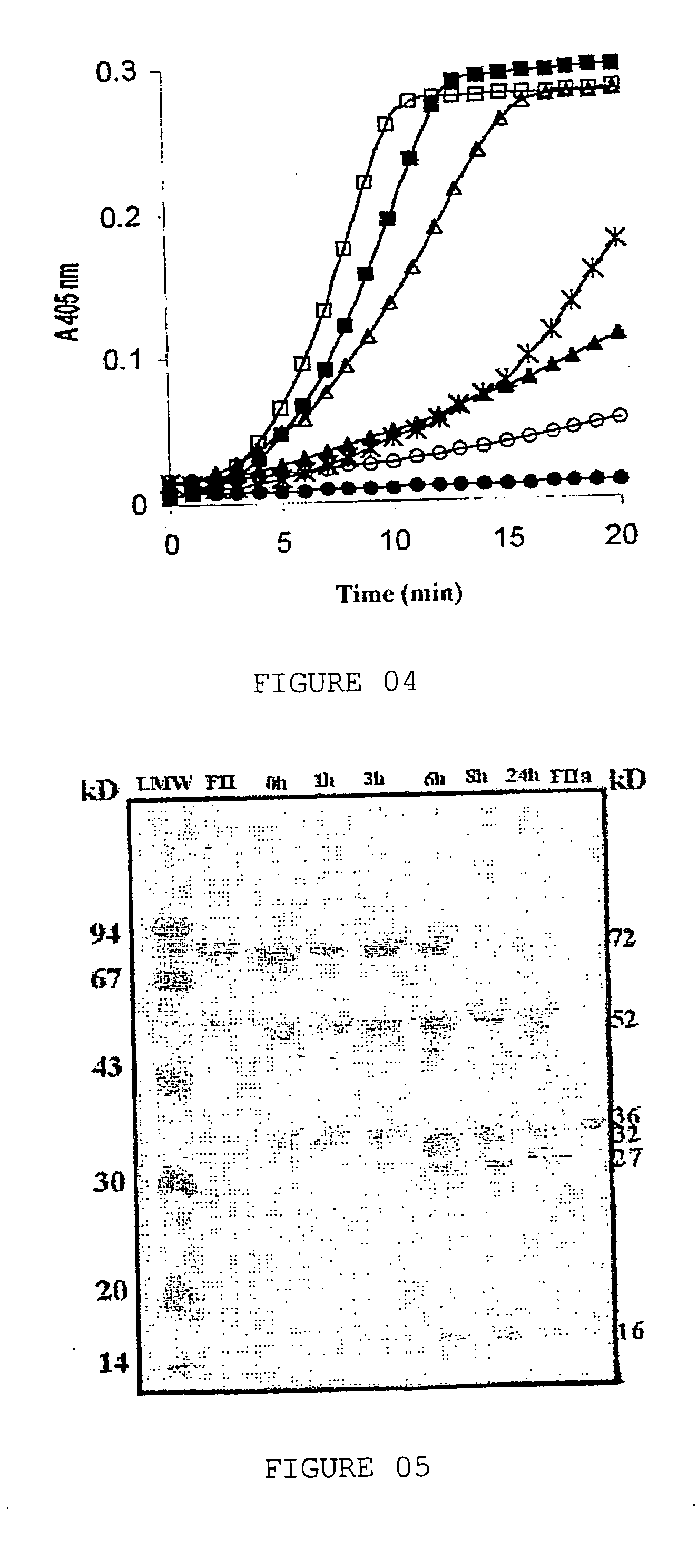
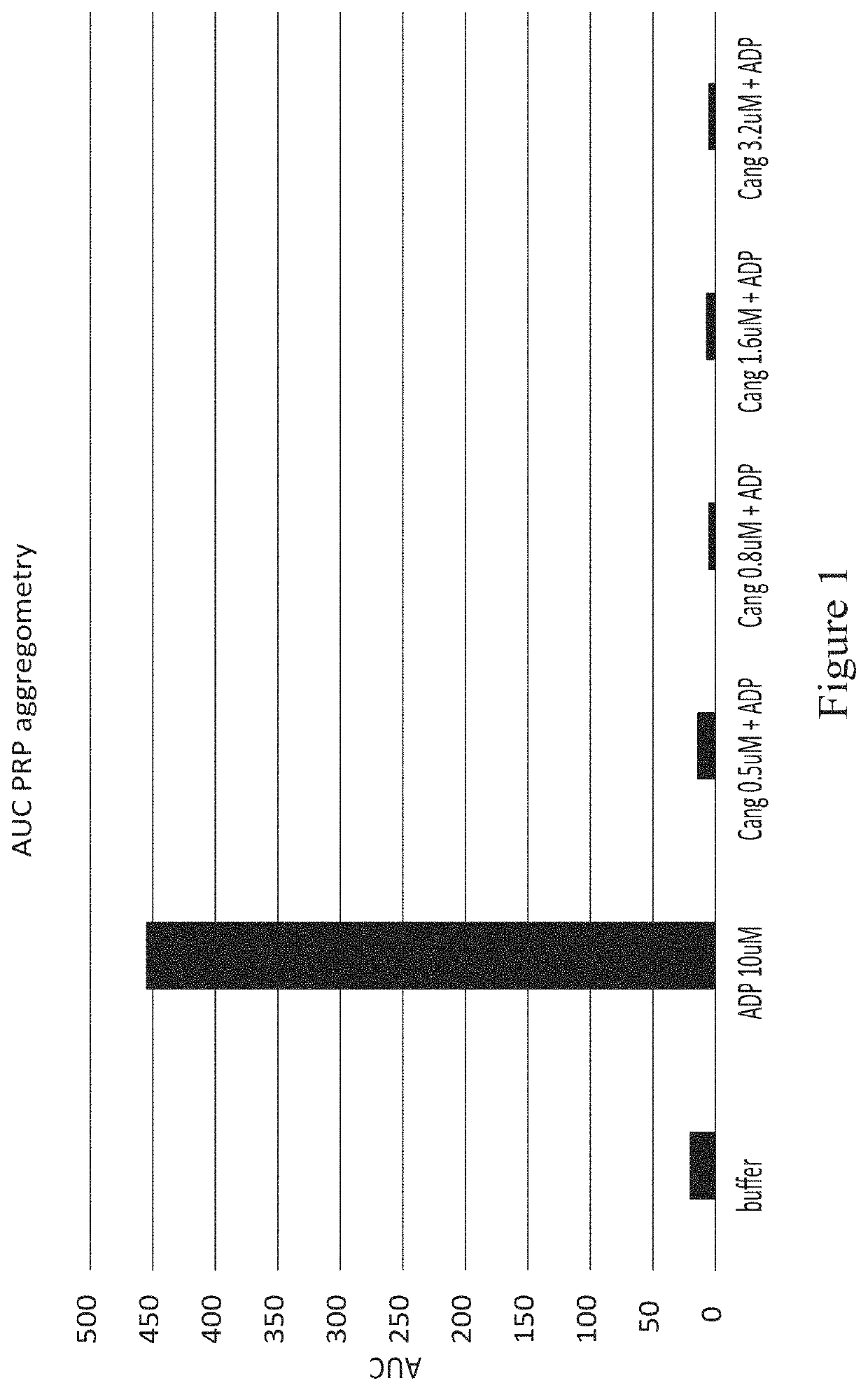
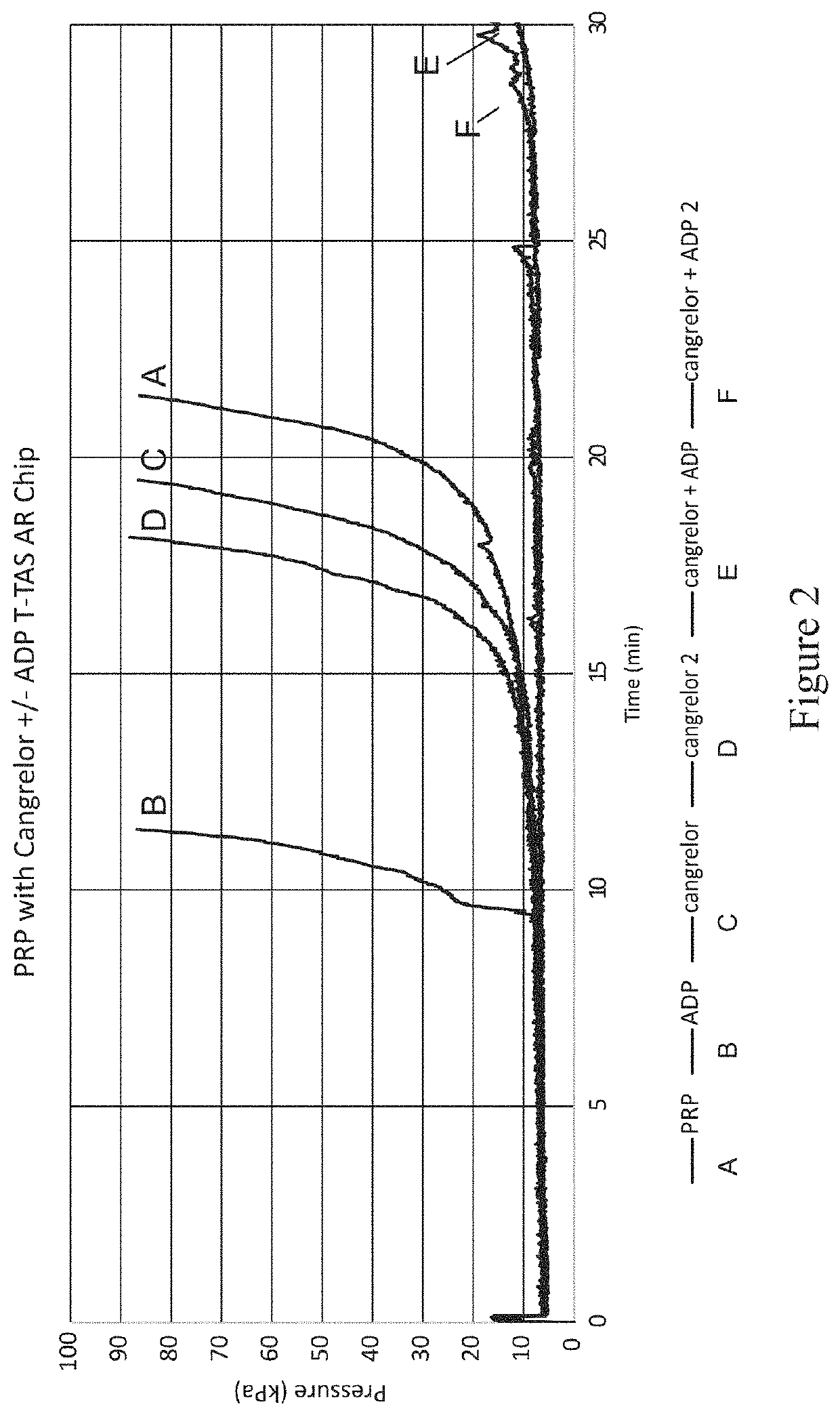
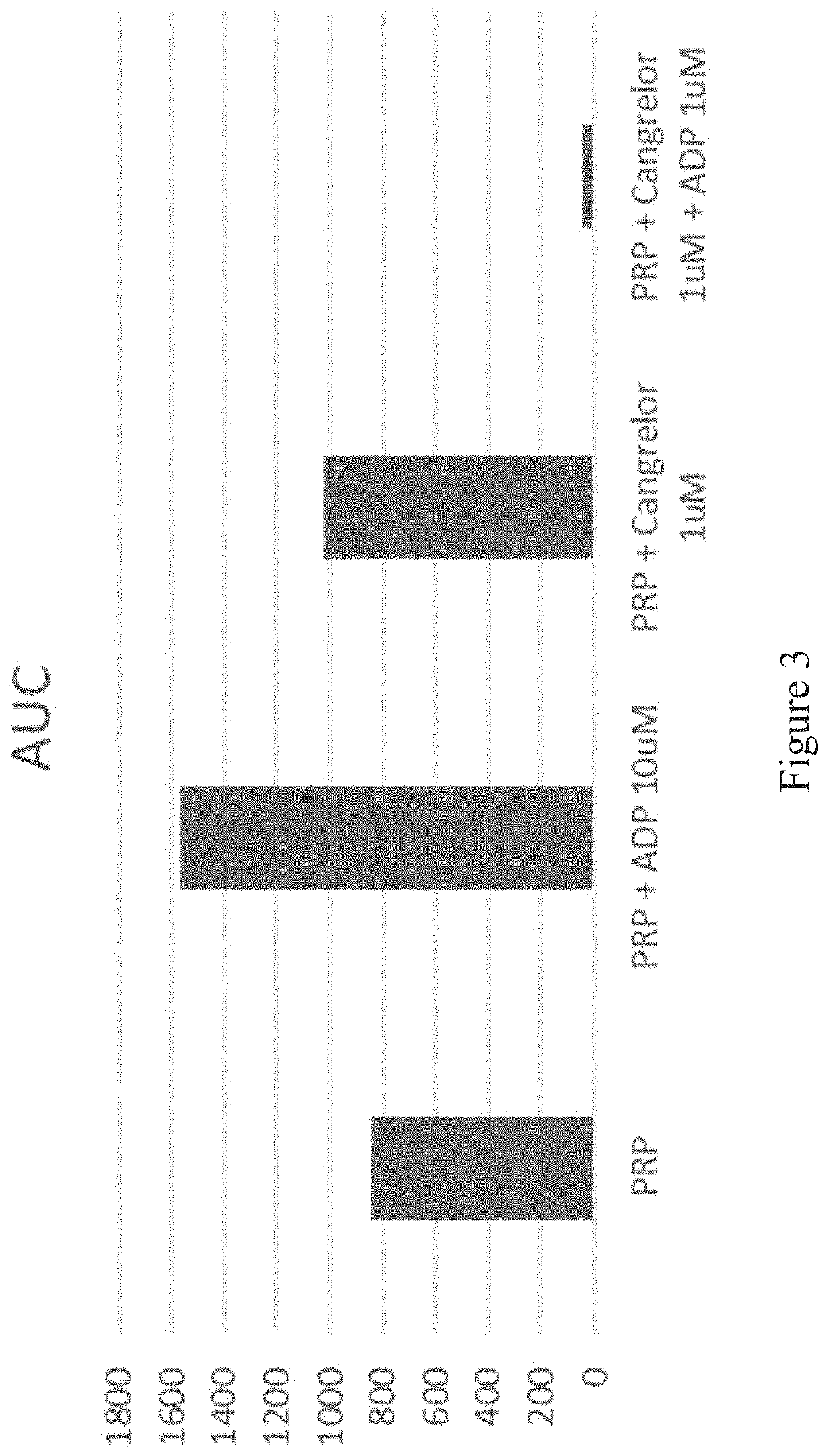
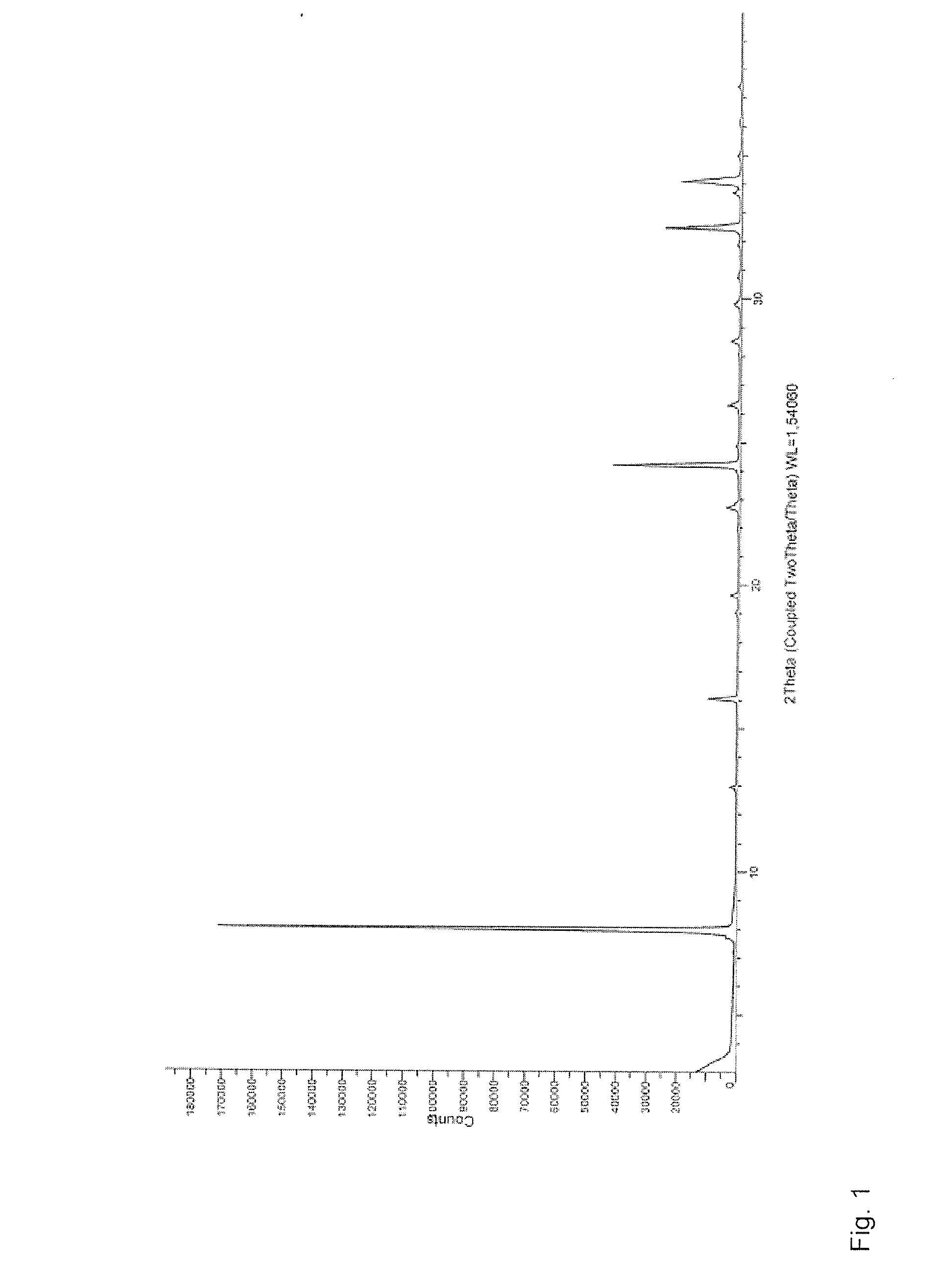
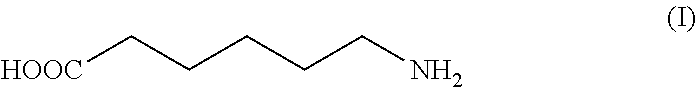
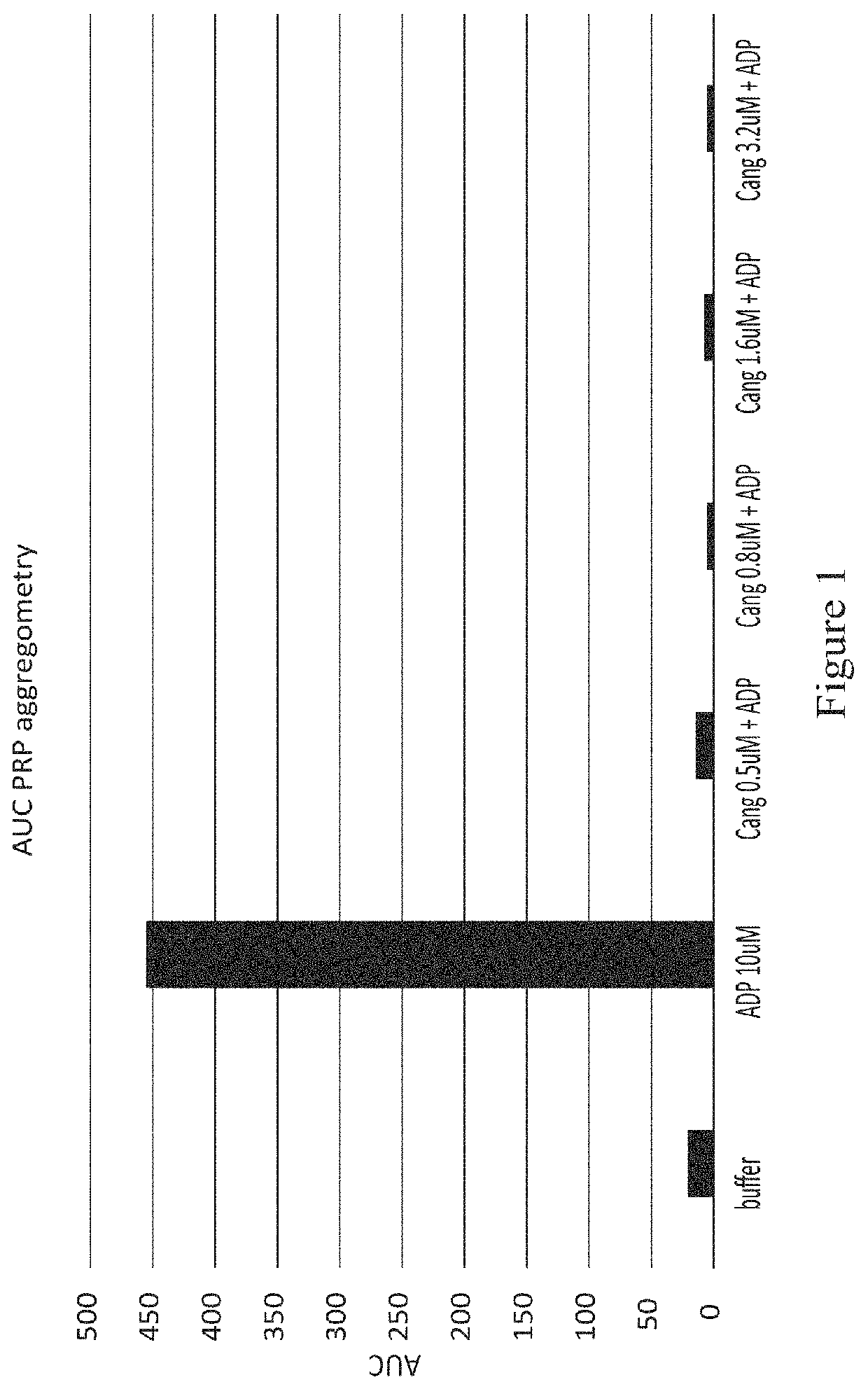
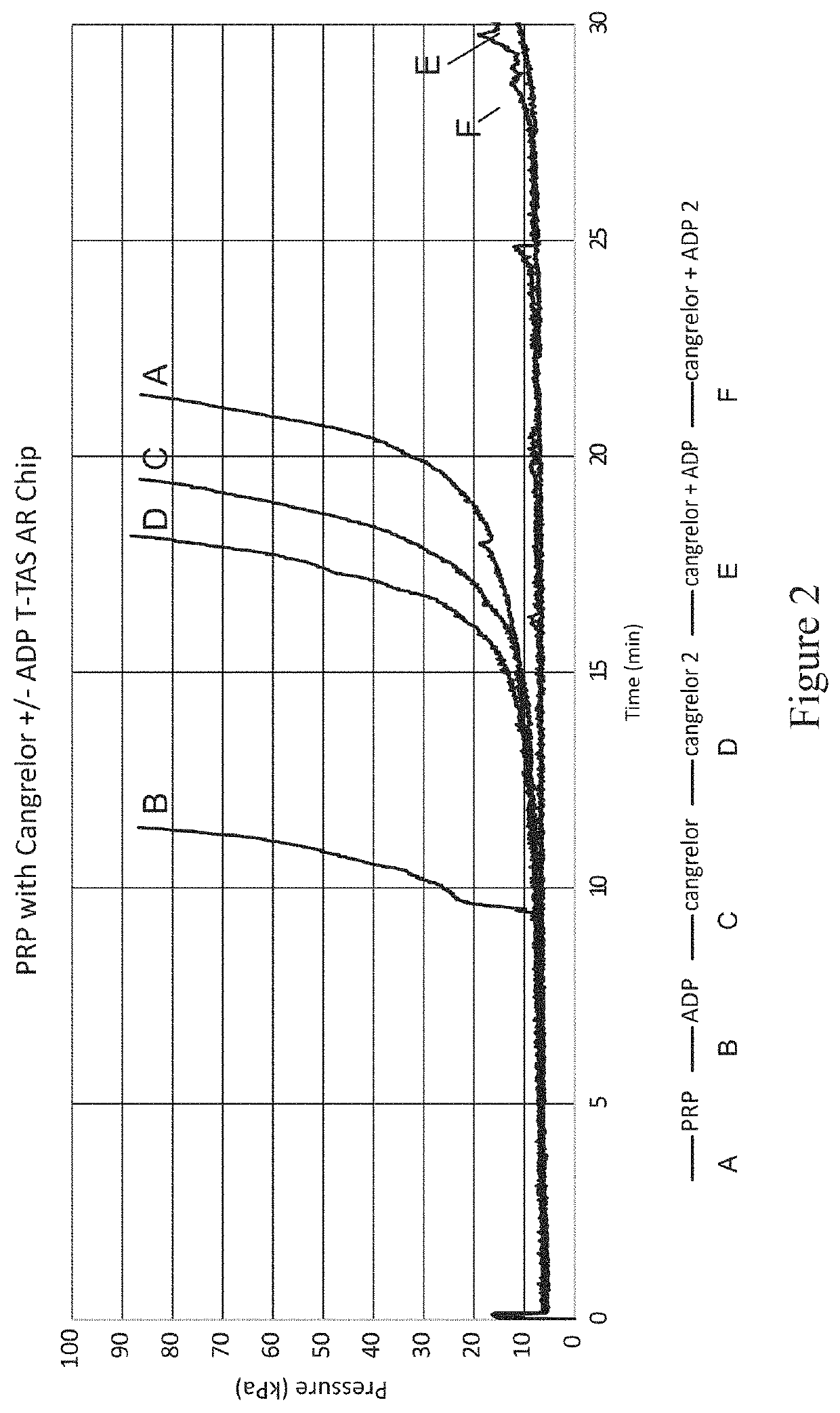
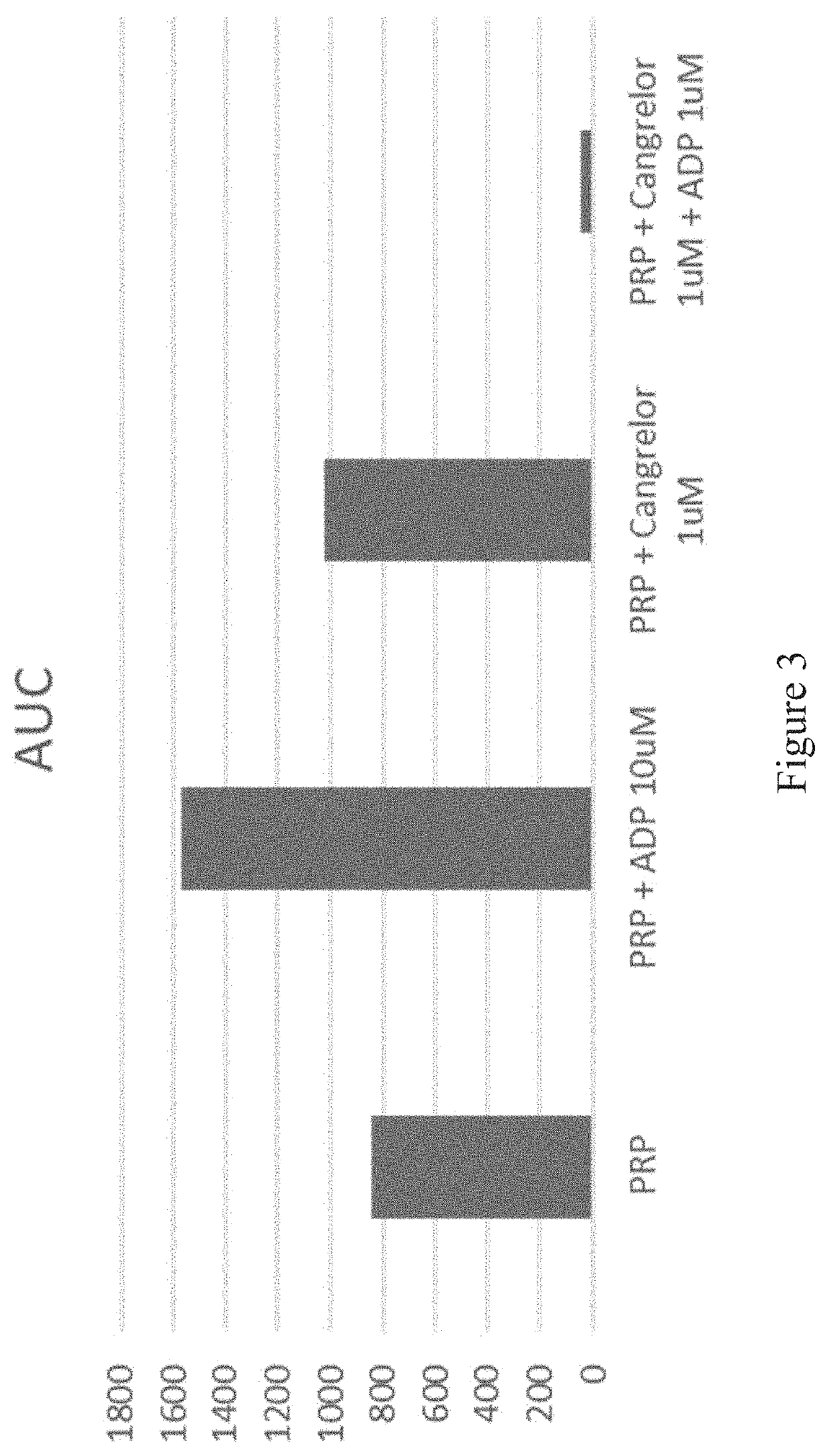
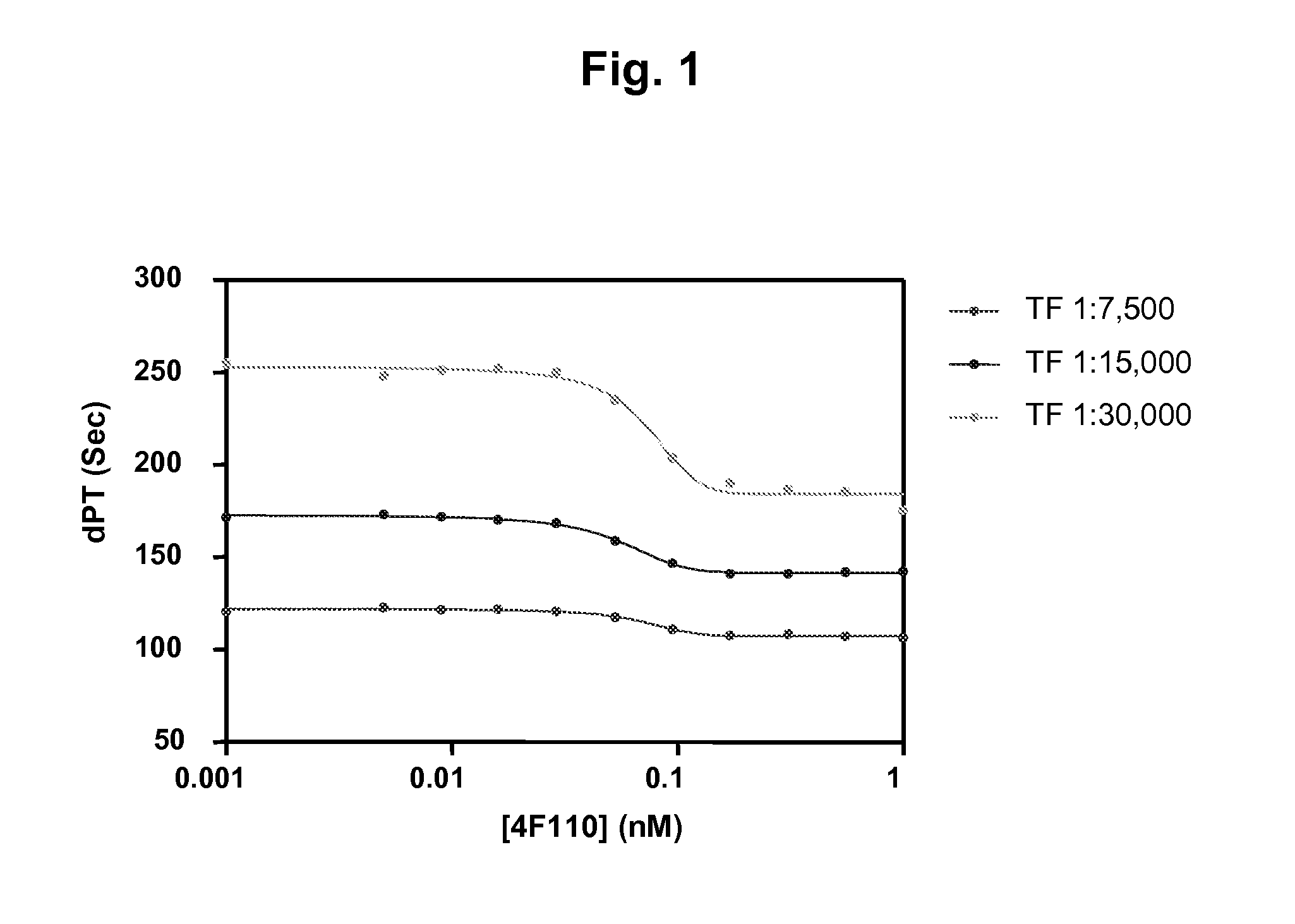
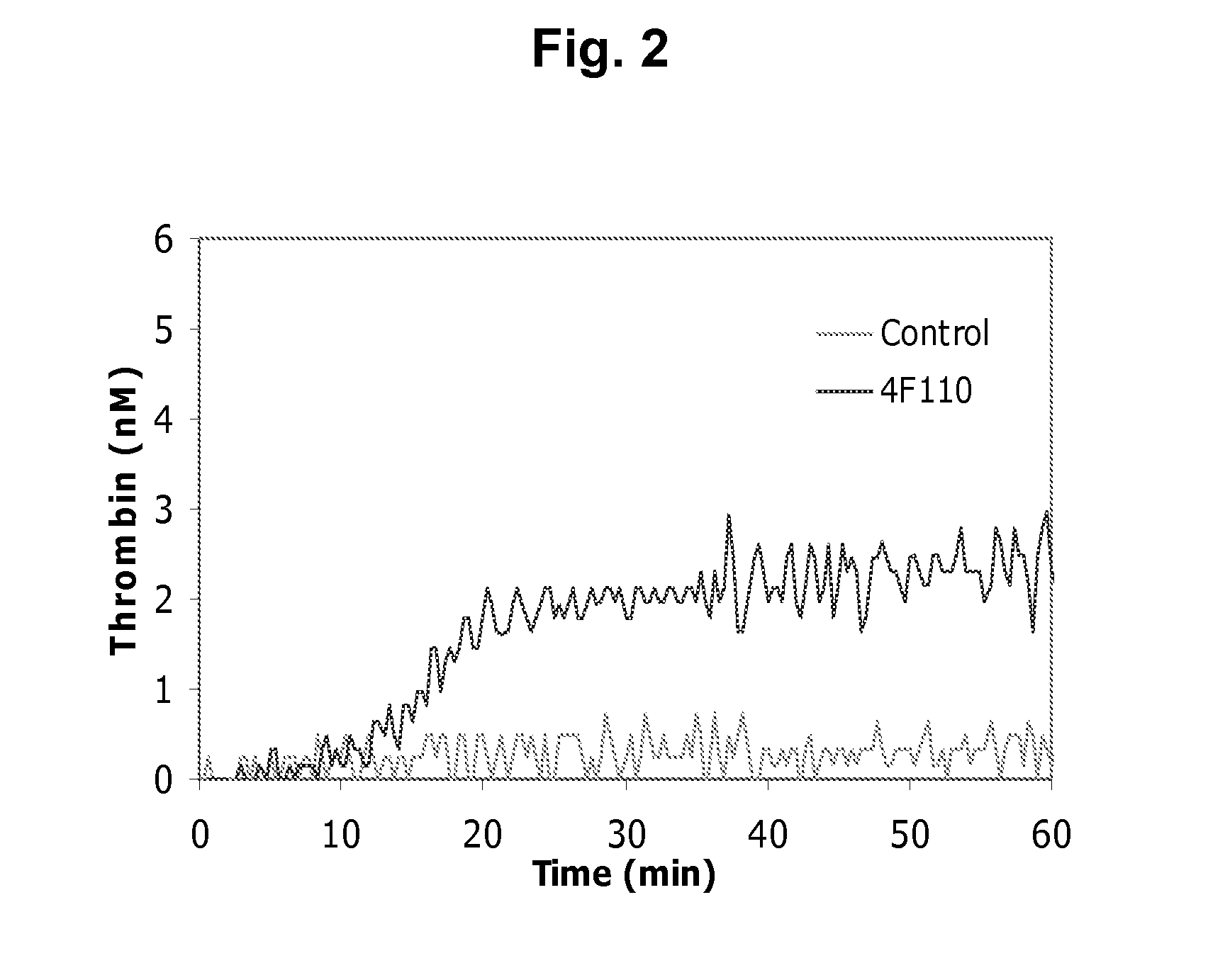
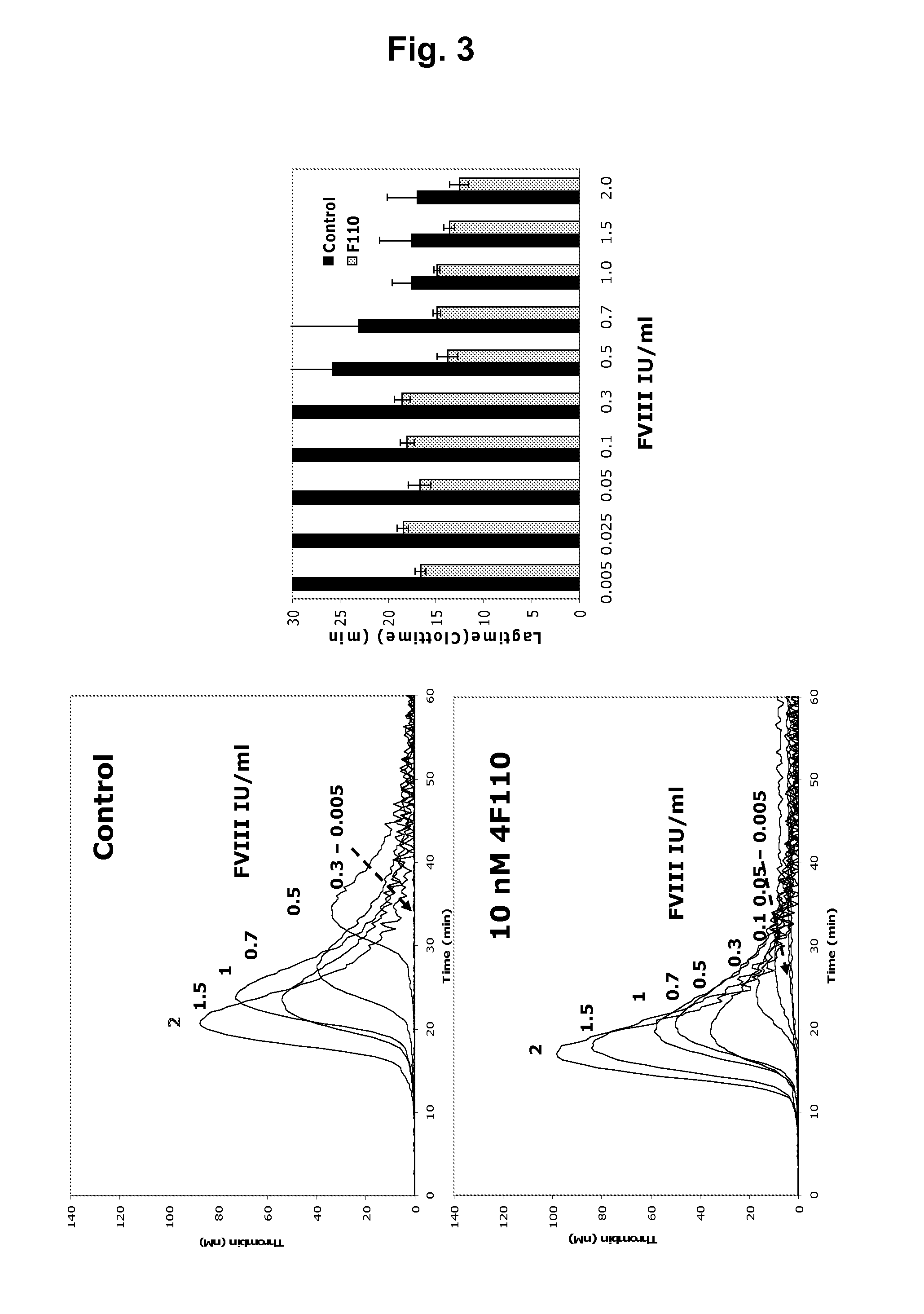
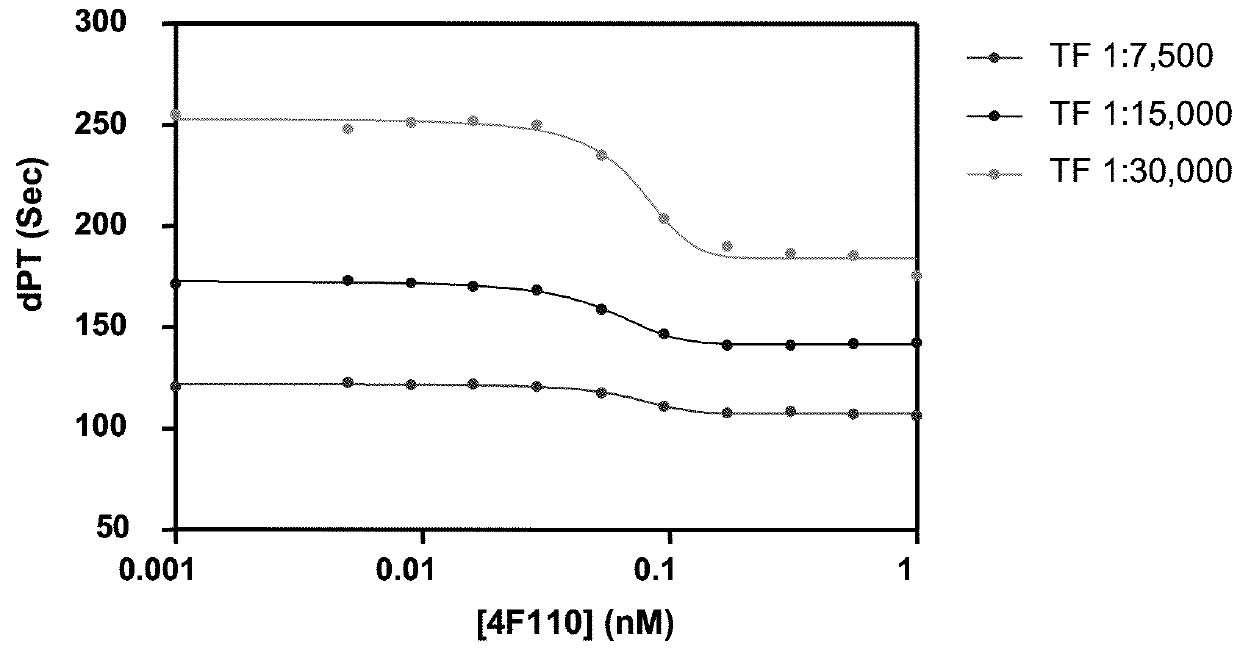
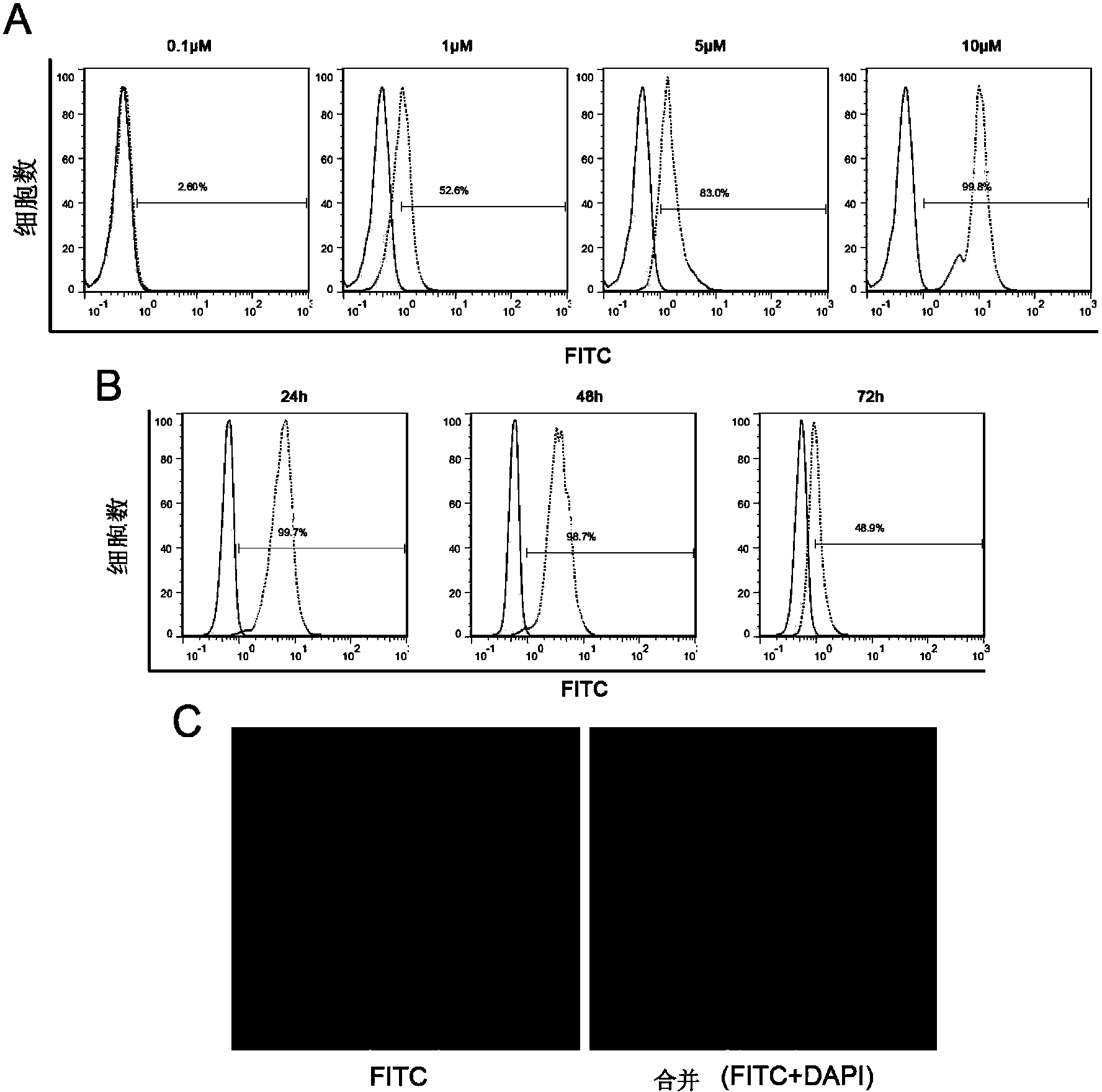
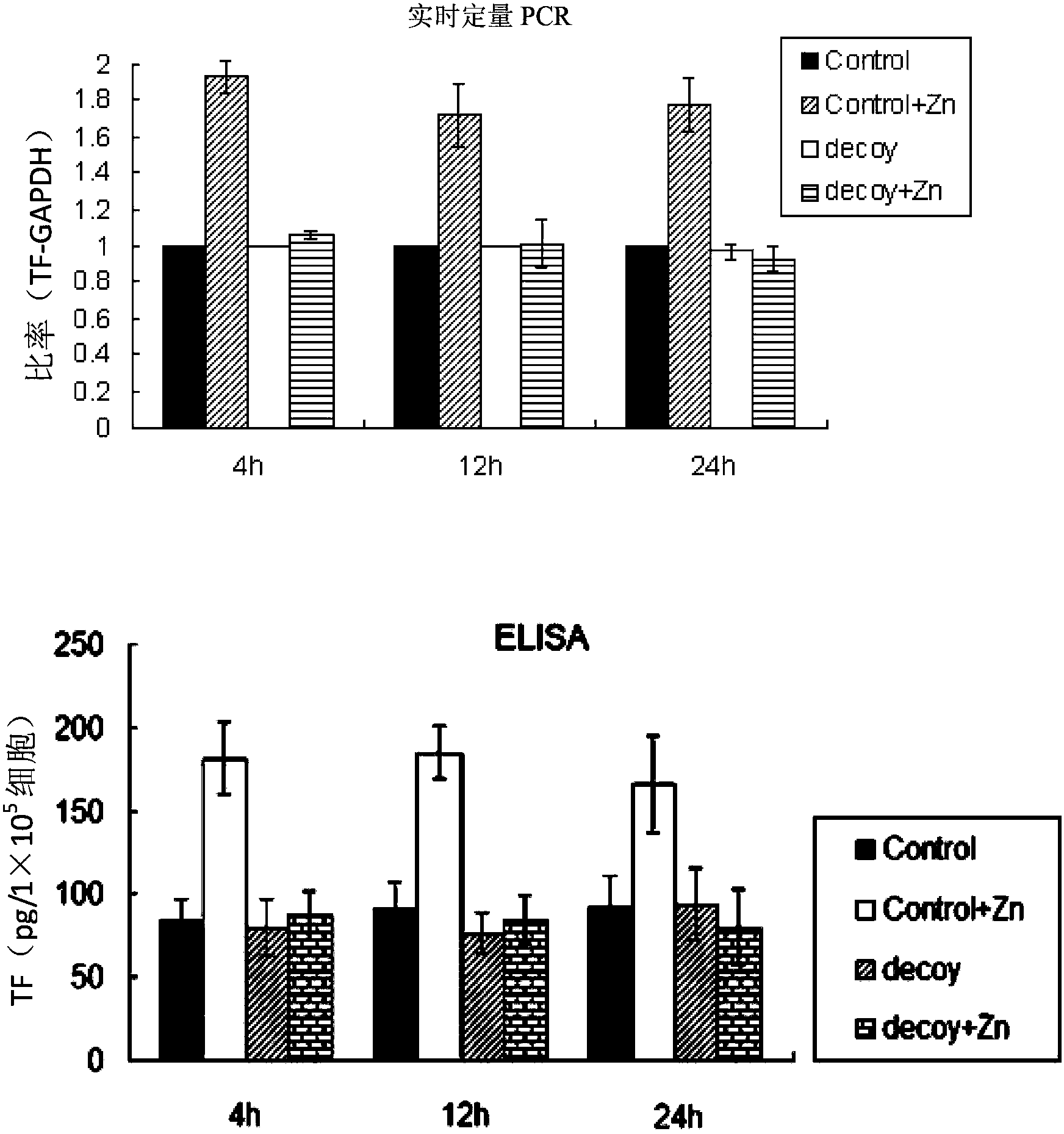
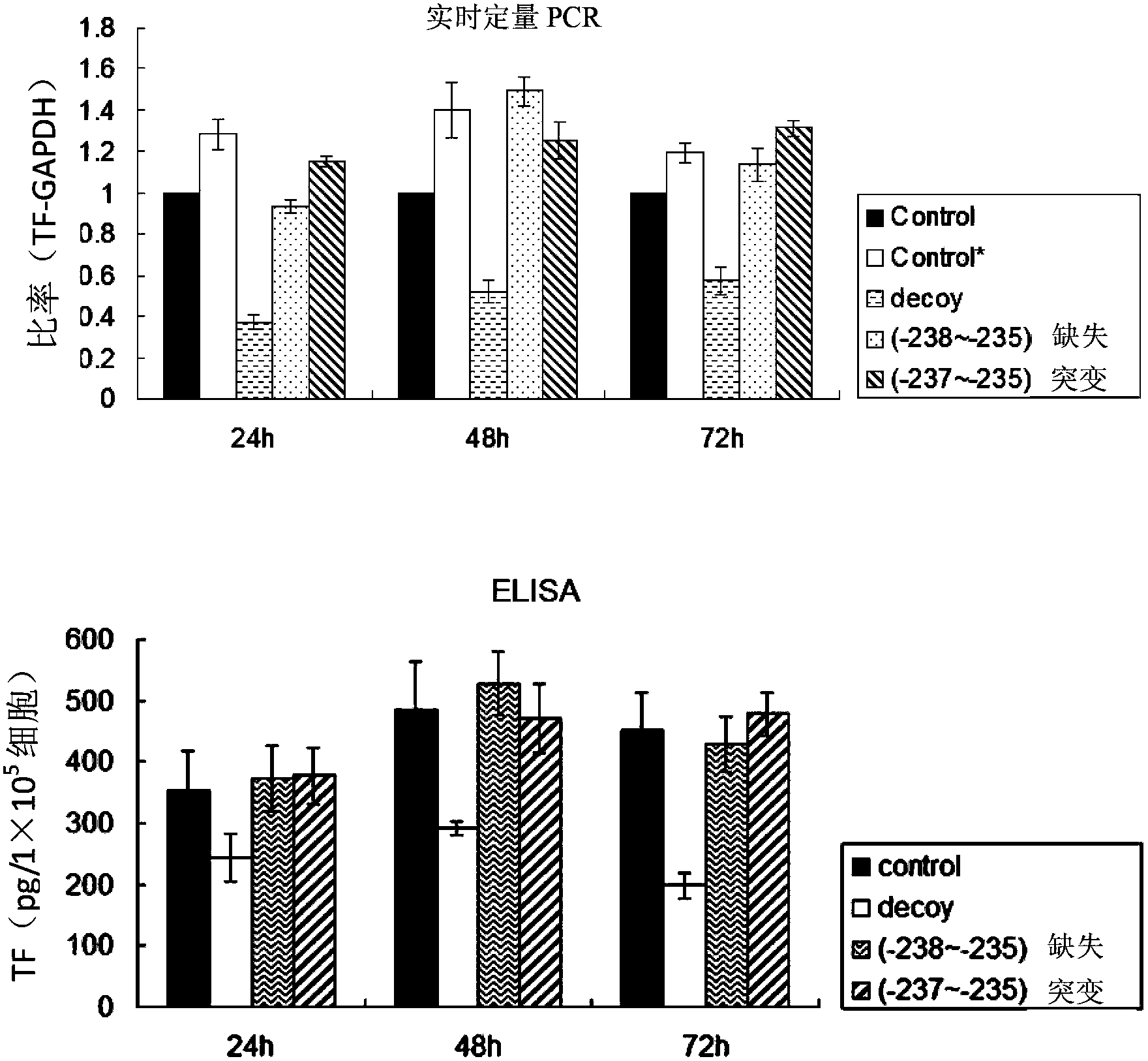
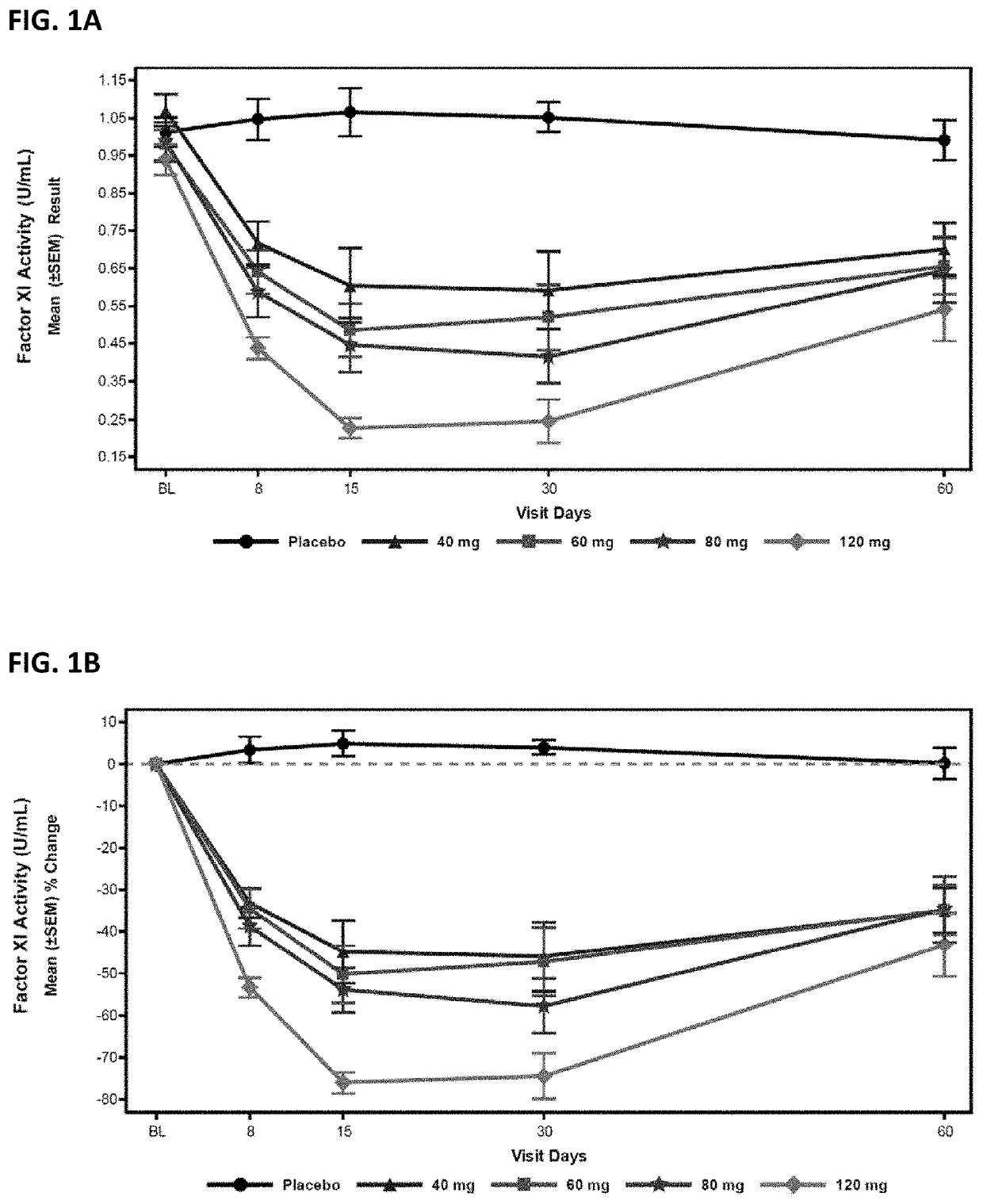
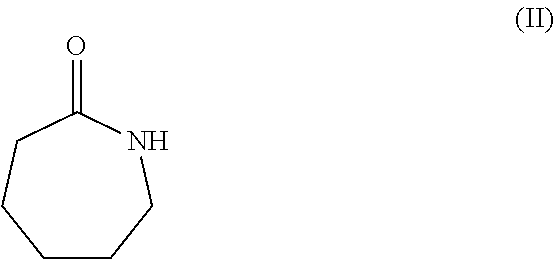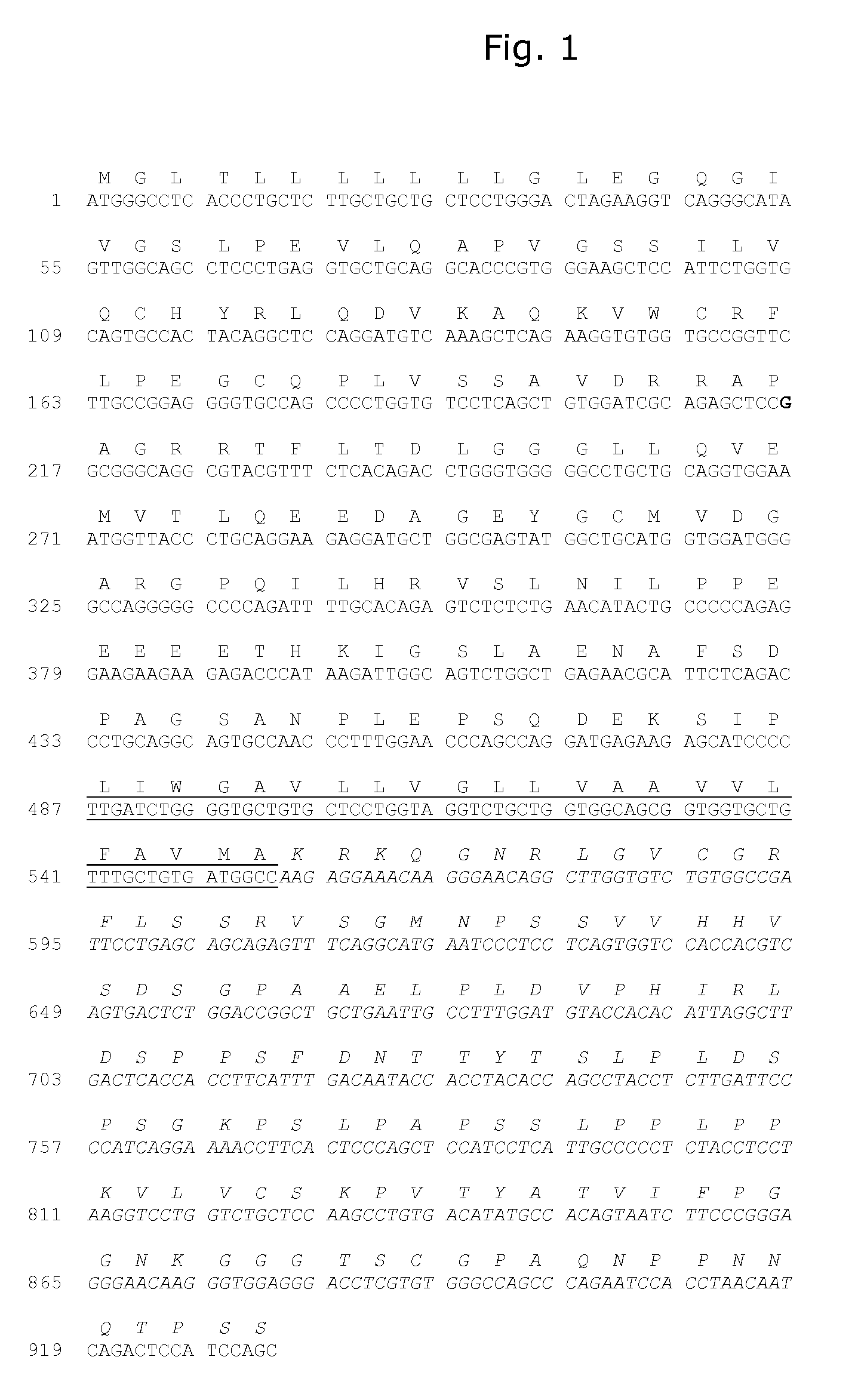Patents
Literature
42 results about "Coagulopathy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood’s ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding (bleeding diathesis), which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures. Of note, coagulopathies are sometimes erroneously referred to as "clotting disorders"; a clotting disorder is a predisposition to clot formation (thrombus), also known as a hypercoagulable state or thrombophilia.
Antibodies Against Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
ActiveUS20110318356A1Shorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFungiCoagulopathyTissue factor pathway inhibitor
The invention relates to antibodies that specifically bind to tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) and that reduce the clotting time of blood. Such antibodies have utility in the treatment of subjects with a coagulopathy.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Diagnostic tool detecting the degradation status of Von Willebrand Factor multimers
InactiveUS20080306346A1Quick checkQuick identificationDiagnostics using lightDrug and medicationsDiseaseHuman body
A method in which the cleavage profile and size distribution of von Willebrand factor (VWF) multimers is analyzed, includes: providing a sample medium of human body fluids comprising a plurality of VWF multimers of different size; enrichment or purification of the VWF multimers by cryoprecipitation or chromatography to obtain a separated preparation of the VWF multimers from said sample medium; exposing the separated preparation of VWF multimers to a light source to produce signals obtained by vibrational spectroscopy; detecting said signals; transformation by mathematical alogrithms; generation of patterns based on computing of data of original resonance spectra and determining the cleavage profile and the size distribution of said separated VWF multimers by chemometrics; and acquisition of a databank obtained from healthy individuals for identifying subjects at risk of developing at least one of the following diseases: sepsis, coagulopathy, thrombotic disease, infection, and inflammation.
Owner:BOCKMEYER CLEMENS +2
Cell membrane directed drugs
Drugs in which peptides having affinity specific for phospholipids, preferably those which are contained in the constituents of lipid bilayers forming the surface layers of cells and of which the proportion in the outer part of each lipid bilayer increases when the cell is not normal, for example, in the case where it is damaged, denatured or activated, and biologically active substances bind to each other, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which codes for the amino acid sequence of the drug in the case where the biologically active substance is a peptide, and processes for producing such drugs. The drugs and novel peptides are useful as preventives and therapeutics of diseases involving coagulopathy, inflammations and immune response.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
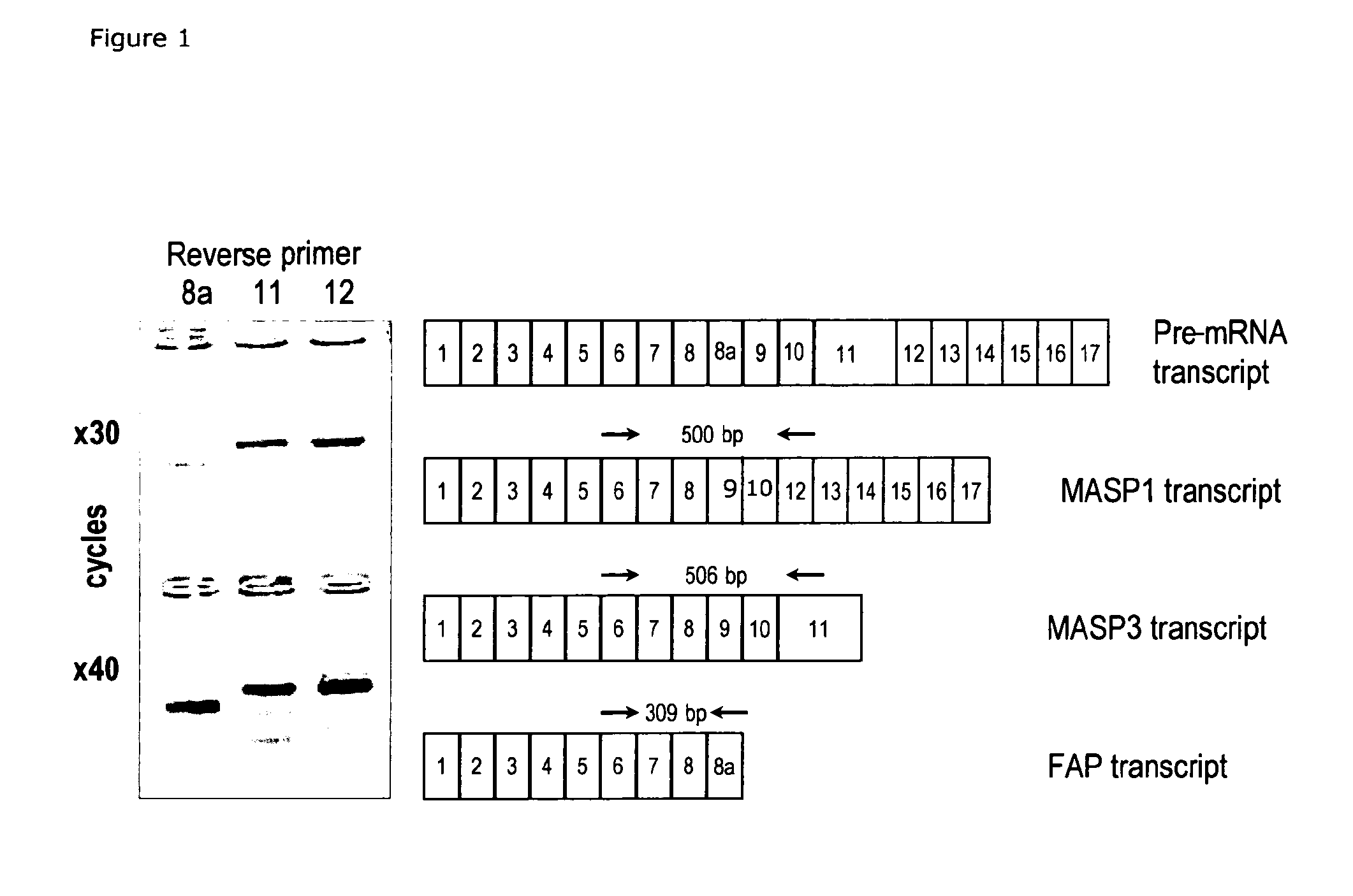
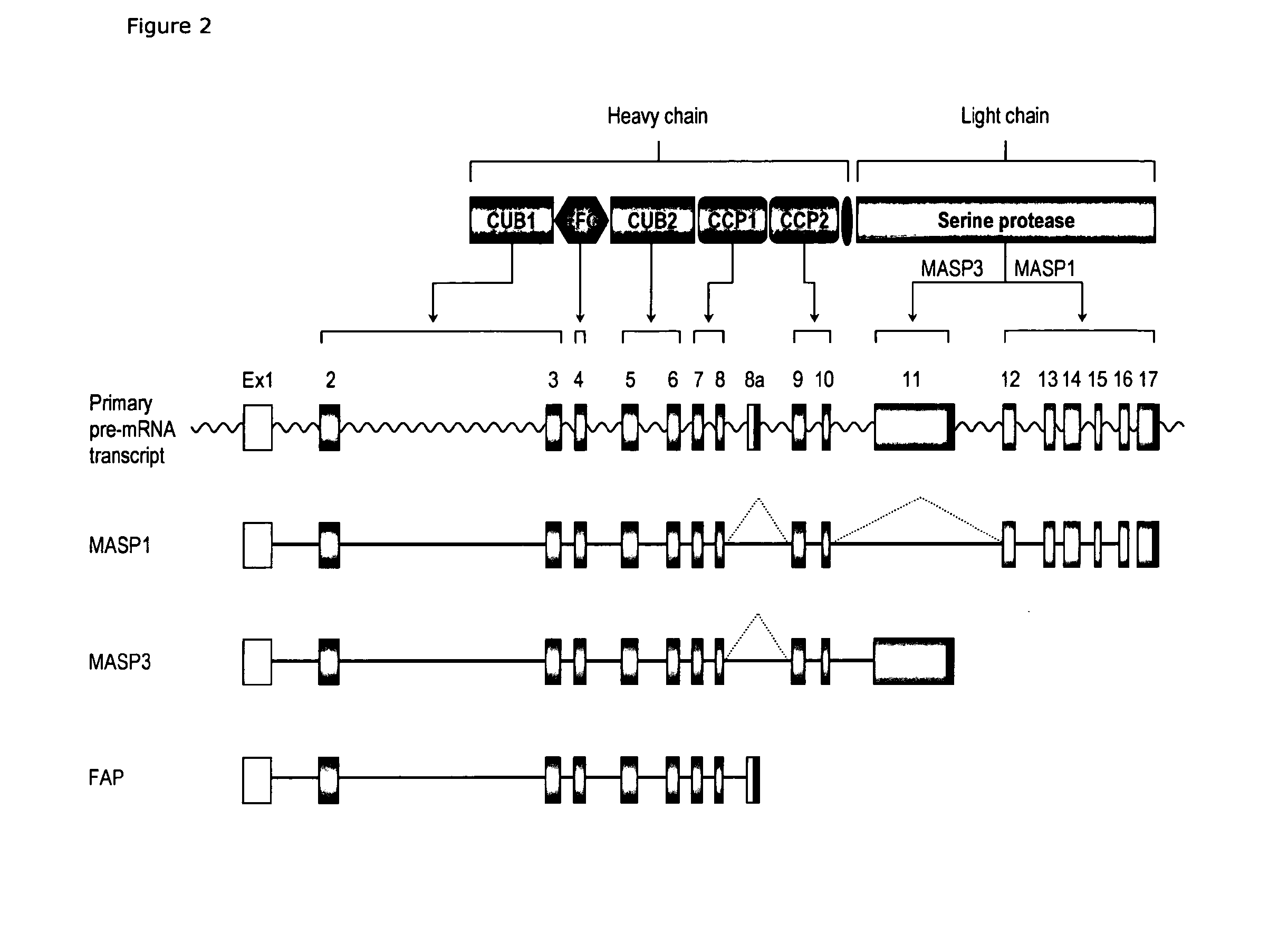
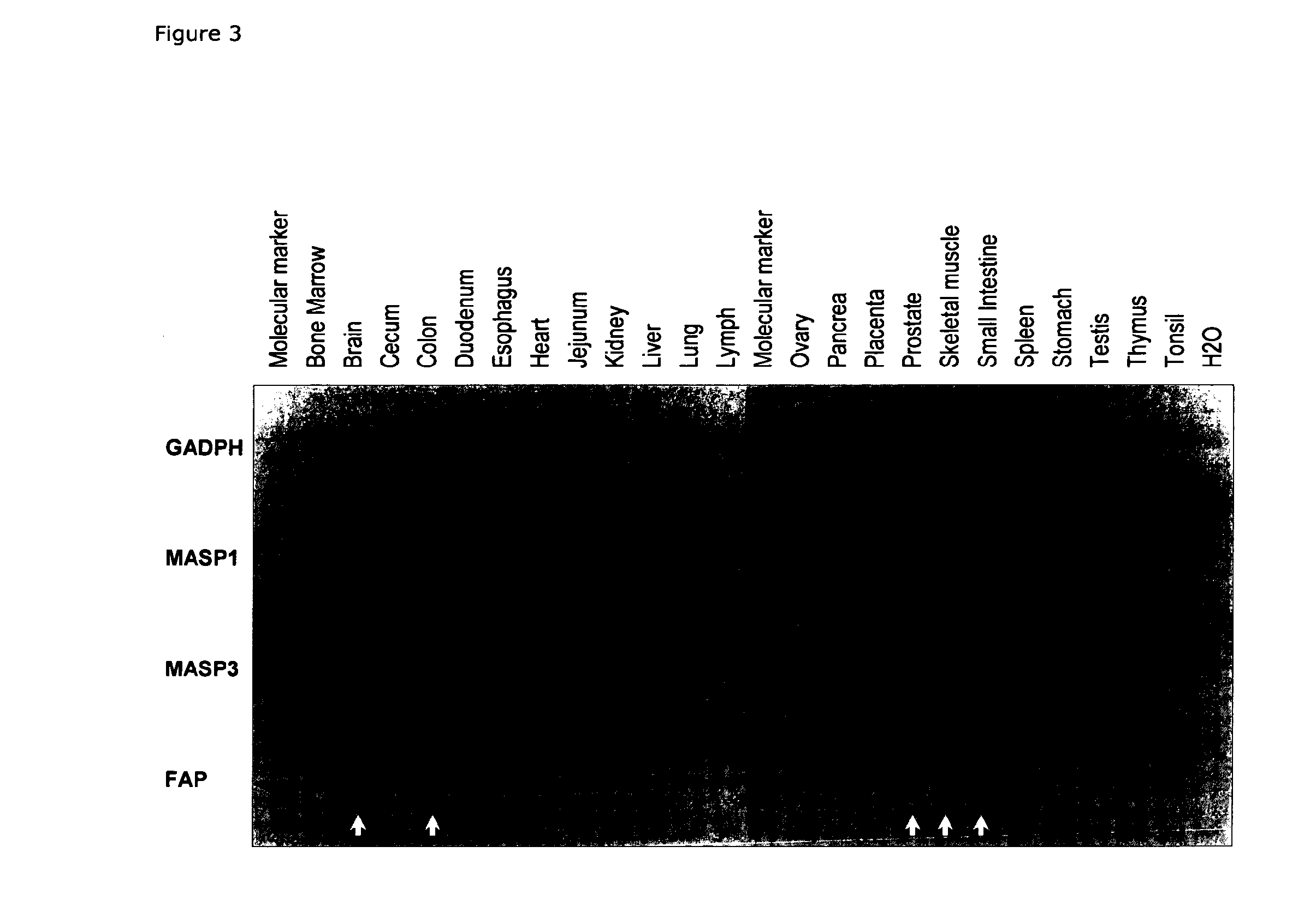
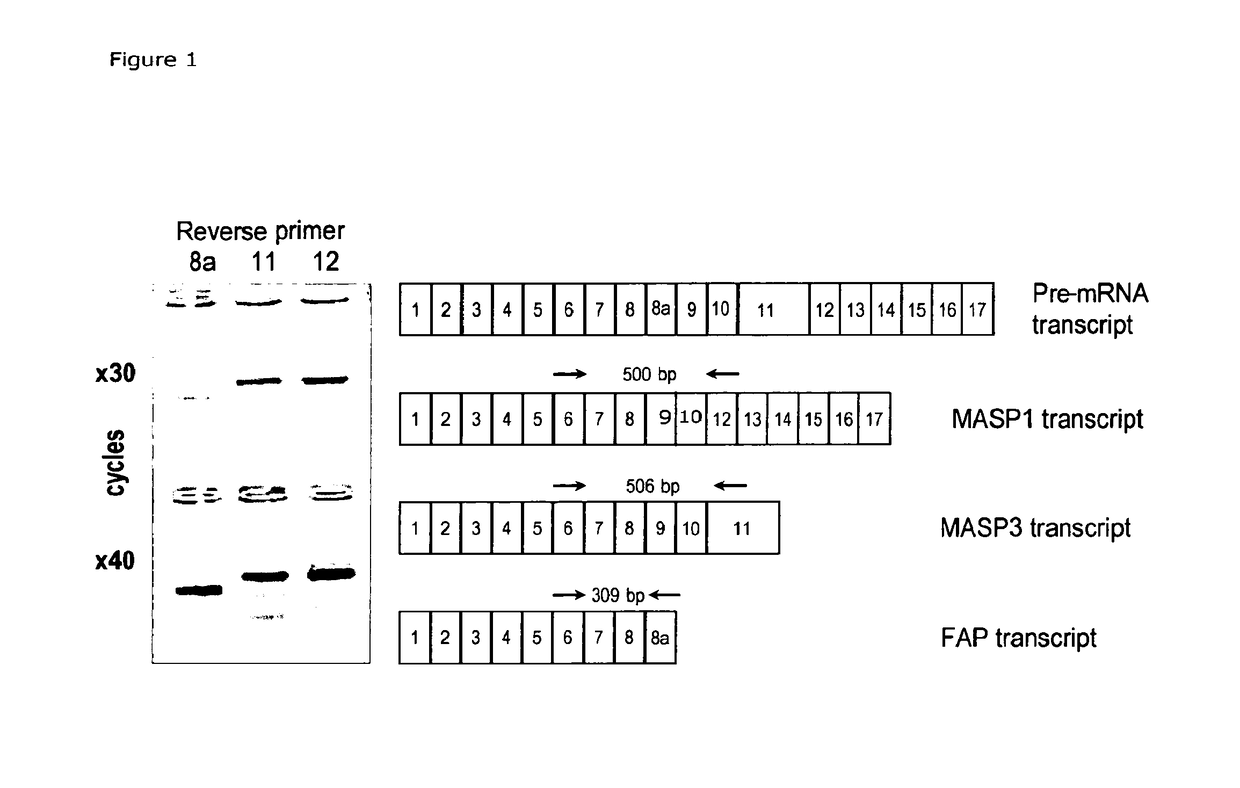
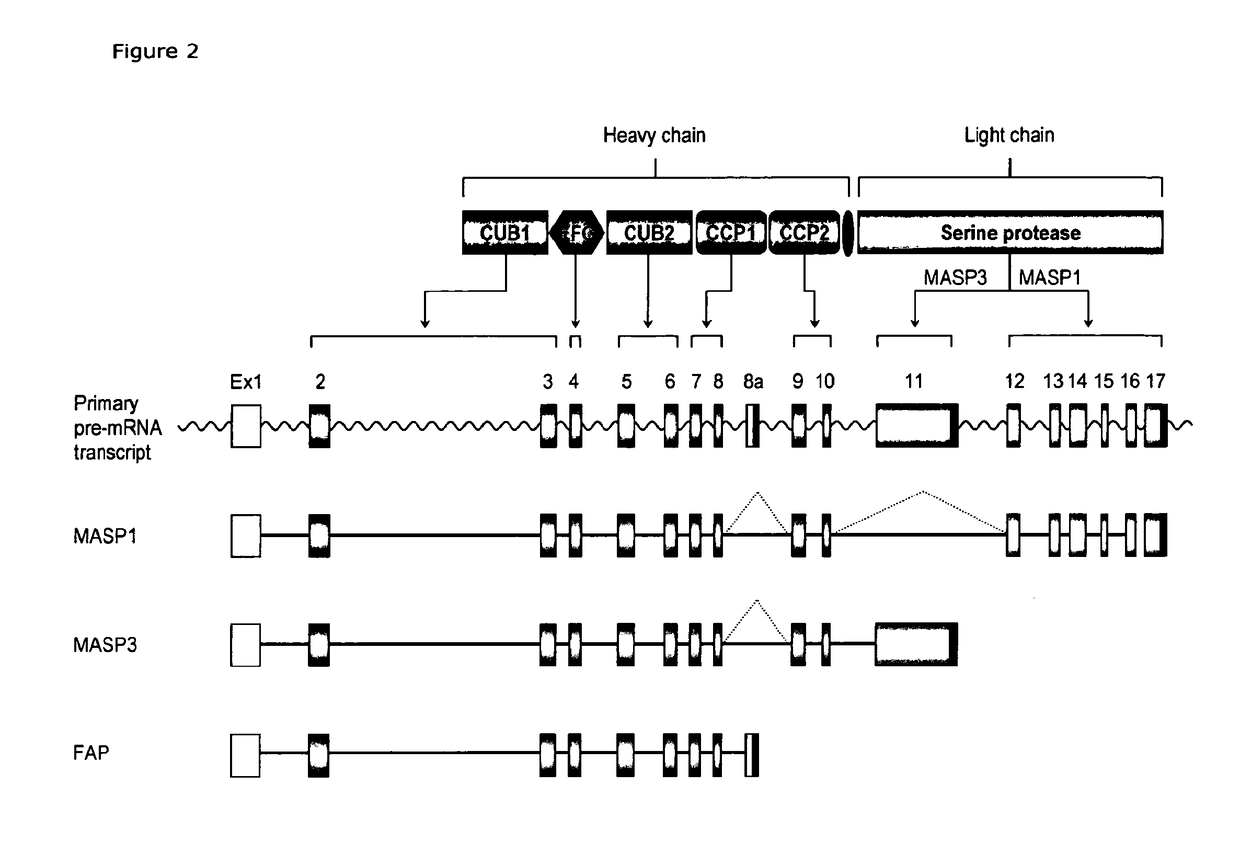
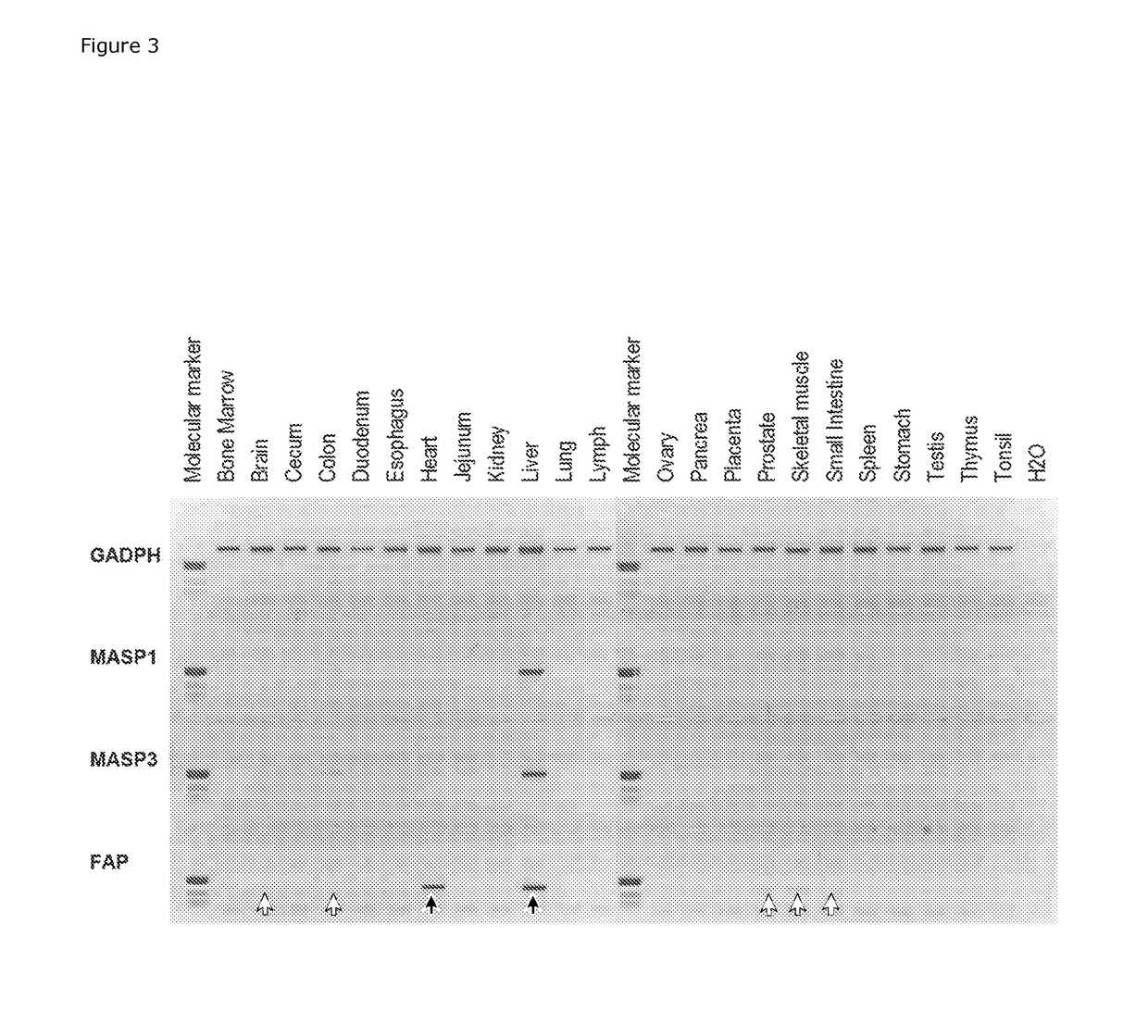
Masp isoforms as inhibitors of complement activation
InactiveUS20120282285A1Avoid it happening againAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseAutoimmune responses
The present invention relates to novel ficolin-associated polypeptides, and polypeptides derived from these ficolin-associated polypeptides for the use in the treatment of conditions associated with inflammation, apoptosis, autoimmunity, coagulation, thrombotic or coagulopathic related diseases, as well as the use as biomarkers. The present invention further relates to anti-bodies recognising such novel ficolin-associated polypeptides, and polypeptides derived thereof, nucleic acid molecules encoding such polypeptides, vectors and host cells used in the production of the polypeptides.
Owner:RIGSHOSPITALET +2
Antibodies against tissue factor pathway inhibitor
ActiveUS8361469B2Shorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPeptide/protein ingredientsCoagulopathyTissue factor pathway inhibitor
The invention relates to antibodies that specifically bind to tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) and that reduce the clotting time of blood. Such antibodies have utility in the treatment of subjects with a coagulopathy.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Targeting Tissue Factor To Activated Platelets
ActiveUS20160272710A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTissue factorPlatelet
The current invention relates to procoagulant fusion proteins, polynucleotides that encode said fusion proteins and cells that expresses said fusion proteins. Furthermore, the current invention relates to fusion proteins for use as a medicament. Individuals that have a coagulopathy, such as haemophilia A and B with or without inhibitors, may be treated with fusions proteins of the current invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Methods of treating diabetic cardiomyopathy using glycogen phosphorylase inhibitors
The present invention provides methods of treating diabetic cardiomyopathy, the methods comprising administering to a patient having or at risk of having diabetic cardiomyopathy a therapeutically effective amount of a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor. The present invention also provides methods of treating diabetic cardiomyopathy, the methods comprising administering to a patient having 1) diabetes and 2) having cardiovascular disease, ischemic heart disease, congestive heart failure, congestive heart failure but not having coronary arteriosclerosis, hypertension, diastolic blood pressure abnormalities, microvascular diabetic complications, abnormal left ventricular function, myocardial fibrosis, abnormal cardiac function, pulmonary congestion, small vessel disease, small vessel disease without atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or luminal narrowing, coagulopathy, cardiac contusion, or having had or at risk of having a myocardial infarction a therapeutically effective amount of a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Purifying process of soluble proteins of the l.obliqua bristles through prothrombin activation: process for a partial determination of the amino acids sequence of the prothrombin activator; process for determining the prothrombin activation of fraction II, n-terminal and internal fragments sequences
InactiveUS20050130287A1Prolong coagulation timePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDysprothrombinemiaConsumption Coagulopathy
The herein invention refers to a purifying process of soluble proteins of the L. obliqua bristles through prothrombin activation; a partial deterrination of the amino acids sequence of the prothrombin activator; a process for determining the fraction II of the prothrombin activation as well as the N-terminal sequence and the sequence of internal fragments of the prothrombin activator fraction, the prothrombin activator and the utilization of the prothrombin activator through the homogenization of the L. obliqua bristles. The herein invention has shown that only one component of the Lonomia obliqua venom, the Lopap, causes the hemorrhagic syndrome directly by activating prothrombin and, therefore, a patient should be conducted to a therapy when in contact with the Lonomia obliqua venom. According to the herein invention, Lopap is a new prothrombin activator, showino to be a quite important factor responsible for consumption coagulopathy, found in patients exposed to the venom of the L. obliqua caterpillar. In low doses of purified protein, due to its capacity of activating prothrombin and generating thrombin, it is possible, in controlled conditions, to withdraw fibrinogen from circulation, transforming it in fibrin microthrombs. The decrease on the concentration of plasmatic fibrinogen promotes the increasing of blood coagulation time and therefore it will avoid acute vascular thrombosis. Since protein does not present proteolytic activity, it could maintain the coagulating capacity of the fibrinogen not consumed in the process. The fibrinogen plasmatic concentration would decrease, however there would not be predisposition for hemorrhagic state. Besides that, it could be used to produce diagnosis KITS for detecting dysprothrombinemias.
Owner:BIOLAB SANUS FARMACEUTICA LTD
Method of treatment of hemorrhagic disease using a factor VIIa/tissue factor inhibitor
ActiveUS7132398B2Decrease or prevent said coagulopathy and/or inflammatory responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIaNematode
The present invention provides methods of treating hemorrhagic fevers where selective inhibitors of fVIIa / TF are used as a treatment for hemorrhagic fevers and have therapeutic effects which include ameliorating and / or preventing coagulopathy and inflammatory responses. These inhibitors include certain proteins which are part of a family termed Nematode-Extracted Anticoagulant Proteins (“NAPs”). Other inhibitors include Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (“TFPI”) and TFPI analogs.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
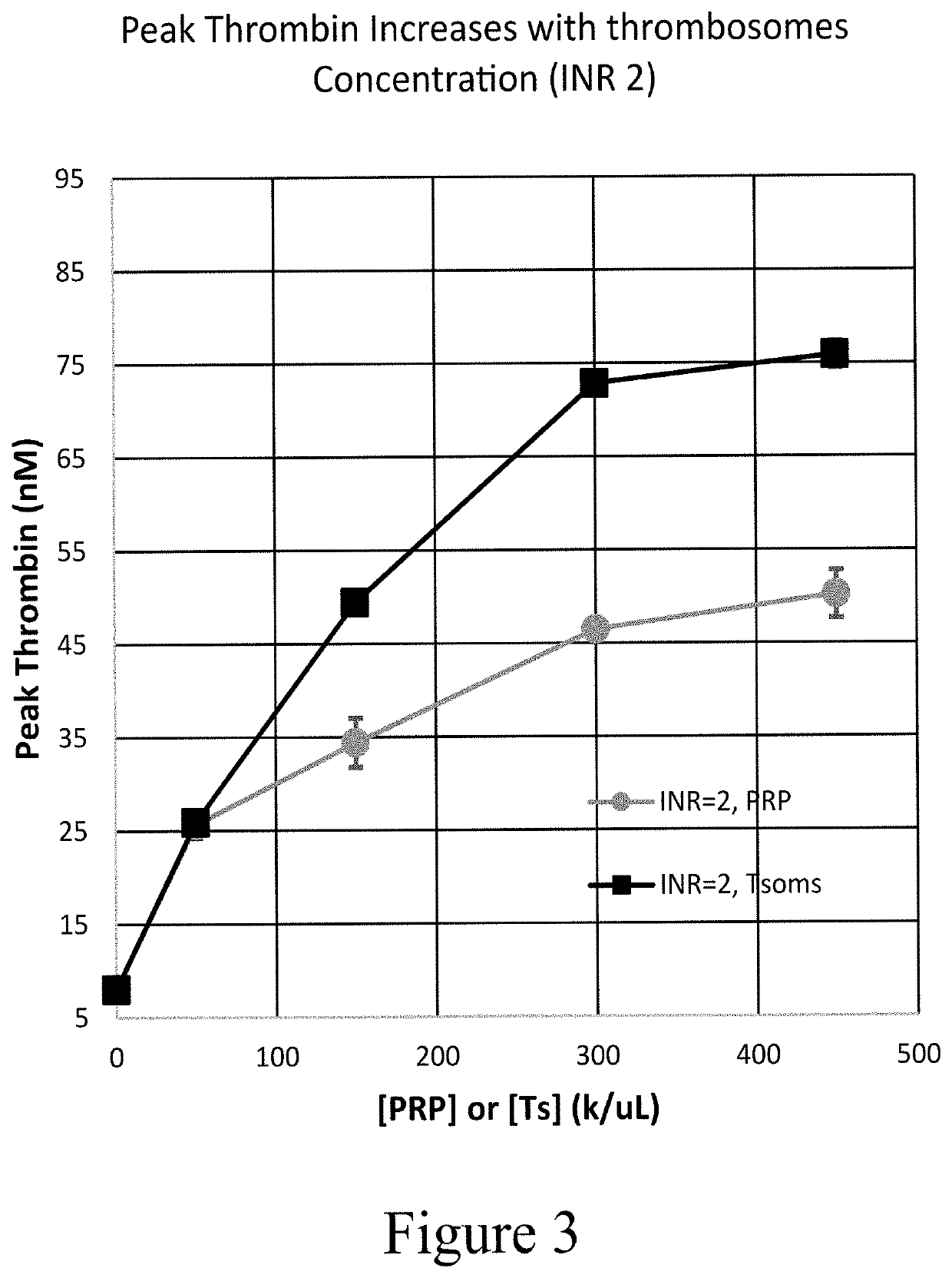
Thrombosomes as an antiplatelet agent reversal agent
ActiveUS20210046121A1Treatment being stoppedTreatment with the antiplatelet agent can be continuedOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic solventThrombus
In some embodiments provided herein is a method of treating a coagulopathy in a subject, the method including administering to the subject in need thereof an effective amount of a composition including platelets or platelet derivatives and an incubating agent including one or more salts, a buffer, optionally a cryoprotectant, and optionally an organic solvent, wherein the subject has been treated or is being treated with an antiplatelet agent.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
Isolation and purification of 6-aminocaproic acid
ActiveUS20170036991A1Organic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAminocaproic acidPost operative
The present invention relates to a new process for the isolation and purification of 6-aminocaproic acid, which is a known inhibitor of enzymes responsible for fibrinolysis and is used in the treatment of coagulopathies and severe post-operative bleedings.
Owner:DIPHARMA FRANCIS
Freeze-dried platelet derivative compositions for treating antiplatelet induced coagulopathy
PendingUS20220168353A1Restore hemostasisIncreased bleeding potential of a subjectPeptide/protein ingredientsSulfonylurea active ingredientsOrganic solventAnti platelet
In some embodiments provided herein is a method of treating a coagulopathy in a subject that is being administered or has been administered an antiplatelet agent, the method comprising: (a) determining that the subject has an abnormal result for evaluation of one or more clotting parameters; and (b) after (a), administering to the subject in need thereof an effective amount of a composition comprising platelets or platelet derivatives and an incubating agent comprising one or more salts, a buffer, optionally a cryoprotectant, and optionally an organic solvent.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
Targeting tissue factor to activated platelets
InactiveUS20120178908A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsTissue factorPlatelet
The current invention relates to procoagulant fusion proteins, polynucleotides that encode said fusion proteins and cells that expresses said fusion proteins. Furthermore, the current invention relates to fusion proteins for use as a medicament. Individuals that have a coagulopathy, such as haemophilia A and B with or without inhibitors, may be treated with fusions proteins of the current invention.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Antibodies That Are Capable of Specifically Binding Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
ActiveUS20130142804A1Suitable for useImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsNucleotideFactor ii
The invention relates to antibodies that are capable of specifically binding tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), neutralising free TFPI and reducing the clotting time of blood. Furthermore, the invention relates to polynucleotides that encode such antibodies and to cells that comprise the polynucleotides or that express the antibodies of the invention. Such antibodies have utility in the treatment of subjects with a coagulopathy, alone as well as in combination with a second agent.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Antibodies that are capable of specifically binding tissue factor pathway inhibitor
The invention relates to antibodies that are capable of specifically binding tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), neutralizing free TFPI and reducing the clotting time of blood. Furthermore, the invention relates to polynucleotides that encode such antibodies and to cells that comprise the polynucleotides or that express the antibodies of the invention. Such antibodies have utility in the treatment of subjects with a coagulopathy, alone as well as in combination with a second agent.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Methods of treating coagulopathy
ActiveUS20100285028A1Increased activationPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesNeuraminidaseCoagulopathy
The invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing clearance of coagulation factors {e.g., VWF) and platelets from the blood stream of a patient in need thereof. The methods comprise administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of an agent that increases clearance of coagulation factors or platelets. Such an agent can be, for example, a neuraminidase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of treatment of hemorrhagic disease using a factor VIIa/tissue factor inhibitor
ActiveUS20040266672A1Reduce incidence deathPrevent coagulationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIaNematode
The present invention provides methods of treating hemorrhagic fevers where selective inhibitors of fVIIa / TF are used as a treatment for hemorrhagic fevers and have therapeutic effects which include ameliorating and / or preventing coagulopathy and inflammatory responses. These inhibitors include certain proteins which are part of a family termed Nematode-Extracted Anticoagulant Proteins ("NAPs"). Other inhibitors include Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor ("TFPI") and TFPI analogs.
Owner:DENDREON PHARMA LLC
Thrombosomes as an anticoagulant reversal agent
PendingUS20210046120A1Treatment being stoppedTreatment with the anticoagulant can be continuedInorganic non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOrganic solventThrombus
In some embodiments provided herein is a method of treating a coagulopathy in a subject, the method including administering to the subject in need thereof an effective amount of a composition including platelets or platelet derivatives and an incubating agent including one or more salts, a buffer, optionally a cryoprotectant, and optionally an organic solvent.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
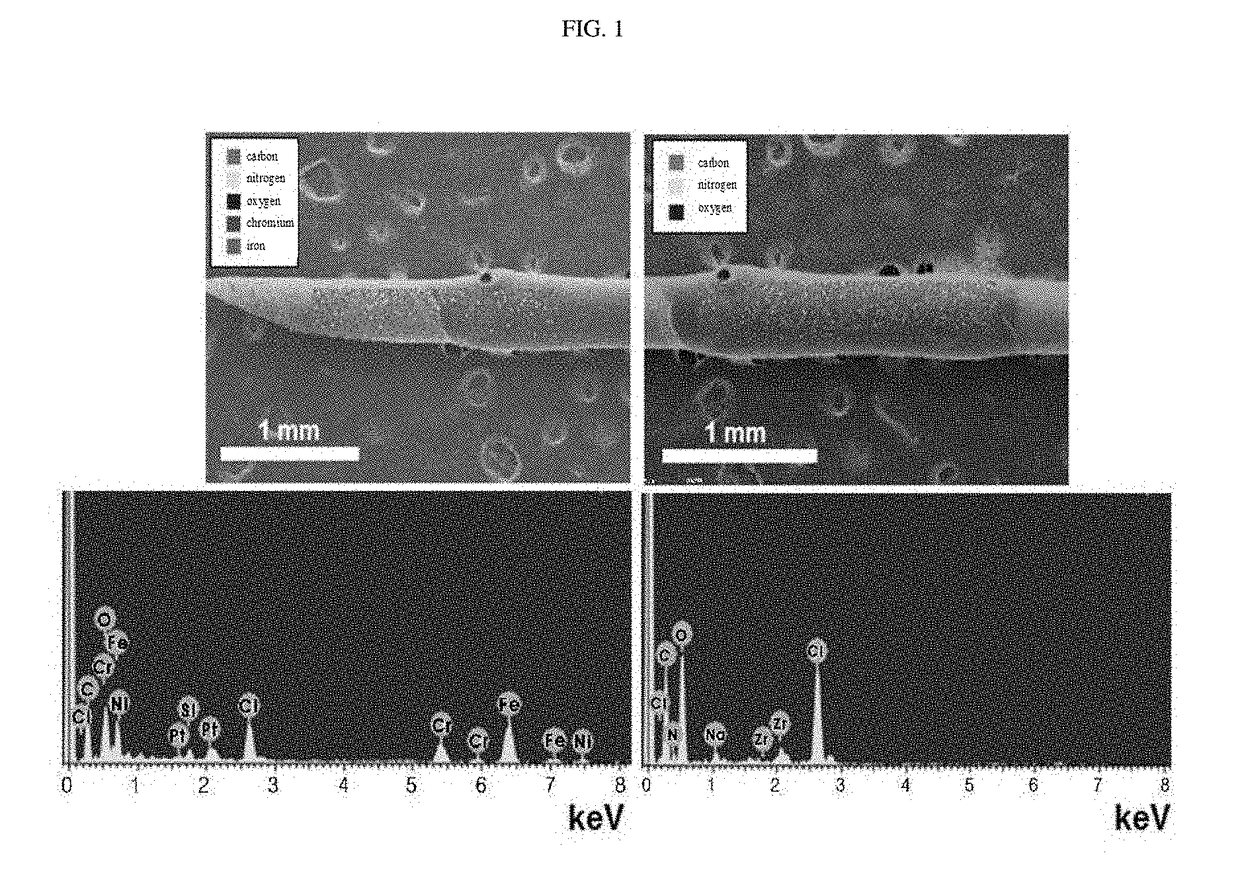
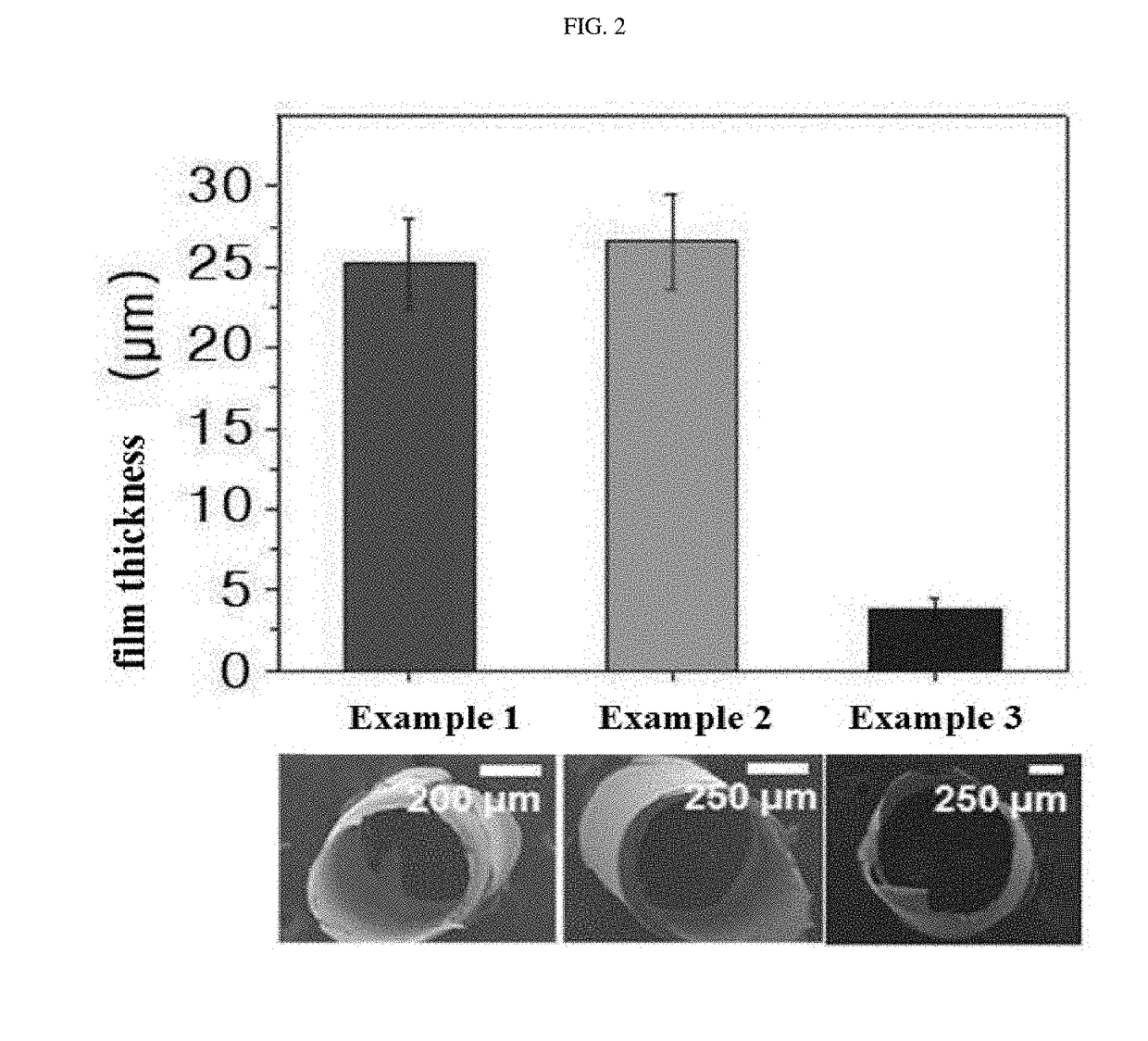
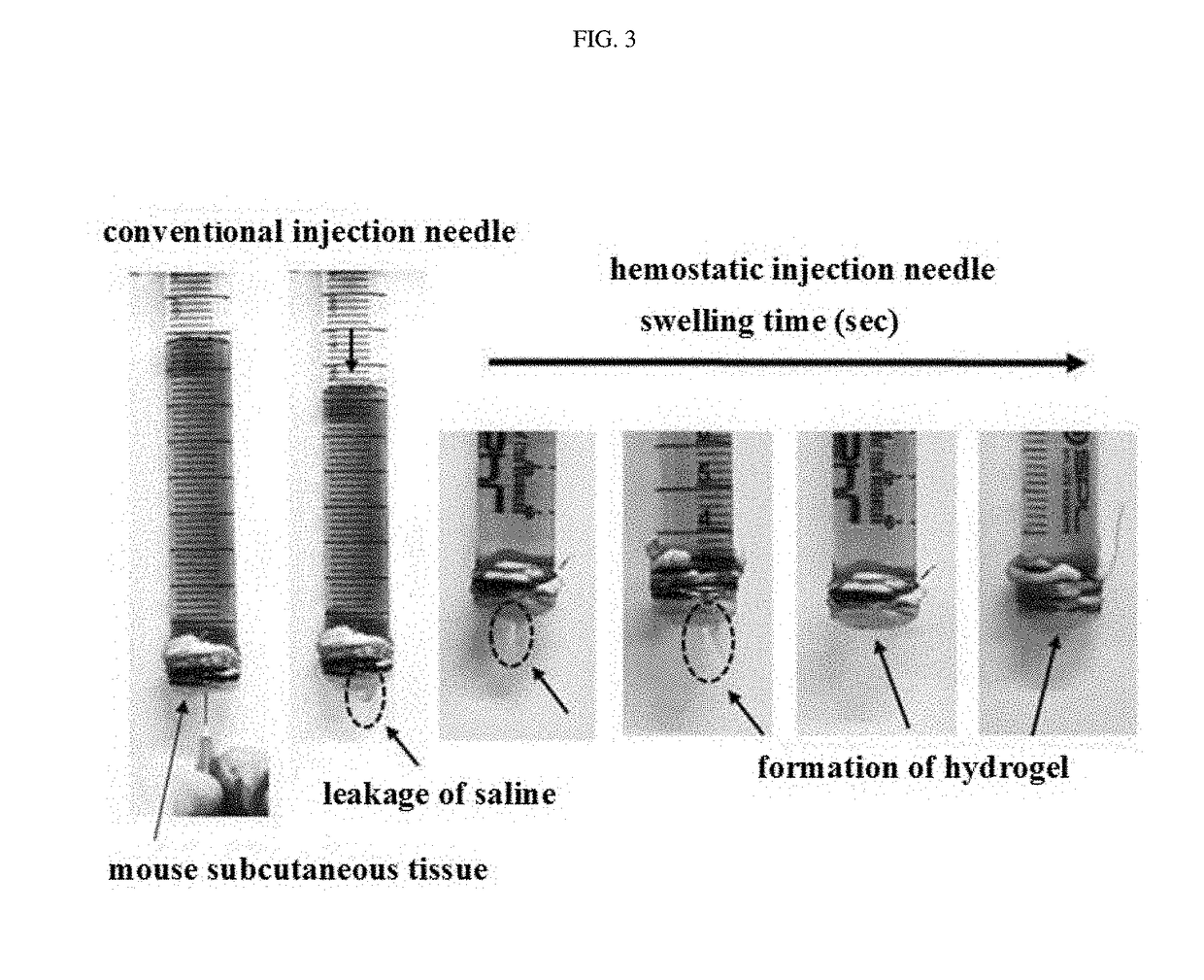
Hemostatic injection needle coated with crosslinked chitosan having catechol group and oxidized catechol group
ActiveUS20180085500A1Avoid bleedingSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCrosslinked chitosanCross-link
The present invention relates to a hemostatic injection needle coated with a chitosan in which a catechol group and an oxidized catechol group are introduced and cross-linked. The hemostatic injection needle according to the present invention can suppress bleeding during and after injection, and thus can be effectively used for injection not only into coagulopathy patients, including diabetic patients, patients under anticancer treatment, and haemophilia patients, who have a low hemostatic ability, but also into patients showing blood rejection responses, and children.
Owner:INNOTHERAPY
Freeze-dried platelet derivative compositions for treating anticoagulant-induced coagulopathy
PendingUS20220279777A1Restore hemostasisIncreased bleeding potential of a subjectPeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processAnticoagulant AgentPlatelet
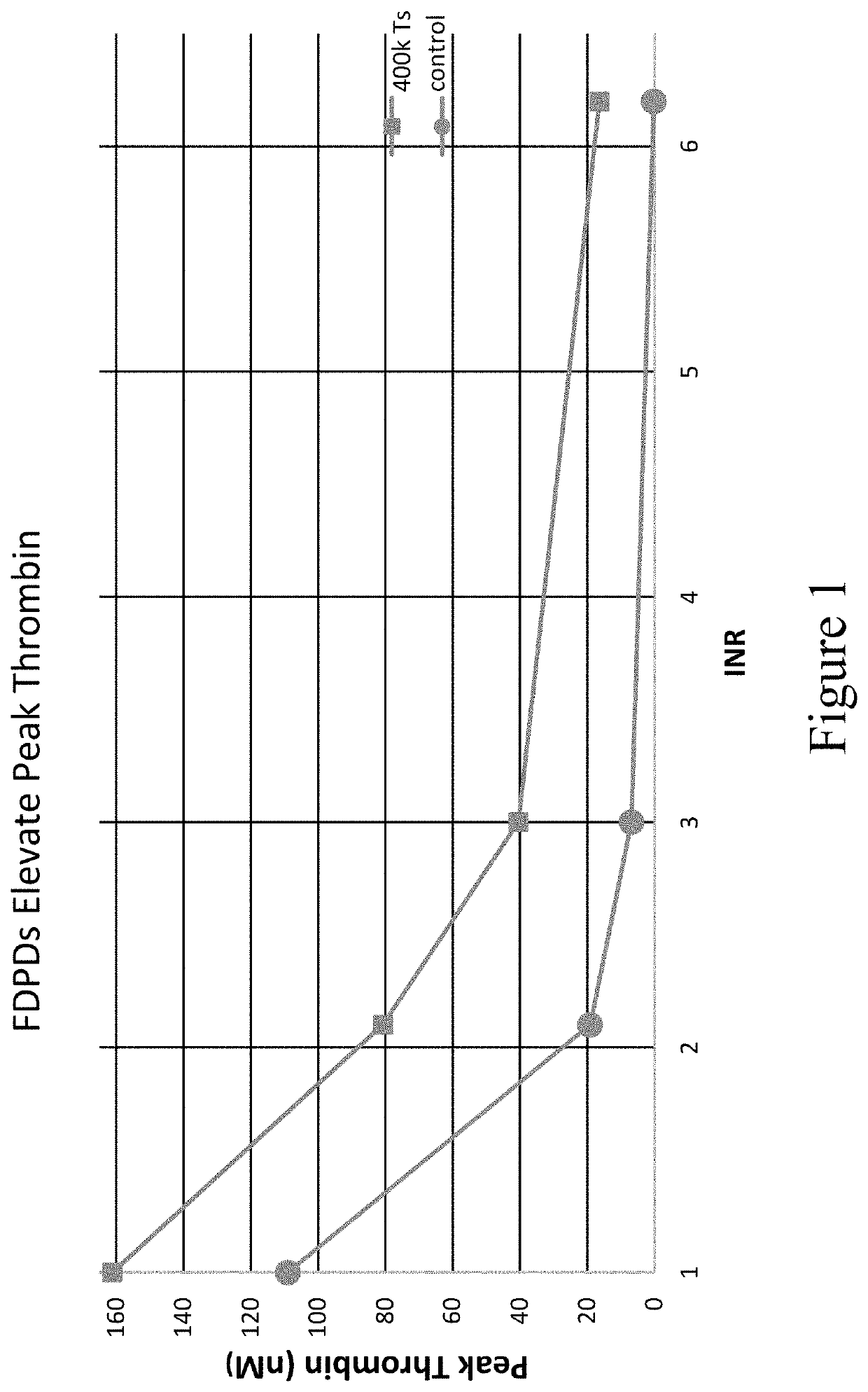
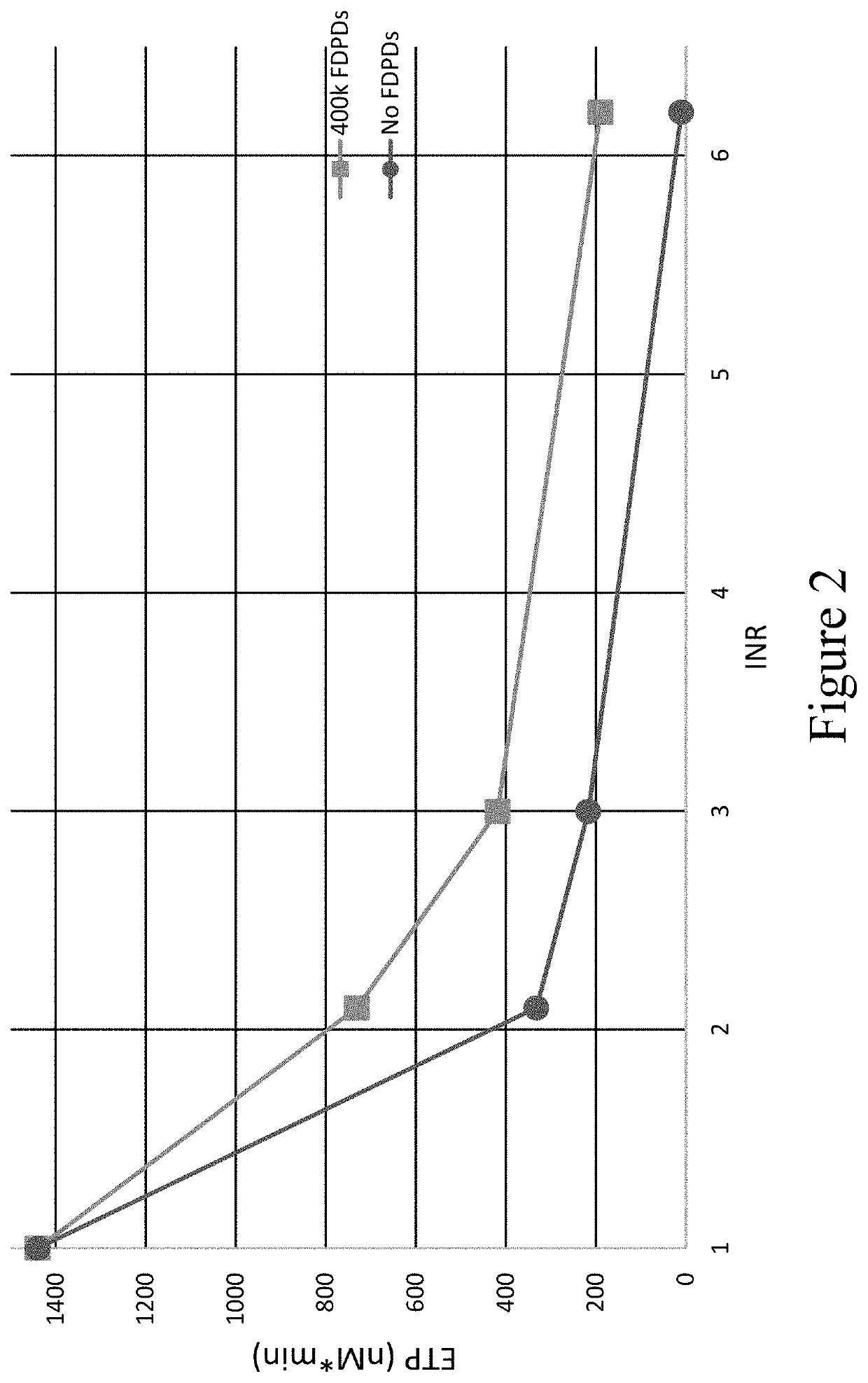
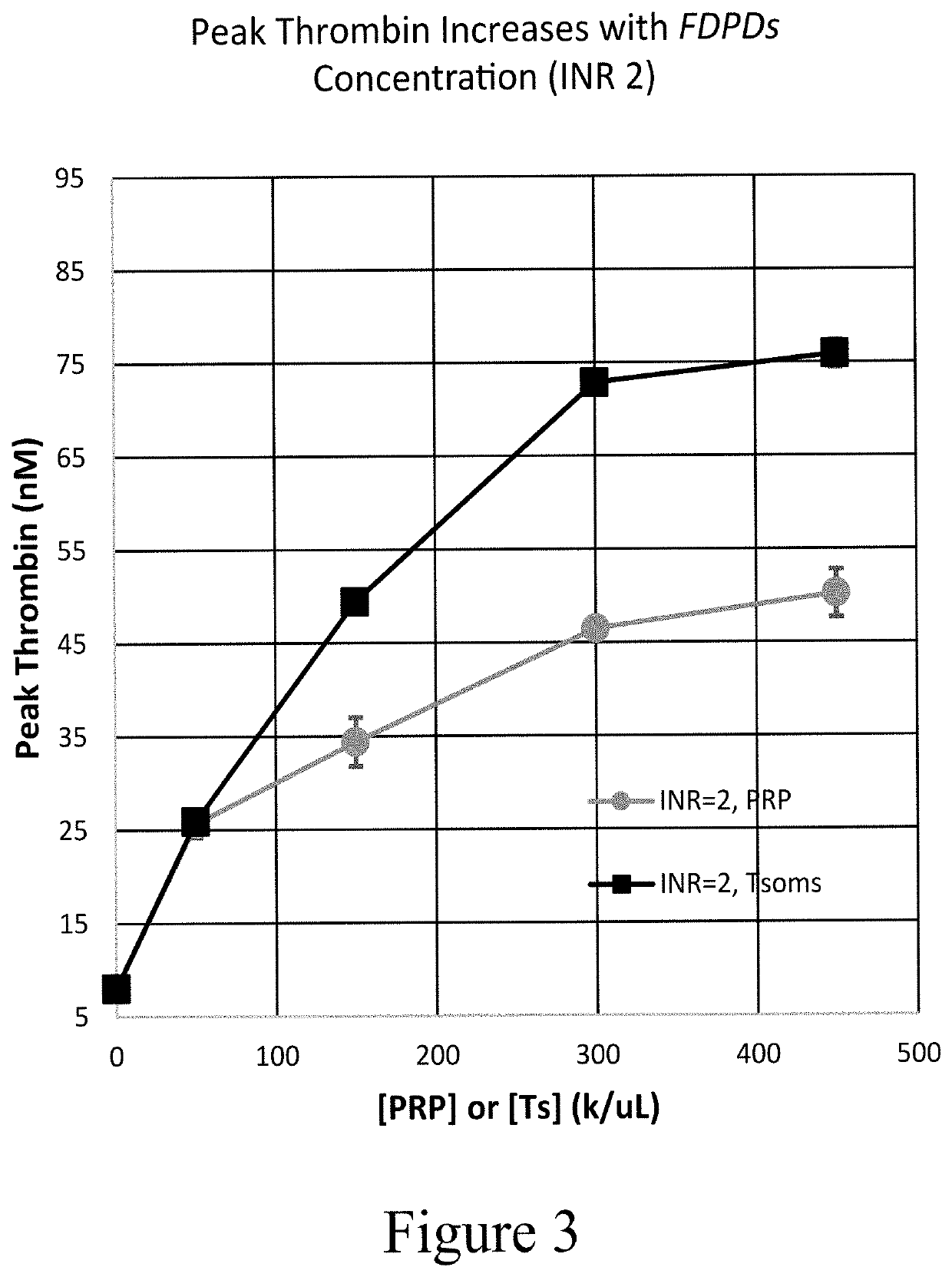
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a coagulopathy in a subject. Such methods can include administering to the subject in need thereof, for example because they have been administered an anticoagulant agent, an effective amount of a composition including platelets, or in illustrative embodiments platelet derivatives, and in further illustrative embodiments freeze-dried platelet derivatives (FDPDs). Various properties of exemplary embodiments of such methods and platelet derivatives used therein, as well as numerous additional aspects and embodiments are provided herein.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
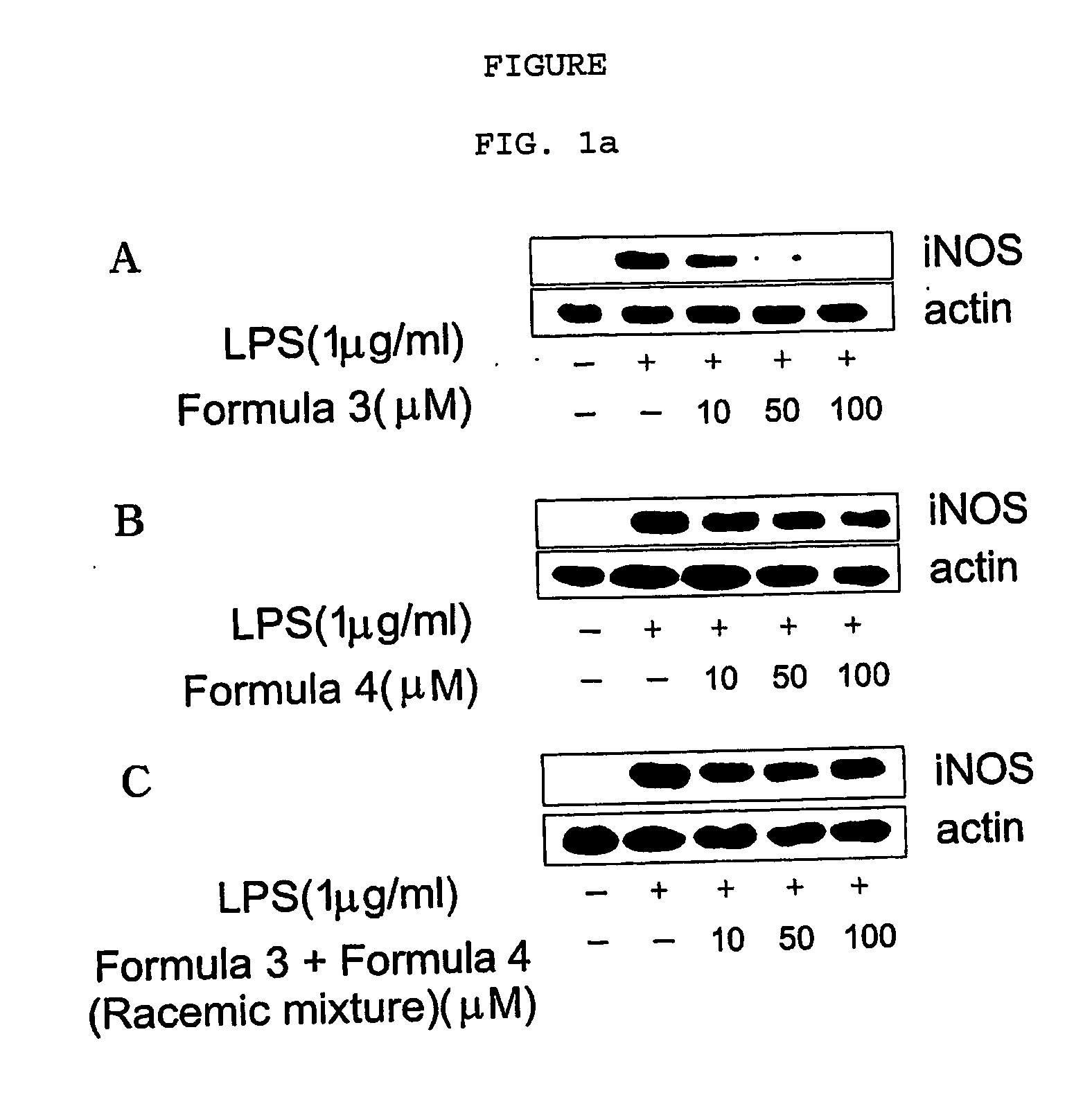
Novel enantiomers of etrahydroisoquinoline derivatives and theirpharmaceutically acceptable salts, their preparations and pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS20060058346A1Suppress inductionReduce the possibilityBiocideOrganic chemistryEnantiomerPlatelet inhibition
The disclosure concerns novel enantiomers of tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, their preparations and pharmaceutical compositions. The enantiomers of tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives are provided which are useful in stimulating heart rate and hypotensive activity, inhibitory activity against platelet aggregation, and suppressive against inducible NO synthase. The enantiomers of tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are effective for treating congestive heart failure, hypertension, thrombosis, inflammation, septicemia, cardiac insufficiency, and disseminated intravascular coagulopathy.
Owner:YUN CHOI HYE SOOK +1
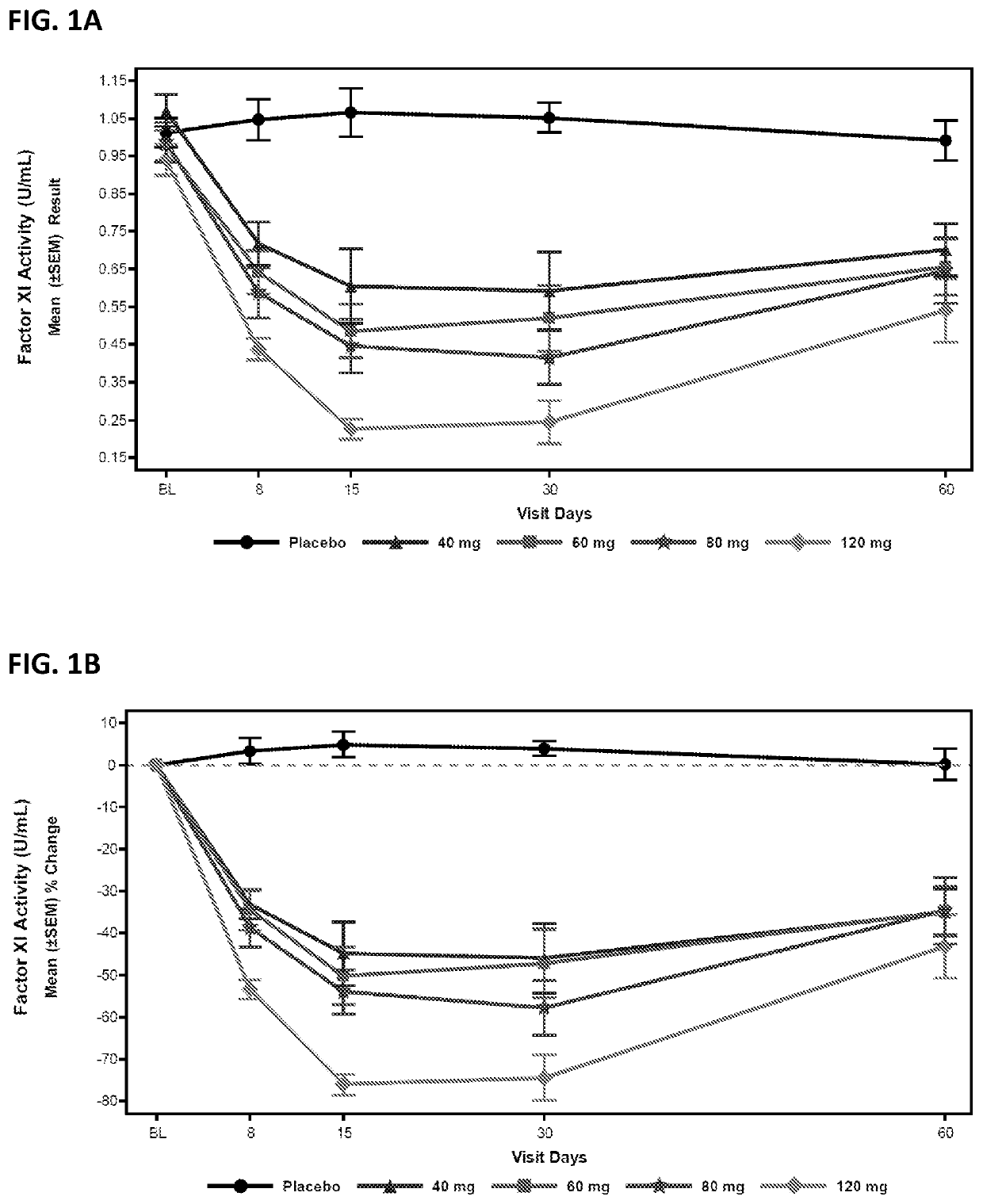
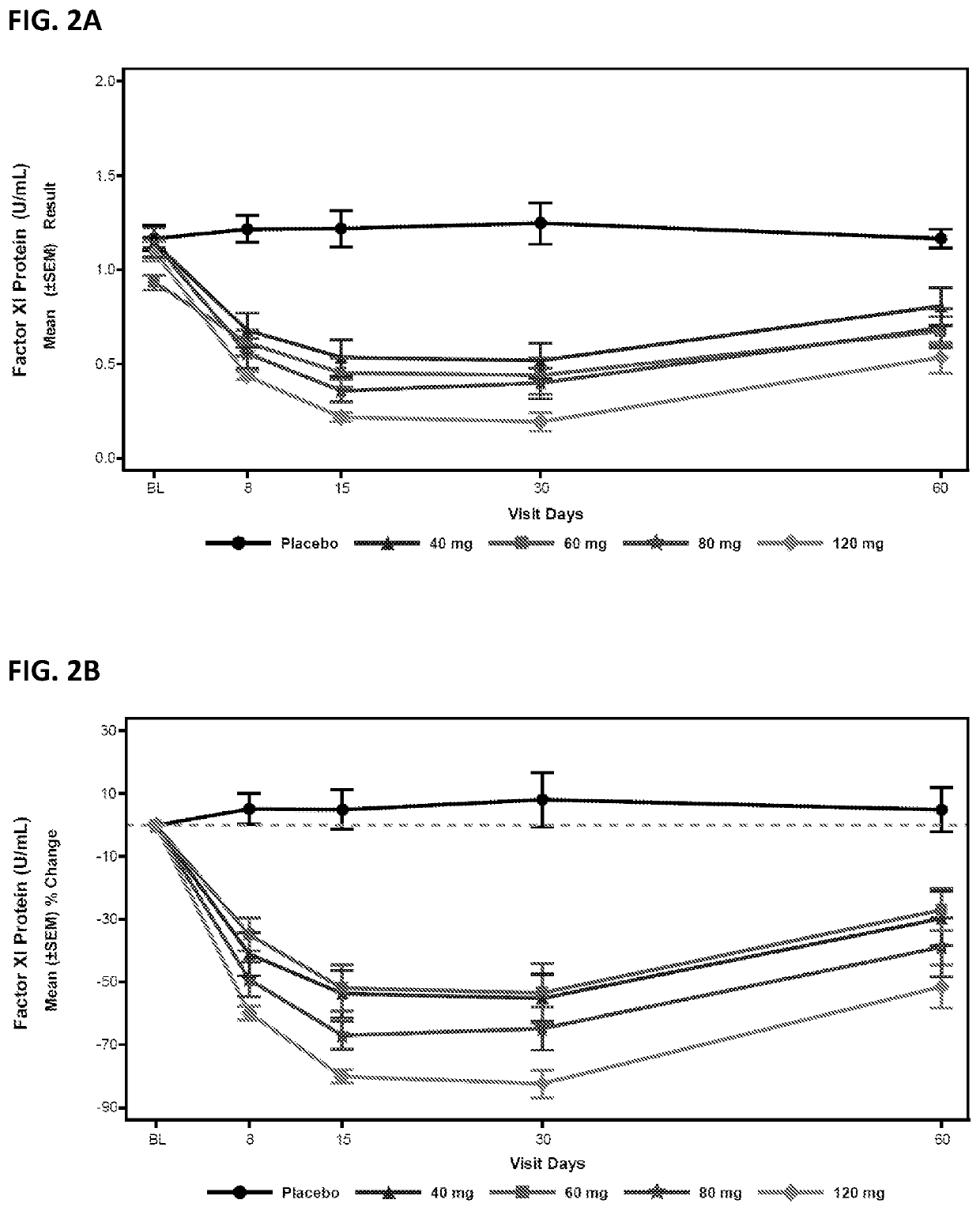
Compounds and methods for reducing fxi expression
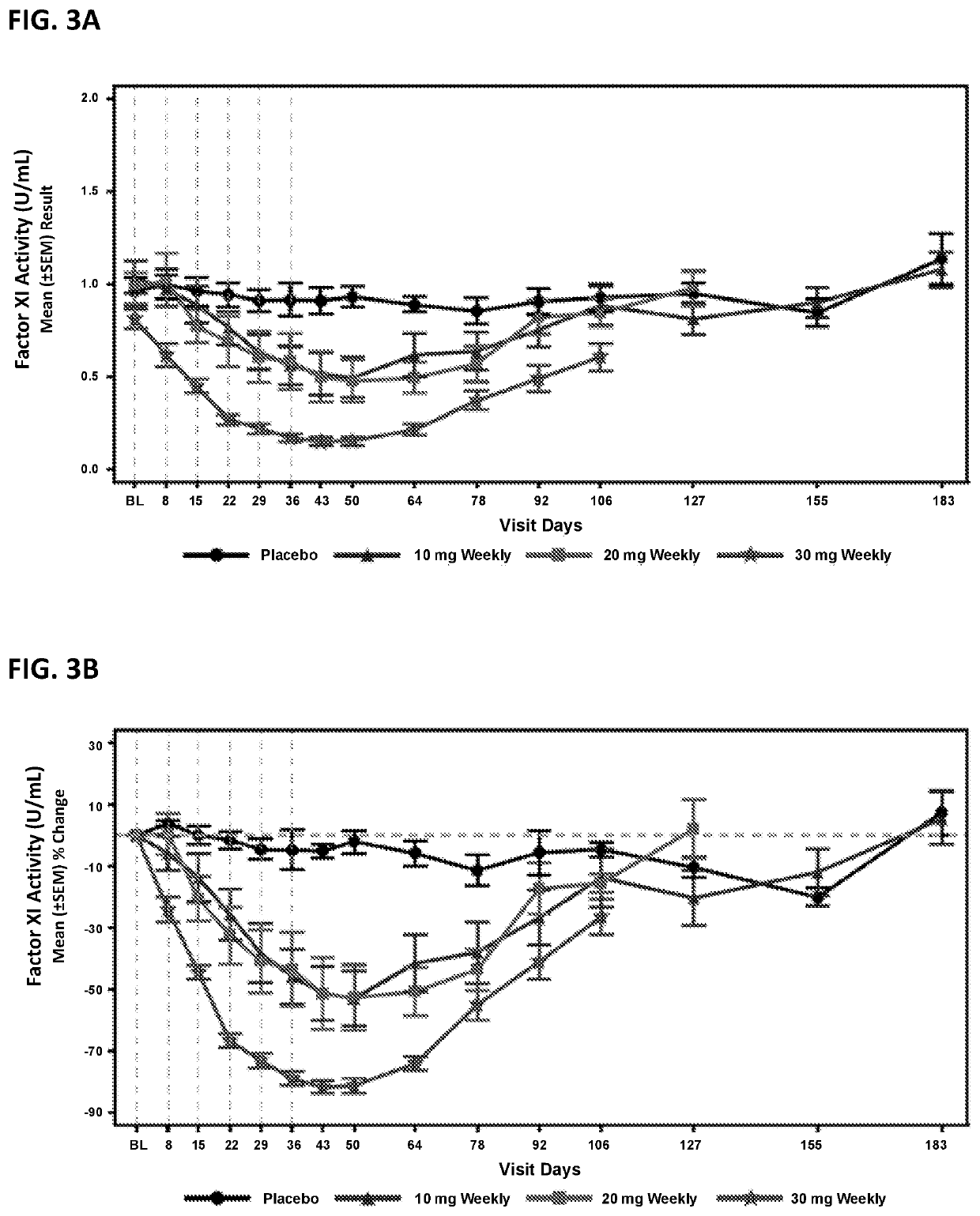
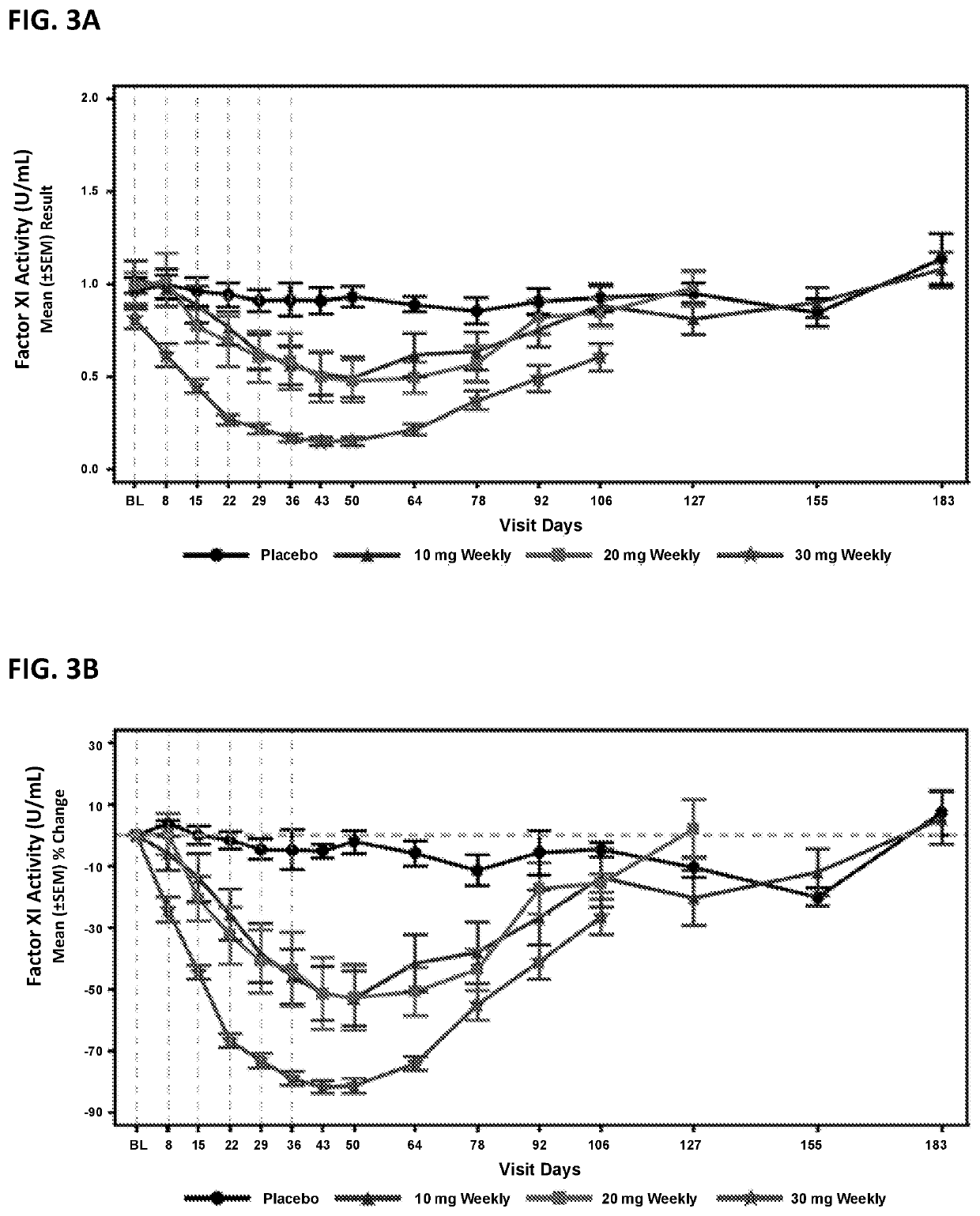
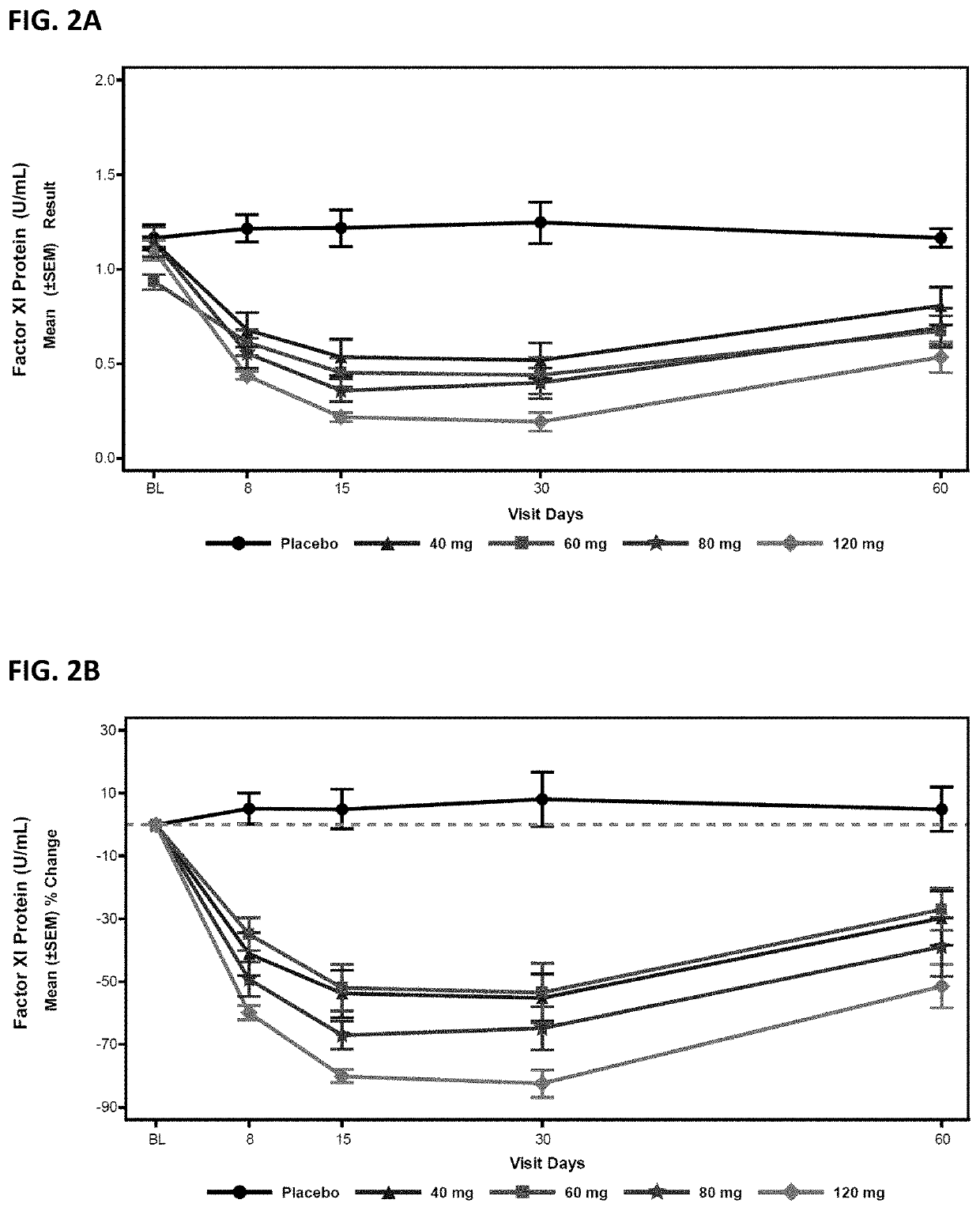
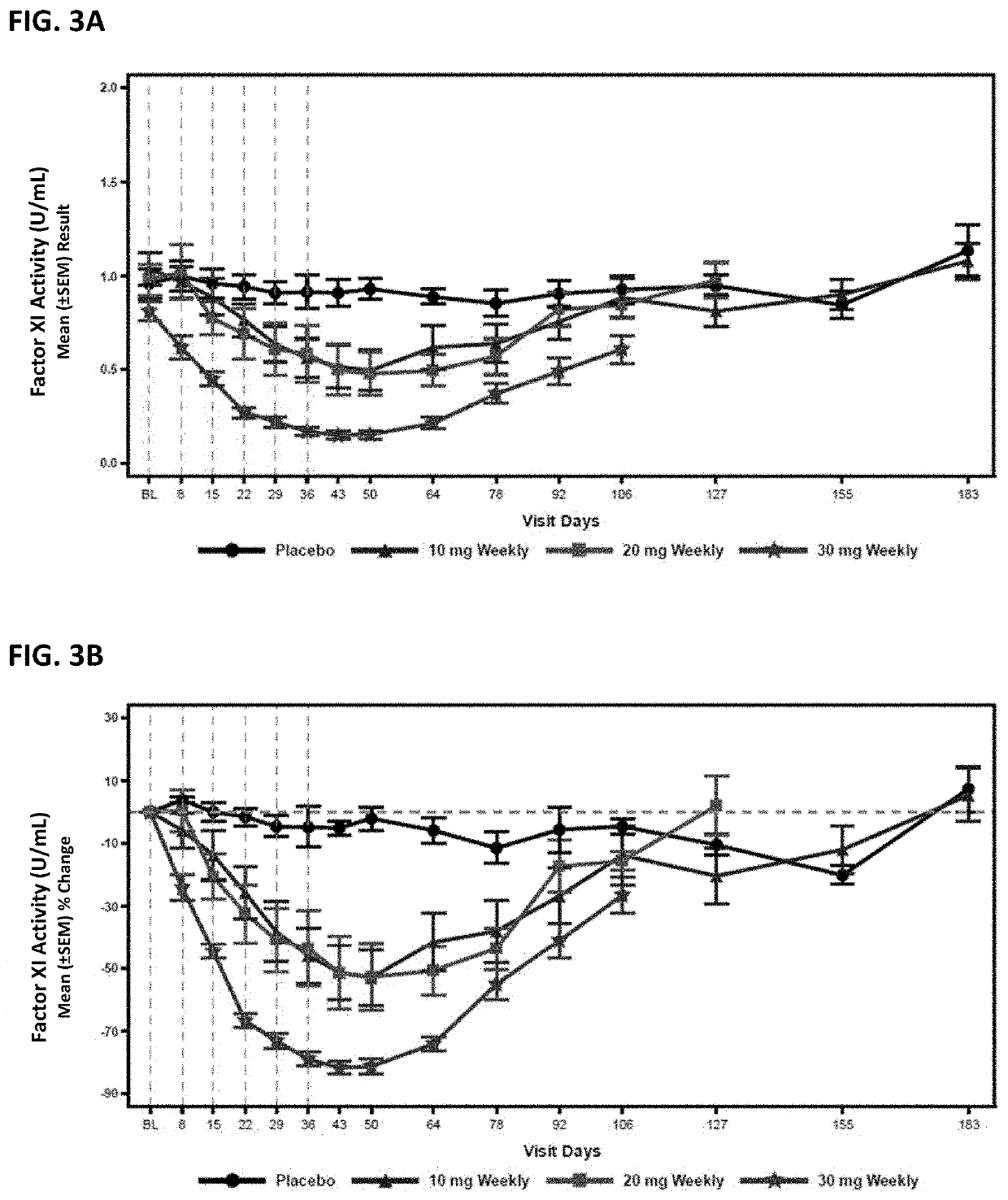
ActiveUS20210087569A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce FXI protein activityCarbohydrate active ingredientsUrinary disorderDiseaseThrombus
Provided are compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the amount or activity of FXI RNA in a cell or subject, and in certain instances reducing the amount of FXI protein in a cell or subject. Such compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions are useful to prevent, treat, or ameliorate at least one symptom of a thromboembolic condition without a significant increase in a bleeding risk. Such thromboembolic conditions include deep vein thrombosis, venous or arterial thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, thrombosis associated with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), including thrombosis associated with dialysis, or other procoagulant condition. Such symptoms include decreased blood flow through an affected vessel, death of tissue, and death.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Antibodies Against Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor
ActiveUS20130251722A1Shorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsFactor iiCoagulopathy
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Masp isoforms as inhibitors of complement activation
The present invention relates to novel ficolin-associated polypeptides, and polypeptides derived from these ficolin-associated polypeptides for the use in the treatment of conditions associated with inflammation, apoptosis, autoimmunity, coagulation, thrombotic or coagulopathic related diseases, as well as the use as biomarkers. The present invention further relates to antibodies recognising such novel ficolin-associated polypeptides, and polypeptides derived thereof, nucleic acid molecules encoding such polypeptides, vectors and host cells used in the production of the polypeptides.
Owner:OMEROS CORP
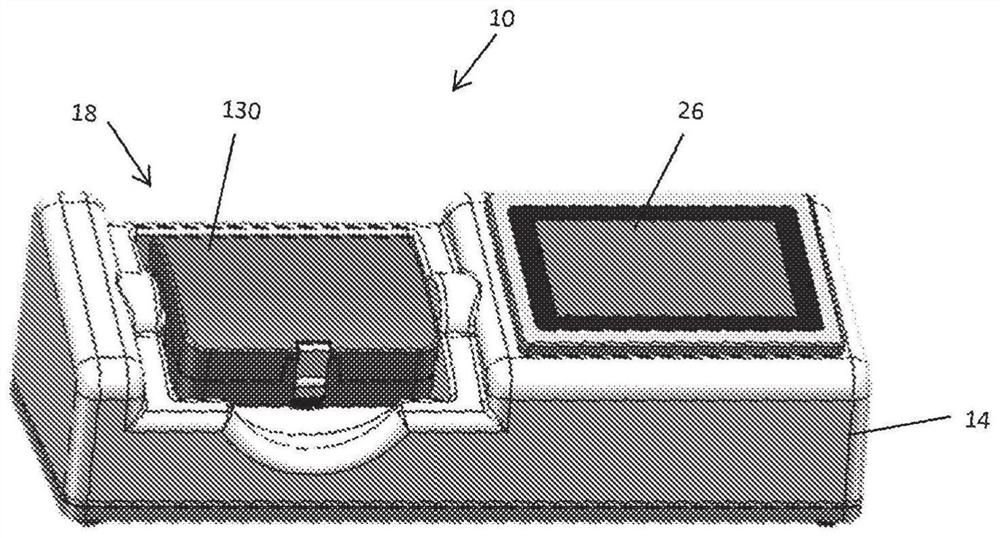
Coagulation test device, system, and method of use
PendingCN113906295ASolve key problemsFlow propertiesLaboratory glasswaresEtiologyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A coagulation test device for measuring clotting time and clot characteristics of a whole blood sample under different hemostatic conditions. Results of the test are used as an aid in management of patients with coagulopathy of unknown etiology in order to help the physician determine appropriate clinical action to arrest bleeding in a patient.
Owner:COAGULATION SCI LLC
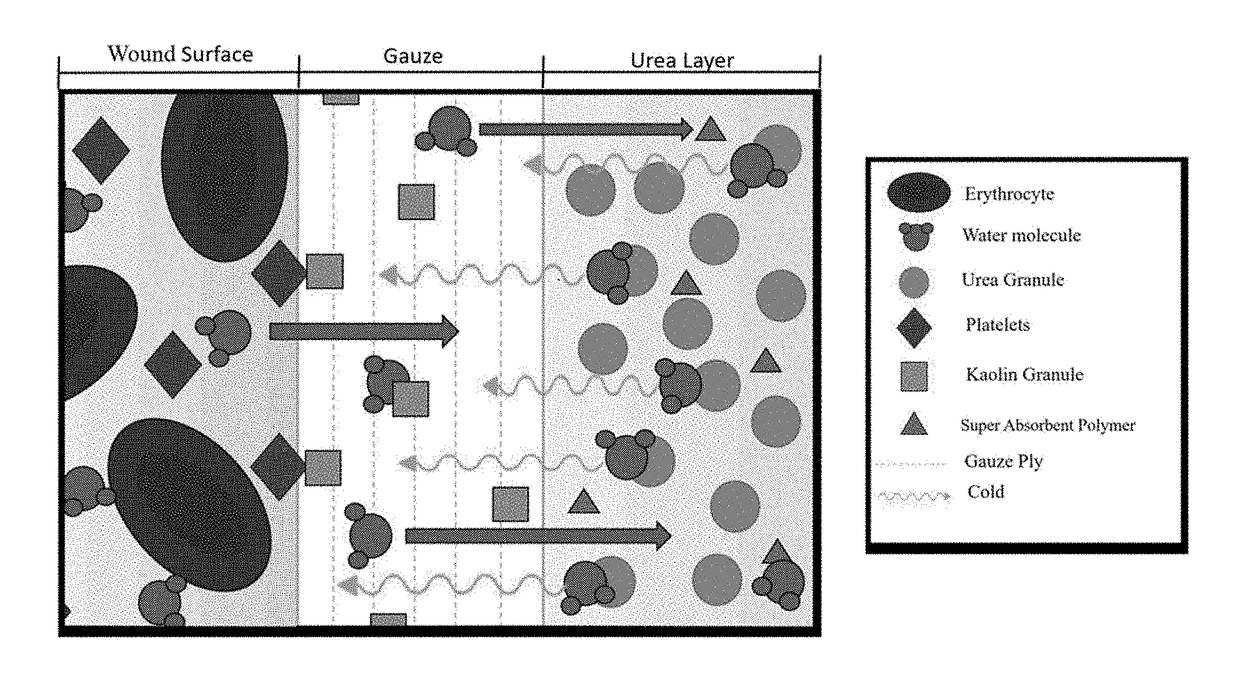
Factor concentration gauze combined with endothermic reaction used to combat very proximal traumatic amputation hemorrhaging
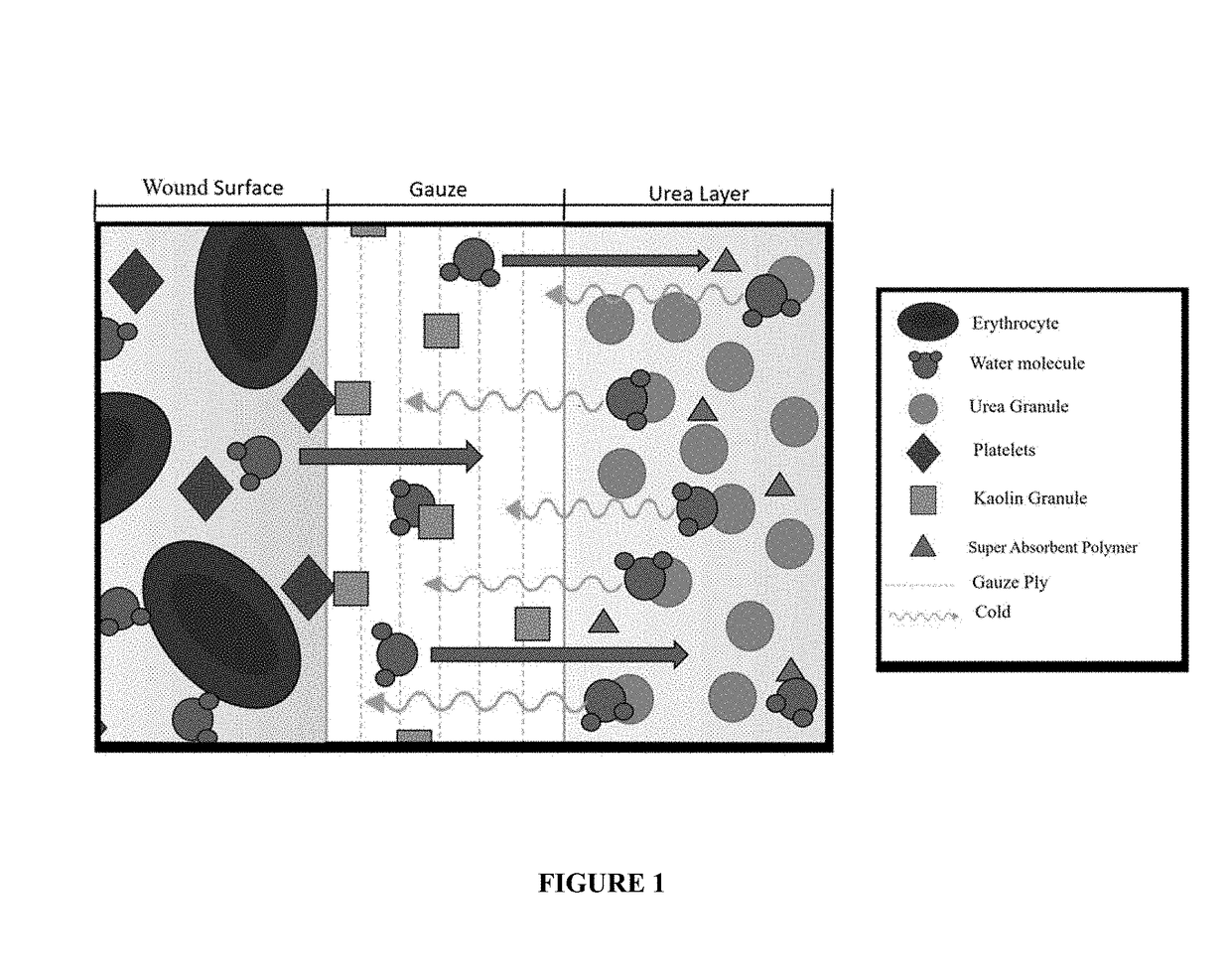
InactiveUS20180303675A1Minimize bleedingEnhanced platelet activityNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersArteriolar VasoconstrictionInjury mouth
The disclosed invention is a device and method of use for gauze utilized in the treatment of hemorrhage. In an embodiment the device combines clotting factor concentrator gauze and urea in order to slow hemorrhage and prevent hemorrhage induced coagulopathy. In an embodiment, the gauze is comprised of a first layer comprised of gauze and a second layer embedded with urea. The urea reacts spontaneously when it comes into contact with water, and undergoes an endothermic reaction. This endothermic reaction cools the smaller blood vessels exposed from soft tissue trauma, causing enhanced platelet activity as well as vasoconstriction to minimize the bleeding that occurs before and after the clotting cascade is activated over the entire wound surface.
Owner:JONES HANNAH MAE +4
Compounds and methods for reducing FXI expression
ActiveUS11021710B2Reduce riskDecreased blood flowCarbohydrate active ingredientsUrinary disorderDiseaseThrombus
Provided are compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the amount or activity of FXI RNA in a cell or subject, and in certain instances reducing the amount of FXI protein in a cell or subject. Such compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions are useful to prevent, treat, or ameliorate at least one symptom of a thromboembolic condition without a significant increase in a bleeding risk. Such thromboembolic conditions include deep vein thrombosis, venous or arterial thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, thrombosis associated with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), including thrombosis associated with dialysis, or other procoagulant condition. Such symptoms include decreased blood flow through an affected vessel, death of tissue, and death.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Systems and methods for identifying coagulopathies
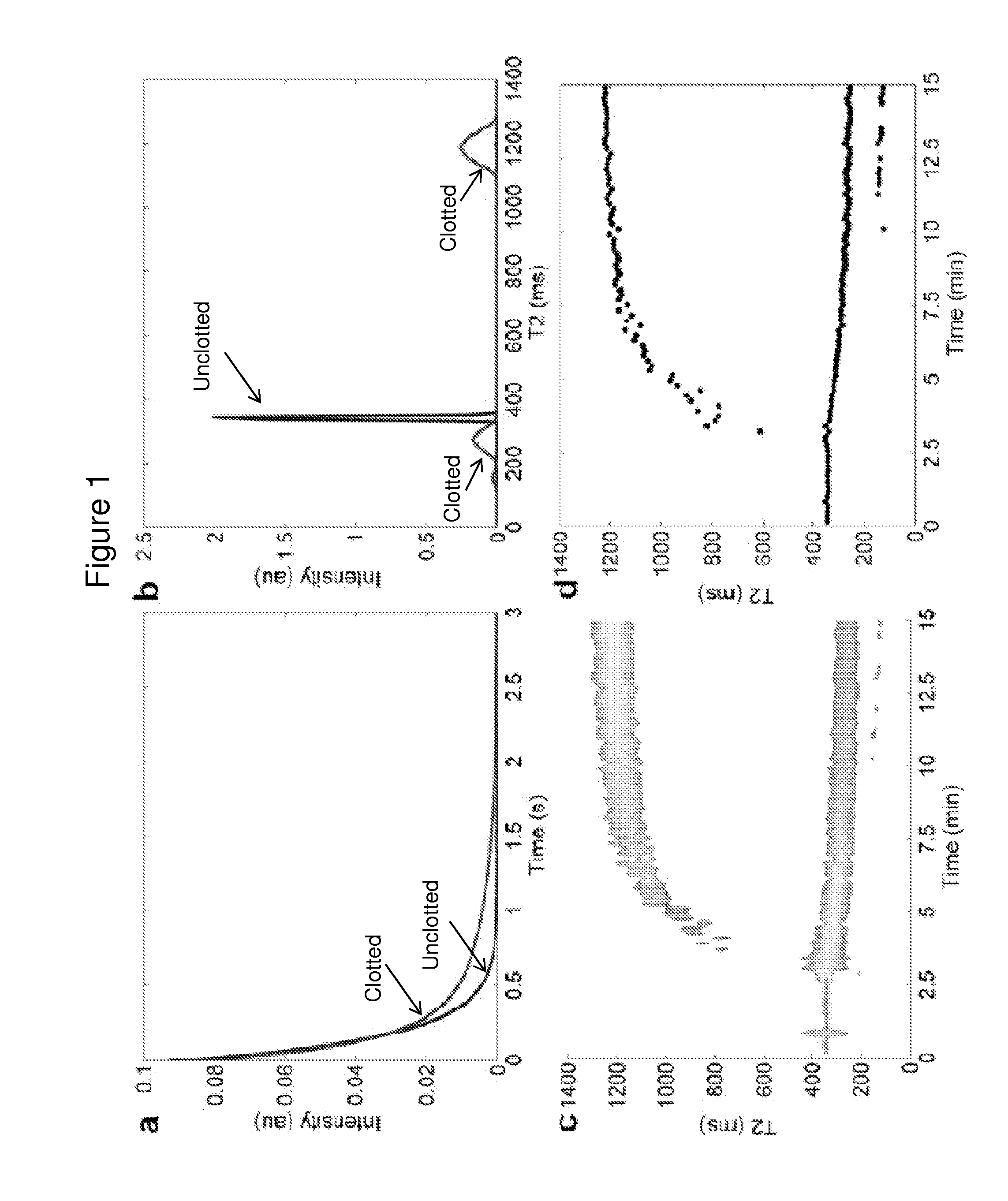
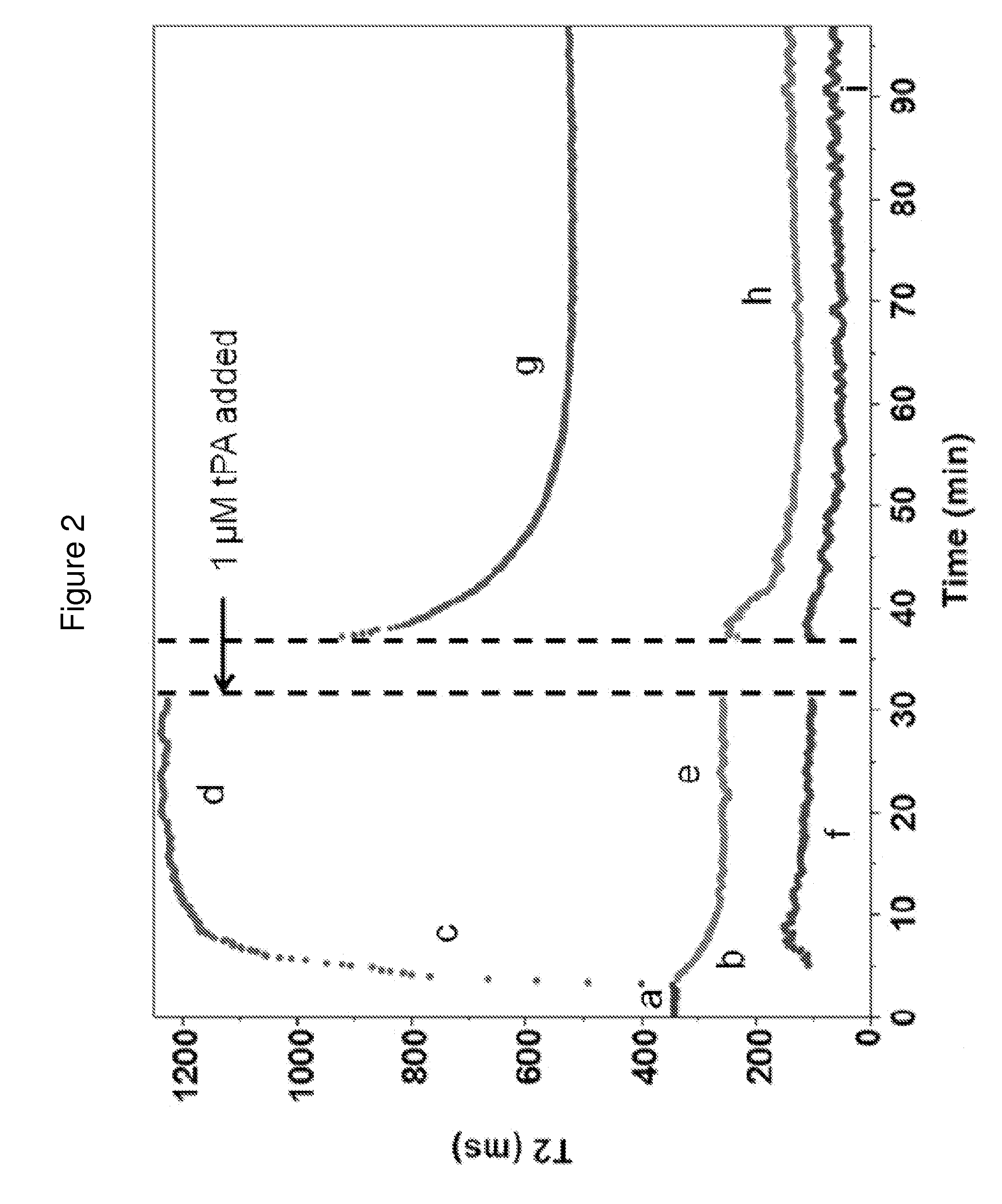
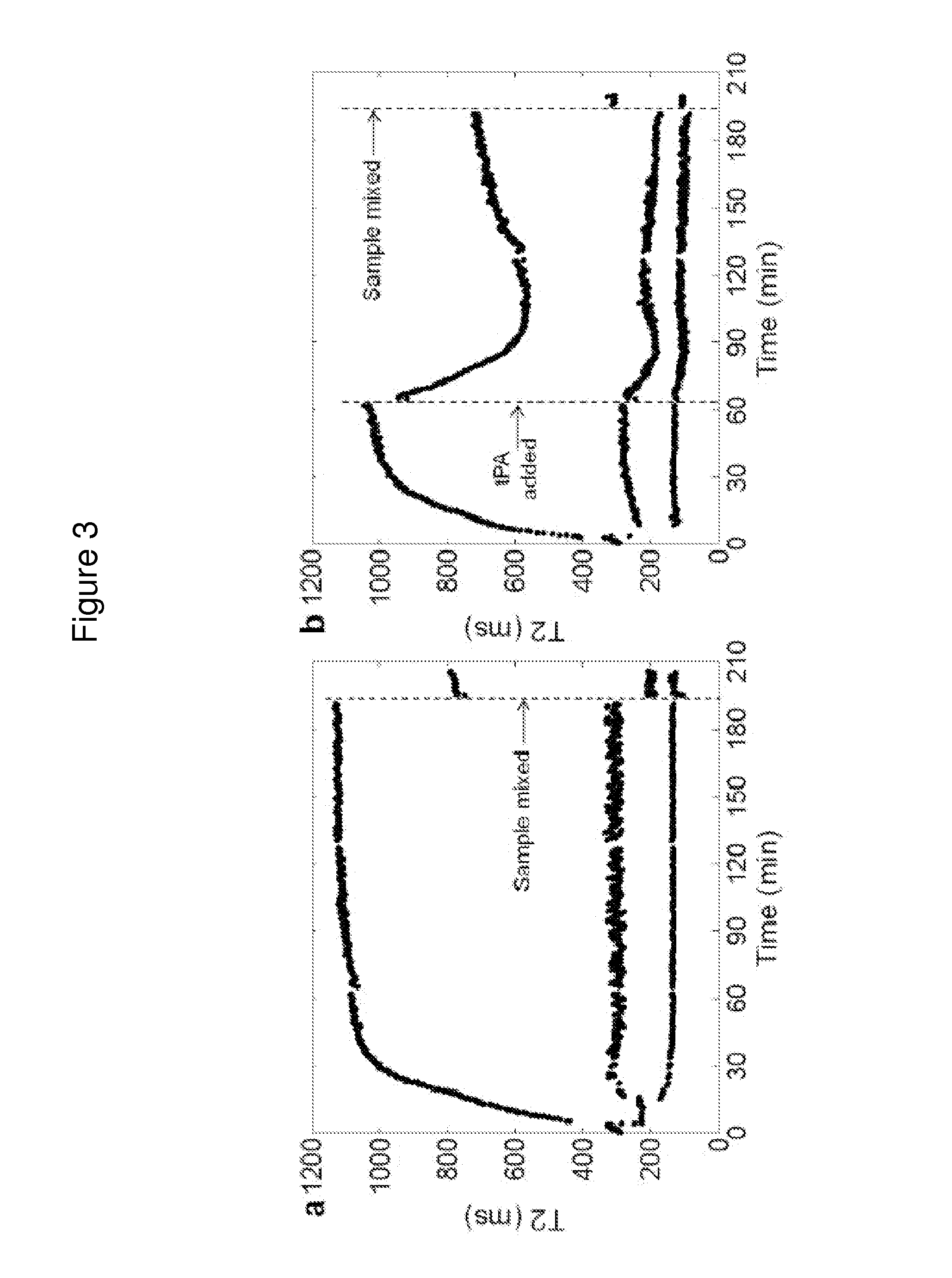
InactiveUS20170045494A1Practical and convenientRapid and reliableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceRadiology
The invention features a diagnostic platform utilizing T2 magnetic resonance to directly measure integrated reactions in whole blood samples such as clotting, clot contraction, and fibrinolysis to provide a comprehensive assessment of hemostatic parameters on a single instrument in minutes. The methods of the invention can be performed with less than 1 mL of blood and minimal sample handling.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Oligonucleotide and its derivatives, and applications thereof
InactiveCN103484460AReduced transcriptional activityAvoid influenceGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTissue factorDisease
The invention provides an oligonucleotide (5'-cagctccgcgctcggtgg-3') capable of reducing the high expression of a PML / RARalpha fusion protein related tissue factor (TF), and its derivatives, and applications of the oligonucleotide (5'-cagctccgcgctcggtgg-3') and its derivatives in the prevention and / or treatment of acute leukemia and its complications and / or other PML / RARalpha related tissue factor abnormal-high-expression or its acceptor activity abnormal-change related diseases, and / or the improvement of TF high-expression related pathology phenomena, such as coagulopathy.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compounds and methods for reducing fxi expression
PendingUS20210355497A1Reduce riskDecreased blood flowCarbohydrate active ingredientsUrinary disorderDiseaseThrombus
Provided are compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the amount or activity of FXI RNA in a cell or subject, and in certain instances reducing the amount of FXI protein in a cell or subject. Such compounds, methods, and pharmaceutical compositions are useful to prevent, treat, or ameliorate at least one symptom of a thromboembolic condition without a significant increase in a bleeding risk. Such thromboembolic conditions include deep vein thrombosis, venous or arterial thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, thrombosis associated with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), including thrombosis associated with dialysis, or other procoagulant condition. Such symptoms include decreased blood flow through an affected vessel, death of tissue, and death.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com