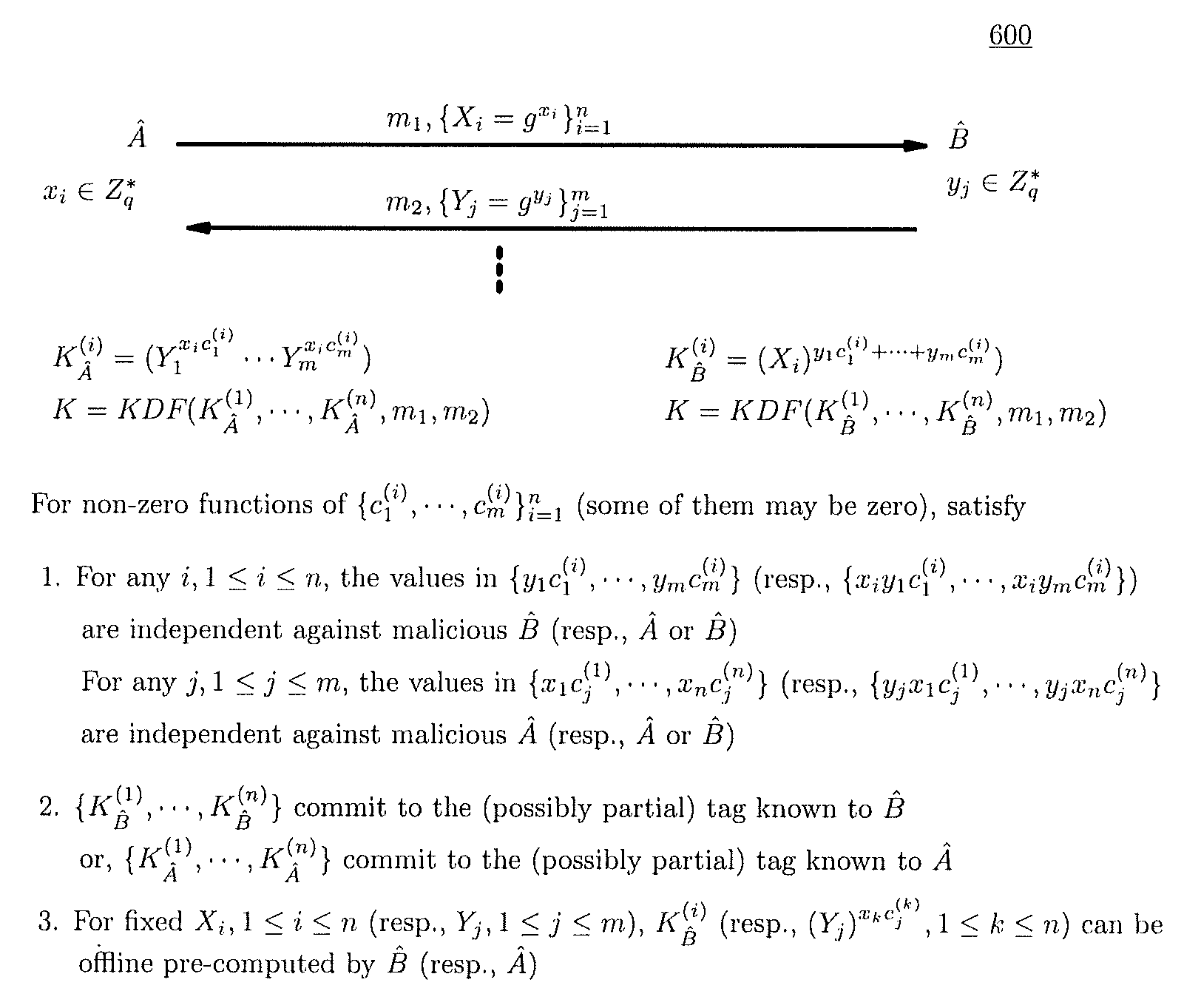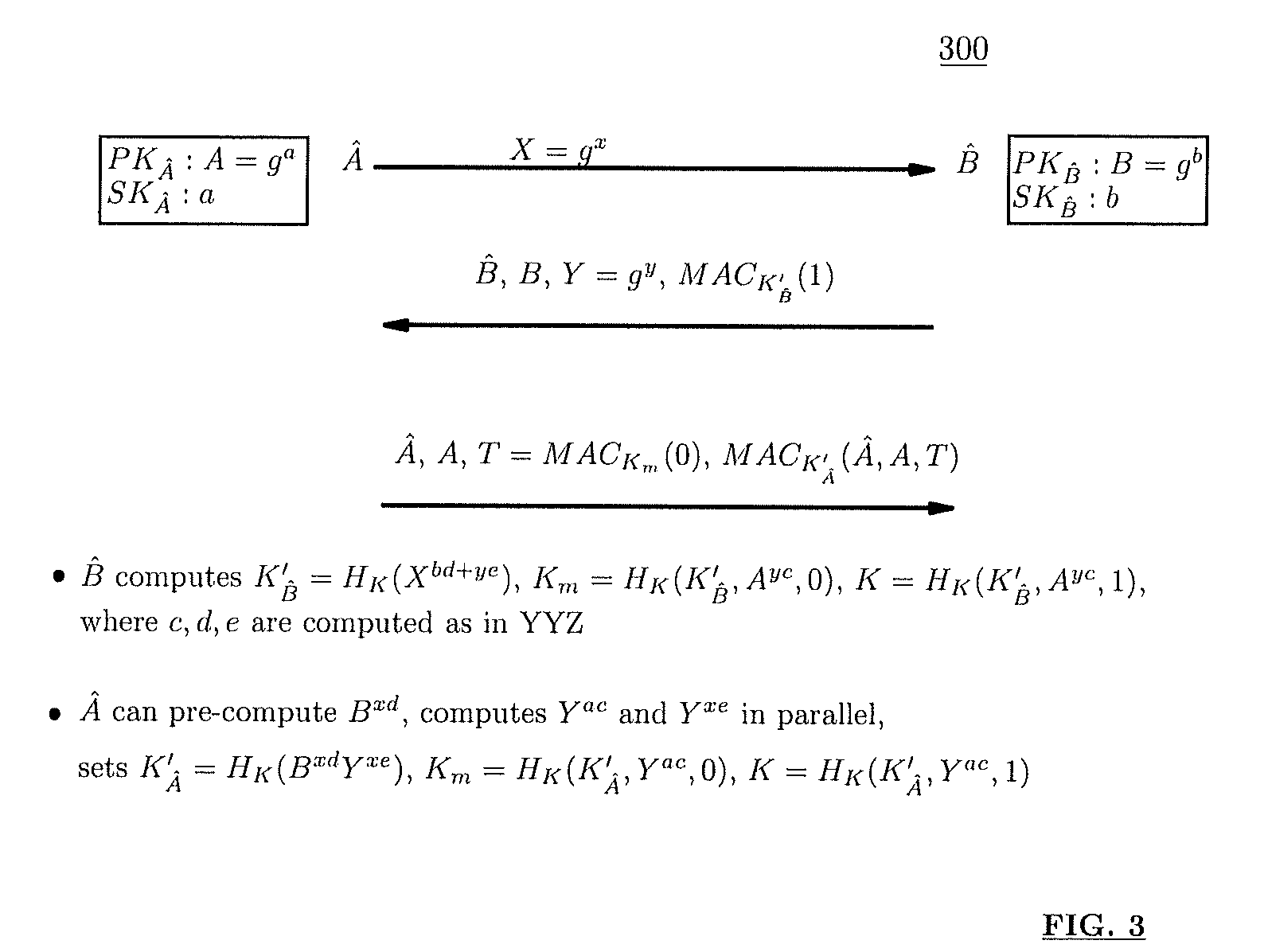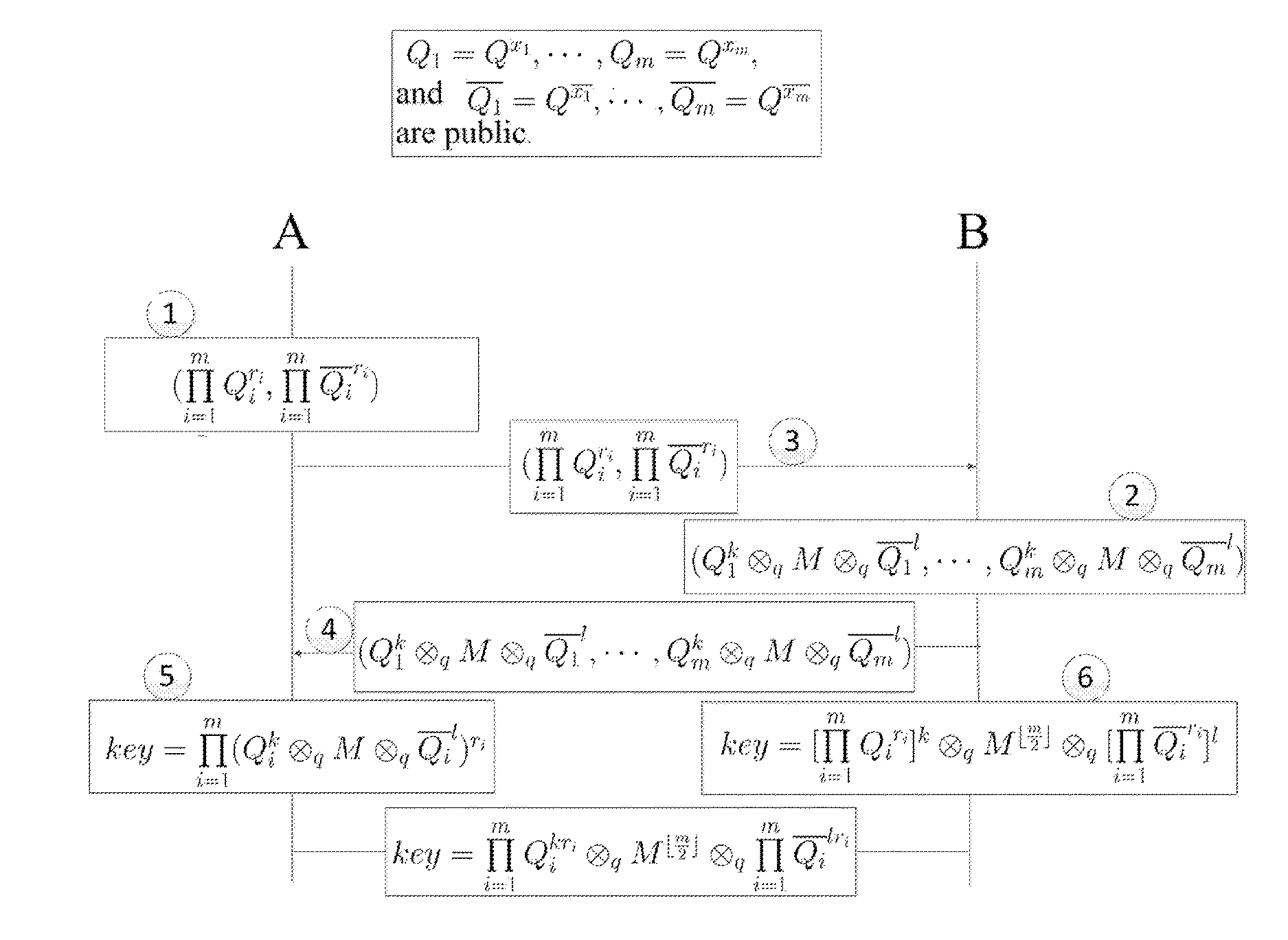Patents
Literature
34 results about "Diffie–Hellman key exchange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
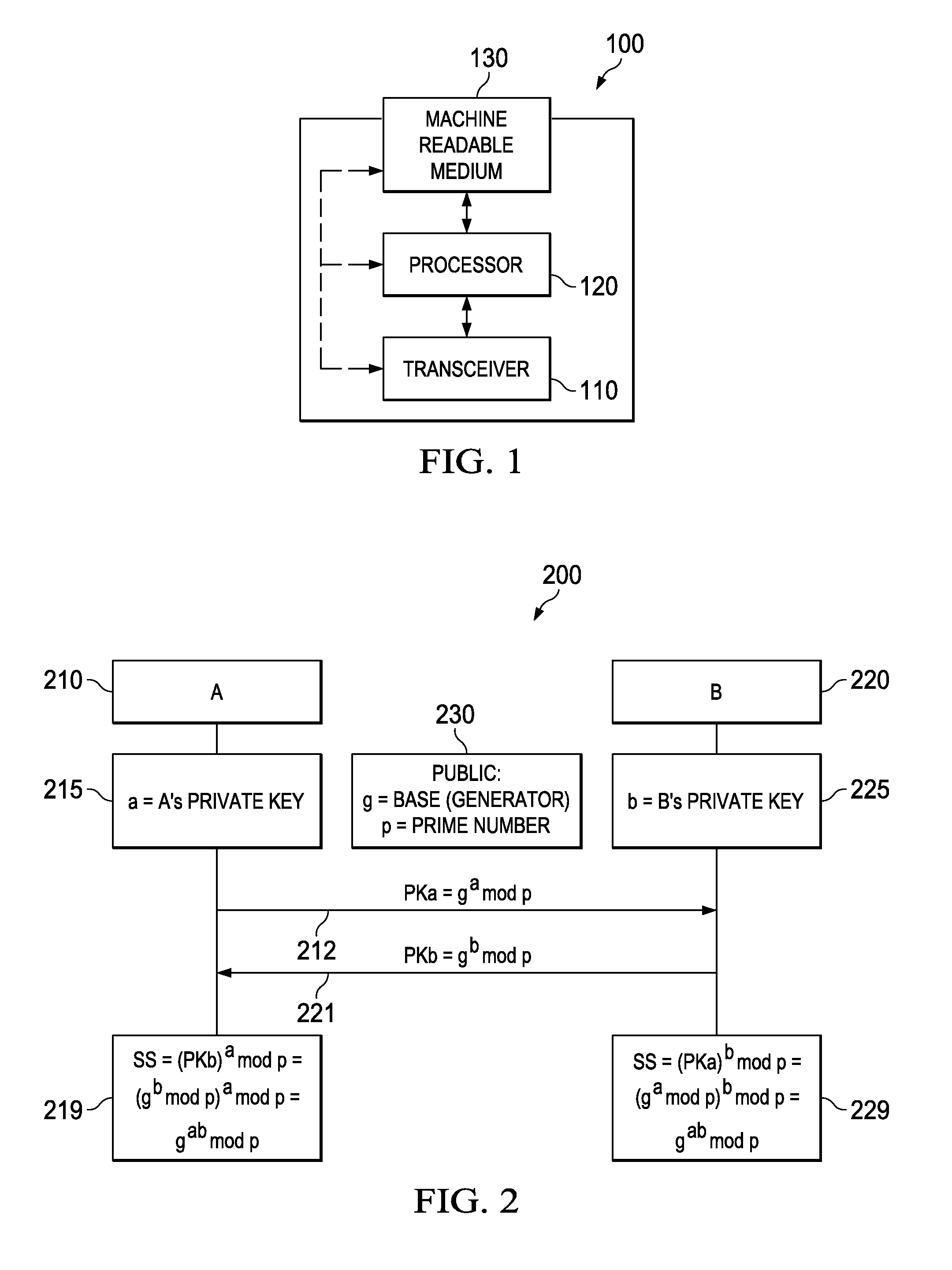
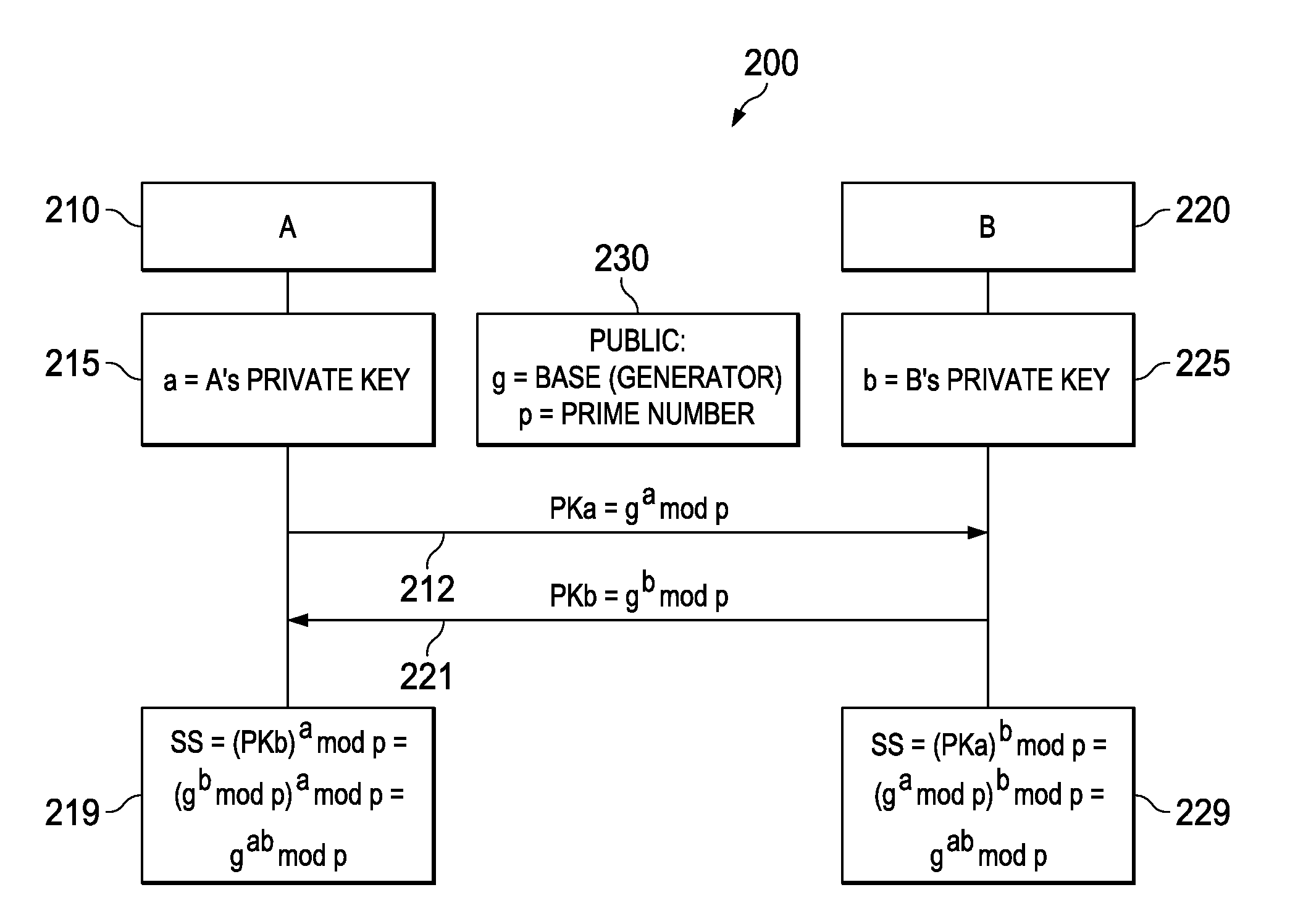
Diffie–Hellman key exchange (DH) is a method of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over a public channel and was one of the first public-key protocols as originally conceptualized by Ralph Merkle and named after Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman. DH is one of the earliest practical examples of public key exchange implemented within the field of cryptography.
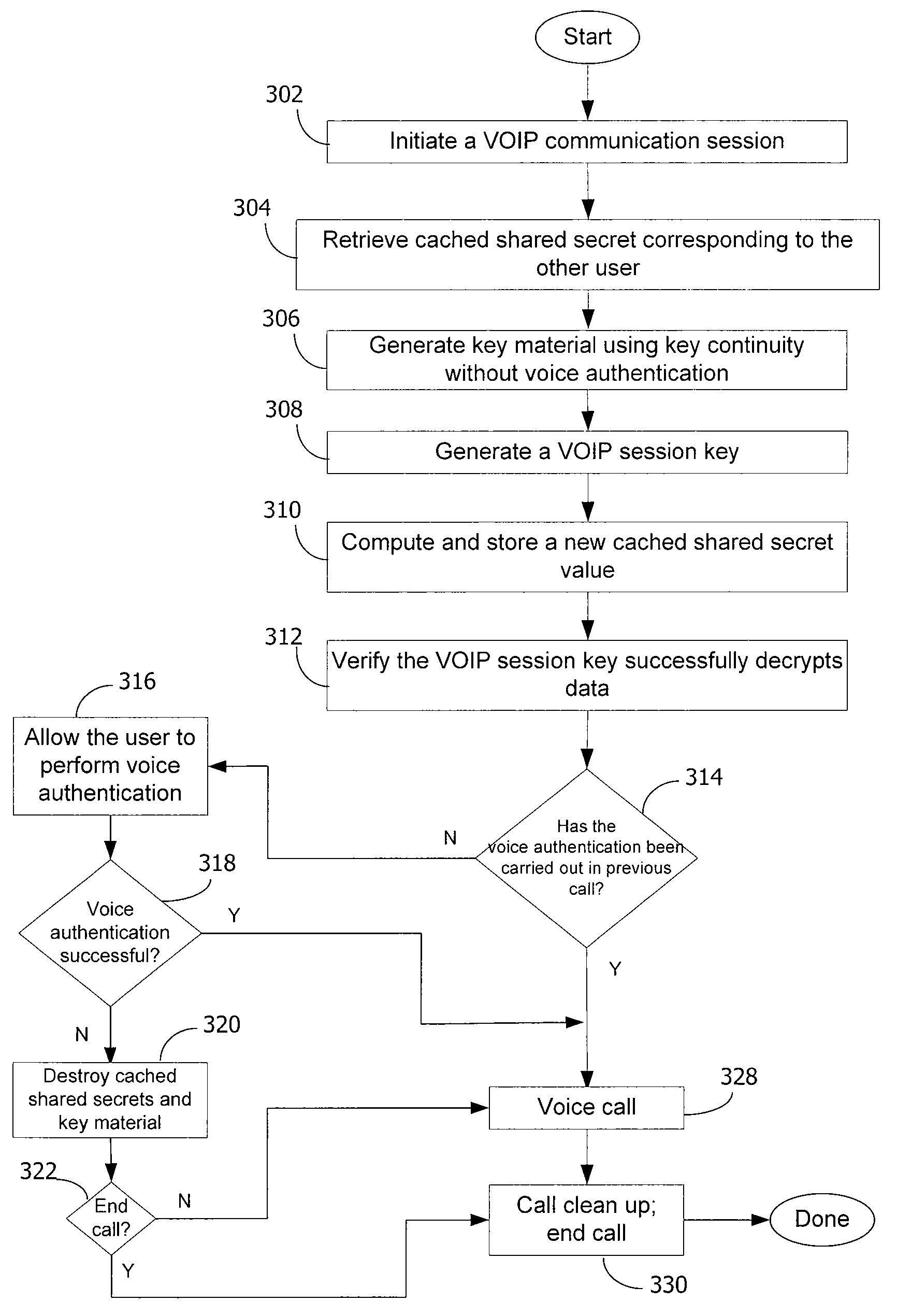
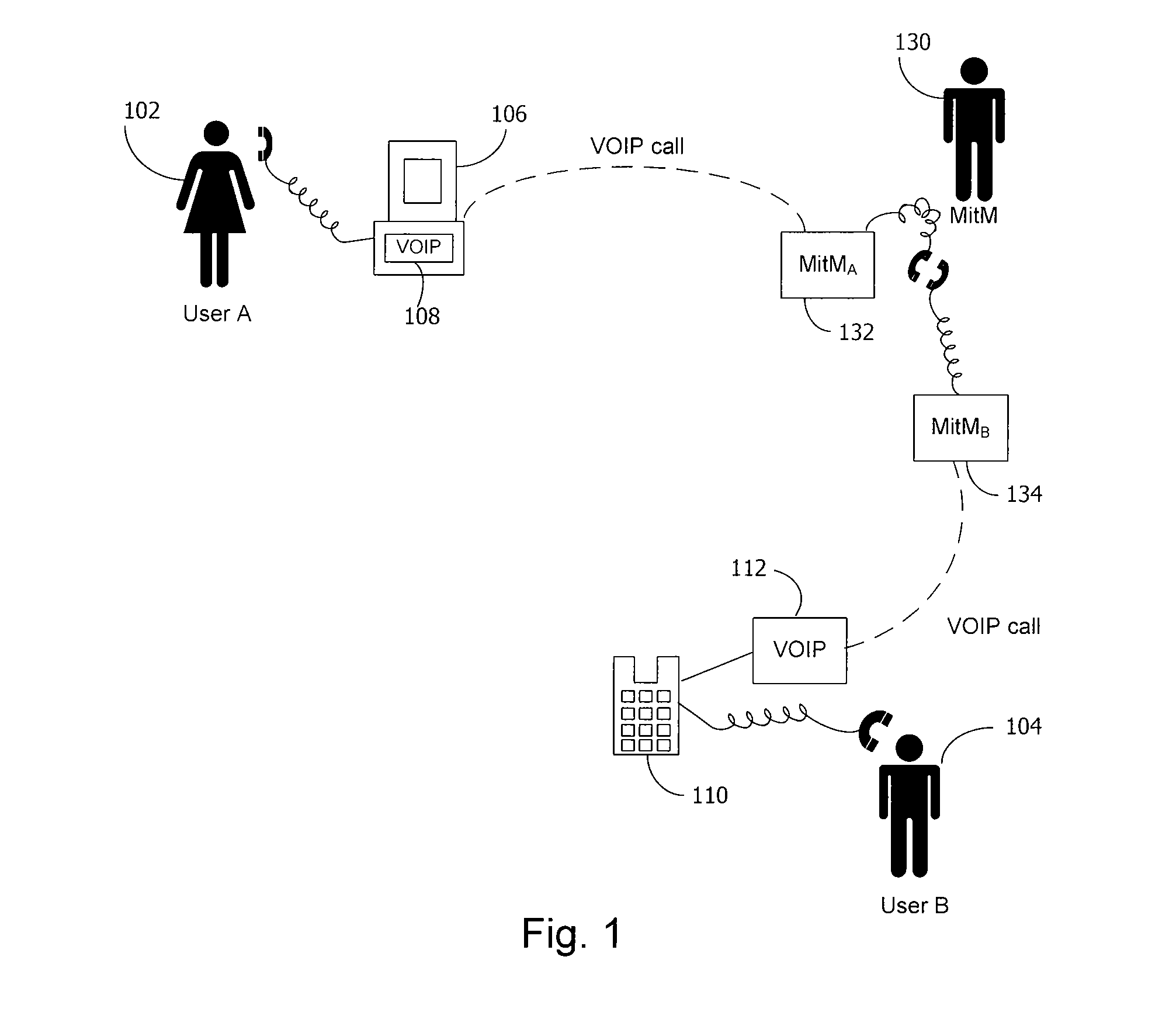
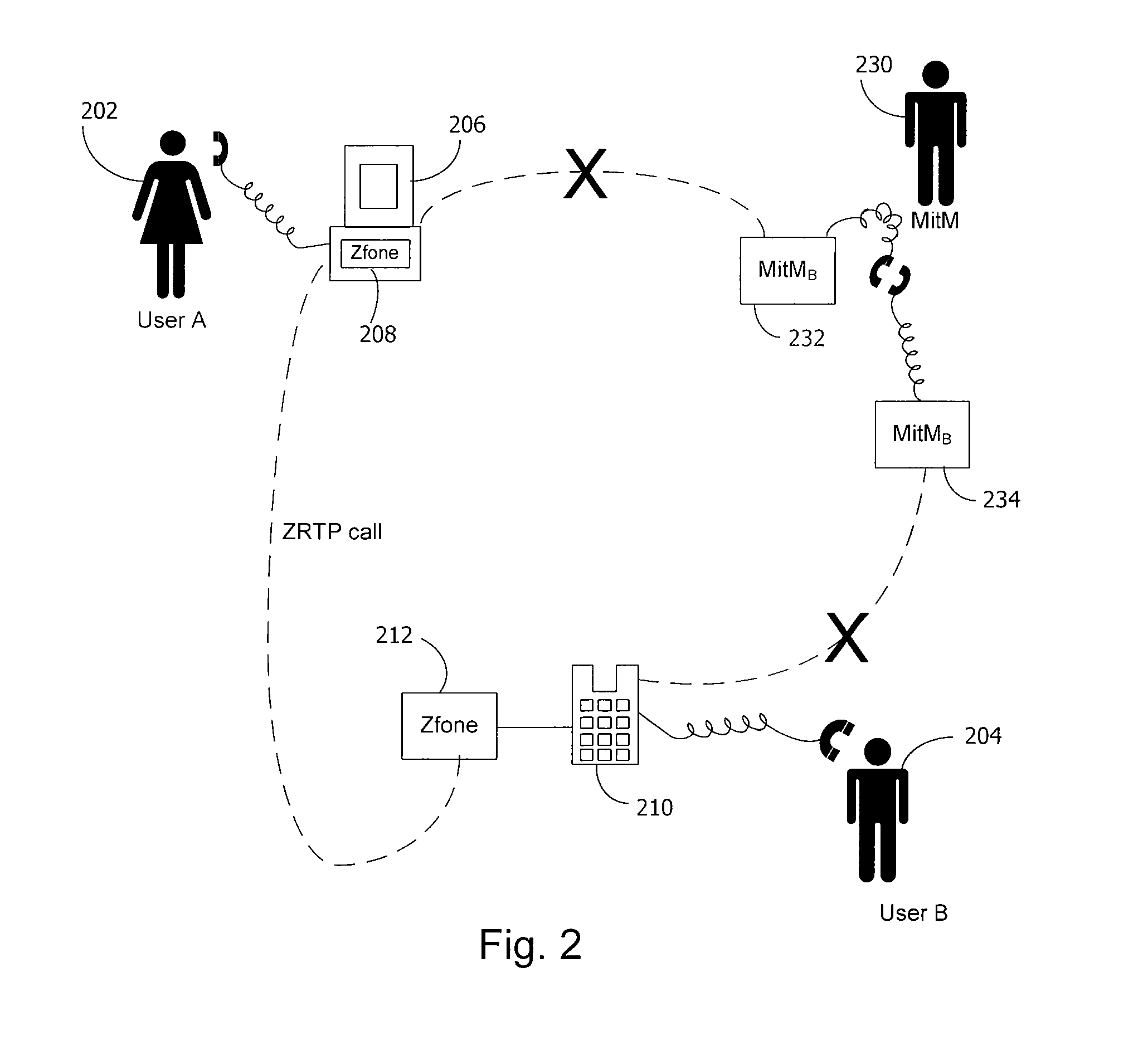
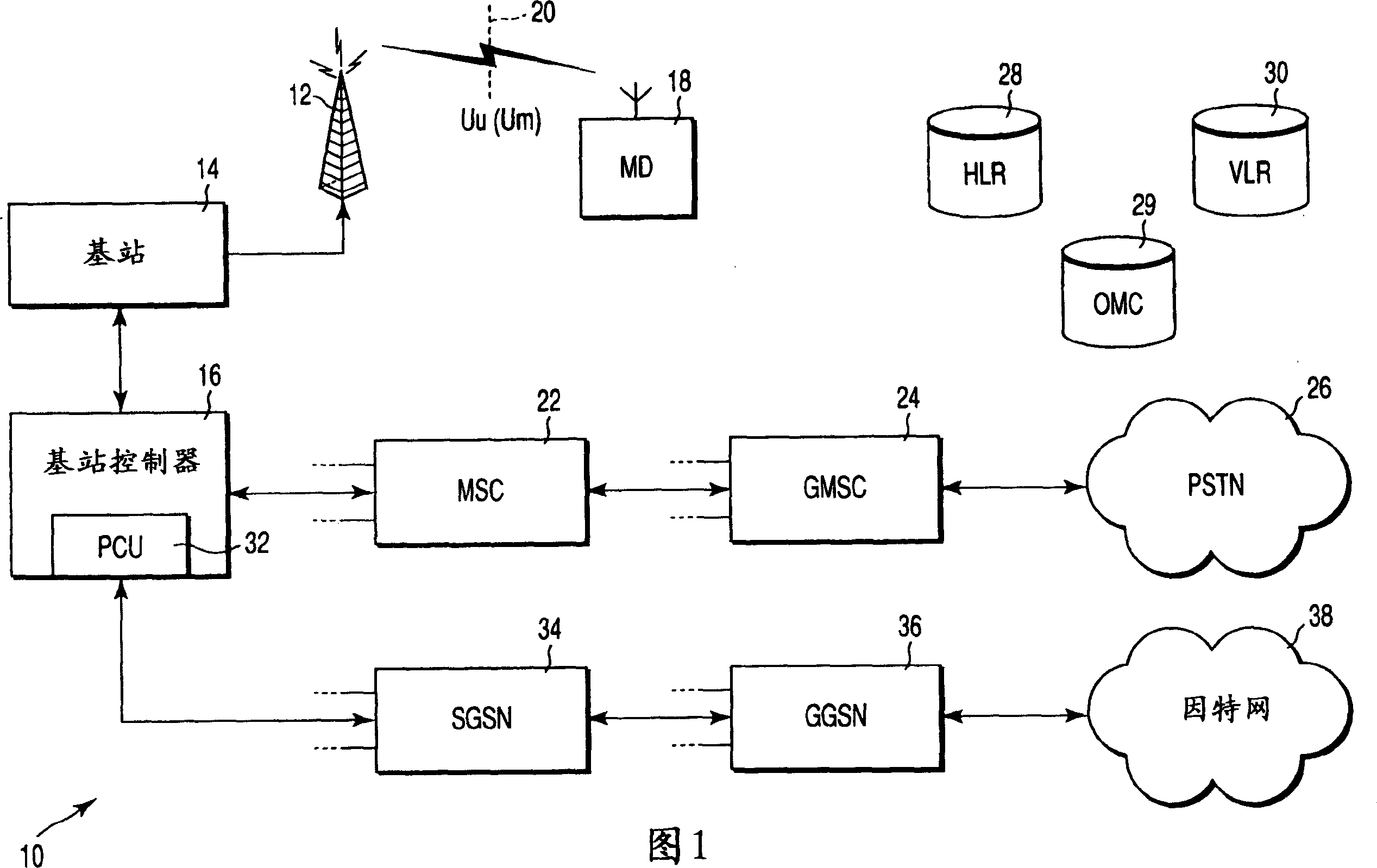
Method and system for key management in voice over internet protocol
InactiveUS7730309B2Eliminate needEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSession Initiation ProtocolDiffie–Hellman key exchange
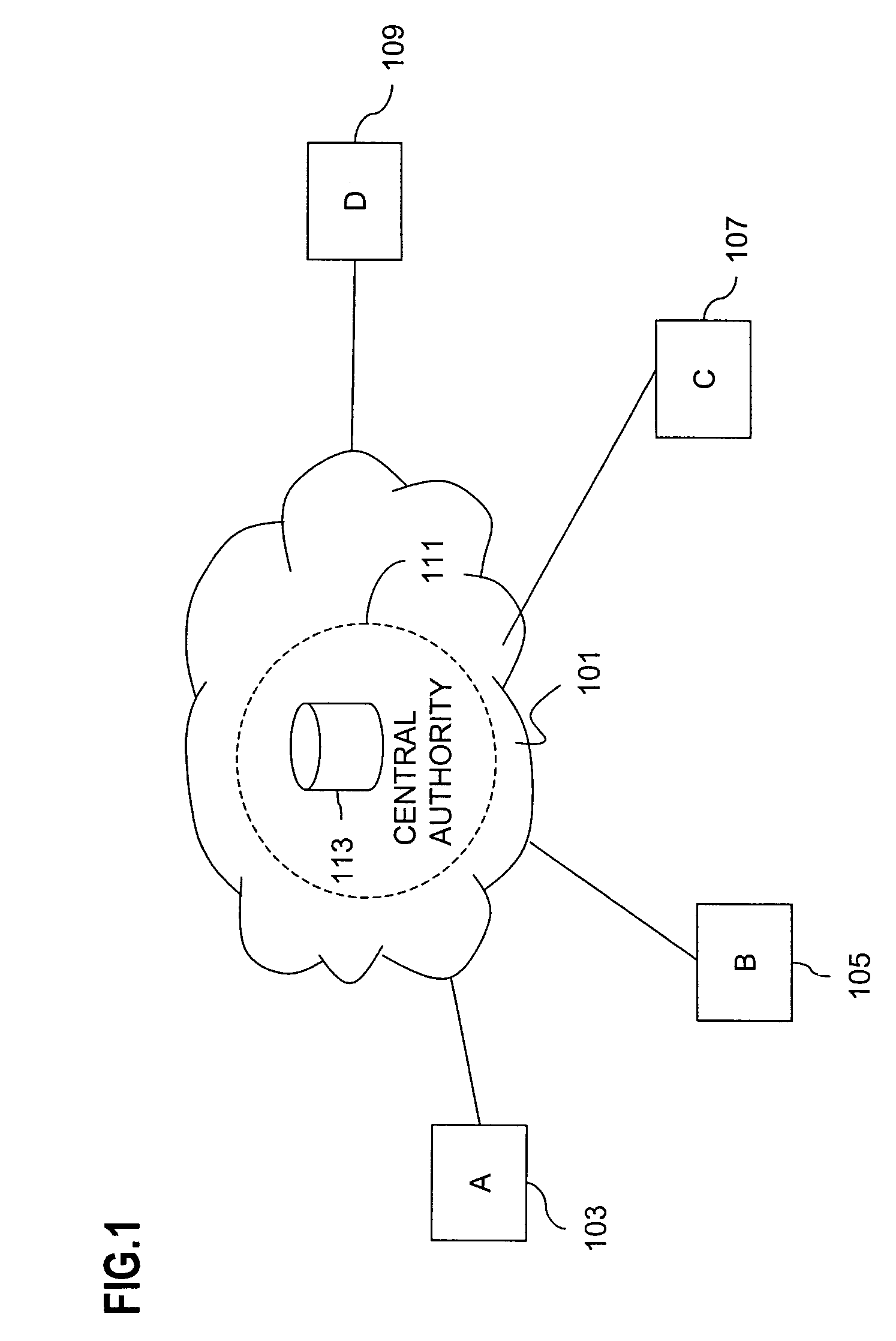
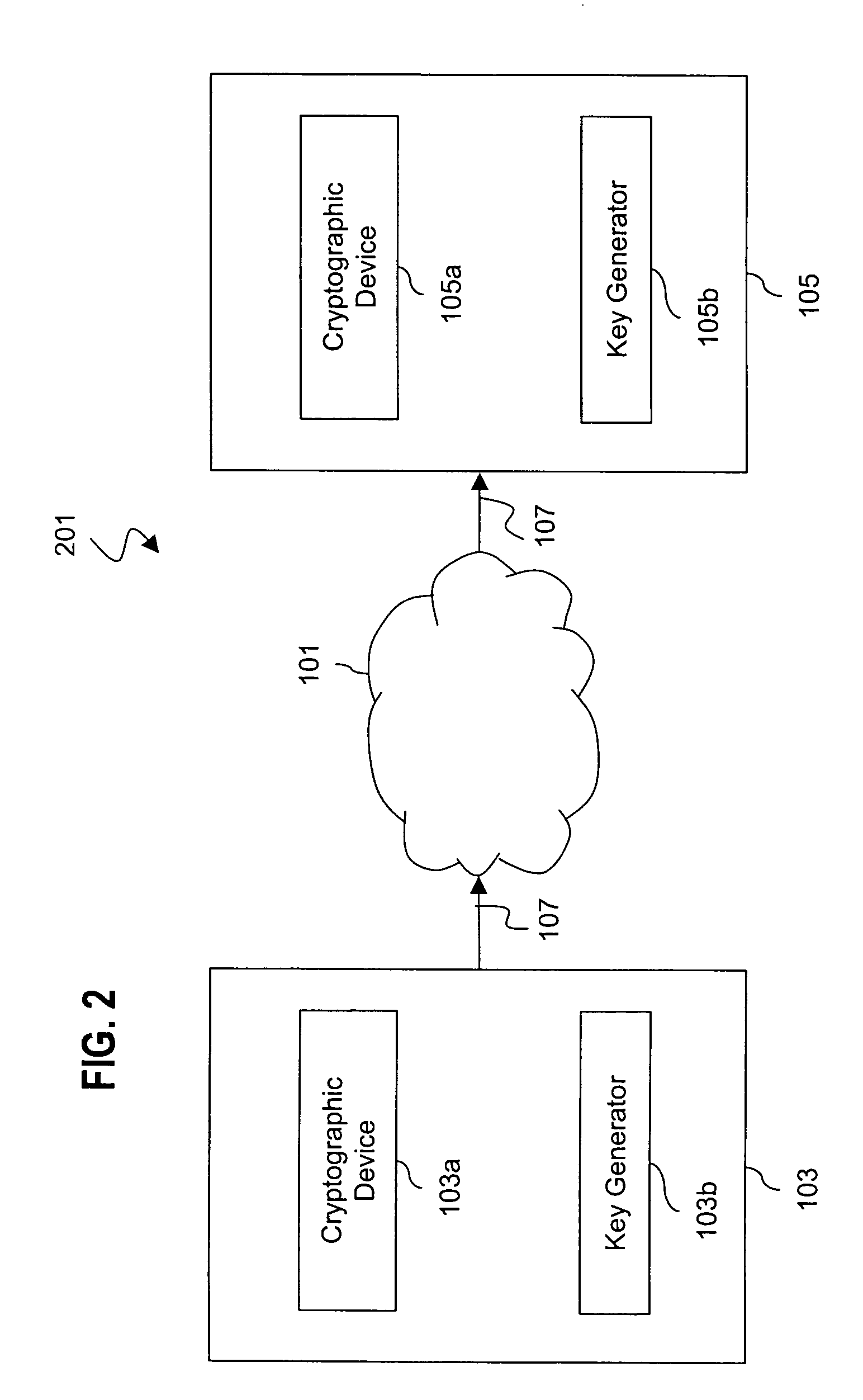
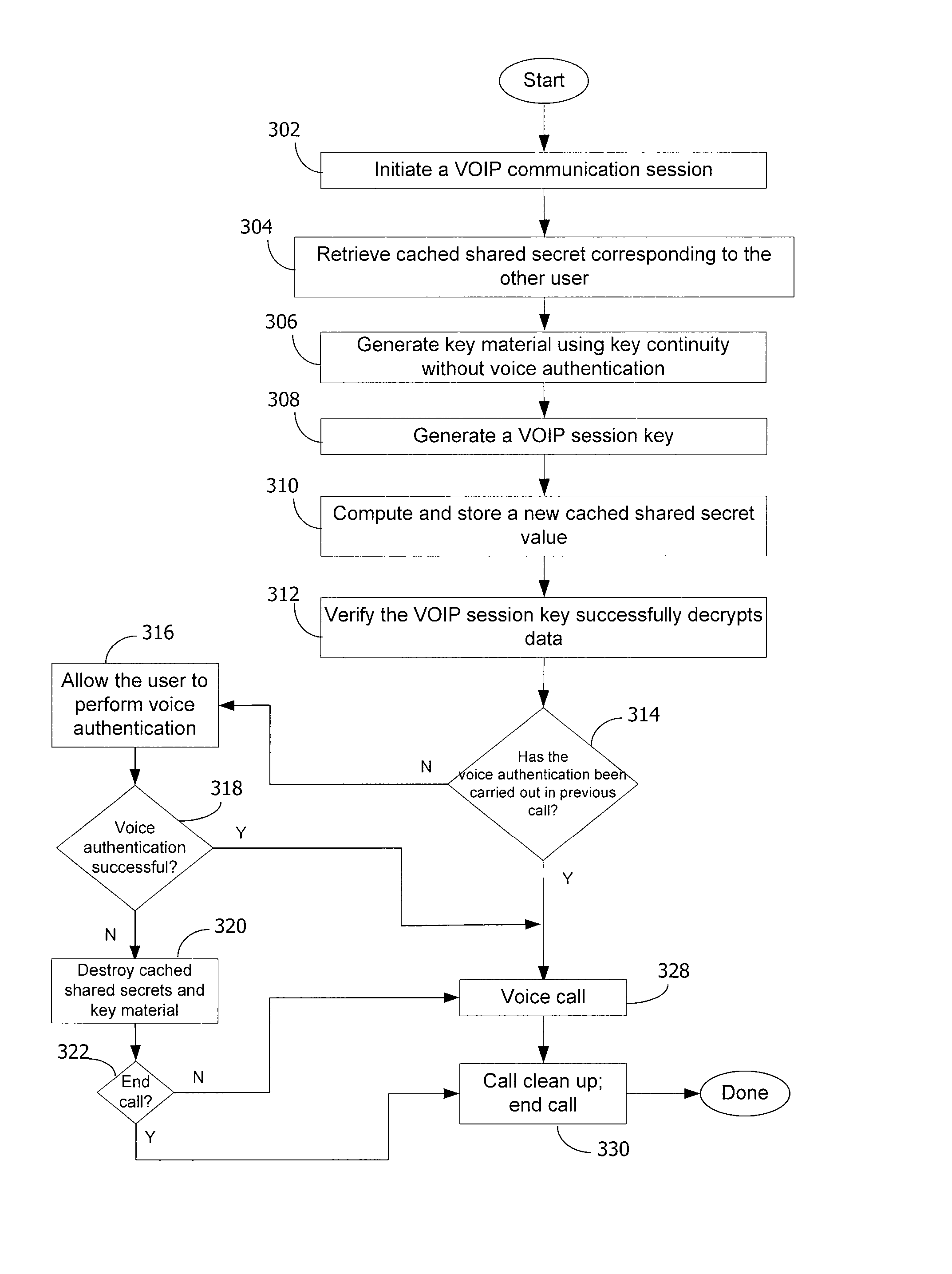
A method and system for a secure telephone protocol are disclosed, which can be implemented using current Voice over IP (VoIP) protocols, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP, as specified in the Request for Comment (RFC) 3261 from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)), Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP, as specified in RFC 3550), and Secure RTP (SRTP, as specified in RFC 3711). The secure telephone protocol can include a shared secret value that is cached and then re-used later to authenticate a long series of session keys to be used for numerous separate secure phone calls over a long period of time, thereby providing cryptographic key continuity without the need for voice authentication. In an embodiment, the secure telephone protocol can utilize the Diffie-Hellman key exchange during call setup, and AES for encrypting the voice stream.
Owner:ZIMMERMANN PHILIP R
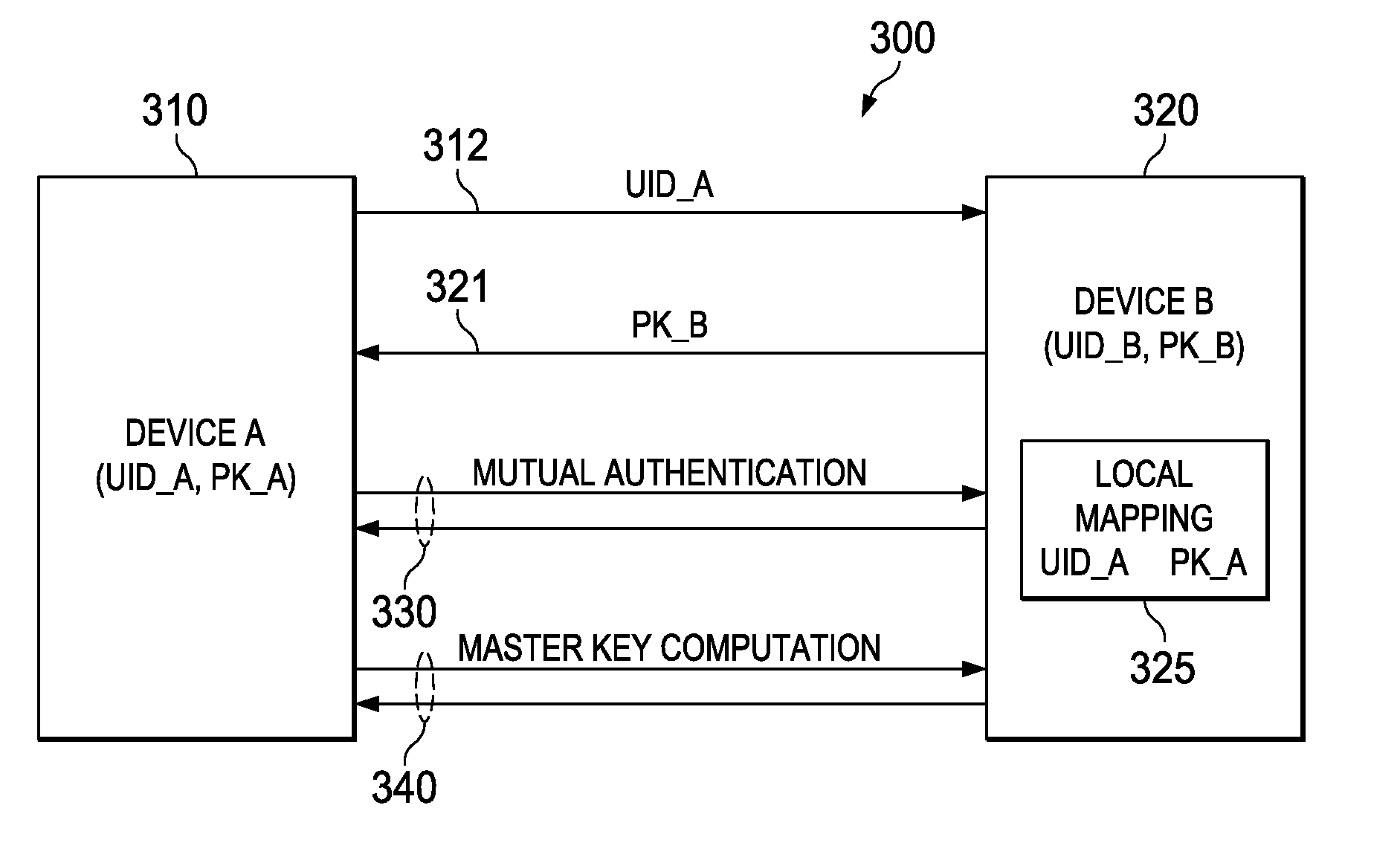
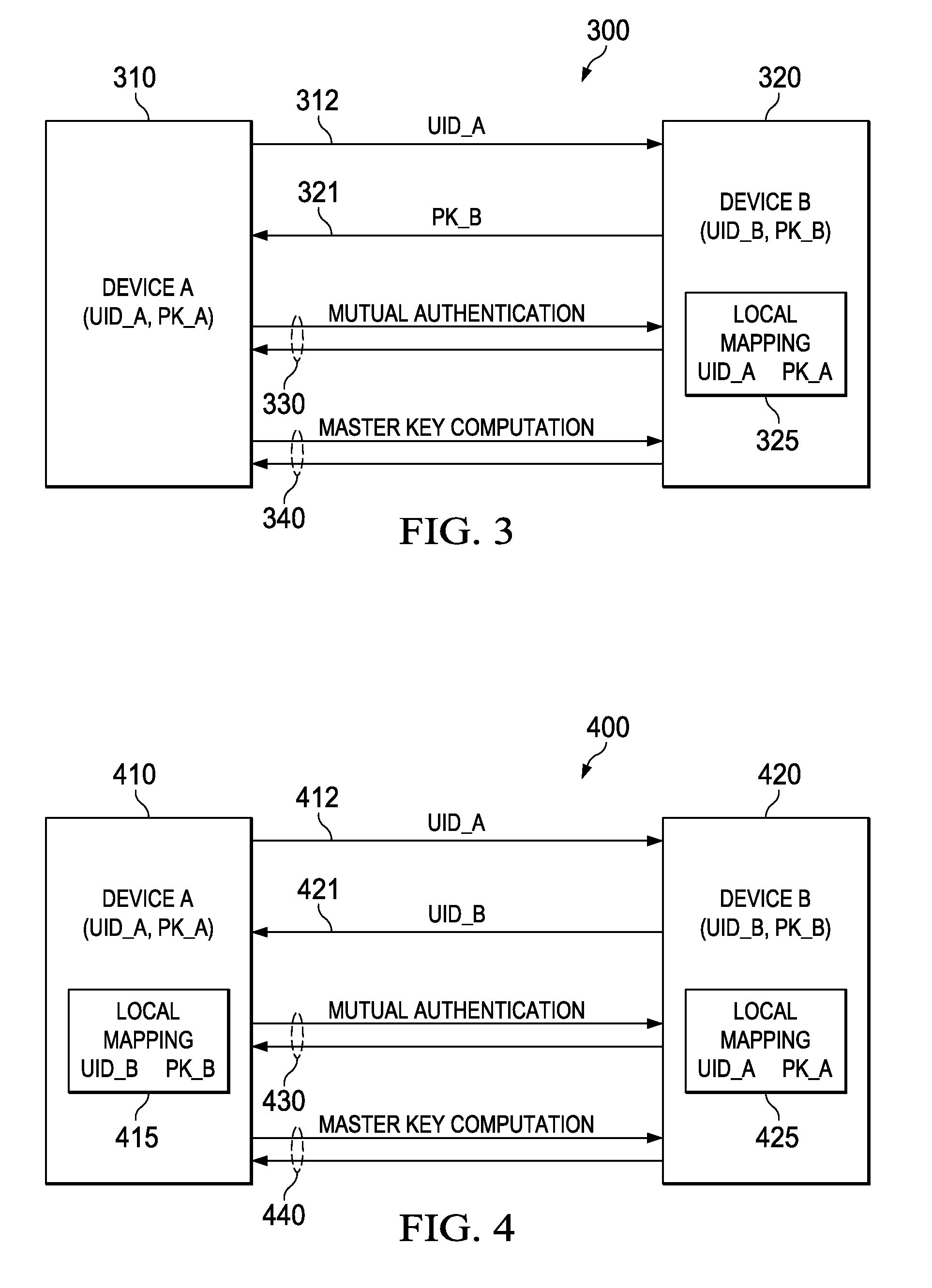
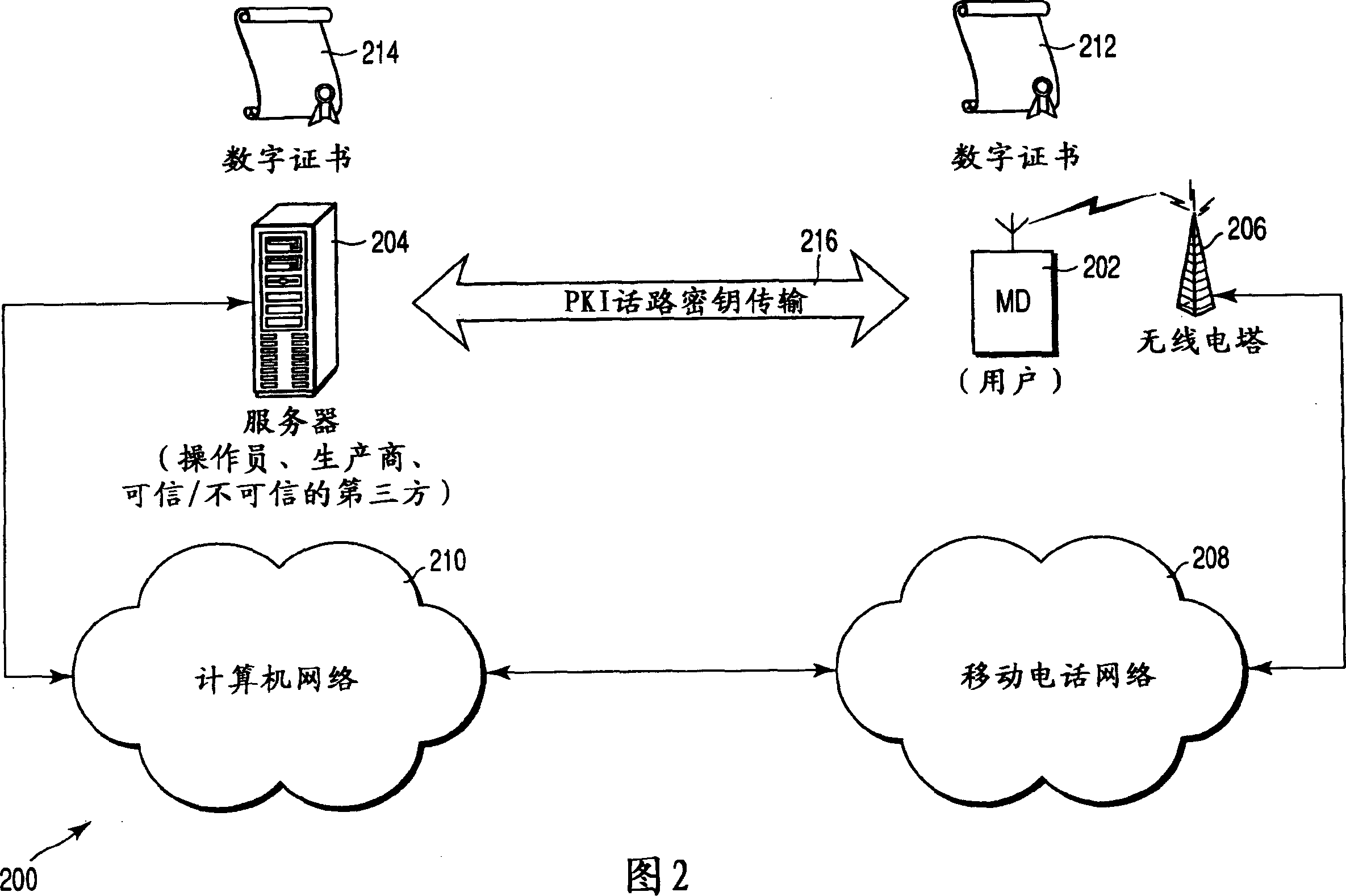
Public Key Out-of-Band Transfer for Mutual Authentication
ActiveUS20100042838A1User identity/authority verificationSecure communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchange
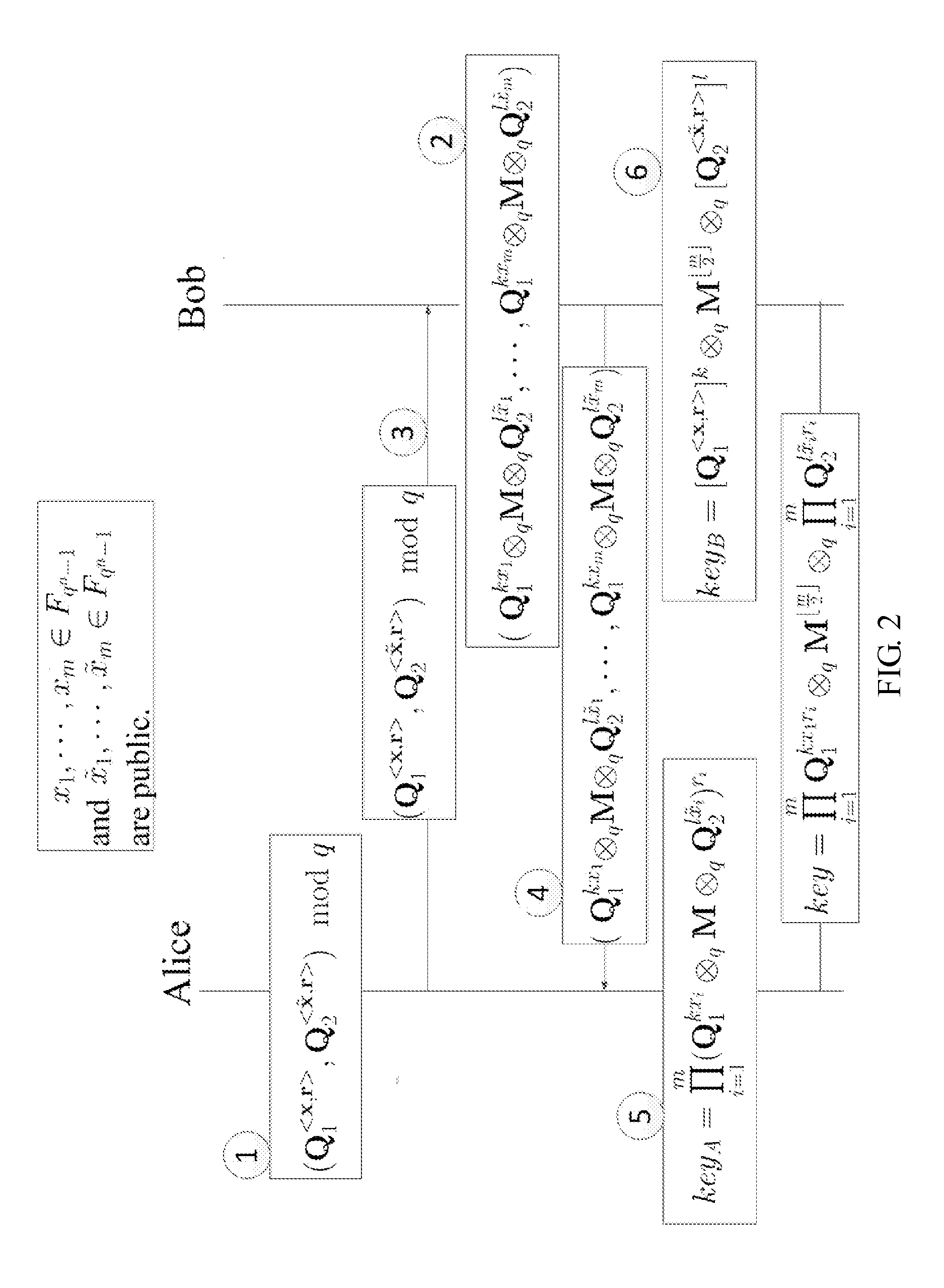
Methods for key exchange and mutual authentication are provided that allow for inherent authentication and secret key derivation of parties communicating through an unsecured medium. These methods allow for greater security than existing key exchange and authentication methods while requiring little or no additional energy or time compared with a basic Diffie-Hellman key exchange. These methods allow for secure communication with small, low-power devices and greater security for any devices communicating through an unsecured medium.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Providing forward secrecy in a terminating SSL/TLS connection proxy using ephemeral Diffie-Hellman key exchange
ActiveUS20150067338A1Promote exchangeKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageTerminal serverDigital signature
An infrastructure delivery platform provides a proxy service as an enhancement to the TLS / SSL protocol to off-load to an external server the generation of a digital signature, the digital signature being generated using a private key that would otherwise have to be maintained on a terminating server. Using this service, instead of digitally signing (using the private key) “locally,” the terminating server proxies given public portions of ephemeral key exchange material to the external server and receives, in response, a signature validating the terminating server is authorized to continue with the key exchange. In this manner, a private key used to generate the digital signature (or, more generally, to facilitate the key exchange) does not need to be stored in association with the terminating server. Rather, that private key is stored only at the external server, and there is no requirement for the pre-master secret to travel (on the wire).
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Method and structure for self-sealed joint proof-of-knowledge and diffie-hellman key-exchange protocols
InactiveUS20100205443A1Robust resistance against malicious disclosureImproving security and privacy and efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeCryptographic protocol
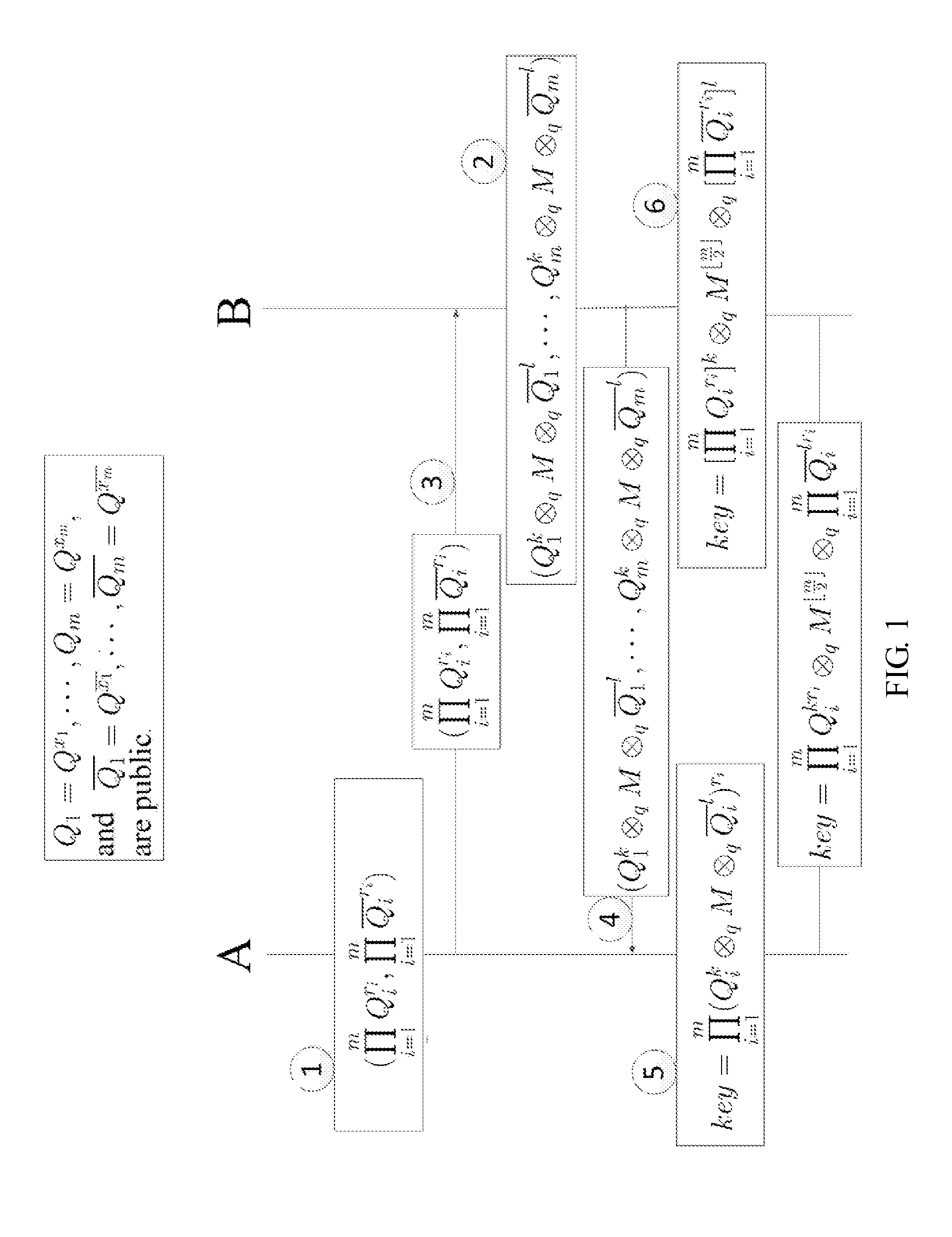
A method (and structure) for a party (the prover) to prove its knowledge, jointly and non-malleably, of multiple secret (fixed and / or ephemeral) Diffie-Hellman exponents (DH-exponents), corresponding to its public (fixed and / or ephemeral) DH-components and with respect to the public (fixed and / or ephemeral) challenging DH-components from another party (the verifier). The joint proof-of-knowledge (JPOK) consists of secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets, which can be generated and verified by each party by its own secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties. To ensure the non-malleability of the JPOK, the method invented herein makes all these multiplied DH-secrets to be independent, and makes the session-tag committed to the multiplied DH-secrets. To preserve players' privacy and / or to improve protocol efficiency, the invented method makes the DH-secrets to be multiplied to further satisfy at least one of the following (besides above independence and commitments properties): (1) Deniability: all the DH-secrets to be multiplied can be computed out merely from the ephemeral secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties; (2) Pre-computability: a DH-secret involving a fixed DH-component of a party can be offline pre-computed by its peer; (3) Post-ID computability: a DH-secret involving an ephemeral DH-component of a party can be computed by its peer without knowing that party's identity and / or fixed DH-components. The secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets can then be used to derive session-keys and to generate and verify authenticators between the parties. The invented method can also be used in parallel or subsequently by the parties, possibly with reserved player roles in different runs of the method, for mutual identifications, key confirmations, and for achieving more advanced cryptographic protocols in various settings.
Owner:ANDREW C YAO
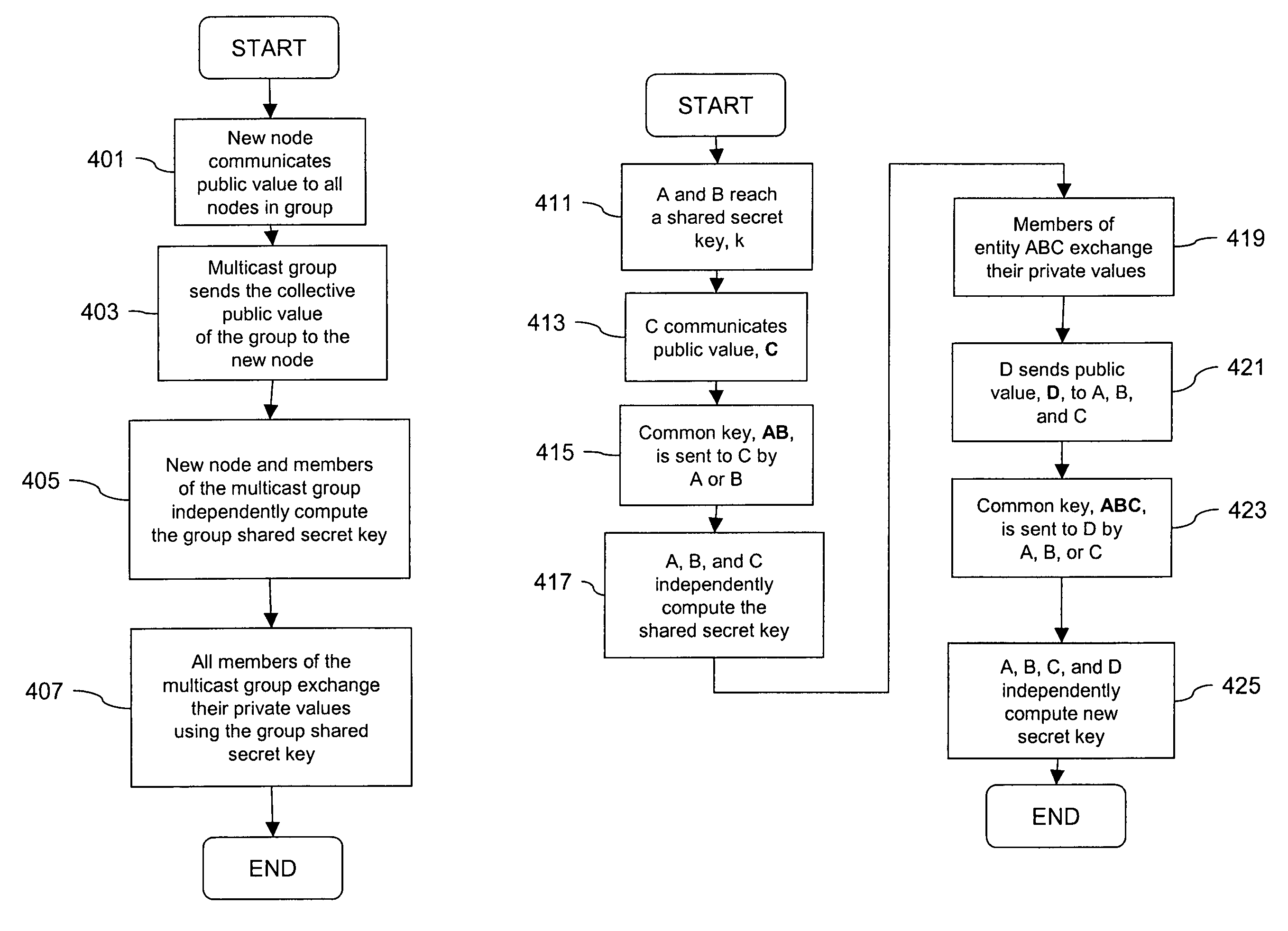
Processing method for key exchange among broadcast or multicast groups that provides a more efficient substitute for Diffie-Hellman key exchange
InactiveUS7181014B1Communication securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeBroadcasting
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for key management in voice over internet protocol
InactiveUS20070157026A1Eliminate needEasy to implementKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSession Initiation ProtocolDiffie–Hellman key exchange
A method and system for a secure telephone protocol are disclosed, which can be implemented using current Voice over IP (VoIP) protocols, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP, as specified in the Request for Comment (RFC) 3261 from the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)), Real Time Transport Protocol (RTP, as specified in RFC 3550), and Secure RTP (SRTP, as specified in RFC 3711). The secure telephone protocol can include a shared secret value that is cached and then re-used later to authenticate a long series of session keys to be used for numerous separate secure phone calls over a long period of time, thereby providing cryptographic key continuity without the need for voice authentication. In an embodiment, the secure telephone protocol can utilize the Diffie-Hellman key exchange during call setup, and AES for encrypting the voice stream.
Owner:ZIMMERMANN PHILIP R
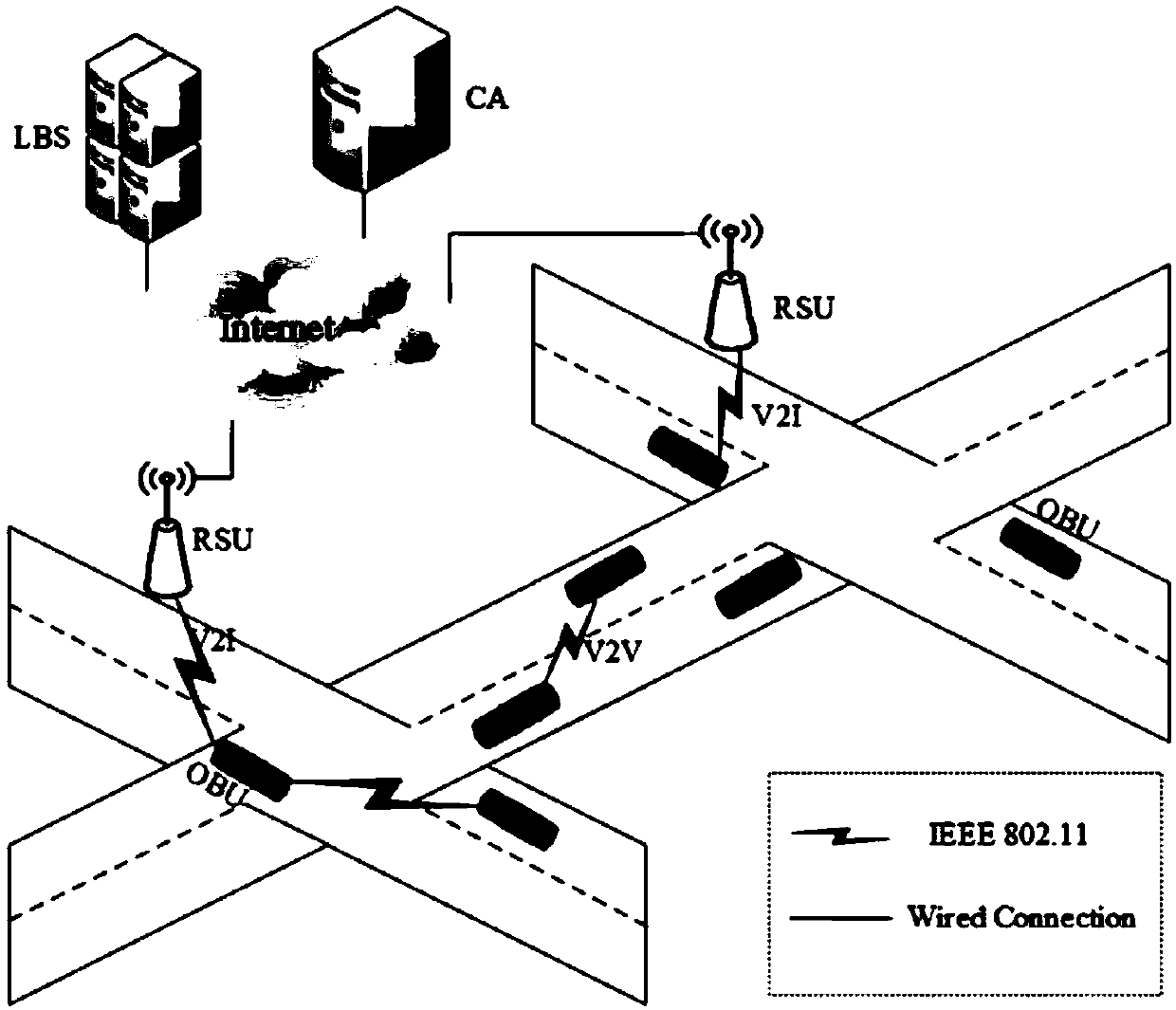
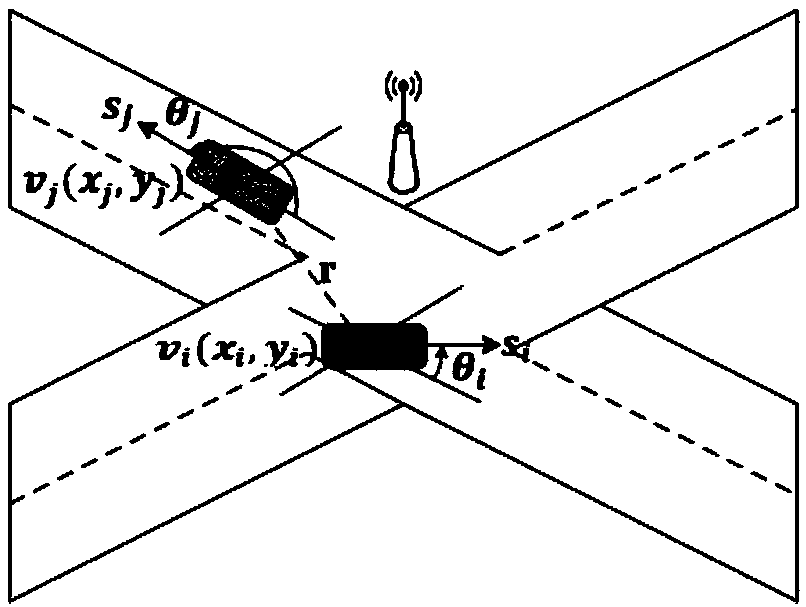
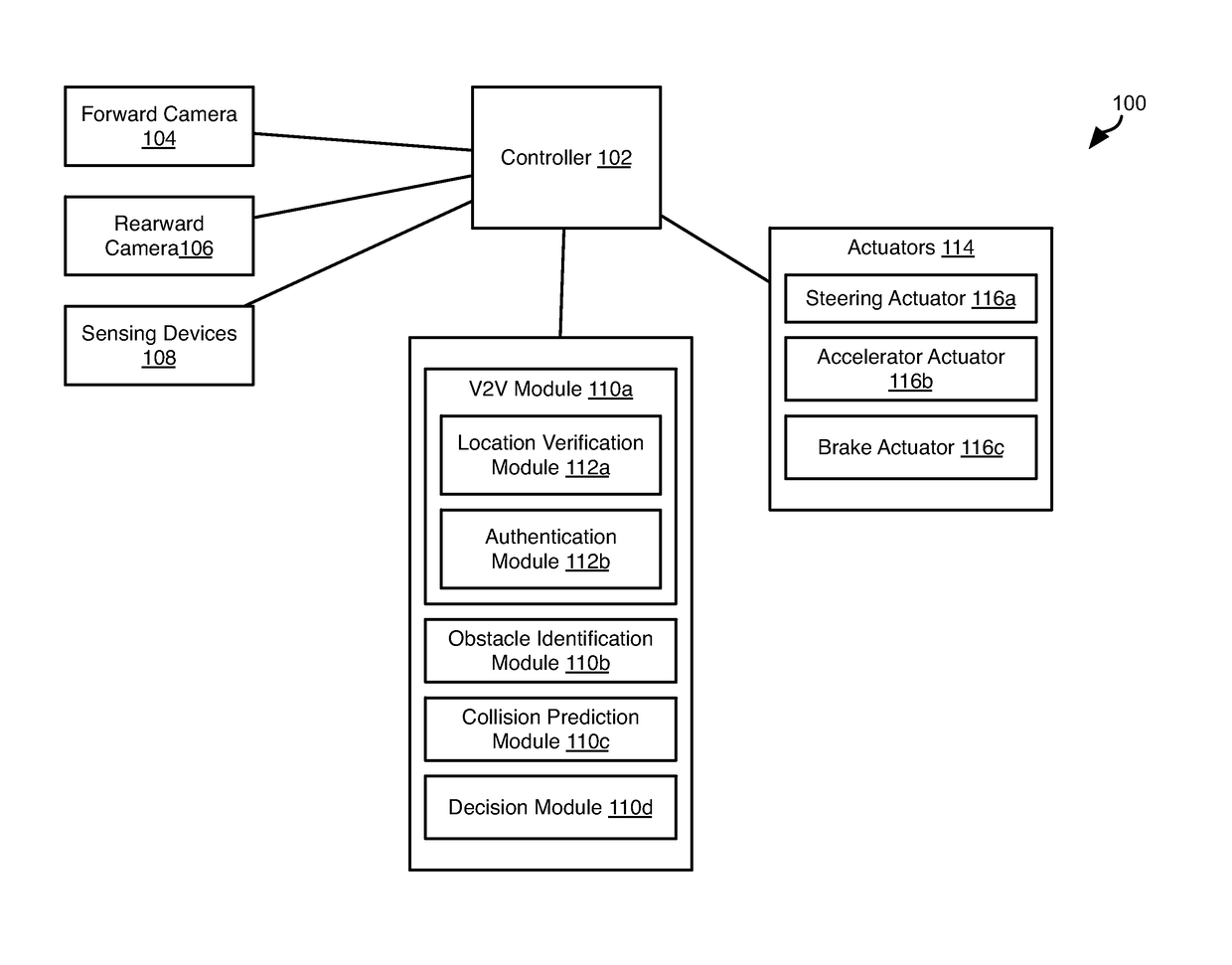
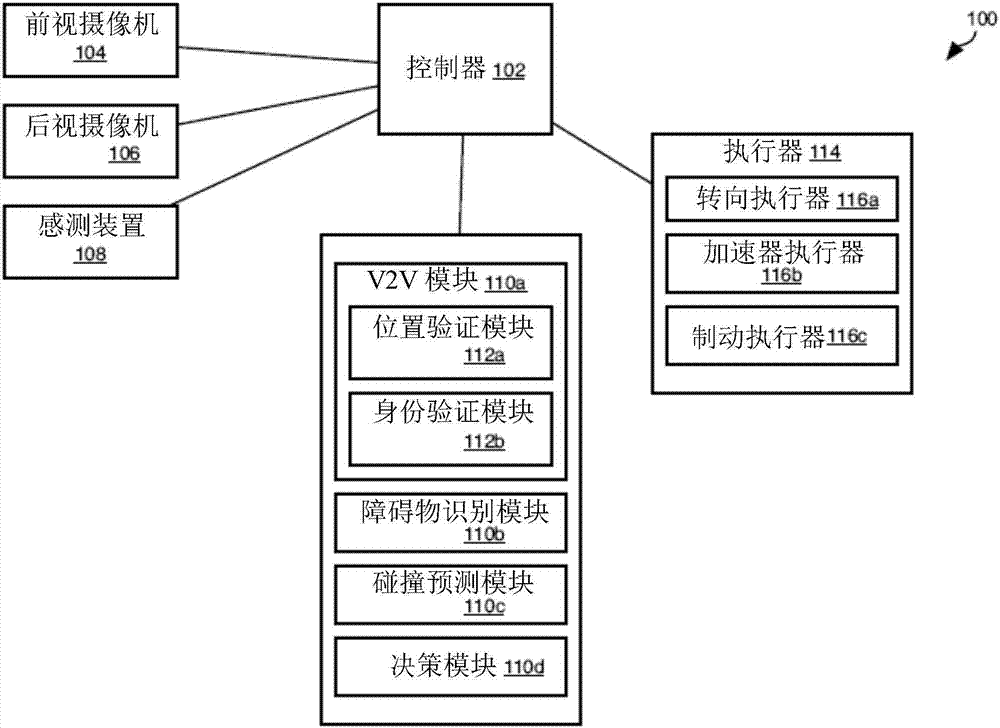
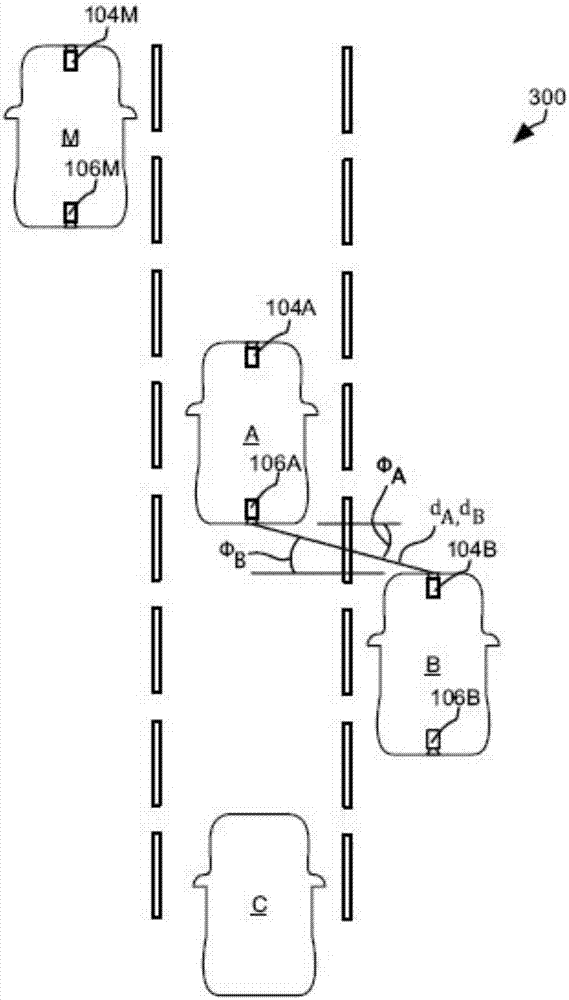
Inter-Vehicle Authentication Using Visual Contextual Information
ActiveUS20170132477A1Television system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeVisual perception
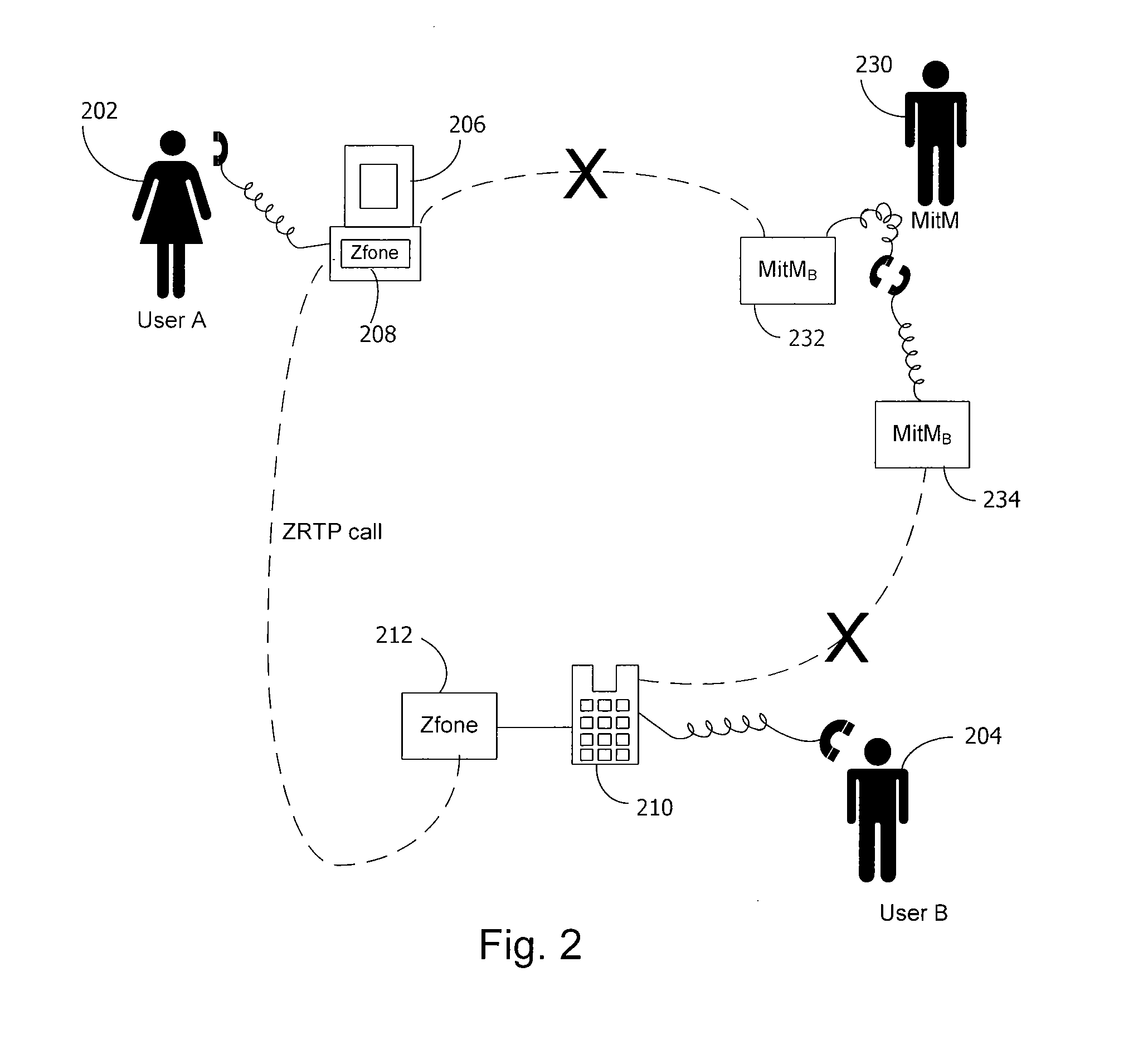
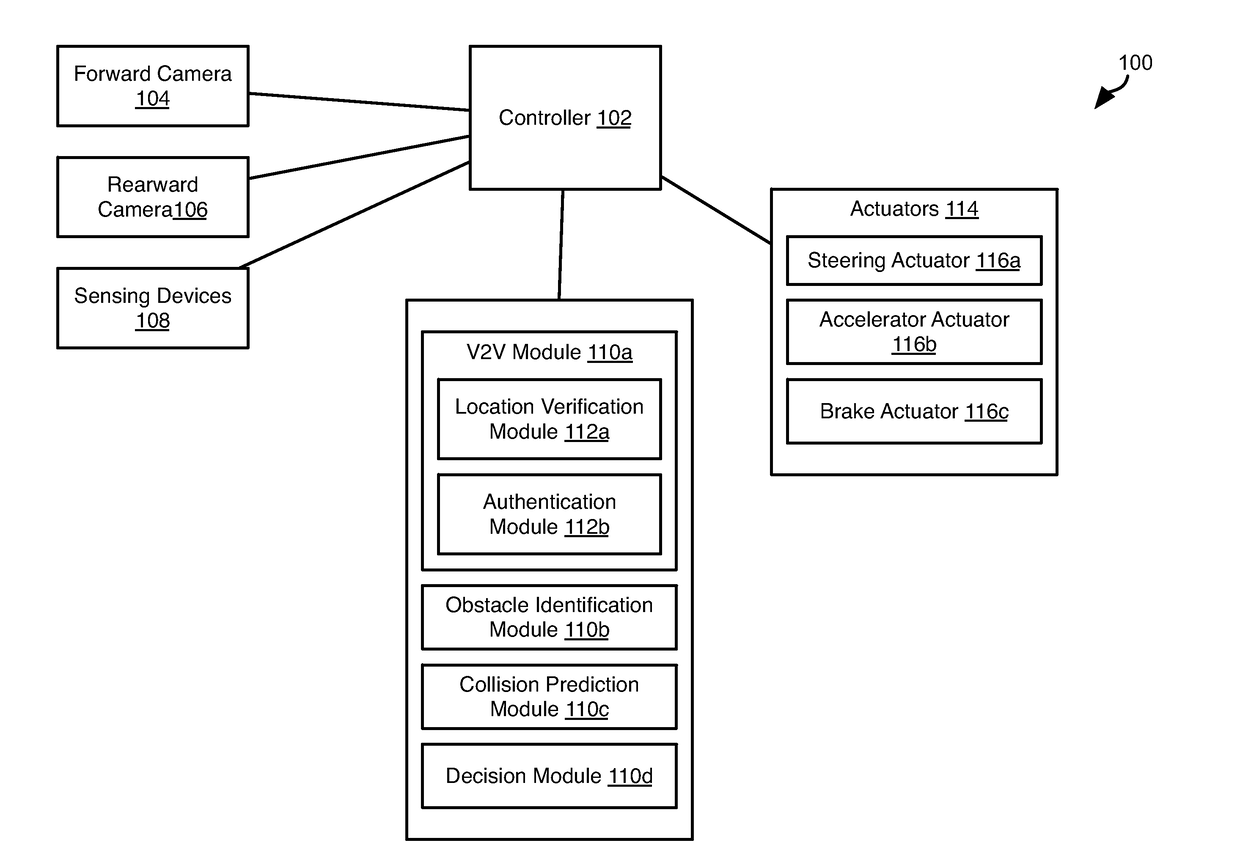
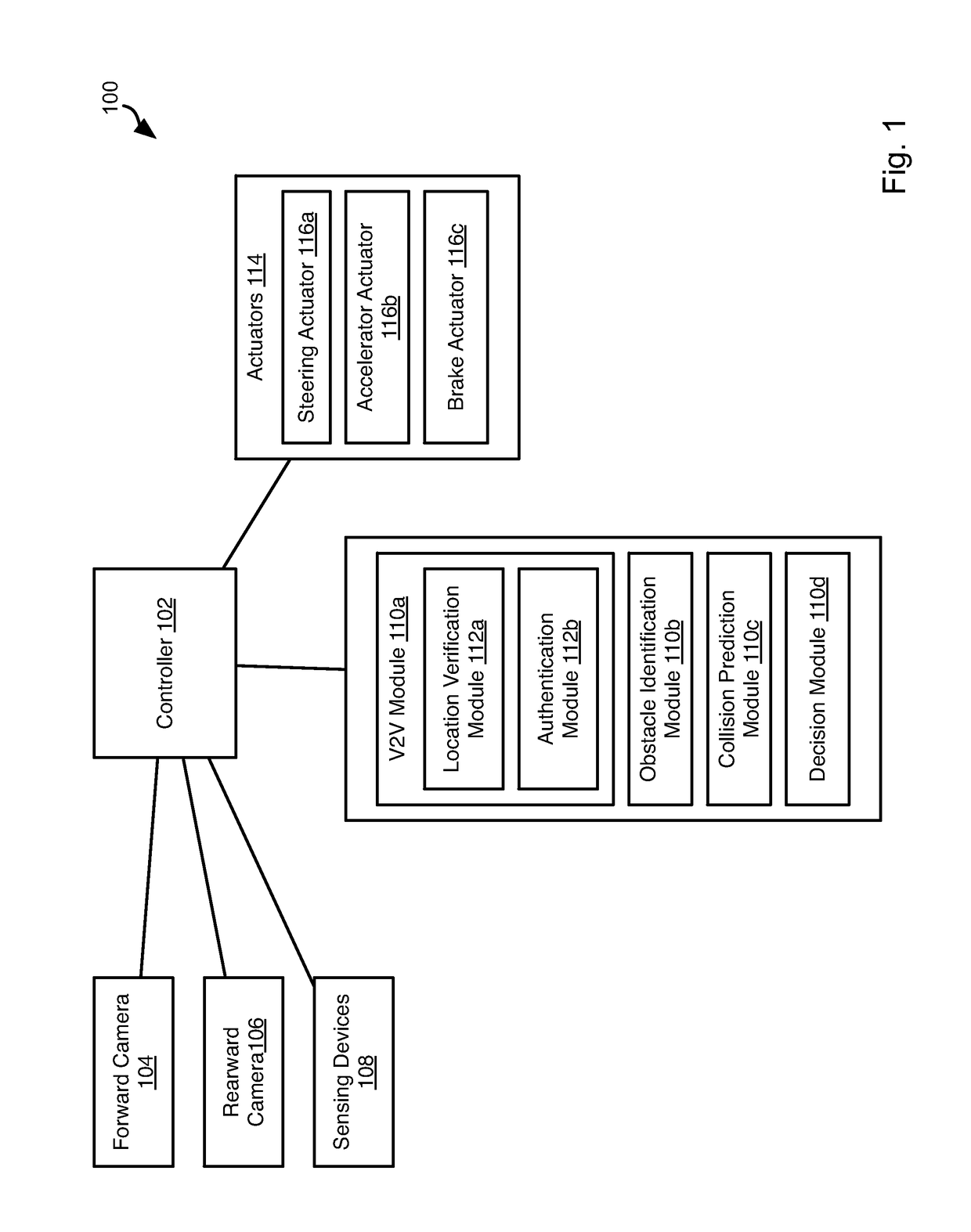
Authentication of vehicles in preparation for V2V communication includes vehicle A taking a picture of vehicle B (VA) and vehicle B taking a picture of vehicle A (VB). These pictures are then shared. Vehicle A determines the relative location of vehicle B indicated in VA and VB. If they agree, then vehicle A and B authenticate one another, such as using Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Identifying vehicle A and vehicle B in the pictures may include identifying the license plates of vehicle A and vehicle B in the pictures. Vehicles A and B may exchange license plate numbers prior to taking of the pictures. Image spoofing may be prevented by taking both forward and rearward facing pictures by both vehicles. Objects in pictures facing the same direction may be identified to verify that the pictures were taken nearly simultaneously.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
System and method for initializing a simple network management protocol (SNMP) agent
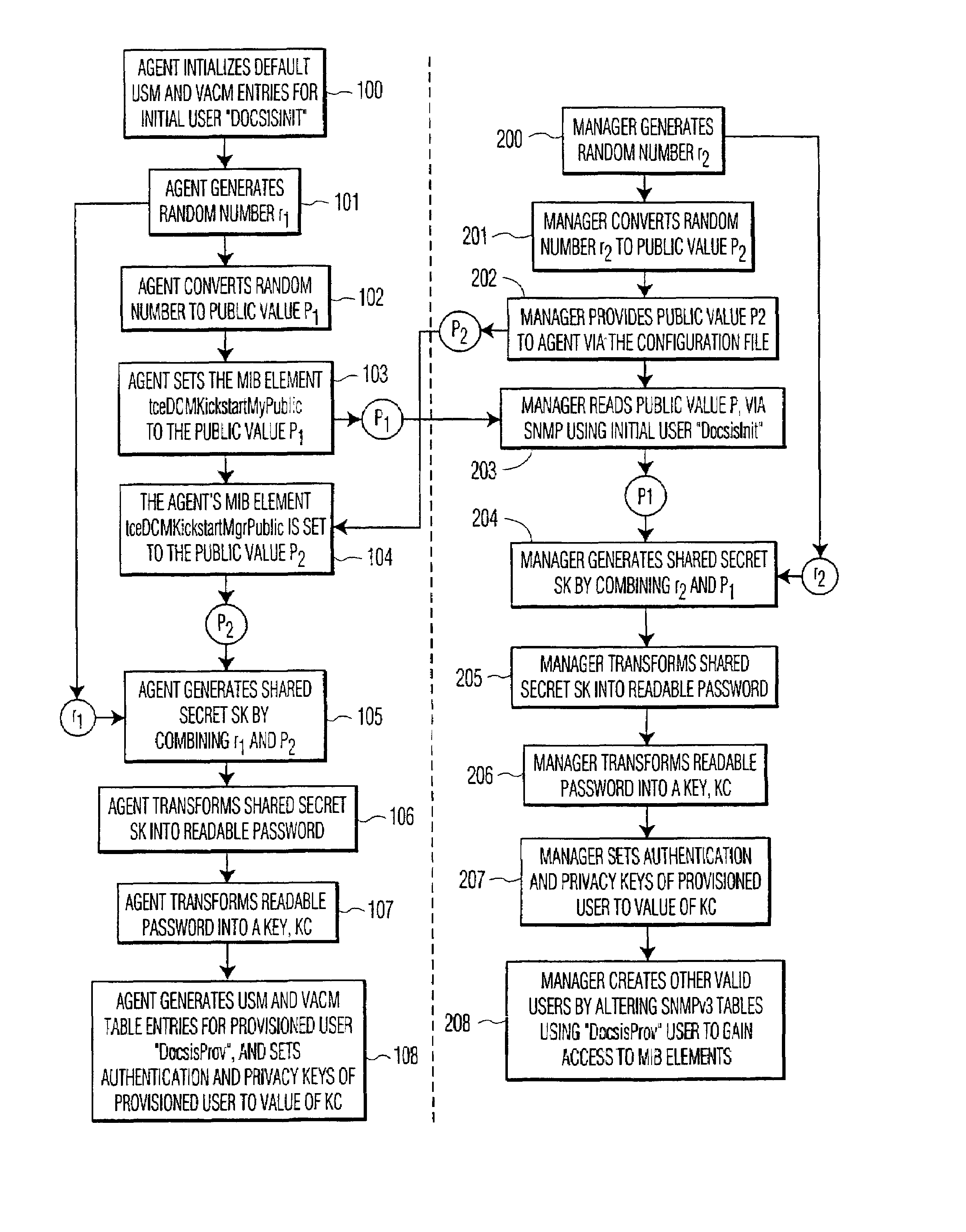
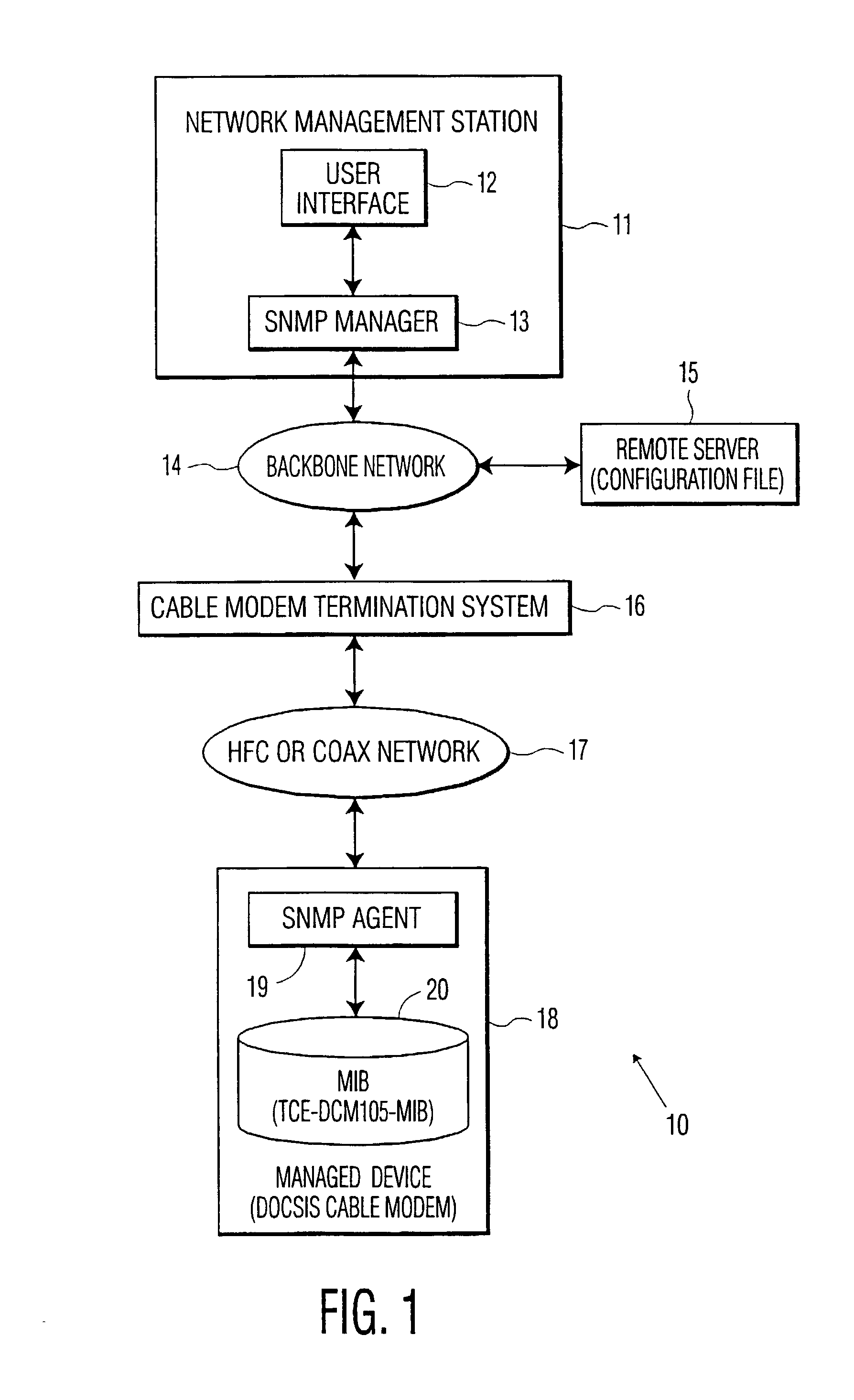
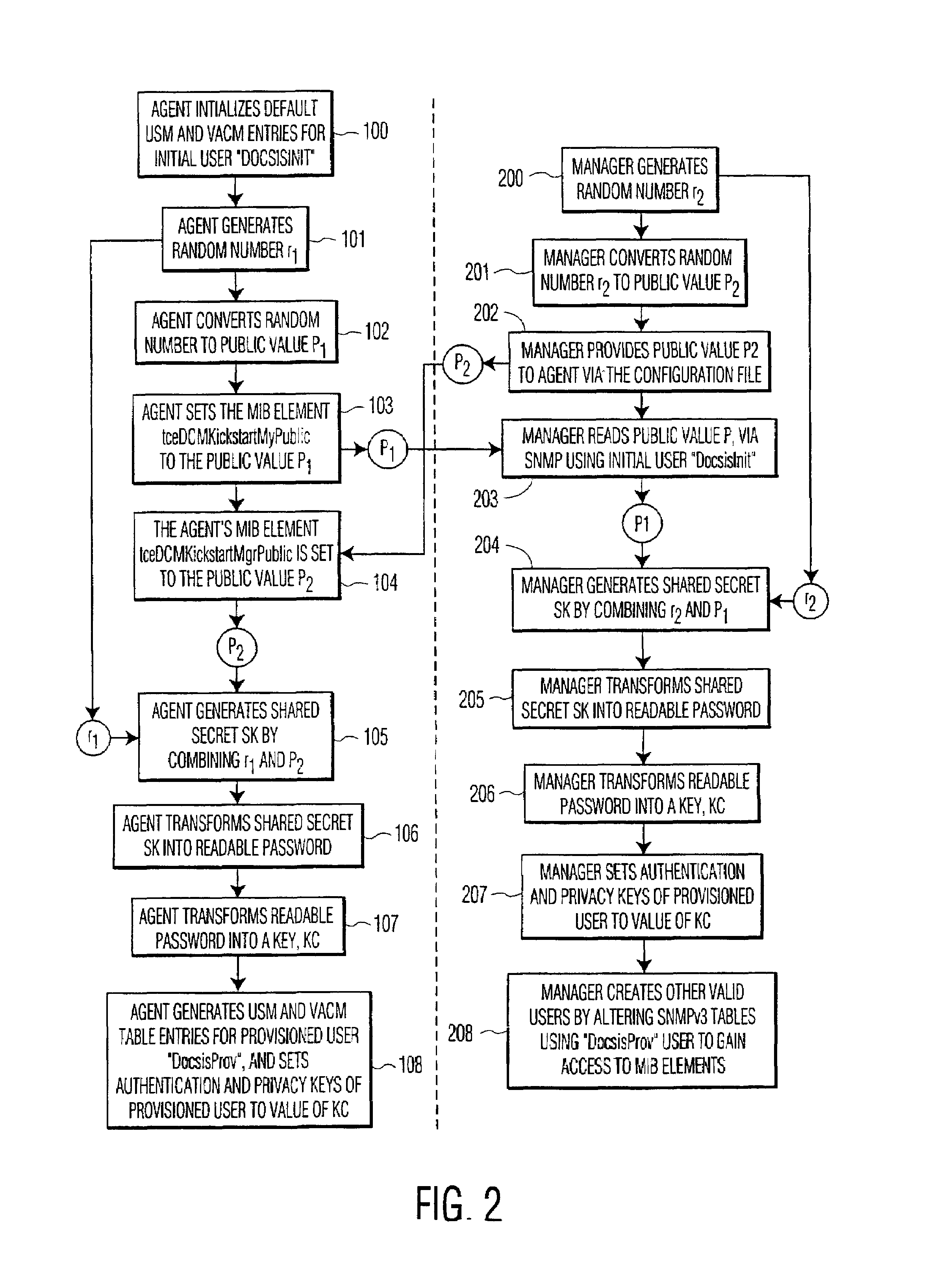
InactiveUS7290142B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordDiffie–Hellman key exchange
A system and method for initializing a SNMP agent in SNMPv3 mode. In one aspect of the invention, a method is provided that allows an operator to securely enter the initial SNMPv3 privacy and authentication keys into a SNMPv3 device and cause the device to enter in SNMPv3 mode. The SNMP manager and SNMP agent both generate an associated random number and public value. The SNMP manager passes its public value to the SNMP agent in a configuration file, which causes a proprietary MIB element in the SNMPv3 device to be set with the public value of the SNMP manager. The SNMP manager reads the public value of the SNMP agent through a SNMP request using an initial valid user having access to the public value of the SNMP agent. The SNMP agent and SNMP manager each independently compute a shared secret using the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol. The SNMP manager and SNMP agent each independently convert the shared secret into the same readable password, convert the readable password into the same secret key and set the initial authentication key and the initial privacy key to the value of the secret key.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
ASYMMETRIC-COMPUTING TYPE SHARED KEY ESTABLISHING METHOD SUITABLE FOR CLOUD COMPUTING AND IoT
ActiveUS20150358157A1Improve efficiencyWide applicationKey distribution for secure communicationCoprocessorDiffie–Hellman key exchange
An asymmetric-computing type shared key establishing method suitable for cloud computing and IoT has the following advantages. The realization efficiency and the security level are high, and a cryptographic algorithm coprocessor is not needed. The method can be applied to occasions in which the computing capabilities are asymmetric, and attacks from quantum computers can be resisted. Compared with a conventional key exchange protocol such as the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol, the method can be more effective between servers and mobile equipment in the security fields as the IoT and cloud computing, and the method can be used in both the electronic environment and the quantum environment. Thus, the asymmetric-computing type shared key establishing method suitable for cloud computing and IoT provided by the invention can be widely applied to the field of information security systems such as network security and e-commerce.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Digital copyright management method and device for protecting digital content consumer privacy
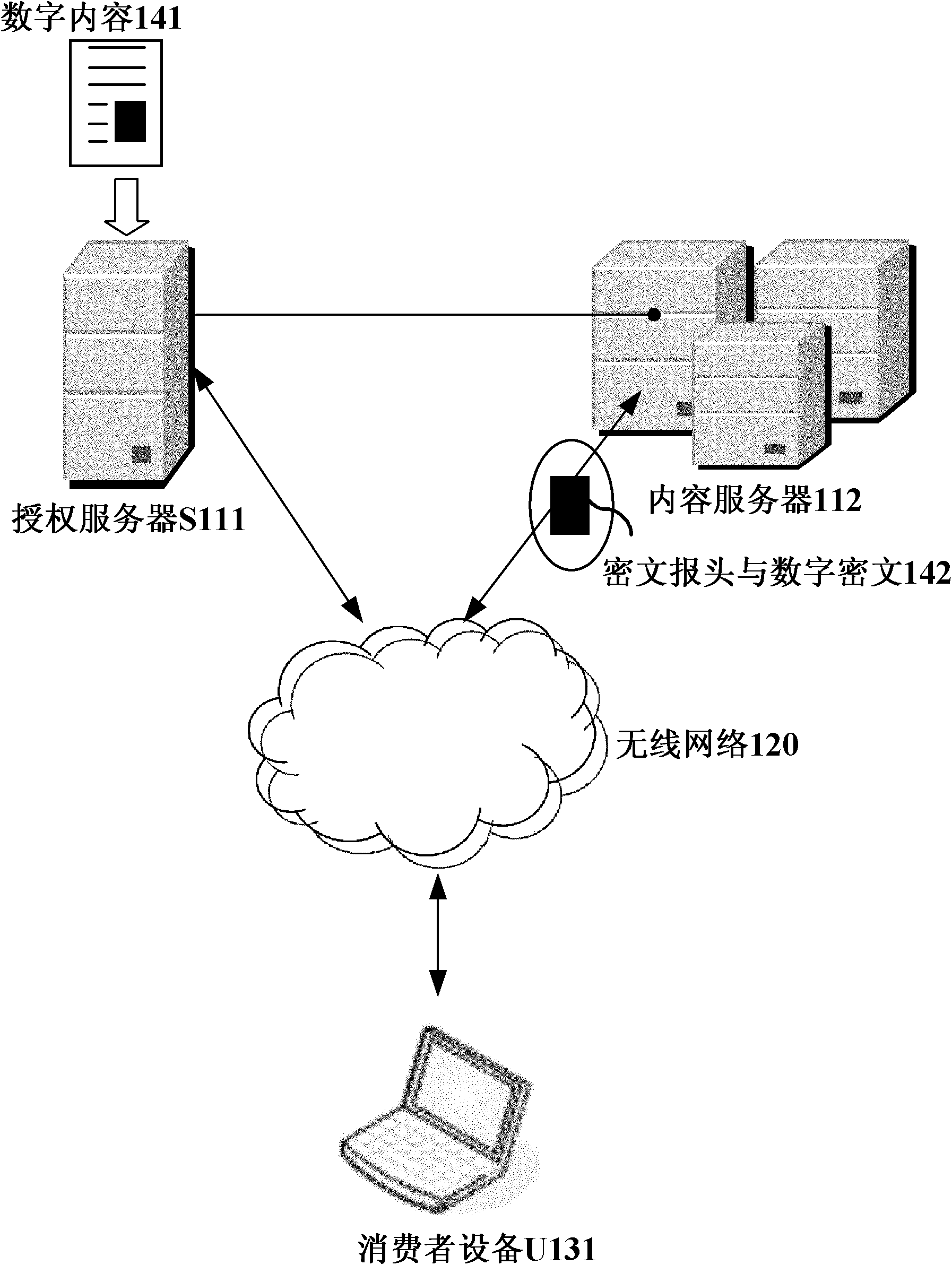
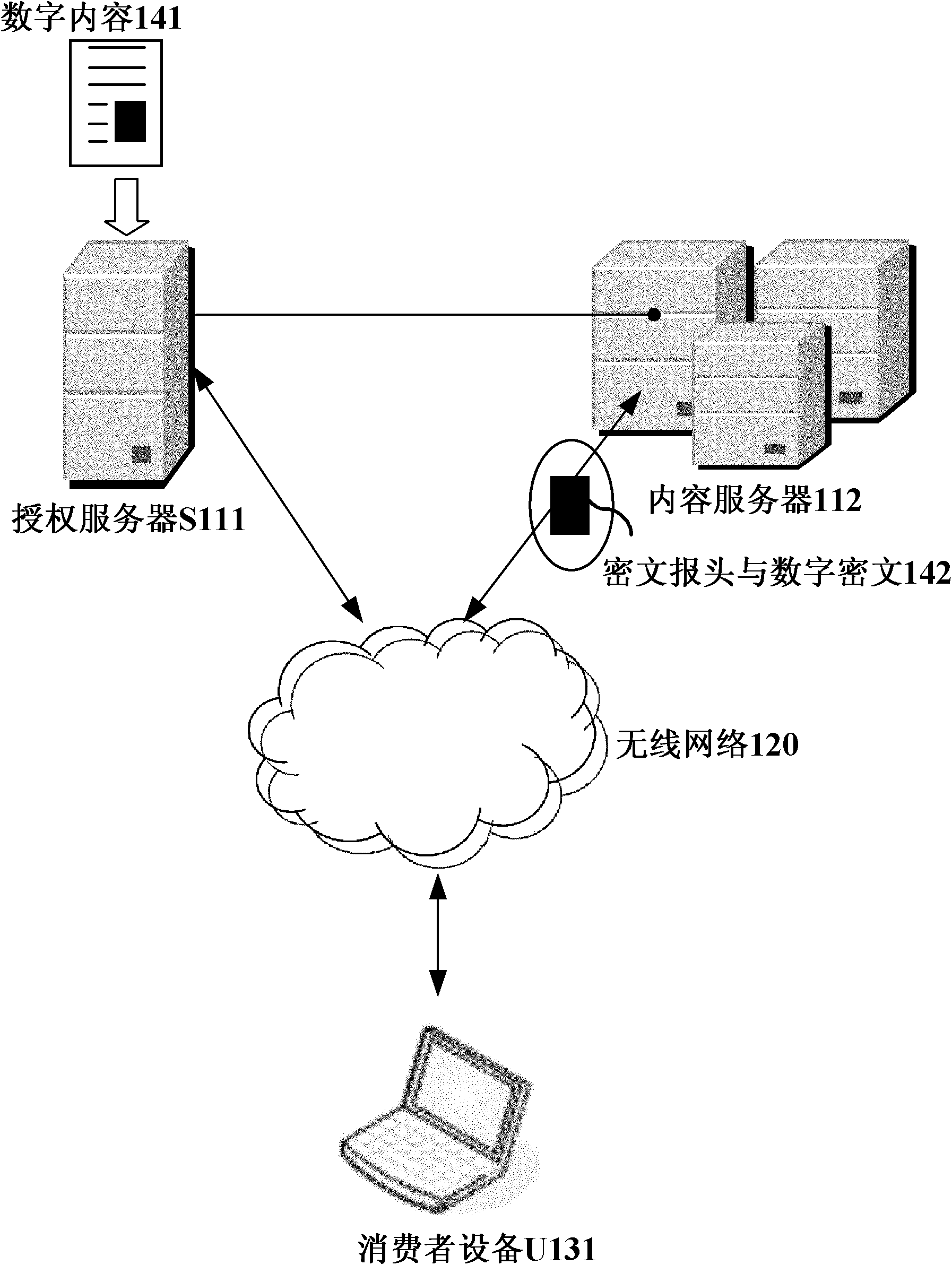
InactiveCN102025507APrivacy protectionPrevent Tampering AttacksUser identity/authority verificationProgram/content distribution protectionHash functionCiphertext
The invention discloses a digital copyright management method and device for protecting digital content consumer privacy. The method comprises the following steps: randomly generating an encrypted master key by utilizing the Chameleon hash function, and generating a copyright license; grouping the digital contents, then generating different symmetrical encrypted keys and cryptograph headers according to different groups of digital contents by adopting the Diffie-Hellman key exchange technology, encrypting the digital contents to acquire digital cryptographs, and then, storing the cryptograph headers and the digital cryptographs into a content server; and as required by users, decrypting from the cryptograph headers by utilizing the copyright license to acquire the symmetrical encrypted keys of the authorized digital contents, and then, decrypting the corresponding digital cryptographs to acquire the required digital contents. The device comprises an authorized server, a content serverand consumer equipment. Under the same security level, the invention can reduce the calculated amount, save the storage space and lower the requirements for network bandwidth.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
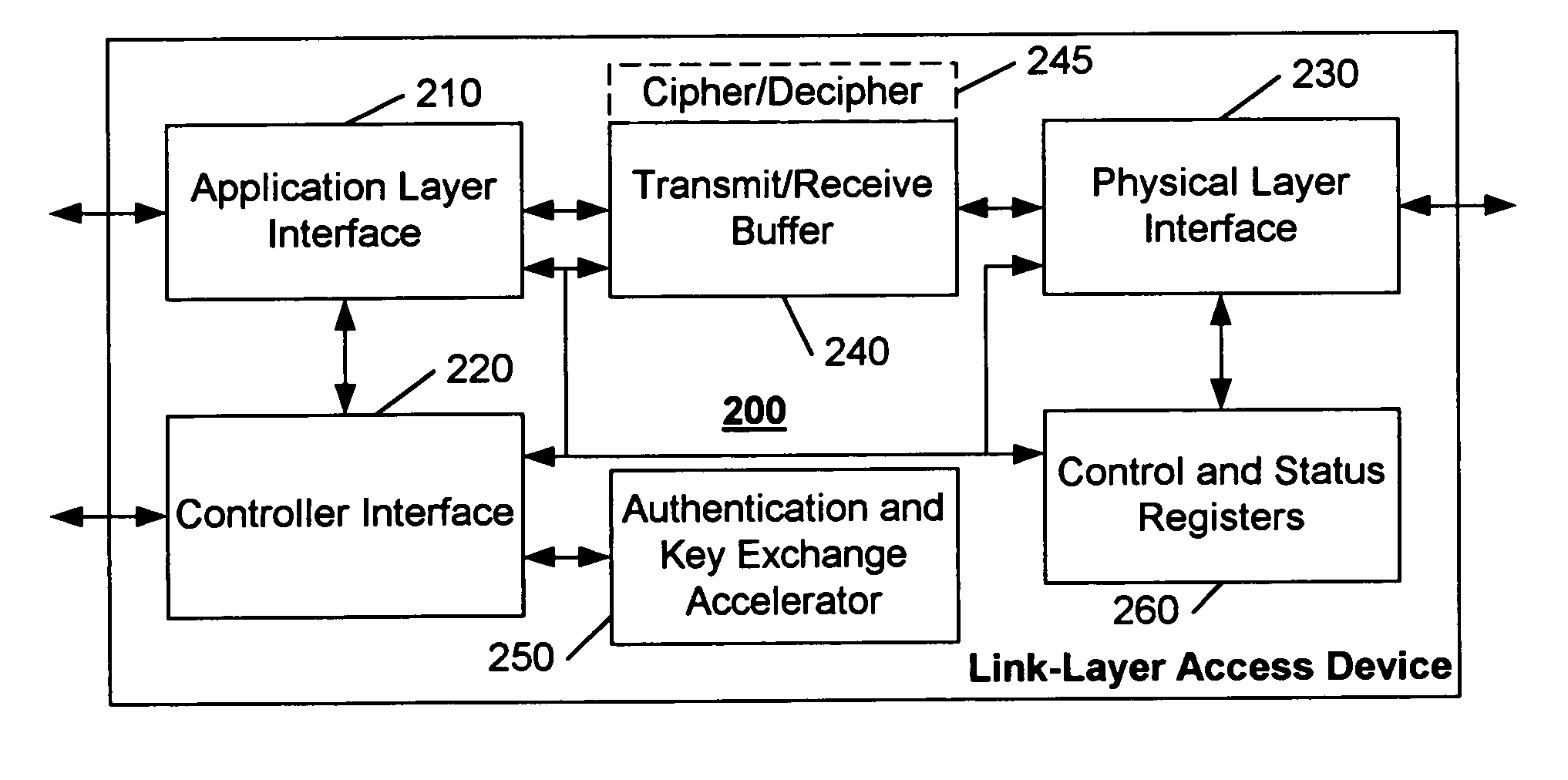
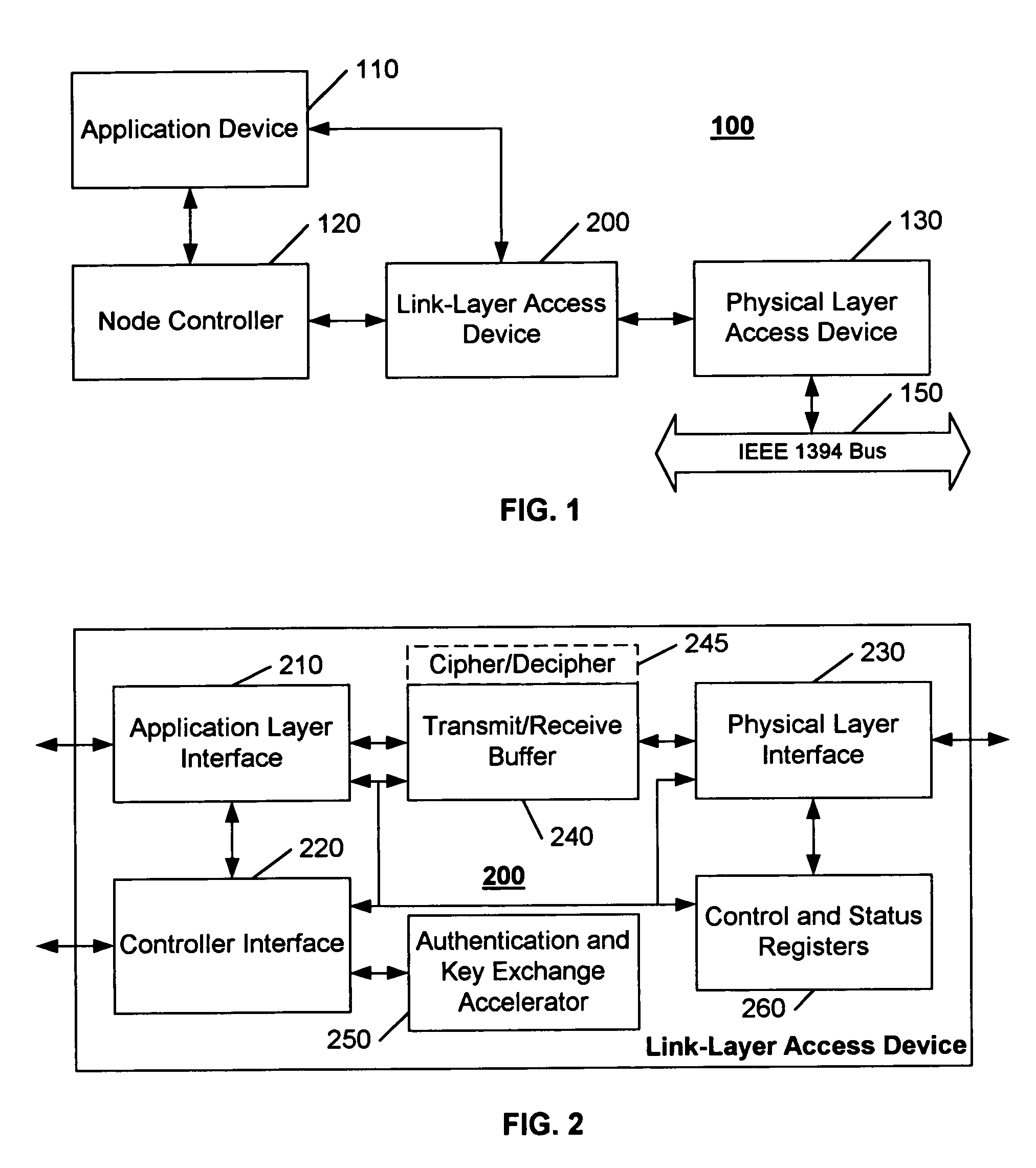
IEEE 1394 link layer chip with "5C" authentication and key exchange accelerator
InactiveUS7103769B1Facilitates taskReduce the burden onInternal/peripheral component protectionTransmissionDigital signatureDiffie–Hellman key exchange
Authentication and key exchange functions, such as those conforming to the Digital Transmission Licensing Authority's (DTLA) Digital Transmission Content Protection (5C) Specification, are incorporated into a link-layer access device of a conventional processing system. Because of the suitability of IEEE 1394 for transferring audio / video information, these functions are preferably embodied in an IEEE 1394 compatible link-layer access device. The link-layer access device of this invention is configured to support, for example, the elliptic curve multiplication functions of a Diffie-Hellman key exchange process, as well as digital signature generation and digital signature verification. By incorporating the authentication and key exchange functions into a link-layer access device, the system architecture and devices that are commonly used in conventional processing systems can be used, thereby providing an incremental path toward increased protection of copyright material. In a preferred embodiment, the conventional link-layer controller is configured to implement the authentication and key exchange processes, via calls to the link-layer access device to perform the complex mathematical operations, thereby eliminating the need for each application-layer program or device to implement these processes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
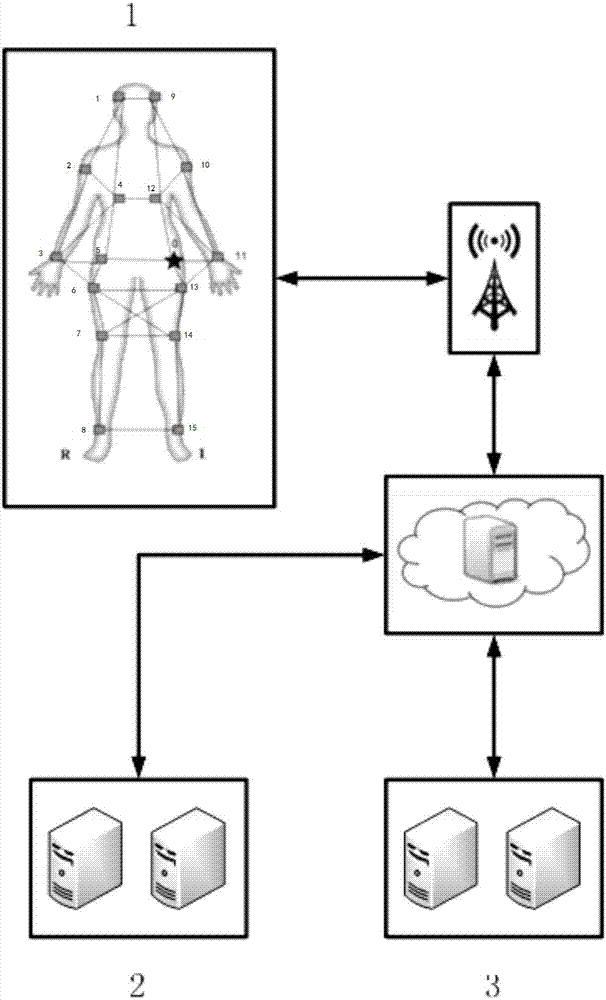
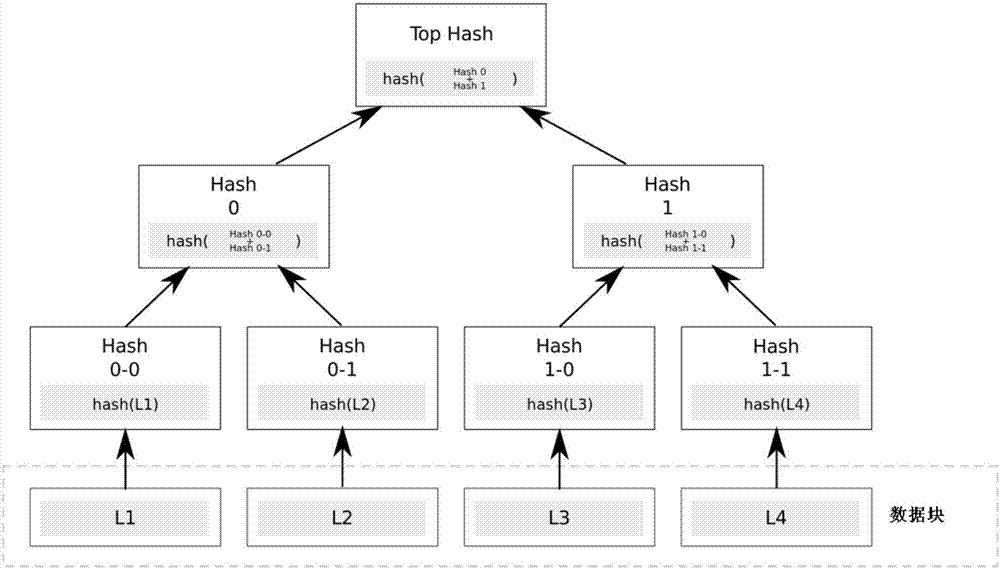
Medical big data processing method based on body area network and cloud computing
ActiveCN107040510AEnsure safetyReduce transmissionInput/output to record carriersTransmission systemsReal time analysisDiffie–Hellman key exchange
The invention discloses a medical big data processing method based on a body area network and cloud computing. The method comprises the steps that a physiological sensor senses user physiological data, generates a symmetric key for encryption of data through utilization of an APTEEN protocol and a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol, signs the data through utilization of a Merkle tree and transmits the processed data to a mobile device; the mobile device decrypts the data uploaded by the physiological sensor, verifies a user identity and completeness of the transmission data and sends verified user data to a cloud server for data storage and data analysis; and the cloud server stores a data analysis result and sends the data analysis result to the mobile device. According to the method, the medical data is stored and protected through adoption of a transmission encryption technology, so the problem that the privacy of a patient is leaked is effectively solved; and the data is transmitted to the cloud server in real time through a wireless network, redundancy eliminated storage and real-time decision analysis problems for the real-time transmission data are solved through utilization of a big data technology, and the security protection and real-time analysis of the medical big data are realized.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Public key out-of-band transfer for mutual authentication
ActiveUS8156334B2User identity/authority verificationSecure communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchange
Methods for key exchange and mutual authentication are provided that allow for inherent authentication and secret key derivation of parties communicating through an unsecured medium. These methods allow for greater security than existing key exchange and authentication methods while requiring little or no additional energy or time compared with a basic Diffie-Hellman key exchange. These methods allow for secure communication with small, low-power devices and greater security for any devices communicating through an unsecured medium.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and structure for self-sealed joint proof-of-knowledge and diffie-hellman key-exchange protocols
InactiveUS8464060B2Robust resistance against malicious disclosureImproving security and privacy and efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeComputer science
A method (and structure) for a party (the prover) to prove its knowledge, jointly and non-malleably, of multiple secret (fixed and / or ephemeral) Diffie-Hellman exponents (DH-exponents), corresponding to its public (fixed and / or ephemeral) DH-components and with respect to the public (fixed and / or ephemeral) challenging DH-components from another party (the verifier). The joint proof-of-knowledge (JPOK) consists of secrets made by multiplying multiple DH-secrets, which can be generated and verified by each party by its own secret DH-exponents and the public DH-components of both parties. To ensure the non-malleability of the JPOK, the method makes all these multiplied DH-secrets to be independent, and makes the session-tag committed to the multiplied DH-secrets. In addition, the invented method makes the DH-secrets to be multiplied to further satisfy at least one of the following: (1) deniability; (2) pre-computability; and (3) post-ID computability.
Owner:ANDREW C YAO
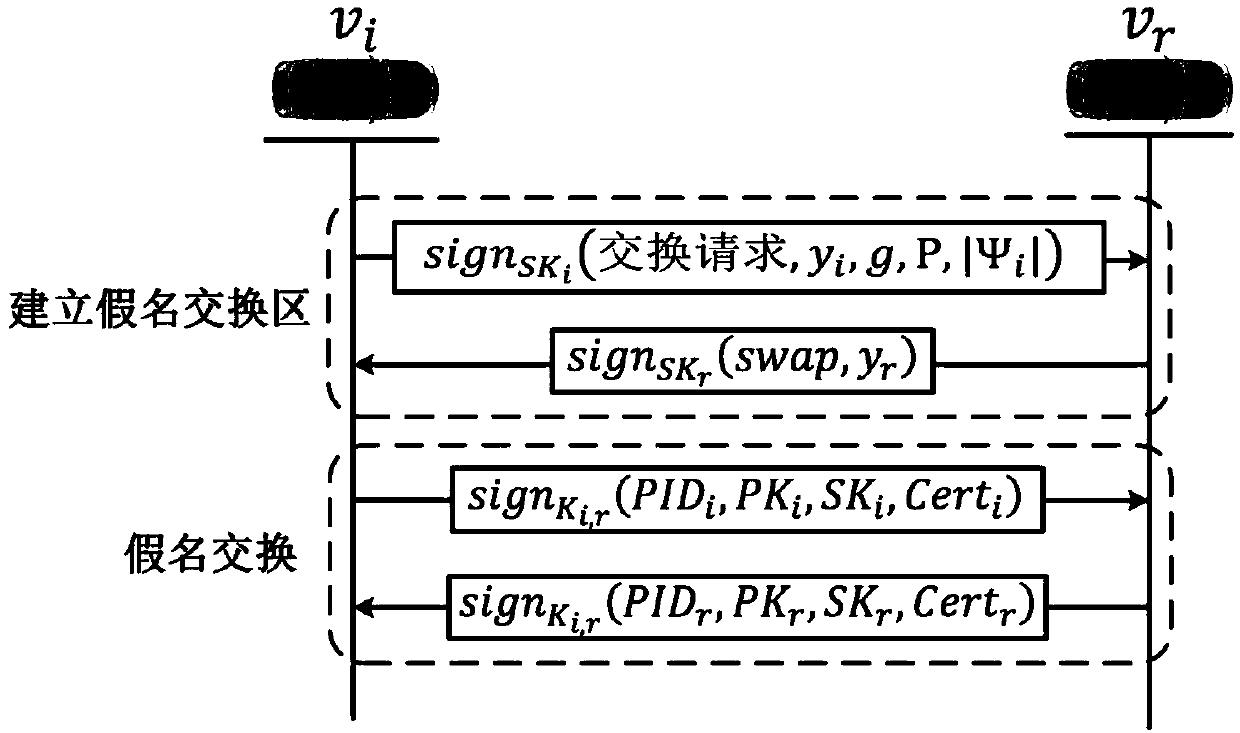
Location privacy protection method based on dynamic pseudonym exchange area
InactiveCN109561383AImprove privacy protectionGuaranteed anonymityParticular environment based servicesVehicle wireless communication serviceDiffie–Hellman key exchangeThe Internet
The invention discloses a location privacy protection method based on a dynamic pseudonym exchange area, and belongs to the field of location privacy protection of the Internet of vehicles. The methodcomprises the steps that a vehicle in the vehicular ad hoc network registers and generates a dynamic pseudonym in the driving process and periodically updates the pseudonym, then the vehicle dynamically establishes a pseudonym exchange area, carries out pseudonym exchange to enhance the location privacy, embeds an improved Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol in the pseudonym exchange process atthe same time to protect the pseudonym exchange process, the vehicle initiating the pseudonym exchange uploads a pseudonym exchange log to a certification authority (CA) of the area after the completion of the pseudonym exchange, the CA re-establishes the relationship between a real ID and the pseudonym of the vehicle through analyzing the pseudonym exchange log so as to enable the CA to perform identity tracking and violation processing. The location privacy protection method solves a problem of location privacy of the vehicle in the driving process, and is an effective location privacy protection method which adapts to the communication environment of the Internet of vehicles and can claim the responsibility of violation vehicles.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for authenticating identity of mobile terminal and constructing safety channel
InactiveCN104618113AAvoid attackImprove effectivenessUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDiffie–Hellman key exchangeData transmission
The invention belongs to the field of identity authentication and image recognition, and specifically relates to a method for authenticating identity of a mobile terminal and constructing a safety channel. The method comprises the steps of 1) authenticating the identity, namely, mutually shooting by two data transmission sides through a front camera and a rear camera of an intelligent terminal, extracting the characteristics values of the image shot by the front camera of a first user and image shot by the rear camera of a second user, performing image matching for the first time, and entering the next step after successful matching; 2) constructing the safety channel, namely, generating a random key according to the background noise of the image shot in step 1), constructing a temporary channel through the random key, and then constructing the safety channel on the basis of the temporary channel by the Diffie-Hellman key exchange method. The communication channel constructed by the method is stable, safe and high in effectiveness; the identity can be authenticated and the safety channel can be constructed simply by shooting the images; the method has the advantages of being safe, efficient, convenient and fast and can be generally applied in the field of mobile data transmission for a long term.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and system for updating preshared key
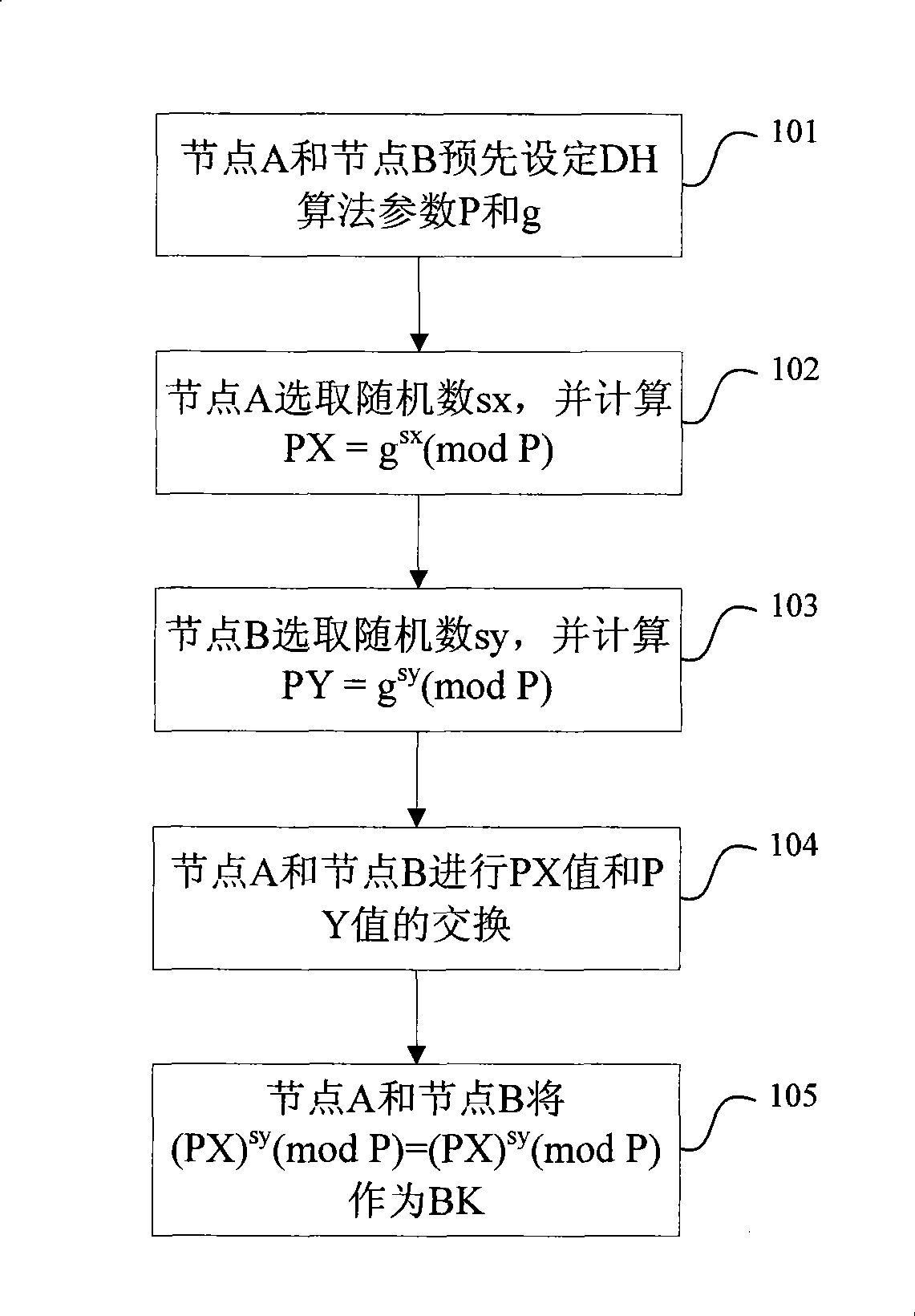
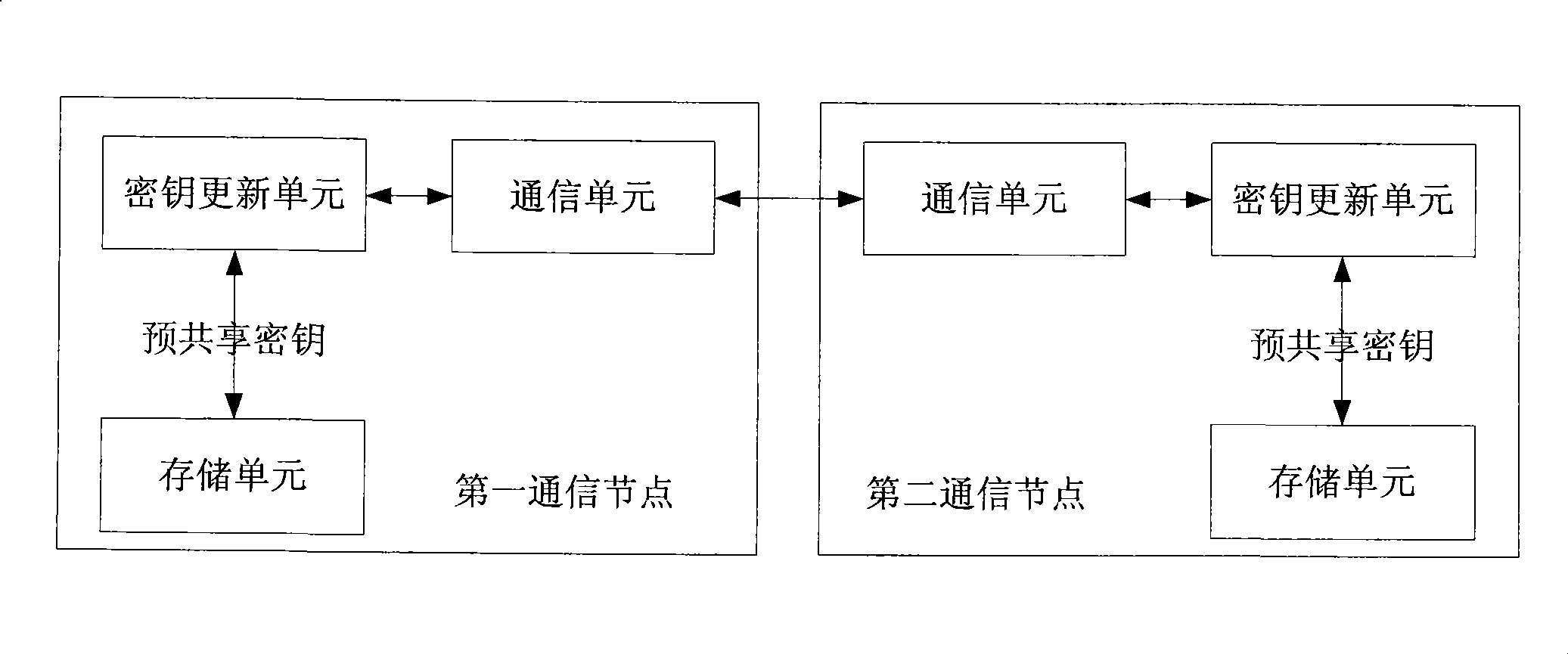
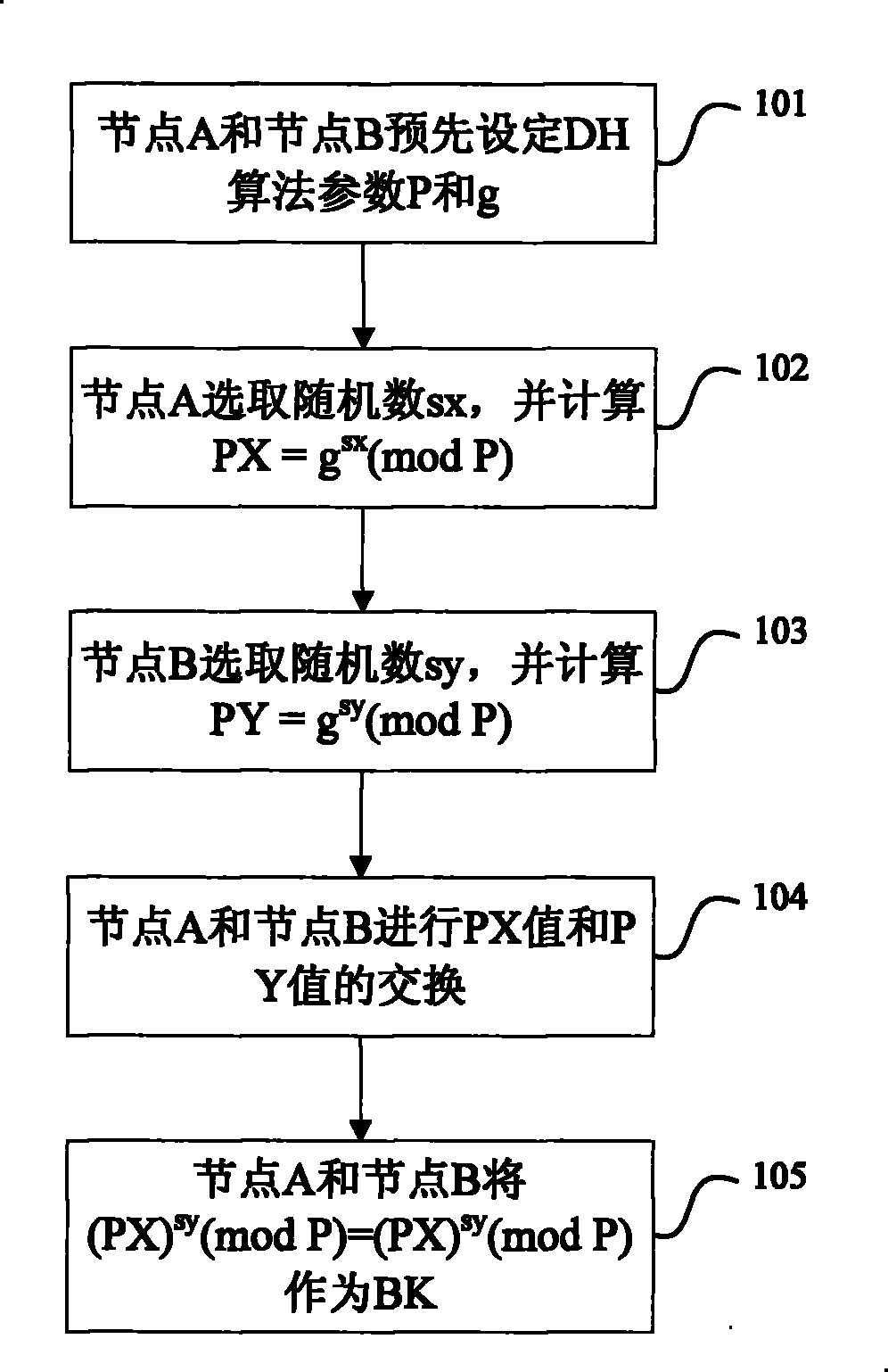
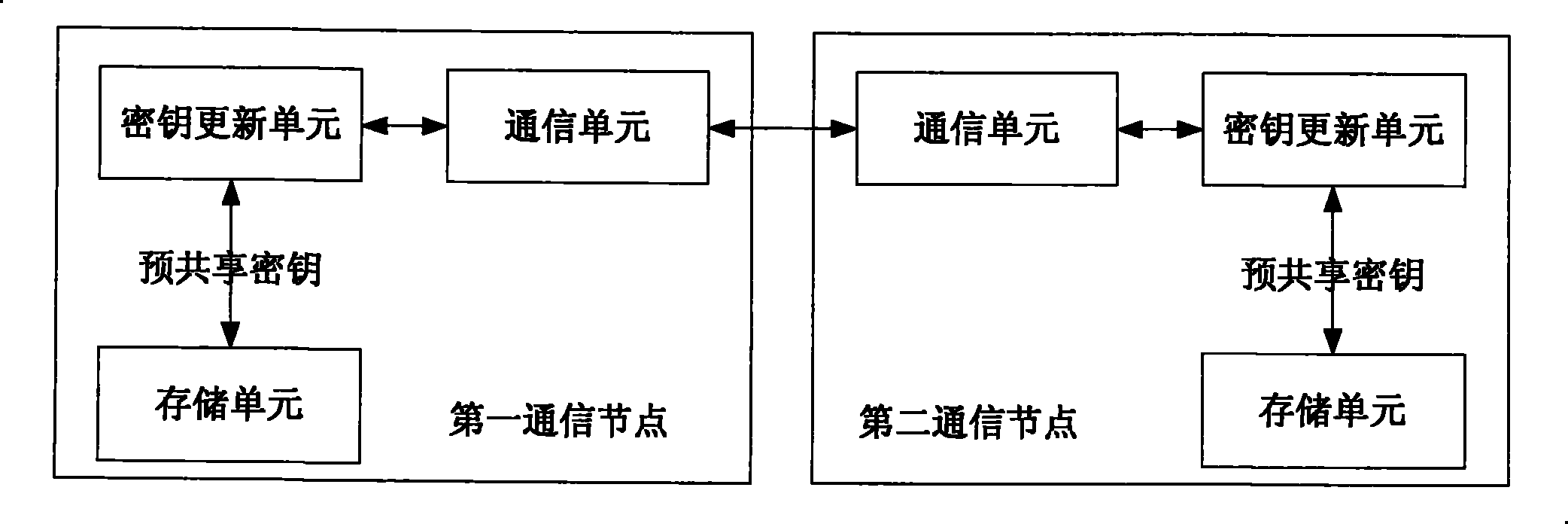
InactiveCN101521882AIncrease randomnessImprove dynamic rangeNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesComputer hardwareDiffie–Hellman key exchange
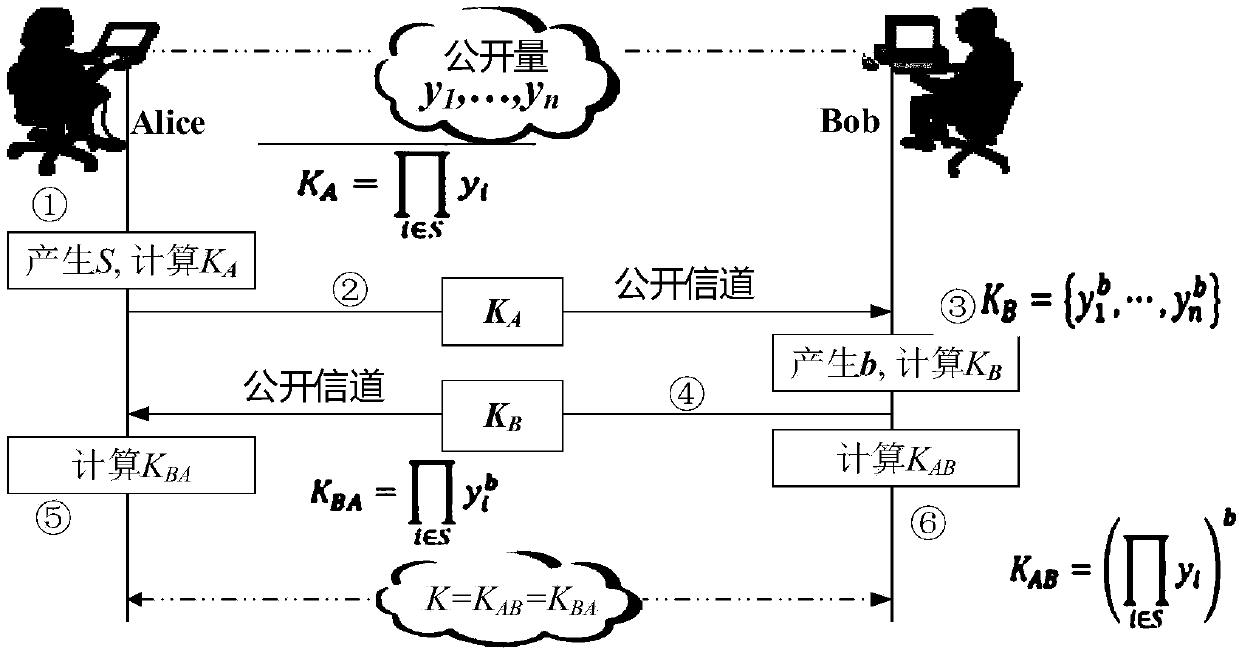
The invention relates to a method and a system for updating a preshared key. The method comprises the following steps: both communication sides take prime numbers which correspond to a preshared key to be updated as prime number parameters P for Diffie-Hellman Key exchange algorithm; both communication sides use prime number parameters P, positive integers g which are less than the prime number parameters P and random numbers sx and sy generated by respective communication side for calculating PX and PY, wherein PX= g<sx>(mod P) and PY = g<sy>(mod P); and both communication sides exchange the PX and the PY and take (PY)<sx>(mod P)= (PX)<sy>(mod P) as a new preshared key.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Asymmetric-computing type shared key establishing method suitable for cloud computing and IoT
ActiveUS9548860B2Improve efficiencyWide applicationKey distribution for secure communicationCoprocessorDiffie–Hellman key exchange
An asymmetric-computing type shared key establishing method suitable for cloud computing and IoT has the following advantages. The realization efficiency and the security level are high, and a cryptographic algorithm coprocessor is not needed. The method can be applied to occasions in which the computing capabilities are asymmetric, and attacks from quantum computers can be resisted. Compared with a conventional key exchange protocol such as the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol, the method can be more effective between servers and mobile equipment in the security fields as the IoT and cloud computing, and the method can be used in both the electronic environment and the quantum environment. Thus, the asymmetric-computing type shared key establishing method suitable for cloud computing and IoT provided by the invention can be widely applied to the field of information security systems such as network security and e-commerce.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
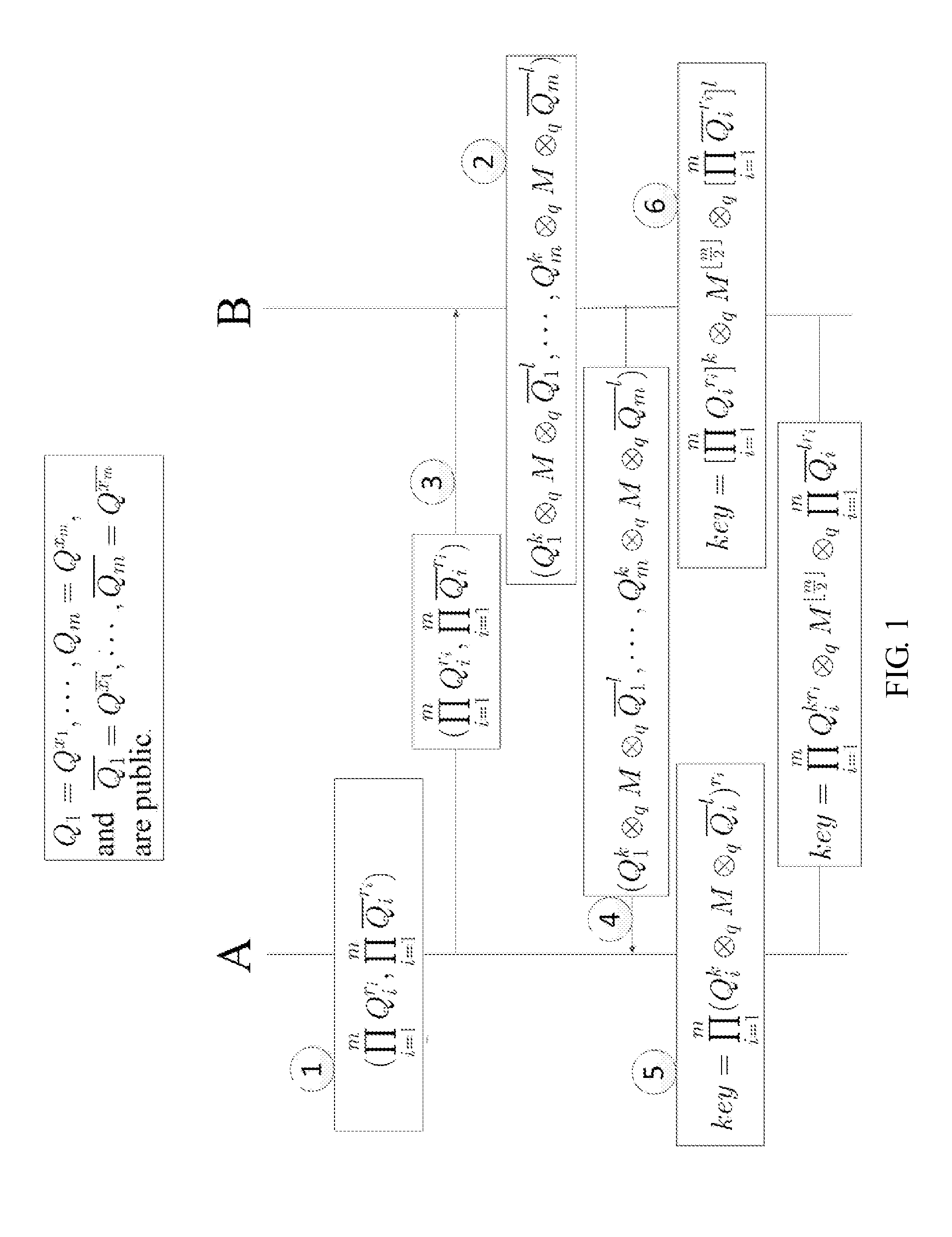
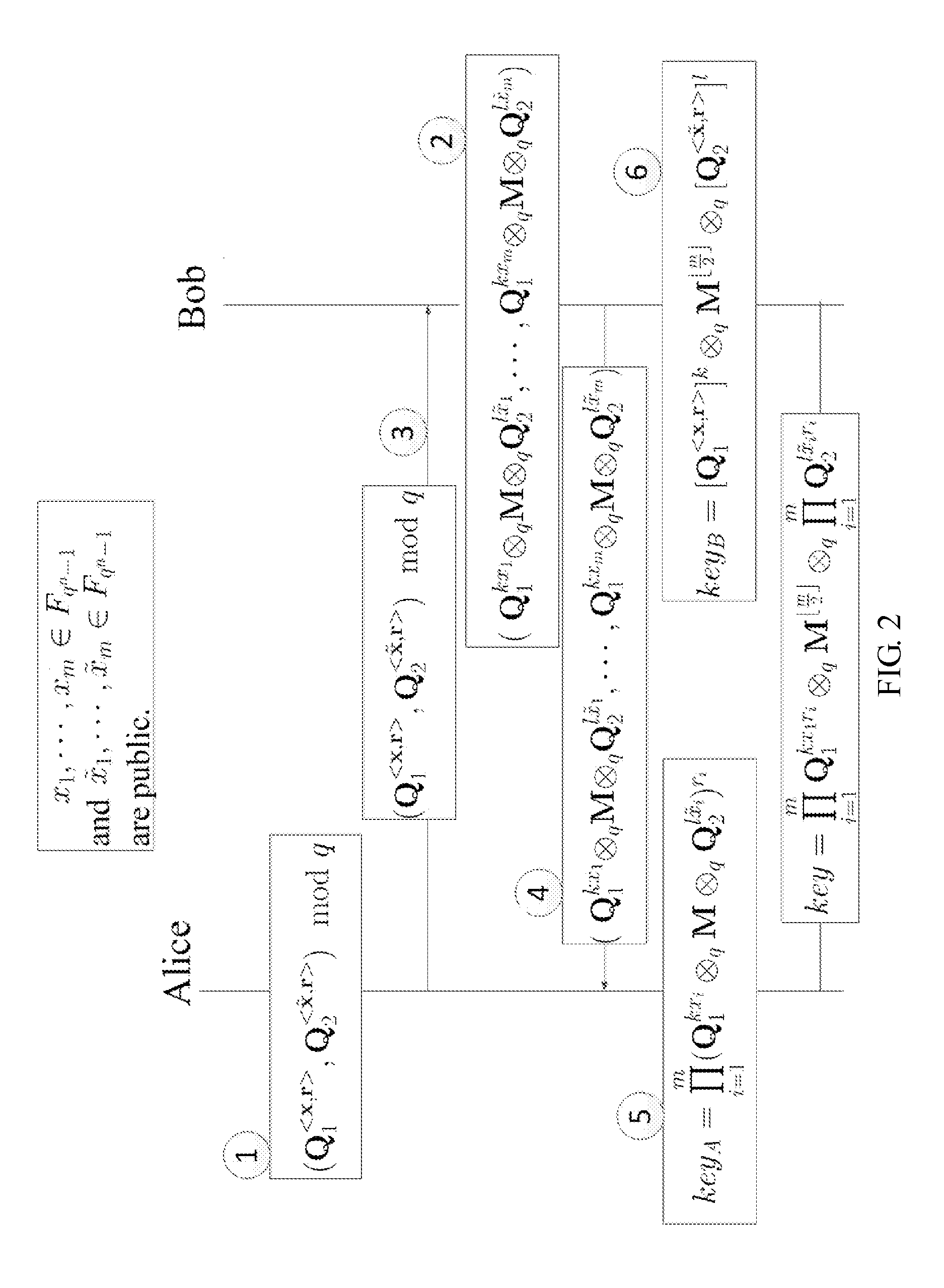
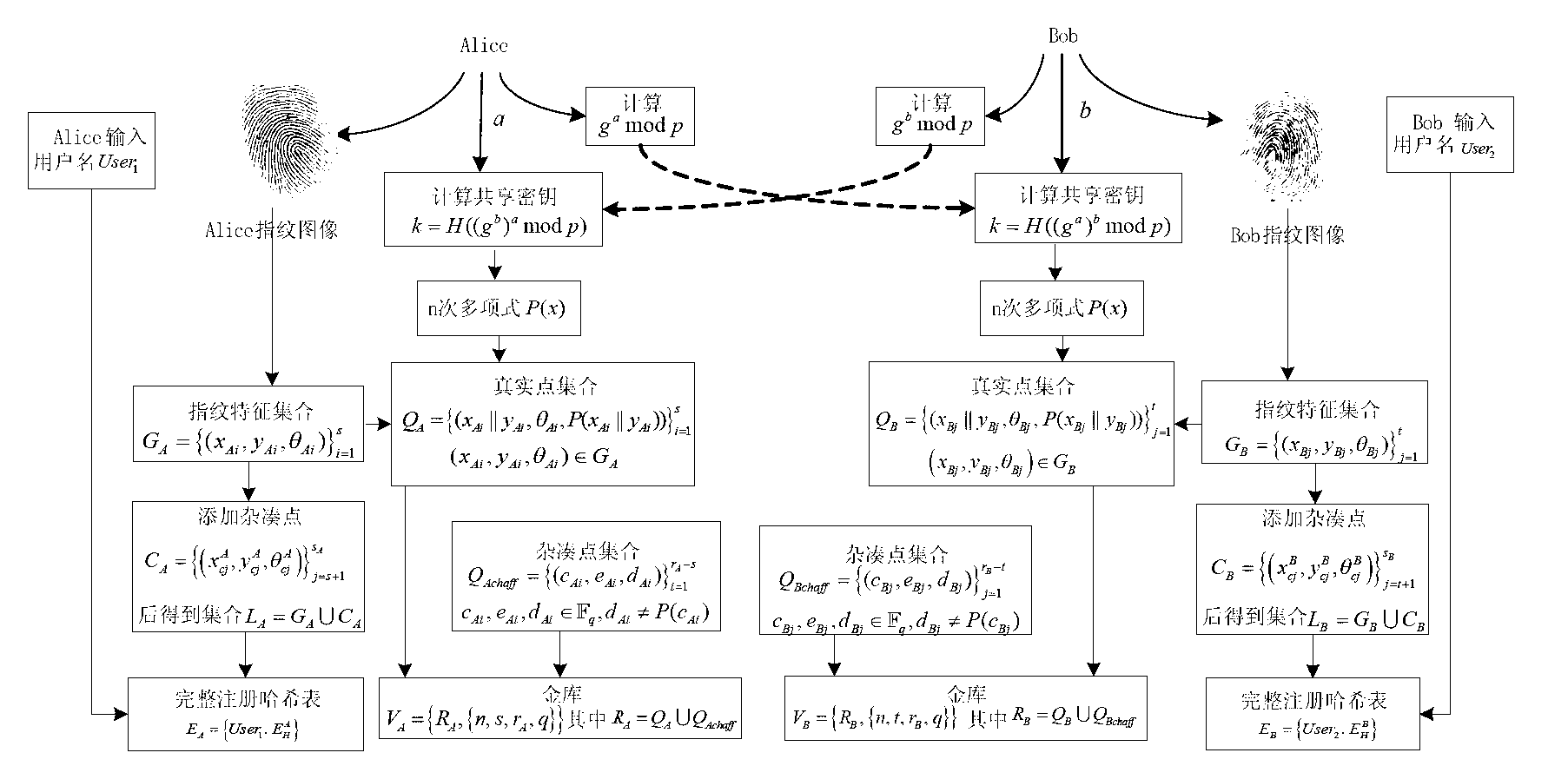
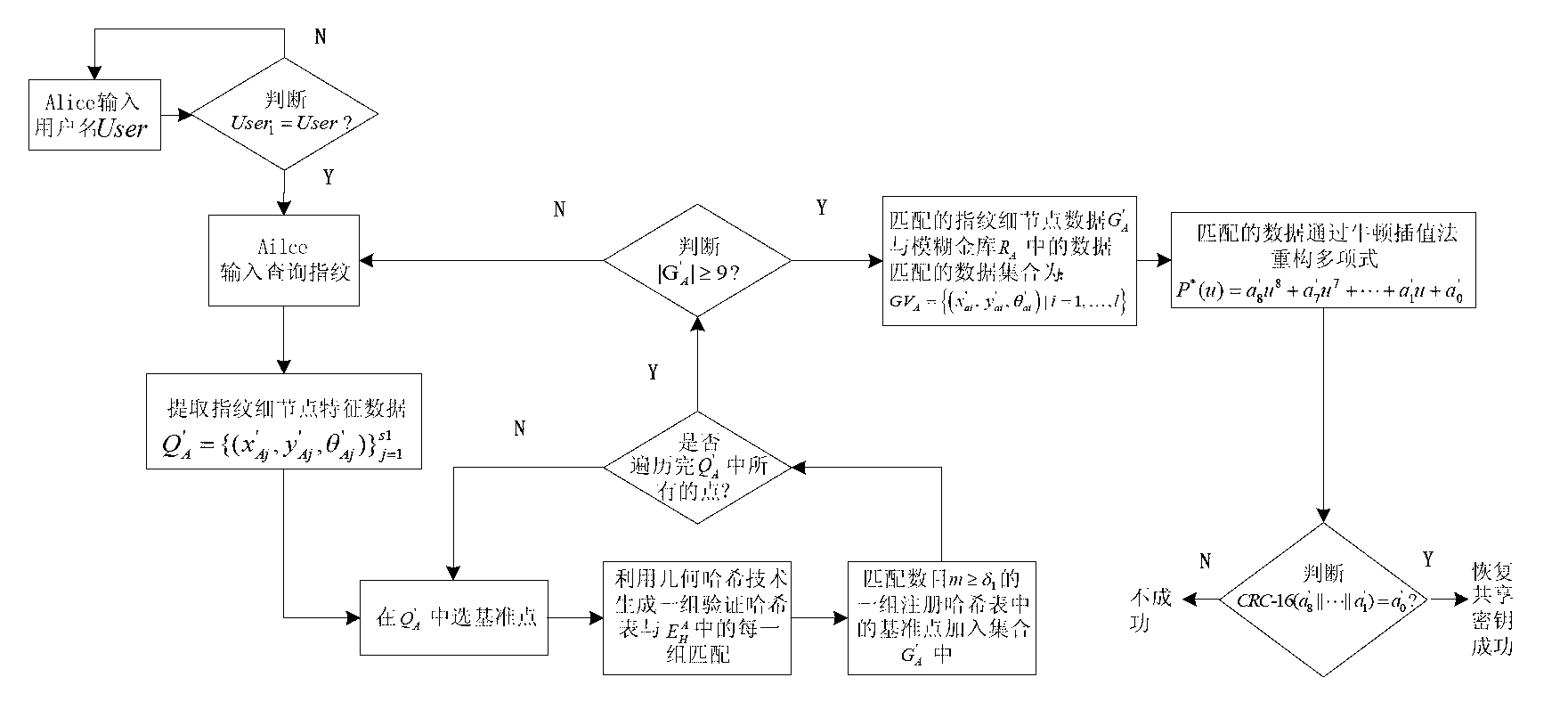
Fuzzy vault method based on fingerprint features and Internet key exchange protocol
InactiveCN102710417AKey distribution for secure communicationCharacter and pattern recognitionInternet Key ExchangeDiffie–Hellman key exchange
The invention relates to a fuzzy vault method based on fingerprint features and an Internet key exchange protocol. The existing method has the problems that security storage users share one key. The method comprises the steps of a shared key generation step of a diffie-hellman key exchange protocol and a binding and releasing step of a finger fuzzy vault and the shared key, wherein the shared key generation step is that the shared key is generated on the basis of the Diffie-Hellman protocol. The binding step of the fingerprint fuzzy vault and the shared key is that original fingerprint information is adopted as a polynomial element, and a polynomial is constructed by utilizing the shared key. The releasing step of the fingerprint fuzzy vault and the shared key is that the polynomial is reconstructed by inquiring the fingerprint information, and the shared key is restored. Due to the adoption of the fingerprint fuzzy vault algorithm, while the shared key is protected, the shared key can be safely and conveniently released through the fingerprint features of the user, so that the key sharing scheme has better practicability.
Owner:海宁鼎丞智能设备有限公司
Secure data transmission links
InactiveCN1507720AQuick to useKey distribution for secure communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer hardwareSecure communication
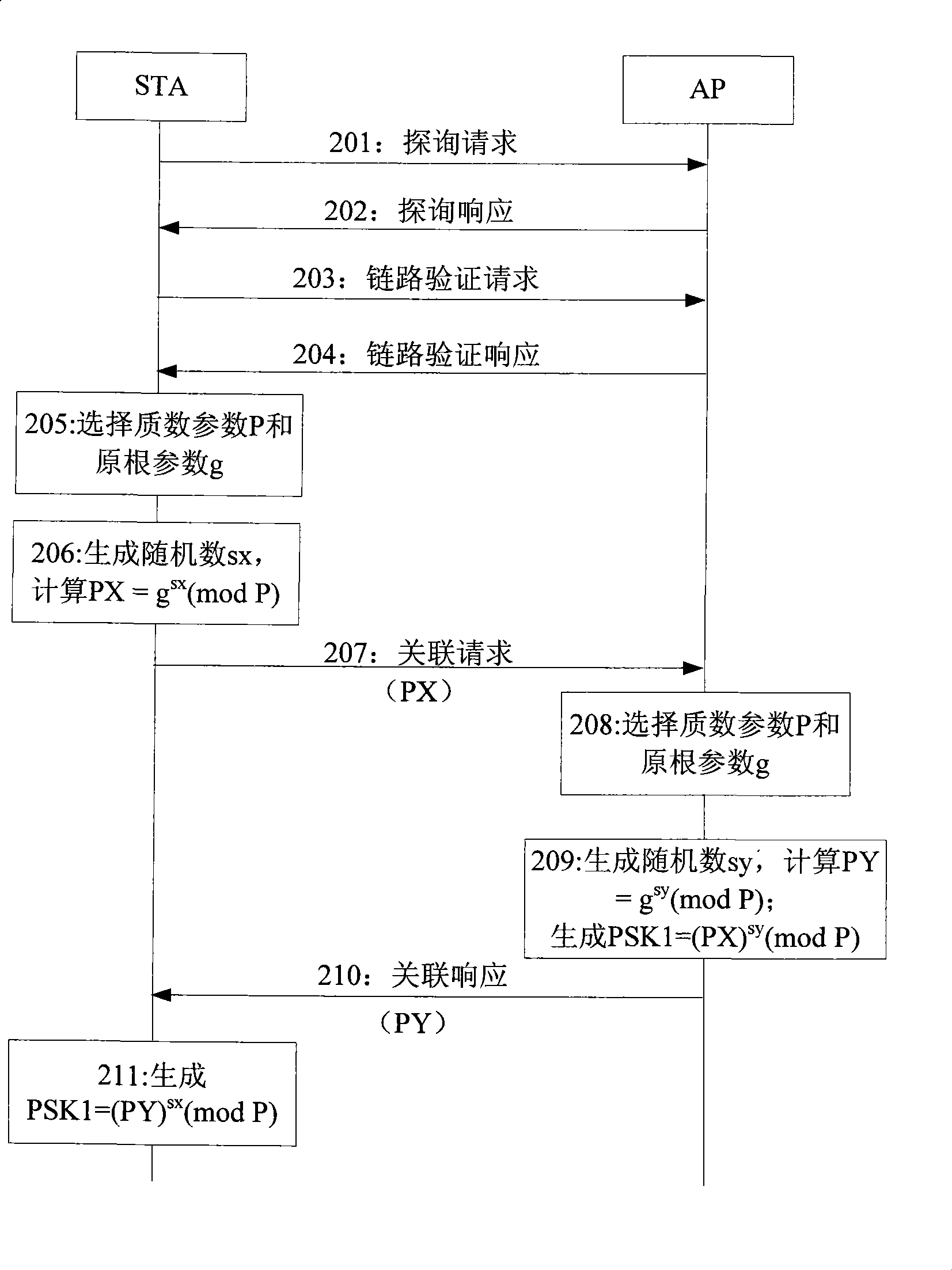
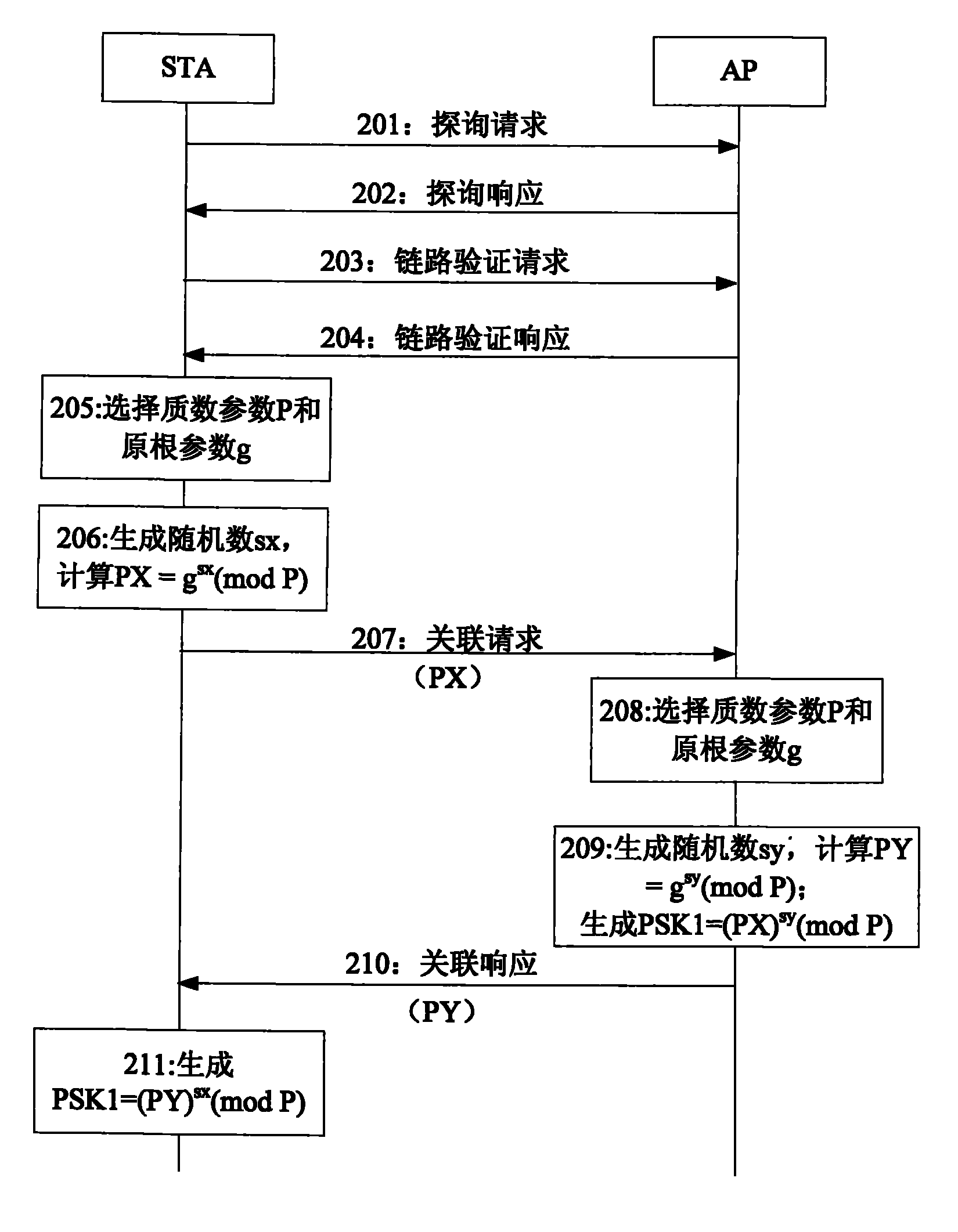
A method of establishing a secure communications link between a mobile terminal and a server, the method comprising retrieving from storage, in the mobile terminal a prime number, p, and generator, g, for a Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol, generating a positive integer b at the terminal, sending a message including the value of (g<=[b] mod p) from the terminal to the server, determining a shared secret number for the terminal and the server by calculating the value of g<=[ab] mod p, where a is a positive integer, using b and a public value for the server y=g<=[a] mod p at the terminal, and using a, b, g and p at the server, and using the shared secret number to establish the secure communications between the terminal and the server. The method facilitates download of software to a mobile communications system terminal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
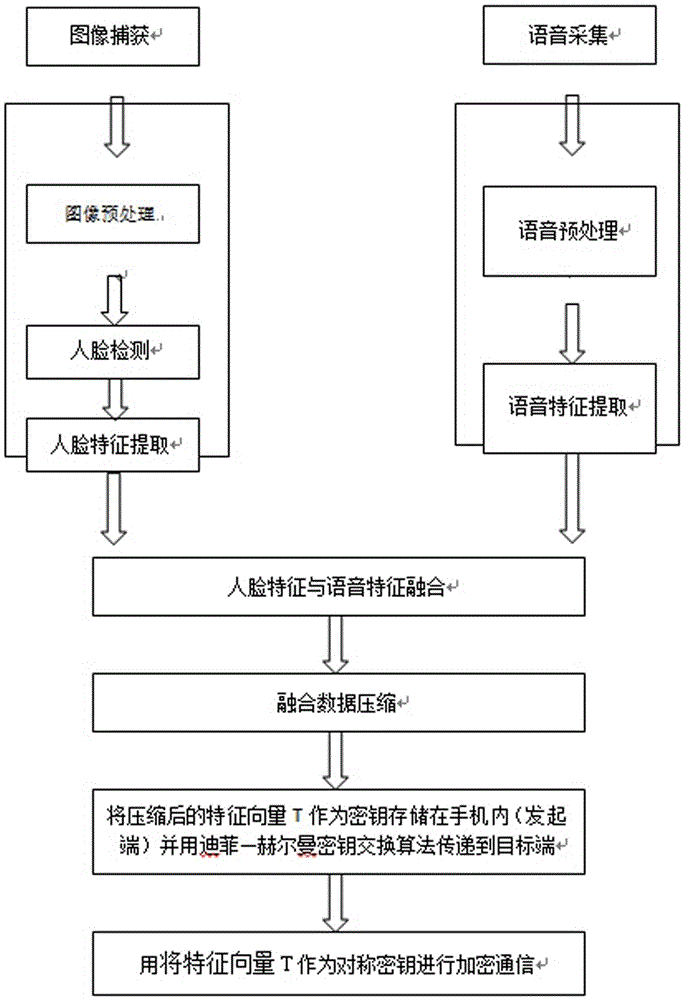
Handset NFC safety payment method based on integrated voiceprint and face characteristic encryption
The invention discloses a handset NFC safety payment method based on integrated voiceprint and face characteristic encryption. The method is characterized by comprising steps that, image acquisition and voice acquisition are carried out; the acquired image and the acquired voice are respectively processed; integrated processing on a face characteristic vector and a voice characteristic vector is carried out to acquire a characteristic vector P; the characteristic vector P is compressed to be in 256-bit bytes, and a characteristic vector T is acquired; the characteristic vector T is taken as a secret key and is stored in a handset as an initiation end, and the characteristic vector T is transmitted by utilizing a Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm to a target end; the characteristic vector T is taken as a symmetric secret key by two communication parties to carry out encryption communication. The method is carried out in an NFC point-to-point mode, and through the method, information safety interaction during handset NFC payment can be realized.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF AEROSPACE TECH
Inter-vehicle authentication using visual contextual information
ActiveUS9842263B2Television system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeVisual perception
Authentication of vehicles in preparation for V2V communication includes vehicle A taking a picture of vehicle B (VA) and vehicle B taking a picture of vehicle A (VB). These pictures are then shared. Vehicle A determines the relative location of vehicle B indicated in VA and VB. If they agree, then vehicle A and B authenticate one another, such as using Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Identifying vehicle A and vehicle B in the pictures may include identifying the license plates of vehicle A and vehicle B in the pictures. Vehicles A and B may exchange license plate numbers prior to taking of the pictures. Image spoofing may be prevented by taking both forward and rearward facing pictures by both vehicles. Objects in pictures facing the same direction may be identified to verify that the pictures were taken nearly simultaneously.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
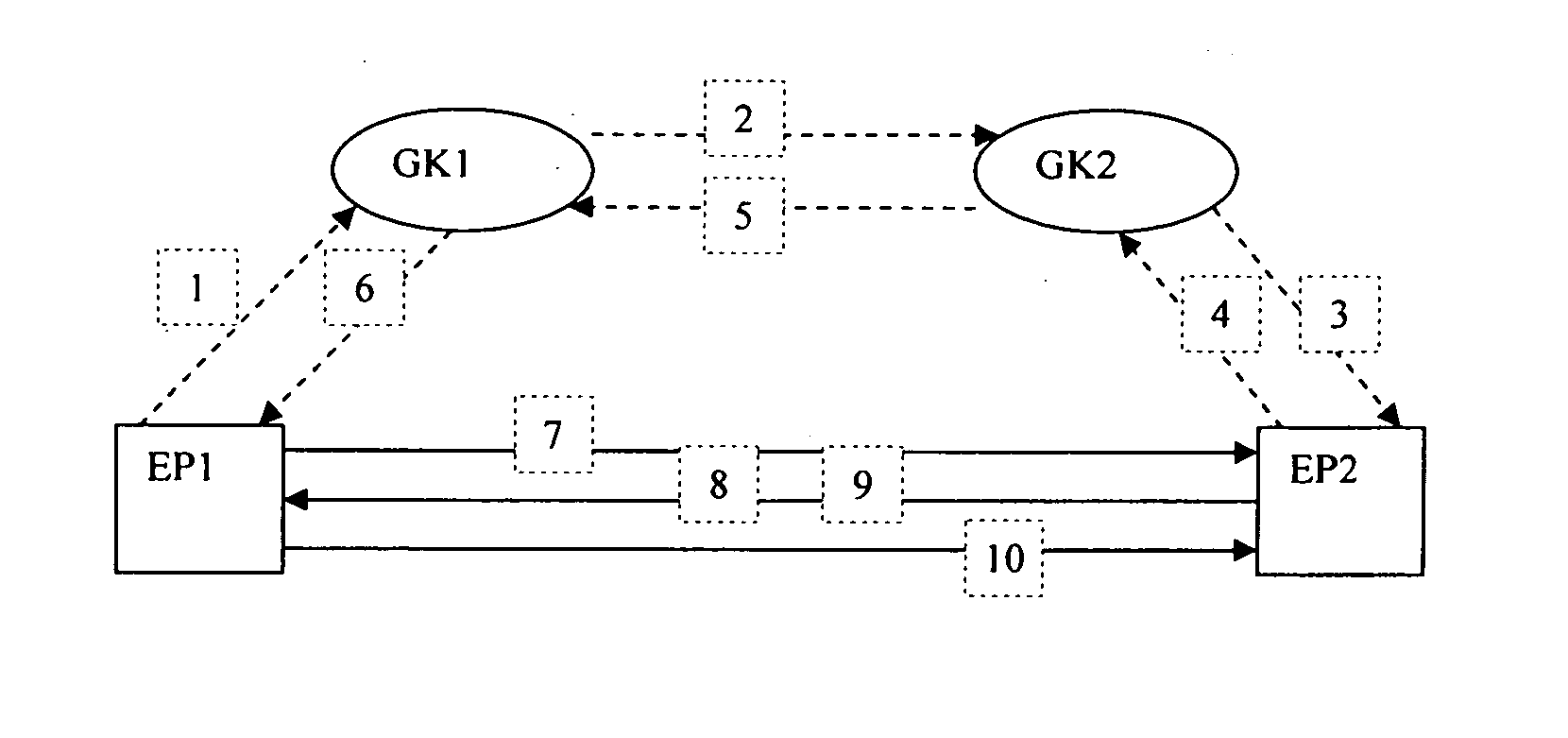
Method for providing message transmission in H.323 communication system
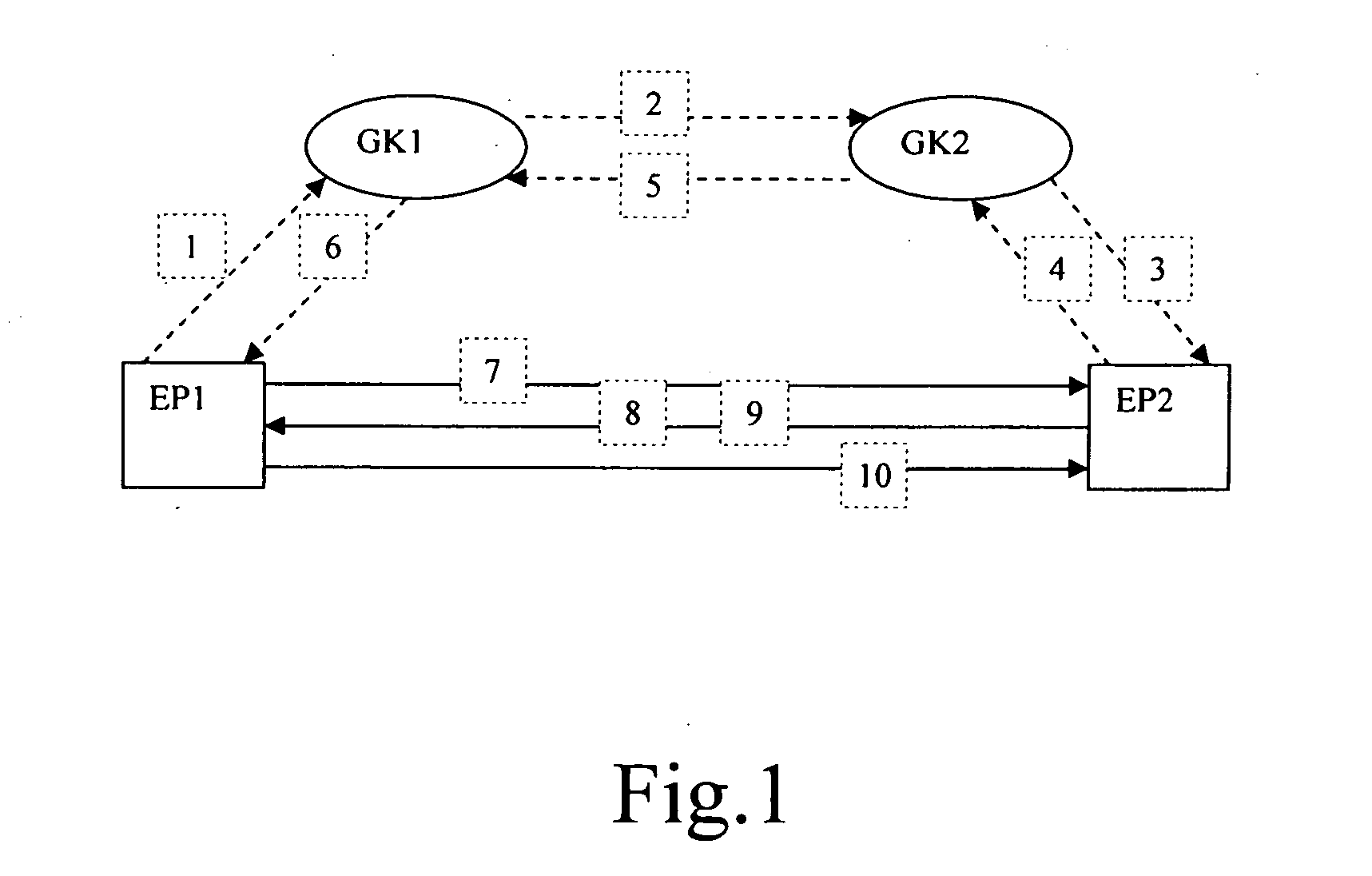
InactiveUS20070074022A1Improve securityImprove scalabilityInterconnection arrangementsUser identity/authority verificationRouting modelCommunications system
The present invention provides a method for providing message transmission in H.323 communication system. The method includes: the first endpoint and second endpoint confirming authentication information through a GK; according to said authentication information, the first endpoint and second endpoint exchanging message directly. Since H.235 protocol of ITU-T describes the authentication and privacy technique used in H.323 systems and provides security service for message transmission in GK-routed model, the present invention can guarantee the security of the authentication information. The functions of middle entities need not to be modified for applying the method provided by the present invention because Diffie-Hellman key exchange technology is adopted in this method. The present invention increases the network scalability of the symmetric key system by adopting negotiation mode. The present invention designates and improves the security framework of message transmission in direct-routed model of H.323 system, thereby improving the security of H.323 system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Inter-Vehicle Authentication Using Visual Contextual Information
ActiveCN107040506ATelevision system detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlDiffie–Hellman key exchangeVisual perception
The invention relates to inter-vehicle authentication using visual contextual information. Authentication of vehicles in preparation for V2V communication includes vehicle A taking a picture of vehicle B (VA) and vehicle B taking a picture of vehicle A (VB). These pictures are then shared. Vehicle A determines the relative location of vehicle B indicated in VA and VB. If they agree, then vehicle A and B authenticate one another, such as using Diffie-Hellman key exchange. Identifying vehicle A and vehicle B in the pictures may include identifying the license plates of vehicle A and vehicle B in the pictures. Vehicles A and B may exchange license plate numbers prior to taking of the pictures. Image spoofing may be prevented by taking both forward and rearward facing pictures by both vehicles. Objects in pictures facing the same direction may be identified to verify that the pictures were taken nearly simultaneously.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
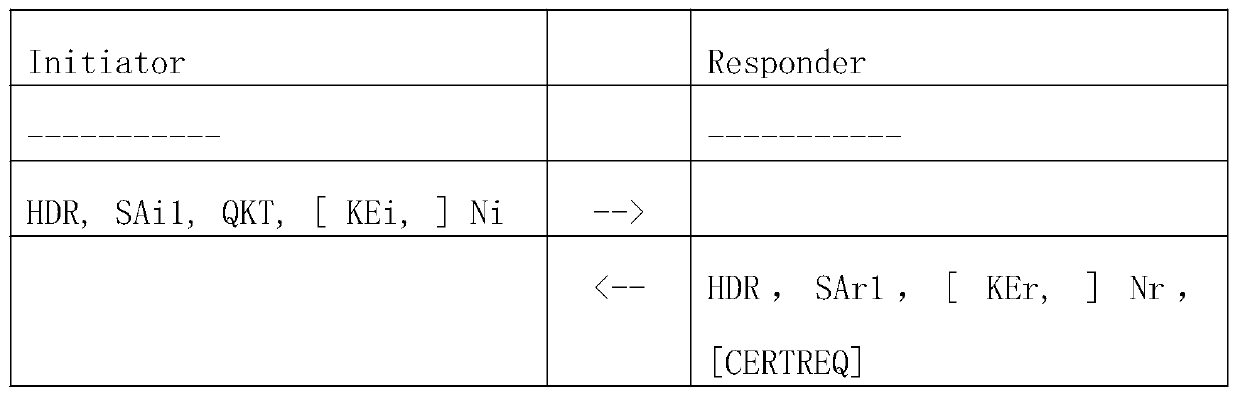
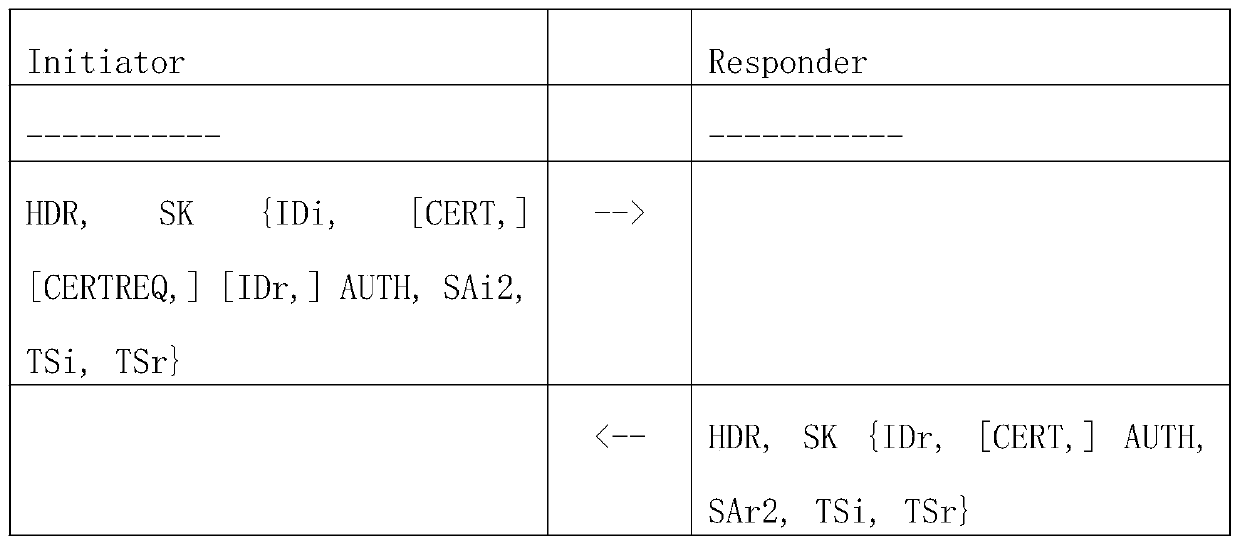
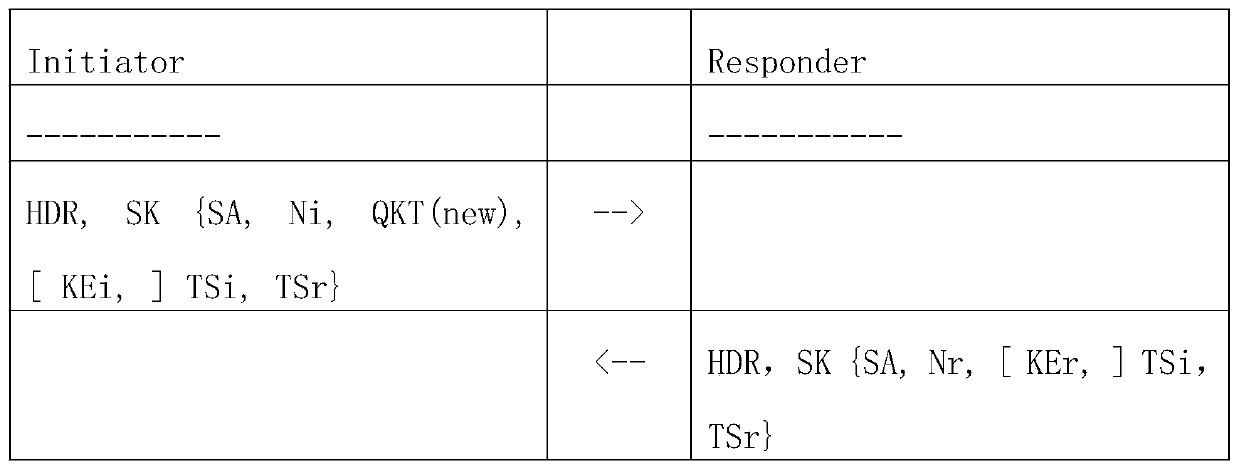
A method for using a quantum key through IKEv2 negotiation
ActiveCN109714164AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeIPsec
The invention discloses a method for using a quantum key through IKEv2 negotiation, and relates to the technical field of communication. The technical problem that an existing network encryption method is easy to crack and is not safe enough can be solved. The method comprises the following steps: generating a quantum key QK by using a quantum key distribution protocol QKD, and replace the sharedkey g^ir generated by QK or combined with Diffie-Hellman key exchange giving a specific step of calculating a key material and a HASH value by using a QK value, so that generated IKE SA and IPSEC SA keys indirectly use a quantum key; A quantum key bill QKT load is newly added in an ISAKMP protocol, the QK key generated this time is uniquely identified, and the QKT load is used for replacing or combining with the KE load of Diffie-Hellman key exchange to carry out on the KE load of Hellman key exchange, and a specific exchange step during IKEv2 negotiation is given. According to the invention,a novel quantum encryption technology can be combined, so that the traditional IPSEC technology can generate IKE SA and CHILD SA by using a quantum key in an IKEv2 negotiation stage, and the encryption in the negotiation stage and the encryption of a tunnel message are improved in security due to the use of the quantum key.
Owner:ANHUI WANTONG POSTS & TELECOMM CO LTD
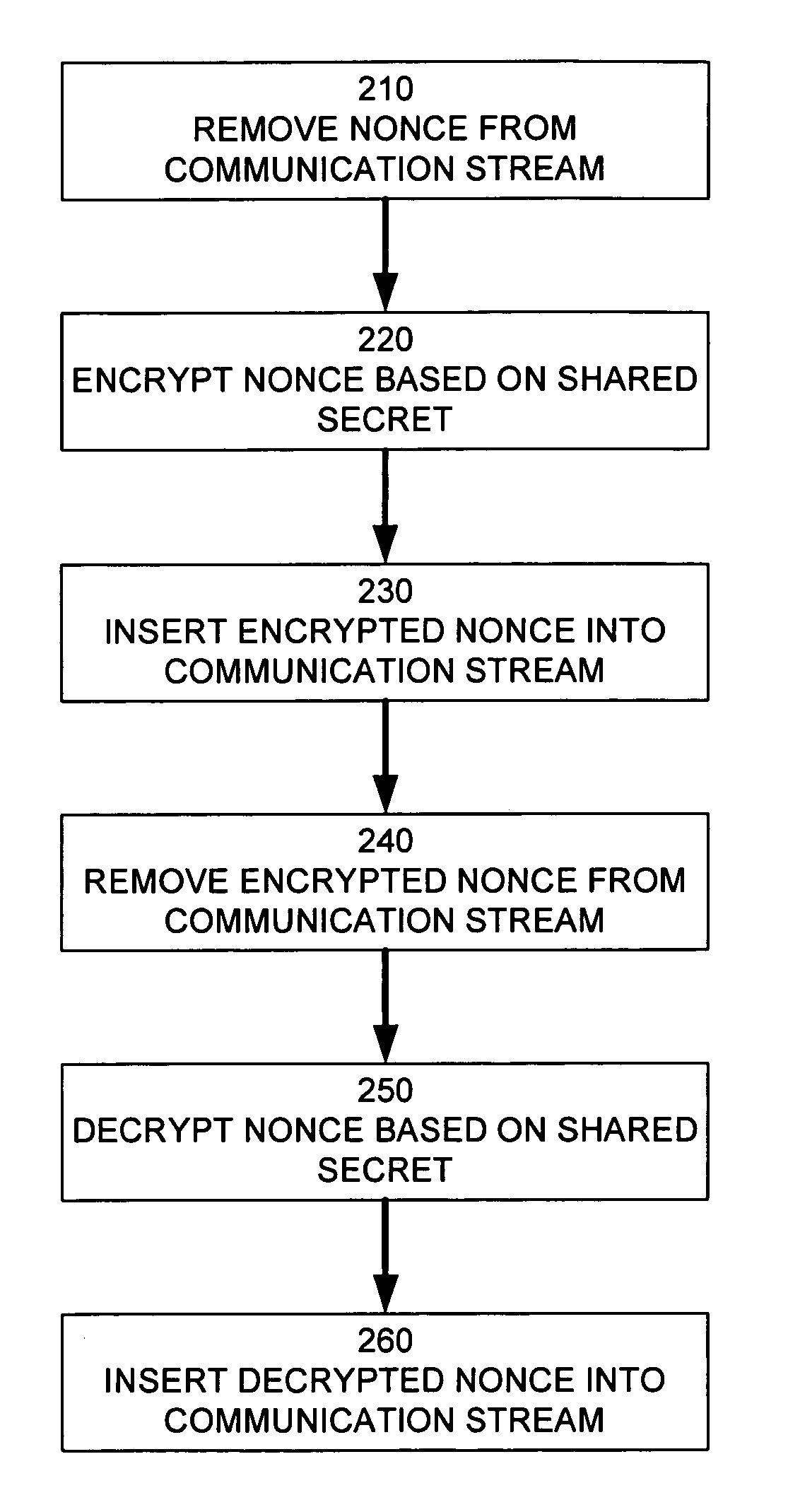
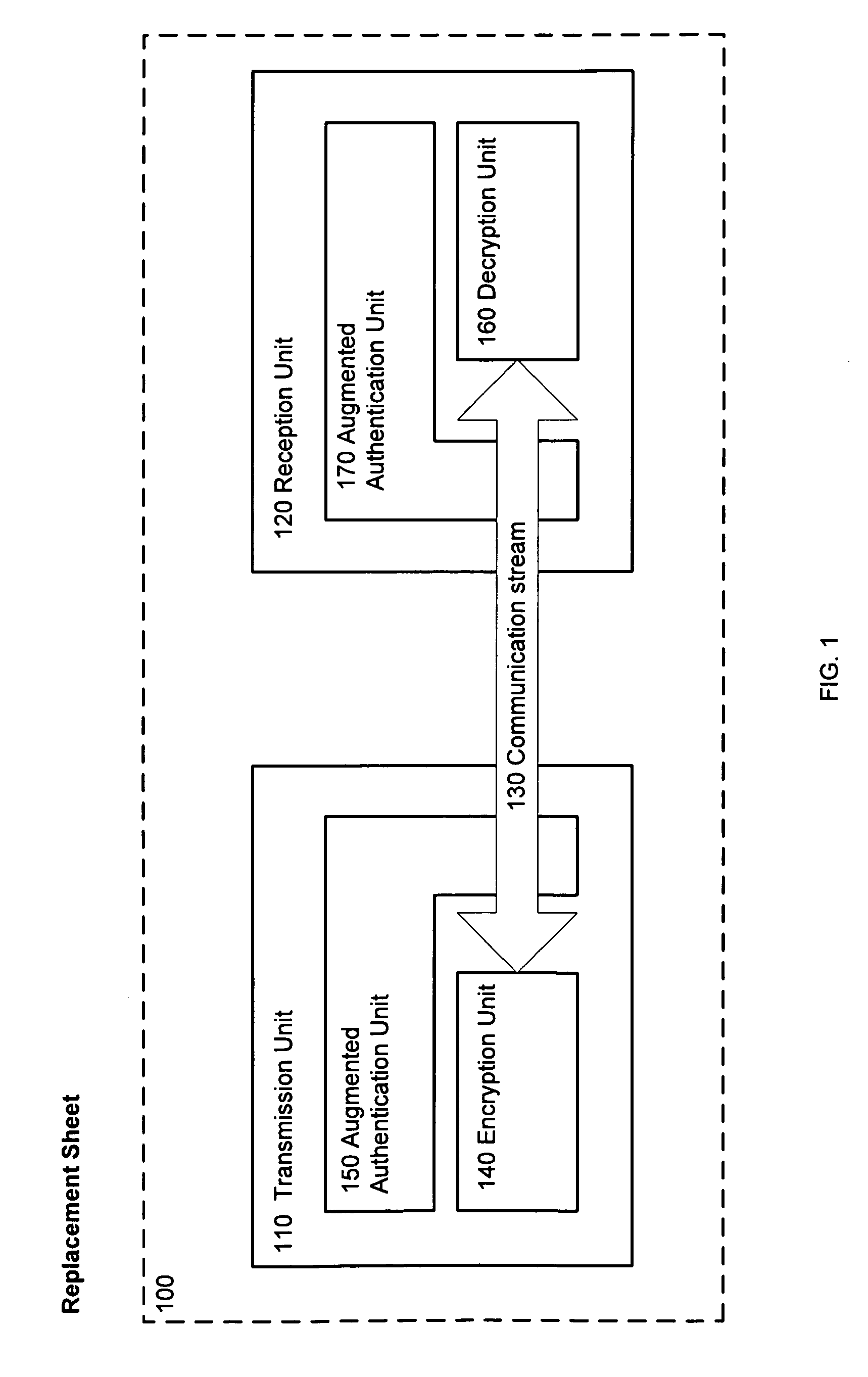
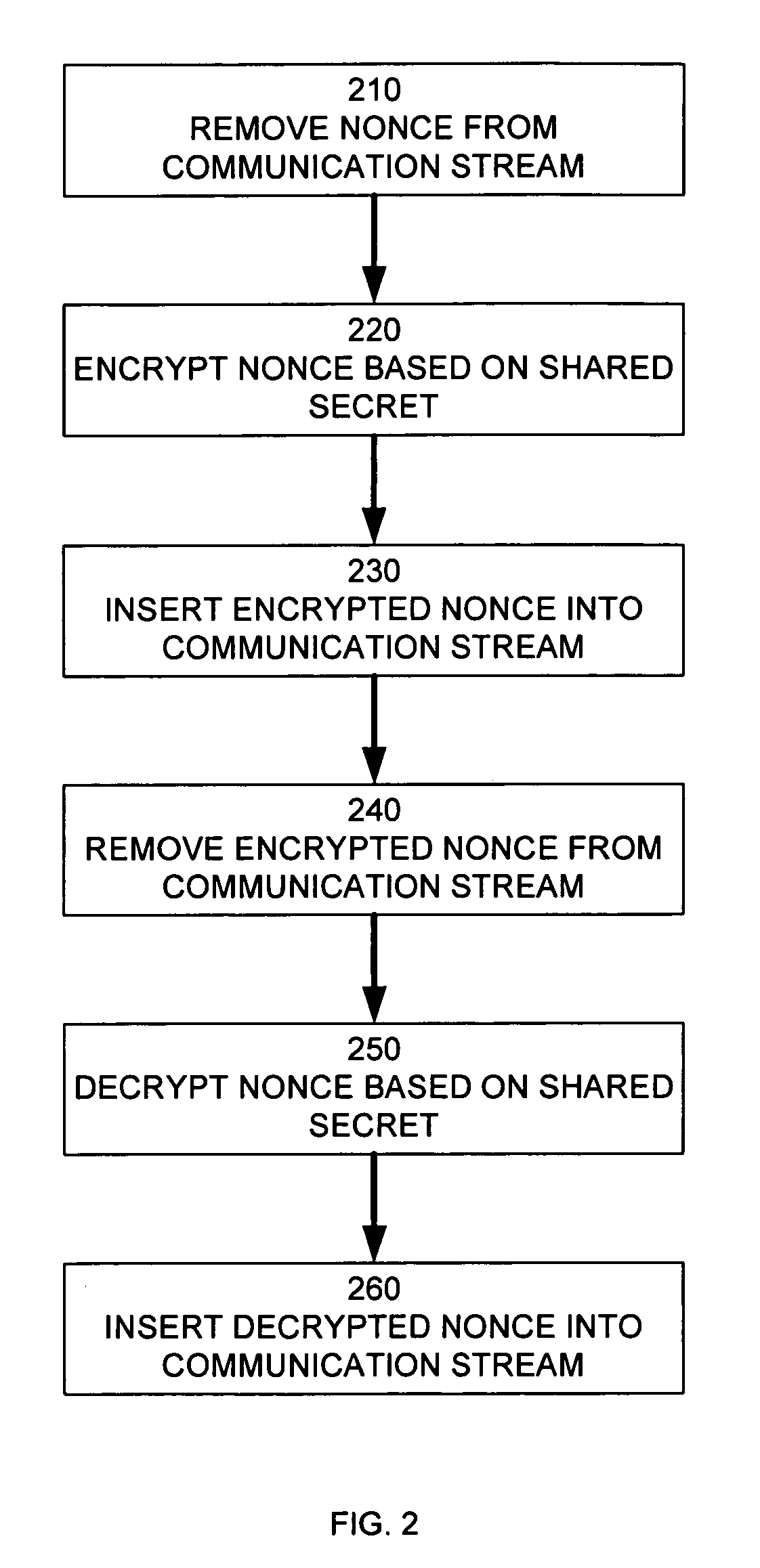
Method and apparatus for augmenting authentication in a cryptographic system
ActiveUS7600118B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeCryptographic nonce
In a cryptographic system, a nonce is removed from a communication stream. The nonce is encrypted based on a shared secret. The encrypted nonce is inserted into the communication stream. The encrypted nonce is removed from the communication stream. The encrypted nonce is decrypted based on the shared secret formed by an authenticated key exchange. The decrypted nonce is inserted into the communication stream. The nonce may be an An value generated by a HDCP function. The authenticated key exchange may use Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for updating preshared key
InactiveCN101521882BIncrease randomnessEnsure safetyNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesComputer hardwareDiffie–Hellman key exchange
The invention relates to a method and a system for updating a preshared key. The method comprises the following steps: both communication sides take prime numbers which correspond to a preshared key to be updated as prime number parameters P for Diffie-Hellman Key exchange algorithm; both communication sides use prime number parameters P, positive integers g which are less than the prime number parameters P and random numbers sx and sy generated by respective communication side for calculating PX and PY, wherein PX= g<sx>(mod P) and PY = g<sy>(mod P); and both communication sides exchange the PX and the PY and take (PY)<sx>(mod P)= (PX)<sy>(mod P) as a new preshared key.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Digital copyright management method for protecting digital content consumer privacy
InactiveCN102025507BPrivacy protectionPrevent Tampering AttacksUser identity/authority verificationProgram/content distribution protectionHash functionCiphertext
The invention discloses a digital copyright management method and device for protecting digital content consumer privacy. The method comprises the following steps: randomly generating an encrypted master key by utilizing the Chameleon hash function, and generating a copyright license; grouping the digital contents, then generating different symmetrical encrypted keys and cryptograph headers according to different groups of digital contents by adopting the Diffie-Hellman key exchange technology, encrypting the digital contents to acquire digital cryptographs, and then, storing the cryptograph headers and the digital cryptographs into a content server; and as required by users, decrypting from the cryptograph headers by utilizing the copyright license to acquire the symmetrical encrypted keys of the authorized digital contents, and then, decrypting the corresponding digital cryptographs to acquire the required digital contents. The device comprises an authorized server, a content serverand consumer equipment. Under the same security level, the invention can reduce the calculated amount, save the storage space and lower the requirements for network bandwidth.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Shared key establishment method suitable for computing resource dissymmetric fields
ActiveCN107682150AImprove implementation efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsComputer hardwareElliptic curve discrete logarithm problem
The invention discloses a shared key establishment method suitable for computing resource dissymmetric fields. The shared key establishment method is provided by adopting a knapsack problem and a discrete logarithm problem (comprising an elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem), which is characterized in that computing resources necessary for both protocol parties in an implementation process are dissymmetric, thereby greatly improving the implementation efficiency of one of the protocol parties. The shared key establishment method is particularly suitable for the computing resource dissymmetric fields of servers and mobile terminals in the Internet of Things, cloud computing and other security fields, and has more advantages than the traditional key exchange protocols such as Diffie Hellman key exchange protocol and the like in these fields. The method provided by the invention can be widely used in the field of information security systems such as network security, electronic commerce and so on.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
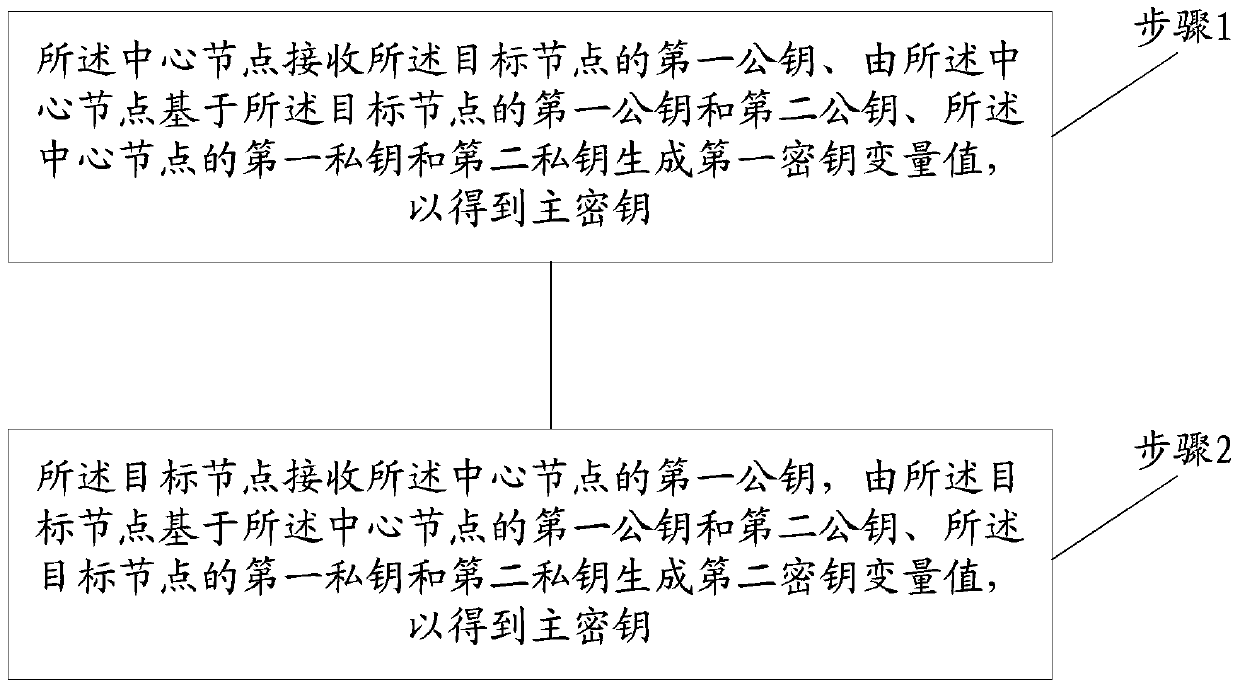
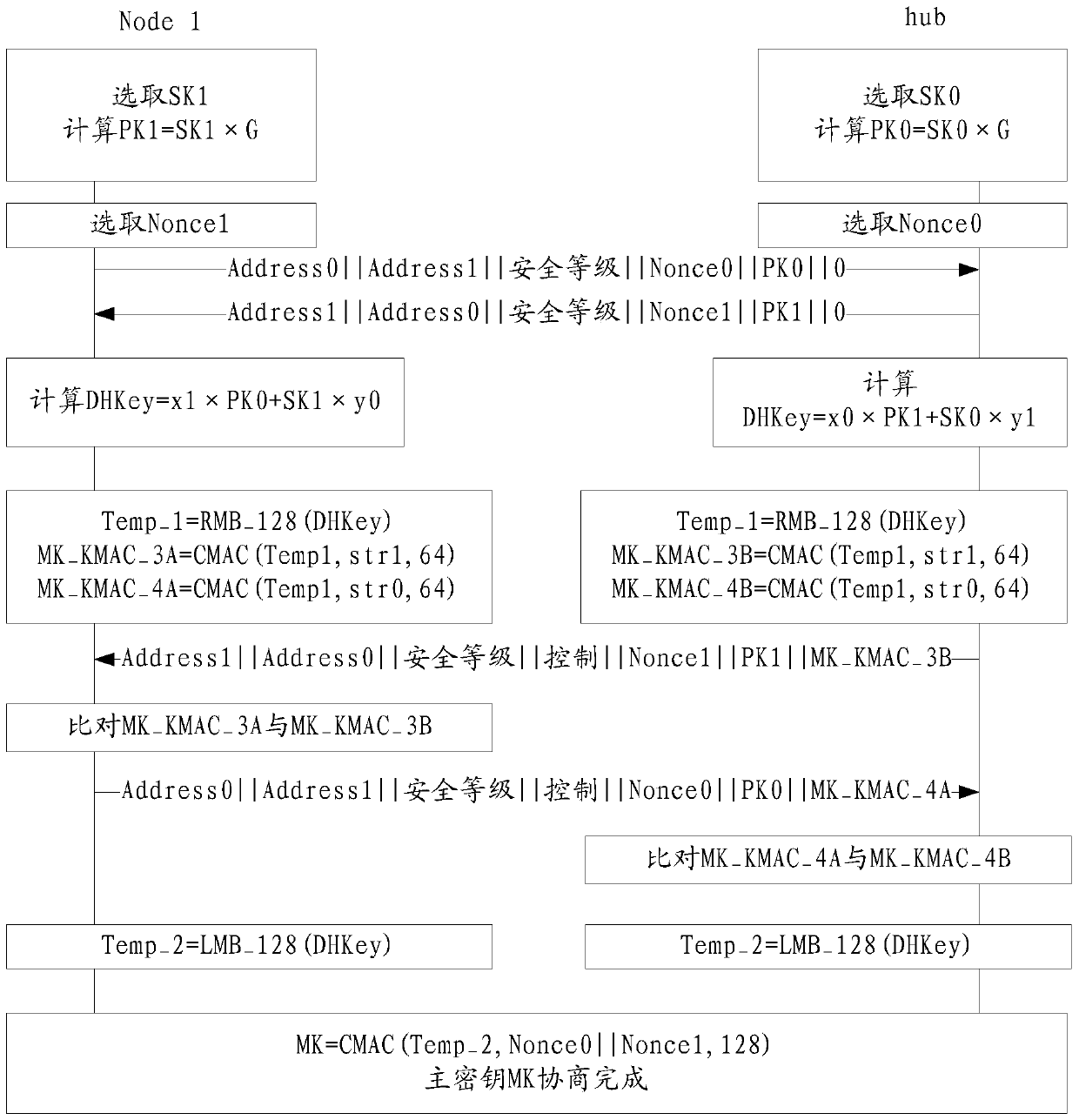
A body area network master key generation method
ActiveCN104836661BSolve the problem of not being able to resist the middlemanImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationArea networkBody area network
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com