Patents
Literature
255 results about "Digital holography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
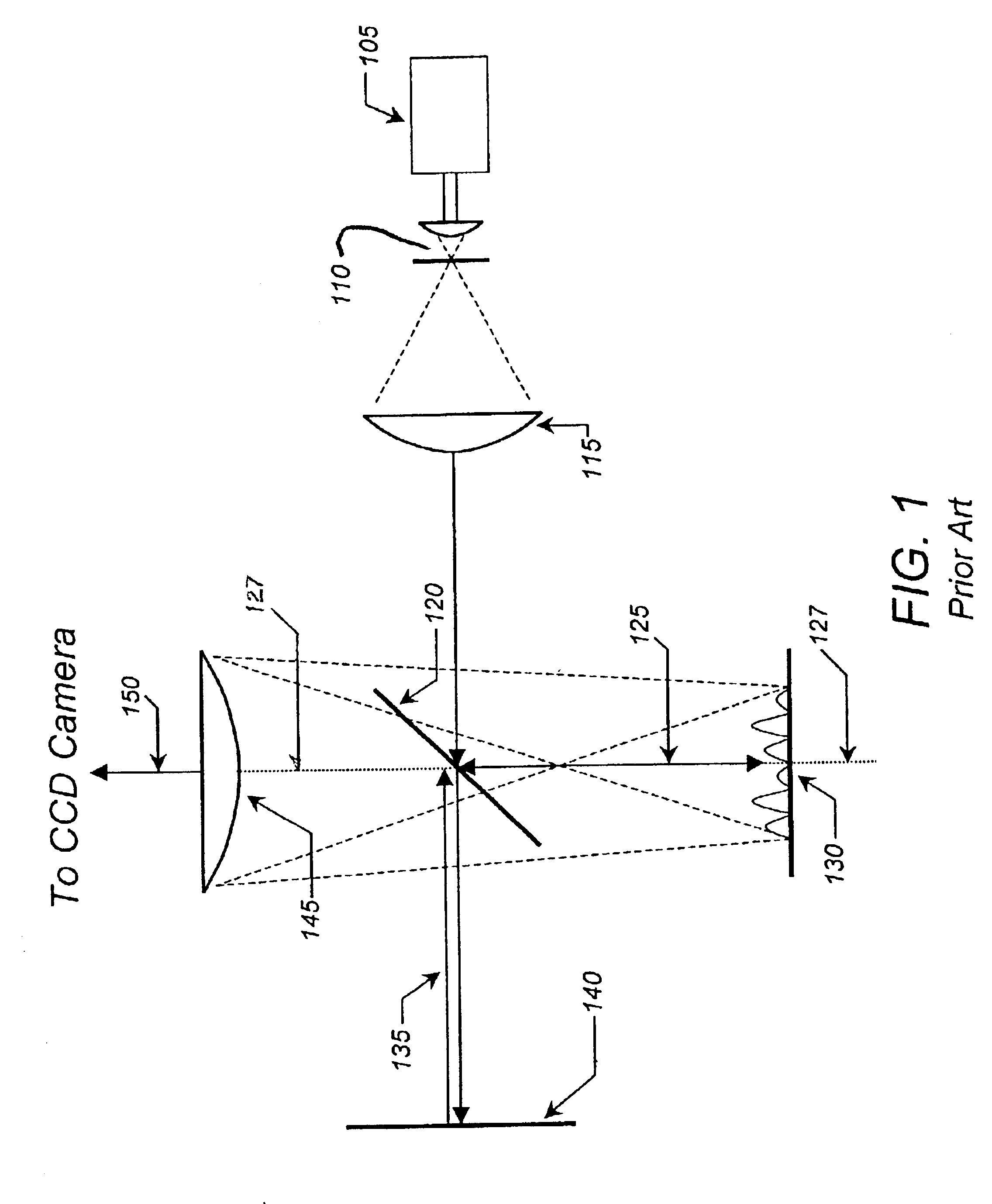
Digital holography refers to the acquisition and processing of holograms with a digital sensor array , typically a CCD camera or a similar device. Image rendering, or reconstruction of object data is performed numerically from digitized interferograms. Digital holography offers a means of measuring optical phase data and typically delivers three-dimensional surface or optical thickness images. Several recording and processing schemes have been developed to assess optical wave characteristics such as amplitude, phase, and polarization state, which make digital holography a very powerful method for metrology applications .
Wave front sensing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7649160B2Reduce fieldHigh resolutionImage enhancementOptical measurementsWavefront sensorMetrology
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Wave Front Sensing Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080265130A1Improve performanceHigh imaging performanceImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueWavefront sensorMetrology
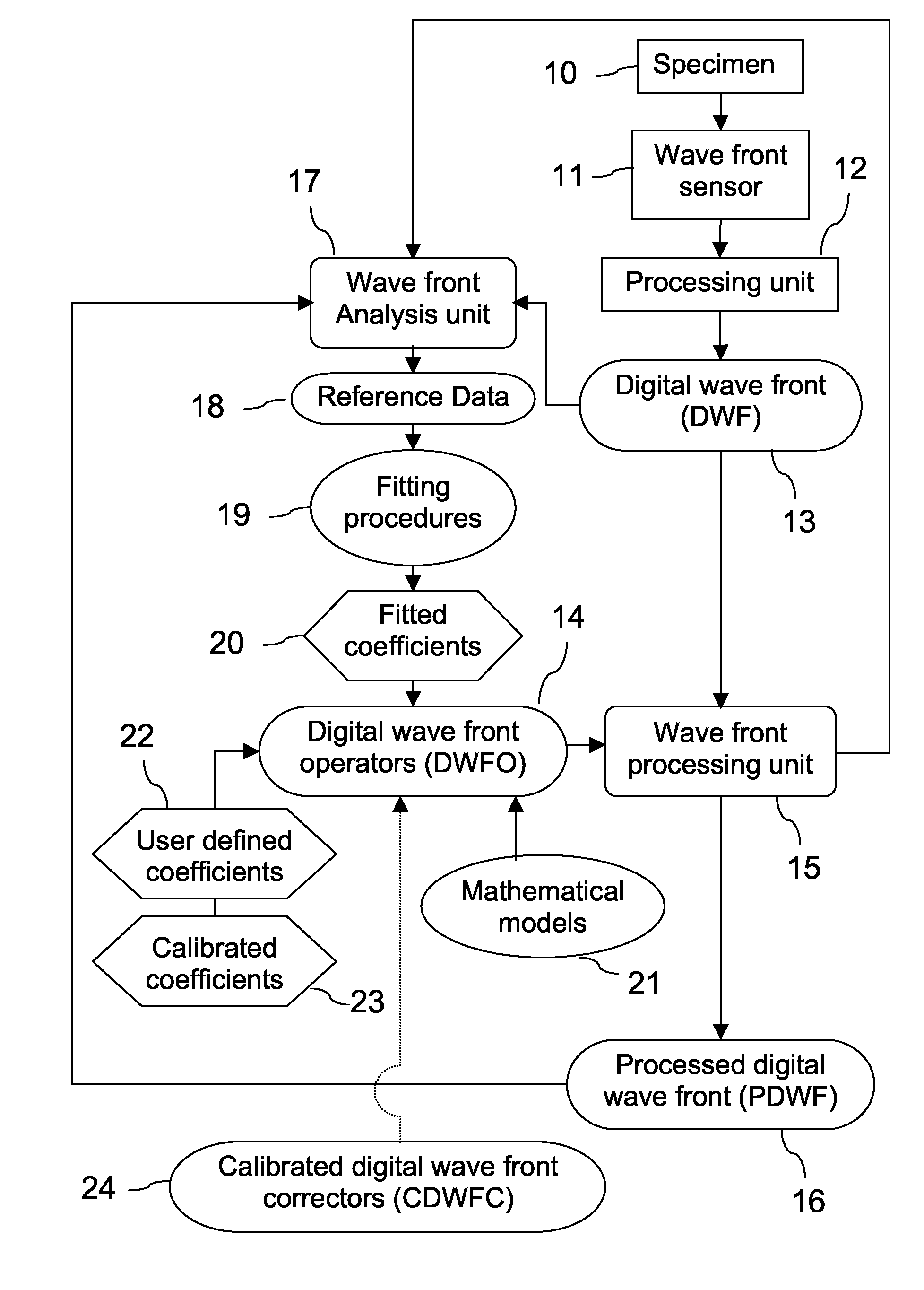
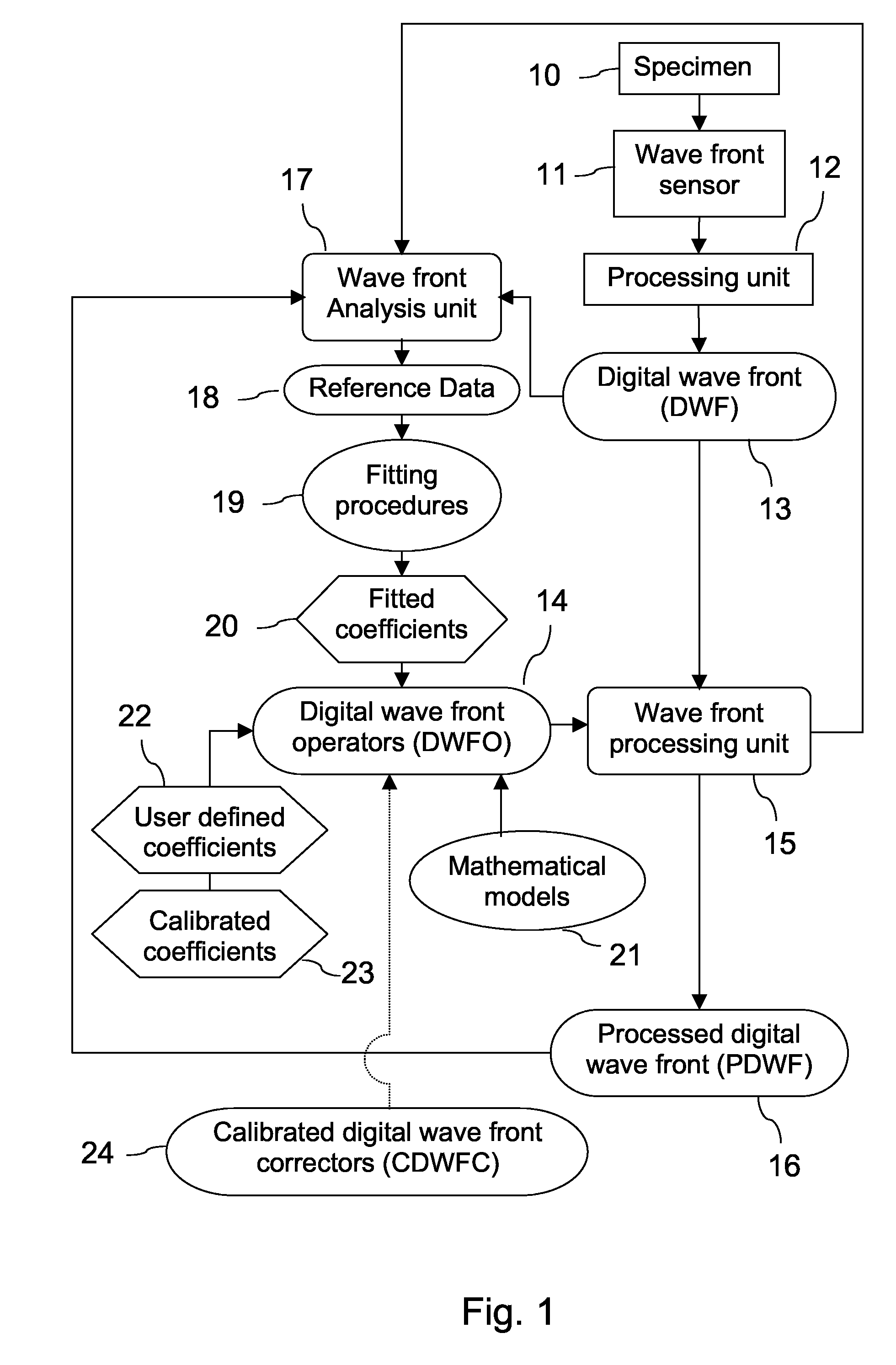
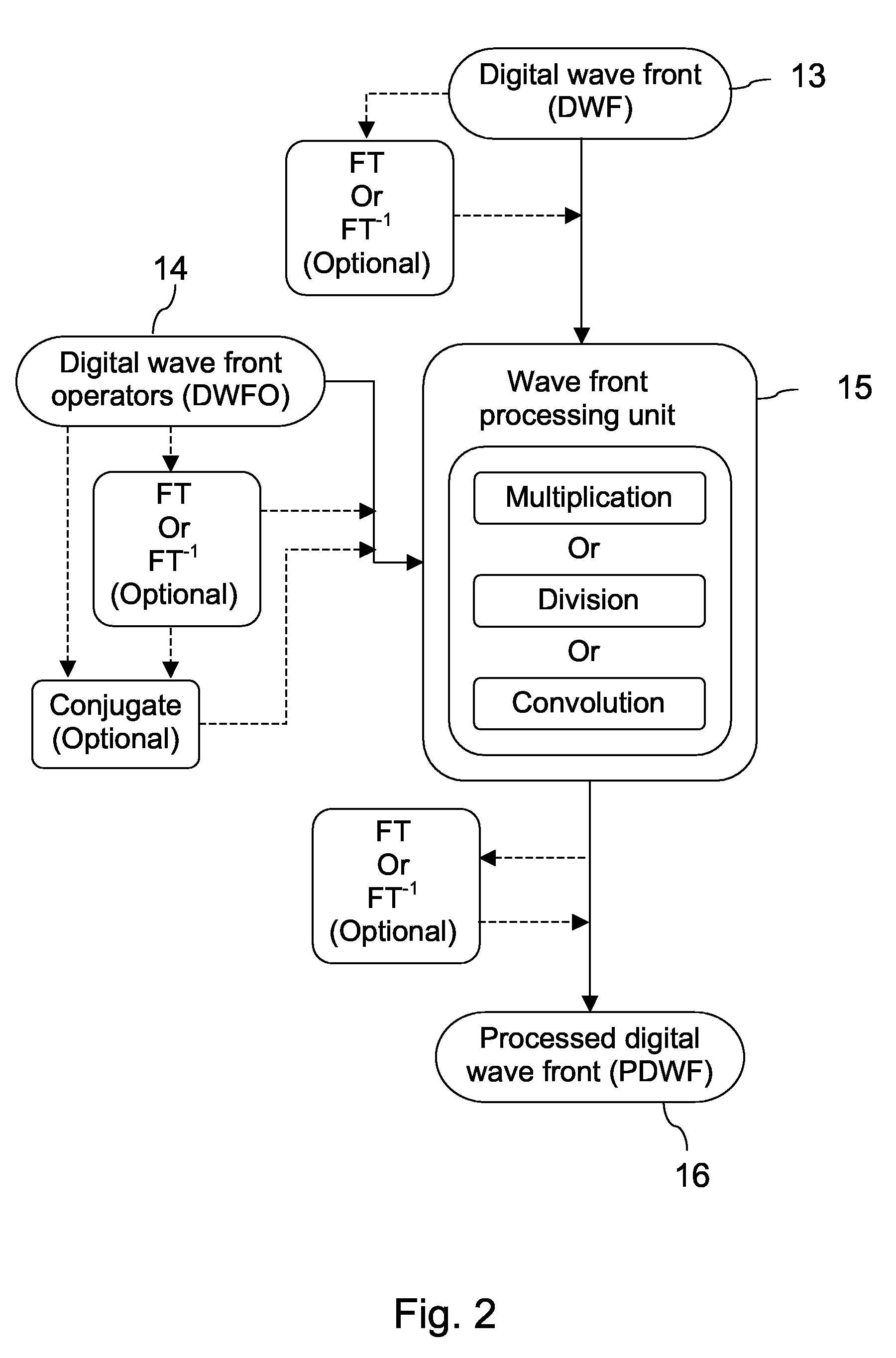
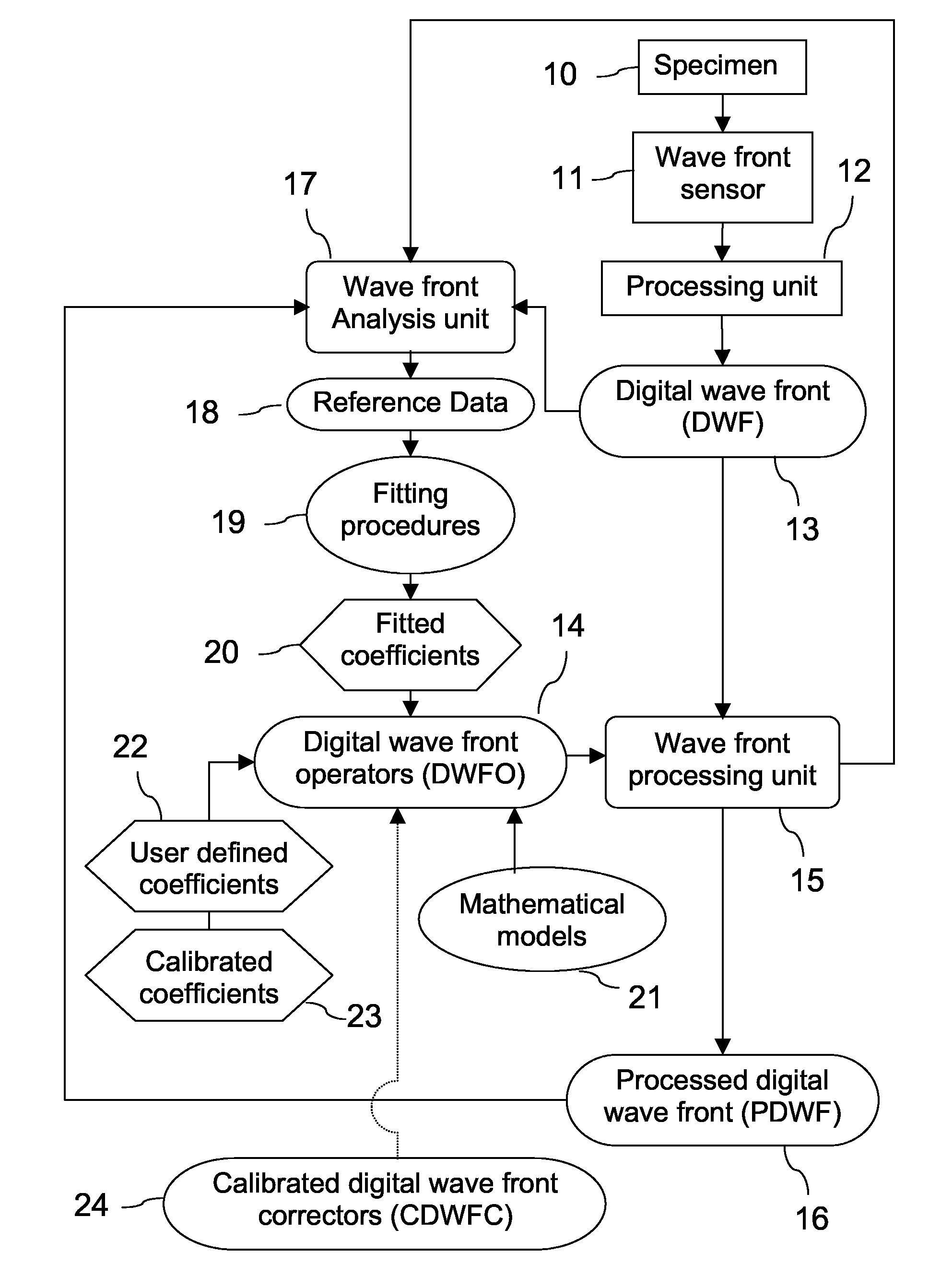
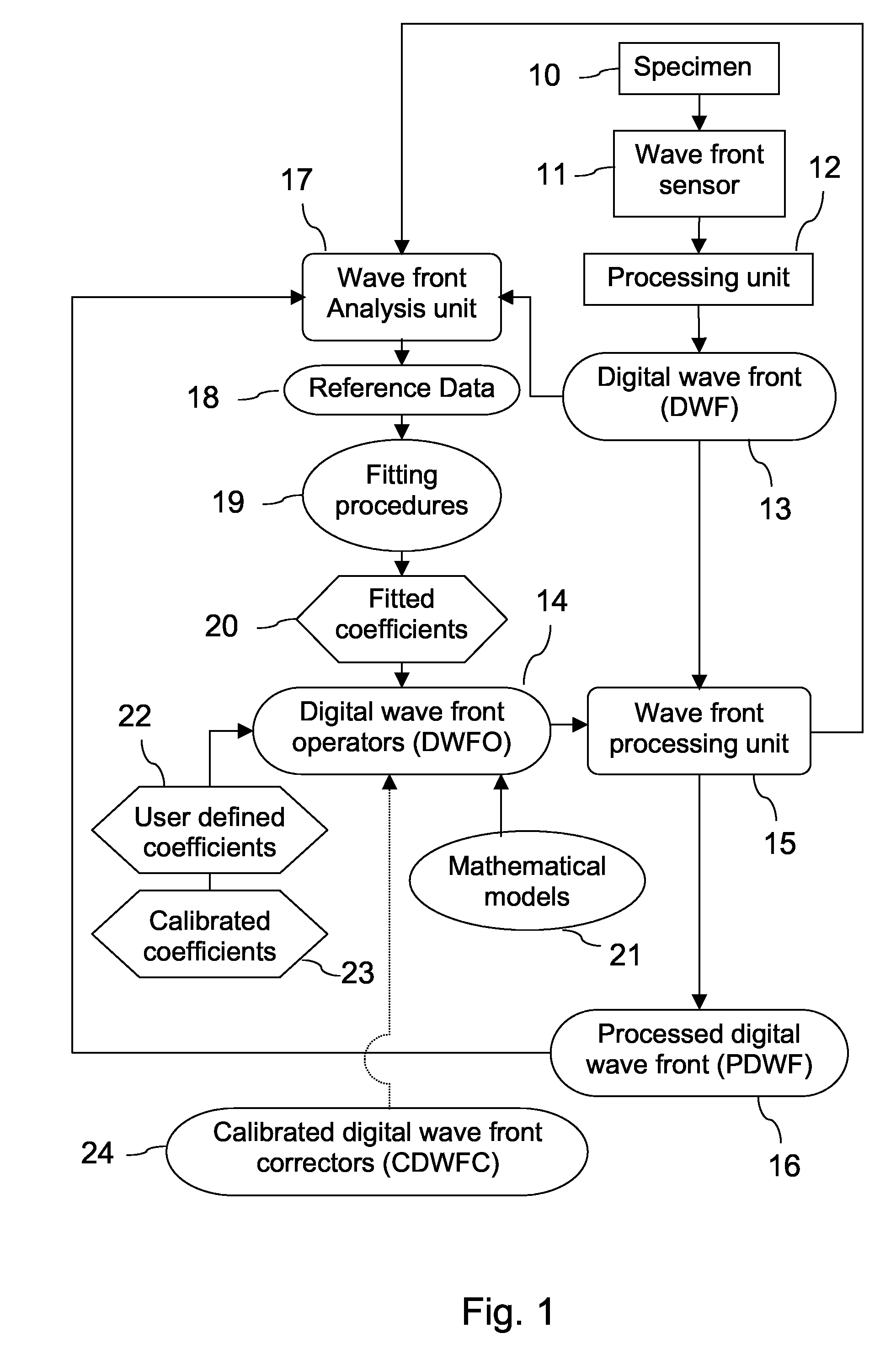
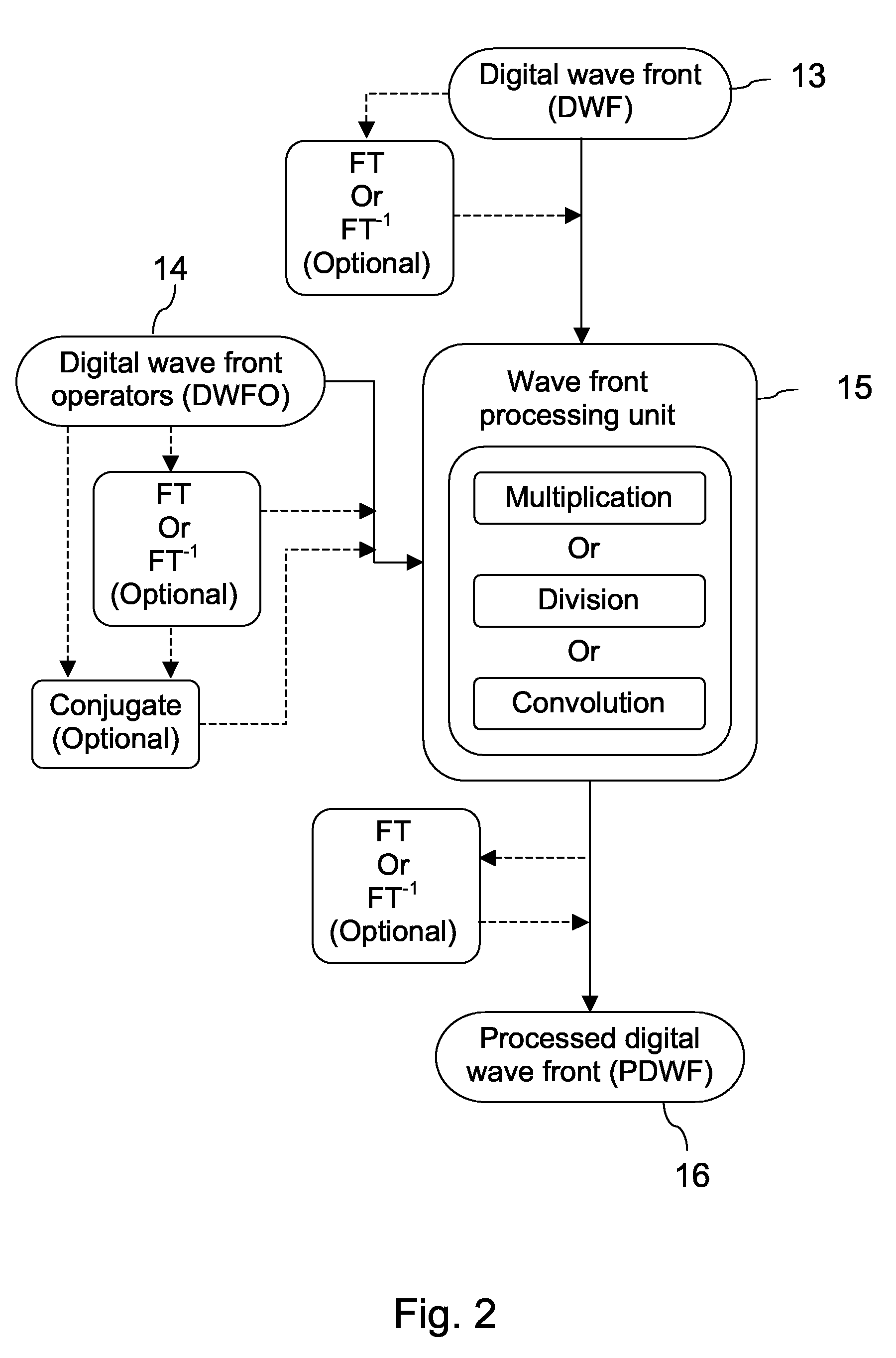
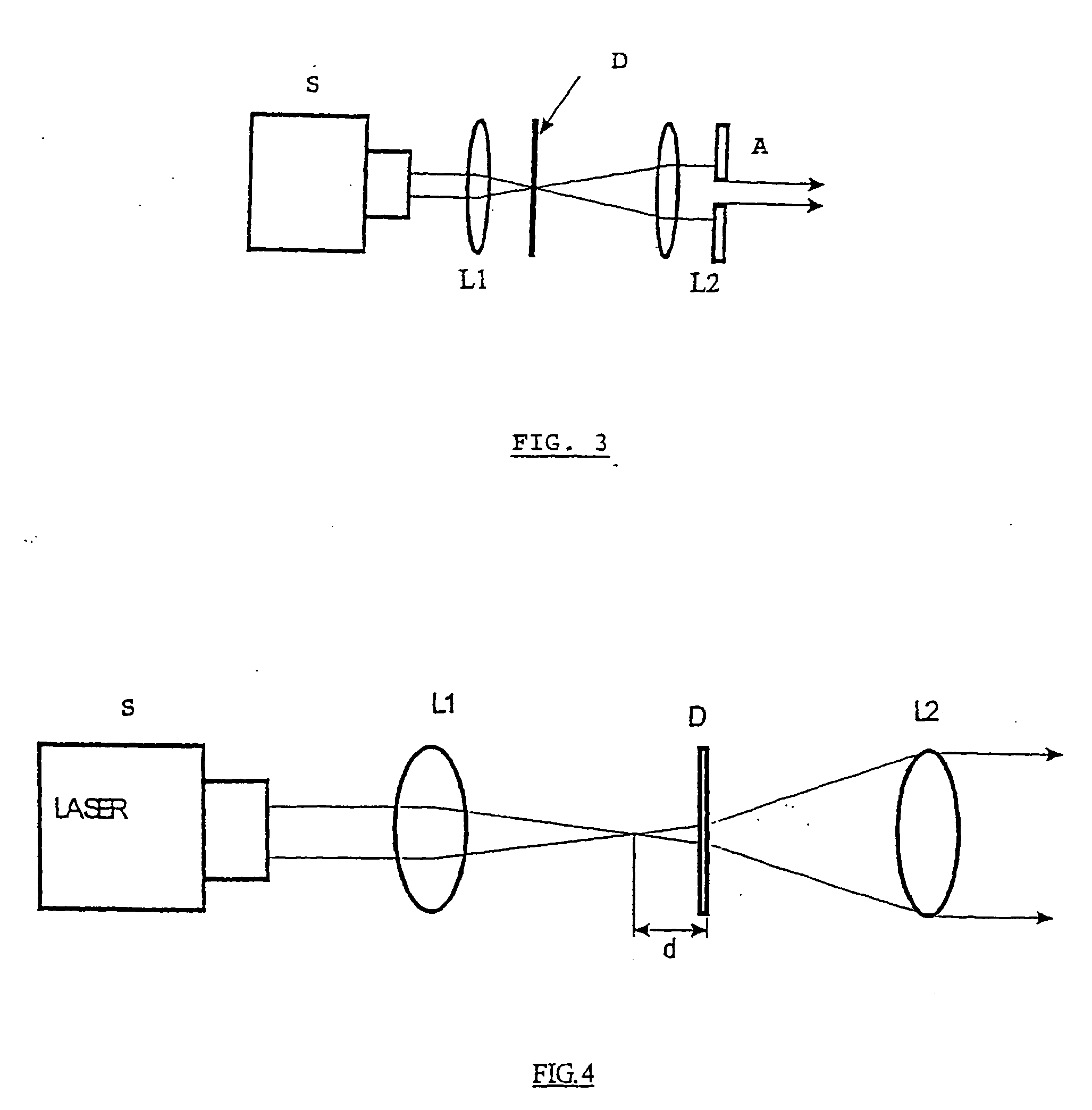
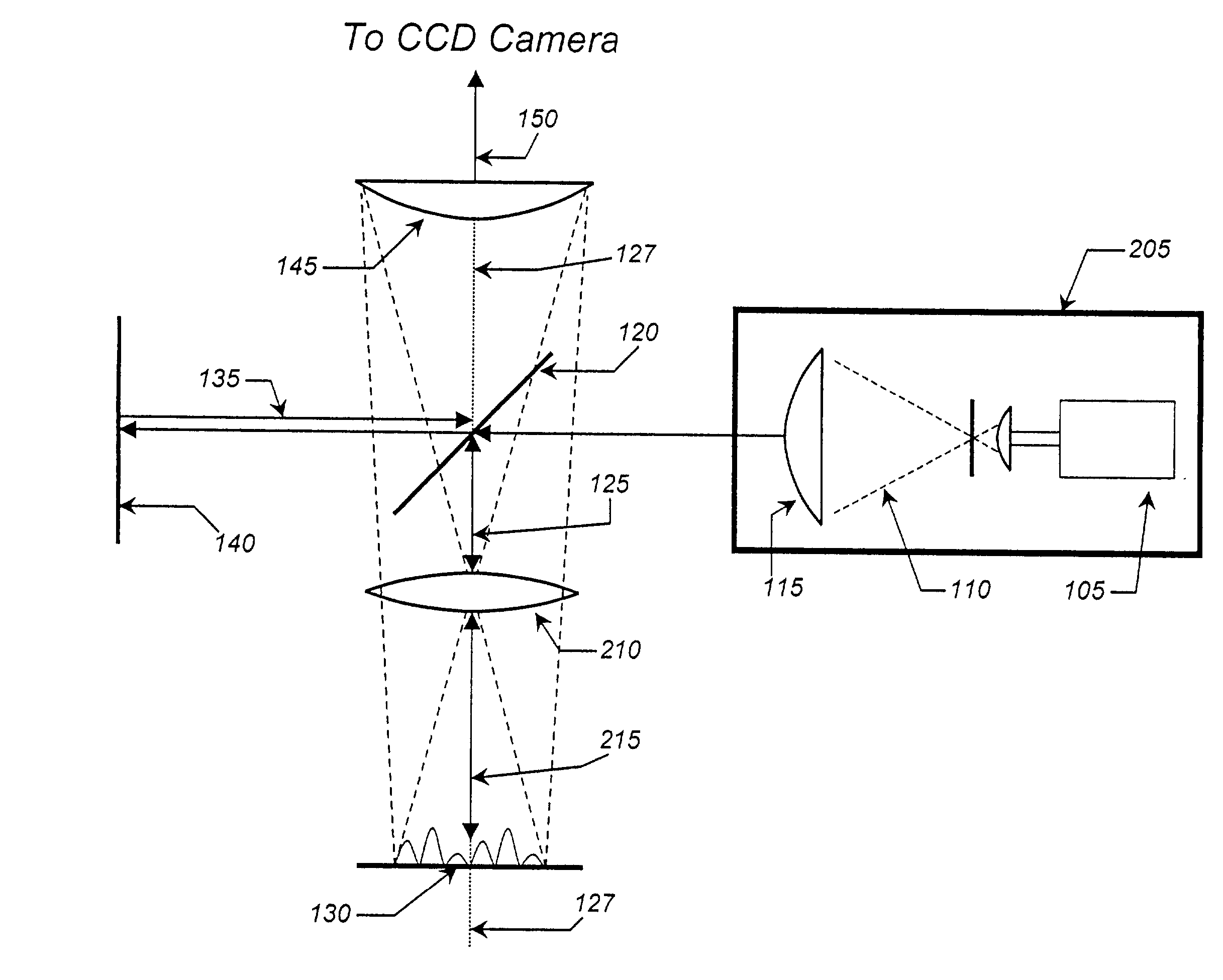
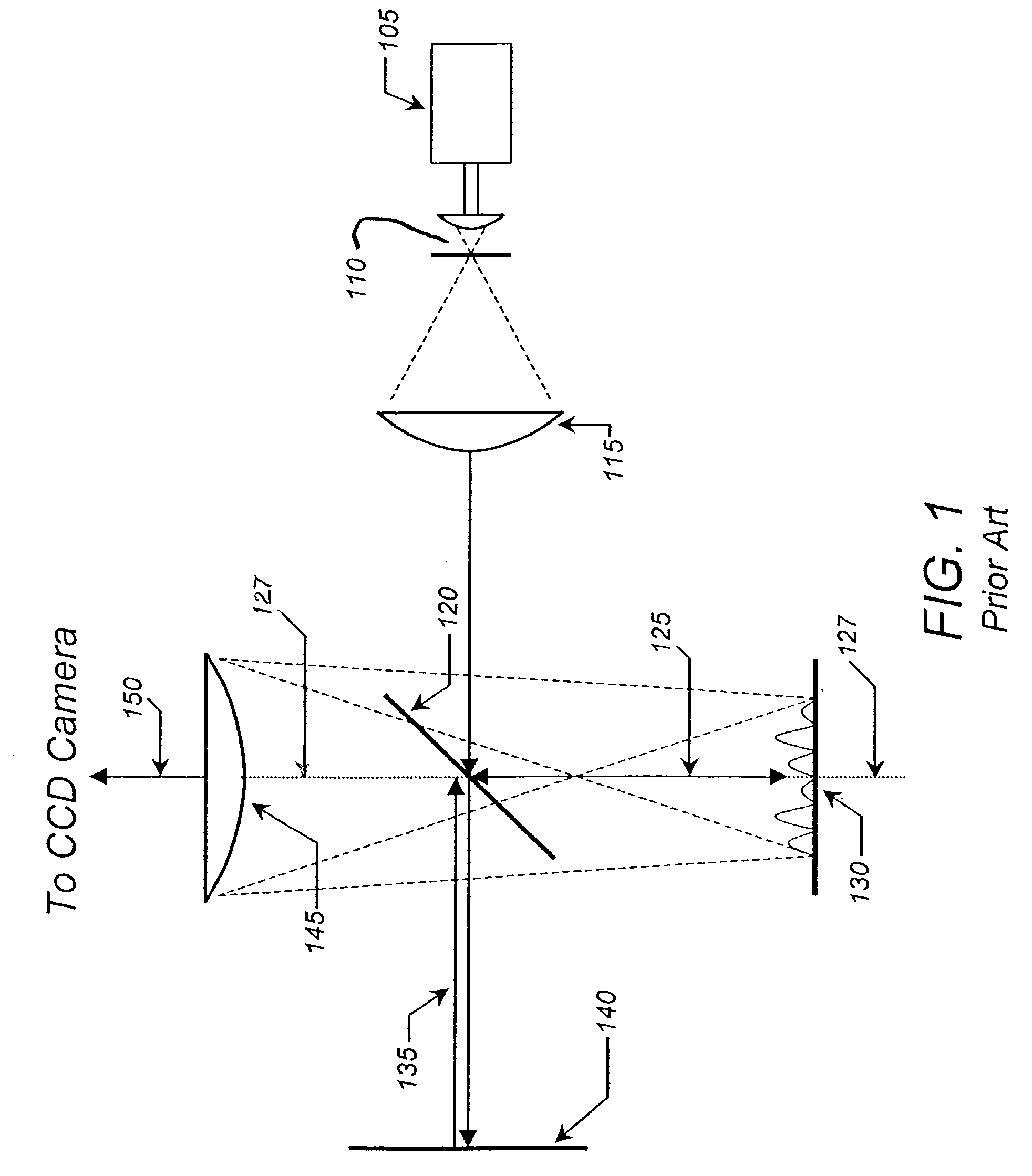
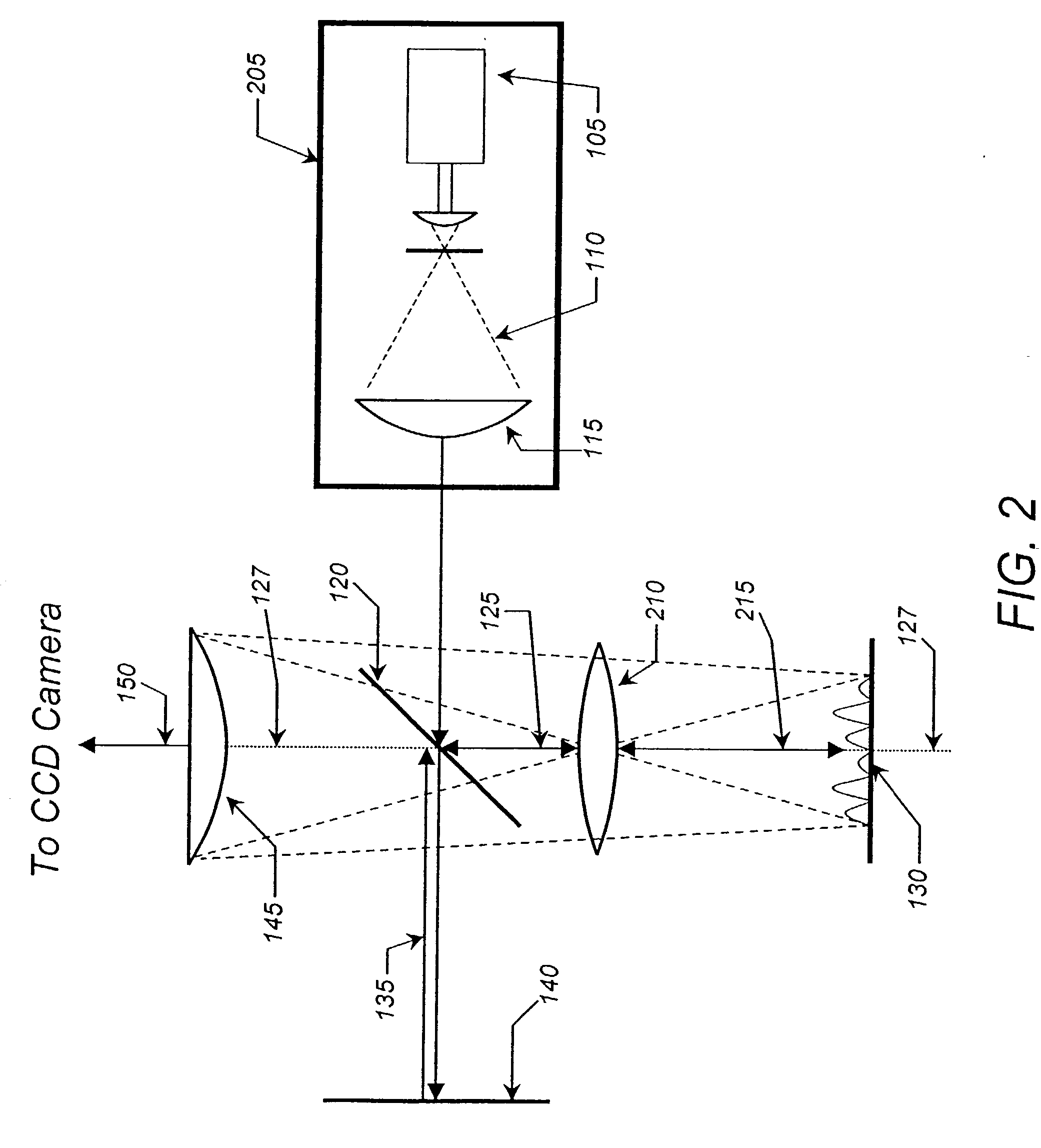
A new way of mixing instrumental and digital means is described for the general field of wave front sensing. The present invention describes the use, the definition and the utility of digital operators, called digital wave front operators (DWFO) or digital lenses (DL), specifically designed for the digital processing of wave fronts defined in amplitude and phase. DWFO are of particular interest for correcting undesired wave front deformations induced by instrumental defects or experimental errors. DWFO may be defined using a mathematical model, e.g. a polynomial function, which involves coefficients. The present invention describes automated and semi-automated procedures for calibrating or adjusting the values of these coefficients. These procedures are based on the fitting of mathematical models on reference data extracted from specific regions of a wave front called reference areas, which are characterized by the fact that specimen contributions are a priori known in reference areas. For example, reference areas can be defined in regions where flat surfaces of a specimen produce a constant phase function. The present invention describes also how DWFO can be defined by extracting reference data along one-dimensional (1D) profiles. DWFO can also be defined in order to obtain a flattened representation of non-flat area of a specimen. Several DWFO or DL can be combined, possibly in addition with procedures for calculating numerically the propagation of wave fronts. A DWFO may also be defined experimentally, e.g. by calibration procedures using reference specimens. A method for generating a DWFO by filtering in the Fourier plane is also described. All wave front sensing techniques may benefit from the present invention. The case of a wave front sensor based on digital holography, e.g. a digital holographic microscope (DHM), is described in more details. The use of DWFO improves the performance, in particular speed and precision, and the ease of use of instruments for wave front sensing. The use of DWFO results in instrumental simplifications, costs reductions, and enlarged the field of applications. The present invention defines a new technique for imaging and metrology with a large field of applications in material and life sciences, for research and industrial applications.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
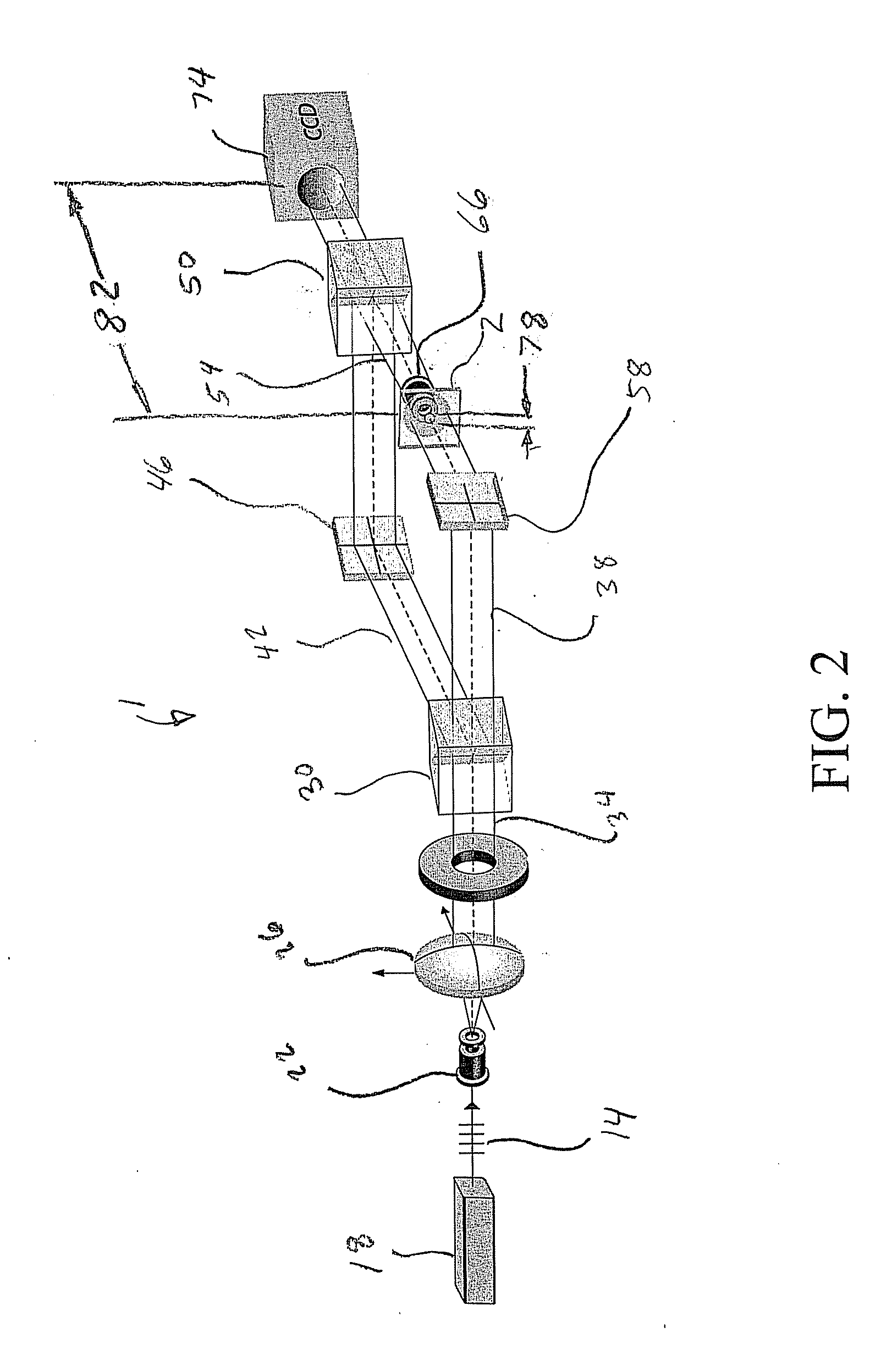
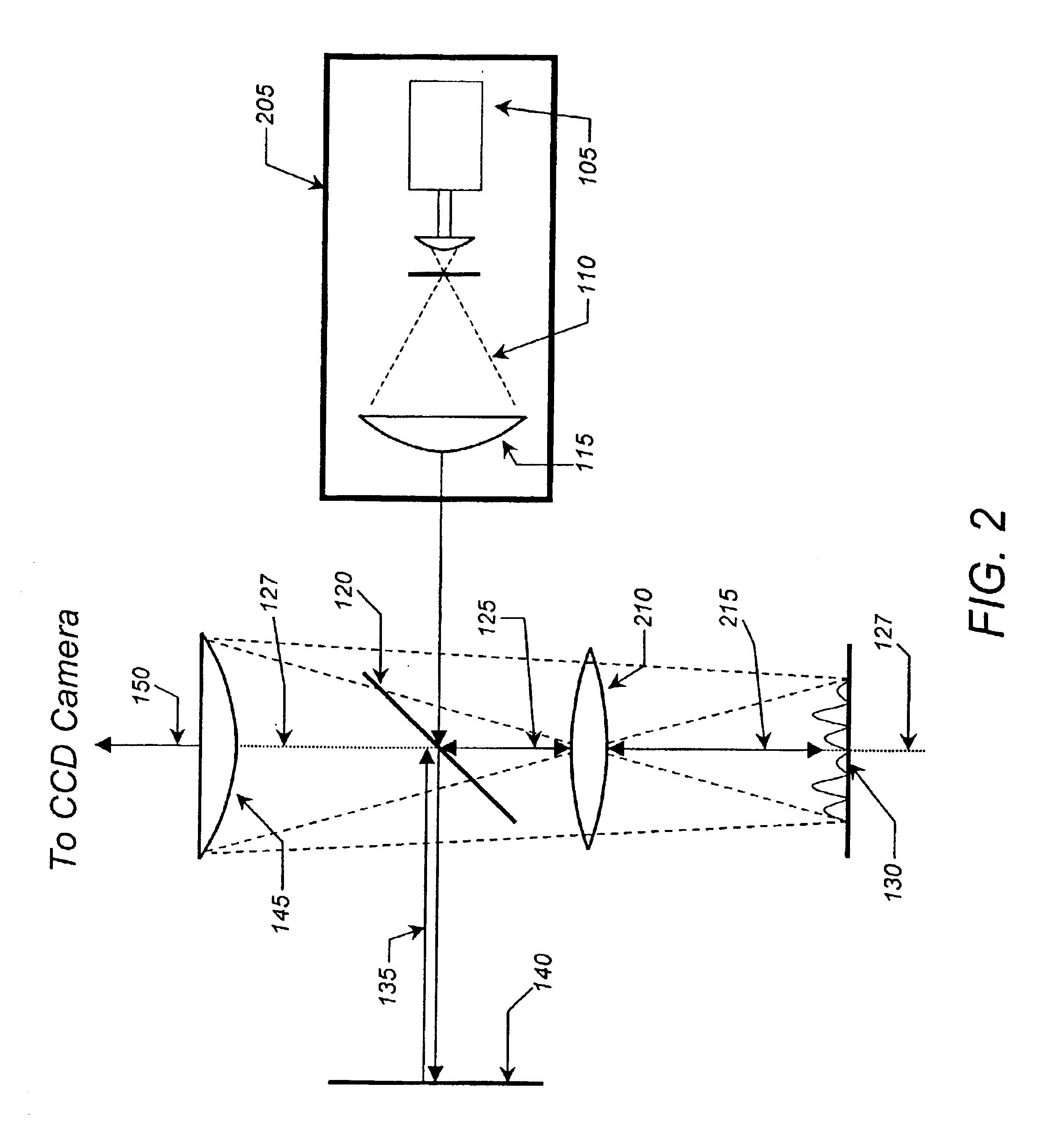
Digital holographic microscope for 3D imaging and process using it
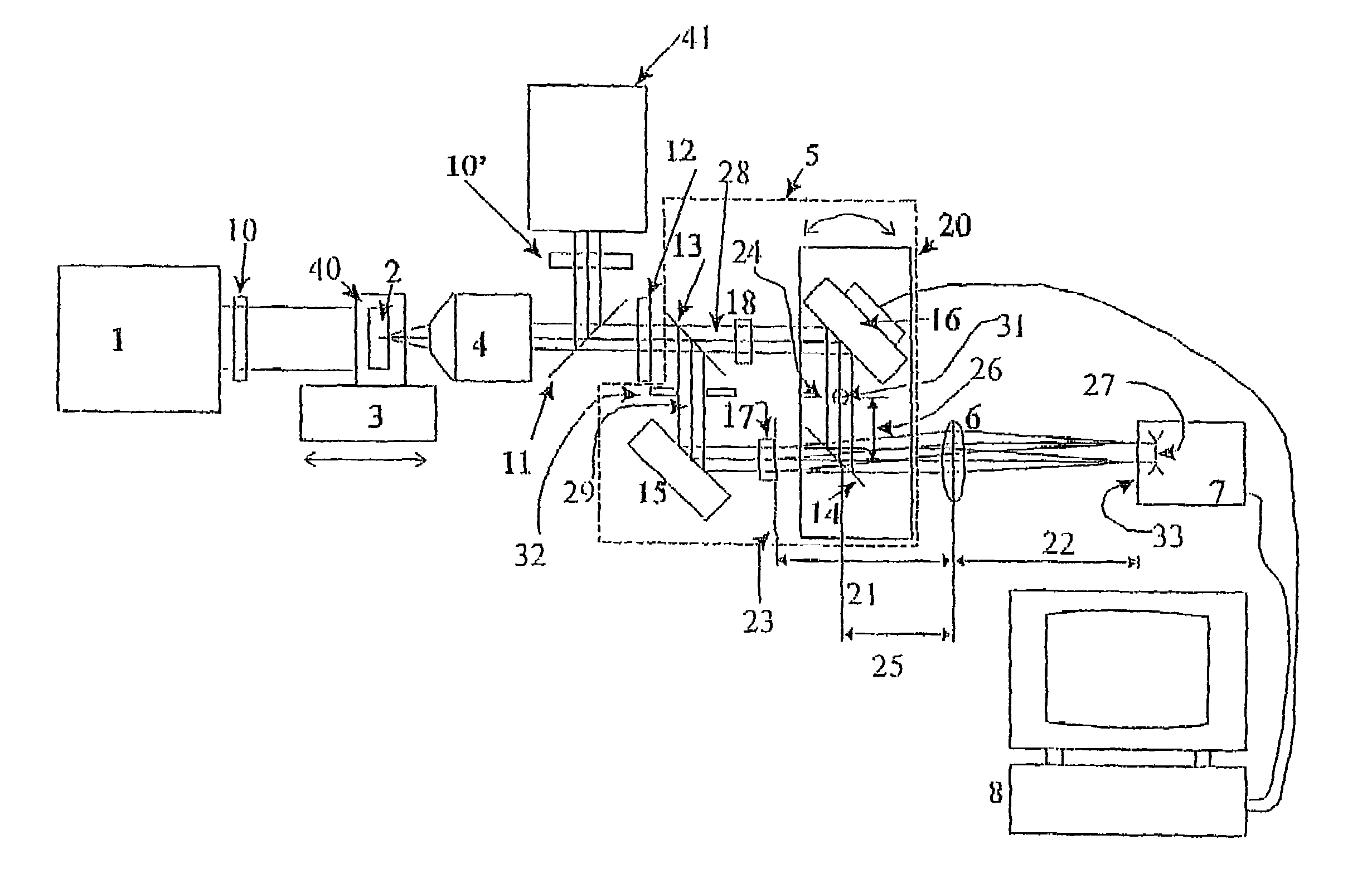
InactiveUS20080018966A1Reduce spatial coherenceReduce coherent noiseHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopes3d imageDigital holographic microscopy
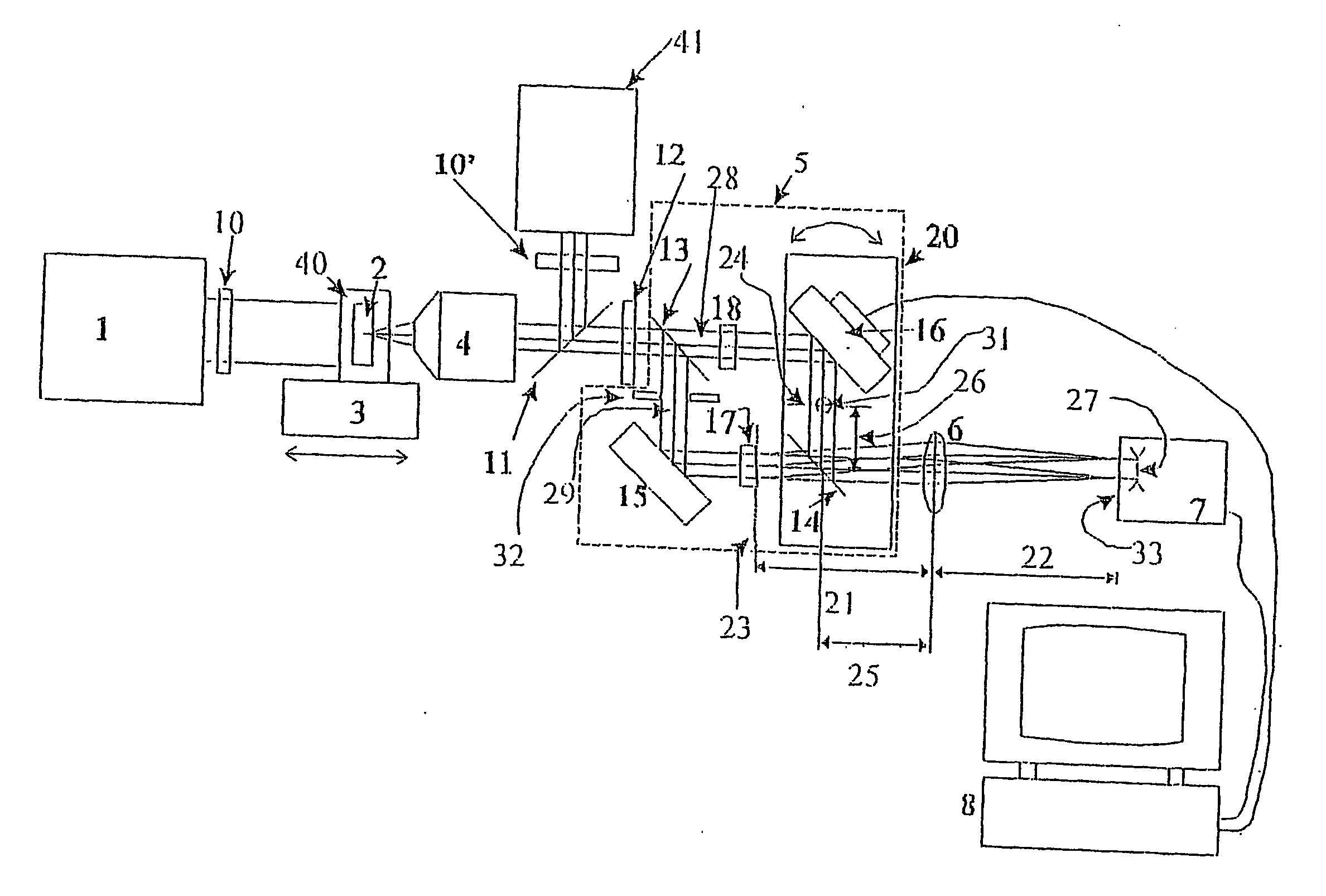
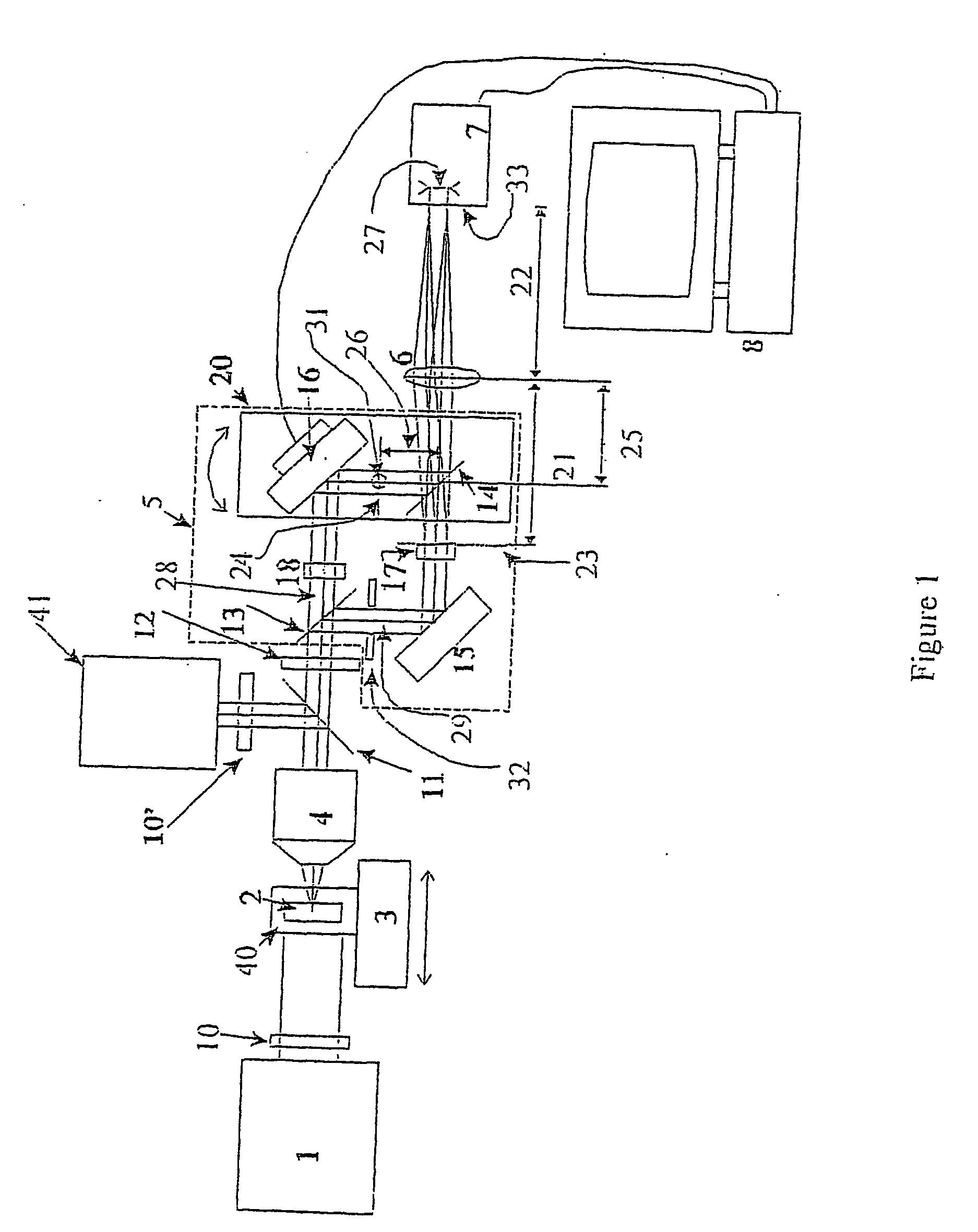
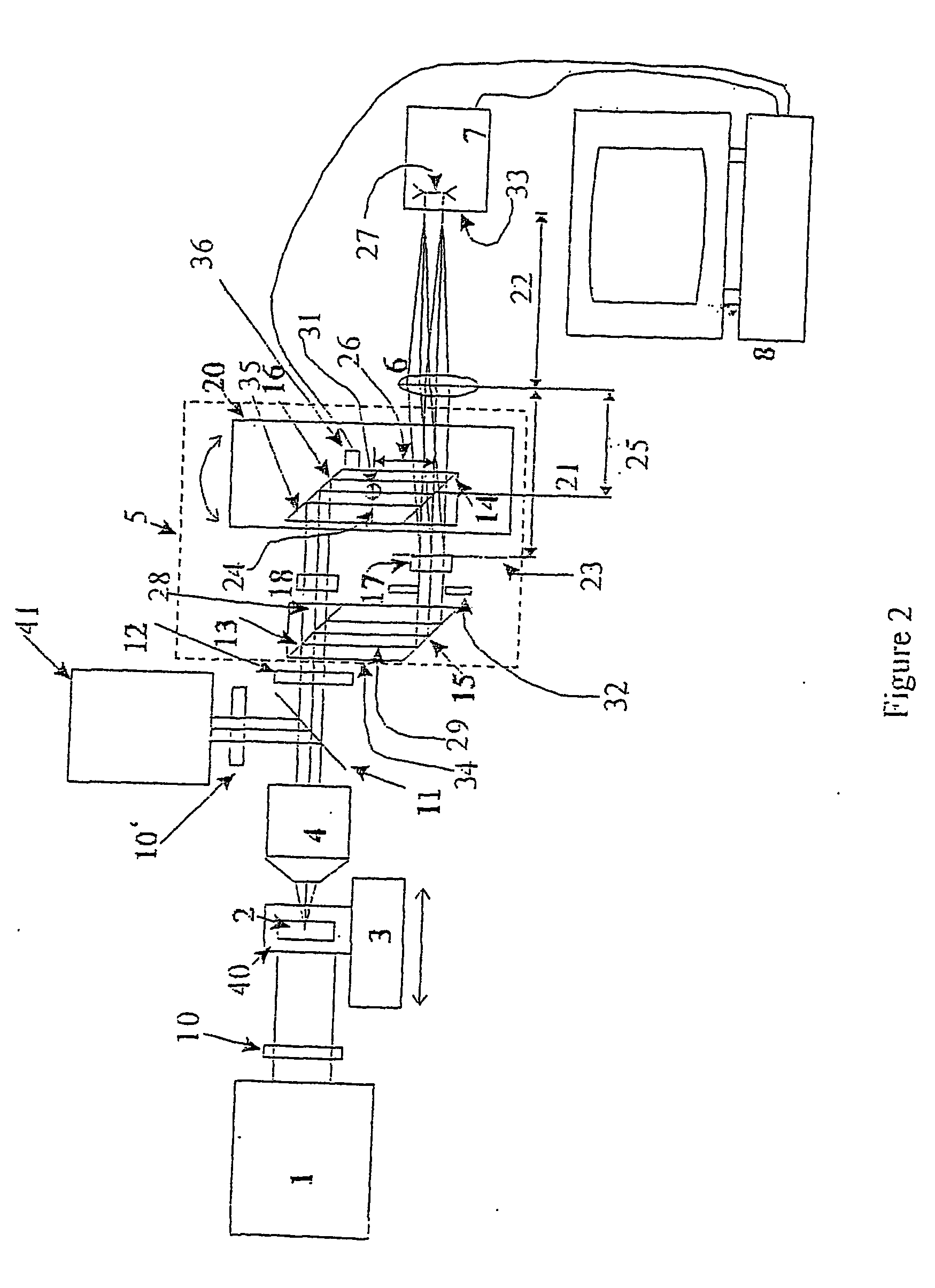
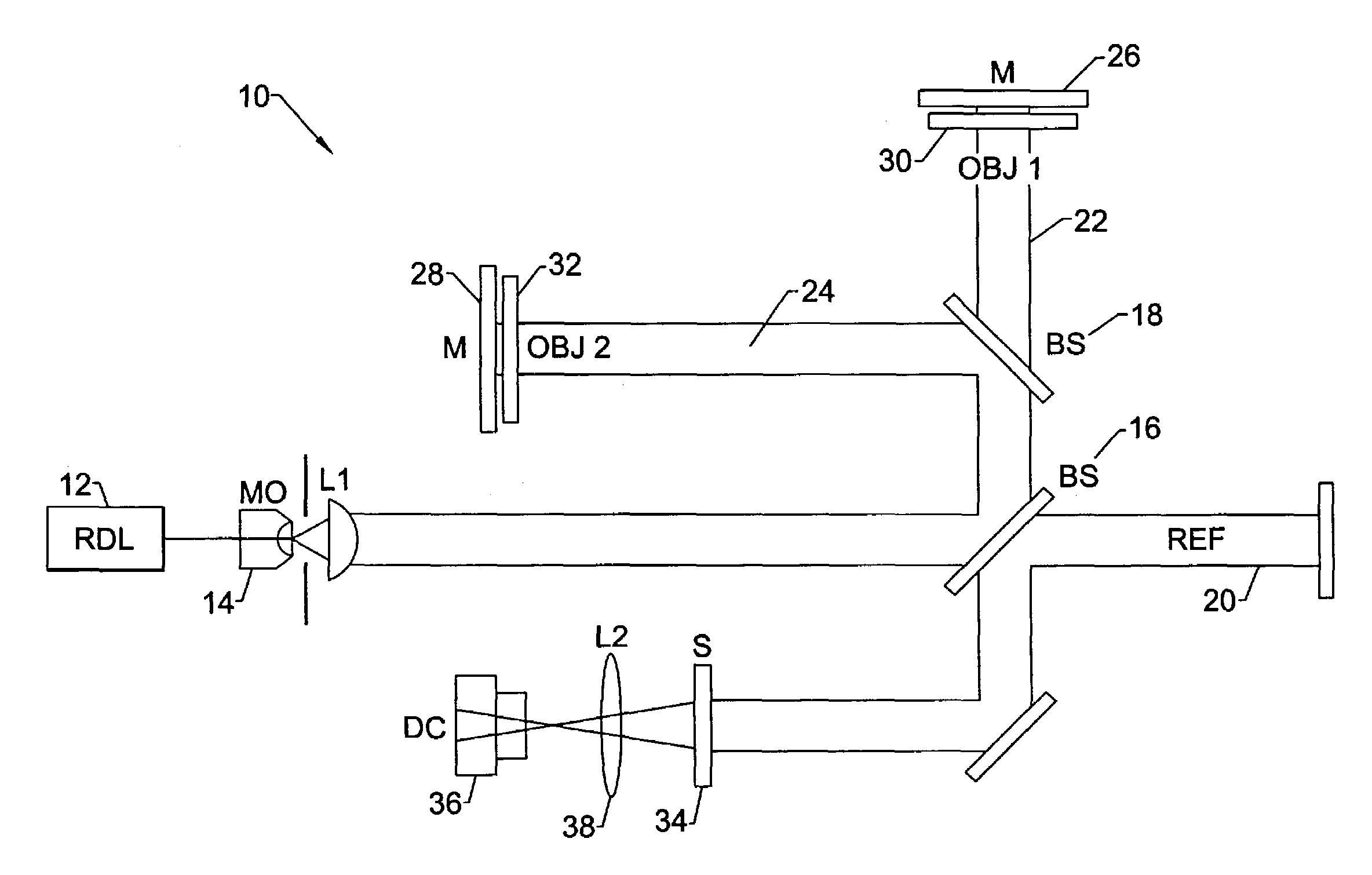
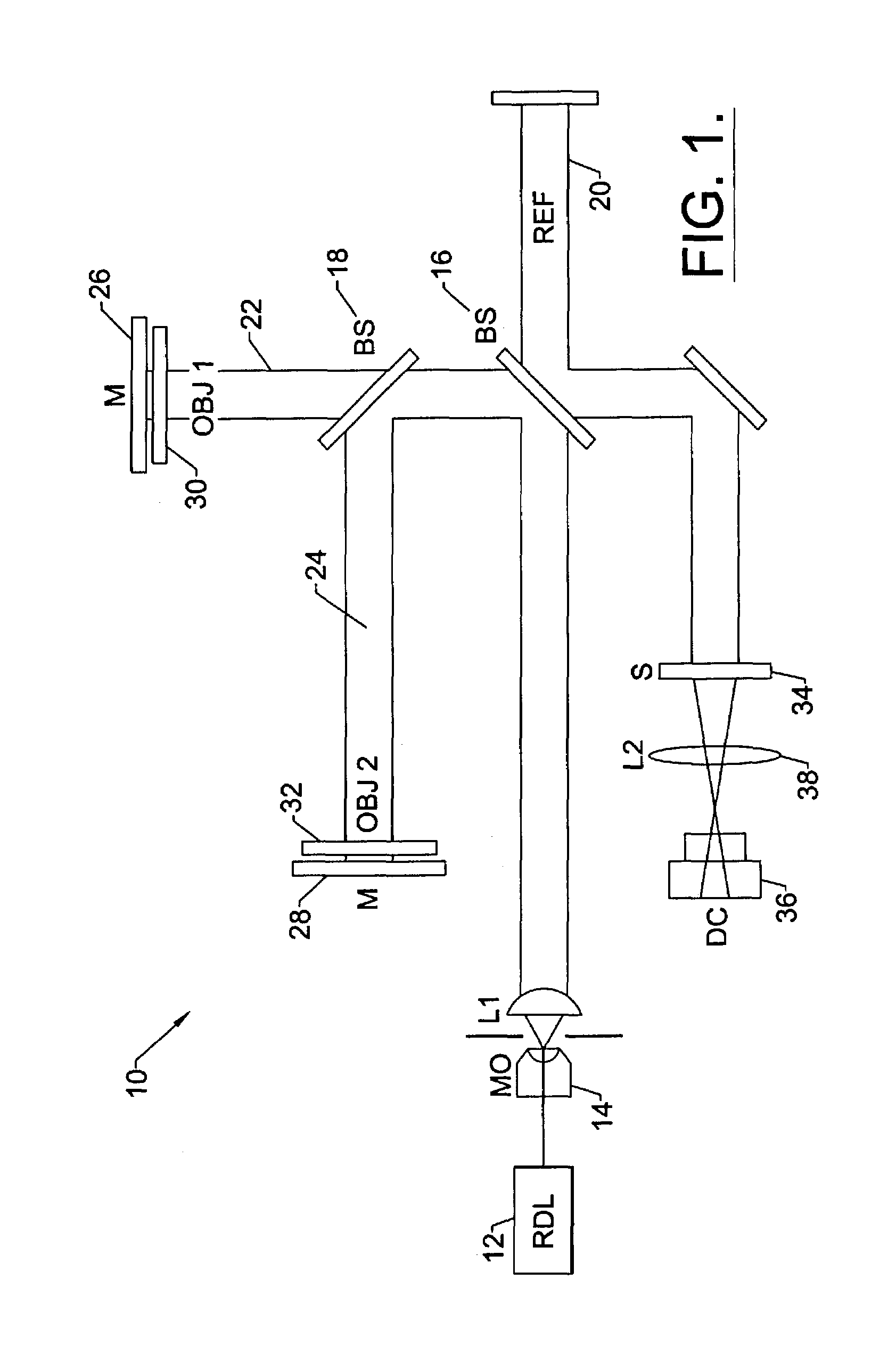
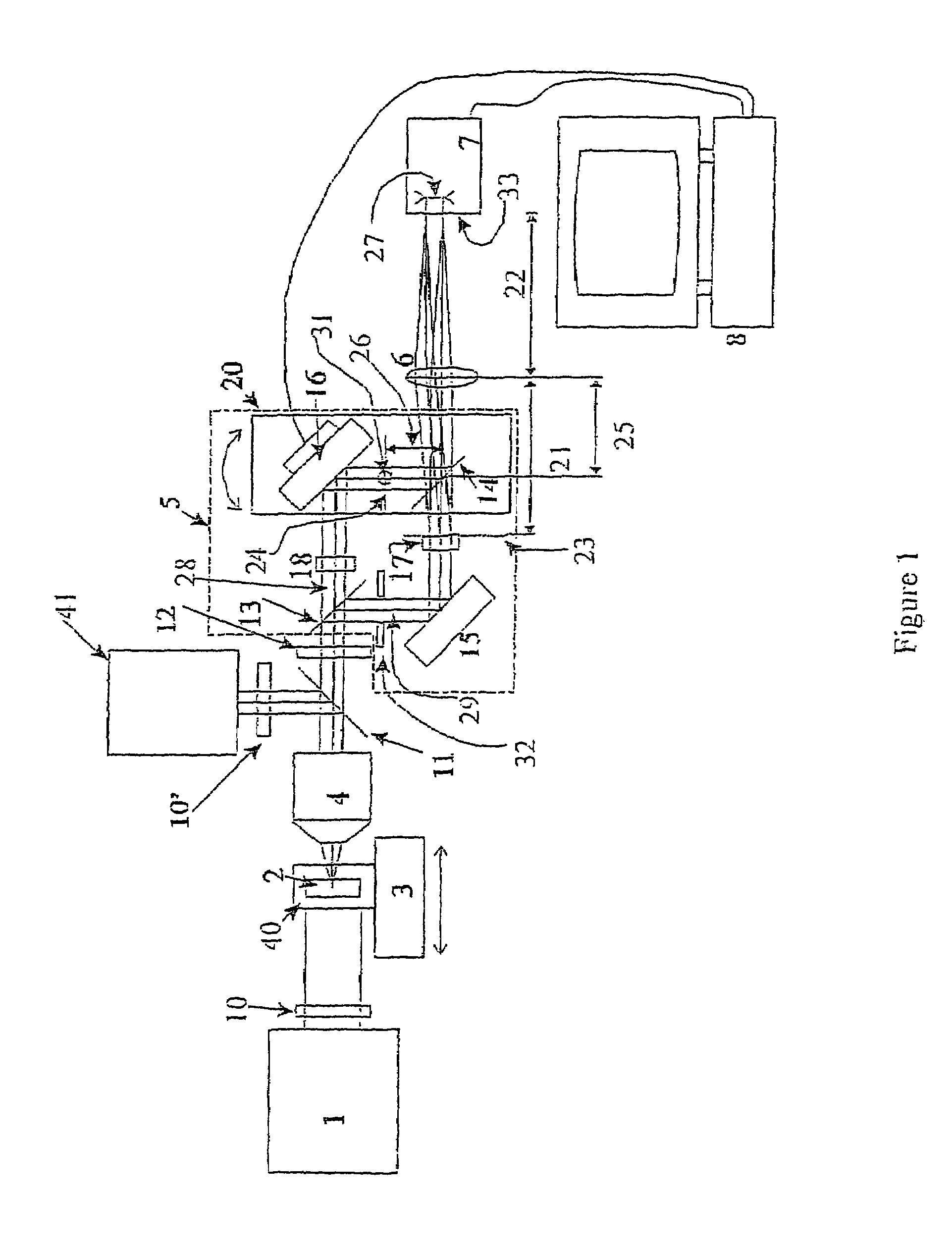
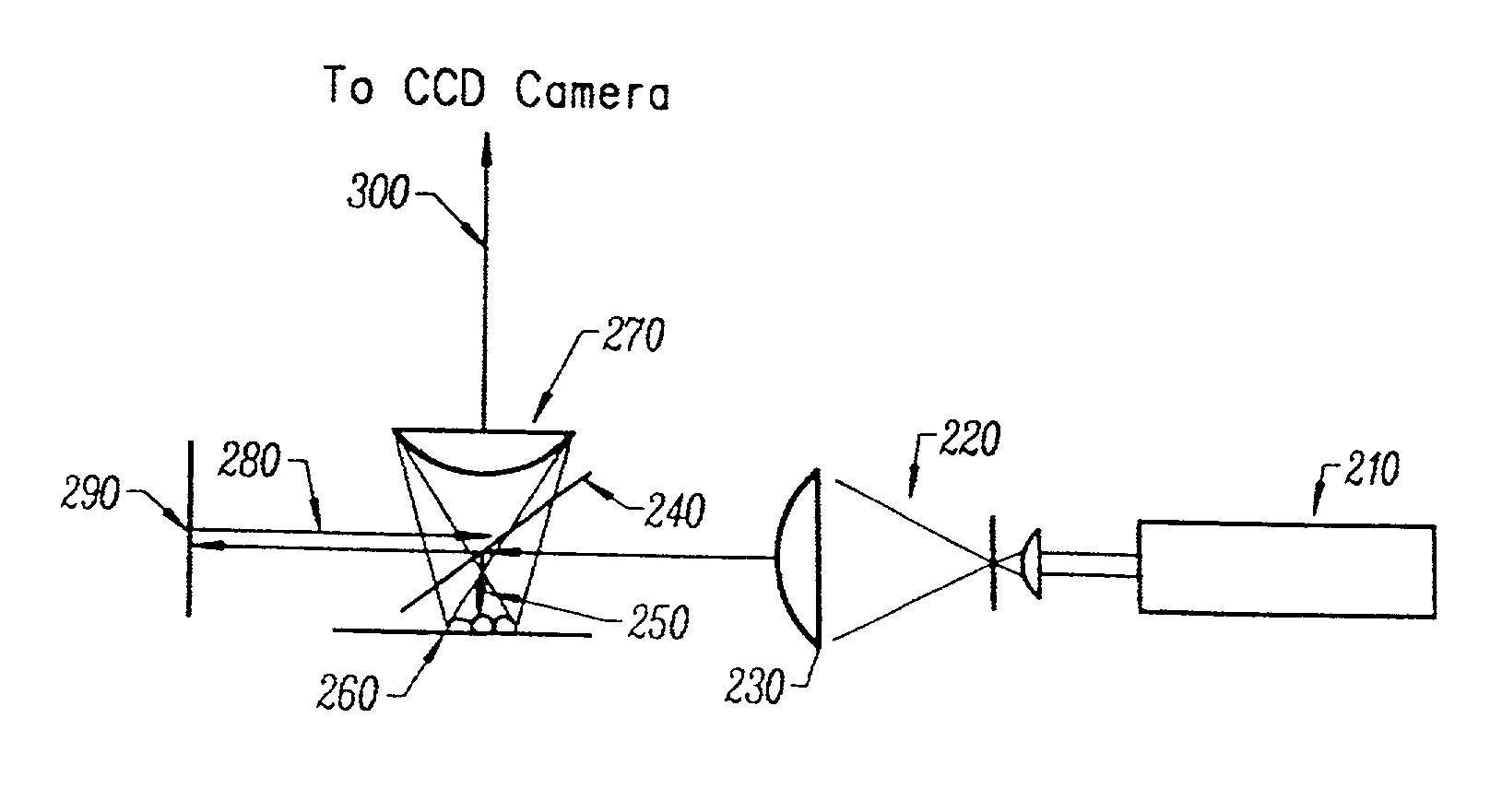
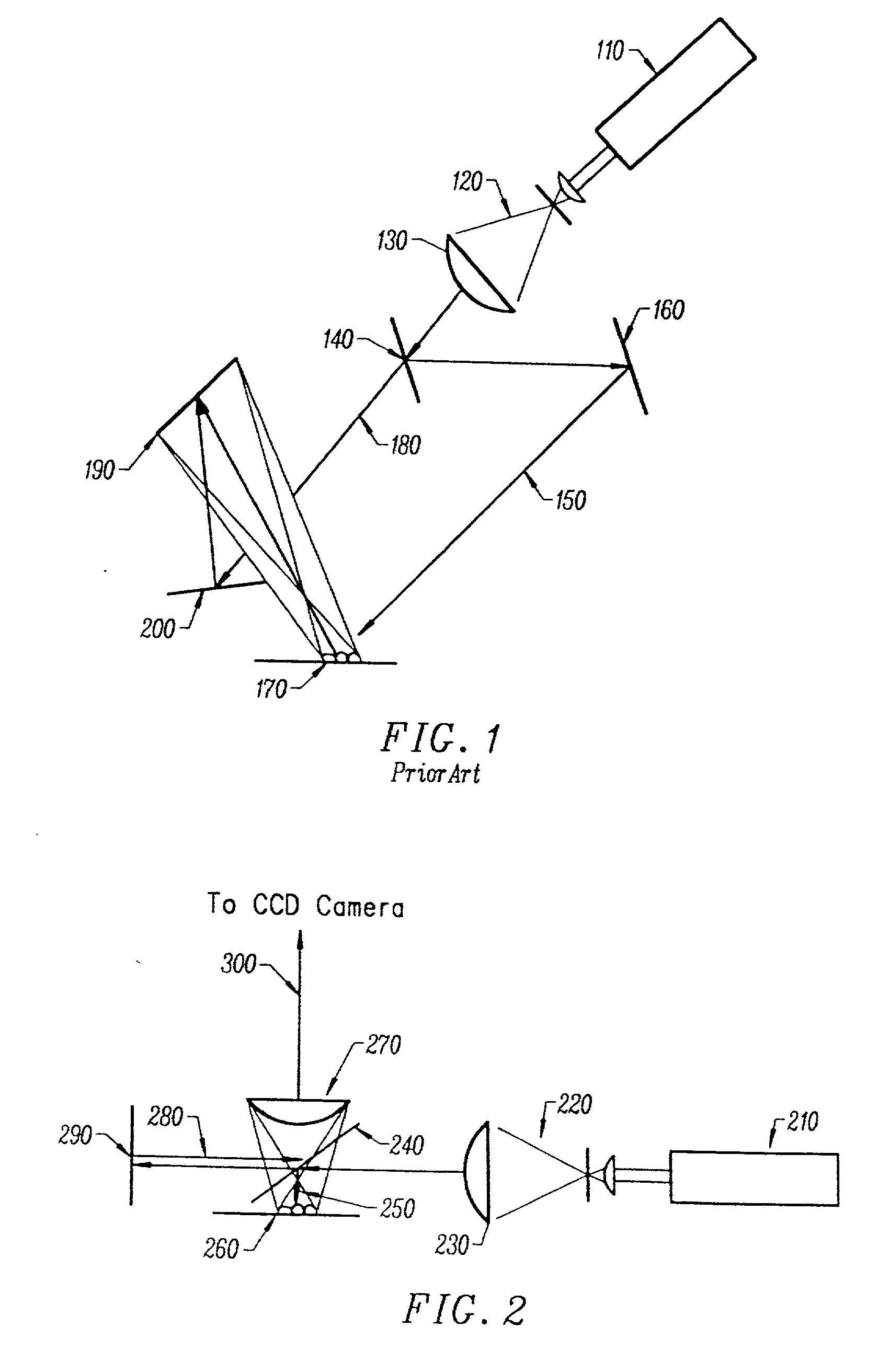
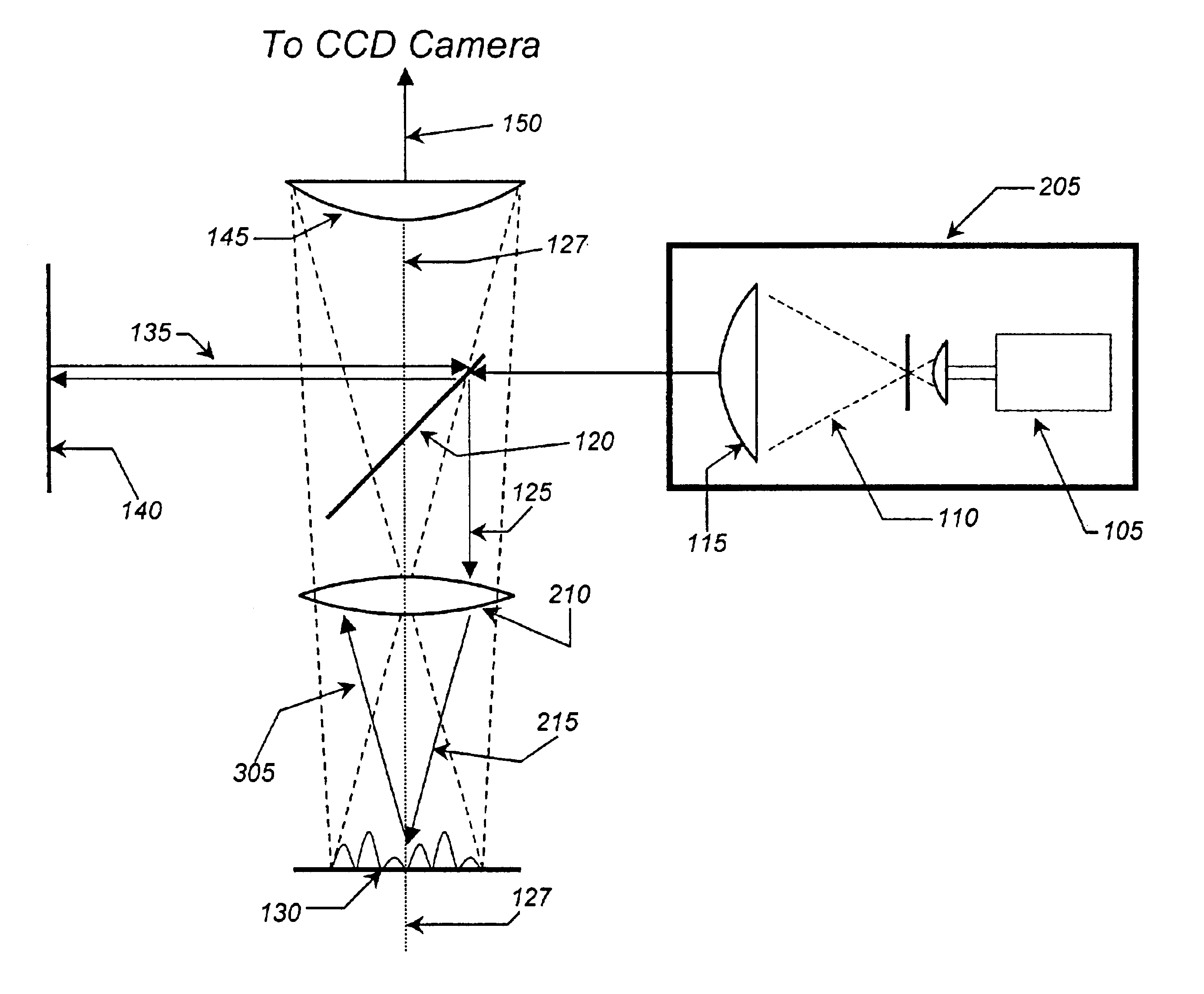
The present invention is related to a compact microscope able to work in digital holography for obtaining high quality 3D images of samples, including fluorescent samples and relatively thick samples such as biological samples, said microscope comprising illumination means (1,41) at least partially spatially coherent for illuminating a sample (2) to be studied and a differential interferometer (5) for generating interfering beams from said sample (2) on the sensor (33) of an electronic imaging device (7), said interferometer (5) comprising namely tilting means (17) for tilting by a defined angle one the interfering beams (28 or 29) relatively to the other, said tilting resulting into a defined shift (27) of said interfering beam on the sensor of the electronic imaging device (7), said shift (27) being smaller than spatial coherence width of each beam, said microscope being able to be quasi totally preadjusted independently from the samples so that minimum additional adjustments are required for obtaining reliable 3D images of samples.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Information security using digital holography
InactiveUS20060078113A1User identity/authority verificationHolographic optical componentsComputer visionPhase mask
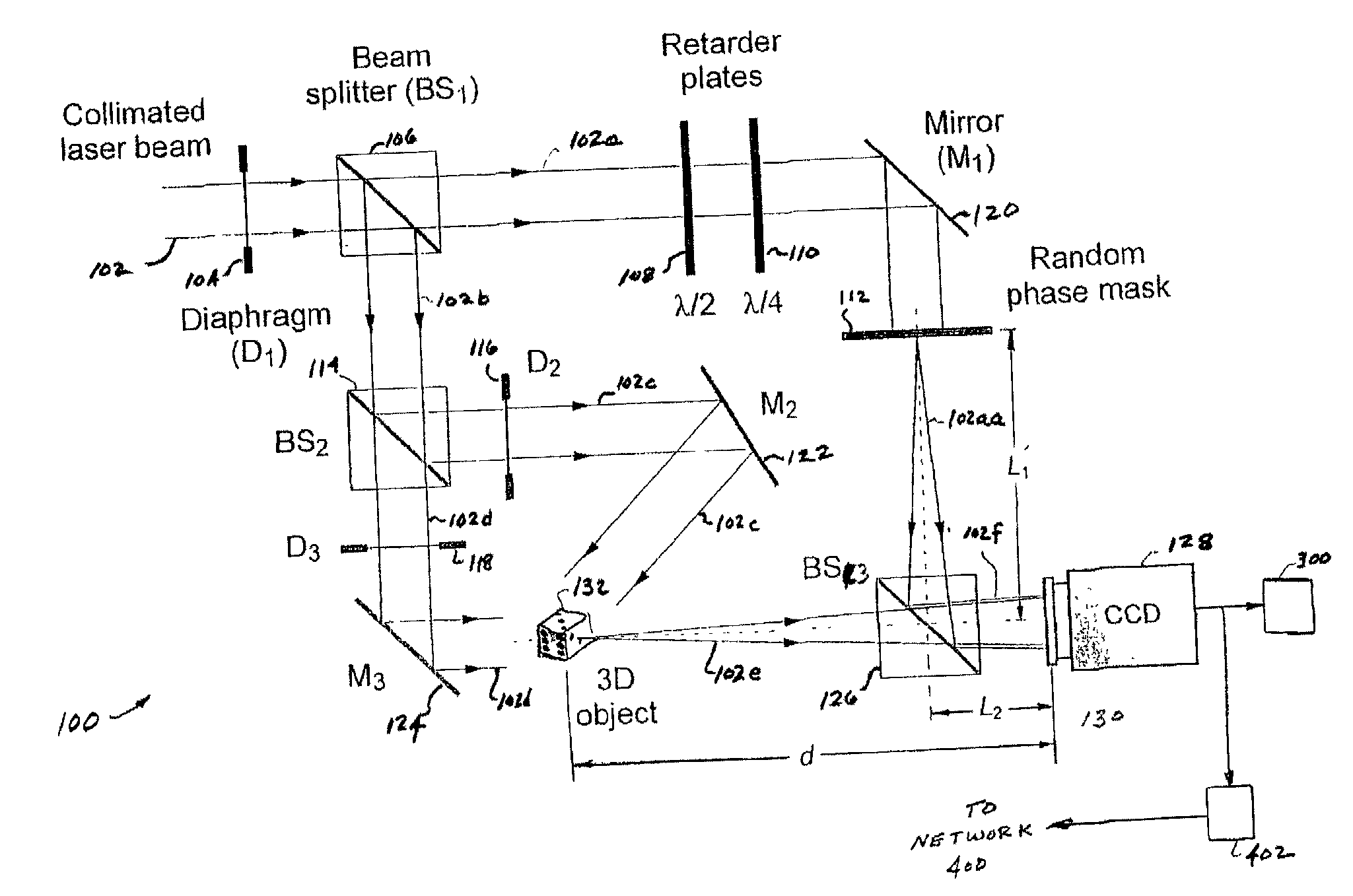
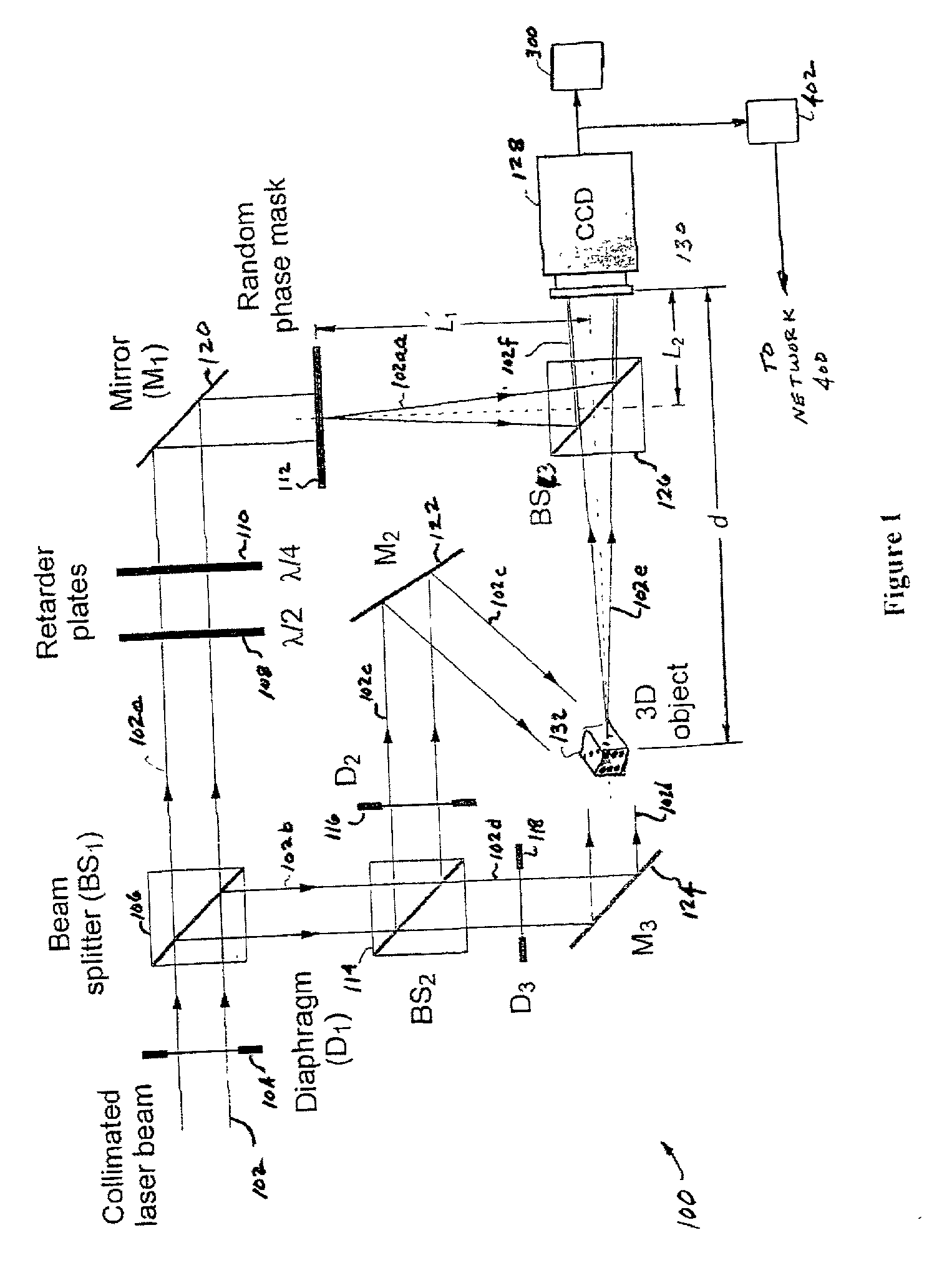
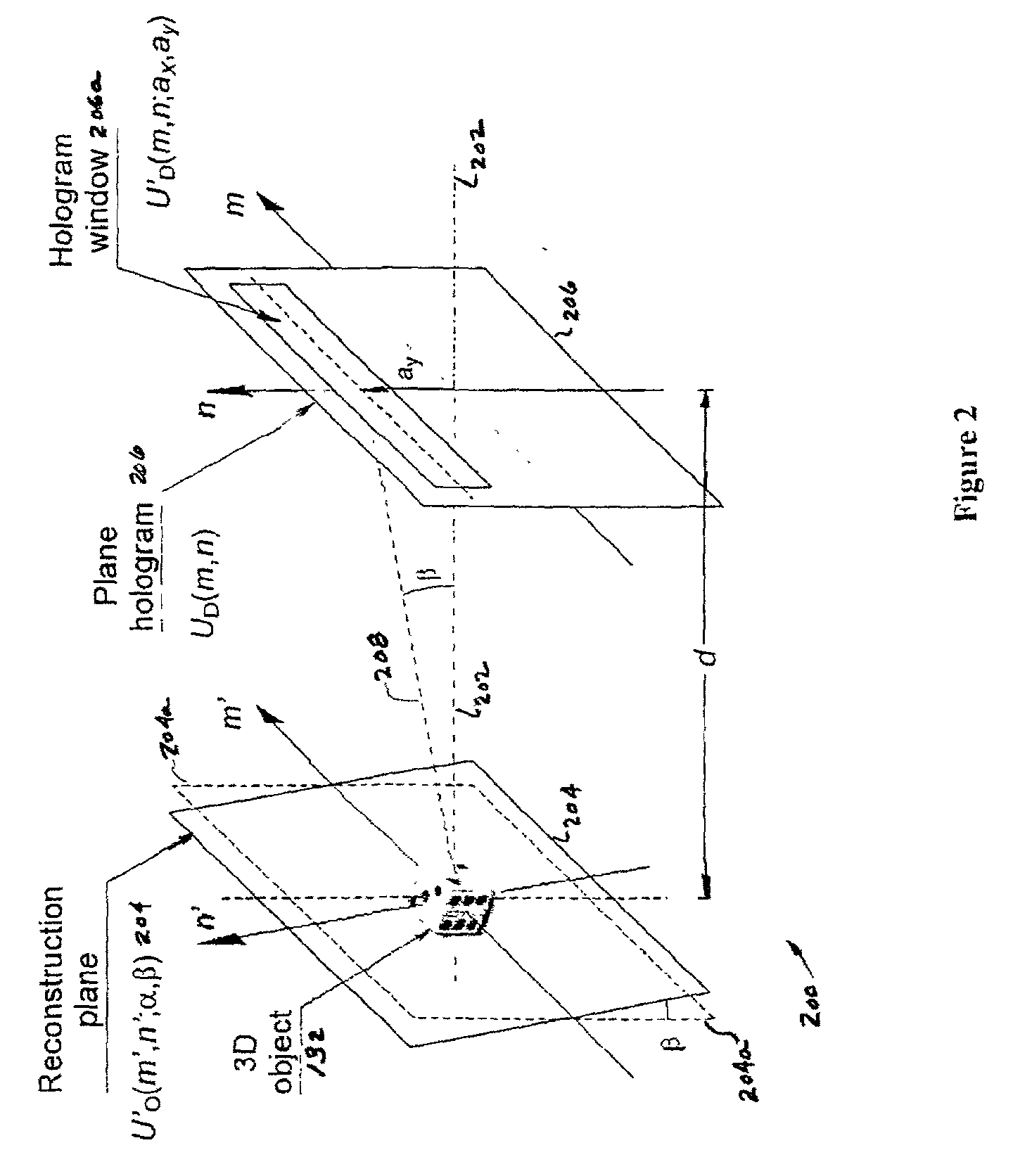
A method and system for encrypting multi-dimensional information utilizing digital holography is presented. A phase-shifting interferometer records the phase and amplitude information generated by a three-dimensional object at a plane located in the Fresnel diffraction region with an intensity-recording device. Encryption is performed by utilizing the Fresnel diffraction pattern of a random phase mask. Images of different perspectives of the three-dimensional object focused at different planes can be generated digital or optically with the proper key after decryption. After decryption, images of the object, focused at different planes, can be generated digitally or optically. The method allows for the reconstruction of the object with different perspectives from a single encrypted image. The method does not require sending the key exclusively through a digital communication channel. Instead, a copy of the random phase key itself can be sent to the authorized user. A method of forming an image of an object is disclosed. The method comprises forming an original hologram of the object; compressing the original hologram of the object to form a compressed hologram; decompressing the compressed hologram of the object to form a decompressed hologram; and reconstructing the object from the decompressed hologram to form a multi-dimensional image of the object.
Owner:CONNECTICUT UNIV OF THE
Digital interference holographic microscope and methods
InactiveUS7127109B1Simple processExtend to reconstructionHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionLength wave
A simple digital holographic apparatus and method allow reconstruction of three-dimensional objects with a very narrow depth of focus or high axial resolution. A number of holograms are optically generated using different wavelengths spaced at regular intervals. They are recorded, such as on a digital camera, and are reconstructed numerically. Multiwavelength interference of the holograms results in contour planes of very small thickness and wide separation. Objects at different distances from the hologram plane are imaged clearly and independently with complete suppression of the out-of-focus images. The technique is uniquely available only in digital holography and has applications in holographic microscopy.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
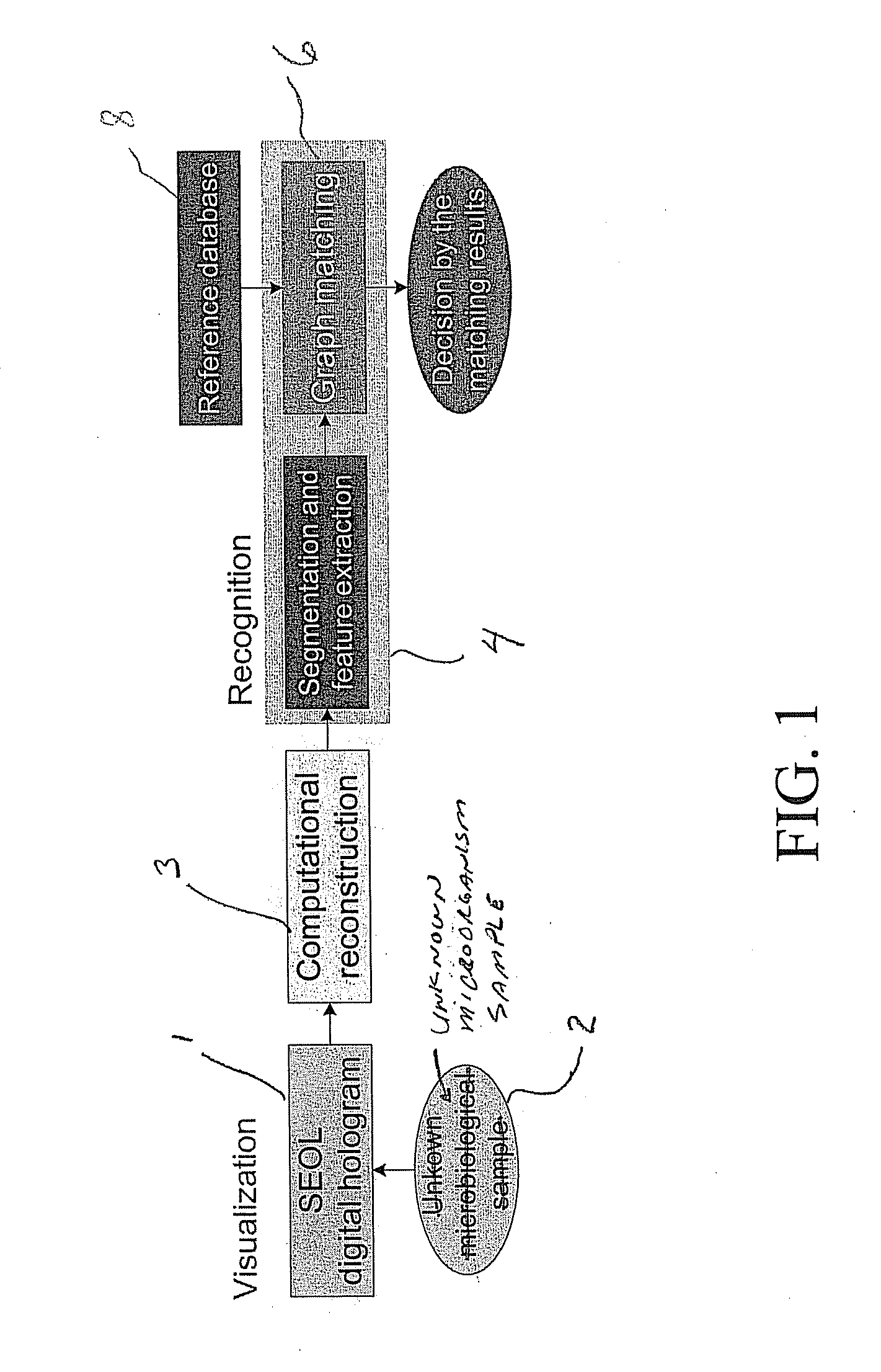
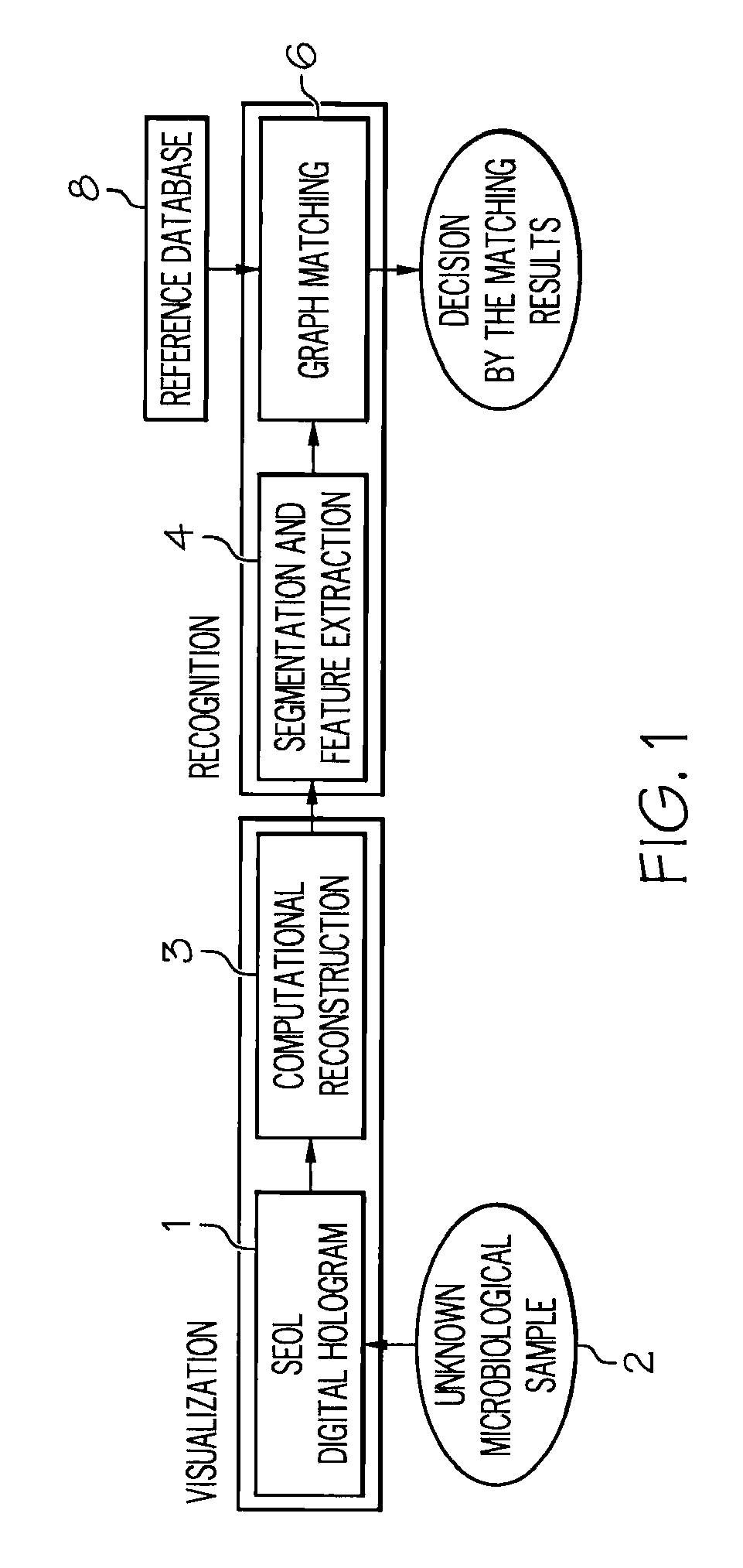
Method and apparatus for recognition of microorganisms using holographic microscopy
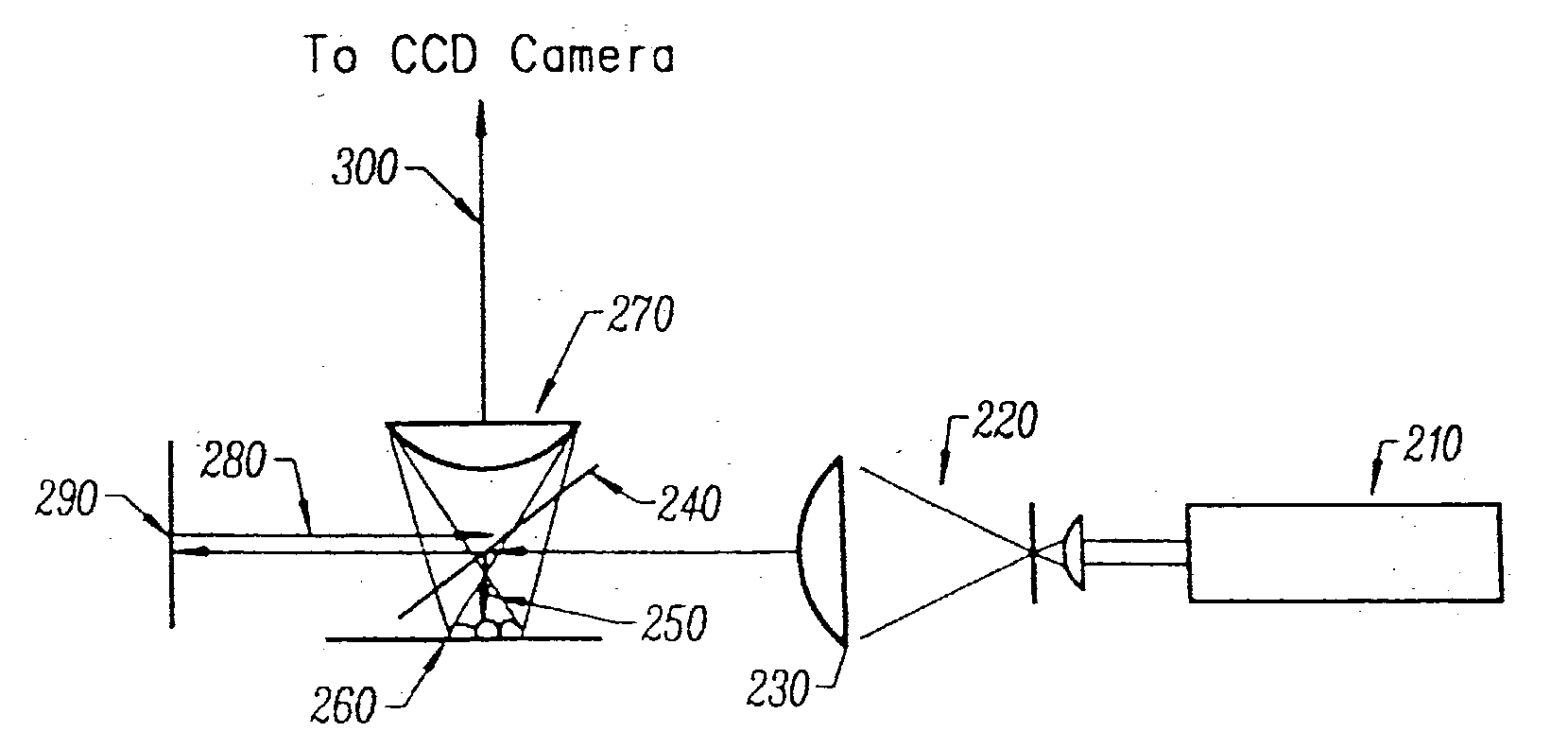
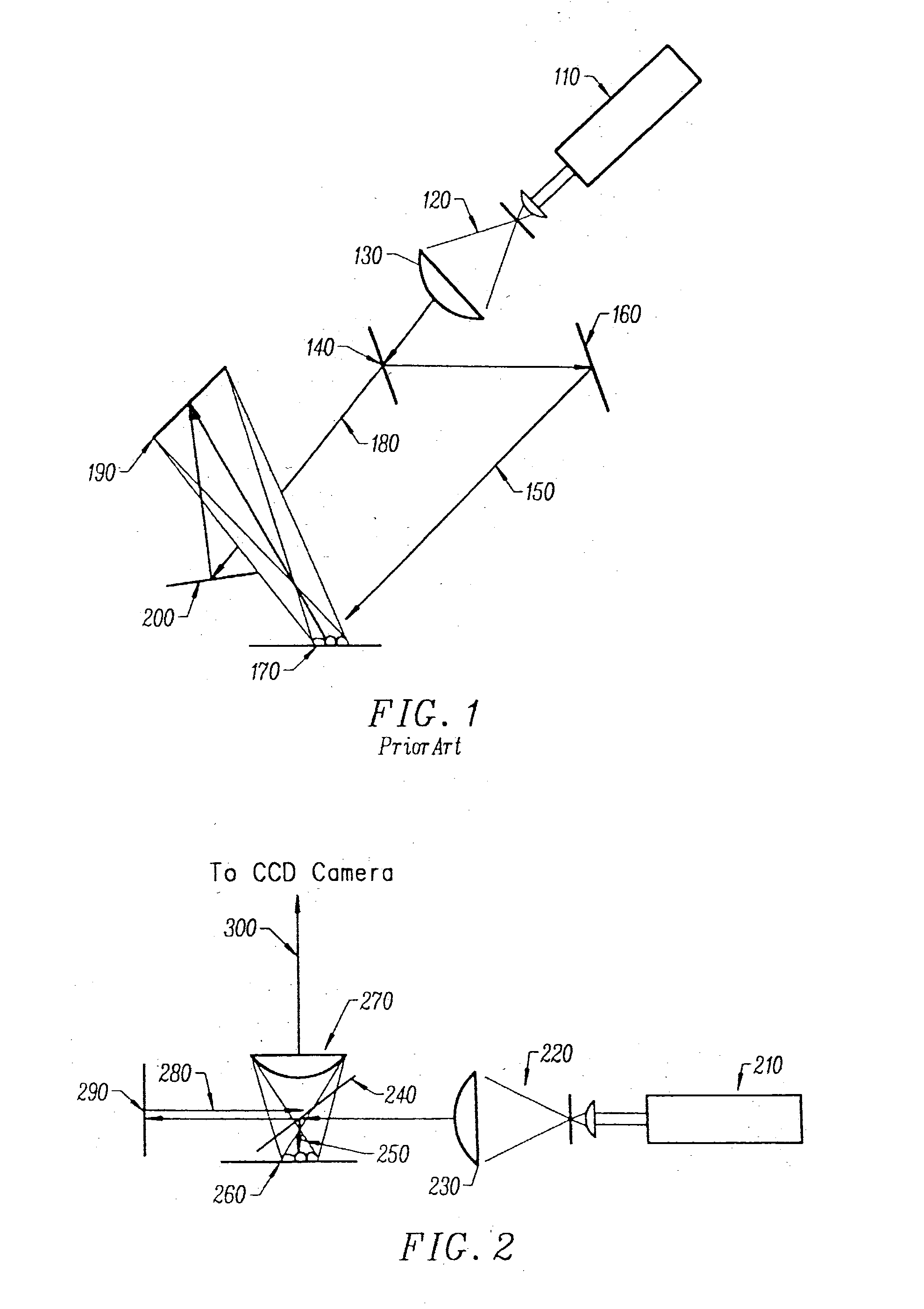
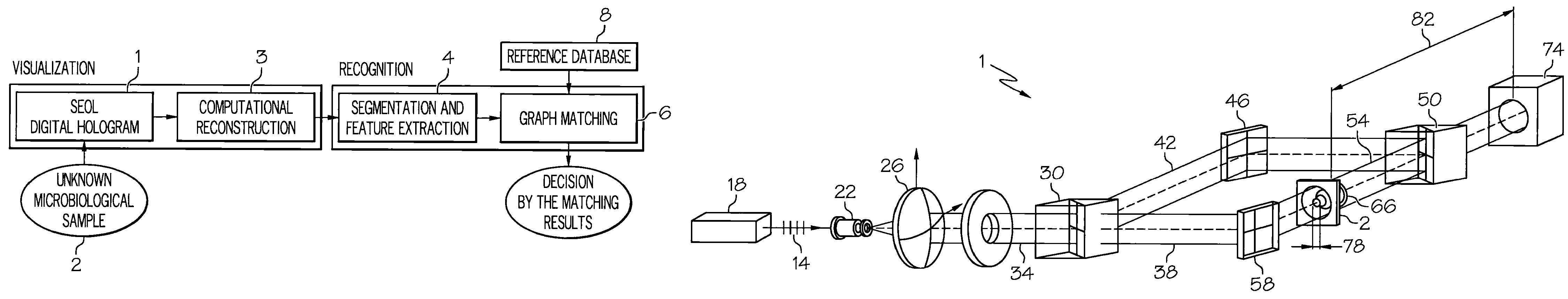
ActiveUS20070216906A1Material analysis by optical meansHolographic object characteristicsDetector arraySingle exposure
Disclosed herein is a method that relates to identifying a microorganism. The method comprising, diffracting laser light through a microorganism, combining a reference beam with the diffracted light on a single axis, and recording the combined light holographically as a three-dimensional image with a single exposure on a detector array. The method further comprising, reconstructing the holographic image and matching the reconstructed image with reference images of known microorganisms. Further disclosed herein is an apparatus for identifying a microorganism. The apparatus comprising, an interferometer to record an image of an unknown microorganism using single-exposure on-line (SEOL) digital holography, a means for reconstructing the recorded image, and a means for matching the reconstructed image with images of known microorganism.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Incoherent digital holography three-dimensional dynamic microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN103257441ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical diffractionSpatial light modulator
The invention provides an incoherent digital holography three-dimensional dynamic microscopic imaging system and method and belongs to the field of an optical diffraction imaging and incoherent digital holography technology. Three-dimensional microscopic imaging of dynamic samples is achieved through adoption of a single exposure phase shift technology based on a phase spatial light modulator on the condition of incoherent light illumination. In a hologram shooting light path, incident light is incoherent light transmitted or reflected by the samples, is subjected to convergence of a collimation lens and modulation of the spatial light modulator, and is received by an image sensor. The image sensor and the spatial light modulator are respectively connected with a computer. Diffraction spectroscopic phase mask patterns which are made and generated in the computer are loaded on the spatial light modulator. In order to enable a plurality of phase holograms to be recorded by the system through one-time exposure, a phase loading method on the spatial light modulator needs to be adjusted to a regional phase shift loading method. The incoherent digital holography three-dimensional dynamic microscopic imaging system and method can be used for simultaneously recording the plurality of incoherent digital holograms through one-time exposure, and can be used for carrying out real-time three-dimensional imaging with low requirements for coherence of light sources. Moreover, any moving components or scanning components are not needed in the system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for obtaining a sample with three-dimensional microscopy
InactiveUS7009700B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFluorescenceDigital holographic microscopy
A method and device for obtaining a sample with three-dimensional microscopy, in particular a thick biological sample and the fluorescence field emitted by the sample. One embodiment includes obtaining interferometric signals of a specimen, obtaining fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, recording these signals, and processing these signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time. Another embodiment includes a digital holography microscope, a fluorescence excitation source illuminating a specimen, where the microscope and the fluorescence excitation source cooperate to obtain interferometric signals of the specimen and obtain fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, means for recording the interferometric signals and fluorescence signals, and means for processing the interferometric signals and the fluorescence signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
Single-pixel terahertz holographic imaging device and method
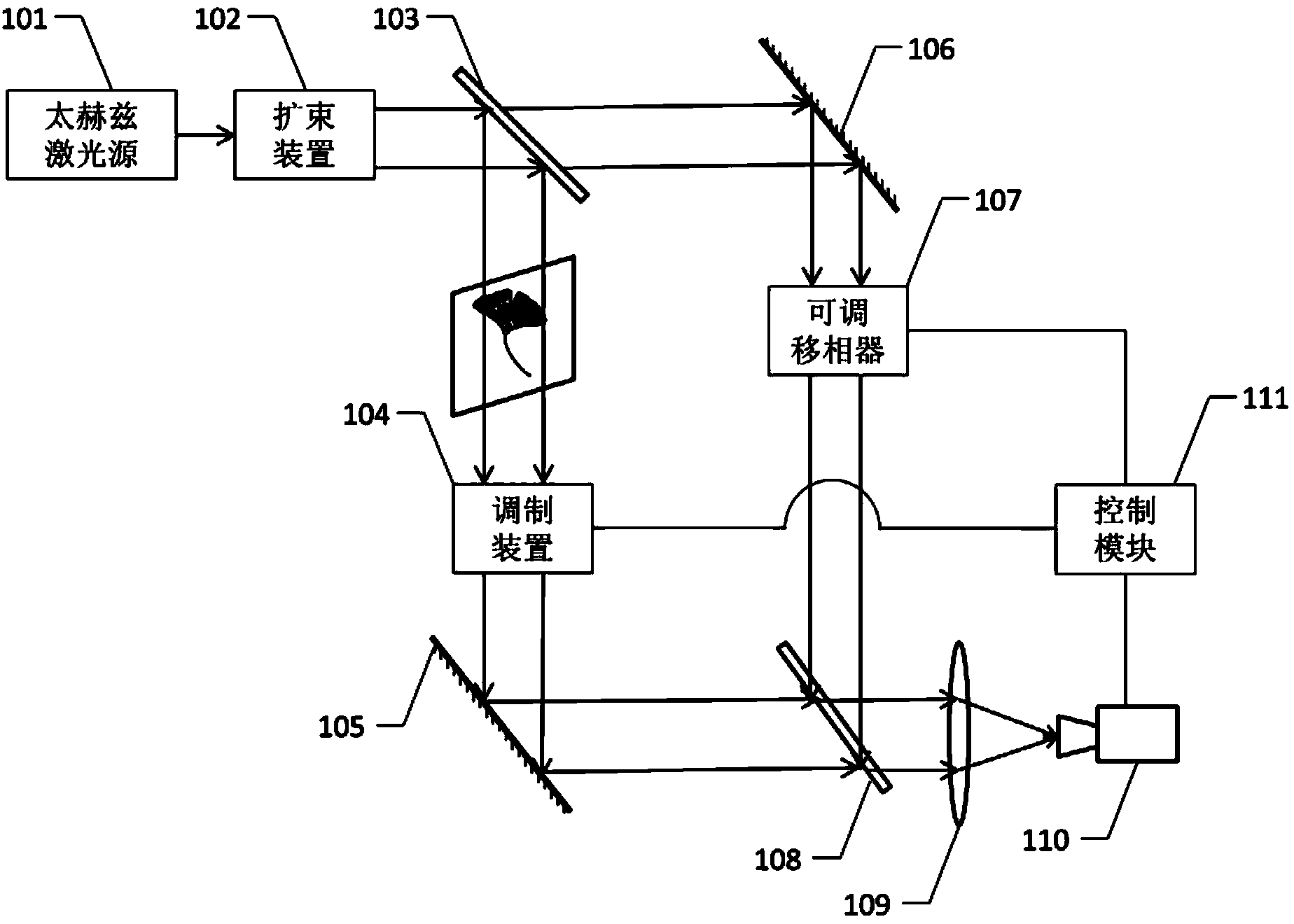
ActiveCN103822577ARealize true 3D imagingEasy to refactorMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansBeam splitterPlane mirror
The invention discloses a single-pixel terahertz holographic imaging device and method. Monochromatic terahertz light emitted by a terahertz laser source is transformed into parallel light with larger beamwidth by a beam expander device, and then divided into object light and reference light through a beam splitter; the object light is encoded by a modulation device in airspace after irradiating an object; the reference light passes through an adjustable phase shifter on the light path after being reflected by a plane mirror; the object light is converged with the reference light on a second beam splitter after being reflected by the plane mirror, enters a single-pixel detector at the focus point of a condenser lens after being converged by the condenser lens; a signal output by the single-pixel detector is fed to a control module to carry out image reconstruction; and terahertz holographic compression sensing imaging of the object is achieved by changing combination of a space code on the modulation device and a phase on the adjustable phase shifter for a plurality of times. The single-pixel terahertz holographic imaging device and method have the advantages that real three-dimensional imaging of the tested object is achieved by combining phase-shifting digital holography with a compression sensing principle, and the single-pixel terahertz holographic imaging device and method are pioneering inventions in the field of terahertz imaging.
Owner:博微太赫兹信息科技有限公司
Digital holographic microscope for 3D imaging and process using it
InactiveUS7362449B2Reduce spatial coherenceHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesMicroscopesFluorescence3d image
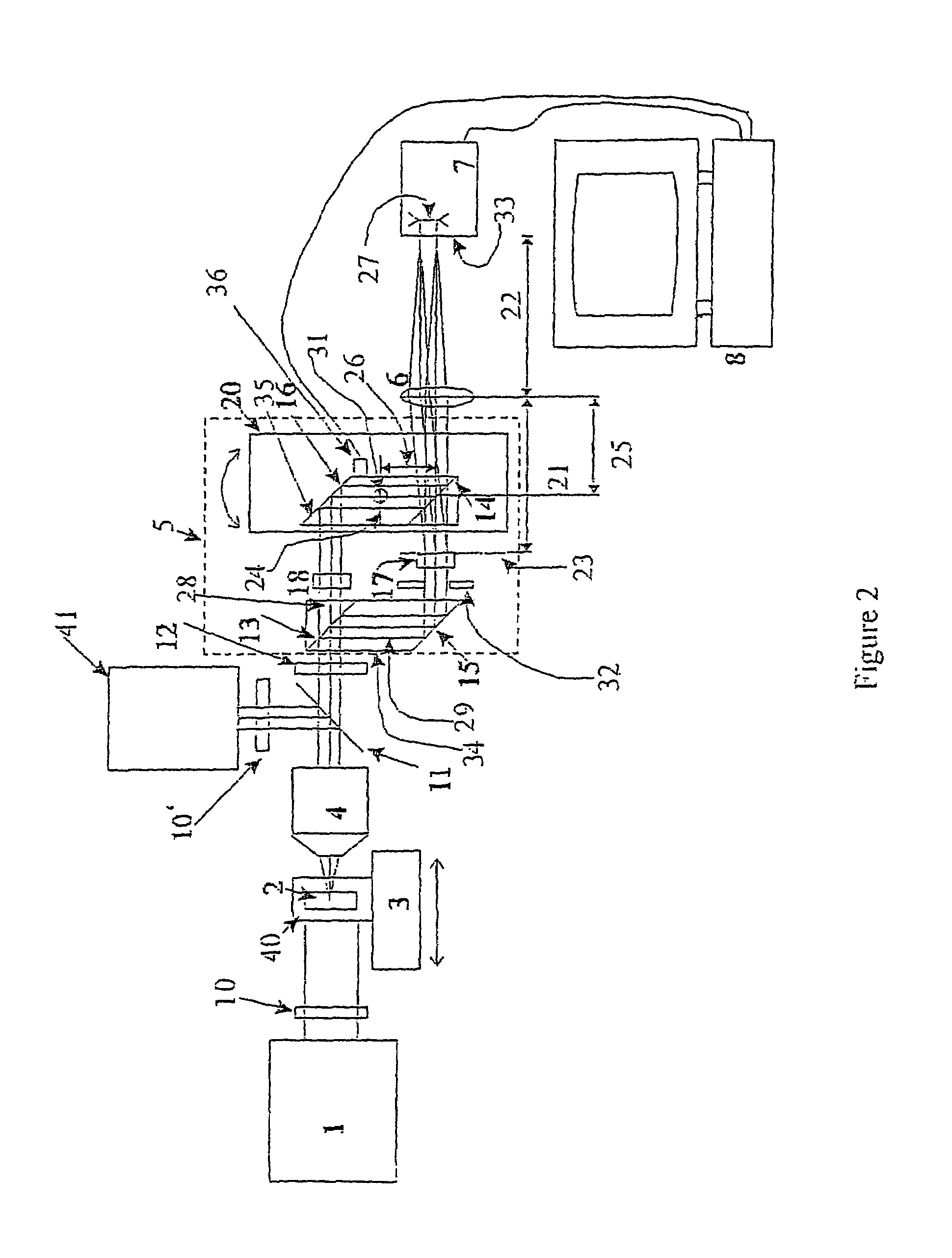
The present invention is related to a compact microscope able to work in digital holography for obtaining high quality 3D images of samples, including fluorescent samples and relatively thick samples such as biological samples, said microscope comprising illumination means (1,41) at least partially spatially coherent for illuminating a sample (2) to be studied and a differential interferometer (5) for generating interfering beams from said sample (2) on the sensor (33) of an electronic imaging device(7), said interferometer (5) comprising namely tilting means (17) for tilting by a defined angle one the interfering beams (28 or 29) relatively to the other, said tilting resulting into a defined shift (27) of said interfering beam on the sensor of the electronic imaging device (7), said shift (27) being smaller than spatial coherence width of each beam, said microscope being able to be quasi totally preadjusted independently from the samples so that minimum additional adjustments are required for obtaining reliable 3D images of samples.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
All-solid digital holography imaging system capable of reducing speckle noise
InactiveCN103092049AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce speckle noiseInstrumentsInformation controlOptical diffraction
The invention discloses an all-solid digital holography imaging system capable of reducing speckle noise, and belongs to the technical field of optical diffraction imaging and digital holography. The all-solid digital holography imaging system capable of reducing the speckle noise comprises a hologram shooting light path, a spatial light modulator, a sample to be detected, an image sensor and a computer. The reference light in the hologram shooting light path is directly incident to the image sensor, the object light in the hologram shooting light path passes through the spatial light modulator and the sample to be detected and then is incident to the image sensor, both the image sensor and the spatial light modulator are connected with the computer, under the control of different phase information provided by the computer, the spatial light modulator is loaded with different random phase mask plates, every time a random phase mask plate is loaded, the image sensor is controlled to record a hologram for one time, multiple holograms are continuously and automatically obtained, and all reproductive images of the holograms are overlapped. The speckle noise of the reproductive images of the digital holography imaging system can be automatically reduced, and the all-solid digital holography imaging system capable of reducing the speckle noise can be used for imaging detection which is relatively high in requirements for instantaneity and distinguishability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
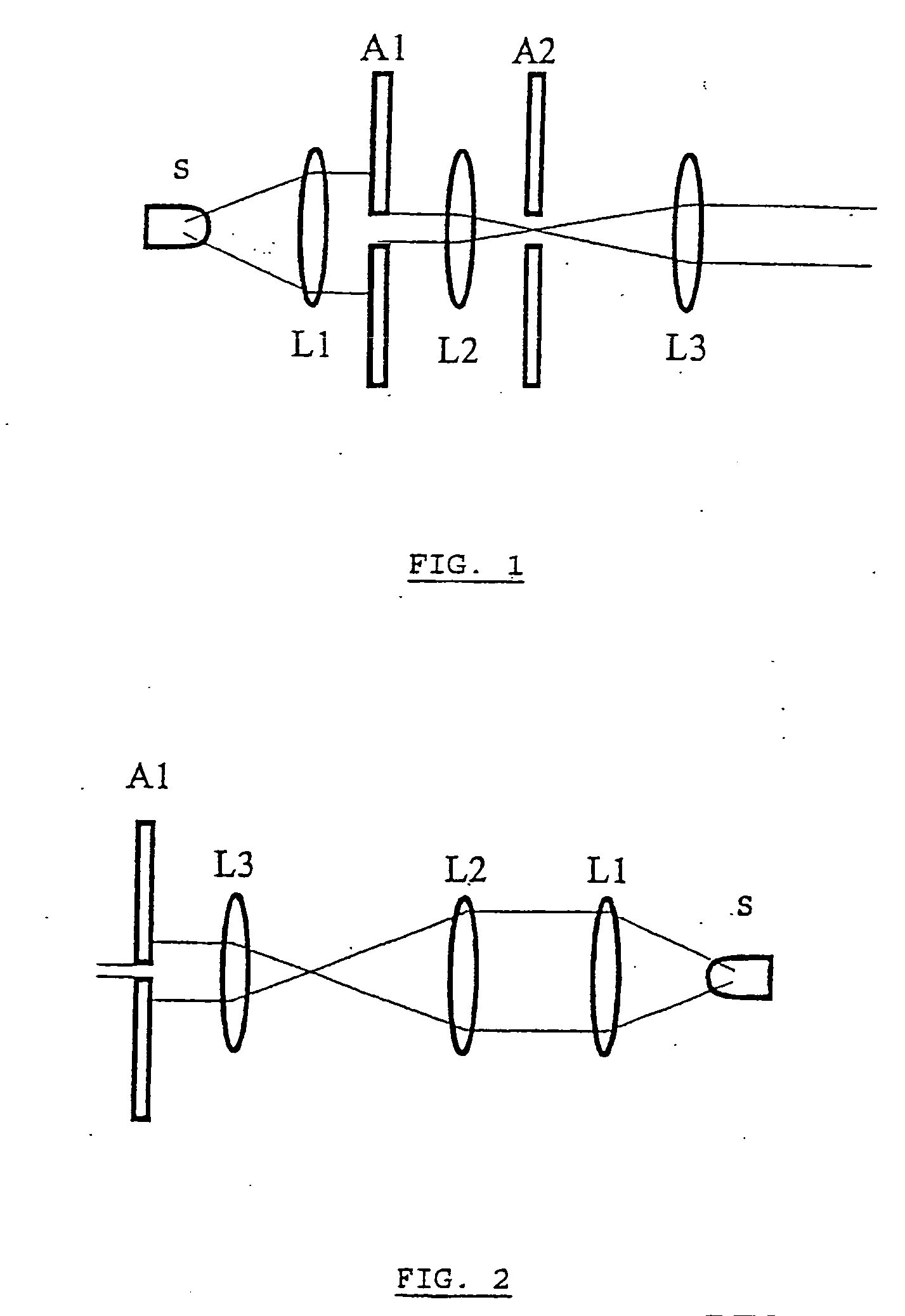
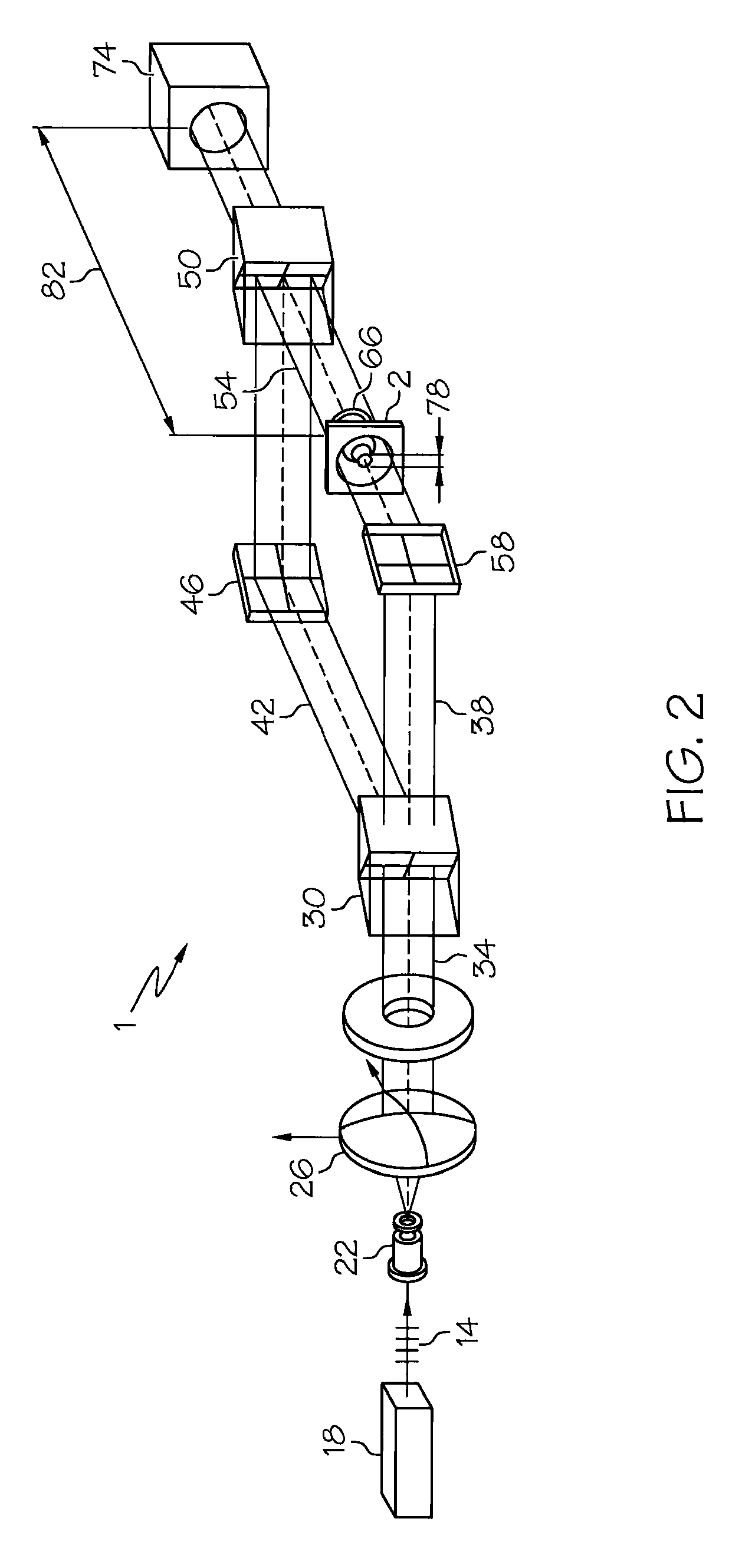
Acquisition and replay systems for direct-to-digital holography and holovision
InactiveUS20030016364A1Cost effectiveLow densityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic object characteristicsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
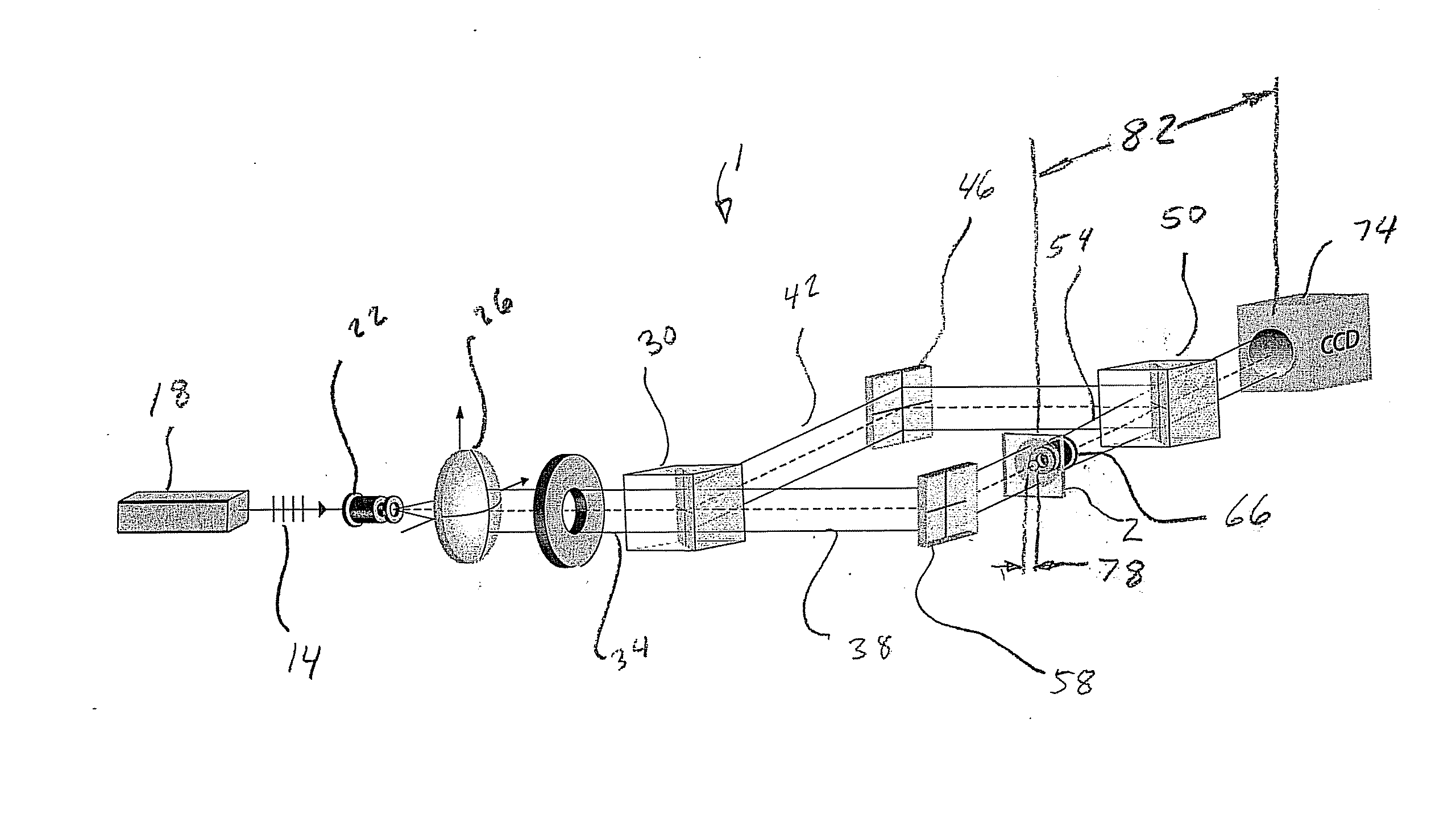
Improvements to the acquisition and replay systems for direct-to-digital holography and holovision are described. A method of recording an off-axis hologram includes: splitting a laser beam into an object beam and a reference beam; reflecting the reference beam from a reference beam mirror; reflecting the object beam from an illumination beamsplitter; passing the object beam through an objective lens; reflecting the object beam from an object; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form an off-axis hologram; digitally recording the off-axis hologram; and transforming the off-axis hologram in accordance with a Fourier transform to obtain a set of results. A method of writing an off-axis hologram includes: passing a laser beam through a spatial light modulator; and focusing the laser beam at a focal plane of a photorefractive crystal to impose a holographic diffraction grating pattern on the photorefractive crystal. A method of replaying an off-axis hologram includes: illuminating a photorefractive crystal having a holographic diffraction grating with a replay beam.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS6747771B2Cost effectiveImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method of recording an off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis, includes: reflecting a reference beam from a reference mirror at a non-normal angle; reflecting an object beam from an object at an angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; digitally recording the off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded off-axis illuminated spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Digital holographic microscope
InactiveUS20060132799A1Minimum delayCompetitive costHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsFluorescenceDigital holographic microscopy
A method and device for obtaining a sample with three-dimensional microscopy, in particular a thick biological sample and the fluorescence field emitted by the sample. One embodiment includes obtaining interferometric signals of a specimen, obtaining fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, recording these signals, and processing these signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time. Another embodiment includes a digital holography microscope, a fluorescence excitation source illuminating a specimen, where the microscope and the fluorescence excitation source cooperate to obtain interferometric signals of the specimen and obtain fluorescence signals emanating from the specimen, means for recording the interferometric signals and fluorescence signals, and means for processing the interferometric signals and the fluorescence signals so as to reconstruct three-dimensional images of the specimen and of the field of fluorescence emitted by the specimen at a given time.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES
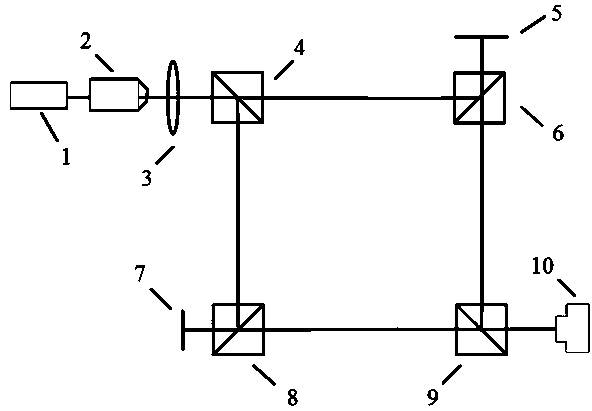
Device and method for detecting topological charge number of vortex beams based on improved Mach-Zehnder interferometer
InactiveCN103940520AEasy to operateImprove stabilityOptical measurementsBeam splitterSpatial light modulator
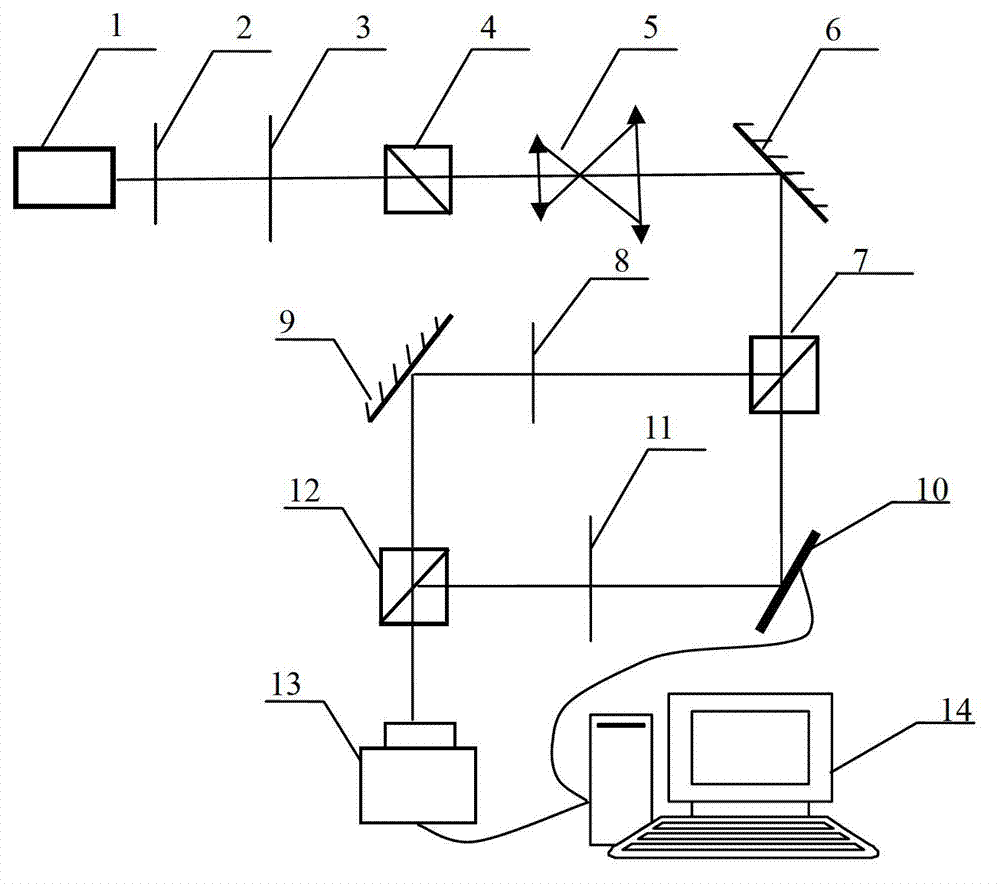
The invention relates to a device and method for detecting the topological charge number of vortex beams based on an improved Mach-Zehnder interferometer, and belongs to the technical field of digital holography. The device comprises a semiconductor laser unit, a microscope objective spatial fiber, a collimating lens, a beam splitter prism I, a plane mirror, a beam splitter prism II, a spatial light modulator, a beam splitter prism III, a beam splitter prism IV and a photoelectric coupled device. According to the method, one arm of the device is used for generating the vortex beams to be used as object light, the other arm of the device is used for generating the vortex beams to be used as reference light, the holographic interferometry principle is used for recording the wave front phase information of the vortex beams in an interference fringe mode, phase distribution is digitally reconstructed in the later period, and the topological charge number of the vortex beams can be obtained according to the reconstructed phase distribution in accordance with the definition of the vortex beams. The device and method solve the problem that at present, specific instruments or equipment is needed in the method for detecting the topological charge number of the vortex beams, or an existing detecting method is complex to operate, poor in stability and low in reliability.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
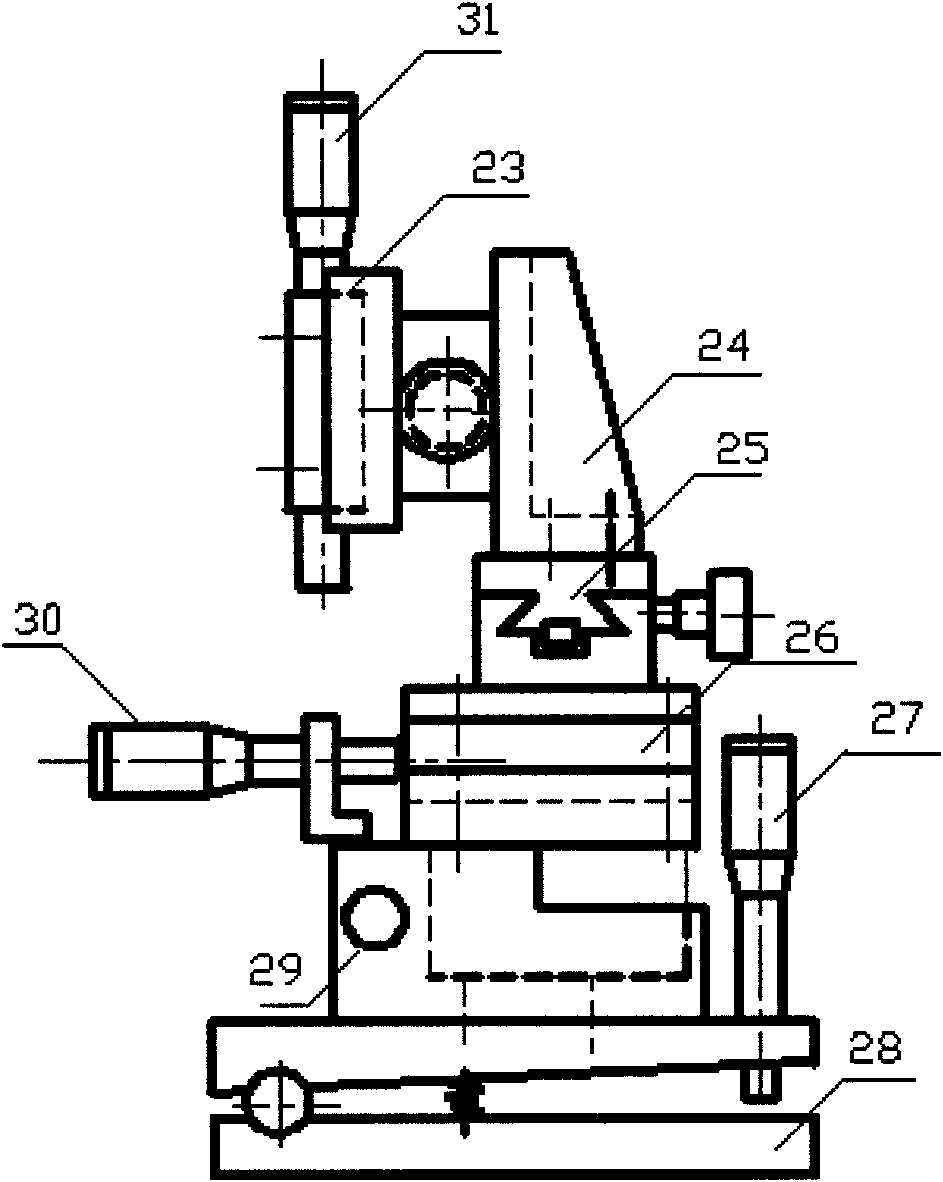
Multifunction three-dimensional displacement and topography laser interferometry system
InactiveCN101608904AEasy to convertImprove dynamic performanceUsing optical meansPhotoswitchTopography
The invention discloses a multifunction three-dimensional displacement and topography laser interferometry system, belonging to the technical fields of photo mechanics, engineering material, structural member deformation, displacement testing, topography measurement and the like. The invention consists of a laser device, a image collecting and shooting system, a light split coupler, a light split photoswitch, a DC electrical source controller, a three-dimensional laser interference optical path system, a loading charging floor for putting test pieces, a bracket adjusting system, a computer and the like. The laser interferometry system can realize high-precision measurement of u, v and w displacement fields, and displacement measurement sensitivity can reach wavelength magnitude; the laser interferometry system has two displacement measurement modes of digital holography and electronic speckle pattern interferometry, and also has the mode of digital holographic measurement of surface topography. The invention can realize the adjustment of degrees of freedom on multiple directions by using the bracket adjusting system, brings convenience for system imaging and measurement adjustment, and has the characteristics of convenient use, compact structure, high measurement precision and the like; because the system is provided with a phase shifting device, the displacement measurement precision of the system of the invention can reach nanometer magnitude after phase shifting treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
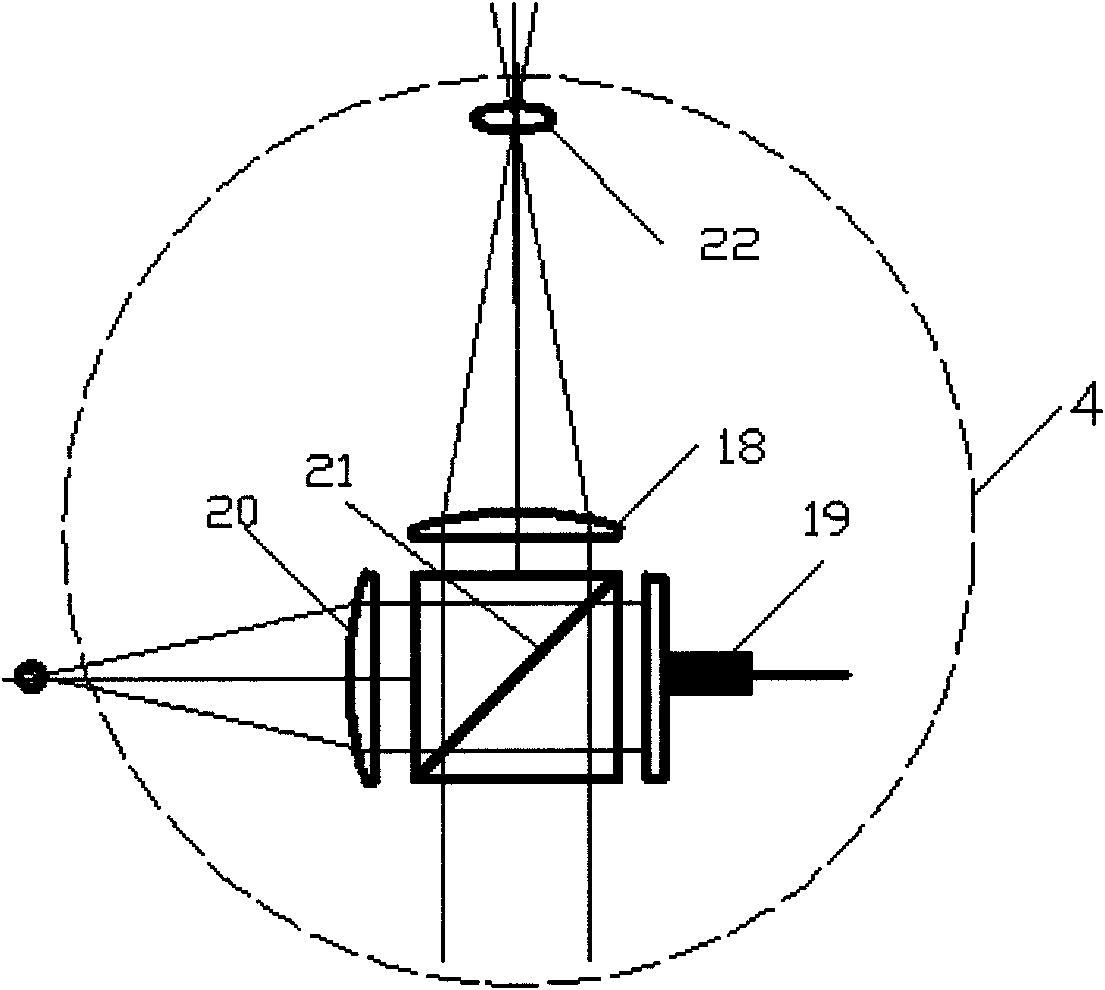
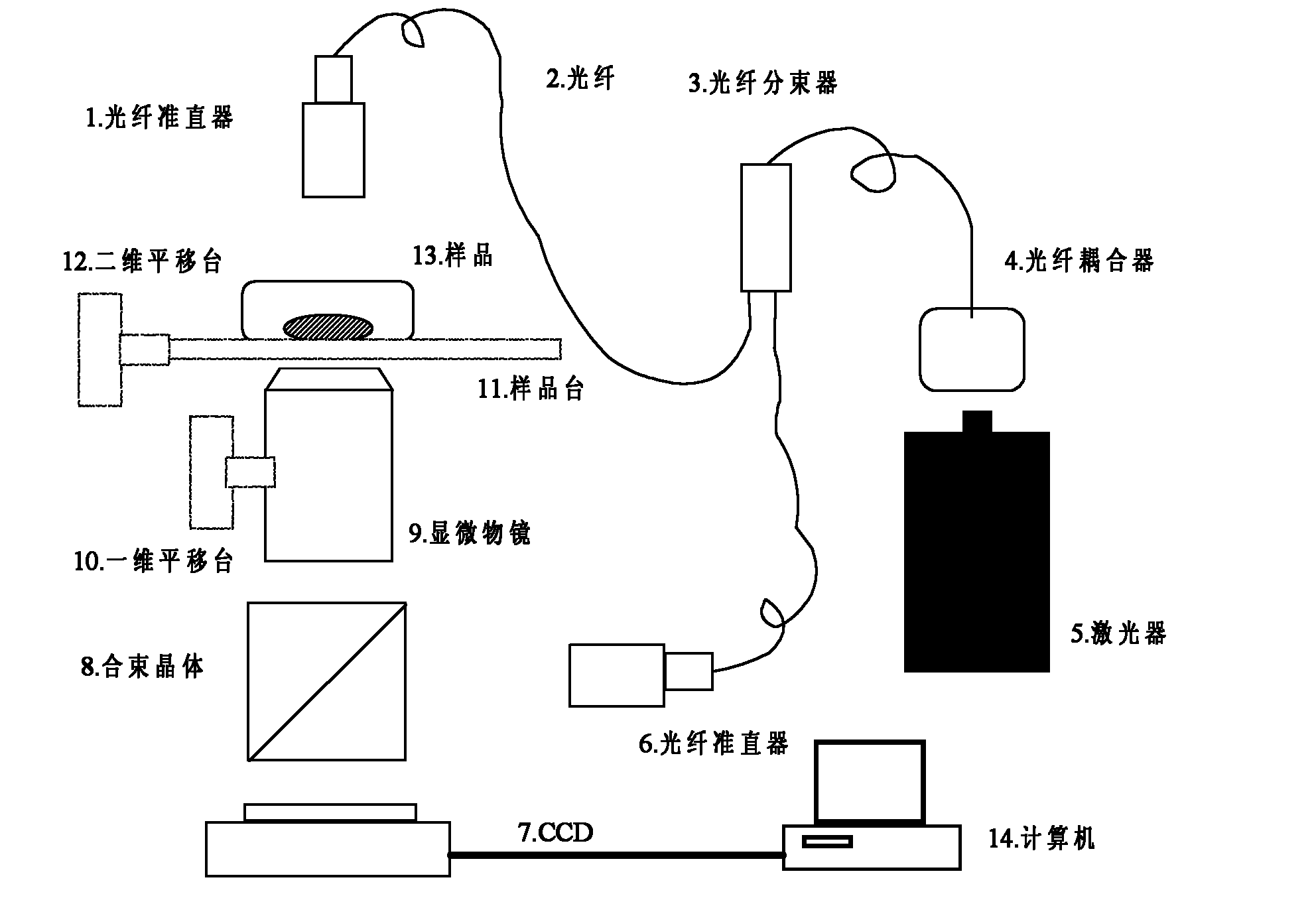
Inverted digital holographic microscope
InactiveCN102122063AHighly integratedReduce volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansBeam splitterDigital holographic microscopy
The invention discloses an inverted digital holographic microscope, which belongs to the digital holographic technical field, and can be used for three-dimensional real-time appearance measurement and biological cell imaging. In the inverted digital holographic microscope, an optical fiber coupler 4 is arranged in front of a laser 5 and connected with an optical fiber beam splitter 3 through an optical fiber; the optical fiber beam splitter 3 is connected with two paths of optical fibers respectively connected with an optical fiber collimator 1 and an optical fiber collimator 6, a sample stage 11 for placing a sample 13 is arranged under the optical fiber collimator 1, and the sample stage 11 is connected with a two-dimensional translation stage 12; a micro objective mounted on a one-dimensional translation stage 10 is located under the sample stage 11, and the micro objective 9 and the optical fiber collimator 6 are aligned with two mutually vertical sides of a beam combination crystal 8; and a CCD (charge-coupled device) camera 7 is located under the beam combination crystal 8. The inverted digital holographic microscope can be used for observing the living cell which is located at the bottom of a culture dish and grows along a wall of the culture dish with a high resolution ratio for long time, and is highly integrated and small in volume; moreover, with the optical fiber connection, the laser can be freely mounted on other parts of the system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Spatially-heterodyned holography
InactiveUS20030227658A1Cost effectiveLow densityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic object characteristicsSpatial light modulatorEngineering
Improvements to the acquisition and replay systems for direct-to-digital holography and holovision are described. A method of recording an off-axis hologram includes: splitting a laser beam into an object beam and a reference beam; reflecting the reference beam from a reference beam mirror; reflecting the object beam from an illumination beamsplitter; passing the object beam through an objective lens; reflecting the object beam from an object; focusing the reference beam and the object beam at a focal plane of a digital recorder to form an off-axis hologram; digitally recording the off-axis hologram; and transforming the off-axis hologram in accordance with a Fourier transform to obtain a set of results. A method of writing an off-axis hologram includes: passing a laser beam through a spatial light modulator; and focusing the laser beam at a focal plane of a photorefractive crystal to impose a holographic diffraction grating pattern on the photorefractive crystal. A method of replaying an off-axis hologram includes: illuminating a photorefractive crystal having a holographic diffraction grating with a replay beam.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method and apparatus for recognition of microorganisms using holographic microscopy
ActiveUS7616320B2Material analysis by optical meansHolographic object characteristicsDigital holographic microscopyDetector array
Disclosed herein is a method that relates to identifying a microorganism. The method comprising, diffracting laser light through a microorganism, combining a reference beam with the diffracted light on a single axis, and recording the combined light holographically as a three-dimensional image with a single exposure on a detector array. The method further comprising, reconstructing the holographic image and matching the reconstructed image with reference images of known microorganisms. Further disclosed herein is an apparatus for identifying a microorganism. The apparatus comprising, an interferometer to record an image of an unknown microorganism using single-exposure on-line (SEOL) digital holography, a means for reconstructing the recorded image, and a means for matching the reconstructed image with images of known microorganism.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
High-resolution digital holographic diffraction tomography
InactiveCN108519728AEnabling 3D tomography measurementsImprove imaging resolutionUsing optical meansImage resolutionDiffraction tomography
Provided is high-resolution digital holographic diffraction tomography, belonging to the field of digital holography and diffraction tomography. A digital holographic diffraction tomography device isused for obtaining N synthetic high-resolution holograms by utilizing a synthetic aperture method, and then the high-resolution three-dimensional refractive index reproduction of a tested sample is obtained. In order to improve the imaging resolution of the system, the synthetic aperture method is introduced into a digital holographic diffraction tomography system, a two-dimensional electric translation platform is used for moving the CCD, the high-frequency information around the original hologram is acquired, and m*m (m>=3) sub-holograms are recorded when the angle of a galvanometer is theta), the m*m sub-holograms are subjected to intensity registration and image dislocation sub-pixel micro-displacement, so that a synthetic high-resolution hologram is obtained. The high-resolution three-dimensional imaging is realized by combining a digital holographic diffraction tomography method and the synthetic aperture method. The digital holographic diffraction tomography system can realize non-contact, non-marking, lossless and three-dimensional tomography measurement.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
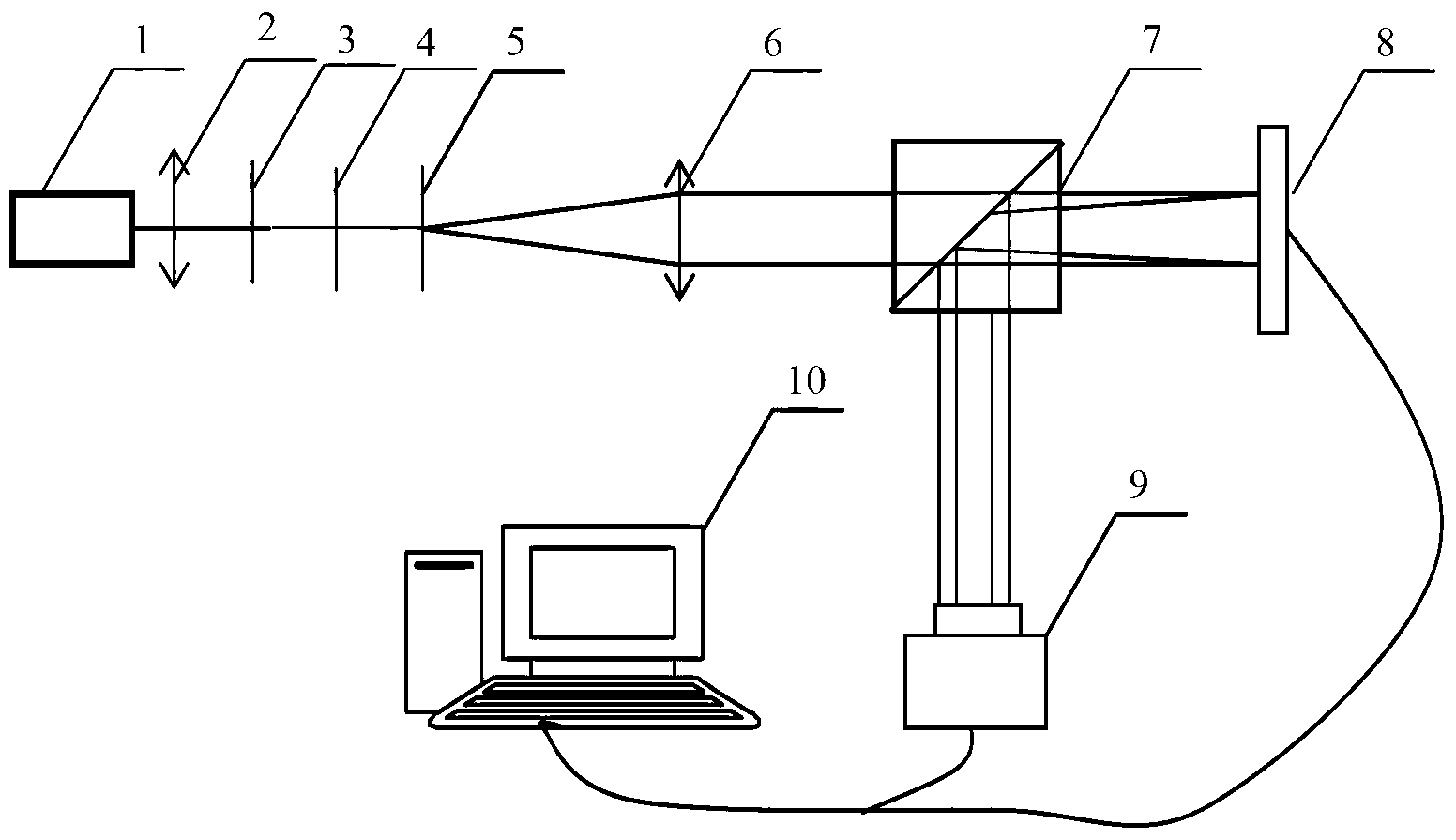
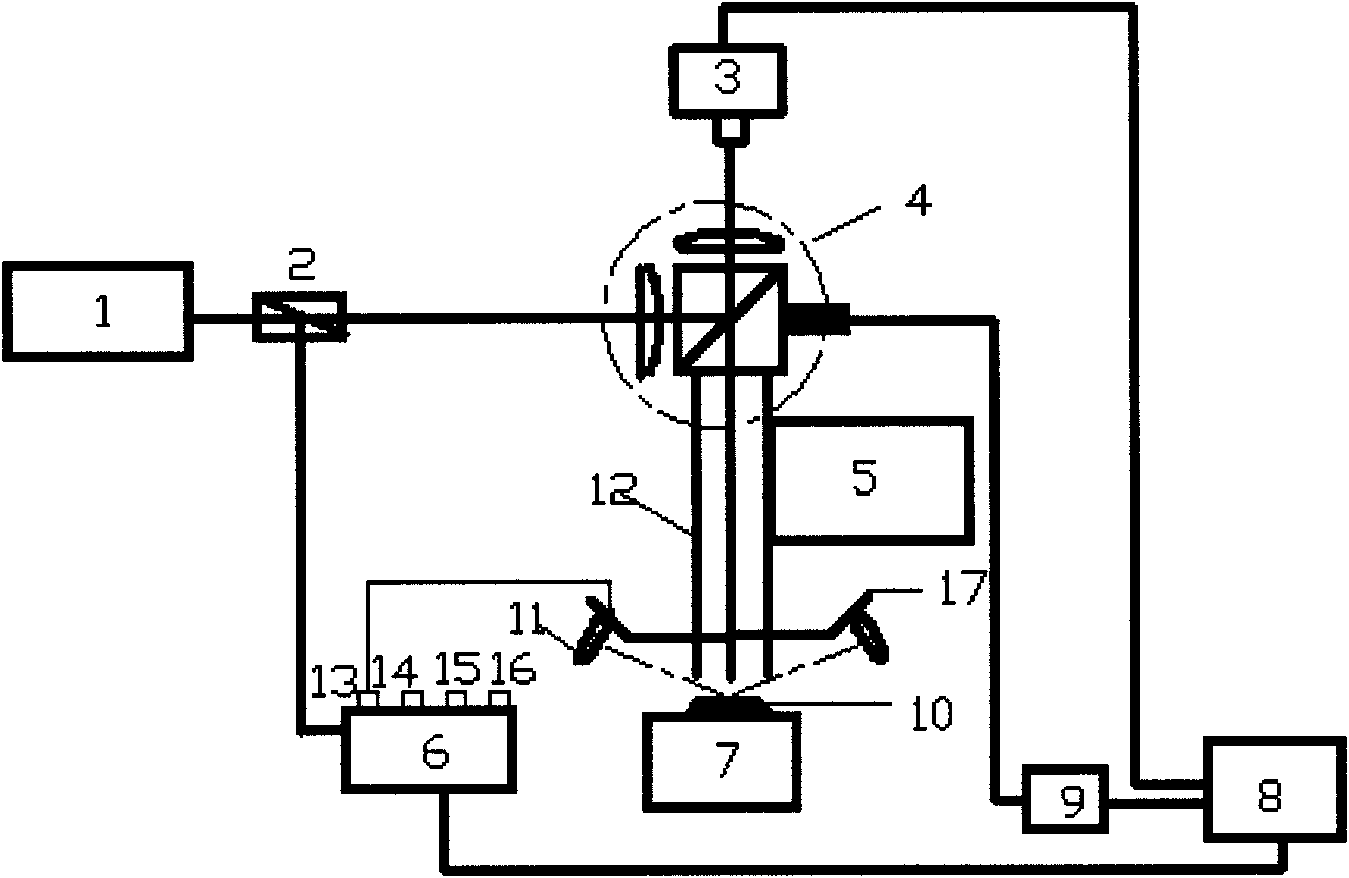
A dynamic three-dimensional microscopic observation device for biological living cells based on digital holography
InactiveCN102278951AWith non-contactNon-destructiveUsing optical meansDistance correctionMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a digital holography-based three-dimensional micro-observation apparatus for cell dynamic of a living organism. According to the apparatus provided in the invention, a microscopic technology of digital holography is employed, so that dynamic three-dimensional microscopic observation without contact, damage and pretreatment on a cell of a living organism can be realized; a fiber optical path is utilized to realize object light illumination and an optical path portion of the object light employs a vertical type structure, so that it is convenient to carry out observationon the cell of the living organism; reference light utilizes a light beam turnover device to control an included angle between the reference light and the object light so as to realize off-axis digitholography; and an infinite distance correction microscopic object lens is employed to carry out pre-amplification and imaging on the cell; simultaneously, a relay lens is utilized to adjust an imaging position and a wavefront curvature of the object light, so that observation resolution is improved. According to the apparatus, layout structures of a plurality of optical elements are compact, flexible and stable thorough a platform; moreover, the apparatus can be applied to dynamic observation on the cell of the living organism for a long time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
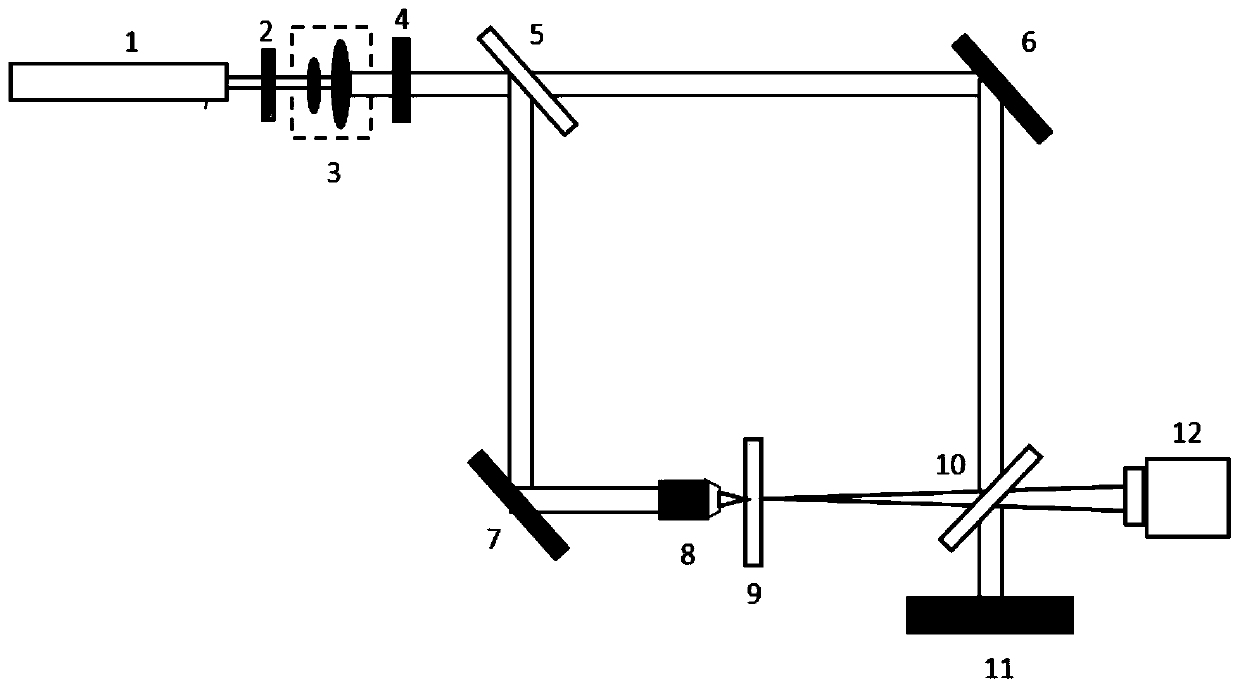
Digital holographic three-dimensional appearance detecting device based on multiple wavelengths
The invention relates to a digital holographic three-dimensional appearance detecting device based on multiple wavelengths. The device carries out surface appearance measurement on the surface of a three-dimensional object by adopting the multiple wavelengths through a digital holographic method. In an optical path structure, the object to be measured is illuminated by planar optical waves, reflected object light is collected, and the included angle between reference light and the object light is controlled through a light beam deflector to achieve off-axis digital holography. In order to enlarge the measurement range while the observation resolution ratio is ensured, the object to be measured can be measured through light beams with the different wavelengths, obtained holographic spectrograms are processed in a subtractive iteration mode, and then three-dimensional appearance information of the object which is to be measured and free of phase position wrapping is obtained. Due to an integrated optical platform, all the optical elements are compact in layout structure, flexible to use and stable, and the detecting device can be used for observing three-dimensional appearances of optical elements large in height and high in accuracy and roughness and mechanical assemblies including mechanical rotors and the like on line.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Super-resolution digital holographic imaging system and imaging method
ActiveCN109709786AHigh resolutionImprove scalabilityInstrumentsSpatial light modulatorHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a super-resolution digital holographic imaging system and a super-resolution digital holographic imaging method. The super-resolution digital holographic imaging system is characterized in that a trnasmissive spatial light modulator (SLM) is additionally arranged in front of a conventional Mach-Zehnder holographic optical path, fringe patterns in different directions are generated in the SLM so as to generate structured light in different directions, and an image sensor acquires a series of holograms formed by illumination of the structured light. The super-resolution digital holographic imaging method comprises the steps of performing Fourier transform on each hologram in a computer, superimposing the series of holograms in a spatial frequency domain, then demodulating high-frequency information of the holograms, and finally using a classical reconstruction algorithm of digital holography to achieve higher resolution imaging of objects. The super-resolution digital holographic imaging method provides a new solution for improving the resolution of the digital holographic imaging system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Content-based fused off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography
InactiveUS20040042015A1Cost effectiveHigh resolutionUsing optical meansOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
Systems and methods are described for content-based fused off-axis illumination direct-to-digital holography. A method includes calculating an illumination angle with respect to an optical axis defined by a focusing lens as a function of data representing a Fourier analyzed spatially heterodyne hologram; recording a content based spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes for Fourier analysis; Fourier analyzing the recorded content based spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes by transforming axes of the recorded content based spatially heterodyne hologram including spatially heterodyne fringes in Fourier space to sit on top of a heterodyne carrier frequency defined as an angle between the reference beam and the object beam; applying a digital filter to cut off signals around an original origin; and then performing an inverse Fourier transform.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Double charge-coupled-device (CCD) mirror image overlap adjustment and single-exposure coaxial digital holographic record device
InactiveCN103034109AAddressing Insufficient Recording CapabilitiesIncrease freedomInstrumentsBeam splitterThree dimensional shape
The invention relates to a double charge-coupled-device (CCD) single-exposure coaxial digital holographic record device, and belongs to the technical field of digital holography. The device utilizes double CCD mirror image overlap union record and single step phase shift cepstrum technology, achieves real-time record and reproduction of the coaxial digital holography, and can be used for dynamical measurement of small transparent phase position objects such as plankton. The basic principle of the device includes that a laser emitted by a laser device is divided into two beams after beam expansion and collimation, wherein one beam of the laser vertically irradiates the transparent phase position objects to form object light, after the other beam of the laser passes through a one half wave plate, the polarization direction is rotated by 90 degrees, the other beam serves as reference light, and at the moment, the polarization directions of the object light and the reference light are orthogonal; wave combination is conducted through a beam splitter, one of the two beams of the laser is recorded by a first CCD camera after polarization inspection and interference through a polarization analyzer, after the other one of the two beams of the laser passes through a one quarter wave plate, the phase position of the reference light is delayed by one half of pi, the phase position of the object light is not changed, and the other one of the two beams of the laser is recorded by a second CCD camera after polarization inspection and interference through the polarization analyzer; and a computer reads and reproduces the three-dimensional shapes of measured objects in real time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Digital holography three-directional shape detection device based on multi-wavelengths and multi-polarization states
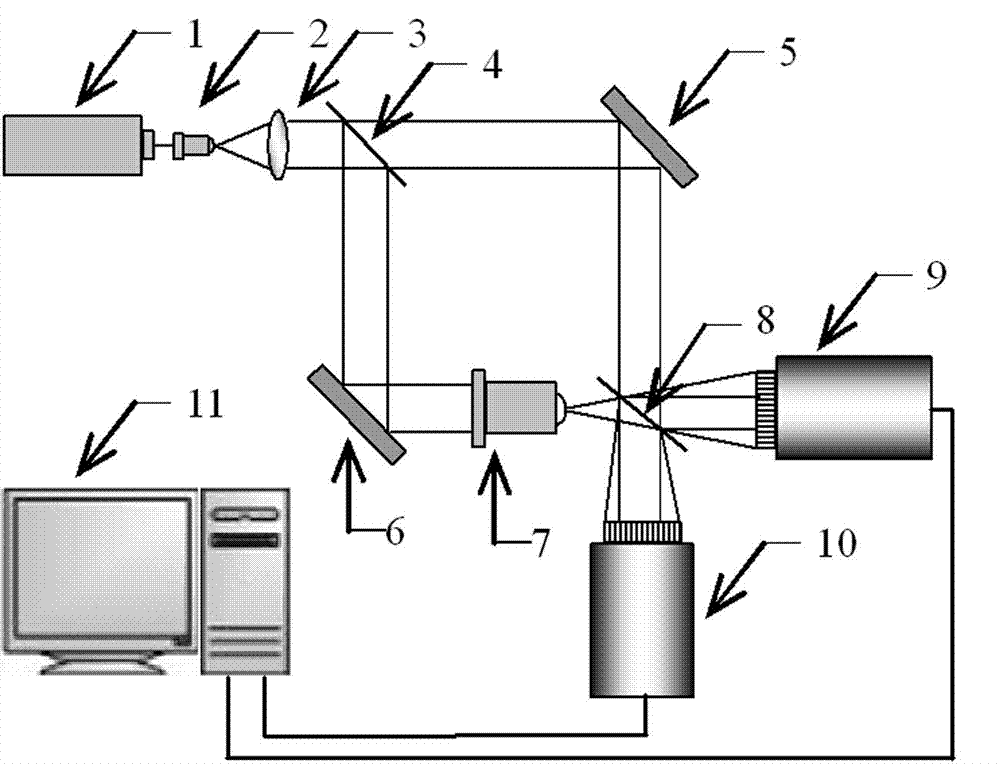
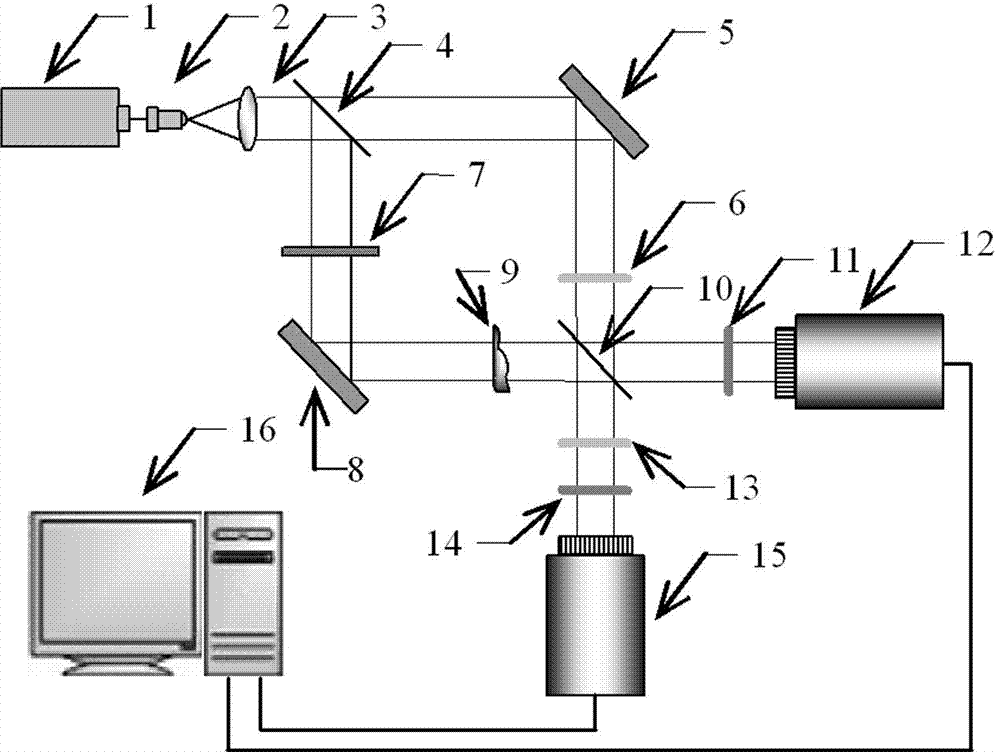
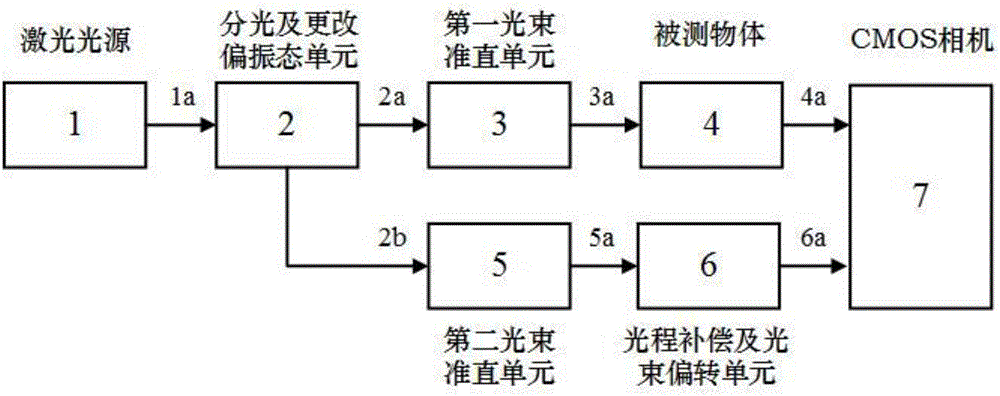
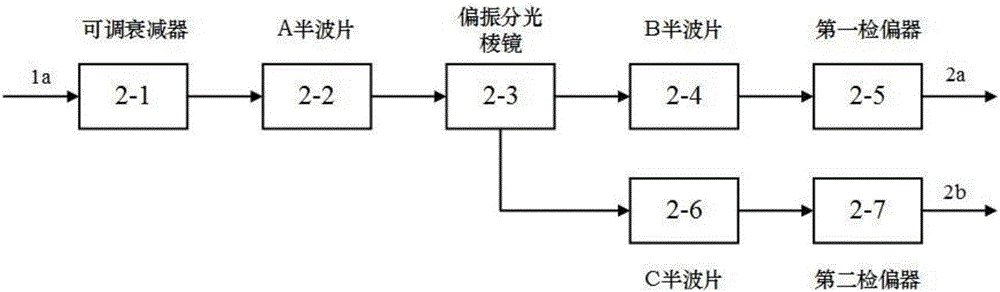
InactiveCN105066908AAvoid wrappingAvoid uncertaintyUsing optical meansCMOSSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a digital holography three-directional shape detection device based on multi-wavelengths and multi-polarization states. The detection device comprises a laser light source, a light dividing and changing polarization state unit, a first light beam aligning unit, a to-be-detected object, a second light beam aligning unit, an optical length compensation and light beam deflecting unit and a CMOS camera. By combining the digital holography method and the multi-wavelength measuring technology, the detection device can be used for three-dimensional shape detection of an object whichis highly roughwith a non-optically smooth surface and an incontinuous and highly uneven surface structure. Based on effects on speckle distribution imposed by light wave polarization states, the detection device is capable of integrating information for multiple holograms in different polarization states, so effects on reconstructed images by speckles can be effectively restrained and signal to noise ratio can be increased.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Direct-to-digital holography reduction of reference hologram noise and fourier space smearing
Systems and methods are described for reduction of reference hologram noise and reduction of Fourier space smearing, especially in the context of direct-to-digital holography (off-axis interferometry). A method of reducing reference hologram noise includes: recording a plurality of reference holograms; processing the plurality of reference holograms into a corresponding plurality of reference image waves; and transforming the corresponding plurality of reference image waves into a reduced noise reference image wave. A method of reducing smearing in Fourier space includes: recording a plurality of reference holograms; processing the plurality of reference holograms into a corresponding plurality of reference complex image waves; transforming the corresponding plurality of reference image waves into a reduced noise reference complex image wave; recording a hologram of an object; processing the hologram of the object into an object complex image wave; and dividing the complex image wave of the object by the reduced noise reference complex image wave to obtain a reduced smearing object complex image wave.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
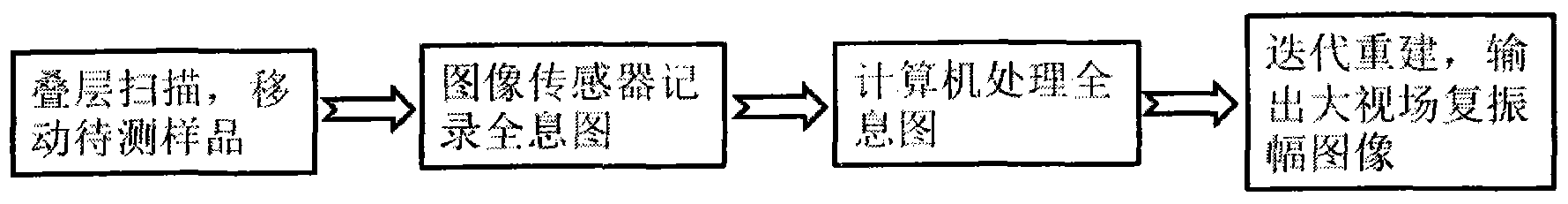
Imaging-view-field-increase-oriented lamination scanning digital holography
InactiveCN103838124ALarge field of viewEnable complex amplitude imagingInstrumentsComplex amplitudeReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses an imaging-view-field-increase-oriented lamination scanning digital holography. According to the imaging-view-field-increase-oriented lamination scanning digital holography, samples to be measured are sequentially moved transversely in a measuring plane in a lamination scanning mode, and corresponding holograms are recorded with an image sensor. The recorded series holograms are processed with a digital holography reconstruction algorithm based on lamination scanning, and complex amplitude images of increased view fields of the samples to be measured can be obtained. Information redundancy constraints of adjacent view fields are provided through lamination scanning, so that the problems of view field splicing and image fusing in large-view-field digital holography imaging are solved. Meanwhile, the convergence rate and the noise jamming resisting capacity of lamination iteration are substantially improved through the holographic record data processing mode. The imaging-view-field-increase-oriented lamination scanning digital holography is high in imaging efficiency, good in transportability and suitable for phase position quantitative measurement and microimaging of various transmission type or reflection type objects.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
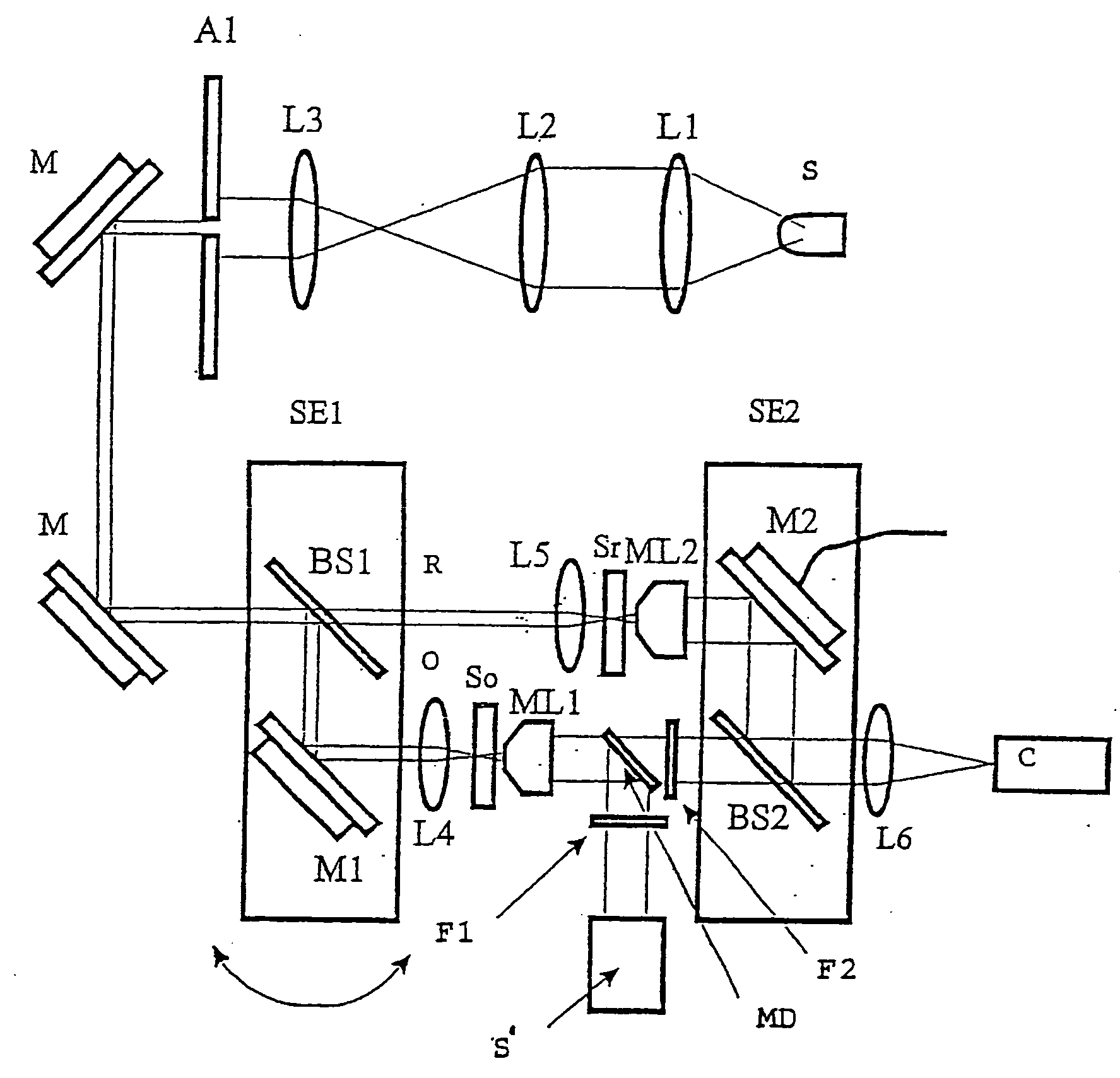
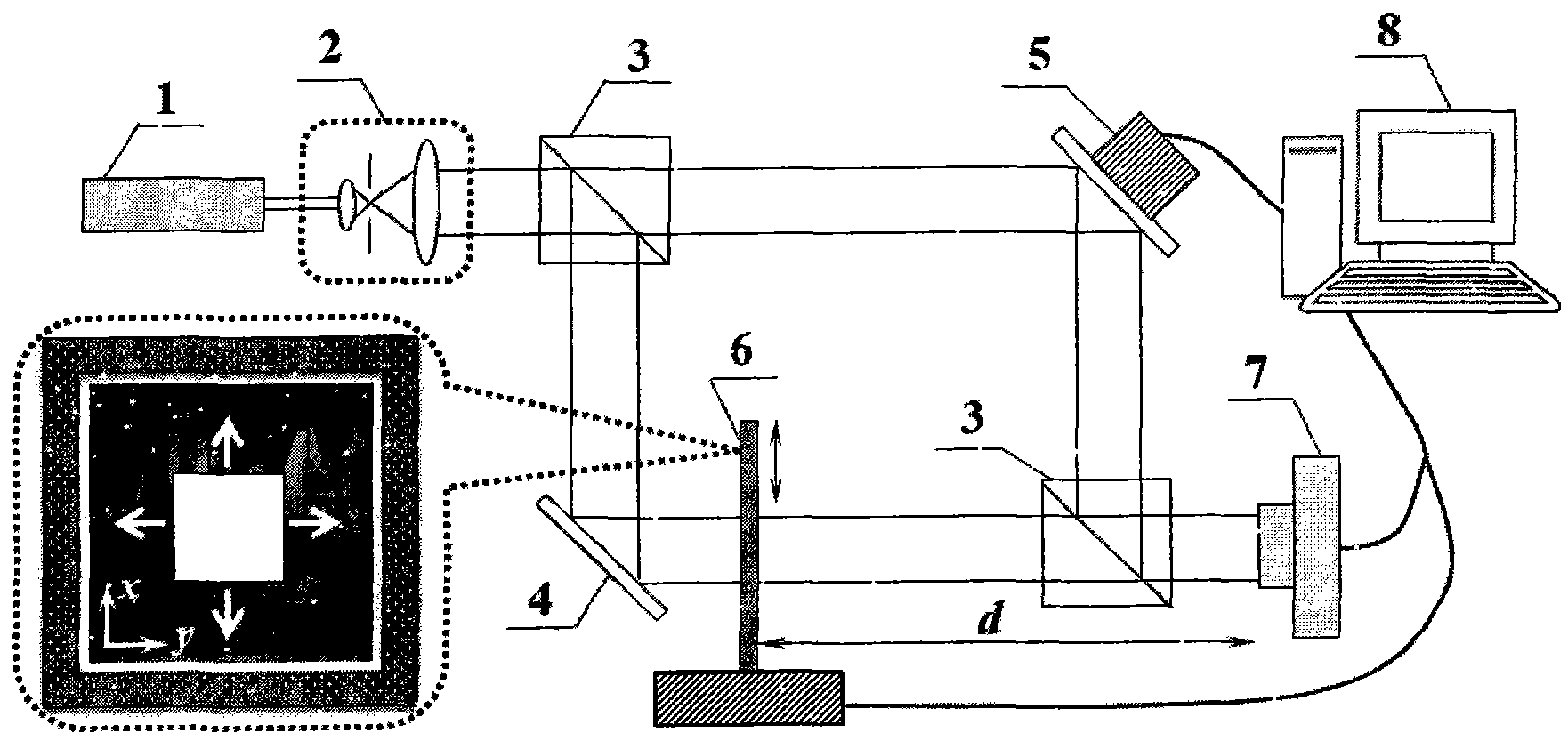
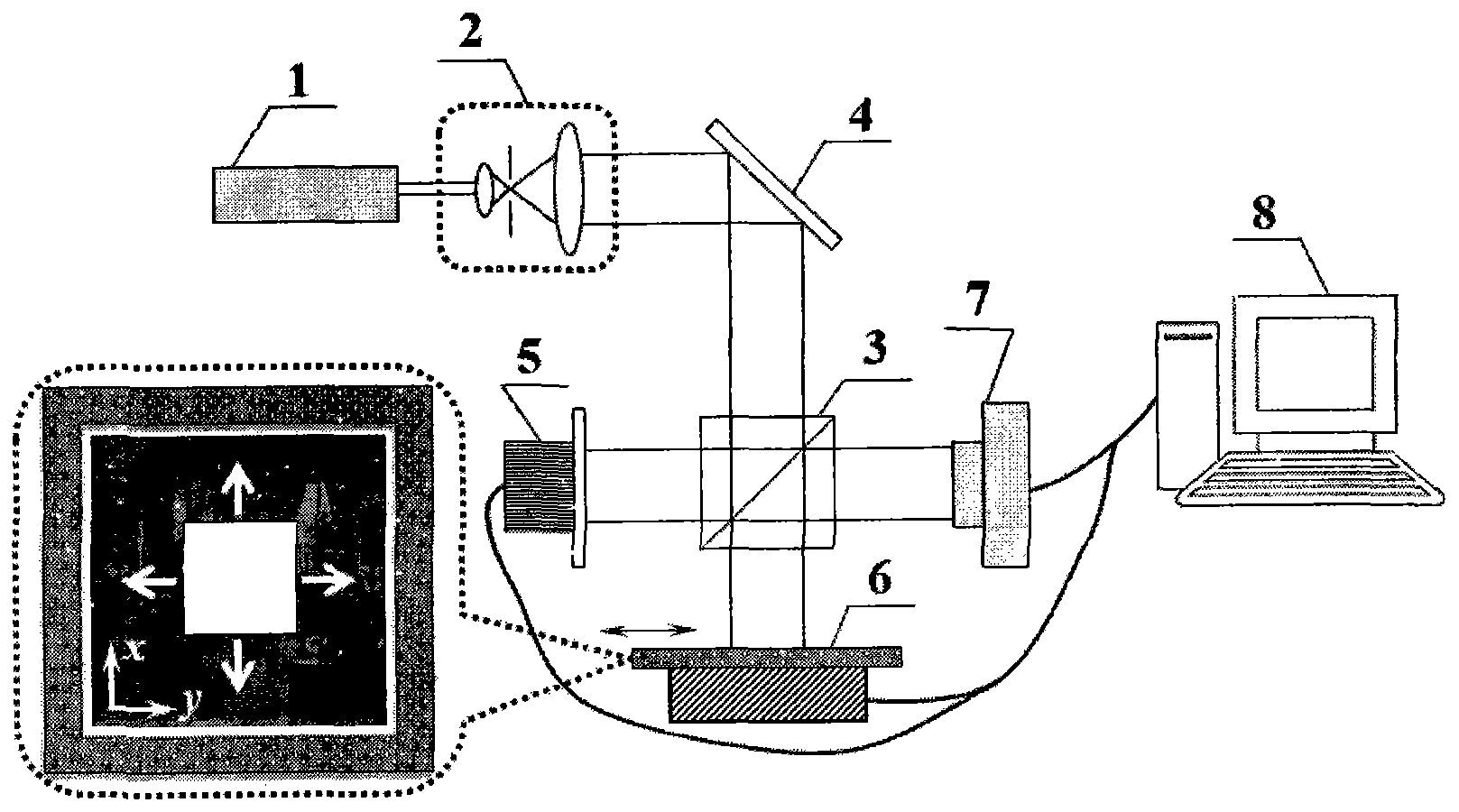
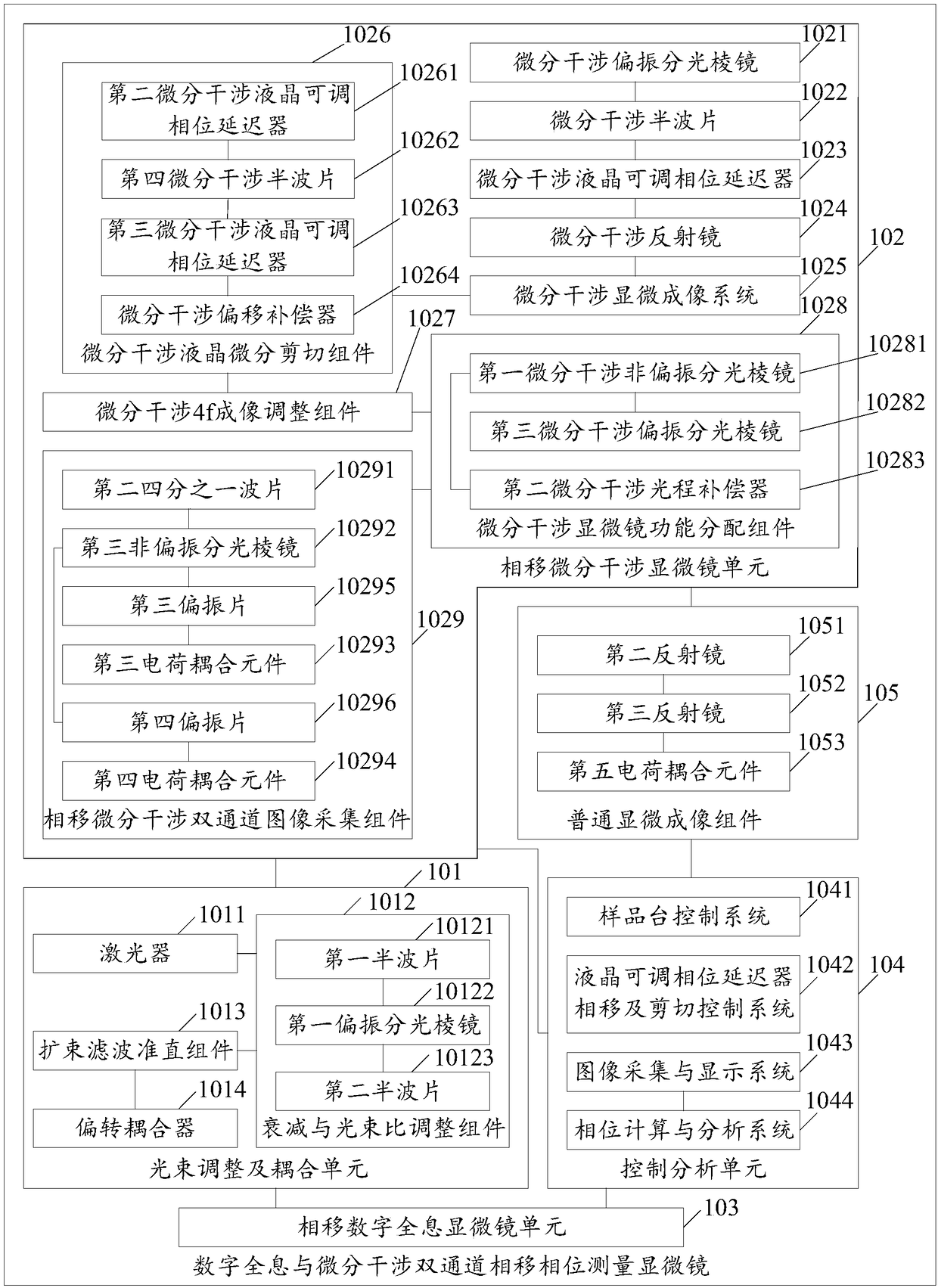
Digital holography and differential interference combined dual-channel phase-shift phase measuring microscope
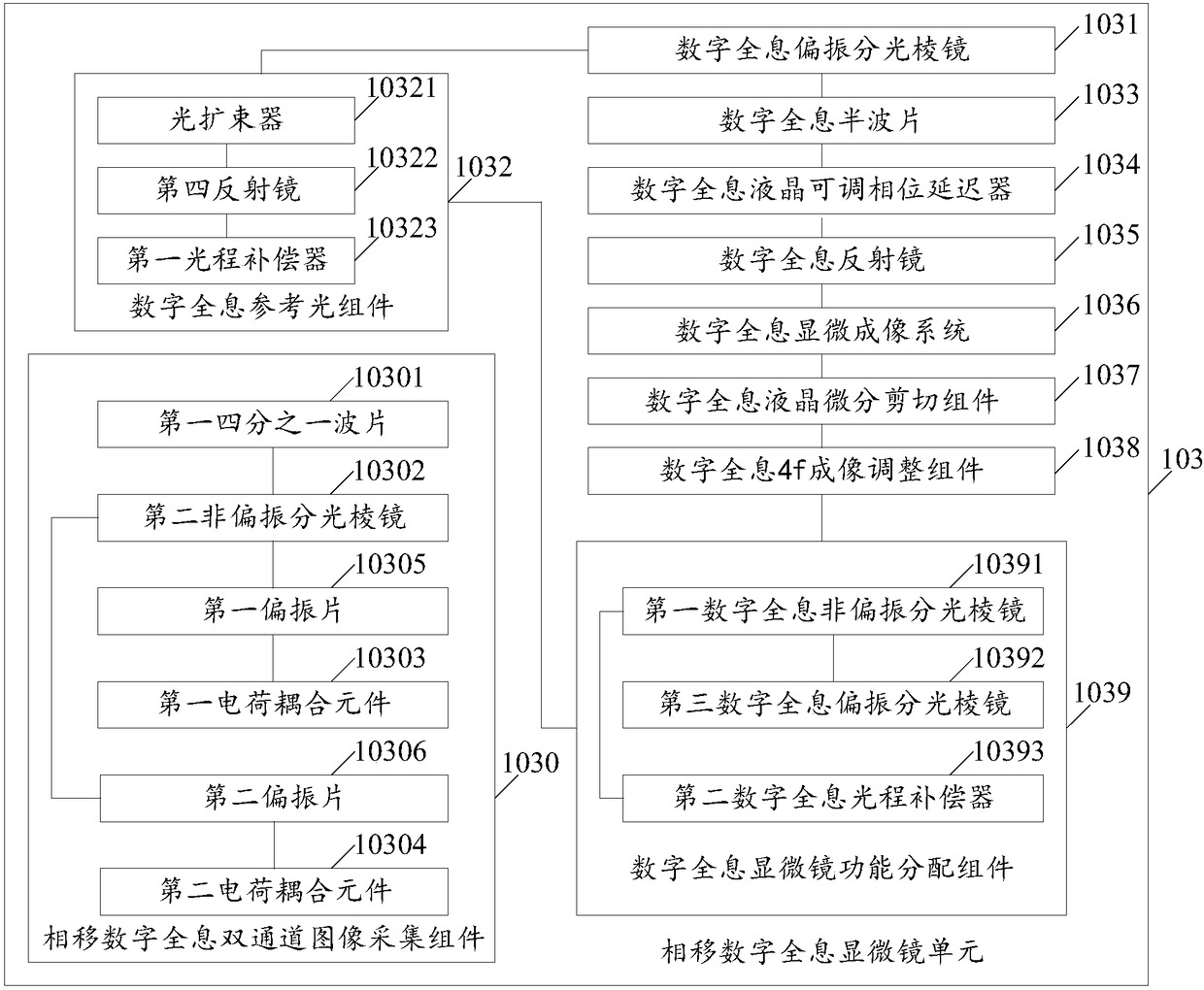
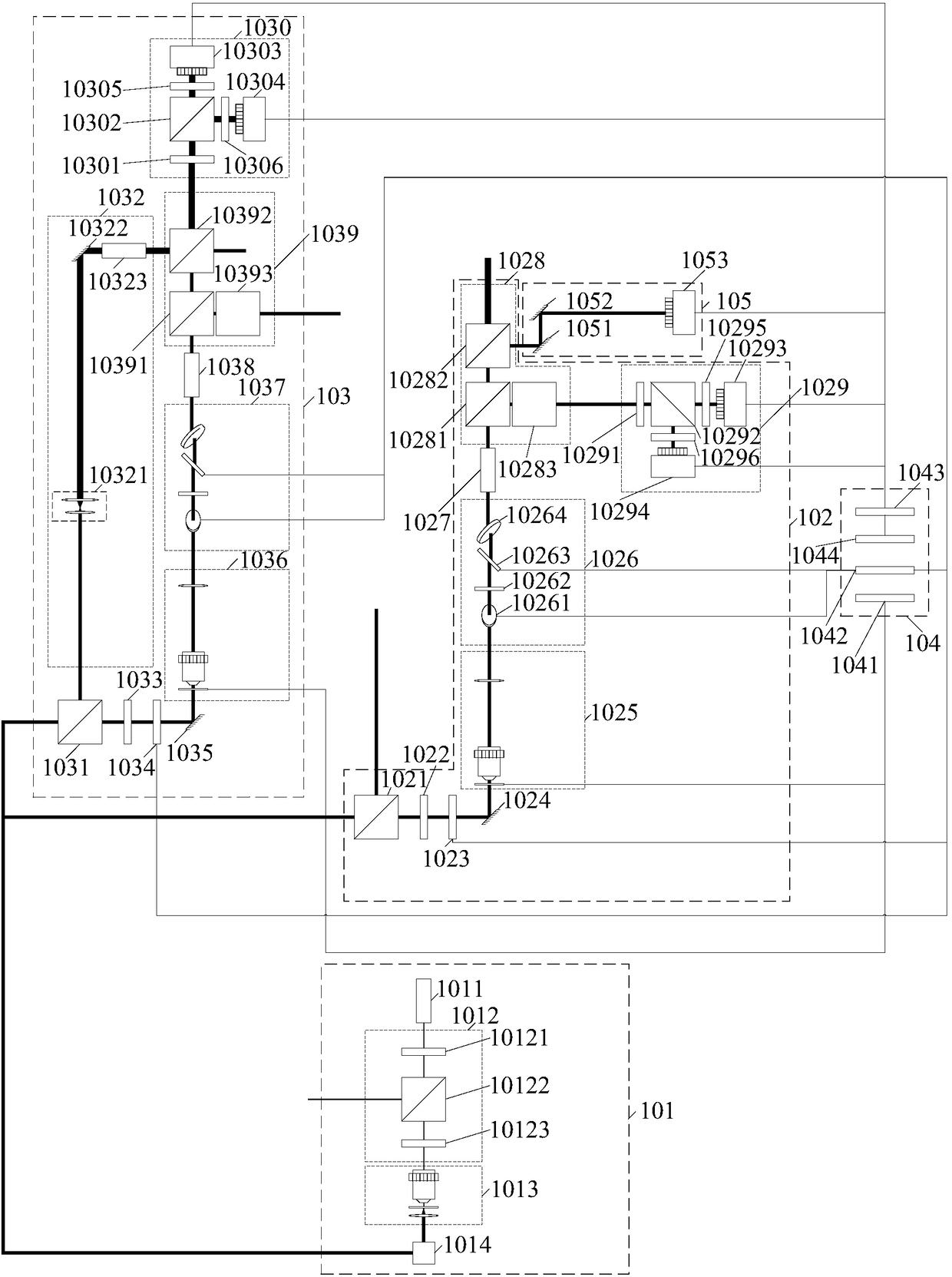
The invention relates to a digital holography and differential interference combined dual-channel phase-shift phase measuring microscope. The measuring microscope includes: a light beam adjusting andcoupling unit used for generating a measuring light beam; a phase shift phase shift differential interference microscope unit used for receiving the measuring light beam to form a corresponding imaging light beam and a first adjusting shear phase shift orthogonal polarized light; a phase shift digital holographic microscope unit used for receiving the measuring light beam and forming a corresponding imaging light beam; a common microscope imaging assembly used for receiving the first adjusting shear phase shift orthogonal polarized light and outputting the corresponding imaging light beam; anda control analysis unit used for controlling the formed imaging light beam and performing phase shift calculation and analysis on the imaging light beam to obtain a phase shift calculation and analysis result. Therefore, the embodiment of the invention increases accuracy of real-time three-dimensional dynamic phase measurement of a minimal transparent sample and provides a new quantified measuring means for cell, micro-flow field and micro-device research and correlated engineering application.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A Synthetic Aperture Digital Holographic 3D Microscopic Observation Device with Smooth Reflective Surface
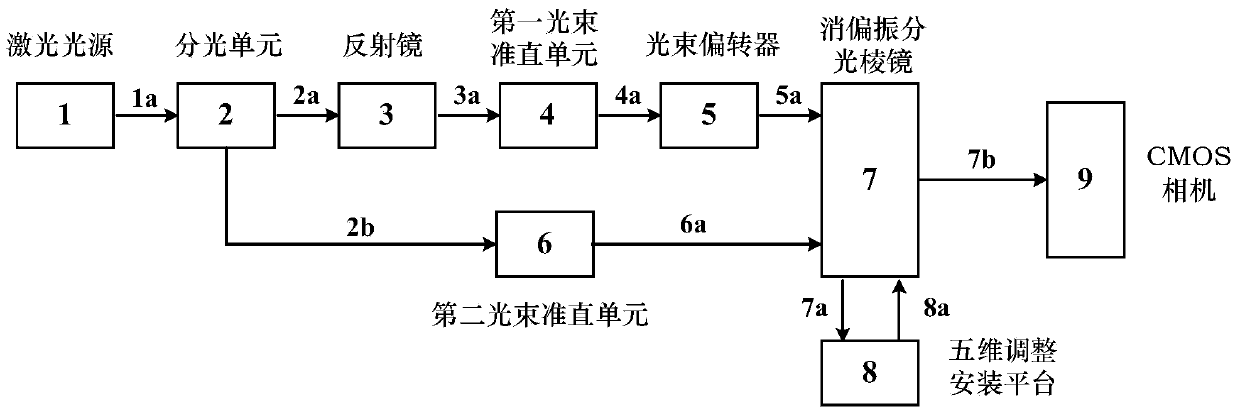
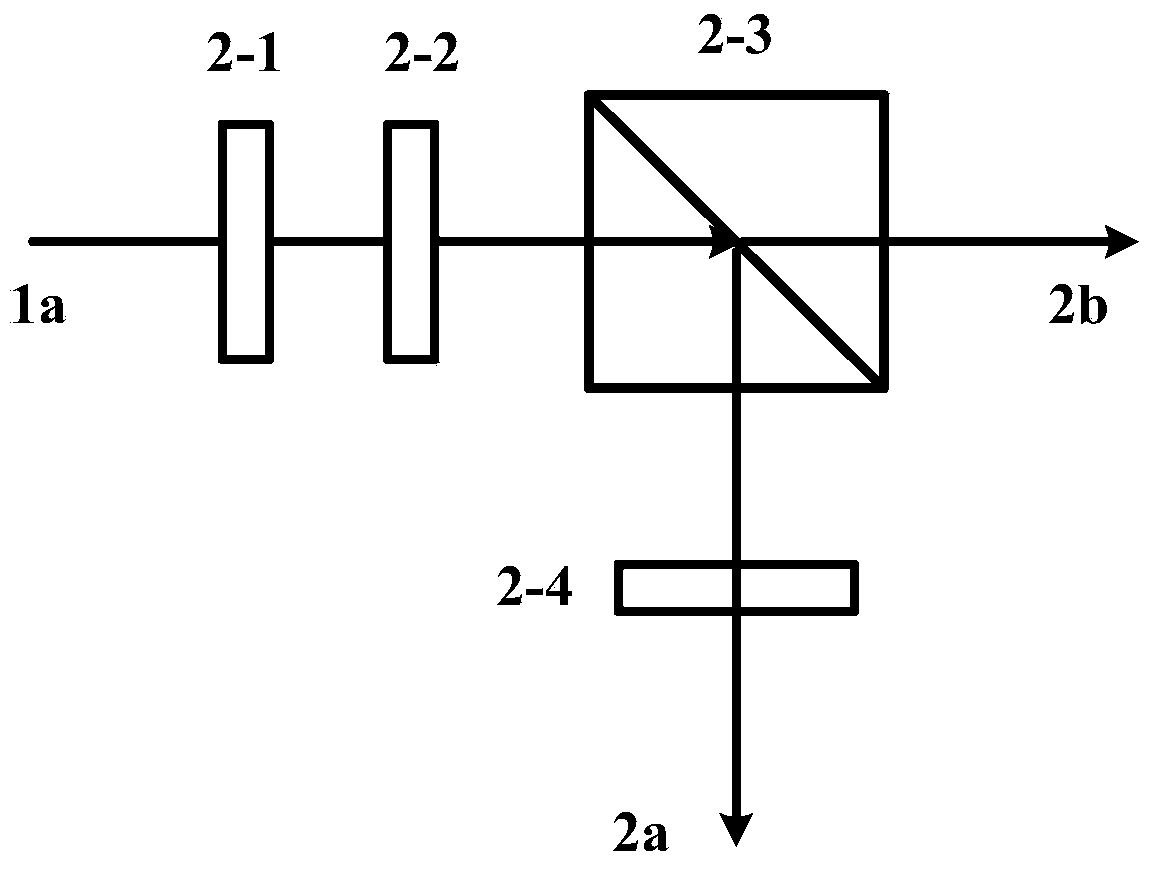
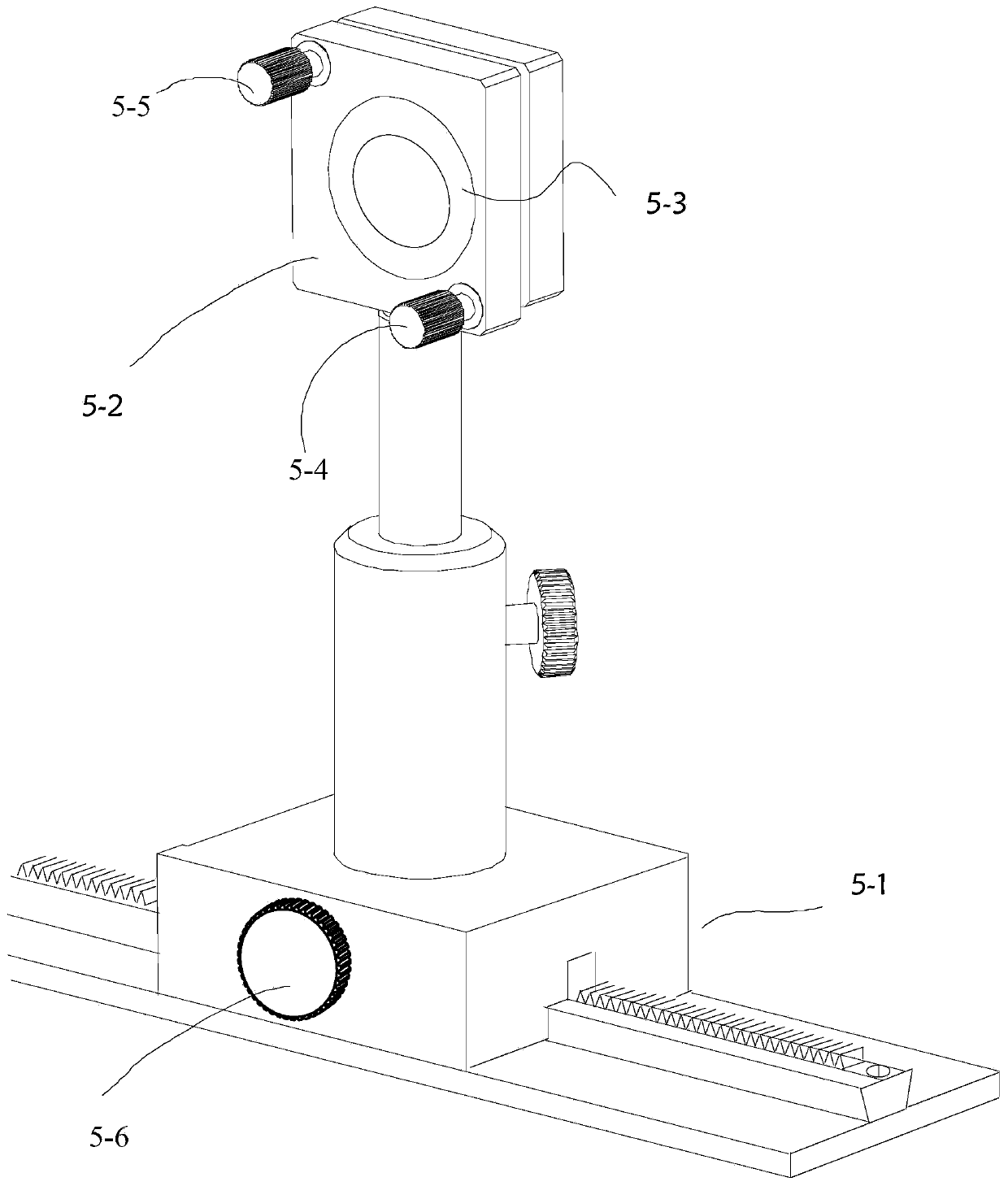
The invention discloses a three-dimensional micro-observation apparatus for a smooth reflective surface and the apparatus is based on synthetic aperture in digital holography. The apparatus comprises a light source, light splitting unit, space filters, plano-convex lenses, a planar mirror, a depolarization beam splitter prism, a beam adjuster, a rotating stage and a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) camera. A light path of the apparatus is characterized in that: a laser emitted by the light source is incident to the light splitting unit; after a light splitting processing is carried out by the light splitting unit, illuminating light and reference light are output; two beams of light respectively pass through the space filters and the plano-convex lenses in order so as to be processed by beam expansion and shaping; the illuminating light passes through the planar mirror and outputs parallel light that penetrates the depolarization beam splitter prism and is incident inclinedly to a surface of an observed object on the rotating stage; and then reflected light of the object surface is again incident to the depolarization beam splitter prism; an angle and a position of the reference light are adjusted by the beam adjuster and the reference light is also incident to the depolarization beam splitter prism; and light composition processing is carried out on the incidentreference light and an object light by the depolarization beam splitter prism so as to obtain a combined light beam; and an interference hologram formed by the combined light beam is captured by a photosensitive surface of the CMOS camera. During the obtaining process, the rotating stage is rotated and an incident angle of the illuminating light is adjusted many times, so that an object surface hologram that contains different frequency components is obtained; and then fusion is carried out, thereby realizing a three-dimensional micro-observation based on the synthetic aperture in digital holography.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com