Novel phospholipase D
A technology of phospholipase and phosphatidylinositol, applied in the field of phospholipase D, can solve the problems of low alkali conversion rate and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
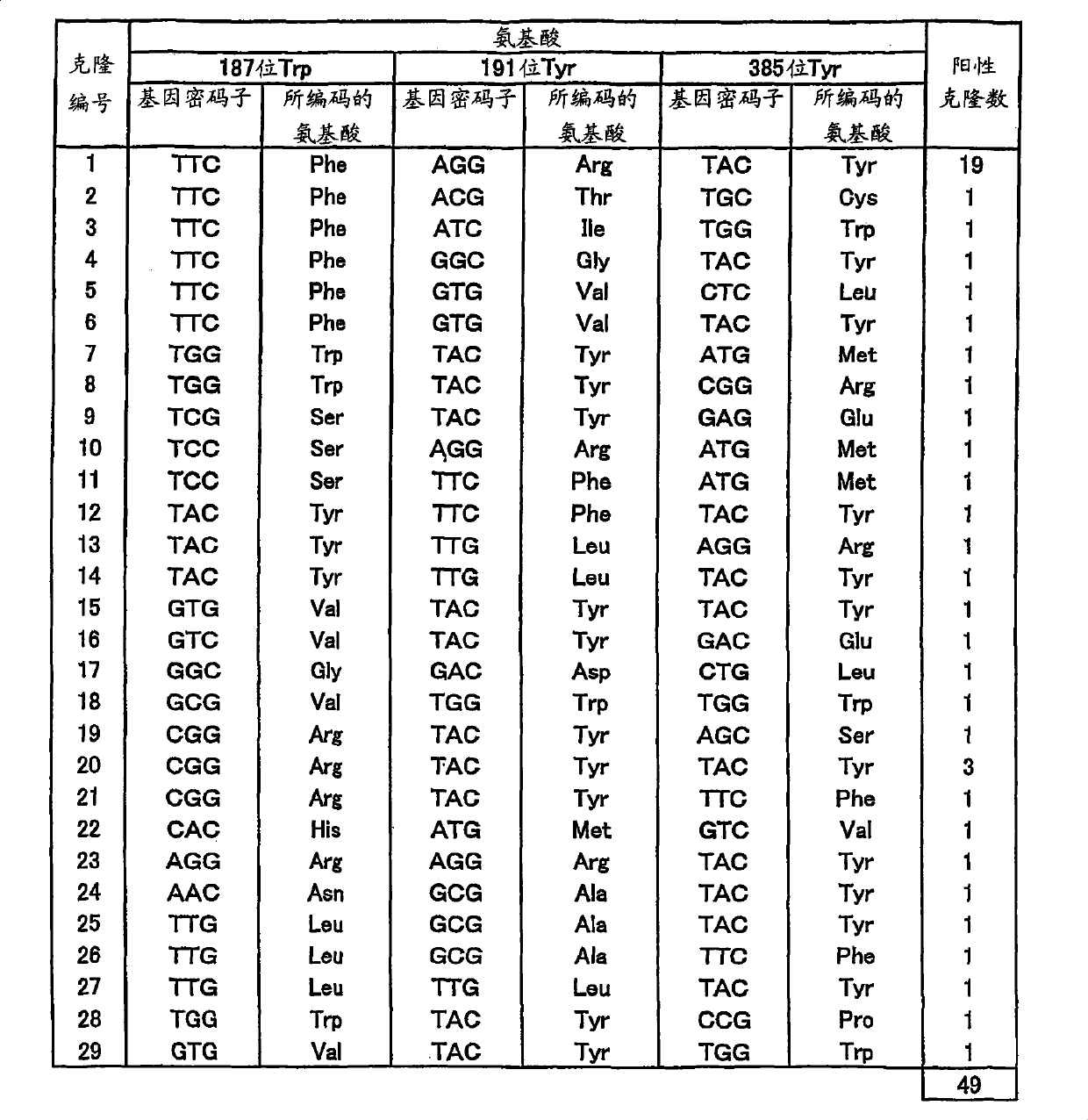
[0144] (Example 1: Preparation of library)
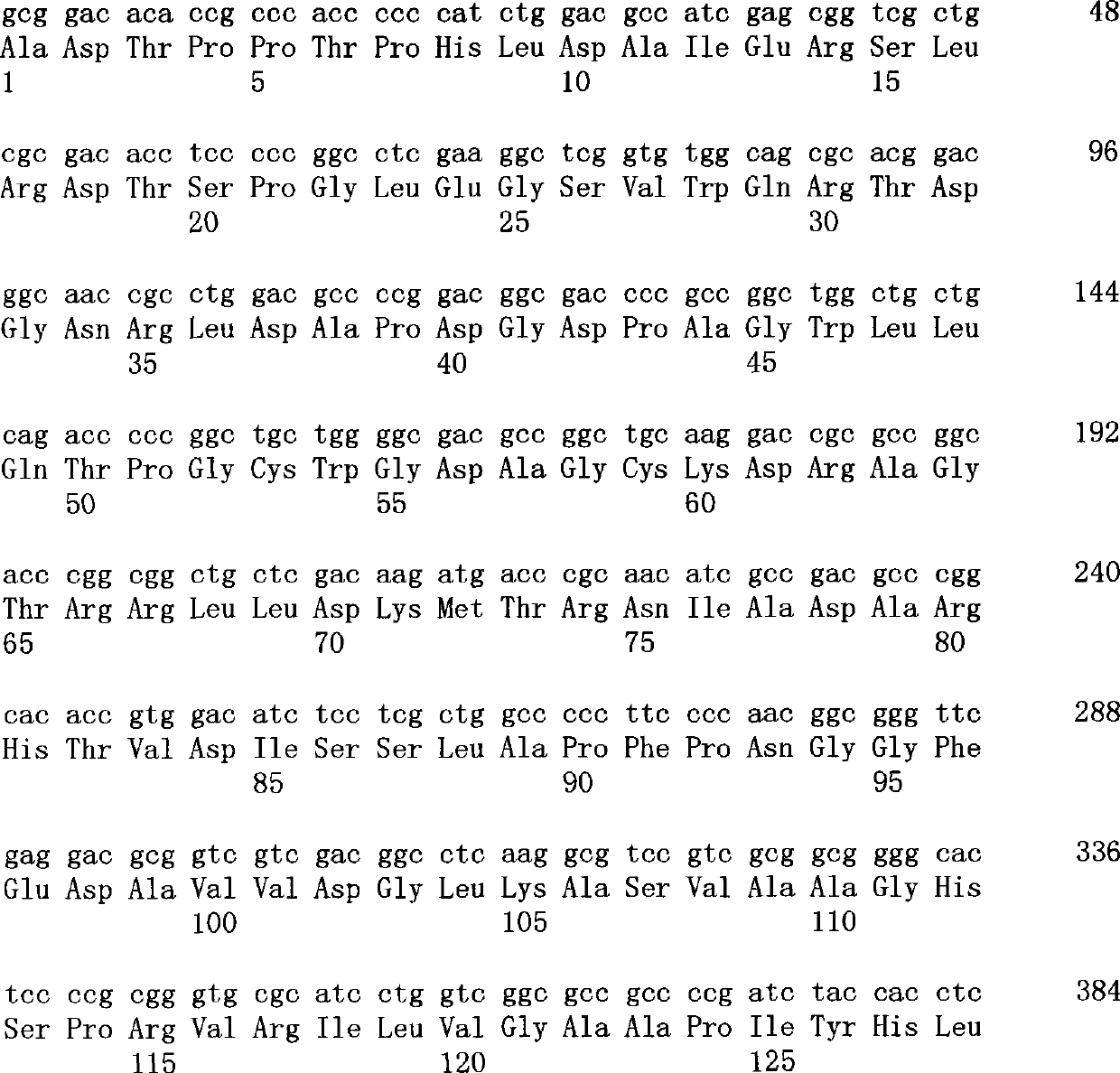
[0145] pPELB-PLD1 (prepared according to Y.Iwasaki et al., J.Ferment.Bioeng., 1995, Vol. 79, pages 417-421) was digested with restriction enzymes XbaI and XhoI, and the liposome-binding site, The pelB signal from pET22b (Novagen) and the fragment of the full-length (1530bp; base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 of the sequence listing) of the PLD gene from the resistant Streptomyces were inserted into the pBluescriptII KS digested with XbaI and XhoI in advance +(manufactured by Toyobo), pPELB-PLD-KS was prepared. This was digested with the restriction enzyme ApaI, together with the fragment around the stop codon of the PLD gene, the inverted repeat sequence downstream of the PLD gene was removed. On the other hand, pSA1 (prepared according to Y.Iwasaki et al., Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol., 1994, volume 42, pages 290-299) was digested with restriction enzymes BamHI and SalI, and the second half of the PLD gene containing it was excise...
Embodiment 2
[0153] (Example 2: Expression of plasmid library)
[0154] The above-mentioned plasmid mixture was introduced into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) as an expression host, and grown on LB agar medium having the same composition as in Example 1 at 37°C for 16 hours. A nitrocellulose membrane (HybondC, manufactured by Amasyam) was placed on the obtained colonies, and the colonies were transferred. Next, the membrane is transferred to a synthetic medium (the composition is as follows (indicates the quality per 1 L): 5g KH 2 PO 4 , 5g K 2 HPO 4 , 4.4g Na 2 HPO 4 , 3g (NH 2 ) 2 SO 4 , 5g glucose, 3g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 40mg FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 40mg CaCl 2 , 10mgMnSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 2.9mg CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O, 3mg CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O, 0.36mgNa 2 MoO·2H 2 O, 10 mg H3 BO 3 , 10mg ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 1.5% agar was added to O) and incubated at 30°C for 8 hours to allow colonies to grow on the membrane. Colonies on LB agar medium were kept in the refrigerator as master plates. The membrane was trans...
Embodiment 3
[0155] (Example 3: Screening of clones expressing modified PLDs that synthesize PI)
[0156] The above membrane was immersed in a substrate solution (10% soybean lecithin (manufactured by SLP-PC70ツルレシチン), 20% inositol, 2% calcium chloride and 50 mM acetate buffer, pH 5.6) at 30°C For 14 hours, the enzymatic reaction was carried out on the membrane. Phosphatidylinositol (PI), which is an acidic phospholipid, is produced by this enzymatic reaction, and these form water-insoluble salts with coexisting calcium ions, and precipitate at the site where the reaction occurs. After the reaction, the excess substrate solution was rinsed with water, and the membrane was immersed in a 10% aqueous sodium periodate solution at room temperature for 10 minutes. By this sodium periodate treatment, the diol moiety of the precipitated PI is oxidatively cleaved to derivatize to an aldehyde. The excess sodium periodate solution was rinsed with water, and the membrane was coated with an aqueous NB...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com