Optical Semiconductor Device
An optical semiconductor and device technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as higher modulation efficiency and narrower wavelength bandwidth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0028] will refer to Figure 1 to Figure 14 An optical semiconductor device according to the first embodiment is described.
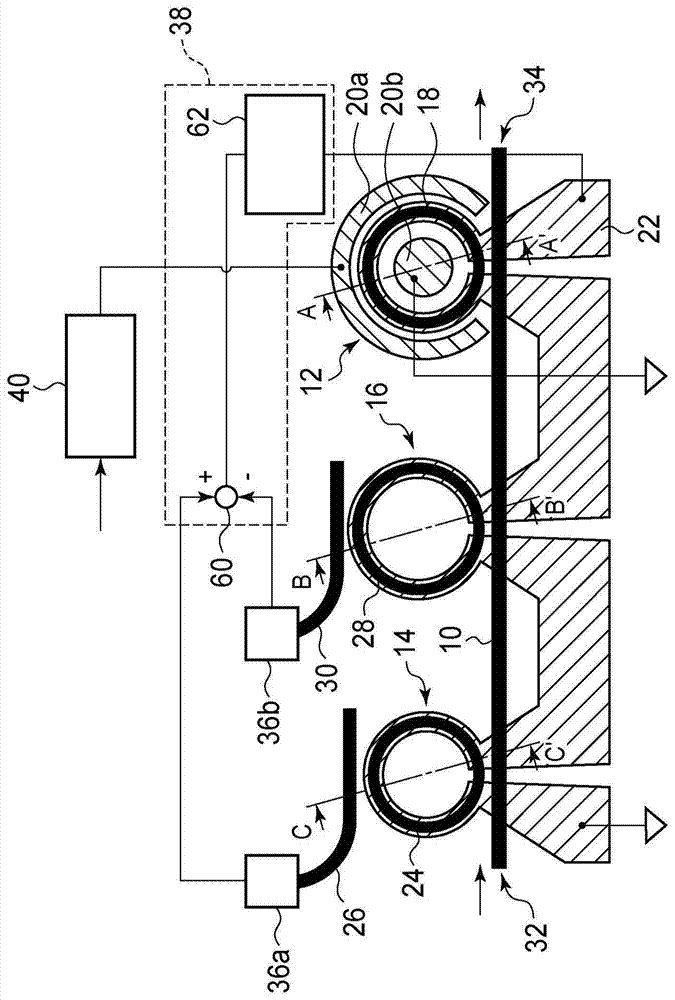
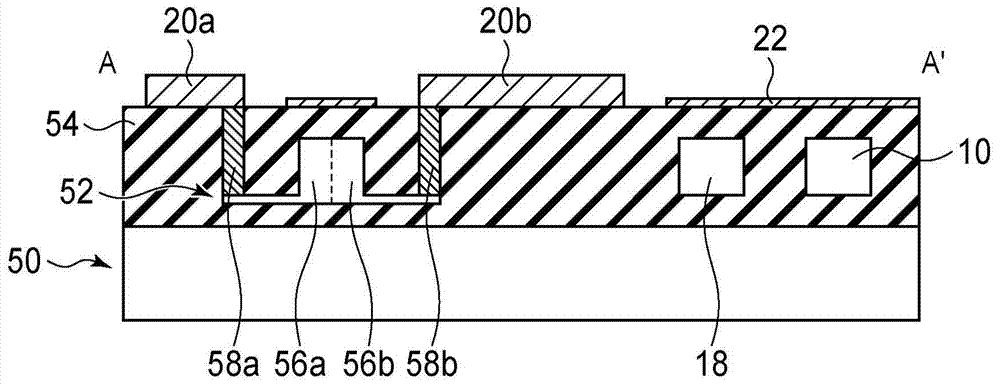
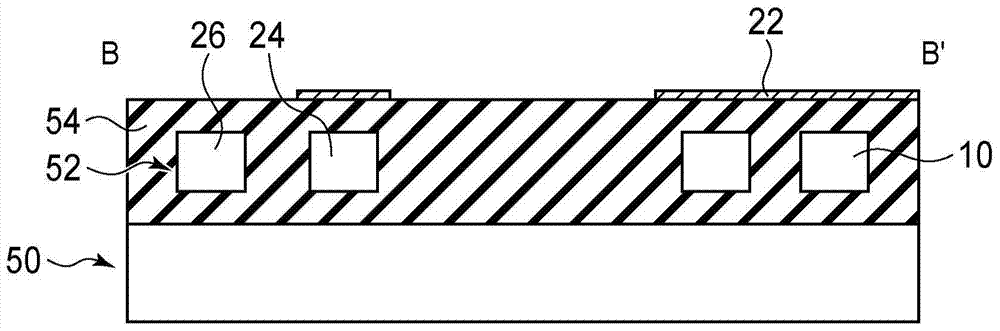
[0029] figure 1 is a schematic diagram showing the optical semiconductor device according to the present embodiment. Figure 2 to Figure 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the optical semiconductor according to the present embodiment. Figure 5 , Figure 6 , Figure 10 as well as Figure 11 is a graph showing the relationship between the modulated light output power of an optical resonator and the wavelength of input light. Figure 7 and Figure 8 is a graph showing the relationship between the monitored current and the wavelength of input light. Figure 9 and Figure 13 is a schematic diagram showing an optical semiconductor device according to a reference example. Figure 12 is a graph showing the relationship between the monitored light power and the wavelength of the input light. Figure 14 is a graph showing the relationship between the ...
no. 2 example
[0084] will refer to Figure 15 An optical semiconductor device according to a second embodiment is described. Denote this embodiment with the same reference numerals according to Figure 1 to Figure 14 The same components are shown as the optical semiconductor device of the first embodiment so as not to repeat or simplify the description.
[0085] Figure 15 is a schematic diagram showing the optical semiconductor device according to the present embodiment.
[0086] The optical semiconductor device according to the present embodiment is the same as the optical semiconductor device according to the first embodiment except for the planar configuration of the ring waveguide.
[0087] That is, the optical semiconductor device according to the present embodiment includes ring waveguides 18a, 24a, 28a instead of ring waveguides 18, 24, 28 each having four linear portions and four arcuate portions. Composite Structure.
[0088] The arc of the ring waveguides 18a, 24a, 28a is a ...
no. 3 example
[0094] will refer to Figure 16 An optical semiconductor device according to a third embodiment is described. Denote this embodiment with the same reference numerals according to Figure 1 to Figure 15 The same components of the optical semiconductor devices of the first and second embodiments are shown so as not to repeat or simplify the description.
[0095] Figure 16is a schematic sectional view showing the optical semiconductor device according to the present embodiment.
[0096] The optical semiconductor device according to the present embodiment is the same as the optical semiconductor device according to the first embodiment except that the second optical resonator 14 and the third optical resonator 16 are disposed opposite to each other.
[0097] With the second optical resonator 14 and the third optical resonator 16 disposed oppositely, the optical semiconductor device can operate in the same manner as the optical semiconductor device according to the first embodi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com