Patents
Literature
1009 results about "Inter-domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
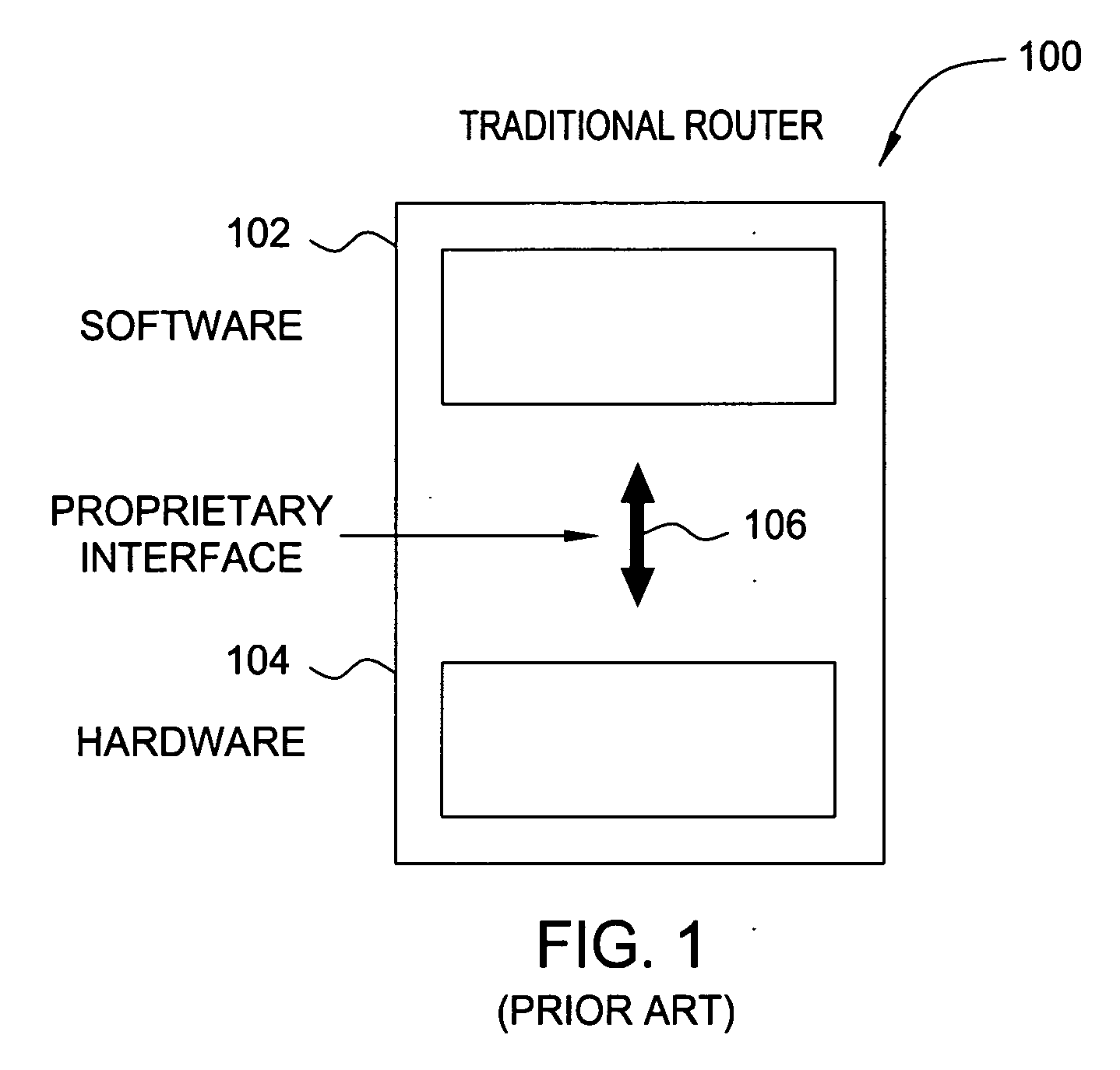
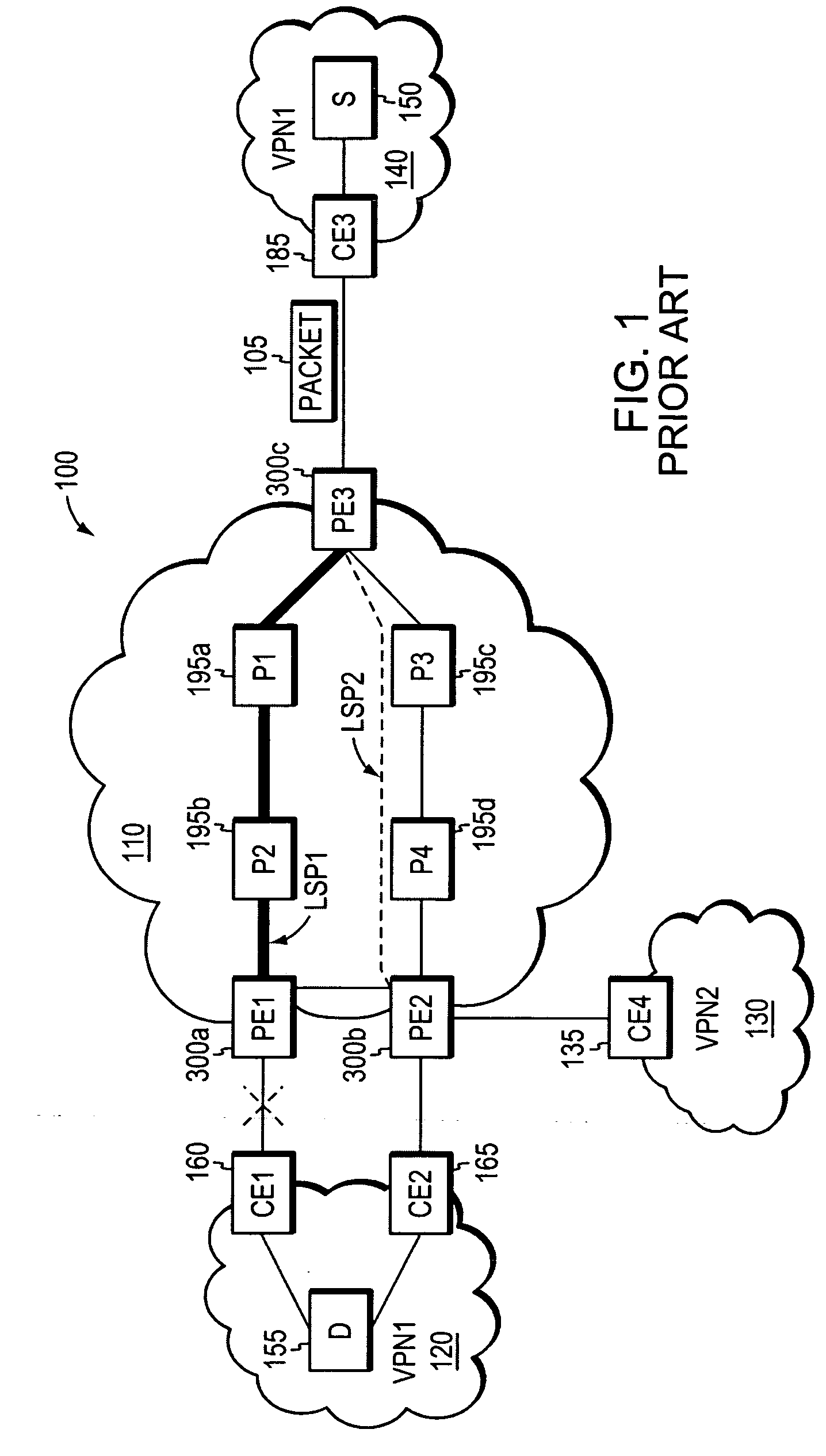
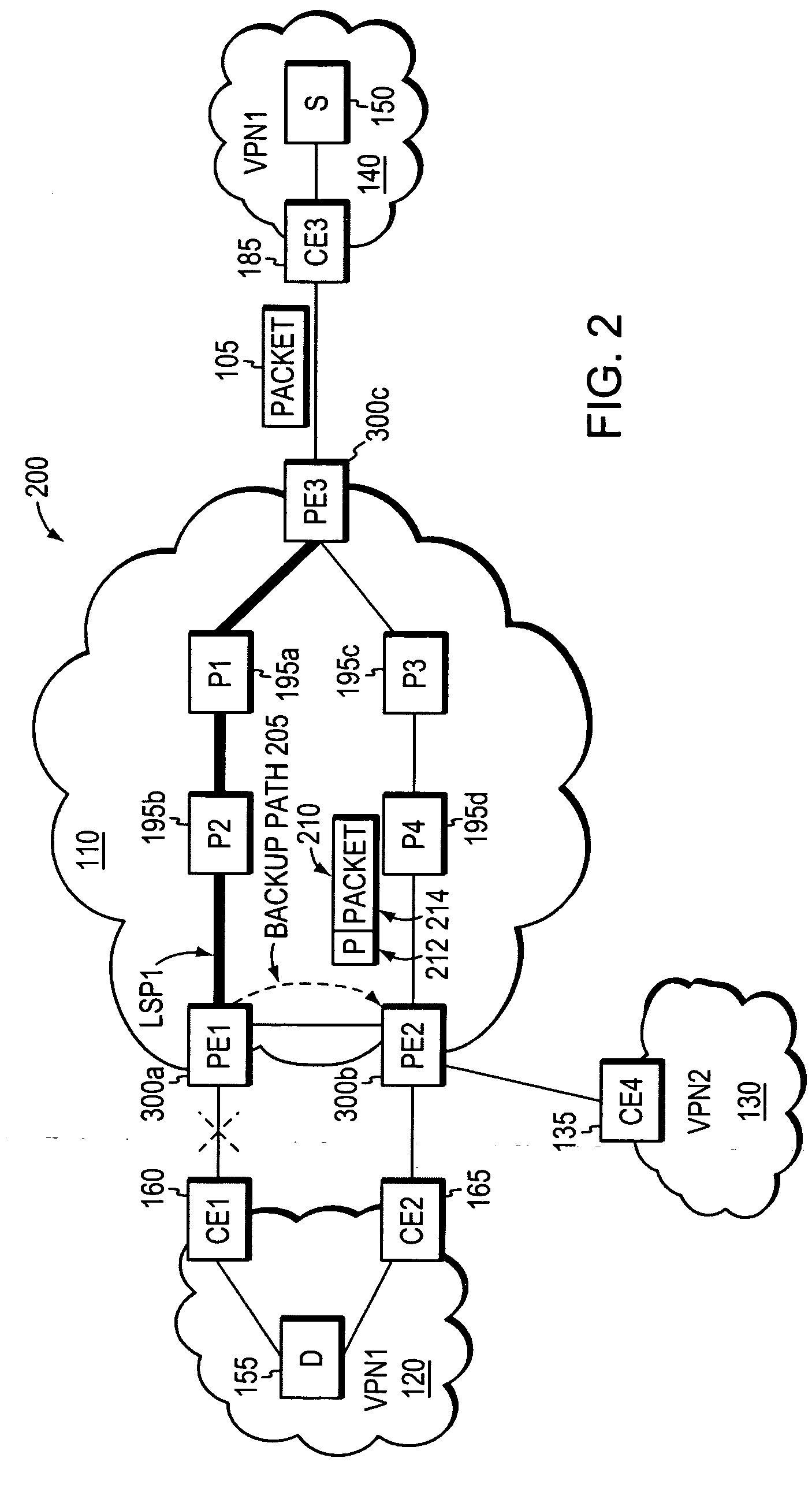
Inter-domain is data flow control and interaction between Primary Domain Controller (PDC) computers. This type of computer uses various computer protocols and services to operate. It is most commonly used to multicast between internet domains.
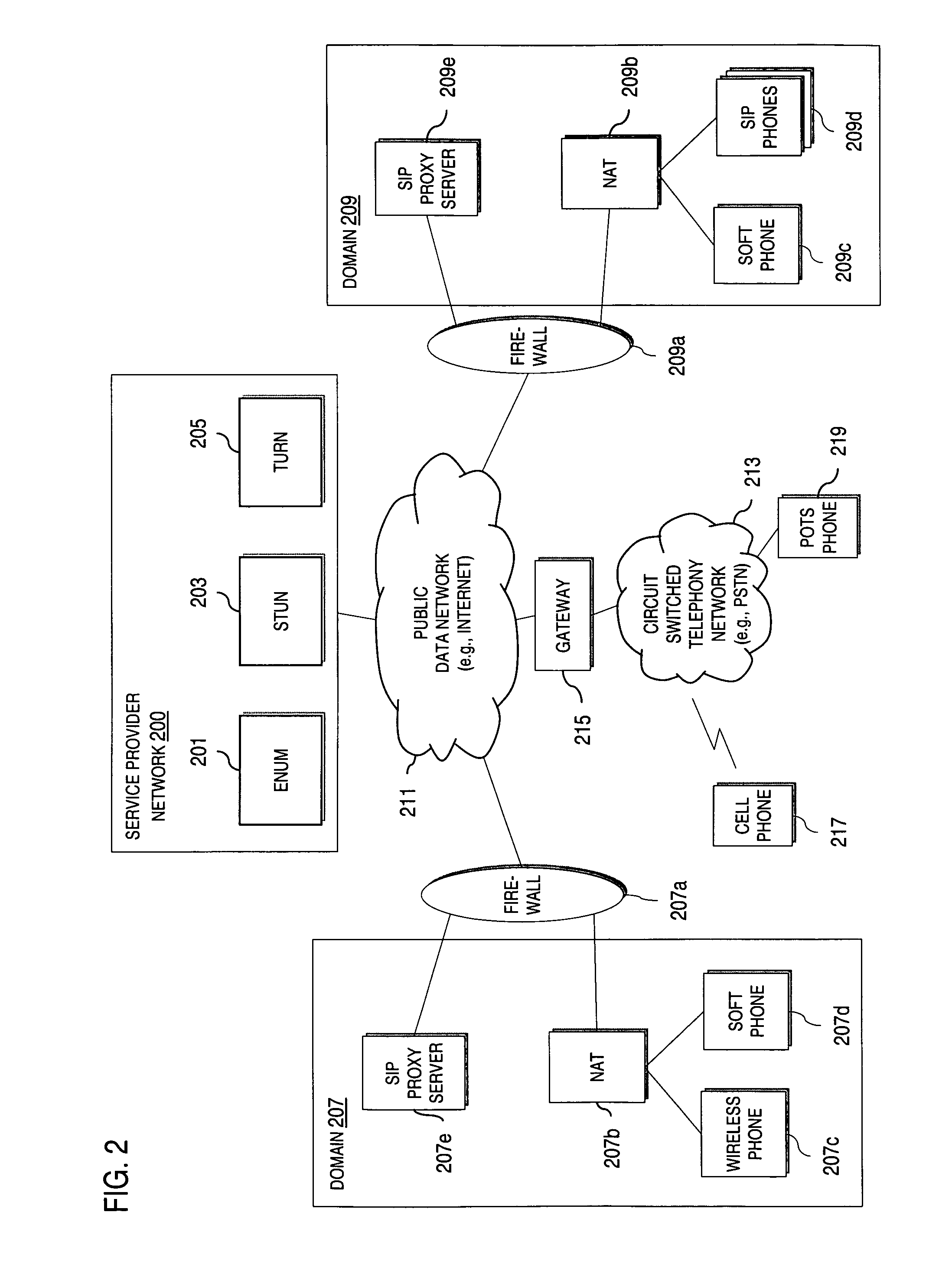
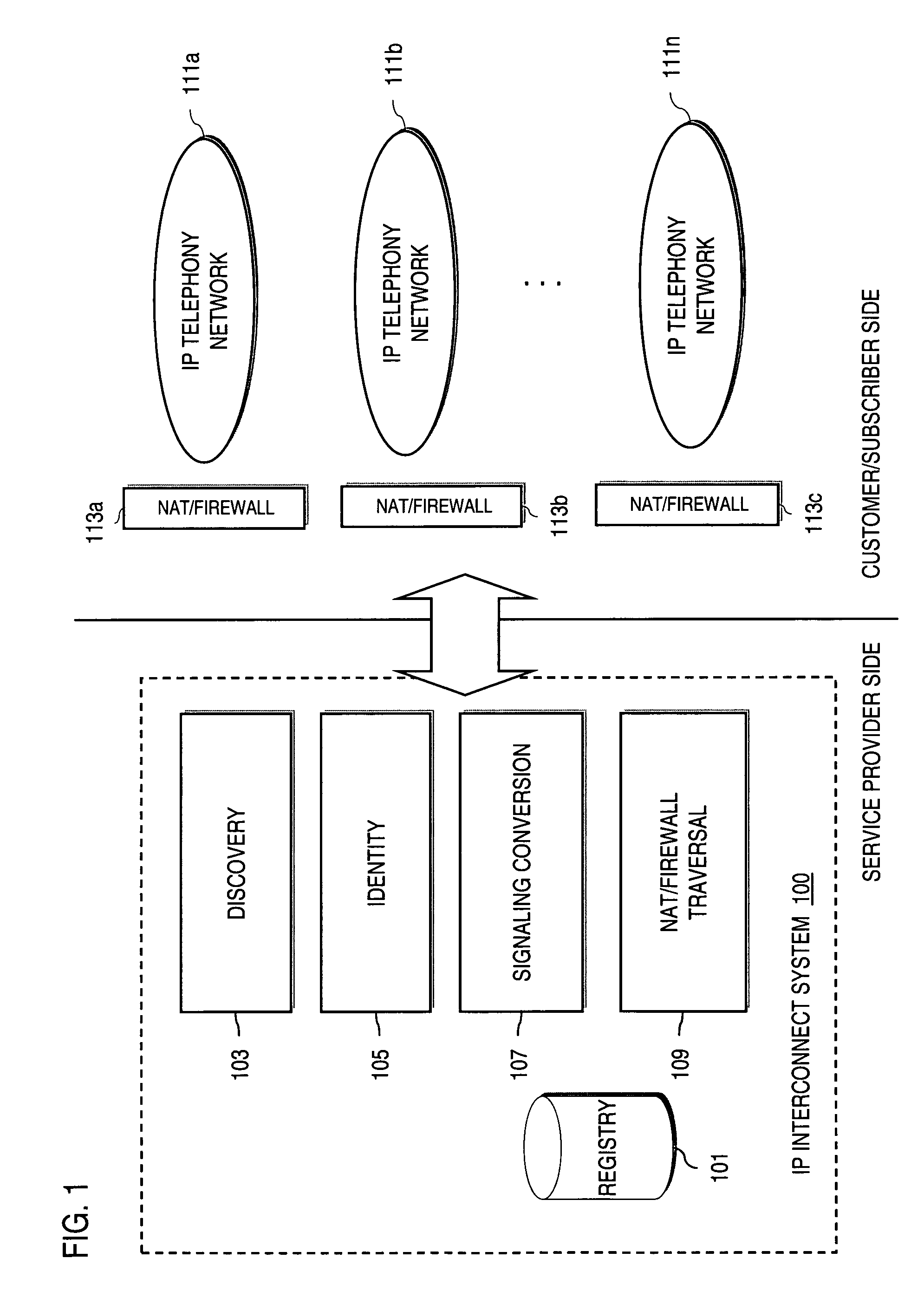
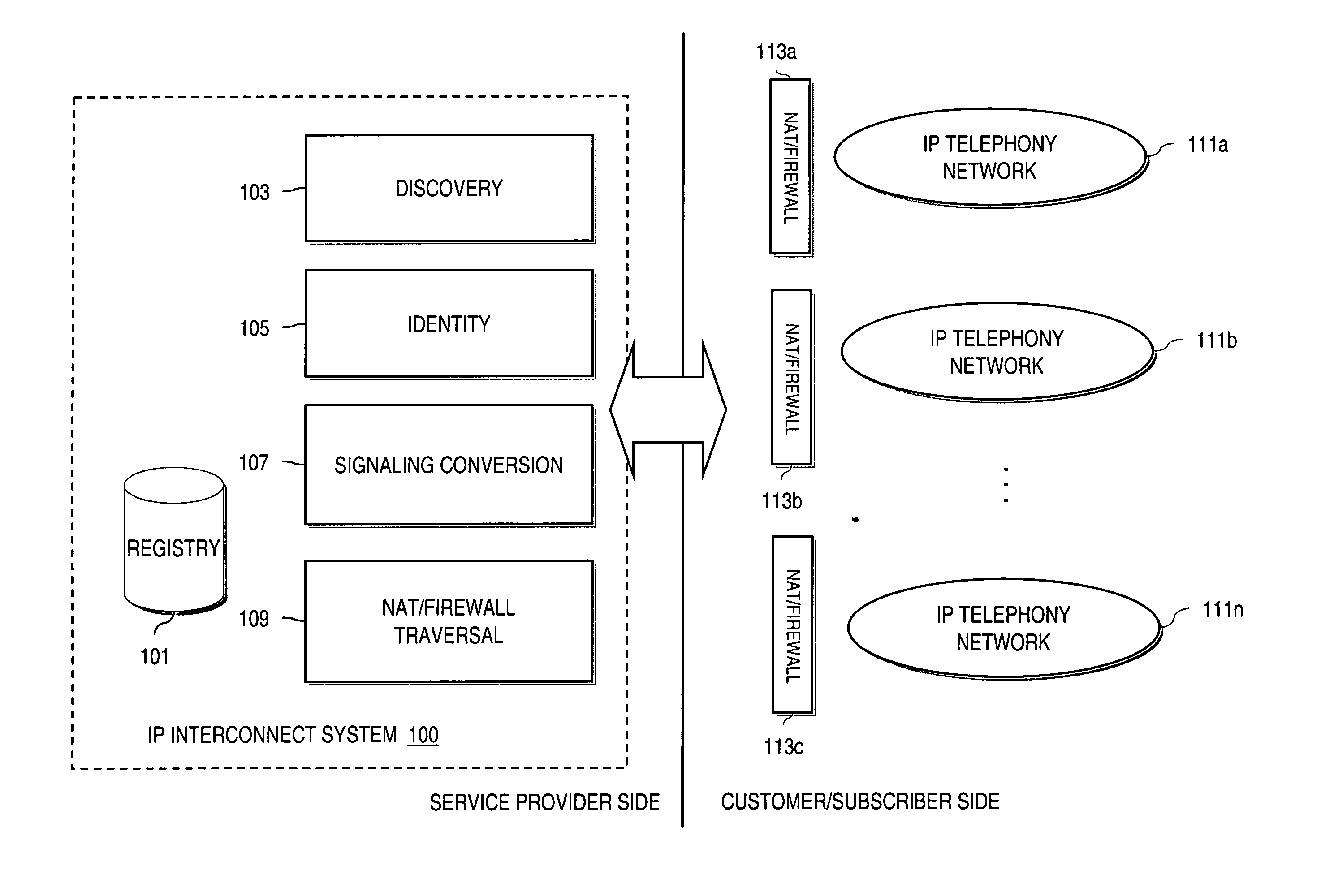
Method and system for providing secure credential storage to support interdomain traversal
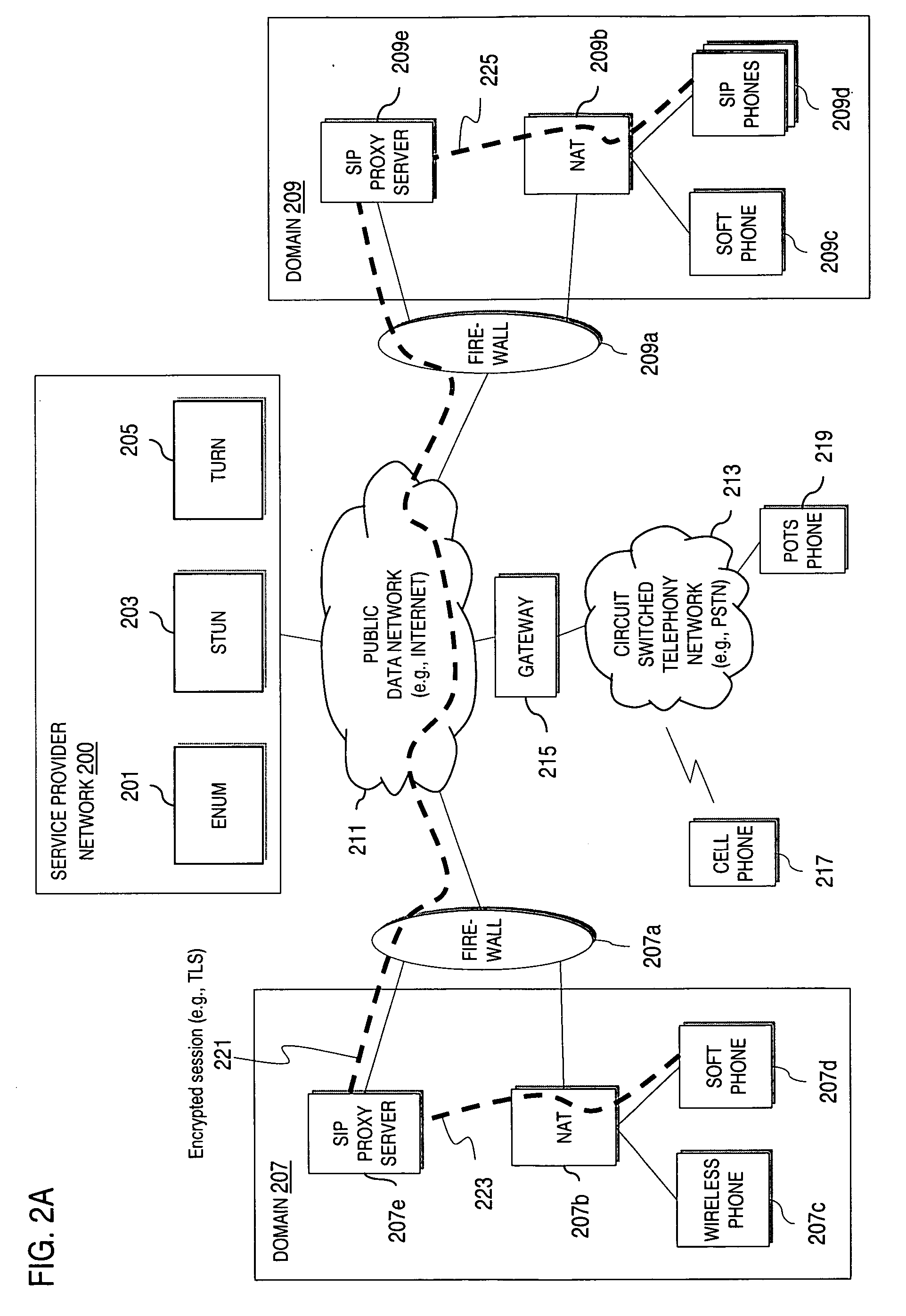
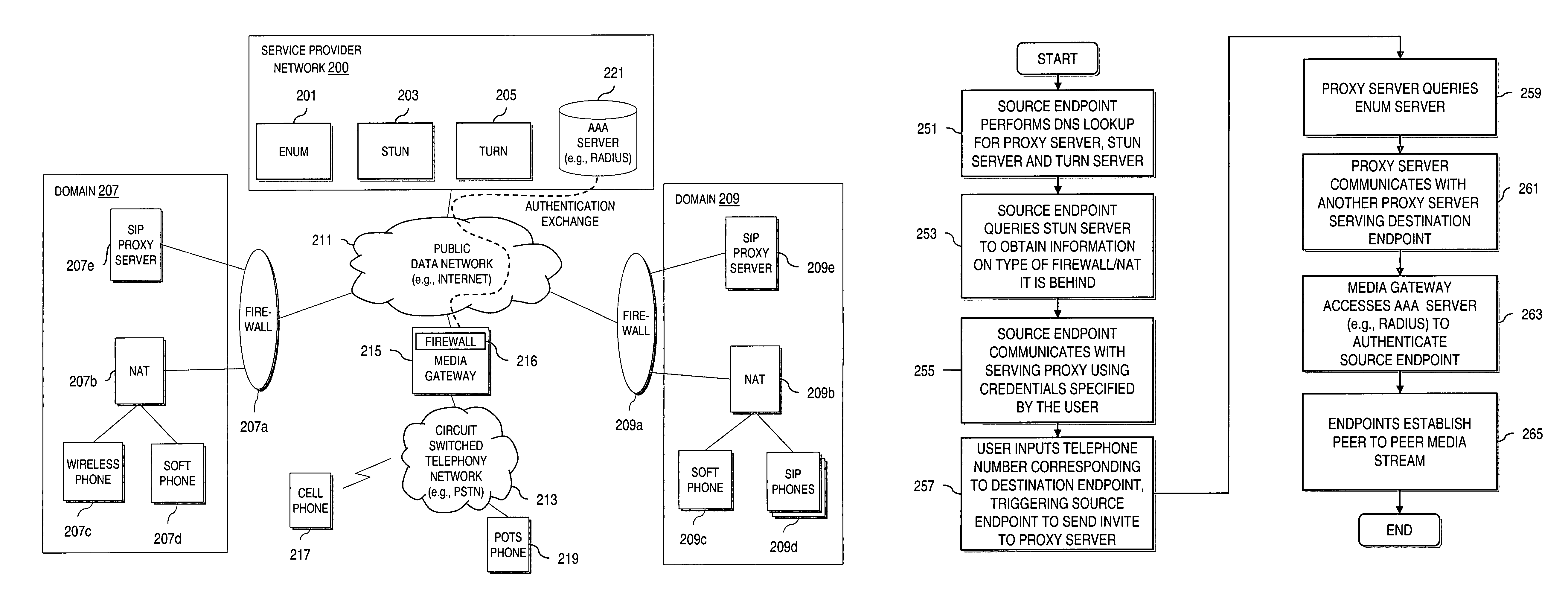
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A request is received from a first endpoint of a first domain for establishing a communication session with a second endpoint of a second domain. Encrypted user credential information is retrieved from a credentials database resident within the first domain, wherein the encrypted user credential includes a password associated with a user associated with the first endpoint. Further, the encrypted user credential information is transmitted to a tunneling server in response to the request, wherein the tunneling server is configured to selectively setup a tunnel to support the communication session based on the encrypted user credential information. The tunnel traverses a first firewall and a first network address translator of the first domain and a second firewall and a second network address translator of the second domain to reach the second endpoint.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
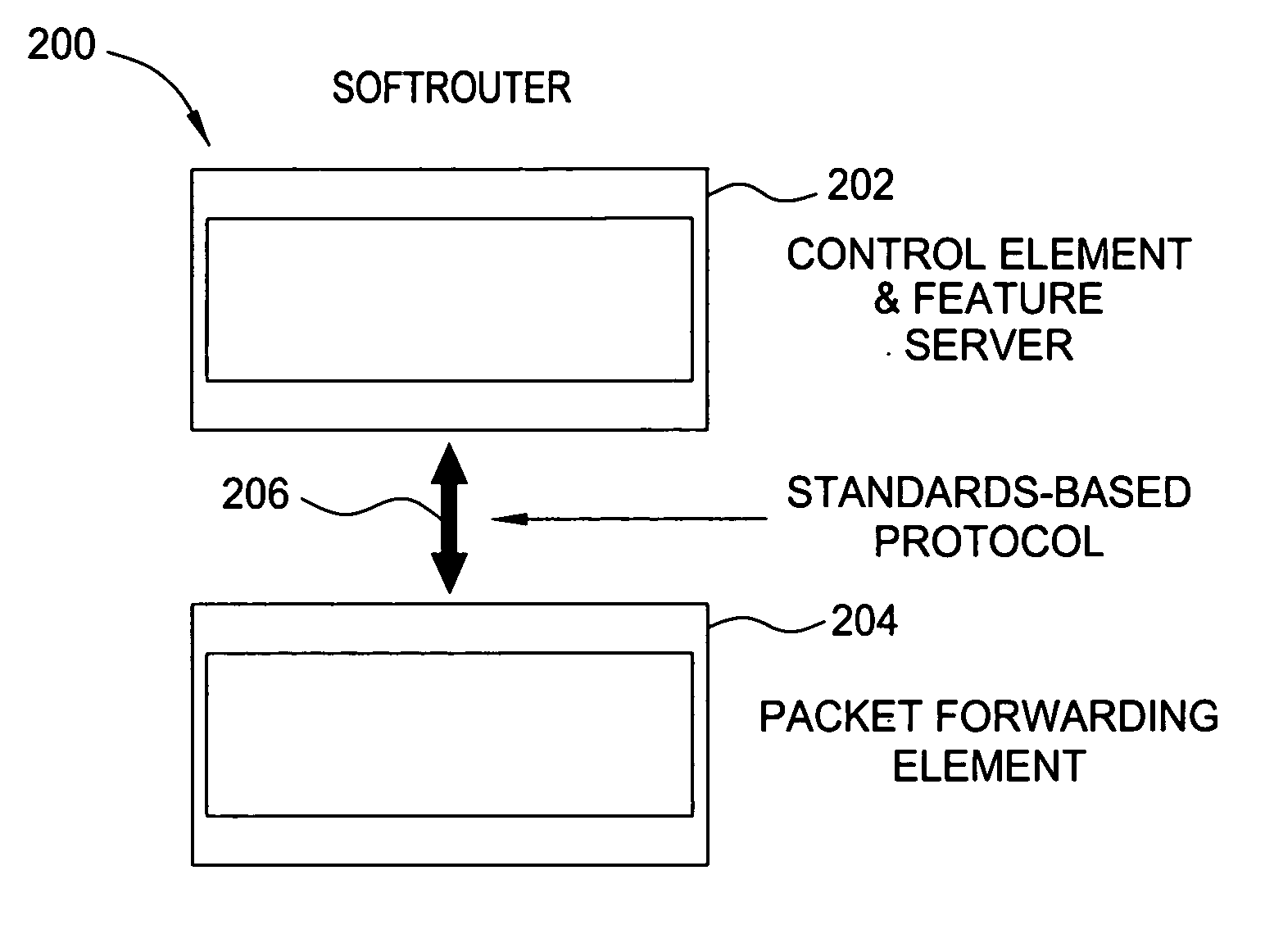
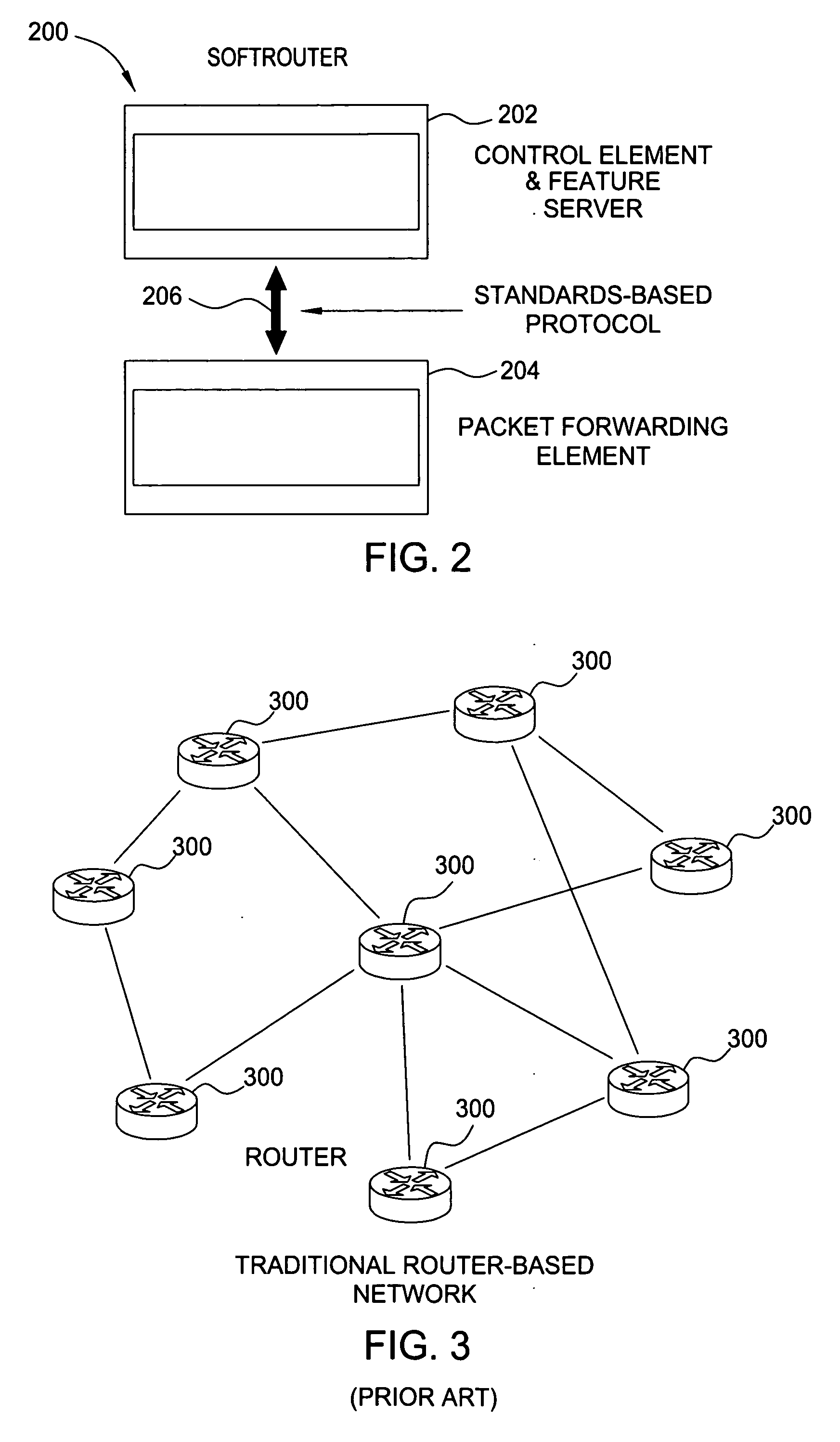
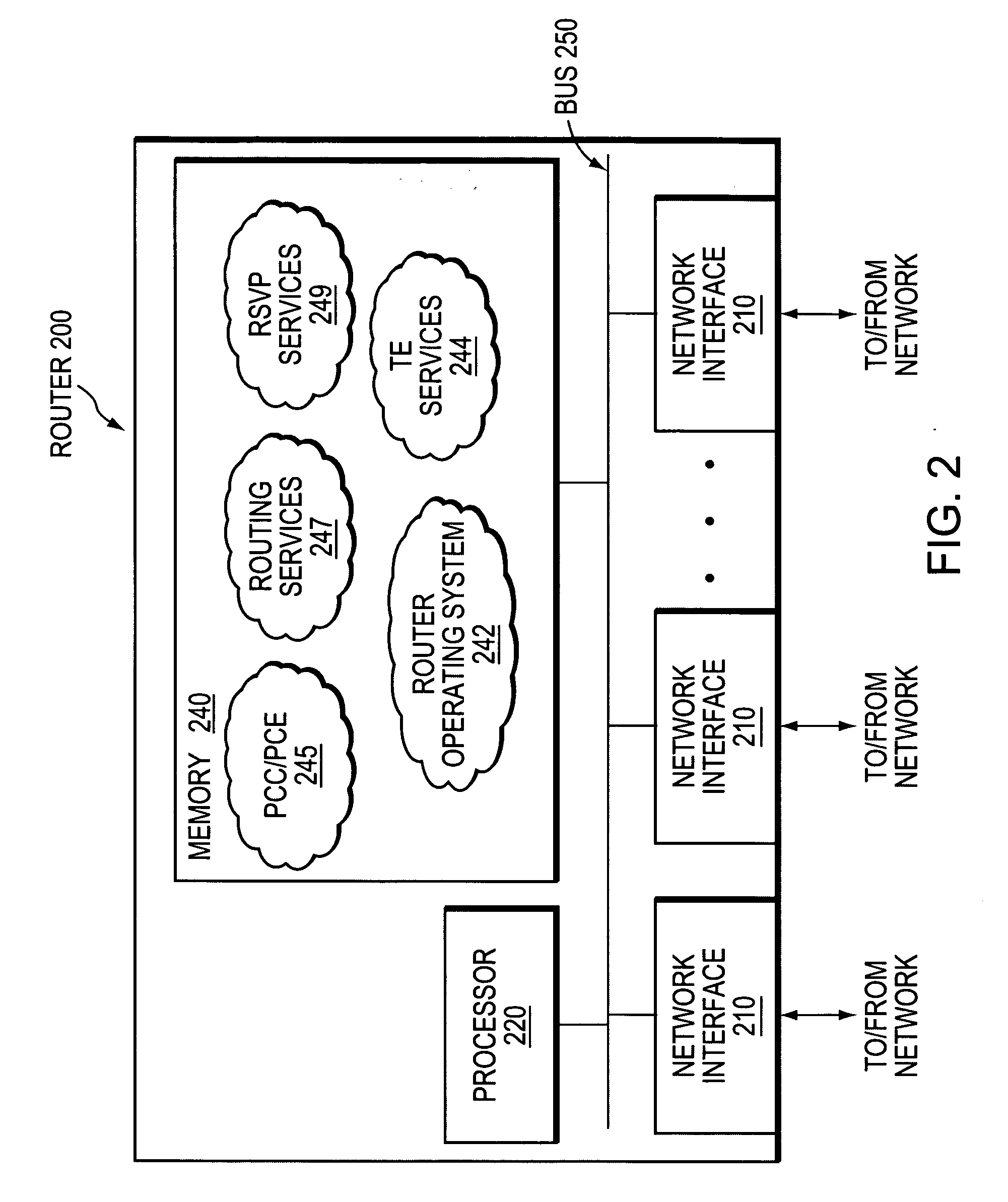
Softrouter protocol disaggregation
ActiveUS20060092940A1Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationFailoverRate of convergence
A SoftRouter architecture deconstructs routers by separating the control entities of a router from its forwarding components, enabling dynamic binding between them. In the SoftRouter architecture, control plane functions are aggregated and implemented on a few smart servers which control forwarding elements that are multiple network hops away. A dynamic binding protocol performs network-wide control plane failovers. Network stability is improved by aggregating and remotely hosting routing protocols, such as OSPF and BGP. This results in faster convergence, lower protocol messages processed, and fewer route changes following a failure. The SoftRouter architecture includes a few smart control entities that manage a large number of forwarding elements to provide greater support for network-wide control. In the SoftRouter architecture, routing protocols operate remotely at a control element and control one or more forwarding elements by downloading the forwarding tables, etc. into the forwarding elements. Intra-domain routing and inter-domain routing are also included.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and system for providing voice over IP managed services utilizing a centralized data store
ActiveUS20070036143A1Interconnection arrangementsData switching by path configurationVoice over IPData memory
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A centralized data store, maintained by a service provider, stores one or more user identifiers and an associated directory number. The centralized data store also stores routing information including one or more communication paths corresponding to the user identifier, wherein the routing information includes a data path or a circuit-switched path for establishing a call to the user. In response to a request for establishing the call to the directory number, the data store retrieves the routing information for use to establish the call.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
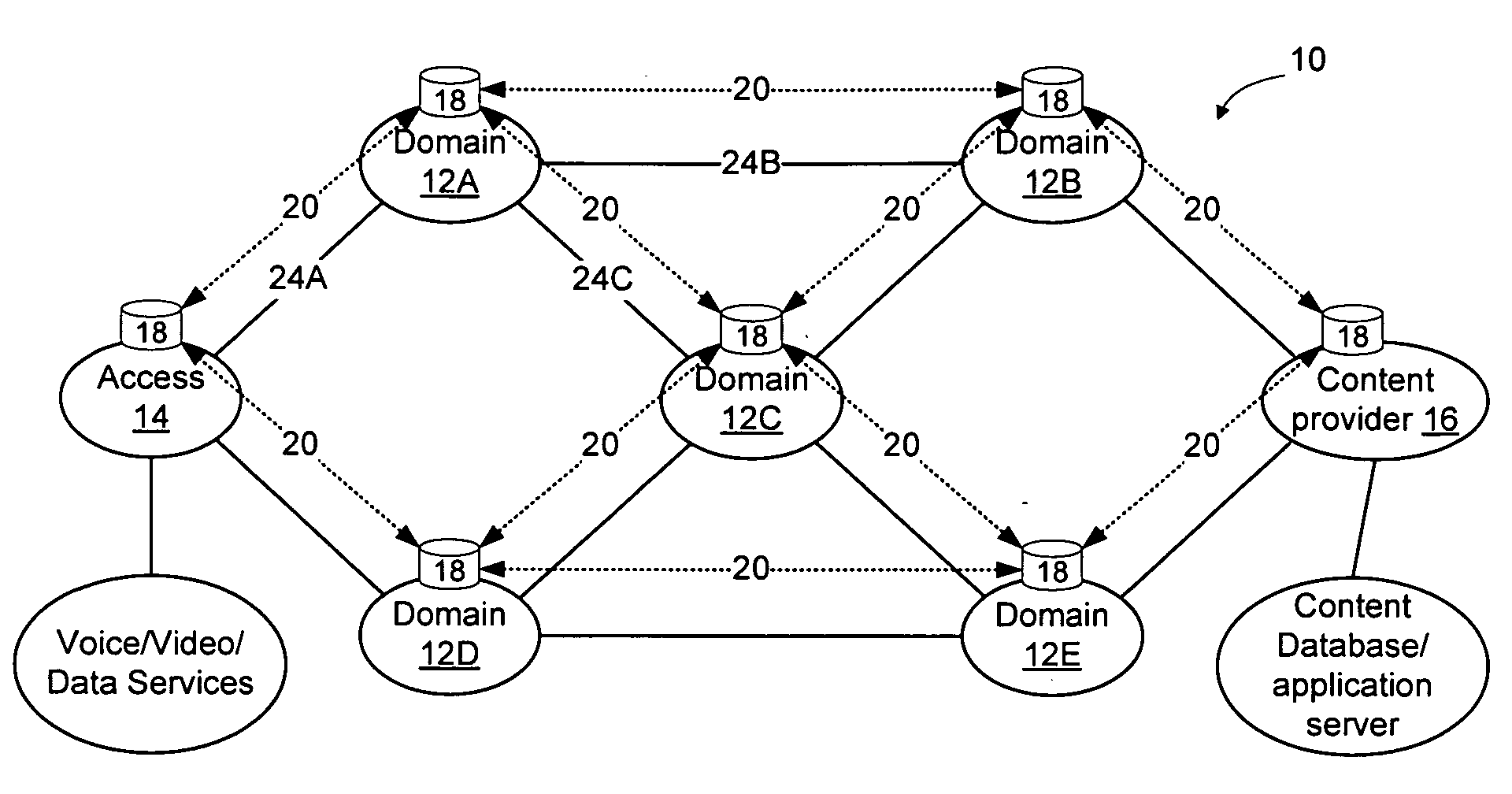
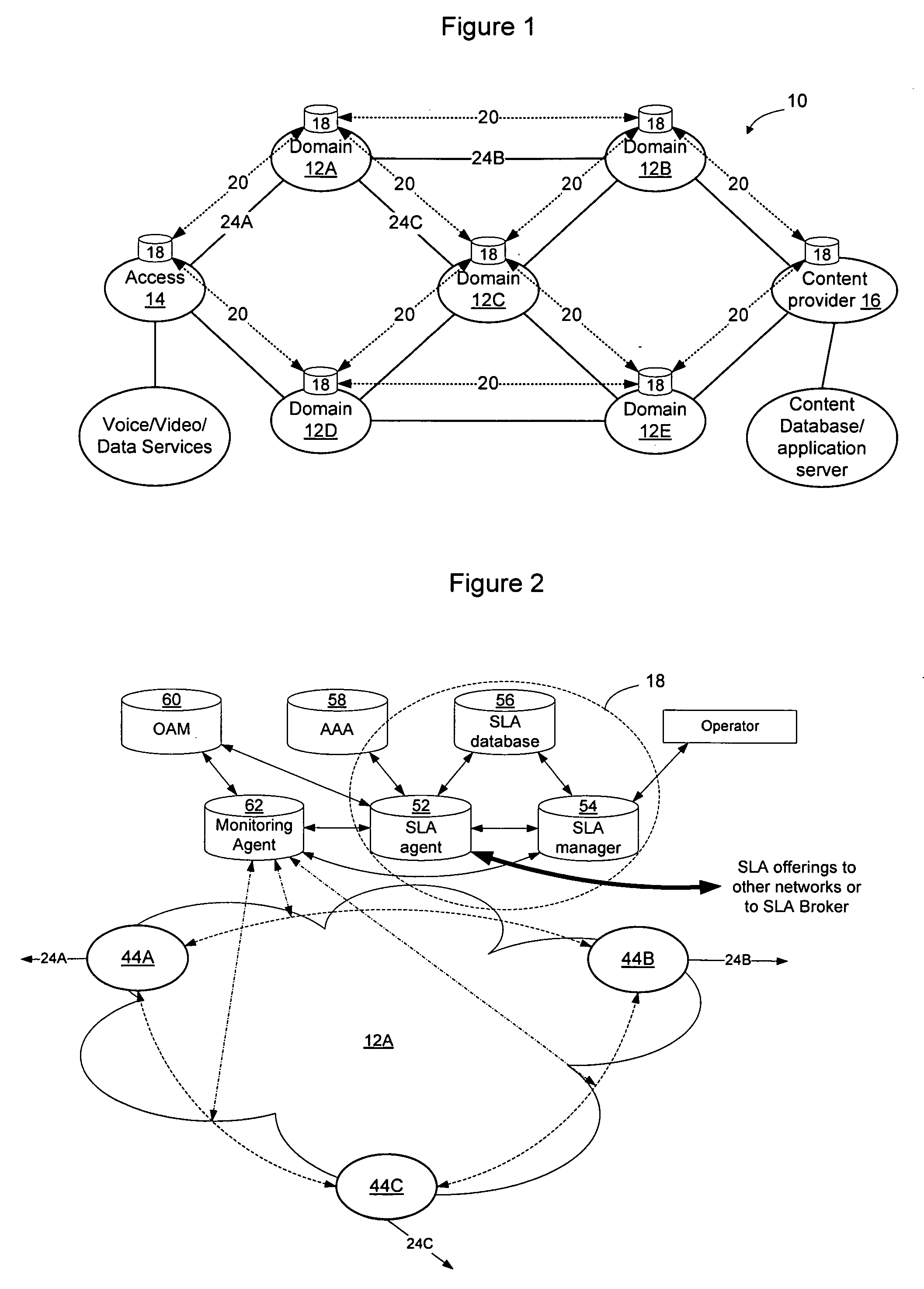
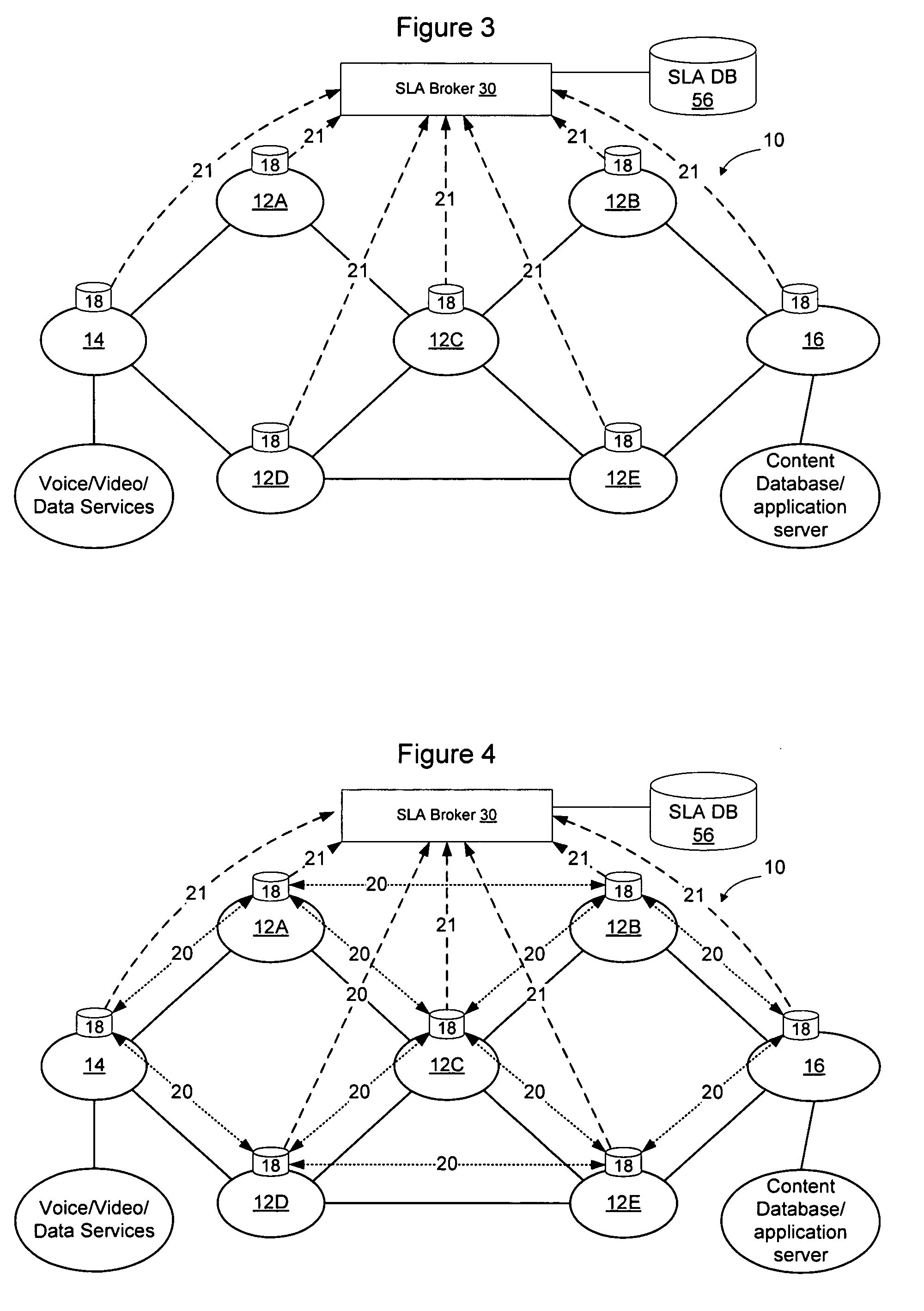
Method and apparatus for discovering, negotiating, and provisioning end-to-end SLAs between multiple service provider domains
Domains (multiple collaborating service providers) create service offerings between pairs of edge nodes that interconnect with other domains in the network. The service offerings may specify the available bandwidth, quality of service, reliability, available security, price, subscriber and service contextual specific and other SLA information. When a new service is to be created, the service definition is used along with information about the available service offerings to determine a set of networks to implement the service. Information associated with the service offerings may be flooded to all other networks. Alternatively, the service offering information may be provided to a trusted third party (SLA broker) which may provide SLA services on the network to select sets of domains to implement inter-domain services, and may also proxy to set up the service for the SLA requesting party. A hybrid approach may also be used wherein some SLA information is flooded and other information is retained in secret and provided only to the SLA broker.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
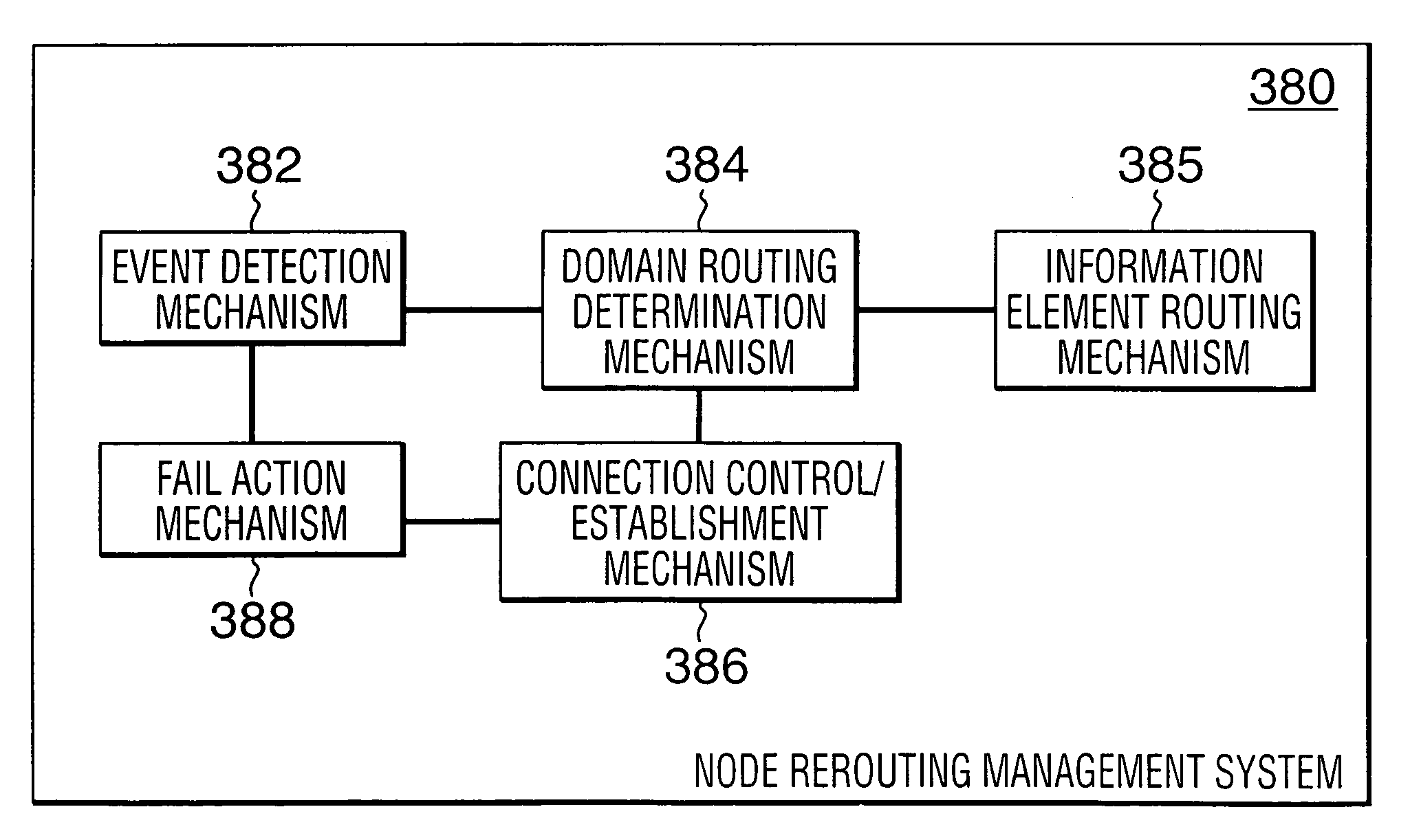
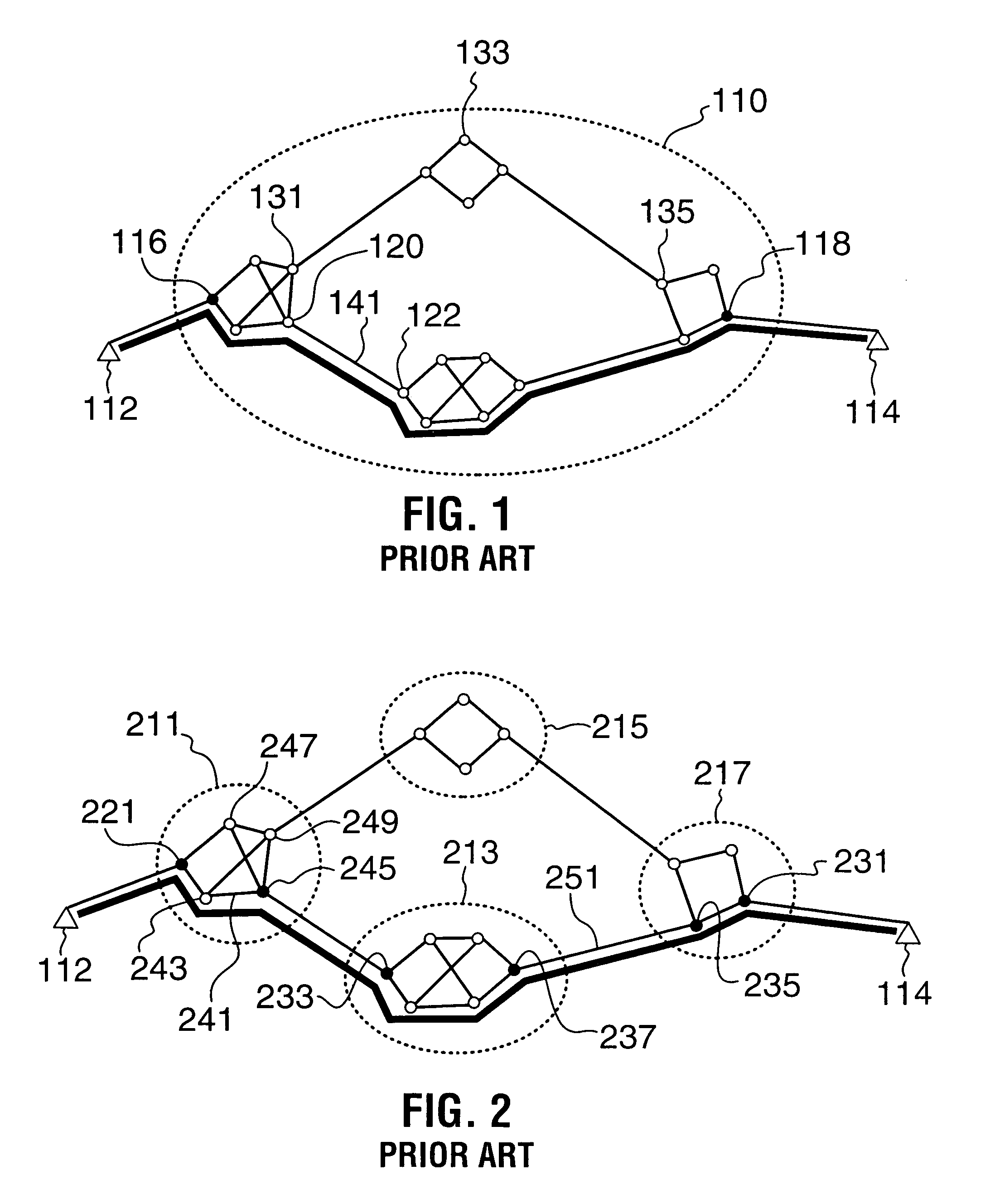
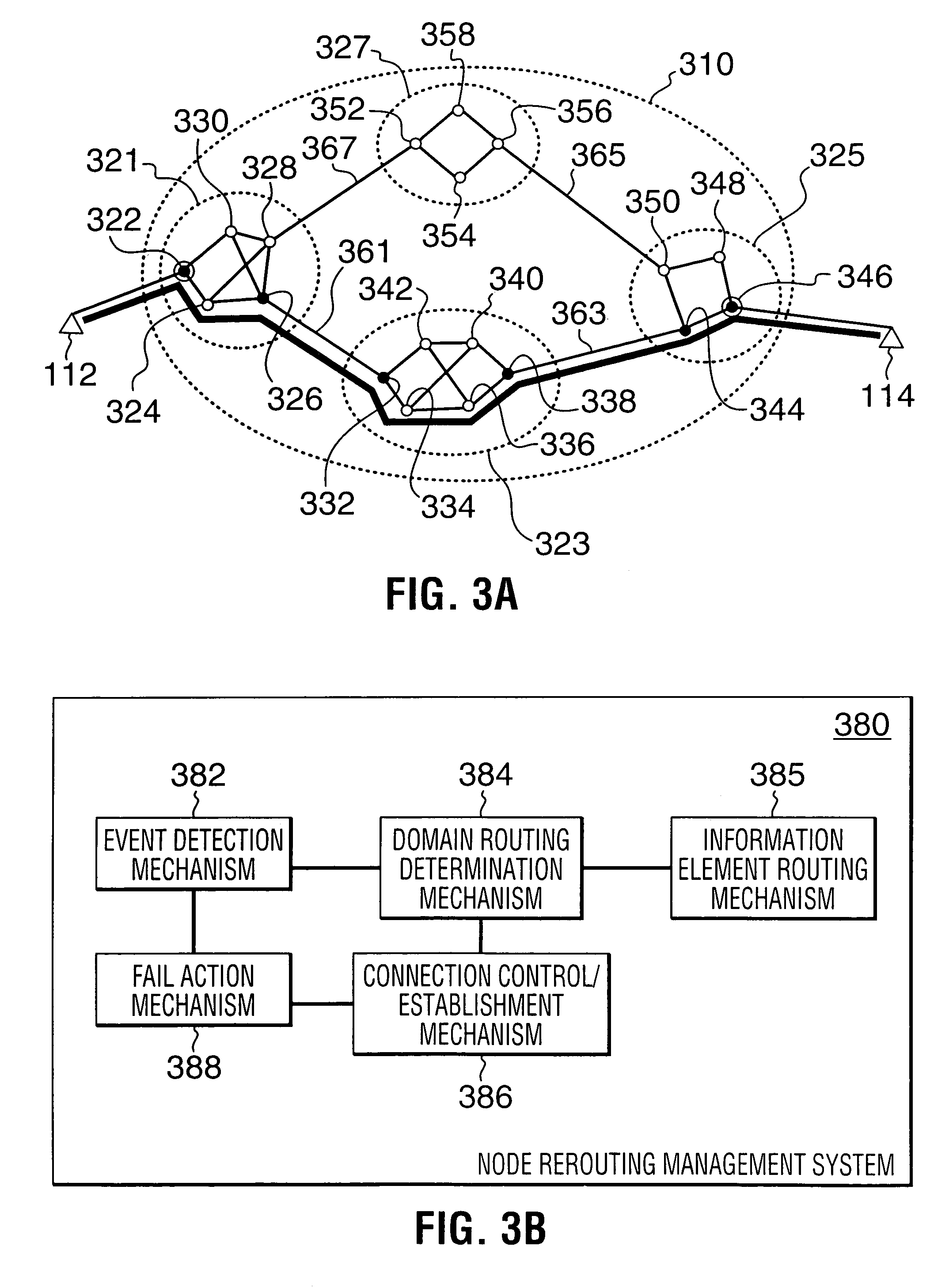
Rerouting in connection-oriented communication networks and communication systems
InactiveUS7180866B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionDouble faultCommunications system
A Private Network-Network Interface (PNNI) network including interconnected nodes is defined as a single rerouting domain (“global domain”) and the global domain is further defined by multiple divided domains (“local domains”). Each of the local domains is defined to include multiple nodes that are included in the network. Connection recovery and path optimization in the global domain (the entire PNNI network) are performed in accordance with a global rerouting protocol. The global rerouting protocol is a modification of the standard Domain-Based Rerouting (DBR) protocol, by adding information elements of domain identifier, rerouting for the global domain. The DBR protocol does not support the connection recovery from a link failure between local domains (“inter-domains”) and the global path optimization. The global rerouting method is capable of connection recovery and path optimization outside of any rerouting local domains. The global rerouting provides double fault recovery within the rerouting domain (“intra-domain”) as covered by the DBR and outside of the domains (“inter-domain”) or when the initial fault recovery within the domain has failed. Also, the global rerouting method provides maximum path optimization across all domains and within the rerouting local domain.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Multiple clock domain microprocessor
ActiveUS20070016817A1High frequencyImprove good performanceEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingComputer scienceInter-domain
A multiple clock domain (MCD) microarchitecture uses a globally-asynchronous, locally-synchronous (GALS) clocking style. In an MCD microprocessor each functional block operates with a separately generated clock, and synchronizing circuits ensure reliable inter-domain communication. Thus, fully synchronous design practices are used in the design of each domain.
Owner:ALBONESI DAVID +5
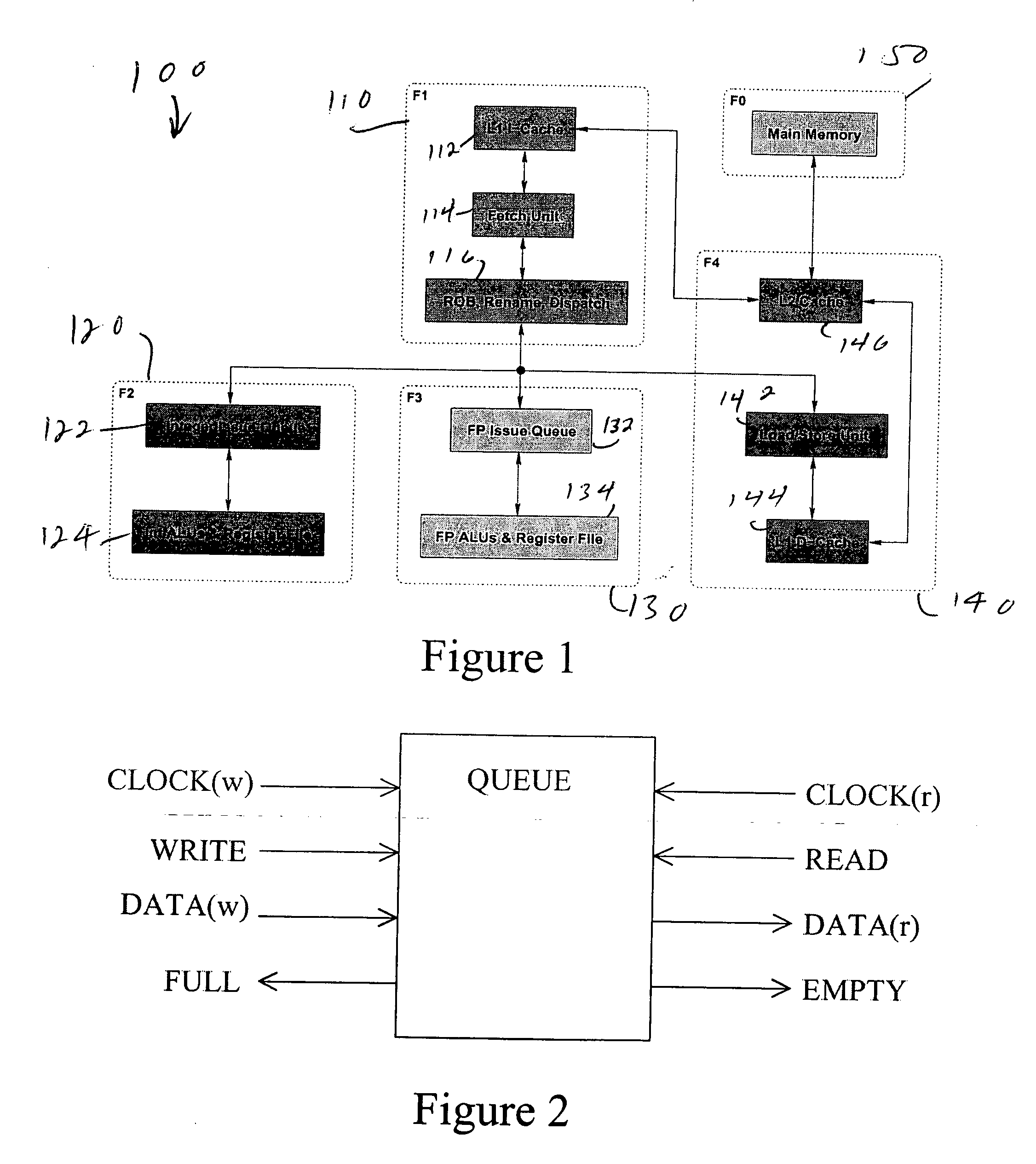
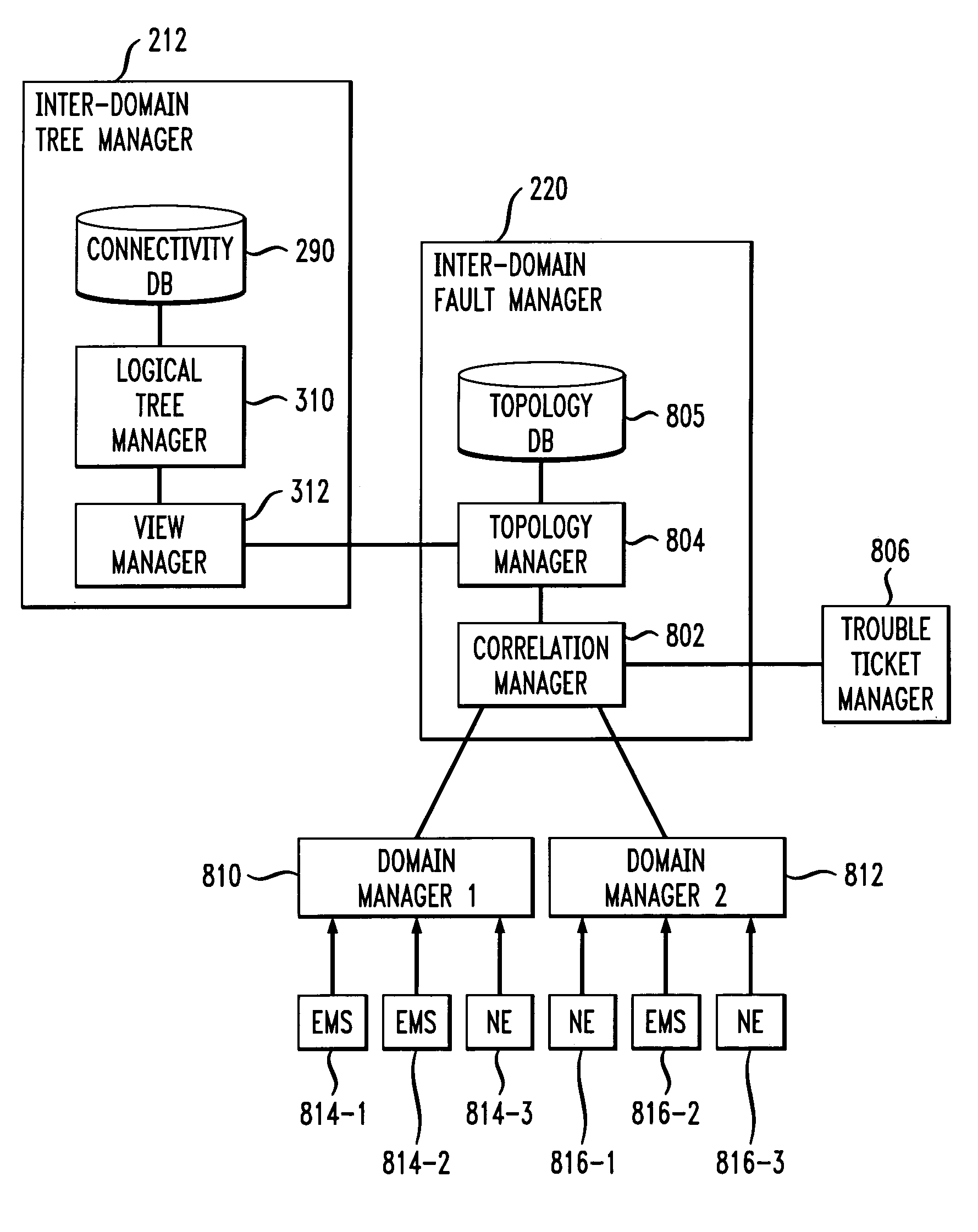
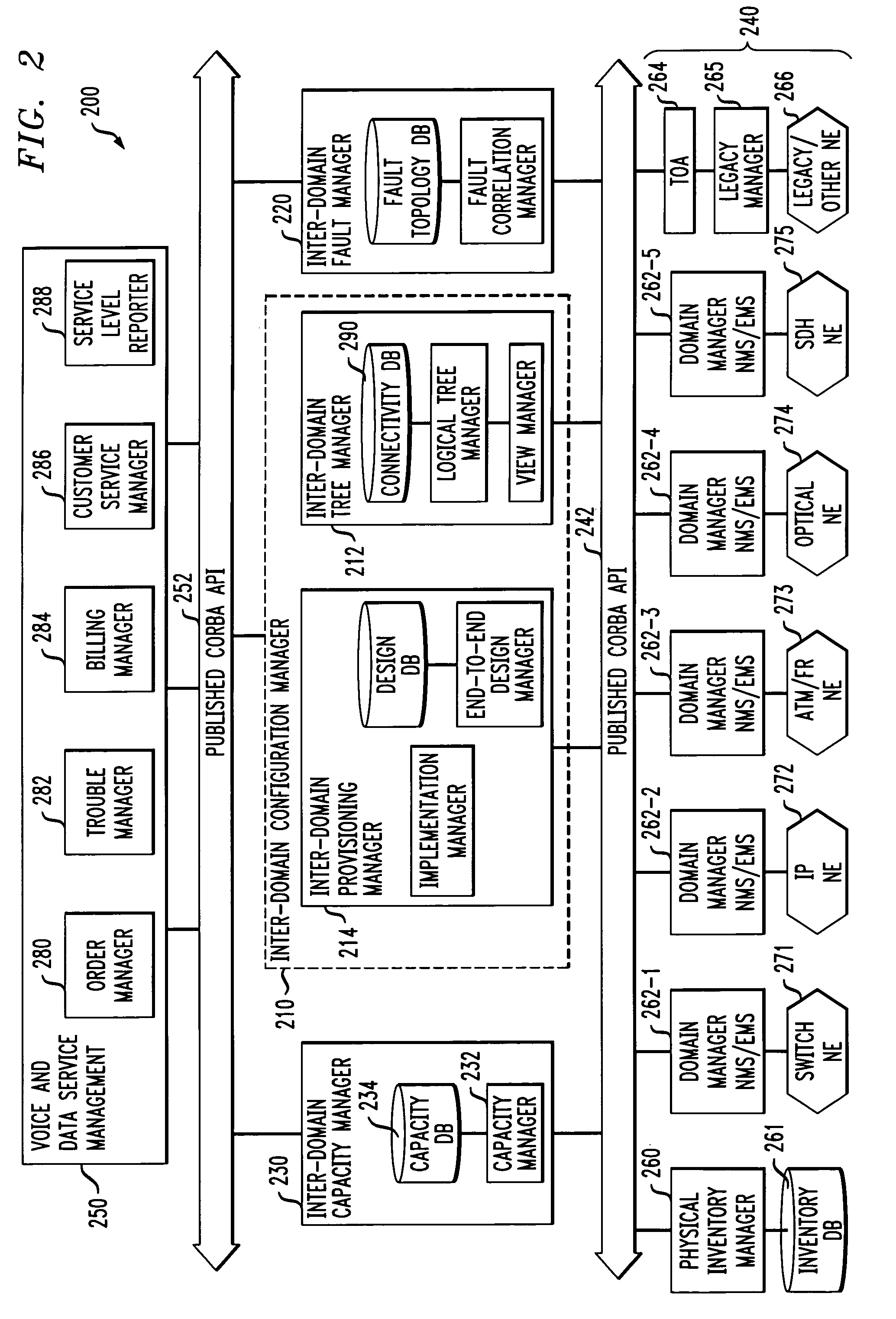
Inter-domain network management system for multi-layer networks
InactiveUS7197546B1High activityEasy maintenanceData processing applicationsTime-division multiplexNetwork managementApplication software
A network management system for a multi-layer network having multiple architectural or technological domains includes an inter-domain configuration manager arranged between a set of one or more network service management applications and a set of network element domain managers, each of the domain managers being associated with a particular domain of the multi-layer network. The configuration manager implements network service design and provisioning functions across the domains of the network in conjunction with stored connectivity information characterizing the multi-layer network. The network management system further includes an inter-domain fault manager and an inter-domain capacity manager, which provide respective fault management and transport capacity management functions across the domains of the multi-layer network. The inter-domain configuration manager, inter-domain fault manager and inter-domain capacity manager may be interfaced to the set of network service management applications and the set of network element domain managers through corresponding published Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
System and method for provisioning of route information in a meshed communications network
InactiveUS20050105524A1Quantity minimizationReduce overheadData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionCommunications systemNetwork addressing
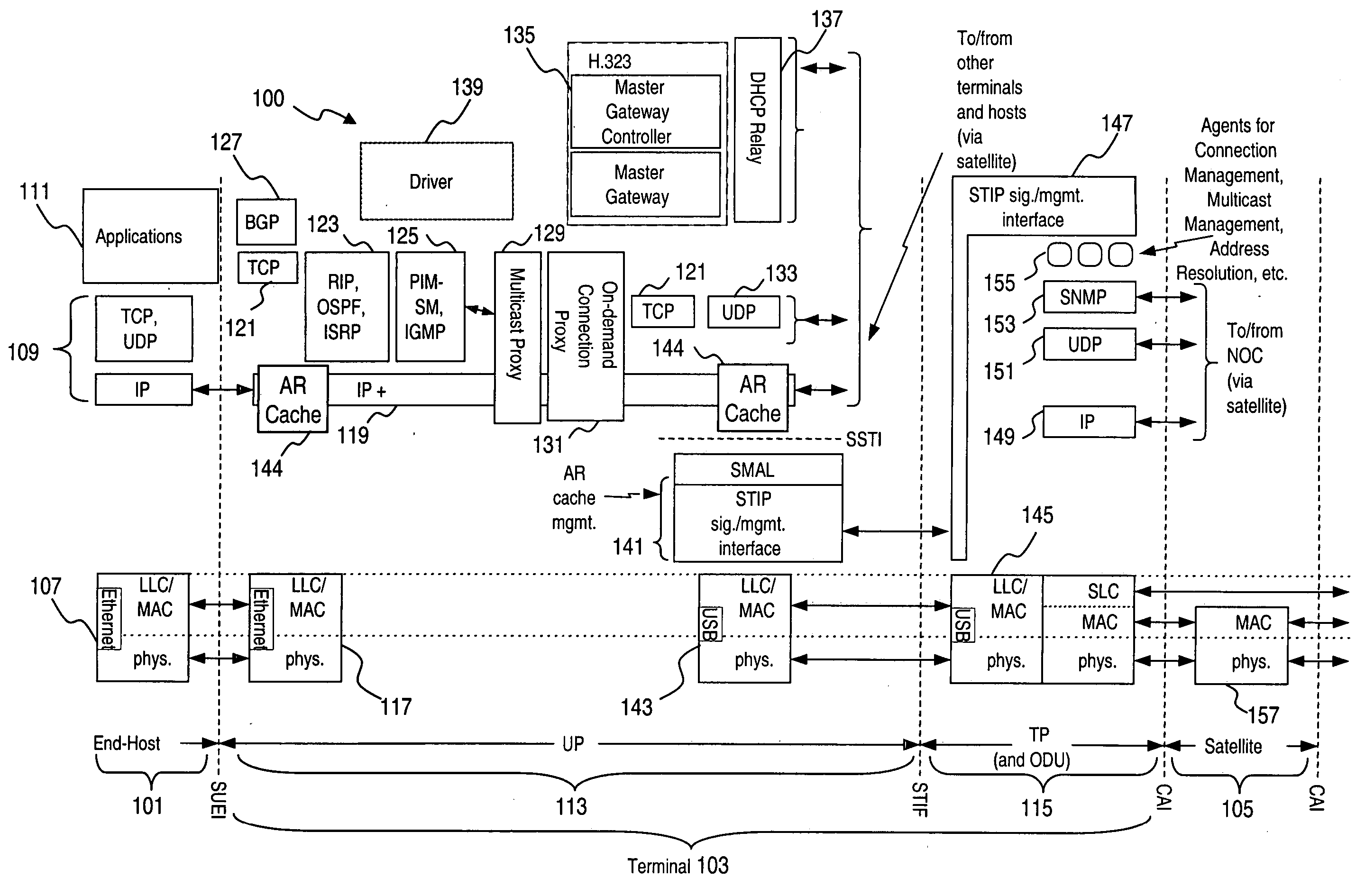
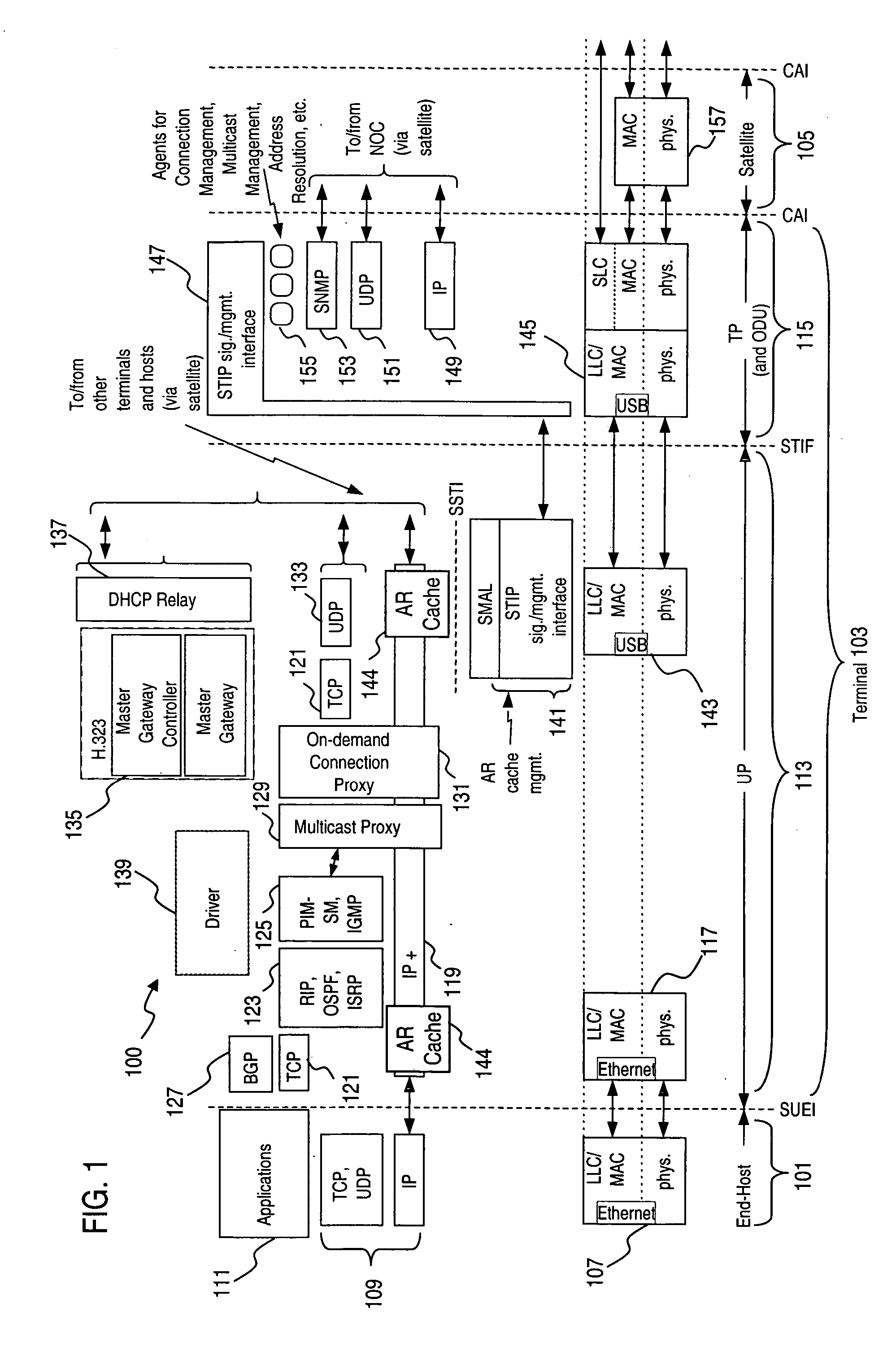
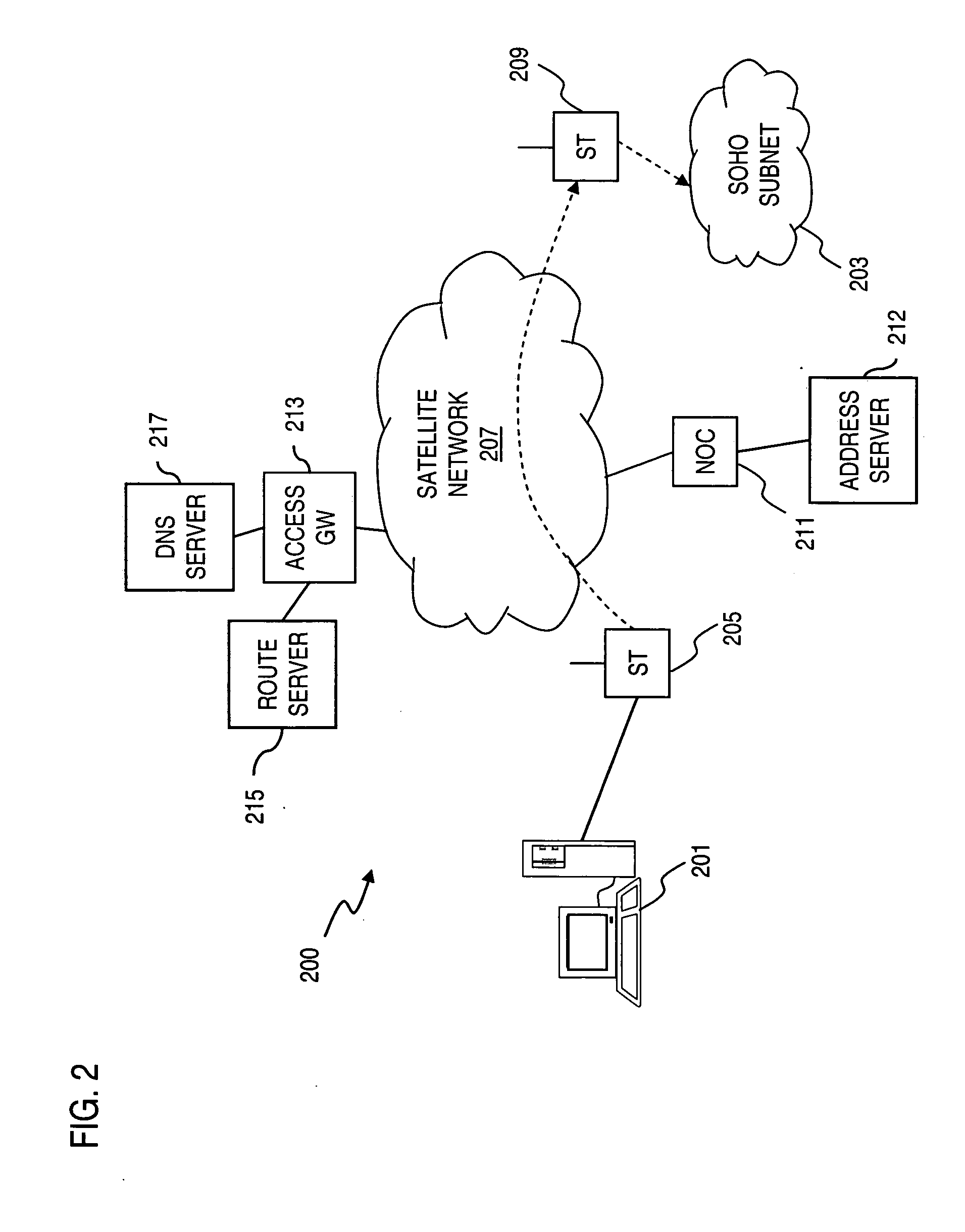
An approach for supporting inter-domain routing of a packet is provided. A communication system includes a plurality of terminals having full meshed connectivity, in which each of the terminals is configured to route the packet to one of a plurality of address domains (i.e., terminal is multi-homed) and to notify a source terminal originating the packet of a correct one of the terminals. An address server assigns a network address corresponding to the one address domain based on a destination address associated with the packet, wherein the source terminal routes the packet according to the assigned network address. The present invention has particular applicability to a fully meshed satellite network.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
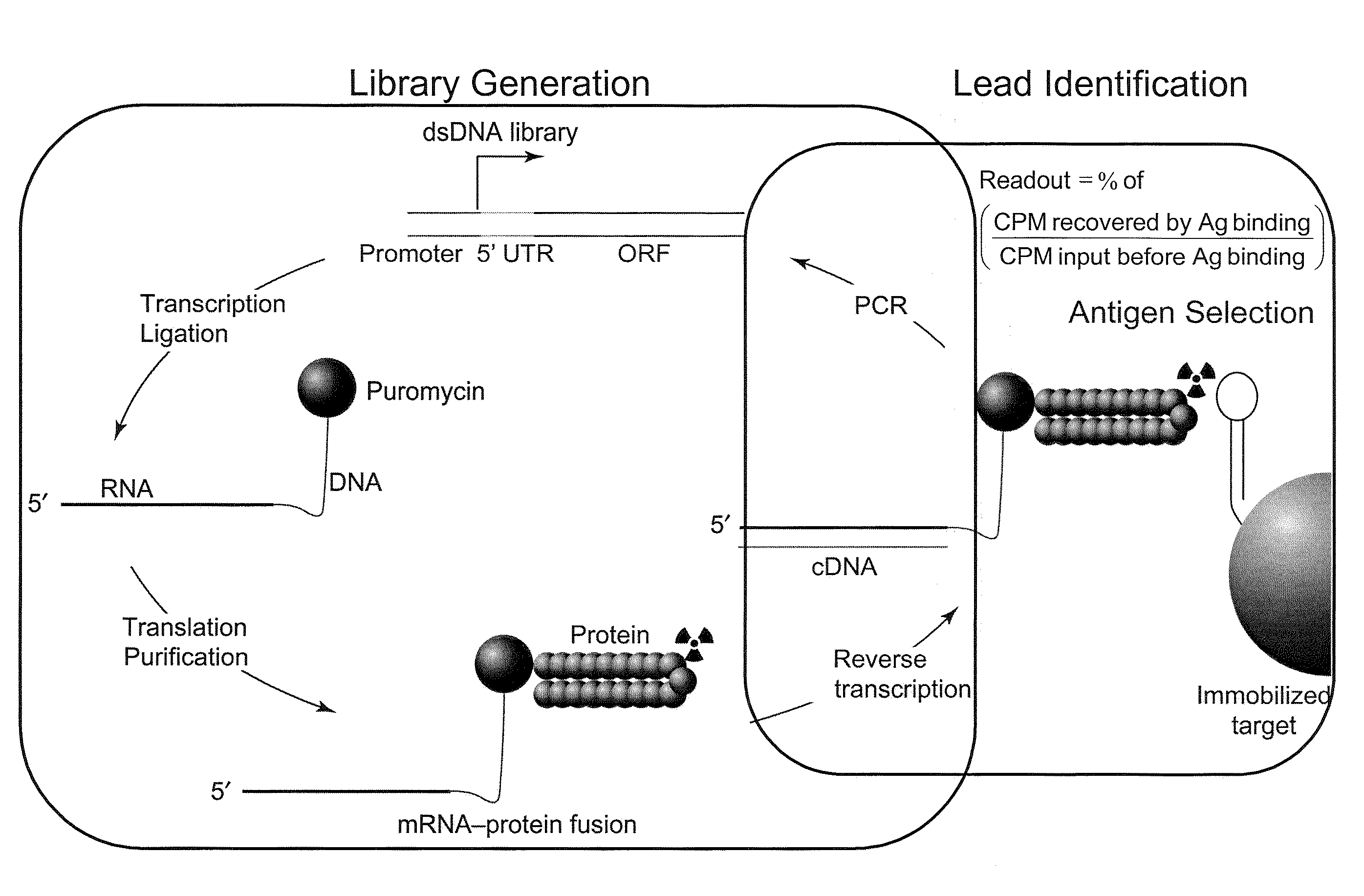
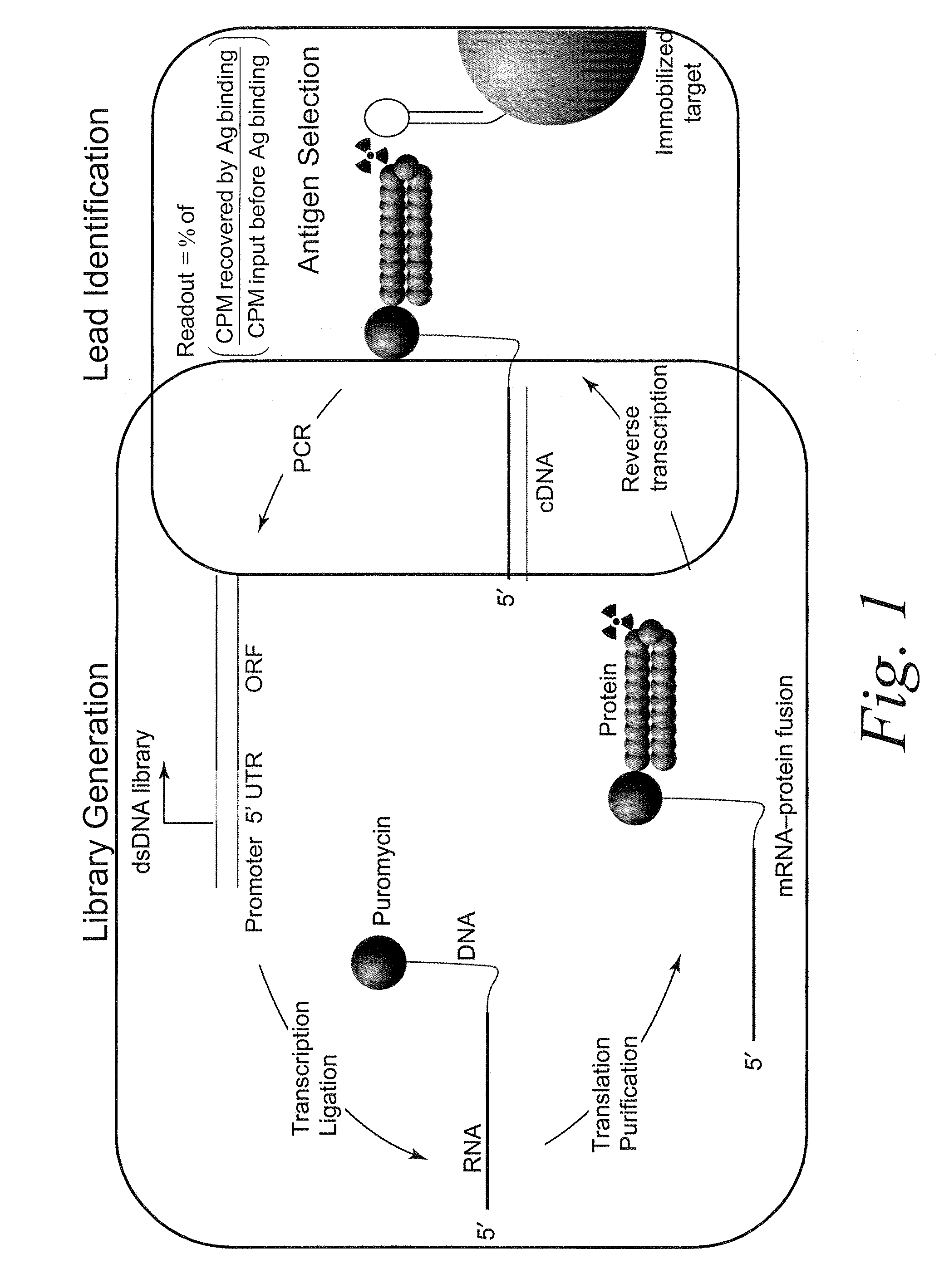
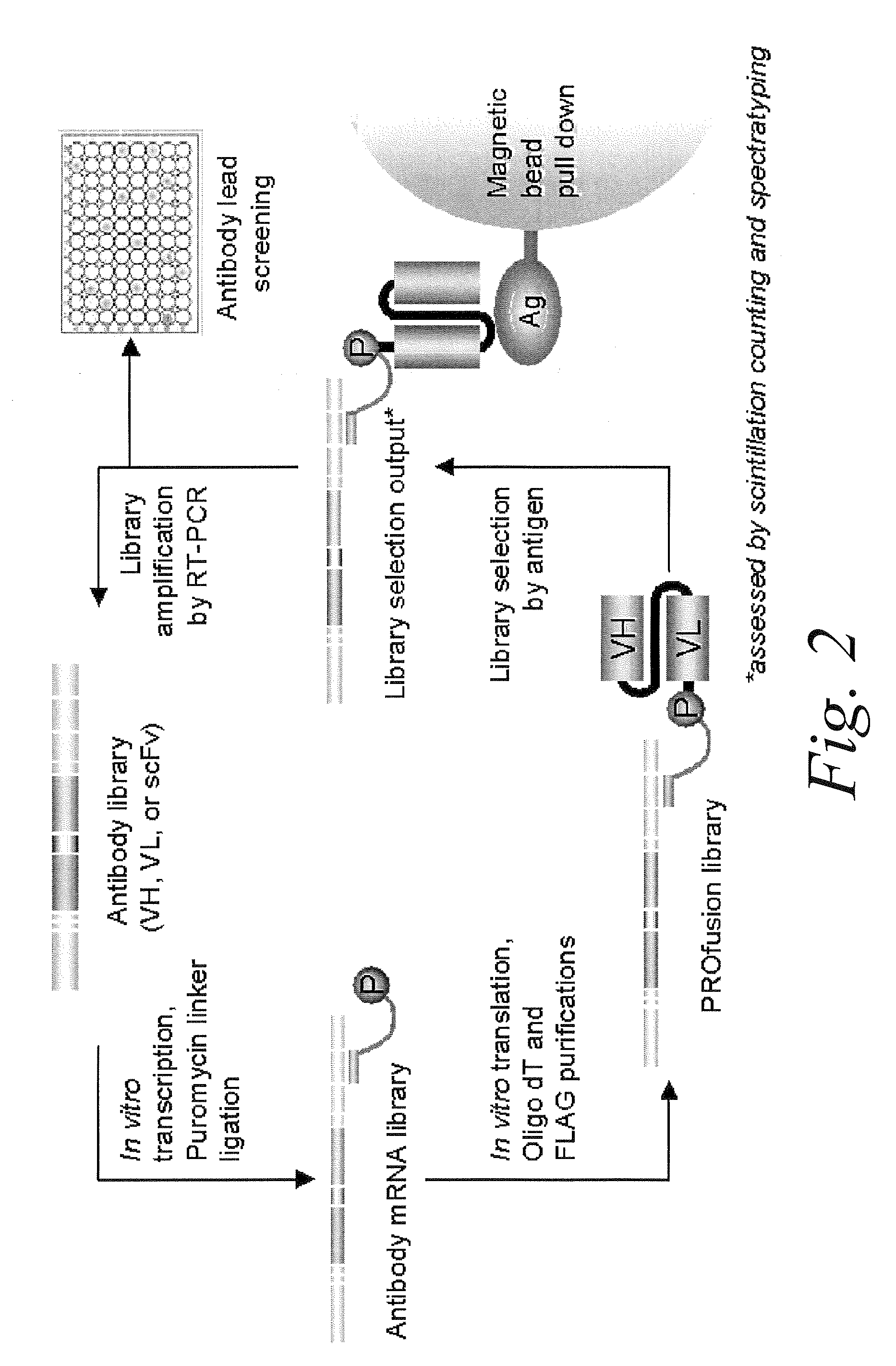
Antibody Libraries
InactiveUS20100099103A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementExpression LibraryScFv Antibodies
The present invention features improved in vitro RNA display libraries to allow reliable expression and selection of scFv antibody molecules from expression libraries. The scFv antibody libraries of the invention contain an optimized, shortened inter-domain linker that improves expression scFv antibody expression. The scFv antibody libraries also include short nucleic acid barcodes that allow for identification of individual library clones, libraries or subsets thereof. Primers for generating, amplifying and spectratyping the scFv antibody libraries of the invention are also provided.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
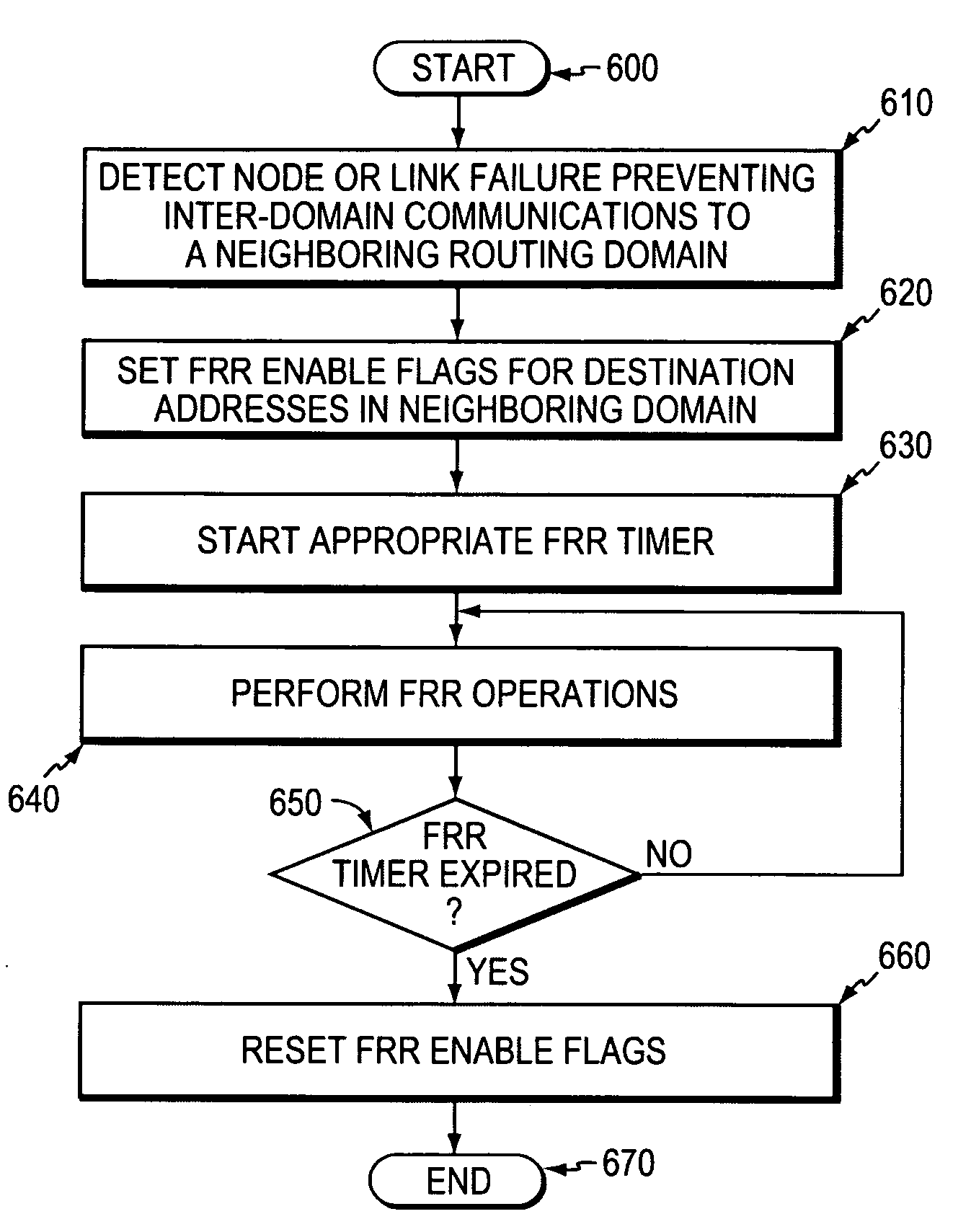
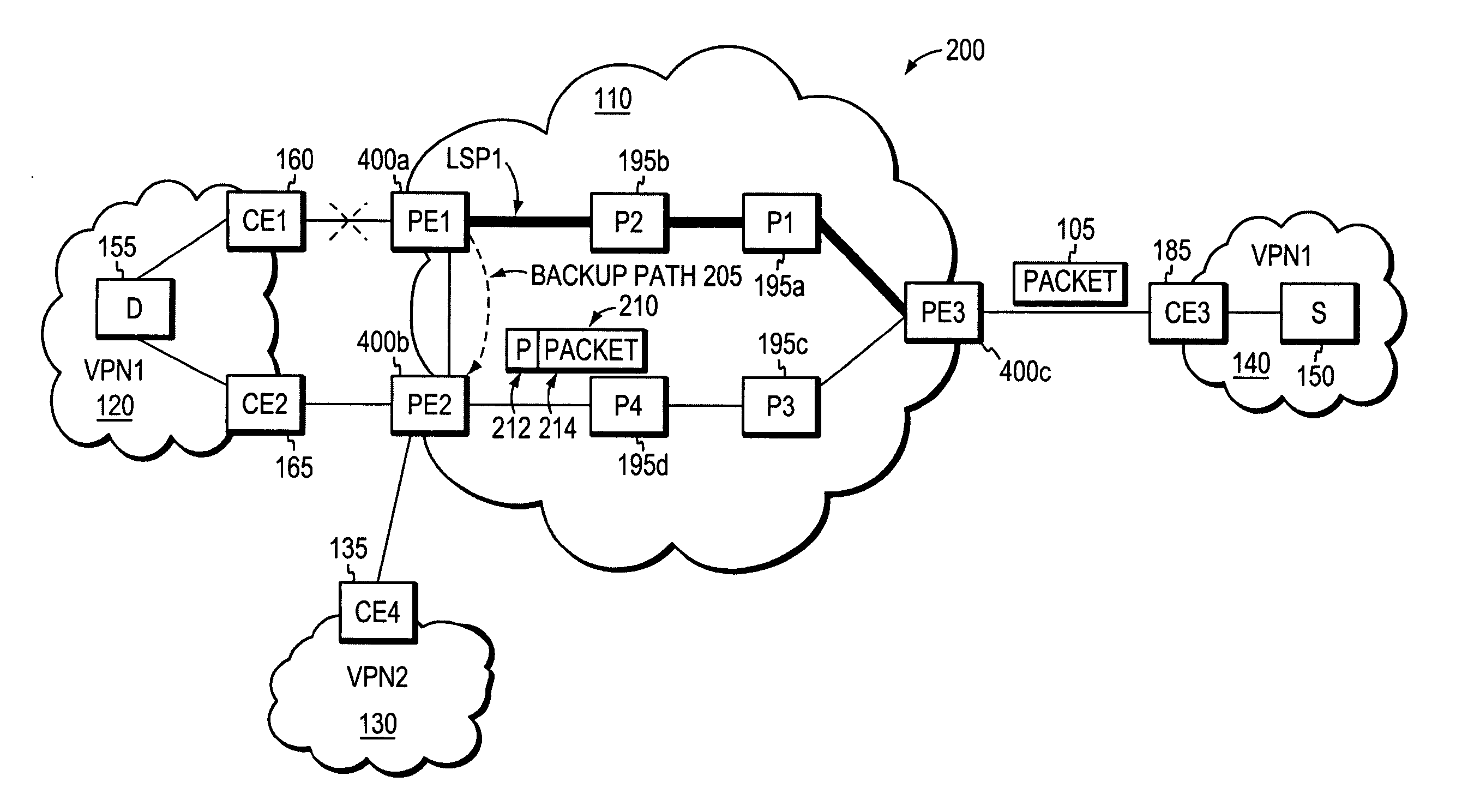
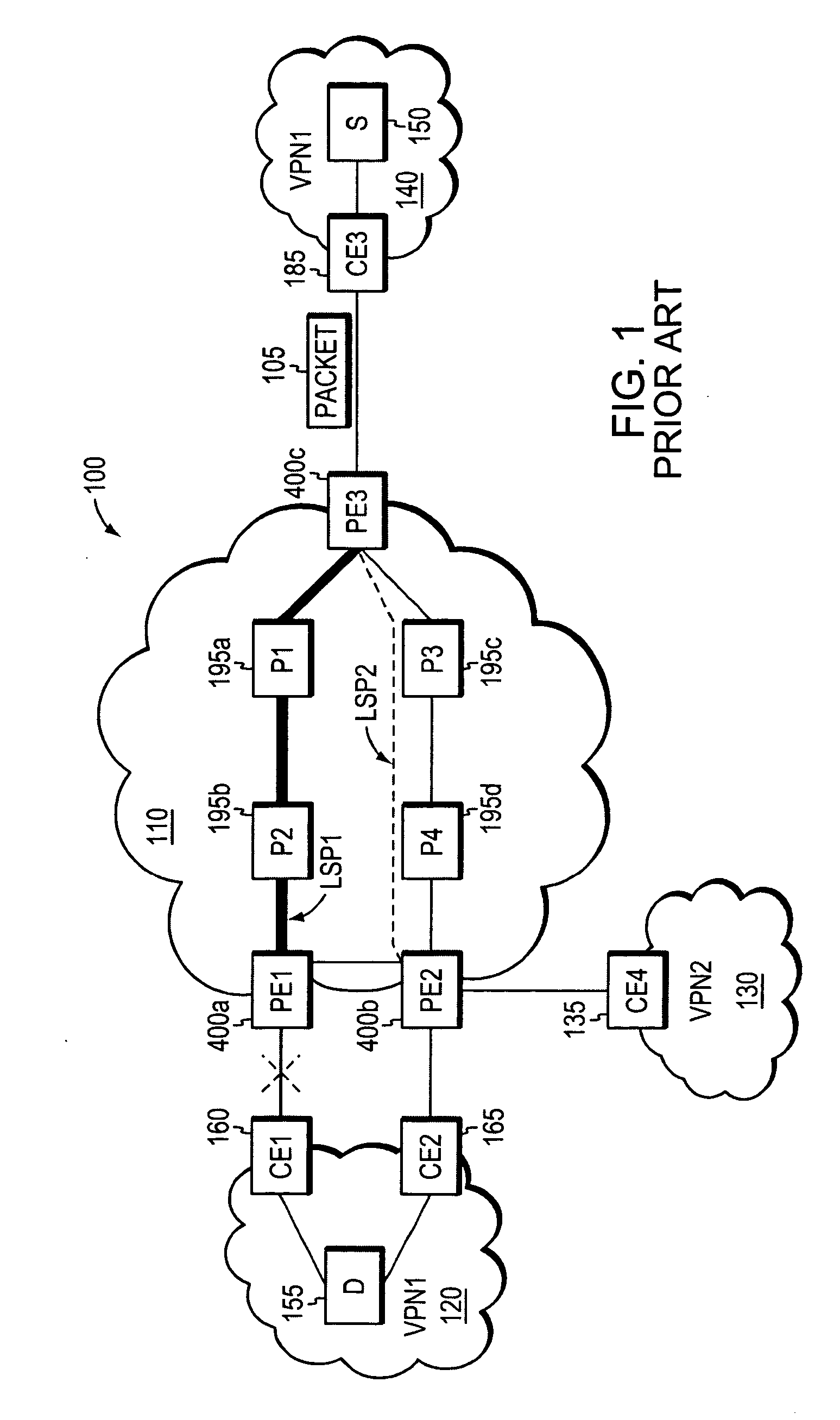
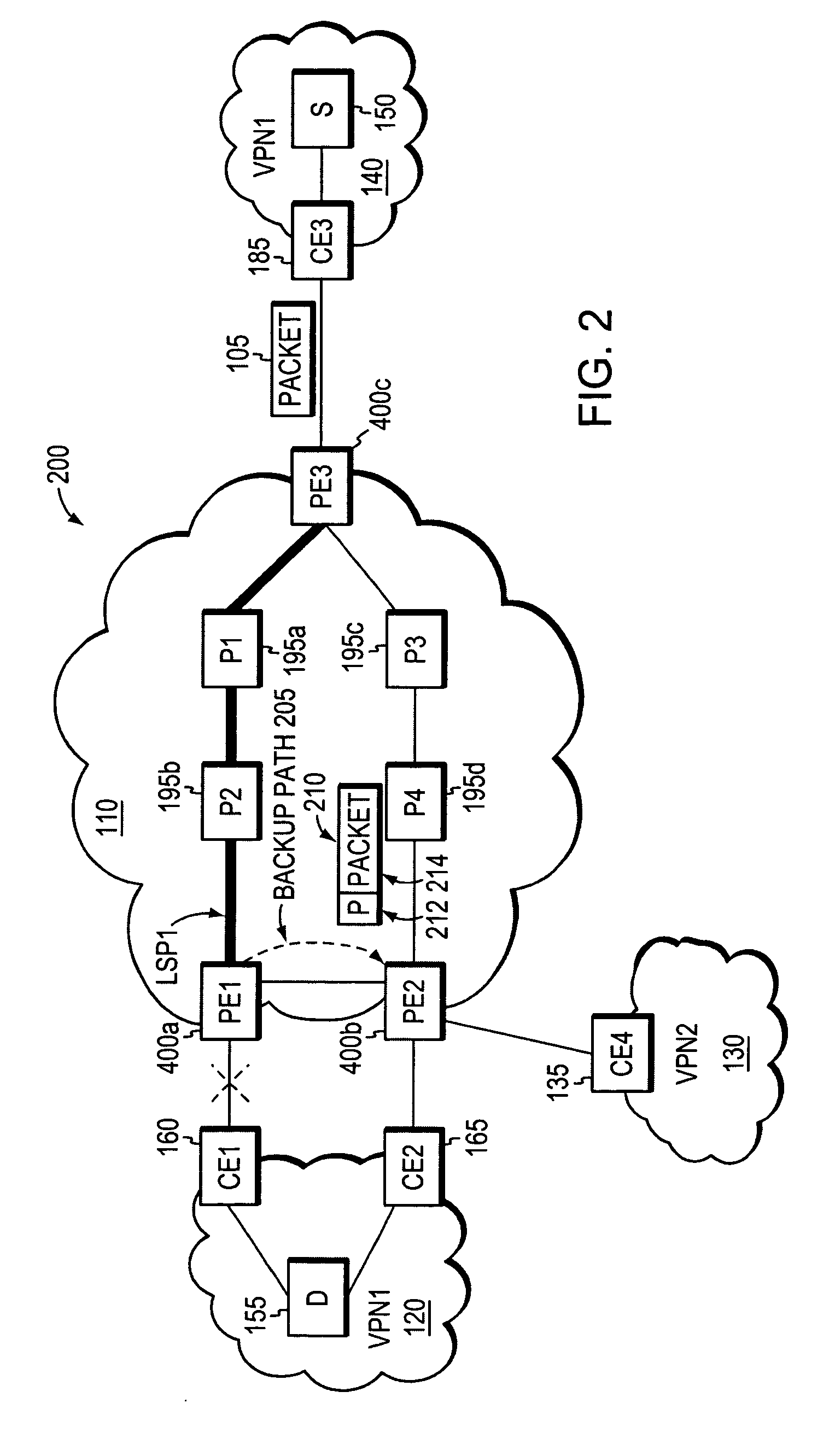
Fast reroute (FRR) protection at the edge of a RFC 2547 network
InactiveUS20060126496A1Quickly and efficiently forwardedFast reroute (FRR)Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting domainInter-domain
A fast reroute (FRR) technique that may be deployed at the edge of a network having first and second edge devices coupled to a neighboring routing domain. If the first edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with the neighboring domain, the first edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to the neighboring domain to the second edge device. The second edge device receives the rerouted packets and then forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. Notably, the second edge device is not permitted to reroute the received packets a second time, e.g., upon identifying another inter-domain node or link failure. As such, loops are avoided at the edge of the network and packets are rerouted to the neighboring routing domain faster and more efficiently than in prior implementations.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Separation of copy protection rules
InactiveUS20050071669A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDigital rights management systemCopy protection
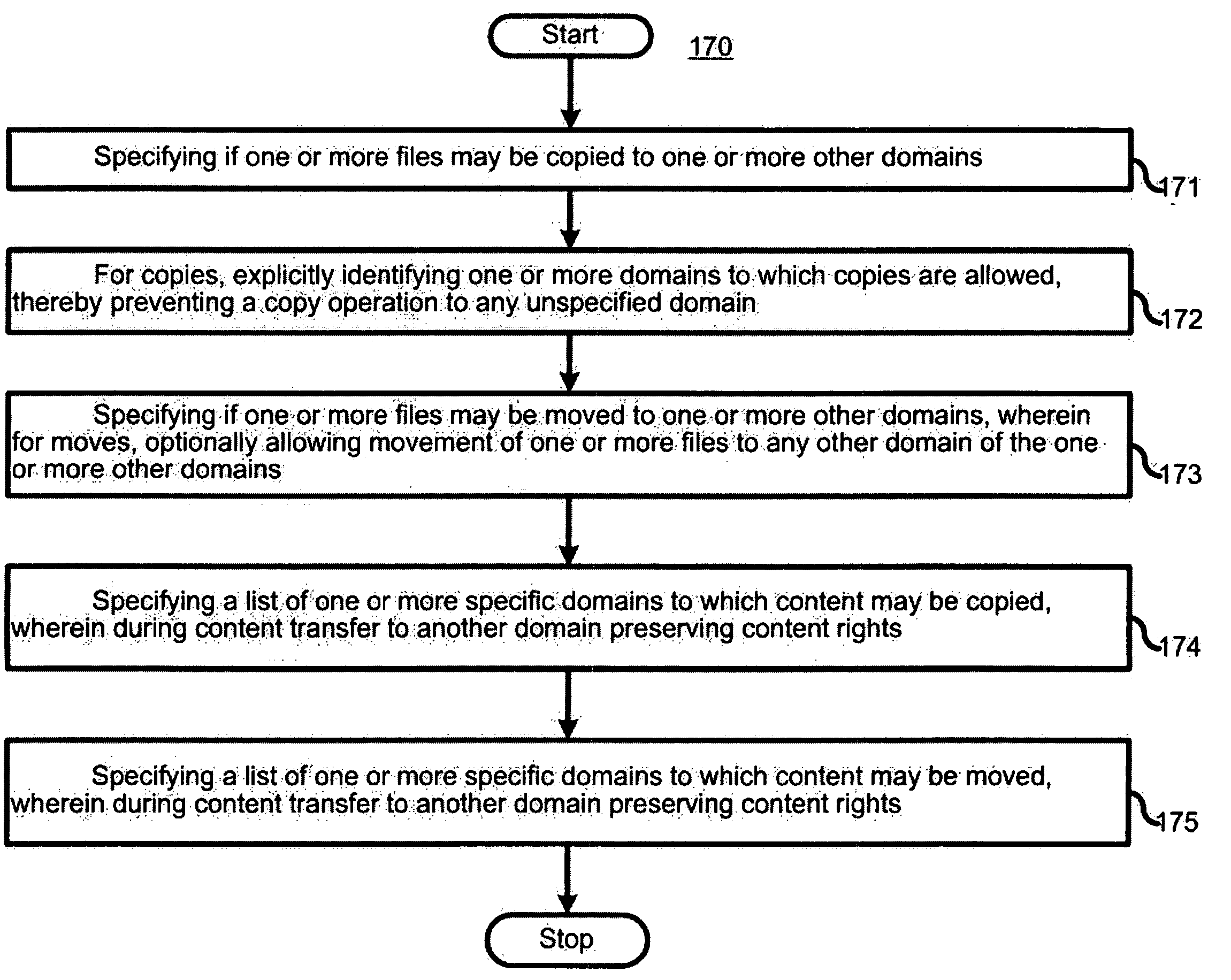
A copyright protection method (150) and apparatus (190) employs (151) a first protection scheme (160) within a single authorized domain (195), in which all interfaces (194a-c) are protected with digital rights management system and employs (152) a second protection scheme (170) for use in inter-domain file transfers. The method (150) and apparatus (190) may employ (153) a third protection scheme (180) for external outputs (197a-c) not protected by a digital rights management system. The first protection scheme (160) includes specifying (161) whether a copy of files is allowed to be stored anywhere within the single authorized domain; specifying (162) whether files may be stored only on specific devices within the single authorized domain; or specifying (163) how many simultaneous rendering devices are permitted when rendering files. The second protection scheme (170) may include: specifying (171) if the files may be copied to other domains; and explicitly identifying (172) domains to which copies are allowed; specifying (173) if files may be moved to other domains, and optionally allowing movement of files to any other domain; specifying (174) a list of specific domains to which content may be copied, and preserving content rights during content transfer to another domain; or specifying (175) specific domains to which content may be moved, and preserving content rights during content transfer. The third protection scheme (180) may include: specifying (181) copy protection information separately for analog, digital uncompressed and digital compressed outputs; specifying (182) a CGMS Copy protection state; specifying (183) MACROVISION parameters for analog outputs; specifying (184) if a particular type of output is allowed at all; or disabling (185) the particular type of output if the particular output type is not allowed.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
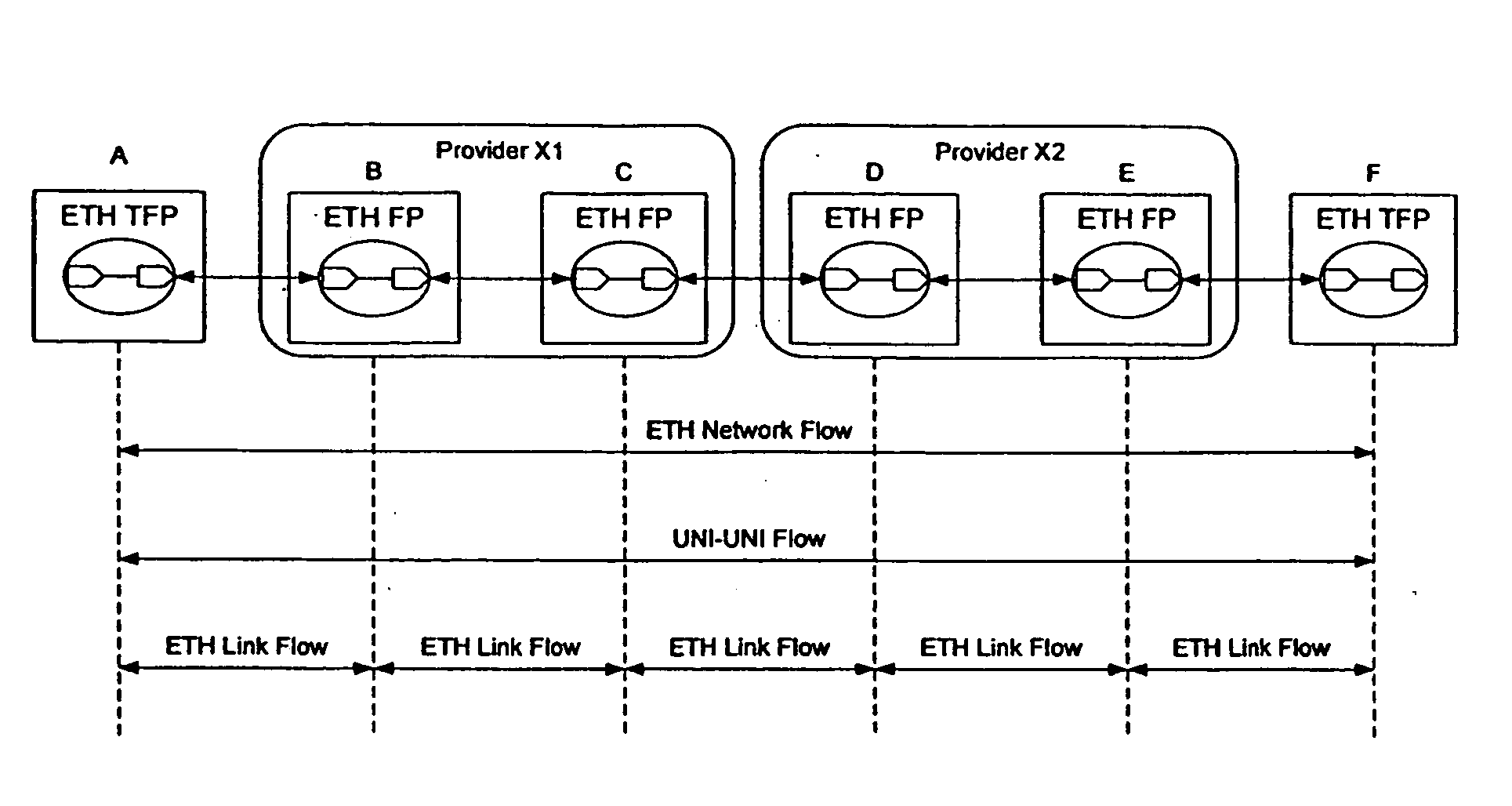
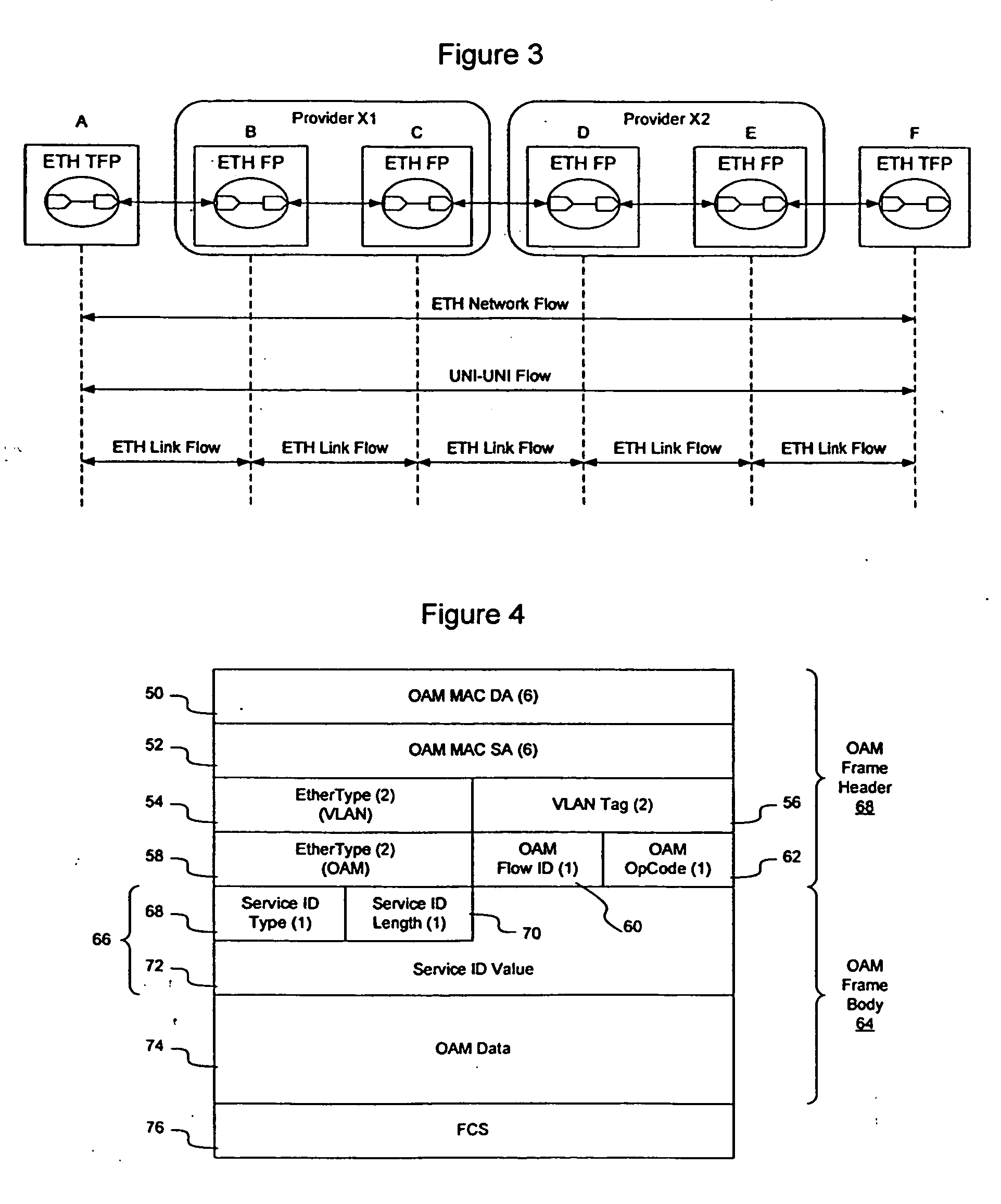
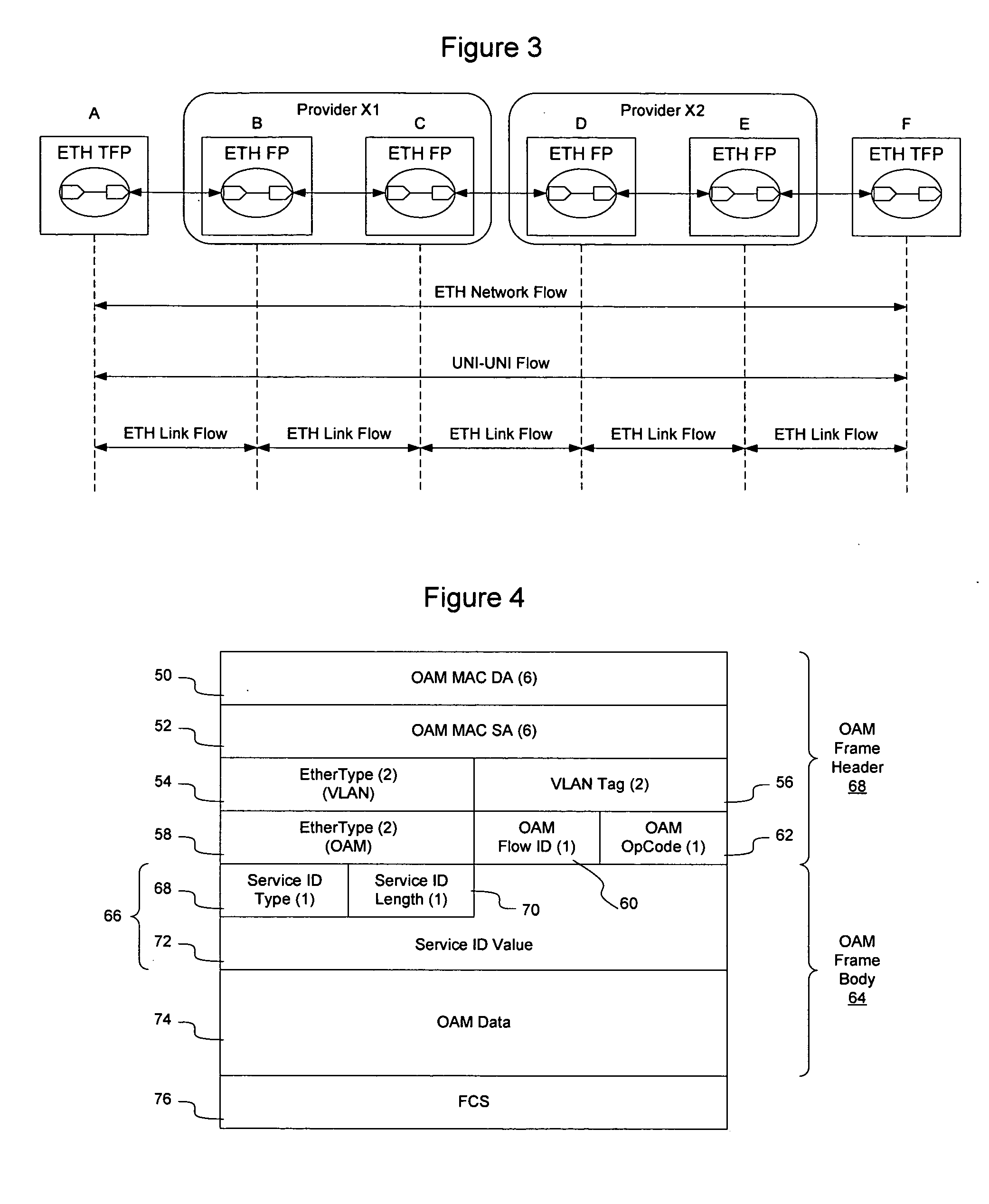
Method and apparatus for providing availability metrics for measurement and management of Ethernet services
InactiveUS20060092847A1Measurement performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEthernetDistributed computing
Maintenance entities may be defined between customer and provider flow points to allow performance management to take place on an Ethernet network. The maintenance entities may be defined for access link, intra-domain, and inter-domain, and may be defined on a link or service basis. Performance parameters, including availability metrics, may be collected for the maintenance entities. The provision of such availability metrics in an Ethernet based solution to facilitate consistency of service management and operations for carriers transitioning to the Ethernet solution.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
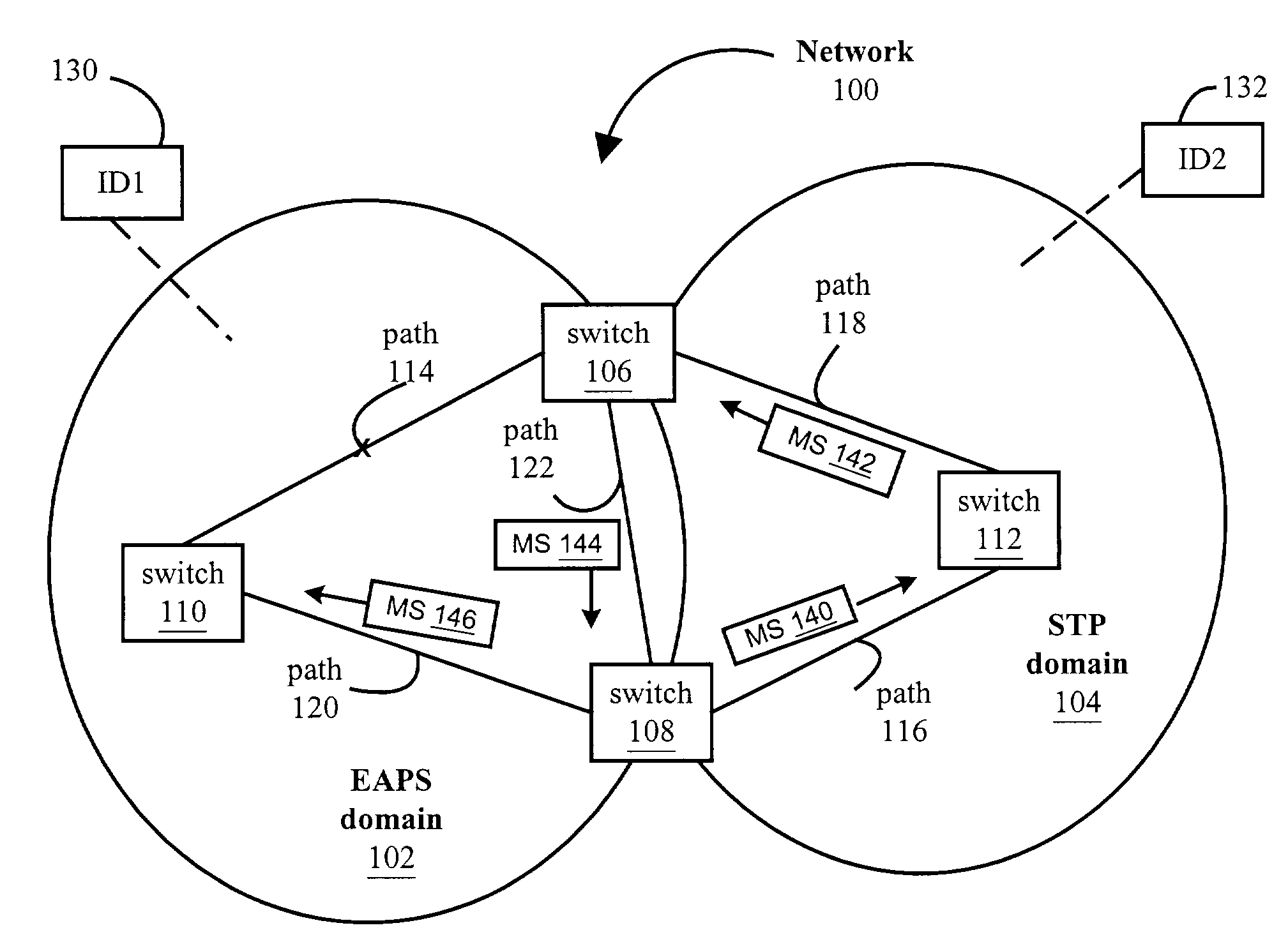
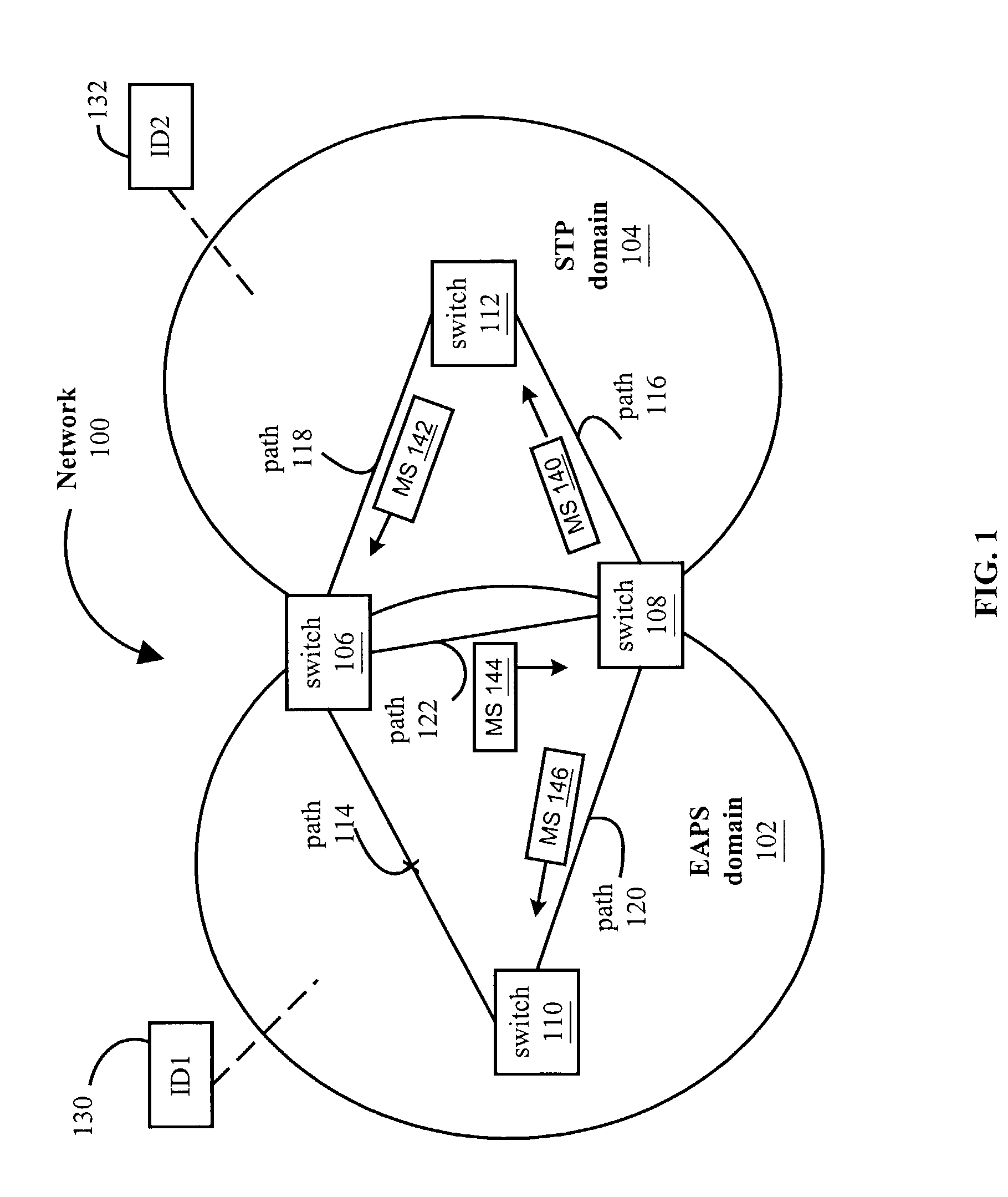
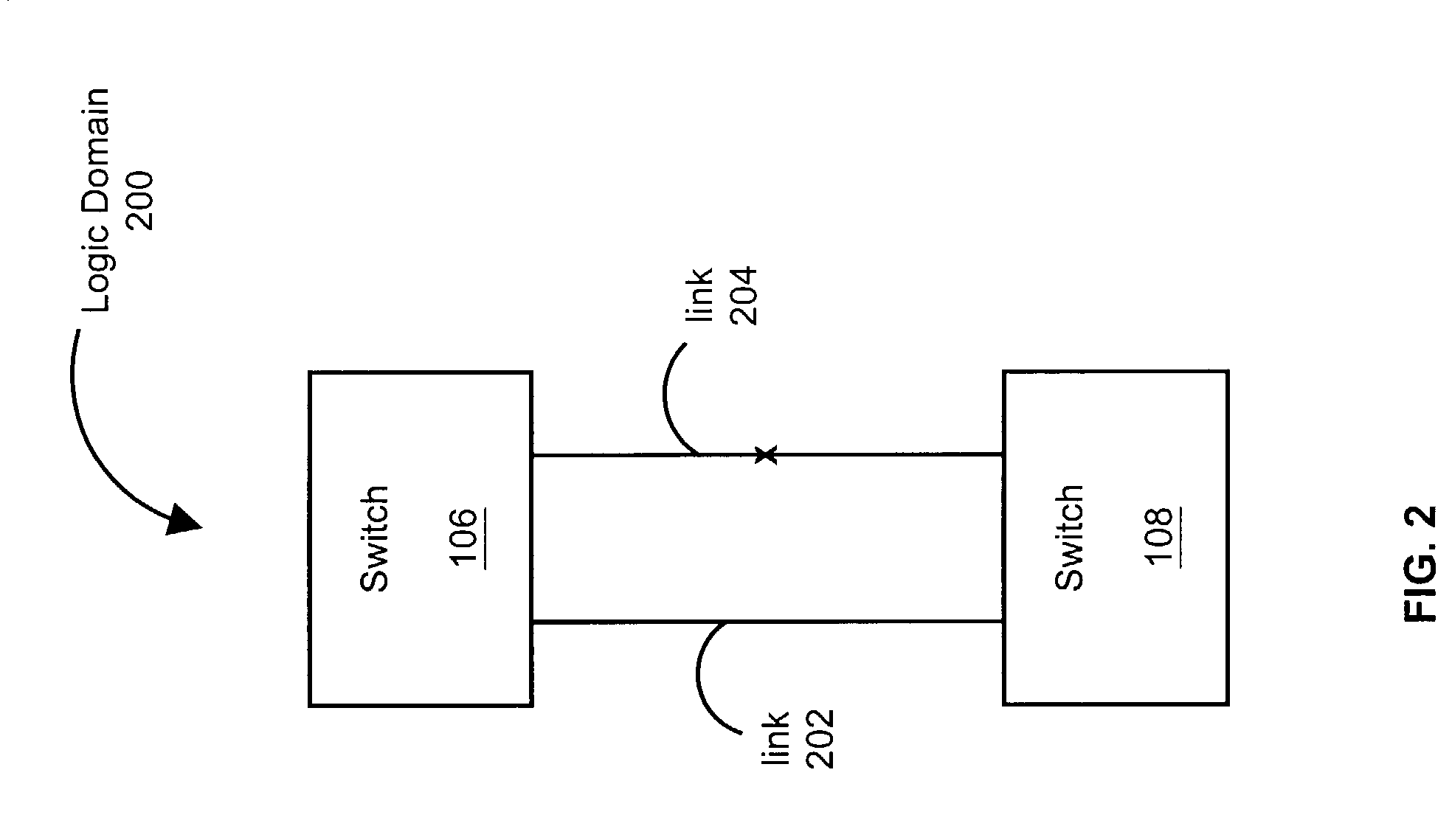
Method and system for inter-domain loop protection using a hierarchy of loop resolving protocols
A method and system is provided for inter-domain loop protection using a hierarchy of loop resolving protocols. The method includes receiving messages from inter-domain switches. The inter-domain switches belong to a plurality of loop-free network topology domains. A logical domain is abstracted that includes the inter-domain switches and logical links that connect the switches. Each logical link represents one of the physical loop free network topology domains that the inter-domain switches belong to. Then, the loops in the logical domain are eliminated. One or more logical links and ports associated with those logical links may be blocked to break the loops. This provides for a network free of inter-domain loops.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
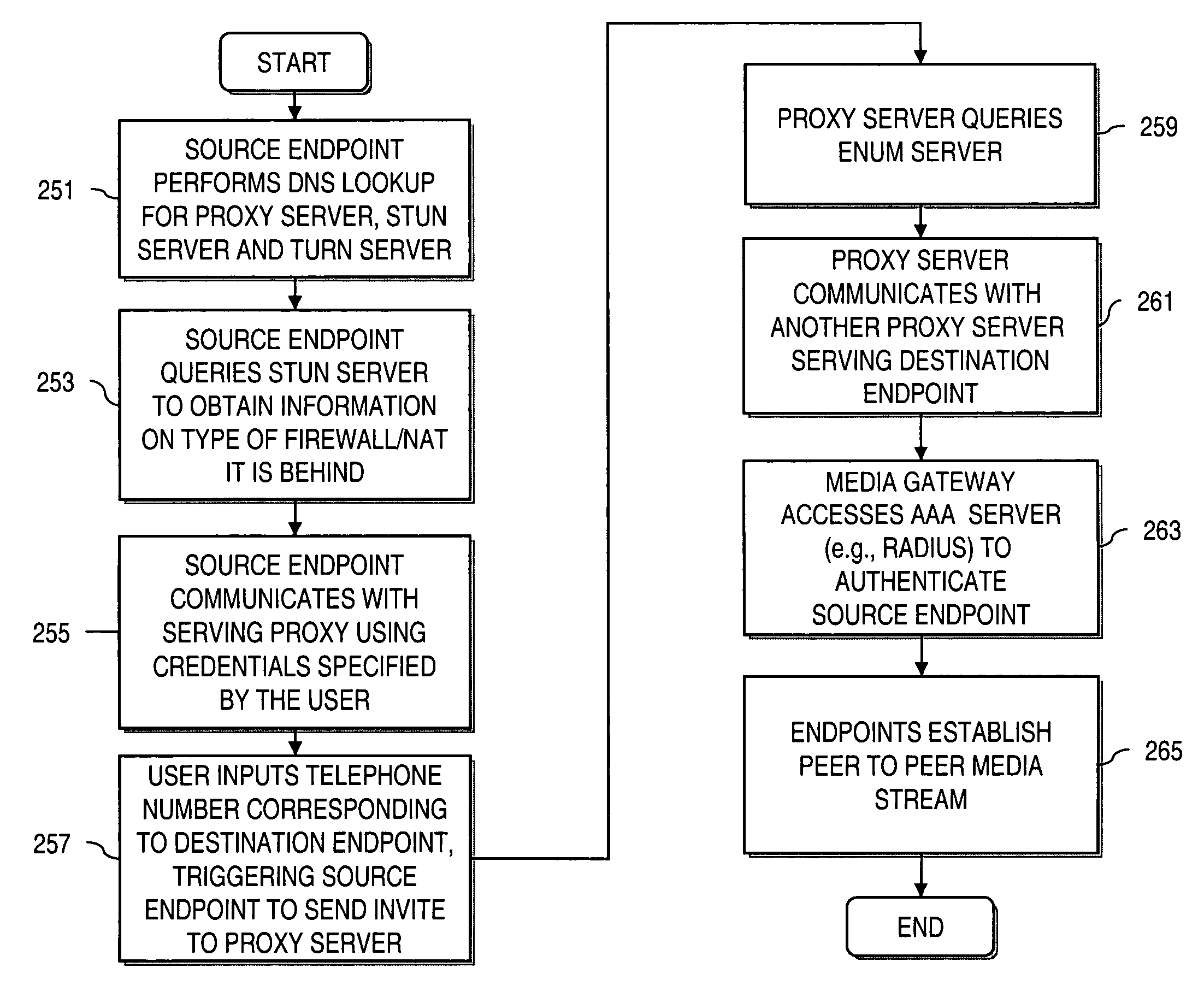
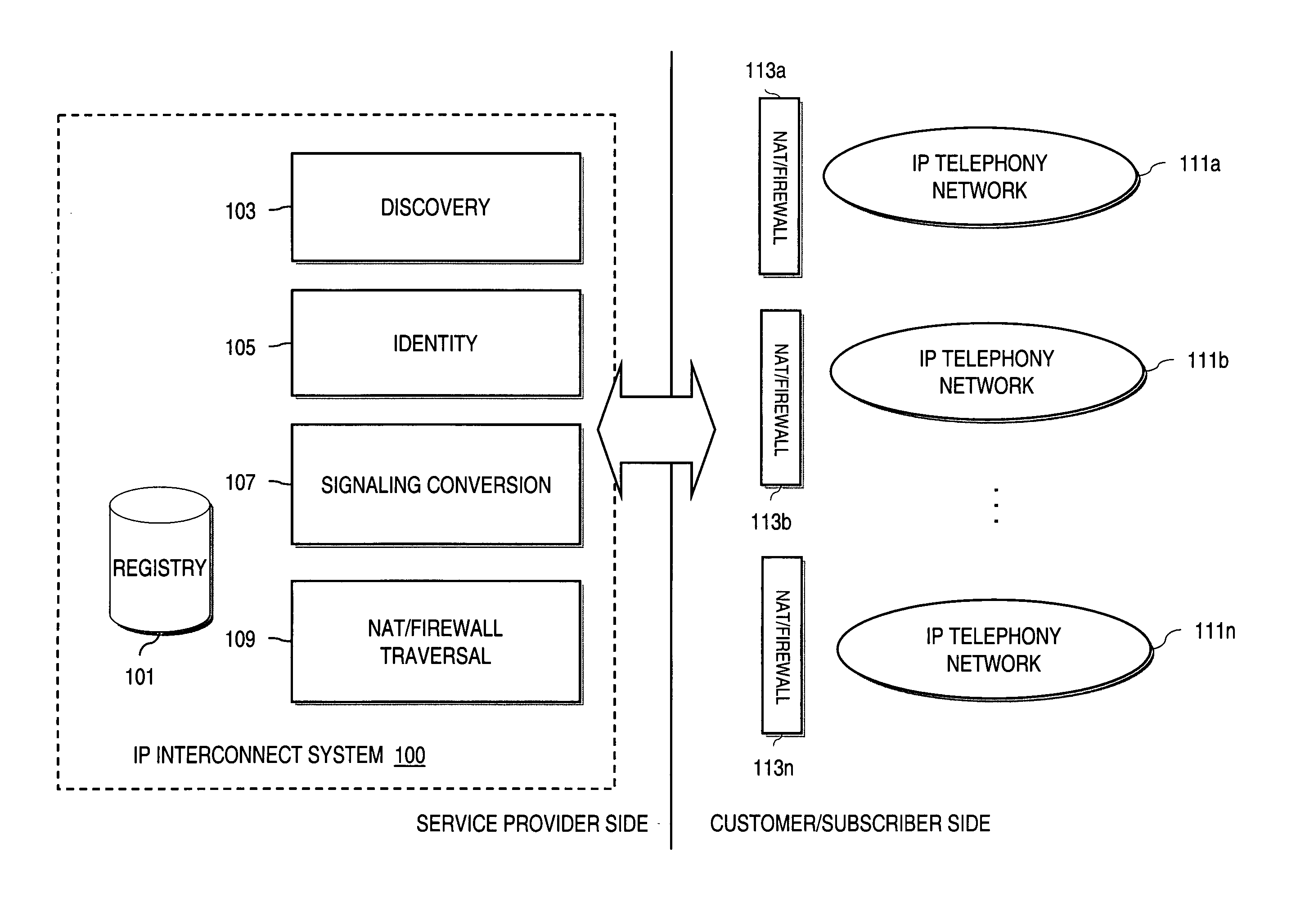
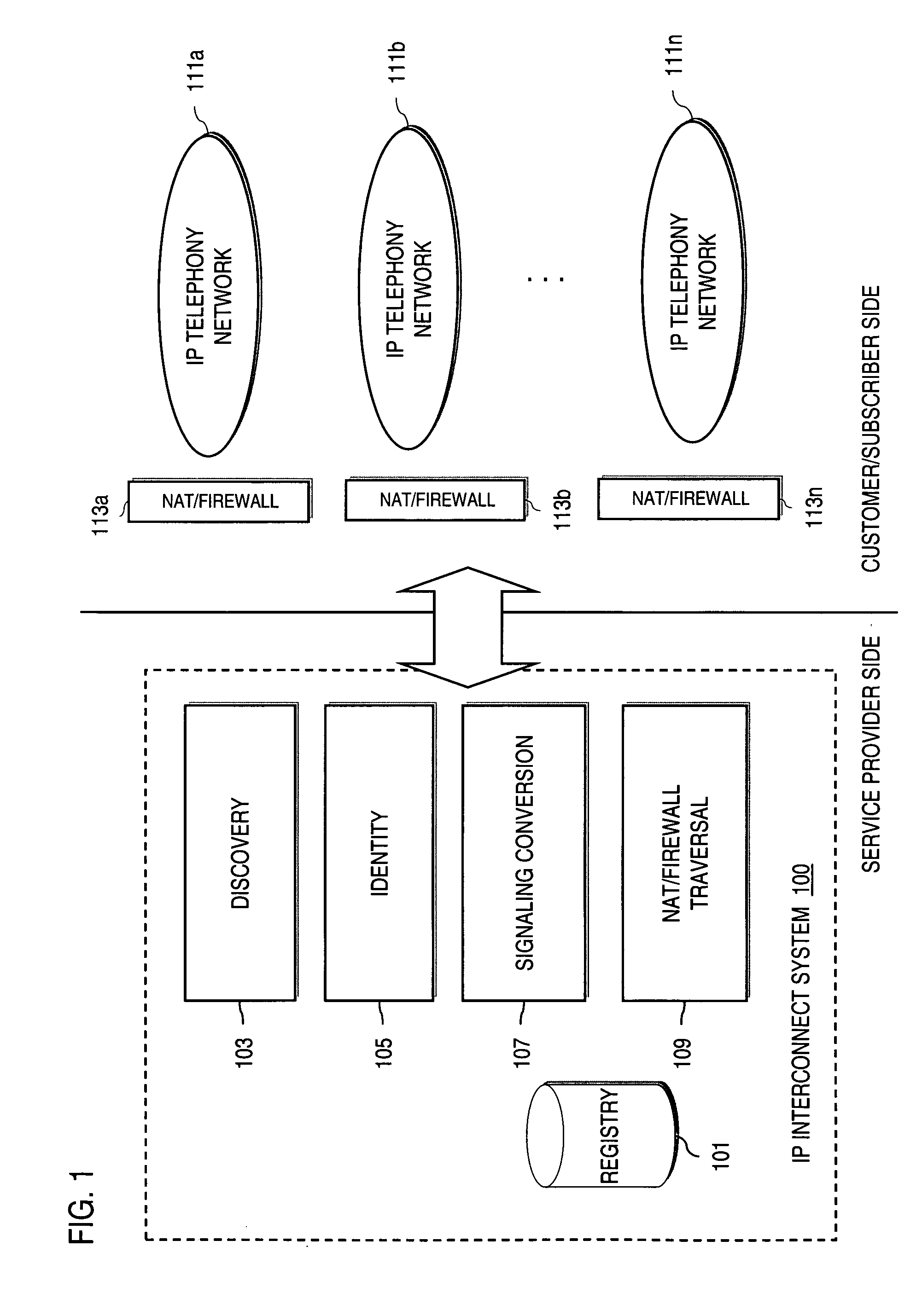
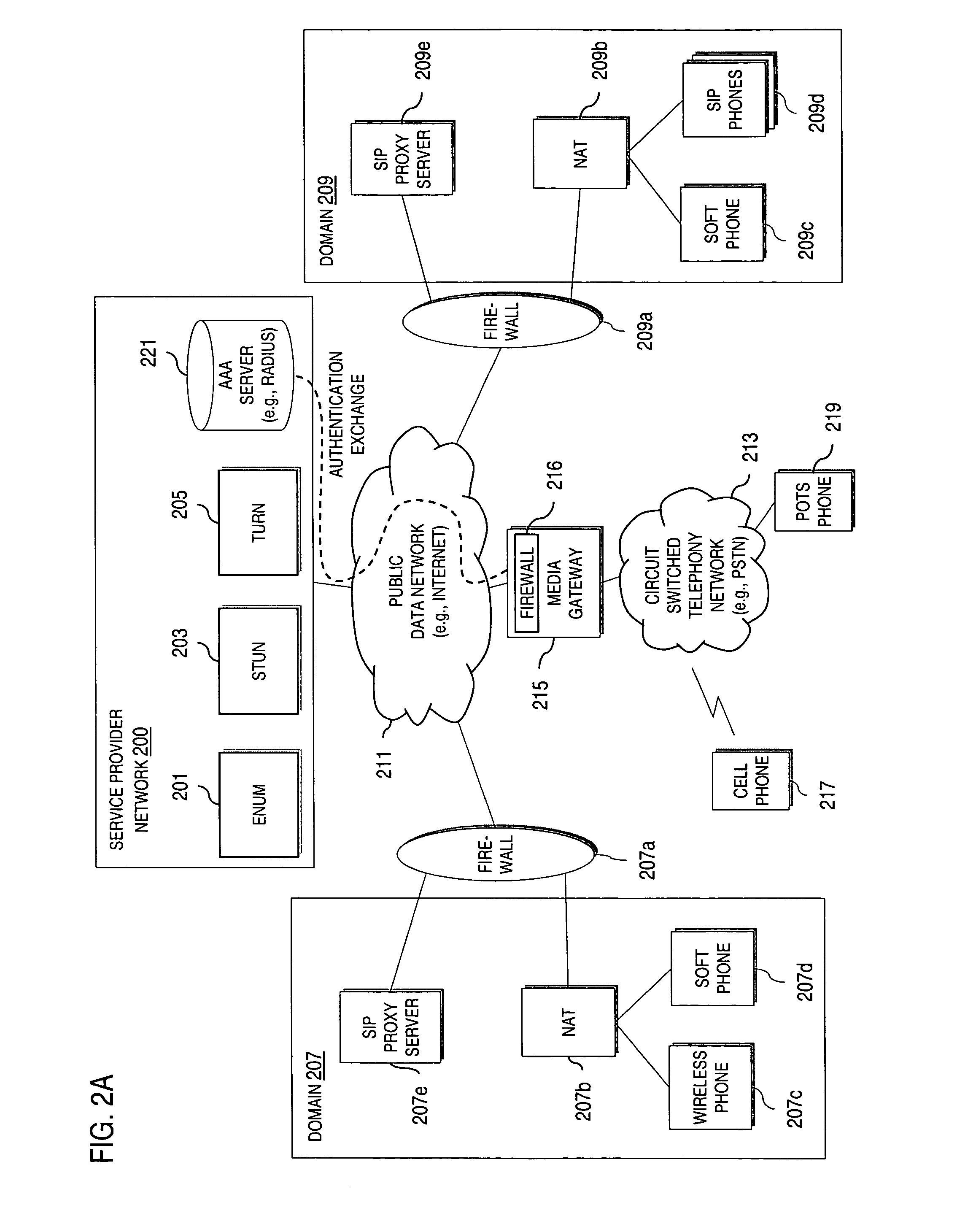
Method and system for providing interdomain traversal in support of packetized voice transmissions
ActiveUS20060209794A1Interconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexNetwork addressingNetwork address translation
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A request for establishing a voice call is received from a source endpoint behind a first network address translator of a first domain, wherein the request specifies a directory number of a destination endpoint within a second domain. A network address is determined for communicating with the destination endpoint based on the directory number. Additionally, existence of a second network address translator within the second domain is determined. If the network address can be determined, a media path is established between the source endpoint and the destination endpoint based on the network address to support the voice call.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Ethernet OAM performance management
InactiveUS20050099952A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCollection methodsEthernet
Maintenance entities may be defined between customer and provider flow points to allow performance management to take place on an Ethernet network. The maintenance entities may be defined for access link, intra-domain, and inter-domain, and may be defined on a link or service basis. The maintenance entities may be used to monitor performance within a network or across networks, and may be used to monitor various performance parameters, such as frame loss, frame delay, frame delay variation, availability, errored frame seconds, service status, frame throughput, the number of frames transmitted, received or dropped, the status of a loopback interface, the amount of time a service has been unavailable, and many other parameters. Several management mechanisms may be used, and the measurements may be collected using a solicited collection method, in which a responses are required and collected, or an unsolicited collection method in which a response is not required.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE +1
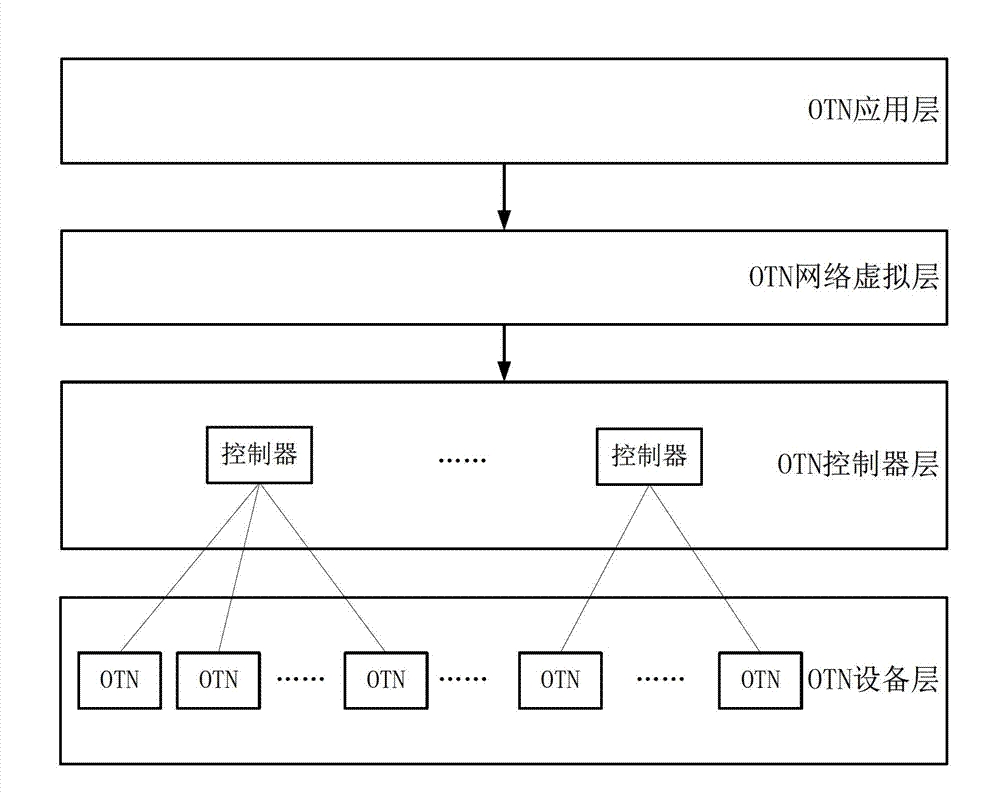
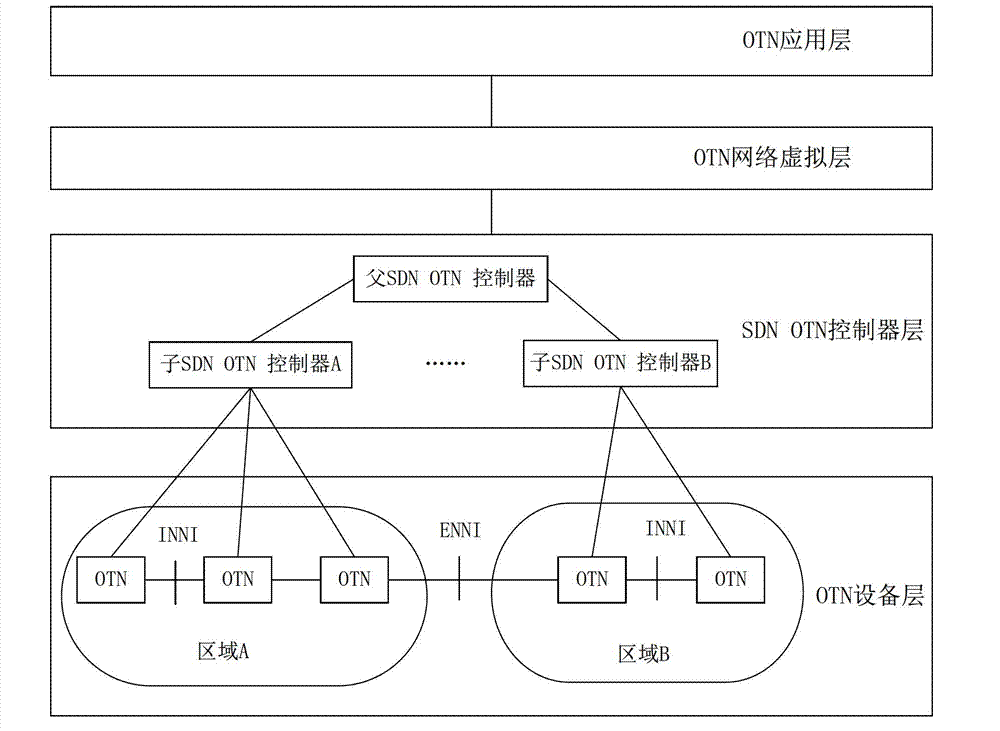
Framework system of grade software defined network software controller and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN103051565AResolve resource conflictsAvoid asyncData switching networksStructure of Management InformationNetwork control
The invention discloses a framework system of a grade software defined network software controller and an implementation method thereof. The framework system and the implementation method are applied in a multi-domain optical transport network (OTN); an inter-domain mapping relation of a whole network view and a physical device network is established according to whole network topologic information by a primary (SDNOTN) controller; an inter-domain mapping processing request of the whole network view and the physical device network in each domain is sent to each auxiliary SDNOTN; and the domain mapping relation of the whole network view and the physical device network is established by the auxiliary SDNOTN controllers. Grade structures of the primary SDNOTN controller and the auxiliary SDNOTN controllers are arranged in the framework system, so that the mapping relation of the multi-domain whole network view and the overall physical device network in real sense is realized, and a whole network resource optimizing algorithm is realized in the real sense, so that the problem that the inter-domain link resource conflict occurs in a cross-domain service connection signaling process can be thoroughly solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Loop prevention technique for MPLS using two labels
InactiveUS20060164975A1Fast and efficientProtect dataError preventionTransmission systemsInternet trafficRouting domain
A fast reroute (FRR) technique is implemented at the edge of a network. In accordance with the technique, if an edge device detects a node or link failure that prevents it from communicating with a neighboring routing domain, the edge device reroutes at least some data packets addressed to that domain to a backup edge device which, in turn, forwards the packets to the neighboring domain. The rerouted packets are designated as being “protected” (i.e., rerouted) data packets before they are forwarded to the backup edge device. To differentiate which data packets are protected and which are not, the backup edge device employs different sets of VPN label values for protected and non-protected network traffic. That is, the backup edge device may allocate two different VPN label values for at least some destination address prefixes that are reachable through the neighboring domain: a first VPN label value for FRR protected traffic and a second VPN label value for non-protected traffic. Upon receiving a data packet containing a protected VPN label value, the backup edge device is not permitted to reroute the packet a second time, e.g., in response to another inter-domain node or link failure, thereby preventing loops from developing at the edge of the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
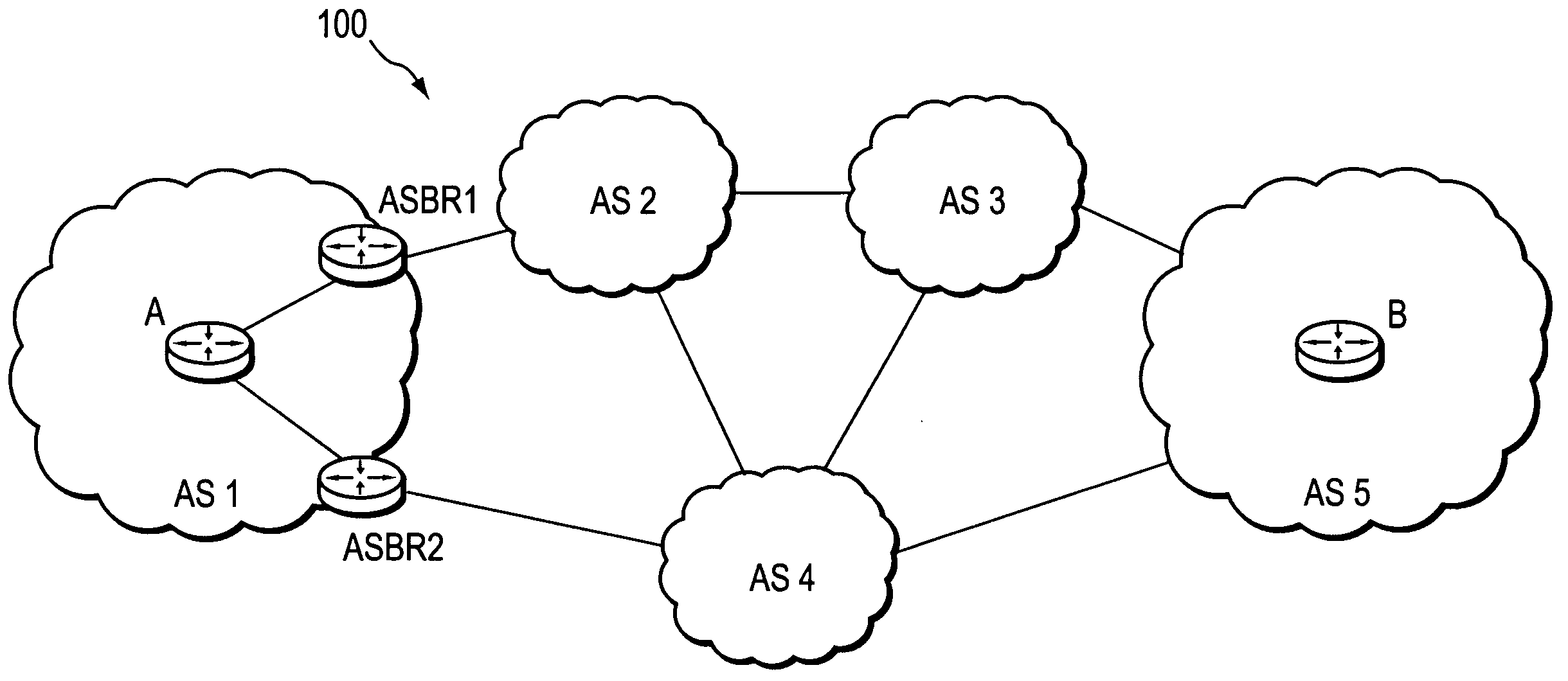
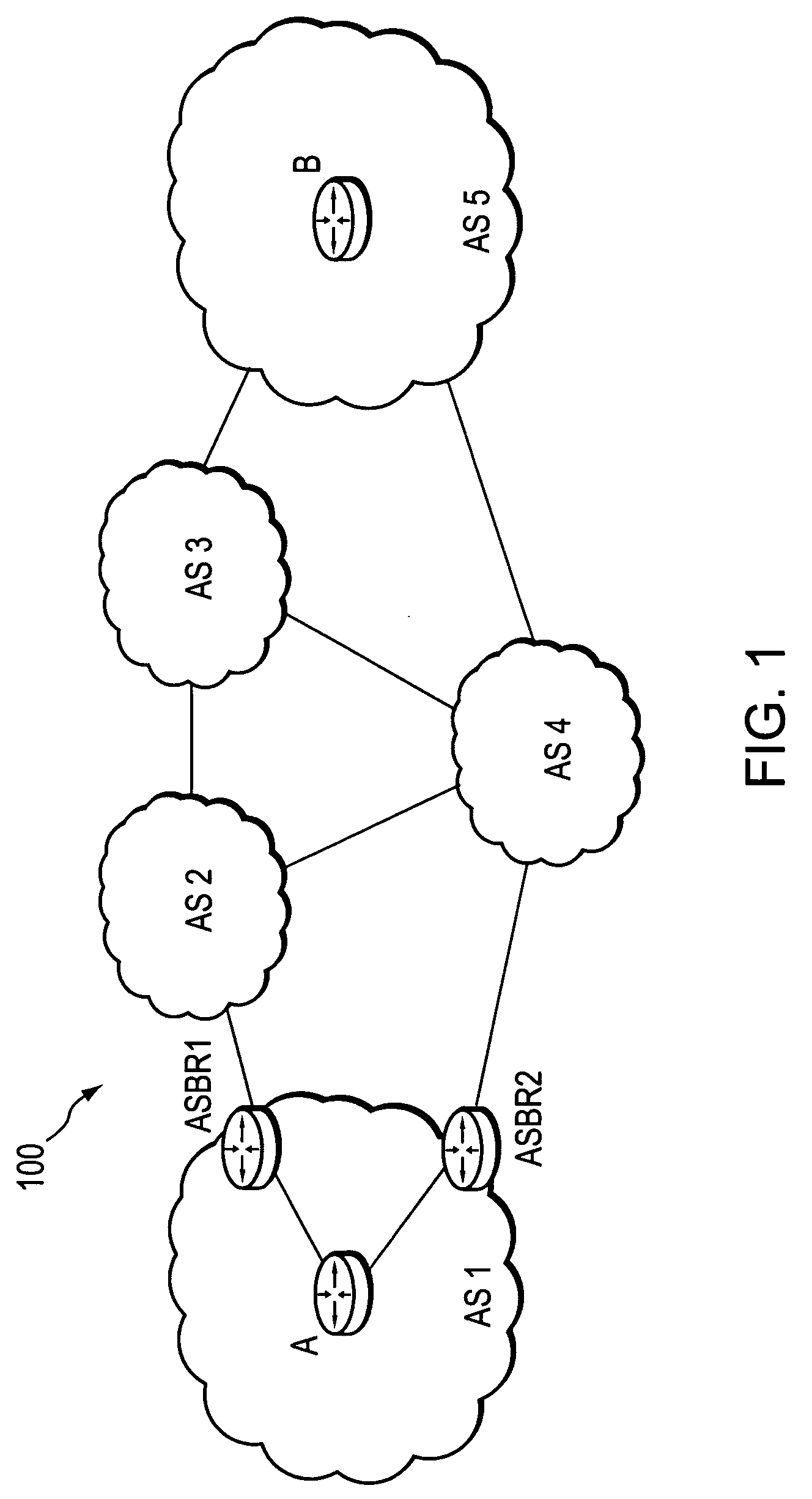
Computation of a shortest inter-domain TE-LSP across a set of autonomous systems
A technique calculates a shortest path for a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) from a head-end node in a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain in a computer network. The novel path calculation technique determines a set of different remote domains through which the TE-LSP may traverse to reach the tail-end node (e.g., along “domain routes”). Once the set of possible routes is determined, the head-end node sends a path computation request to one or more path computation elements (PCEs) of its local domain requesting a computed path for each domain route. Upon receiving path responses for each possible domain route, the head-end node selects the optimal (shortest) path, and establishes the TE-LSP accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Secure intra-and inter-domain handover
ActiveUS20070064647A1Fast and secure handoverConnection securityNetwork traffic/resource managementUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionHandoff controlFast handover
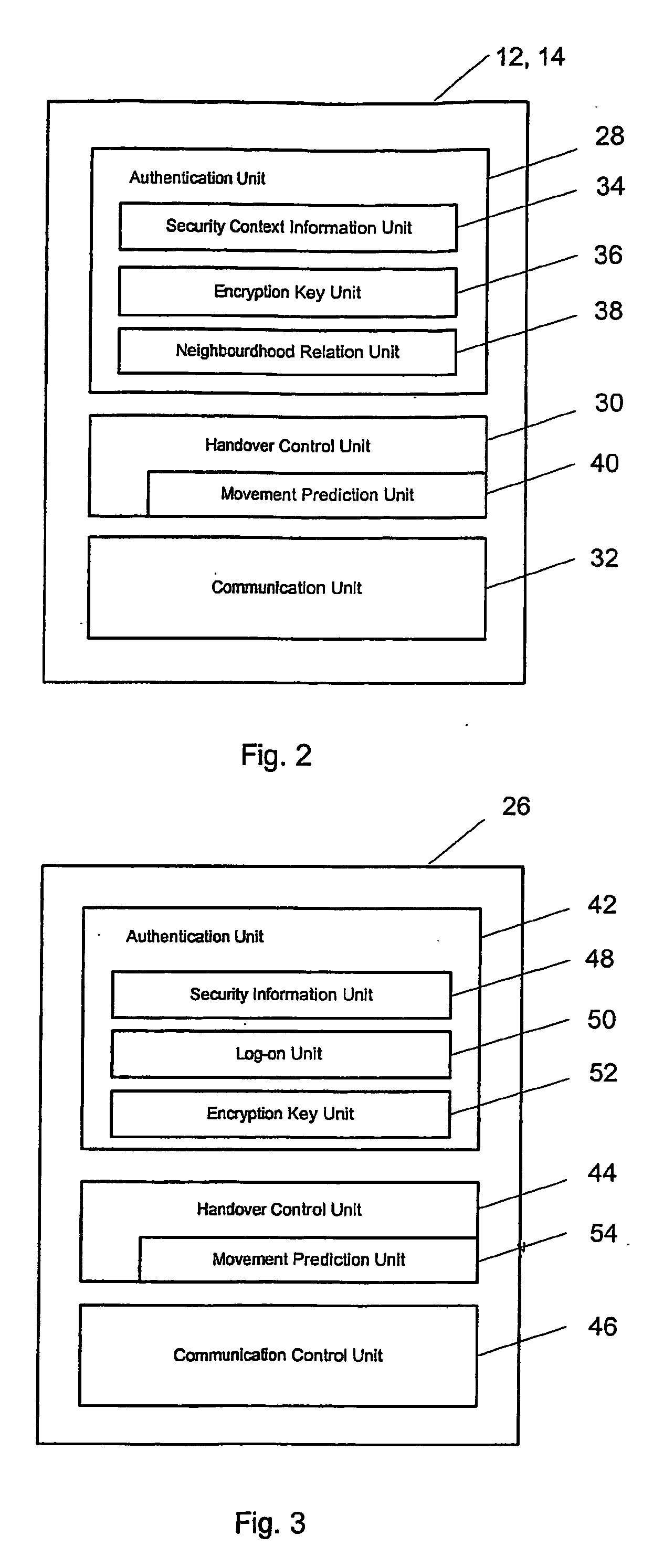
To achieve a secure and fast handover in a distributed mobile communication environment (10), the control functionality is lying at the borderline between wireless and wire-bound communication network elements, and it is proposed to, firstly, execute a mutual authentication between a mobile device (26) and a new access point (14) using security context information previously transmitted to the new access point. Then, after successful mutual authentication, a handover will be executed from the current access point (12) to the new access point (14).
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method for tunable inter domain egress selection
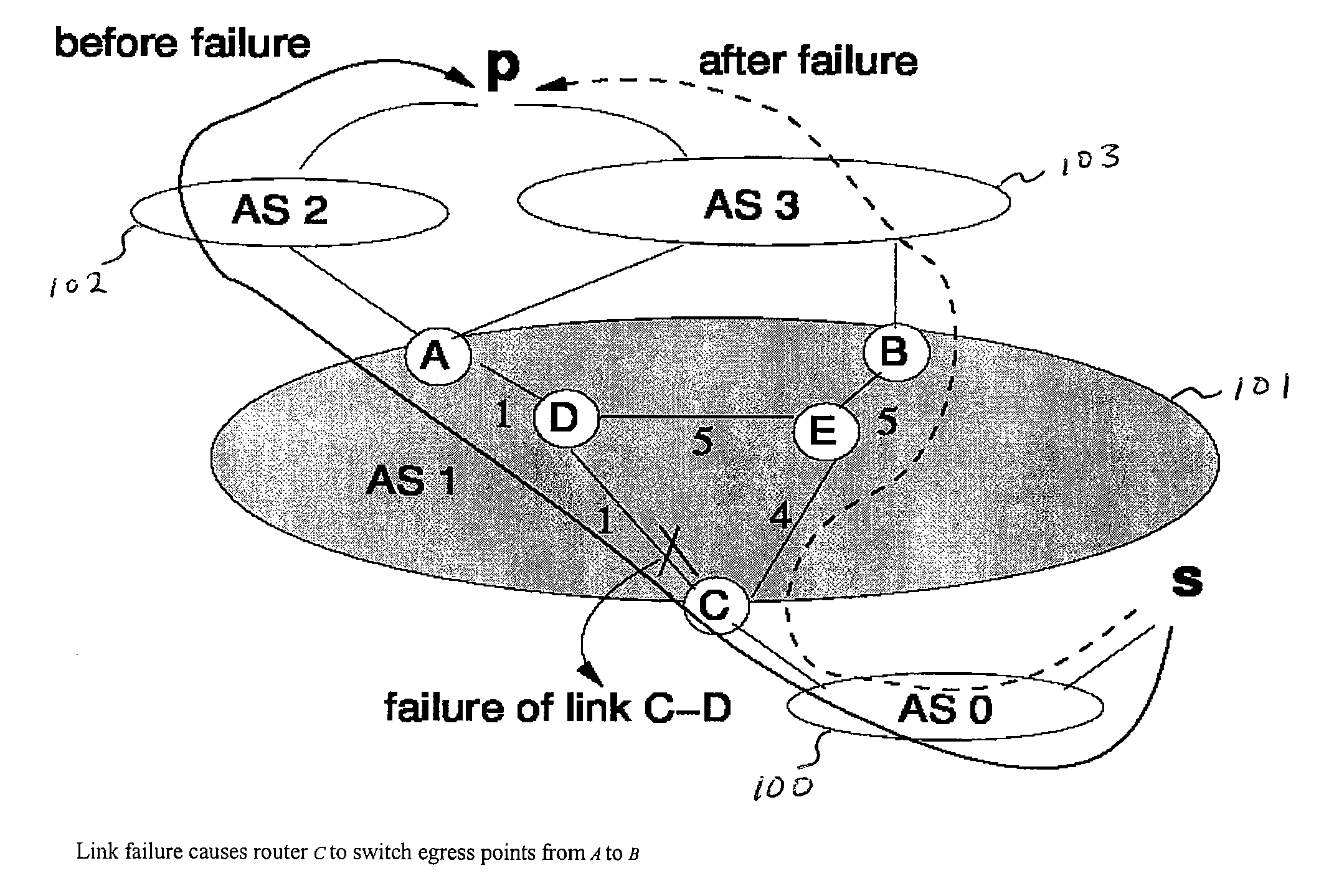
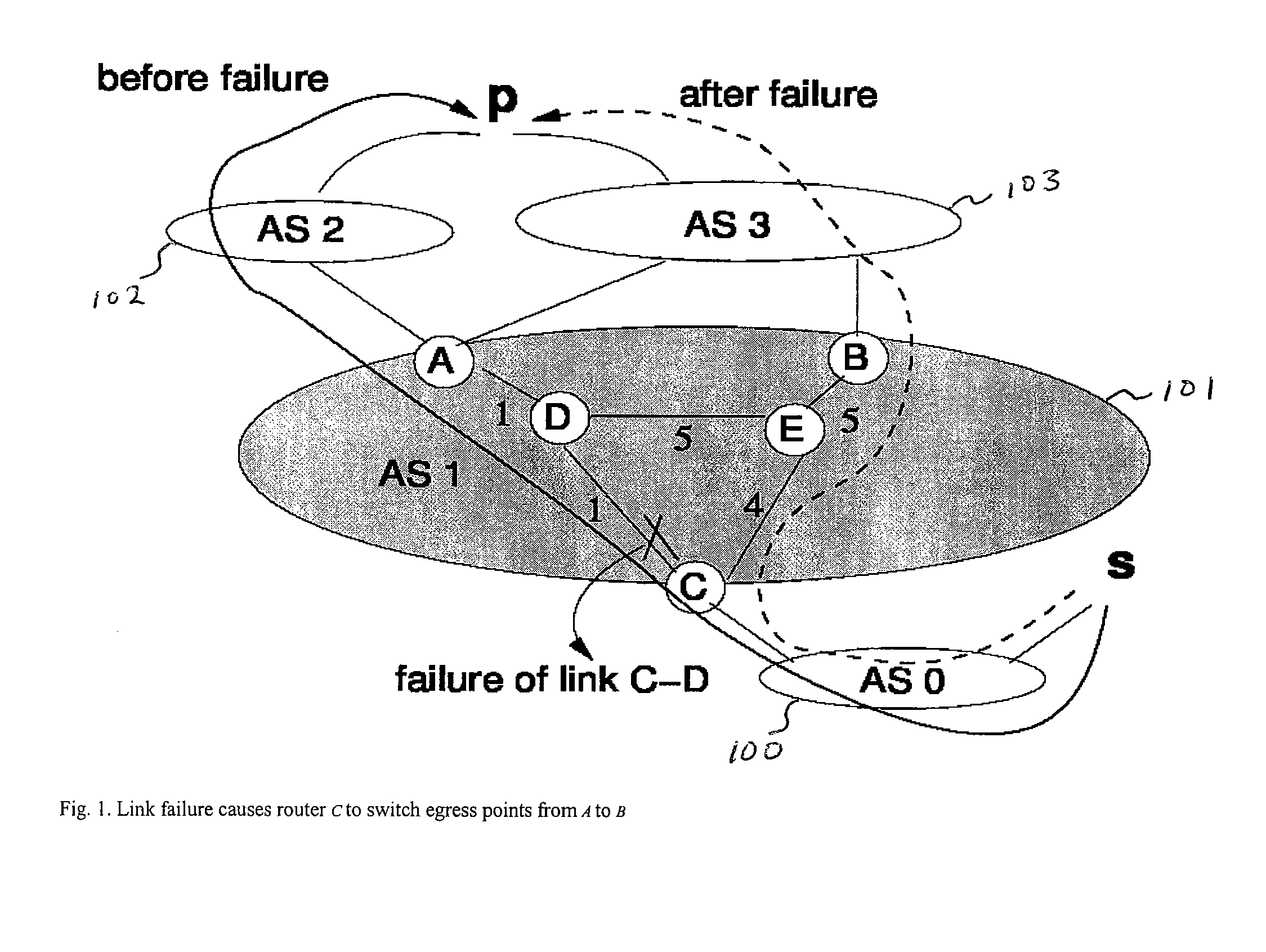
InactiveUS7581022B1Simple to executeError preventionTransmission systemsFlexible MechanismsInter-domain
A flexible mechanism and method for routers to select the egress point for each destination comprises identifying a plurality of points of egress from an autonomous system, ranking the plurality of points of egress according to a metric having variable and fixed terms, selecting a point of egress having the smallest rank, and transmitting packets from a point of ingress via a path to the selected point of egress. The metric is across a plurality of destinations and respective possible points of egress from the autonomous system and the metric is m(i, p, e) equaling α(i, p, e)·d(G,i,e)+β(i, p, e) where a and β are configurable values, i is the identity of the router, p is the destination, G is an undirected weighted graph, the d function is the interior gateway protocol distance and e is a point of egress.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Method of monitoring calls in an internet protocol (IP)-based network
InactiveUS6839323B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet protocol suiteTTEthernet
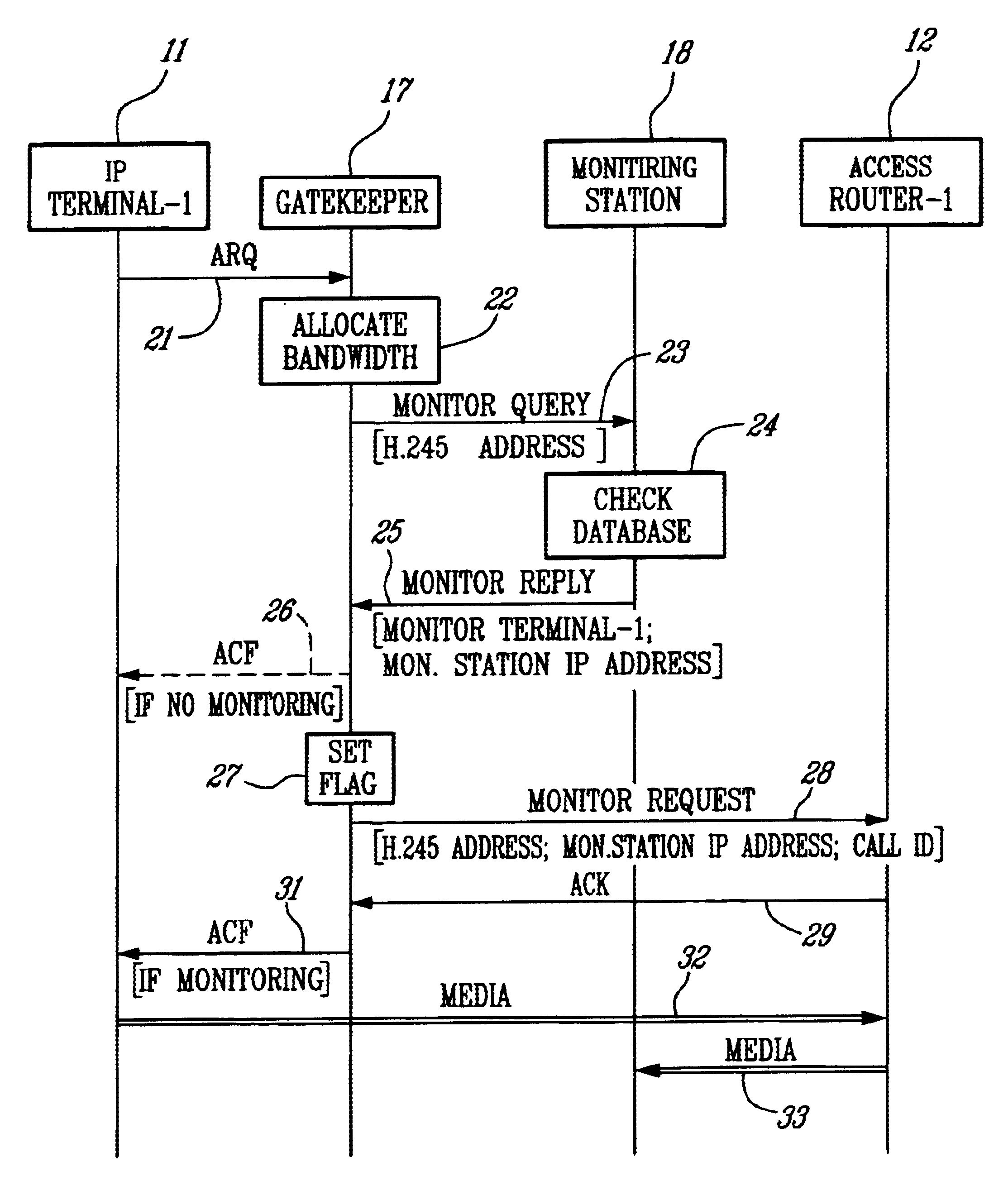
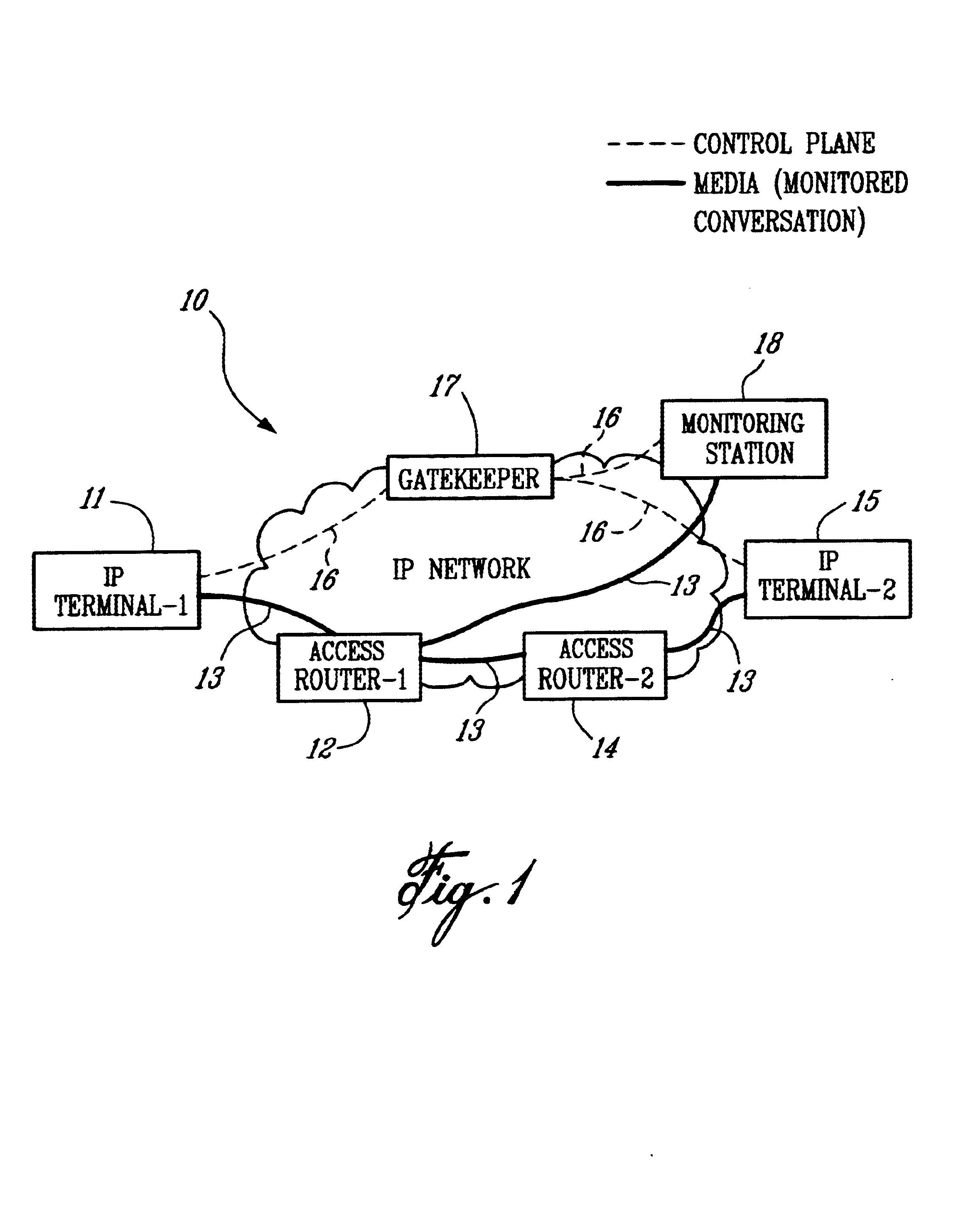
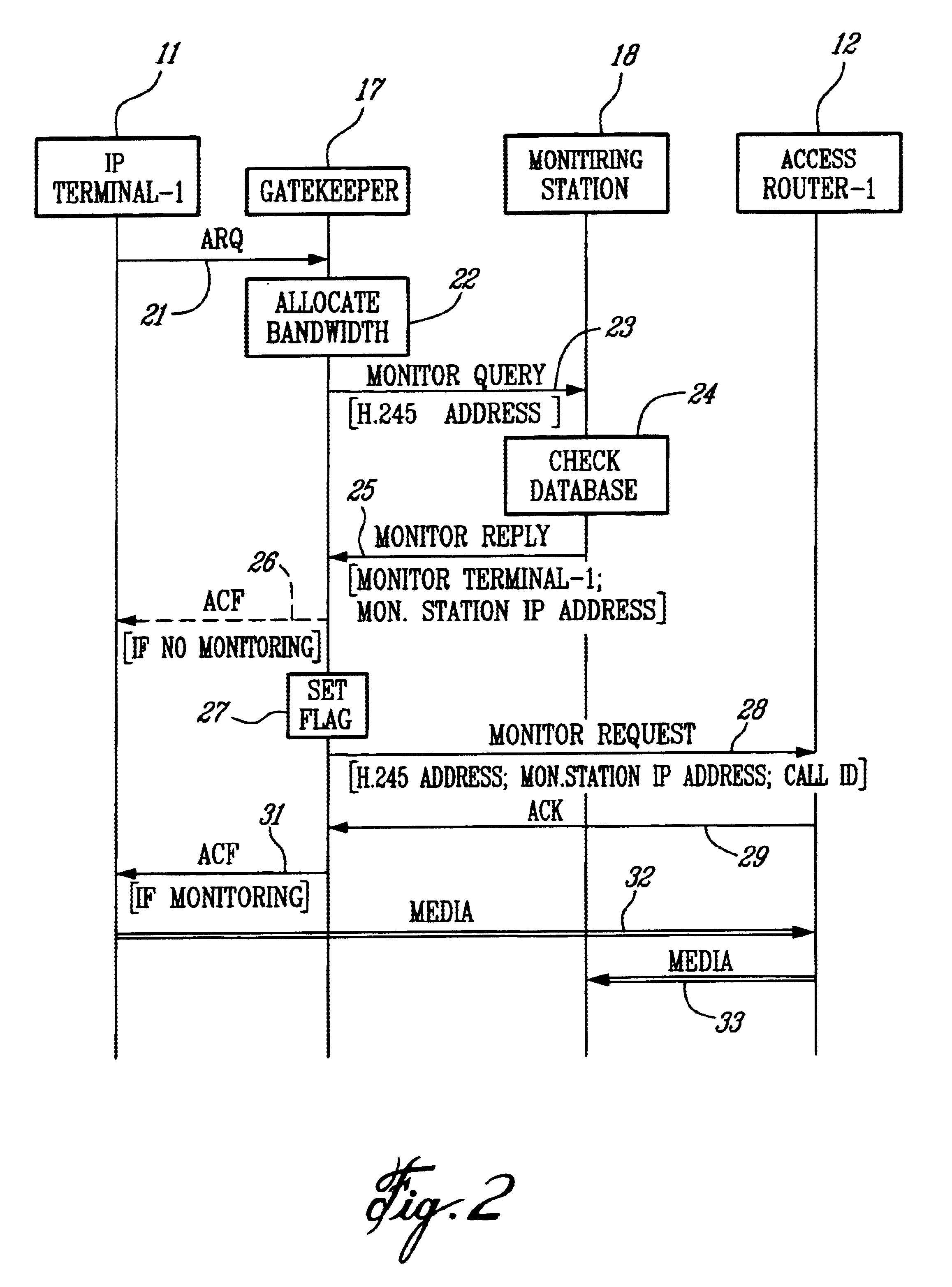
A method of monitoring a call with a mobile terminal (MT) in an Internet Protocol (IP)-based network having a Gatekeeper that controls the network, a plurality of access routers that provide access to the network, and a Monitoring Station having monitoring facilities and a database of MTs to be monitored. When the MT sends an Admission Request message to the Gatekeeper, the Gatekeeper sends a query to the Monitoring Station asking whether the MT is to be monitored. The Monitoring Station sends a reply to the Gatekeeper indicating that the MT is to be monitored and providing an IP address where monitored packets are to be sent. The Gatekeeper then sends a monitoring request message to the access router associated with the MT. The request identifies the MT to be monitored, instructs the access router to monitor the MT, and provides a unique call identification (Call ID) and the IP address where monitored packets are to be sent. When the access router detects a packet associated with the MT, the router sends all packets associated with the MT to the Monitoring Station. The method also controls monitoring during intra-domain and inter-domain handoffs of the MT.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
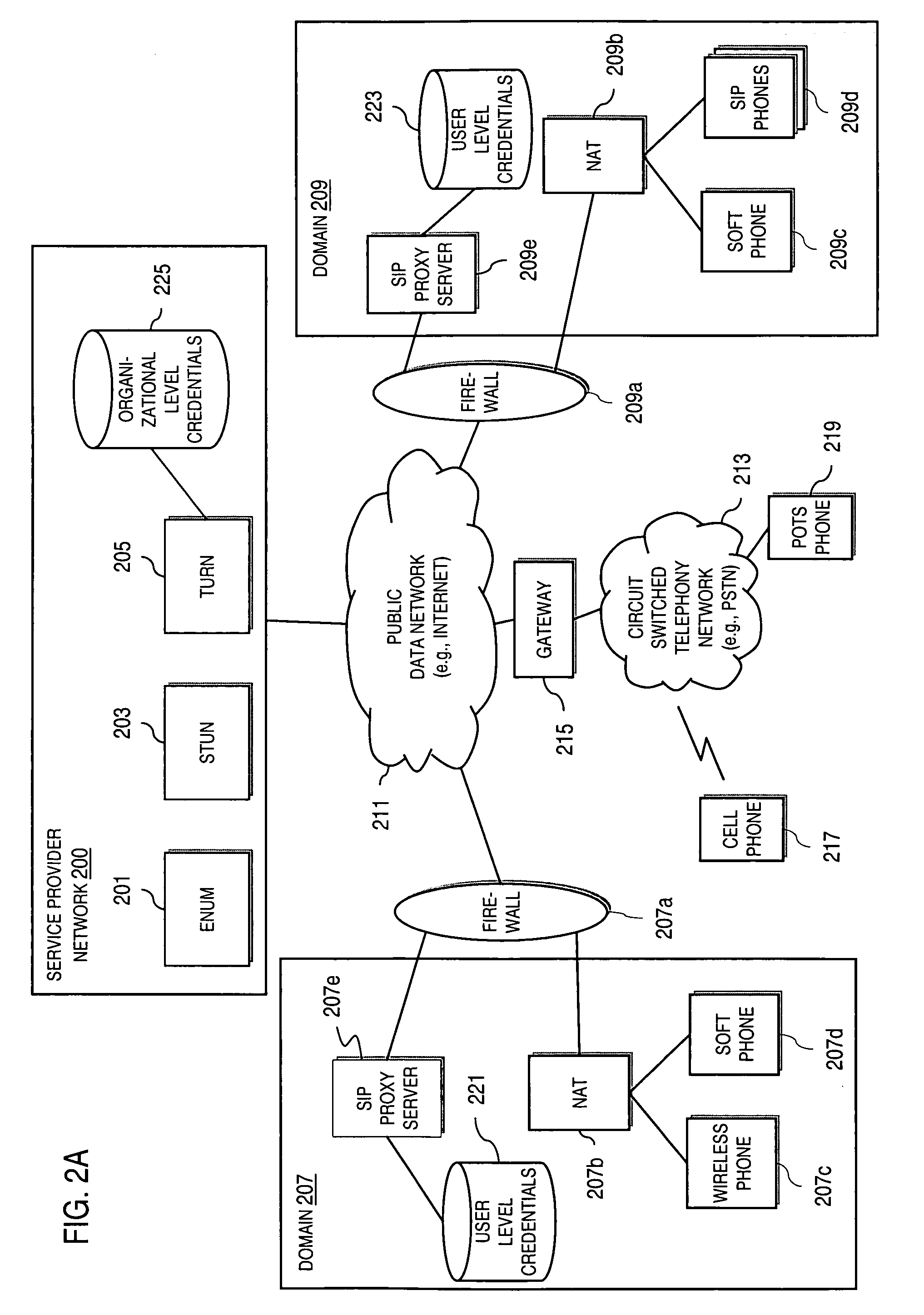
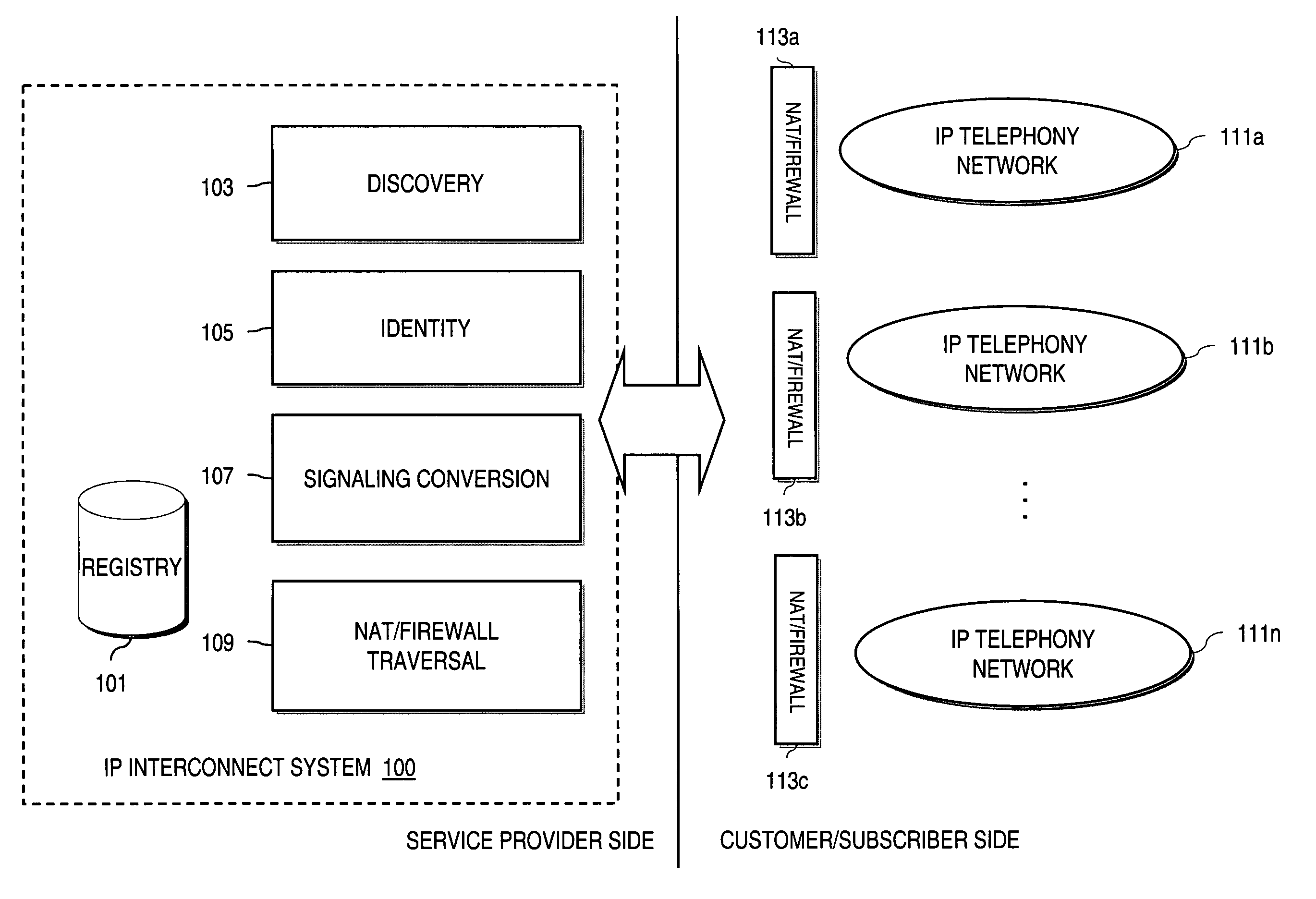
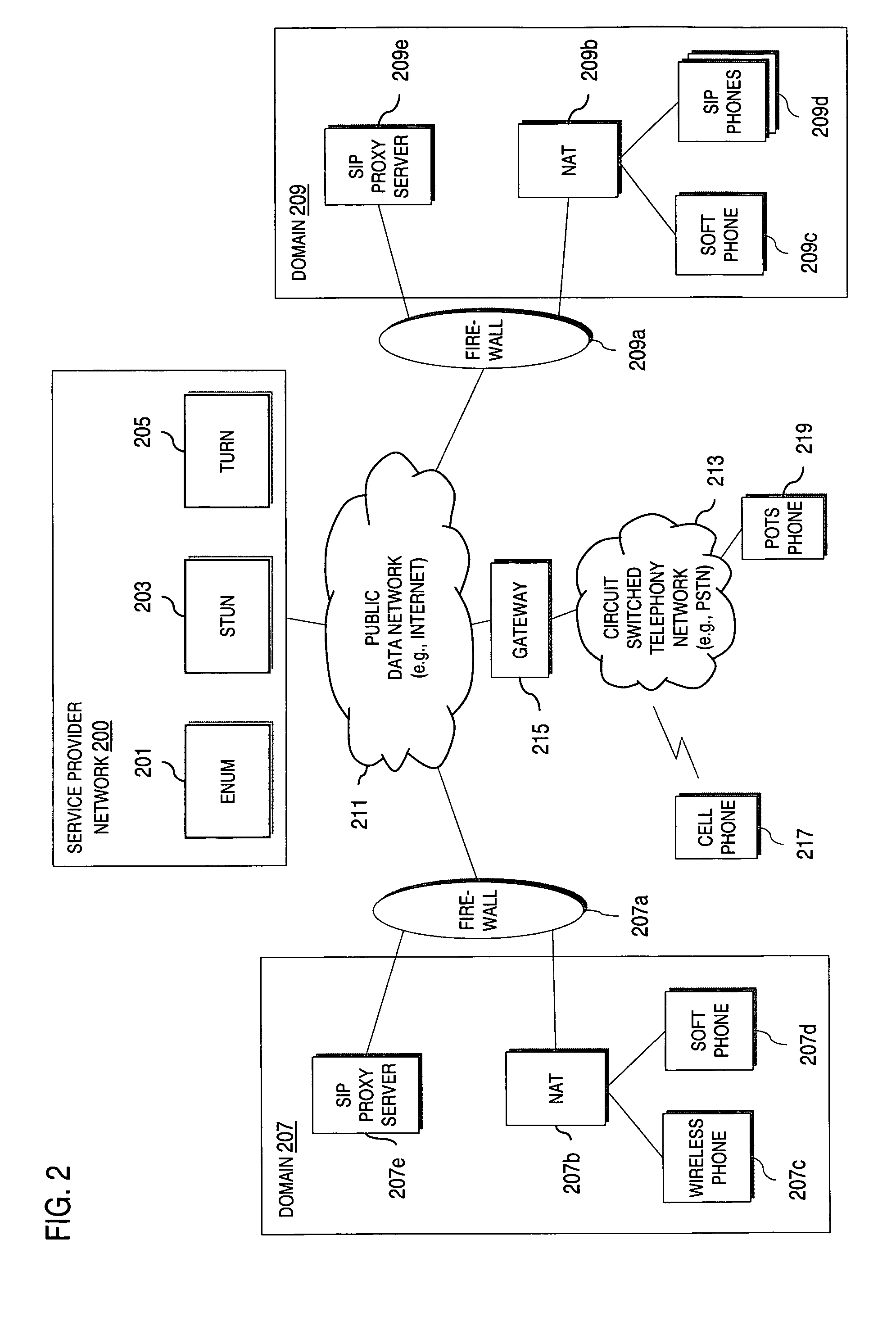
Method and system for providing secure media gateways to support interdomain traversal
ActiveUS20070019623A1Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationNetwork addressNetwork address translation
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A signaling message is received for establishing a voice call from a first endpoint associated with a first domain to a second endpoint associated with a second domain. The first endpoint queries a STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP (User Datagram Protocol)) server to determine information relating to a firewall and network address translator that the first endpoint is behind, and to log into a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server configured to establish a media path between the first endpoint and the second endpoint. A first proxy server serving the first endpoint communicates with an ENUM (Electronic Number) server to convert a directory number corresponding to the second endpoint to a network address. The first proxy server communicates with a second proxy server serving the second endpoint to establish the voice call. The STUN server, the TURN server and the ENUM server are maintained by service provider. The first endpoint is authenticated to permit exchange of a media stream over the media path. The media stream is relayed, if the first endpoint is successfully authenticated.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Method and system for providing secure communications between proxy servers in support of interdomain traversal
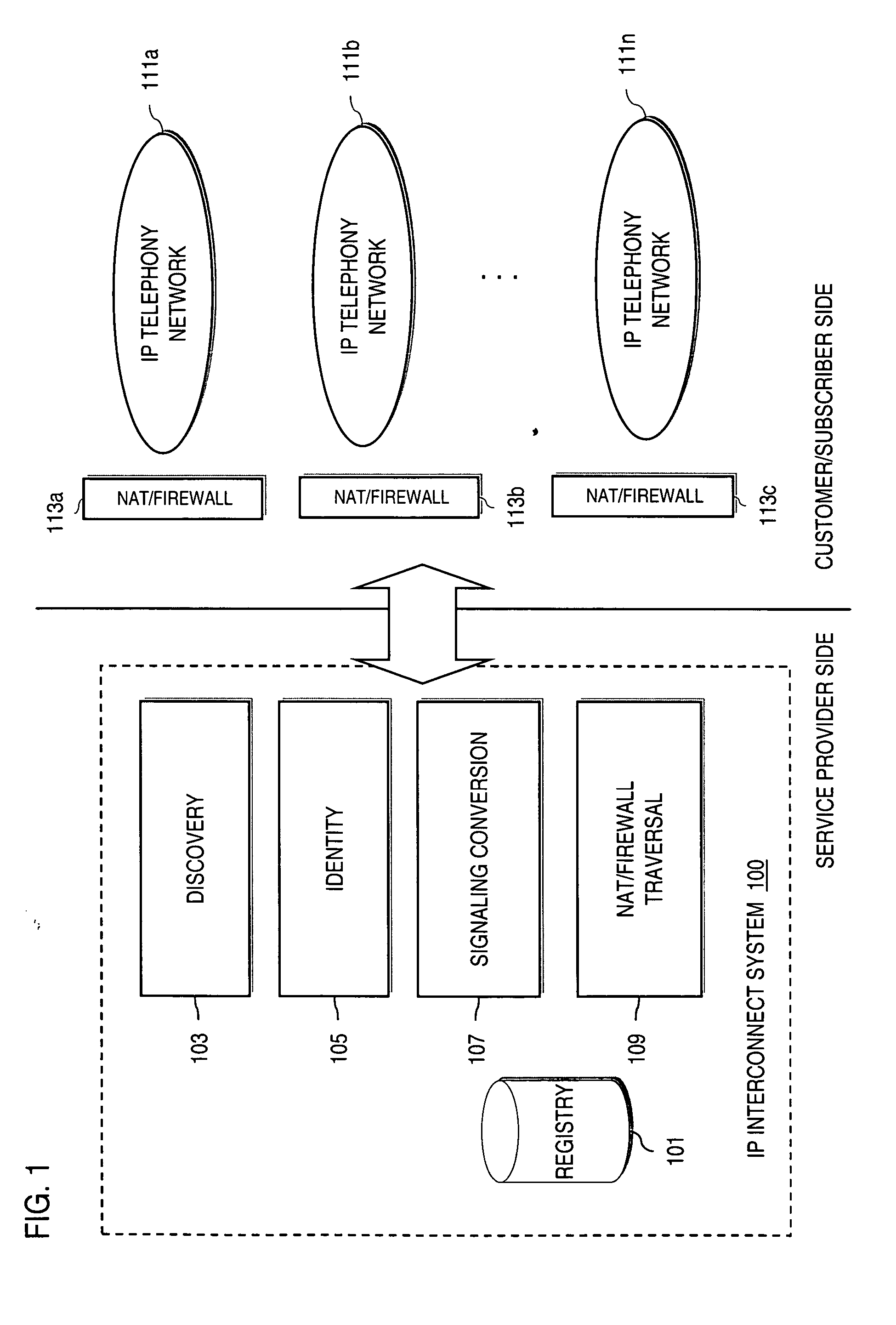
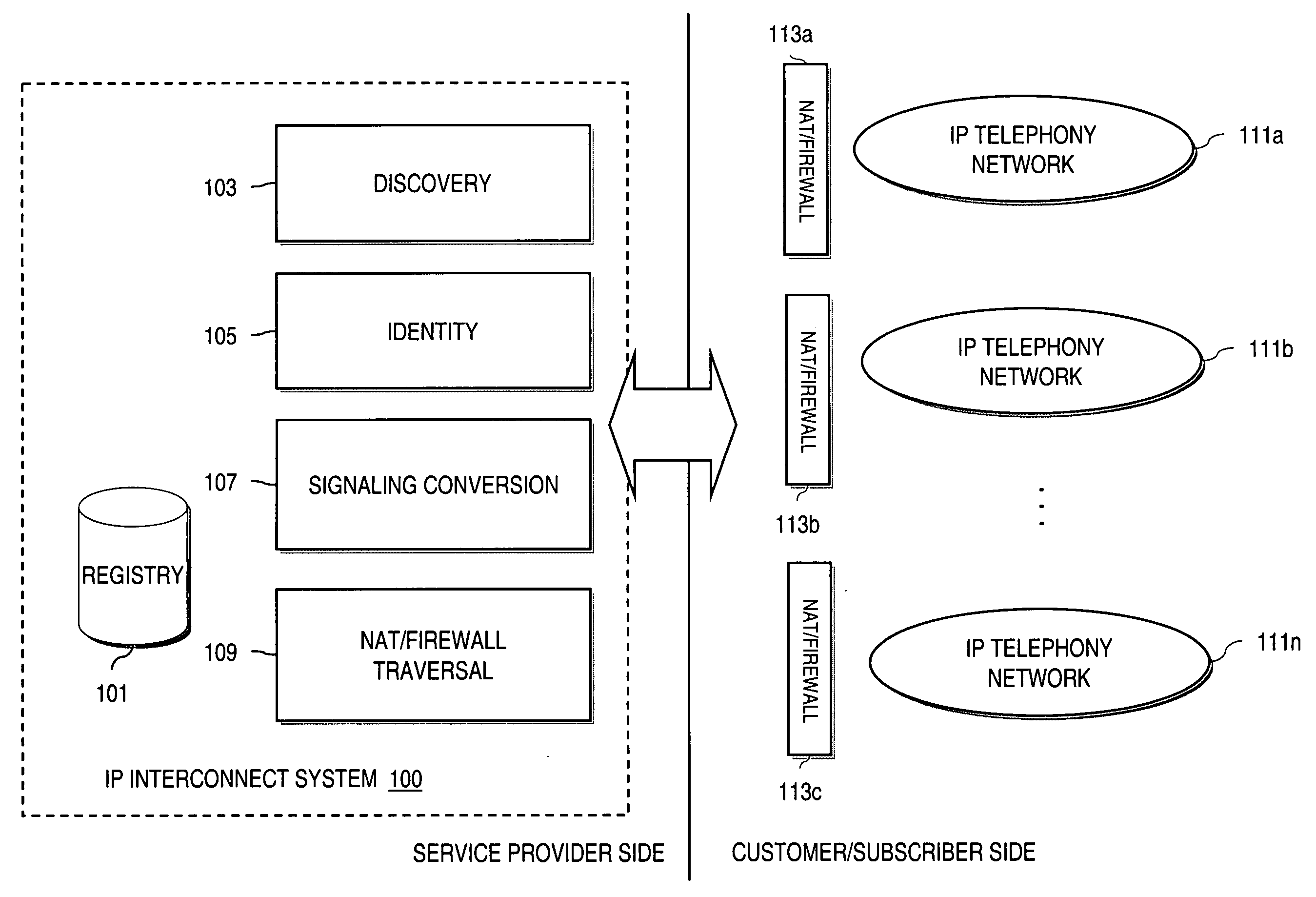
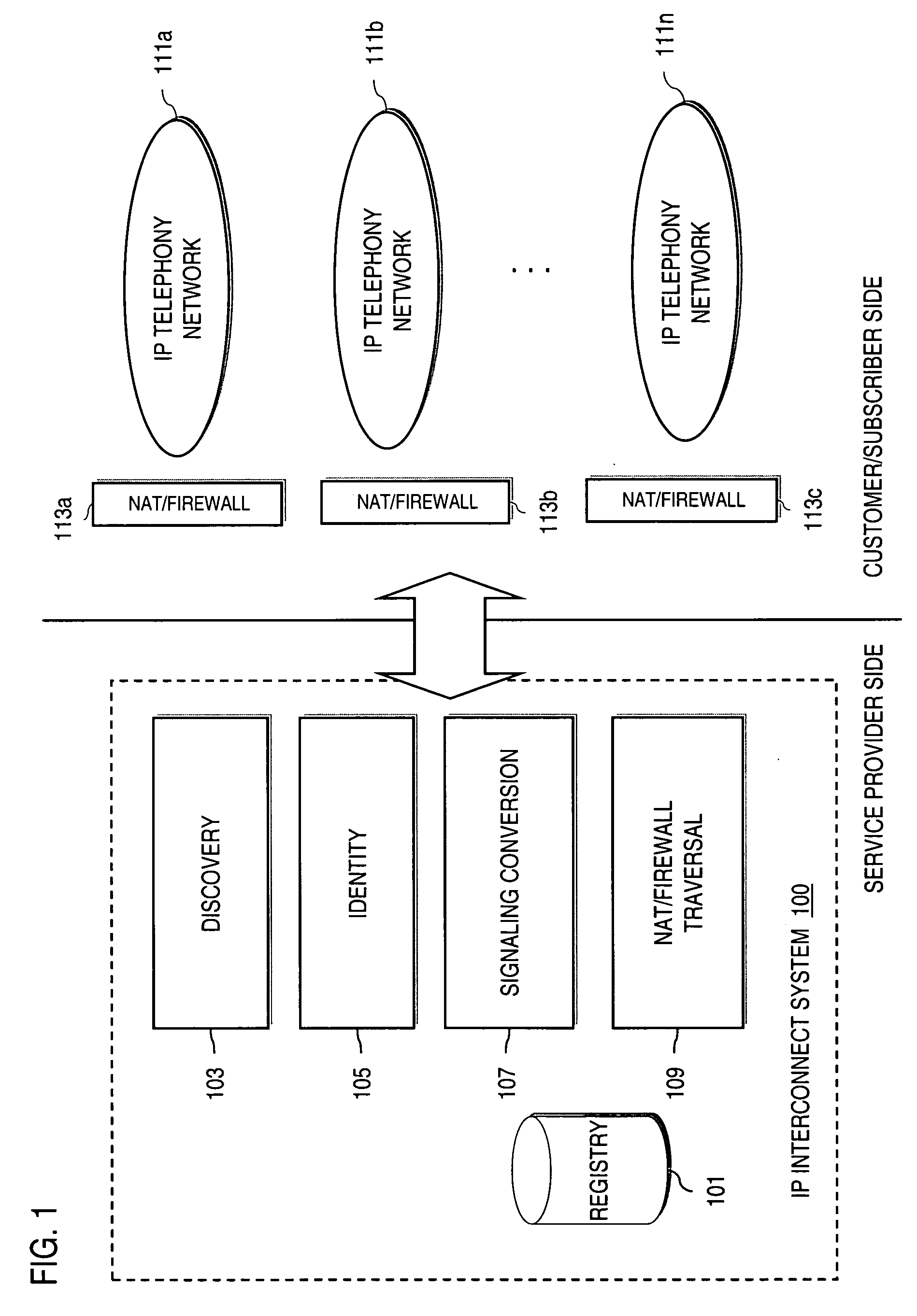
ActiveUS20070019622A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationSecure communicationService provision
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A request is received and specifies a directory number for establishing a communication session from a first endpoint to a second endpoint. The first endpoint is behind a first network address translator of a first domain, and the second endpoint is within a second domain. A service provider network is accessed to determine a network address for communicating with the second endpoint based on the directory number, to determine existence of a second network address translator within the second domain, and to establish, if the network address can be determined, a media path between the first endpoint and the second endpoint based on the network address to support the communication session. An encrypted session is established with a proxy server according to a cryptographic protocol to support the media path. The proxy server resides within the second domain.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Network system of Internet of things and data processing method thereof
InactiveCN102025577ARelieve pressureIncrease profitData switching by path configurationMobile application execution environmentsIot gatewayThe Internet
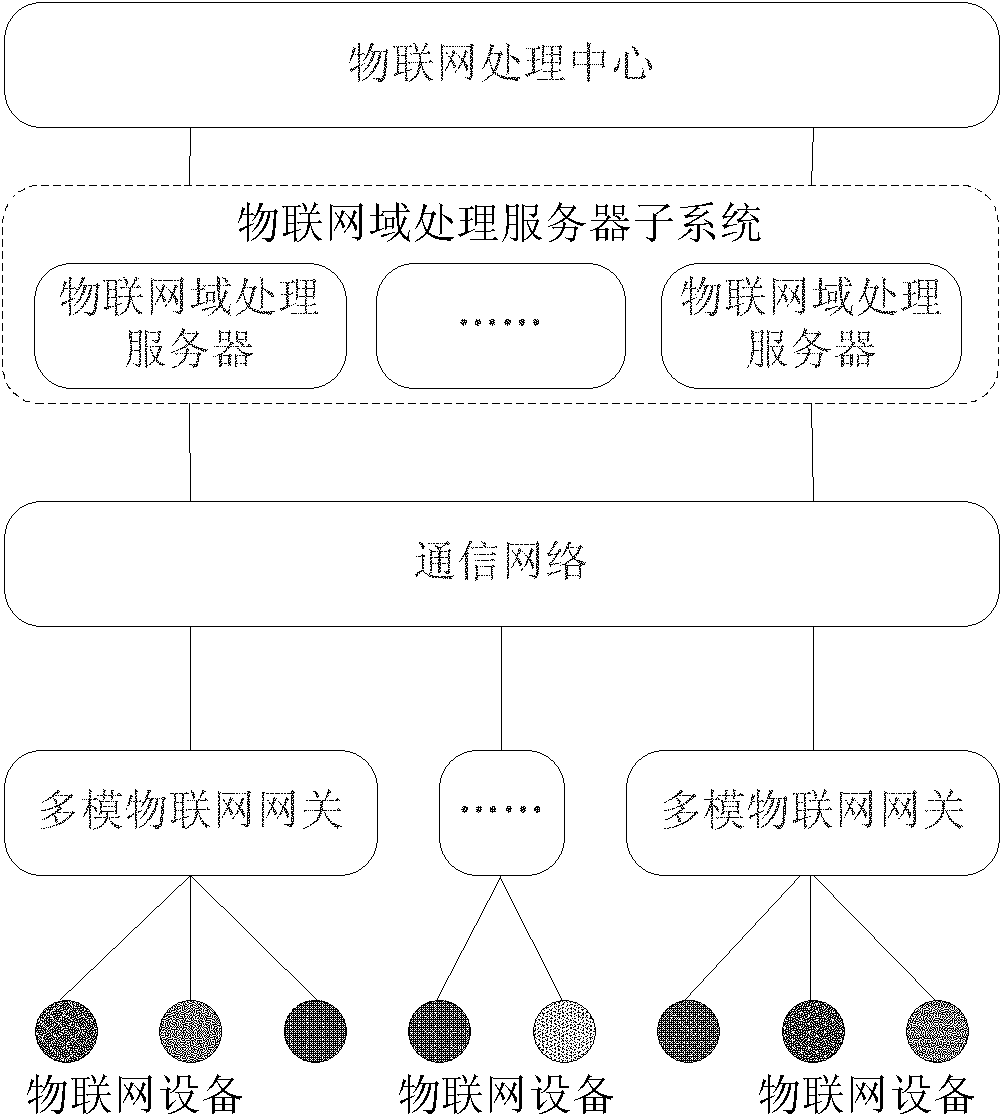
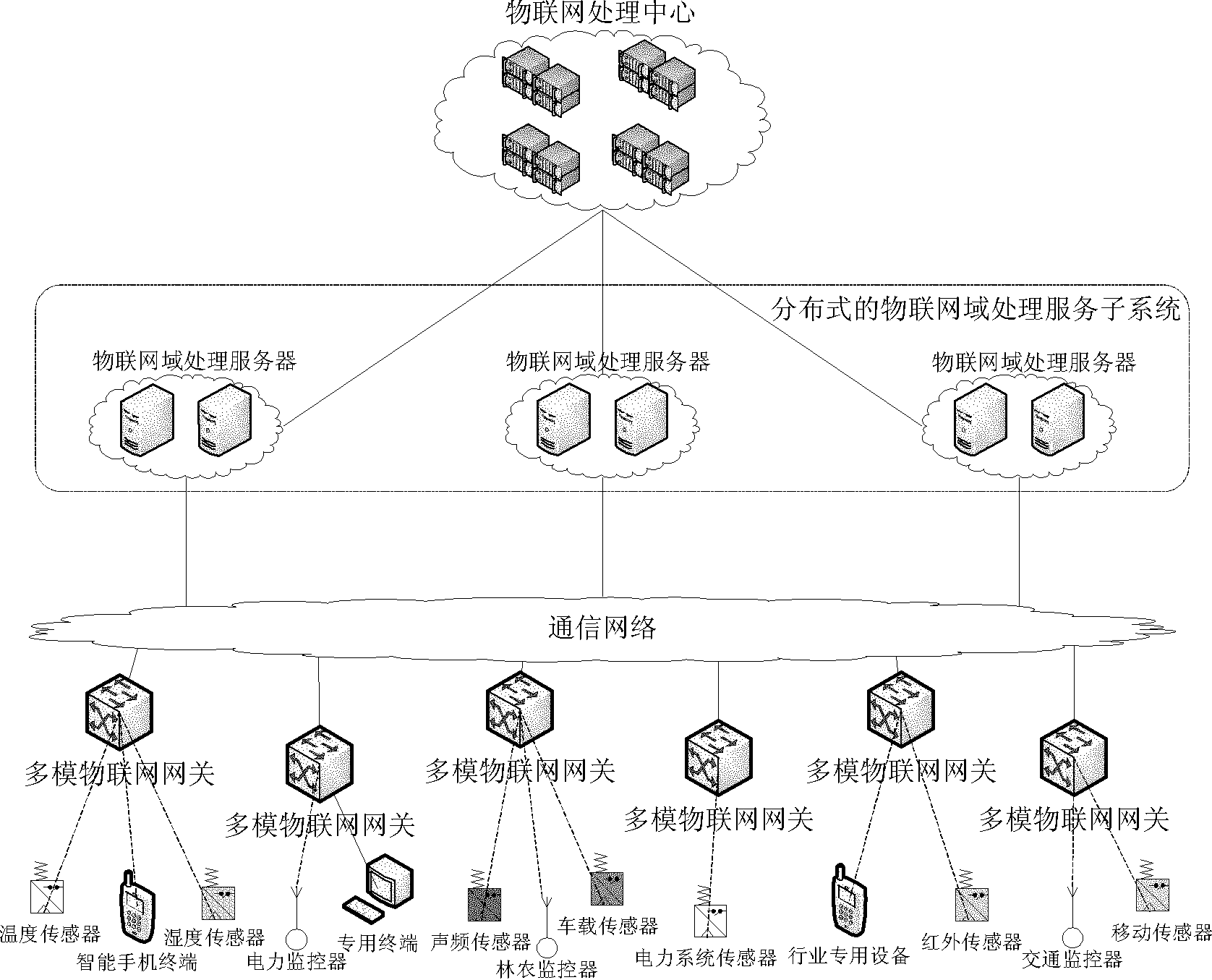
The invention discloses a network system of Internet of things and a data processing method thereof, mainly solving the problems of unavailable heterogeneous network integrated access, difficult resource sharing and poor security control of the existing network of Internet of things. The network system mainly comprises an Internet of things processing center, a distributed Internet of things domain processing and servicing subsystem, a multimode Internet of things gateway, and Internet of things devices. The Internet of things processing center provides service and a development platform for the public, the distributed Internet of things domain processing and servicing subsystem assists the Internet of things processing center to provide the service for the user, the multimode Internet of things gateway provides the protocol conversion and the security service, and the Internet of things devices are used to receive and transmit the Internet of things data or to execute instruction, and perform the inter-domain processing or the intra-domain processing on the network data according to different services when processing the network data in the network system of Internet of things. According to the invention, the problem of heterogeneous network integrated access is solved, the resource sharing rate of the Internet of things is enhanced, and the security control of the Internet of things information is strengthened, therefore, the system and the method can be used in designing and building of the Internet of things network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for providing secure media gateways to support interdomain traversal
ActiveUS7920549B2Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationNetwork addressNetwork address translation
An approach provides interdomain traversal to support packetized voice transmissions. A signaling message is received for establishing a voice call from a first endpoint associated with a first domain to a second endpoint associated with a second domain. The first endpoint queries a STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP (User Datagram Protocol)) server to determine information relating to a firewall and network address translator that the first endpoint is behind, and to log into a TURN (Traversal Using Relay NAT (Network Address Translation)) server configured to establish a media path between the first endpoint and the second endpoint. A first proxy server serving the first endpoint communicates with an ENUM (Electronic Number) server to convert a directory number corresponding to the second endpoint to a network address. The first proxy server communicates with a second proxy server serving the second endpoint to establish the voice call. The STUN server, the TURN server and the ENUM server are maintained by service provider. The first endpoint is authenticated to permit exchange of a media stream over the media path. The media stream is relayed, if the first endpoint is successfully authenticated.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Method and apparatus for managing forwarding of data in an autonomous system
ActiveUS20070091793A1Minimize packet lossRapid responseError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork Communication ProtocolsInter-domain
A method of managing forwarding of data in a first autonomous system (AS) is described. The first AS includes a plurality of border routers having inter-domain links to one or more remote AS's and an associated exterior communications protocol. The border routers use an interior communications protocol with other border routers in the first AS using primary tunnels. The method comprises the steps, performed at a first border router having a primary route via an inter-domain link to a remote AS, of constructing an alternate route to the remote AS via second border router in the first AS, instigating a backup tunnel to the second border router upon failure of the primary route and sending a failure message to the other border routers.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Inter-domain path computation technique
ActiveUS20060171320A1Computationally efficientOptimization pathError preventionTransmission systemsPath computation elementLabel switching
A technique computes a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) that spans multiple domains of a computer network from a head-end node of a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain. The novel inter-domain TE-LSP computation technique comprises a computation algorithm executed by the head-end node, which utilizes Path Computation Elements (PCEs) located within the remote domains (i.e., other than the local domain). Specifically, the head-end node requests path segments from a PCE in each of the remote domains, in which the path segments represent paths between all entry border routers to either all exit border routers of the particular remote domain (i.e., through the domain), or to the tail-end node. Upon receiving path segments from each remote domain, the head-end node combines the path segments with local domain information, and performs a forward path computation from the head-end node to the tail-end node to find the best (i.e., “shortest”) path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
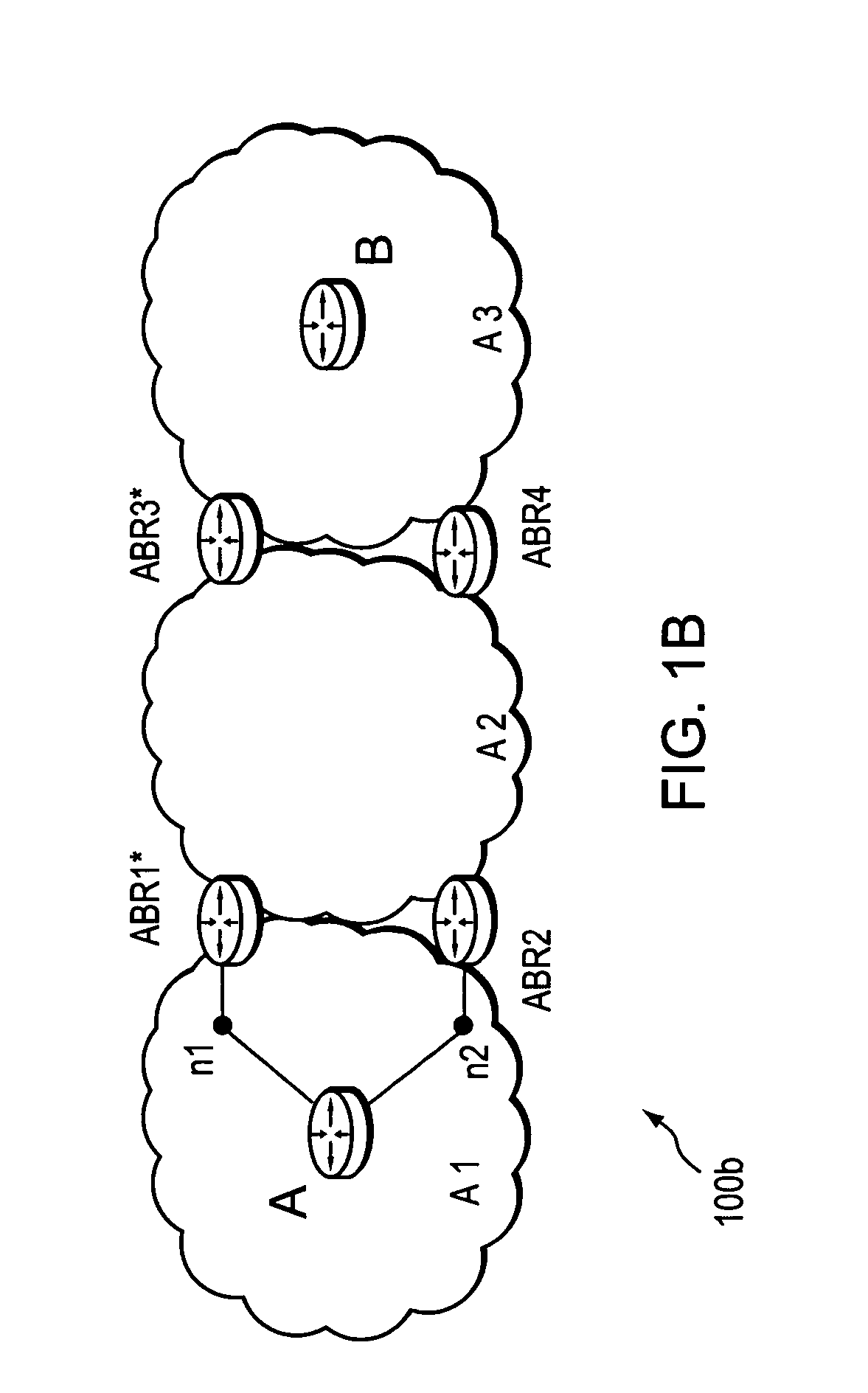
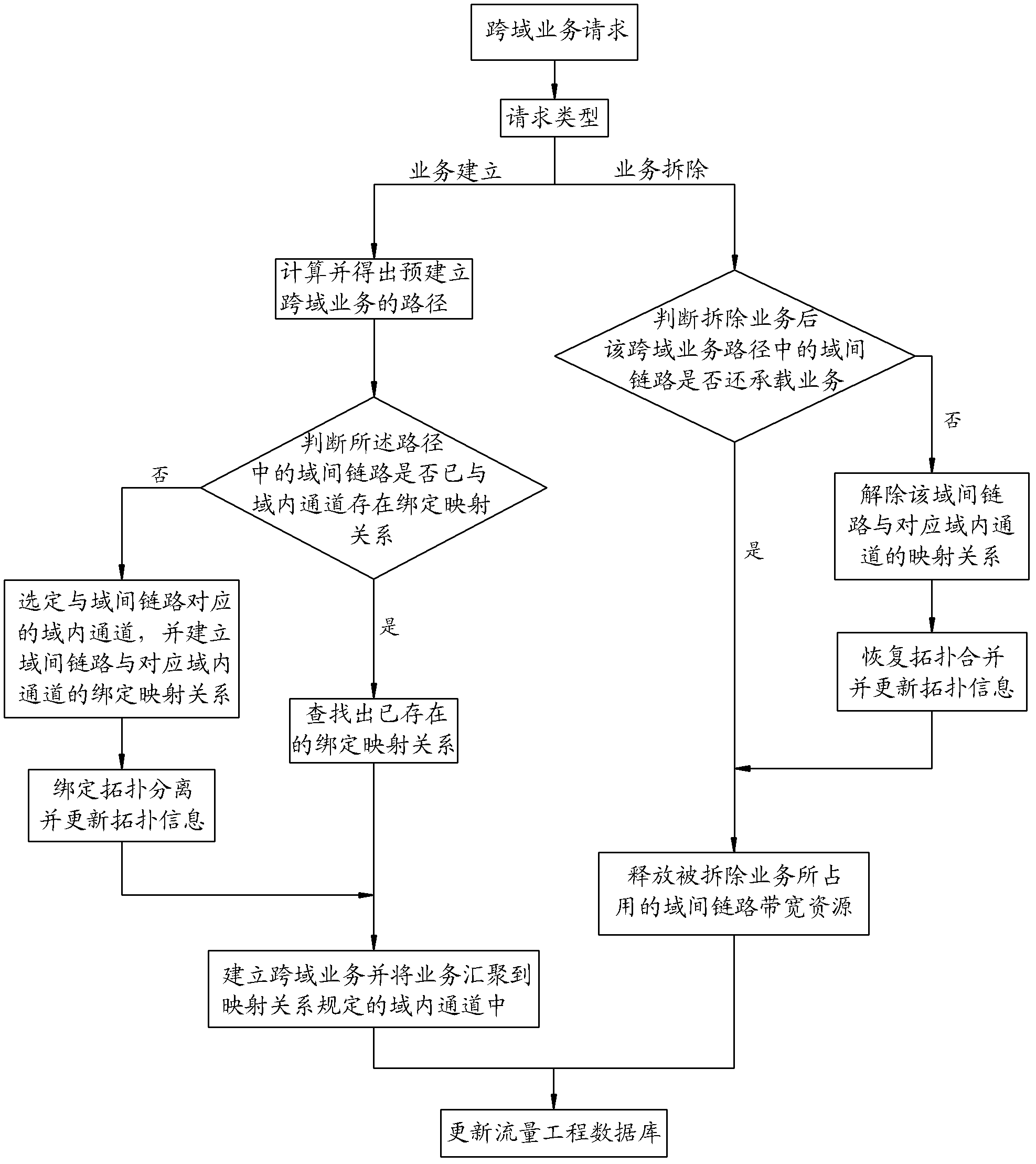
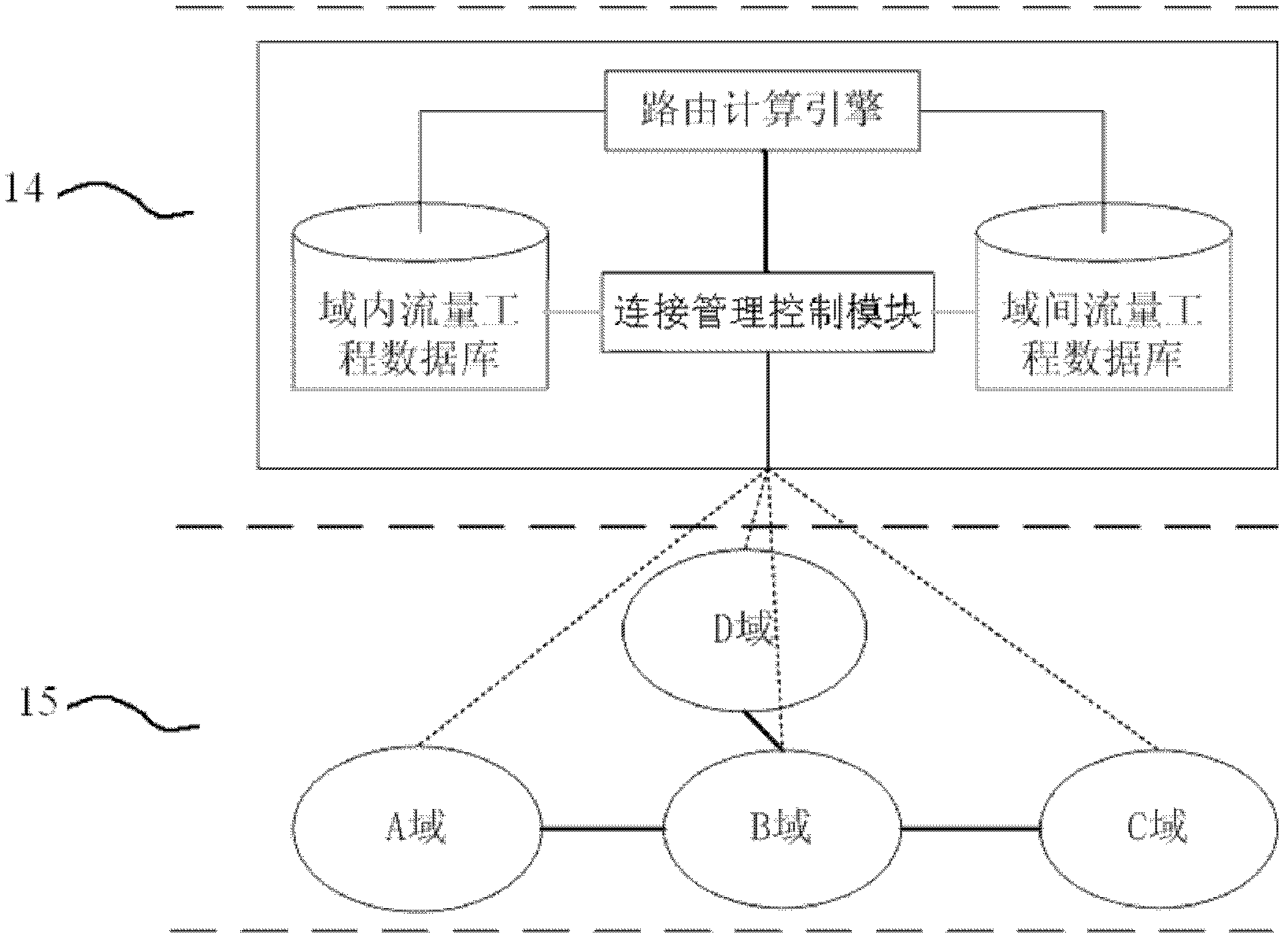
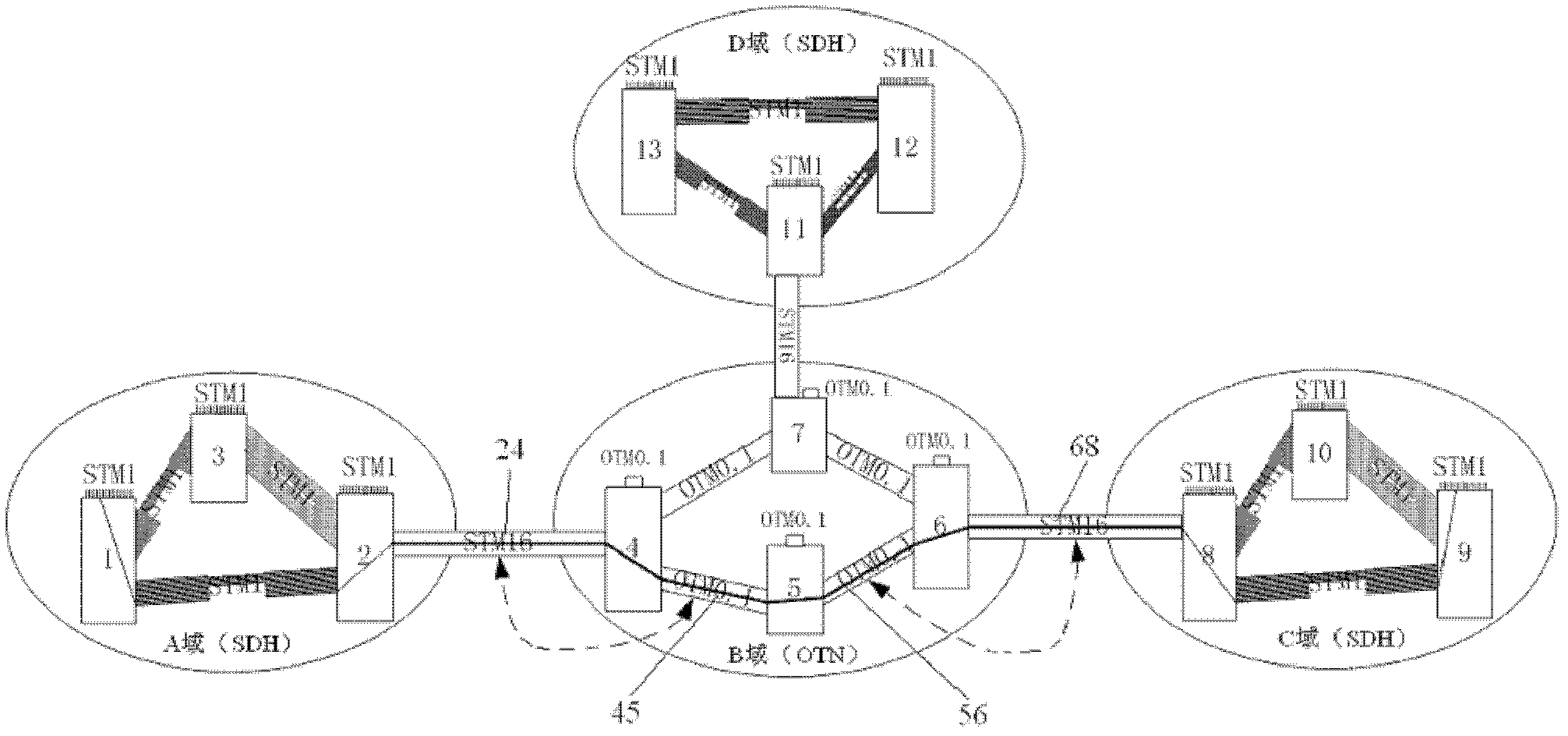
Method and device for binding and mapping control of inter-domain links and intra-domain channels for cross-domain services
InactiveCN102299852ARealize dynamic controlAvoid routing failureData switching networksComputer scienceInter-domain
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Dual-tier security architecture for inter-domain environments
InactiveUS6996716B1Communication securityUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsCost effectivenessSecurity information
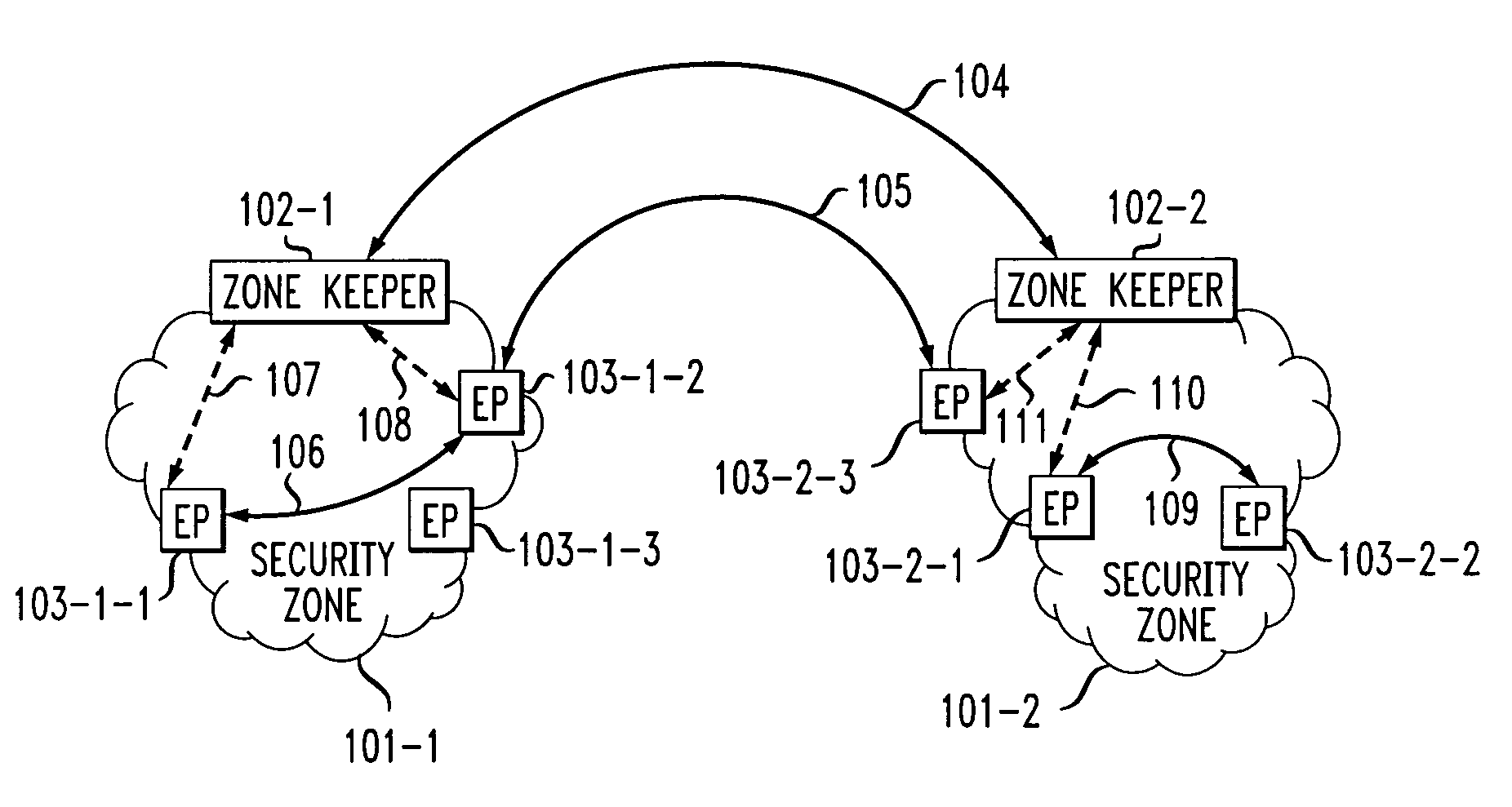
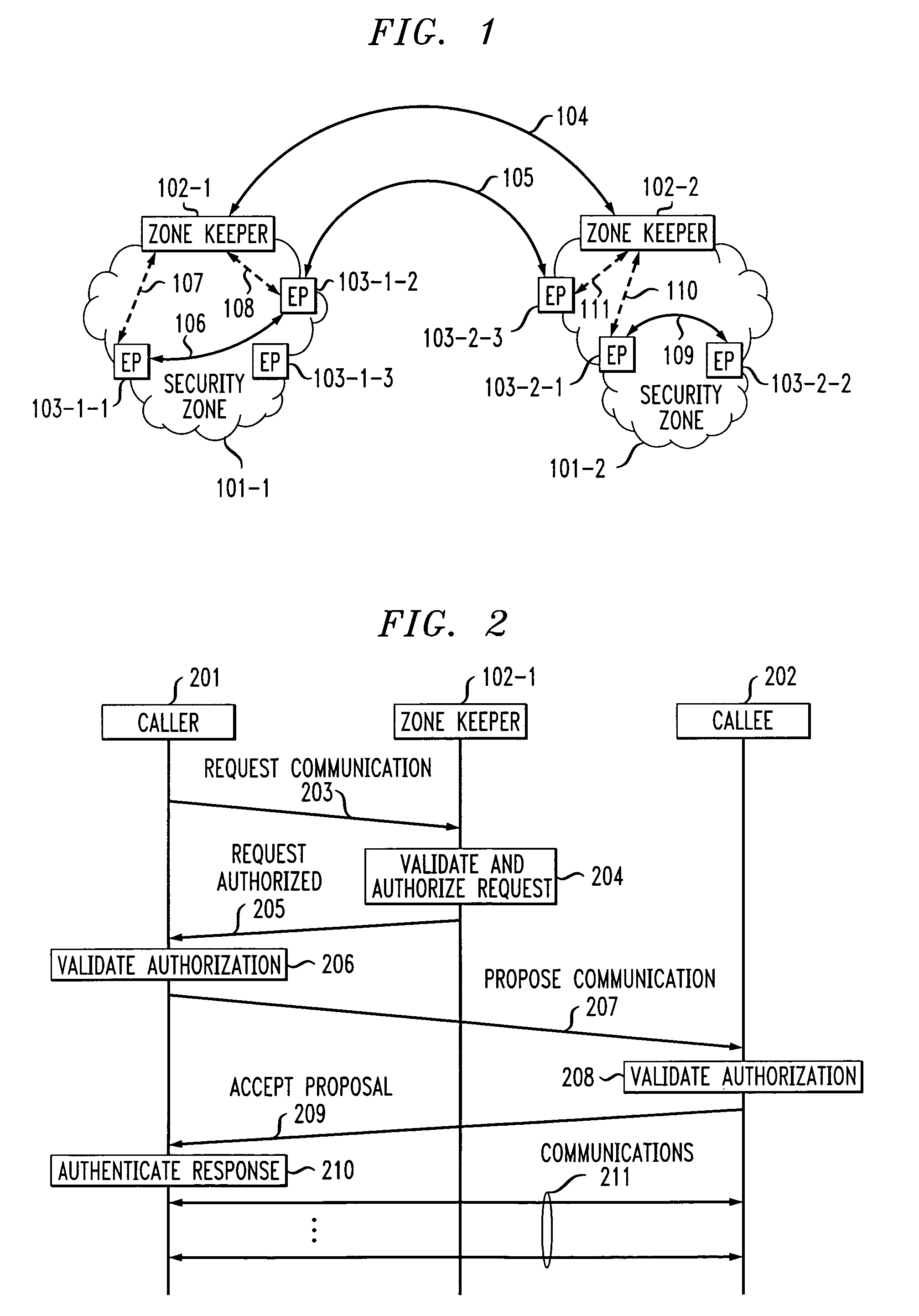
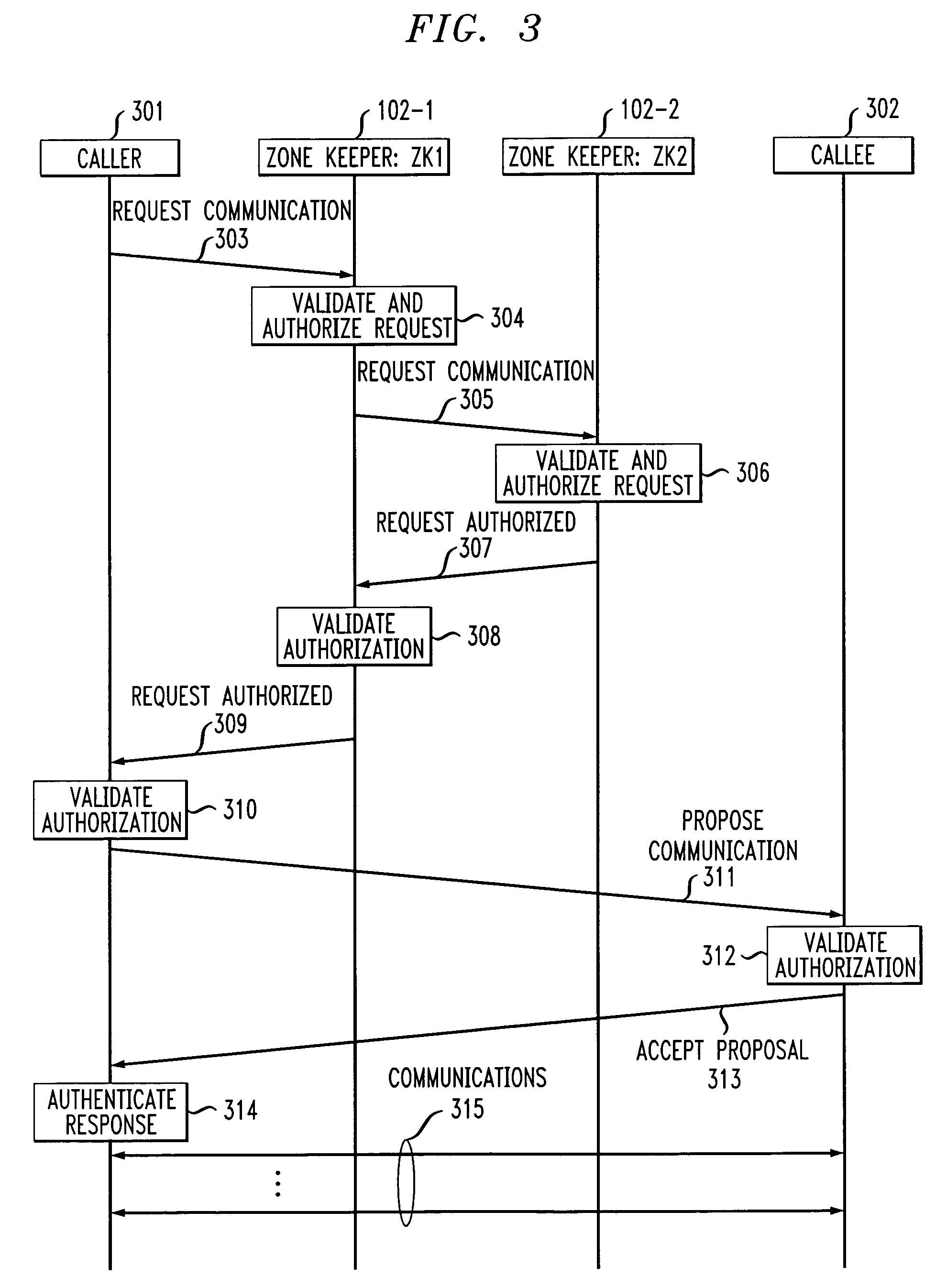
A two-tier security architecture that provides balance between the use of public and secret-key cryptography to realize cost-effectiveness and scalability of security. One tier is an intra-zone tier and the other tier is an inter-zone tier. The intra-zone tier addresses communication between users employing endpoints within a prescribed Security Zone and is designed to achieve cost-effectiveness. The inter-zone tier specifies how communication between users employing endpoints from different Security Zones can be established and is designed to provide scalability for intra-enterprise and / or inter-enterprise communications. Specifically, each Security Zone has a “Zone Keeper” and one or more endpoints that may be employed by users. The Zone Keeper authenticates, i.e., validates, users employing an endpoint in the Security Zone and determines whether a caller and a callee are security compatible. When setting up a communication, the caller provides the Zone Keeper security information in order for the caller to prove its identity. The callee supplies to the caller information confirming its identity. A proposal on how the communication is to be Set-up is sent from the caller to the callee, and if they agree to the proposal and their security is authenticated, the communication is started. For inter-zone, inter-domain, communications, the caller provides information as described above to its Zone Keeper. Then, the caller's Zone Keeper forwards the caller's request to the Zone Keeper of the security associated with the callee. Additionally, the caller's Zone Keeper also supplies the callee's Zone Keeper with its security identity so that the callee's Zone Keeper may authenticate that the request is from the caller's Zone Keeper. Then, the callee's Zone Keeper sends back an authorization to the Caller's Zone Keeper. This authorization includes the callee's Zone Keeper security identity so that the caller's Zone Keeper can authenticate that the authorization is from the callee's Zone Keeper.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Controlled distribution of inter-area routing information
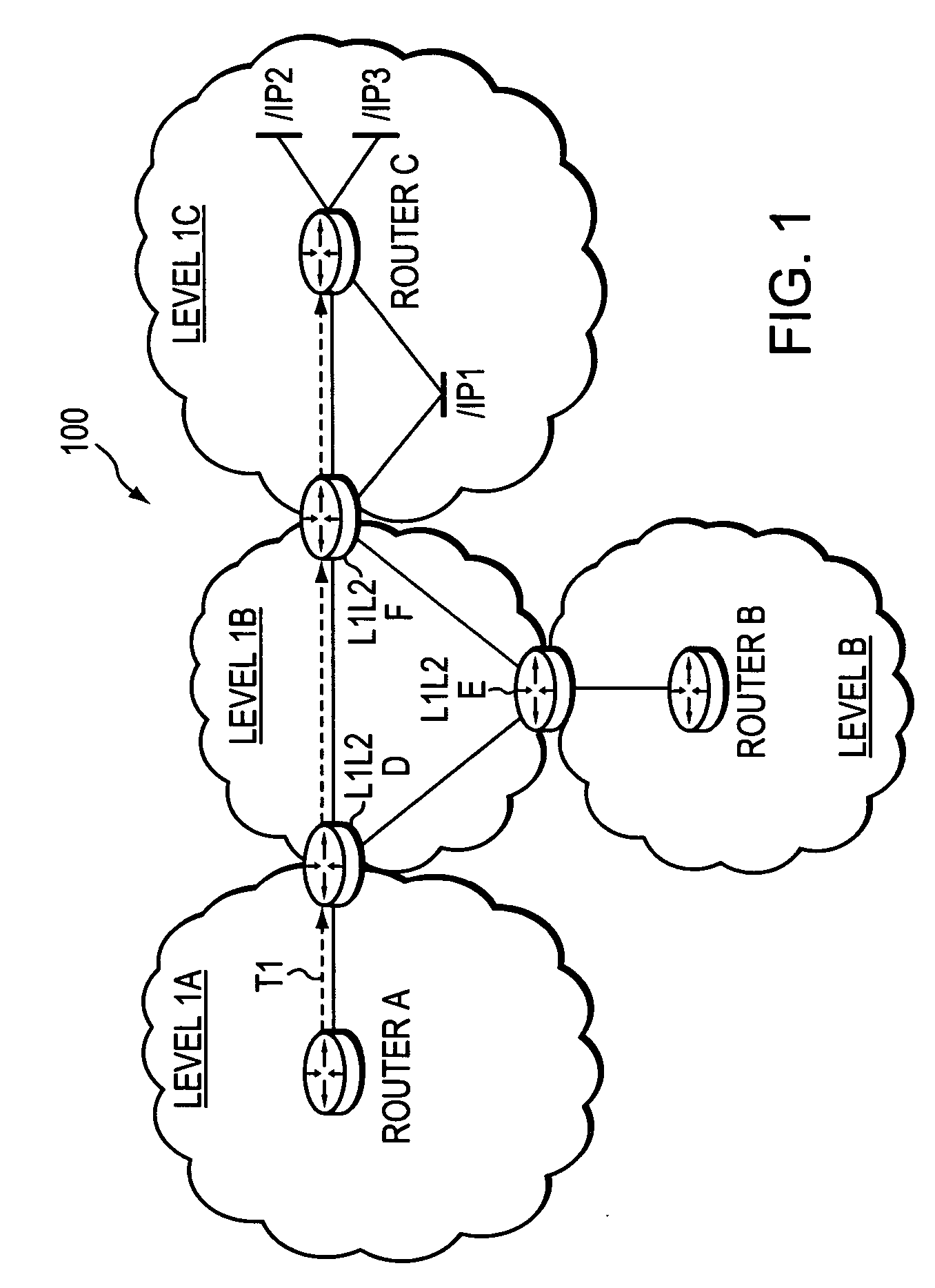
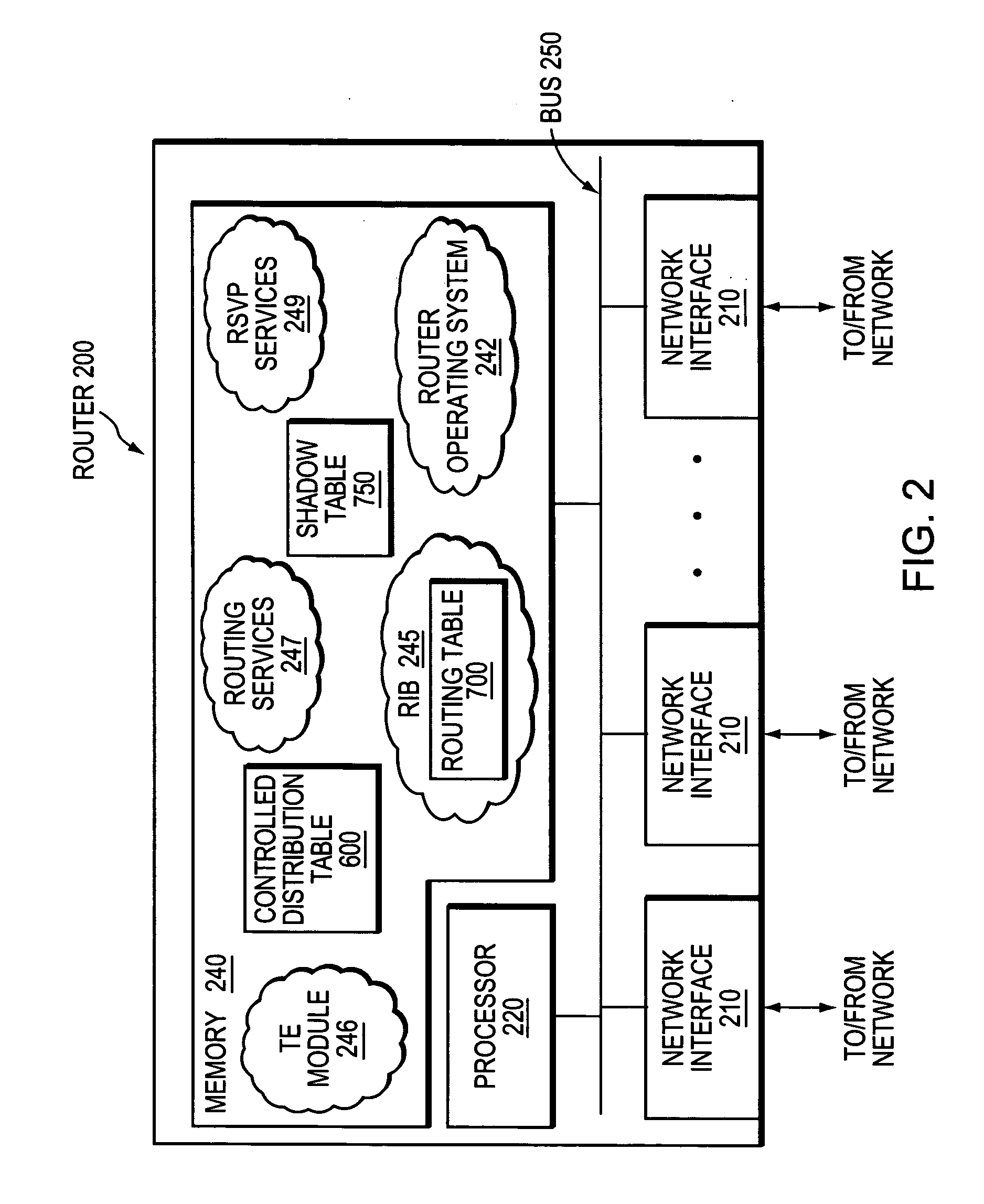
InactiveUS20070058568A1Limit excess distributionData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityRouting table
A technique controls distribution of reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain (“tail-end domain”) that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node (“head-end domain”). According to the inter-domain information distribution technique, the head-end node requests the remote reachability information from the tail-end node, which may employ an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the information to a border router of the tail-end domain. The tail-end domain border router then shares this information with at least a head-end domain border router. The head-end node thereafter requests that the head-end domain border router release the reachability information into the head-end domain. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com