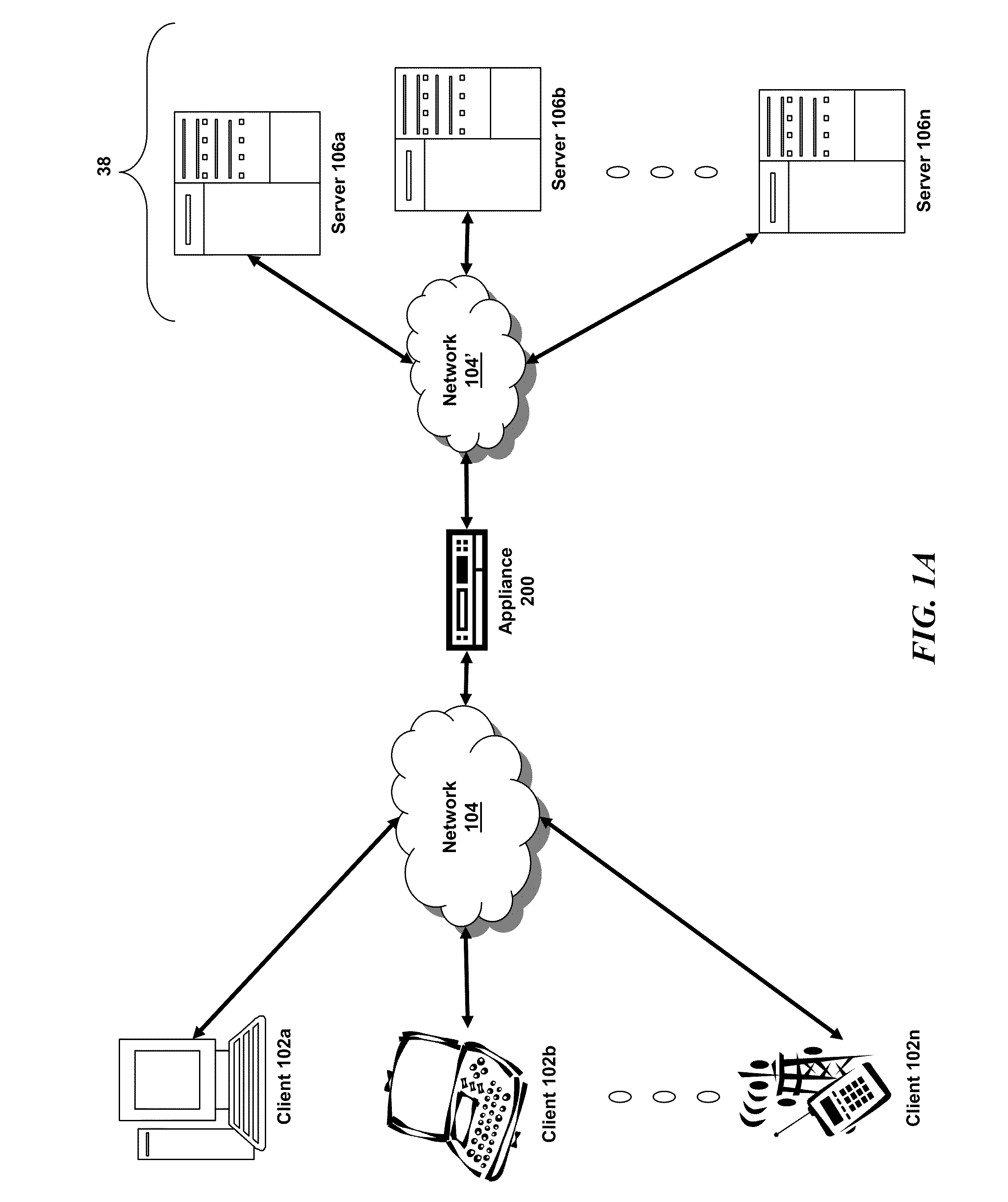
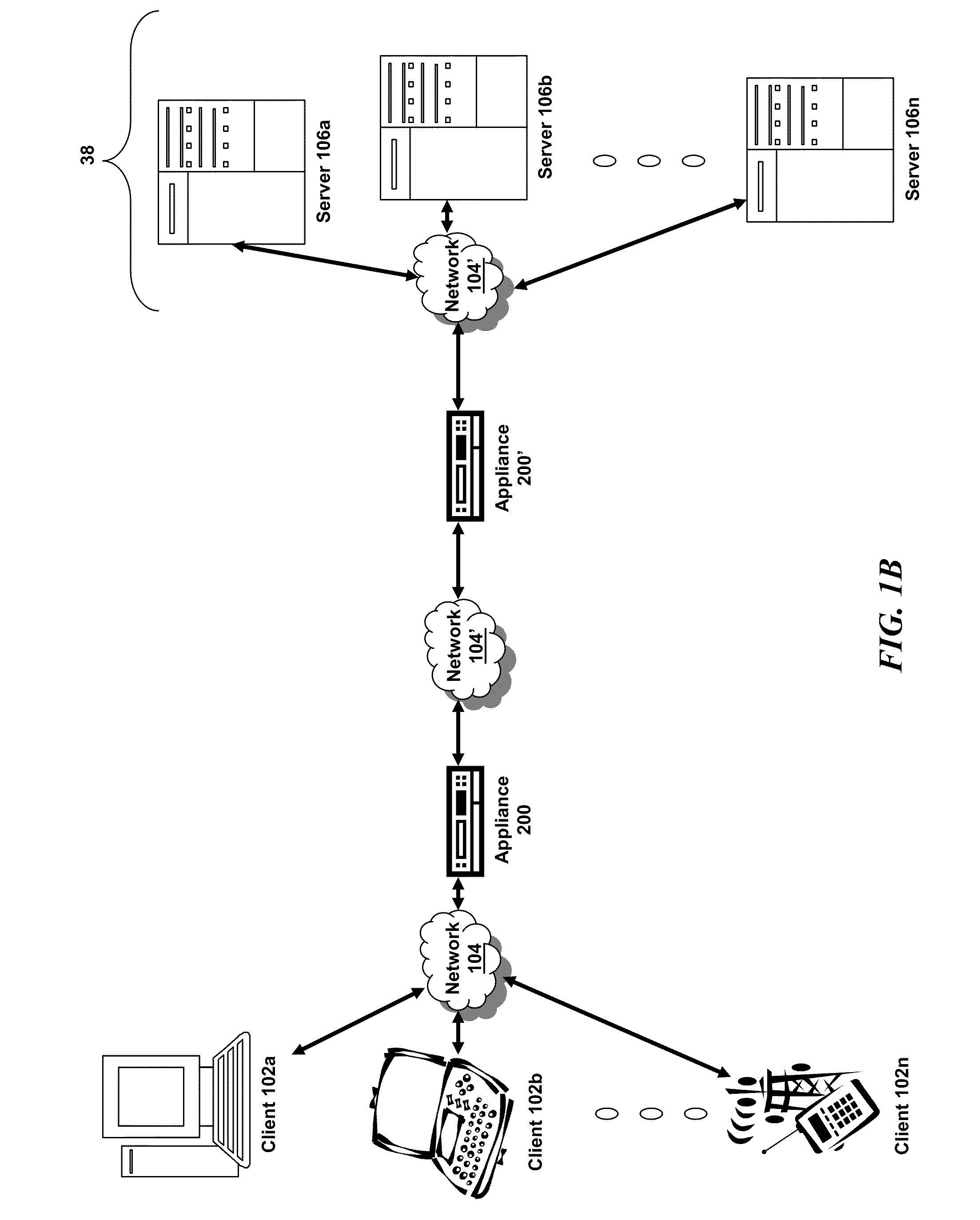
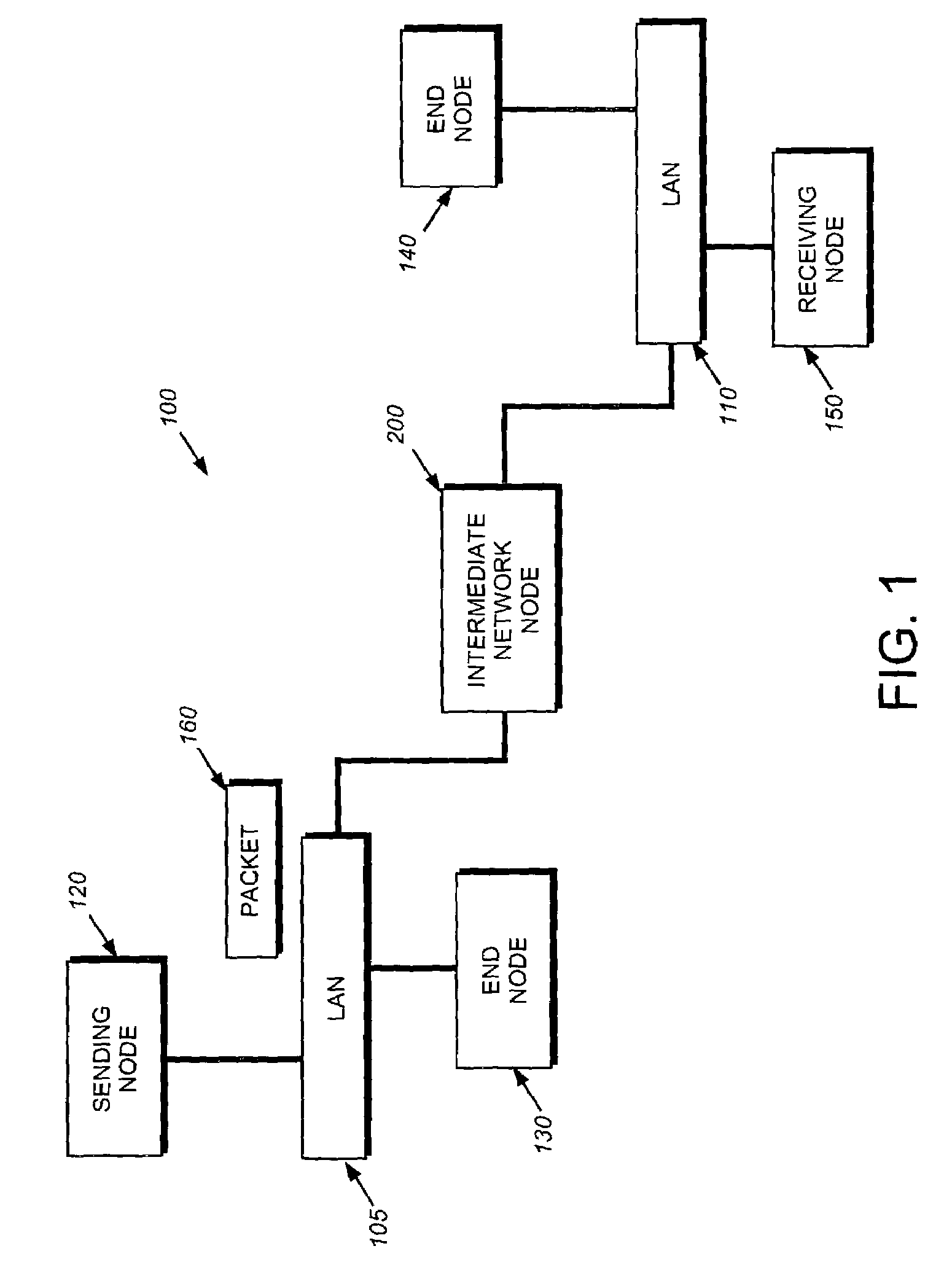
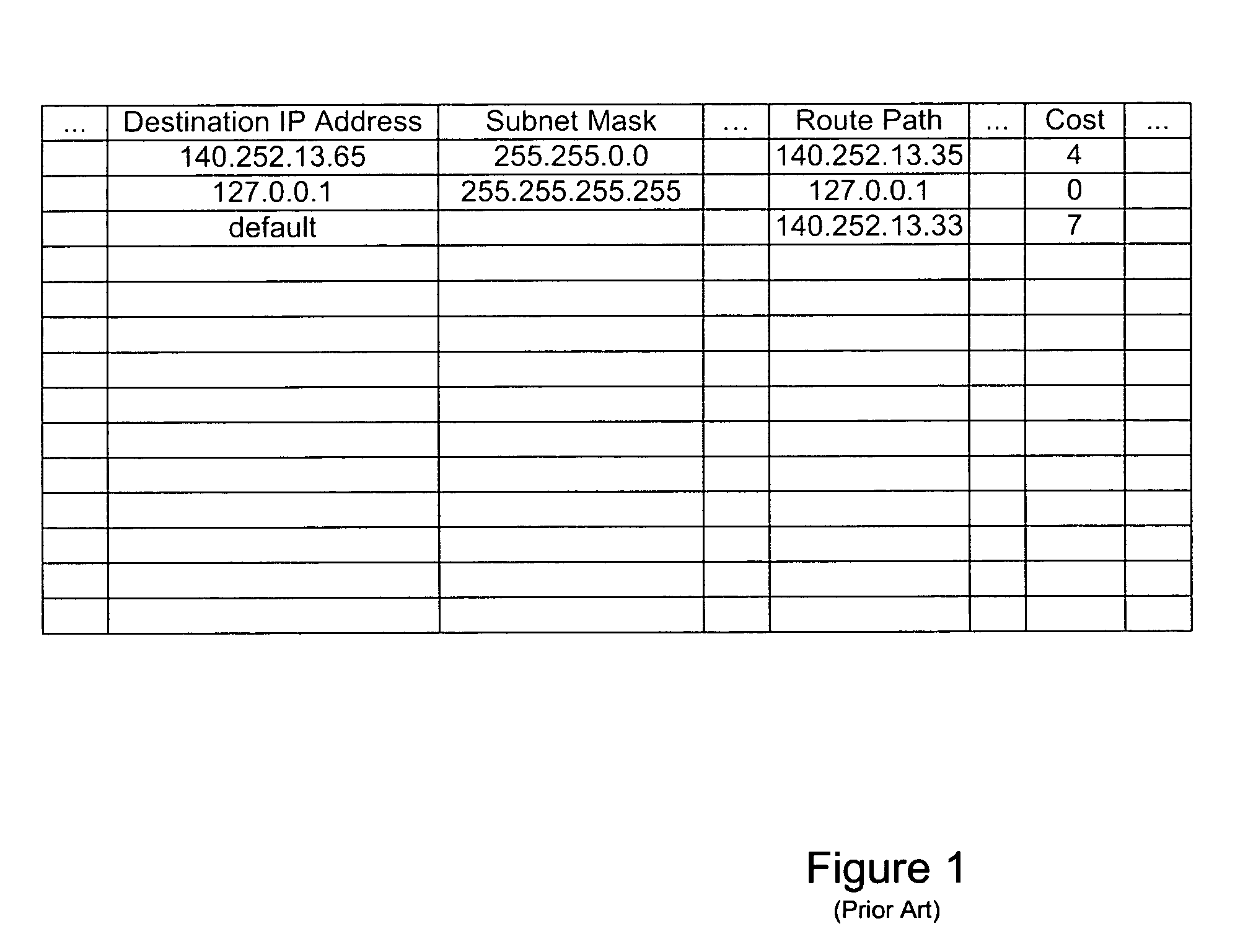
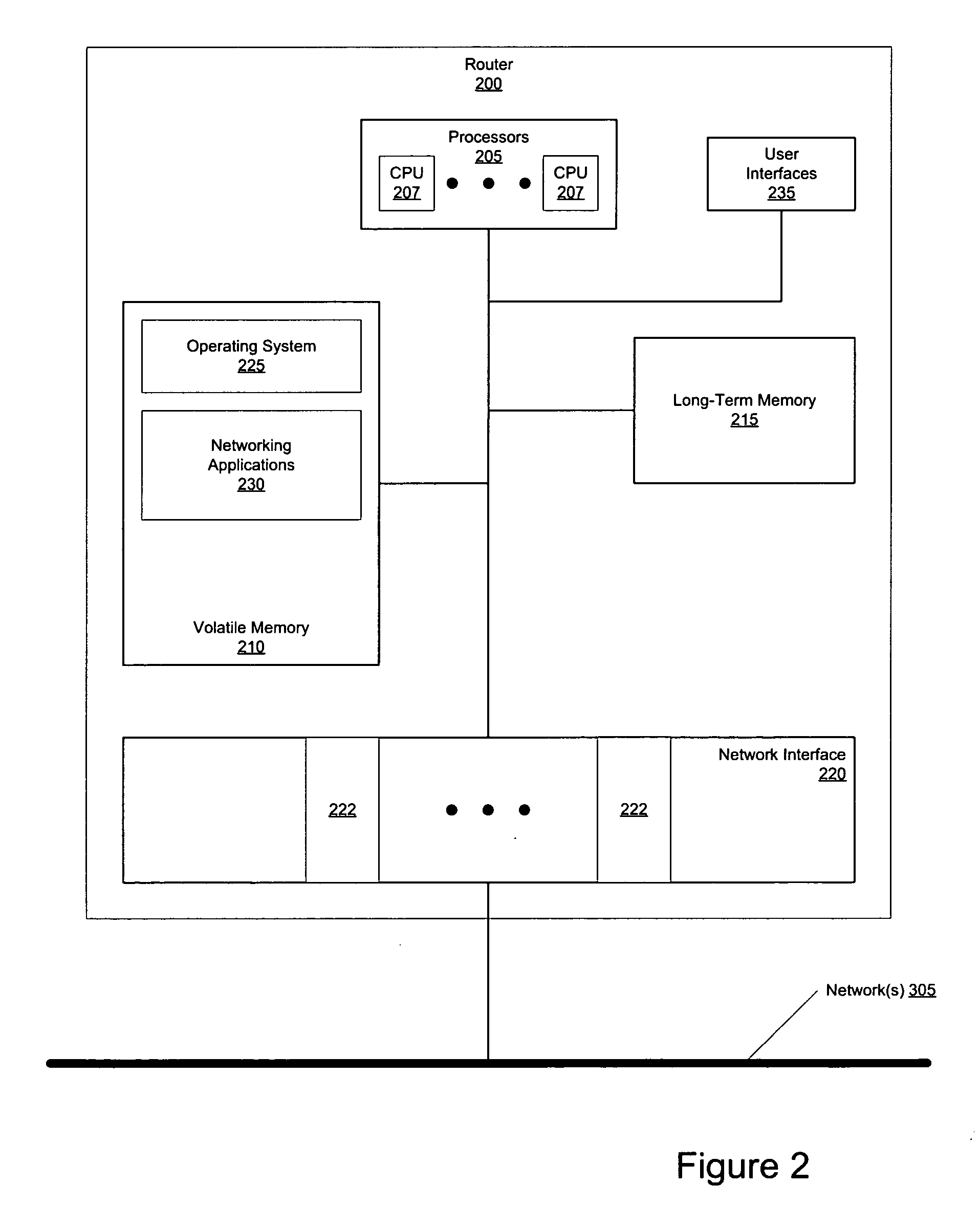
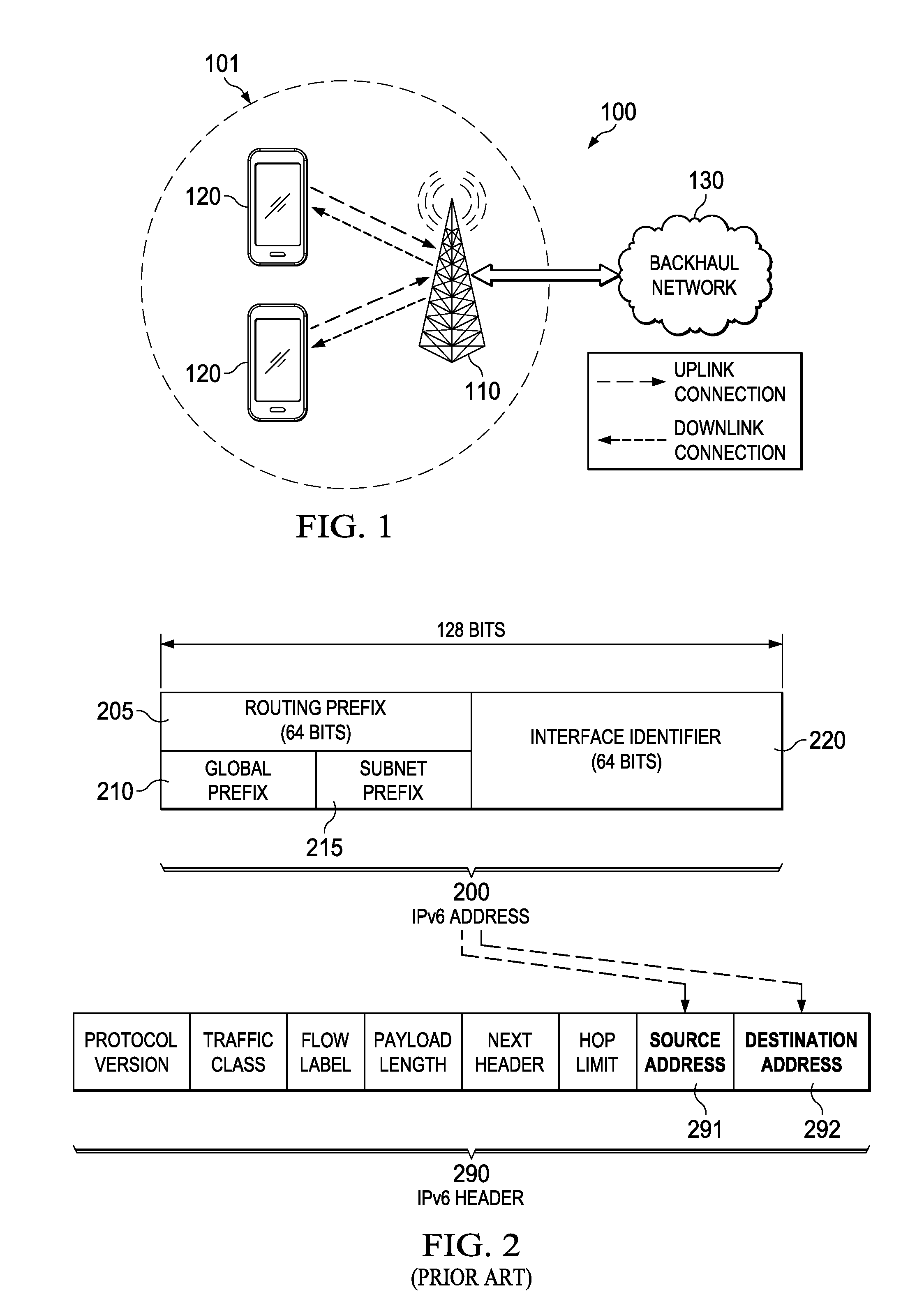
Patents
Literature
1215 results about "IPv6 address" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
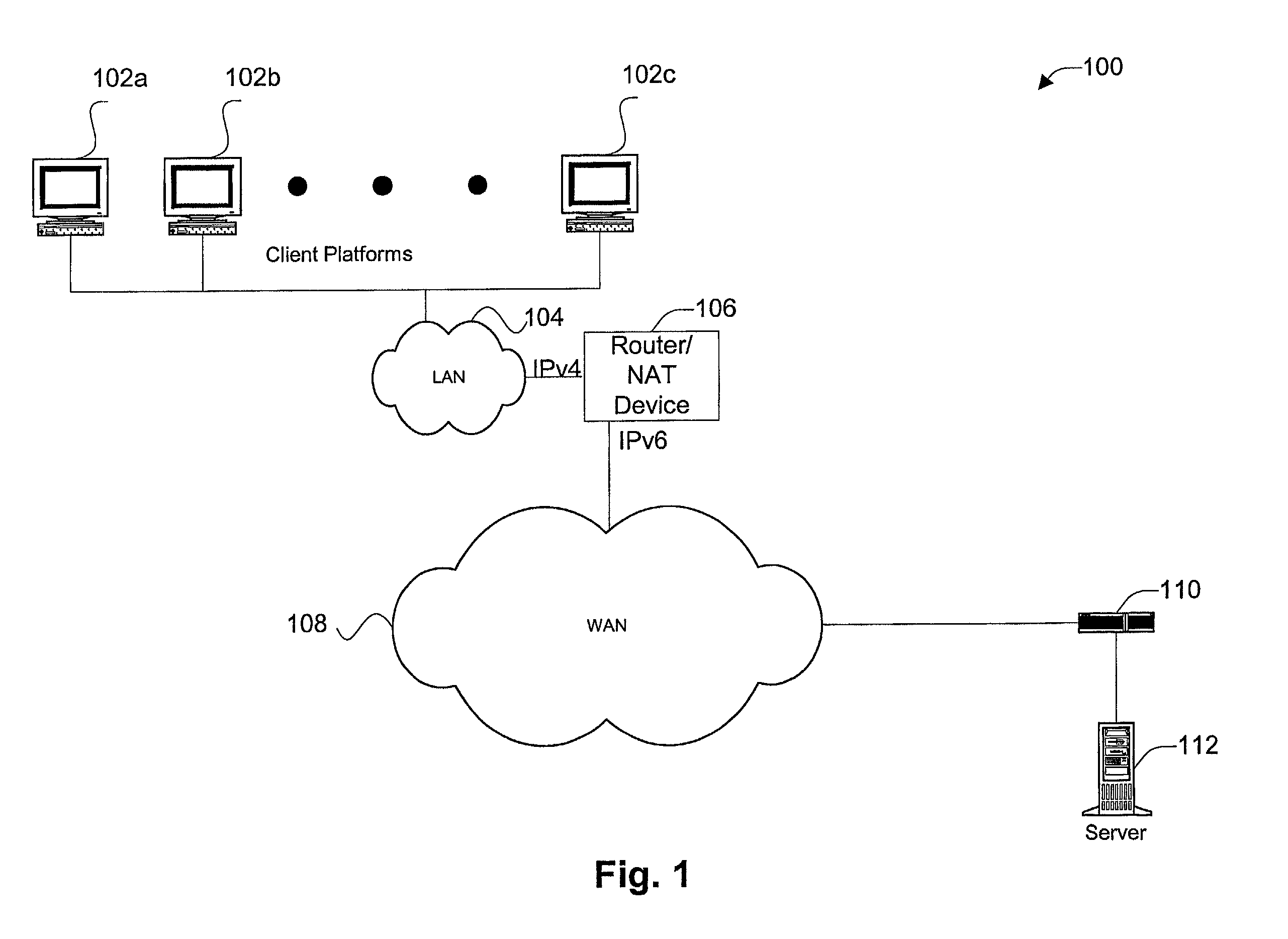
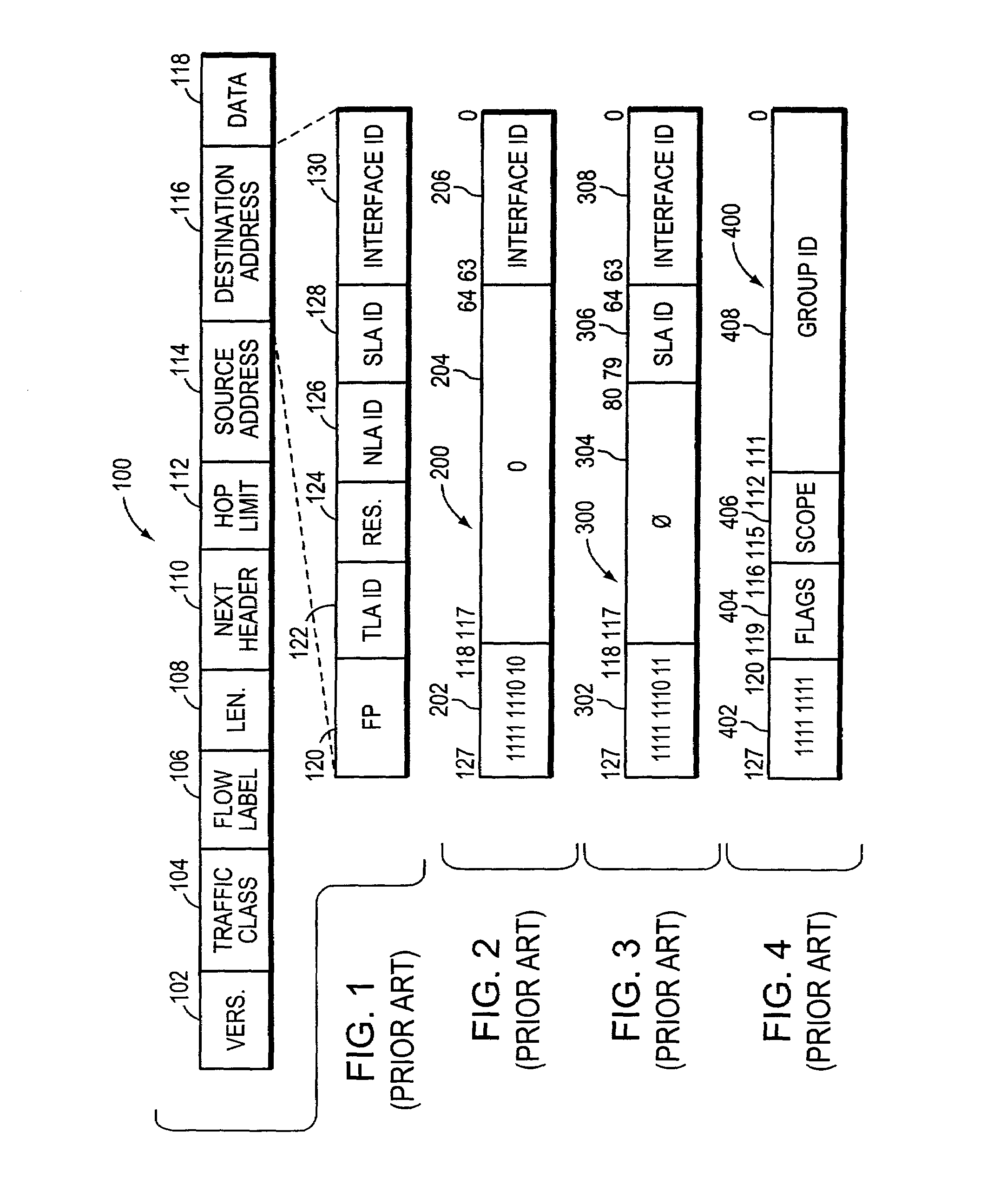
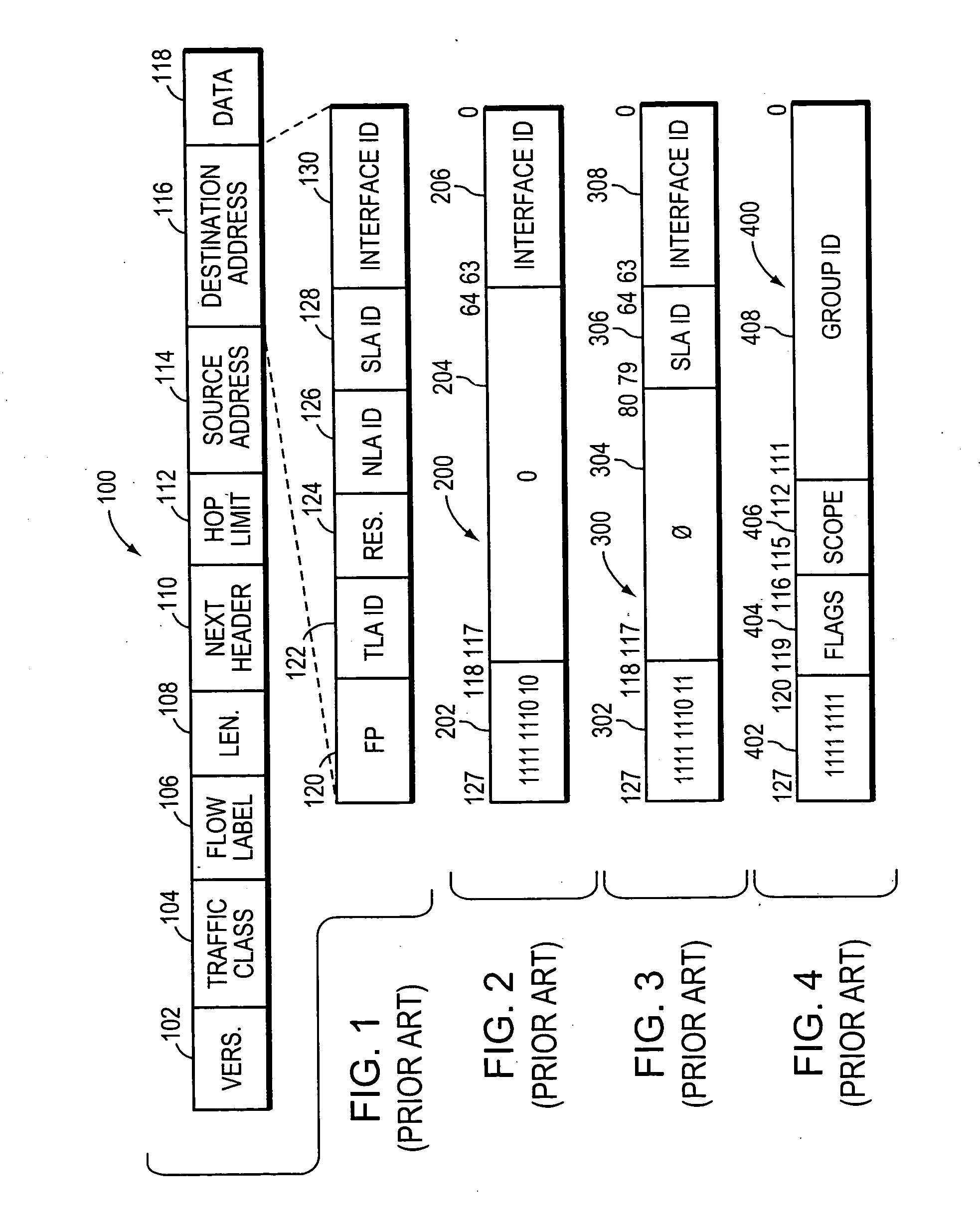
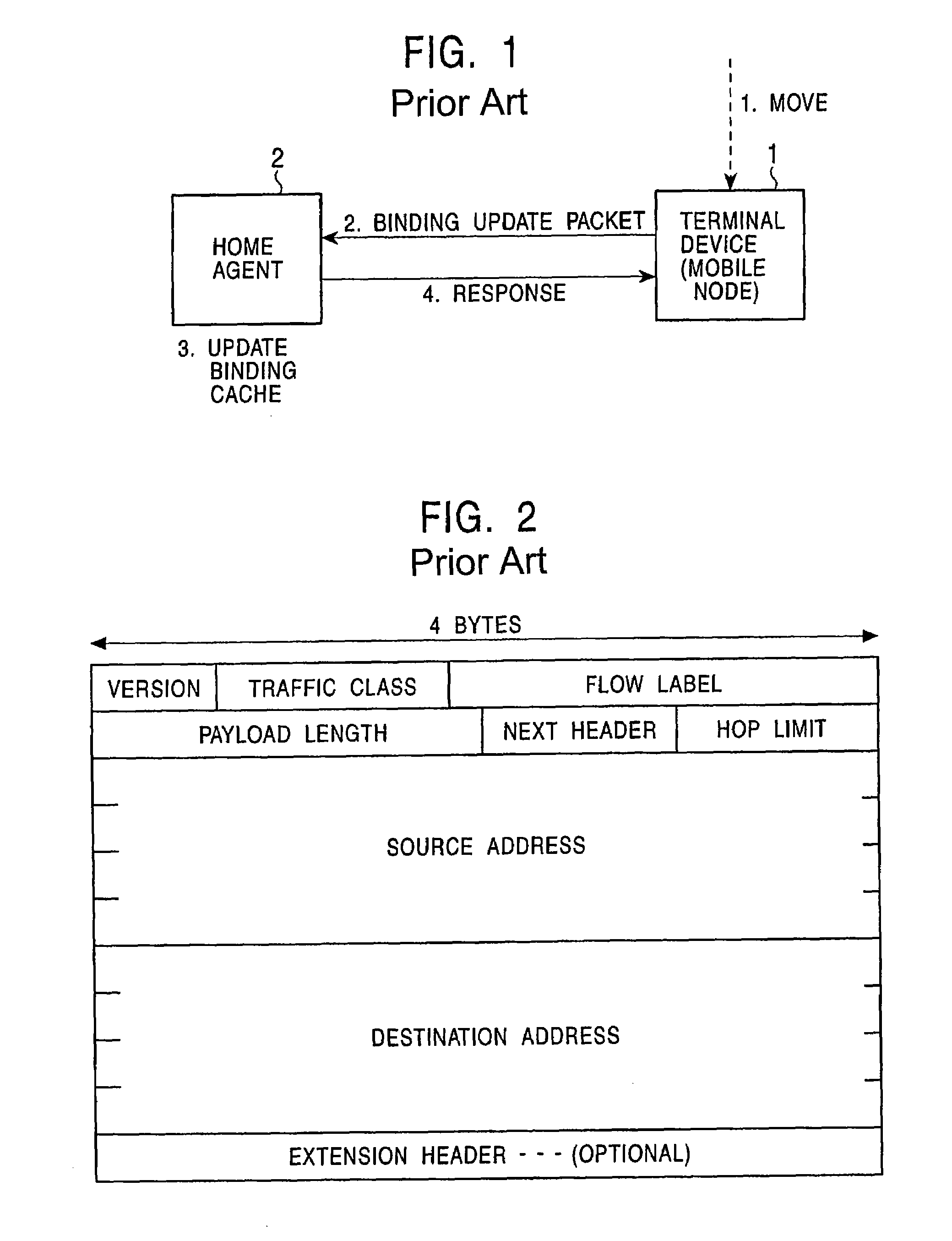
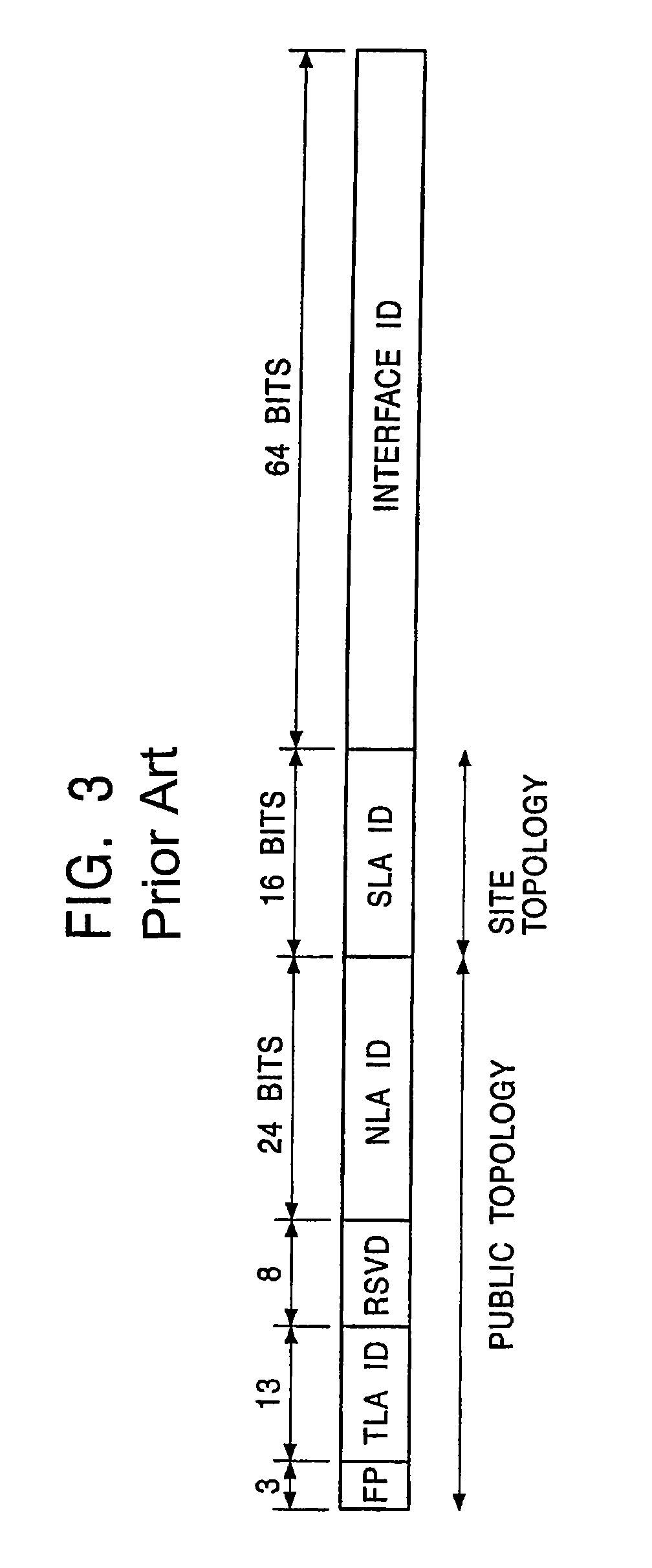
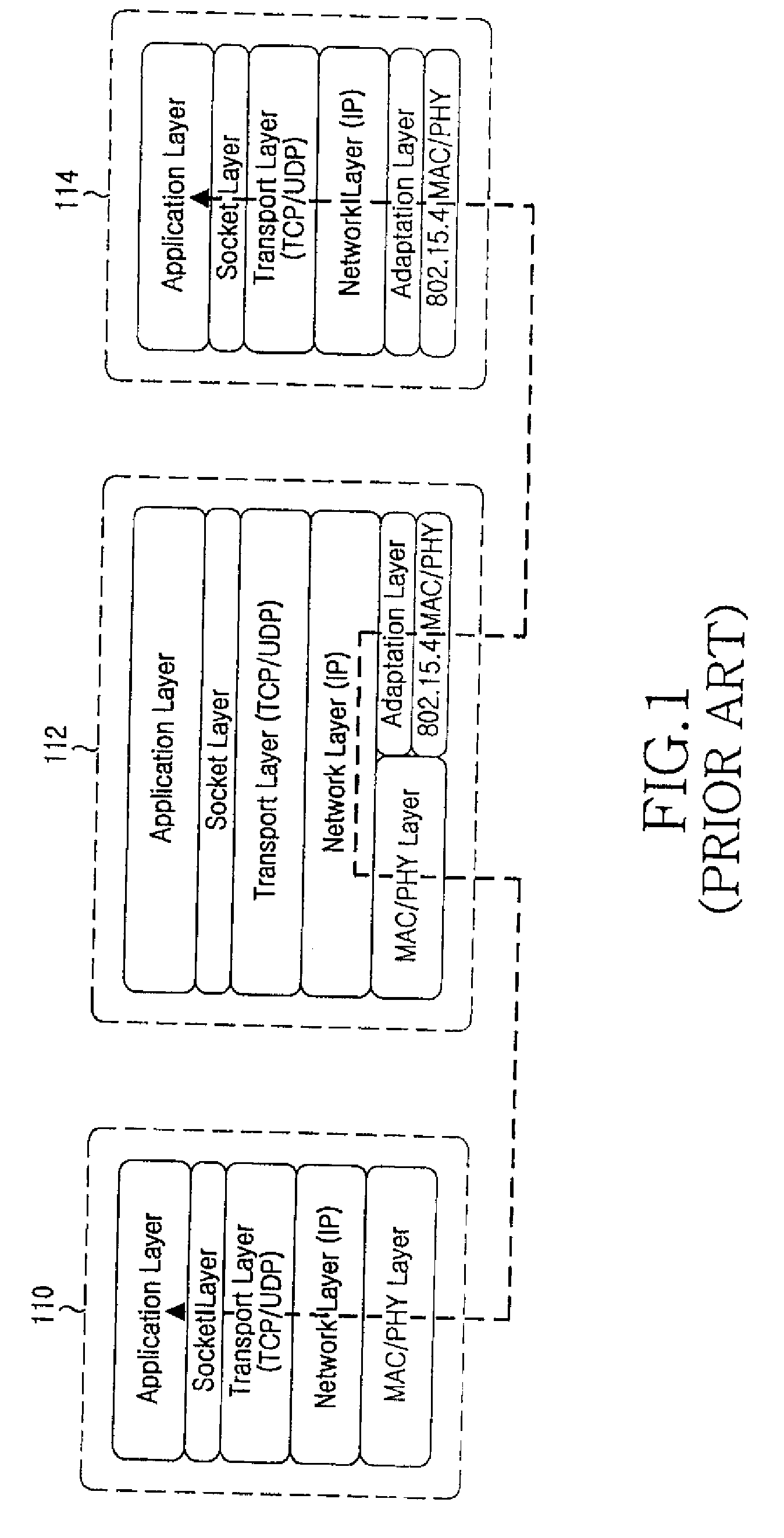
An Internet Protocol Version 6 address (IPv6 address) is a numerical label that is used to identify a network interface of a computer or a network node participating in an IPv6 computer network. An IP address serves the purpose of identifying an individual network interface of a host, locating it on the network, and thus permitting the routing of IP packets between hosts. For routing, IP addresses are present in fields of the packet header where they indicate the source and destination of the packet.
Stateless Protocol Translation
Some aspects of the methods and systems presented relate to performing stateless address translation between IPv4 capable devices to IPv6 capable networks and devices. Stateless address translation may form a new IPv6 addresses by combining the IPv4 address of a device with an IPv6 prefix address assigned to the translator. The translation may also combine the IPv4 destination address and UDP port information with the new IPv6 address. Existing Domain Name Systems (DNSs) may be leveraged for resolving the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses across different networks.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Mechanisms for avoiding problems associated with network address protocol translation
ActiveUS7006526B1Avoid problemsReduce morbidityError preventionTransmission systemsSize differenceSize increase
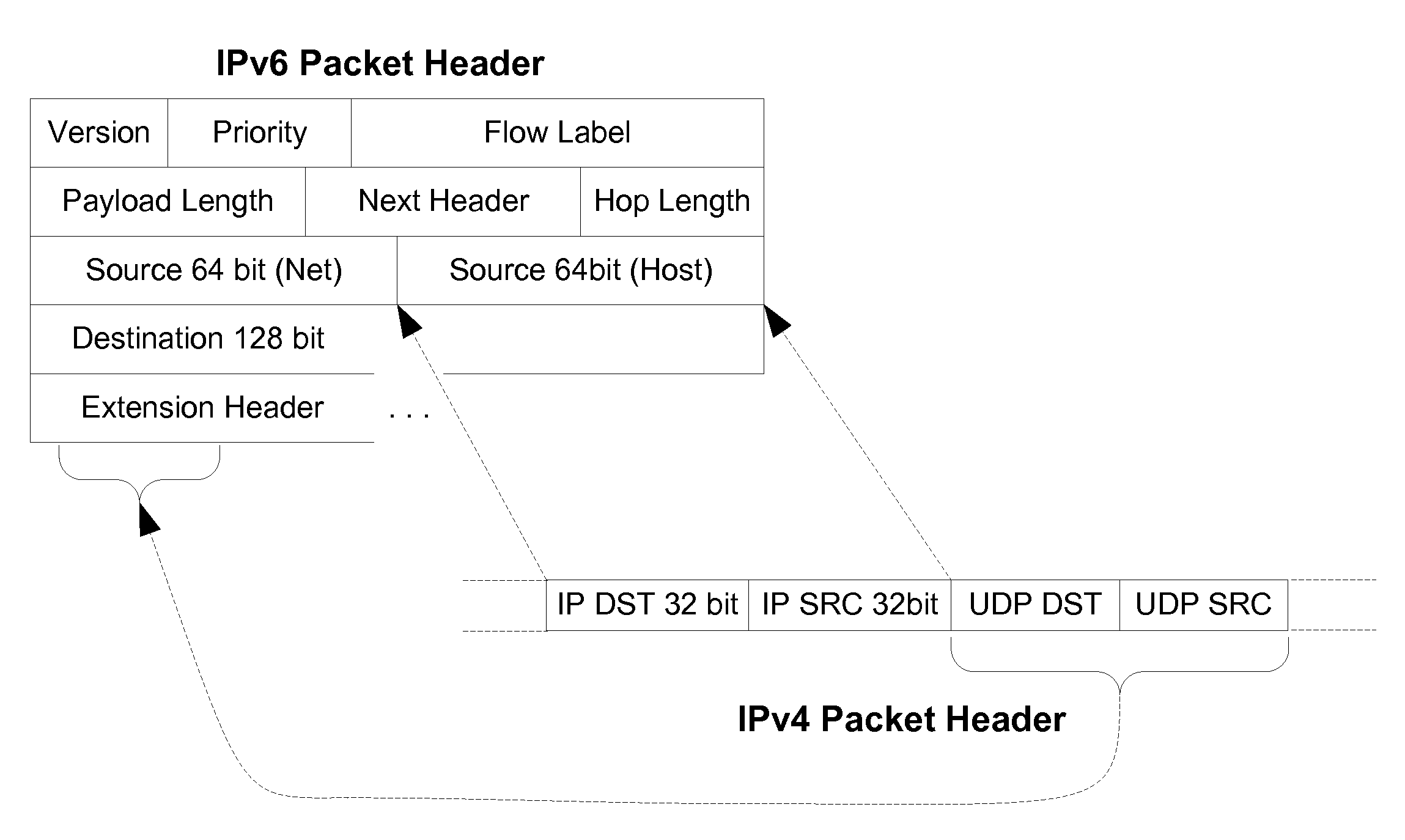
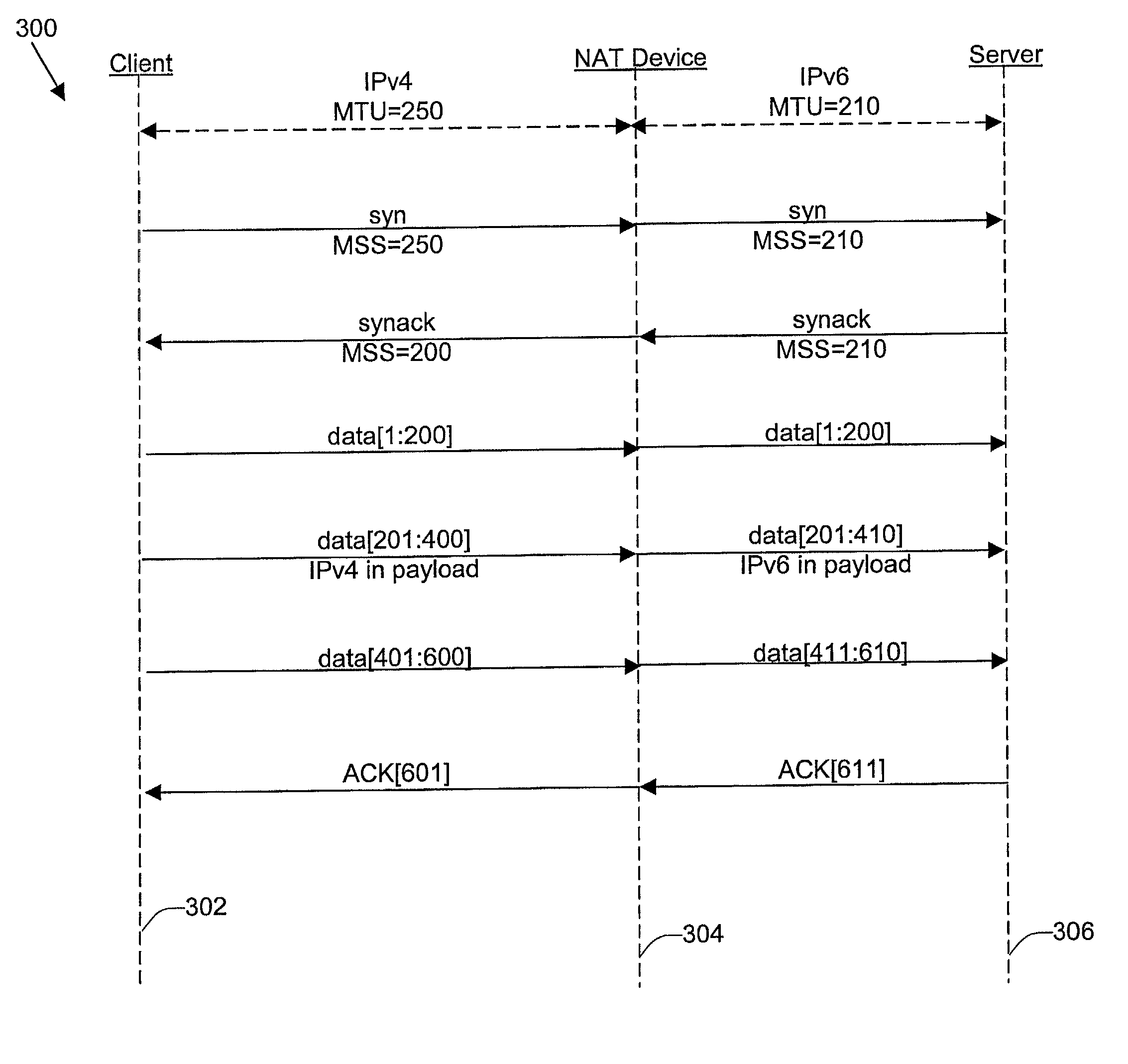
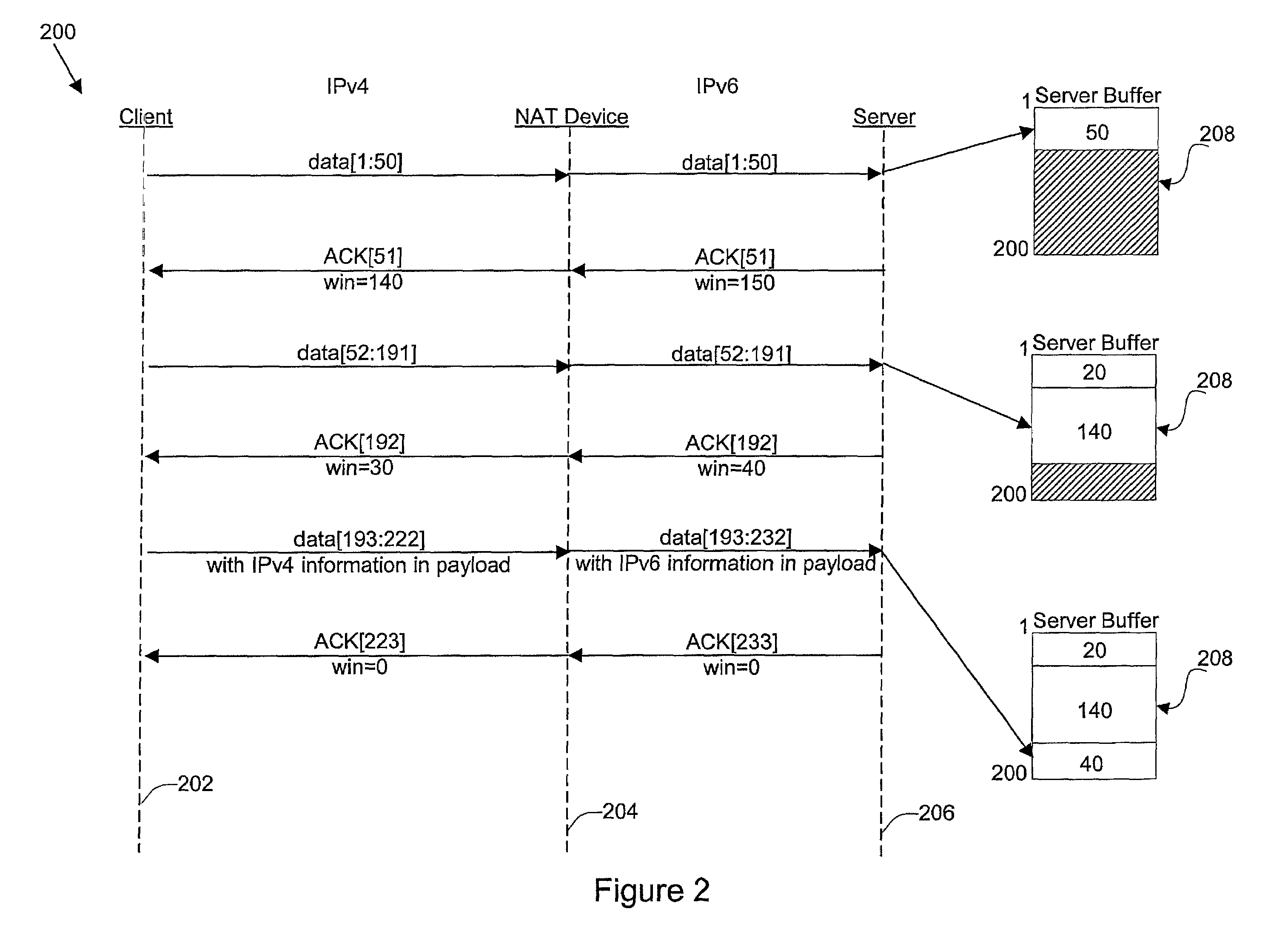
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for avoiding problems caused by converting between two different protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6. These problems may include, but are not limited to, fragmentation of packets, dropping of packets, and retransmission of packets. Avoiding these problems will reduce the incidence of transmission delays, bandwidth degradation, and additional processing in the packet's transmission path due to such problems. In general terms, the present invention provides mechanisms for modifying a protocol parameter, such as a TCP or UDP parameter, to avoid problems associated with protocol translation, such as fragmentation. In one implementation, the protocol parameter limits the size of a particular portion of the a packet transmitted by a sending computer node or device. For example, a packet size indicator is communicated to the sending computer node so that the sending computer node sends packets limited by the packet size indicator to thereby avoid associated with the size of such packets. In specific TCP embodiments, the size indicator specifies a window size and / or a maximum segment size. For example, if packets transmitted by a sending node to a receiving node are converted from IPv4 to IPv6 and the window size indicated to the sending node (e.g., by the receiving node) is 512 bytes, the window size is adjusted to 500 bytes before reaching the sending node. The adjustment amount may be based on an estimated size increase resulting from converting from IPv4 to IPv6. In this example, the window size is decreased by 12 bytes since a conversion from IPv4 to IPv6 where one 4 byte IPv4 address is changed to a 16 byte Ipv6 address has an associated size difference of 12 bytes. In a specific embodiment, actual changes in packet size may tracked and the adjusted size indicator may be dynamically based on such tracked changes. In other embodiments, the changes in packet size are predicted, and the adjusted size is preemptively changed as needed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for extending network address translation for unsupported protocols
InactiveUS6886103B1Ensure safetyMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlExpiration TimeIp address
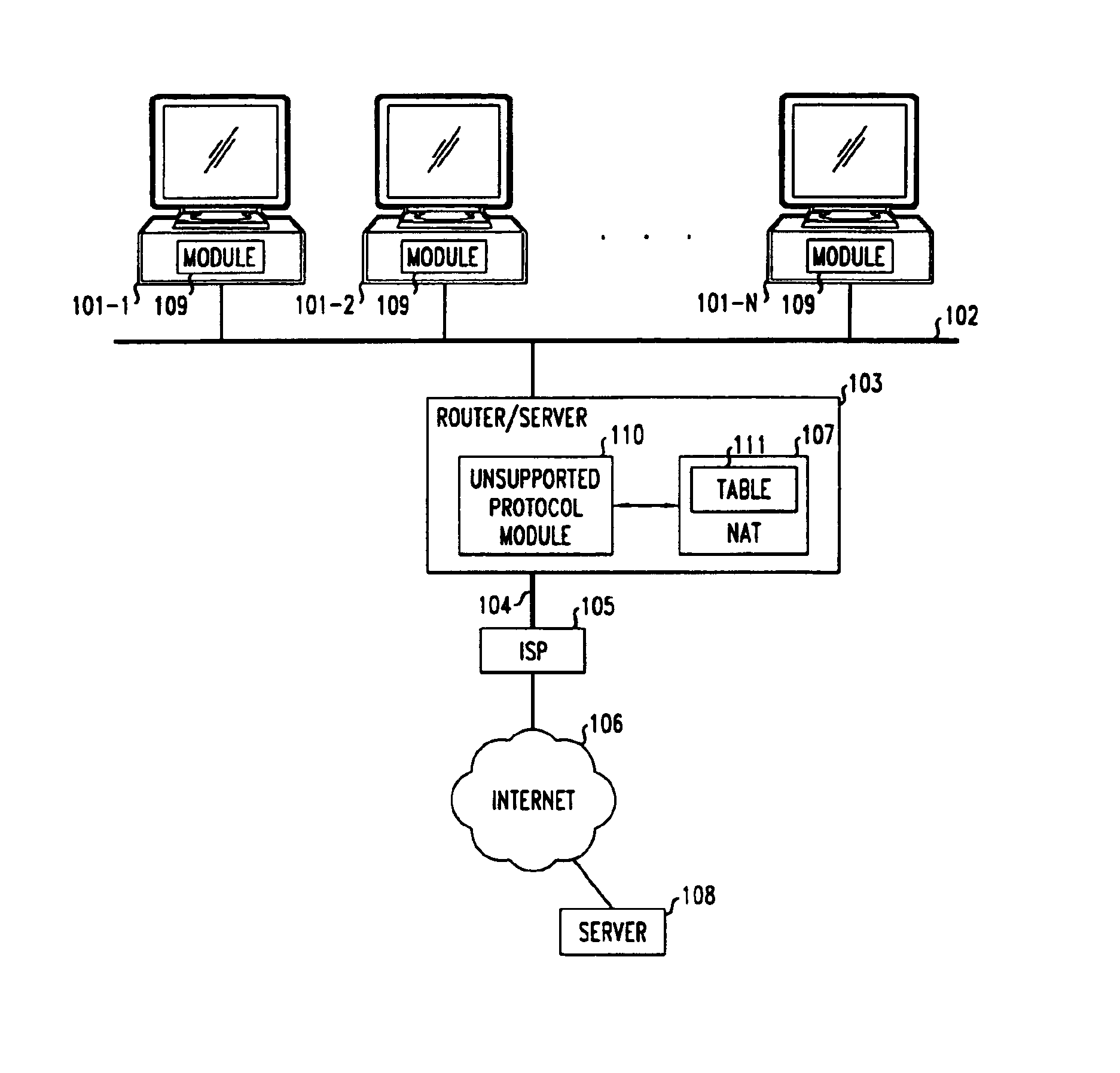
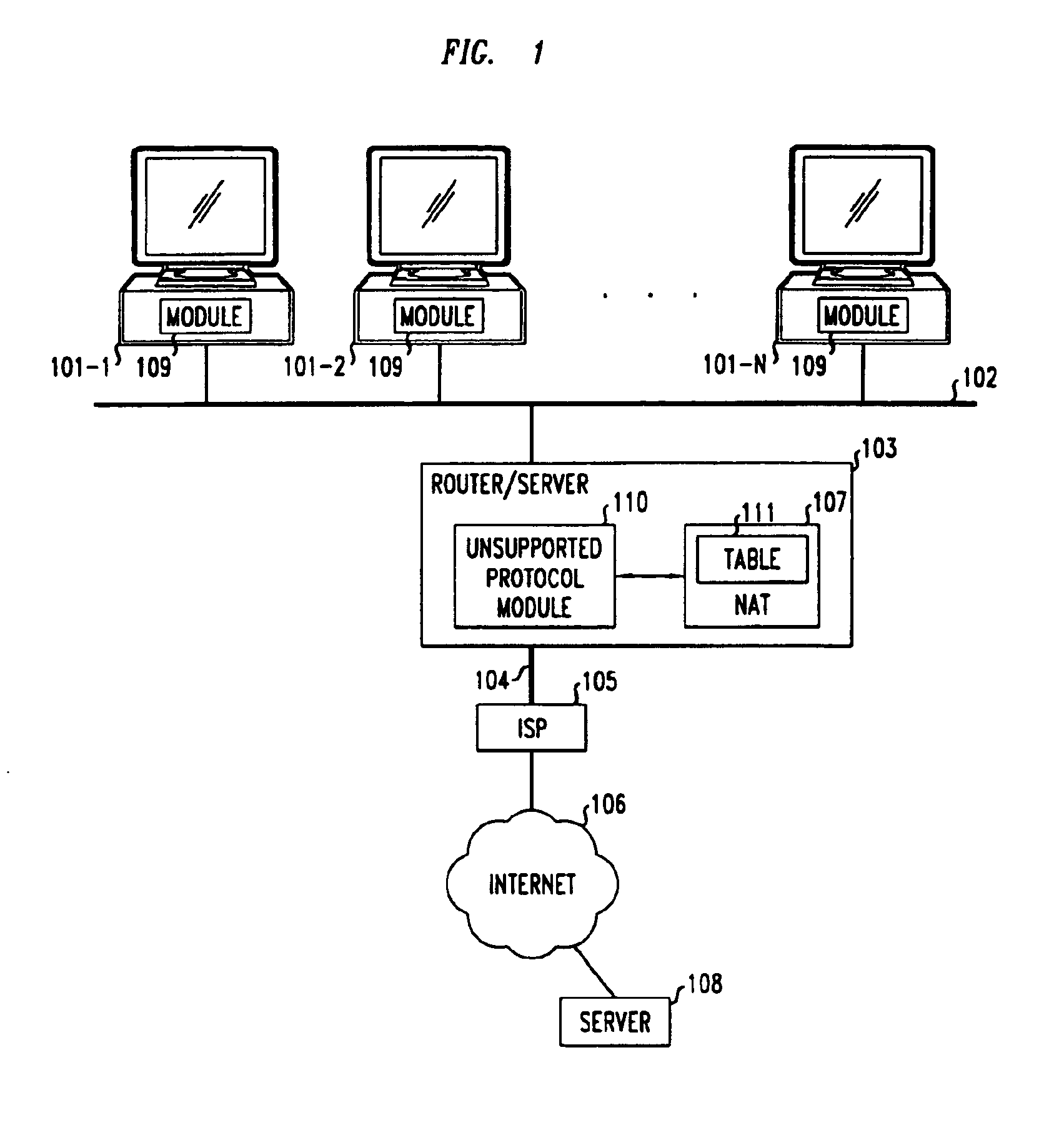
Clients that are connected on a private network and which are assigned a private IP address that is not routable on the Internet can connect to the Internet through a router / server that includes a network address translator (NAT). For outgoing packets, the NAT translates the client's private source IP address and generalized port number (GPN) to the NAT's global IP address and GPN. For incoming packets sent to the NAT's global IP address and GPN, the NAT translates the global destination IP address and GPN to the client's private IP address and GPN. For protocols which cannot be directly supported by the NAT, such as those in the IPSec security protocol suite, the NAT is extended by creating in the NAT's translation table an entry that associates, for a specific unsupported protocol, a client's private IP address and GPN, the NAT's global IP address and GPN, and a foreign address on the Internet, that is valid until a specified or default expiration time. Outgoing packets from the client to that foreign address and incoming packets from that foreign address to the NAT's global IP address and GPN are translated according to the entry until the entry expires. In associations with these translations to outgoing and incoming packets, the client implements any Application Layer Gateway (ALG) that would otherwise be implemented at the NAT. Further, at the client, outgoing packets are modified before being transmitted so as to pre-compensate for the effects of the translations. Incoming packets at the client from the NAT are similarly modified so as to post-compensate for the effects of the translations. For the IPSec protocol, these modification include adjusting the checksum in the TCP or UDP header to account for IP address and TCP or UDP port number translations.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Hierarchical mobility management for wireless networks
InactiveUS6947401B2Network traffic/resource managementInformation formatWireless mesh networkMobility management
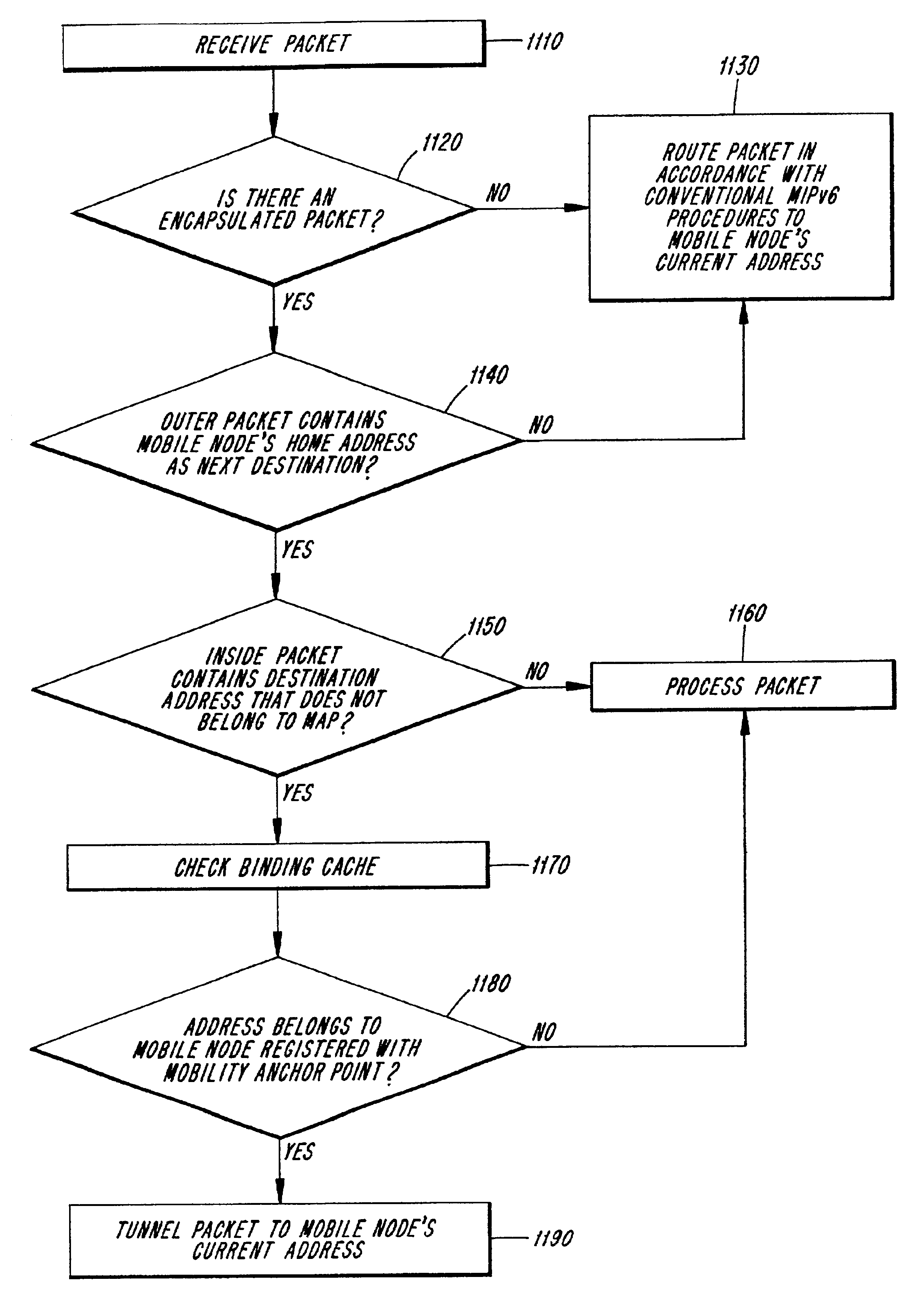
Methods and apparatus for providing a hierarchical mobility management function for routing packets to mobile nodes are provided. The hierarchical mobility management function may be placed anywhere within the network and provide efficient use of IPv6 addresses. A node implementing the hierarchical mobility management function receives packets intended for the mobile node and routes the packets to the mobile node's current address. Load sharing of packets intended for a mobile node may be implemented across several access routers. Additional, bi-casting of packets is provided to allow for seamless handoff of the mobile node as it switches from one access router to another access router.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of and apparatus for adaptively managing connectivity for mobile devices through available interfaces
InactiveUS20050058112A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMobile deviceSelf adaptive
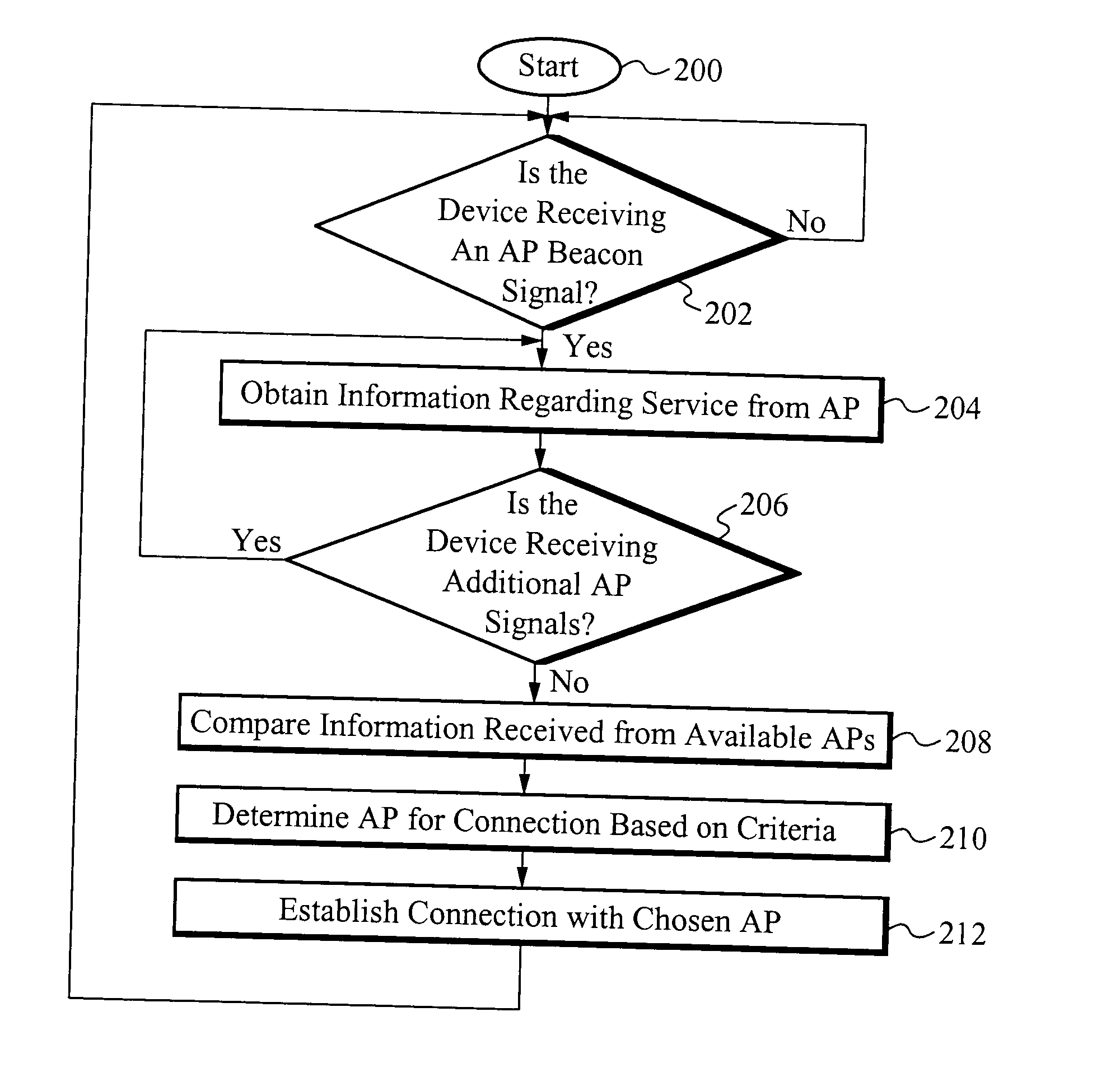
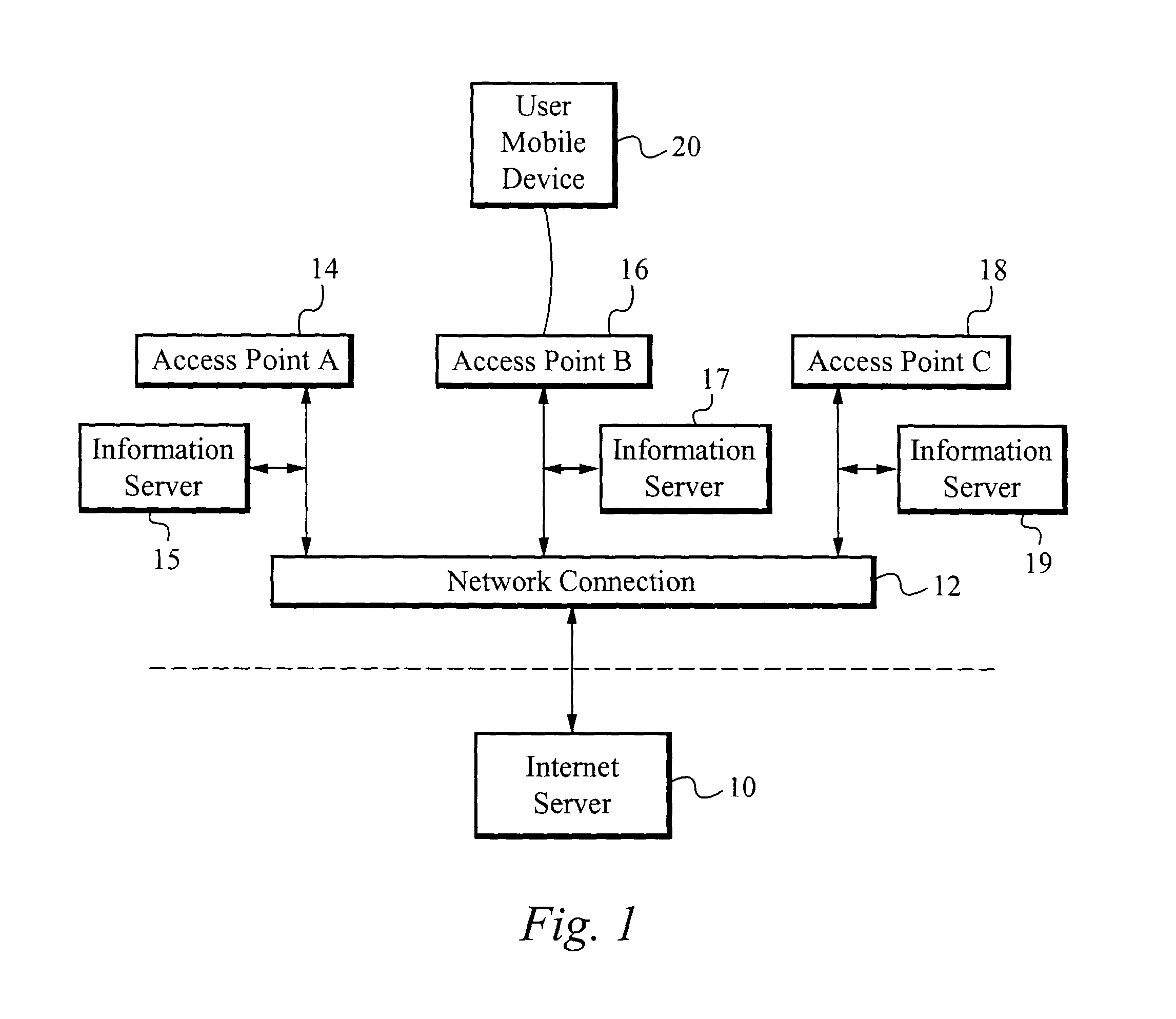
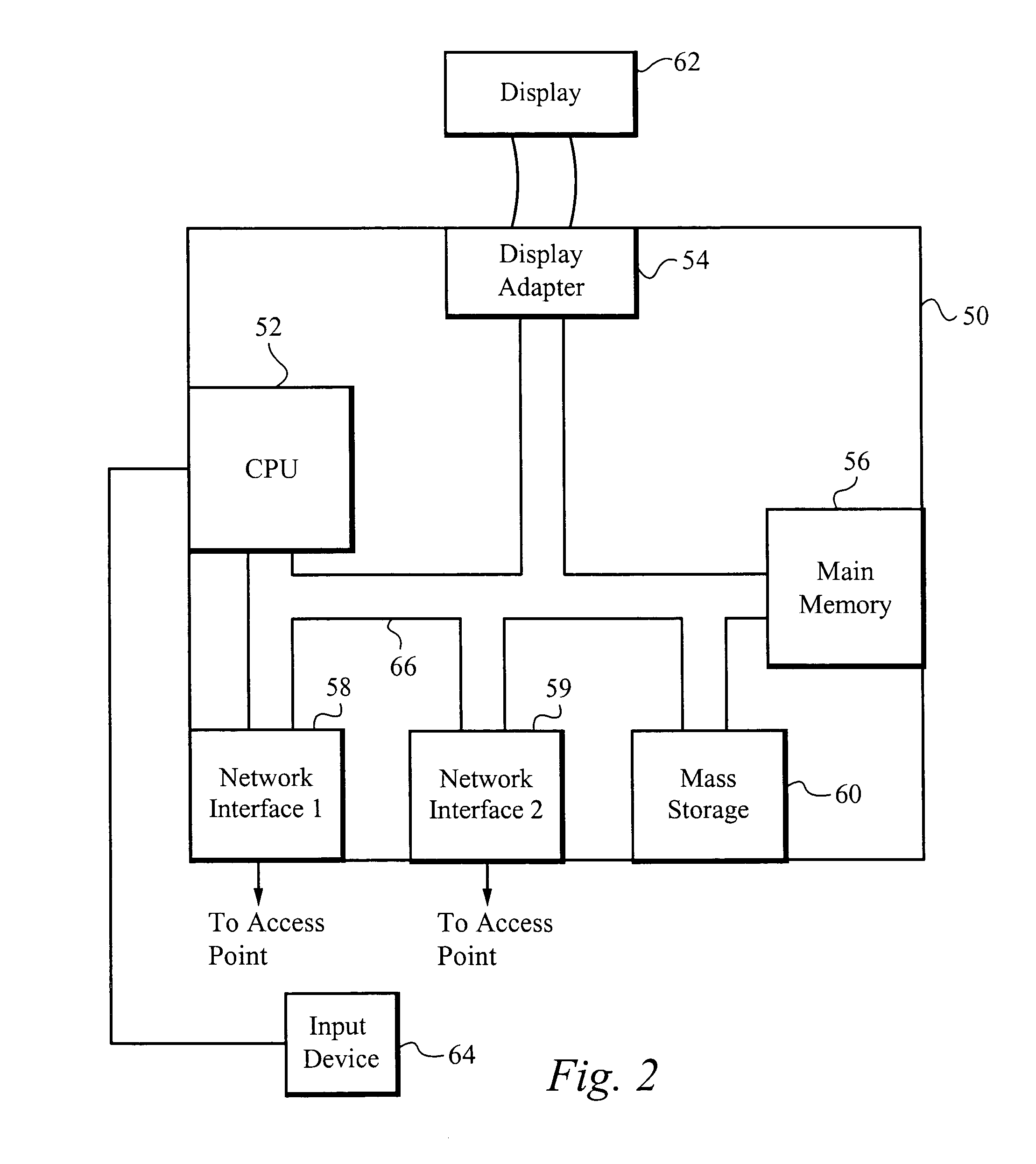
A method of and apparatus for adaptively managing connectivity for mobile devices through available interfaces allows a user to seamlessly move from one access point to another while the user's mobile device manages the connection for the user. The user's mobile device continuously probes for access points, identifies access points within range of the device and chooses to connect to the access point that fits defined criteria. Information within the access point's beacon signal is used to obtain information regarding the access point and the characteristics of service provided by the access point through out of band communications. Preferably, the mobile device utilizes a separate IPv6 address for each application used by the mobile device so that communications are associated with the appropriate application utilizing this address.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
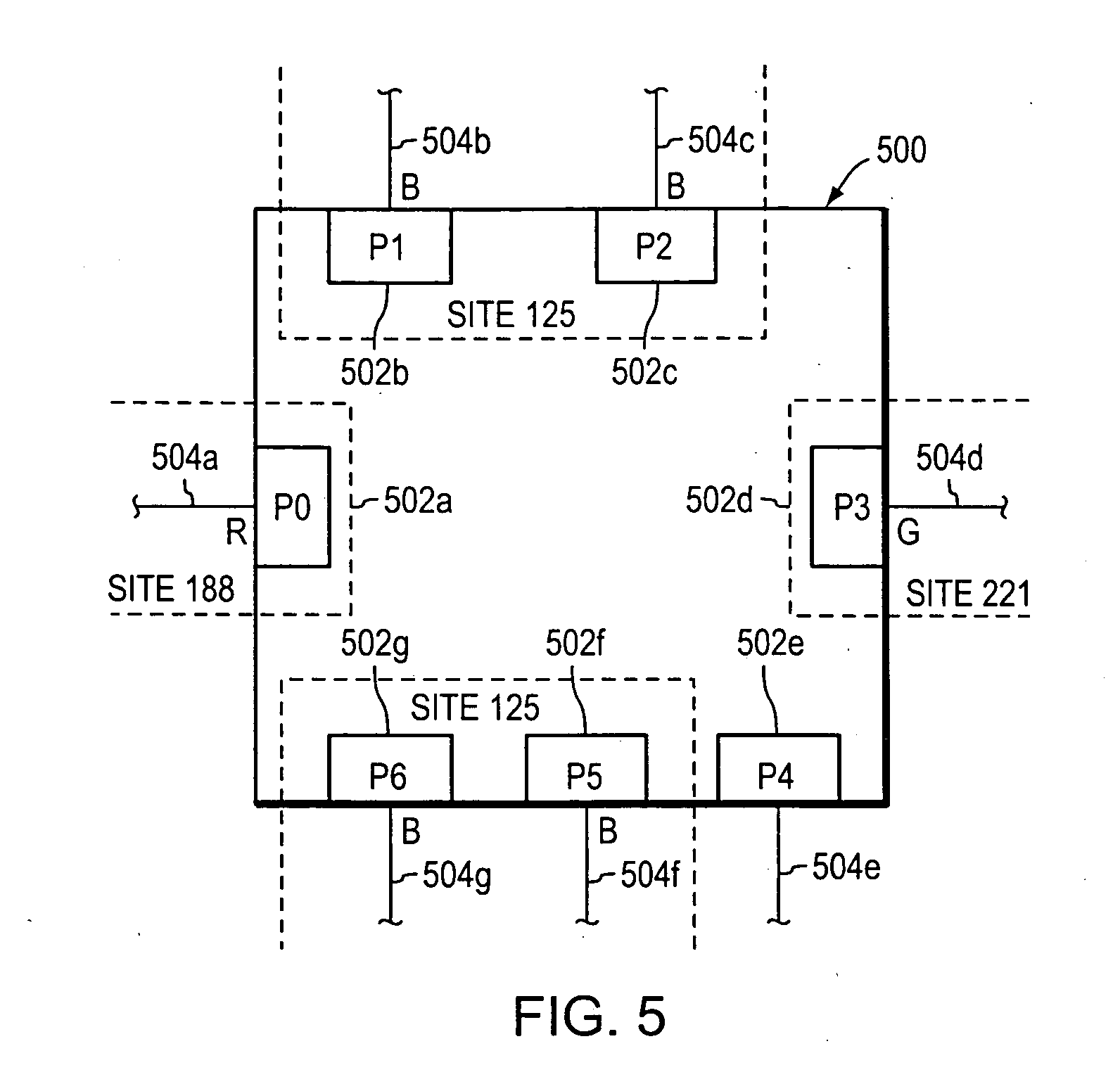
System and method for deriving IPv6 scope identifiers and for mapping the identifiers into IPv6 addresses
InactiveUS7095738B1Efficient and high-speedSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsInformation repositoryVirtual LAN
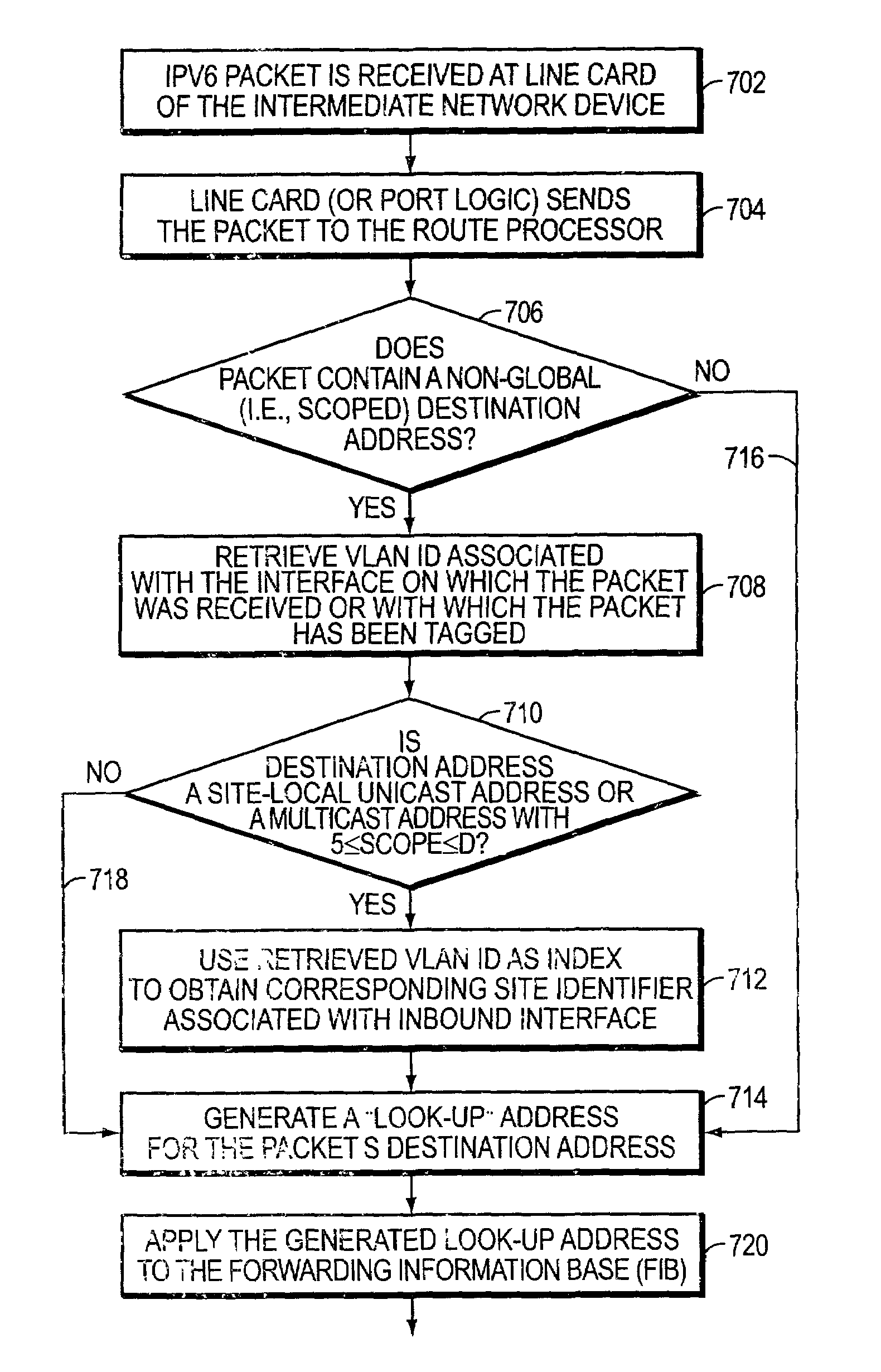
A system and method for use at an intermediate network device employs Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations as Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) link identifiers, and maps VLAN designations to IPv6 site identifiers (IDs). The system also generates a compacted look-up address based on the destination address specified within a received network message, such as an IPv6 packet. For a network message having a link-local unicast destination address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a site-local unicast address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a multicast destination address, if the address's scope value is between hexadecimal “2” and “4” inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. If the scope value is between hexadecimal “5” and “D”, inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. The look-up addresses are applied to a forwarding information base (FIB) to derive the outbound interface(s) from which the message is to be forwarded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
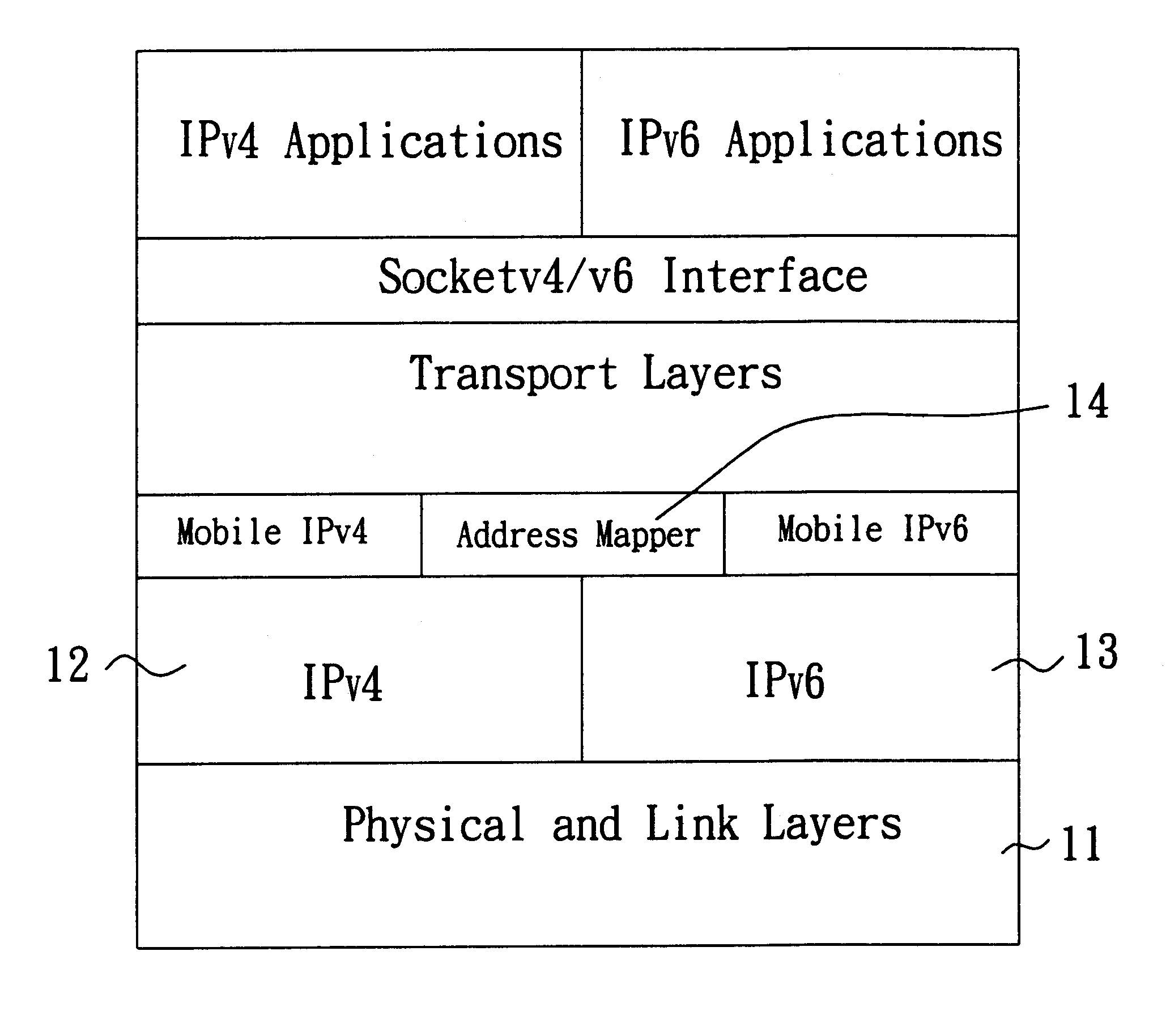
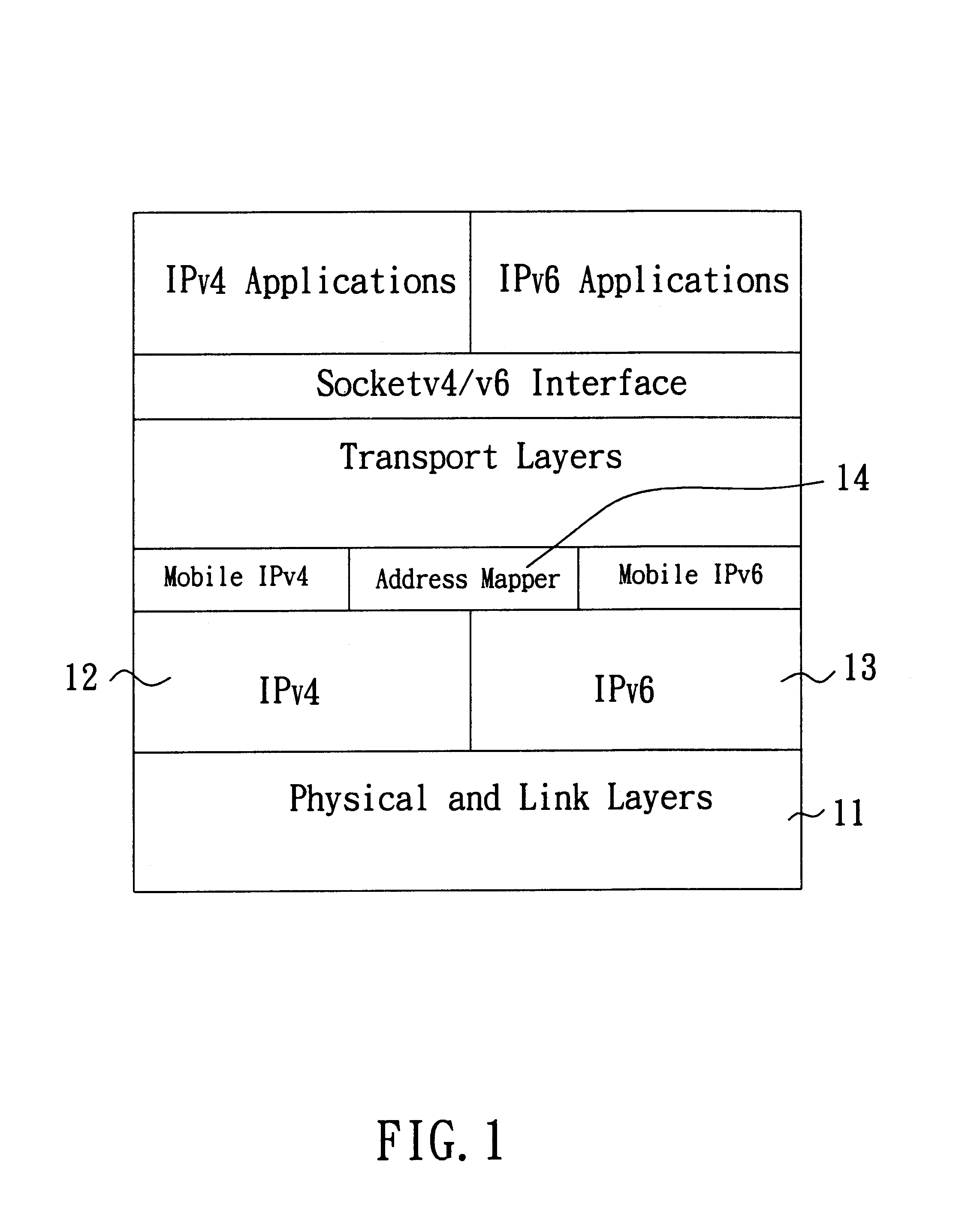
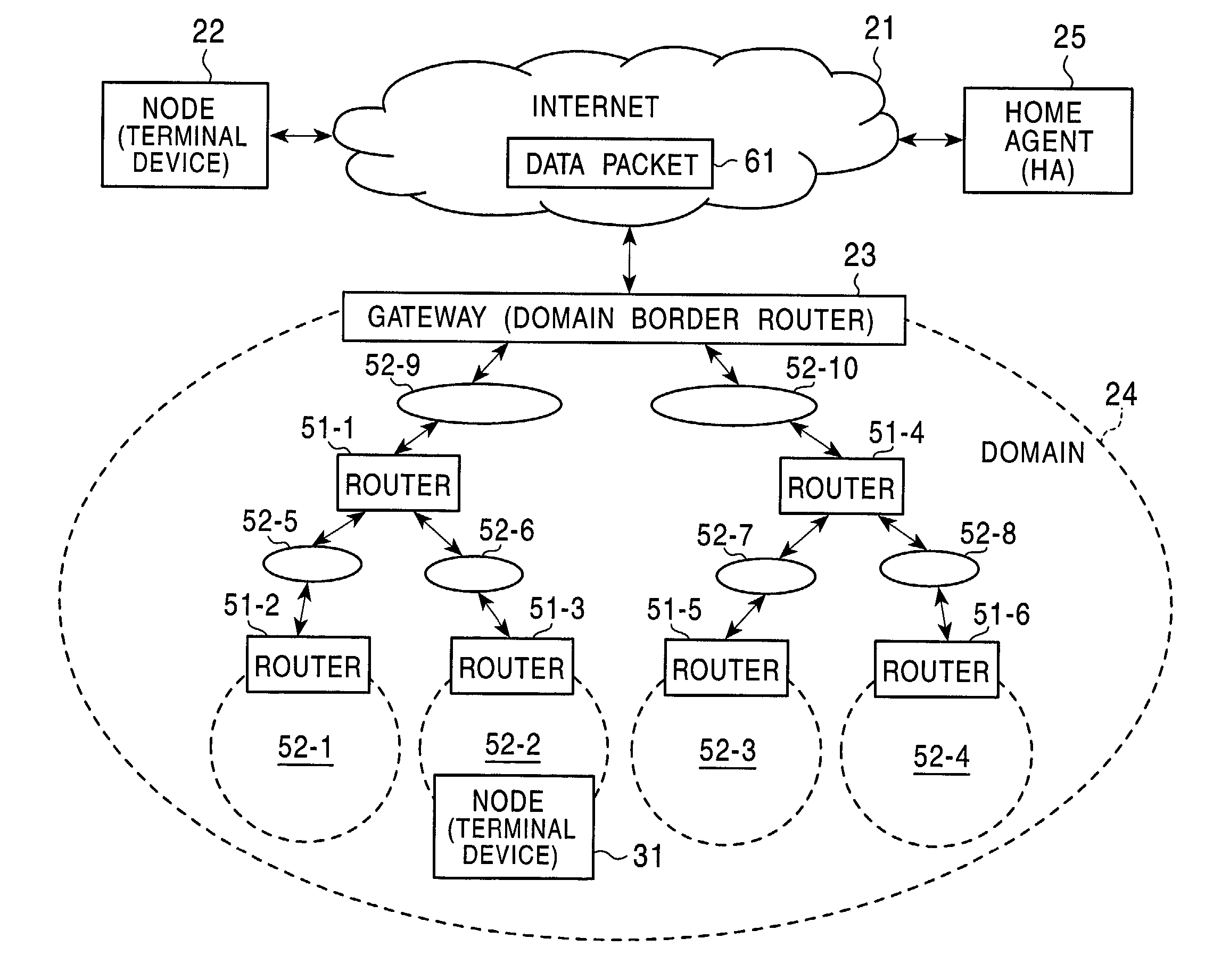
Method and system capable of providing mobility support for IPv4/IPv6 inter-networking
InactiveUS6862274B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork packetForeign agent
A method and system capable of providing mobility support for IPv4 / IPv6 inter-networking to a mobile node is disclosed. The mobile node in the system has an address mapper, an IPv4 protocol stack and an IPv6 protocol stack in the network layer. When moving from IPv4 to IPv6 networks, the mobile node registered an IPv4 address receives router advertisement packets from an IPv6 router, so as to obtain a IPv6 care-of-address, and resolve the IPv6 care-of-address by an IPv4 care-of-address. The address mapper issues an IPv4 message to register the IPv4 care-of-address. When moving from IPv6 to IPv4 networks, the mobile node registered an IPv6 address receives agent advertisement messages from a foreign agent, so as to obtain an IPv4 care-of-address, resolve the IPv4 care-of-address by an IPv6 care-of-address. The address mapper issues an IPv6 message to register and update binding information by the IPv6 care-of-address.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for automatically registering intelligent home appliance in network by one key
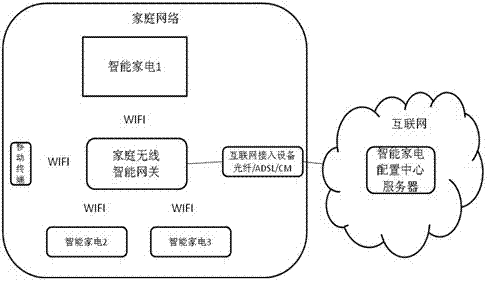
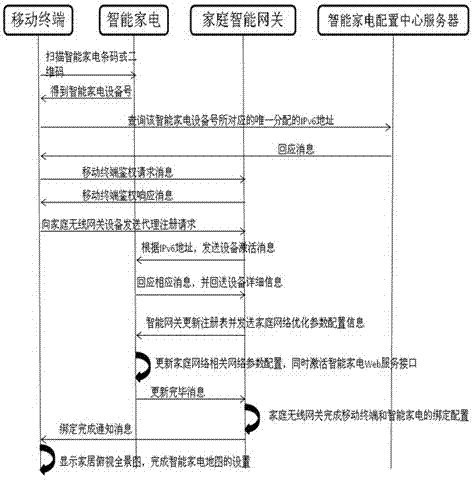
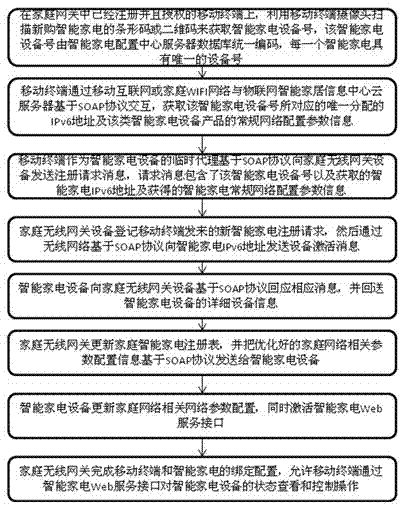
InactiveCN102769619ASimplify complex configurationEasy remote controlTransmissionWeb serviceRemote control
The invention discloses a method for automatically registering an intelligent home appliance in a network by one key. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the device number of the newly purchased intelligent home appliance by scanning; obtaining the IPv6 address and the general network configuration parameters of the home appliance from a server; sending registration request information to a home wireless gateway by a mobile terminal; sending device activation information to the home appliance by the home wireless gateway; returning detailed device information to the home wireless gateway by the home appliance; updating a home appliance registry and sending optimized home network configuration parameters to the home appliance by the home wireless gateway; updating home network relevant parameter configuration and activating a home appliance Web service interface by the home appliance; and finishing the binding configuration of the mobile terminal and the home appliance by the home wireless gateway. By the method, the configuration for finishing the registration of the intelligent home appliance in a computer is simplified for users and professional staffs, the binding of the mobile terminal and the intelligent home appliance is finished automatically, and the later safer remote control on the Web service interface of the intelligent home appliance through an authorized mobile terminal is facilitated.
Owner:NANJING XIAOWANG SCI & TECH
Name-based routing system and method
Owner:128 TECH
Packet communication method and apparatus and a recording medium storing a packet communication program
InactiveUS6580717B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareInformation processing
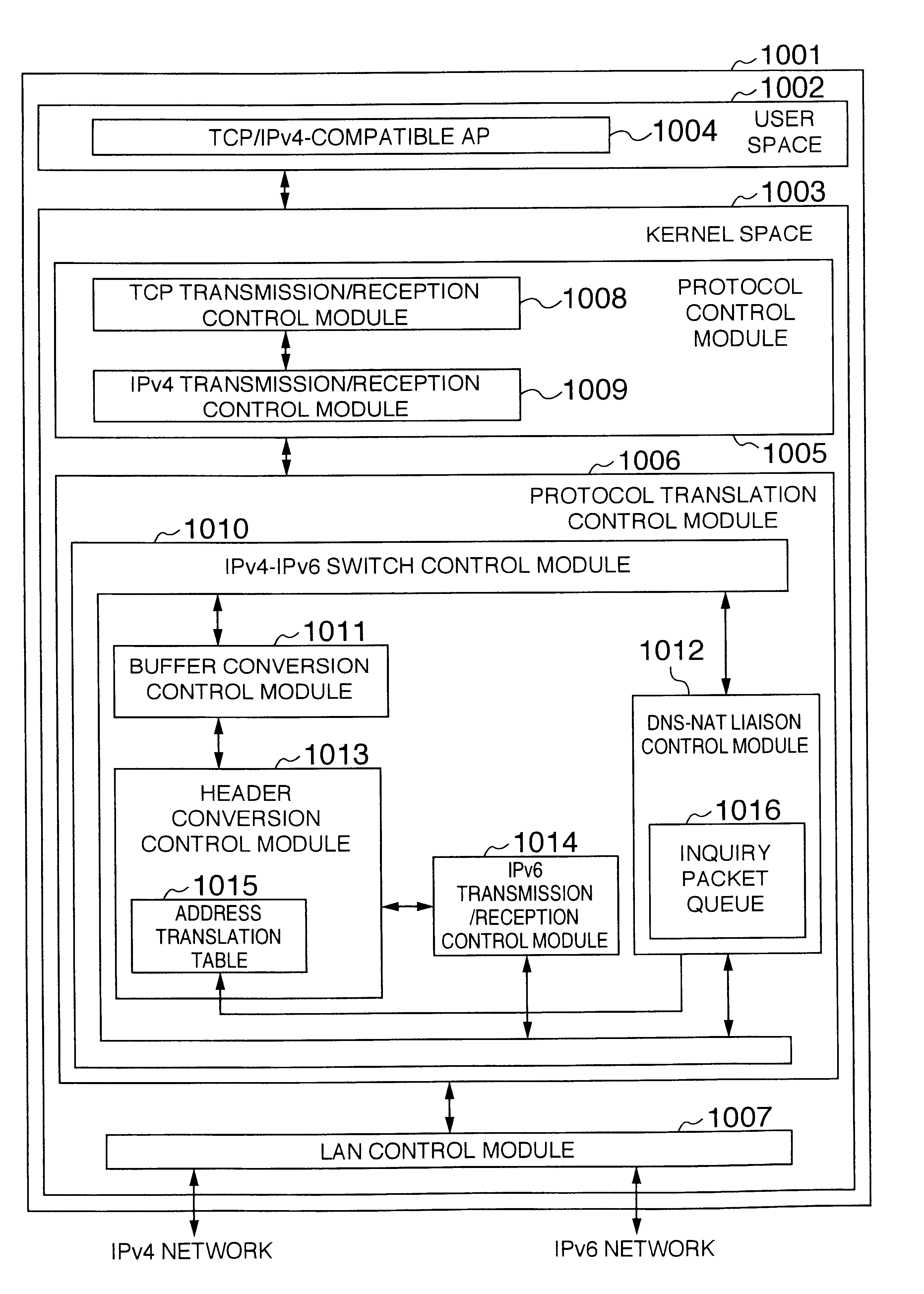
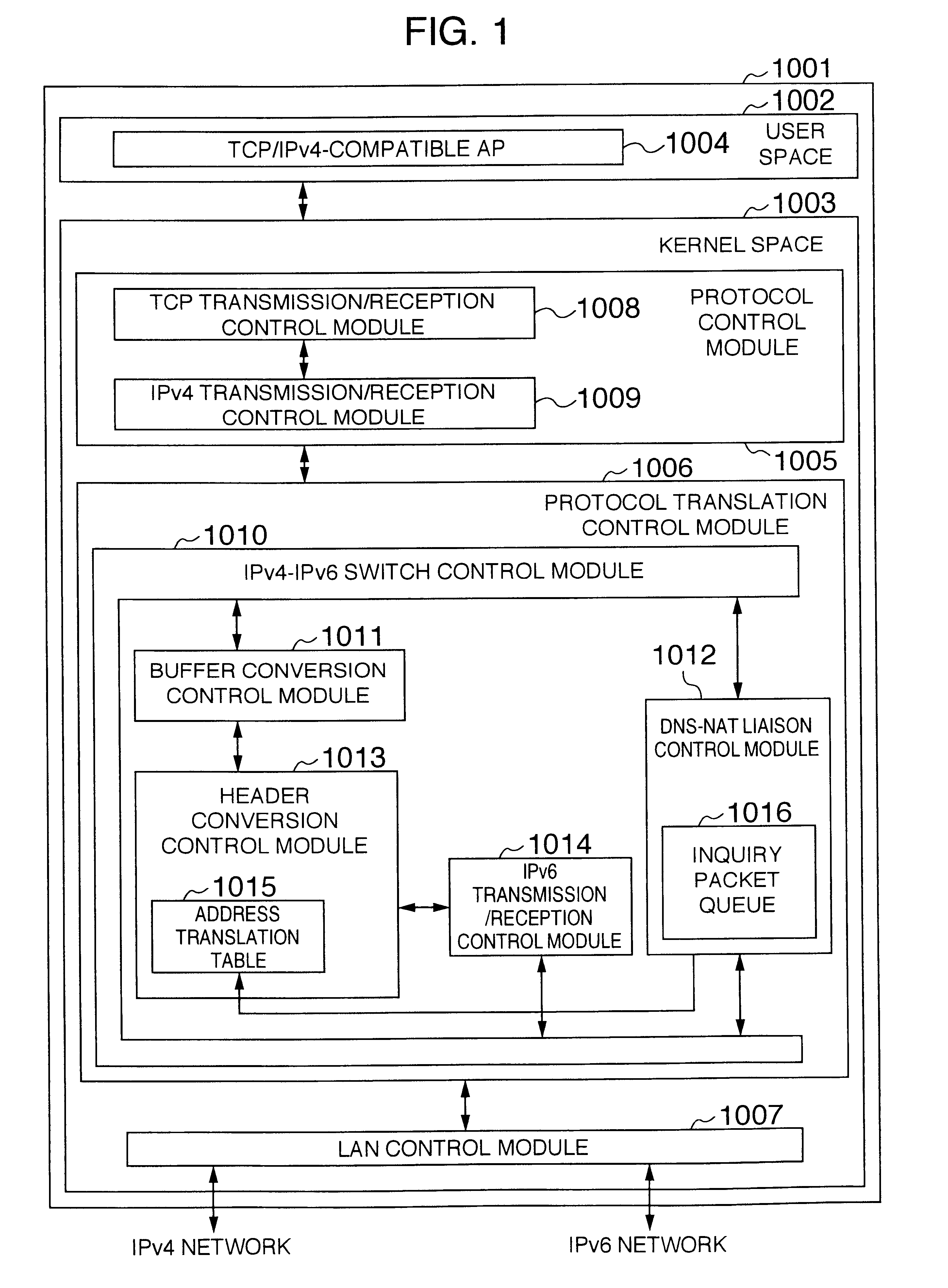
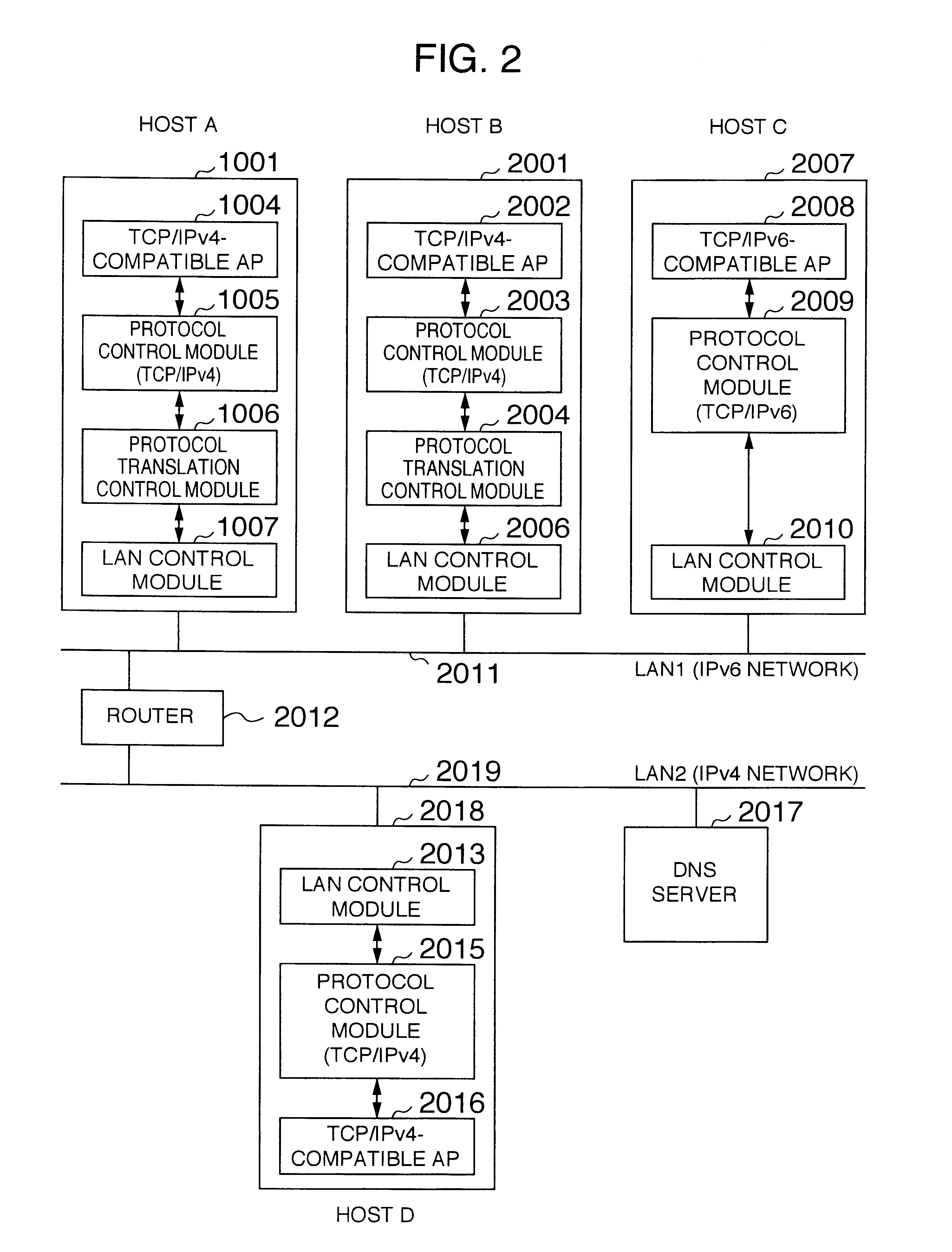
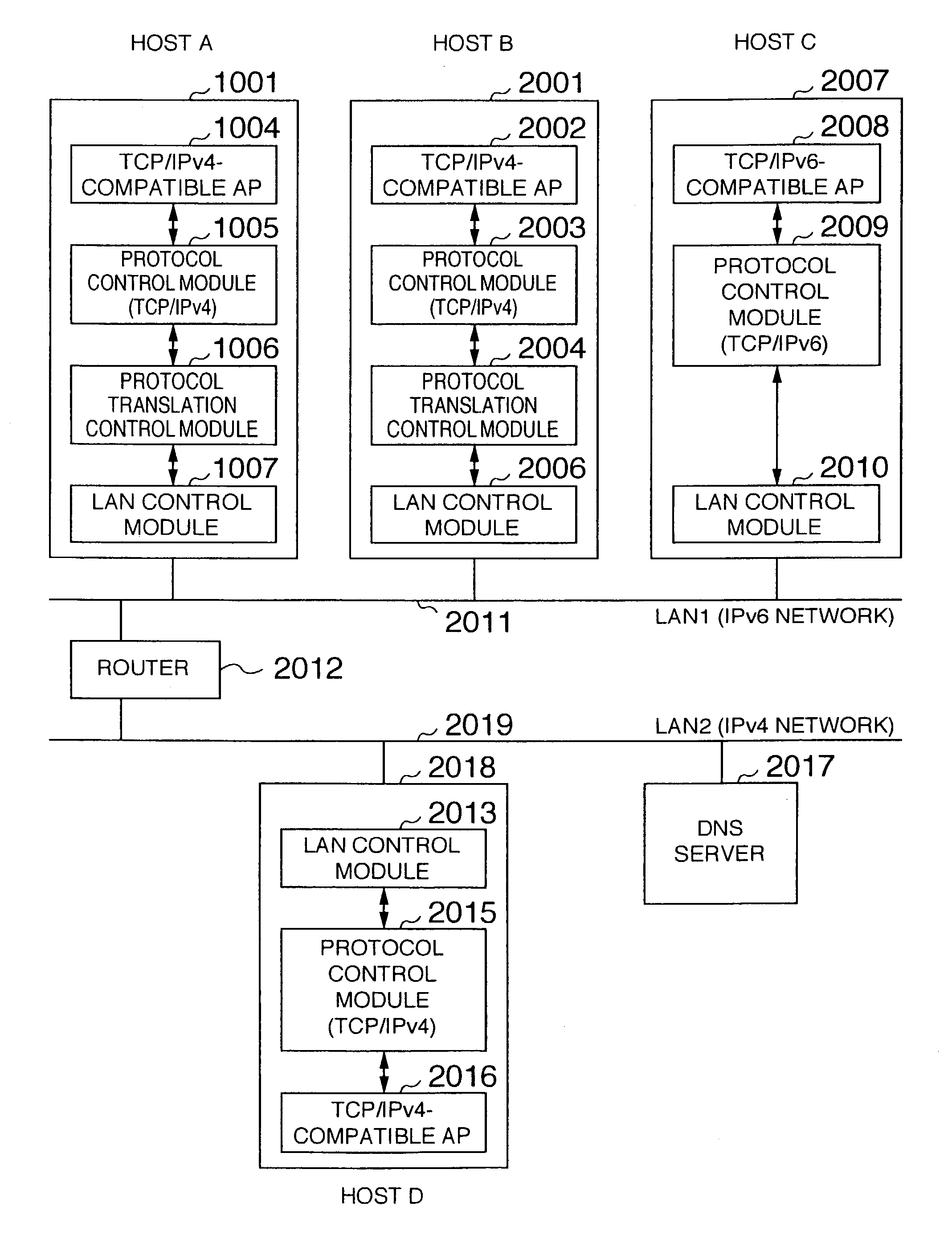
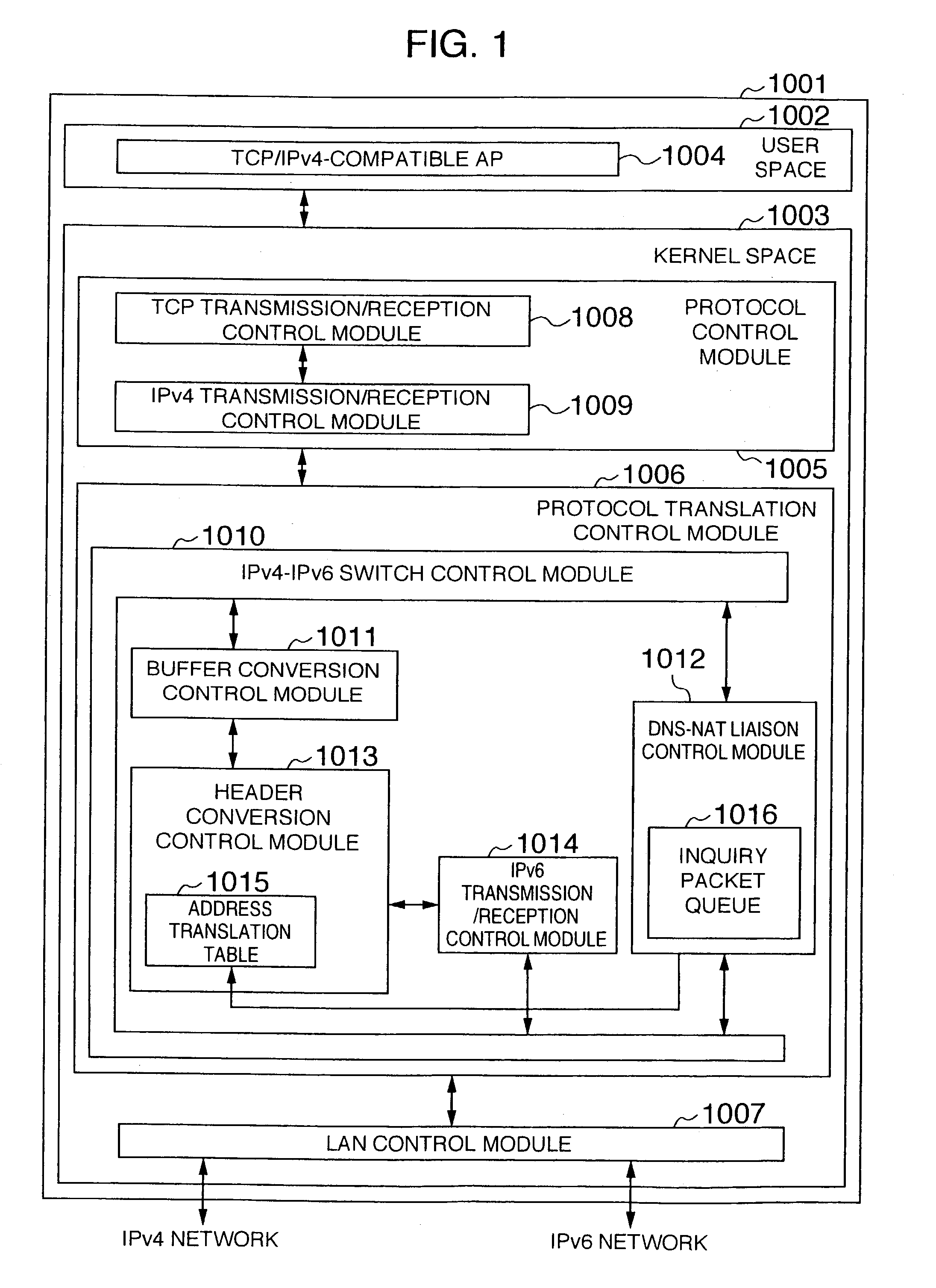
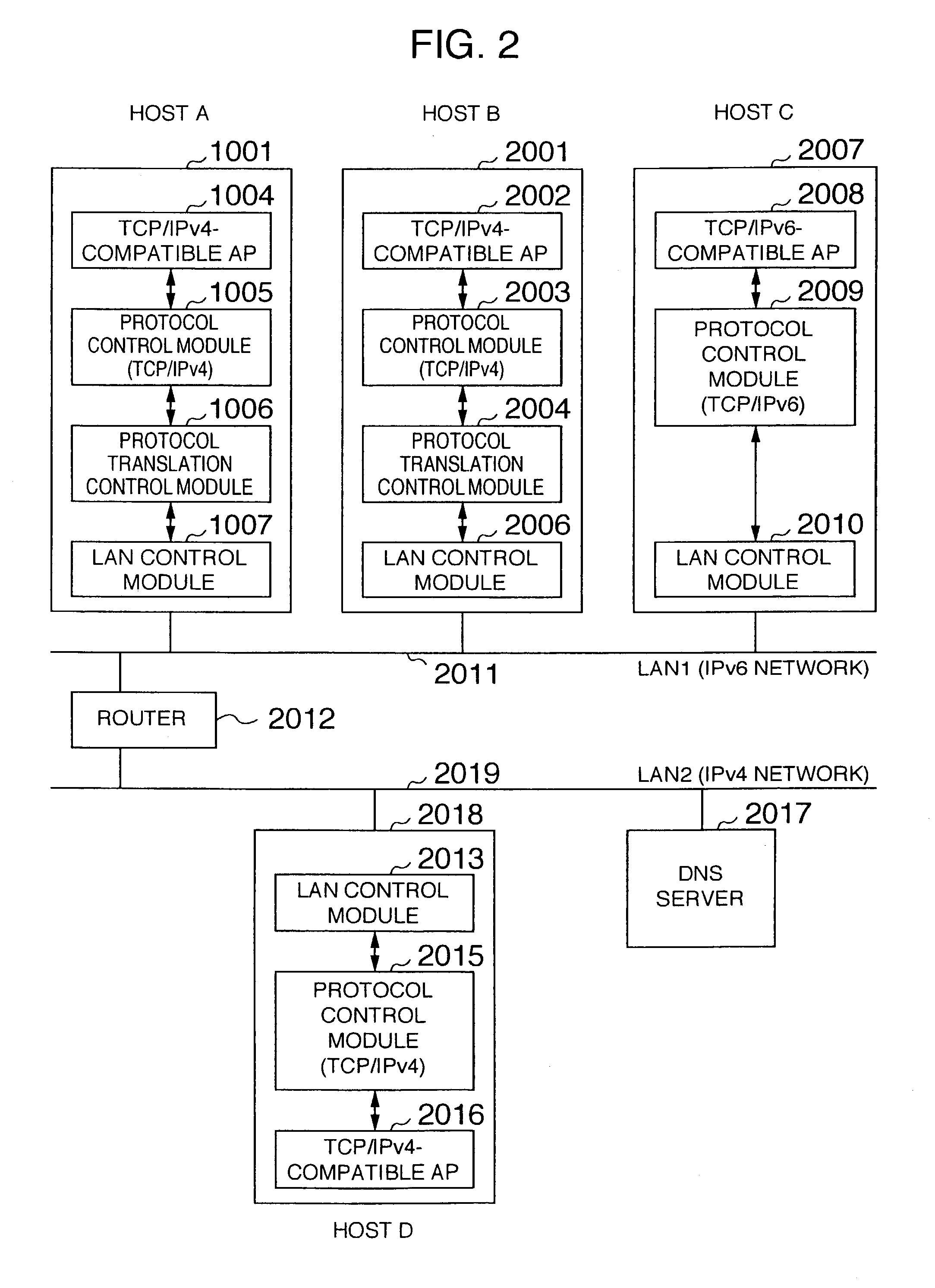
A packet communication method and a packet communication system capable of making an IPv4-compatible application operating on an information processing apparatus communicate with another information processing apparatus connected to an IPv6 network without using an address translation router. In the information processing apparatus connected to the IPv6 network incorporates, an IPv4-to-IPv6 protocol conversion control function is incorporated in a LAN driver. A protocol conversion control module receives an IPv4 packet from a protocol control module. When a send destination IPv4 address contained in a header of the packet is registered in an address translation table incorporated in the protocol conversion control module, an IPv6 address is generated to be sent onto a LAN. Unless the send destination IPv4 address contained in the packet header is registered in the address translation table incorporated in the protocol conversion control module, the IPv4 packet as received is intactly sent onto the LAN.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for deriving IPv6 scope identifiers and for mapping the identifiers into IPv6 addresses
InactiveUS20060280192A1Efficient and high-speedSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsComputer networkComputer science
A system and method are employed for forwarding multicast packets among a plurality of interfaces. A multicast packet having a scope value and a multicast group identifier (ID) value is received on an inbound interface. A VLAN designation associated with the inbound interface is identified. If the scope value in the received multicast packet indicates that the multicast packet has a link-local scope, a look-up address is generated that includes the identified VLAN designation and the multicast group ID value of the multicast packet. If the scope value in the received multicast packet indicates that the multicast packet has a site-local scope or an organization-local scope, the identified VLAN designation is used to retrieve a site identifier associated with the VLAN designation, and a look-up address is generated that includes the retrieved site identifier and the multicast group ID value. Finally, the look-up address is used to render a forwarding decision for the multicast packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Communication processing system, communication processing method, communication terminal device, and program
InactiveUS7257104B2Reduce network loadTake advantageNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCommunications systemTerminal equipment
In a communication system for a mobile node according to IPv6, a virtual network prefix is configured as a prefix specific to a mobile node in a domain having a plurality of subnetworks. In the domain, a packet is sent to the mobile node by host-based routing on an IPv6 address formed of the virtual network prefix and an interface ID. The communications process with the mobile node which cannot identify a virtual network prefix is performed using a physical network prefix according to IPv6. Accordingly, nodes which can and cannot identify a virtual network prefix can coexist in the domain.
Owner:SONY CORP
Network system and an interworking apparatus
InactiveUS20050041671A1Improve user convenienceImprove convenienceData switching by path configurationNetworked systemUser equipment
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for mixed mode of ipv6 and ipv4 DNS of global server load balancing
Systems and methods for providing one or more GSLB vServers to support both IPv4 and IPv6. The IPv6 support can be provided by permitting both A and AAAA domain name resolution. In other embodiments, the IPv6 support can be provided by modifying data structures to support IPv6 addresses.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
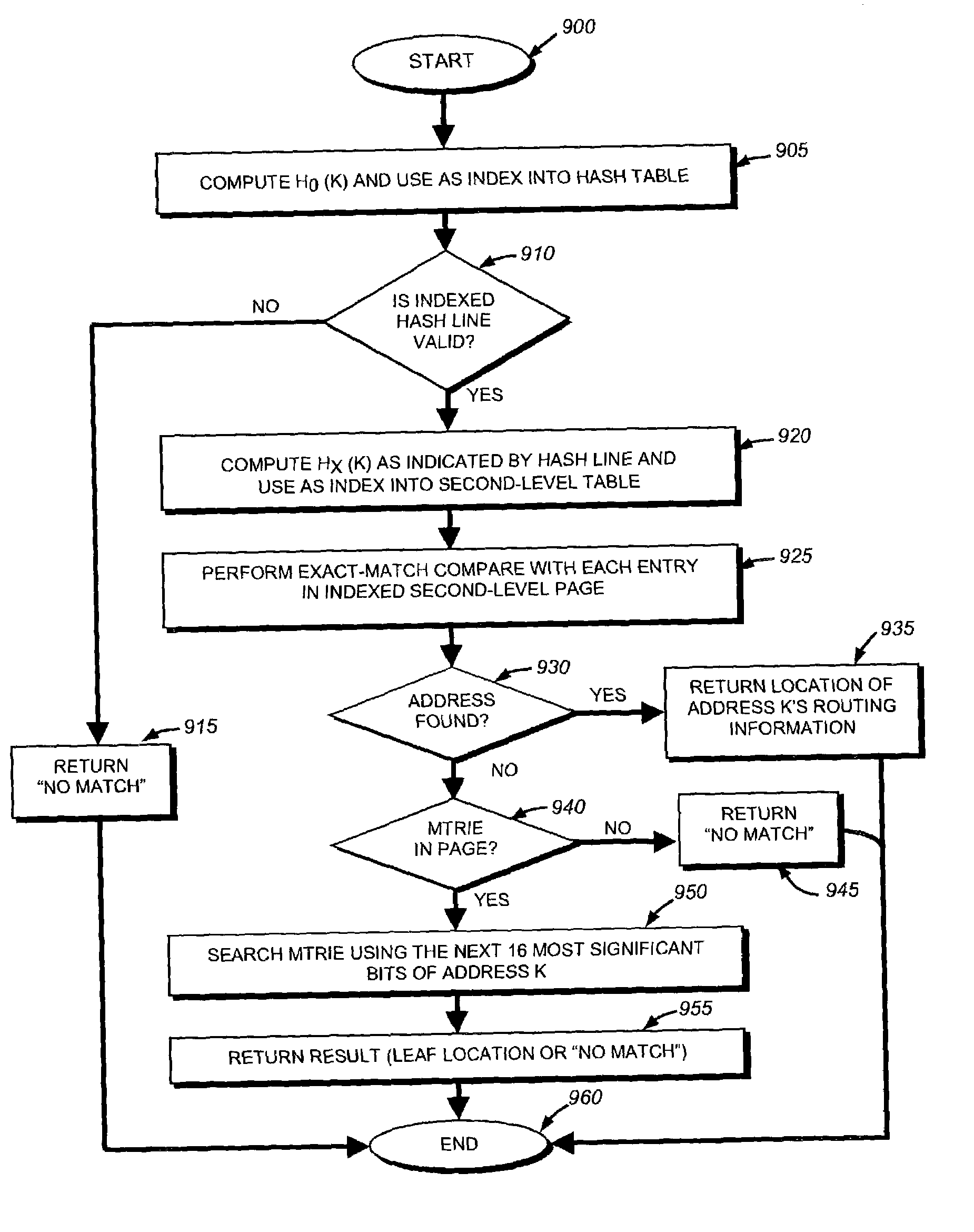
Bounded index extensible hash-based IPv6 address lookup method
InactiveUS7325059B2Increasing memory consumptionIncrease power consumptionMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksComputer architectureNetwork addressing
The present invention provides a technique for efficiently looking up address-routing information in an intermediate network node, such as a router. To that end, the node locates routing information stored in its memory using one or more “lookup” tables (LUT) which can be searched using a small, bounded number of dependent lookups, thereby reducing the number of dependent lookups conventionally performed. The LUTs are arranged so each table provides routing information for network addresses whose subnet mask lengths are within a different range (“stride”) of mask lengths. According to the technique, the node locates a network address's routing information by searching the LUTs, in order of decreasing prefix lengths, until the routing information is found. Preferably, several tables are searched in parallel. A match in a LUT may further point to a small MTRIE that enables the final bits of a prefix to be matched. That final MTRIE is searched using a relatively small, bounded number of dependent lookups.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
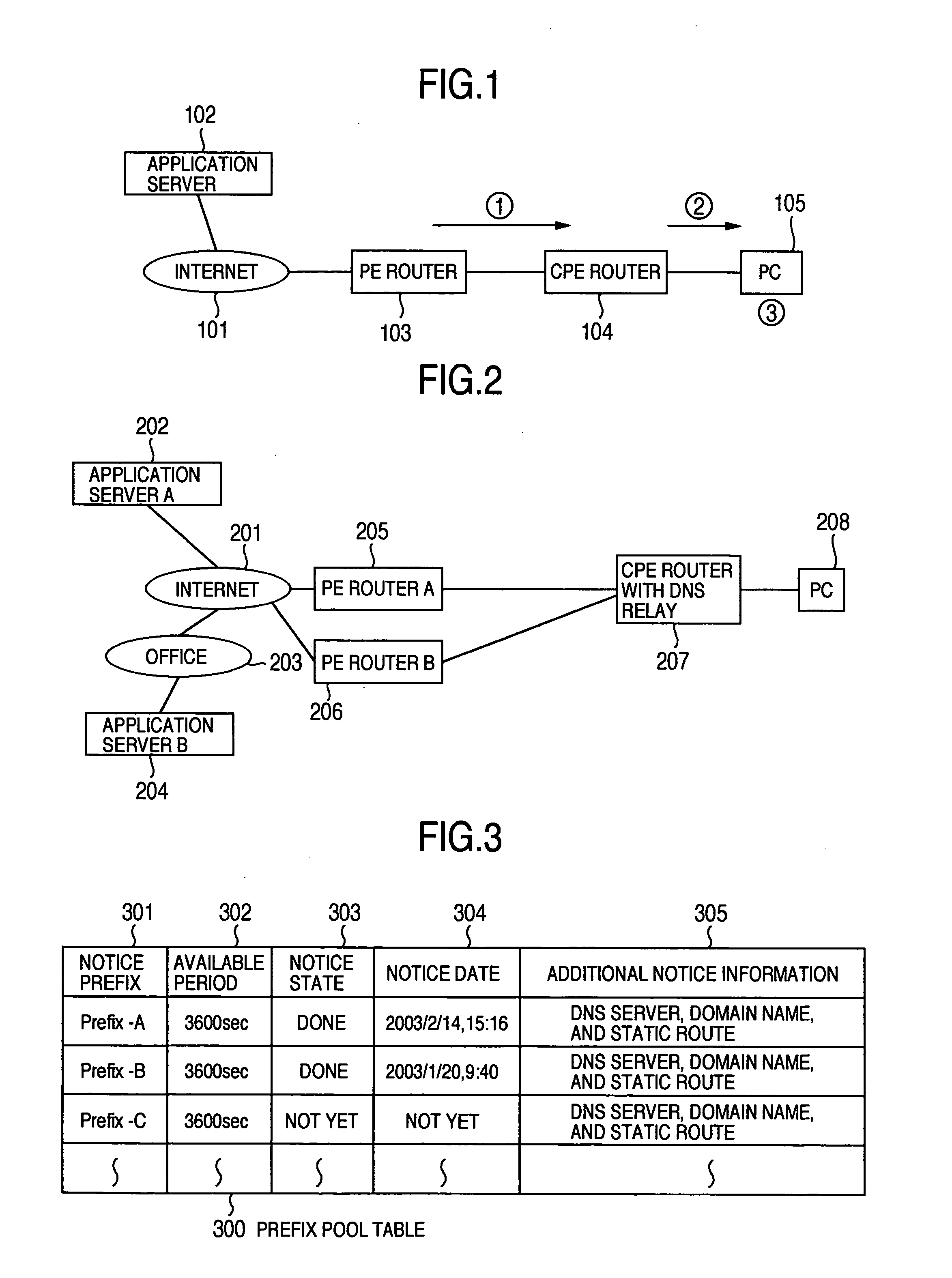
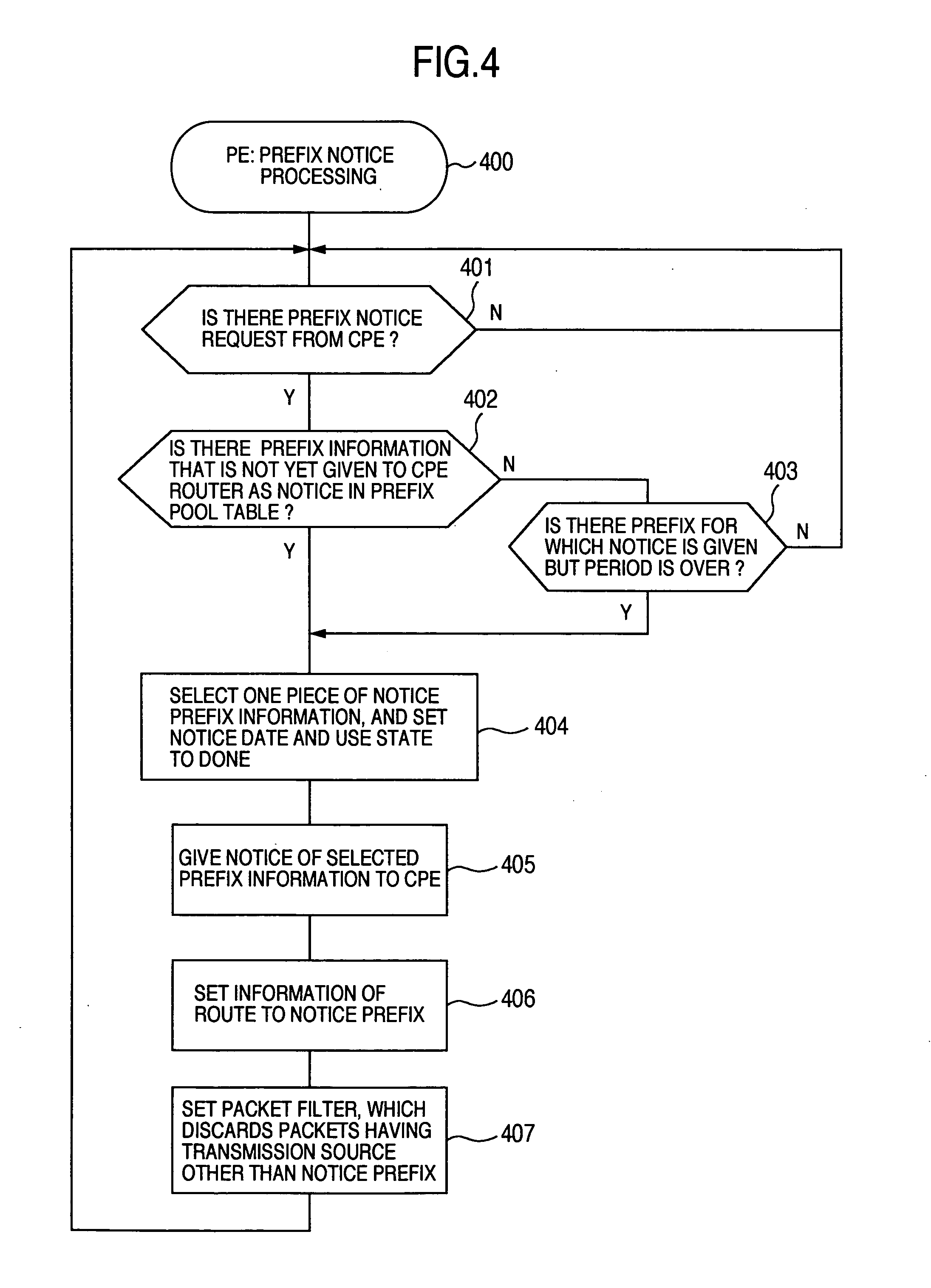
Resource allocation and reclamation for on-demand address pools
InactiveUS7788345B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer scienceResource allocation
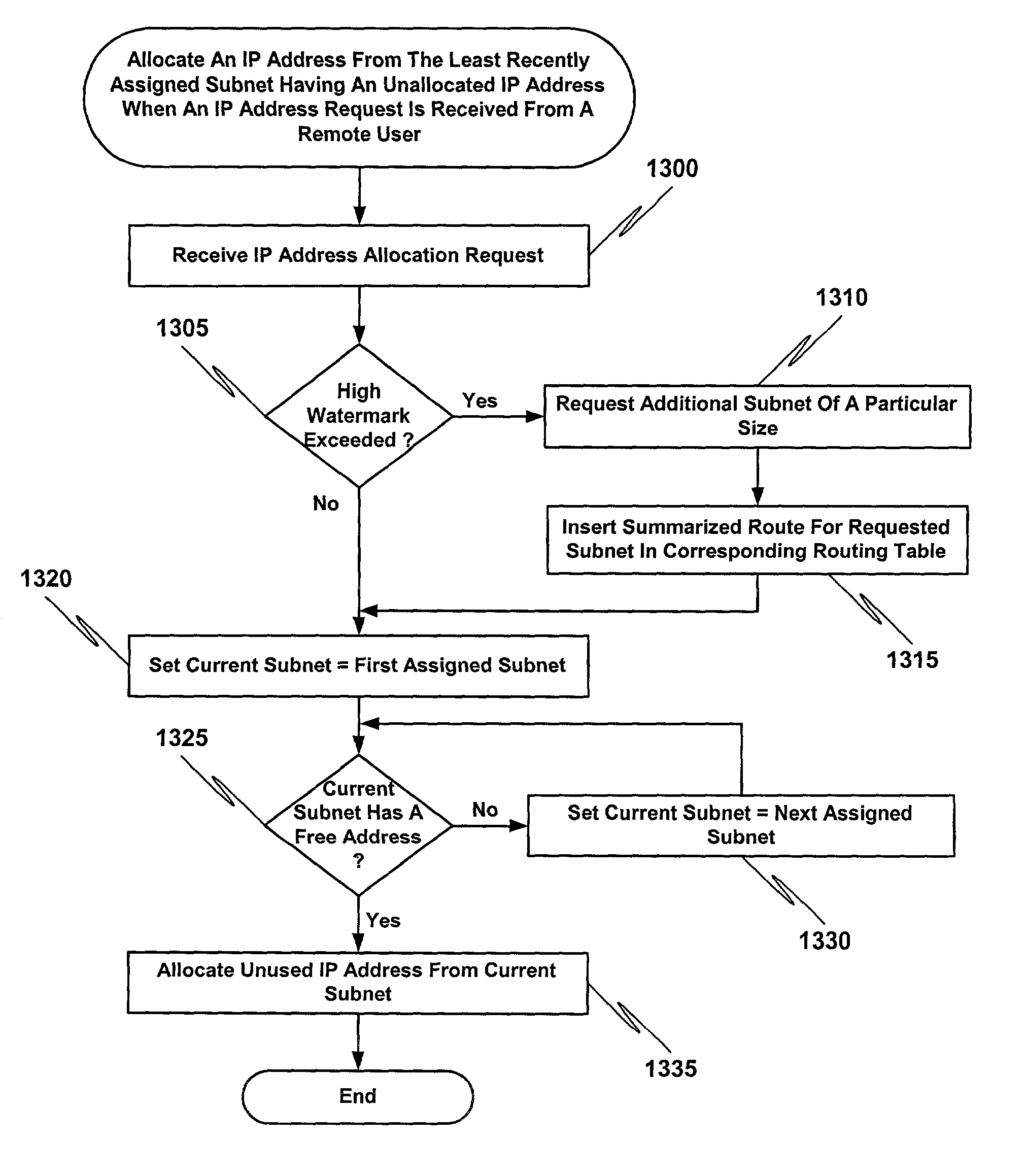
A method for on-demand management of Internet Protocol (IP) address pools includes allocating an unused IP address from a local IP address pool designated for a remote domain if a request to connect to the remote domain is received and deallocating an IP address if the IP address is released. The local IP address pool includes at least one subnet dynamically assigned from a global IP address pool. Each of the subnets specifies a contiguous set of one or more IP addresses. IP addresses are allocated using a first-assigned-subnet-first policy, wherein an IP address is allocated from a least recently assigned subnet having at least one unallocated IP address. According to one aspect, subnets are deassigned using a last-assigned-subnet-first policy, wherein the deassigned subnet is the most recently assigned subnet having no allocated IP addresses.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for improving high speed internetwork data transfers
InactiveUS6631137B1Improving high speed traffic operationHigh speed data transmissionNetworks interconnectionSecuring communicationVirtual LANIp address
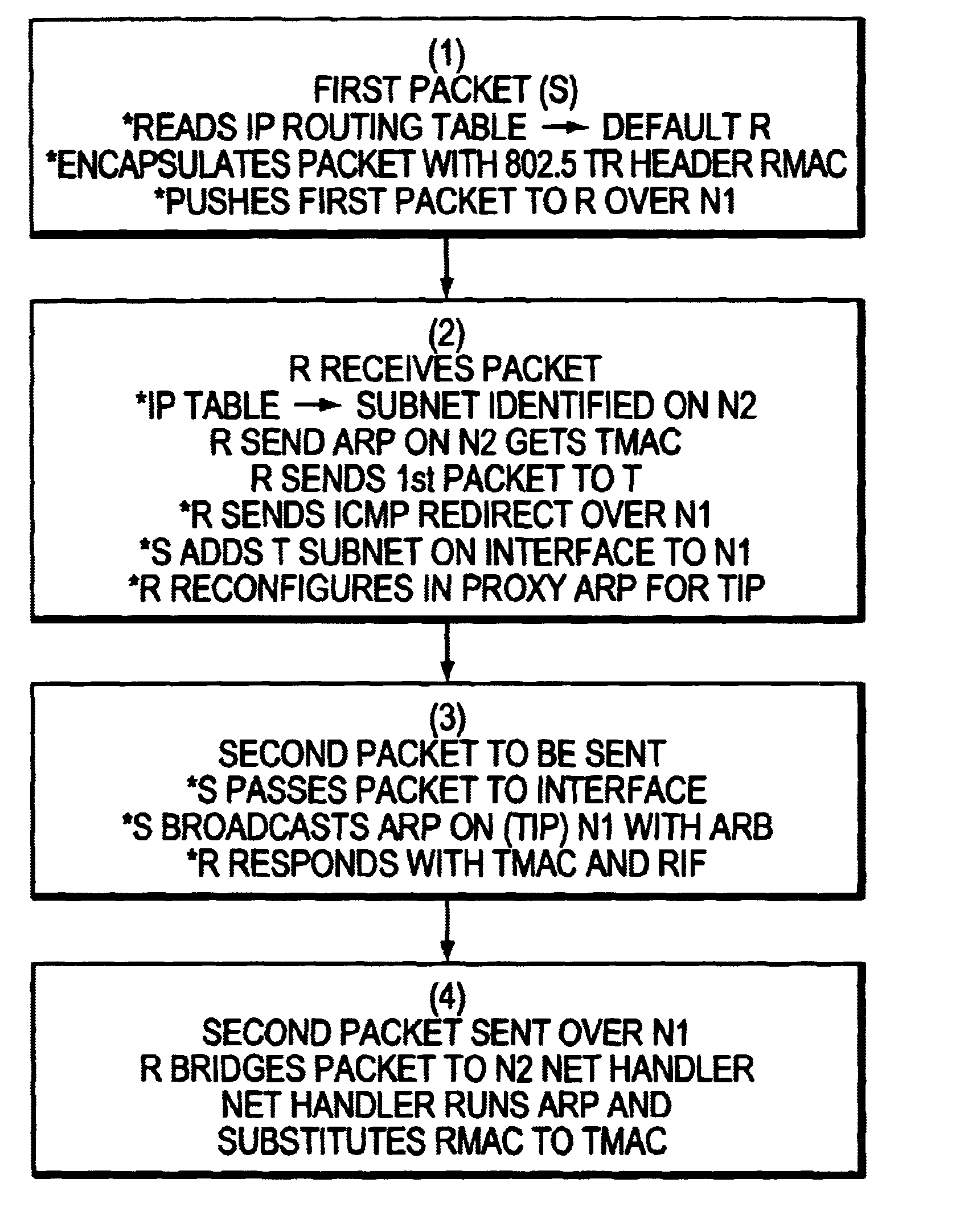
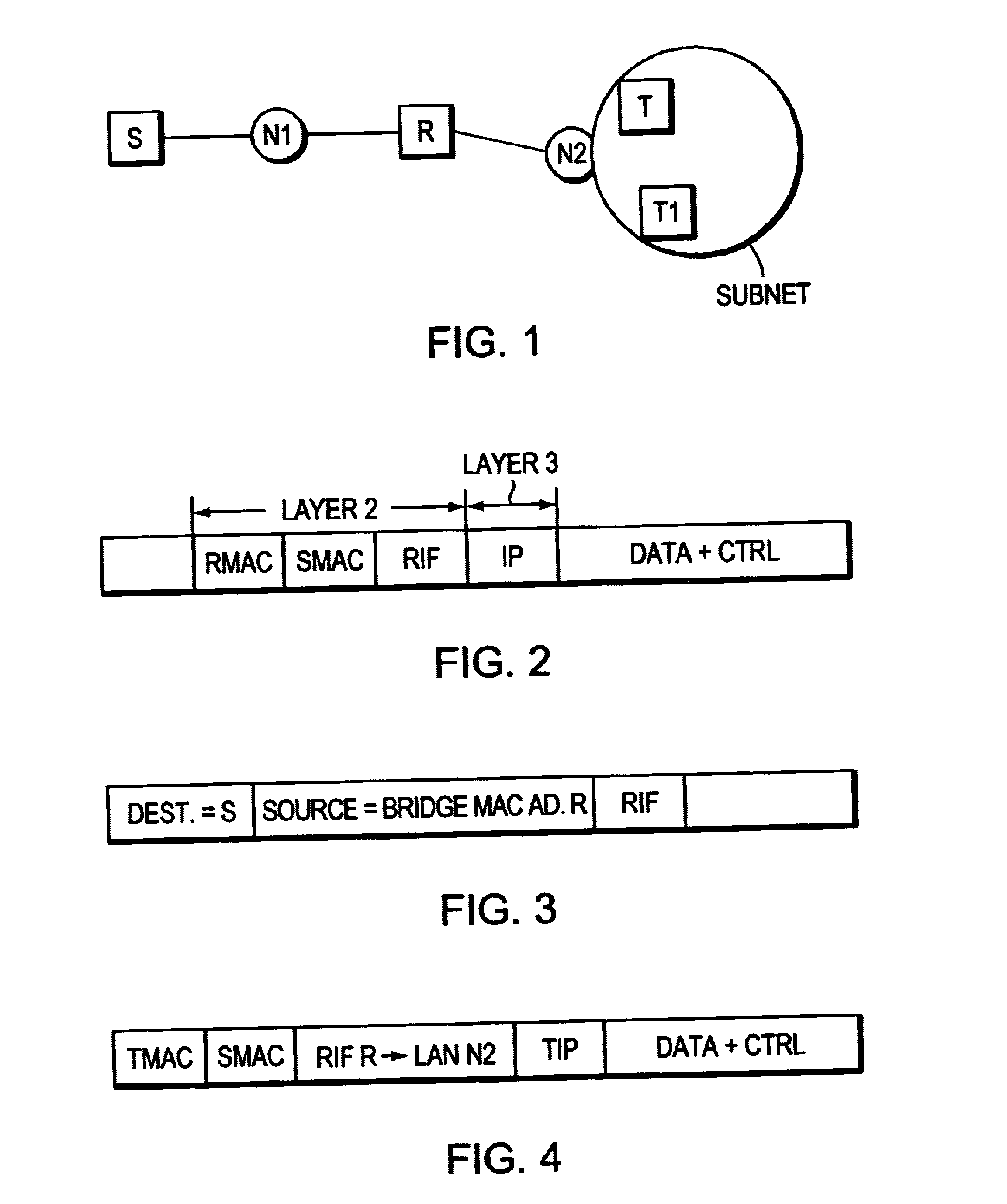
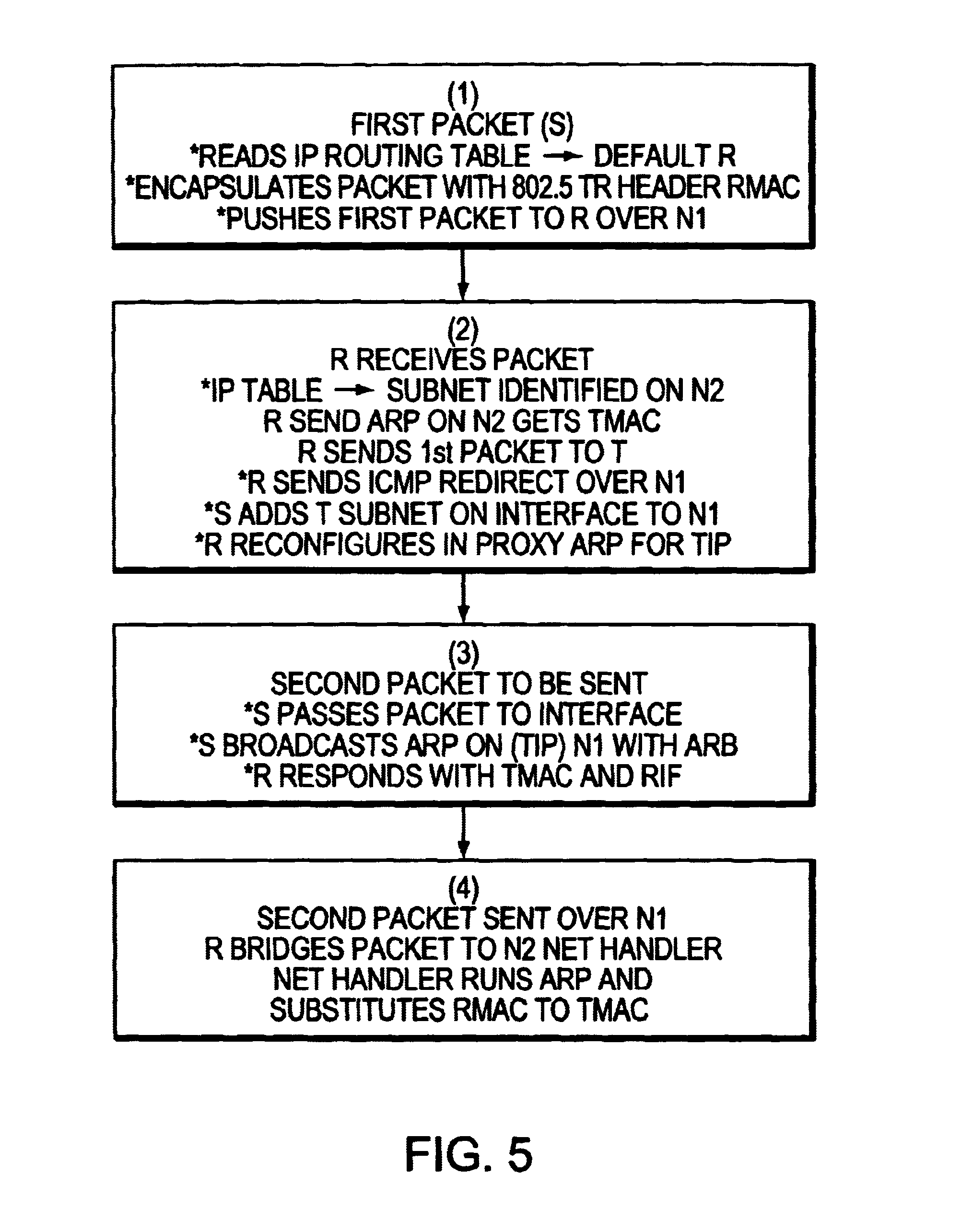
A method for creating a single virtual LAN including a source (S) attached to a first Token ring LAN (N1), a target (T) within a subnet attached to a different Token ring LAN (N2), and an interconnecting router (R). The source (S) encapsulates the first packet with a Token ring header including the router MAC address (RMAC), SMAC as source MAC address as layer 2 information, and IP address of T (TIP) as layer 3 data and sends this packet over N1 toward the router. When receiving the first packet, R reads its IP table for best match with TIP address to identify the subnet including T. The net handler runs an ARP protocol to identify TMAC address, substitutes the MAC header with said TMAC address into said first packet destination MAC address field and forwards said first packet over N2. R then sends a conventional ICMP message over N1 limited broadcast and reconfigures itself in proxy ARP for the defined subnet. For the second packet, S runs an ARP and R answers with RMAC address and the RIF data to be used for next packets.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for efficient sftorage and processing of IPV6 addresses
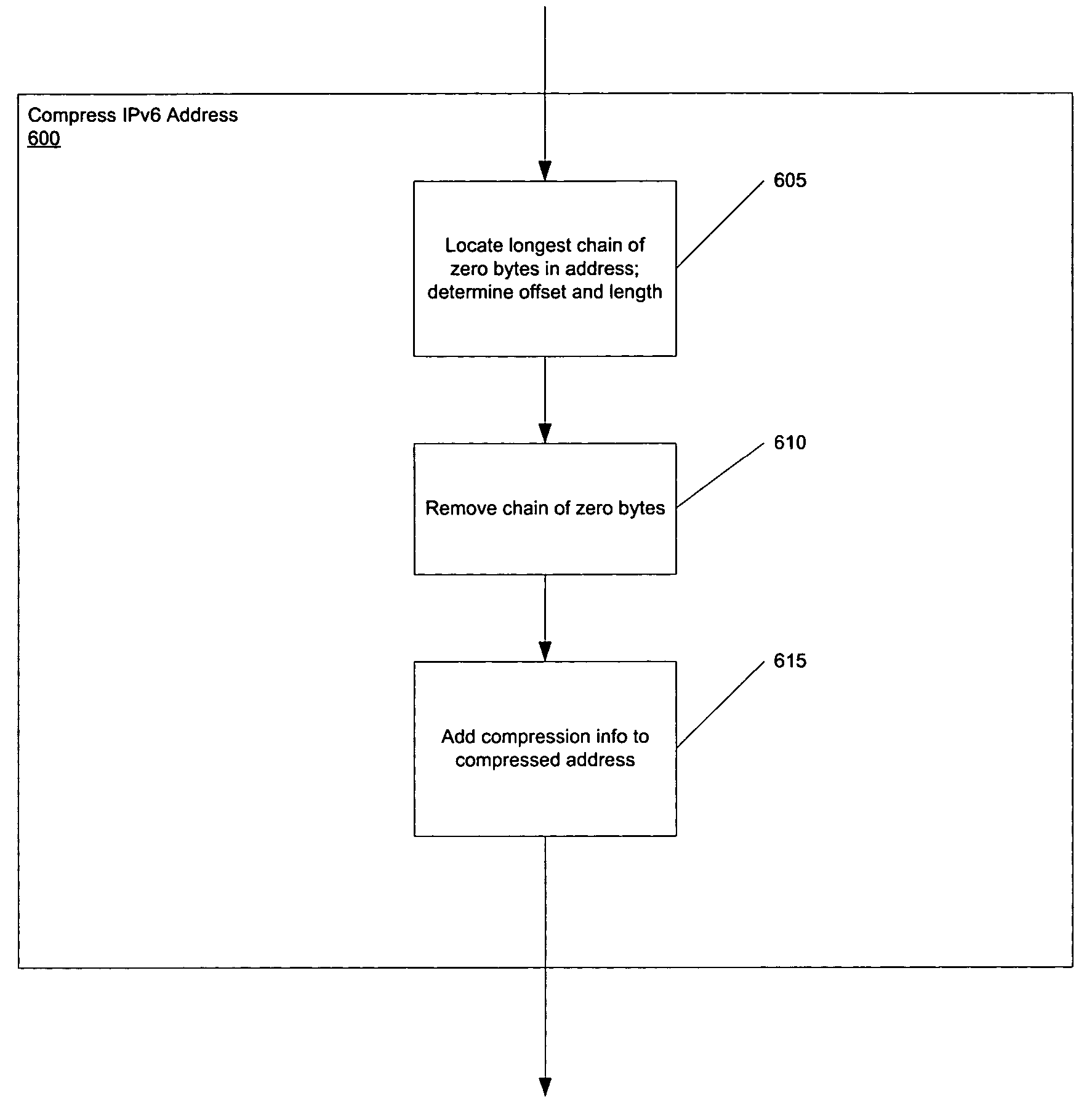
InactiveUS20050111494A1Eliminating compression informationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRouting tableMemory footprint
A preferred method and algorithm of compressing IPv6 addresses is presented which ensures smaller memory occupancy for IPv6 routing tables and databases in general (applicability to particular case of databases of the routing protocol OSPF for IPv6 is described). A method and algorithm of comparison of such compressed IPv6 addresses without decompression is presented, a method of comparison that ensures in the majority of cases better comparison performance than for the case of comparing uncompressed IPv6 addresses. Also, a preferred method and algorithm of decompressing IPv6 addresses that were compressed using this preferred format is given, and a method and algorithm of comparison of an uncompressed IPv6 address with a compressed IPv6 address without decompression. The exemplary comparison methods may achieve or exceed comparable performance with the performance of comparing uncompressed addresses. Illustrations for the particular case of the routing protocol OSPF for IPv6 are presented for all cases.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
System and Method for Flow-Based Addressing in a Mobile Environment
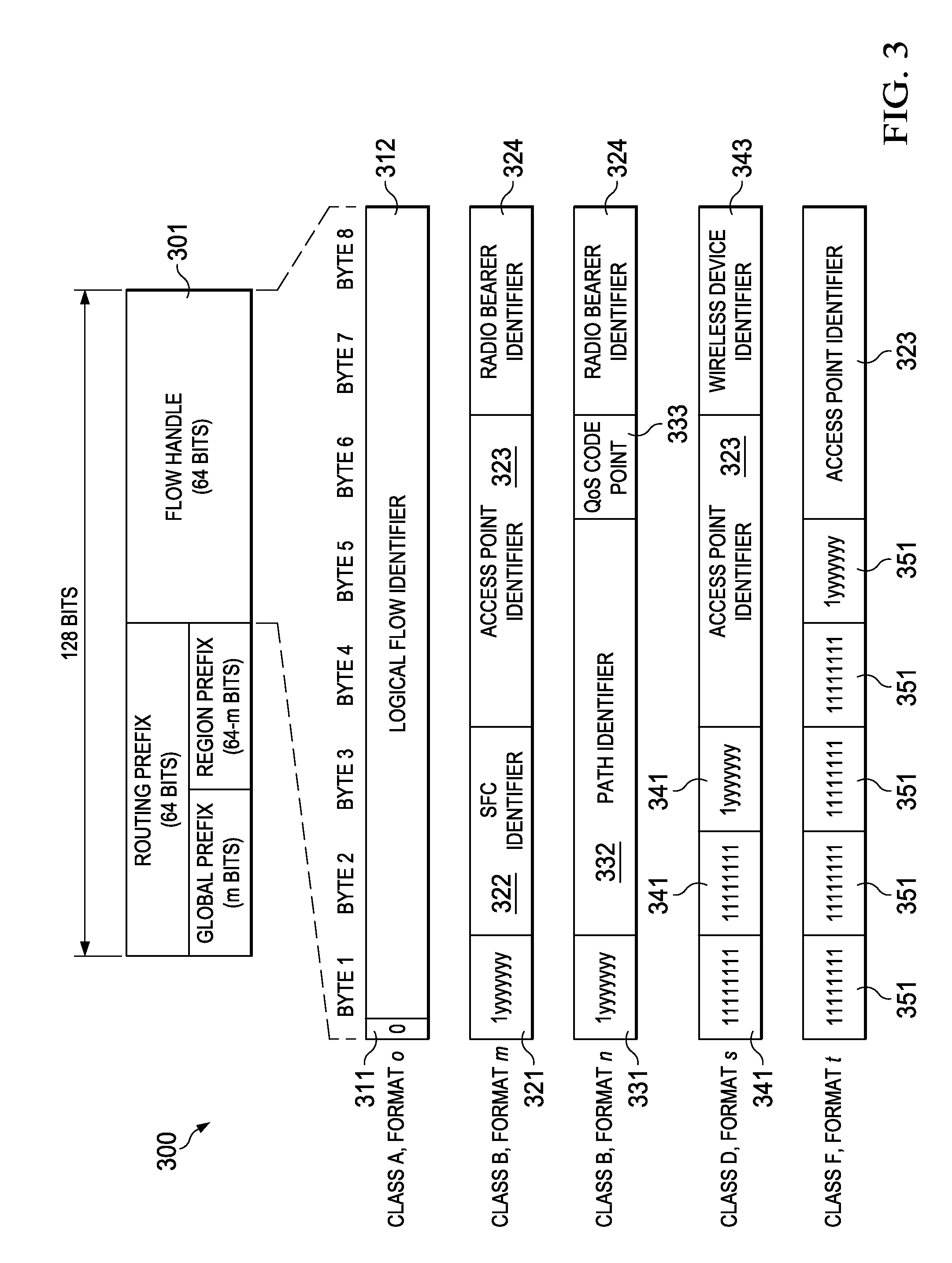
Embedding a flow handle (FH) in an IPv6 address portion of a packet may reduce the amount of overhead needed to support path selection in flow-based packet forwarding. The FH may replace an interface identifier in a standard IPv6 address such that the FH does not add any additional overhead to the IPv6 packet itself. Information specified by the FH embedded in the IPv6 address may be used to select the path or next-hop. In addition, the FH may identify a quality of service (QoS) requirement associated with the packet, and the route selection function may identify a path capable of satisfying the QoS requirement, a service function chain (SFC) ID, an access point (AP) ID, a radio bearer ID, a path ID, and / or a device ID.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Service-oriented IPv6 address specification and distribution method, terminal and system for implementing the same
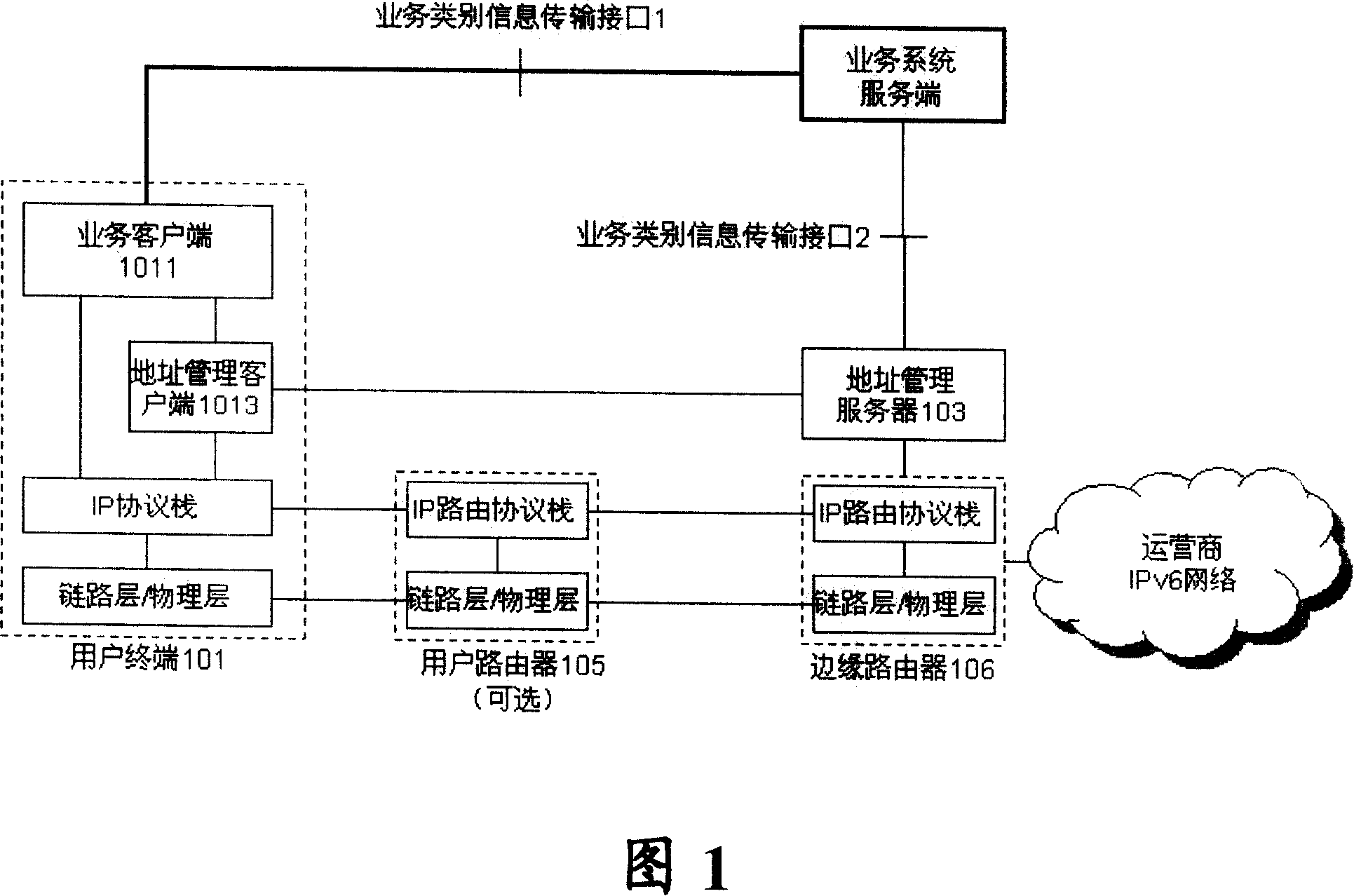
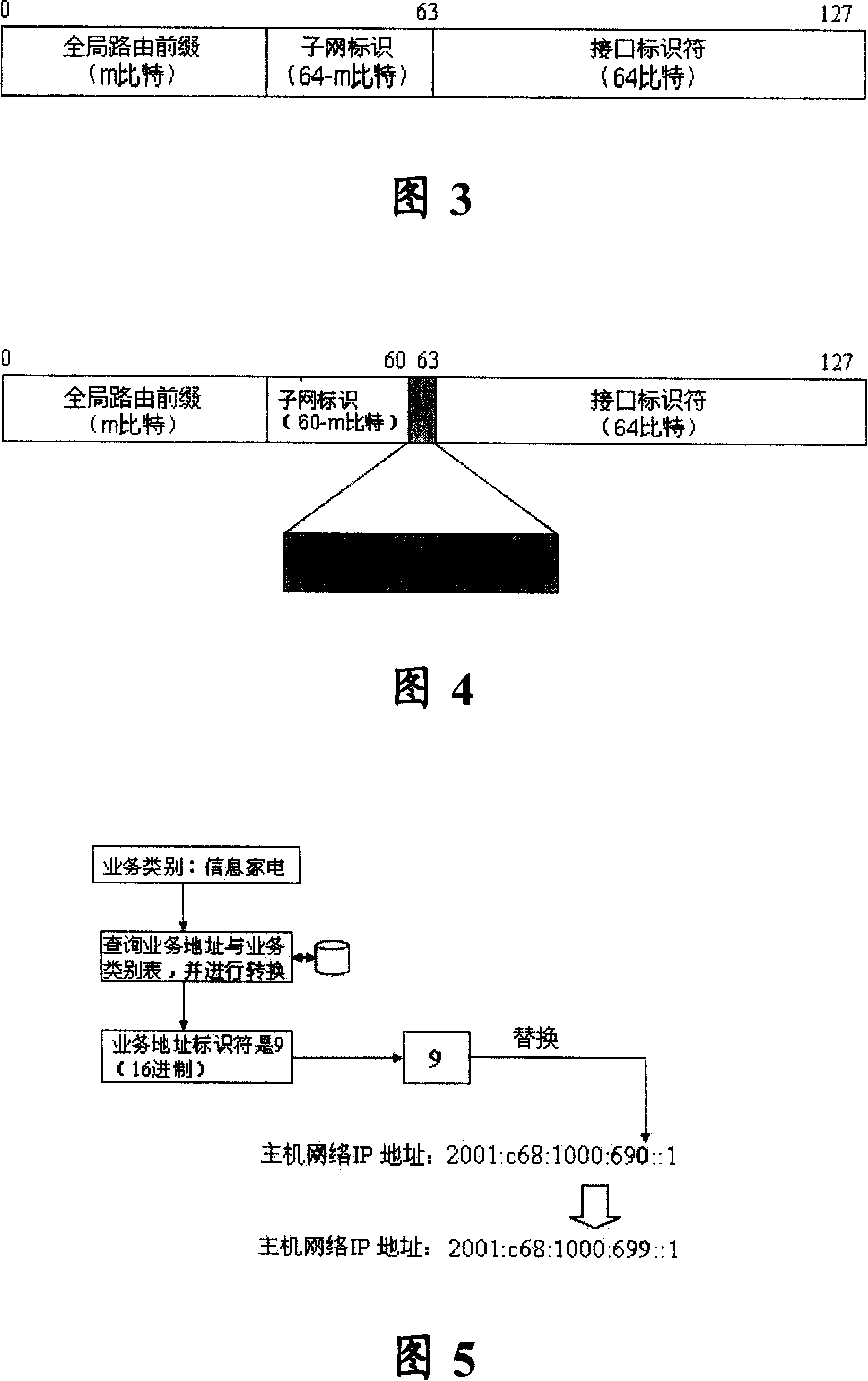
ActiveCN101155196AEasy and efficient managementConvenient and efficient controlTransmissionQuality of serviceDistribution method
The present invention relates to IPv6 address class facing business as well as distributing method, corresponding system frame and user terminal. The method includes: dividing the IPv6 address to network address and business address; classing the business address further according to the business provided by telecommunication, so as to form a plurality of addresses relative to various businesses. Wherein, distributing network address to user terminal; distributing business address to various business client of user terminal, the business client applies the business address of its business to operator address management server according to business address apply and distributing protocol, then taking the business address as the source address of communication of client. According to the present invention, it is easy to implement the function of business statistics, user tracing to the source as well as data redirection, and to establish transparent server quality acceptance and realization mechanism between the operator and users, also the management and control to internet of operator is more convenient and efficient.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Address information display system and address information display program
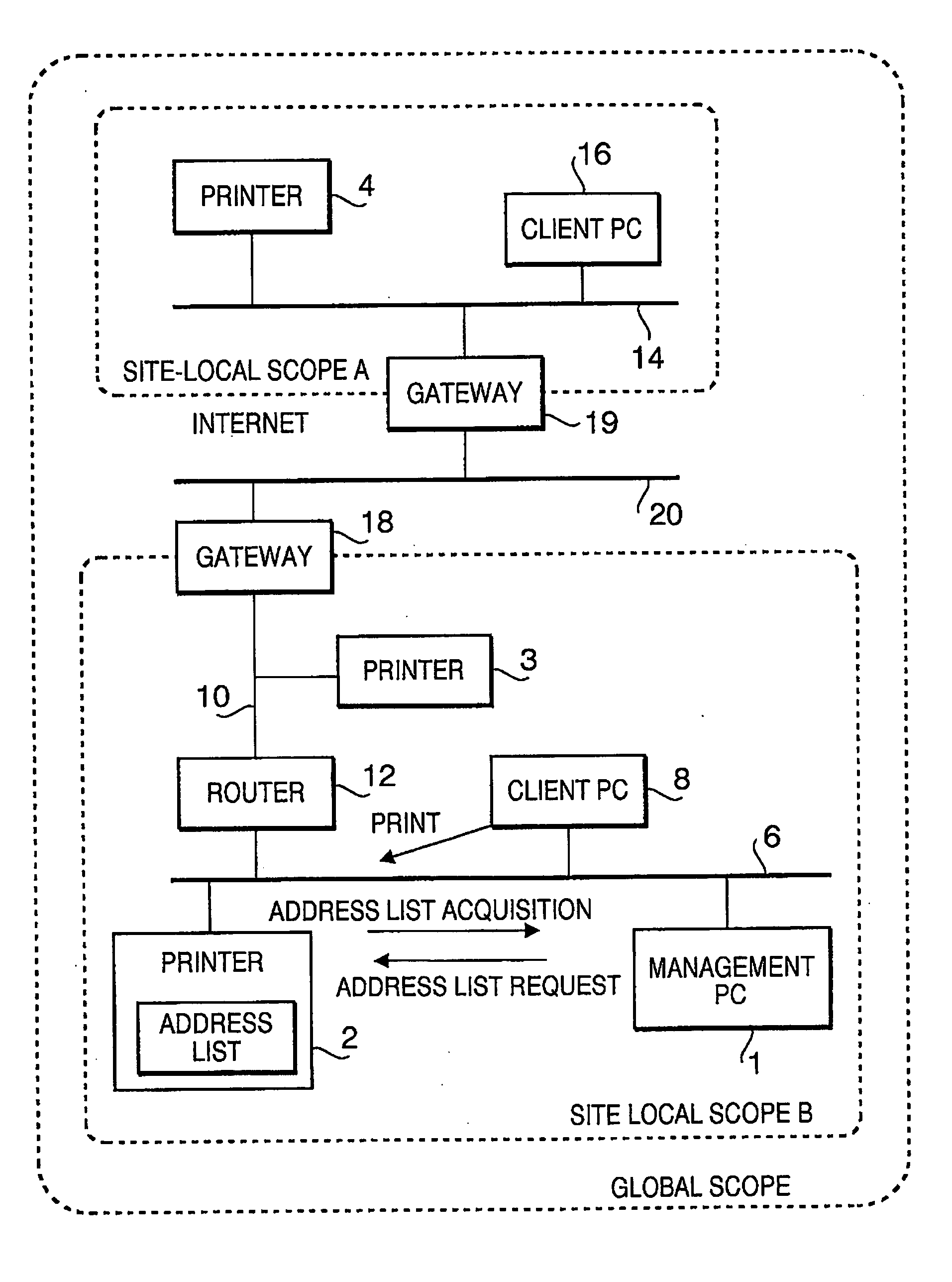
ActiveUS20060067343A1Easy to understandMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data processing detailsInformation display systemsDisplay Order
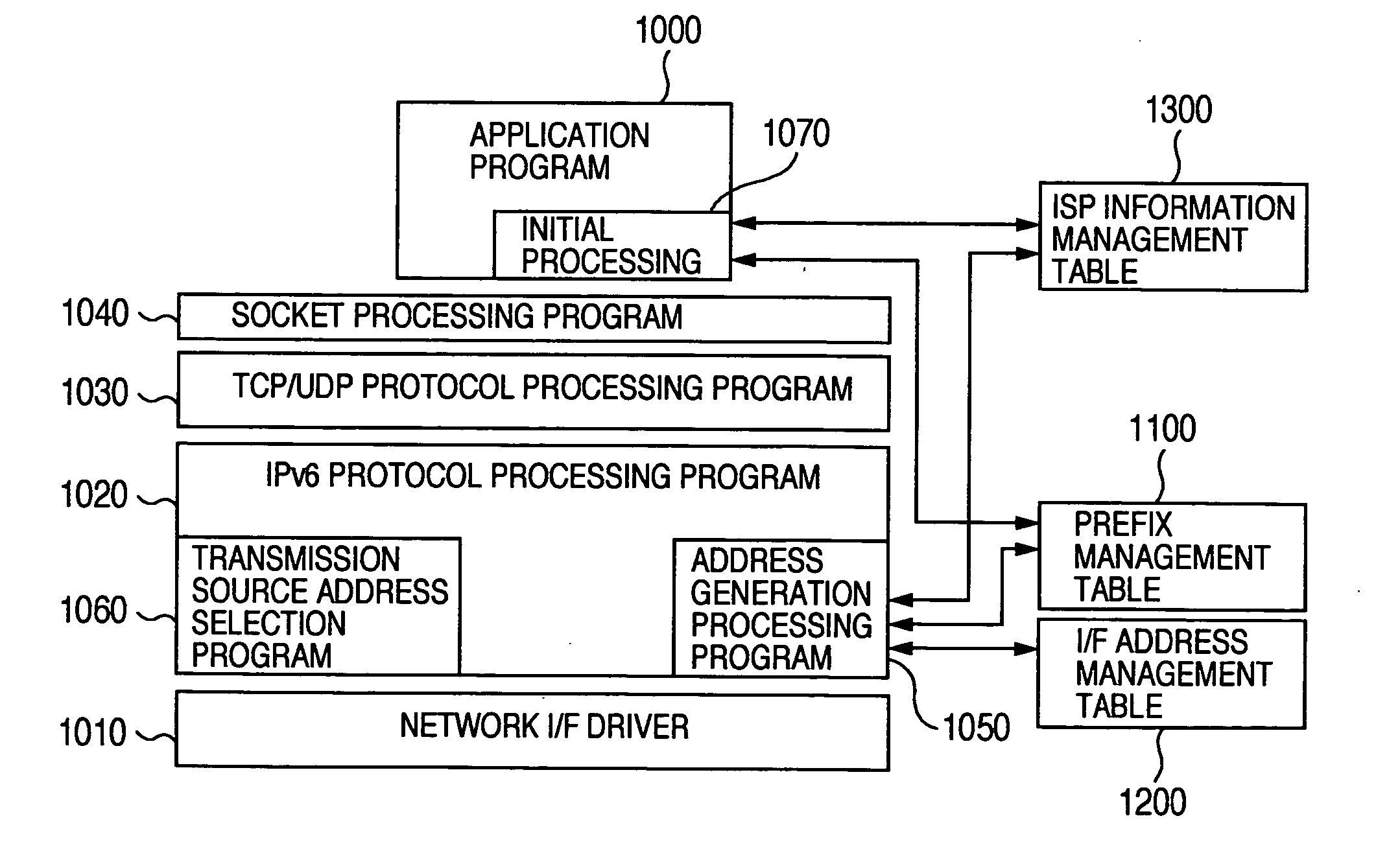
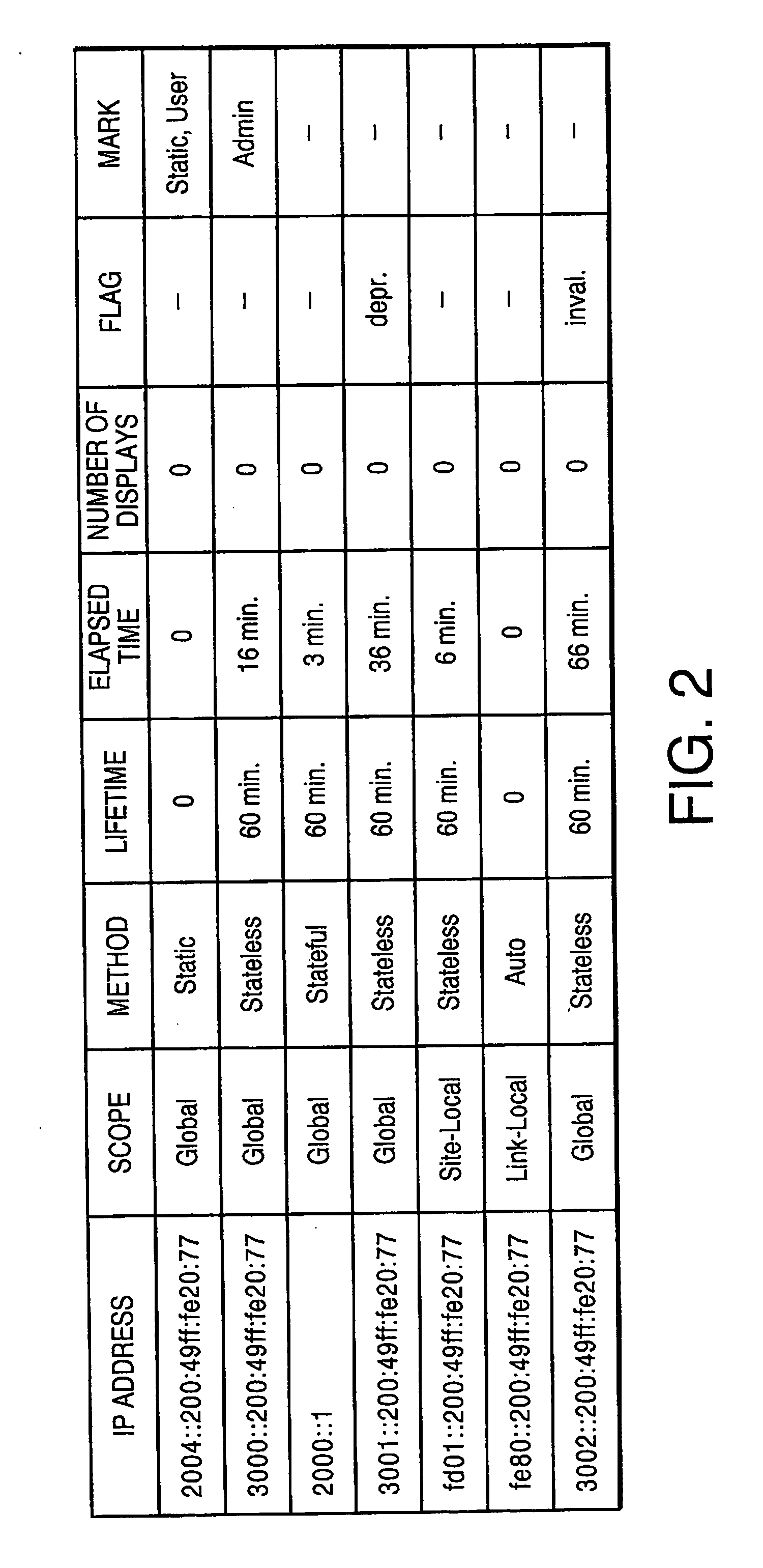
When a management PC (as an address information display device in an address information display system) displays IPv6 addresses that have been assigned to a device in the system, the addresses may be displayed in a pull-down menu, for example. The display order in the pull-down menu may be determined according to a priority order which can be set arbitrarily by the user. Further, addresses judged to be important (according to settings by the user) may be displayed using a bold font, local addresses are displayed in italic, addresses close to the expiration of term of validity may be grayed out) and invalid addresses (addresses already expired) may be grayed out with strikethroughs. As a result, an address information display system may be realized that is capable of displaying addresses assigned to a device in a style easy for the user to understand.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING GATEWAY TO TRANSMIT IPv6 PACKET IN A WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SYSTEM
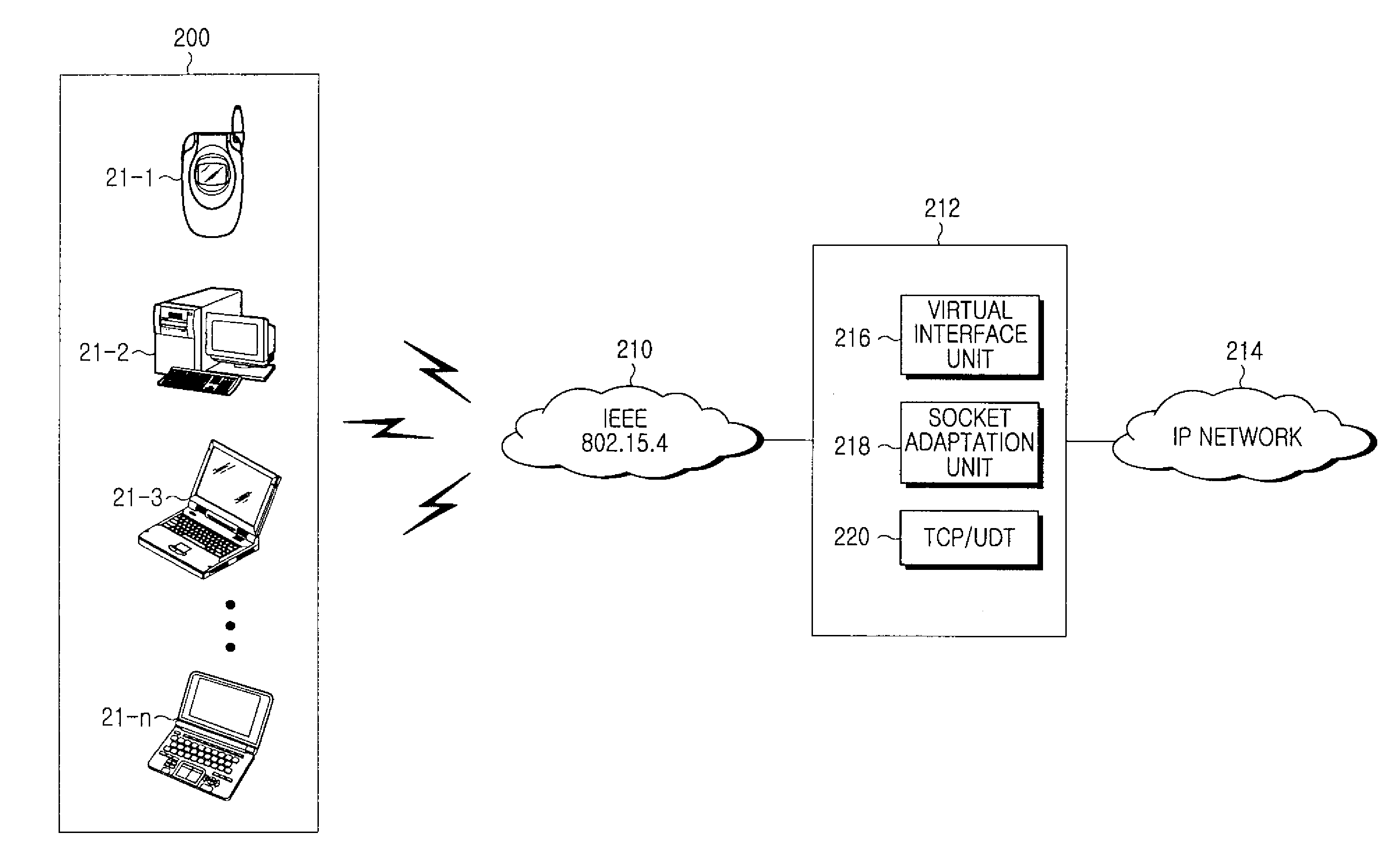
InactiveUS20090073983A1Simplify protocol stackError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetIPv6 packet
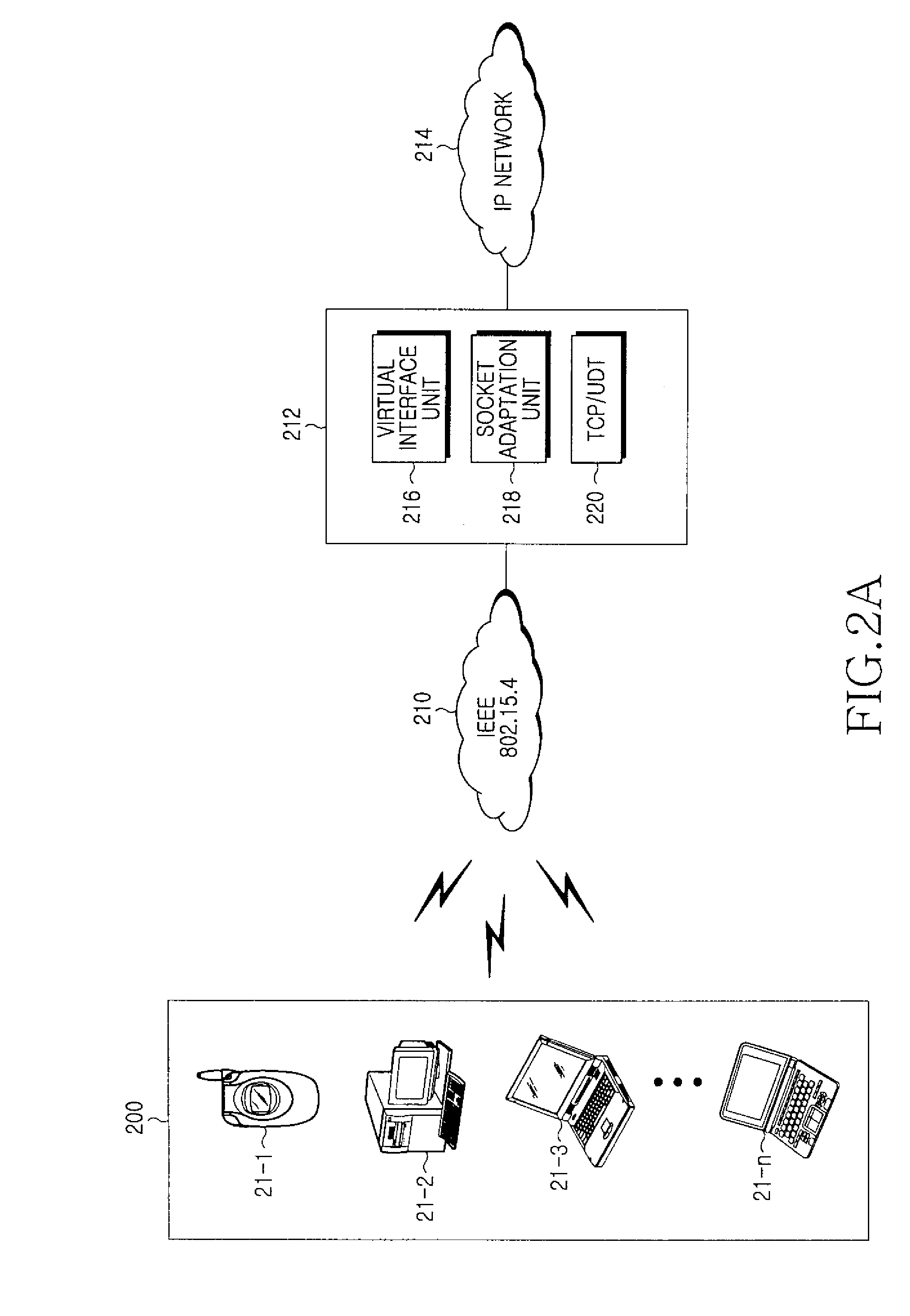
A method and apparatus for providing a gateway for IPv6 packet transmission in a WLAN system are provided, in which a gateway takes over a TCP / IP protocol stack from a legacy 6LoWPAN node for providing a gateway for IPv6 packet transmission in a WLAN system. One or more service request messages for data communications are received from a plurality of 6LoWPAN nodes, and a virtual interface is generated for allocating IPv6 addresses to the 6LoWPAN nodes by adding a predetermined IPv6 address prefix to addresses of the 6LoWPAN nodes set in the service request messages. A socket adaptation layer is interfaced for receiving the IPv6 addresses from the virtual interface and transmitting data packets to the 6LoWPAN nodes, and when data packets are transmitted and received to and from the 6LoWPAN nodes, an on-going file is controlled and managed, and the data packets are routed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for Route Transmission Based on Single IPv6 Address Prefix, and Wireless Device
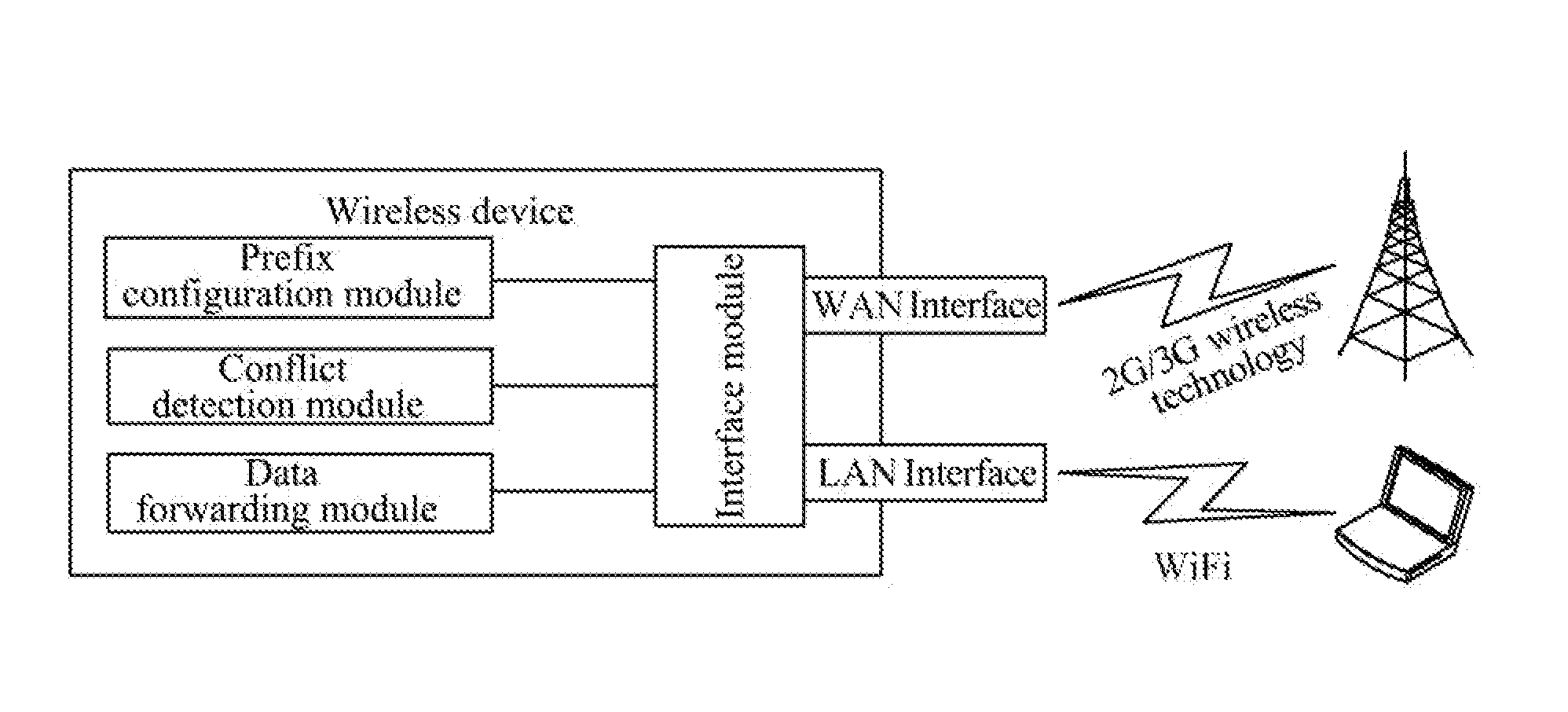
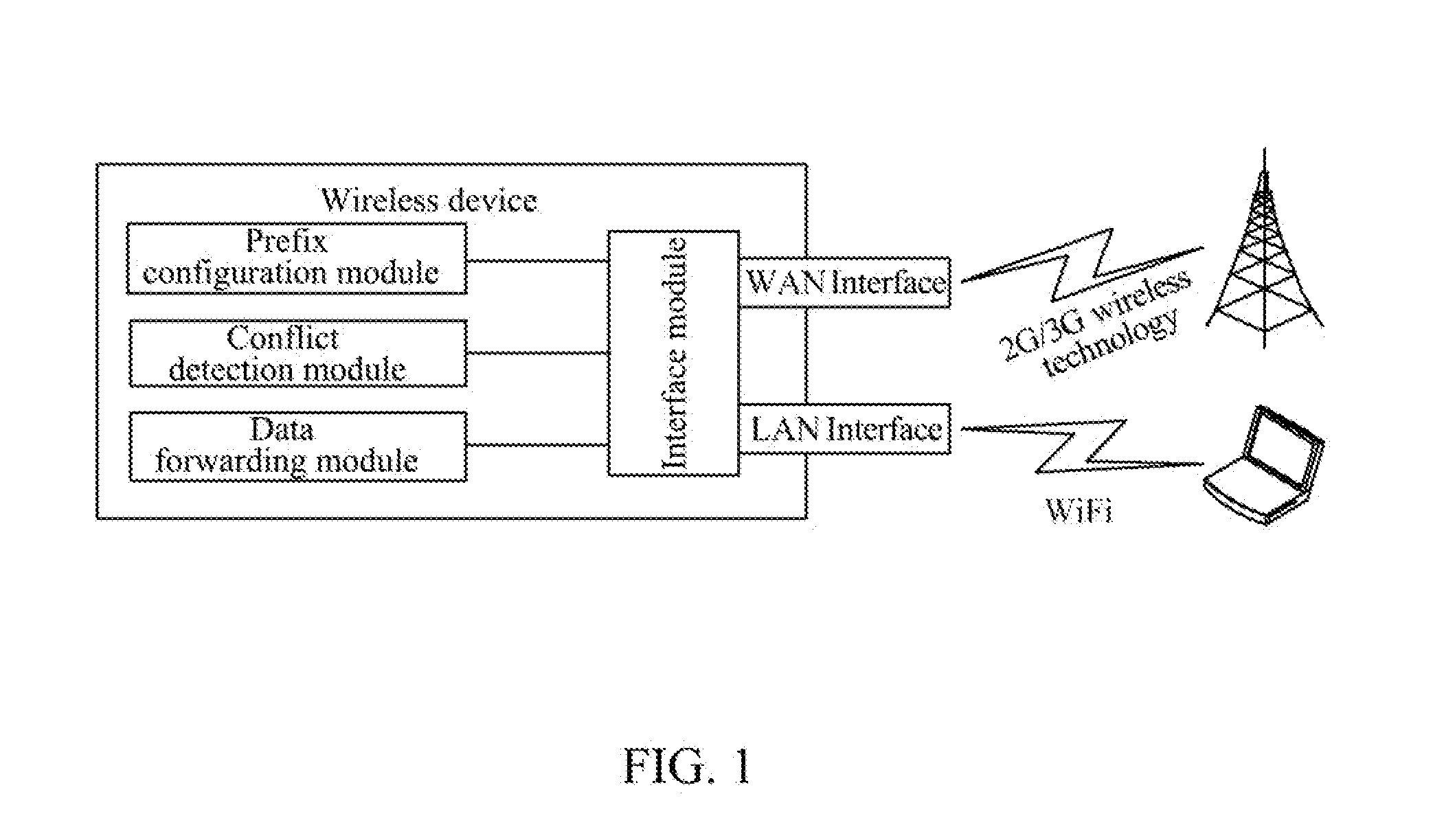
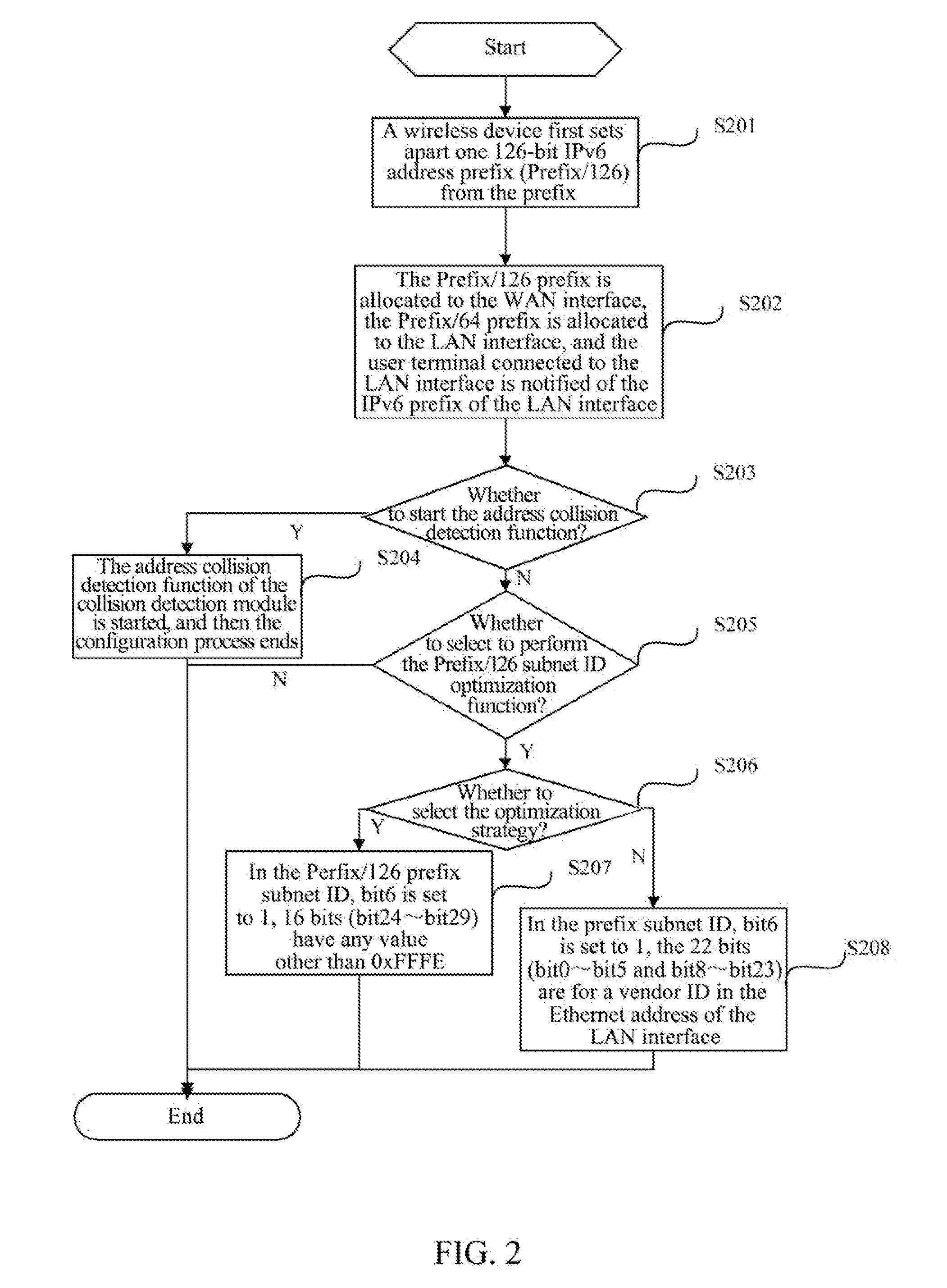
ActiveUS20140215087A1Reduce resource consumptionNetwork topologiesMultiple digital computer combinationsAuto-configurationComputer terminal
The present document provides a method and wireless device for implementing route transmission based on a single IPv6 address prefix. The method includes: when a wireless device succeeds in IPv6-based dialing and obtains one 64-bit-long IPv6 address prefix from a network side, the wireless device first setting apart a 126-bit IPv6 address prefix from the prefix, and then allocating the 126-bit IPv6 address prefix to a WAN interface, allocating the 64-bit-long IPv6 address prefix to a LAN interface, and notifying a user terminal connected to the LAN interface of the IPv6 prefix of the LAN interface, so that the user terminal connected to the LAN interface generates its own IPv6 address through a stateless address auto-configuration mechanism for communication. With the technical solutions of the present document, in an IPv4 / IPv6 dual stack mode, IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks operate normally, and the radio resource consumption is reduced.
Owner:DRNC HLDG INC
IPv6/IPv4 translator
InactiveUS20050185672A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPacket communicationData transmission
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Packet communication method and apparatus and a recording medium storing a packet communication program
A packet communication method and a packet communication system capable of making an IPv4-compatible application operating on an information processing apparatus communicate with another information processing apparatus connected to an IPv6 network without using an address translation router. In the information processing apparatus connected to the IPv6 network incorporates, an IPv4-to-IPv6 protocol conversion control function is incorporated in a LAN driver. A protocol conversion control module receives an IPv4 packet from a protocol control module. When a send destination IPv4 address contained in a header of the packet is registered in an address translation table incorporated in the protocol conversion control module, an IPv6 address is generated to be sent onto a LAN. Unless the send destination IPv4 address contained in the packet header is registered in the address translation table incorporated in the protocol conversion control module, the IPv4 packet as received is intactly sent onto the LAN.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
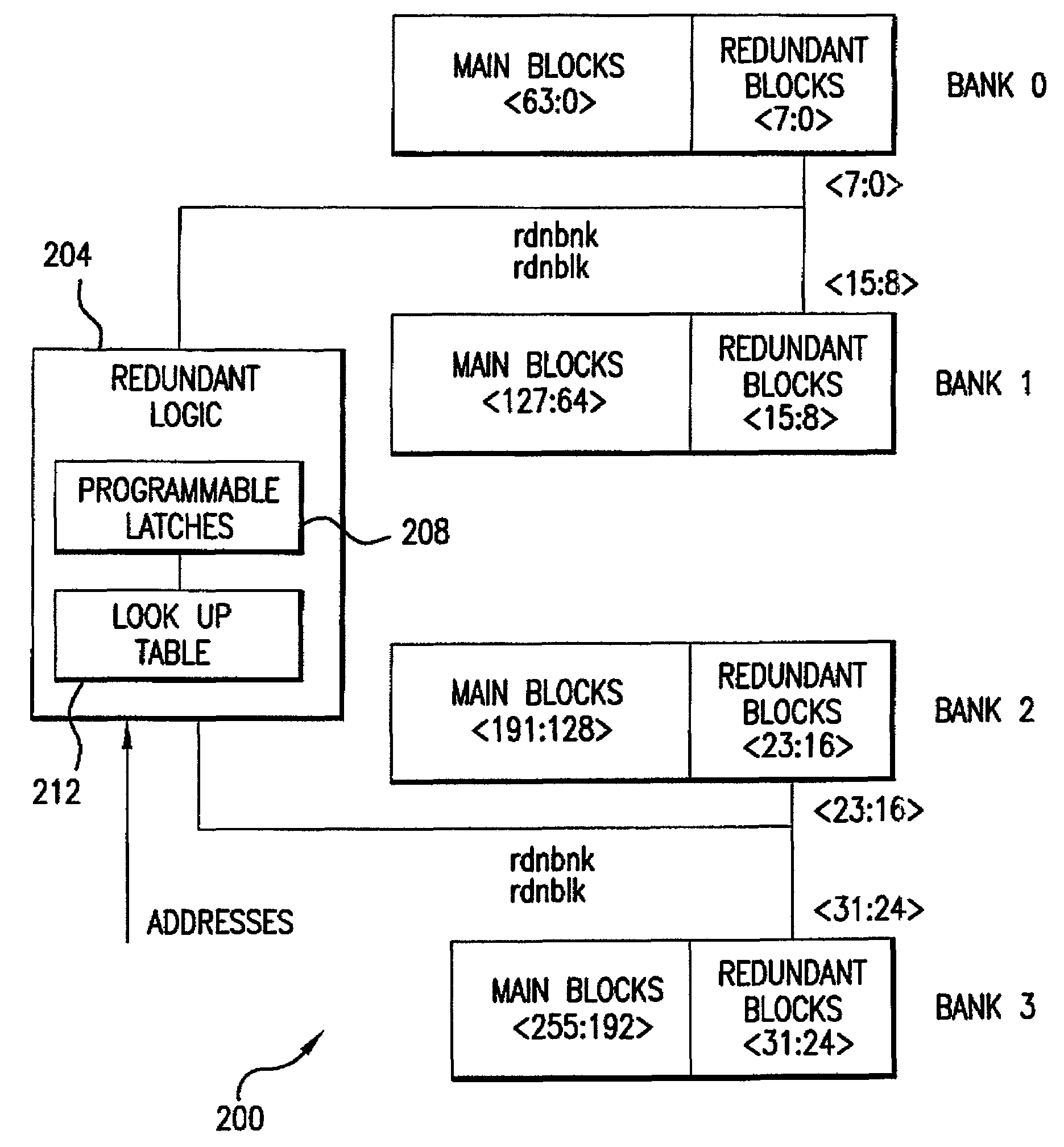
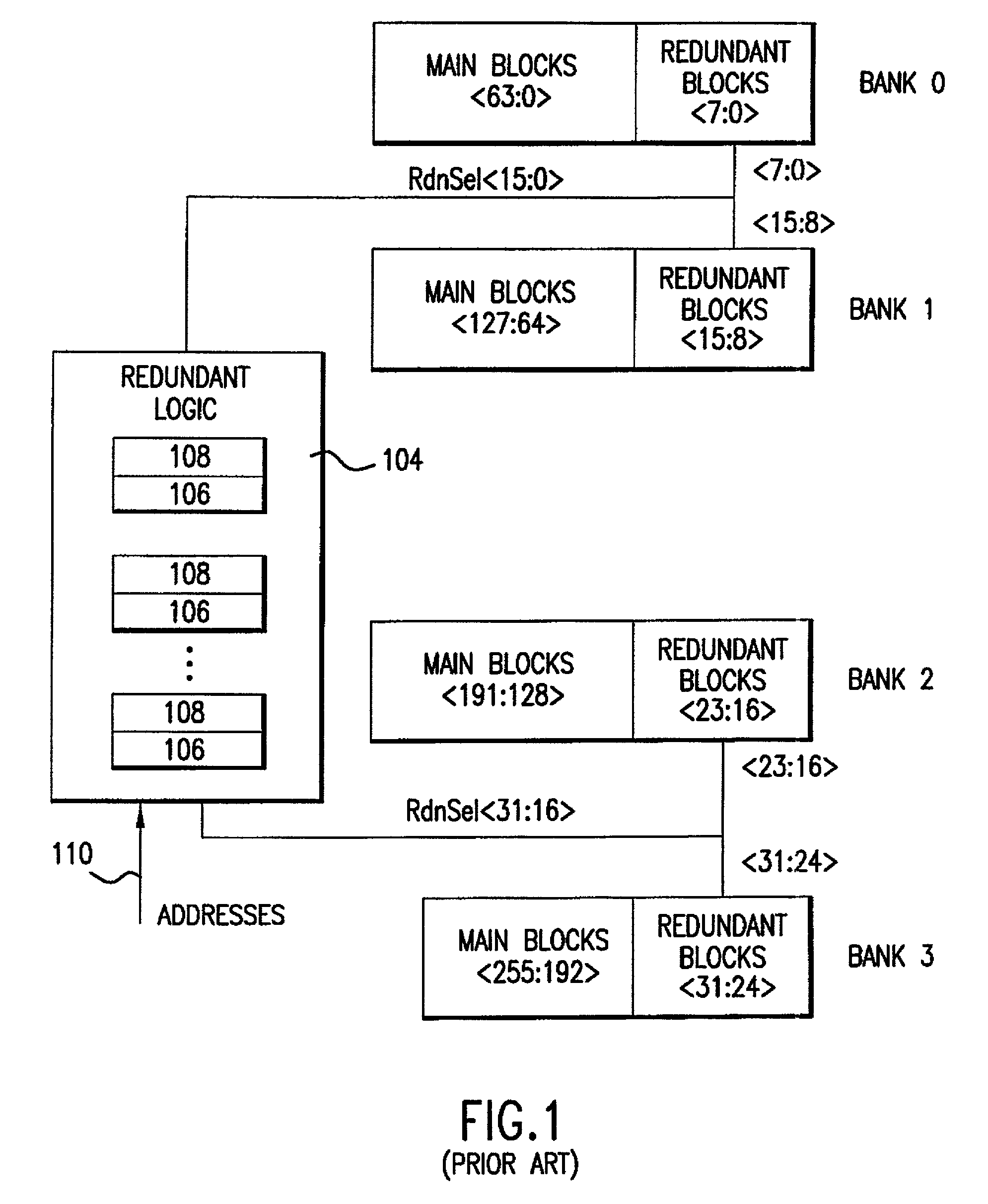
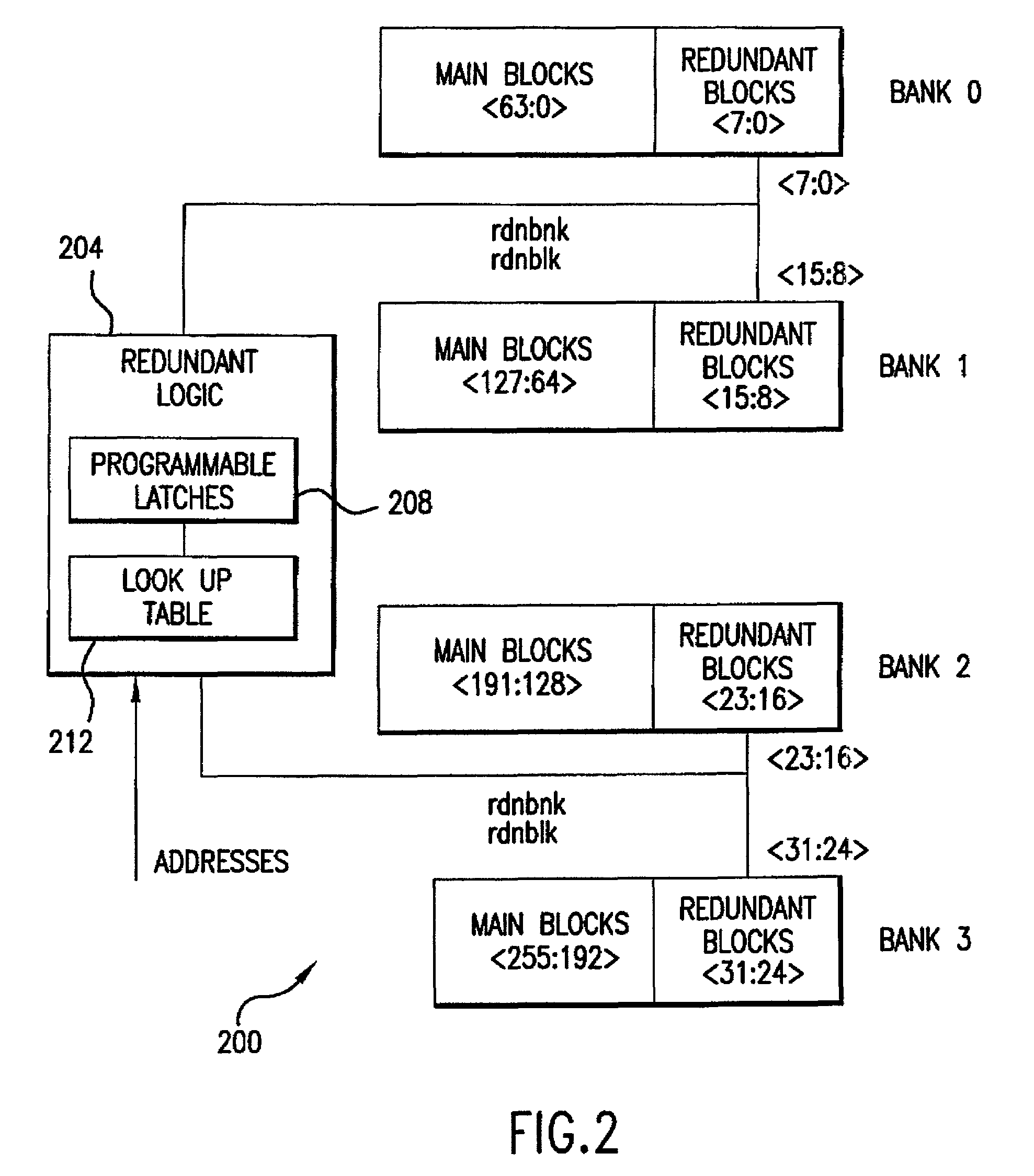
Repairable block redundancy scheme
A scheme for block substitution within a flash memory device is disclosed which uses a programmable look-up table to store new addresses for block selection when certain input block addresses are received. The new addresses are loaded into a programmable fuse latch each time an address transition is detected in the input address. The new addresses may contain block addresses or block and bank addresses.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Peer-to-peer communication between different types of internet hosts
ActiveUS20090248800A1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsSession Initiation ProtocolPeer-to-peer
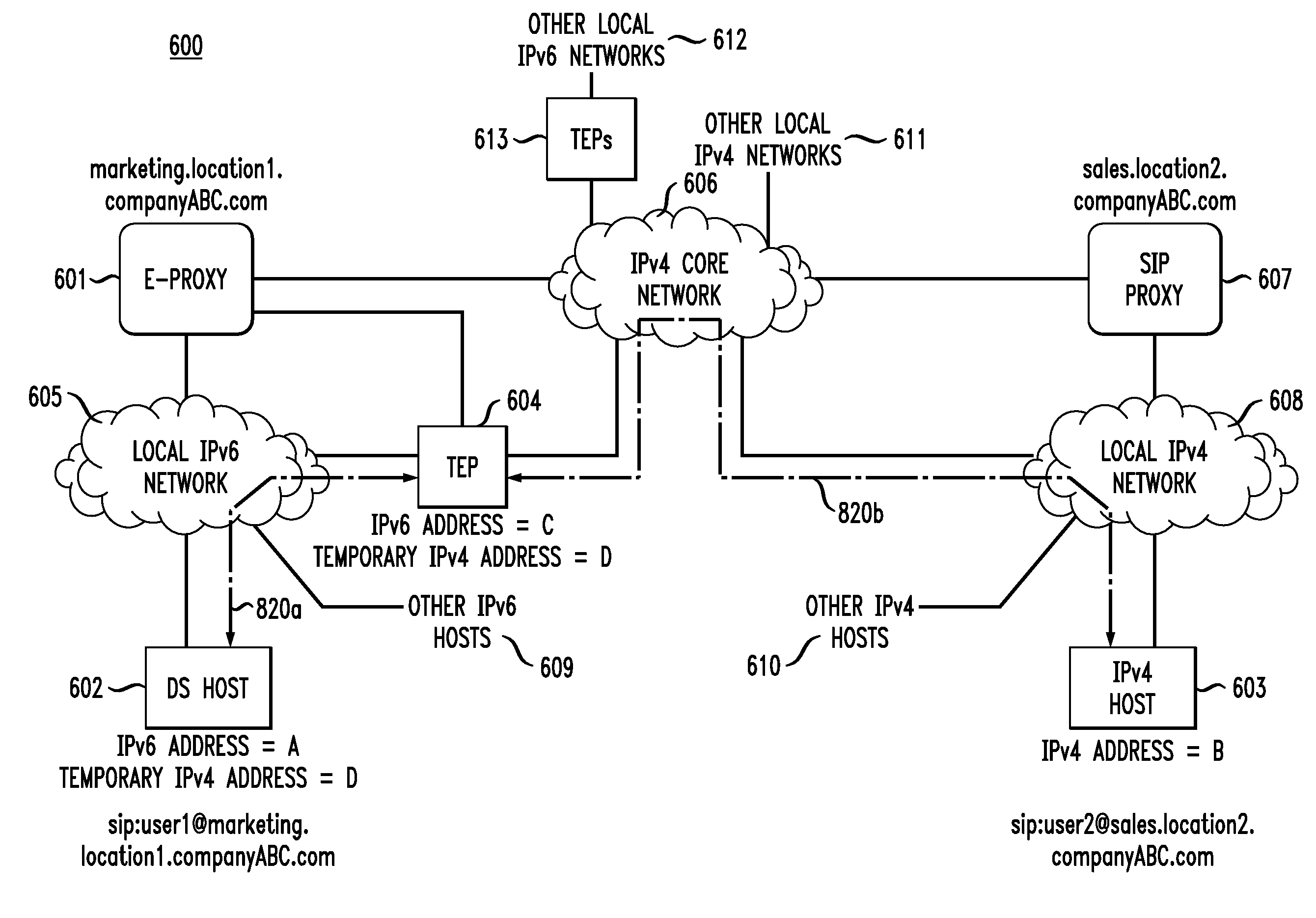
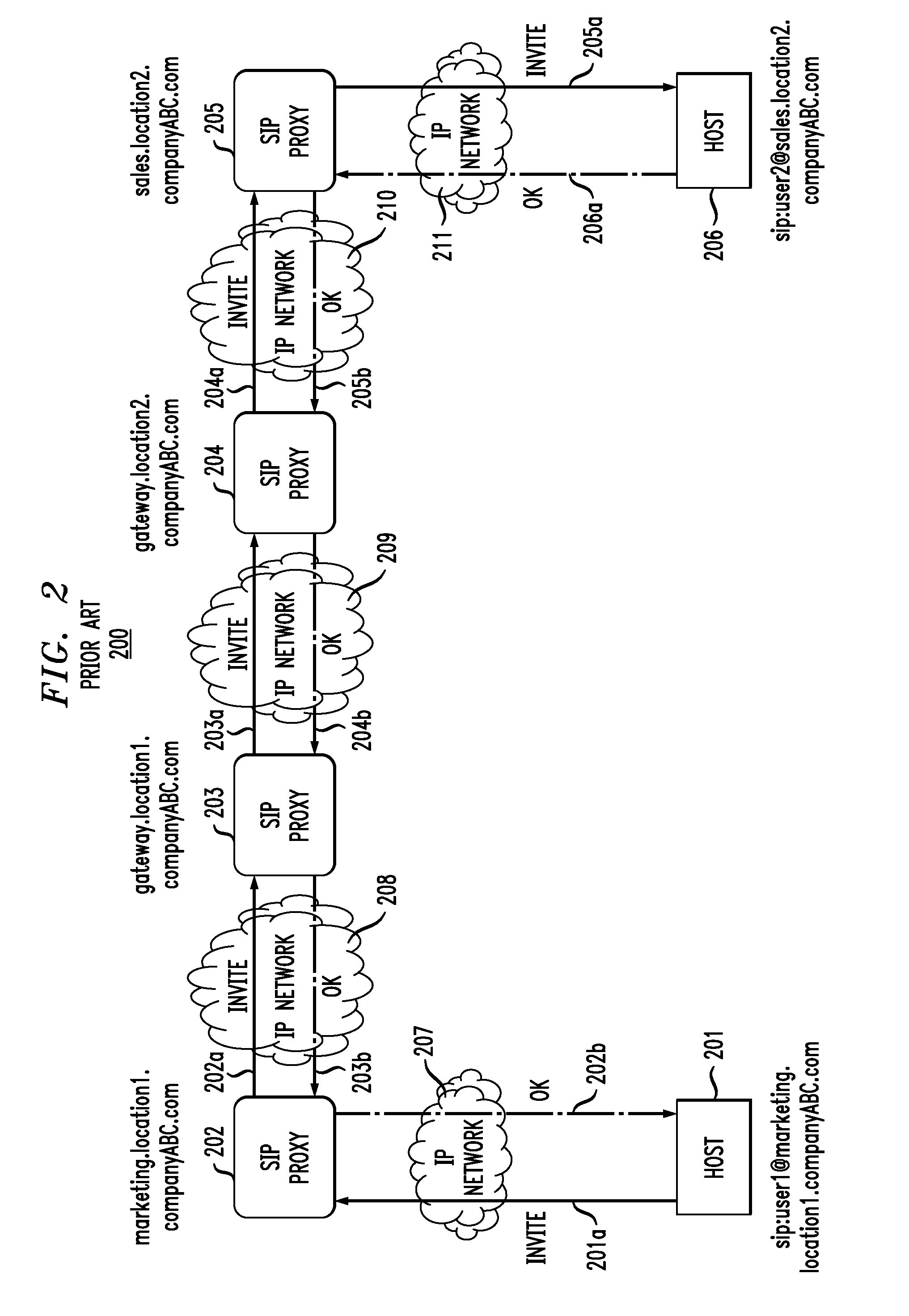
In one embodiment, a method for processing, at an enhanced Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) proxy (e-proxy), (1) a SIP INVITE message to a first user at an IPv4 / IPv6 dual-stack (DS) host, connected to an IPv6 network, from a second user at an IPv4 host, connected to an IPv4 network. The e-proxy receives the SIP INVITE message from the IPv4 network. When the e-proxy determines that Dual Stack Transition Mechanism (DSTM) service is required, the e-proxy obtains a temporary IPv4 address for the DS host, finds a suitable tunnel end-point (TEP), and sends a corresponding, but modified, INVITE message to the DS host. The modified INVITE message body includes invocation of DSTM service, the temporary IPv4 address, the TEP's IPv6 address, and the IPv4 host's IPv4 address. The e-proxy sends a BIND message to the TEP to bind the DS host's IPv6 address to the temporary IPv4 address for proper tunneling.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Method and system of collocating IPV6 (internet protocol version 6) addresses
InactiveCN101753635AEasy to achieve unified updateEasy to manageData switching networksInternet protocol suiteComputer science
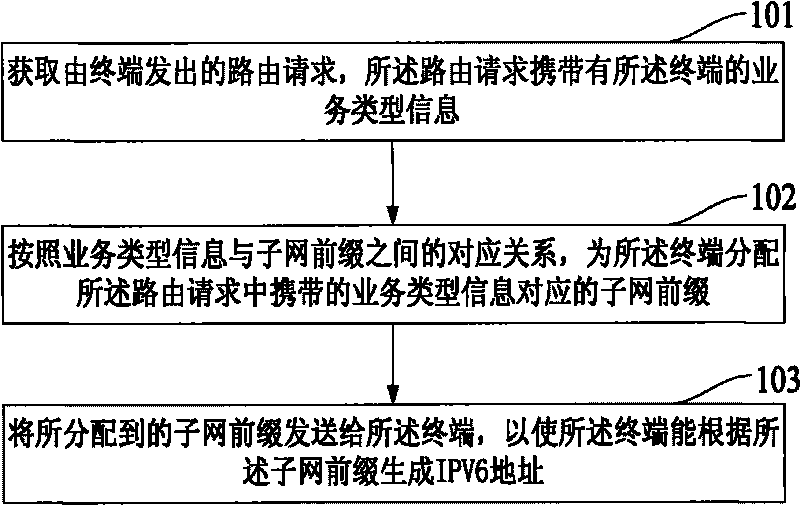
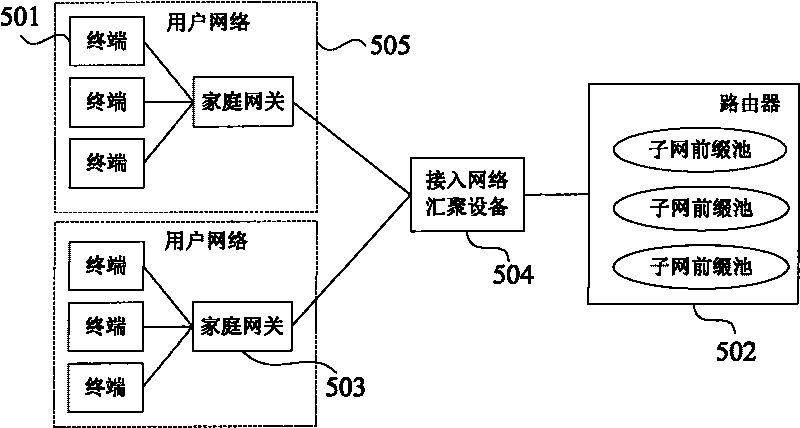
The embodiment of the invention discloses an IPv6 address collocation method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring a route request send from a terminal, wherein the route request carries the service type information of the terminal; allocating a subnet prefix corresponding to the service type information carried by the route request for the terminal according to the correspondence relation between the service type information and the subnet prefix; sending the allocated subnet prefix to the terminal so as to ensure that the terminal can generate an IPV6 address according to the subnet prefix. The method for automatically collocating the IPV6 addresses in the embodiment of the invention is convenient for service management. The invention also further discloses an IPV6 address collocating system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
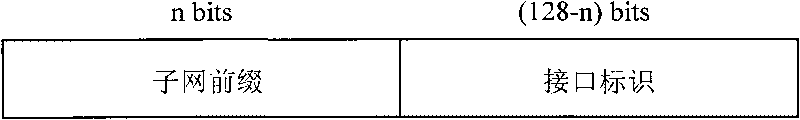
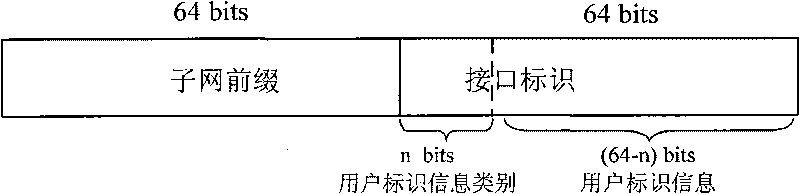
IPv6 address structure and method and device for allocating and tracing same
The invention relates to an IPv6 address structure and a method and a device for allocating and tracing the same. The structure comprises a network prefix and an interface identifier, wherein the interface identifier is obtained by calculating bits for recording user identification information with the asymmetrical encryption algorithm; and the network prefix or the interface identifier also comprises pre-defined bits used for identifying the used encryption algorithm, the class of the user identification information and other information. During tracing, enciphered bits in the interface identifier are deciphered by using a private key to obtain the user information. When allocating addresses, the invention adds the user identification information having the identification function, and then finds out the hose corresponding to the source address based on the user identification information during tracing, thereby solving the problem of IPv6 network tracing.
Owner:THE RES INST OF TELECOMM TRANSMISSION MIIT
System, an arrangement and a method relating to IP-addressing
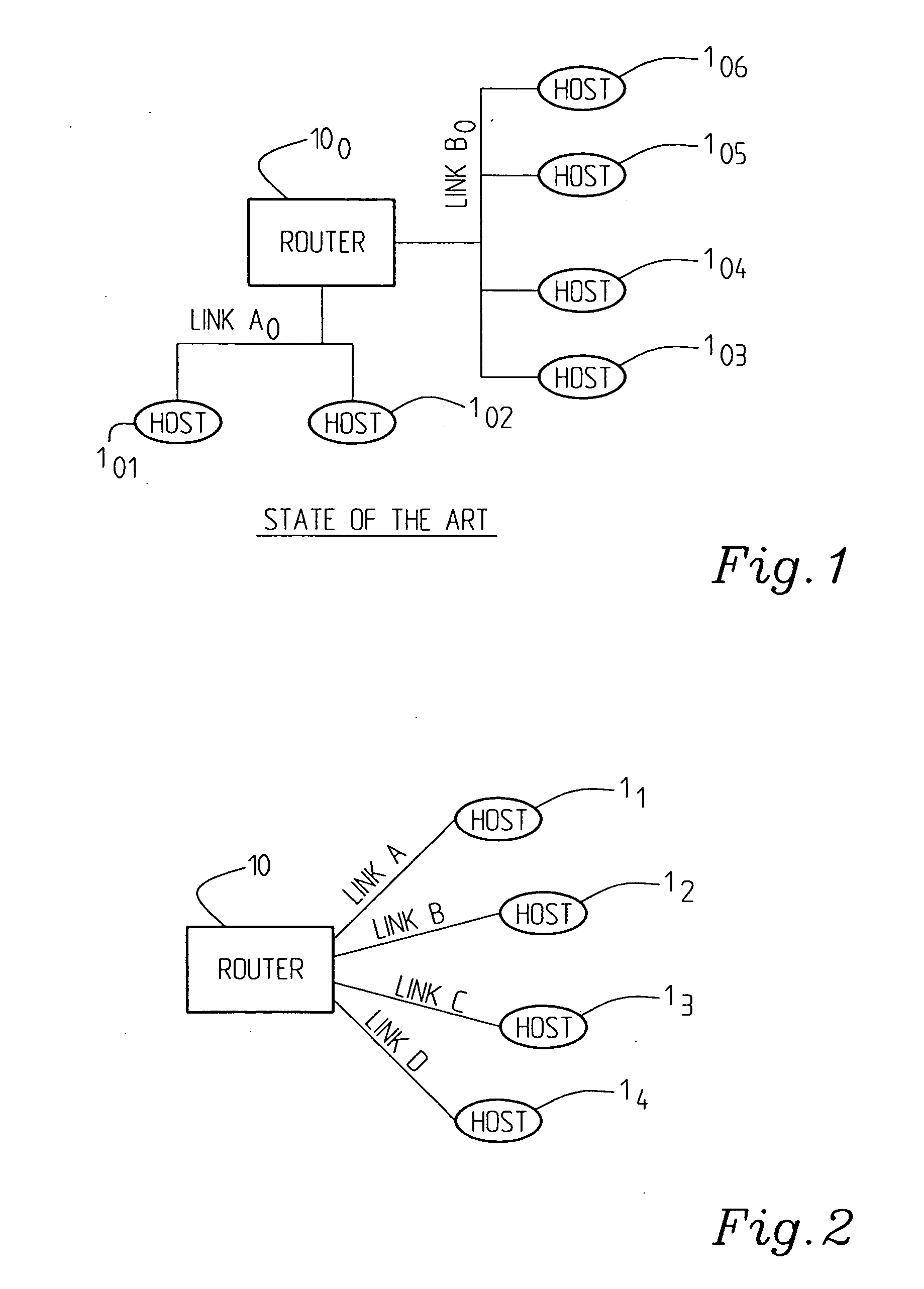
ActiveUS20050117590A1Create quicklyGenerate fastData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsAccess networkCommunications system
The present invention relates to a communication system comprising a number of end user stations (hosts) connected over access networks and routing arrangements. The system supports a IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) addressing scheme, wherein the end user stations are connected to the routing arrangements over links, and sending of router advertisements from router arrangements to end user stations (hosts) being implemented to support provisioning of IPv6 addresses for the end user station. Router advertisements (RAs) from a routing arrangement to an end user station are sent with a controllable and variable frequency during an initial phase. During said initial phase, the frequency is higher at the beginning and lower at the end.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com