Patents
Literature
501 results about "Real-time Transport Protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applications including WebRTC, television services and web-based push-to-talk features.
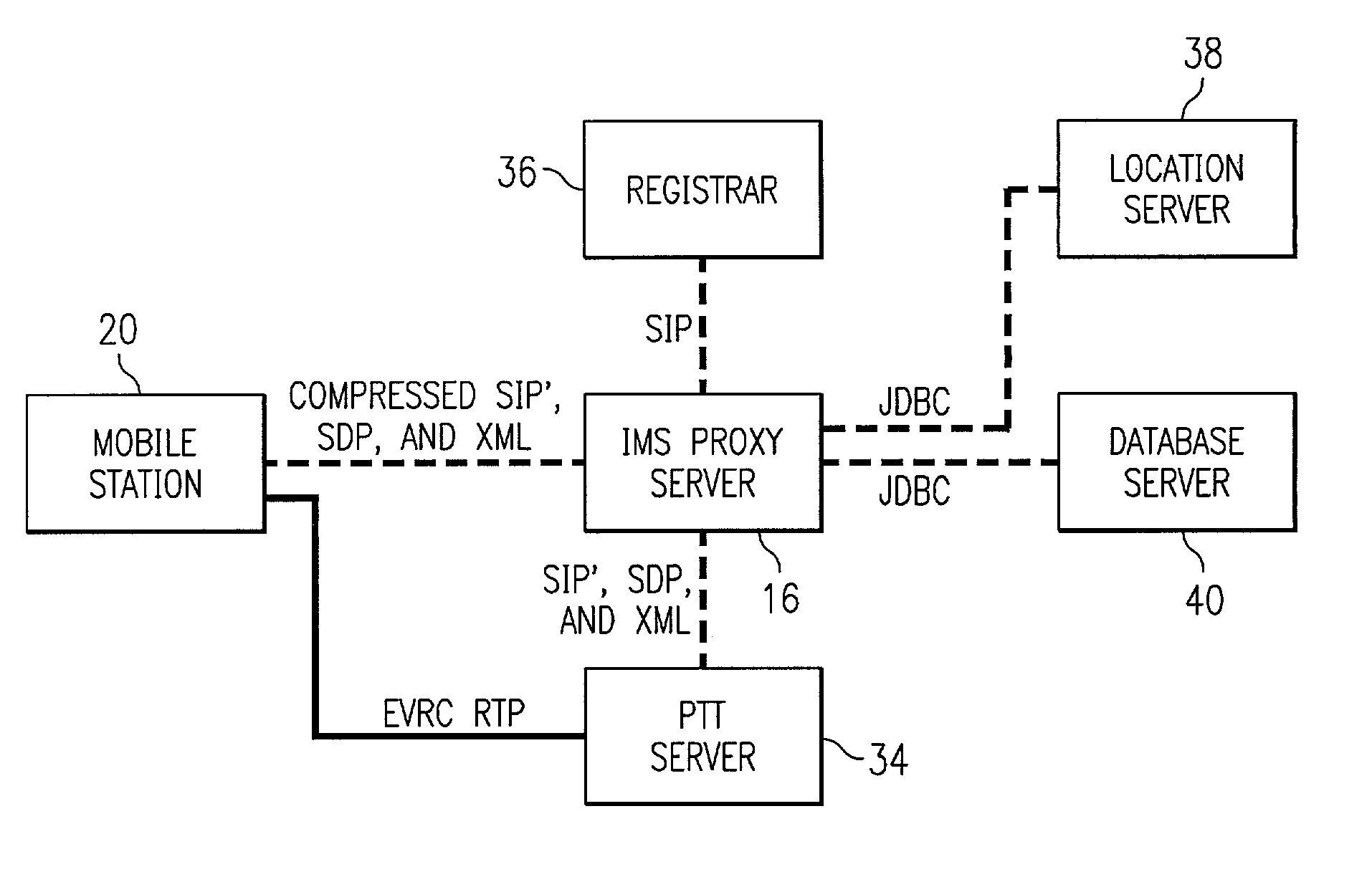
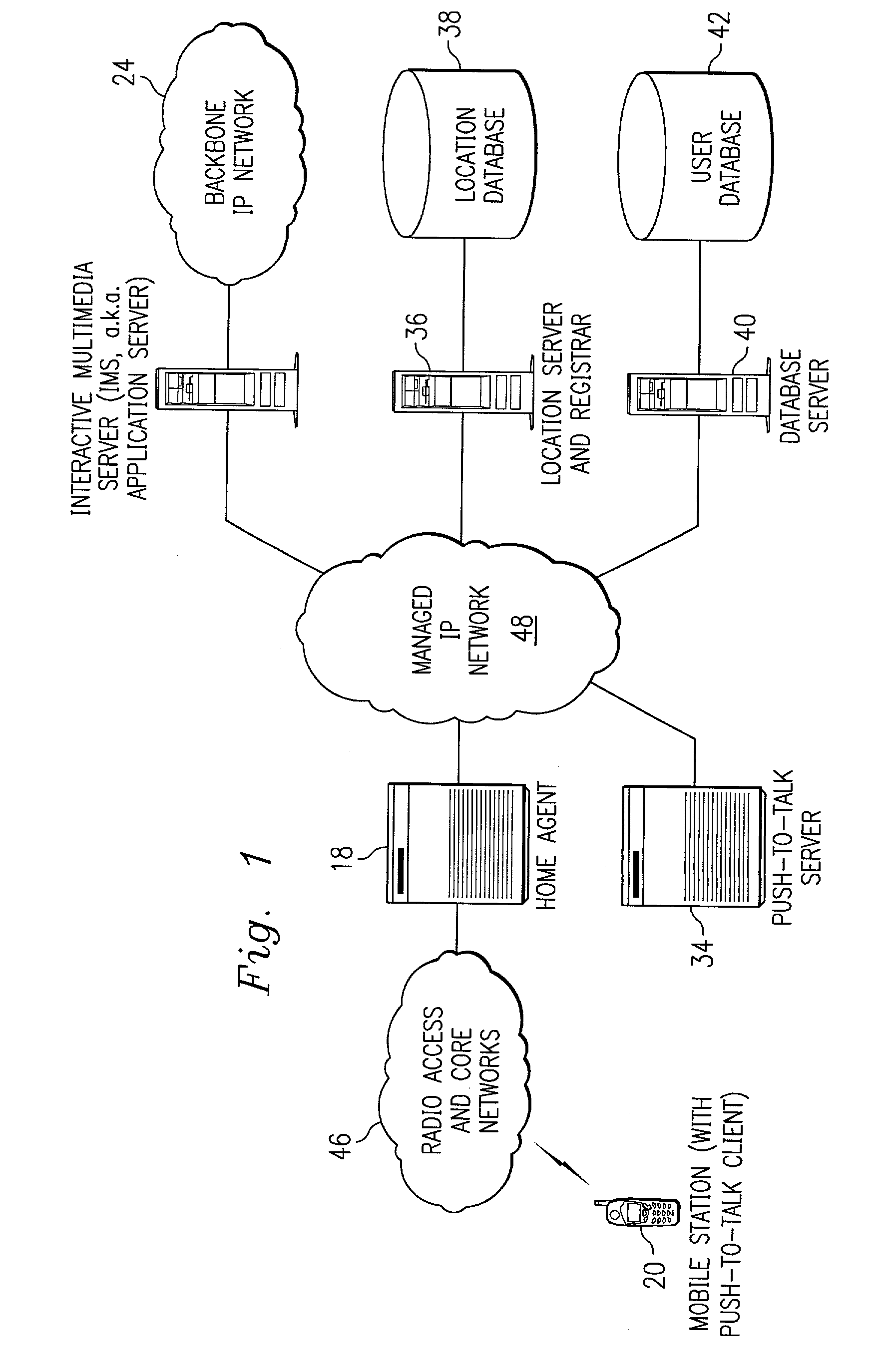
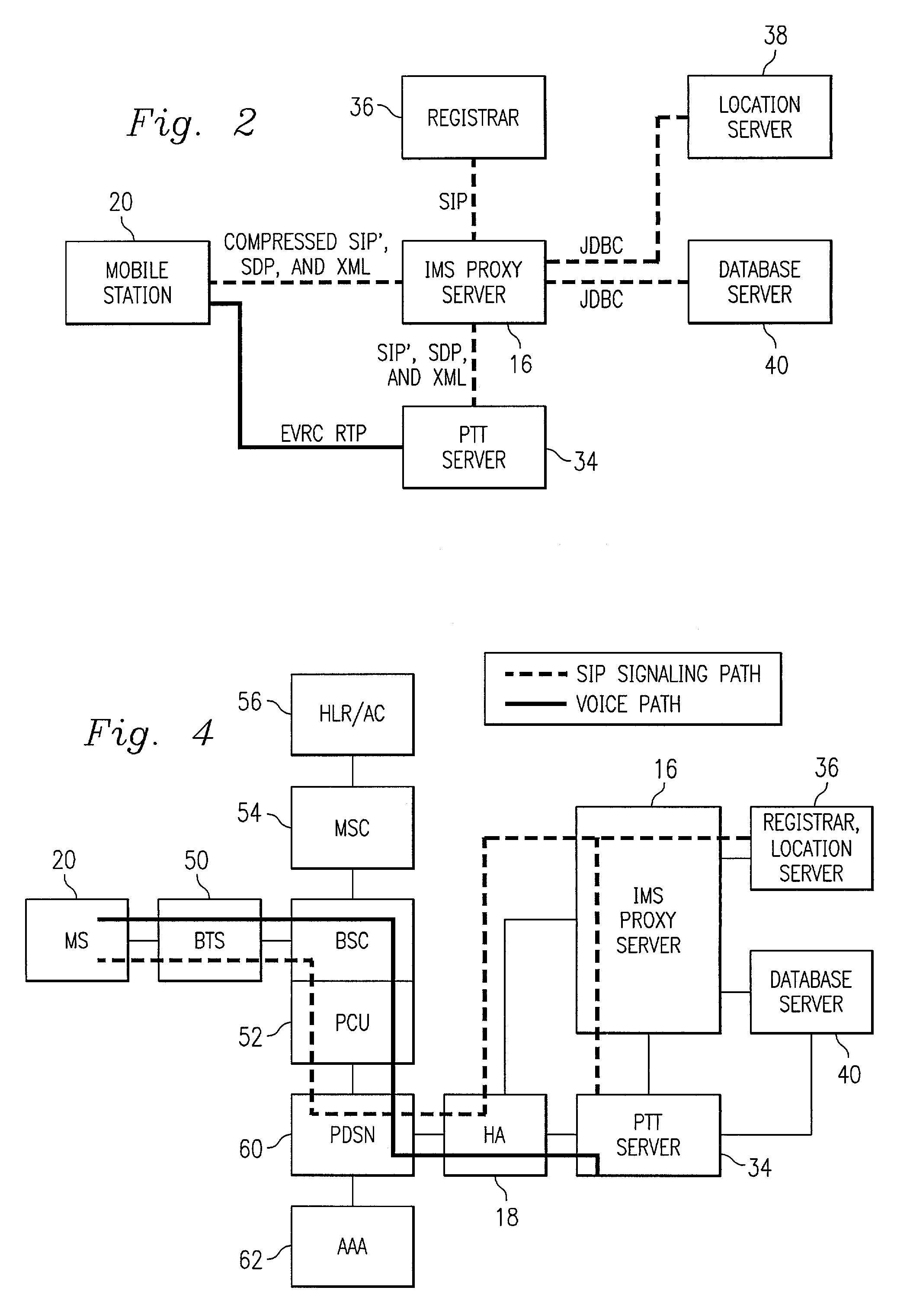
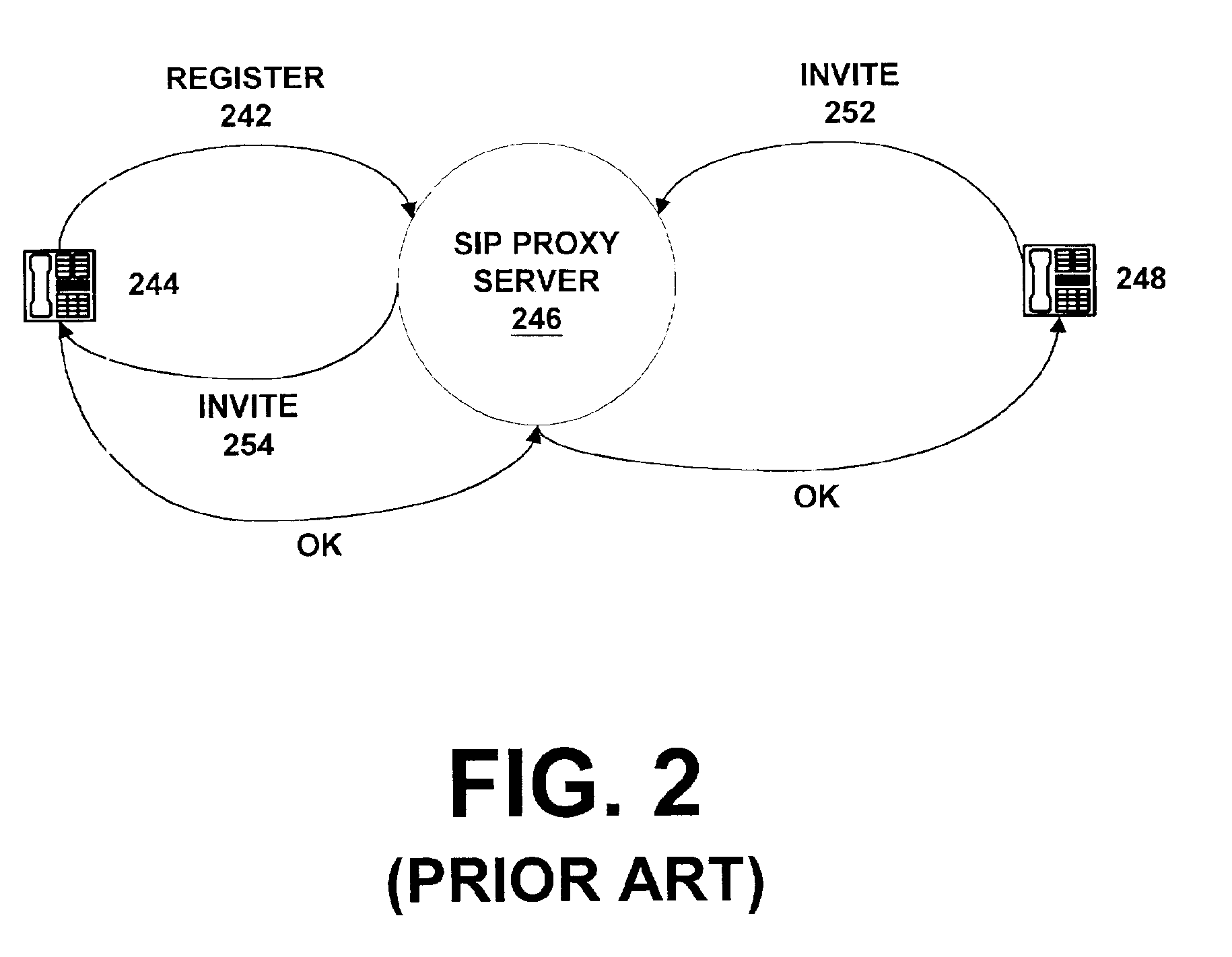
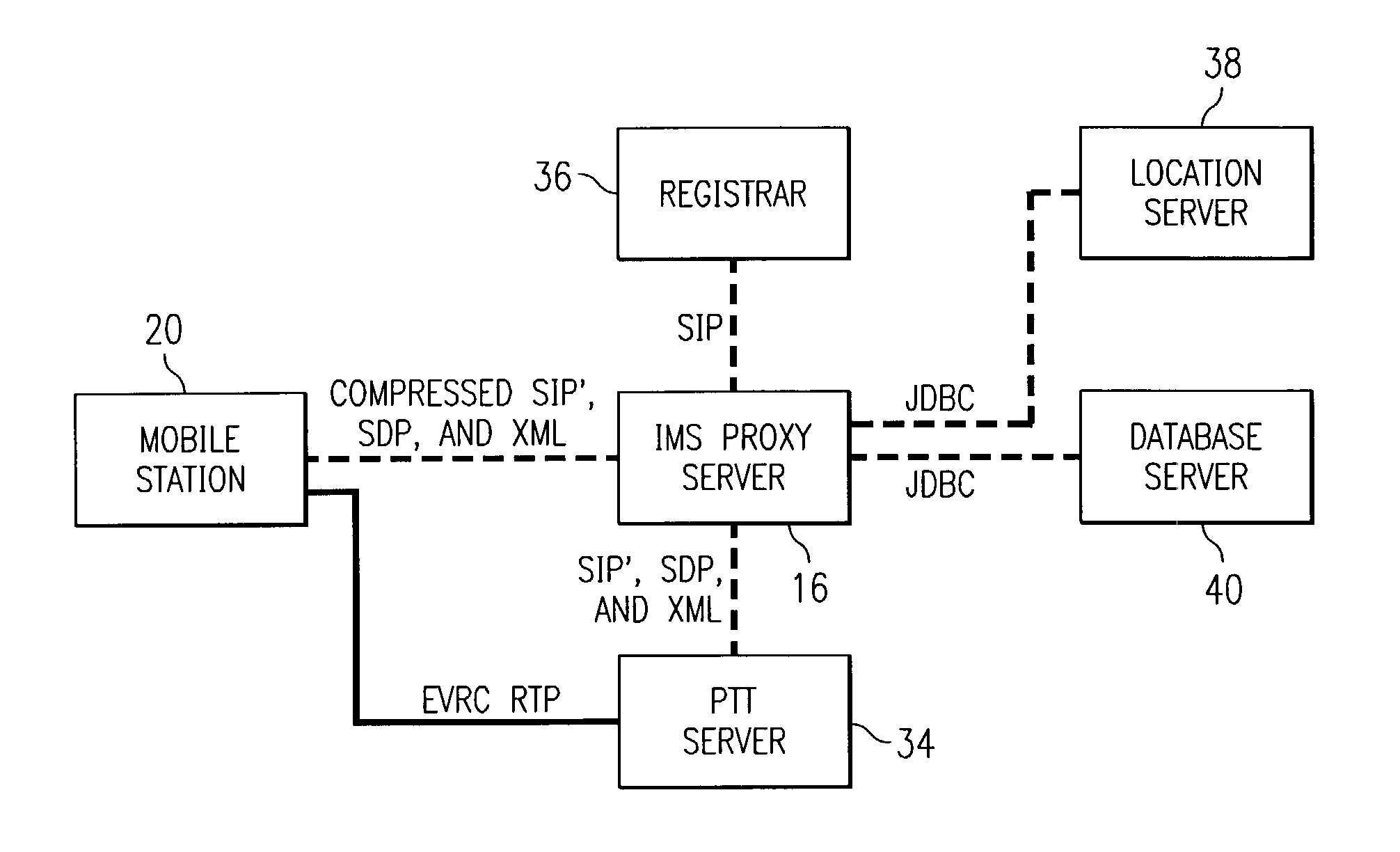
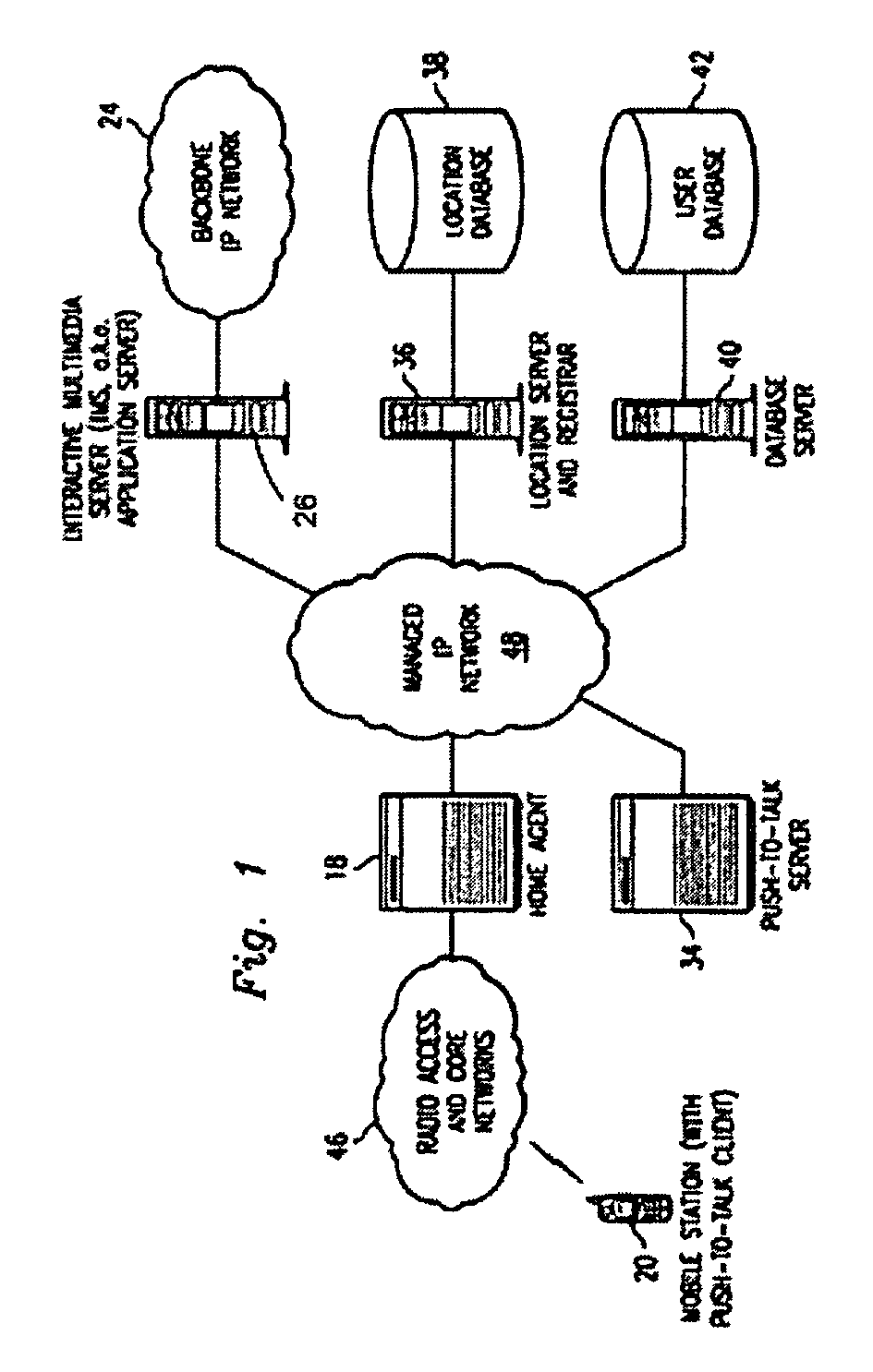
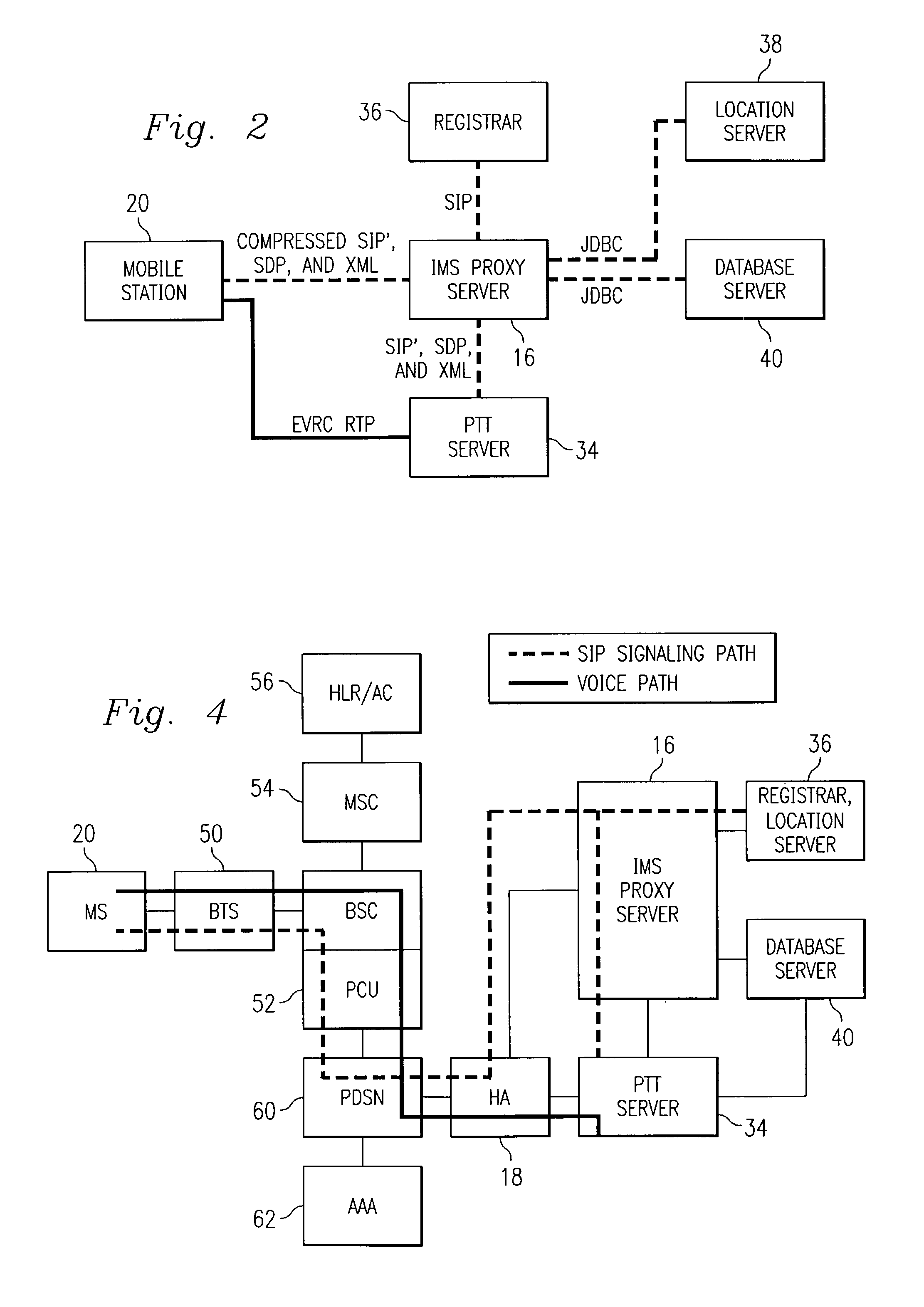
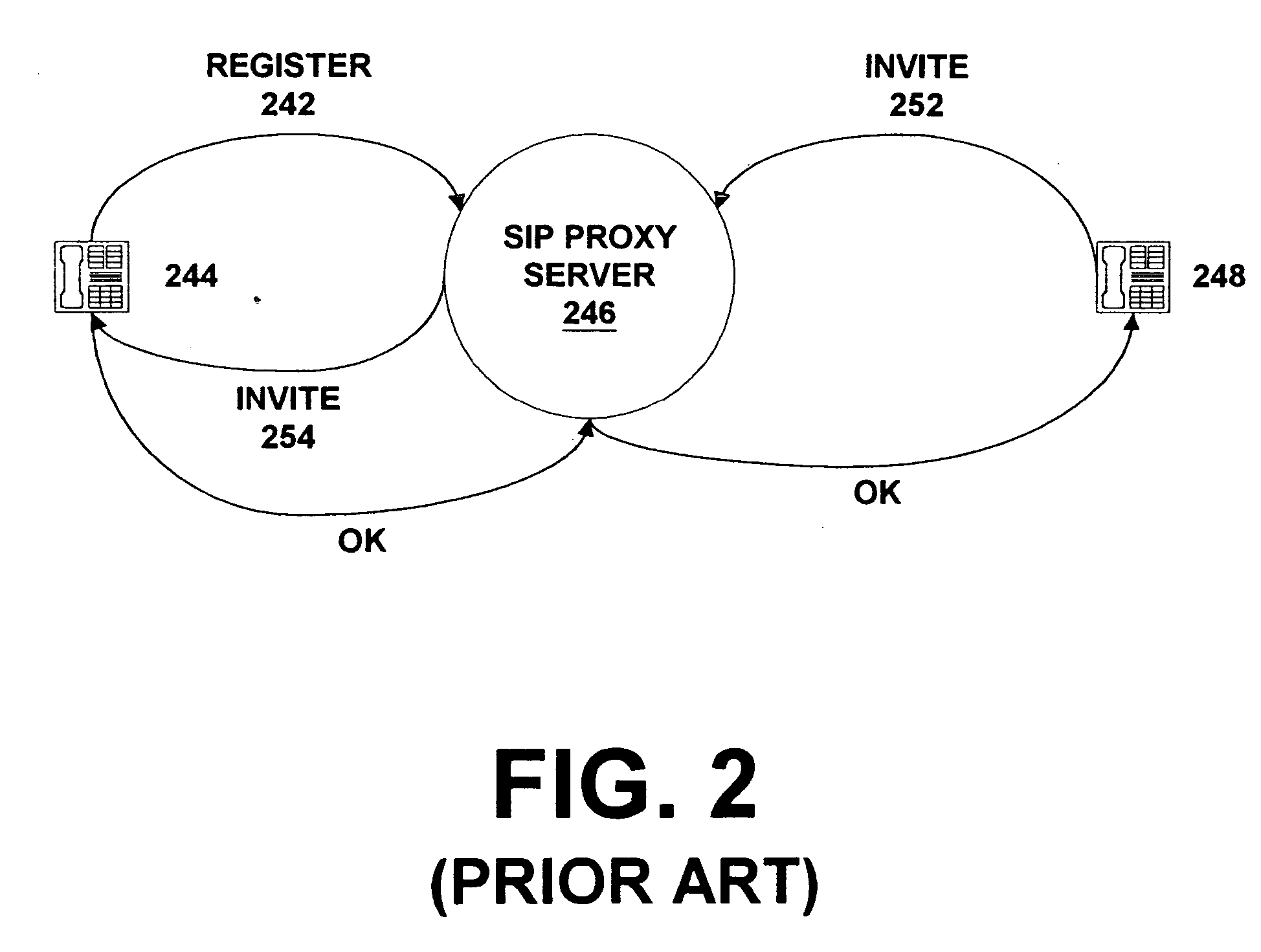
Push-to-talk wireless telecommunications system utilizing a voice-over-IP network
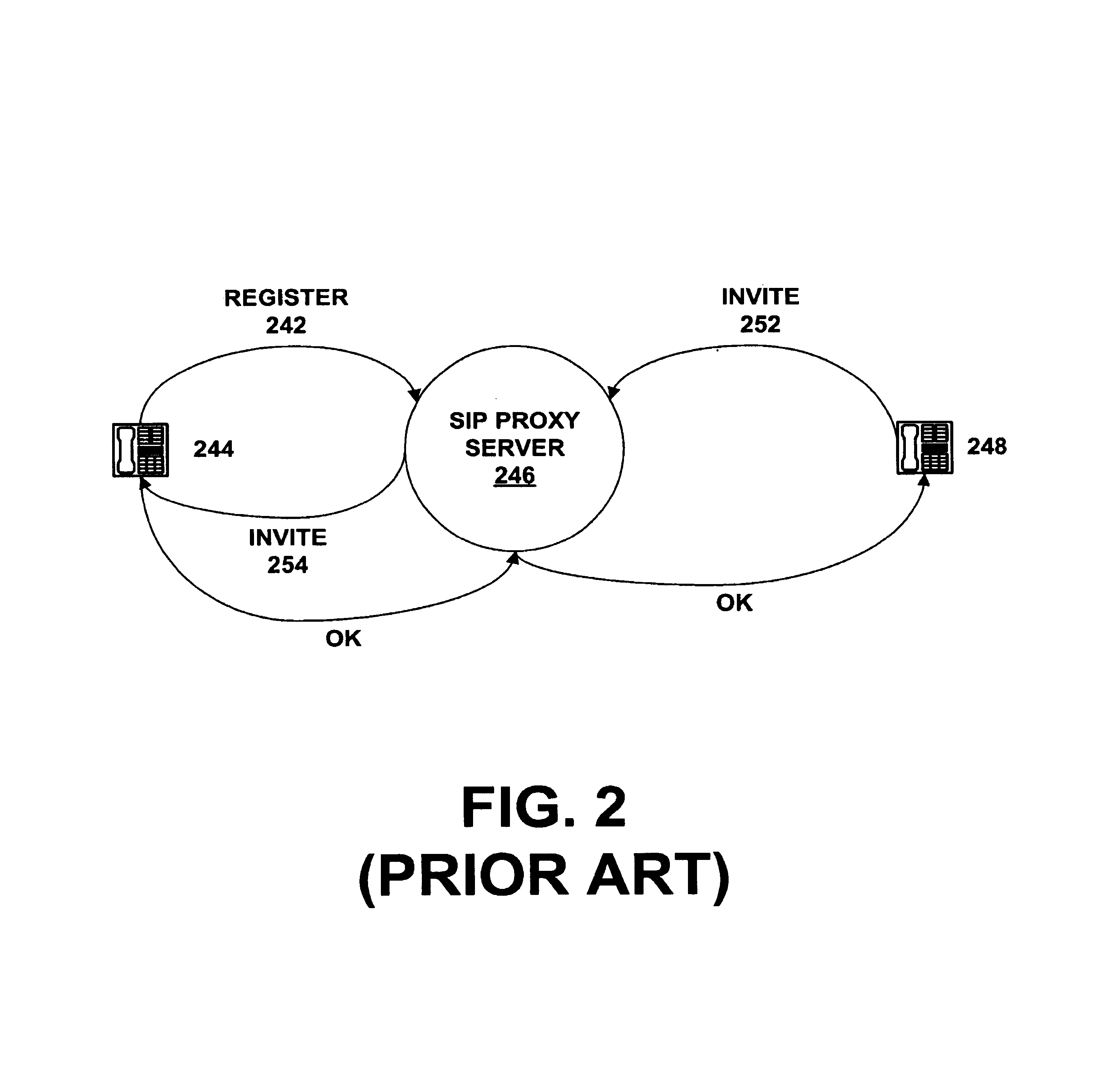
ActiveUS7170863B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationSession Initiation ProtocolTelecommunications network
A method and system to provide push-to-talk from one user to another in a wireless packet data telecommunications network is described. The system may include: a wireless communication network including push-to-talk (PTT) functionality, with a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Proxy Server; a SIP Registrar and Location Server operable to store contact addresses of active mobile devices; a Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP) Media Gateway (PTT Server) operable to function as a call endpoint for each of a plurality of mobile devices wherein the plurality of mobile devices are segmented into membership groups, the PTT Server further operable to multicast a communication from one member of the group to the other members of the group; and an Internet Protocol (IP) network interconnecting the SIP Proxy server, the SIP Registrar and Location Server, and the PTT Server.
Owner:APPLE INC
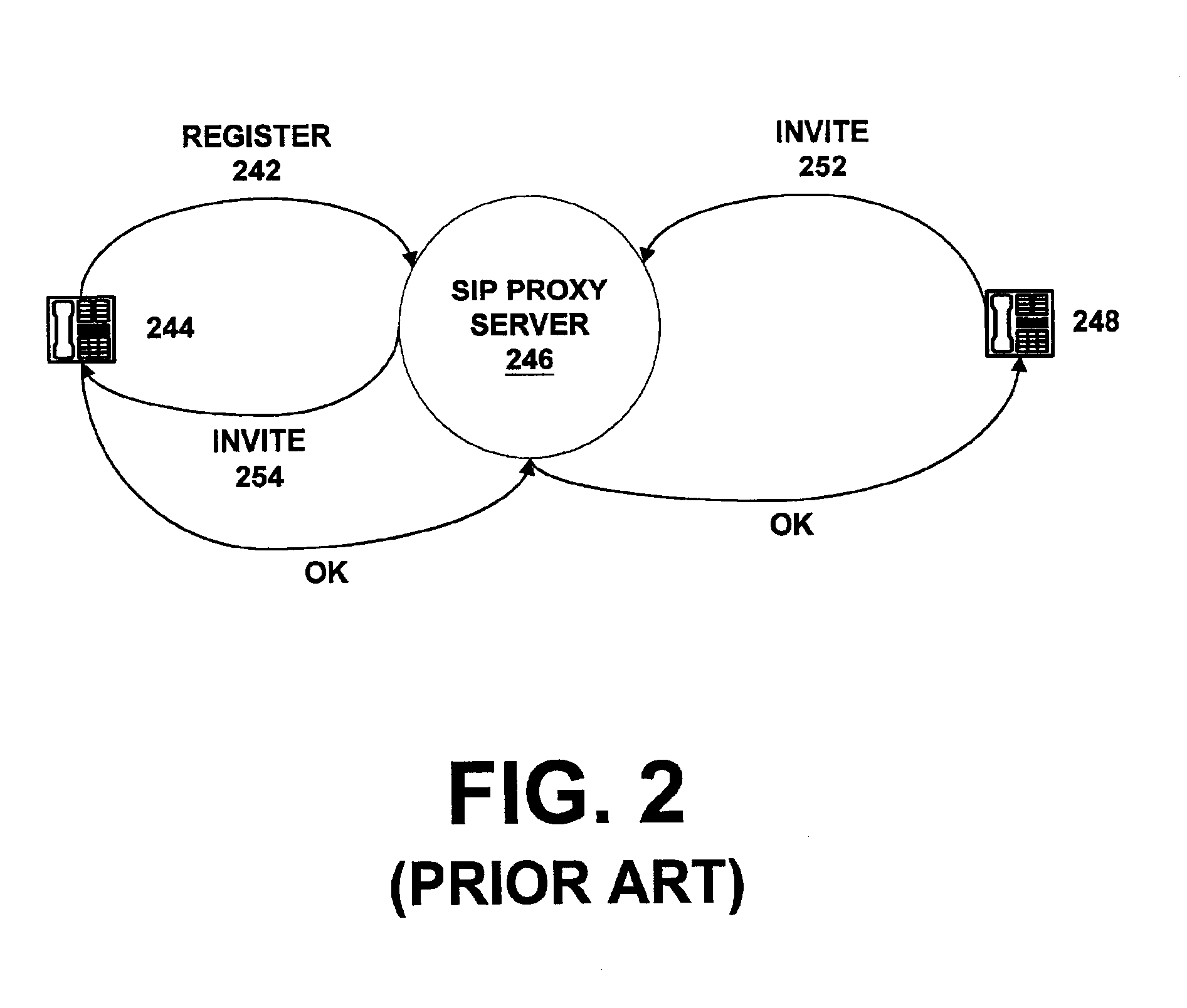
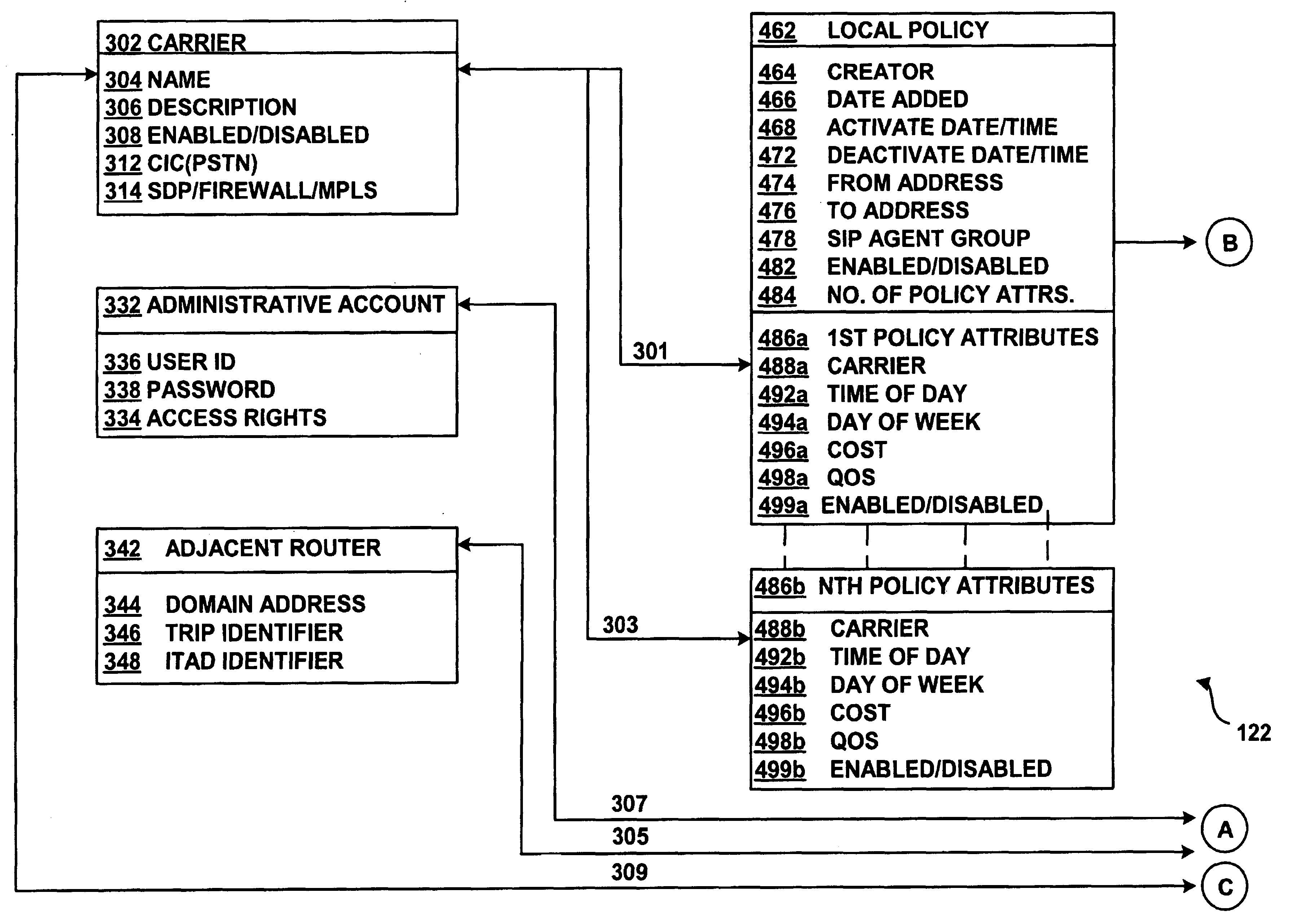
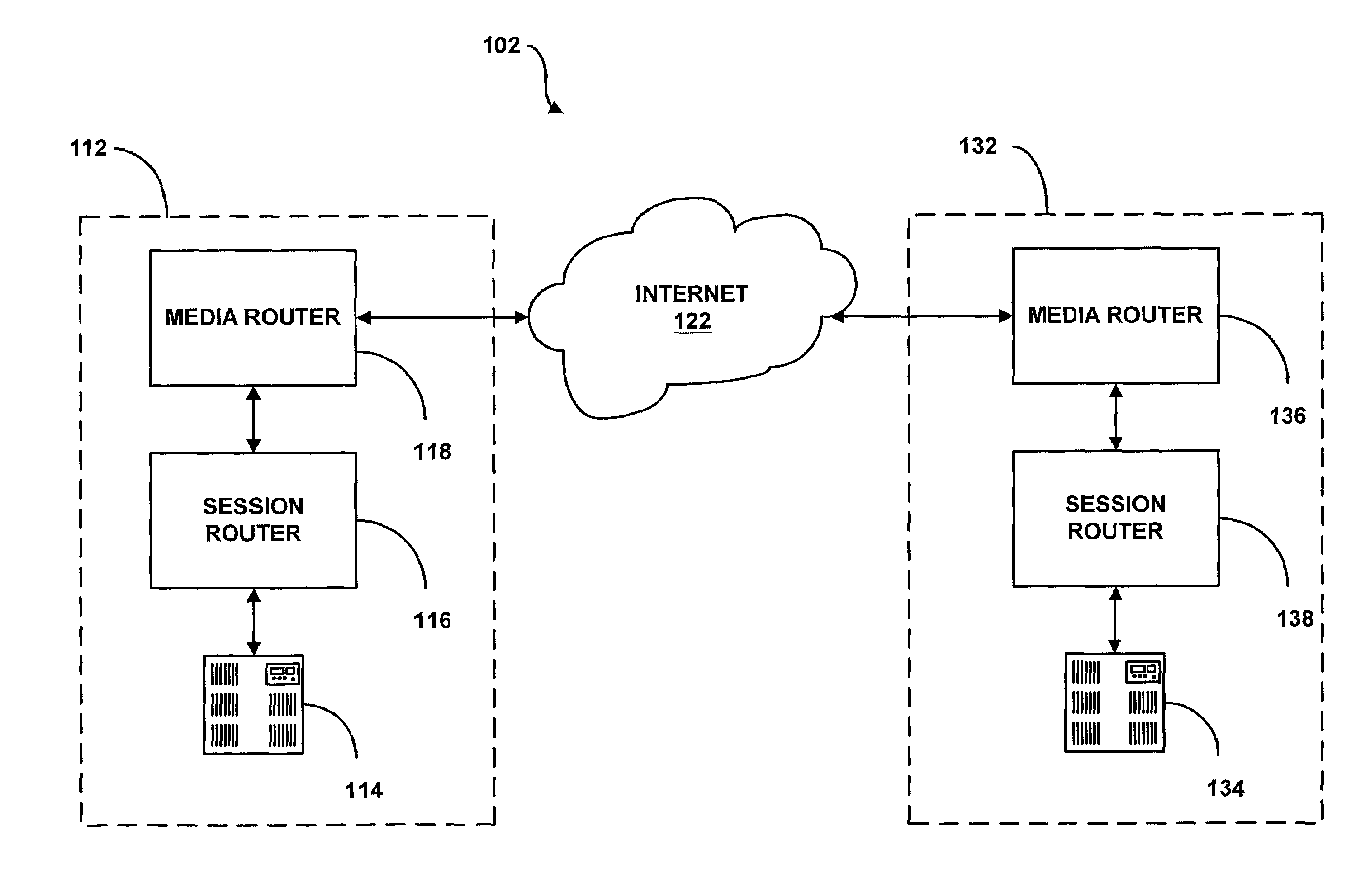
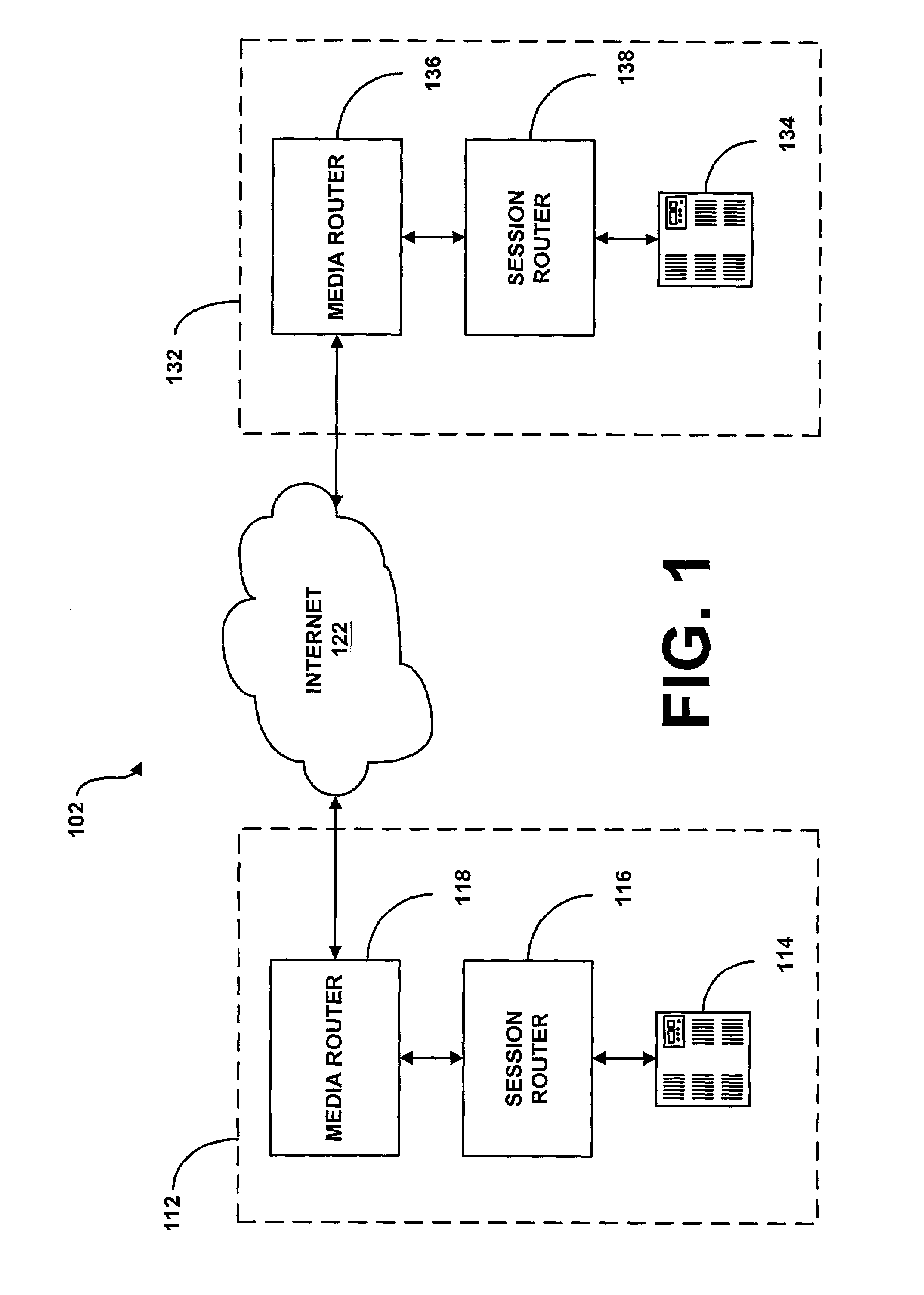
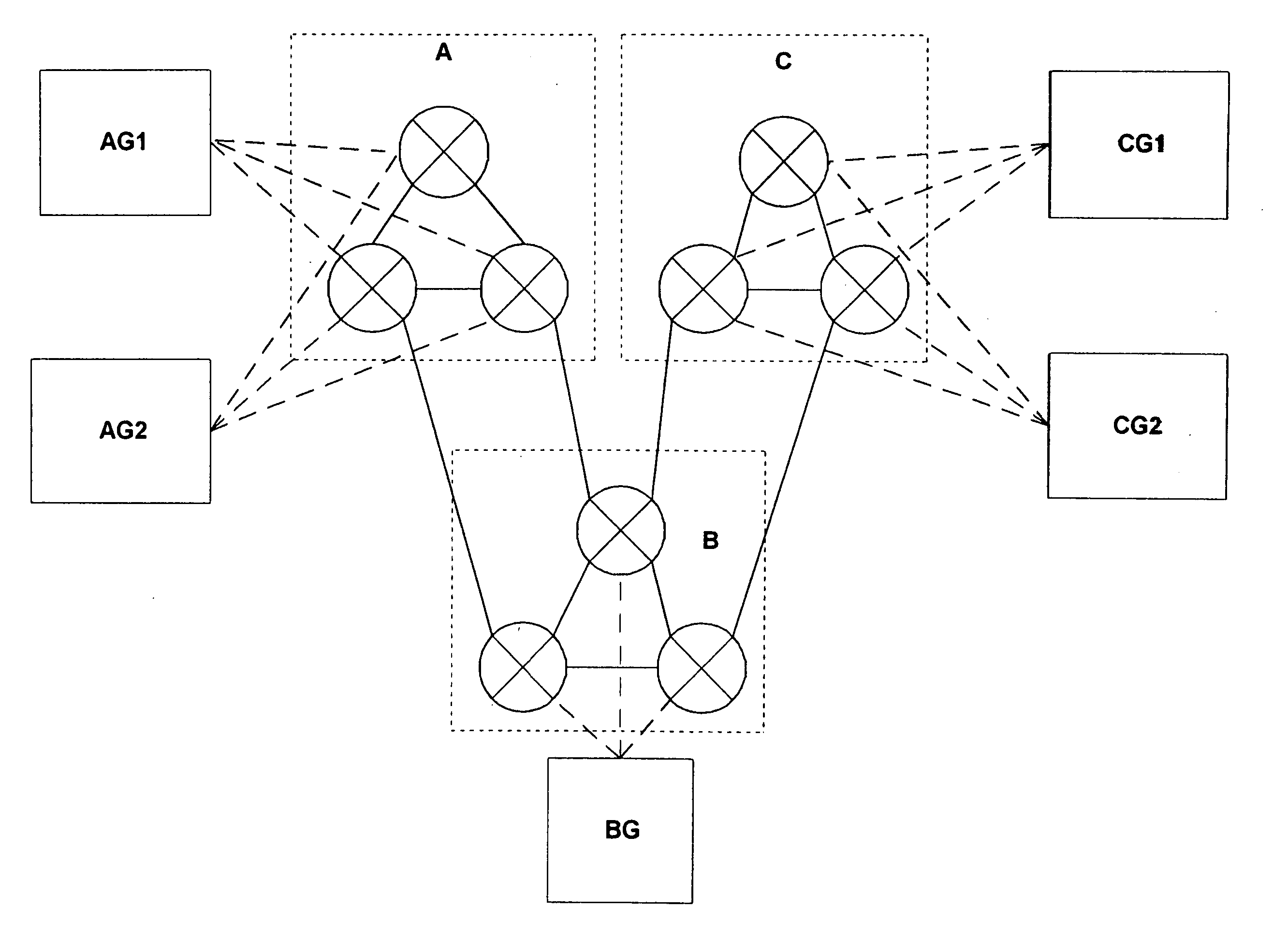
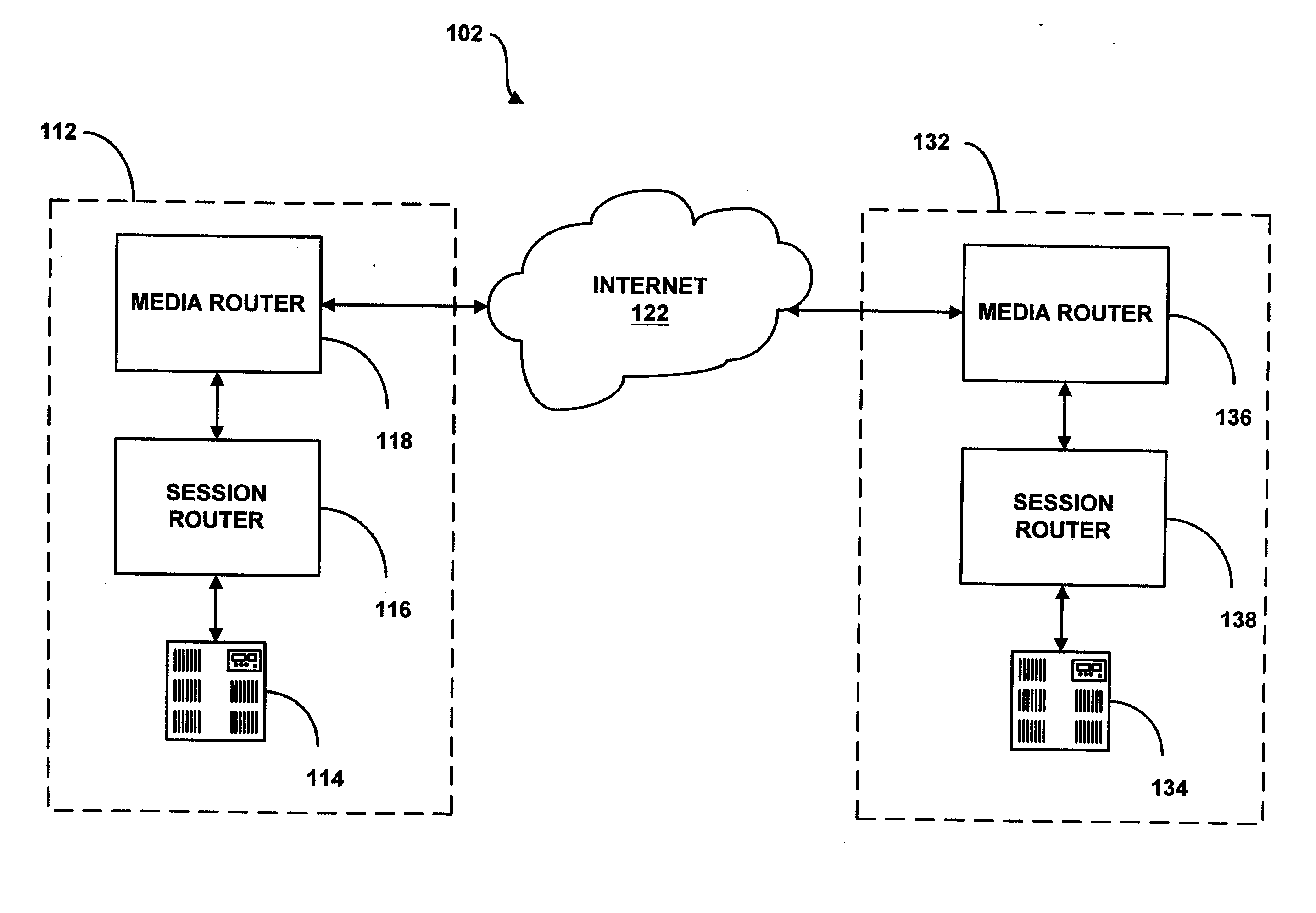
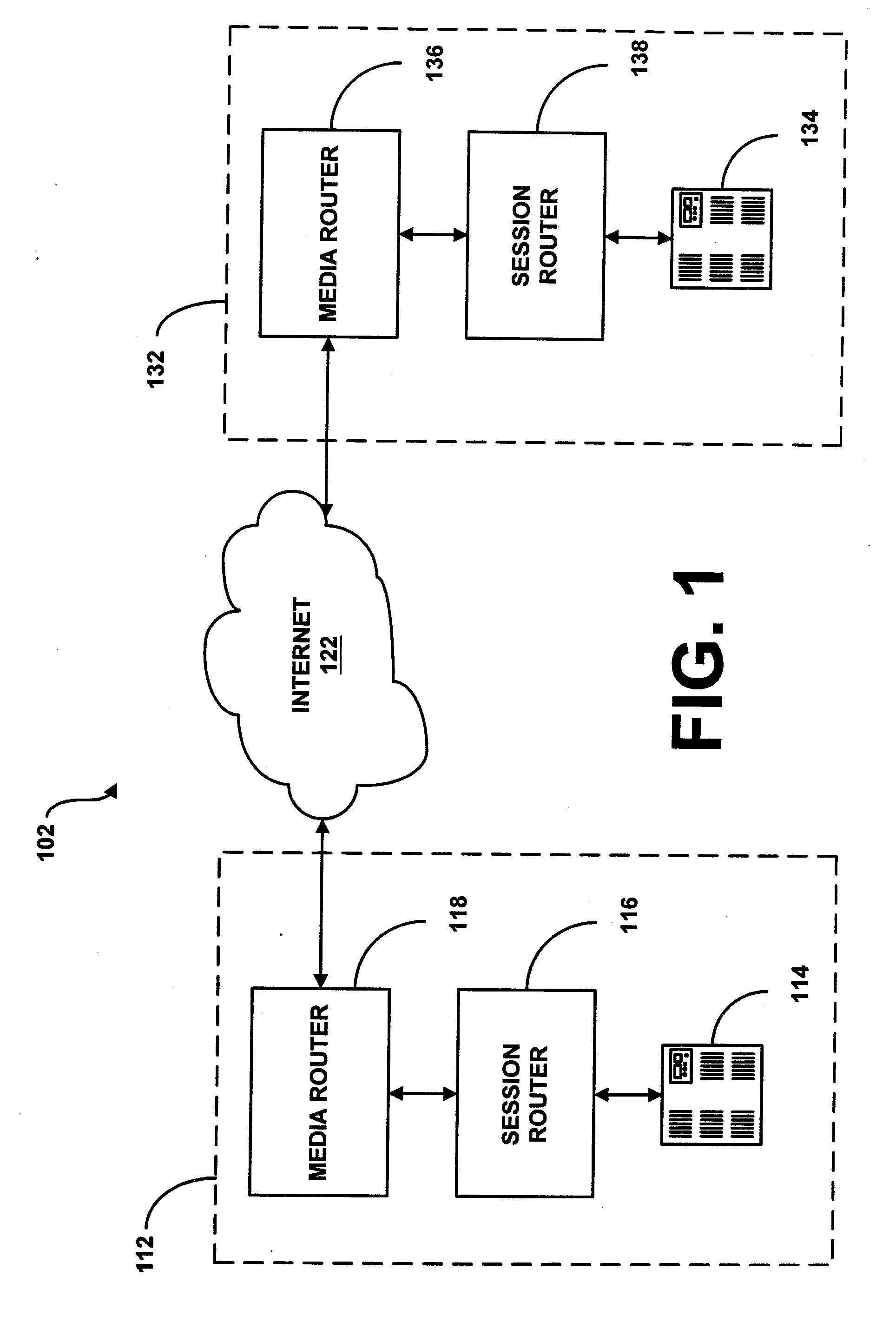
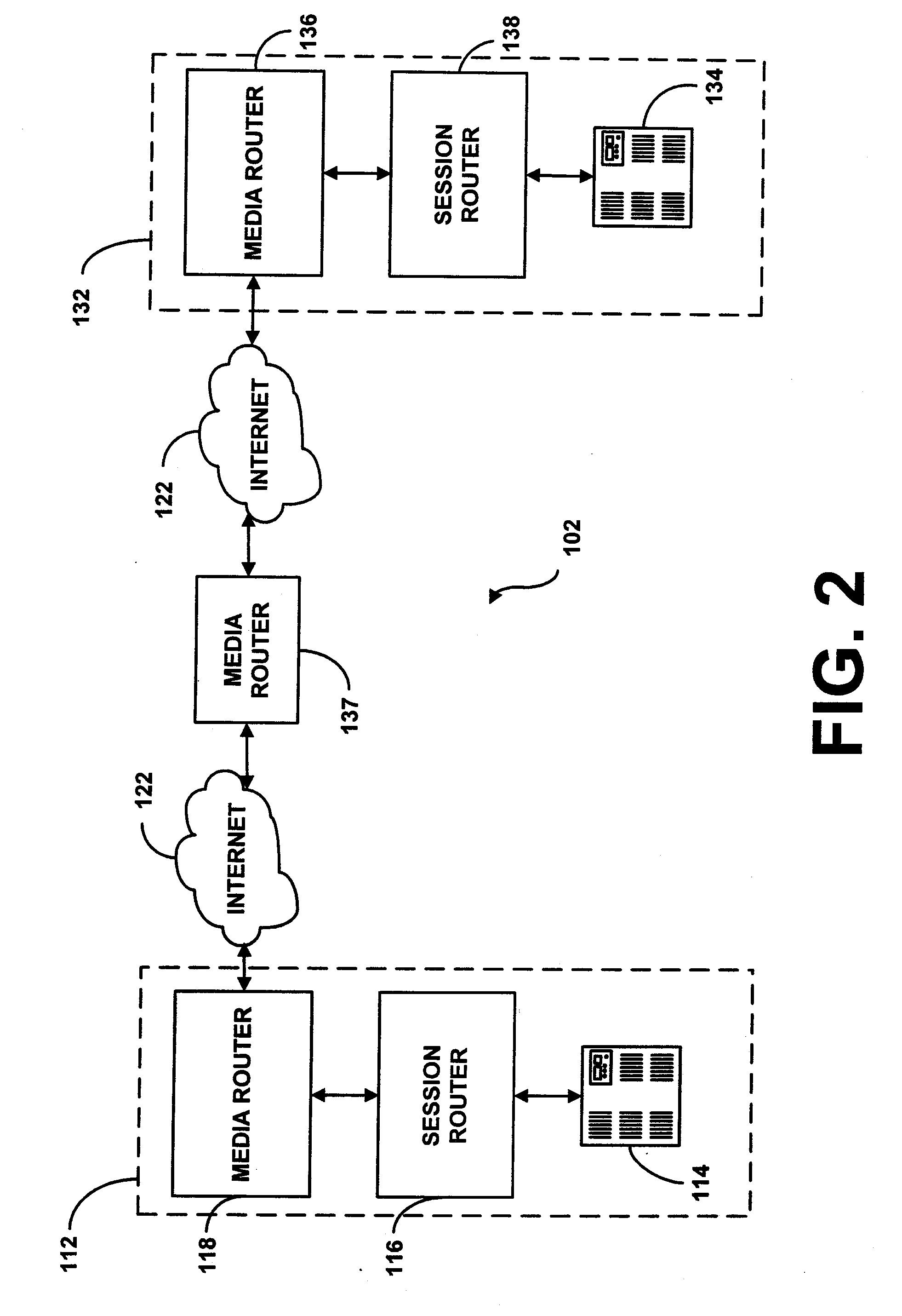
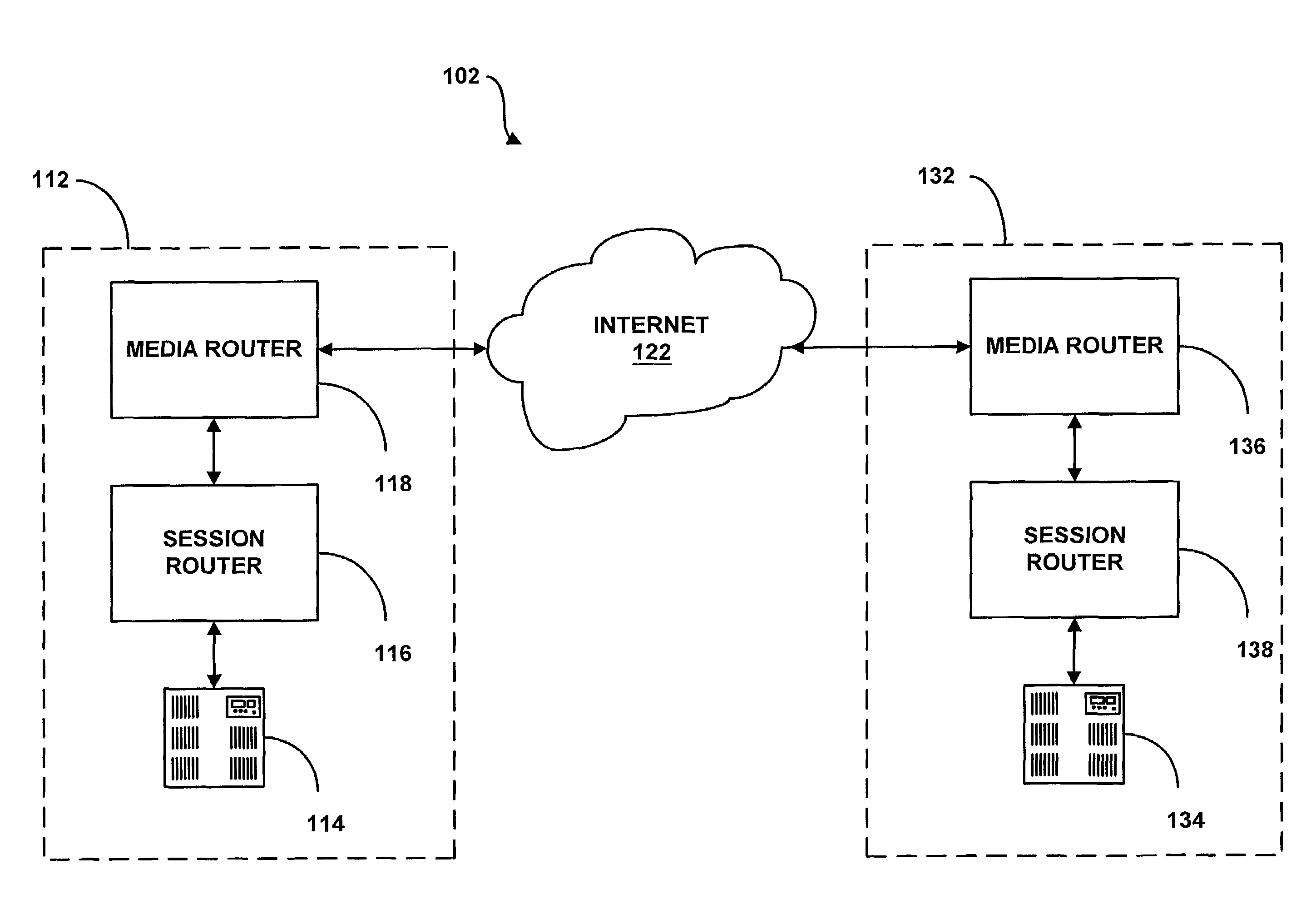
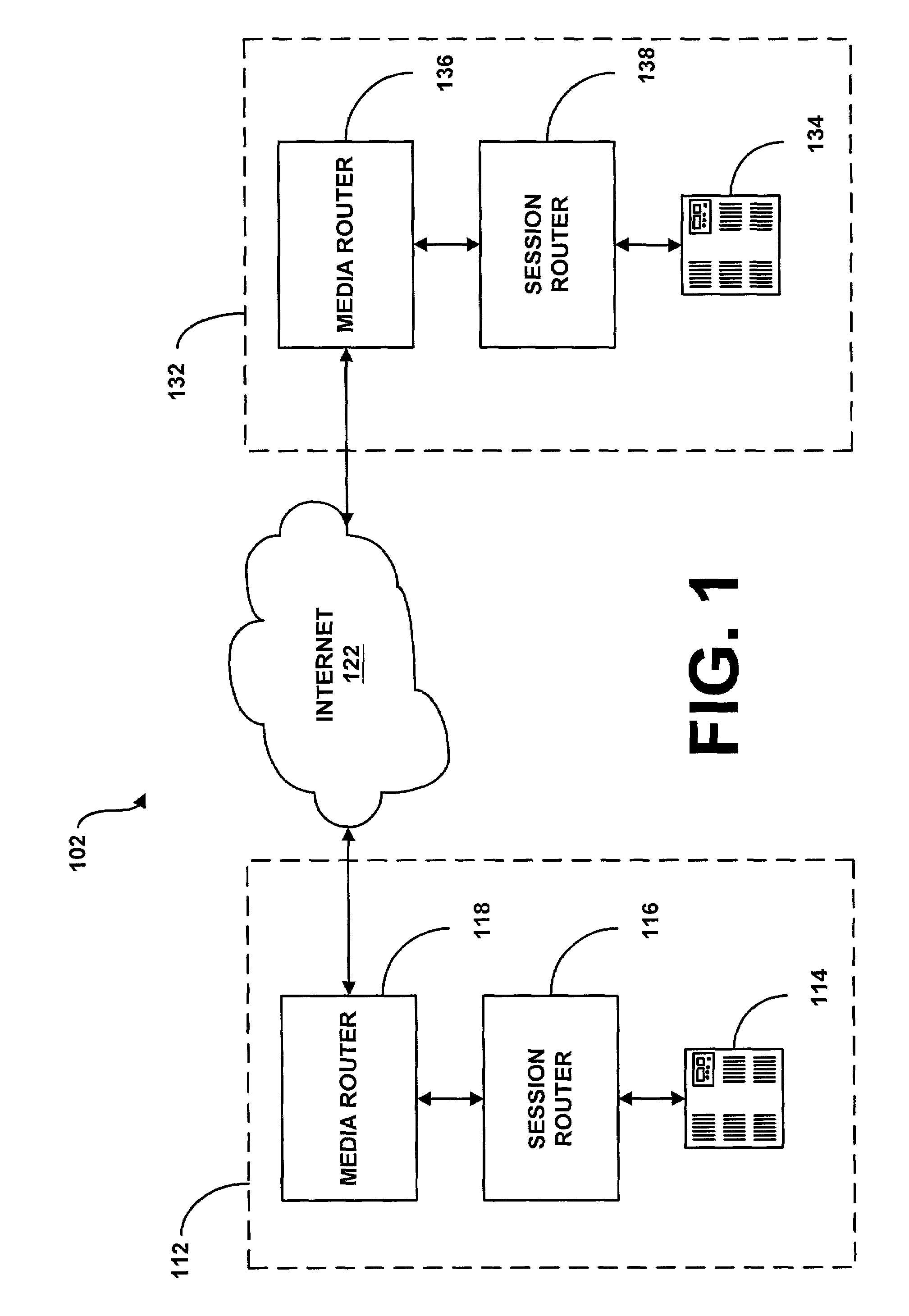
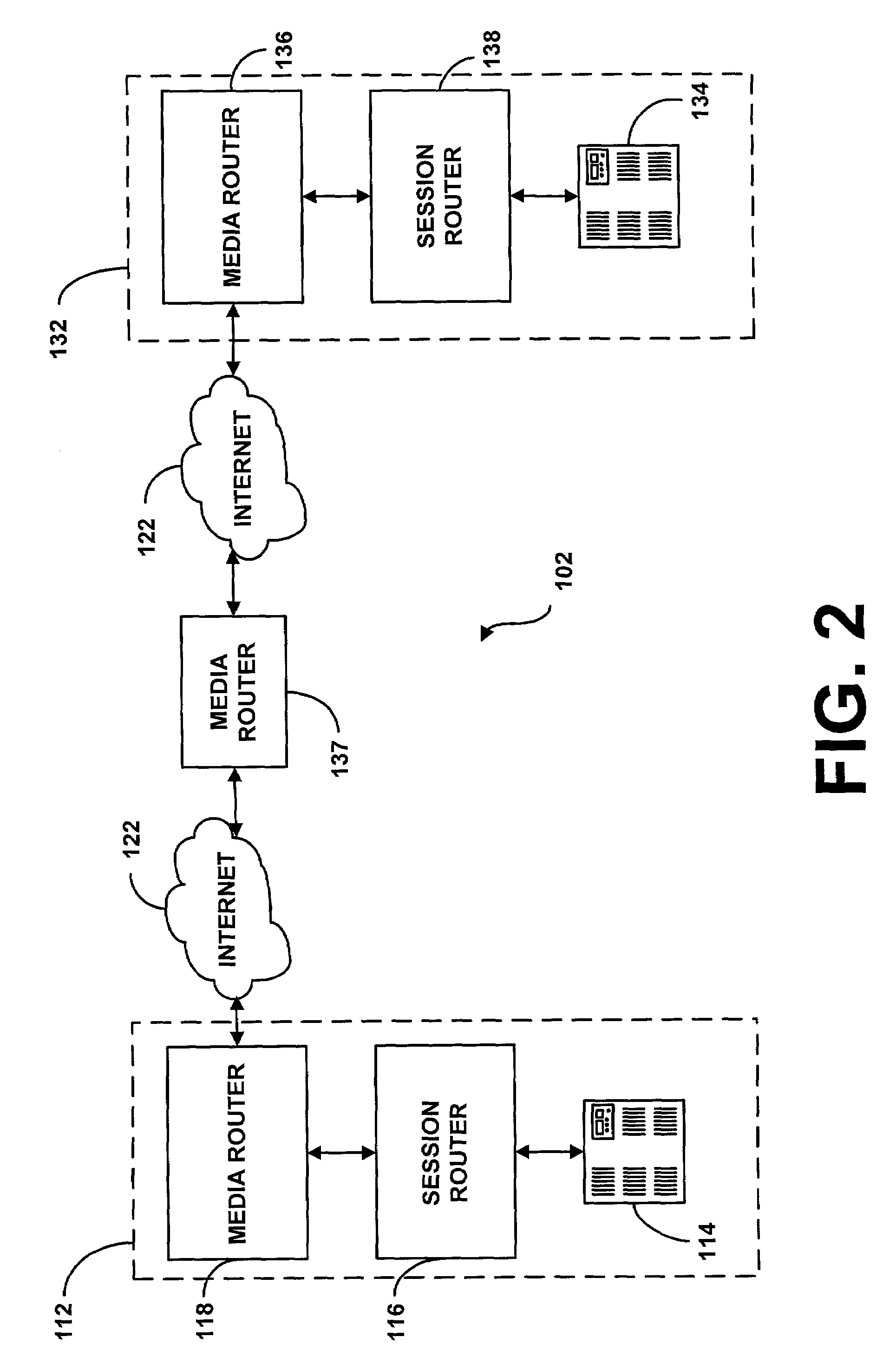
System and method for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks via use of a cluster of session routers
InactiveUS7002973B2Not easy to changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTransceiverComputer cluster
A system for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks via use of a cluster of session routers is disclosed. The system utilizes a first computer and a cluster of computers, wherein the cluster of computers comprises at least two associated computers that are connected to the first computer. Each of the associated computers comprises a second transceiver, a second memory having logic stored therein defining functions to be performed by the associated computers, and a second processor. The second processor is configured by the second memory to perform the functions of: performing an inbound screen on route information received by an associated computer, from the first computer, to determine if the received route information should be discarded; if the route information is not discarded, comparing the received and screened route information to a local policy defined within the cluster of computers; and performing an outbound screen on the received and screened information prior to transmitting the received and screened information outside the cluster of computers.
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
System and method for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks via media flow routing
InactiveUS7028092B2Not easy to changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTransceiverReal-time Transport Protocol
A system and method for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks via media flow routing is disclosed. The system utilizes a first computer and a second computer connected to the first computer, via a group of associated computers, wherein each of the first computer, second computer, and group of associated computers comprise a transceiver, a memory, and a processor. The processor is configured by the memory to perform the functions of: performing an inbound screen on route information received from the first computer, to determine if the received route information should be discarded; if the route information is not discarded, comparing the received and screened route information to a local policy defined within the second computer; performing an outbound screen on the received and screened information prior to transmitting the received and screened route information to the first computer; and selecting a primary route from the received route information and local route information in accordance with the local policy, wherein the primary route is a path from the second computer to the first computer via the group of associated computers.
Owner:ACME PACKET +1
System and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time multi-media flows
A system and method for providing rapid rerouting of real-time transport protocol (RTP) multi-media flows is disclosed. Generally, a first endpoint is connected to a second endpoint, wherein the first endpoint comprises a transceiver, software stored within the first endpoint defining functions to be performed by the first endpoint, and a processor configured by the software. The processor is configured to perform the steps of, performing flow processing on a data packet received at a first endpoint, from a second endpoint, removing a multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) tag from the data packet, translating a source address and destination address of the data packet, and determining a forwarding destination if more than one destination address of the data packet is provided.
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
Medium streaming distribution system
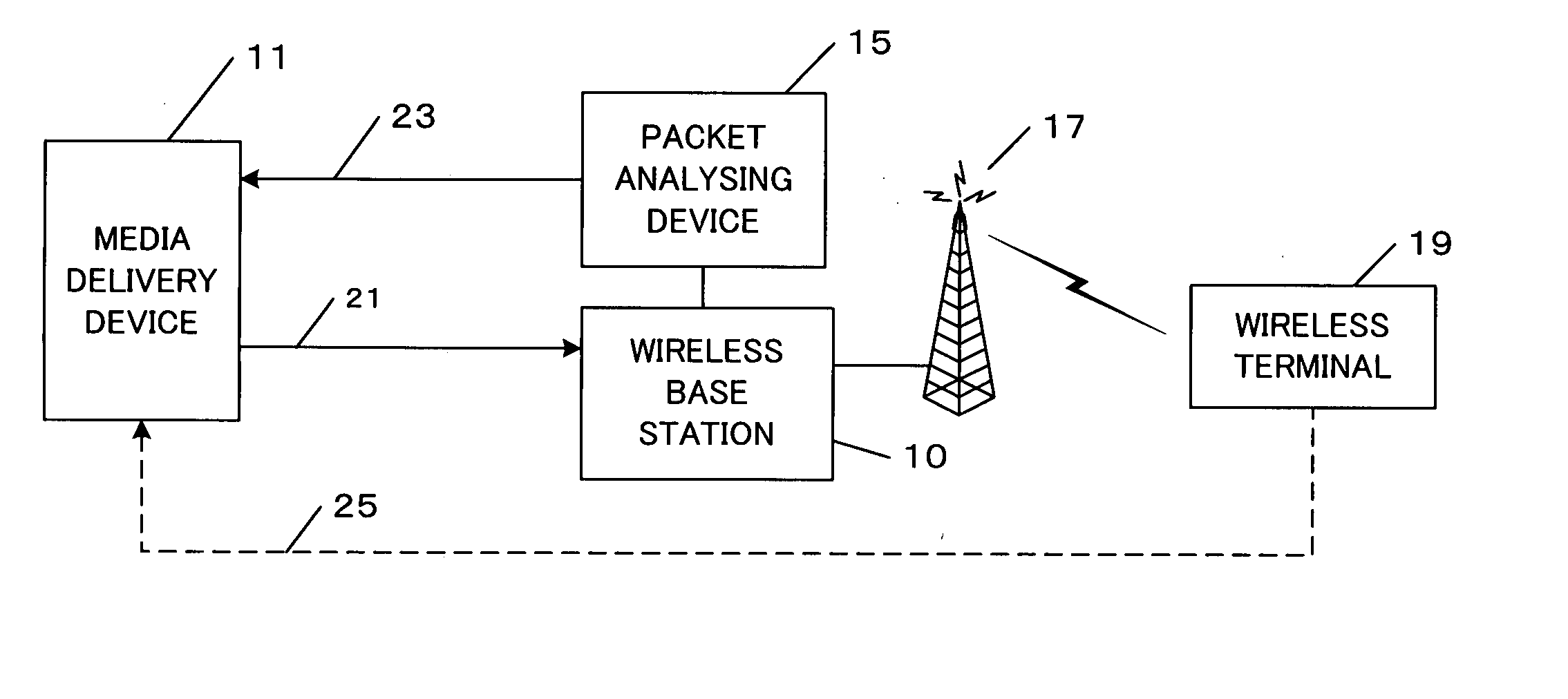
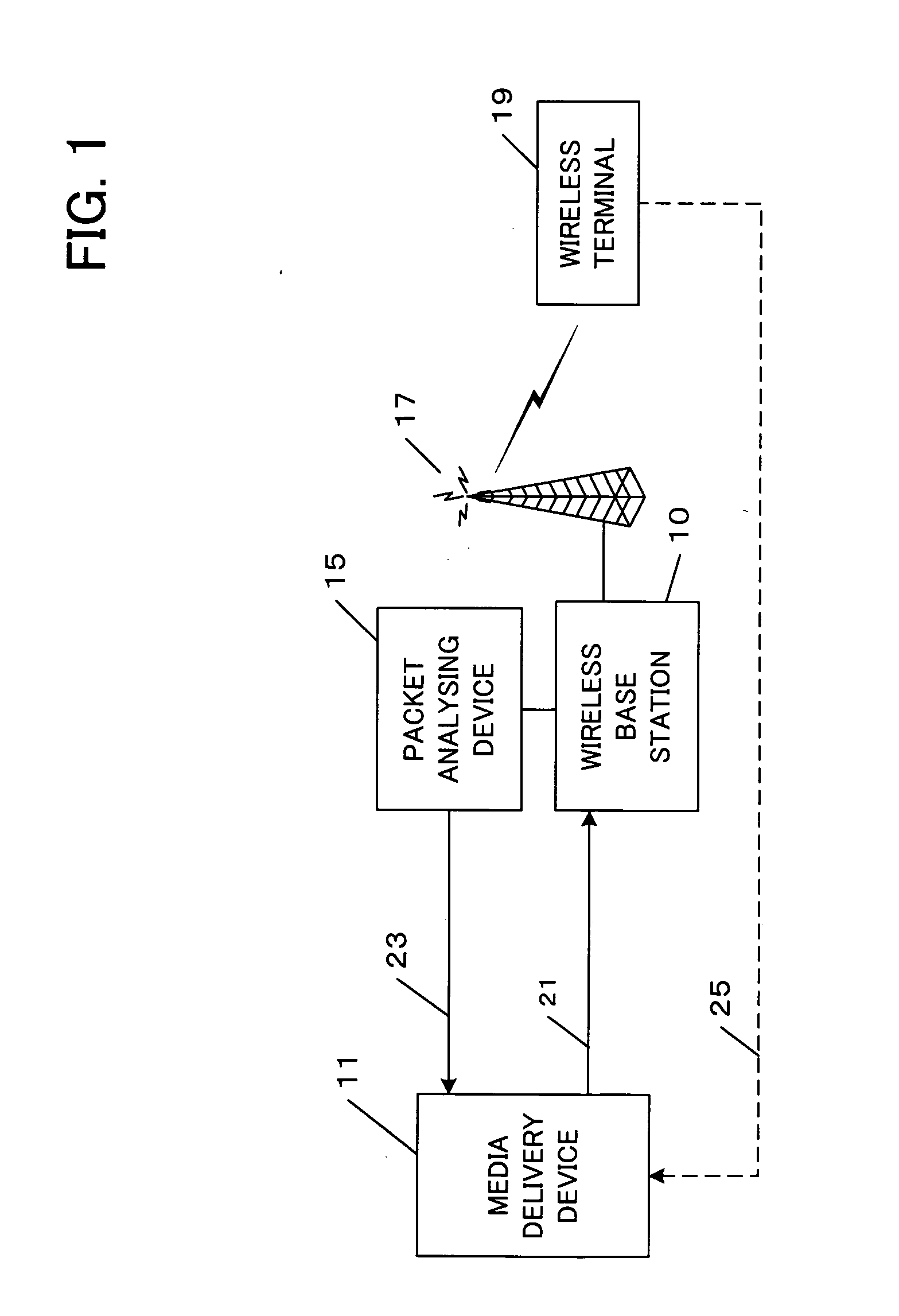
ActiveUS20050180415A1Improve communication qualityReduce impactError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket lossDistribution system
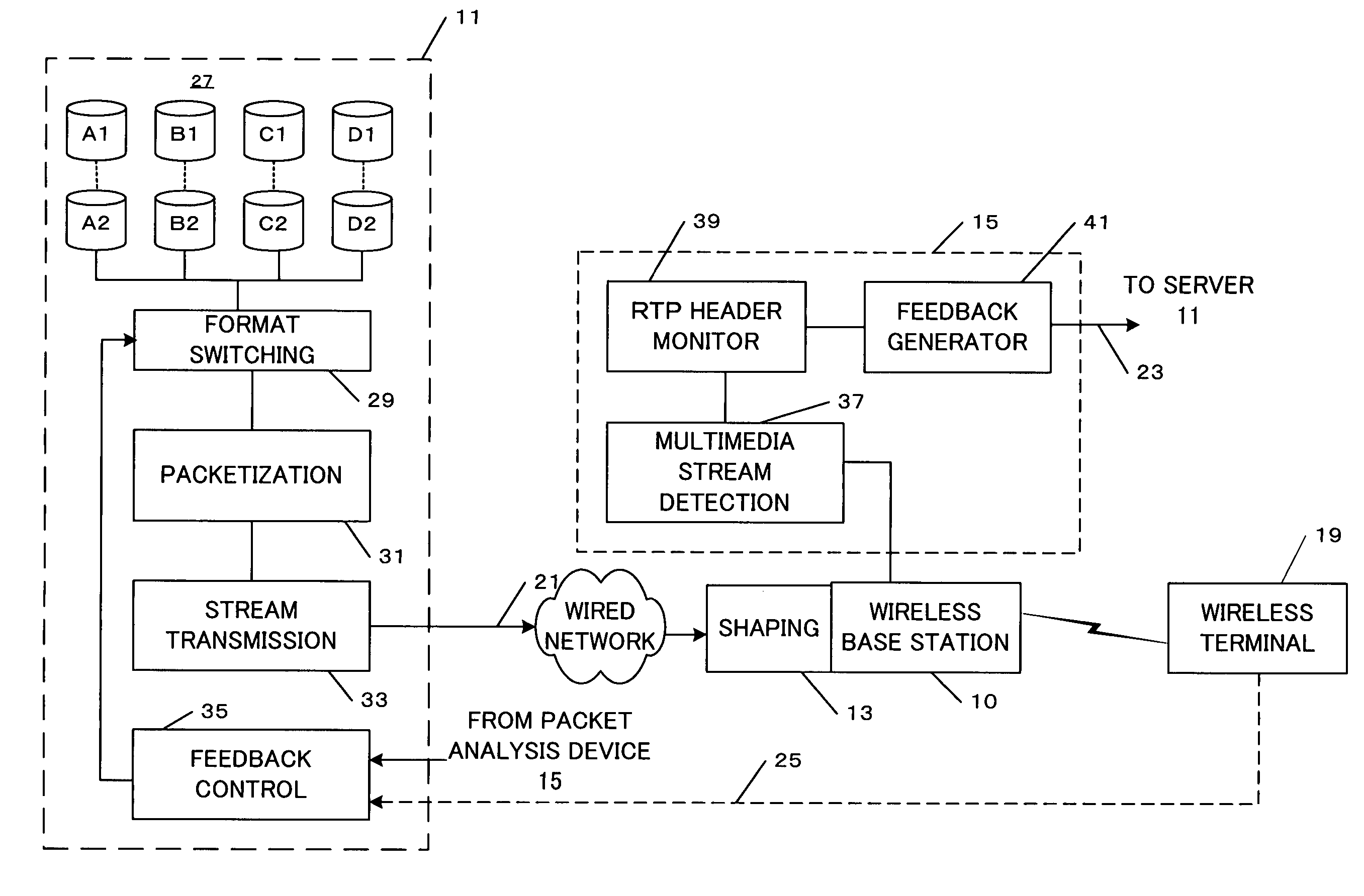
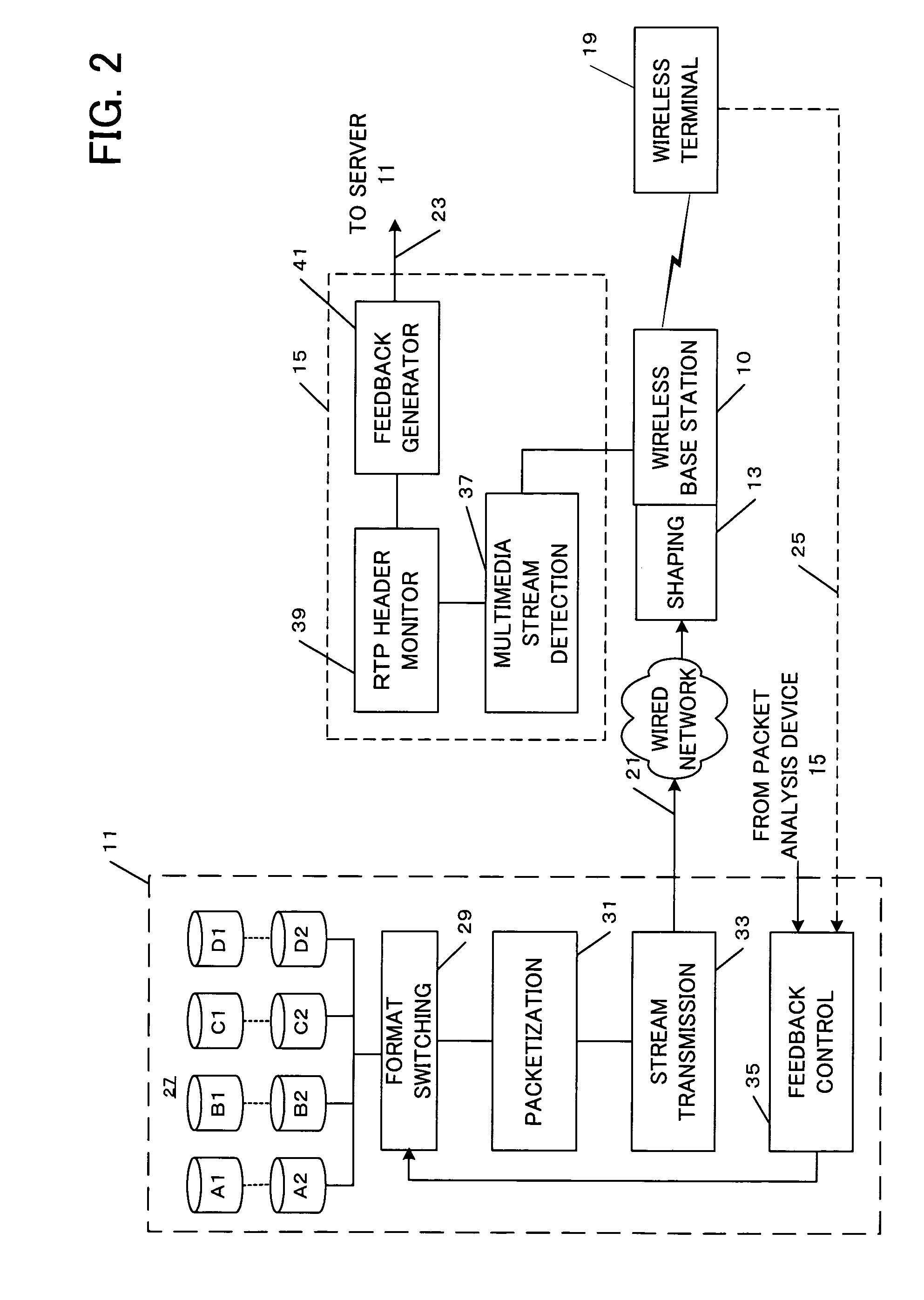
A medium streaming distribution system reduces effects of packet loss in a network before the packet reaches radio base station. A medium distribution device for packet-transmits via the base station, a medium stream to the network by a real time transmission protocol. A packet analyzer monitors the packet arriving at the radio base station and transmits feedback Information associated with loss of a packet to the medium distribution device. Based on the feedback from a relay device and a terminal device of the medium stream, the transmission rates from the medium distribution device to the relay device and from the relay device to the terminal device are obtained to provide a greater transmission rate in a surplus band for re-transmission or a forward error correction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
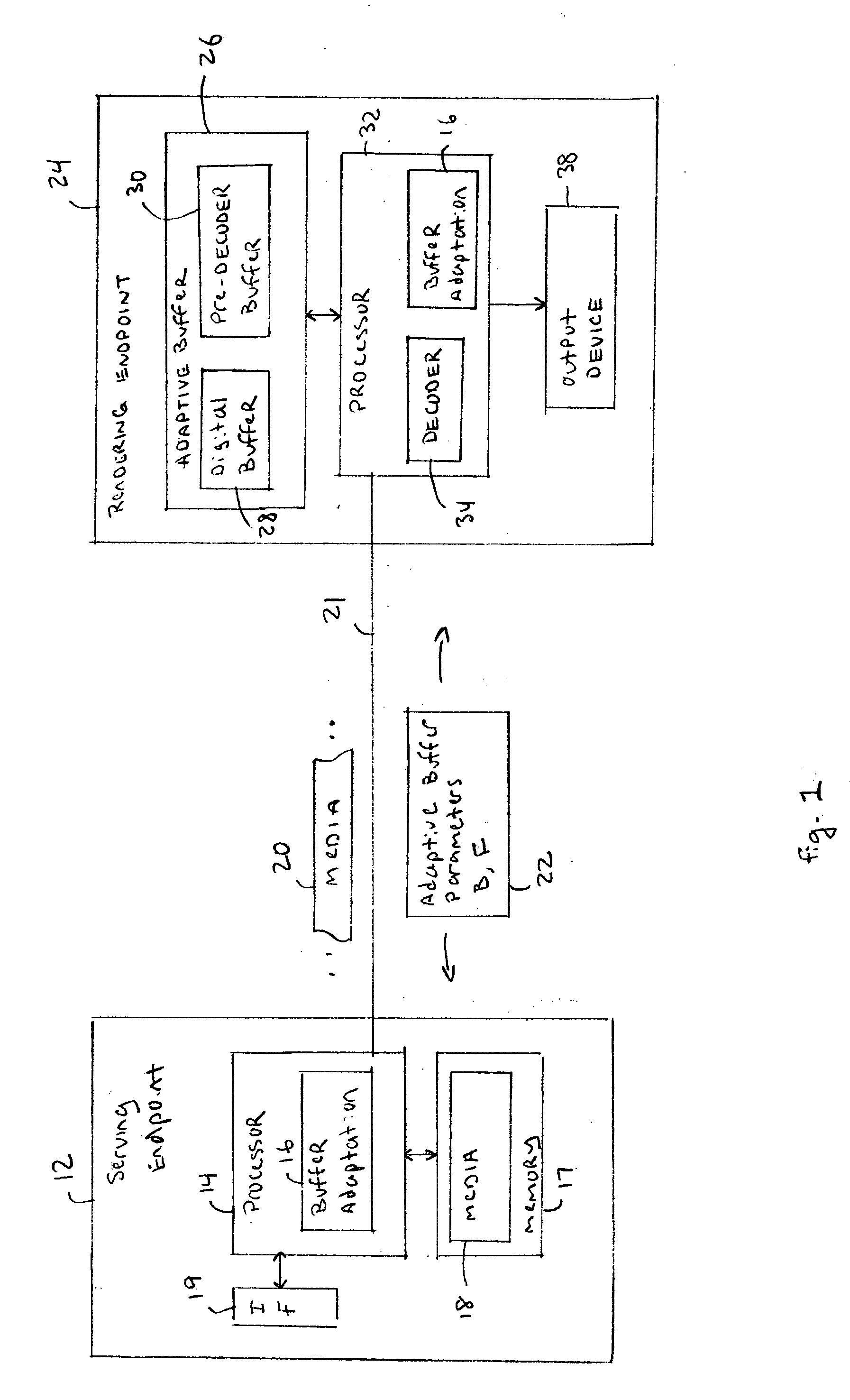
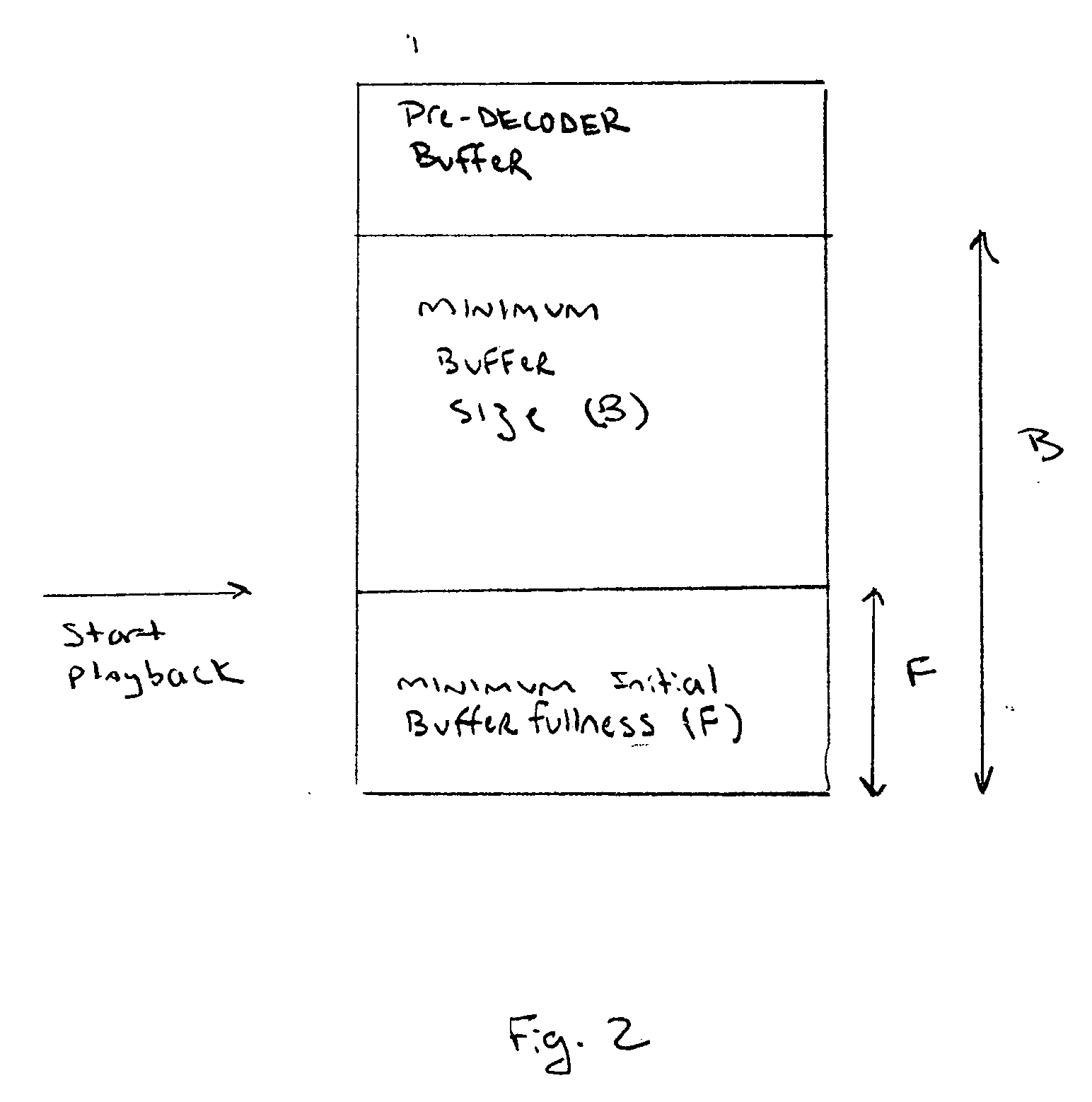
Method and apparatus for adaptive buffering
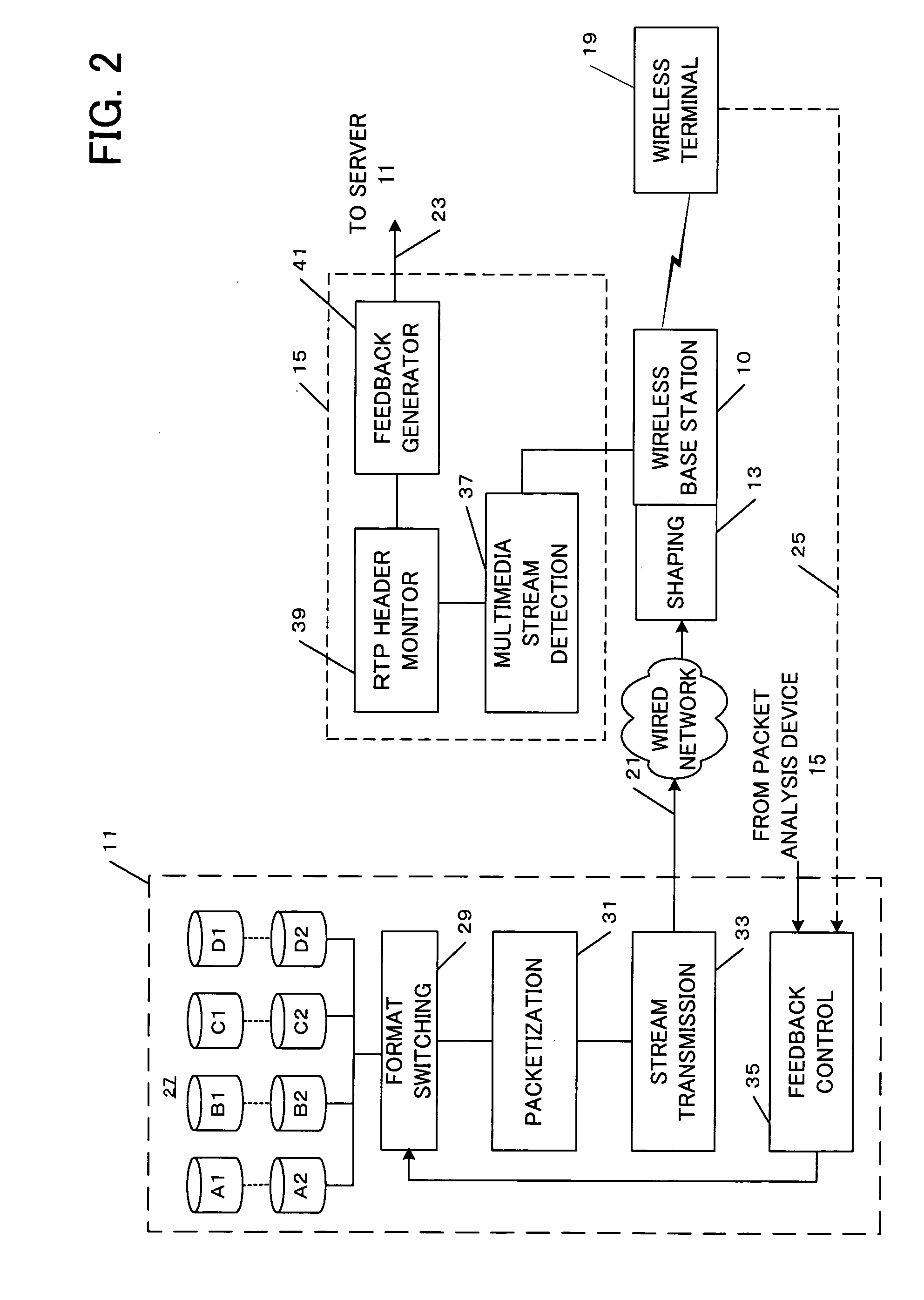
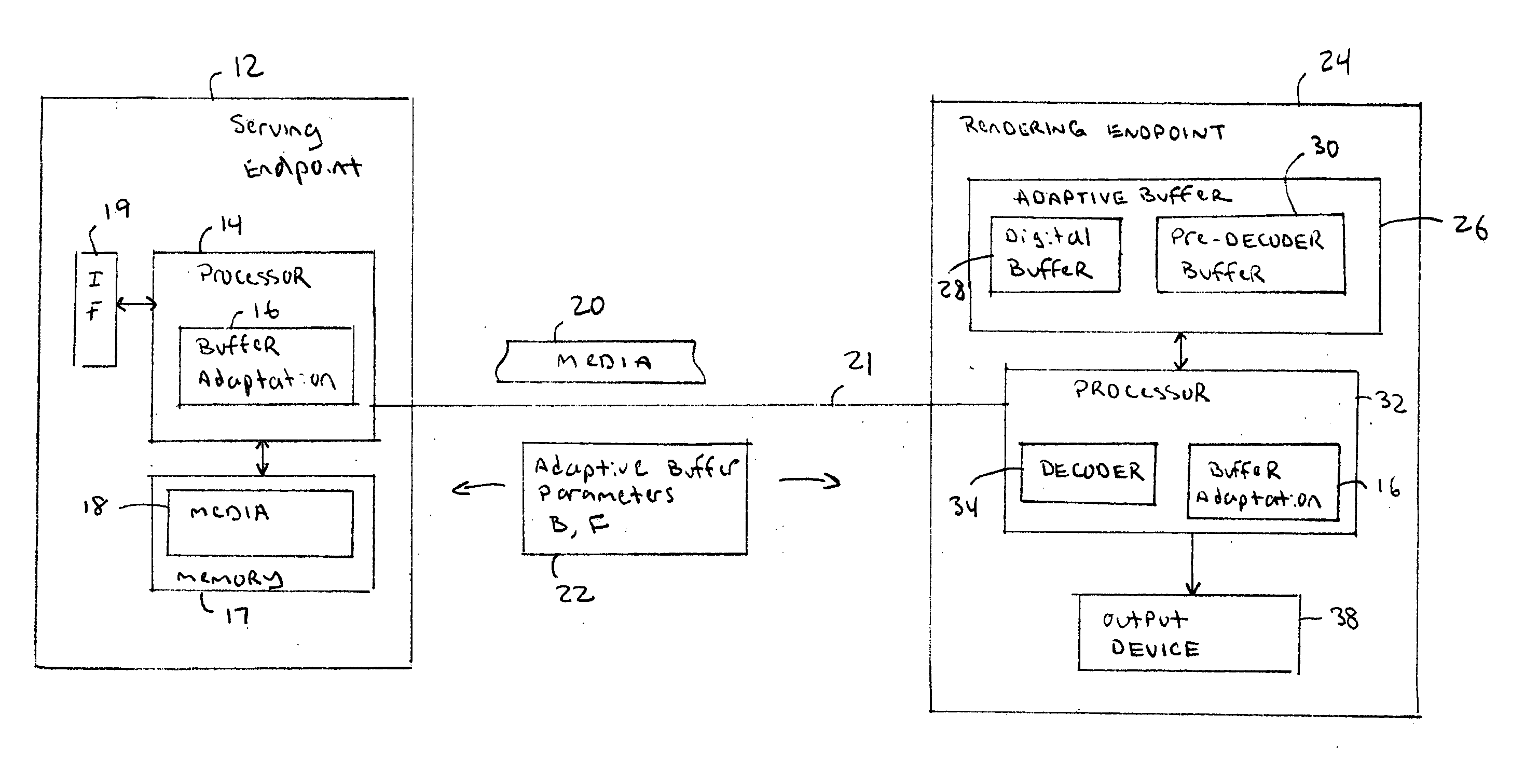
InactiveUS20060109856A1Efficient transportReadily apparentNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTime controlReal-time Transport Protocol
An adaptive buffering scheme allows more effective media transport and buffering. In one aspect of the adaptive buffering scheme, buffering parameters are adapted to different media characteristics, such as media play commands or the amount of encoding / transcoding required for the particular media stream. In another aspect of the adaptive buffering scheme, buffering is adapted to different transmission or memory conditions, such as transmission rate, packet jitter, or the amount of available buffer memory. In one example, the adaptive buffering is supported using Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), and / or Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP) and associated Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP), and / or Session Description Protocol (SDP) messages.
Owner:SHARP KK
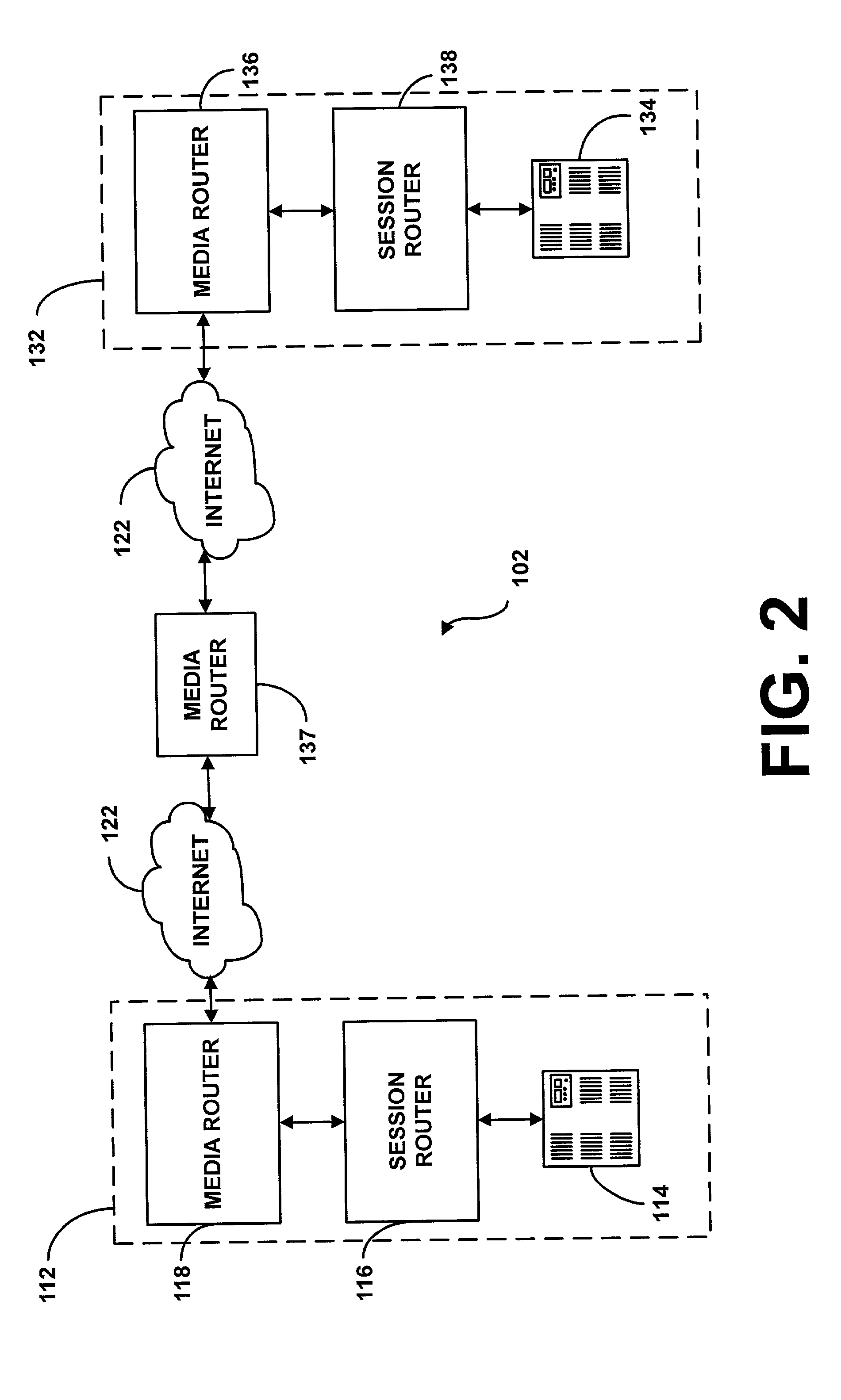
System and method for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks via screening
ActiveUS7133923B2Not easy to changeMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTransceiverReal-time Transport Protocol
A system for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks via screening is disclosed. The system utilizes a transceiver, a memory having logic stored therein defining functions to be performed by the system, and a processor. The processor is configured by the memory to perform the functions of: determining if route information received by the transceiver is from an external source or an internal source; if the route information is from an external source, performing a first internal screen of the route information, wherein a destination address defined by the received route information is compared to a local destination address defined by the first internal screen; and if the route information is from an internal source, performing a second internal screen of the route information, wherein an origin address defined by the received route information is compared to a local origin address defined by the second internal screen.
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
Dynamically selecting codecs for managing an audio message
InactiveUS20060256721A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSession Initiation ProtocolTransport control protocol
A system, method, and apparatus are directed towards managing a Voice over IP (VOIP) messages over a network, employing the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The VOIP messages are sent by a source device to a destination device through a relay server. The relay server may throttle the VOIP messages employing buffer management. When the buffer is substantially full, the relay server will drop packets from the source device. Indication of the lost packets may be provided to the source device through a Real-time Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) report. The source device may then employ the RTCP report to modify a type of codec employed, and thereby adjust a rate of flow of VOIP packets sent towards the destination device. Additionally, the relay server may provide port translation services for RTP / RTCP packets between the source and destination devices.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Digital rights management for local recording and home network distribution
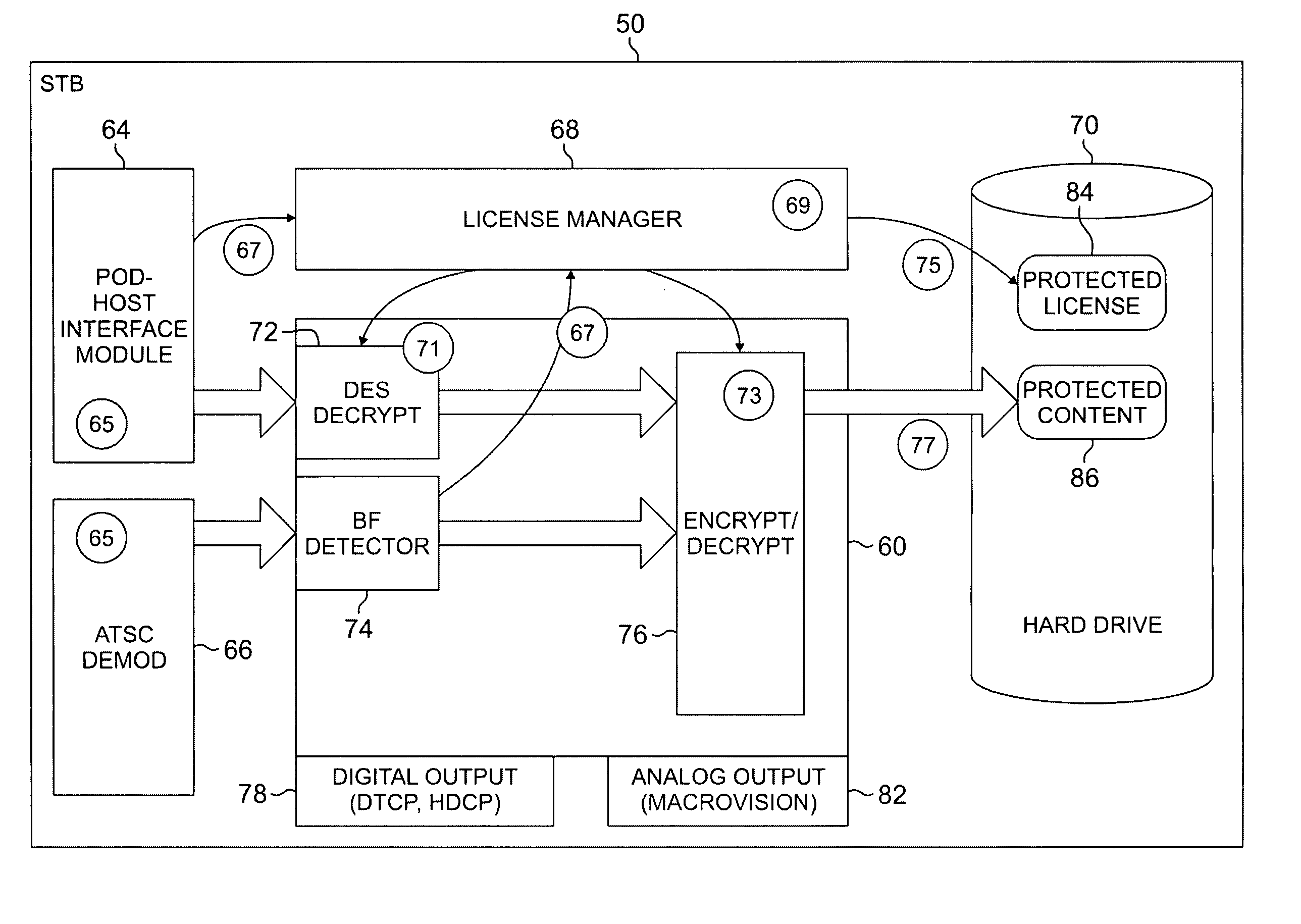
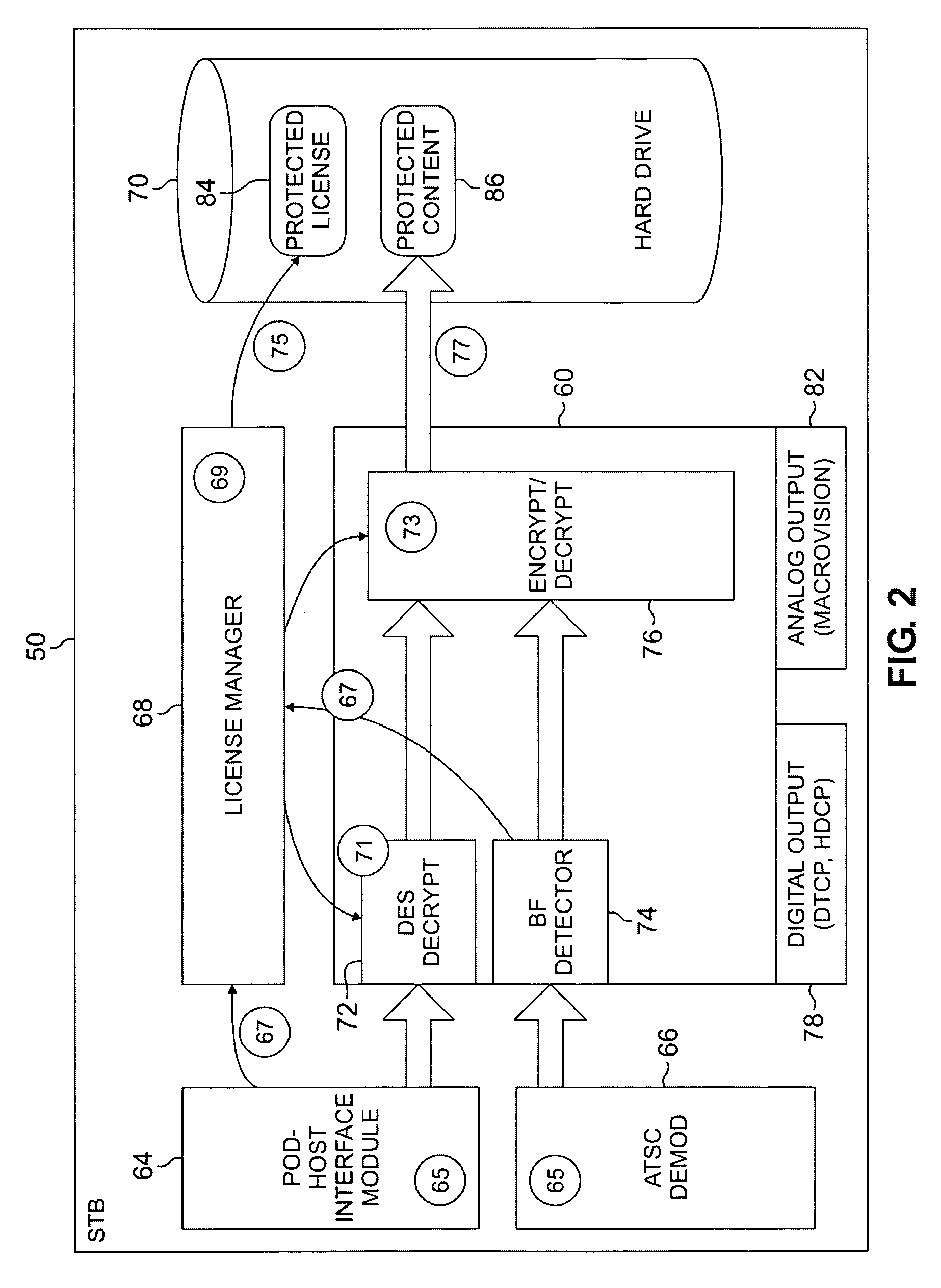
The systems disclosed here provide a complete standards-based end-to-end scalable system for storage, delivery and in-home distribution of digital content over IP networks using standard protocols such as Real-time Transport Protocol (“RTP”) or IP-encapsulated MPEG-2 Transport Stream, or traditional MPEG-2 networks. Mechanisms are provided for receiving content from one security domain, re-encrypting that content uniquely for a receiving device, persistently storing that content, and playing back that content at a later time to and within another security domain. The systems also provide the ability to stream the persistently-stored content from the initial receiving device to another device that has been authenticated as part of a, e.g., home network. This allows a media server, e.g., a dual-tuner set-top box (“STB”) with hard drive, to deliver recorded content to any TV in the house by streaming to media clients such as STBs.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Push-to-talk wireless telecommunications system utilizing an voice-over-IP network
InactiveUS7801953B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationSession Initiation ProtocolTelecommunications network
A method and system to provide push-to-talk from one user to another in a wireless packet data telecommunications network is described. The system may include: a wireless communication network including push-to-talk (PTT) functionality, with a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Proxy Server; a SIP Registrar and Location Server operable to store contact addresses of active mobile devices; a Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP) Media Gateway (PTT Server) operable to function as a call endpoint for each of a plurality of mobile devices wherein the plurality of mobile devices are segmented into membership groups, the PTT Server further operable to multicast a communication from one member of the group to the other members of the group; and an Internet Protocol (IP) network interconnecting the SIP Proxy server, the SIP Registrar and Location Server, and the PTT Server.
Owner:APPLE INC
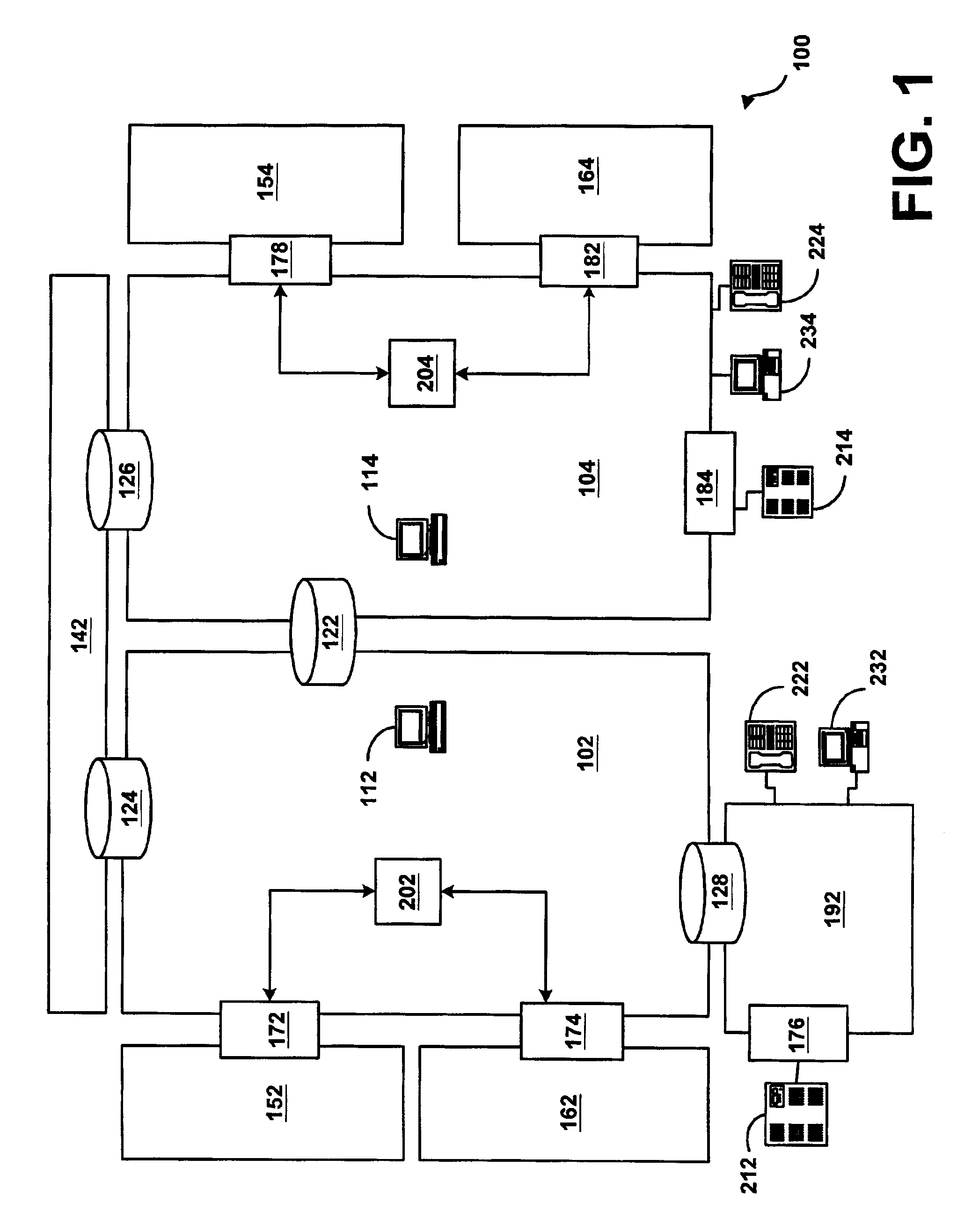
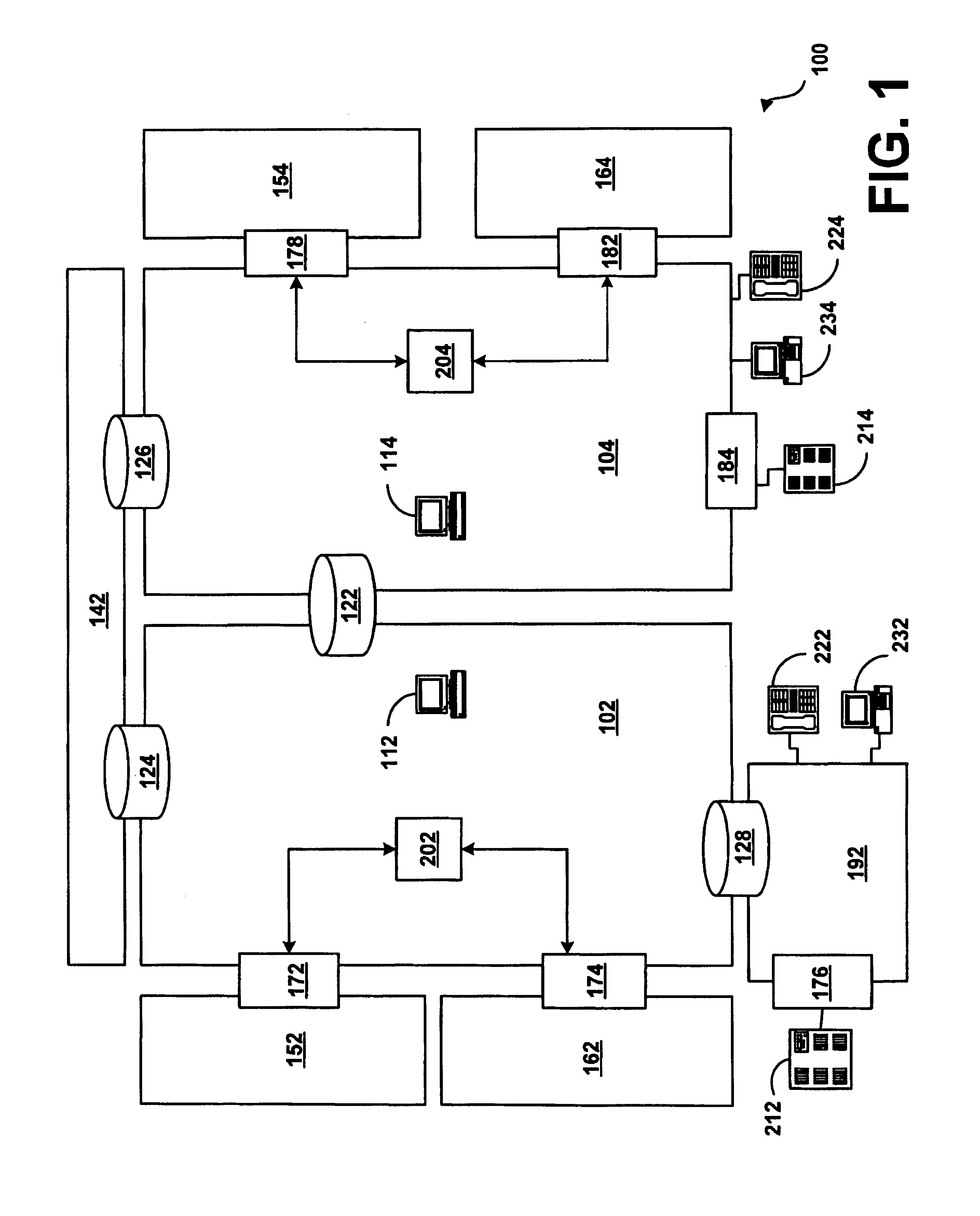
System and method for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks
InactiveUS20060098577A1Reduce effortMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTransceiverReal-time Transport Protocol
A system for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks is disclosed The system utilizes at least a first computer and a second computer that is connected to the first computer, wherein the second computer comprises a second transceiver, a second memory having logic stored therein defining functions to be performed by the second computer, and a second processor The second processor is configured by the second memory to perform the functions of: performing an inbound screen on route information received by the second computer, from the first computer, to determine if the received route information should be discarded; if the route information is not discarded, comparing the received and screened route information to a local policy defined with the second computer; and performing an outbound screen on the received and screened information prior to transmitting the received and screened information.
Owner:ACME PACKET
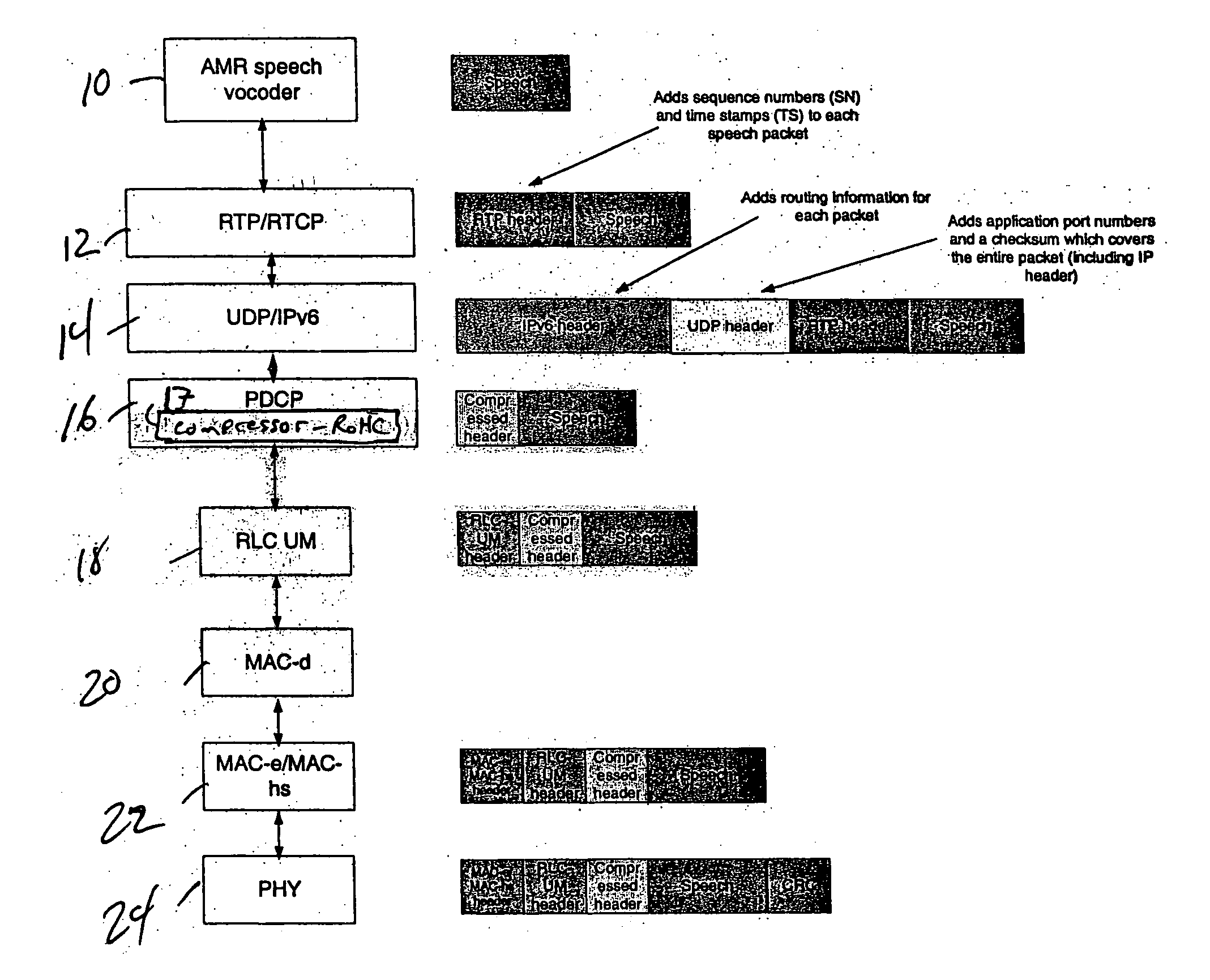
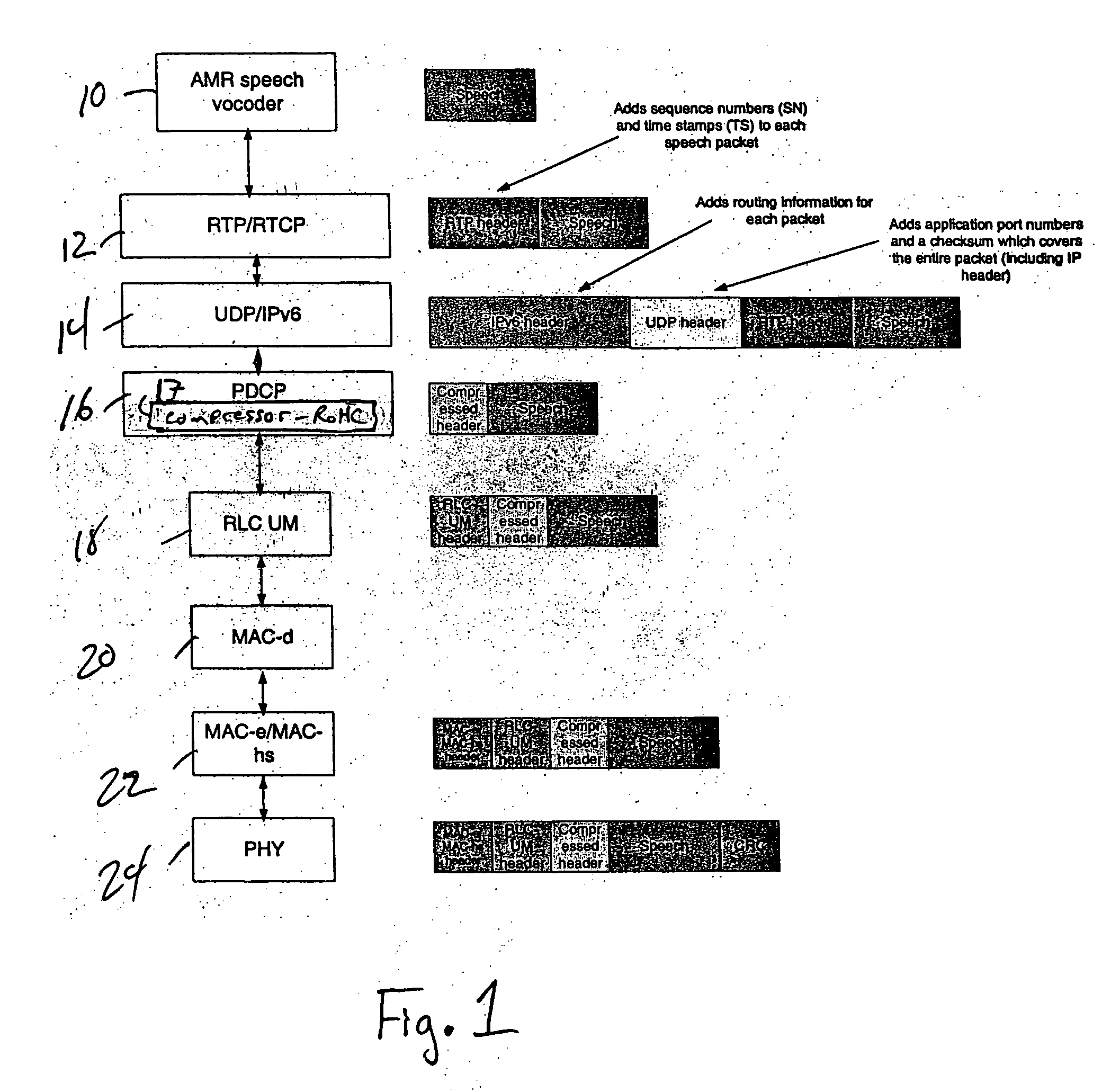
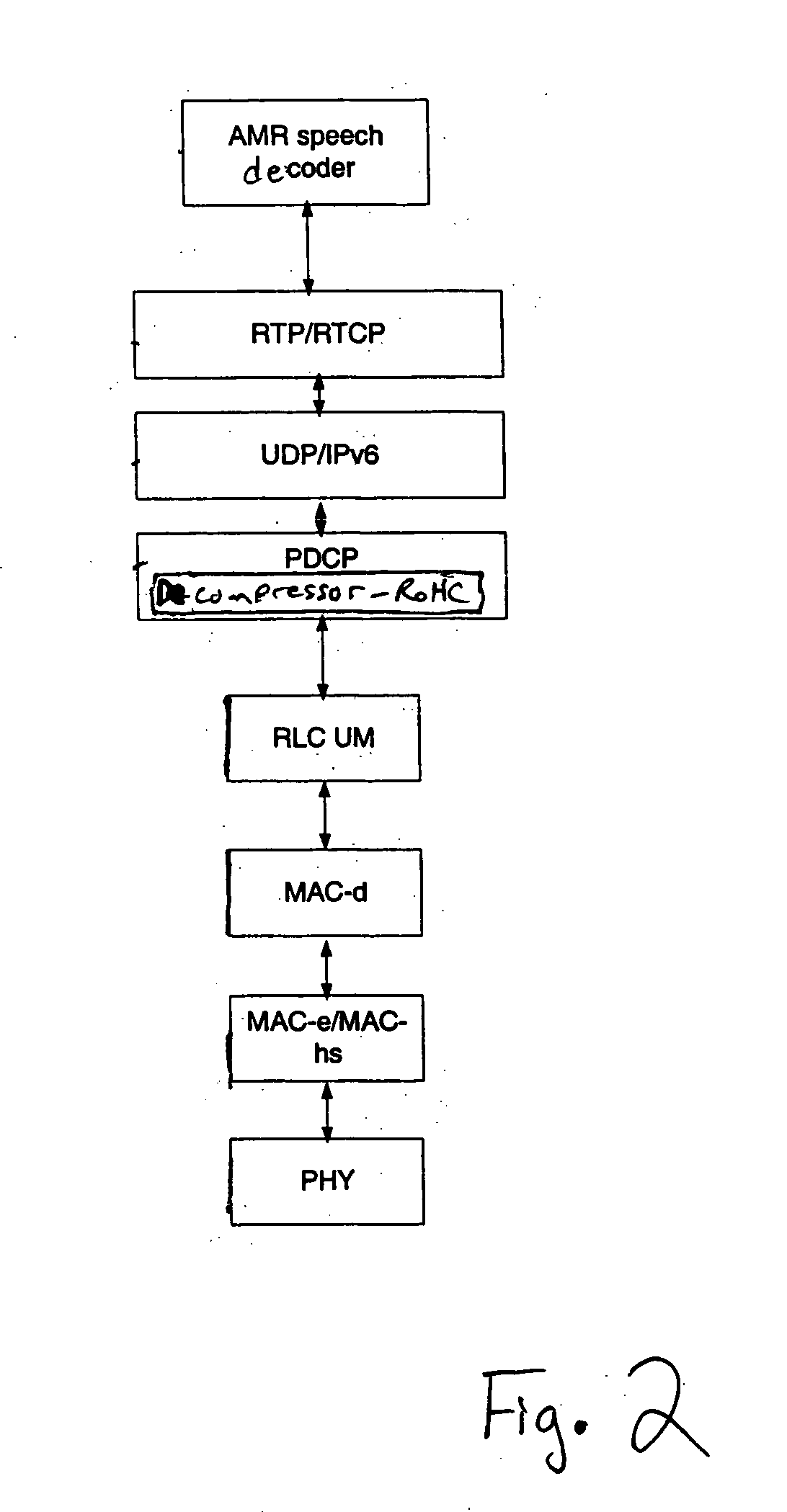
Header elimination for real time internet applications
ActiveUS20070047547A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationChecksumThe Internet
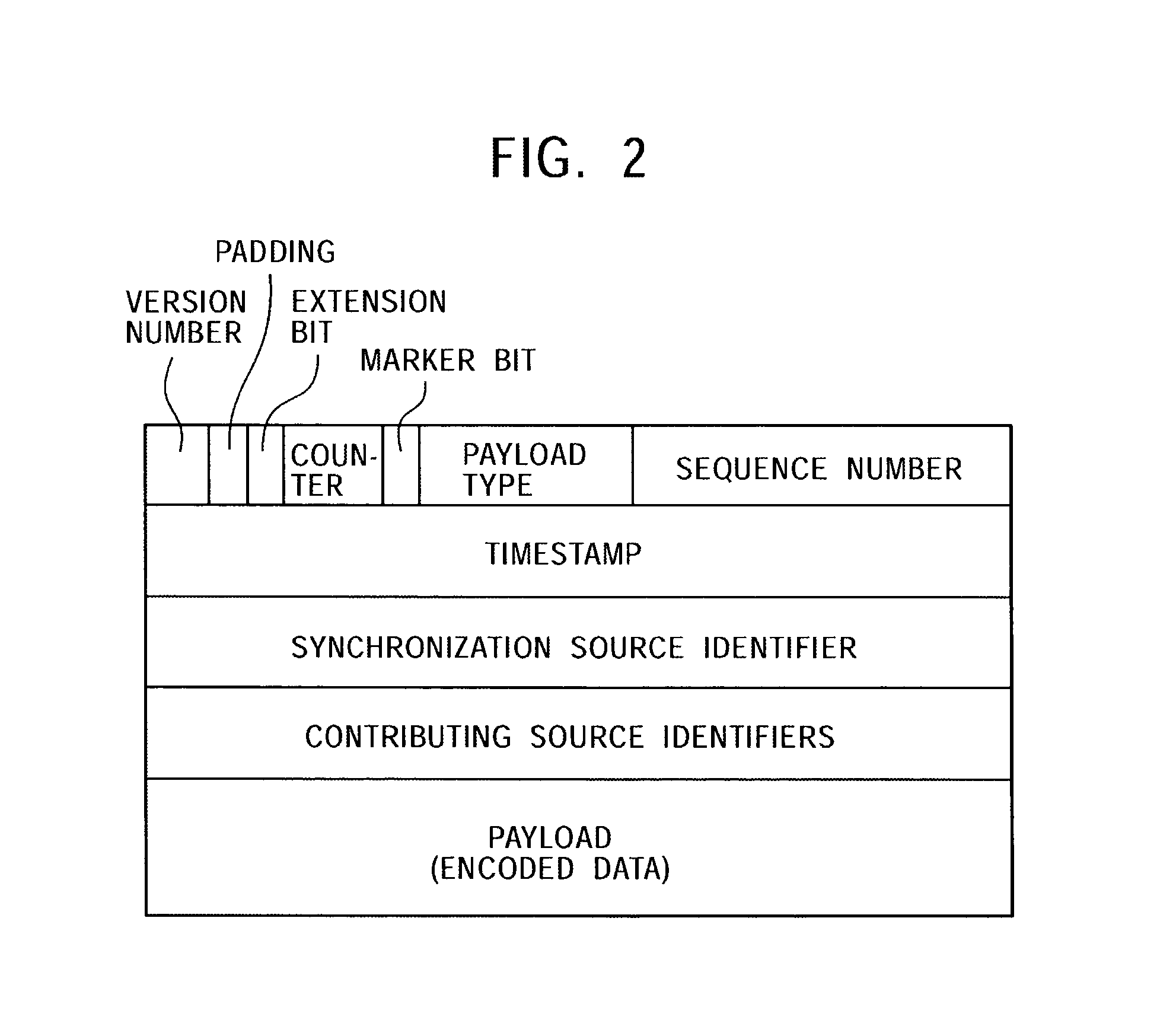
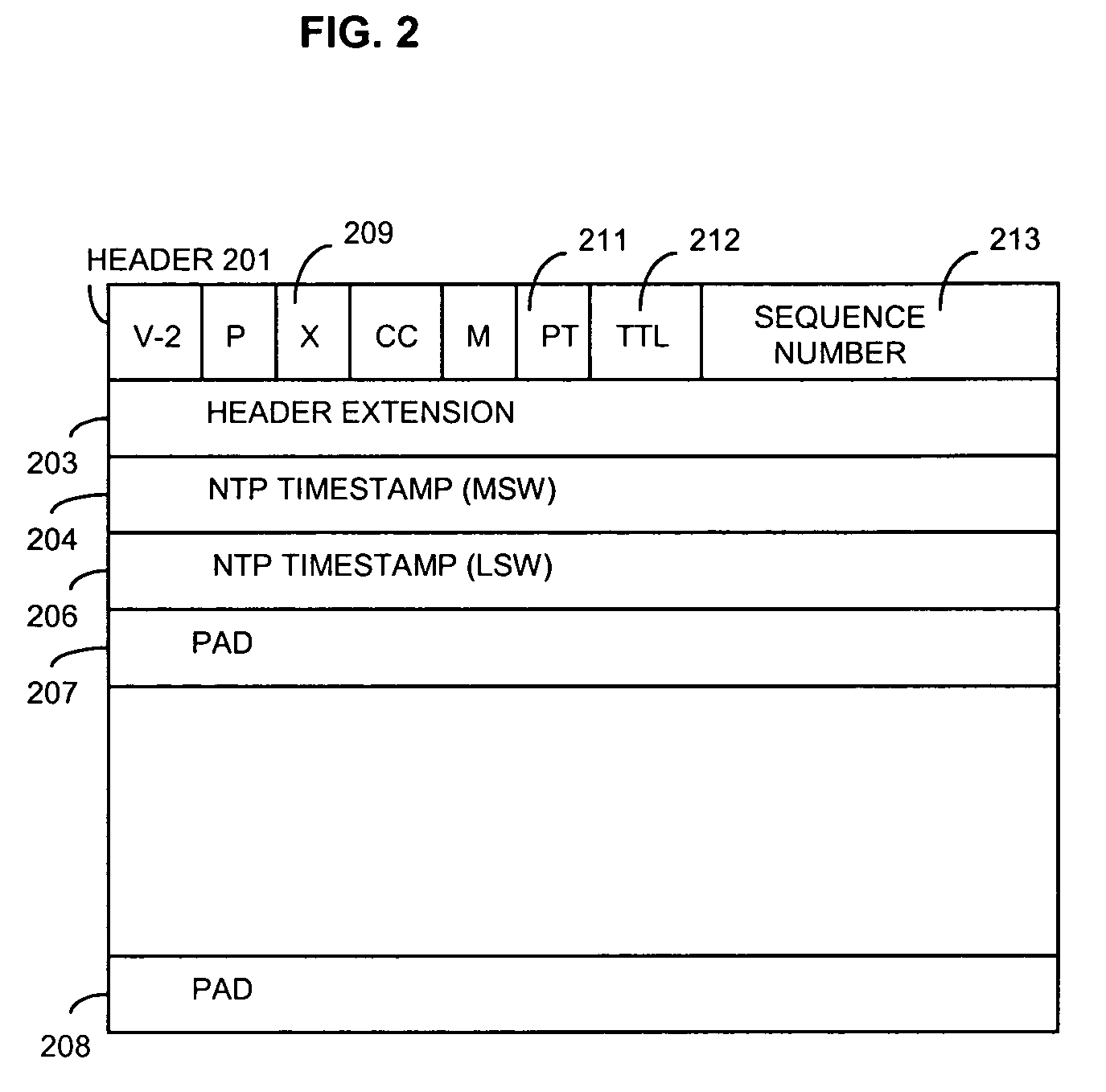
The disclosed techniques provide for eliminating real-time transport protocol, RTP, extension bit X, marker bit M, time stamp and sequence number information and / or user data protocol, UDP, checksum information from the header of a packet for transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Data communication system, data transmission apparatus, data reception apparatus, data communication method, and computer program
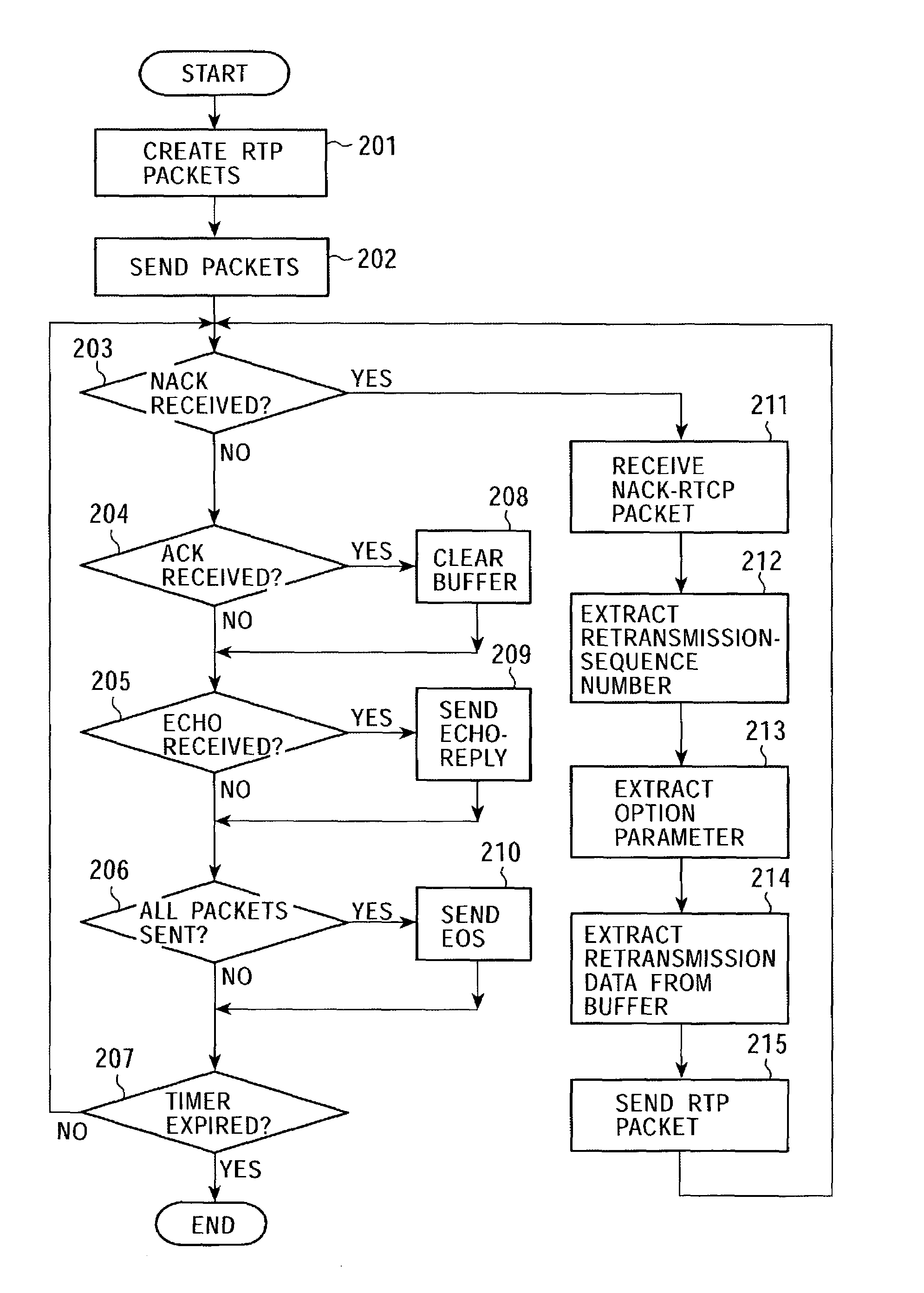
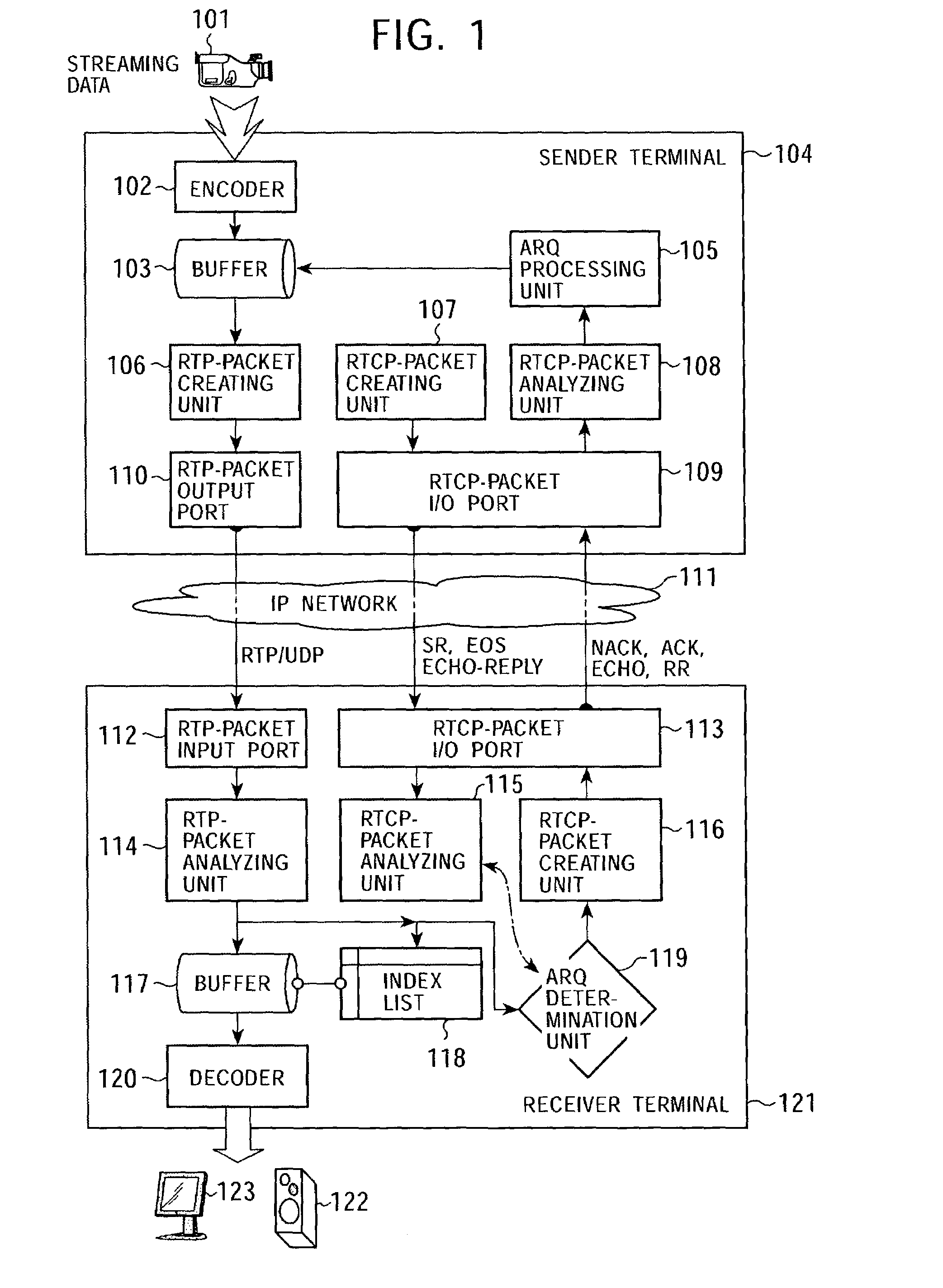
ActiveUS7315898B2Quality improvementEfficient transferError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemAutomatic repeat request
In a data communication system, the function of automatic repeat request is provided for transmission of packets based on a data communication protocol such as the Real-Time Transport Protocol or the User Datagram Protocol. Lost packets are detected at various timings, for example, when the beginning packet of each frame is received, the final frame of each frame is received, at a time limit of processing, and at a regular interval, and retransmission requests are issued accordingly. A data reception terminal does not issue a retransmission request if associated retransmission data will not be in time for playing with consideration of processing time and roundtrip time, thereby avoiding the transmission of useless retransmission request packets and retransmission packets.
Owner:SONY CORP
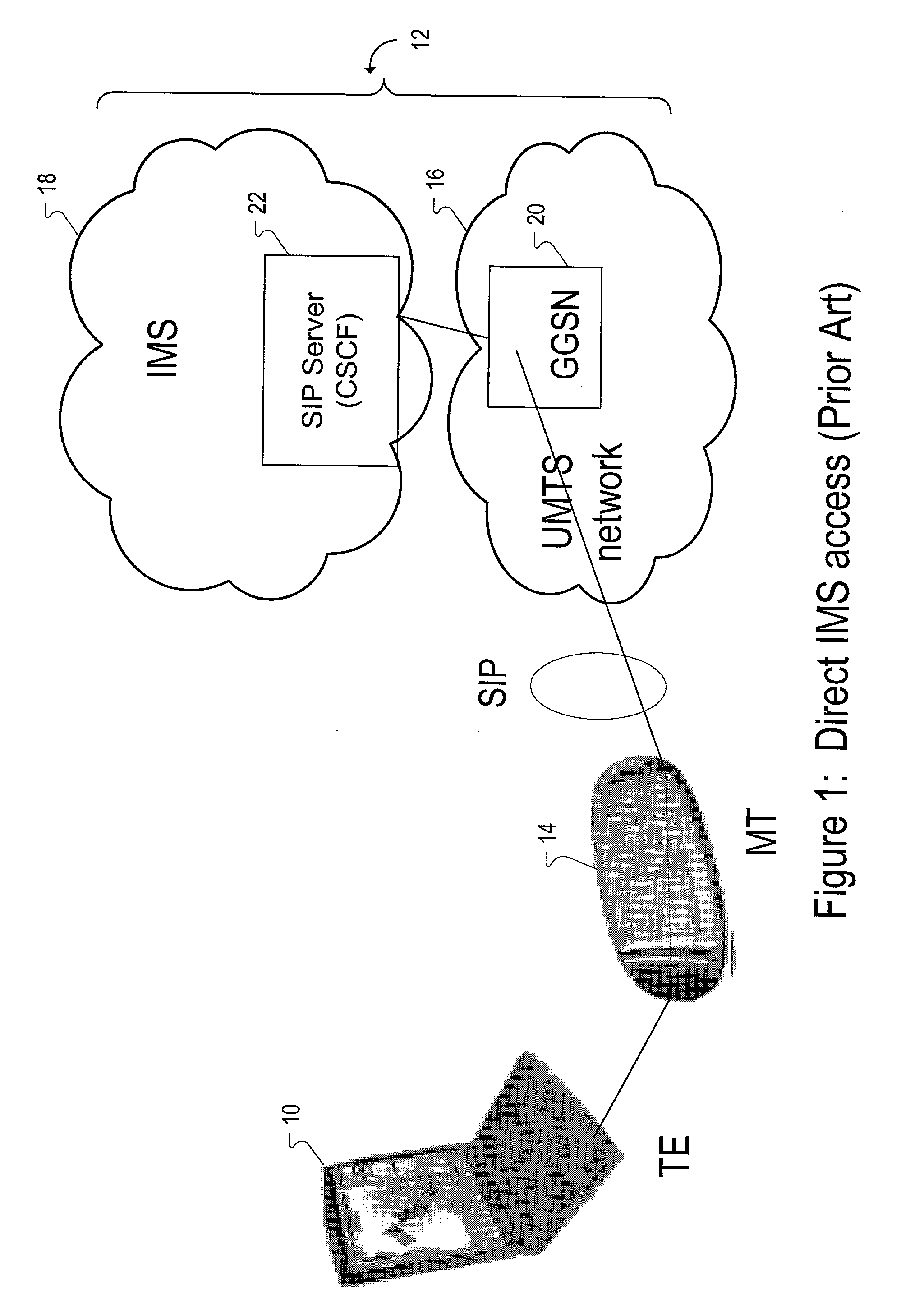
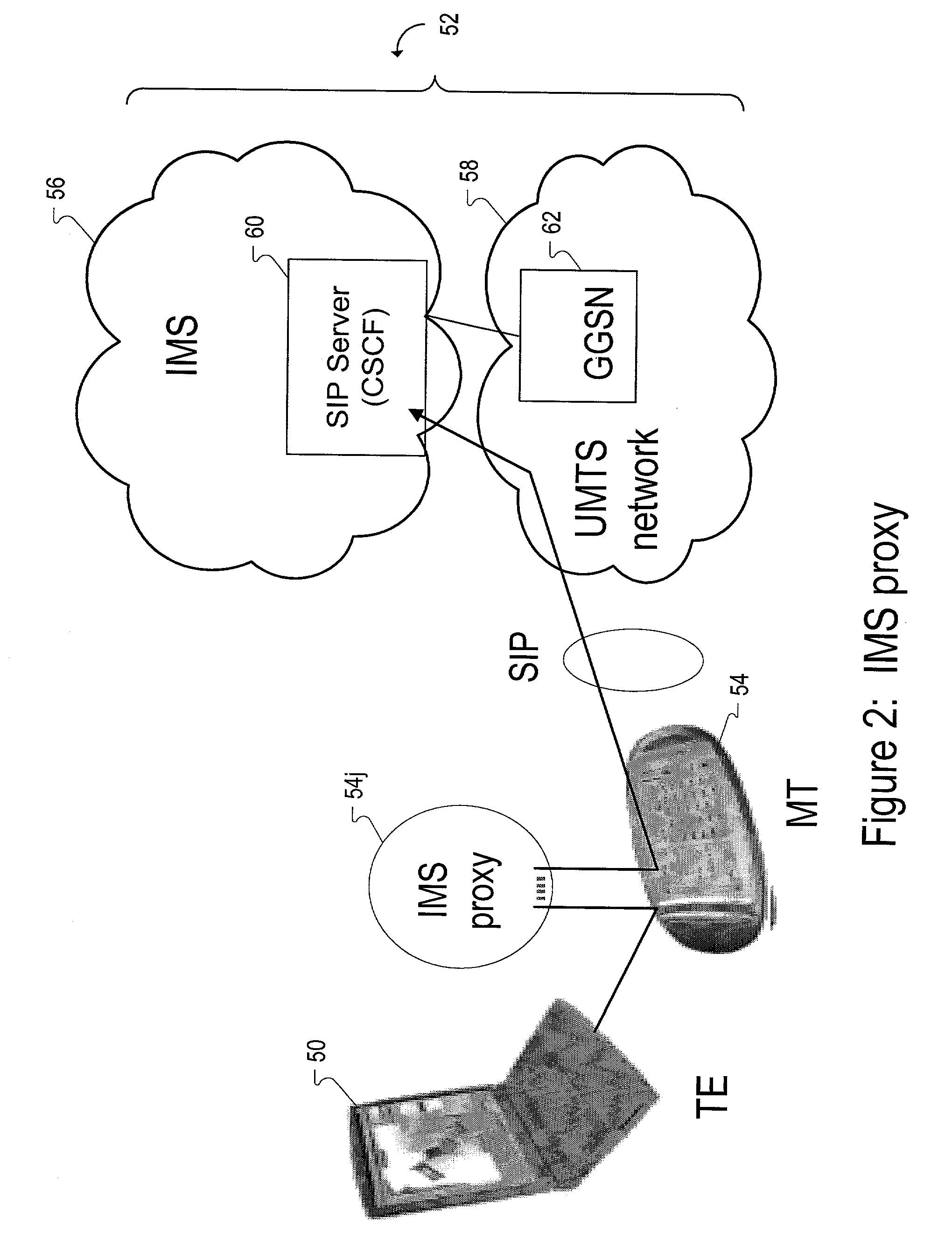
Functionality split between mobile terminal and terminal equipment for internet protocol multimedia signal exchange
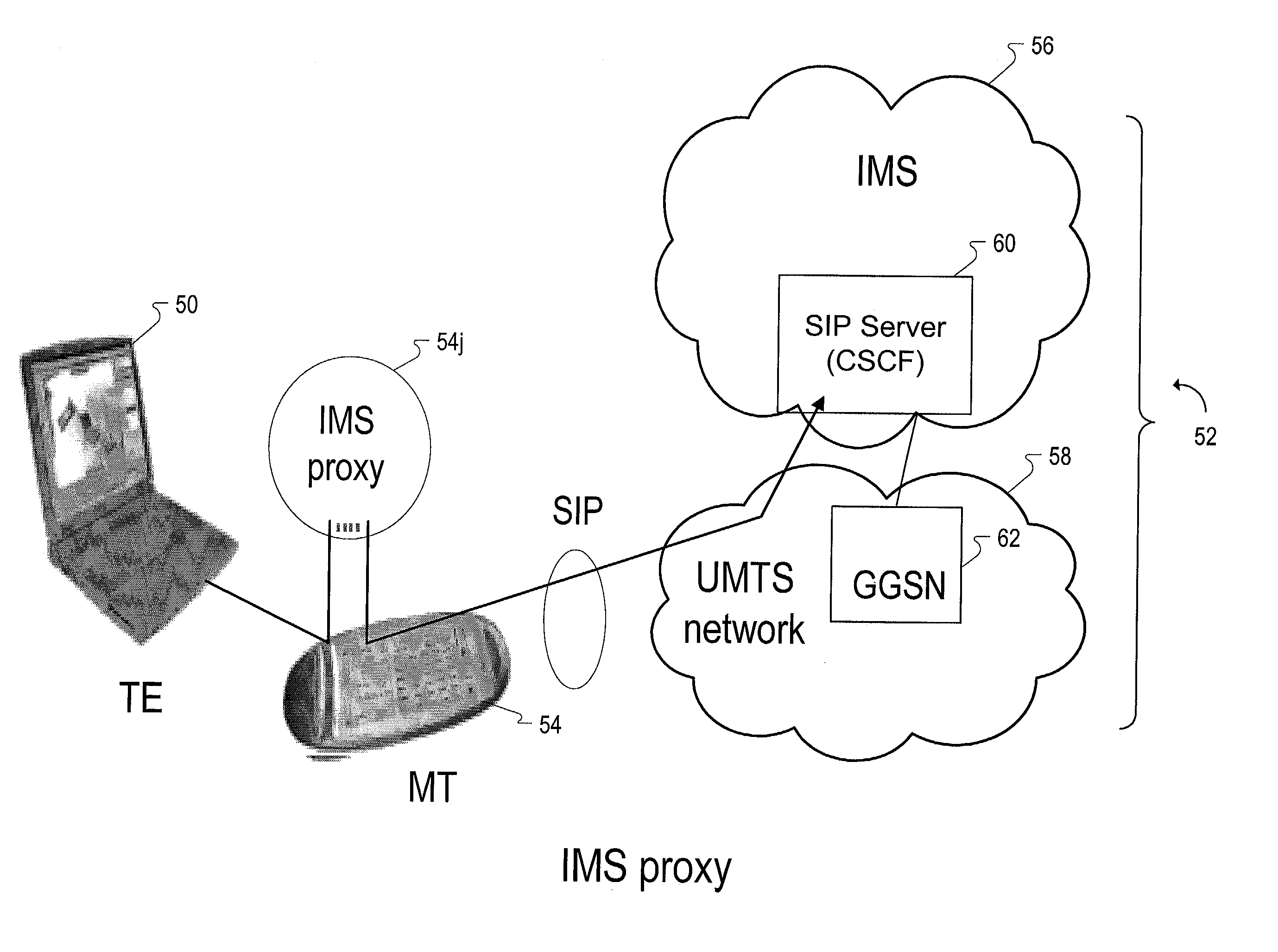
InactiveUS20030210678A1Viewing comfortEnhances the mobile terminal's controller roleNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationSession Initiation ProtocolTransport control protocol
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for connecting terminal equipment to a wireless network with a mobile terminal, wherein the mobile terminal is assigned proxy functions that control access of the terminal equipment to an internet protocol multimedia subsystem (IMS) in the wireless network. The proxy control functions include identification or authentication functions, as well as call control functions. The terminal equipment performs protocol stream processing functions for communicating with the internet protocol multimedia subsystem (IMS). The protocol stream processing functions include real-time transport protocol (RTP) and real-time transport control protocol (RTCP) functions. The wireless network includes a universal mobile telecommunications system (UMTS) network coupled to the internet protocol multimedia subsystem (IMS). The internet protocol multimedia subsystem (IMS) includes a session initiation protocol (SIP) server for providing internet protocol multimedia information signals.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
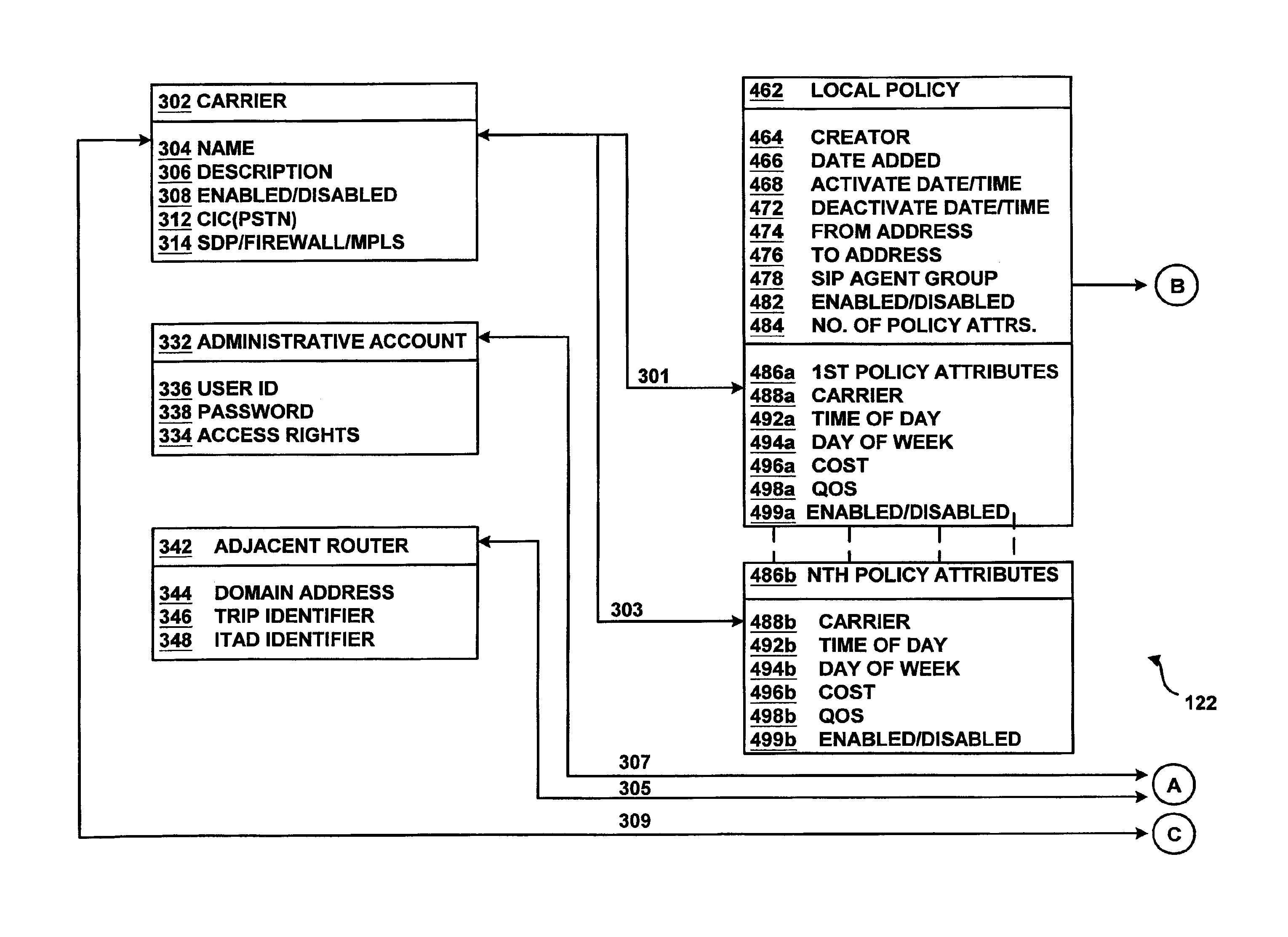
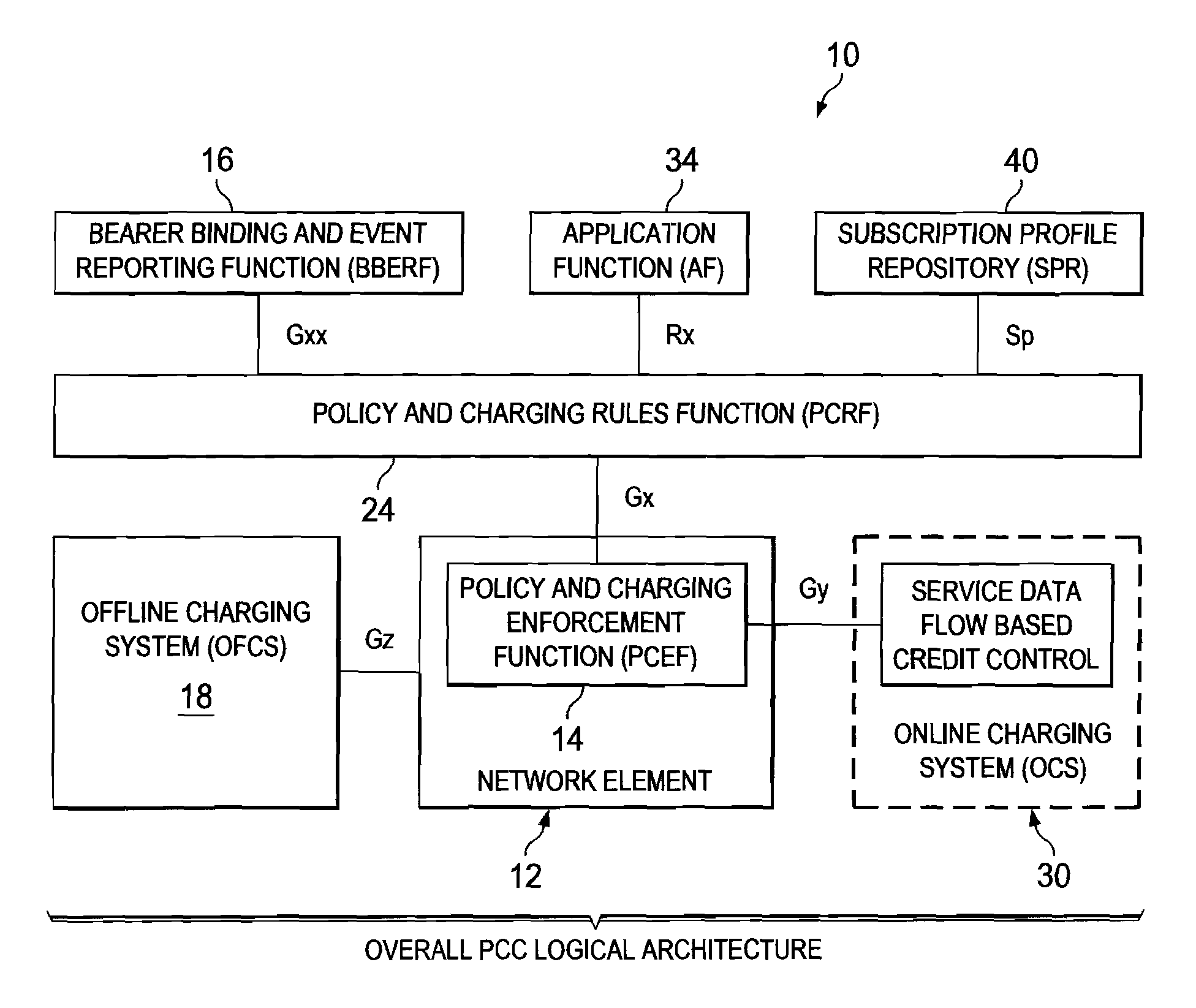
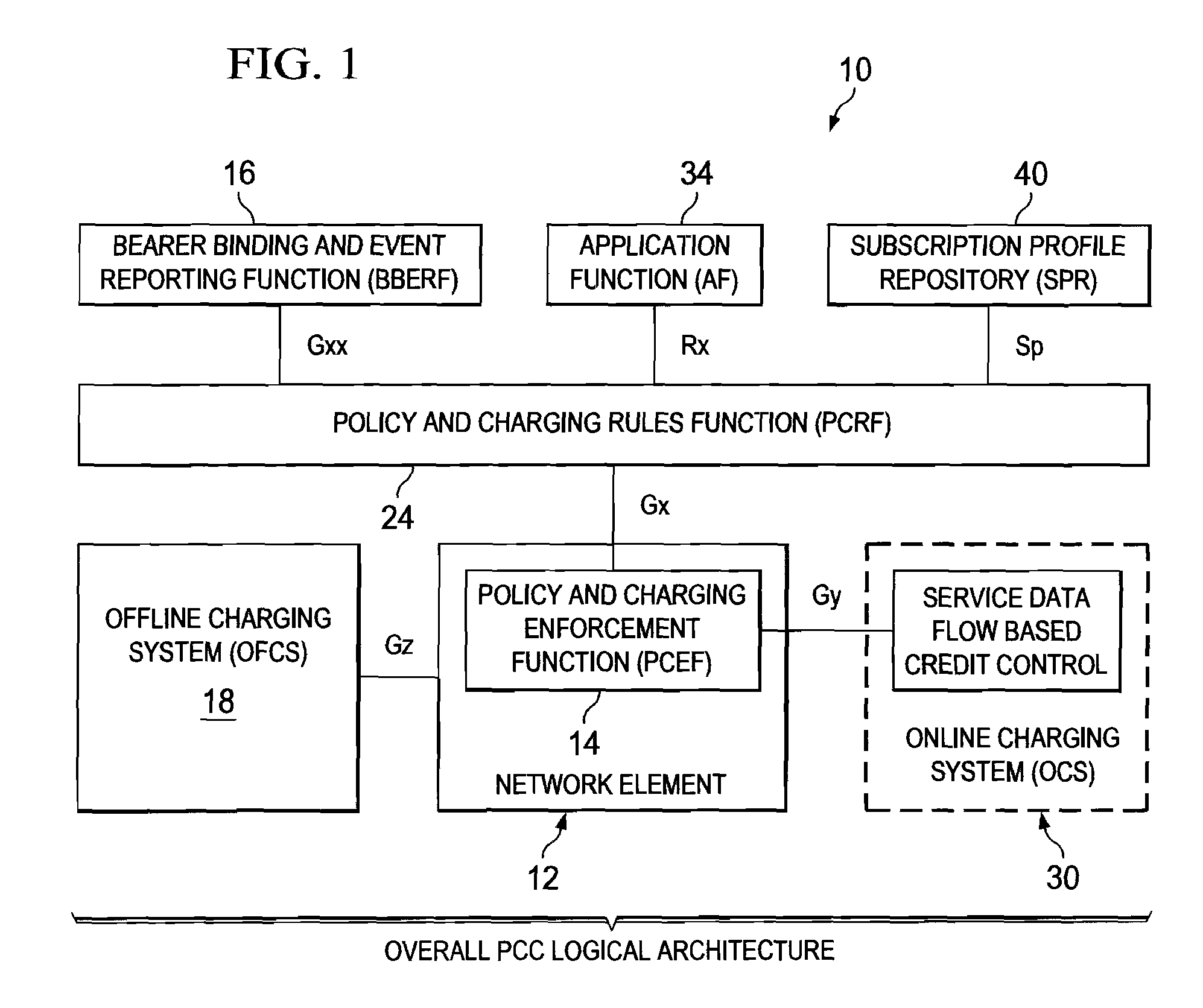
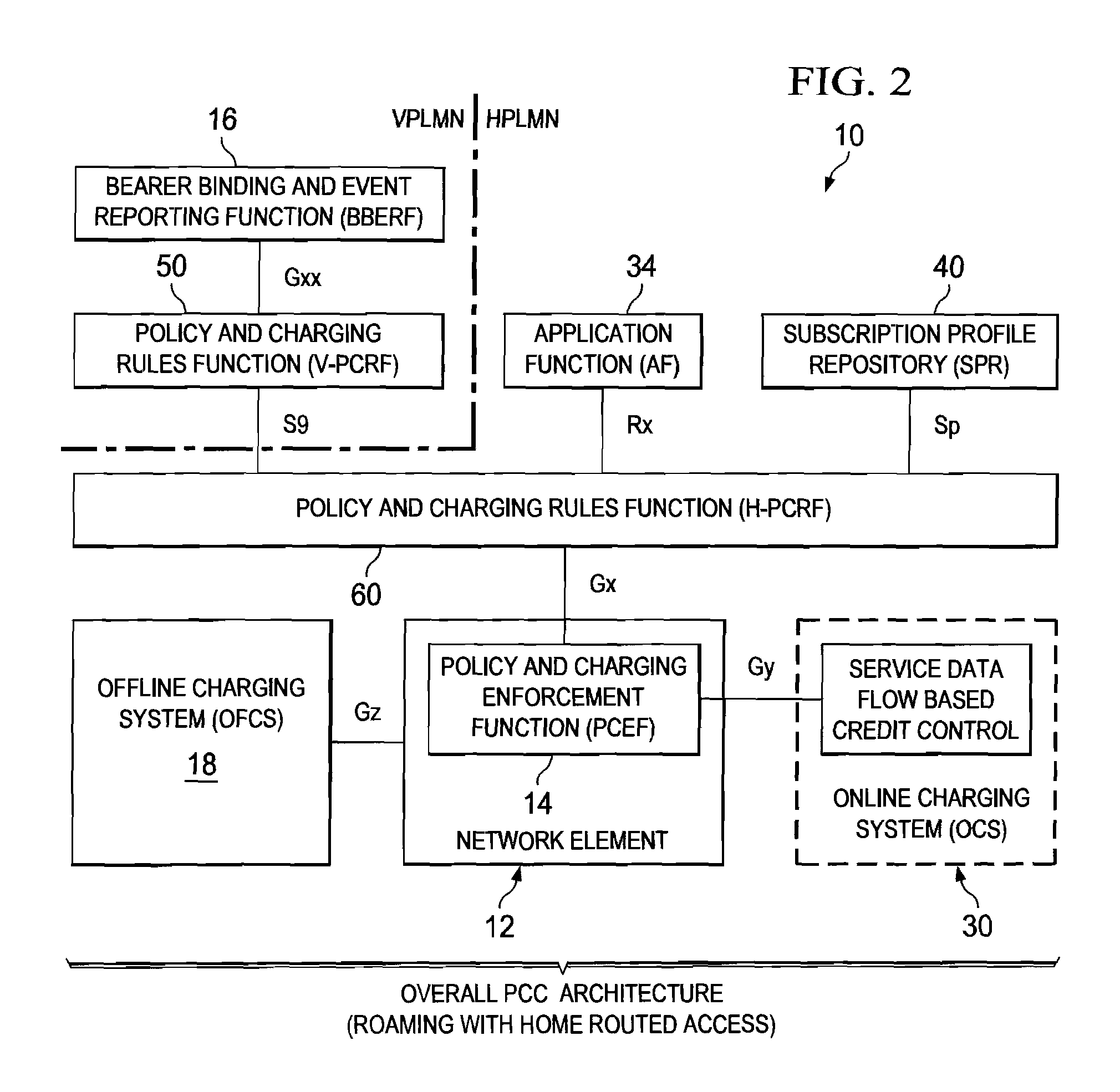
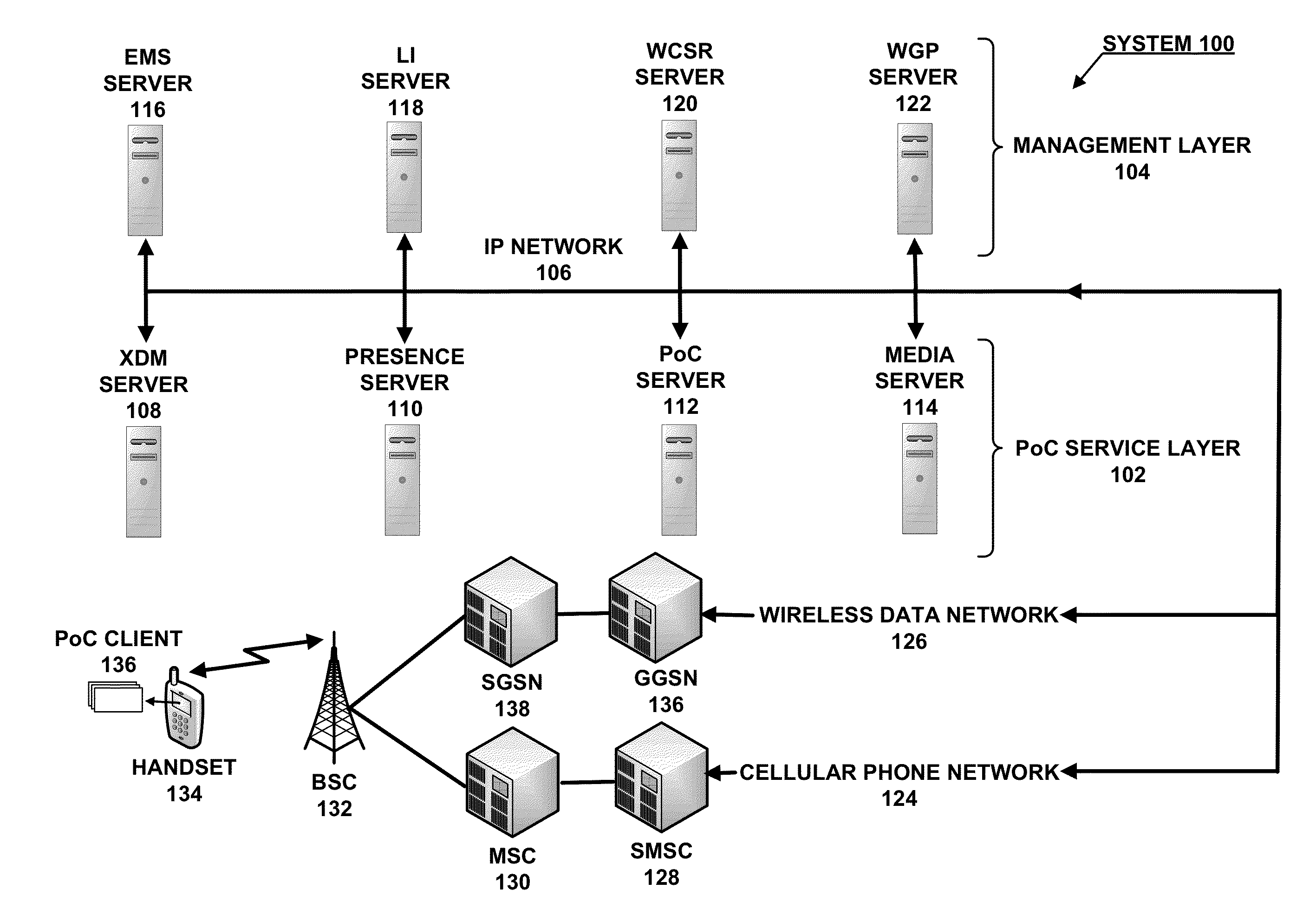
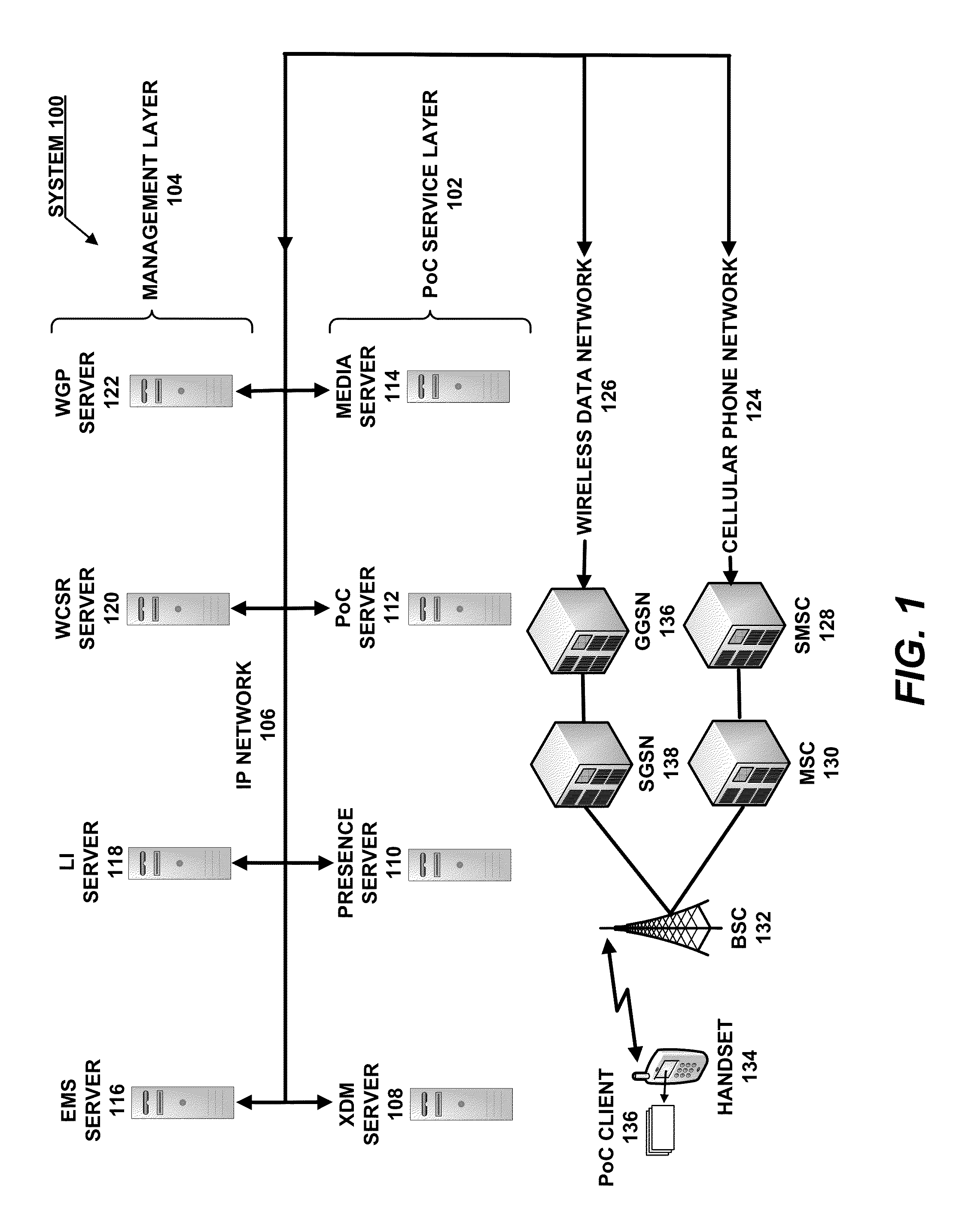
System and Method for Provisioning Charging and Policy Control in a Network Environment
A method is provided in one example embodiment and includes requesting real-time transfer protocol (RTP) quality metrics to be generated by a network for a specific flow in the network. The method also includes recording the RTP quality metrics and reporting the metrics as accounting data associated with the flow. In more specific embodiments, the accounting data includes a correlator with application level accounting and the accounting data is used for quality monitoring and troubleshooting on a per-subscriber basis, on a per-flow basis, or on a per-call basis. An application function can request RTP quality monitoring with a trigger that identifies if a quality parameter reaches a certain threshold.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and Method for Determining Flow Quality Statistics for Real-Time Transport Protocol Data Flows
Systems and methods for determining lost packets for real-time transport protocol (RTP) data flows is disclosed. Generally, a first endpoint is connected to a second endpoint, wherein the first endpoint comprises a transceiver, software stored within the first endpoint defining functions to be performed by the first endpoint, and a processor. The processor is configured by the software to perform the steps of determining a sequence number of a received RTP data packet within said RTP data flow, storing said determined sequence number, calculating whether said determined sequence number sequentially falls within a predetermined numerical order, and if said sequence number of said received RTP data packet does not sequentially fall within said numerical order, storing said sequence number as a missed RTP data packet.
Owner:ACME PACKET
Method and system for key management in voice over internet protocol
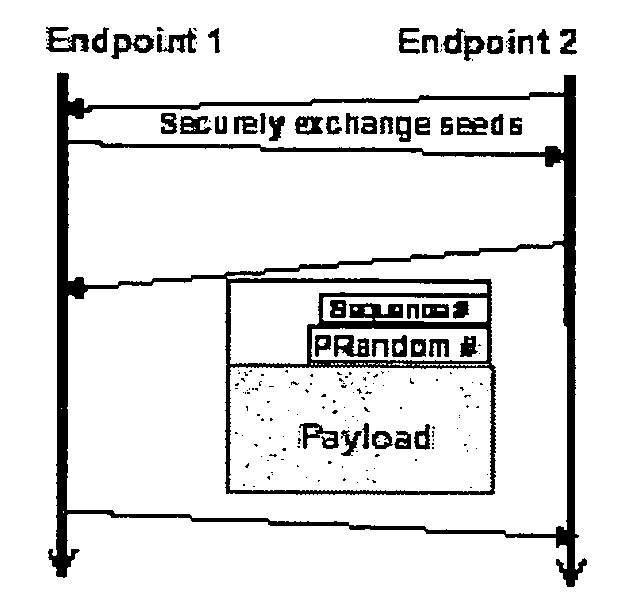
InactiveUS7730309B2Eliminate needEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSession Initiation ProtocolDiffie–Hellman key exchange
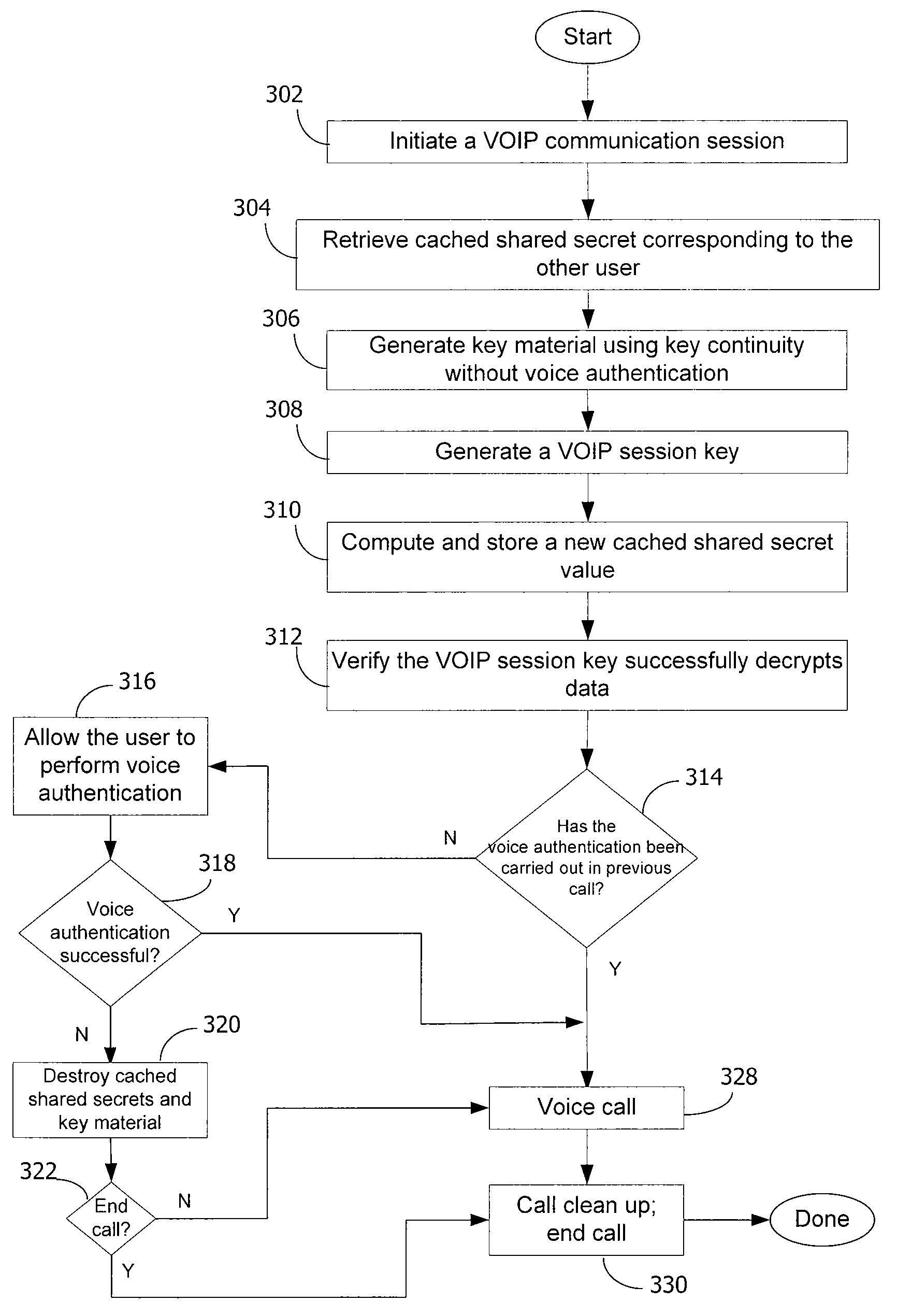
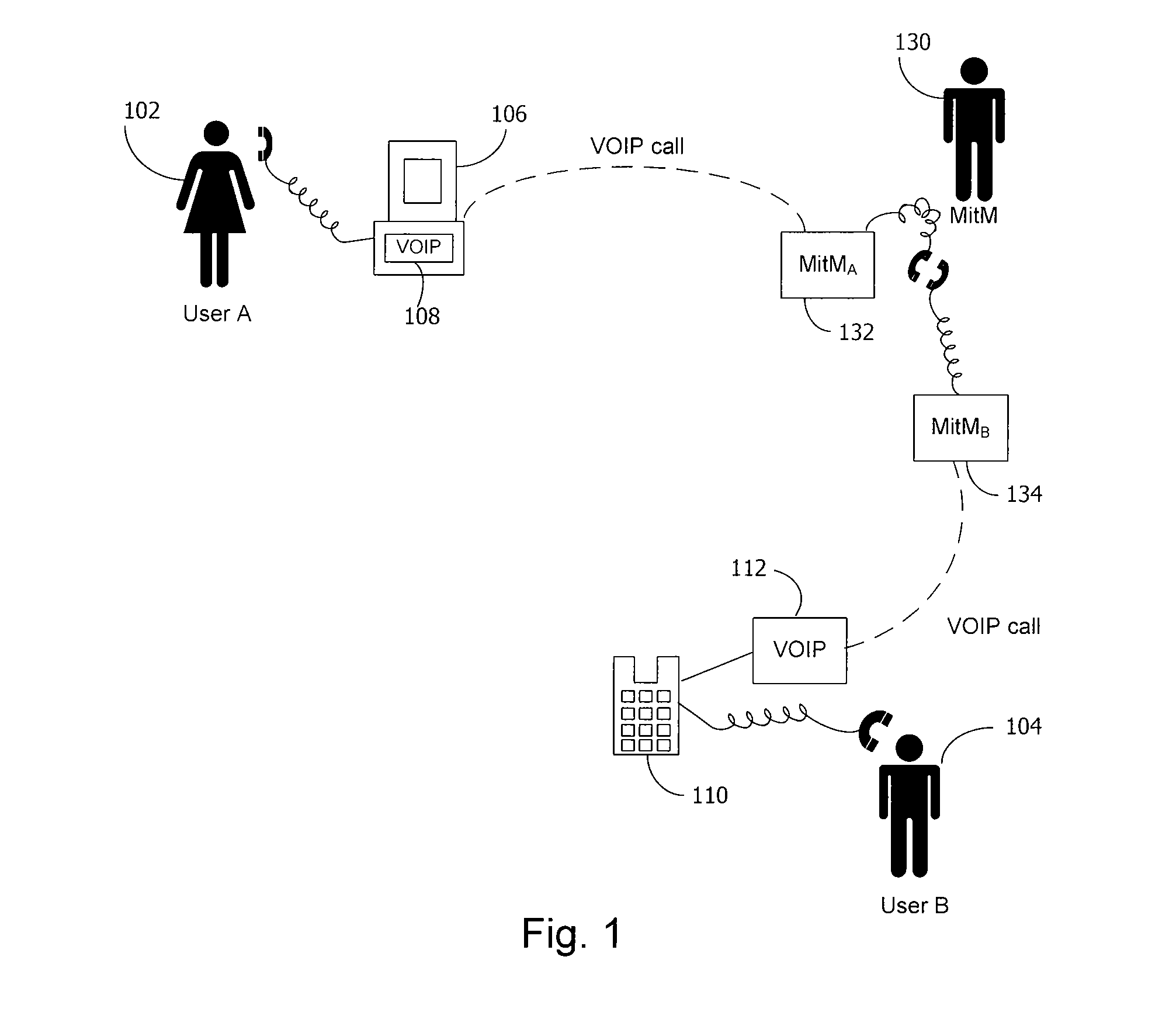
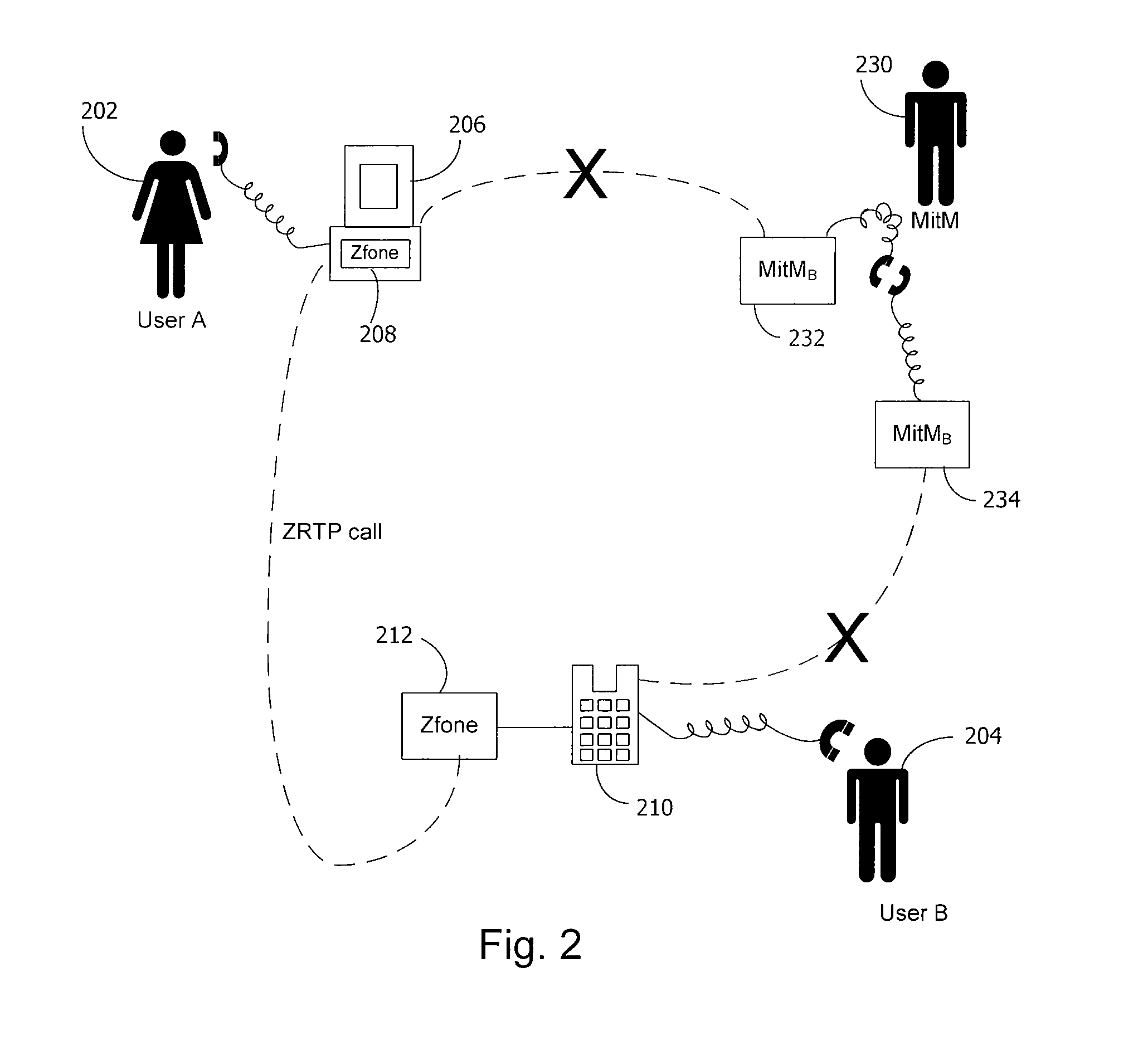
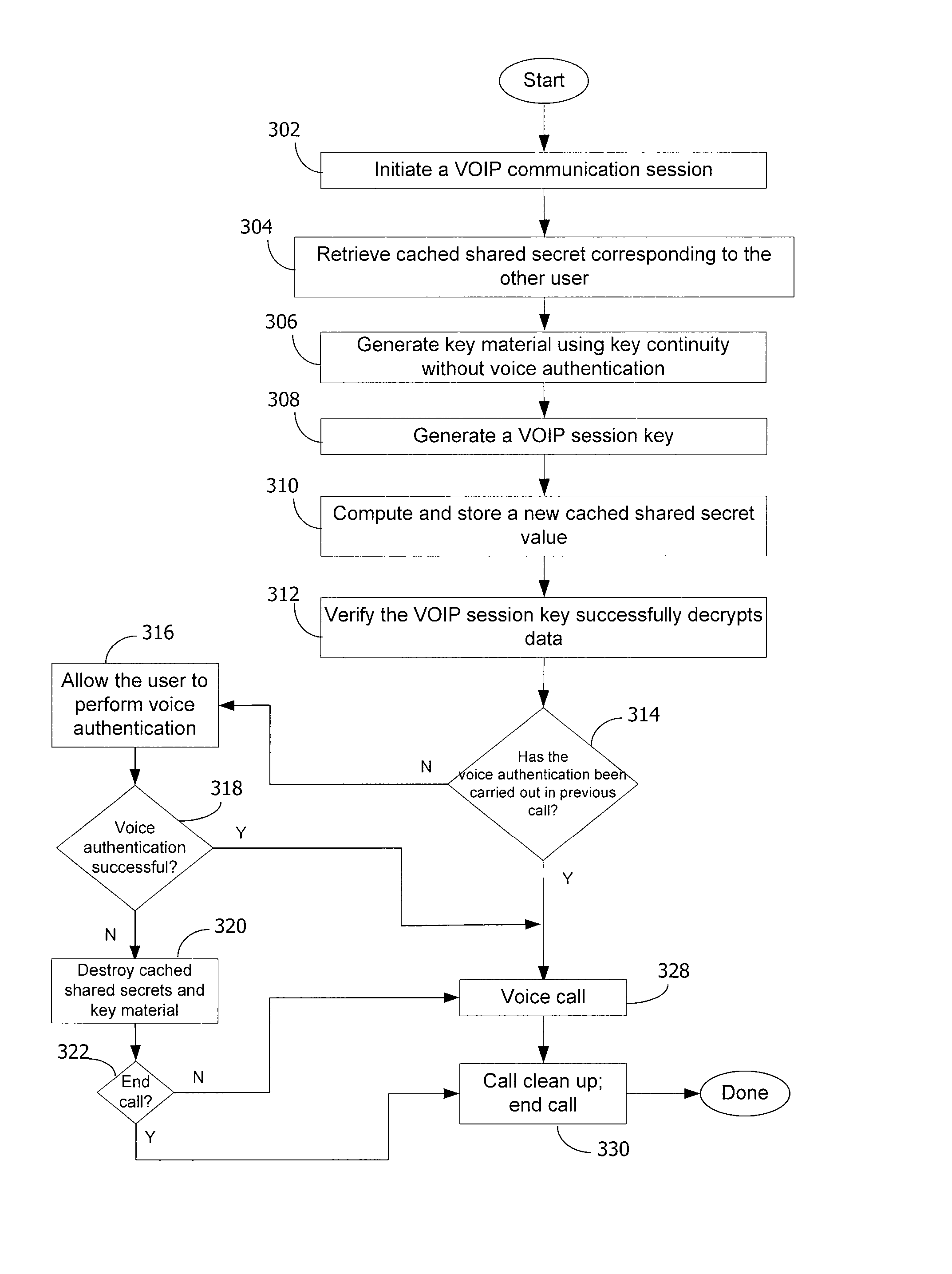
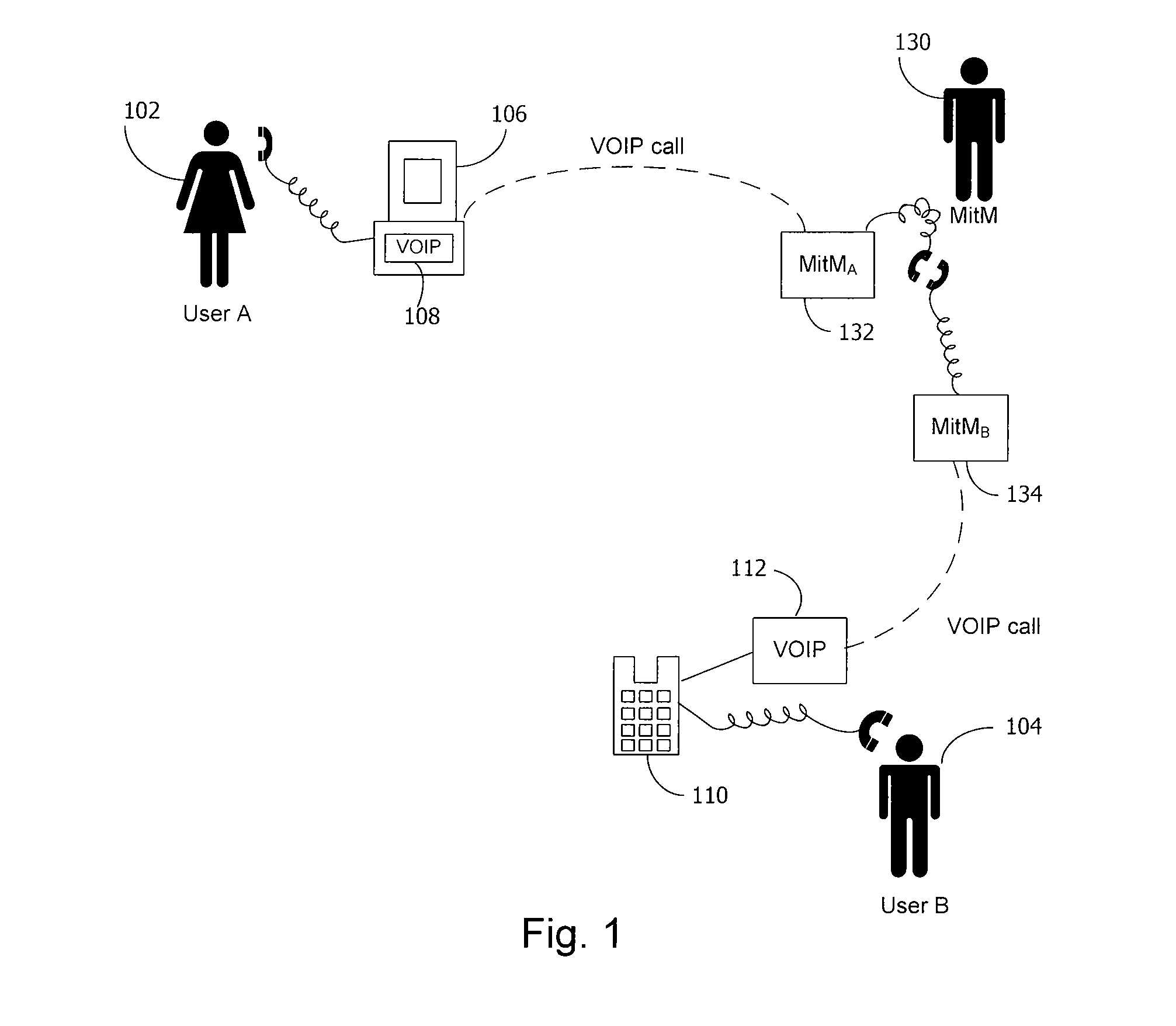
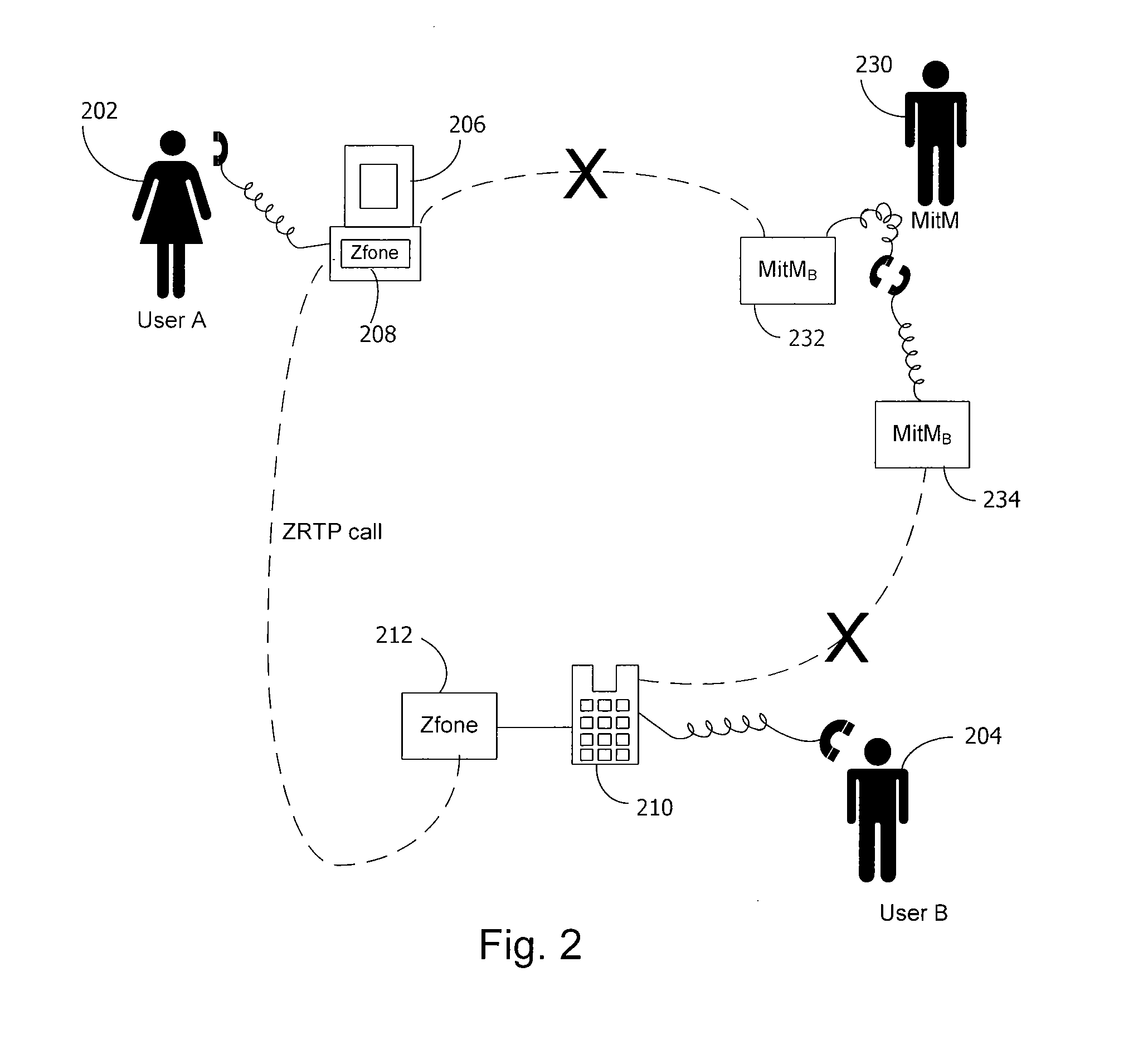
A method and system for a secure telephone protocol are disclosed, which can be implemented using current Voice over IP (VoIP) protocols, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP, as specified in the Request for Comment (RFC) 3261 from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)), Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP, as specified in RFC 3550), and Secure RTP (SRTP, as specified in RFC 3711). The secure telephone protocol can include a shared secret value that is cached and then re-used later to authenticate a long series of session keys to be used for numerous separate secure phone calls over a long period of time, thereby providing cryptographic key continuity without the need for voice authentication. In an embodiment, the secure telephone protocol can utilize the Diffie-Hellman key exchange during call setup, and AES for encrypting the voice stream.
Owner:ZIMMERMANN PHILIP R
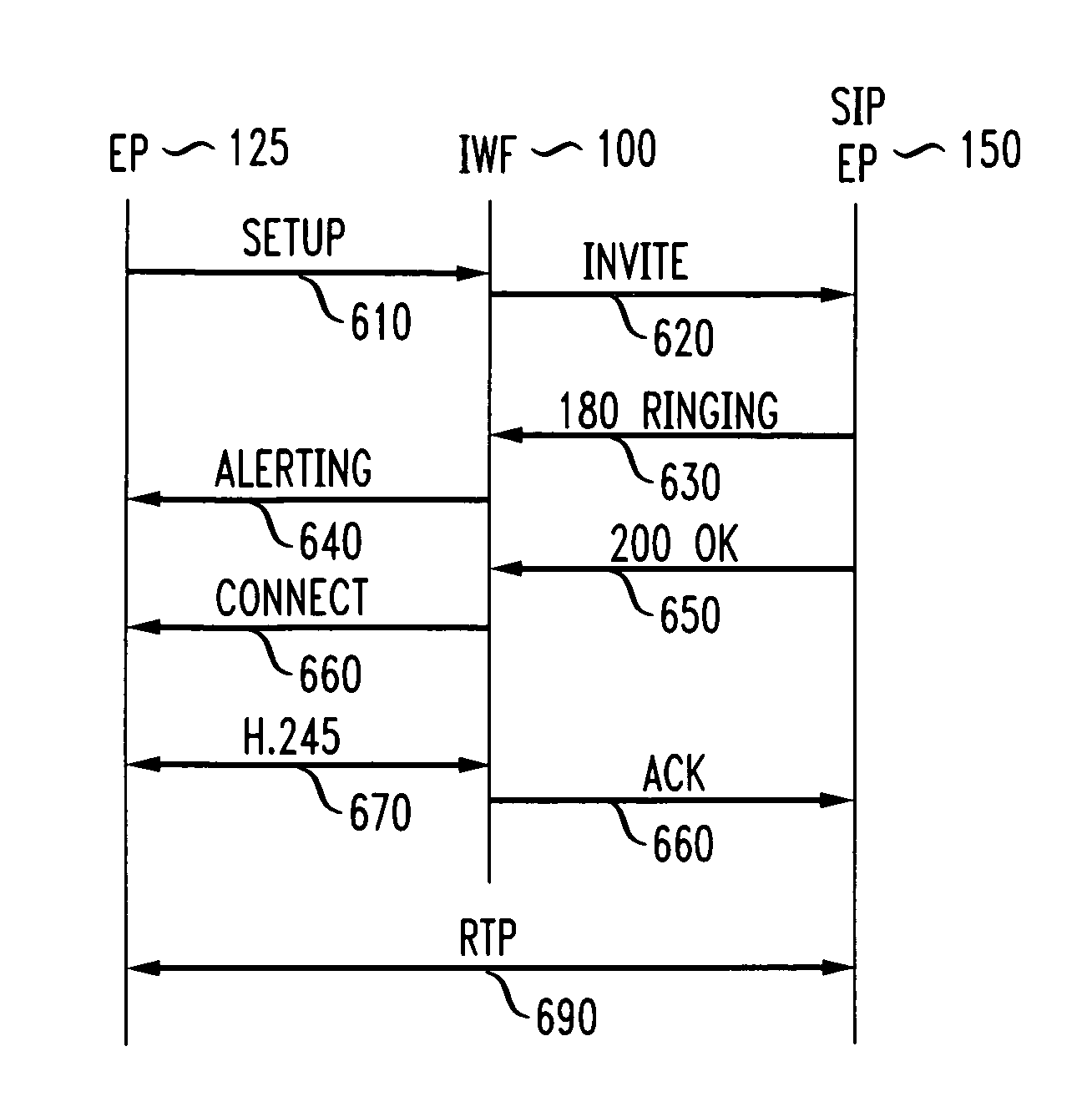
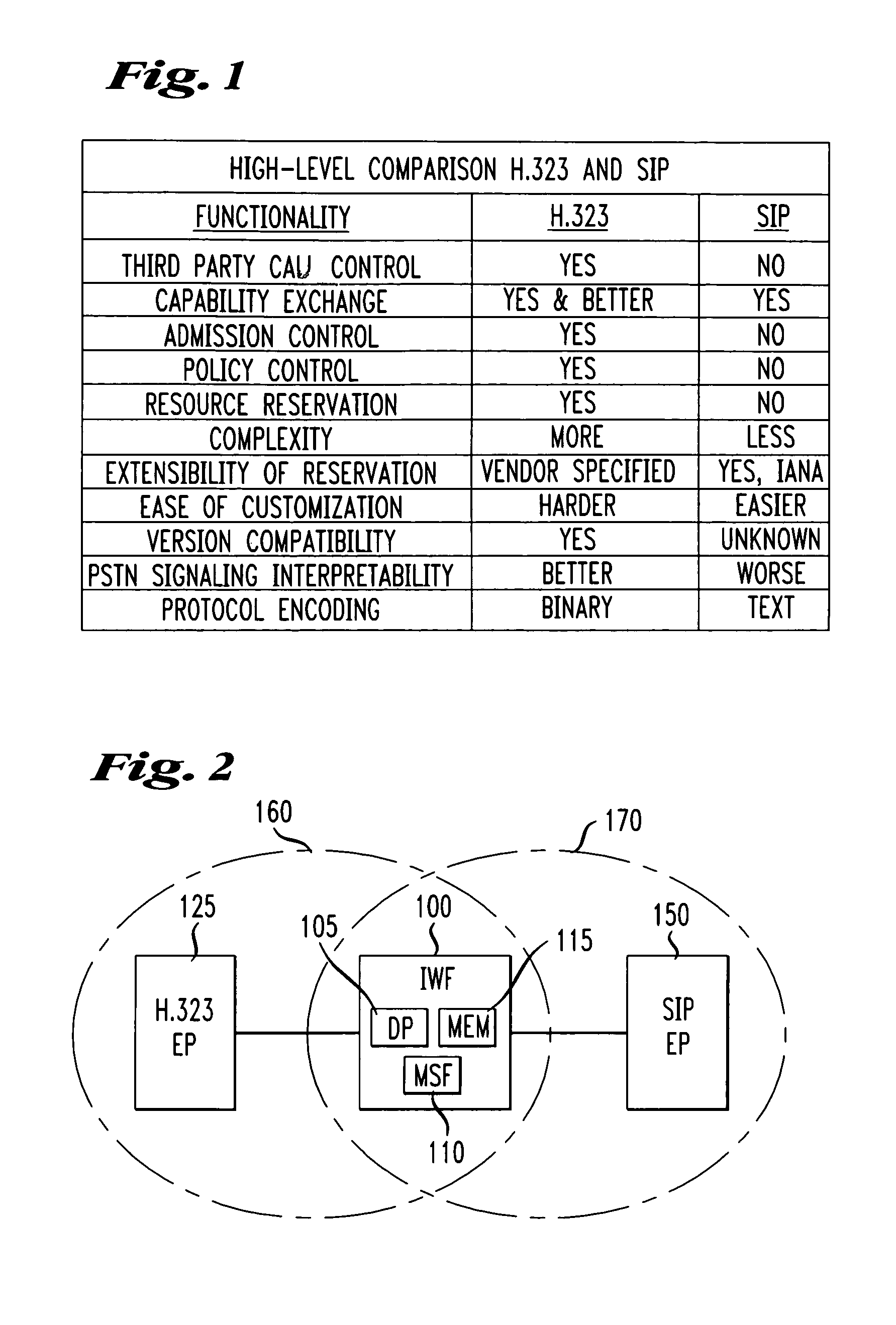
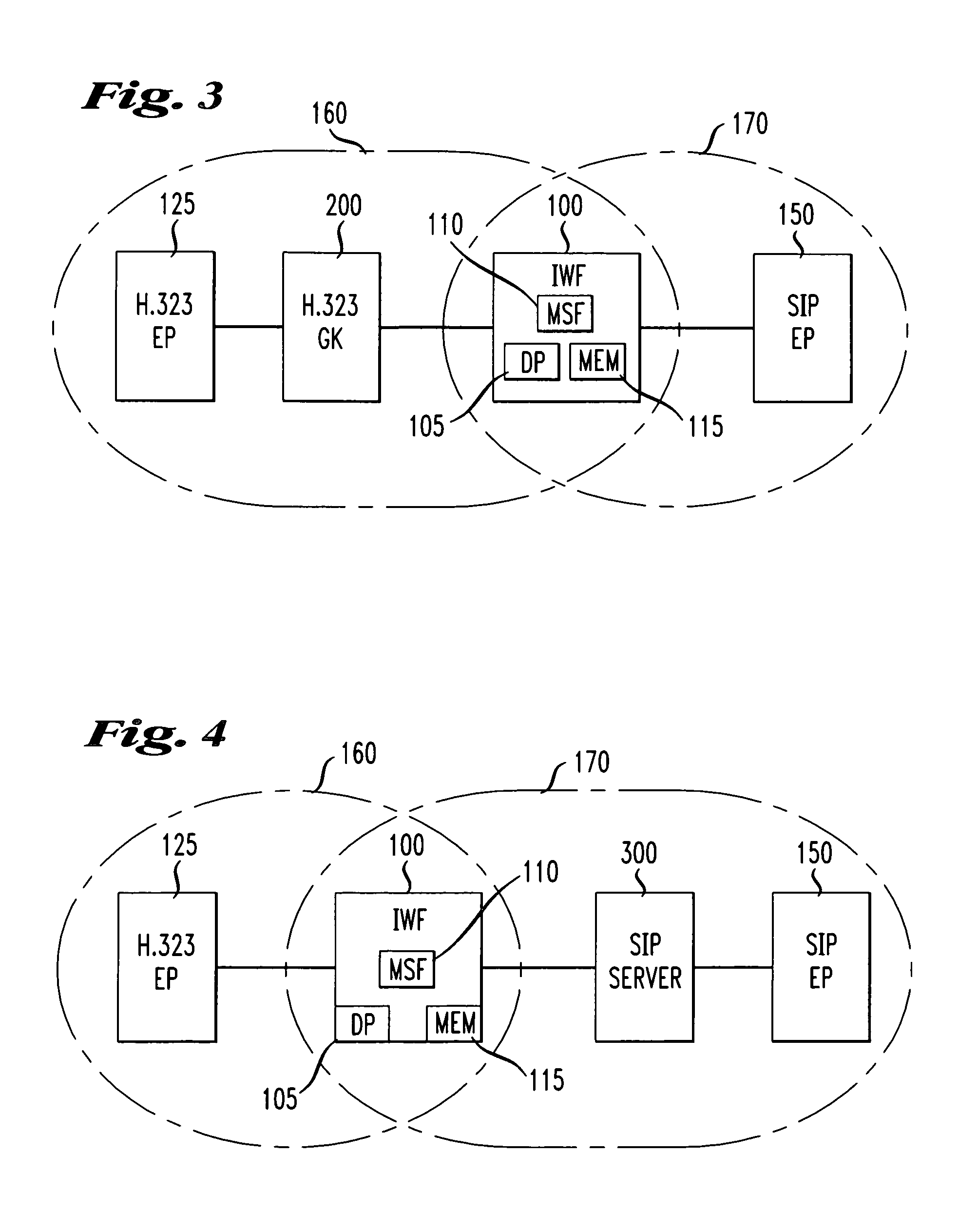
Method and apparatus for S.I.P./H. 323 interworking
ActiveUS7002989B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationState dependentStructure of Management Information
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
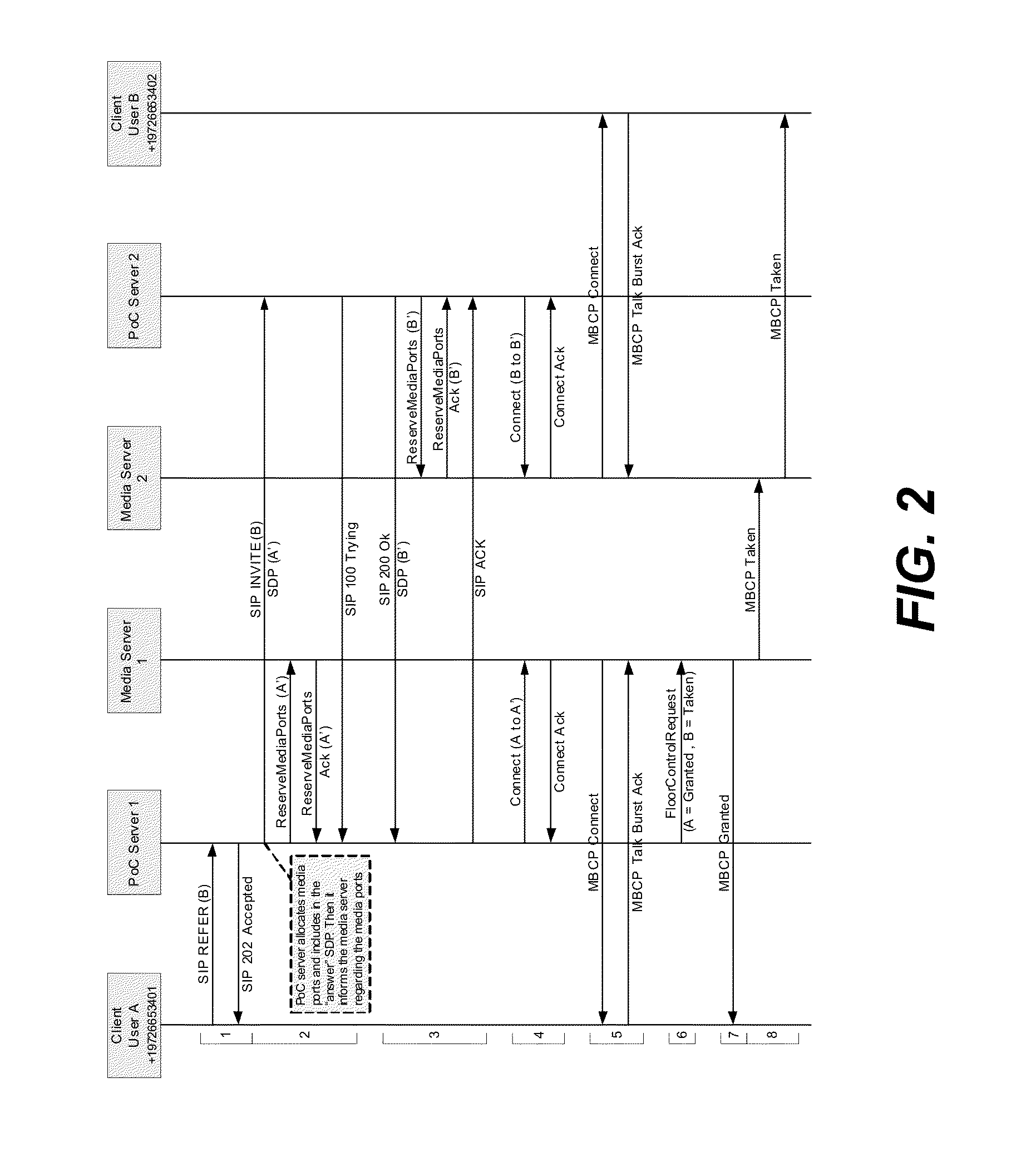
Push-to-talk-over-cellular (POC)
ActiveUS20130155875A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationSession Initiation ProtocolTransport control protocol
A Push-to-Talk-over Cellular (PoC) implementation for use in a wireless communications network, wherein one or more servers interface to the wireless communications network to perform the PoC call sessions. Both the servers and the mobile units that use the PoC call sessions communicate with each other using SIP / IP (Session Initiation Protocol / Internet Protocol) control messages within the wireless communications network, and one or more of the servers switches RTP / IP (Realtime Transport Protocol / Internet Protocol), RTCP / IP (Realtime Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol), or MBCP / IP (Media Burst Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) voice packets for the PoC call sessions between the mobile units across the wireless communications network.
Owner:KODIAK NETWORKS
System and method for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks
ActiveUS7072303B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTransceiverReal-time Transport Protocol
A system for assisting in controlling real-time transport protocol flow through multiple networks is disclosed. The system utilizes at least a first computer and a second computer that is connected to the first computer, wherein the second computer comprises a second transceiver, a second memory having logic stored therein defining functions to be performed by the second computer, and a second processor. The second processor is configured by the second memory to perform the functions of: performing an inbound screen on route information received by the second computer, from the first computer, to determine if the received route information should be discarded; if the route information is not discarded, comparing the received and screened route information to a local policy defined with the second computer, and performing an outbound screen on the received and screened information prior to transmitting the received and screened information.
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
System and method for determining flow quality statistics for real-time transport protocol data flows
Owner:PRIMARY NETWORKS +1
Measuring speech quality over a communications network
InactiveUS20020193999A1Reduction of informationSpeech analysisSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsNetwork measurementPESQ
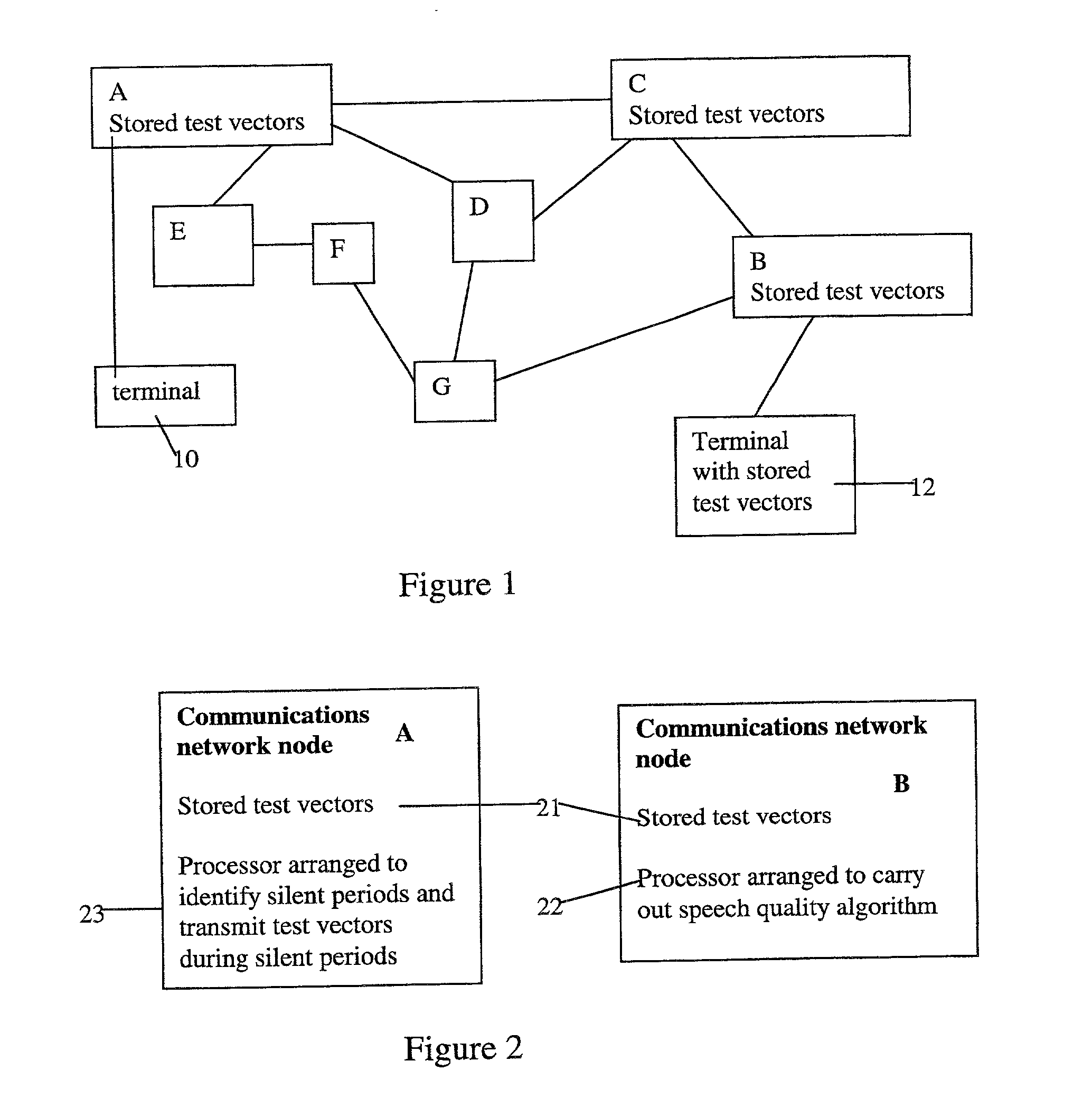
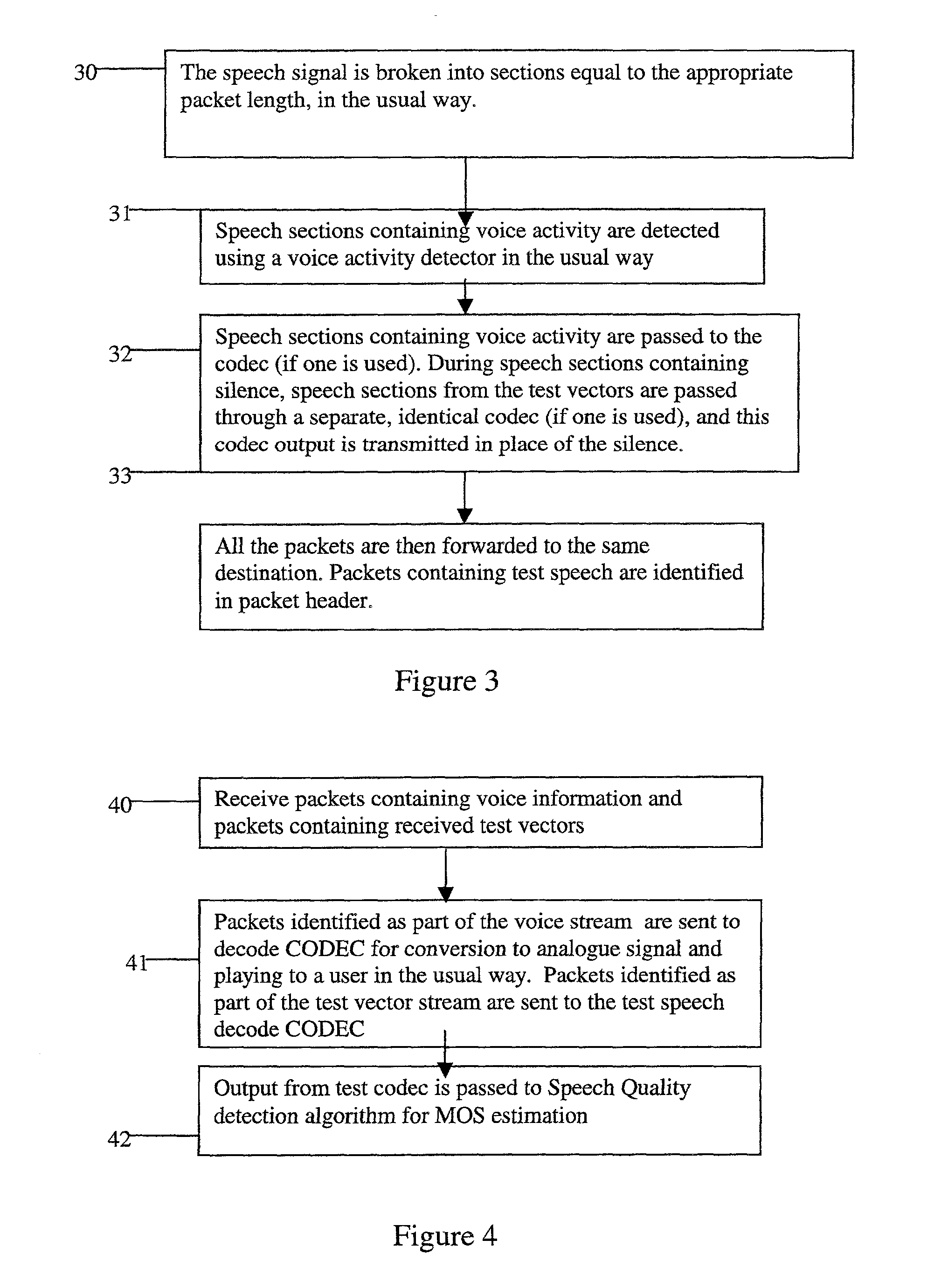
When the PESQ and similar algorithms are used to measure speech quality, a particular voice call is set up to transmit only test voice signals over a communications network. This enables the test voice signals to be easily identified and provides a means of determining the amount of degradation that occurs as a result of transmission of the test voice signals. However, one problem is that in packet switched networks the transmission characteristics change with time. Thus the estimated MOS score obtained cannot be assumed to give an accurate speech quality measure for a voice call later made between the same two points. By adding test voice information to an ongoing voice call and transmitting that test voice information integrally with the ongoing voice call these problems are addressed. The test voice information is sent in packets during silent periods in the voice call such that the voice call is not affected by the test voice information. An identifier is used to identify or label the packets comprising test voice information. In the case that real-time transport protocol is used, the identifier is preferably a payload type value.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
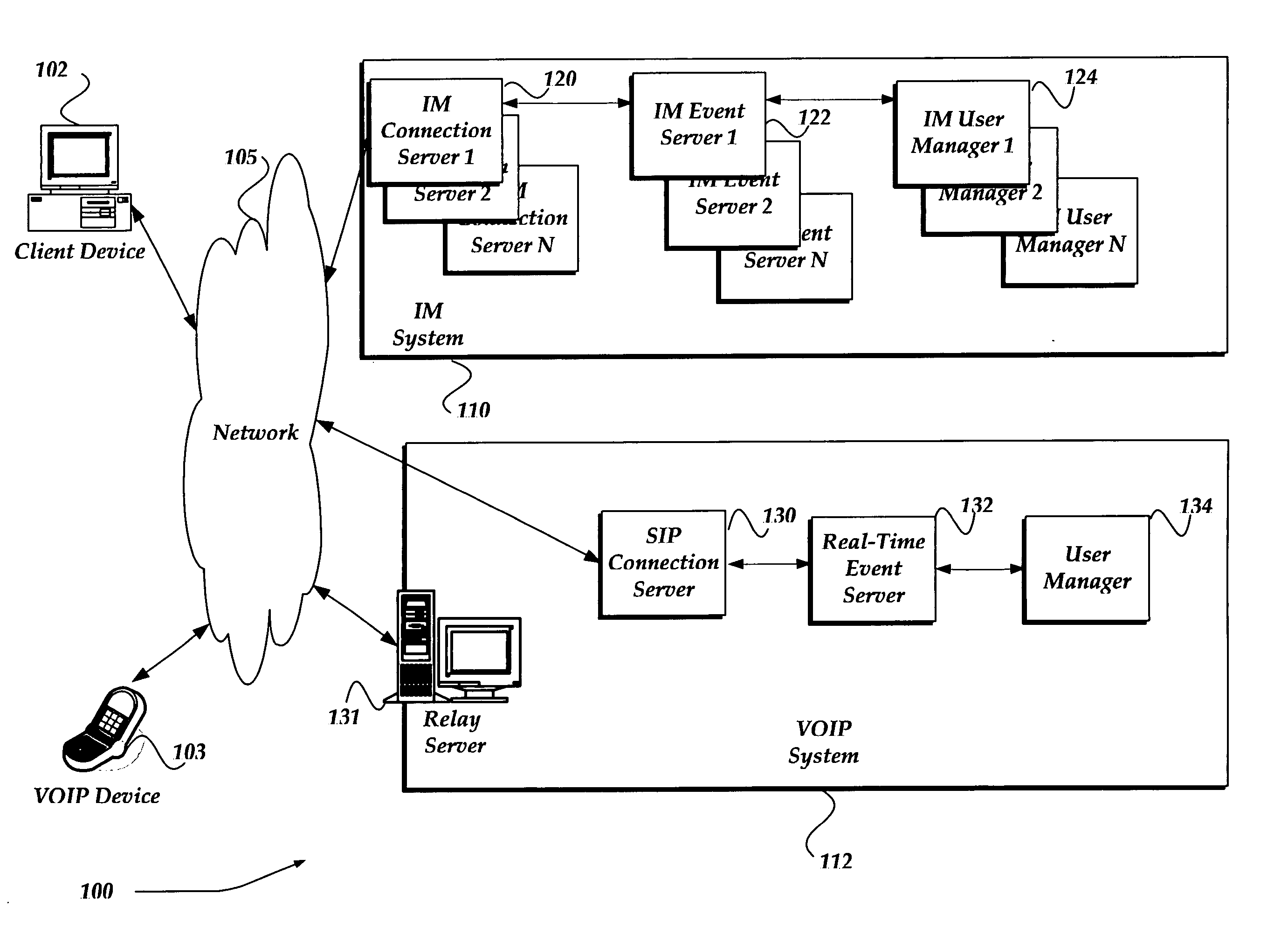
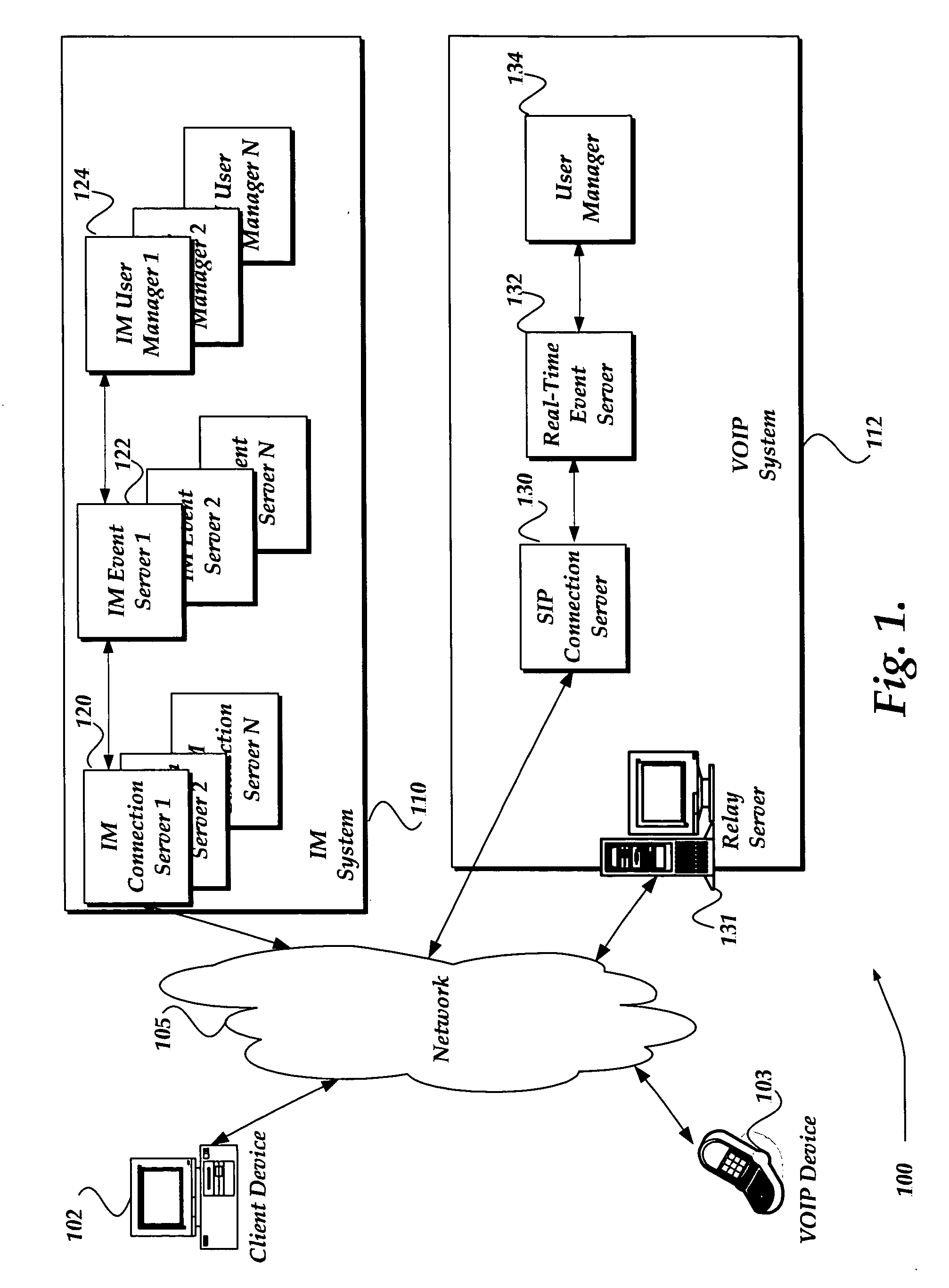
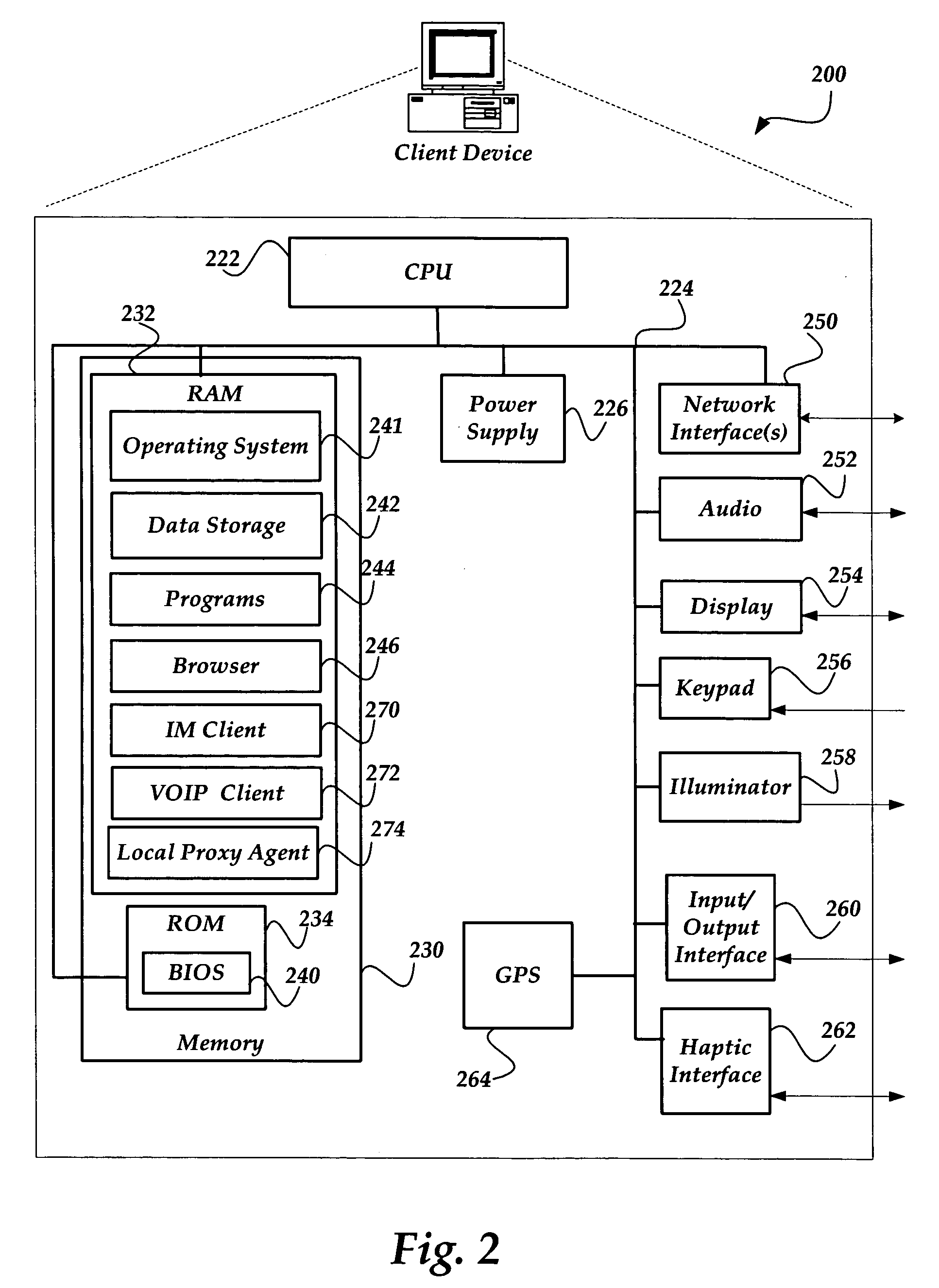
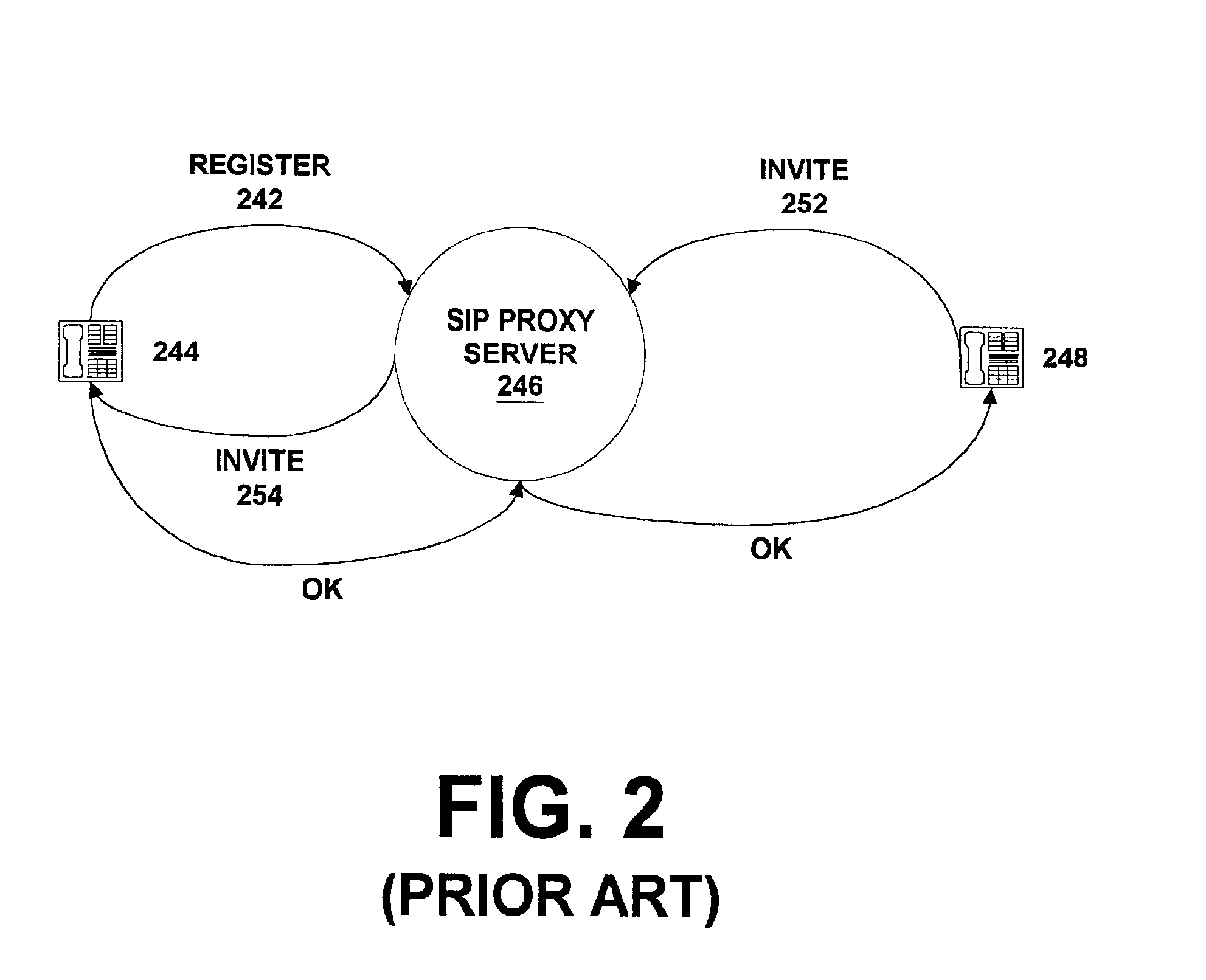
Proxy server for relaying VOIP messages
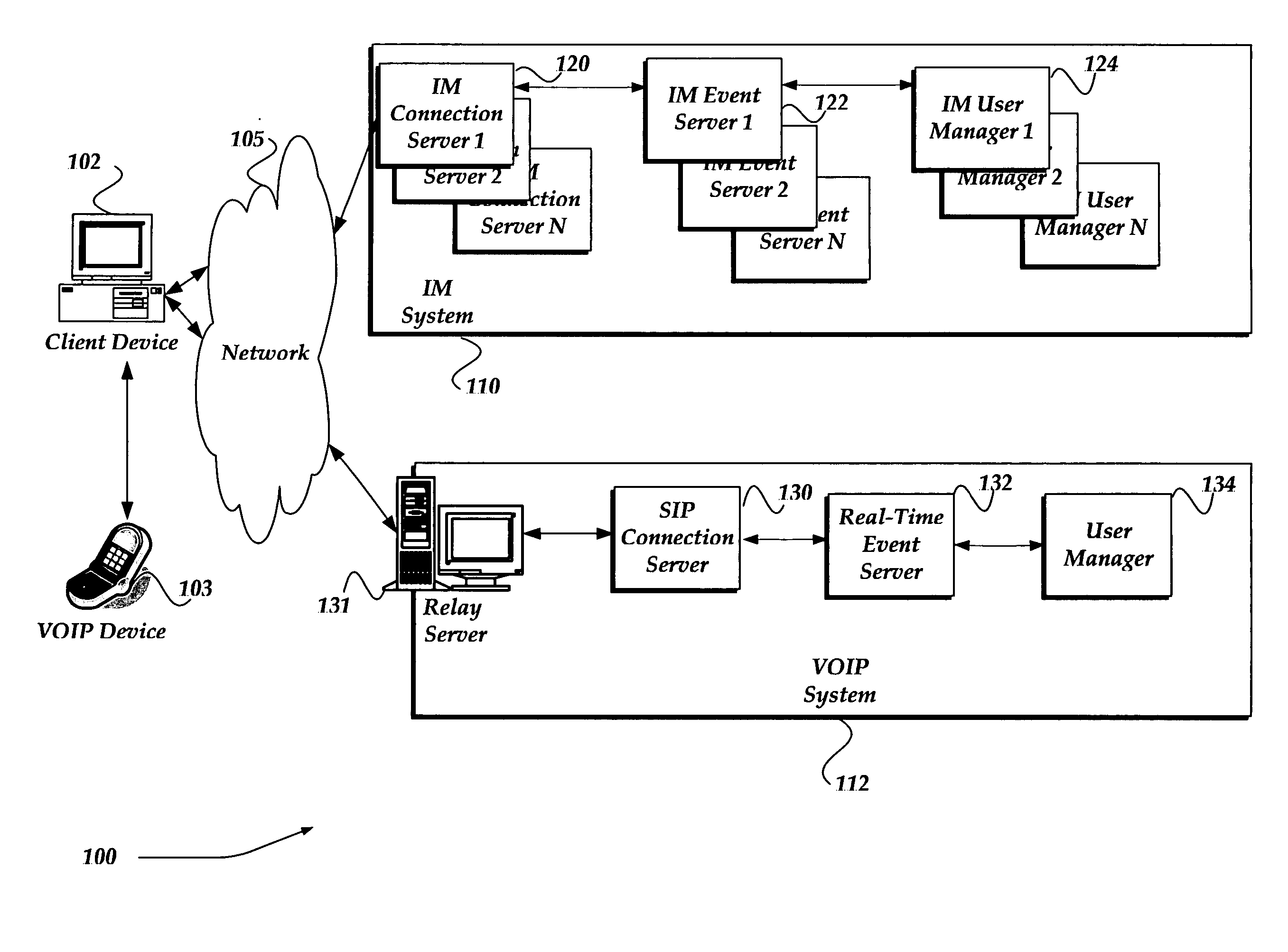
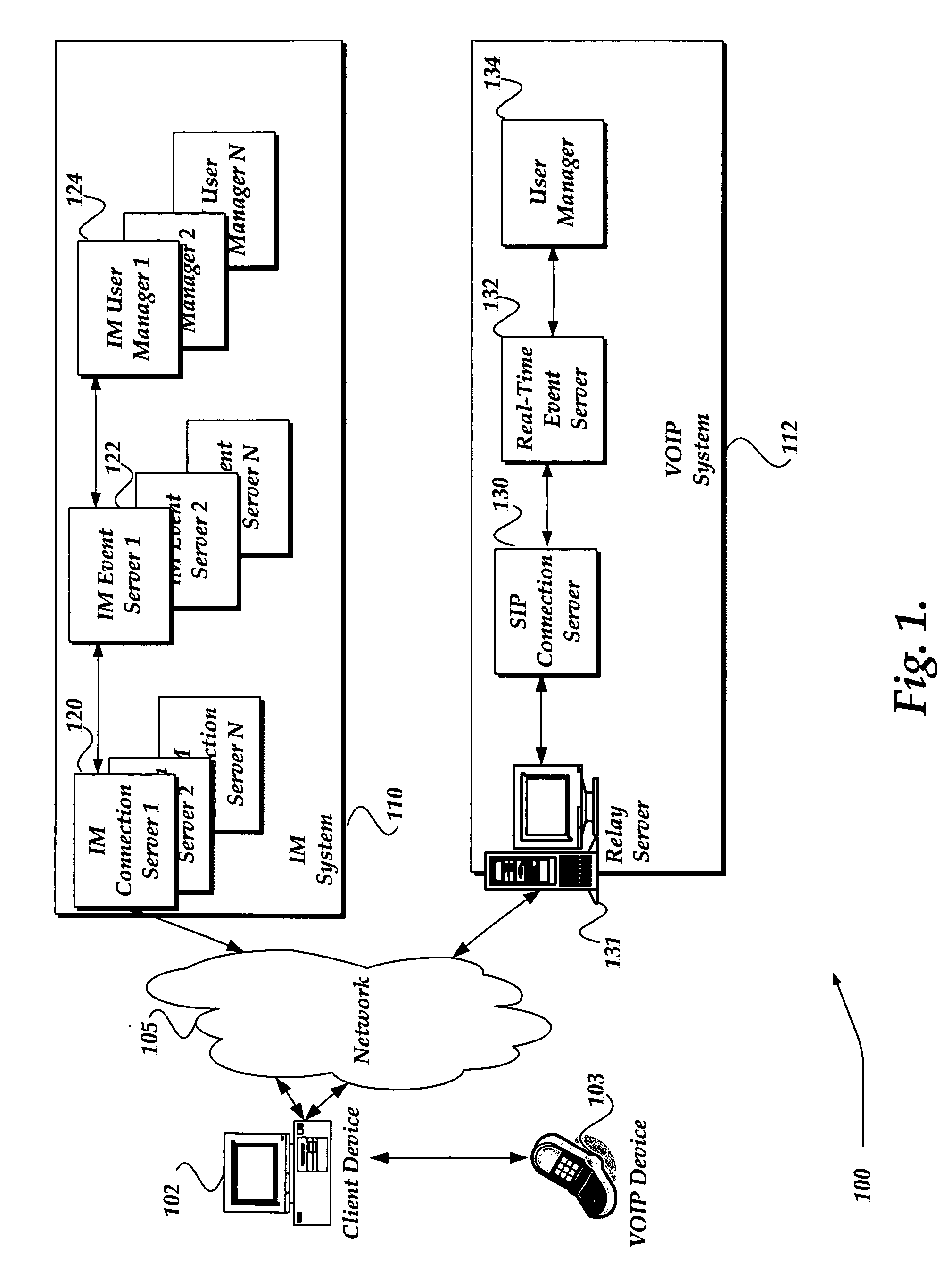
ActiveUS20060256771A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTransmission protocolSession Initiation Protocol
A system, method, and apparatus are directed towards managing a Voice over IP (VOIP) message over a network, where the VOIP message may employ the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and possibly Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). The invention enables a VOIP client device, such as an IP phone, and the like, to communicate a message to a local proxy residing on a local computing device. The communications between the VOIP device and the local proxy may employ SIP / RTP over UDP. Upon receipt of the communications, the local proxy converts the transport protocol to another transport protocol, such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The local proxy may also perform a port translation on the message. The converted communications may then be sent to a remote server, where it may be employed in its present SIP / RTP over TCP format, or be converted back to using UDP.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Method and system for key management in voice over internet protocol
InactiveUS20070157026A1Eliminate needEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSession Initiation ProtocolDiffie–Hellman key exchange
A method and system for a secure telephone protocol are disclosed, which can be implemented using current Voice over IP (VoIP) protocols, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP, as specified in the Request for Comment (RFC) 3261 from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)), Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP, as specified in RFC 3550), and Secure RTP (SRTP, as specified in RFC 3711). The secure telephone protocol can include a shared secret value that is cached and then re-used later to authenticate a long series of session keys to be used for numerous separate secure phone calls over a long period of time, thereby providing cryptographic key continuity without the need for voice authentication. In an embodiment, the secure telephone protocol can utilize the Diffie-Hellman key exchange during call setup, and AES for encrypting the voice stream.
Owner:ZIMMERMANN PHILIP R
Medium streaming distribution system
ActiveUS7443797B2Reduce impactError propagationError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket lossDistribution system
A medium streaming distribution system reduces effects of packet loss in a network before the packet reaches radio base station. A medium distribution device for packet-transmits via the base station, a medium stream to the network by a real time transmission protocol. A packet analyzer monitors the packet arriving at the radio base station and transmits feedback information associated with loss of a packet to the medium distribution device. Based on the feedback from a relay device and a terminal device of the medium stream, the transmission rates from the medium distribution device to the relay device and from the relay device to the terminal device are obtained to provide a greater transmission rate in a surplus band for re-transmission or a forward error correction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
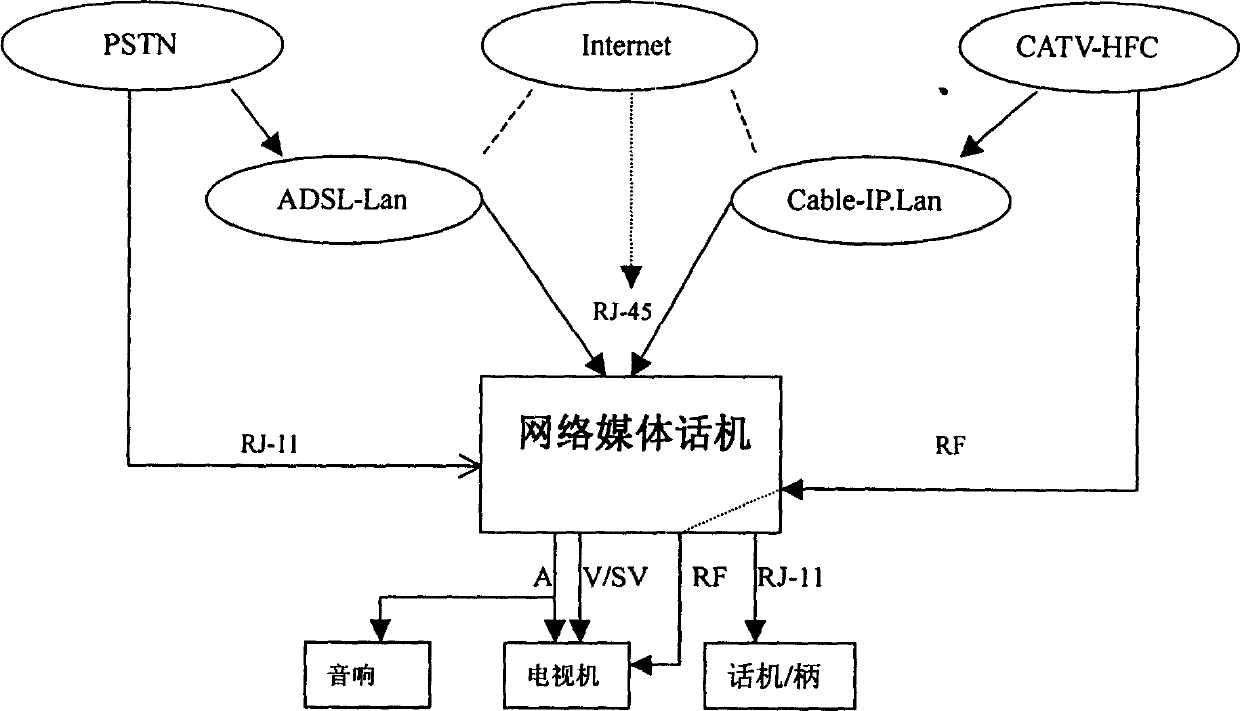
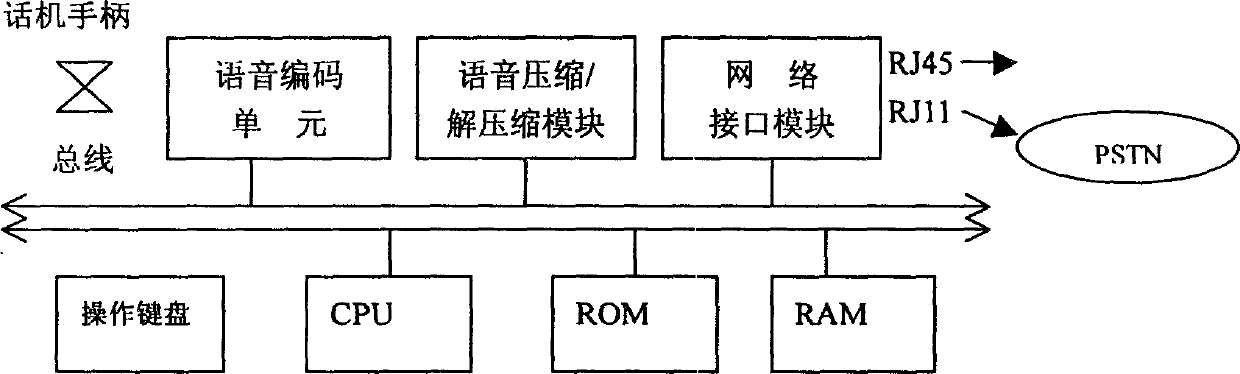
Application and communication method of terminal of network media phone
InactiveCN1599376A--Wide range of applicationsSupport application systemTransmissionIp addressTelephone terminal
This invention relates to the application and communication method for network media telephone terminals. The terminal includes a phone module and IP phone module imaging the target called number into related network IP address for Volp communication, PCI bus with Ethernet interface and phone / multimedia processor controlled by CPU, the media port is connected by D / A conversion, a special inserted CPU, TCP / IP protocol stack the real time transmission protocol of the transmission stream media. The terminal and the software exchange center based on IP interact synchronously or asynchronously, and the IP calling cetral platform provides support to communication for stream media forms and speech.
Owner:SHANGHAI TT&S TELECOM TECH CO LTD
Division distributed storage method of program source based on cluster video server
InactiveCN1434386AImprove versatilityVarietyTelevision system detailsProgram control using stored programsClient-sideReal-time Transport Protocol
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
internet based TV stream data real time transmission and service apparatus and method
InactiveCN101083756AImprove reliabilityImprove real-time performancePulse modulation television signal transmissionTwo-way working systemsQuality of serviceStreaming data
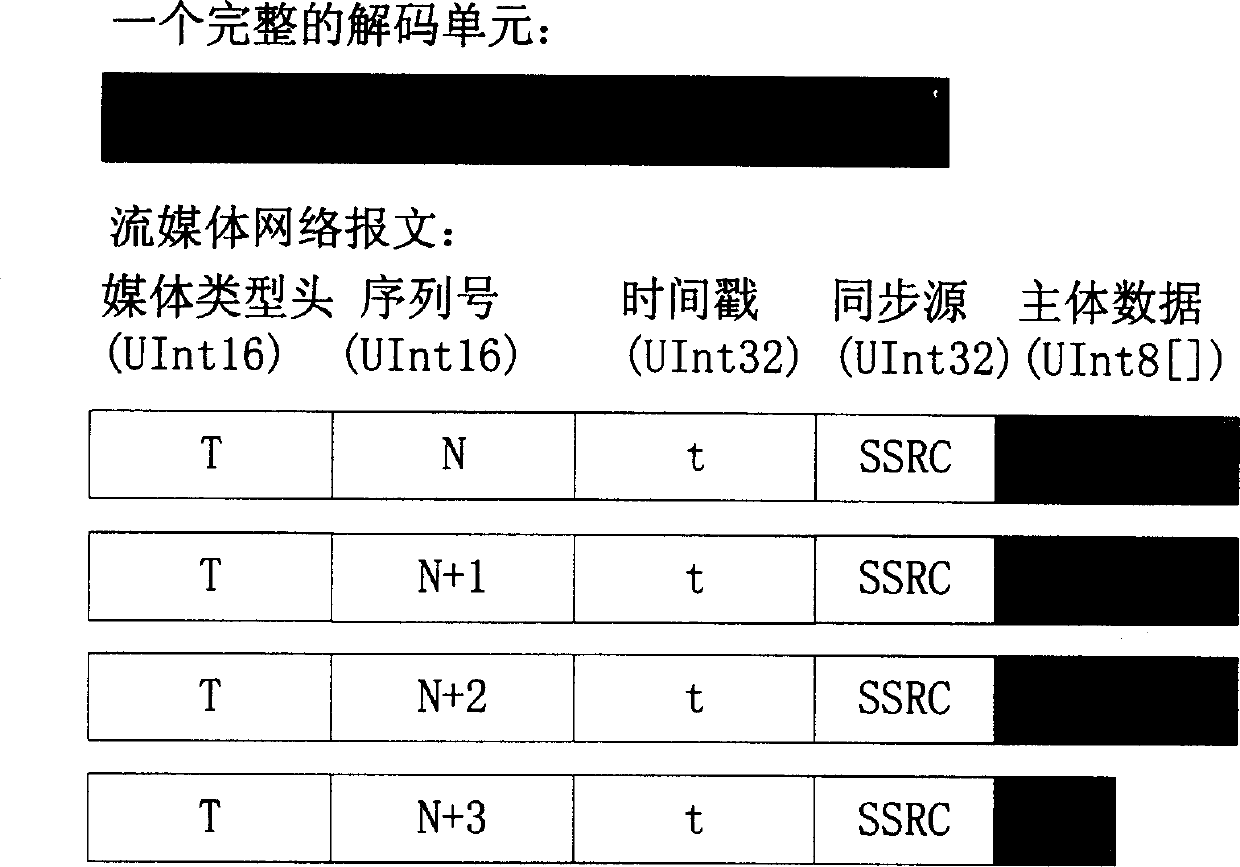
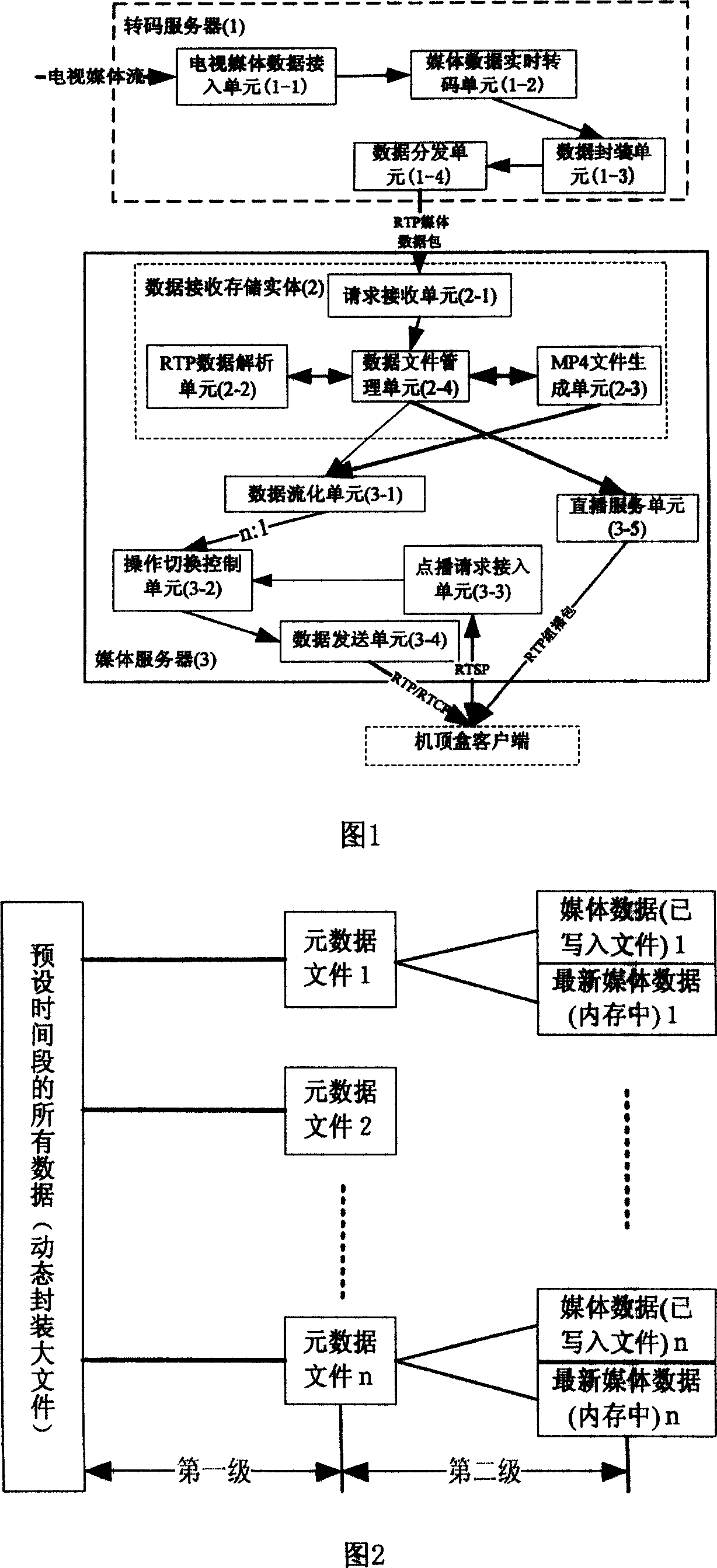
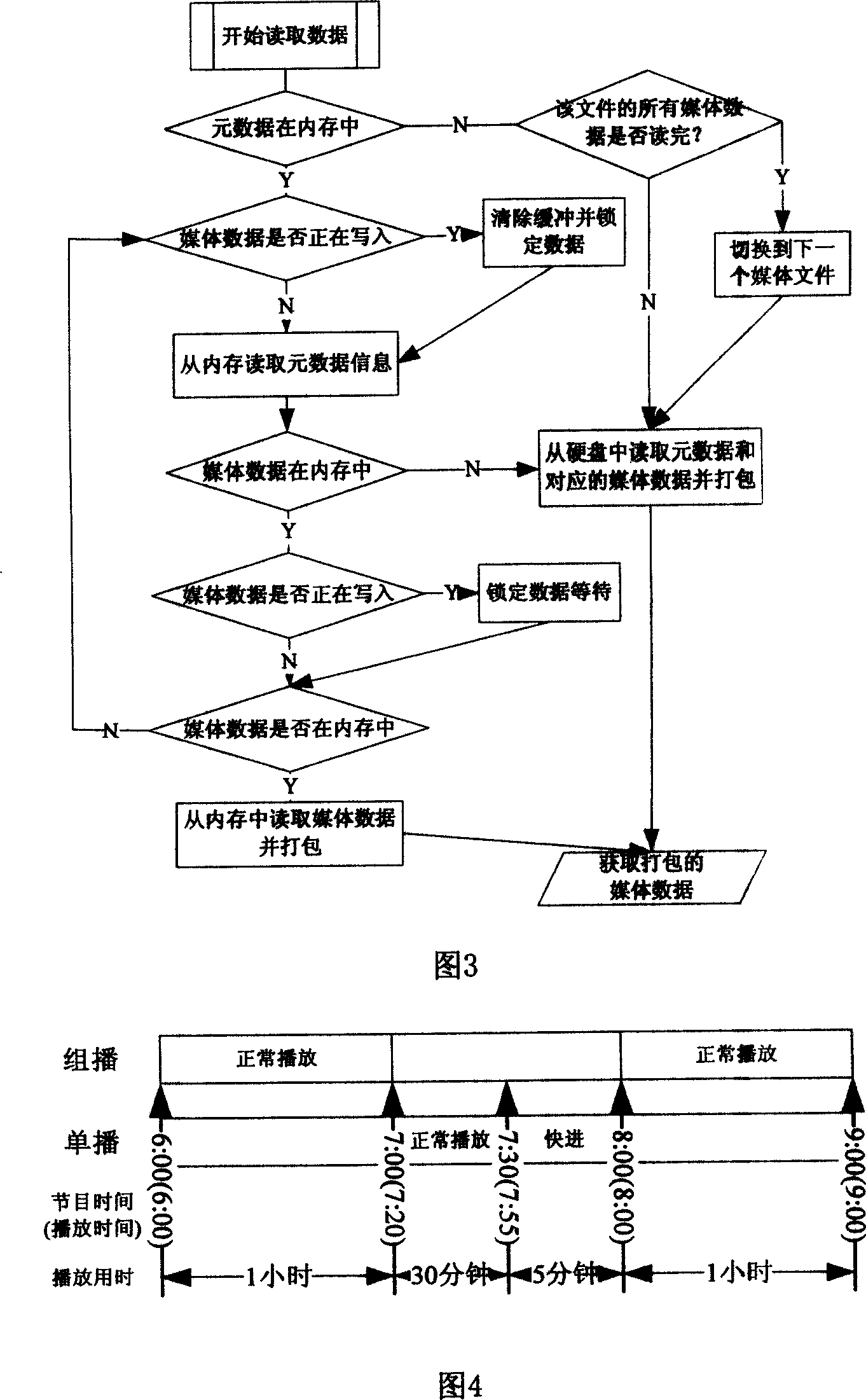
In internet, this invention uses the code-converting server (CS) real time to code-convert the received directly TV media (TM) data, then distributes the code-converted TM data toward all cell media server (CMS). CMS stores these data and offers the TM program ordering service and the real time (RT) directly playing service. These two services can be switched seamlessly. The transferring and service of RT TM operation is realized in Internet and its service quality can be ensured. This device consists of CS, the data receiving / storing entity and media servers. Here, the data receiving entity is the data front end of CMS. Both reside on the same physical server and connect to CS via Internet to execute RT transferring protocol.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
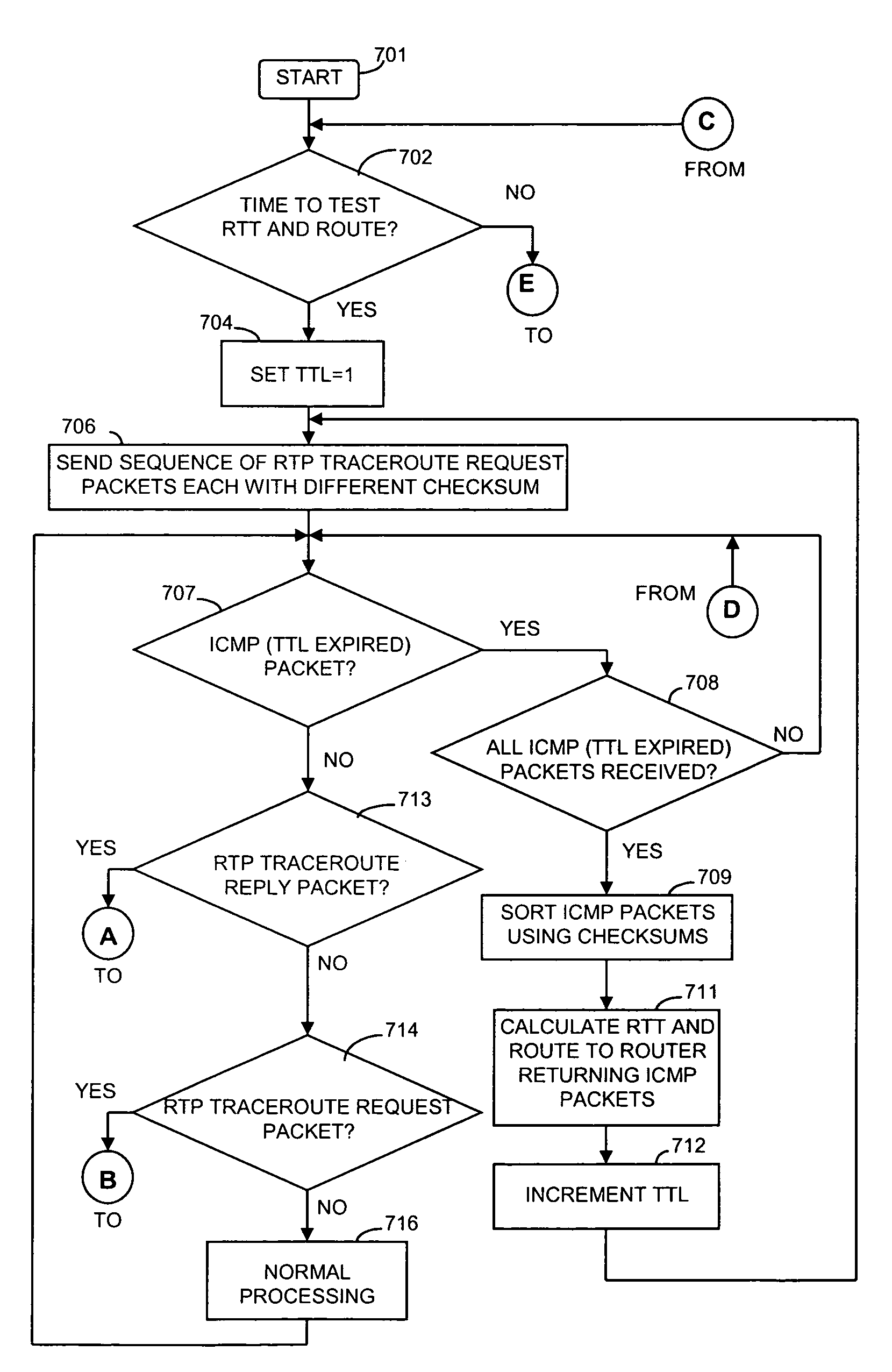
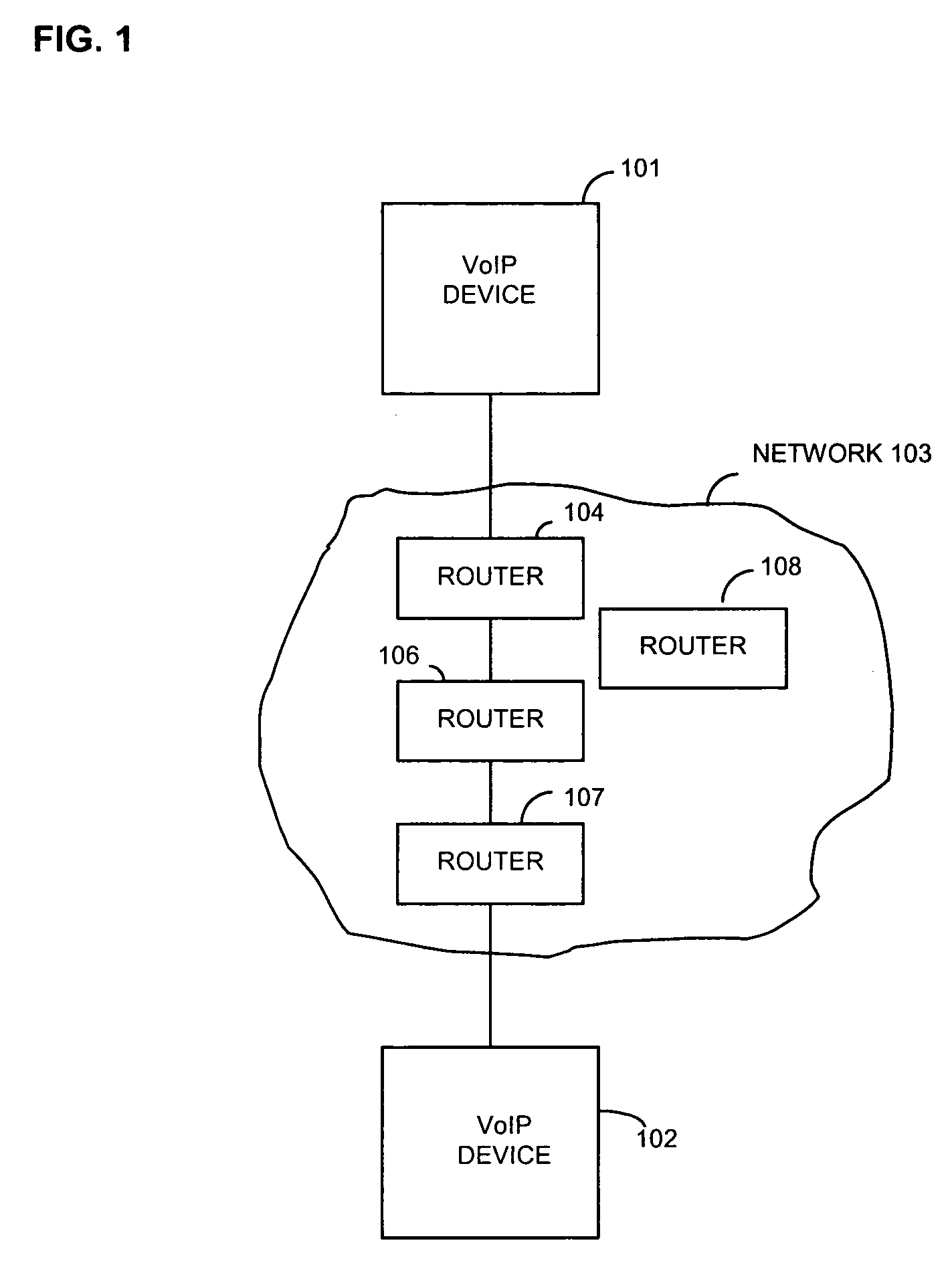
Method and apparatus for providing trace route and timing information for media streams
An apparatus and method that use media packets, such as Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP), packets with a specially define profile to determine the route and round-trip-time information. The route is determined by transmitting by a first network endpoint one or a group of media packets having a number of hops equal to a predefined number and the network address of a second endpoint, incrementing the number of hops upon a non-media packet being received in response to the one or group by a network node because the number of hops was exceeded at that network node. After recording the identification of that network node and incrementing the number of hops, the network endpoint re-transmits the one or group of media packets. The round-trip-time information is determined by timestamp information inserted into the one or group of media packets by the first network endpoint and timestamp information inserted into another one or another group of media packets transmitted from the second network endpoint to the first network endpoint in response to receipt of the one or group of media packets.
Owner:AVAYA INC
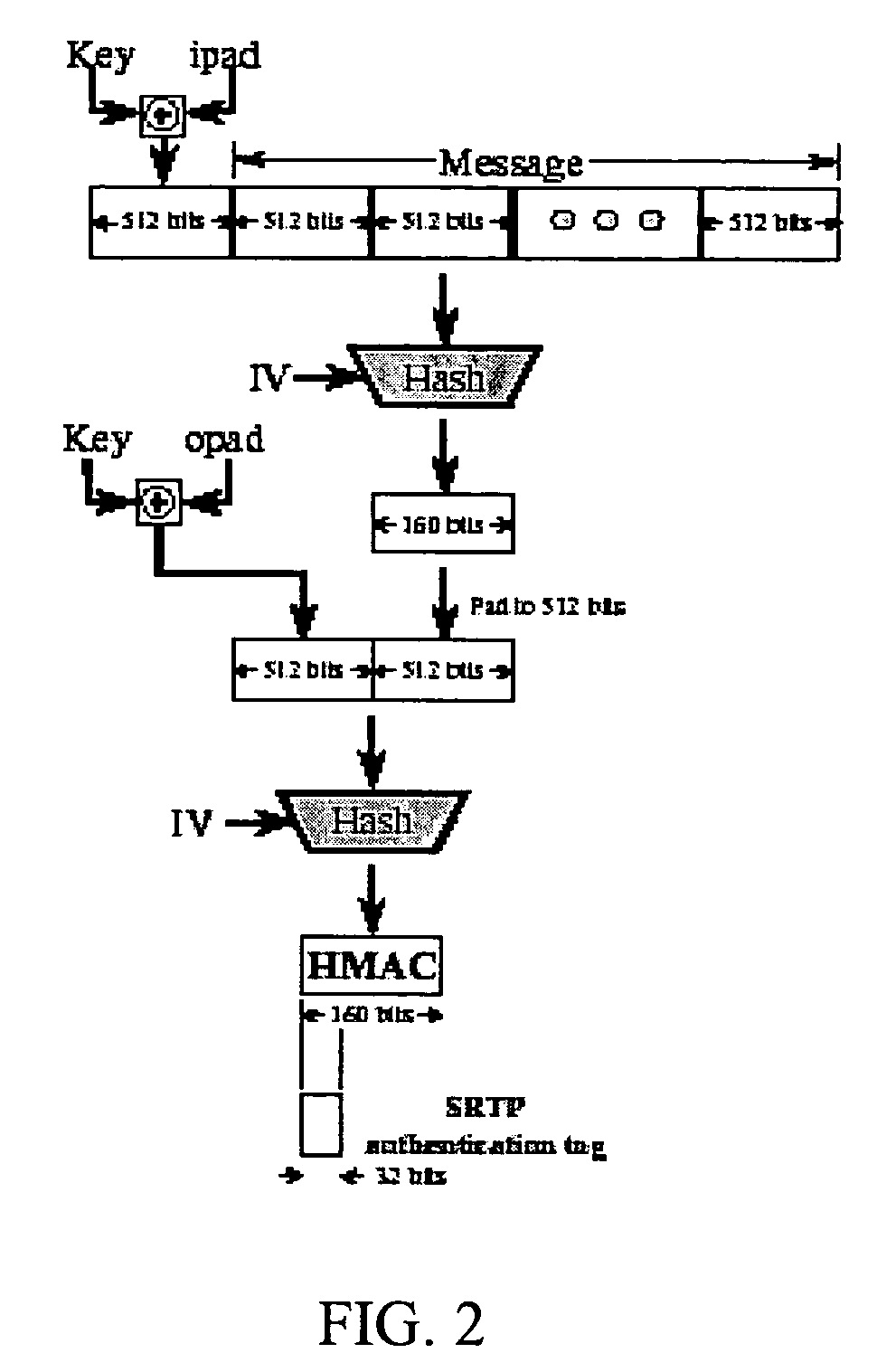
Method for real-time transport protocol (RTP) packet authentication
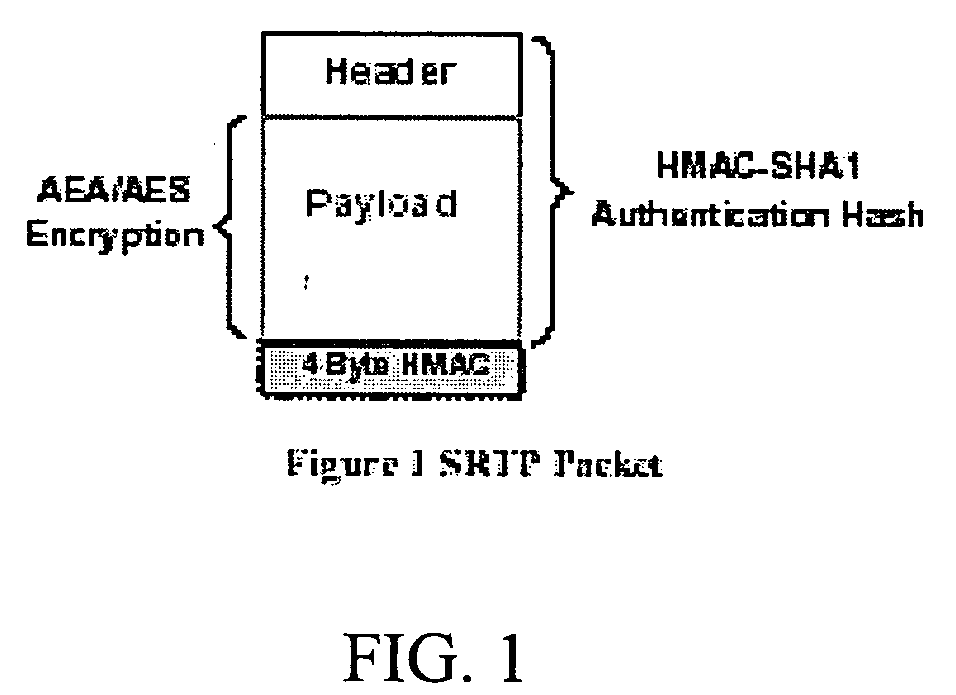
ActiveUS20050265349A1Reduce maximum processor cycle consumedConstant overheadMultiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationTraffic capacityConfidentiality
A method for Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) packet authentication on a packet data network. In particular, the invention relates to a method for preventing toll fraud, privacy compromise, voice quality degradation, or denial of service (DoS) on Voice over IP networks. The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is susceptible to several security attacks, including thirdparty snooping of private conversations, injection of forged content, and introduction or modification of packets to degrade voice quality. The Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) provides confidentiality, message authentication, and replay protection for RTP traffic. However, SRTP incurs an additional overhead to verify the HMAC-SHA1 message authentication code for each packet. SRTP+ significantly decrease the verification overhead compared to SRTP and thereby increases the number of faked packets required to mount a successful denial of service attack. SRTP+ provides packet authentication but not integrity. SRTP+ is compatible with SRTP.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com