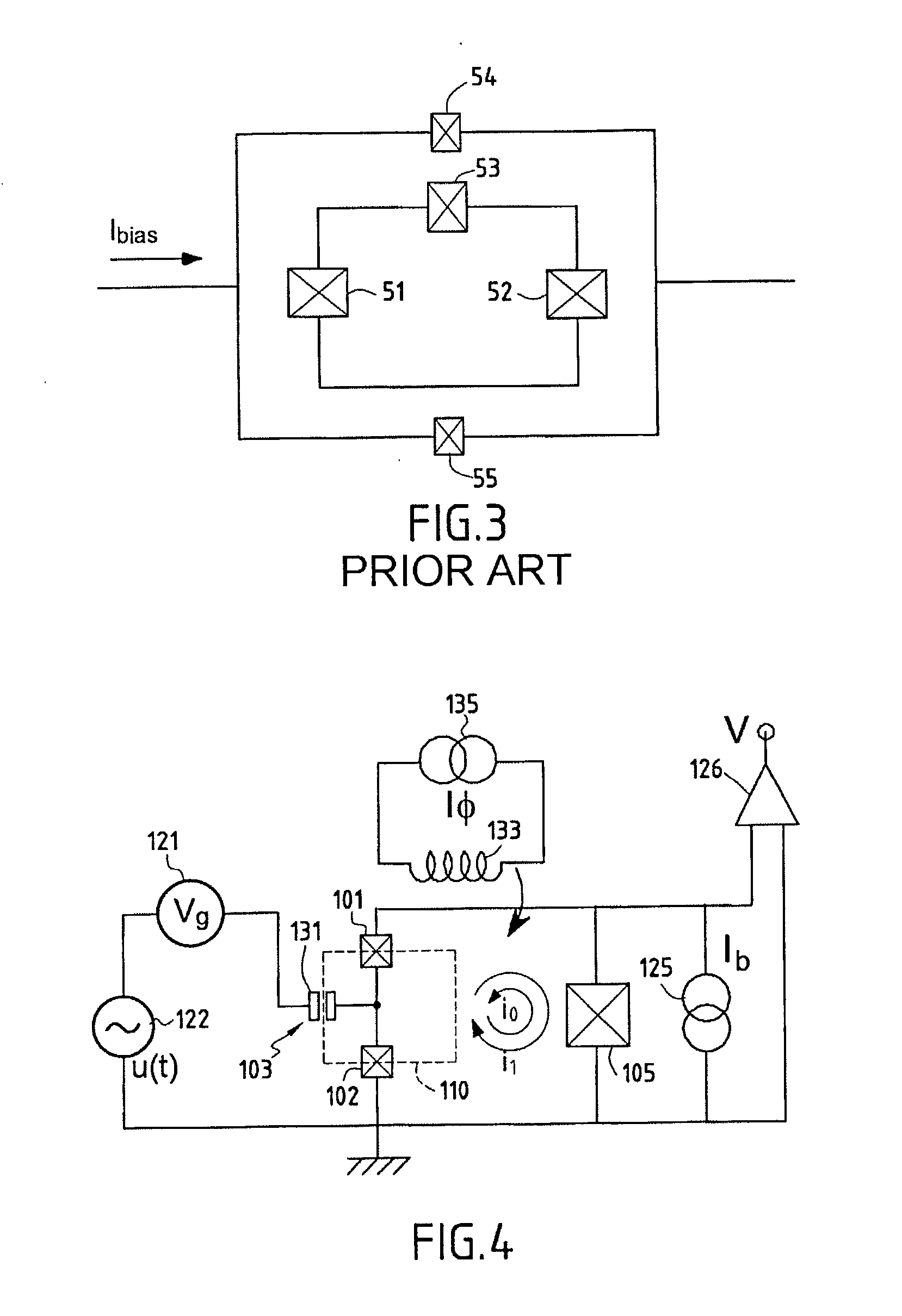
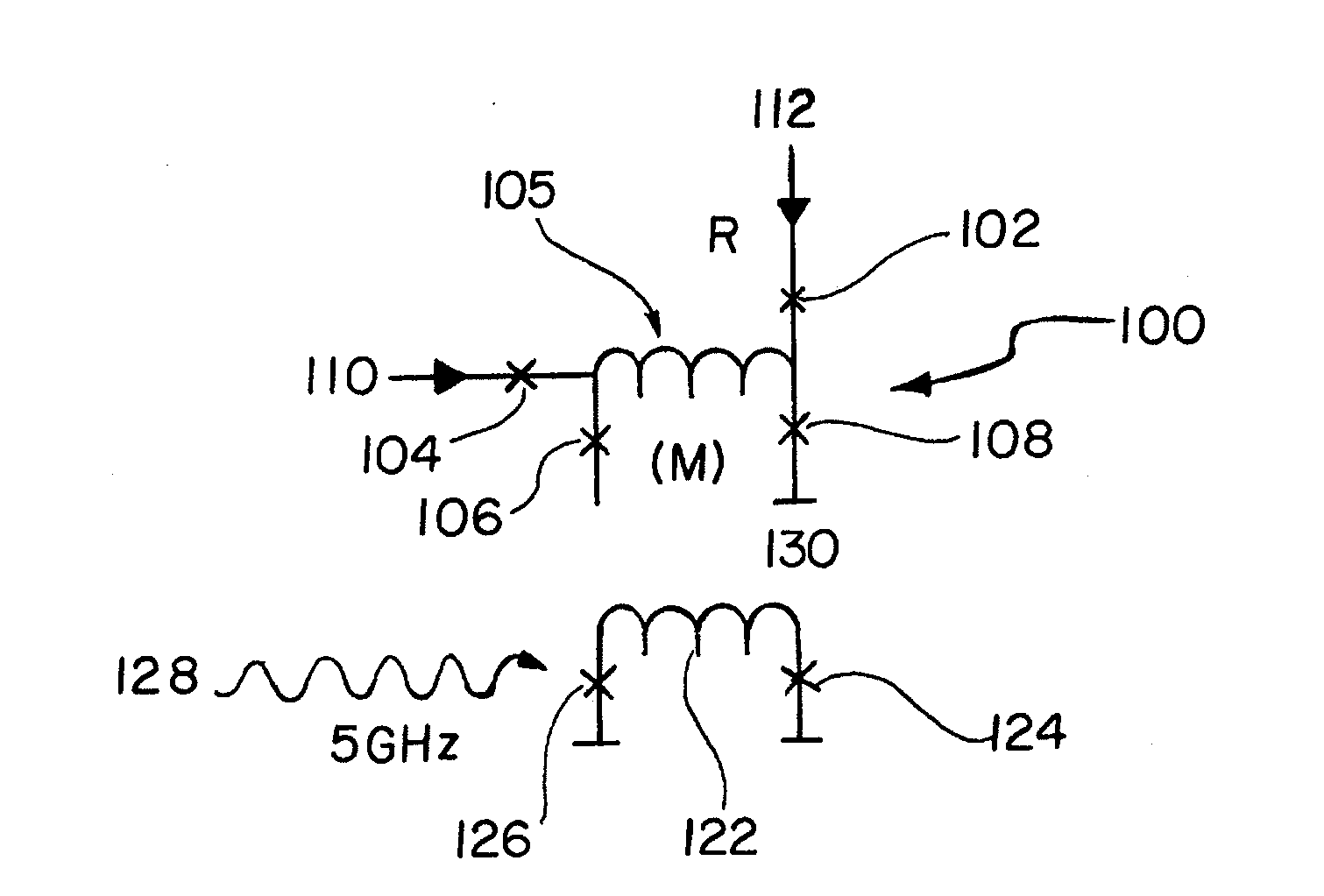
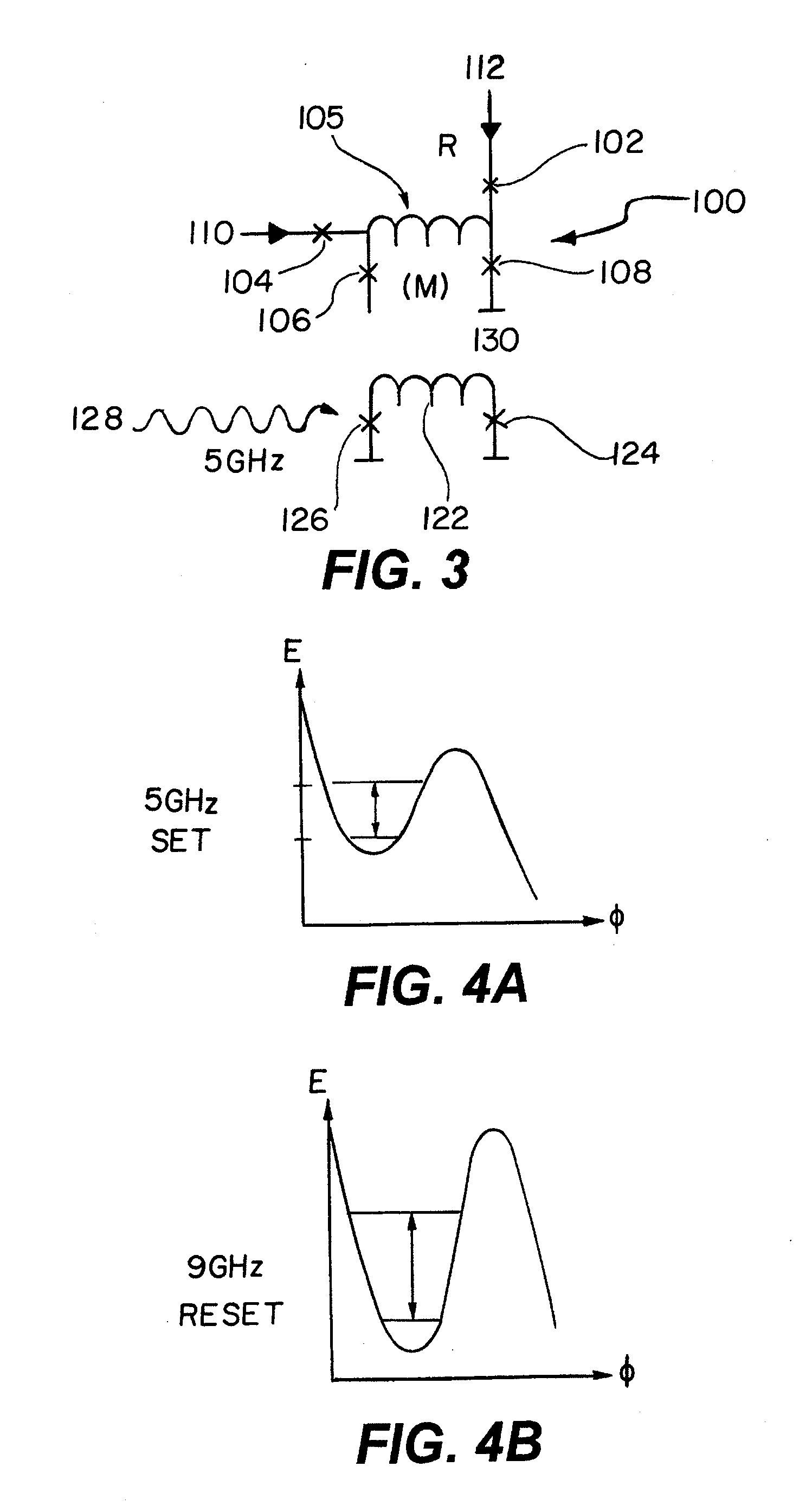
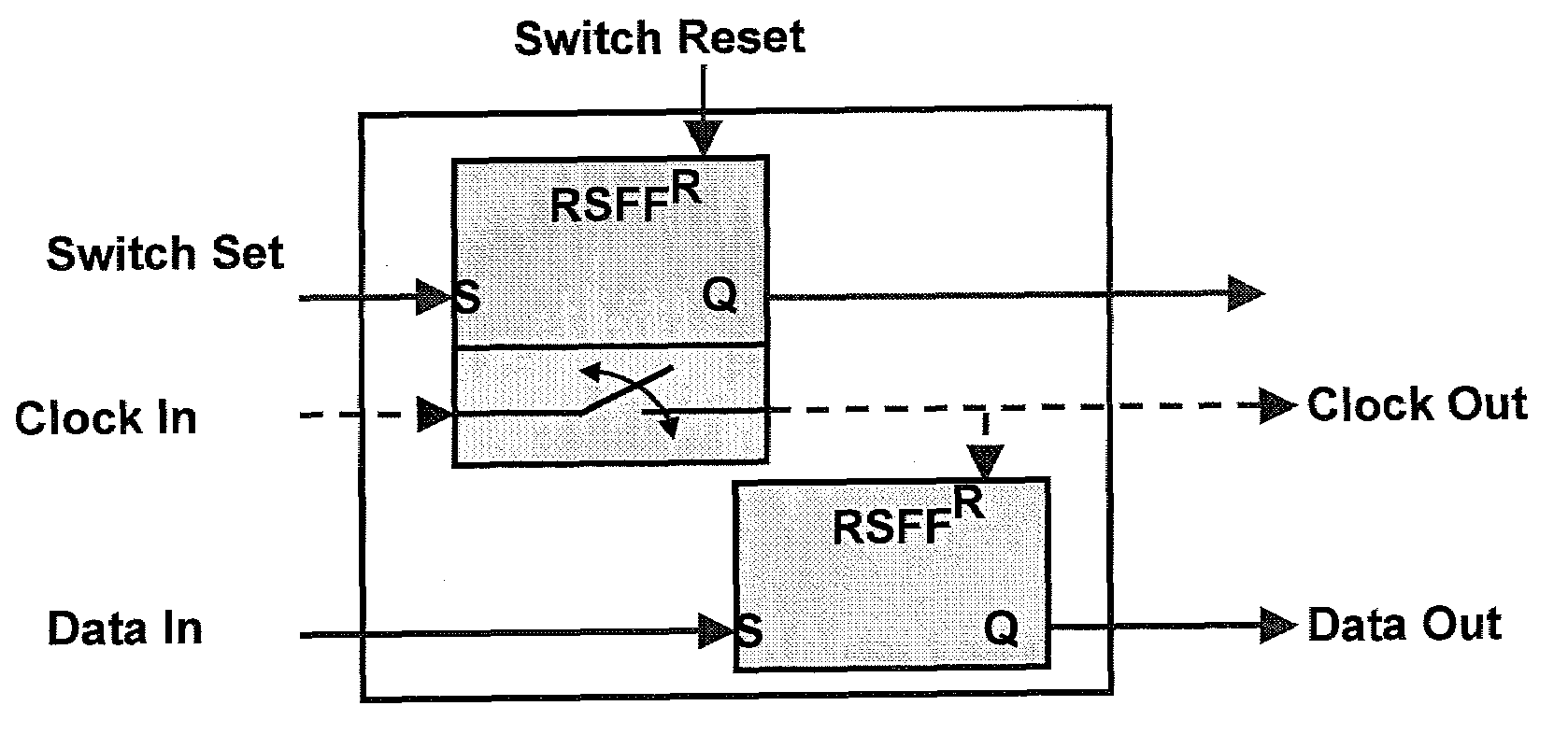
Method and apparatus for controlling qubits with single flux quantum logic
In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for controlling the energy state of a qubit by bringing the qubit into and out of resonance by coupling the qubit to a flux quantum logic gate. The qubit can be in resonance with a pump signal, with another qubit or with some quantum logic gate. In another embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method for controlling a qubit with RSFQ logic or through the interface between RSFQ and the qubit.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling qubits with singel flux quantum logic
In one embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for controlling the energy state of a qubit by bringing the qubit into and out of resonance by coupling the qubit to a flux quantum logic gate. The qubit can be in resonance with a pump signal, with another qubit or with some quantum logic gate. In another embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method for controlling a qubit with RSFQ logic or through the interface between RSFQ and the qubit.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
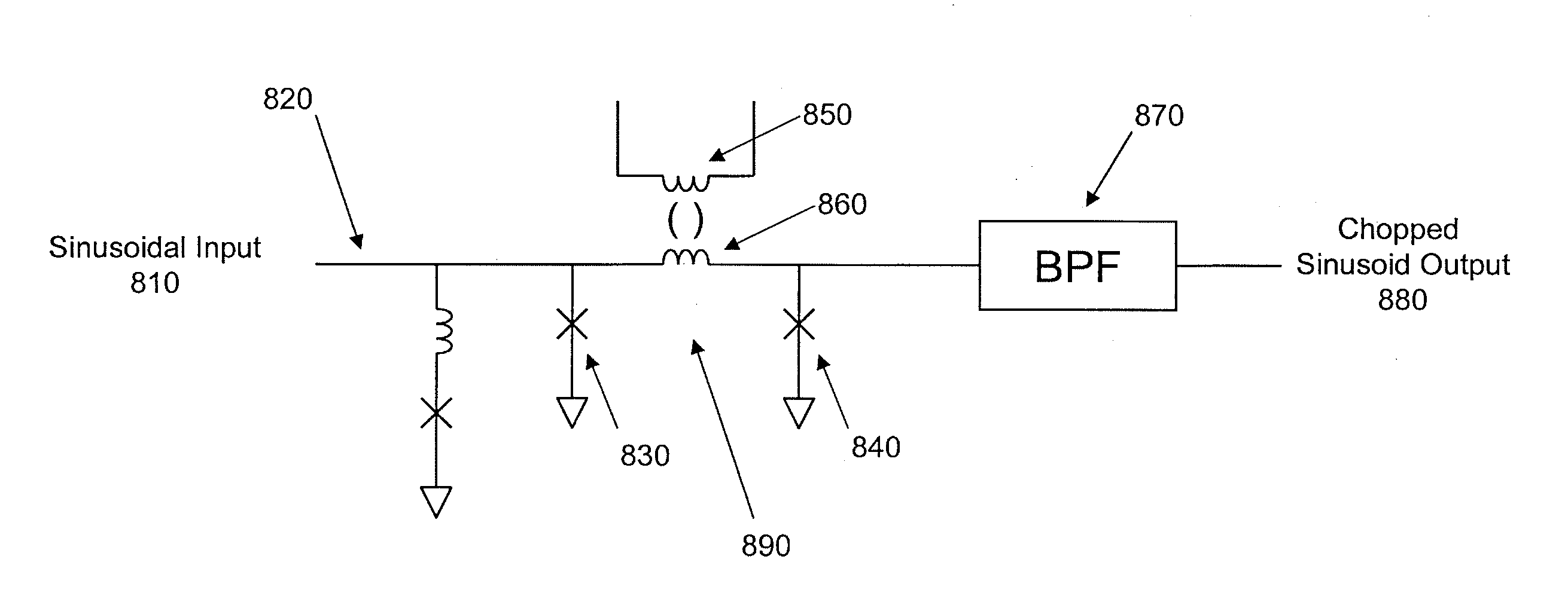
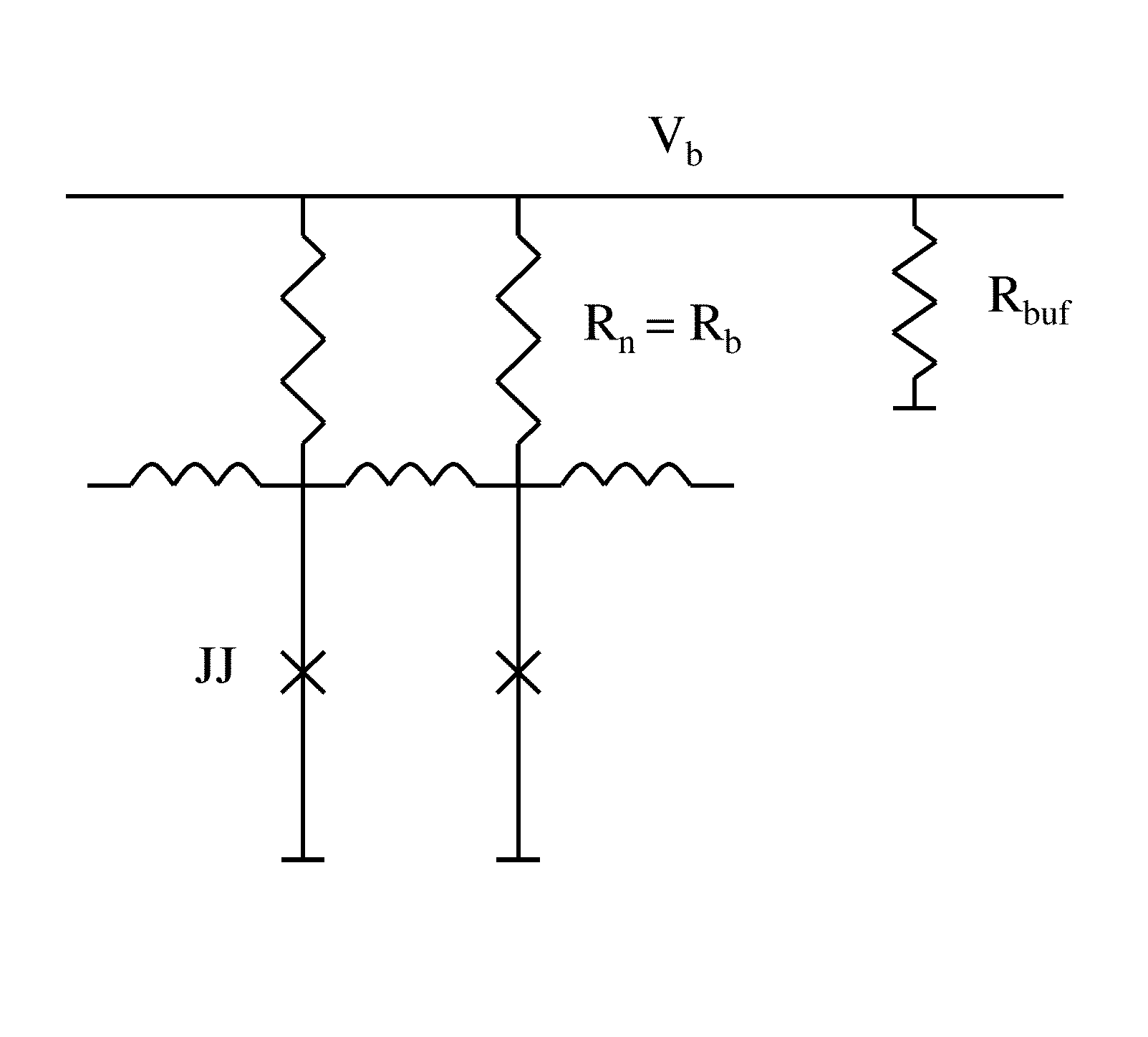
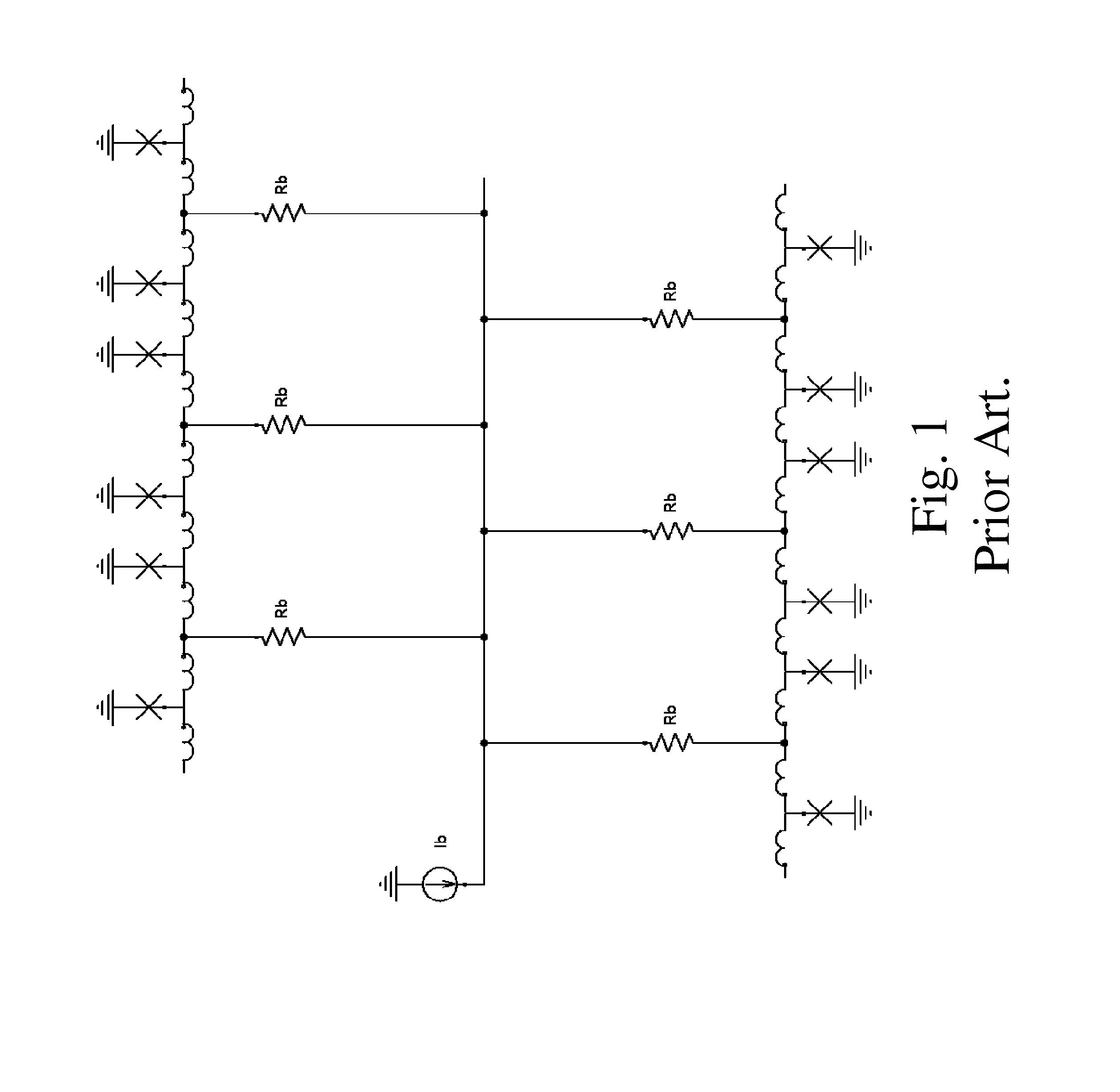
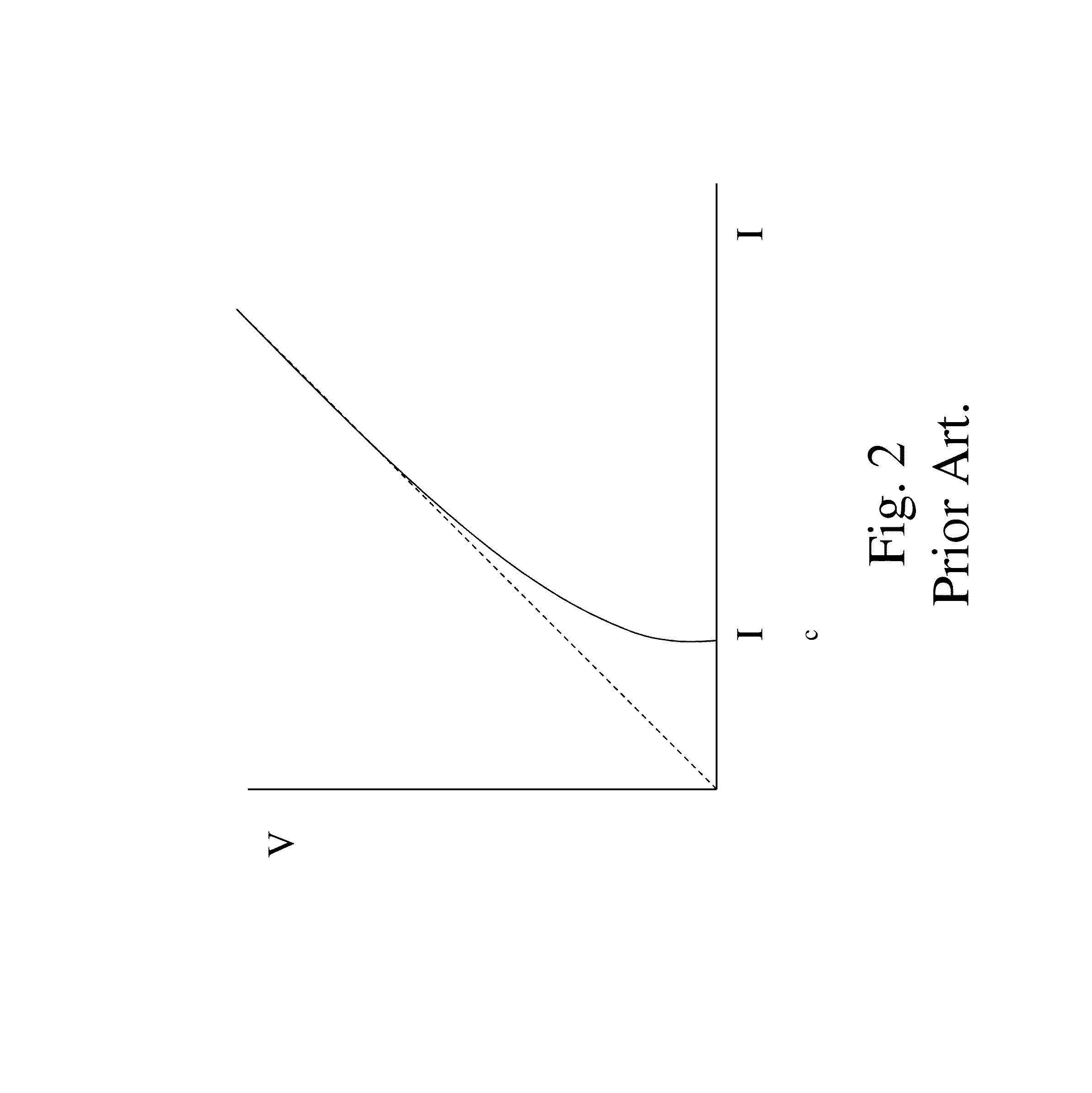
Low-power biasing networks for superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS8571614B1Maintain stabilityHigh dynamic impedanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSuperconducting integrated circuits
A superconducting integrated circuit, comprising a plurality of superconducting circuit elements, each having a variation in operating voltage over time; a common power line; and a plurality of bias circuits, each connected to the common power line, and to a respective superconducting circuit element, wherein each respective bias circuit is superconducting during at least one time portion of the operation of a respective superconducting circuit element, and is configured to supply the variation in operating voltage over time to the respective superconducting circuit element.
Owner:SEEQC INC
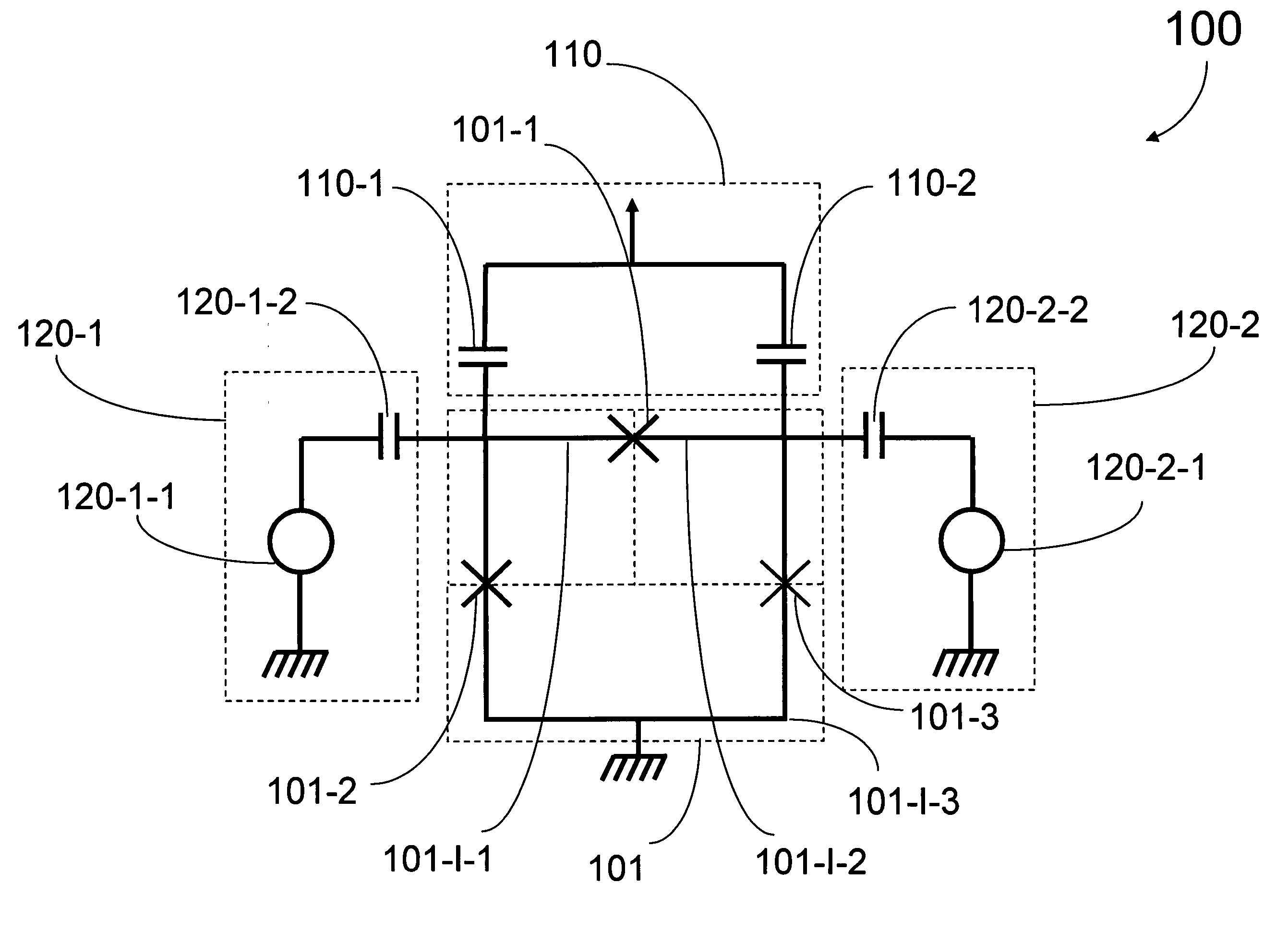
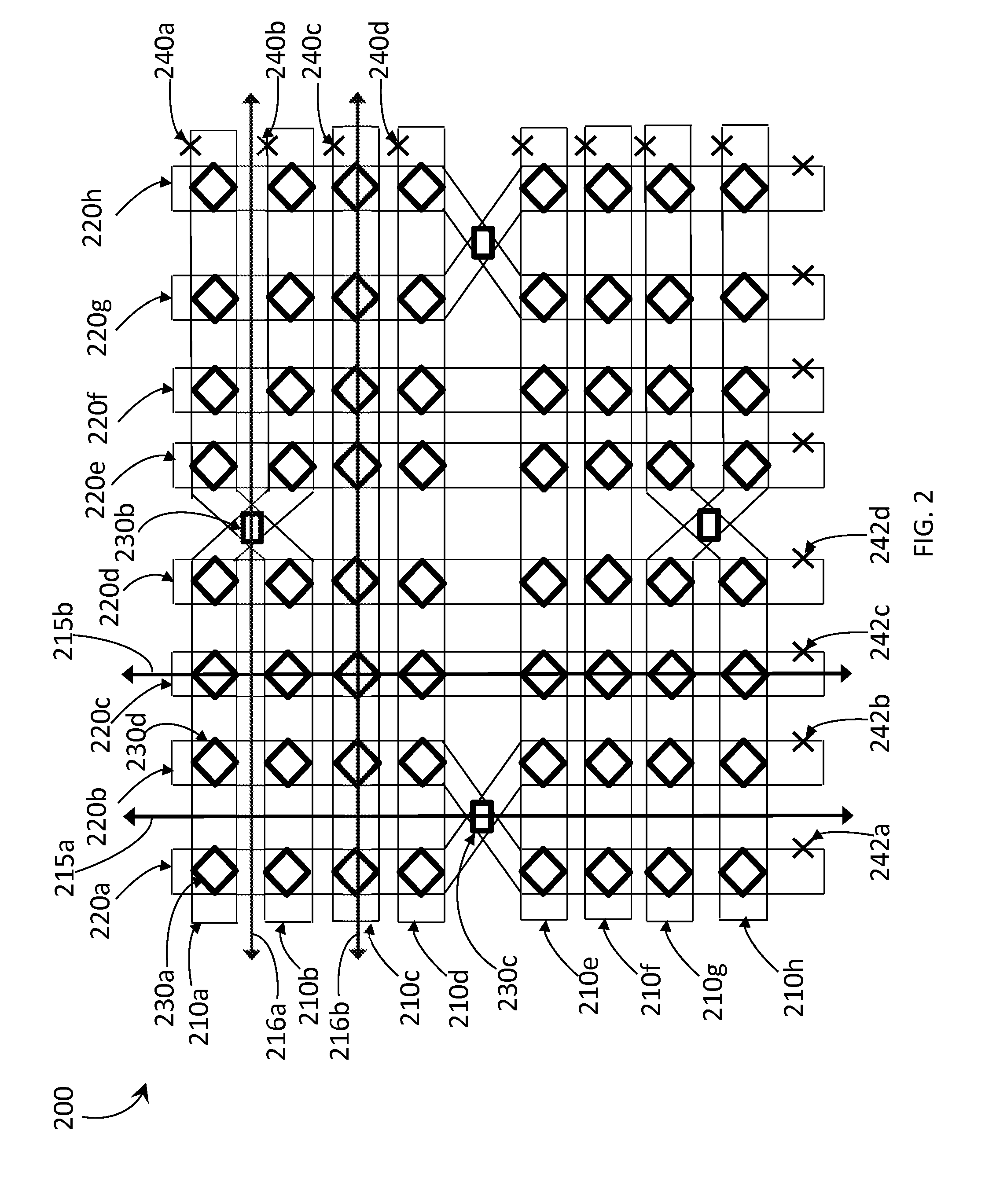
Systems and devices for quantum processor architectures
ActiveUS20150046681A1Improve drawing legibilityQuantum computersGeneral purpose stored program computerAngular deviationCell coupling
Quantum processor architectures employ unit cells tiled over an area. A unit cell may include first and second sets of qubits where each qubit in the first set crosses at least one qubit in the second set. Angular deviations between qubits in one set may allow qubits in the same set to cross one another. Each unit cell is positioned proximally adjacent at least one other unit cell. Communicatively coupling between qubits is realized through respective intra-cell and inter-cell coupling devices.
Owner:D-WAVE SYSTEMS
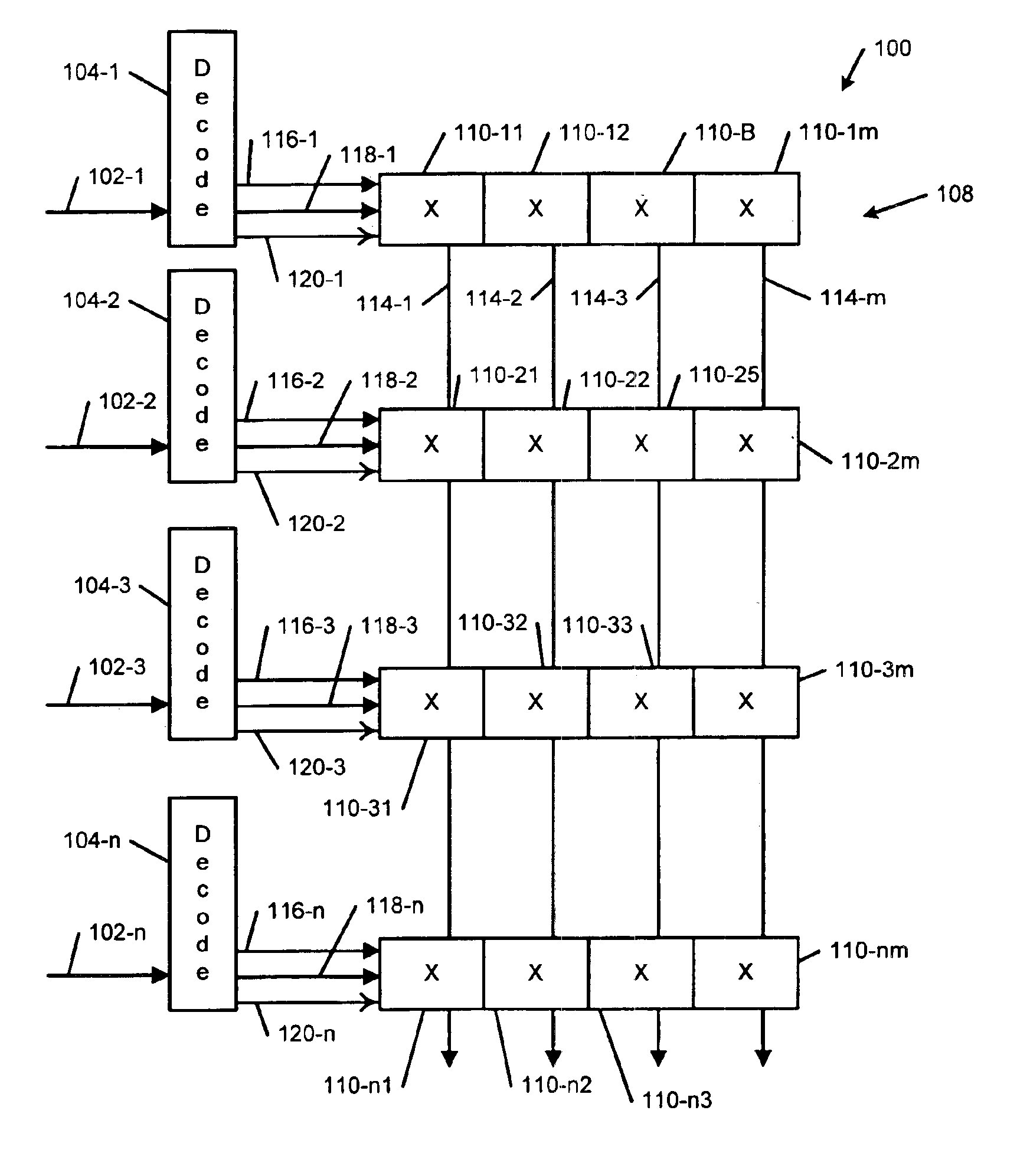
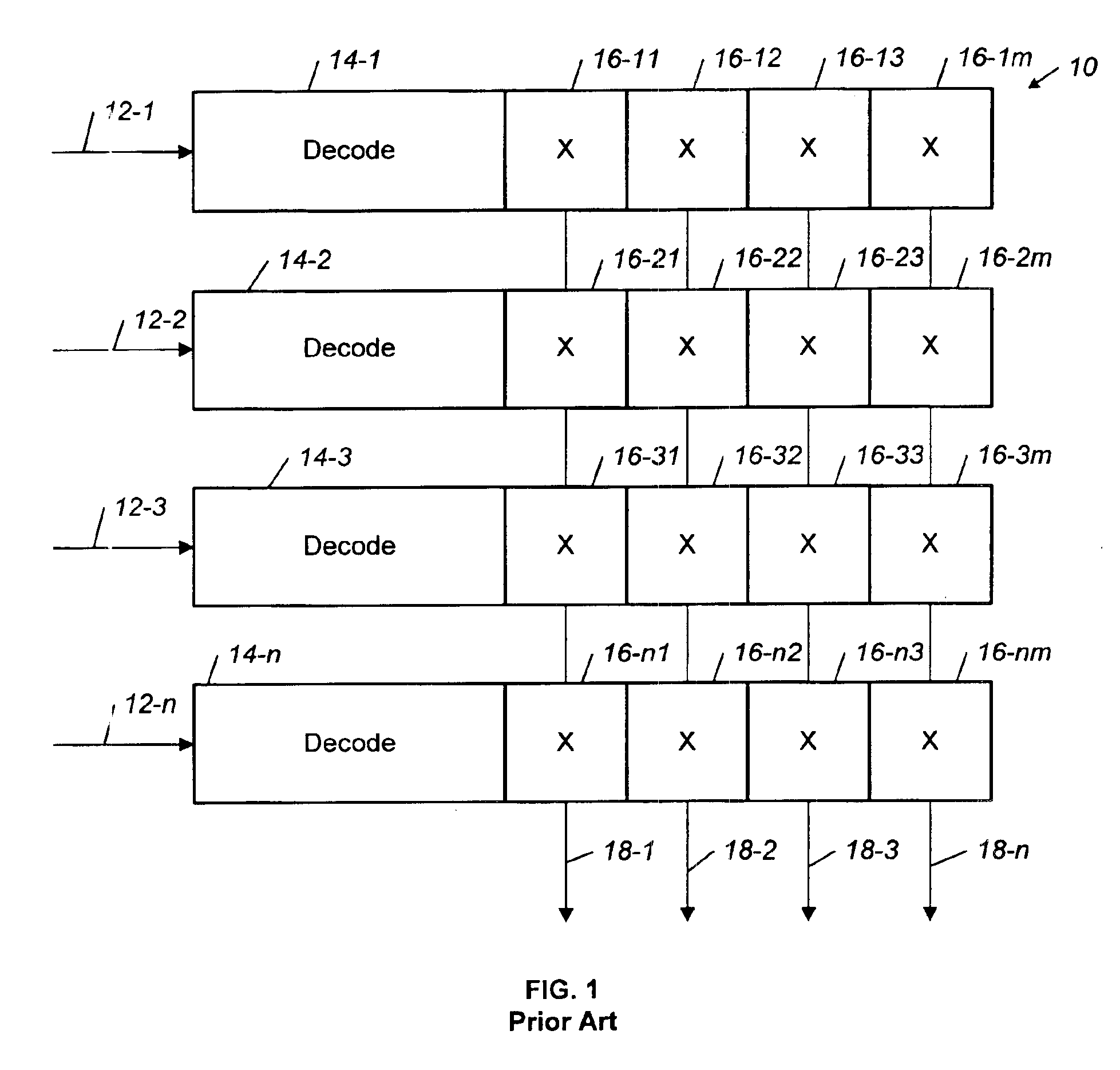
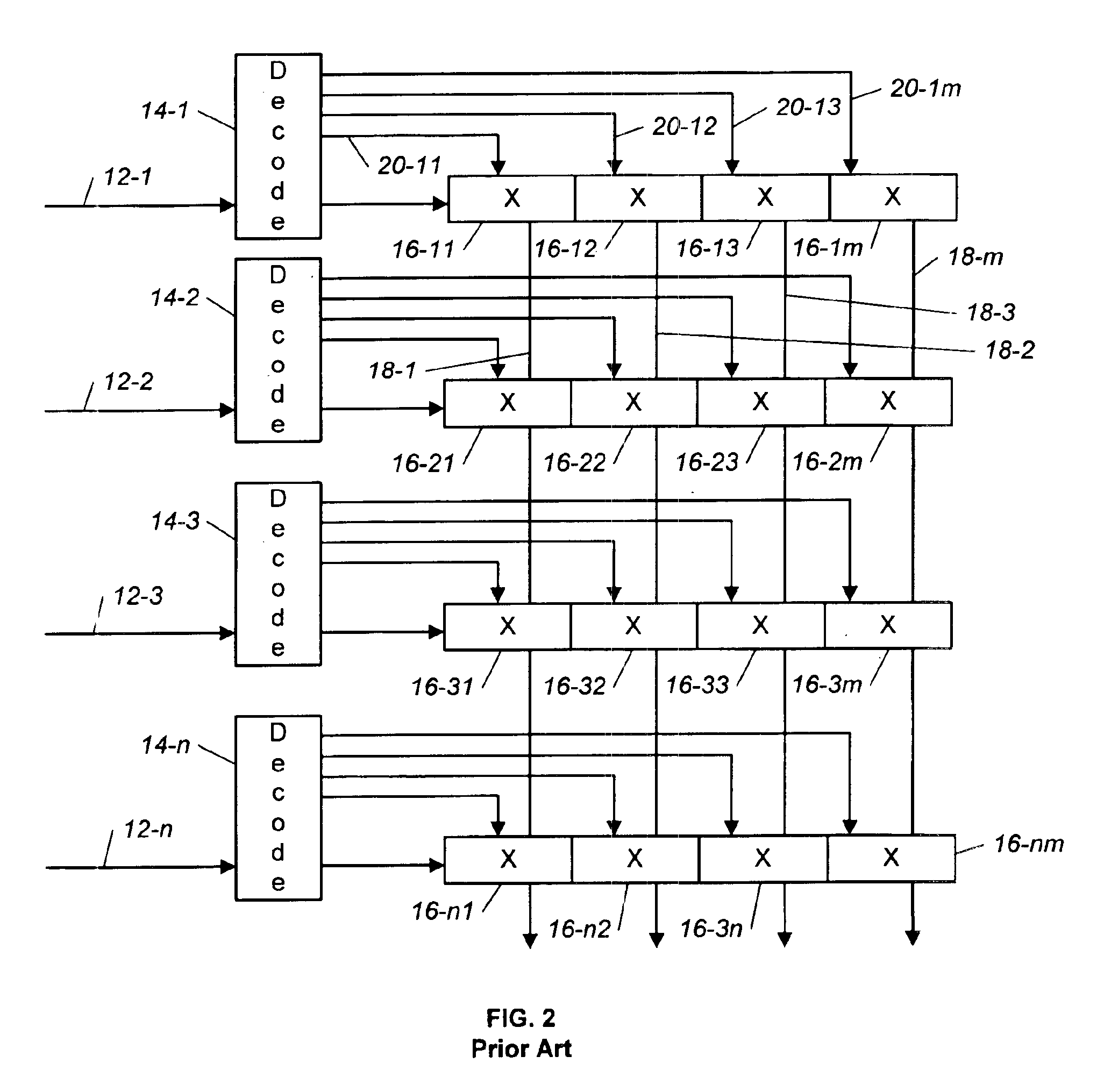
Scalable self-routing superconductor switch
A crossbar switch includes a cross-point matrix with n input rows of cross-points and m output columns of cross-points. The crossbar switch further includes n decoders connected to the n input rows. Each of the n rows includes a single serial address input, a shift input and a data input. A serial address and data enter the address input and the data input in parallel. A shift sequence is transmitted on the single shift input. The data flows before the shift sequence on the shift input is complete. The data is shifted through the crossbar switch using a clock that is generated on-chip using a clock recovery circuit. The decoder converts a binary address input into a serial address and includes an N-bit counter with a plurality of toggle flip-flops. The crossbar switch is implemented using superconductor digital electronics such as rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) logic.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
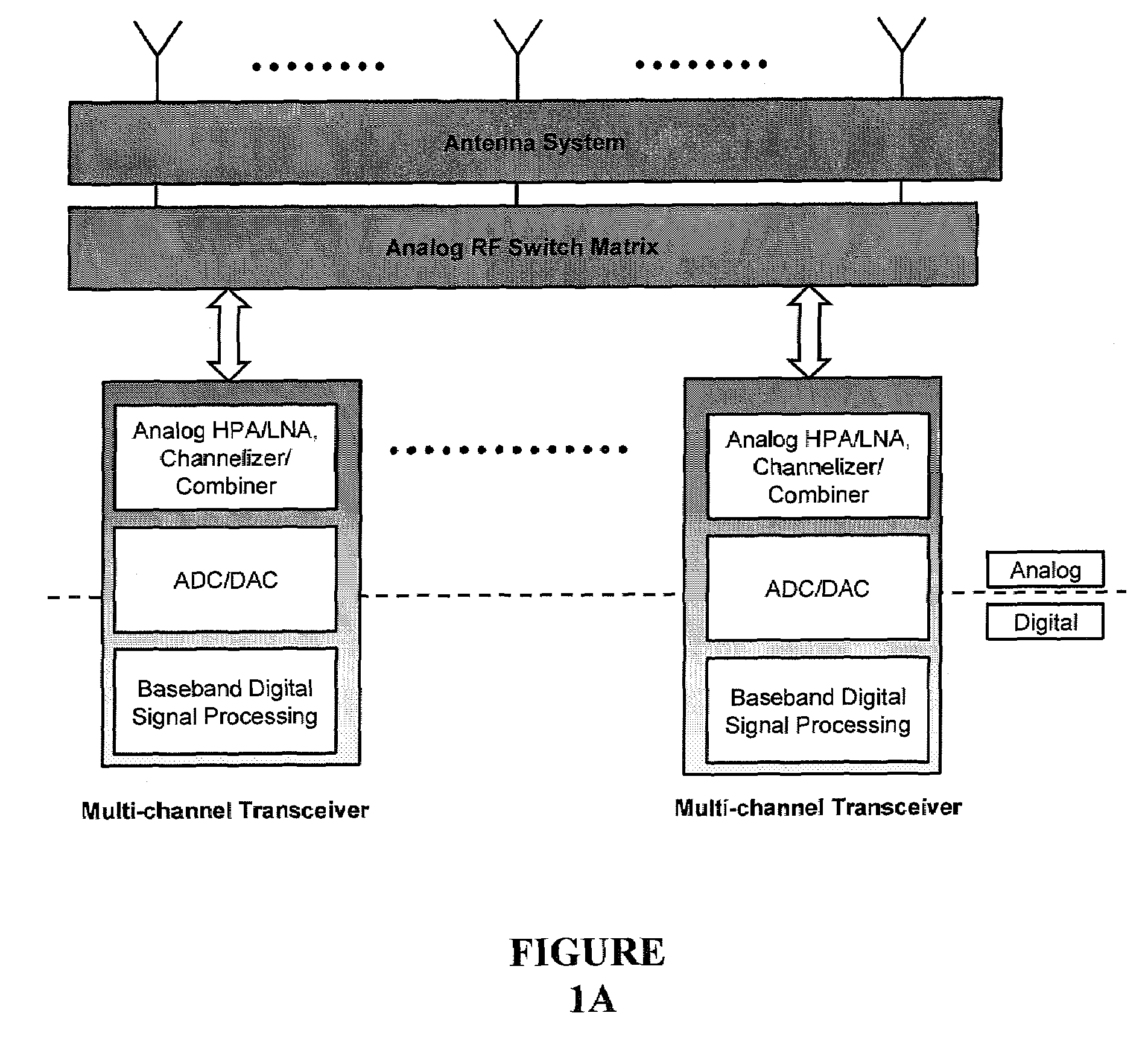
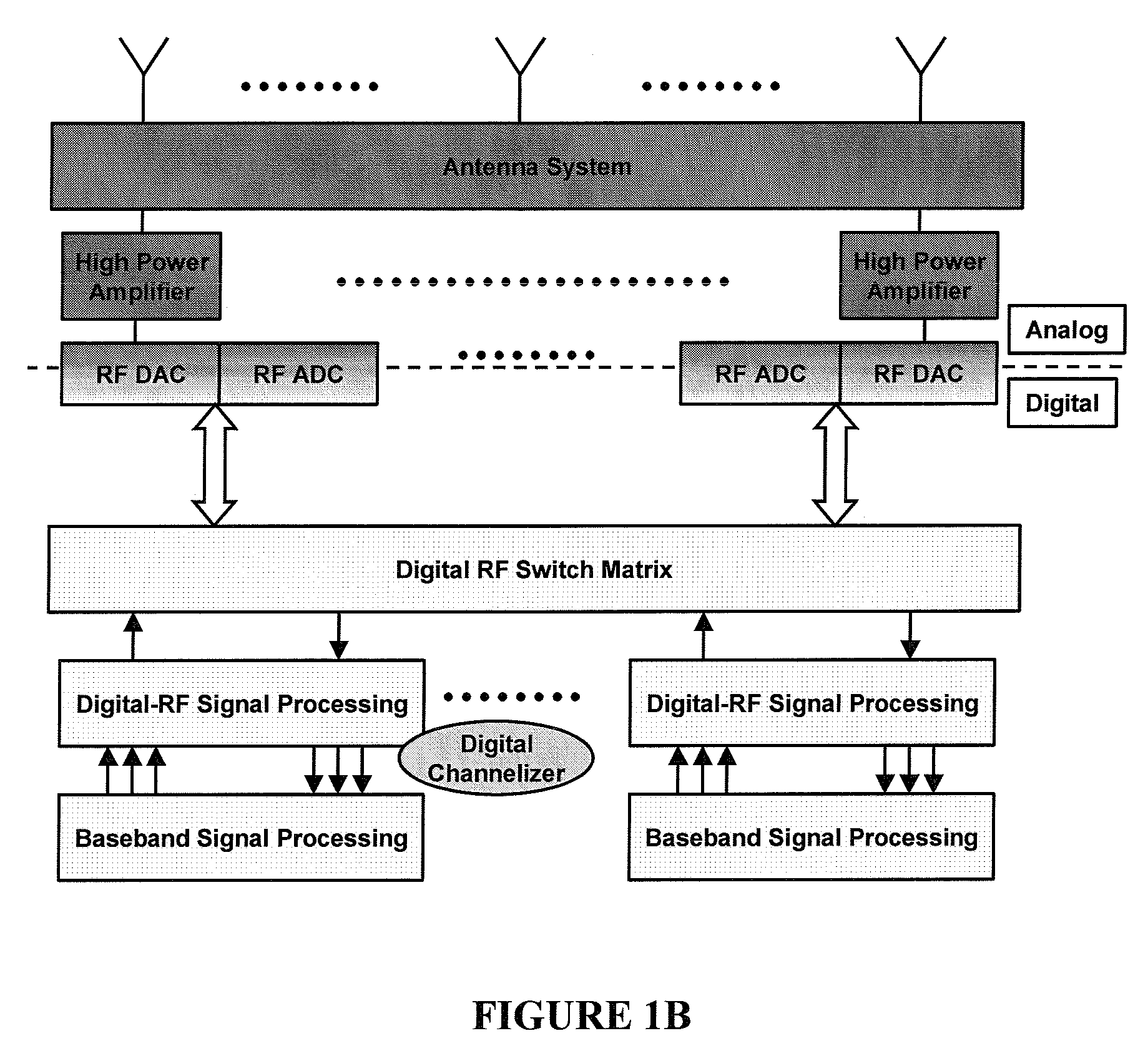
Digital routing switch matrix for digitized radio-frequency signals
InactiveUS7362125B2Efficient executionPrecise processingElectronic switchingSubstation equipmentMulti bandTransceiver
Routing and distribution of radio-frequency (RF) signals is commonly achieved in the analog domain. However, improved performance and simplified circuit architectures may be obtained by first digitizing the RF signal, and then carrying out all routing in the digital domain. A new generation of scalable digital switches has been developed, which routes both the data and clock signals together, this being necessary to maintain the integrity of the digitized RF signal. Given the extremely high switching speeds necessary for these applications (tens of GHz), this is implemented using Rapid-Single-Flux-Quantum (RSFQ) logic with superconducting integrated circuits. Such a digital switch matrix may be applied to either the receiver or transmitter components of an advanced multi-band, multi-channel digital transceiver system, and is compatible with routing of signals with different clock frequencies simultaneously within the same switch matrix.
Owner:HYPRES
Systems and methods for superconducting flux qubit readout
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems and methods for solving computational problems
Solving computational problems may include generating a logic circuit representation of the computational problem, encoding the logic circuit representation as a discrete optimization problem, and solving the discrete optimization problem using a quantum processor. Output(s) of the logic circuit representation may be clamped such that the solving involves effectively executing the logic circuit representation in reverse to determine input(s) that corresponds to the clamped output(s). The representation may be of a Boolean logic circuit. The discrete optimization problem may be composed of a set of miniature optimization problems, where each miniature optimization problem encodes a respective logic gate from the logic circuit representation. A quantum processor may include multiple sets of qubits, each set coupled to respective annealing signal lines such that dynamic evolution of each set of qubits is controlled independently from the dynamic evolutions of the other sets of qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
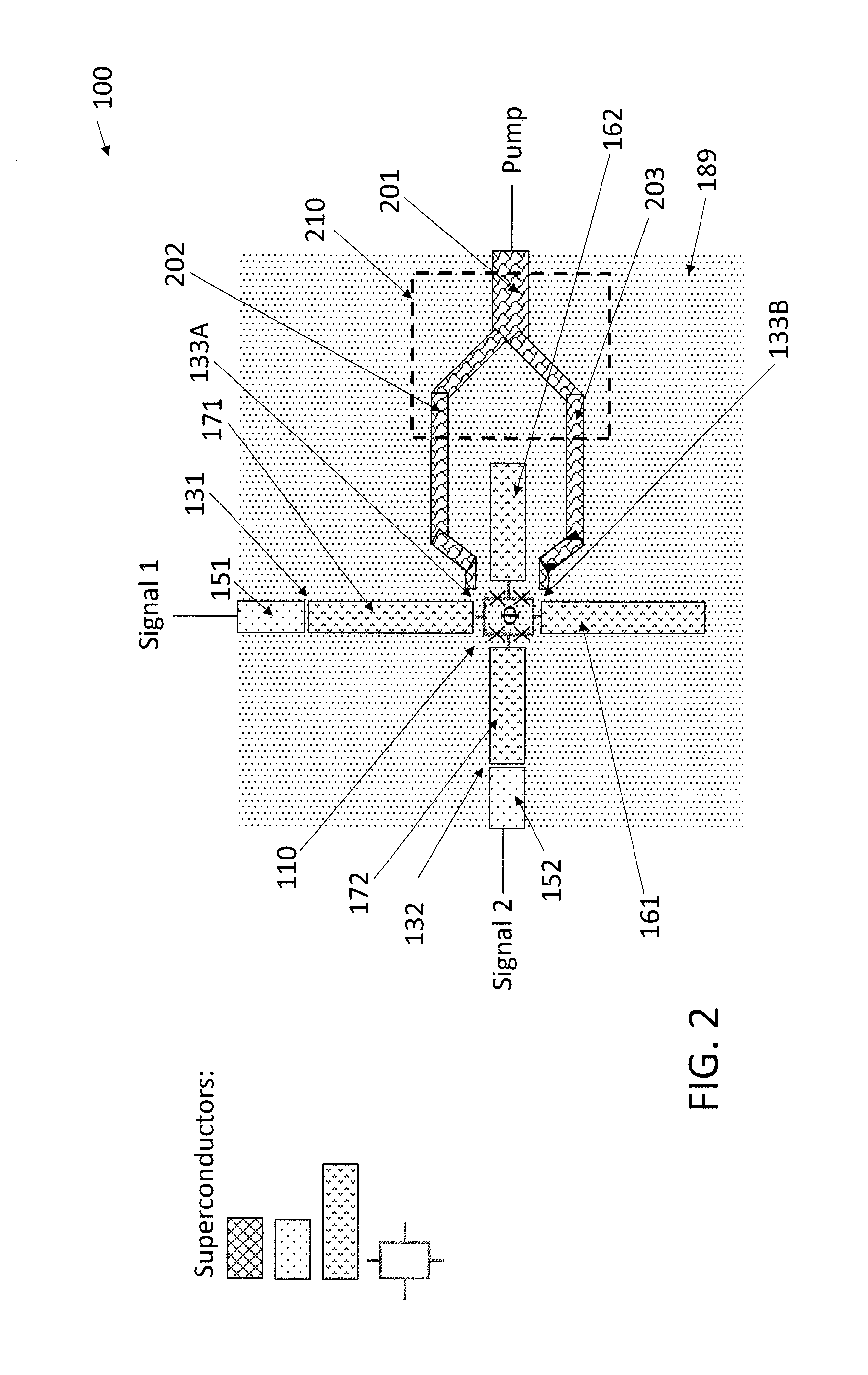
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
ActiveUS20160380636A1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:IBM CORP
Single flux quantum circuits
ActiveUS20090153180A1Reduce and eliminate unnecessary power dissipationQuantum computersPower consumption reductionQuantum circuitTransformer
Superconducting single flux quantum circuits are disclosed herein, each having at least one Josephson junction which will flip when the current through it exceeds a critical current. Bias current for the Josephson junction is provided by a biasing transformer instead of a resistor. The lack of any bias resistors ensures that unwanted power dissipation is eliminated.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Active timing arbitration in superconductor digital circuits
InactiveUS6507234B1Electronic switchingDissimilar materials junction devicesInductorSuperconducting transmission lines
A superconductor circuit (50) for providing active timing arbitration between SFQ pulses. The superconductor circuit (50) includes a first superconducting transmission line (52) having at least one inductor (54) for transmitting first input pulses, and a second superconducting transmission line (62) having at least one inductor (64) for transmitting second input pulses that are correlated to the first input pulses. The first and second superconducting transmission lines (52, 62) are coupled together in order to generate a flux attraction between the first and second input pulses for reducing relative timing uncertainty.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Superconducting quantum logic and applications of same
ActiveUS9998122B2Avoid flowExclusive-OR circuitsPulse generation by super conductive devicesVoltage pulseLogic cell
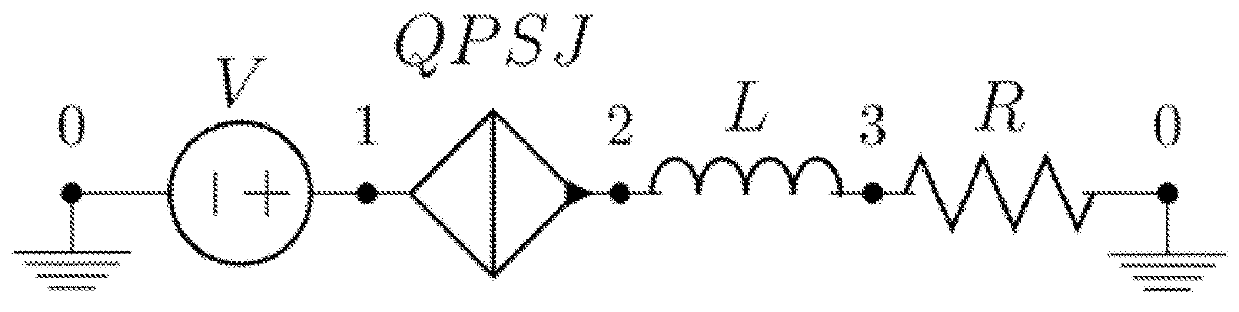
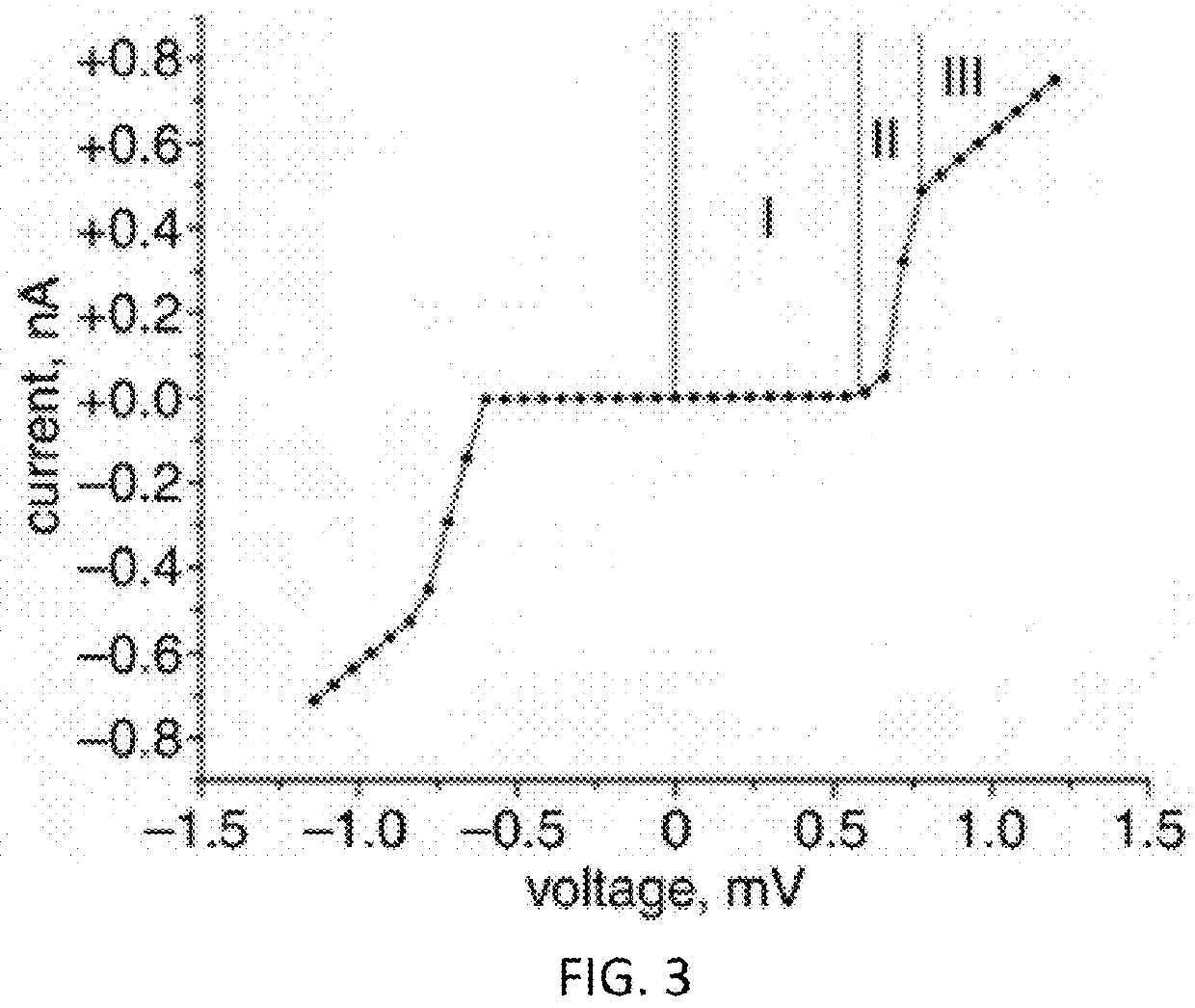
A superconducting logic cell includes at least one quantum phase-slip junction (QPSJ) for receiving at least one input and responsively providing at least one output, each QPSJ being configured such that when an input voltage of an input voltage pulse exceeds a critical value, a quantized charge of a Cooper electron pair tunnels across said QPSJ as an output, when the input voltage is less than the critical value, no quantized charge of the Cooper electron pair tunnels across said QPSJ as the output, where the presence and absence of the quantized charge in the form of a constant area current pulse in the output form two logic states, and the at least one QPSJ is biased with a bias voltage. The superconducting logic cell further includes at least one Josephson junction (JJ) coupled with the at least one QPSJ to perform one or more logic operations.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com