Patents
Literature
39 results about "Ring modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
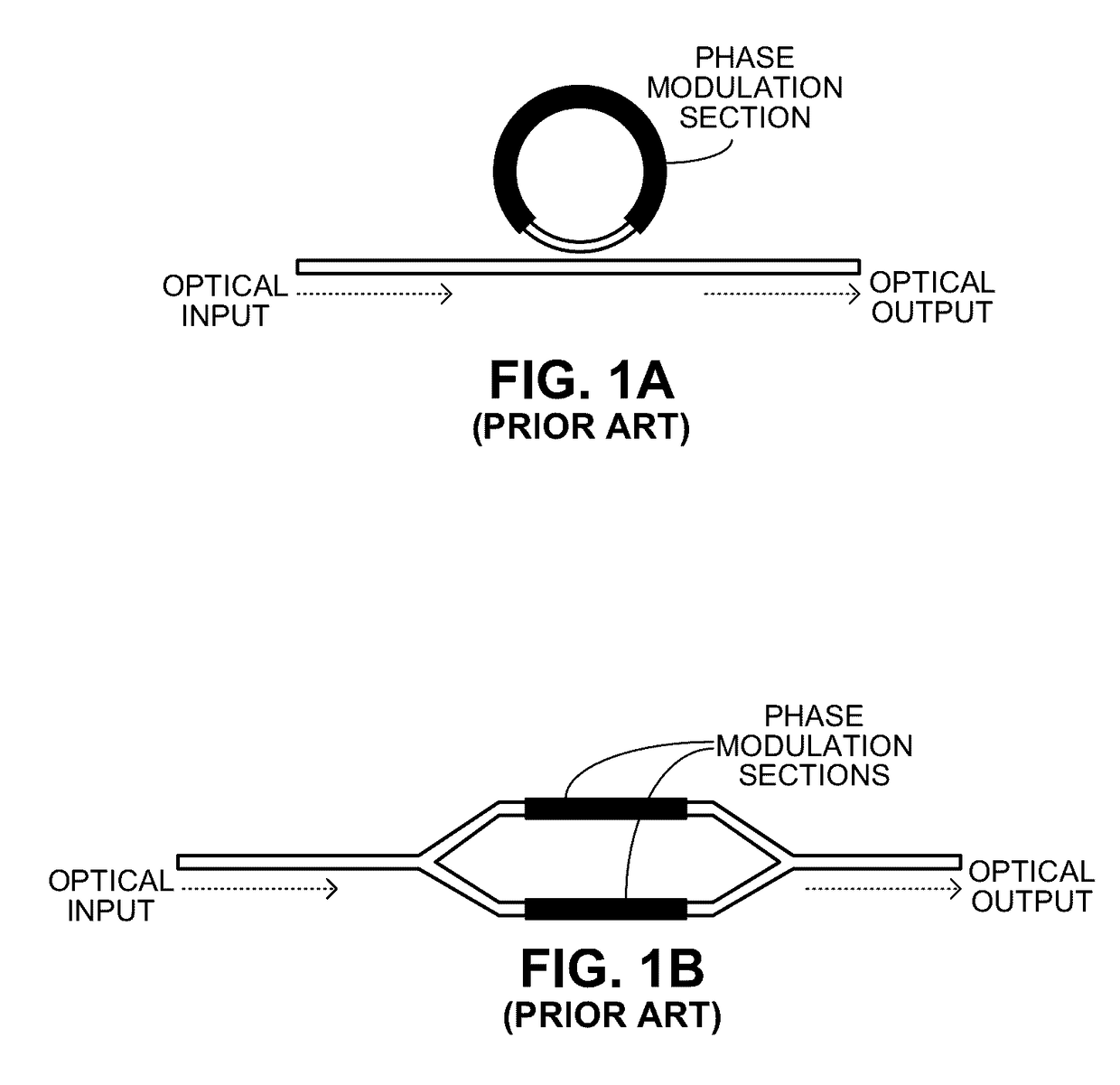
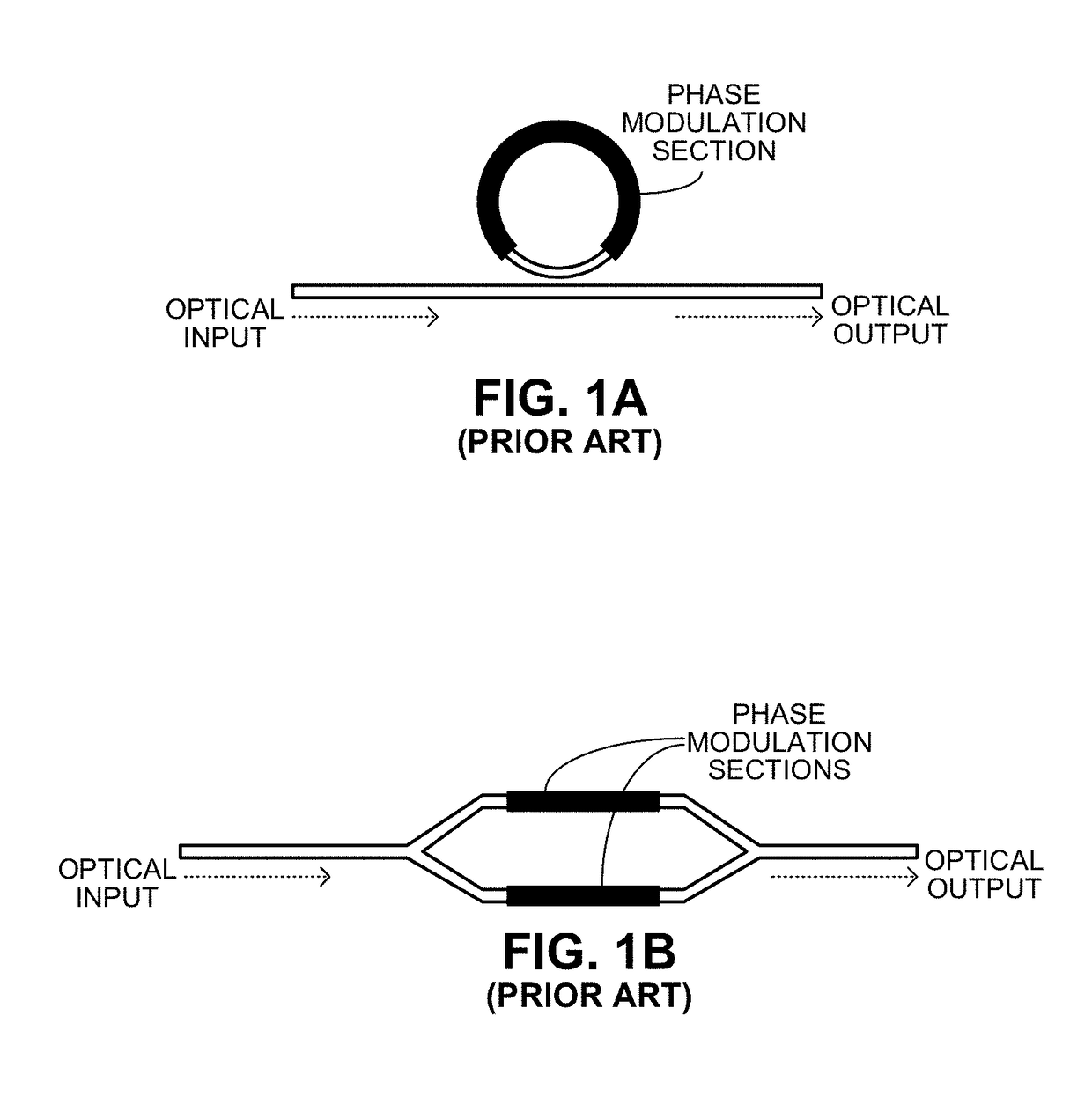
In electronics, ring modulation is a signal-processing function, an implementation of frequency mixing, performed by multiplying two signals, where one is typically a sine wave or another simple waveform and the other is the signal to be modulated. A ring modulator is an electronic device for ring modulation. A ring modulator may be used in music synthesizers and as an effects unit.
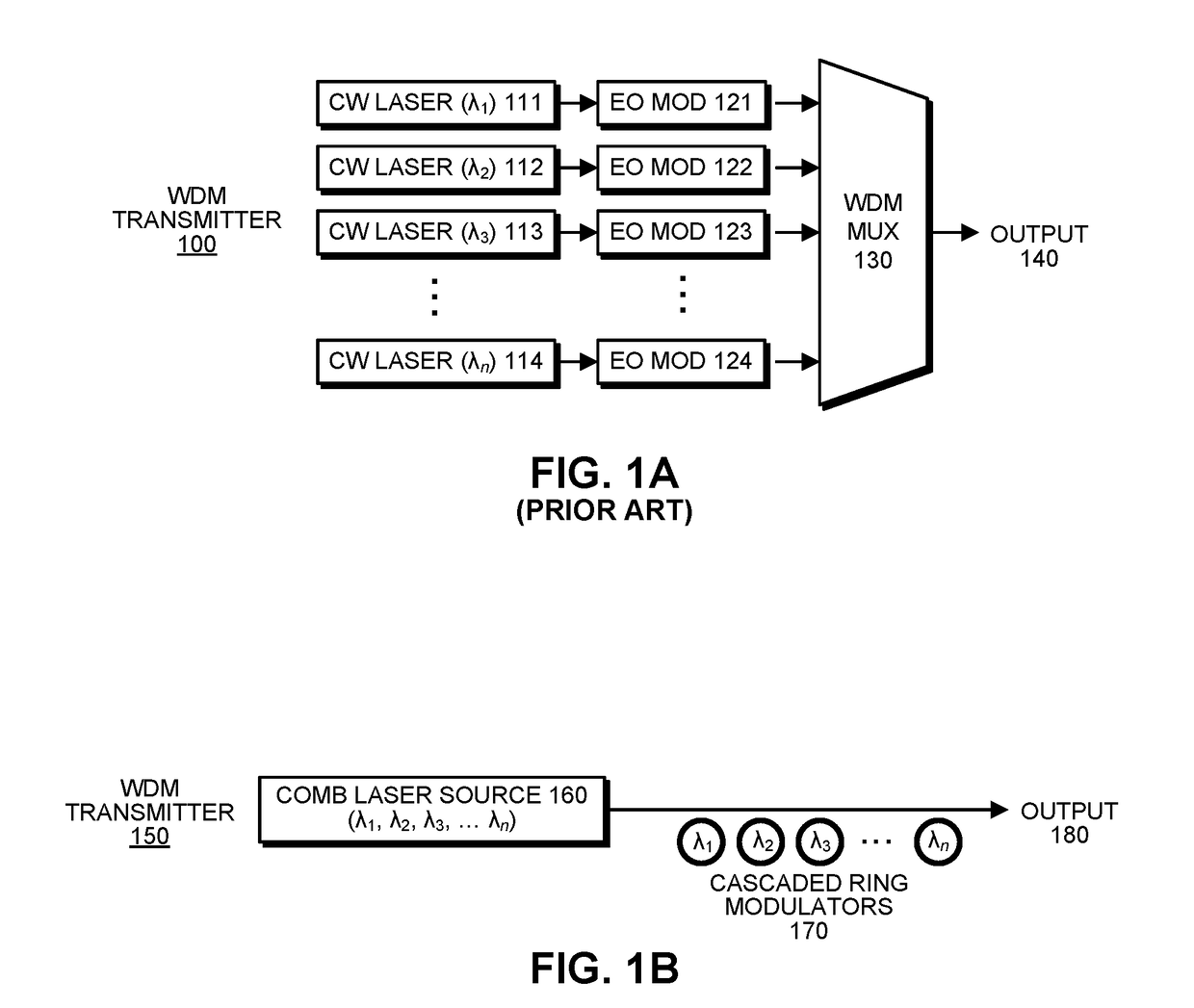
Method and circuit for encoding multi-level pulse amplitude modulated signals using integrated optoelectronic devices
ActiveUS20100060972A1Electromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerEngineering
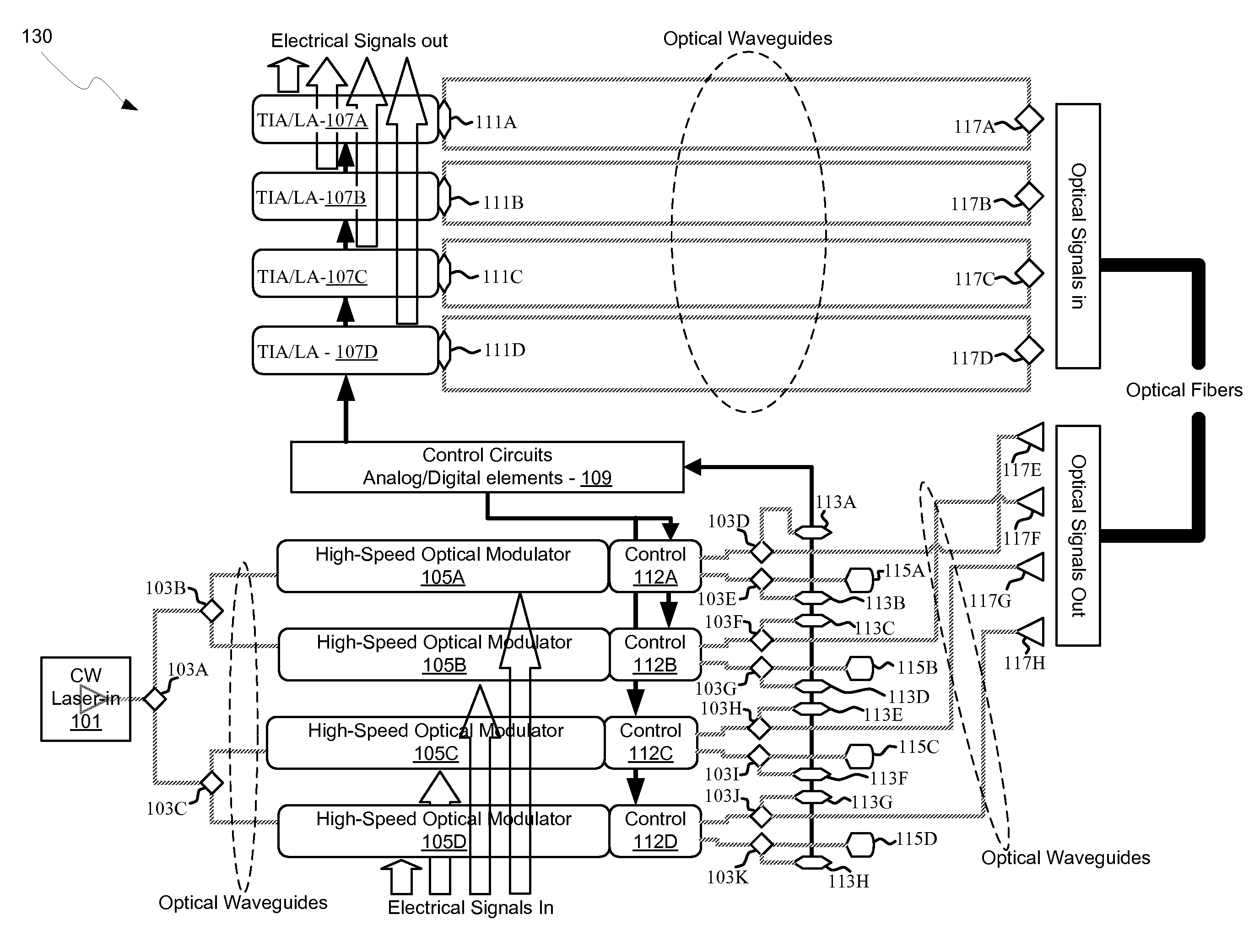
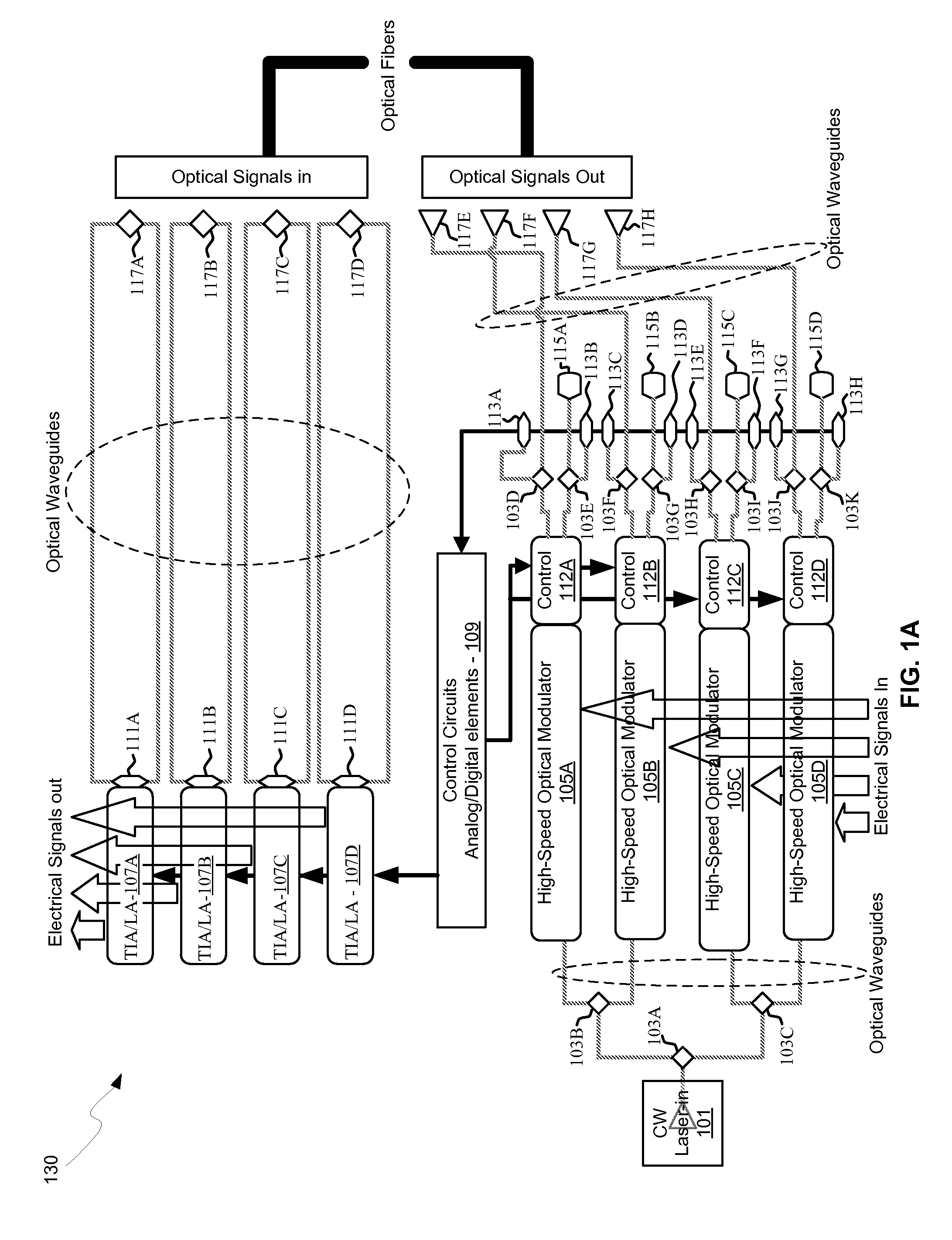
Methods and systems for encoding multi-level pulse amplitude modulated signals using integrated optoelectronics are disclosed and may include generating a multi-level, amplitude-modulated optical signal utilizing an optical modulator driven by two or more electrical input signals. The optical modulator may include optical modulator elements coupled in series and configured into groups. The number of optical modular elements and groups may configure the number of levels in the multi-level amplitude modulated optical signal. Unit drivers may be coupled to each of the groups. The electrical input signals may be synchronized before communicating them to the unit drivers utilizing flip-flops. Phase addition may be synchronized utilizing one or more electrical delay lines. The optical modulator may be integrated on a single substrate, which may include one of: silicon, gallium arsenide, germanium, indium gallium arsenide, polymers, or indium phosphide. The optical modulator may include a Mach-Zehnder interferometer or one or more ring modulators.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and circuit for encoding multi-level pulse amplitude modulated signals using integrated optoelectronic devices
ActiveUS8238014B2Electromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerEngineering
Methods and systems for encoding multi-level pulse amplitude modulated signals using integrated optoelectronics are disclosed and may include generating a multi-level, amplitude-modulated optical signal utilizing an optical modulator driven by two or more electrical input signals. The optical modulator may include optical modulator elements coupled in series and configured into groups. The number of optical modular elements and groups may configure the number of levels in the multi-level amplitude modulated optical signal. Unit drivers may be coupled to each of the groups. The electrical input signals may be synchronized before communicating them to the unit drivers utilizing flip-flops. Phase addition may be synchronized utilizing one or more electrical delay lines. The optical modulator may be integrated on a single substrate, which may include one of: silicon, gallium arsenide, germanium, indium gallium arsenide, polymers, or indium phosphide. The optical modulator may include a Mach-Zehnder interferometer or one or more ring modulators.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
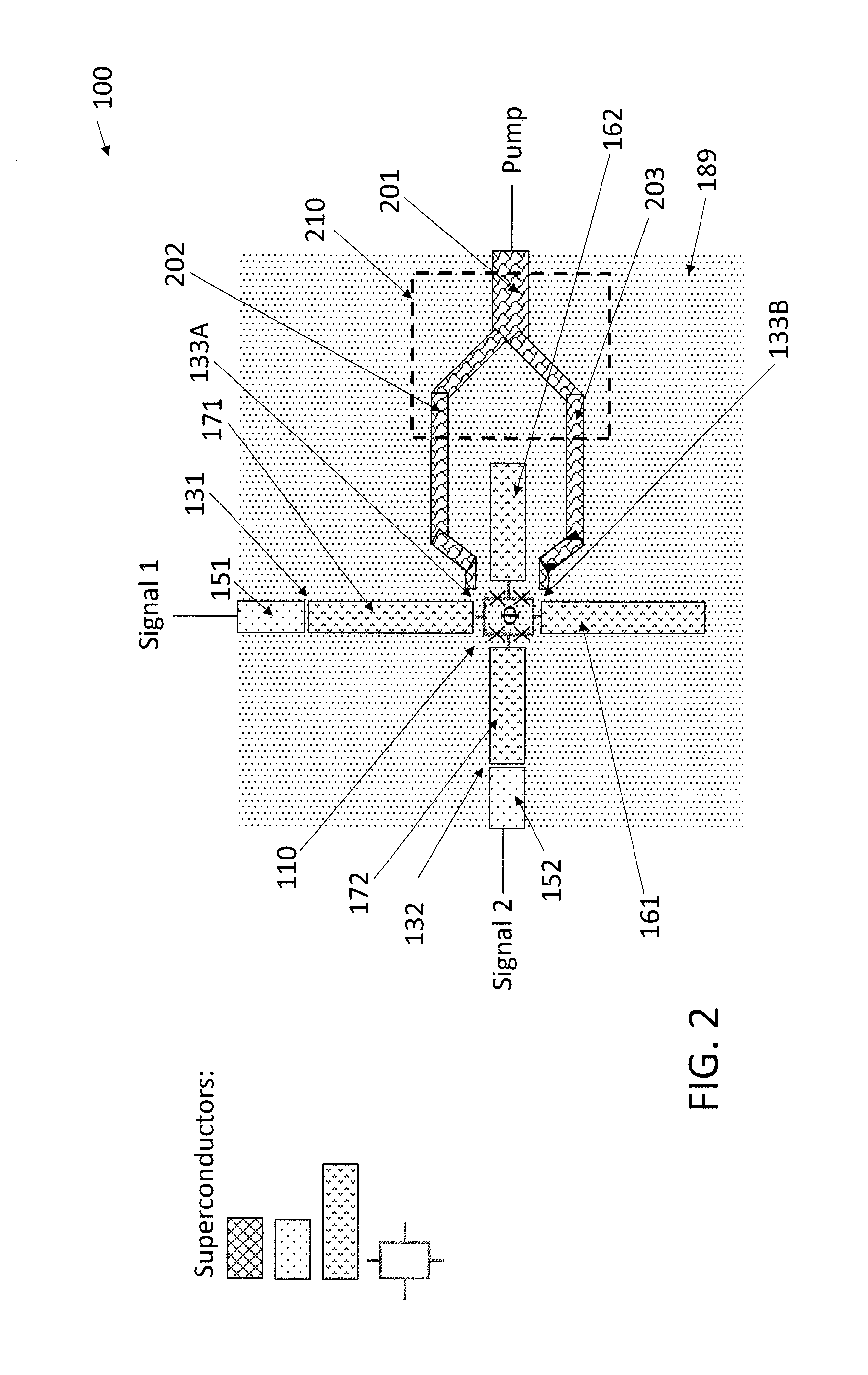
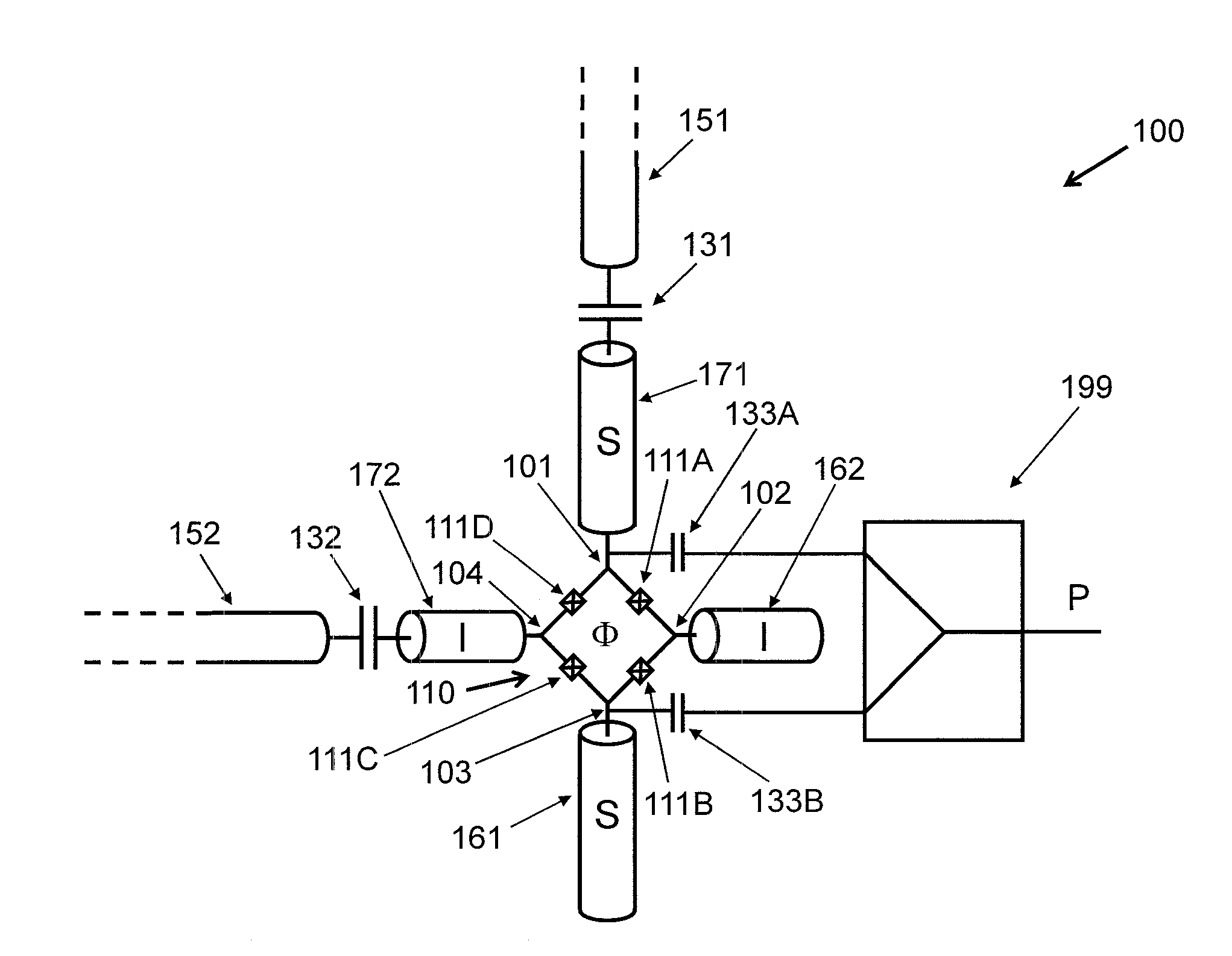
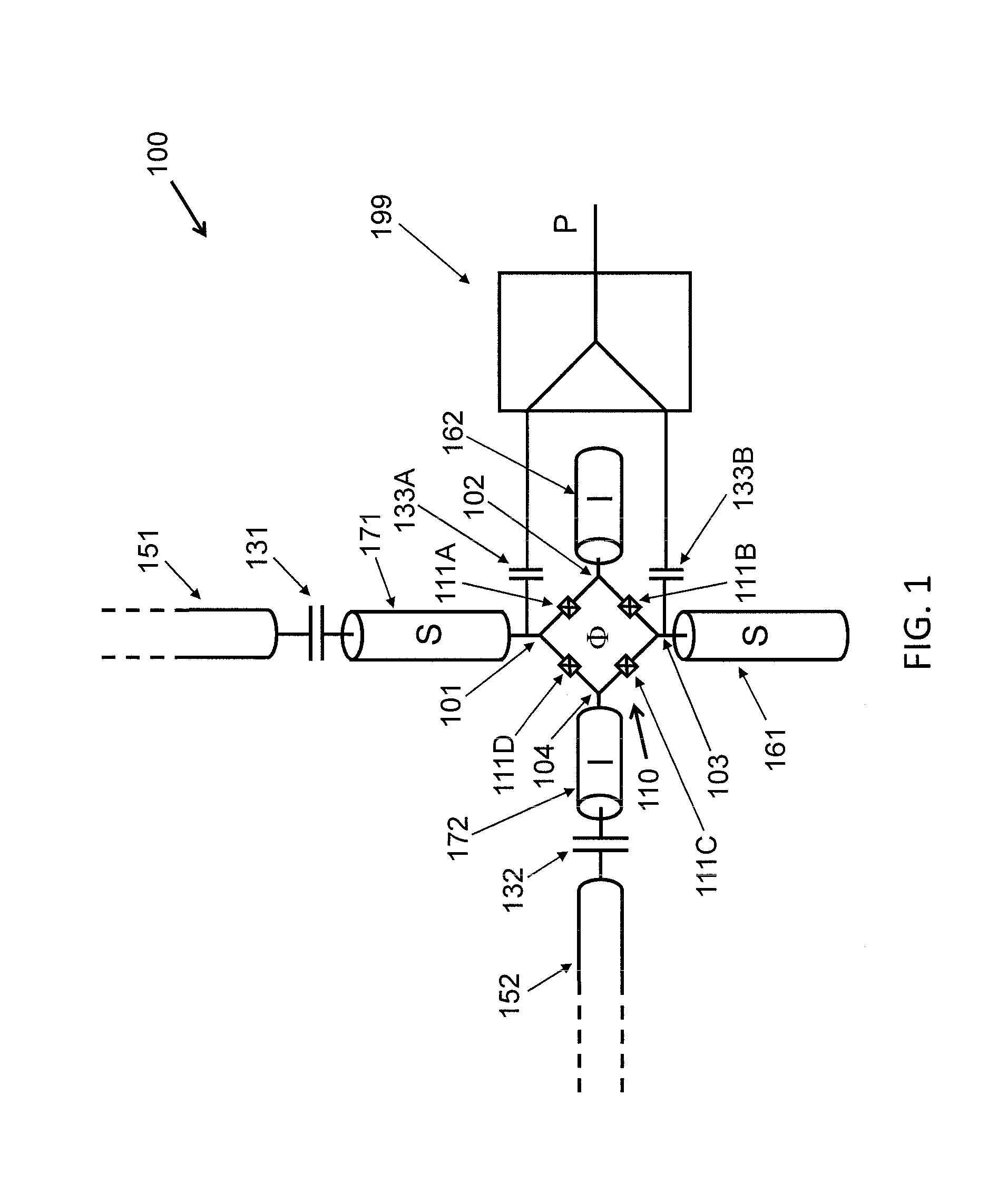
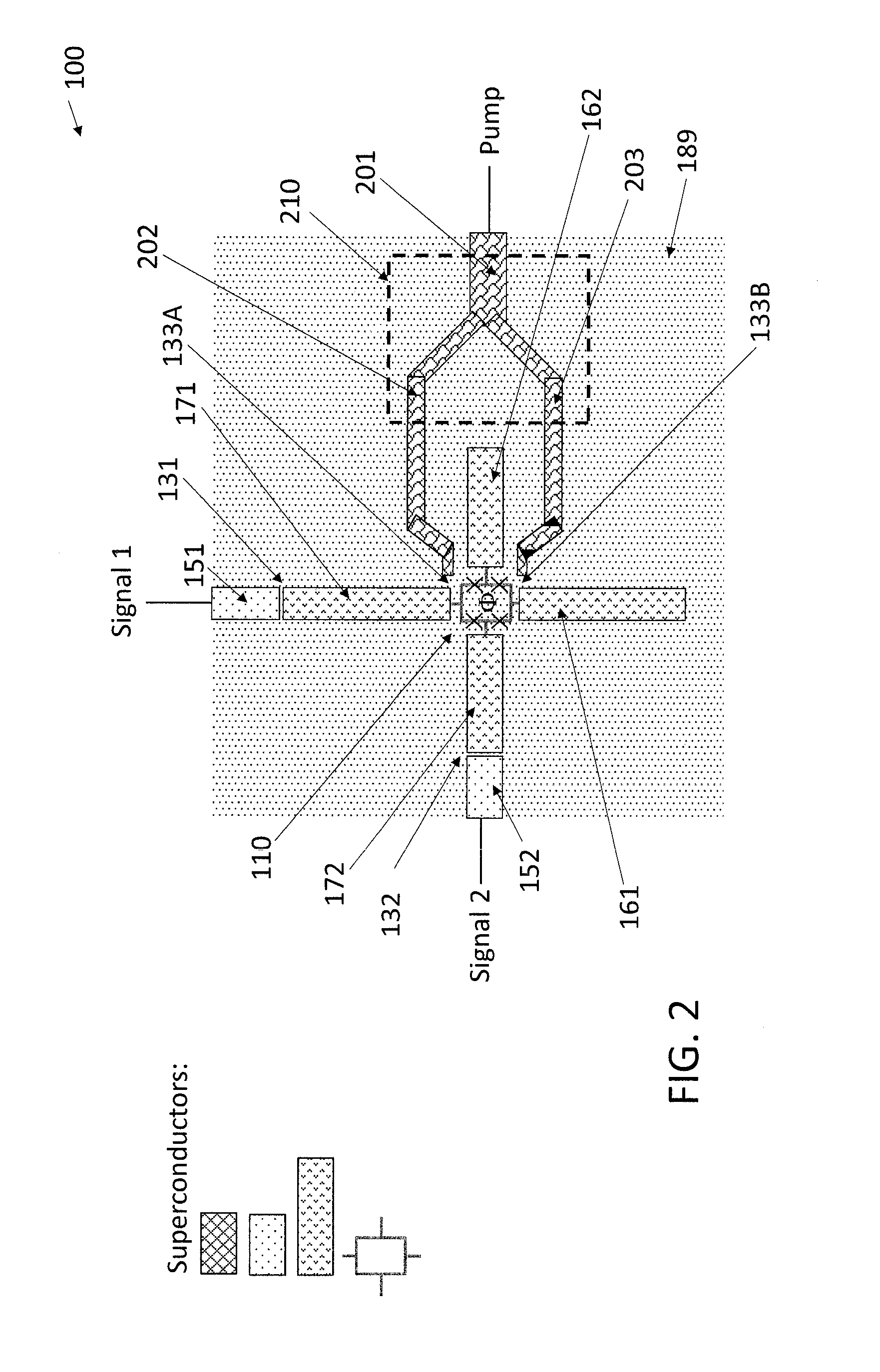
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
ActiveUS20160380636A1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:IBM CORP
Driving the common-mode of a josephson parametric converter using a three-port power divider
ActiveUS9548742B1Modulation transference by superconductive devicesParametric amplifiersRing modulationEngineering
An on-chip Josephson parametric converter is provided. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter includes a Josephson ring modulator. The on-chip Josephson parametric converter further includes a lossless power divider, coupled to the Josephson ring modulator, having a single input port and two output ports for receiving a pump drive signal via the single input port, splitting the pump drive signal symmetrically into two signals that are equal in amplitude and phase, and outputting each of the two signals from a respective one of the two output ports. The pump drive signal excites a common mode of the on-chip Josephson parametric converter.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
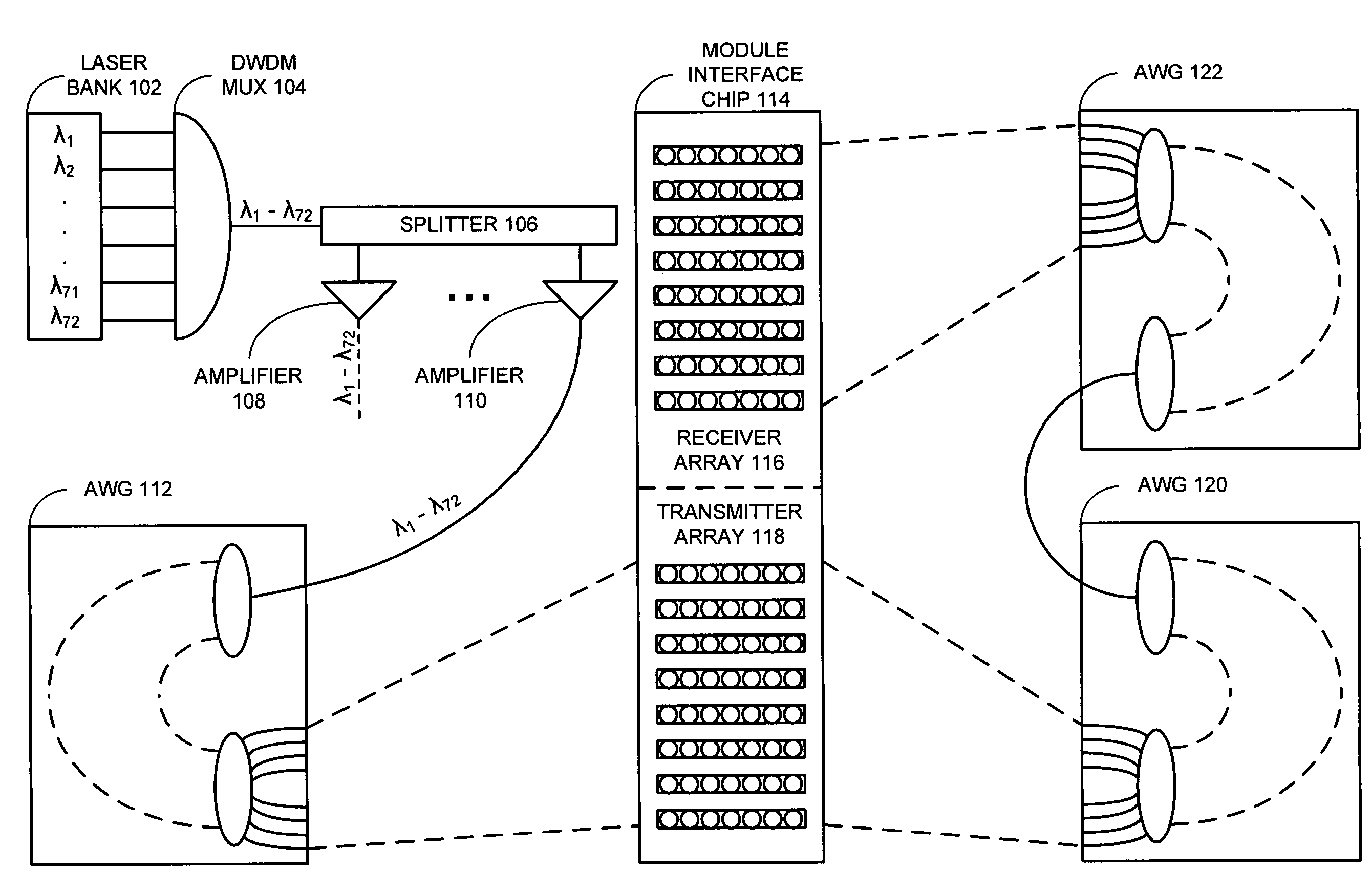
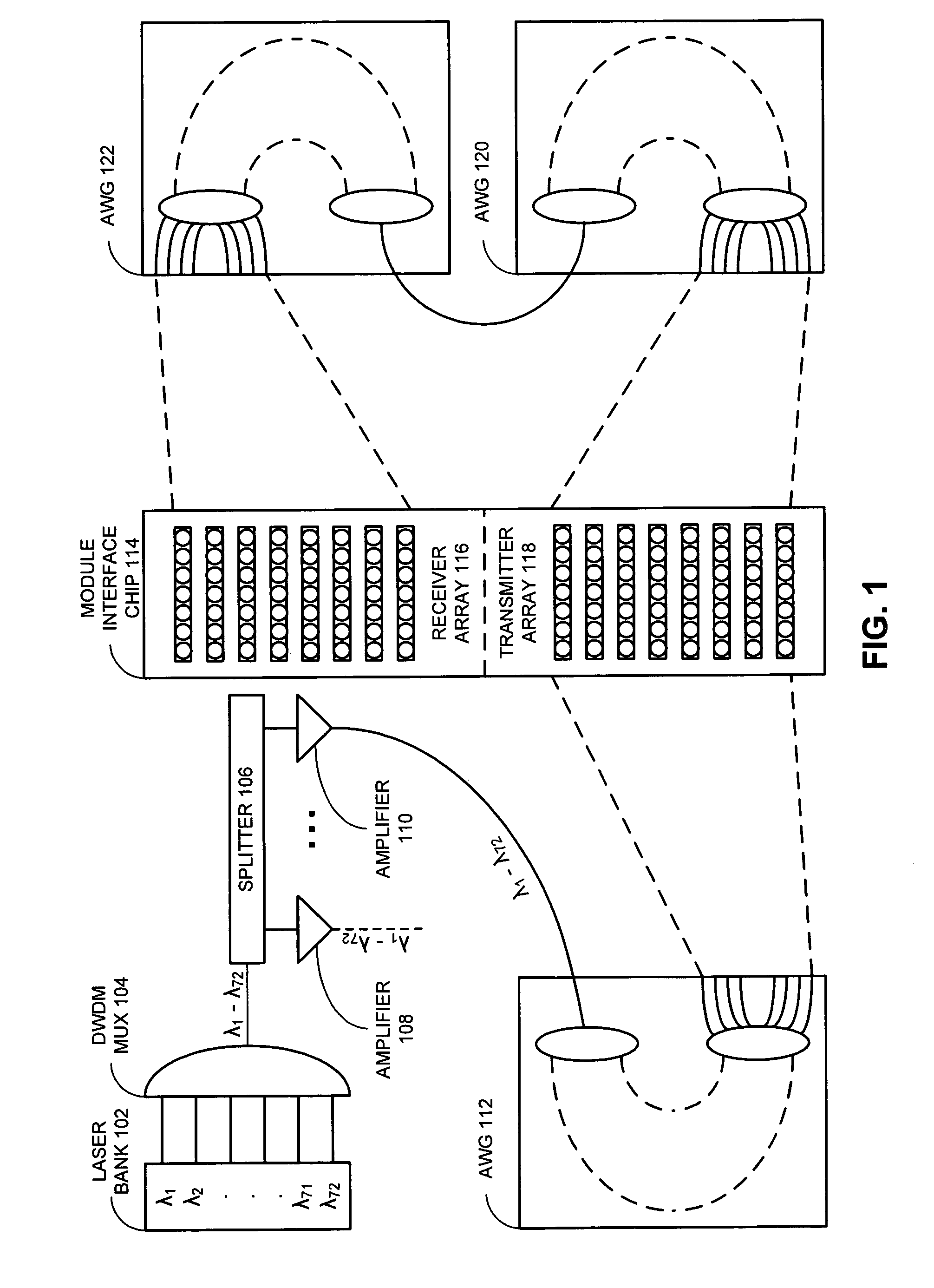
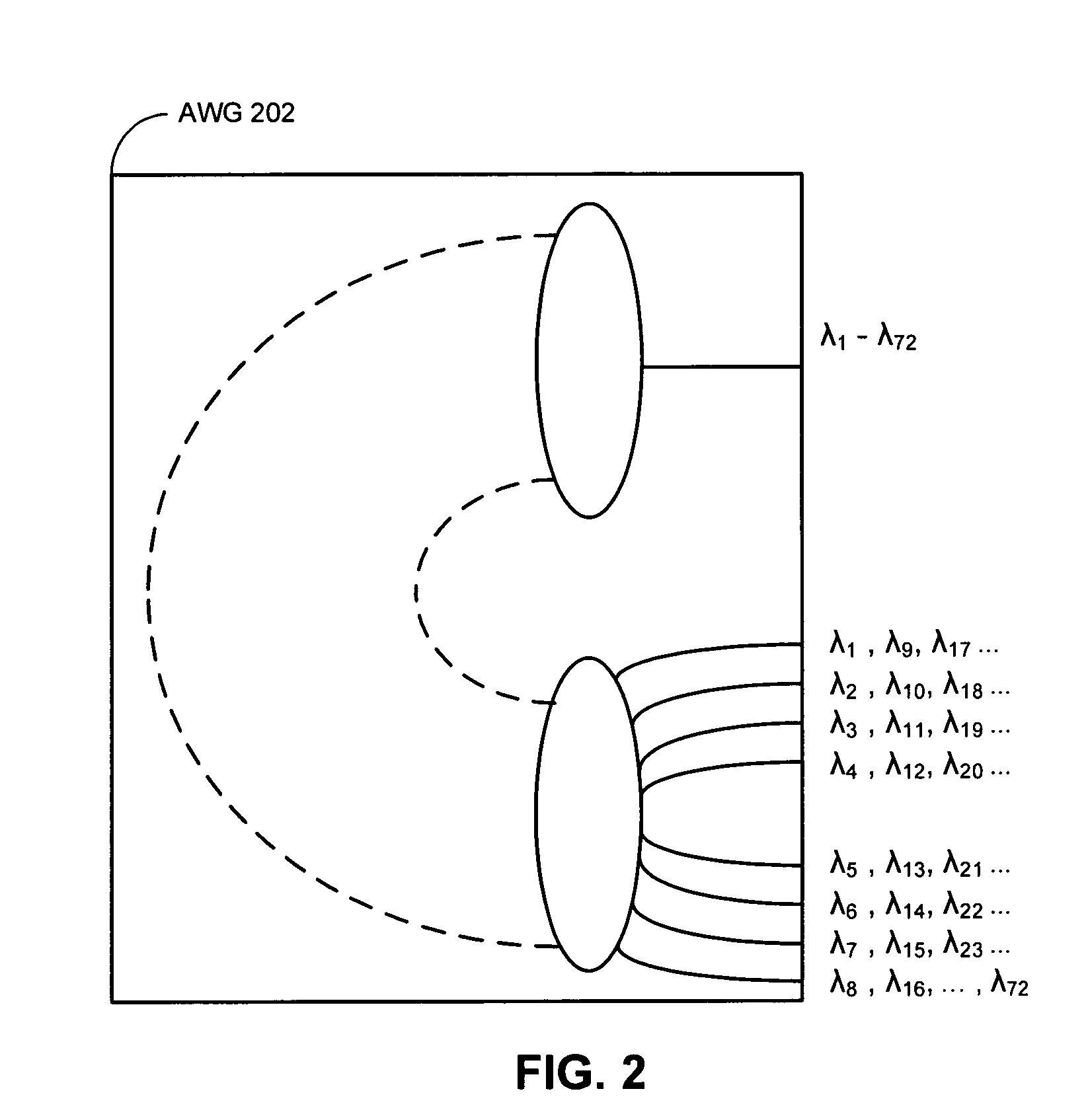
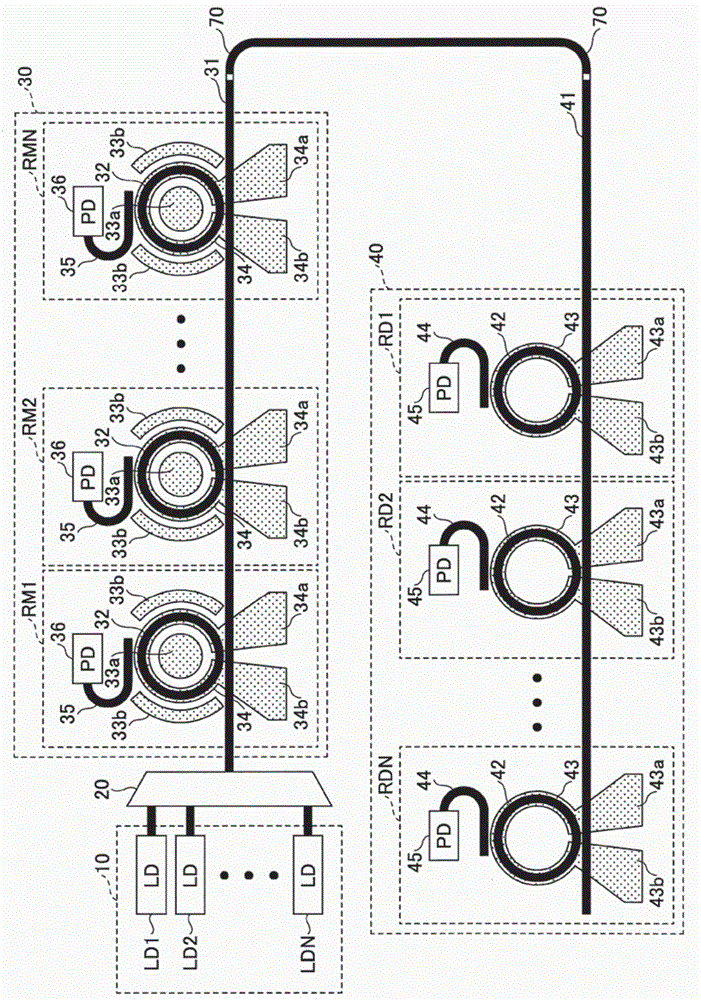
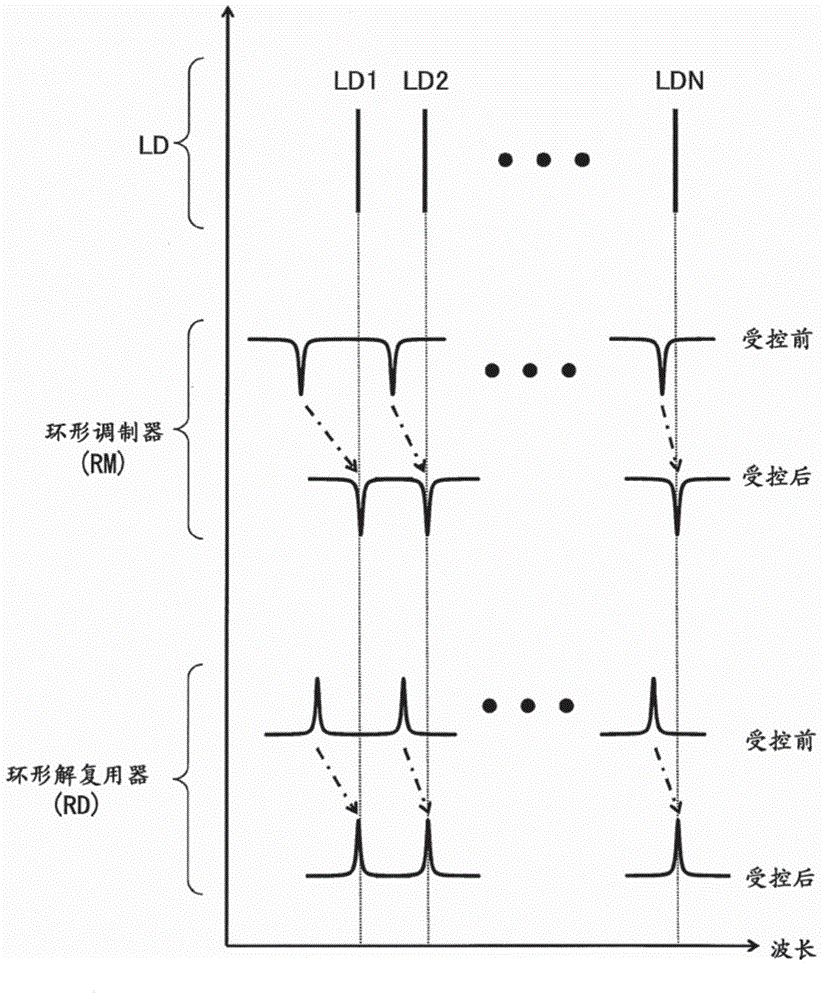
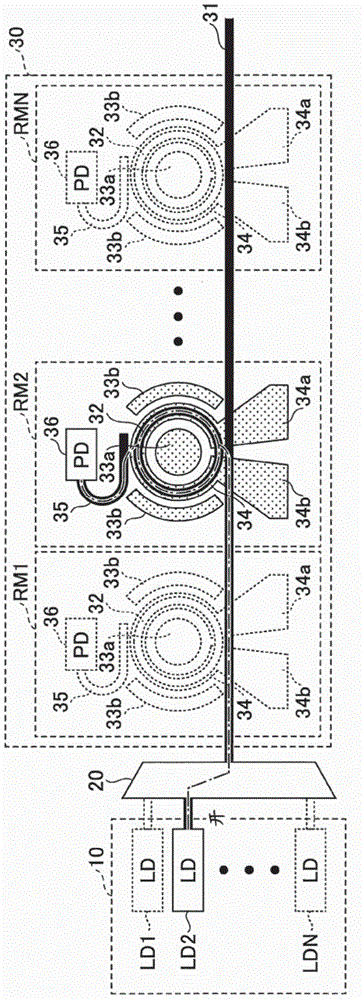
Integrated ring modulator array WDM transceiver
ActiveUS7539418B1Facilitates optical multiplexingFacilitates demultiplexingWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionMultiplexingRing modulation
A system that facilitates optical multiplexing and demultiplexing. The system includes an optical transmitter which is structured in the following way. A wavelength-splitting mechanism is coupled to the optical transmitter, which separates the wavelengths of light onto an array of input-optical-waveguide busses within the optical transmitter. An array of ring modulators within the optical transmitter is coupled to each optical-waveguide bus, wherein the input-end of a given ring modulator is coupled to a corresponding input-optical-waveguide bus. Output-optical-waveguide busses within the optical transmitter are coupled to the array of ring modulators, wherein the output-end of each ring modulator is coupled to a corresponding output-optical-waveguide bus. When a modulation signal is applied to a given ring modulator within the array of ring modulators, a specific wavelength of light is directed to the corresponding output-optical-waveguide bus.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dual-ring-modulated laser that uses push-pull modulation
ActiveUS20170139237A1Large tuning rangeLaser detailsLaser active region structureRing modulationResonance
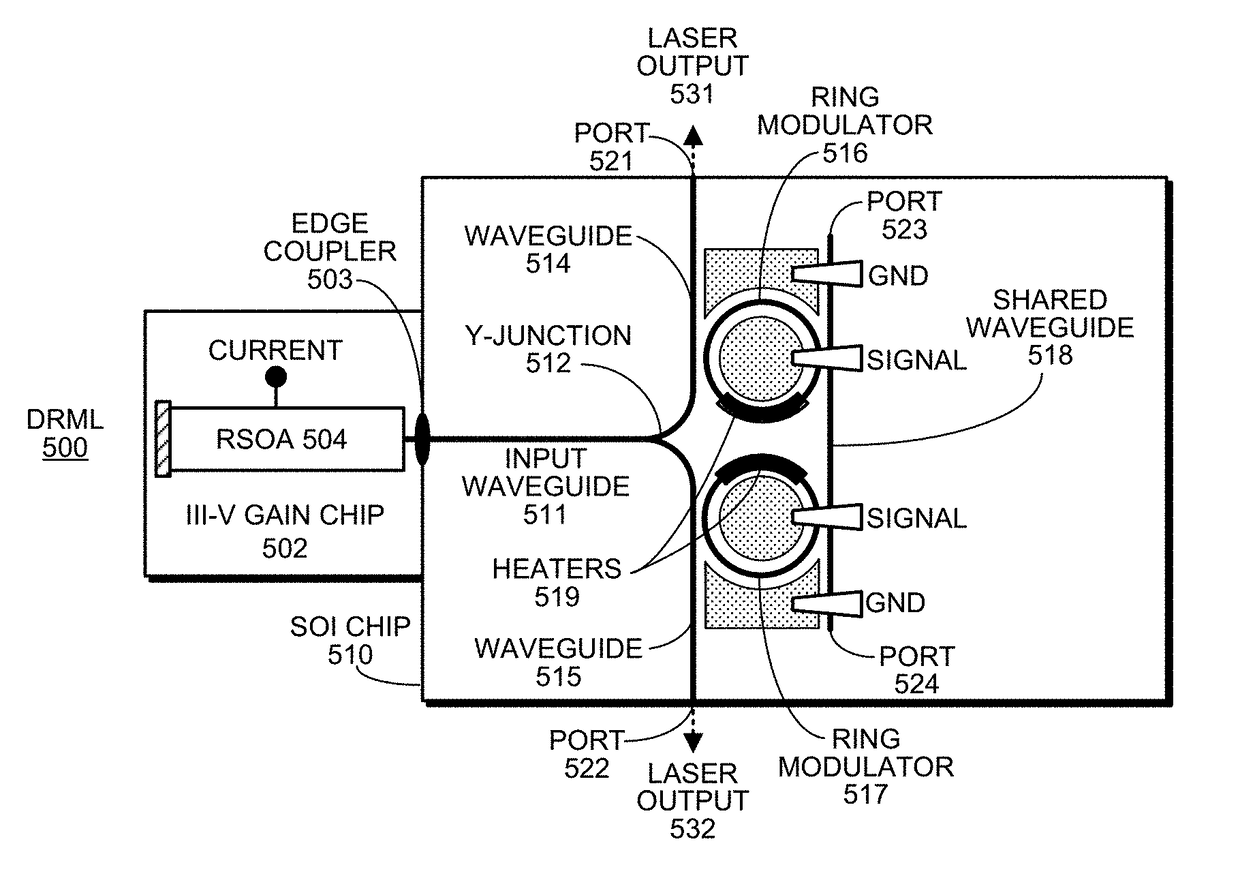
A dual-ring-modulated laser includes a gain medium having a reflective end coupled to a gain-medium reflector and an output end coupled to a reflector circuit to form a lasing cavity. This reflector circuit comprises: a first ring modulator; a second ring modulator; and a shared waveguide that optically couples the first and second ring modulators. The first and second ring modulators have resonance peaks, which are tuned to have an alignment separation from each other. During operation, the first and second ring modulators are driven in opposing directions based on the same electrical input signal, so the resonance peaks of the first and second ring modulators shift wavelengths in the opposing directions during modulation. The modulation shift for each of the resonance peaks equals the alignment separation, so the resonance peaks interchange positions during modulation to cancel out reflectivity changes in the lasing cavity caused by the modulation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
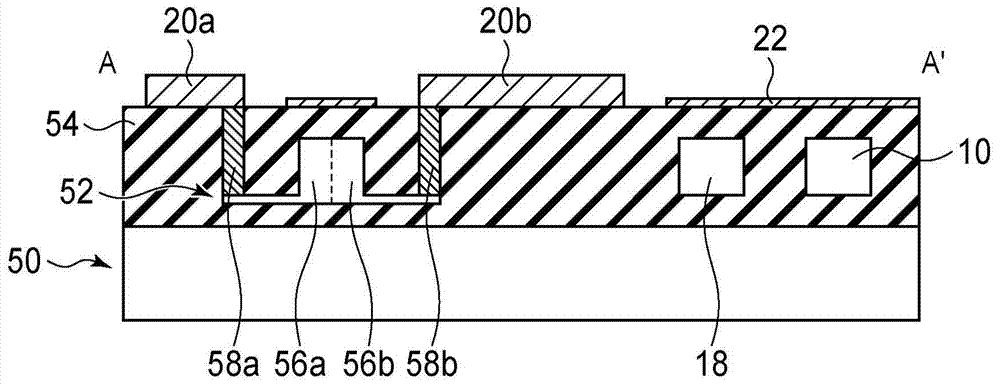
Optical semiconductor device
InactiveCN102955265APhotometry using reference valueNon-linear opticsPhotodetectorResonance wavelength
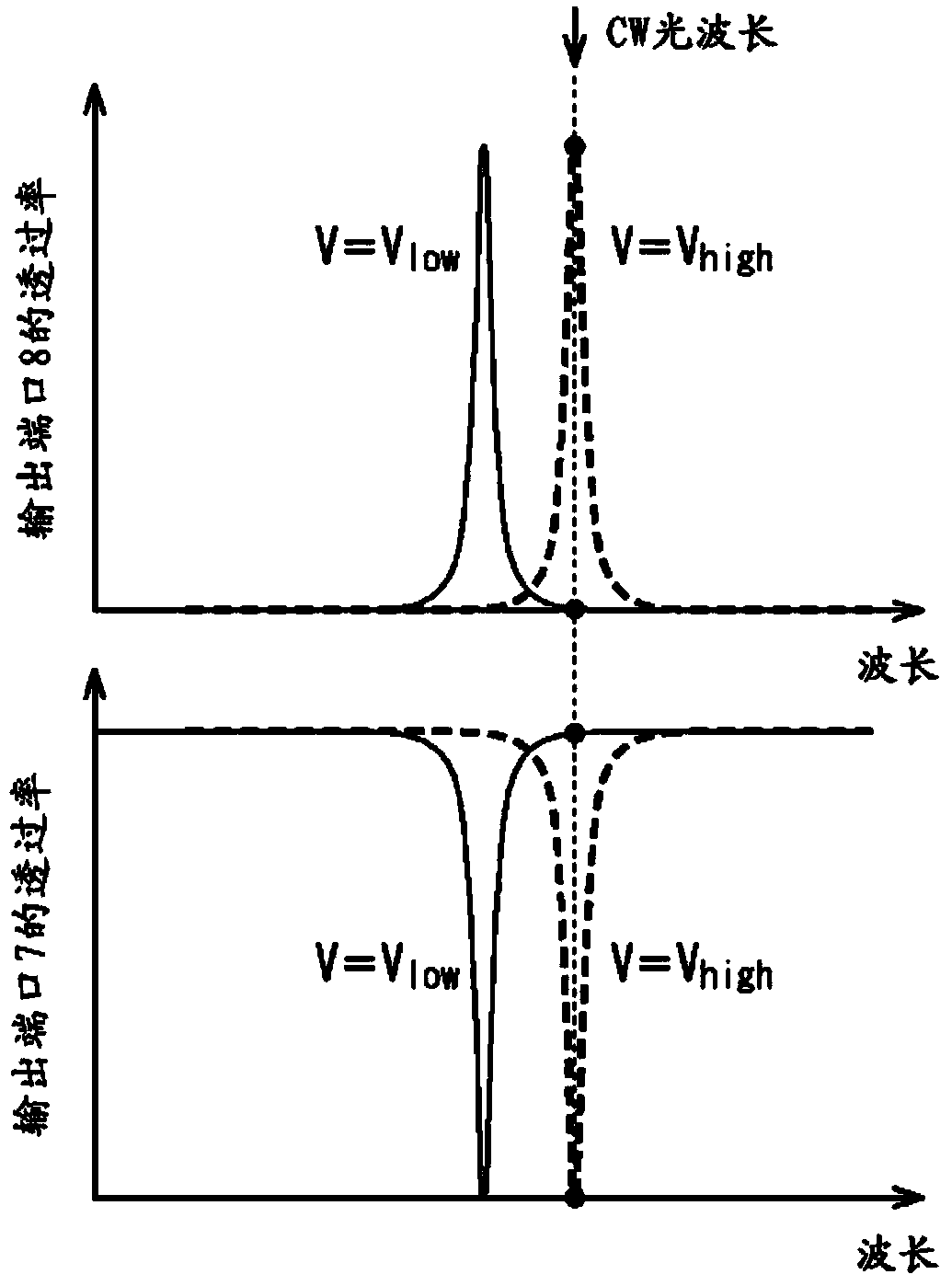
An optical semiconductor device includes a waveguide that an input light to be inputted, a ring modulator optically coupled with the waveguide, a first ring resonator optically coupled with the waveguide and having an optical path length smaller than an optical path length of the ring modulator, a second ring resonator optically coupled with the first waveguide and having an optical path length larger than the optical path length of the ring modulator, a heater arranged adjacent to the ring modulator, the first ring resonator and the second ring resonator, a first photodetector monitoring a light power in the first ring resonator, a second photodetector monitoring a light power in the second ring resonator, and a controller controlling the heater so that a resonance wavelength of the ring modulator agrees with a wavelength of the input light, based on signals detected by the first and second photodetectors.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Dual-ring-modulated laser that uses push-push/pull-pull modulation
ActiveUS9778493B1Large tuning rangeLaser detailsLaser active region structureRing modulationResonance
A dual-ring-modulated laser includes a gain medium having a reflective end coupled to an associated gain-medium reflector and an output end, which is coupled to a reflector circuit through an input waveguide to form a lasing cavity. The reflector circuit comprises: a first ring modulator; a second ring modulator; and a shared waveguide that optically couples the first and second ring modulators together. The first and second ring modulators have resonance peaks that are tuned to be offset in alignment from each other to provide an effective reflectance having a flat-top response, which is aligned with an associated lasing cavity mode. The first and second ring modulators are driven in tandem based on the same electrical input signal, whereby the resonance peaks of the first and second ring modulators shift wavelengths in the same direction during modulation, and an effective reflectance stays within the flat-top wavelength range.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
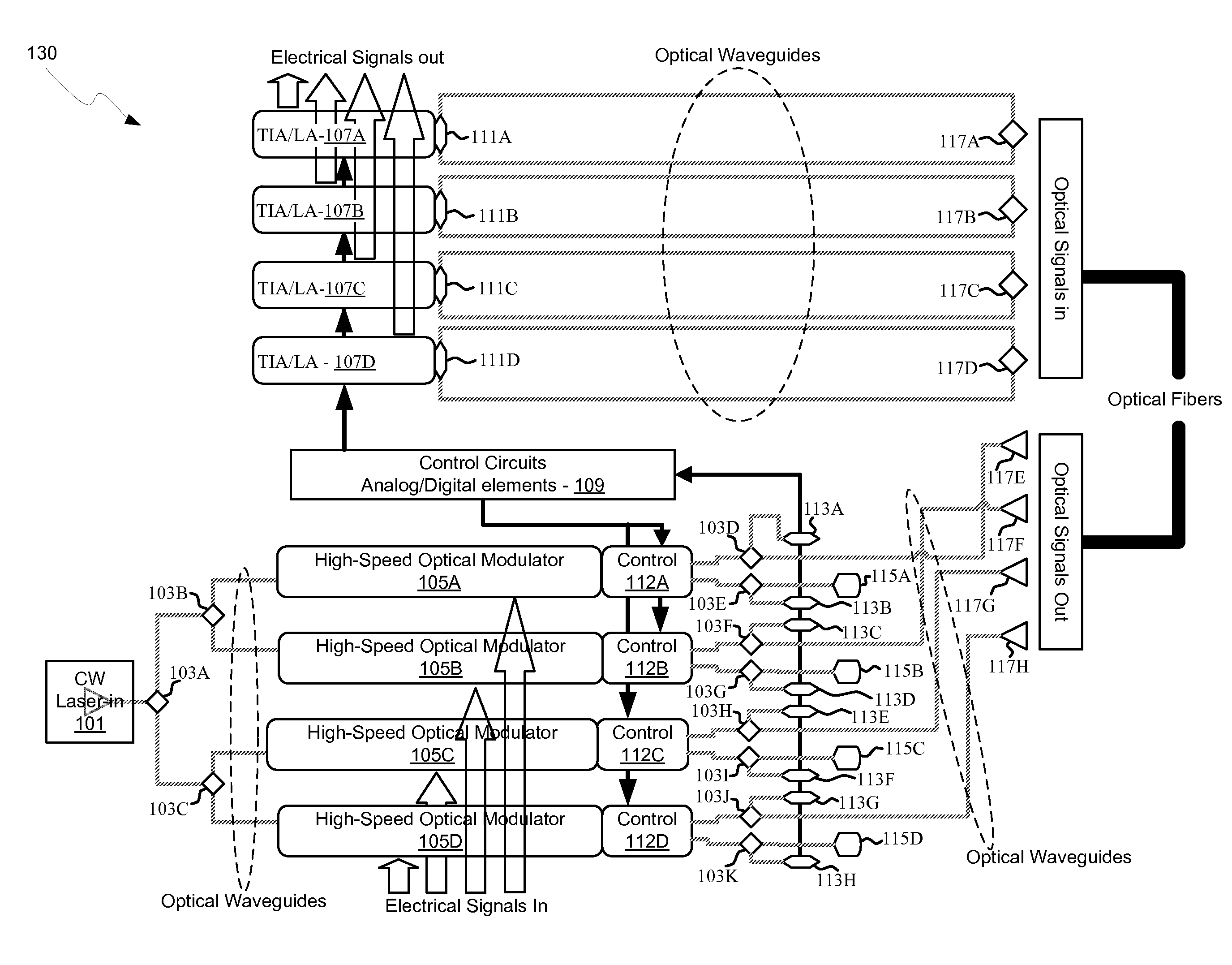
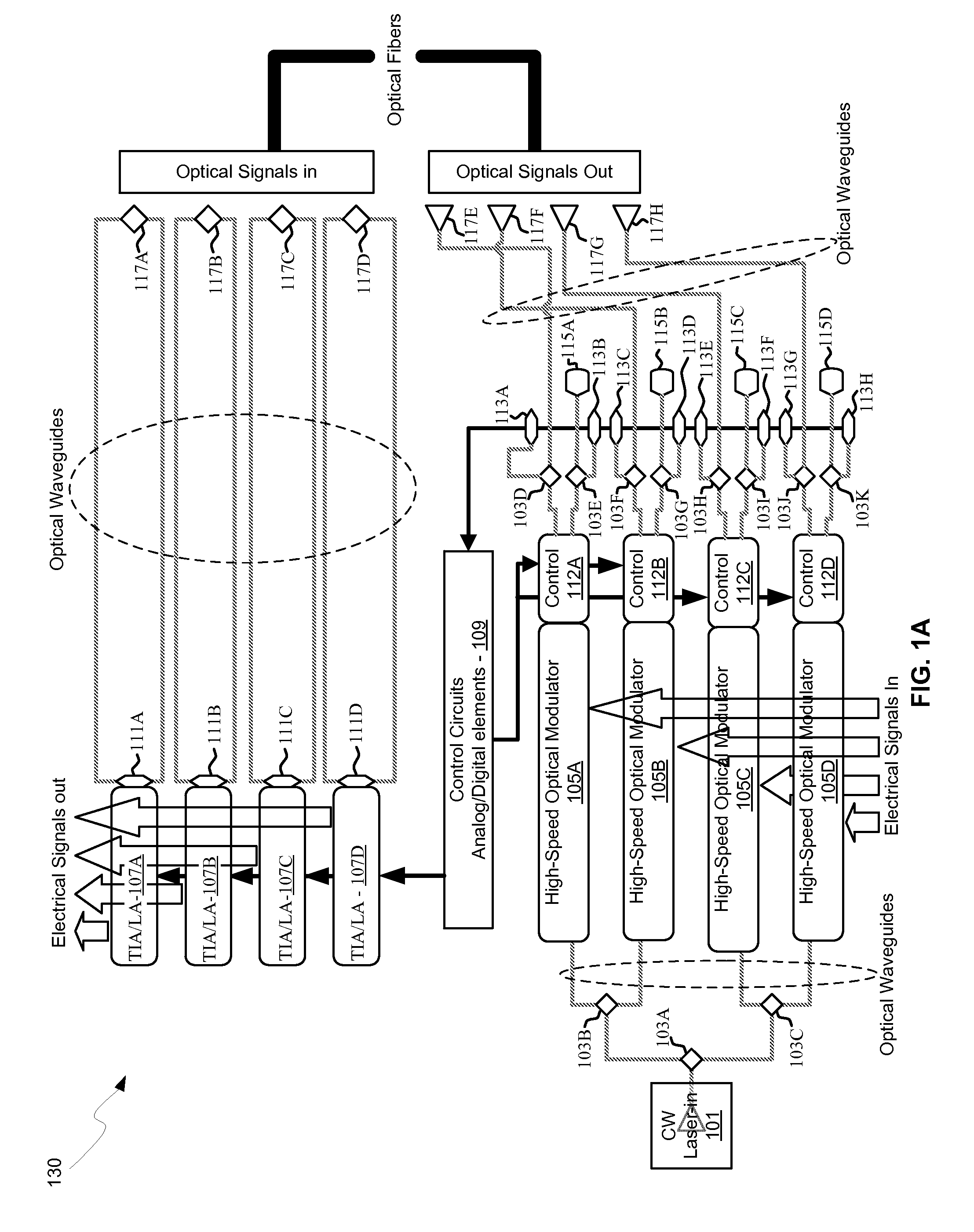
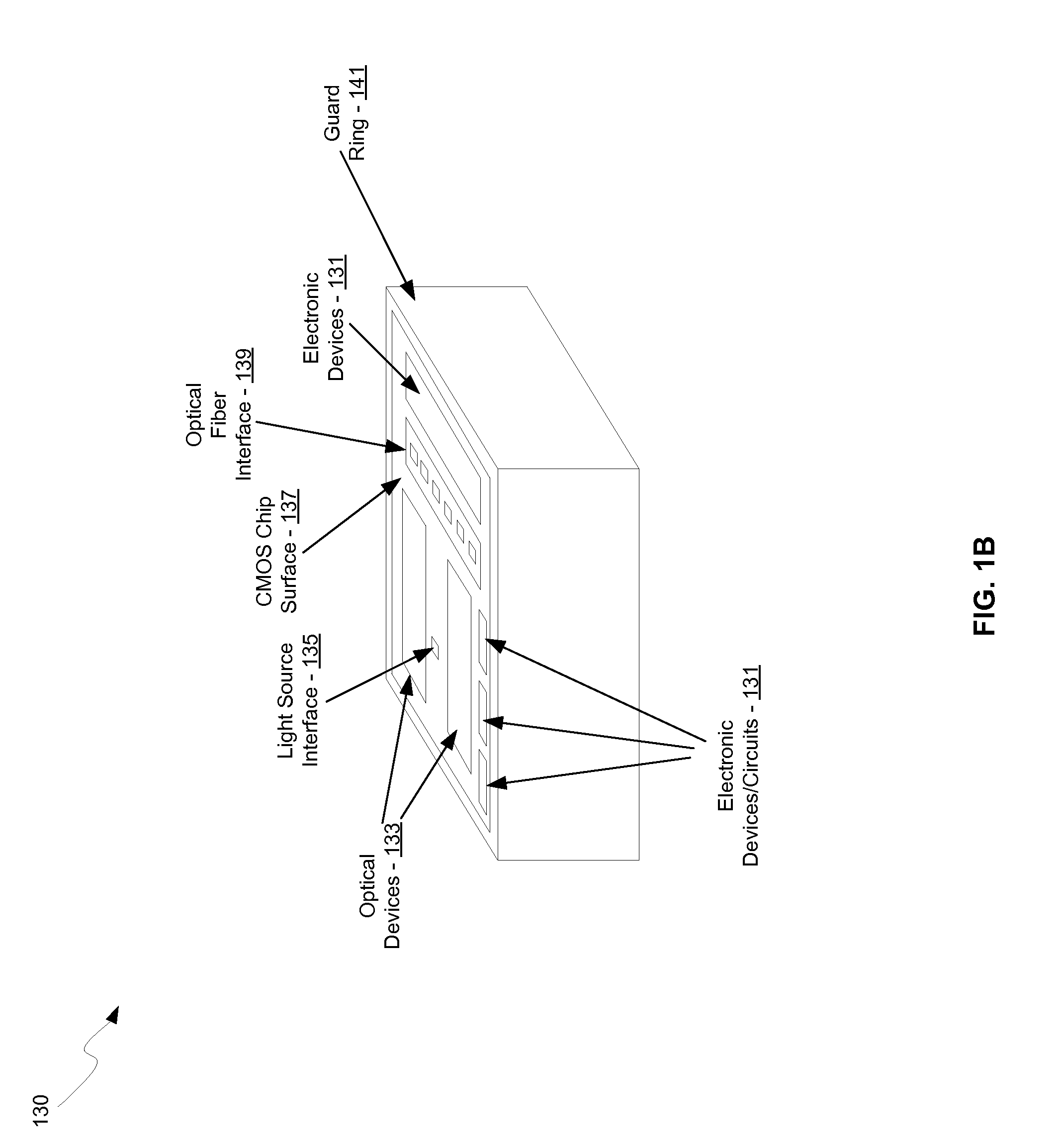
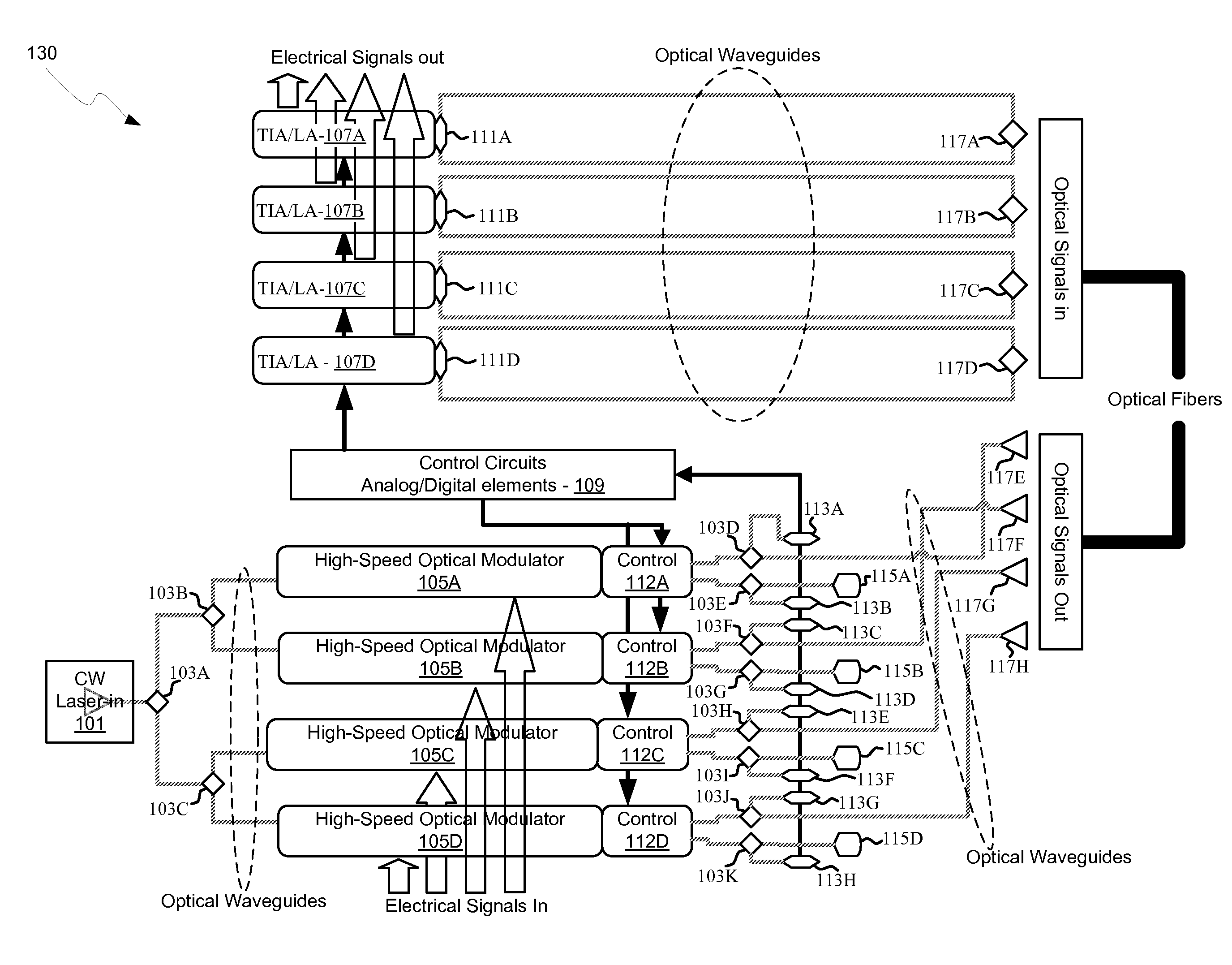
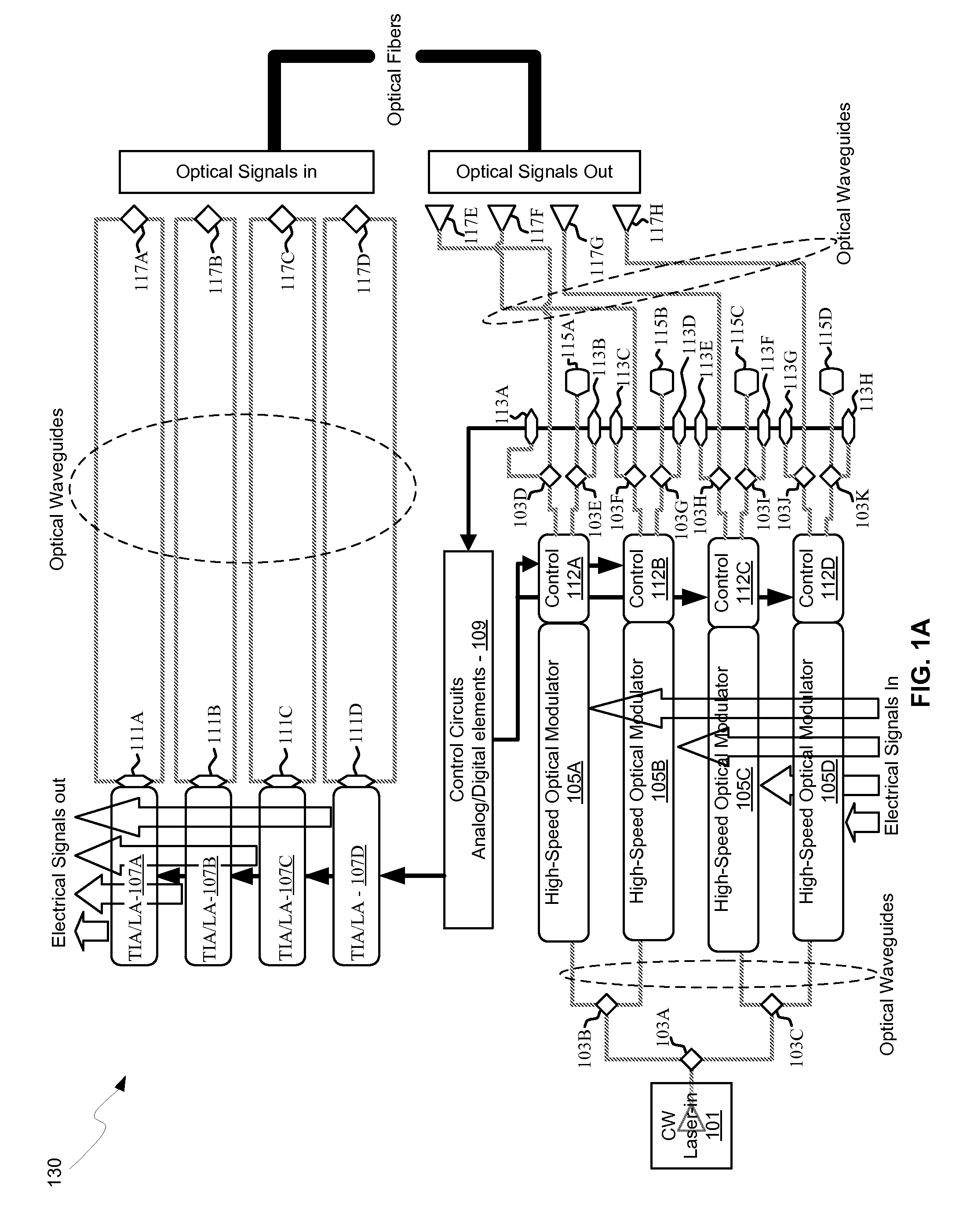
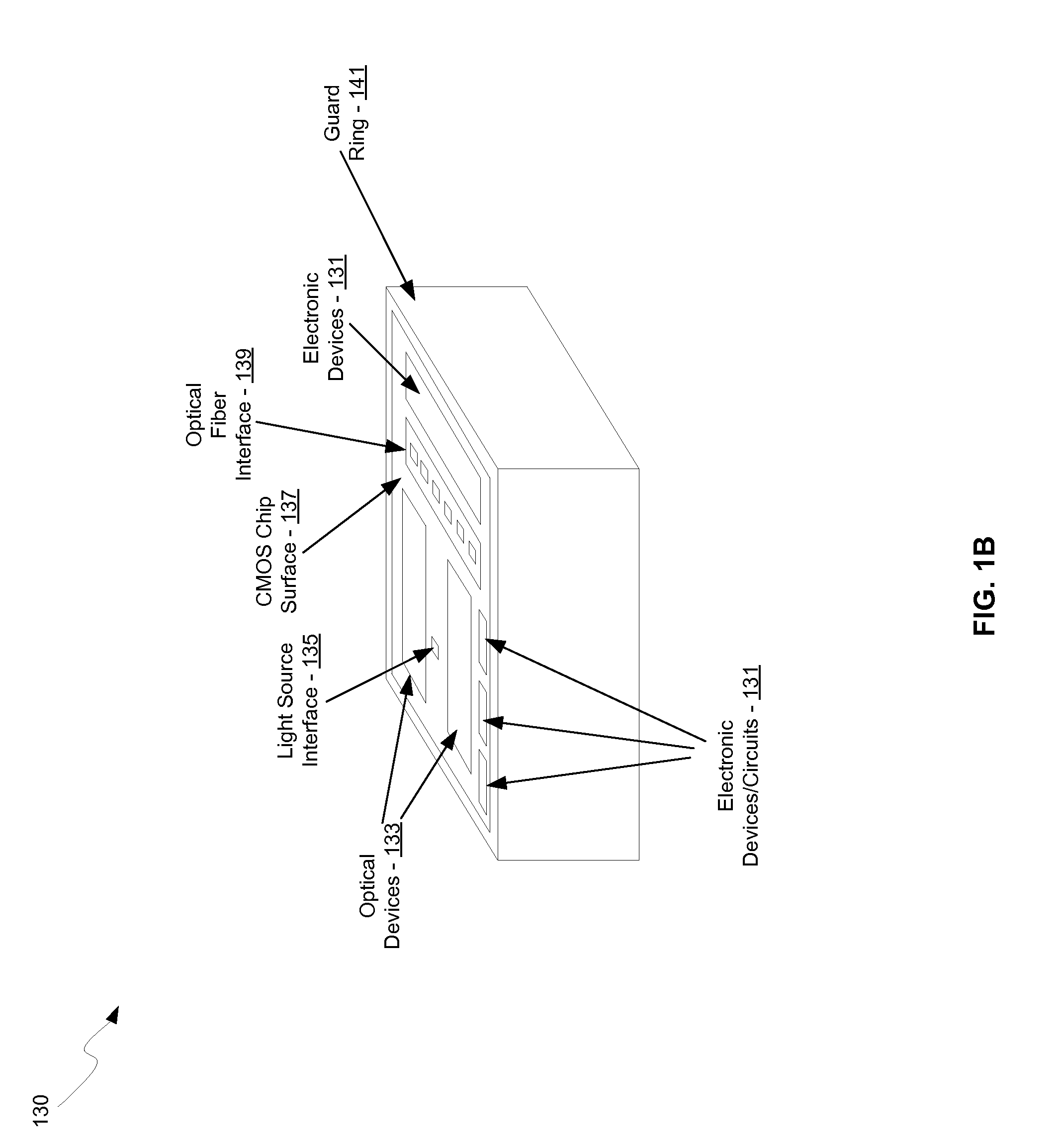
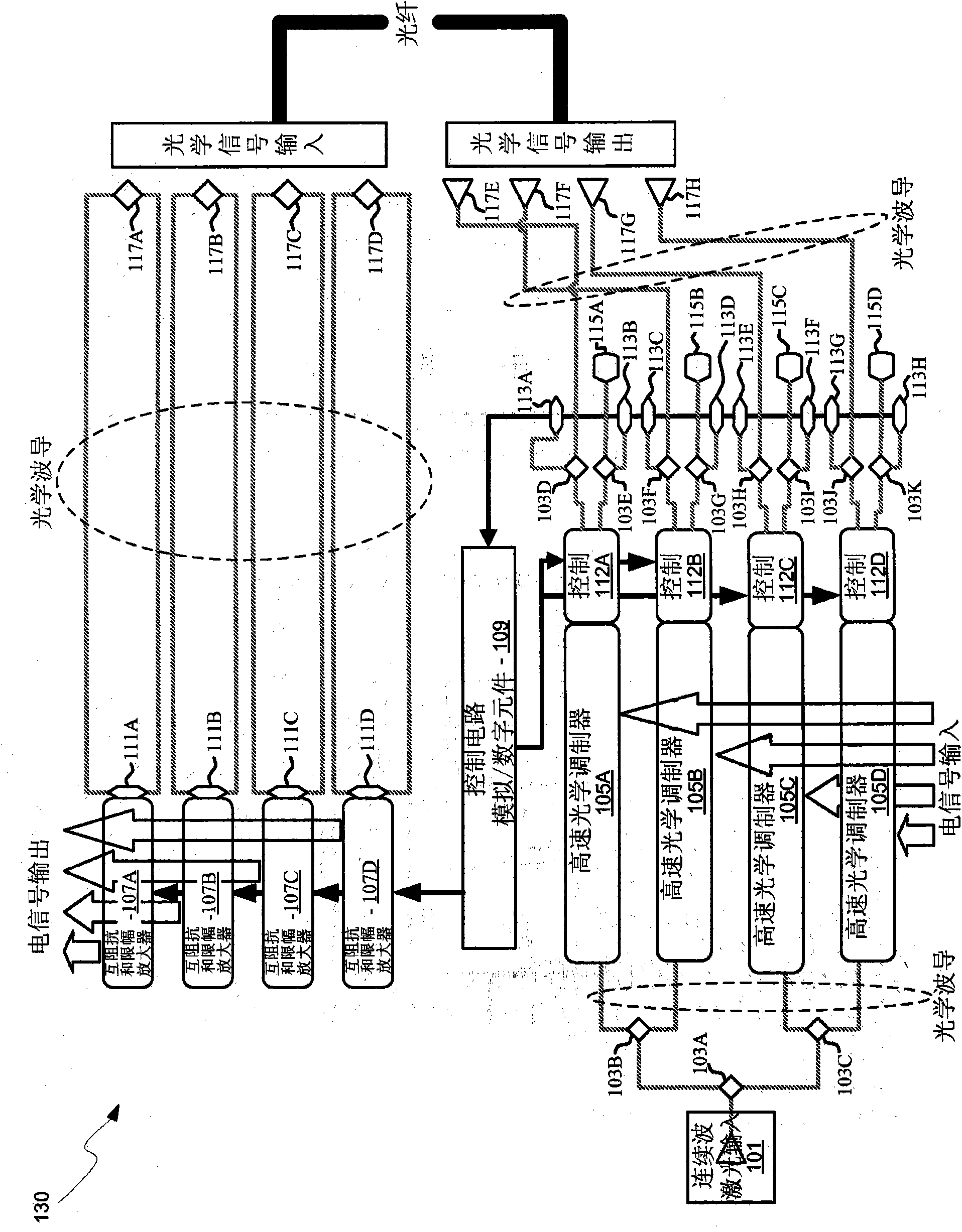
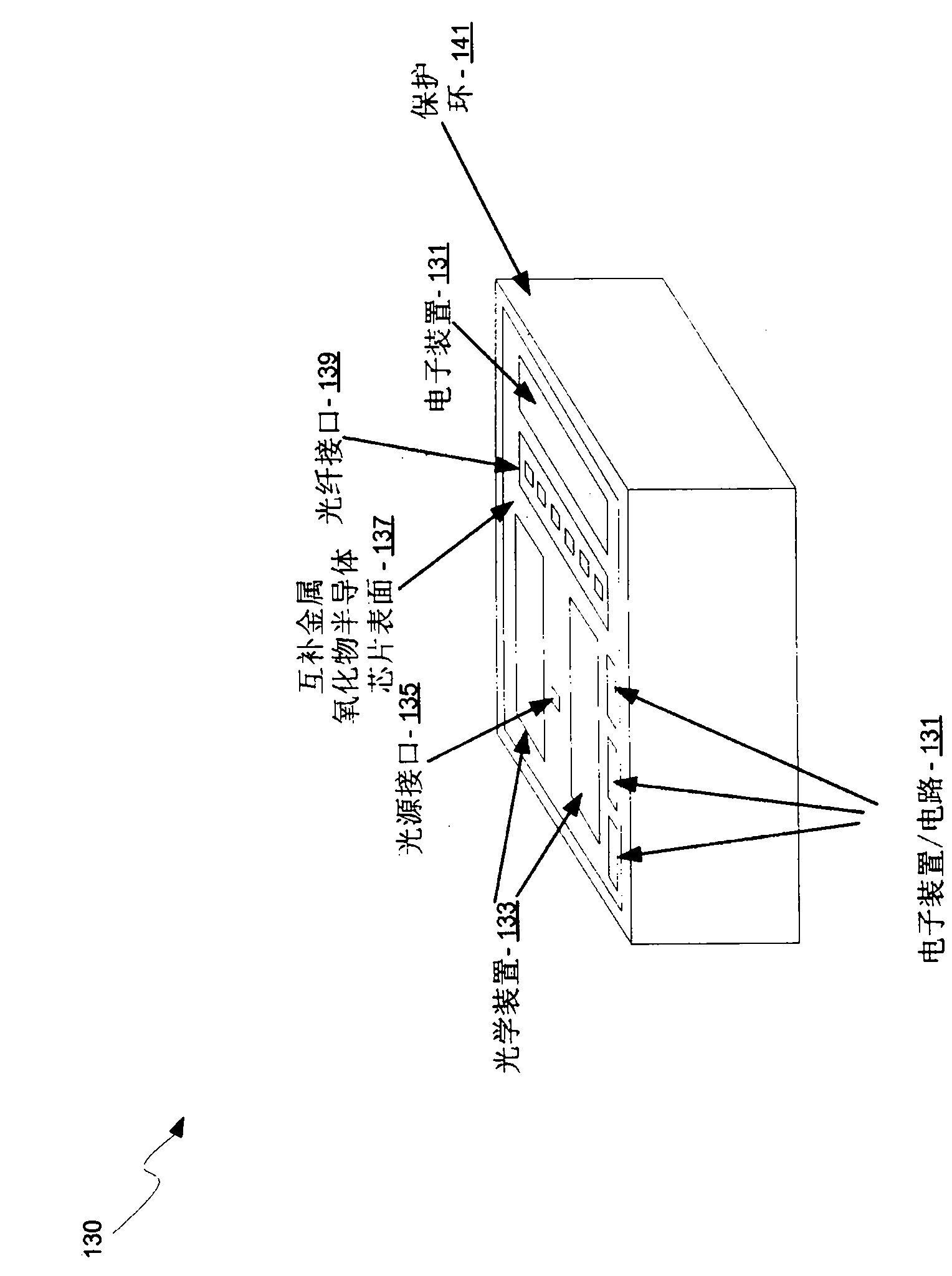
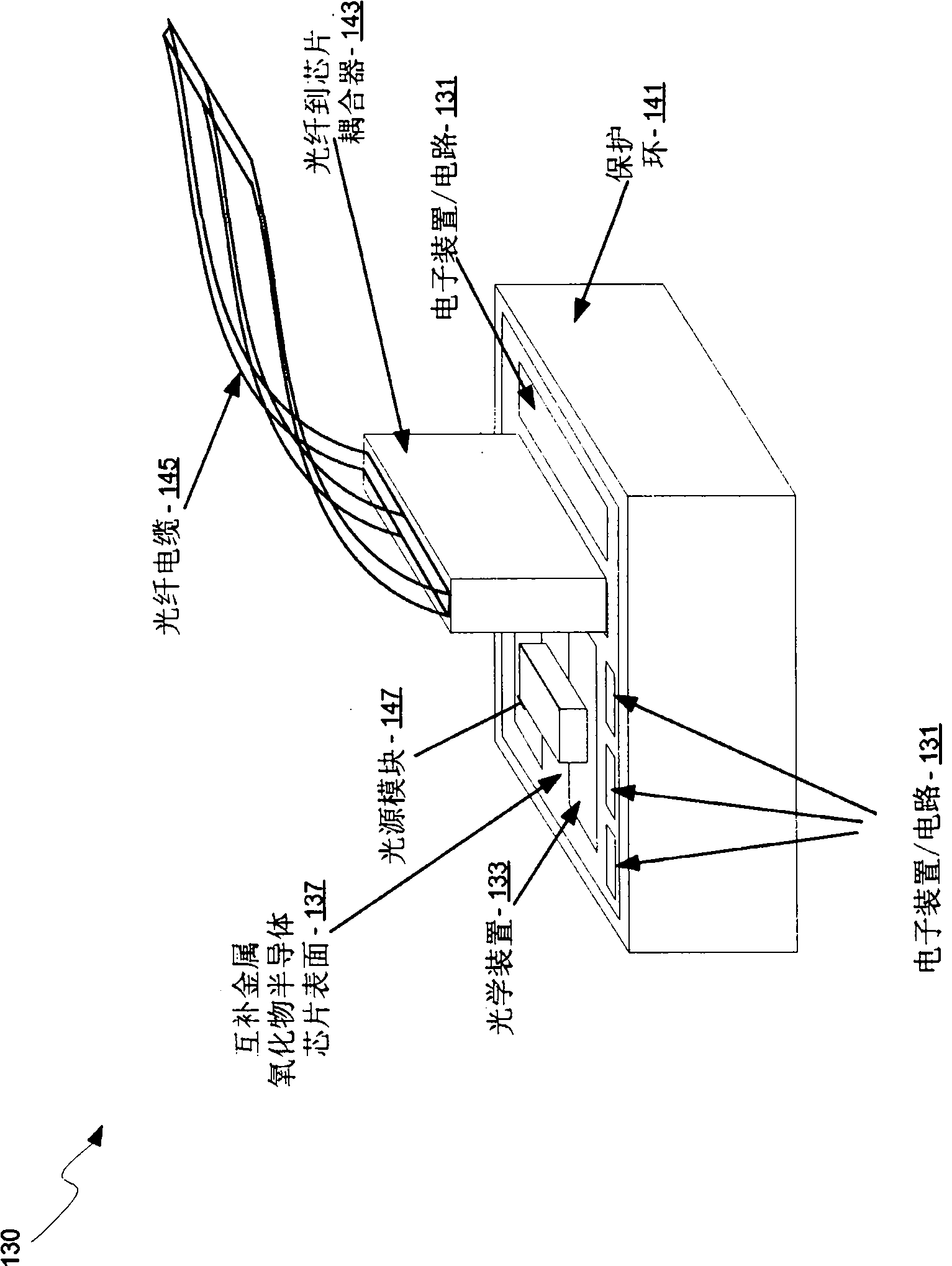
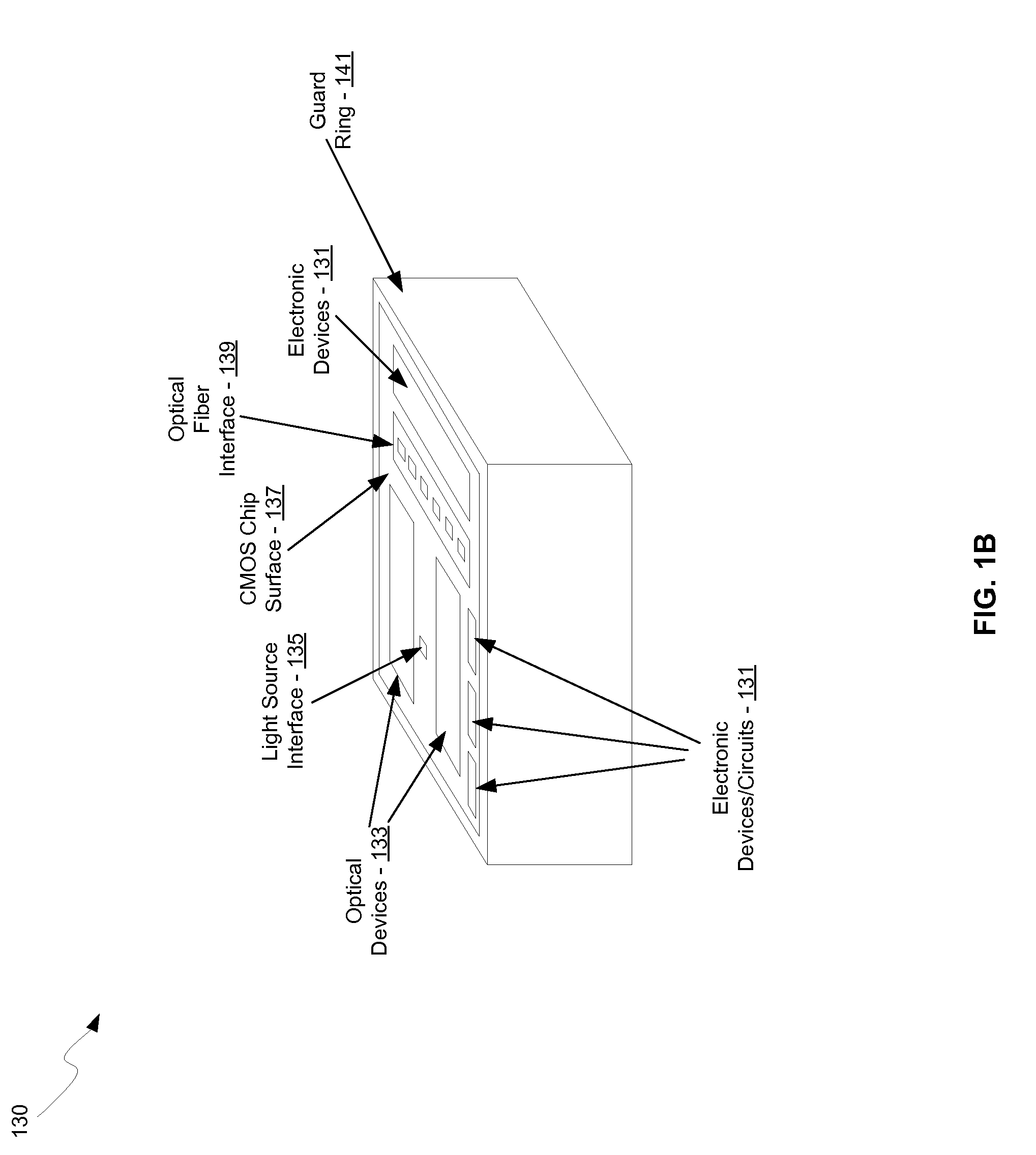
Method and system for optoelectronics transceivers integrated on a CMOS chip
Methods and systems for optoelectronics transceivers integrated on a CMOS chip are disclosed and may include receiving optical signals from optical fibers via grating couplers on a top surface of a CMOS chip, which may include a guard ring. Photodetectors may be integrated in the CMOS chip. A CW optical signal may be received from a laser source via grating couplers, and may be modulated using optical modulators, which may be Mach-Zehnder and / or ring modulators. Circuitry in the CMOS chip may drive the optical modulators. The modulated optical signal may be communicated out of the top surface of the CMOS chip into optical fibers via grating couplers. The received optical signals may be communicated between devices via waveguides. The photodetectors may include germanium waveguide photodiodes, avalanche photodiodes, and / or heterojunction diodes. The CW optical signal may be generated using an edge-emitting and / or a vertical-cavity surface emitting semiconductor laser.
Owner:LUXTERA
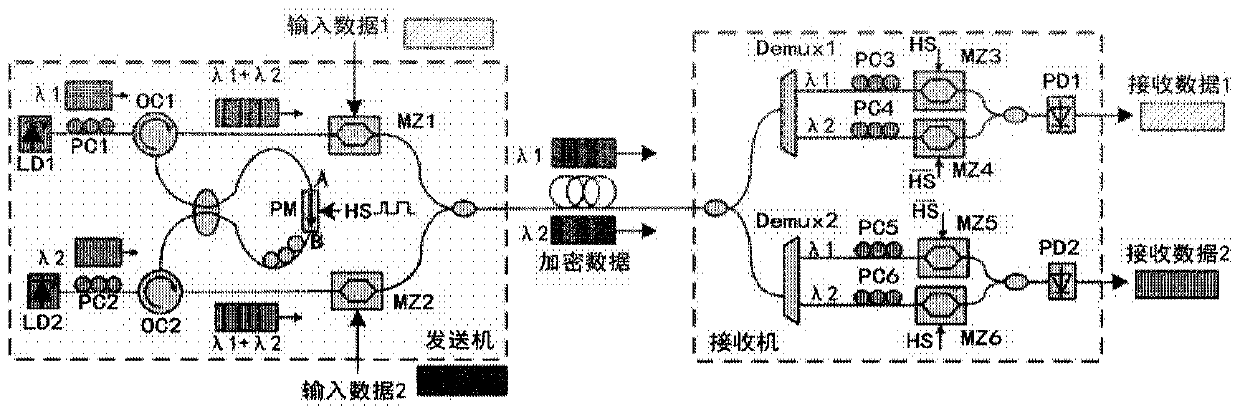
Optical frequency hopping system based on optical circulator and transmitter
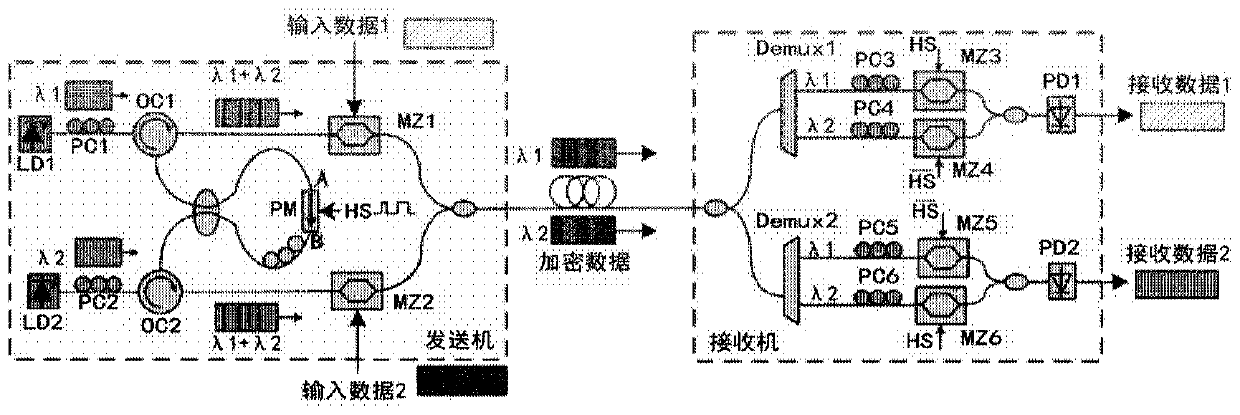
ActiveCN109981174AImplement encrypted transmissionReliable transmissionRing-type electromagnetic networksEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesConfidentialityCarrier signal
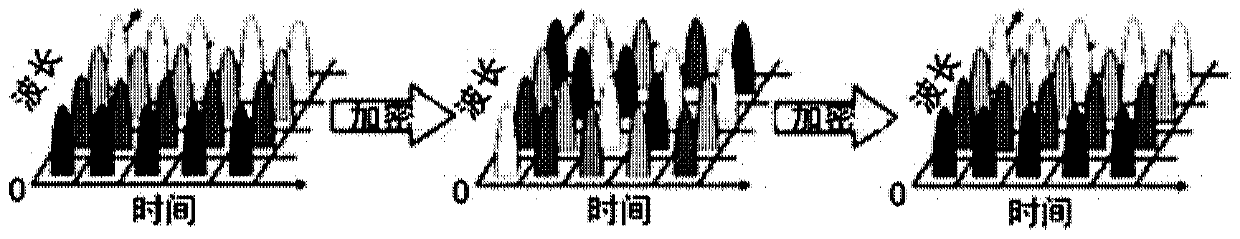
The invention discloses an optical frequency hopping system based on an optical circulator and a transmitter. The optical frequency hopping system includes: an annular modulation unit, whereinthe annular modulation unit comprises a plurality of optical circulators; the first port of each optical circulator receives different optical carriers; a second port of each optical circulator is connected with an optical coupler, each optical coupler is connected with a phase modulator and is combined with frequency hopping coding in a pseudo-random code generator to realize coding modulation of an optical carrier signal, and a third port of each optical circulator respectively outputs the coded and modulated optical carrier signal; a transmitter which is internally provided with the annular modulation unit and is used for transmitting the optical carrier signal encrypted by the annular modulation unit; a receiver which is used for receiving the encrypted optical carrier signal and decrypting the encrypted optical carrier signal through frequency hopping coding; and an optical fiber which is used for realizing carrier communication between the transmitter and the receiver. According to the invention, high-speed optical frequency hopping coding can be realized, a flexible and simple unit structure is provided, expansion to a multi-channel optical frequency hopping system is facilitated, and a communication system with higher confidentiality is provided.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and system for split voltage domain transmitter circuits
ActiveUS20090087196A1Electromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversBoundary valuesRing modulation
Methods and systems for split voltage domain transmitter circuits are disclosed and may include amplifying a received signal in a plurality of partial voltage domains. Each of the partial voltage domains may be offset by a DC voltage from the other partial voltage domains. A sum of the plurality of partial domains may be equal to a supply voltage of the integrated circuit. A series of diodes may be driven in differential mode via the amplified signals. An optical signal may be modulated via the diodes, which may be integrated in a Mach-Zehnder or a ring modulator. The amplified signals may be communicated to the diodes, connected in a distributed configuration, via even-mode coupled transmission lines. The partial voltage domains may be generated via stacked source follower or emitter follower circuits. The voltage domain boundary value may be at one half the supply voltage due to symmetric stacked circuits.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
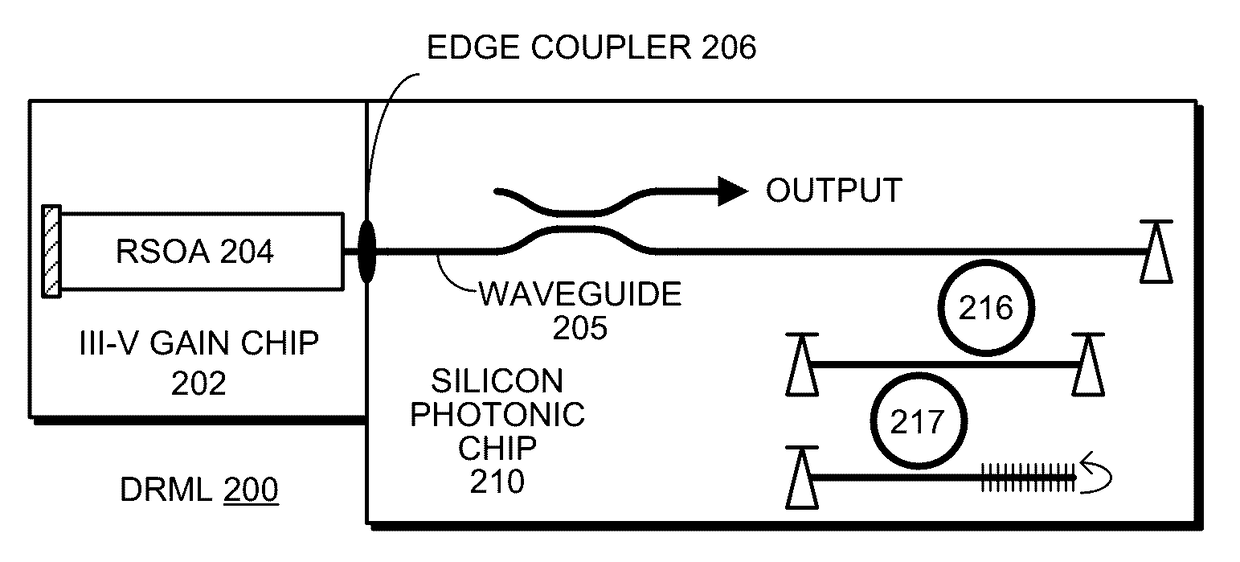
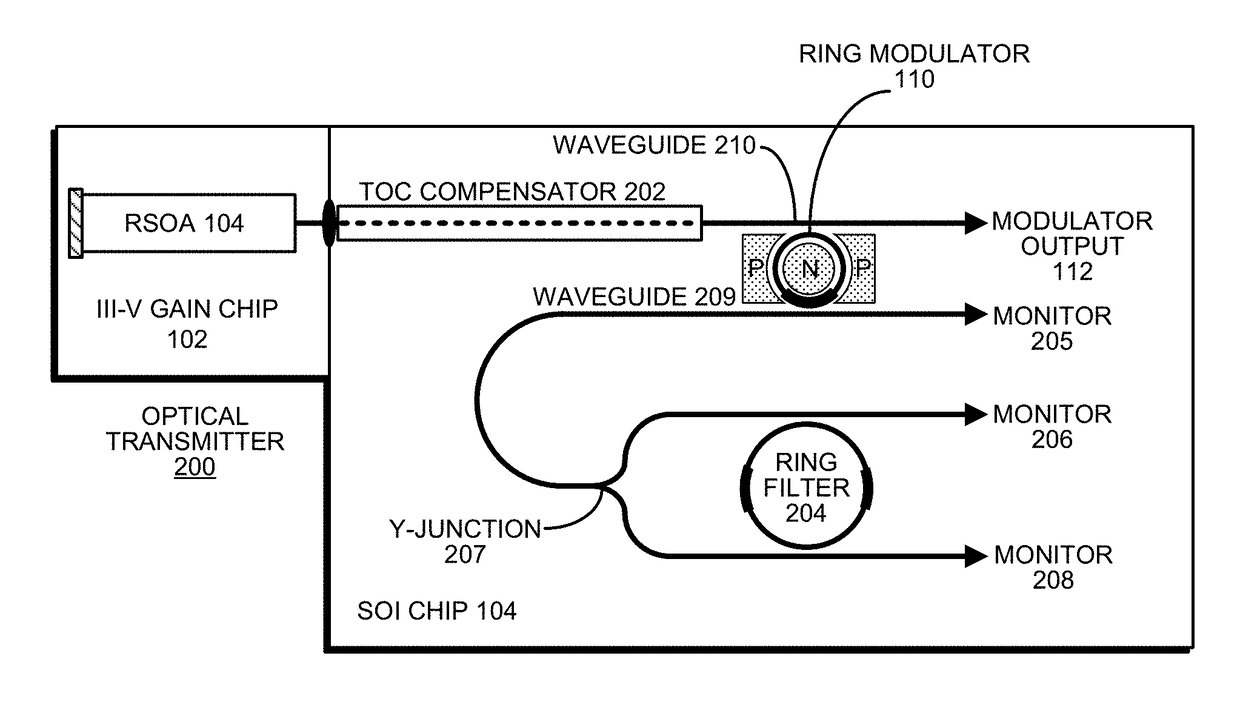
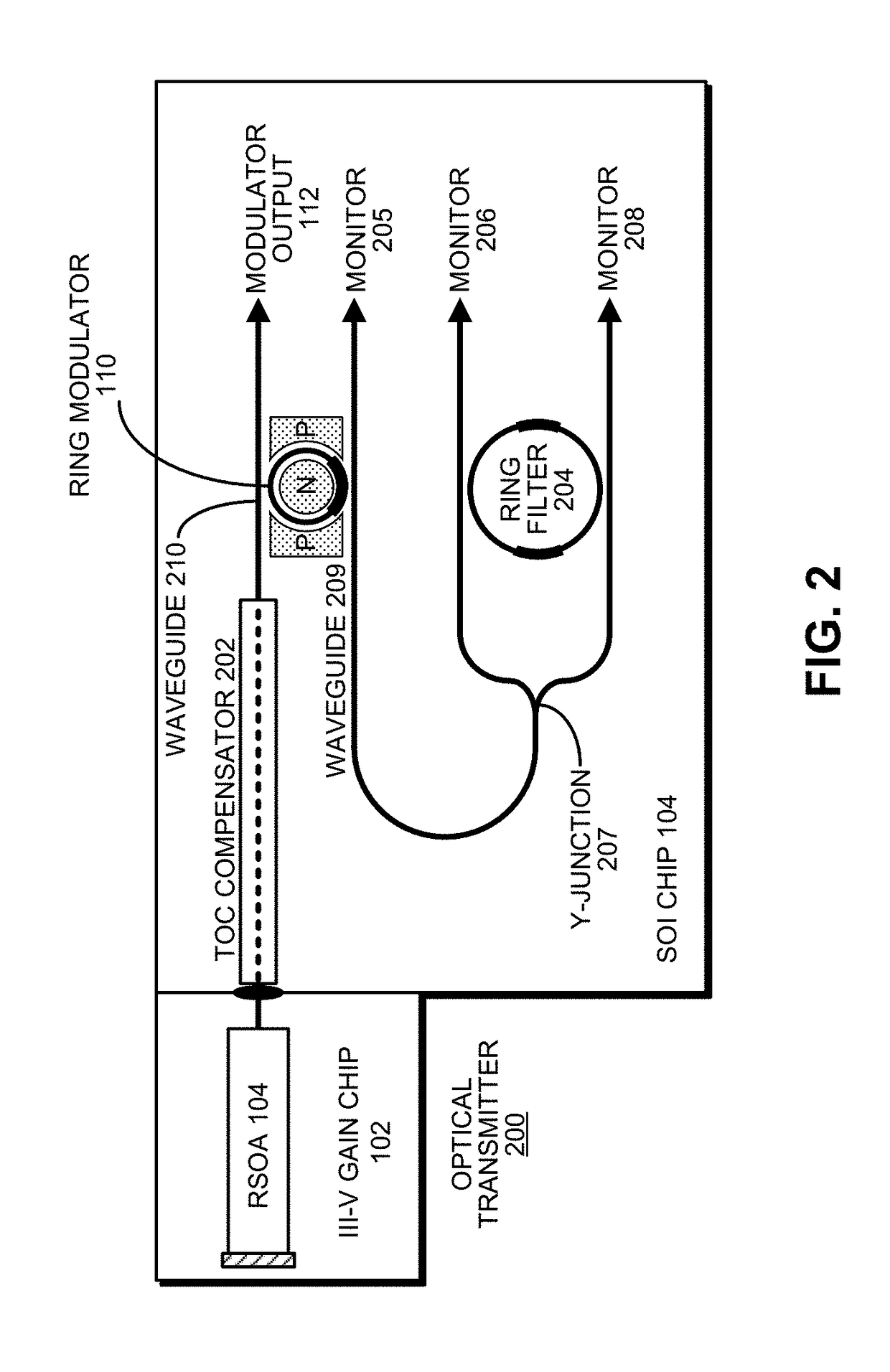
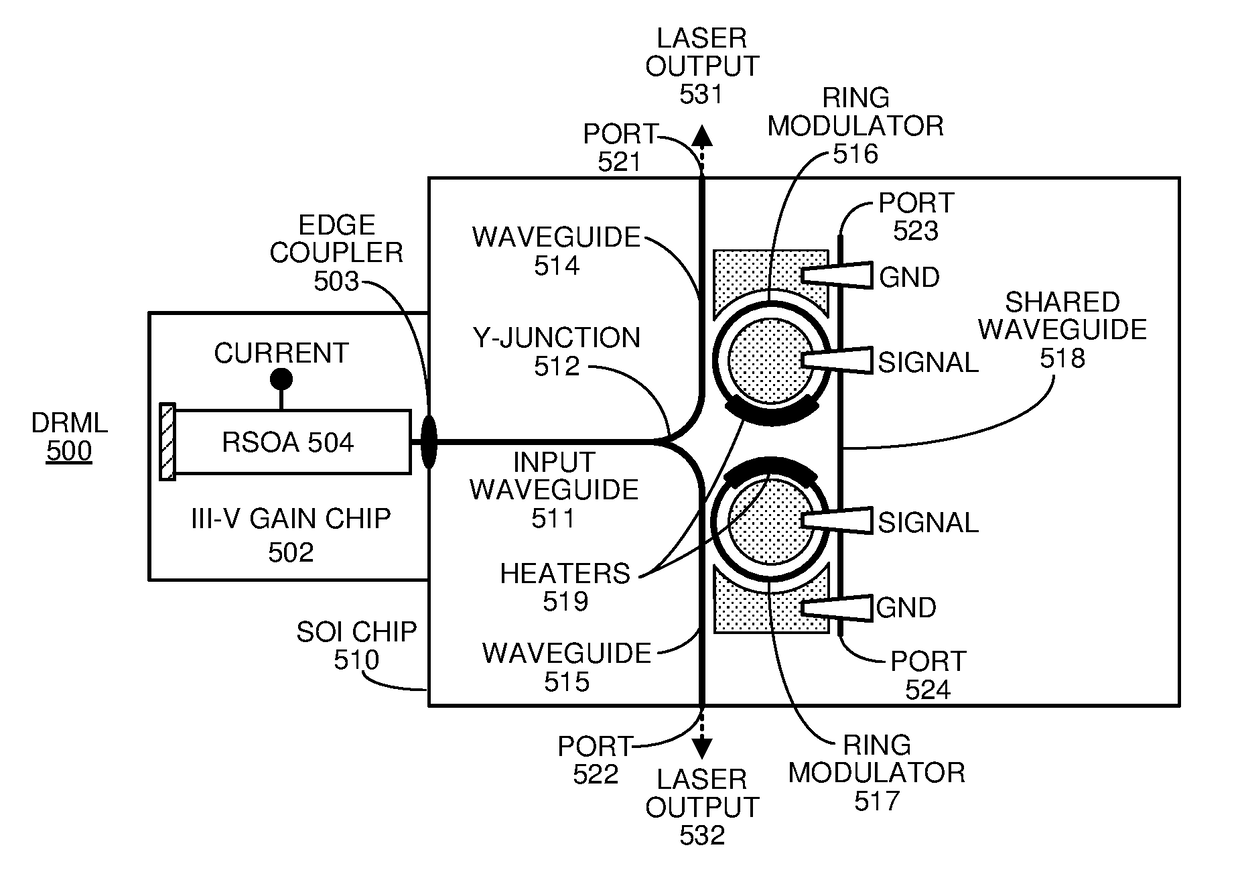
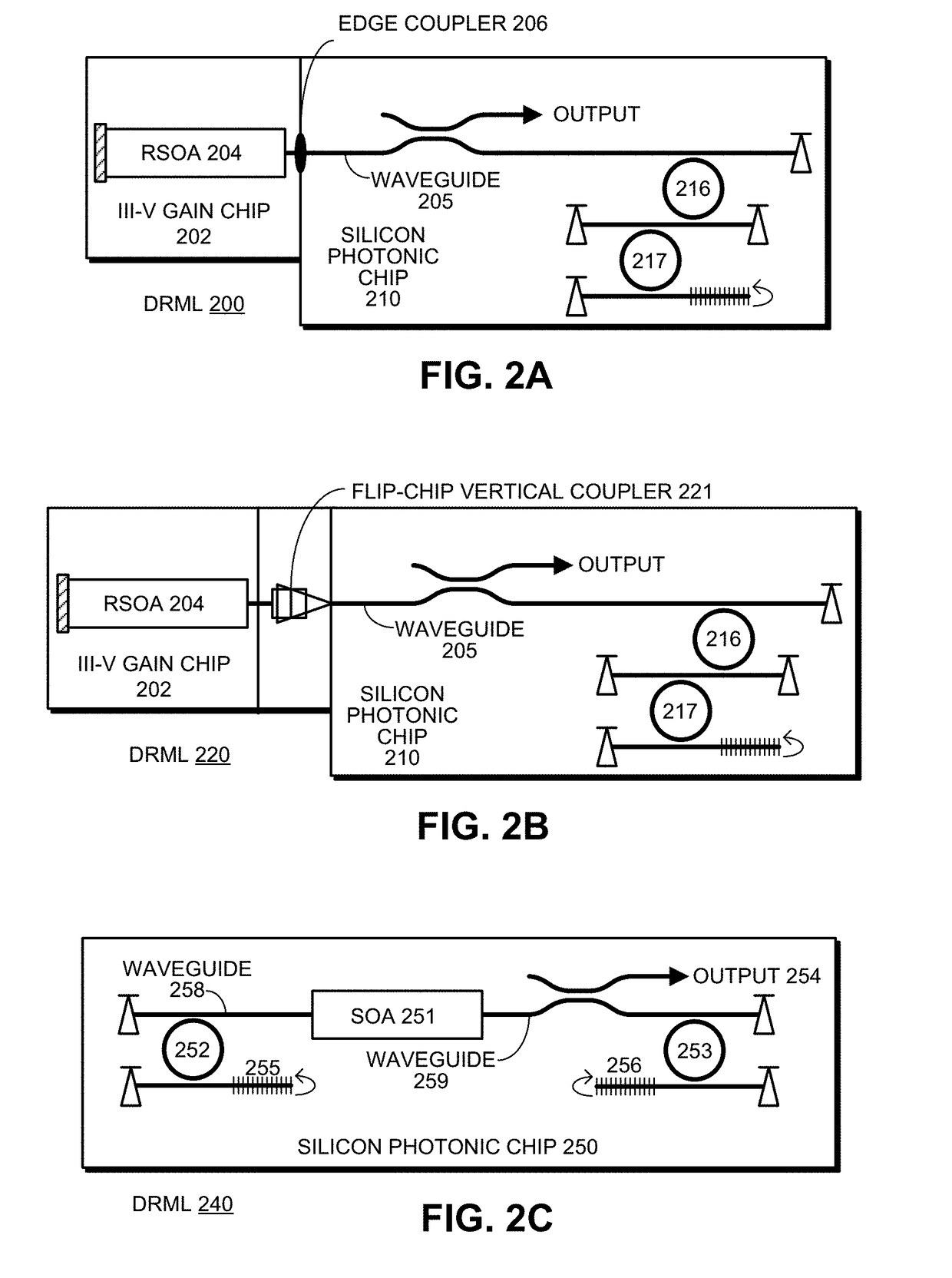
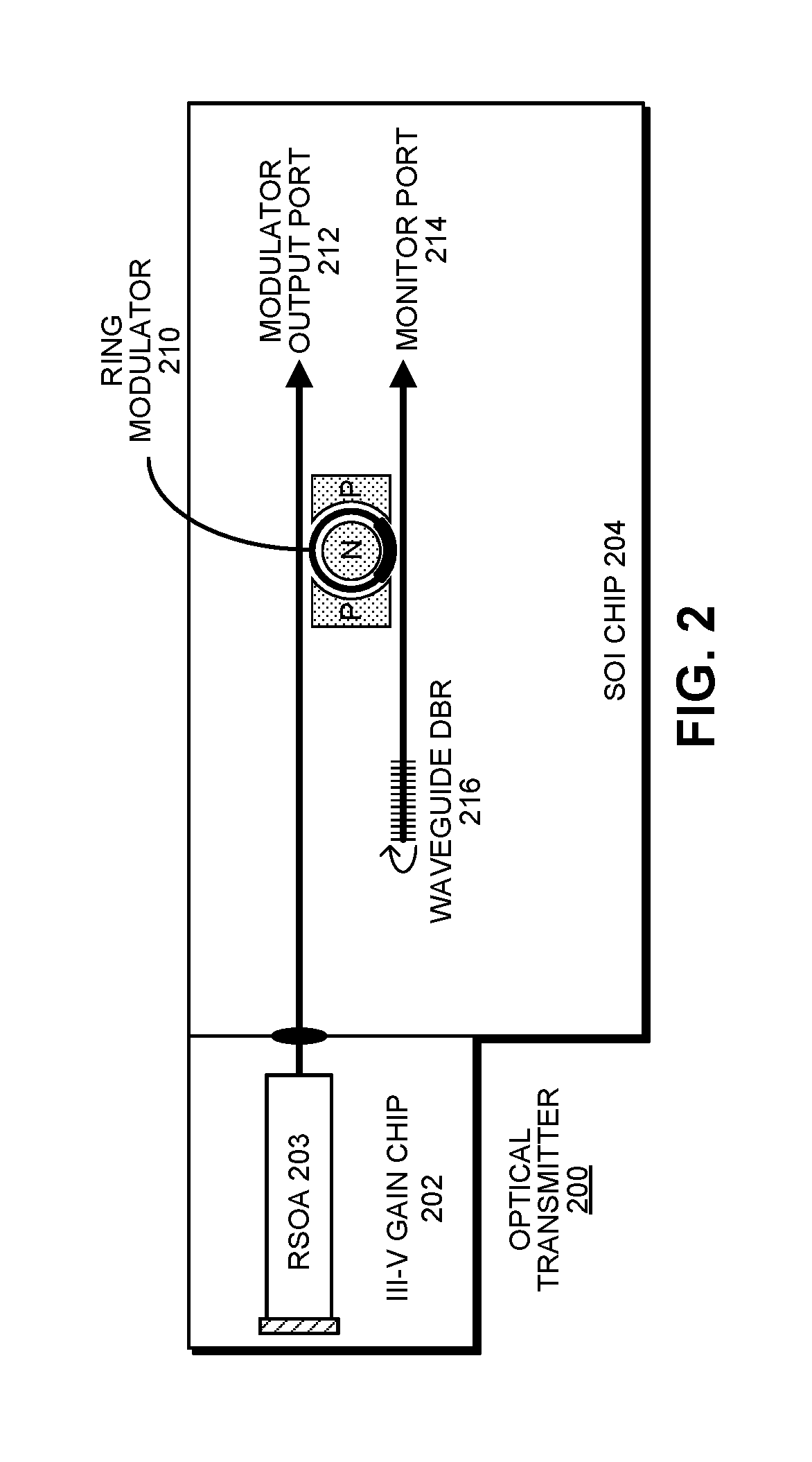
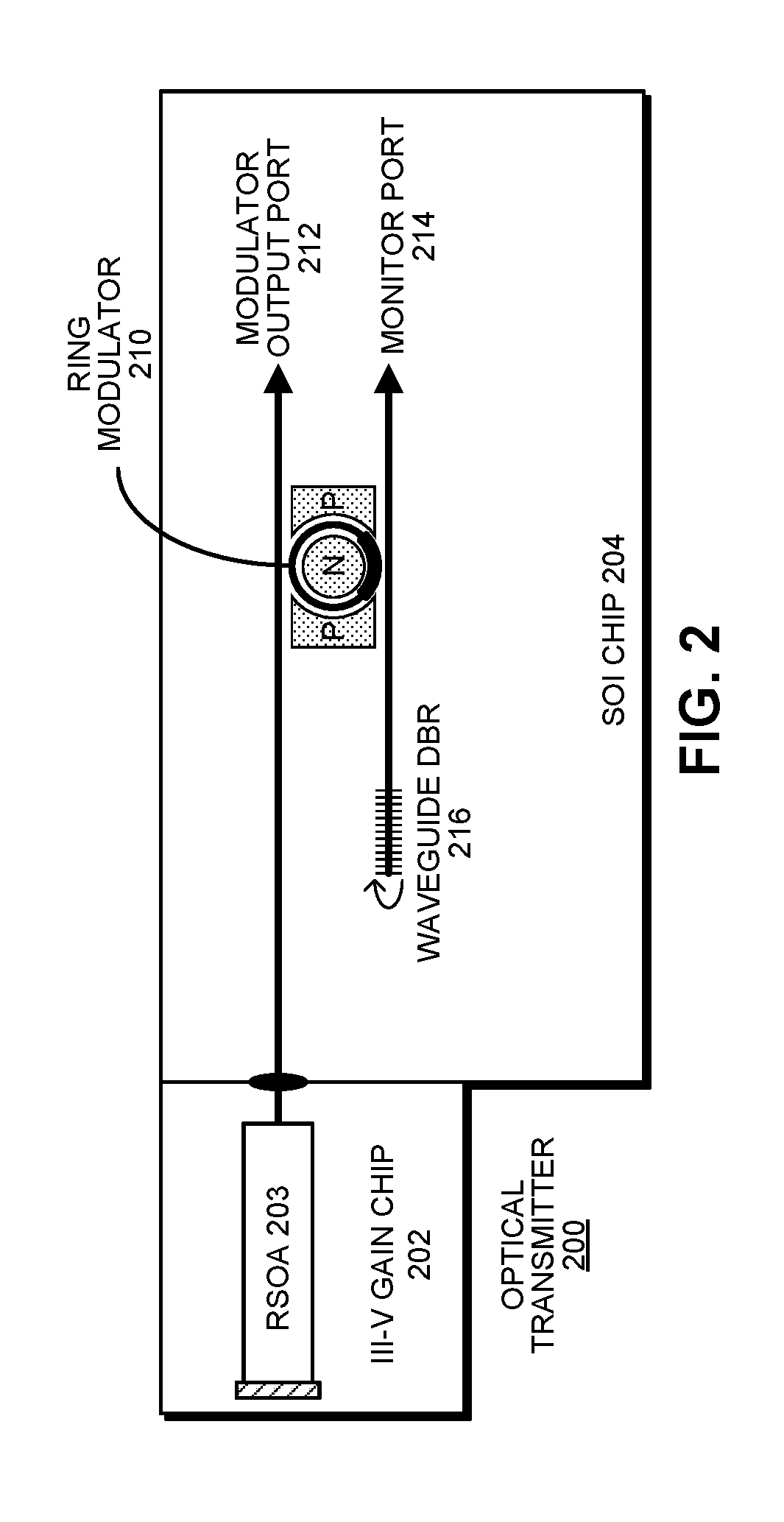
WAVELENGTH-TUNABLE III-V/Si HYBRID OPTICAL TRANSMITTER
ActiveUS20180143461A1Large wavelength tuning rangeEasy to adjustLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsEngineering
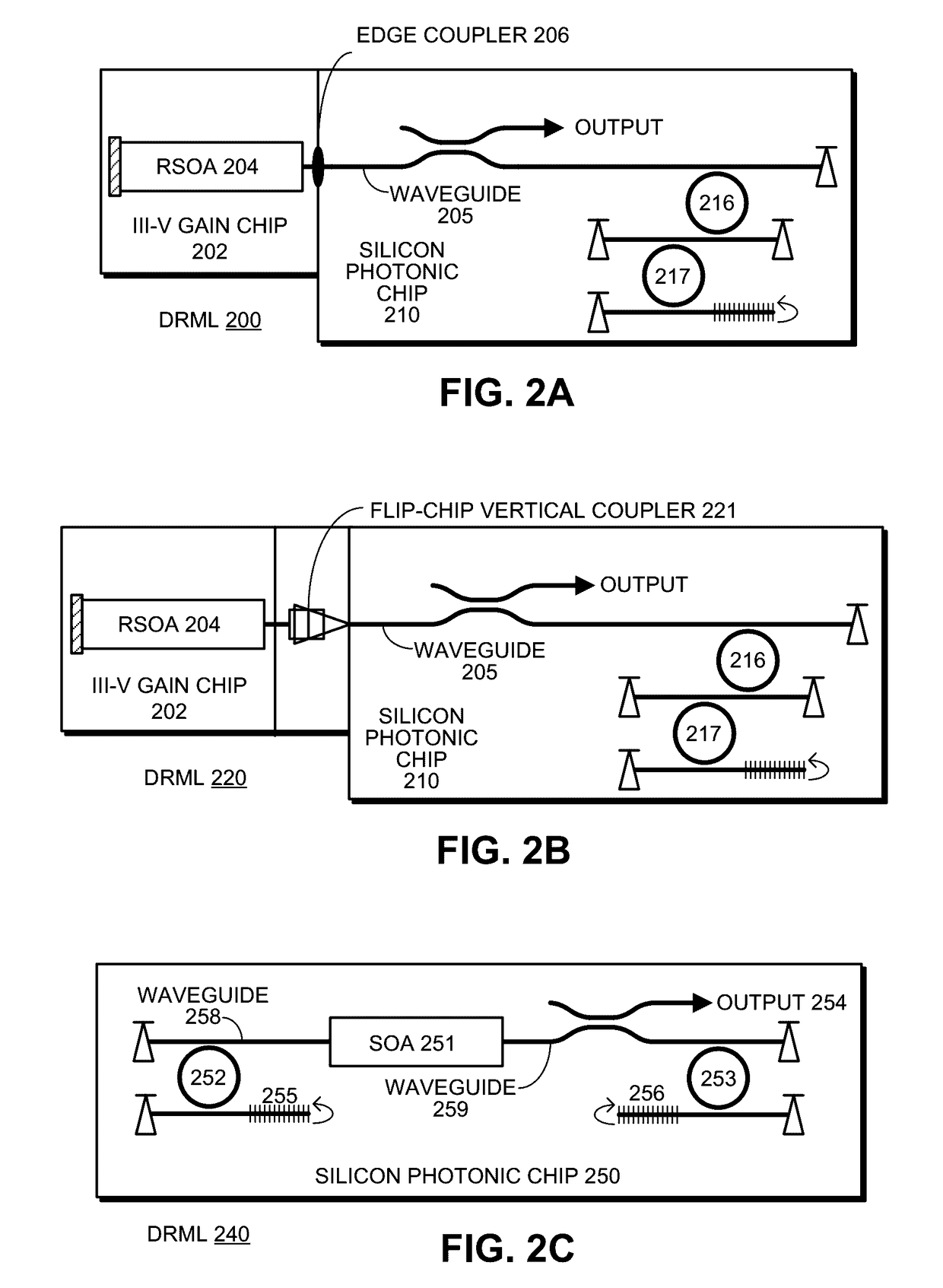
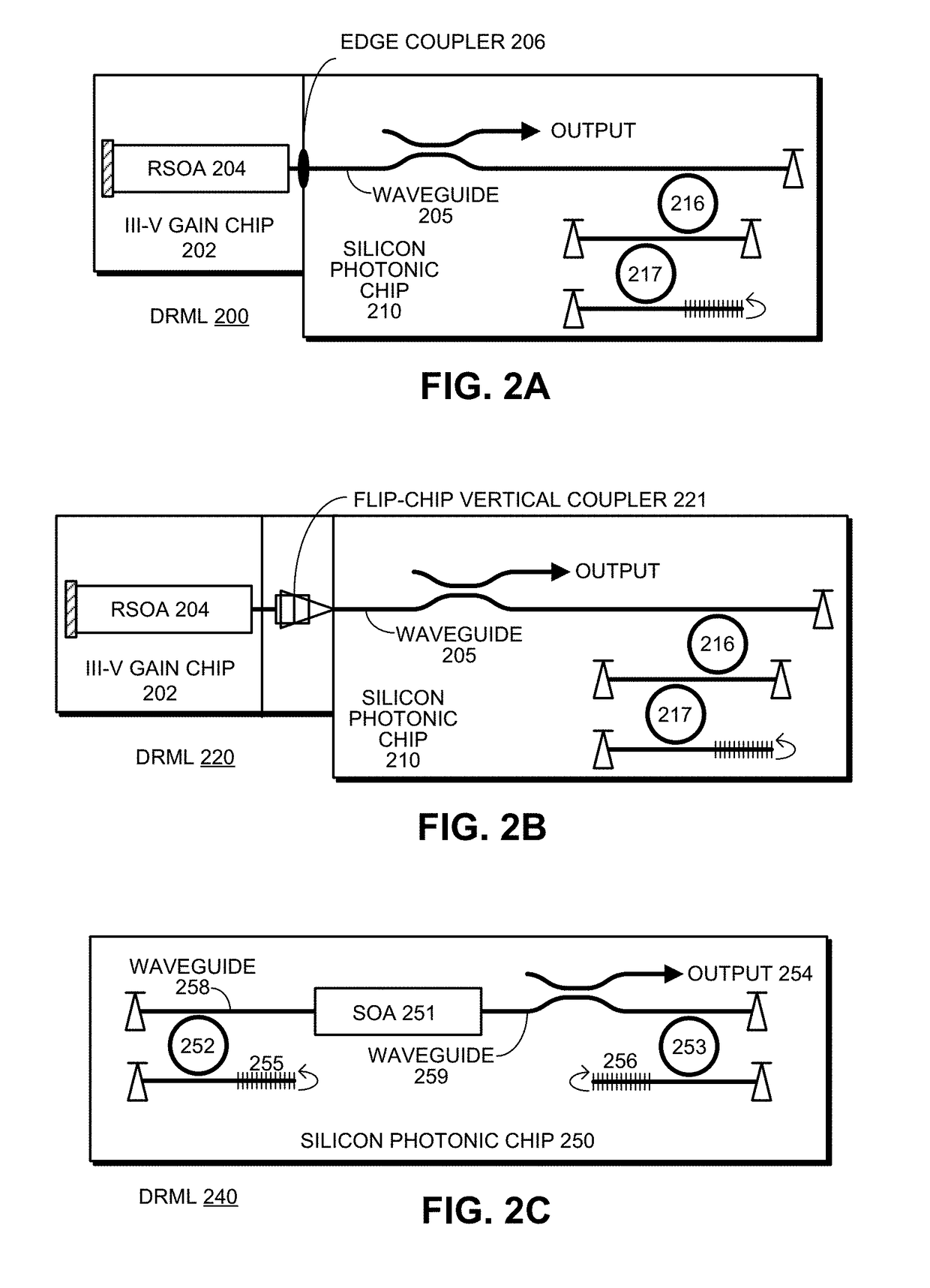
An optical transmitter includes a reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA) coupled to an input end of a first optical waveguide. An end of the first optical waveguide provides a transmitter output for the optical transmitter. Moreover, a section of the first optical waveguide between the input end and the output end is optically coupled to a ring modulator that modulates an optical signal based on an electrical input signal. A passive ring filter (or a 1×N silicon-photonic switch and a bank of band reflectors) is connected to provide a mirror that reflects light received from the second optical waveguide back toward the RSOA to form a lasing cavity. Moreover, the ring modulator and the passive ring filter have different sizes, which causes a Vernier effect that provides a large wavelength tuning range for the lasing cavity in response to tuning the ring modulator and the passive ring filter.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Hybrid electro-optic annular modulator of Si-PLZT heterojunction structure based on SOI
ActiveCN105954892APossesses the characteristic of electro-optic modulationEvenly distributedNon-linear opticsModulation bandwidthHybrid type
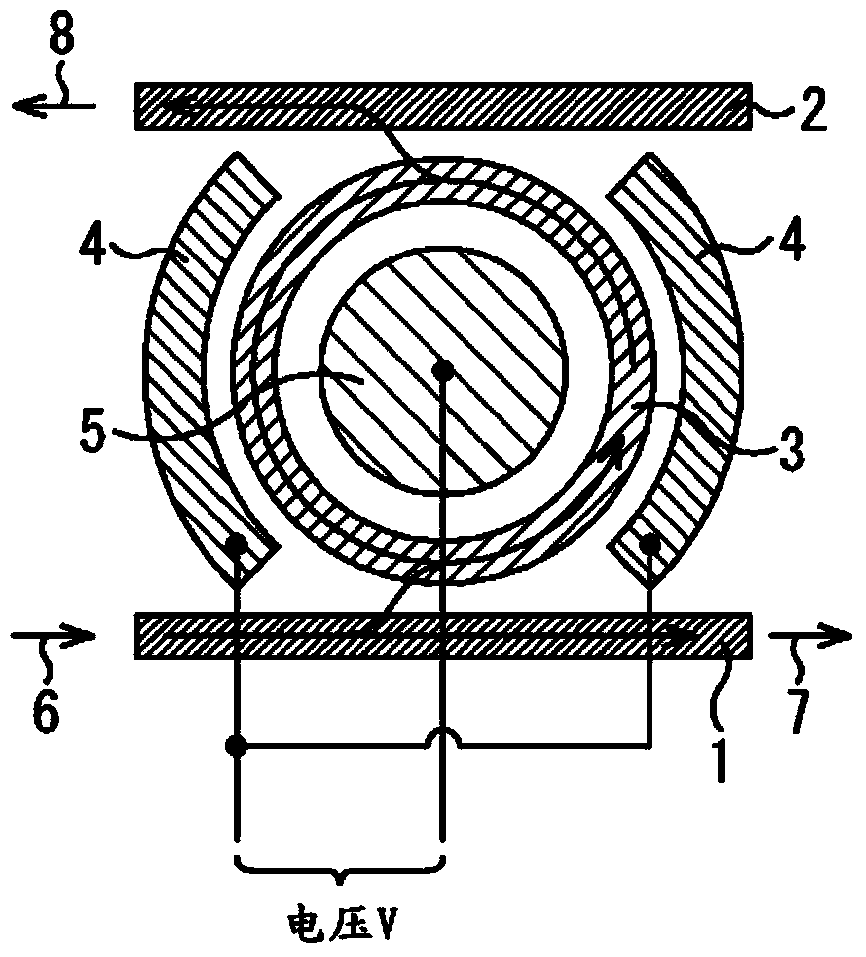
The invention discloses a hybrid electro-optic annular modulator of a Si-PLZT heterojunction structure based on an SOI. The hybrid electro-optic annular modulator comprises a silicon rectangular panel straight waveguide and a silicon rectangular panel annular waveguide, wherein the silicon rectangular panel straight waveguide and the silicon rectangular panel annular waveguide are coupled, the silicon rectangular panel straight waveguide is used as a direct-connection end of the hybrid electro-optic annular modulator, and the silicon rectangular panel annular waveguide is used as a resonant ring of the hybrid electro-optic annular modulator; the silicon rectangular panel straight waveguide and the silicon rectangular panel annular waveguide are completely wrapped by a PLZT rectangular channel to form a Si-PLZT hybrid structure; the inner side and the outer side of the annular waveguide part are provided with a pair of semi-wrapped curved coplanar traveling wave electrode couples, and the hybrid electro-optic annular modulator is electrified to be modulated by virtue of the curved coplanar traveling wave electrode couples, so that a refractive index of a PLZT rectangular channel is changed. The hybrid electro-optic annular modulator has the characteristics of high modulation sensitivity, small device size, good reliability, large modulation bandwidth and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
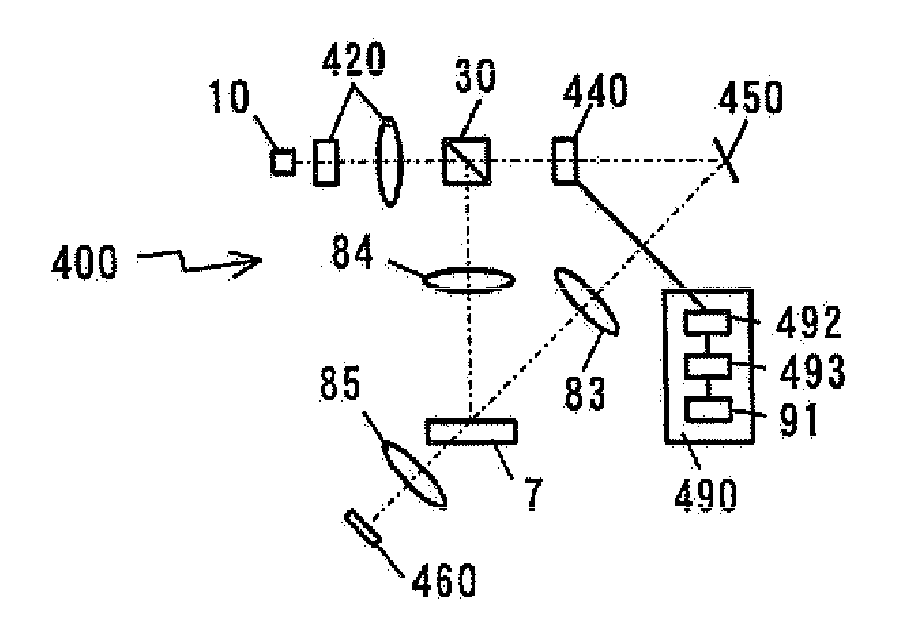
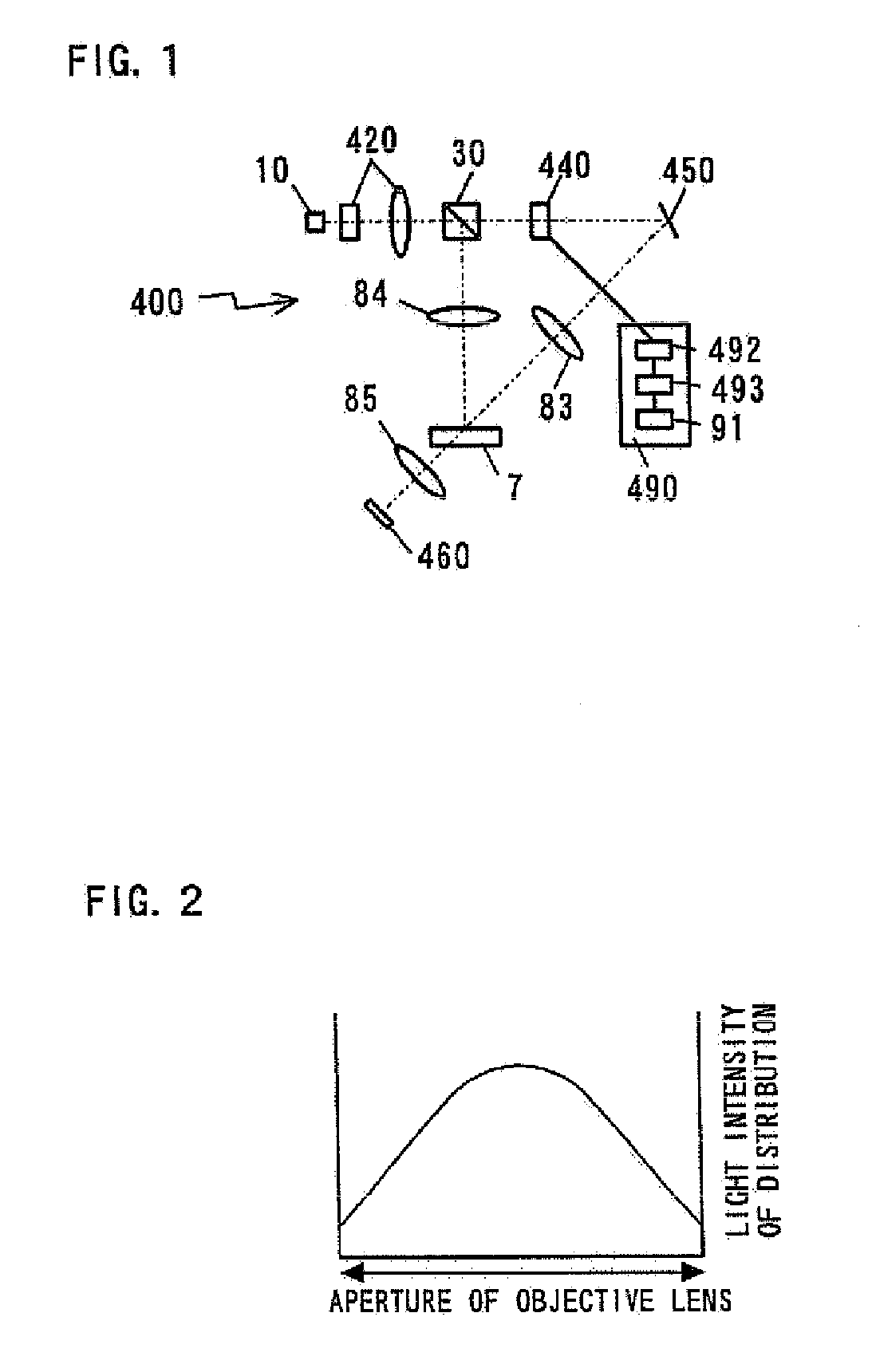
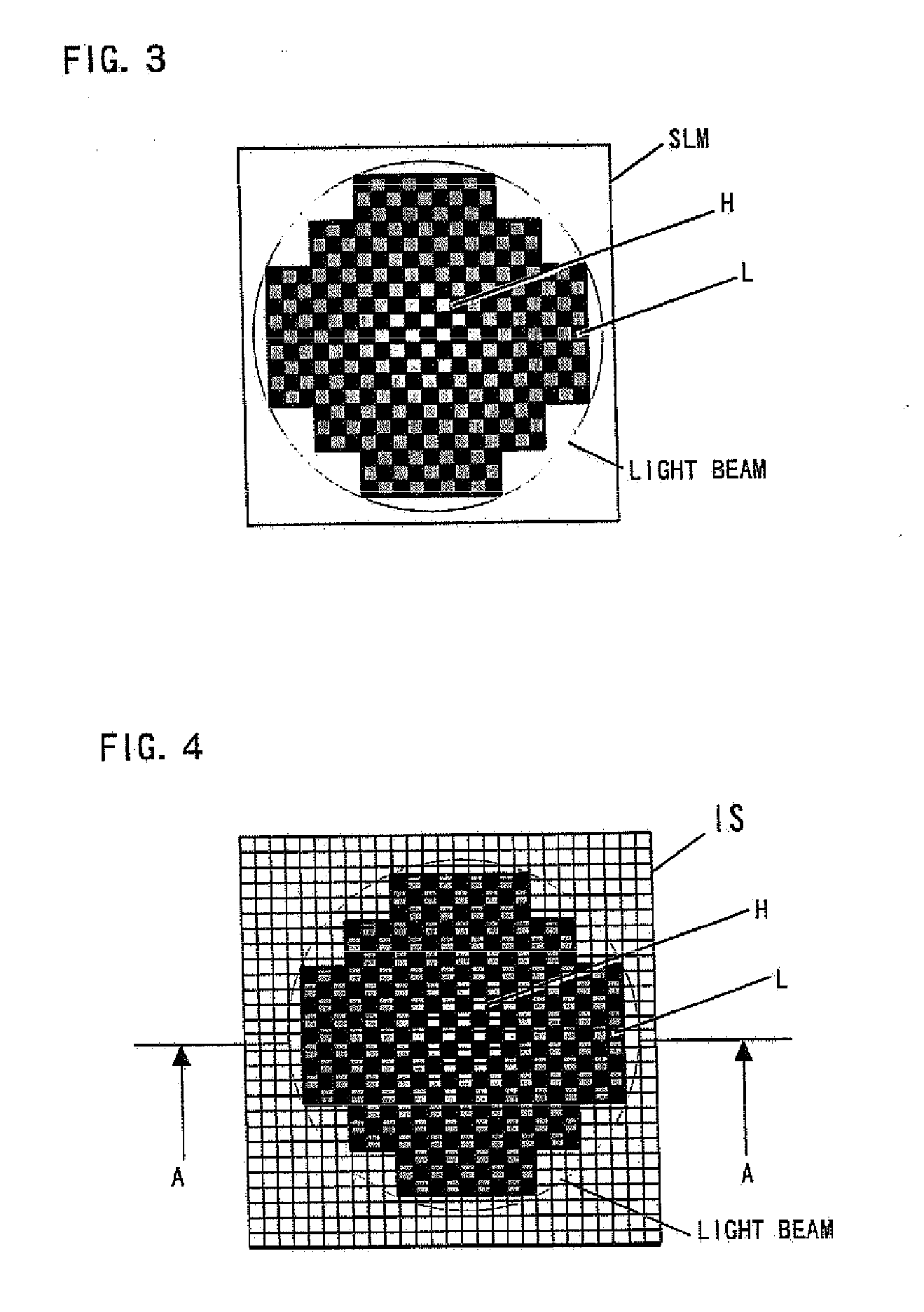
Hologram Recording and Reproducing Apparatus and Hologram Recording Method
InactiveUS20080247010A1Improve recording densityIncrease recording capacityRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsSpatial light modulatorOptical axis
There is provided a hologram recording and reproducing apparatus for a hologram recording medium that stores optical interference fringes therein as a diffraction grating generated by coherent reference light and signal light. The hologram recording and reproducing apparatus includes a control circuit that is connected to a spatial light modulator and controls each pixel in such a way that the reference light is modulated according to information data to produce the signal light. The control circuit spatially classifies a plurality of pixels in the spatial light modulator into a central modulation area disposed on the optical axis and at least one annular modulation area sequentially disposed around the central modulation area in a concentric manner, and controls the pixels in the central modulation area and the pixels in the annular modulation area using respective different recording modulation methods to deliver the signal light through the central modulation area and the annular modulation area.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Dual-ring-modulated laser that uses push-pull modulation
A dual-ring-modulated laser includes a gain medium having a reflective end coupled to a gain-medium reflector and an output end coupled to a reflector circuit to form a lasing cavity. This reflector circuit comprises: a first ring modulator; a second ring modulator; and a shared waveguide that optically couples the first and second ring modulators. The first and second ring modulators have resonance peaks, which are tuned to have an alignment separation from each other. During operation, the first and second ring modulators are driven in opposing directions based on the same electrical input signal, so the resonance peaks of the first and second ring modulators shift wavelengths in the opposing directions during modulation. The modulation shift for each of the resonance peaks equals the alignment separation, so the resonance peaks interchange positions during modulation to cancel out reflectivity changes in the lasing cavity caused by the modulation.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
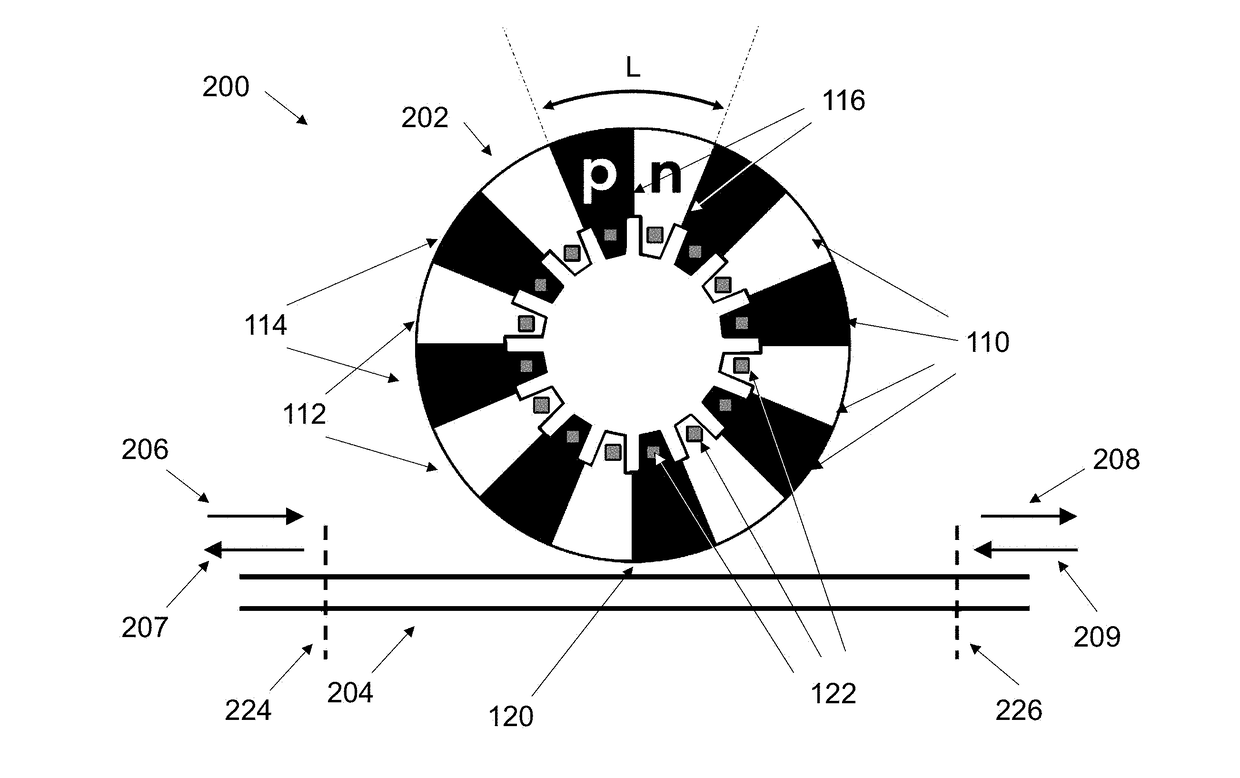
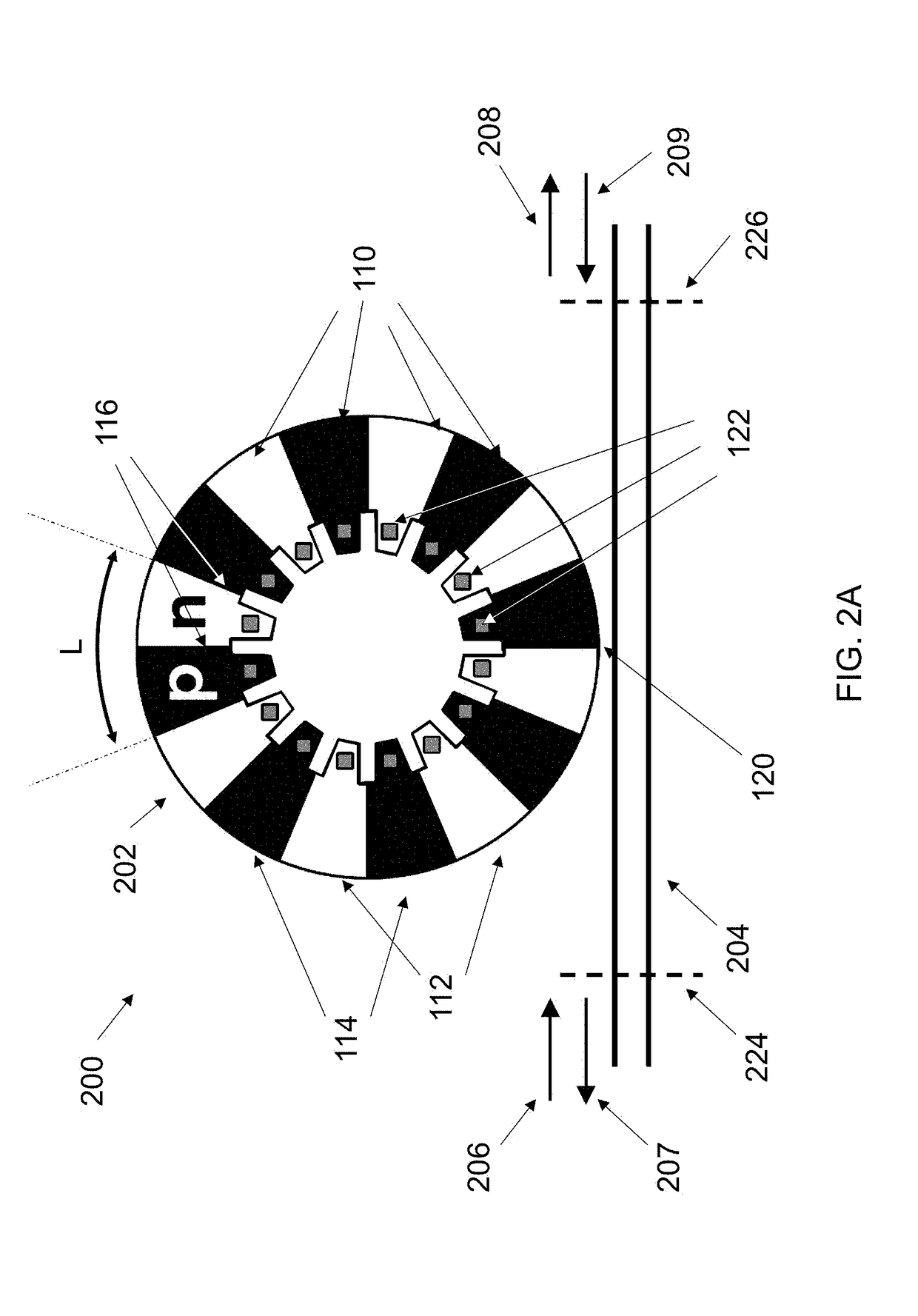
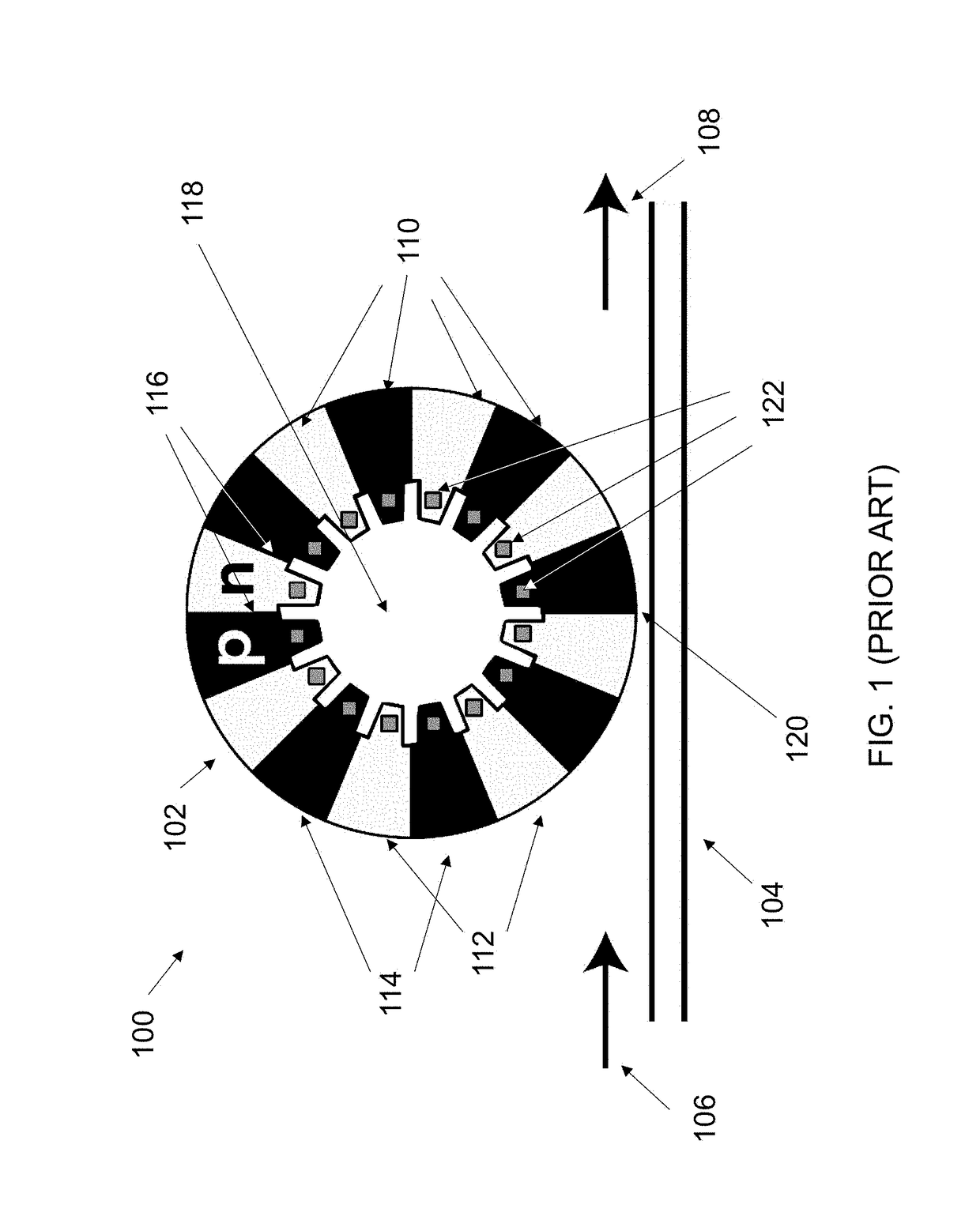
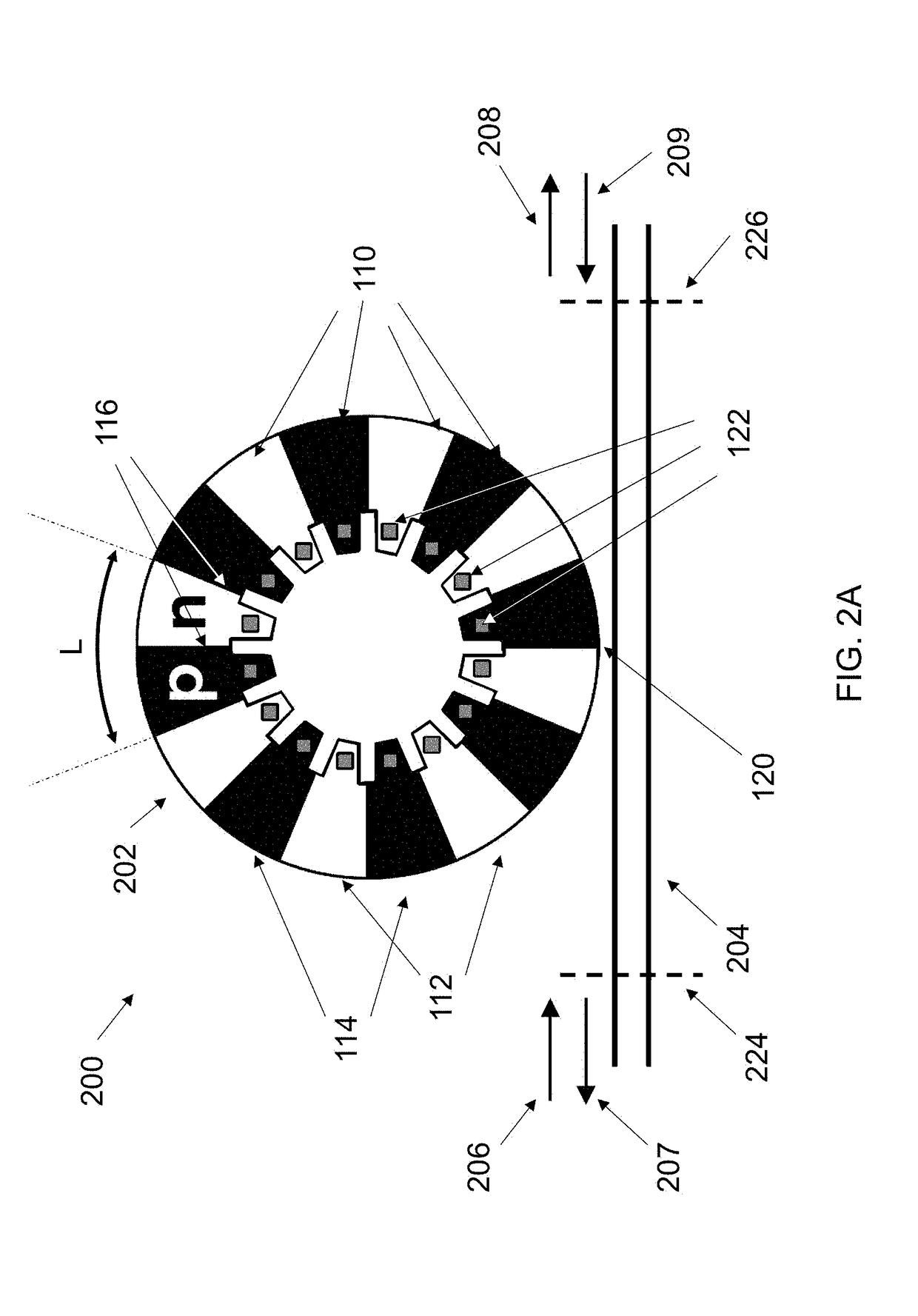
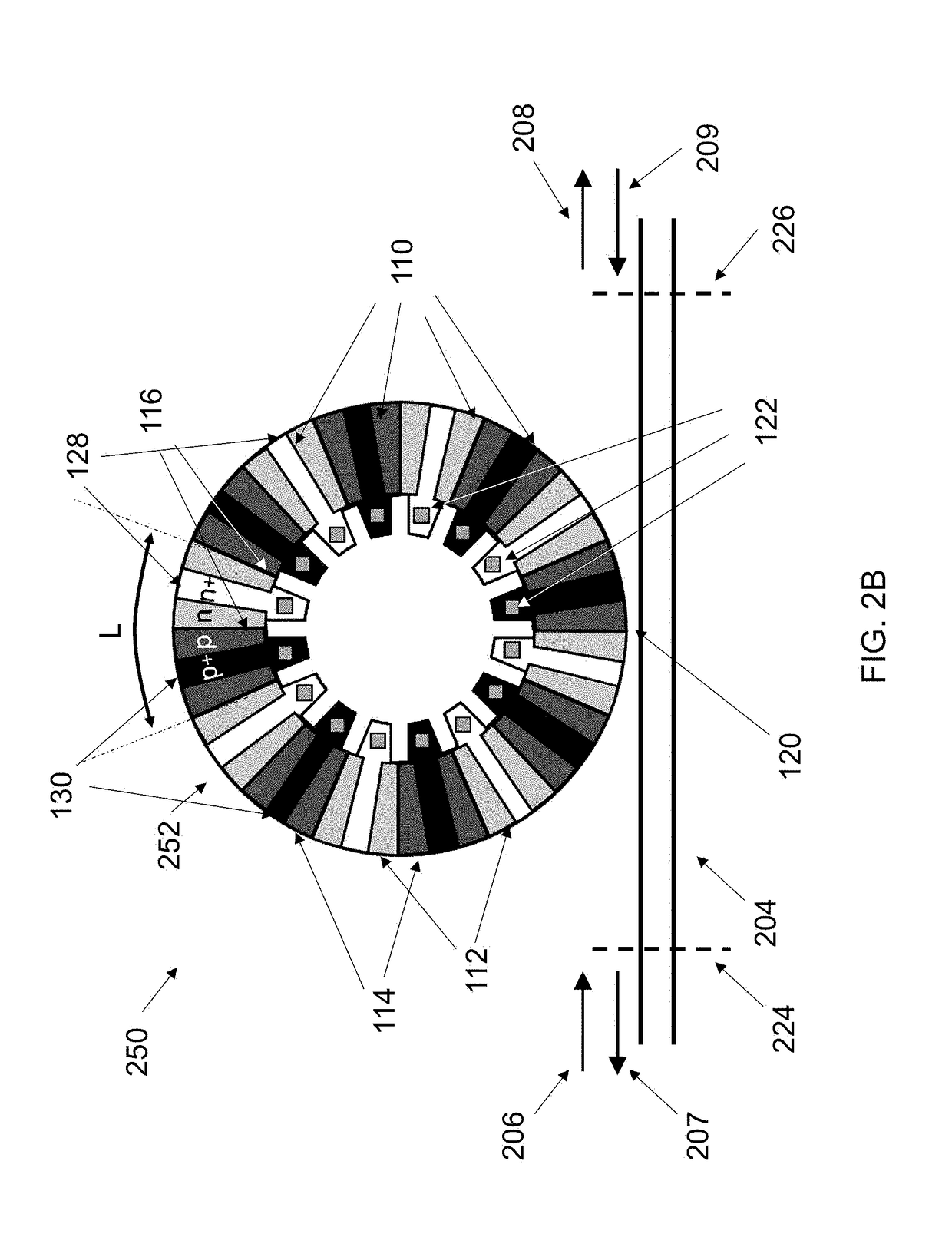
CMOS Compatible Optical Modulators
InactiveUS20170315421A1Maximize modulationLight loss is minimizedNon-linear opticsResonant cavityRing modulation
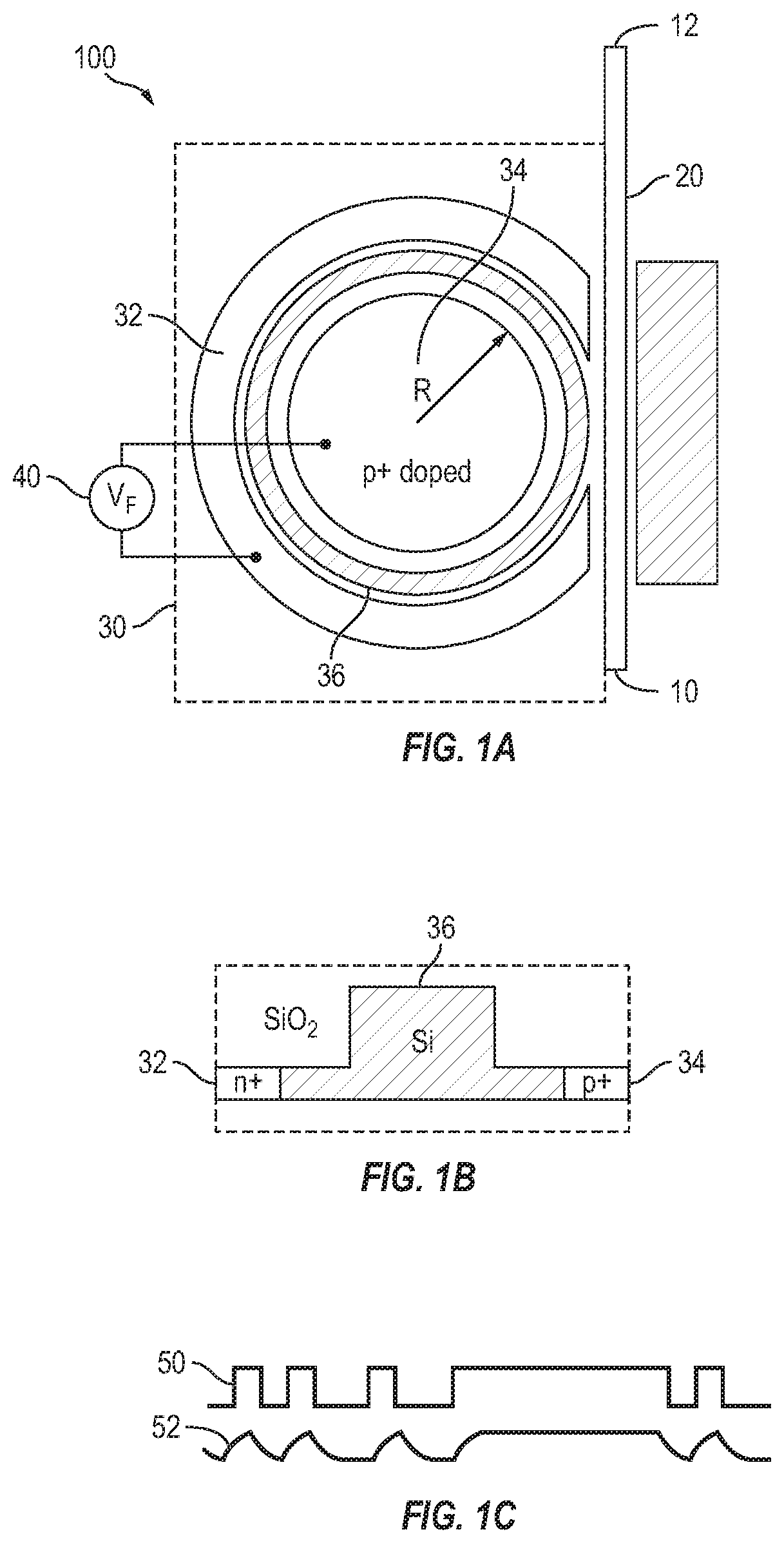
Ring modulators based on interdigitated junctions may be driven in full or partial standing wave mode and, active regions (providing the modulation) and light-absorptive regions (e.g. providing electrical conduction) are placed in a pattern inside a resonant cavity in order to match the maxima and minima of the optical field, respectively. The pattern may be periodic to match the periodicity of a typical electromagnetic field which is periodic with the wavelength. It may also be aperiodic in the case that the cross-section or materials are engineered along the direction of propagation such that the propagation constant (and thus wavelength, i.e. optical wave “local periodicity”) change along the propagation direction.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
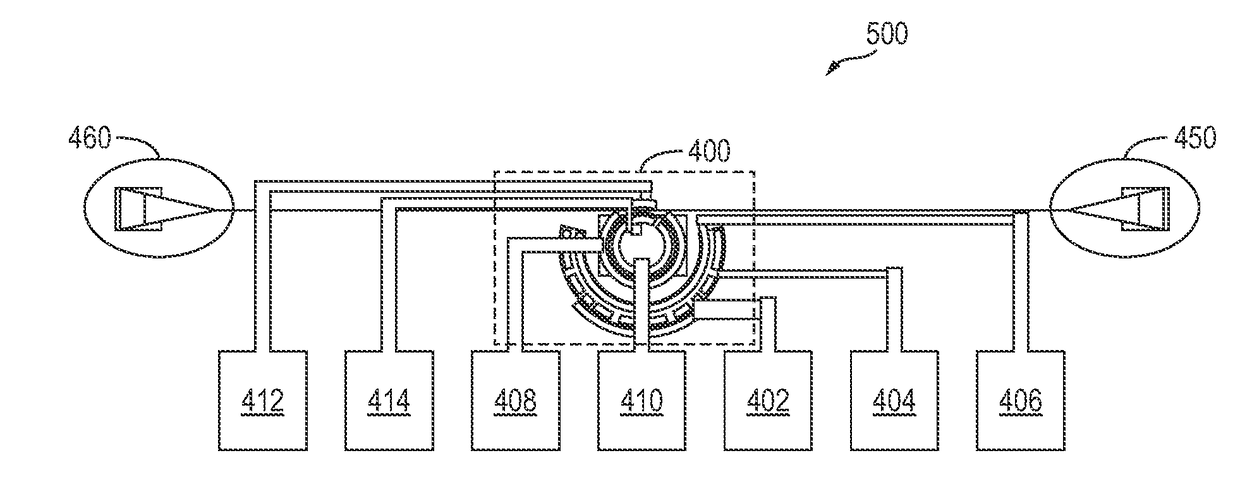
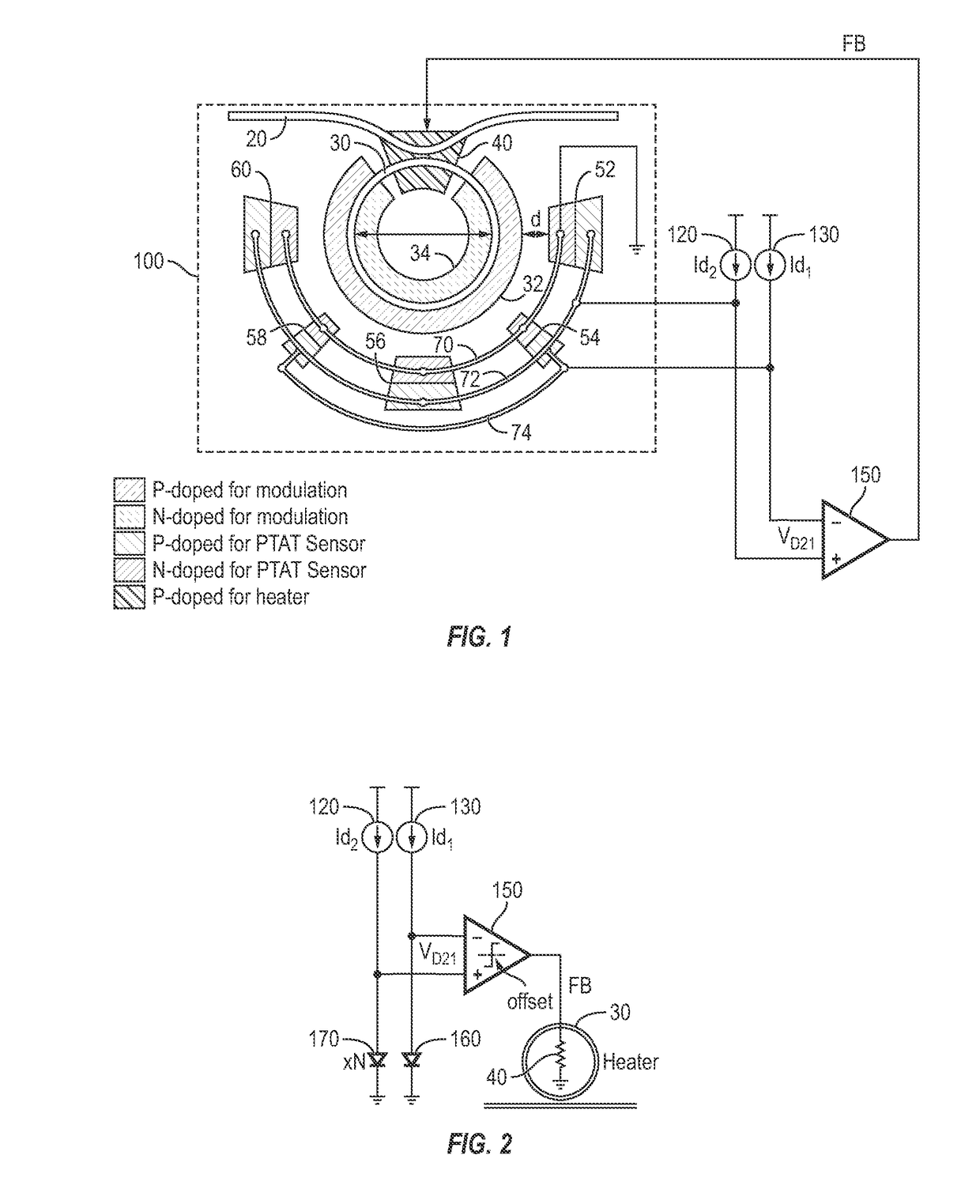
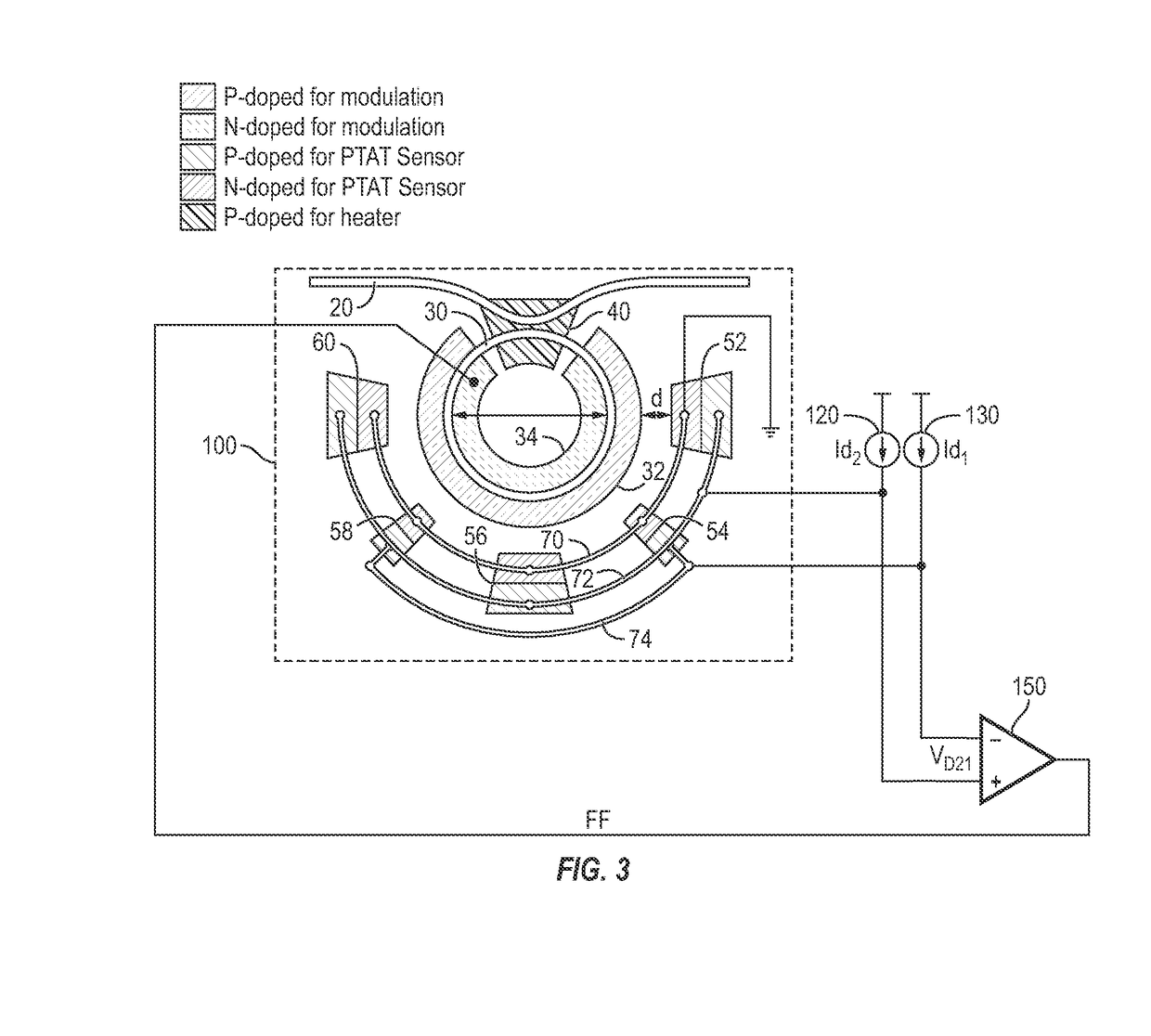
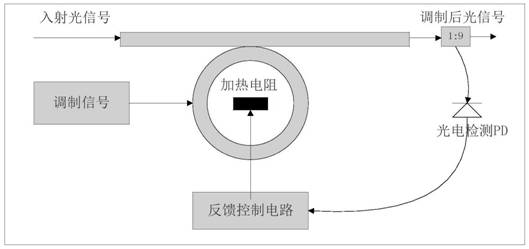
Optical Ring Modulator Thermal Tuning Technique
An optical signal modulator (modulator) includes, in part, a first multitude of diodes coupled in parallel and disposed along an outer periphery of the optical ring of the modulator, a second multitude of diodes coupled in parallel and disposed along the outer periphery of the optical ring, and a doped region adapted to supply heat to the optical ring. A pair of current sources supply substantially constant currents to the first and second multitude of diodes to generate a pair of electrical signals. The modulator further includes, in part, a control circuit adapted to control the temperature of the optical ring in accordance with the pair electrical signals. To achieve this, the control circuit varies the voltage applied to the doped region to vary the supplied heat. Alternatively, the control circuit applies a voltage to the optical ring to maintain a substantially constant resonant wavelength in the optical ring.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Photonic crystal micro-ring modulator chip based on lithium niobate film
PendingCN111897146ACompatible with CMOS processEasy monolithic integrationNon-linear opticsResonant cavitySlow light
The invention discloses a photonic crystal micro-ring modulator chip based on a lithium niobate film. The photonic crystal micro-ring modulator chip comprises a chip substrate, a chip lower cladding layer, a waveguide core layer and a chip upper cladding layer. According to the invention, an input optical waveguide, a photonic crystal micro-ring modulation structure and an output optical waveguideare integrated on a waveguide core layer, wherein the photonic crystal micro-ring modulation structure is composed of a single straight-through waveguide and a closed annular waveguide, the straight-through waveguide is of a two-dimensional line defect photonic crystal waveguide structure, the annular waveguide is of a two-dimensional circular lattice annular resonant cavity type photonic crystalwaveguide structure, a modulation electrode is arranged on the annular waveguide, the waveguide core layer is made of a lithium niobate film material, the device size can be greatly reduced and the integration degree can be improved while the high electro-optical coefficient is achieved, the electro-optical effect is enhanced in combination with the photonic crystal waveguide slow light effect, the modulator works at a low driving voltage, and the structural size is further reduced. The modulator chip is simple in manufacturing process and easy to integrate and expand, and has good reliability and performance stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SCI & IND ELECTRIC APPLIANCE RES INST
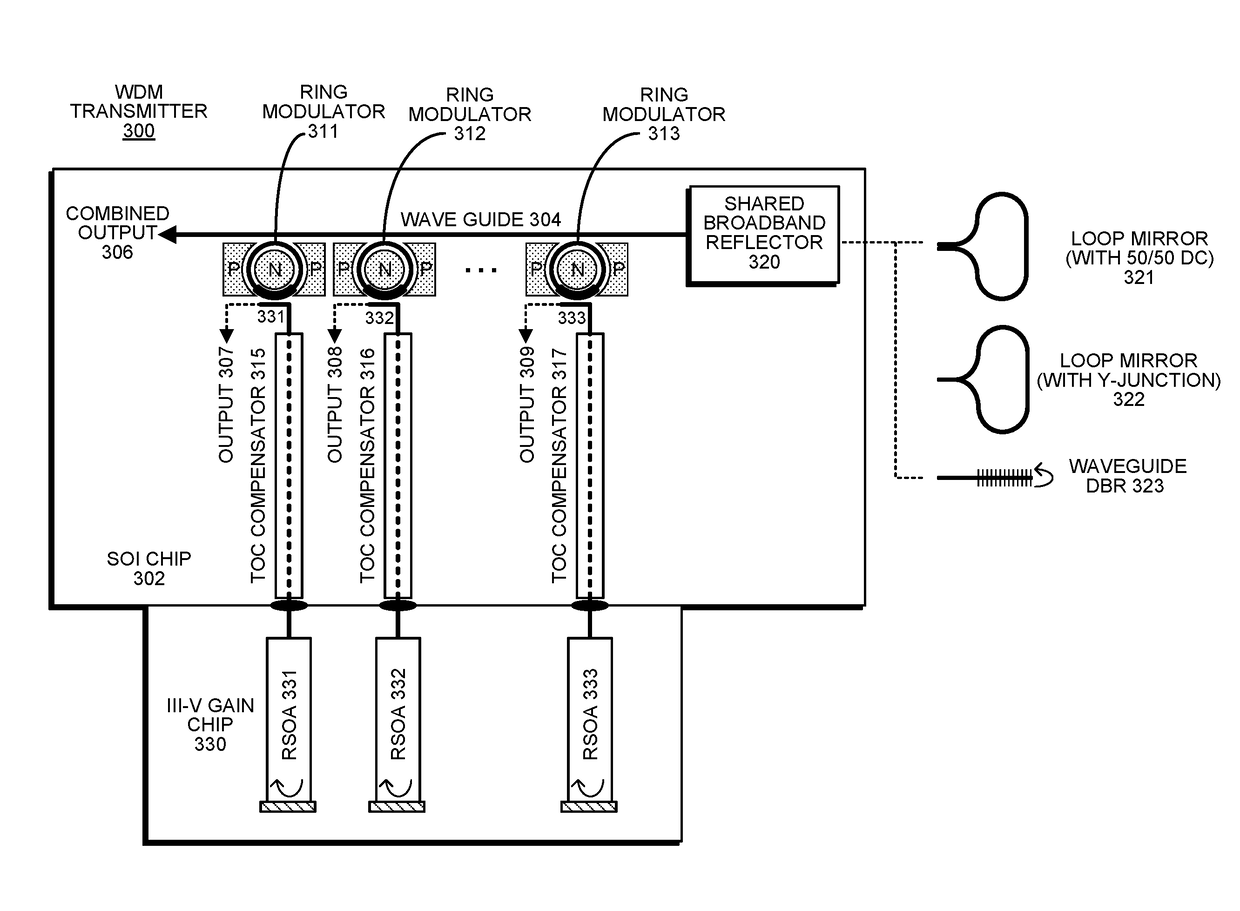
Self-tuned silicon-photonic WDM transmitter
ActiveUS10120211B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionResonanceRing modulation
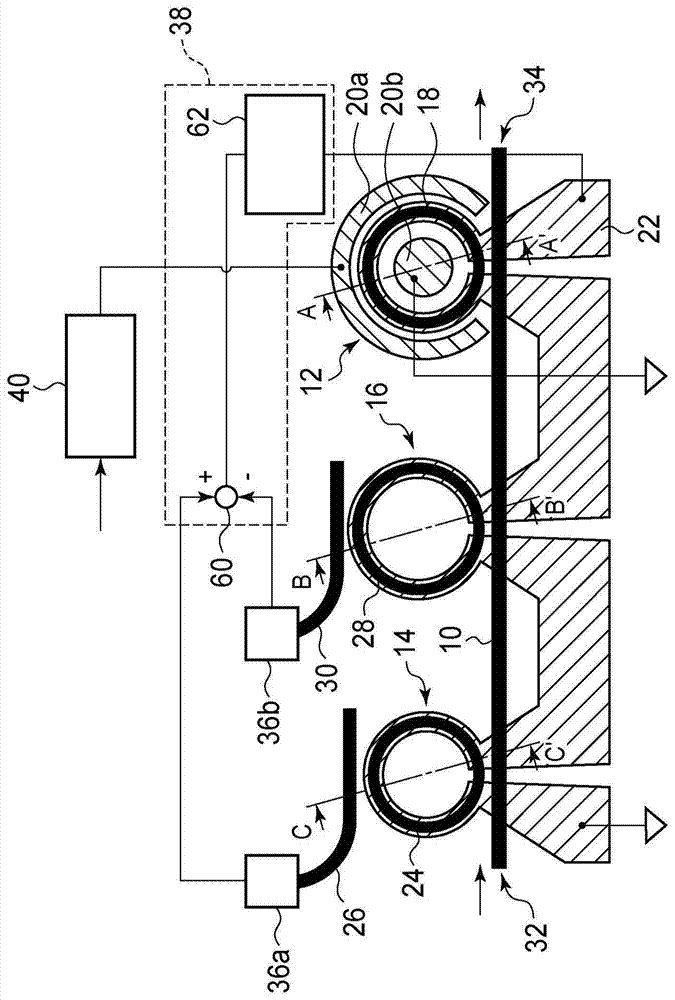
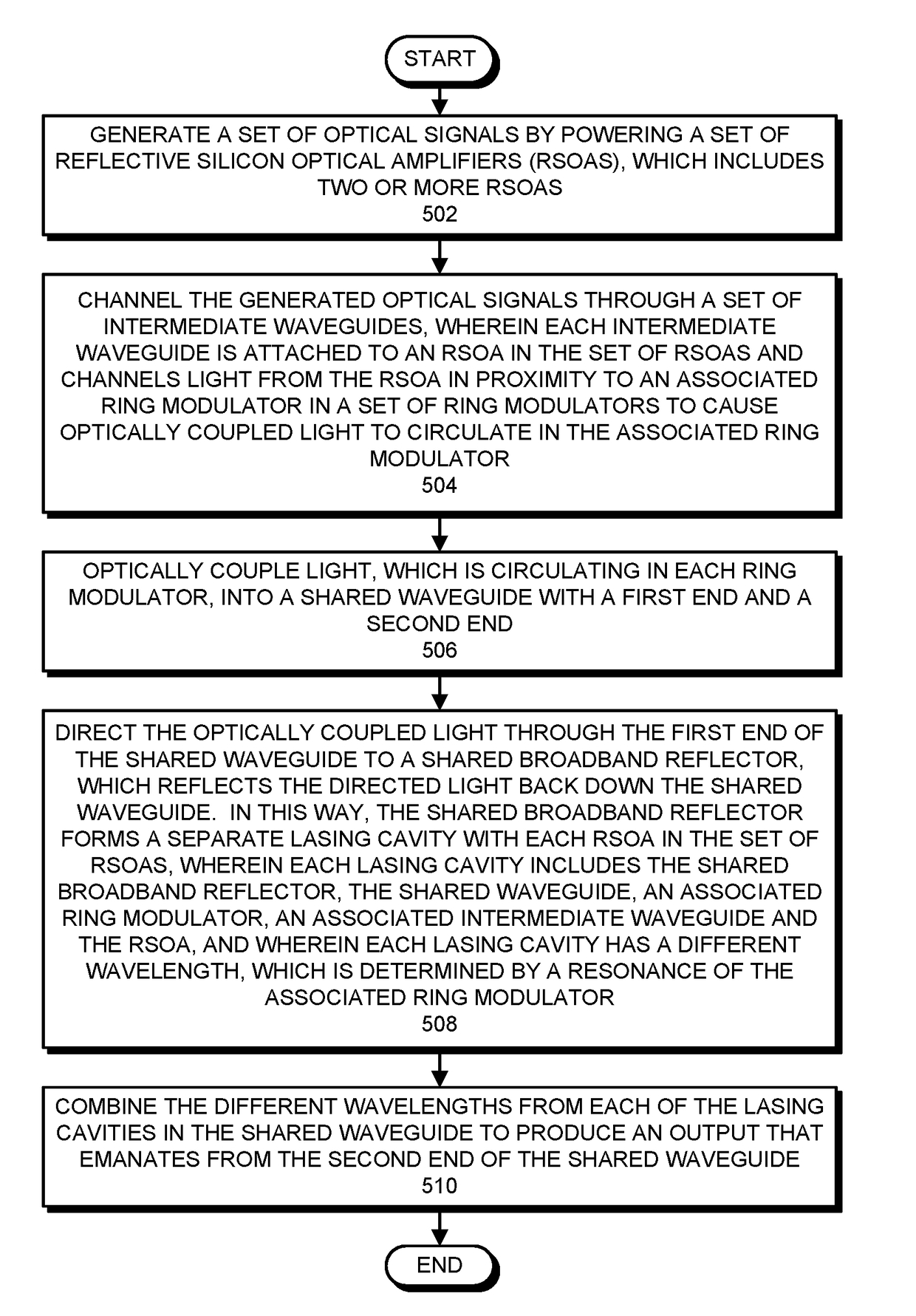
An optical transmitter includes: a set of reflective silicon optical amplifiers (RSOAs), a set of ring modulators, a shared broadband reflector, a set of intermediate waveguides, and a shared waveguide. Each intermediate waveguide channels light from an RSOA in proximity to an associated ring modulator to cause optically coupled light to circulate in the associated ring modulator. The shared waveguide is coupled to the shared broadband reflector, and passes in proximity to the set of ring modulators, so that light circulating in each ring modulator causes optically coupled light to flow in the shared optical waveguide. During operation, each RSOA forms a lasing cavity with the shared broadband reflector, wherein each lasing cavity has a different wavelength, which is determined by a resonance of the associated ring modulator. The different wavelengths are combined in the shared waveguide to produce a combined output.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
CMOS compatible optical modulators
Ring modulators based on interdigitated junctions may be driven in full or partial standing wave mode and, active regions (providing the modulation) and light-absorptive regions (e.g. providing electrical conduction) are placed in a pattern inside a resonant cavity in order to match the maxima and minima of the optical field, respectively. The pattern may be periodic to match the periodicity of a typical electromagnetic field which is periodic with the wavelength. It may also be aperiodic in the case that the cross-section or materials are engineered along the direction of propagation such that the propagation constant (and thus wavelength, i.e. optical wave “local periodicity”) change along the propagation direction.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Optical semiconductor element, method for controlling optical semiconductor element, and method for manufacturing optical semiconductor element
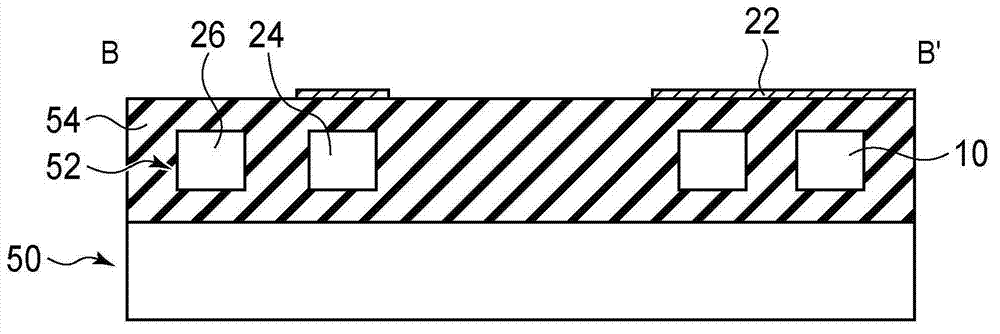
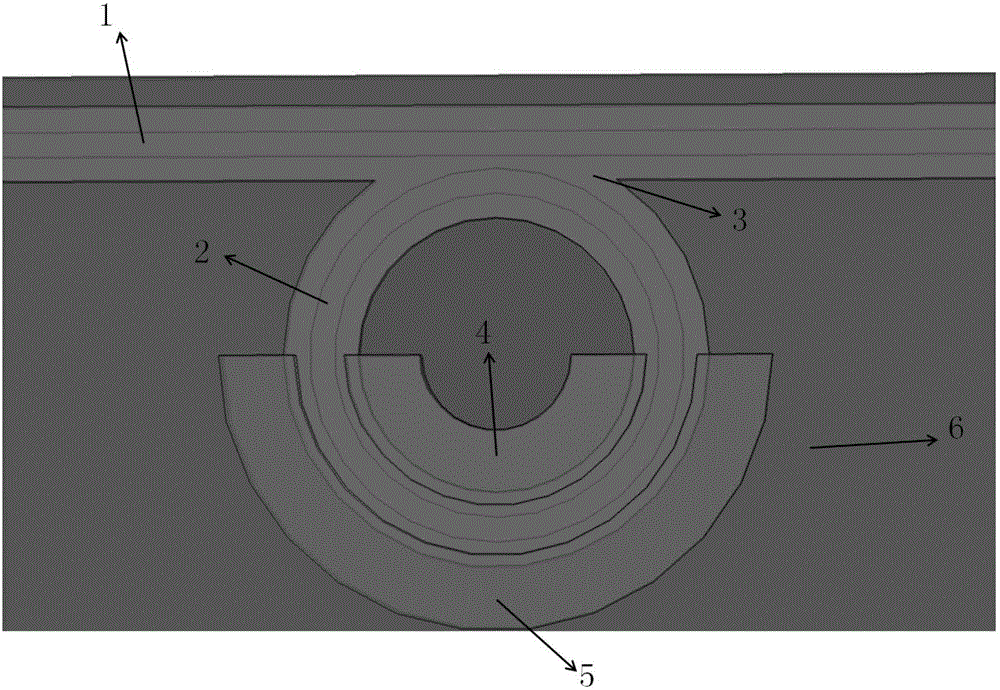
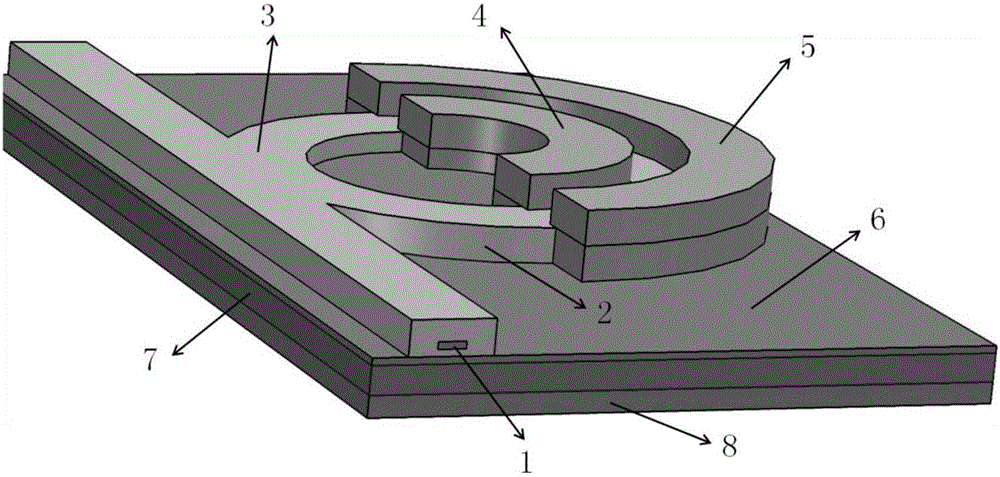
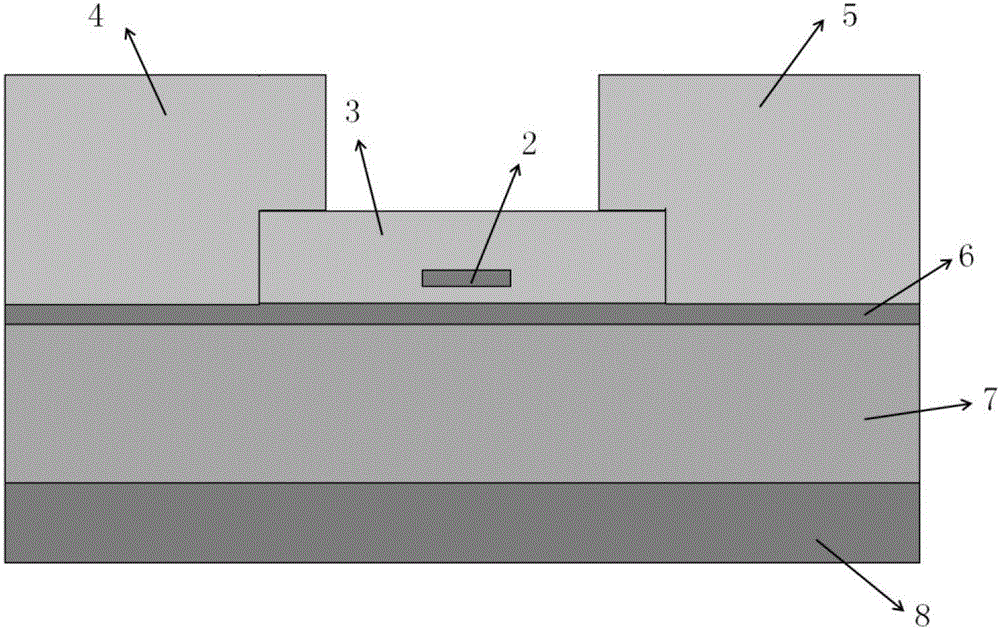
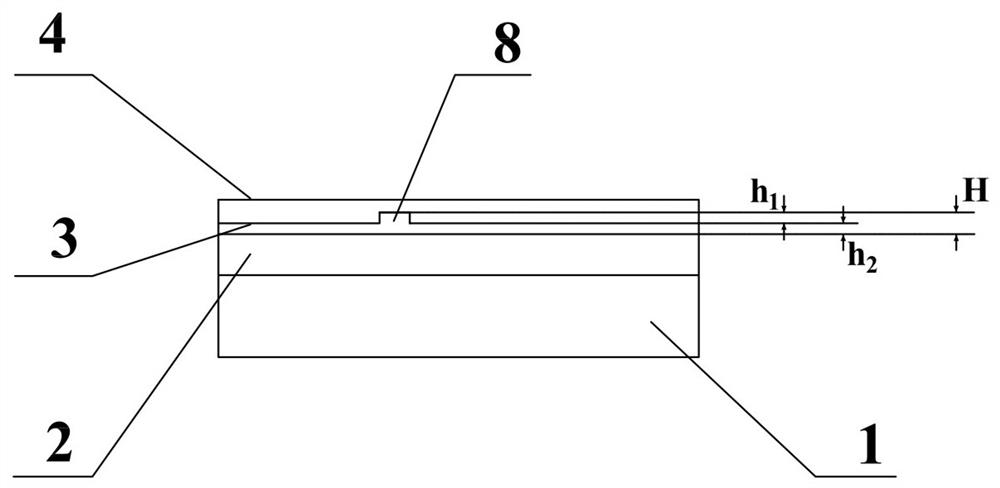
InactiveCN103827737ARing Resonant Wavelength ControlOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsRing modulationWaveguide
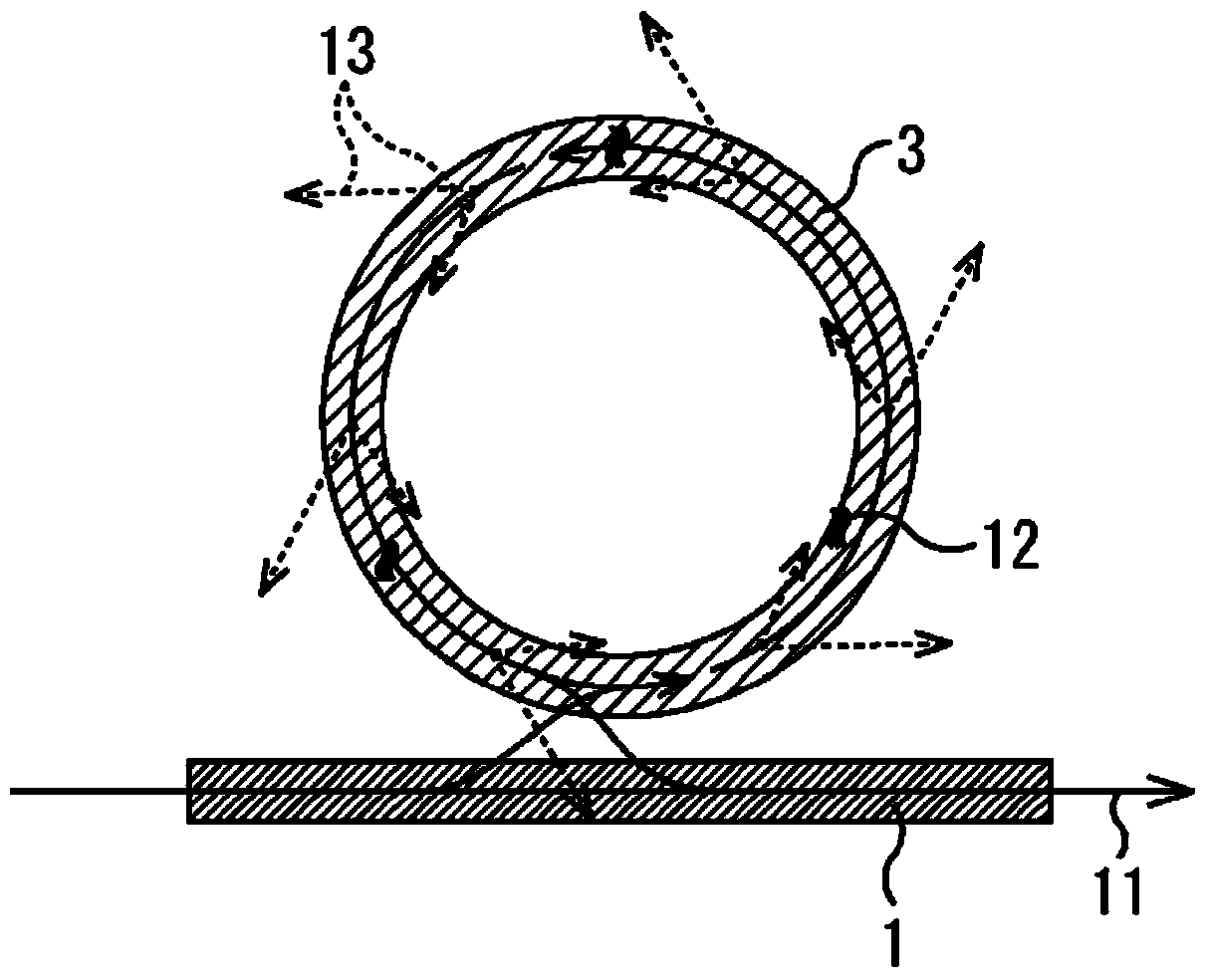
This optical semiconductor element is provided with: a ring modulator; and a light absorbing material (9), which is provided at a position separated from a path of light to be modulated, said path guiding waves in the ring modulator, absorbs light leaked from a ring waveguide (3) of the ring modulator, and increases a temperature of the ring waveguide (3).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical Semiconductor Device
An optical semiconductor device includes a waveguide that an input light to be inputted, a ring modulator optically coupled with the waveguide, a first ring resonator optically coupled with the waveguide and having an optical path length smaller than an optical path length of the ring modulator, a second ring resonator optically coupled with the first waveguide and having an optical path length larger than the optical path length of the ring modulator, a heater arranged adjacent to the ring modulator, the first ring resonator and the second ring resonator, a first photodetector monitoring a light power in the first ring resonator, a second photodetector monitoring a light power in the second ring resonator, and a controller controlling the heater so that a resonance wavelength of the ring modulator agrees with a wavelength of the input light, based on signals detected by the first and second photodetectors.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
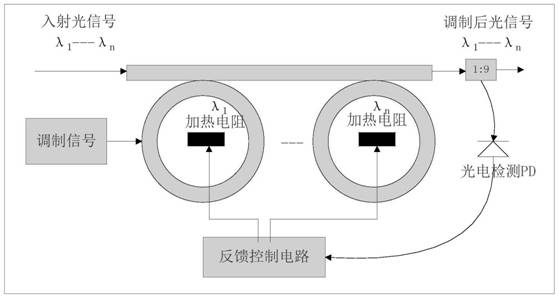
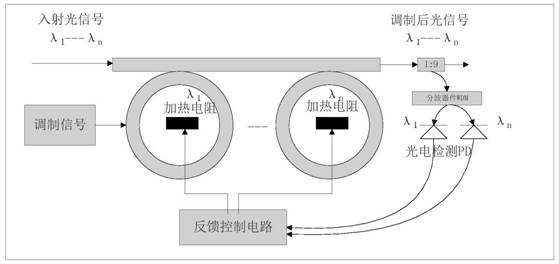
Wavelength multiplexing micro-ring modulator and wavelength locking method
PendingCN113608370AModulation efficiency dropsOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsMultiplexingRing modulation
The invention discloses a wavelength multiplexing micro-ring modulator. The wavelength multiplexing micro-ring modulator comprises a micro-ring modulation main arm, a feedback control circuit unit and n heating resistors, wherein n paths of output ends of the feedback control circuit unit are respectively, correspondingly and electrically connected with the first heating resistor, the second heating resistor... and the nth heating resistor; and the first heating resistor, the second heating resistor... and the nth heating resistor are correspondingly arranged in a first micro-ring modulator, a second micro-ring modulator... and an nth micro-ring modulator respectively. The invention also discloses a wavelength locking method for the wavelength multiplexing micro-ring modulator. The method comprises the steps of S1, modulating a multi-wavelength multiplexing optical signal; S2, acquiring an optical signal of the currently modulated resonant wavelength of each micro-ring; and S3, locking the working wavelength of the micro-ring modulator. The wavelength multiplexing micro-ring modulator and the wavelength locking method have the beneficial effect that a relatively complex and expensive wavelength division demultiplexing device in a traditional wavelength division multiplexing system can be omitted.
Owner:吴弟书
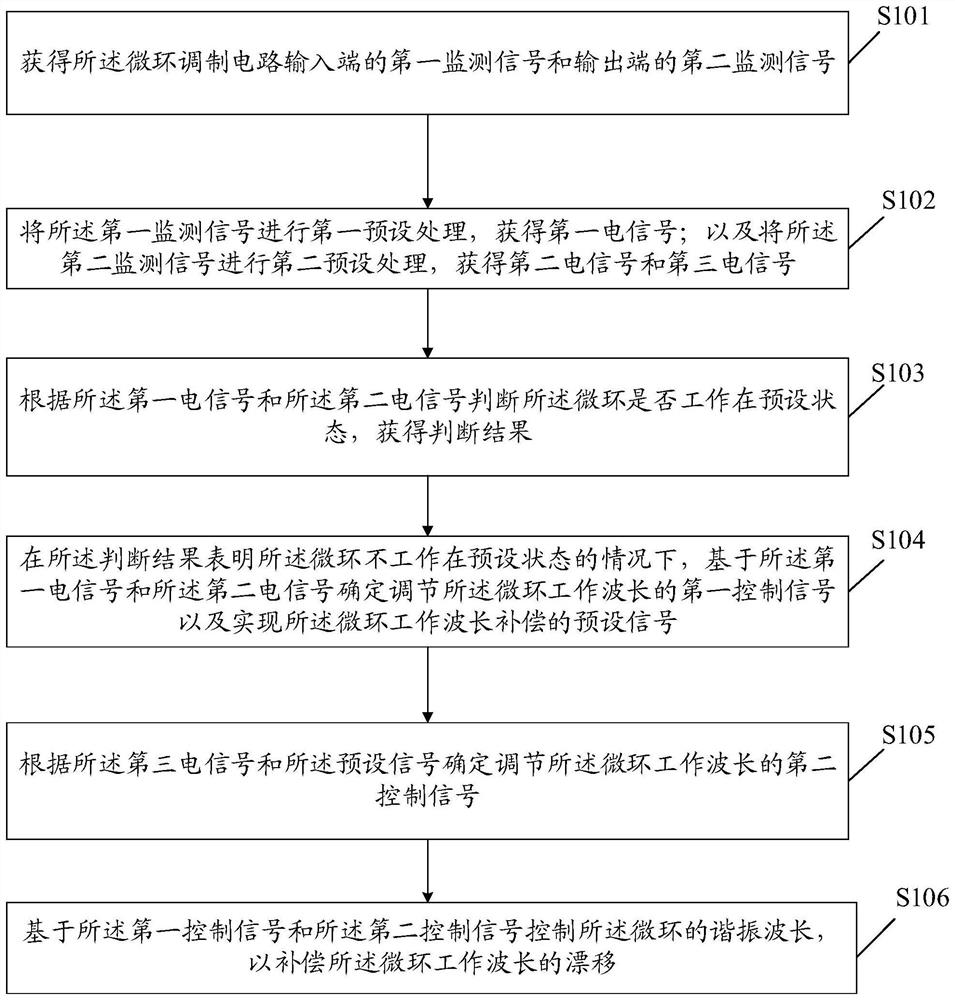
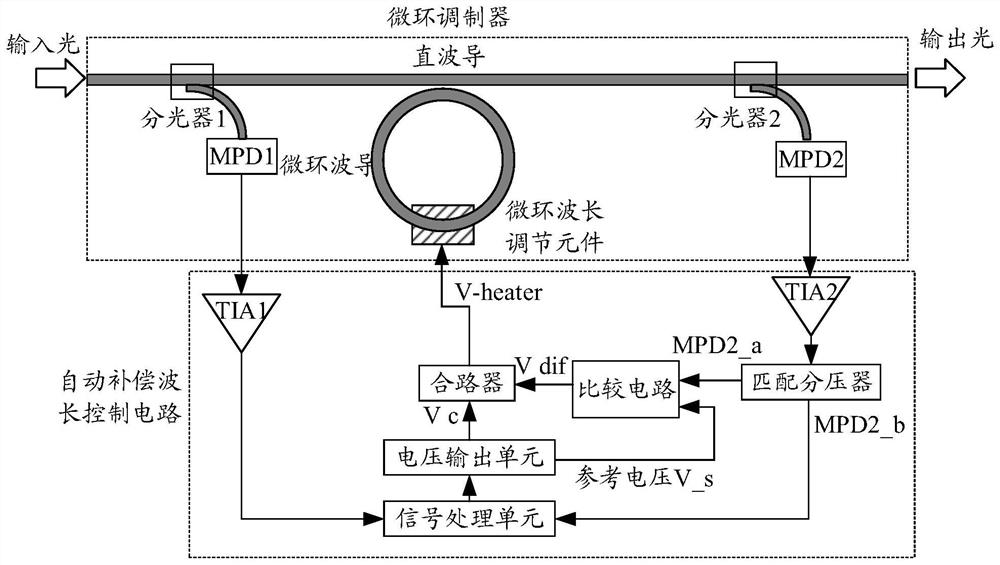
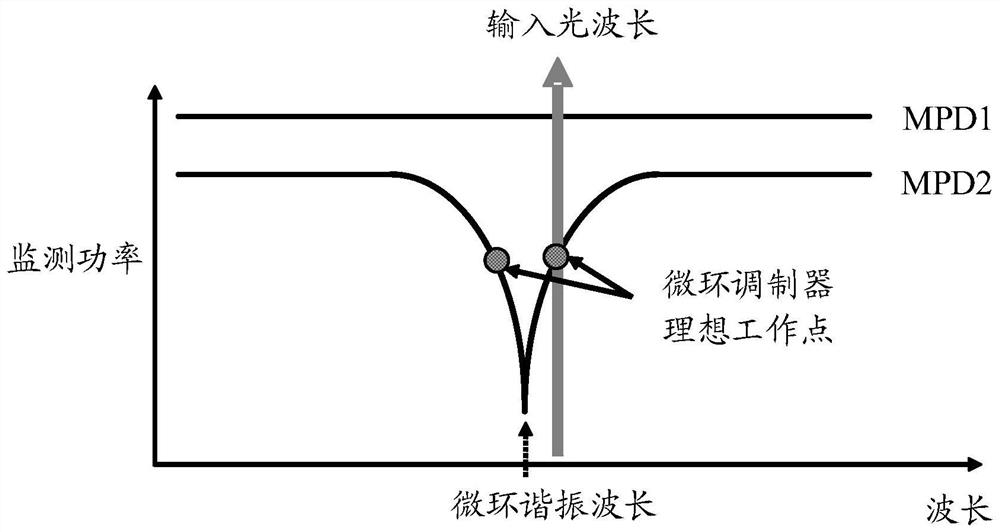
Micro-ring wavelength control method, system, device and storage medium
The invention discloses a micro-ring wavelength control method, a system, a device and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps that a first monitoring signal of the input end of a micro-ring modulation circuit and a second monitoring signal of the output end of the micro-ring modulation circuit are obtained; performing first preset processing on the first monitoring signal to obtain a first electric signal; performing second preset processing on the second monitoring signal to obtain a second electric signal and a third electric signal; judging whether the micro-ring works in a preset state according to the first electric signal and the second electric signal to obtain a judgment result; under the condition that the judgment result shows that the micro-ring does not work in the preset state, determining a first control signal for adjusting the working wavelength of the micro-ring and a preset signal for realizing the working wavelength compensation of the micro-ring based on the first electric signal and the second electric signal; determining a second control signal for adjusting the working wavelength of the micro-ring according to the third electric signal and a preset signal; and controlling the resonant wavelength of the micro-ring based on the first control signal and the second control signal so as to compensate the drift of the working wavelength of the micro-ring.
Owner:WUHAN OPTICAL VALLEY INFORMATION OPTOELECTRONICS INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Differential ring modulator
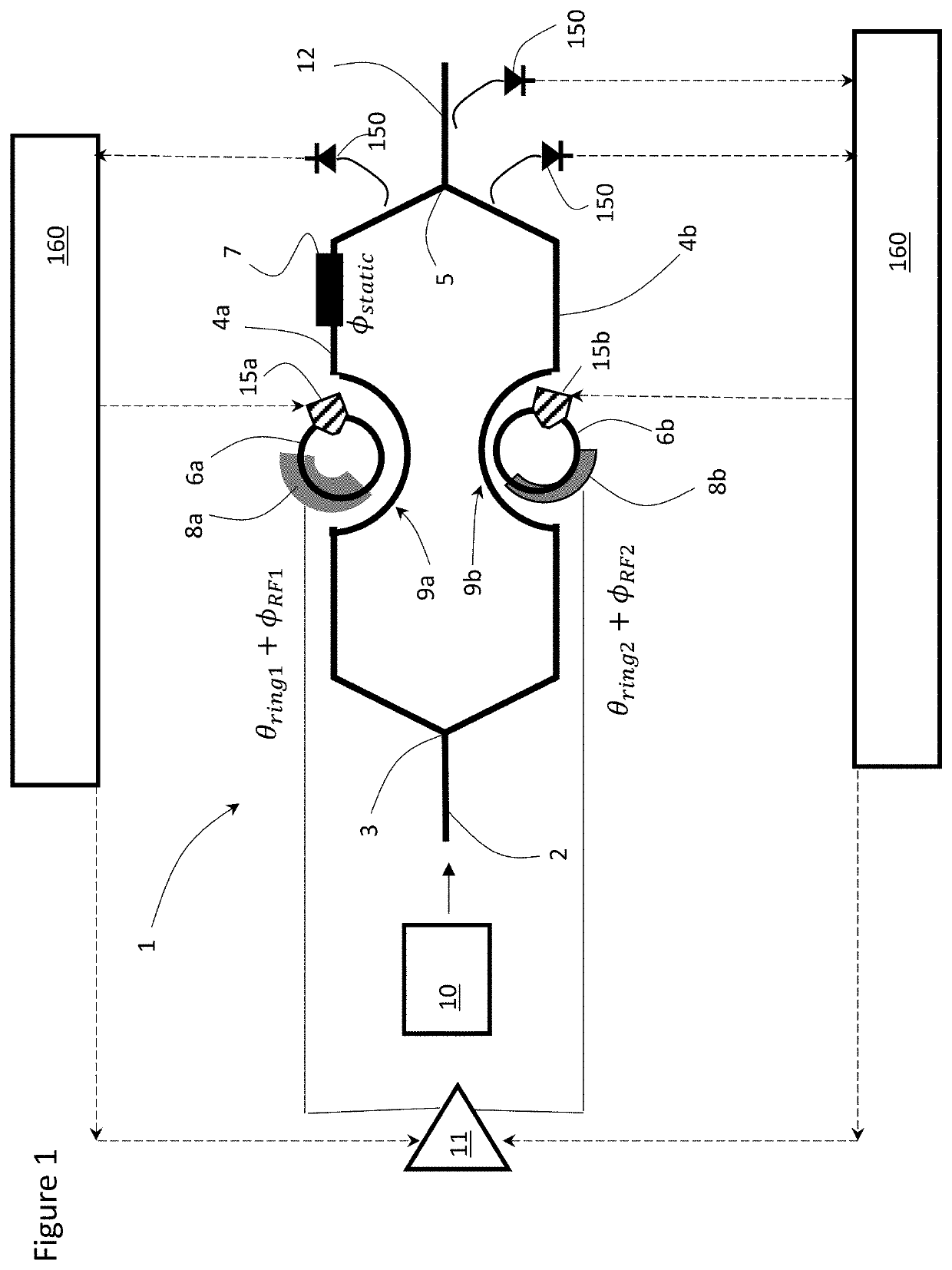
ActiveUS10527871B2Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersRing modulationSoftware engineering
A differential optical modulator includes, in part, a splitter splitting an incoming optical signal into first and second input signals, a first variable coupler generating a first differential output signal in response to the first input signal, and a second variable coupler generating a second differential output signal in response to the second input signal. The first variable coupler includes, in part, first and second couplers and a phase shifter disposed therebetween. The first coupler generates a pair of internal signals in response to the first input signal. The second coupler generates the first differential output signal. The second variable coupler includes, in part, third and fourth couplers and a phase shifter disposed therebetween. The third coupler generates a pair of internal signals in response to the second input signal. The fourth coupler generates the second differential output signal.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
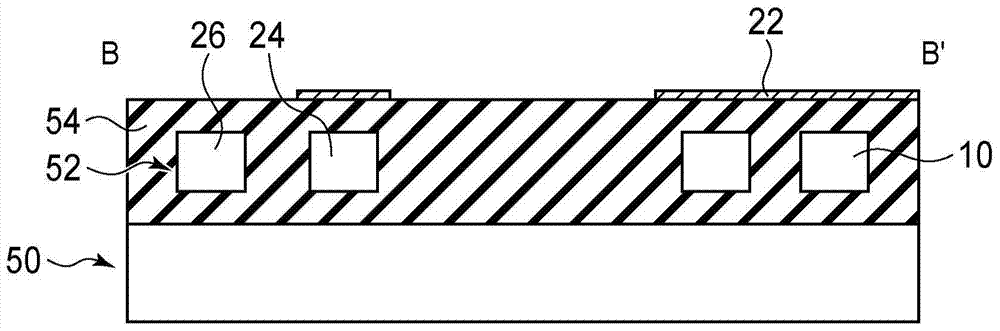
Sensor device with alternating excitation fields
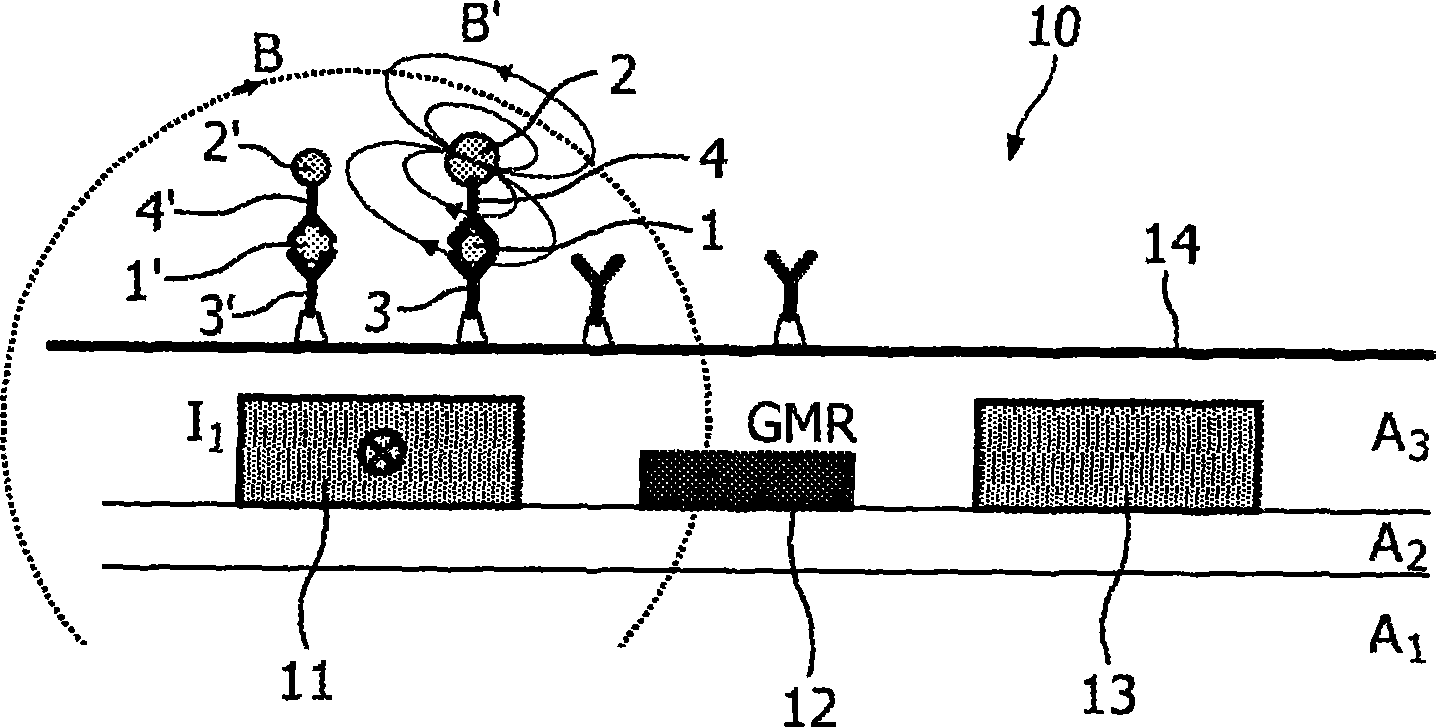
InactiveCN101400984AAvoid Dynamic Range IssuesNanomagnetismMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRing modulationMagnetic response
The invention relates to a magnetic sensor device comprising excitation wires (11, 13) for generating a magnetic excitation field and a magnetic sensor element, particularly a GMR sensor (12), for sensing magnetic fields generated by labeling particles in reaction to the excitation field. The magnetic excitation fields are generated with non-sinusoidal forms, particularly as square-waves, such that their spectral range comprises a plurality of frequency components. Magnetic particles with different magnetic response characteristics can then be differentiated according to their reactions to the different frequency components of the excitation fields. The magnetic excitation field and the sensing current driving the GMR sensor (12) are preferably generated with the help of ring modulators (22, 24). Moreover, ring modulators (27, 29) may be used for the demodulation of the sensor signal.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optical Ring Circuit with Electrical Filter
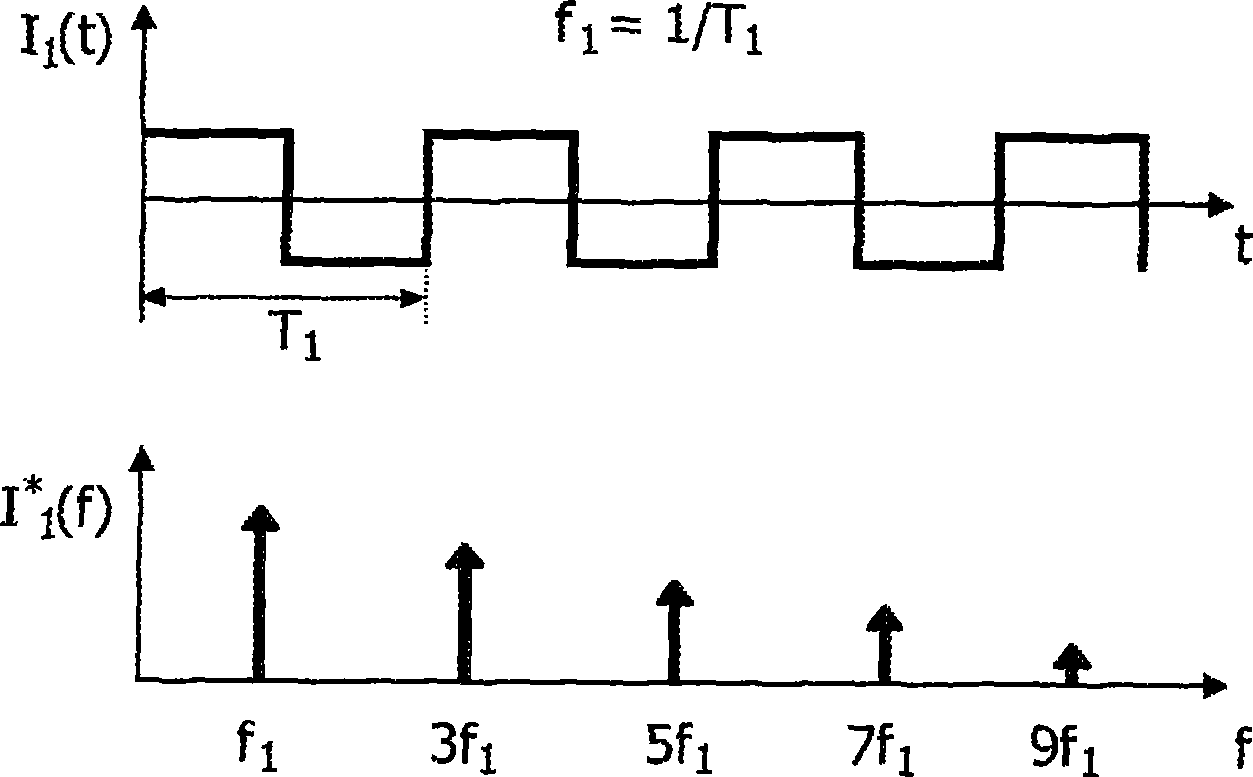
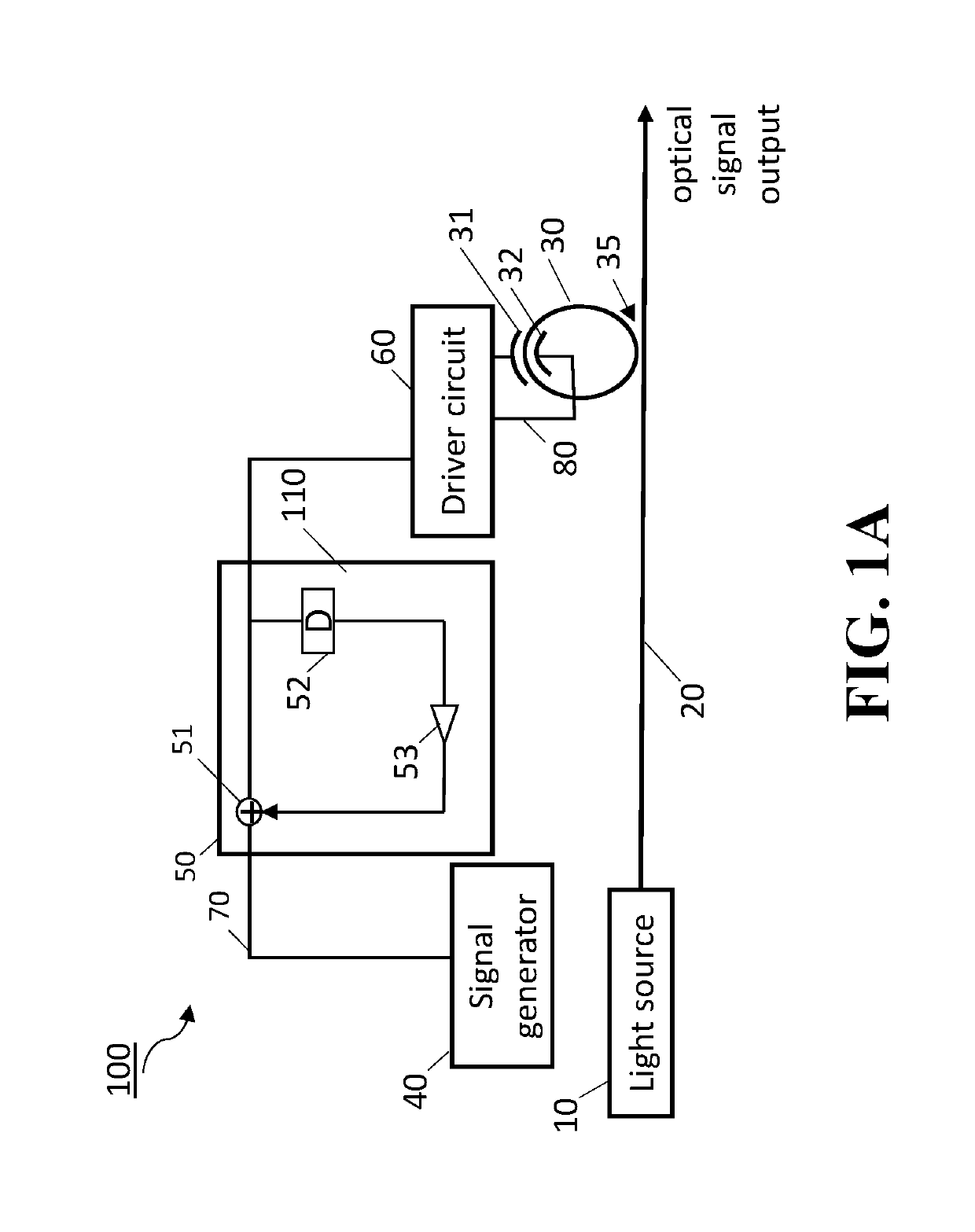
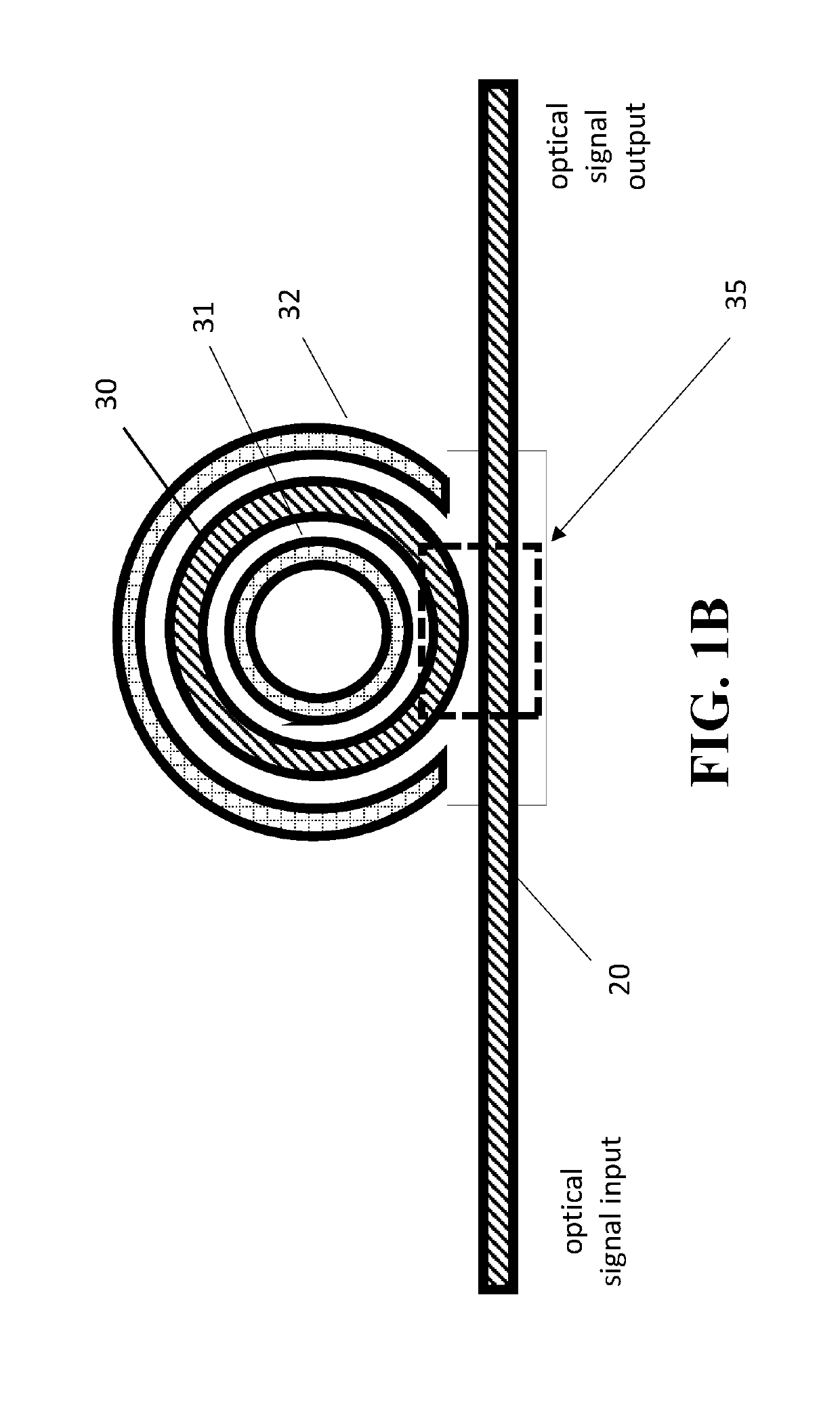
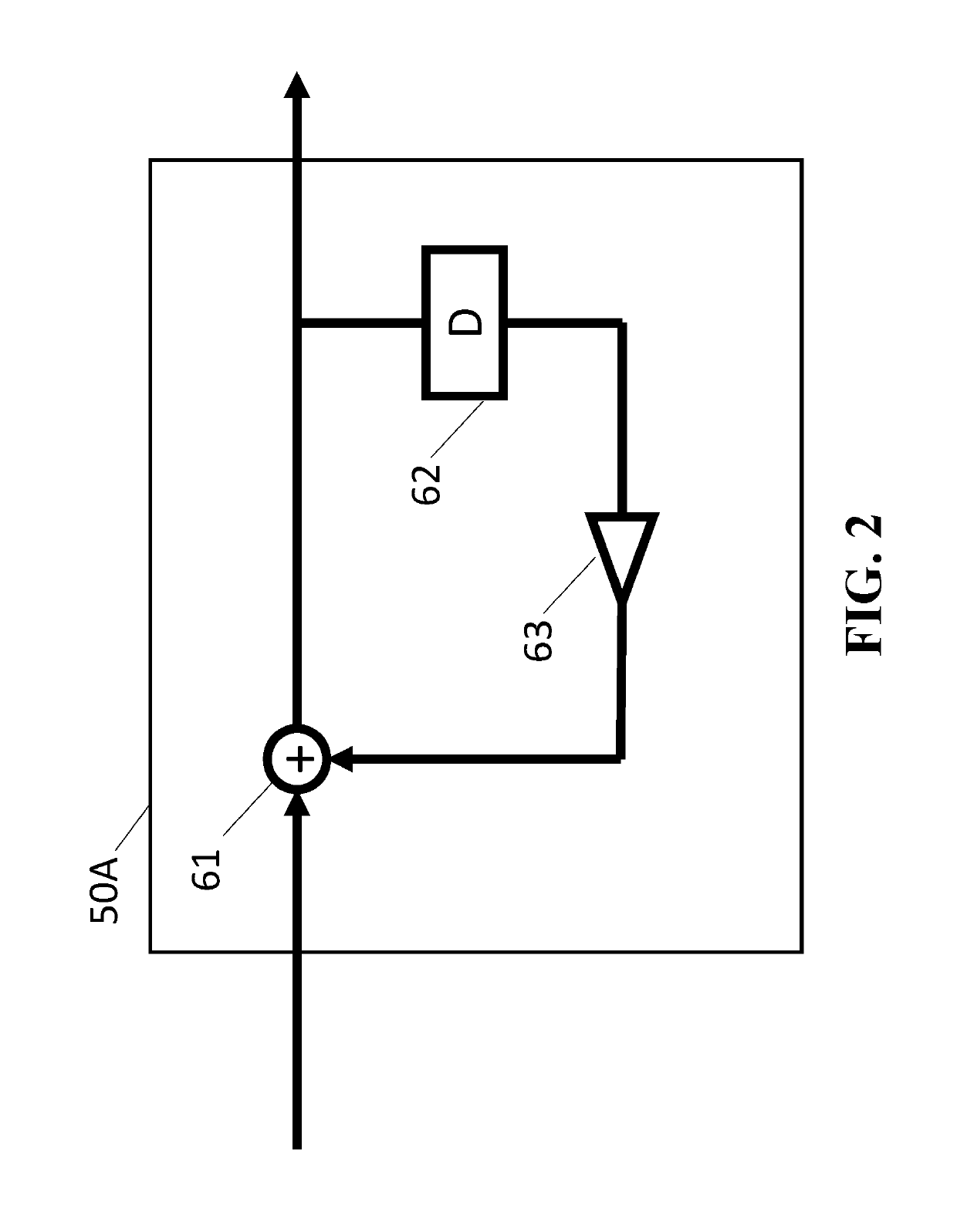
An optical ring circuit for modulating light from a light source into an optical signal includes a ring modulator located near a waveguide to couple a light propagating the waveguide, the ring modulator including a pair of electrodes, a signal generator to transmit an electrical signal corresponding to the optical signal, a filter circuit to generate an output signal, wherein the filter circuit includes an adder unit and at least one tap unit having a delay unit and a coefficient unit, wherein the adder unit adds the electrical signal from the signal generator and a signal passed from the tap unit for pre-compensating signal components of the electrical signal by at least twice delay time of the delay unit, and a driver circuit to apply a voltage to the electrodes based on the output signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Self-tuned silicon-photonic WDM transmitter
ActiveUS20180231808A1Large tuning rangeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionPhotonicsTransmitter
An optical transmitter includes: a set of reflective silicon optical amplifiers (RSOAs), a set of ring modulators, a shared broadband reflector, a set of intermediate waveguides, and a shared waveguide. Each intermediate waveguide channels light from an RSOA in proximity to an associated ring modulator to cause optically coupled light to circulate in the associated ring modulator. The shared waveguide is coupled to the shared broadband reflector, and passes in proximity to the set of ring modulators, so that light circulating in each ring modulator causes optically coupled light to flow in the shared optical waveguide. During operation, each RSOA forms a lasing cavity with the shared broadband reflector, wherein each lasing cavity has a different wavelength, which is determined by a resonance of the associated ring modulator. The different wavelengths are combined in the shared waveguide to produce a combined output.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Control Method Of Optical Element
A control method of an optical element, including light sources to emit lights having different wavelengths from each other, and ring modulators connected in cascade along a light waveguide, is disclosed. Each ring modulator includes a ring resonator, and a wavelength adjustment electrode to adjust a resonance wavelength in the ring resonator, wherein the lights from the light sources are multiplexed to enter the light waveguide. The method includes having a light source emit the light; adjusting power to the wavelength adjustment electrode in each ring modulator, to obtain a value of the power causing the resonance wavelength of the ring resonator, equivalent to the wavelength of the light emitted from the light source; obtaining a relationship between the light sources and the values of the power corresponding to the ring modulators; and selecting the ring modulators corresponding to the light sources based on the relationship.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
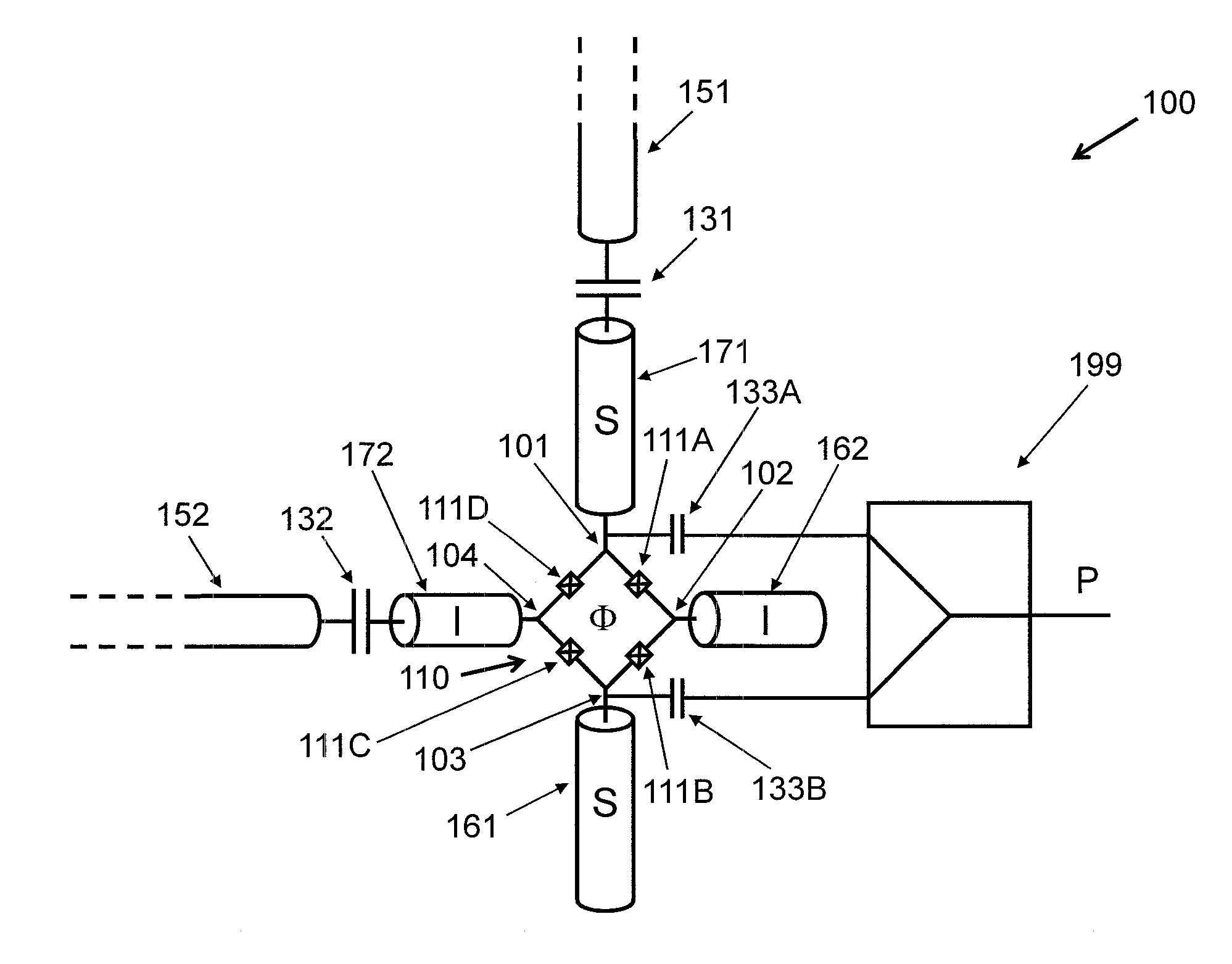
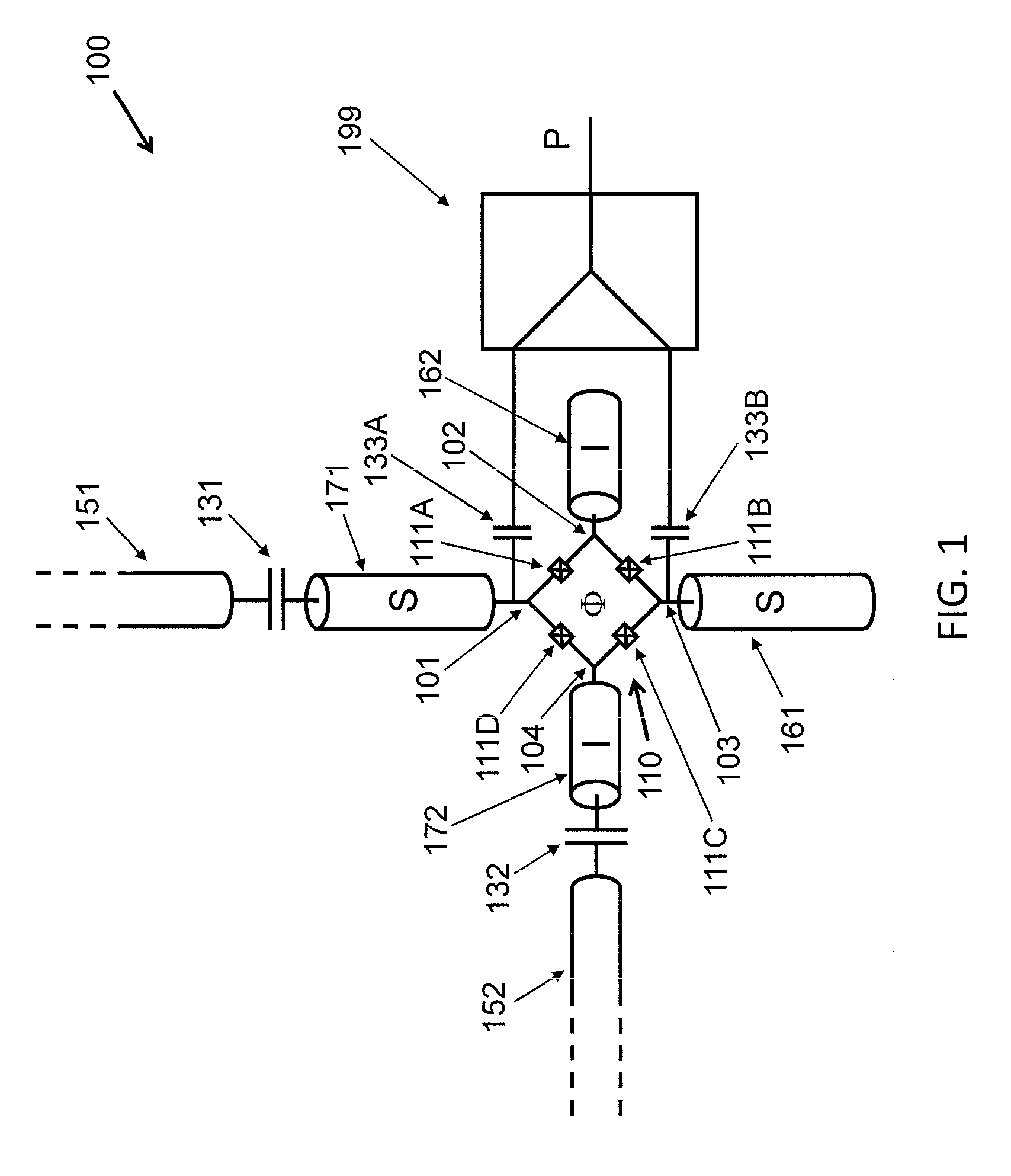
Null bias mach-zehnder interferometer with ring resonators
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com