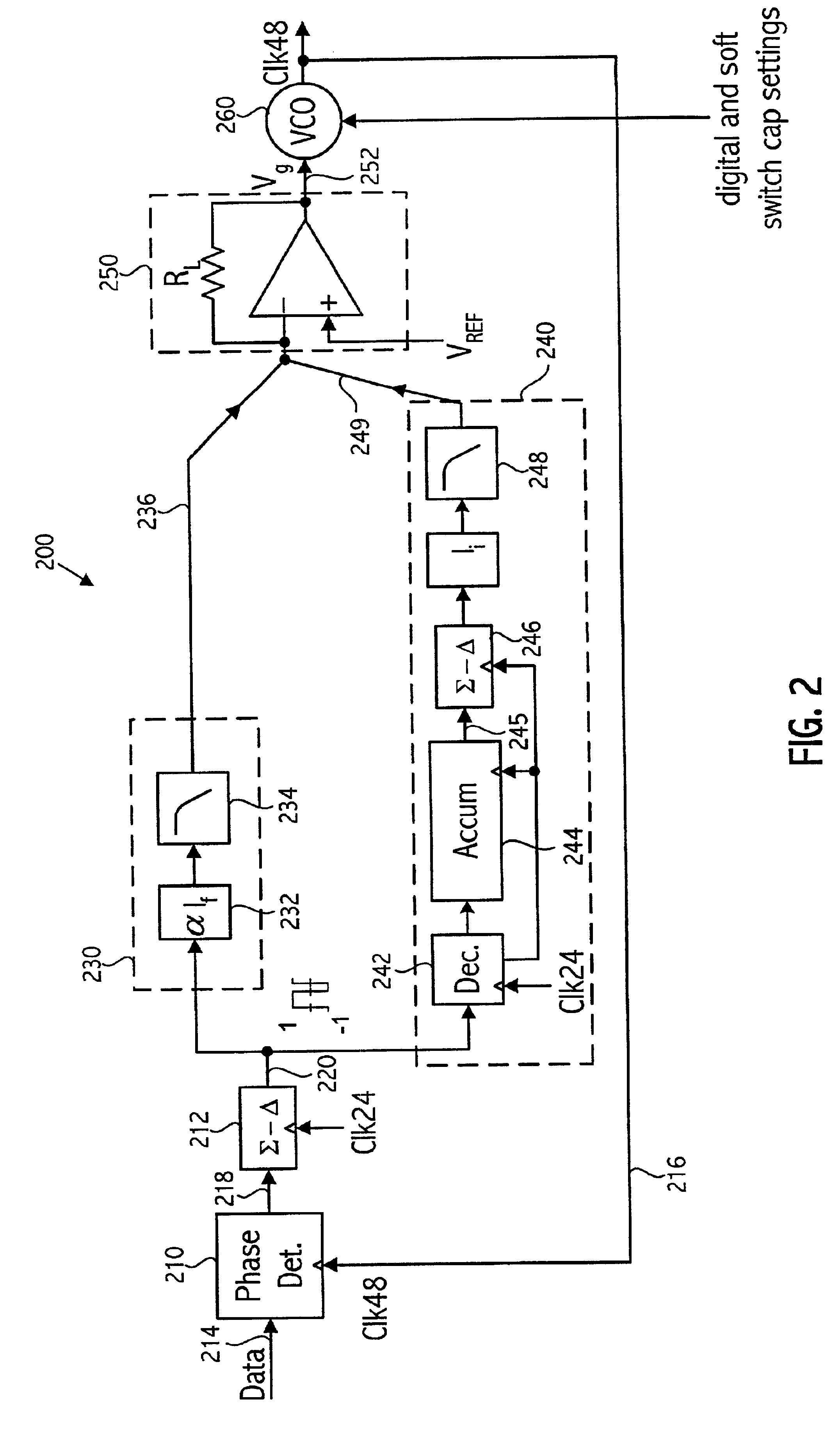
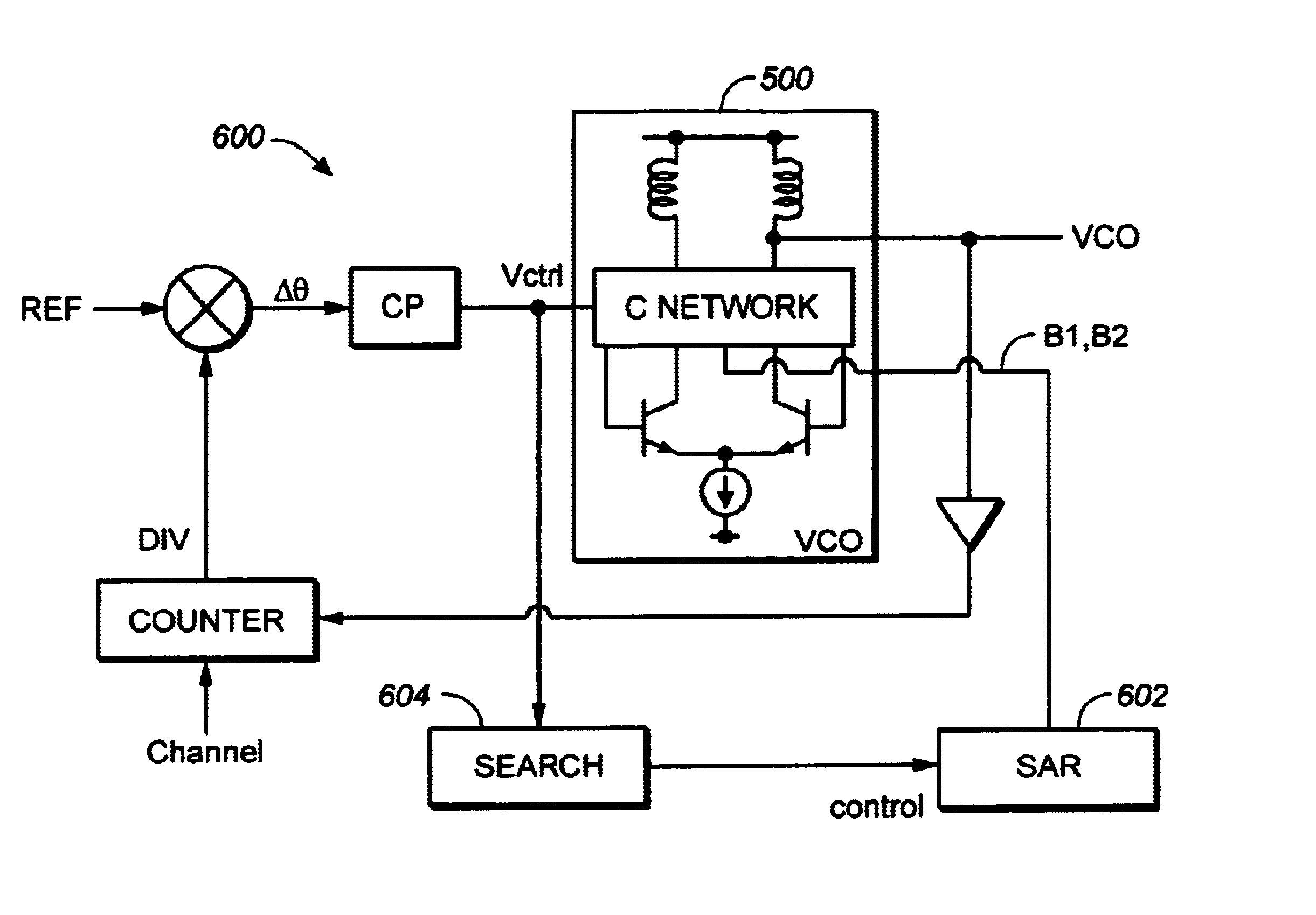
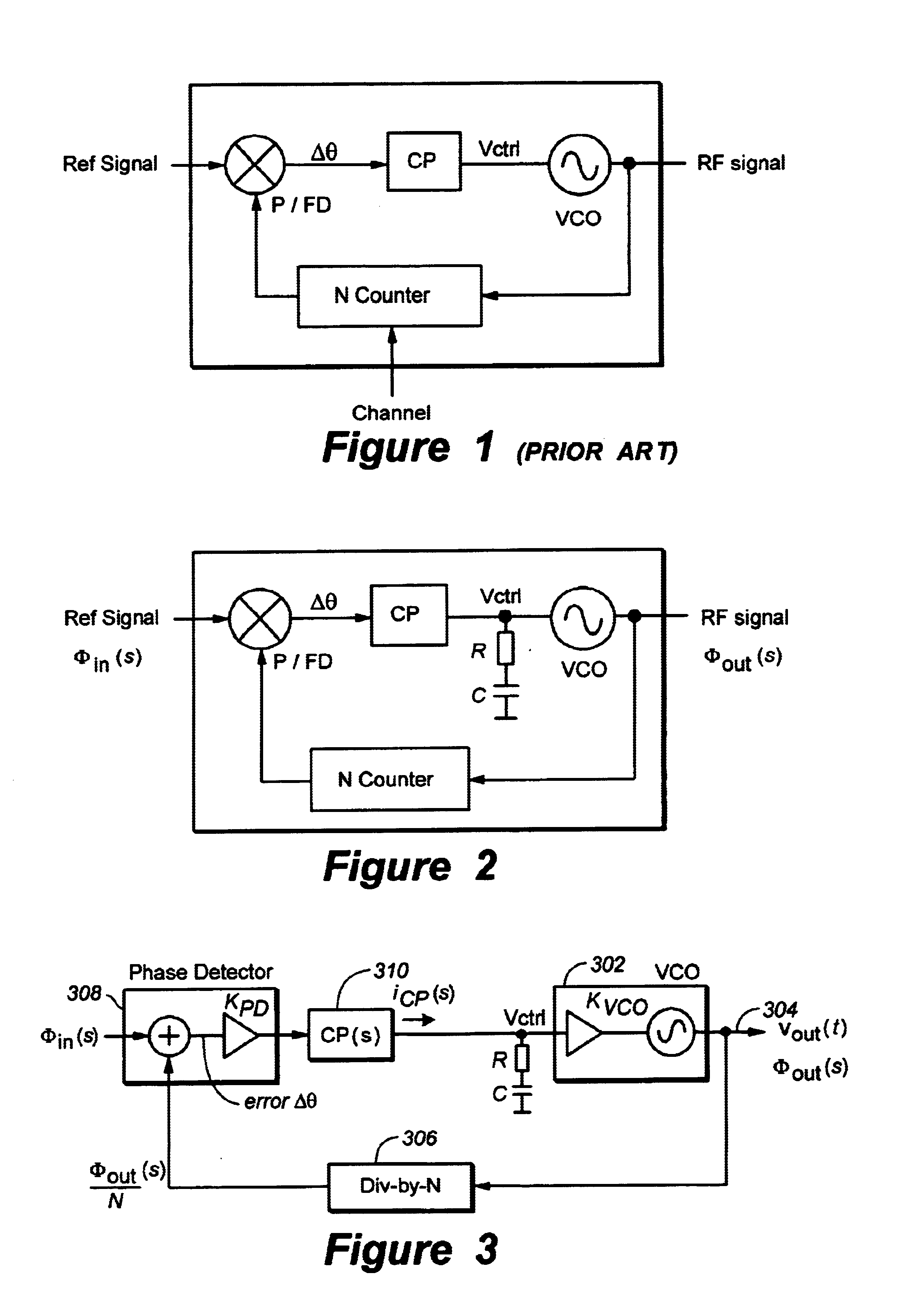
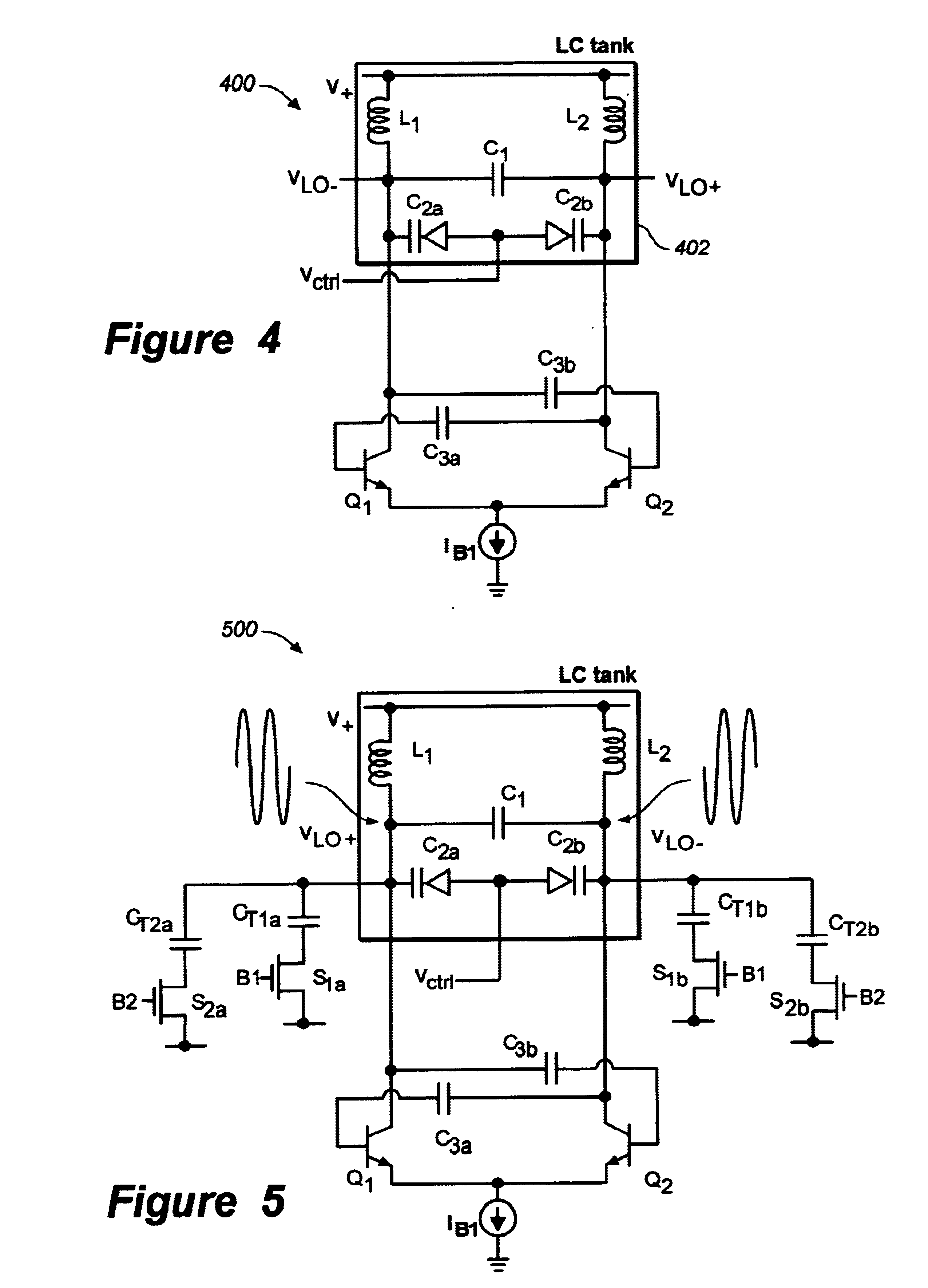
Patents
Literature
144results about "Oscillator tubes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
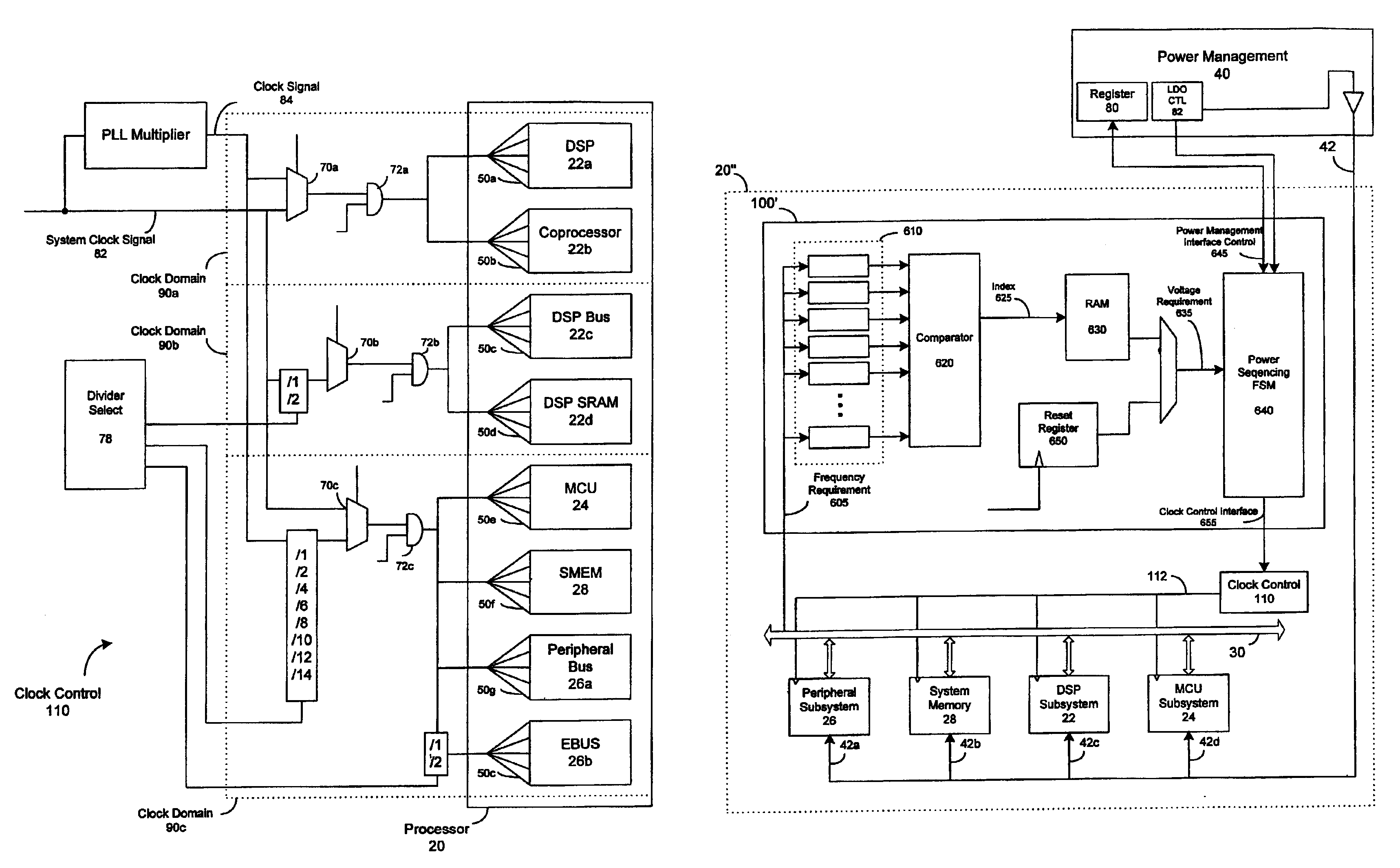
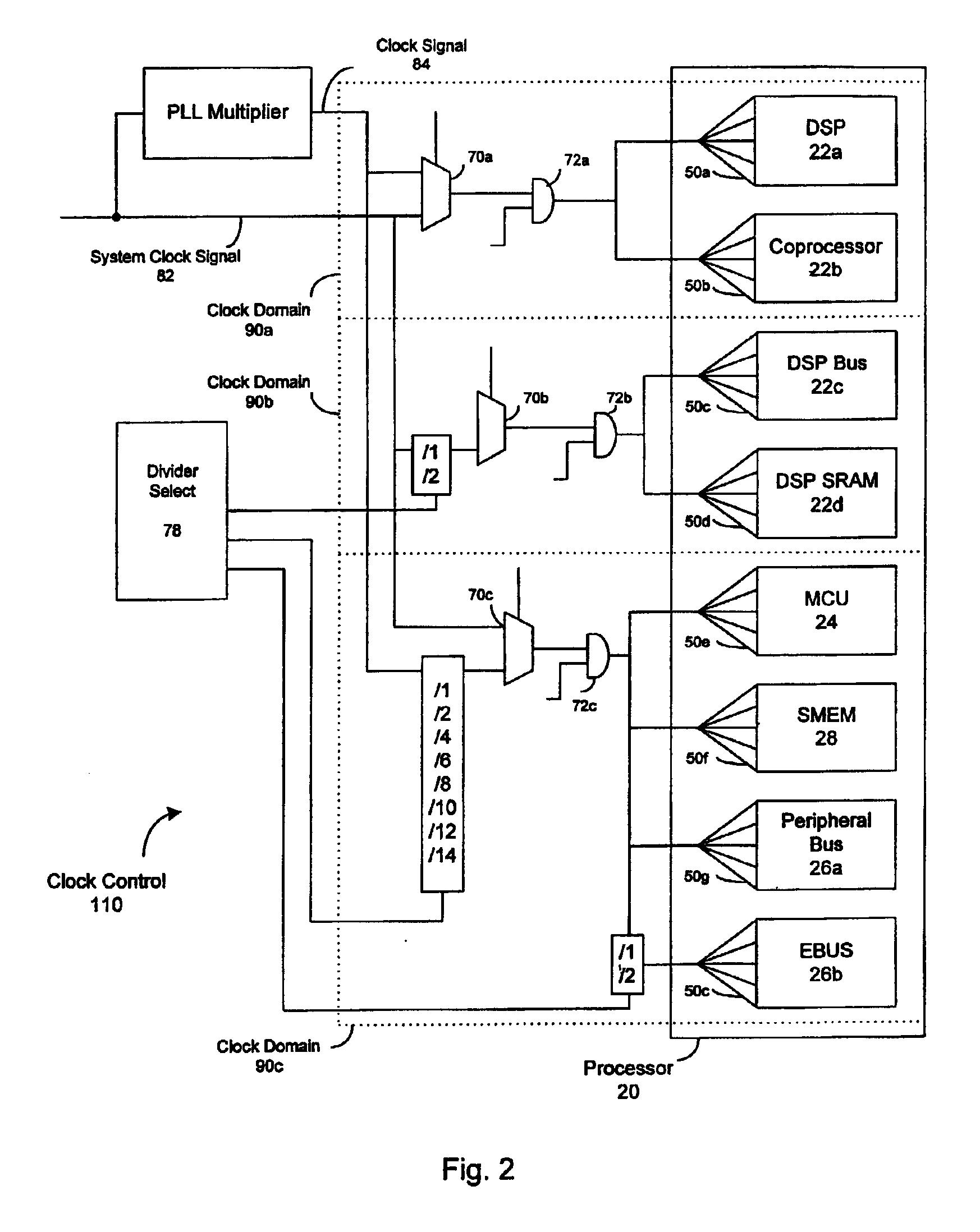
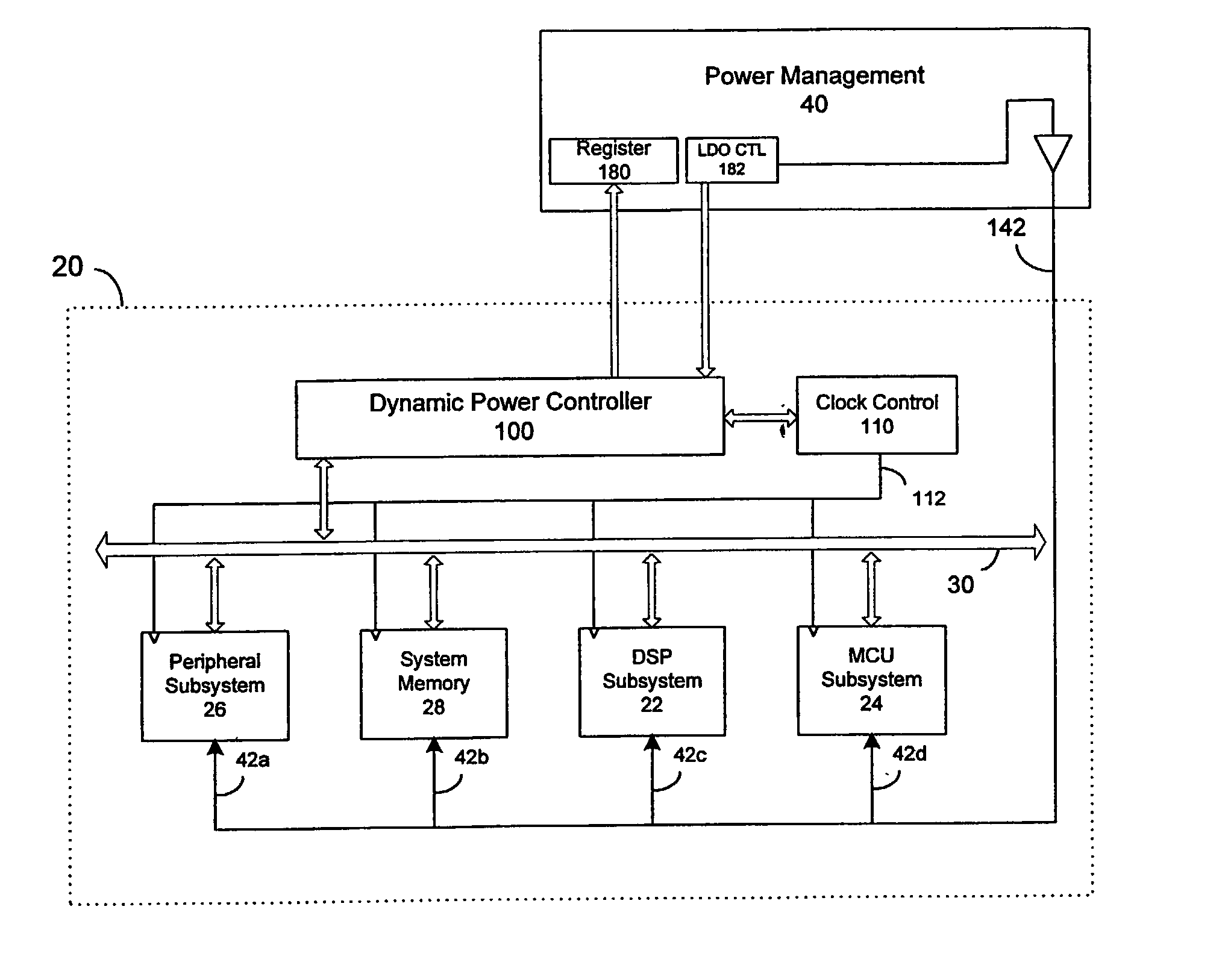
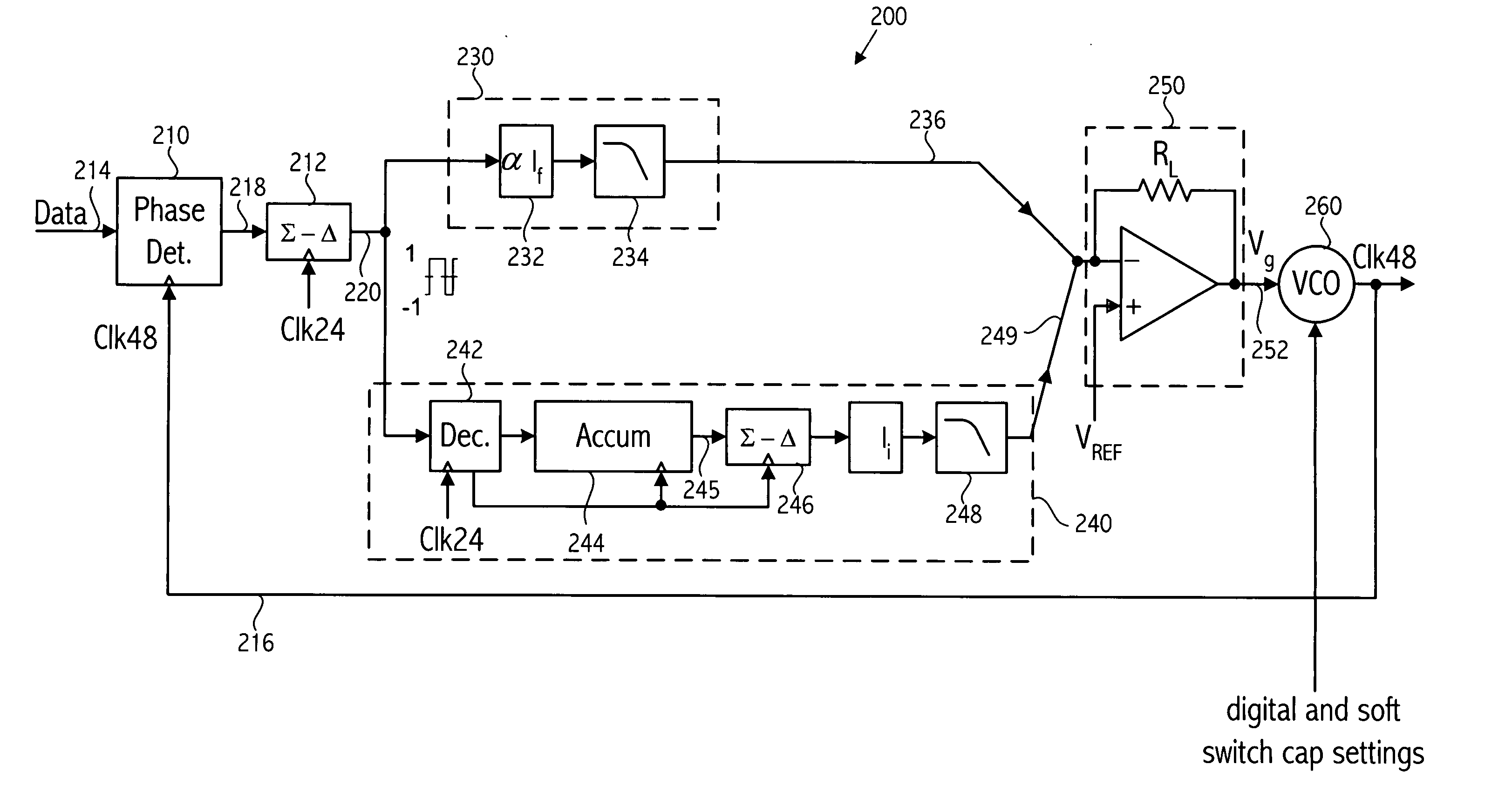
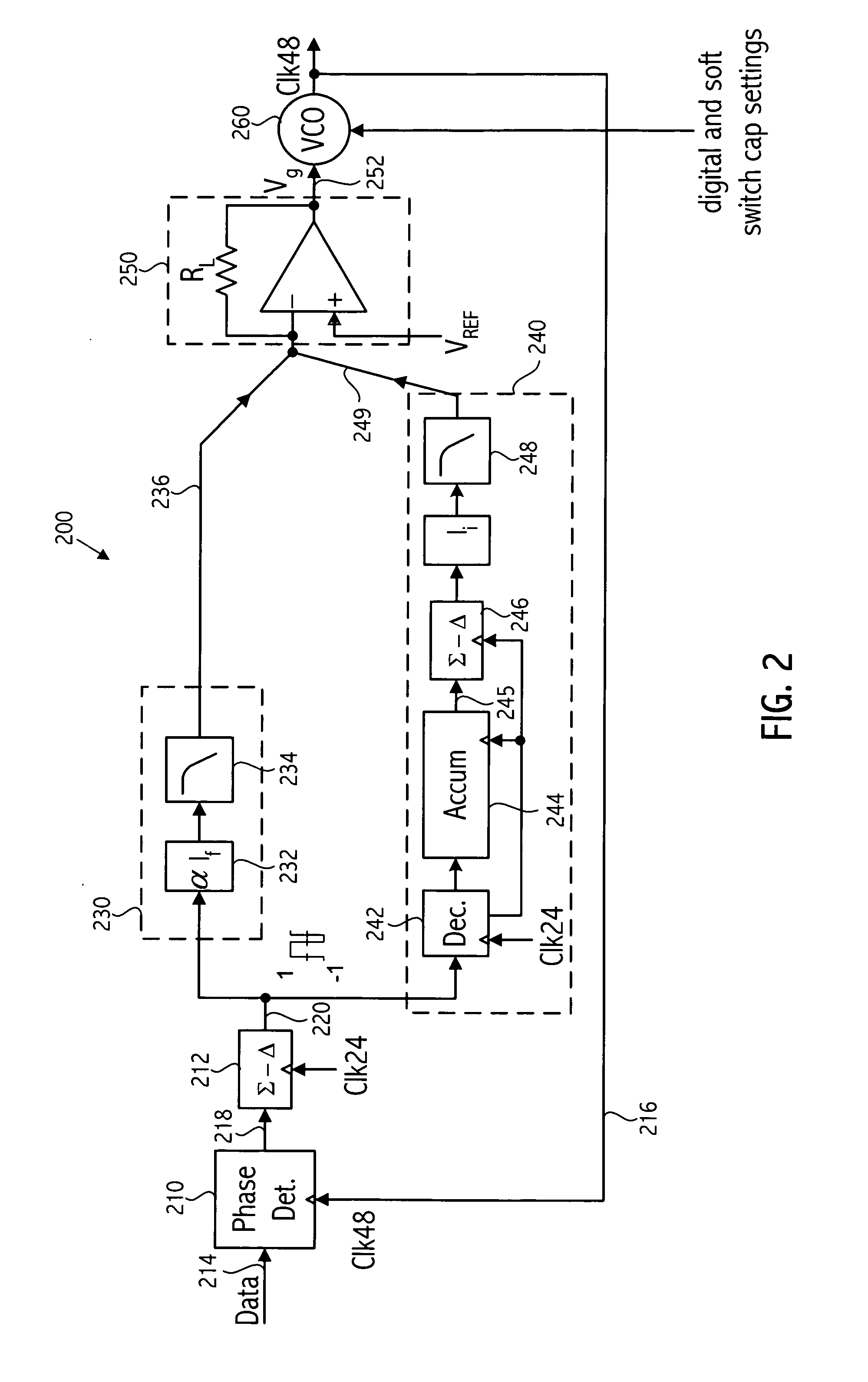
Dynamic voltage control method and apparatus
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Dynamic voltage control method and apparatus
A dynamic power controller is provided that identifies a clock frequency requirement of a processor and determines a voltage requirement to support the clock frequency requirement. The dynamic power controller transitions the processor to a power state defined by the clock frequency requirement and the voltage requirement. In particular, a voltage level indicated by the voltage requirement is supplied to the processor and the frequency distribution indicated by the frequency requirement is provided to the clocks signals of the processor.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
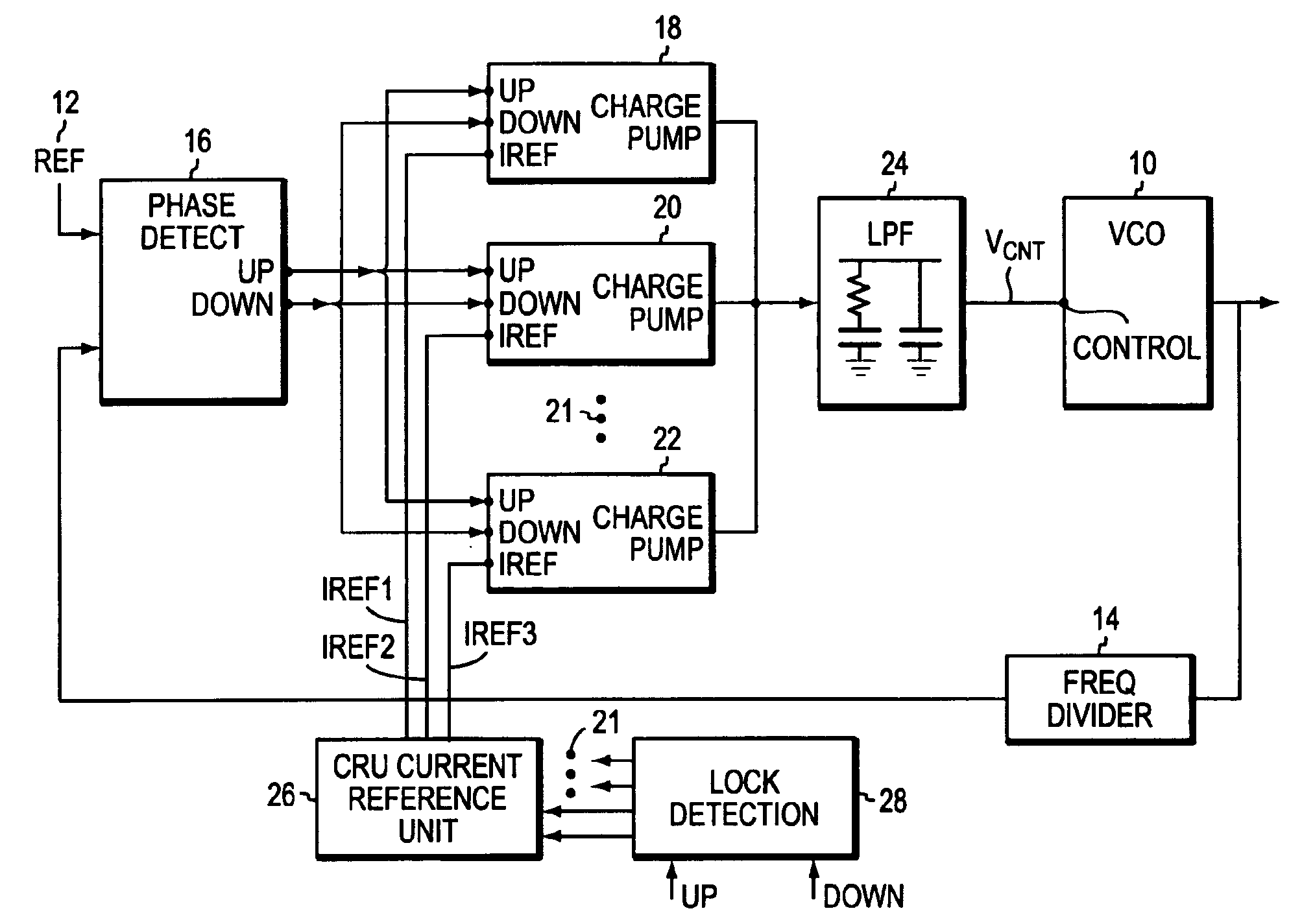
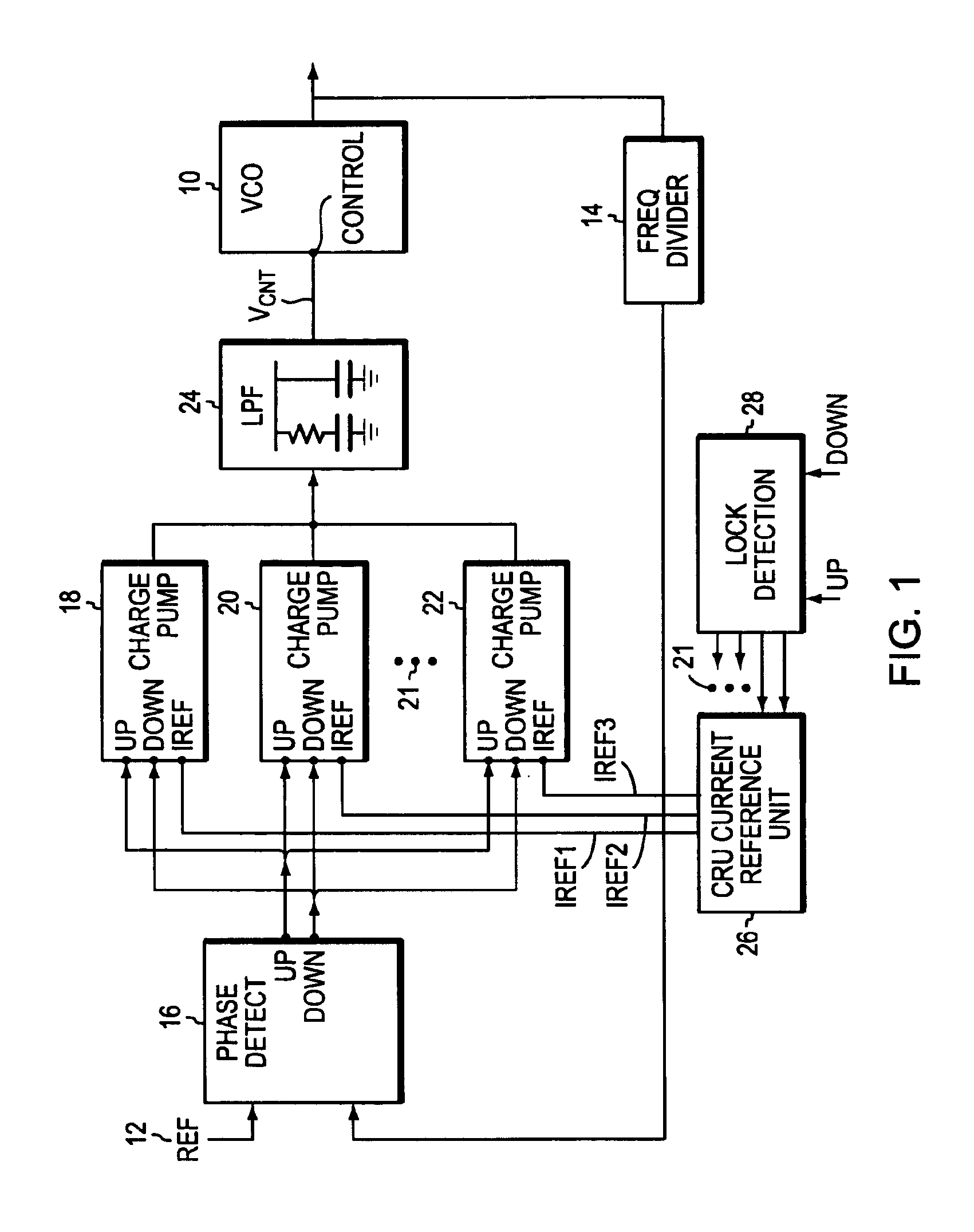
Circuitry to reduce PLL lock acquisition time
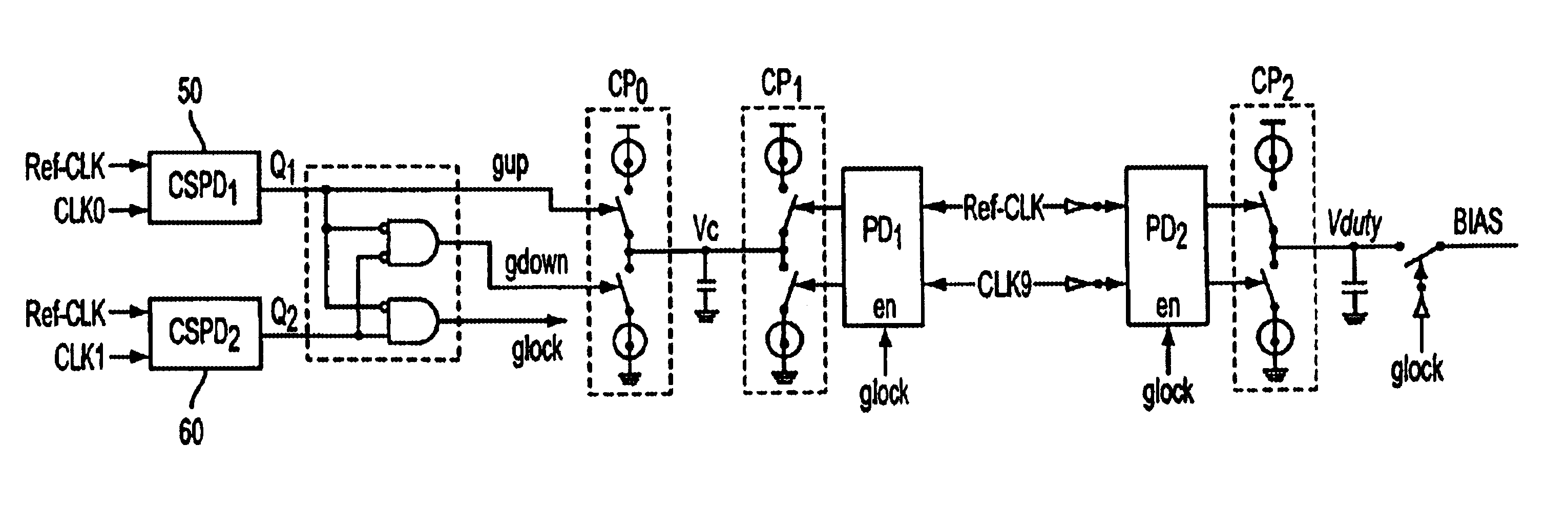
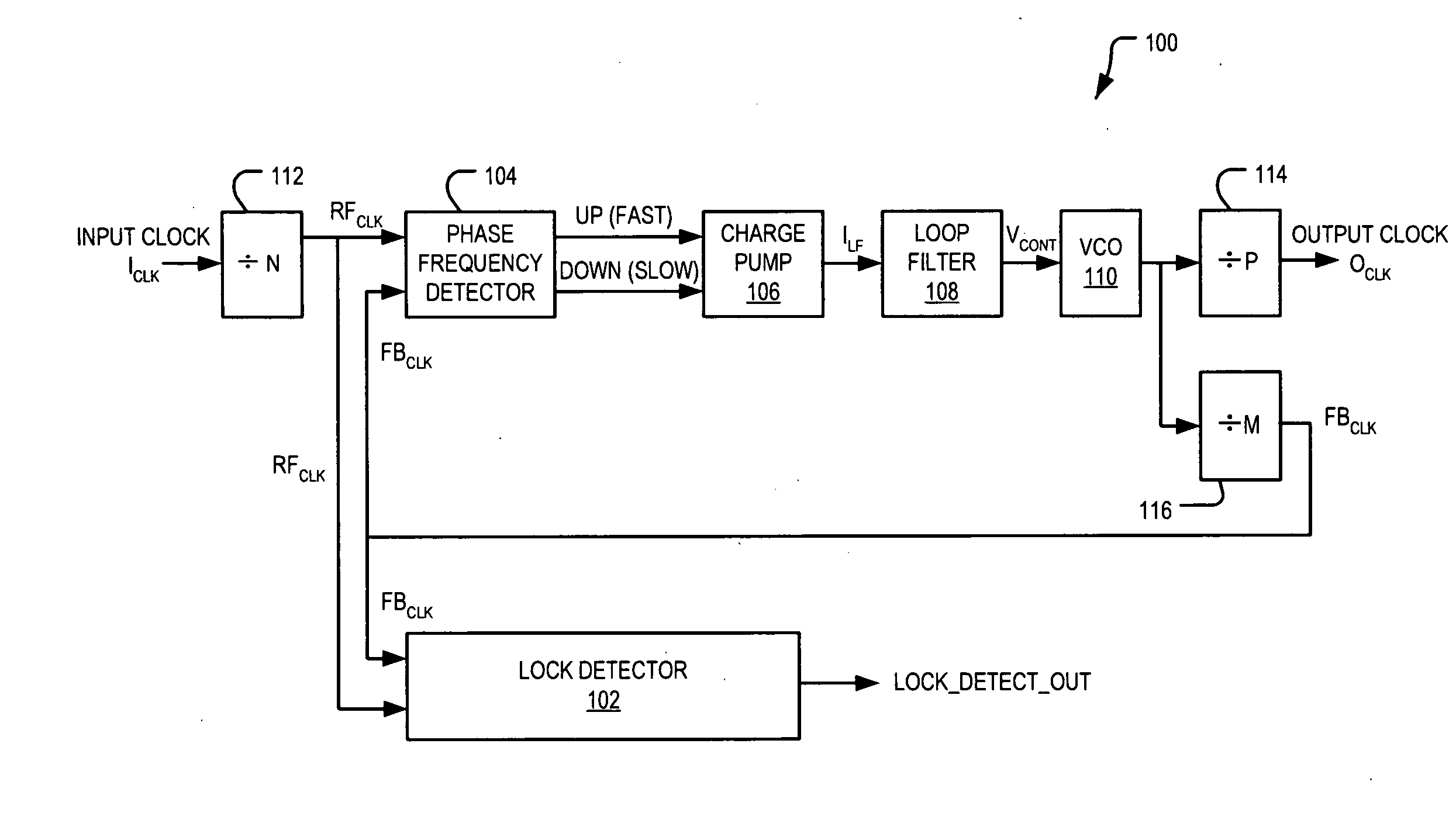
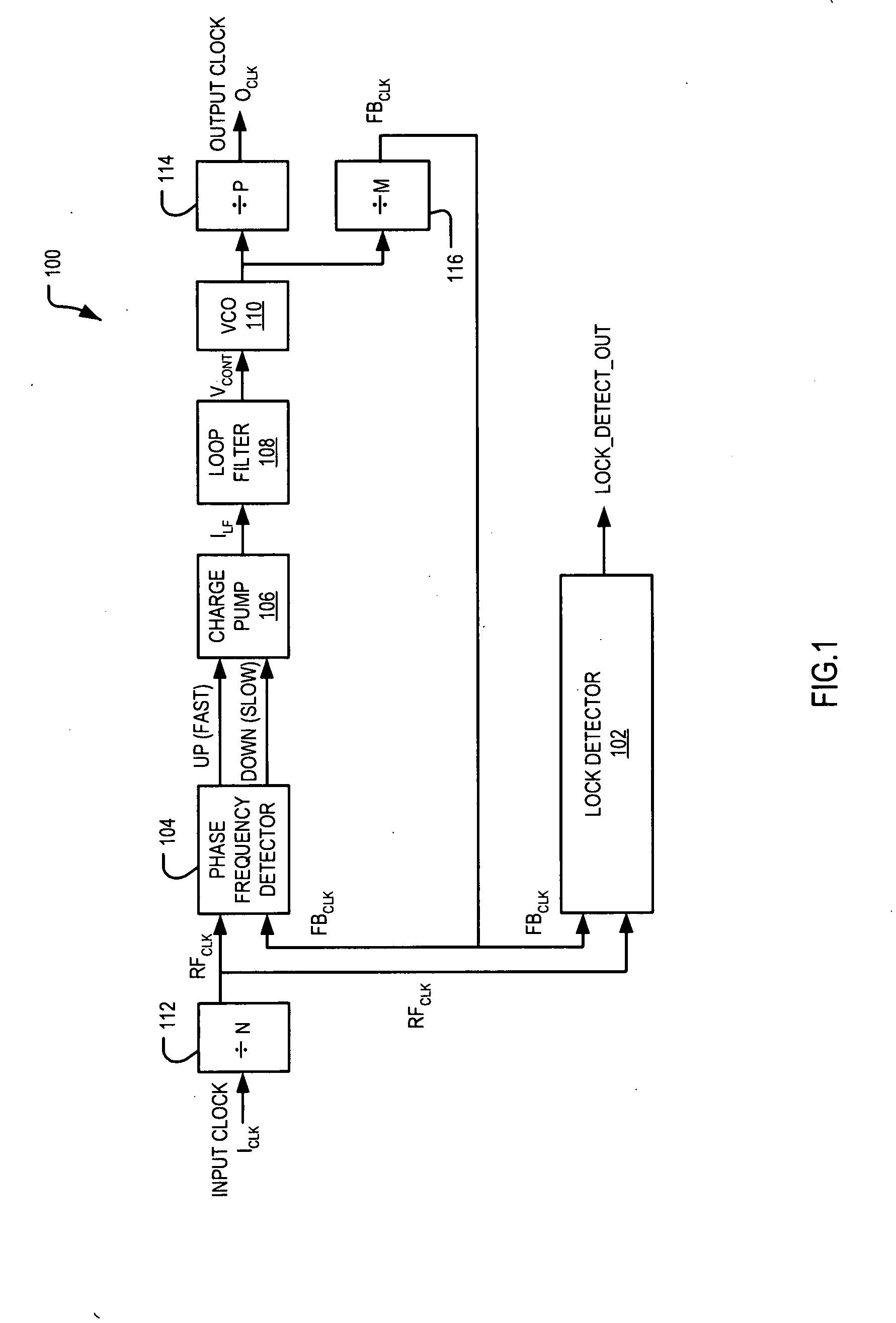
ActiveUS6940356B2Decrease frequency/phase errorFast frequencyPulse automatic controlOscillator tubesPhase detectorSwitched current
A phase locked loop, PLL, is described with multiple parallel charge pumps that are selectively disabled as phase lock is approached. A lock detection circuit is described that enabled reference currents to be fed to the parallel charge pumps. The error signal from a phase detector is arranged as UP and a DOWN signals that are averaged in the lock detector. When the average error is large, all the reference currents feed the charge pumps that provide a high loop gain to reduce the lock time. As the lock becomes closer selective reference currents are disabled to reduce loop gain so that a smooth transition to lock is made. Selectively switching currents into a low pass filter that usually follows a charge pump in a PLL circuit automatically reduces switching noise by the operation of the low pass filter.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Phase lock loop with coarse control loop having frequency lock detector and device including same
ActiveUS7102446B1Improve portabilitySynchronization is simplePulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersTransceiverPhase locked loop circuit
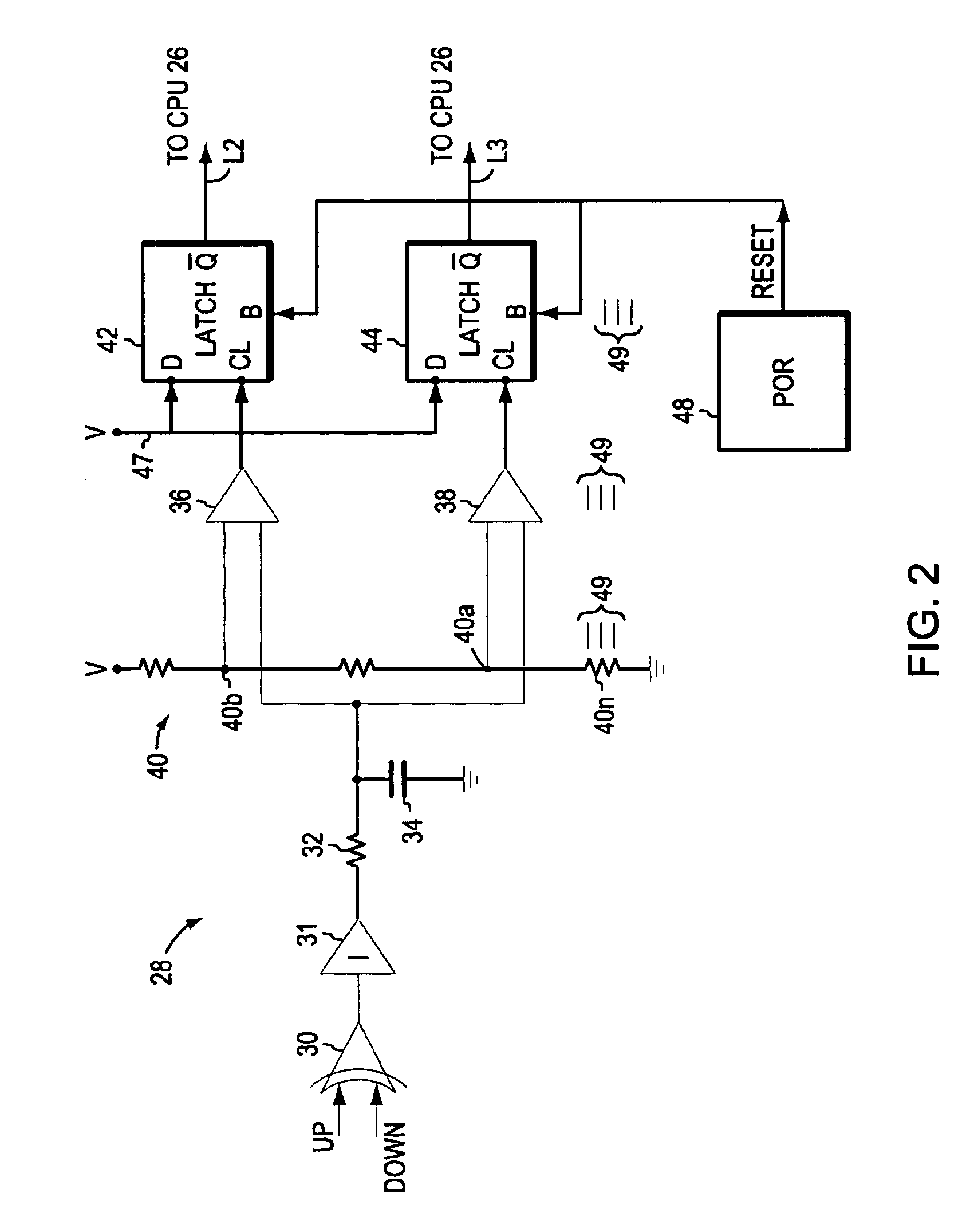
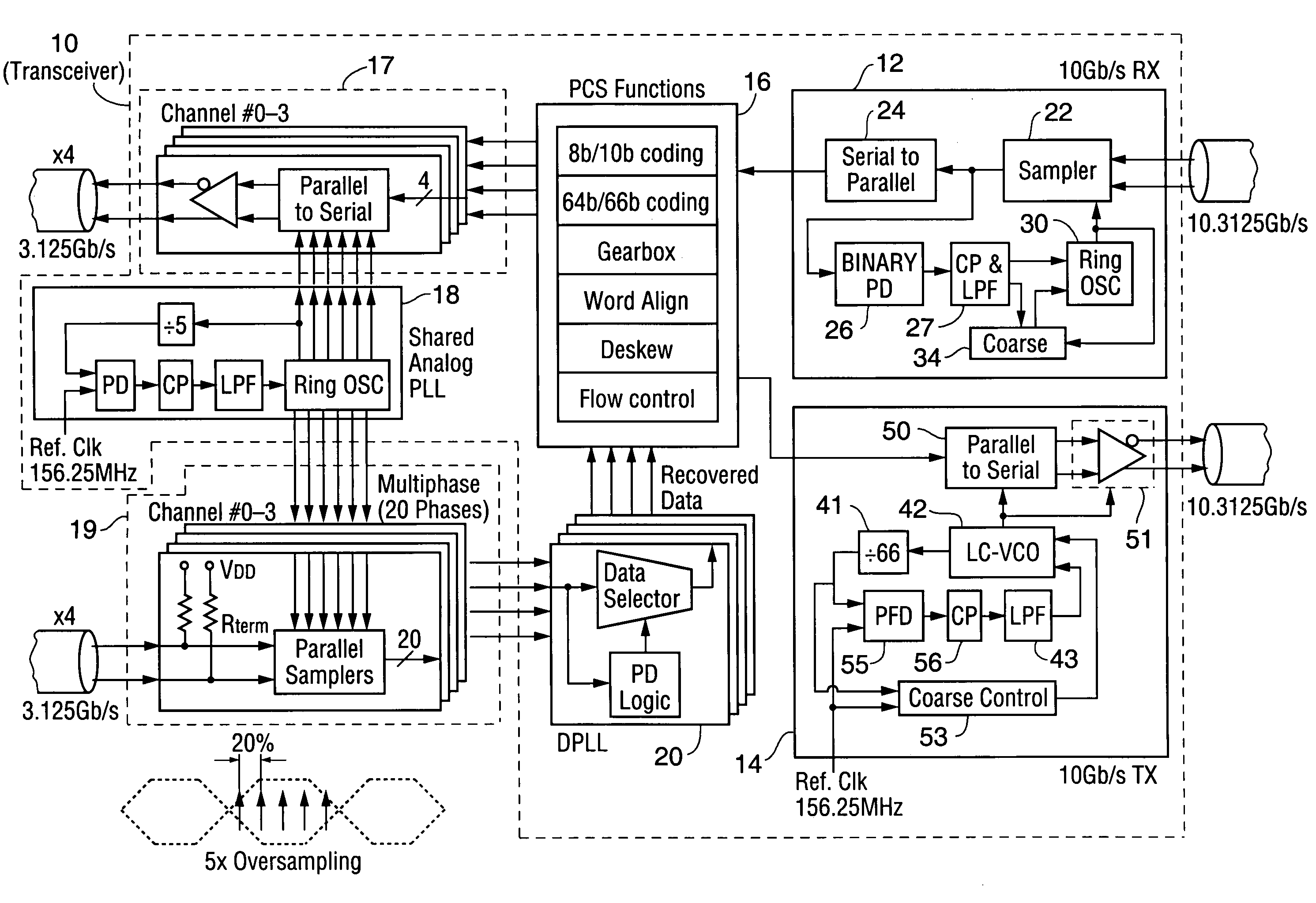
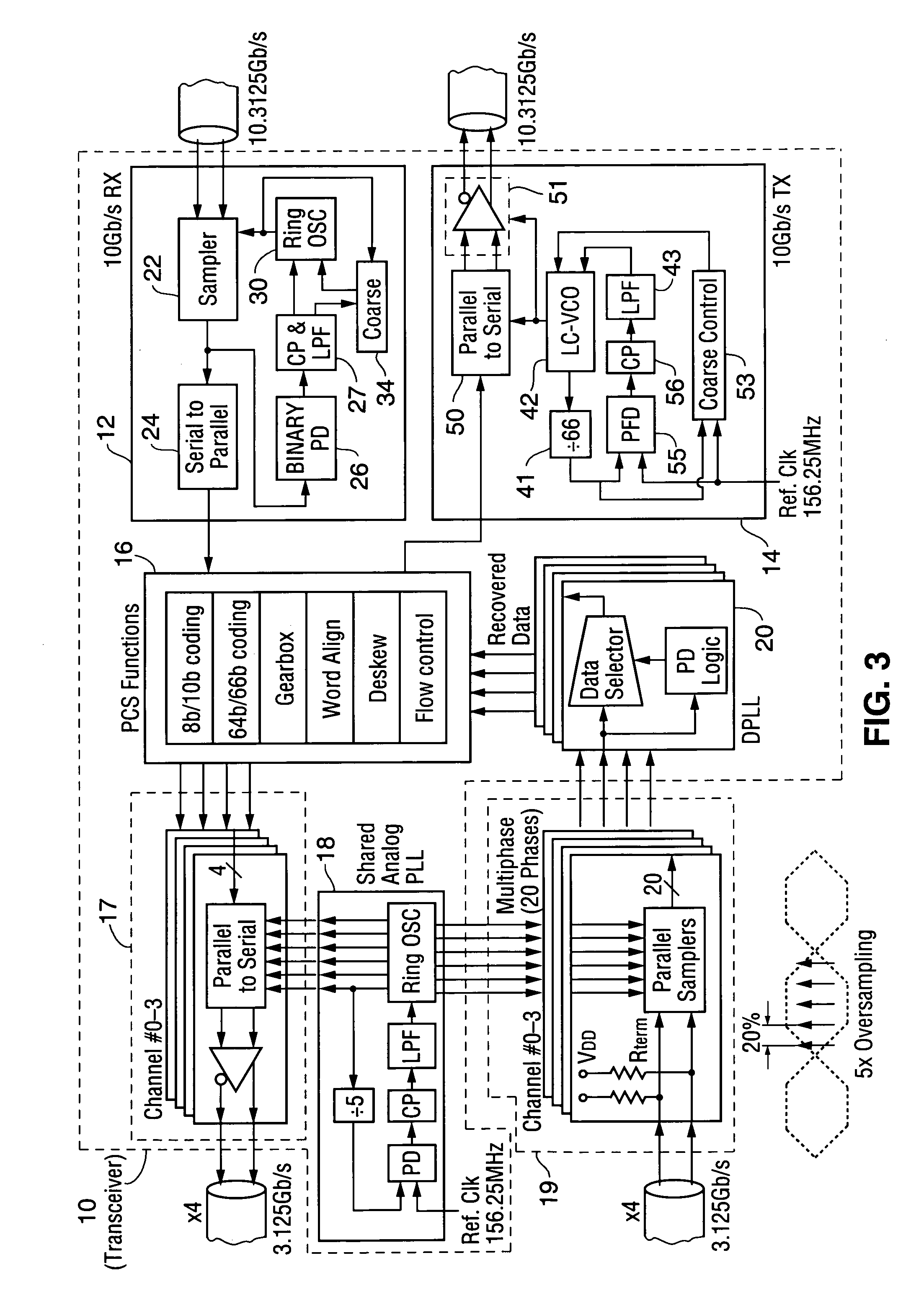
A phase lock loop (PLL) for controlling a sampling clock or other clock, and a data sampling circuit, transceiver, or other device including such a PLL. The PLL includes a multi-range VCO, at least one fine control loop for controlling the VCO, and a coarse control loop for controlling the VCO by changing its frequency-voltage characteristic. The coarse control loop includes a frequency lock detector and voltage range monitoring logic. Typically, the frequency lock detector locks operation of the coarse control loop when the difference between the VCO output clock frequency and a reference frequency decreases to within a predetermined threshold, and the unlocked coarse control loop employs the voltage range monitoring logic to change the VCO frequency-voltage characteristic when the VCO's fine control voltage leaves a predetermined range. Other aspects are a transceiver (including at least two receiver interfaces and a transmitter interface) implementing a clocking scheme employing no more than three PLLs for clock generation, and a transceiver having a multi-layered receiver interface including digital circuitry and a single clock-generating PLL (an analog PLL for generating a multiphase clock to be shared by all layers of the receiver interface). Each receiver interface layer performs blind oversampling on a different received signal using the multiphase clock and the digital circuitry includes multilayered digital phase lock loop circuitry which receives the oversampled data.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Phase/frequency detector and phase lock loop circuit
ActiveUS6856202B2Avoid the needHigh frequencyPulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleDetector circuitsControl signal
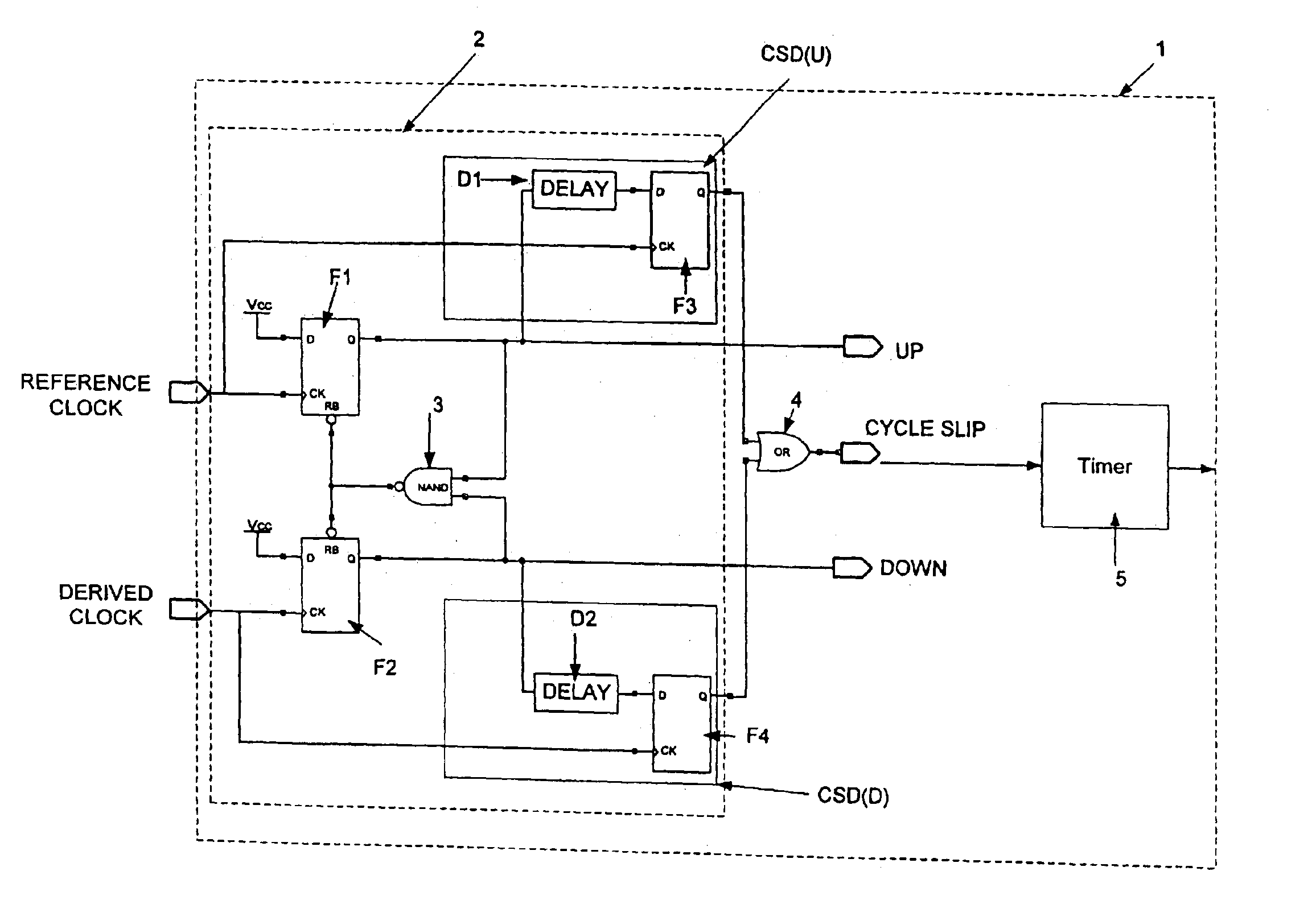
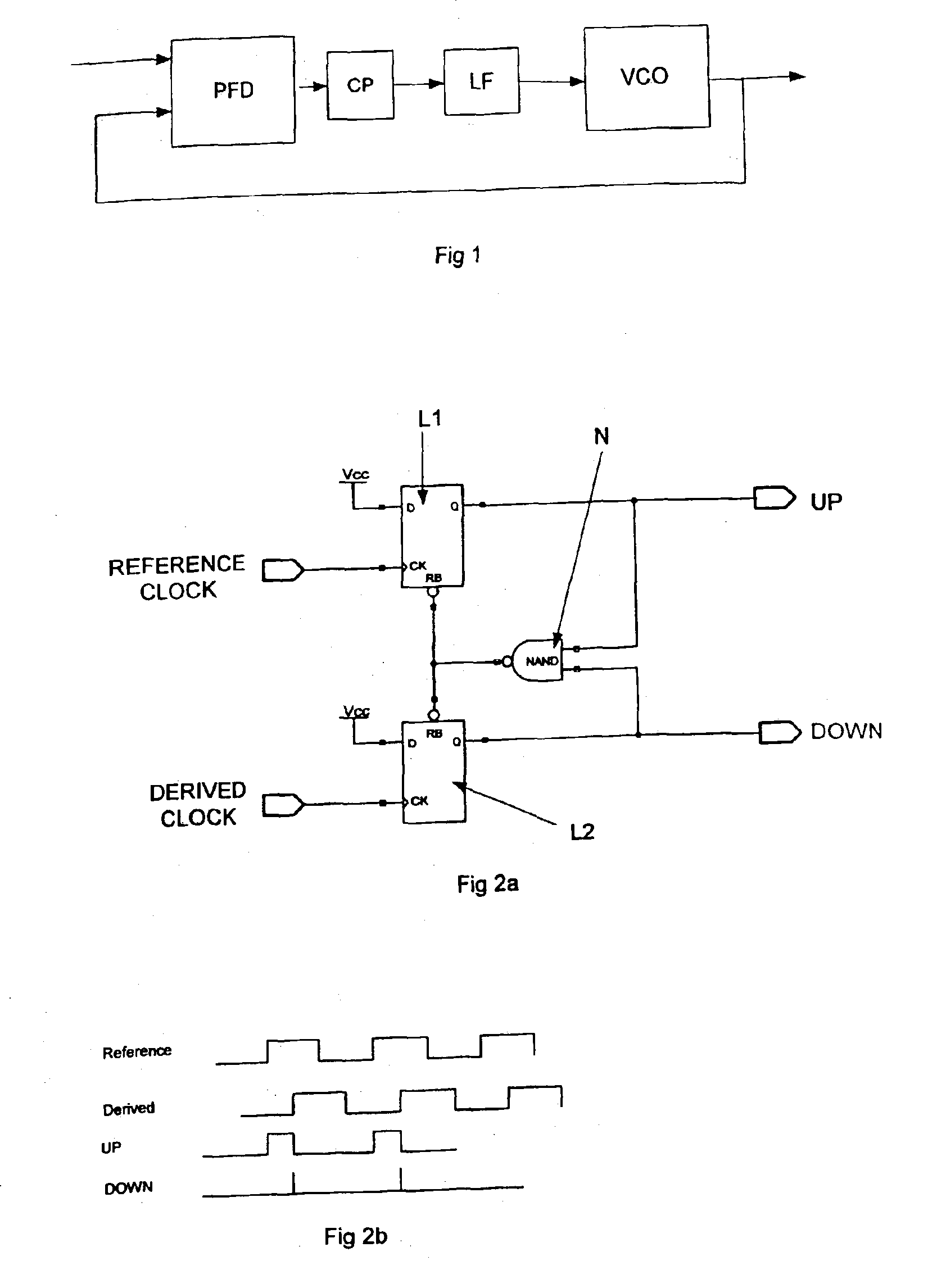
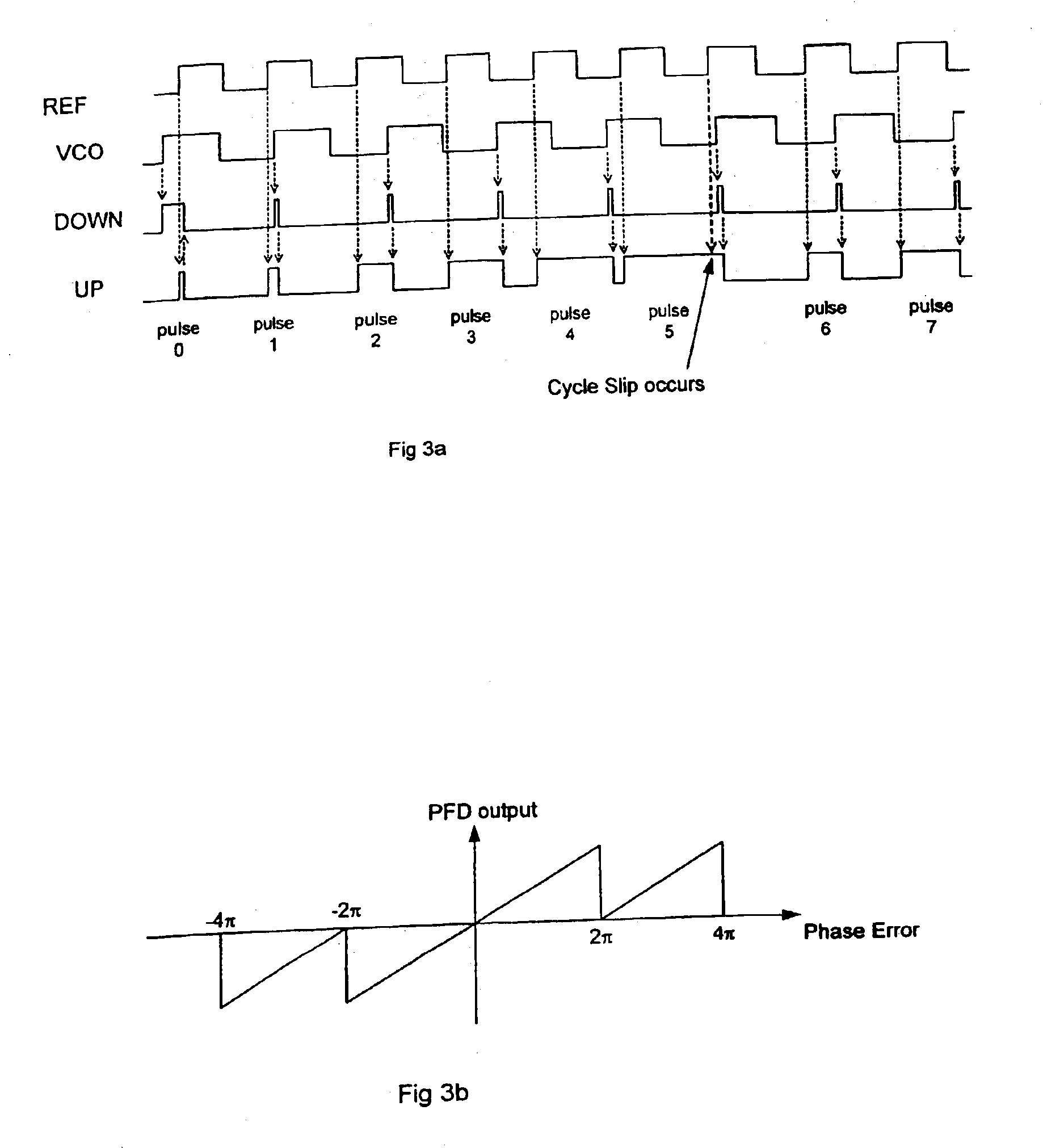
The present invention relates to cycle slip detectors for phase and frequency detectors (PFD) and to lock detectors for phase lock loop (PLL) circuits. The present invention provides a cycle slip detector circuit for use with a phase and frequency detector circuit having first and second signal inputs, and arranged to provide first and second PLL control signal outputs responsive to clock edges in the first and second input signals respectively; the cycle slip detector circuit comprising: means for determining a cycle slip between said input signals by determining when a delayed output signal coincides with a respective input signal.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Lock detector for phase locked loops
InactiveUS6580328B2Improve system performanceEliminate high frequency noisePulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDetector circuitsControl system
A detector circuit for determining whether synchronization lock has been optimally achieved in feedback-type control systems. The detector circuit evaluates an error signal developed by a phase / frequency detector and compares the absolute magnitude of the error signal to a first threshold signal corresponding to a magnitude metric. When the value of the error signal is less than the magnitude threshold value, an event signal initiates a time interval counter which continues counting so long as the error signal remains below the magnitude threshold value. The time interval counter continues until it counts to a second threshold value corresponding to a timing metric. At this point, synchronization lock is declared.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Ring oscillator using current mirror inverter stages
InactiveUSRE37124E1Limit maximum frequencyPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsLow voltageEngineering
A ring oscillator having an odd number of single ended stages, each stage including two transistors connected as a current mirror. The stage provides for low-voltage performance and improved process tolerance characteristics.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
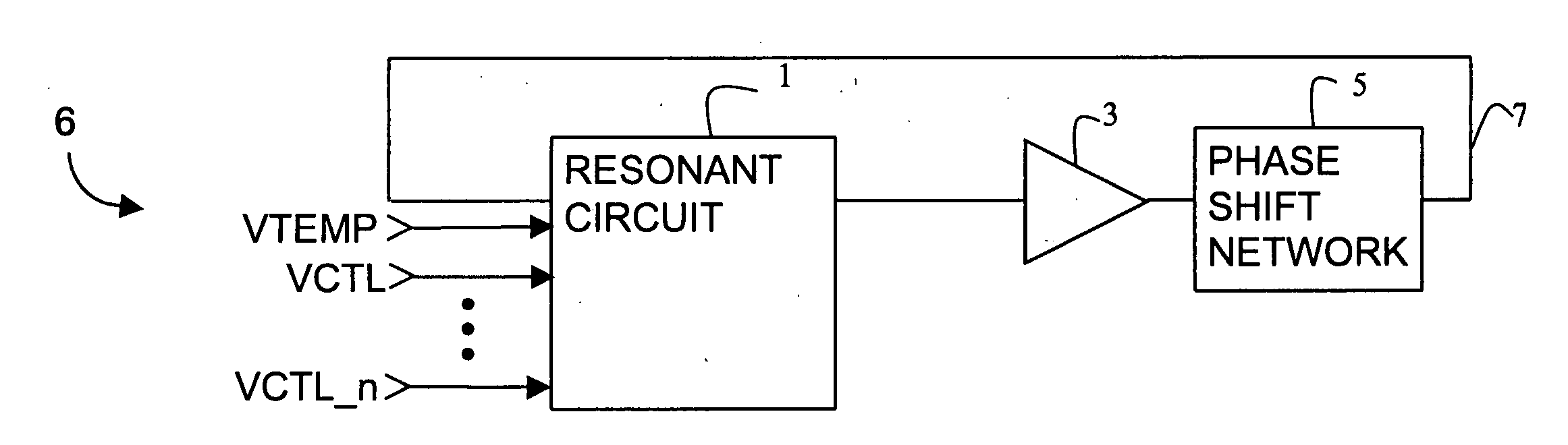
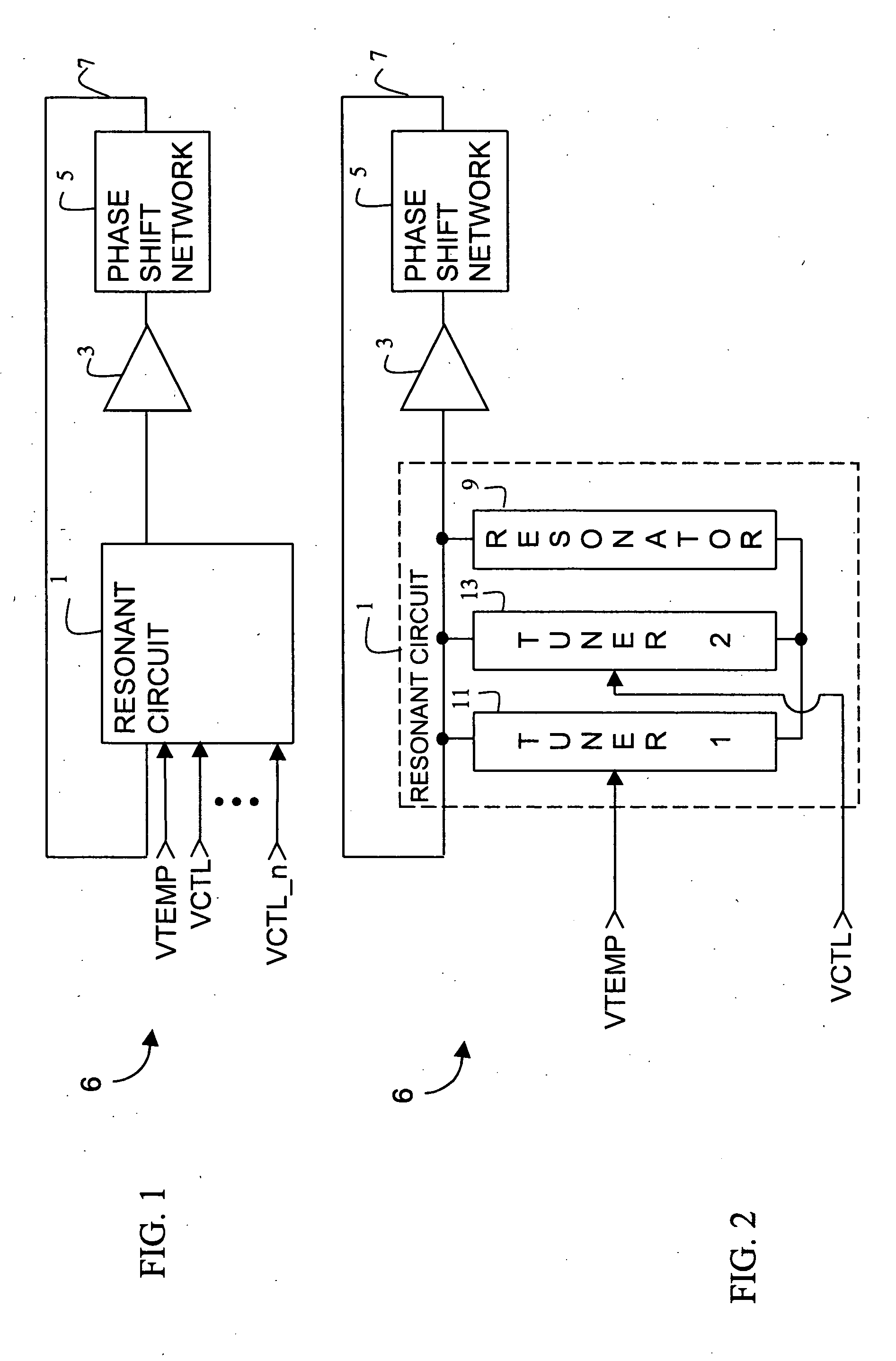
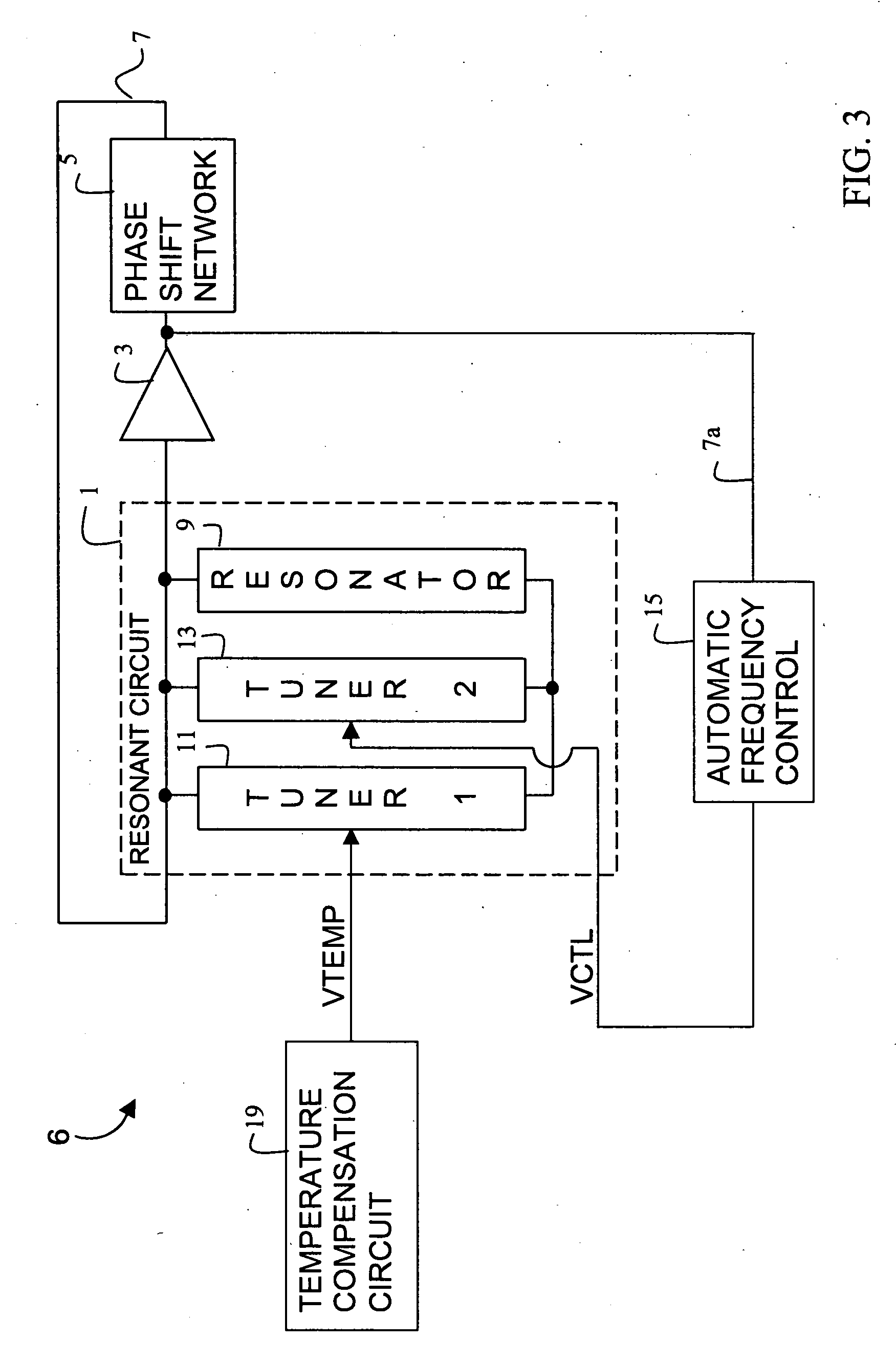
Temperature compensation circuit
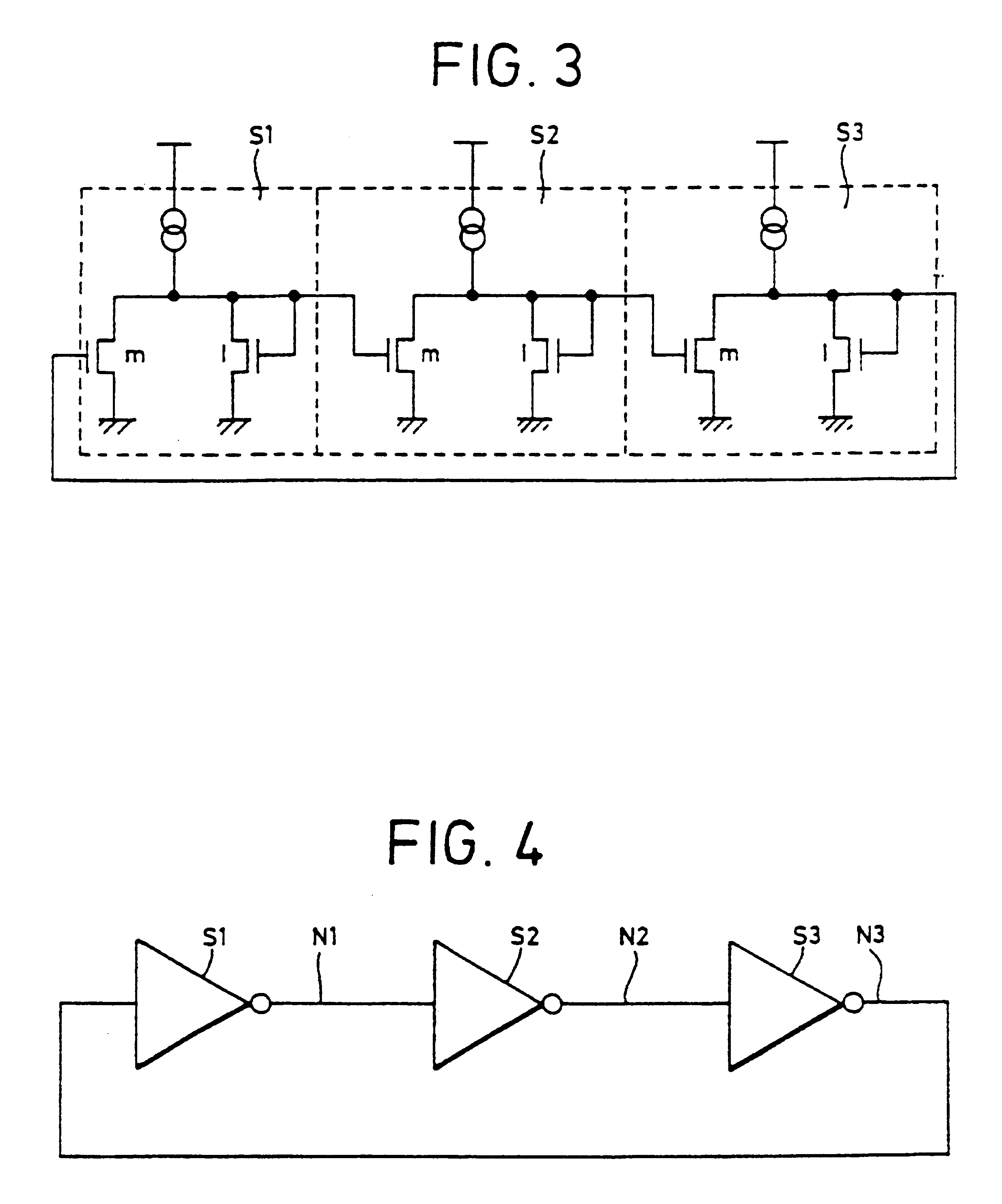
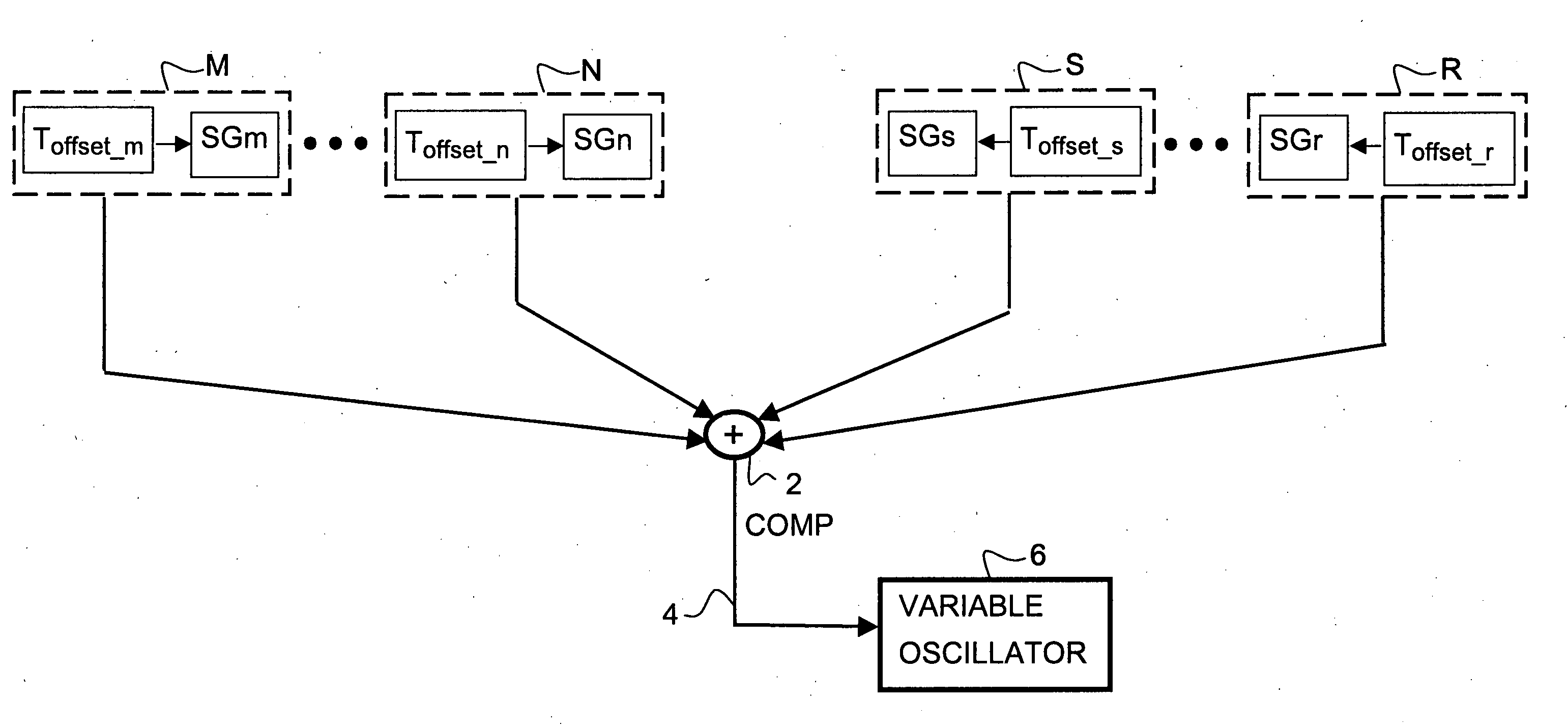
A temperature compensation circuit has multiple configurable modules to produce a compensation signal whose temperature characteristic curve is the inverse of the frequency-to-temperature characteristic curve of a specified oscillator. A set of first modules that produce first sub-signals directly proportional to temperature and a set of second modules that produce second sub-signals inversely proportional to temperature have their outputs summed at a summation node. Each module may adjust the strength and shaped of its temperature characteristic sub-signal, and each module may optionally be assigned a temperature offset that impedes the output of its corresponding sub-signal until the assigned temperature offset is reached. Each of the first and second modules includes a signal generator and an optional temperature offset circuit, which may be incorporated into the operation of the signal generator. To produce a compensation signal to compensate a SAW resonator, a first module having a temperature offset and being directly proportional to temperature is summed with a second module having no temperature offset and being inversely proportional to temperature.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Phase lock detection circuit for phase-locked loop circuit
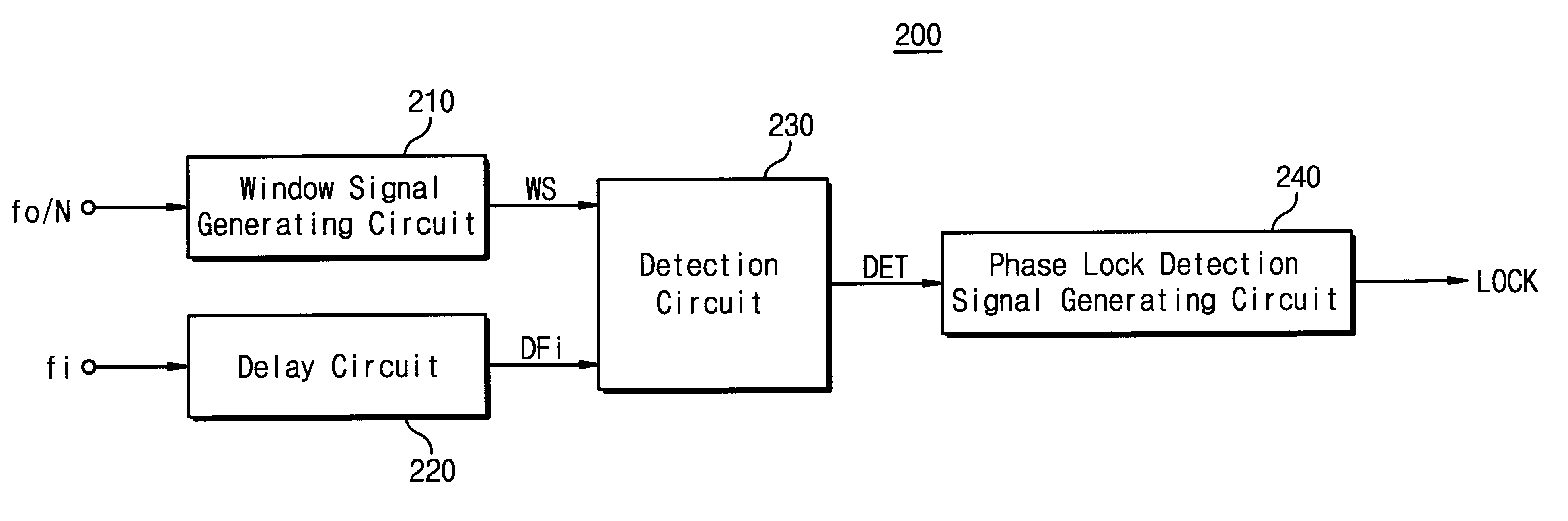
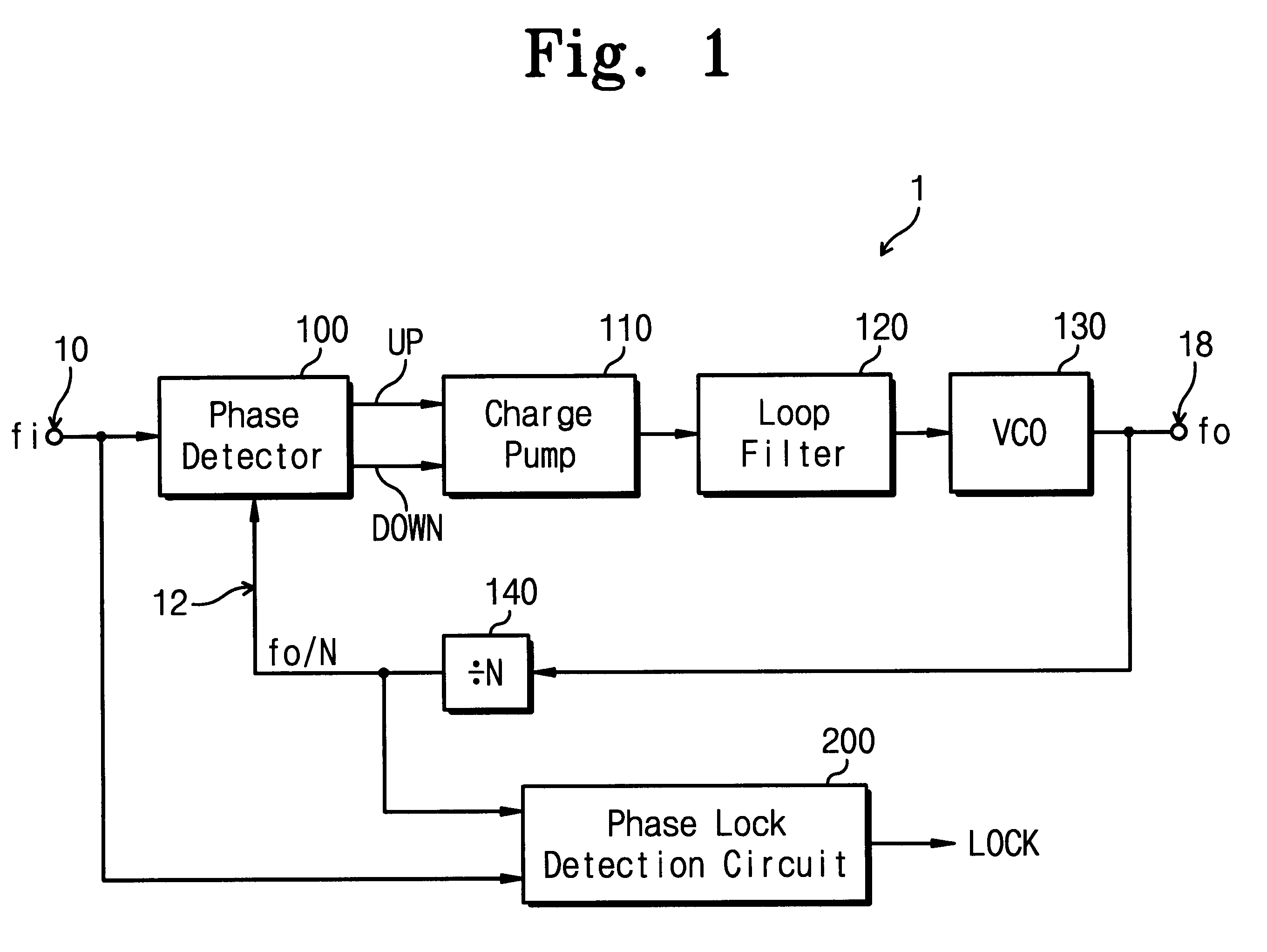
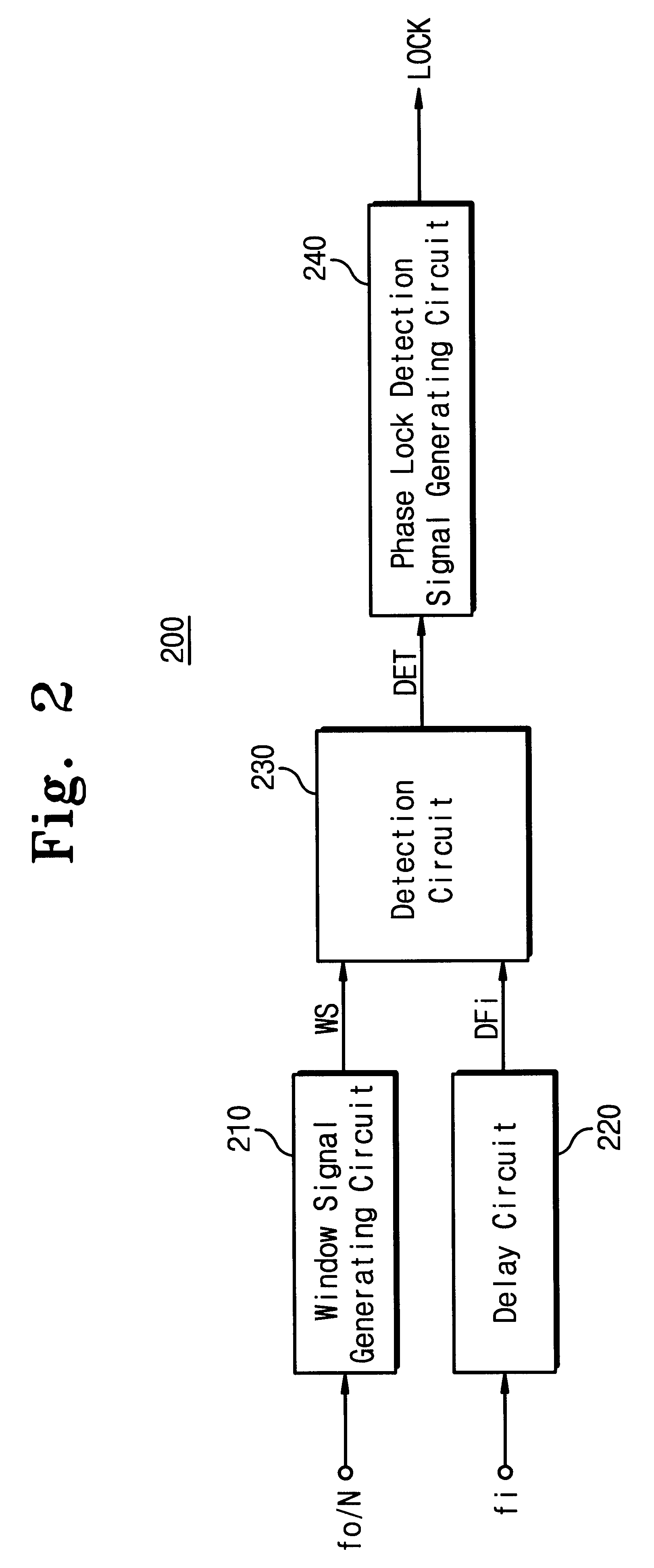
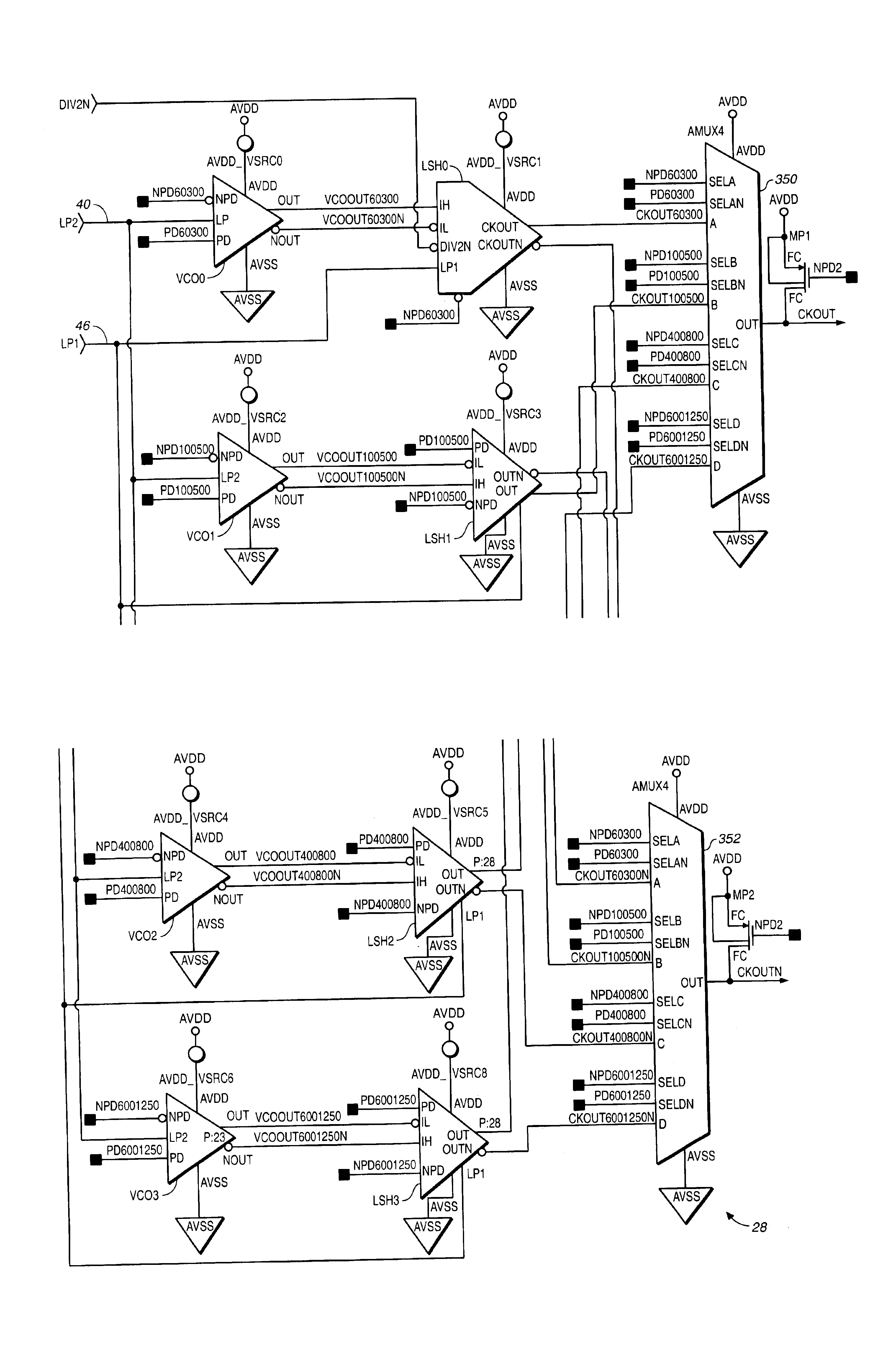
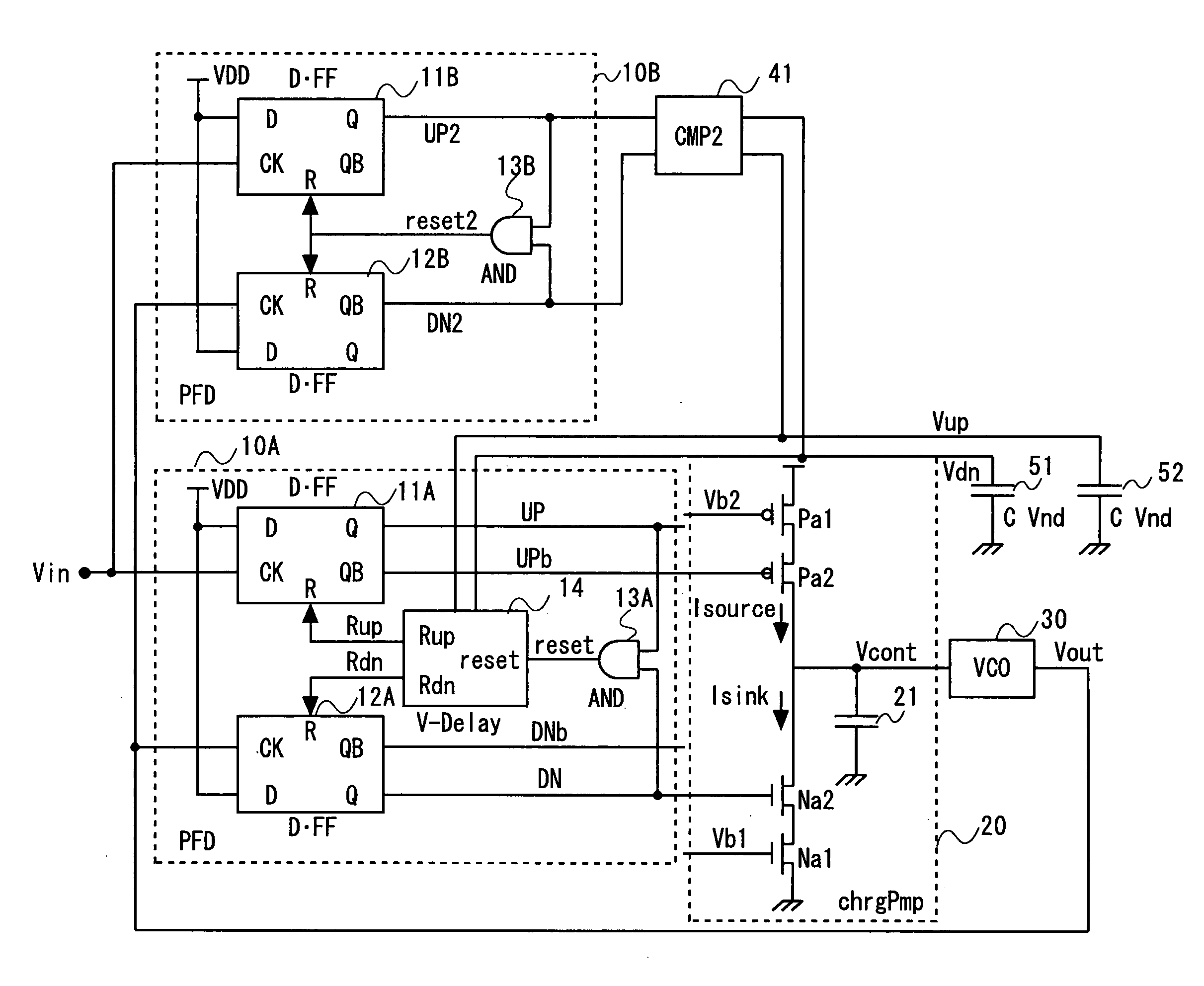
The present invention relates to a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit and, more particularly to a PLL with a phase lock detection circuit. The PLL circuit includes a phase detector, a charge pump, a loop filter, a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), a frequency divider, and a phase lock detection circuit having two current charging / discharging circuits with first and second constant current sources for generating a phase lock signal having a pulse form through charging / discharging a capacitor. A voltage level of the capacitor is changed with a hysteresis characteristic. In the out-of-lock state of the PLL circuit, the discharging speed of the capacitor is faster than the charging speed thereof. In the phase lock state of the PLL circuit, the charging speed of the capacitor is faster than the discharging speed thereof. Since the charging / discharging operation of the capacitor is executed linearly and symmetrically, the phase lock detection circuit according to the present invention can obtain stable phase lock information. In addition, it is able to forecast the result of the phase lock state apart from a process variation by using the current mirror.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
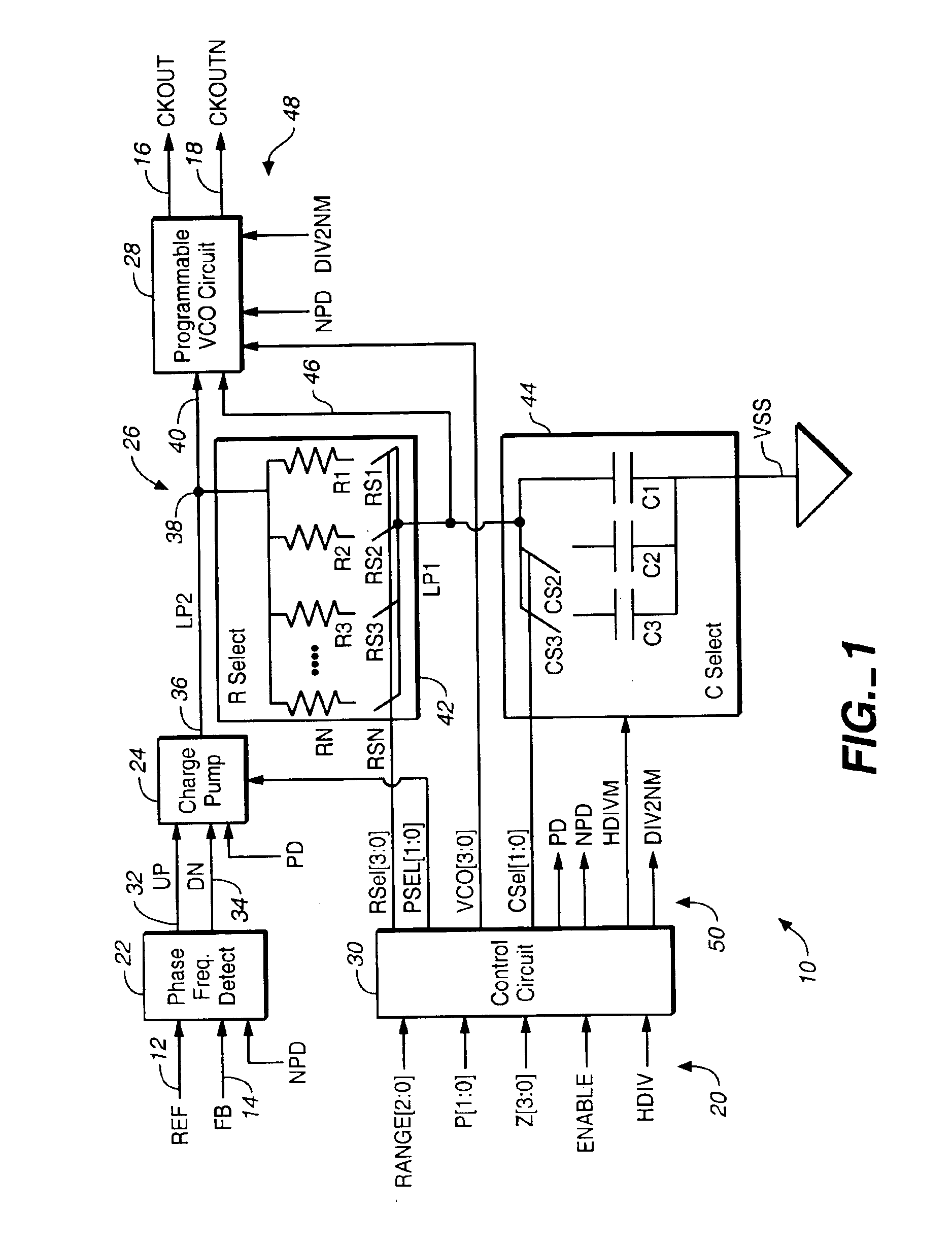
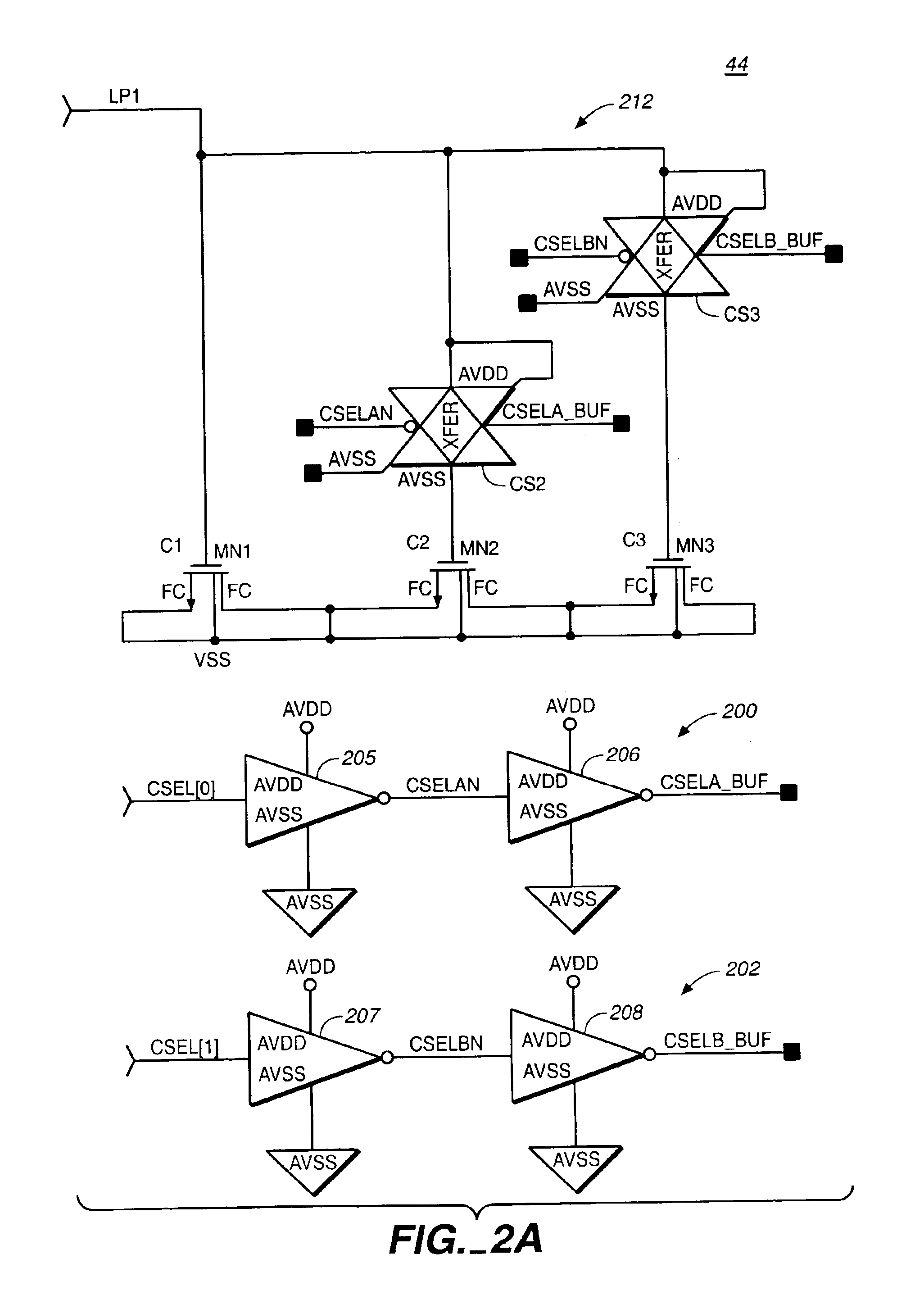
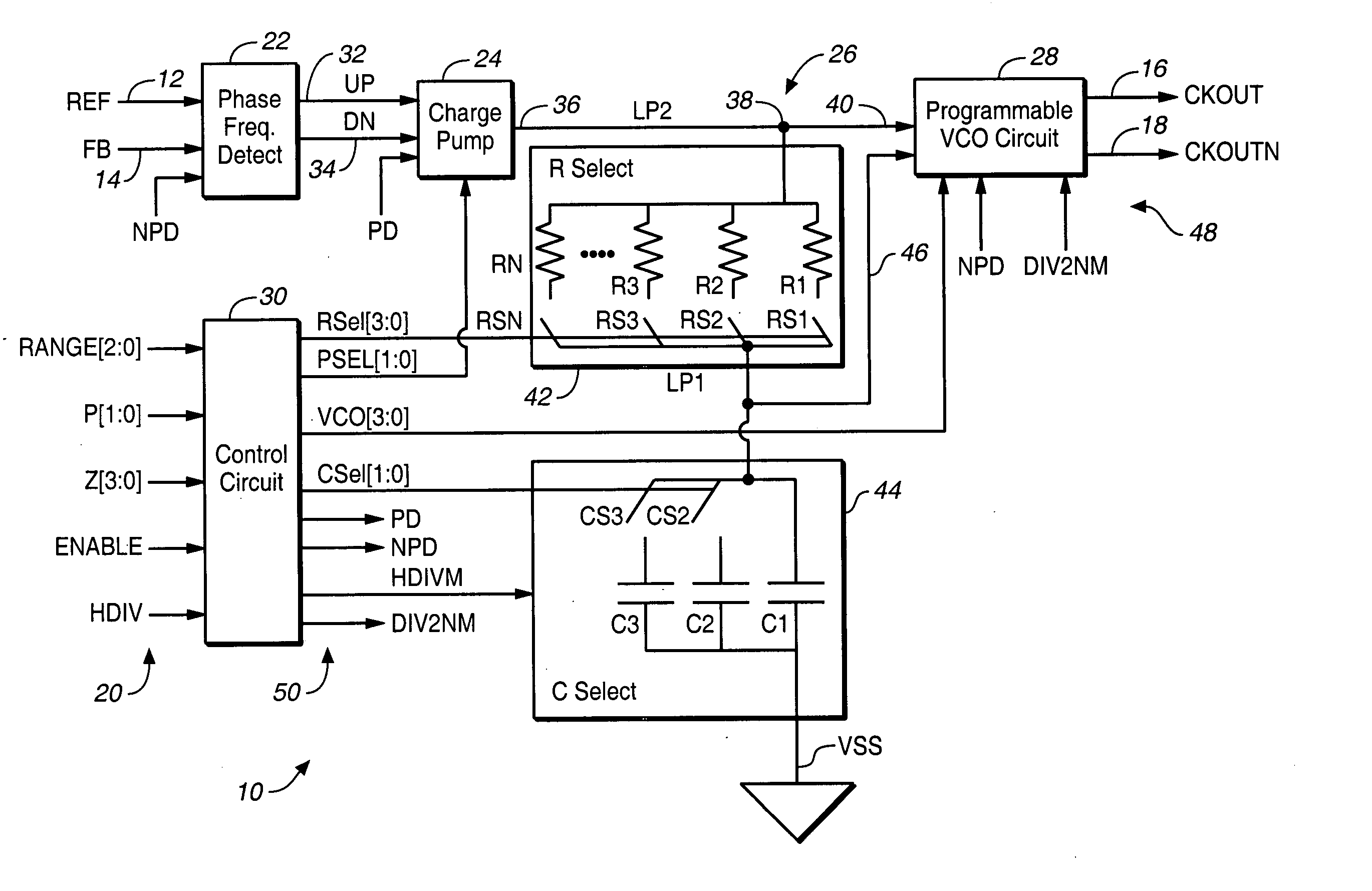
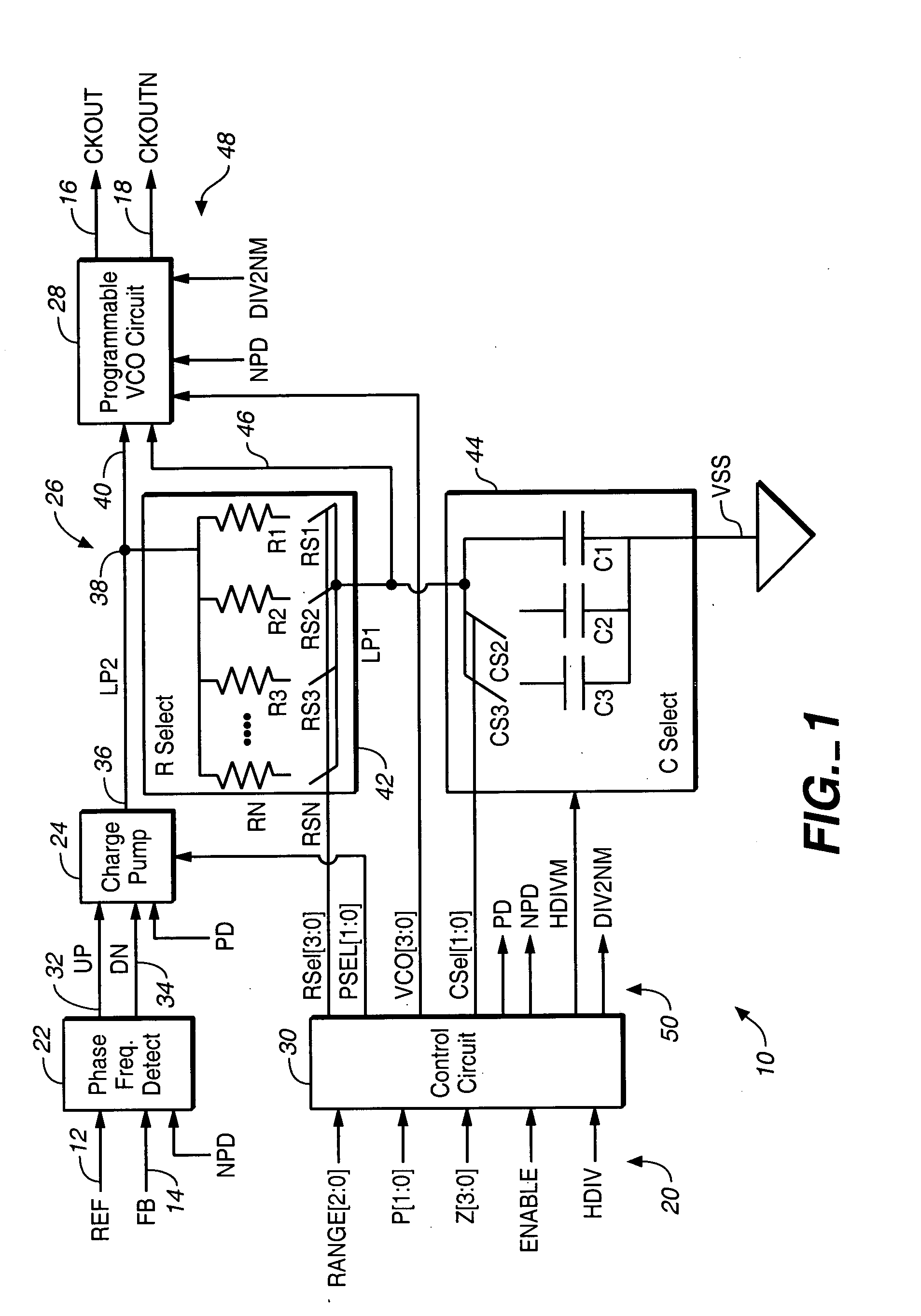
Programmable phase-locked loop
An integrated circuit is provided, which includes a phase-locked loop (PLL) that is fabricated on the integrated circuit and has a selectable loop filter capacitance and a selectable output frequency range.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Temperature compensation for a variable frequency oscillator without reducing pull range
InactiveUS20050128017A1Reducing its voltage range for functional frequency pull controlPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationInductorBiological activation
A variable frequency oscillator having multiple, independent frequency control inputs, each coupled to a respective tuning sub-circuit. The tuning sub-circuits are connected in parallel with each other and with a resonator module, which may be a quartz crystal, inductor, or other reactance component. Each tuning sub-circuit consists of two varactors with their respective cathodes coupled to each other and to their corresponding frequency control input. By having the tuning sub-circuits connected in parallel to the resonator, the overall frequency pull range of each frequency control input remains unaffected by the activation of any other frequency control input. Preferably, at least one frequency control input is a temperature compensation control input that can maintain the variable oscillator insensitive to temperature variations while the remaining frequency control inputs provide functional frequency control.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
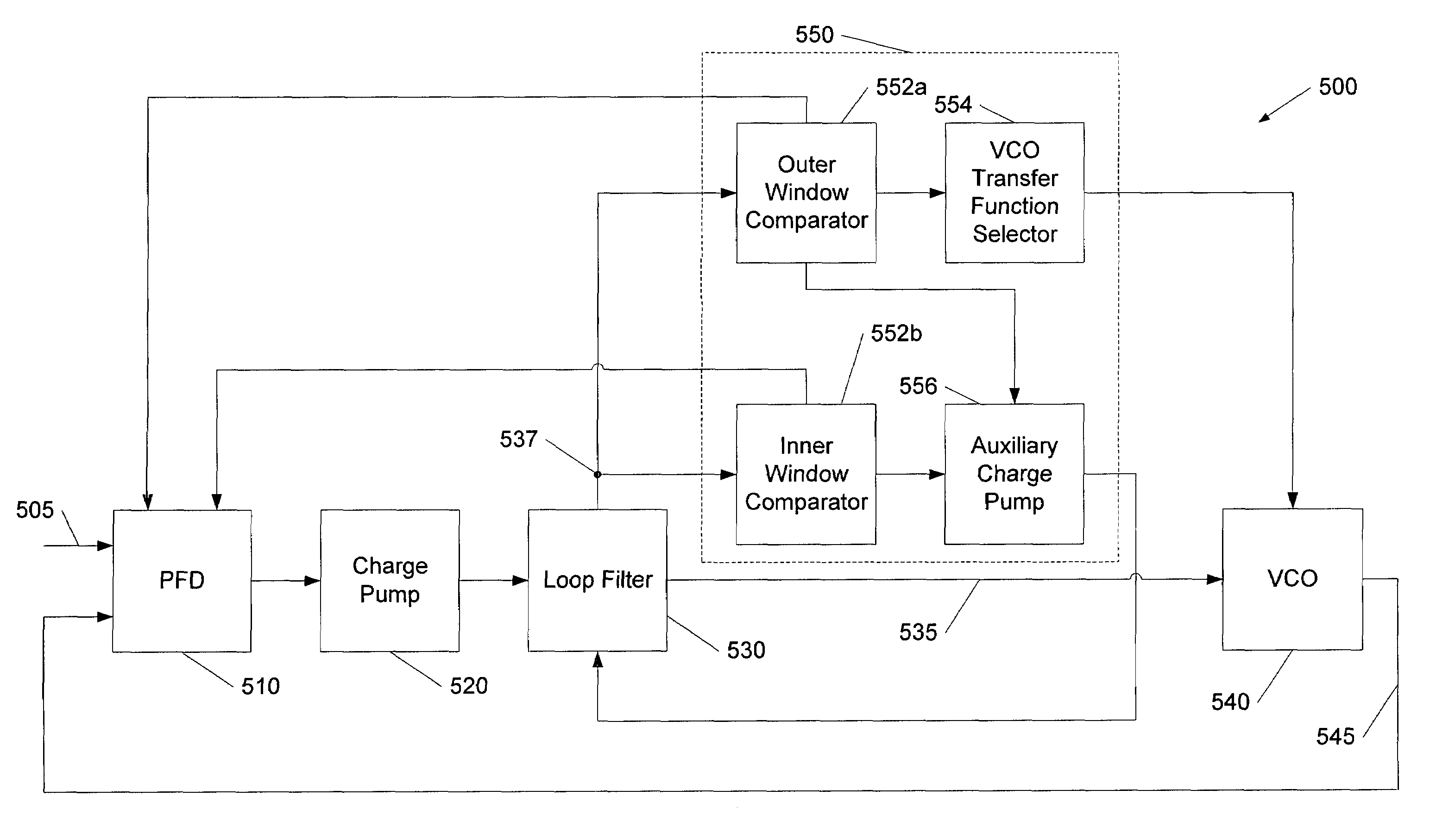
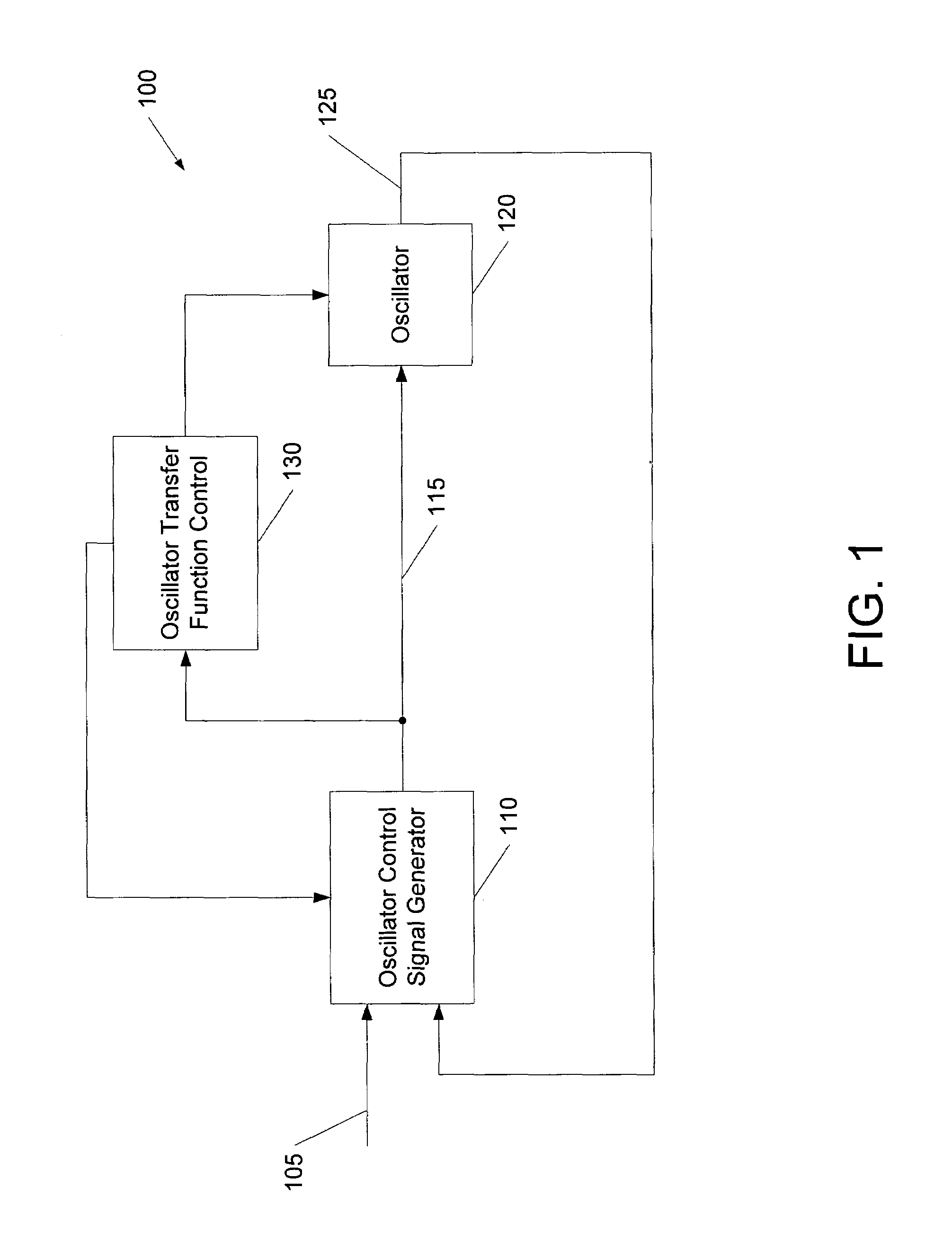
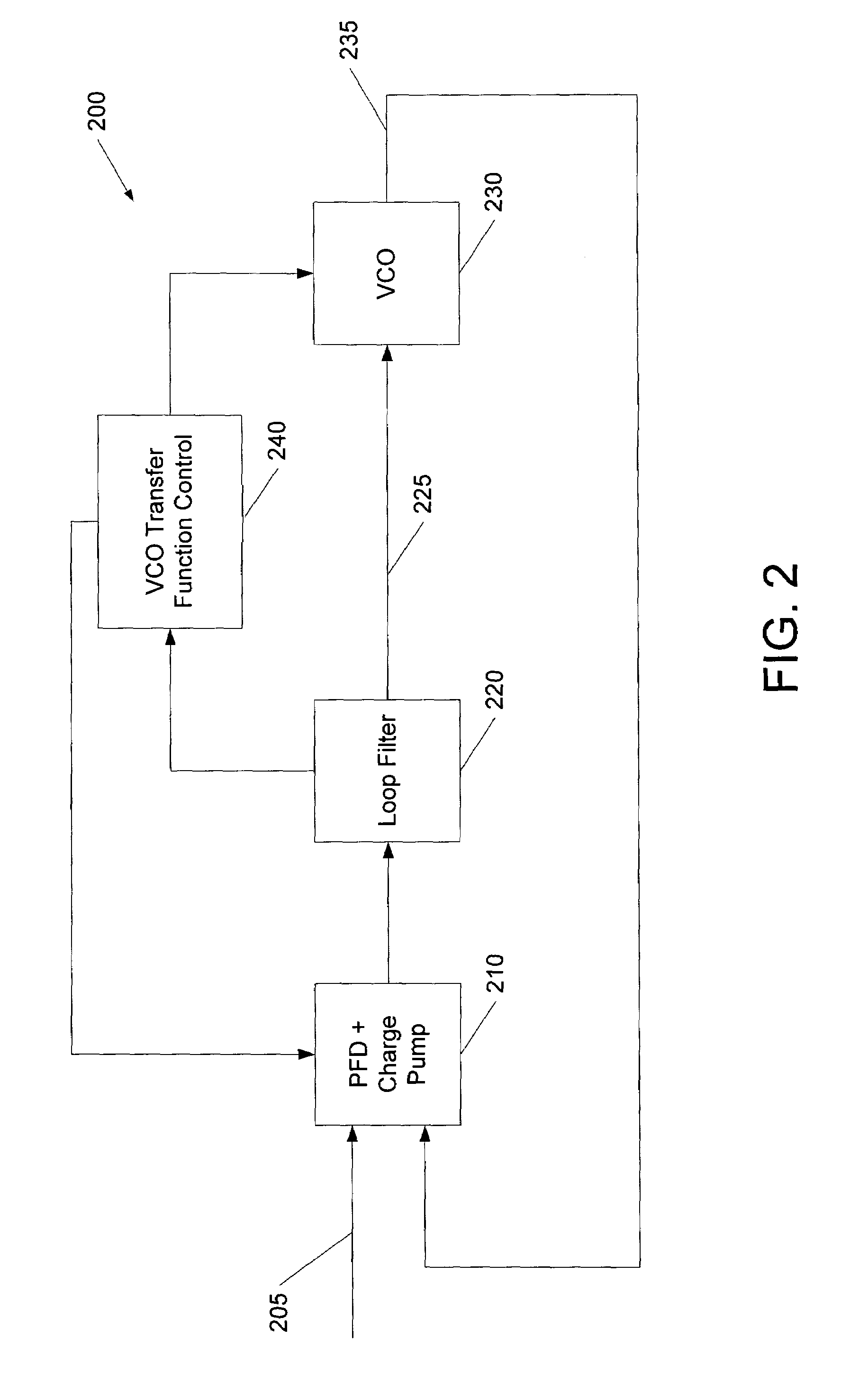
Dynamic phase-locked loop circuits and methods of operation thereof
A phase locked loop (PLL) circuit includes a controlled oscillator circuit that is operative to generate an output clock signal responsive to an oscillator control signal according to a plurality of selectable transfer functions, and an oscillator control signal generator circuit that is operative to generate the oscillator control signal responsive to the output clock signal and a reference clock signal. The PLL circuit further includes a transfer function control circuit operative to transition operation of the controlled oscillator from a first one of the transfer functions to a second one of the transfer functions responsive to the oscillator control signal. For example, the transfer function control circuit may step the controlled oscillator circuit through a succession of the transfer functions in response to a change in a frequency of the reference clock signal and may enable a closed loop including the oscillator control signal generator circuit and the controlled oscillator circuit upon selection of each of the succession of transfer functions.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Wide range multi-phase delay-locked loop
InactiveUS6876240B2Pulse automatic controlSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlHarmonicDelay-locked loop
A delay locked loop apparatus includes a first delay element to receive a reference signal, to delay the reference signal by a delay time, and to output a first delayed signal. A second delay element is used to receive the first delayed signal, to delay the first signal delayed signal by the delay time, and to output a second delayed signal. Also included is a harmonic lock prevention circuit to receive the reference signal, the first delayed signal, and the second delayed signal, and to adjust the delay time so that a period of each delayed signal is within a predetermined range.
Owner:SUPER INTERCONNECT TECH
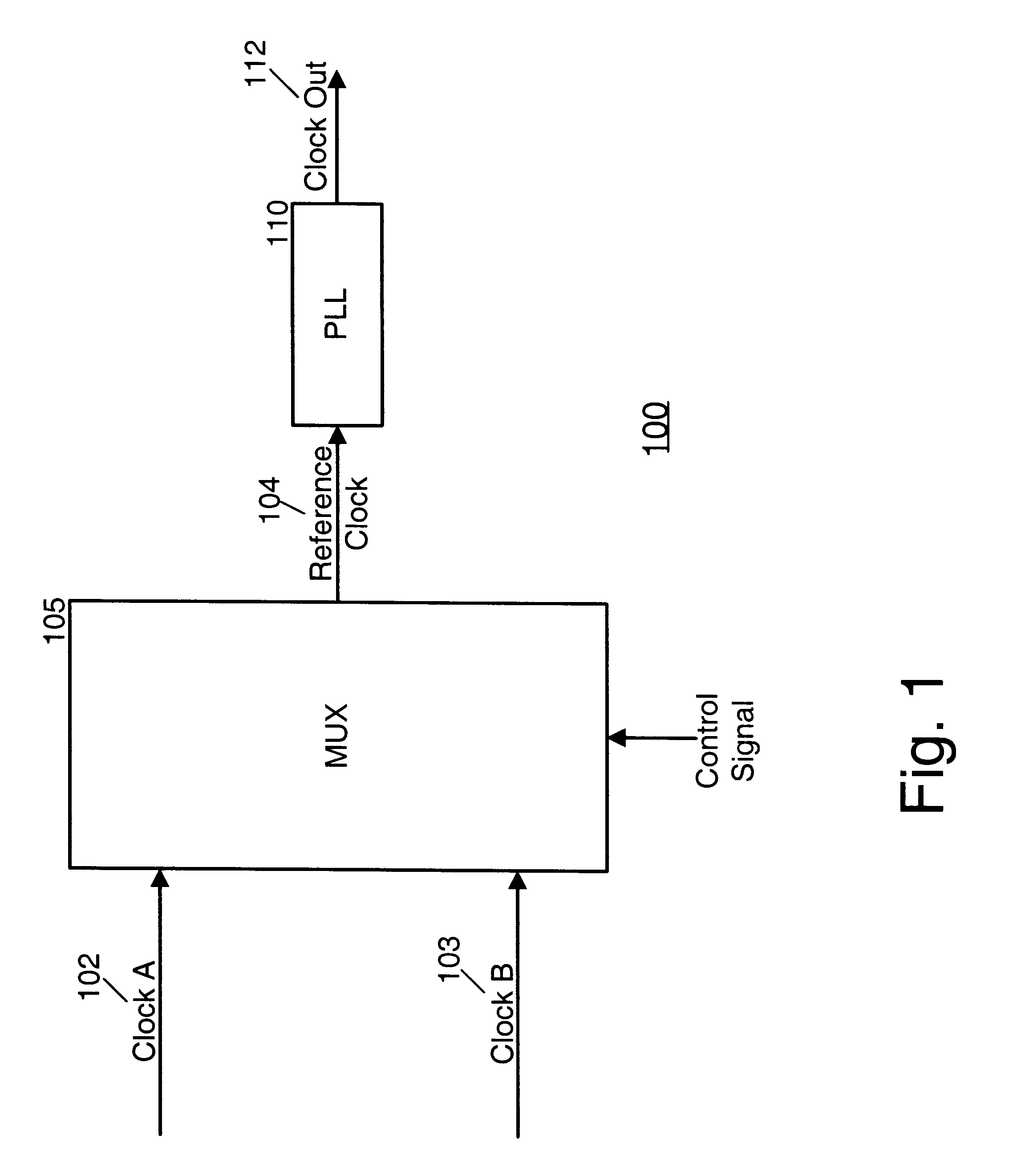
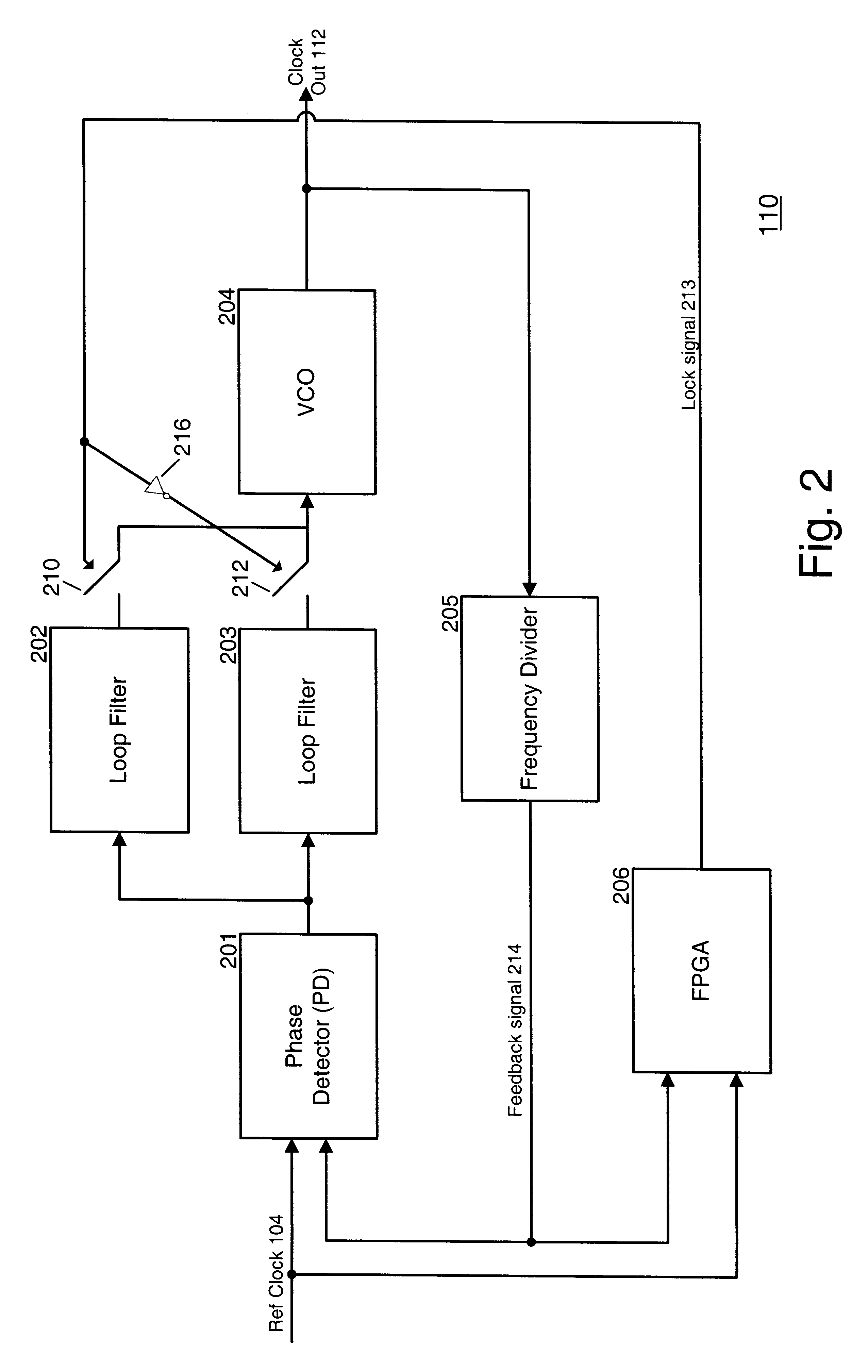
Multi-loop phase lock loop for controlling jitter in a high frequency redundant system
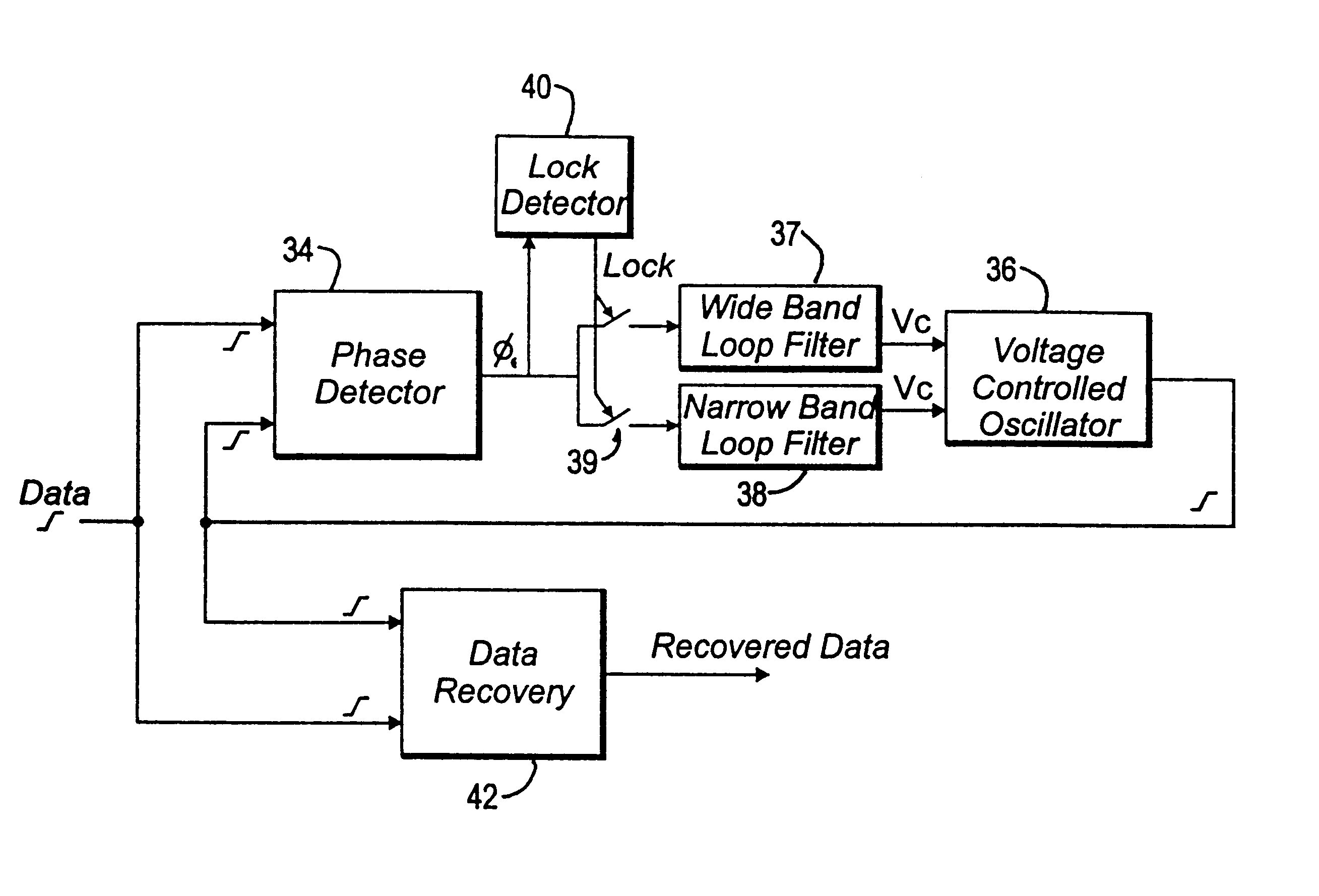
A multi-loop phase lock loop (PLL) contains multiple loop filters, each having different bandwidths. The multi-loop PLL receives one of multiple high-frequency clock signals as an input. A phase detector outputs a signal, based on the phase difference between the high-frequency clock signal and a feedback signal to the loop filters. A voltage controlled oscillator generates an output clock signal based on signals received from the loop filters. During a clock switch over sequence between the multiple high-frequency input clock signals, the multi-loop PLL uses one of its loop filters with a wide bandwidth to quickly lock the input clock signal. Once the clock signal is locked, a narrower bandwidth loop filter in the PLL is then used to reduce jitter in the locked signal.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and apparatus for acquiring a frequency without a reference clock
InactiveUS6856206B1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPulse automatic controlData streamEvaluation Interval
A clock and data recovery system acquires a clock embedded in an input data stream by detecting the occurrence of transitions in the input data stream falling into a predetermined phase zone of a sample clock used to sample the input data stream. A control circuit counts how many evaluation intervals have at least one transition in the predetermined phase zone. The control circuit determines if lock is achieved according to the count. If it is determined that lock is not achieved, an output of a variable oscillator circuit used in the clock recovery operation is adjusted until the number of evaluation intervals having one or more transitions in the predetermined phase zone is below a level indicating lock.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
VCO with automatic calibration
InactiveUS6856205B1Automatically calibrateAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlControl signalEngineering
Voltage-controlled oscillator with apparatus for automatic calibration. The voltage-controlled oscillator includes switches connecting associated coarse-tuning capacitors to an LC resonant tank of the oscillator. The voltage-controlled oscillator also comprises a calibration loop used to appropriately set the switches associated with the coarse tuning apparatus based on a oscillator control signal.
Owner:QUINTIC MICROELECTRONICS WUXI
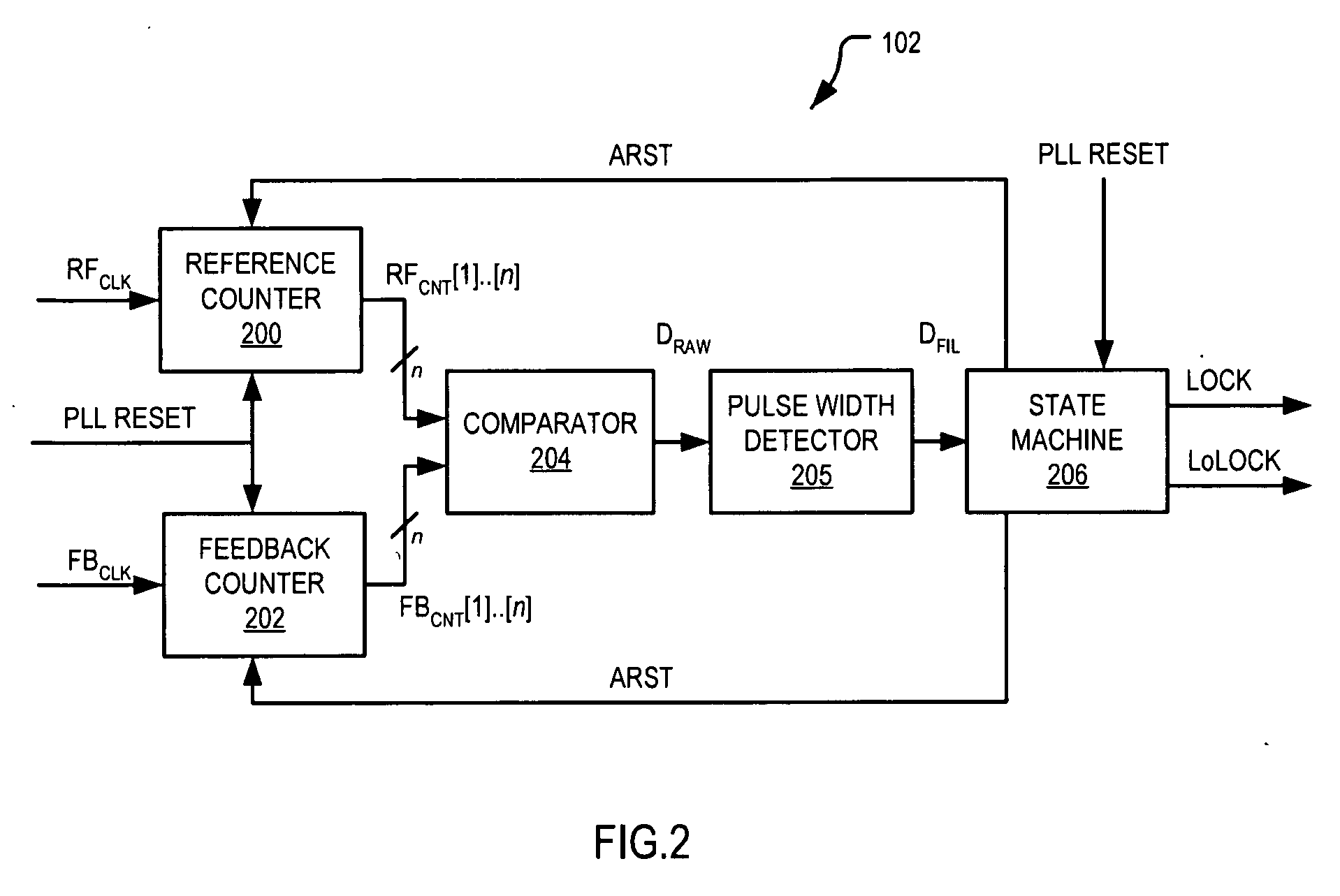
Lock detection circuit for phase locked loop
InactiveUS20090251226A1Pulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase angleDetector circuitsMachine control
A lock detector circuit for detecting a lock condition between a reference signal and a feedback signal includes a first counter for outputting a first counter value indicative of a number of clock cycles of the reference signal, and a second counter for outputting a second counter value indicative of a number of clock cycles of the feedback signal. An asynchronous comparator receives the first and second counter values and provides an output signal having a pulse width that is proportional to the difference between the first and second counter values. A pulse width detector receives the comparator output signal and produces an output signal that is indicative of the relationship between the pulse width of the comparator output signal and a predetermined threshold value. A state machine controls the state of at least one lock indication signal according to the pulse width detector output signal.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
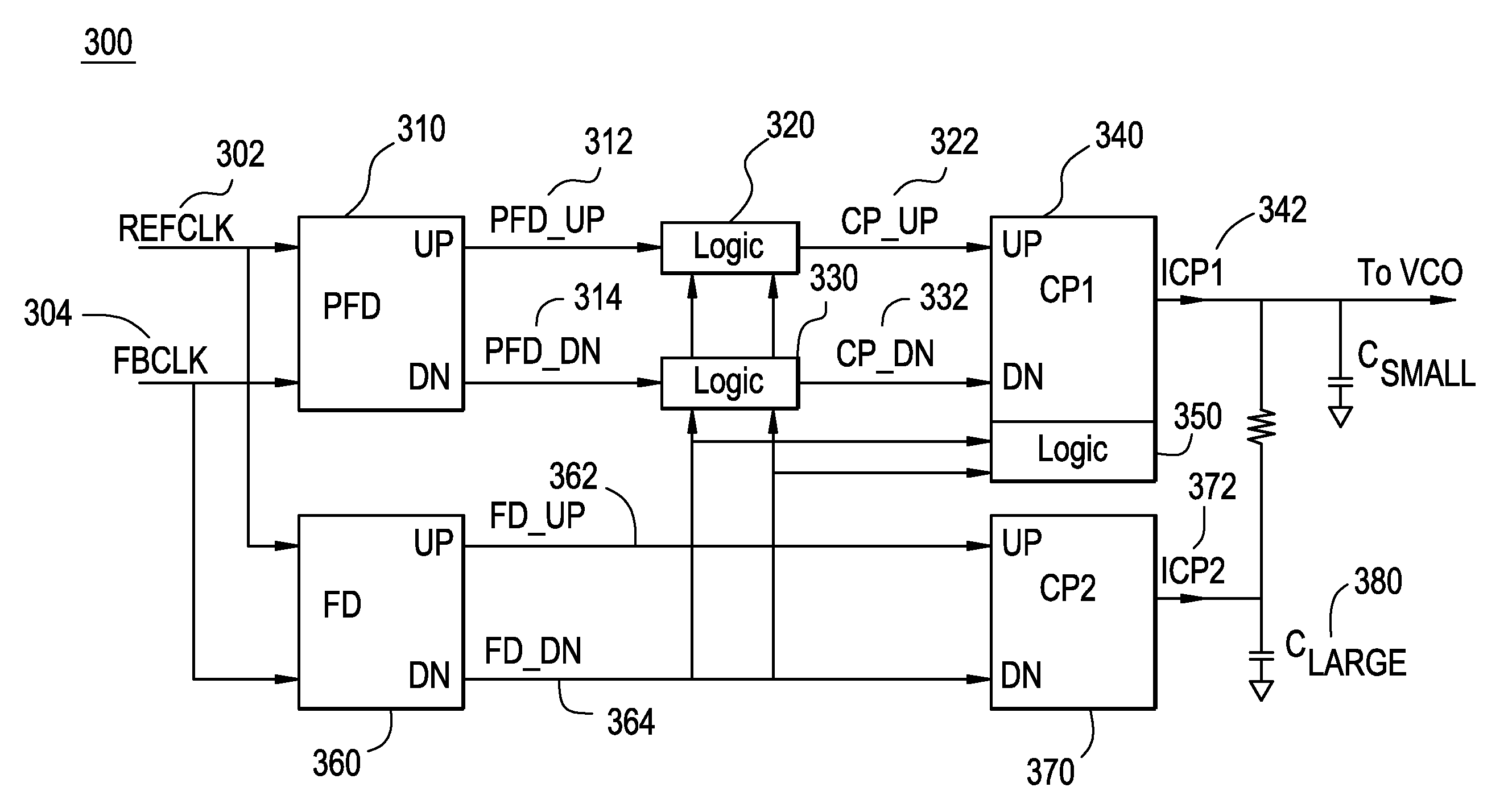
Fast lock circuit for a phase lock loop
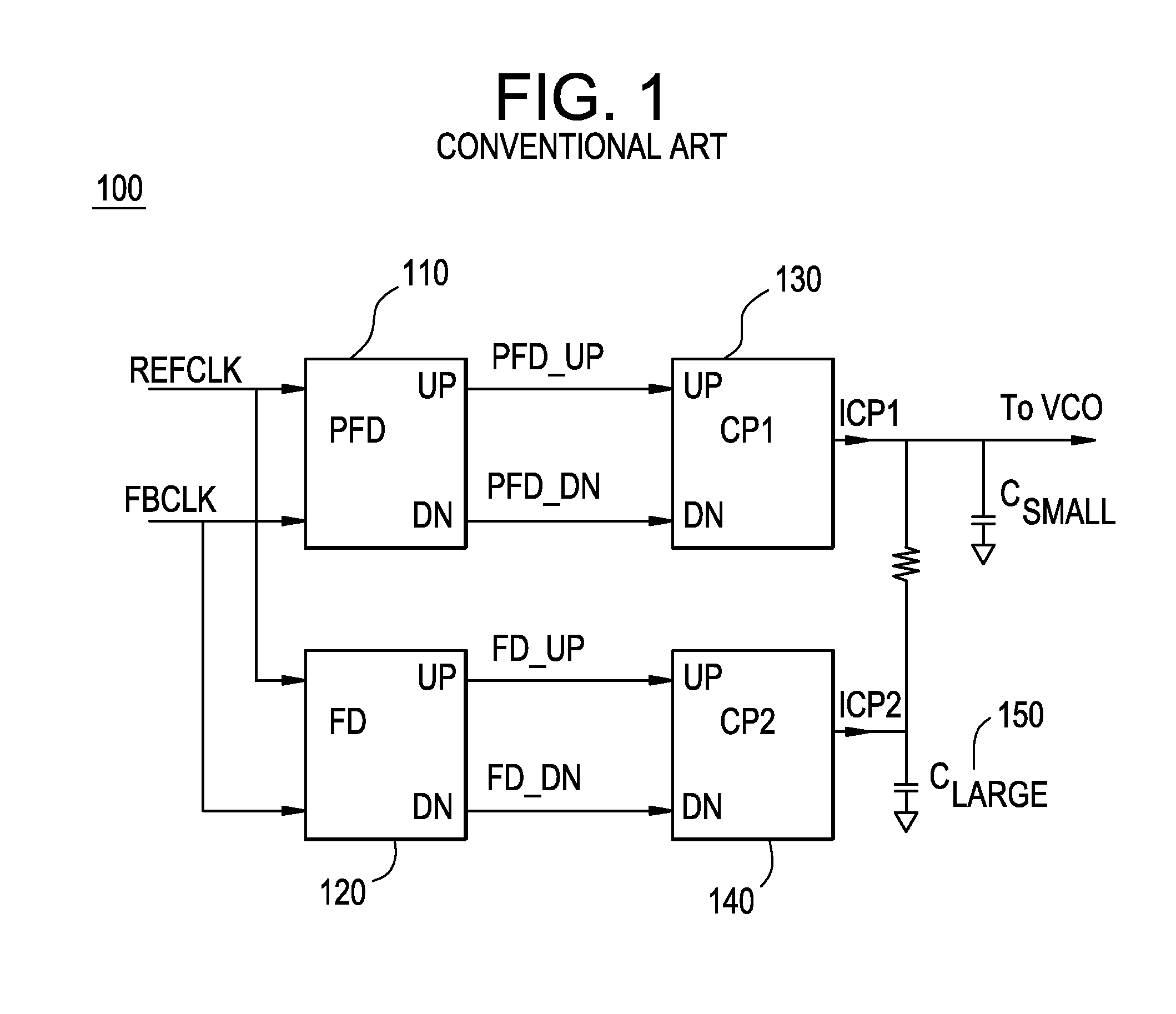
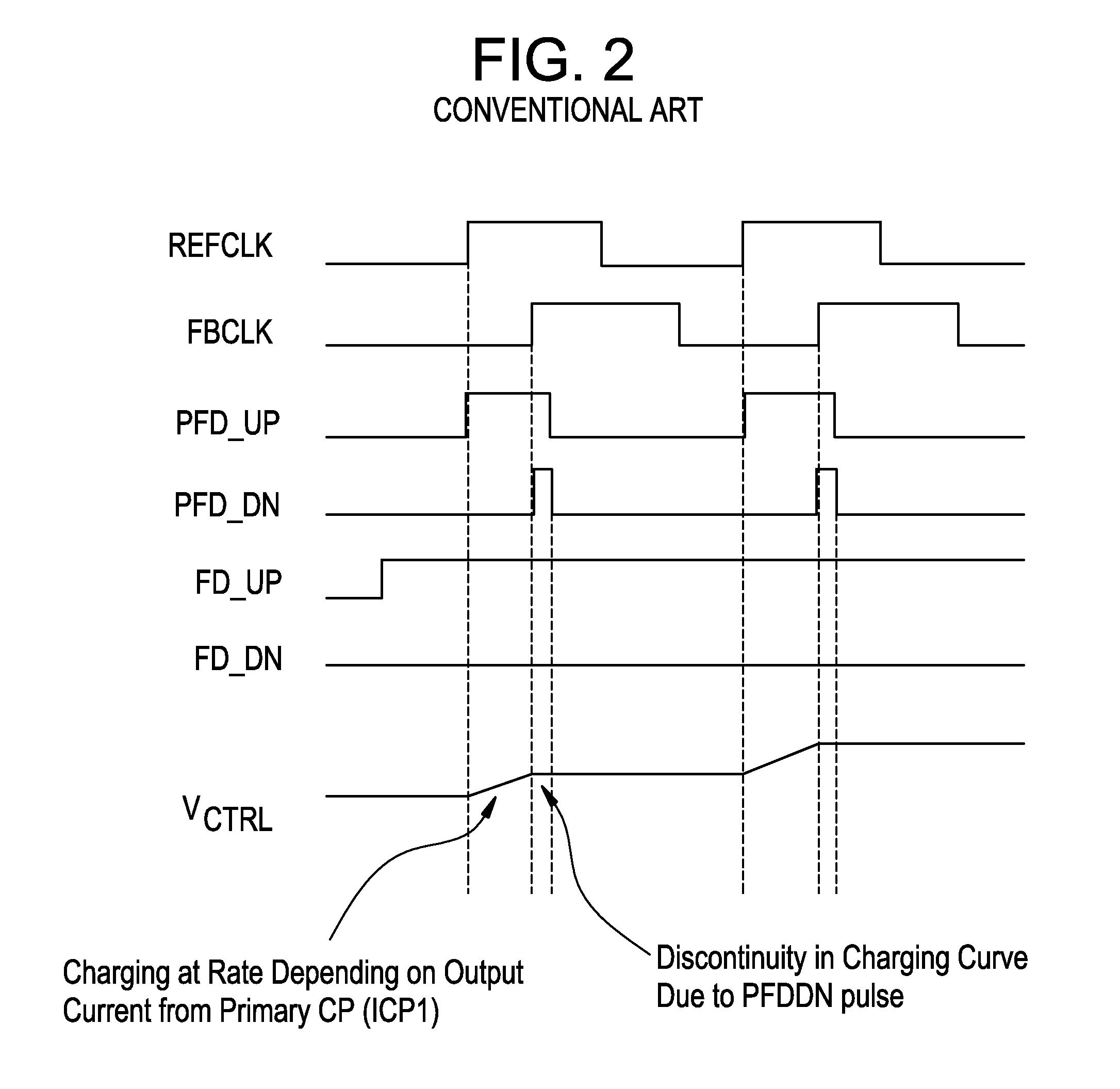
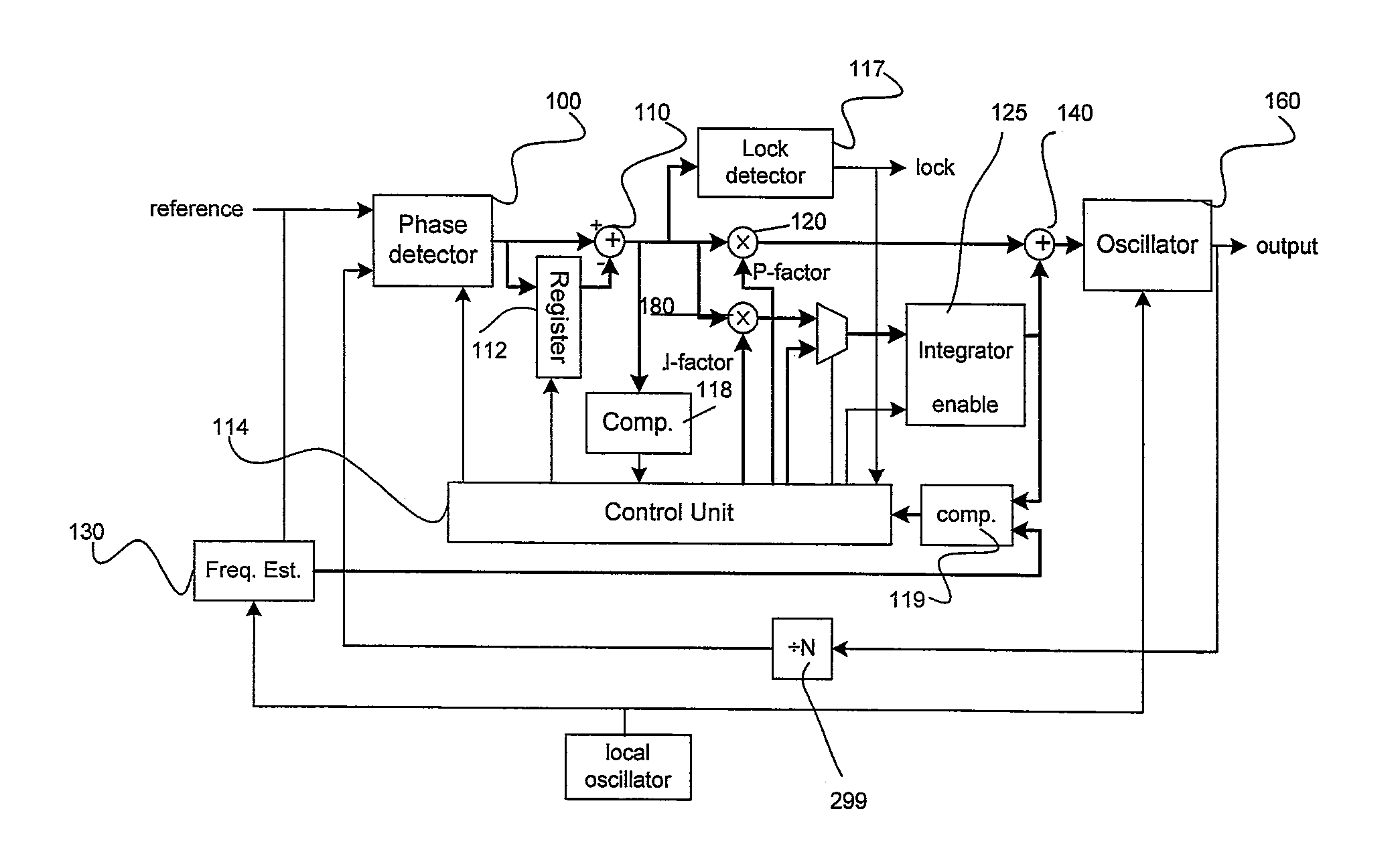
InactiveUS7728675B1Increase volumeSlow chargingPulse automatic controlOscillator tubesLoop filterDetector circuits
A fast lock circuit for phase lock loop comprising a frequency detector, a phase frequency detector, a logic unit and a corresponding charge pump for the frequency and the phase frequency detectors. Embodiments of the present invention use the logic unit to relay signals from the phase frequency detector circuit to the charge pump when the PLL is in lock. The logic circuit relay signals from the frequency detector circuit before the PLL is in lock. As a result, a constant current is supplied to a large loop filter capacitor before lock. In one embodiment, additional logic circuit may be used to maximize the output current. Therefore, using the logic circuit to supply constant current charges the large loop filter capacitor continuously and avoids a slow down in charging the large loop filter. Accordingly, current is no longer wasted and the lock time is improved.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Efficient tuning circuit for on-chip voltage controlled oscillator and method
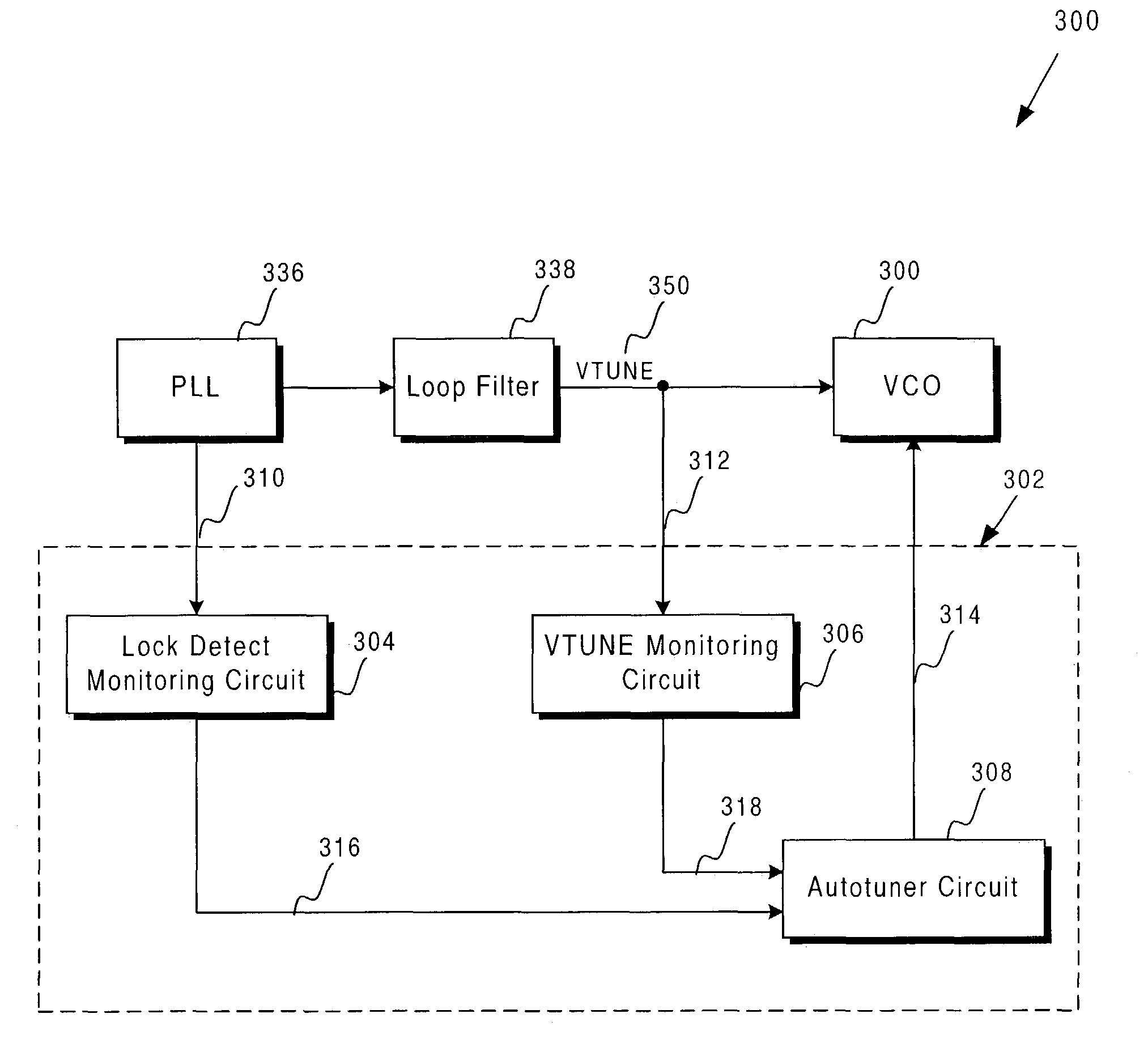
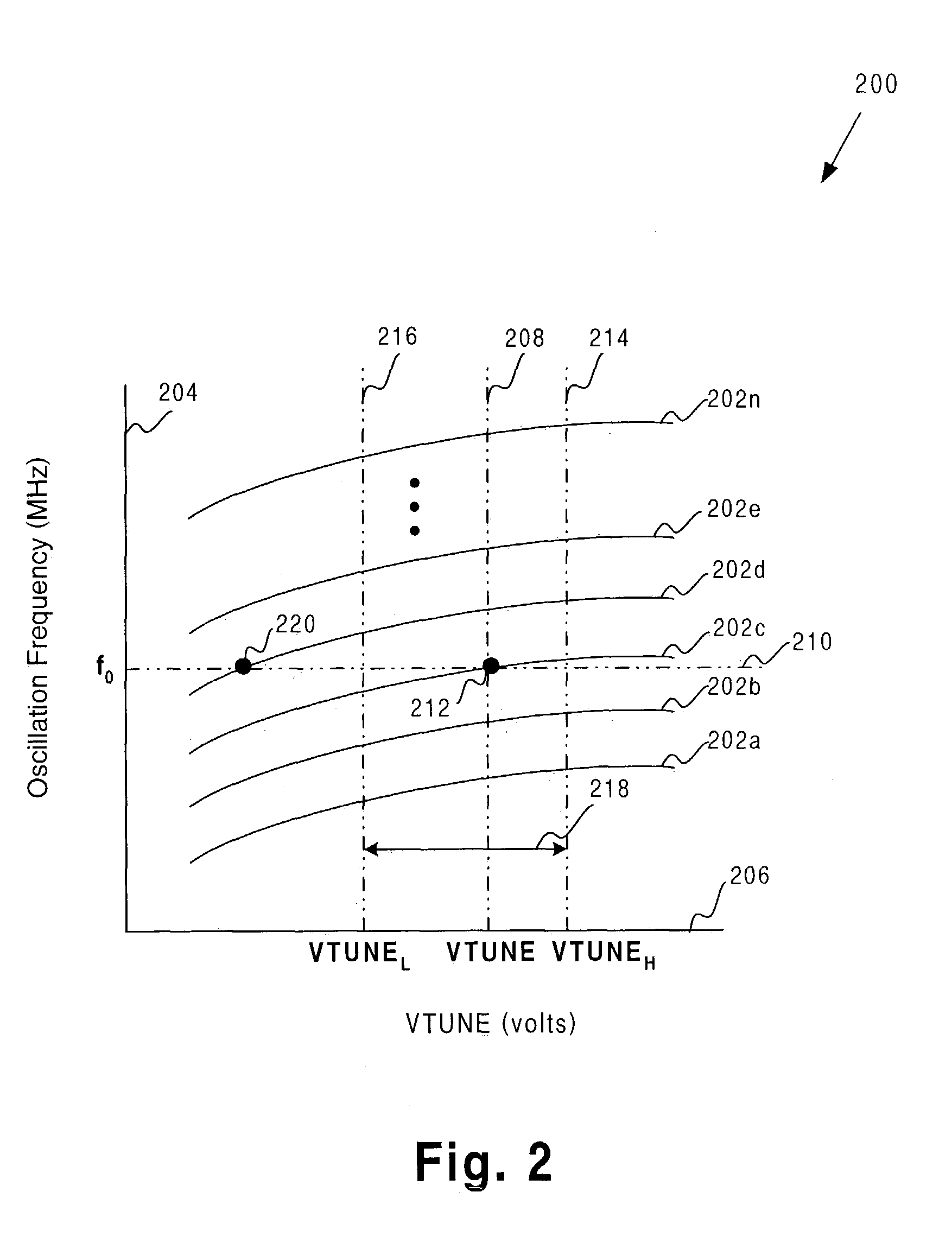
ActiveUS6927637B1Efficient coarse tuningReduce the valueAngle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlLoop filterVoltage-controlled oscillator
An exemplary tuning circuit is coupled to, a voltage controlled oscillator. The tuning circuit comprises a lock detect monitoring circuit, a VTUNE monitoring circuit and an autotuner circuit. The lock detect monitoring circuit is coupled to a phase locked loop of the voltage controlled oscillator and is configured to determine a state of the phase locked loop. The VTUNE monitoring circuit is coupled to a loop filter of the voltage controlled oscillator and is configured to determine the fine tuning voltage generated by the loop filter. The autotuner circuit is connected to the lock detect monitoring circuit and the VTUNE monitoring circuit and is configured to provide coarse tuning of the voltage controlled oscillator based on the fine tuning voltage and the state of the phase locked loop.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Sigma-delta fractional-N PLL with reduced frequency error
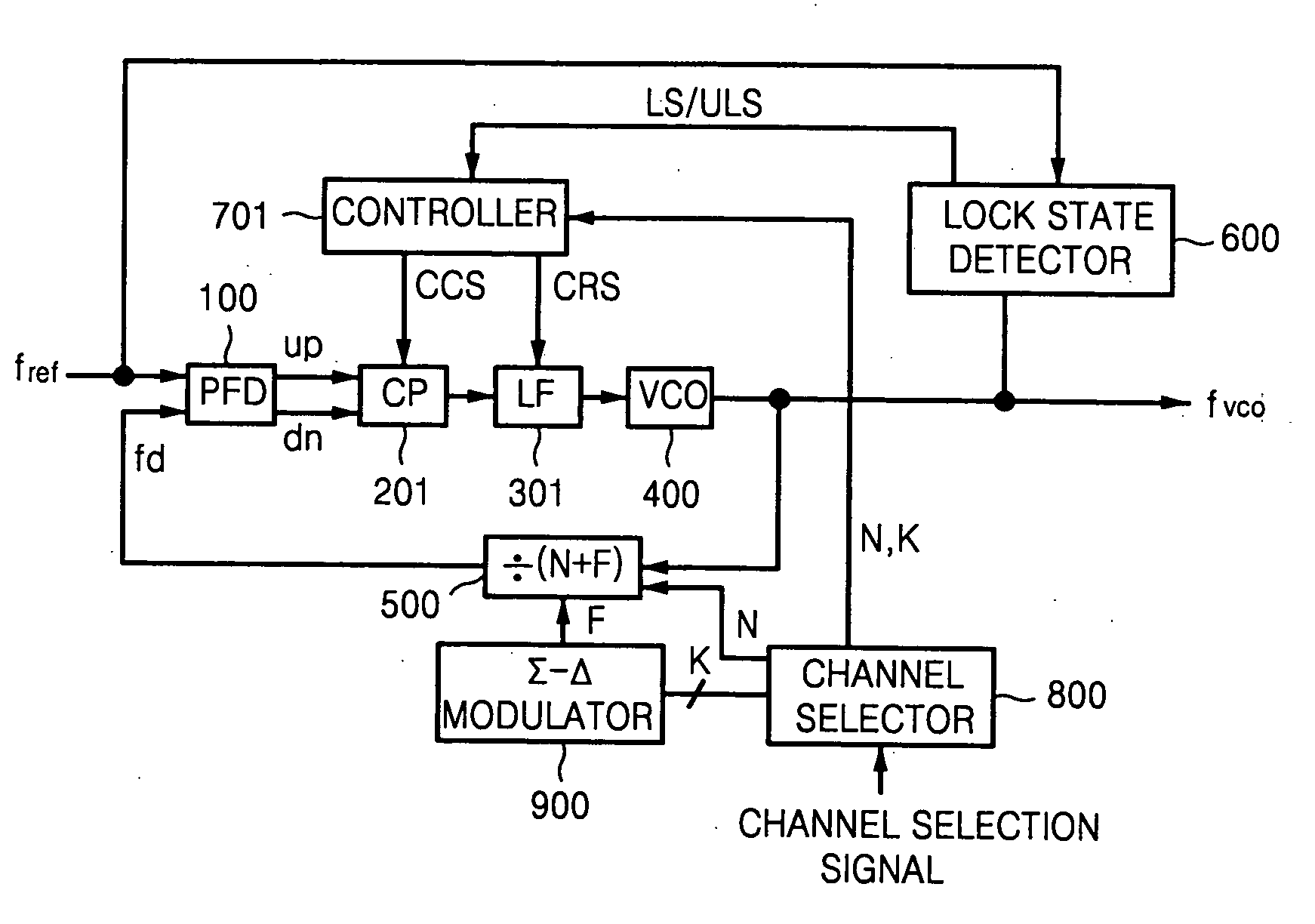
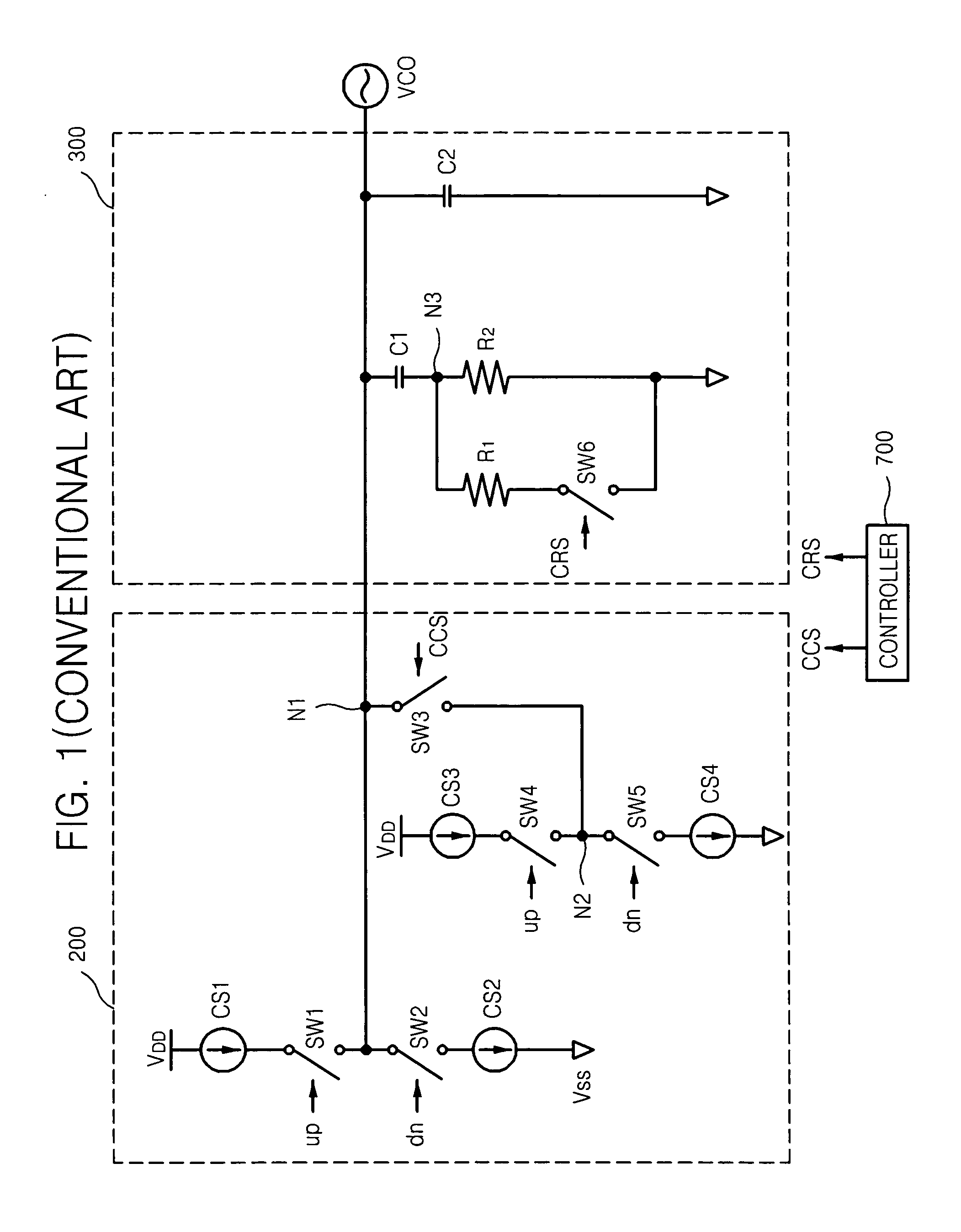
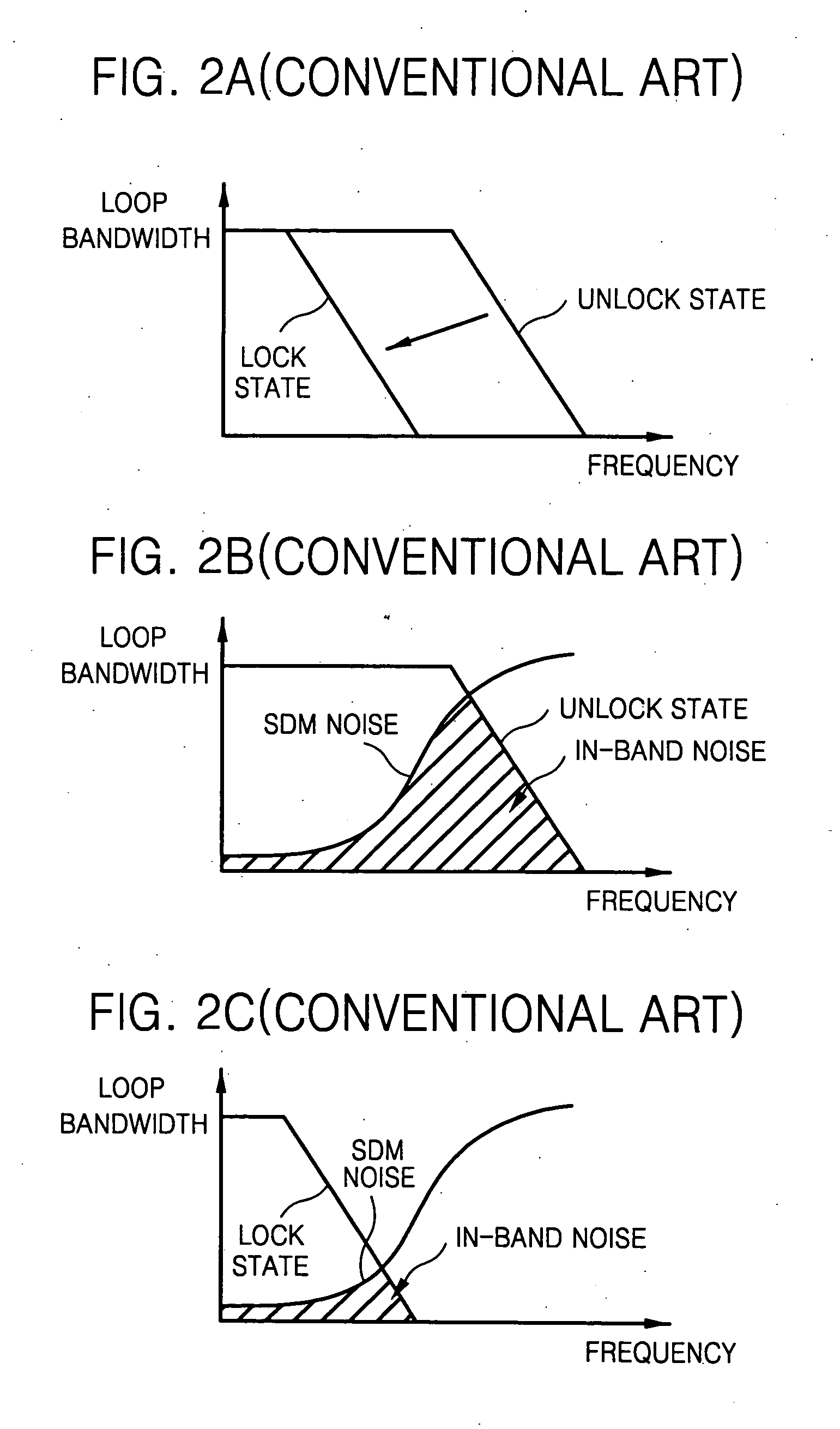
ActiveUS20070164829A1Reduce frequencyImprove the immunityPulse automatic controlOscillator tubesLoop filterLow noise
A sigma-delta fractional-N phase locked loop has faster lock time with increased charge pump current and decreased loop filter resistance in the unlock state. On the other hand, the sigma-delta fractional-N phase locked loop has lower noise susceptibility and lower frequency error with gradual decrease in charge pump current and gradual increase in loop filter resistance, in the lock state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Time-to-digital converter using stochastic phase interpolation
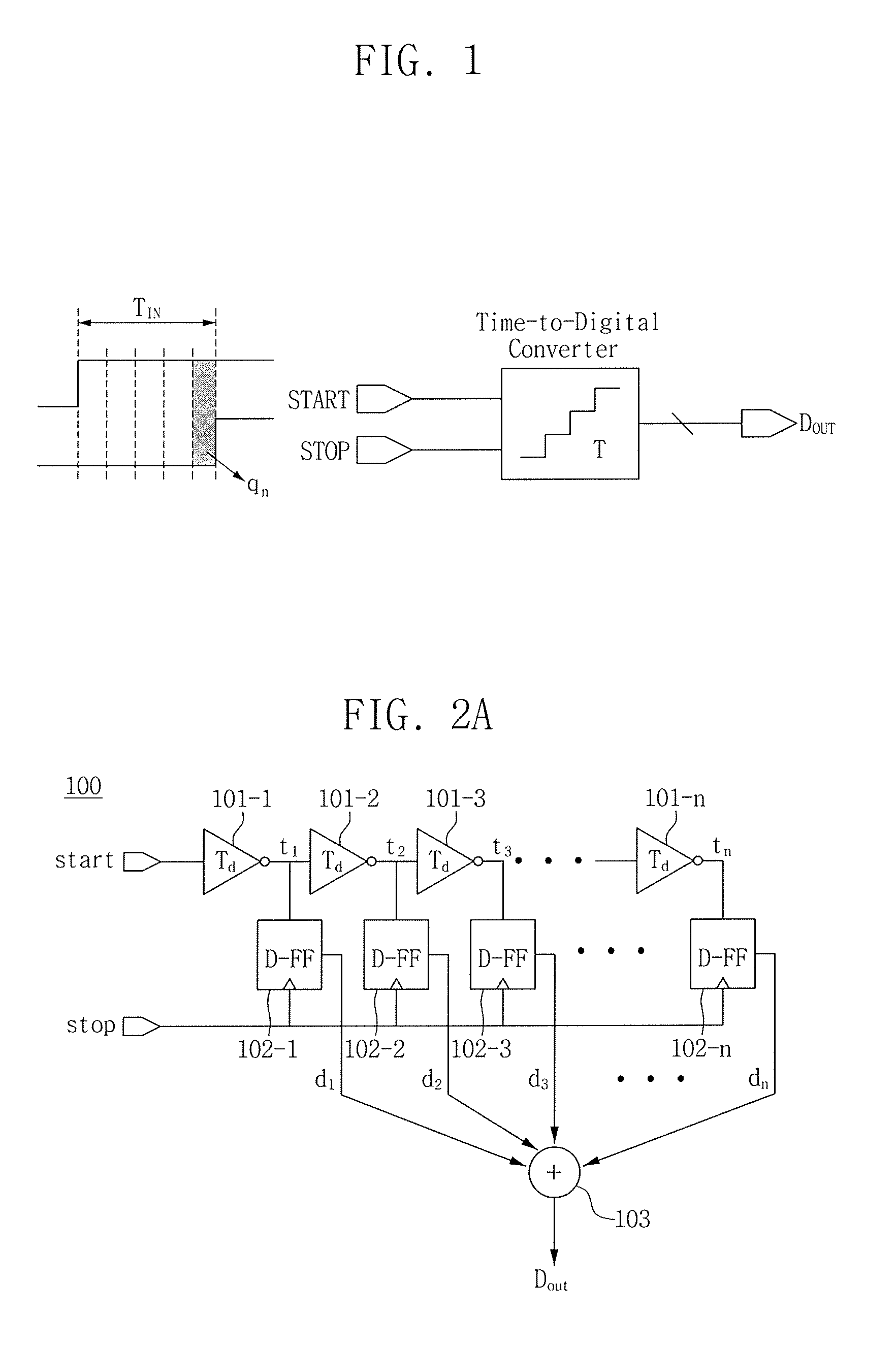
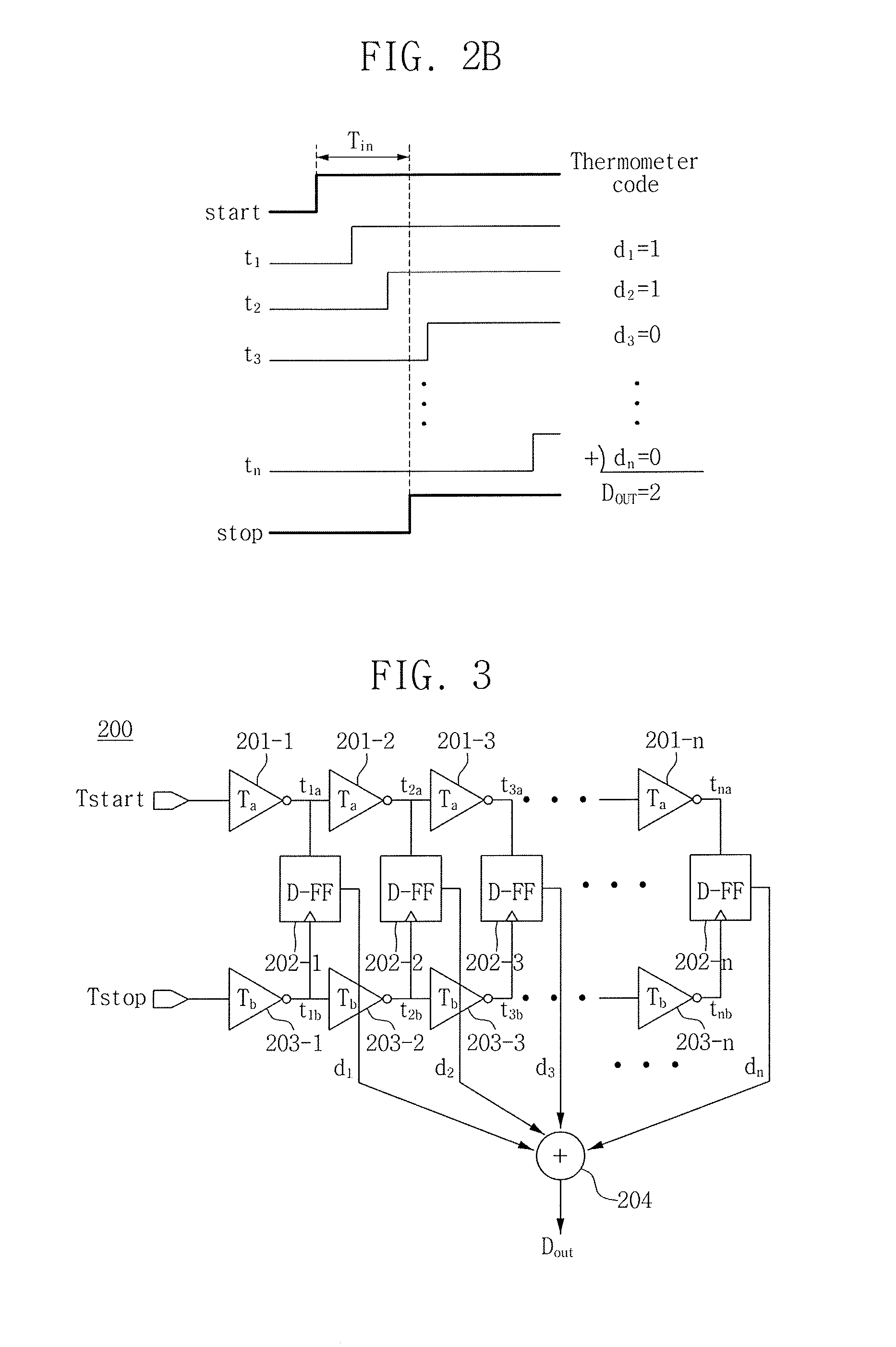
ActiveUS20160156362A1High resolution operationHigh operating requirementsAnalogue/digital conversionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLeast significant bitDigital converter
Provided is a time-to-digital converter. The time-to-digital converter includes several delay circuits, an adder configured to count outputs of the delay circuits, and a least significant bit (LSB) truncation circuit configured to truncate a predetermined number of LSBs from a result output by the adder. The time-to-digital converter is configured to determine a time interval between a start signal and a stop signal within one cycle of a clock having a predetermined period.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Phase-locked loop circuit with dynamic backup
InactiveUS6111442APulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsLow-pass filterPhase locked loop circuit
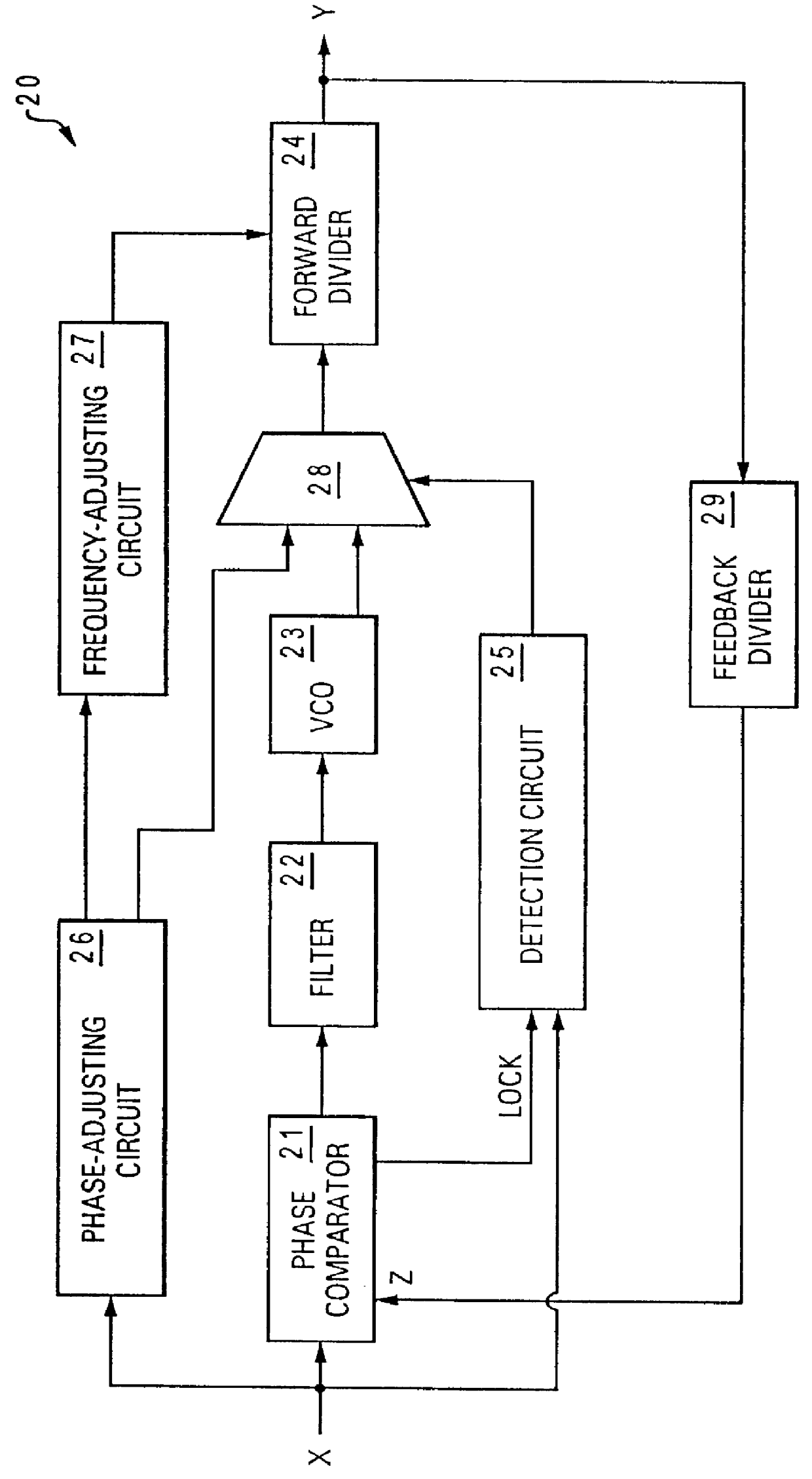
A phase-locked loop circuit with dynamic backup is disclosed. The phase-locked loop circuit with dynamic backup includes a phase comparator, a lowpass filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator, and a detection circuit. The phase comparator compares an input reference signal and a feedback output signal from an output of the phase-locked loop circuit for generating a voltage signal representing the phase difference between the input reference signal and the feedback output signal. After the voltage signal is filtered by the lowpass filter, the filtered voltage signal is sent to the voltage-controlled oscillator for generating the feedback output signal. Coupled to the phase comparator, the detection circuit detects whether or not the phase-locked loop circuit is in lock with the input reference signal. In response to a determination that the phase-locked loop circuit is not in lock with the input reference signal, the detection circuit directs the input reference signal to bypass the phase comparator, the lowpass filter, and the voltage-controlled oscillator.
Owner:IBM CORP
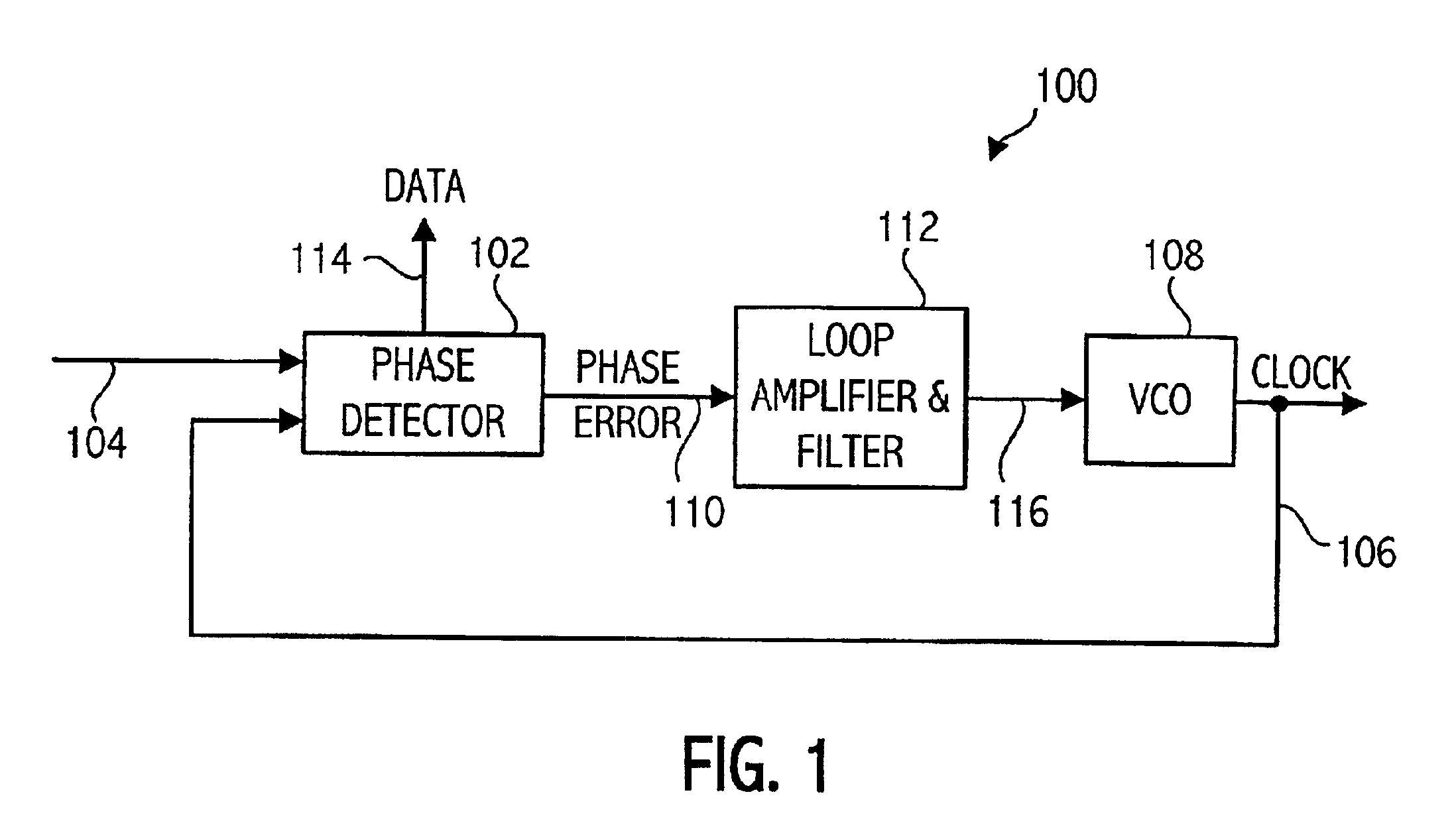
Phase Locked Loop Fast Lock Method
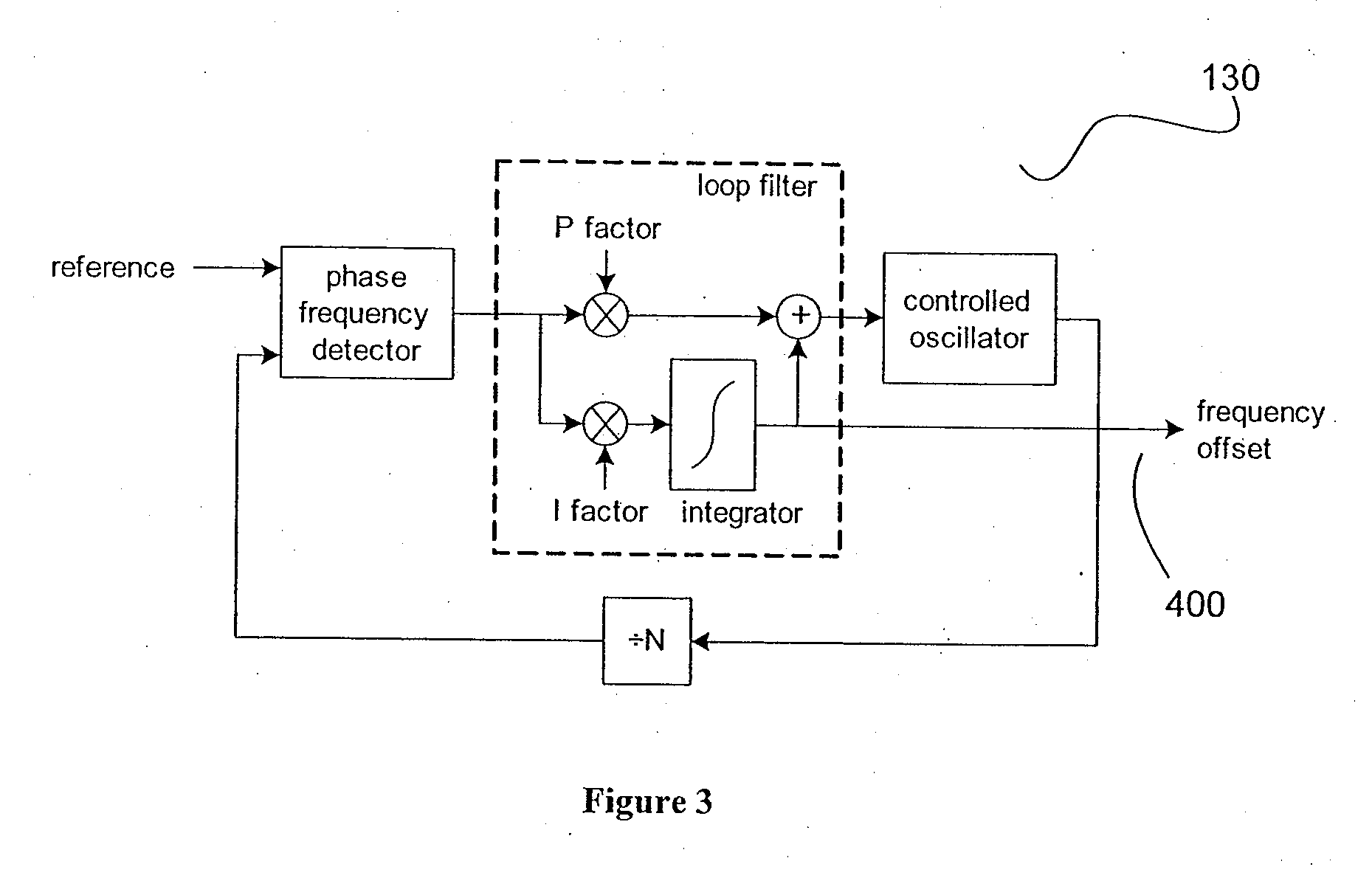
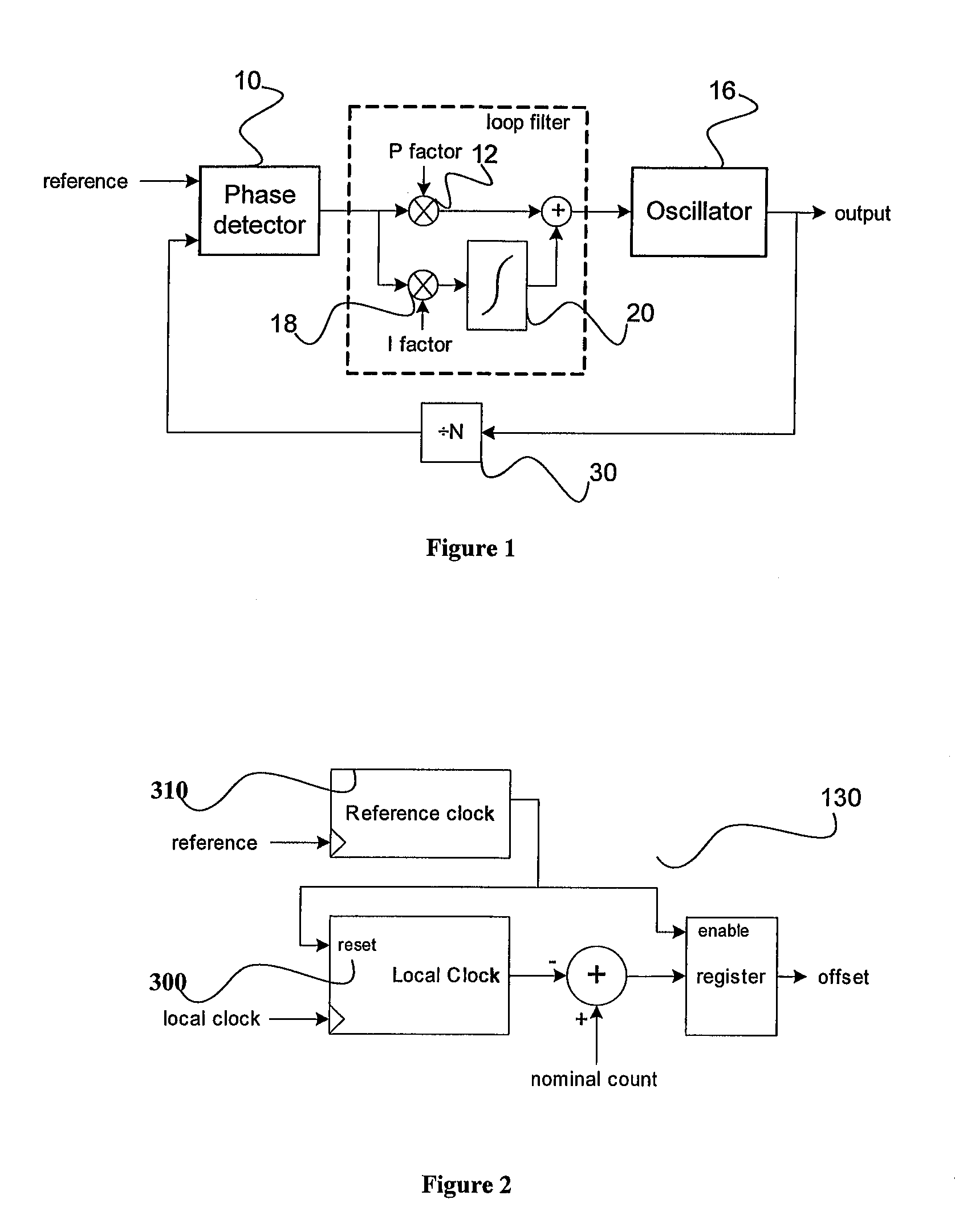
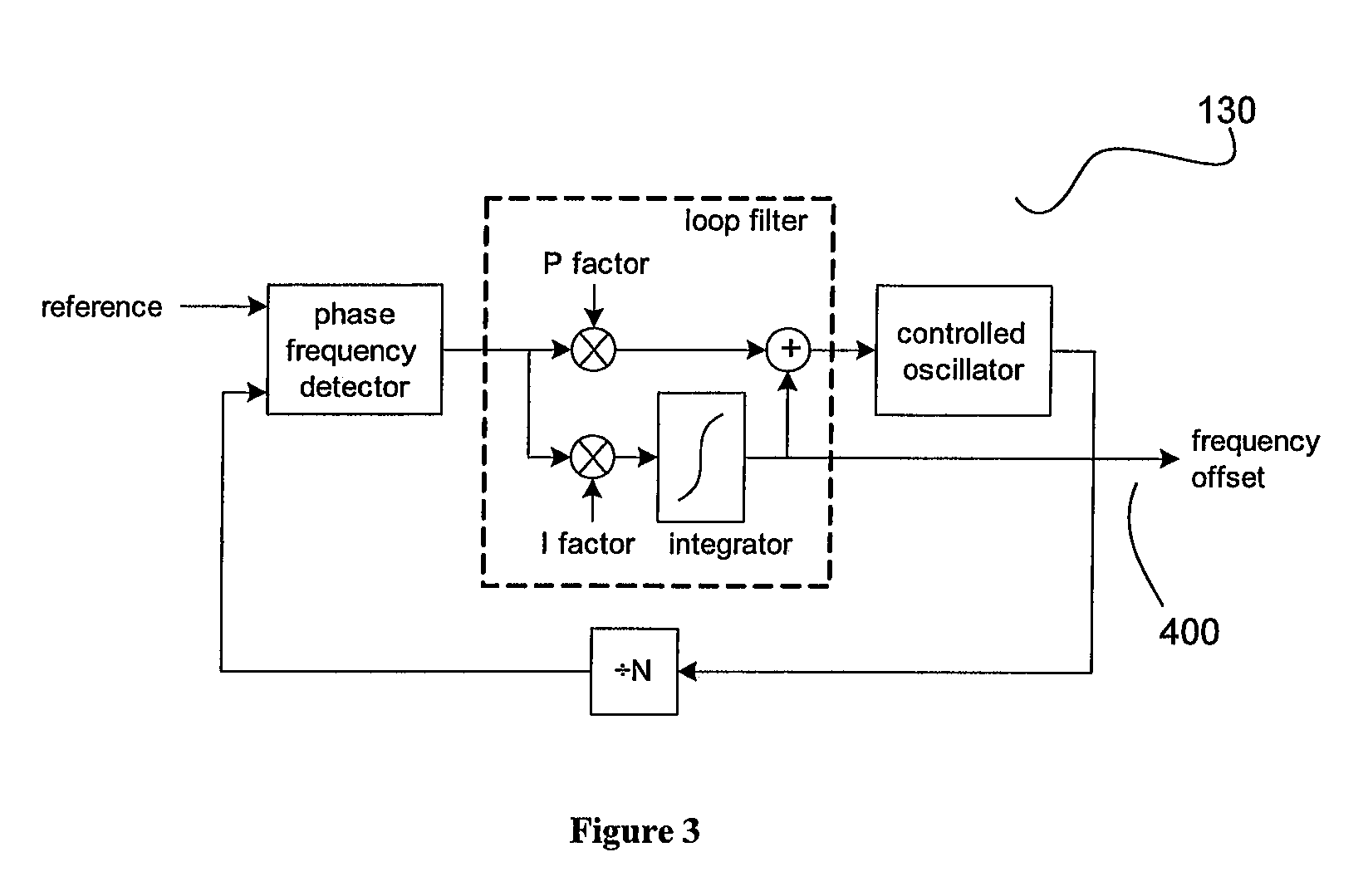
ActiveUS20070024383A1Quality improvementReduced settling timePulse automatic controlOscillator tubesLoop filterIntegrator
The present invention is a method to rapidly lock a type II phase locked loop (PLL) after a frequency jump without degrading the output signal much. The method to decrease the settling time and improve the quality of the output clock during the settling disclosed herein comprises of the following broad steps: Estimate new frequency offset with a separate circuit outside the PLL loop to measure the frequency of the input signal accurately. Ramp integrator to the new frequency offset. Do phase build out or phase pull-in. The remaining phase offset is build out when no edge to edge alignment is required. Otherwise, the remaining phase offset is pulled in while the integrator in the PLL's loop filter is disabled. Reduce the PLL bandwidth and / or lower damping to let the PLL settle. Switch the PLL to final bandwidth and damping required by the application.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
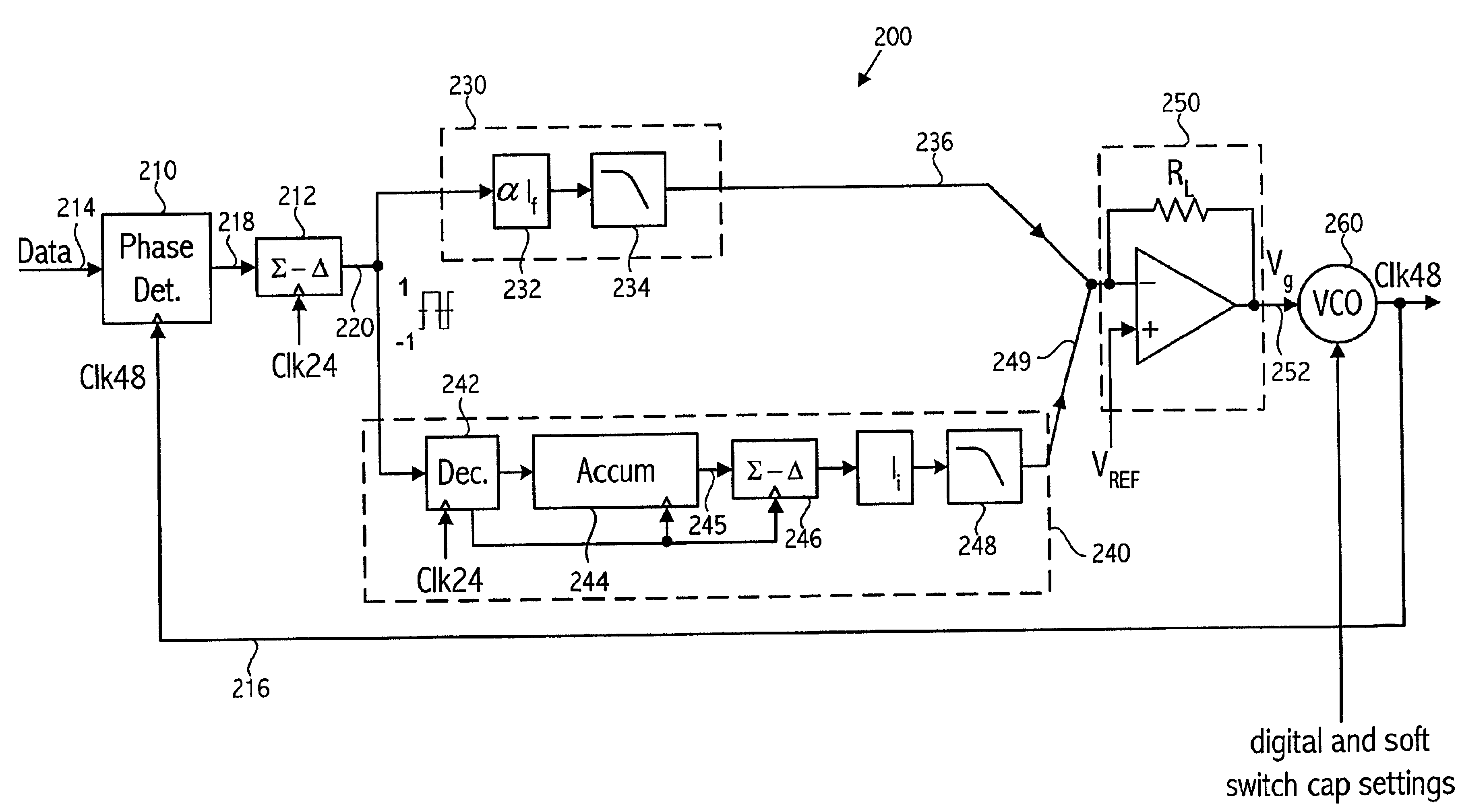
Hybrid analog/digital phase lock loop frequency synthesizer
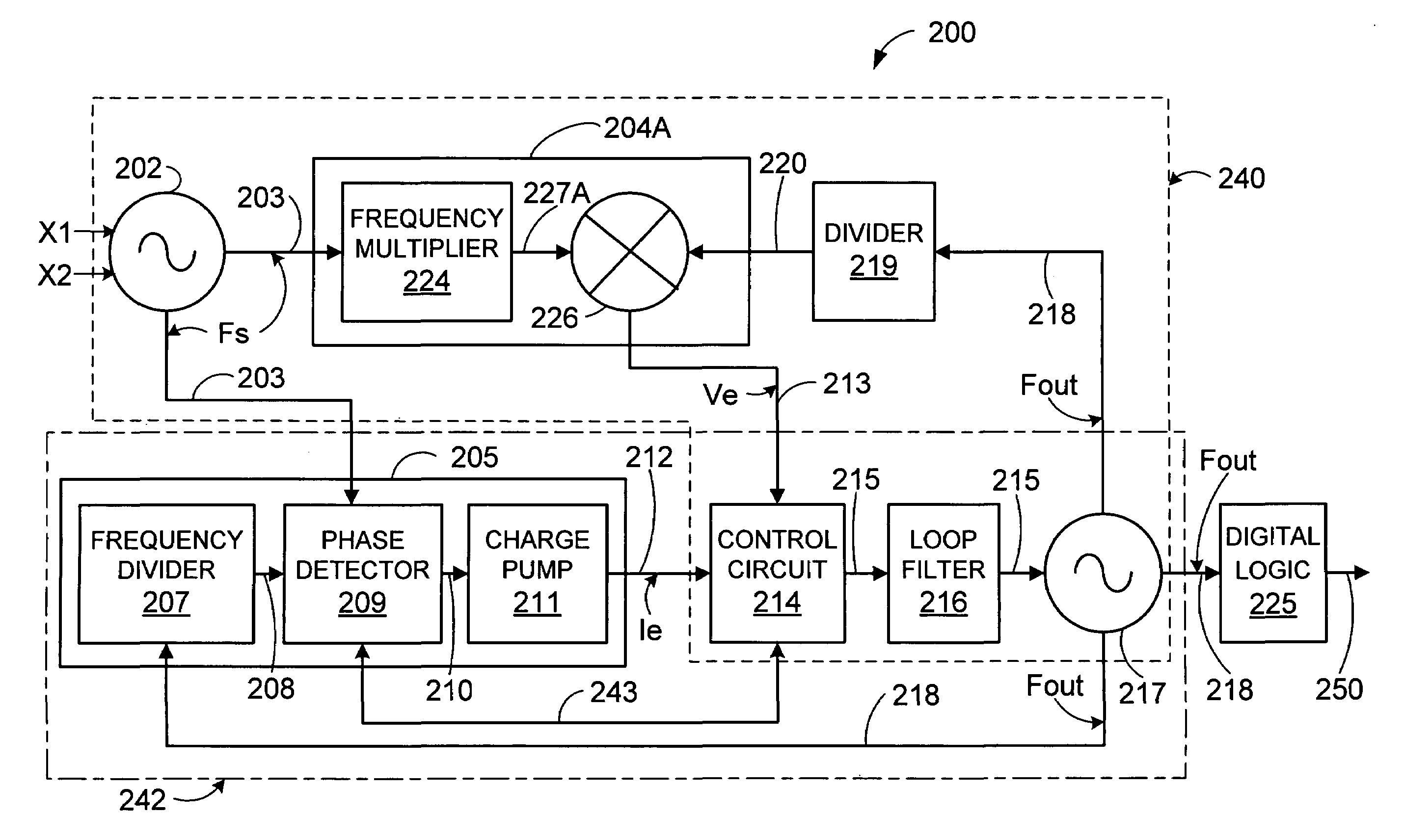
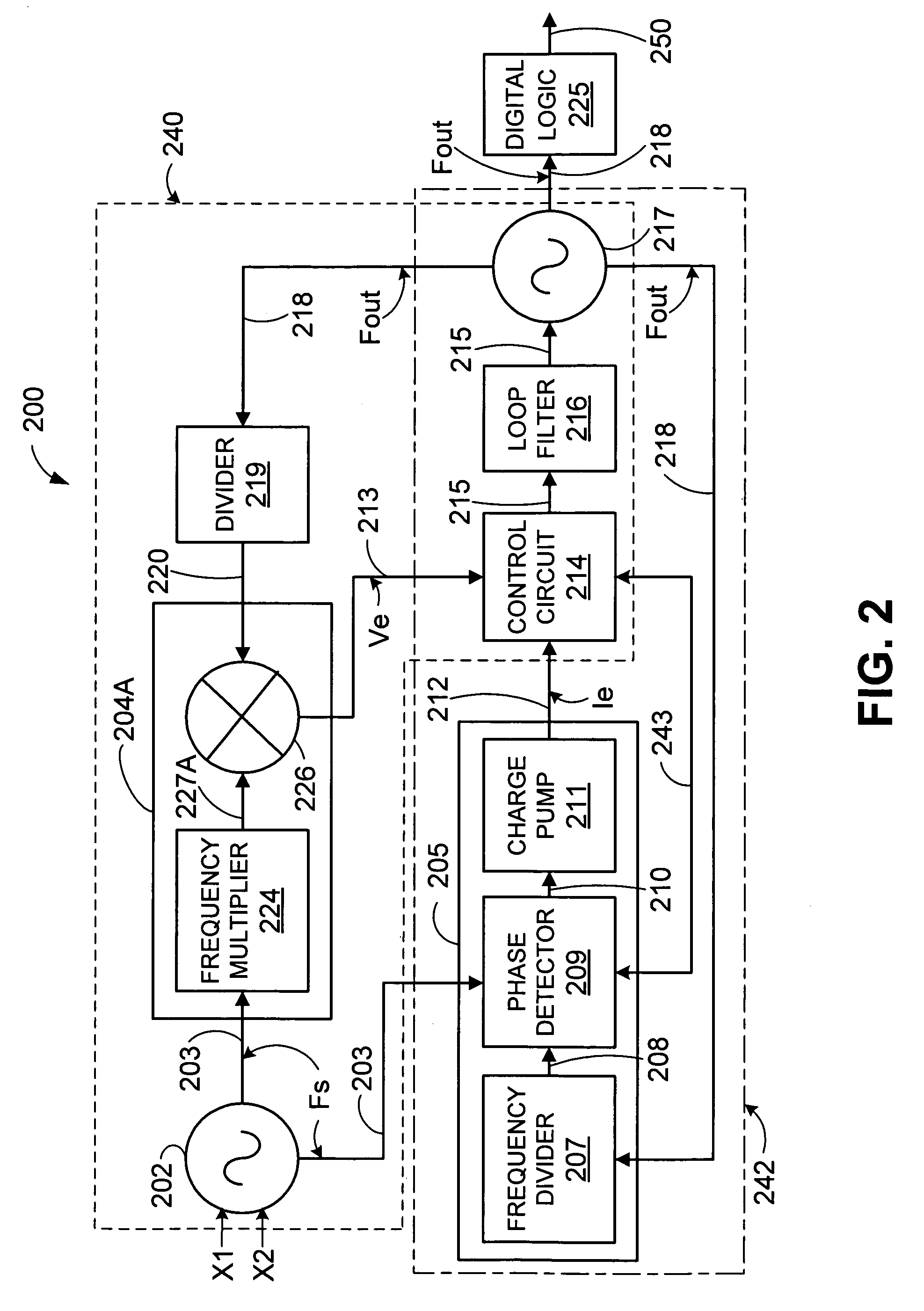
ActiveUS7084709B1Rapid and accurate and robust acquisitionLow noise operationPulse automatic controlOscillator tubesLow noiseControl signal
A hybrid frequency synthesizer includes an analog phase lock loop (PLL), a PLL, and a control circuit to control an output oscillator. The control circuit combines a control signal from the analog PLL with a control signal from the digital PLL to form a composite control signal. The composite control signal is conditioned depending on a state of lock of the analog PLL and / or the digital PLL. The composite signal controls the phase and frequency of the output oscillator. The analog control signal and the digital PLL control signal may be given a percentage of over the hybrid frequency synthesizer depending on the state of lock of the PLL and / or the digital PLL. The composite control signal provides both rapid, accurate, and robust acquisition by the digital PLL, and a smooth transition thereafter to low noise phase lock by the analog PLL.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Method and apparatus for acquiring a frequency without a reference clock
InactiveUS20050147197A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPulse automatic controlData streamEvaluation Interval
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
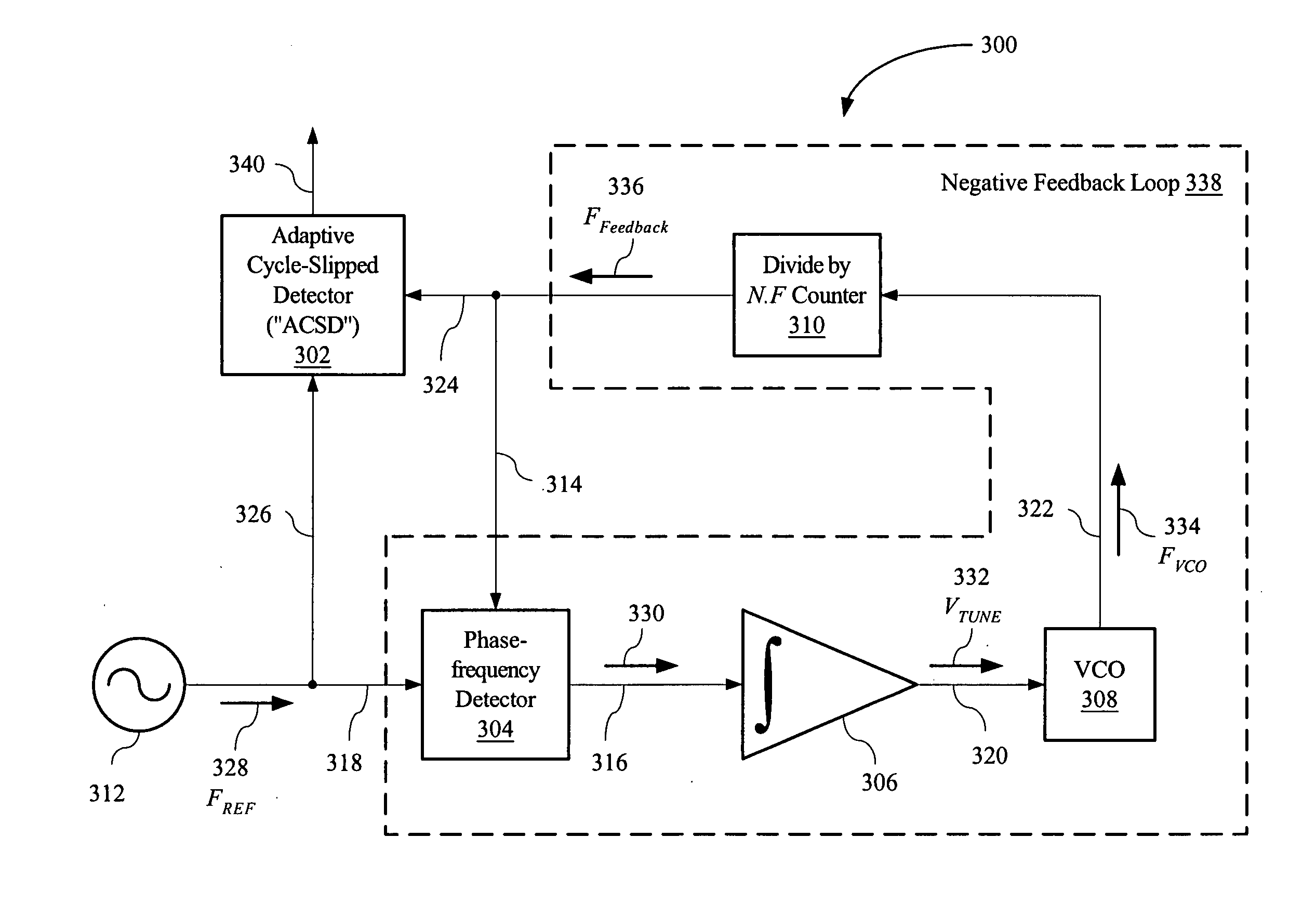
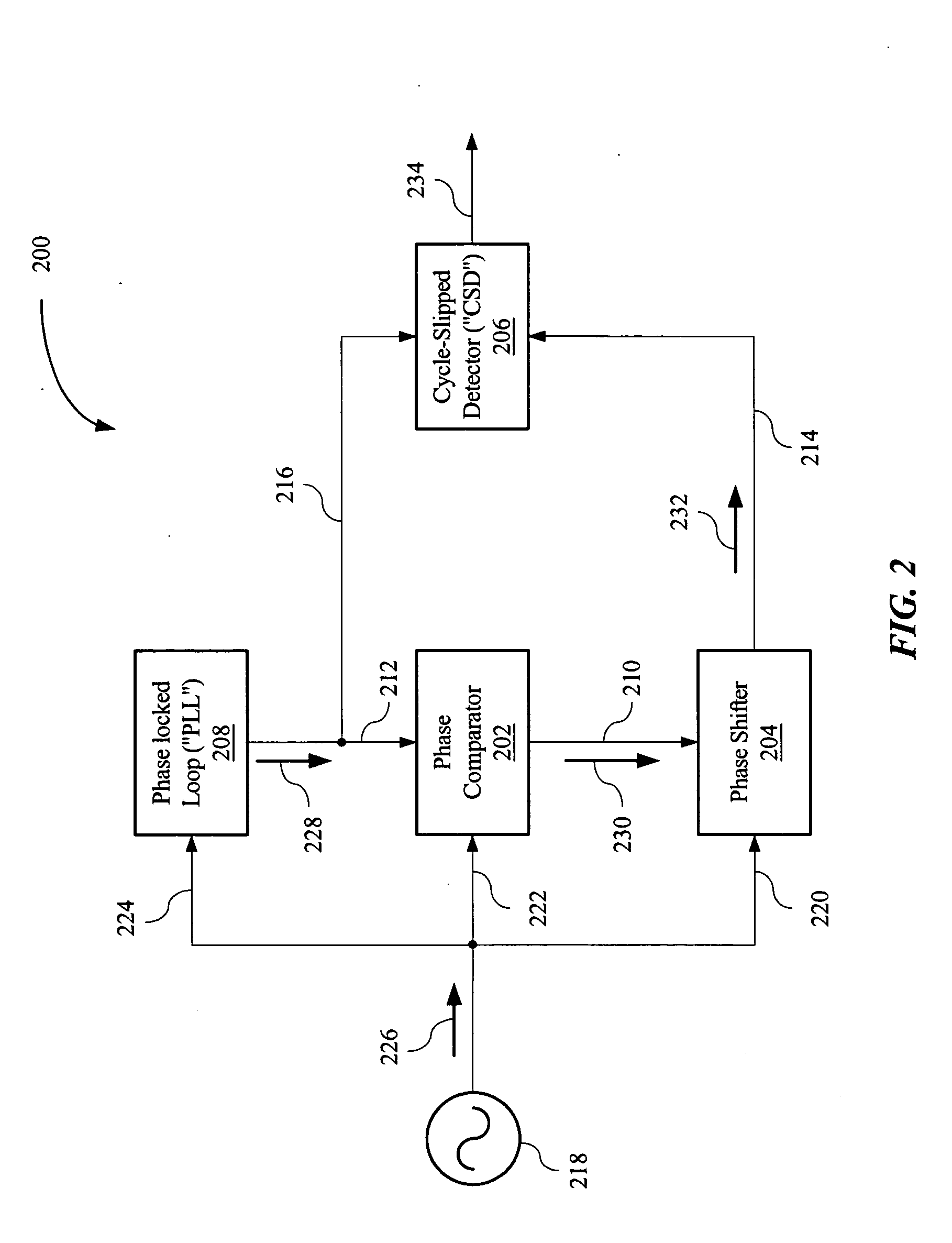
Adaptive cycle-slipped detector for unlock detection in phase-locked loop applications
An adaptive cycle-slipped detector (“ACSD”) for use in a Phase-Locked Loop (“PLL”) circuit. The ACSD may include a phase comparator, a phase shifter in signal communication with the phase comparator, and a cycle-slipped detector (“CSD”) in signal communication with the phase shifter.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Programmable phase-locked loop
An integrated circuit is provided, which includes a phase-locked loop (PLL) that is fabricated on the integrated circuit and has a selectable loop filter capacitance and a selectable output frequency range.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Phase-lock loop having programmable bandwidth
InactiveUS6853252B2Reducing PFD gainReducing PLL bandwidthPulse automatic controlCounting chain pulse countersPhase differencePhase frequency detector
A phase-locked loop having a programmable loop bandwidth is provided. A PLL comprises an oscillator operable to receive an error-correction signal and to generate an oscillator signal having a frequency that is related to the error-correction signal. The PLL further comprises a phase-frequency detector (PFD) coupled to the oscillator and operable to receive a reference signal and to generate the error-correction signal based upon a phase difference between the reference signal and a feedback signal derived from the oscillator signal. The PLL further comprises an error-correction signal suppression circuit coupled to the PFD and operable to control the loop bandwidth of the PLL by periodically enabling the PFD.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Phase locked loop fast lock method
ActiveUS7369002B2Quality improvementReduced settling timePulse automatic controlOscillator tubesLoop filterIntegrator
The present invention is a method to rapidly lock a type II phase locked loop (PLL) after a frequency jump without degrading the output signal much. The method to decrease the settling time and improve the quality of the output clock during the settling disclosed herein comprises of the following broad steps: Estimate new frequency offset with a separate circuit outside the PLL loop to measure the frequency of the input signal accurately. Ramp integrator to the new frequency offset. Do phase build out or phase pull-in. The remaining phase offset is build out when no edge to edge alignment is required. Otherwise, the remaining phase offset is pulled in while the integrator in the PLL's loop filter is disabled. Reduce the PLL bandwidth and / or lower damping to let the PLL settle. Switch the PLL to final bandwidth and damping required by the application.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
PLL circuit
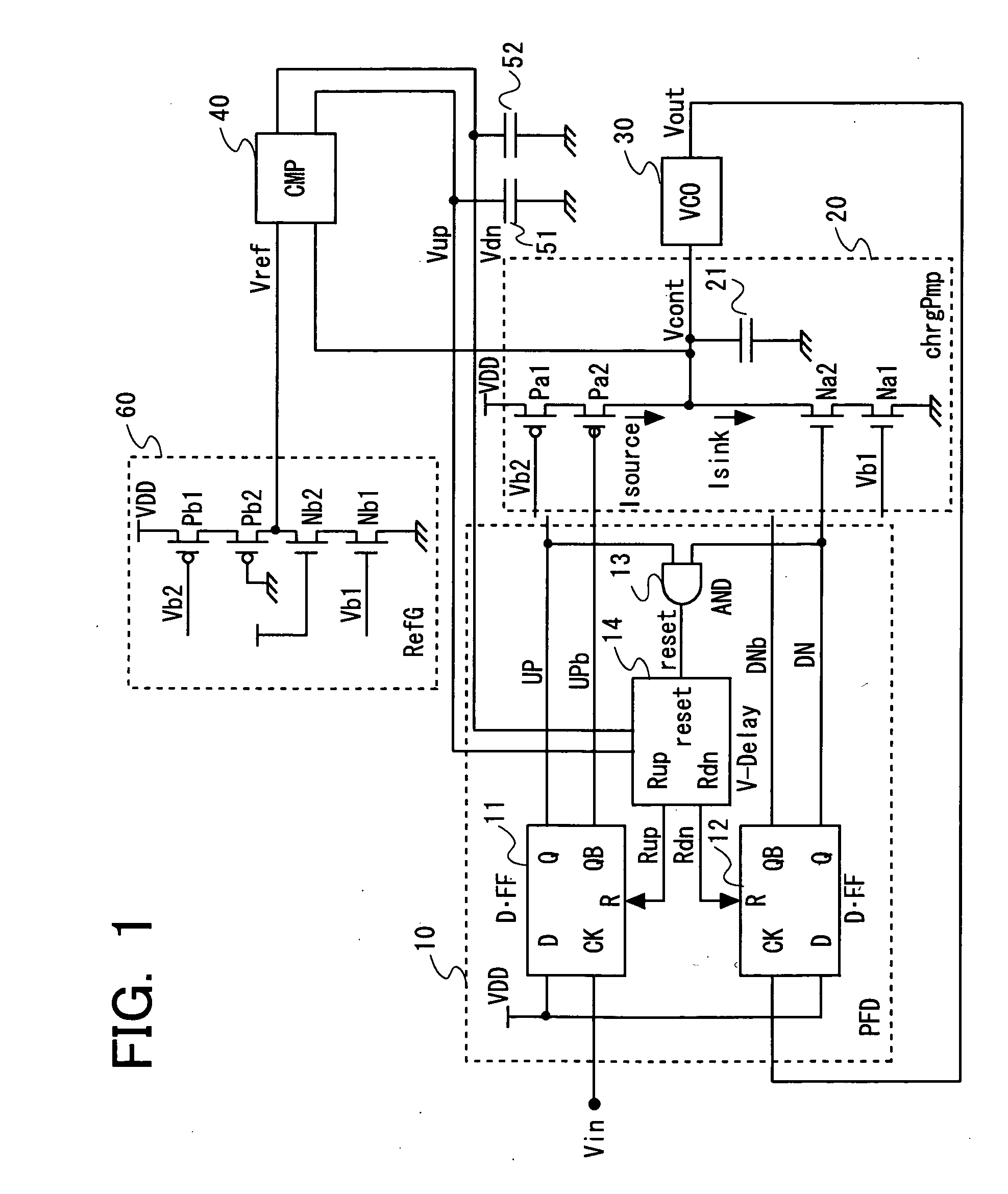
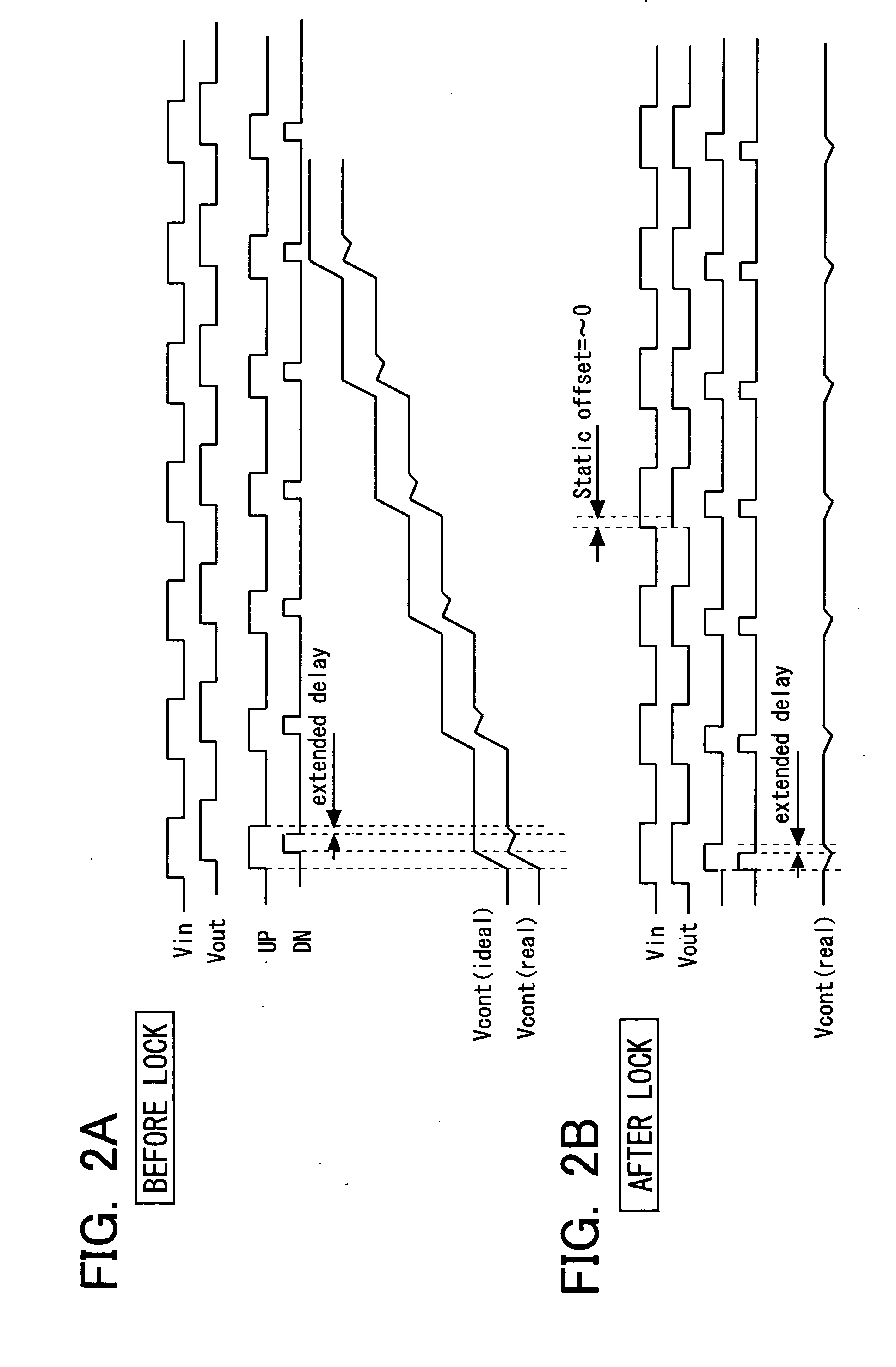
InactiveUS20060119405A1Less-gain adjustment rangeReduce phase offsetPulse automatic controlFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAudio power amplifierTerminal voltage
Disclosed is a PLL circuit including a phase frequency detector (PFD) for comparing phase and frequency between an input signal and an output signal, a charge pump circuit for charging a capacitor when an up-signal from the PFD is activated, discharging the capacitor when a down-signal is activated, and for outputting the terminal voltage of the capacitor as a control voltage, and a VCO for outputting an output signal of a frequency in accordance with the control voltage. An output of the VCO is fed back as an output signal to the PFD as input. The PFD includes a delay adjustment circuit for exercising control for resetting the up-signal and the down-signal with a preset delay as from a time point both up-signal and the down-signal have been activated. There is also provided a comparator amplifier circuit for comparing a reference voltage, corresponding to a control voltage when both up-signal and down-signal are activated, to supply first and second control signals to the delay adjustment circuit. The pulse widths of up and down-signals are adjusted depending on current offset characteristics of the charge pump circuit.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com