Patents
Literature
64 results about "Absolute magnitude" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absolute magnitude (M) is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object, on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were viewed from a distance of exactly 10.0 parsecs (32.6 light-years), without extinction (or dimming) of its light due to absorption by interstellar matter and cosmic dust. By hypothetically placing all objects at a standard reference distance from the observer, their luminosities can be directly compared on a magnitude scale.
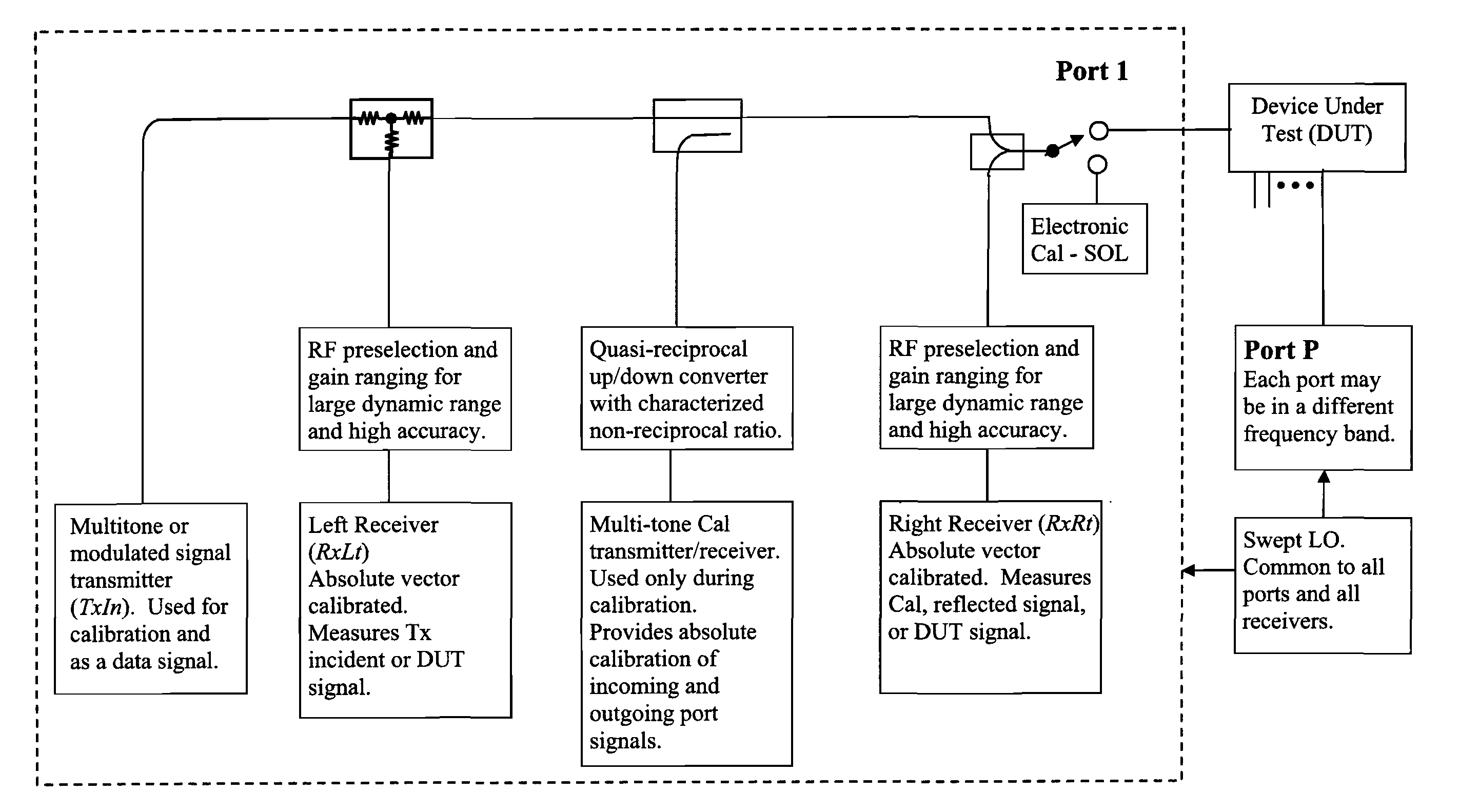
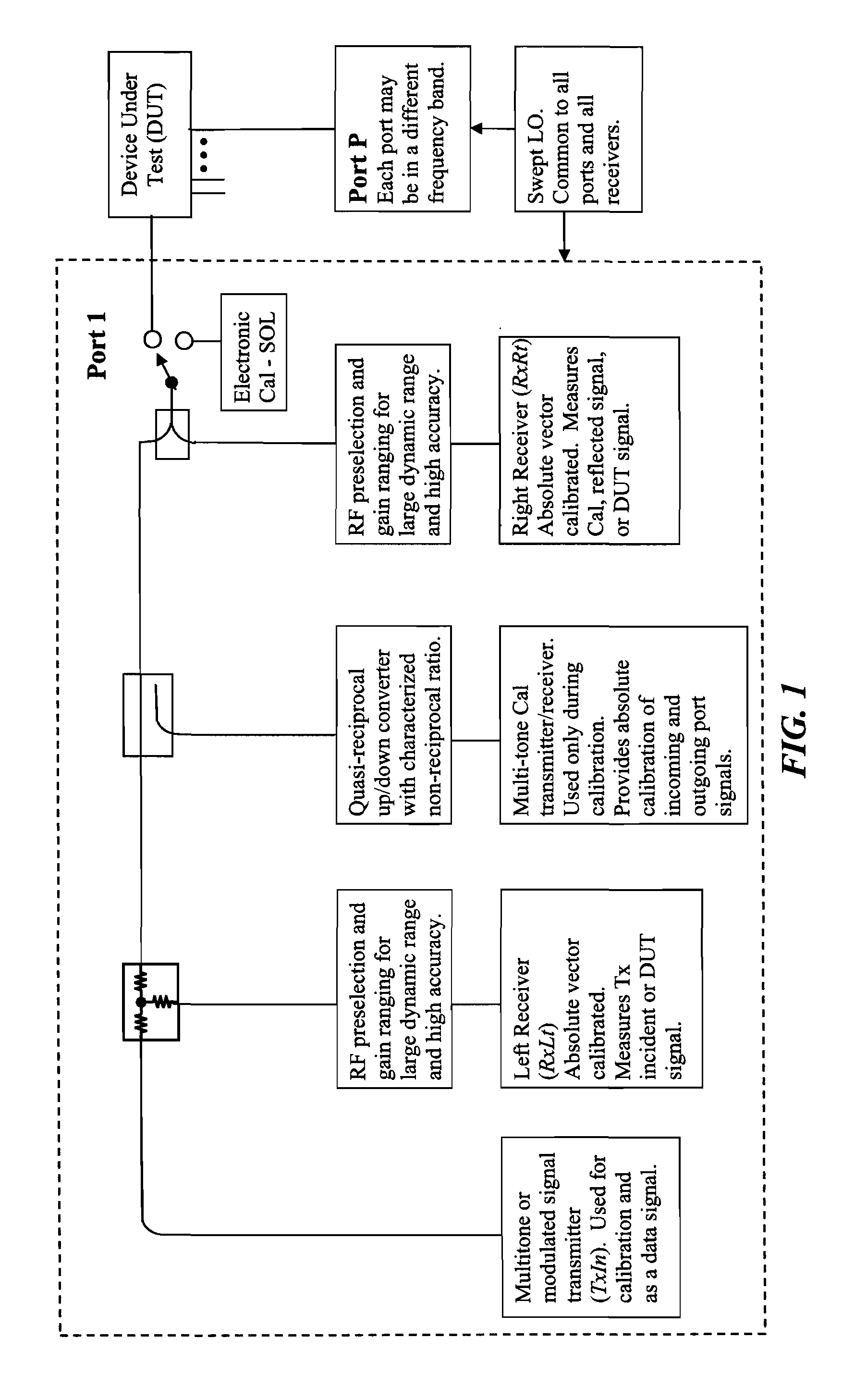
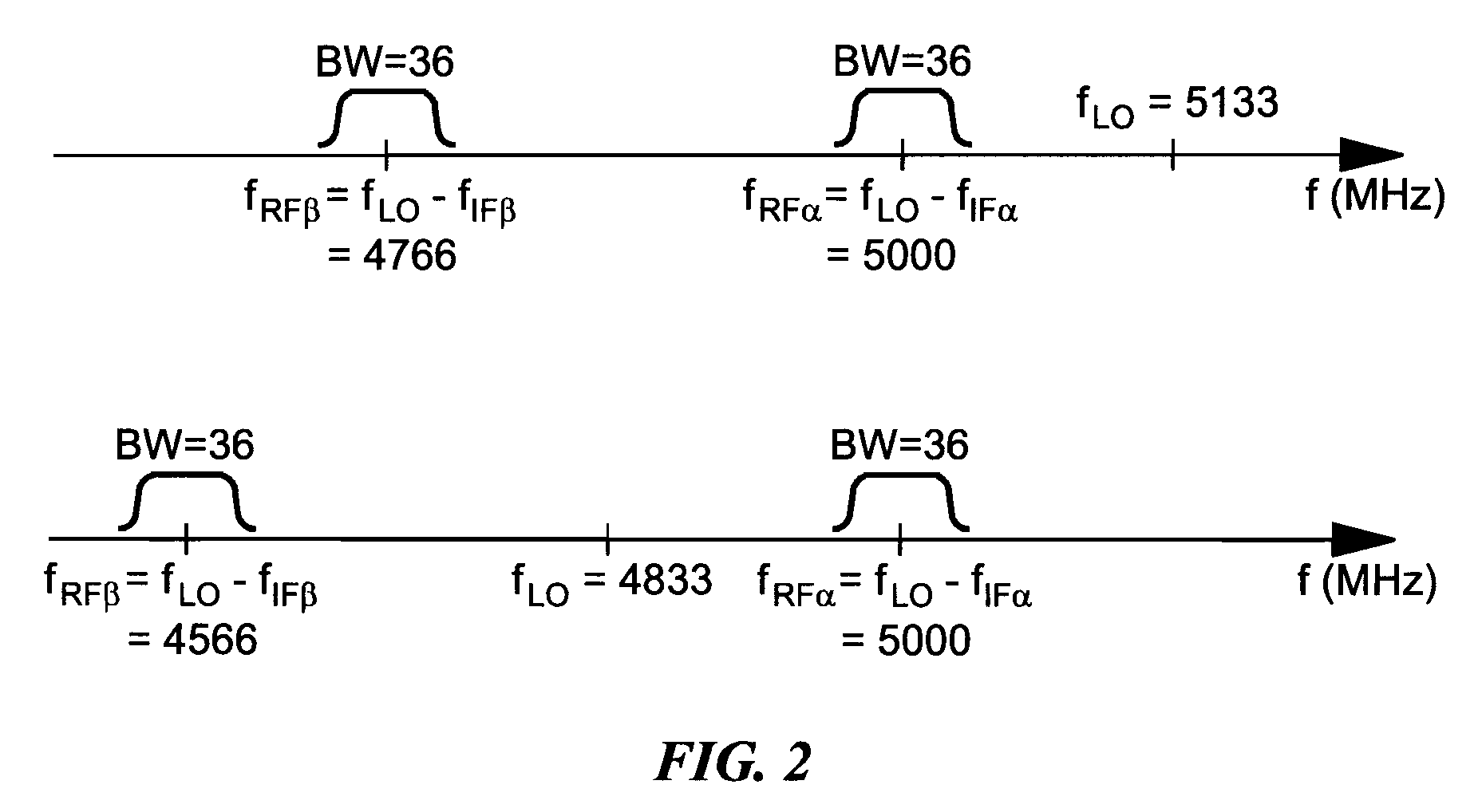
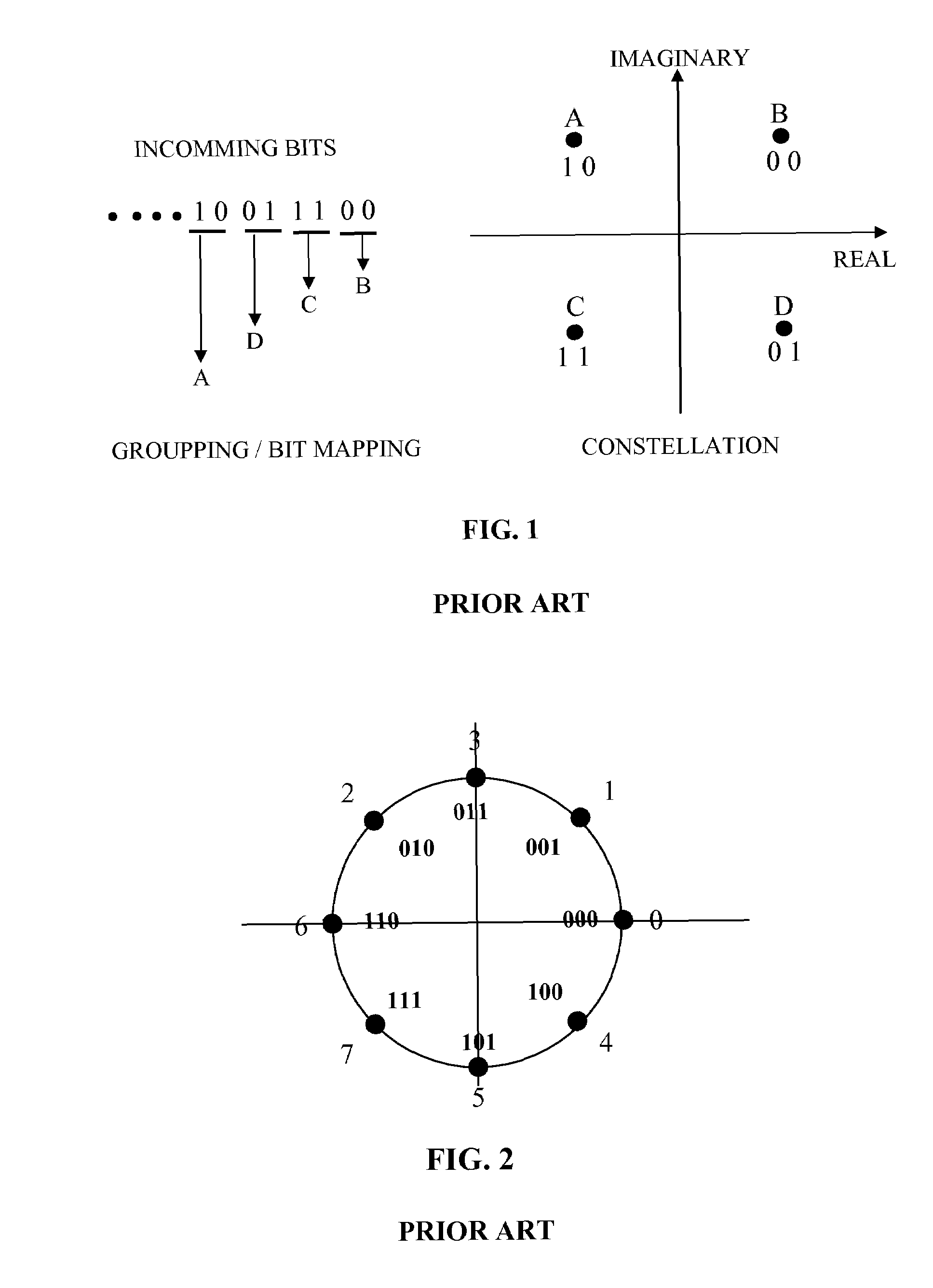
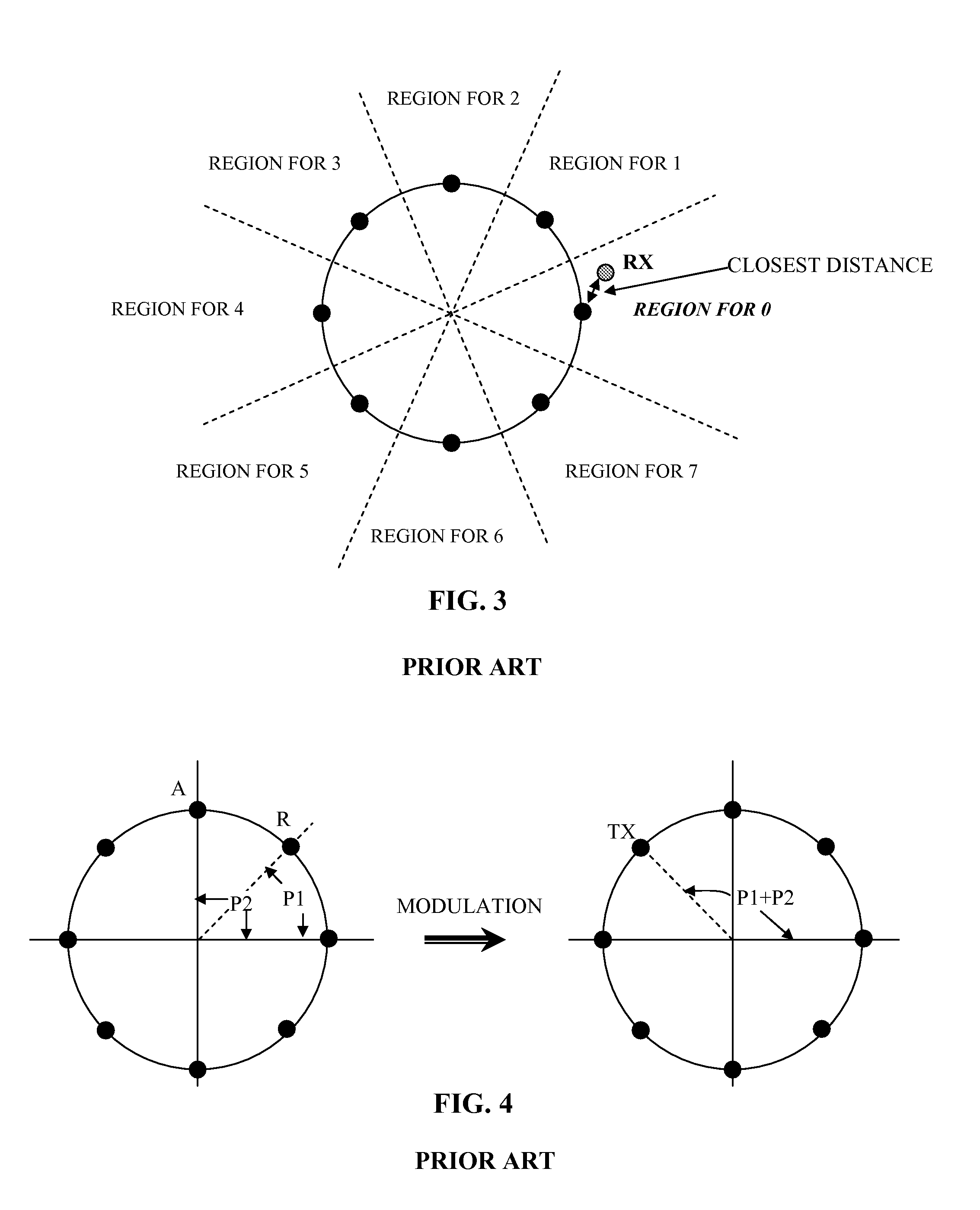
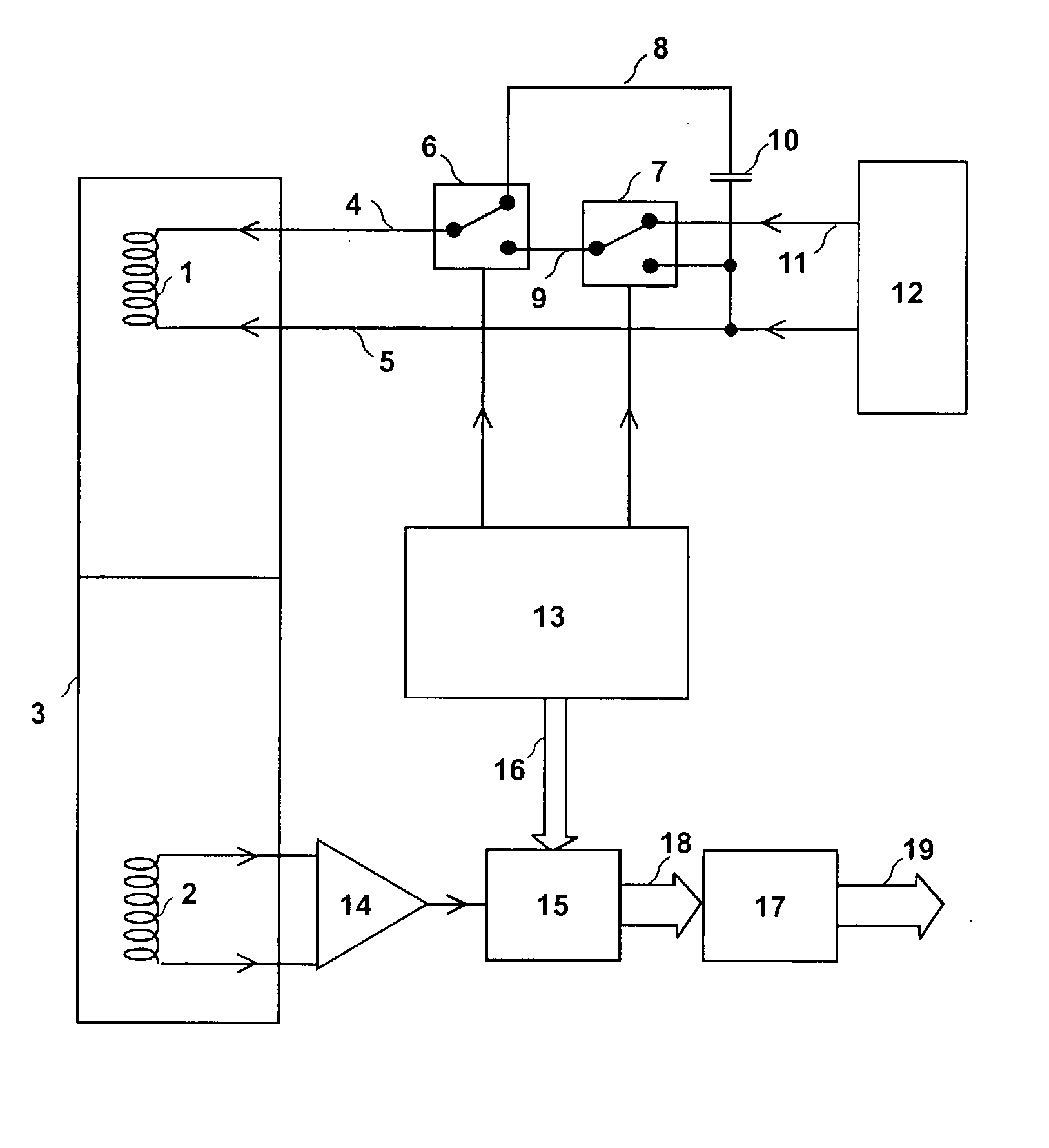
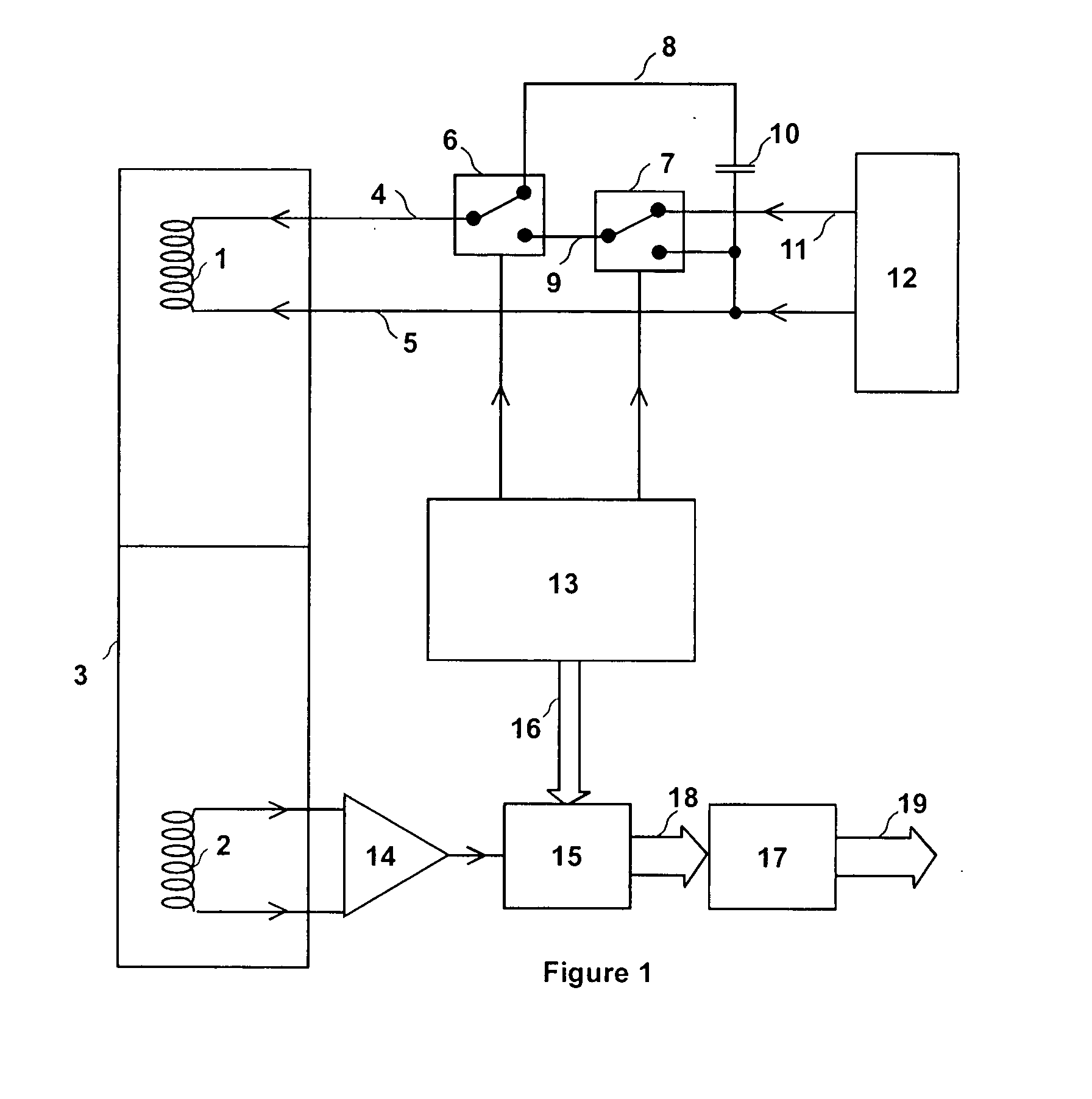
Vector signal measuring system, featuring wide bandwidth, large dynamic range, and high accuracy
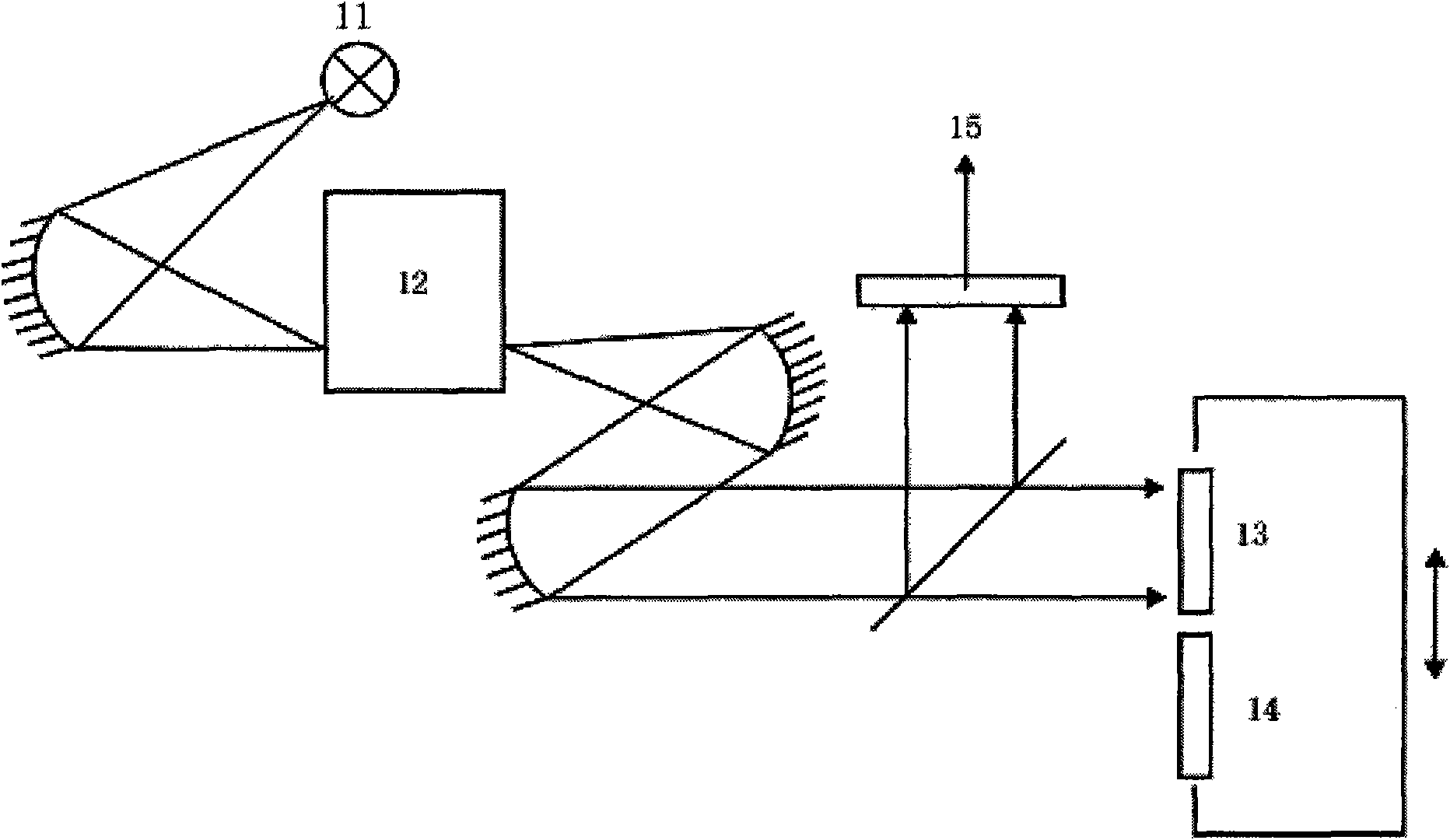
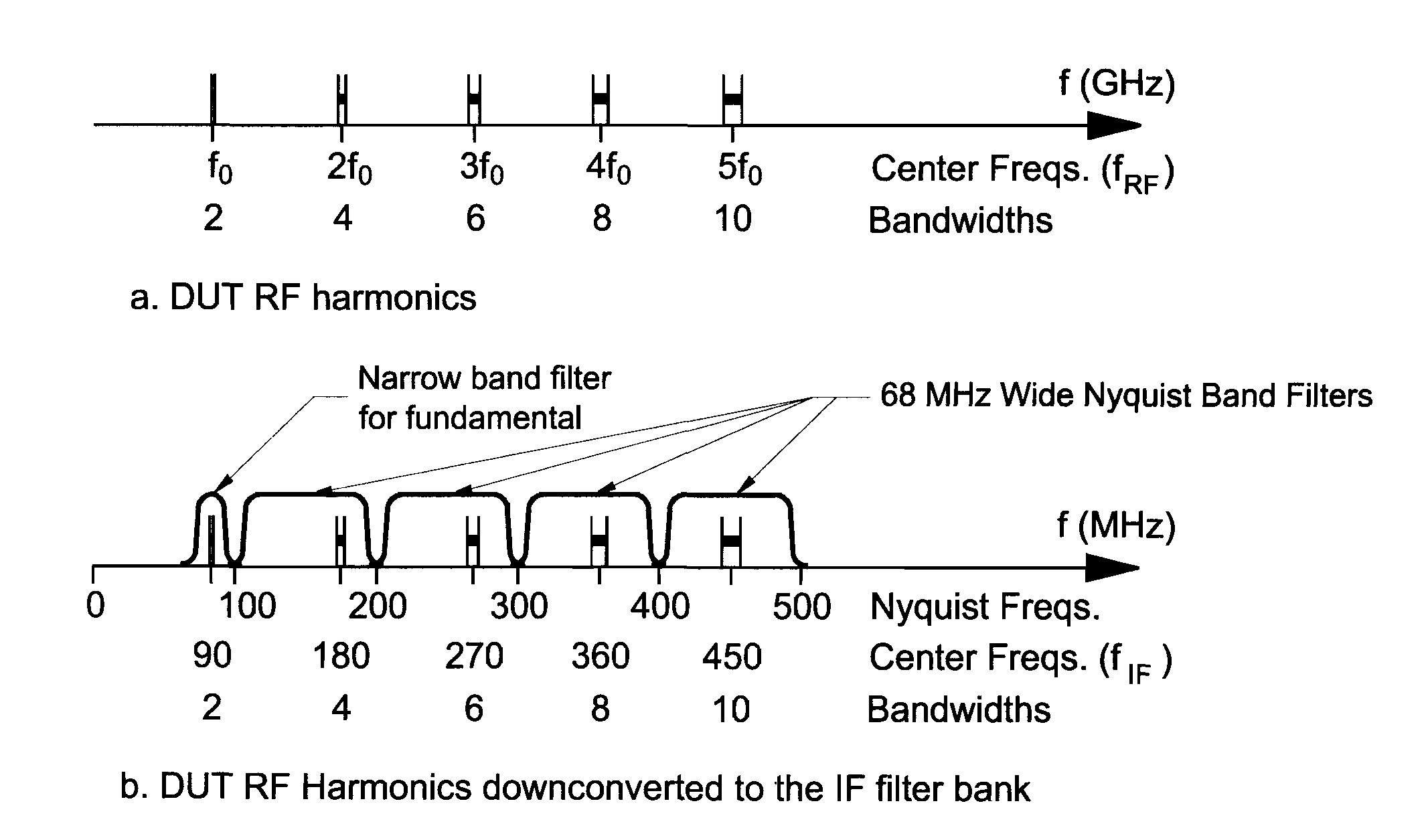
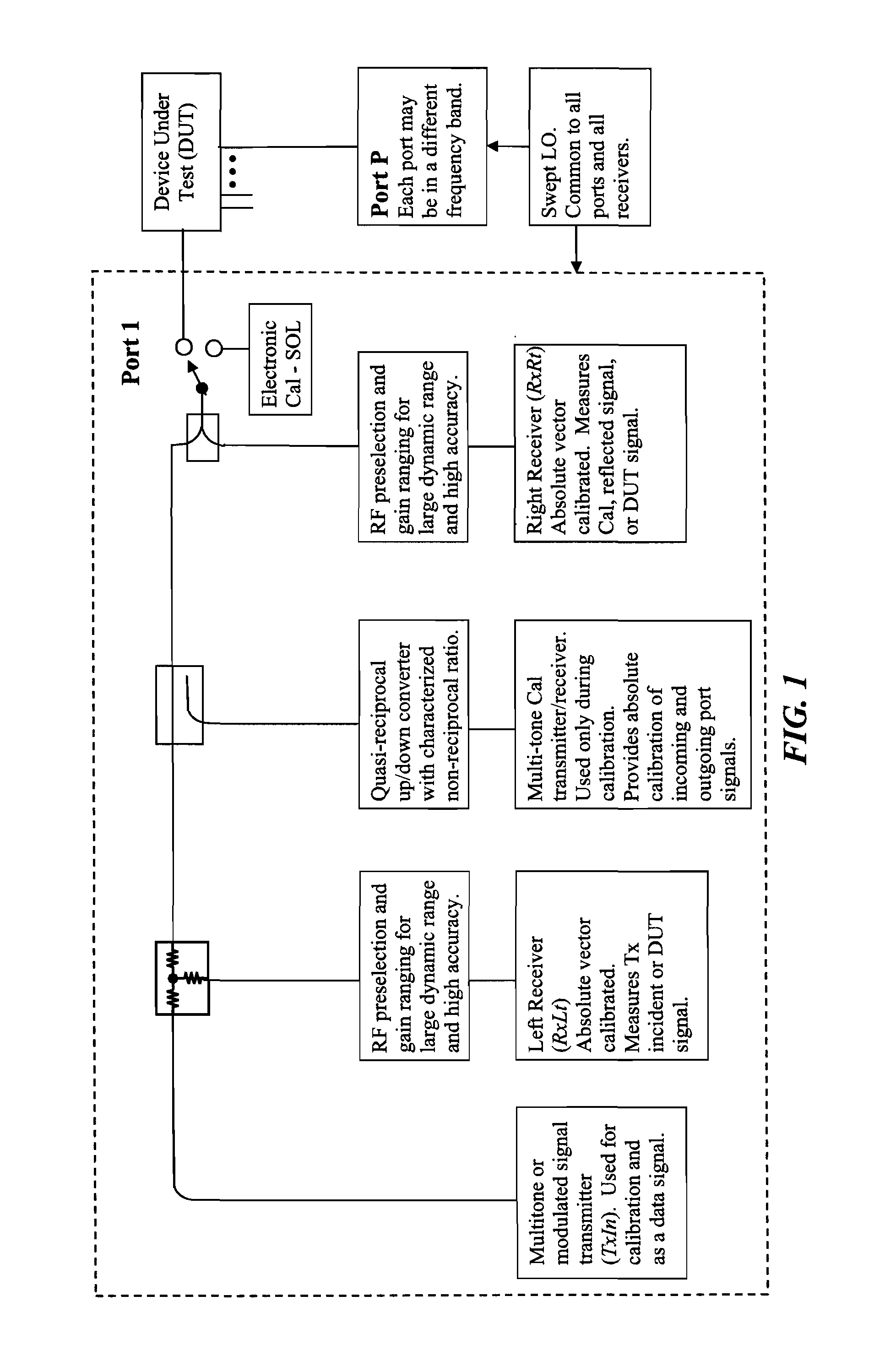
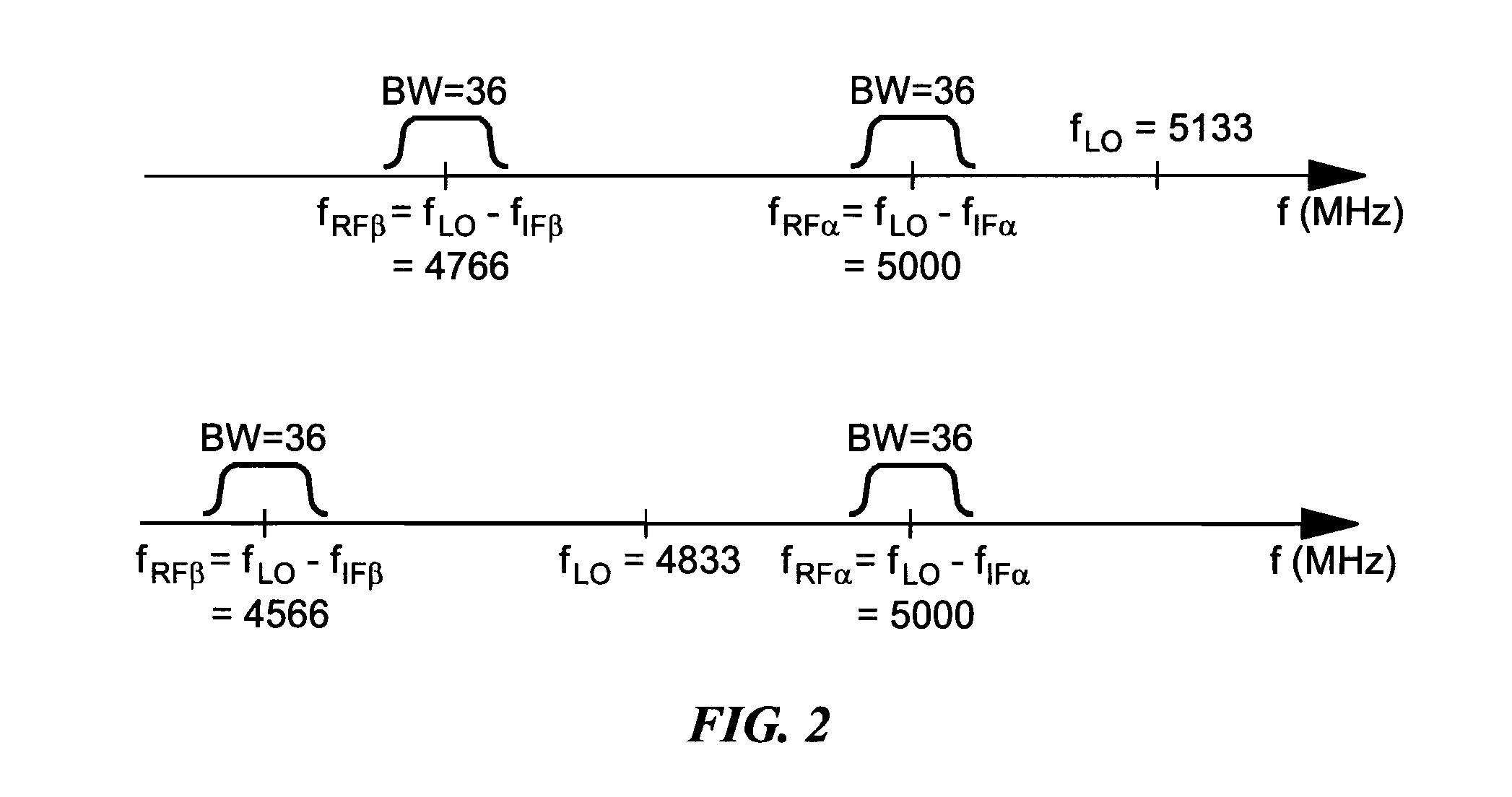
A new measurement system, with two receiver channels per measurement port, has been developed that provides absolute magnitude and absolute phase relationship measurements over wide bandwidths. Gain ranging is used at RF to provide optimum noise performance and a swept YIG preselector filter is used to avoid spurious signals. A new absolute vector error correction method is used to calibrate the measurement system in order to allow for absolute vector measurements, and it also removes the time-varying responses caused by the swept YIG preselector filters. A quasi-reciprocal mixer with a characterized non-reciprocal ratio is used to provide the absolute calibration standard. The two receiver channels can be adapted to a wide variety of applications, including wide bandwidth vector signal analyzer measurements, mixer measurements, and harmonic measurements. The two-channels can also be used as an absolute calibrated transmitter / reflectometer.
Owner:DVORAK STEVEN L +1
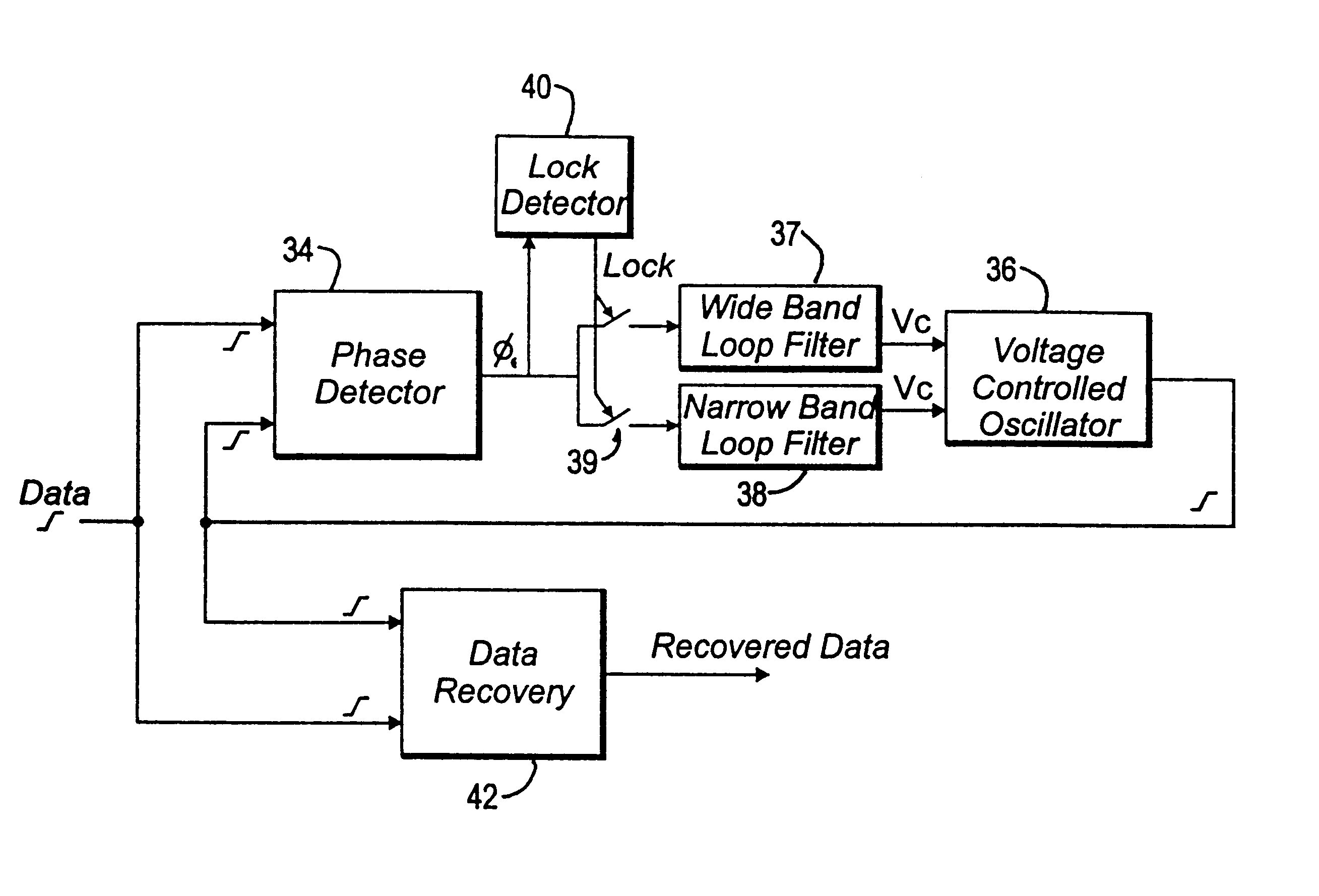
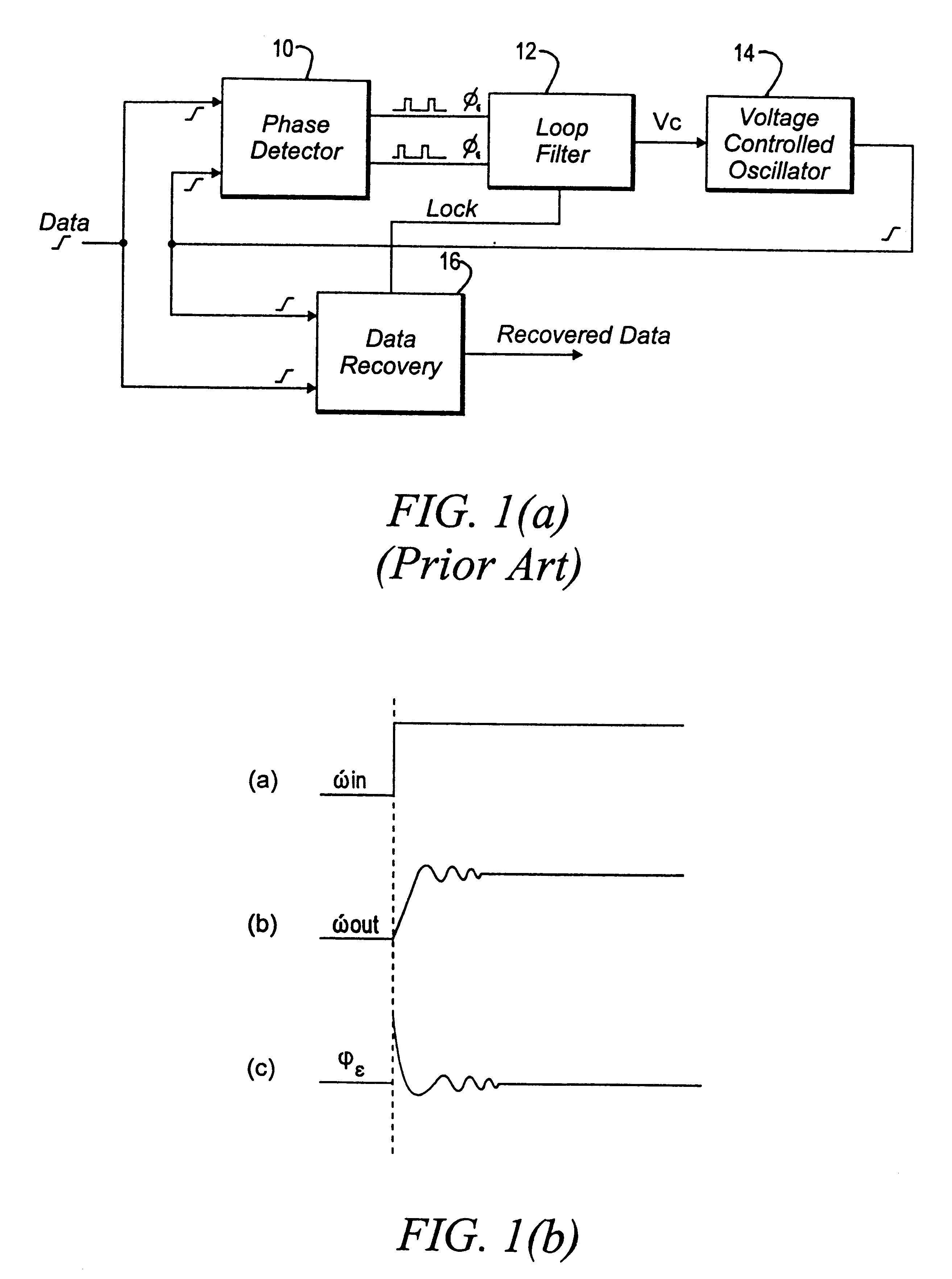
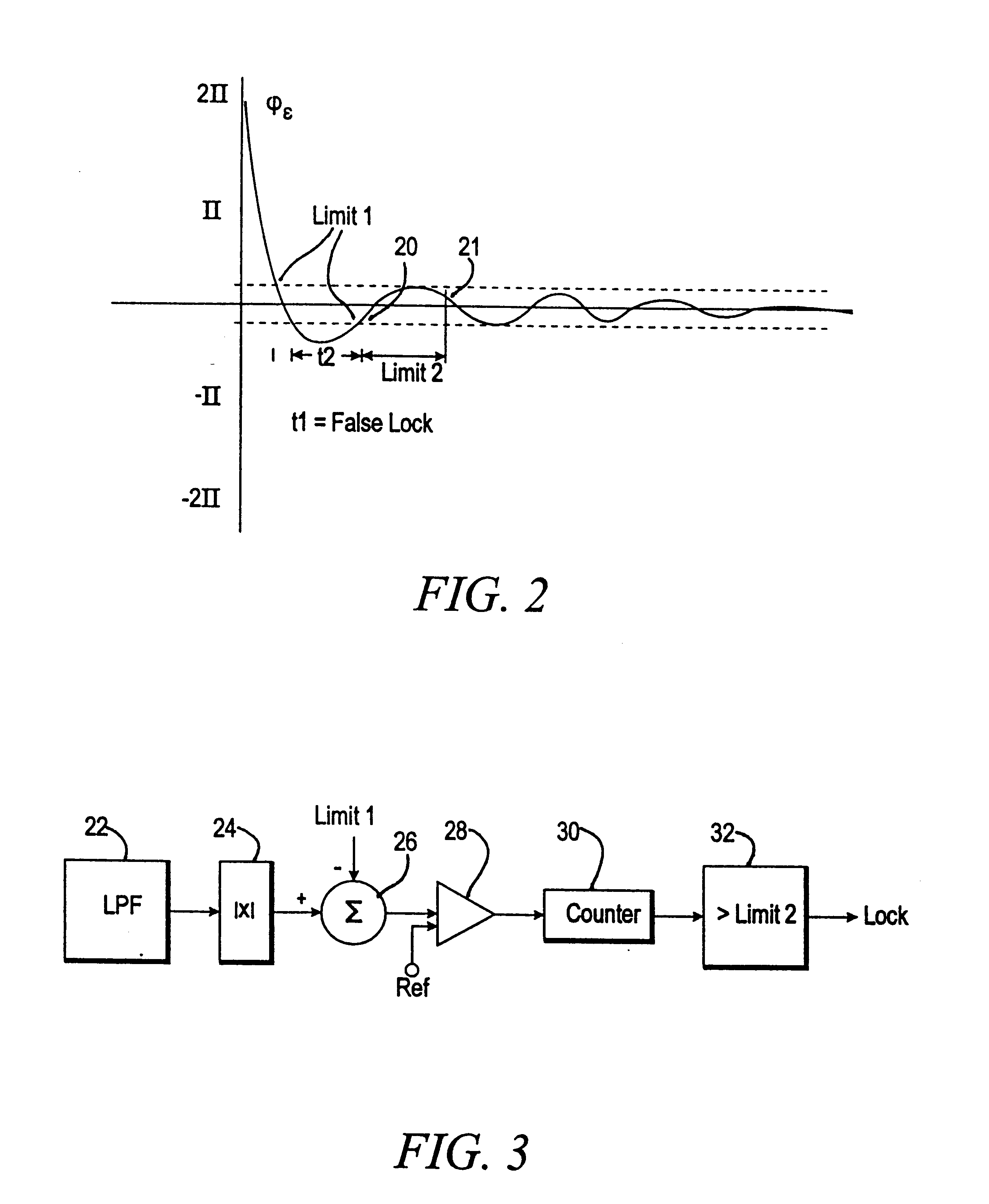
Lock detector for phase locked loops
InactiveUS6580328B2Improve system performanceEliminate high frequency noisePulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDetector circuitsControl system
A detector circuit for determining whether synchronization lock has been optimally achieved in feedback-type control systems. The detector circuit evaluates an error signal developed by a phase / frequency detector and compares the absolute magnitude of the error signal to a first threshold signal corresponding to a magnitude metric. When the value of the error signal is less than the magnitude threshold value, an event signal initiates a time interval counter which continues counting so long as the error signal remains below the magnitude threshold value. The time interval counter continues until it counts to a second threshold value corresponding to a timing metric. At this point, synchronization lock is declared.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
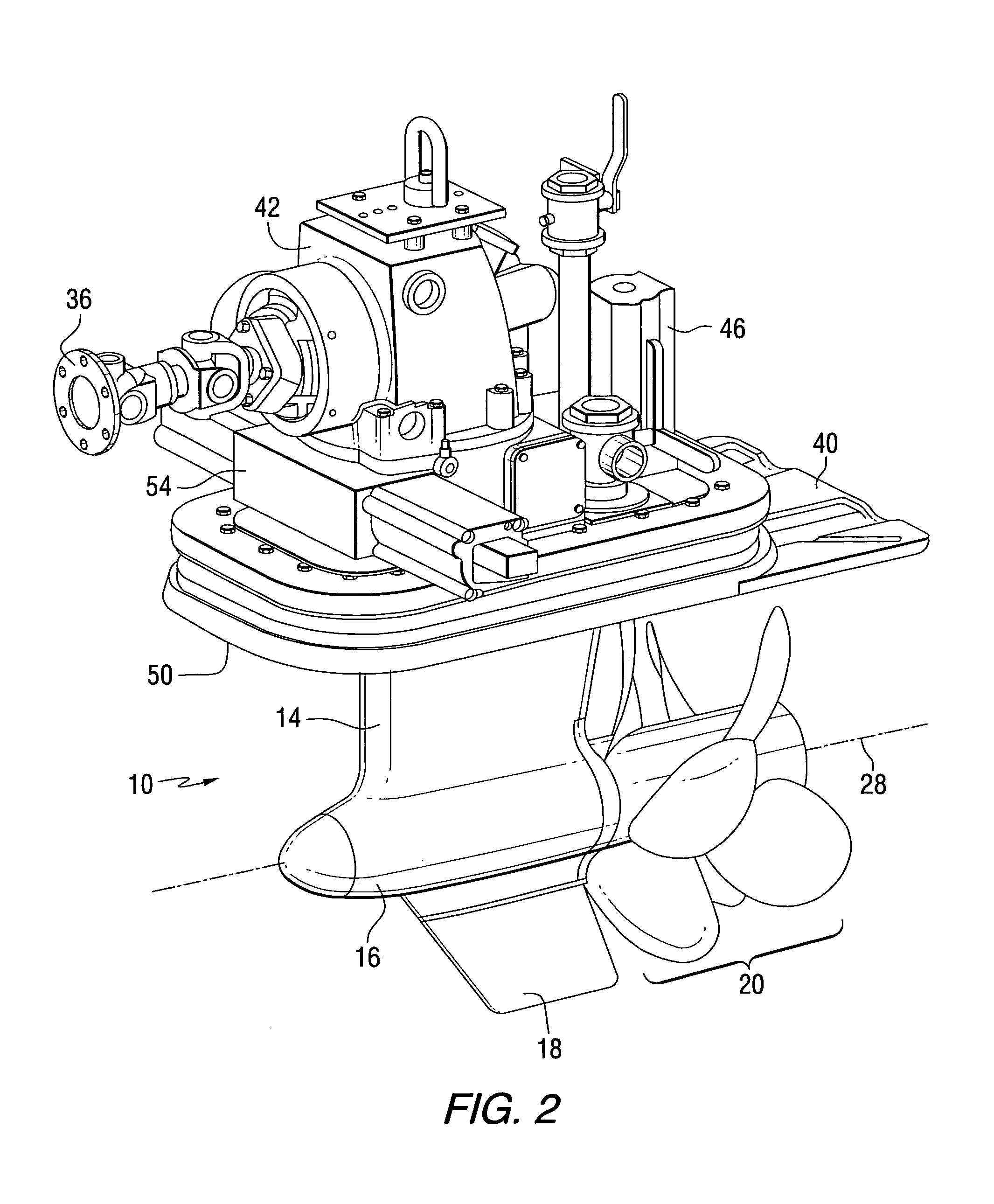
Method for braking a vessel with two marine propulsion devices
InactiveUS7131385B1Steering by extensible flapsSteering by propulsive elementsMarine propulsionMarine engineering
A method for controlling the movement of a marine vessel comprises steps that rotate two marine propulsion devices about their respective axes in order to increase the hydrodynamic resistance of the marine propulsion devices as they move through the water with the marine vessel. This increased resistance exerts a braking thrust on the marine vessel. Various techniques and procedures can be used to determine the absolute magnitudes of the angular magnitudes by which the marine propulsion devices are rotated.
Owner:BRUNSWICK CORPORATION
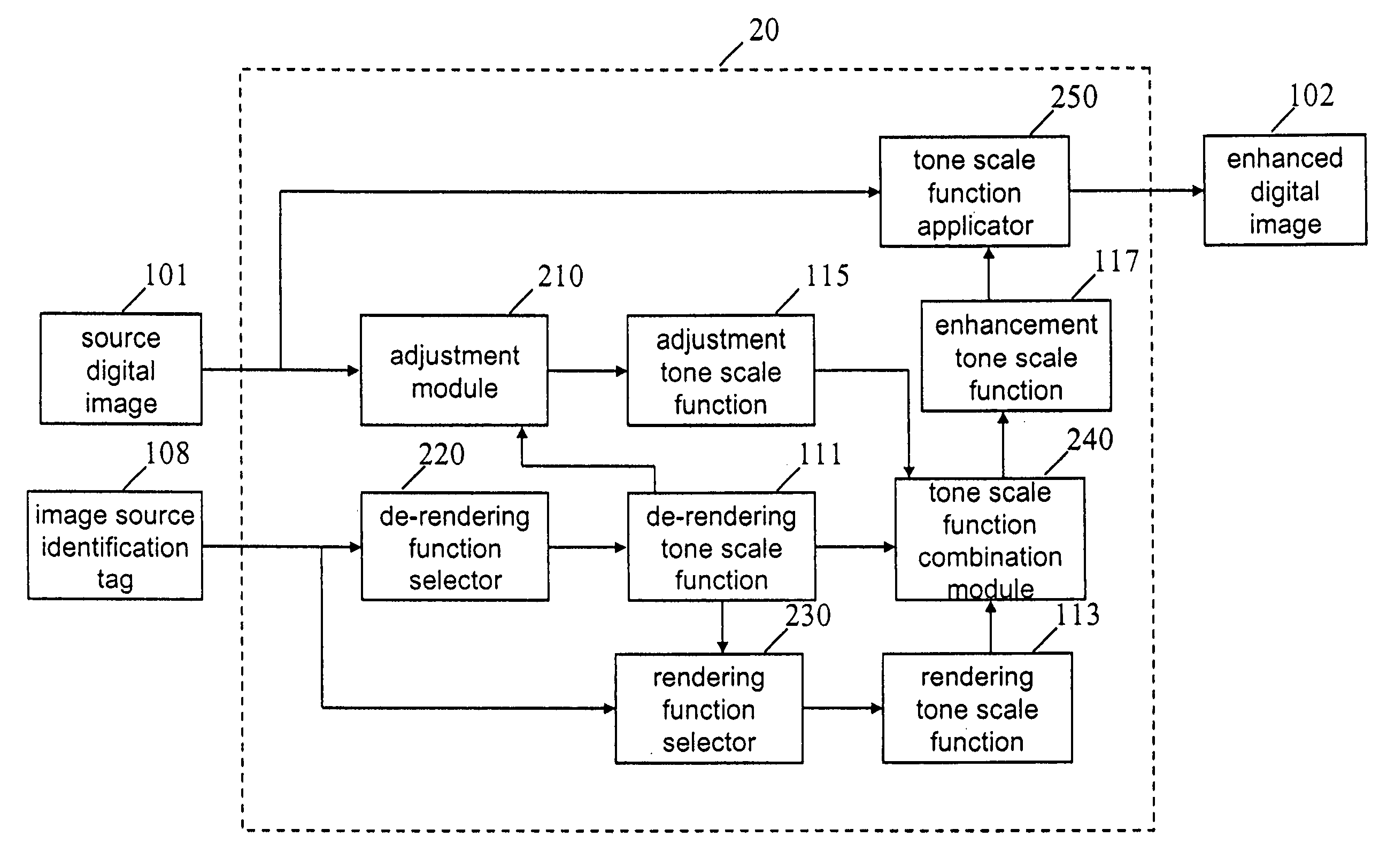
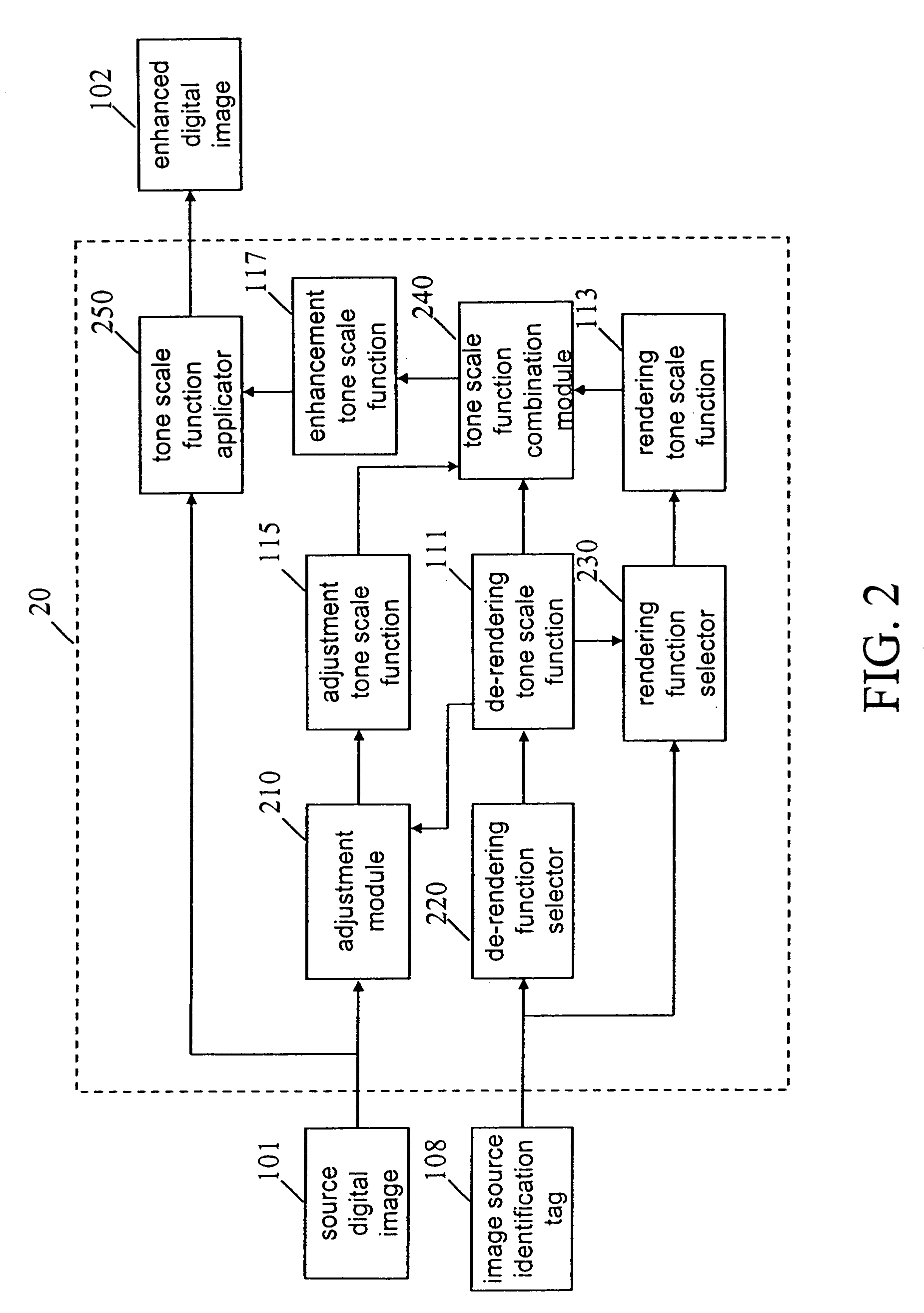
Adjusting the color, brightness, and tone scale of rendered digital images
A method of processing a digital image to produce an enhanced digital image including receiving a source digital image; receiving a rendering tone scale function wherein the rendering tone scale function is a nonlinear function that has an absolute magnitude slope in the middle of the function domain that is greater than or equal to the absolute magnitude slope at either extreme of the function domain; and using the rendering tone scale function to calculate a de-rendering tone scale function. The method also includes receiving or calculating an adjustment tone scale function; combining the de-rendering, rendering, and adjustment tone scale functions to form an enhancement tone scale function; and using the enhancement tone scale function and the source digital image to produce an enhanced digital image.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
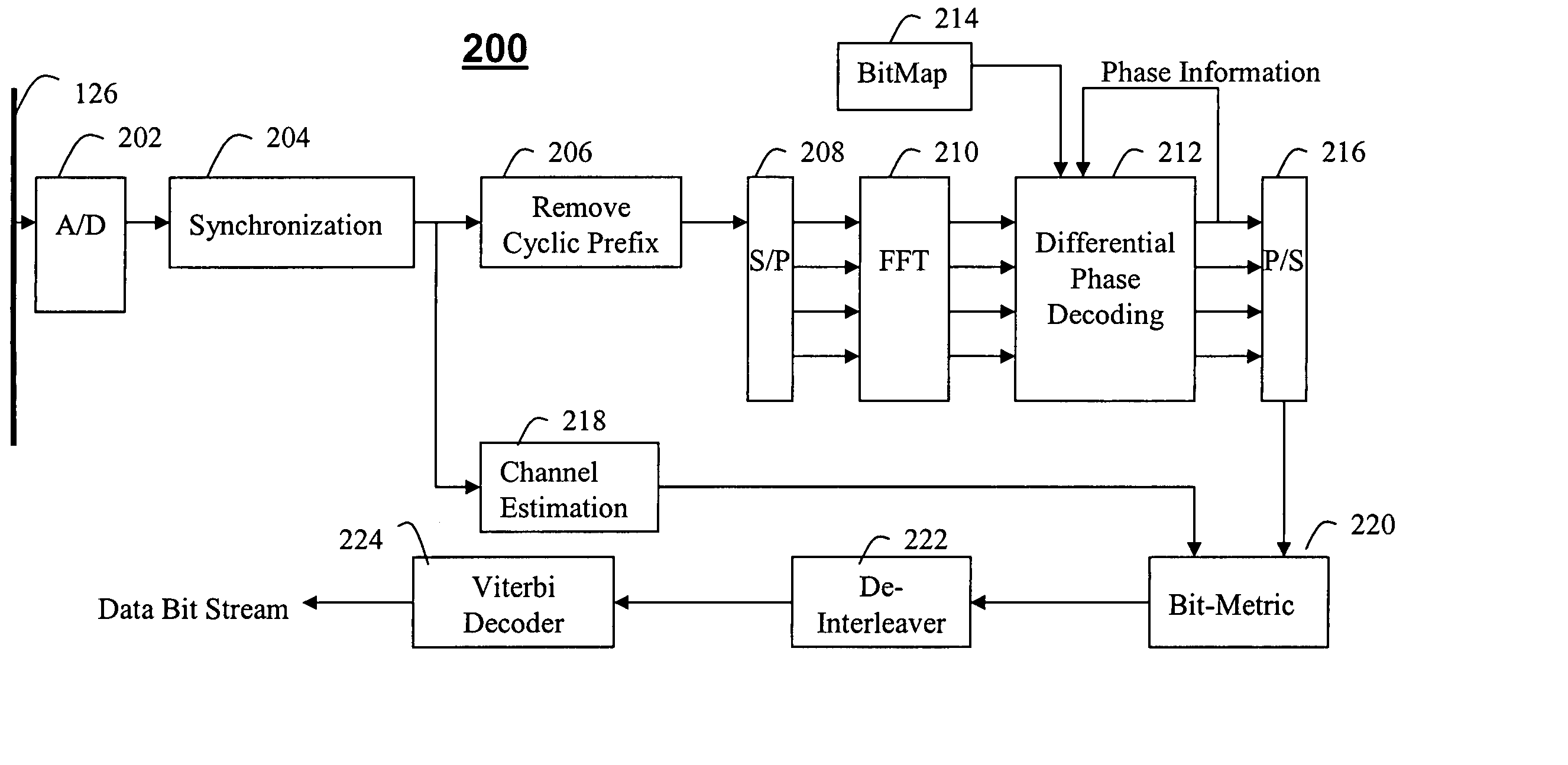
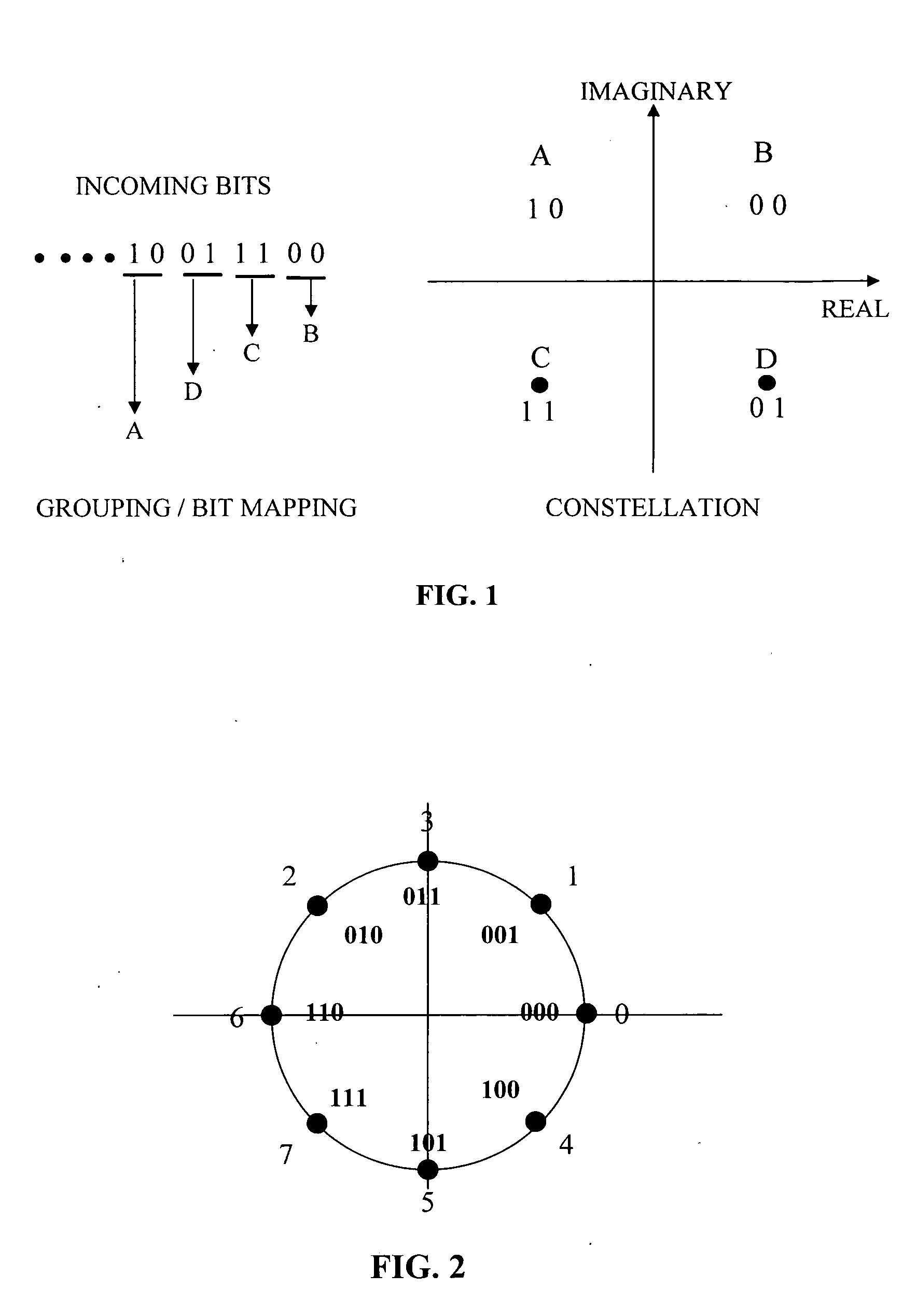
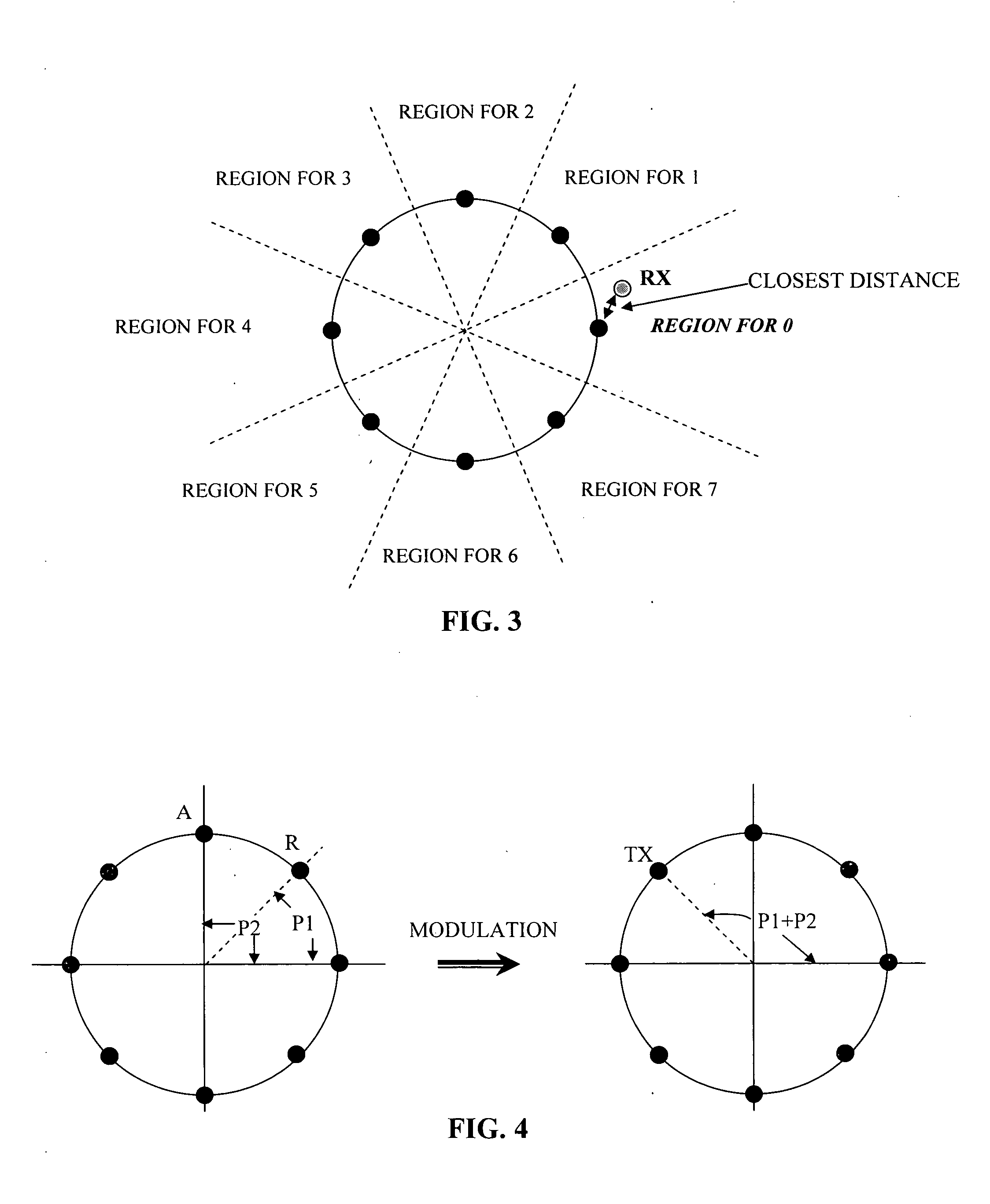
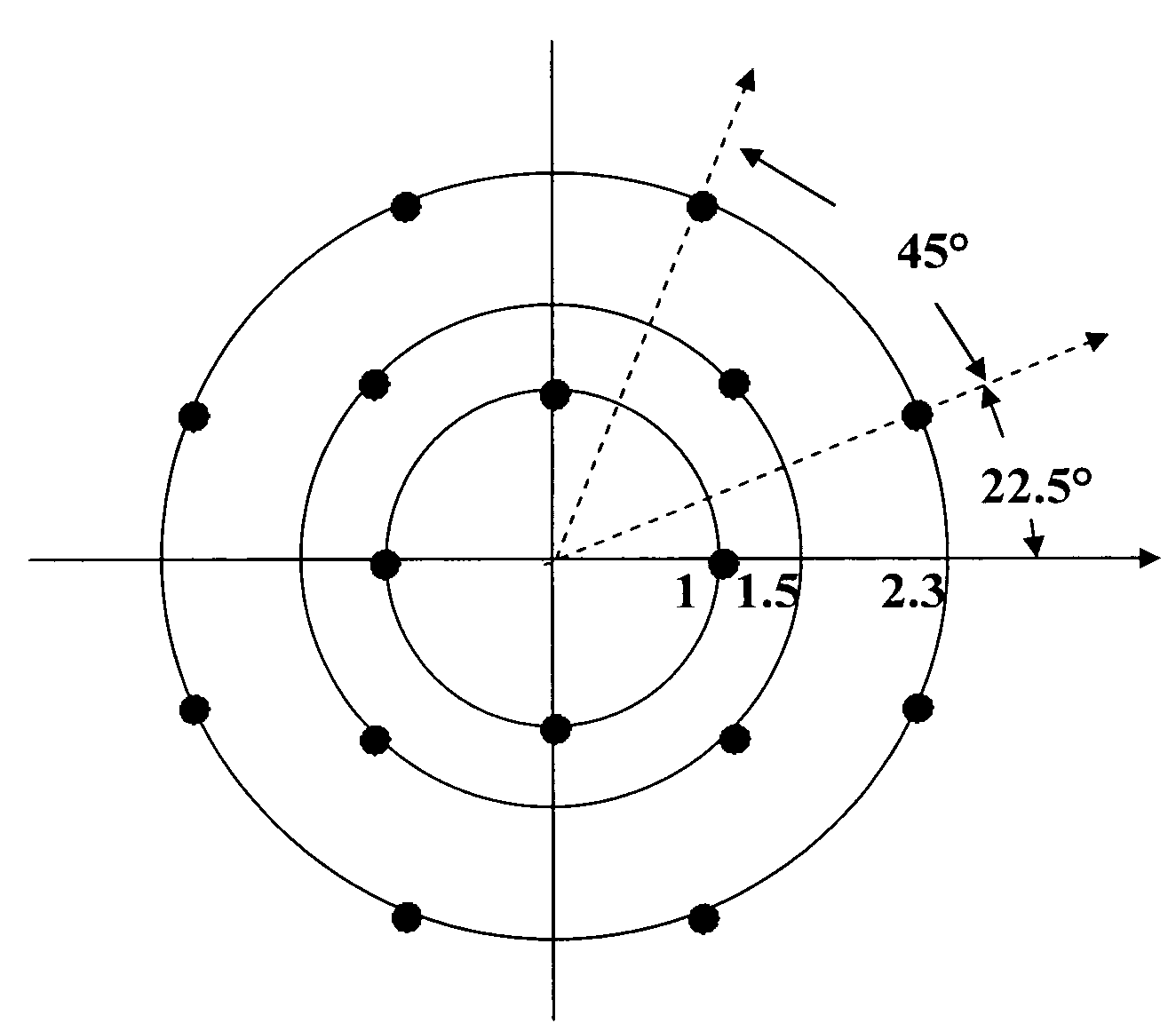
Multi-layer differential phase shift keying with bit-interleaved coded modulation and OFDM
InactiveUS20050111590A1Increase data rateEfficient methodAngle modulationSecret communicationEngineeringDifferential modulation
An efficient system and method for modulation and demodulation to achieve a high data rate using Bit-Interleaved Coded Modulation and OFDM uses either a coherent or a non-coherent transmission scheme using differential modulation. In order to maintain a high data rate impervious to sudden phase changes, a communication system uses an efficient constellation having multiple rings with different sizes and modulation / demodulation schemes utilizing this constellation. In power line communications, the channel gain information is obtained easily at a receiver (100) while the phase information is not. Thus, the communication system uses an absolute magnitude and differential phase coding for modulation and demodulation of the signals.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
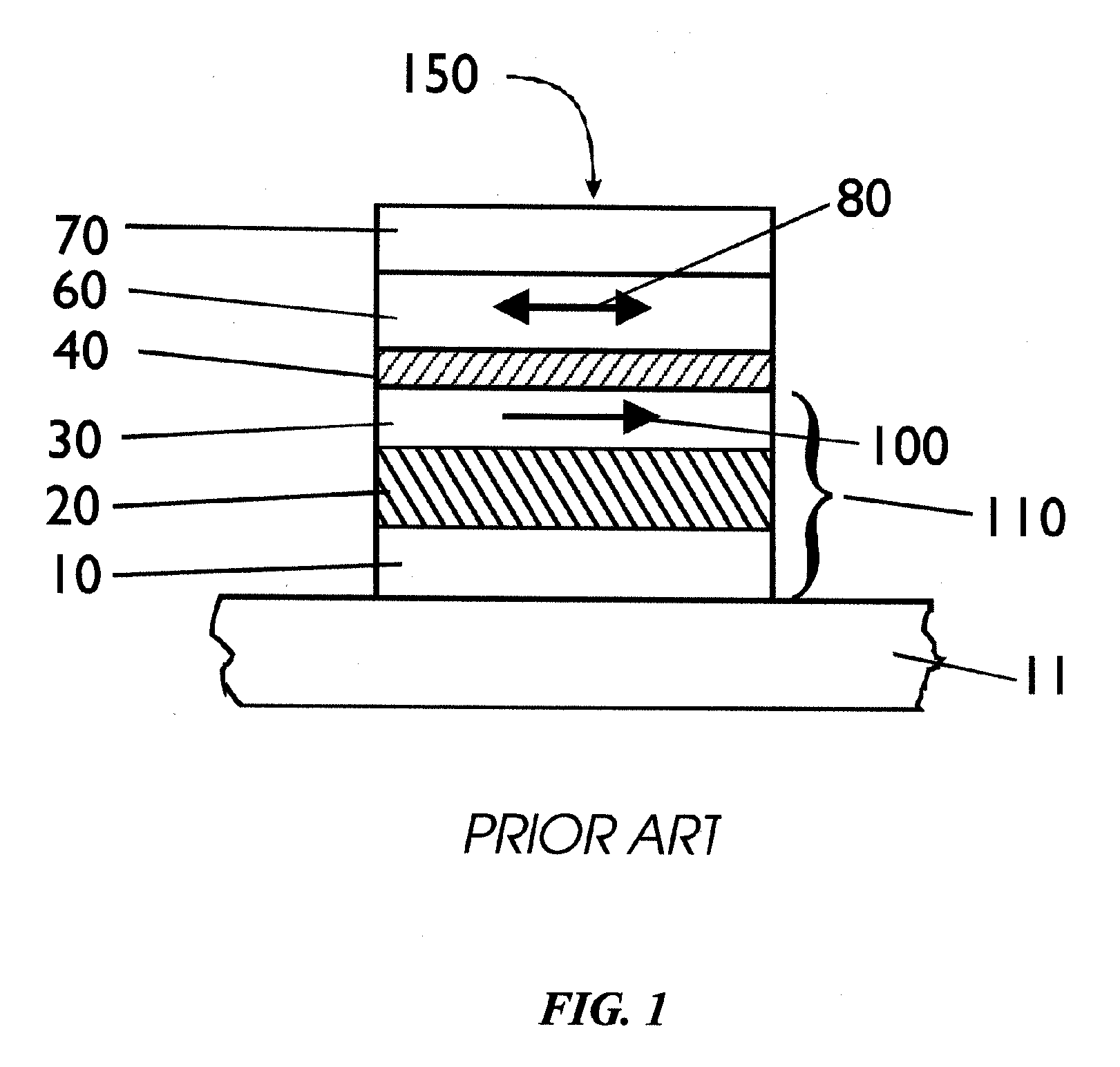
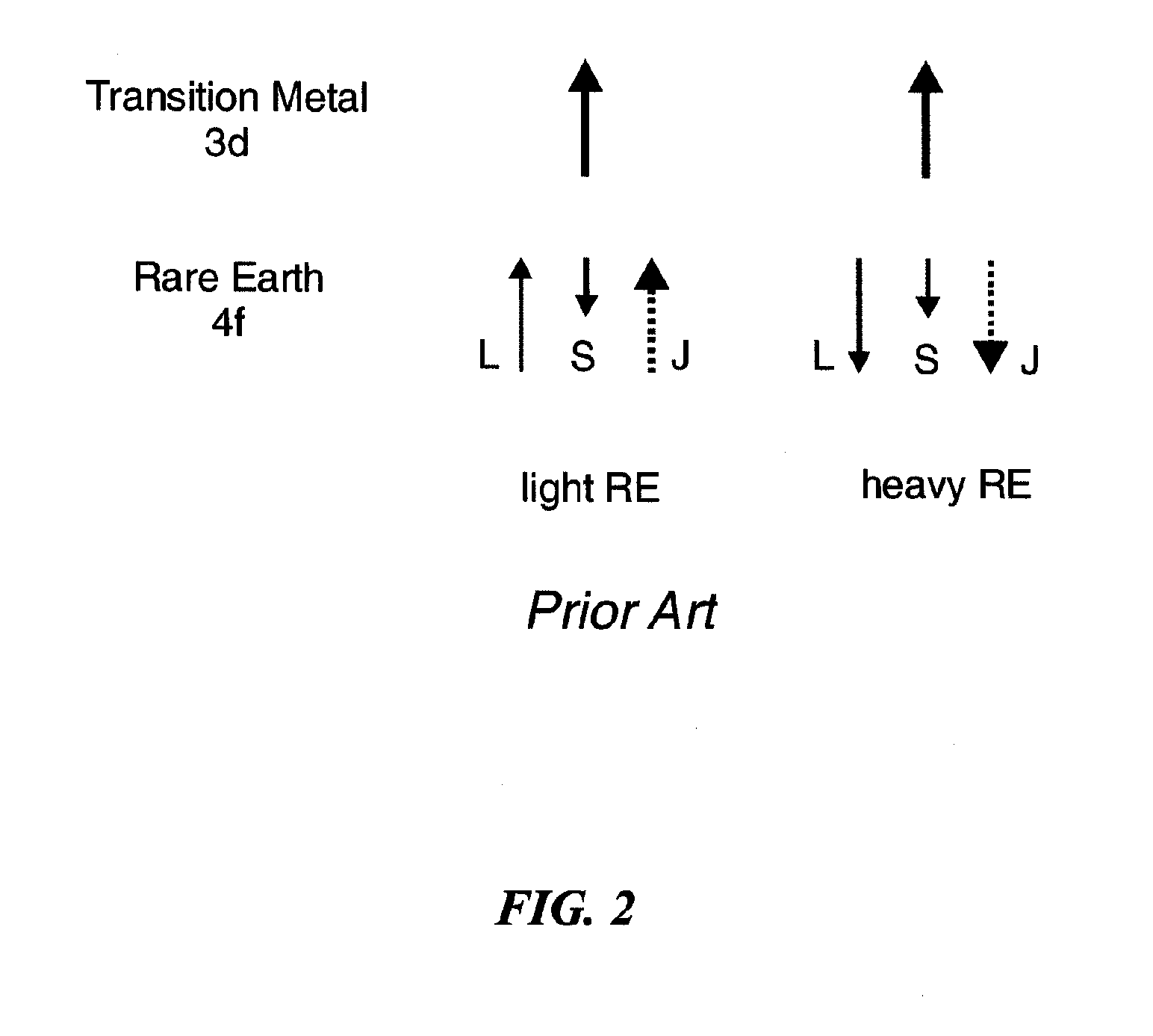
Spin-Polarization Devices Using Rare Earth-Transition Metal Alloys
ActiveUS20060255383A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionRare-earth elementCombined use
A tunnel barrier in proximity with a layer of a rare earth element-transition metal (RE-TM) alloy forms a device that passes negatively spin-polarized current. The rare earth element includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb. The RE and TM have respective sub-network moments such that the absolute magnitude of the RE sub-network moment is greater than the absolute magnitude of the TM sub-network moment. An additional layer of magnetic material may be used in combination with the tunnel barrier and the RE-TM alloy layer to form a magnetic tunnel junction. Still other layers of tunnel barrier and magnetic material may be used in combination with the foregoing to form a flux-closed double tunnel junction device.
Owner:IBM CORP
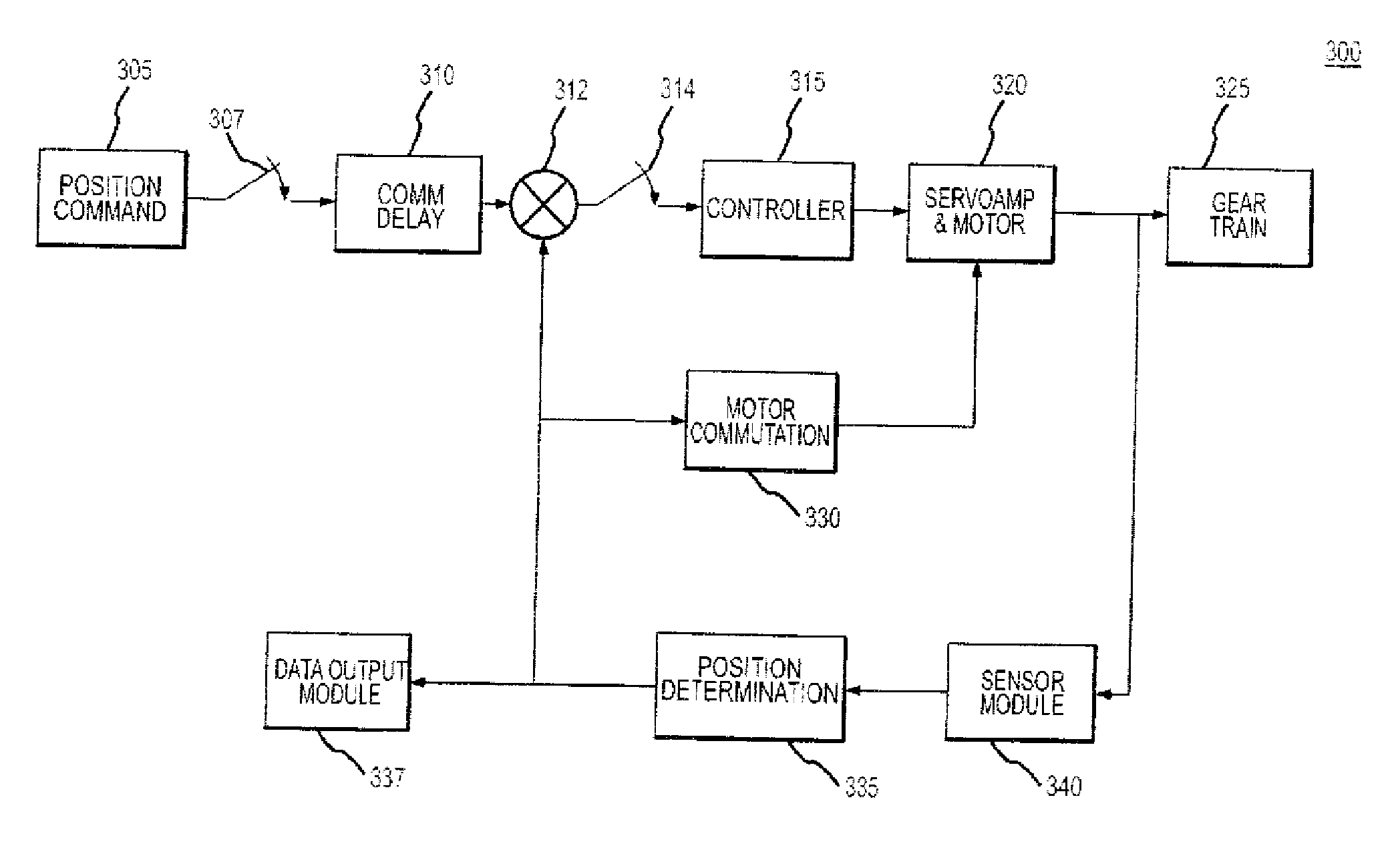
System and method for determining angular position and controlling rotor orientation
ActiveUS20070176568A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersAmplitude scalingAngular orientation
Methods and devices for determining the position and / or angular orientation of a rotating shaft. Exemplary features include a sensor module and a position determination module. Sensor module may include a plurality of Hall Effect devices (HEDs) arranged at a specified angular separation to produce a signal in response to rotation of the shaft. Position module may be responsive to sensor module to produce a converted signal, determine an error term, and produce a position estimate. Converted signal may be produced by processing the HED signals into sinusoidal reference signals having offset scale and amplitude scale factors. Error term may be determined by processing the converted signals to produce an estimated position signal. Position estimate may be produced by processing the error term. Refined position measurement may be achieved by iterative elimination of regressive differences between position estimates with minimization of absolute magnitude of error term.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method And Circuitry for Improving the Magnitude and Shape of the Output Current of Switching Power Converters
InactiveUS20100097827A1Not to damageReduce total powerAc-dc conversionElectric lighting sourcesControl signalEngineering
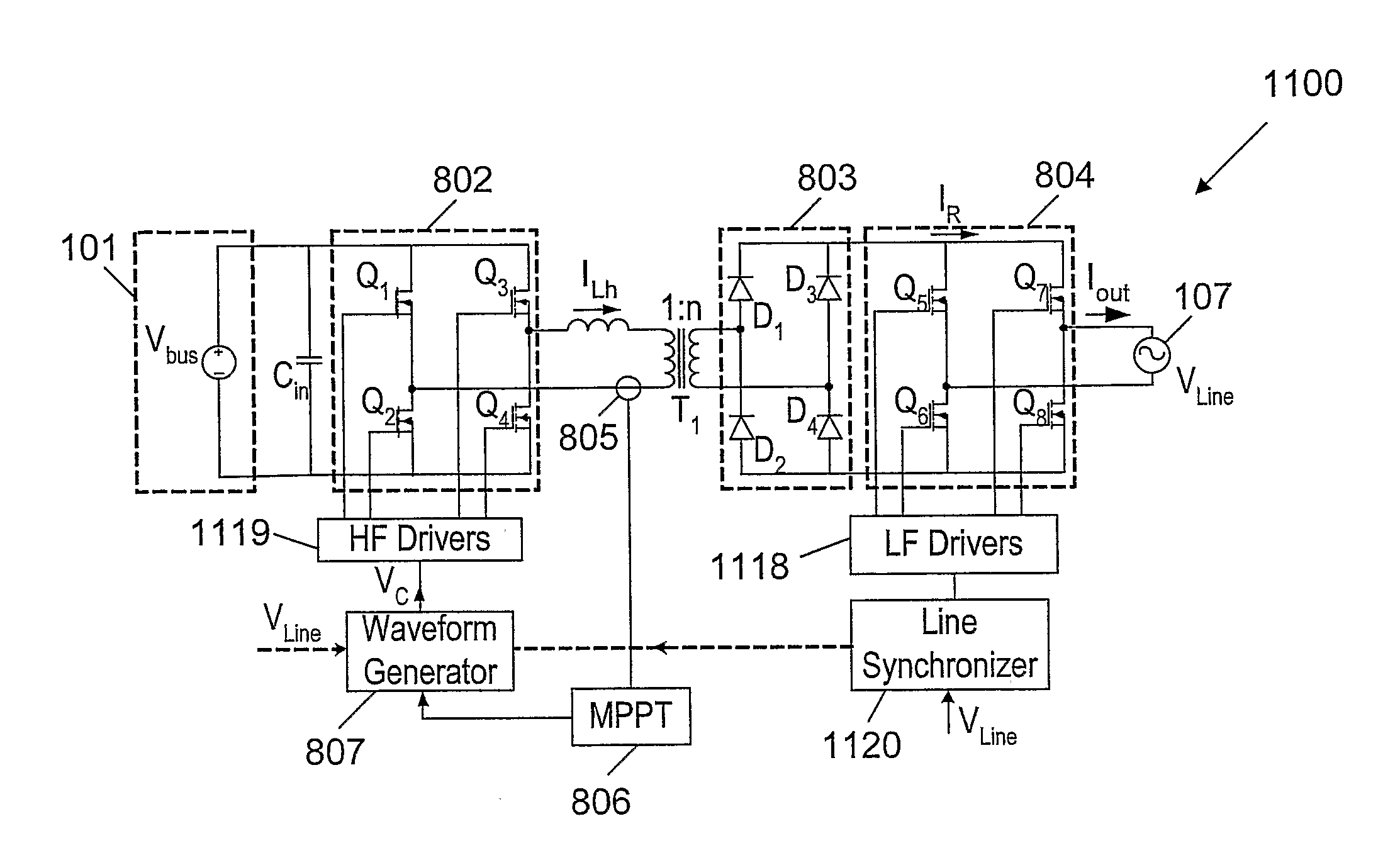
Apparatus of a grid-connected switching inverter for injecting it current into a power line comprises: (a) an electrical energy source for providing the substantially DC voltage to the apparatus; (b) a switching inverter connected to the electrical energy source for converting the substantially DC voltage of the electrical energy source to a high frequency alternating voltage; (c) a waveform generator for controlling the magnitude and shape of the alternating high frequency voltage outputted from the switching inverter by means of a control signal fed into the switching inverter; (d) an inductor connected to an output of the switching inverter for generating an alternating current from the alternating high frequency voltage, wherein the magnitude of the alternating current depends on a frequency of the alternating high frequency voltage: (e) a rectifier connected in series with the inductor for rectifying the alternating current and for outputting a rectified unipolar alternating current, wherein the rectified average value of the alternating current is proportional to the absolute magnitude of the power line voltage; and (t) a polarity commutator connected to an output of the rectifier for converting the rectified unipolar alternating current into a bipolar alternating current, and for injecting the bipolar alternating current into a power line, wherein the bipolar alternating current is substantially in phase with and of shape of the power line voltage of the power line.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
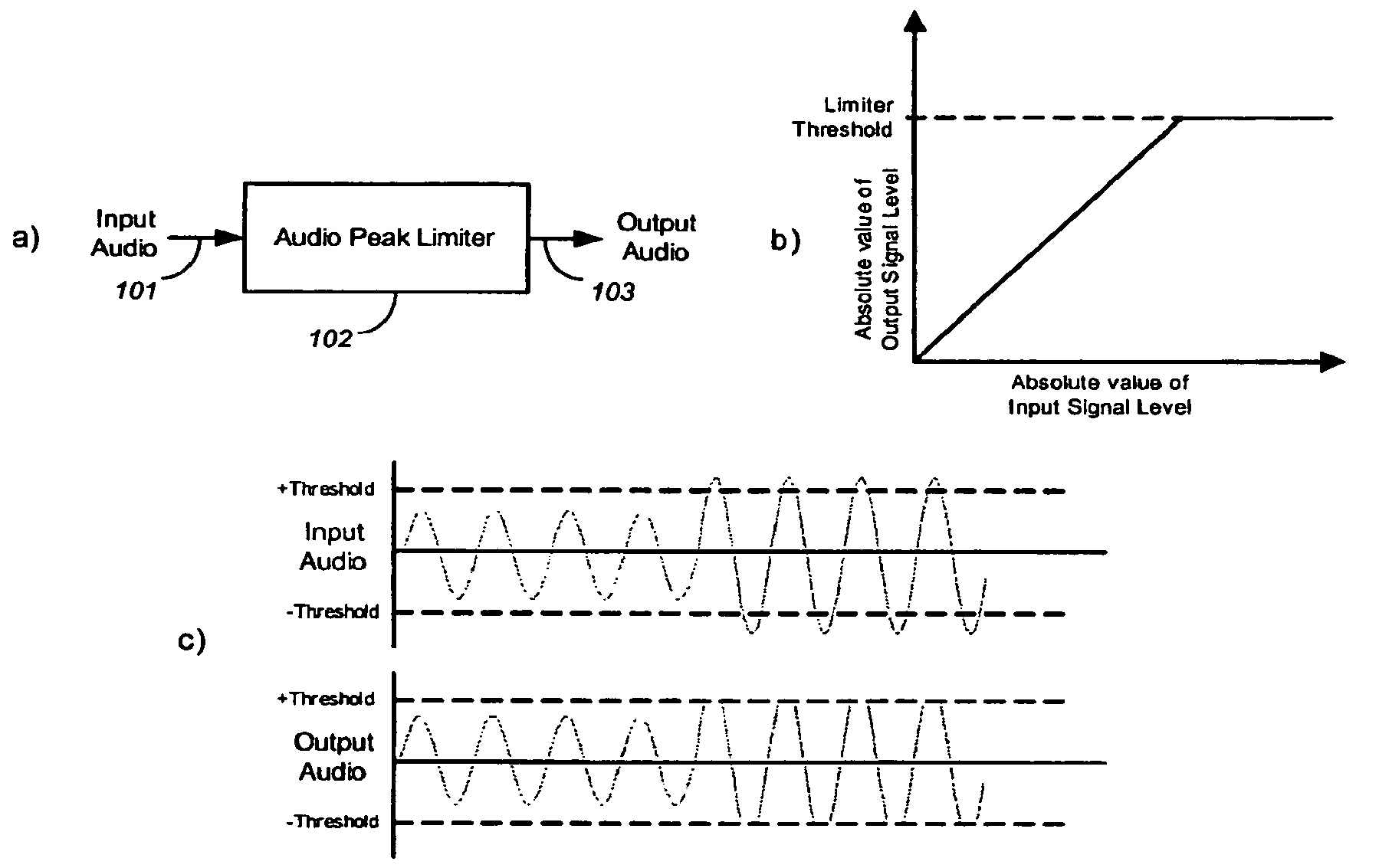
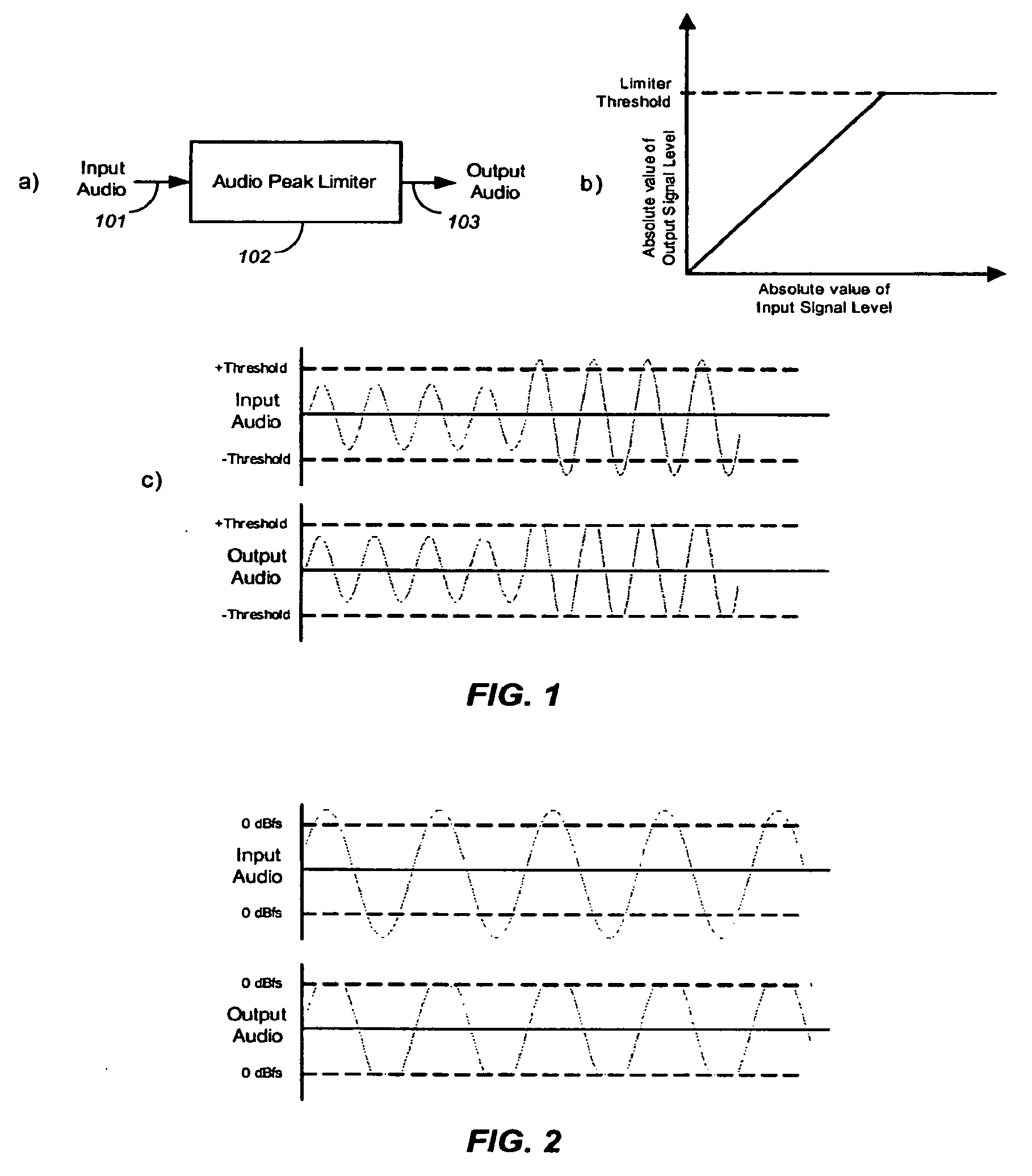
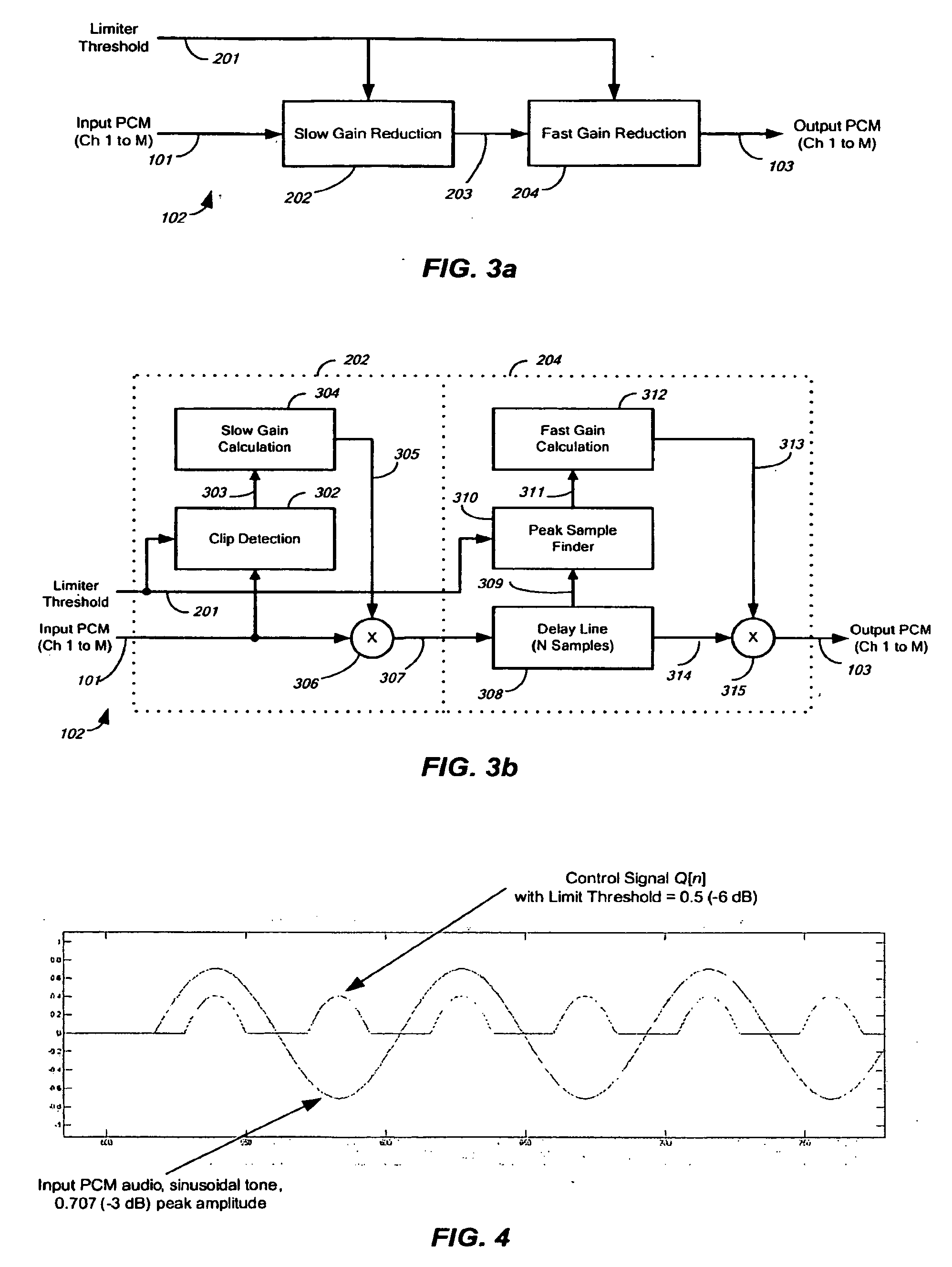
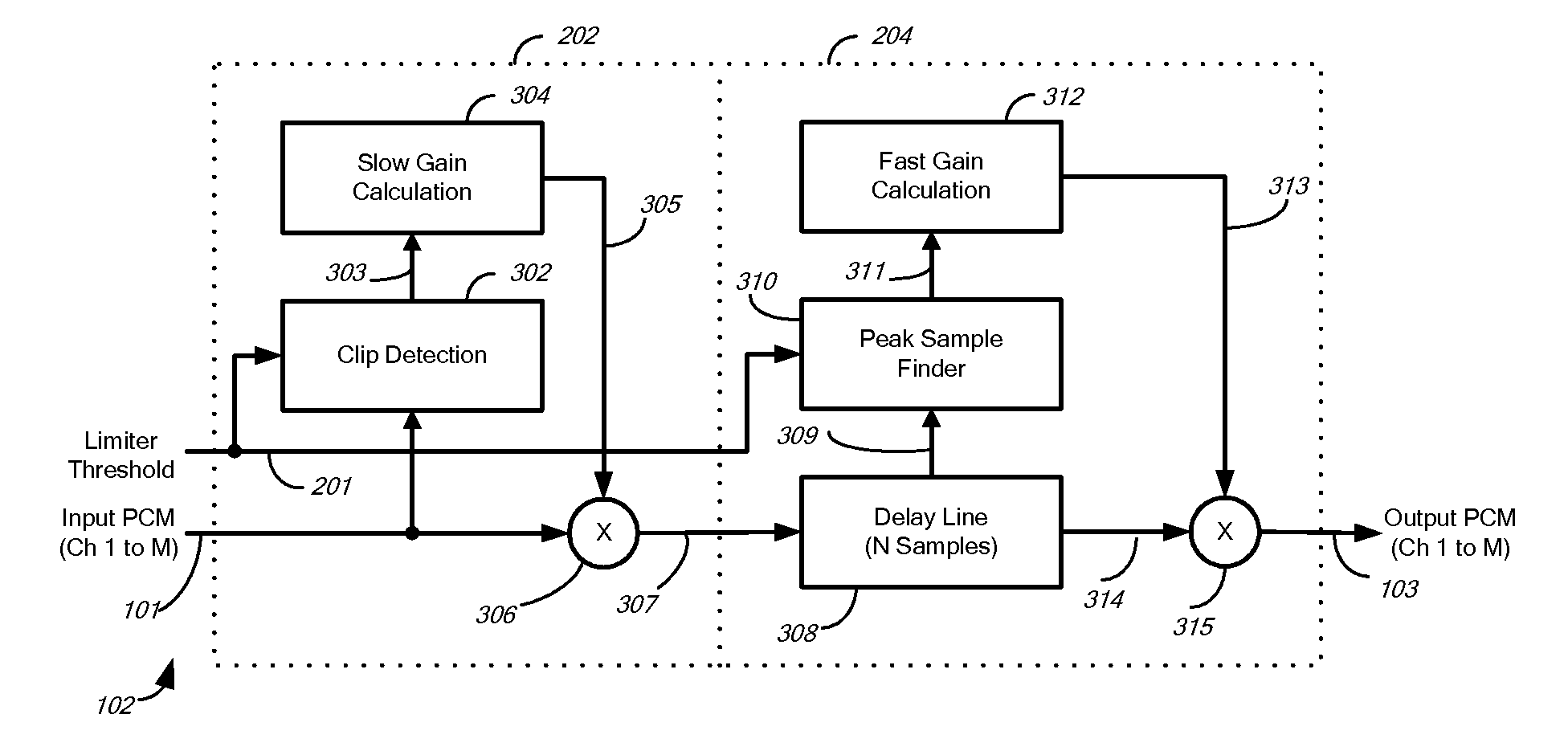
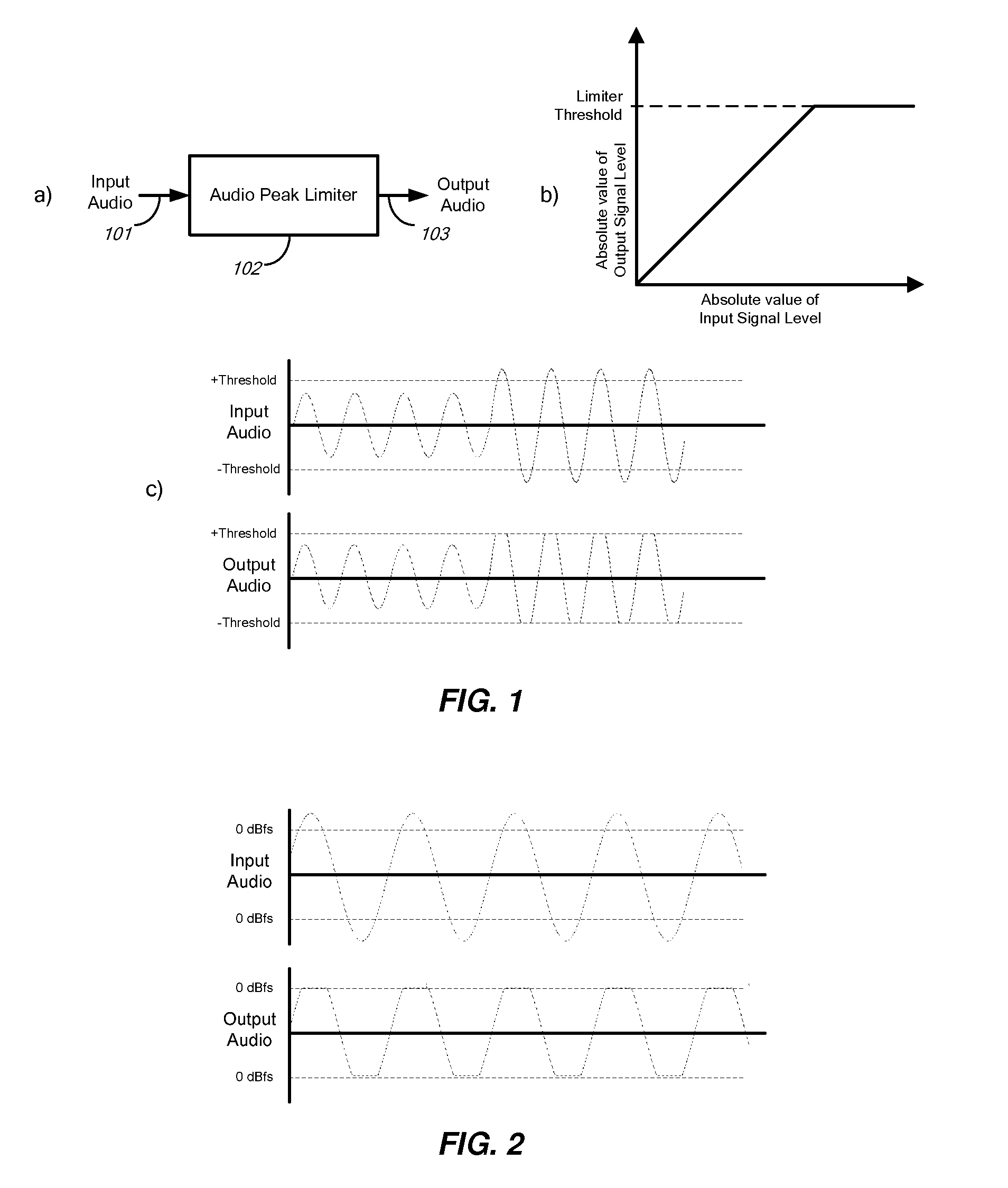
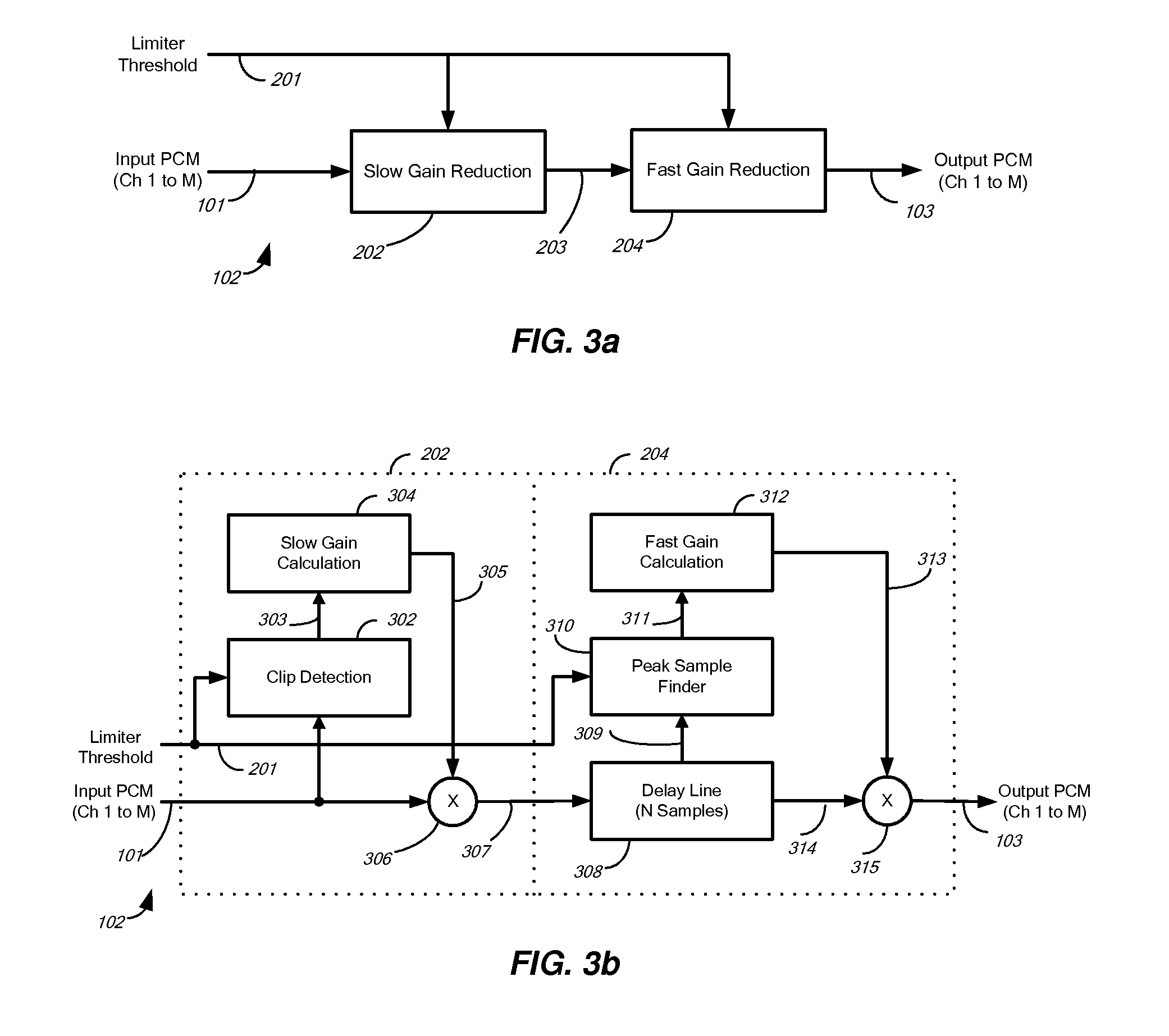
Audio-peak limiting in slow and fast stages
A method and apparatus for limiting the absolute magnitude of an audio signal. The method may include firstly variable-gain reducing the gain of an audio signal, and then secondly variable-gain reducing the gain of the audio signal faster than the first variable-gain reduction, thereby limiting the absolute magnitude of the audio signal to a threshold. The first variable-gain reduction may include variable-gain reducing the gain of the audio signal in a first stage, and the second variable-gain reduction may include variable-gain reducing the gain of the audio signal in a second stage that reduces the gain faster than the first stage. The second variable-gain reduction may include delaying the audio signal, finding a peak among the delayed audio signal, calculating a fast gain from a found peak, and modifying the delayed audio signal with the calculated fast gain.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
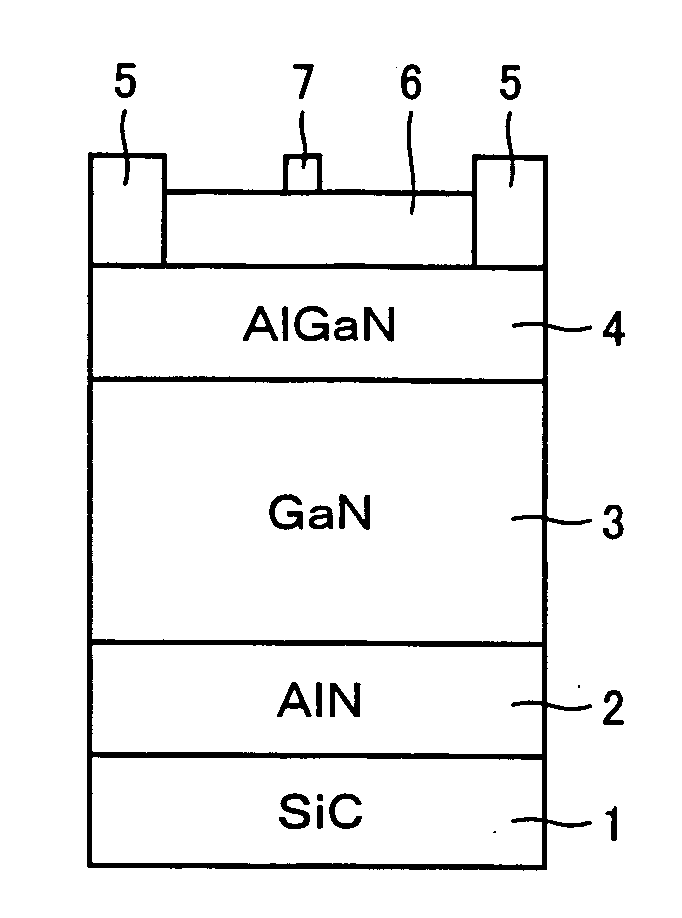
Field-effect transistor
InactiveUS20060237711A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorLattice constant
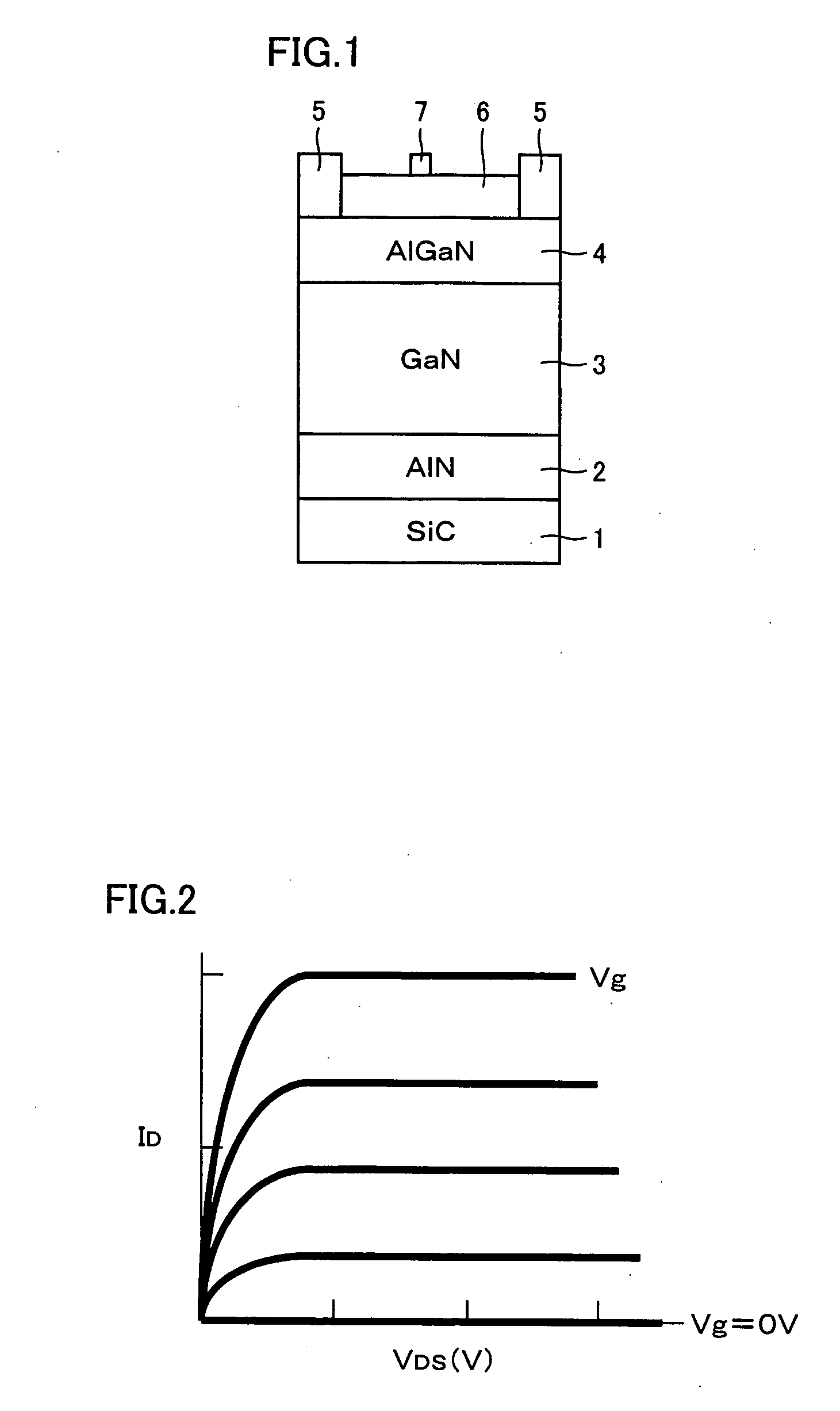
A nitride-based group III-V compound semiconductor device includes a buffer layer, a first nitride semiconductor layer and a second nitride semiconductor layer successively stacked on a substrate, the first and the second nitride layers having their respective lattice constants a1 and a2 in the relation a1>a2, an ohmic source electrode and an ohmic drain electrode formed on the second nitride layer, and a piezoelectric effect film formed on at least a partial region between the electrodes, wherein the piezoelectric film exerts compressive stress of an absolute magnitude at least equivalent to that of tensile stress applied to the second nitride layer due to the difference (a1−a2) between the lattice constants of the first and second nitride layers.
Owner:SHARP KK
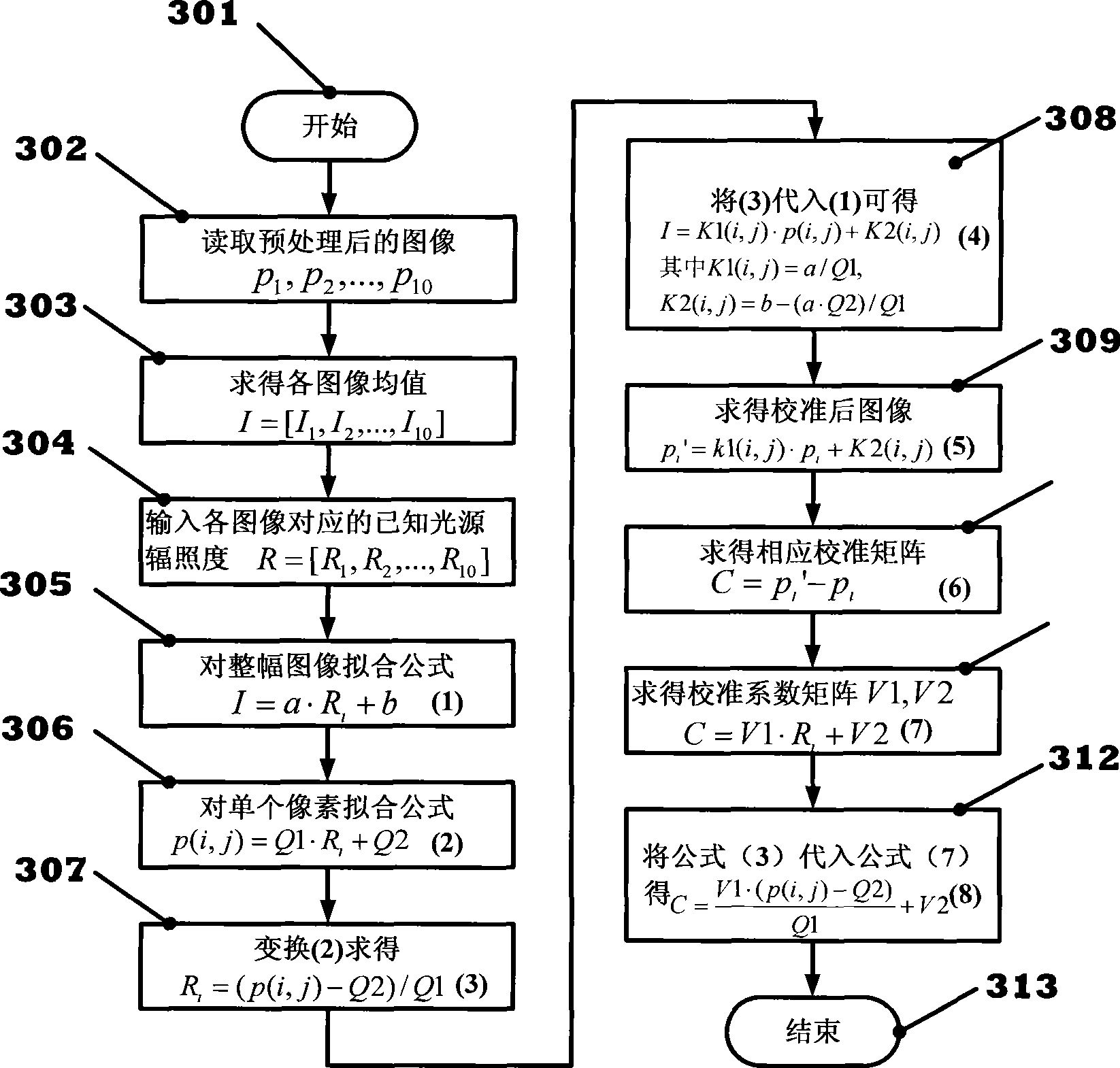
Calibration method for CCD camera imaging application
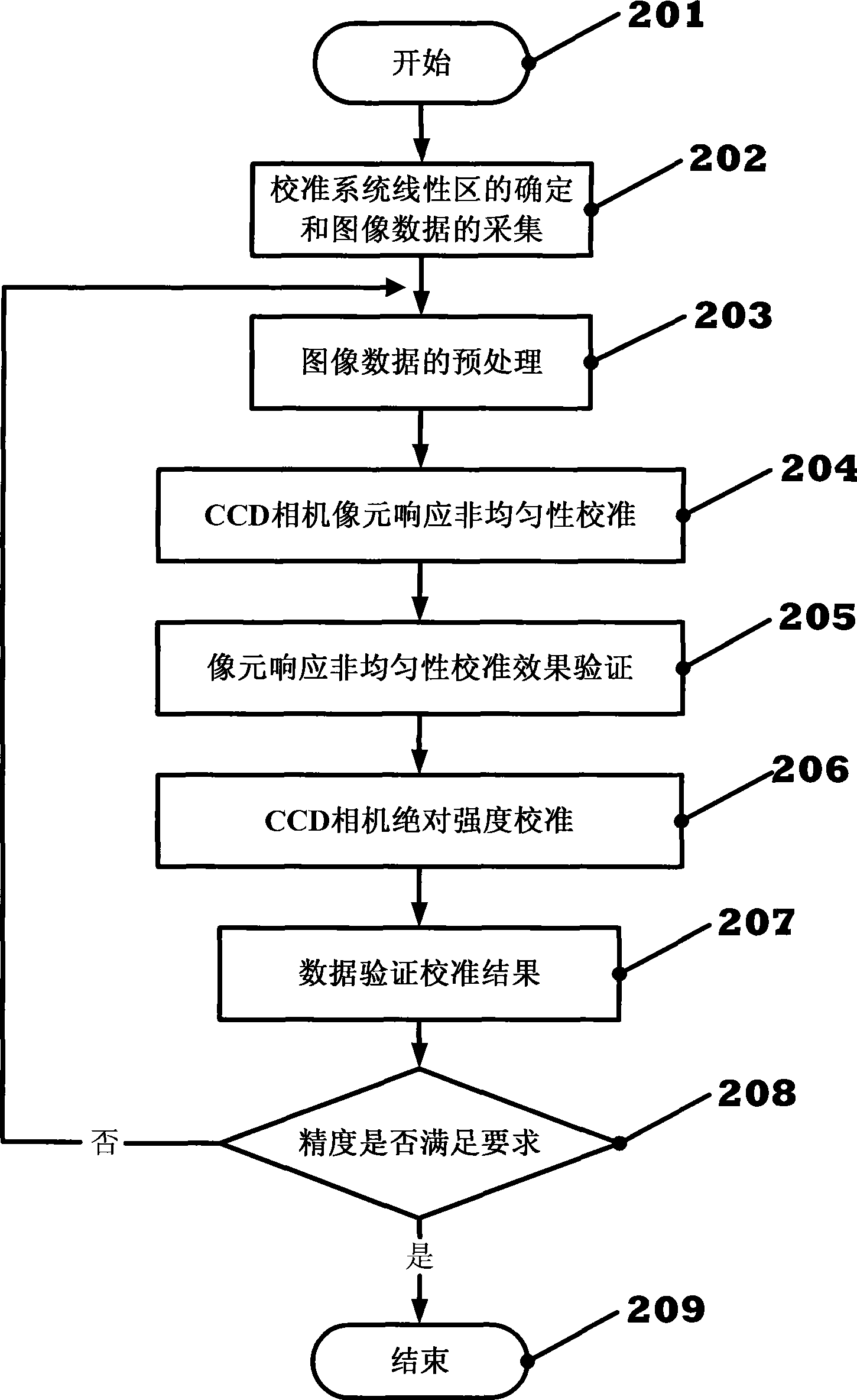
InactiveCN101532948AIdeal non-uniformity calibration effectMeet the requirement of accuracy less than 0.5%PhotometryDiagnostic recording/measuringCcd cameraFunctional relation
The invention provides a calibration method for CCD camera imaging application, which comprises a calibration method for the pixel-response nonuniformity of a CCD camera, and a calibration method for reversely calculating the absolute intensity of a corresponding light source by utilizing the known absolute magnitude of an integrating sphere uniform light source and the pixel gray of an image captured by the corresponding CCD camera, wherein the calibration method for pixel-response nonuniformity automatically obtains a compensation matrix of a full-width image according to the gray information of each pixel on the image, and the calibration method for absolute intensity reversely calculates the quantitative information of the functional relation of the absolute intensity of the corresponding light source through the exposure time of the image and the gray of each pixel on the image. The calibration method for pixel-response nonuniformity and the calibration method for absolute intensity can follow the changes of the exposure time of the CCD camera and the pixel gray of the image to automatically calibrate pixel-response nonuniformity and the absolute intensity of the corresponding light source according to the calibration functional relation obtained in the calibration method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
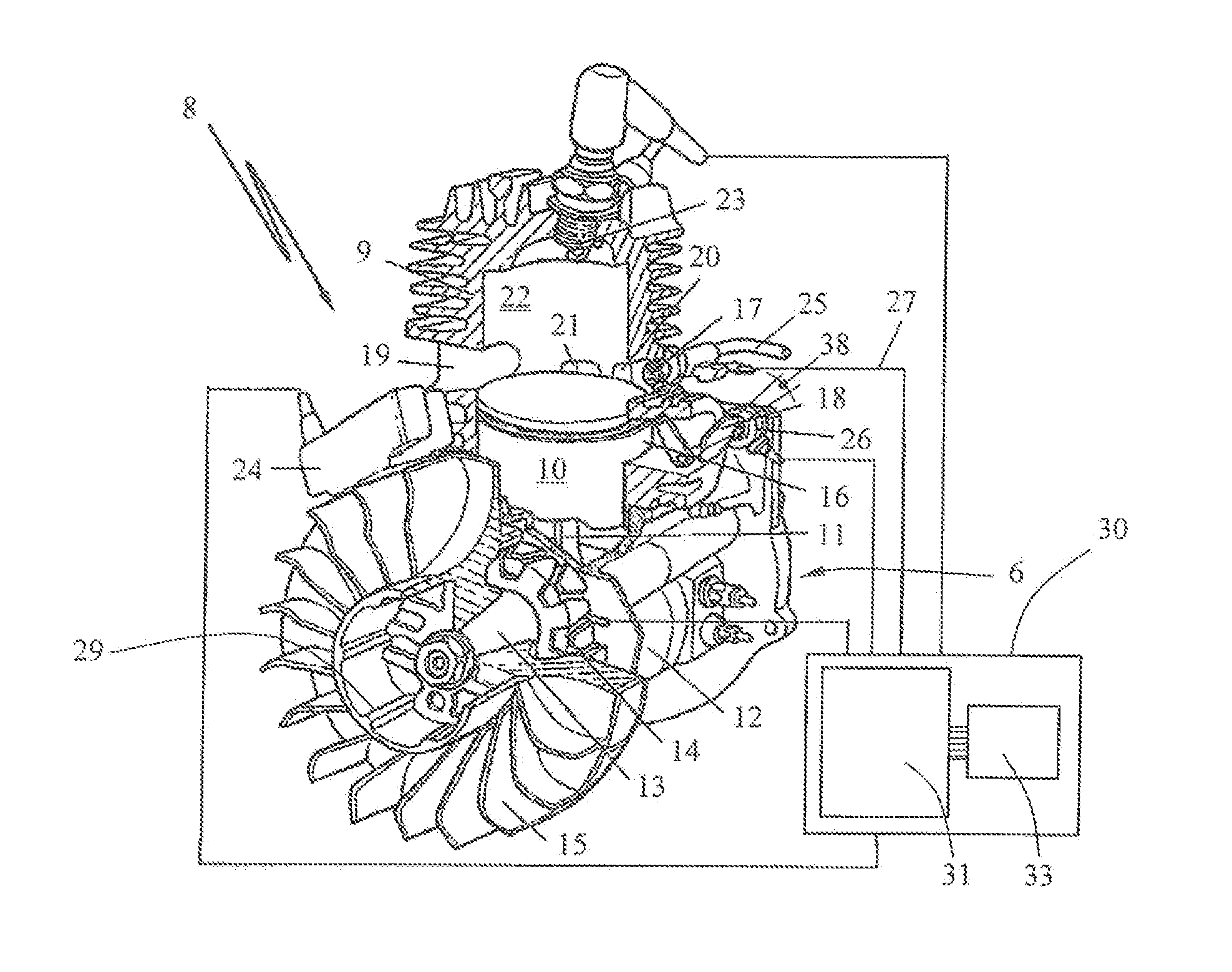
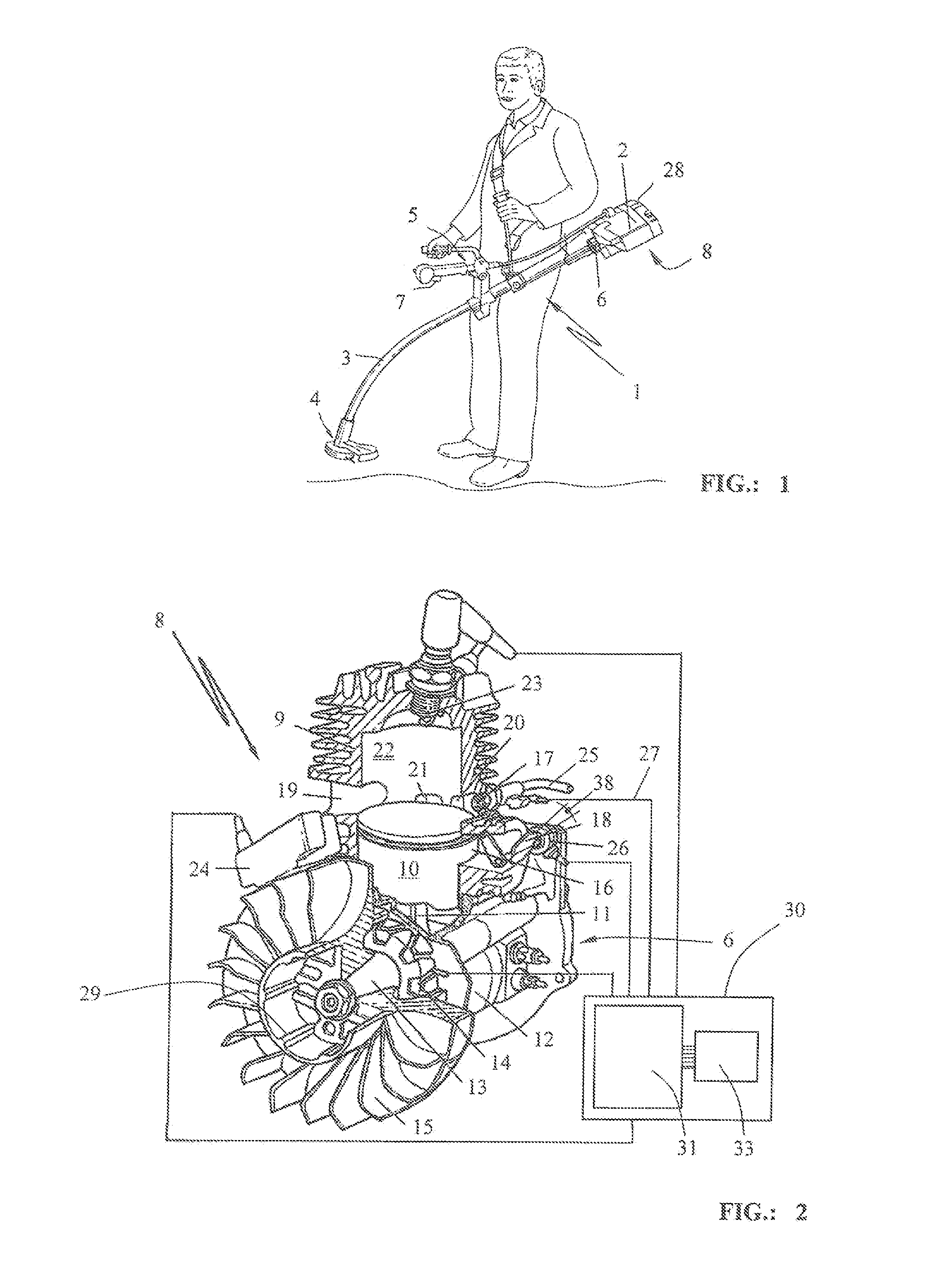
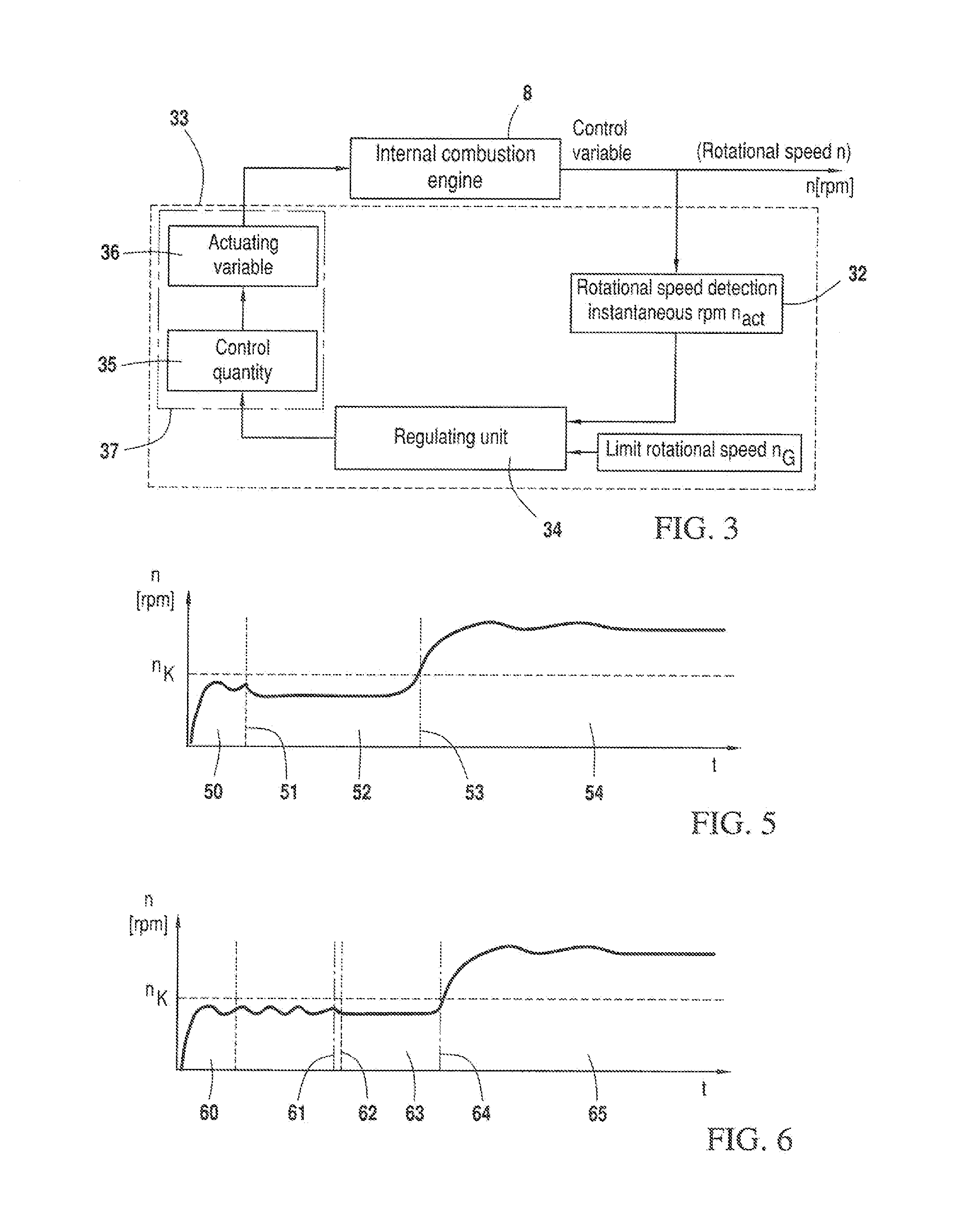
Method for switching off a rotational speed limit in an internal combustion engine
A method controls the rpm of a combustion engine in a hand-held work apparatus such as a brushcutter. The engine drives a work tool via a clutch which engages as a function of the engine rpm (n). A spark plug is arranged in the combustion chamber and is driven by an ignition unit. During start of the engine, an rpm lock circuit is active and defines a control variable as a function of the instantaneous rpm (nact) of the engine. According to the magnitude of this control variable, operating parameters of the engine are adapted to change the instantaneous rpm (nact). A control variable is determined for the adaptation of the operating parameters by the rpm lock circuit. The switch-off of the rpm lock circuit is provided when the control variable of the control lies outside a predetermined bandwidth of the absolute magnitude of the control variables.
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
Multi-layer differential phase shift keying with bit-interleaved coded modulation and OFDM
InactiveUS7324613B2Increase data rateReliable and high data rate transmissionAngle modulationSecret communicationDifferential modulationEngineering
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
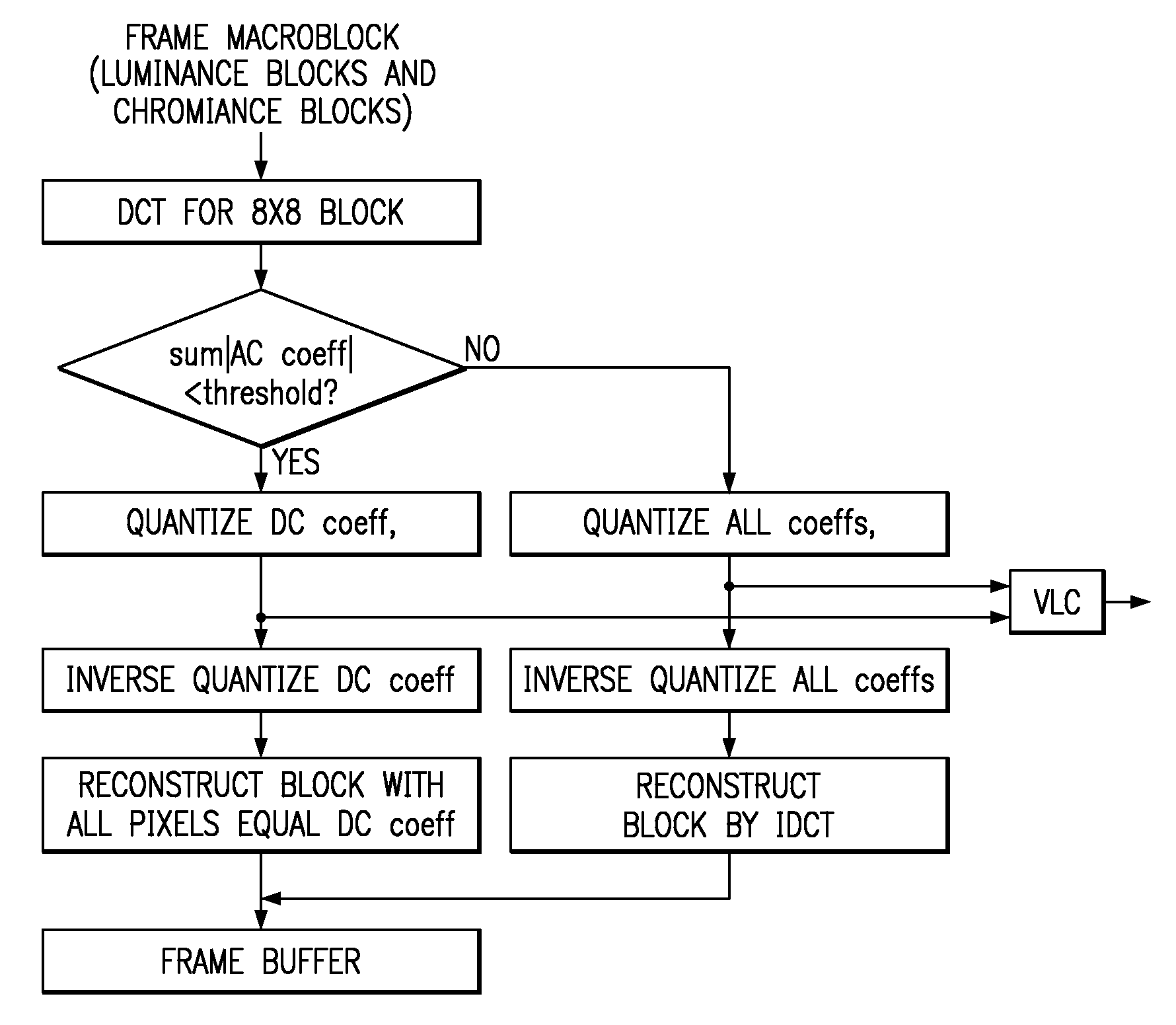
Image compression with transform coefficient analysis
ActiveUS7079697B2Reduce encoding complexitySignificant complexityImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionCoding blockAc coefficient
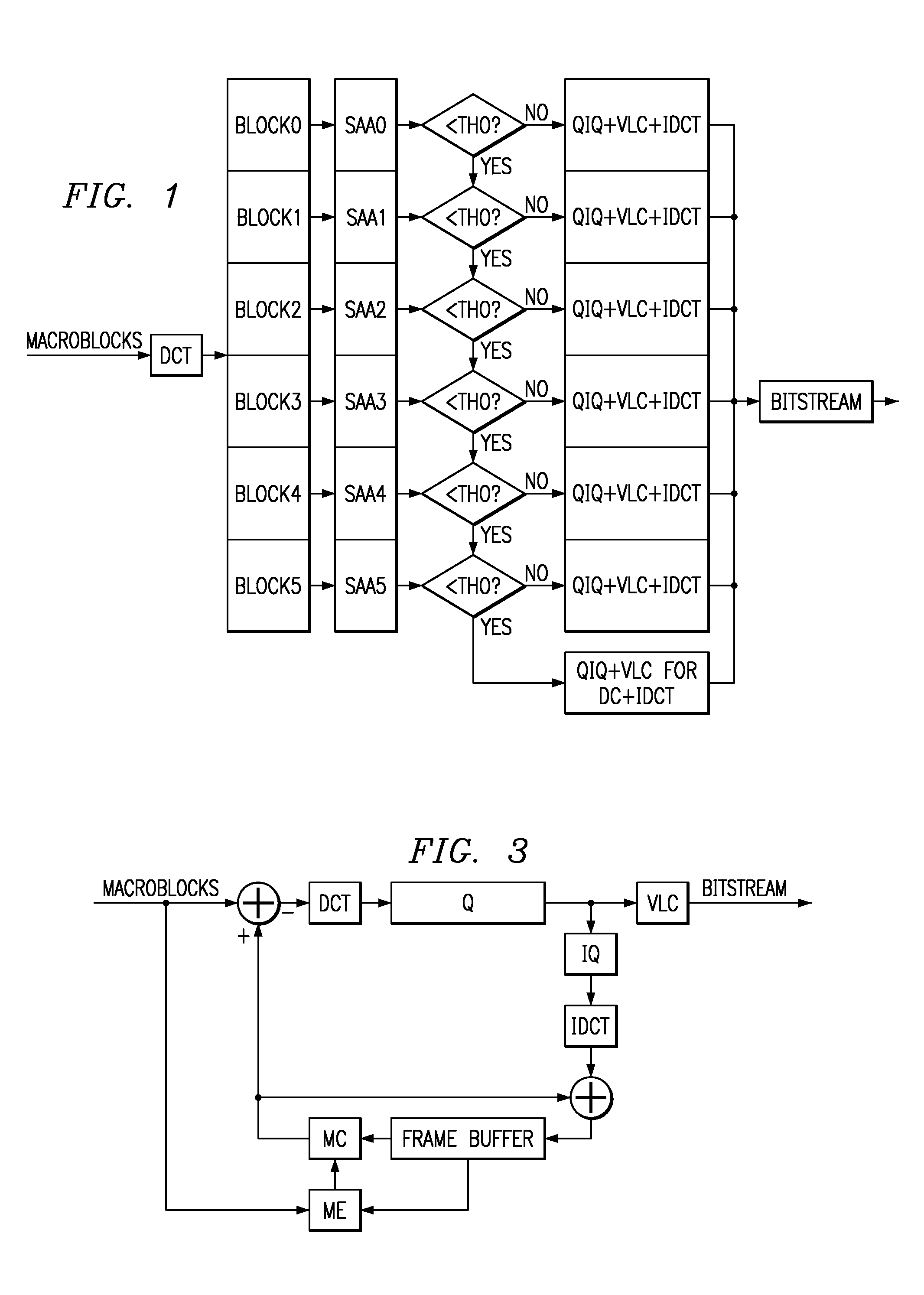
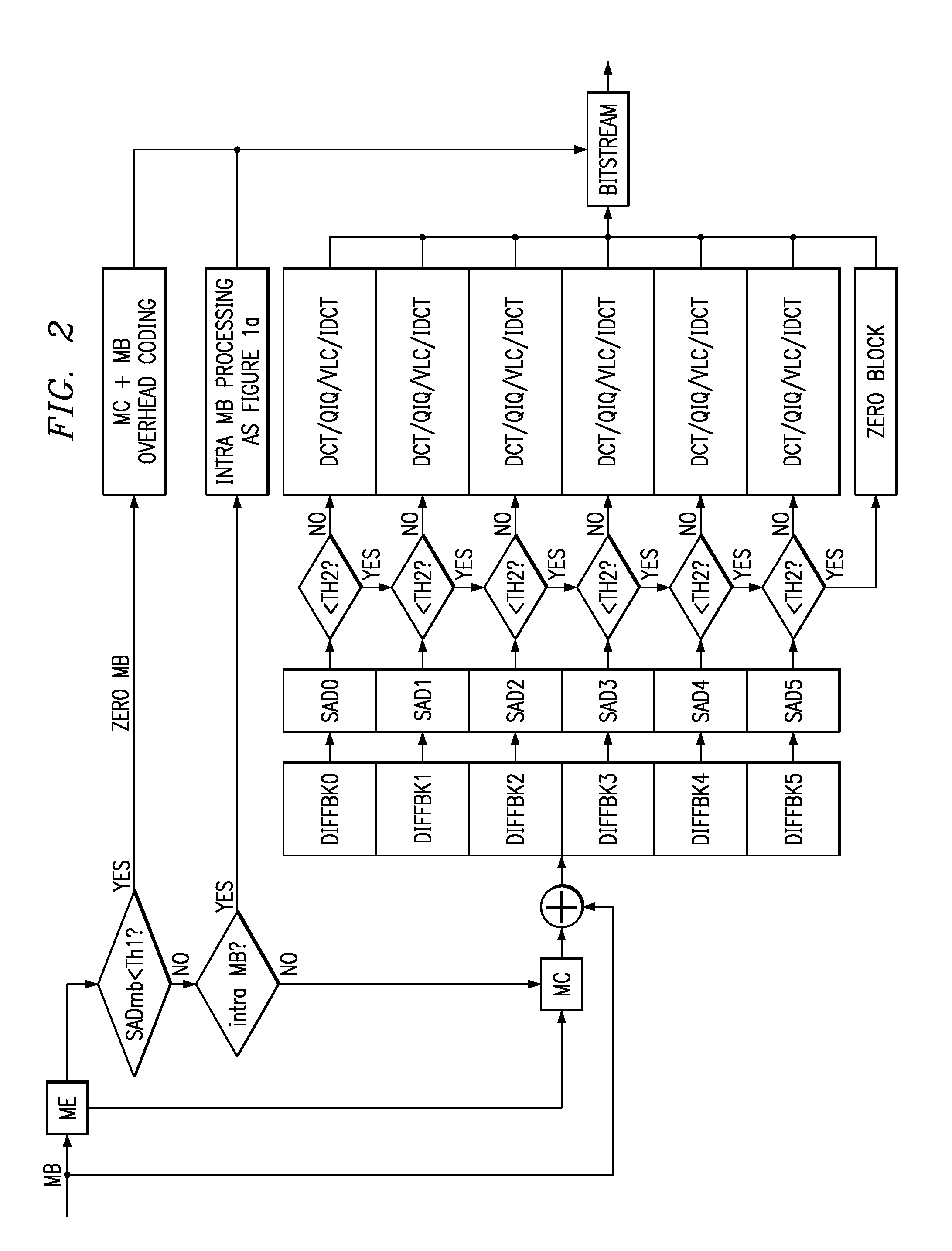
A method of image / video compression with intra-coding blocks analyzed for sum of absolute magnitudes of AC coefficients of DCT of block to determine whether to approximate the block with 0 AC coefficients, and with inter-coding blocks analyzed for sum of absolute differences of block and predicted block to determine whether to approximate the block with a 0 block.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Spectrum self-correction photometer and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN101782428AImprove measurement repeatabilityEasy and time-saving measurementPhotometry using reference valueOptical radiationLuminescence
The invention discloses a spectrum self-correction photometer and a measuring method thereof. The spectrum self-correction photometer comprises a light entrance, an optical spectroscope, a spectrometer and a silicon photovoltaic cell with a color filter, wherein light to be measured is divided into at least two beams by the optical spectroscope according to a set proportion; one part of beams is received by the spectrometer, the other part of beams is received by the silicon photovoltaic cell, and the light to be measured is simultaneously measured by the beams. The spectrum self-correction photometer of the invention can greatly reduce errors brought by the mismatch of the spectrum, has less reliance on the spectrum of the light to be measured, overcomes the problems brought by inconsistent special spectrum power distribution of a light source to be measured, time-varying luminescence, and the like, has relative smaller system measuring error and random error and high measuring repetitiveness and is calibrated by utilizing an absolute spectrum radiometer as a standard source so that the absolute magnitude transmission chain of an optical radiation degree is very short. The spectrum self-correction photometer has higher precision and reliable absolute magnitude value and can be applied to various optical radiation measuring systems for measuring a plurality of important optical radiation parameters.
Owner:HANGZHOU EVERFINE PHOTO E INFO
Method for measuring absolute magnitudes and absolute phase relationships over a wide bandwidth
Owner:STERNBERG BEN K +1
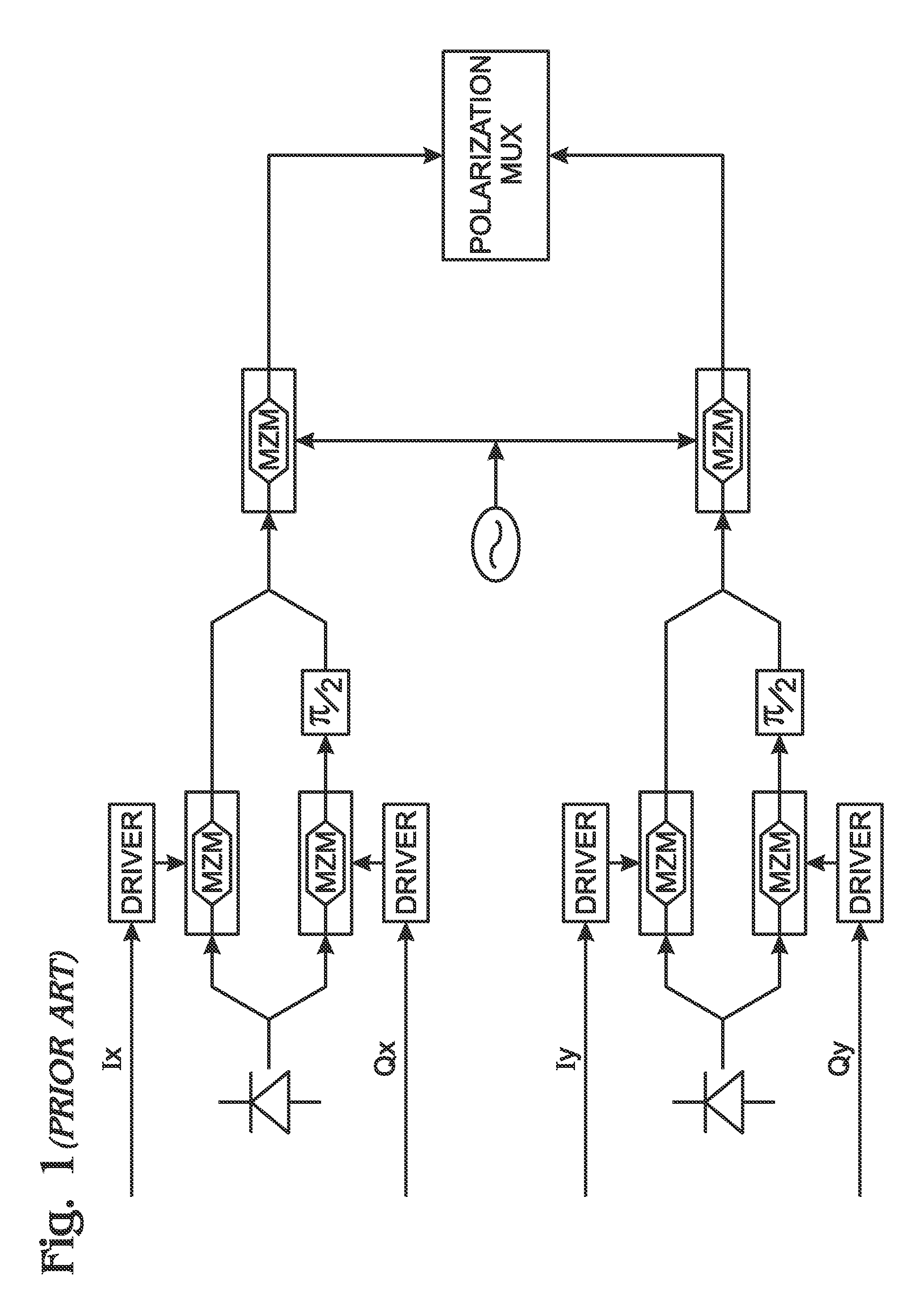
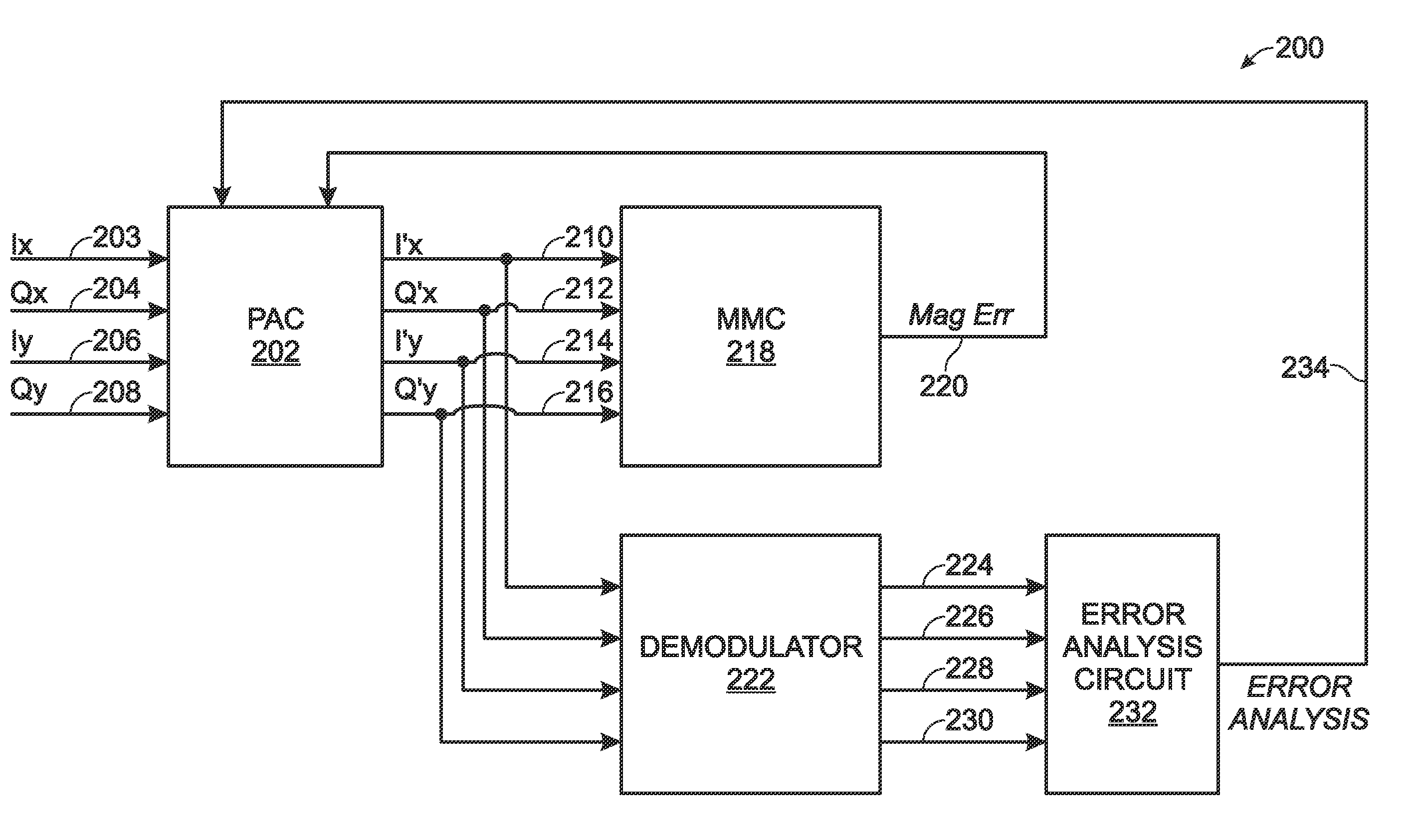
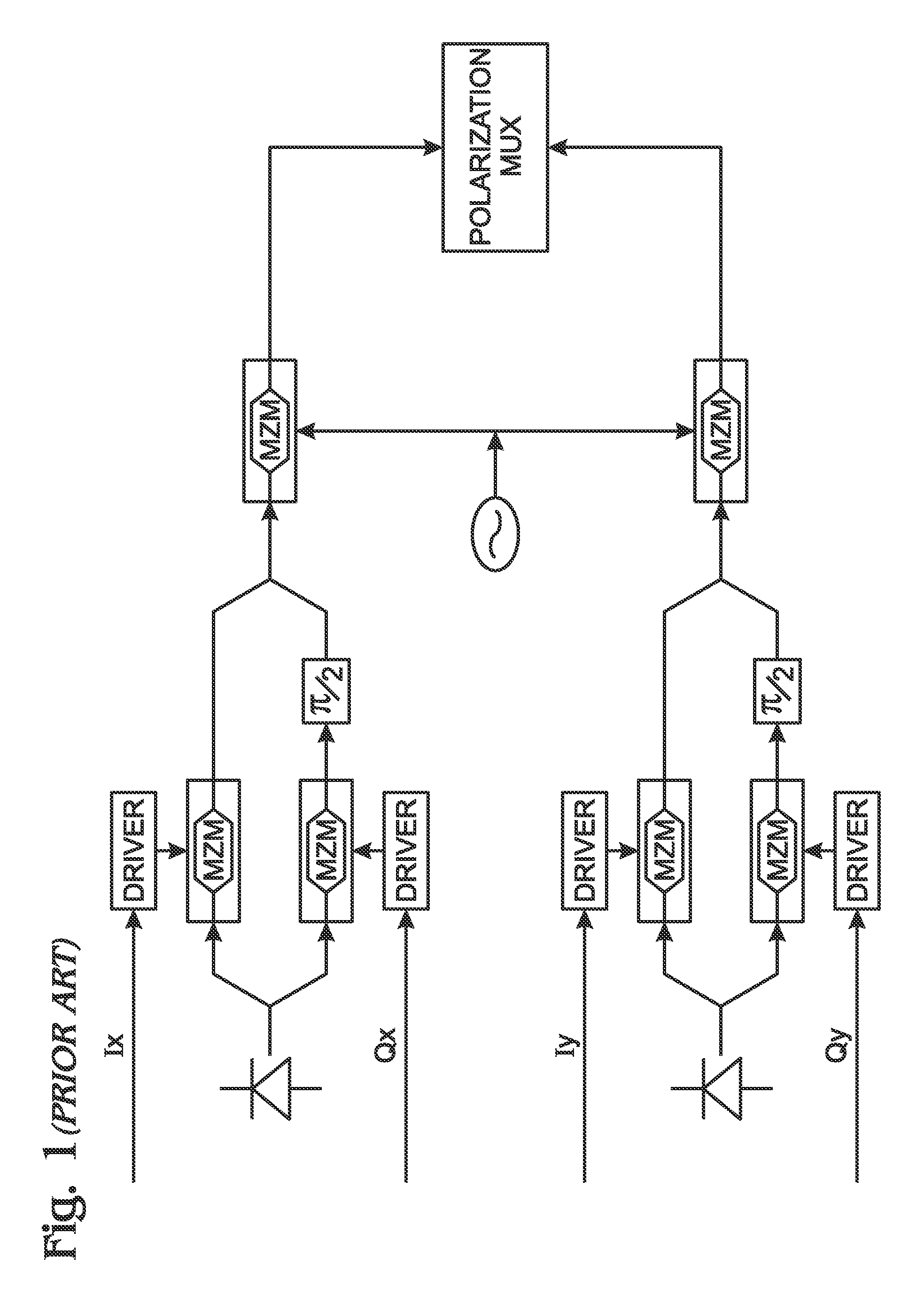
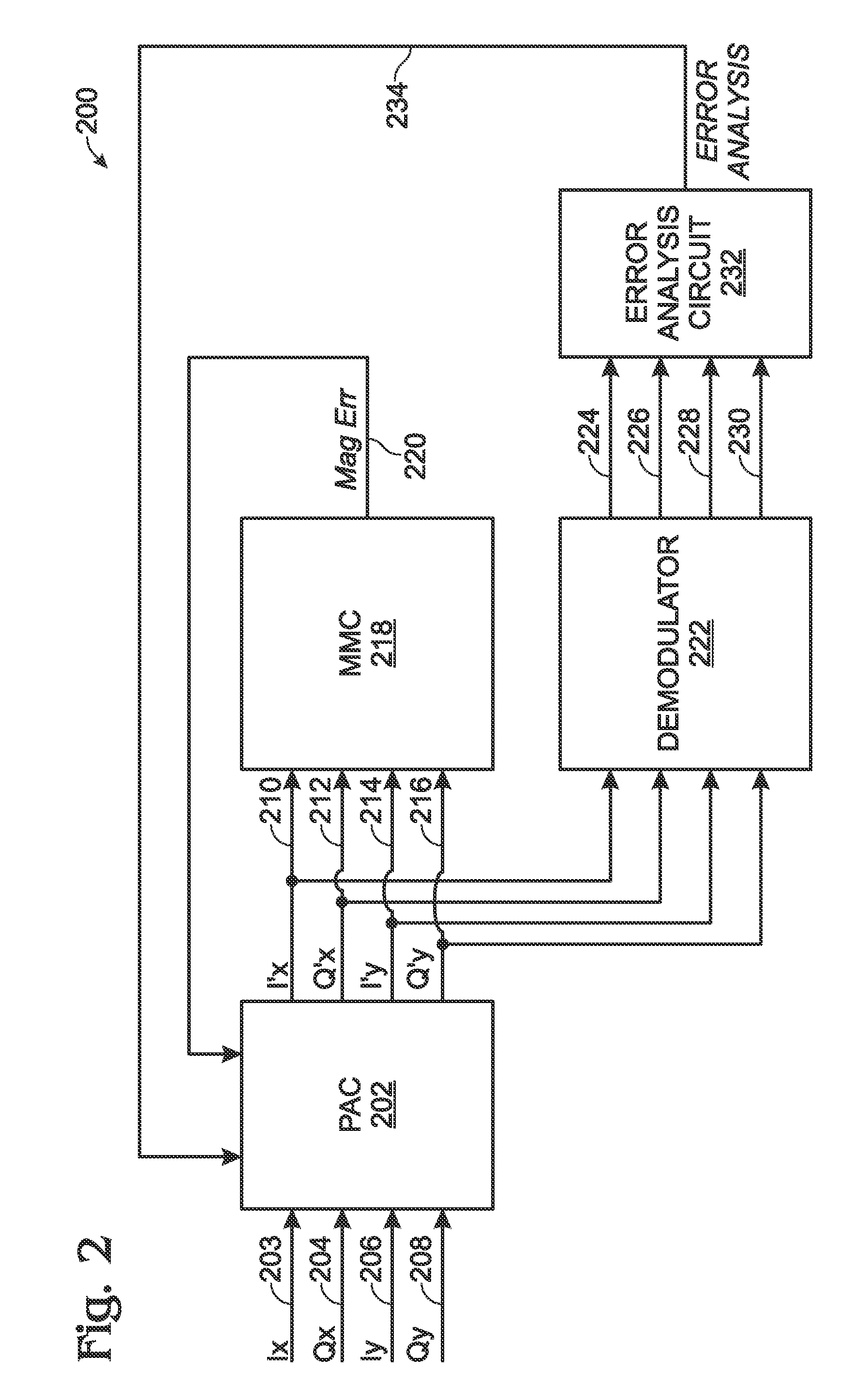
Polarization control for multichannel and polarization multiplexed optical transport networks
ActiveUS7603044B1Improve overall utilizationPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversPolarization multiplexedPeak value
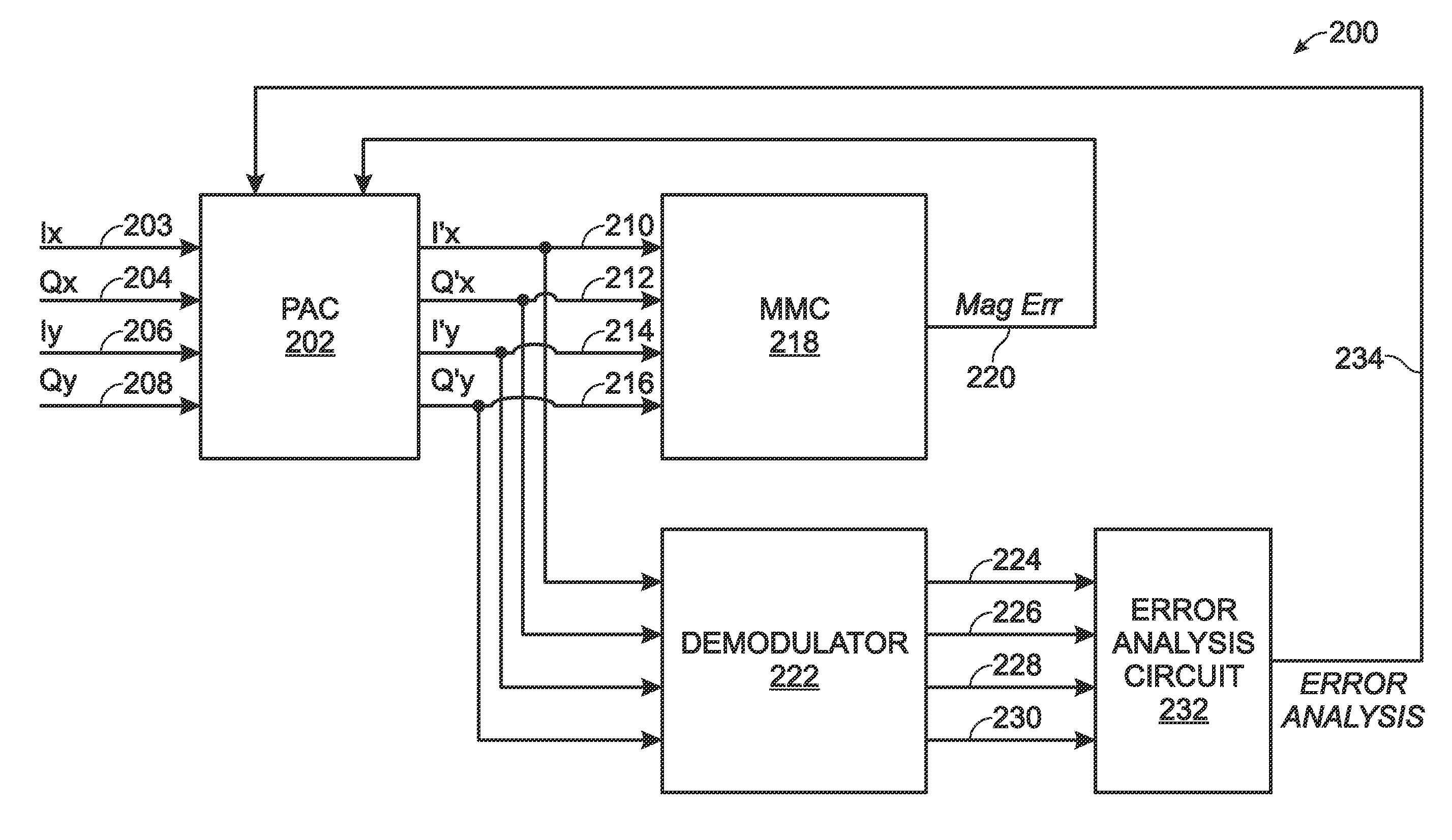
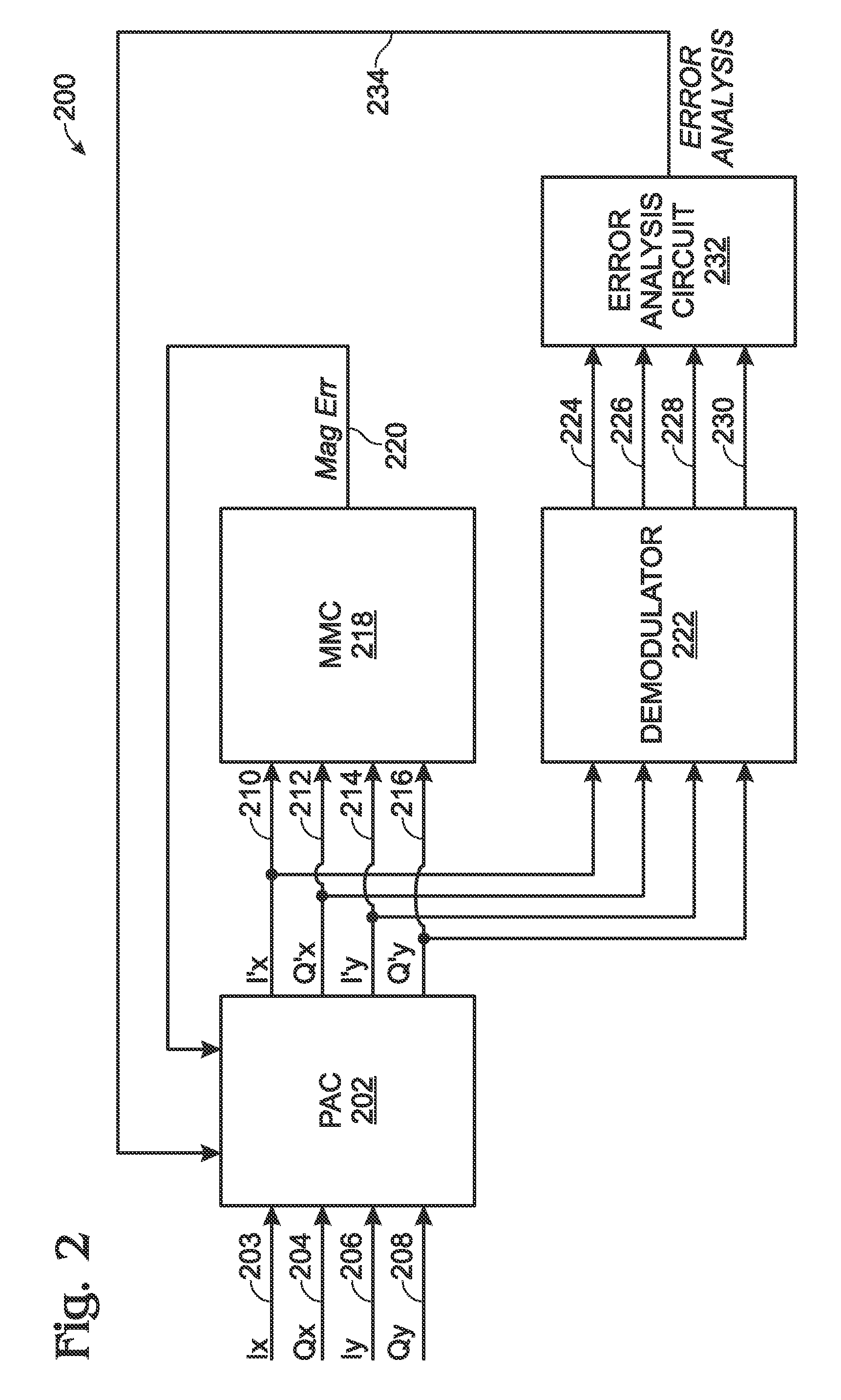
A system and method are provided for calibrating orthogonal polarity in a multichannel optical transport network (OTN) receiver. The method accepts a composite signal and separates the polarization of the signal into a pair of 2n-phase shift keying (2n-PSK) modulated input signals via Ix and Qx optical signal paths, where n≧1. Likewise, a pair of 2p-PSK modulated input signals are accepted via Iy and Qy optical signal paths where p≧1. Polarization-adjusted I′x, Q′x, I′y, and Q′y signals are generated. An average magnitude is compared to either 2×the absolute magnitude of (I′x and Q′x), or 2×the absolute magnitude of (I′y and Q′y). The average magnitude value can be used that is either 2×(a predetermined peak signal amplitude), or the sum of the absolute magnitudes of (I′x and Q′x) and (I′y and Q′y). The polarization-adjusted I′x, Q′x, I′y, and Q′y signals are modified until the magnitude comparison is about zero.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
System and method for determining angular position and controlling rotor orientation
ActiveUS7579799B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersAmplitude scalingAngular orientation
Methods and devices for determining the position and / or angular orientation of a rotating shaft. Exemplary features include a sensor module and a position determination module. Sensor module may include a plurality of Hall Effect devices (HEDs) arranged at a specified angular separation to produce a signal in response to rotation of the shaft. Position module may be responsive to sensor module to produce a converted signal, determine an error term, and produce a position estimate. Converted signal may be produced by processing the HED signals into sinusoidal reference signals having offset scale and amplitude scale factors. Error term may be determined by processing the converted signals to produce an estimated position signal. Position estimate may be produced by processing the error term. Refined position measurement may be achieved by iterative elimination of regressive differences between position estimates with minimization of absolute magnitude of error term.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
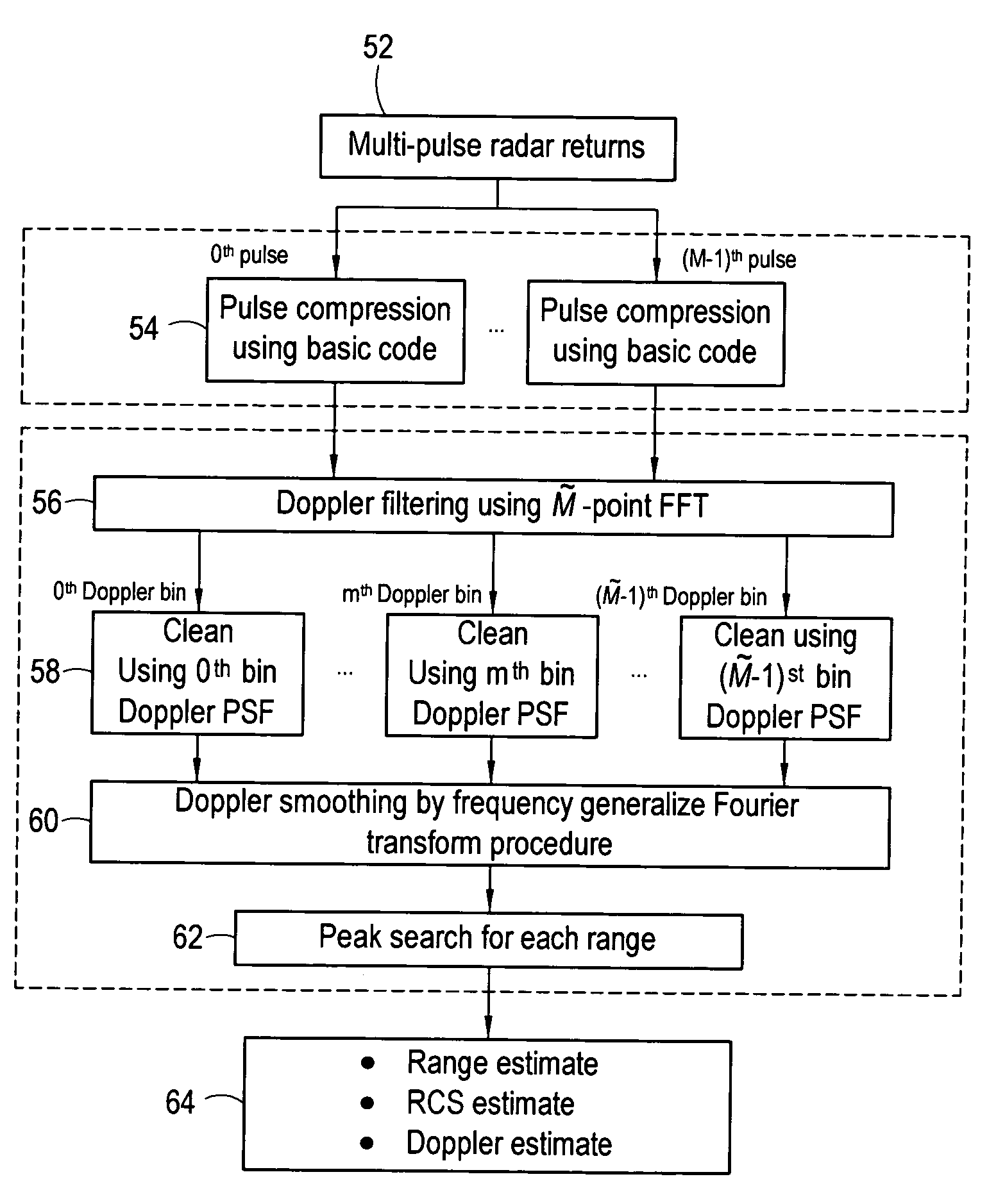
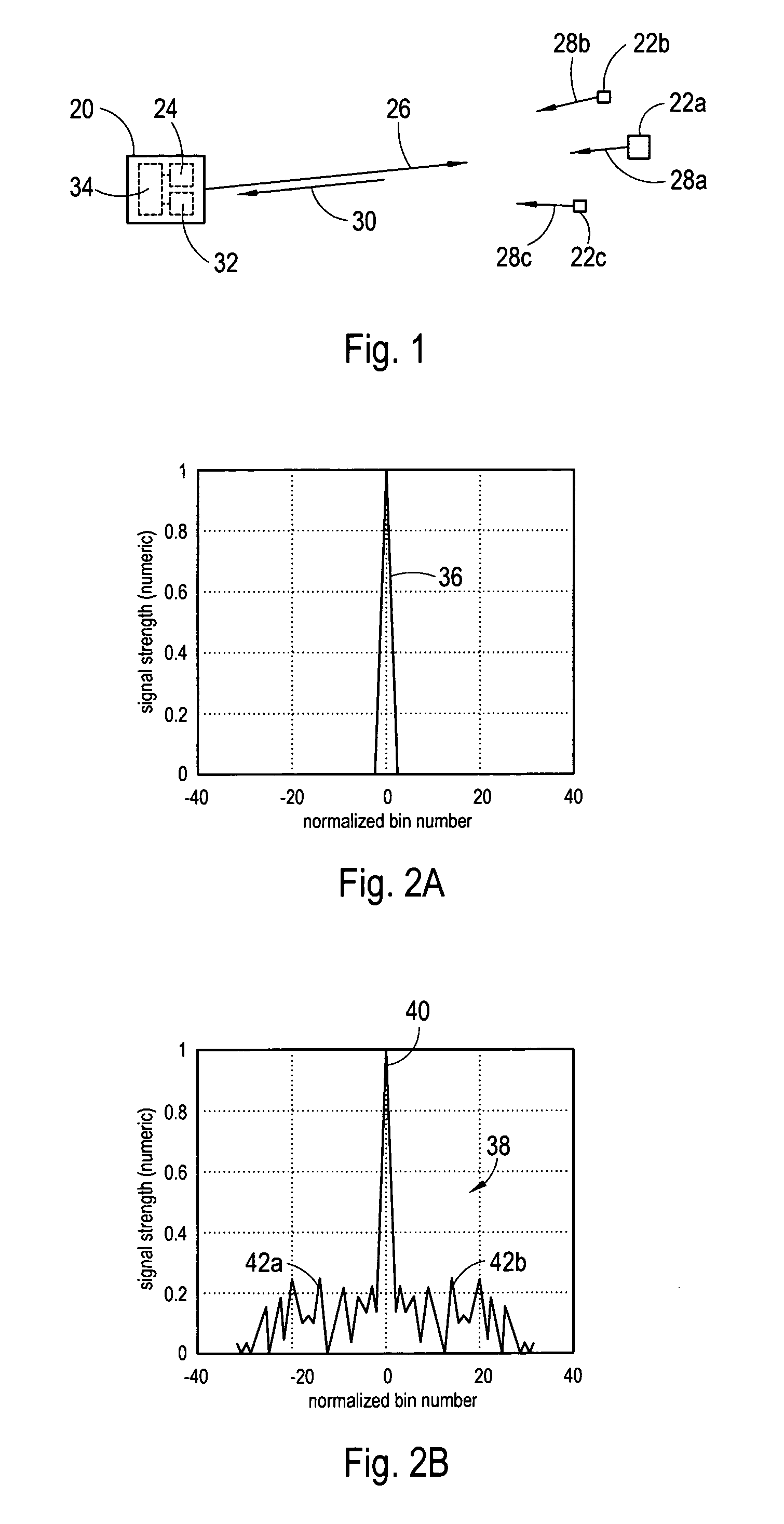
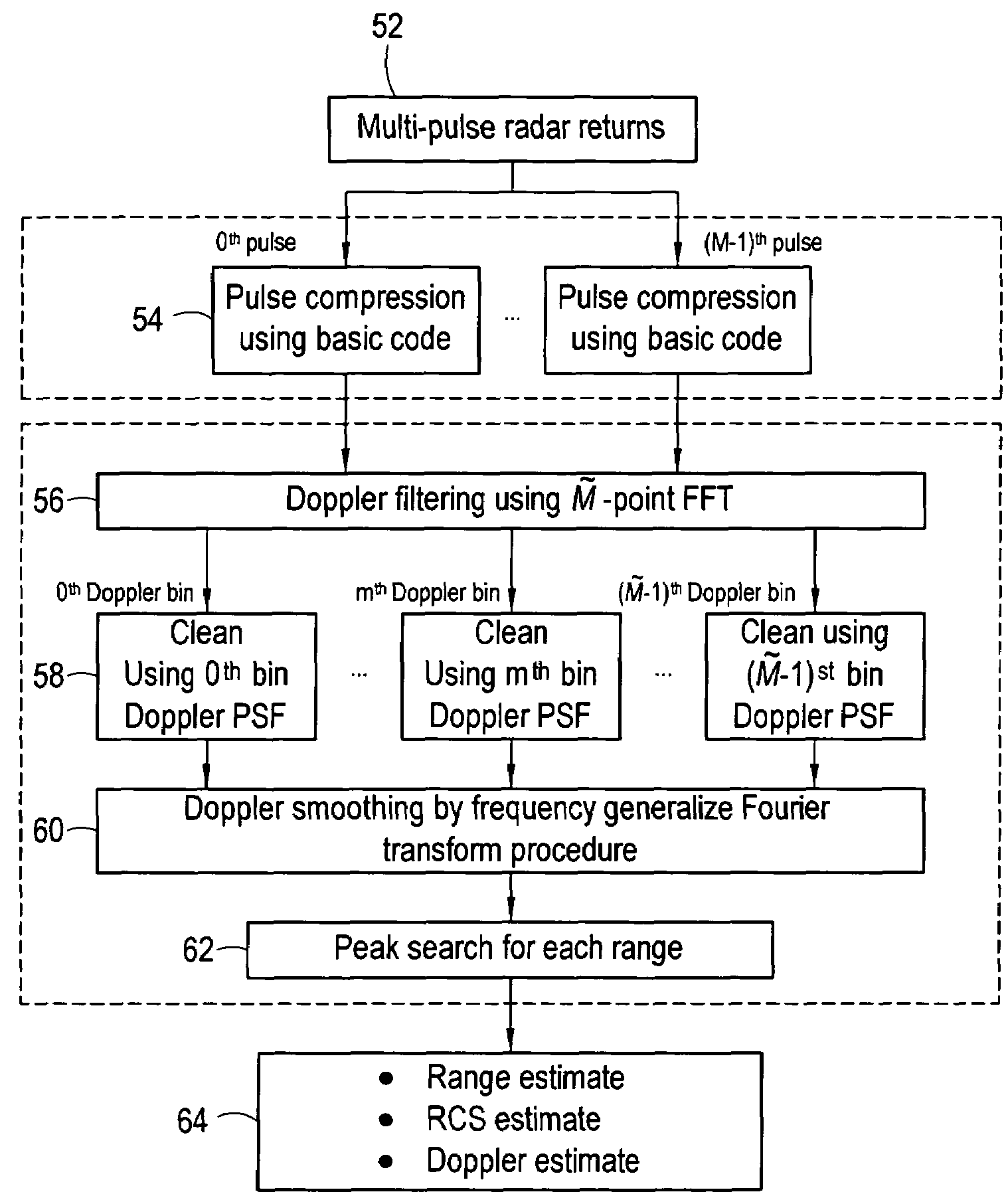
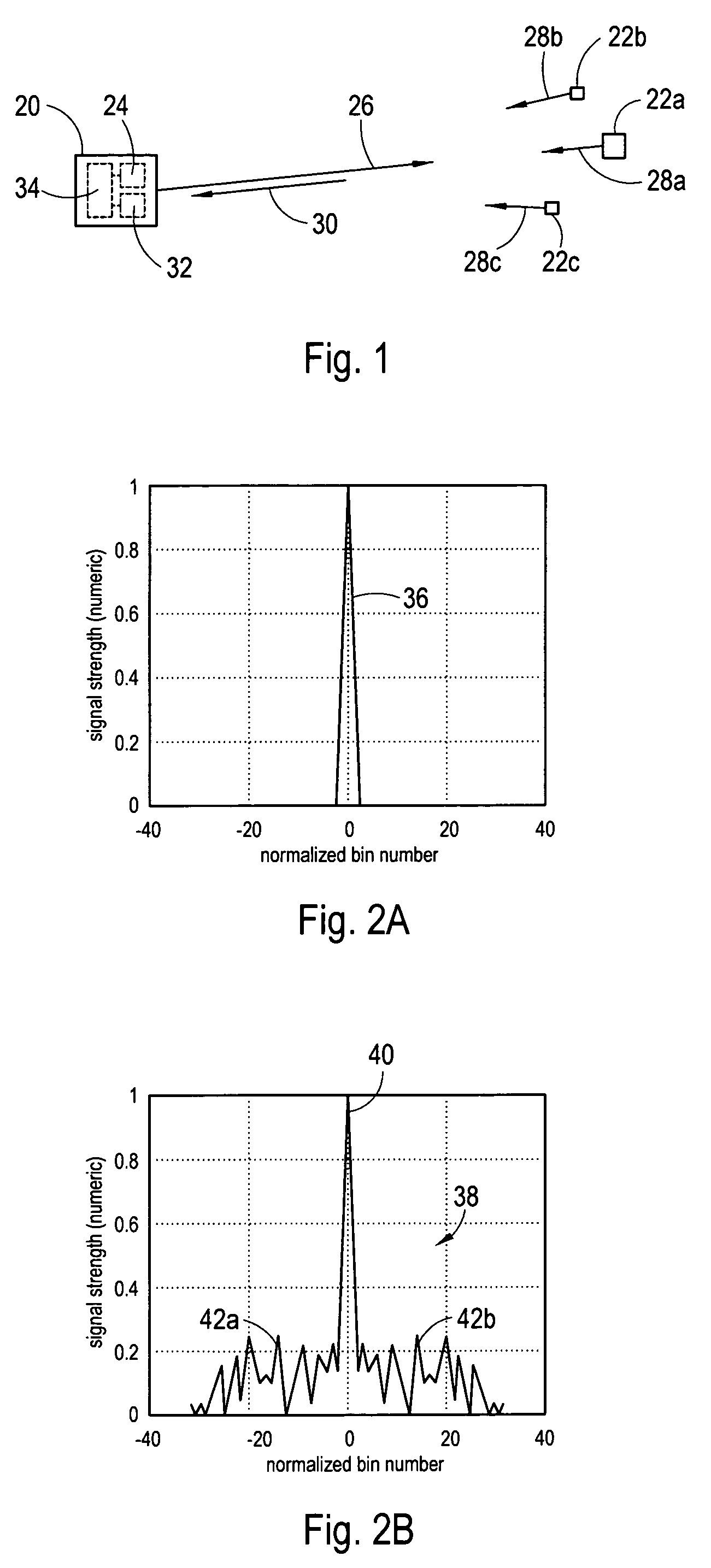
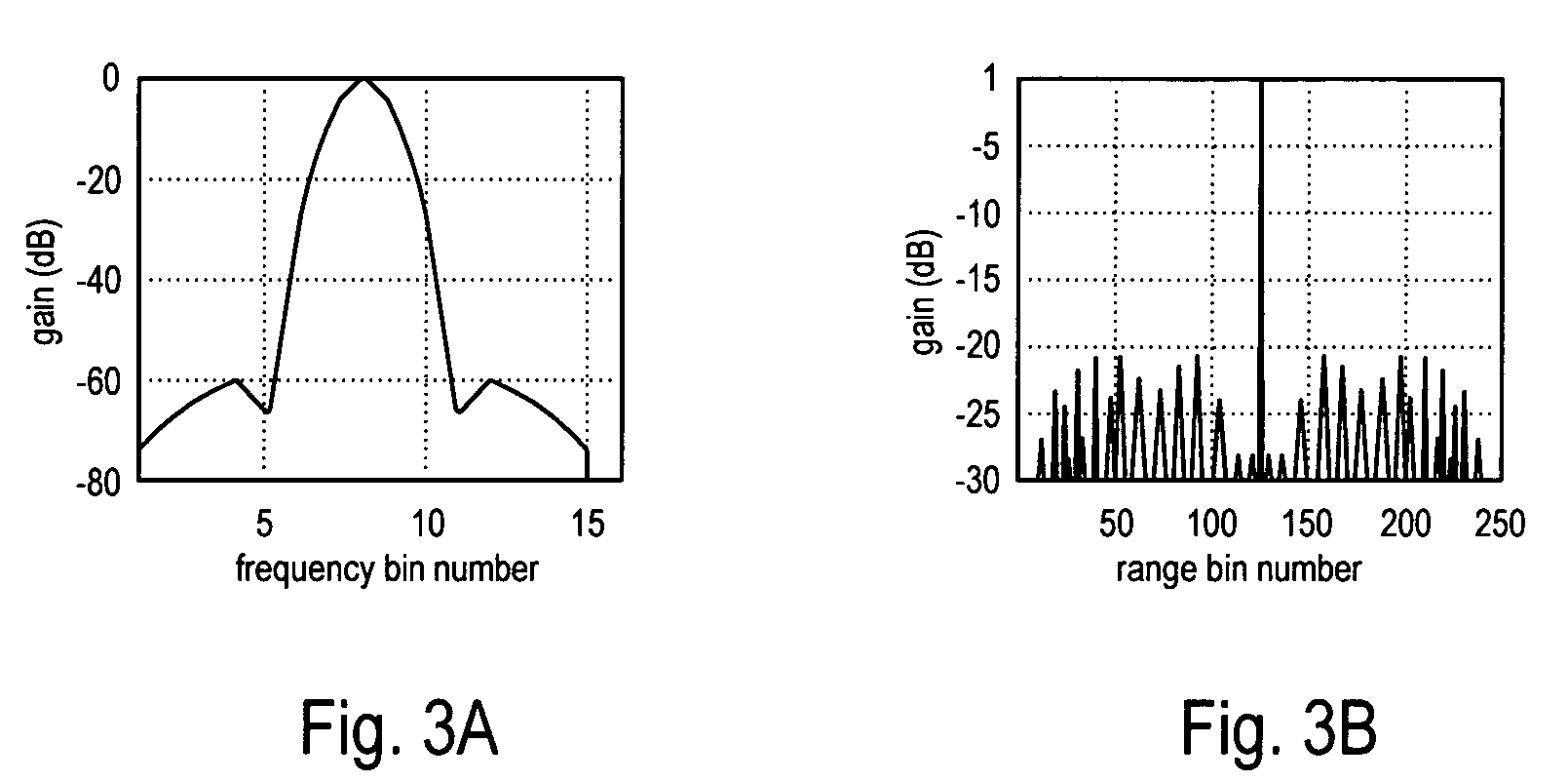
System and method for sidelobe reduction using point spread function expansion
InactiveUS20060227038A1Reduce Doppler filter sidelobesIncreasing mainlobe widthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmPoint spread function
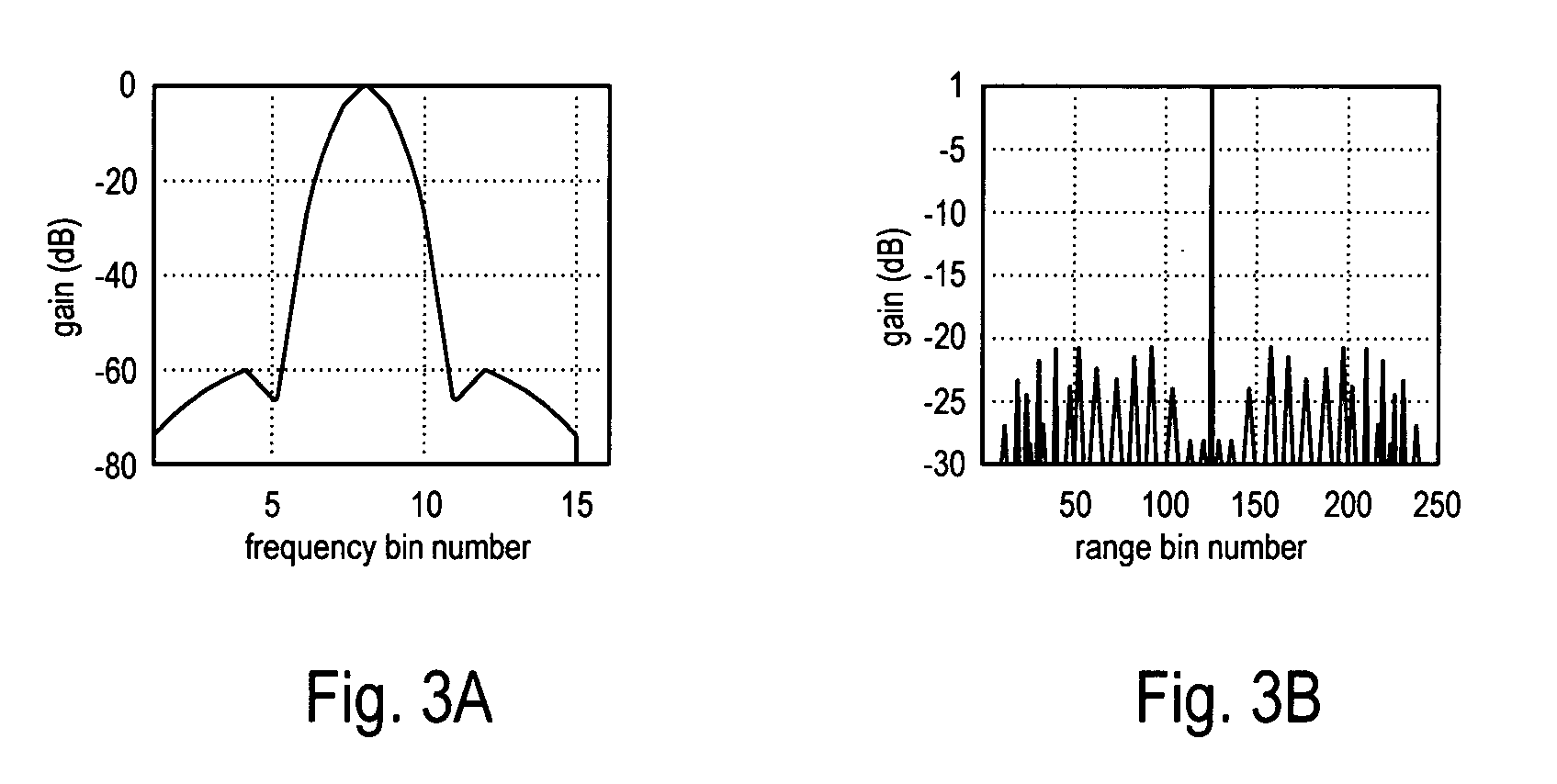
Systems and methods for detecting targets using pulse-compressed radar signals are disclosed. In one application, relatively small targets that are masked by the time-sidelobes of a larger target's return signal can be detected. The methods include a signal expansion type algorithm that is used to process the pulse-compressed return signal. Specifically, a generalized Fourier expansion expression having a summation of PSF terms is used to expand the pulse-compressed signal. Each term represents a respective target and includes a point spread function and a complex coefficient. The signal expansion procedure can be used to determine a set of optimum complex coefficients, with one coefficient for each range bin. Doppler frequency can be used together with range to optimize the complex coefficients. Next, targets are detected by analyzing each range bin to determine whether the corresponding complex coefficient has an absolute magnitude greater than a pre-determined threshold.
Owner:INFORMATION SYST LAB
Near time-optimal jerk trajectory for positioning a control object
InactiveUS7208898B2DC motor speed/torque controlRecord information storageTransducerElectrical polarity
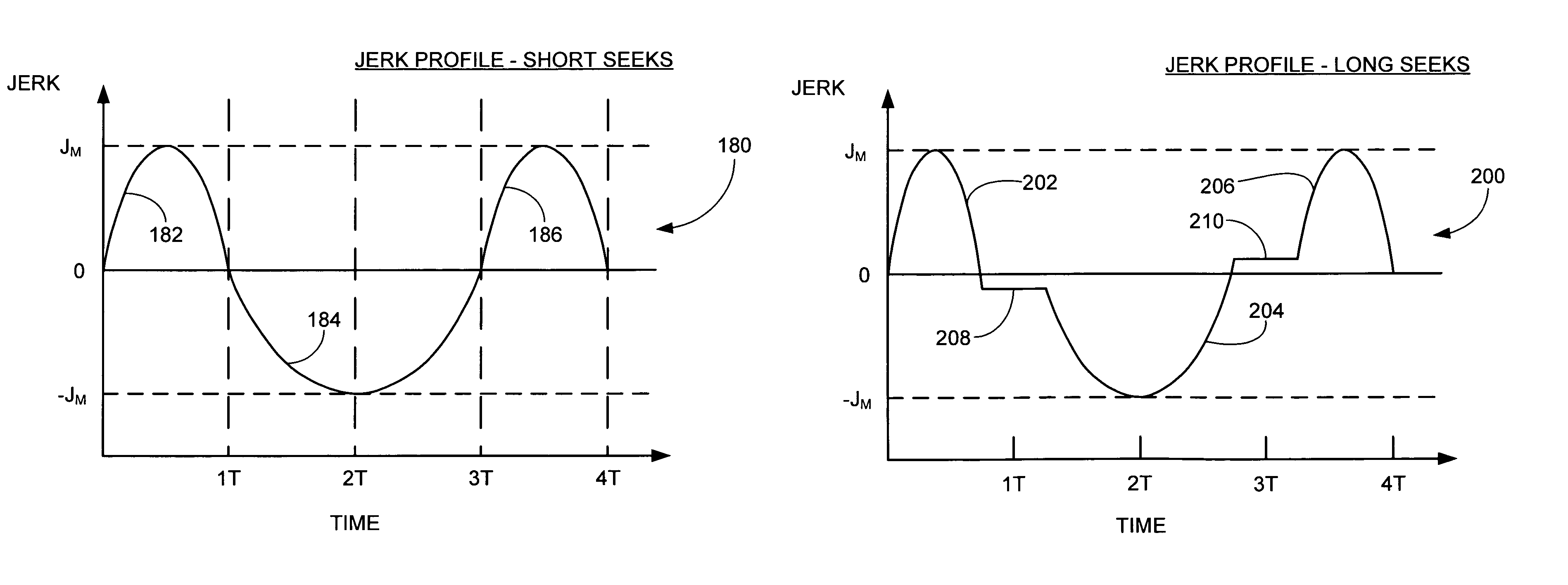
Method and apparatus for control object manipulation from an initial position to a final position. A jerk control profile describes a near time-optimal jerk trajectory for the control object and includes a sequence of first, second and third sinusoidal pulses of respectively alternating polarity and common absolute magnitude. The area of the second pulse is nominally equal to the combined area of the first and third pulses, and the pulses are preferably symmetric about the respective maximum pulse values. Associated control profiles (control voltage, current, velocity, displacement, etc.) are derived from the jerk control profile. For longer seeks, constant, non-zero jerk segments are inserted into the profile between the pulses, during which control voltage is maintained near saturation. The control object preferably comprises a transducer in a data storage device and the jerk control profile is stored in a memory location of the device.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
System and method for sidelobe reduction using point spread function expansion
InactiveUS7248207B2Increasing mainlobe widthReduce Doppler filter sidelobesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmDiffusion function
Owner:INFORMATION SYST LAB
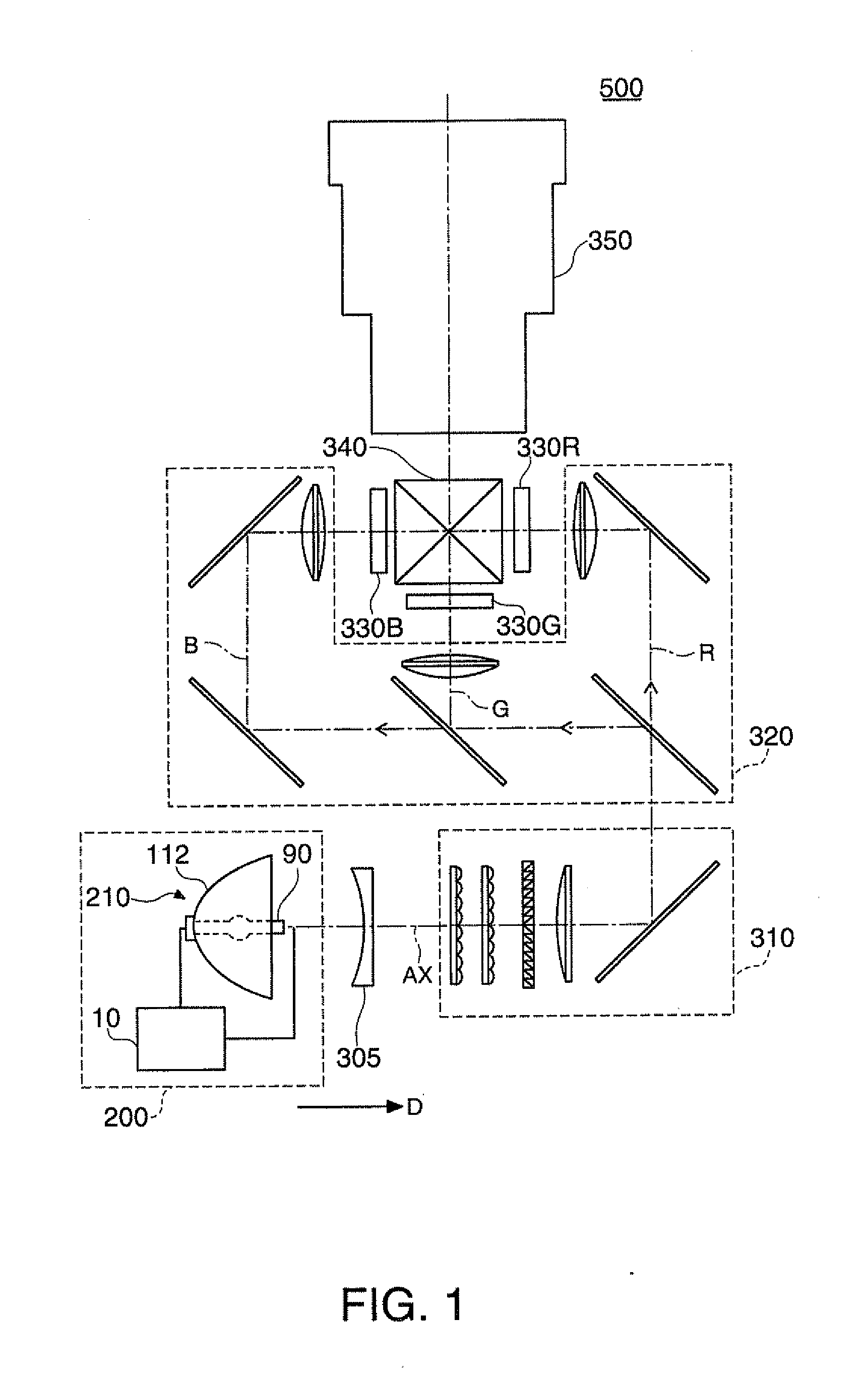
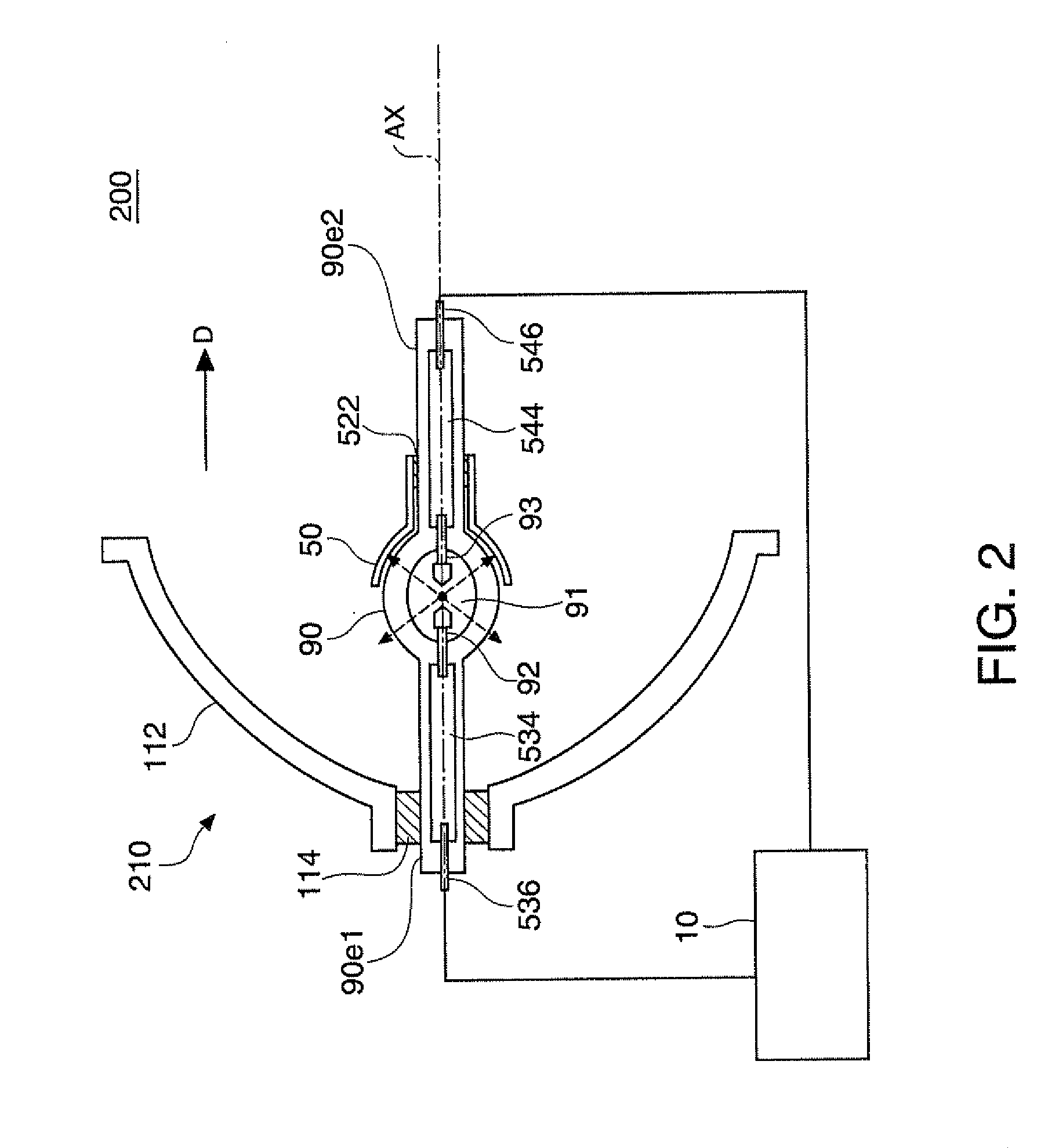
Projector
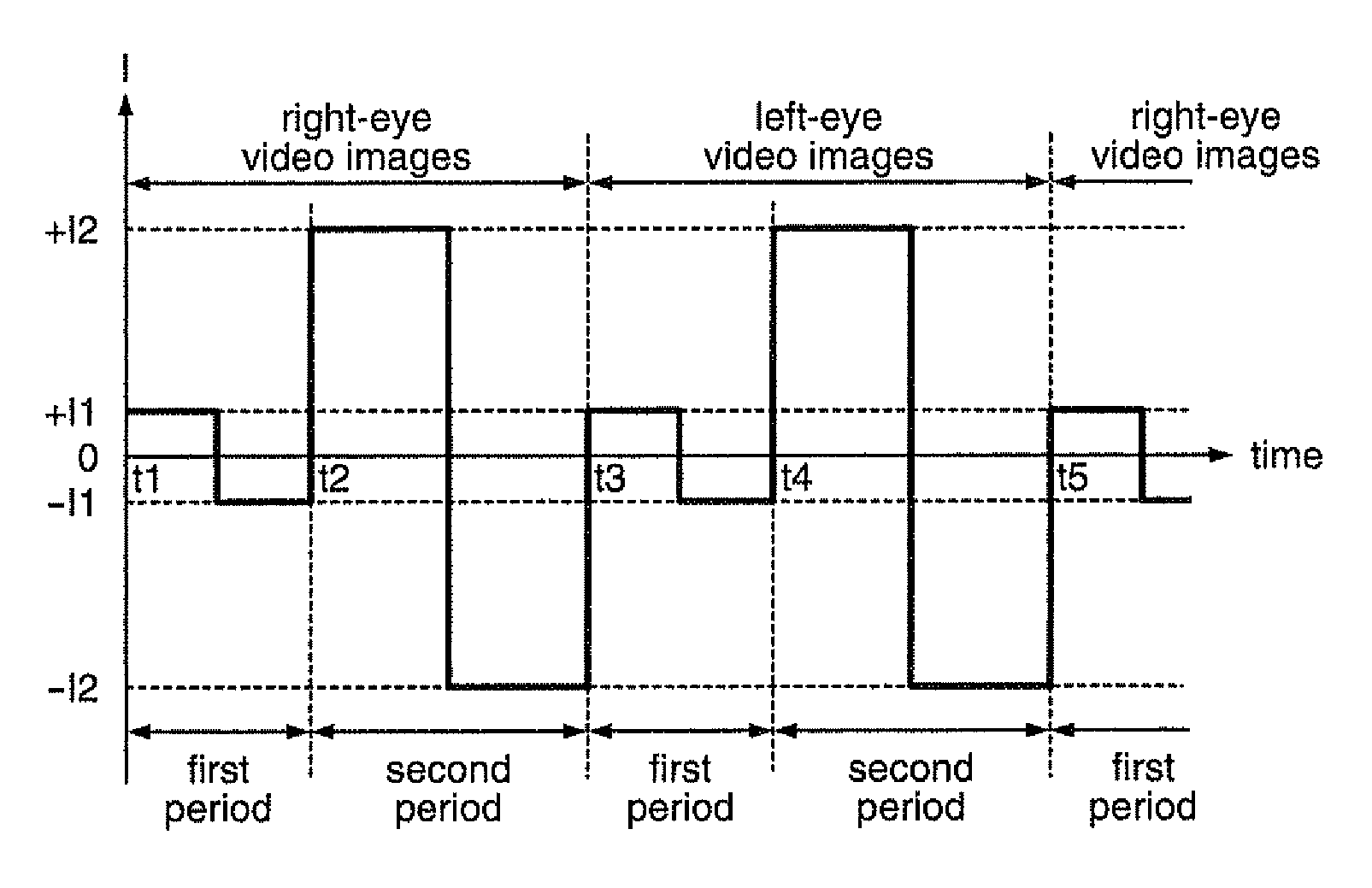
A projector includes a discharge lamp, a discharge lamp driver that supplies the discharge lamp with a current, a voltage detector that detects a drive voltage for driving the discharge lamp, and a controller that controls the discharge lamp driver. The controller carries out a first control process in which the discharge lamp driver is so controlled that an absolute magnitude of the drive current in a first period is smaller than that in a second period and that an AC current is supplied to the discharge lamp in a second period. The first control process includes a first electric power control process in which first average drive electric power is determined based on the voltage detected by the voltage detector and a current is supplied to the discharge lamp in such a way that average drive electric power is set at the first average drive electric power.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Apparatus and method of AC driving OLED
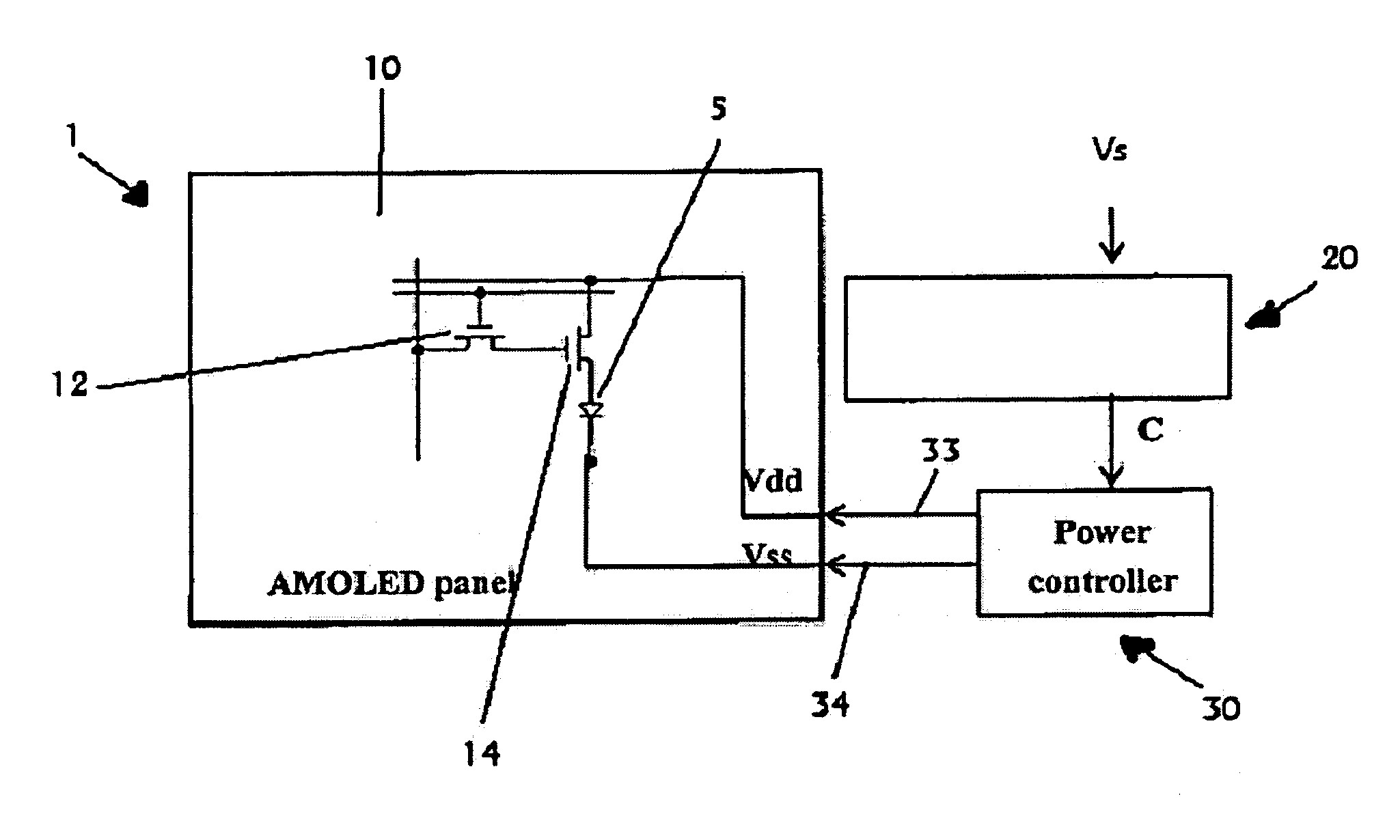
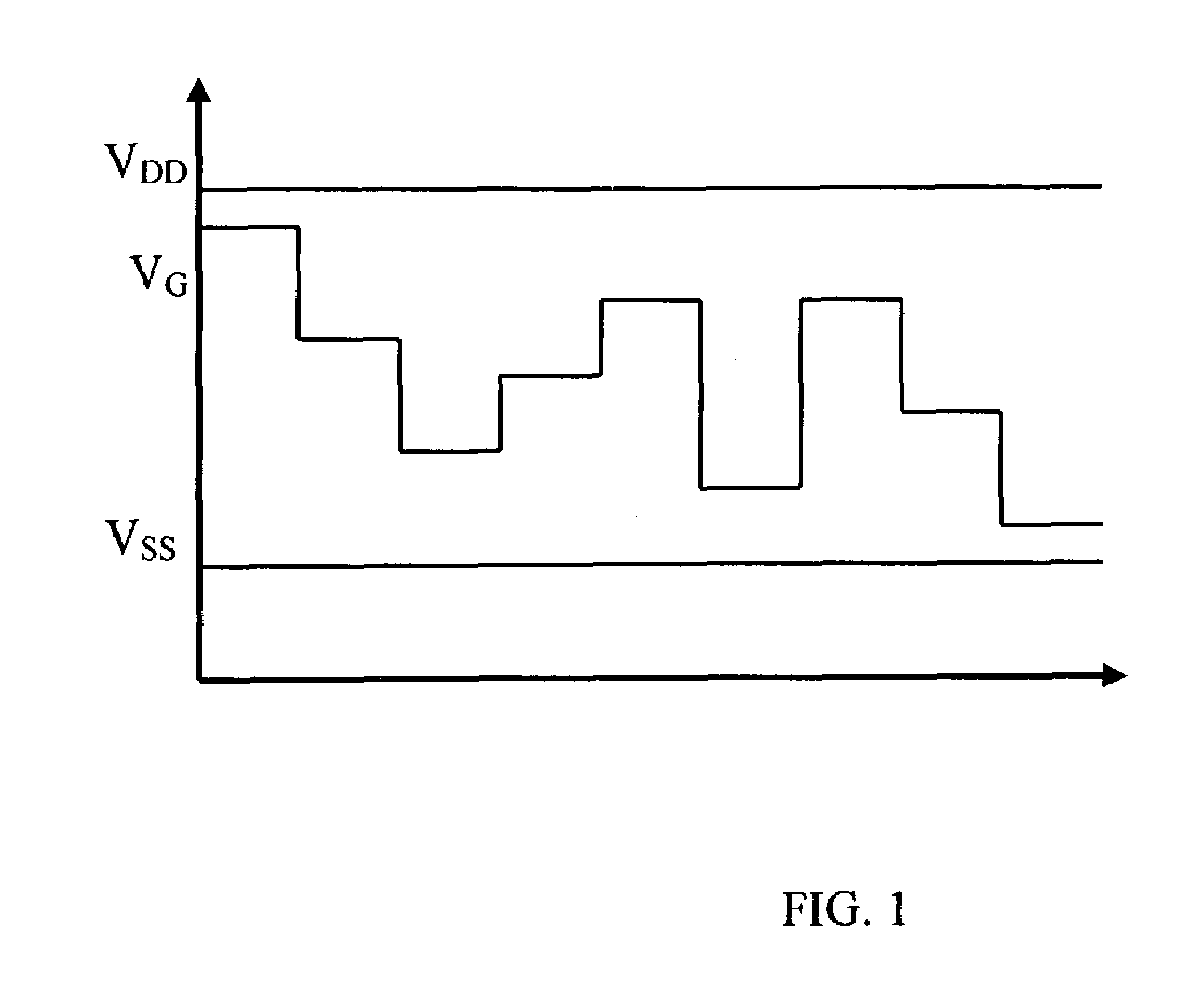
An apparatus and method for providing switched power to an AMOLED is disclosed. During certain time intervals, voltage and / or polarity provided to active devices such as thin film transistors (TFT) driving the AMOLEDs may be changed to reverse polarity or differ in absolute magnitude of voltage. During a subsequent time interval, the changed power may be changed again and / or reverted to an original state. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Rectangular-wave transmitting metal detector
InactiveUS20080048661A1Improve efficiencyCurrent/voltage measurementMagnetic property measurementsElectrical polarityEngineering
This invention relates to an electronic metal detector having transmit electronics comprising switching electronics arranged and adapted to generate a transmit signal, the transmit electronics comprising at least two power sources, a first power source and a second power source, the transmit electronics being connected to a transmit coil arranged and adapted to transmit an alternating magnetic field, wherein the switching electronics are adapted and arranged to switch a first voltage of the first power source to the transmit coil for at least a first period and also a third period, the switching electronics being adapted and arranged to switch a second voltage of the second power source to the transmit coil for at least a second period. The switching electronics are further adapted and arranged to switch approximately zero volts to the transmit coil for at least a fourth period, the second voltage being opposite in polarity to the first voltage, and an absolute magnitude of the first voltage being at least ten times an absolute magnitude of the second voltage, the said first voltage, second voltage, first period, second period and third period and fourth period being selected so that a transmit coil current increases in a second polarity sense during the second period and changes sign during the second period, and the transmit coil current increases in an opposite polarity sense to the second polarity sense during the first period and also the third period, receive electronics is adapted and arranged to receive and process a receive magnetic field during at least some of the second period and fourth period to produce an indicator output, the indicator output at least indicating the presence of at least some metal targets under the influence of the said alternating magnetic field and indicating at least a characteristic of the metal targets.
Owner:MINELAB ELECTRONICS
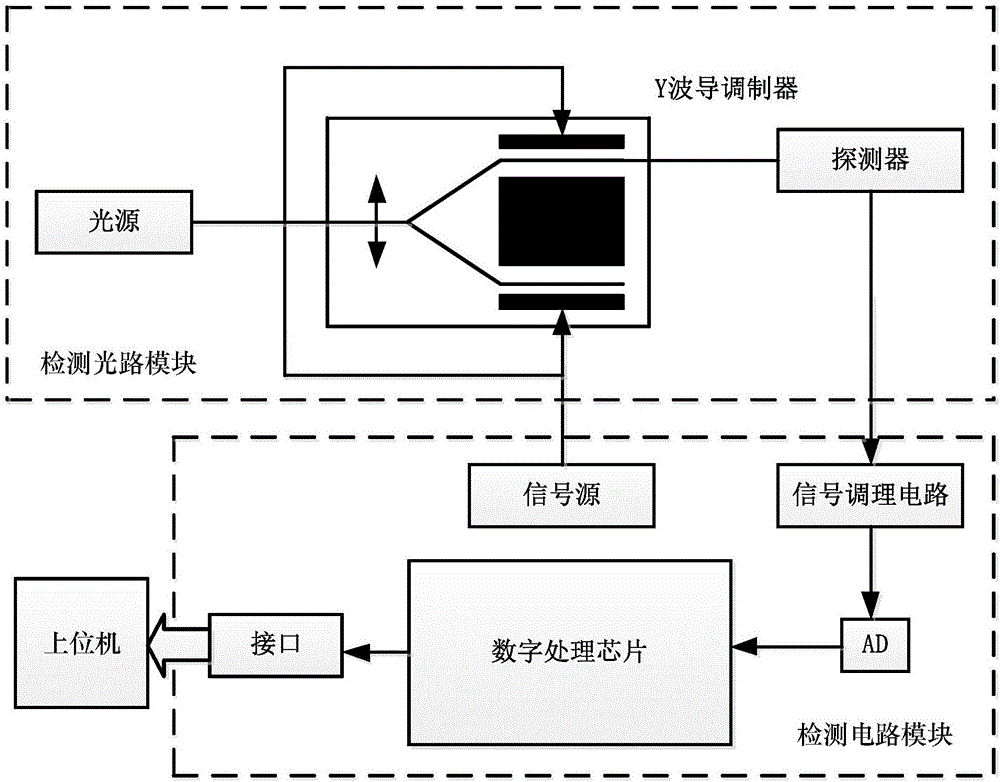
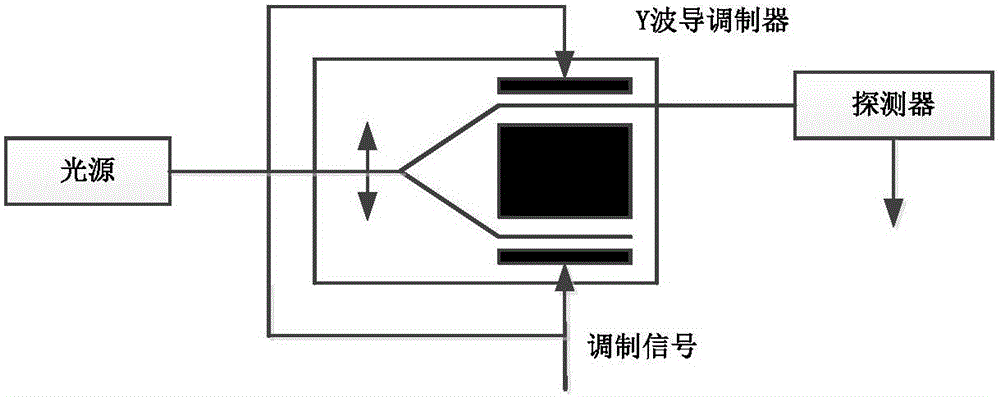
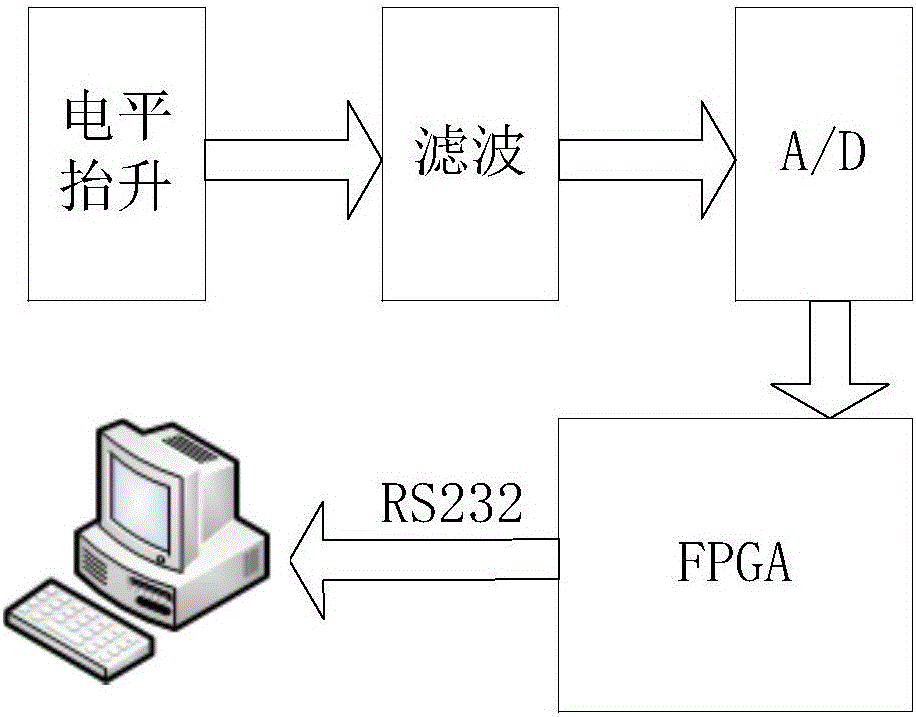
Online testing device and method for residual strength modulation of Y-waveguide modulator
InactiveCN105953818ASolve the problem of low precision and low measurement speedFast measurementSagnac effect gyrometersResidual strengthFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an online testing device and method for residual strength modulation of a Y-waveguide modulator. The online testing device comprises a detecting optical path module, a detecting circuit module and a host computer. The working principle of the device is that a light source sends an optical signal to the Y-waveguide modulator, one end of an output branch of the Y-waveguide modulator is connected to a detector, and the optical signal is subjected to photovoltaic conversion through the detector, then passes through the level elevation circuit, a filter circuit and a high-speed A / D conversion chip, is processed by an FPGA (field-programmable gate array) and is finally sent to the host computer through an RS232 serial port for display. With design of the online testing device for residual strength modulation of the Y-waveguide modulator, the absolute magnitude of residual strength modulation can be obtained directly and rapidly, the problems of low precision and low testing speed are solved, one objective real-time online method is provided, and compared with the conventional methods adopting an oscilloscope, a lock-in amplifier, spectral analysis and the like, the testing precision is higher, the speed is higher and the functions are more complete.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Audio-peak limiting in slow and fast stages
A method and apparatus for limiting the absolute magnitude of an audio signal. The method may include firstly variable-gain reducing the gain of an audio signal, and then secondly variable-gain reducing the gain of the audio signal faster than the first variable-gain reduction, thereby limiting the absolute magnitude of the audio signal to a threshold. The first variable-gain reduction may include variable-gain reducing the gain of the audio signal in a first stage, and the second variable-gain reduction may include variable-gain reducing the gain of the audio signal in a second stage that reduces the gain faster than the first stage. The second variable-gain reduction may include delaying the audio signal, finding a peak among the delayed audio signal, calculating a fast gain from a found peak, and modifying the delayed audio signal with the calculated fast gain.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
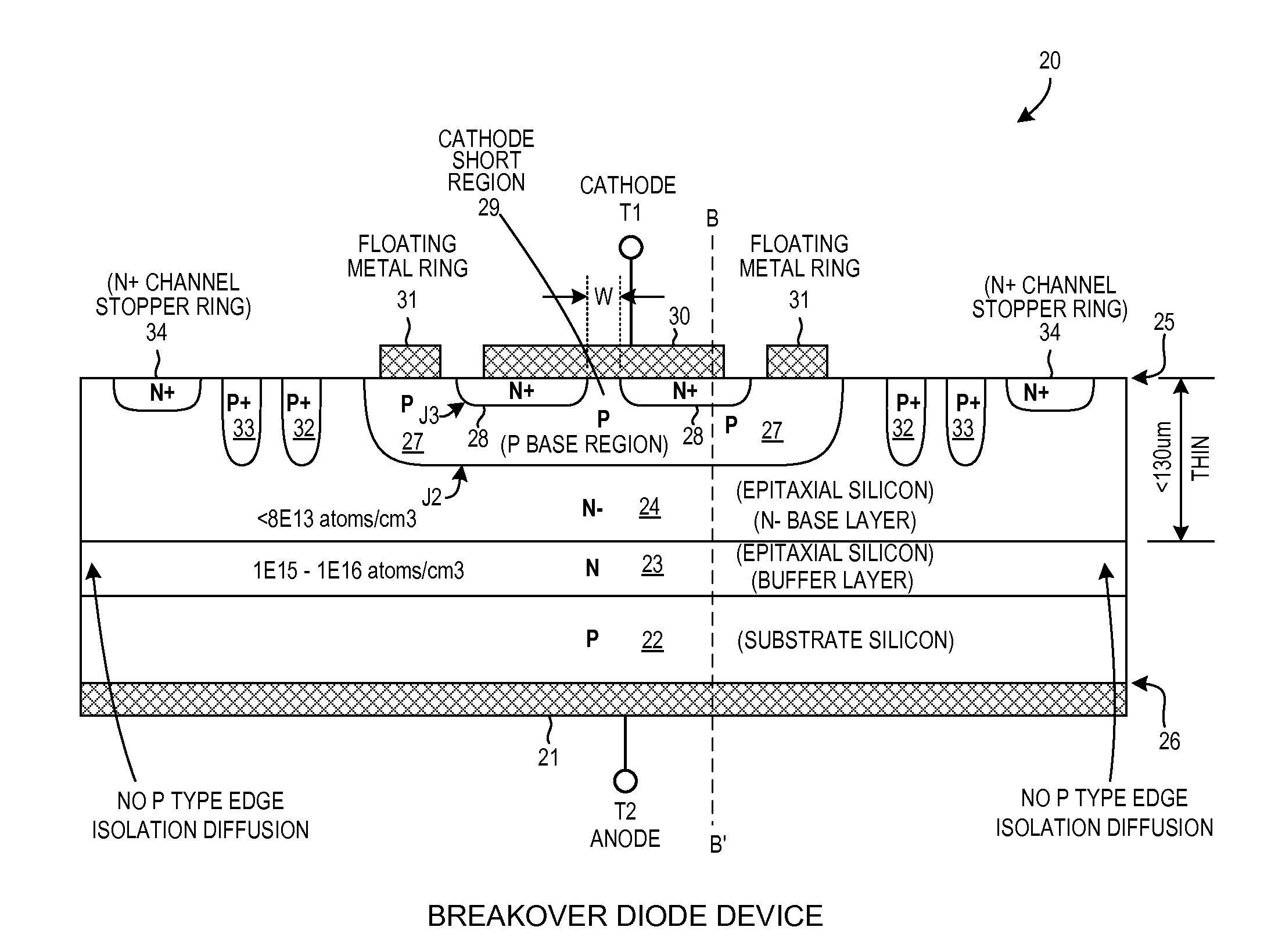
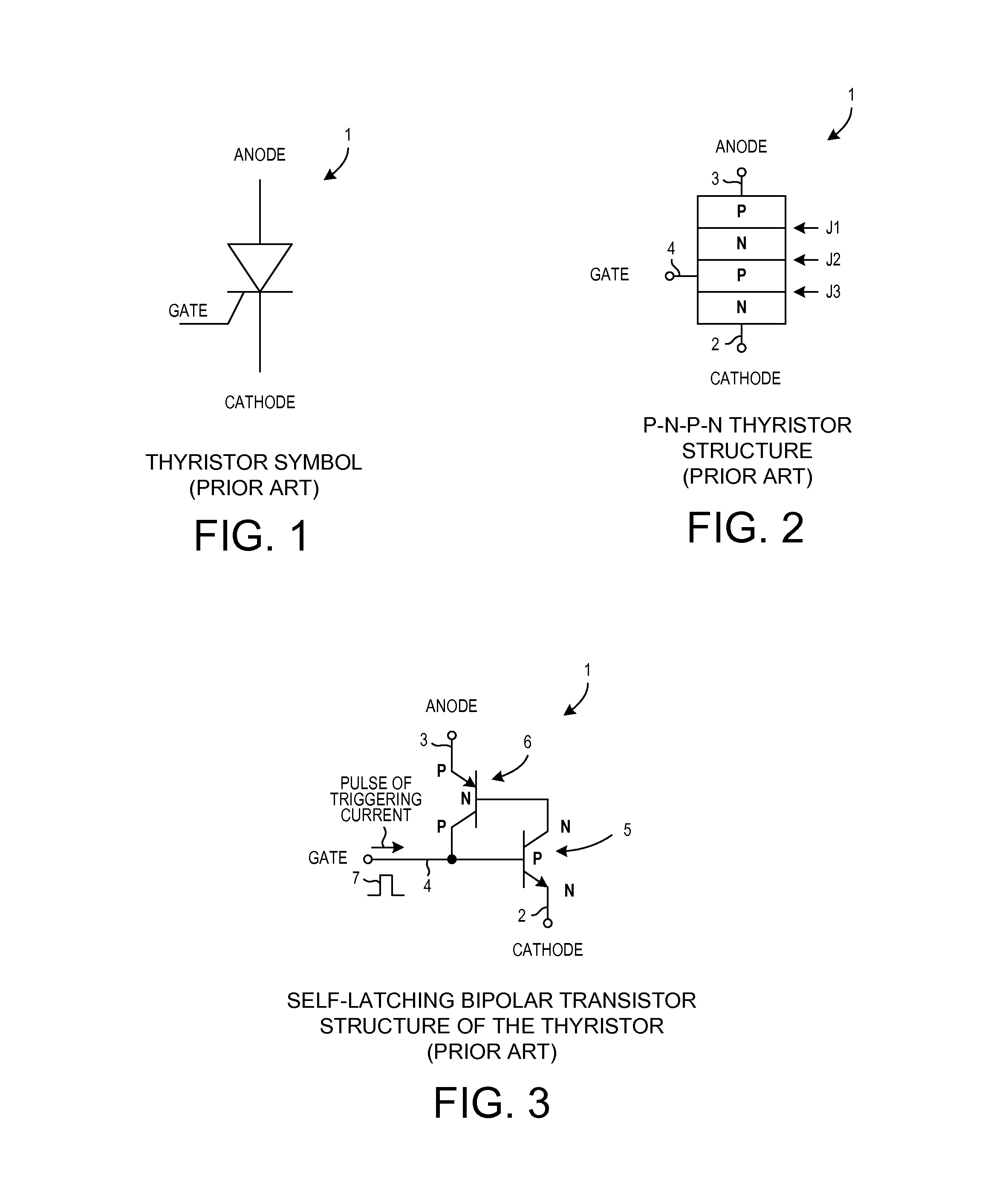
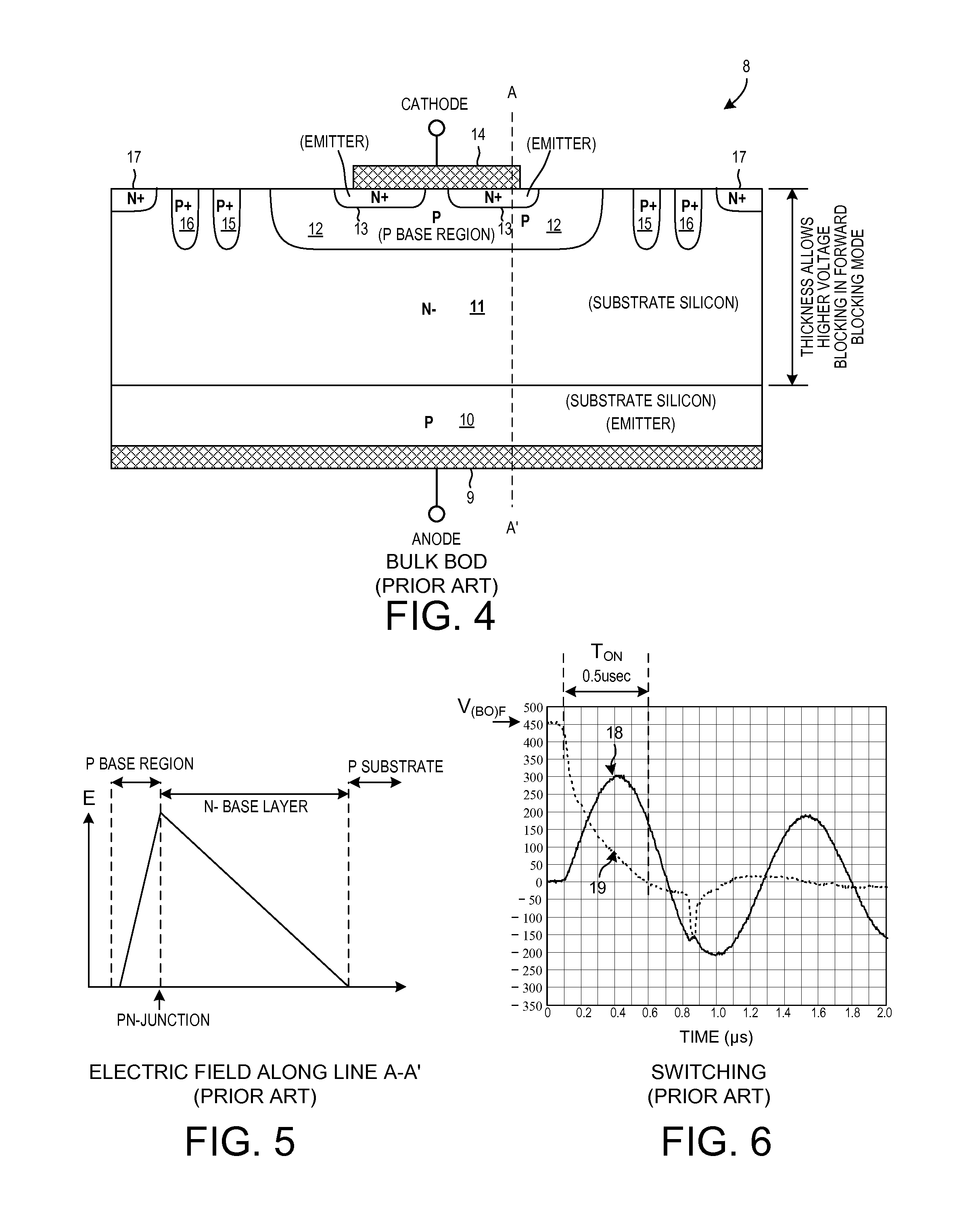
Packaged overvoltage protection circuit for triggering thyristors
ActiveUS20140332842A1Reduce voltageNot to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOvervoltageCelsius Degree
In a first embodiment, an ultra-fast breakover diode has a turn on time TON that is less than 0.3 microseconds, where the forward breakover voltage is greater than +400 volts and varies less than one percent per ten degrees Celsius change. In a second embodiment, a breakover diode has a reverse breakdown voltage that is greater, in absolute magnitude, than the forward breakover voltage, where the forward breakover voltage is greater than +400 volts. In a third embodiment, a string of series-connected breakover diode dice is provided, along with a resistor string, in a packaged circuit. The packaged circuit acts like a single breakover diode having a large forward breakover voltage and a comparably large reverse breakdown voltage, even though the packaged circuit includes no discrete high voltage reverse breakdown diode. The packaged circuit is usable to supply a triggering current to a thyristor in a voltage protection circuit.
Owner:LITTELFUSE INC
Multichannel Polarization Control for Polarization Multiplexed Optical Transport Networks
ActiveUS20100135655A1Improve overall utilizationPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversPolarization multiplexedPeak value
A system and method are provided for calibrating orthogonal polarity in a multichannel optical transport network (OTN) receiver. The method accepts a composite signal and separates the polarization of the signal into a pair of 2n-phase shift keying (2n-PSK) modulated input signals via Ix and Qx optical signal paths, where n≧1. Likewise, a pair of 2p-PSK modulated input signals are accepted via Iy and Qy optical signal paths where p≧1. Polarization-adjusted I′x, Q′x, I′y, and Q′y signals are generated. An average magnitude is compared to either 2×the absolute magnitude of (I′x and Q′x), or 2×the absolute magnitude of (I′y and Q′y). The average magnitude value can be used that is either 2×(a predetermined peak signal amplitude), or the sum of the absolute magnitudes of (I′x and Q′x) and (I′y and Q′y). The polarization-adjusted I′x, Q′x, I′y, and Q′y signals are modified until the magnitude comparison is about zero.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Projector
ActiveUS8506092B2Reduce wearTelevision system detailsElectric lighting sourcesDriving currentEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Supersonic deformeter
The invention is a kind of ultrasonic deformeter, which is mainly made up of emission piezo-electric, sound insulating material, metal shell, transmitting end power outgoing line, receiving end power outgoing line. It has merits of high accuracy, low cost, no electromagnetism interference, no loose, adjustable strain absolute magnitude, small size. It especially is suitable for long time strain measurement and the rheopectic measurement of construction structure safe monitoring, hill arpon.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com