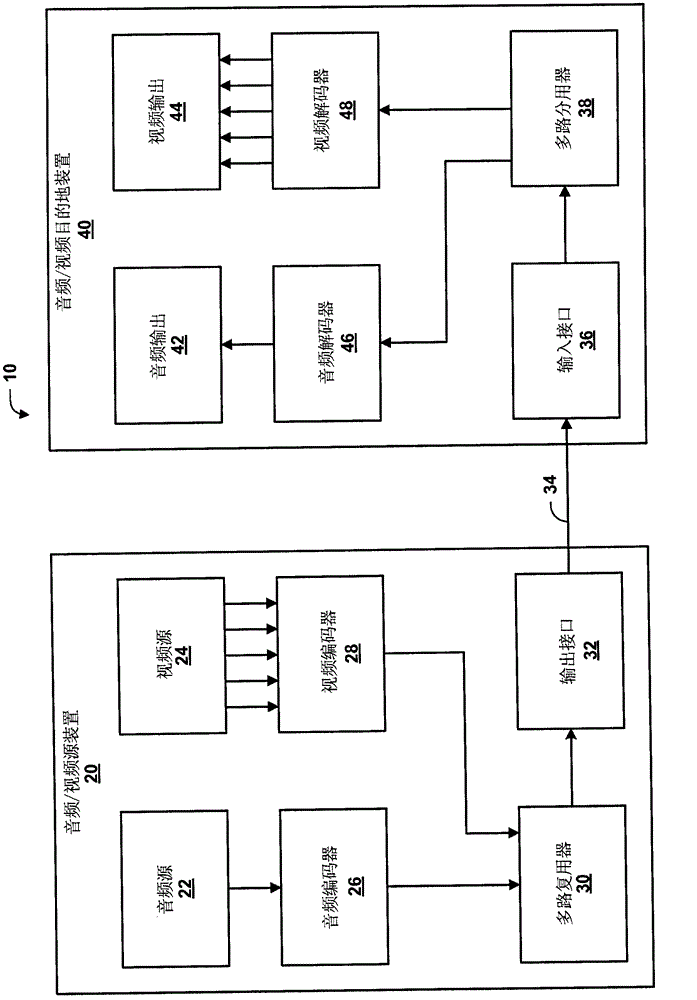
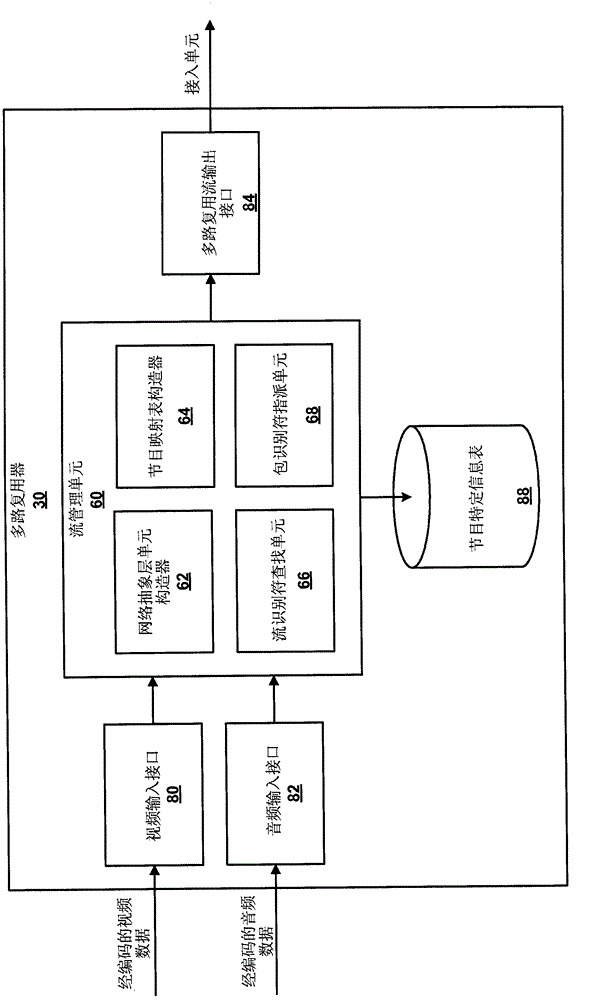
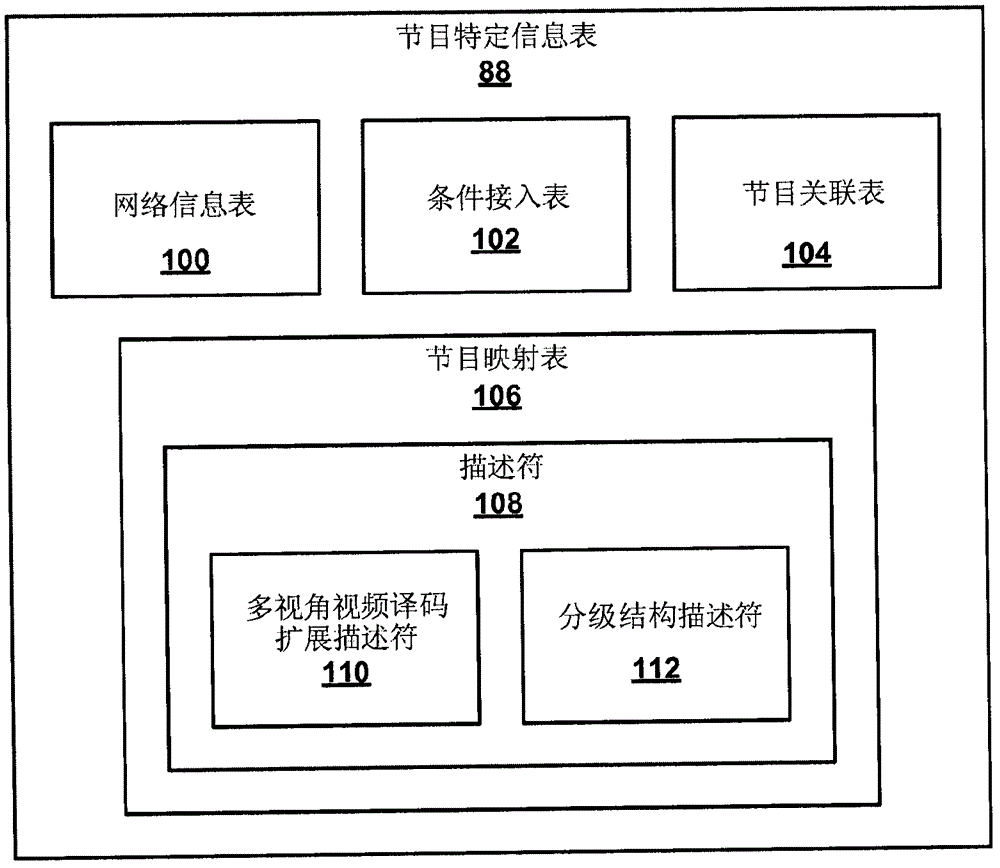
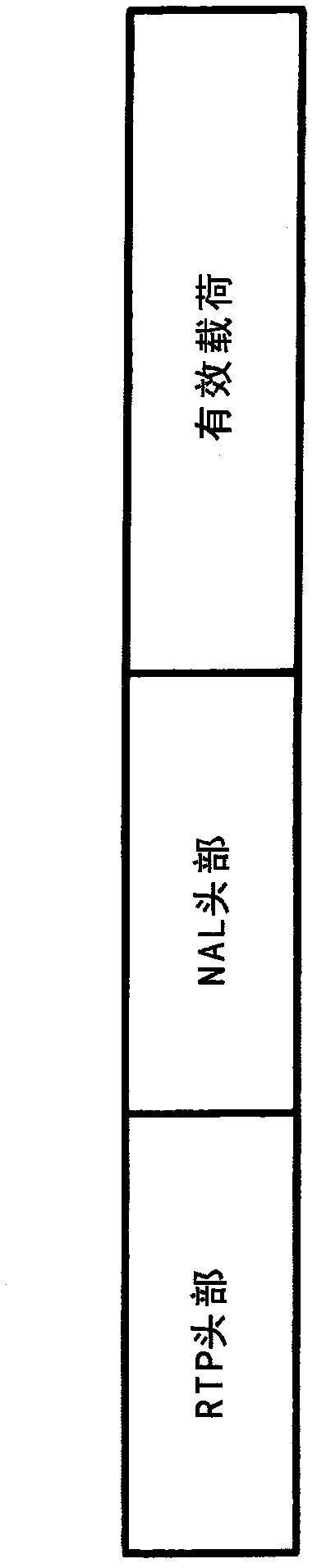
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Network Abstraction Layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
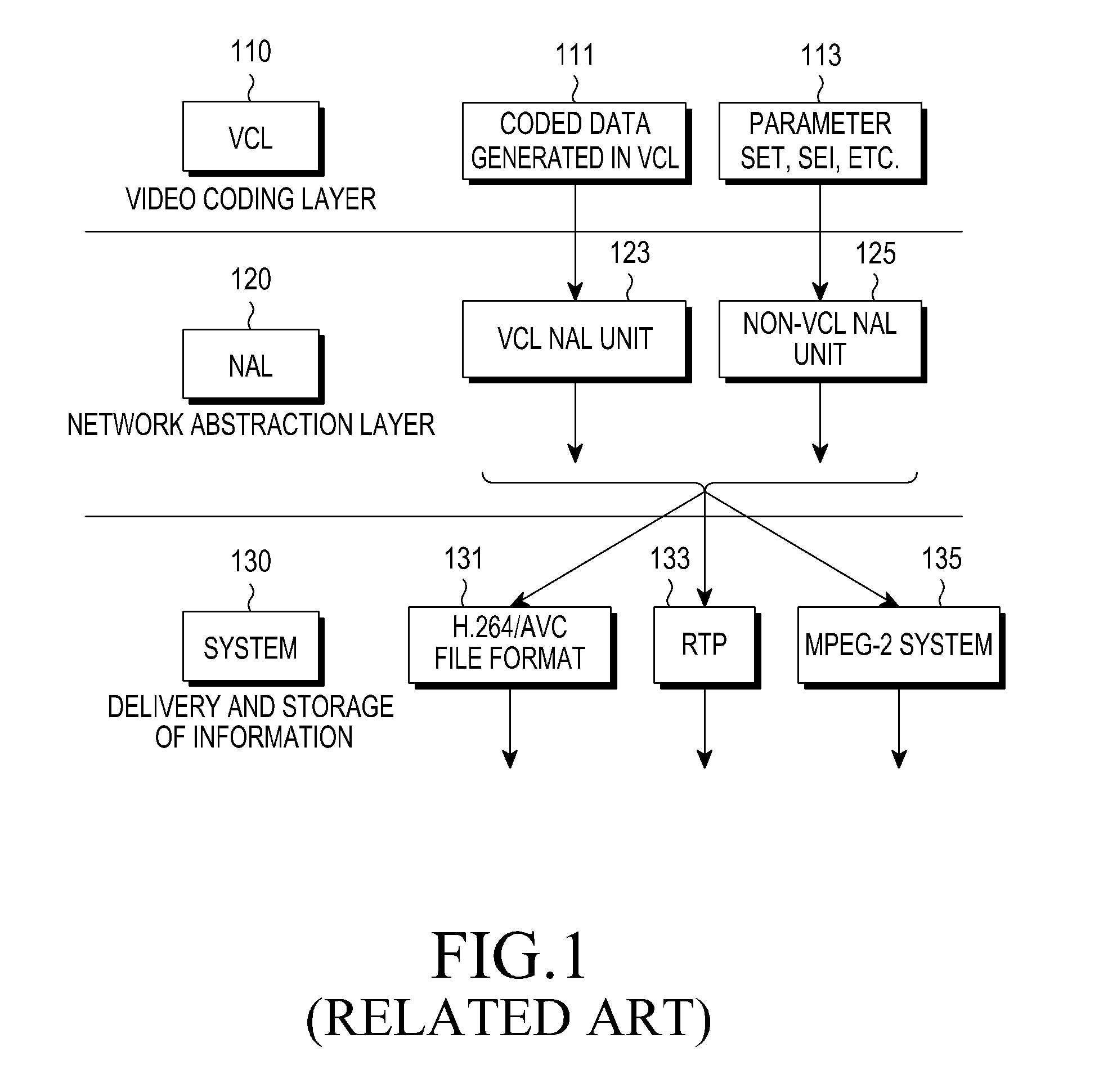
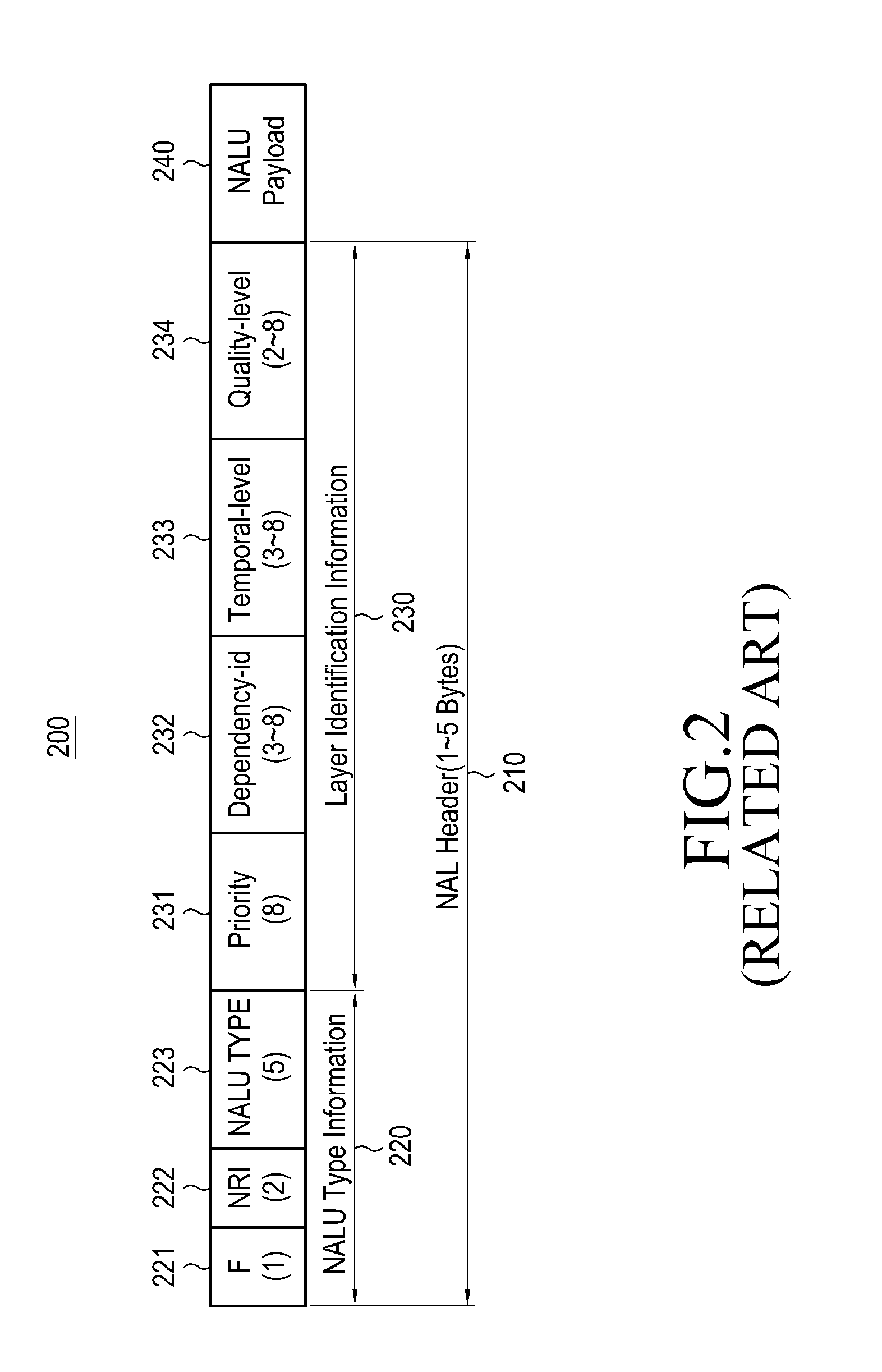
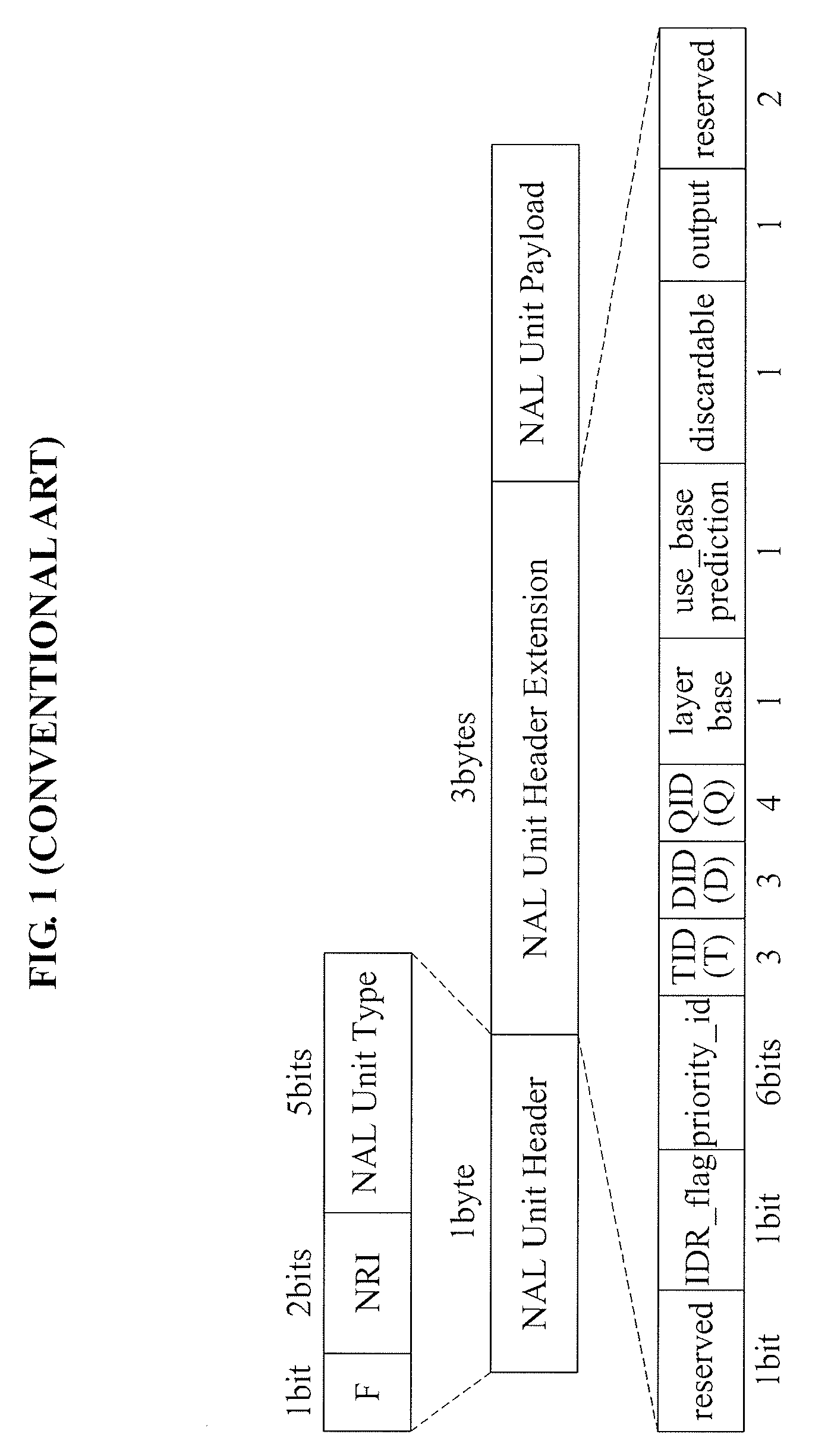
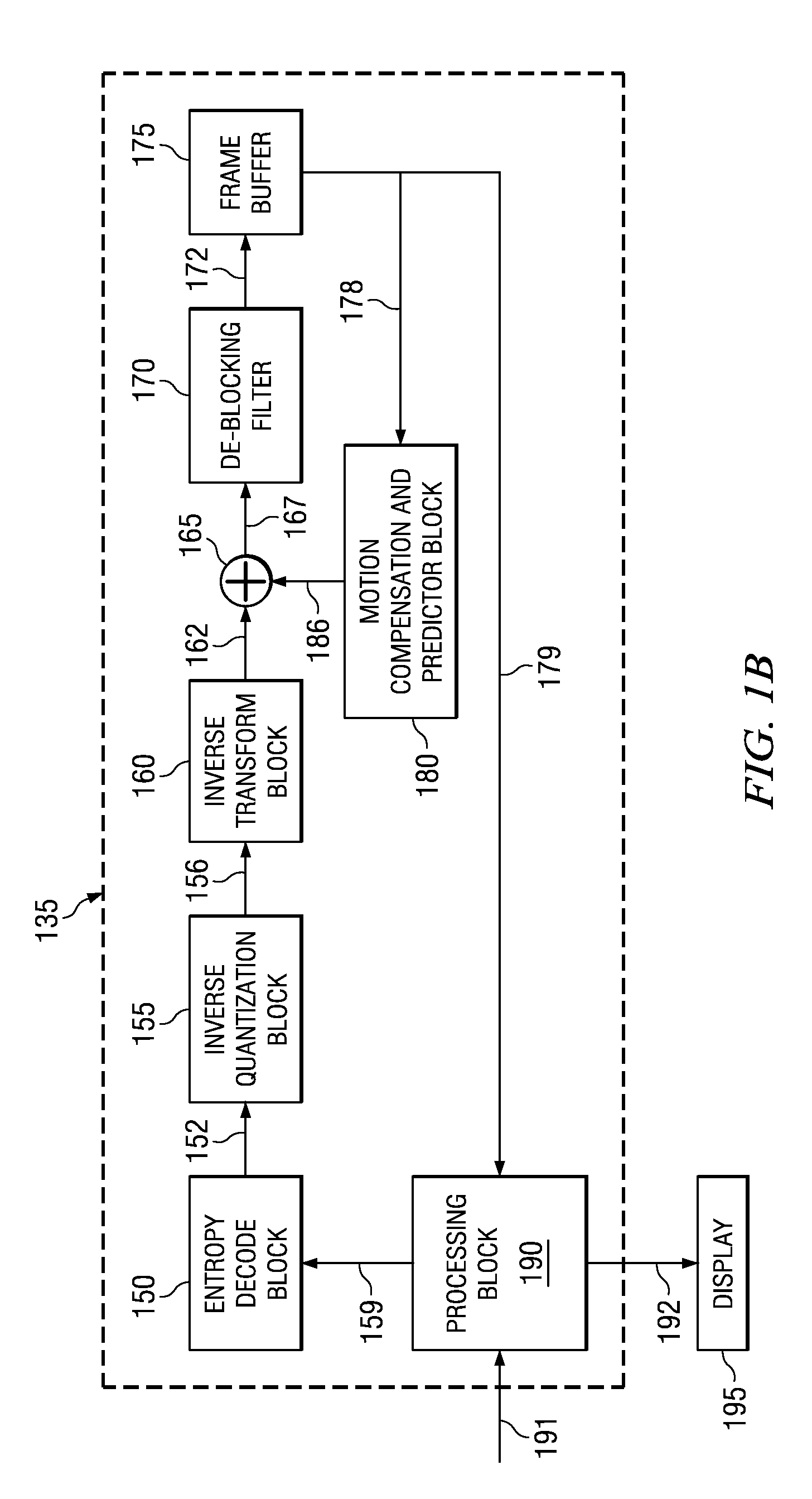
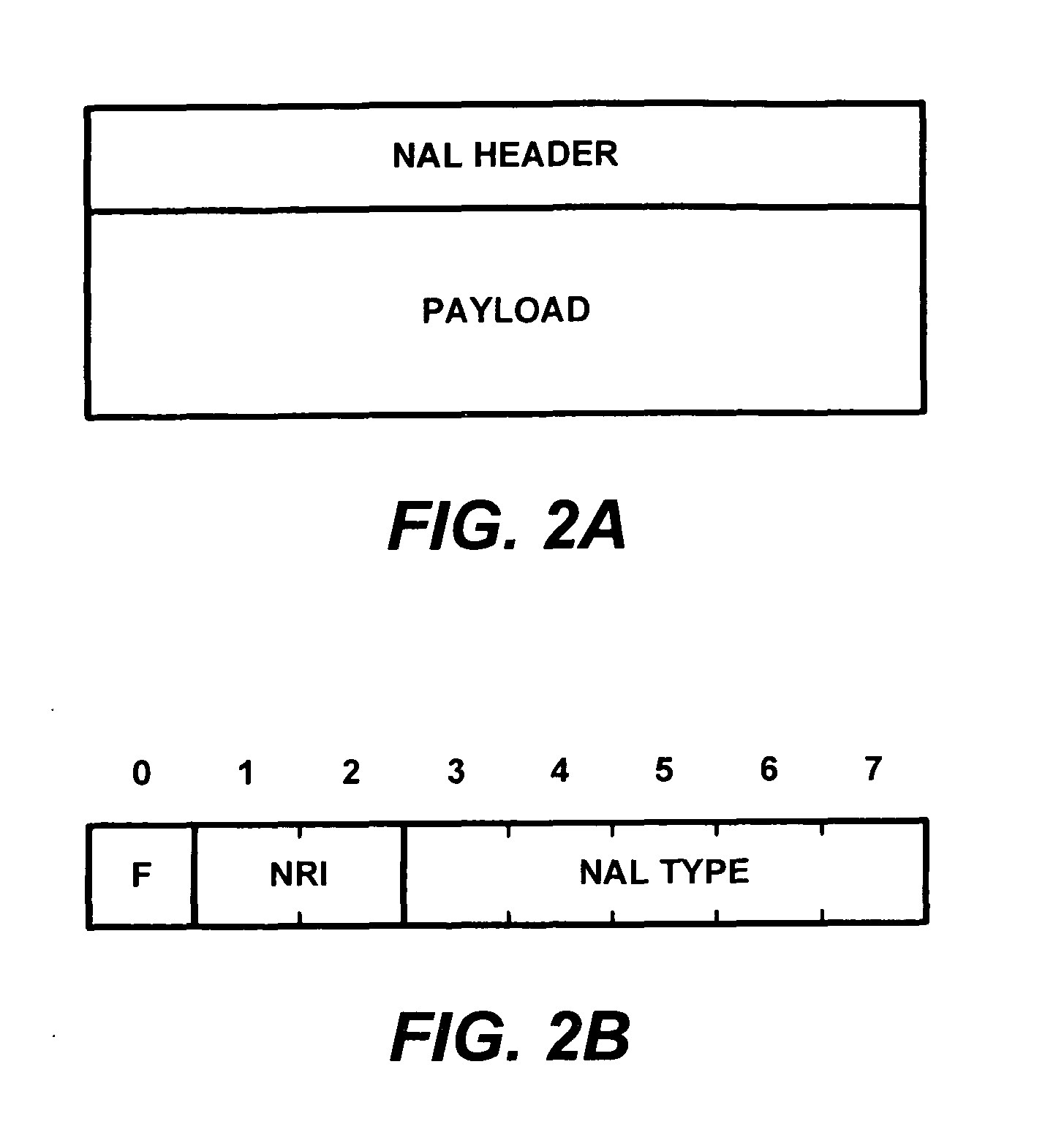
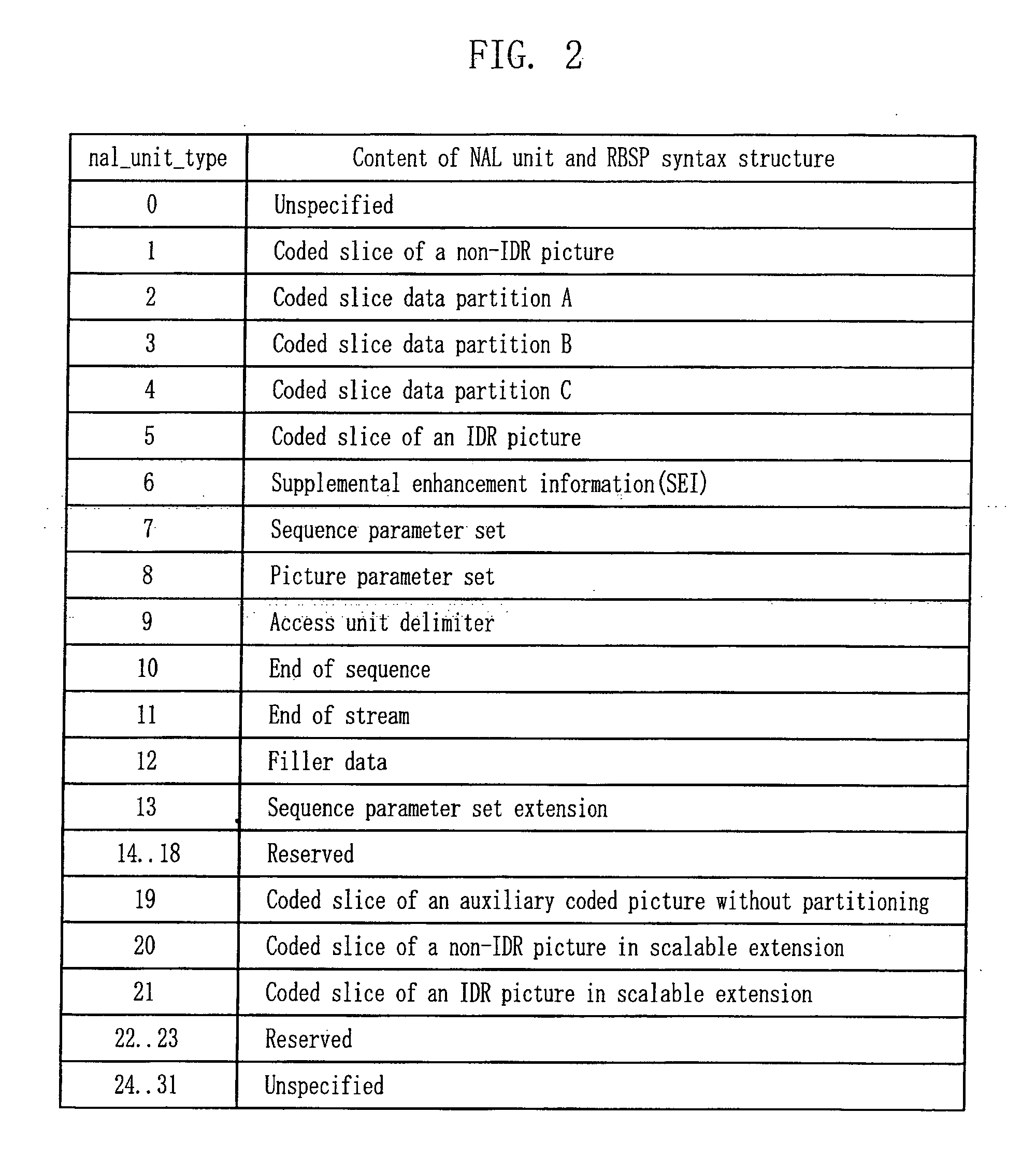
The Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) is a part of the H.264/AVC and HEVC video coding standards. The main goal of the NAL is the provision of a "network-friendly" video representation addressing "conversational" (video telephony) and "non conversational" (storage, broadcast, or streaming) applications. NAL has achieved a significant improvement in application flexibility relative to prior video coding standards.
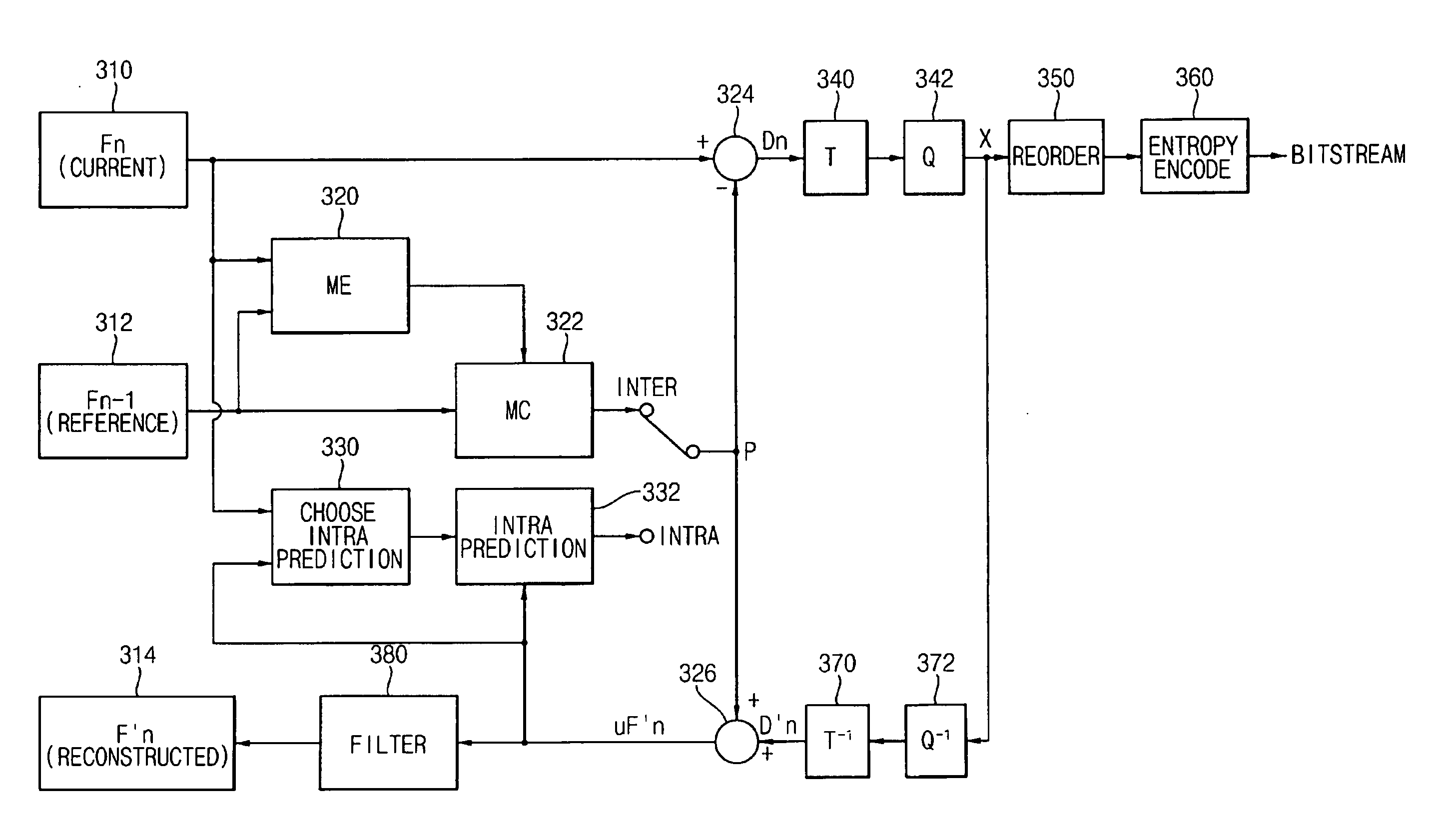
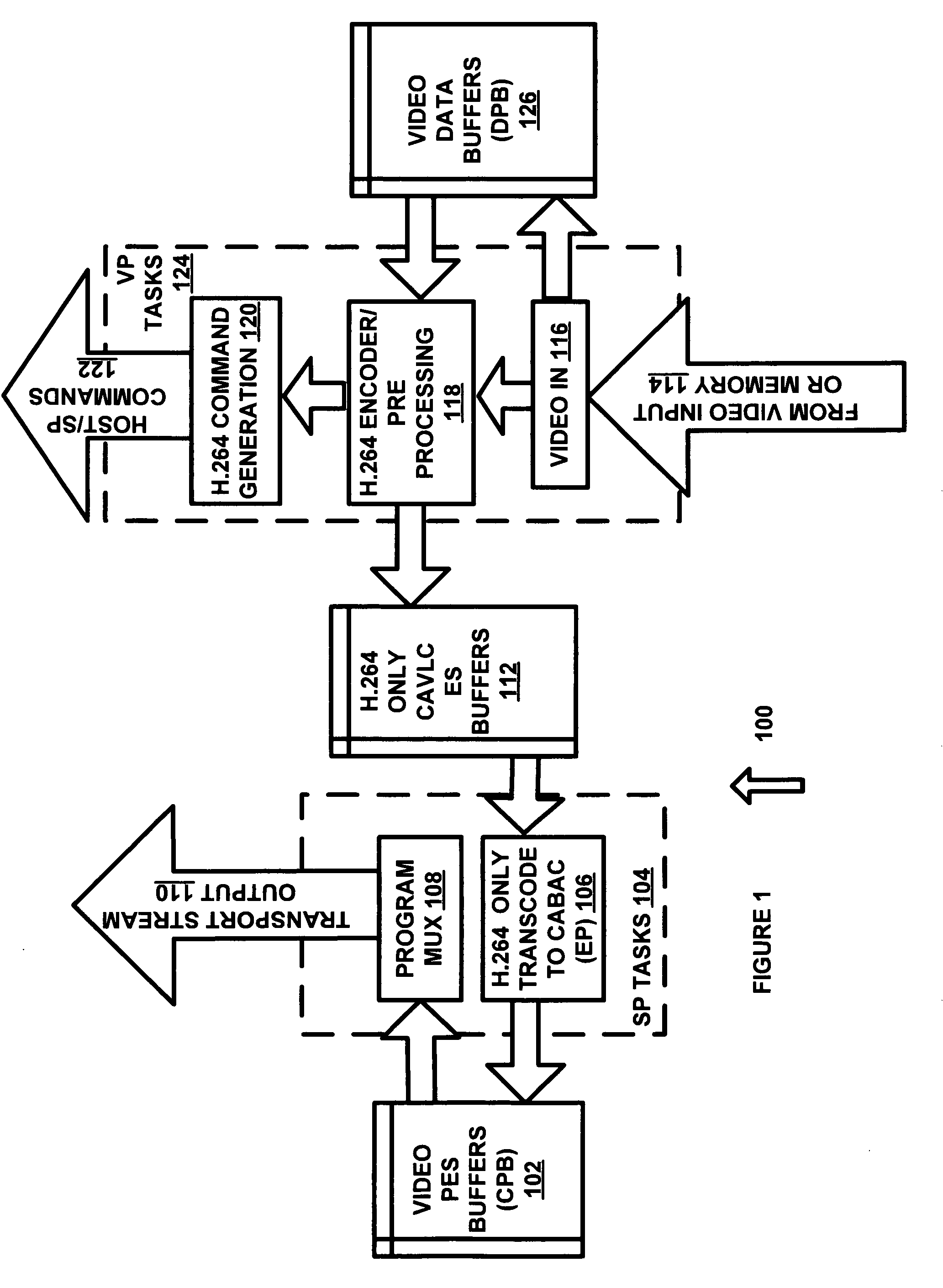
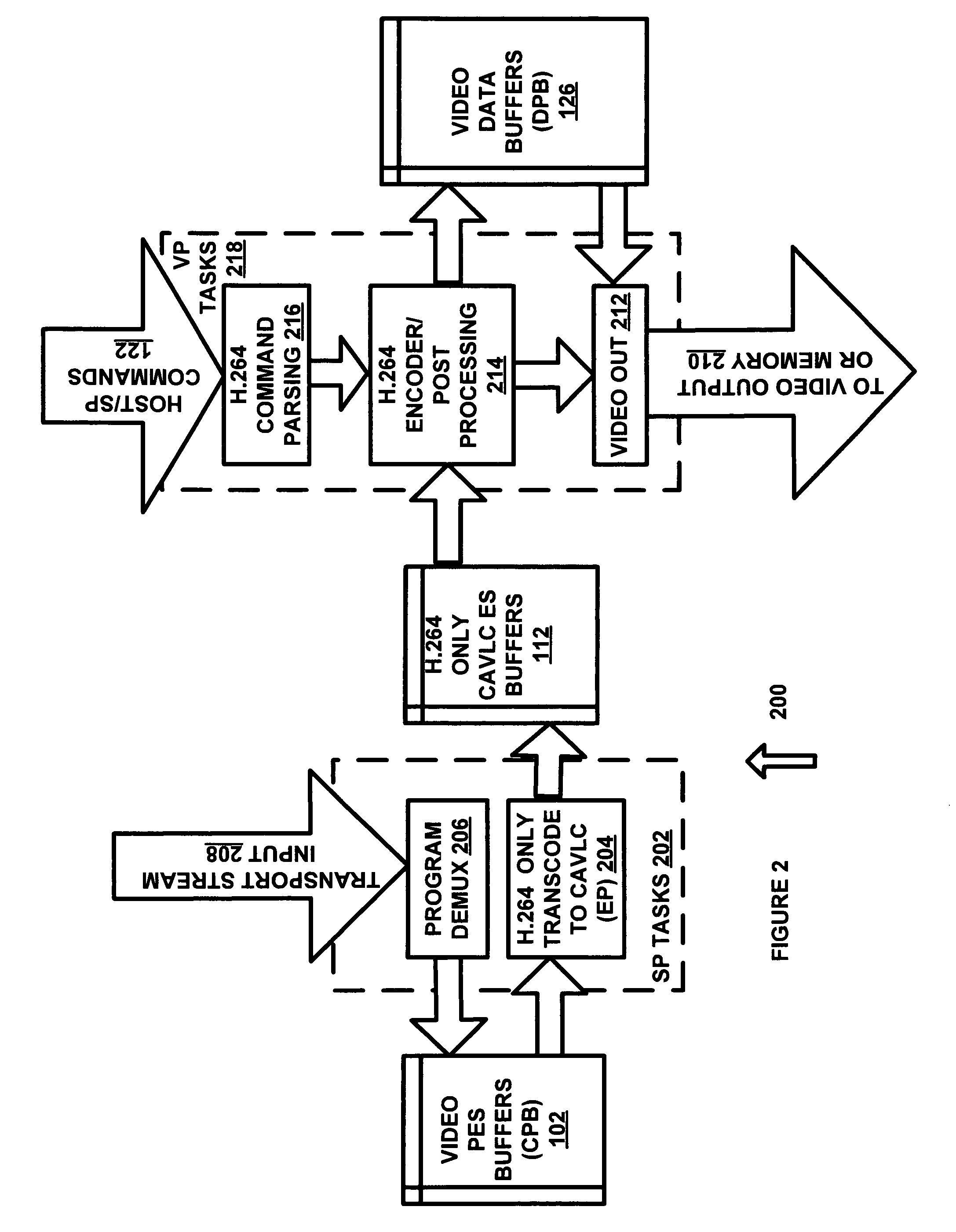
Method and apparatus for skipping pictures
ActiveUS20070030911A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer graphics (images)Network Abstraction Layer
In a video decoder having a picture skip function, the video decoder may obtain reference information from a network abstraction layer (NAL) unit, and upon receipt of a skip command, skips frames / pictures from where a non-reference frame / picture begins. The video decoder may execute a picture skip function, either at a fast speed or at a normal speed, according to the skip mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
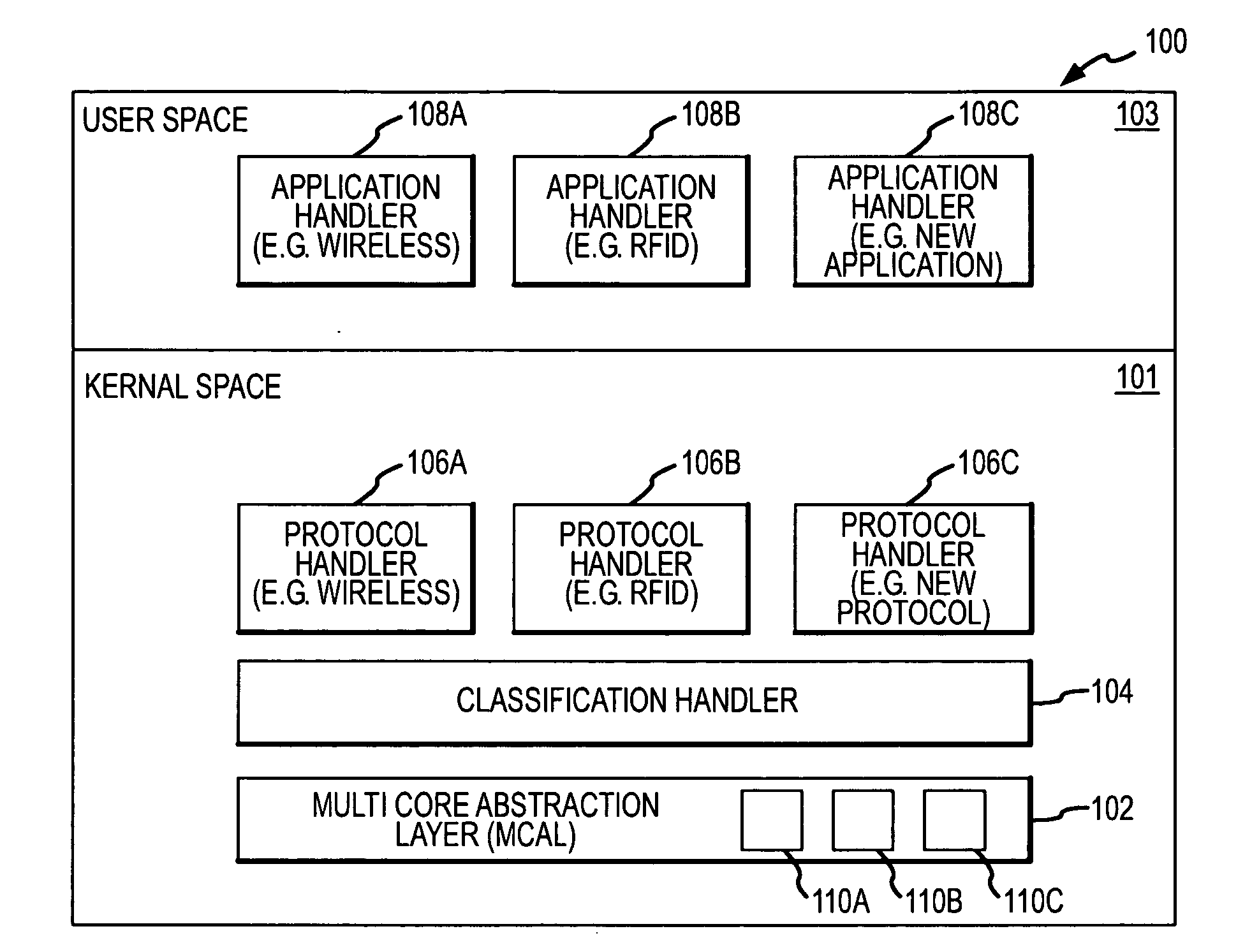
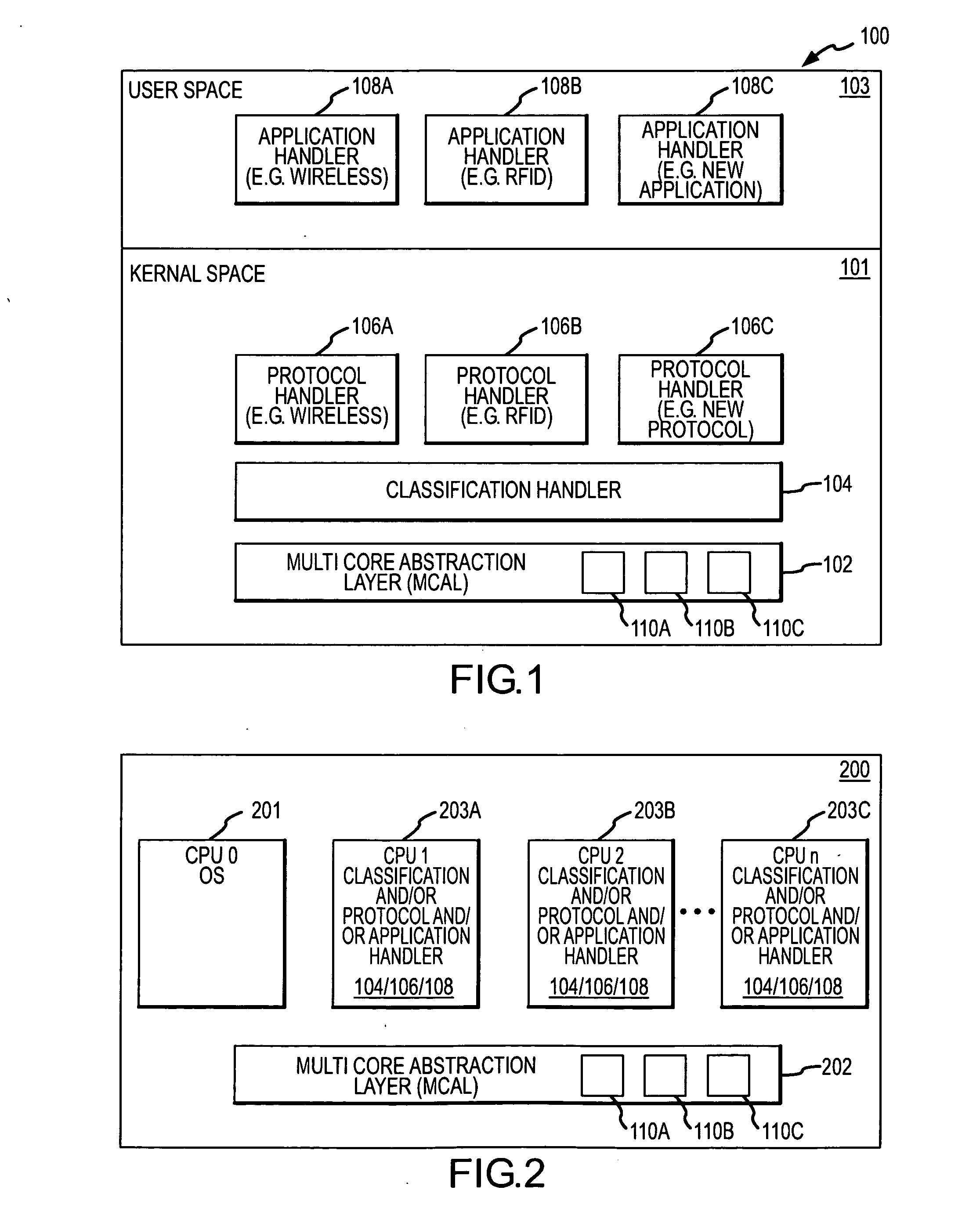
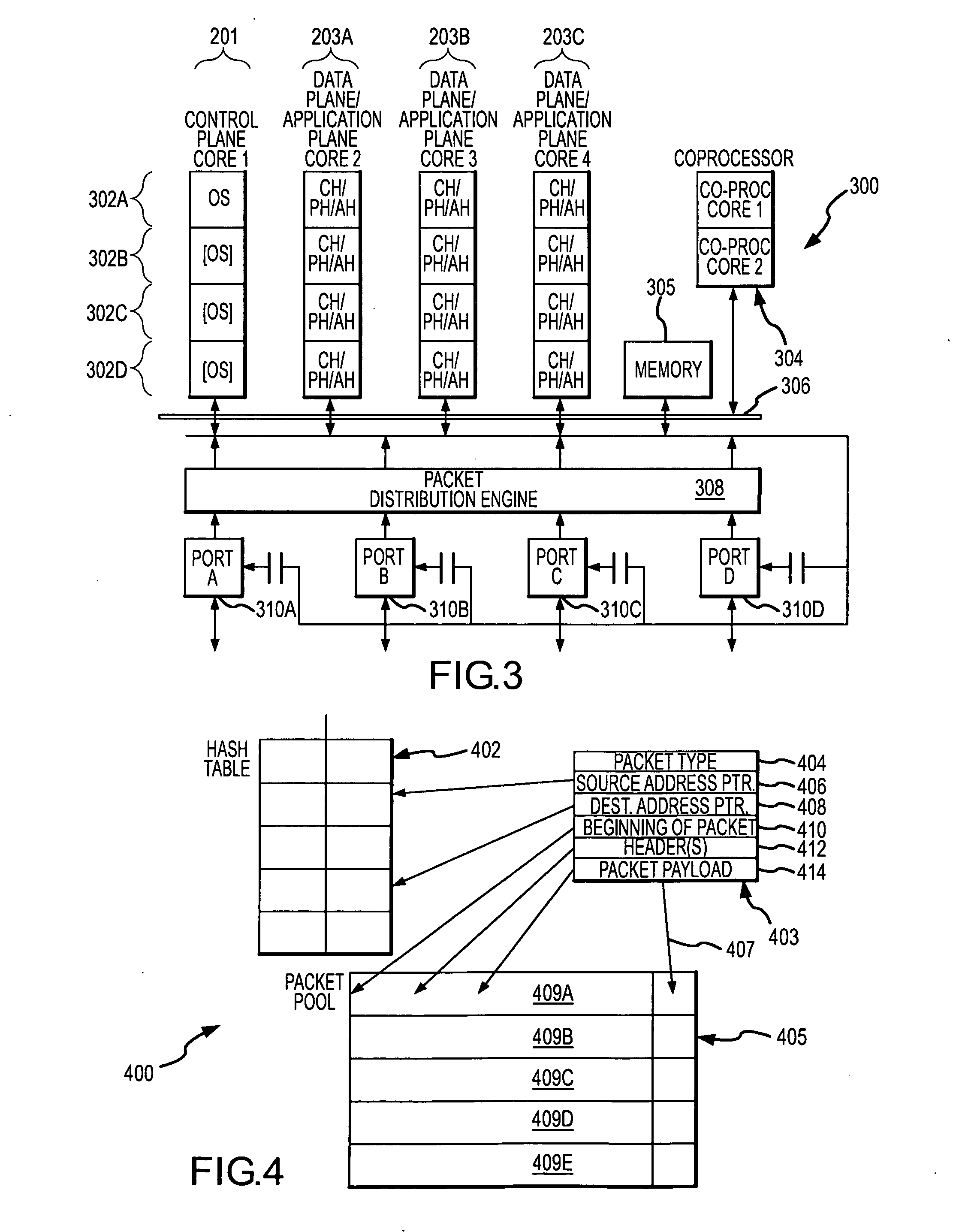
Systems and methods for processing data packets using a multi-core abstraction layer (MCAL)
InactiveUS20080002702A1Improve system flexibilityData switching by path configurationProgram controlAbstraction layerOperational system
System flexibility and ease-of-design is greatly enhanced by using a multicore abstraction layer (MCAL) to interface between a multicore hardware platform, a device operating system and the packet transfer functions of the system. Systems and techniques are described for processing a data packet received at a network interface of a network infrastructure device (such as a wireless switch) or other computing system, particularly using multi-core processors. A classification handler initially classifies the data packet. A plurality of protocol handlers each associated with a data protocol processes the data packet if the classification of the data packet matches the data protocol associated with the protocol handler, and one of several application handlers each associated with a user applications processes the data packet if the classification of the data packet matches the user application associated with the application handler. The MCAL is configured to send the data packet to the classification handler after the packet is initially received, and to subsequently direct the packet toward one of the protocol or application handlers in response to the classification of the data packet. MCAL further contains a set of the containers for handlers. Real application, protocol and classification handlers register with MCAL and are modules developed outside of the MCAL.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
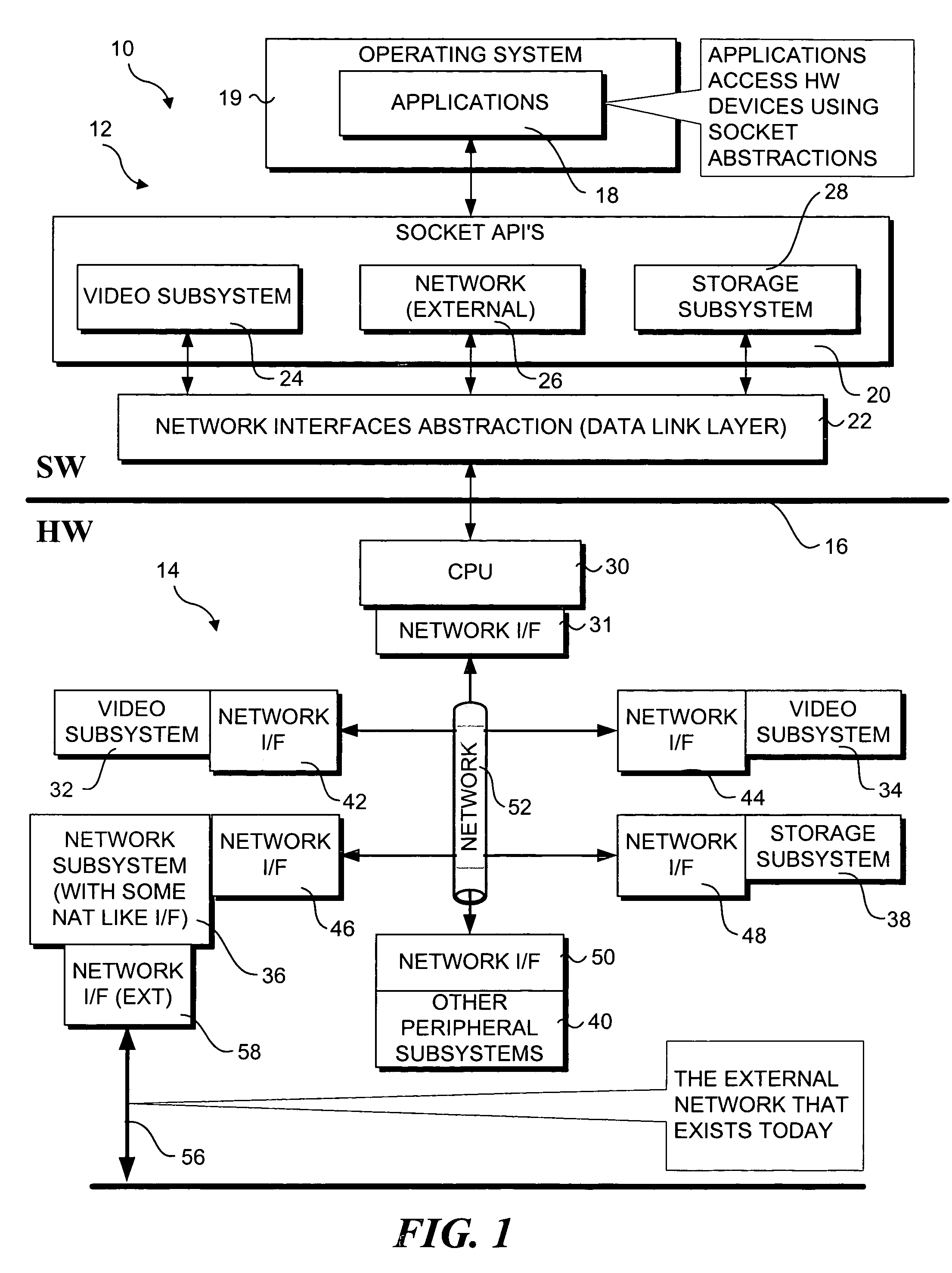
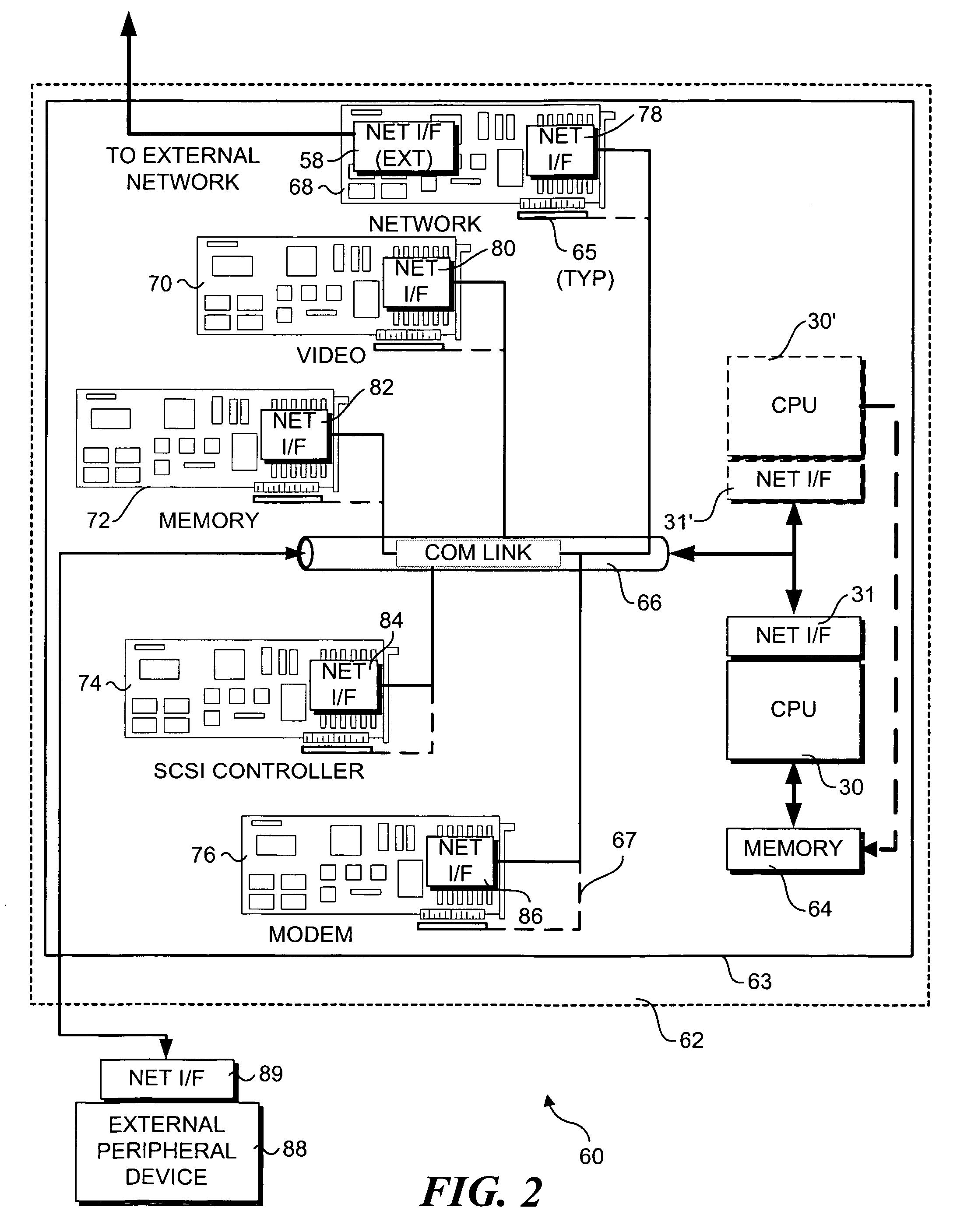
Network based intra-system communications architecture
InactiveUS7117280B2Multiple digital computer combinationsComponent plug-in assemblagesNetwork socketNetwork address
An architecture and method that enables communication between applications and peripheral devices through use of network-type messaging. The architecture is exemplified by a machine having a mainboard that includes memory and one or more processors. The mainboard also includes one or more expansion slots for receiving various peripheral device cards. The processor(s) is enabled to communicate with peripheral devices via an internet network that includes network interfaces for both the processor and each of the peripheral devices. The network interfaces include a network port and a network address that is bound to the network port by means of a network socket. Socket application program interface (API) and network abstraction layers are provided by software means to enable applications to communicate with the peripheral devices using network messaging and protocols, such as TCP / IP over an Ethernet.
Owner:INTEL CORP
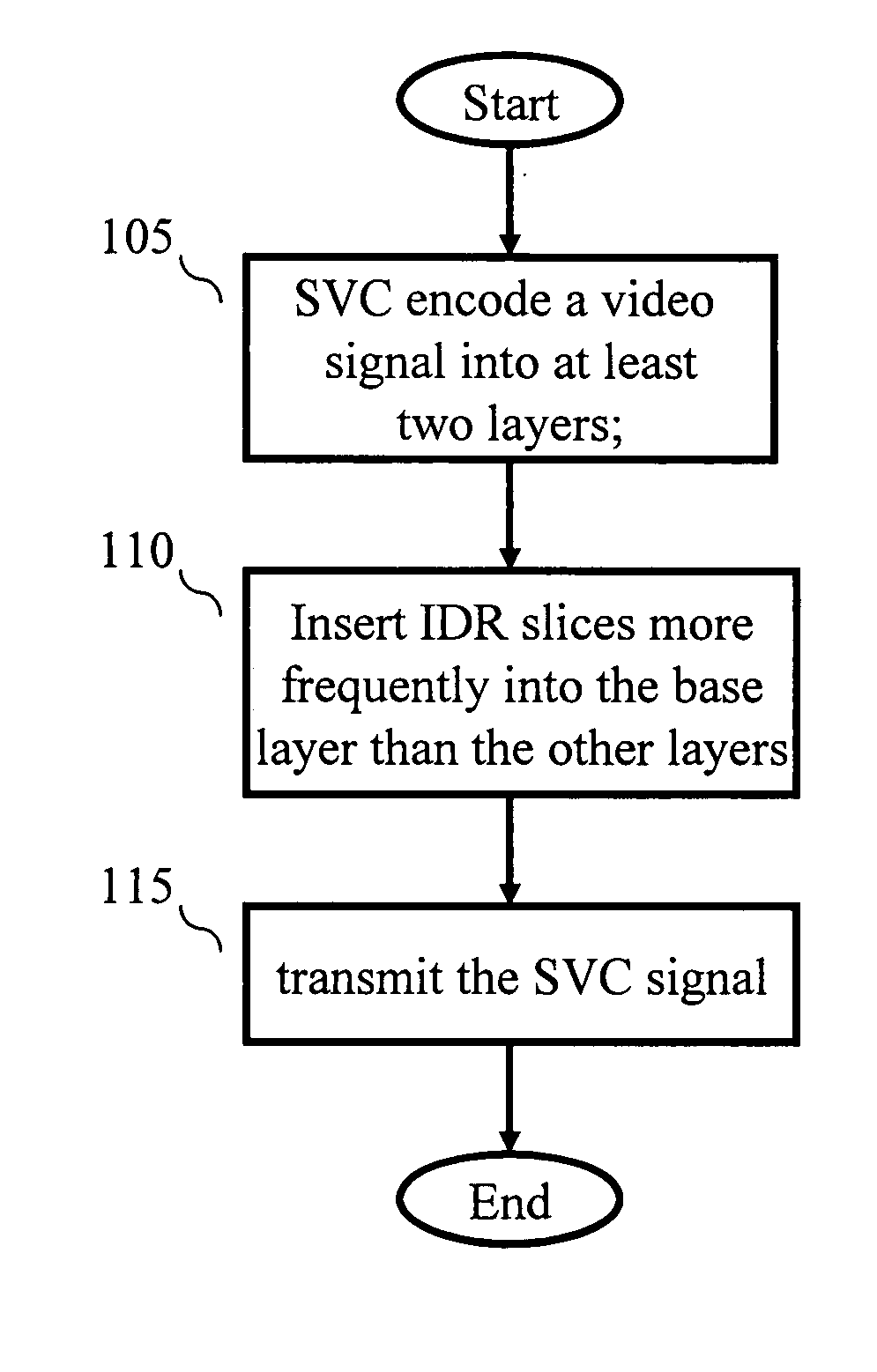
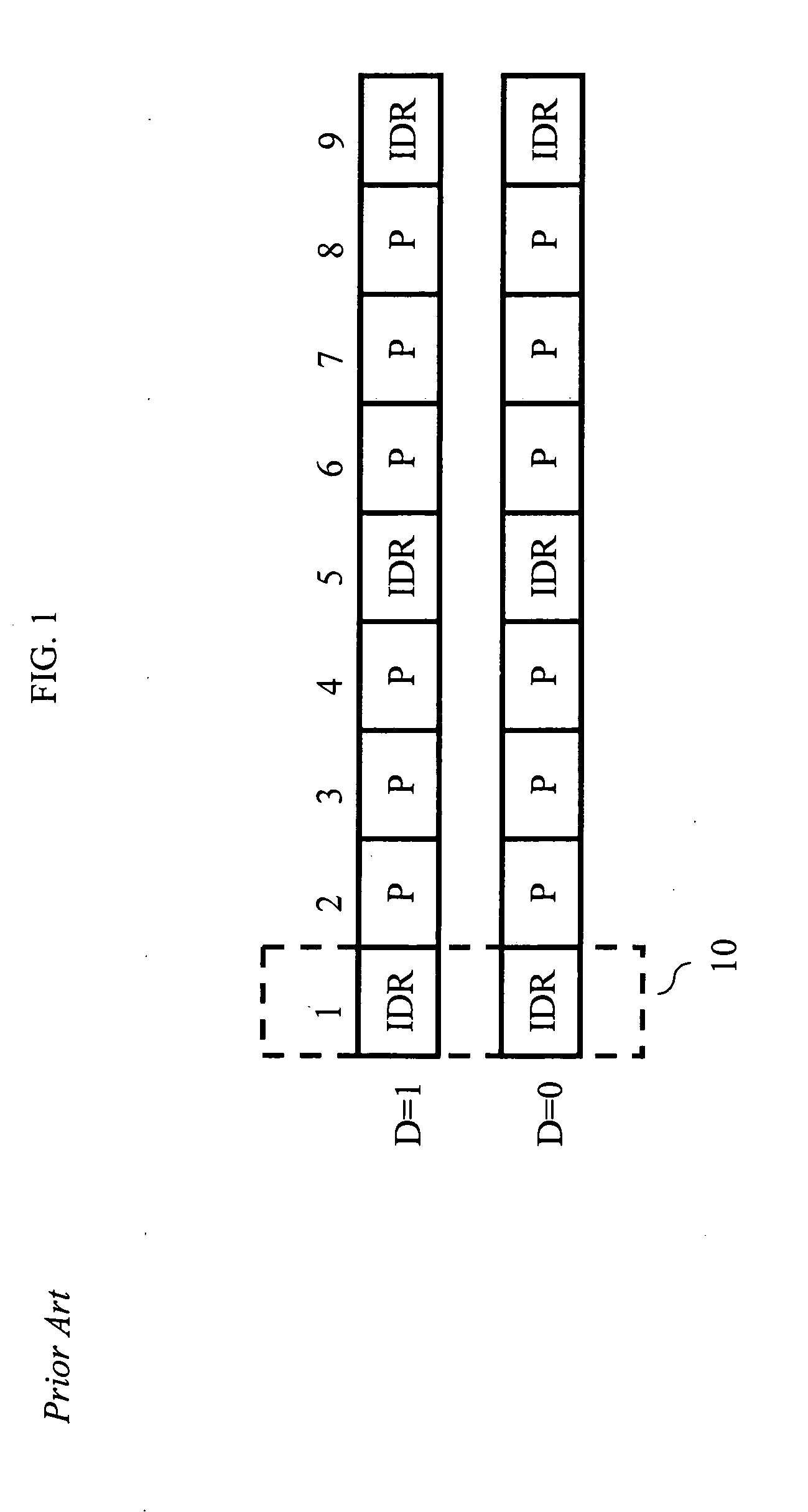
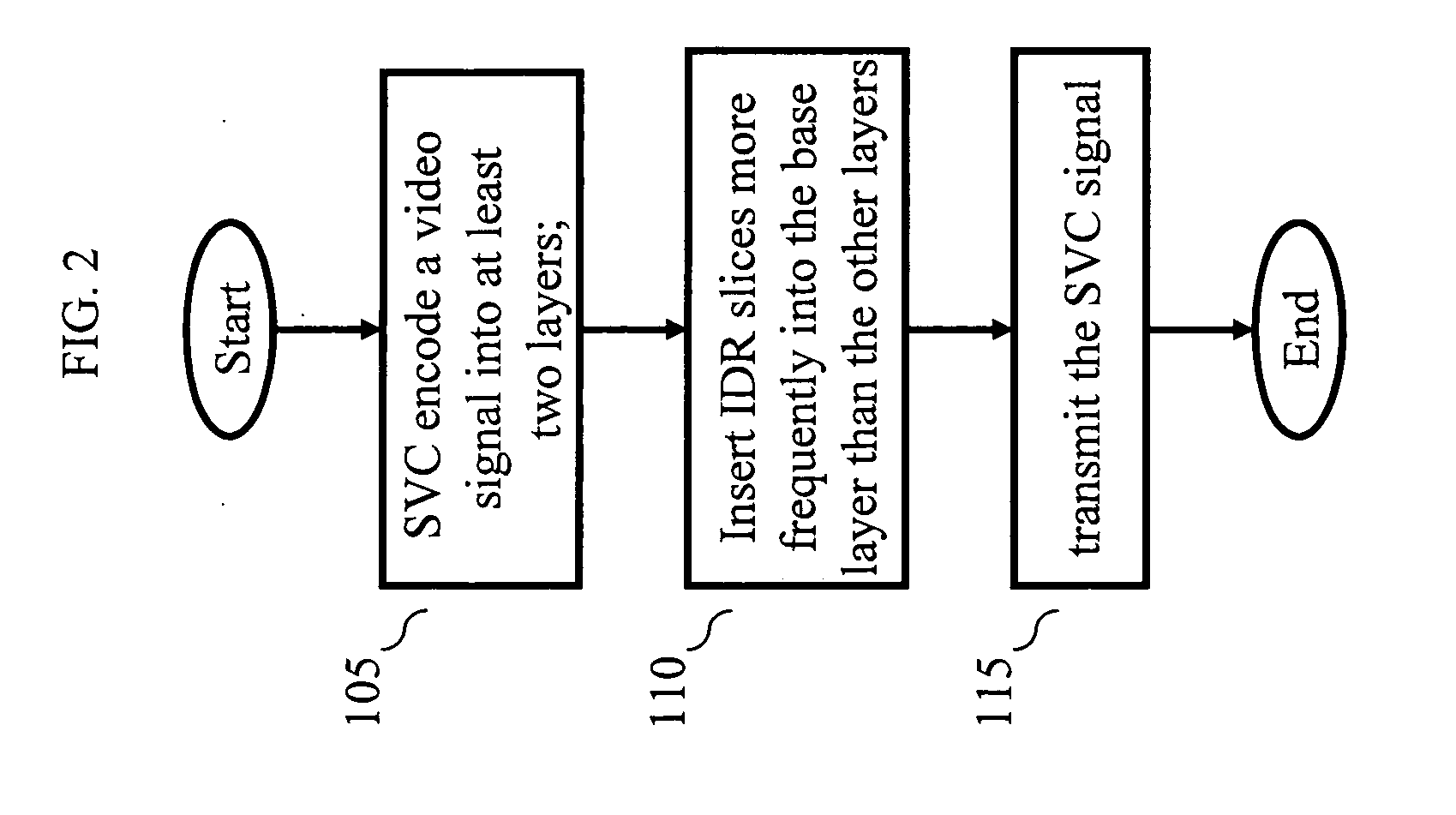
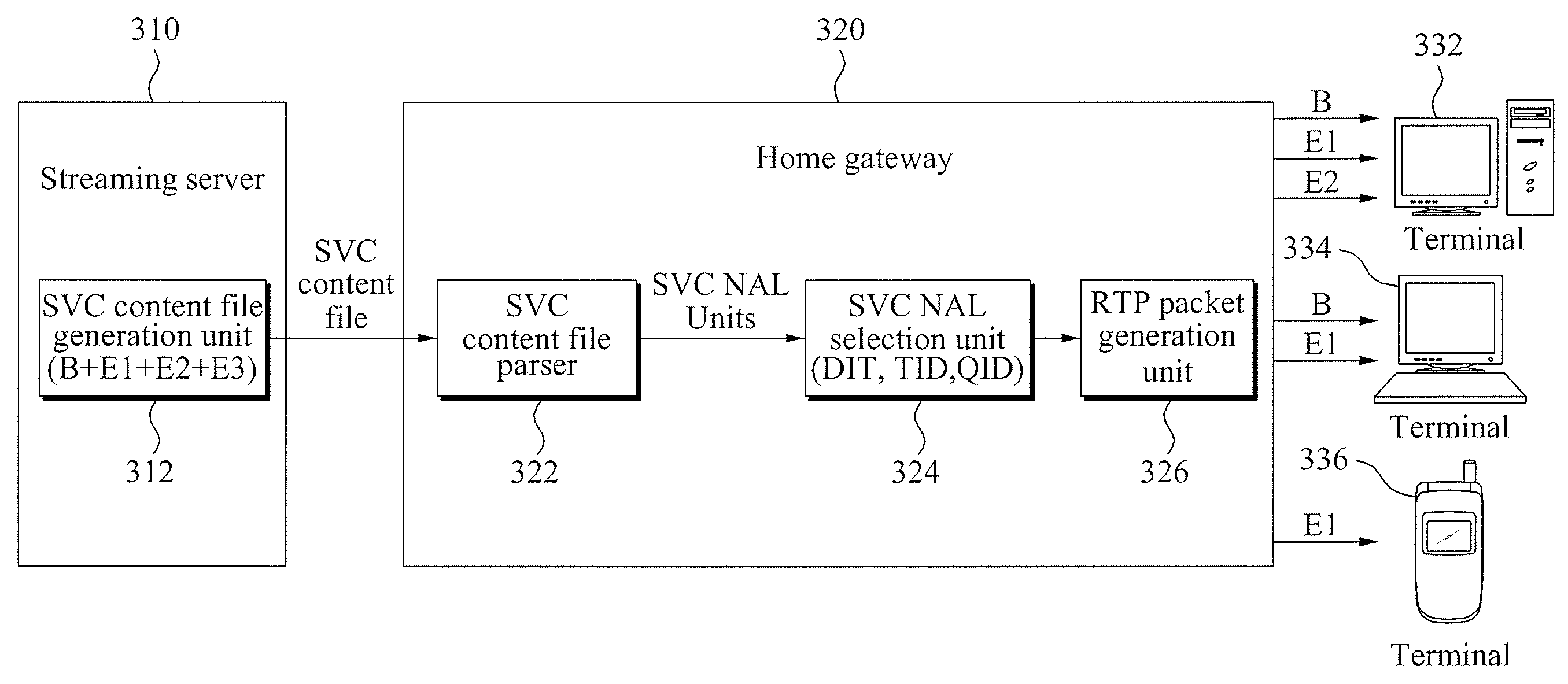
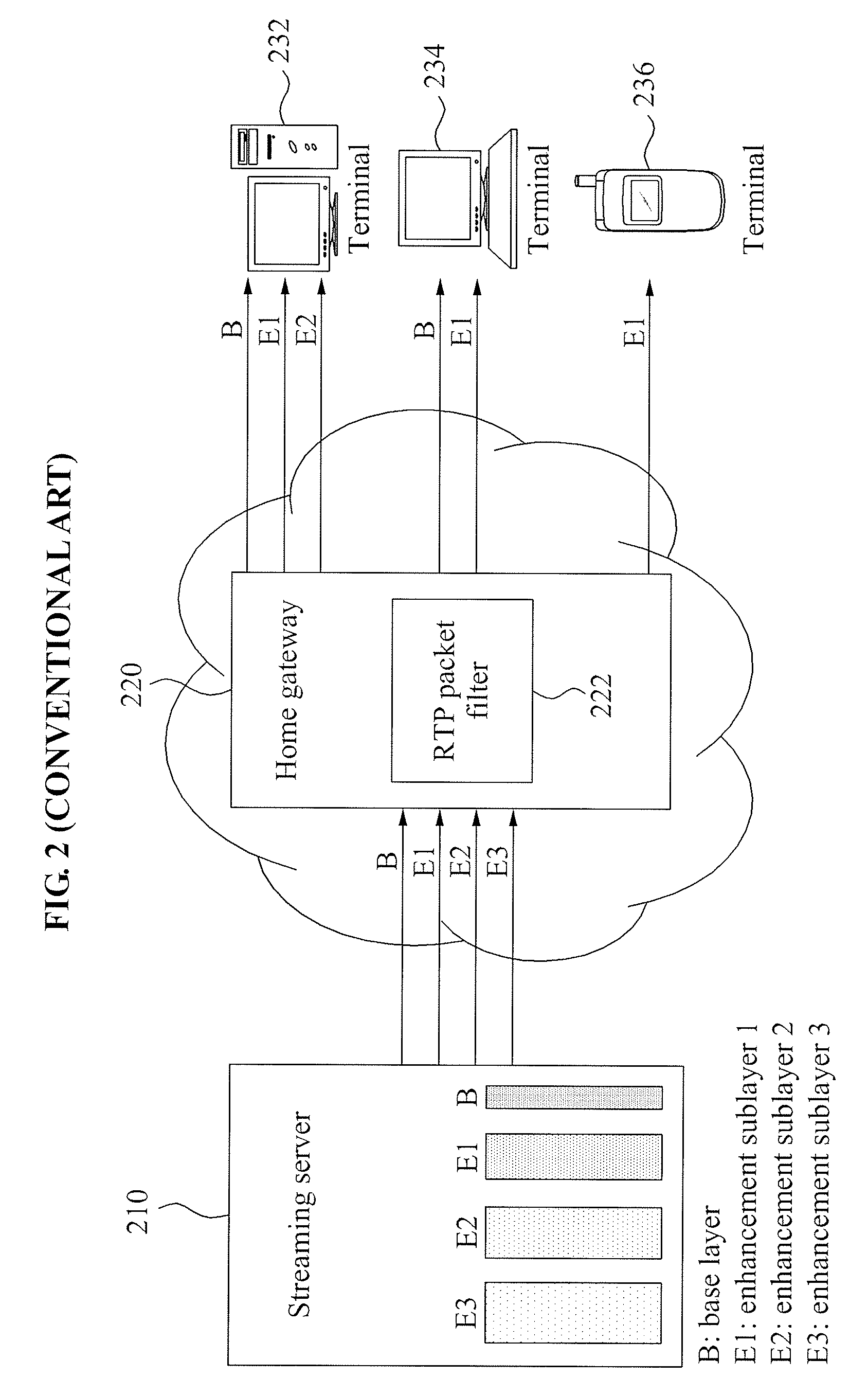
Real-time transport protocol (RTP) packetization method for fast channel change applications using scalable video coding (SVC)
InactiveUS20110134994A1Improve quality of experienceImprove transmission efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesNetwork Abstraction LayerReal-time Transport Protocol
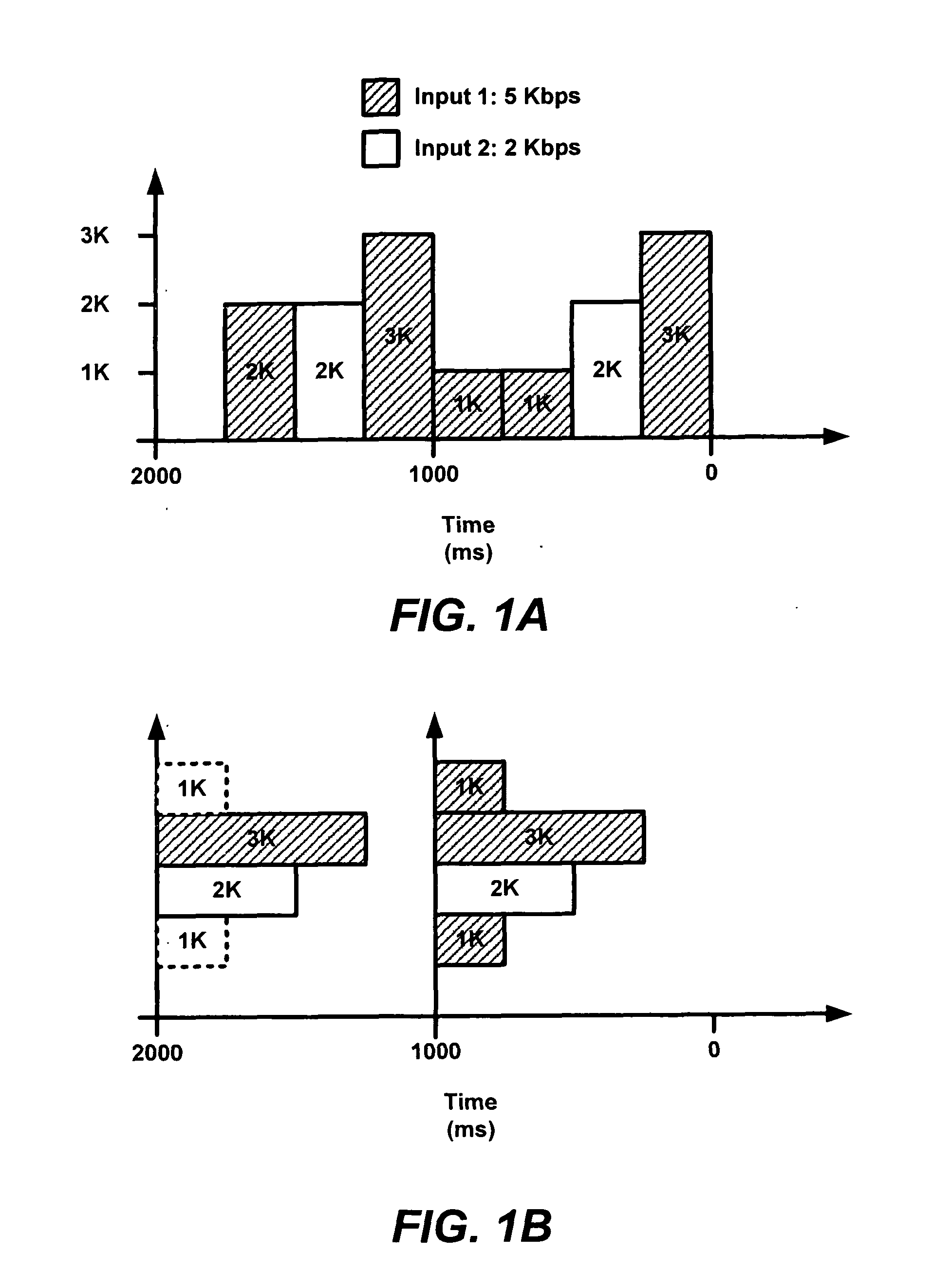
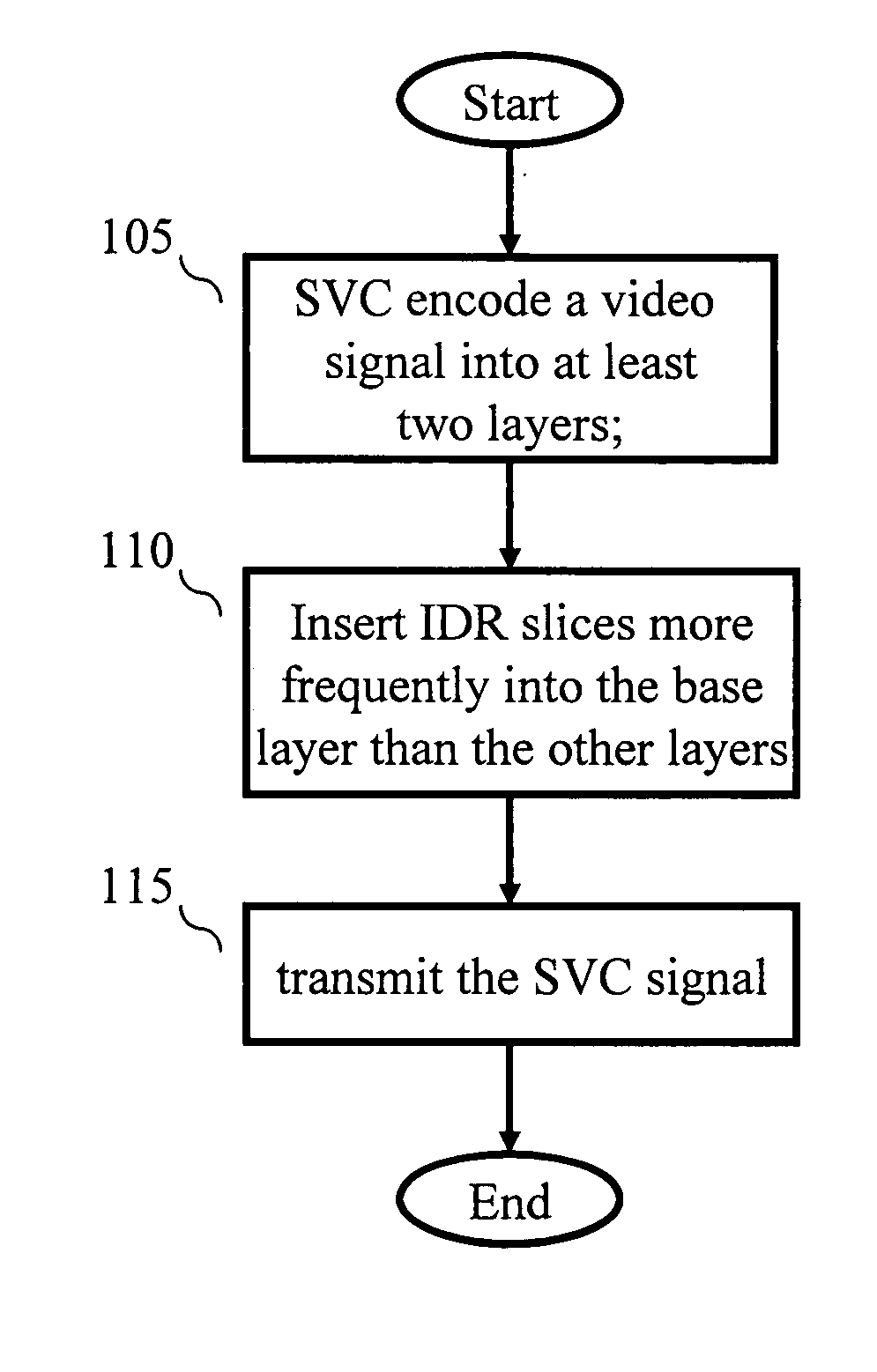
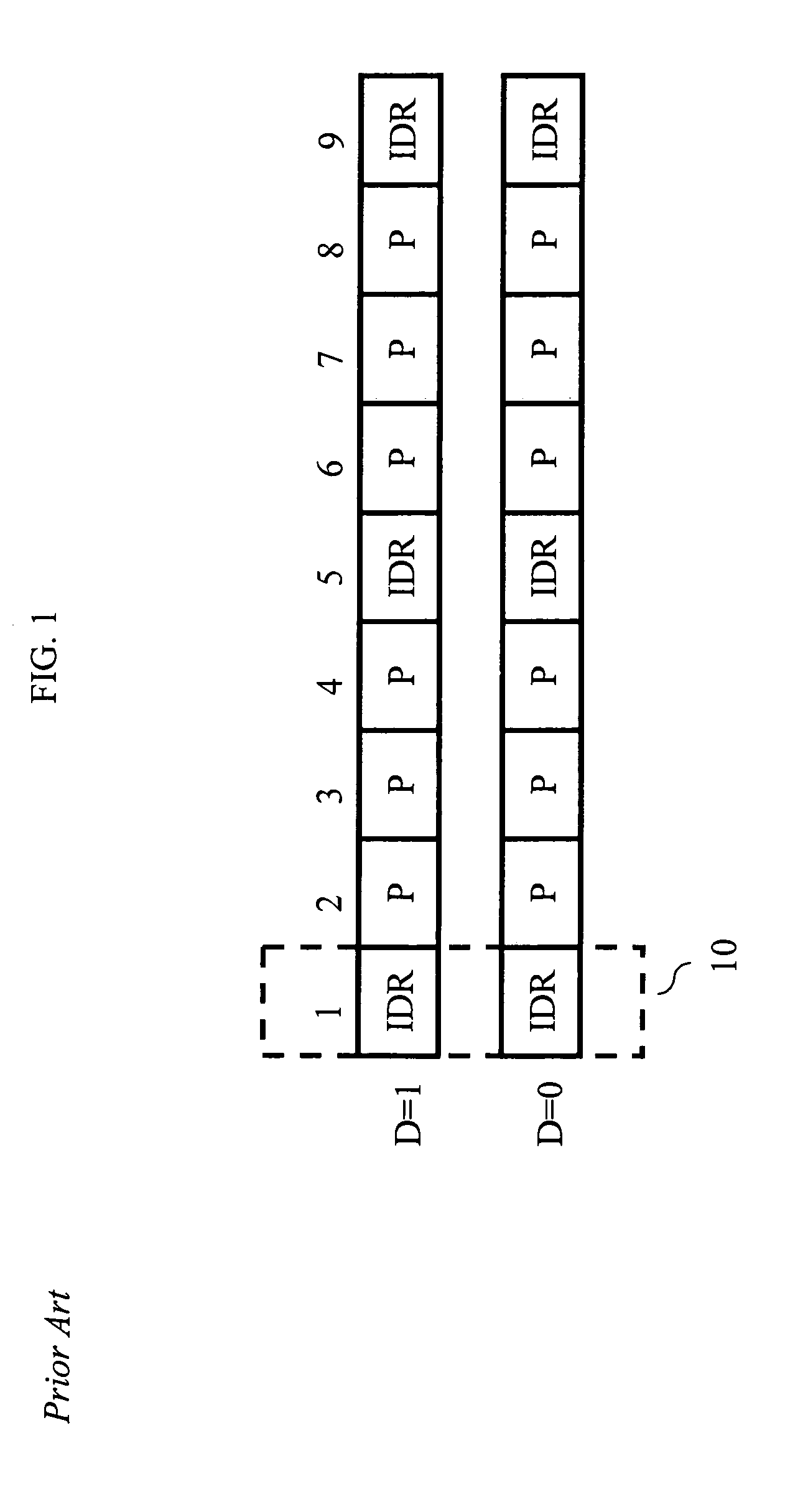
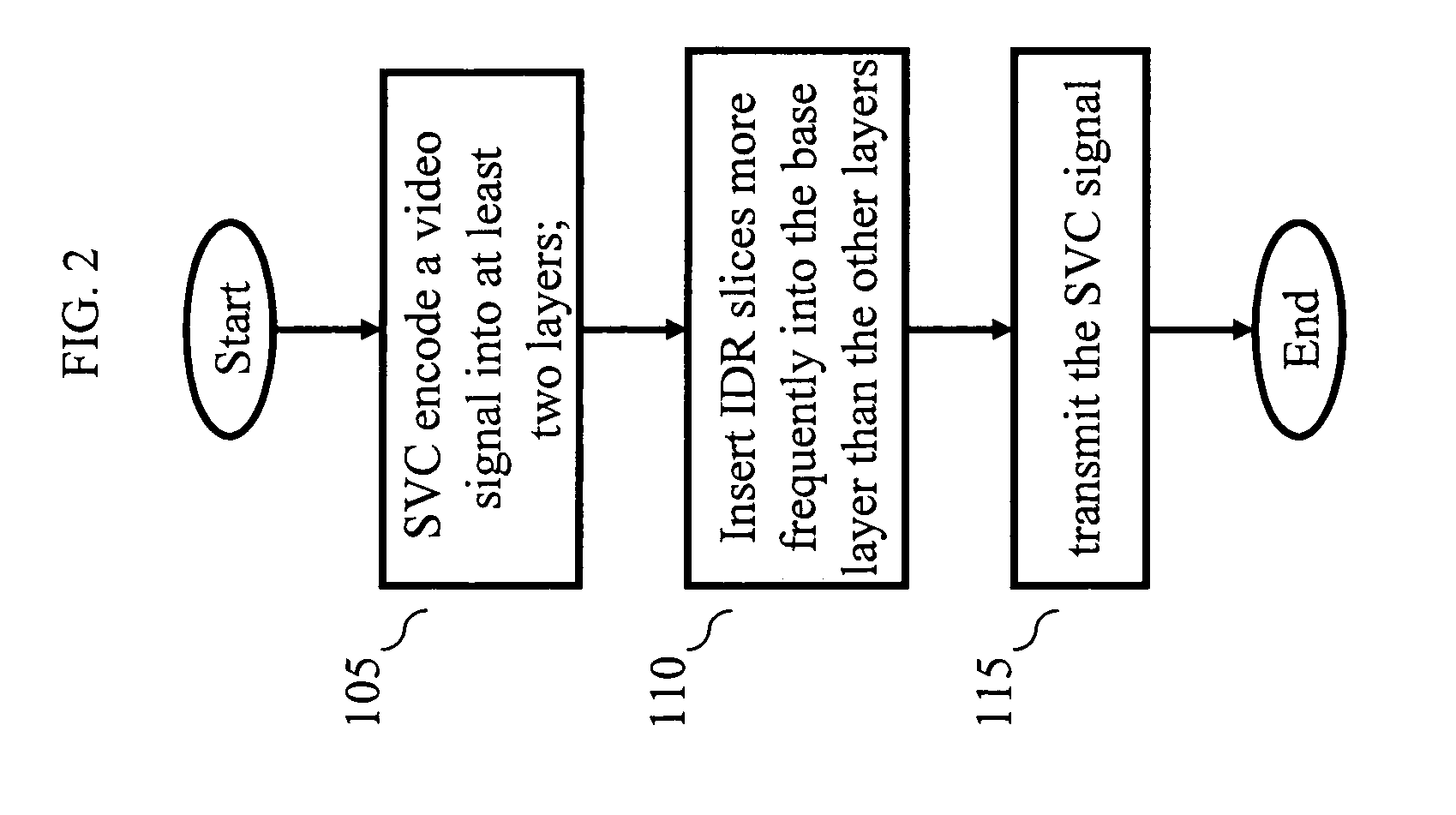
An apparatus encodes a video signal for providing a scalable video coded (SVC) signal comprising a base layer video coded signal and an enhancement layer video coded signal, wherein the base layer video coded signal has more random access points, e.g., Instantaneous Decoder Refresh (IDR) slices, than the enhancement layer and in those access units where the enhancement layer has an IDR slice, the base layer has a non-IDR slice. Transmission of the SVC occurs in packet form using the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) such that non-random access point slices are conveyed in Simple Time Aggregation Packets (STAP), each Simple Time Aggregation Packet comprising a Payload Content Scalability Information (PACSI) Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) Unit.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Method for protecting multimedia data using additional network abstraction layers (NAL)
InactiveUS20090177949A1Increase the lengthCode conversionCyclic codesComputer networkNetwork Abstraction Layer
A method for protecting multimedia data encoded by the H.264 standard, the data being encapsulated in a structure of the network abstraction layer or NAL type, characterized in that the user inserts at least one redundancy NAL containing the error-correcting code used for transmitting the data.
Owner:THALES SA
System and method for reducing storage requirements for content adaptive binary arithmetic coding
ActiveUS7595743B1Data storage requirement is reducedReduce storage requirementsCode conversionDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareData stream
A system for reducing storage requirements for content-adaptive binary arithmetic coding (CABAC) is provided. The system includes a transcode engine performing CABAC on a video data stream. The transcode engine receives save data, stops CABAC, and converts the video data stream into sub-network abstraction layer (NAL) unit state data. An entropy state data storage system receiving the sub-NAL unit state data and stores the sub-NAL unit state data. The transcode engine subsequently receives restore data, extracts the sub-NAL unit state data from the entropy state data storage system, and re-starts CABAC on the video stream data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
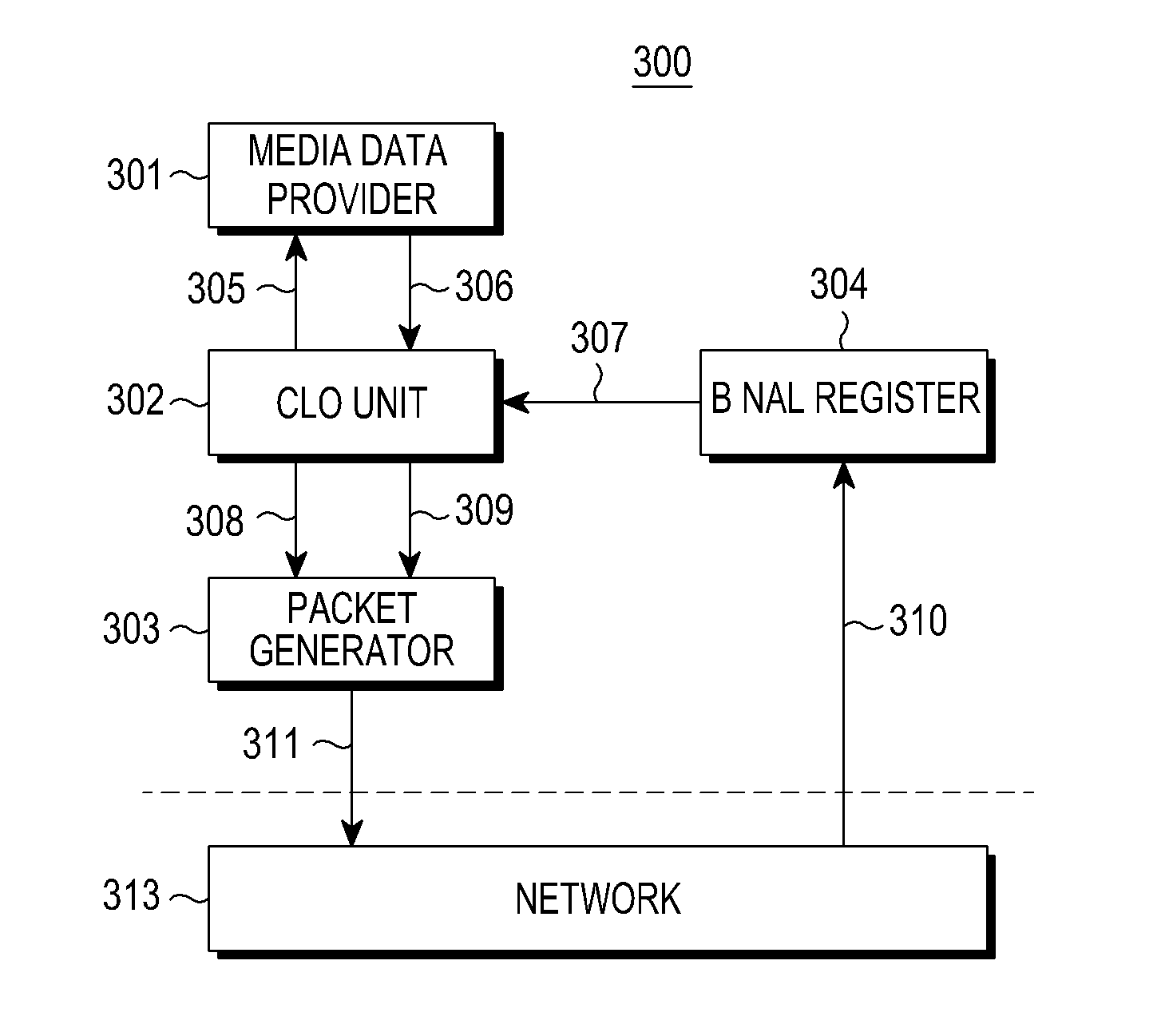
Method and apparatus for transmitting a multimedia data packet using cross layer optimization
InactiveUS20120250690A1Easy to useData switching by path configurationSelective content distributionCross-layer optimizationNetwork packet
A method and apparatus for transmitting a multimedia data packet are provided. The method includes receiving Bottom-up Network Abstraction Layer (B-NAL) information from a network entity, generating Top-down Network Abstraction Layer (T-NAL) information on the multimedia data to be transmitted, generating a multimedia data packet containing said T-NAL information, and transmitting the multimedia data packet generated in the previous process, to the network entity, in consideration of said B-NAL information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
A streaming service system and method for universal video access based on scalable video coding
InactiveUS20100161823A1Convenient verificationBroadcast information characterisationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo encodingNetwork Abstraction Layer
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Video coding system with low delay and method of operation thereof
ActiveUS20140003535A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo bitstreamVideo encoding
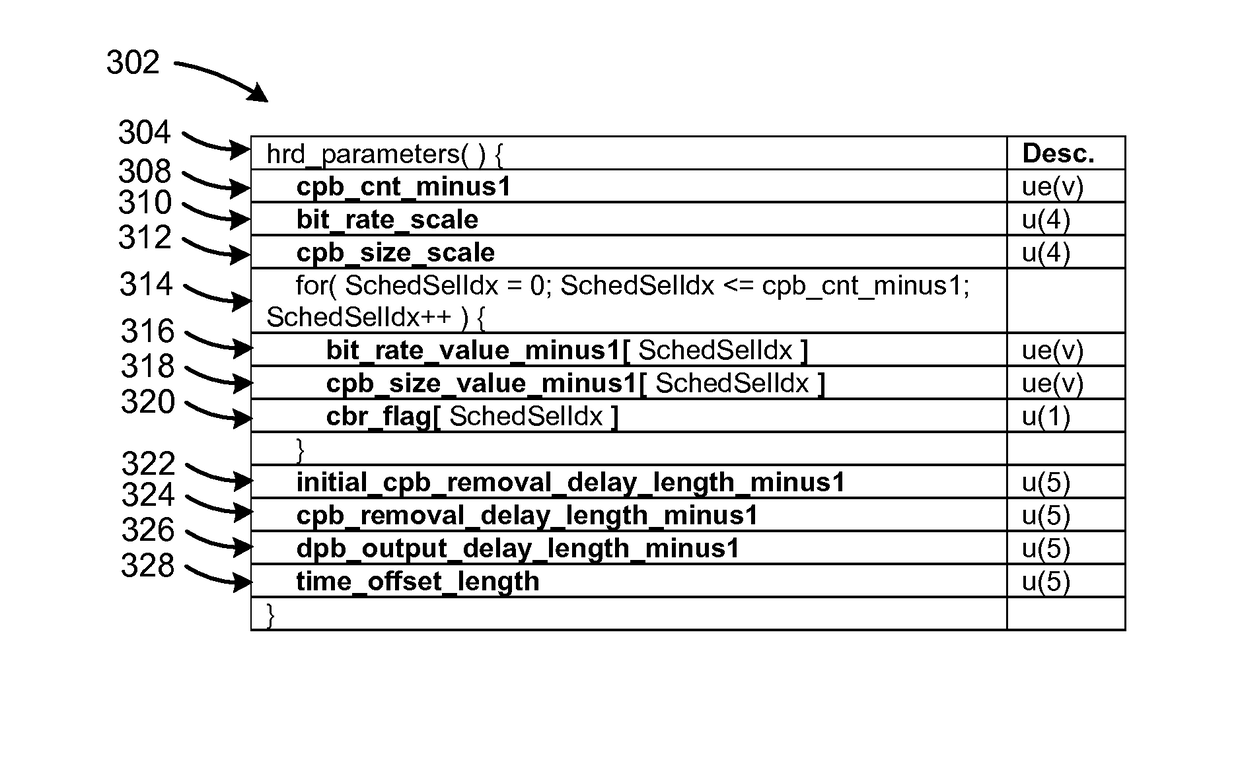
A method of operation of a video coding system includes: receiving a video bitstream as a serial bitstream; extracting a video syntax from the video bitstream; extracting a low delay flag, a network abstraction layer (NAL) hypothetical reference decode (HRD) parameters present flag, and a video coding layer (VCL) HRD parameters present flag from the video syntax extracting a HRD syntax from the video bitstream based on the low delay flag, the NAL HRD parameters present flag, and the VCL HRD parameters present flag; extracting a temporal layer from the video bitstream based on the video syntax having the HRD syntax; and forming a video stream based on the temporal layer for displaying on a device.
Owner:SONY CORP
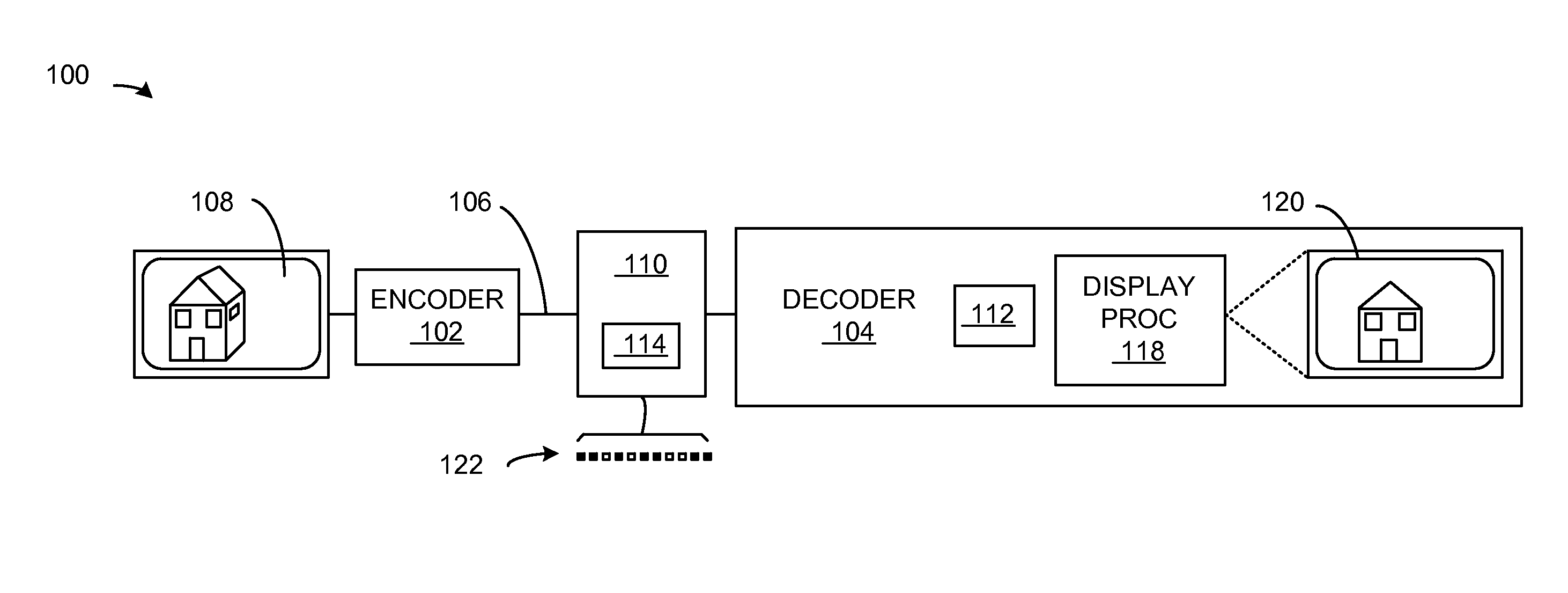
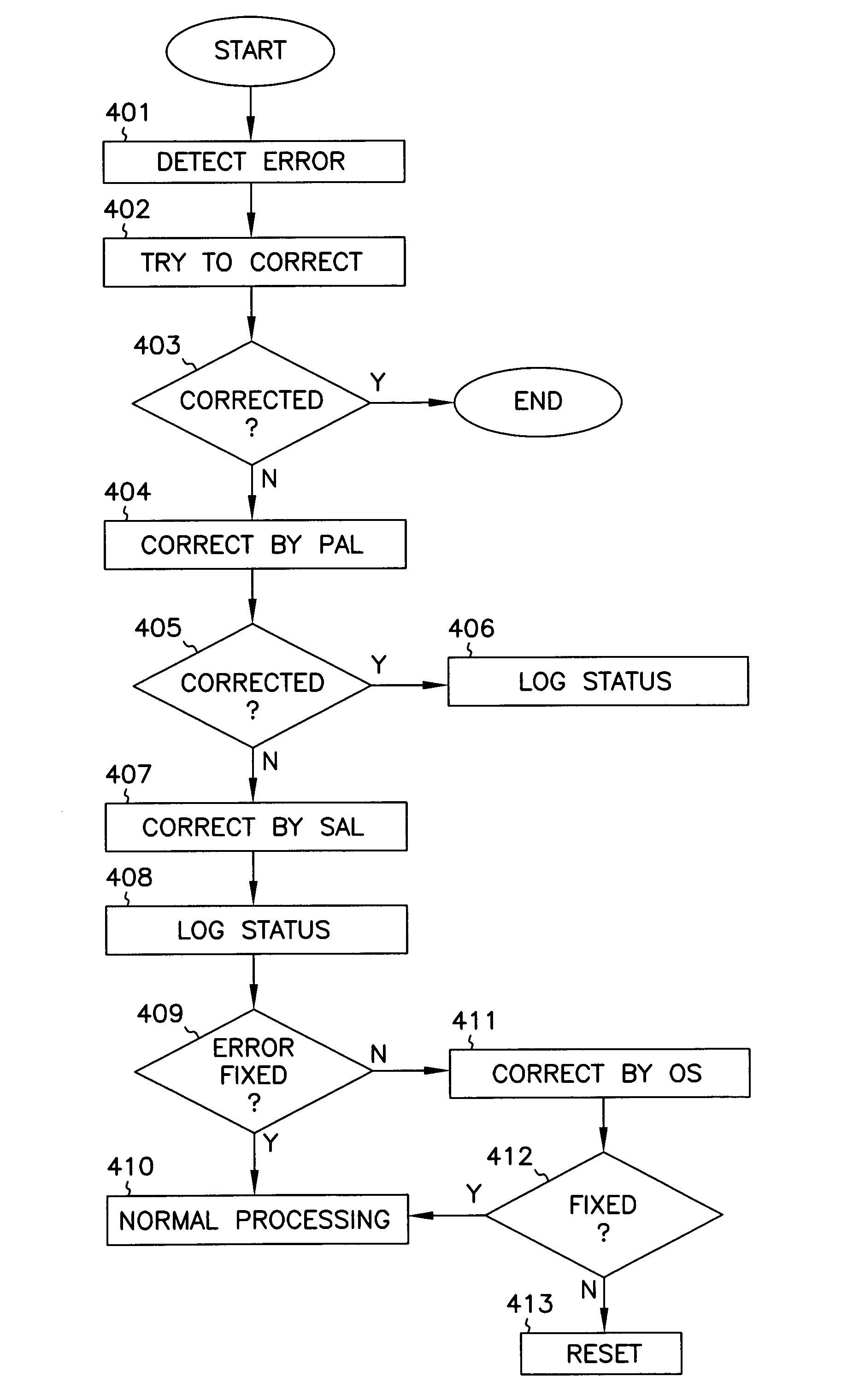
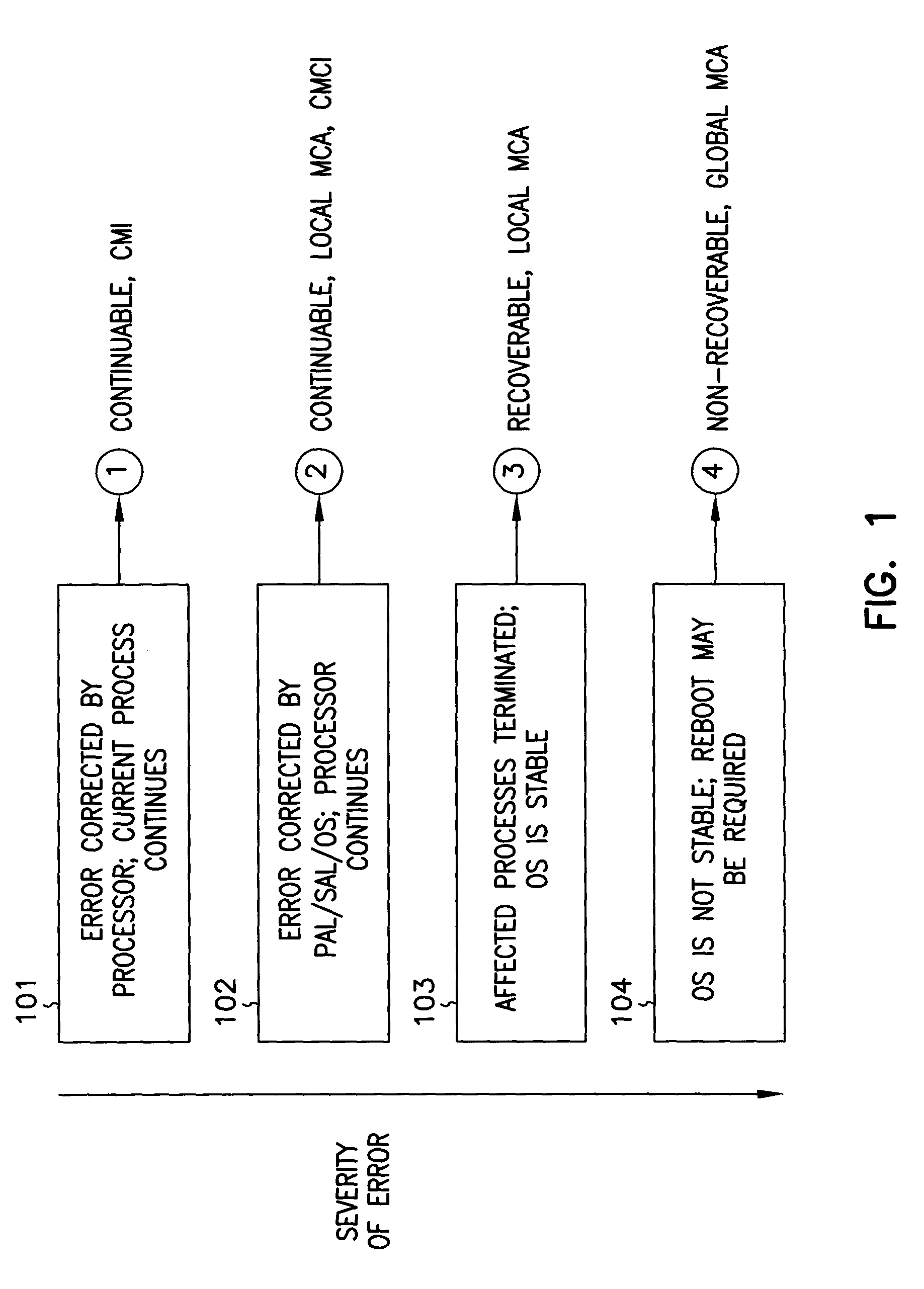
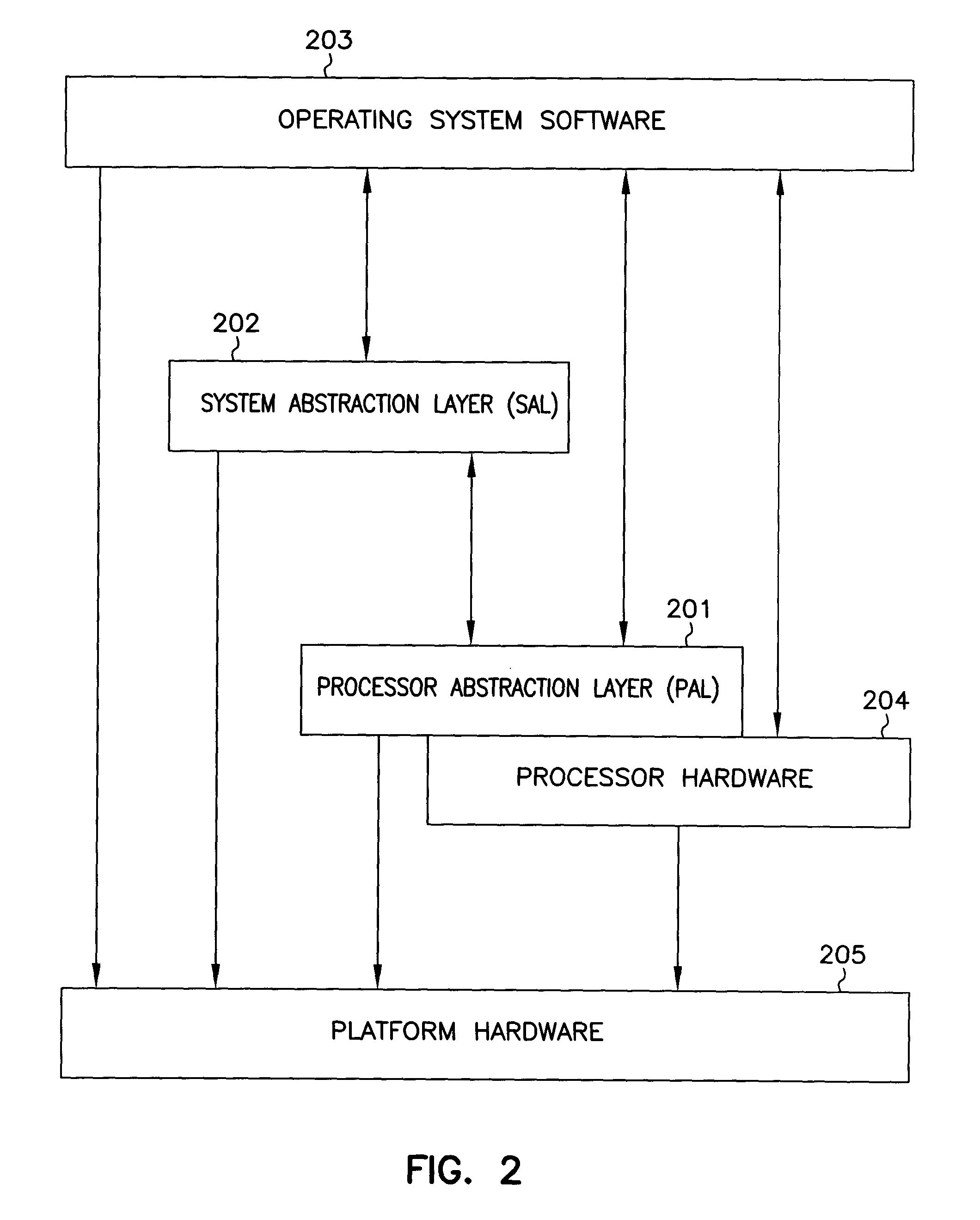
System abstraction layer, processor abstraction layer, and operating system error handling
Systems and methods for error handling are disclosed. The systems and methods may be utilized for single or multiple processor computer systems to handle errors in a coordinated manner between hardware and any firmware or software layers. A computer system includes a non volatile memory and at least one processor. A firmware error handling routine is stored on the non volatile memory. The firmware error handling routine is for handling errors. Each of the at least one processors detects errors. Each processor executes the firmware error handling routine on detecting an error. The executed firmware error handling routine handles the error. The executed firmware error handling routine also logs error information to a log.The systems and methods provide for coordinated error handling that enhance error recovery, provide error containment and maintain system availability.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for processing packet loss in international protocol television (IPTV) system as well as server
InactiveCN102130821AReduce the impact of decodingImprove experienceData switching networksPacket lossNetwork Abstraction Layer
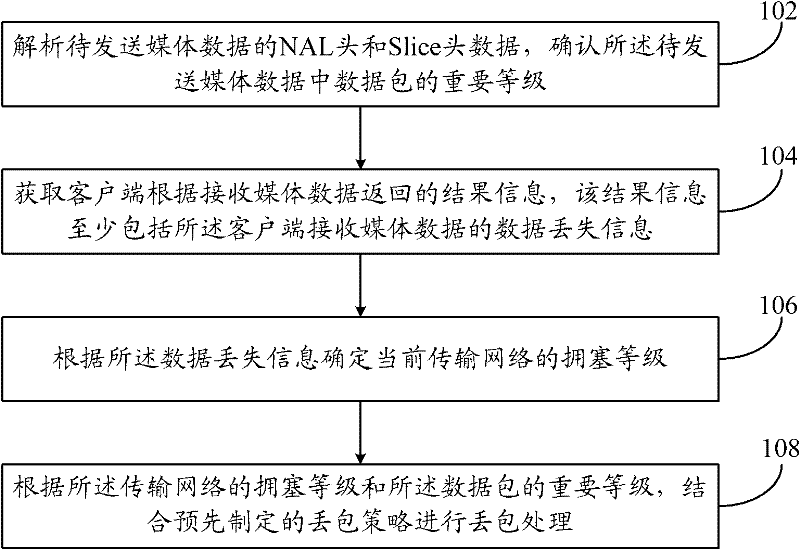
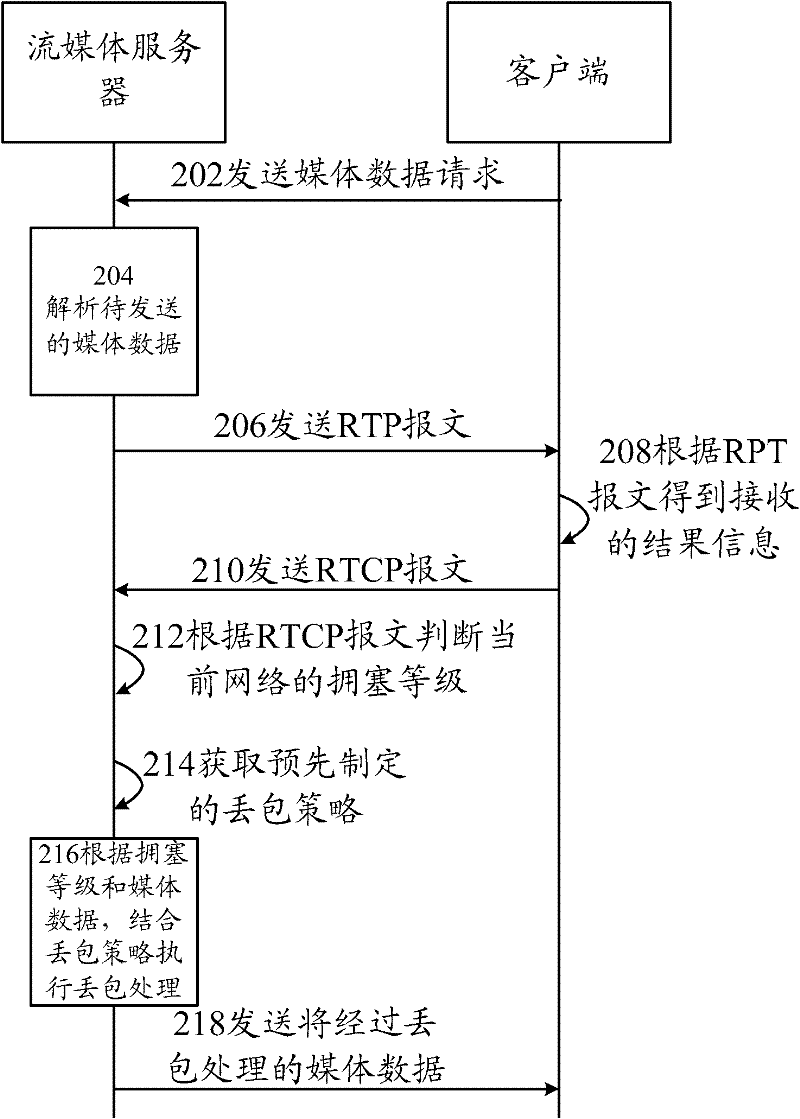
The invention discloses a method for processing packet loss in an international protocol television (IPTV) system, comprising the following steps: analyzing network abstraction layer (NAL) head and Slice head data of media data to be sent, and confirming order of precedence of data packets in the media data to be sent; acquiring the result information returned by a client-side in accordance with the received media data, wherein the result information at least comprises data loss information of the media data received by the client-side; according to the data loss information, determining the congestion level of the current transmission network; and according to the congestion level of the current transmission network and the order of the precedence of the data packets, combining with preset packet loss strategies to process the packet loss. The invention discloses a stream media server and a system for processing packet loss in an IPTV system. By judging the congestion level of the network and combining with the preset packet loss strategies, the data packets are abandoned selectively and actively. The problem that decoding can not be performed so as to seriously influence the decoding quality of information destination ends because key data packets in the media data are abandoned at random can be avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
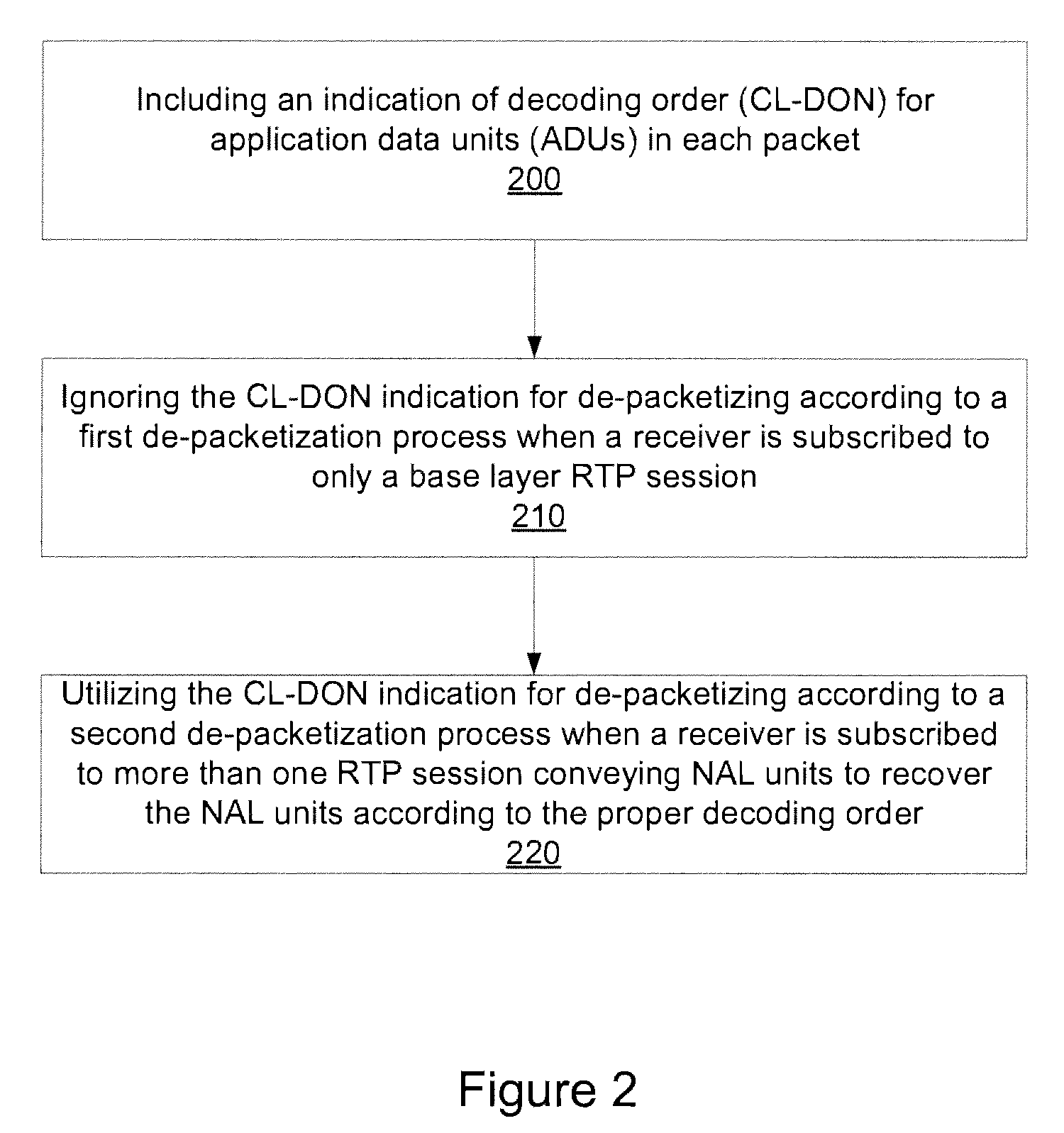
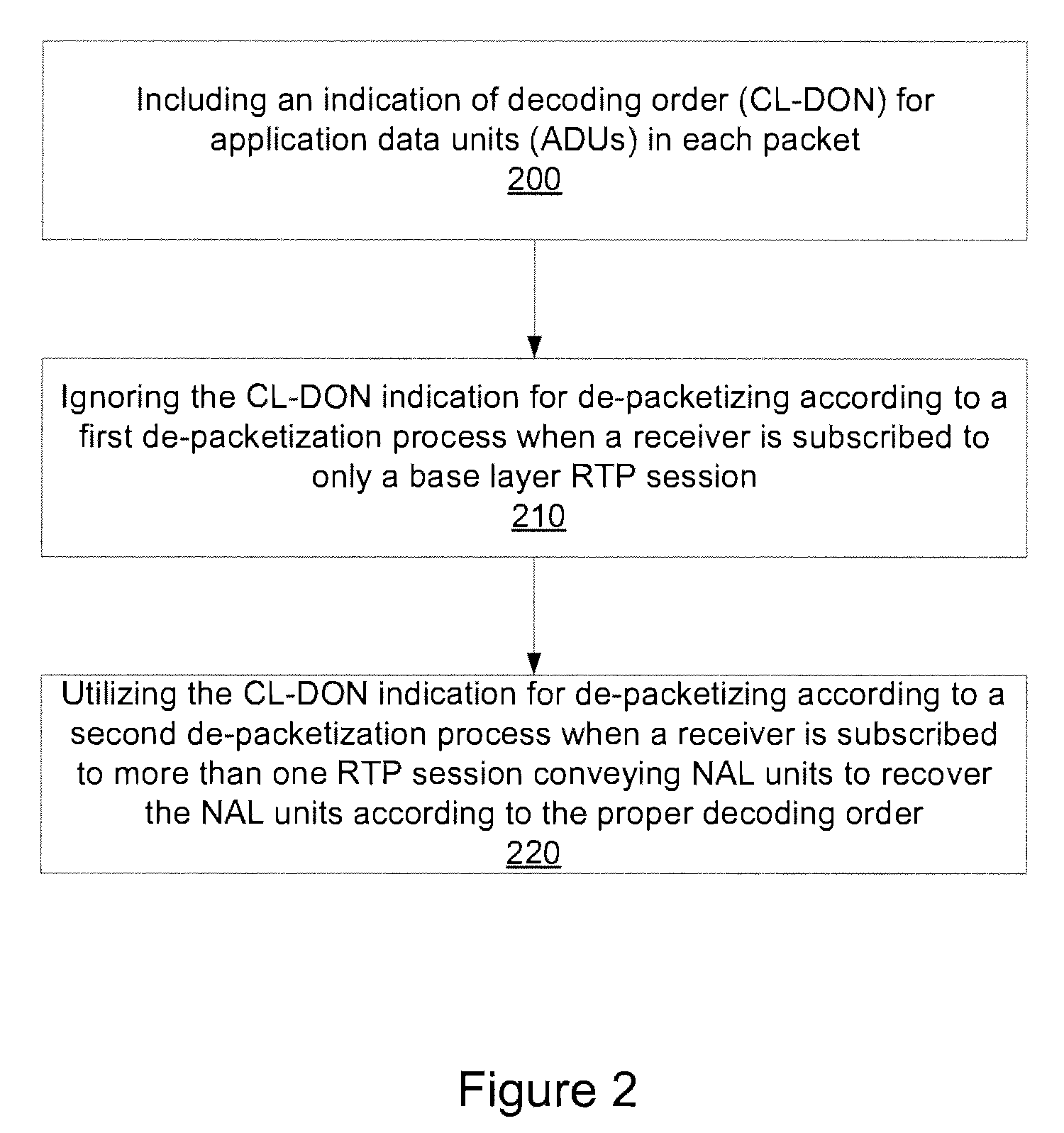
Coded application data unit order recovery in layered multicast
ActiveUS20090083434A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTime ProtocolNetwork Abstraction Layer
Systems and methods are provided which allow receivers to recover the decoding order of network abstraction layer (NAL) units conveyed in different Real Time Protocol (RTP) sessions. An indication of decoding order for application data units (ADUs) in each packet is included in the packet structure of a PACSI NAL unit, when the PACSI NAL unit is a single-time aggregation packet type A (STAP-A) packet and the PACSI NAL unit is the first NAL unit in an aggregation packet (e.g., when a receiver is subscribed to different RTP session that convey NAL units). If the receiver is subscribed to only a base layer RTP session, the CL-DON indication can be ignored.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
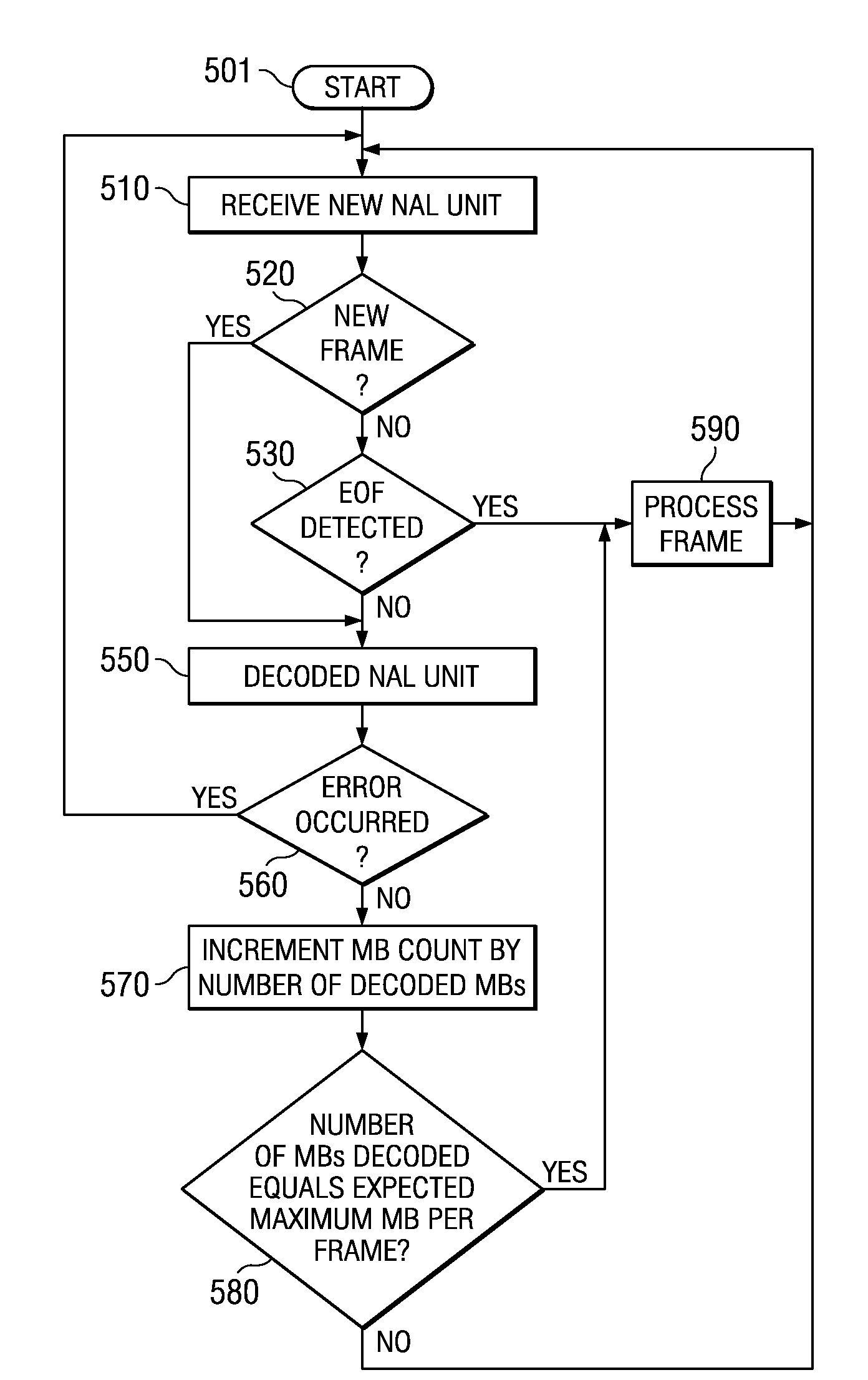
Decoder with resiliency to handle errors in a received data stream
ActiveUS20090144596A1Reliable detectionAvoid problemsTransmission systemsFault responseData streamOriginal data
A decoder provided according to an aspect of the present invention determines a type of each network abstraction layer (NAL) unit, and discards a NAL unit when the size of the NAL unit is inconsistent with the size according to the determined type. According to another aspect, a decoder corrects for errors in the non-pay load portions and uses the corrected non-pay load portions to recover the original data contained in the payload portions of the data stream. In an embodiment, various global parameters (which are applicable to the data stream unless changed further in the data stream) and the values in the slice headers are examined to correct the parameters in the slice headers. According to one more aspect, an end of frame is reliably detected by using an expected number of macro-blocks in a frame and a set of logical conditions of slice header parameters.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Source-channel combined coding method and satellite broadcasting system using the same
InactiveUS20110131615A1Efficient solutionReduce decreaseSatellite broadcast receivingGHz frequency transmissionSatellite broadcastingChannel signal to noise ratio
A source-channel combined coding method including: determining whether a channel signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is varied or not; when it is determined that the channel SNR is varied, selecting a MODCOD suitable for the channel SNR by referring to a first table defining an SNR threshold value at which data transmission is performed without an error, for each MODCOD designating a low density parity check (LDPC) code rate and a modulation scheme; calculating a source coding rate by using an effective information bit rate of the selected MODCOD; extracting network abstraction layer (NAL) units for each layer from an inputted video frame so as to satisfy the calculated source coding rate, and packetizing the extracted NAL units; binding packets to configure a baseband (BB) frame; and LDPC coding and modulating the BB frame through the code rate and the modulation scheme which are designated by the selected MODCOD.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
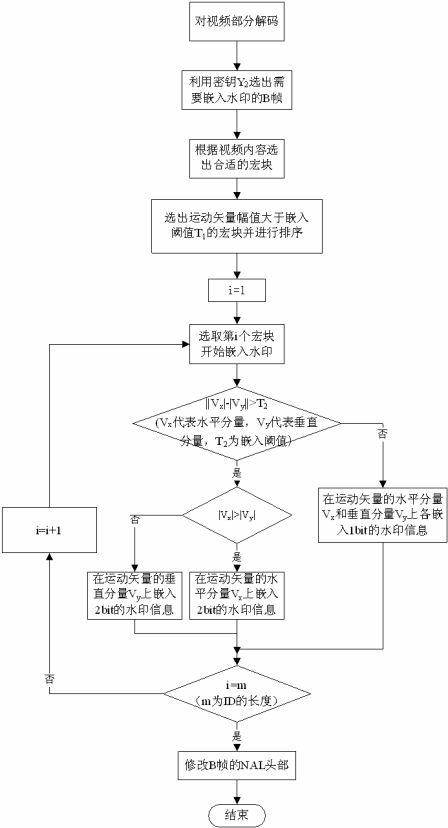
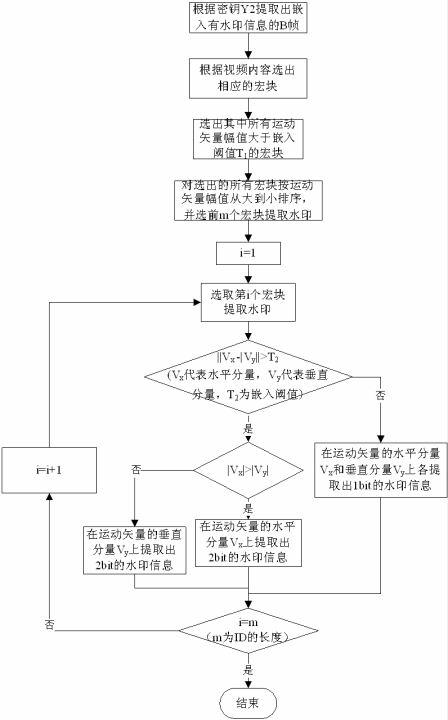
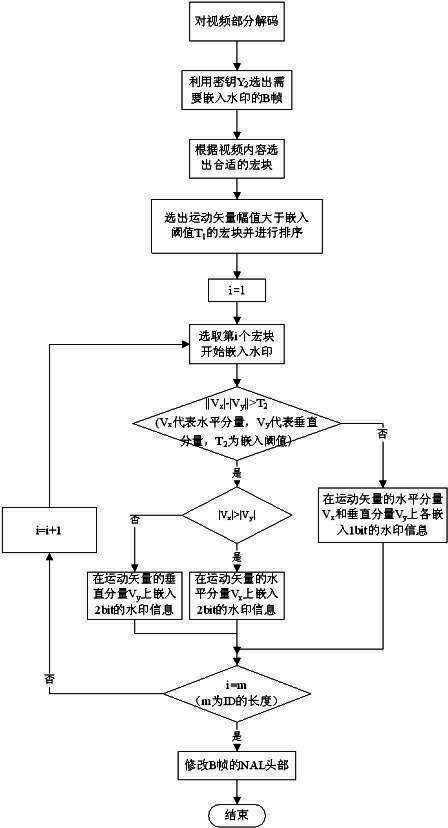
Piracy tracing watermarking method applicable to streaming media environment
ActiveCN102307320AImprove real-time performanceReduce complexityTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationWatermark methodMotion vector
The invention relates to a piracy tracing watermarking method applicable to streaming media environment, and belongs to the multimedia information safety field. The method comprises the following steps: firstly segmenting video before the watermark embedding procedure; according to content of streaming video, selecting macroblocks meeting the conditions to be embedded with watermarks during the watermark embedding process; and determining the macroblock which is best suited for being embedding with watermark information by adopting a quicksort algorithm. In the piracy tracing watermarking method, based on difference between horizontal direction and vertical direction of motion vector of the macroblock, appropriate motion components are adaptively selected to be embedded with 2-bit watermark information, and the NAL (network abstraction layer) head of a B-frame is modified after the watermark embedding procedure so that the watermark can cope with the situations such as frame loss and the like resulting from network transmission. By adopting the piracy tracing watermarking method, the watermark information can be embedded into the streaming video in real time so as to achieve the purpose of piracy tracing.
Owner:JIANGSU YITONG HIGH TECH
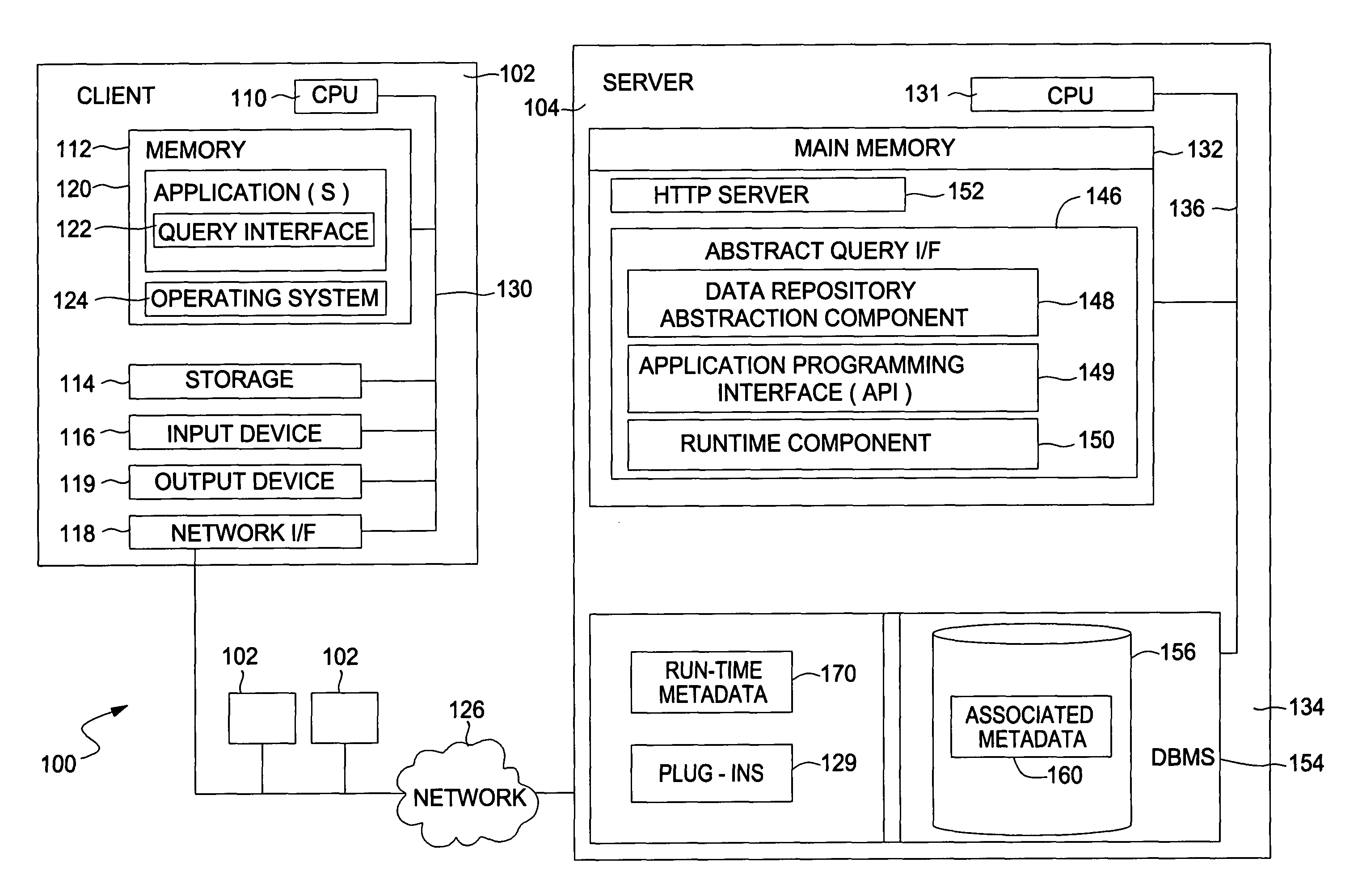
Dynamic functional module availability
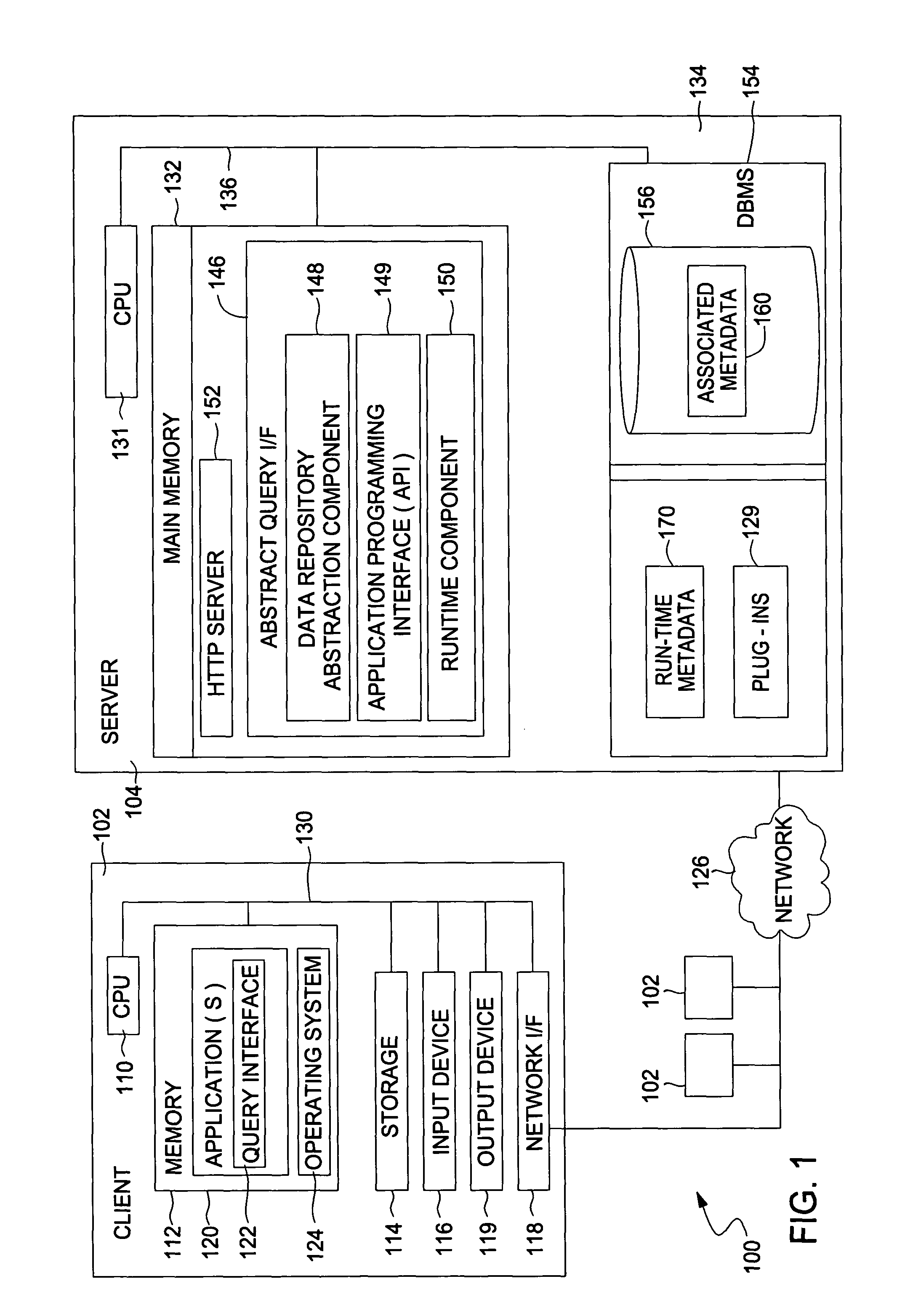
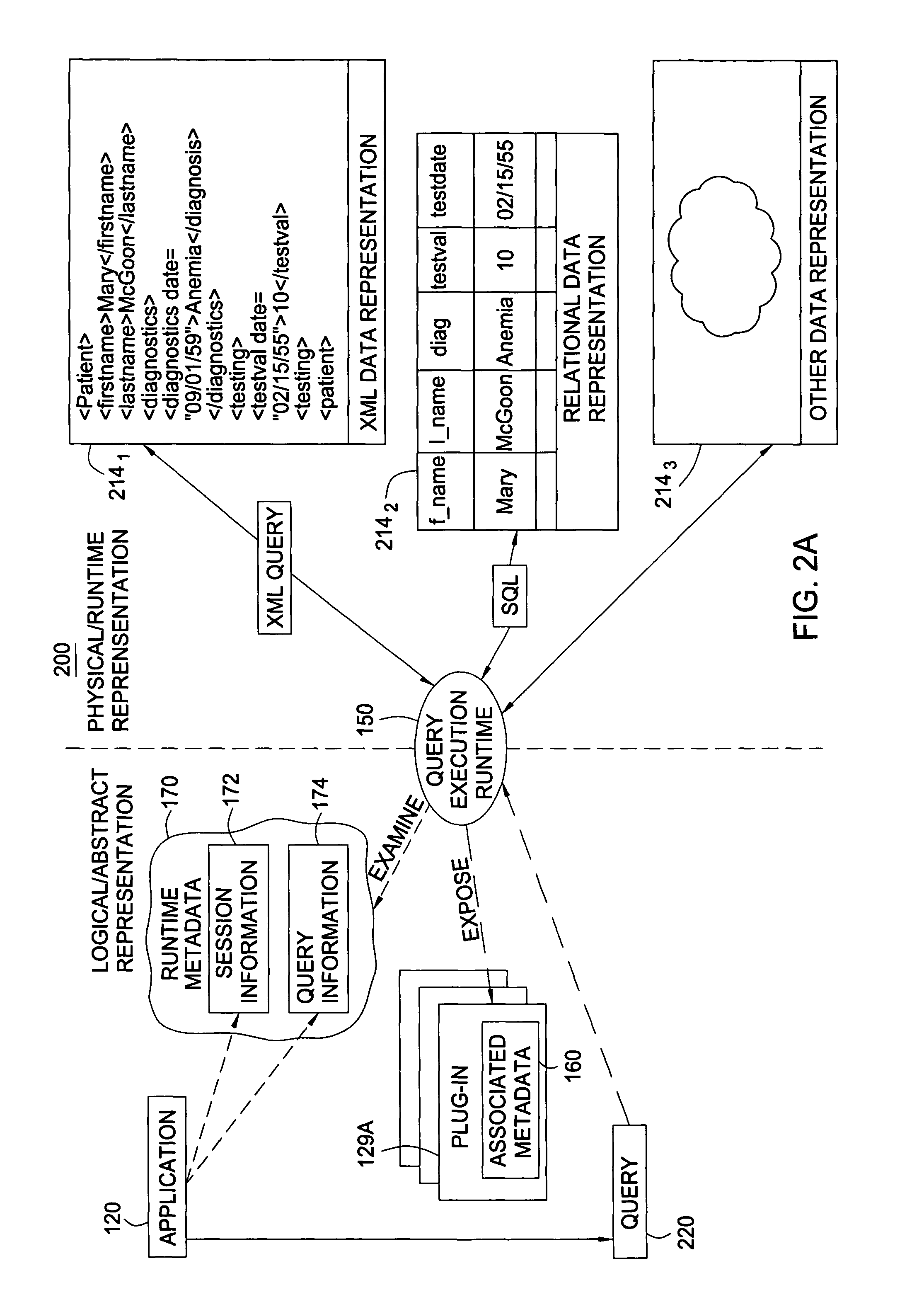
ActiveUS8458215B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAbstraction layerComputer module
The present invention generally is directed to a system, method and article of manufacture for accessing data independent of the particular manner in which the data is physically represented. In one embodiment, a data repository abstraction layer provides a logical view of the underlying data repository that is independent of the particular manner of data representation. A query abstraction layer is also provided and is based on the data repository abstraction layer. A runtime component performs translation of an abstract query into a form that can be used against a particular physical data representation.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
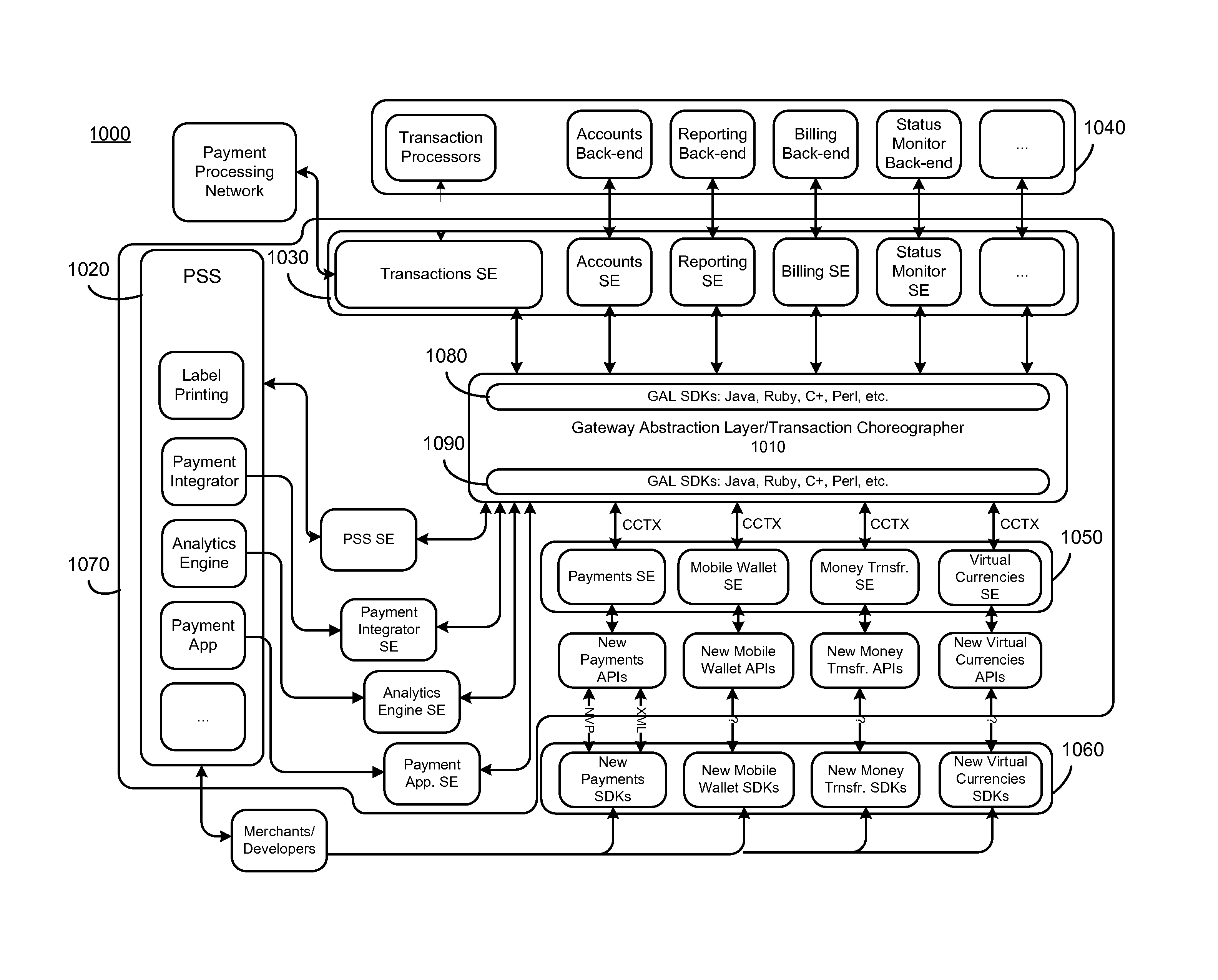
Gateway abstraction layer
Systems, gateway computers, and methods for using a gateway abstraction layer and application platform interfaces for conducting service transactions are disclosed. A gateway abstraction layer computers can receive service requests in multiple message formats or communication protocols, transform those service requests into other message formats to process the service using one or more networks or third-party service providers. The results of the service request can then be translated back to the message format in which the original service request was received. The gateway abstraction layer can be maintained using update messages received from service providers.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
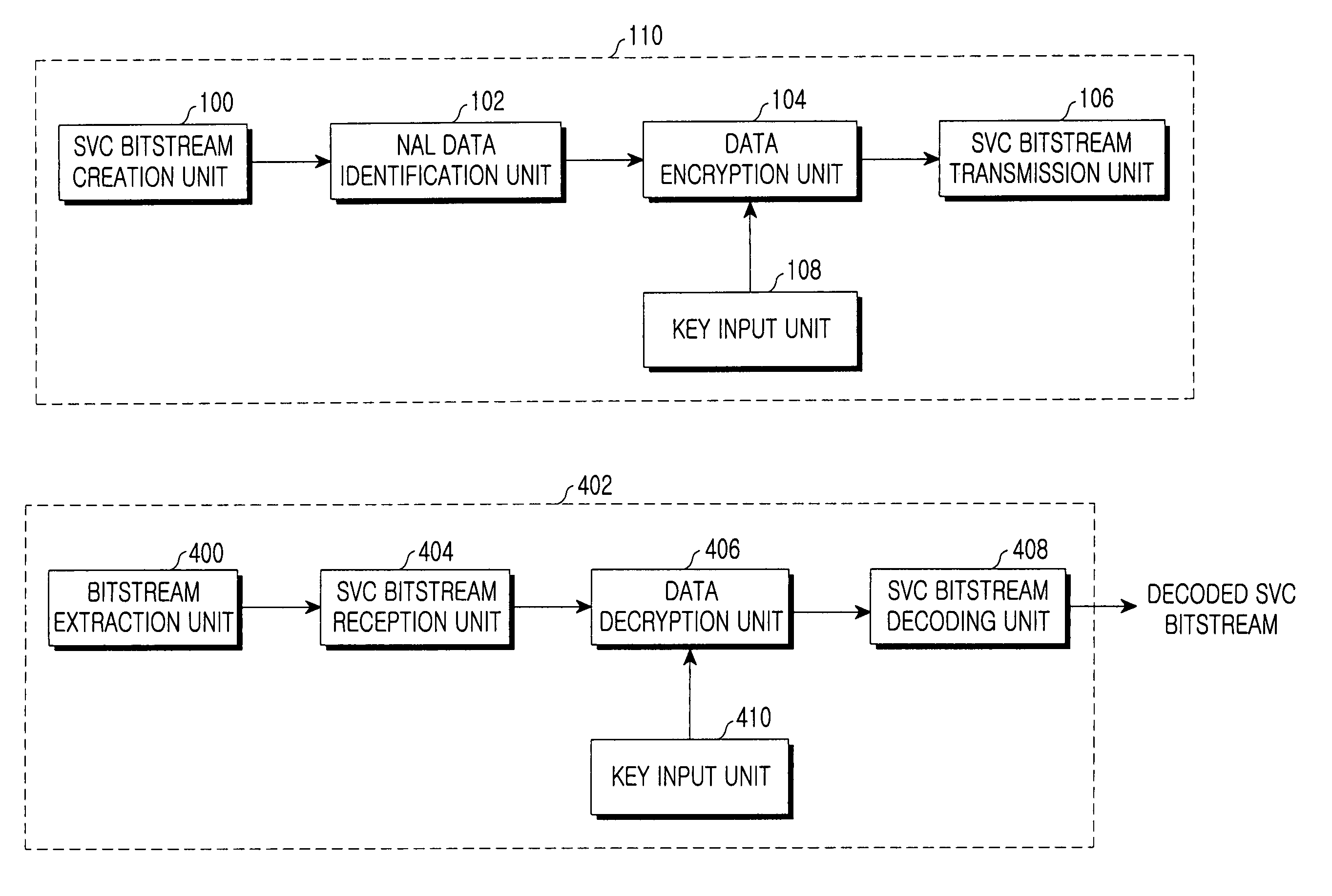
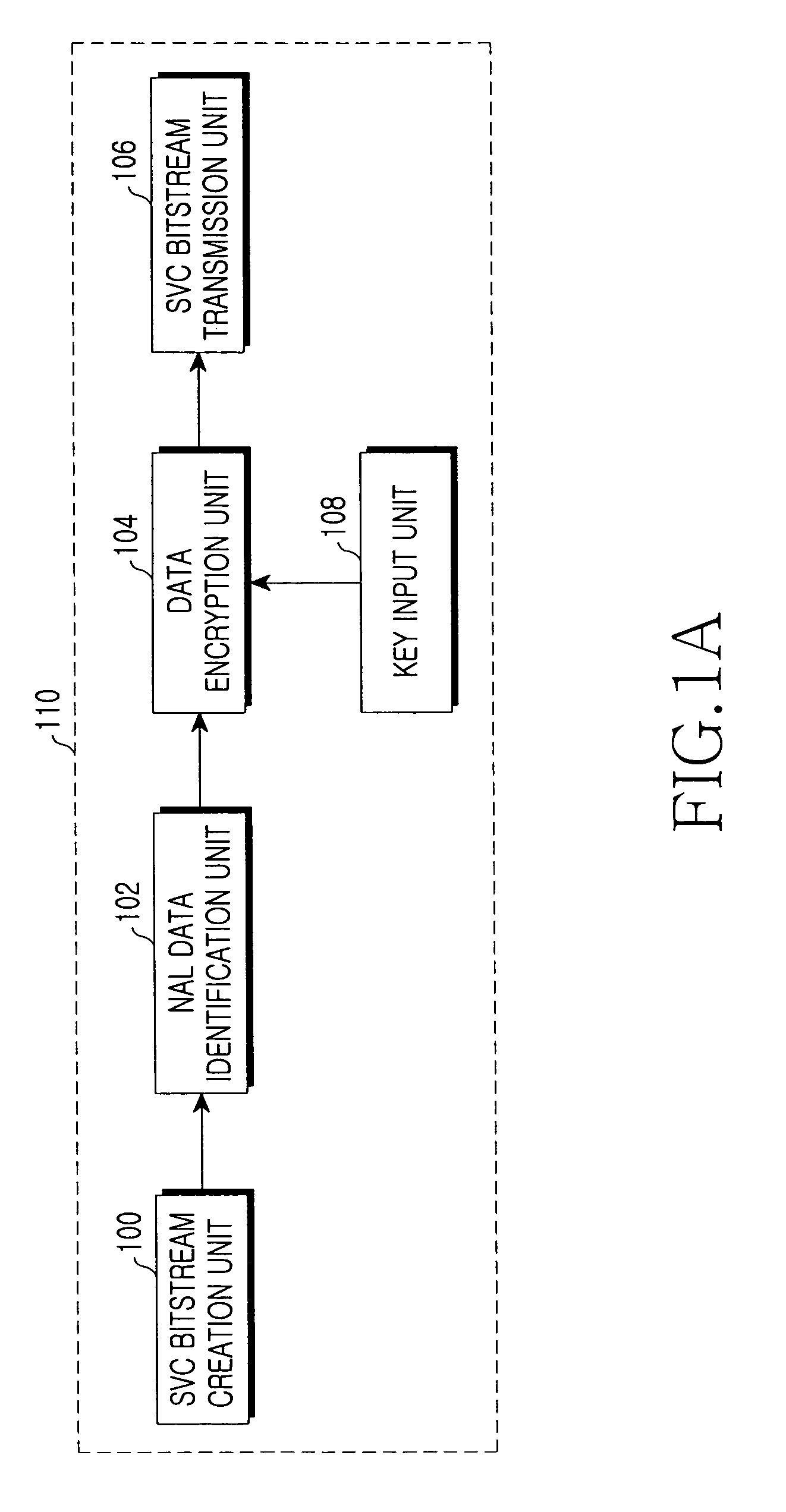
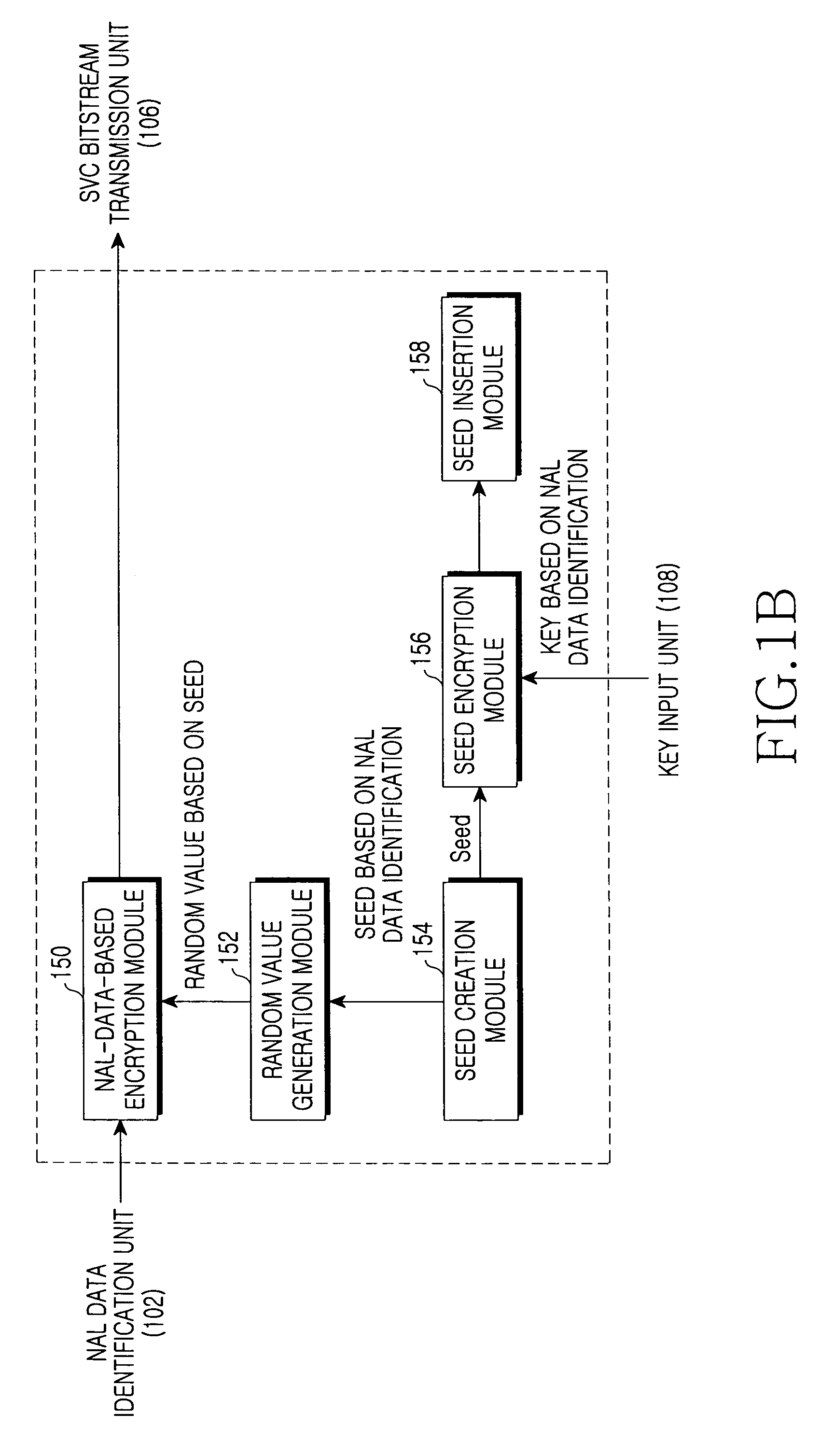
Method and system for encryption/decryption of scalable video bitstream for conditional access control based on multidimensional scalability in scalable video coding
InactiveUS8514926B2Easy to implementIncreased complexityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningExtensibilityVideo bitstream
Disclosed is a system and method for encryption of a scalable video coding (SVC) bitstream, which is the next-generation coding technology. The encryption method encrypts Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) data identified according to multidimensional scalability for space, time, and quality with respect to a bitstream created after an SVC encoding, thereby providing a multidimensional scalability function for space, time, and quality even after the encryption, so that the scalability is also maintained even in a bitstream extraction process after the encryption. According to such a scalable encryption method, a specific portion of an encrypted bitstream is removed in a bitstream extraction process, and user access to the bitstream is limited based on a combination of keys for accessing a specific scalability. Therefore, it is possible to protect scalable video content and to access the video content based on scalabilities.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Staggercasting method and apparatus using type of service (TOS) information
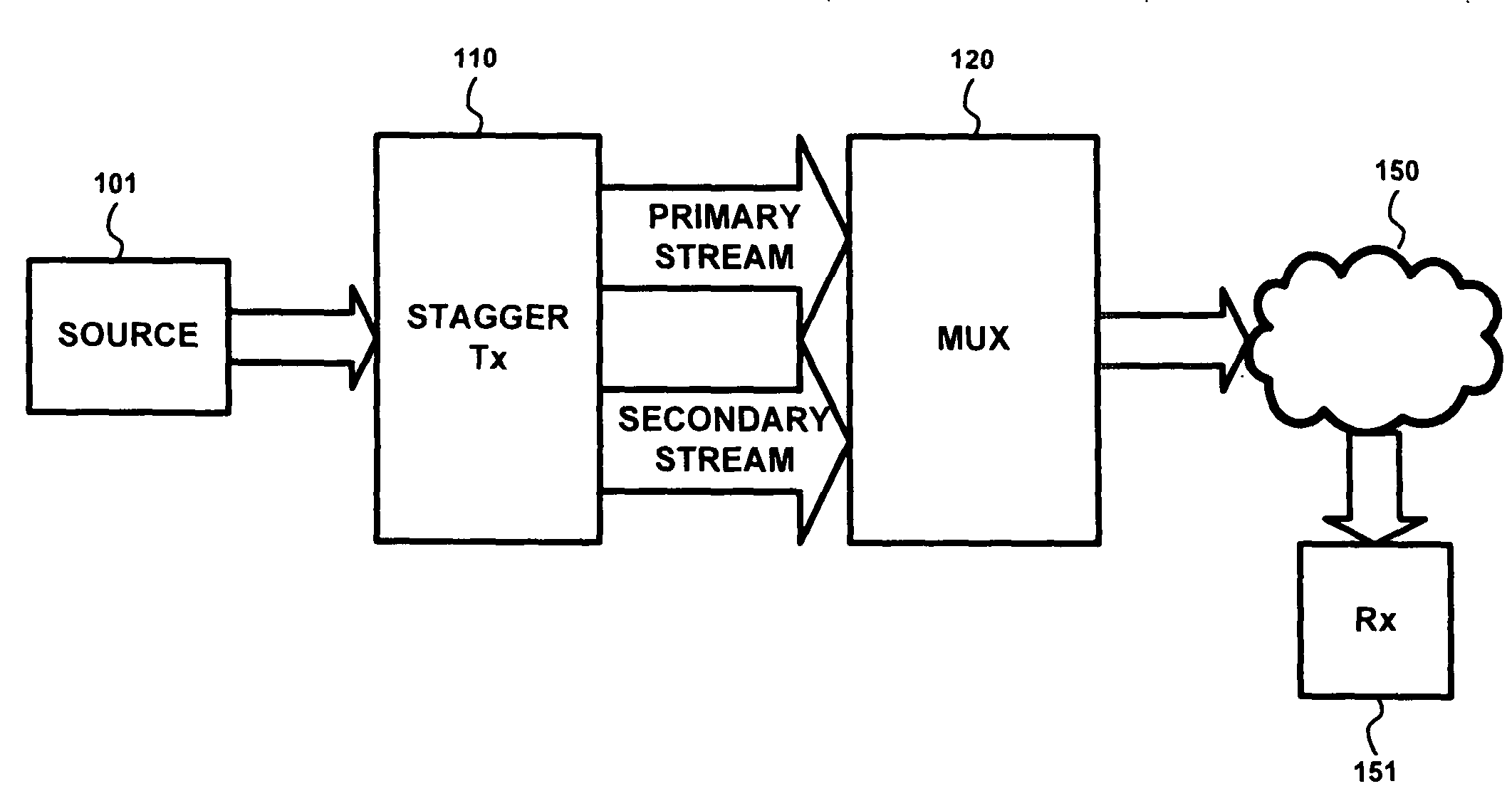
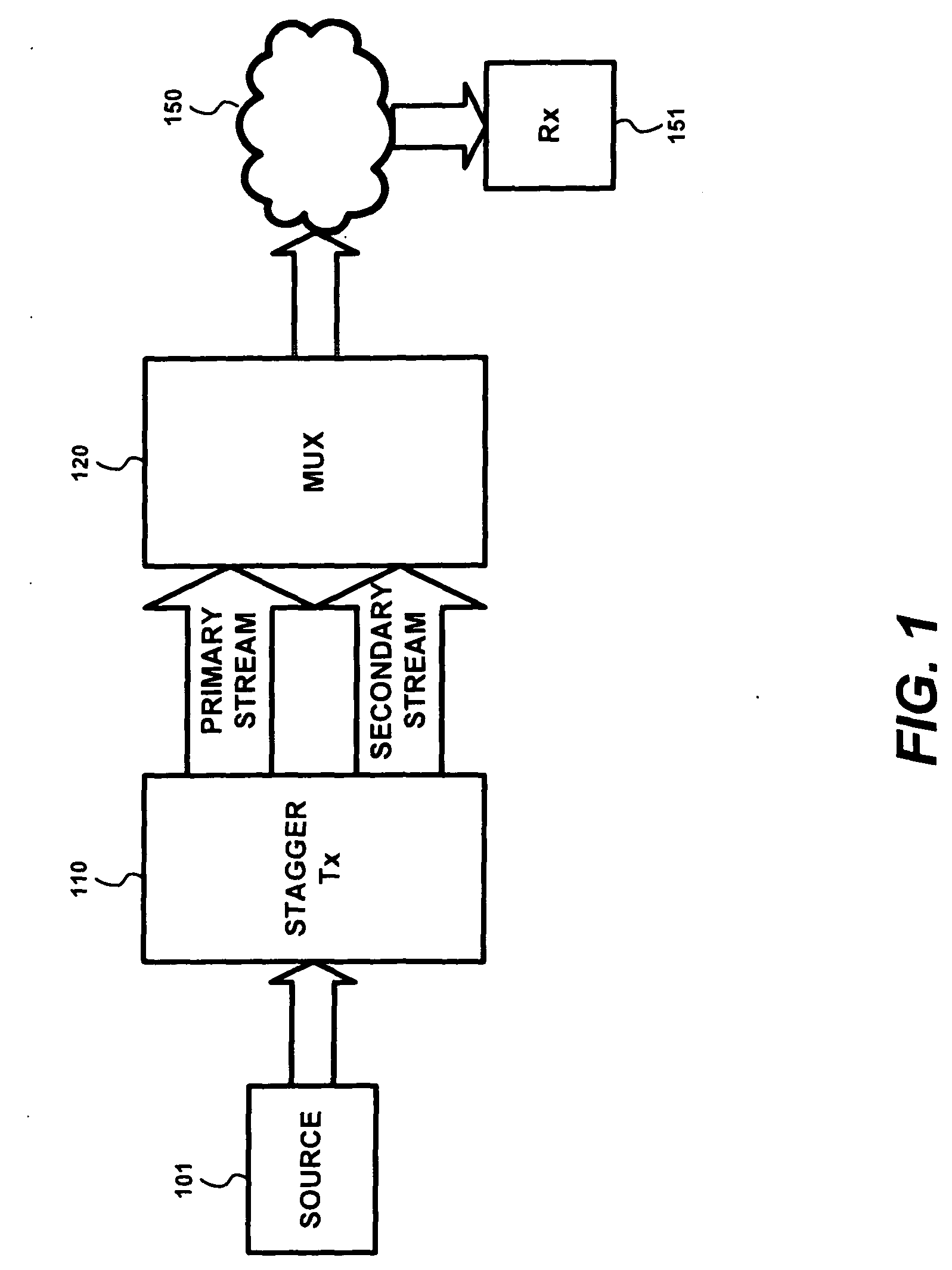
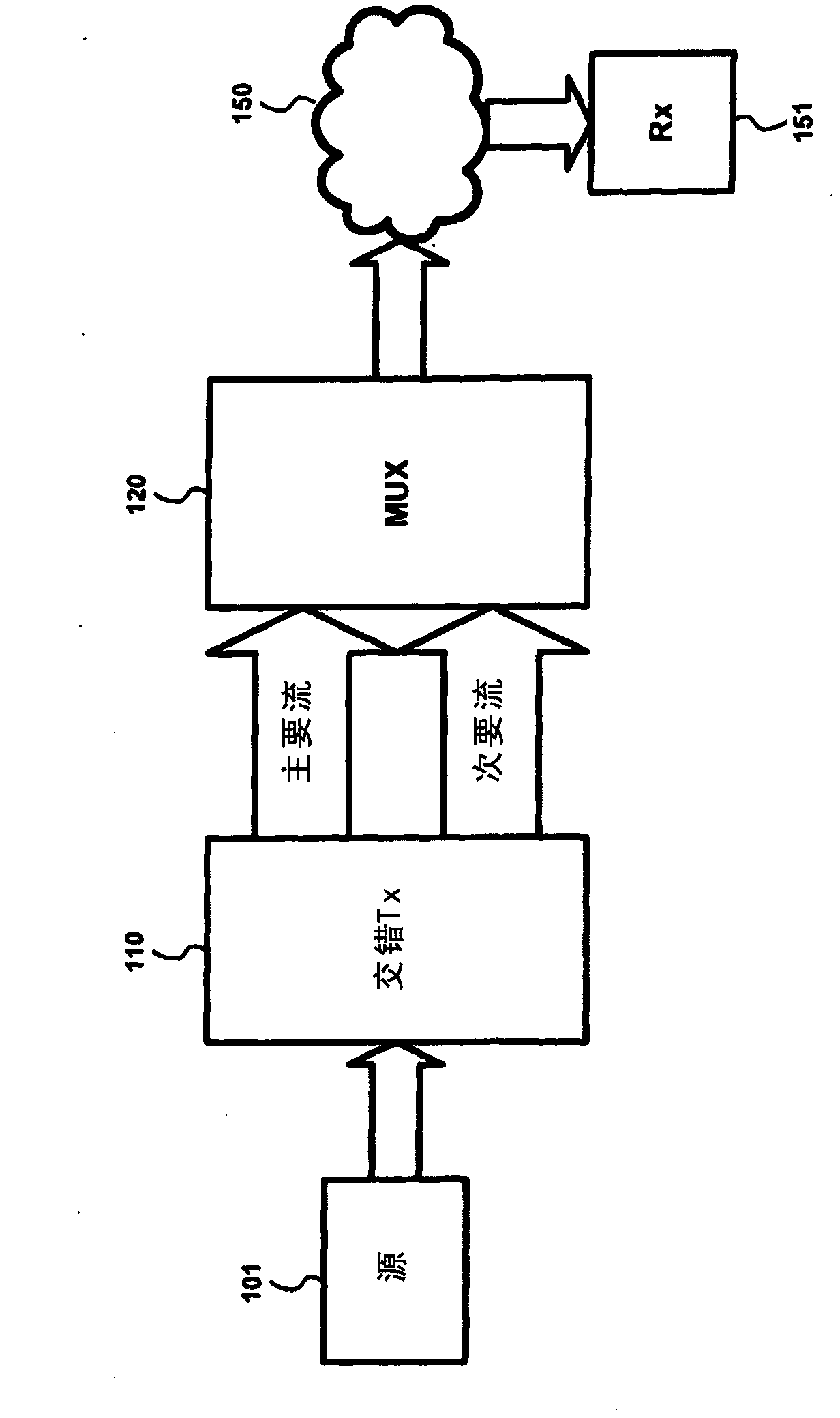
InactiveUS20110085551A1Redundancy and error protectionTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionNetwork packetMultiplexer
A stagger transmitter manipulates the Type of Service (TOS) information contained in packets transmitted therefrom. Downstream network devices, such as a network Multiplexer (MUX), use the TOS information to handle the packets. A MUX controls the bandwidth allocated to each of the original and staggered streams in accordance with the TOS information. The stagger transmitter manipulates the TOS information of packets in accordance with other information contained in the packets, such as Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) information. As such, the staggered stream copies of more important packets, as indicated by their NAL information, can have their TOS information set by the stagger transmitter so that a network MUX will forward such staggered packets in addition to the original packets, thereby providing redundancy and error protection for such packets.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Network abstraction layer (NAL)-aware multiplexer with feedback
InactiveUS20110090958A1Effect video qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesAbstraction layerMultiplexing
Advanced multiplexing methods and apparatus that are especially useful in multiplexing variable bit rate input video streams onto a fixed bandwidth output stream with minimum effect on video quality are described. A multiplexer provides feedback to a stagger transmitter to help it maintain its output bit rate. In addition, the stagger transmitter parses Network Abstraction Layers (NALs) from the given streams and makes decisions on which NALs to forward to the MUX.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Method for determining packet type for svc video bitstream, and rtp packetizing apparatus and method using the same
InactiveUS20100067522A1Efficiently determinedGuaranteed normal transmissionColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo bitstreamVideo encoding
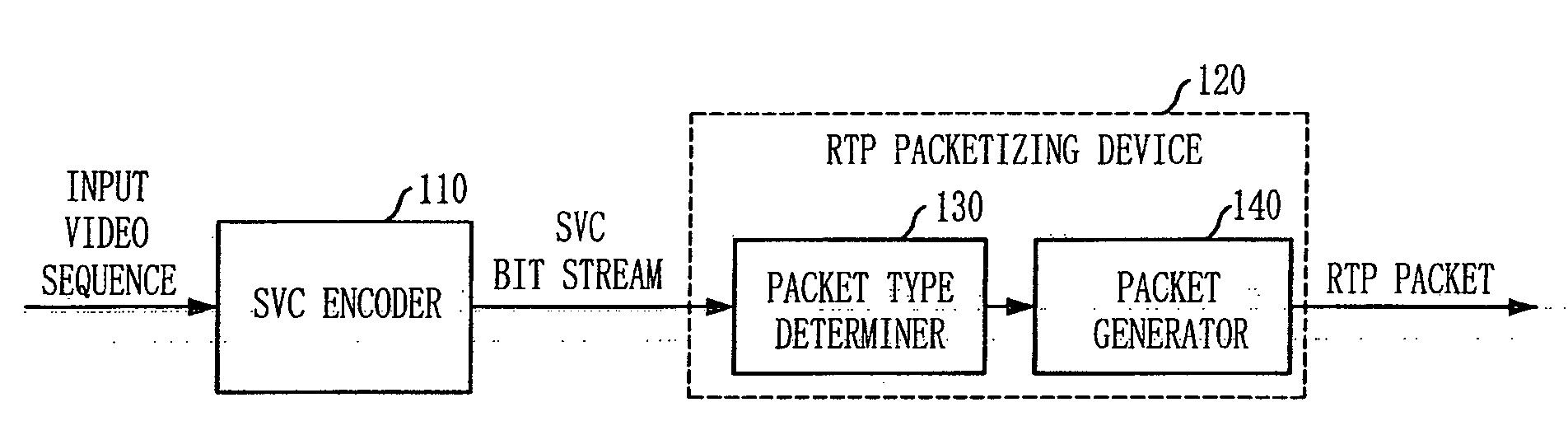
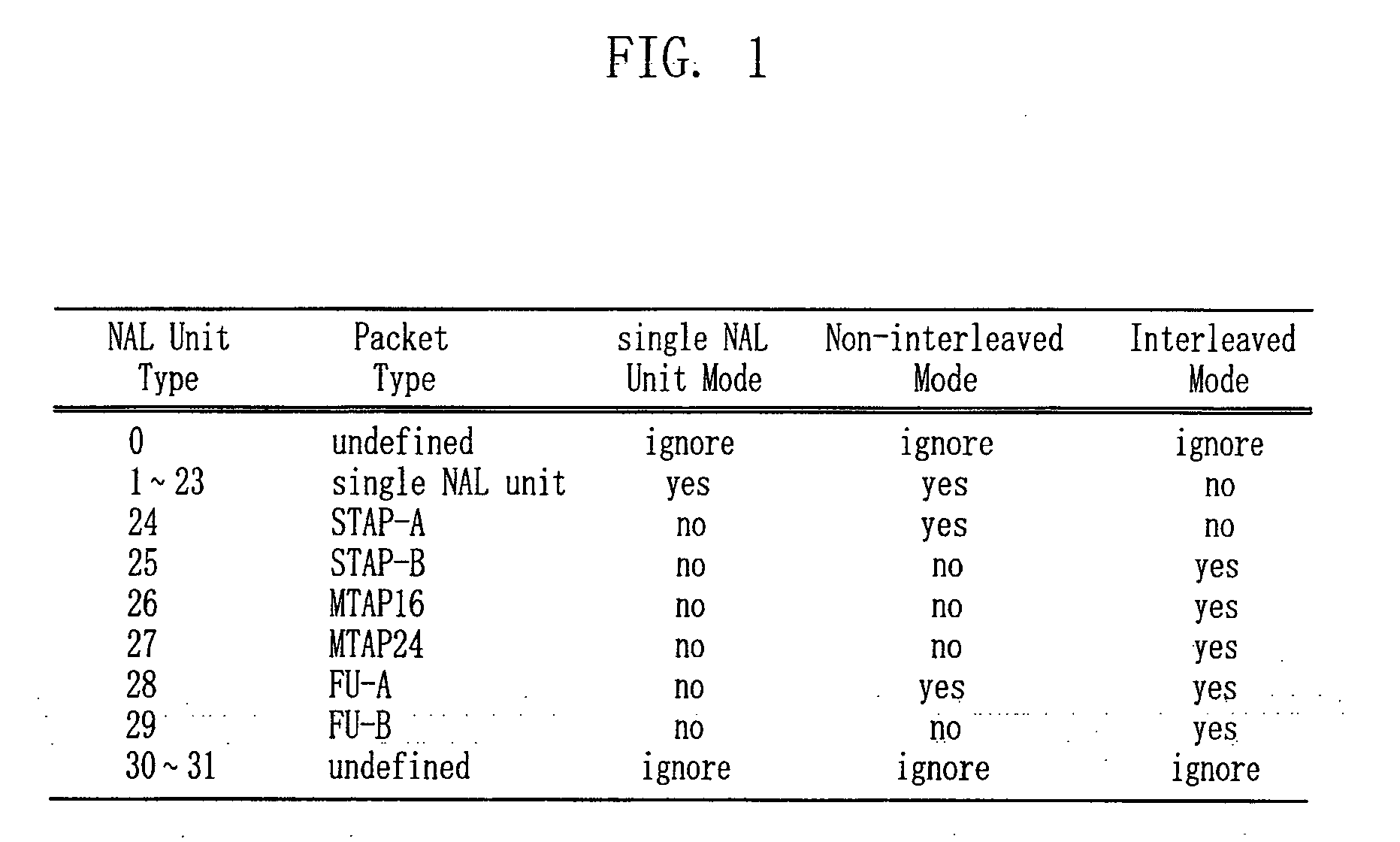
Provided are a method for determining the packet type for a Scalable Video Coded (SVC) video bitstream, and a Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) packetizing apparatus and method using the same. The method for determining a packet type for a Scalable Video Coded (SVC) video bitstream, which includes the steps of: a) deriving temporal and spatial hierarchy information between Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) units from field information defined in the NAL unit headers of scalable layers; b) detecting the type of encoding information by applying combined scalability encoding to the hierarchical structure of the Scalable Video Coding (SVC); and c) determining a Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) packet type for the corresponding SVC video bitstream by using the derived temporal and spatial hierarchy information between the NAL units and the detected type of encoding information.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Real-time transport protocol (RTP) packetization method for fast channel change applications using scalable video coding (SVC)
InactiveUS8582644B2Minimal impactImprove efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesNetwork Abstraction LayerReal-time Transport Protocol
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
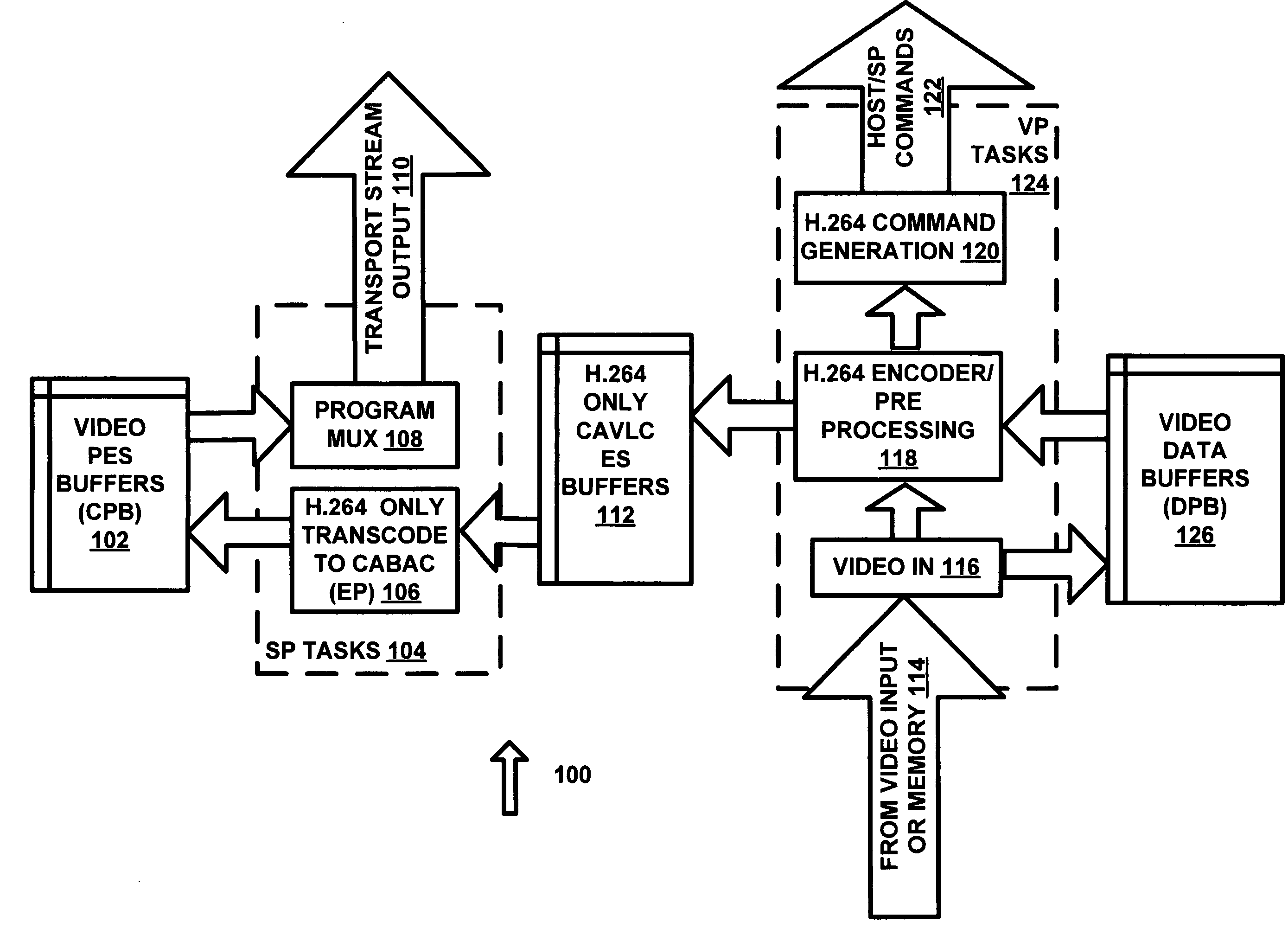
NAL (network abstraction layer) module of video codec and implementation method thereof
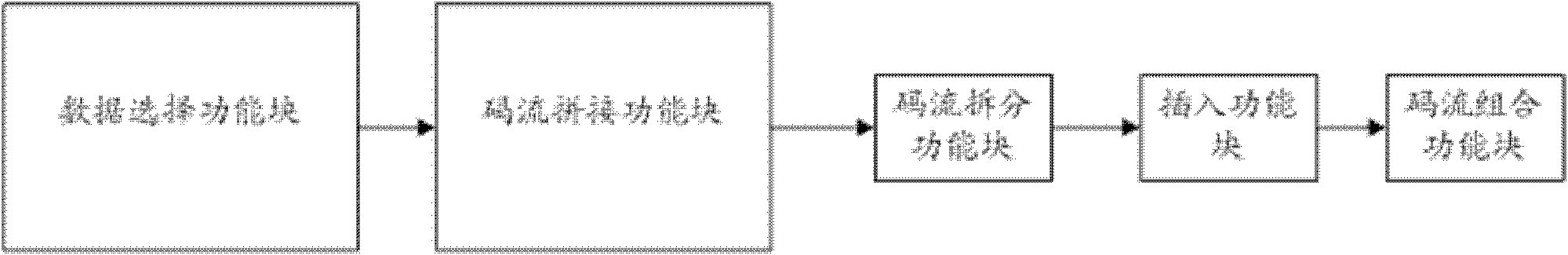
ActiveCN102123286AImprove design efficiencyHardware area balanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationAbstraction layerData selection
The invention discloses an NAL (network abstraction layer) module of a video codec, and the NAL module provided by the invention comprises a data selection function block, a code stream splicing function block, a split function block, an insert function block and a code stream combination function block, wherein the data selection function block is used for controlling data output; the code stream splicing function block is used for splicing the code streams output by the data selection function block; the split function block is used for splitting the code streams output by the code stream splicing function block; the insert function block is used for judging whether to insert bytes and carry out processing according to the judging result; and the code stream combination function block is used for splicing the results output by the insert function block. According to the invention, the efficiency of hardware design can be improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
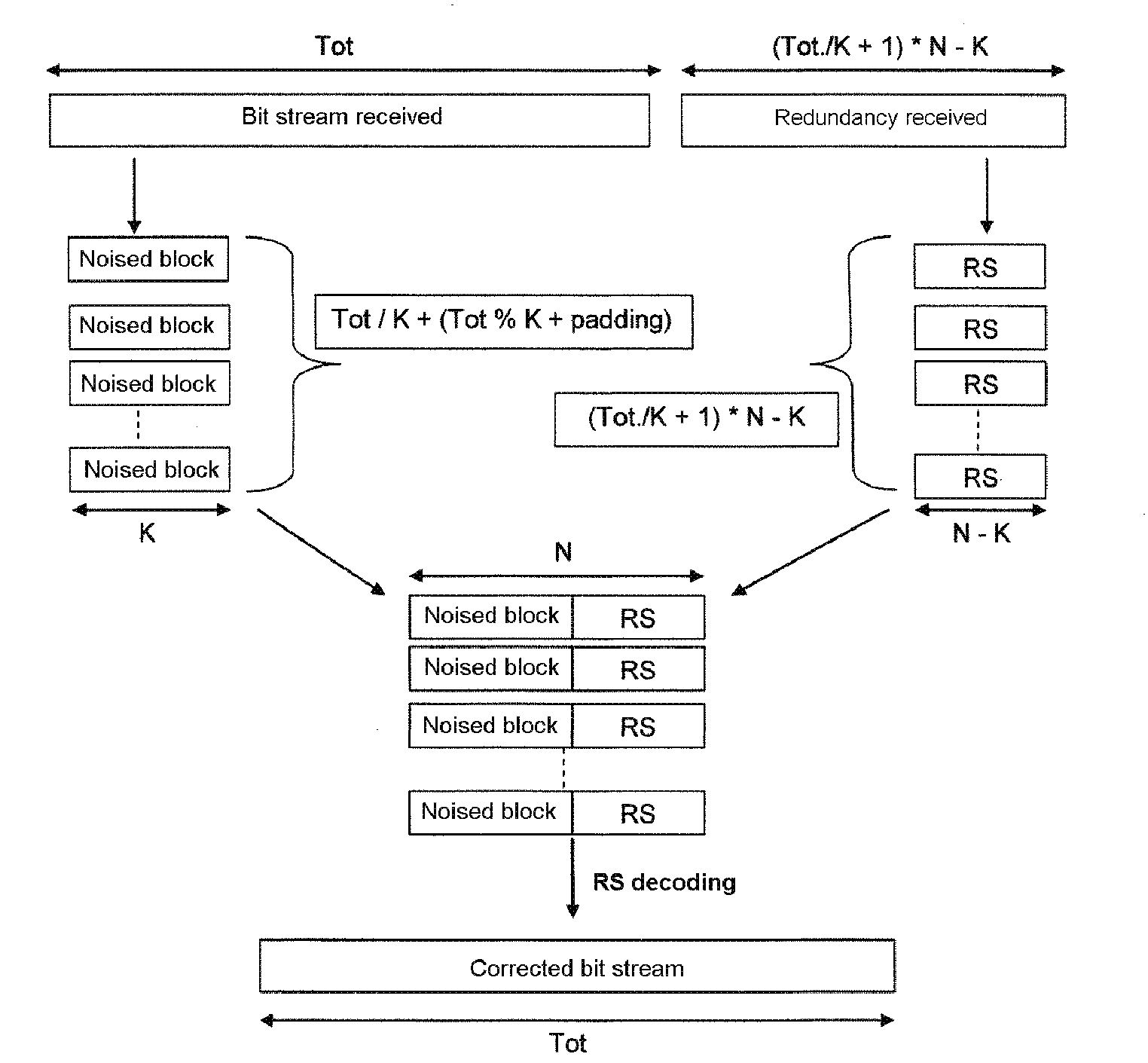
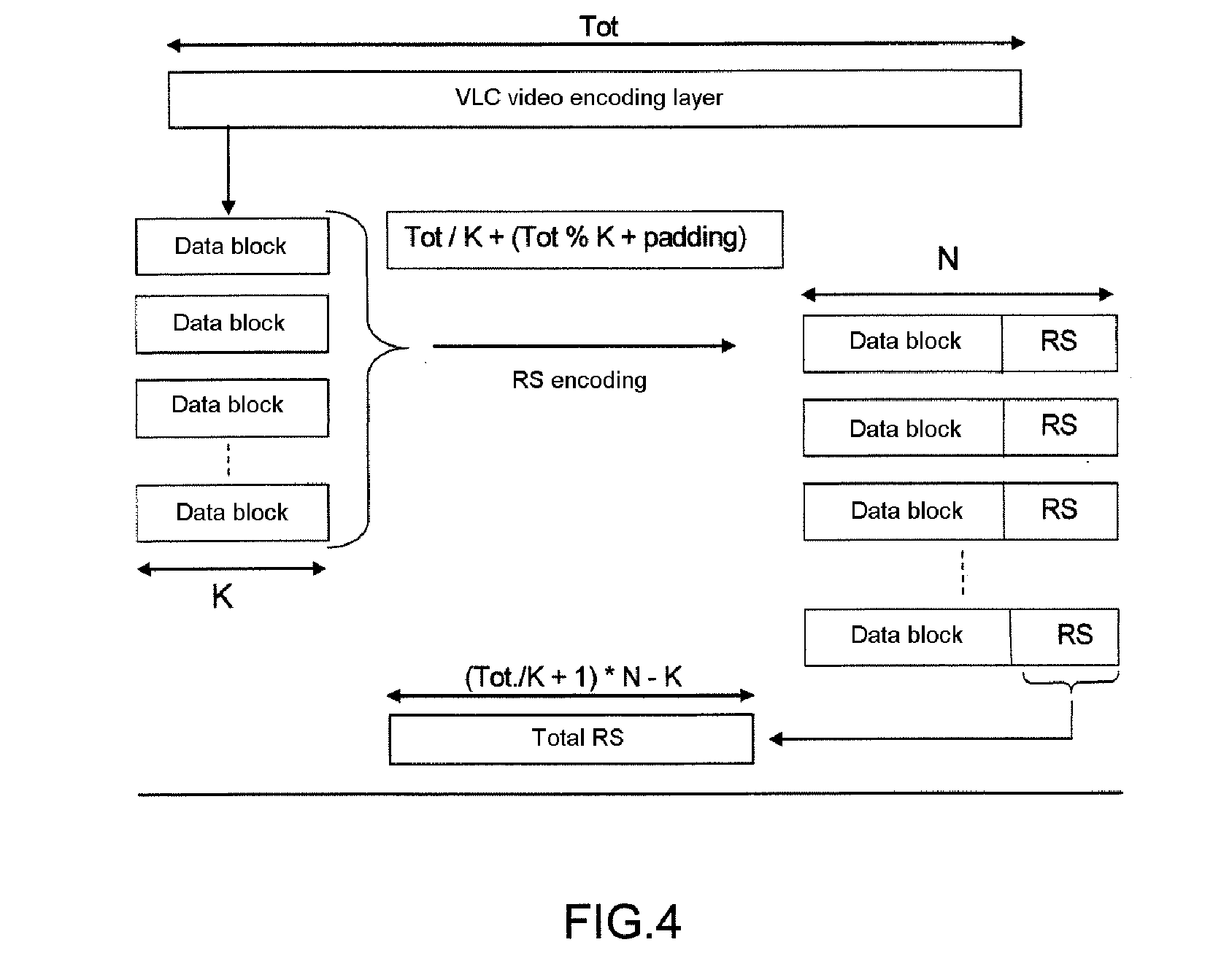
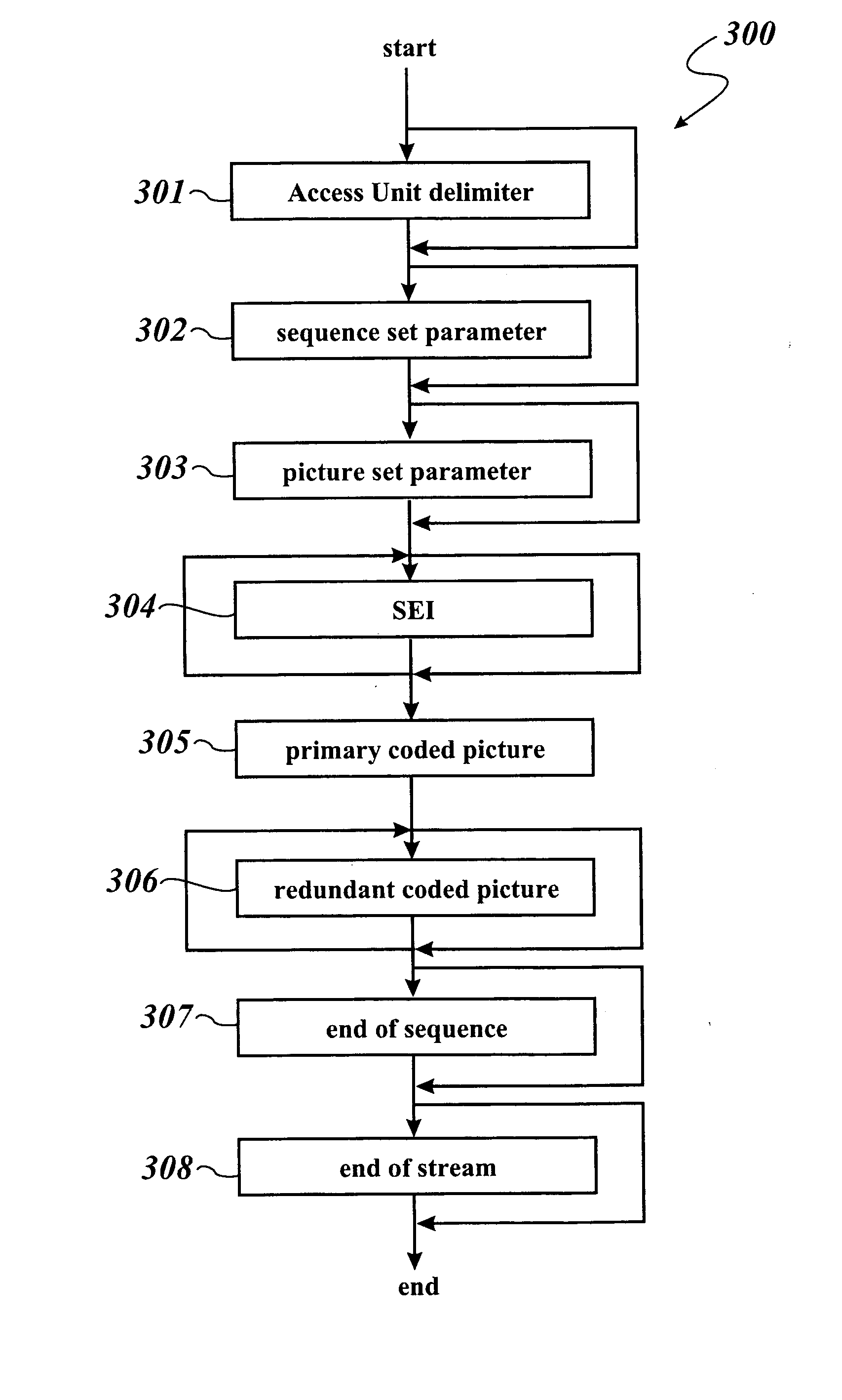
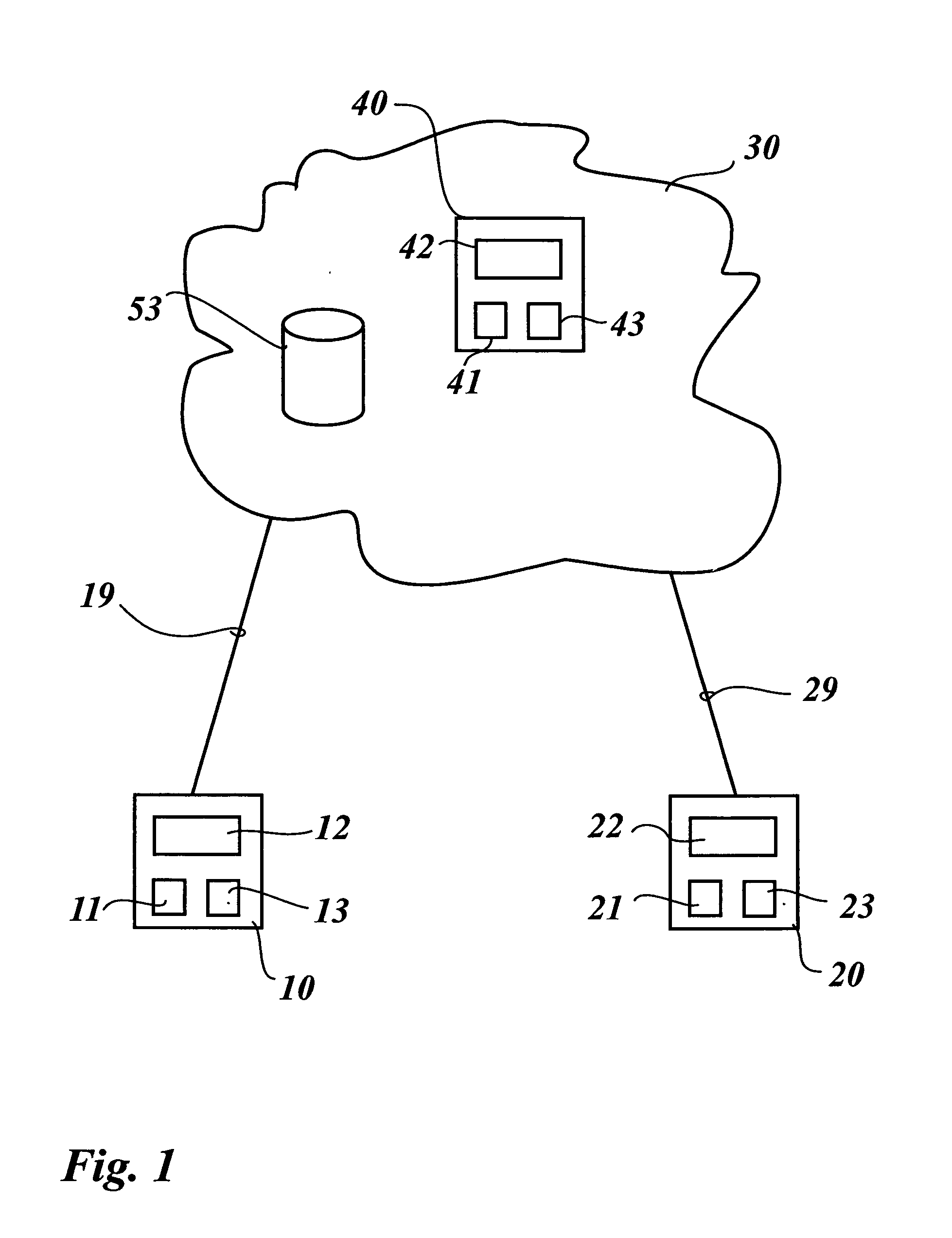
Method of transmitting video data
ActiveUS8068721B2Spread the wordIncrease powerTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionRedundant codeVideo processing
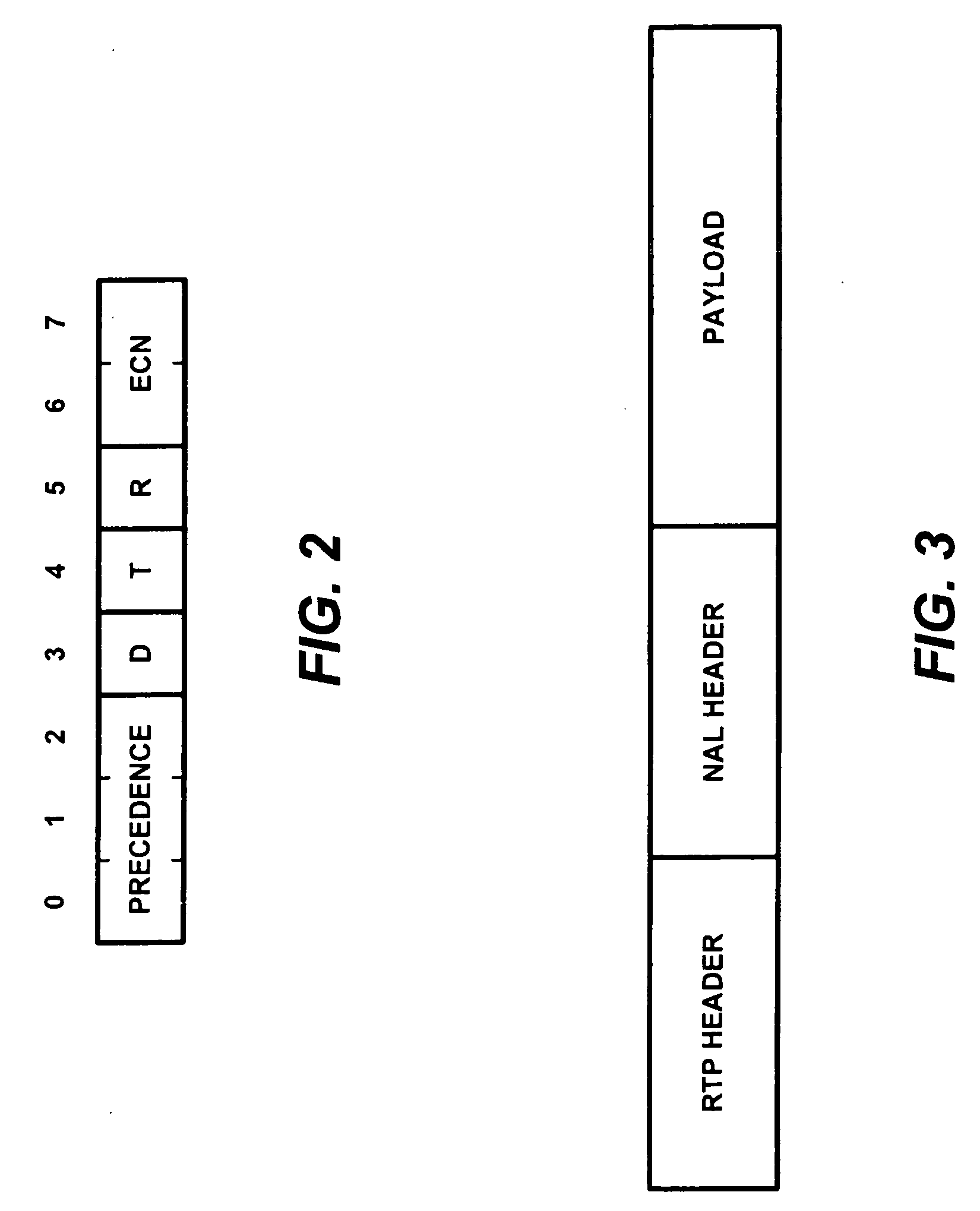
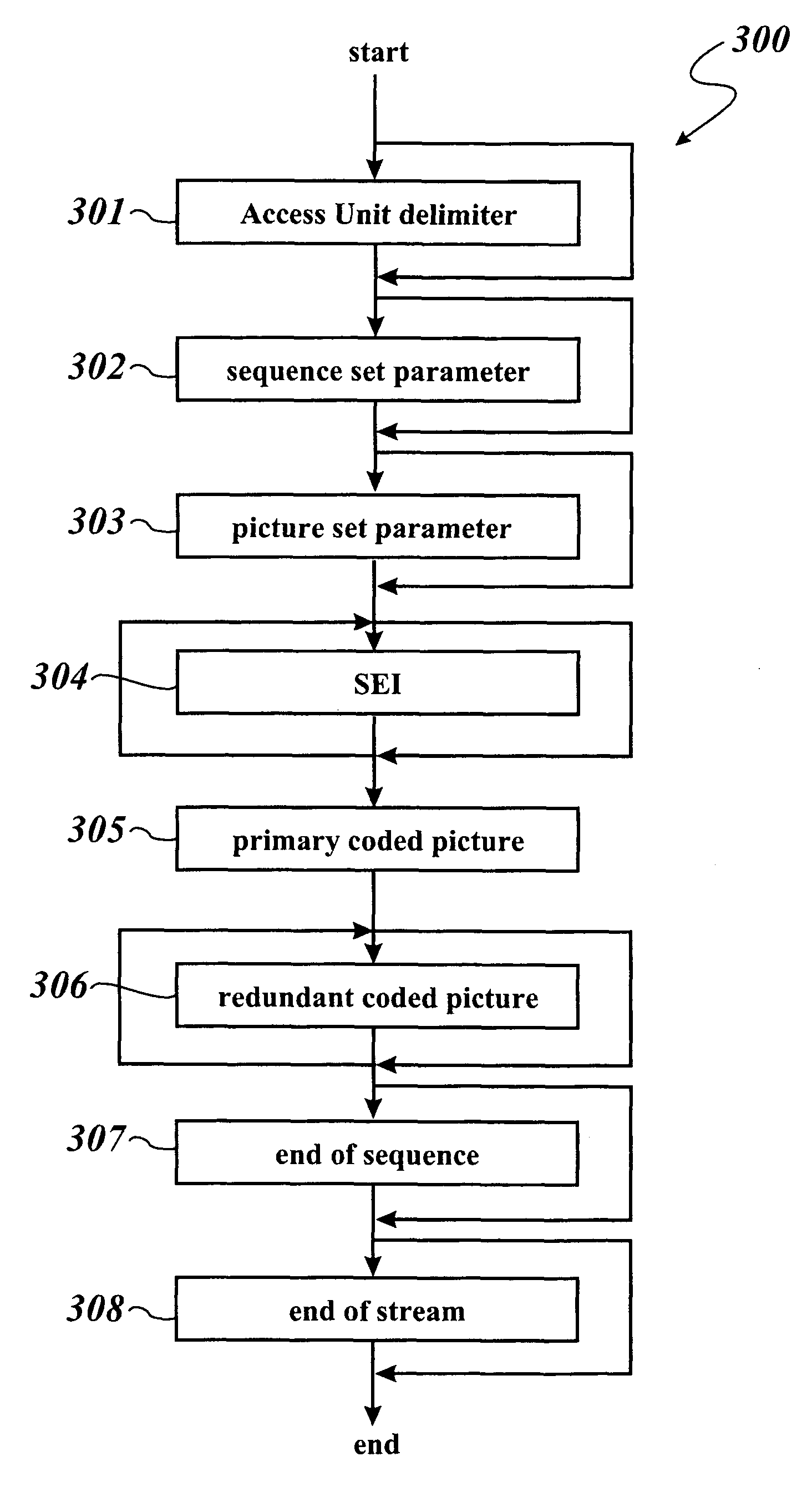
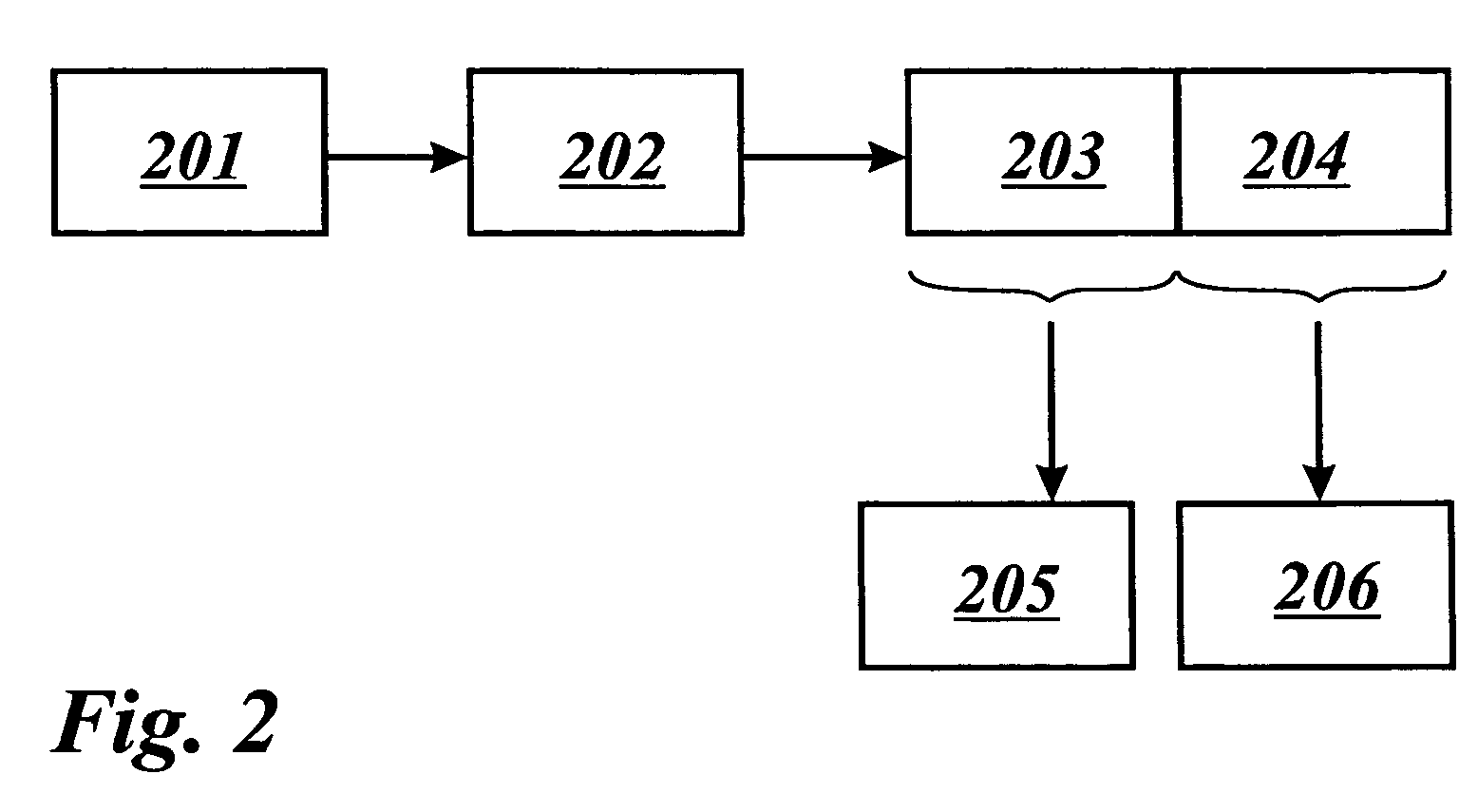
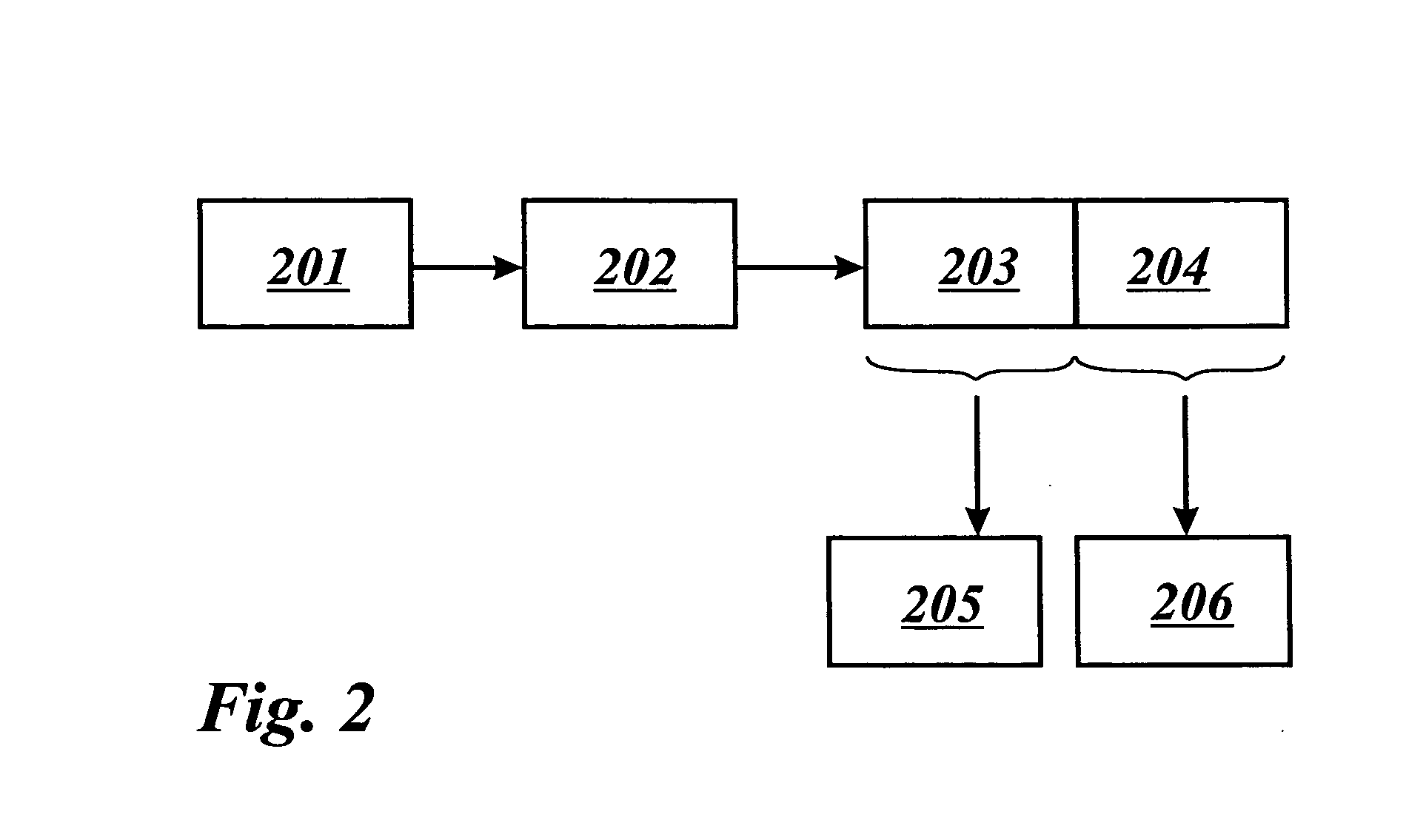
The invention concerns a method of transmitting video data comprising information bits (201), a video processing unit (10, 20, 40) with a control unit (12, 22, 42) for sending and / or receiving such video data, and a computer program product for the execution of said method. The method comprises the application of a systematic channel encoding (202) on the information bits (201) of the video data and obtaining a sequence comprising the encoded information bits (203) and error correction bits (204, 403) of the information bits (201). For transmission to another video processing unit (10, 20, 40), the encoded information bits (203) and the error correction bits (204, 403) are inserted into a primary coded picture network abstraction layer (205, 401) and a redundant coded picture network abstraction layer (206, 402), respectively. At the other video processing unit (10, 20, 40), the error correction bits (204, 403) in the redundant coded picture network abstraction layer (206, 402) are used for detecting (404) and correcting (405) errors in the received primary coded picture network abstraction layer (205, 401) and for performing the video decoding (407) of the corrected primary coded picture network abstraction layer (406).
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Assembling multiview video coding sub-bistreams in mpeg-2 systems
ActiveCN102804773ASuccessfully decodedPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationComputer graphics (images)Network Abstraction Layer
A demultiplexer may assemble view components of sub-bitstreams. In one example, an apparatus comprises a demultiplexer that produces a multiview video coding (MVC) standard compliant bitstream from a received bitstream comprising a primary sub-bitstream and an embedded sub-bitstream. To produce the MVC standard compliant bitstream, the demultiplexer determines whether a view component of the primary sub-bitstream has a view order index that is greater than a view order index of a view component of the embedded sub-bitstream, and to add the view component from the sub-bitstream for which the view order index is lower to the produced bitstream. The received bitstream may comprise delimiter network abstraction layer (NAL) units between each view component to differentiate the view components. The apparatus may further comprise a video decoder to decode the bitstream produced by the demultiplexer.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
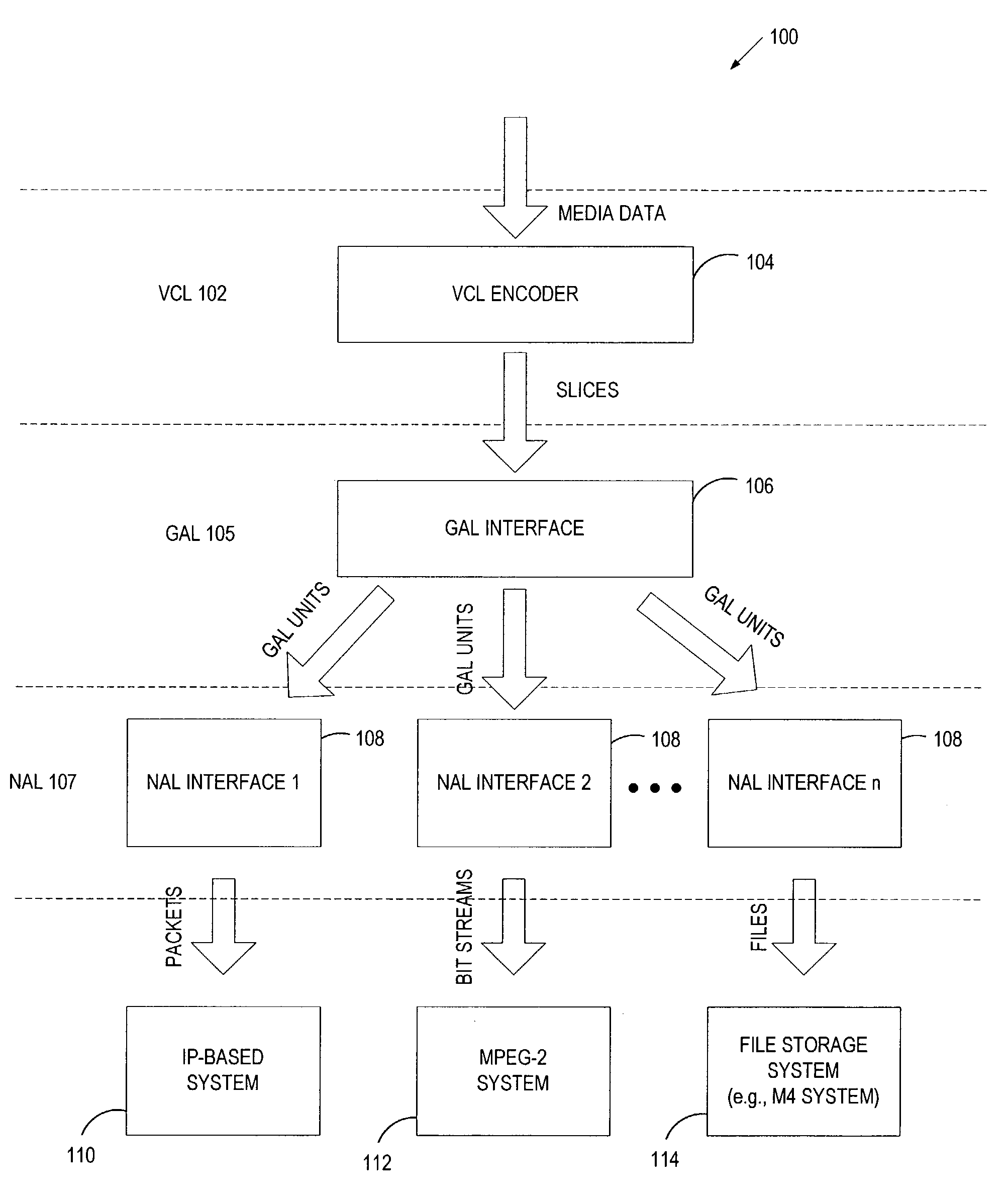
Generic adaptation layer for JVT video
ActiveUS7831990B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningTransport systemNetwork Abstraction Layer
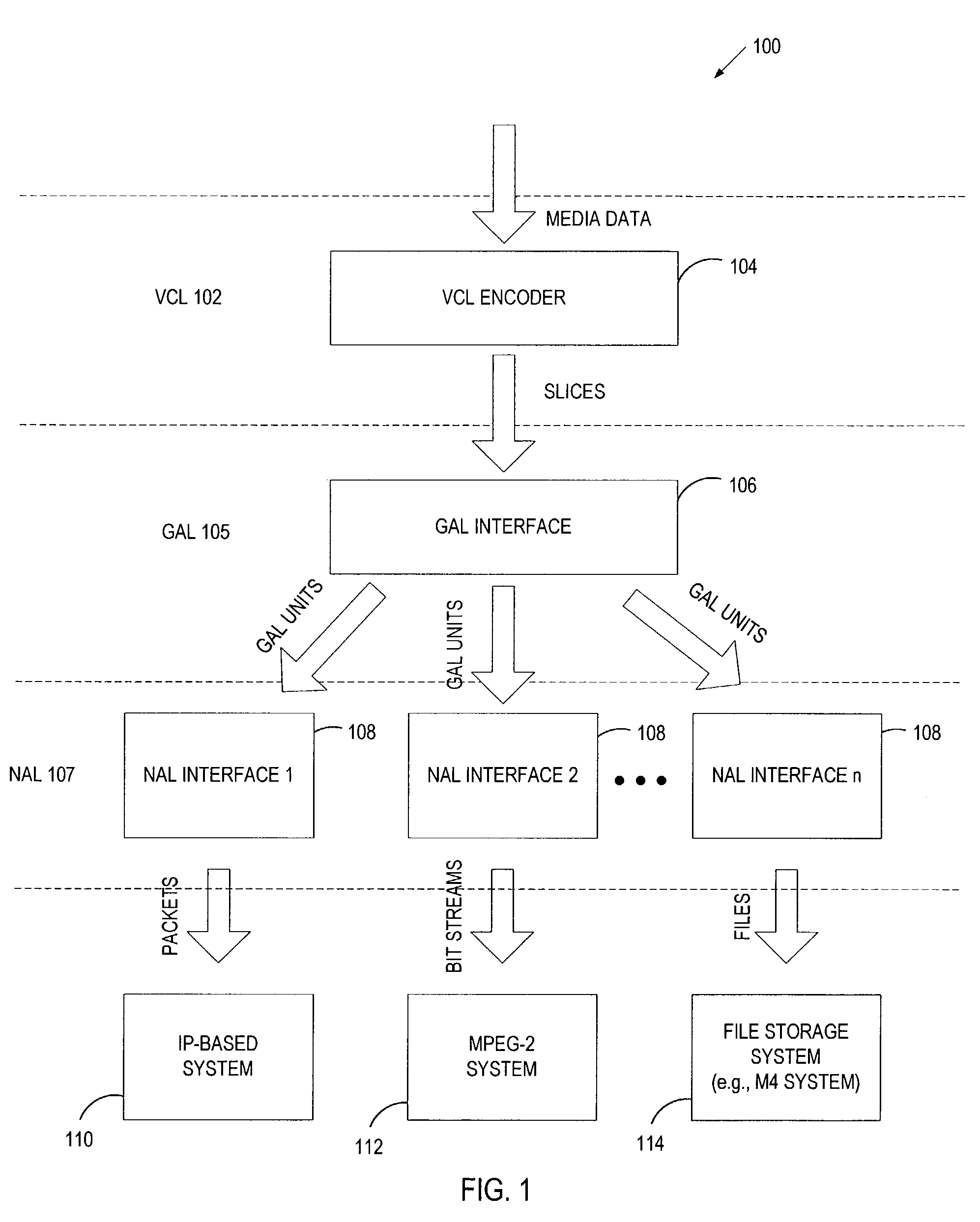
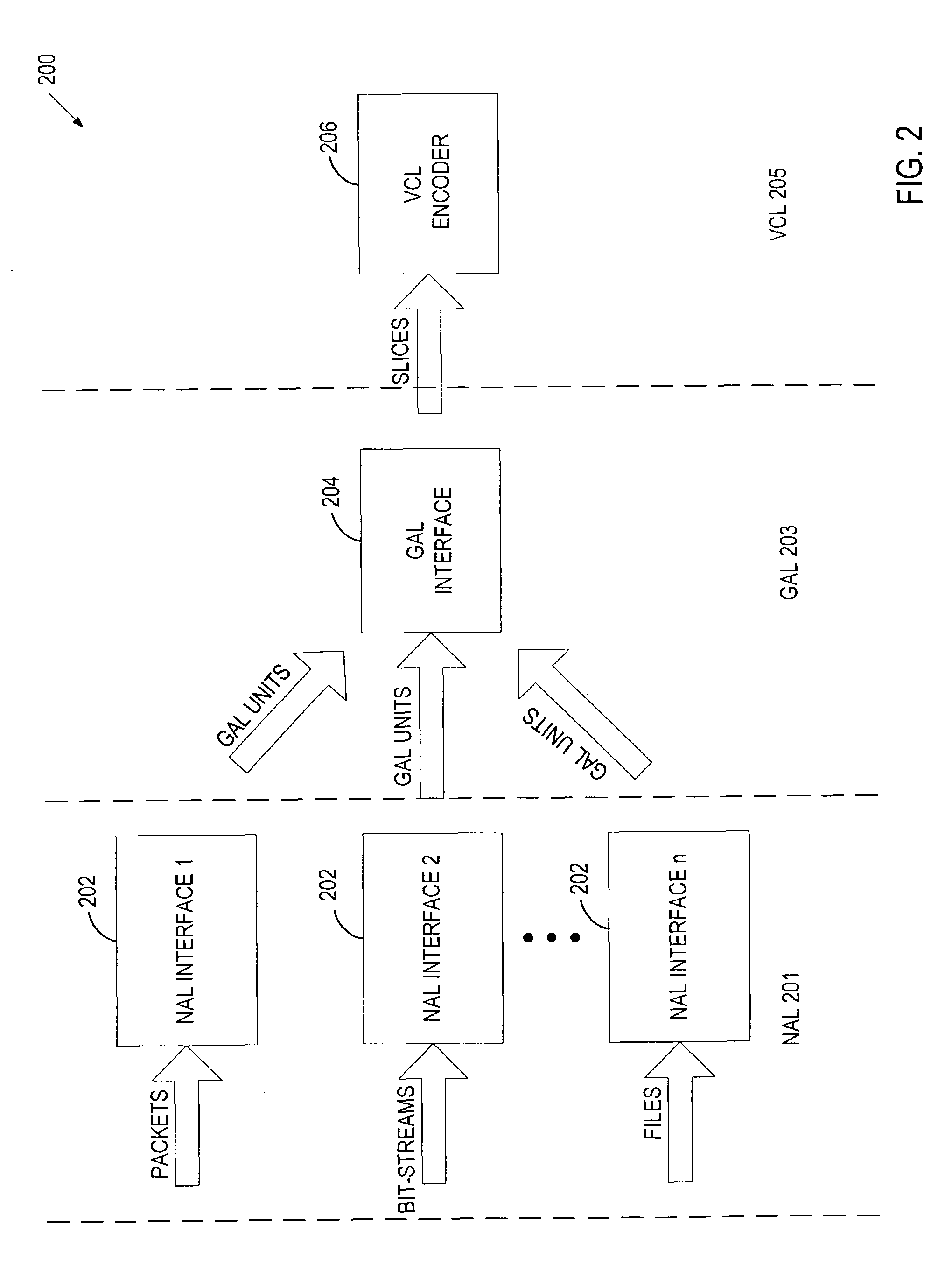
An encoding system includes a video coding layer (VCL) to generate slices when encoding multimedia data, a generic adaptation layer (GAL) to create, from the slices, a set of GAL units having a format that is generic to various transport systems, and a network adaptation layer (NAL) associated with a specific transport system to map the set of GAL units to the format of the specific transport system.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Staggercasting method and apparatus using type of service (TOS) information
InactiveCN102067618ATelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexerEngineering
A stagger transmitter manipulates the Type of Service (TOS) information contained in packets transmitted therefrom. Downstream network devices, such as a network Multiplexer (MUX), use the TOS information to handle the packets. A MUX controls the bandwidth allocated to each of the original and staggered streams in accordance with the TOS information. The stagger transmitter manipulates the TOS information of packets in accordance with other information contained in the packets, such as Network Abstraction Layer (NAL) information. As such, the staggered stream copies of more important packets, as indicated by their NAL information, can have their TOS information set by the stagger transmitter so that a network MUX will forward such staggered packets in addition to the original packets, thereby providing redundancy and error protection for such packets.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Coded application data unit order recovery in layered multicast
ActiveUS8352625B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTime ProtocolStructure of Management Information
Systems and methods are provided which allow receivers to recover the decoding order of network abstraction layer (NAL) units conveyed in different Real Time Protocol (RTP) sessions. An indication of decoding order for application data units (ADUs) in each packet is included in the packet structure of a PACSI NAL unit, when the PACSI NAL unit is a single-time aggregation packet type A (STAP-A) packet and the PACSI NAL unit is the first NAL unit in an aggregation packet (e.g., when a receiver is subscribed to different RTP session that convey NAL units). If the receiver is subscribed to only a base layer RTP session, the CL-DON indication can be ignored.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method of transmitting video data
ActiveUS20060256235A1Spread the wordIncrease powerTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionRedundant codeVideo processing
The invention concerns a method of transmitting video data comprising information bits (201), a video processing unit (10, 20, 40) with a control unit (12, 22, 42) for sending and / or receiving such video data, and a computer program product for the execution of said method. The method comprises the application of a systematic channel encoding (202) on the information bits (201) of the video data and obtaining a sequence comprising the encoded information bits (203) and error correction bits (204, 403) of the information bits (201). For transmission to another video processing unit (10, 20, 40), the encoded information bits (203) and the error correction bits (204, 403) are inserted into a primary coded picture network abstraction layer (205, 401) and a redundant coded picture network abstraction layer (206, 402), respectively. At the other video processing unit (10, 20, 40), the error correction bits (204, 403) in the redundant coded picture network abstraction layer (206, 402) are used for detecting (404) and correcting (405) errors in the received primary coded picture network abstraction layer (205, 401) and for performing the video decoding (407) of the corrected primary coded picture network abstraction layer (406).
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com