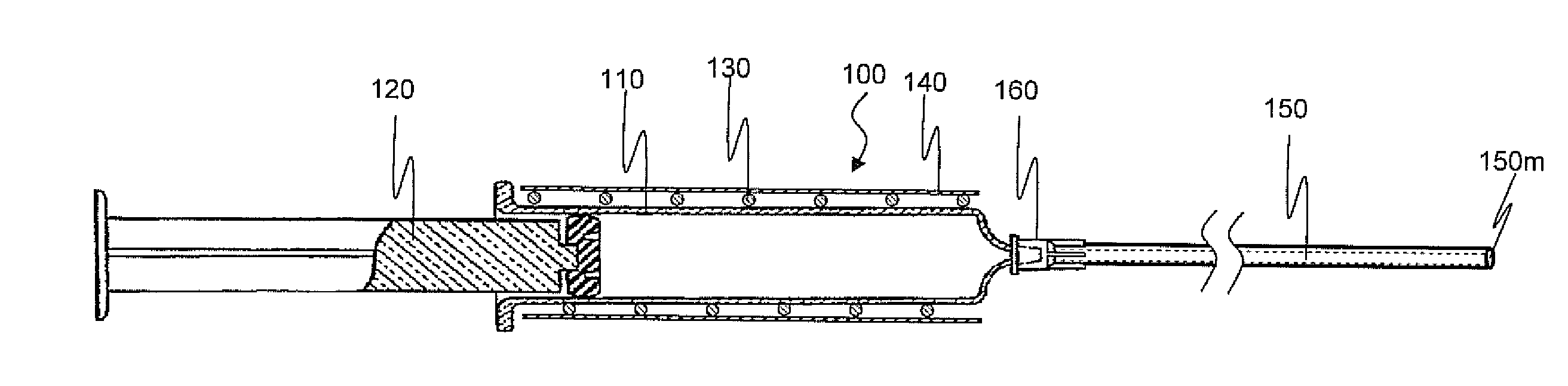
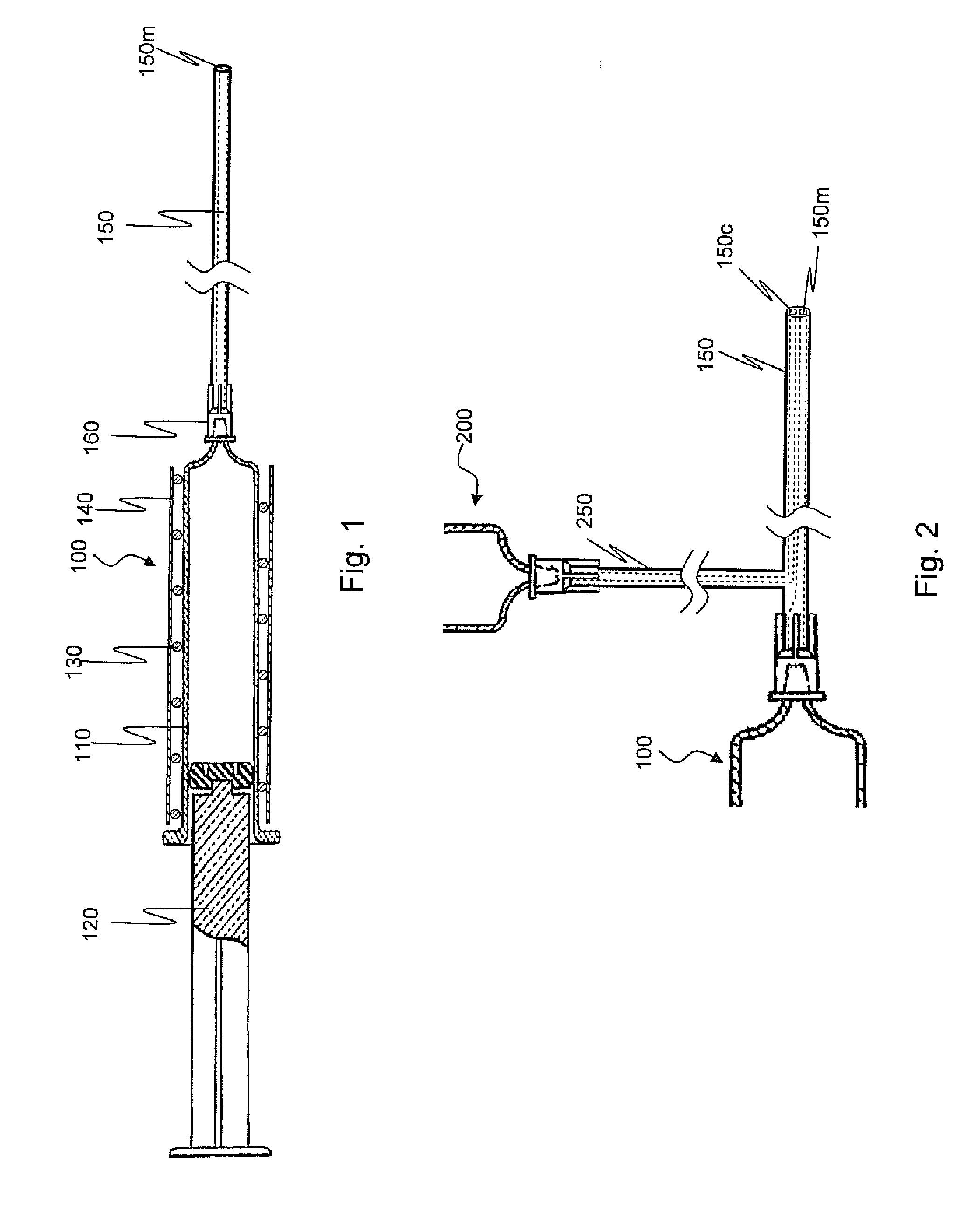
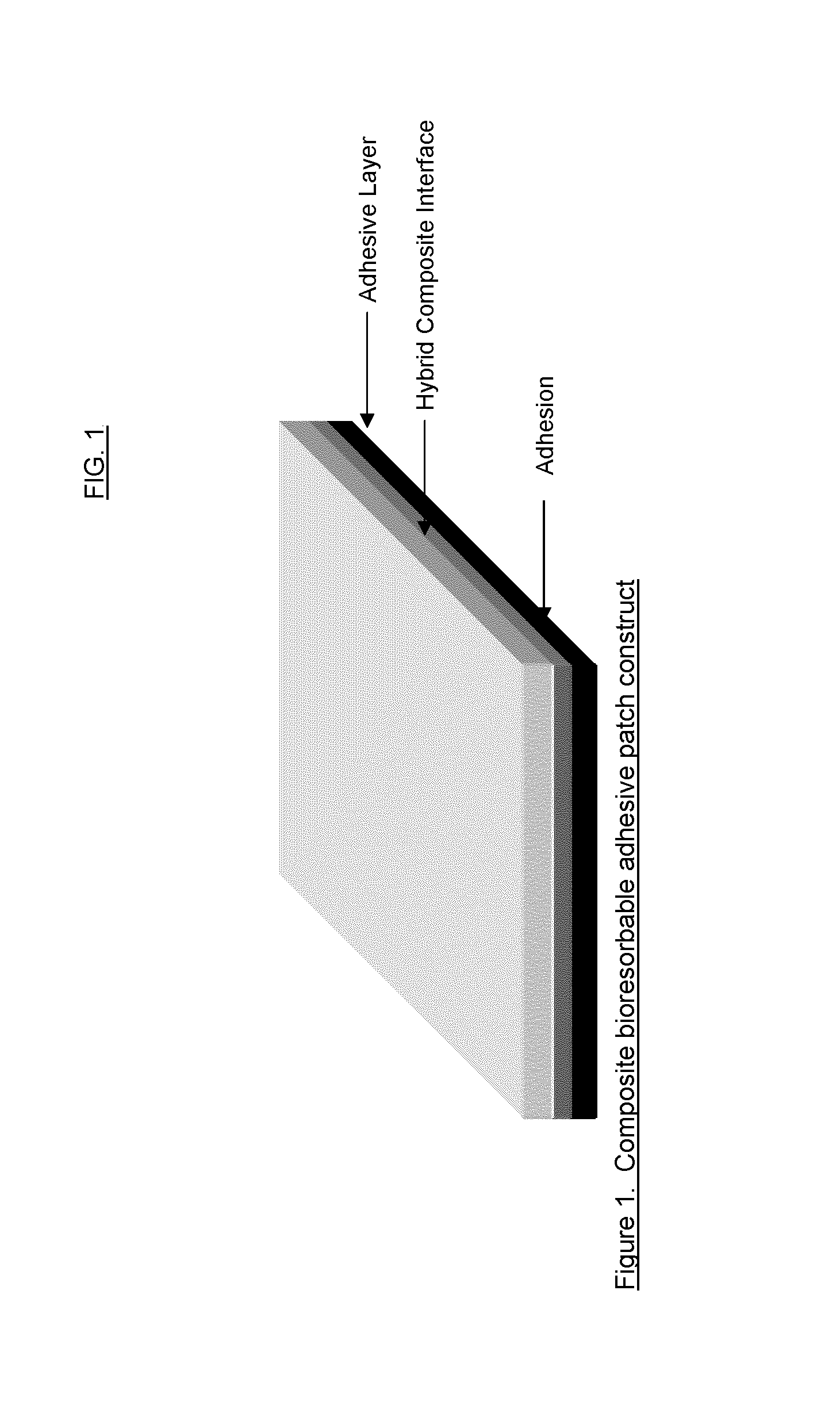
Patents
Literature
60 results about "Adhesion barrier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
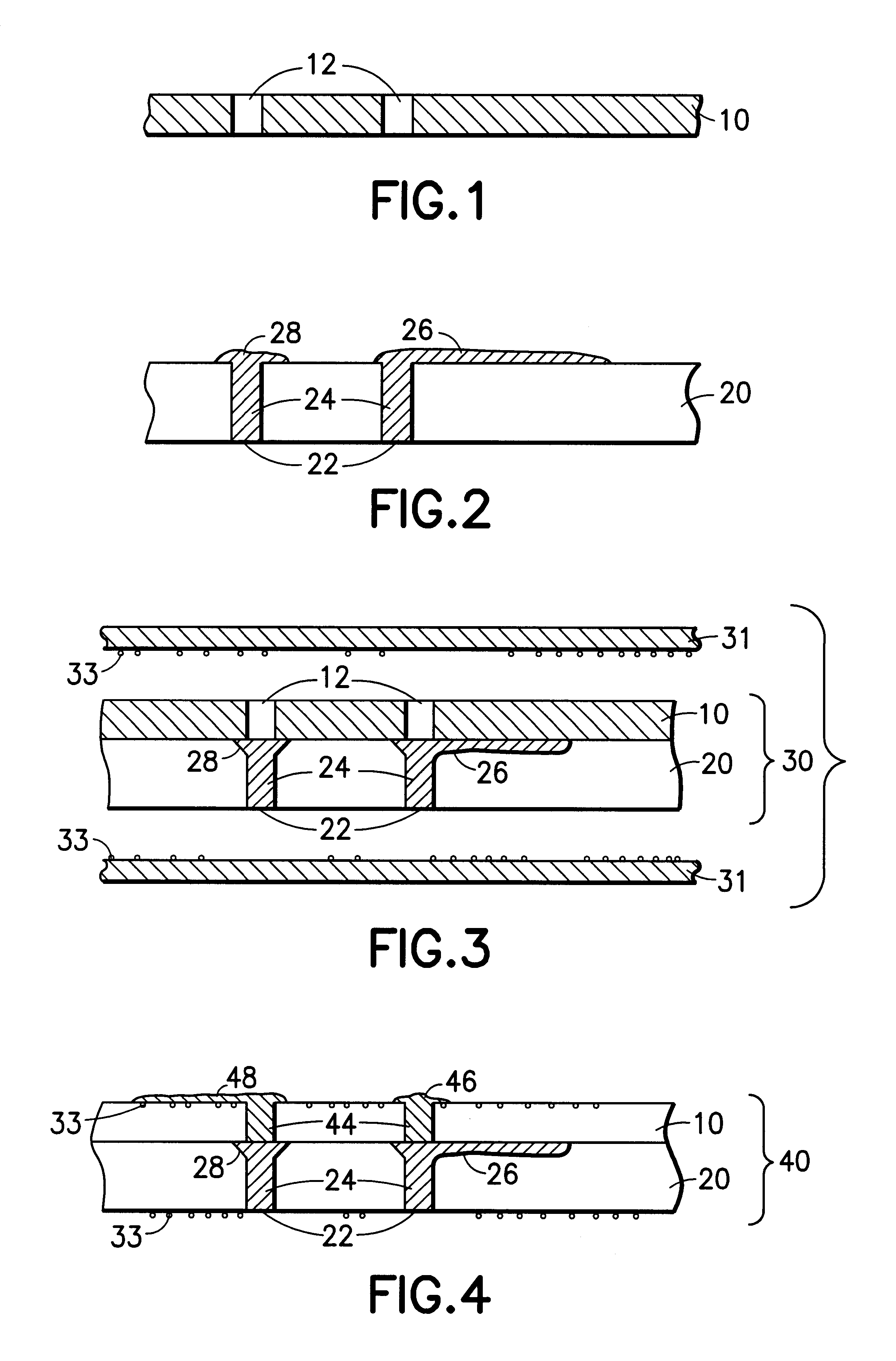
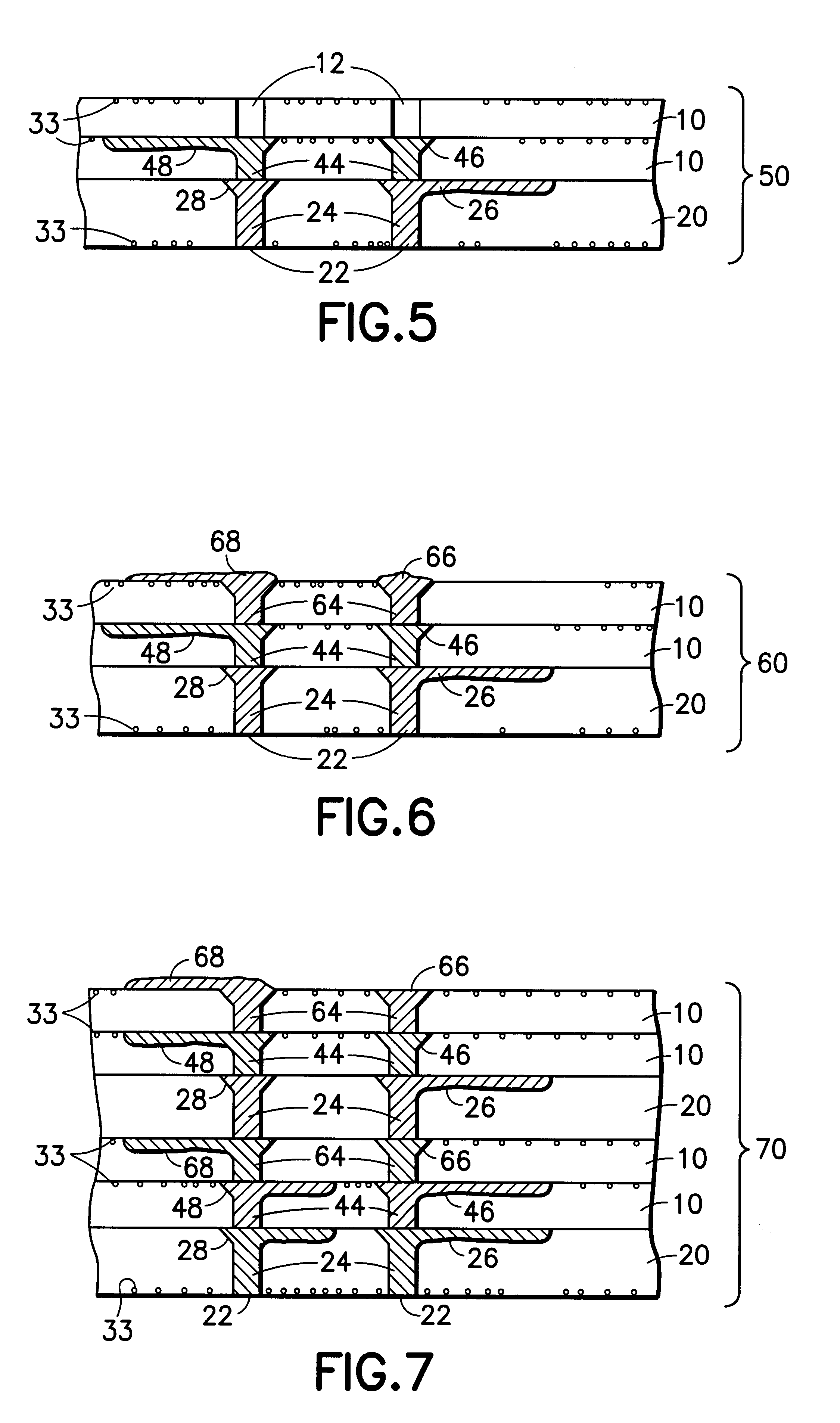
An adhesion barrier is a medical implant that can be used to reduce abnormal internal scarring (adhesions) following surgery by separating the internal tissues and organs while they heal. Surgeons have realized that proper surgical technique is crucial to reduce adhesion formation. In addition, for more than a century, adjuvants including drugs and materials such as animal membranes, gold foil, mineral oil, sheets made of rubber and Teflon, have been used to reduce the risk of adhesion formation. Nevertheless, adhesions do occur and appear to be, to some degree, an almost unavoidable consequence of abdominal and pelvic surgery. Adhesions can lead to significant post-surgical morbidity, bowel obstruction, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain or chronic abdominal pain.
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
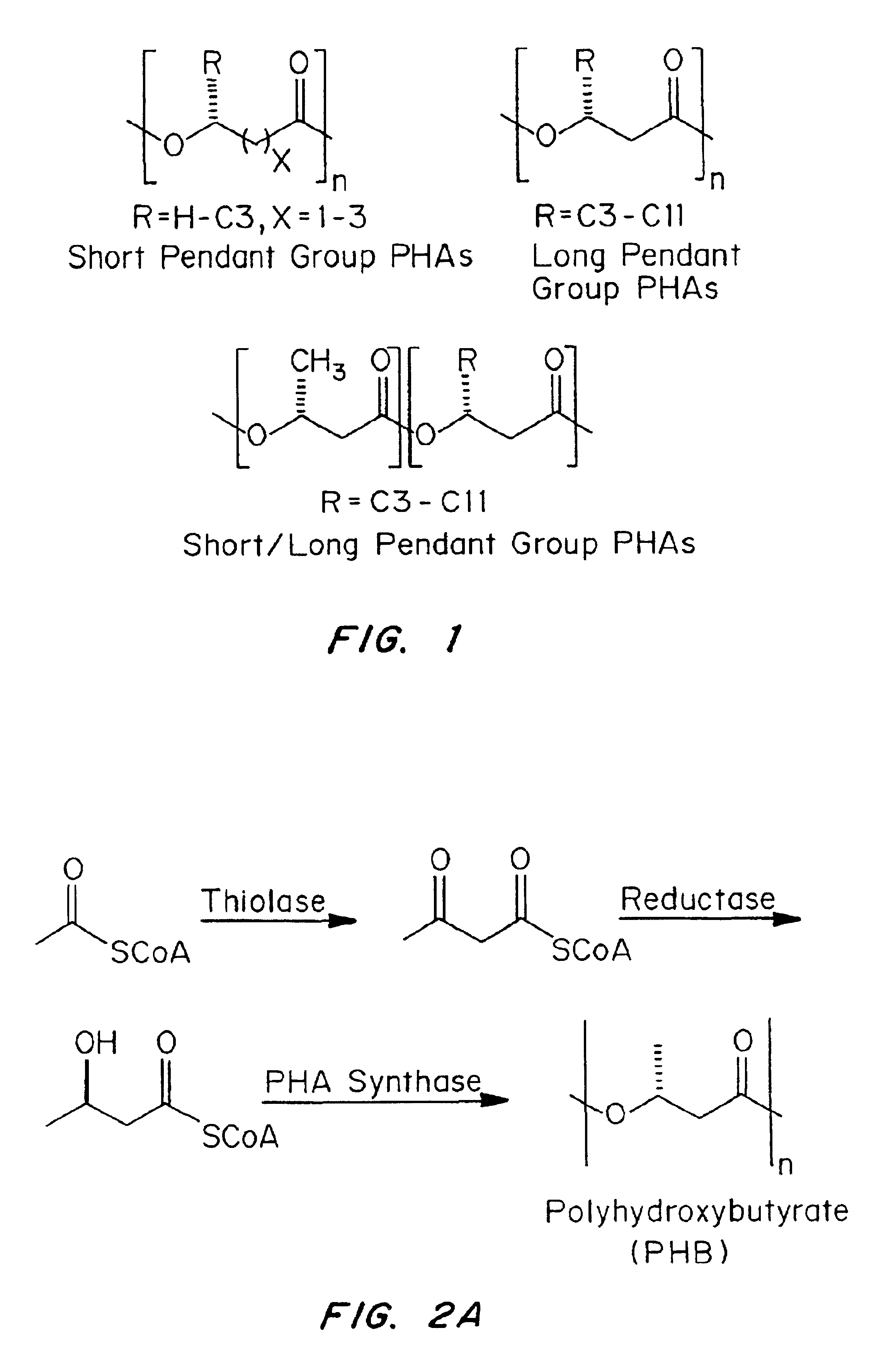
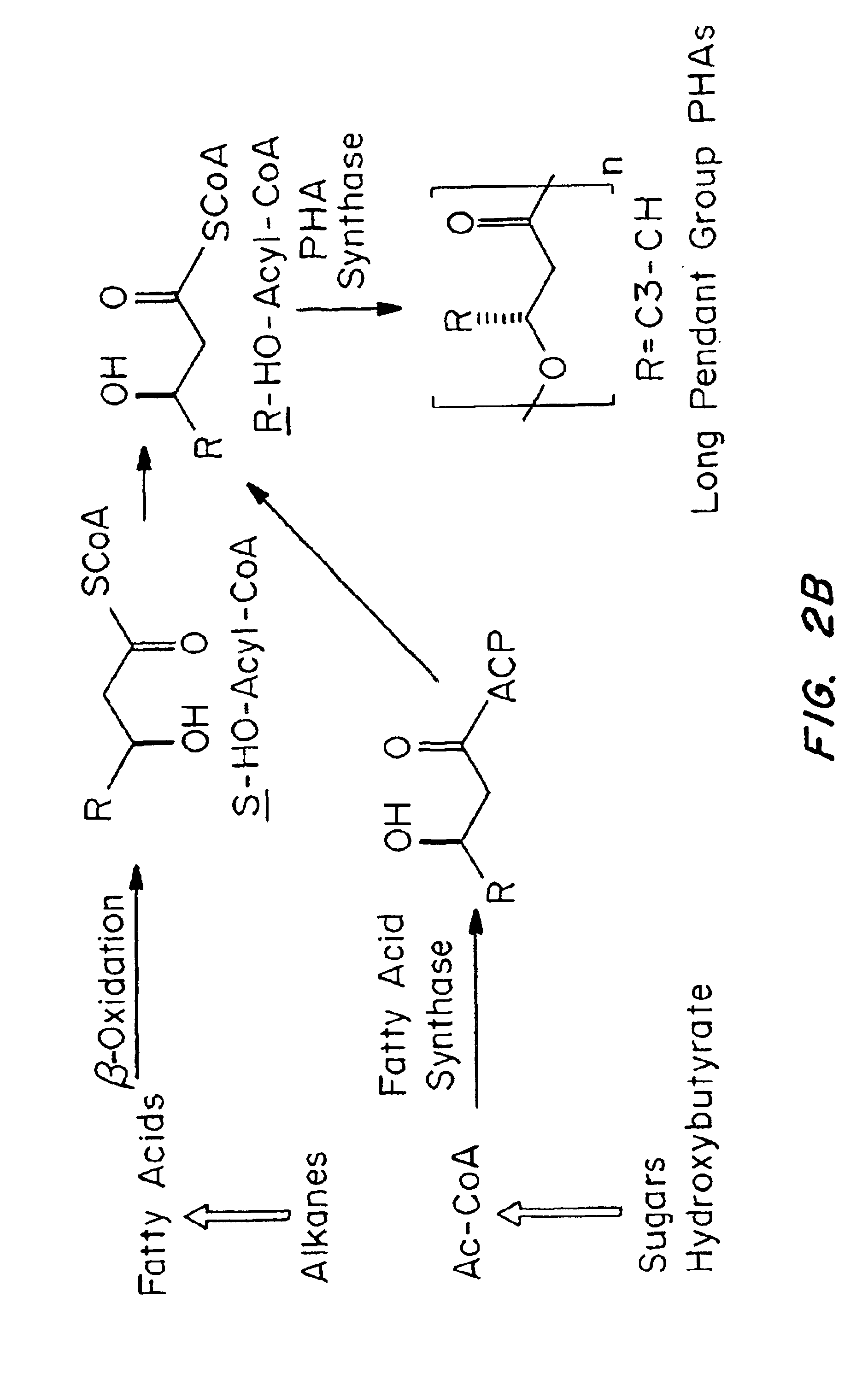
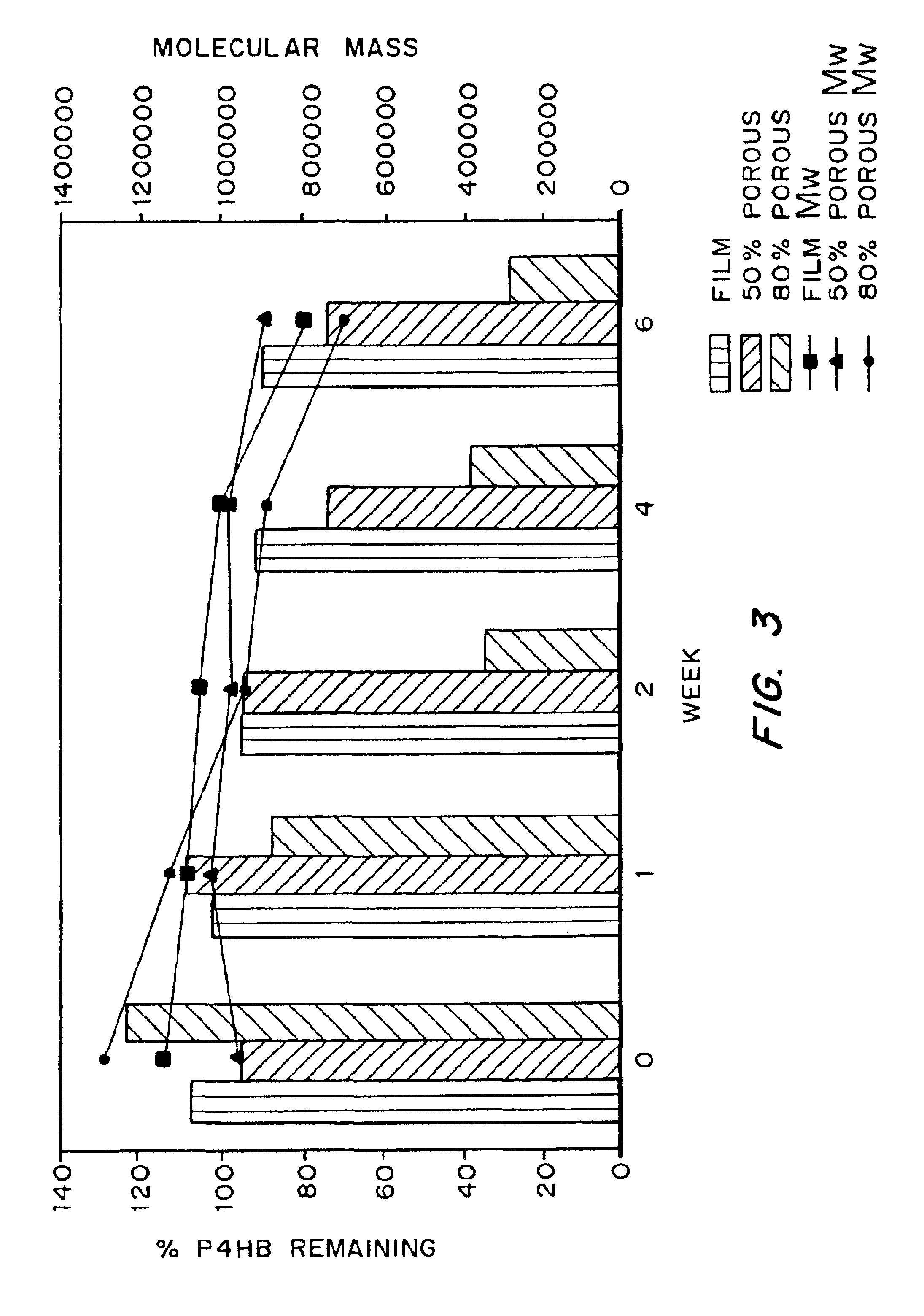
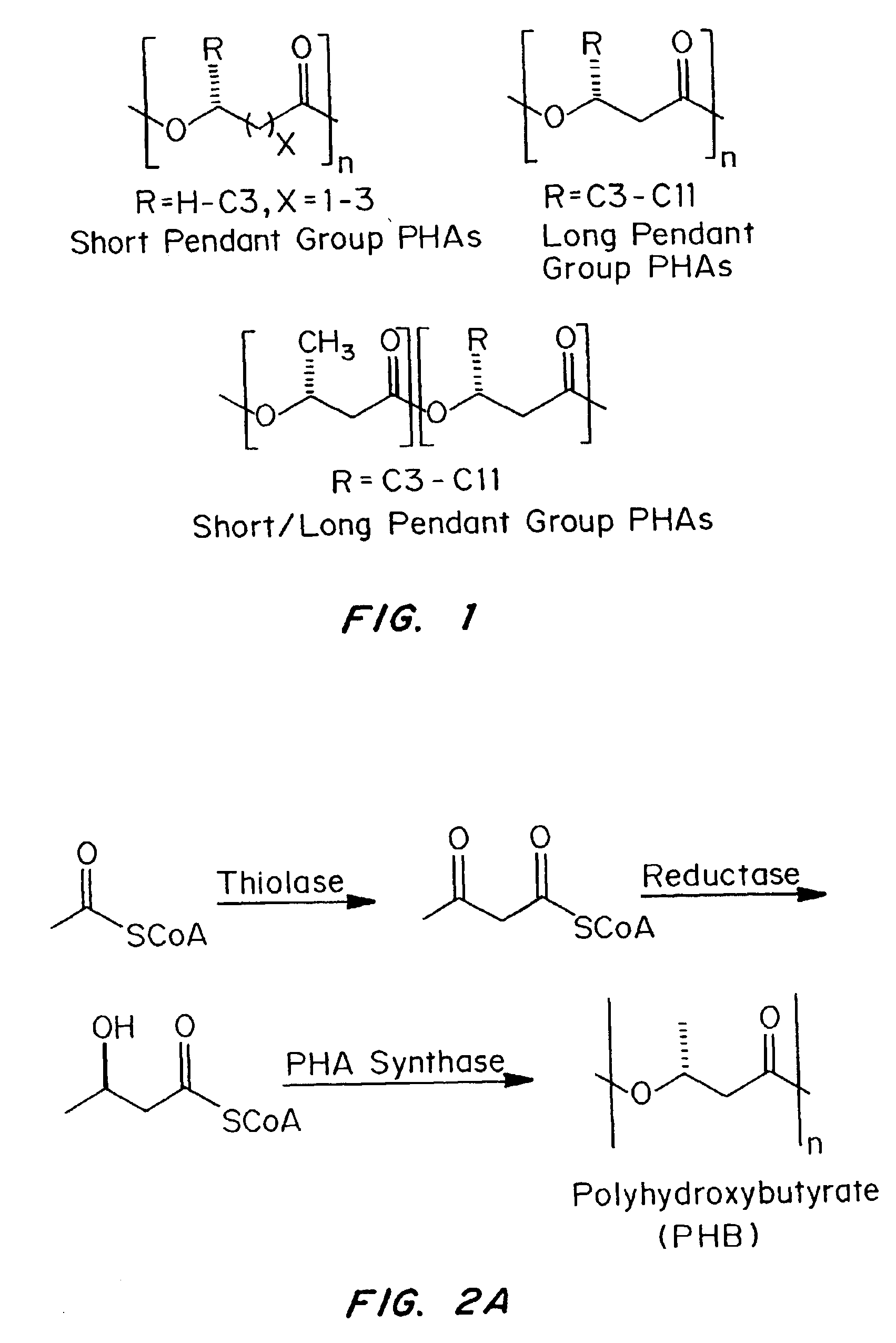
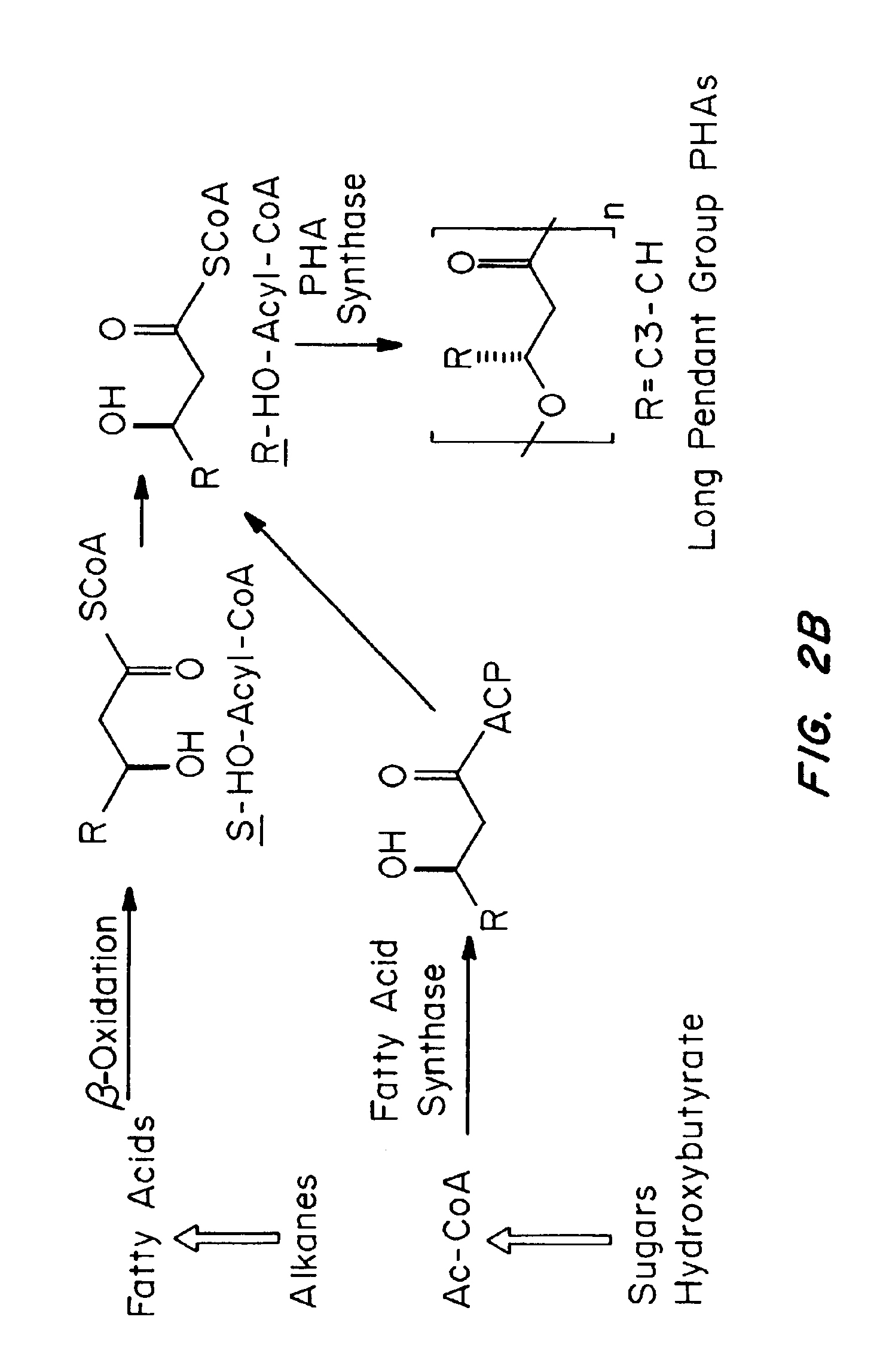
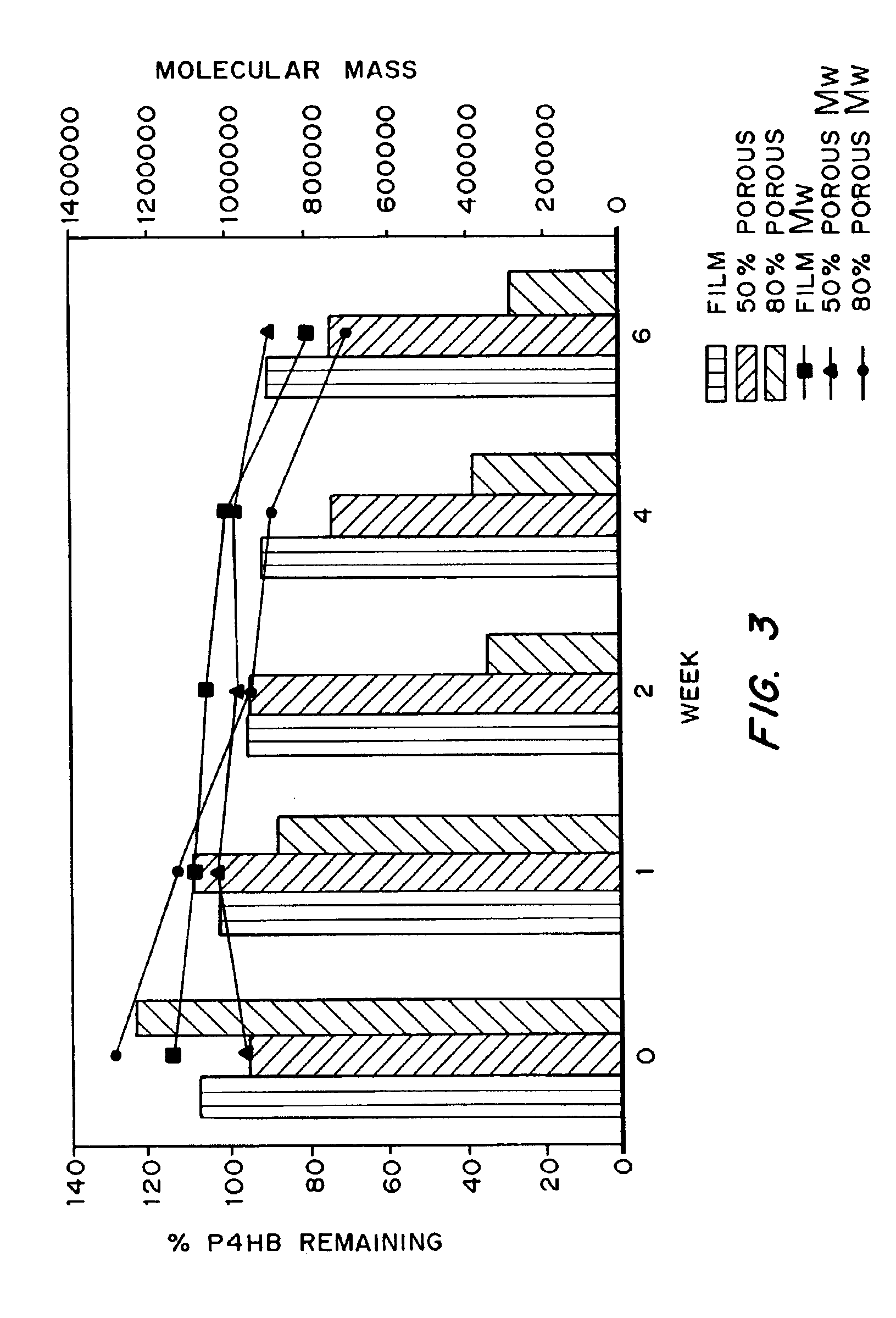
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
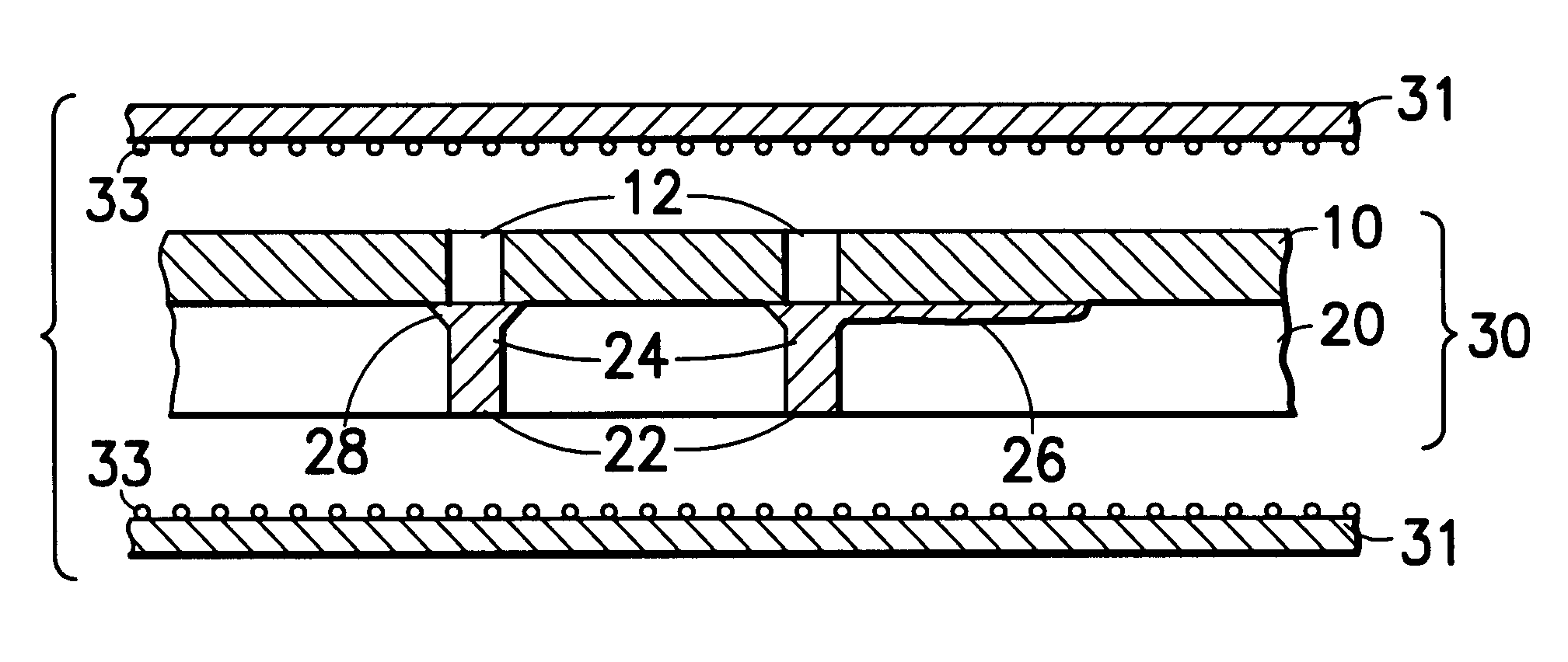
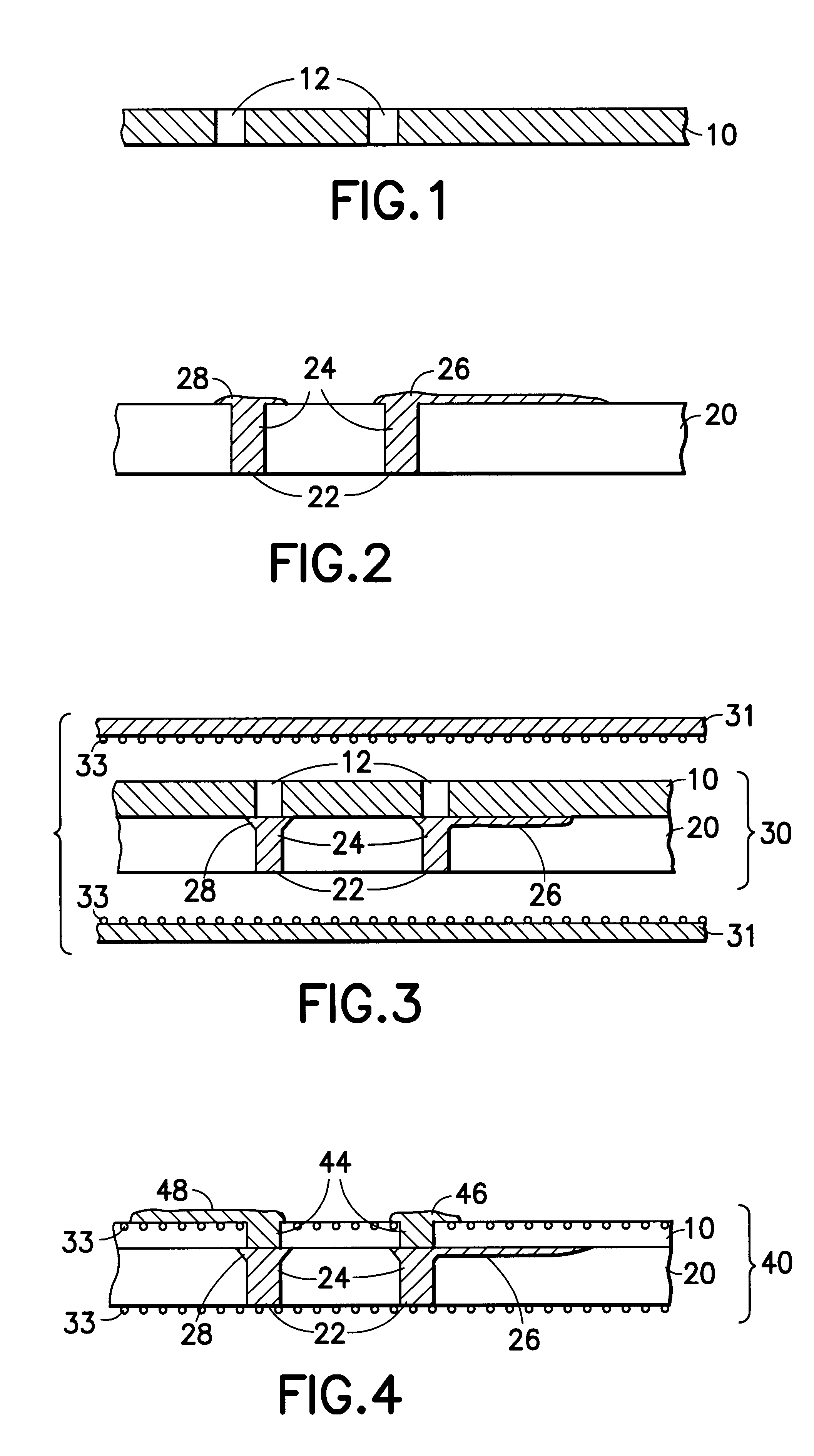
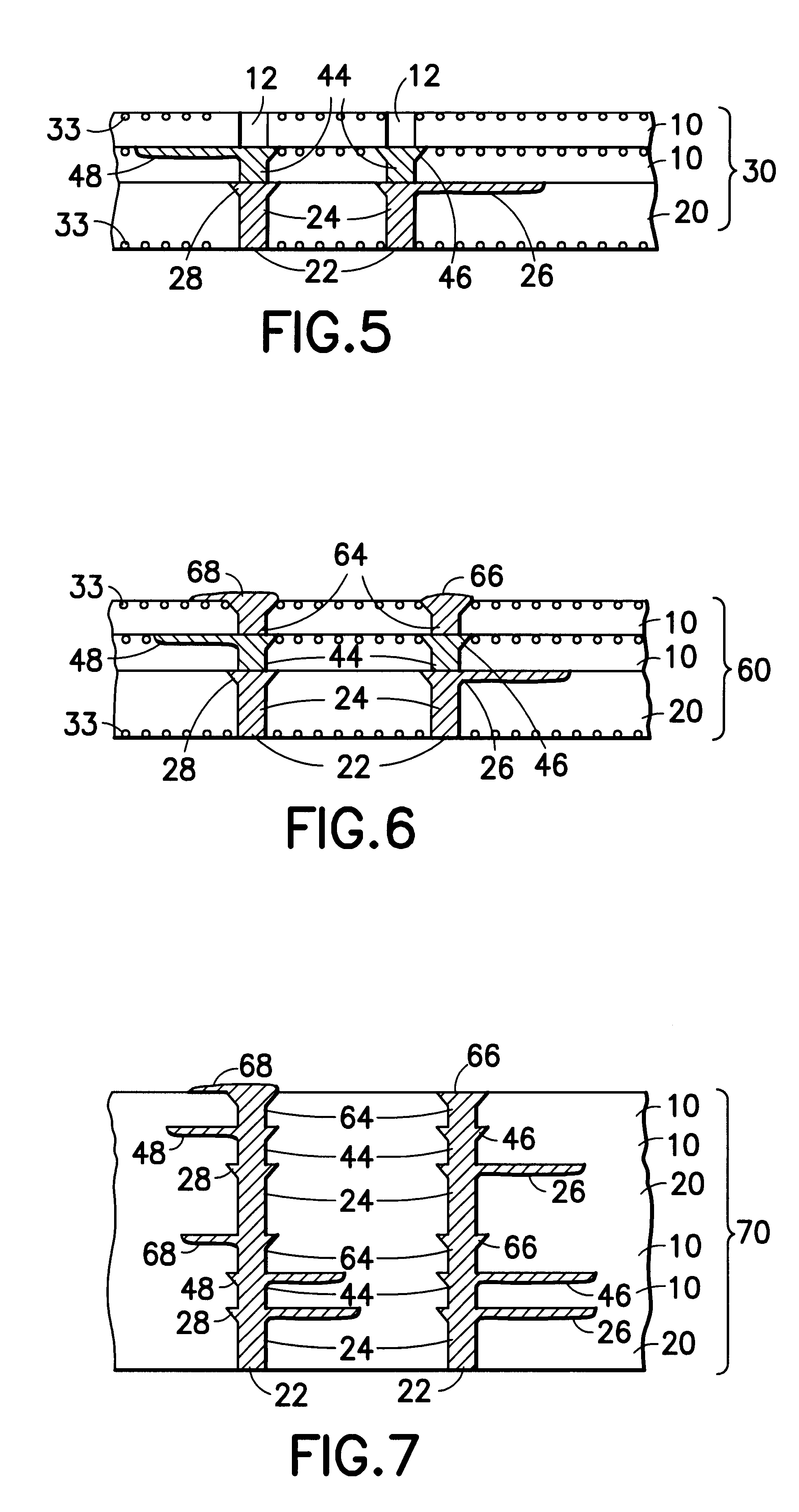
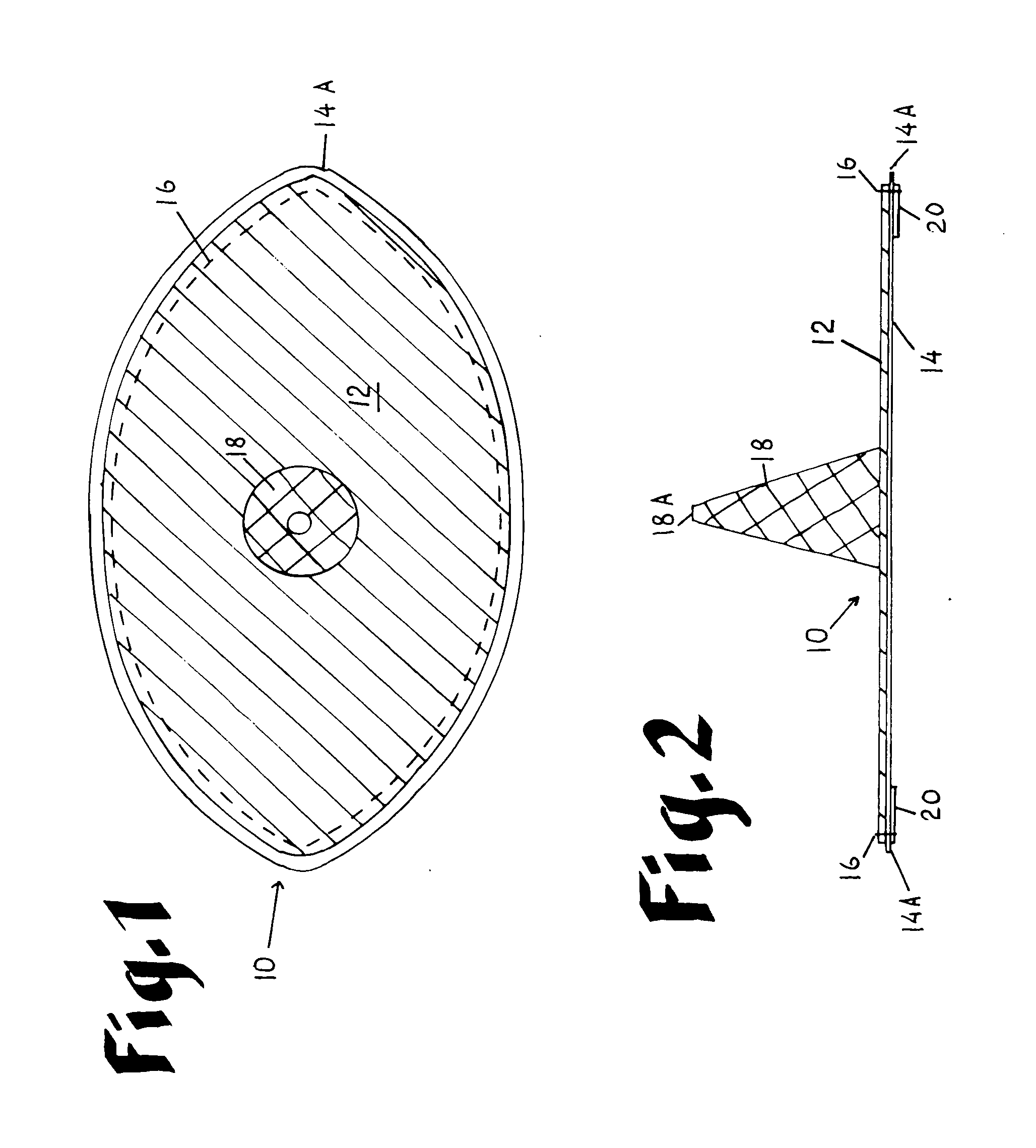
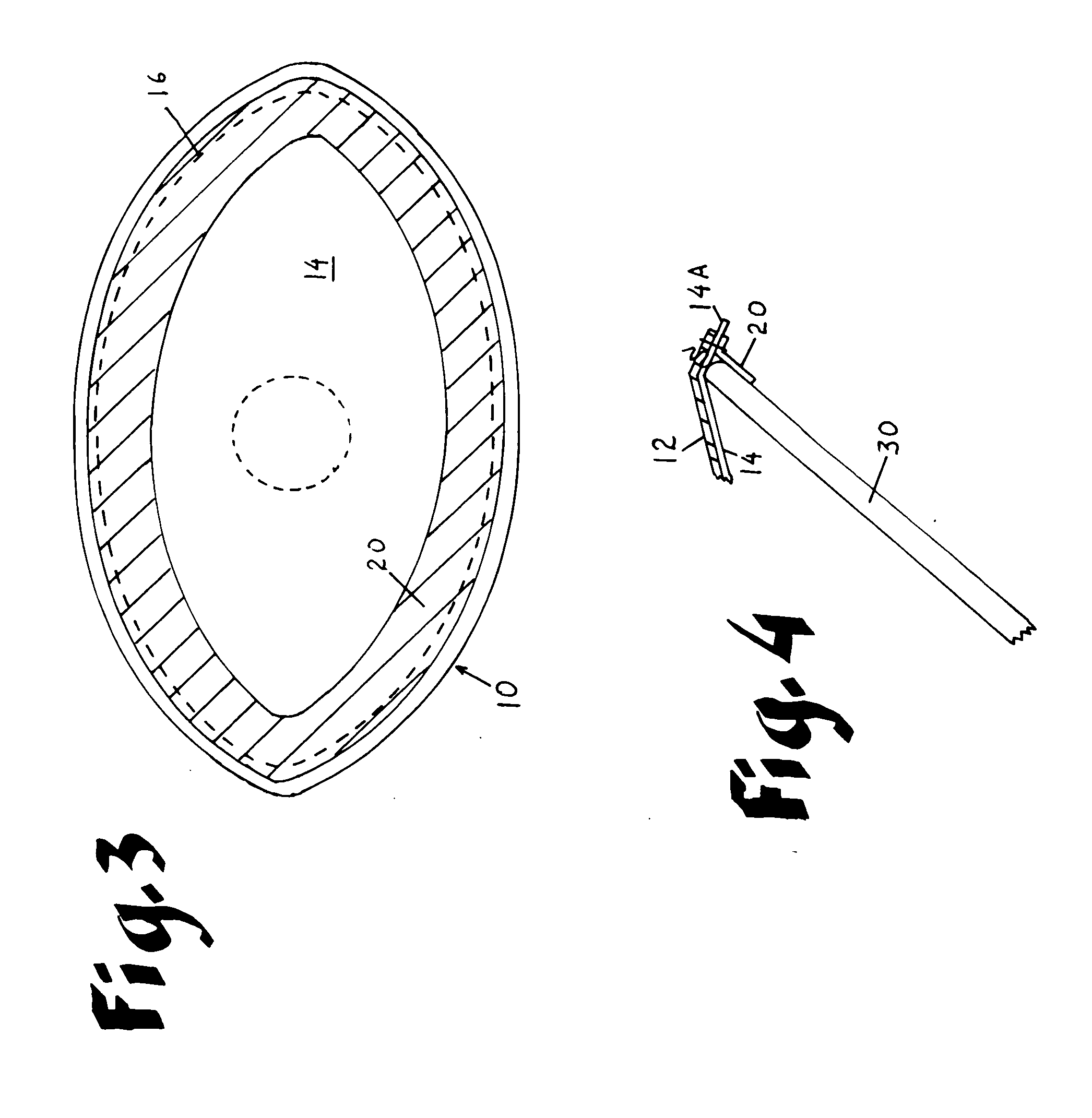
Adhesion barriers applicable by minimally invasive surgery and methods of use thereof
Biocompatible crosslinked polymers, and methods for their preparation and use with minimally invasive surgery applicators are disclosed. The disclosure includes compositions and methods for in situ formation of hydrogels using minimally invasive surgical techniques.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
Collagen device and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20050283256A1Minimize presenceEasy to operateSurgeryTissue regenerationMeningesUltimate tensile strength
A laminated, bioimplantable dural graft product is configured for use as both an onlay graft and a suturable graft. The dural graft product is sufficiently pliable so as to sufficiently conform to a curvature of a tissue surface to which it is applied, such as the curved surface of a meningeal membrane. The use of the graft product can have improved properties, including suture retention strength and fluid impermeability. To use the dural graft product as an implant to replace, reinforce or strengthen bodily tissue, or to act as an adhesion barrier, the dural graft is placed in contact with bodily tissue and conforms to the curvature of the bodily tissue. Sutures can be used to maintain the contact between the dural graft and the bodily tissue.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Collagen device and method of preparing the same
InactiveUS20050175659A1Easy to operateEasy to handlePeptide/protein ingredientsSurgeryBody tissuePurified water
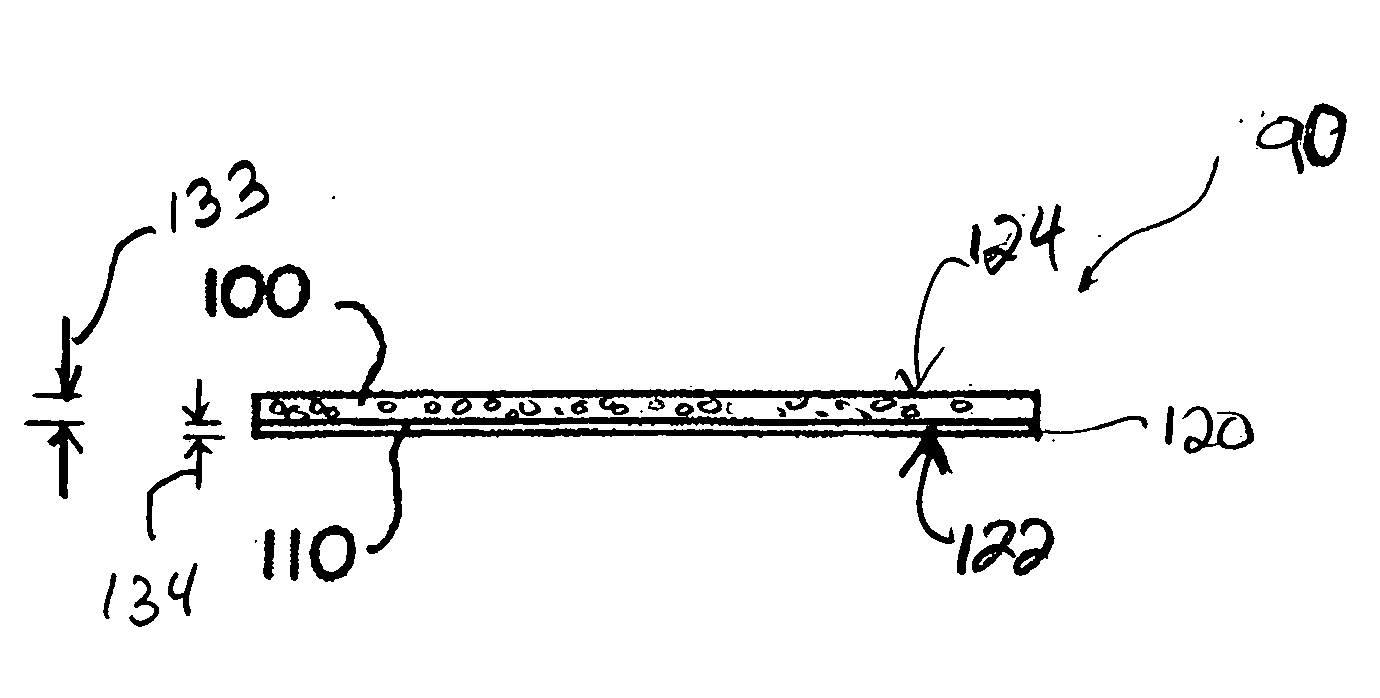
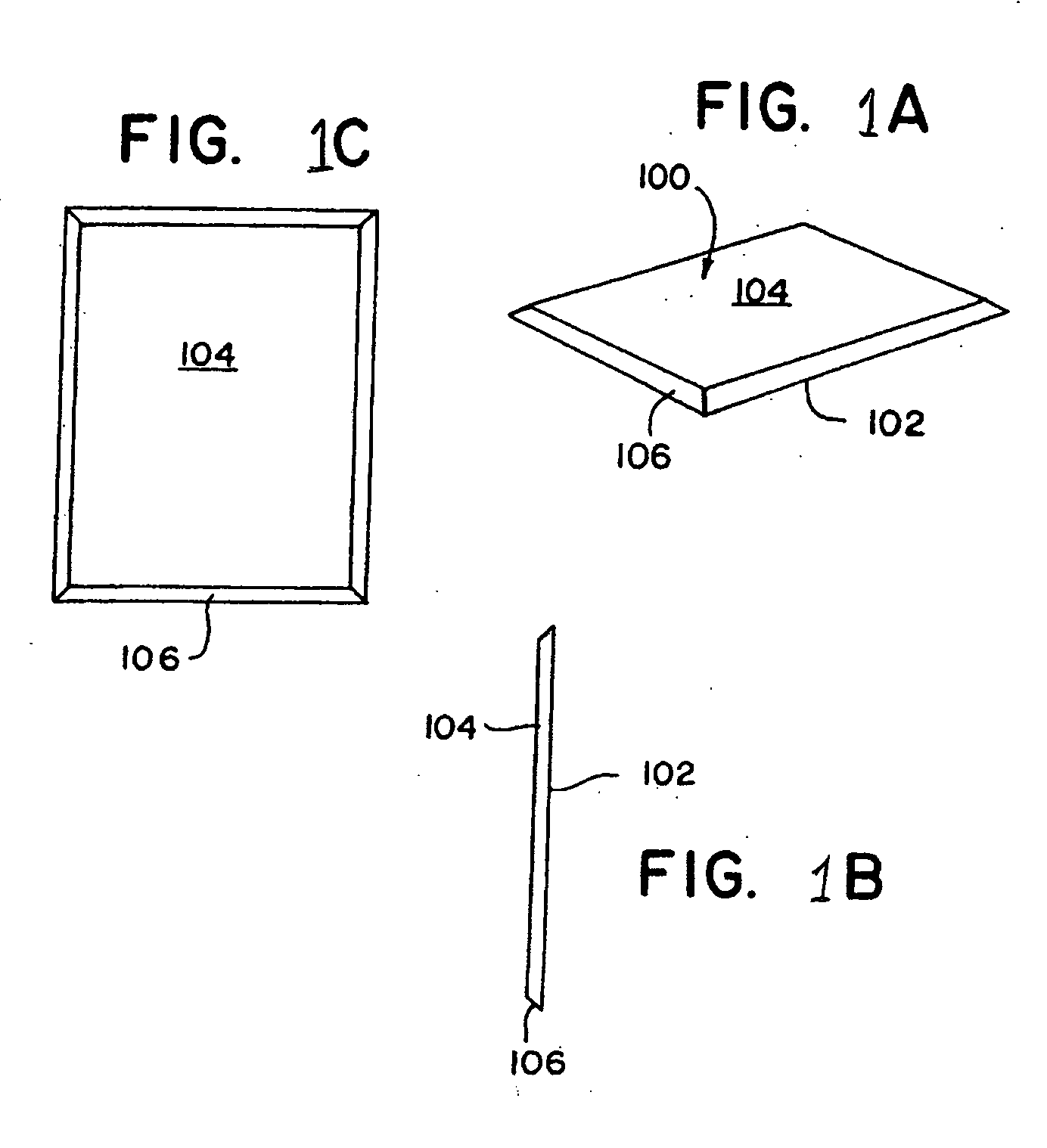
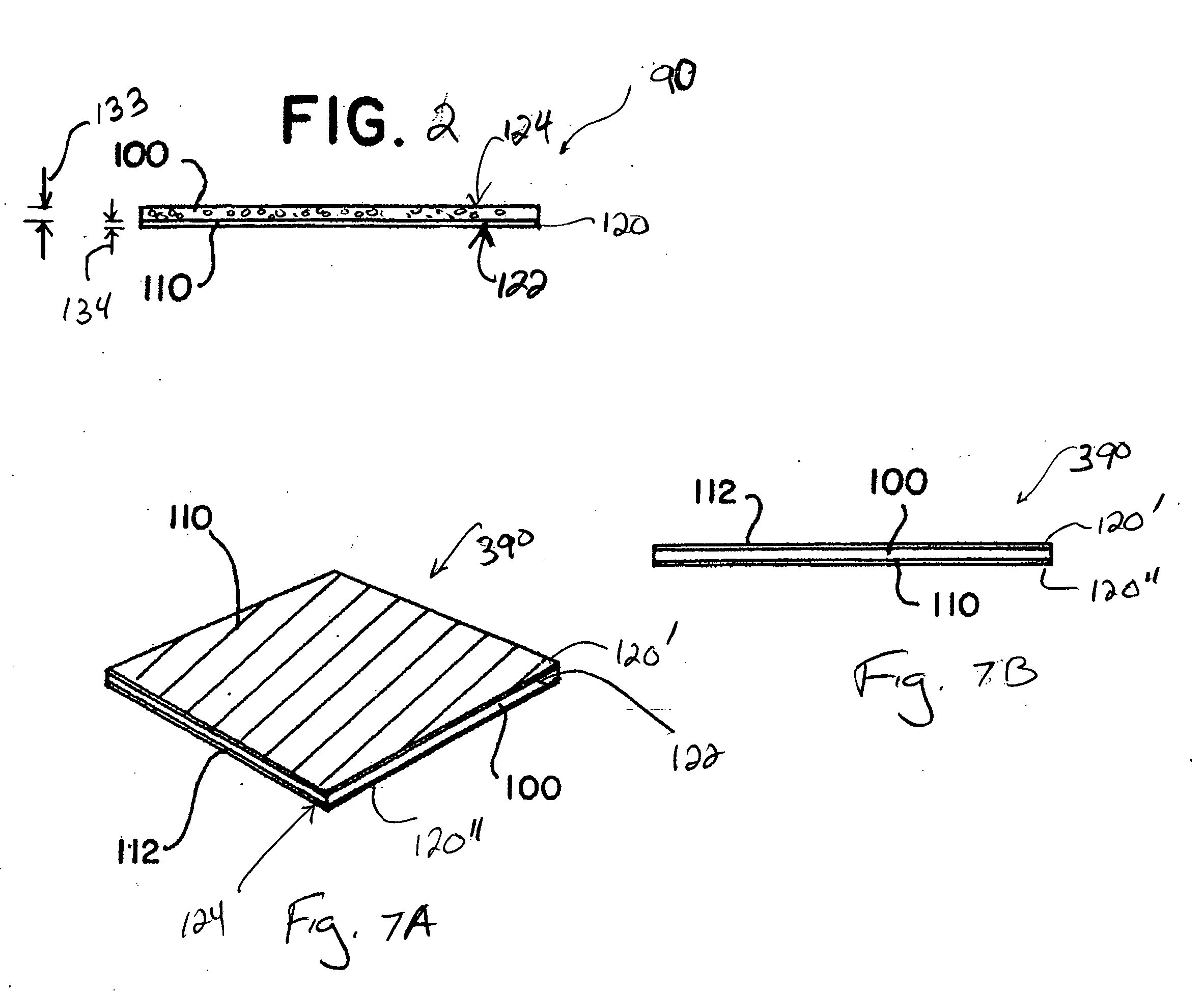
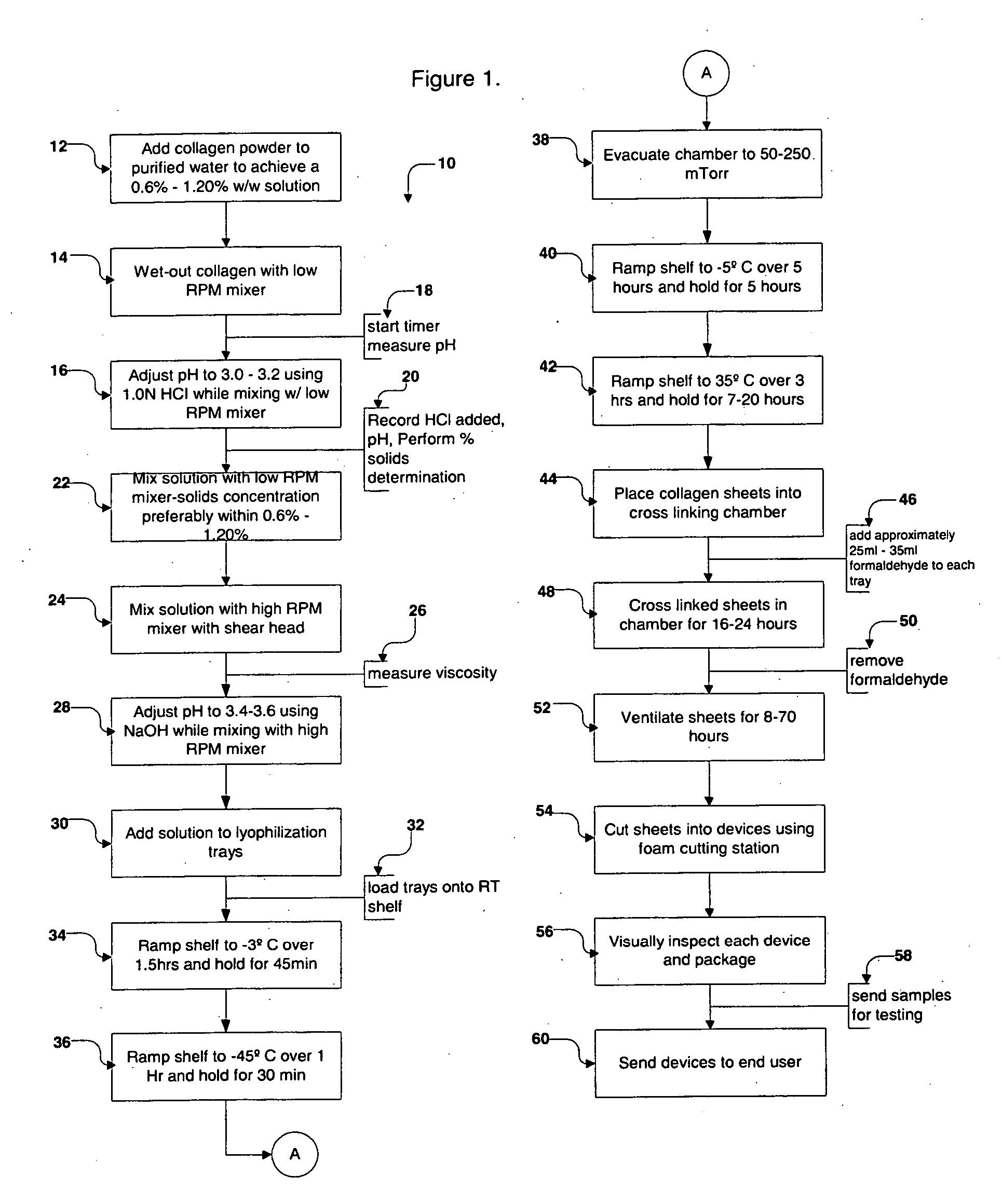
A collagen device is prepared by mixing collagen with purified water for a period of time sufficient to form a mixture. The pH of the mixture is adjusted to a pH level sufficient to substantially solubilize the collagen. A first predetermined amount of the mixture is placed into a container. The mixture is subject to a lyophilizing process and formed into a collagen device. The collagen device is also cross-linked. The collagen device has a plurality of pores wherein a majority of the pores have a diameter of less than 10 μm. To use the collagen device as an implant to replace, reinforce or strengthen bodily tissue, or to act as an adhesion barrier, the collagen device is placed in contact with bodily tissue and that contact is maintained until the collagen device is substantially resorbed within the bodily tissue.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Fibrin material and method for producing and using the same
This invention describes a bioerodible fibrin material which is obtained by mixing fibrinogen and thrombin reconstituted or diluted with a particular high tonic strength medium, free of calcium. Such a fibrin-based biomaterial develops a tight structure with thin fibers and small pore size suitable for use as an anti-adhesion barrier. In this invention, thrombin is no longer the variable which governs the tightness and the porosity of the fibrin material obtained, but still controls the clotting time. The mechanical behavior, high-water capacity, and releasable retention properties for therapeutic agents of this fibrin structure causes the fibrin material to be ideally suited for use as a drug delivery device, capable of delivering proteins, hormones, enzymes, antibiotics, antineoplastic agents and even cells for local and systemic treatment of human and non-human patients.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Multi-thickness, multi-layer green sheet processing
InactiveUS6258192B1Free from damageIncrease capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsMaterials scienceElectrically conductive
The present invention relates generally to using at least one green sheet that is originally very thin with the help of at least one thicker green sheet. At least one organic adhesion barrier is used to build the multi-layer ceramic laminates. Basically, the present invention relates to a structure and method for forming laminated structures and more particularly to a structure and method for fabricating multi-density, multi-layer ceramic products using at least one very thin green sheet and / or at least one green sheet with very dense electrically conductive patterns secured to at least one thicker green sheet using at least one organic adhesion barrier.
Owner:IBM CORP
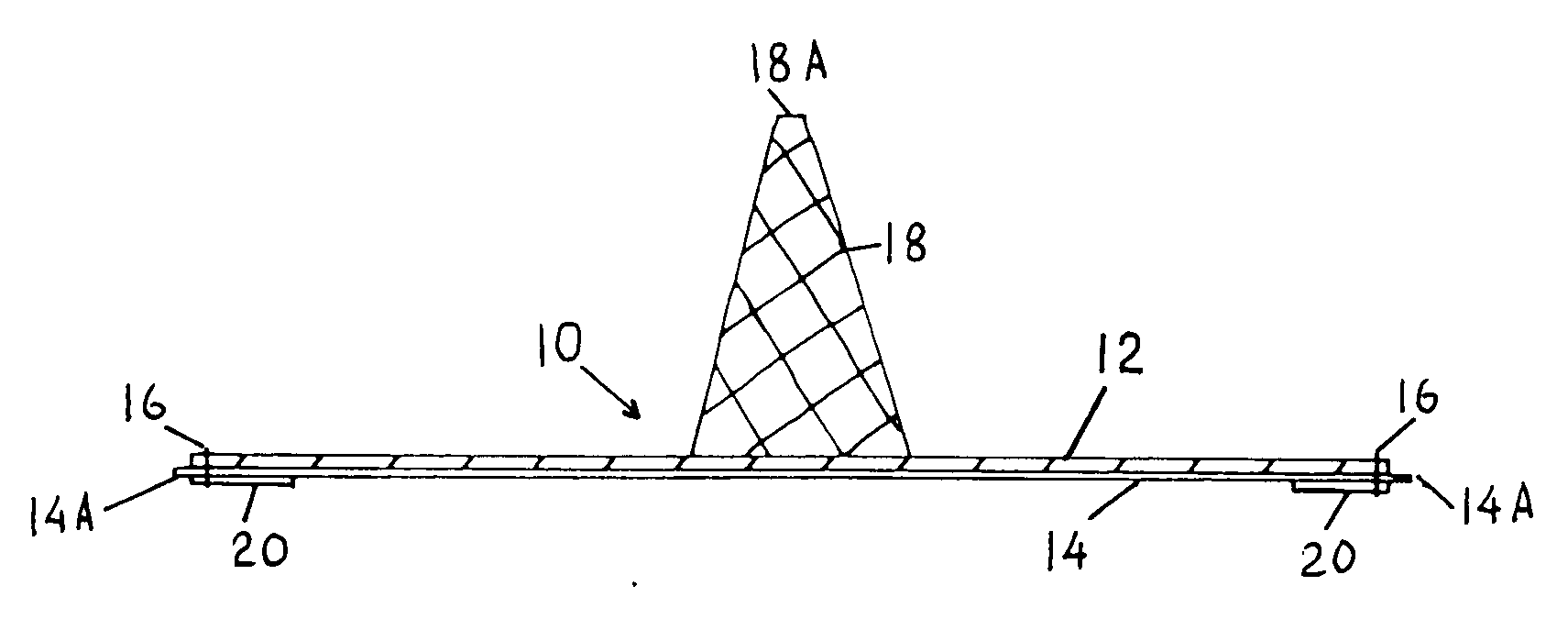
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia prosthesis
InactiveUS20060015143A1Overcome limitationsPromote tissue ingrowthSurgical veterinaryProsthesisIntestinal structurePolypropylene mesh
An improved composite prosthesis for laparoscopic repair of inguinal or femoral hernias, and also for the laparoscopic repair of large incisional ventral hernias incorporates two different layers, namely an upper layer made of polypropylene mesh to promote tissue ingrowth, and a lower layer formed with an adhesion barrier material to prevent adhesions to the intestines. Both layers are secured together with a highly visible dark seam at the perimeter of the prosthesis to assist the surgeon in visualizing the peripheral edge. The lower layer is slightly larger than the polypropylene mesh so there is an adhesion barrier edge around the prosthesis to conceal the edges of the polypropylene mesh. The upper layer includes a guiding cone to facilitate placement of the prosthesis at the exact center of the hernial defect. The base of this cone is attached to the central part of the prosthesis, and the apex of the cone will be attached later to a guiding thread that is inserted to from the outside of the abdomen using a long straight needle through the skin and hernial sac. Furthermore the laparoscopic hernia prosthesis lower layer is provided with a bounding rim to guide the tip of the spiral tacker to the very edges of the prosthesis in order to stretch the prosthesis in place, and also to conceal the staples or tacks.
Owner:ALVARADO ALFREDO
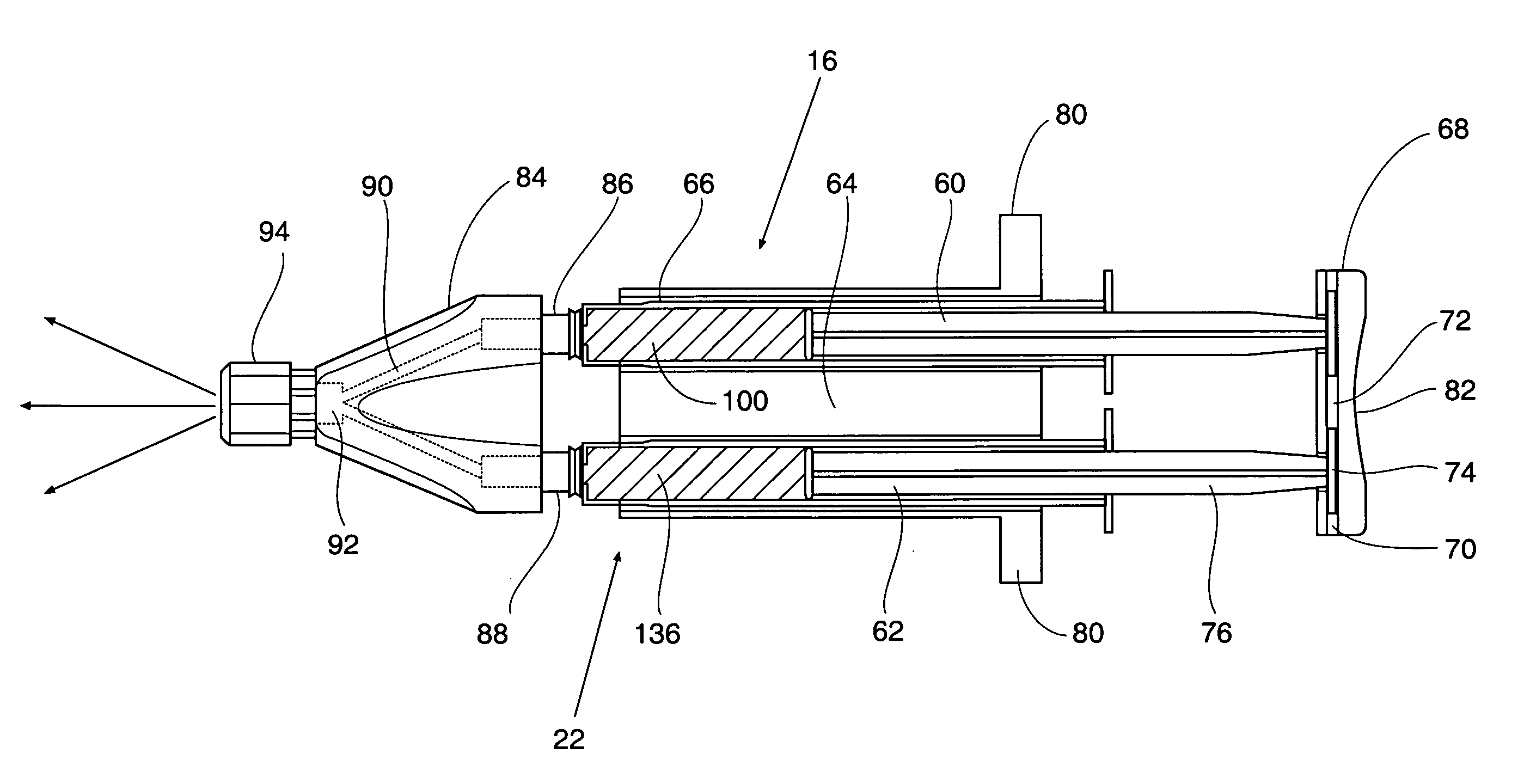
Systems, methods, and compositions for prevention of tissue adhesion
A blended electrophilic material with a first component having a functionality of at least three and a second component having a functionality of two is mixed with a nucleophilic material. The blended electrophilic material cross-links with the nucleophilic material to form a non-liquid, three dimensional structure which can applied, e.g., as an adhesion barrier.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
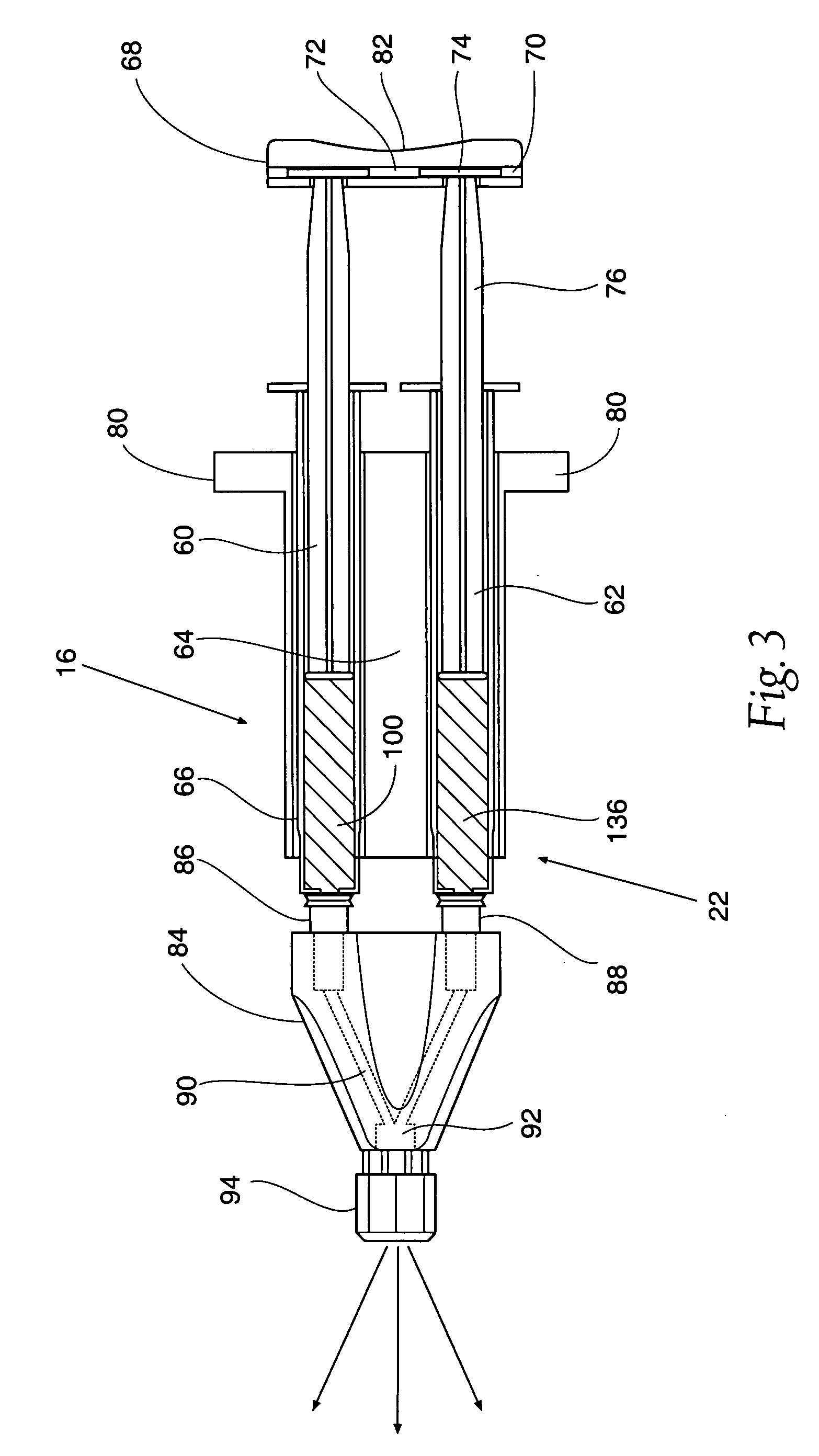
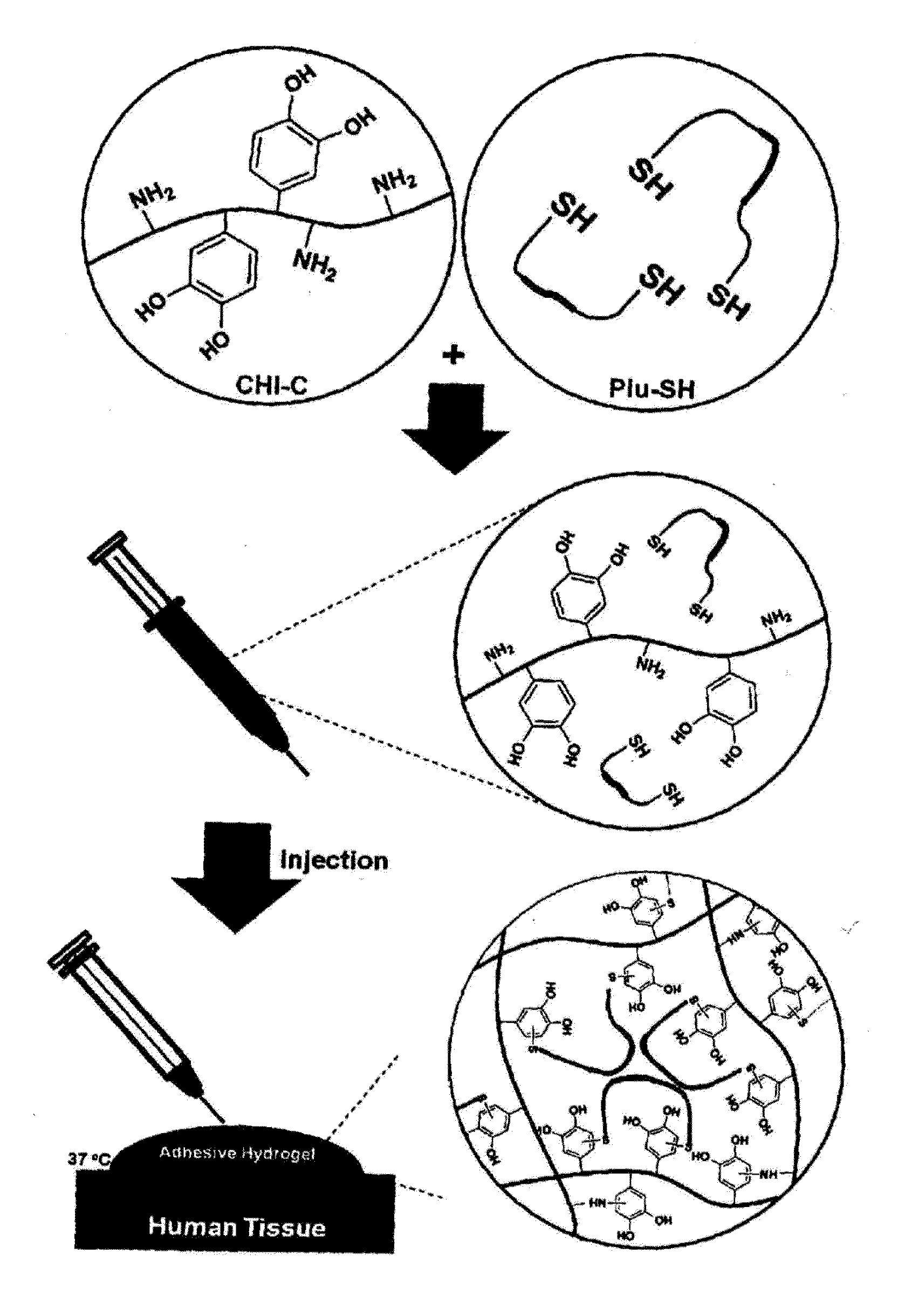
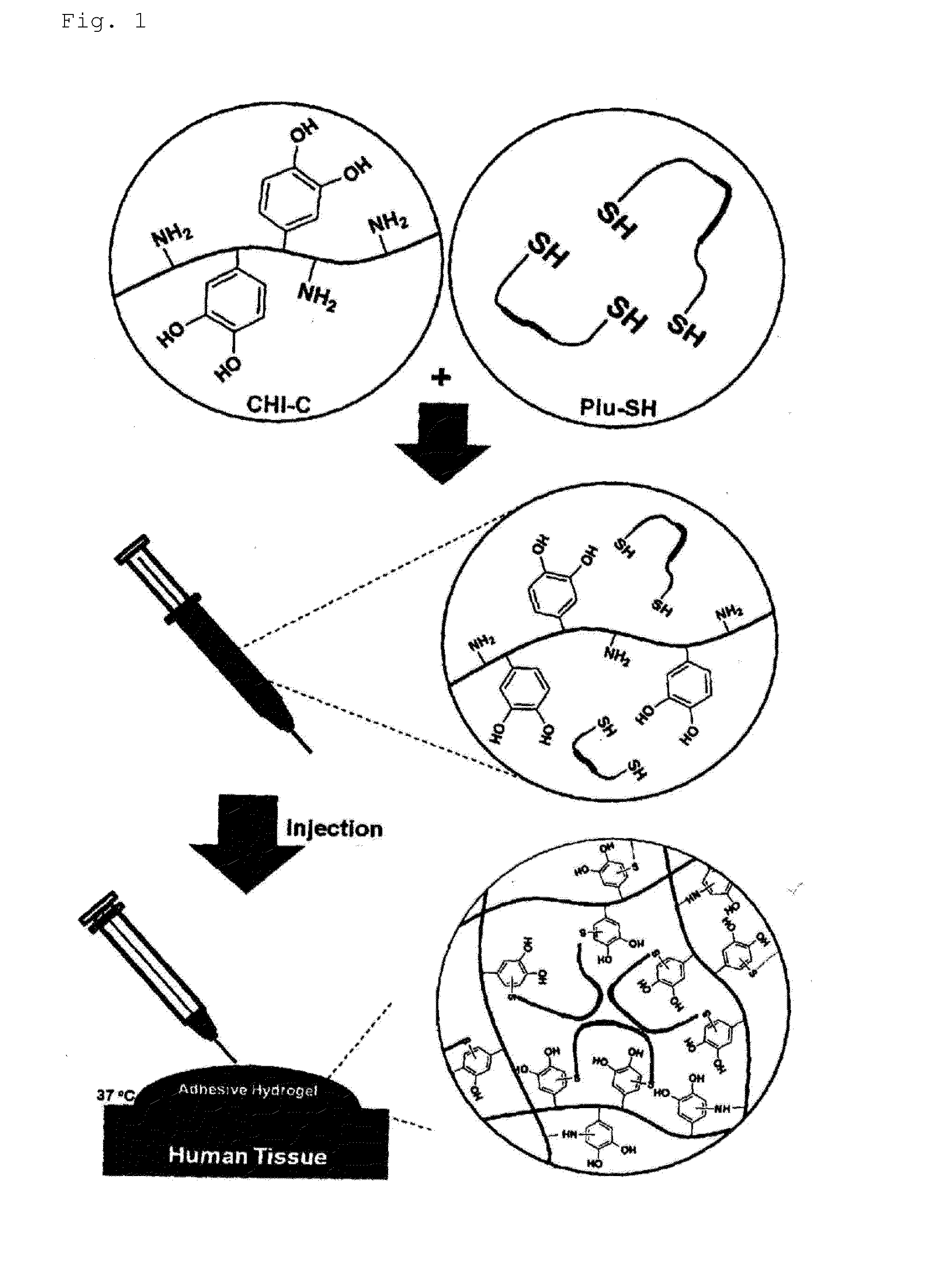
Hydrogel comprising catechol group-coupled chitosan or polyamine and poloxamer comprising thiol group coupled to end thereof, preparation method thereof, and hemostat using same
The present invention relates to an adhesive hydrogel composition containing catechol group-coupled chitosan and Pluronic comprising a thiol group coupled to the end thereof, and more specifically, to an adhesive composition which is safe in vivo and in vitro, is temperature sensitive, and has an excellent hemostatic effect and thus can be used as a bioadhesive, and a medical adhesive, an adhesion barrier and a surface adsorption inhibitor comprising the same.
Owner:INNOTHERAPY
Multi-layer barrier layer stacks for interconnect structures
ActiveUS20140021615A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStress levelDielectric layer
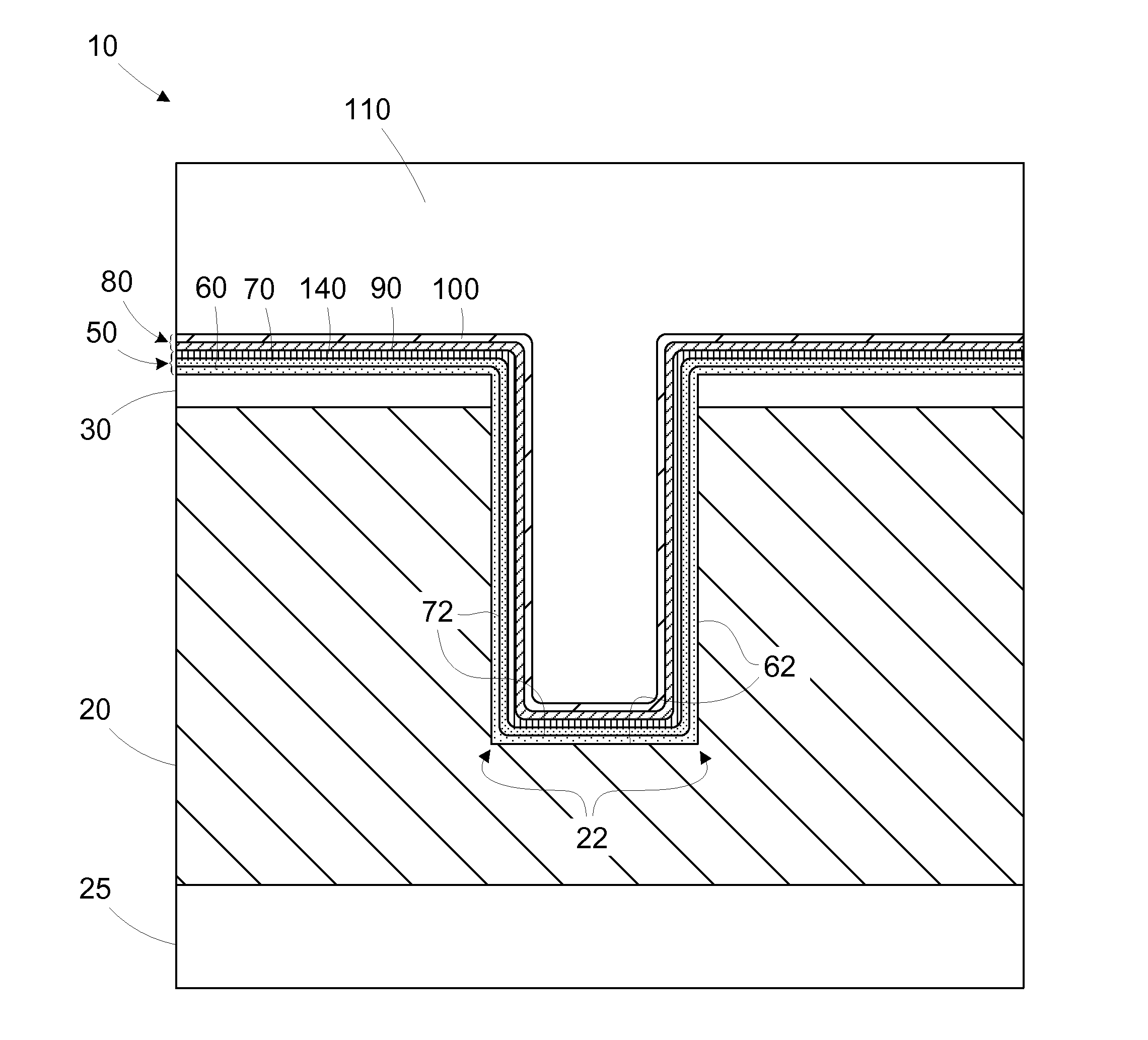
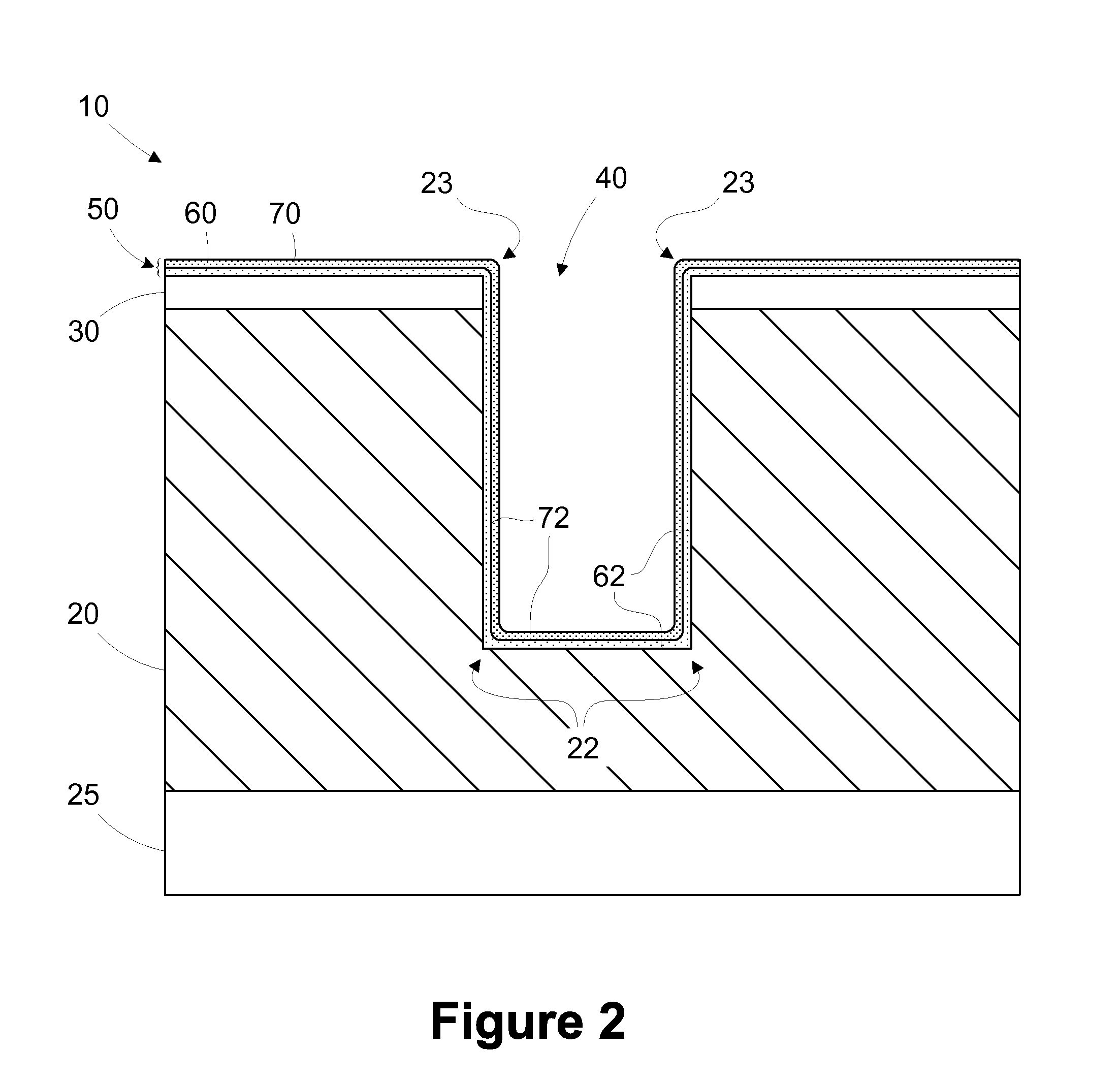
The present disclosure is generally directed to multi-layer barrier layer stacks for interconnect structures that may be used to reduce mechanical stress levels between the interconnect structure and a dielectric material layer in which the interconnect structure is formed. One illustrative method disclosed herein includes forming a recess in a dielectric layer of a substrate and forming an adhesion barrier layer including an alloy of tantalum and at least one transition metal other than tantalum to line the recess, wherein forming the adhesion barrier layer includes creating a first stress level across a first interface between the adhesion barrier layer and the dielectric layer. The method also includes forming a stress-reducing barrier layer including tantalum over the adhesion barrier layer, wherein the stress-reducing barrier layer reduces the first stress level to a second stress level less than the first stress level, and filling the recess with a fill layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Multi-thickness, multi-layer green sheet lamination and method thereof
InactiveUS6245171B1Free from damageIncrease capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMaterials scienceElectrically conductive
The present invention relates generally to using at least one green sheet that is originally very thin with the help of at least one thicker green sheet. An adhesion barrier to build multi-layer ceramic laminates and process thereof is also disclosed. Basically, the present invention relates to a structure and method for forming laminated structures and more particularly to a structure and method for fabricating multi-density, multi-layer ceramic products using at least one very thin green sheet and / or at least one green sheet with very dense electrically conductive patterns on top of at least one thicker green sheet.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High-barrier water-based adhesive
ActiveCN109161363ALow costNo emissionsNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesLamination ancillary operationsAdhesive cementPolymer science
The invention relates to the field of packaging materials, in particular to a high-barrier water-based adhesive as well as a preparation method and an application of the water-based adhesive. The invention further relates to a composite film, a preparation method and an application of the composite film and a package comprising the composite film. The composite film comprises an adhesion barrier layer formed by the water-based adhesive.
Owner:刘建林
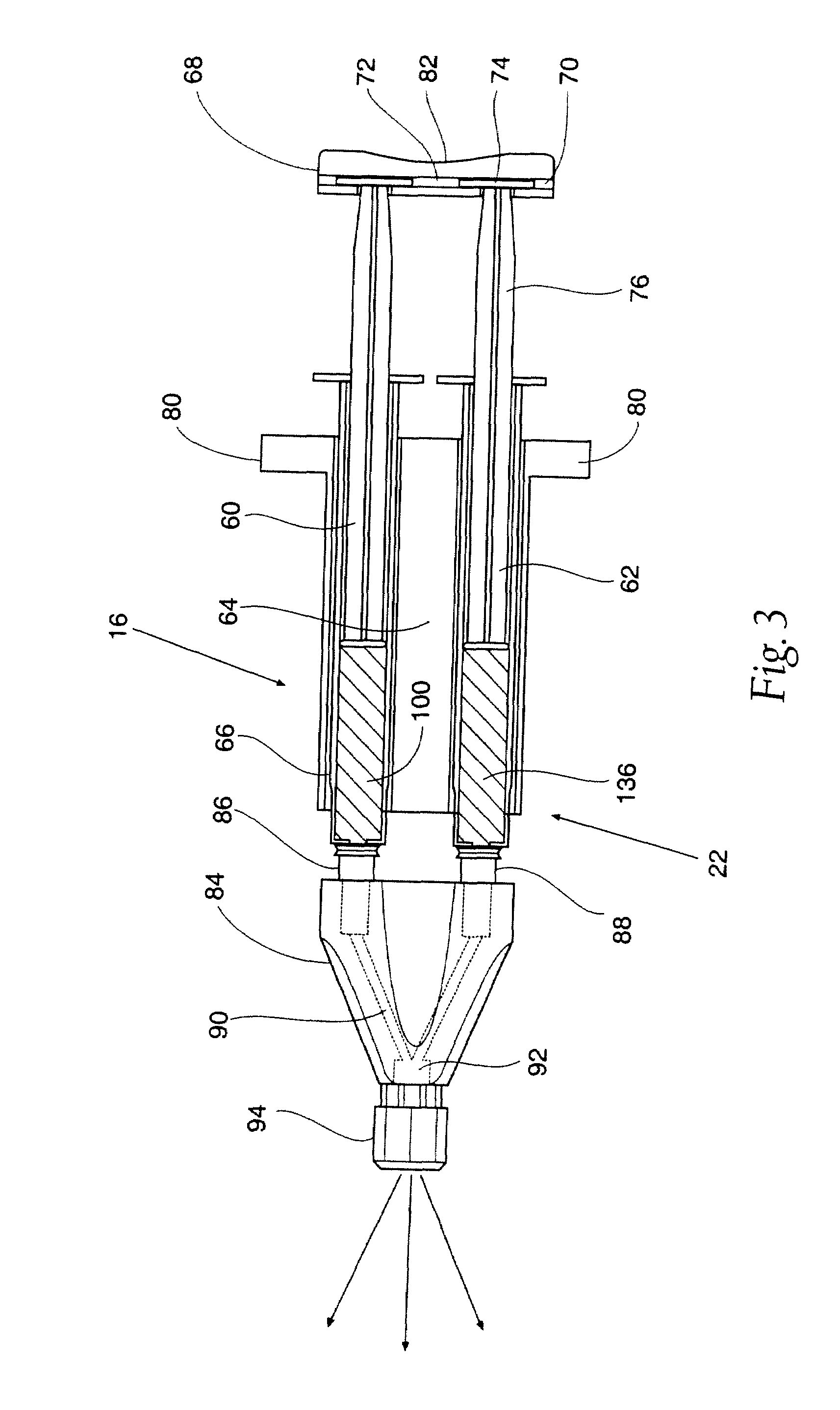
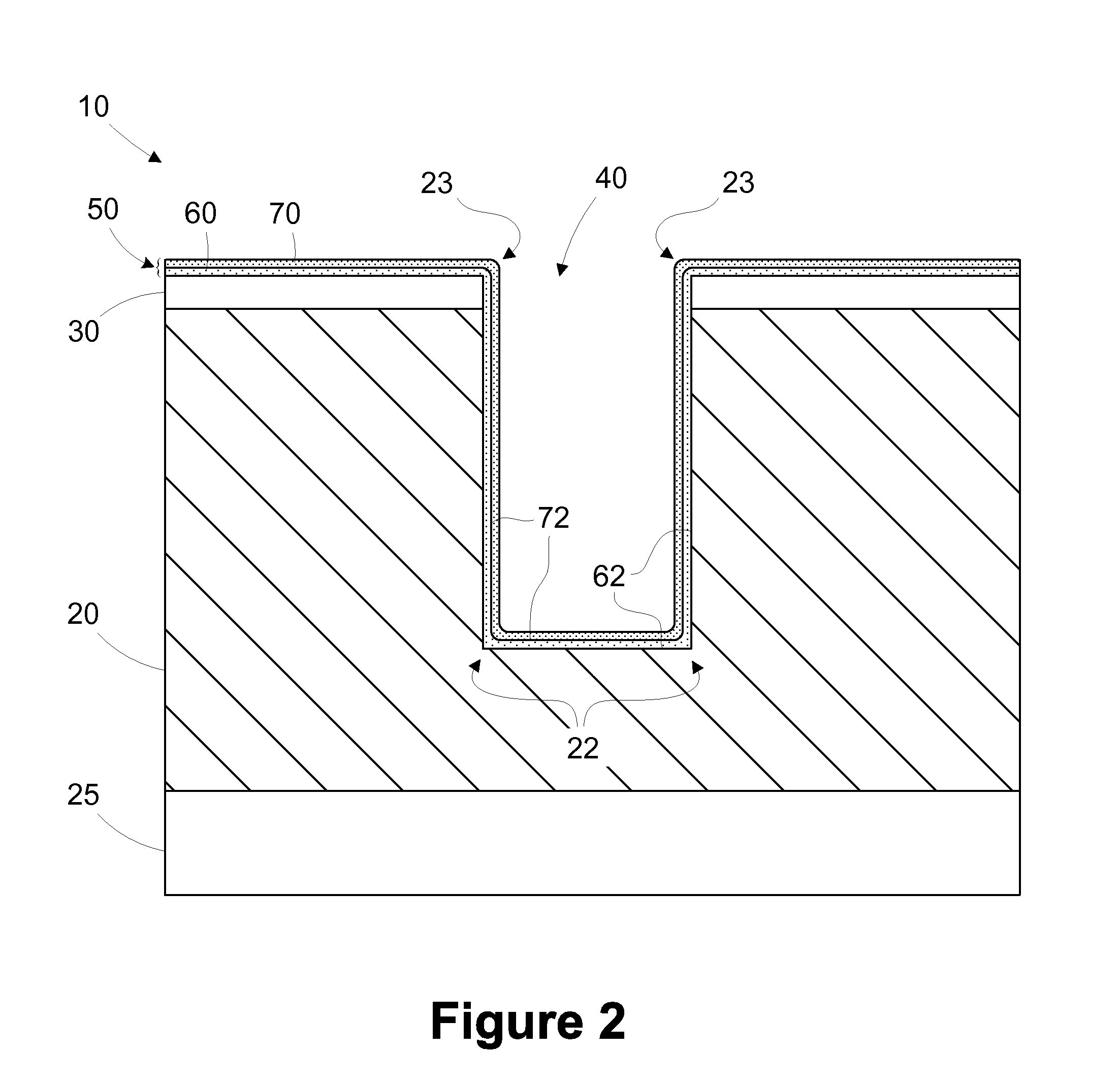
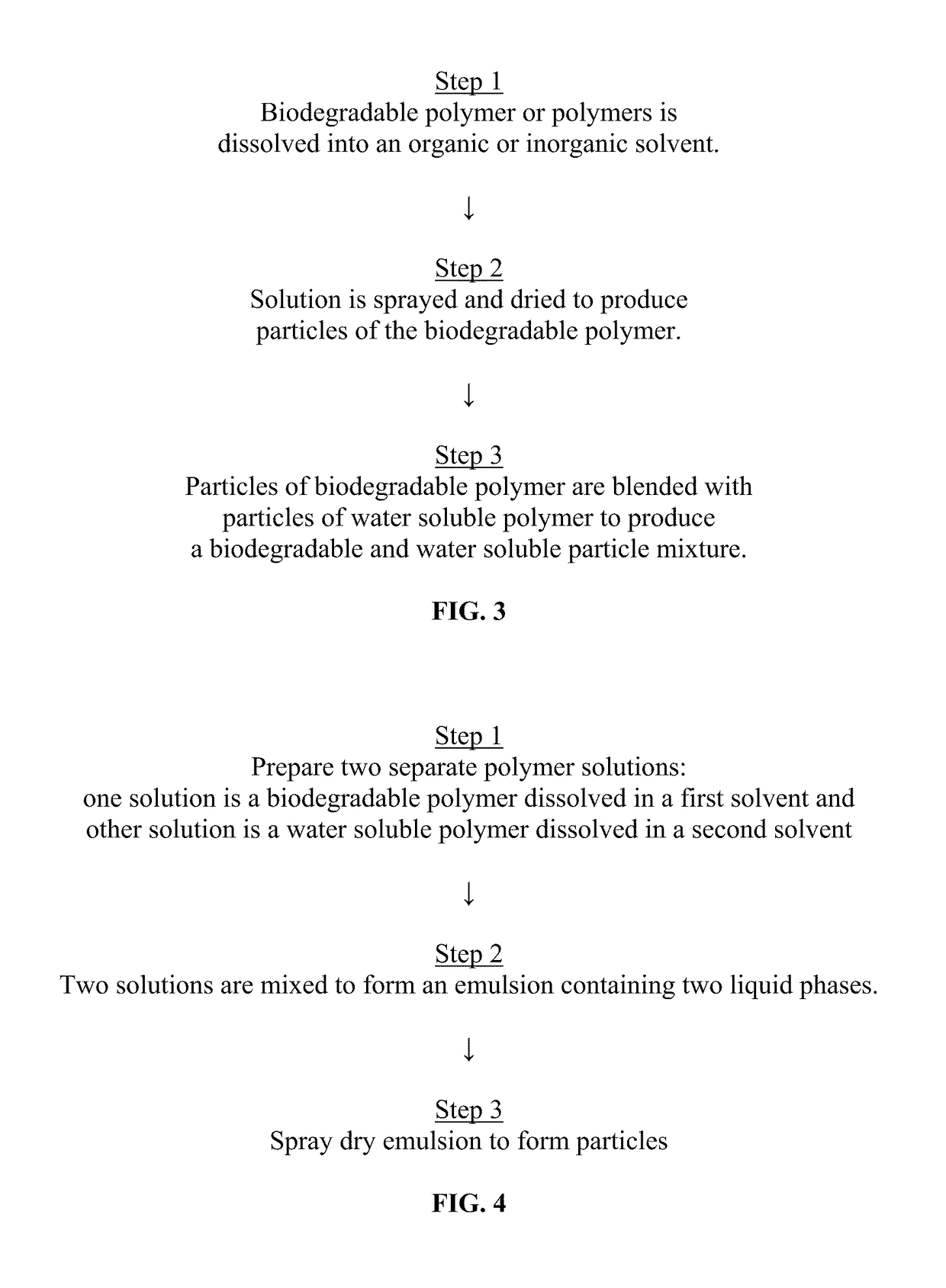
Sprayable Polymers As Adhesion Barriers
A formulation for generating an adhesion barrier that includes a plurality of particles or a dry powder that is made of a polymer combination of at least one biodegradable polymer and at least one water soluble polymer is disclosed. Methods of making and delivering the formulation are further disclosed. The formulation of particles is deposited on a surface of internal body tissue and the deposited formulation absorbs moisture from the tissue and forms a film over the surface. The film acts as an adhesion barrier by reducing or preventing adhesion of the surface to other body tissue.
Owner:ARA MEDICAL
Multi-thickness, multi-layer green sheet lamination and method thereof
InactiveUS6406778B1Increase capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMaterials scienceElectrically conductive
The present invention relates generally to using at least one green sheet that is originally very thin with the help of at least one thicker green sheet. An adhesion barrier to build multi-layer ceramic laminates and process thereof is also disclosed. Basically, the present invention relates to a structure and method for forming laminated structures and more particularly to a structure and method for fabricating multi-density, multi-layer ceramic products using at least one very thin green sheet and / or at least one green sheet with very dense electrically conductive patterns on top of at least one thicker green sheet.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Single plane tissue repair patch
A novel single plane tissue repair device such as a patch is disclosed. The device has a base member with an opening therethrough, and a closure member associated with the opening. The mesh has a biaborbable polymeric adhesion barrier attached to the bottom side of the base member about its periphery to form a pocket that is accessible through the opening. The mesh may be used in open surgical procedures for hernia repairs and other repairs of body wall defects.
Owner:ETHICON INC
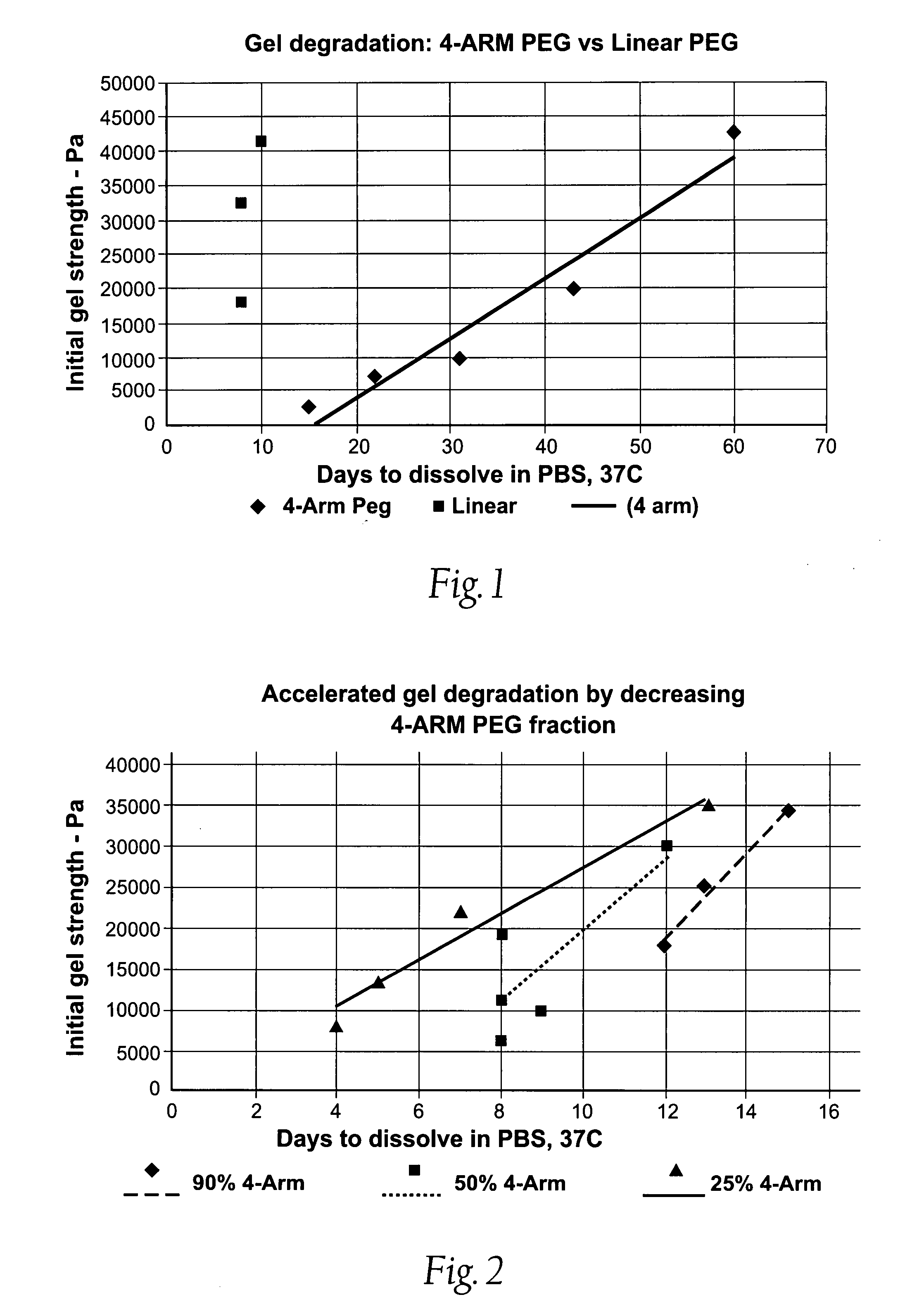
High swell, long-lived hydrogel sealant
A high swell, long-lived hydrogel sealant formed by reacting a highly oxidized polysaccharide containing aldehyde groups with a multi-arm amine is described. The hydrogel sealant may be particularly suitable for applications requiring high swell and slow degradation, for example, tissue augmentation, both cosmetic and reconstructive; void filling; tissue bulking, for example treatment of urinary incontinence and acid reflux; and embolization. The high swell, long-lived hydrogel sealant may also be useful as a tissue sealant and adhesive, and as an anti-adhesion barrier.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Postsurgical adhesion barrier of carboxymethylchitosan and carboxymethylcellulose and method for preparation of the same
The present invention relates to a postsurgical adhesion barrier of carboxymethylchitosan, carboxymethylchitosan / carboxymethylcellulose cross-linked with multivalent ions and a method for preparation of the barrier. The method of preparation comprises: preparing a carboxymethxylchitosan polymer aqueous solution and carboxymethylcellulose polymer aqueous solution in purified water respectively, applying the carboxymethxylchitosan solution, or a mixed solution of carboxymethxylchitosan and carboxymethylcellulose with certain weight ratio on a smooth plate, drying the plate with the applied polymer aqueous solution to obtain a film thereon, socking the dried film on the plate in a aqueous solution of cross-linking agent selected from Ca++ ion, Fe+++ ion, a mixture of Ca++ and Fe+++, or a mixture of Ca++ and Al+++ to complete cross-linking reaction, and drying and detaching the cross-linked film. The obtained postsurgical adhesion barrier is biocompatible and bioresorbable.
Owner:DALIAN YONGXING MEDICAL MATERIAL
Collagen device and method of preparing the same
ActiveUS20090030526A1Easy to operateGood strength performanceTissue regenerationProsthesisMeningesUltimate tensile strength
A laminated, bioimplantable dural graft product is configured for use as both an onlay graft and a suturable graft. The dural graft product is sufficiently pliable so as to sufficiently conform to a curvature of a tissue surface to which it is applied, such as the curved surface of a meningeal membrane. The use of the graft product can have improved properties, including suture retention strength and fluid impermeability. To use the dural graft product as an implant to replace, reinforce or strengthen bodily tissue, or to act as an adhesion barrier, the dural graft is placed in contact with bodily tissue and conforms to the curvature of the bodily tissue. Sutures can be used to maintain the contact between the dural graft and the bodily tissue.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Adhesive composition comprising tannin, polyethylene glycol, and water, lower alcohol or mixture thereof
ActiveCN103459542ANot easily soluble inNo toxicitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismControlled releaseAlcohol
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Systems, methods, and compositions for prevention of tissue adhesion
A blended electrophilic material with a first component having a functionality of at least three and a second component having a functionality of two is mixed with a nucleophilic material. The blended electrophilic material cross-links with the nucleophilic material to form a non-liquid, three dimensional structure which can applied, e.g., as an adhesion barrier.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
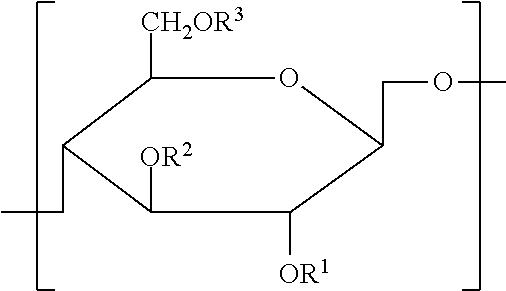
Cellulose derivative and method for production thereof
InactiveUS8455001B2Improve viscoelasticity and therefore retentionImprove barrier propertiesPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceAlkaline earth metal
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Adhesion barrier containing hyaluronic acids and l-arginine
InactiveUS20130252921A1Extended stayMaintain good propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSurgical operationArginine
The present invention relates to an anti-adhesive agent containing hyaluronic acid and L-arginine, which has increased in vivo residence time and excellent anti-adhesive properties. According to the present invention, adhesion can be prevented from occurring due to surgical operation, infection and trauma.
Owner:HUMEDIX
Systems, methods, and compositions for prevention of tissue adhesion
A blended electrophilic material with a first component having a functionality of at least three and a second component having a functionality of two is mixed with a nucleophilic material. The blended electrophilic material cross-links with the nucleophilic material to form a non-liquid, three dimensional structure which can applied, e.g., as an adhesion barrier.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
Methods for preventing or inhibiting post-surgical adhesions
InactiveUS20080300319A1Preventing and inhibiting post-surgical adhesionInhibition formationBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsSurgical siteIn vivo
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, a method is provided in which post-surgical adhesions at a surgical site in a patient are prevented or inhibited. The method comprises topically applying a liquid composition comprising a hydrophobic species, which has a melting point above normal body temperature, to tissue at the surgical site in an amount effective to prevent or inhibit the formation of adhesions during healing. Application of the liquid composition results in the formation of a solid adhesion barrier layer on the tissue. Moreover, the properties of the hydrophobic species are such that the adhesion barrier sublimes in vivo after the surgical site is closed. In another aspect, A medical device that comprises first and second lumens, wherein the medical device is configured to deliver a first fluid medium through the first lumen at a temperature above normal body temperature and to concurrently or sequentially deliver a second fluid medium through the second lumen at a temperature below normal body temperature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
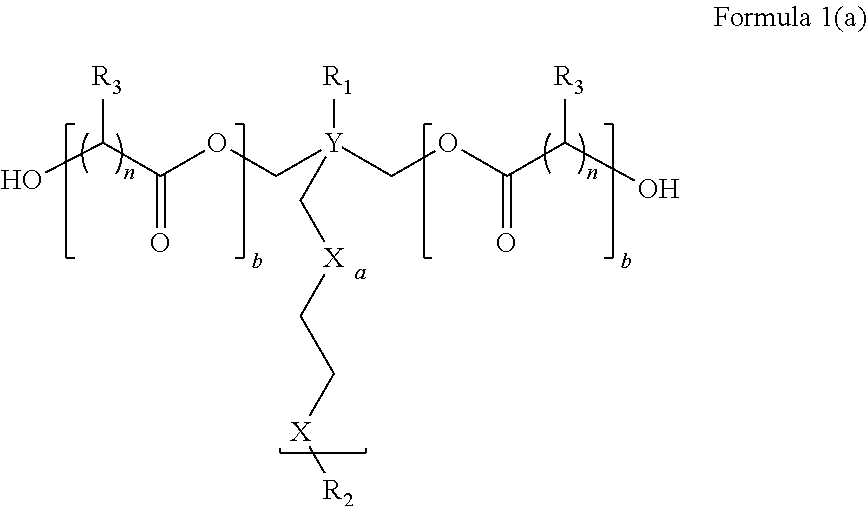
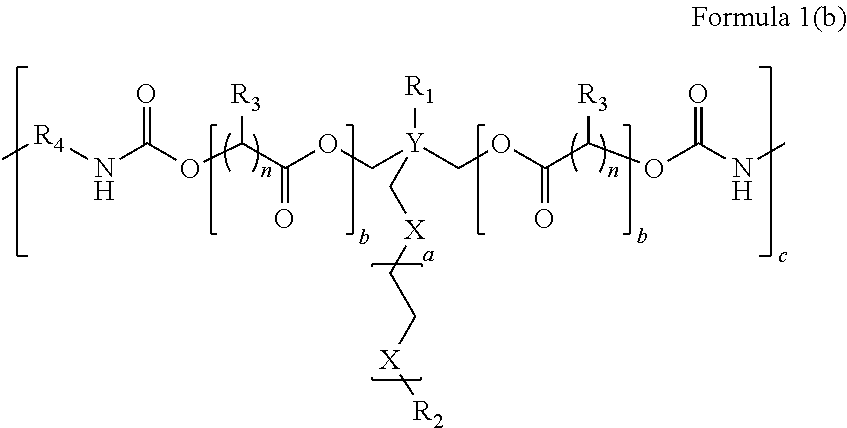
Pendant hydrophile bearing biodegraadable compositions and related devices
ActiveUS20140037711A1Improve functional propertiesPrevent postoperative adhesionsBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationPolyesterWound healing
The instant invention relates to a composition comprising at least one polymer having the structure A-B-A′, wherein A and A′ may be the same or different and each is a degradable polyester component and wherein B is the reaction product resulting from the reaction between a diol, having one or more pendant oligomeric or polymeric groups, and A and A′.Additionally, the invention also relates to the development of a bioresorbable patch comprising:(a) an adhesion barrier component comprising a composition according to the invention in the form of a film; and(b) an adhesive component comprising:(i) at least one synthetic adhesive polymer; and / or(ii) at least one polysaccharide.The present invention provides a method of wound healing, comprising administering the composition or patch.
Owner:INNOCORE TECH HLDG BV
Multi-layer barrier layer stacks for interconnect structures
ActiveUS8772158B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStress levelDielectric layer
The present disclosure is generally directed to multi-layer barrier layer stacks for interconnect structures that may be used to reduce mechanical stress levels between the interconnect structure and a dielectric material layer in which the interconnect structure is formed. One illustrative method disclosed herein includes forming a recess in a dielectric layer of a substrate and forming an adhesion barrier layer including an alloy of tantalum and at least one transition metal other than tantalum to line the recess, wherein forming the adhesion barrier layer includes creating a first stress level across a first interface between the adhesion barrier layer and the dielectric layer. The method also includes forming a stress-reducing barrier layer including tantalum over the adhesion barrier layer, wherein the stress-reducing barrier layer reduces the first stress level to a second stress level less than the first stress level, and filling the recess with a fill layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Sprayable polymers as adhesion barriers
A formulation for generating an adhesion barrier that includes a plurality of particles or a dry powder that is made of a polymer combination of at least one biodegradable polymer and at least one water soluble polymer is disclosed. Methods of making and delivering the formulation are further disclosed. The formulation of particles is deposited on a surface of internal body tissue and the deposited formulation absorbs moisture from the tissue and forms a film over the surface. The film acts as an adhesion barrier by reducing or preventing adhesion of the surface to other body tissue.
Owner:ARA MEDICAL
Cellulose derivative and hydrogel thereof
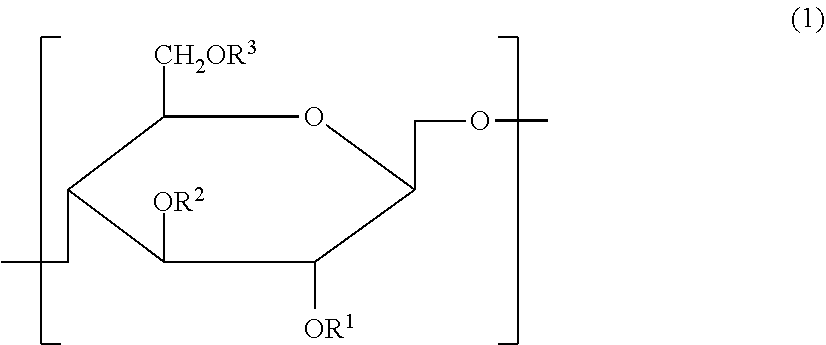
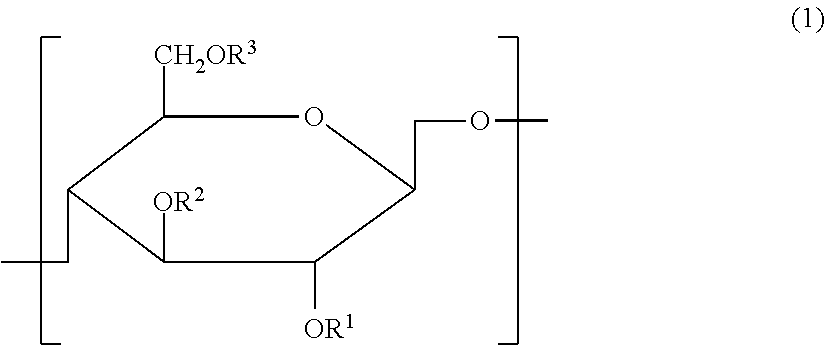
The invention is a cellulose derivative wherein some of the carboxyl groups of the cellulose derivative carboxymethylcellulose are replaced with —CO—NH—X—CO—Y—Z, and a hydrogel of the same. In the formula, X is a C1-10 divalent hydrocarbon group, Y is a divalent group derived from polyalkylene oxide having oxygen atoms at both ends, and Z is a C1-24 hydrocarbon group or —CO—R4, where R4 is a C1-23 hydrocarbon group. The hydrogel has excellent viscoelasticity and can be injected into prescribed sites with injecting devices such as syringes, and it can thus be utilized as a medical gel or adhesion barrier.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
High temperature hybridized molecular functional group adhesion barrier coating and method
ActiveUS20150099133A1Easy adhesionSimple structureAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentLaminationDerivatizationDegree Fahrenheit
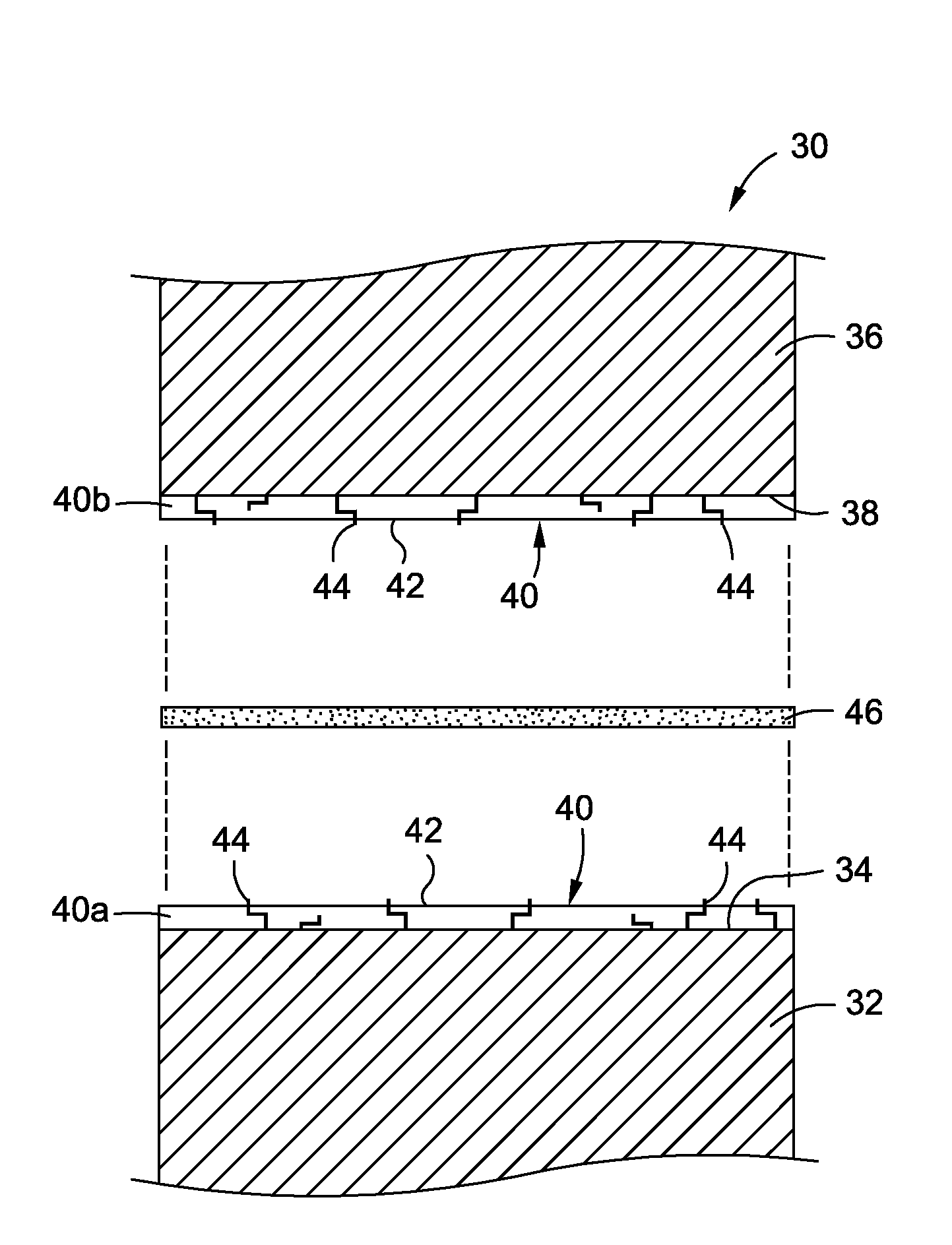
There is provided a high temperature hybridized molecular functional group adhesion barrier coating for a composite structure. The coating has one or more hybridized molecular functional groups attached to a composite surface of the composite structure, wherein the one or more hybridized molecular functional groups are hybridized through a chemical derivatization process. The coating further has one or more chemical derivatization compounds attached to the one or more hybridized molecular functional groups via a condensation reaction. The coating is resistant to high heat temperatures in a range of from about 350 degrees Fahrenheit to about 2000 degrees Fahrenheit, and the coating is a thermally protective, toughened adhesion coating that mitigates effects of a hostile operating environment.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com