Use of lysophosphatidylethanolamine (18:1) and lysophosphatidylinositol to retard senescence and to enhance fruit ripening
A technology of lysophospholipids and fruits, which is applied in the field of promoting fruit ripening and improving stability, and can solve problems such as the lack of research on the relative efficiency of lysophospholipids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1:LPE(18∶1) and LPIPLD Embodiment 1
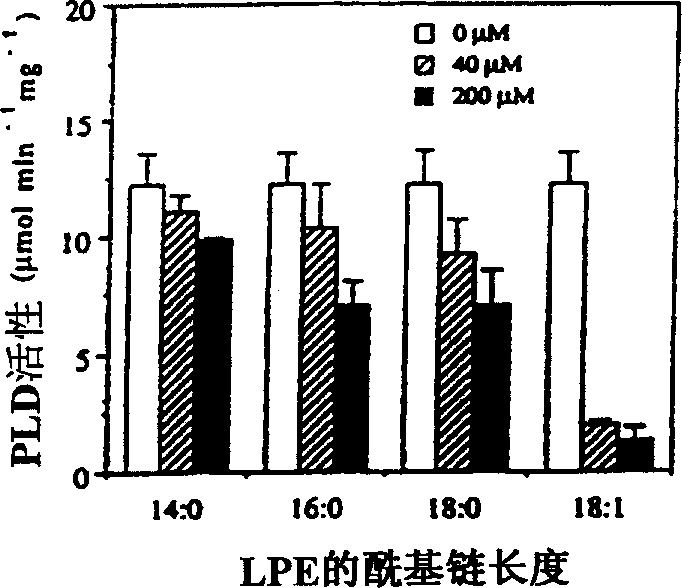
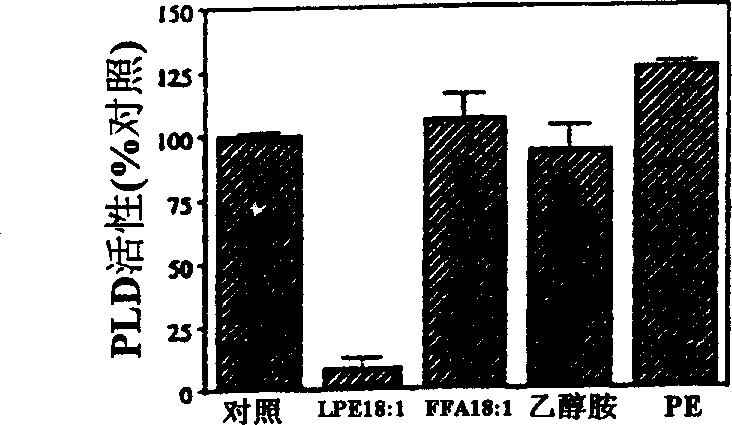
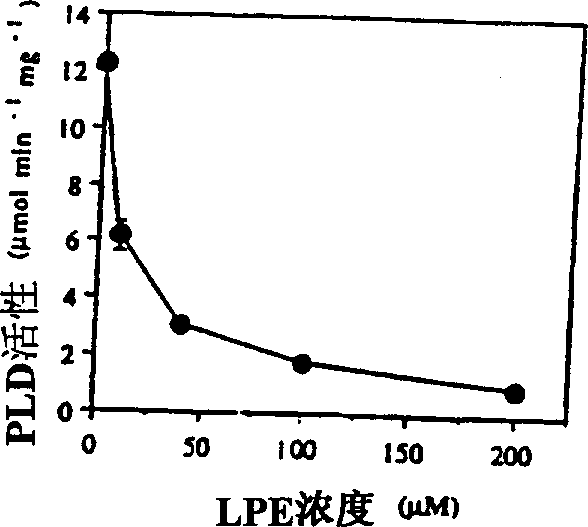
[0022] Examples of the present invention are now given, by way of illustration and not limitation. Example 1: Specific Inhibition of PLD by LPE (18:1) and LPI Example 1a: Chemicals and Plant Material
[0023]Natural lysophospholipids purified from egg yolk, beef liver and soybean as well as synthetic LPEs with different acyl chains (14:0, 16:0, 18:0, 18:1 ) were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, Alabama). The remaining phospholipid chemicals and materials used were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Phospholipids and fatty acids were dissolved in chloroform:methanol:KOH (1N) (95:5:1, v / v). After adding water, the organic solvent was removed by flowing nitrogen. Before adding to the PLD reaction system, the concentration of the stock solution was adjusted to 1 mM with water. LPE solutions for the treatment of fruit and plant tissue were prepared in bulk by sonication of LPE powder suspended in water without the use of organic solvents.
[0024] Partially pur...
Embodiment 1b
[0026] Example 1b: Tissue sorting
[0027] Fully expanded leaves of two-month-old castor plants and cabbage were harvested, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and homogenized with a mortar and pestle cooled on ice (13). An extraction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCL (pH 8.0), 10 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5 mM PMSF and 2 mM DTT was added to the powder sample. After grinding for an additional 5 minutes, the homogenate was centrifuged at 6000 g for 10 minutes to remove debris. The supernatant was centrifuged at 100,000 g for 30 minutes to separate the extract into soluble PLD and membrane-associated PLD. The resulting supernatant was collected as a soluble fraction, and the precipitate was collected as a membrane fraction. Wash the membrane fraction once with extraction buffer to remove soluble impurities. The soluble PLD and membrane-associated PLD samples were added to the reaction system to a final concentration of 100 μg / ml and 10 μg / ml, respectively. Embodiment 1c: PLD activity ...
Embodiment 1c
[0027] Fully expanded leaves of two-month-old castor plants and cabbage were harvested, snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and homogenized with a mortar and pestle cooled on ice (13). An extraction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCL (pH 8.0), 10 mM KCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.5 mM PMSF and 2 mM DTT was added to the powder sample. After grinding for an additional 5 minutes, the homogenate was centrifuged at 6000 g for 10 minutes to remove debris. The supernatant was centrifuged at 100,000 g for 30 minutes to separate the extract into soluble PLD and membrane-associated PLD. The resulting supernatant was collected as a soluble fraction, and the precipitate was collected as a membrane fraction. Wash the membrane fraction once with extraction buffer to remove soluble impurities. The soluble PLD and membrane-associated PLD samples were added to the reaction system to a final concentration of 100 μg / ml and 10 μg / ml, respectively. Embodiment 1c: PLD activity detection method
[0028] The activi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com