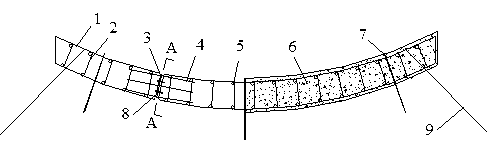
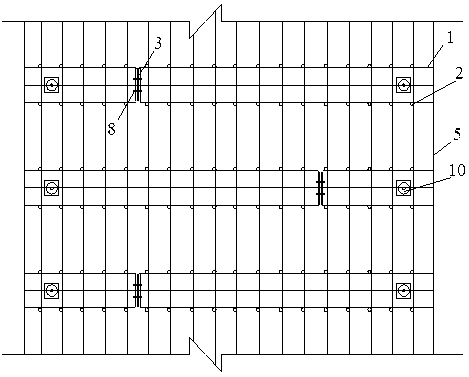
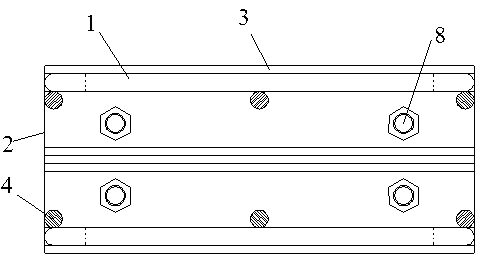
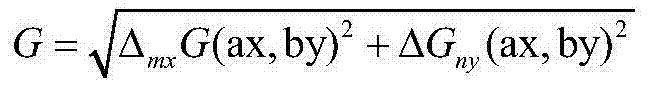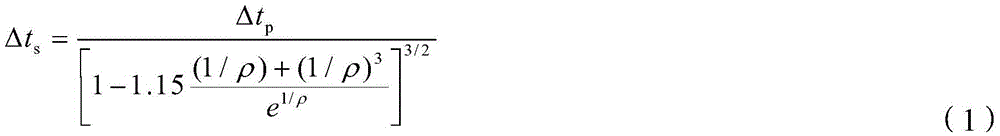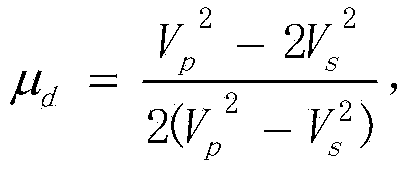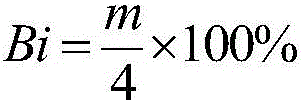Patents
Literature
96 results about "Tectonic stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The major source is tectonic stress; it is primarily a consequence of the slow cooling of the earth. The stress occurs continually as a field within the earth’s crust. However the direction and magnitude of stresses change over space and time. These changes induce strain within the local crust.
Discrete fracture modeling method based on multiscale factor restraint
InactiveCN104730596AReflect spatial heterogeneityAvoid complexityGeological measurementsTectonic stressWrinkle skin
The invention provides a discrete fracture modeling method based on multiscale factor restraint. The discrete fracture modeling method based on multiscale factor restraint comprises the following steps that the fracture parameter of a single well is recognized and described in details; a fault-wrinkle-fracture symbiosis evolution system is established based on the counted fracture parameters, and a key fracture making period is determined; the fracture parameter based on detailed tectonic stress field simulation is calculated in a quantitative mode; main controlling factors for fracture development are optimally selected; the weights of the main controlling factors of the fracture are optimally selected according to the entropy weight method; a multiscale fracture DFN model restrained by multiple factors is established; a double-hole and double-permeability geologic model is established. According to the discrete fracture modeling method based on multiscale factor restraint, the mutual control and influence between multiscale fractures are analyzed based on detailed description, obtained through CT scanning, of one single well, the multiple geological factors, such as the structure and deposition, controlling fracture development are analyzed, the main controlling factors for fracture development are optimally selected according to the entropy weight method, a large-scale discrete fracture model, a medium-scale discrete fracture model and a small-scale discrete fracture model are established, an idea and method for establishing a detailed fracture geologic model are formed, and an important basis is provided for efficient development of a fractured oil reservoir and scheme optimization.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
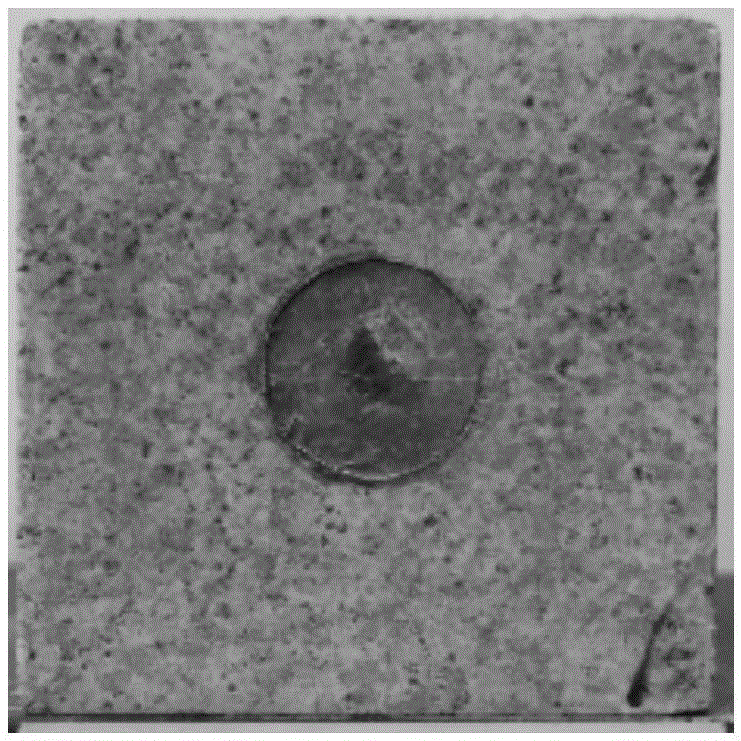
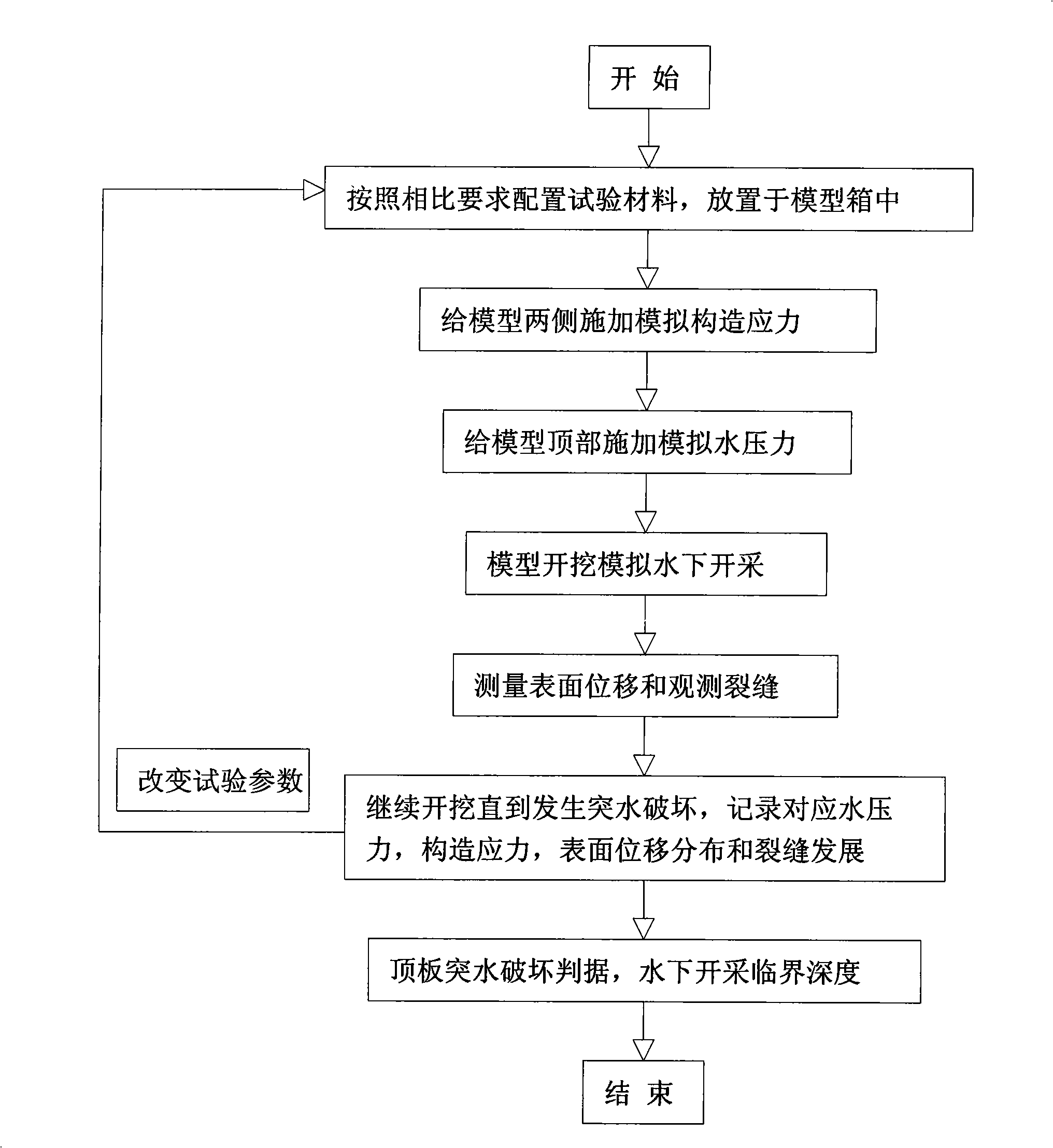
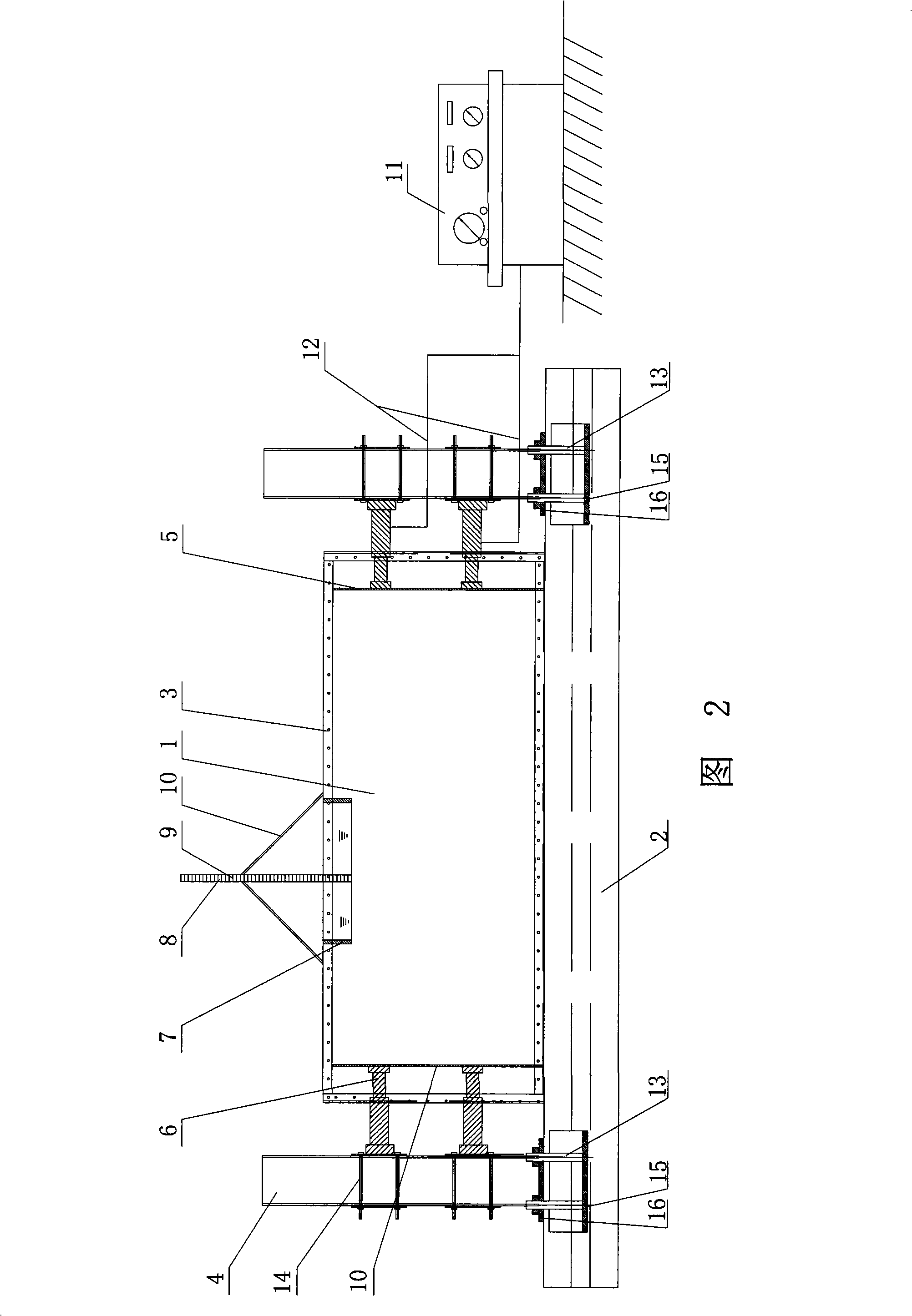
Offshore mining top board seepage flow sudden inflow test method and device
ActiveCN101308126ATo achieve the purpose of waterproofingWon't flow outMaterial analysisTectonic stressExperimental methods
The invention discloses an experimental method for top plate seepage and water inrush when in underwater exploitation as well as an apparatus thereof, comprising the steps of: (1) putting a configured experimental material in a model box according to the practical relative position; (2) exerting lateral pressure on the model material in the model box; (3) sealing the top part of the model box and exerting the stated water pressure on the top part of the model; (4) acquiring water pressure data, tectonic stress data, displacement digital photos and crack digital photos magnified by certain times at regular intervals in the exploitation process until the water inrush destruction takes place; (5) repeating the steps of (1), (2) and (3) to change lateral pressure and water pressure parameters, and repeating the step (4); and (6) obtaining the relation between the water pressure at the top part, the tectonic stress and the model surface displacement, model surface crack. The method and apparatus can embody the combined action of tectonic stress and water pressure at the top part and deadweight function of cover layer more factually, thereby improving the testing precision.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Punching-shear composite drill bit for hard rock drilling
ActiveCN107842317AReduced compressive strengthLow shear strengthDrill bitsTectonic stressPre cracking
The invention discloses a punching-shear composite drill bit for hard rock drilling. The punching-shear composite drill bit comprises three parts of an impactor, an internal punching bore bit and an external cutting drill bit, a lower joint of the impactor can be in threaded connection with the external cutting drill bit, and the upper part of the internal punching bore bit is connected with the impactor in a spline mode; and the lower end face of the internal punching bore bit extends out of the surface of the external cutting drill bit, the central axis of the internal punching bore bit is parallel to or coincident with the central axis of the external cutting drill bit, distributed teeth on the internal punching bore bit and distributed teeth on the external cutting drill bit are combined and can completely cover a downhole, and distributed teeth on the internal punching bore bit and the distributed teeth on the external cutting drill bit are independent of each other. In this way,rock crushing through shearing and rock crushing through impact are creatively combined together, a rock stratum at the hole bottom is pre-cracked first through the internal punching bore bit, the whole tectonic stress of the rock stratum is destroyed, the strength of compression resistance and shearing resistance of rock is reduced so that PDC column teeth and PDC cone teeth can more easily cut / plough-cut the rock, and the rock-breaking efficiency of the super hard rock stratum is greatly improved.
Owner:XIAN RES INST OF CHINA COAL TECH& ENG GROUP CORP
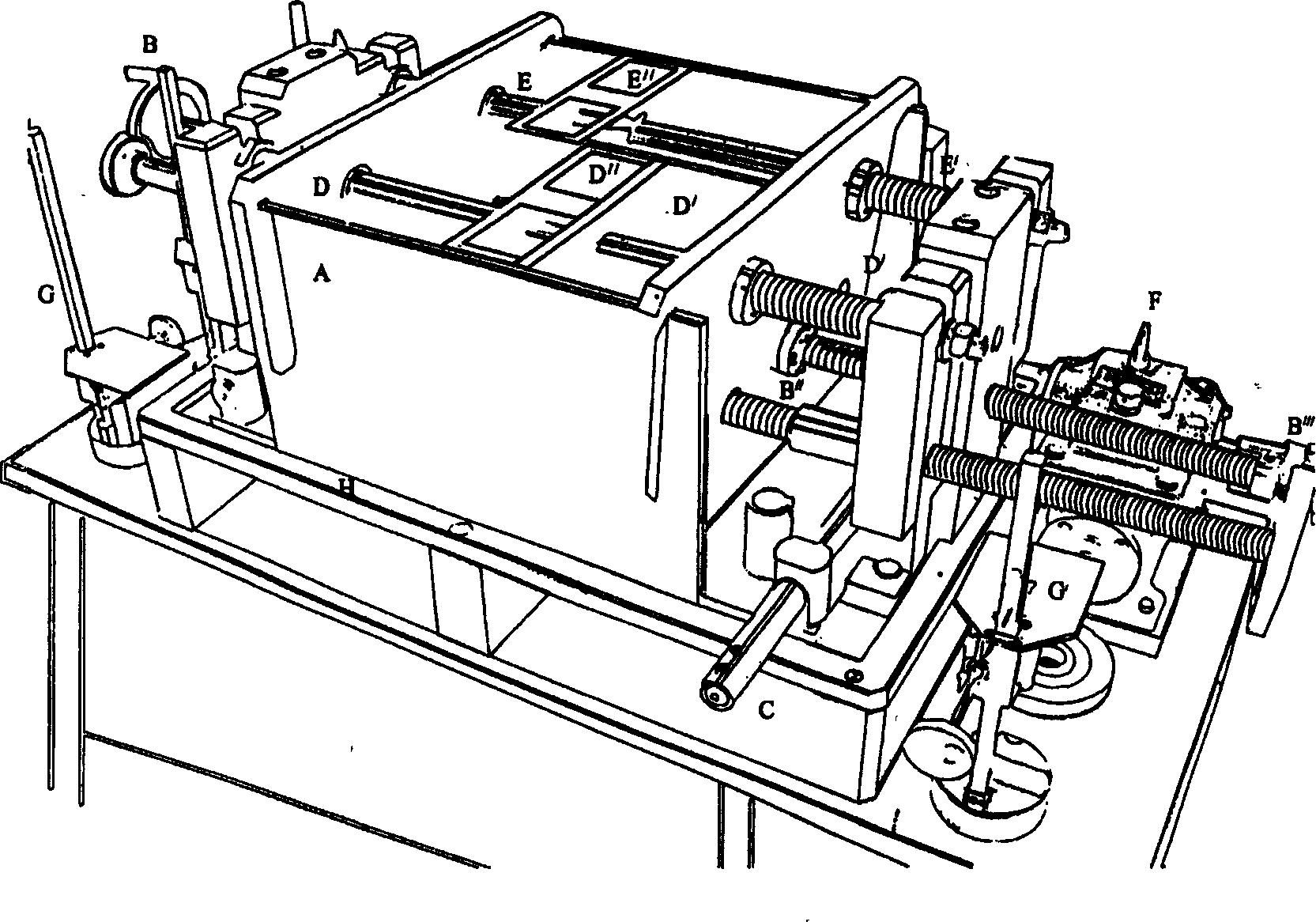
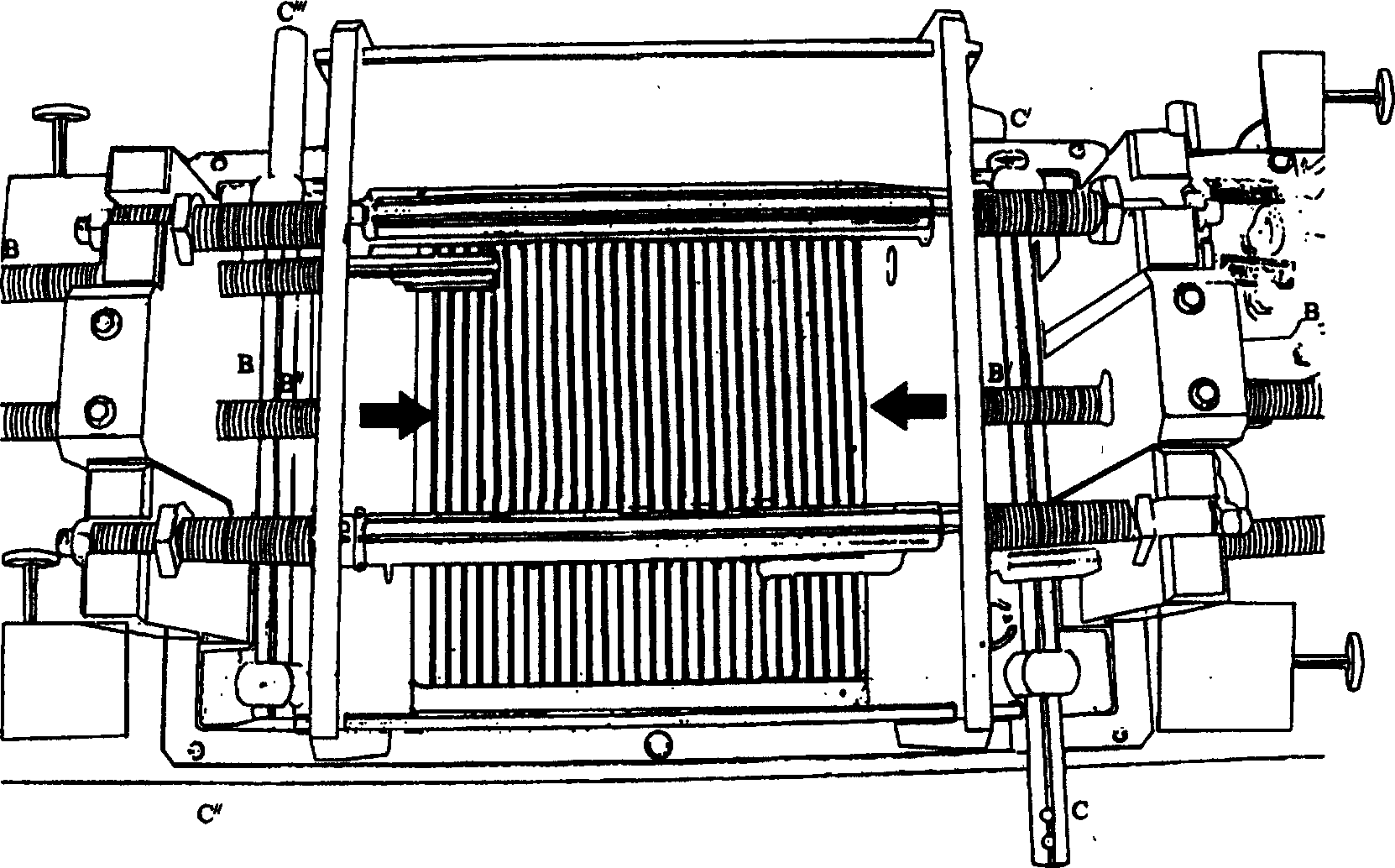
Multifunction tridimension structure analogue testing device
InactiveCN1538359ATo achieve a multi-purpose machineTo achieve the function of one machine with multiple functionsEducational modelsTectonic stressEngineering
The experimental apparatus is stochastic shortened or elongated along X, Y, Z directions under actions of different driving forces in order to show geological structure deformation in evolvement under various driving forces. Accessories can measure horizontal and vertical displacement values of experimental apparatus caused by diversified forces. Values of tectonic stress applied to model are also can be measured so as to realize quantized simulation experiment. Comparing traditional apparatus, invention makes developments: from 2D apparatus to 3 D, from simple functional driving force to multiple functional driving forces including left-lateral and right -lateral sense torsions. Thus, one apparatus serves several purposes so as to raise work efficiency more than several decuples.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fractured rock mass grouting simulation visual test system and test method considering stress effect
Owner:INST OF DEFENSE ENG ACADEMY OF MILITARY SCI PLA CHINA +1
Strike-slip fault structure evolution analytical method
InactiveCN108680952AReduce spendingEasy to operateSeismic signal processingTectonic stressKinematics
The invention belongs to the oil and gas field exploration and development and mineral evaluation and prediction field and relates to a strike-slip fault structure evolution analytical method. According to the strike-slip fault structure evolution analytical method, the fault paleo fall of different positions of a strike-slip fault is calculated, so that the periodic rhythm change of the paleo fall of the fault along a strike-slip direction is analyzed; restored graben-horst structures at two sides of the strike-slip fault in different periods are used to determine basin prototypes at the twosides of the strike-slip fault before the deposition of different strata, and identify the damping sections of the strike-slip fault; the unit movement intensity of the fault is calculated to characterize the strike-slip amount of the strike-slip fault; the calculated strain energy release rate of the strike-slip fault is used to analyze the dynamic mechanisms of different portions of the strike-slip fault; and the numerical simulation of a tectonic stress field is used to explain the fault from the aspect of dynamics and verify the formation mechanism of the strike-slip fault. The method foranalyzing the formation mechanism and evolution process of the strike-slip fault is systematically provided from a time and space four-dimensional perspective in the aspects of geometry, kinematics and dynamics.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
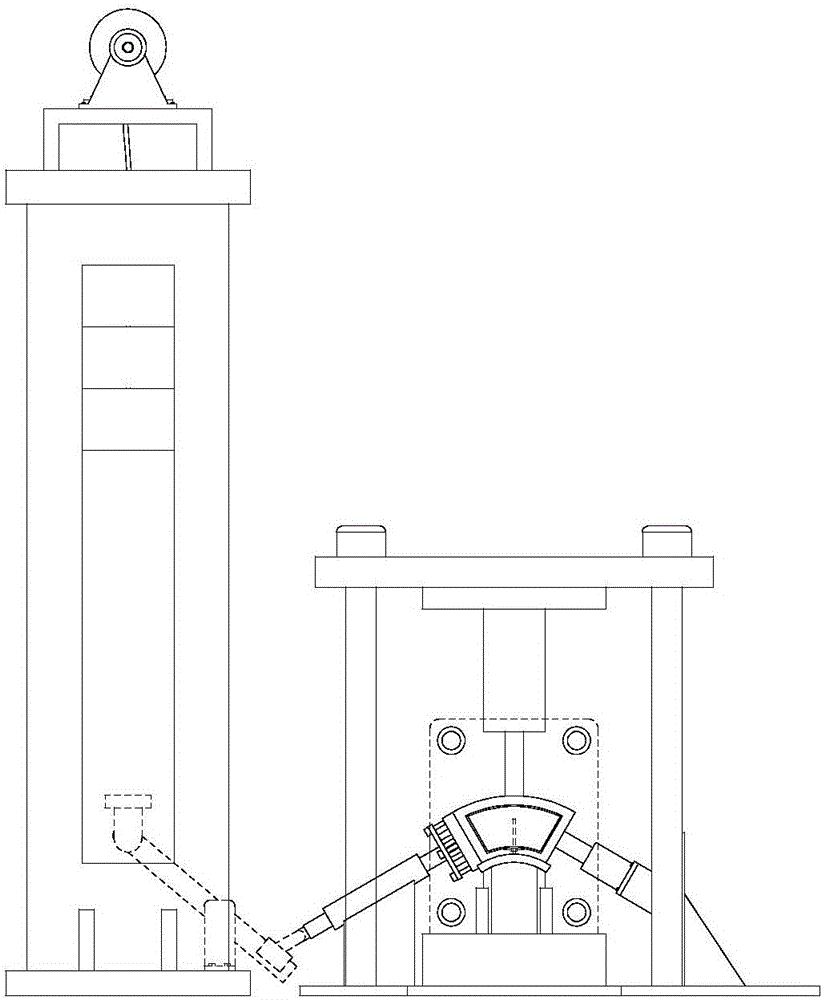
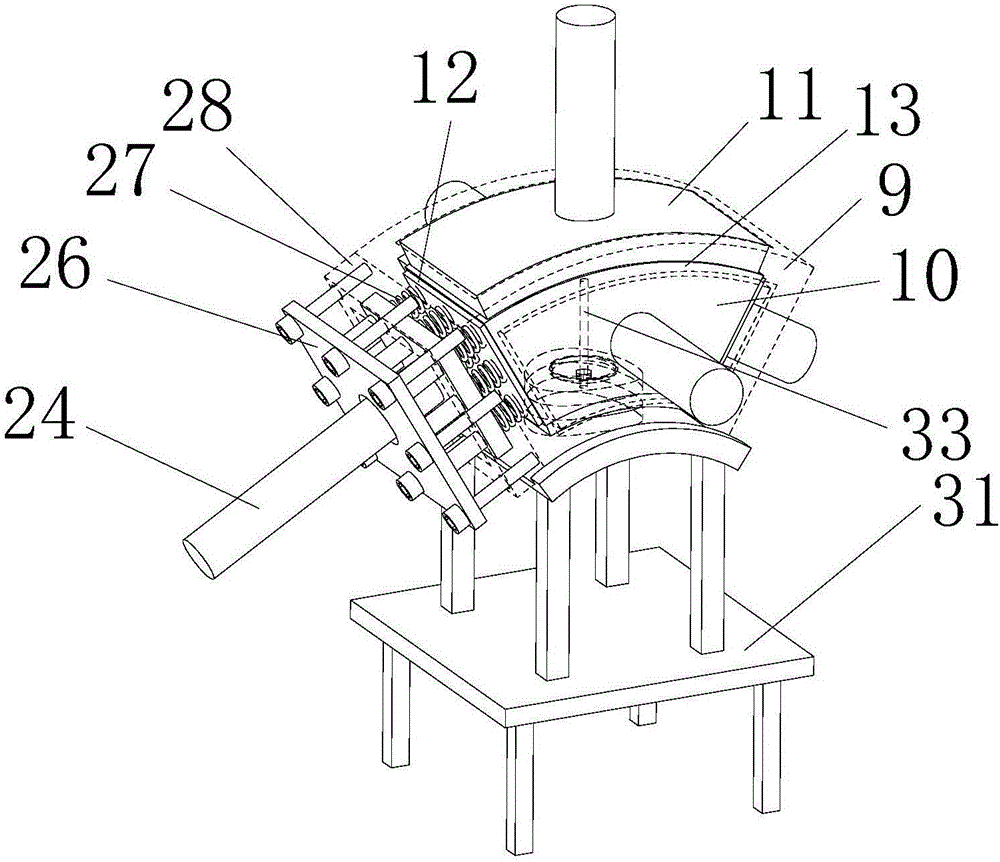
Simulation test apparatus of tectonic stress field and method thereof
ActiveCN105204088AReal-time monitoring of changing characteristicsGood flexibilityGeological measurementsTectonic stressSlide plate
The invention discloses a simulation test apparatus of a tectonic stress field and a method thereof. The apparatus comprises a simulated test bench, a loading module arranged at the top of the test bench, lateral loading systems, and a console. The simulated test bench includes a cuboid frame and baffle plates installed at the periphery of the cuboid frame. A model is laid inside the frame and is formed by successively laying of a plurality of layers of similar materials; and a water capsule and a smooth plate assembly are arranged between the bottom similar material and the similar material at the upper layer. The smooth plate assembly includes at least two smooth plates and a clamp groove part enabling the smooth plates to move relatively; and the water capsule is laid below the smooth plates. At least one separator plate for simulating a facture layer is arranged inside the similar material layer above the smooth plates in advance; and a certain included angle is formed between the separator plate and the water capsule at the horizontal direction. According to the invention, quantitative researches on the stress field evolution process during the tectonic movement formation process can be realized; and a beneficial theory and data basis can be provided for underground activities like mining.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
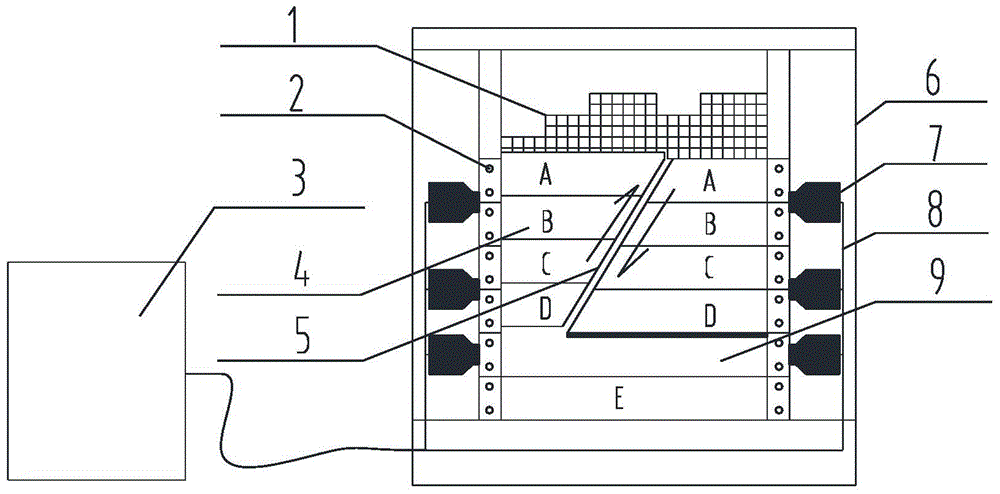
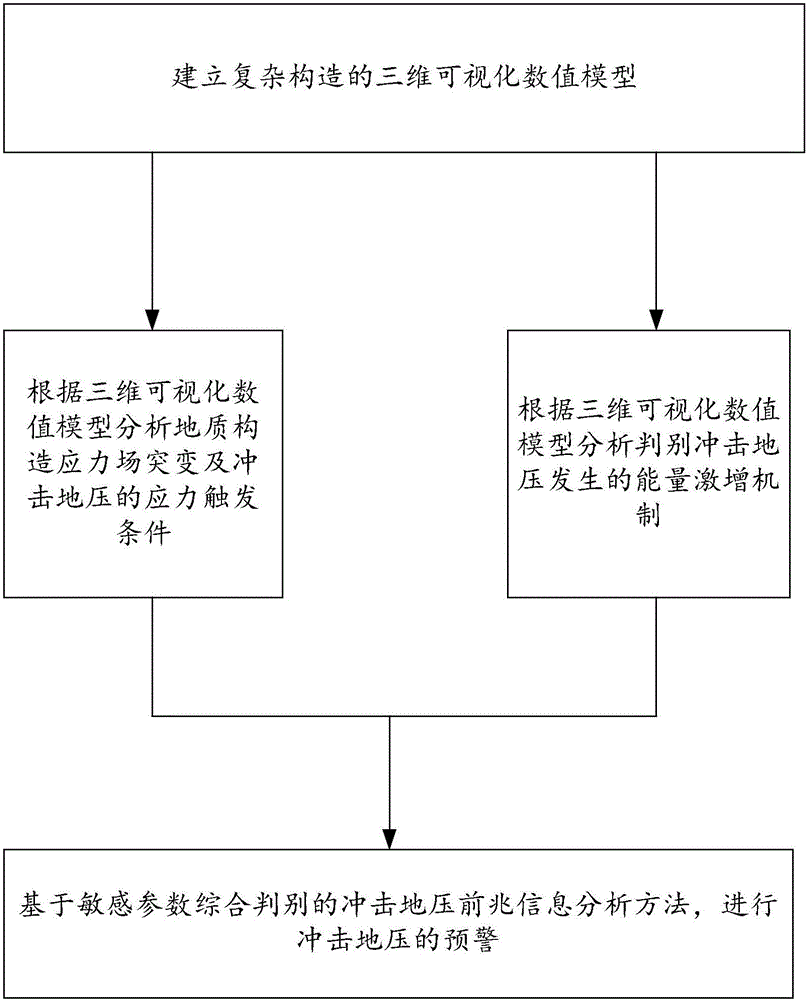
Rock burst early warning method and system in complex geological occurrence environment
ActiveCN106285782AAccurately describe the shape of the spreadPromote research and developmentMining devicesTectonic stressInformation analysis
The invention relates to a rock burst early warning method in a complex geological occurrence environment. The rock burst early warning method in the complex geological occurrence environment comprises the following steps that S1, a three-dimensional visualization numerical model of a complex tectonic belt is built; S2, the stress triggering conditions of geological tectonic stress field sudden changes and rock burst are analyzed according to the three-dimensional visualization numerical model; S3, the power surge mechanism of occurrence of rock burst is researched and judged according to the three-dimensional visualization numerical model; and S4, according to the analysis results in the steps S2 and S3, a rock burst foreboding information analysis method comprehensively judged based on a sensitive parameter is formed, and early warning of rock burst is carried out. The rock burst early warning method in the complex geological occurrence environment can provide a theoretical basis for remote on-line monitoring, intelligent judgment and real-time early warning of rock burst.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
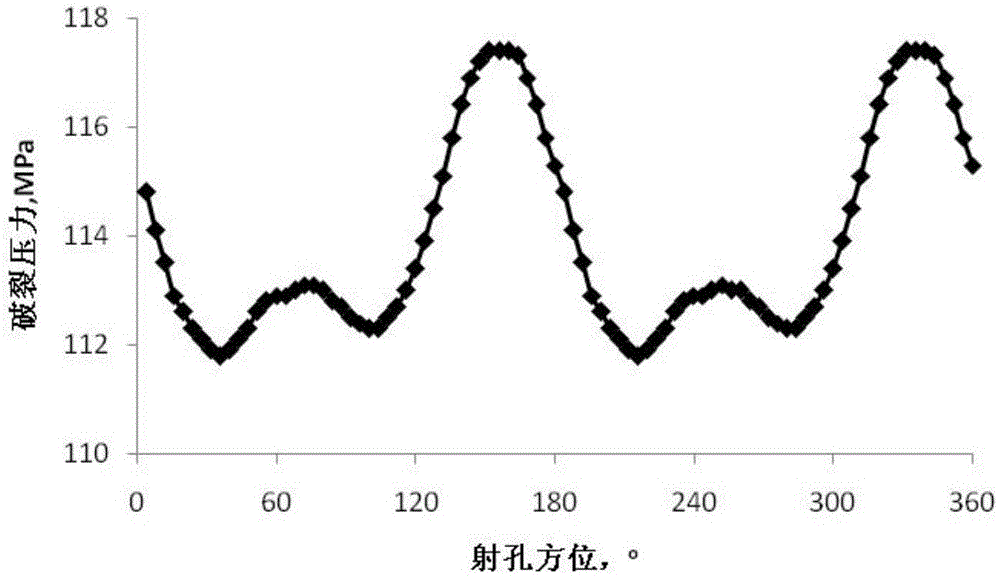
Method for selecting fracturing perforation orientation for inclined shaft
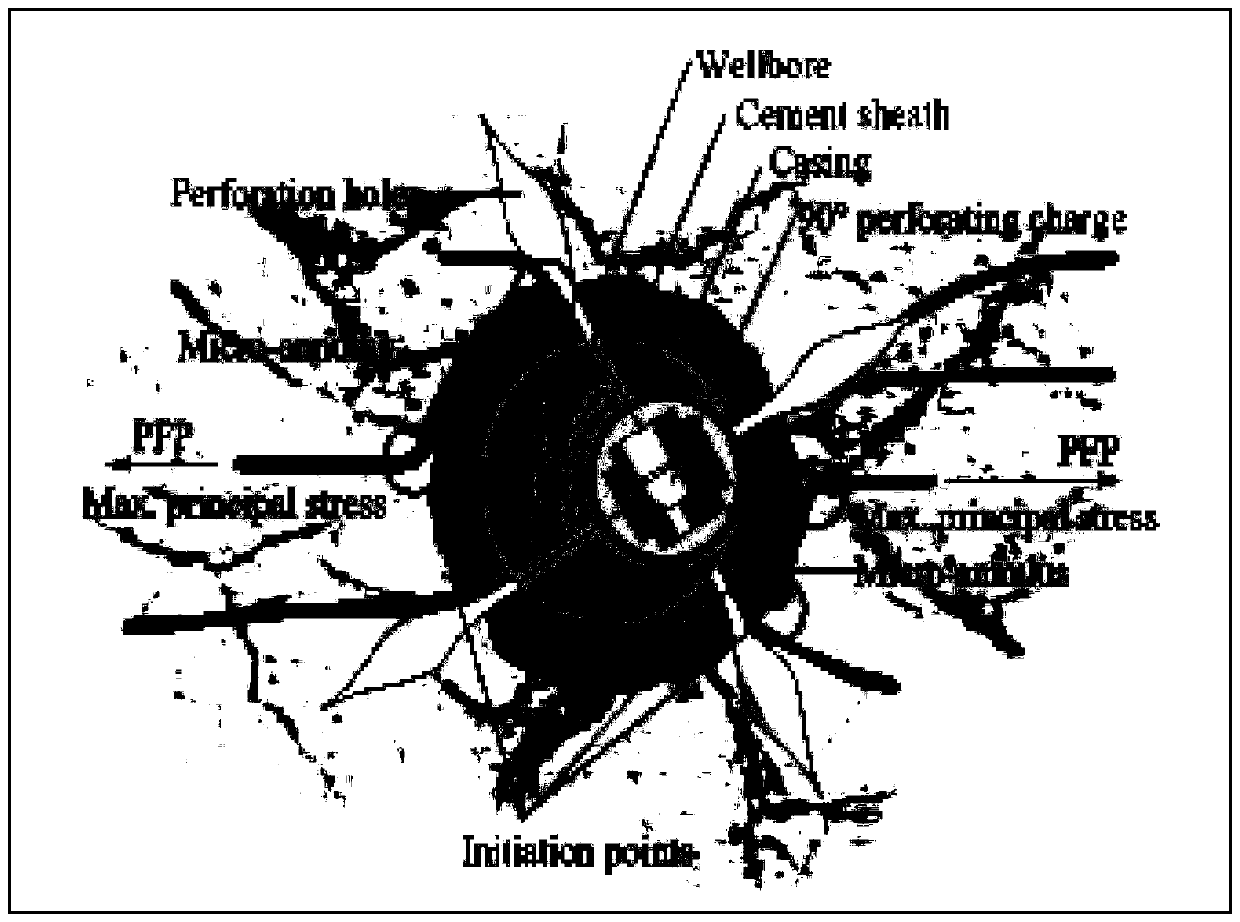
ActiveCN105484710AThe solution to poor fracking performanceImprove the transformation effectFluid removalStress distributionTectonic stress
The invention discloses a method for selecting the fracturing perforation orientation for an inclined shaft. The method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting data, including the hole drift angles, the azimuthal angles and the reservoir permeability, of a fracturing well section of the inclined shaft, calculating the main terrestrial stresses of original fields of three far fields of the inclined shaft through inclined shaft logging and adjoining well fracturing tectonic stress coefficient data, and collecting the fracturing fluid viscosity parameter and the construction displacement parameter; 2, transferring the terrestrial stresses of the original fields of the three far fields into an inclined shaft rectangular coordinate system, so that six corresponding stress components are obtained; 3, calculating a shaft peripheral stress distribution model of an inclined shaft perforation well section in the process of injecting fracturing fluid into the inclined shaft; 4, calculating the fracture pressure of inclined shaft fracturing at different perforation azimuthal angles, and selecting the orientation where the fracturing pressure is the minimum as the optimal perforation orientation of inclined shaft fracturing. By means of the technical scheme of the method, optimization of inclined shaft fracturing perforation orientation can be achieved rapidly, the problem that the inclined shaft fracturing effect is not good is effectively solved, thereby the basis is provided for optimization of inclined shaft fracturing perforation orientation, and the reservoir reconstruction effect is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
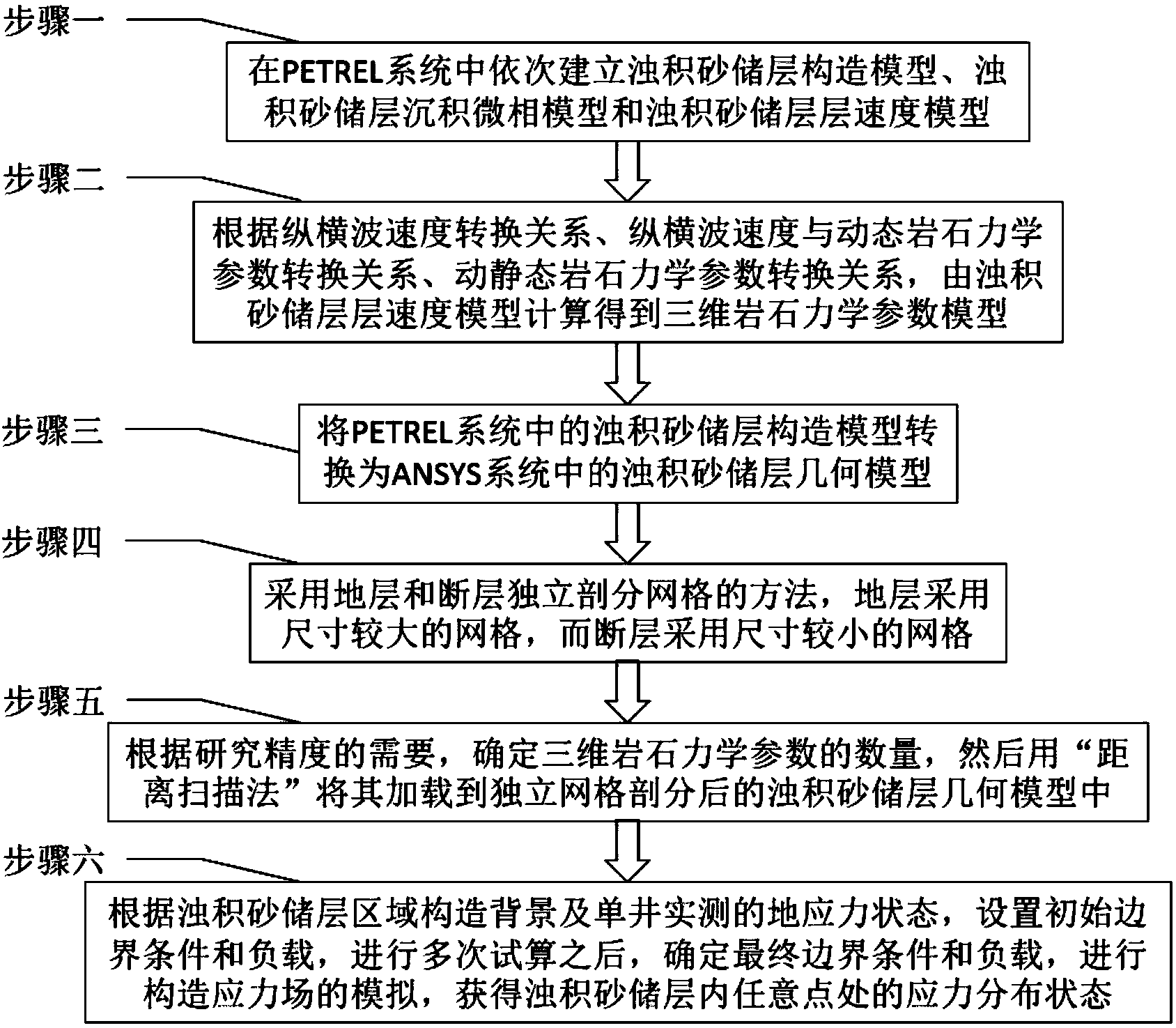
High-precision tectonic stress field simulation method applicable to turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs
InactiveCN103838936AHigh precisionSolve rationalitySpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionTectonic stress
The invention provides a high-precision tectonic stress field simulation method applicable to turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs and belongs to the field of tectonic stress field simulation technologies. The high-precision tectonic stress field simulation method aims at solving the problems that the high-precision simulation can not be carried out on the turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs to direct well network deployment in the oilfield development process and improve the development effect of the low-permeability reservoirs through an existing tectonic stress field simulation method. The method includes the first step of establishing a turbidite sand reservoir tectonic model and a turbidite sand reservoir interval velocity model in a PETREL system, the second step of obtaining a three-dimensional rock mechanics parameter model through calculation on the turbidite sand reservoir interval velocity model, the third step of converting the turbidite sand reservoir tectonic model in the PETREL system to a turbidite sand reservoir geometric model in an ANSYS system, the fourth step of carrying out independent mesh subdivision on a stratum and a geologic fault; the fifth step of loading rock mechanics parameters through a range scanning mode, and the sixth step of carrying out simulation on a tectonic stress field to obtain stress distribution states of any point in the turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs. The method is used for simulating the tectonic stress field in the turbidite sand low-permeability reservoirs.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Achieving method for simulating situation that straining-type rock bursting of roadway is caused by excavating unloading effect
The invention discloses an achieving method for simulating the situation that straining-type rock bursting of a roadway is caused by the excavating unloading effect, and belongs to the field of geology simulating tests. The achieving method includes the following step that a hole is filled with a concrete column, wherein the cement-sand ratio is controlled, flocculating agents are added, the errors between the mechanical parameters and the roadway-surrounding-rock parameters of the concrete column are controlled to be lower than 10% by testing the mechanical parameters including the compressive strength, the extension strength, the poisson ratio and the elasticity modulus of the concrete column, and then the hole is filled with concrete after the concrete is evenly stirred. The achieving method has the advantages that by means of the achieving method for simulating the situation that straining-type rock bursting of the roadway is caused by the excavating unloading effect, the background of the combined effects of different self-weight stress fields and tectonic stress fields in a site can be fully considered, and the straining-type rock bursting process is generated in the roadway digging process in rock mass. In addition, other monitoring means are combined, the various physical-performance-change parameters in the rock bursting breeding process, the rock bursting occurring process and the rupturing process after rock bursting are collected, and reliability is high.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Fabricated grilling anti-invert method for treating pucking
InactiveCN102797486AReinforcement is fast and effectiveEven by forceAnchoring boltsTectonic stressSocial benefits
The invention discloses a fabricated grilling anti-invert method for treating pucking, which aims at treating roadways with serious inverts, such as with large sections, dynamic pressure effect, low strength of surrounding rock, and high tectonic stress. The fabricated grilling anti-invert method for treating pucking comprises the steps as follows: a preprocessed grilling anti-invert is spliced through a bolt and concrete is poured on the anti-invert on the spot, so as to form a grilling anti-invert support with the same intensity as the surrounding rock; the gap between the support and a base plate is eliminated by filling grout behind a wall so as to increase the compactness of the concrete; and two feet of the grilling anti-invert is rigidly connected in a rock layer of the base plate through a construction rigidly-connected anchor rod, so as to further improve the flexural rigidity of the grilling anti-invert, the shearing strength of the base plate and the integrity of the two. According to the invention, the fabricated grilling anti-invert is preprocessed and spliced on the spot, so that the fabricated grilling anti-invert has the advantages of high installation accuracy, high construction speed, short exposure time of the surrounding rock, high integrity, and force evenness of the support. In addition, the grilling anti-invert makes full use of the mechanical property of an arch, so as to have a high bearing capacity, low supporting cost, no contamination, and obvious economic and social benefits, and therefore the problem of pucking control is solved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
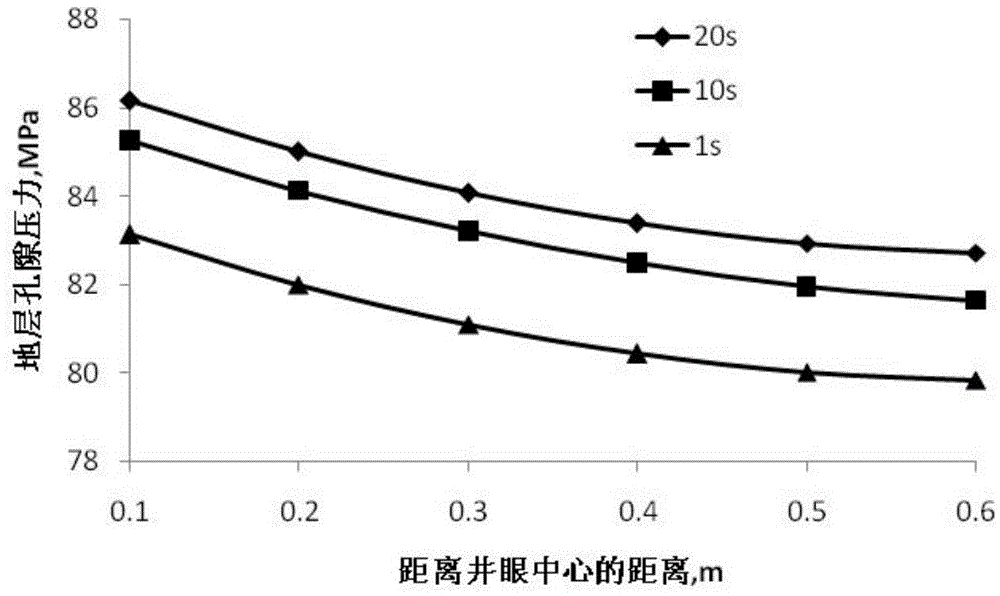
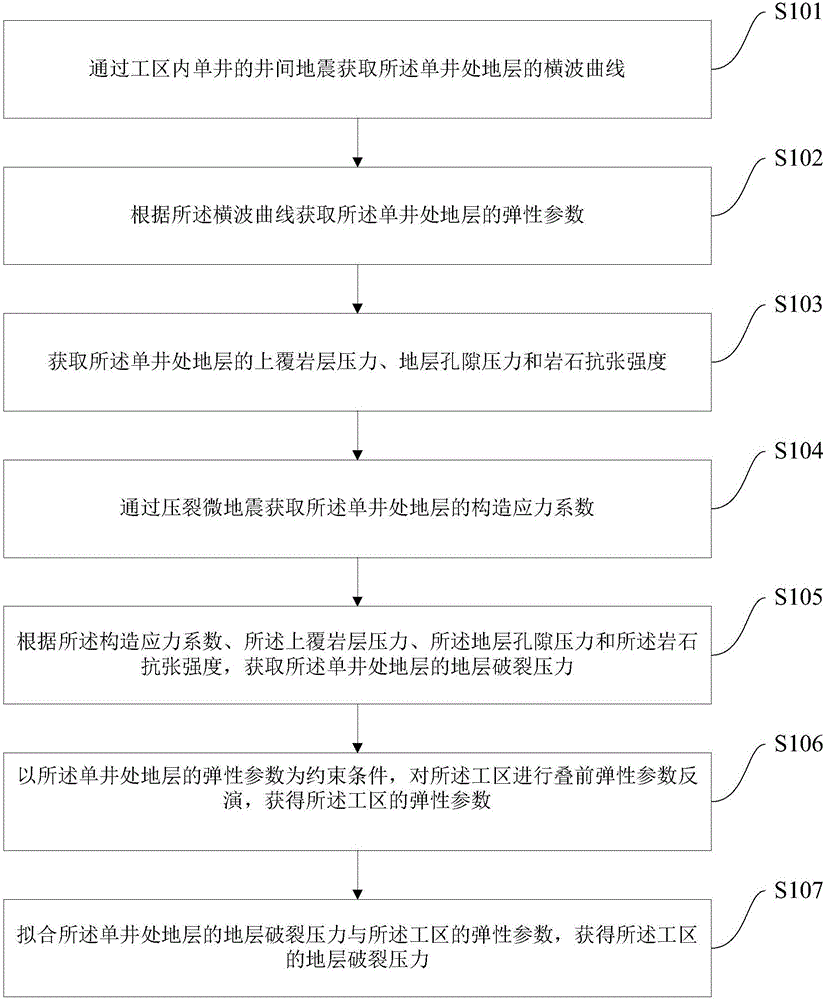
Stratum rupture pressure prediction method
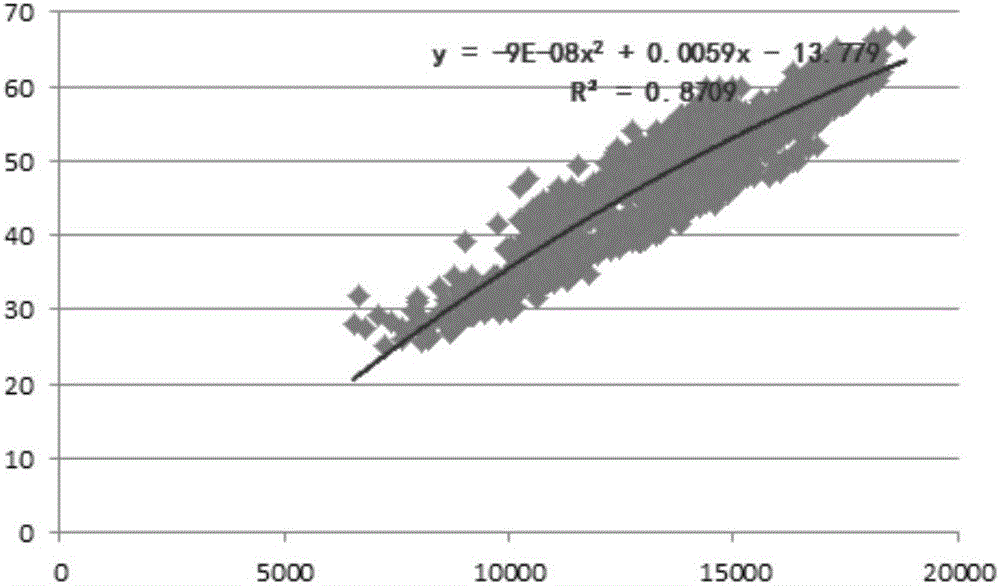
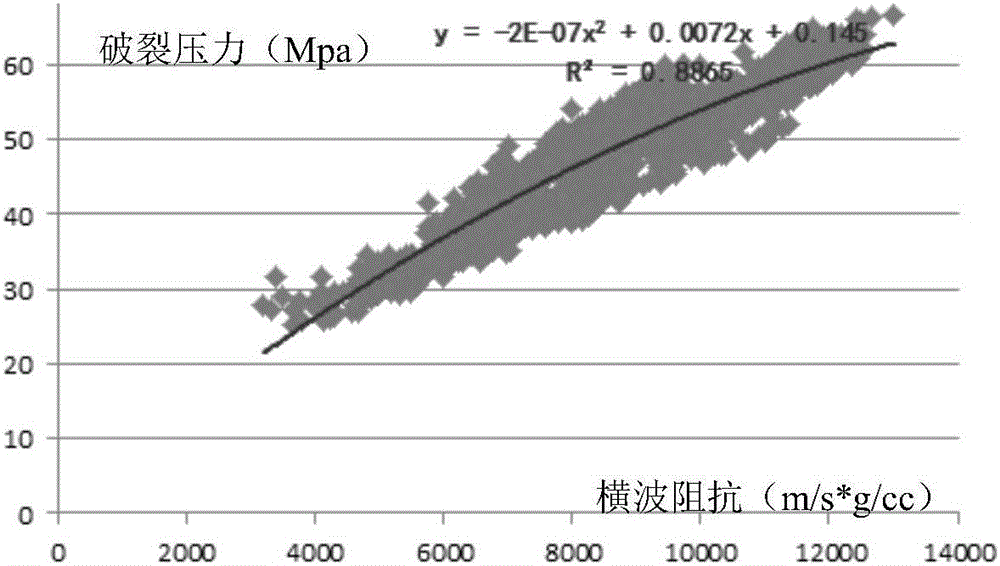
InactiveCN106324680AHigh precisionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingTectonic stressGeomorphology
The invention provides a stratum rupture pressure prediction method. The stratum rupture pressure prediction method comprises steps of obtaining a transverse wave curve of a stratum at a single well through earthquake between single wells in a work area; obtaining an elastic parameter of the single well according to the transverse wave curve; obtaining overlaying rock pressure, the stratum formation pore pressure and rock tension resistance strength of the stratum at the single well; obtaining a tectonic stress coefficient of the single well through a fracture micro-earthquake; obtaining the stratum rupture pressure of the stratum at the single well according to the tectonic stress coefficient, the overlaying rock stratum pressure, the stratum pore pressure and the rock tension resistance strength; performing pre-stack elastic parameter inversion on the work area to obtain the elastic parameter of the work area by using the elastic parameter of the stratum of the single well as a constraint condition; and fitting the stratum rupture pressure of the stratum at the single well and the elastic parameter of the work area to obtain the stratum rupture pressure of the work area. The stratum rupture pressure prediction method can improve the prediction accuracy of the stratum rupture pressure.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
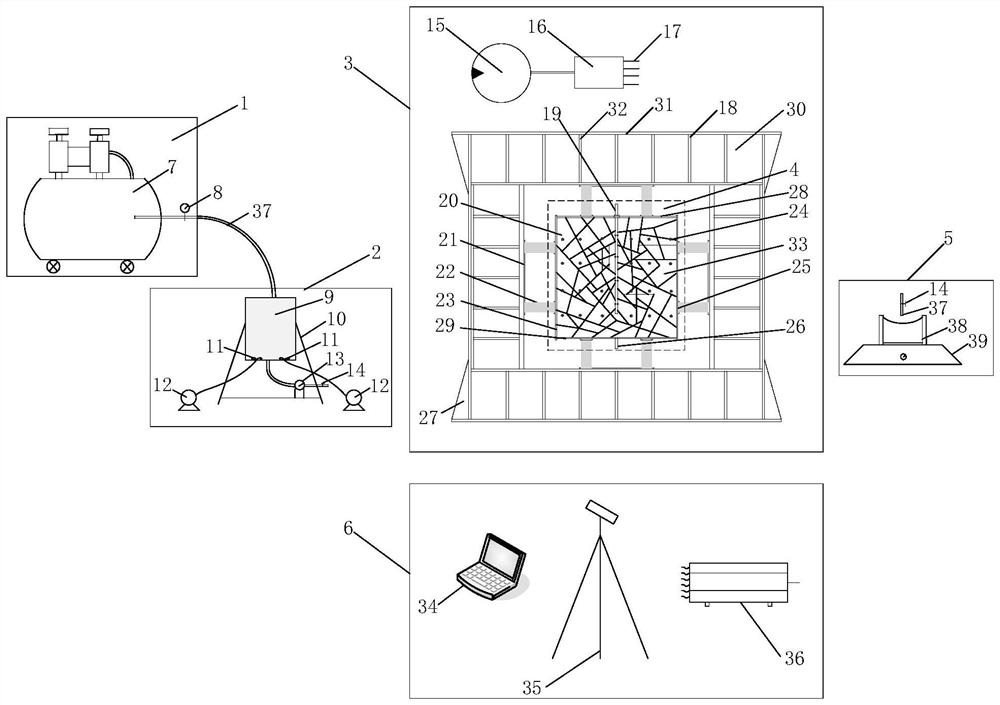
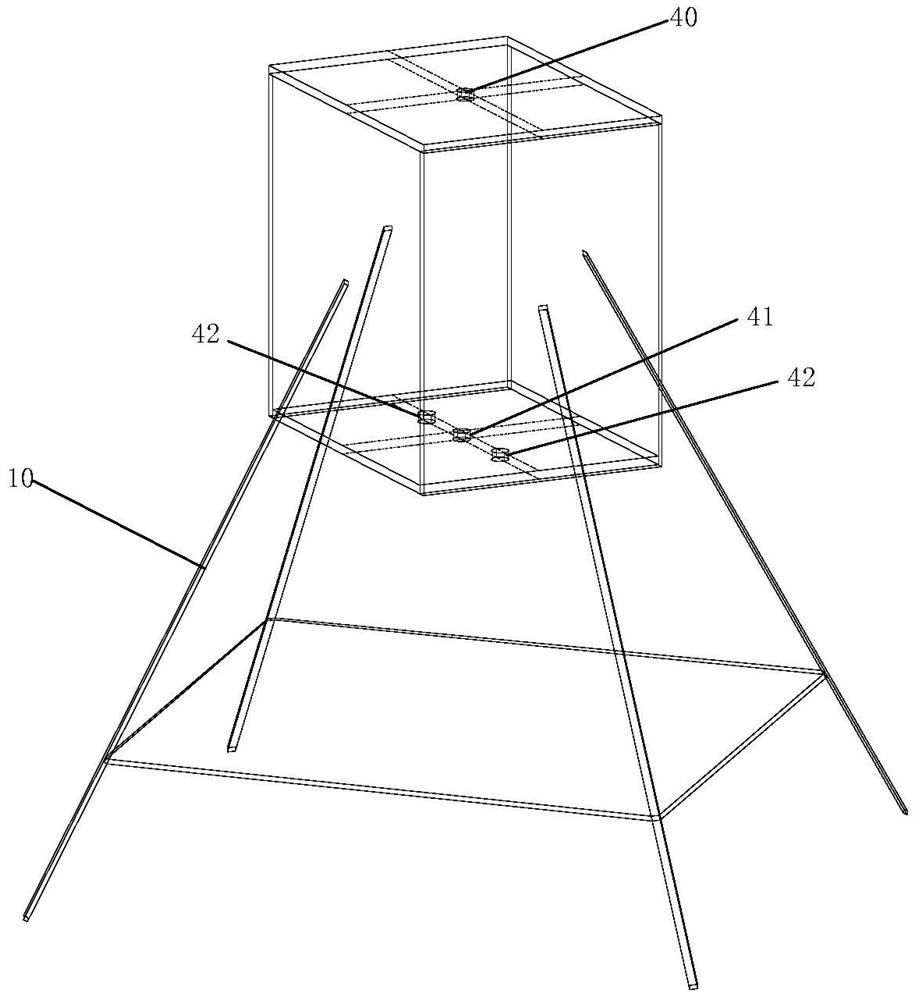
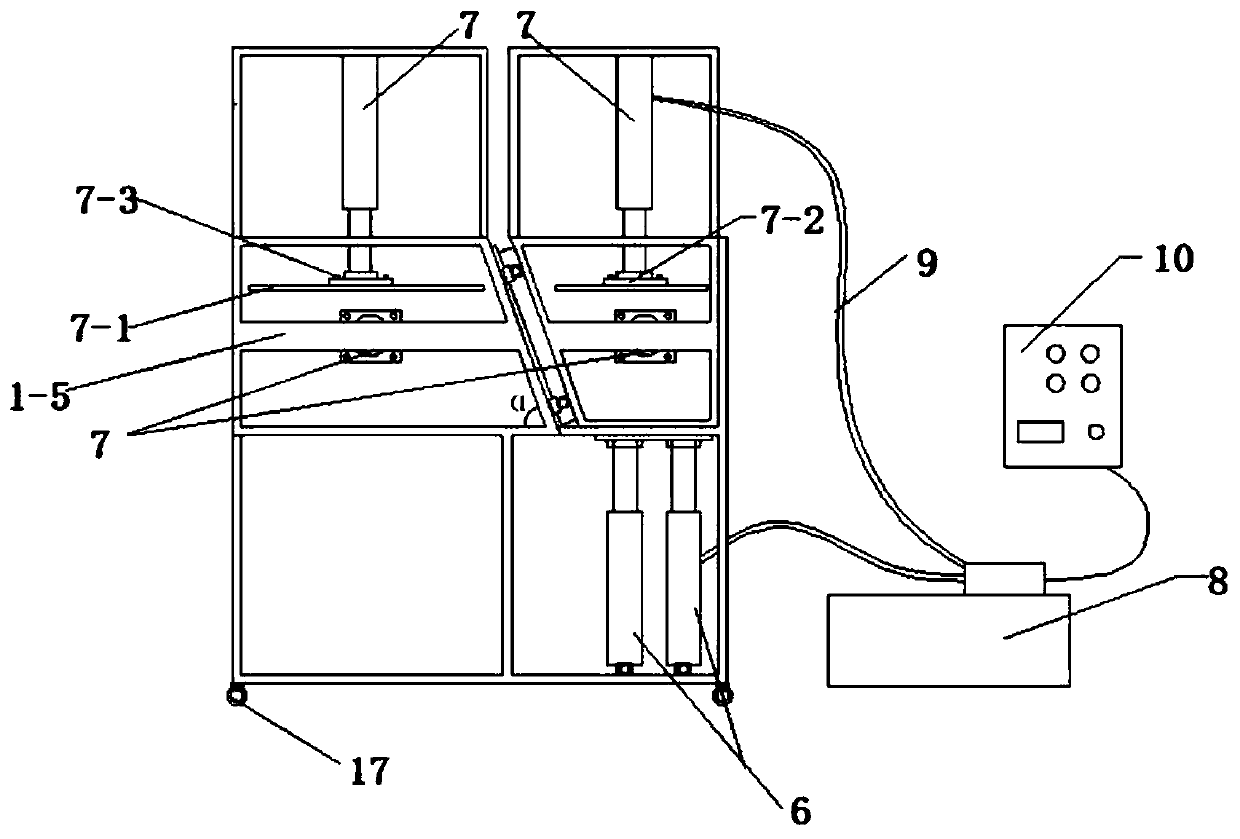
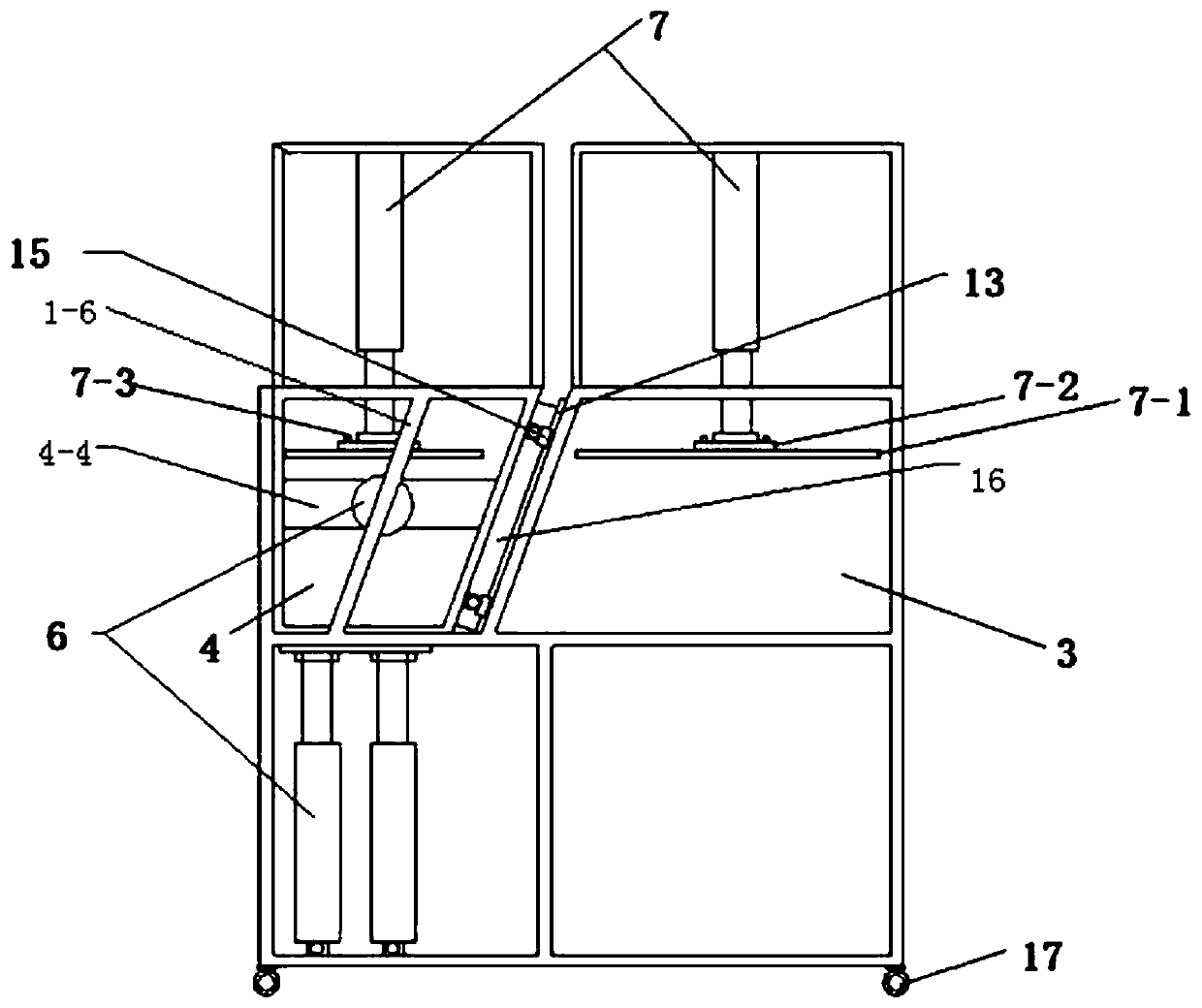
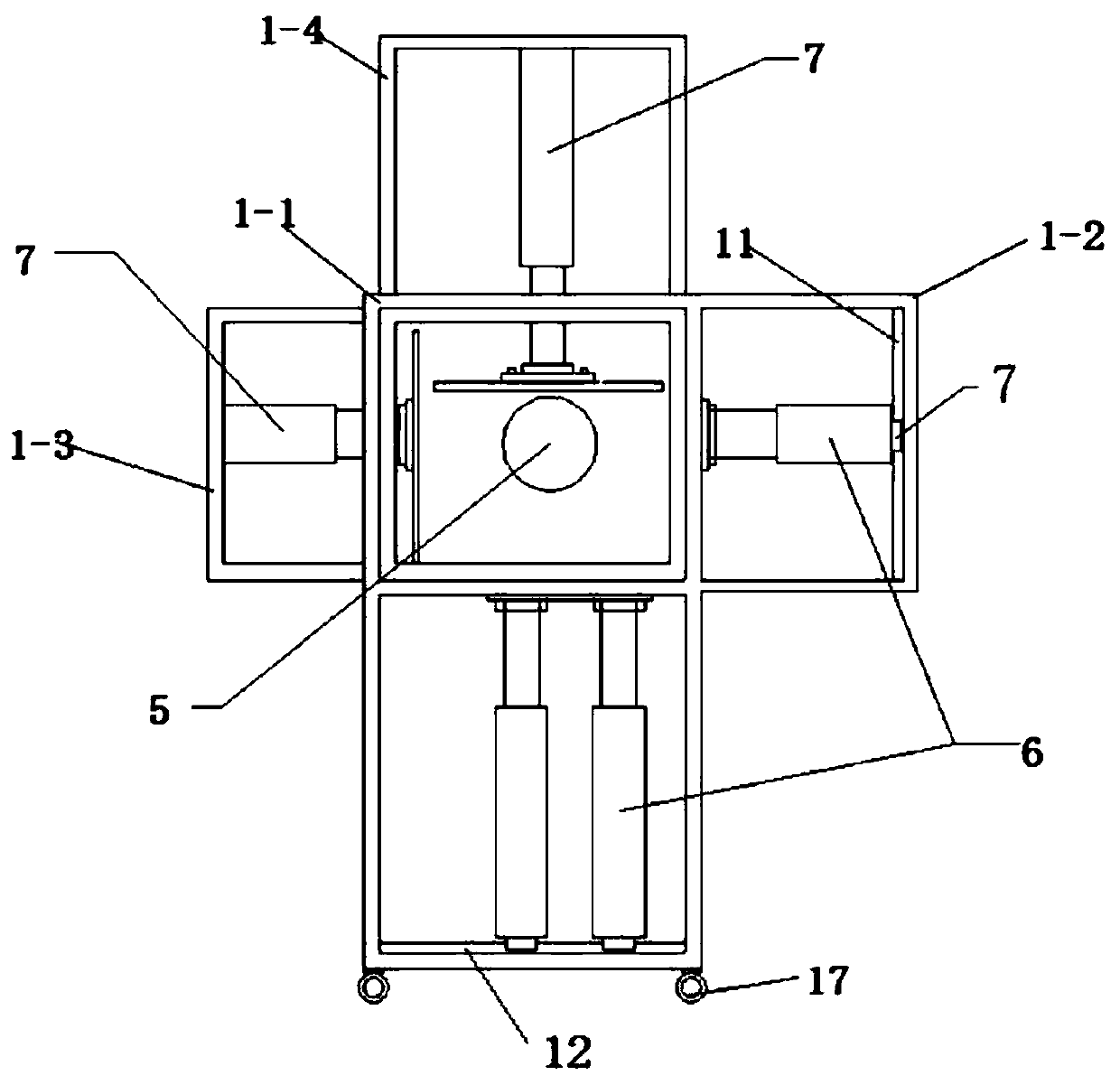
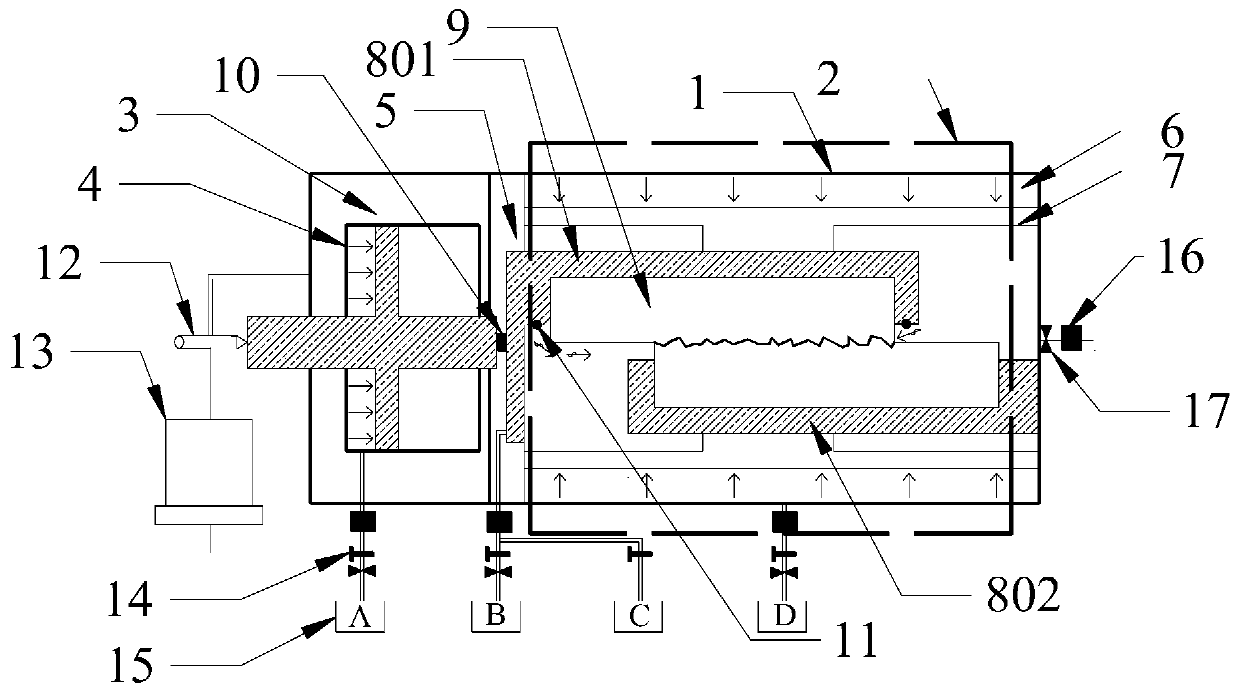
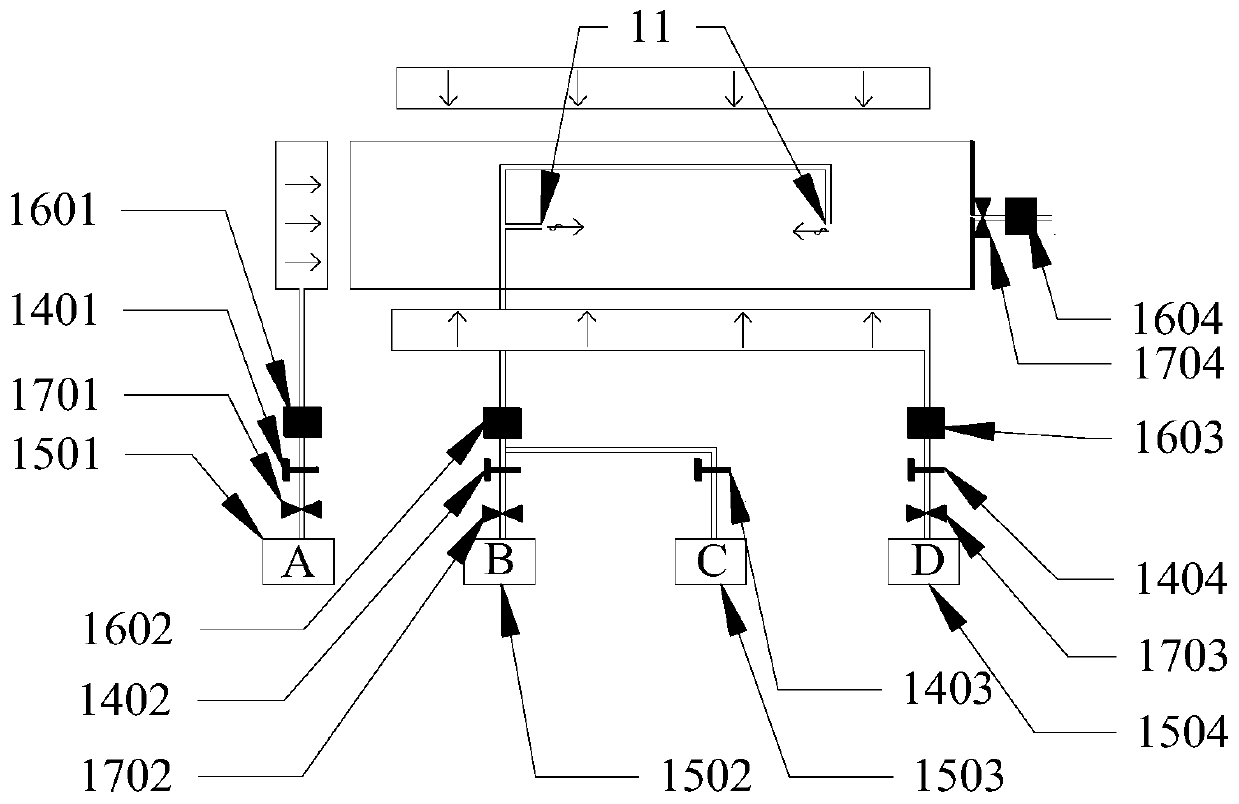
Simulation test device and simulation test method for mechanical behavior characteristics of cross-fault tunnel roadway under different burial depths and different tectonic stresses
PendingCN111081110ATrue restorationImprove accuracyCosmonautic condition simulationsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTectonic stressPhysical model
The invention discloses a simulation test device and a simulation test method for mechanical behavior characteristics of a cross-fault tunnel roadway under different burial depths and different tectonic stresses. The simulation test device comprises a support frame, a loading hopper, a guide rail, a sliding block, a bidirectional power system and a confining pressure loading system. A confining pressure loading system for simulating overlying formation pressure and horizontal tectonic stress is provided for surrounding rock materials in a fixed hopper and a movable hopper. Meanwhile, a bidirectional power system, a guide rail and a sliding block are matched, so that the movable hopper can move in the horizontal direction and the longitudinal direction, complex engineering environment simulation of different burial depths, different tectonic stresses and fault composite diastrophism is achieved, and simulation of tunnel and roadway mechanical behavior characteristics in the environmentis achieved. According to the invention, the engineering actual situation can be restored more truly, the research accuracy of the mechanical behavior characteristics of the cross-fault tunnel roadwayunder the deep high ground stress condition is improved, and the problem that the existing physical model box cannot simulate the influence of the overlying stratum pressure and the tectonic stress on the tunnel roadway is solved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
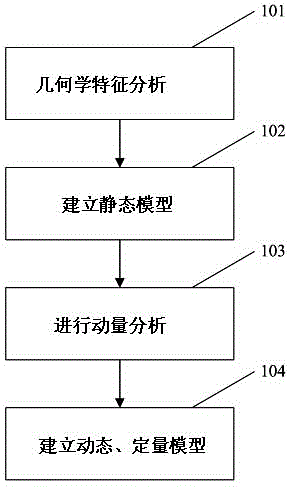
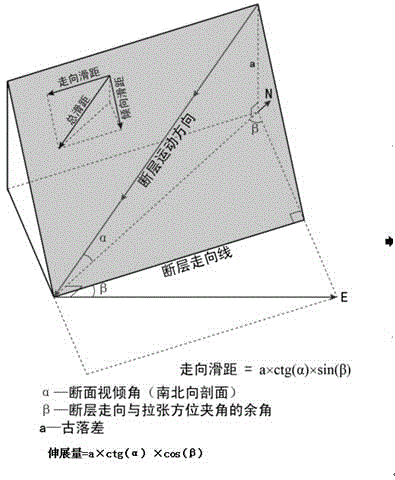
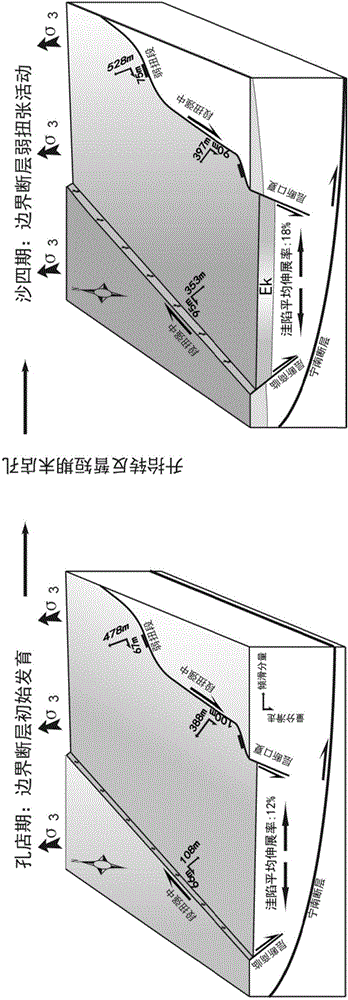
Quantitative description method for torsional/tensional geological structure
ActiveCN105372702AClear controlSolve the low drilling success rateSeismic signal processingTectonic stressWell drilling
The invention provides a quantitative description method for a torsional / tensional geological structure. The quantitative description method for the torsional / tensional geological structure comprises the steps of a step 1, analyzing according to fault geometric features, forming an analog according to a tectonic stress field and a fault, determining the type of a basin torsional / tensional structure; a step 2, establishing a basin and fault forming mechanism and a static model; a step 3, performing dynamic quantitative analysis, obtaining the development characteristic of the basin torsional / tensional structure, performing quantitative calculation for obtaining the vertical displacement and horizontal displacement of a torsional / tensional fault in each key period, and meeting a quantization standard; and a step 4, establishing a dynamic geological structure for torsional / tensional fault of the basin, and defining control function for a basin sedimentary reservoir and oil-and-gas migration and entrapment. The quantitative description method for the torsional / tensional geological structure has functions of defining control function of the torsion / tension structure to deposition, reservoiring and entrapment, settling a problem of low well drilling success rate in torsional / tensional basins, and realizing profound measuring for oil-gas exploration on similar basins.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Device and method for monitoring fault tectonic stress
The invention relates to a method and device for monitoring fault tectonic stress. The method for monitoring fault tectonic stress comprises following steps: stress sensor installation, fault pre-fabrication, load application, critical stress of fault instability determination, theoretical value and experimental value comparison and analysis, and precursory information of fault instability acquisition; the device for monitoring fault stress comprises a fault analogue simulation test platform and a fault stress sensor. According to the device, by use of the stress sensor vertically installed on a fault surface, the normal stress and shearing stress of the fault surface are monitored; through the establishment of a fault dynamic module, the functional relations between the normal stress and shearing stress of the fault surface and horizontal load and vertical load are calculated; the errors between experimental values and theoretical values are analyzed; the critical stress value of fault instability is determined; the device and method provide theoretical basis and experimental data support for researching dynamic disasters such as rock burst and pressure bump caused by fault slip instability in study fields of geotechnical engineering and mining engineering, and provide pre-cursor information for predicting and preventing dynamic disasters.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
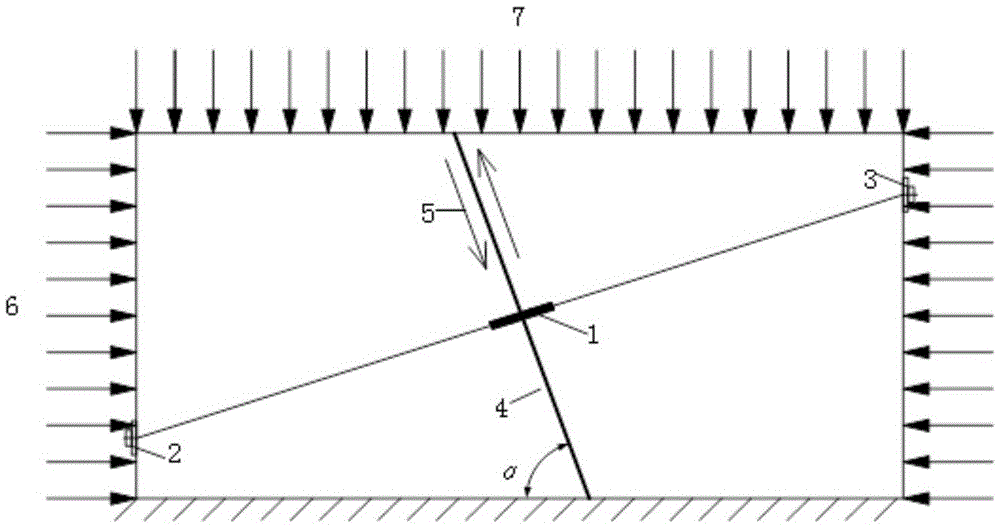
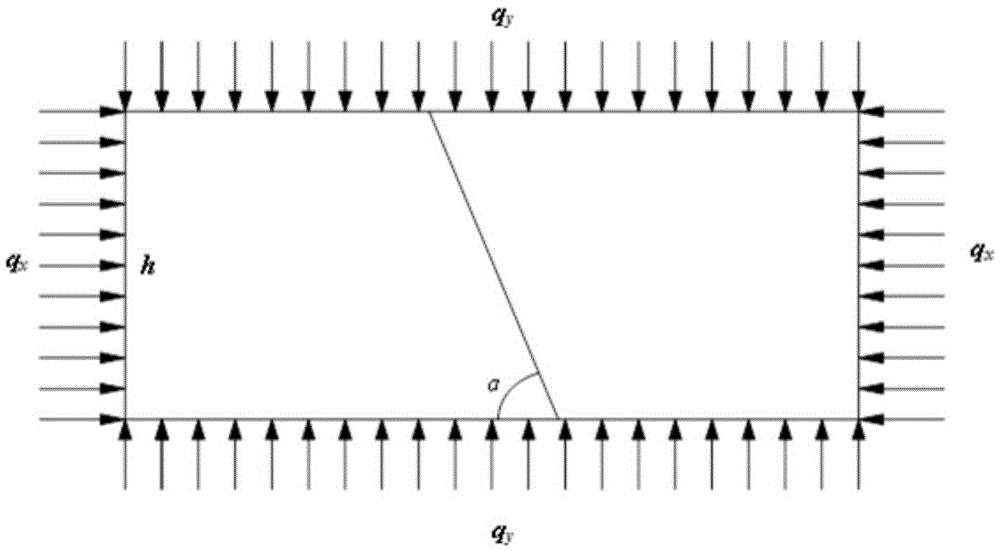
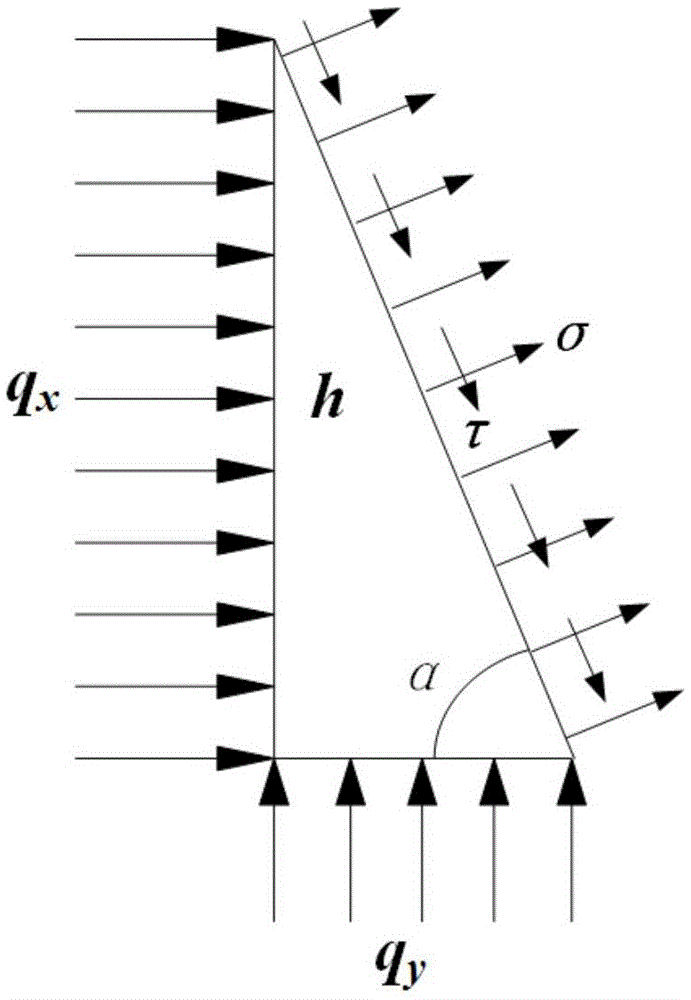
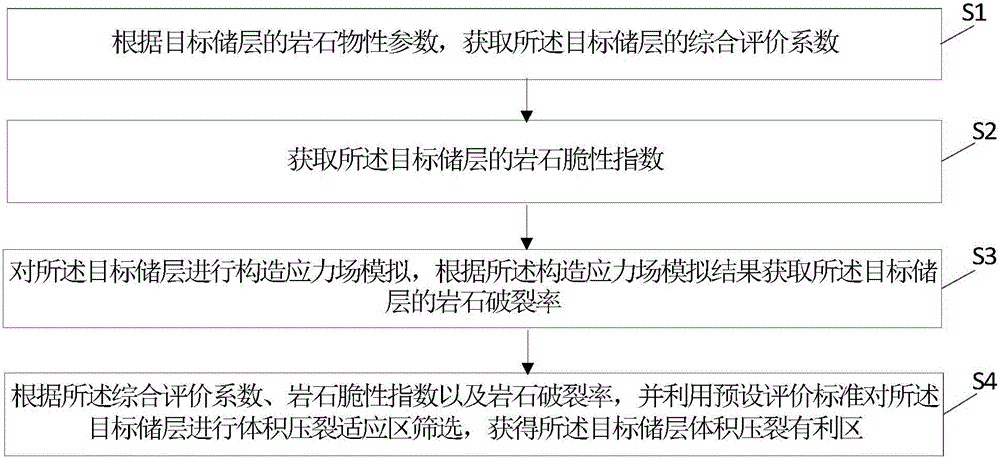
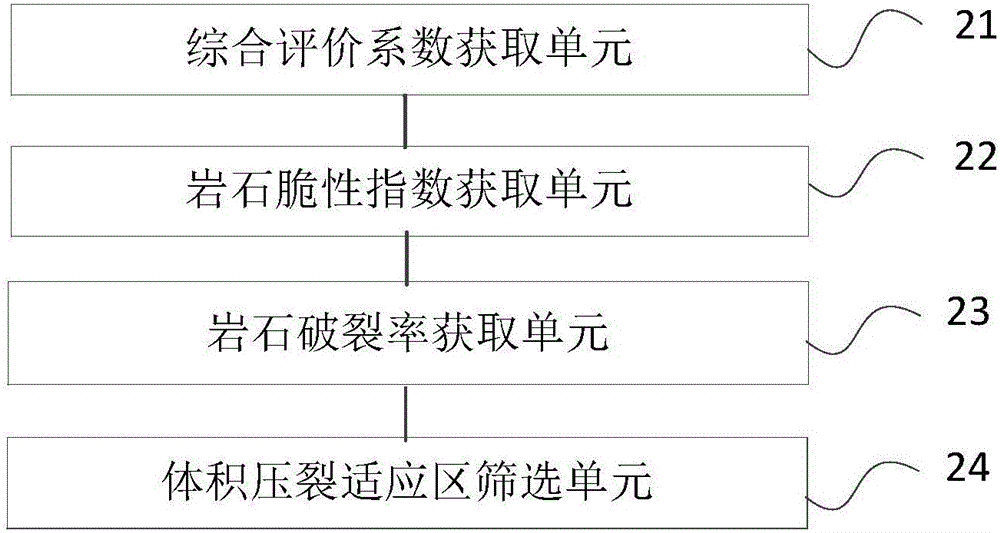
Method and device for screening adaptive volume fracturing area of tight reservoir
ActiveCN106202737AEfficient screeningDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTectonic stressScreening method
The invention relates to the field of seismic exploration, in particular to a method and device for screening the adaptive volume fracturing area of a tight reservoir. The method includes: acquiring the comprehensive evaluation coefficient of a target reservoir according to the rock physical parameters of the target reservoir; acquiring the rock brittleness index of the target reservoir; performing tectonic stress field simulation on the target reservoir, and acquiring the rock fracture rate of the target reservoir according to the tectonic stress field simulation result; according to the comprehensive evaluation coefficient, the rock brittleness index and the rock fracture rate, using preset evaluation standards to screen the adaptive volume fracturing area of the target reservoir so as to obtain the favorable volume fracturing area of the target reservoir. By the method, the adaptive volume fracturing area of the tight reservoir can be evaluated effectively, the definite evaluation standards of the adaptive volume fracturing area of the tight reservoir are built at the same time according to the comprehensive evaluation coefficient, the rock brittleness index and the rock fracture rate, and a foundation is provided for the development of the tight reservoir.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
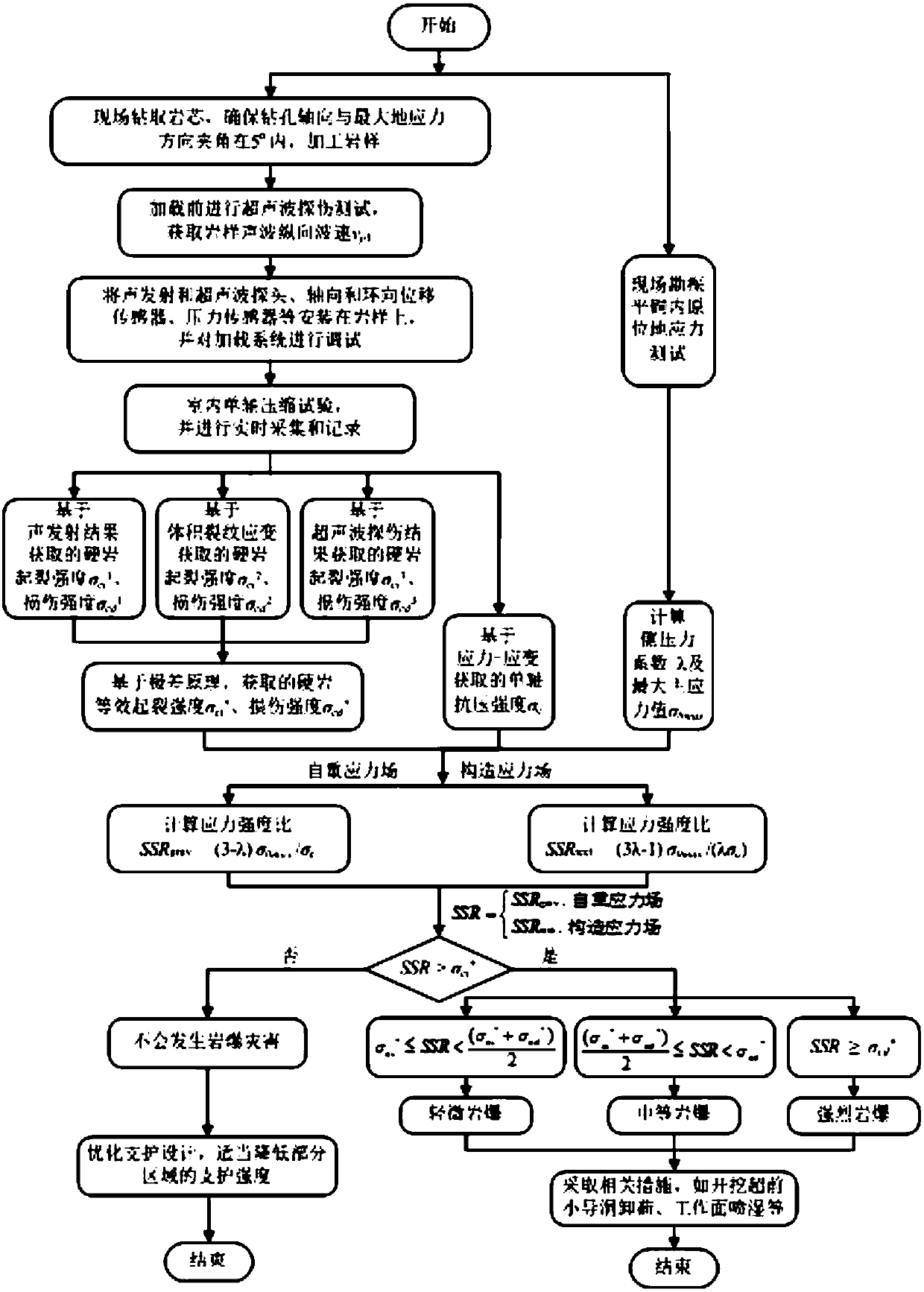
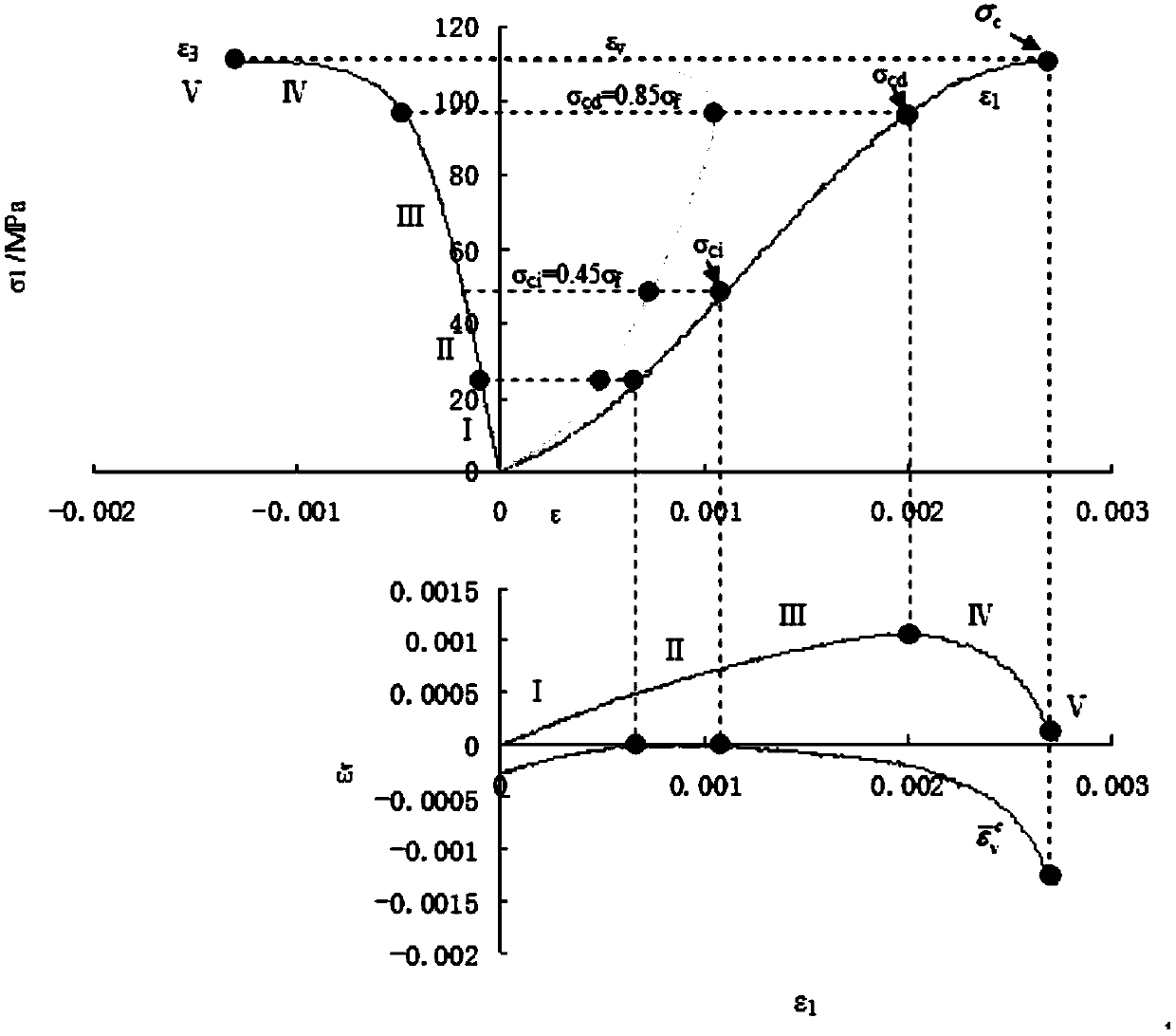
Method for assessing risk level of hard rock burst disaster in great-depth cavern
ActiveCN108871946AWell formedImprove general performanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress ratioStress strength
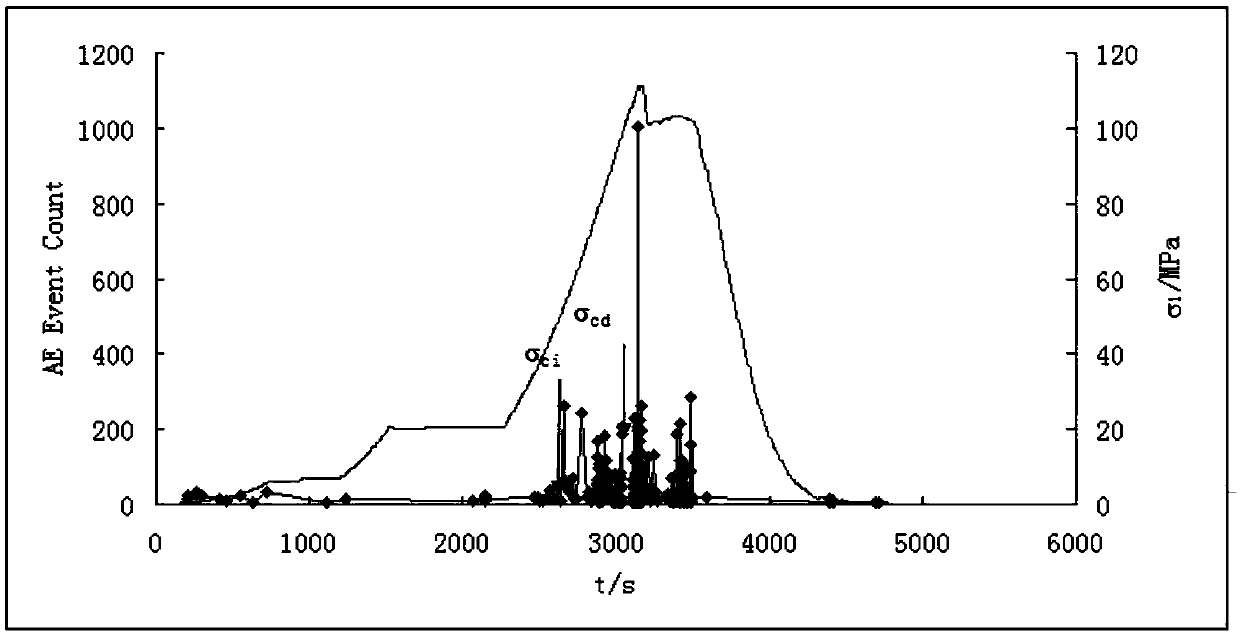
The invention discloses a method for assessing the risk level of a hard rock burst disaster in a great-depth cavern. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out an in-situ ground stress test; drilling a cylindrical rock sample at a ground stress test position; emitting an ultrasonic flaw detection signal to the cylindrical rock sample by using a multi-channel ultrasonic flaw detector, and calculating the crack initiation strength sigma<ci><j> (j=1, 2, 3) and damage strength sigma<cd><j> (j=1, 2, 3) of hard rock in three states; calculating equivalent crack initiation strength sigma<ci><*> and equivalent damage strength sigma<cd><*> according to the range principle; comparing rock strength to stress ratios under a gravity stress field and a tectonic stress field with the equivalent crack initiation strength sigma<ci><*> and the equivalent damage strength sigma<cd><*>, and assessing the level of the hard rock burst disaster in the great-depth cavern. The method is implementedcomprehensively by a field ground stress test, an indoor uniaxial compression test, and an ultrasonic and acoustic emission coupling system. By adopting the method, the equivalent crack initiation strength and equivalent damage strength of the hard rock and the stress-strength ratio of rock after excavation of the cavern can be obtained effectively, and the problem concerned with stability evaluation of the great-depth cavern as well as optimization of level assessment and control measures of the hard rock burst disaster is solved.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Method for judging temporary plugging times of segmented multi-cluster fracturing wellbores of directional well and horizontal well
ActiveCN110580401ANovel angleCalculation method is simpleData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsRelational modelPrincipal stress
The invention discloses a method for judging the temporary plugging times of a segmented multi-cluster fracturing wellbore of a directional well and a horizontal well. The method for the directional well comprises the following steps: building a physical model of fracture initiation of the wellbore of the directional well; establishing a corresponding stress mathematical model; calculating the fracture pressure during fracture initiation; determining the fracture initiation number by utilizing a current limiting principle; subtracting 1 from the ratio of the designed perforation cluster numberto the fracture initiation number by adopting a ceil method to obtain a temporary plugging time; the method for the horizontal well comprises the following steps: obtaining rock mechanical parameters; establishing a dynamic and static relation model of rock mechanics parameters; calculating a tectonic stress coefficient; calculating the minimum horizontal principal stress and the maximum horizontal principal stress; calculating the fracture pressure during fracture initiation; determining the fracture initiation number by utilizing a current limiting principle; subtracting 1 from the ratio ofthe designed perforation cluster number to the fracture initiation number by adopting a ceil method to obtain the temporary plugging times. According to the method, the temporary plugging times of the segmented multi-cluster fracturing wellbores of the directional well and the horizontal well can be accurately judged.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
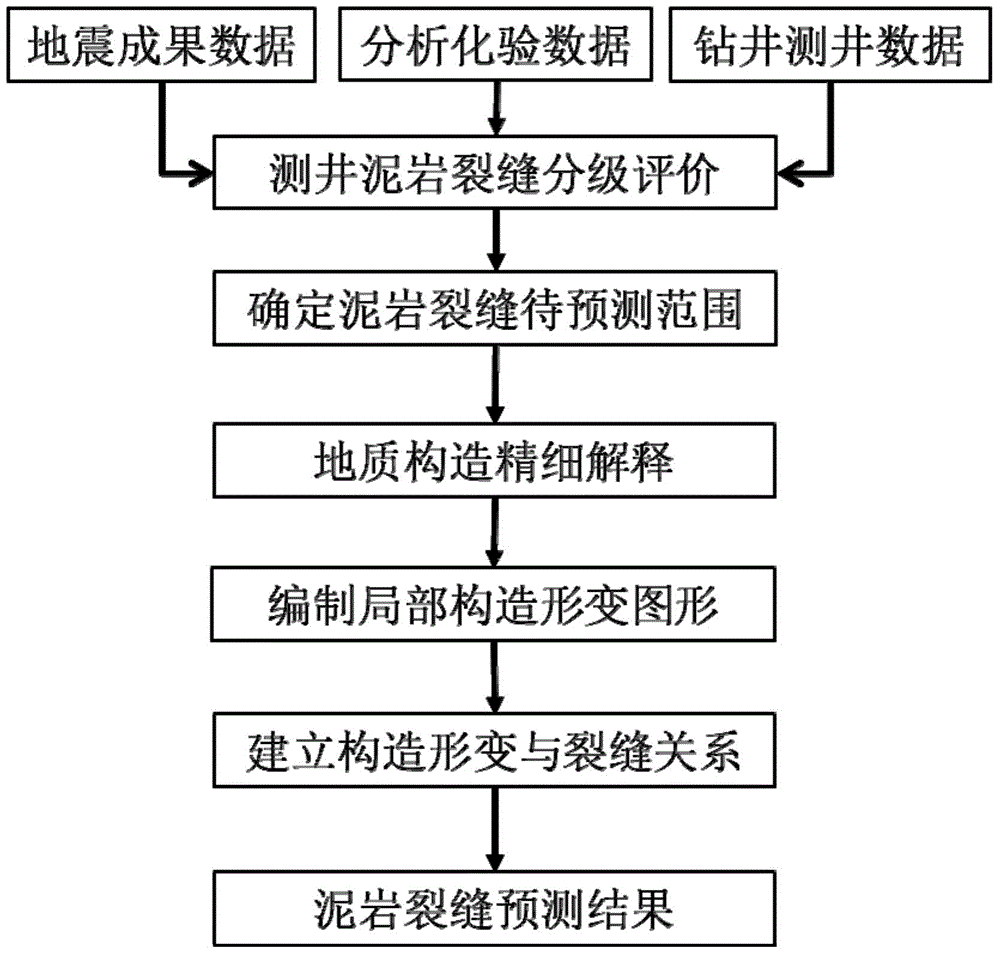
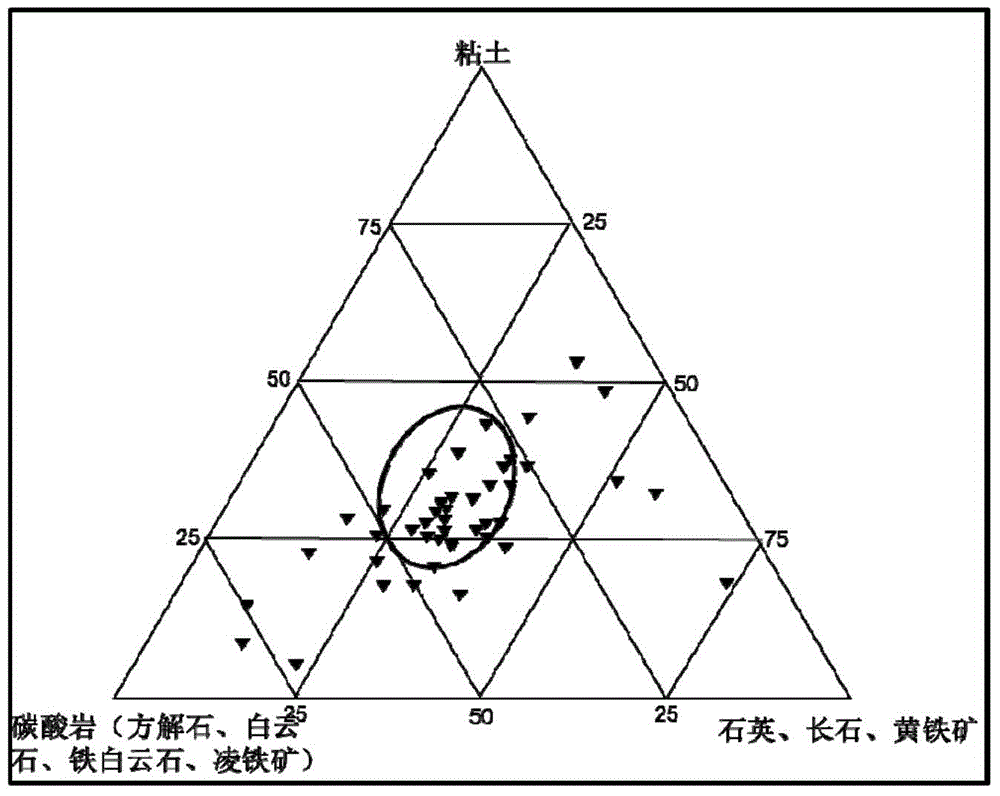
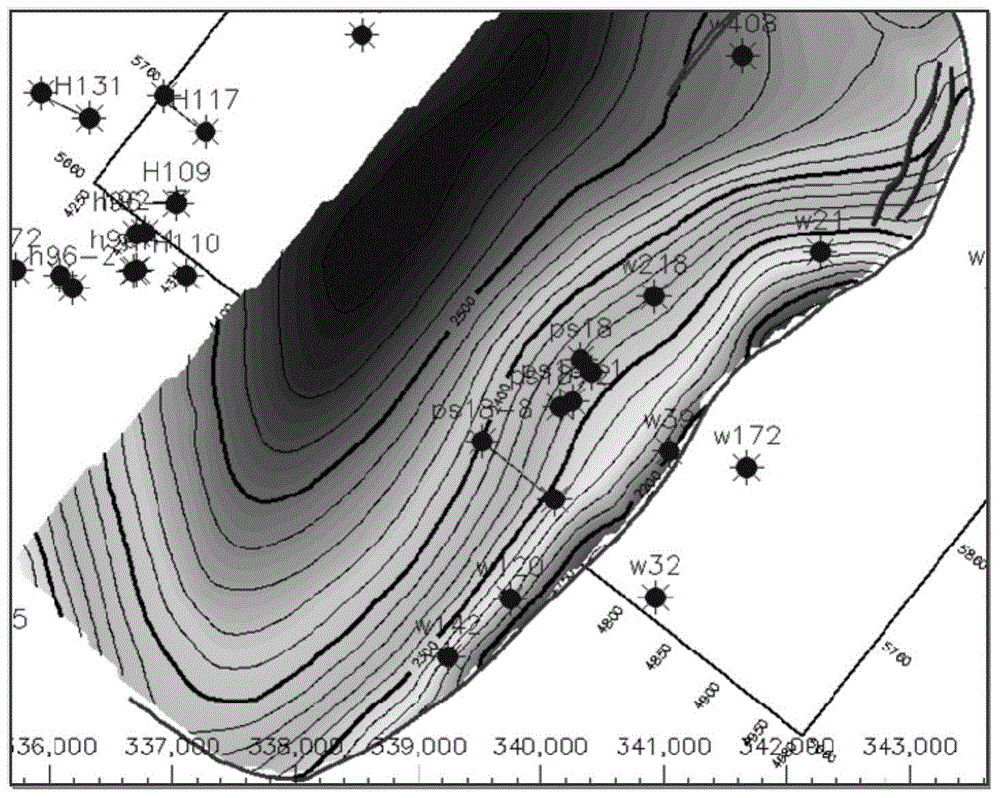
Method for predicting mudstone crack by structure causes
InactiveCN104358564AHigh predictive rateShort research cycleSurveyFluid removalTectonic stressPetroleum exploration
The invention relates to a method for predicting a mudstone crack by structure causes and belongs to the technical field of petroleum exploration and development. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out evaluation and classification on the mudstone crack; (2) determining a range to be predicted of the mudstone crack; (3) obtaining conventional geological structure data of a target layer in a region to be predicted; (4) making a local structure deformation graph of the region to be predicted; (5) establishing a relation between the local structure deformation graph and the mudstone crack; (6) determining a developing range of the mudstone crack. According to the invention, the conventional geological structure is decomposed into a regional structure background, local structure deformation and a random factor, the random factor is eliminated by replacing the regional structure background with a trend surface and adopting a filtering method and micro curvature change generated by the local structure deformation is stressed so as to predict the development range of the mudstone crack caused by structure stress variation; and the method provides a rapid, convenient and efficient technical means for exploration and development of a mudstone crack petroleum reservoir is provided, the prediction coincidence rate is high, the research period is short, and the cost is low.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Test device for simulating anchor rod impact failure under tectonic stress influence
ActiveCN106017842ATimely supplementary loadingReduce intensityShock testingTectonic stressFront loading
The invention discloses a test device for simulating anchor rod impact failure under tectonic stress influence. With the test device of the invention adopted, the technical problem that a test device in the prior art cannot simulate anchor rod impact failure under tectonic stress influence can be solved. The test device of the invention includes a hexahedron test piece, a test box, an anchor rod, a front loading unit, a back loading unit, a left loading unit, a right loading unit and a top loading unit, wherein the front loading unit, the back loading unit, the left loading unit, the right loading unit and the top loading unit are loaded on the test box; the anchor rod is installed in an anchor hole of the test piece; the left loading unit includes an impact weight, a lifting device, a guide rod, an impact base, a warping rod and a loading device; the lifting device provides a vertical stress to the impact weight, the warping rod converts the vertical stress into a lateral force of the test piece, a strong spring expands and elongates instantaneously so as to quickly carry out supplementary loading on the test piece, and therefore, energy can be compensated, and further squeezing work carried out on coal and rock mass by external surrounding rock is simulated; and burst rock blocks impact the anchor rod, so that the impact failure of the anchor rod in an engineering field can be simulated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ground deformation-based method for inversion of tectonic stress field in shale gas exploration area
InactiveCN104866682AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingTectonic stress
The invention relates to a ground deformation-based method for inversion of a tectonic stress field in a shale gas exploration area, and the method comprises the following steps: determining a research region by a satellite, establishing a basic geological data database, determining an earth's surface deformation value of the research region by an earth's surface deformation processing module and establishing an earth's surface deformation database; establishing a geological model of the research region by a geographic information processing module, giving the earth's surface deformation value to the geological model, establishing a displacement calculation model by corresponding to the geological model with a finite element analysis module, obtaining an initial displacement field database of the research region, comparing data of the initial displacement field database, determining a corrected displacement field database, and solving by the finite element analysis module to obtain basic stress data of the research region. The method can accurately simulate a tectonic stress field in the shale gas exploration and development region, and can obtain a large-large scale and high-precision tectonic stress field.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +1
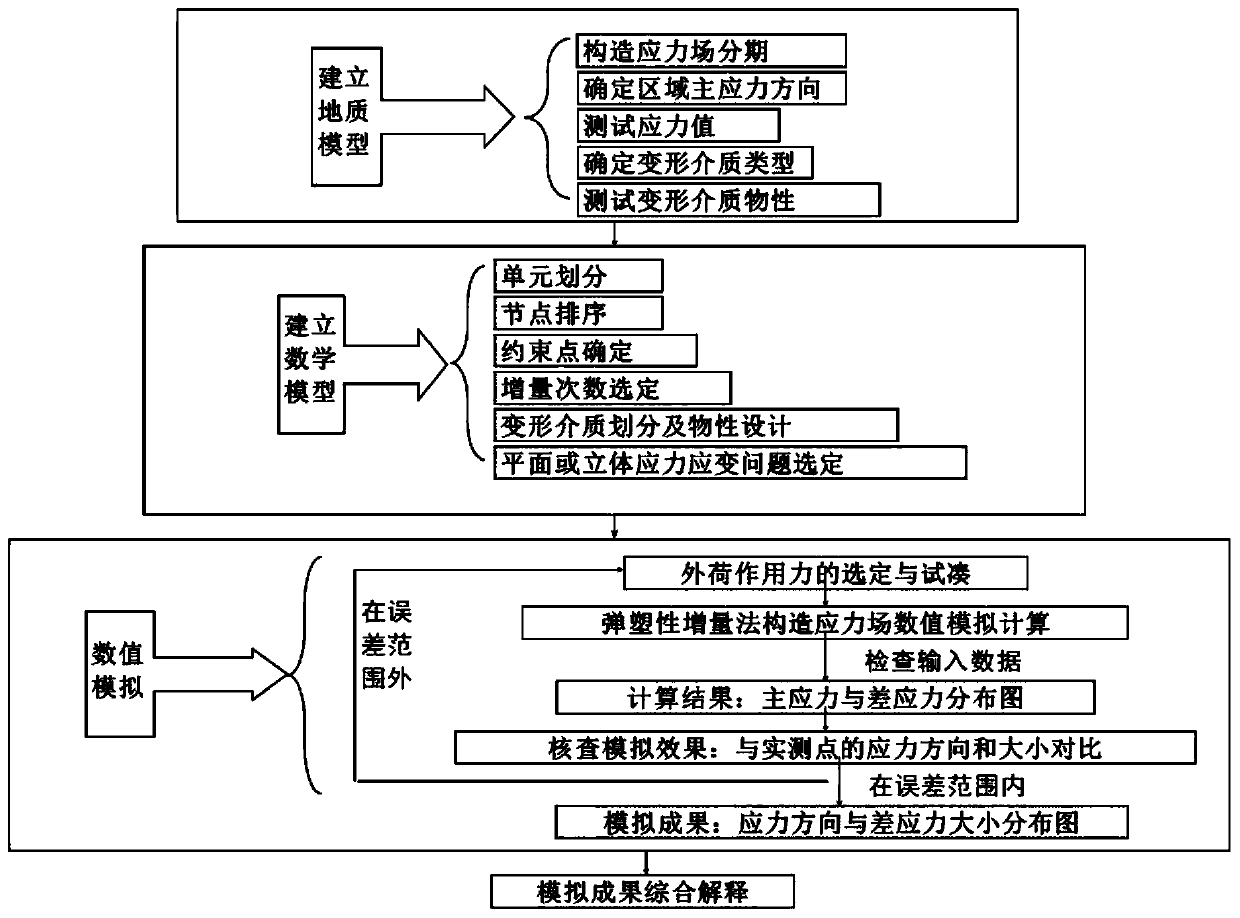
Method for simulating tectonic stress field
PendingCN110705168AReduce economic riskDesign optimisation/simulationTectonic stressMathematical model
The invention provides a method for simulating a tectonic stress field. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a geologic model; establishing a mathematical model; performing numericalsimulation; wherein the numerical simulation comprises selection and calculation of an external load acting force; constructing stress field numerical simulation calculation by an elastic-plastic incremental method; comparing with the stress direction and size of an actual measurement point; and determining whether the stress direction and magnitude are within an error range. According to the method, an elastic-plastic increment method is used for simulating the plastic deformation process of the target geologic body, and an artificial fracture development favorable area can be predicted moreaccurately through research of a tectonic stress field.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
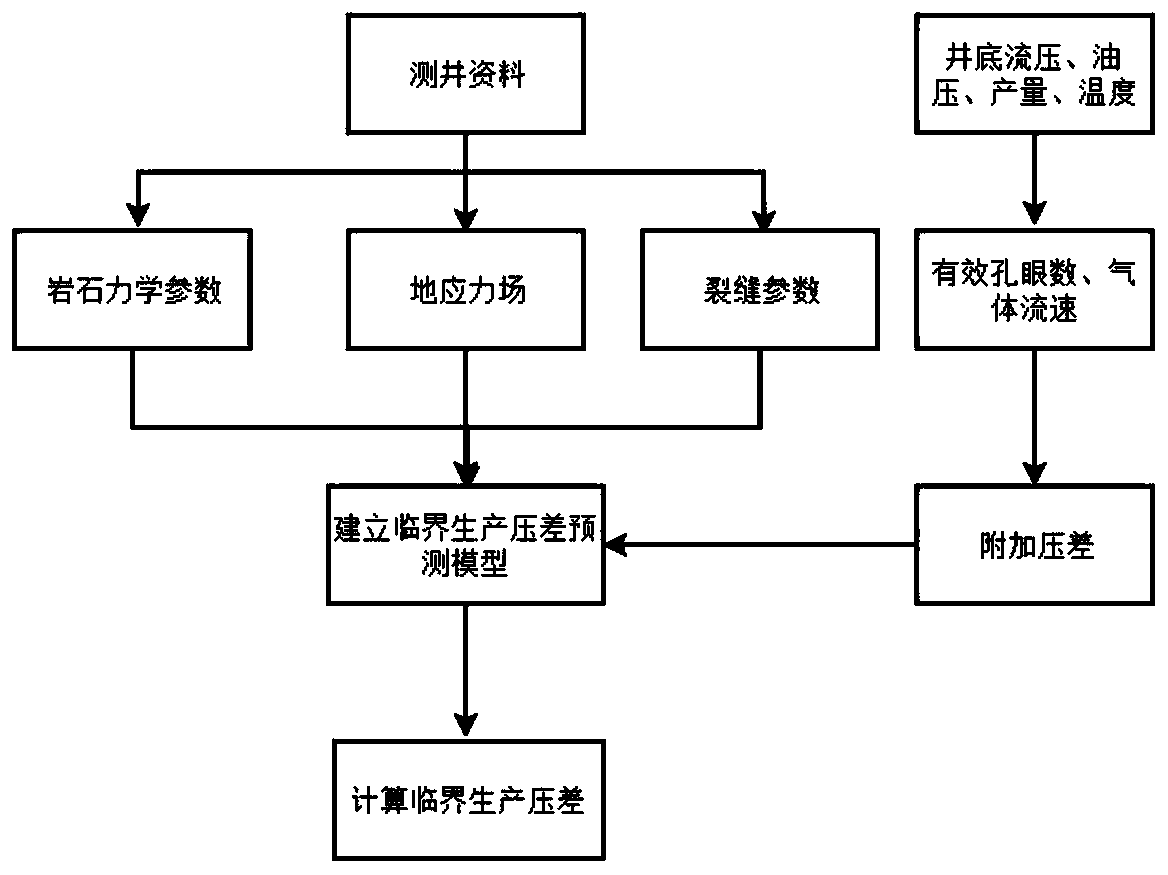
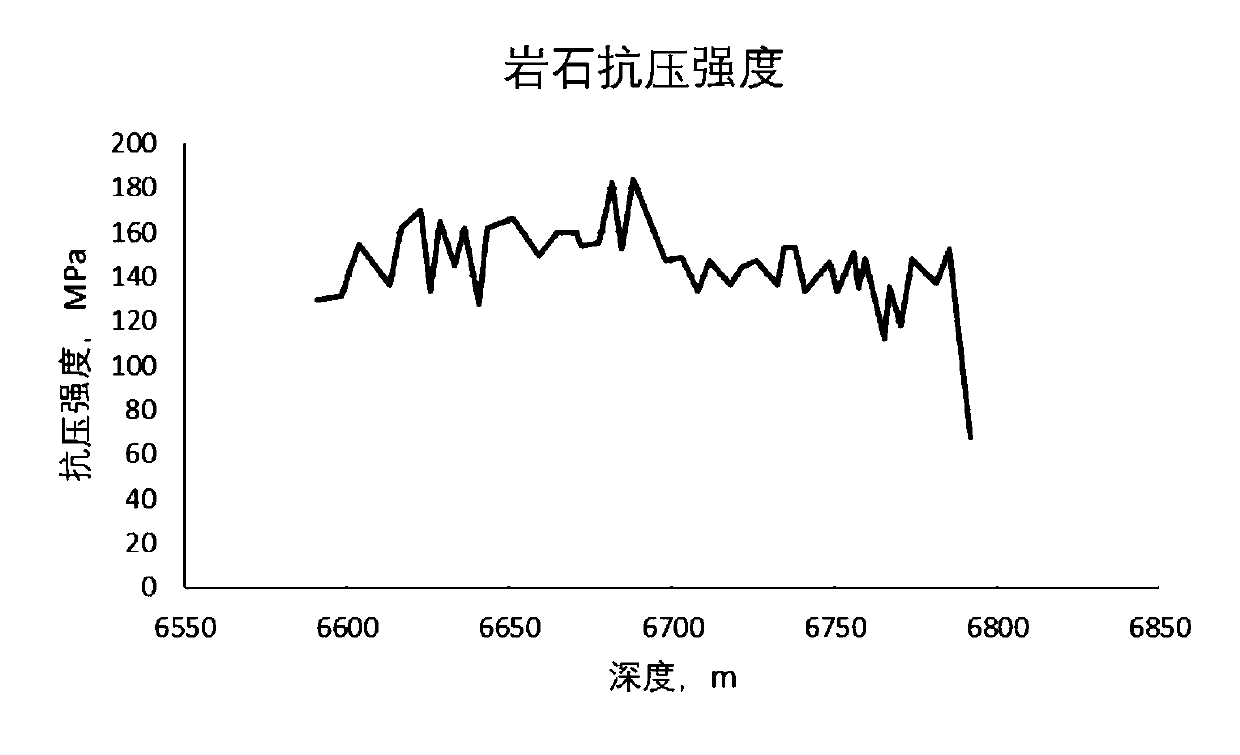
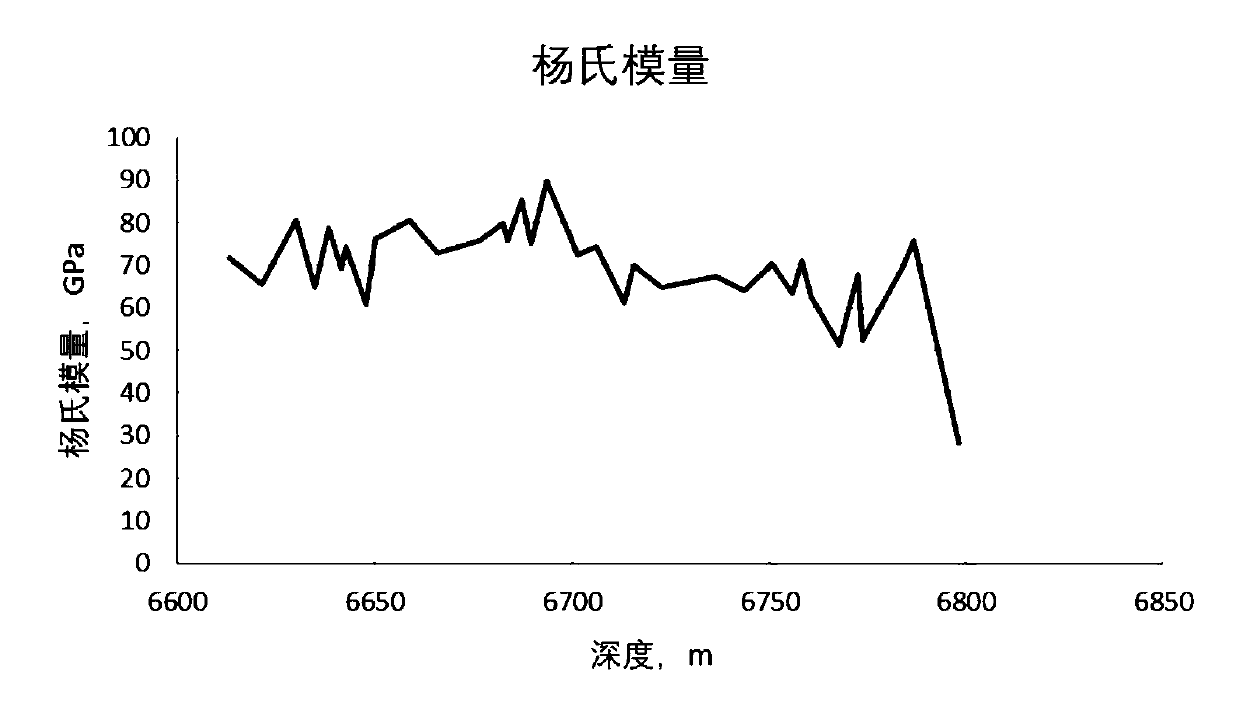
Ultrahigh-pressure tight fractured sandstone gas reservoir sand production prediction method
The invention belongs to the technical field of oil and gas exploitation, and discloses an ultrahigh-pressure tight fractured sandstone gas reservoir sand production prediction method. The method mainly considers the influence of the factors such as reservoir strong tectonic stress, perforation hole blockage, an additional pressure difference, and reservoir fractures of a sand production gas reservoir, and mainly comprises the following steps of (1) acquiring rock mechanical parameters through a well logging curve or experiment; (2) determining the magnitude and directions of a vertical main stress, a horizontal maximum main stress and a horizontal minimum main stress through logging data, and establishing a ground stress model; (3) determining an approximate number of effective holes andthe additional pressure difference; and (4) calculating a sand production critical production pressure difference according to the characteristic factors such as the fractures and the additional pressure difference. According to the method, reference and guidance can be provided for sand prevention work in such gas reservoir development, thus facilitating the recovery of normal and stable production of a gas well, and improving the economic benefit.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Near-field-intensity ground motion estimation method based on finite element model
PendingCN111553103AQuick Estimate ResultsReduce computationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTectonic stressElement model
The invention relates to a near-field-intensity ground motion estimation method based on a finite element model, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a two-dimensional fault fracture surface finite element model, initializing a tectonic stress field in a static finite element model, and triggering a seismic event; setting an artificial boundary with an equivalent boundary unit, extracting seismic oscillation parameters, and realizing bed rock seismic oscillation simulation; and in the static finite element model, obtaining an initial stress state under a fault surface boundary fracture state when a seismic event occurs, and transferring the obtained initial stress state in the static finite element model to the dynamic finite element model for nonlinear analysis to obtain a seismic oscillation acceleration time-history estimated value. According to the method, a two-dimensional finite element model is used for replacing a traditional three-dimensional Green function model,so that the operand is reduced, and meanwhile, the operation time is shortened; and meanwhile, a rapid estimation result of strong ground motion of the earthquake event is provided, and important guiding significance is achieved for command and decision making of earthquake emergency rescue after an earthquake.
Owner:THE FIRST MONITORING CENT OF CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTATION
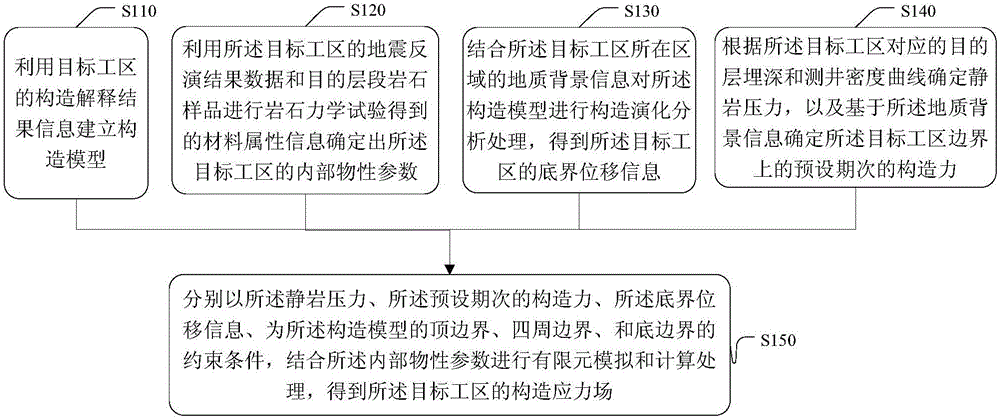
Method and device for simulating tectonic stress field
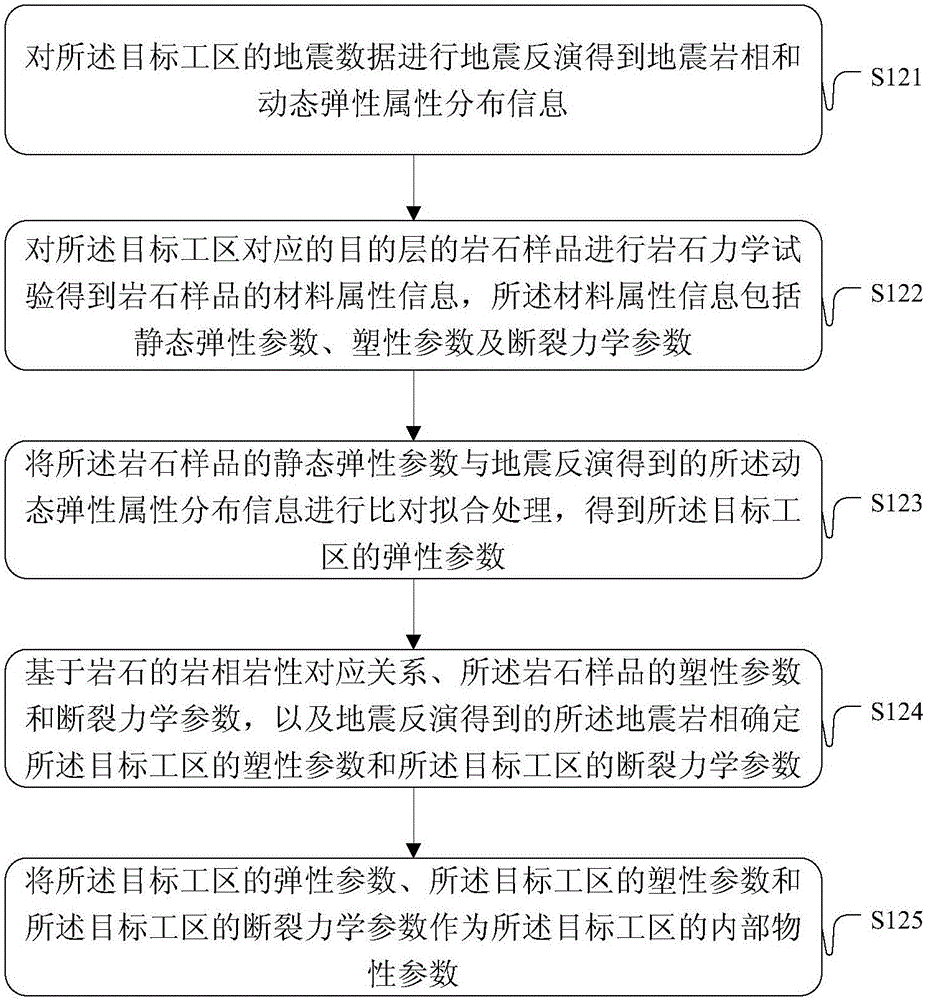
ActiveCN106815412AAdapt to complexityAccurately determineDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTectonic stressDensity curve
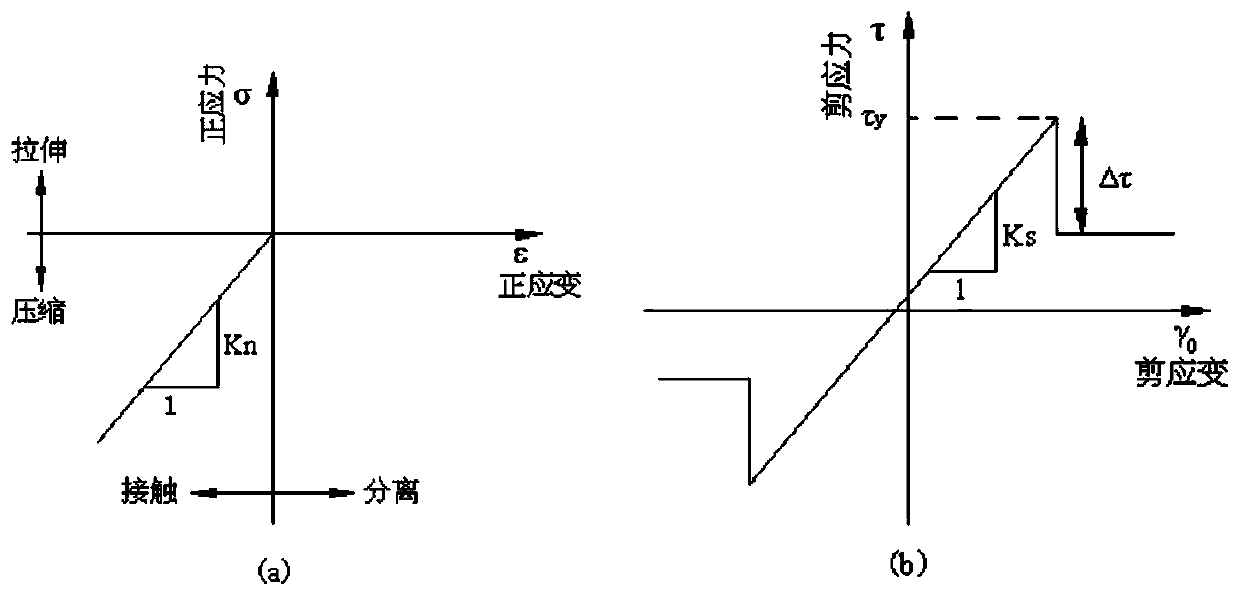
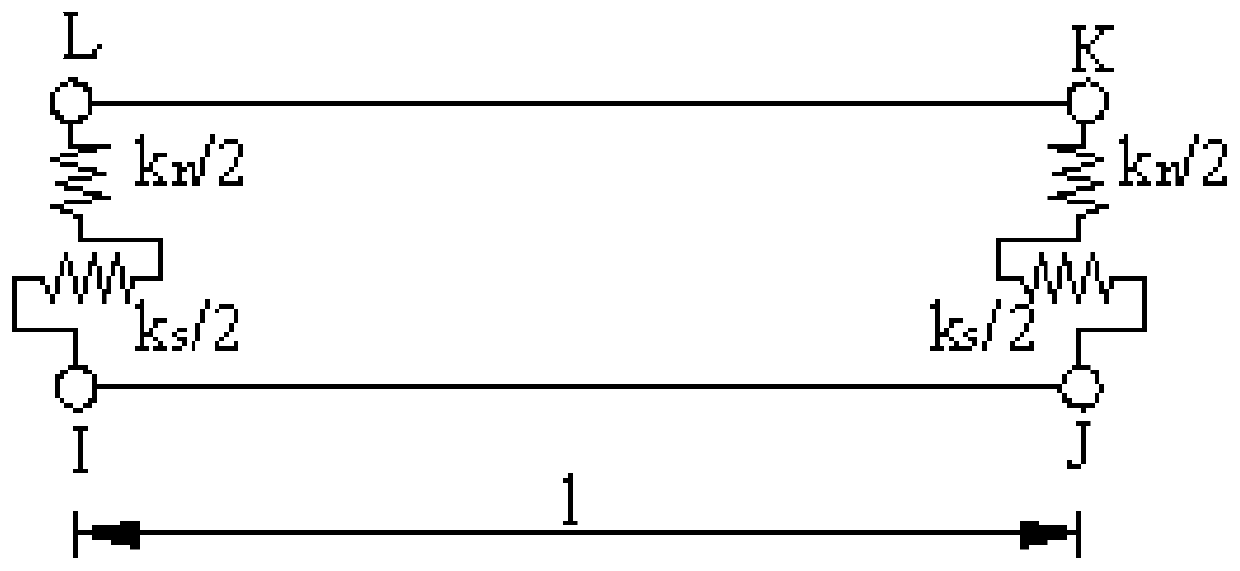
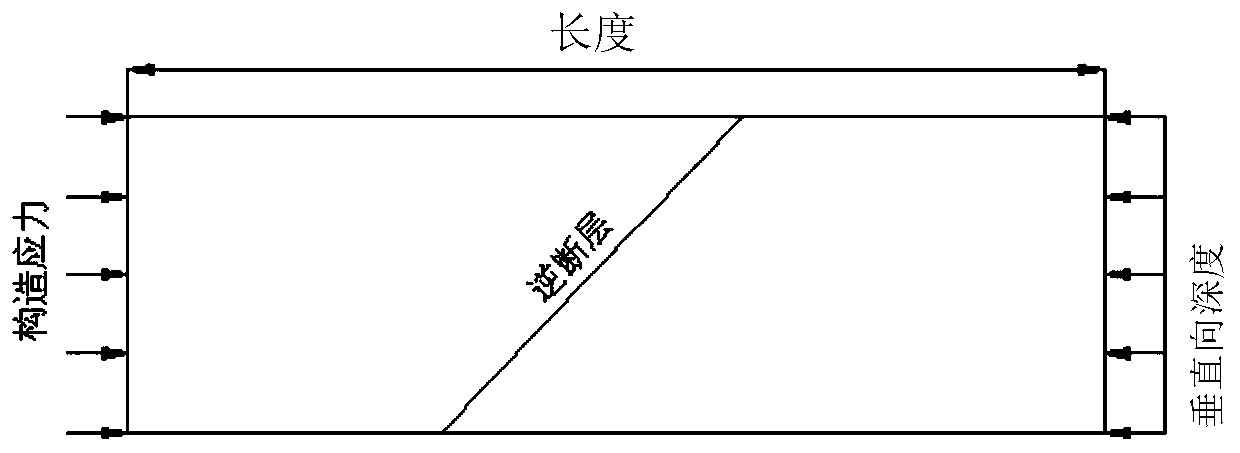
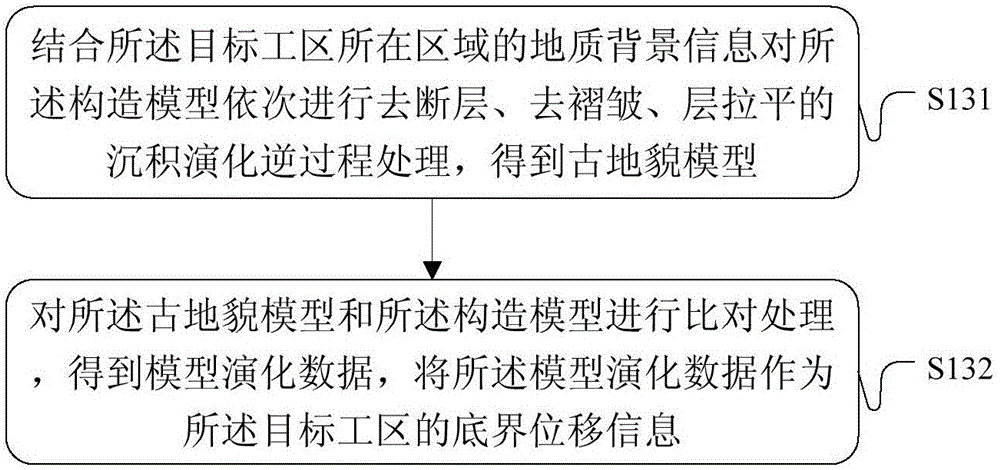
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for simulating a tectonic stress field. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing tectonic explaining result information in a target work area to establish a tectonic model; confirming interior physical property parameters by utilizing material attribute information acquired from a rock mechanical test for seismic inversion result data and an objective interval rock sample in the target work area; performing tectonic evolutionary analysis treatment on the tectonic model in combination with geological background information, thereby acquiring bottom margin displacement information; confirming static rock pressure according to objective interval burial depth and logging density curve and confirming an inferior tectonic force in a preset period at a boundary of a target work area on the basis of the geological background information; respectively utilizing the static rock pressure, the inferior tectonic force in the preset period and the bottom margin displacement information as the constraint conditions of the top boundary, the peripheral boundary and the bottom boundary of the tectonic model and performing finite element modeling and calculating treatment in combination with an interior physical property parameter, thereby acquiring the tectonic stress field in the target work area. The technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention is utilized to more accurately confirm the tectonic stress field in the work area.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Gaseous coal friction-adsorption/desorption test device and test method
The invention discloses a gaseous coal friction-adsorption / desorption test device and test method. The device mainly comprises a gaseous coal friction device system, a gas injection / pressurization pipeline and a real-time data acquisition system. The friction device system and the gas injection / pressurization pipeline can realize a friction sliding action of coal and coupling of adsorption / desorption; and meanwhile, the real-time data acquisition system is used to monitor and acquire data of a friction sliding state and adsorption and desorption features. The gaseous coal friction-adsorption / desorption test device can well describe the adsorption and desorption features of dynamic damage to a coal sample under a tectonic stress environment, which is closer to an actual situation, so that afoundation is laid to researching a forming mechanism of gas expansion energy which induces a coal mine gas disaster and a gaseous coal friction sliding instability inducing and outburst mechanism.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Discrimination method of stability potential energy of overburden strata in metal mine supported by artificial pillars
ActiveCN109682946ADetermine stabilityEarth material testingStrength propertiesStress distributionTectonic stress
The invention provides a discrimination method of the stability potential energy of an overburden strata in metal mine supported by artificial pillars. A goaf overburden strata model is established, when the width of a goaf is larger than the length, the model is simplified to a thin section simply supported beam model, and stress distributions generated by the support force and tectonic stress ofa beam are calculated respectively; when the strata only supported by the beam, a plane-coordinate system is built, the stress function on a plane is calculated, and components of stress are obtained; when the strata is only subjected to the tectonic stress, the components of stress are calculated; when the strata is subjected to the combined action of the supporting force and the tectonic stress, the generated total stress distribution is calculated when the strata is subjected to the combined action of the supporting force and the tectonic stress, the potential energy of the whole strata is calculated, and the stability potential energy of the overburden strata in metal mine supported by artificial pillars is discriminated. The method can be used for analyzing the stress distribution and concentration degree, changing by the artificial pillars, of the goaf overburden strata, and meanwhile the stability of the goaf overburden strata is judged under supporting of the artificial pillars.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
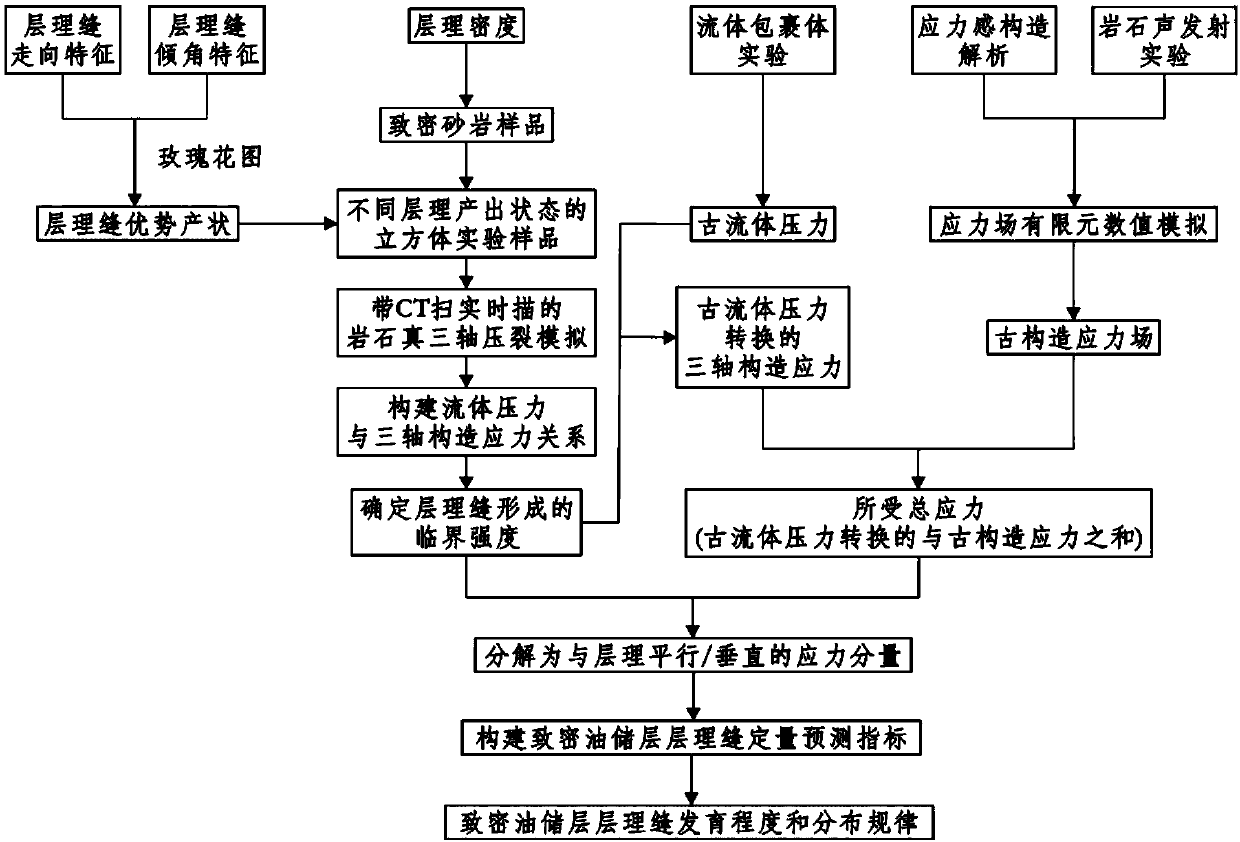
Quantitative prediction method for stratification seam of compact oil reservoir layer
ActiveCN107942381AImprove the effect of exploration and developmentSeismic signal processingTectonic stressStressed state
The invention discloses a quantitative prediction method for a stratification seam of a compact oil reservoir layer. Paleostructure stress states and compact reservoir layer paleo-fluid pressures of aresearch area in different periods are determined; simulation experiment is carried out to construct a relationship between a fluid pressure and a triaxial tectonic stress and critical strengths formed by stratification seams in different tectonic stress states and on different fluid pressure strength conditions are determined; and a quantitative prediction index (I) of a stratification seam of acompact oil reservoir layer is constructed and a growth degree and a distribution rule of the stratification seam of the compact oil reservoir layer are predicted in a quantitative manner. Therefore,a novel idea and path is provided for the stratification seam study of the compact oil reservoir layer; and the exploration and development effects of the compact oil are improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Asymmetrical supporting method of impact ground pressure roadway
ActiveCN109973113AGuarantee the quality of supportImprove support efficiencyUnderground chambersTunnel liningTectonic stressRebar
The invention discloses an asymmetrical supporting method of an impact ground pressure roadway. The asymmetrical supporting method comprises the steps: according to the vertical stress and tectonic stress in surrounding rock of the roadway, and the coal seam dip angle, the direction of main acting force, in the normal direction of a coal seam, in the surrounding rock of the roadway is determined;the top, the hance and side wall parts of the roadway located in the coal seam are supported through anchor cables and inner-layer reinforcing meshes, wherein the anchor cables are densified, lengthened and / or patched at the positions, directly facing the direction of the main acting force, of the roadway, and then the roadway is asymmetrically supported; and the working resistance of the anchor cables at the top, the hance, the side wall parts and / or a bottom plate of the roadway is monitored in real time, the measure of reinforcing supporting or pressure relieving is taken, the supporting quality of the surrounding rock of the roadway is guaranteed, and then the roadway is asymmetrically supported. According to the asymmetrical supporting method, supporting is reinforced only in the direction of the main acting force in the normal direction of the coal seam, and thus the supporting efficiency and effect are improved.
Owner:TIANDI SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com