Patents
Literature
212 results about "IPv6 packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
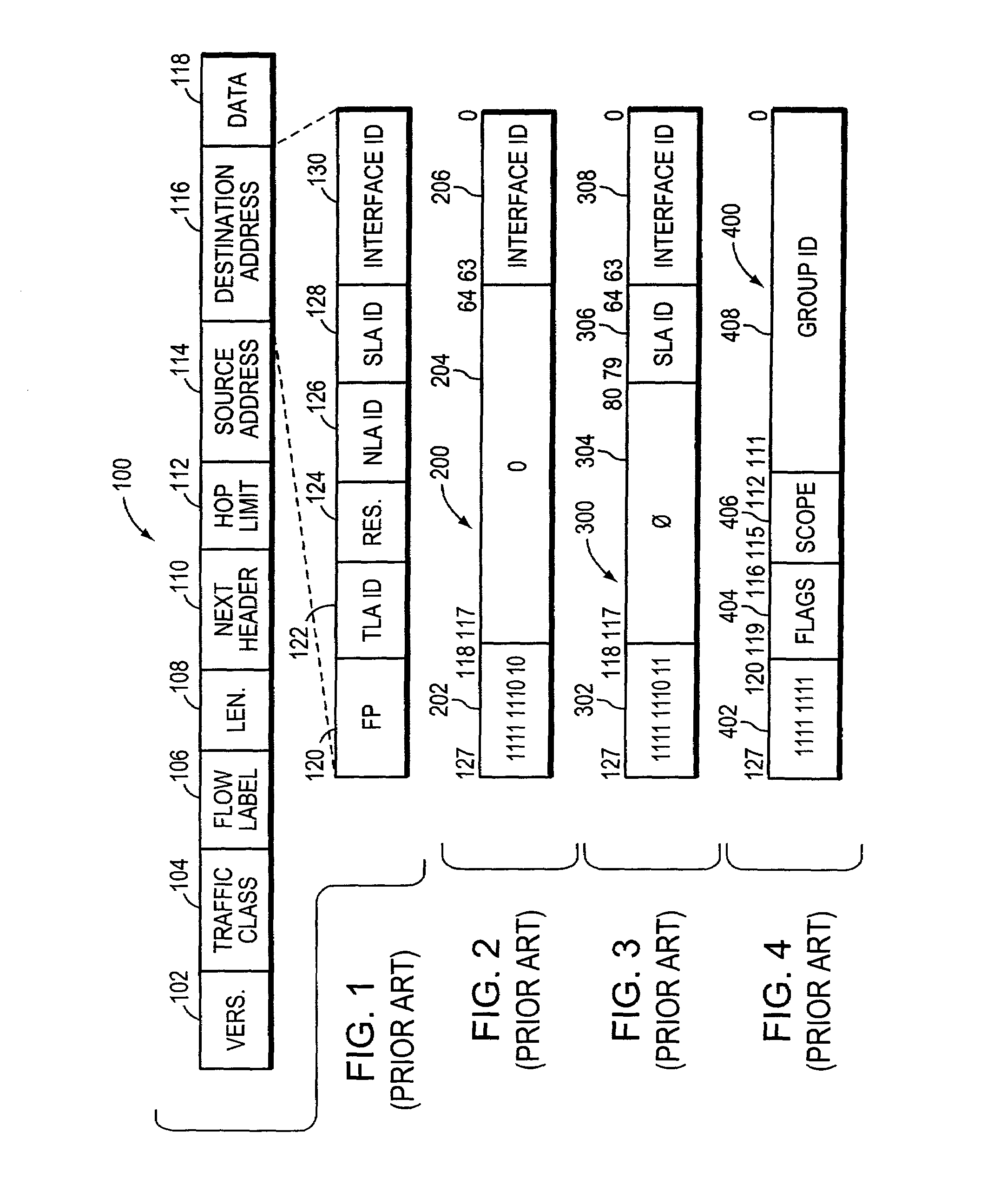
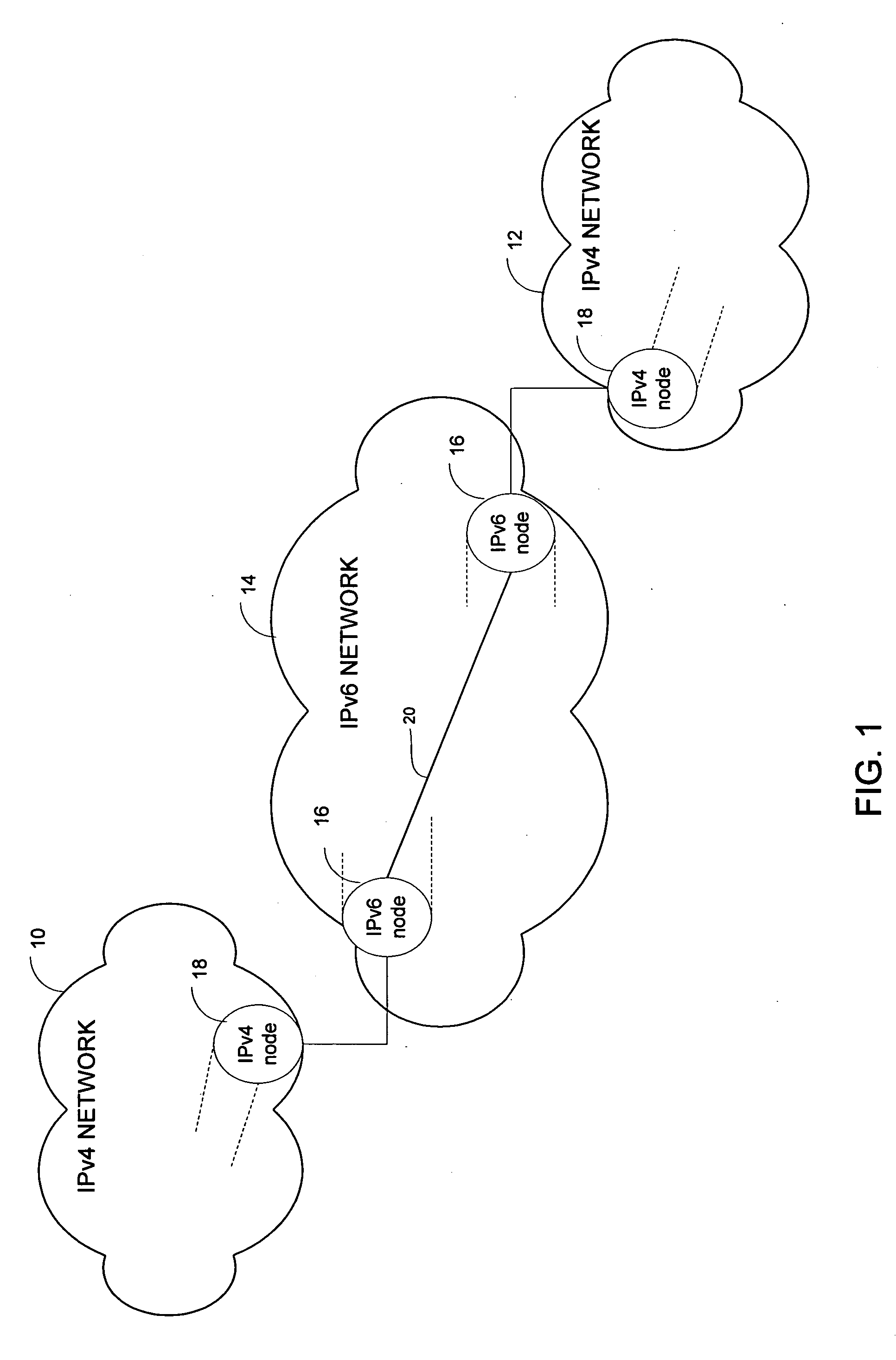
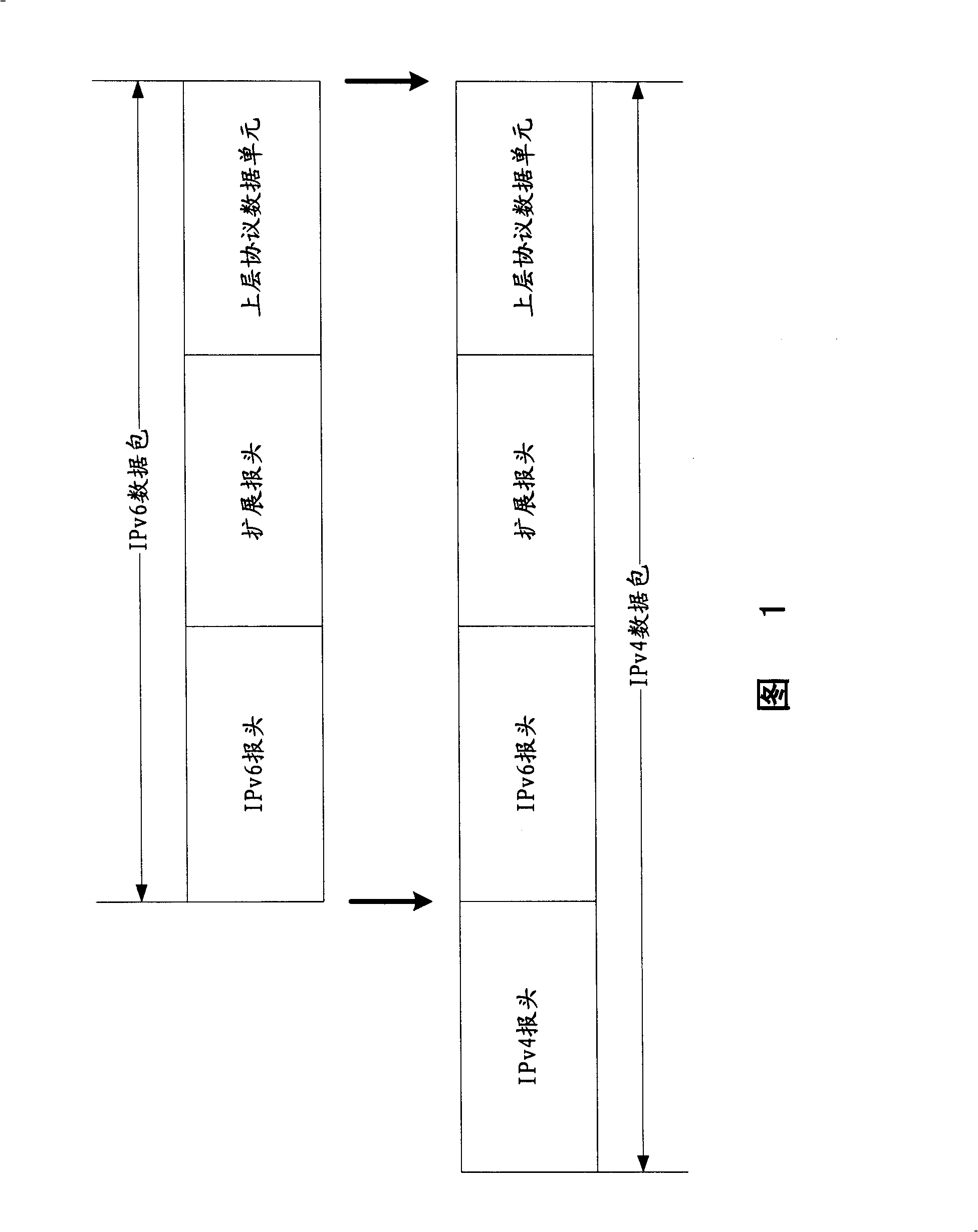
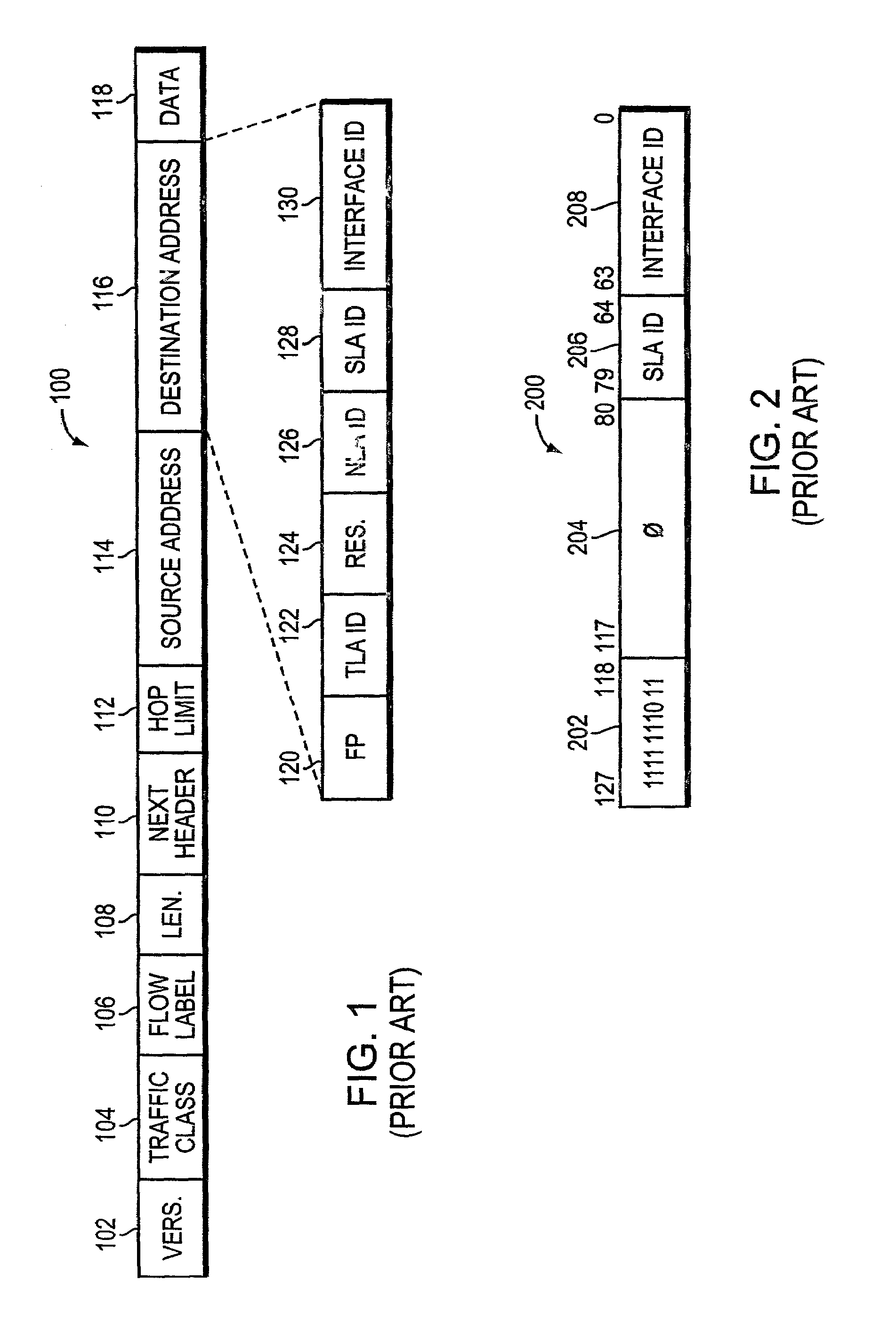
An IPv6 packet is the smallest message entity exchanged via the Internet Protocol across an Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) network. Packets consist of control information for addressing and routing and a payload of user data. The control information in IPv6 packets is subdivided into a mandatory fixed header and optional extension headers. The payload of an IPv6 packet is typically a datagram or segment of the higher-level Transport Layer protocol, but may be data for an Internet Layer (e.g., ICMPv6) or Link Layer (e.g., OSPF) instead.
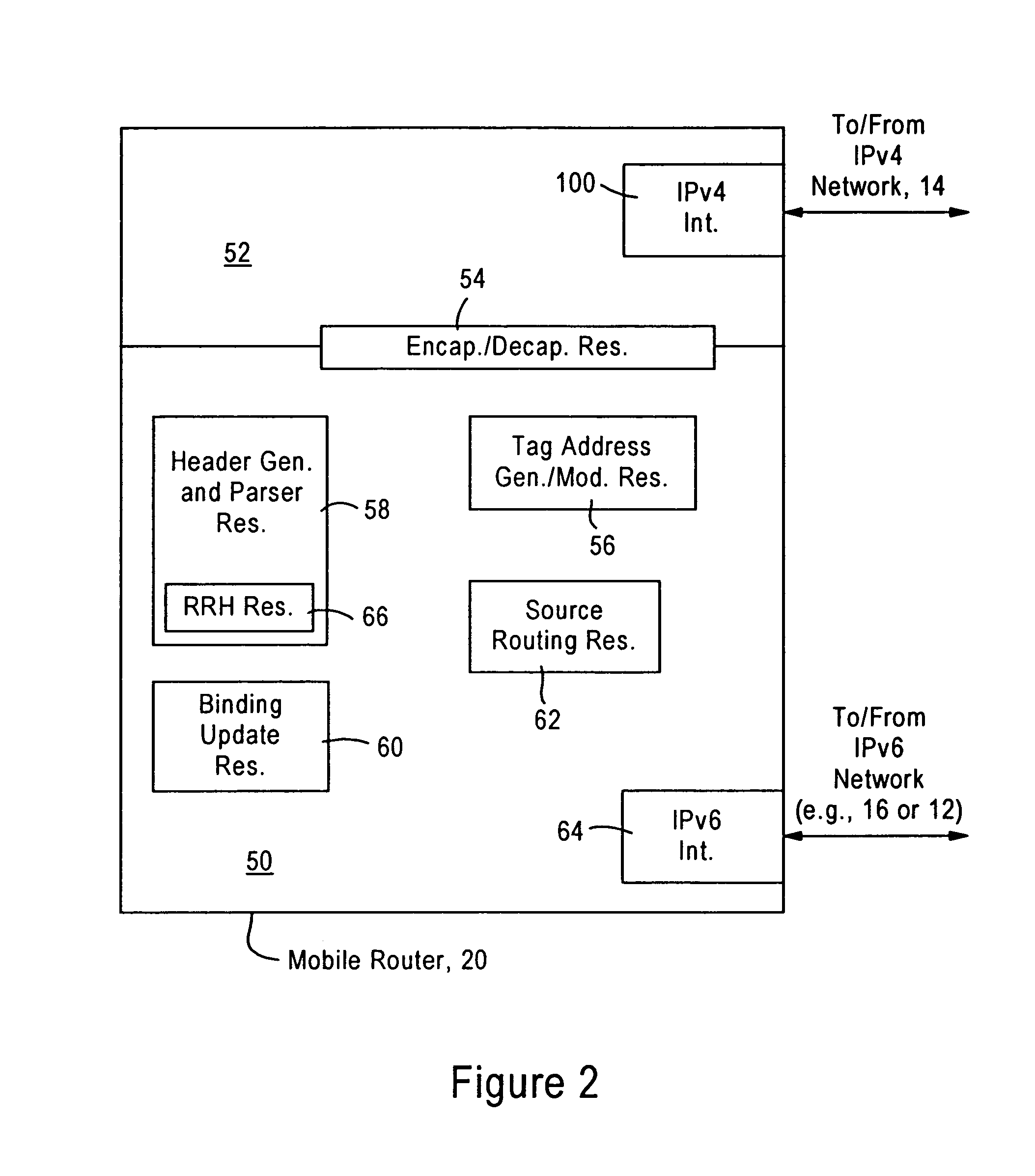
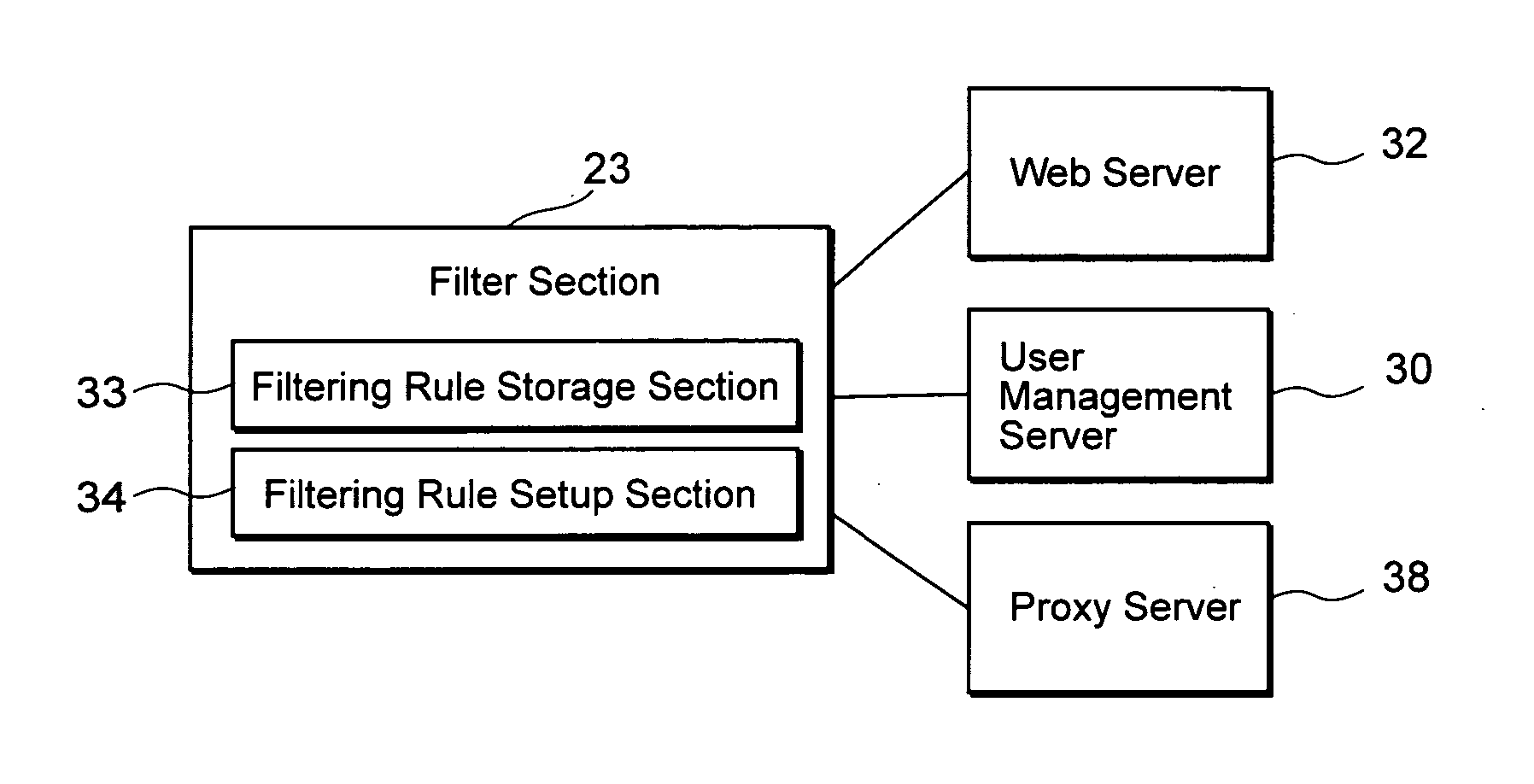
System and method for deriving IPv6 scope identifiers and for mapping the identifiers into IPv6 addresses
InactiveUS7095738B1Efficient and high-speedSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsInformation repositoryVirtual LAN
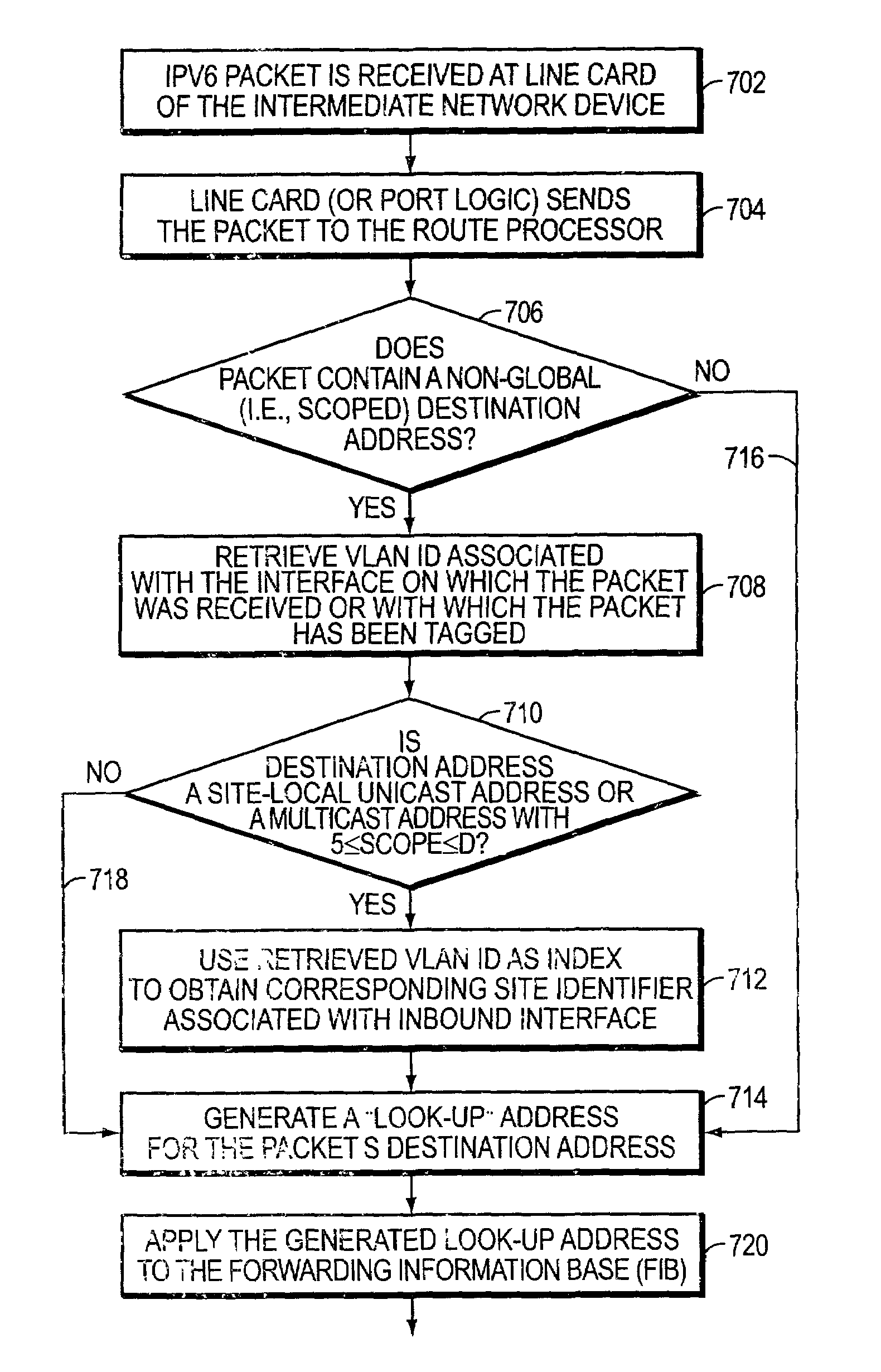
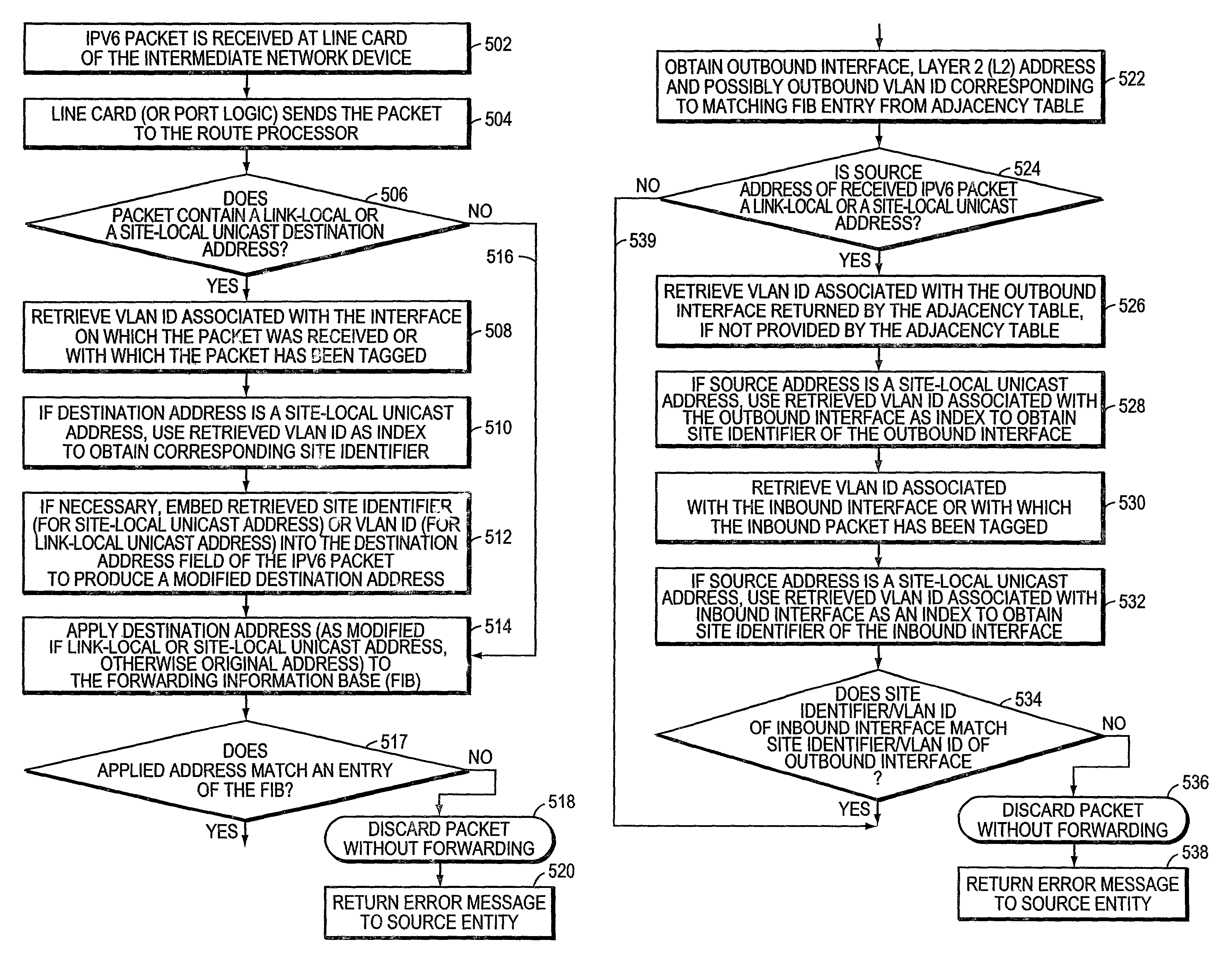
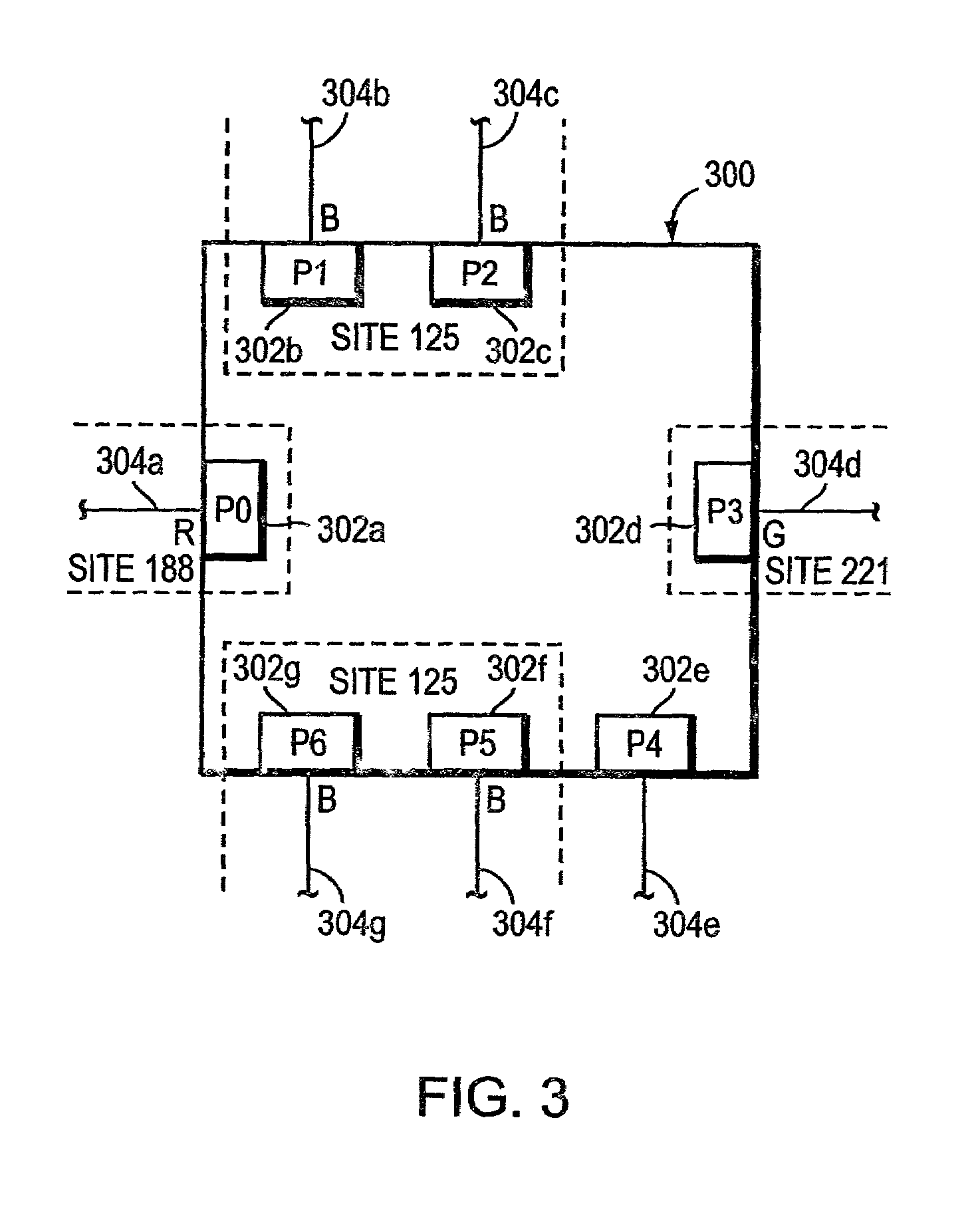
A system and method for use at an intermediate network device employs Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations as Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) link identifiers, and maps VLAN designations to IPv6 site identifiers (IDs). The system also generates a compacted look-up address based on the destination address specified within a received network message, such as an IPv6 packet. For a network message having a link-local unicast destination address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a site-local unicast address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a multicast destination address, if the address's scope value is between hexadecimal “2” and “4” inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. If the scope value is between hexadecimal “5” and “D”, inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. The look-up addresses are applied to a forwarding information base (FIB) to derive the outbound interface(s) from which the message is to be forwarded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
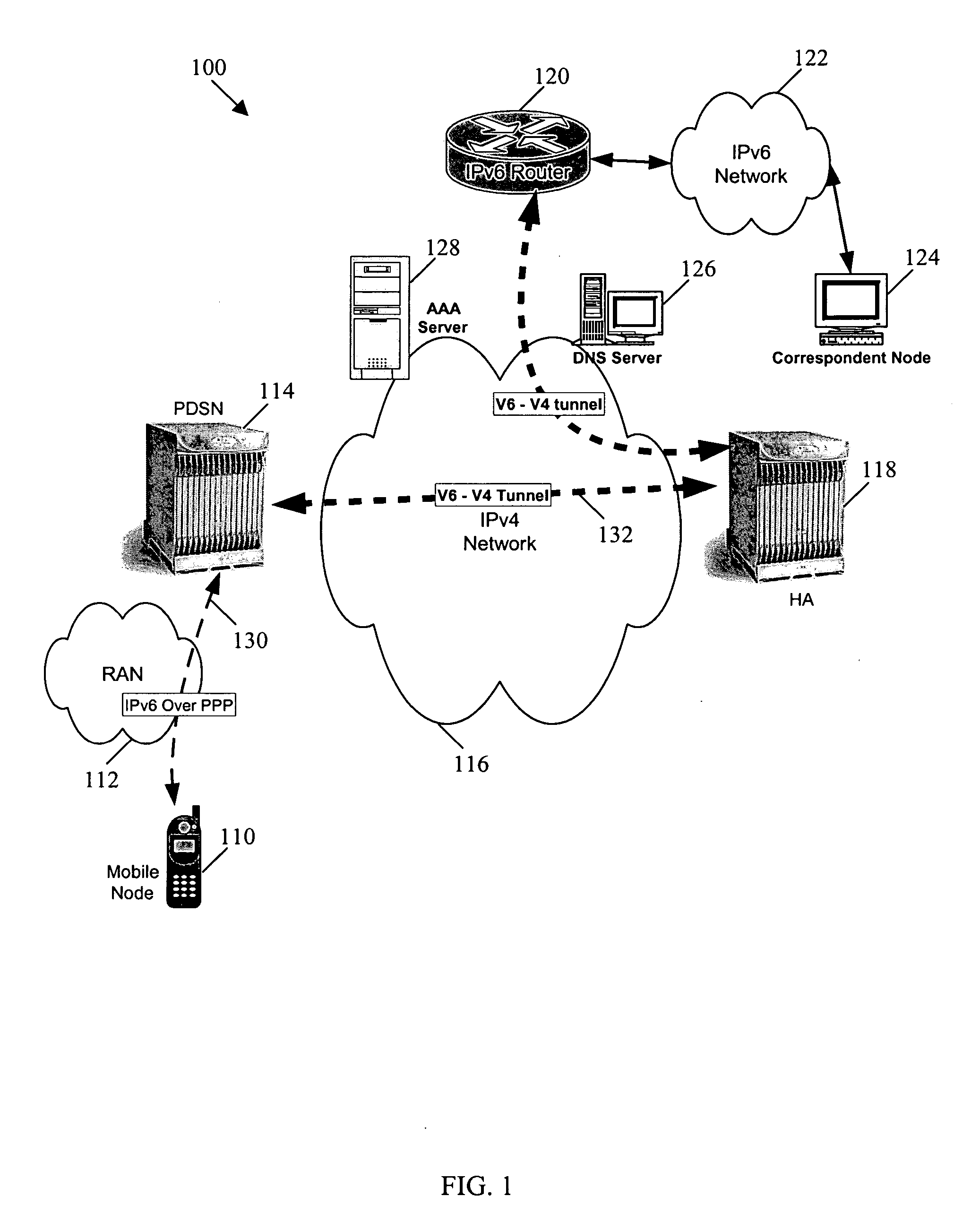
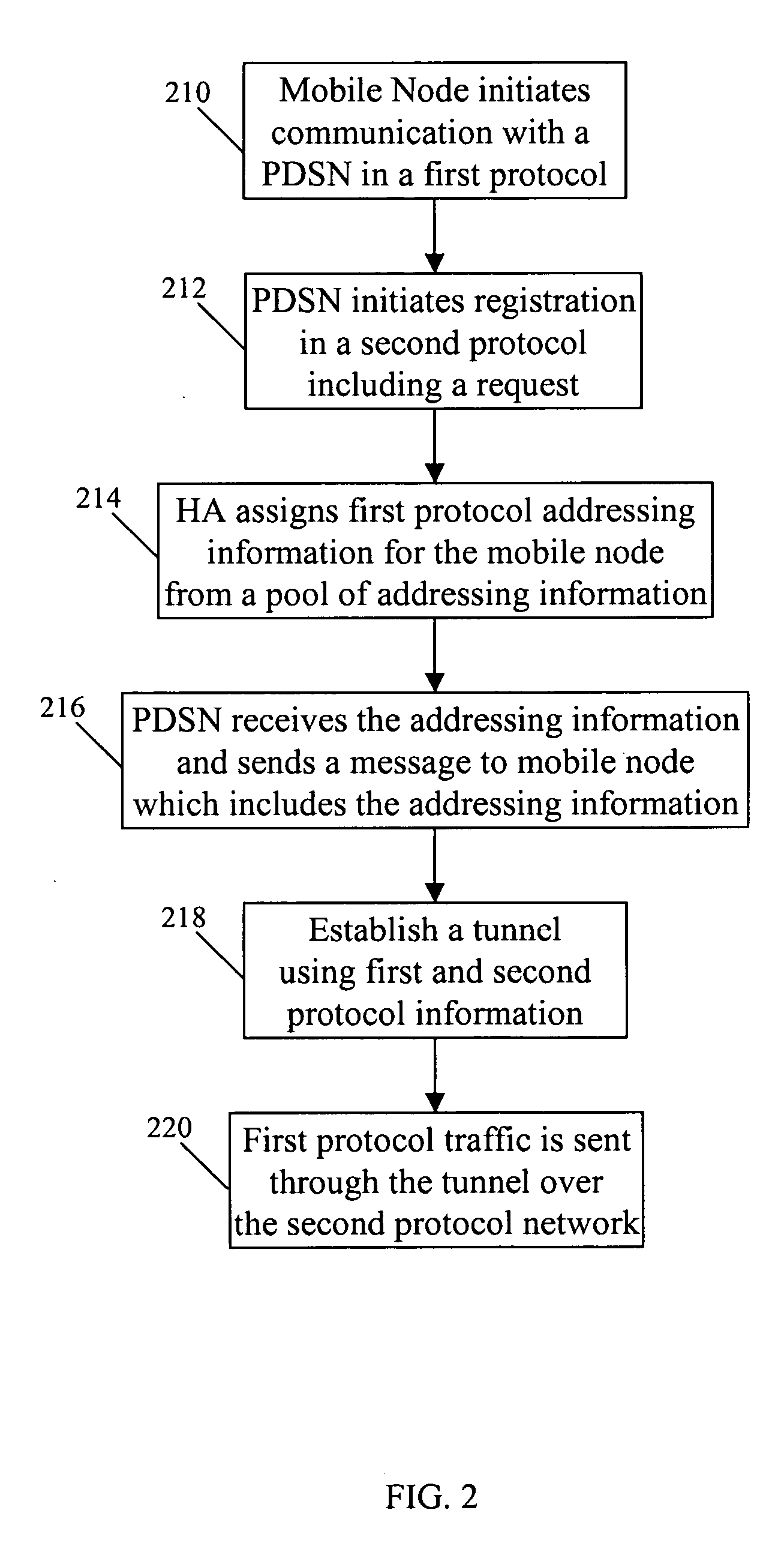
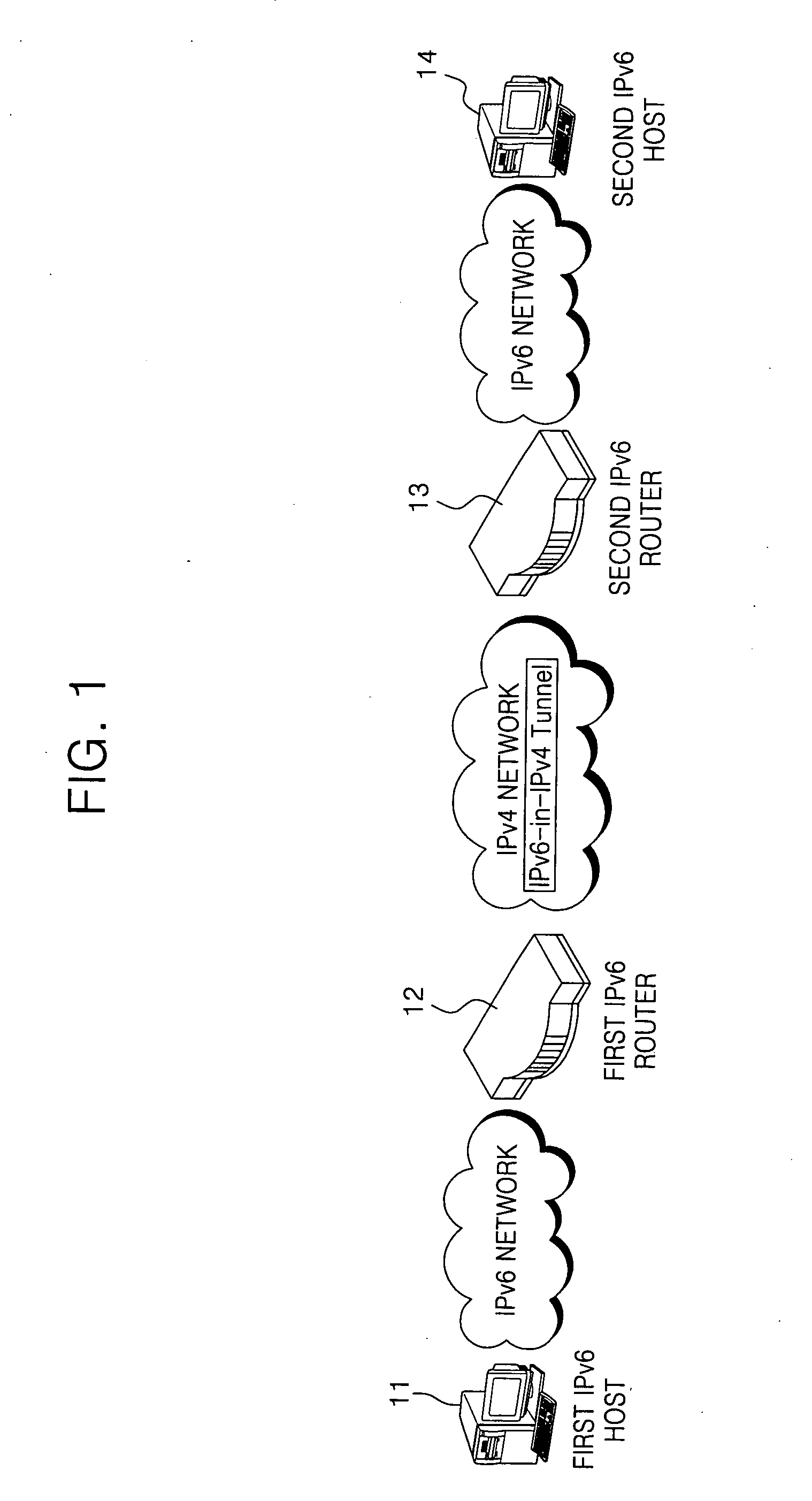
Internet protocol tunneling on a mobile network
InactiveUS20070189219A1Wireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsIp addressIPv6 packet
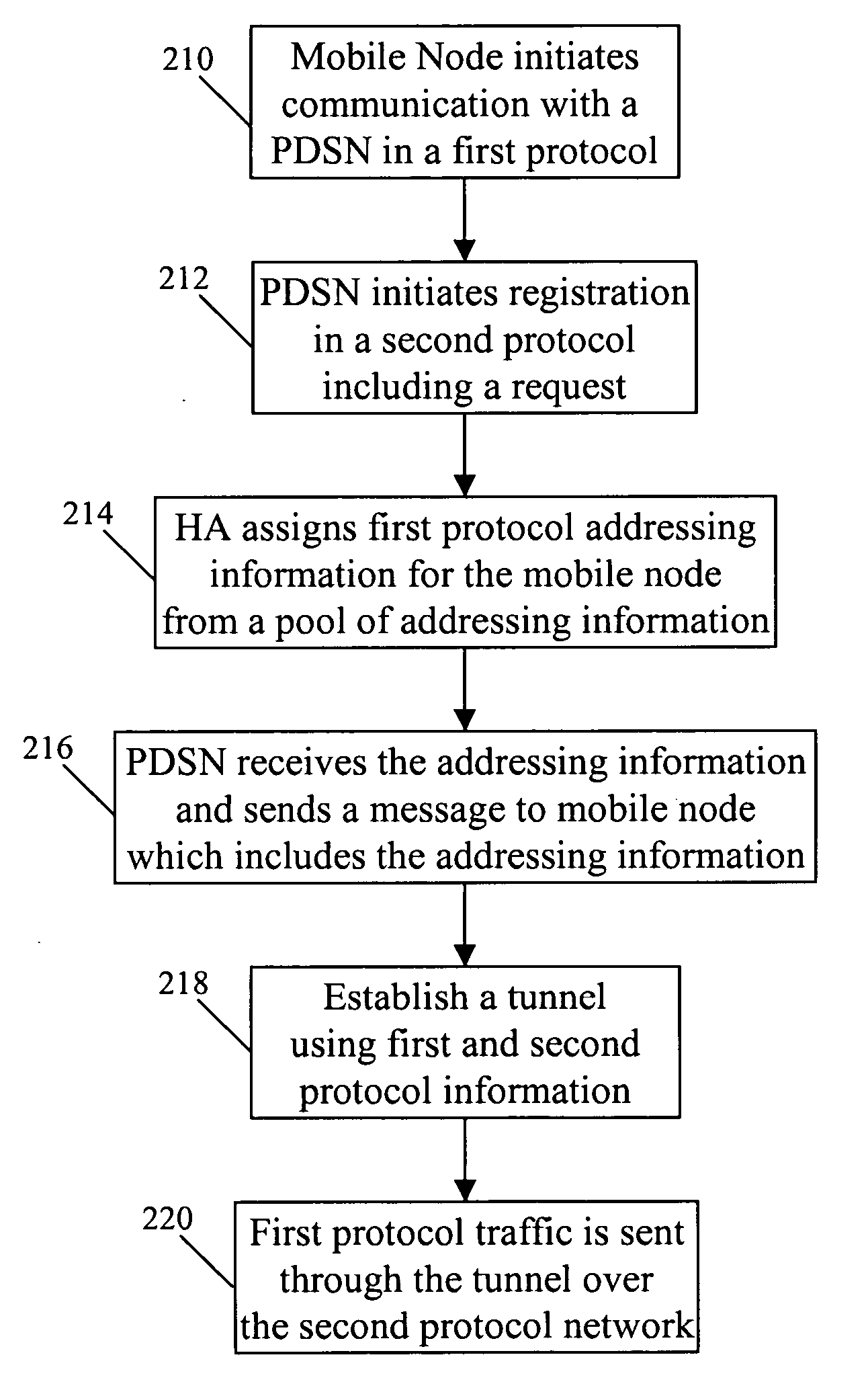
Systems and methods are provided for sending information in a first protocol over a network that supports a second protocol. A tunnel is used to provide a roaming mobile node with IPv6 packet data over an IPv4 core network. When the mobile node is handed off while roaming, the same IP address is provided to the mobile node and the IPv6 packet data is again tunneled over the IPv4 core network. Certain embodiments allow an IPv4 core network to support a mobile node that uses Simple IPv6 or MIPv6 addressing. This system and method can be applicable to situations where the mobile node uses addressing greater than 32 bits, while the core network supports 32 bit addressing.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
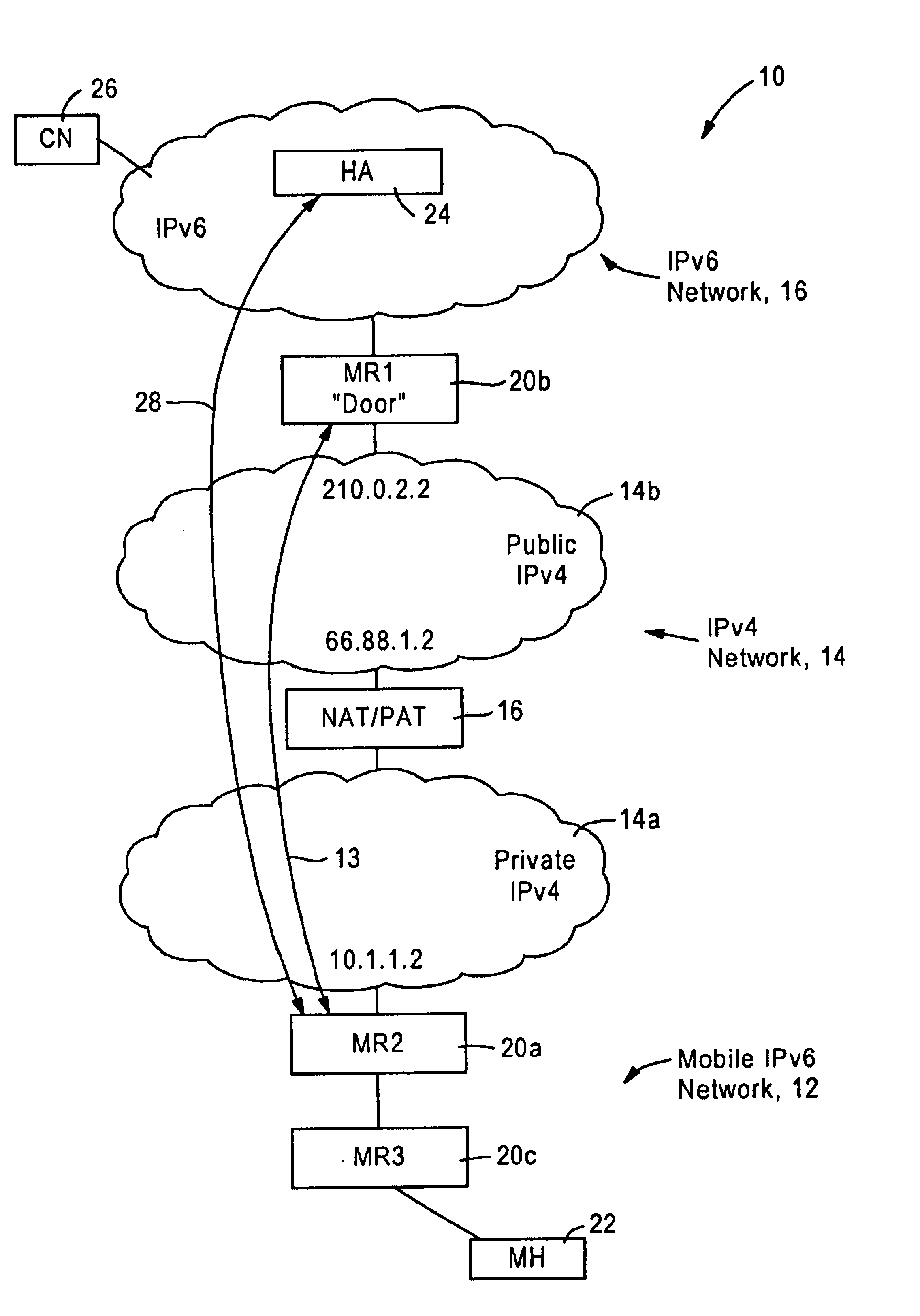
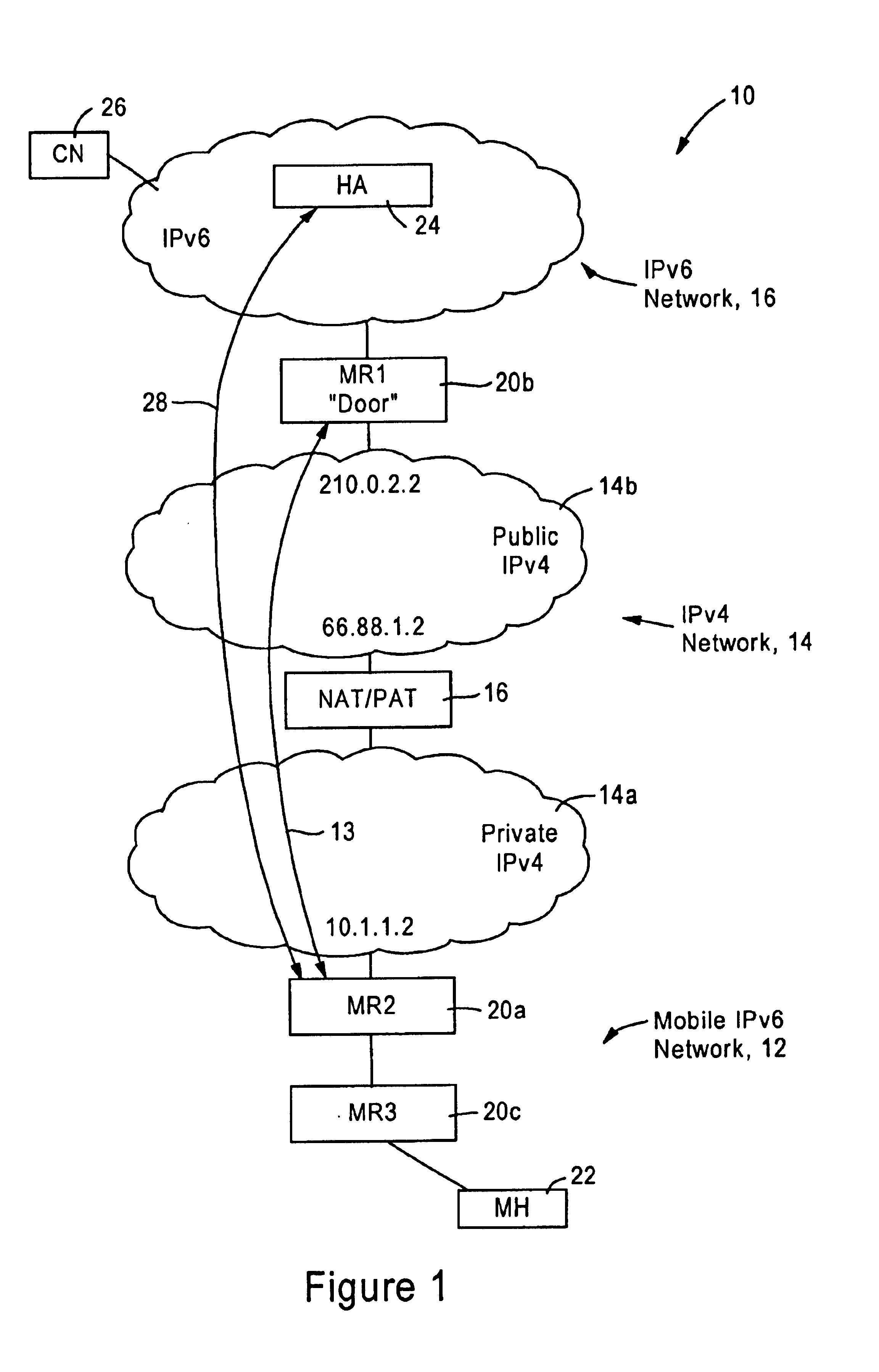
Arrangement for traversing an IPv4 network by IPv6 mobile nodes
InactiveUS6865184B2Use minimizedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetCare-of address
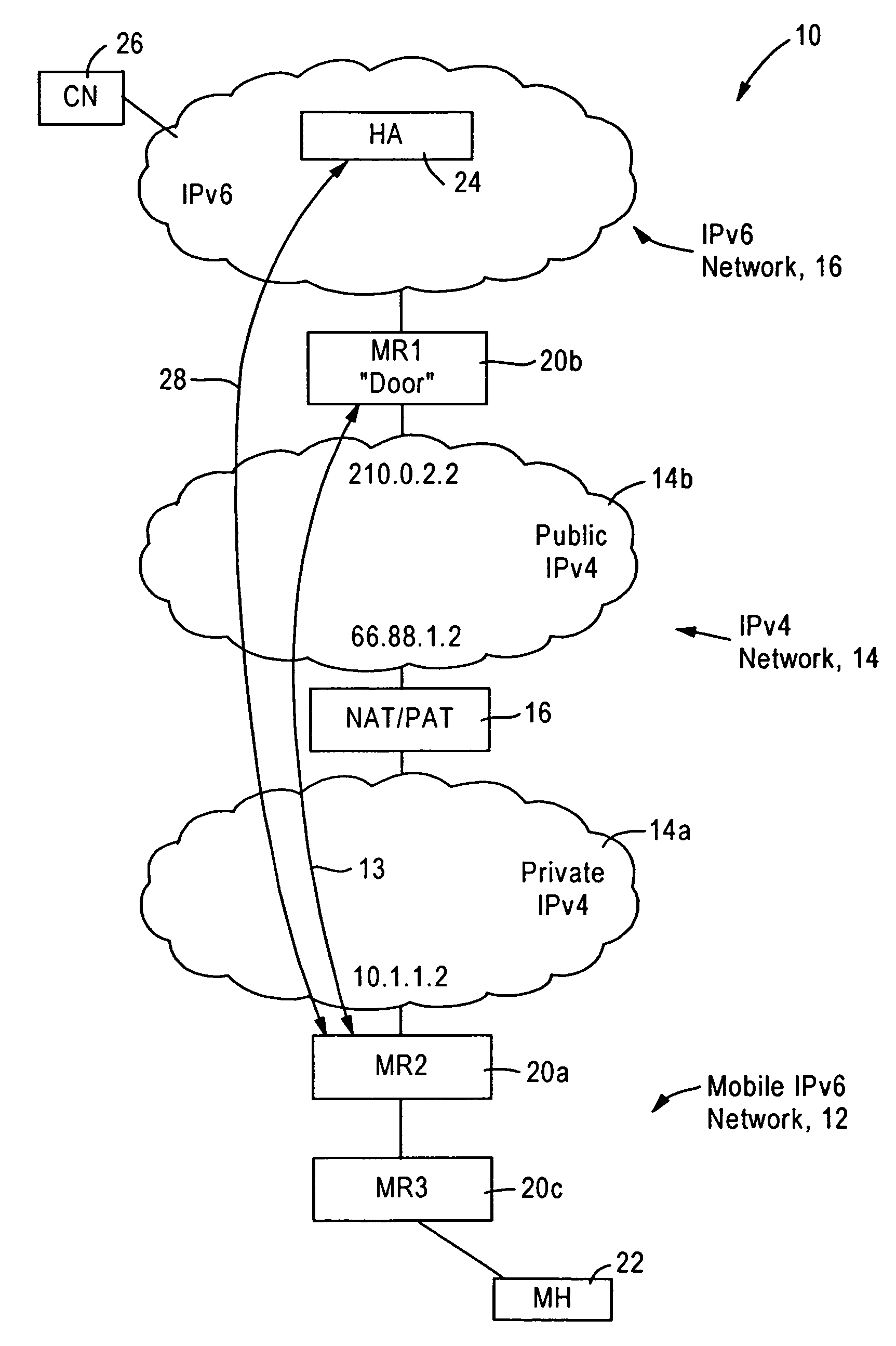
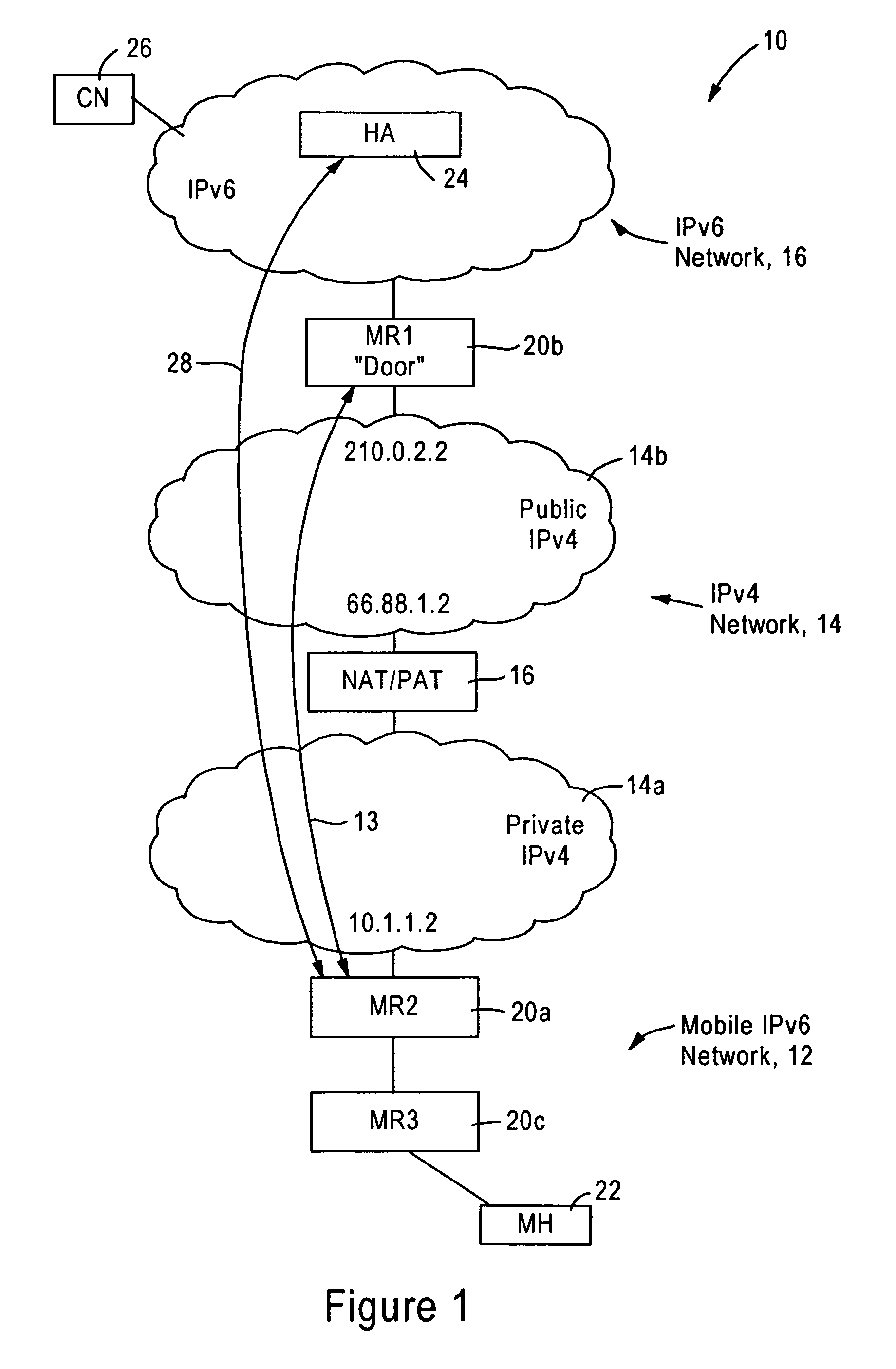
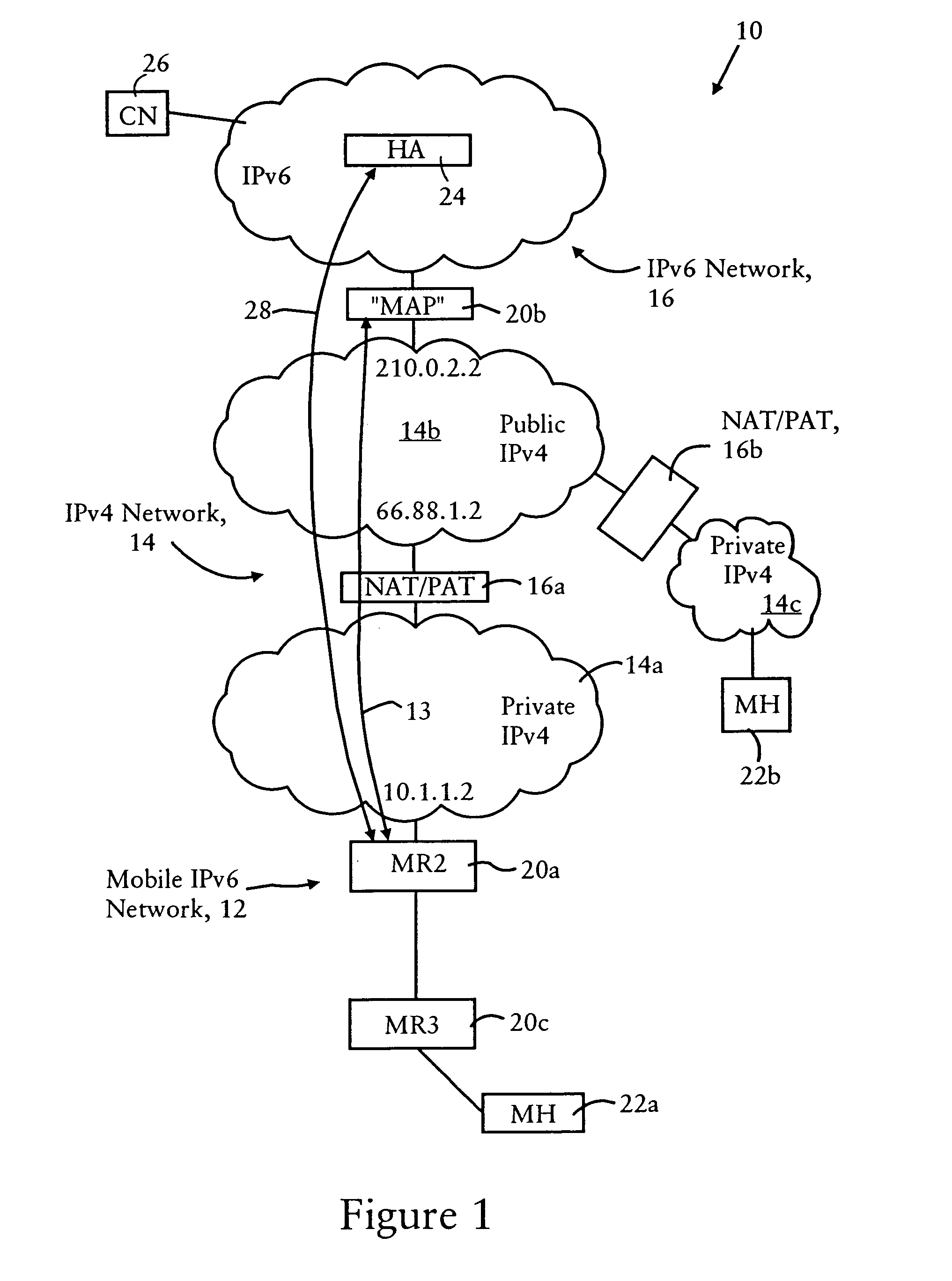
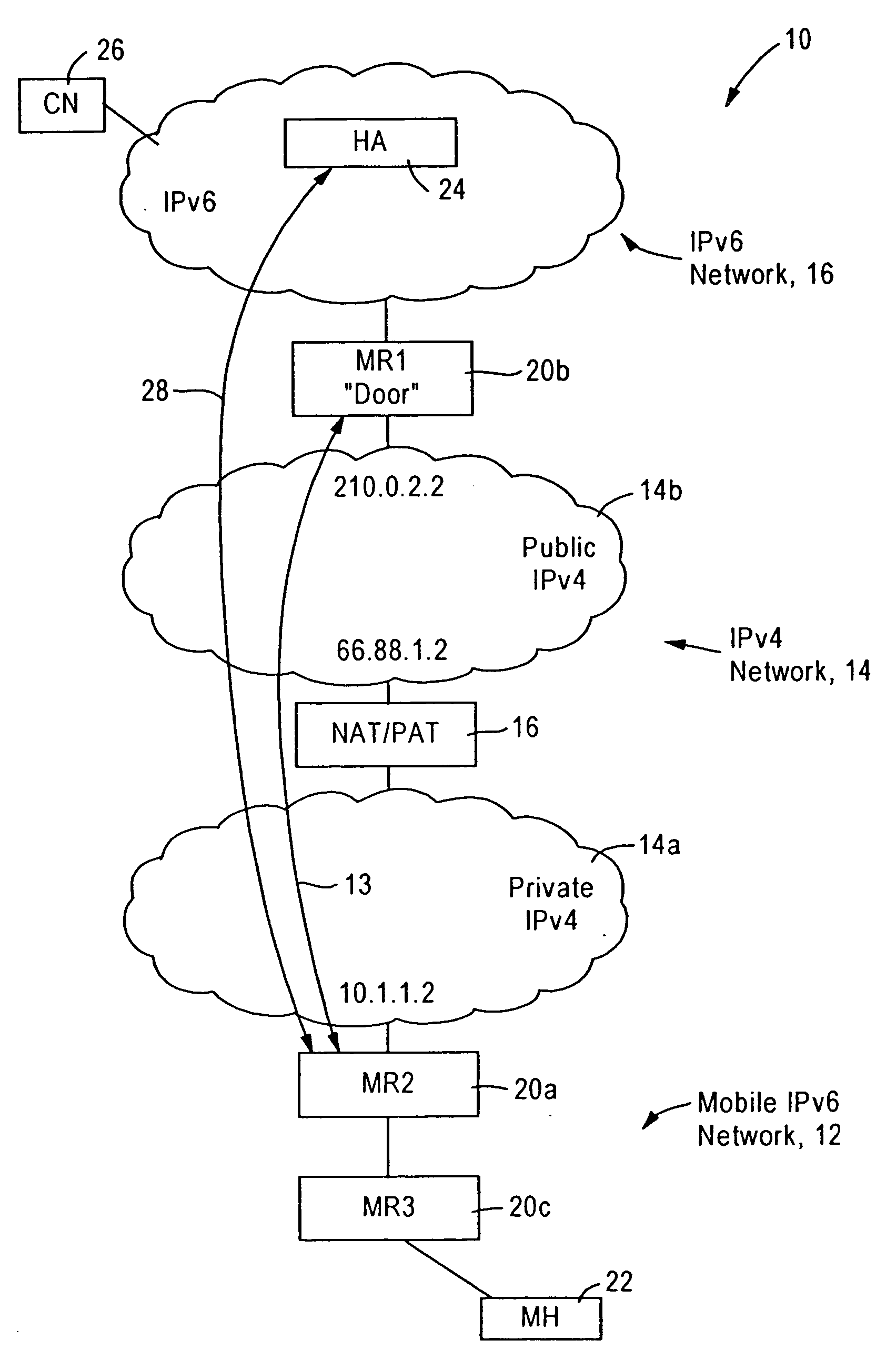
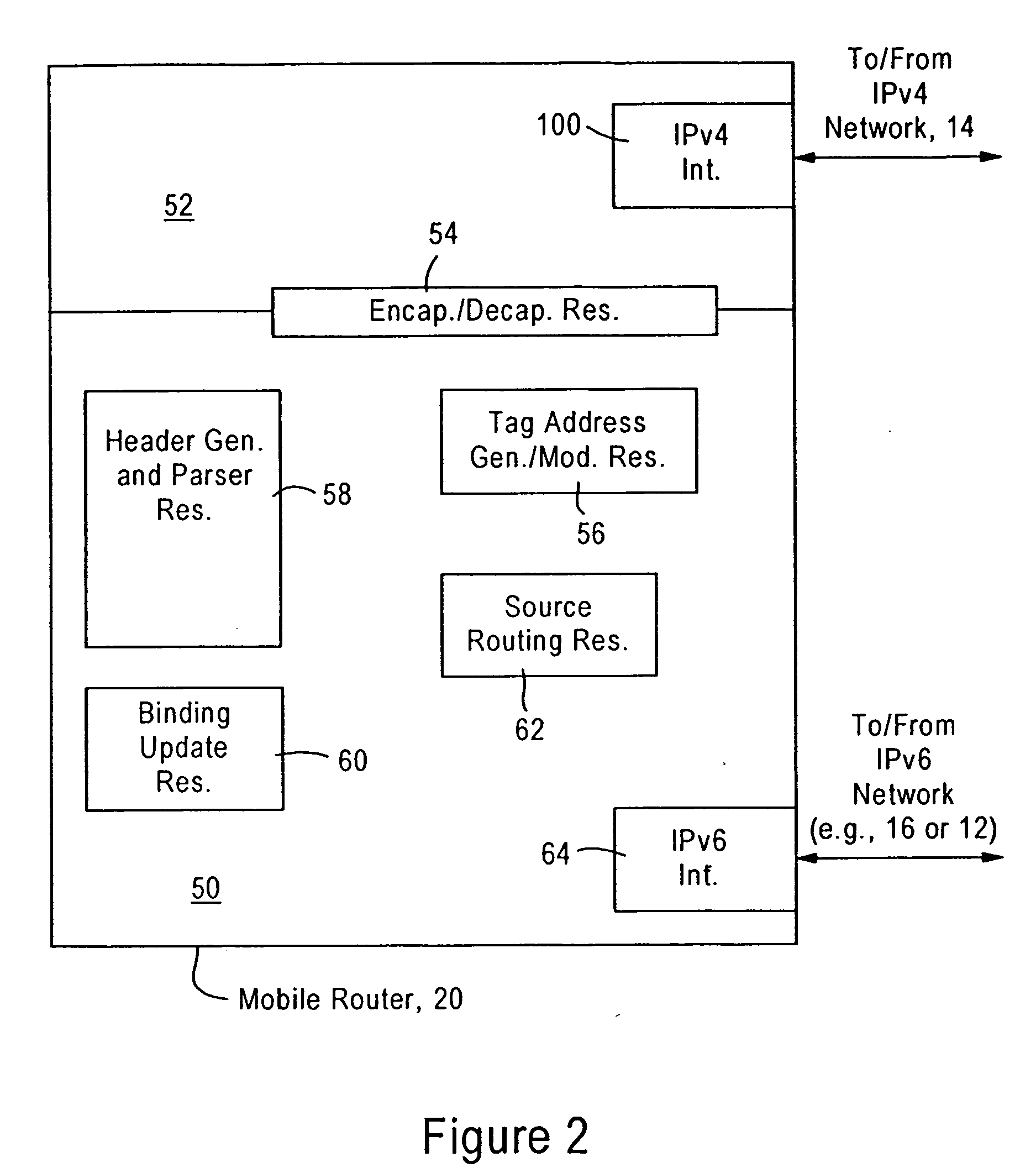
A source IPv6 mobile node is configured for forwarding an IPv6 packet via an IPv4 connection with a destination IPv6 router. The IPv4 packet includes IPv4 source and destination addresses, a UDP source port and UDP destination port, and a synthetic tag address in the IPv6 destination address field. The synthetic tag address, a valid (routable) IPv6 care of address, has an address prefix routed to the IPv6 router. The address prefix specifies a forwarding protocol, the IPv4 destination address for the IPv6 router, and a site-level aggregation identifier. An address suffix for the synthetic tag address specifies the IPv4 source address, the UDP source port and UDP destination port. Hence, the synthetic tag address enables the destination IPv6 router to send an IPv6 reply packet back to the source IPv6 mobile node via the IPv4 network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
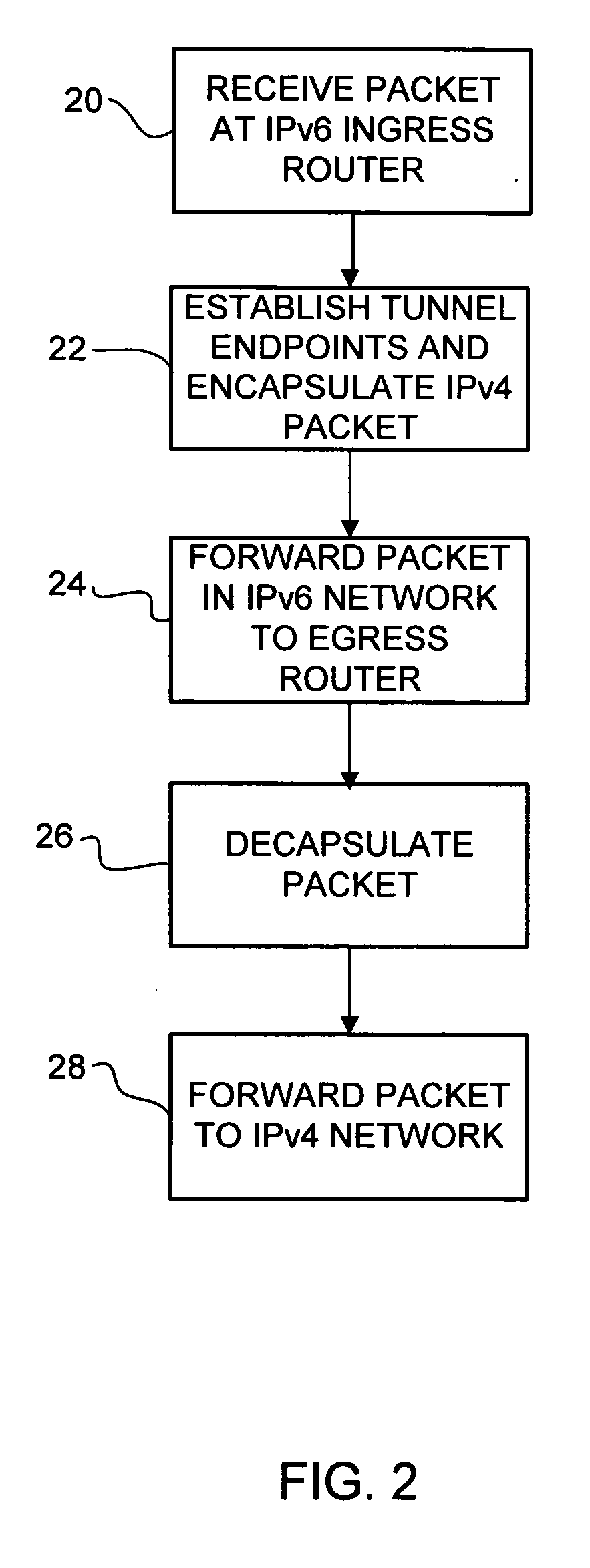
Method and system for automatically interconnecting IPv4 networks across an IPv6 network
InactiveUS20060209885A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetEgress router
A method and system for automatically interconnecting IPv4 networks across an IPv6 network are disclosed. The method includes receiving an IPv4 packet at an ingress router in the IPv6 network and finding the longest match IPv4 routing entry for IPv4 addresses in the received packet to identify an egress router in the IPv6 network. The IPv4 packet is encapsulated to create an IPv6 packet, wherein destination and source addresses of the encapsulated packet identify a subnet router anycast corresponding to the ingress router and the egress router in the IPv6 network. The encapsulated packet is forwarded to the egress router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
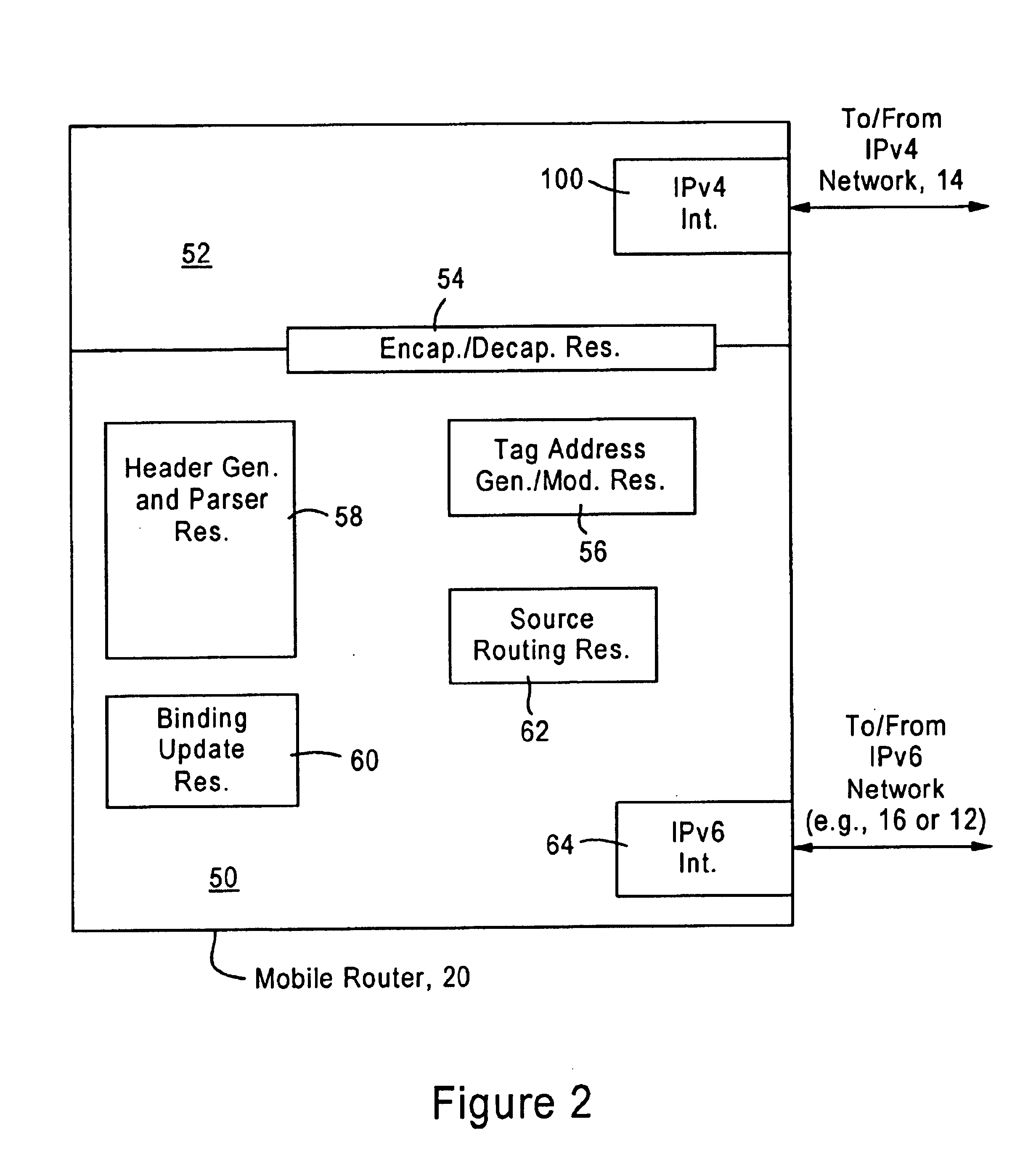
Arrangement for traversing an IPv4 network by IPv6 mobile routers
InactiveUS7031328B2Use minimizedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkIPv6 packet
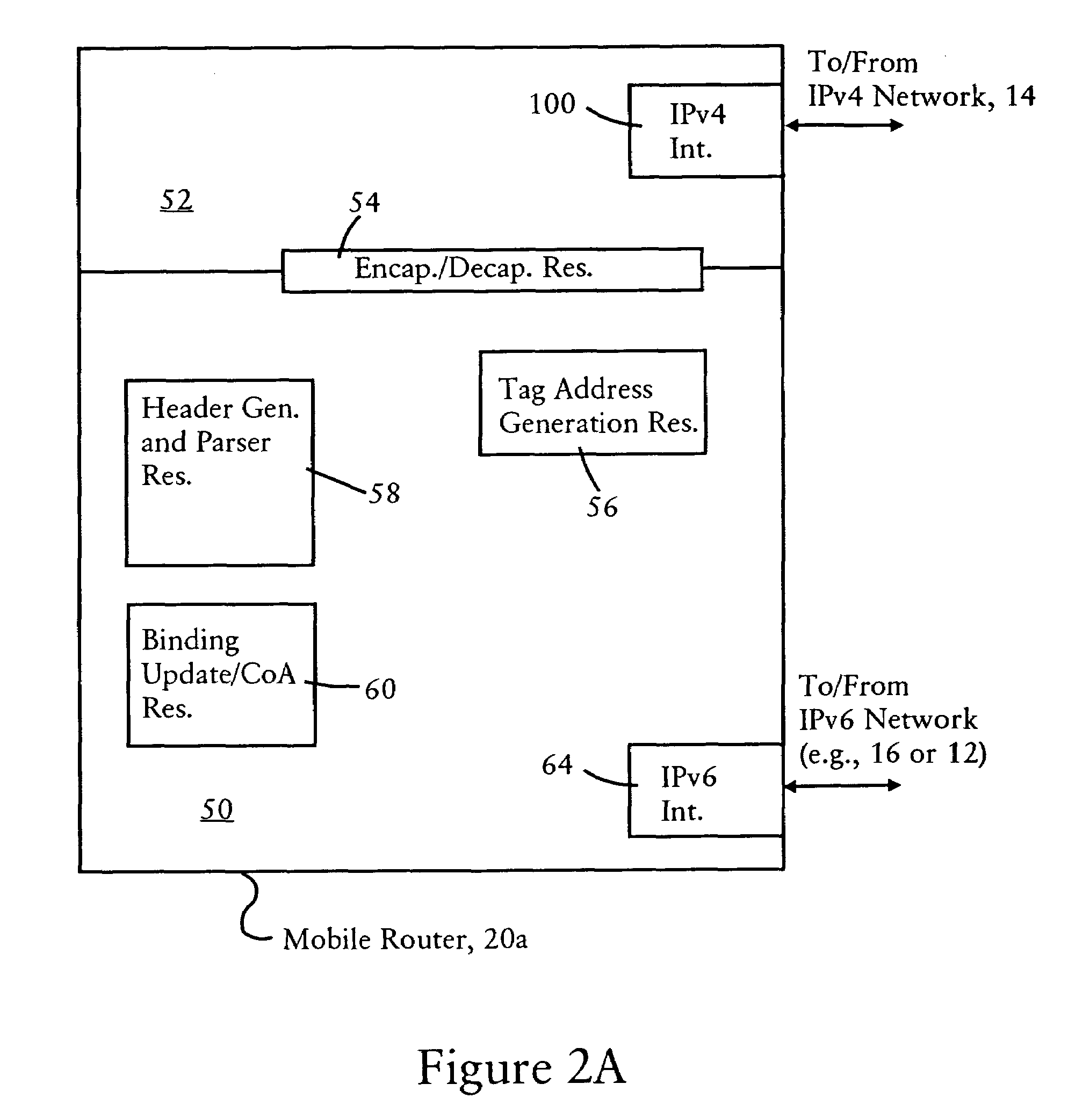
A source IPv6 mobile router is configured for establishing an IPv4 tunnel with destination IPv6 mobile router using a synthetic tag address, specifying a forwarding protocol, and IPv4 source and destination addresses. If an optional transport header is used (e.g, UDP port), the source port and destination port also are added to the synthetic tag address. The IPv6 packet includes a reverse routing header that enables the destination IPv6 mobile router to recover routing information for reaching the source IPv6 mobile router via the IPv4 network. Hence, all IPv4 routing information that may be needed by the destination IPv6 mobile router in sending an IPv6 reply packet back to the source IPv6 mobile router is maintained in the routing header specified in the IPv6 reply packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
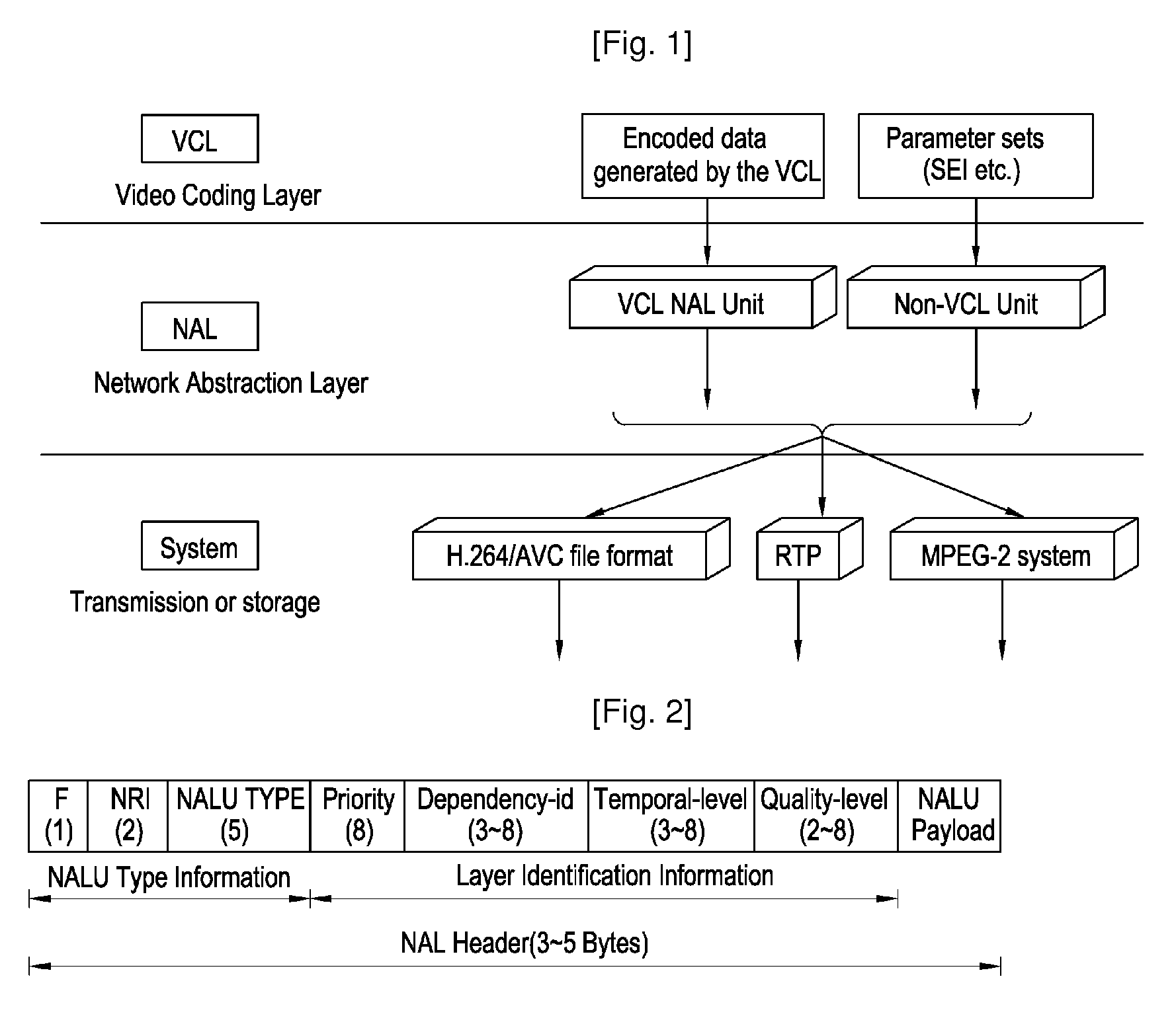
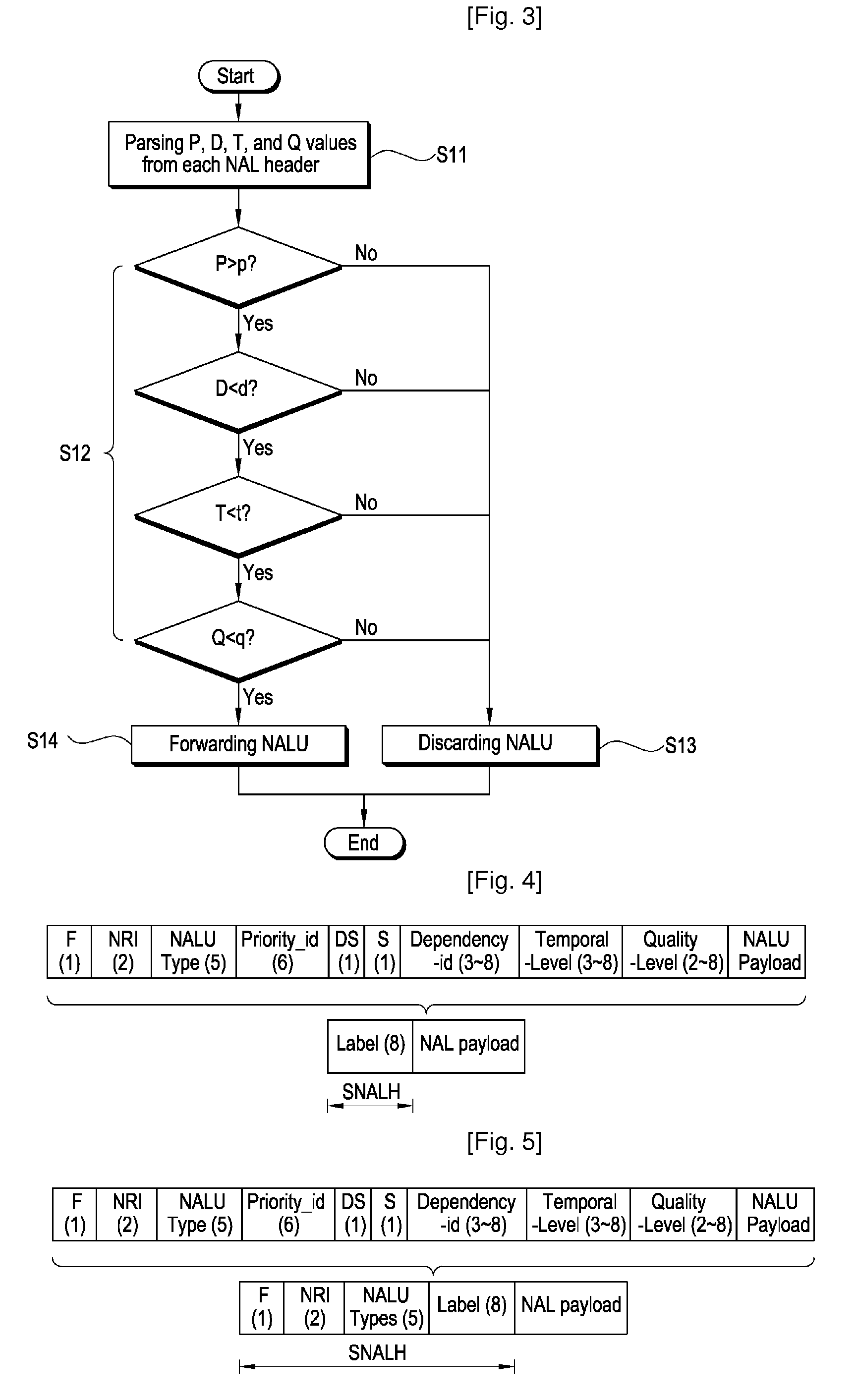
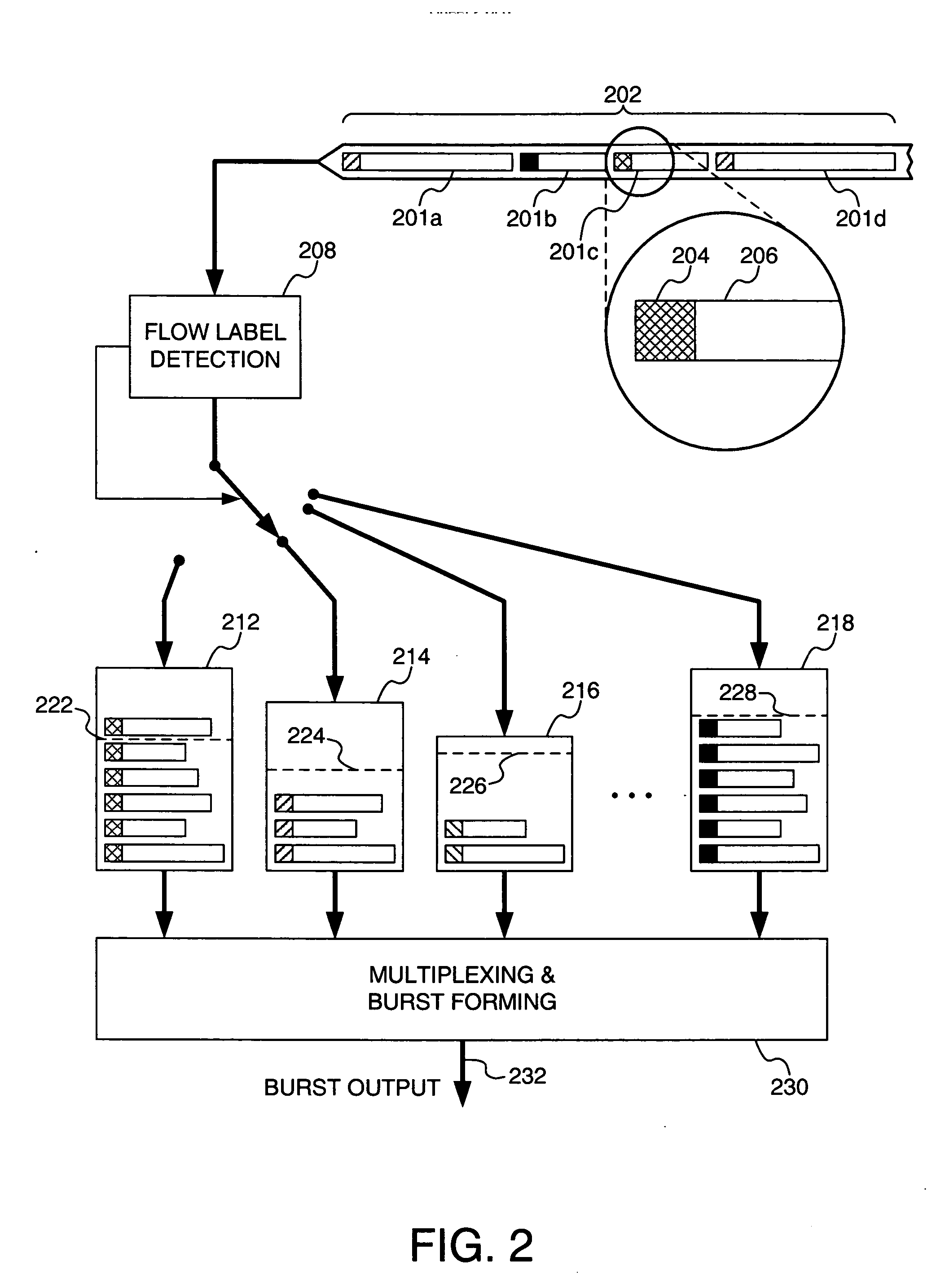
Packet format of network abstraction layer unit, and algorithm and apparatus for video encoding and decoding using the format, QOS control algorithm and apparatus for ipv6 label switching using the format
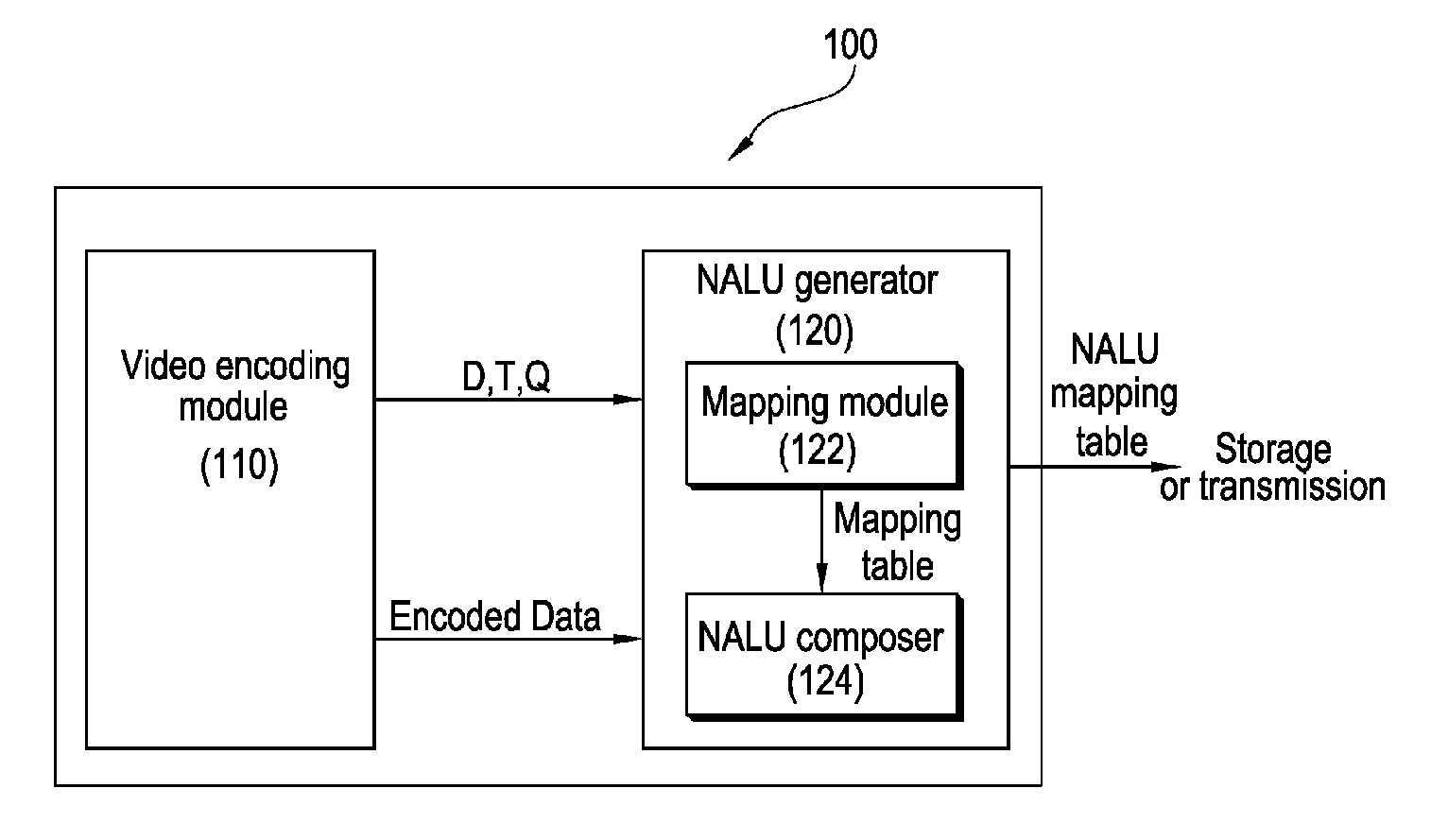
ActiveUS20090175353A1Reduce complexityReduce controlPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData packVideo encoding
The construction method of NALU (Network Abstraction Layer Unit) for IPv6 label switching and its using algorithms of video encoding, QoS control, and decoding are provided. According to an embodiment of the present invention, the NALU format is composed of the NALH (Network Abstraction Layer Header) including the label and the NAL (Network Ab straction Layer) payload. Here, the label is determined based on layer information which is combination of a spatial scalable level, a temporal scalable level, and a quality scalable level of the encoded data. The decoder uses the label to decide which one of multiple decoding modules is used to decode the current NAL payload. Moreover, the label can be included in the packet header so that the MANE (Media Aware Network Element) can use the label to decide whether to forward the packet or drop it. For example, the label in the packet header can be used for QoS control of video service by using the flow label field in IPv6 packet header The IPv6 router can identify priority of the video packet by using the 20 bit long flow label, into which the label in NALH can be inserted. According to the embodiment, the MANE assumed in the MPEG and JVT (Joint Video Team) can be implemented effectively.
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV
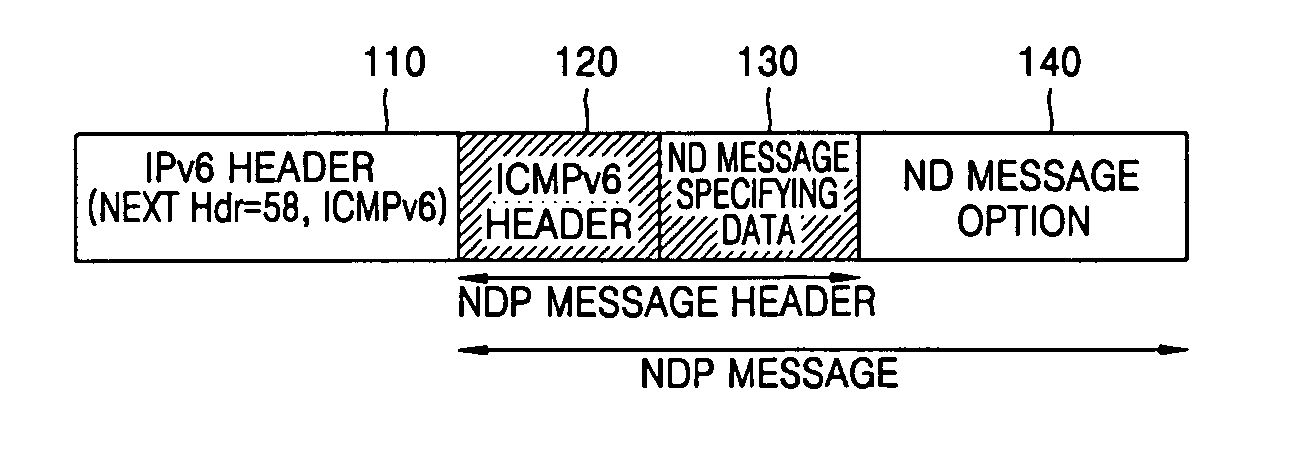
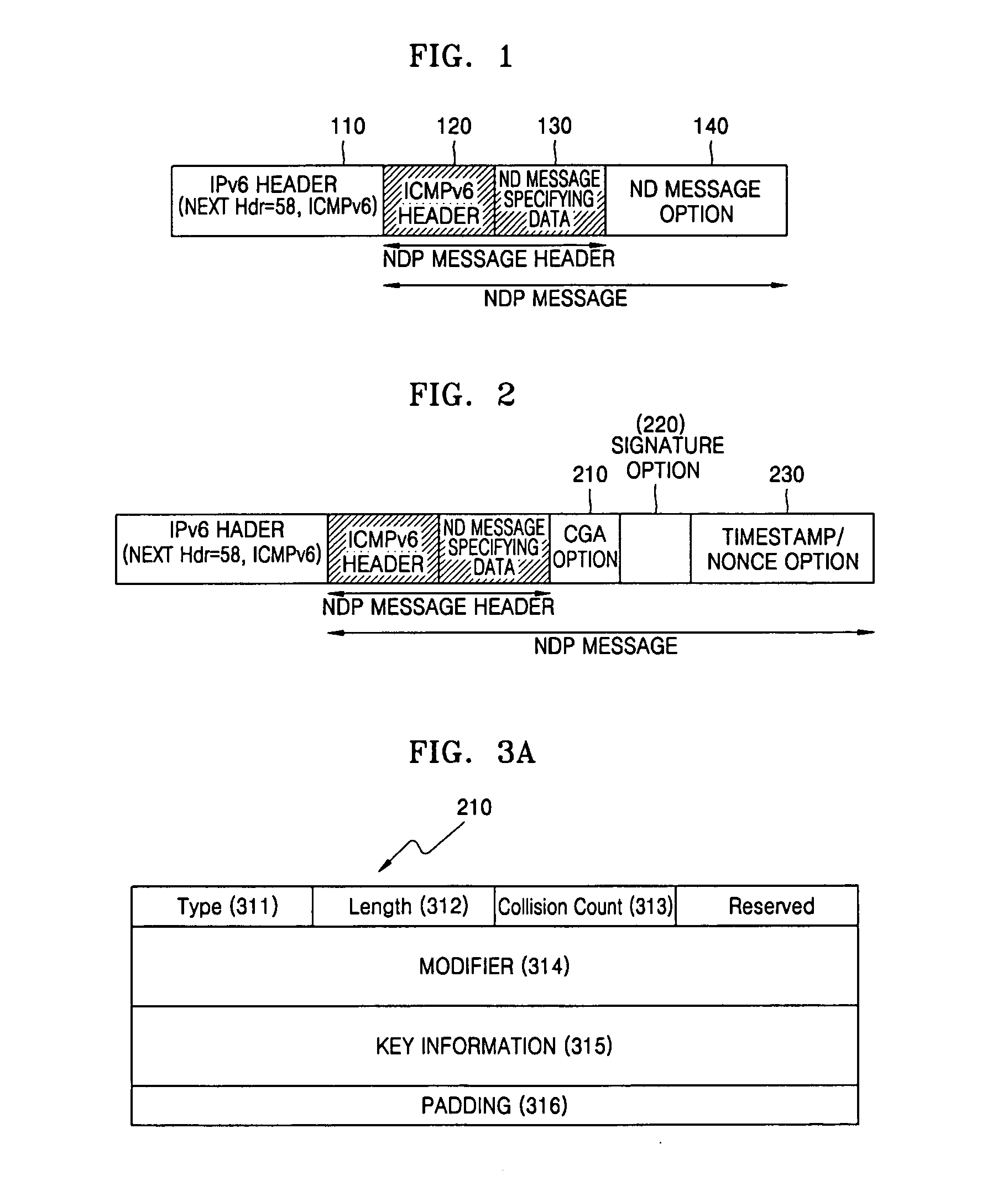
Method for generating and authenticating address automatically in IPv6-based internet and data structure thereof
InactiveUS20060077908A1Protect informationPublic key for secure communicationData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetTimestamp
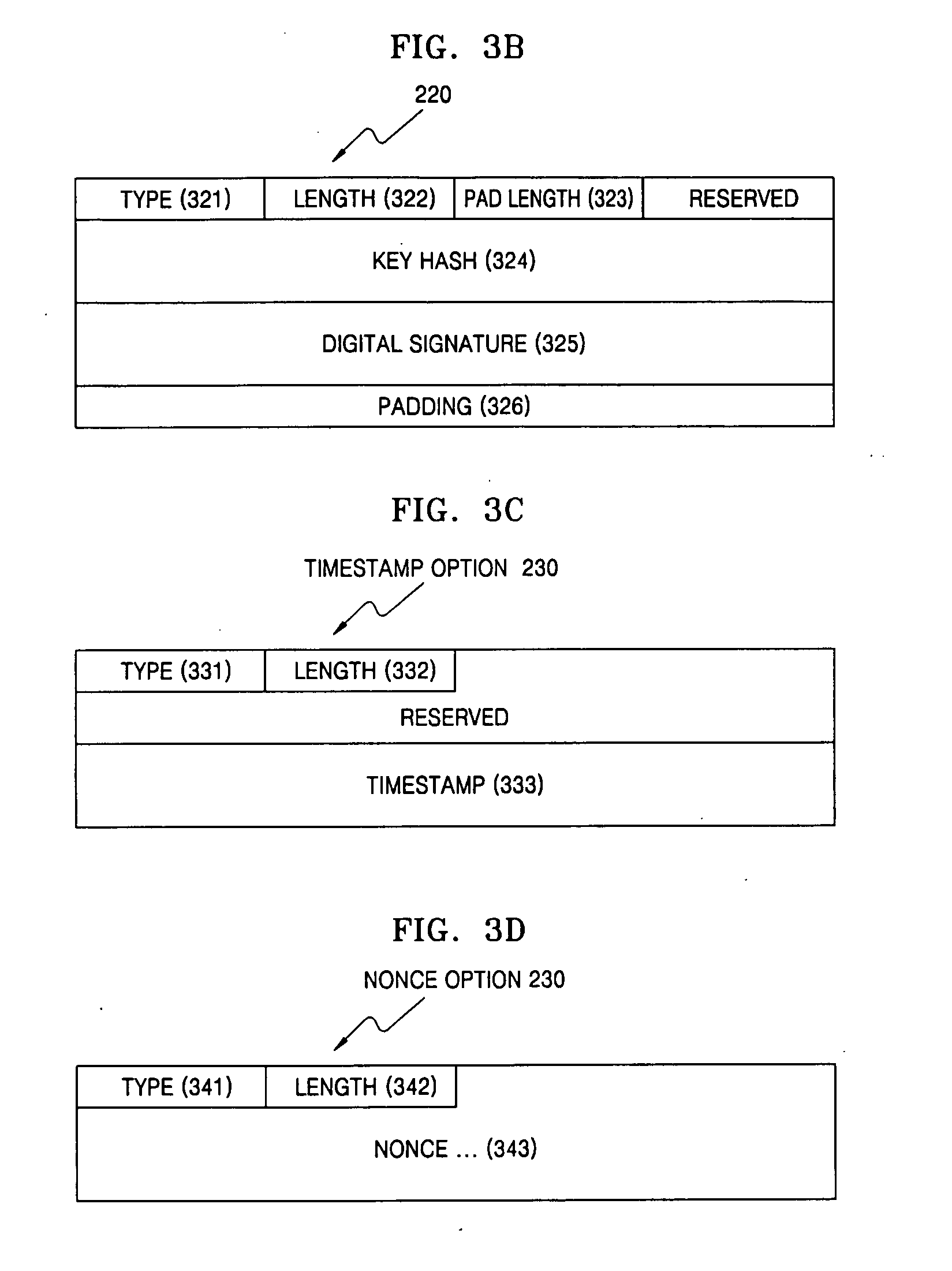
Provided are a method for automatically generating an address in the IPv6-based Internet when a sender having a pair of a public key and a private key establishes a network connection, and a data format thereof. The method includes generating a CGA address and a CGA option based on the public key and a predetermined parameter, generating a signature option for verifying the CGA option, additionally generating a timestamp option in a case where a unidirectional message is transmitted to the network, and additionally generating a nonce option containing random numbers in a case where a bidirectional message is transmitted to the network, and adding the signature option, the timestamp option and the nonce option to a Neighbor Discovery (ND) option field to form an ND message, and transmitting the ND message to the network. When a host enters the network in a Zero Configuration over the IPv6-based Internet, the host can securely generate its own address without using a manual key. The method can also be applied to general IPv6 packet authentication or position authentication of a mobile node.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
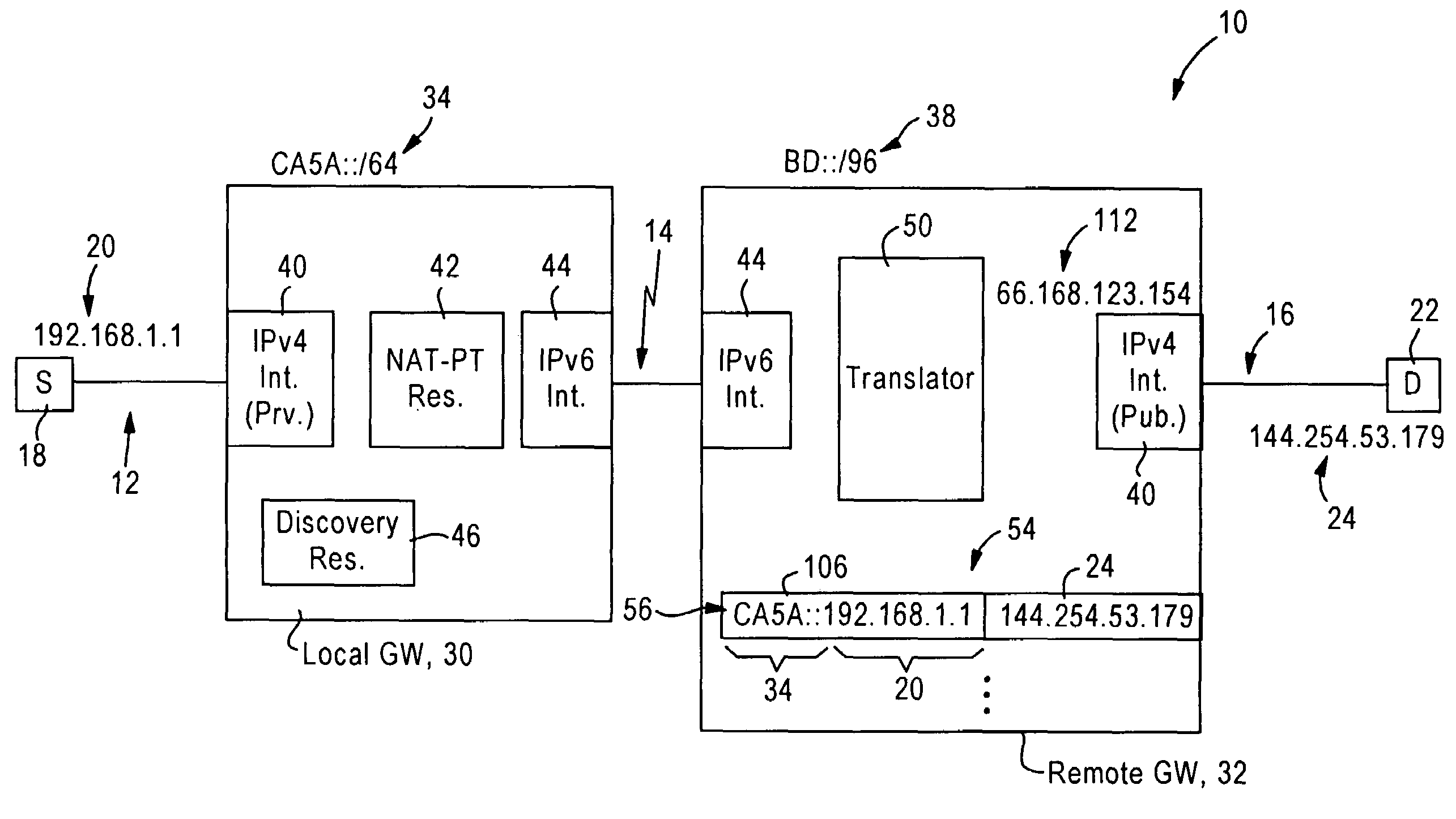
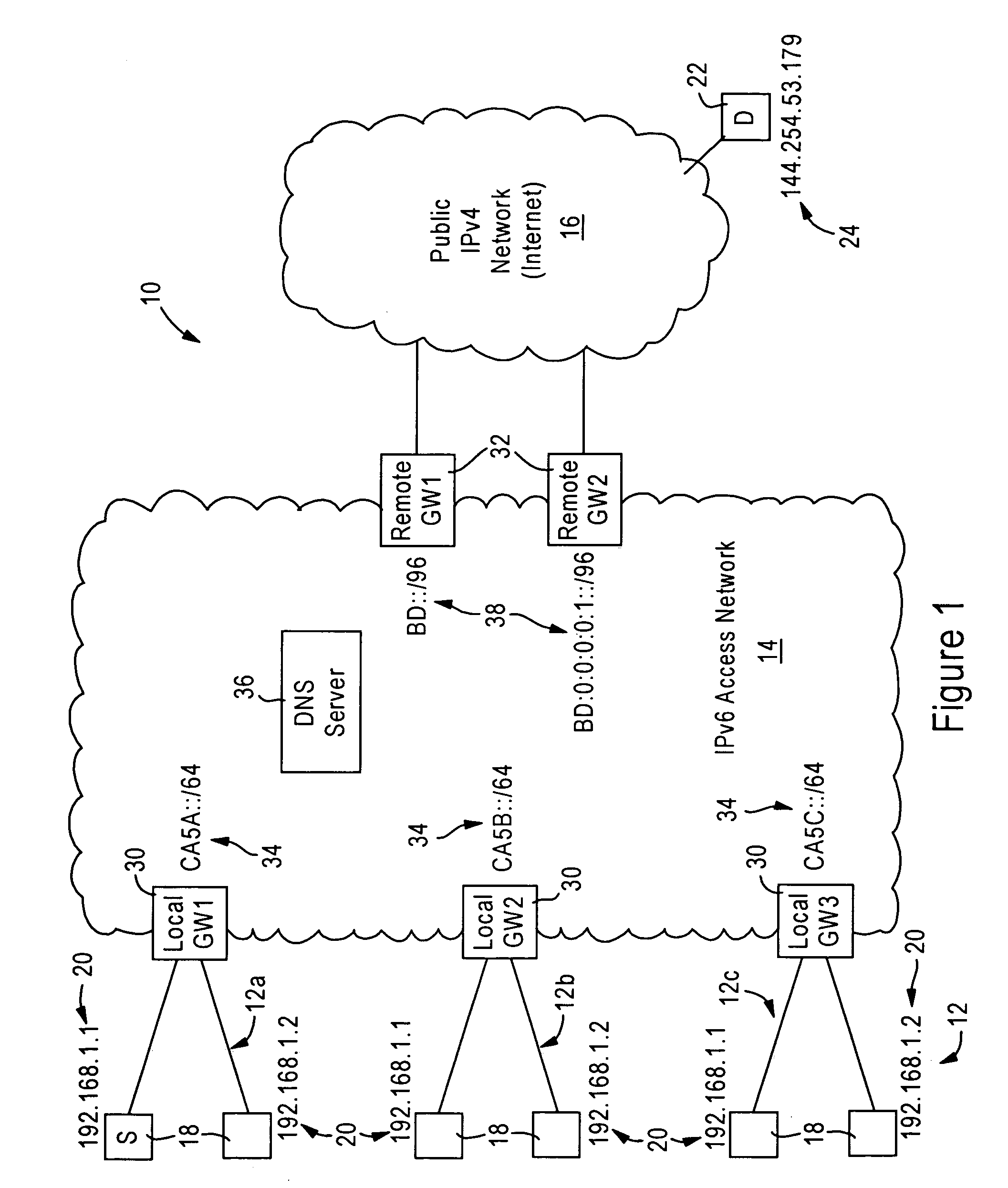
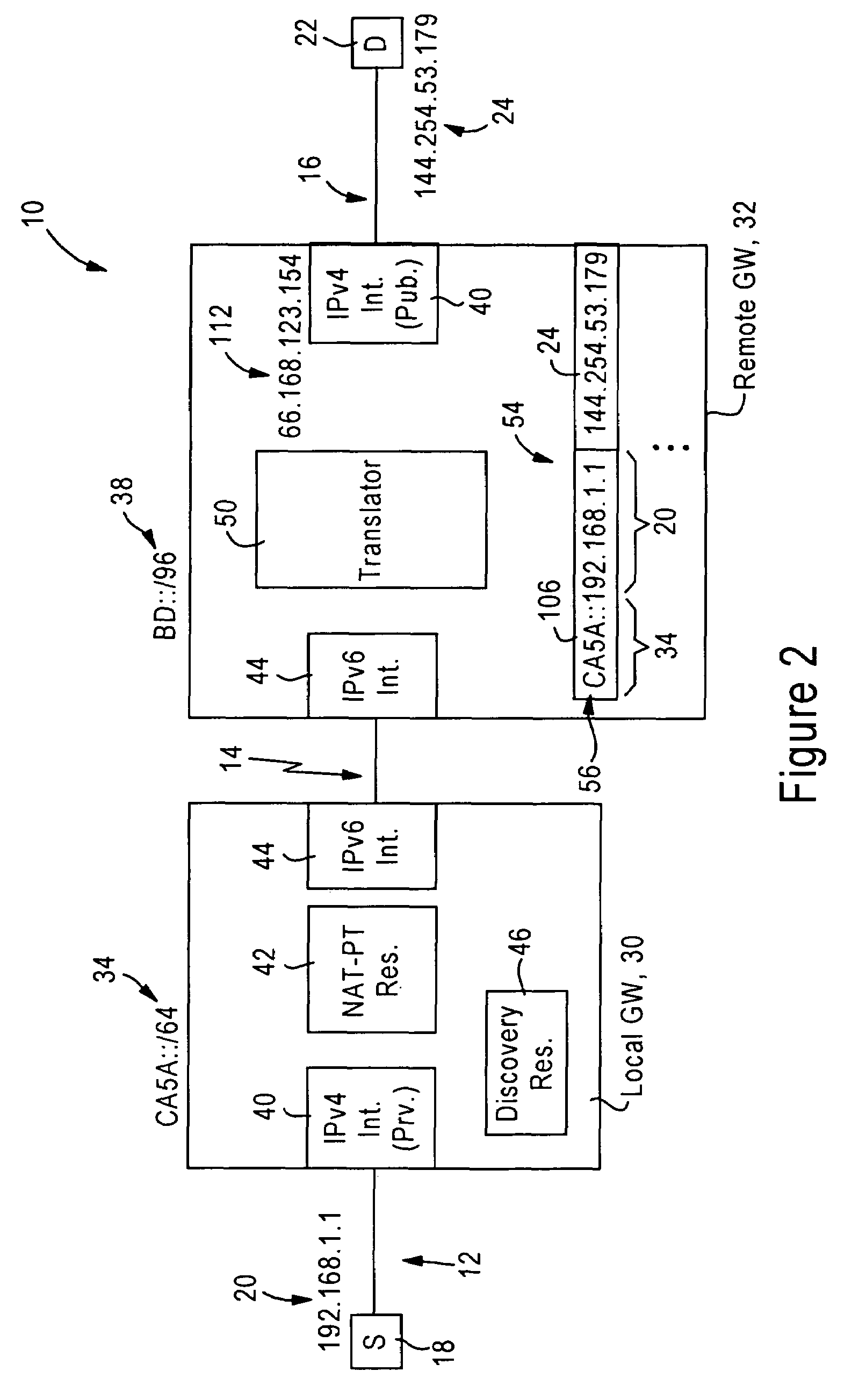
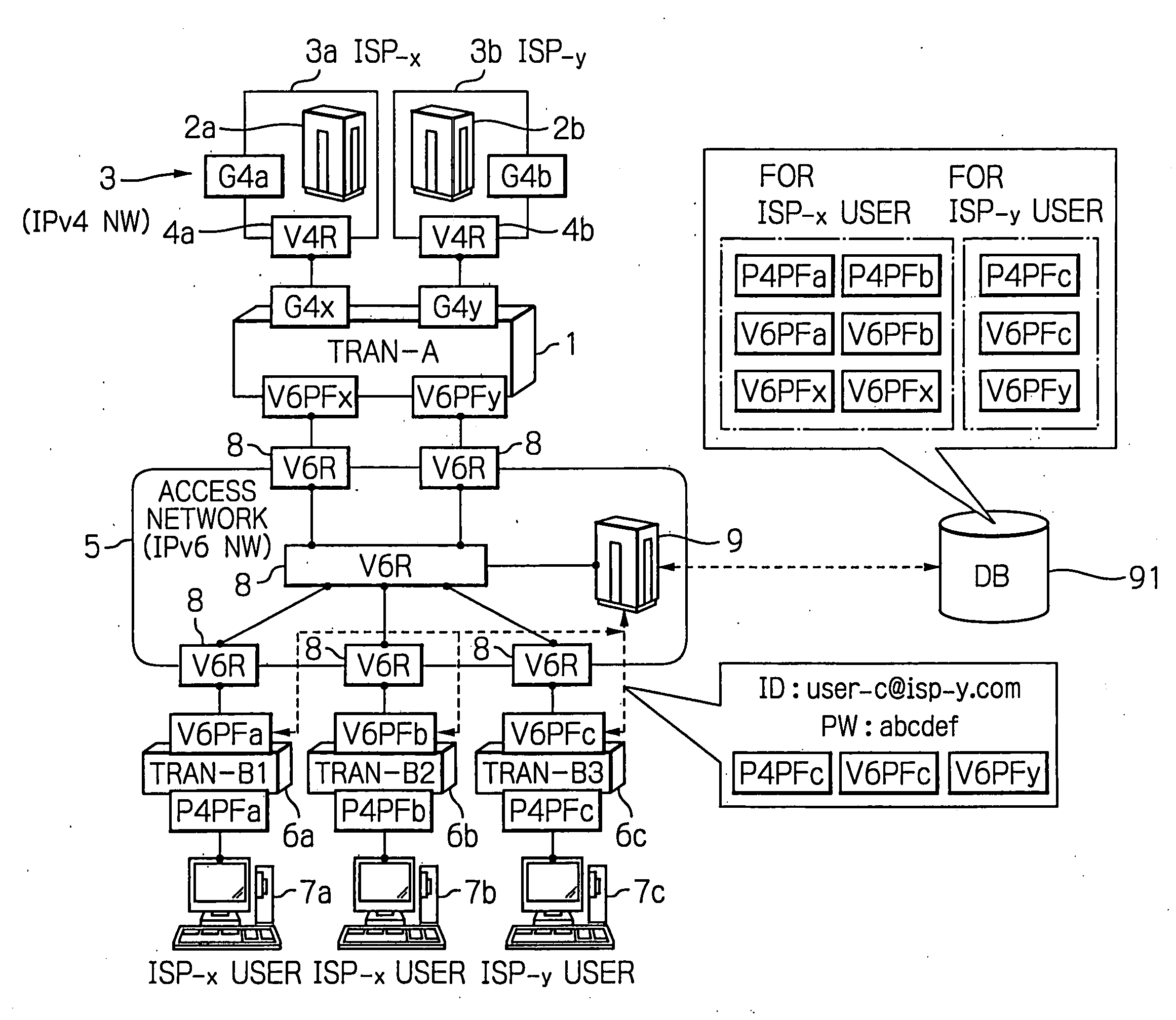
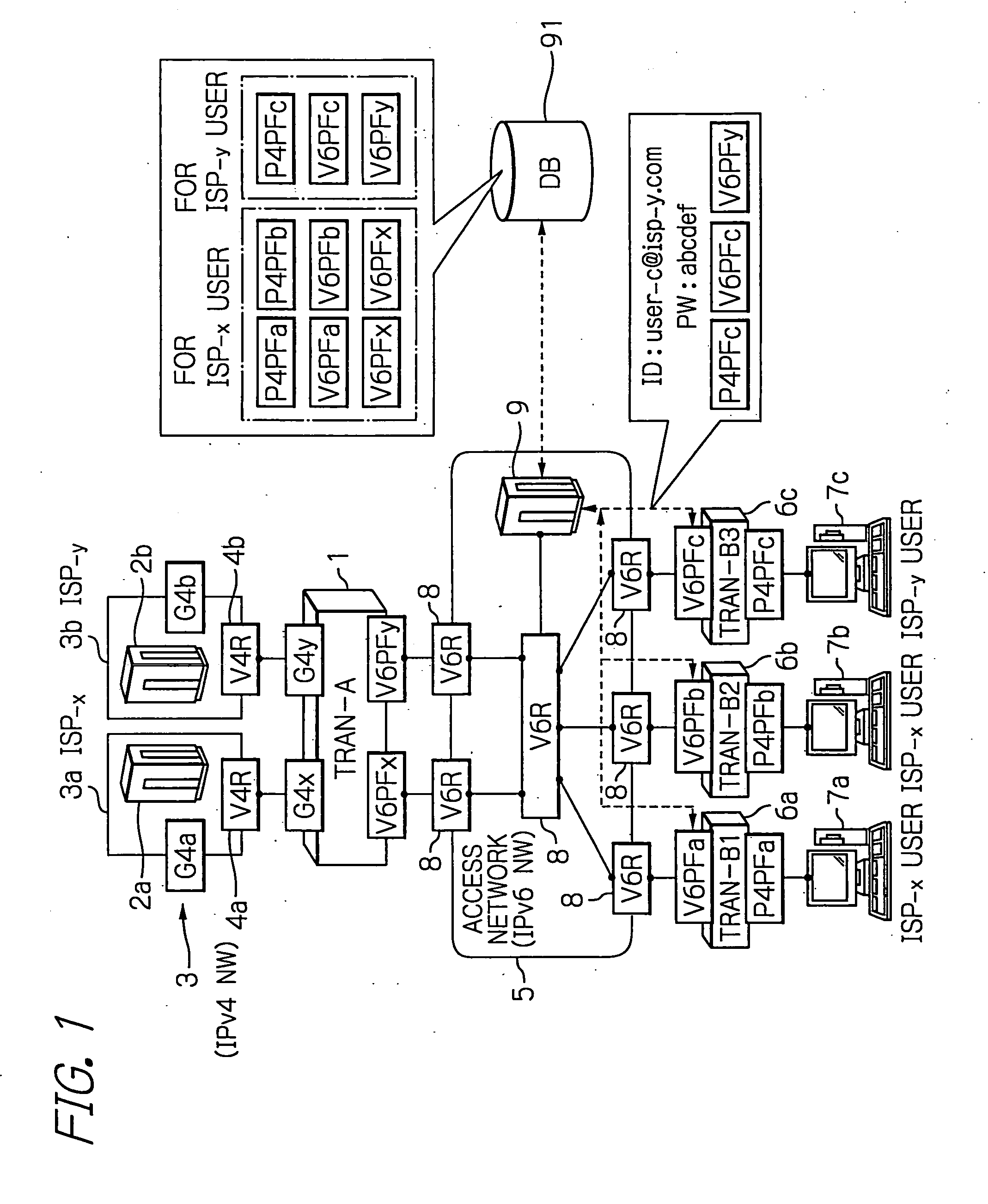
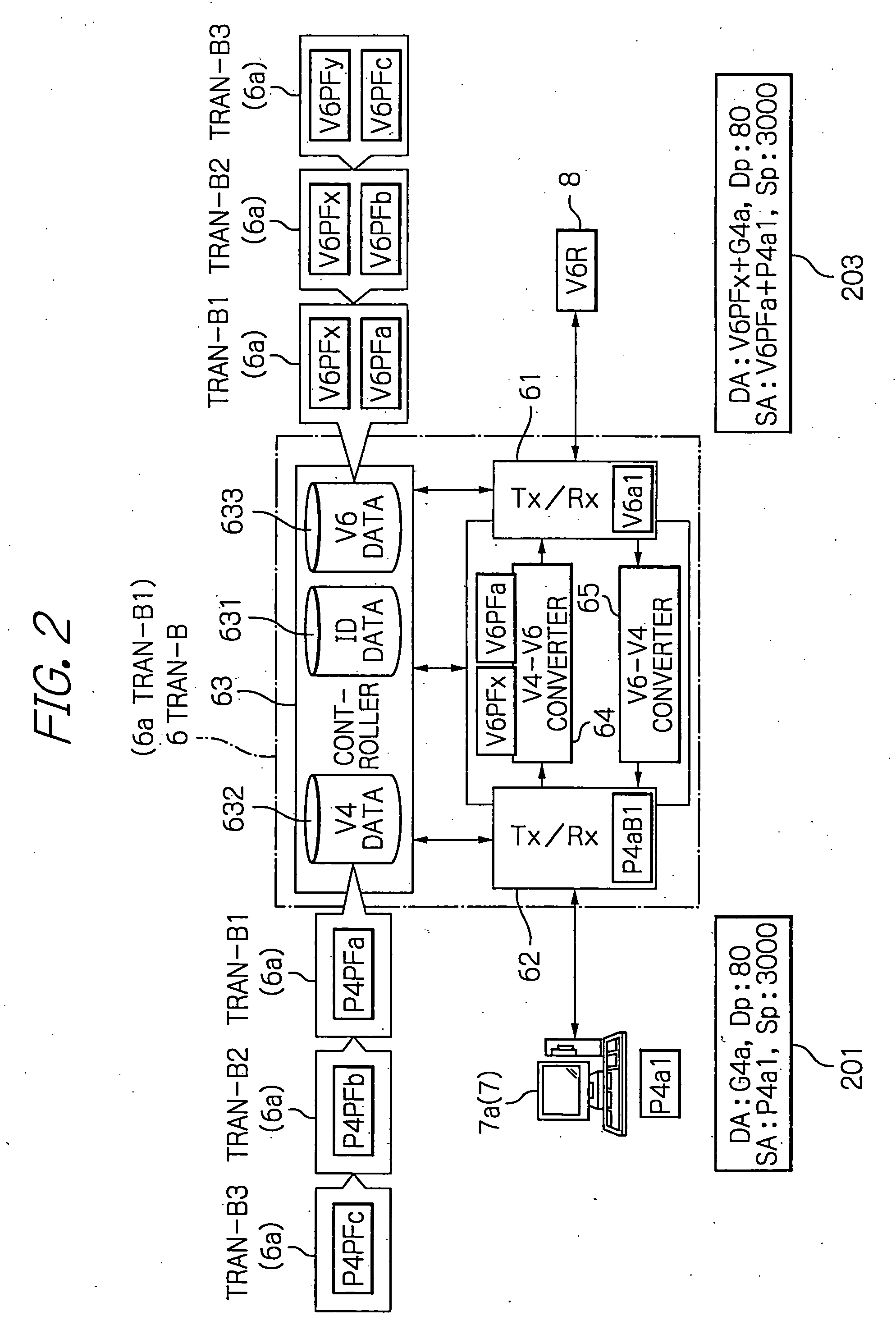
Arrangement for reaching IPv4 public network nodes by a node in an IPv4 private network via an IPv6 access network
ActiveUS20050286553A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetAccess network
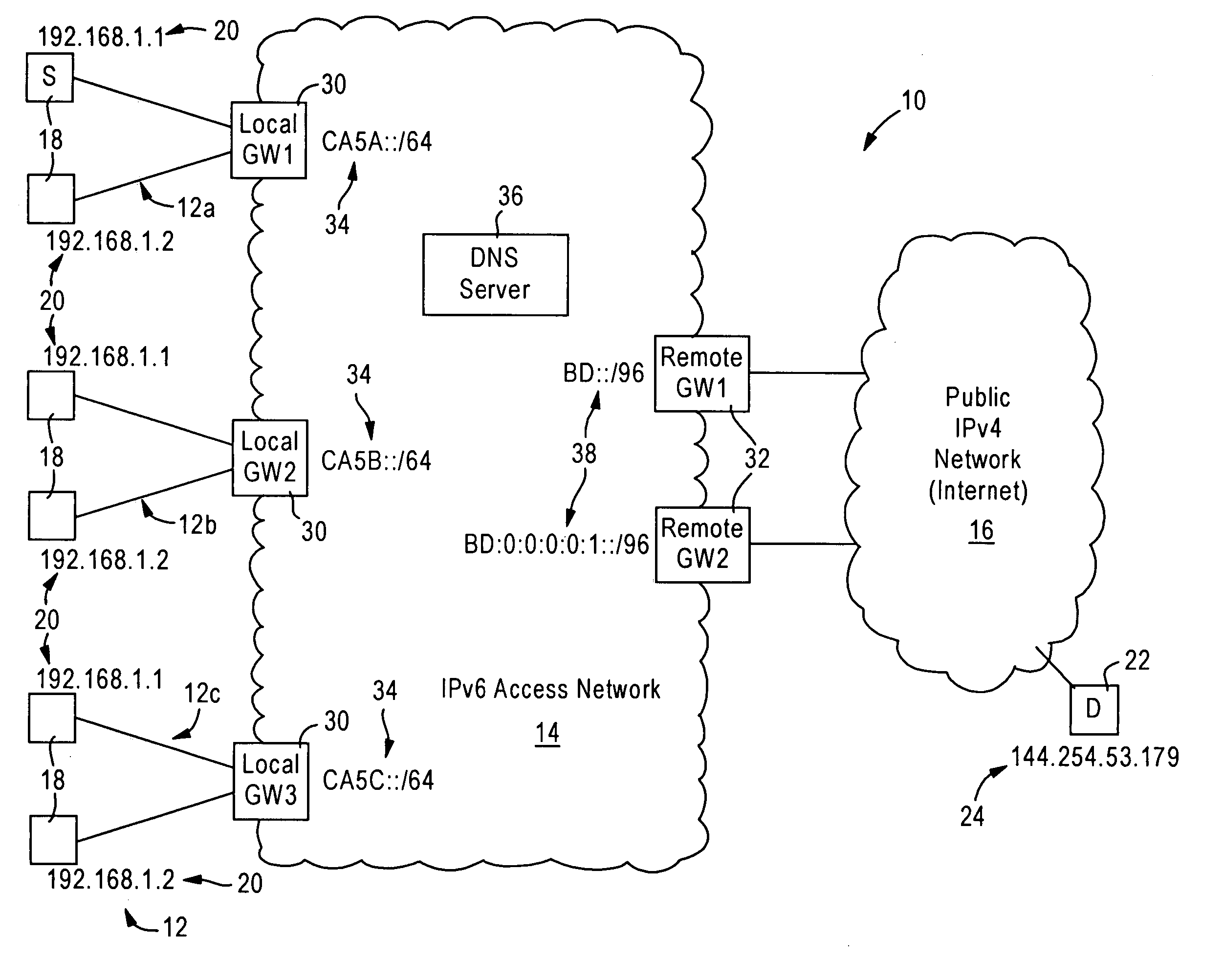
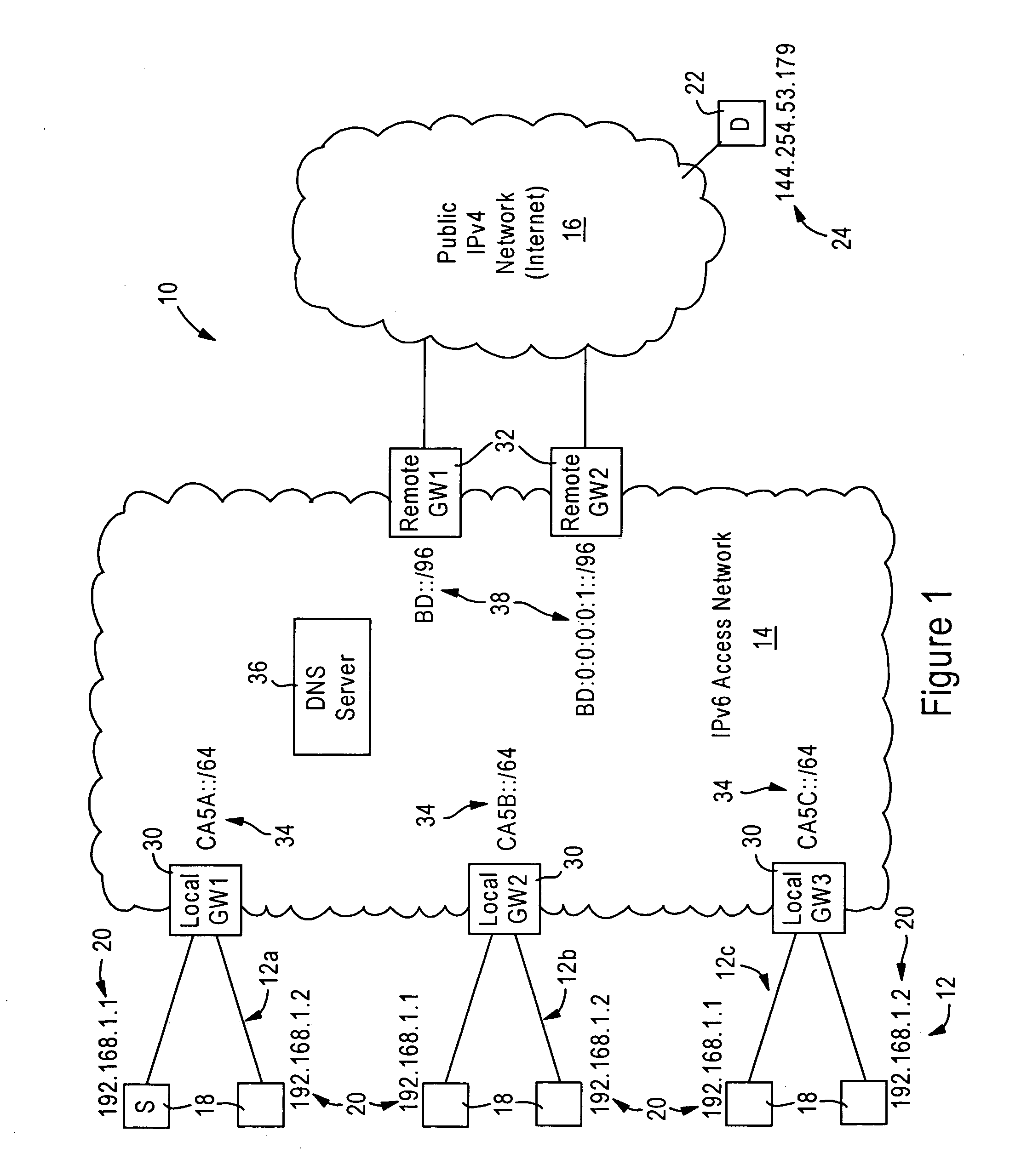
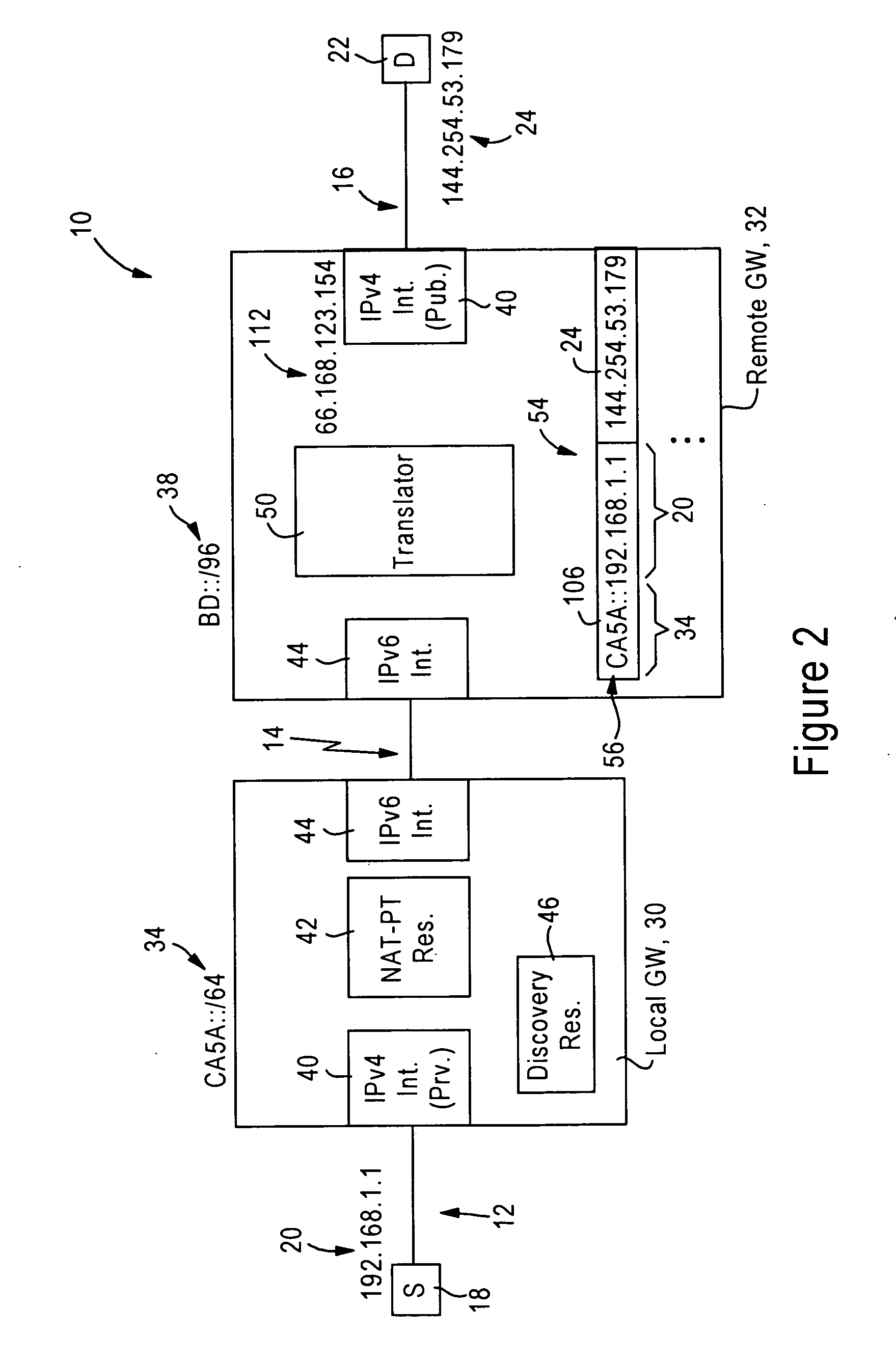
An IPv4 node is able to send an IPv4 packet to an IPv4 destination via an IPv6 access network, based on translation of the IPv4 packet into an IPv6 packet for transmission via the IPv6 access network. The IPv4 packet is translated into the IPv6 packet by a local gateway. The IPv6 packet has an IPv6 source address that includes a prescribed address prefix assigned to the local gateway, and an IPv4 address of the IPv4 node. The IPv6 packet also includes an IPv6 destination address that includes a second address prefix assigned to a remote gateway, and a second IPv4 address of the IPv4 destination. The IPv6 packet is converted by the remote gateway into an IPv4 packet for reception by the IPv4 destination via an IPv4 network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and Method for Flow-Based Addressing in a Mobile Environment
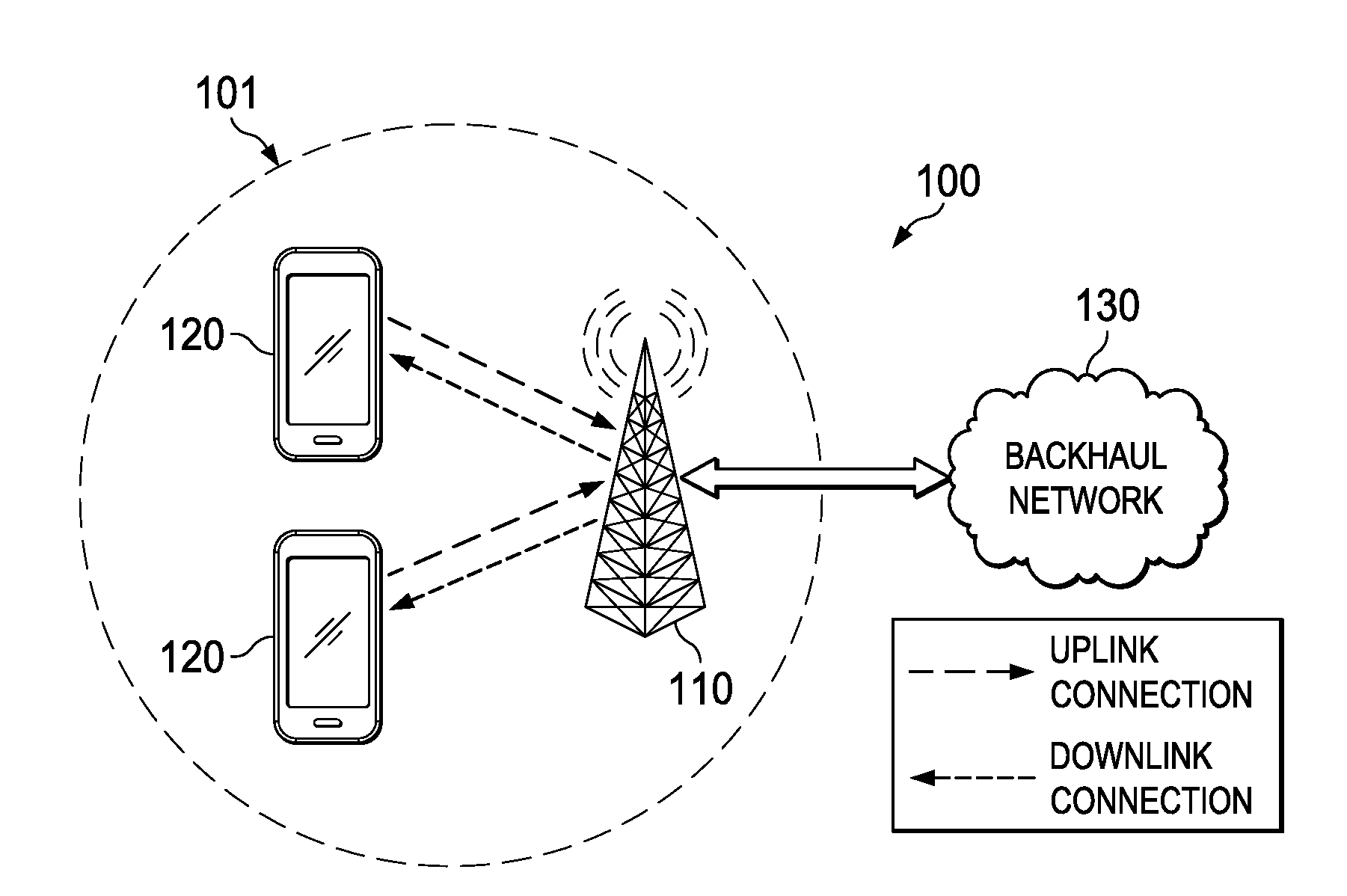
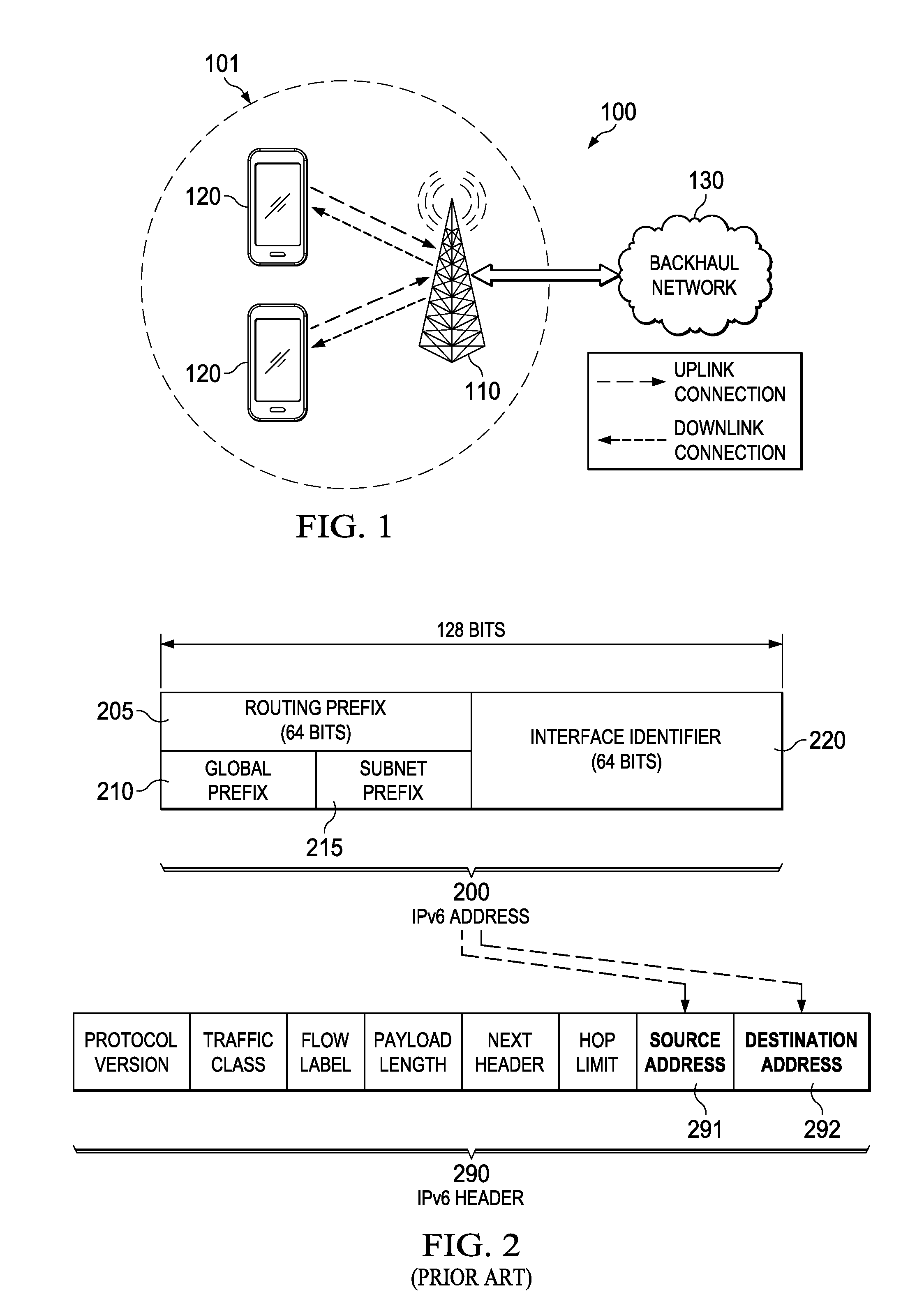
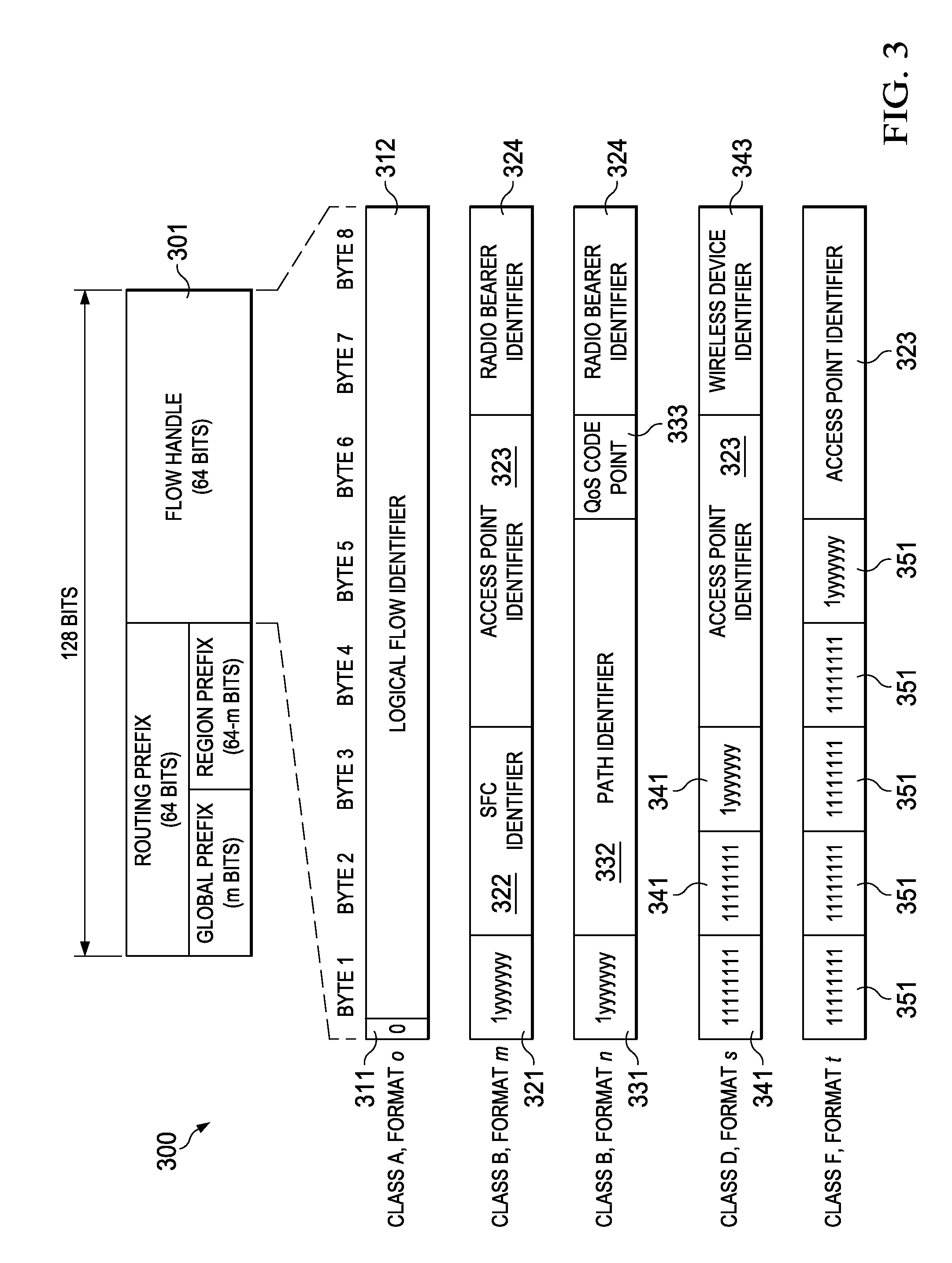
Embedding a flow handle (FH) in an IPv6 address portion of a packet may reduce the amount of overhead needed to support path selection in flow-based packet forwarding. The FH may replace an interface identifier in a standard IPv6 address such that the FH does not add any additional overhead to the IPv6 packet itself. Information specified by the FH embedded in the IPv6 address may be used to select the path or next-hop. In addition, the FH may identify a quality of service (QoS) requirement associated with the packet, and the route selection function may identify a path capable of satisfying the QoS requirement, a service function chain (SFC) ID, an access point (AP) ID, a radio bearer ID, a path ID, and / or a device ID.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Arrangement for traversing an IPv4 network by IPv6 mobile nodes via a mobility anchor point
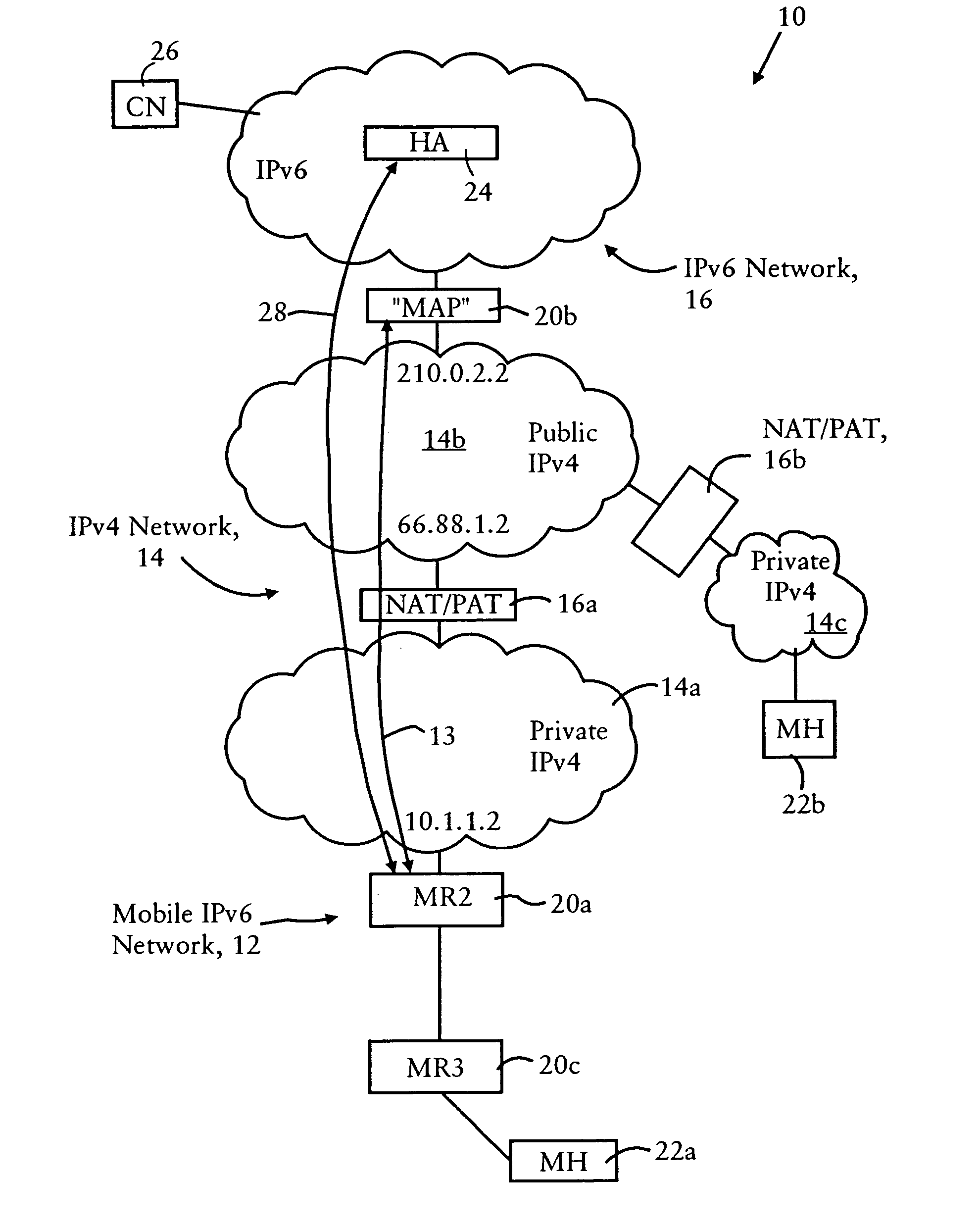
ActiveUS7149225B2Use minimizedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetUnique identifier
An IPv6 mobile node establishes an IPv4 connection with an IPv6 router having an IPv4 interface and configured as a Mobility Anchor Point (MAP) according to Hierarchical Mobile IPv6 Protocol. The MAP assigns a valid IPv6 care-of address to the IPv6 mobile node in response to receiving an IPv4 packet carrying an IPv6 packet requesting a valid care-of address. The IPv4 packet includes IPv4 source and destination addresses, a TCP / UDP source port and TCP / UDP destination port, and a synthetic tag address in the IPv6 source address field. The synthetic tag address includes a unique identifier that enables the MAP to associate the valid IPv6 care-of address with the IPv6 mobile node. Hence, the MAP forwards an IPv6 packet, carried via the IPv4 connection from the source IPv6 mobile node, onto an IPv6 network with an IPv6 source address field that specifies the assigned valid IPv6 care-of address.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
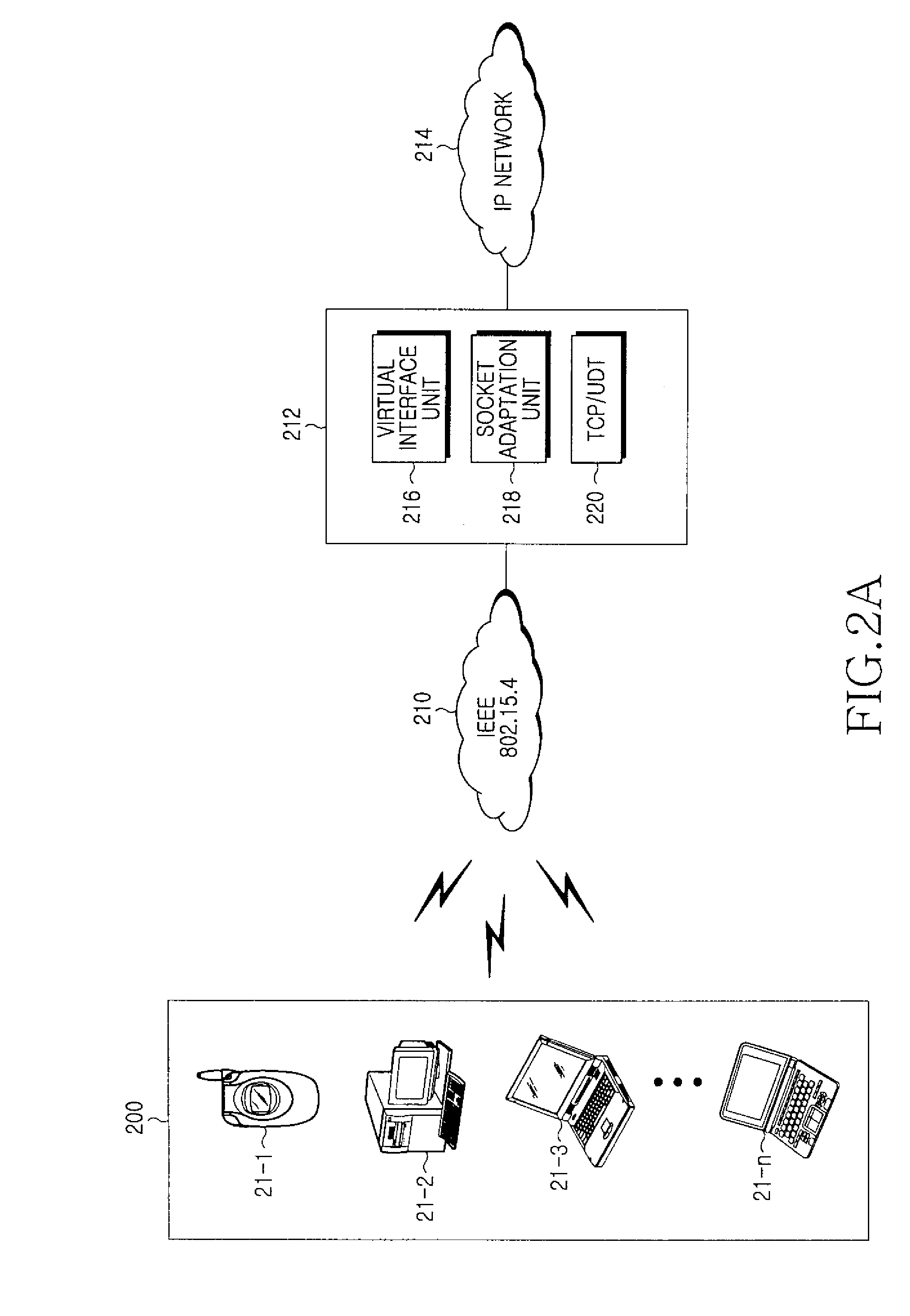
METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING GATEWAY TO TRANSMIT IPv6 PACKET IN A WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK SYSTEM
InactiveUS20090073983A1Simplify protocol stackError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetIPv6 packet
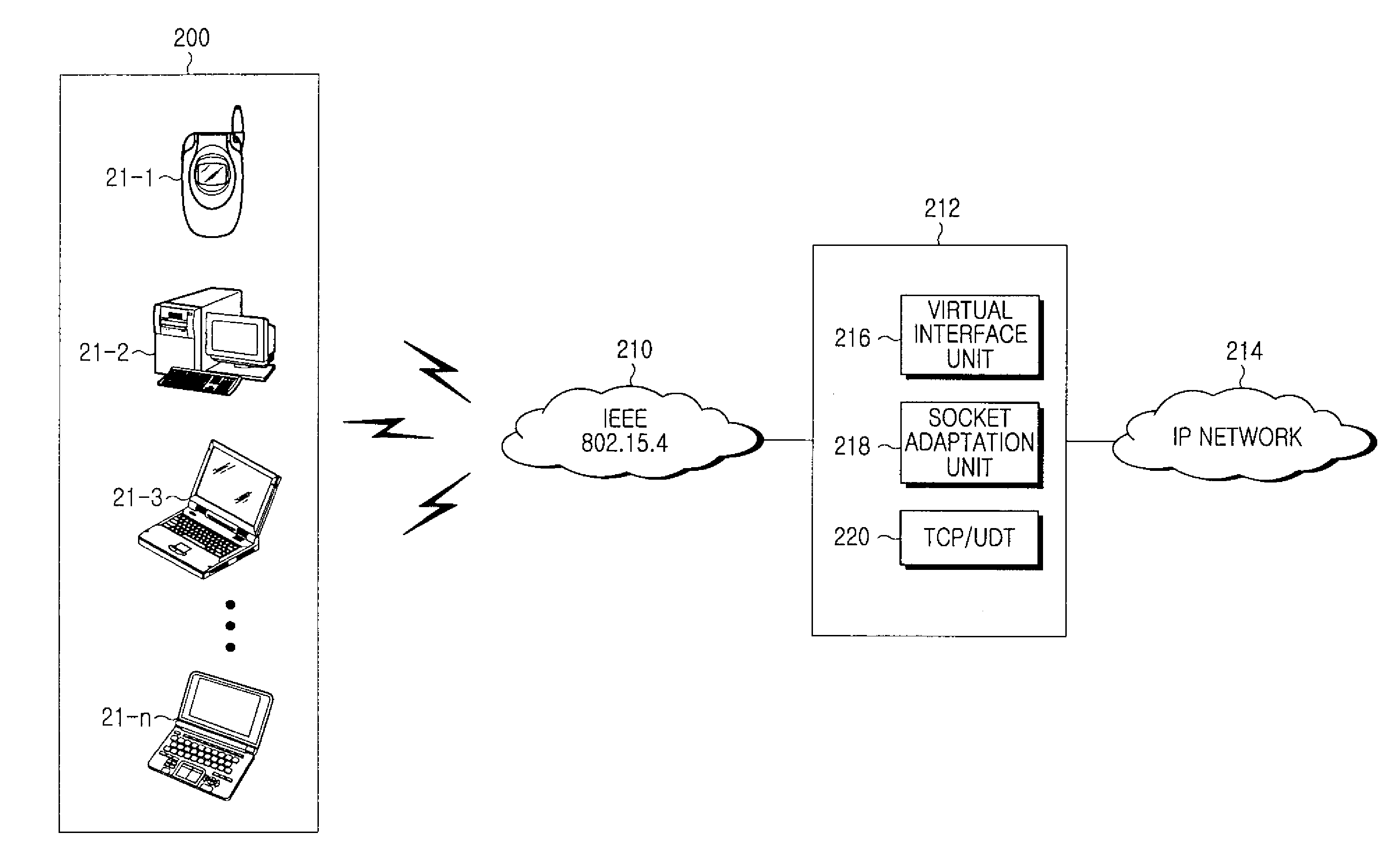
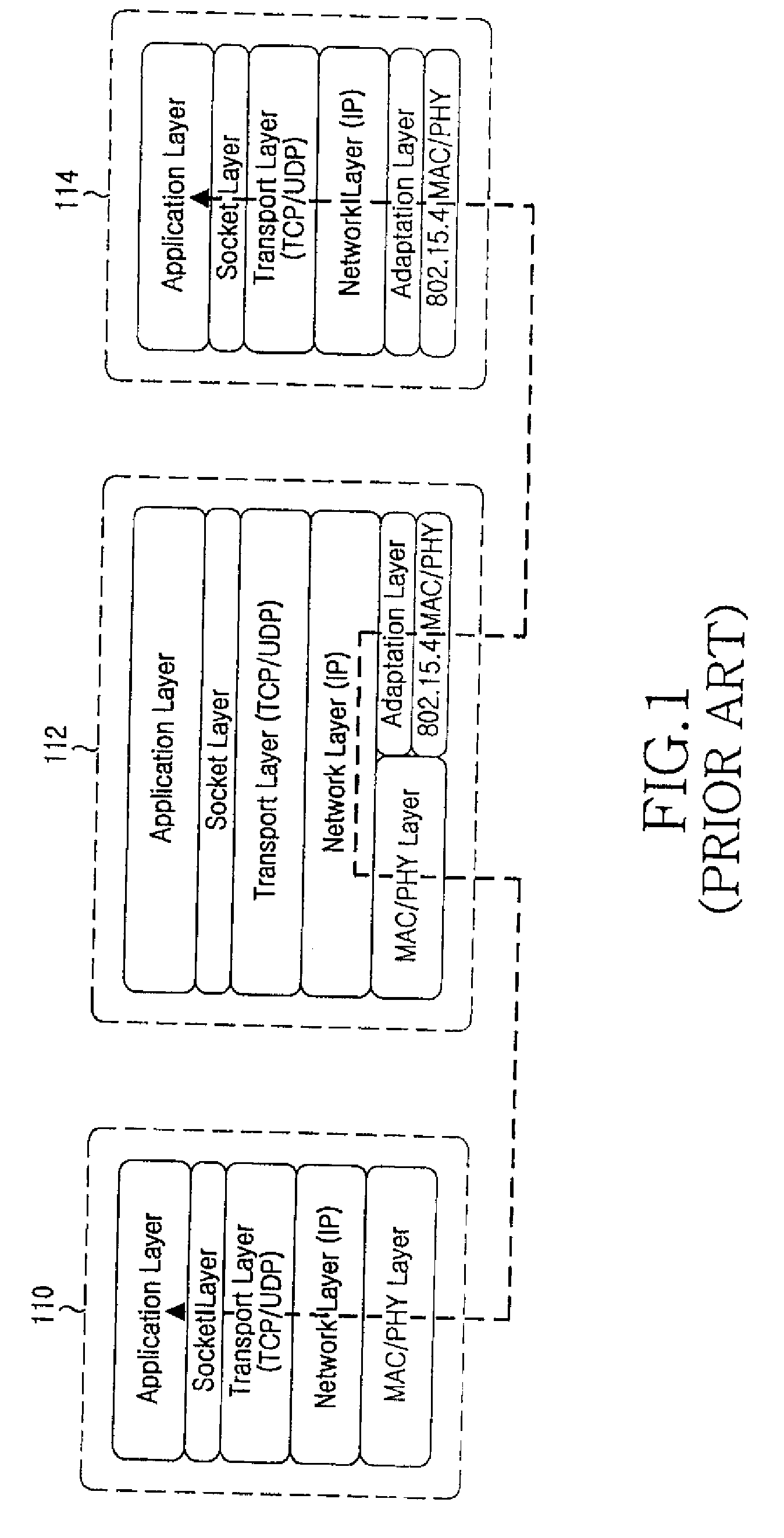
A method and apparatus for providing a gateway for IPv6 packet transmission in a WLAN system are provided, in which a gateway takes over a TCP / IP protocol stack from a legacy 6LoWPAN node for providing a gateway for IPv6 packet transmission in a WLAN system. One or more service request messages for data communications are received from a plurality of 6LoWPAN nodes, and a virtual interface is generated for allocating IPv6 addresses to the 6LoWPAN nodes by adding a predetermined IPv6 address prefix to addresses of the 6LoWPAN nodes set in the service request messages. A socket adaptation layer is interfaced for receiving the IPv6 addresses from the virtual interface and transmitting data packets to the 6LoWPAN nodes, and when data packets are transmitted and received to and from the 6LoWPAN nodes, an on-going file is controlled and managed, and the data packets are routed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
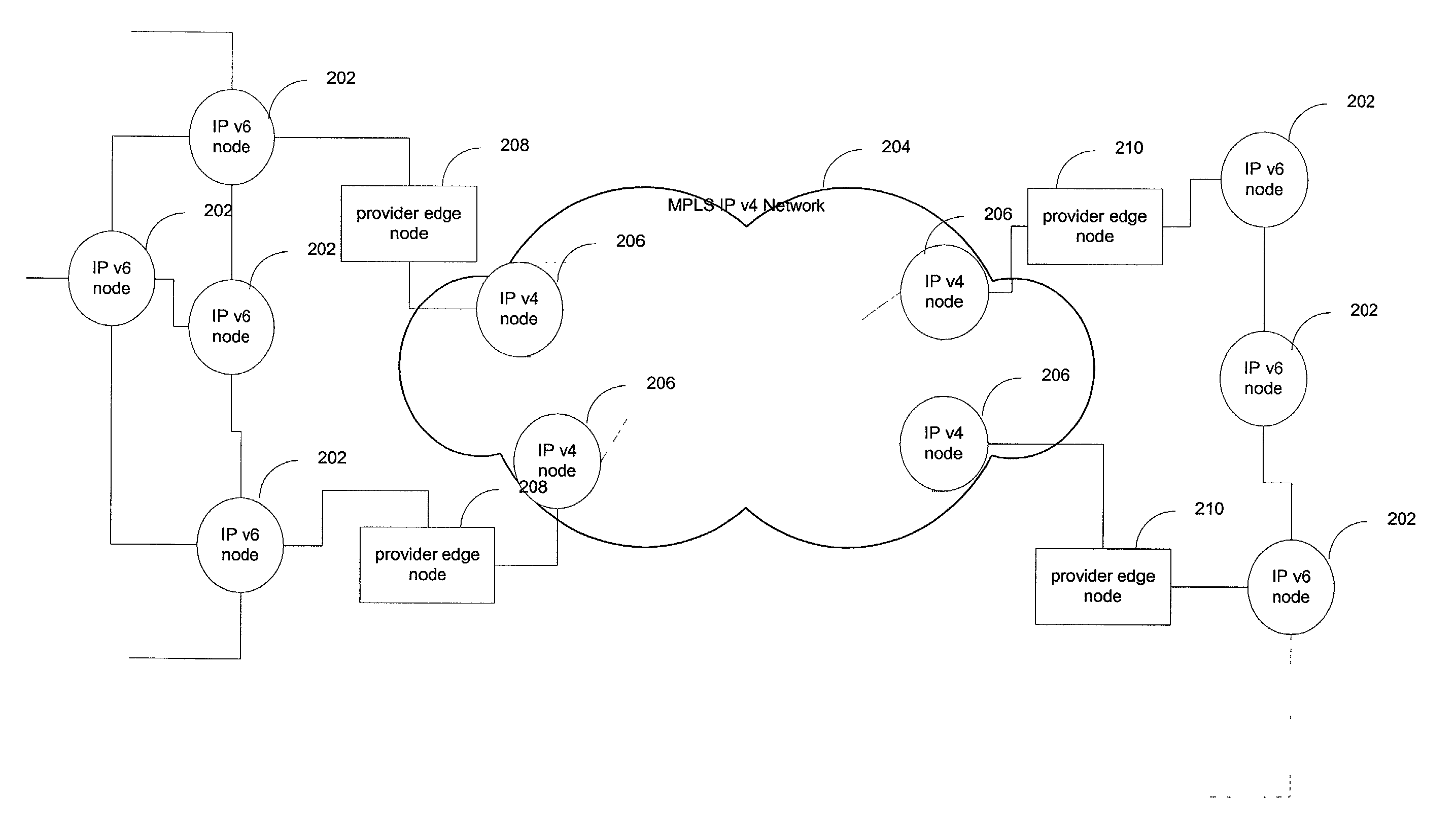
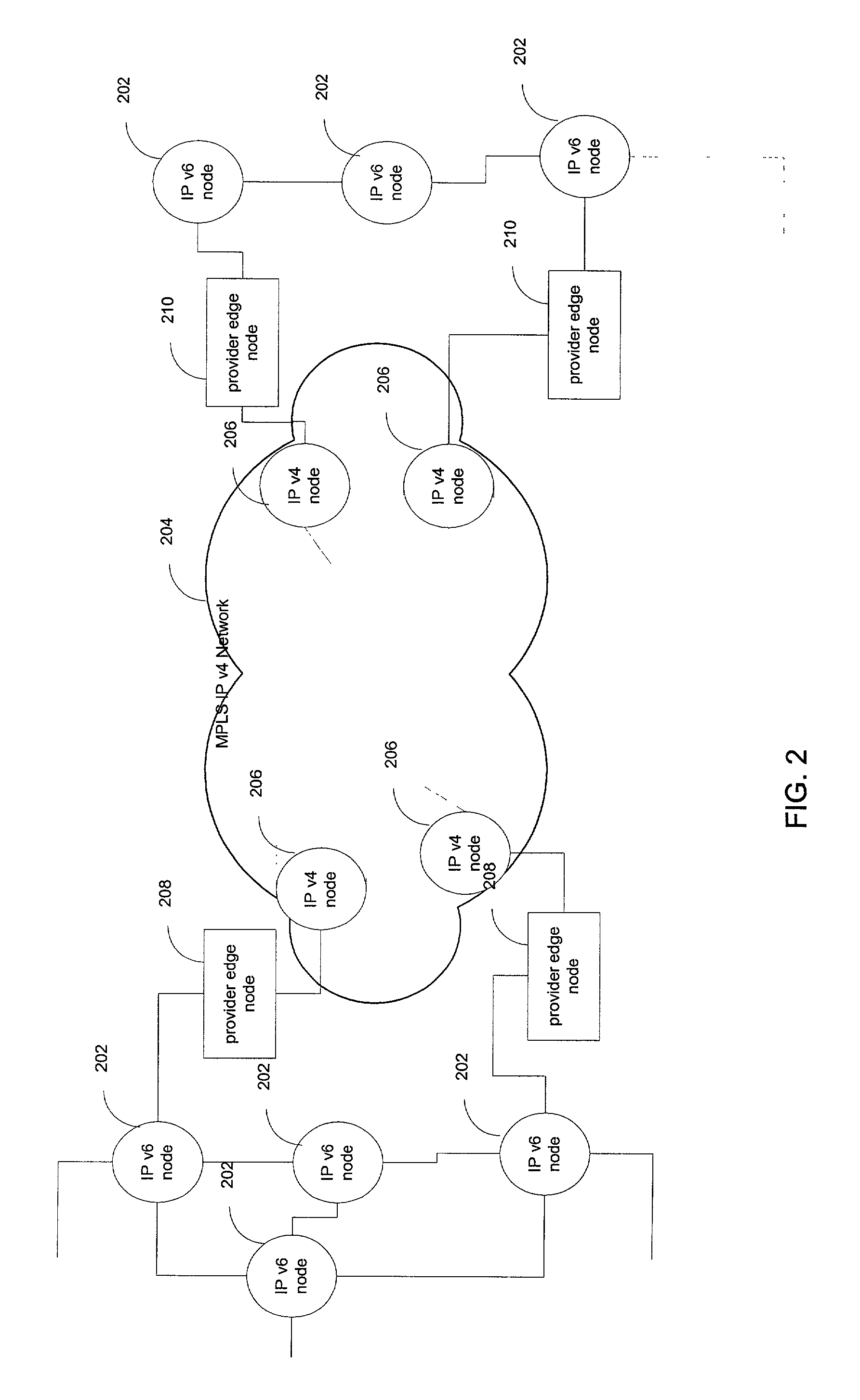
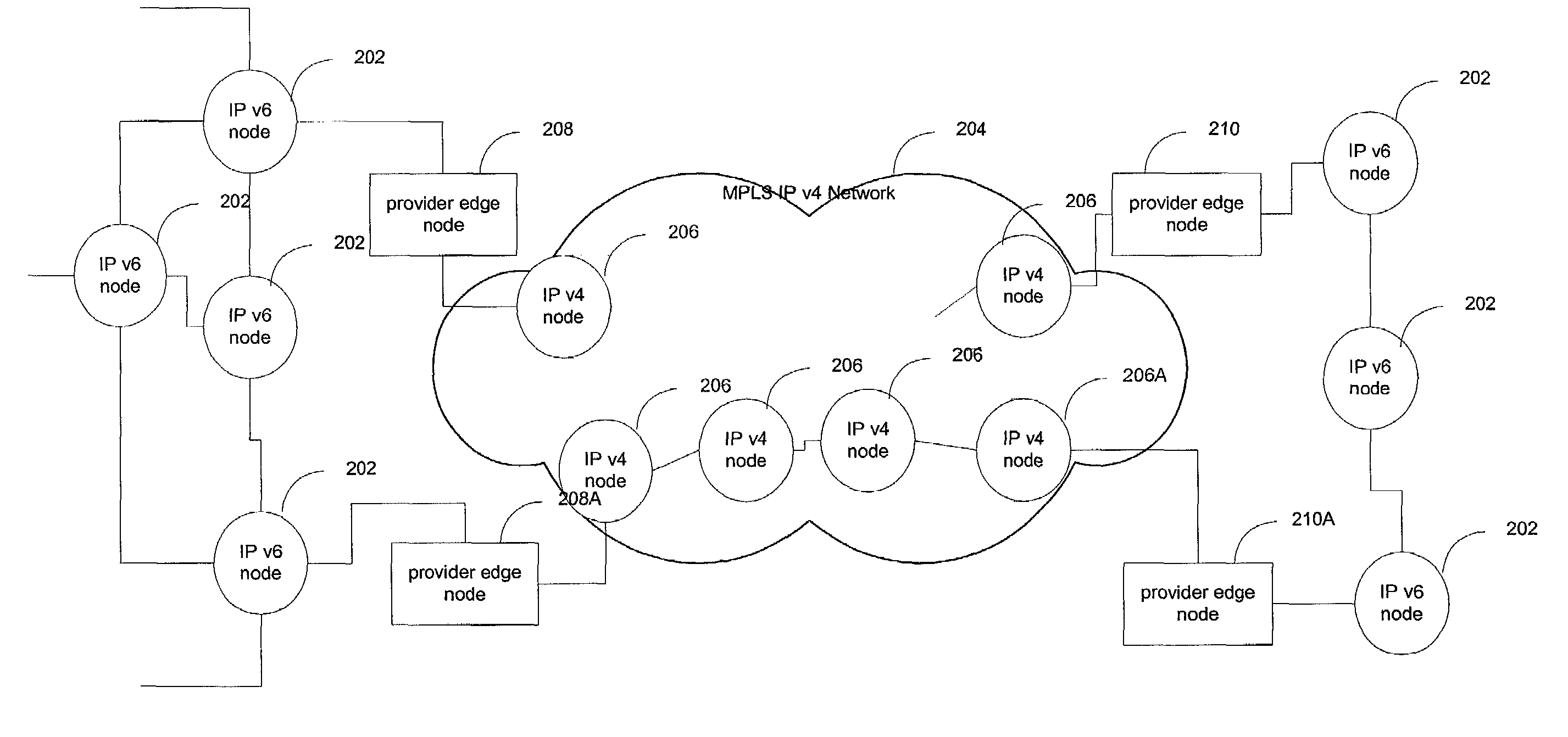
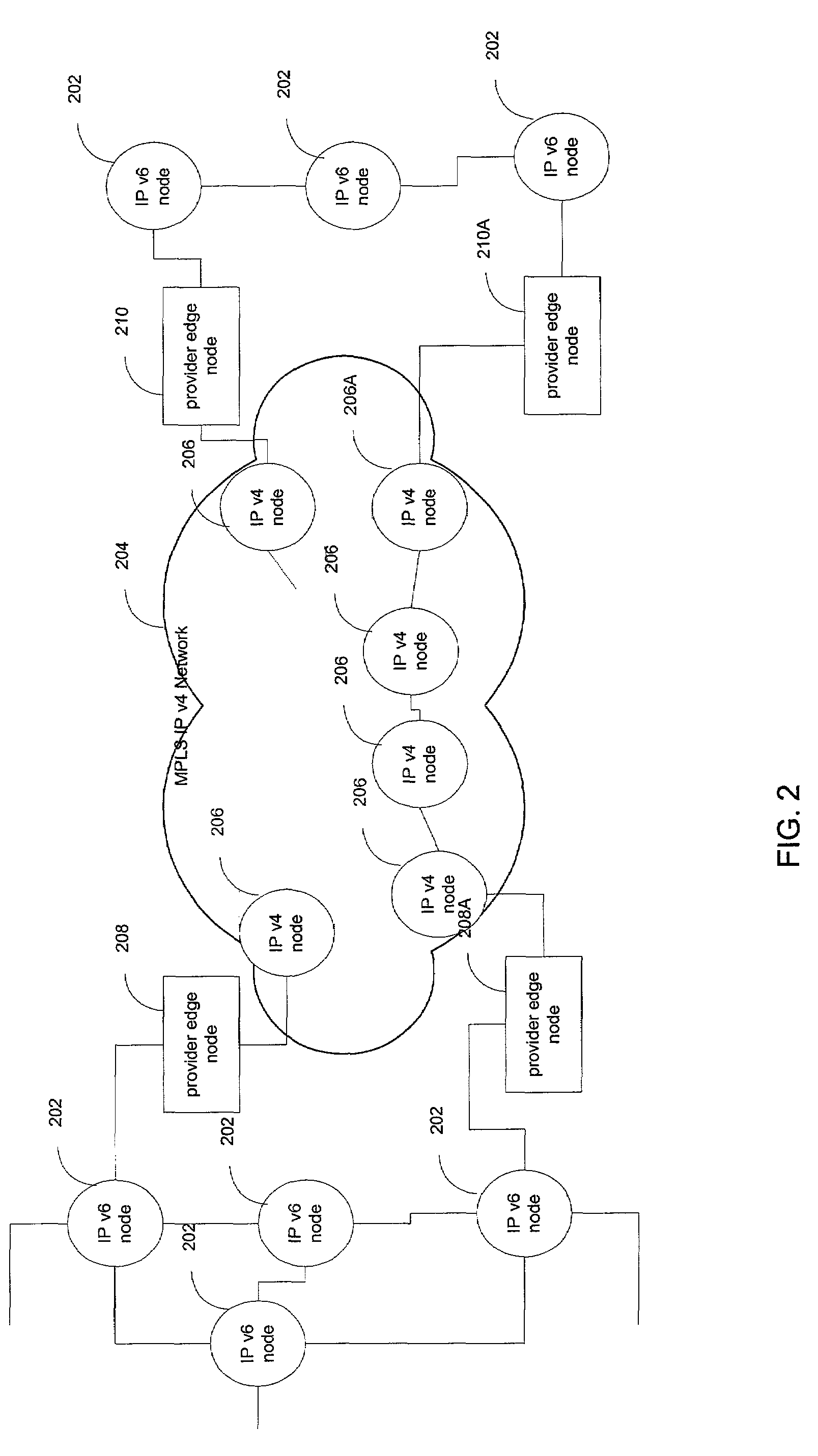
IPv6 over MPLS IPv4 core
ActiveUS7246175B1Save overheadSaving in signalingData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityIPv6 packet
IPv6 traffic may be carried through an MPLS IPv4 network without the use of IPv6-over-IPv4 tunneling. This provides great savings in overhead, signaling, and state information storage and also allows for routing through the MPLS IPv4 network to adjust in response to changes in network state. In one embodiment, an edge node of an MPLS IPv4 network resolves a destination IPv6 network of a received IPv6 packet to an MPLS label switched path. The resolution exploits received inter-domain routing information. This information identifies the IPv4 address of an egress node that is usable as a gateway to the destination network. Within the inter-domain routing information, the IPv4 address may be encoded in IPv6 format.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Arrangement for traversing an IPv4 network by IPv6 mobile nodes
InactiveUS20050152298A1Use minimizedBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsStation
A source IPv6 mobile node is configured for forwarding an IPv6 packet via an IPv4 connection with a destination IPv6 router. The IPv4 packet includes IPv4 source and destination addresses, a UDP source port and UDP destination port, and a synthetic tag address in the IPv6 destination address field. The synthetic tag address, a valid (routable) IPv6 care of address, has an address prefix routed to the IPv6 router. The address prefix specifies a forwarding protocol, the IPv4 destination address for the IPv6 router, and a site-level aggregation identifier. An address suffix for the synthetic tag address specifies the IPv4 source address, the UDP source port and UDP destination port. Hence, the synthetic tag address enables the destination IPv6 router to send an IPv6 reply packet back to the source IPv6 mobile node via the IPv4 network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
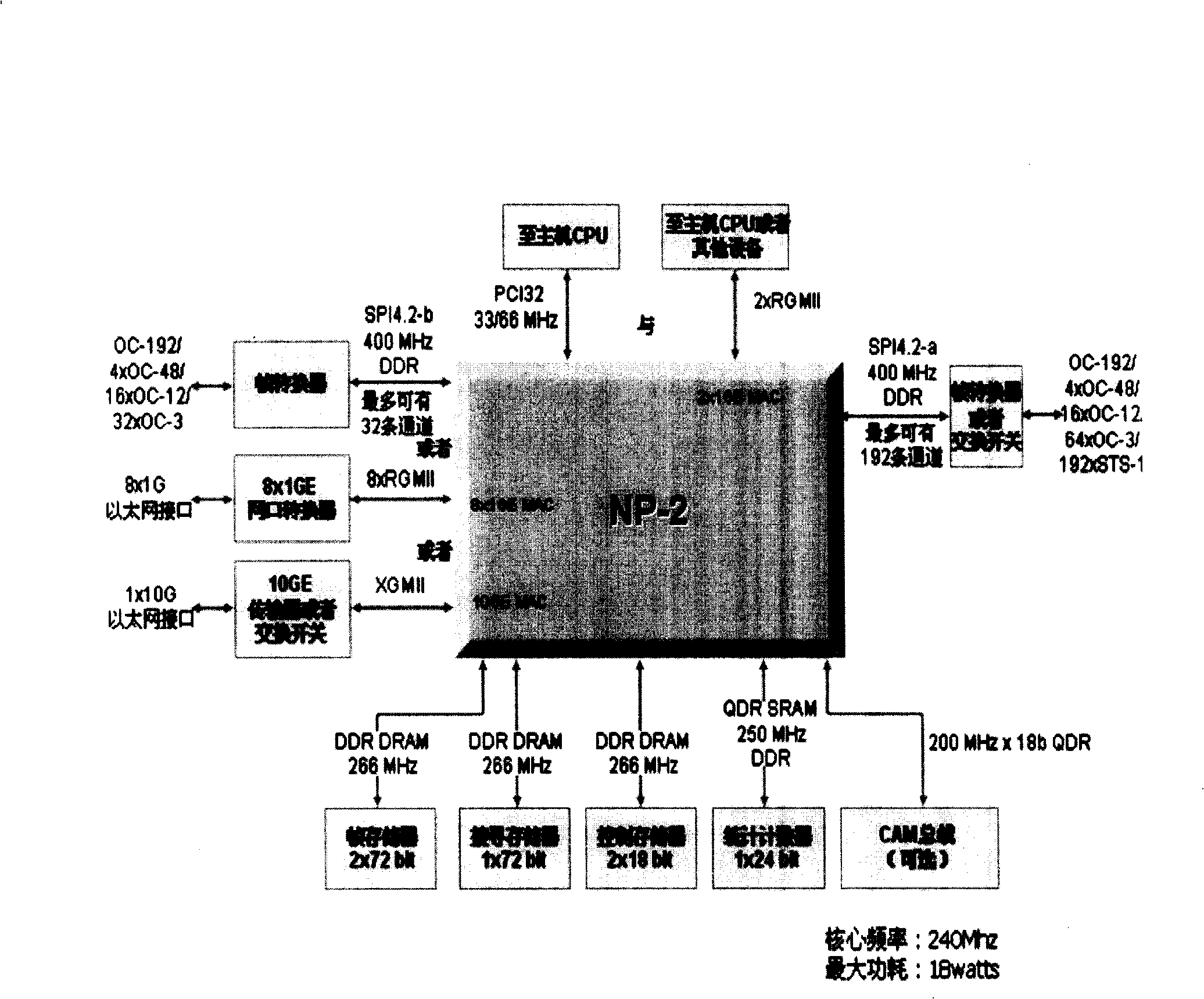
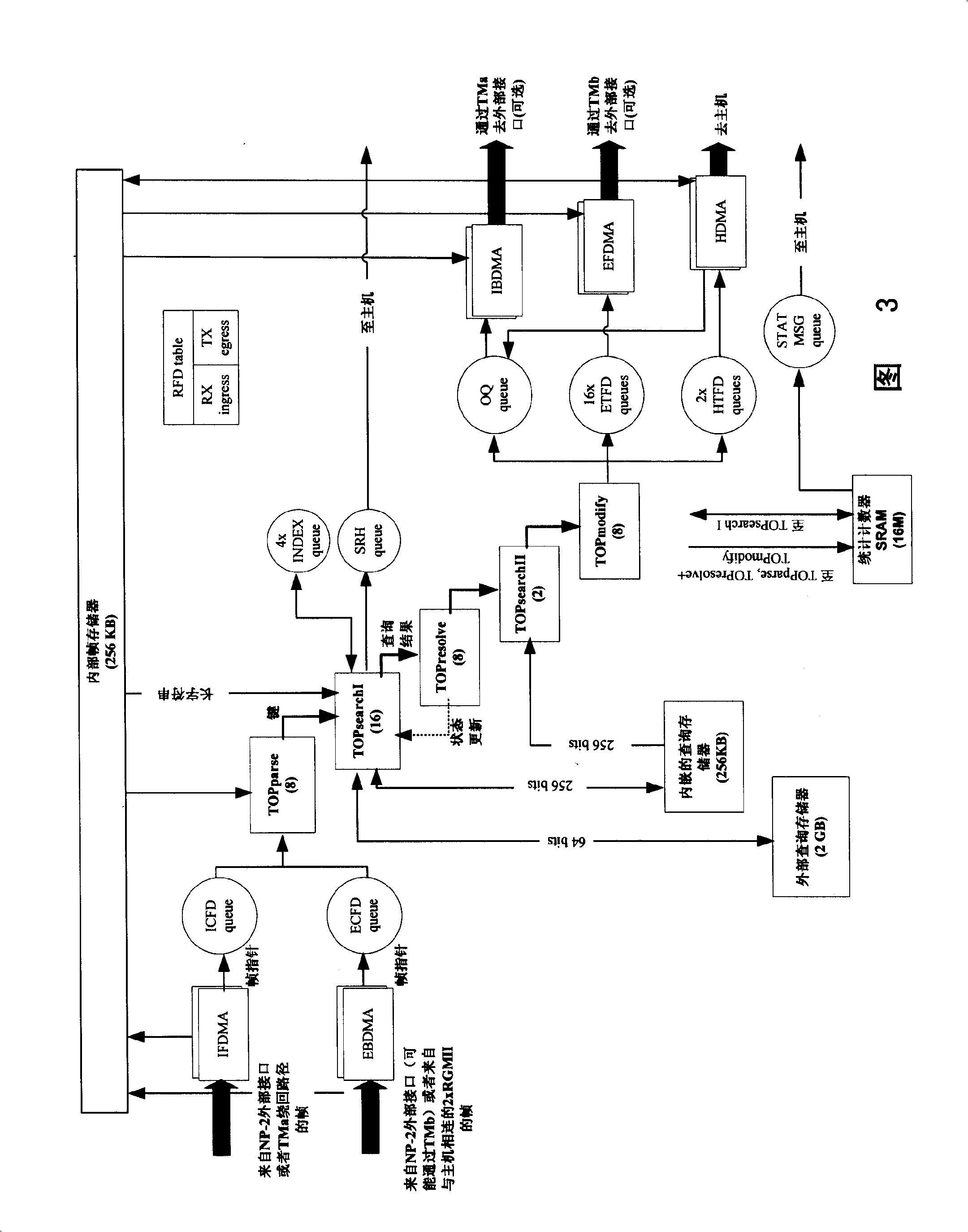
Tunnel packet processing method for implementing IPv6 traversing IPv4 based on network processor
InactiveCN101247308AFlexible configurationMeet the needs of high-speed networkNetworks interconnectionRouting tableRelevant information
The invention discloses a tunnel message processing method for realizing IPv6 passing IPv4 based on network processor. It is characterized in that IPv4 message is adopted to packaging IPv6 data packet, enabling the IPv6 data packet to transmit on IPv4 network. The method comprises the following steps: a, establishing a complete tunnel for IPv6 passing IPv4; b, each tunnel identifies by a tunnel identification code; c, establishing tunnel information table, IPv6 illegal tunnel address list, routing table and conversation table; d, querying the IPv4 package massage obtained by the said tables and forming the tunnel massage passing IPv4; e, judging and delidding according to the protocol number and destination address in the IPv4 message for ordinary IPv6 routing process for the delidding message. When realizing IPv6 passing IPv4, relevant information is cached through the conversation table and inquiry route is simplified, thereby enabling the system to have the data transmission speed with high performance.
Owner:上海亿人通信终端有限公司
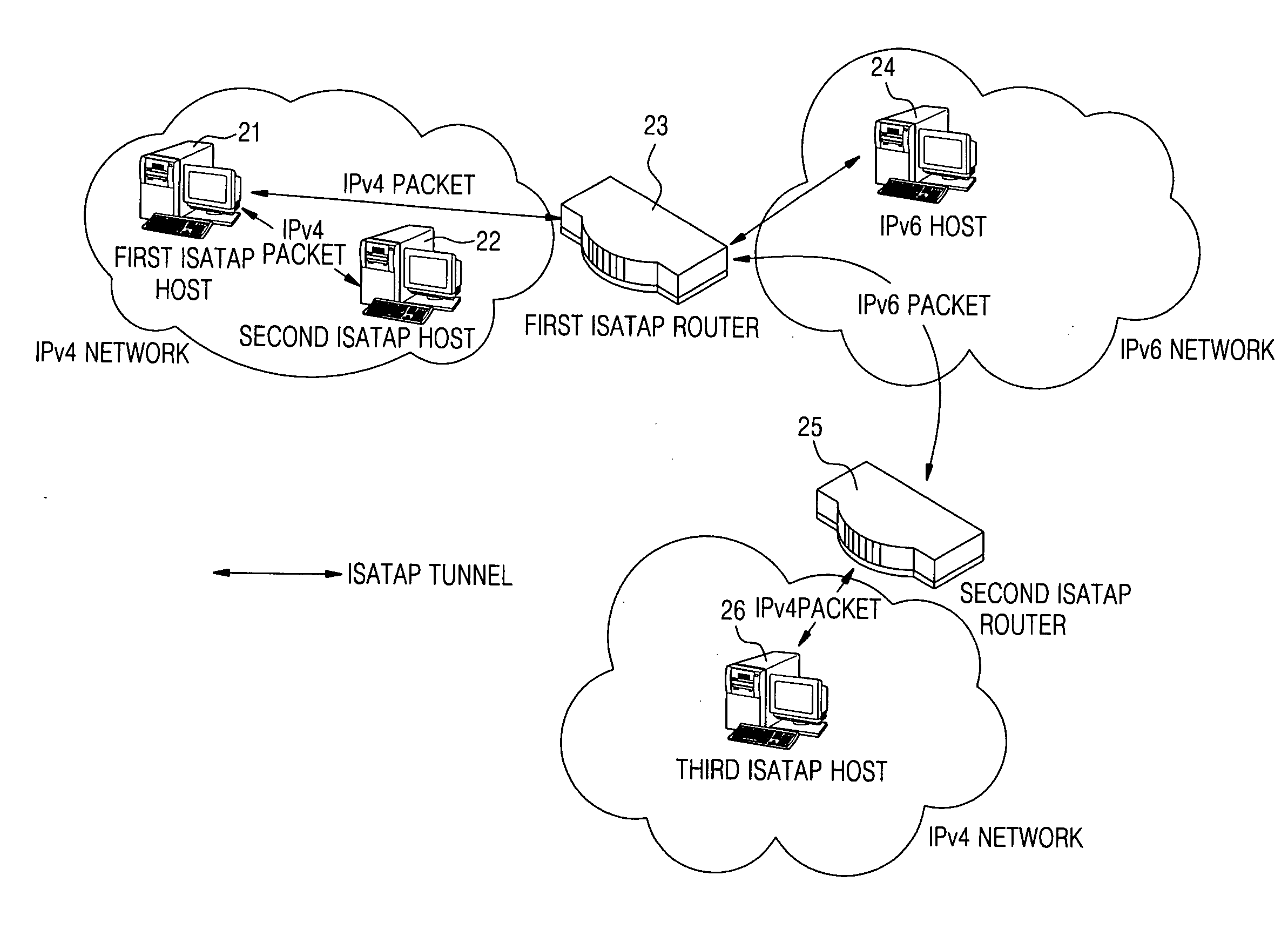
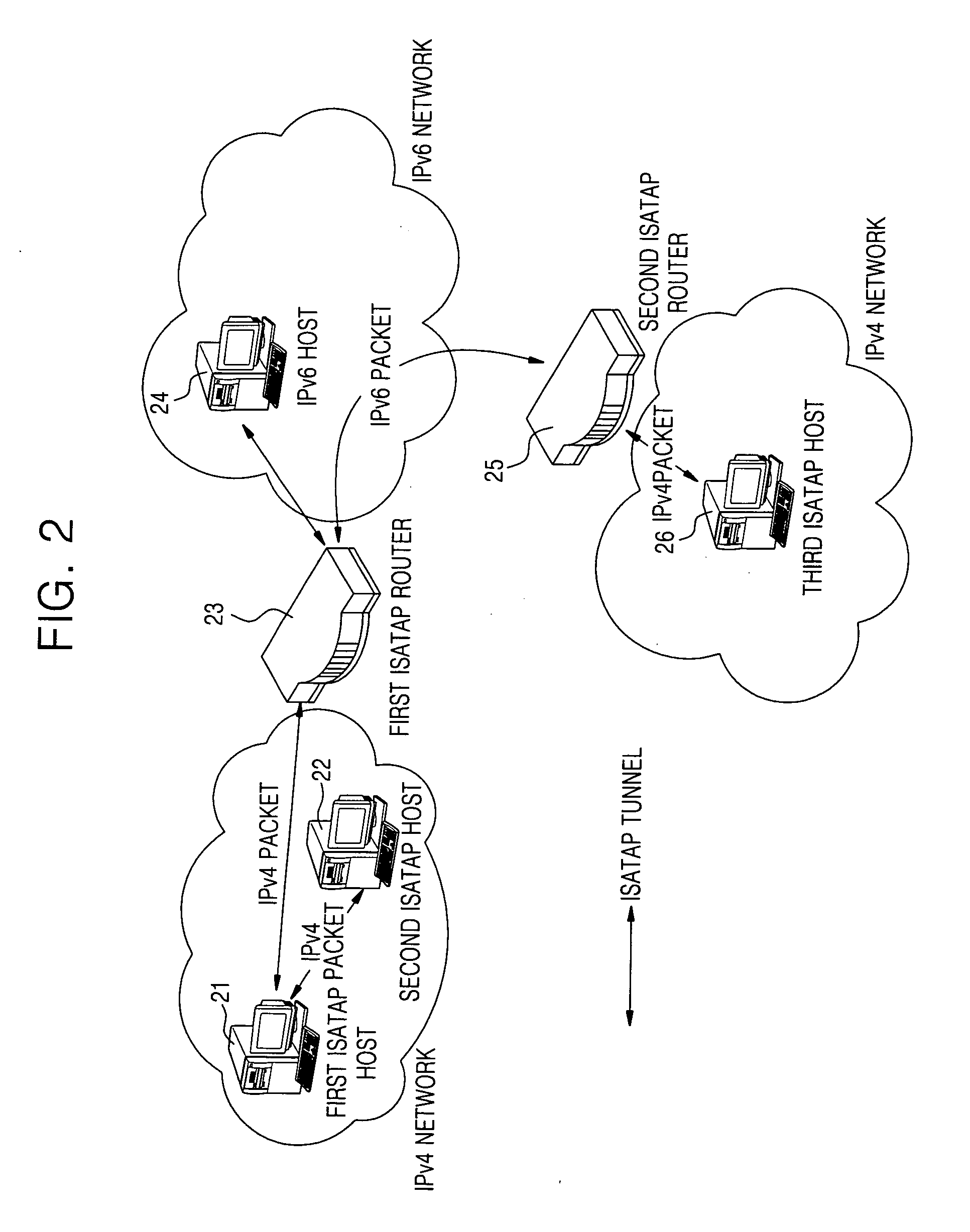
ISATAP router for tunneling packets and method thereof
InactiveUS20070147421A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPrivate IPIPv6 packet
An Intra-Site Automatic Tunnel Address Protocol (ISATAP) router for tunneling packets and a method thereof are provided. A private IP address of an ISATAP host and public IPv4 address information are stored in a mapping table, a public IPv4 address of a Network Address Translator (NAT), to which an IPv6 packet received from the IPv6 host is to be transmitted, is checked using the IPv6 packet and the mapping table, and the IPv6 packet is encapsulated within an IPv4 header whose destination address is the public IPv4 address of the Network Address Translator (NAT), and tunneled to the Network Address Translator (NAT). Thus, the ISATAP host and the IPv6 network can be connected without changing the Network Address Translator (NAT).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
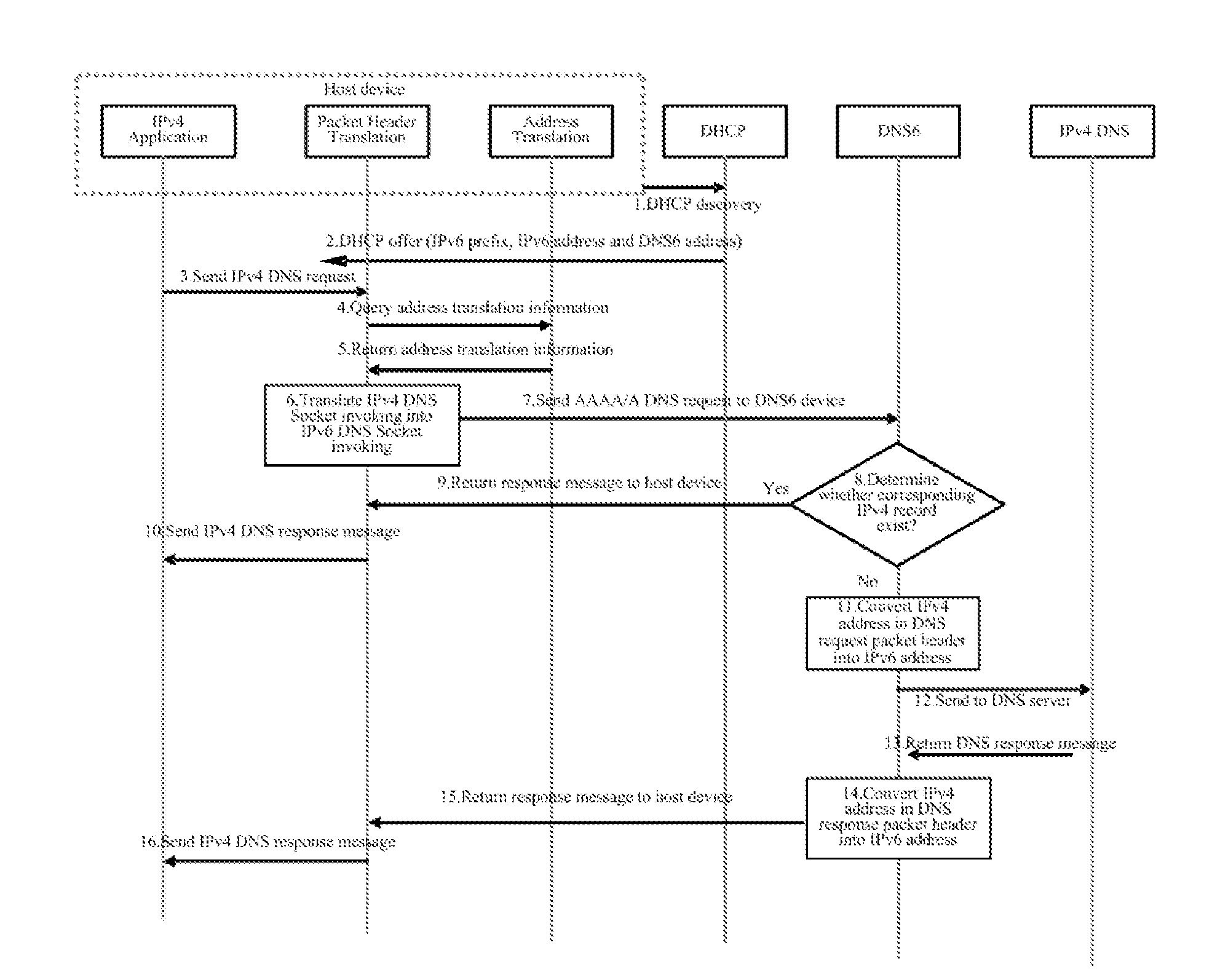
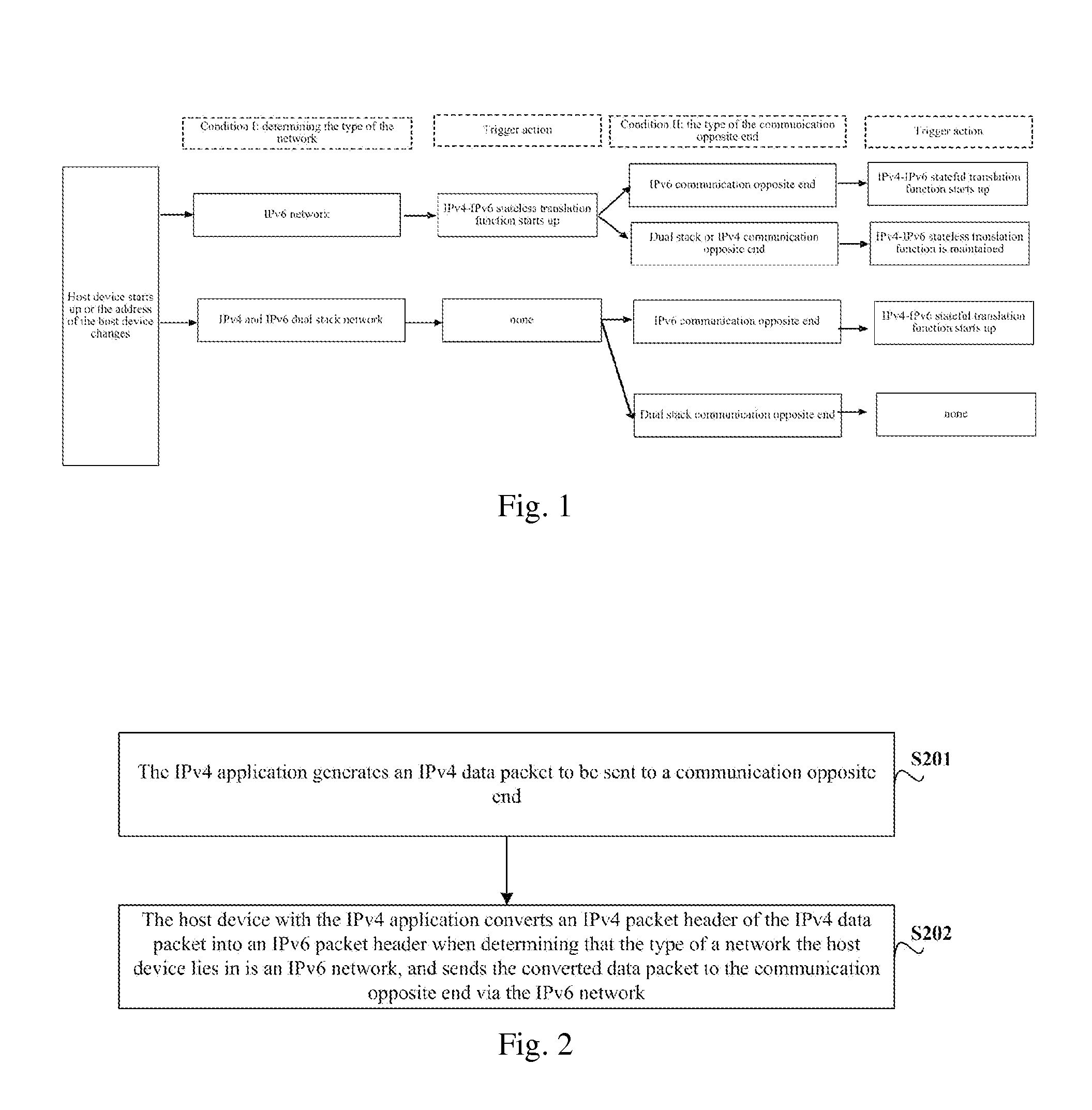
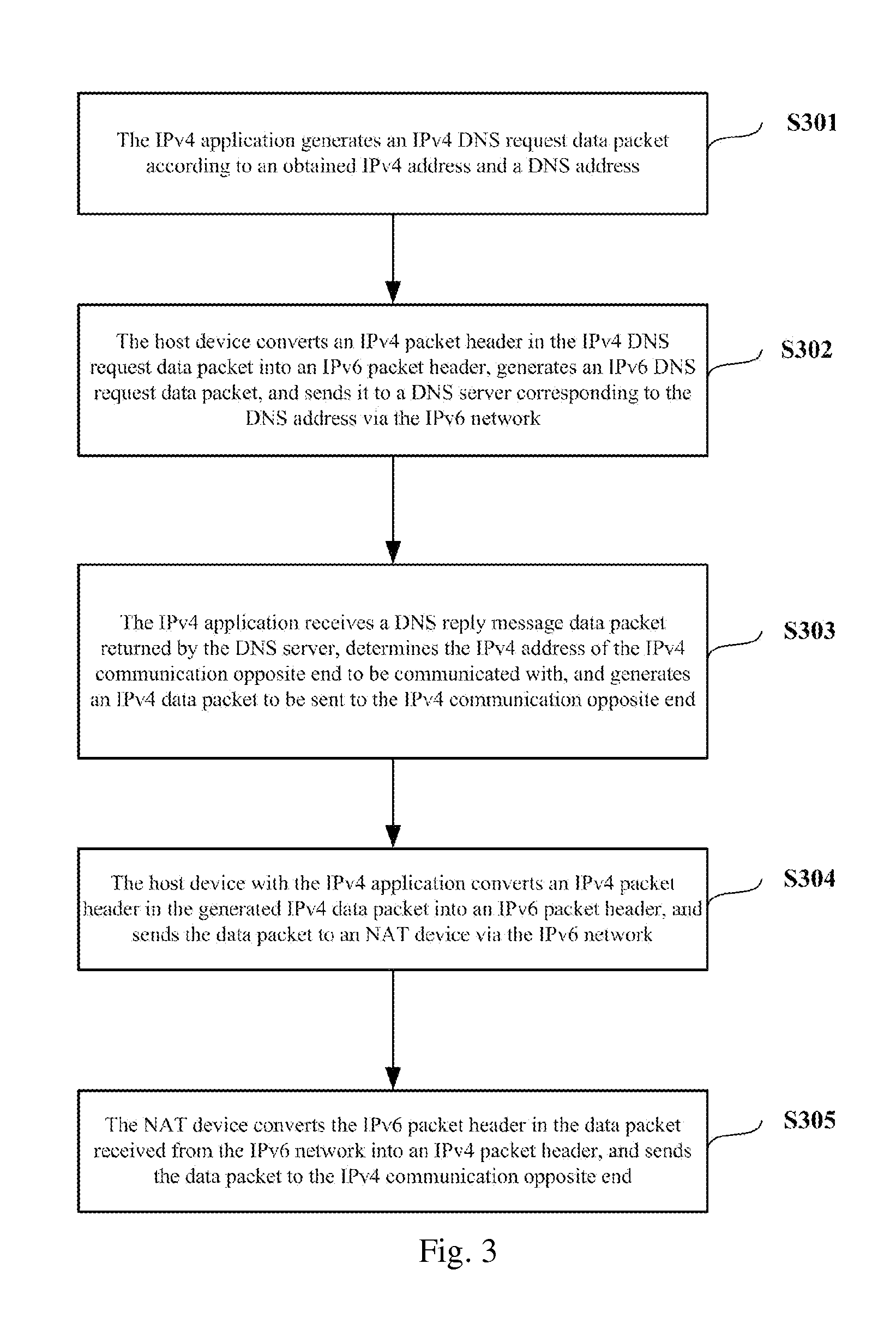
Method and device for communication for host device with ipv4 application
ActiveUS20120110210A1Great system loadImprove communication flexibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData packIPv6 packet
Provided are a method and a device of a host with IPv4 application for performing communication. The method of the host with IPv4 application for performing data communication includes the following steps: the IPv4 application generates an IPv4 packet sent to a communication end; when confirming the type of the network the host is located in is an IPv6 network, the host transforms the IPv4 packet head of the IPv4 packet to an IPv6 packet header, and sends it to the communication end via the IPv6 network. With this invention, it can be accomplished that according to the type of the network the host is located in, the host with IPv4 application communicates with a communication end; the processing load of the system is lightened; the probability that invalidation occurs at a single node is reduced; the smooth migration and transition from original IPv4 application to IPv6 system are facilitated.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
System and method for mapping an index into an IPv6 address
InactiveUS7609689B1Easy to processData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation repositoryInternet Protocol
A system and method maps Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations to Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) site identifiers (IDs), and embeds site IDs into scoped internet addresses in such a way as to facilitate processing by primarily hardware-oriented forwarding tables. A router has a plurality of interfaces for receiving and forwarding packets, and a route processor for making forwarding decisions for received packets. The route processor includes a routing engine, a routing table, a forwarding information base (FIB), a VLAN store and a site ID store. At least some of the router's interfaces are associated with corresponding VLAN IDs, and the site ID store is preconfigured with a mapping of VLAN IDs to site IDs. For IPv6 packets with link-local unicast destination addresses, embedding the VLAN ID associated with the inbound interface into the address, while for packets with site-local unicast destination addresses, using the retrieved VLAN ID as an index to obtain the corresponding site ID, which is then embedded into the address. The modified destination address is then applied to the FIB, which is a forwarding table optimized to permit fast lookups, to derive the outbound interface from which the packet is to be forwarded to reach the destination entity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Data transmission method and network equipment
InactiveCN102170395ASolve the problem of limited deploymentAvoid massive upgradesData switching networksAccess networkNetwork packet
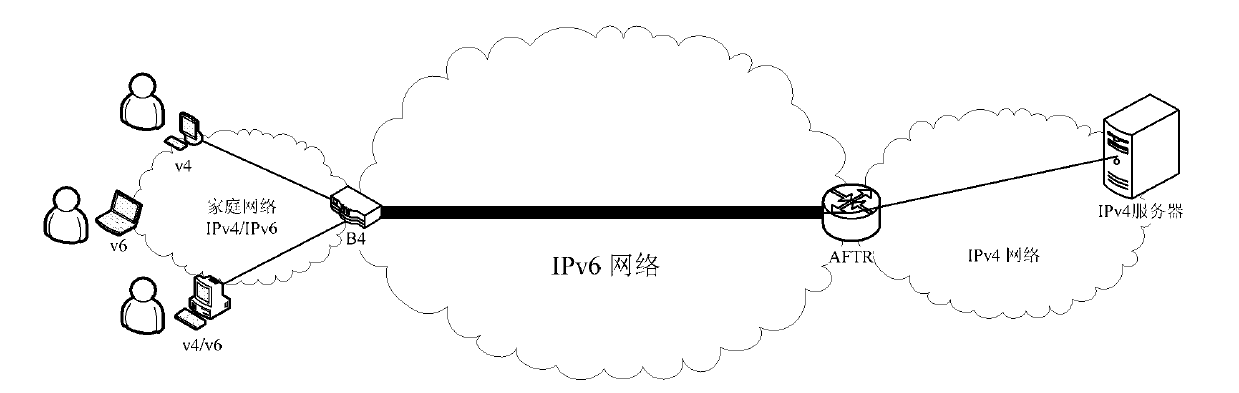
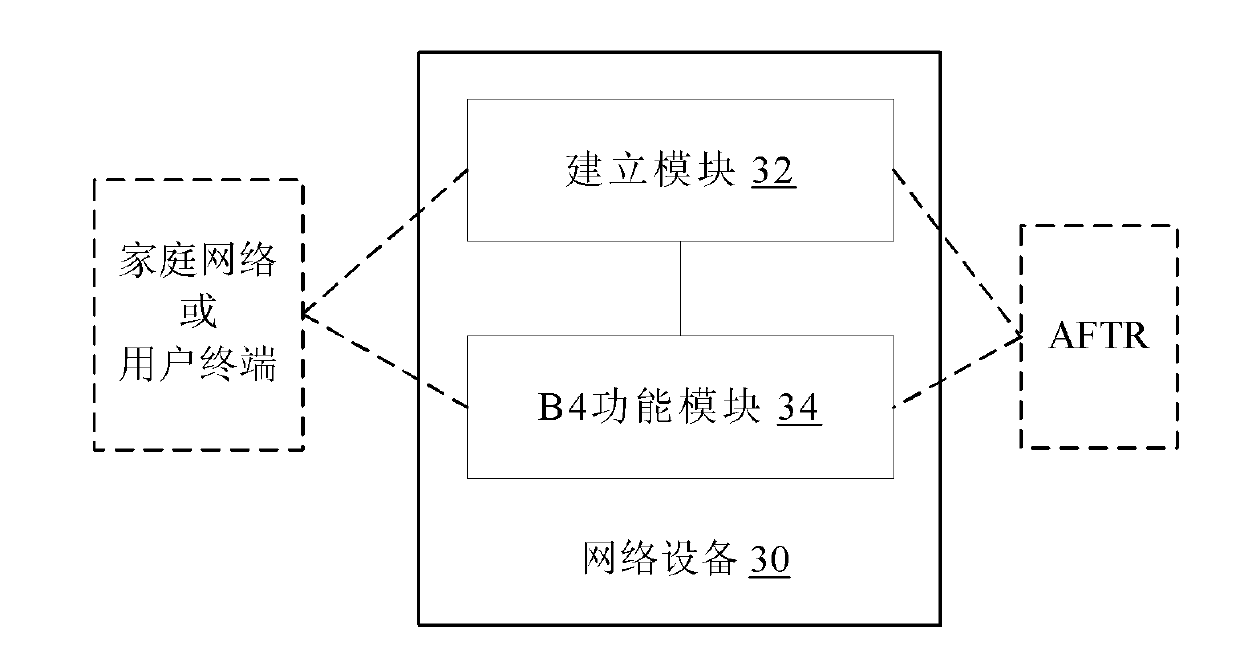
The invention discloses a data transmission method and network equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: the network equipment positioned between a dual stack (DS)-Lite address family transition router element (AFTR) and a home gateway or a user terminal establishes an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6)-based Internet protocol version 4 (IPv4) tunnel from a user side to the AFTR; and the network equipment performs tunnel encapsulation on an IPv4 data packet from a user access network, transmits the encapsulated IPv4 data packet to an IPv4 network, performs decapsulation on an IPv6 data packet from an IPv6 network, and transmits the decapsulated IPv6 data packet to the user side to realize a DS-Lite B4 function. By the data transmission method and the network equipment, the large-scale upgrading of the home gateway or the user terminal is avoided, the DS-Lite technology deployment cost of an operator is reduced, and the evolution rate of the IPv6 network is increased.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Arrangement for reaching IPv4 public network nodes by a node in a IPv4 private network via an IPv6 access network
ActiveUS7443880B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAccess networkPrivate network
An IPv4 node is able to send an IPv4 packet to an IPv4 destination via an IPv6 access network, based on translation of the IPv4 packet into an IPv6 packet for transmission via the IPv6 access network. The IPv4 packet is translated into the IPv6 packet by a local gateway. The IPv6 packet has an IPv6 source address that includes a prescribed address prefix assigned to the local gateway, and an IPv4 address of the IPv4 node. The IPv6 packet also includes an IPv6 destination address that includes a second address prefix assigned to a remote gateway, and a second IPv4 address of the IPv4 destination. The IPv6 packet is converted by the remote gateway into an IPv4 packet for reception by the IPv4 destination via an IPv4 network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Two label stack for transport of network layer protocols over label switched networks
InactiveUS7243161B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
IPv6 traffic may be carried through an MPLS IPv4 network without the use of IPv6-over-IPv4 tunneling. An IPv6 packet is sent through the MPLS IPv4 network through a label switched path (LSP). The IPv6 packet is encapsulated with a label stack associated with the LSP. A second level label is used in the label stack (in addition to the label associated with the LSP). This second level label provides important benefits.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
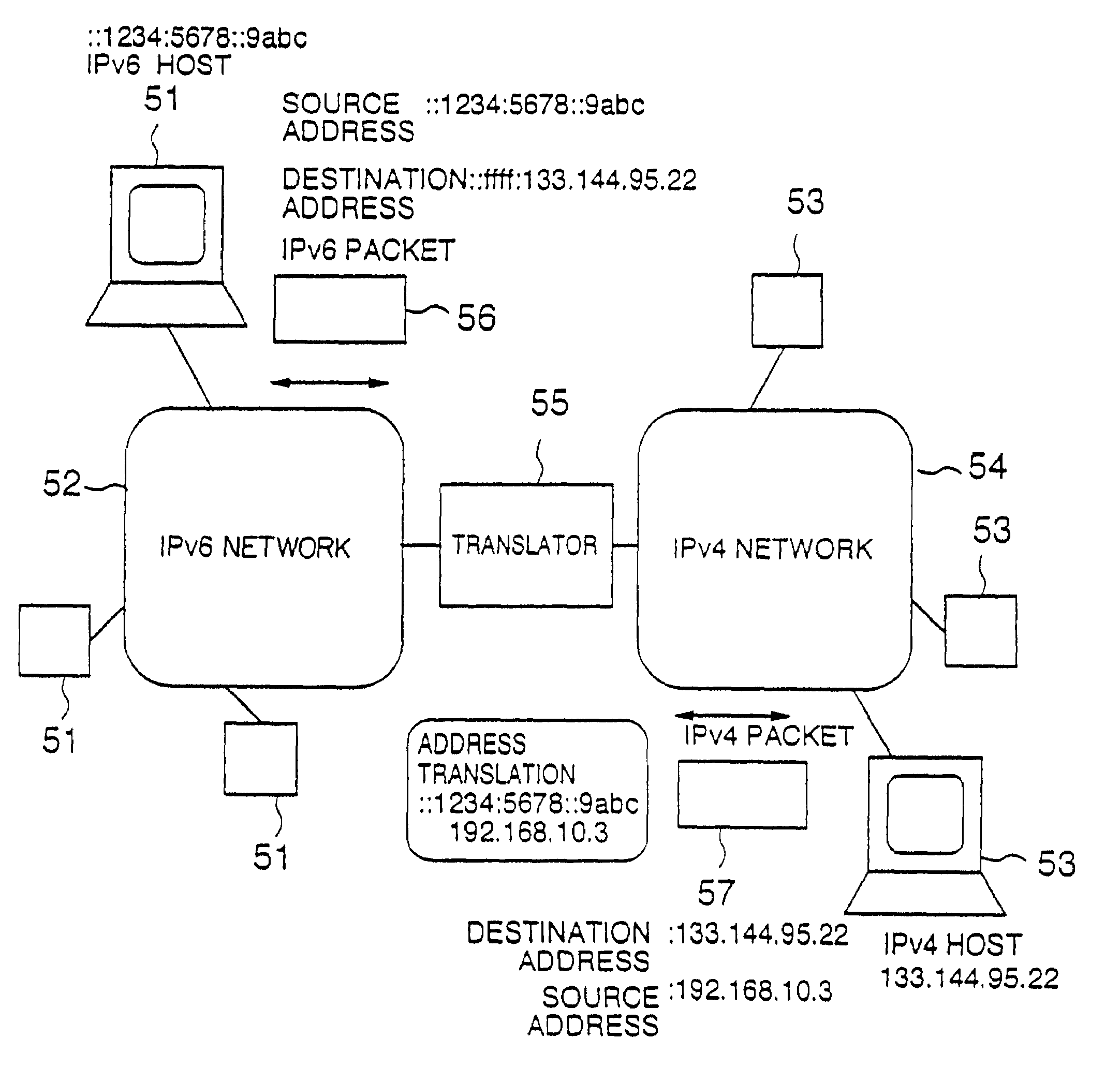
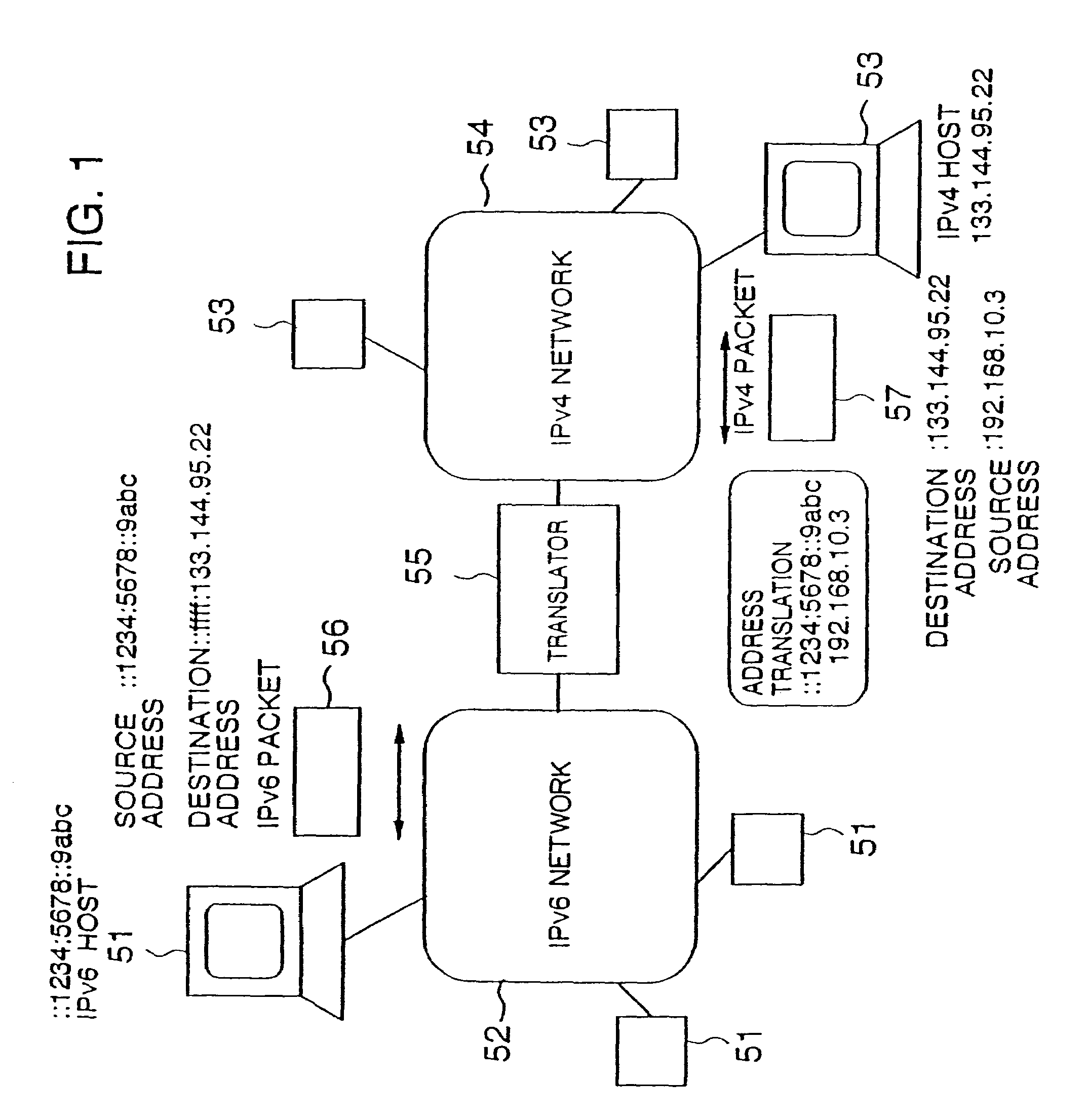
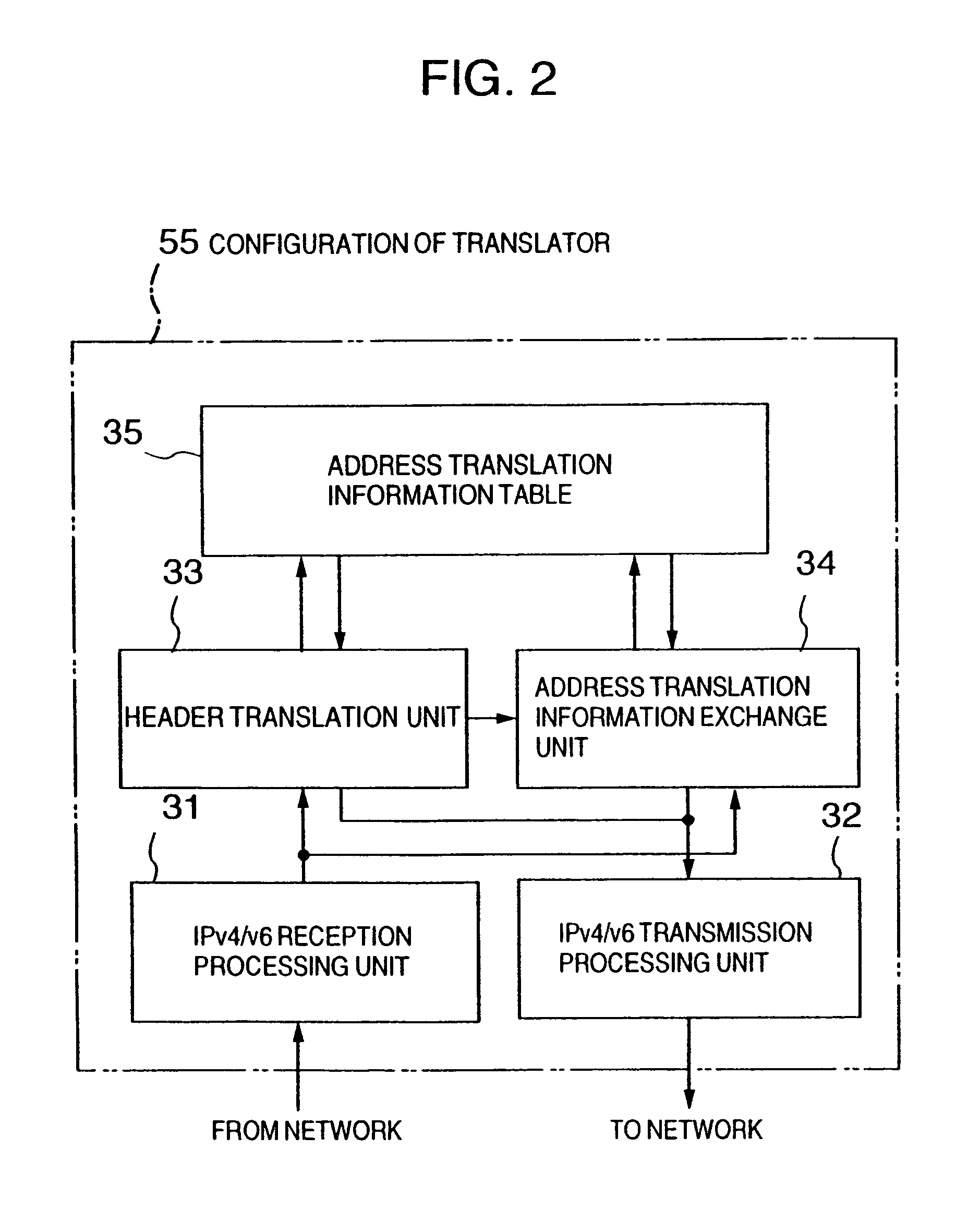
Translator for IP networks, network system using the translator, and IP network coupling method therefor
InactiveUS7088726B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIp addressNetwork packet
A translator for coupling a first network such as an internet protocol version 4 (IPv4) and a second network such as an internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) having different addressing architectures for IP addresses due to a difference in version or the like so as not to exhaust the IP addresses of one of the two networks, a network system using the translator, and a network coupling method therefor are provided. When a packet is transferred from the IPv6 network to the IPv4 network, the translator assigns any of a plurality of previously prepared IPv4 addresses to an IPv6 address stored in a source storing field of the IPv6 packet. The assigned address is stored in a source storing field of an IPv4 packet. A packet translation unit is provided for assigning the foregoing IPv6 address to an IPv4 address stored in a destination storing field of the IPv4 packet, when a packet is transferred from the IPv4 network to the IPv6 network, and for storing this address in a destination storing field of the IPv6 packet.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
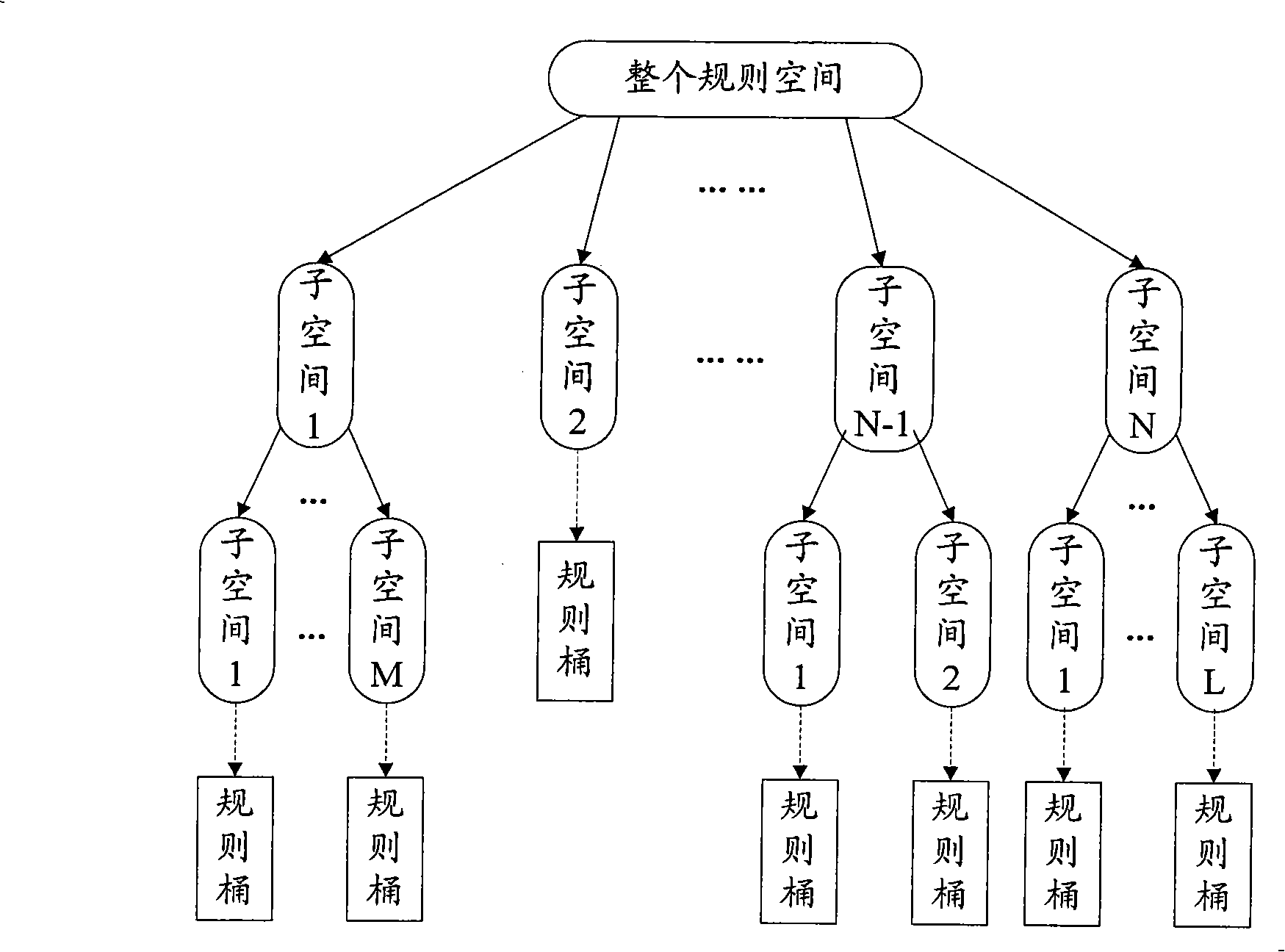
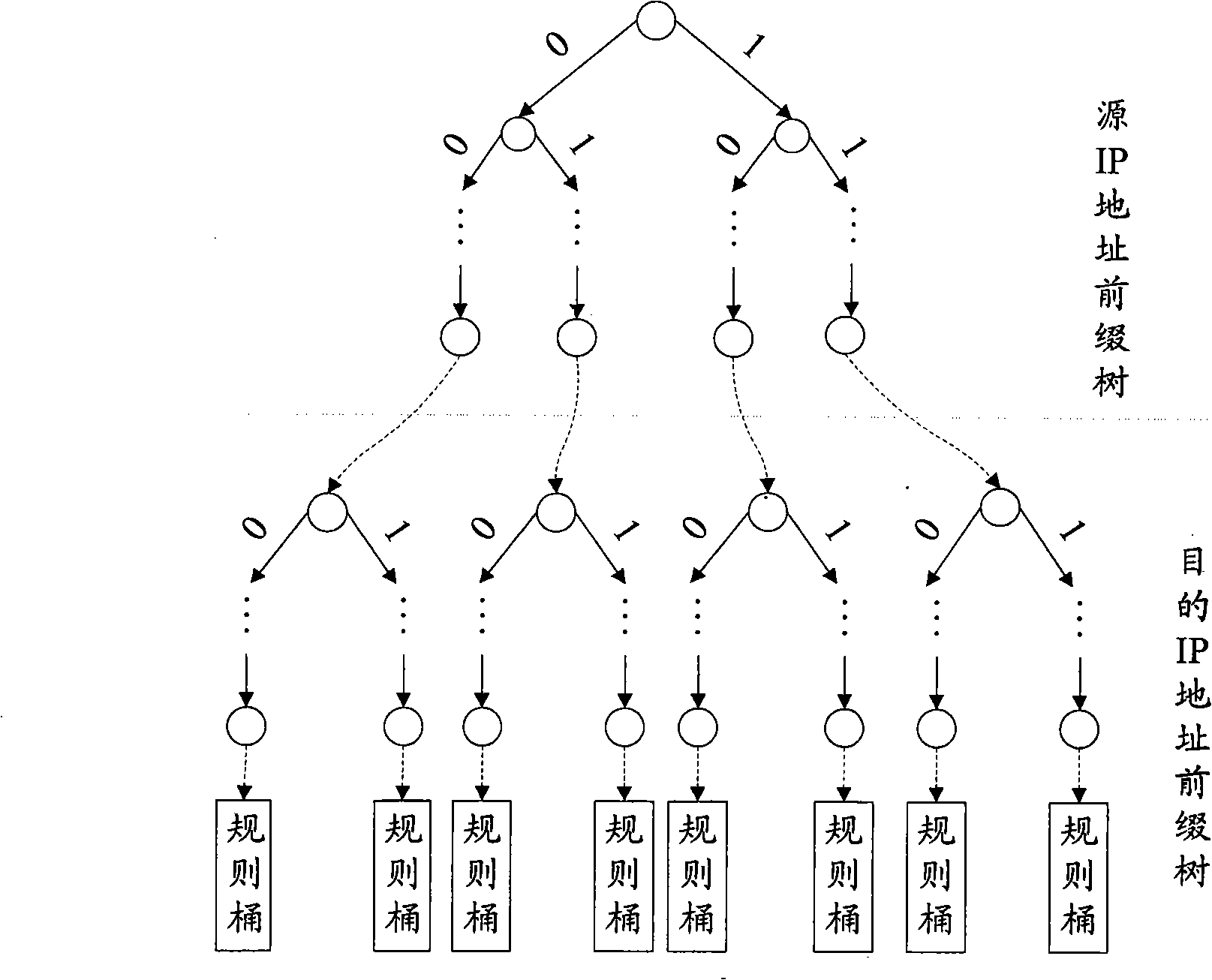
Method and apparatus for implementing IPv6 packet classification
InactiveCN101345707AImprove search speedReduce memory usageData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsIp addressNetwork packet
The invention relates to a method of realizing IPv6 message sorting and a device, wherein an original rule and a centralized rule are both denoted by triple composed of source IP address, object IP address and flow label, and decision trees are constructed according to address prefixing of each rule composite IP address. The method comprises: abstracting the triple of the current data packet, and recording a centralized default rule of the original rule; converting the source IP address and the object IP address of the current data packet from two-dimensional logic operation into compound IP address; determining message classification rule of the current data packet as a matching rule or a default rule with highest priority corresponding to the bit matching result of corresponding nodes by bit in turn according to current data packet composite IP address. The device comprises a structural unit, a processing unit and a sorting unit. The invention is fast in searching speed, small in memory occupancy, excellent in expansibility and simple in updating, widely applied in a network interconnection communication field.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Network system for communicating between different IP versions with multiple translators
ActiveUS20090304026A1Improve transmission efficiencyWithout deteriorating transfer efficiencyTime-division multiplexNetwork connectionsTelecommunications networkIPv6 packet
In a telecommunications network system in which two translators are placed for the conversion of IP version 4 (IPv4)-version 6 (IPv6)-IPv4, one translator converts an IPv4 packet to an IPv6 packet by adding a prefix obtained from a prefix management server managing prefixes to an address contained in an IPv4 packet received from an IPv4 terminal and also converts an IPx6 packet to an IPv4 packet by removing a prefix from the address contained in the IPx6 packet received from the translator. According to the conversion table, the other translator converts the IPv6 packet received from the one translator to an IPv4 packet and an IPv4 packet received from the IPv4 server to an IPv6 packet, thus enhancing the transfer efficiency in the IPv6-IPv4 conversion network.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
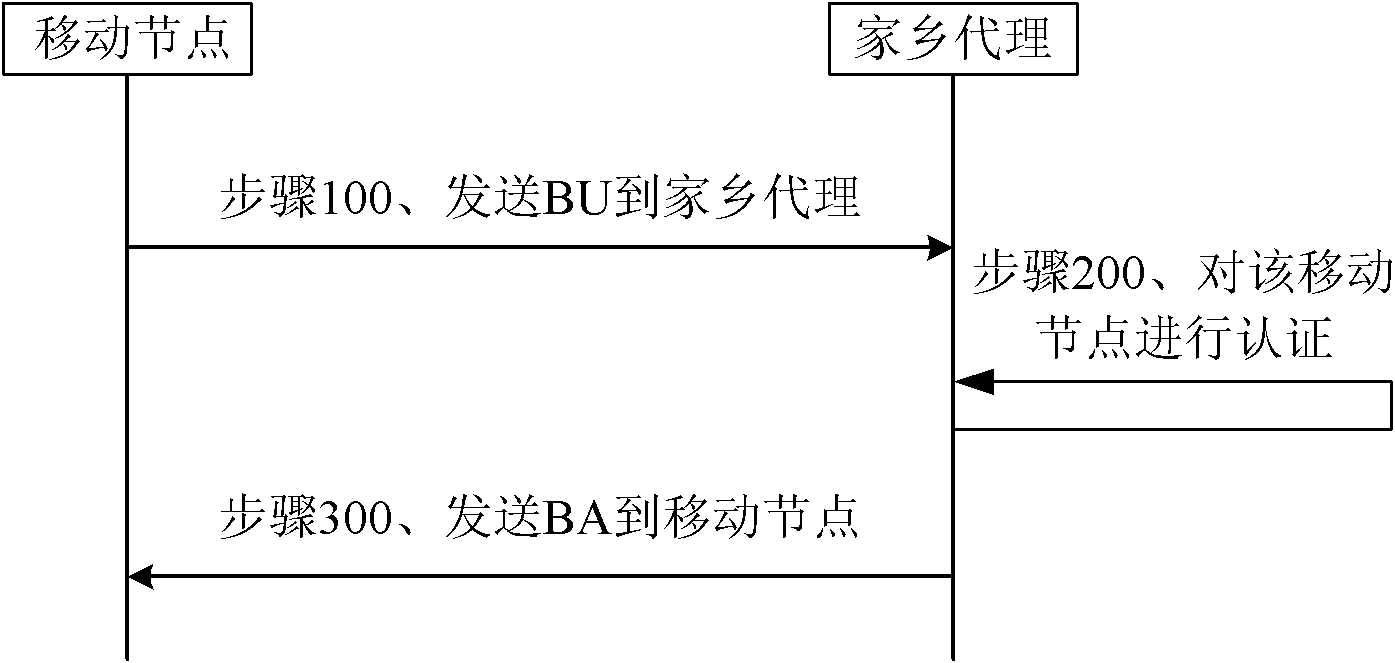
Communication method in mobile IPv6 and mobile IPv6 communication system
ActiveCN101136906ASimple contentSave spaceKey distribution for secure communicationNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemIPv6 packet
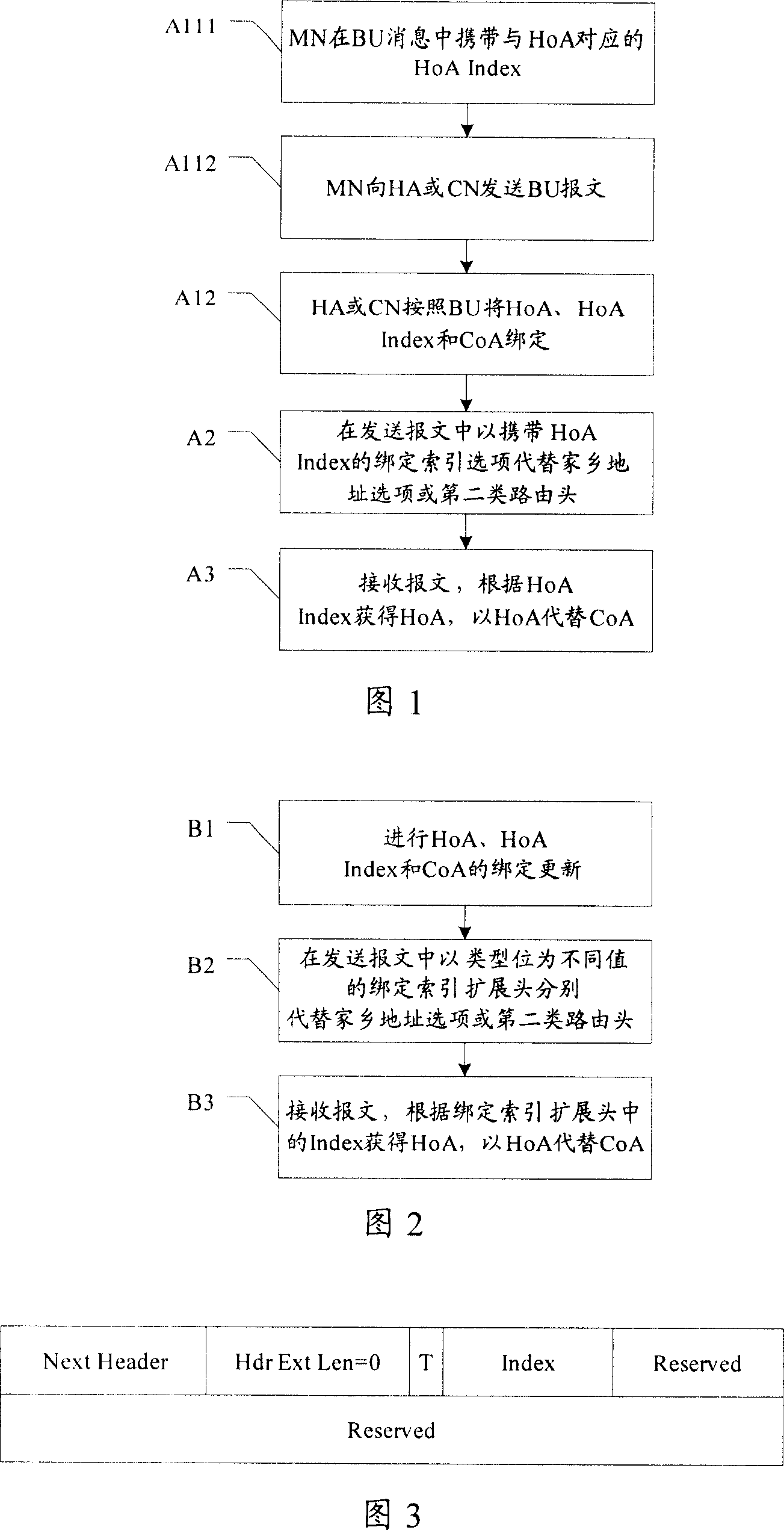
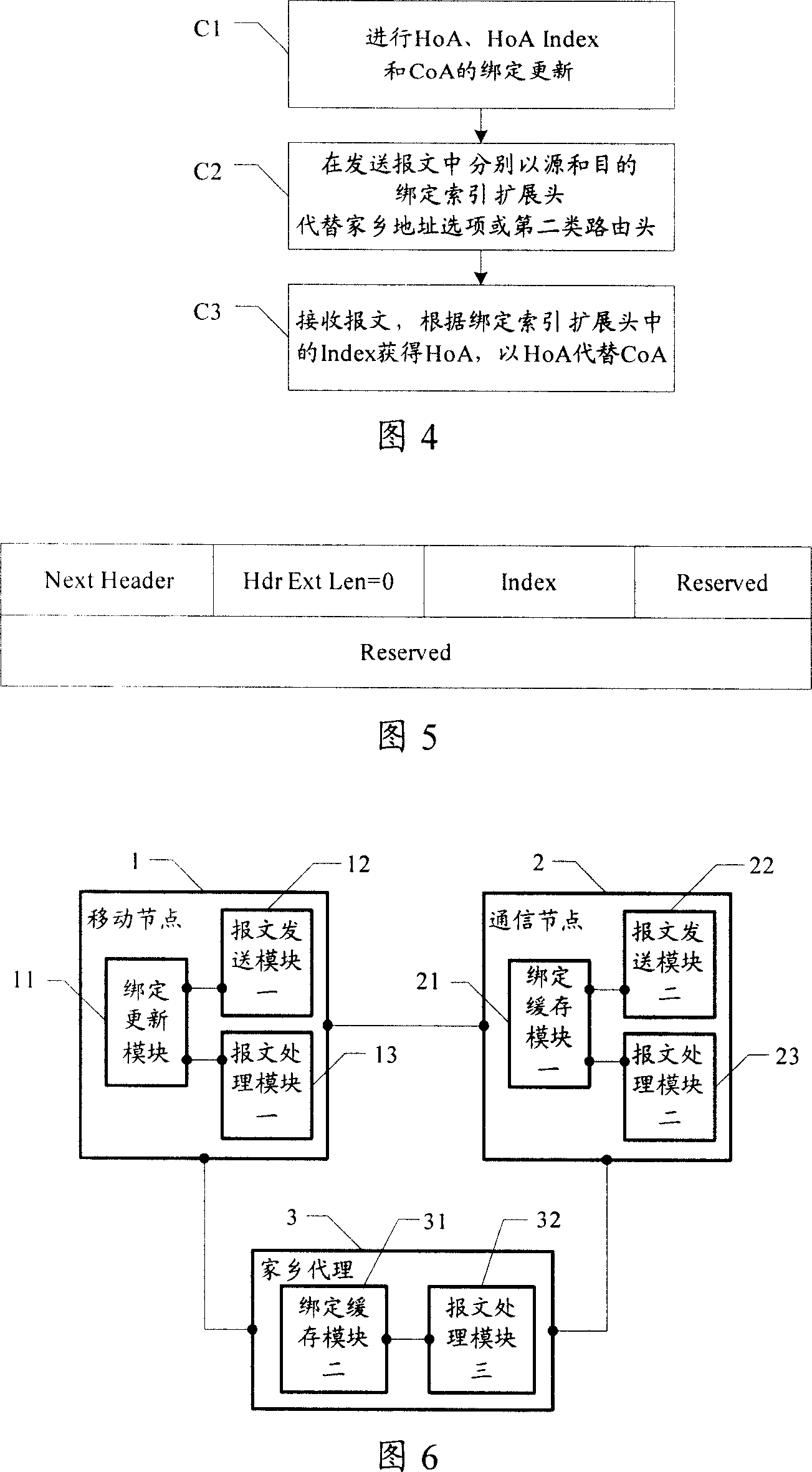
The core idea of the method is that the method informs association relation between the home address index and the home address to corresponding communication end point (CEP); then using one-to-one correspondence between the home address index and the home address stored in buffered list items at each CEP, the method replaces option of home address and second kind of route head by home address index option or expanded head of binding indexes including carried home address indexes in data packet. The invention also discloses corresponding mobile IPv6 transmission system. The invention can reduce overhead of mobile IPv6 packet head effectively. Since content of home address index is simple and is not correlative to any privacy parameter, thus, the invention makes mobile users possess better security in communication.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Combining mobile VPN and internet protocol
ActiveUS20090016253A1Broadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexComputer networkIPv6 packet
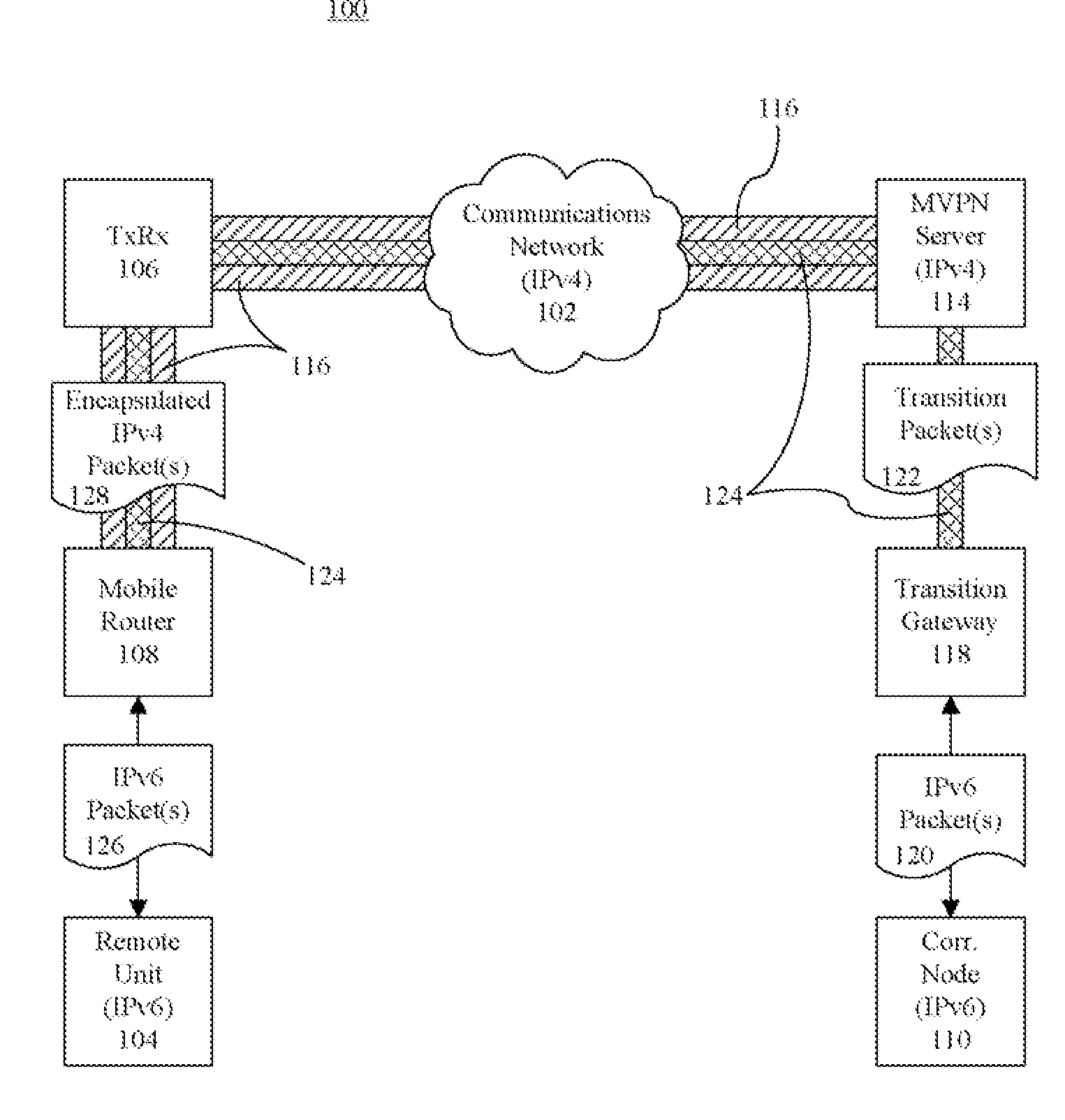
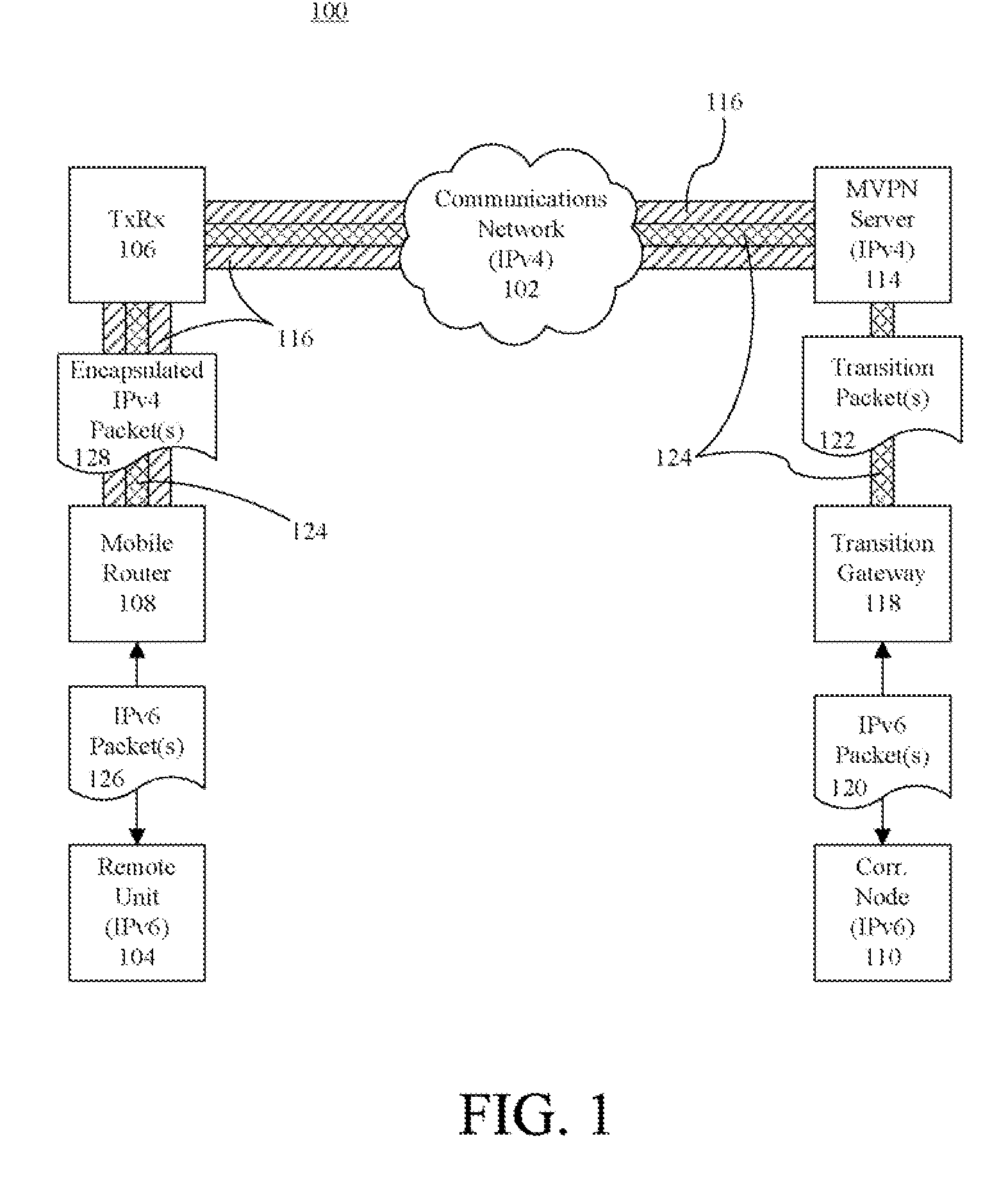
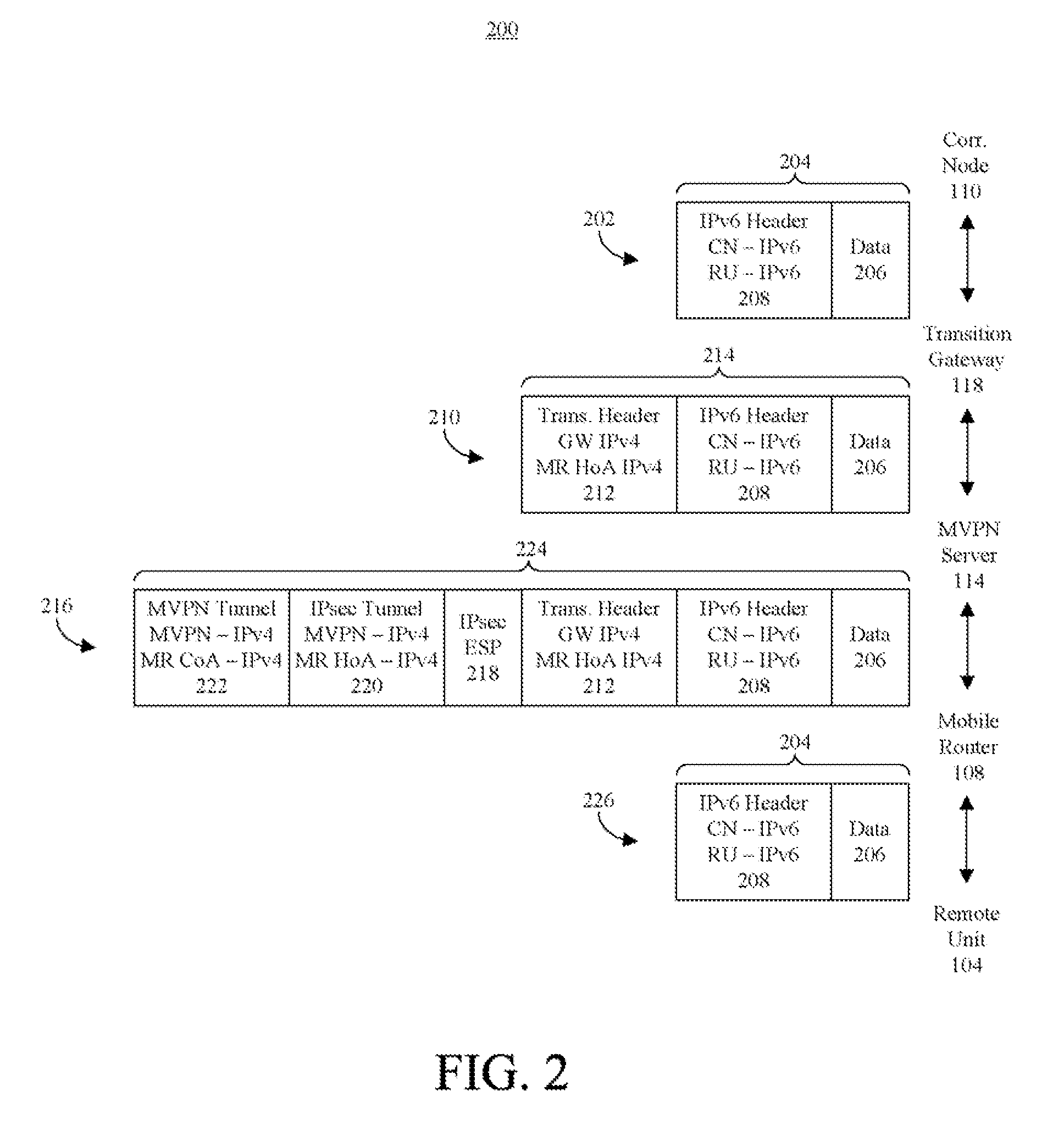
A method (200, 300, 400) of communicating an IPv6 packet (120) over an IPv4 based network (102). The method can include receiving the IPv6 packet to be communicated to a remote unit (104), encapsulating the IPv6 packet in an IPv4 transition packet (122), and communicating the IPv4 transition packet to an IPv4 MVPN (114) server configured to communicate the packet to the remote unit via infrastructure of an IPv4 radio access network. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of processing an IPv6 packet received over an IPv4 based network. The method can include receiving from an MVPN server an IPv4 formatted packet that is being communicated to a remote unit, and removing from the packet at least one IPv4 header to result in the packet being formatted in accordance with IPv6.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Service recognition method of router in ipv6 environment
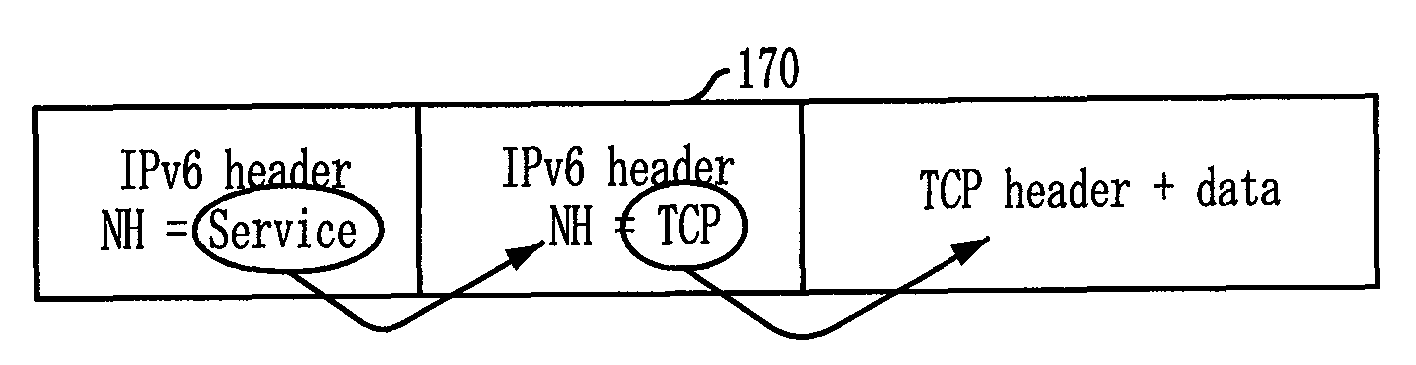
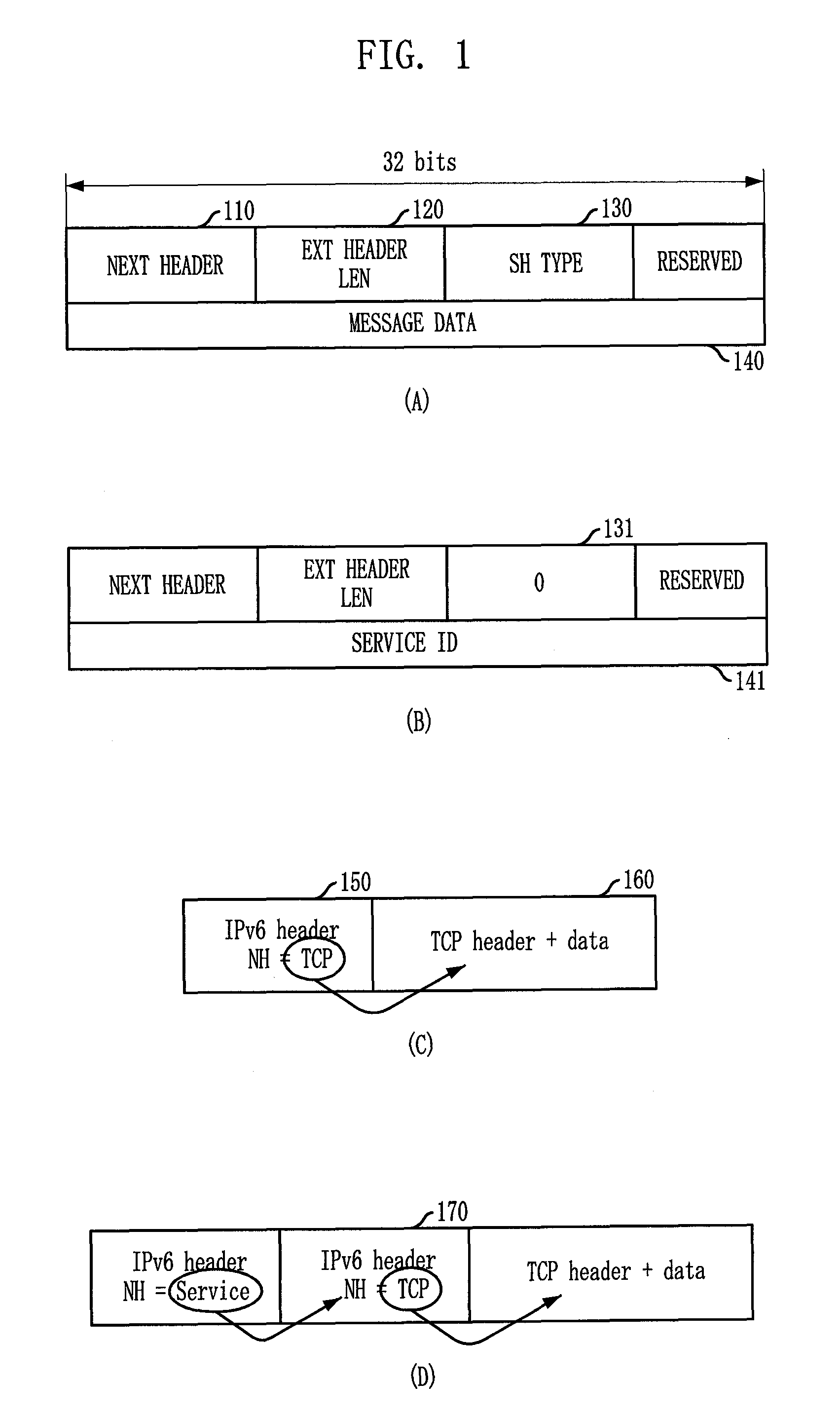
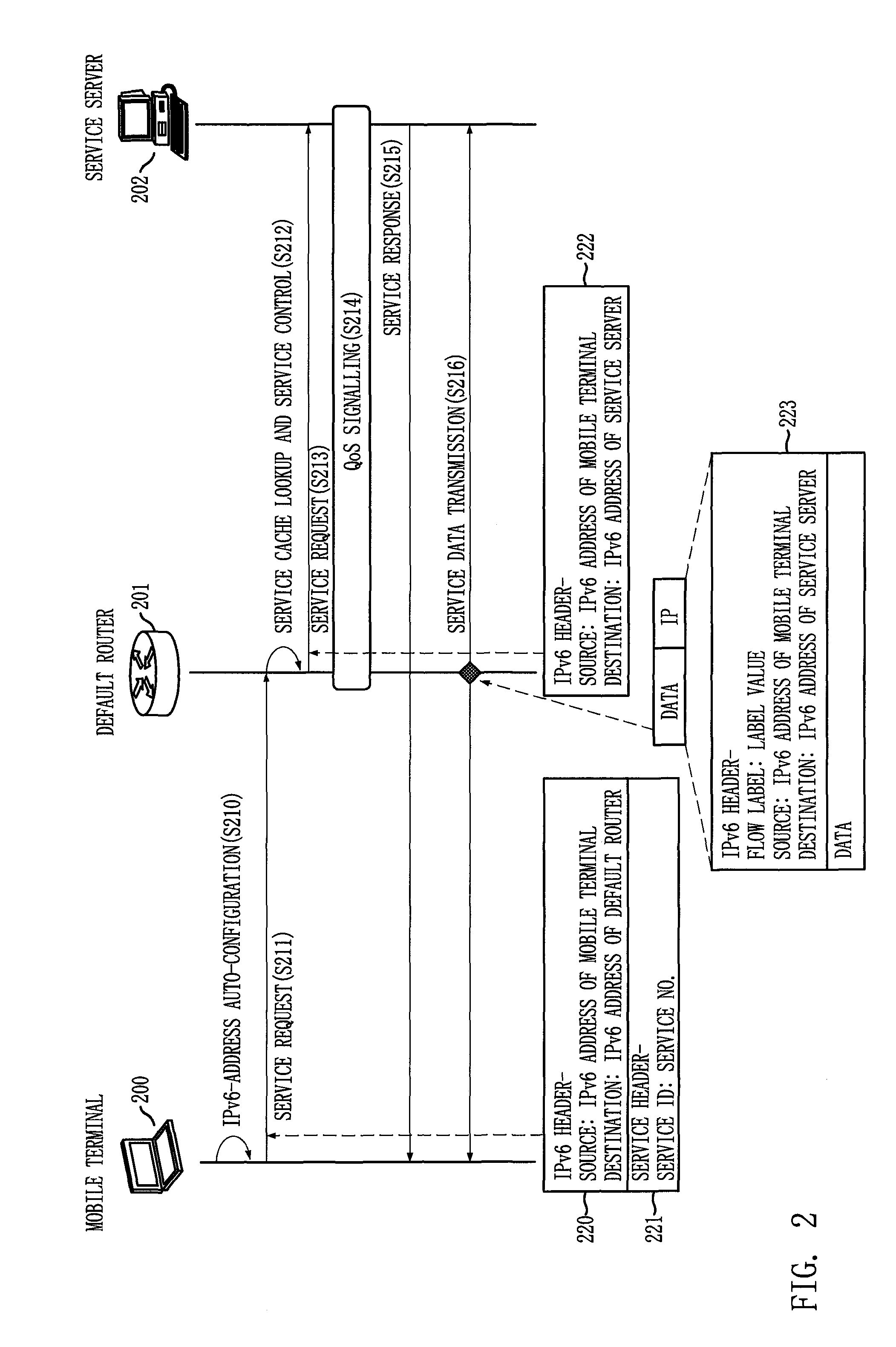
InactiveUS20100074256A1Accurate distinctionPrevented from performing controlData switching by path configurationService controlIPv6 packet
Provided is a service recognition method of a router in IPv6 environment, allowing a router to facilitate access of a mobile terminal to various services by using service information of a service header and identification information of the mobile terminal included in an IPv6 packet transmitted from the mobile terminal. The service recognition method includes: a) looking up predefined service cache by using service identification of IPv6 packet as index key of the service cache when the IPv6 packet including the service ID in a service header is received from the mobile terminal; b) changing destination address into address of the service server when the address of the service server and service control information are determined through the lookup of the service-cache to request service and perform service control; and c) routing to the mobile terminal by using the IPv6 packet when service response is transmitted from the service server.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
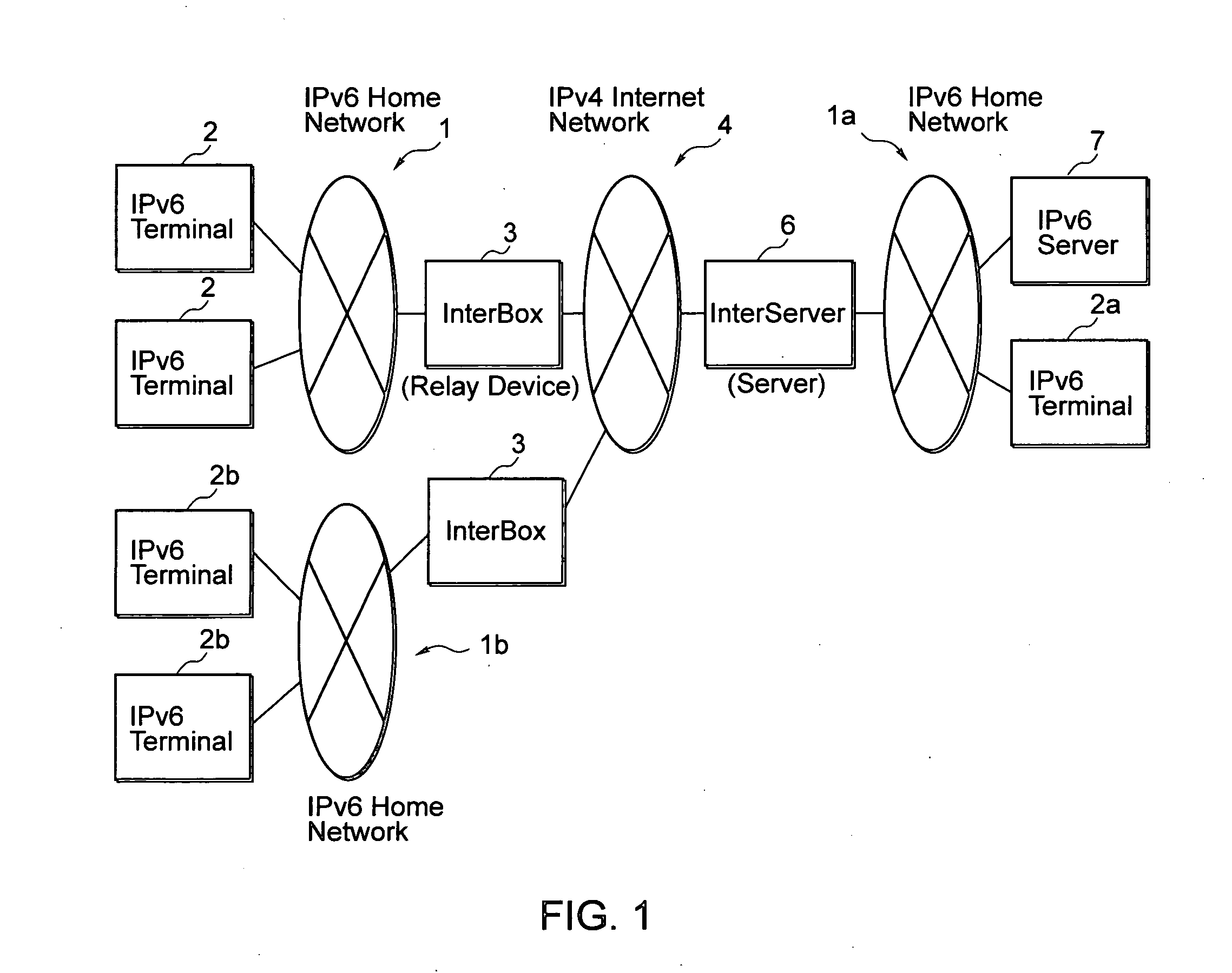
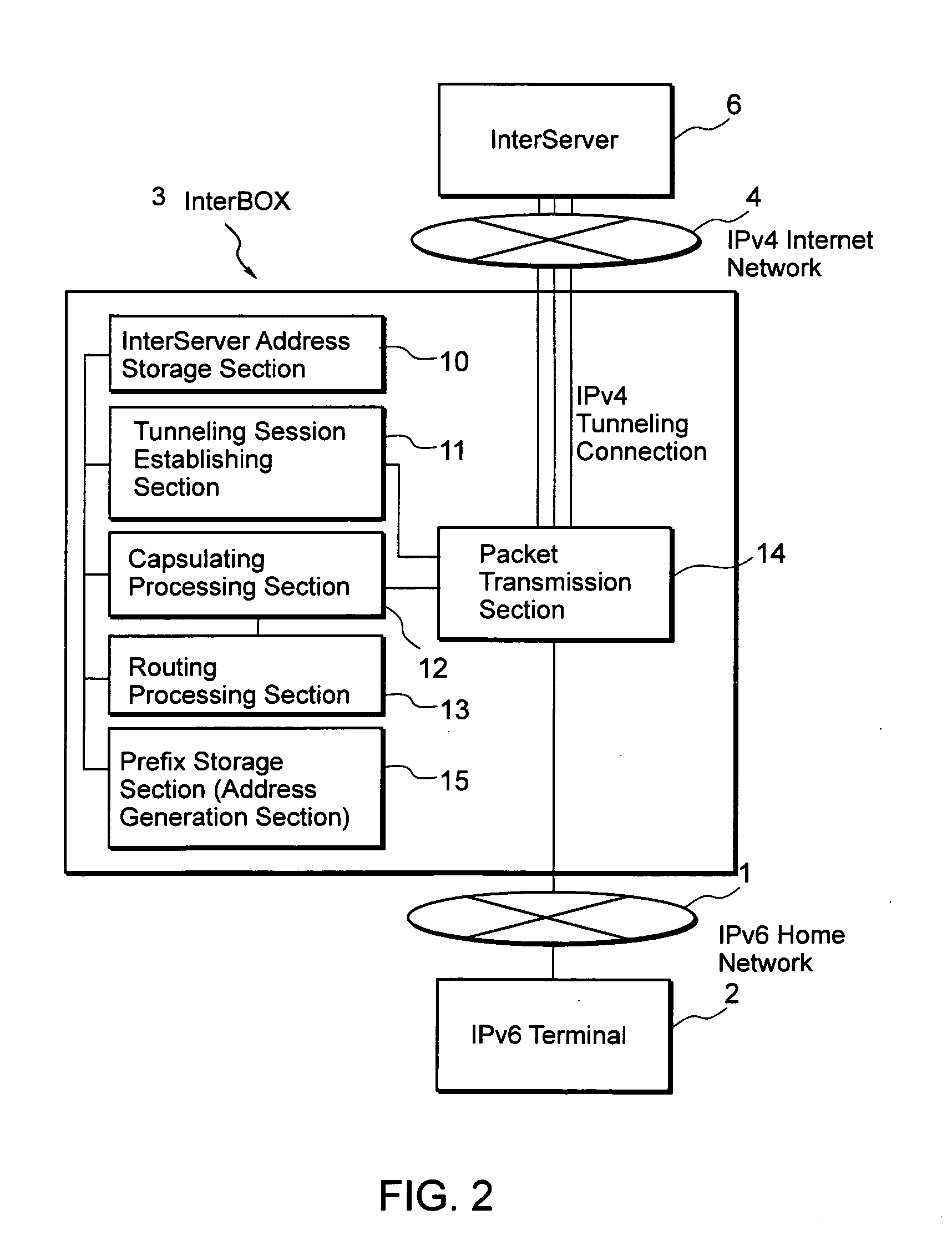
System for the internet connections, and server for routing connections to a client machine
ActiveUS20060129694A1Increase valueMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionTerminal equipmentIPv6 packet
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an Internet connection system which is capable of benefiting from the IPv6 by relatively easy means and in which manufacturers of client-side devices can create added values for users. IPv6 packets are transmitted by a tunneling connection between a home network and a server on the Internet. Also terminal devices present in the home network can be uniquely recognized and controlled from outside via the server. Since all communications are performed via the server on the Internet regardless of the carrier and the ISP, the terminal device and all connections to the terminal device can be freely configured and controlled by the owner or the manufacturer of the server on the Internet.
Owner:FREEBIT
Node access authentication method, access authenticated node, access node and communication system
ActiveCN102065423AGuaranteed costReduce energy requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity arrangementCommunications systemNetwork packet
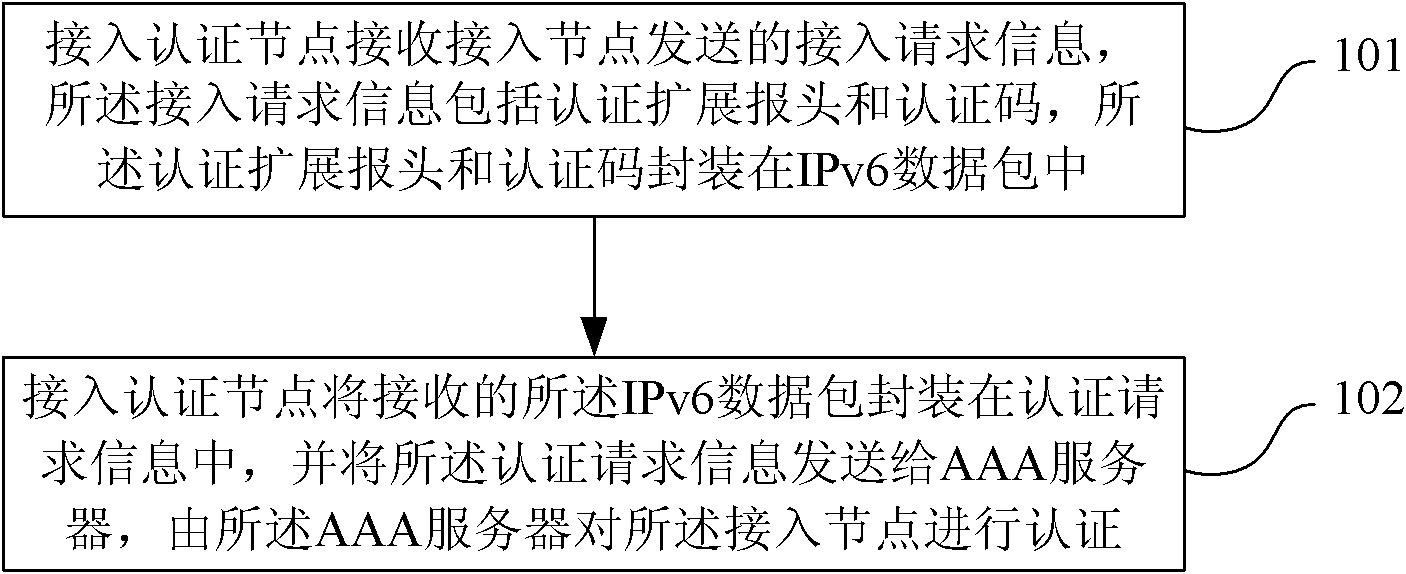
The invention discloses a node access authentication method, an access authenticated node, an access node and a communication system. The method comprises the following steps: the access authenticated node receives the access request information sent by the access node, wherein the access request information comprises an authentication extension header and an authentication code which are packaged in a next-generation IPv6 (internet protocol version 6) data packet; the authentication extension header comprises the algorithm field; and the authentication code is computed by a first computing method according to the algorithm corresponding to the algorithm field, a shared key configured in the access node and the information except the authentication code in the IPv6 data packet; and the access authenticated node packages the received IPv6 data packet in the access request information and sends the access request information to an AAA (authentication, authorization and accounting) server so that the AAA server authenticates the access node. The technical scheme adopted by the invention can be applied in the 6LowPAN (personal area network), realize access authentication of the node on the IP layer and effectively improve the safety of network communication.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
System and method for sending related data over a digital broadcast system
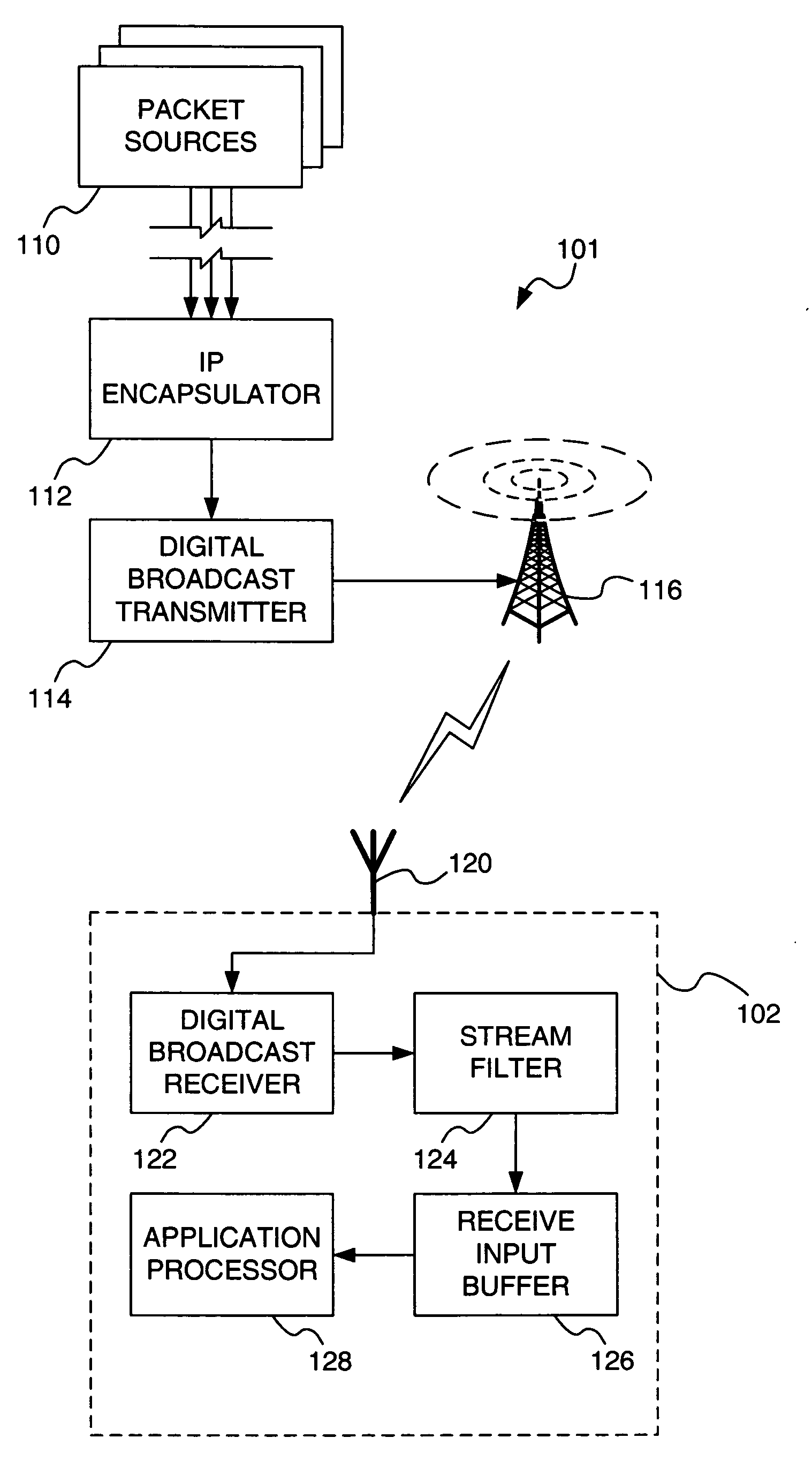
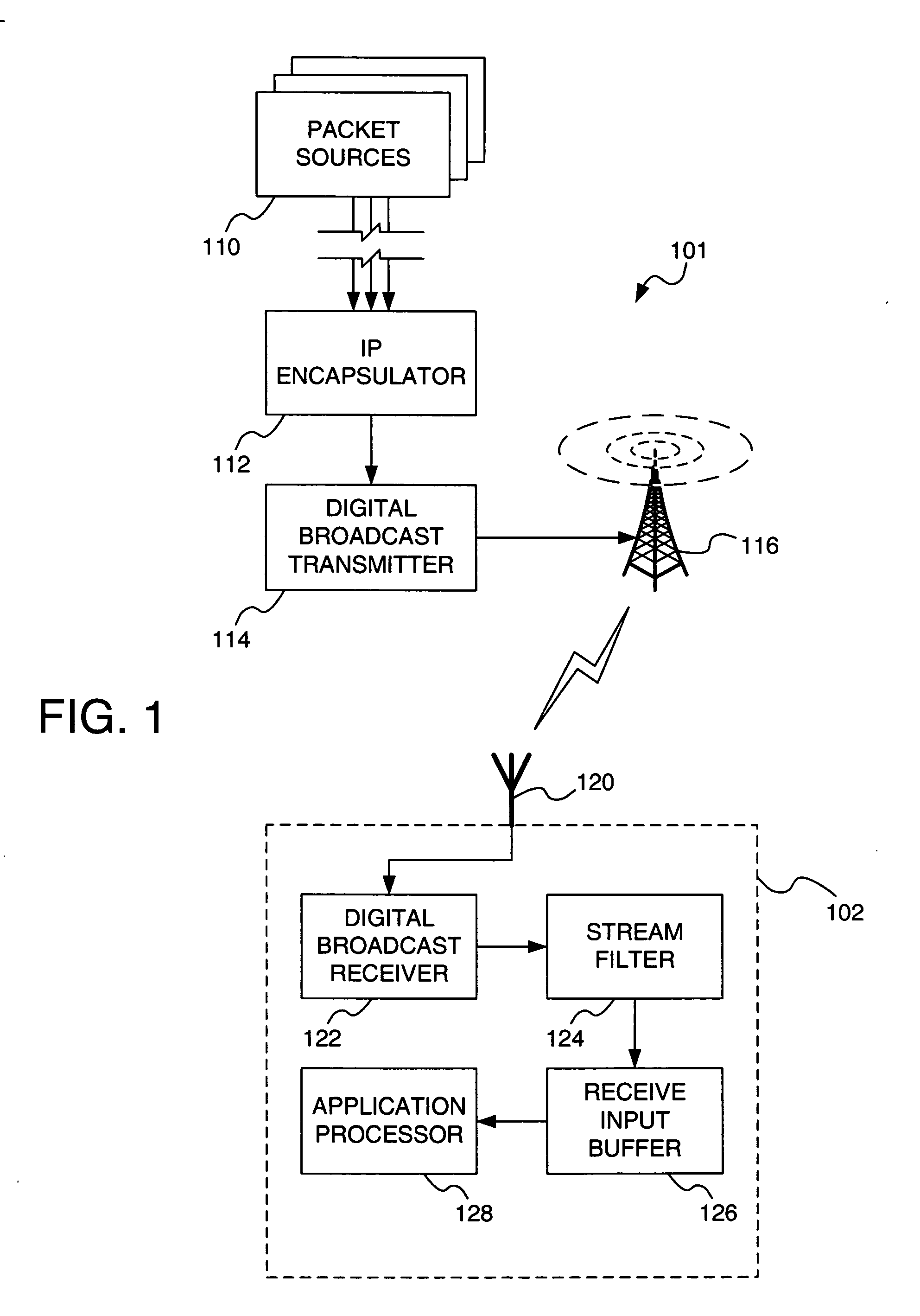
InactiveUS20060146853A1Plural information simultaneous broadcastStore-and-forward switching systemsIPv6 packetDigital broadcasting
A system and method for ensuring that related data packets are transmitted simultaneously in a digital broadcast system are disclosed. Related data packets are provided a common indication, buffered together, and kept together through time-sliced burst formation and digital transmission. The related data packets may include IPv6 packets with common flow label values.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
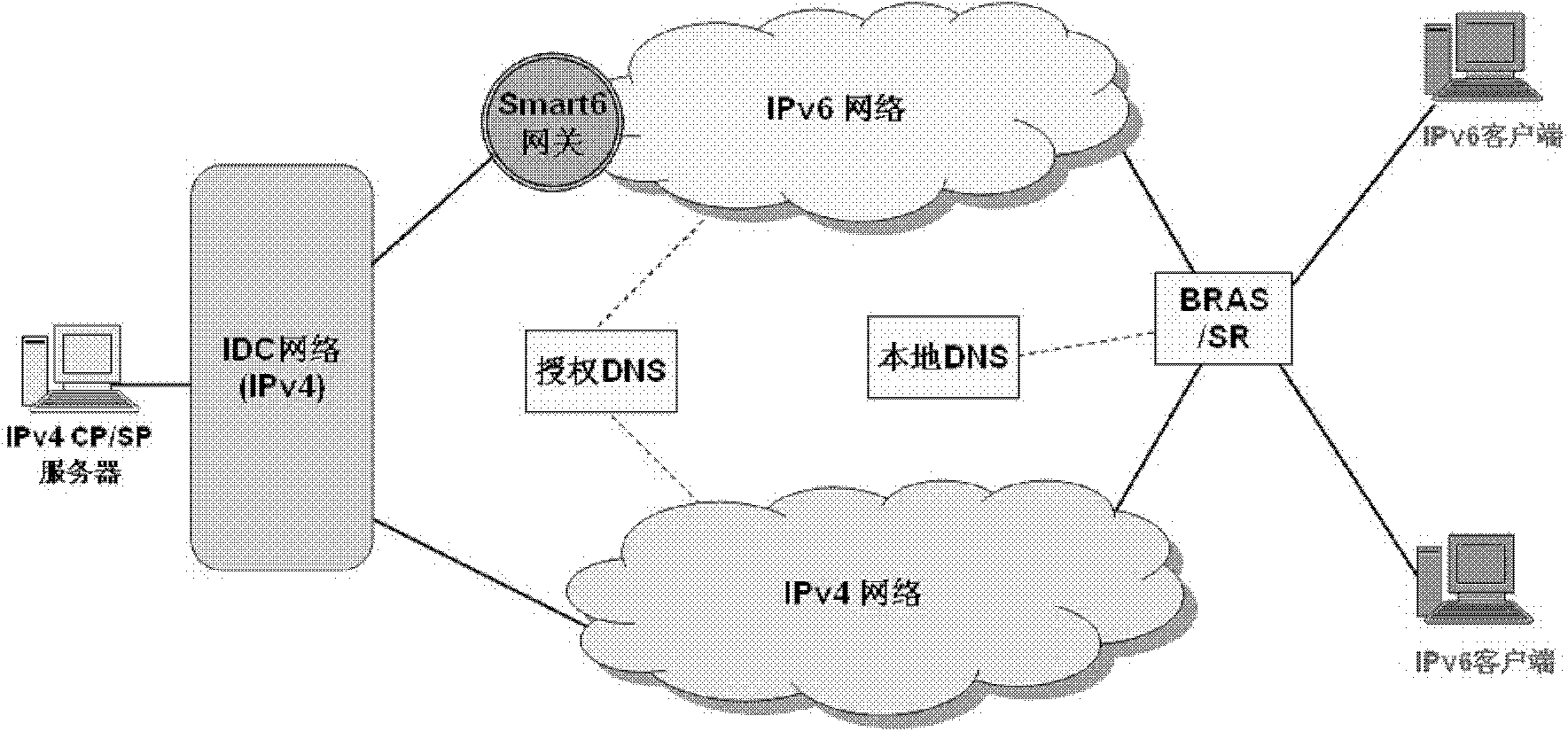
IPv4CP/SP and IPv6 network interworking method and device
The invention provides an IPv4CP / SP and IPv6 network interworking method and device. The method comprises the following steps: an IPv6 client acquires an analyzed and integrated IPv6 address of a CP / SP server from DNS, and sends an access request to the IPv6 address; a gateway acquires an IPv4 address of the CP / SP server according to the IPv6 address; the gateway queries an address mapping table, acquires a private IPv4 address corresponding to the IPv6 client address according to the address mapping table, converts an IPv6 data packet into an IPv4 data packet, and sends the IPv4 data packet to CP / SP; and after CP / SP processes a request from a user, CP / SP returns the IPv4 data packet to the user, and the IPv4 data packet is backward processed by the gateway and then is sent to the IPv6 client. According to the invention, the CP / SP server platform on the existing IPv4 Internet provides services for the users on the IPv6 Internet, thus the traffic on the IPv6 Internet is improved.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com