Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Minimize bleeding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
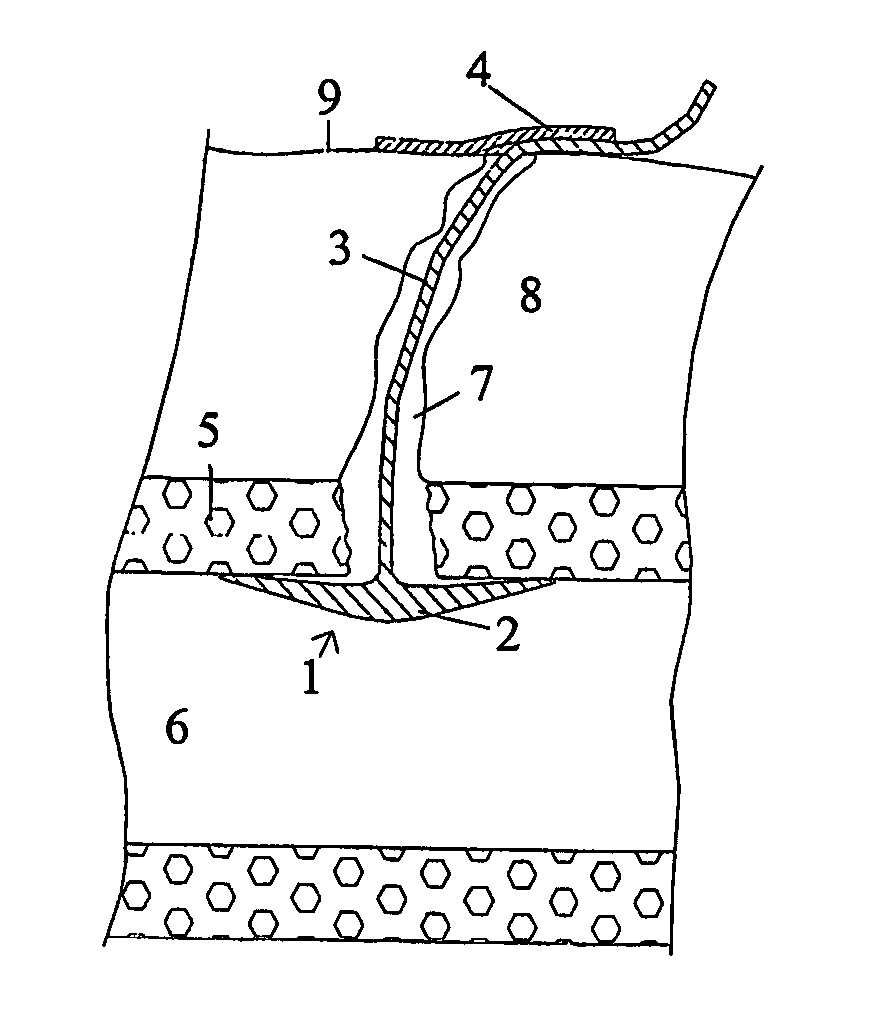
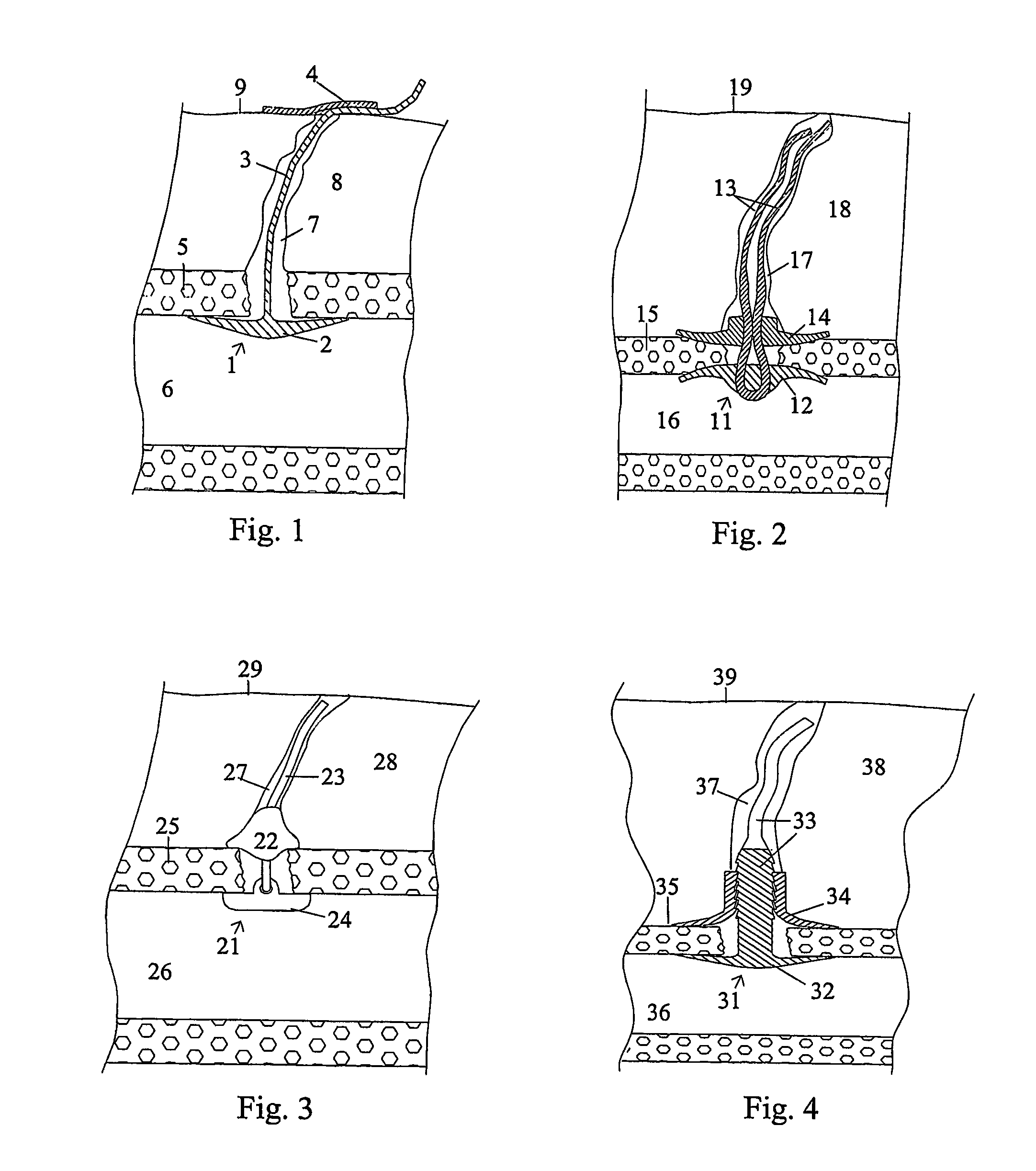
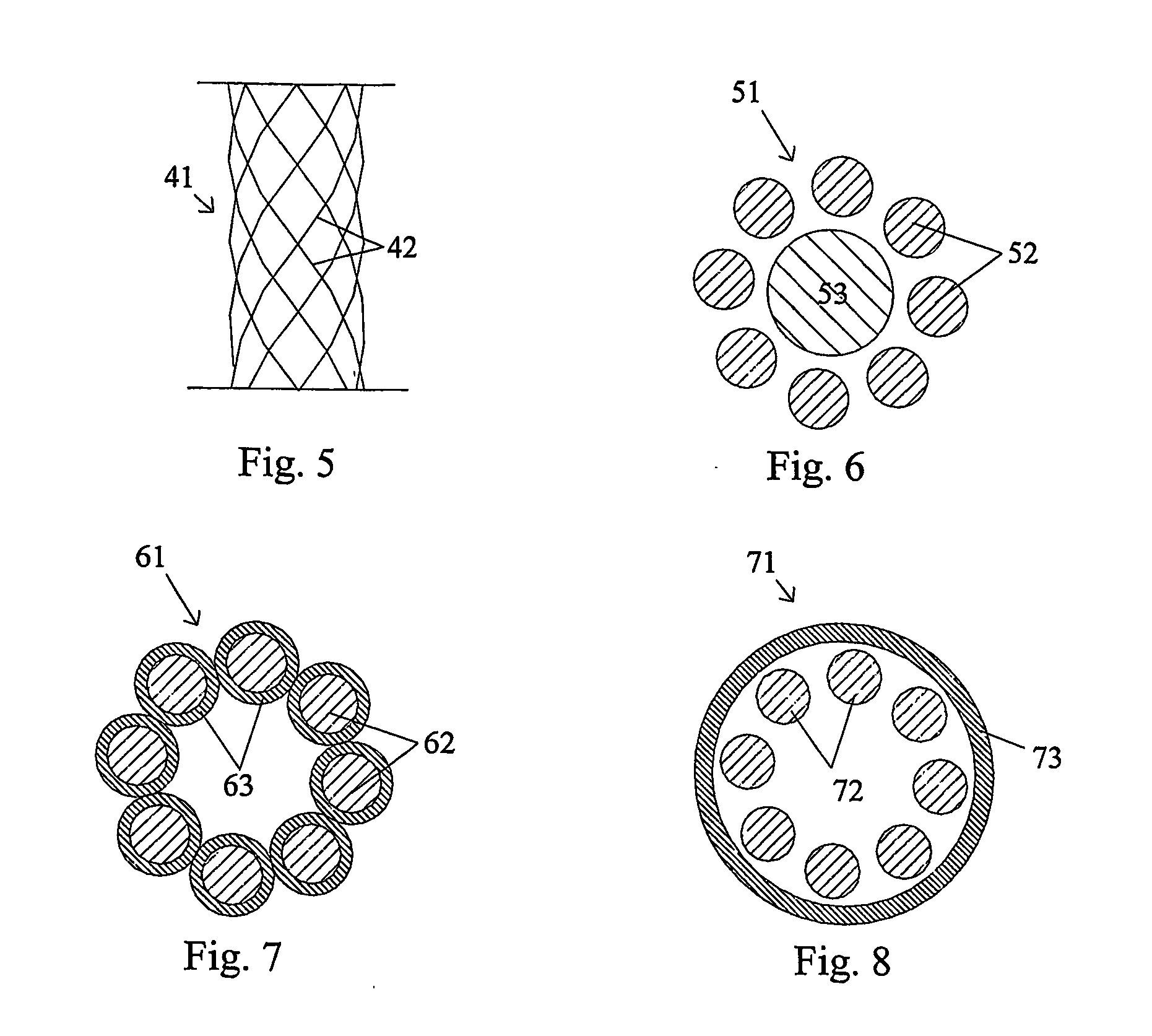
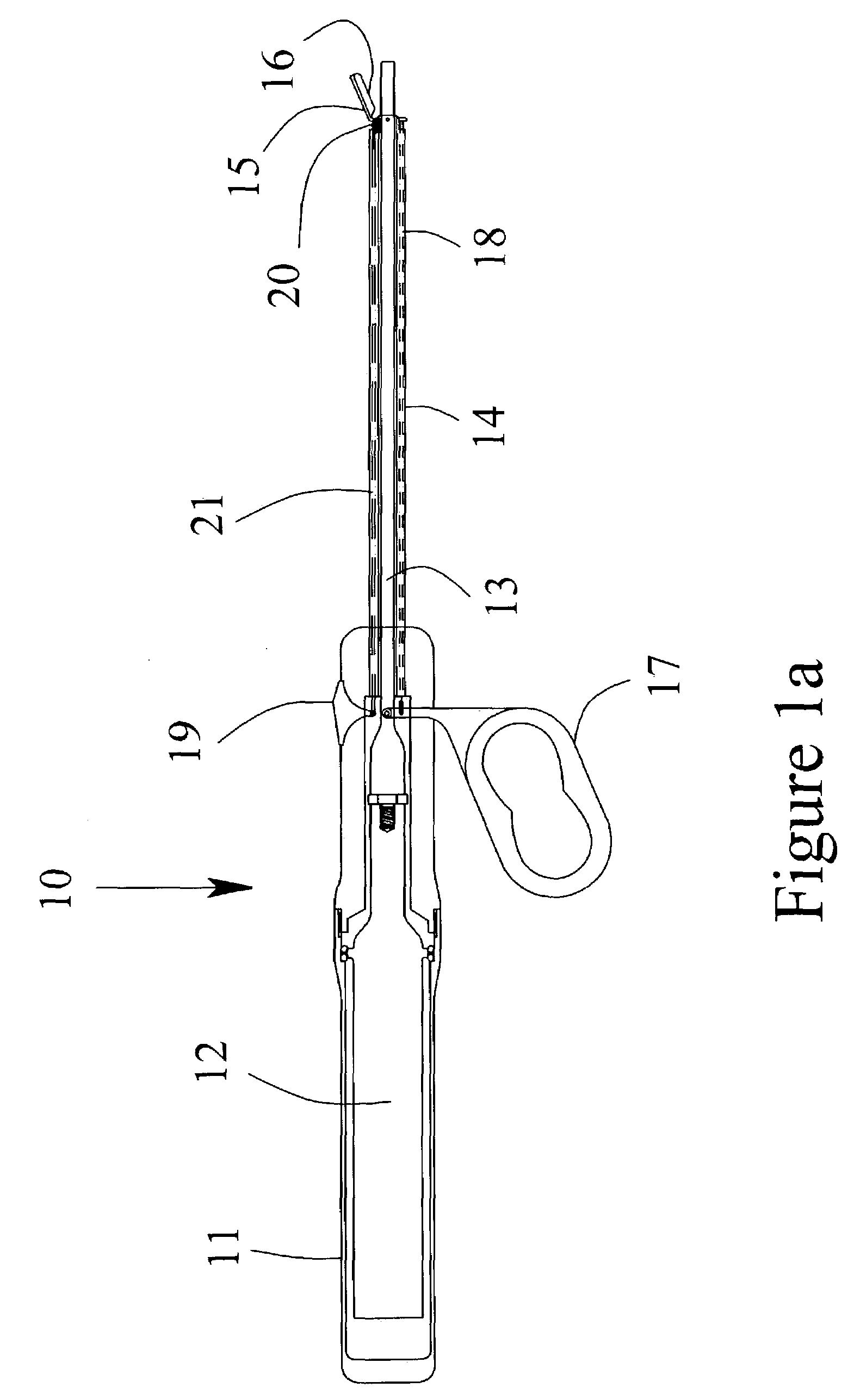
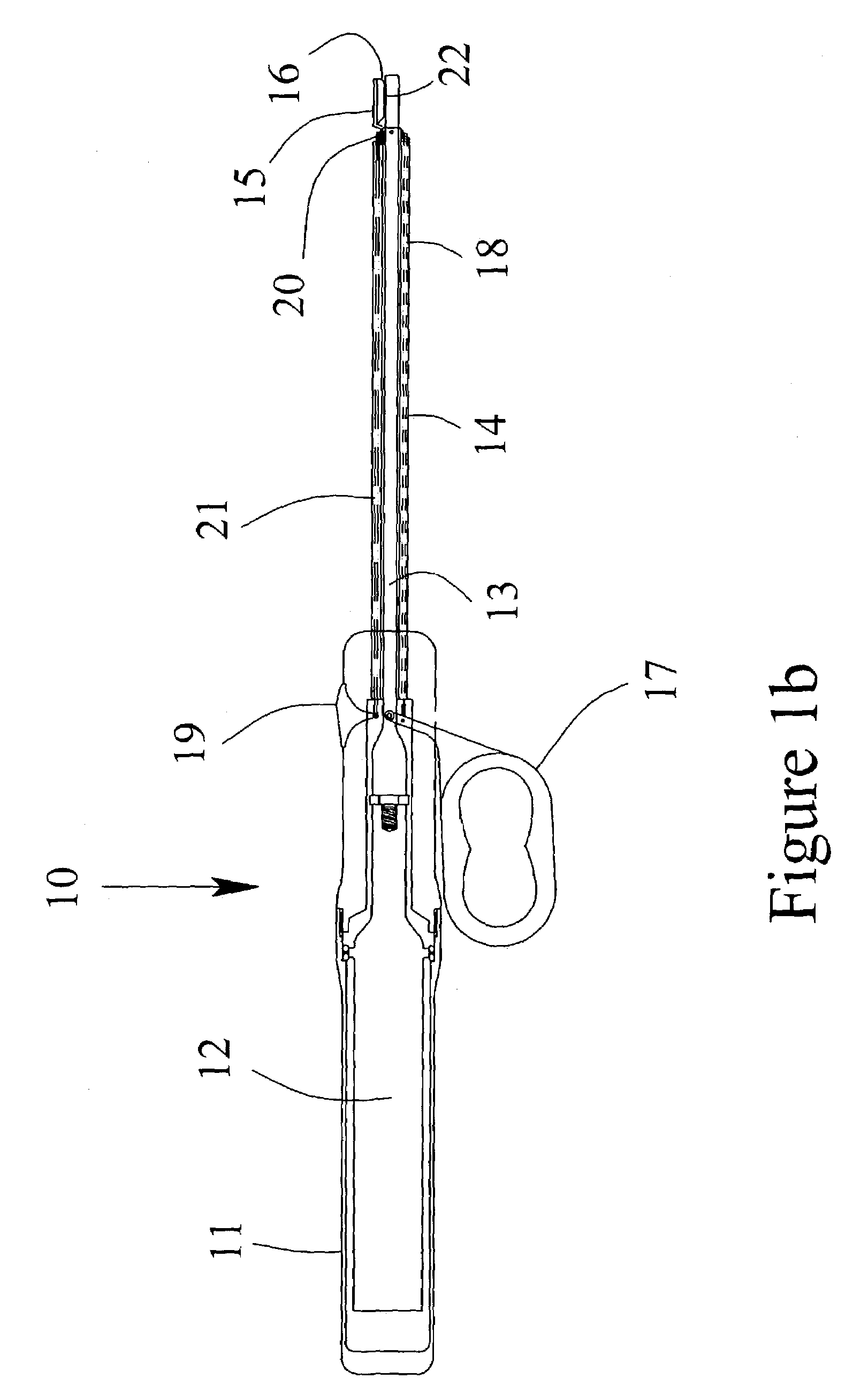
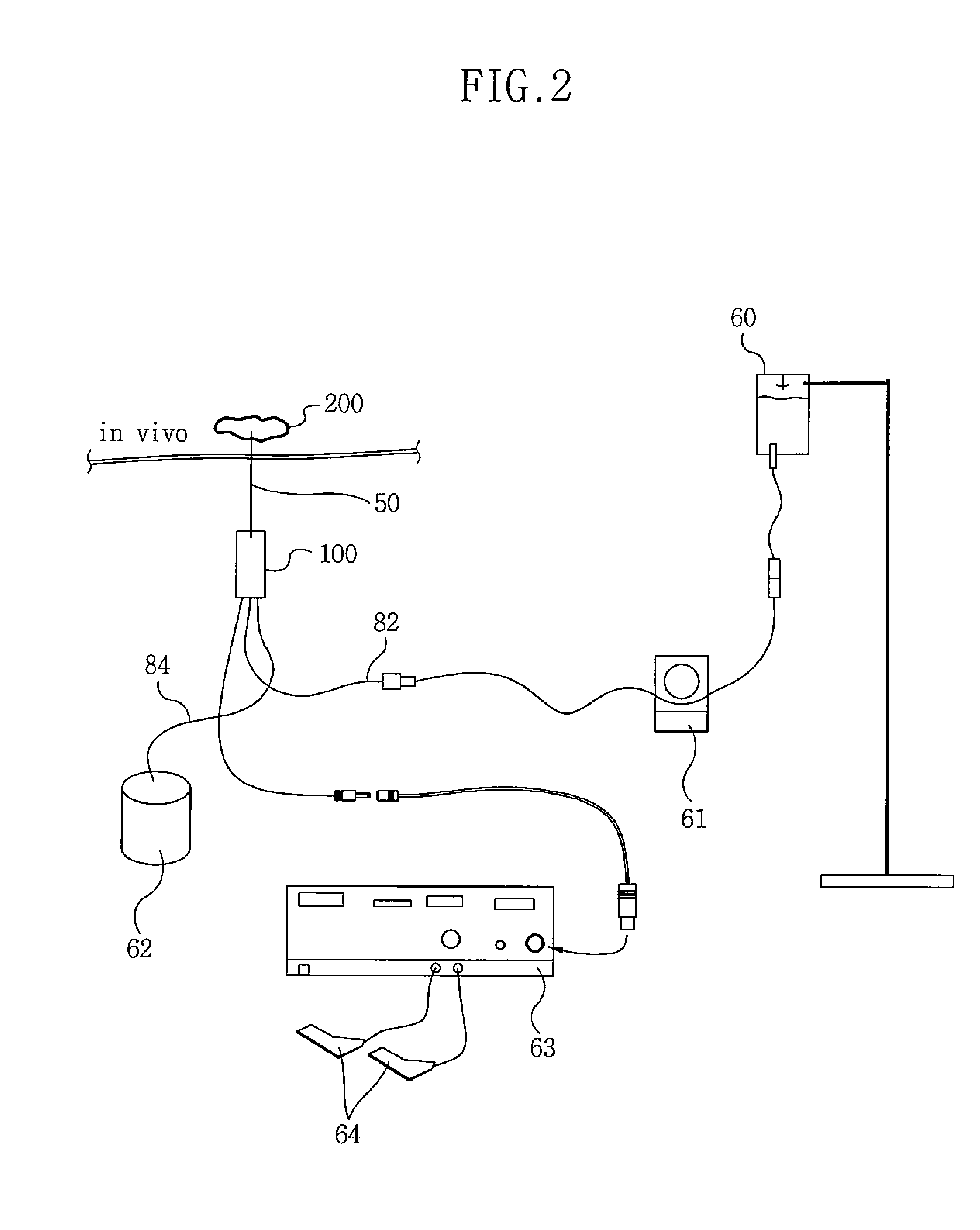
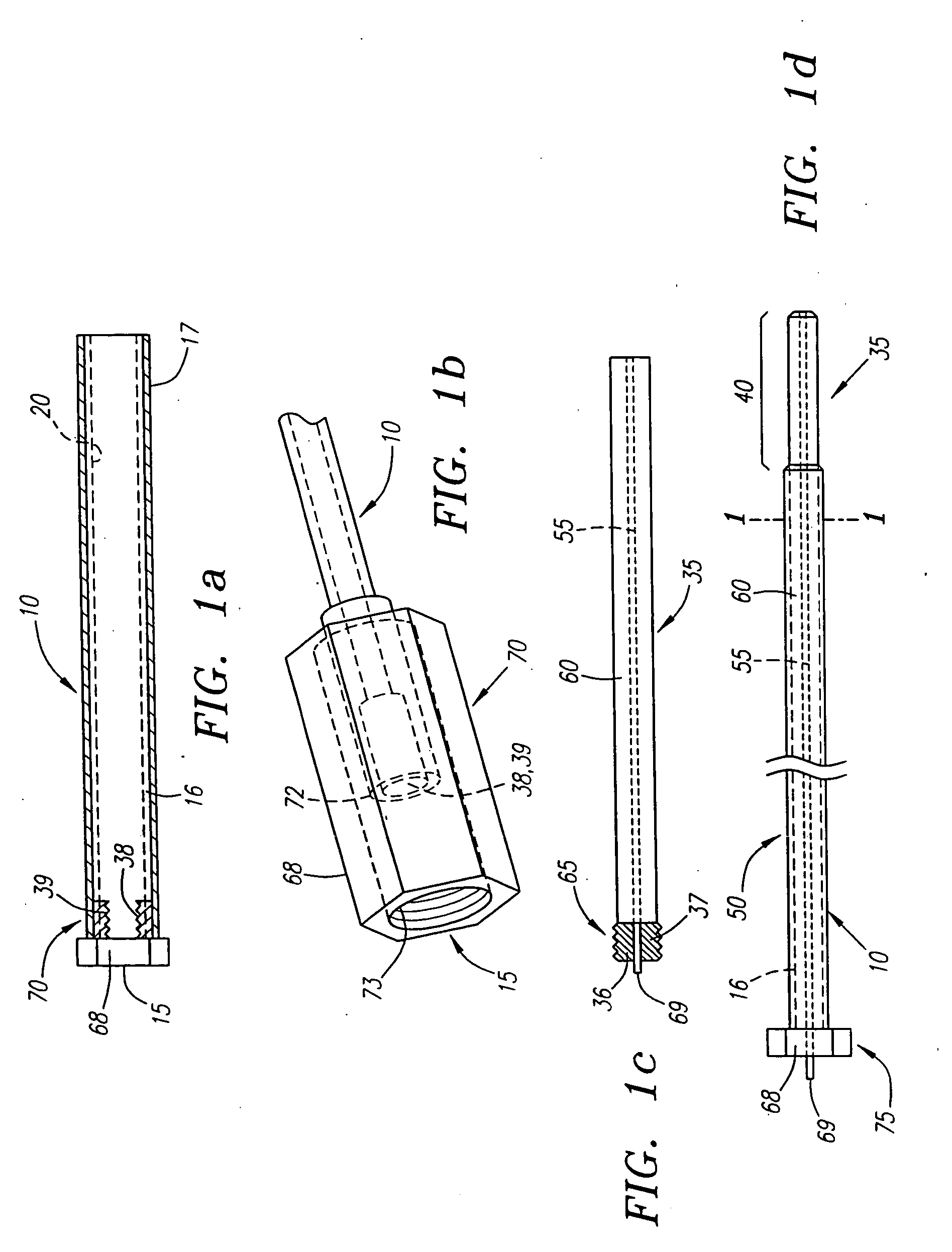
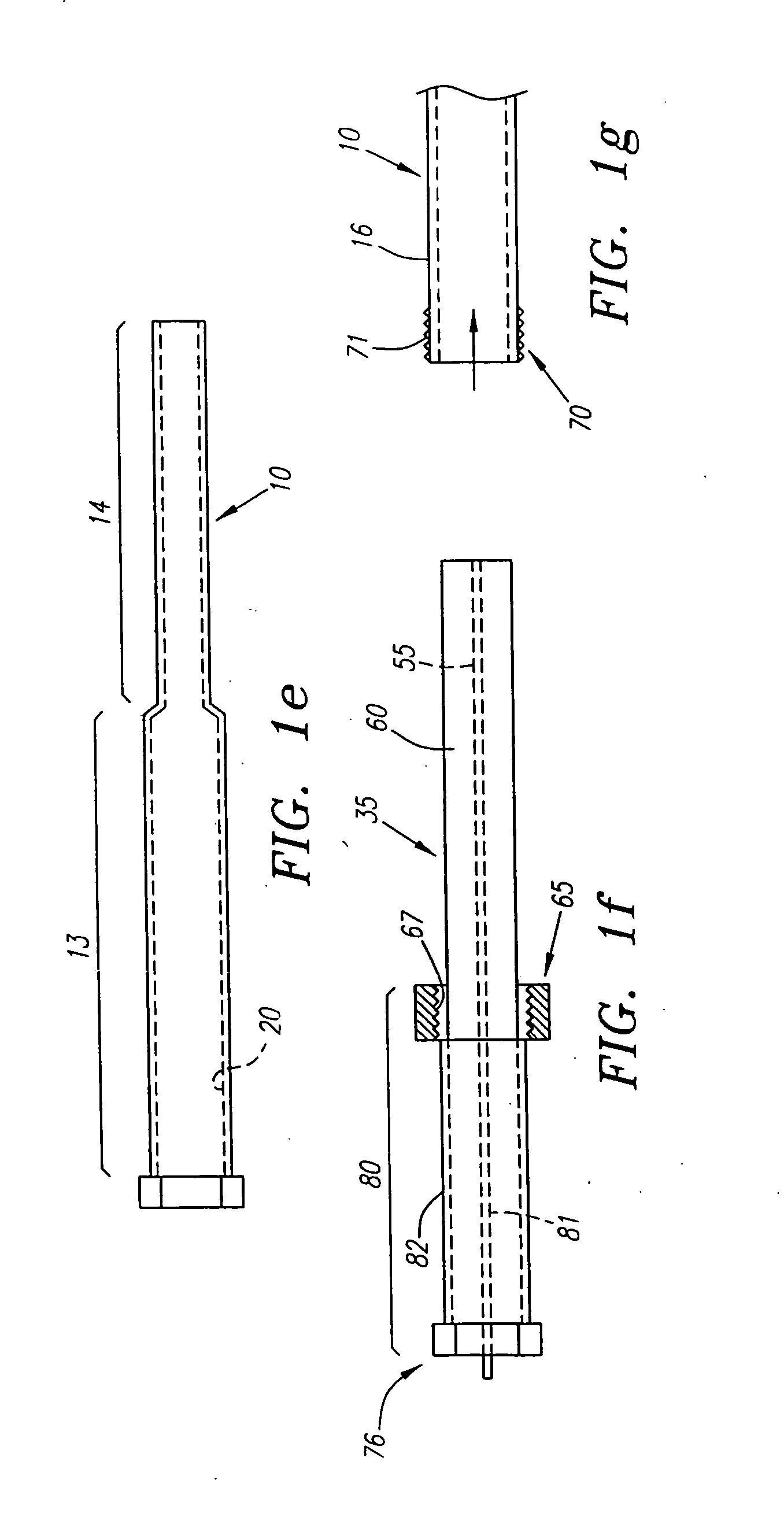
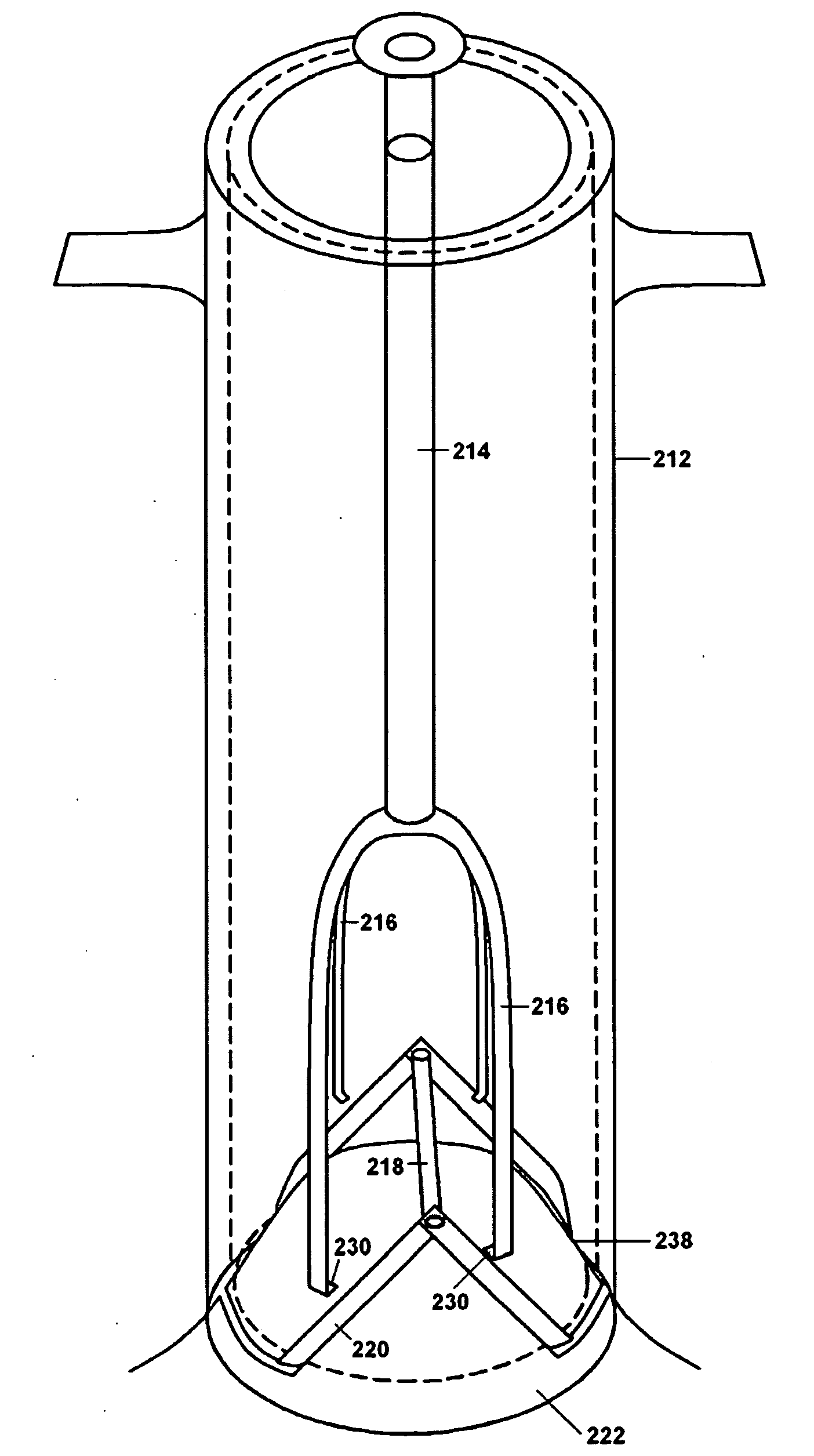
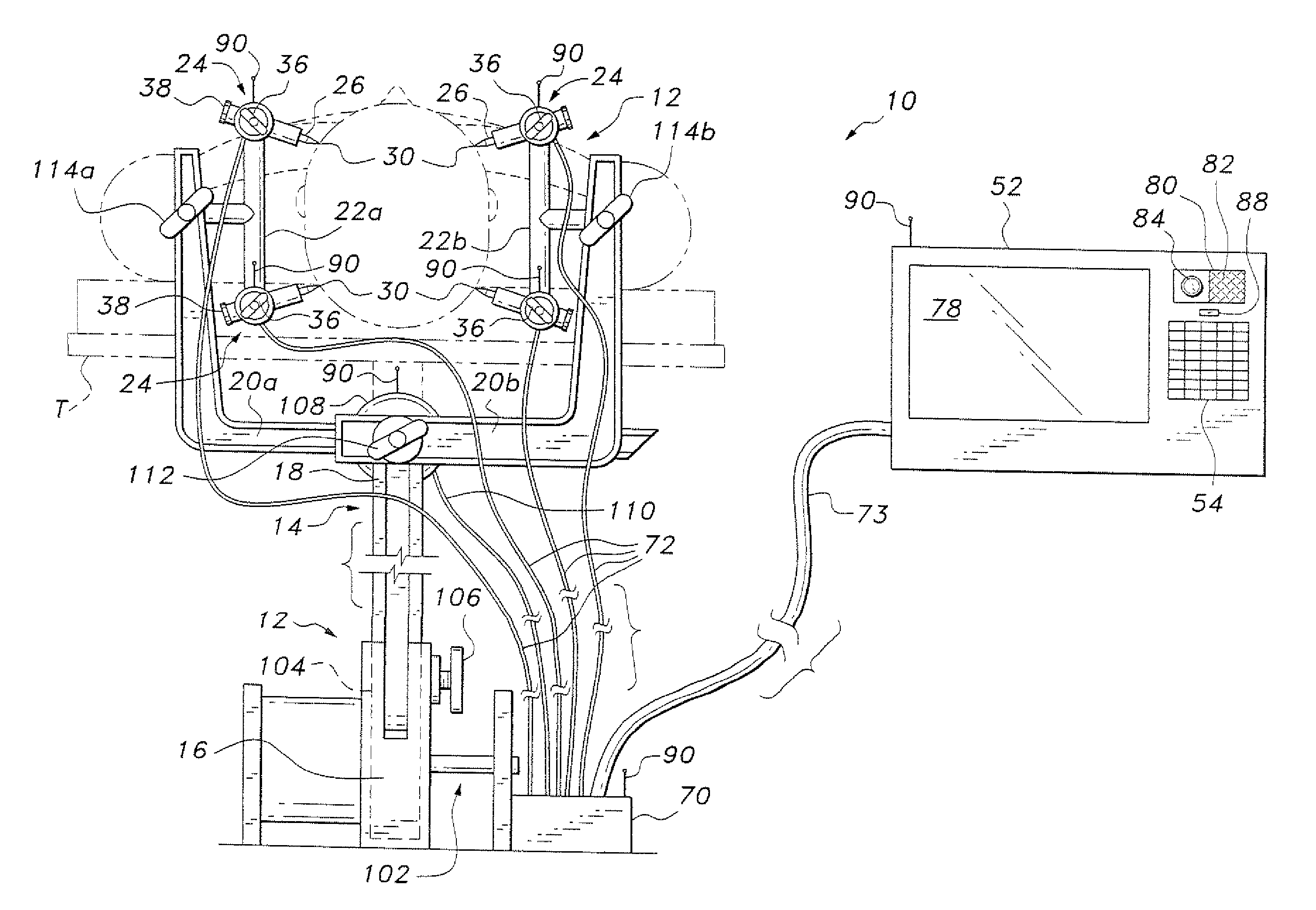
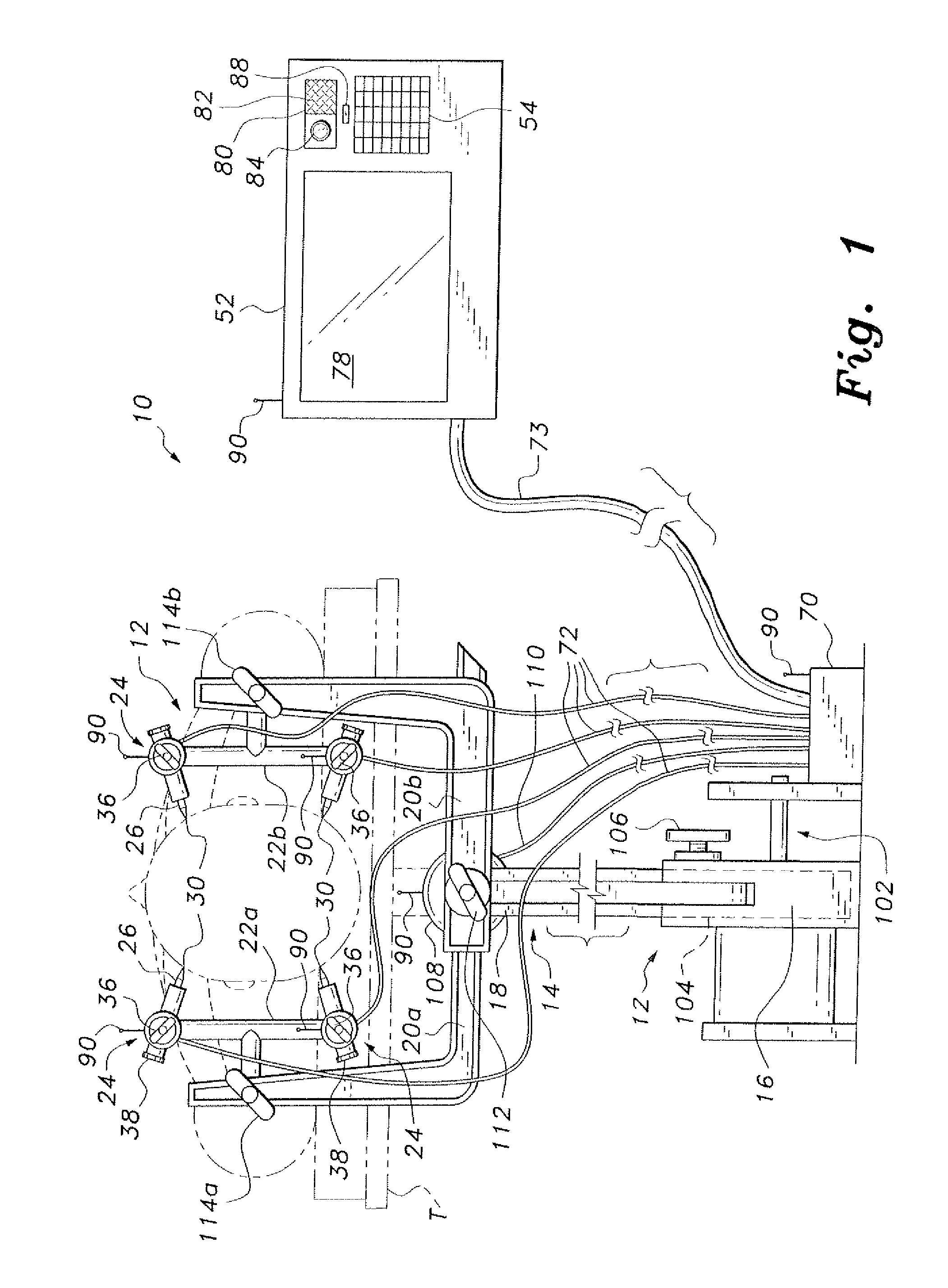
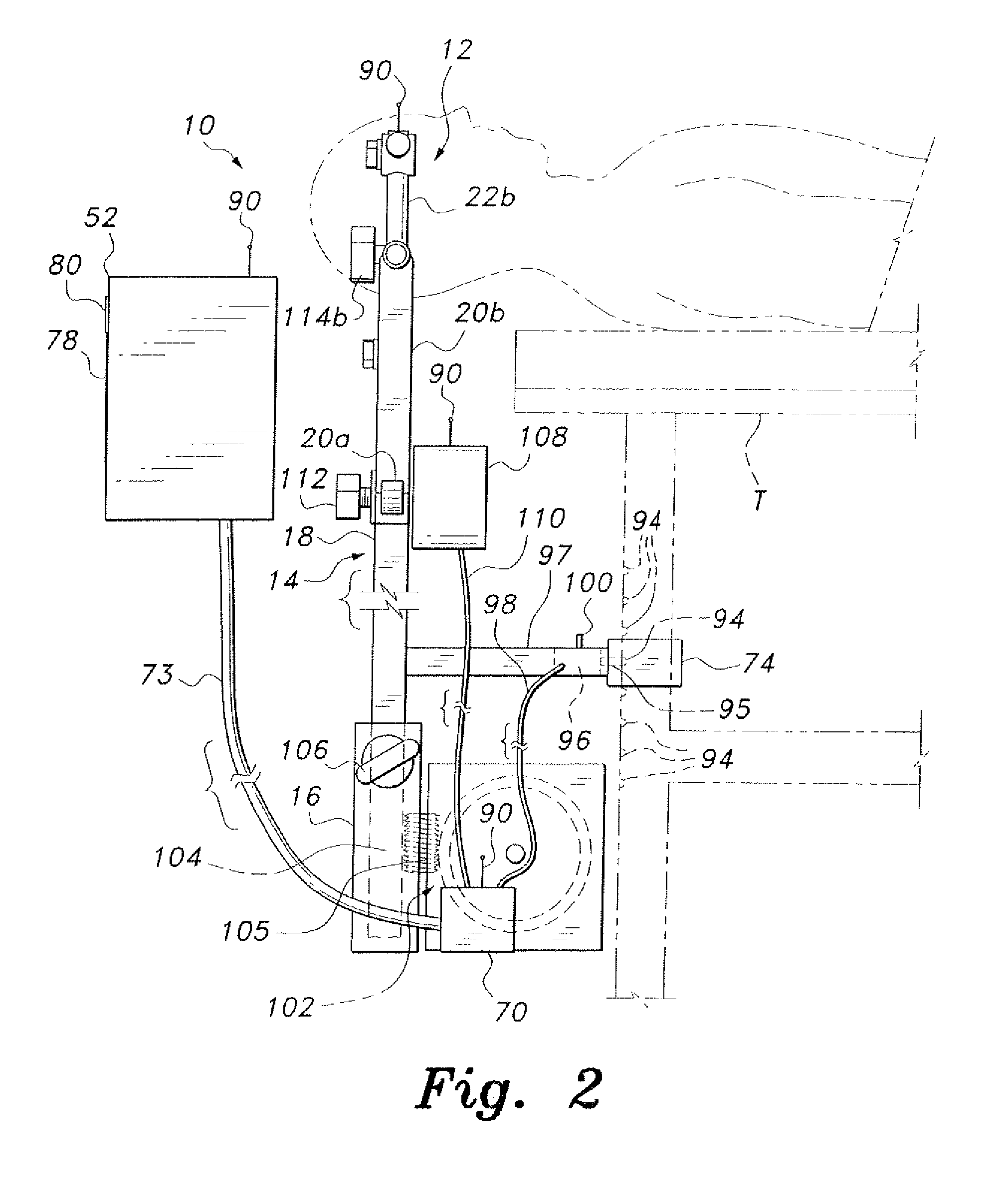
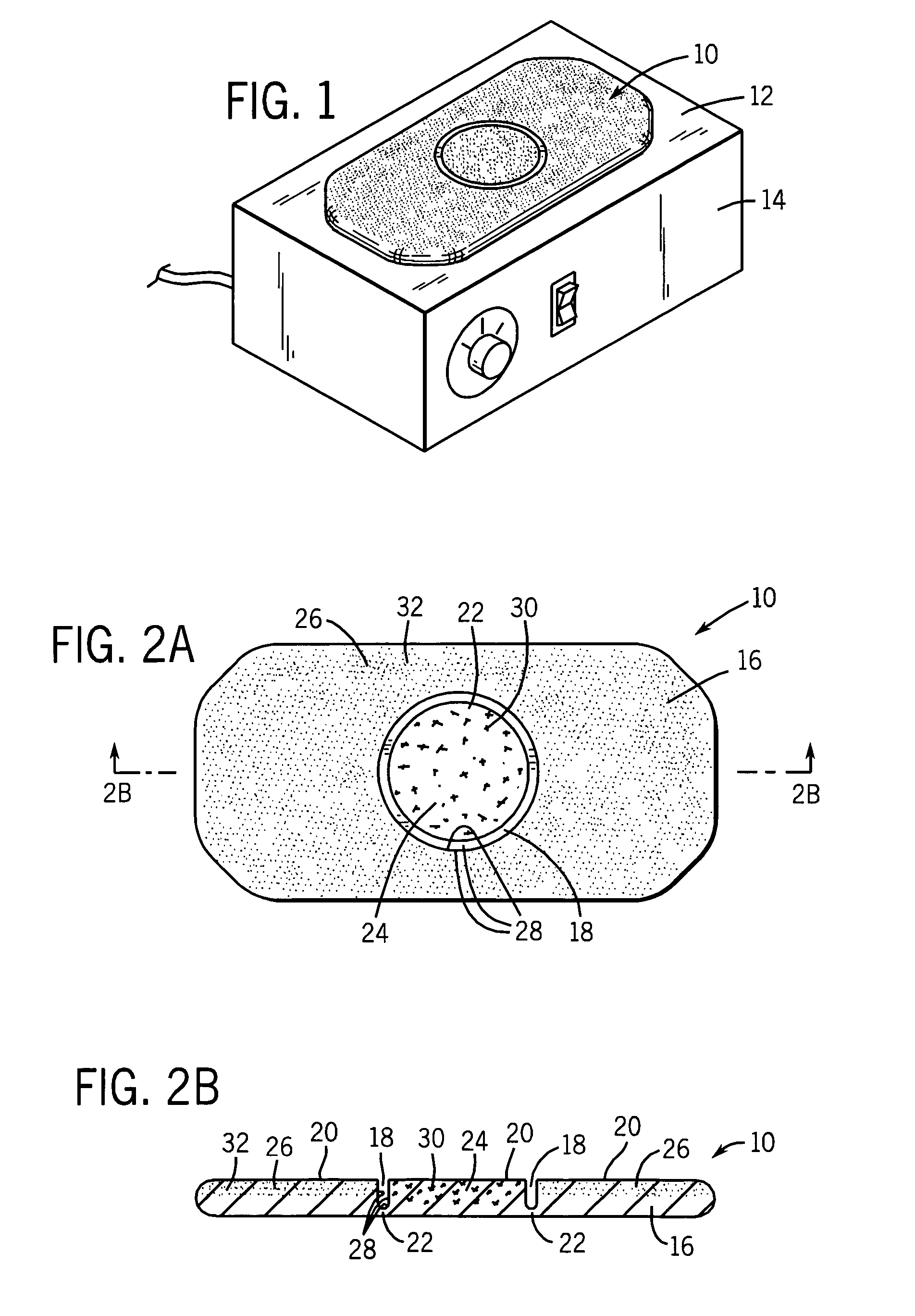
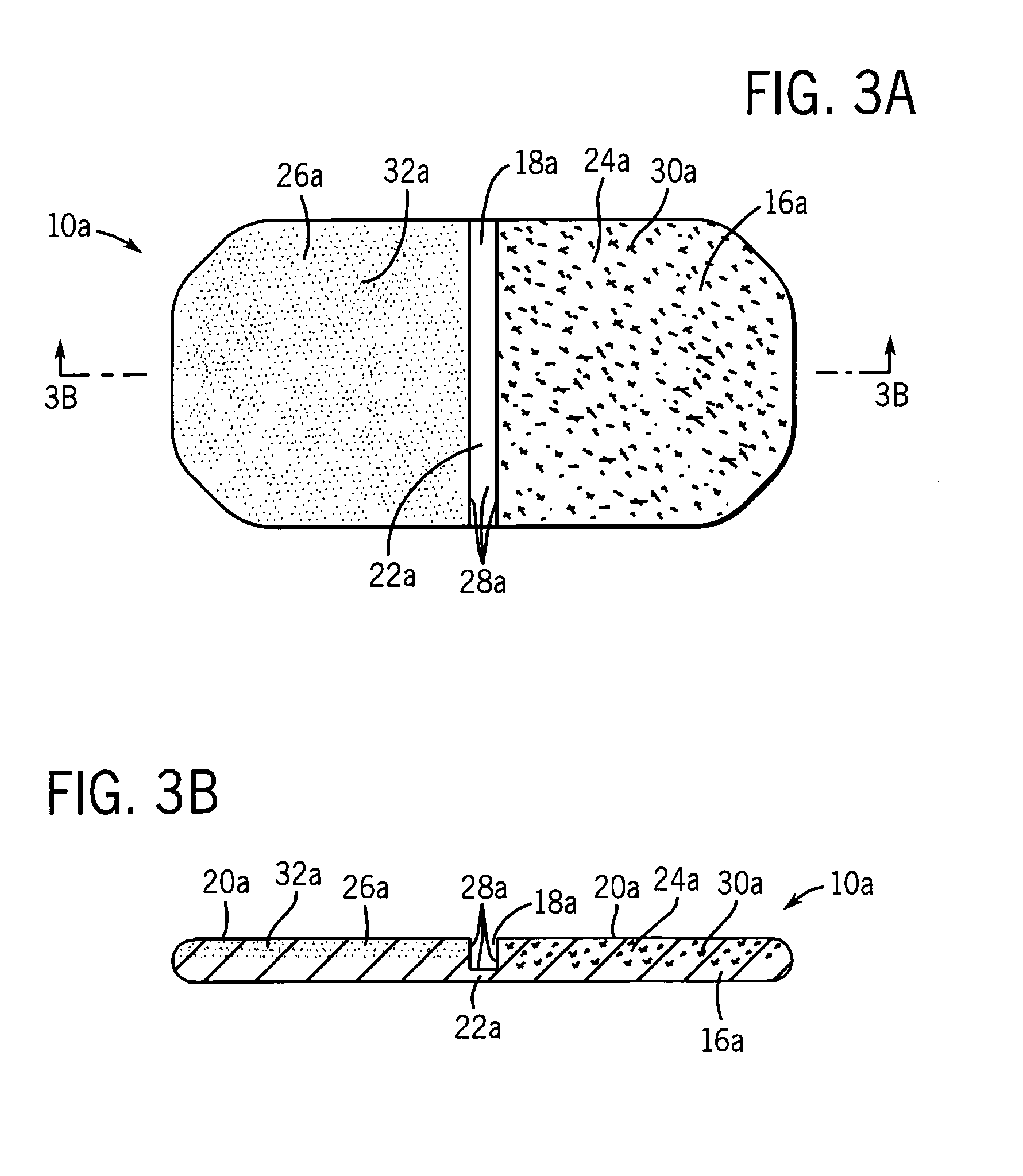
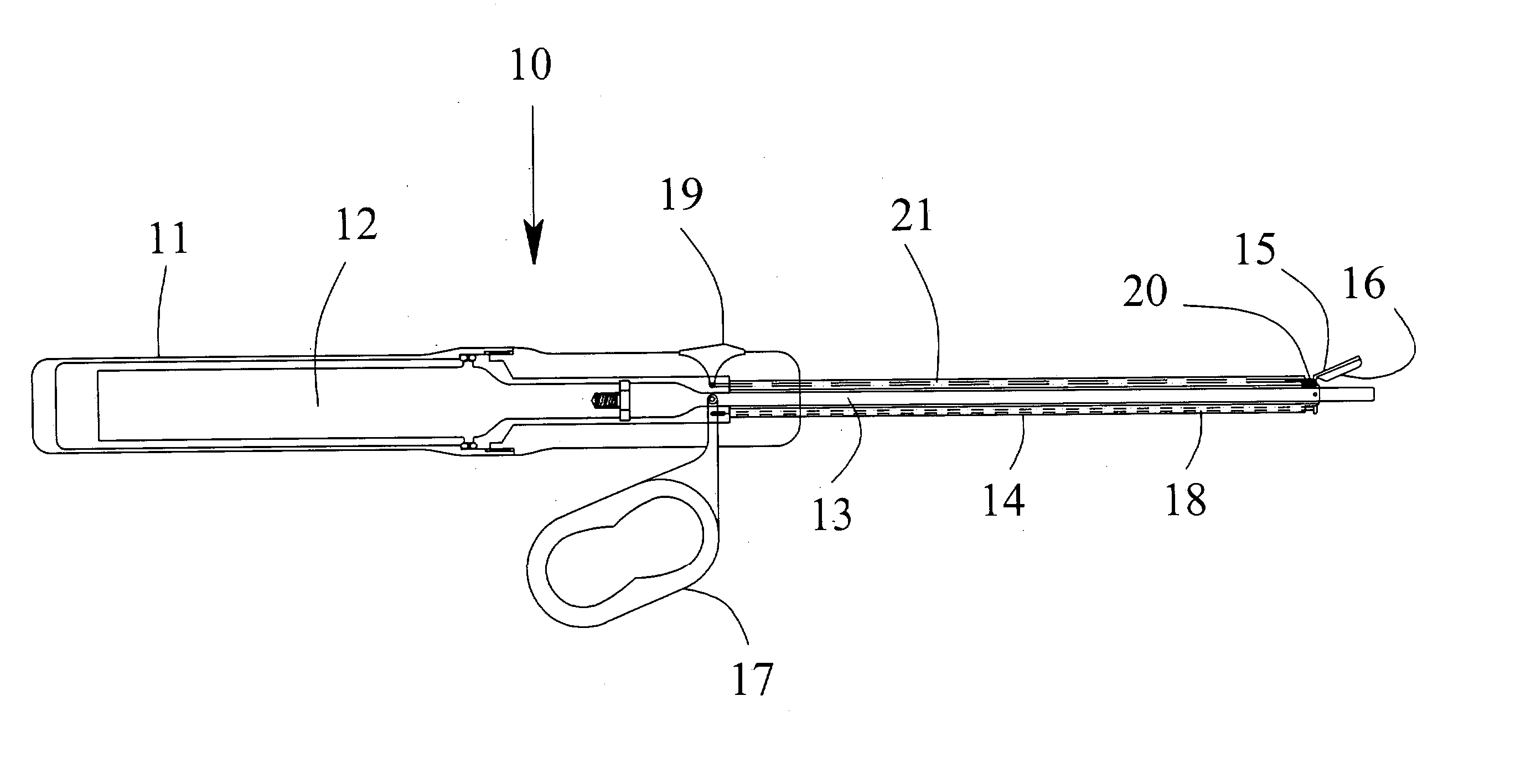
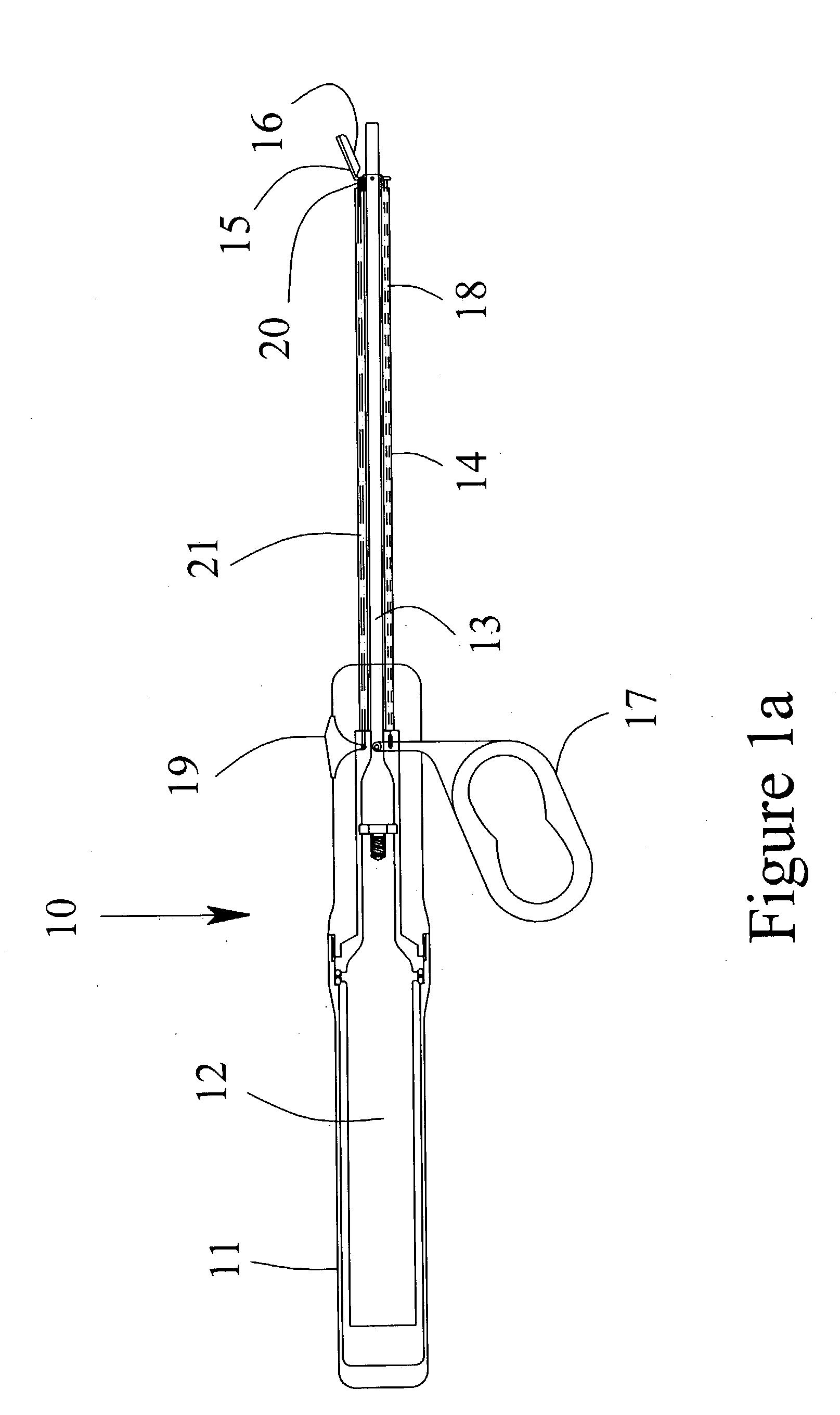
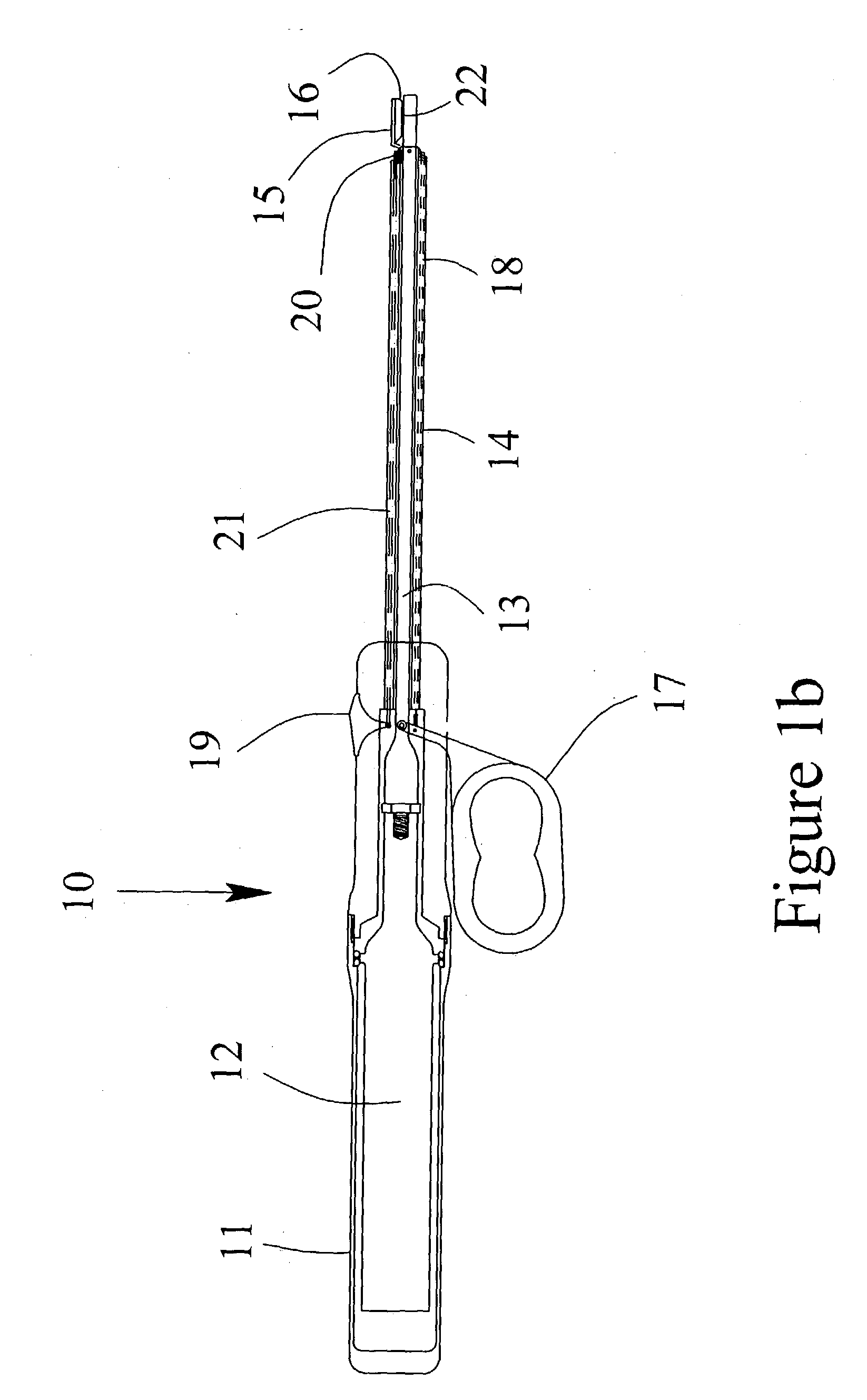
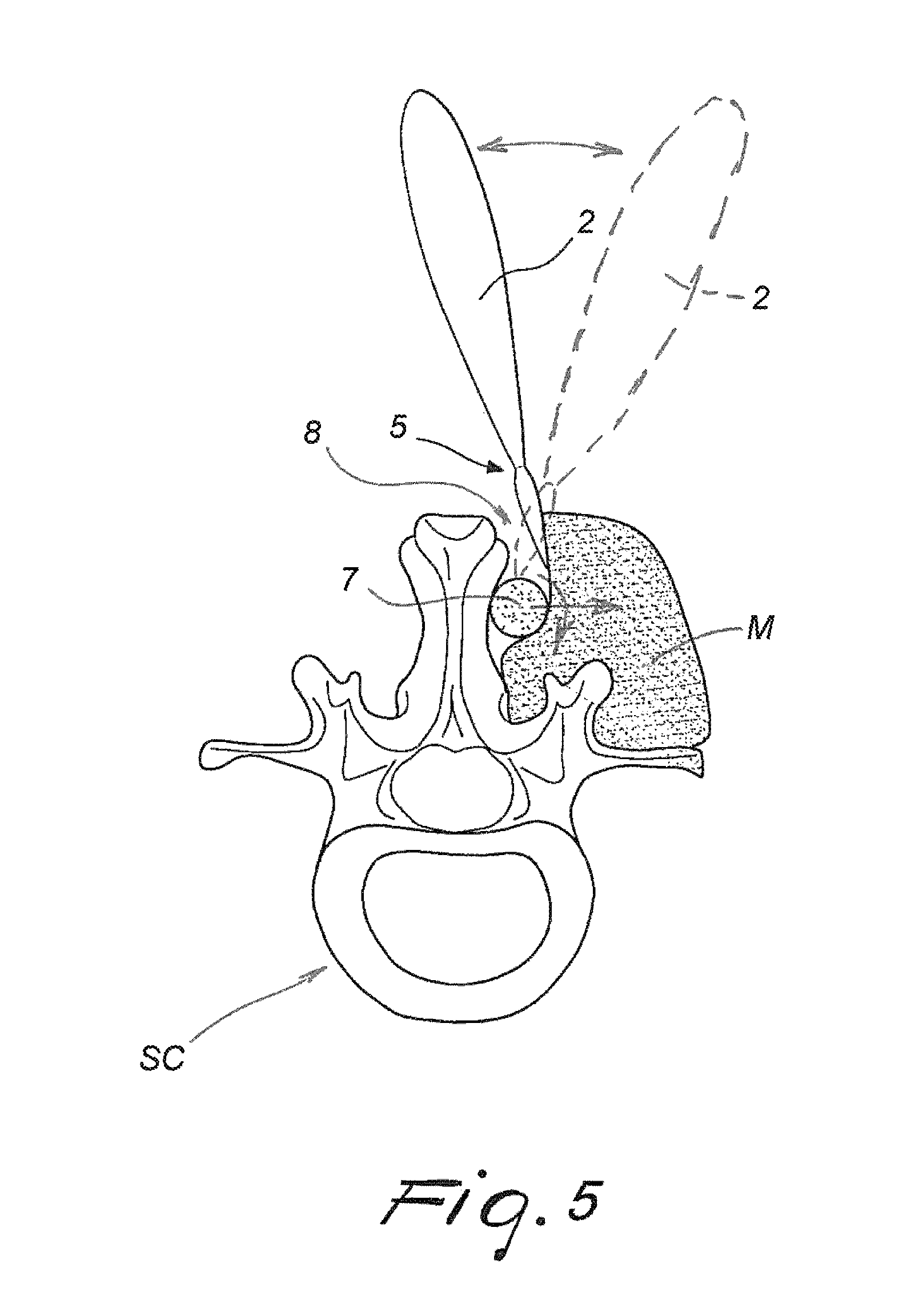
Wound closure and sealing device
InactiveUS20060173492A1Prevented from appearingStops orSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEngineeringBlood vessel
Owner:RADI MEDICAL SYST
Ultrasonic device and method for tissue coagulation
ActiveUS7361172B2Good coagulationImprove the coagulation effectUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesDistal portionSurgical device
An ultrasonic surgical device for the coagulation of animal tissue having an ultrasonic applicator and a movable jaw with a jaw surface adjacent the distal portion of the ultrasonic applicator for movement toward the applicator to a closed position at a predefined clearance of between about 0.075 to about 1.9 millimeters from the applicator. The device may also include a mechanical cutting element that can be extended into the clearance to cut the tissue and means to vary the predefined clearance without removing the applicator from the patient. Tissue coagulating and cutting can be maximized and performed separately and can be easily monitored by the surgeon.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
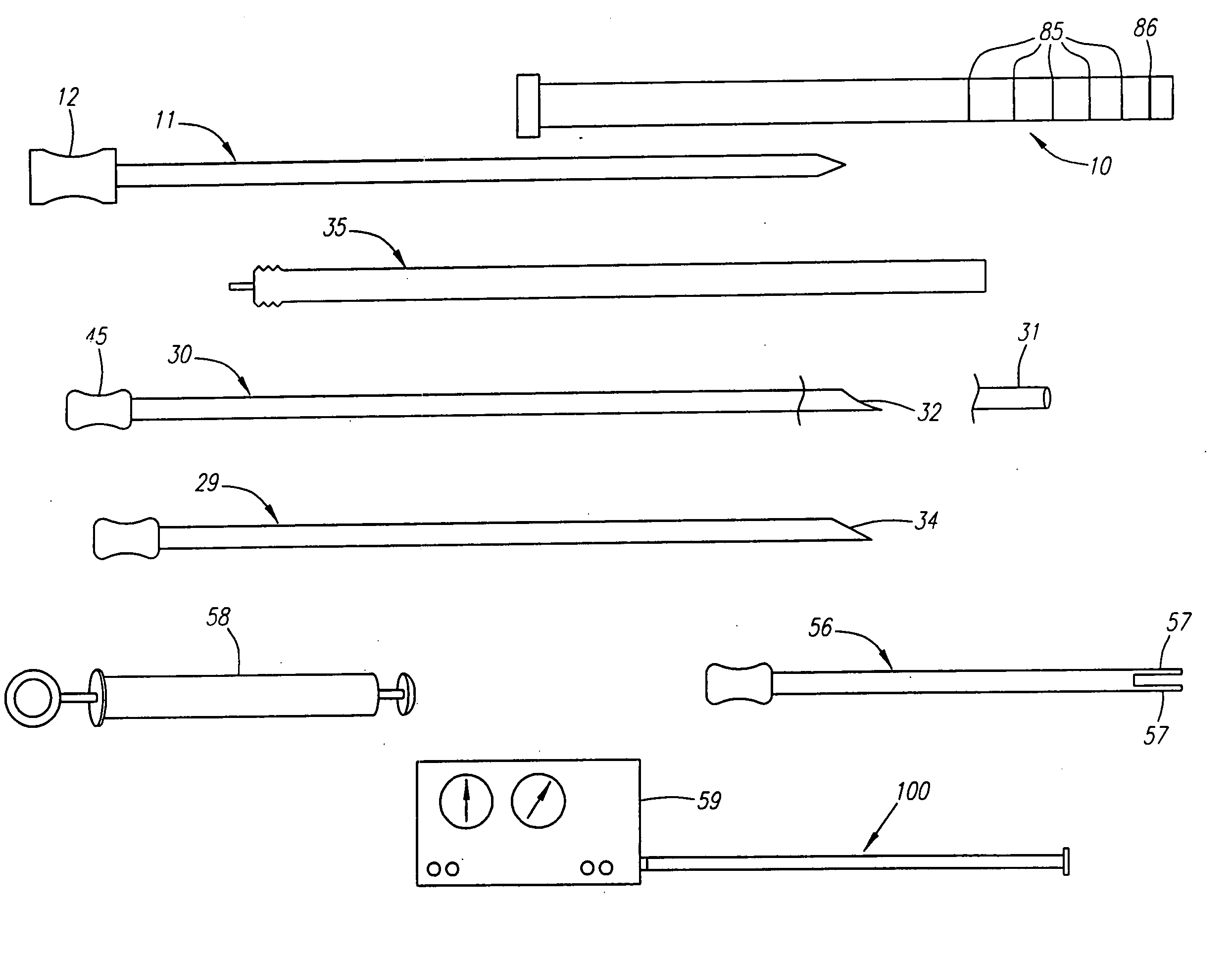
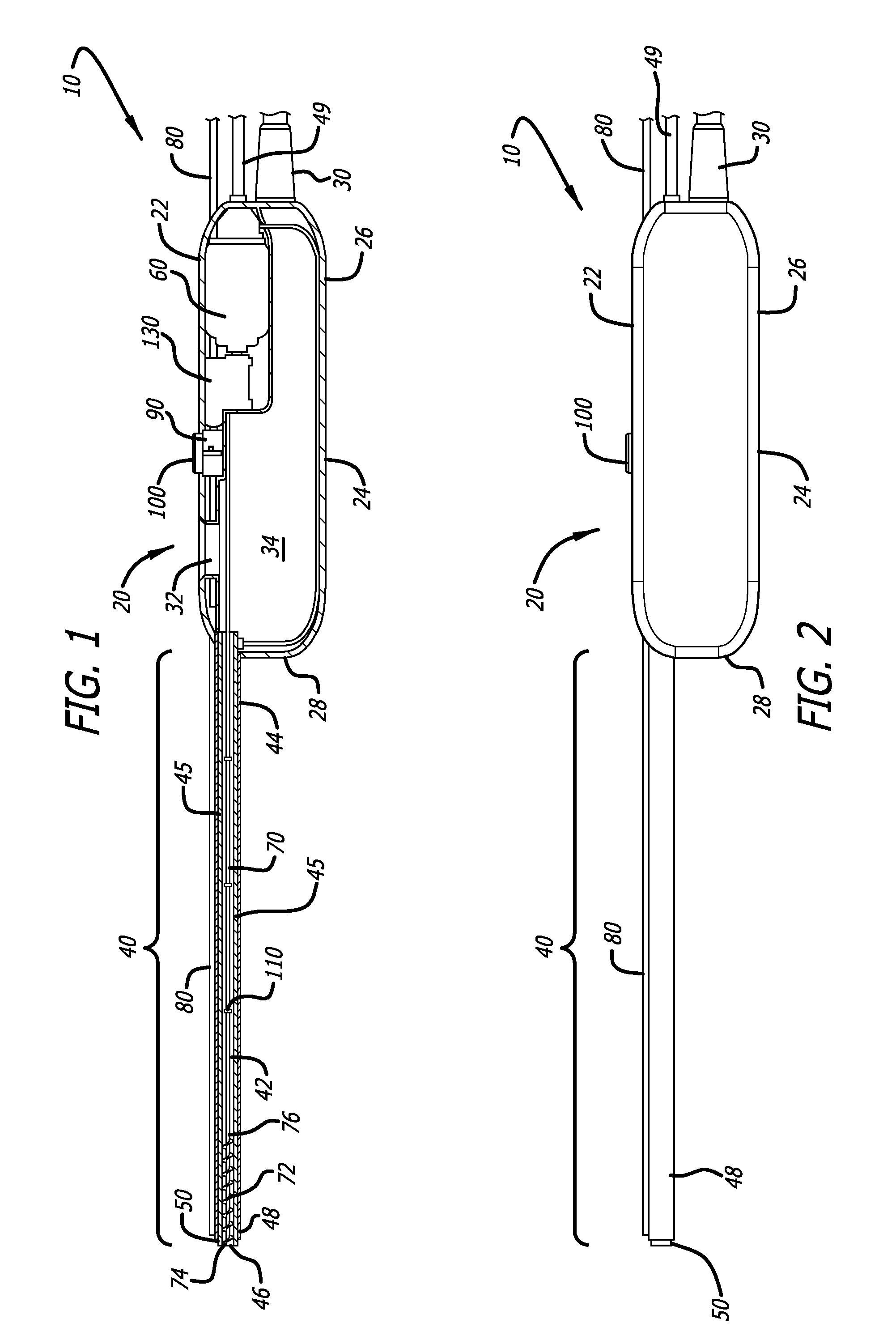
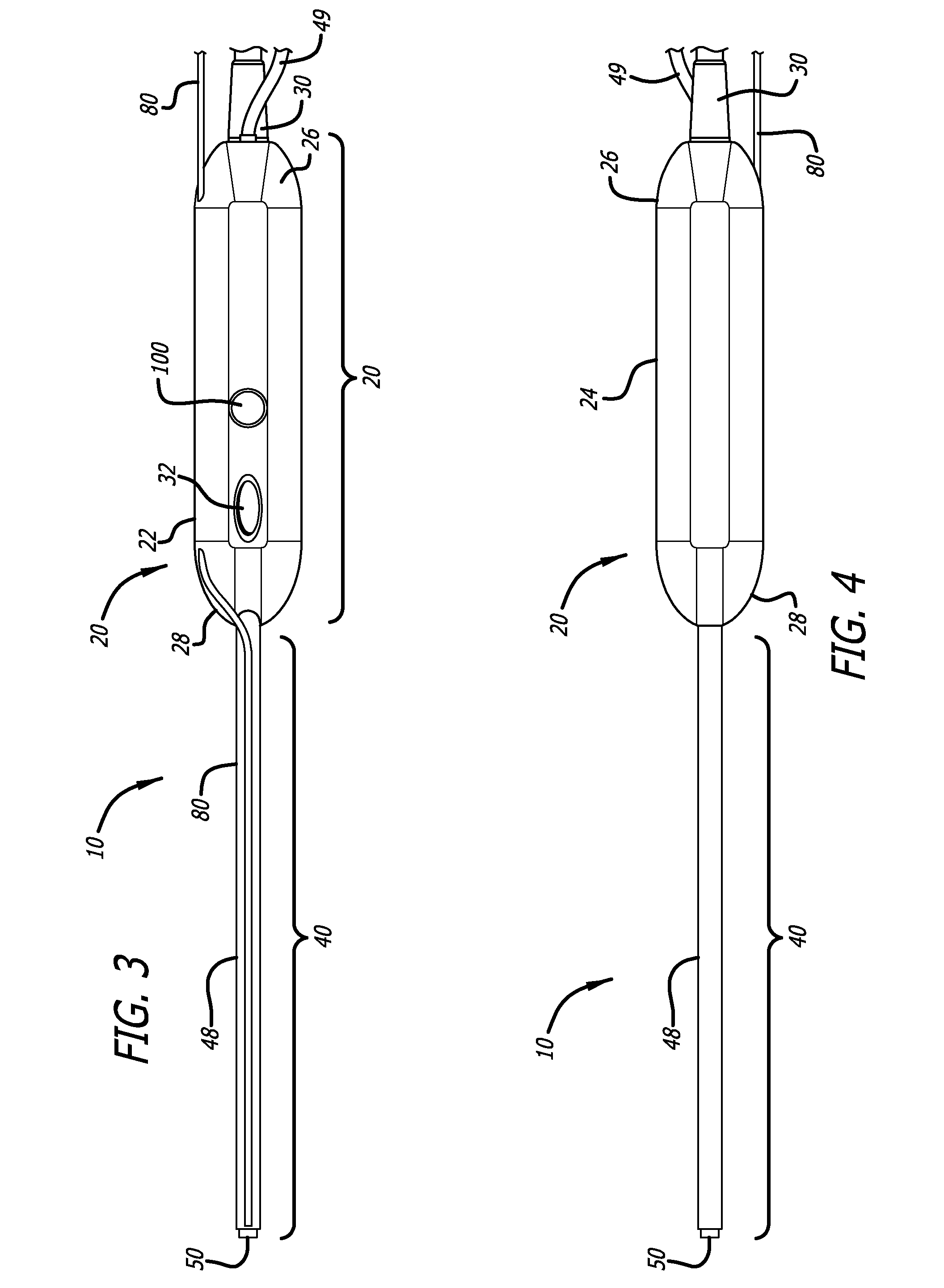
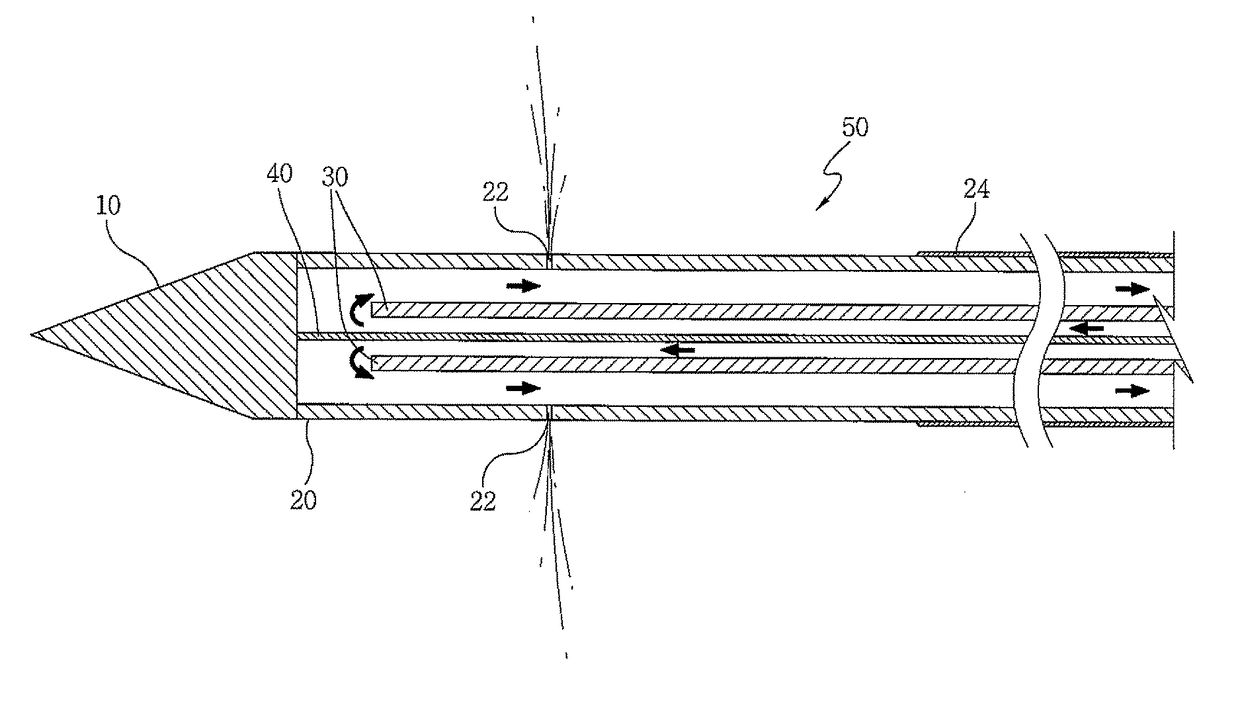
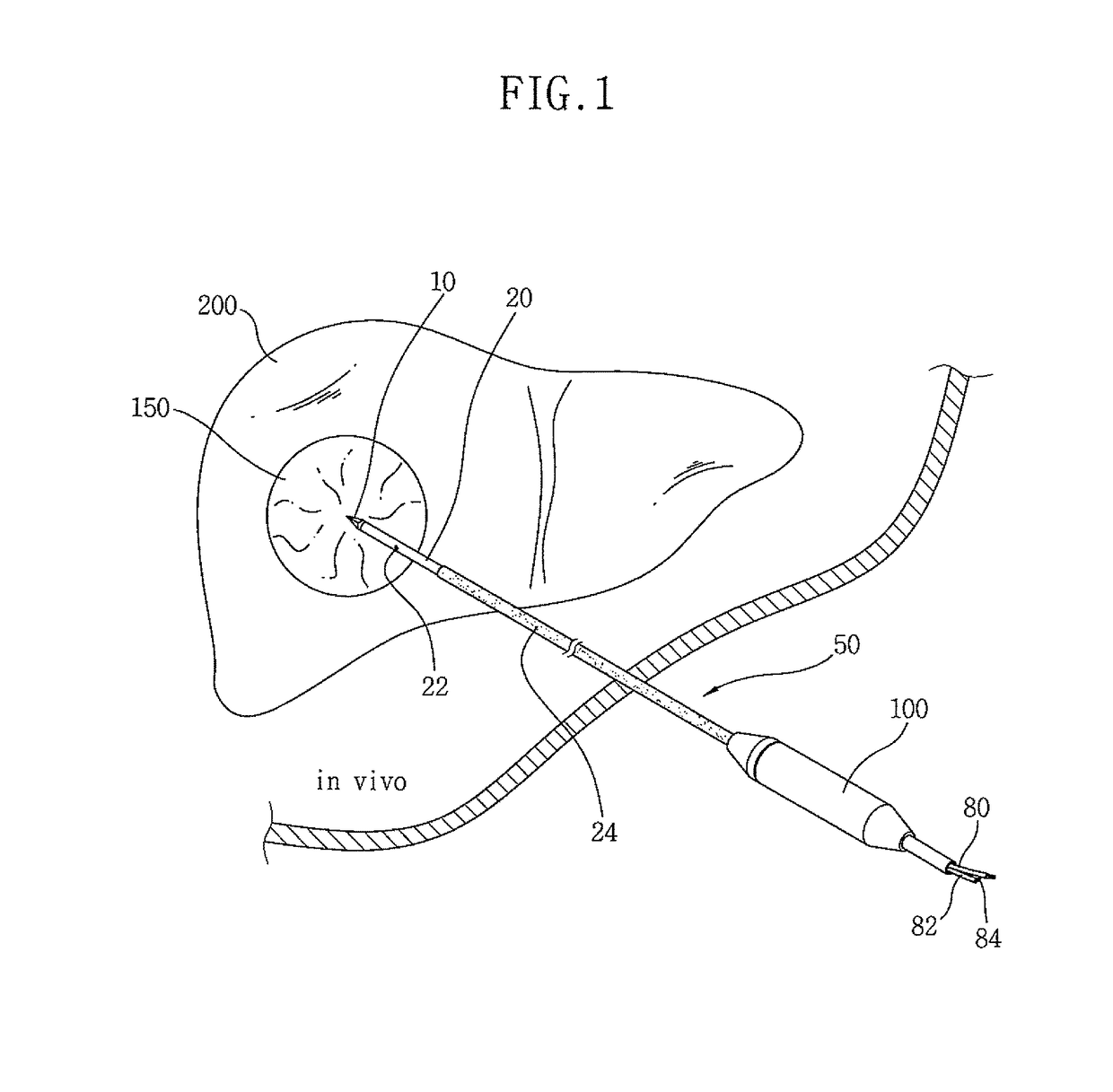
Needle kit and method for microwave ablation, track coagulation, and biopsy
InactiveUS7160292B2Minimize damageMinimize bleedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFungating tumourMicrowave ablation
A modular biopsy, ablation and track coagulation needle apparatus is disclosed that allows the biopsy needle to be inserted into the delivery needle and removed when not needed, and that allows an inner ablation needle to be introduced and coaxially engaged with the delivery needle to more effectively biopsy a tumor, ablate it and coagulate the track through ablation while reducing blood loss and track seeding. The ablation needle and biopsy needle are adapted to in situ assembly with the delivery needle. In a preferred embodiment, the ablation needle, when engaged with the delivery needle forms a coaxial connector adapted to electrically couple to an ablating source. Methods for biopsying and ablating tumors using the device and coagulating the track upon device removal are also provided.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
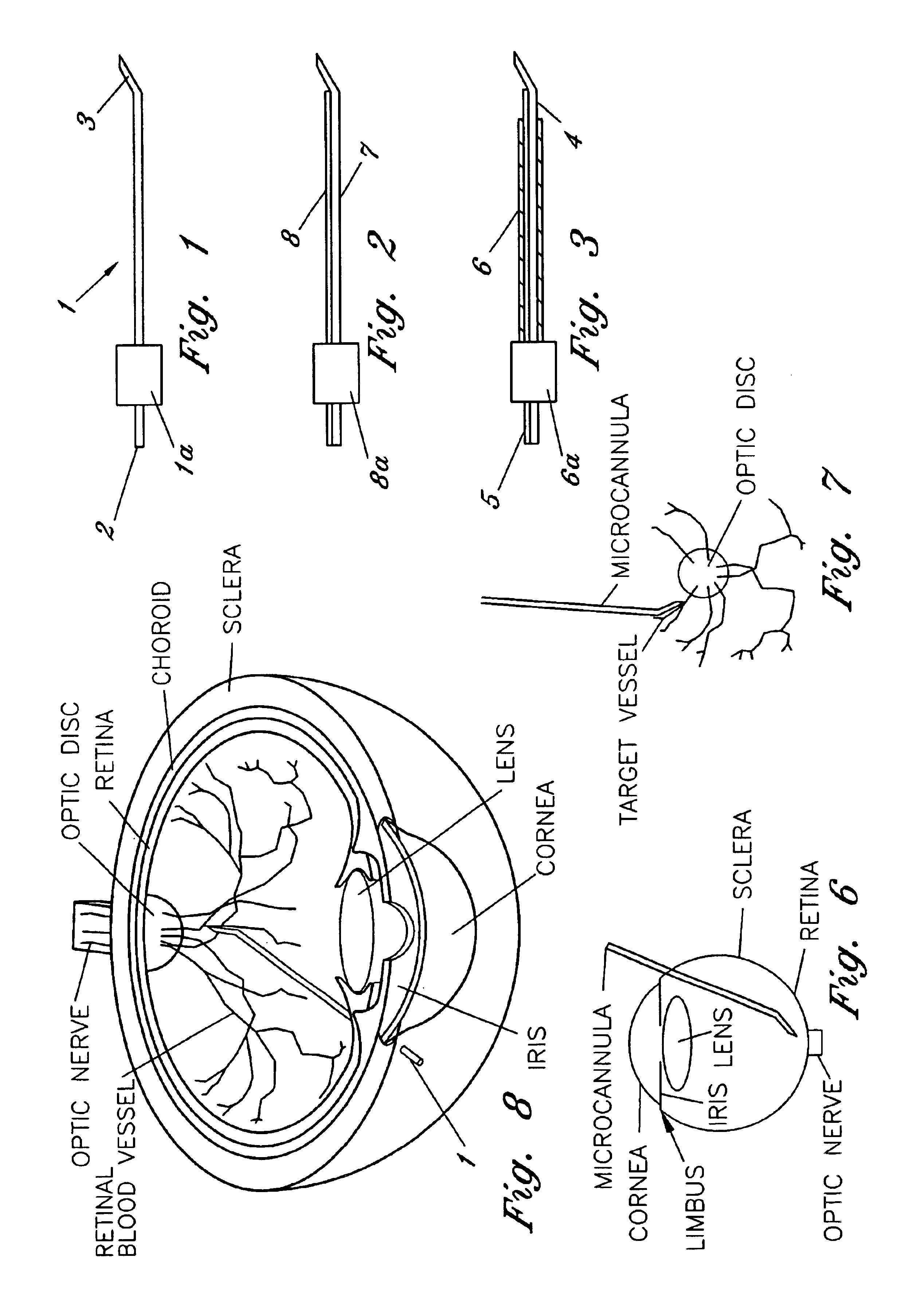
Ocular implant needle
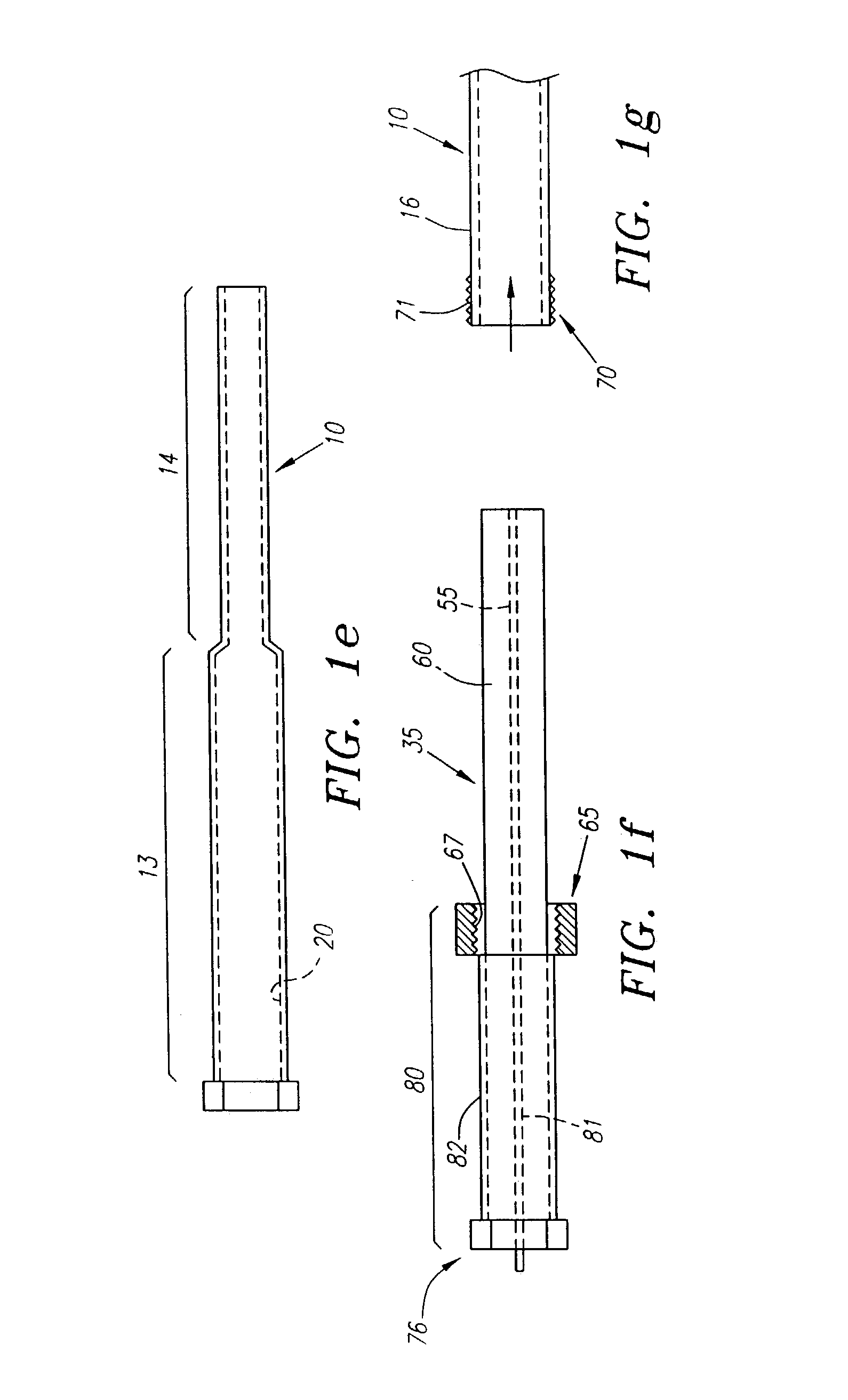
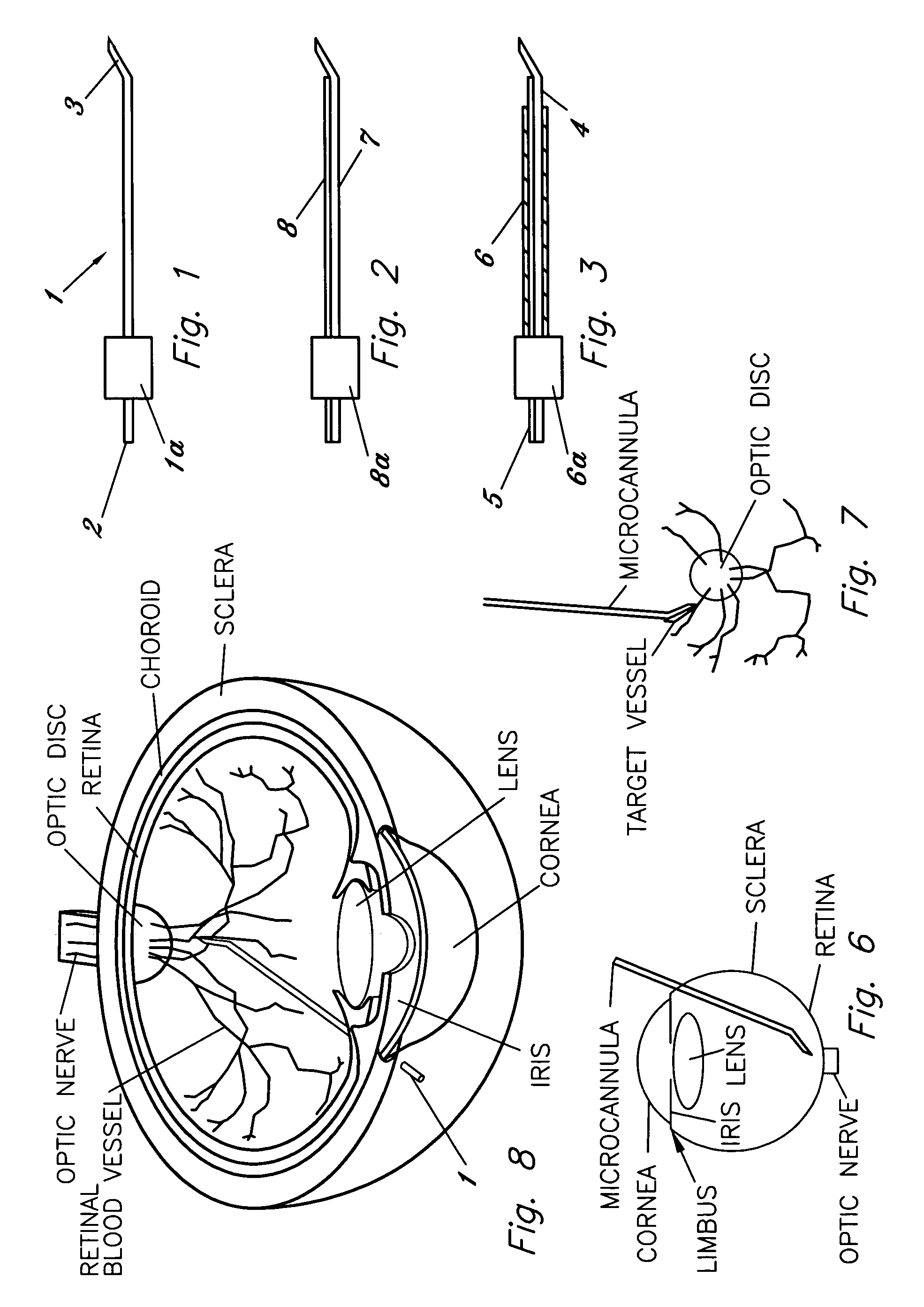
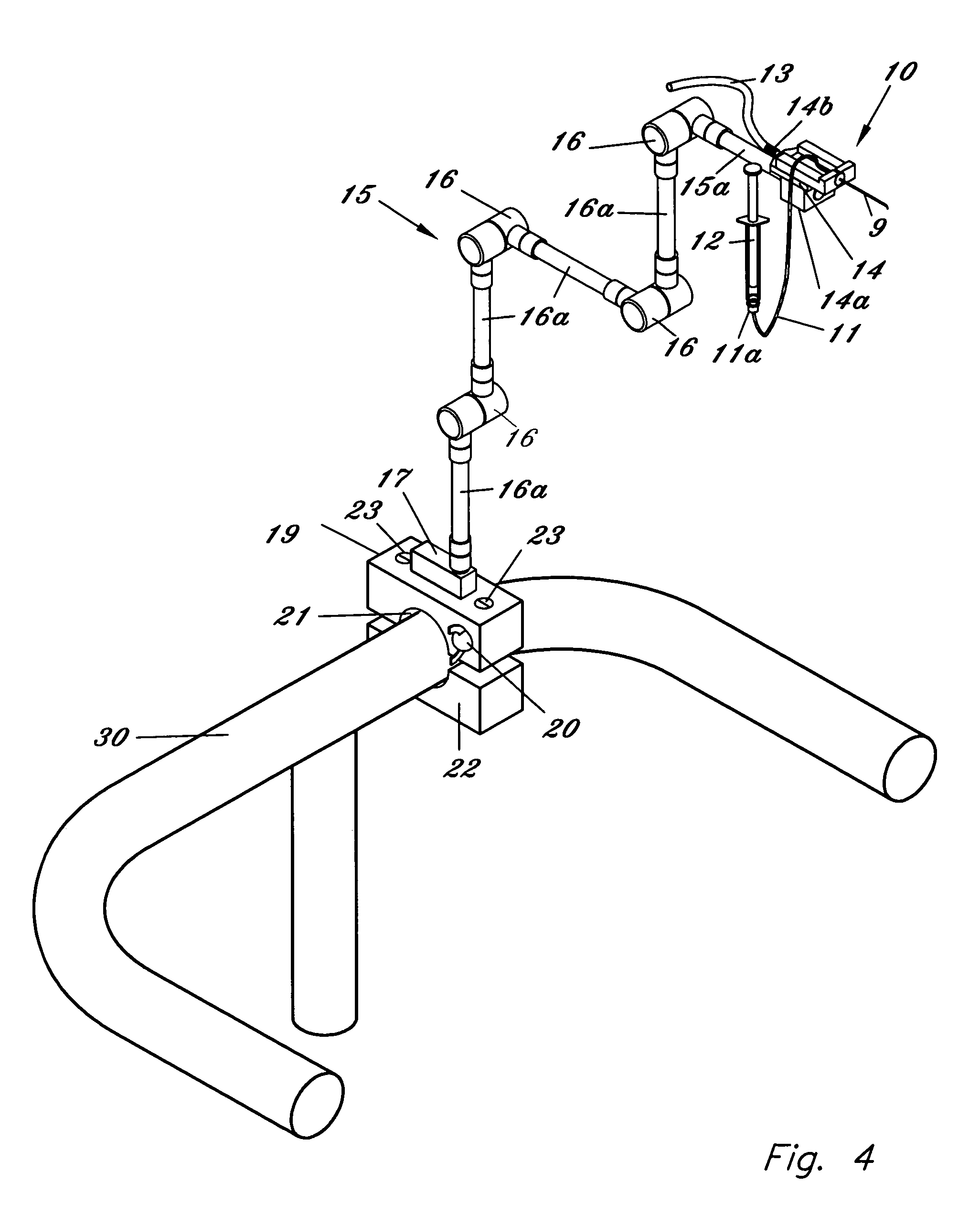
InactiveUS6936053B1Easily perforate designated blood vesselMinimize bleedingStentsEye surgeryDiseaseOptic nerve
An apparatus and method for safely cannulating a blood vessels, including but not limited retinal blood vessels, is described. In one embodiment, the apparatus can consist of a micropipette / microcannula, micromanipulator and positioner mounted to a base, which is attached to a wrist rest commonly used in eye surgery. The micropipette / microcannula is connected to tubing such that a medication may be injected through the micropipette / microcannula into the blood vessel or conversely, a small quantity of material may be removed from a blood vessel. Alternatively, a catheter, wire or stent may be placed through the micropipette / microcannula to treat or diagnose an area remote from the insertion site. The ability to cannulate a retinal blood vessel should be efficacious in the treatment of vein and artery occlusion, ocular tumors and other retinal, vascular and optic nerve disorders that would benefit from diagnosis and / or treatment. In another embodiment, a self-sealing needle is provided which allows the perforation of a blood vessel or other structure and the minimization of hemorrhaging when the needle is withdrawn from the blood vessel / structure. Another embodiment discloses an ocular implant needle.
Owner:JNW PARTNERS
Devices and methods for atrial appendage exclusion
InactiveUS20080039879A1Avoid flowMinimize bleedingSurgical staplesWound clampsLess invasive surgerySurgical site
Devices, tools and methods for occluding fluid flow between two walls of tissue in a patient. Two walls of tissue are compressed together with sufficient compressive force to prevent fluid flow between the two walls, while ensuring that the compressive force is not so great as to cause tissue necrosis. The devices, tools and methods may be carried out using minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as in reduced-access surgical sites. Devices, tools and methods are provided for occluding an atrial appendix.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of fasciitis
InactiveUS20060189971A1Minimize and completely eliminate and damageExpand field of viewStentsHeart valvesFasciitisDamages tissue
Systems, apparatus, and methods are provided for promoting blood flow to a target tissue. In one aspect, the invention involves canalizing or boring channels, divots, trenches or holes through an avascular connective tissue, or through a tissue having sparse vascularity, such as a tendon or a meniscus, in order to increase blood flow within the tissue. In one method, an active electrode is positioned in close proximity to a target site on a tendon, and a high frequency voltage difference is applied between the active electrode and a return electrode to selectively ablate tendon tissue at the target site, thereby forming a channel or void in the tendon. The active electrode(s) may be moved relative to the tendon during, or after, the application of electrical energy to damage or sculpt a void within the tendon, such as a hole, channel, crater, or the like. In another aspect of the invention, an electrosurgical probe is used to elicit a wound healing response in a target tissue, such as an injured tendon, in order to stimulate vascularization of the target tissue. The present invention may also be used for vascularization of a torn or damaged tissue in conjunction with a surgical repair procedure.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation
ActiveUS20090287206A1Easy to liftMaximized economicallySurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingRadiofrequency ablationElectrosurgery
The present invention relates to an electrode for an electrosurgical unit for the use in ablating and necrosing a living tissue by RF electric energy. The present invention provides an electrode for an electrosurgical unit, including: a hollow electrode formed in an elongated hollow tube shape, a non-insulating region of a predetermined length being formed on one side of which, an insulating region being formed on an outer surface of which other than the non-insulating region; a saline solution circulation structure that supplies pressurized saline solution for cooling a living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode from the outside of the living tissue to the inside of the hollow electrode, and discharges the pressurized saline solution from the inside of the hollow electrode to the outside of the living tissue; and one or more saline solution discharge holes formed in the non-insulating region of the hollow electrode to discharge some of the circulating pressurized saline solution to the living tissue which is in contact with the hollow electrode.
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Needle kit and method for microwave ablation, track coagulation, and biopsy
InactiveUS20070161977A1Minimize damageMinimize bleedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAbnormal tissue growthBiomedical engineering
A modular biopsy, ablation and track coagulation needle apparatus is disclosed that allows the biopsy needle to be inserted into the delivery needle and removed when not needed, and that allows an inner ablation needle to be introduced and coaxially engaged with the delivery needle to more effectively biopsy a tumor, ablate it and coagulate the track through ablation while reducing blood loss and track seeding. The ablation needle and biopsy needle are adapted to in situ assembly with the delivery needle. In a preferred embodiment, the ablation needle, when engaged with the delivery needle forms a coaxial connector adapted to electrically couple to an ablating source. Methods for biopsying and ablating tumors using the device and coagulating the track upon device removal are also provided.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Apparatus for punch biopsy
InactiveUS20090018467A1Minimize bleedingMinimize damageVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsCylindromaEngineering
A punch biopsy apparatus for removing all or a portion of a suspect dermal growth. A punch biopsy apparatus has: a hollow cylinder body; a coring blade at the base of the hollow cylinder body; at least one scooping blade pivotally secured by an axle and a pair of pivot seats within the cylinder body, where each scooping blade is semicircular, a longitudinally-moveable plunger secured within the hollow cylinder, where the plunger has at least one plunger leg for contacting each scooping blade, and each plunger leg transfers longitudinal plunger movement to its respective scooping blade, thereby causing rotational scooping-blade movement. This device helps minimize bleeding and minimize damage to the biopsy sample being retrieved.
Owner:CHIU KWOK WAI +2
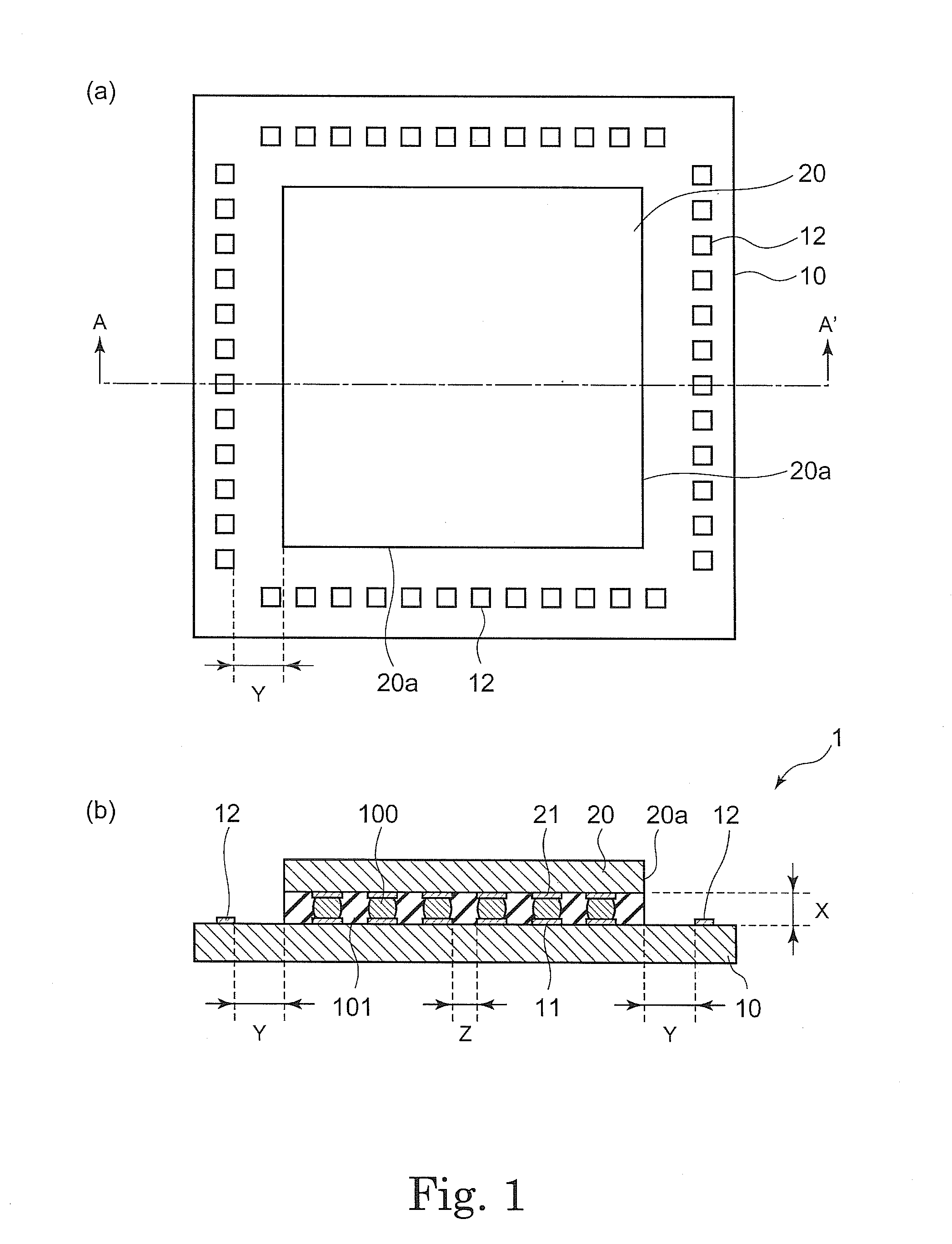
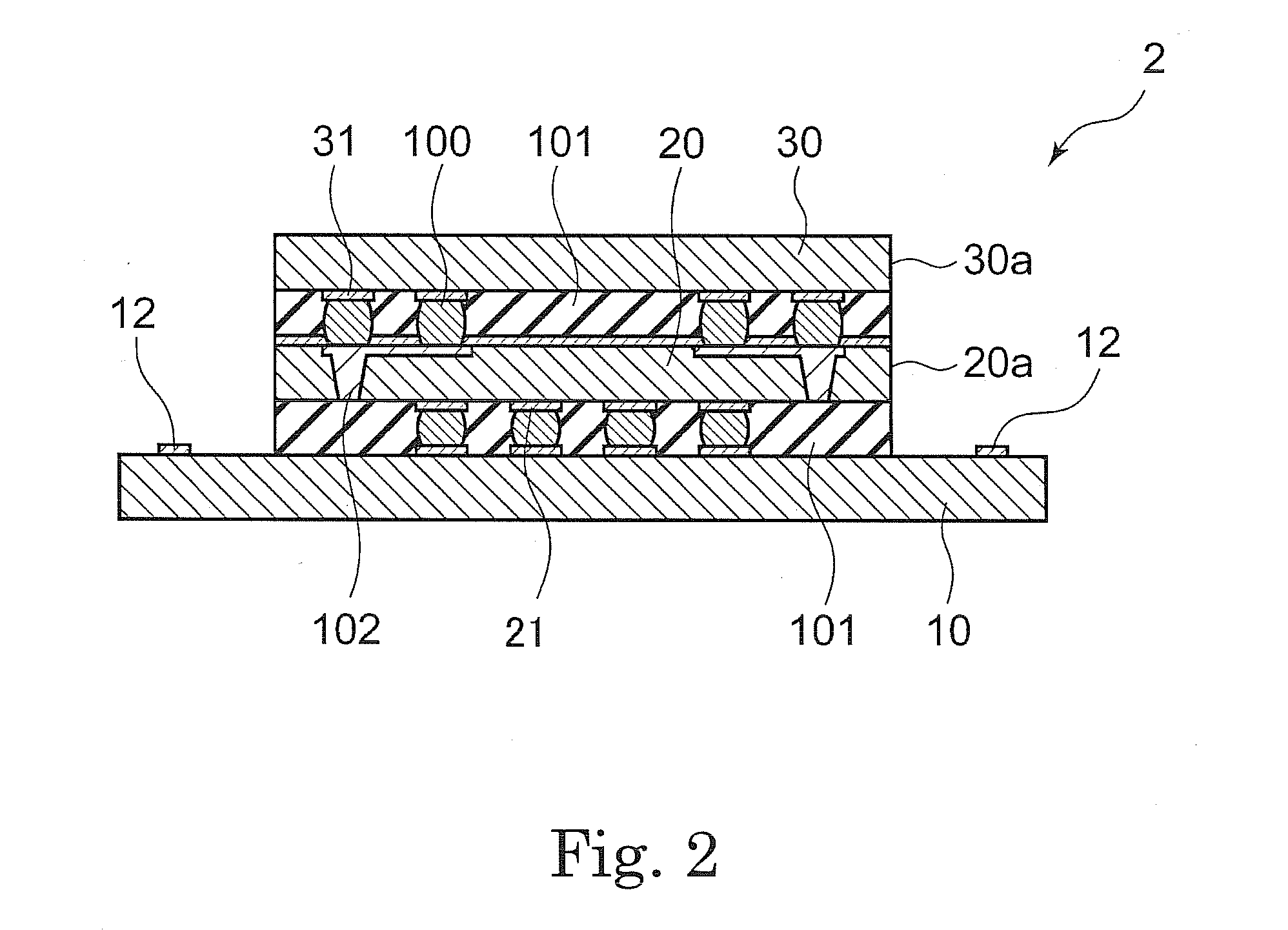
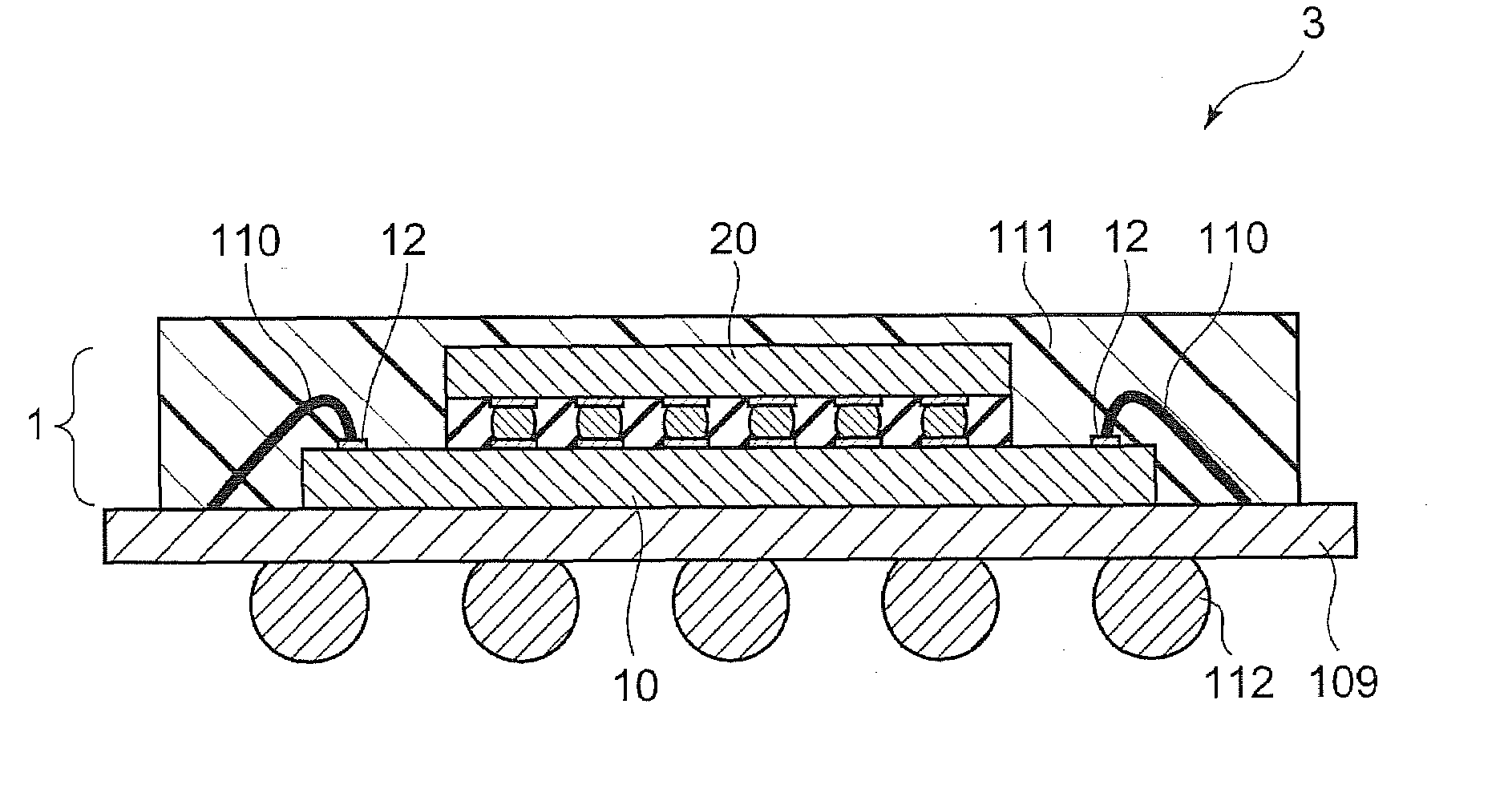
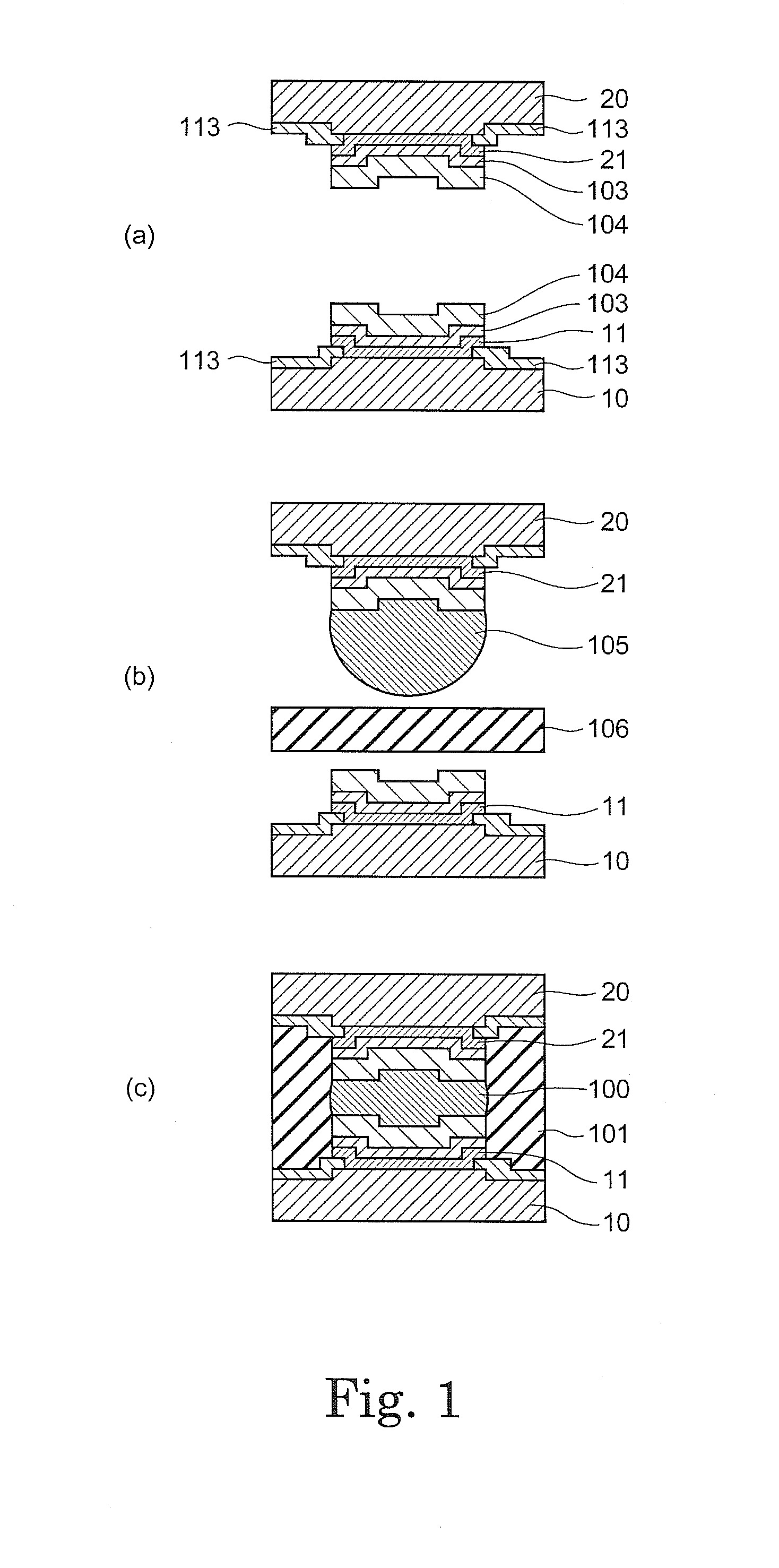
Semiconductor electronic component and semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS20100102446A1Minimize bleedingMeet the requirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChIP-on-chipShortest distance
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Adhesive tape and semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS20100078830A1Good ion migration resistanceGood solder wettabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsChIP-on-chipSemiconductor chip
The present invention relates to an adhesive tape for electrically connecting semiconductor chips in a chip-on-chip type semiconductor device. The adhesive tape comprising: (A) 10 to 50 wt % of film forming resin; (B) 30 to 80 wt % of curable resin; and (C) 1 to 20 wt % of curing agent having flux activity.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Inkjet ink composition, ink cartridge including the same, and inkjet recording apparatus including the ink cartridge
InactiveUS20070040881A1Improve solubilityImprove stabilityMeasurement apparatus componentsInksColoring agentsChemistry
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Head trauma cap bandage and method
InactiveUS20090299259A1Fast and easy to applyAbsorb and control bleedingHead bandagesNeck bandagesCervical spine immobilizationEmergency medicine
An emergency head trauma cap bandage and method of use, which, when applied, applies compression pressure to stop bleeding, doesn't compromise cervical spine immobilization, doesn't come apart during treatment and transport, and doesn't require a caregiver to re-wrap the dressing.
Owner:CUMMING MICHELLE +1
Apparatus and method for cannulating retinal blood vessels
An apparatus and method for safely cannulating a retinal blood vessel is described. The apparatus consists of a micropipette / microcannula, micromanipulator and positioner mounted to a base, which is attached to a wrist rest commonly used in eye surgery. The micropipette / microcannula is connected to tubing such that a medication may be injected through the micropipette / microcannula into the blood vessel or conversely, a small quantity of material may be removed from a blood vessel. Alternatively, a catheter, wire or stent may be placed through the micropipette / microcannula to treat or diagnose an area remote from the insertion site. The ability to cannulate a retinal blood vessel should be efficacious in the treatment of vein and artery occlusion, ocular tumors and other retinal, vascular and optic nerve disorders that would benefit from diagnosis and / or treatment.
Owner:JNW PARTNERS
Cover-integrated gasket
InactiveUS7044475B2Improve adhesionIncrease productivityEngine sealsOther chemical processesVitrificationThermoplastic elastomer
A gasket integrated with a cover wherein a gasket material composed of a thermoplastic elastomer composition is integrally fixed to the cover having a shape of multistep contraction over at least two contraction steps, a gasket wherein the cover and the gasket are integrally molded and after molding, are subjected to a heating treatment at a temperature not lower than the temperature at which an adhesive component in materials constituting the gasket initiates crystal fusion or glass transition, or a gasket wherein the cover and the gasket are integrally molded and a covering layer composed of a fluoropolymer is formed on the gasket surface on atmospheric side are proposed. According to the present invention, a gasket integrated with a cover for a hard disc device which gasket is excellent in adhesive property and productivity, and is minimized in permeability and penetration of substances is provided.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
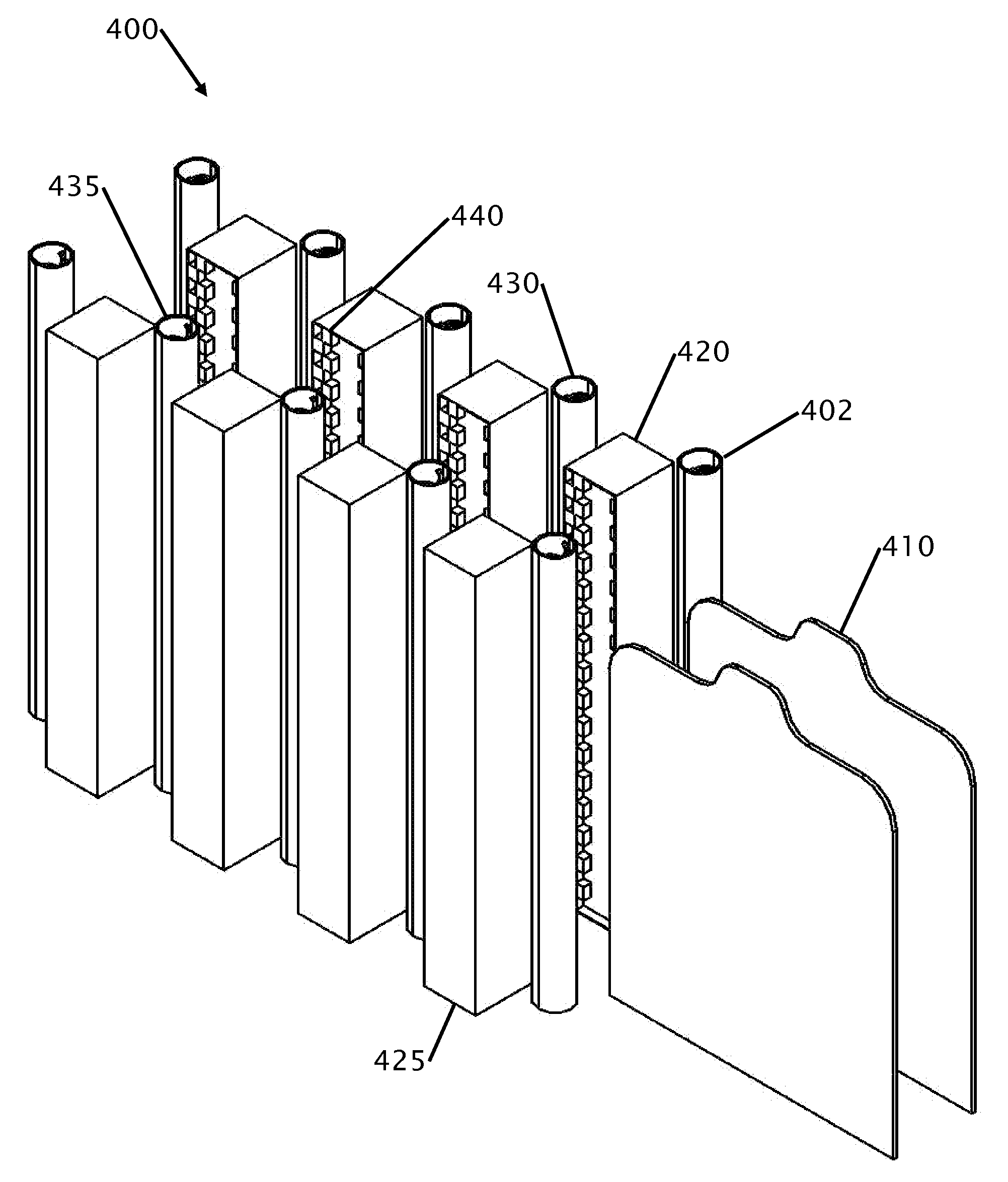
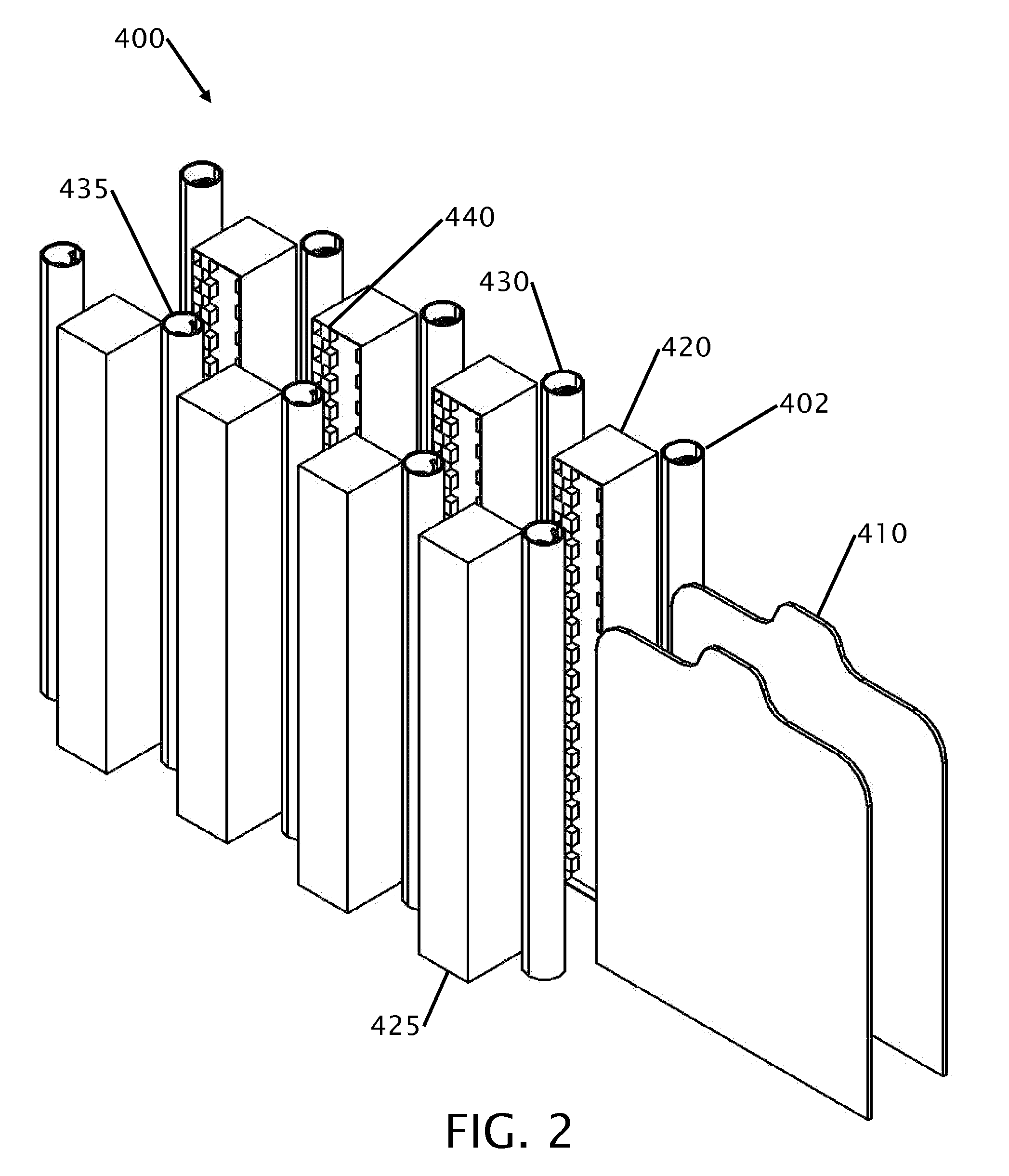
In-line multi-colored clothing printer
InactiveUS20090120309A1Improve productivityMinimize bleedingTypewritersRotary pressesScreen printingHue
Improvements in printing on shirts are disclosed. The shirt printer incorporates multiple elongated single color print heads arranged in-line. As opposed to using standard three or four colors, the clothing printer uses multiple heads where each print head uses a single specific color to eliminate mixing of the colors to obtain a specific hue. Between each print head, a dryer is placed to ensure each color is dry before the application on a subsequent color is applied. The method reproduces a similar method to clothing that is silk-screened. Clothing is placed on blank clothing holders and passes through the printing machine in an assembly line format. Print heads can be arranged on both sides of the blank clothing holder to allow for simultaneous printing on multiple sides of the clothing. Three printing styles are disclosed for a gauntlet style printers and a barrel style printer.
Owner:SZYSZKO ALEXANDER
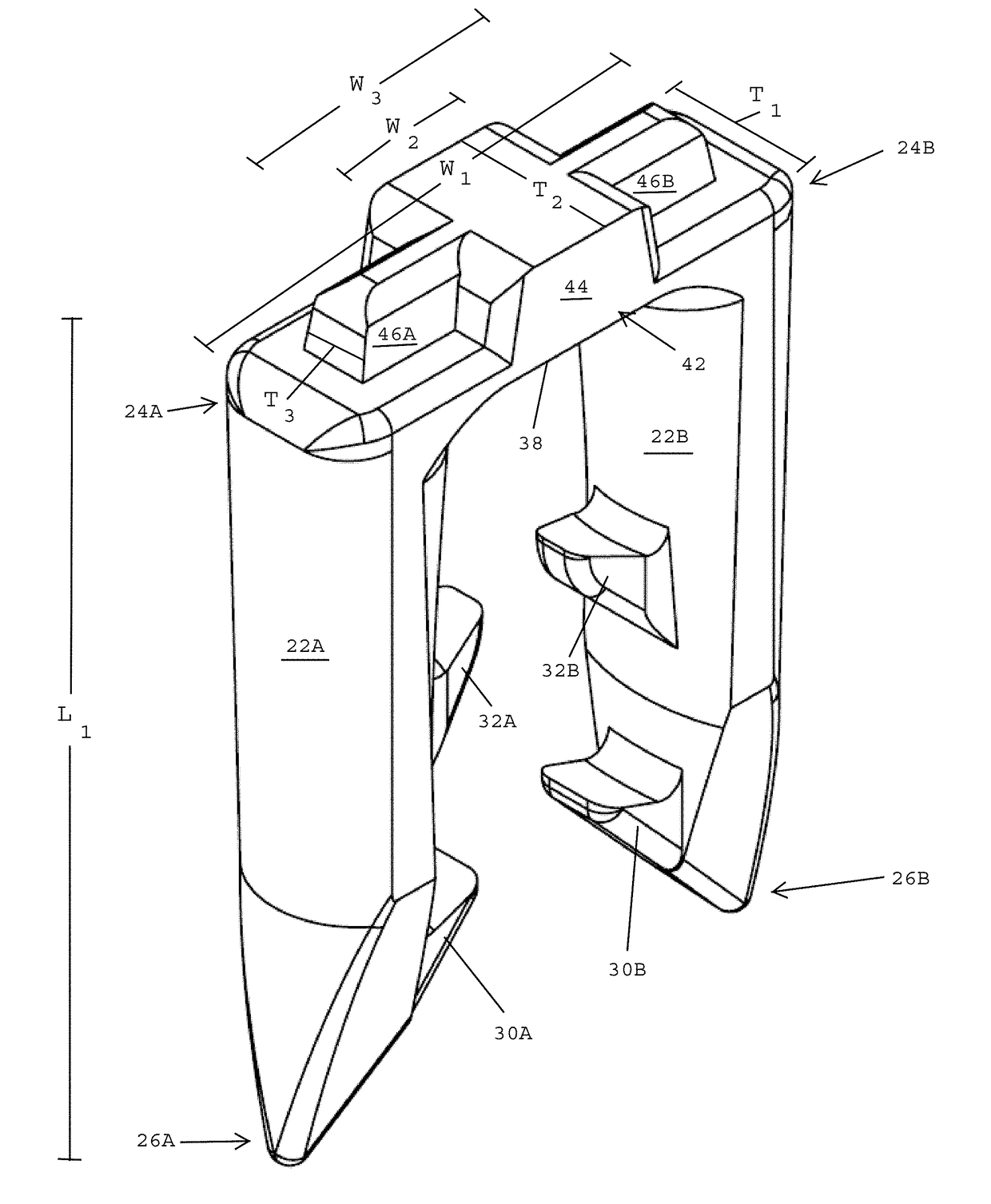
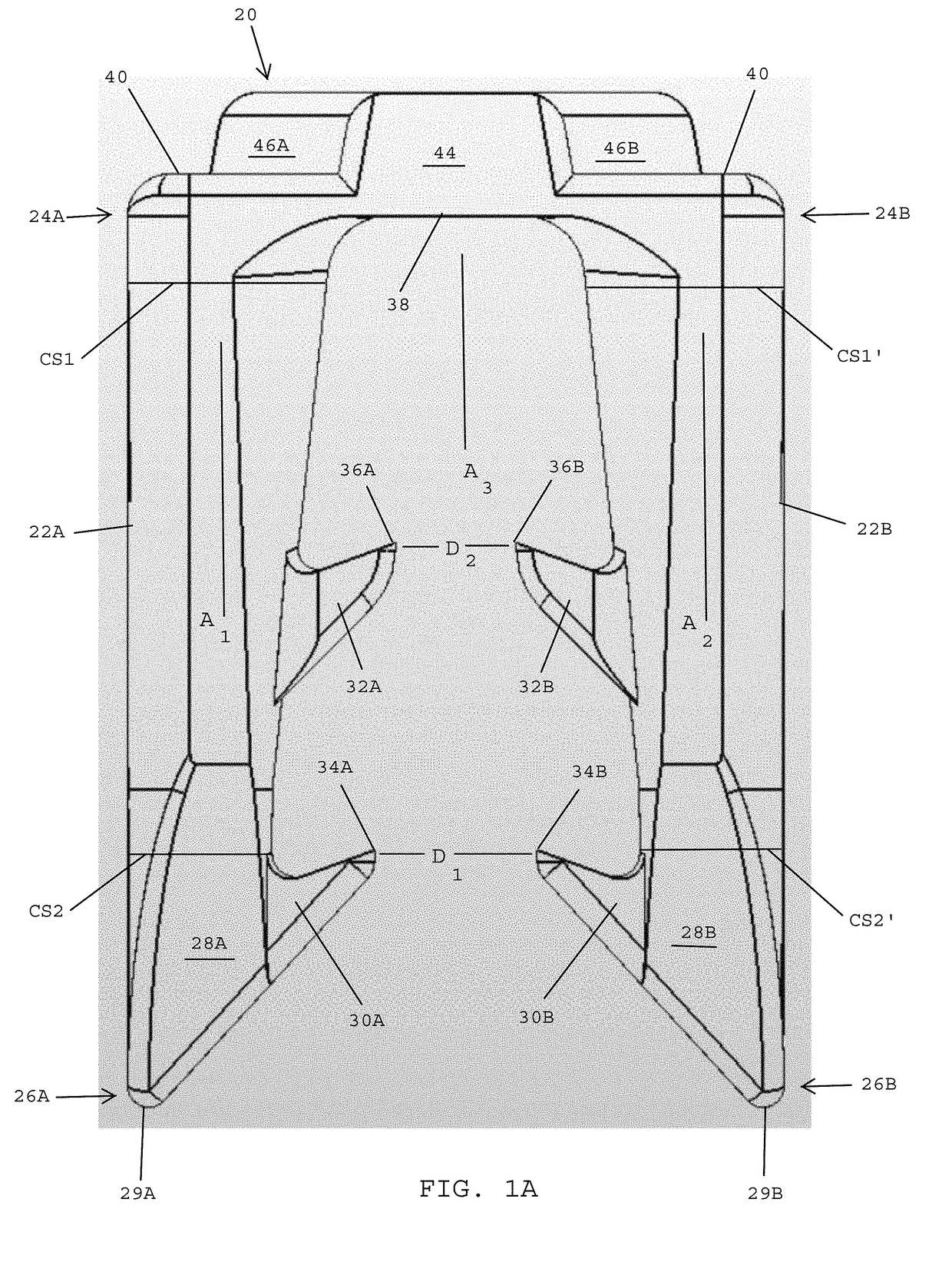
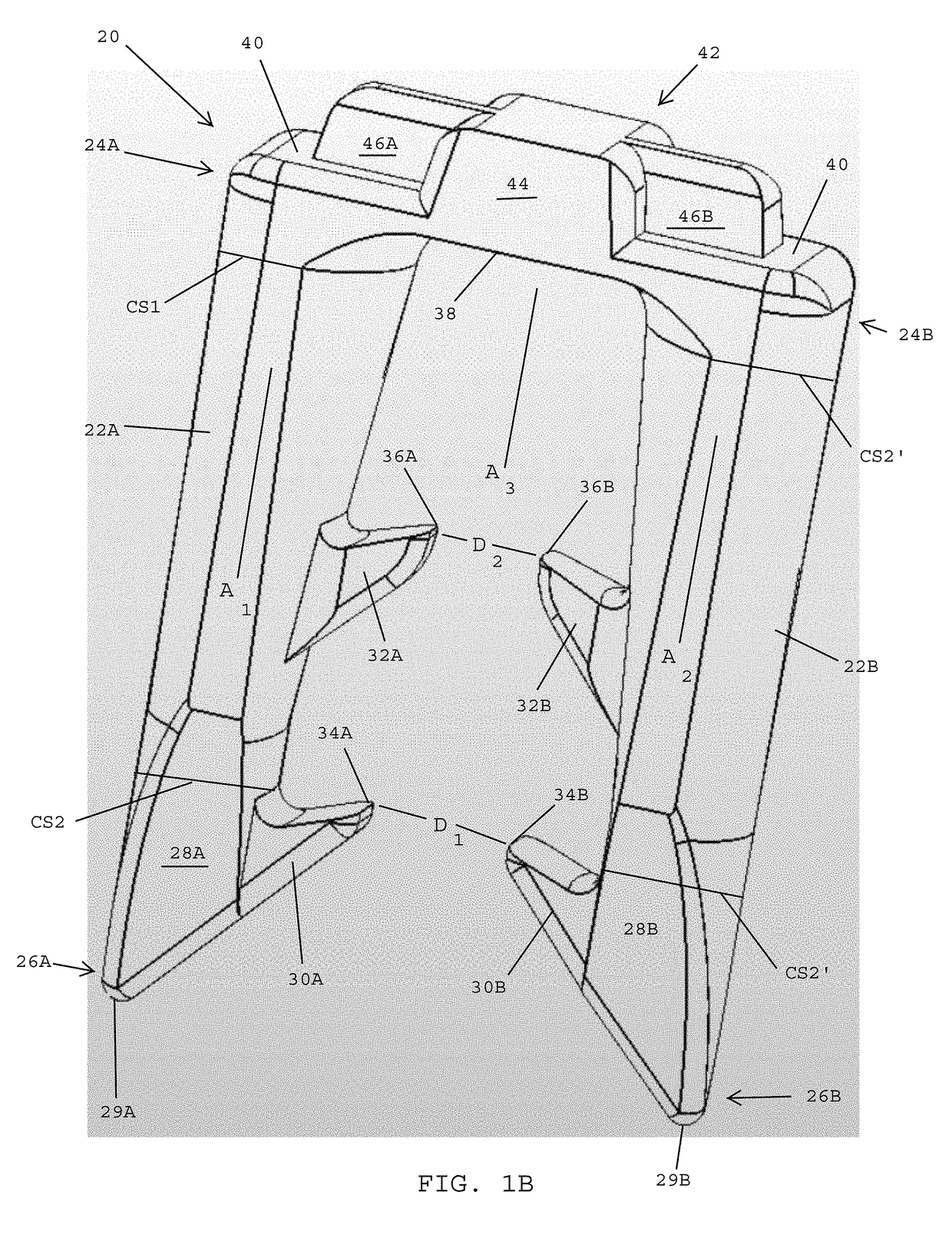
Surgical fasteners for mesh and tissue fixation
A surgical fastener includes a first leg having a first distal barb and a first proximal barb that extend inwardly, and a second leg having a second distal barb and a second proximal barb that extend inwardly. A bridge interconnects proximal ends of the first and second legs. A first distance between opposing inner tips of the first and second distal barbs is greater than a second distance between opposing inner tips of the first and second proximal barbs. The first leg tapers inwardly between the proximal and distal ends thereof and has a cross-sectional area that is greater at the proximal end than at the distal end. The second leg tapers inwardly between the proximal and distal ends thereof and has a cross-sectional area that is greater at the proximal end than at the distal end. An insertion tool engages a crown on the proximal side of the bridge.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Suction electrocautery device having controlled irrigation and rotating auger
InactiveUS20140276813A1More controlled, effective, and less invasive surgeryMinimize bleedingSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesDrive shaftHand held
The present invention is an improved electrocautery device having simplified irrigation controller, a controlled irrigation system and powered rotating auger. Both the rotating auger and the irrigation flow can be turned on and off by operating a controller on the hand-held portion of the device. The auger is part of a flexible rotating drive shaft within malleable suction coagulator conduction tubing. The controller on the handle operates the motor that powers the rotating drive shaft. The motor can also power an irrigation gate to control the flow of fluids through the device's irrigation channel. As an alternative, the irrigation flow can be controlled by mechanical depression of the controller on the handle. The motor can receive power from an AC or DC power source and can be located externally or within the housing of the suction coagulator.
Owner:GAMBRELL LARRY KYLE
Electrode for radiofrequency tissue ablation
ActiveUS9833282B2Simple electrode structureEasy to liftSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingMedicineSaline solutions
Owner:RF MEDICAL
Head trauma bandage and method
InactiveUS20100016775A1Reducing triage timeFast shippingHead bandagesNeck bandagesCervical spine immobilizationEmergency medicine
An emergency head trauma bandage and method of use, which, when applied, applies minimal pressure to stop bleeding, doesn't compromise cervical spine immobilization, allows for fast and effective application of ice / cold packs to control intracranial / internal swelling, doesn't come apart during treatment and transport, and doesn't require a caregiver to re-wrap the dressing.
Owner:CUMMING MICHELLE +1
Skull clamp system with pressure limiting and alarm systems
ActiveUS20120323239A1Eliminate torqueReduce chanceFractureInvalid friendly devicesEngineeringSkull clamp
The skull clamp system with pressure limiting and alarm systems includes at least one and preferably multiple inwardly power driven immobilizing pins adjustably engaging the skull of a patient. The pin power drive systems includes at least one sensor capable of sensing the degree of back pressure on the pin from contact of the pin against the bone of the patient, the sensor being capable of signaling the drive system to stop when the sensor detects a preselected degree of back pressure. The sensor is also capable of signaling an alarm to warn of any reduction of pressure applied to the pins that might result from pin slippage.
Owner:SOLOMON CLIFFORD T +1
Multi-stage dispensing mat
InactiveUS7046920B2Minimize bleedingSacrificing long-term protectionRespiratorsLighting and heating apparatusVolatilesVaporization
Disclosed herein are mats for dispensing volatile materials. A mat of the present invention includes a moat on an upper surface of the mat defining a first mat portion and a second mat portion, preferably connected at the bottom of the moat. Both portions are impregnated with the same or different volatiles. The moat is formed by pressing the upper wall of the mat with a hot forming die. While pressed against the upper wall, the hot die melts the mat material leading to the close of the pores in the material and as a result, a barrier along moat walls is formed. The moat and barrier act to prevent or reduce bleeding of the volatiles between two portions of the mat. The mat provides for both instant burst of volatile and then a sustained vaporization of volatile. Methods for making and using the mat are also disclosed.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Skull clamp system with pressure limiting and alarm systems
The skull clamp system with pressure limiting and alarm systems includes at least one and preferably multiple inwardly power driven immobilizing pins adjustably engaging the skull of a patient. The pin power drive systems includes at least one sensor capable of sensing the degree of back pressure on the pin from contact of the pin against the bone of the patient, the sensor being capable of signaling the drive system to stop when the sensor detects a preselected degree of back pressure. The sensor is also capable of signaling an alarm to warn of any reduction of pressure applied to the pins that might result from pin slippage.
Owner:SOLOMON CLIFFORD T +1
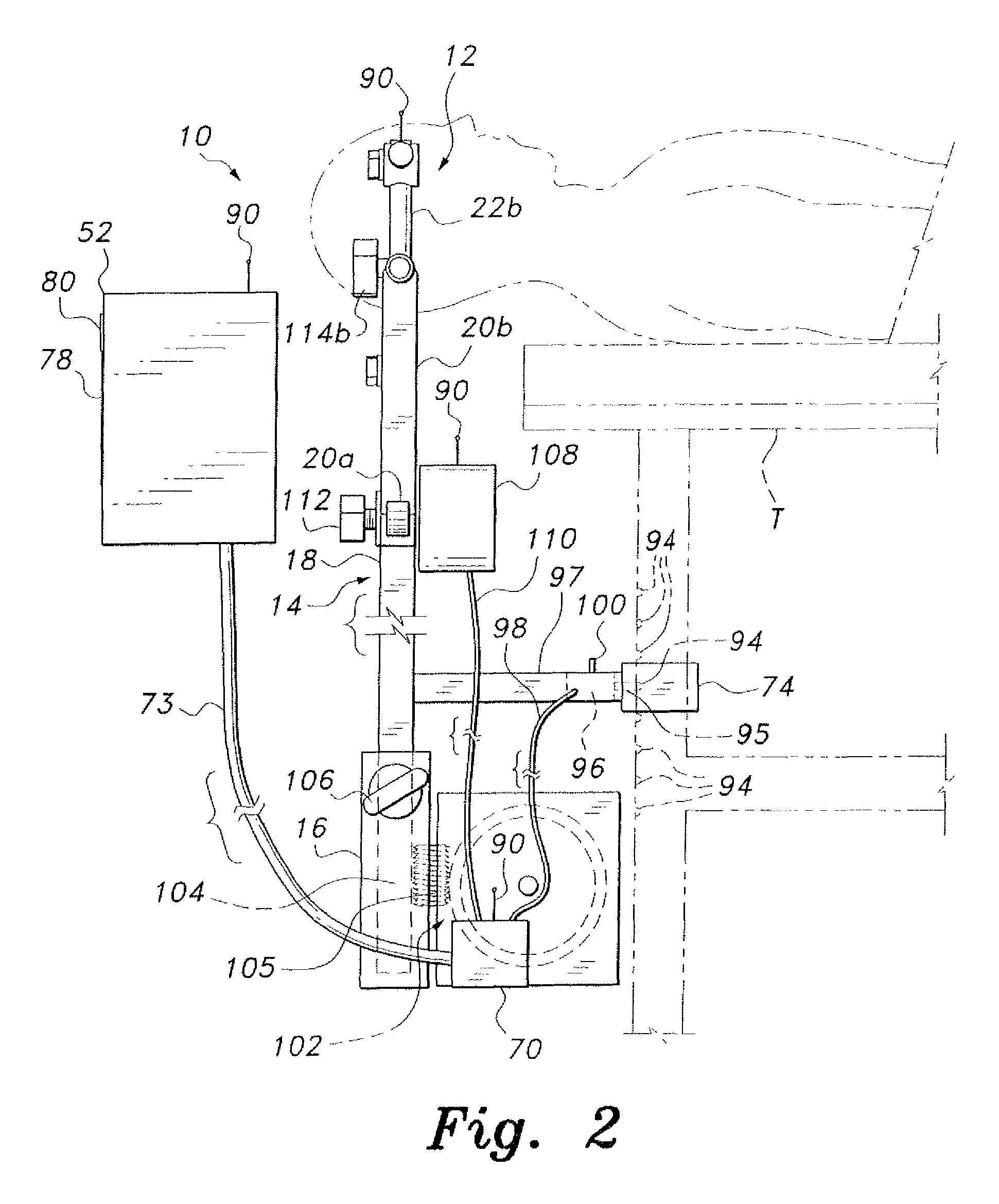
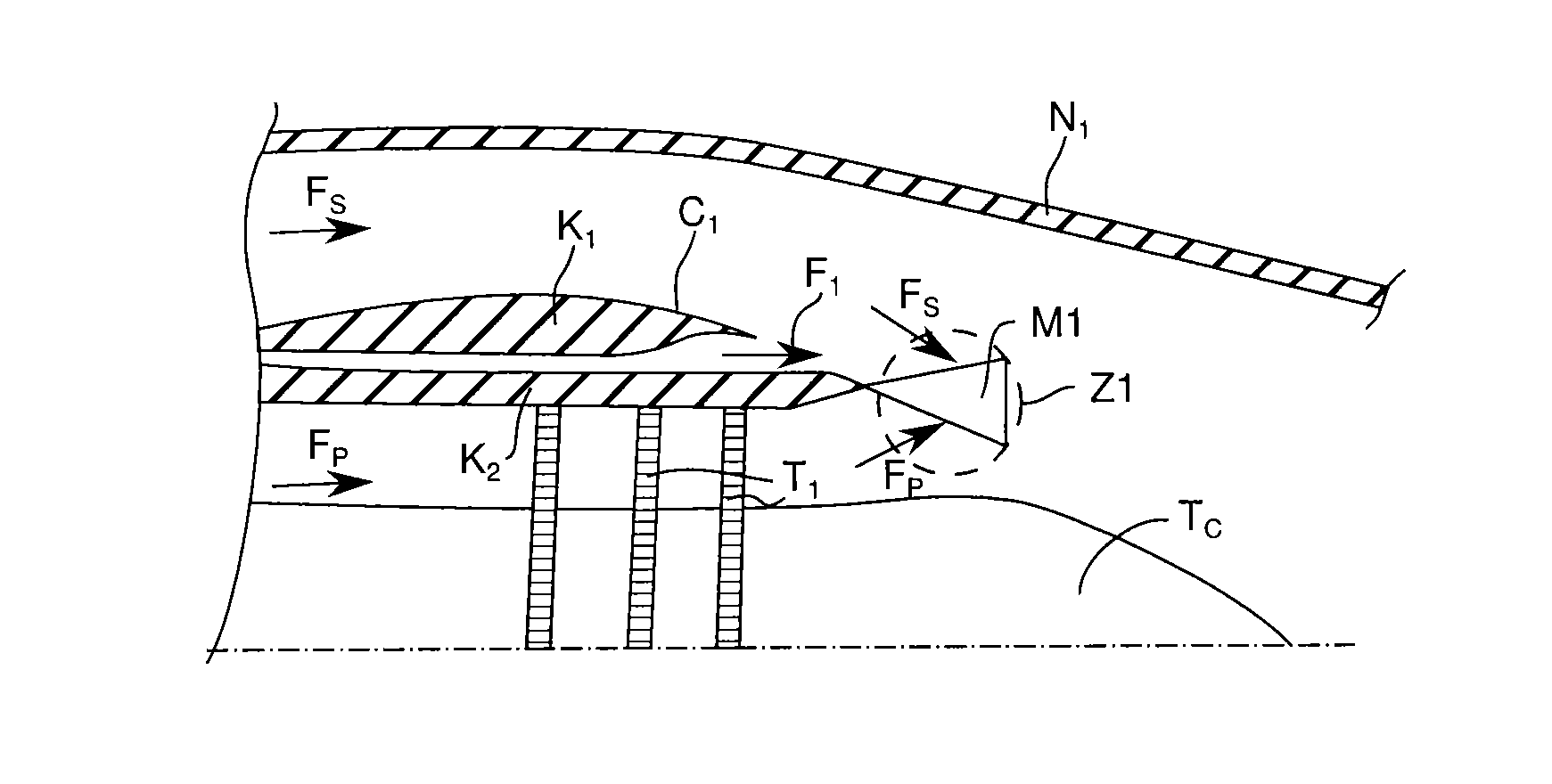
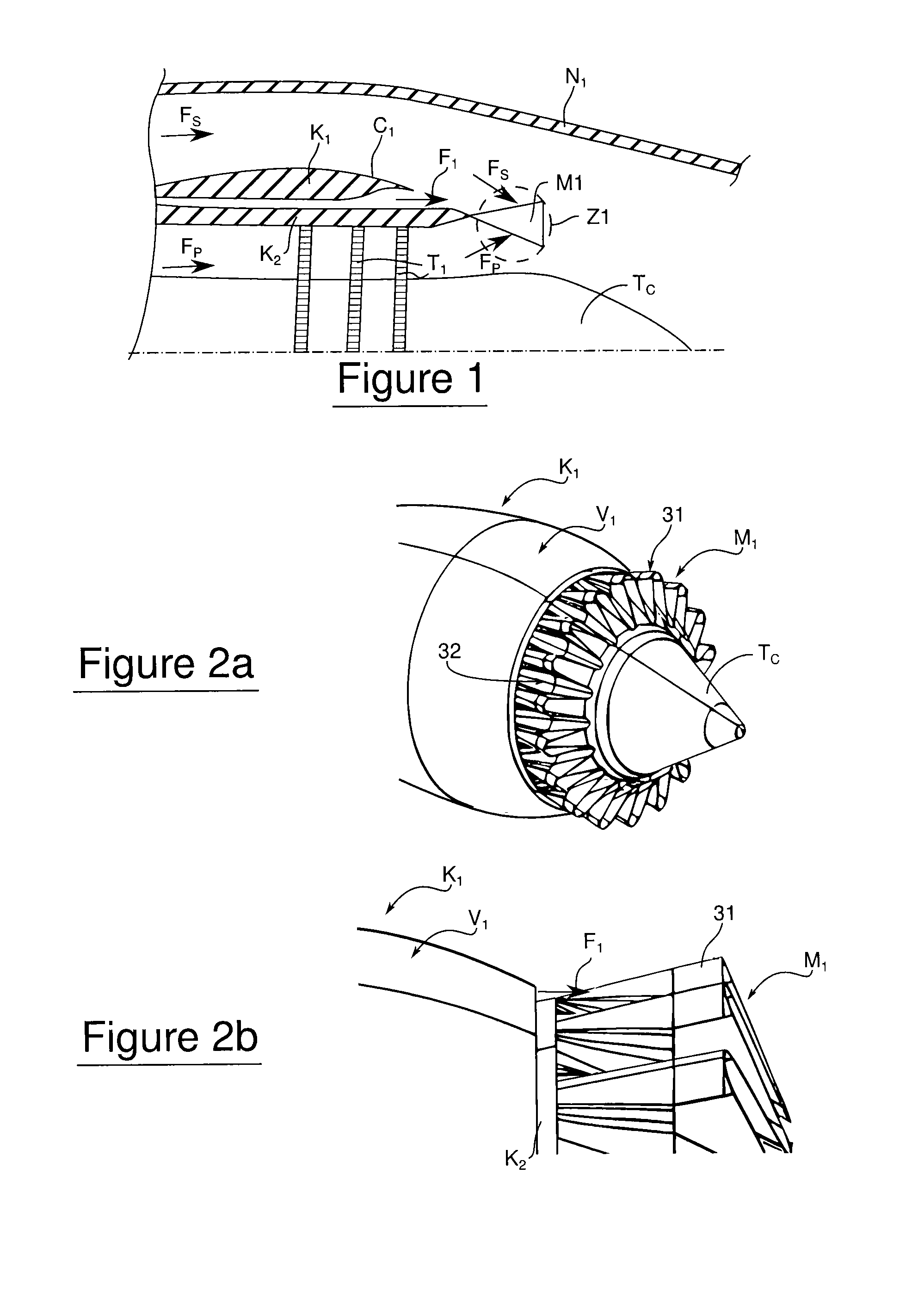
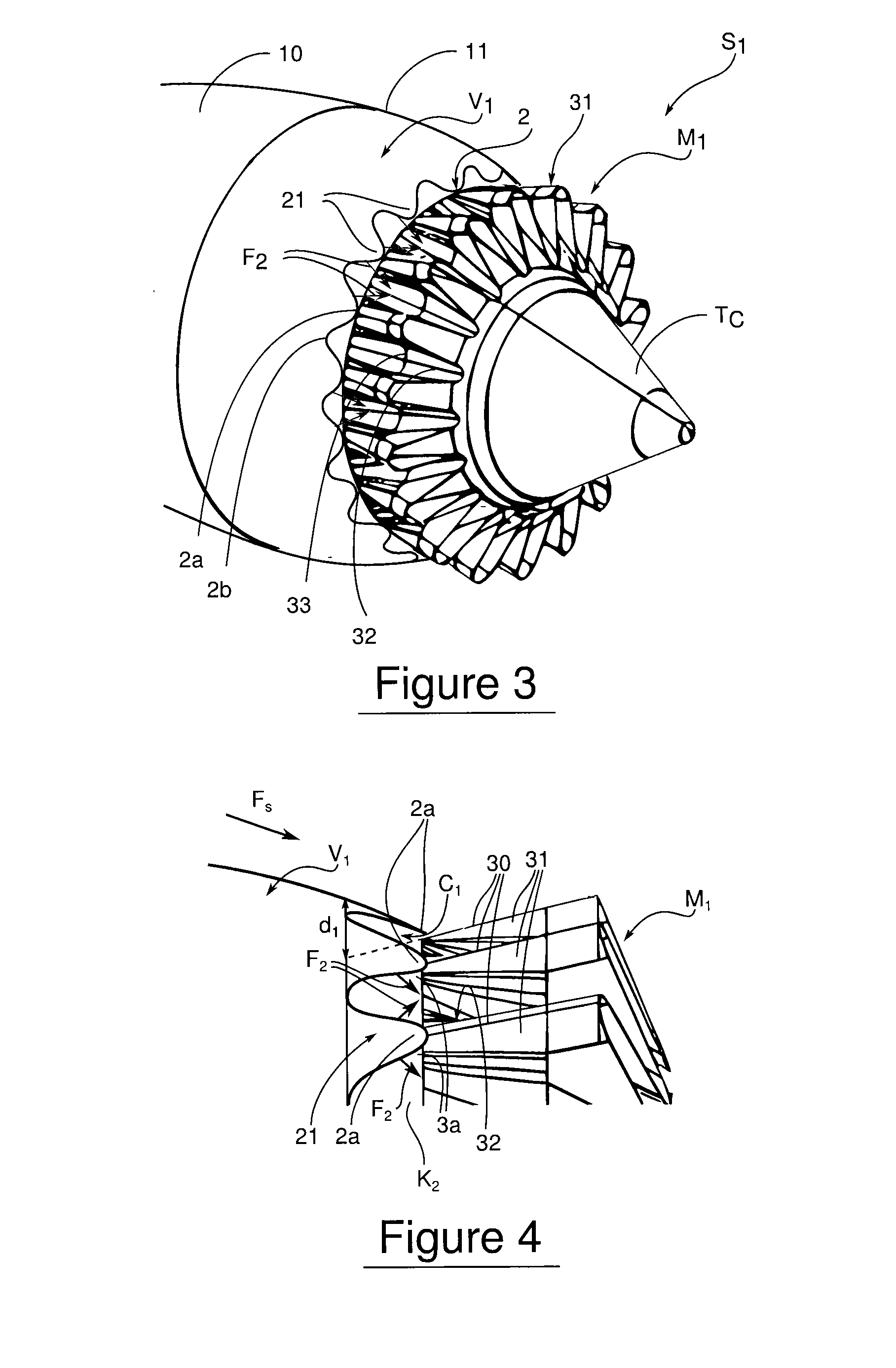
Method for mixing airflows in a turbofan and engine outlet for operation
ActiveUS20130056553A1Small sizeMinimize bleedingAircraft navigation controlPower plant exhaust arrangementsAirflowTurbofan
The invention aims at providing a sufficient air exchange in the engine area without raising the static pressure in the outlet area of the air exchange duct. In order to do this, the invention provides for an outlet section capable of concentrating the outlet of the exchange airflow towards zones with smaller static pressure.An turbojet engine outlet according to the invention provides an engine cowl, which comprises an external wall of a circumferential duct in which circulates an exchange airflow of the turbines, and an airflow mixer. At the outlet, the duct delivers the exchange airflow towards the mixer for the primary and secondary airflows of the turbojet engine. The mixer presents hot and cold lobes. In particular, the engine outlet also comprises guiding means of the exchange airflow towards the cold lobes.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Ultrasonic device and method for tissue coagulation
ActiveUS20040102801A1Coagulating tissueGood coagulationUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesDistal portionUltrasound
An ultrasonic surgical device for the coagulation of animal tissue having an ultrasonic applicator and a movable jaw with a jaw surface adjacent the distal portion of the ultrasonic applicator for movement toward the applicator to a closed position at a predefined clearance of between about 0.075 to about 1.9 millimeters from the applicator. The device may also include a mechanical cutting element that can be extended into the clearance to cut the tissue and means to vary the predefined clearance without removing the applicator from the patient. Tissue coagulating and cutting can be maximized and performed separately and can be easily monitored by the surgeon.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
Surgical fasteners for mesh and tissue fixation
ActiveUS10568627B2Preventing and reducing bleedingPreventing and minimizing bleedingStaplesNailsAnatomyTissue fixing
A surgical fastener includes a first leg having a first distal barb and a first proximal barb that extend inwardly, and a second leg having a second distal barb and a second proximal barb that extend inwardly. A bridge interconnects proximal ends of the first and second legs. A first distance between opposing inner tips of the first and second distal barbs is greater than a second distance between opposing inner tips of the first and second proximal barbs. The first leg tapers inwardly between the proximal and distal ends thereof and has a cross-sectional area that is greater at the proximal end than at the distal end. The second leg tapers inwardly between the proximal and distal ends thereof and has a cross-sectional area that is greater at the proximal end than at the distal end. An insertion tool engages a crown on the proximal side of the bridge.
Owner:ETHICON INC
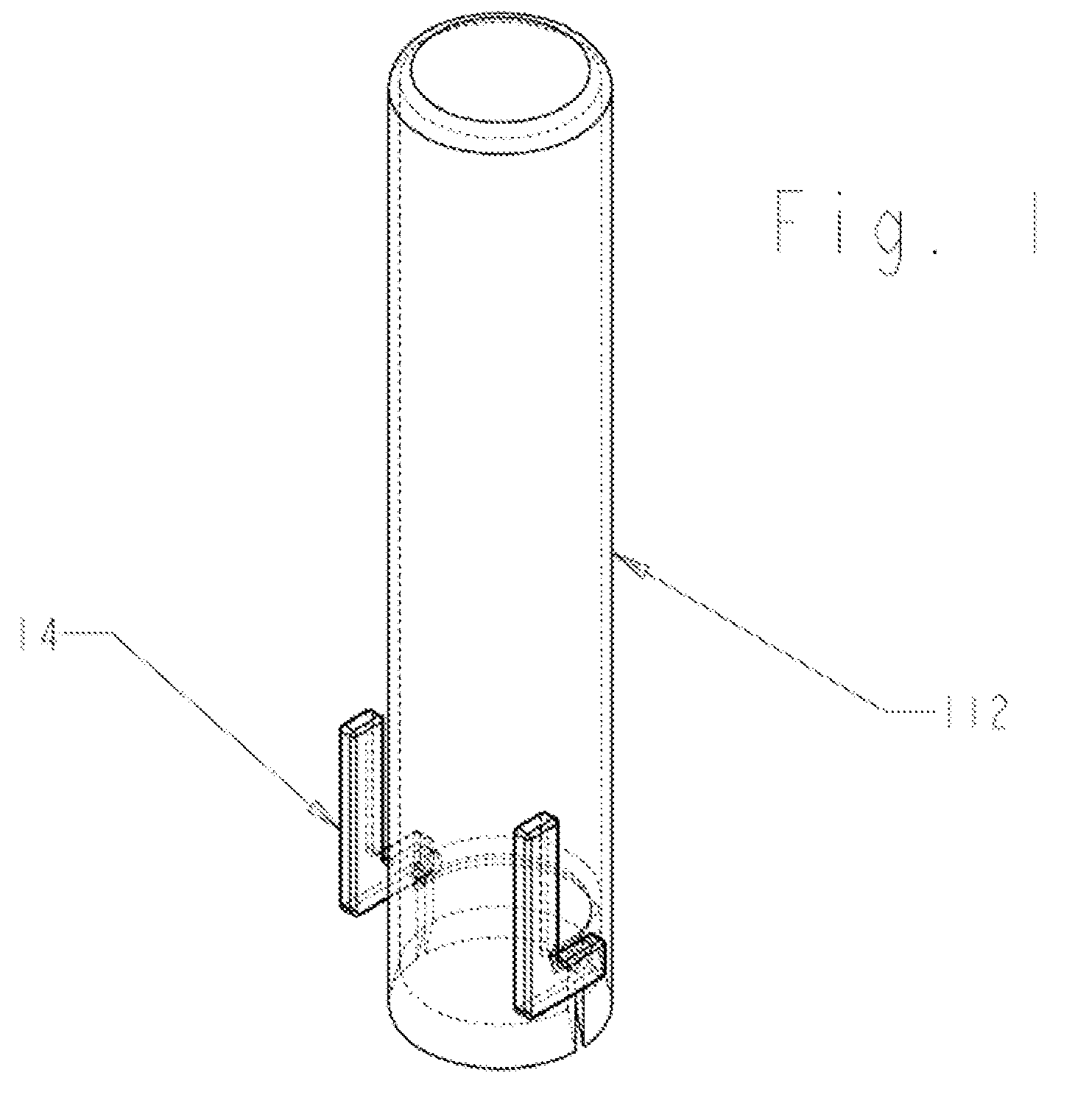
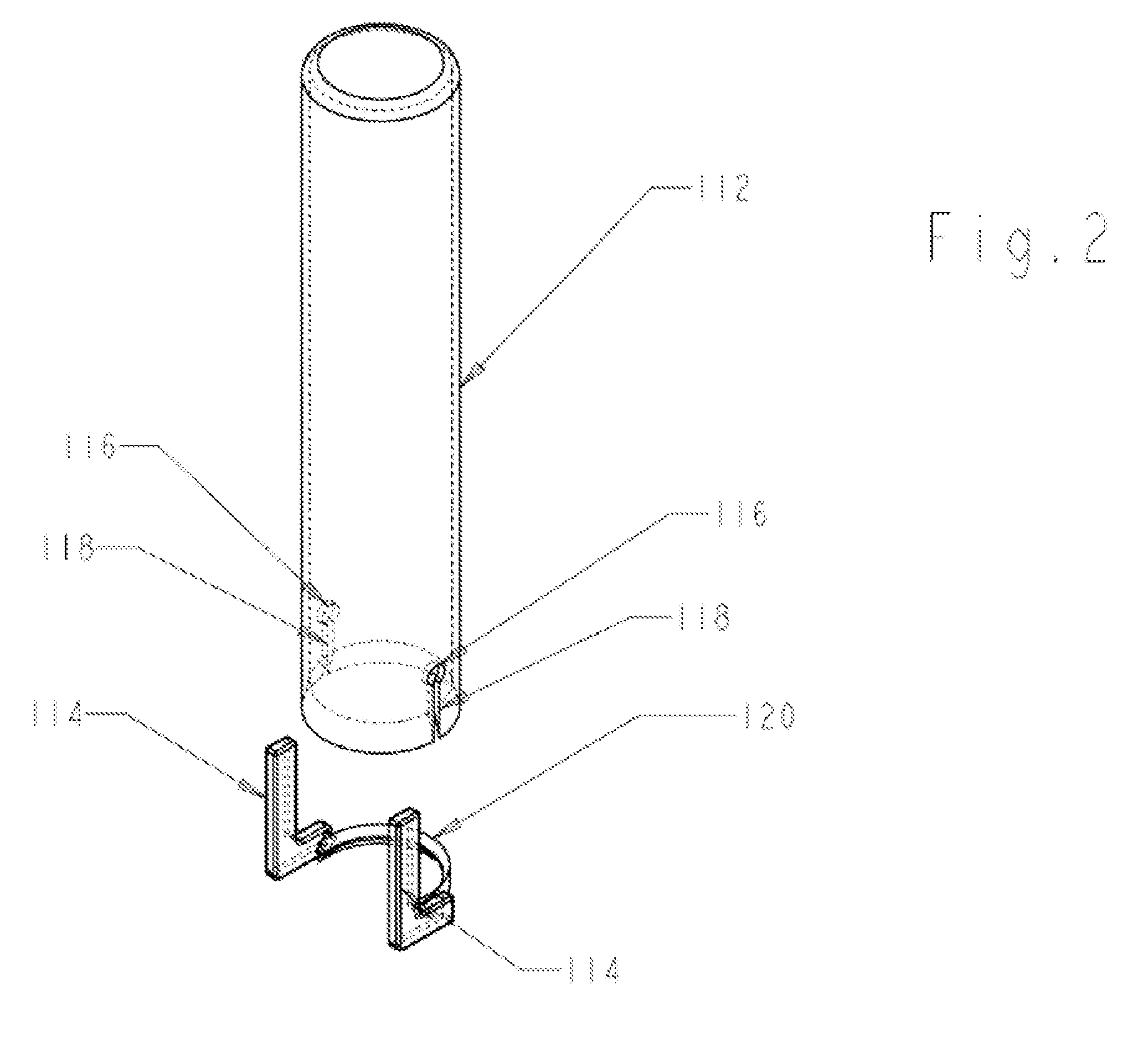
Surgical instrument for operations on the spinal column
ActiveUS8663101B2Easy to splitMinimize bleedingBlunt dissectorsSwabsSpinal columnLumbar vertebral column
A surgical kit for operations on the spinal column includes a surgical instrument having a handle body, the handle body having a substantially flat portion blended with the body, wherein the substantially flat portion is shaped to urge the gauze for draining a wound.
Owner:N B R NEW BIOTECH RES
Needle kit and method for microwave ablation, track coagulation, and biopsy
InactiveUS8690868B2Minimize damageMinimize bleedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFungating tumourBiomedical engineering
A modular biopsy, ablation and track coagulation needle apparatus is disclosed that allows the biopsy needle to be inserted into the delivery needle and removed when not needed, and that allows an inner ablation needle to be introduced and coaxially engaged with the delivery needle to more effectively biopsy a tumor, ablate it and coagulate the track through ablation while reducing blood loss and track seeding. The ablation needle and biopsy needle are adapted to in situ assembly with the delivery needle. In a preferred embodiment, the ablation needle, when engaged with the delivery needle forms a coaxial connector adapted to electrically couple to an ablating source. Methods for biopsying and ablating tumors using the device and coagulating the track upon device removal are also provided.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Ink jet recording apparatus
Owner:CANON KK
Apparatus for punch biopsy
InactiveUS7442170B2Minimize bleedingMinimize damageSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCylindromaEngineering
A punch biopsy apparatus for removing all or a portion of a suspect dermal growth. A punch biopsy apparatus has: a hollow cylinder body; a coring blade at the base of the hollow cylinder body; and a scooping blade assembly installed through a pair of installation channels and pivotally secured by a pair of pivot seats, where the scooping blade assembly comprises a semicircular scooping blade having actuating levers attached at each end via essentially rectangular connectors. This device helps minimize bleeding and minimize damage to the biopsy sample being retrieved.
Owner:CHIU KWOK WAI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com