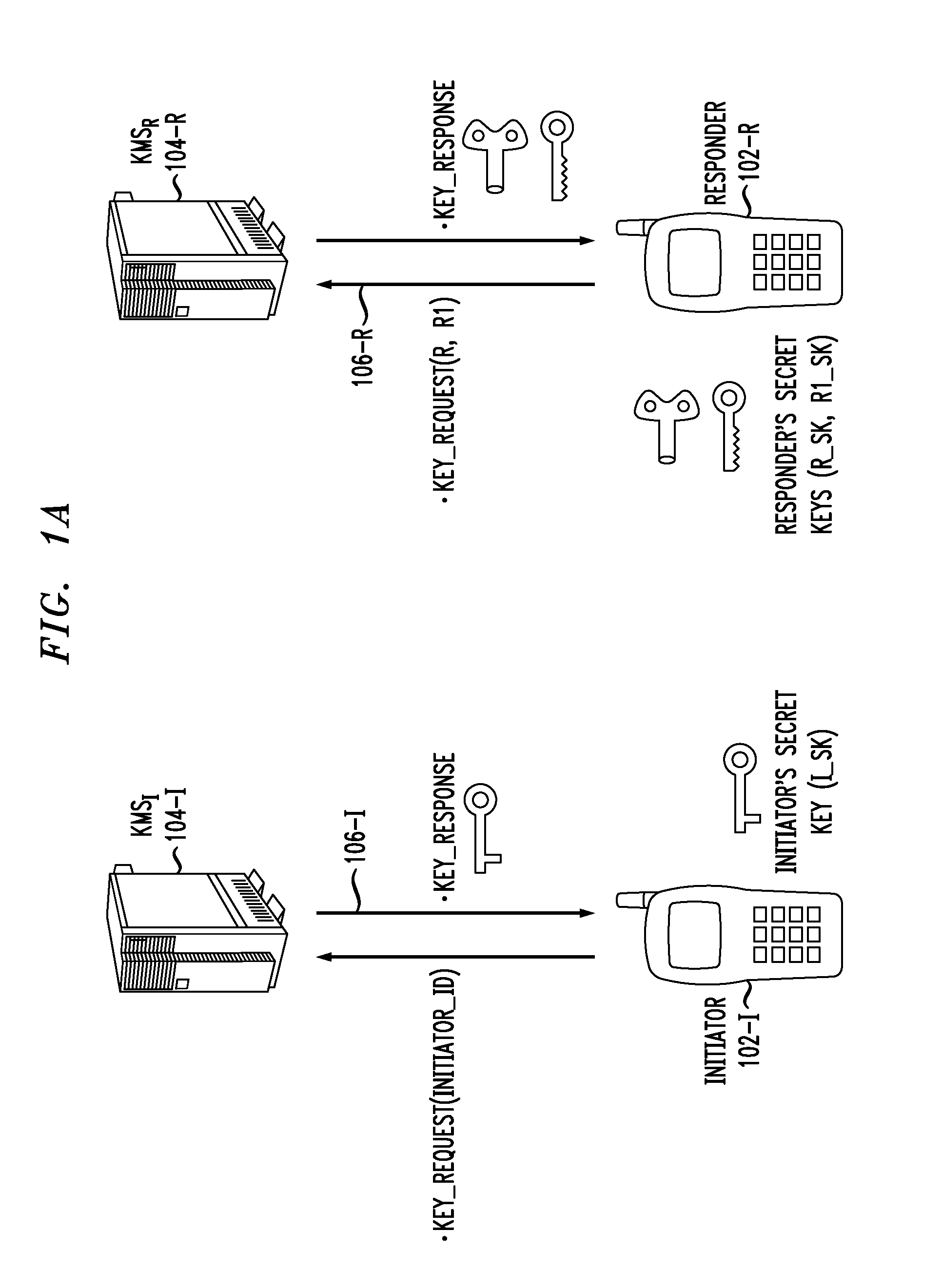
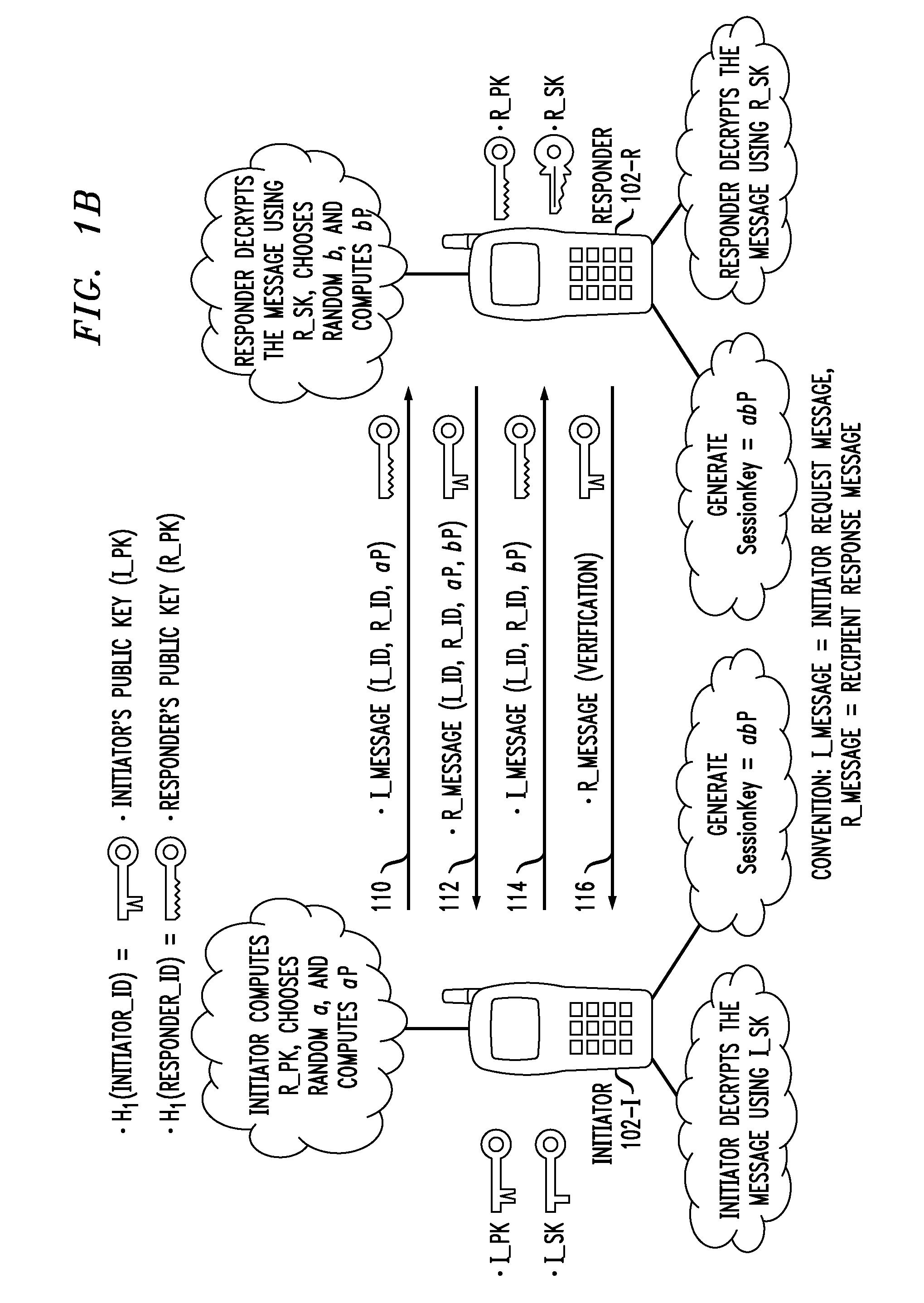
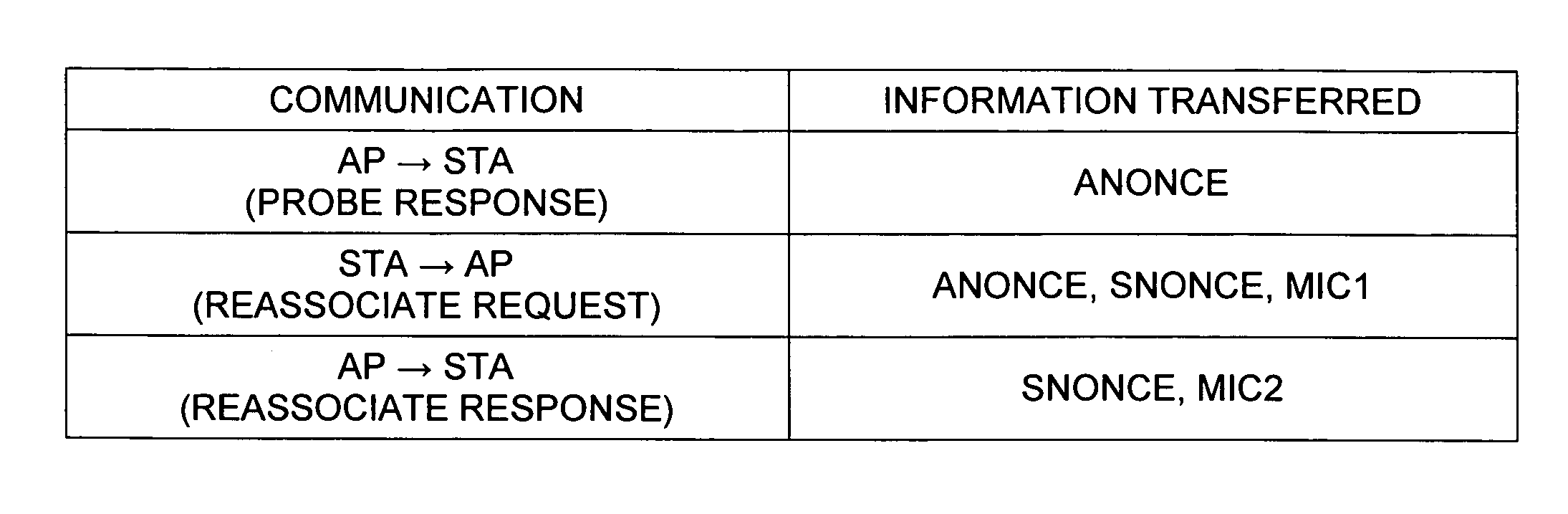
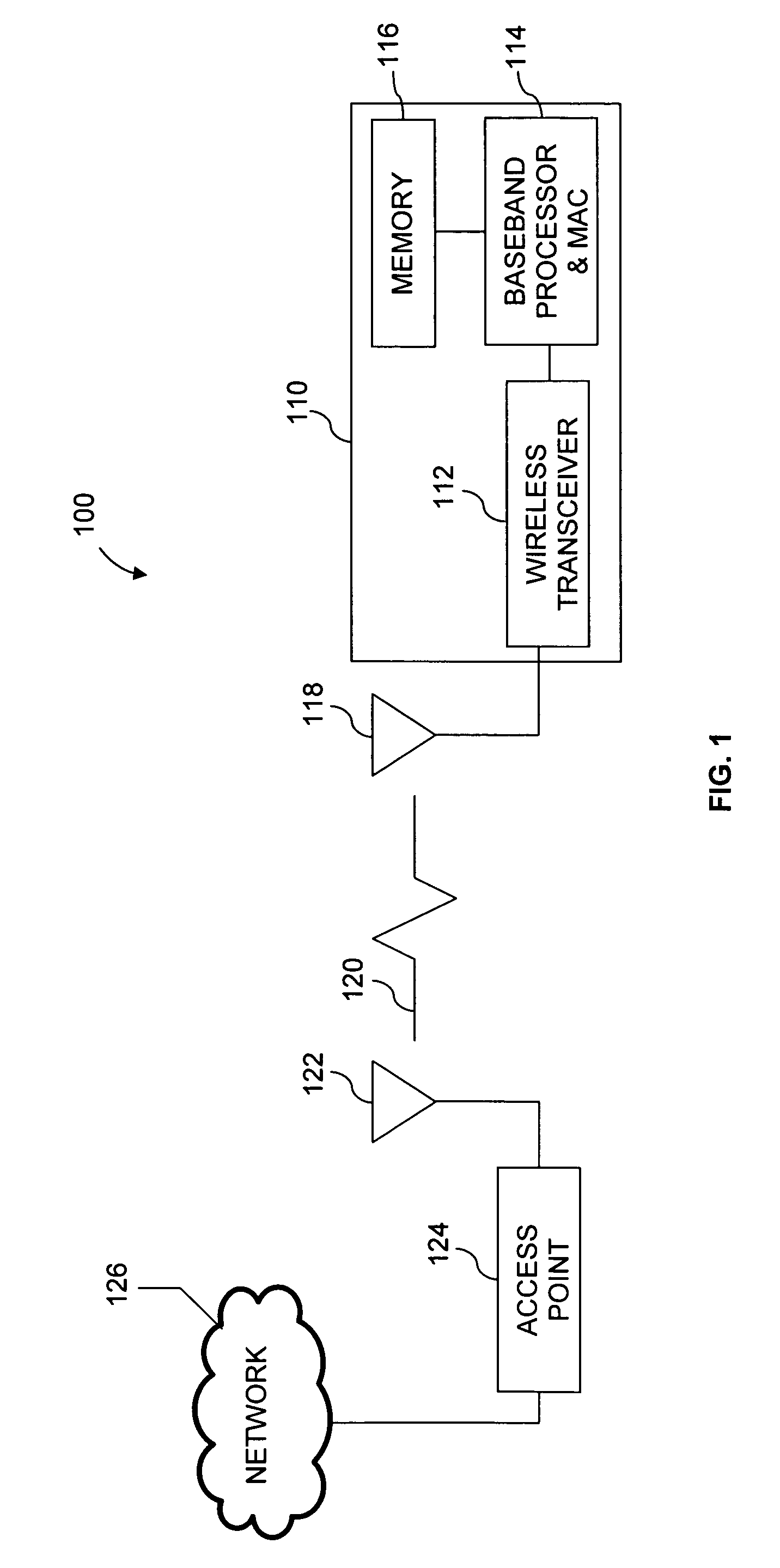
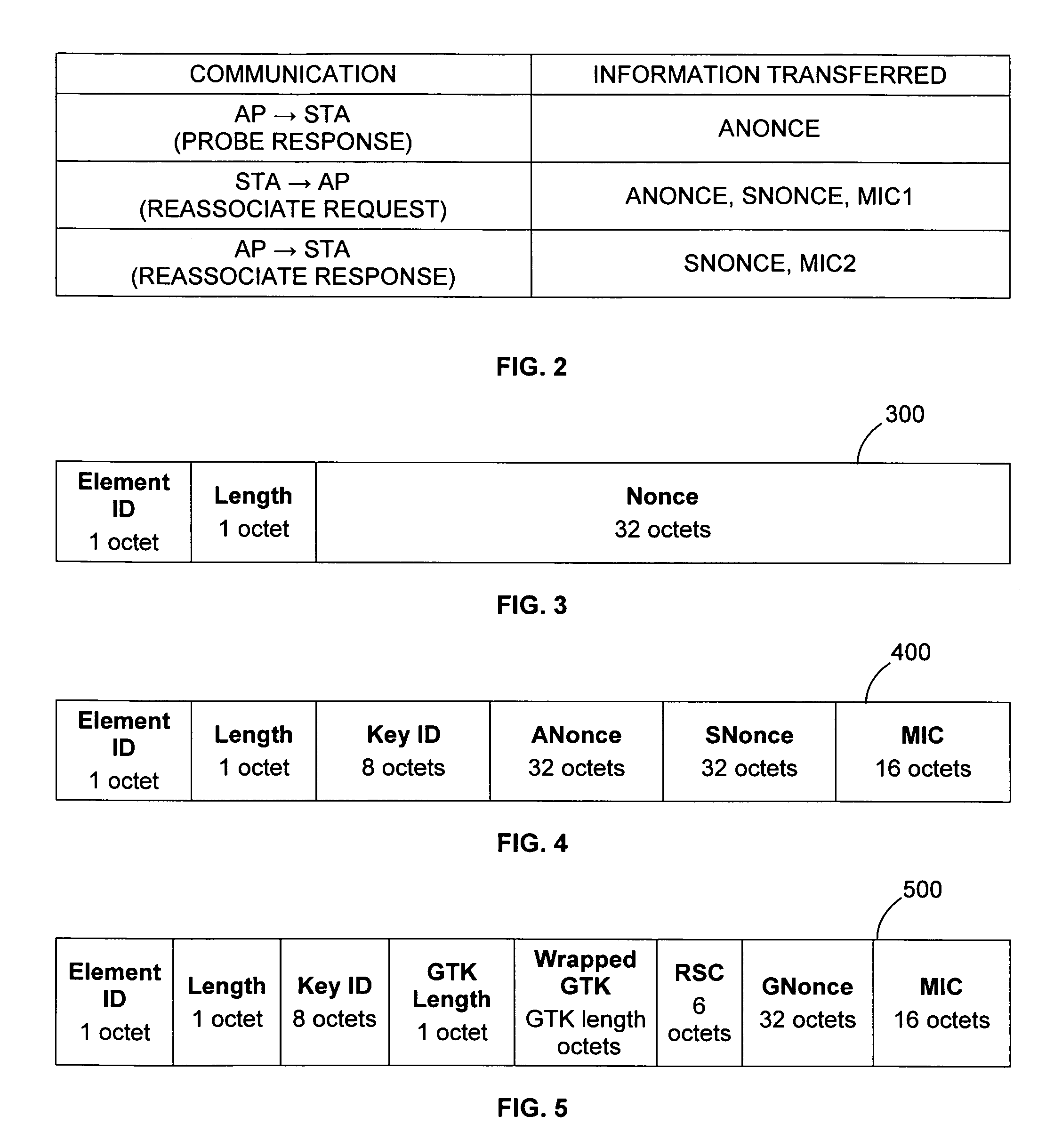
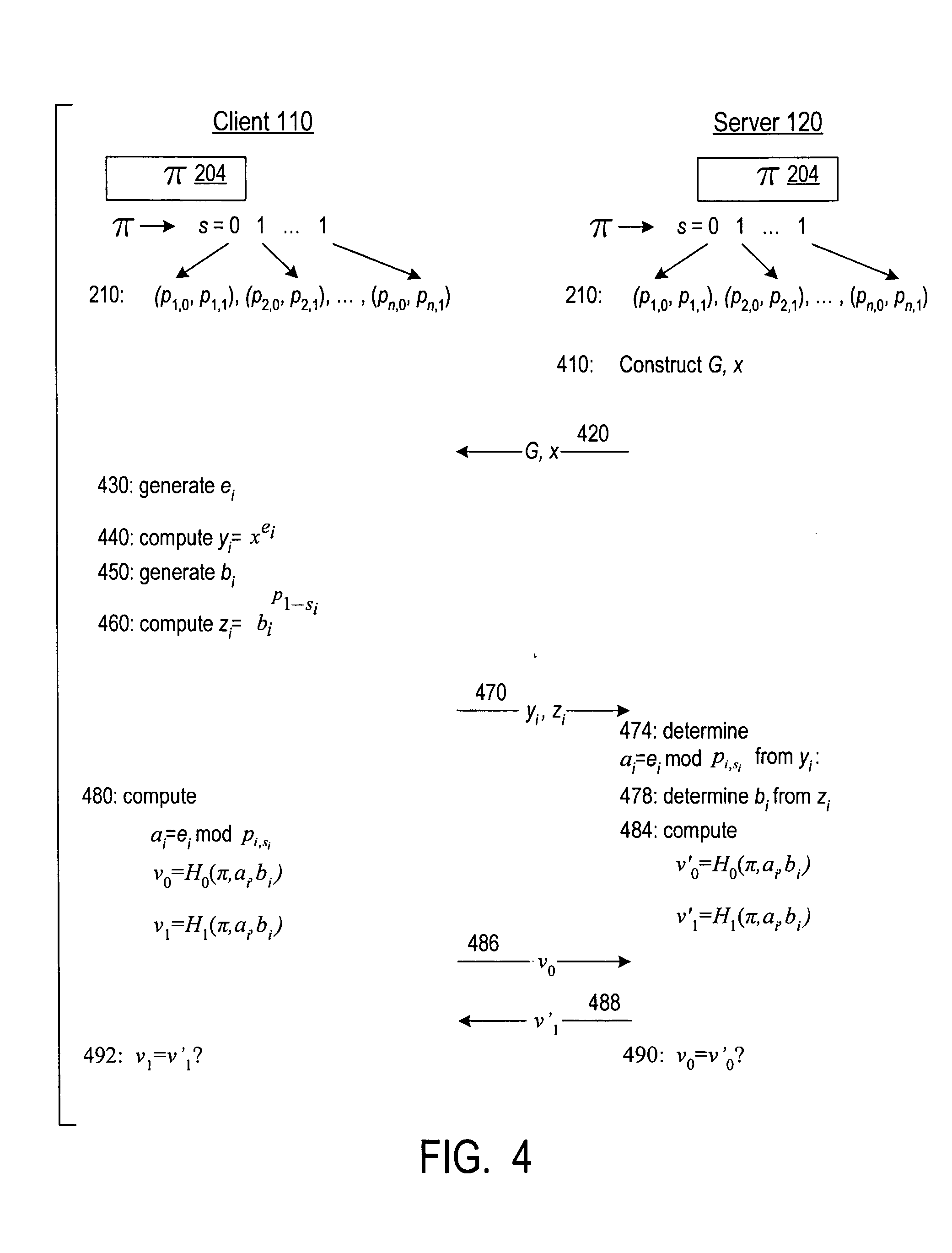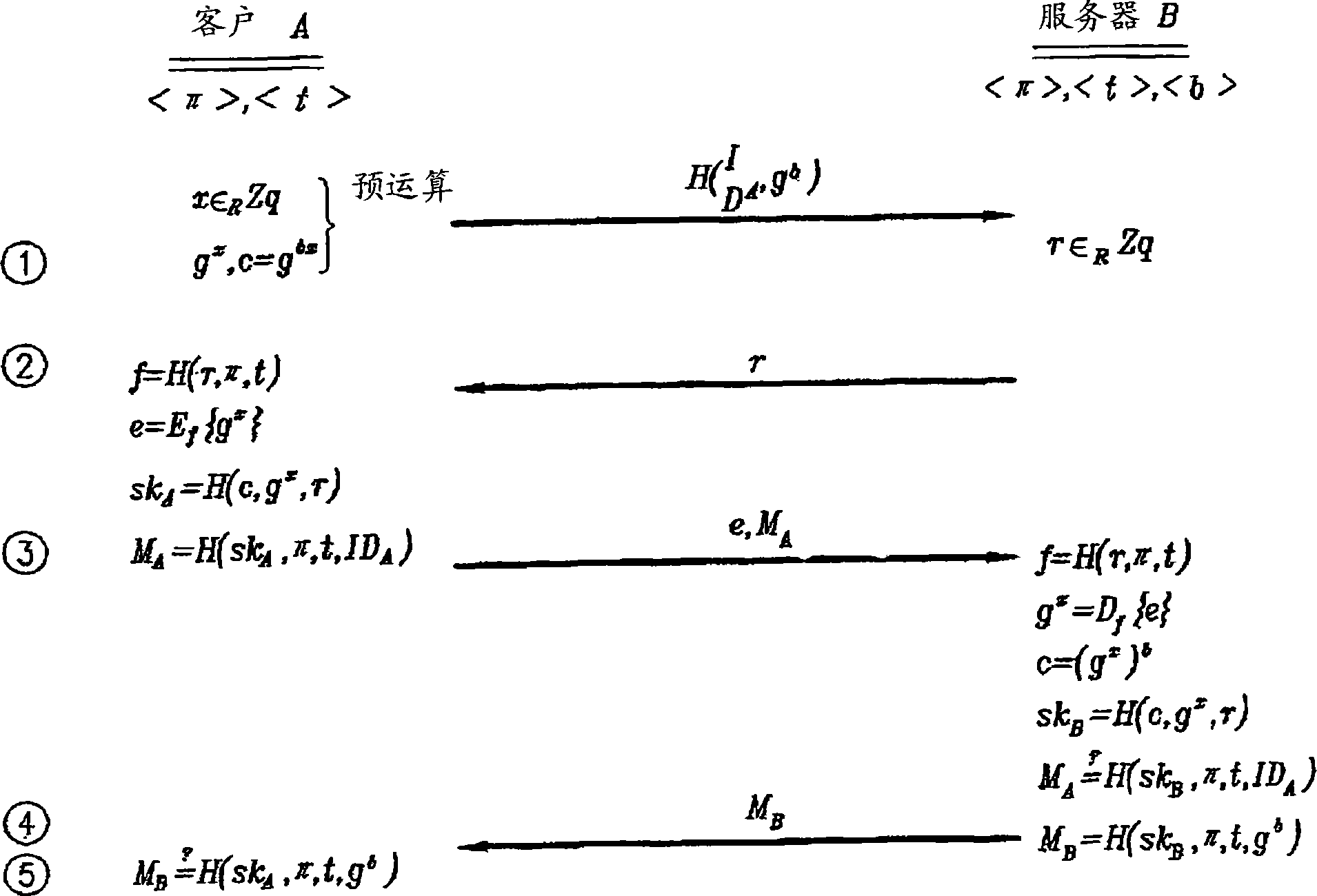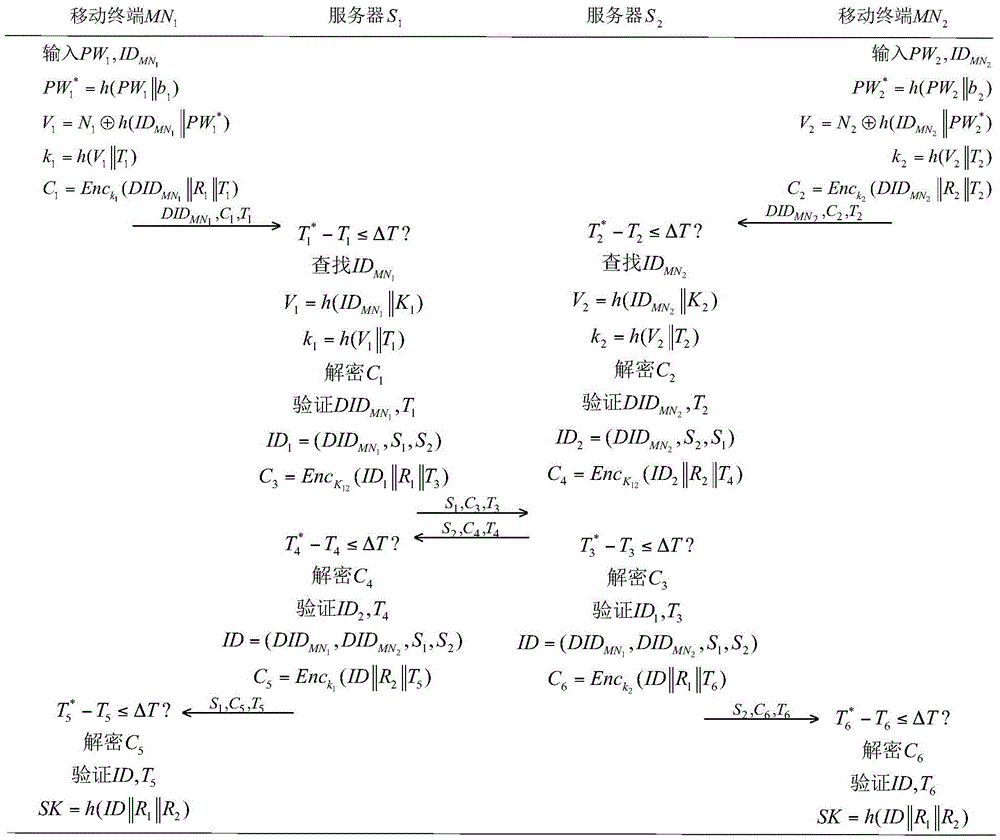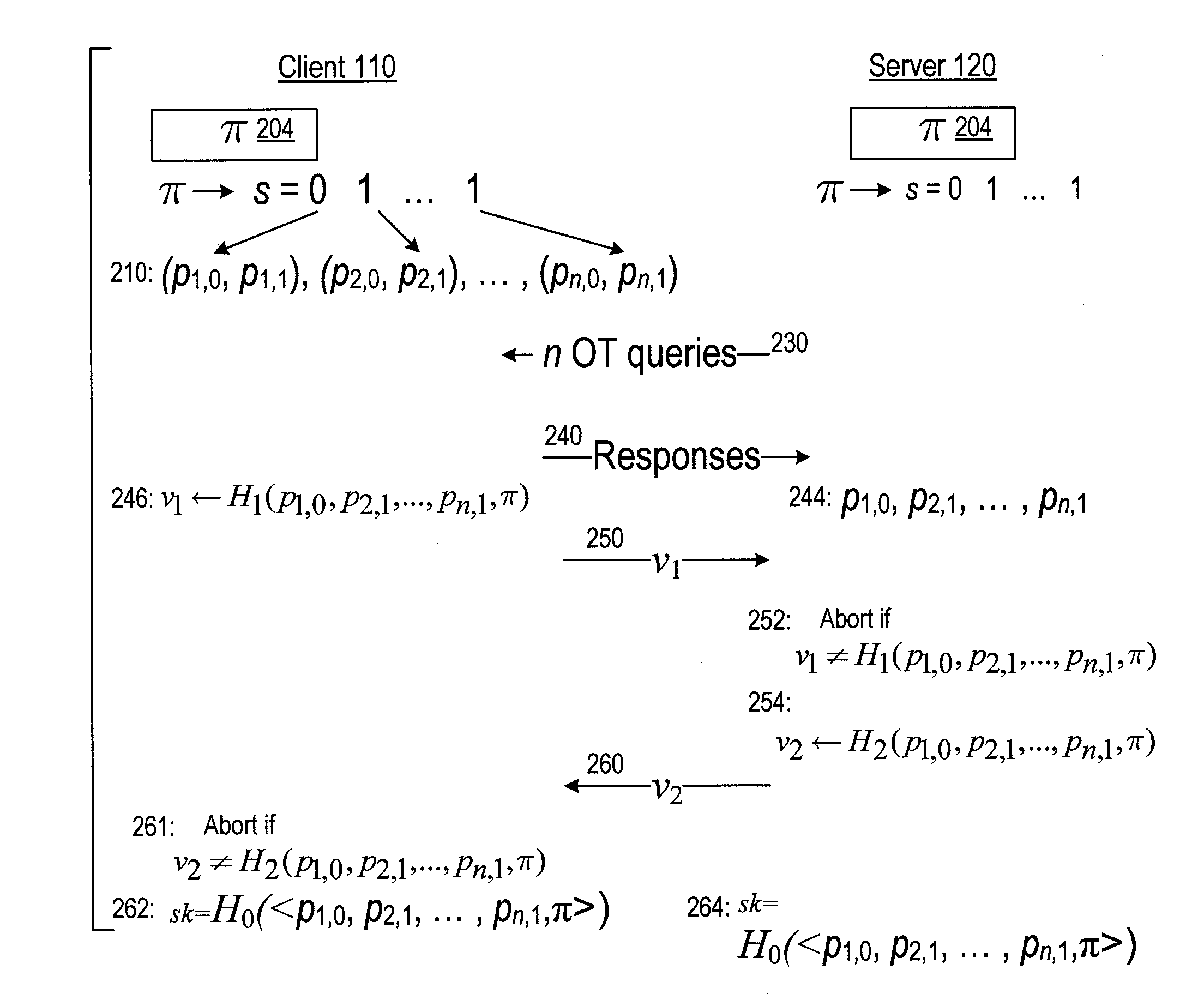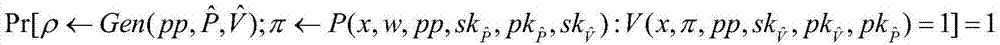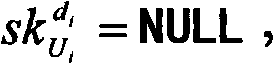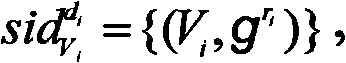Patents
Literature
46 results about "Authenticated Key Exchange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Authenticated Key Exchange (AKE) (or Authenticated Key Agreement) is the exchange of session key in a key exchange protocol which also authenticate the identities of parties involved in the key exchange.
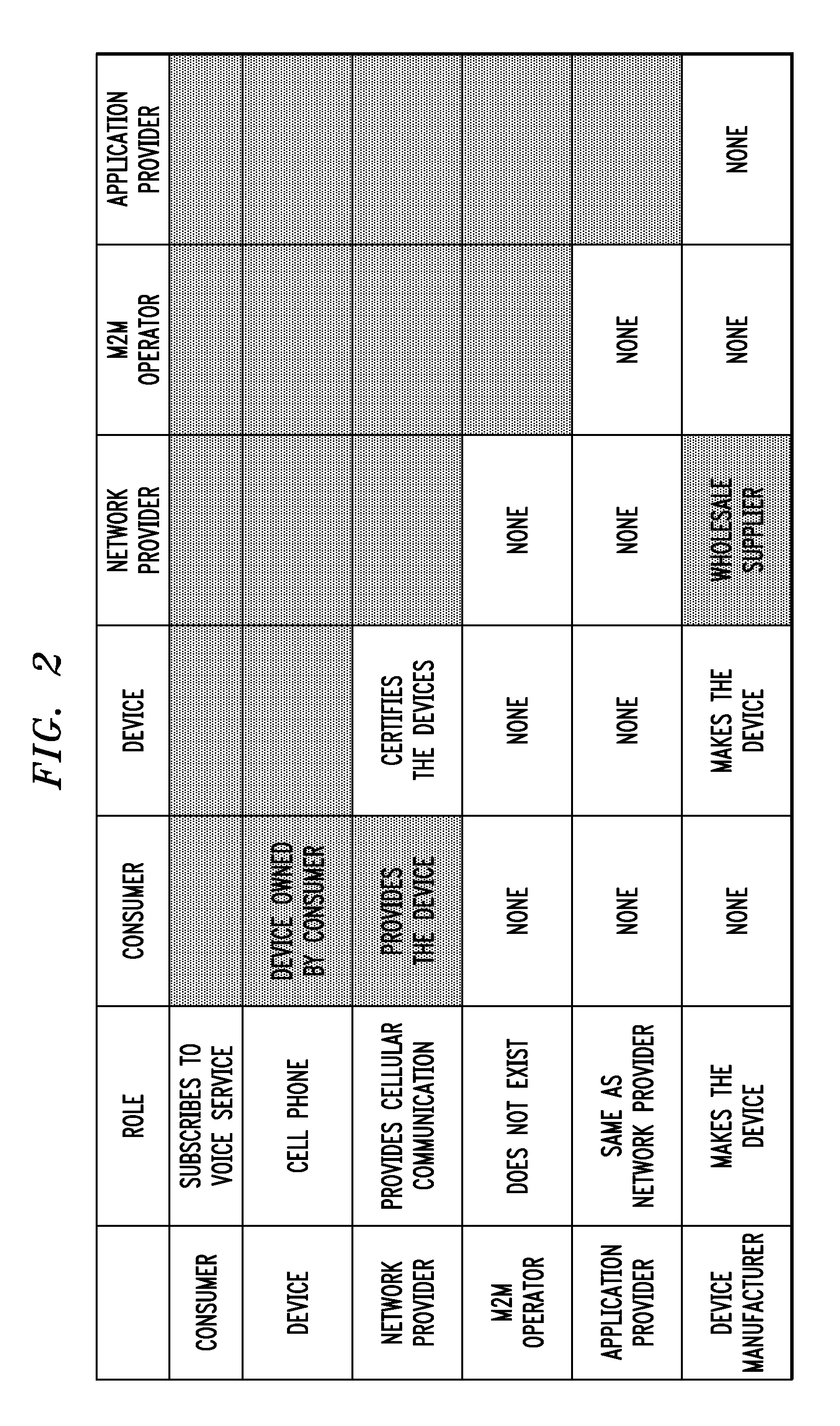
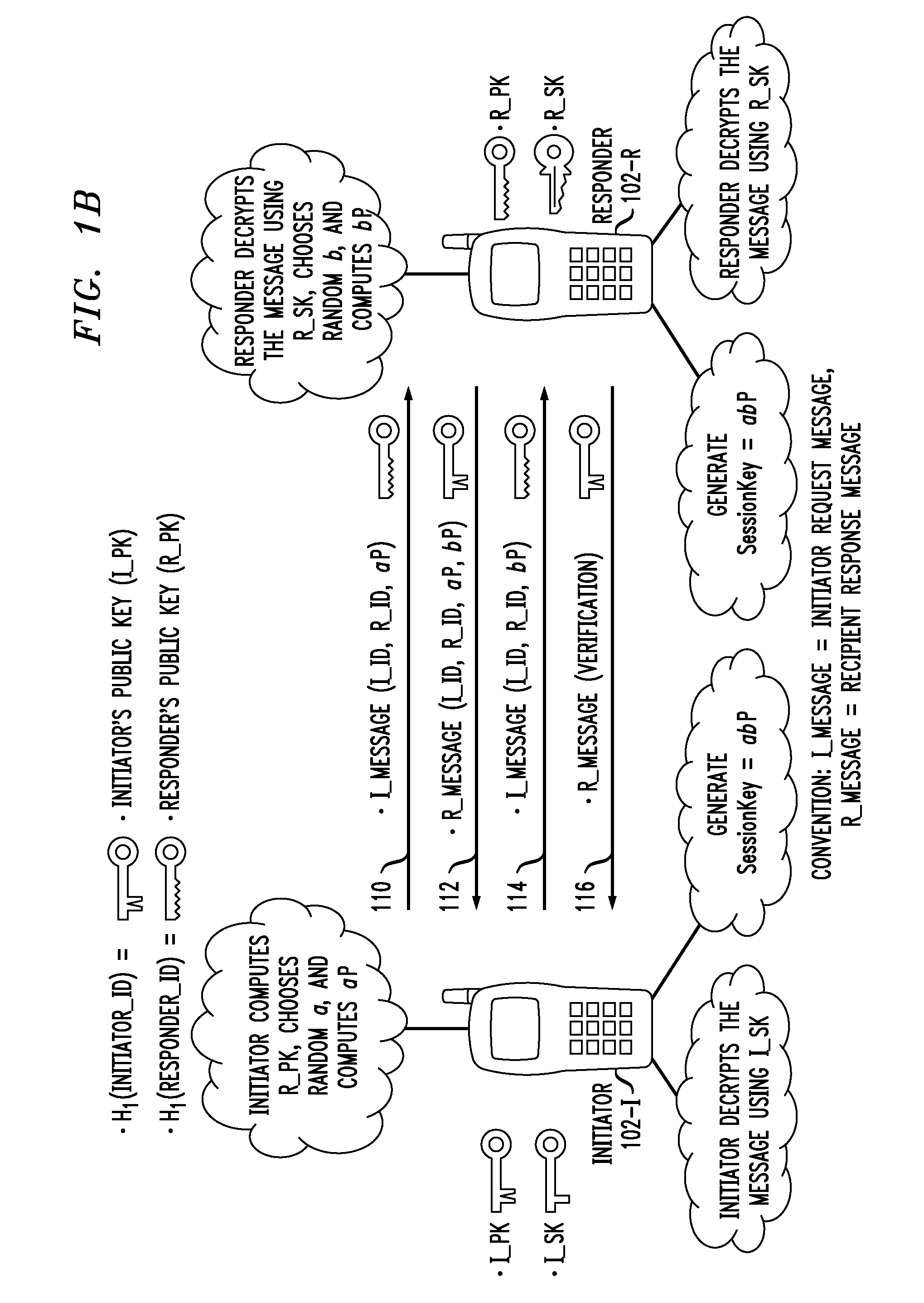
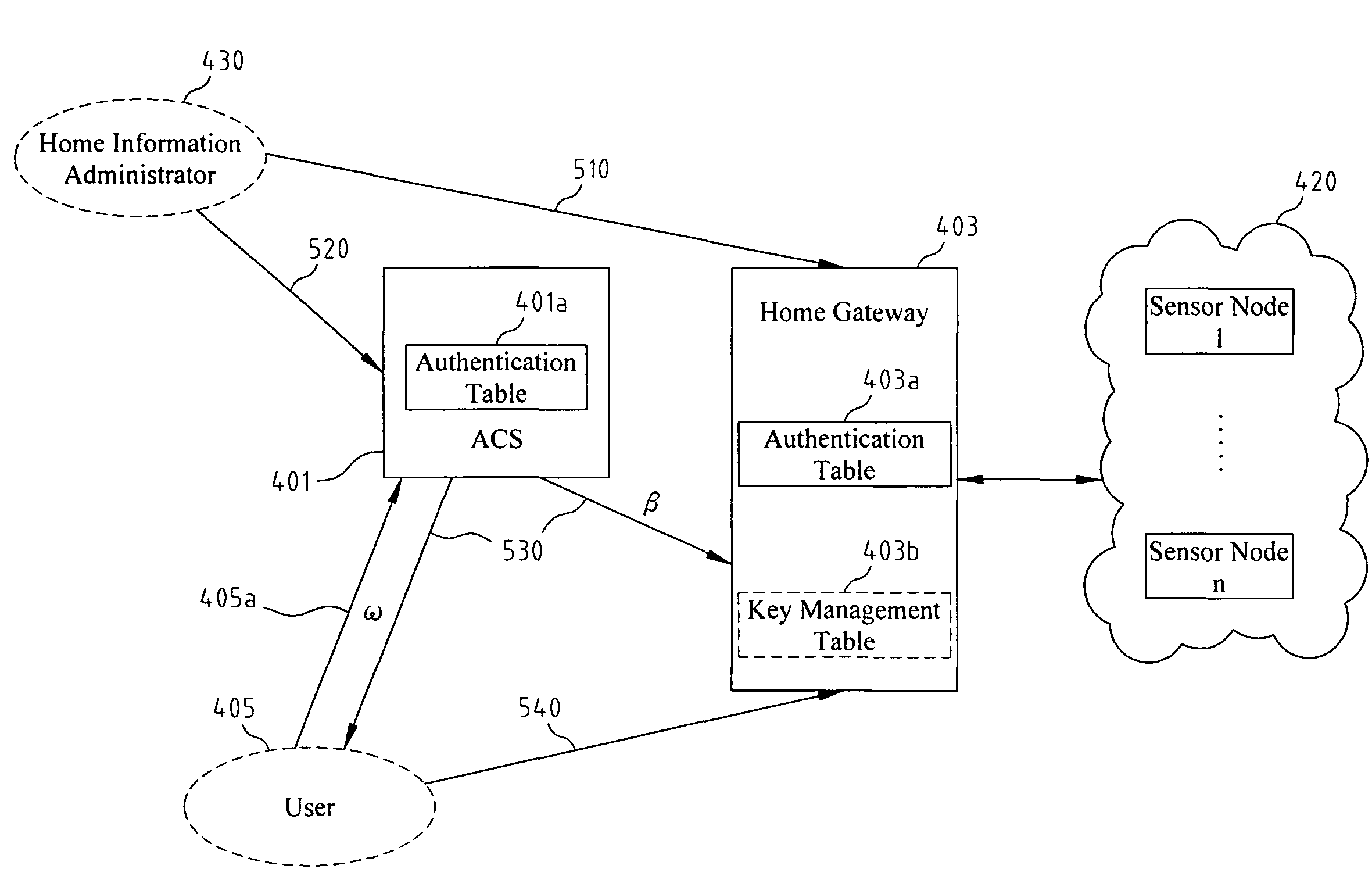
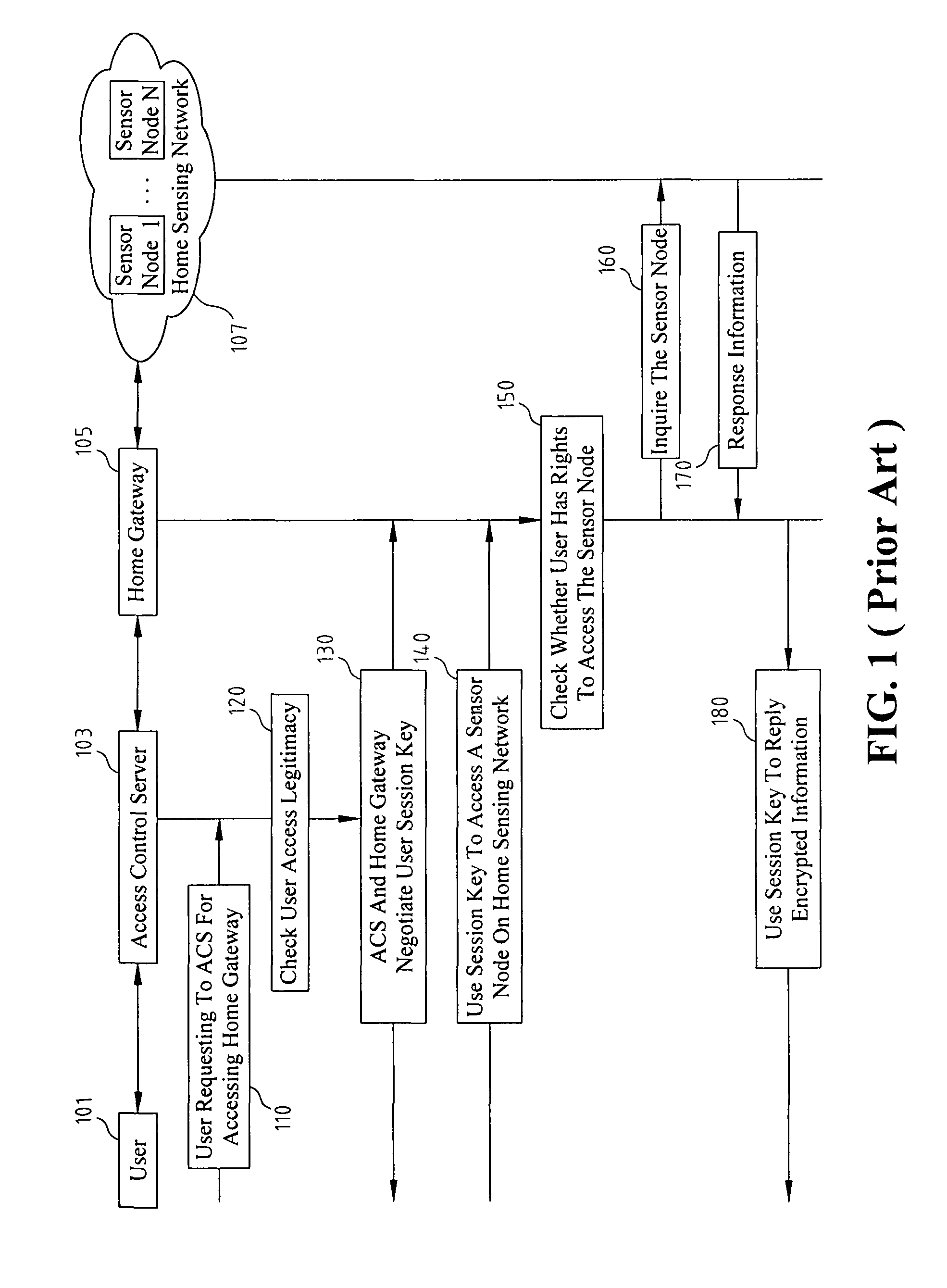
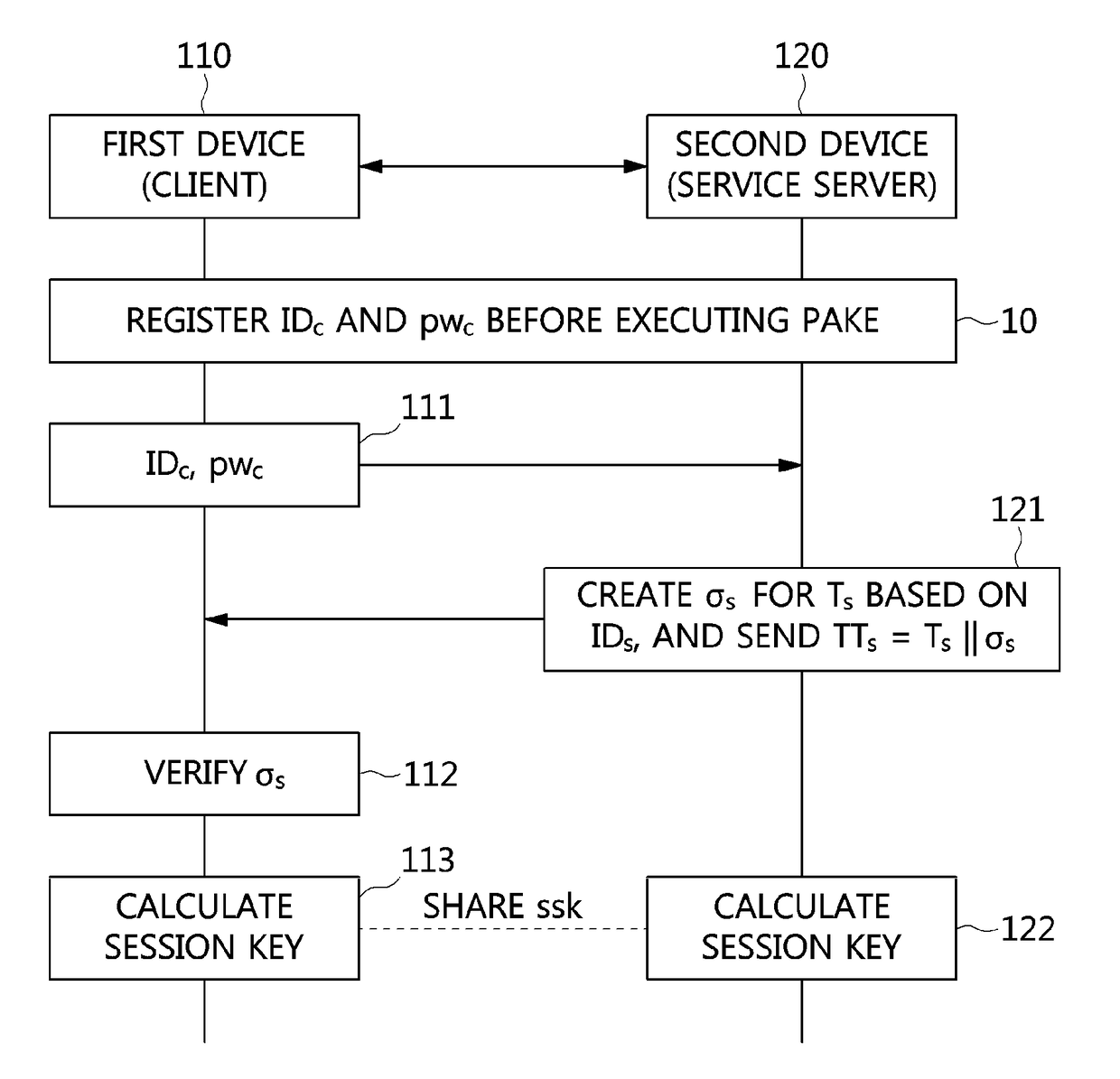
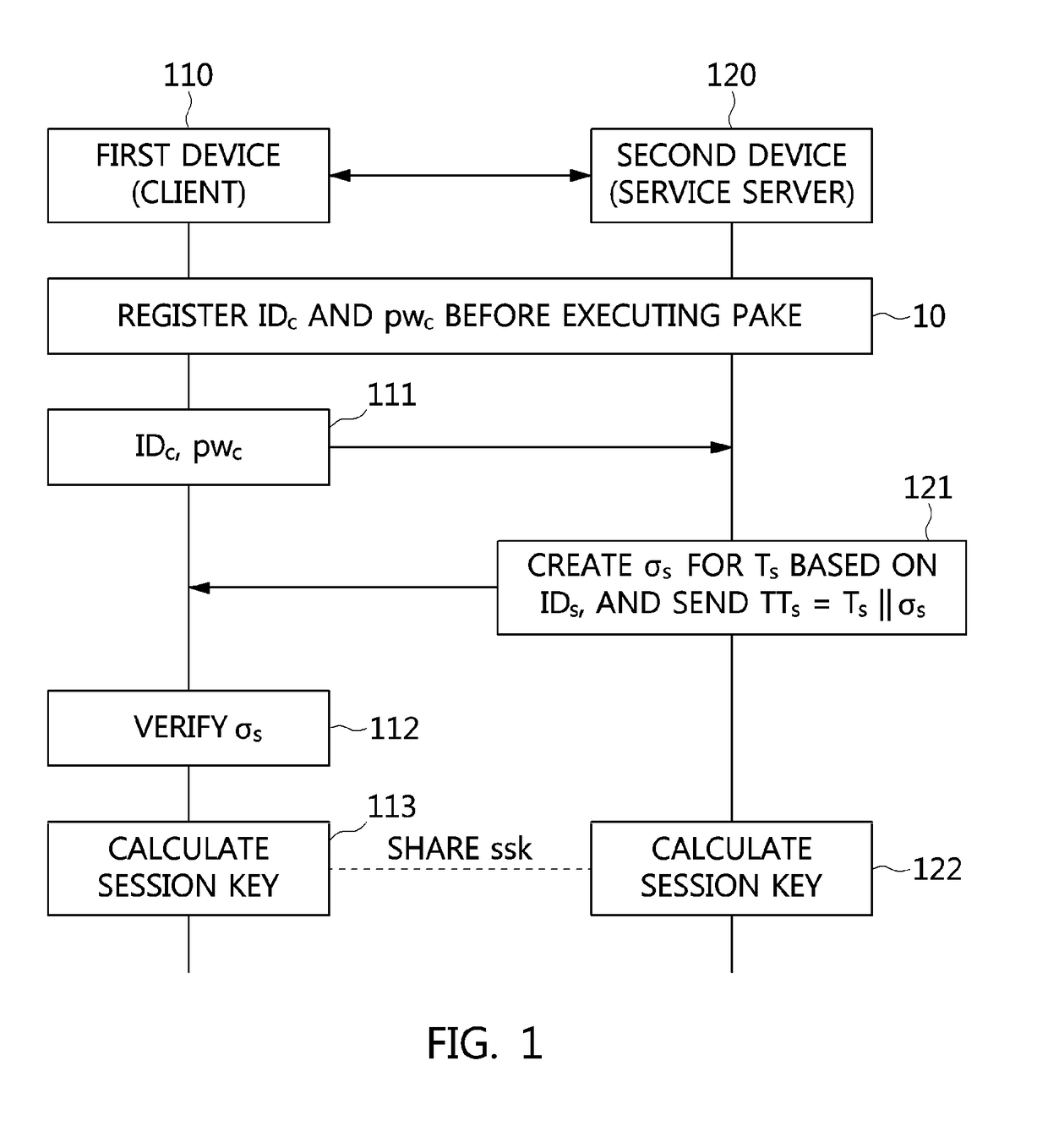
Access Control System And Method Based On Hierarchical Key, And Authentication Key Exchange Method Thereof
ActiveUS20100122091A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPasswordControl system
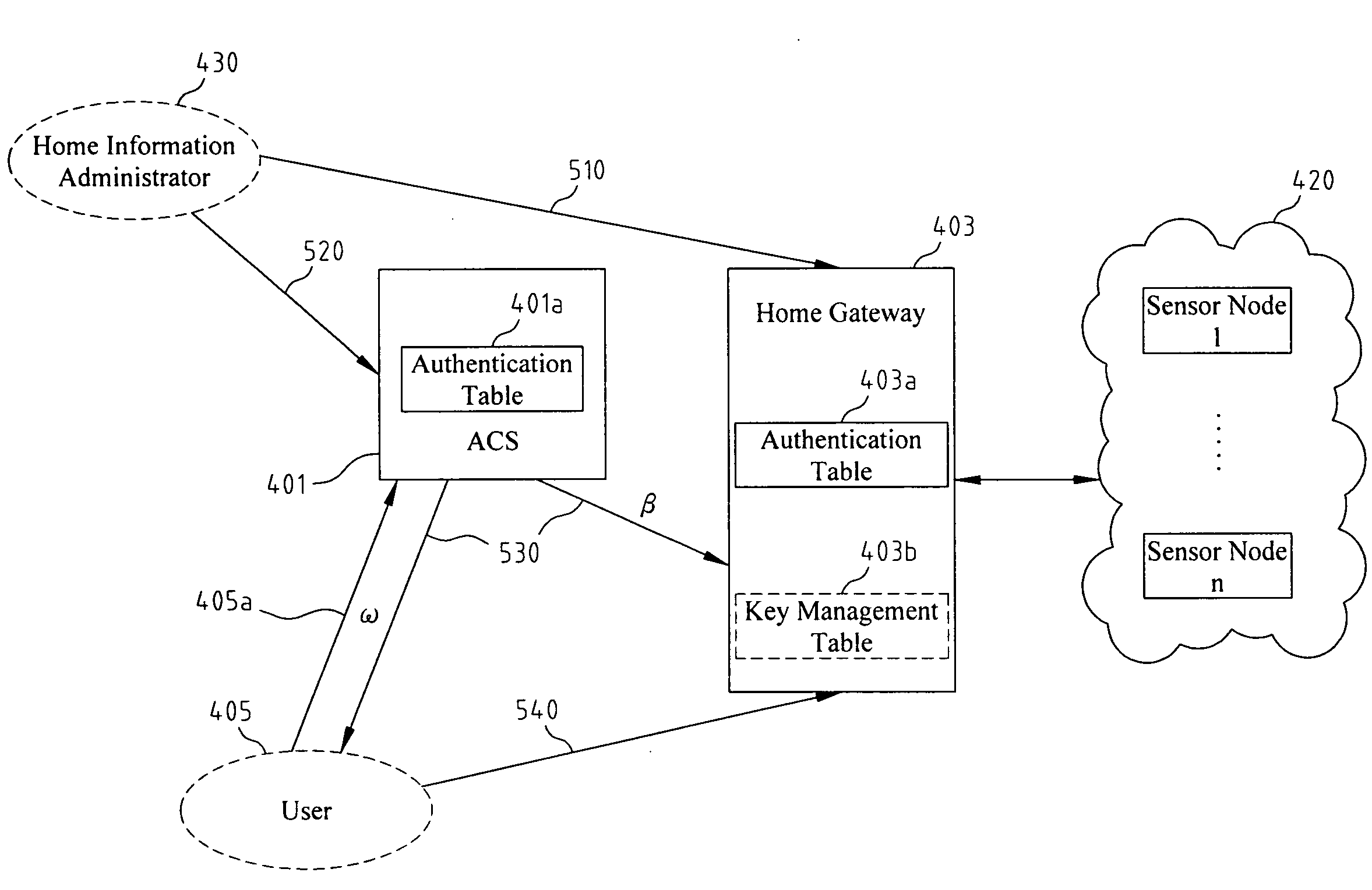
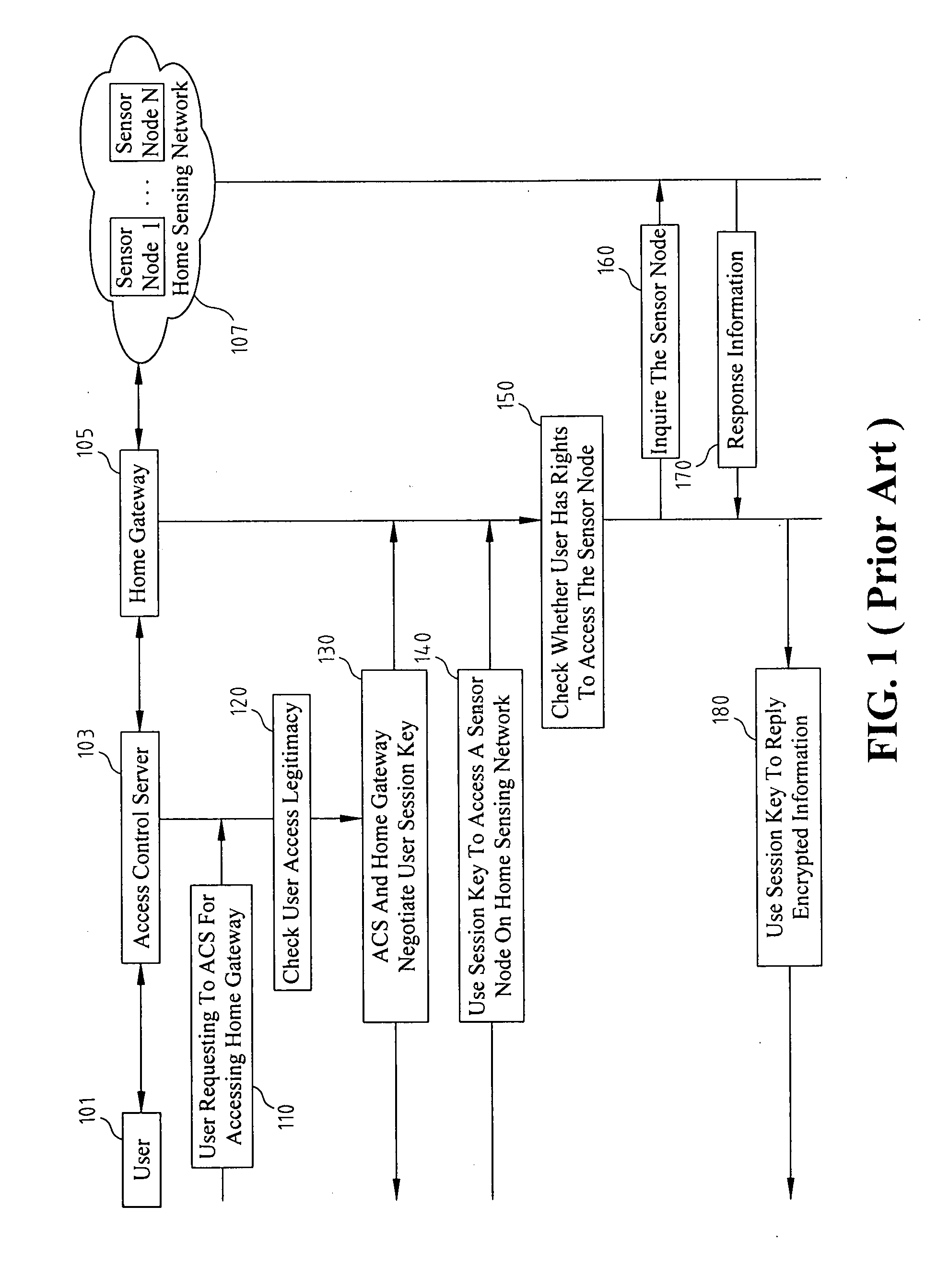
Disclosed relates to an access control system and method based on hierarchical keys. The system comprises an access control server (ACS), a home gateway, and a plurality of sensor devices disposed on a home network. The ACS sets up user's access limits of authority and authorization verifier, and saves the related data of user's password and the user's access limits of authority. The gateway records the authority limits' level and the authority limits' key which are constructed based on a hierarchical key structure. When a user logs in the ACS to request access, an one-time communication key between the user and the home gateway is established by exchanging the ticket and the token that are issued by the ACS. This allows the user to access the information of the sensor devices.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Multi-factor password-authenticated key exchange
ActiveUS20090288143A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsPasswordAuthentication
Apparatus, methods, and computer program products are disclosed that enable a first computer and a second computer to mutually authenticate each other over a network. A first computer sends first authentication evidence to a second computer. The first authentication evidence is used to prove to the second computer that the first computer has access to a first plurality of authentication secrets without exposing the first plurality of authentication secrets. In addition, the second computer sends second authentication evidence to the first computer. The second authentication evidence is used to prove to the first computer that the second computer has access to a second plurality of authentication secrets without exposing the second plurality of authentication secrets. The first plurality of authentication secrets is related to the second plurality of authentication secrets. Thus, the first computer is authenticated to the second computer and the second computer is authenticated to the first computer.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
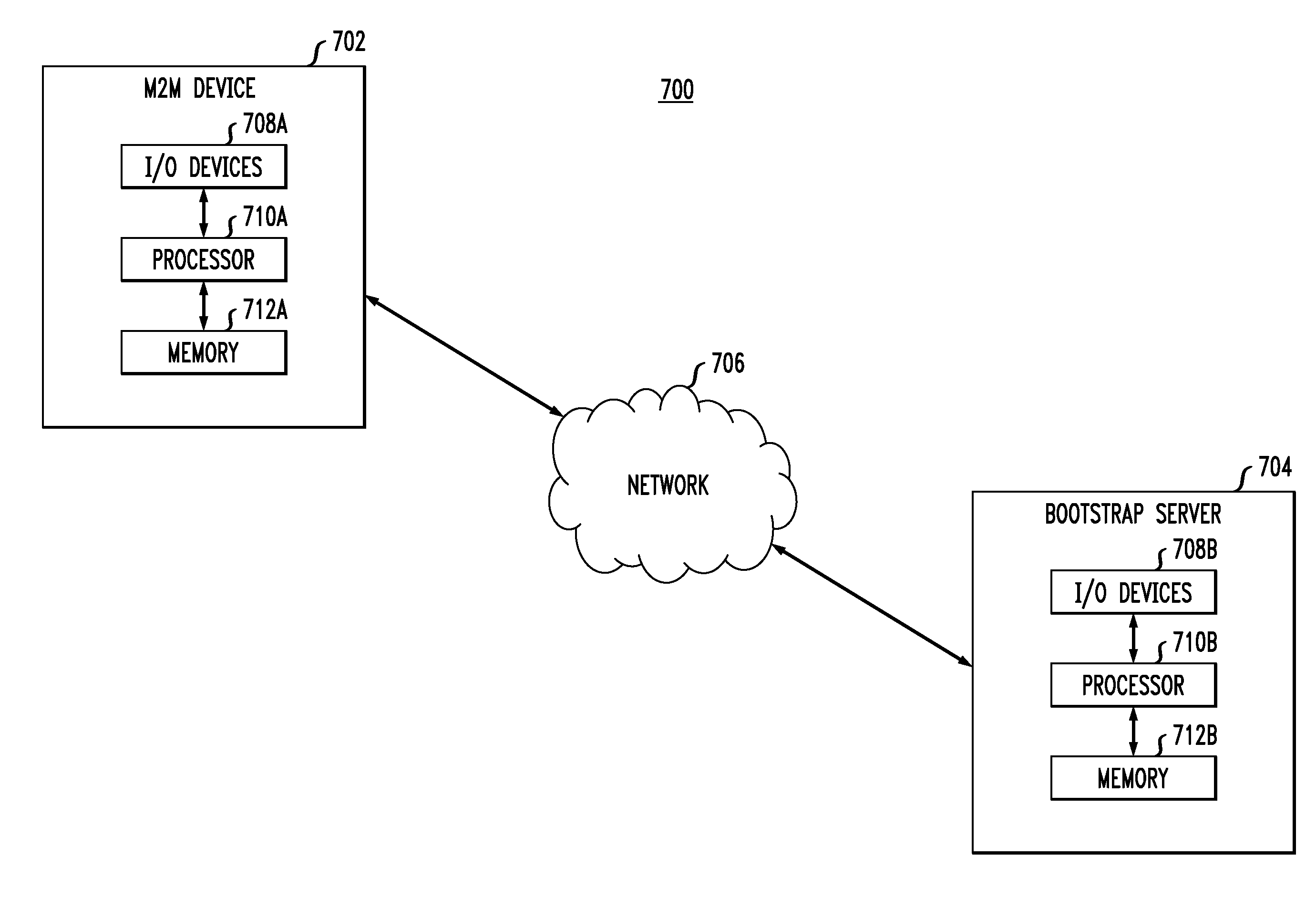
Automated Security Provisioning Protocol for Wide Area Network Communication Devices in Open Device Environment
ActiveUS20110016321A1User identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesSecure communicationCommunication device
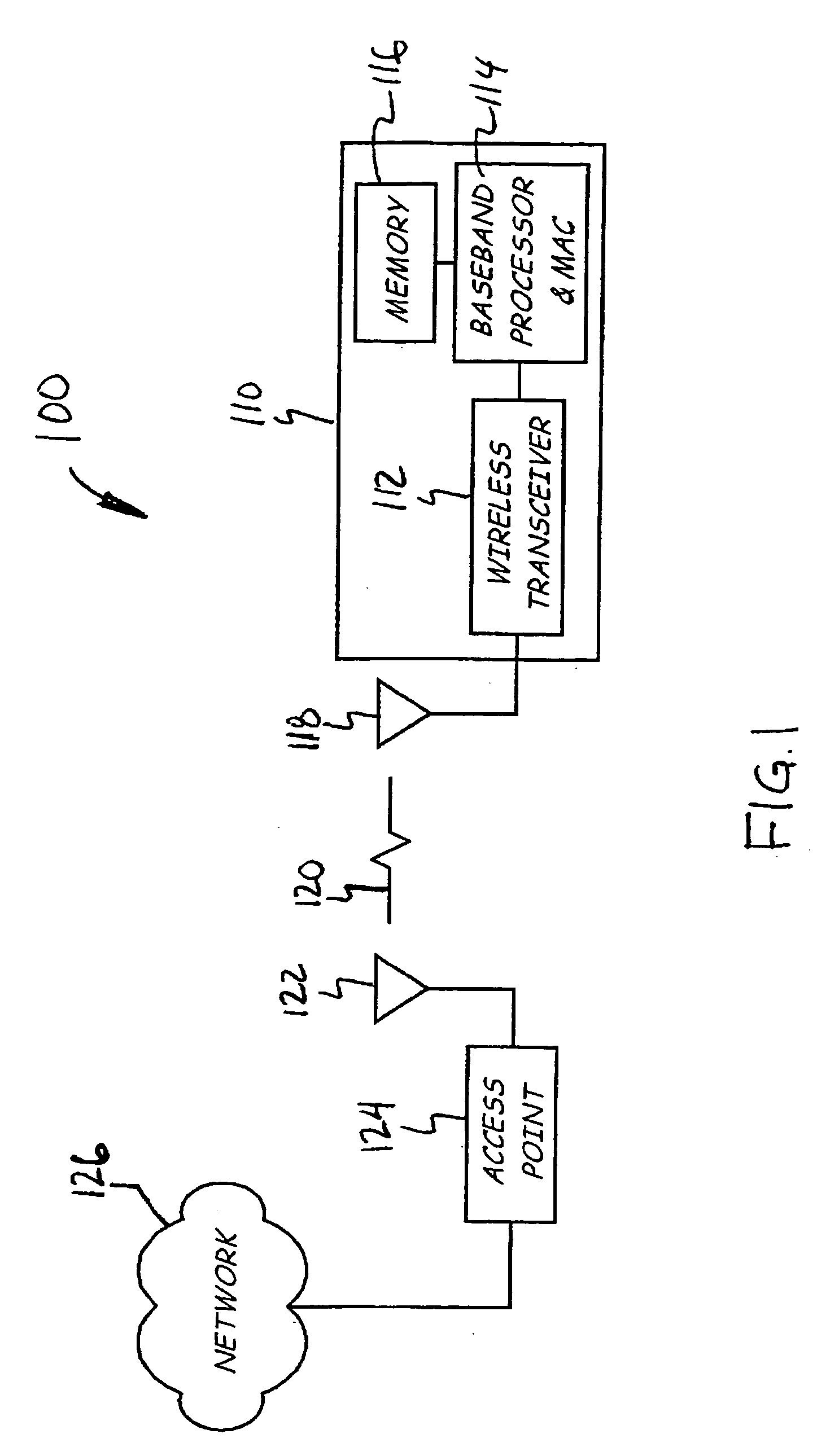
An automated security provisioning protocol is provided for wide area network communication devices in an open device environment, such as cellular communication devices in a machine-to-machine (M2M) environment. For example, a method for performing a security provisioning protocol between a first communication device and a second communication device over at least one wide area communication network comprises the following steps from the perspective of the first communication device. The first communication device automatically uses access information not previously provisioned in the wide area communication network to gain access to the wide area communication network for an initial purpose of communicating with the second communication device. The first communication device, upon gaining access to the wide area communication network, automatically performs an authenticated key exchange operation with the second communication device over the wide area communication network and establishes a secure communication key as a result of the authenticated key exchange operation for subsequent use by the first communication device for secure communications. The wide area communication network is operated by a first entity and the second communication device is operated by a second entity.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
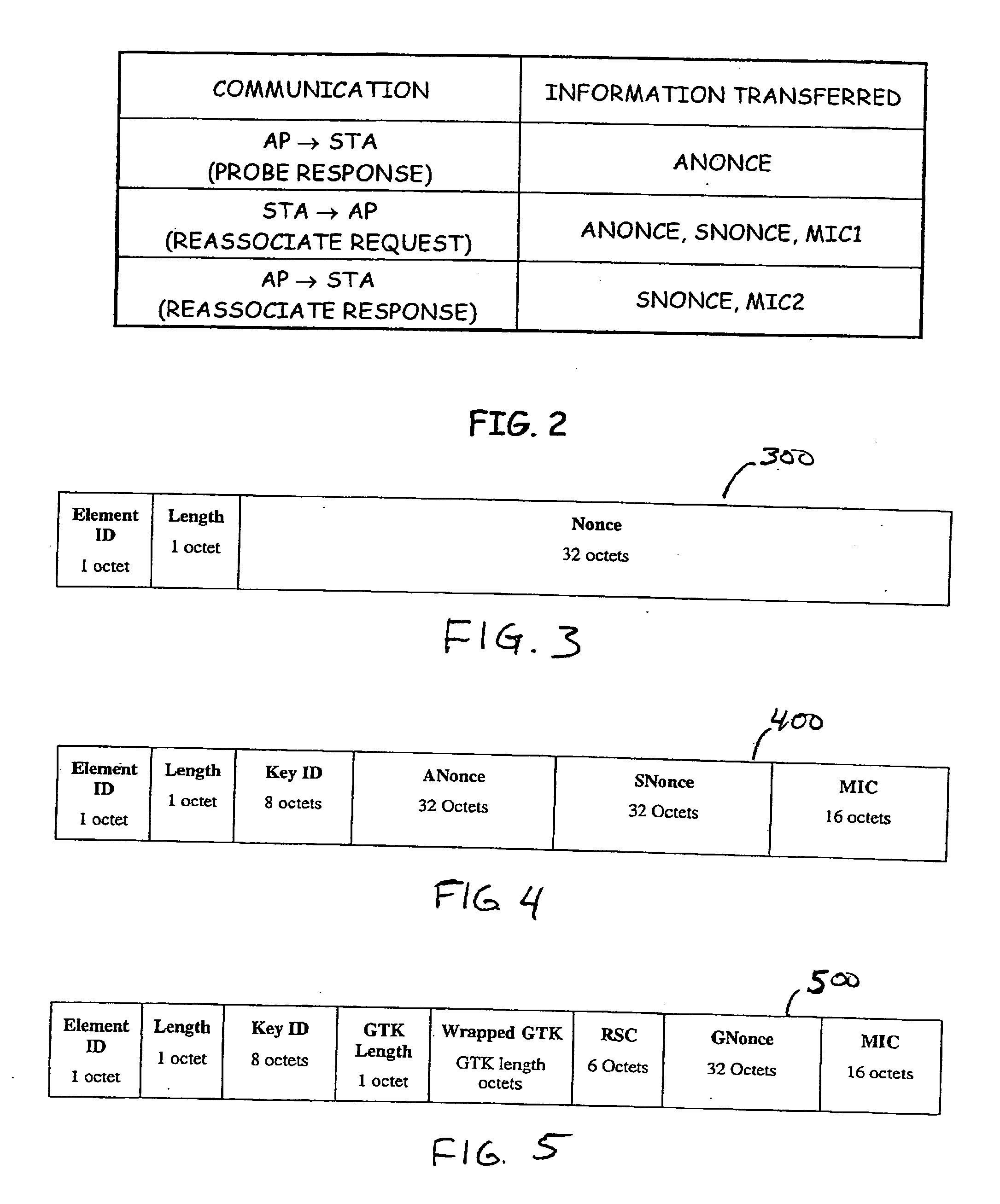
Authenticated key exchange based on pairwise master key
InactiveUS20050032506A1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionWireless lanMaster key
Briefly, in accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a pairwise master key may be utilized to generate nonces for authenticated key exchange during a rekeying event in a wireless local area network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
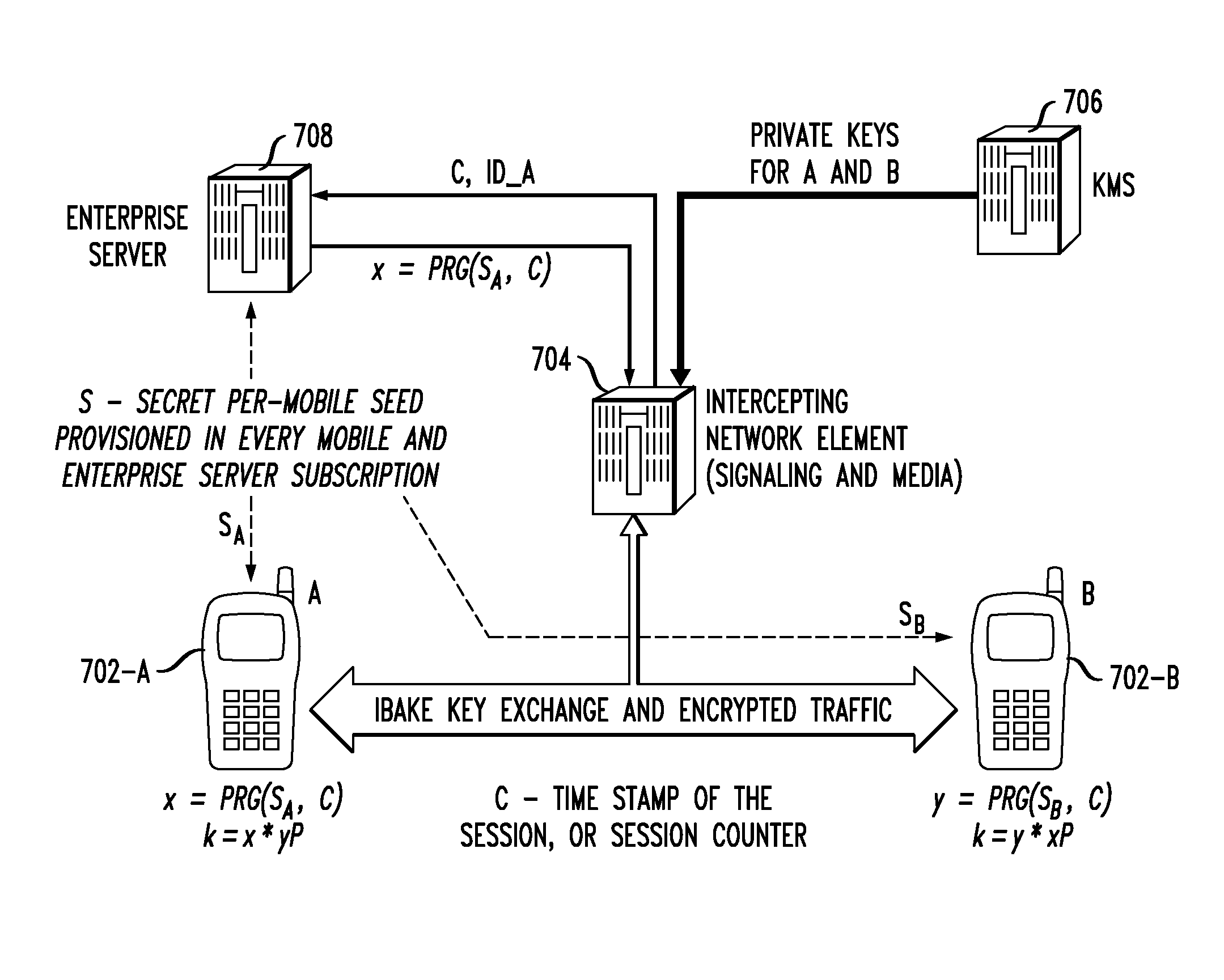
Discovery of security associations
ActiveUS20120272064A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationSecurity association
Techniques are disclosed for discovering security associations formed in communication environments. For example, a method for forming a discoverable security association between a first computing device (e.g., a first client) and a second computing device (e.g., a second client) comprises the following steps. The first computing device is provided with a seed that is used by the first computing device to generate a secret that is used by the first computing device to compute a key for use in securing communications with the second computing device. The secret is re-computable based on knowledge of the seed and the key is re-computable based on knowledge of the secret such that a third computing device (e.g., an intercepting server) can use the re-computed key to intercept communications between the first computing device and the second computing device unbeknownst to the first computing device and the second computing device. By way of example, the key may be a result of an identity based authenticated key exchange.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
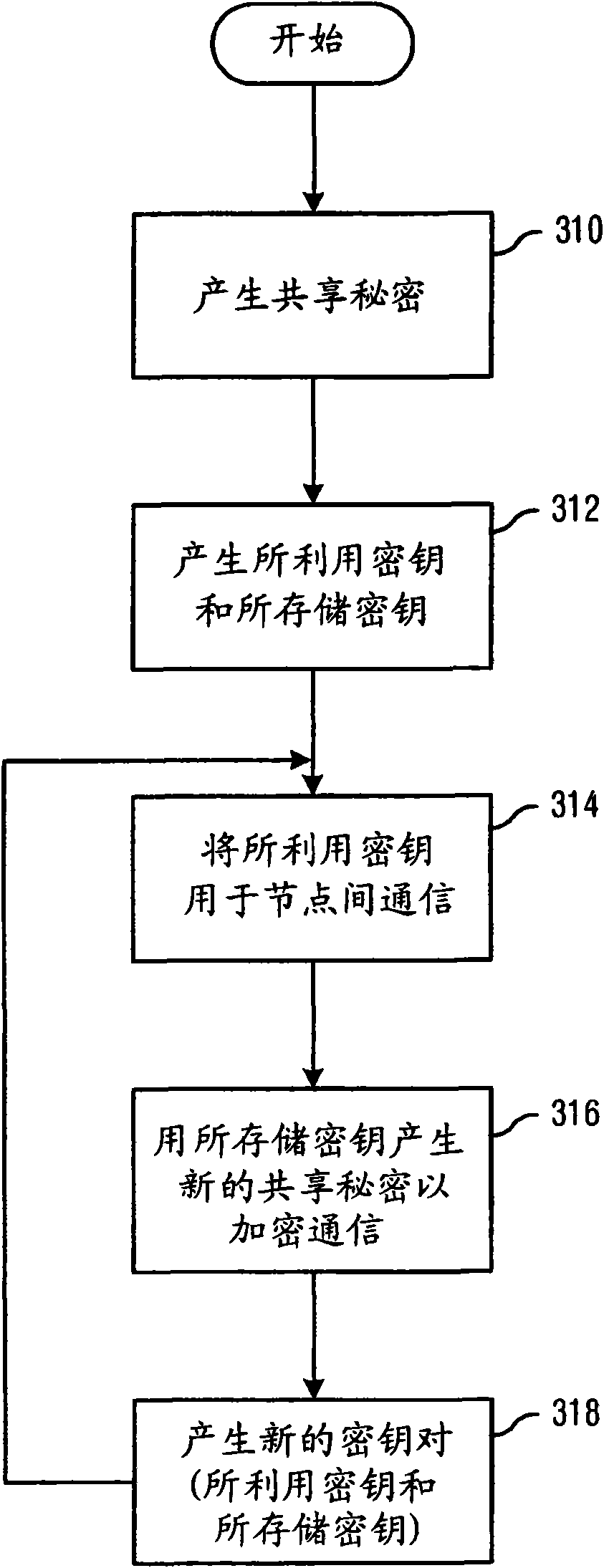
Updating and Distributing Encryption Keys
InactiveUS20100042841A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecure communicationPassword
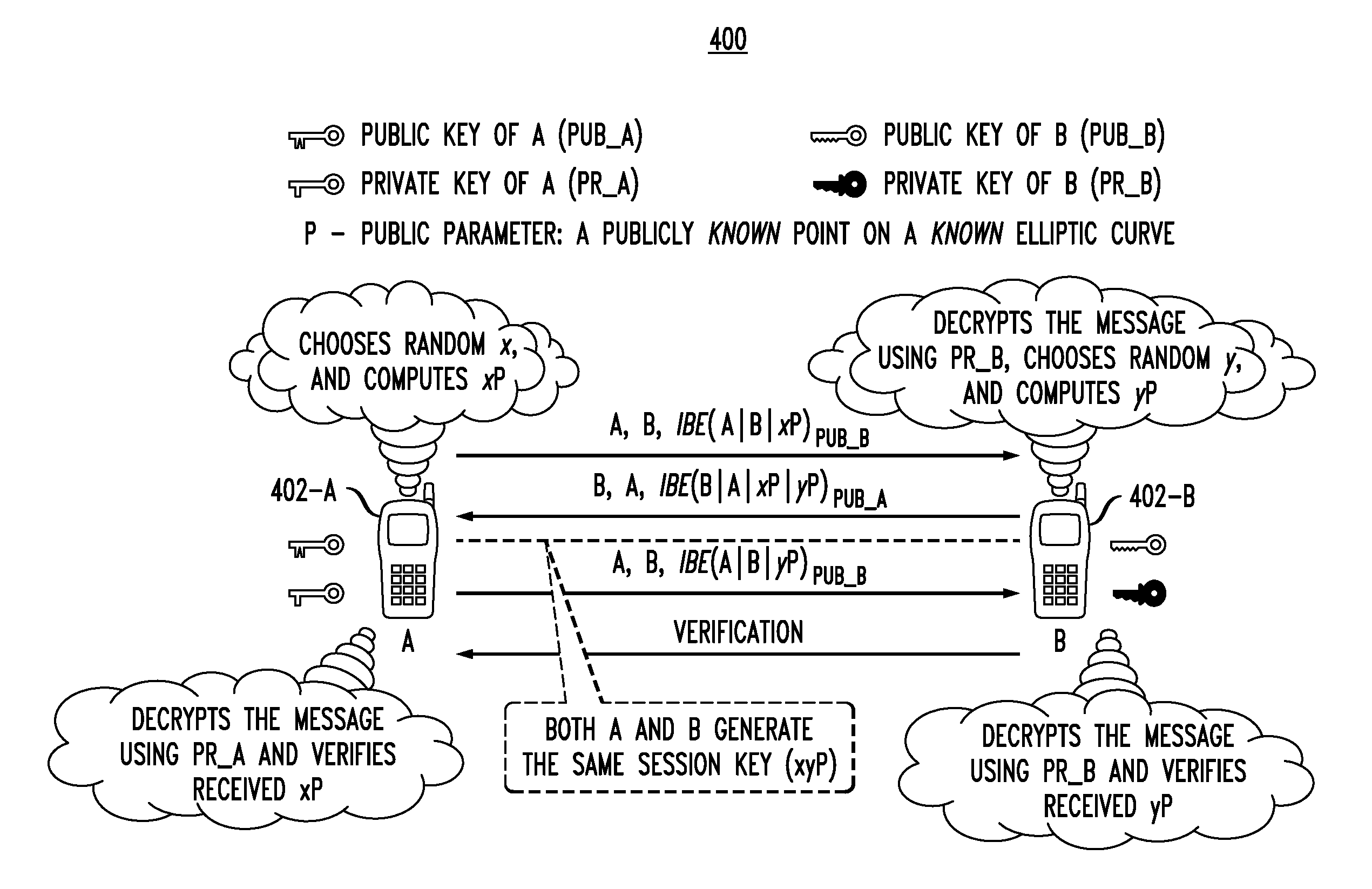
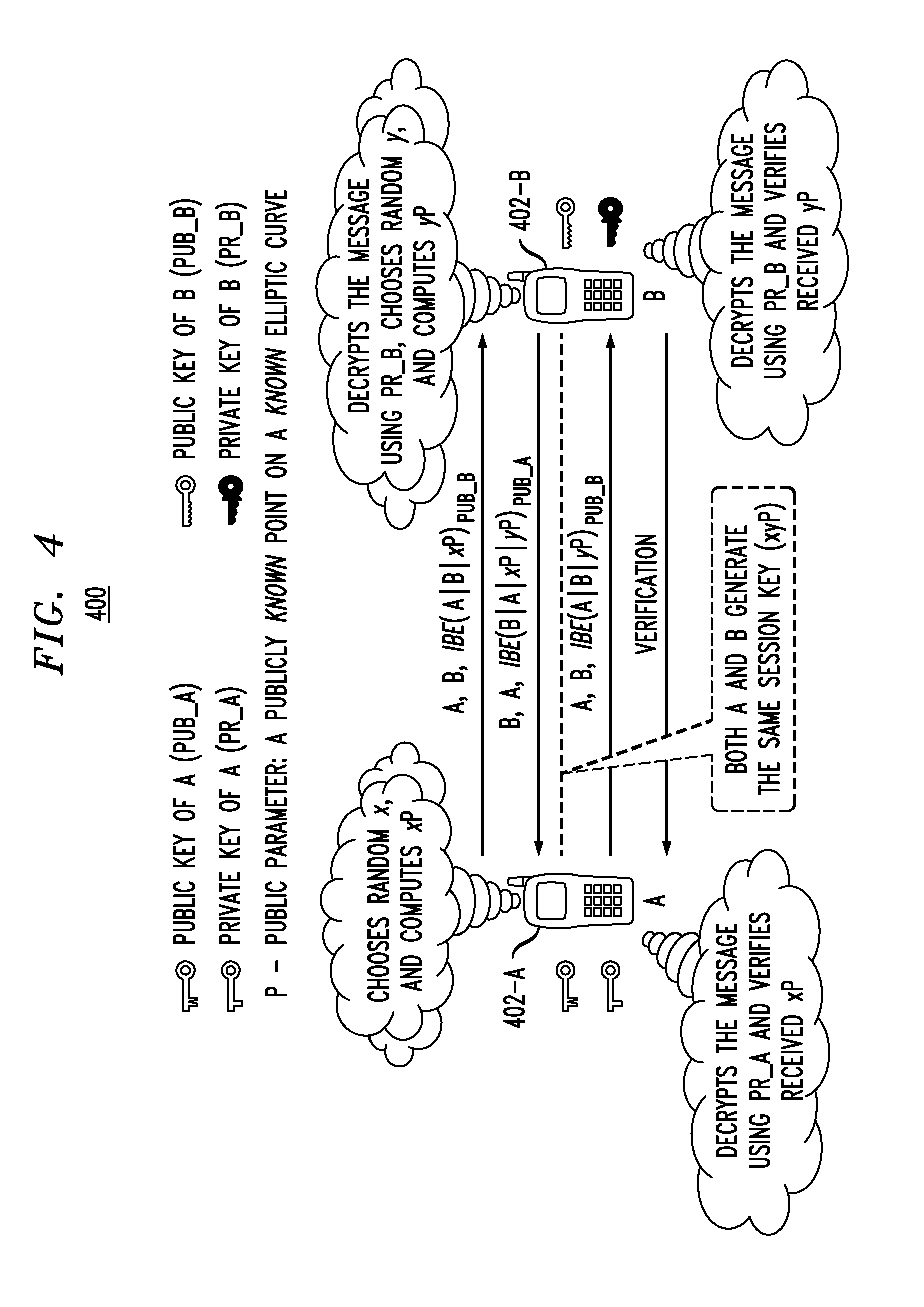
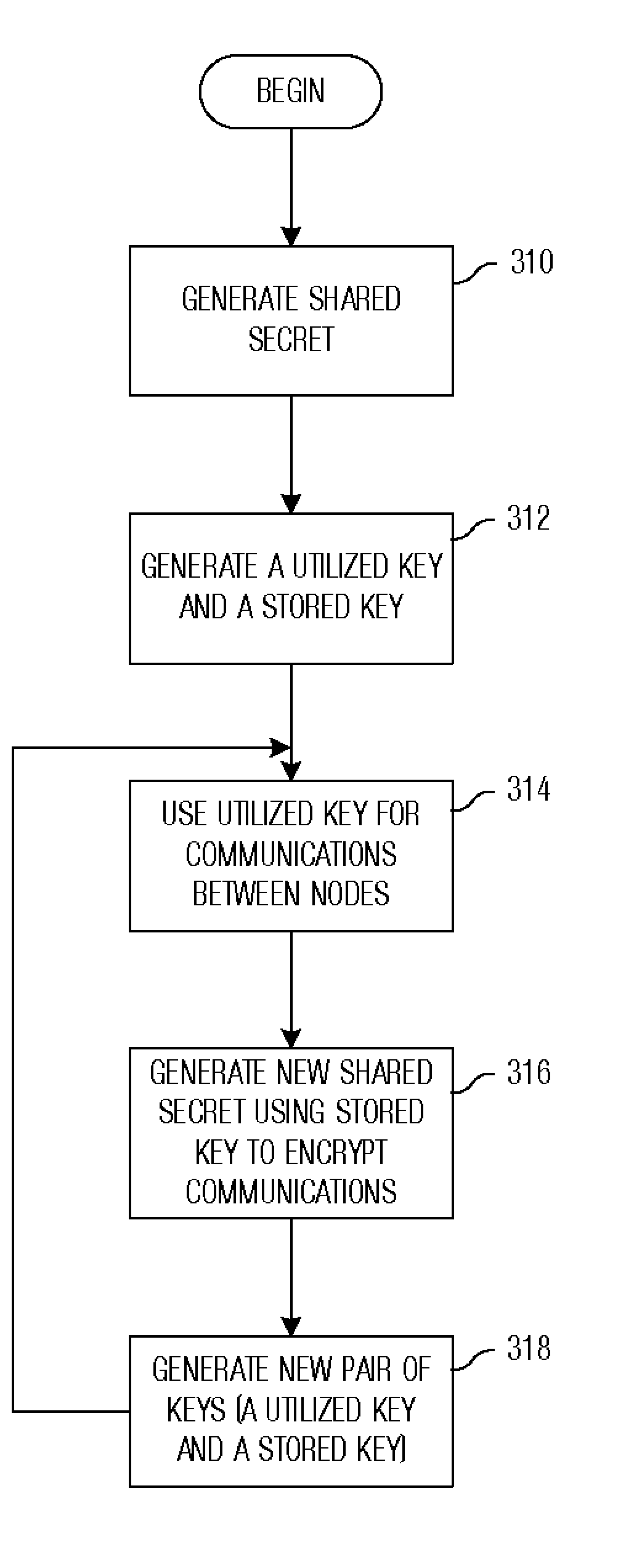
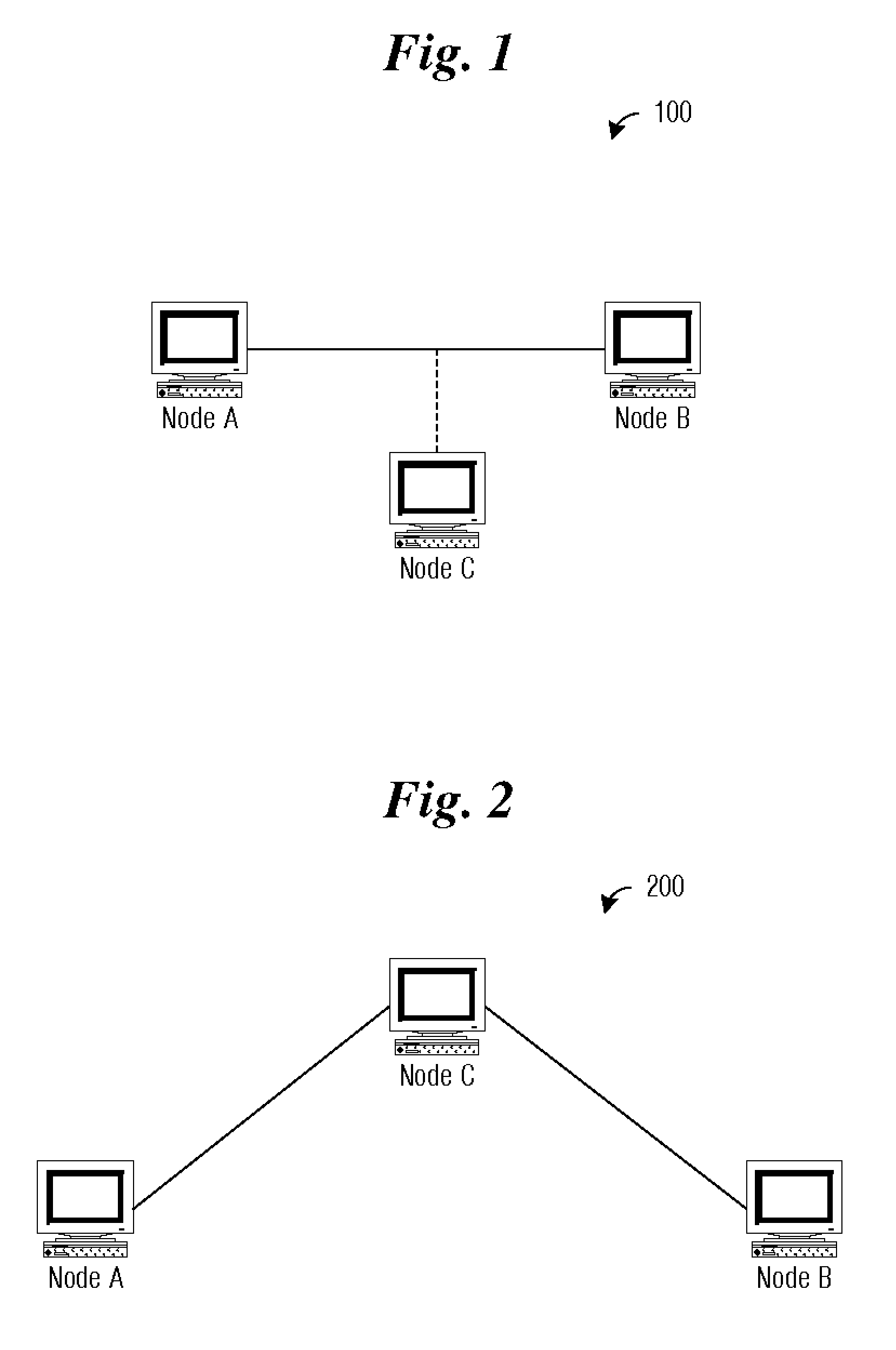
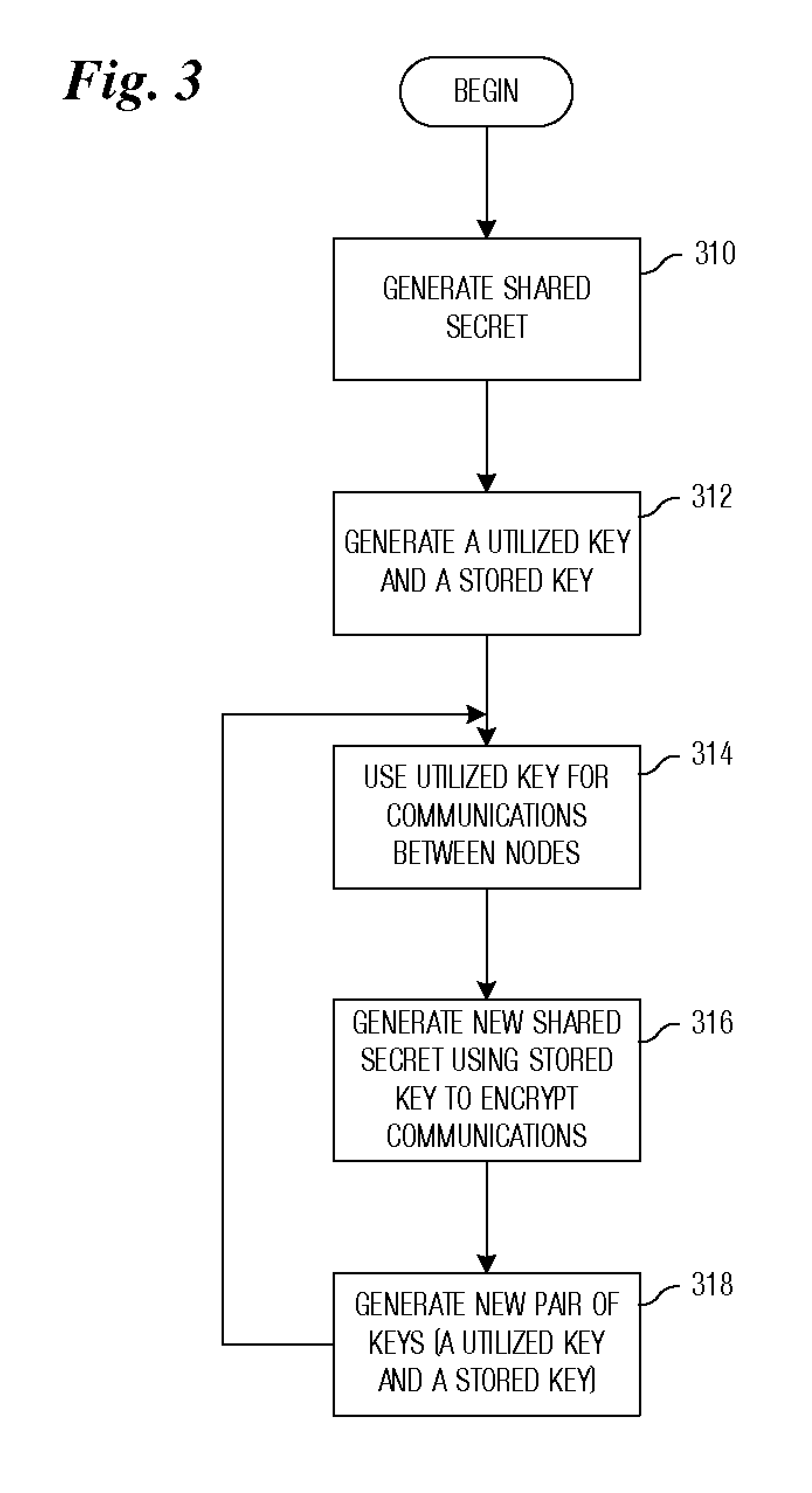
System and method for providing secure communications is provided. Initially, an exchange protocol, such as a password-authenticated key exchange protocol, is used to create a shared secret. From the shared secret, two keys are created: a utilized key and a stored key. The utilized key is used to encrypt messages between nodes. When it is time to replace the utilized key to maintain security, the stored key is utilized to encrypt messages for generating / distributing a new shared secret. The new shared secret is then used to generate a new utilized key and a new stored key. This process may be repeated any number of times to maintain security.
Owner:LANTIQ BET GMBH & CO KG
Secure Key Management in Conferencing System
InactiveUS20110051912A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemConference management
Principles of the invention provide one or more secure key management protocols for use in a communication environment such as a conferencing system. For example, a method for managing a conference between two or more parties in a communication system comprises the following steps. An identity based authenticated key exchange operation is performed between a conference management element of the communication system and each of the two or more parties seeking to participate in the conference, wherein messages exchanged between the conference management element and the two or more parties are encrypted based on respective identities of recipients of the messages, and further wherein the conference management element receives from each party during the key authentication operation a random key component that is computed based on a random number selected by the party. The conference management element sends to each party a set comprising the random key components computed by the parties. The conference management element receives from each party a random group key component, wherein the random group key component is computed by each party via a computation based on the random number used by the party during the key authentication operation and the random key components computed by a subset of others of the two or more parties seeking to participate in the conference. The conference management element sends to each party a set comprising the random group key components computed by the parties such that each party can compute the same group key for use in communicating with each other party through the conference management element.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Methods and apparatus for providing efficient password-authenticated key exchange
InactiveUS7076656B2Reduce computational intensityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPasswordCryptographic protocol
A secure protocol is provided which uses a Diffie-Hellman type shared secret, but modified such that the two parties may authenticate each other using a shared password. In accordance with the invention, a party generates the Diffie-Hellman value gx and combines it with a function of at least the password using a group operation, wherein any portion of a result associated with the function that is outside the group is randomized. The resulting value is transmitted to the other party. The group operation is defined for the particular group being used. Every group has a group operation and a corresponding inverse group operation. Upon receipt of the value, the other party performs the inverse group operation on the received value and the function of at least the password, and removes the randomization of any portion of the result associated with the function that is outside the group, to extract gx such that the other party may then generate the shared secret gxy using its knowledge of y.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
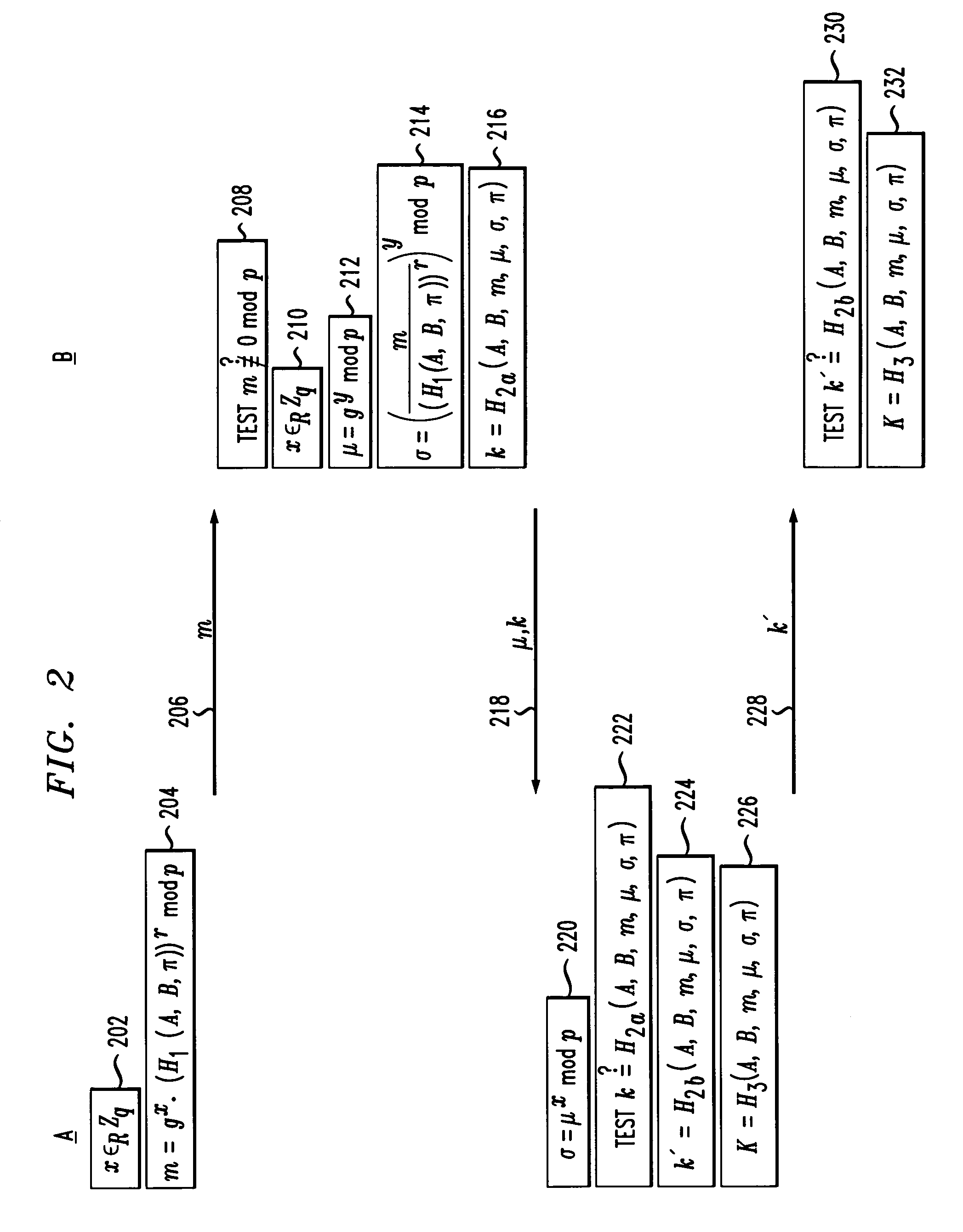
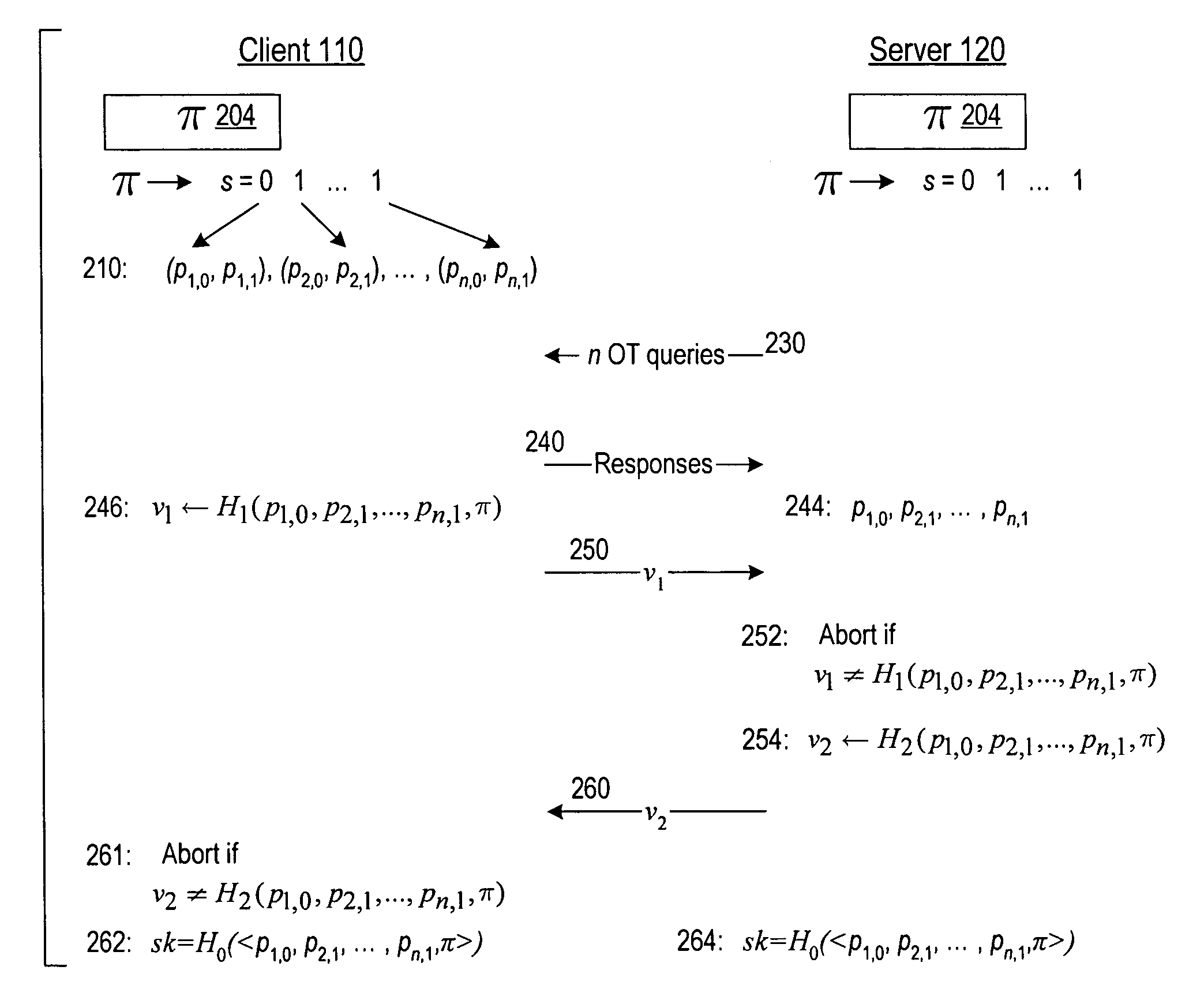
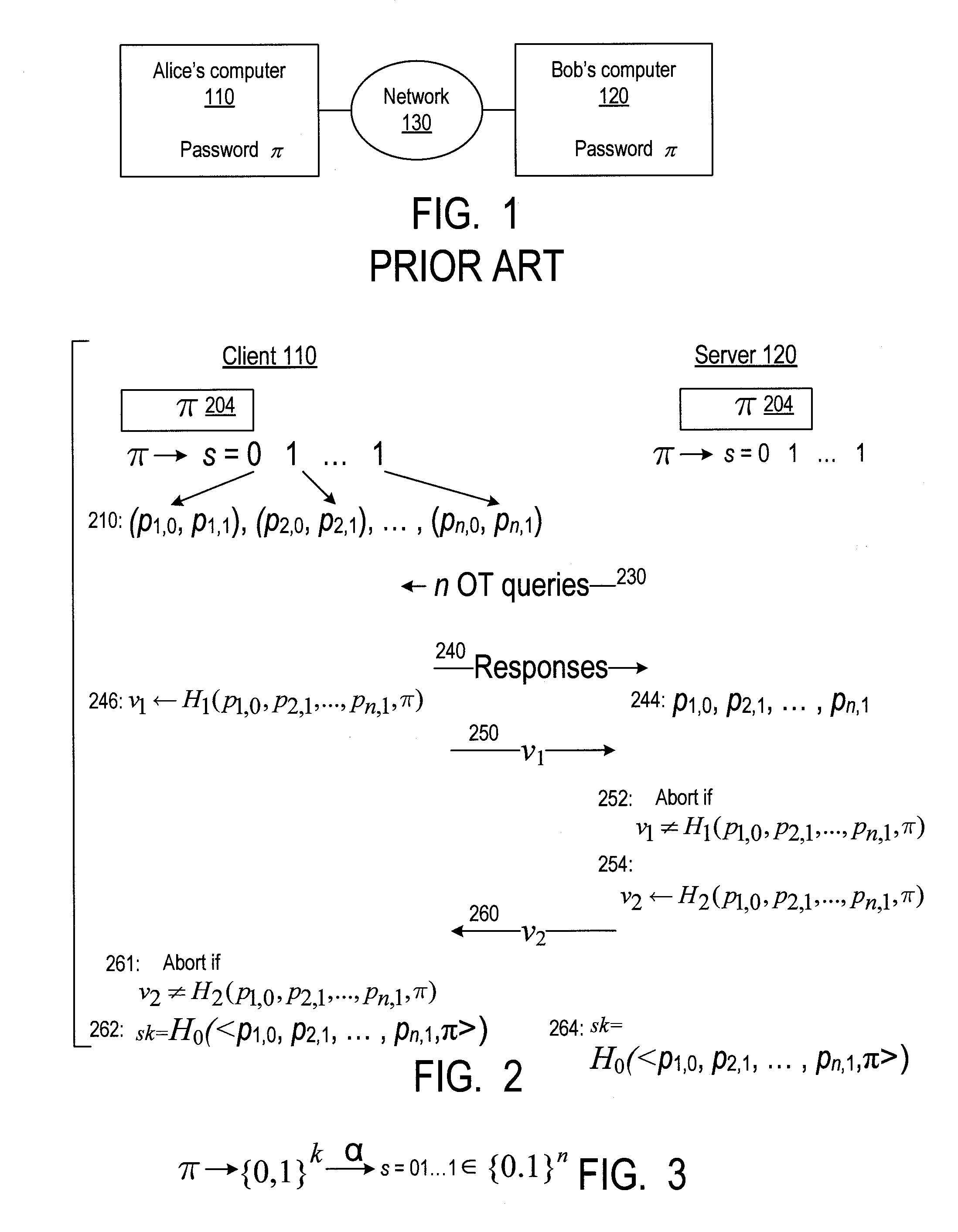
Cryptographic authentication and/or establishment of shared cryptographic keys, including, but not limited to, password authenticated key exchange (PAKE)
ActiveUS20060291661A1Improve efficiencySmall probabilityUser identity/authority verificationTransmission protocolAlgorithm
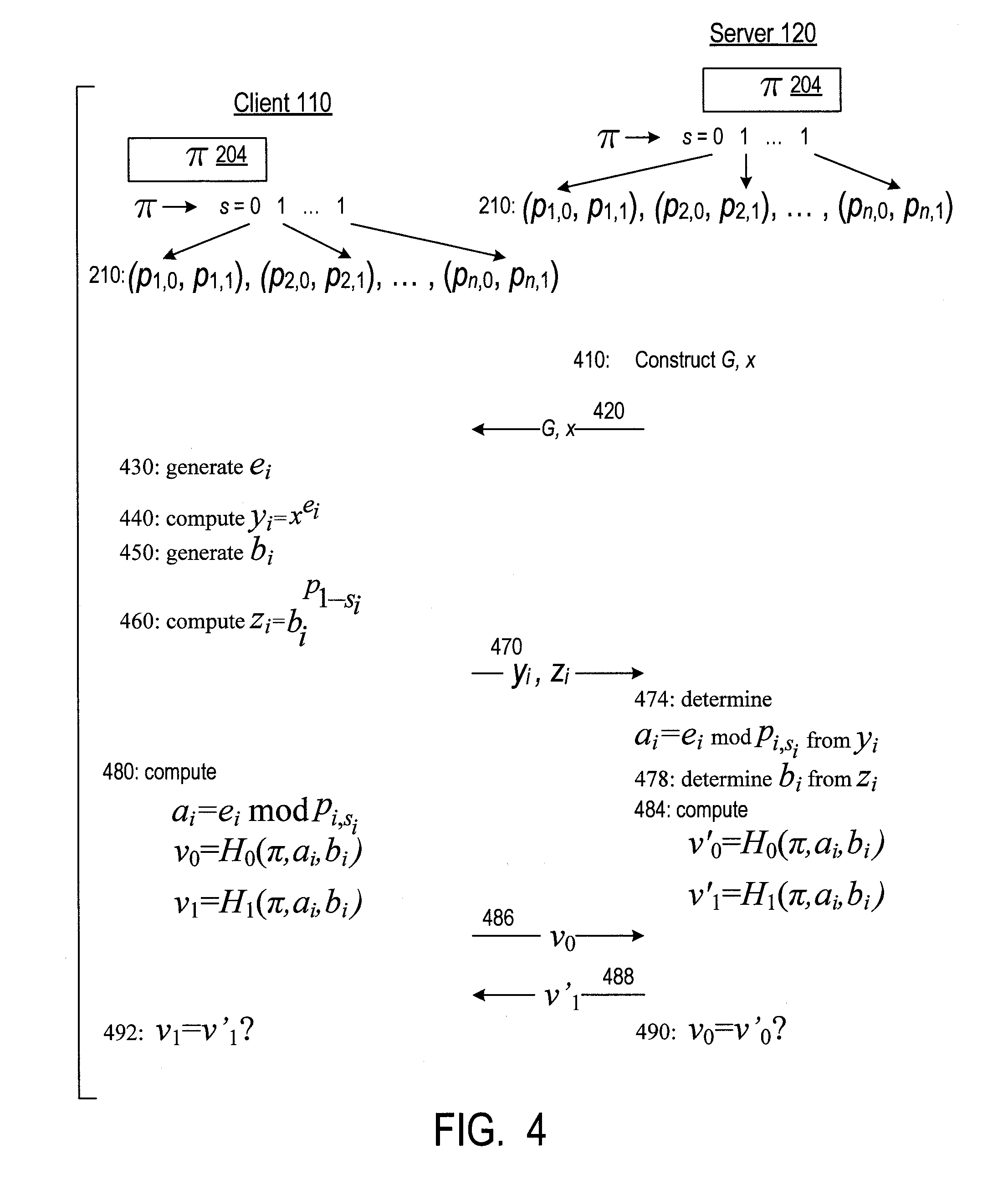
A server (120) uses a password (π) to construct a multiplicative group (ZN*) with a (hidden) smooth order subgroup (<x′>), where the group order (Pπ) depends on the password. The client (110) uses its knowledge of the password to generate a root extraction problem instance (z) in the group and to generate data (y) allowing the server to construct a discrete logarithm problem instance (y′) in the subgroup. The server uses its knowledge of the group order to solve the root extraction problem, and solves the discrete logarithm problem efficiently by leveraging the smoothness of the subgroup. A shared key (sk) can be computed as a function of the solutions to the discrete logarithm and root extraction problem instances. In some embodiments, in an oblivious transfer protocol, the server queries the client (at 230) for data whose position in a database (210) is defined by the password. The client provides (240) such data without knowing the data position associated with the server's query. The client obtains the data position independently from the password. The data positions and / or the respective data are used for authentication and shared secret key generation. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Secure key management in conferencing system
InactiveUS8301883B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationConference managementKey authentication
A method for managing a conference between two or more parties comprises an identity based authenticated key exchange between a conference management element and each of the two or more parties seeking to participate in the conference. Messages exchanged between the conference management element and the two or more parties are encrypted based on respective identities of recipients of the messages. The method comprises the conference management element receiving from each party a random group key component. The random group key component is computed by each party based on a random number used by the party during the key authentication operation and random key components computed by a subset of others of the two or more parties seeking to participate in the conference. The conference management element sends to each party the random group key components computed by the parties such that each party can compute the same group key.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Authenticated key exchange based on pairwise master key
InactiveUS7395427B2Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionMaster keyComputer science
Briefly, in accordance with one embodiment of the invention, a pairwise master key may be utilized to generate nonces for authenticated key exchange during a rekeying event in a wireless local area network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Access control system and method based on hierarchical key, and authentication key exchange method thereof
ActiveUS8239928B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsPasswordData access control
Disclosed relates to an access control system and method based on hierarchical keys. The system comprises an access control server (ACS), a home gateway, and a plurality of sensor devices disposed on a home network. The ACS sets up user's access limits of authority and authorization verifier, and saves the related data of user's password and the user's access limits of authority. The gateway records the authority limits' level and the authority limits' key which are constructed based on a hierarchical key structure. When a user logs in the ACS to request access, an one-time communication key between the user and the home gateway is established by exchanging the ticket and the token that are issued by the ACS. This allows the user to access the information of the sensor devices.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
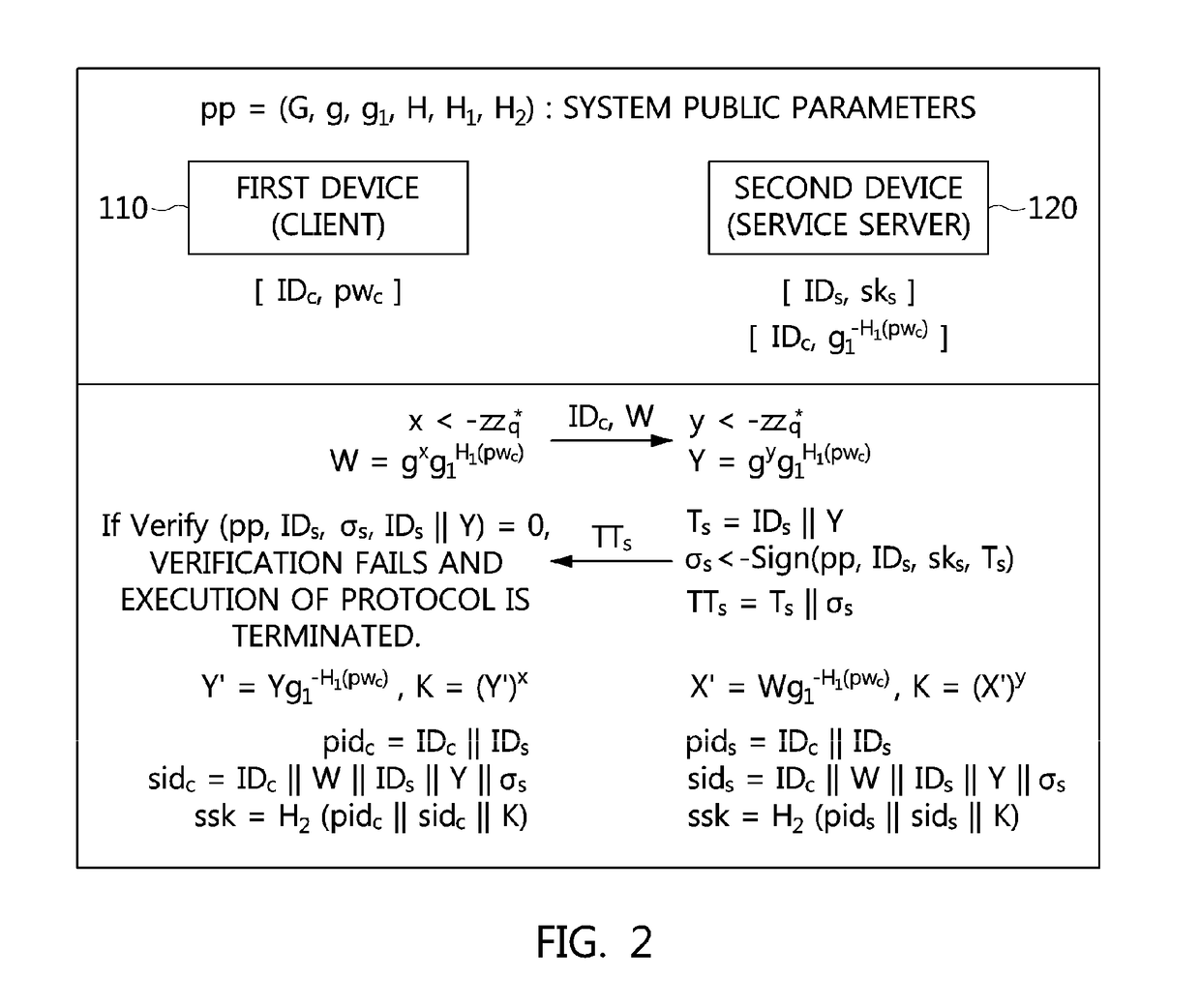
Method and apparatus for authenticated key exchange using password and identity-based signature
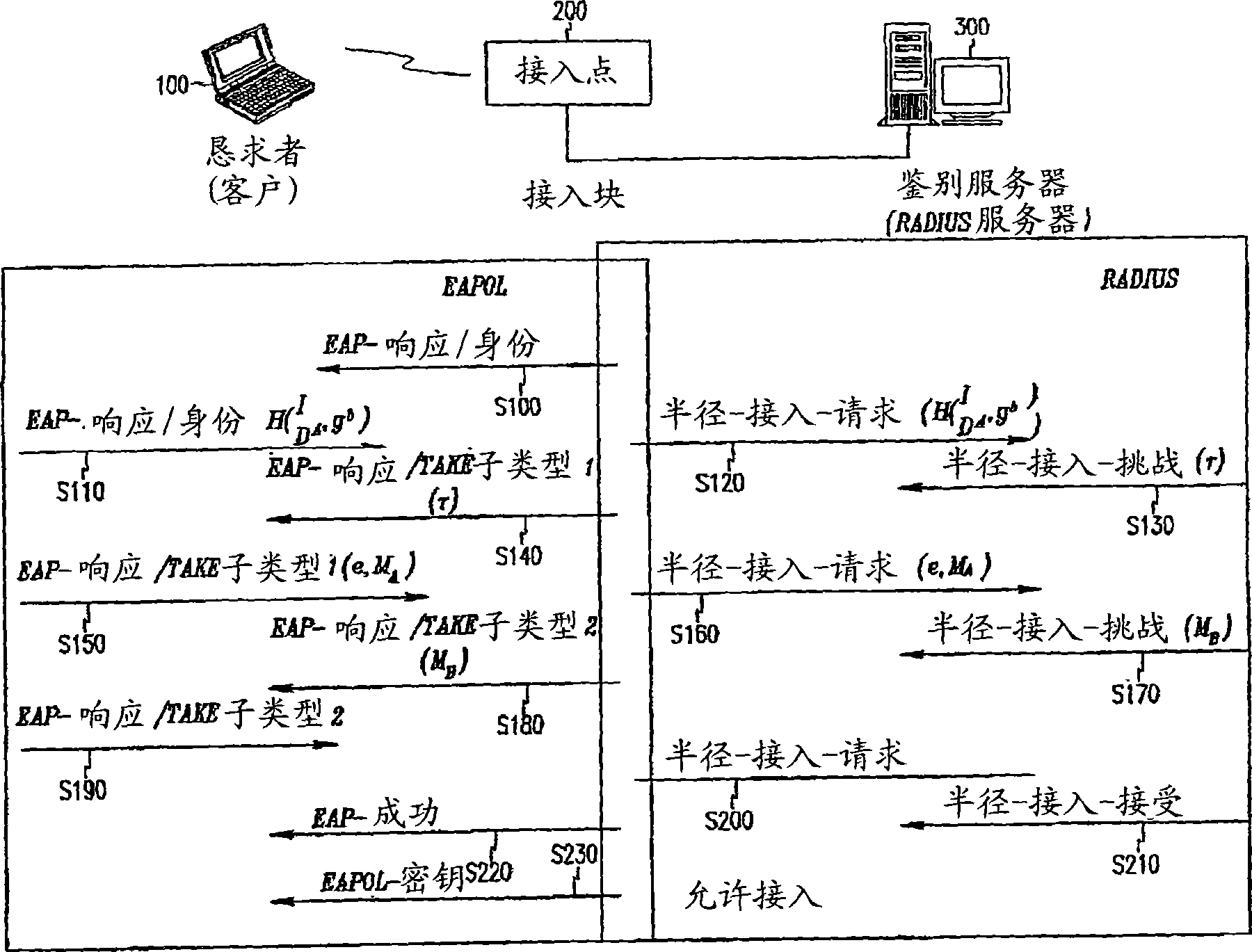
ActiveUS20170339118A1Authentication is convenientEasy to useMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationPasswordImpersonation attack
Disclosed herein are an apparatus and method for authenticated key exchange using a password and an identity-based signature, by which robustness is provided in order to prevent a server impersonation attack when a password is exposed, and by which a client may be provided with convenient authentication using an ID and a password.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
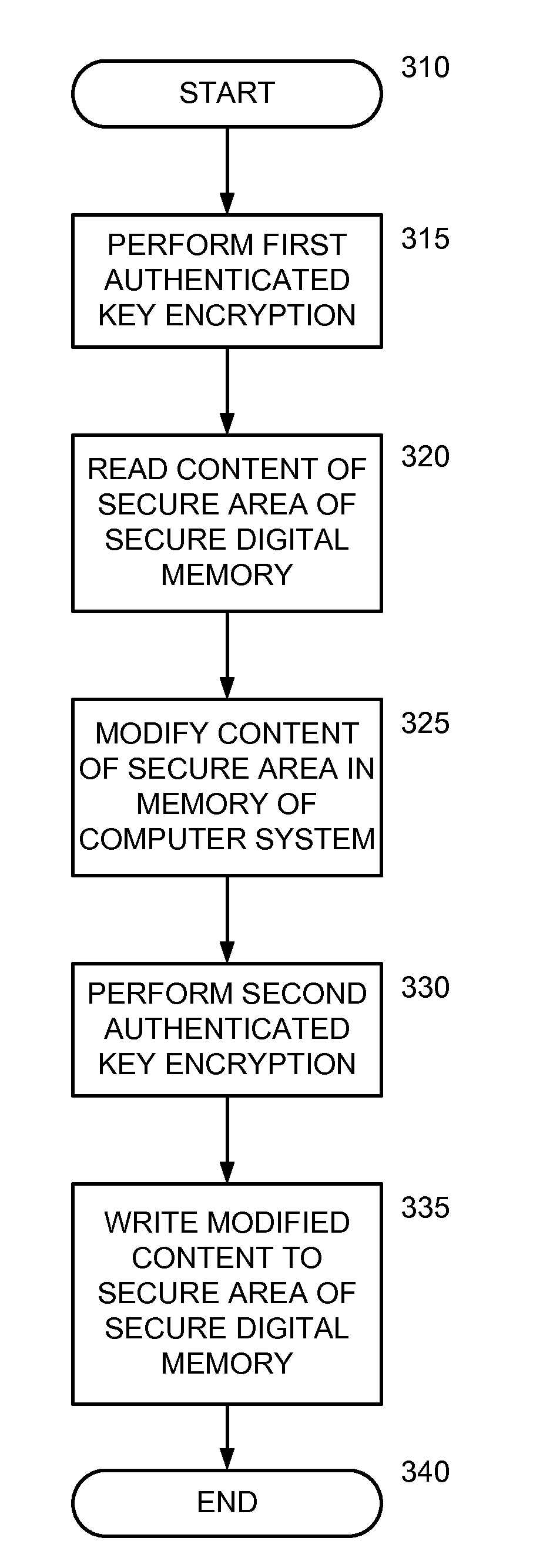
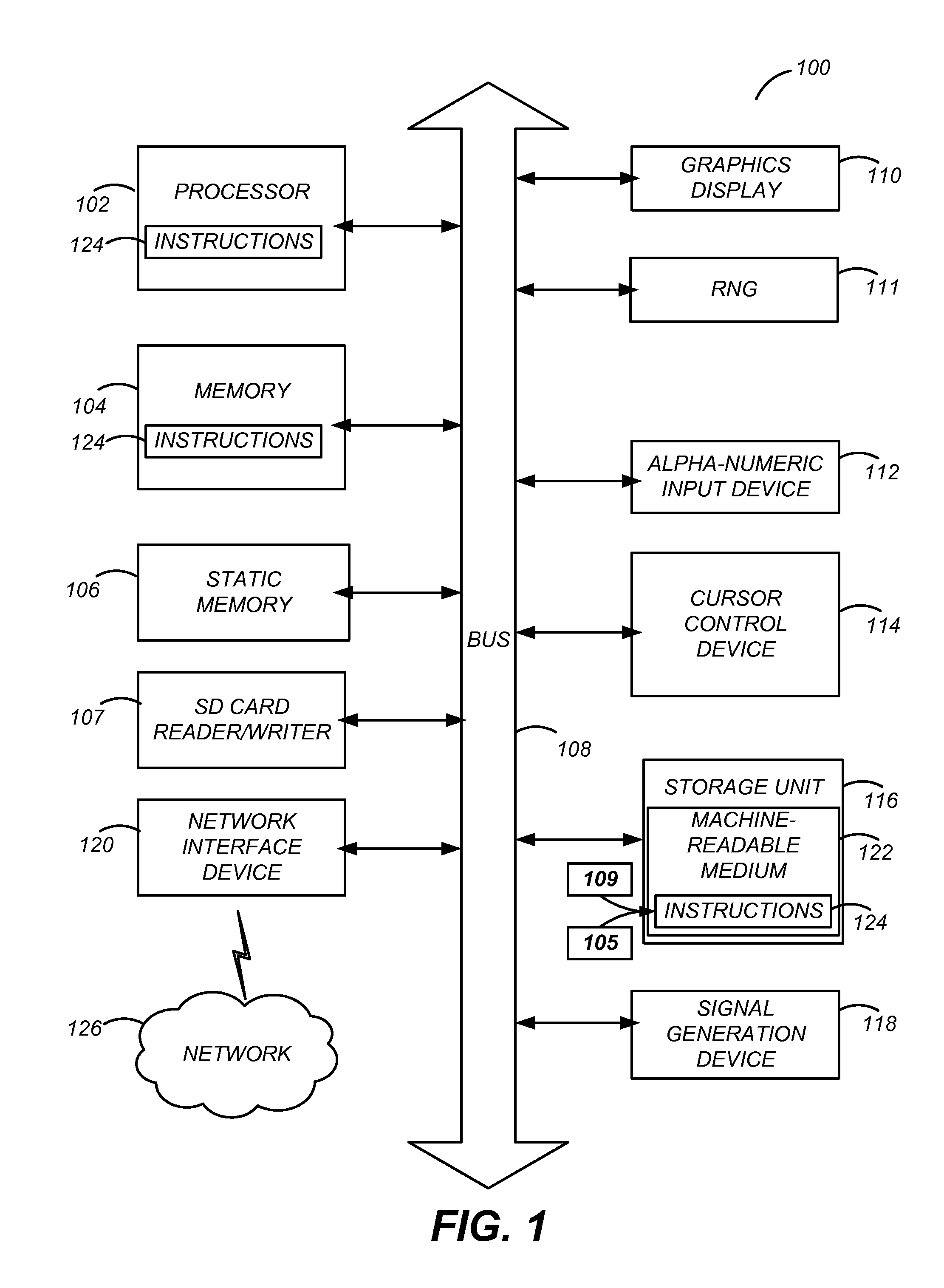
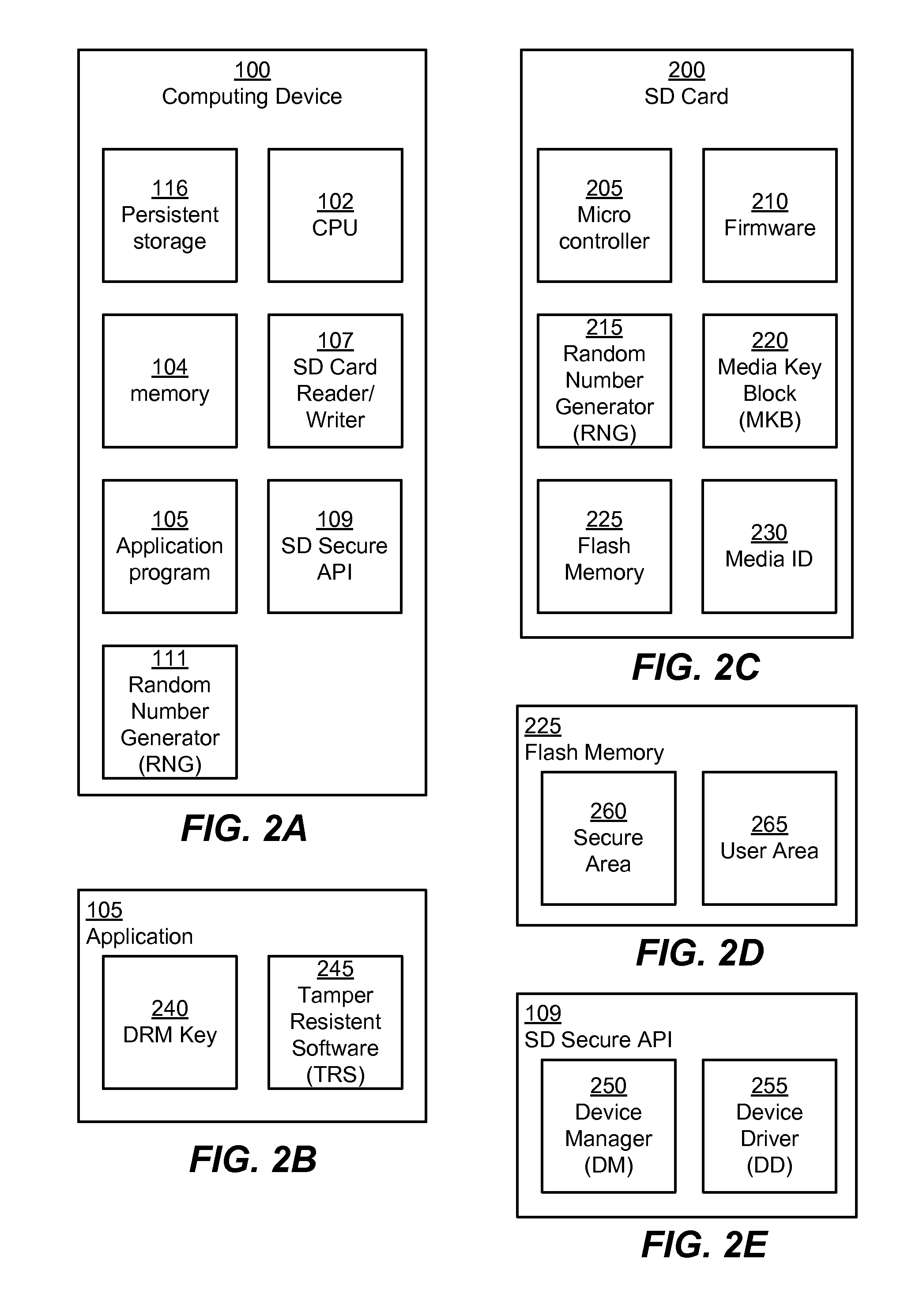
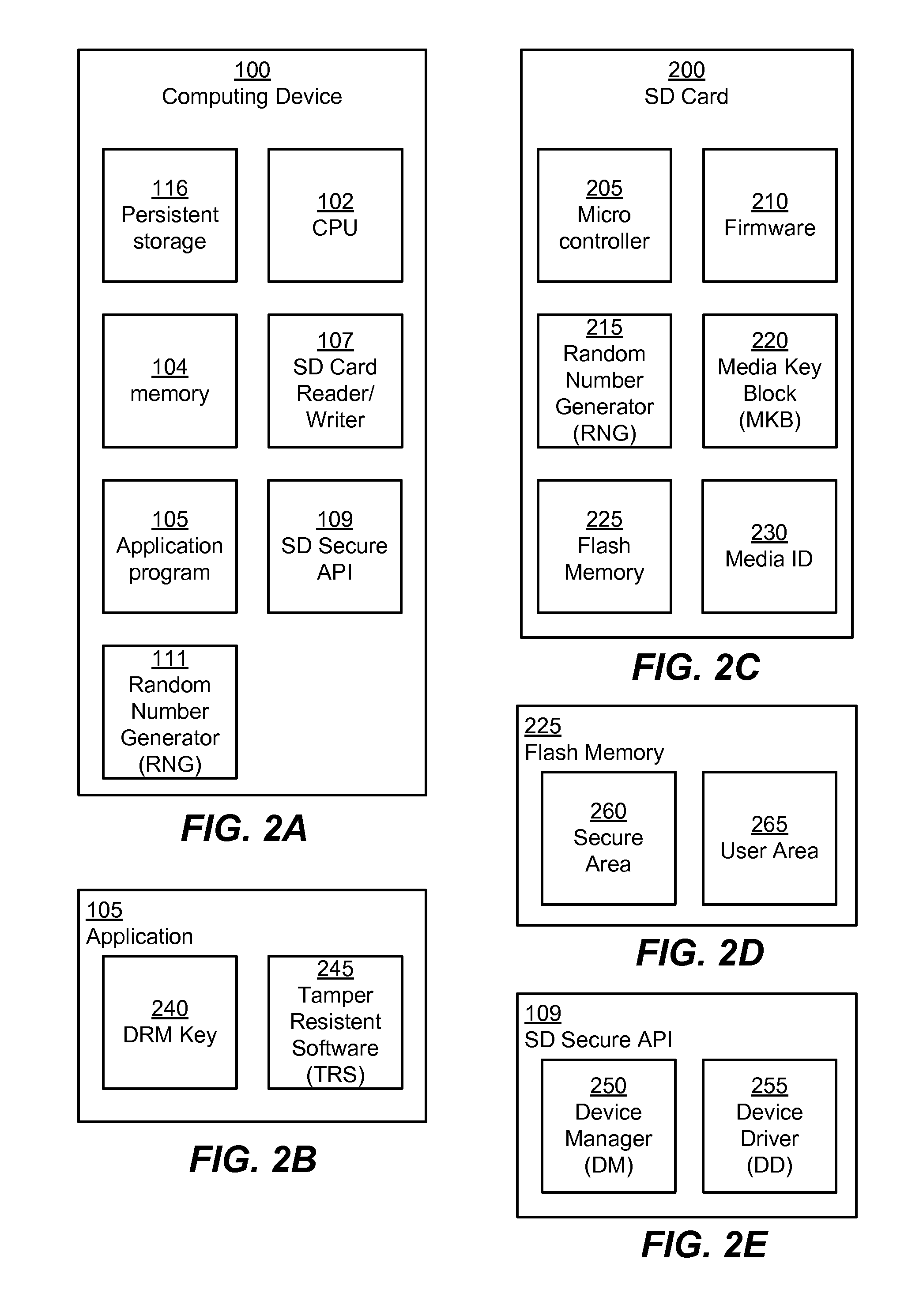
Read and Write Optimization for Protected Area of Memory
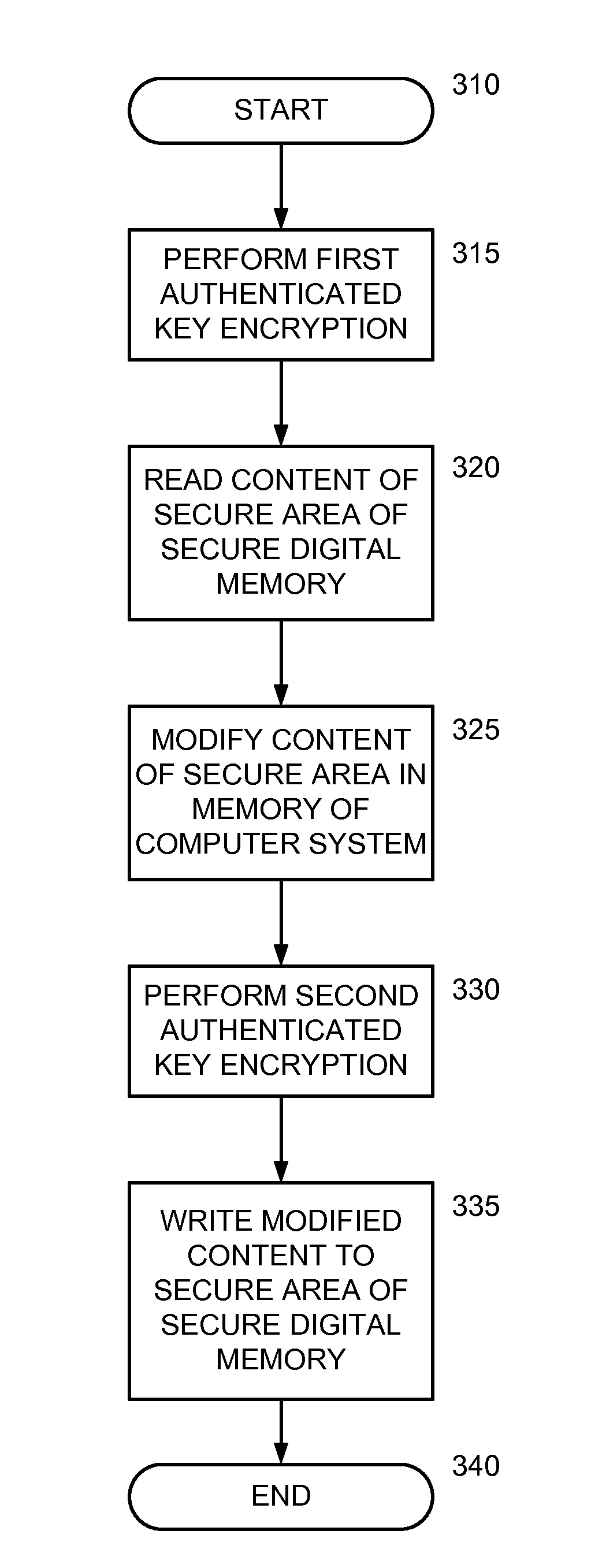
InactiveUS20120254629A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputerized systemDigital memory
A system (and method) to update content of a secure area of a secure digital (SD) card is disclosed. The system performs a first authenticated key exchange to access the secure area of the secure digital memory. The system reads content from the secure area in response to successful performance of the first authenticated key exchange. The system modifies the content in a memory of a computer system. The system performs a second authenticated key exchange to access the secure area of the secure digital card in preparation to write to the secure area of the secure digital memory. The system then writes modified content to the secure area of the secure digital memory in response to successful performance of the second authenticated key exchange.
Owner:MEDIA IP
Updating and distributing encryption keys
The present invention relates to methods for updating and distributing encryption keys. System and method for providing secure communications is provided. Initially, an exchange protocol, such as a password-authenticated key exchange protocol, is used to create a shared secret. From the shared secret, two keys are created: a utilized key and a stored key. The utilized key is used to encrypt messages between nodes. When it is time to replace the utilized key to maintain security, the stored key is utilized to encrypt messages for generating / distributing a new shared secret. The new shared secret is then used to generate a new utilized key and a new stored key. This process may be repeated any number of times to maintain security.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Discovery of security associations
ActiveUS8769288B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationSecurity association
Techniques are disclosed for discovering security associations formed in communication environments. For example, a method for forming a discoverable security association between a first computing device (e.g., a first client) and a second computing device (e.g., a second client) comprises the following steps. The first computing device is provided with a seed that is used by the first computing device to generate a secret that is used by the first computing device to compute a key for use in securing communications with the second computing device. The secret is re-computable based on knowledge of the seed and the key is re-computable based on knowledge of the secret such that a third computing device (e.g., an intercepting server) can use the re-computed key to intercept communications between the first computing device and the second computing device unbeknownst to the first computing device and the second computing device. By way of example, the key may be a result of an identity based authenticated key exchange.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
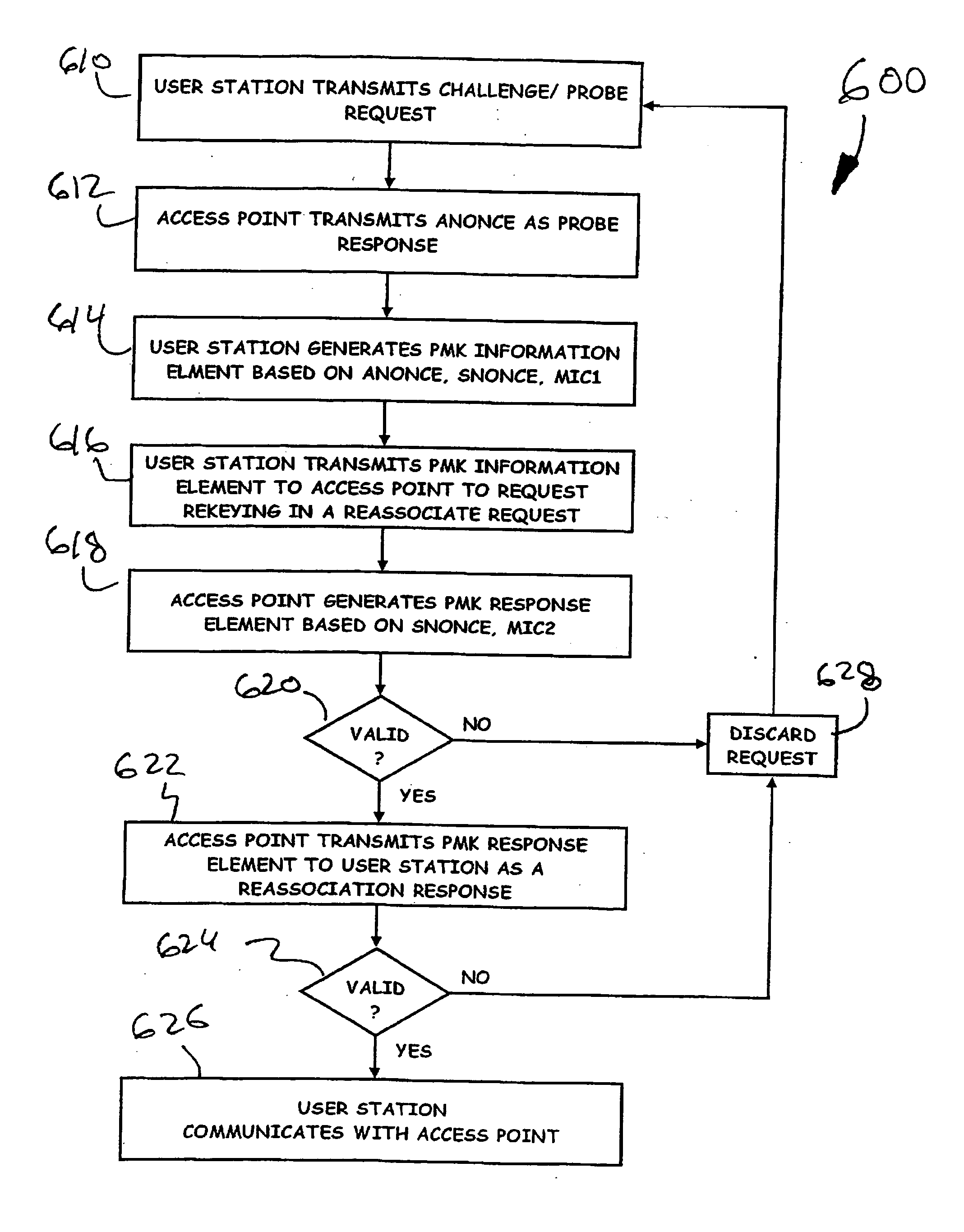
Two-factor authenticated key exchange method and authentication method using the same, and recording medium storing program including the same
InactiveCN1846397AKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePasswordSecret code
A two-factor authentication key exchange method. The user station sends a value generated by using the identifier and the public key of the authentication server to the authentication server via the access point. The authentication server uses this value to check the user's password, the key stored in the token, and the authentication server's secret key to generate a random number. The user station uses the random number, password, and key to send the encrypted value and the user's authentication code to the authentication server. The authentication server creates a second value generated by using the cryptographic key of the decrypted key and the random number to decrypt the encrypted value, verifies the user's authentication code, and sends the authentication server's authentication code to the user station. The user station authenticates the verification code of the verification server by using the key and the password.
Owner:KT CORP
Heterogeneous network end-to-end authentication secret key exchange method based on space-sky information network
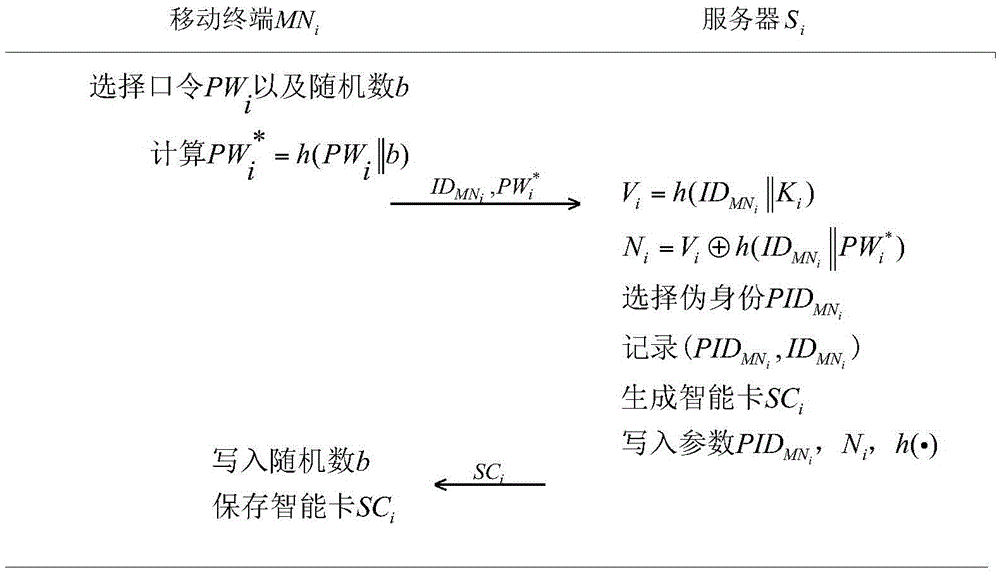
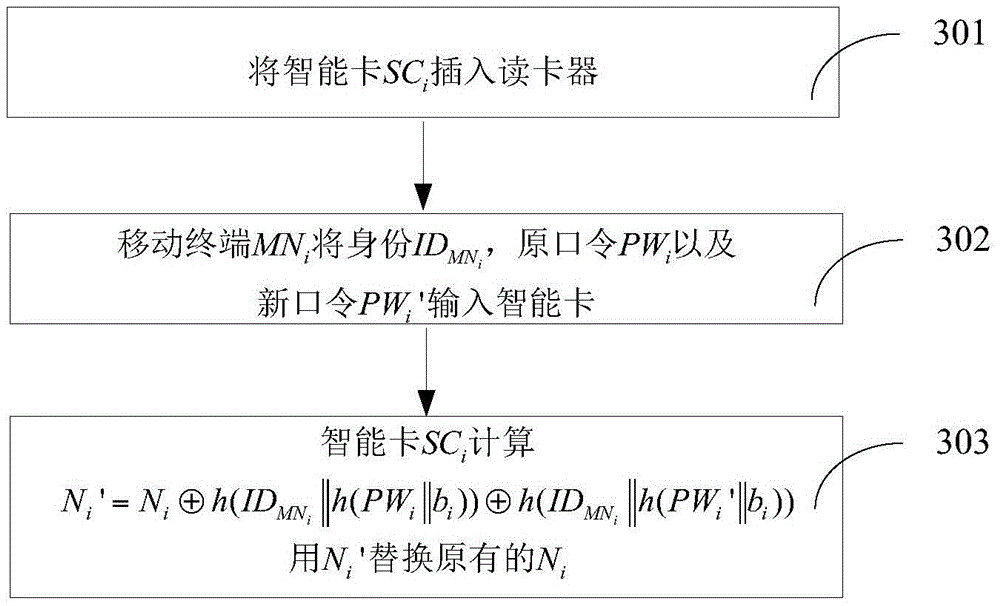
ActiveCN105491076AAchieve identity anonymityReduce computational costTransmissionHash functionInformation networks
The invention discloses a heterogeneous network end-to-end authentication secret key exchange method based on a space-sky information network. The method includes a mobile terminal registering step, a secret key establishment request step, an end-to-end authentication secret key exchange step and a password update step, which are conducted in sequence. A common session key can be established for two mobile terminals in two different trust domains while the identities of the mobile terminals are verified, so end-to-end secure communication is achieved. On the basis of symmetric encryption and the design of a Hash function, public key password operation that is time consuming is not used, so the method completely meets application demands of limited resources of the mobile terminals in a space-sky information network. The calculating cost of a server is low, and congestion will not occur due to frequent requests of the mobile terminals. Moreover, a dual-factor authentication mode of both an intelligent card and a password is adopted, so higher security is exhibited. Identity information of the mobile terminals is hidden in public information, so the mobile terminals are anonymous in identity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
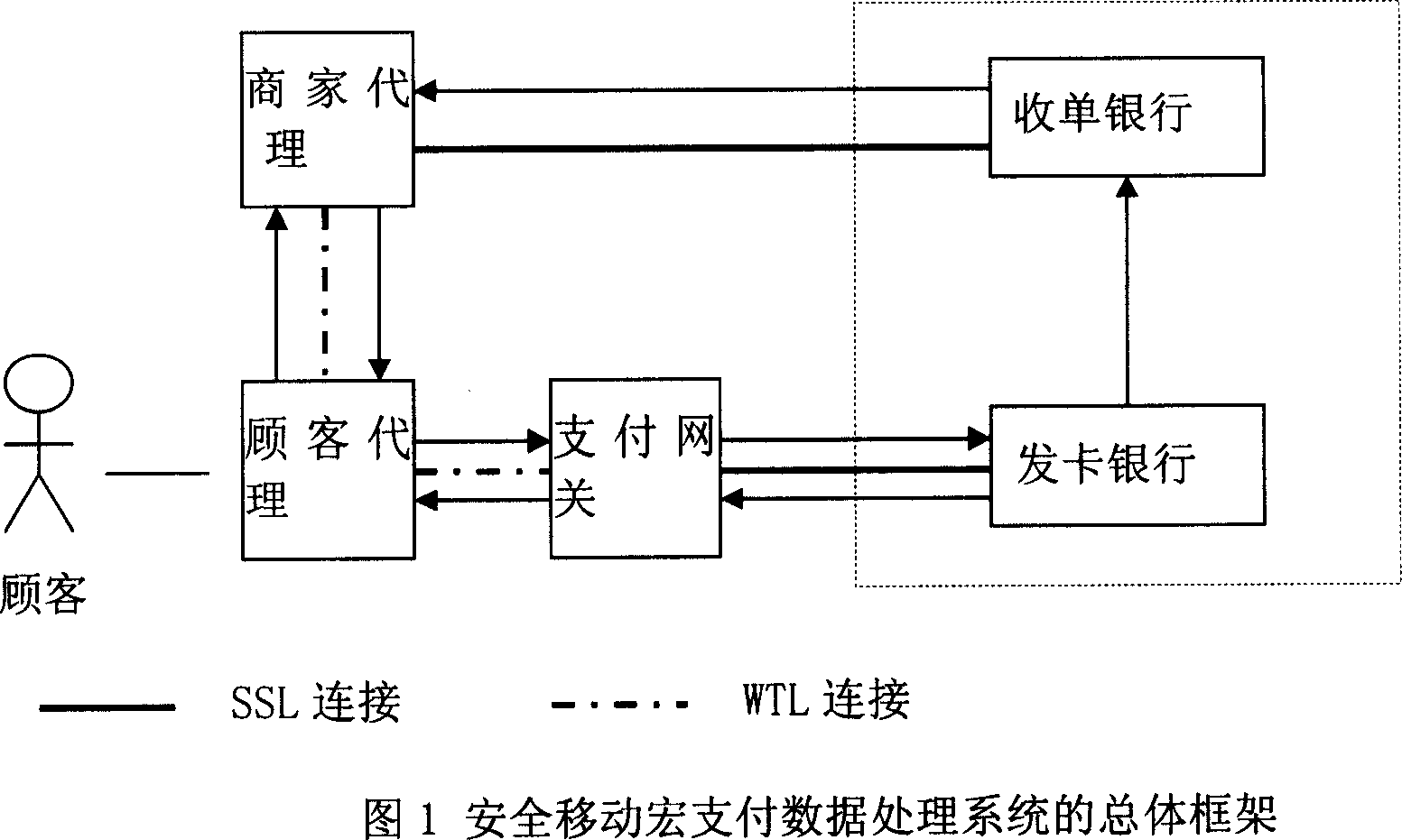
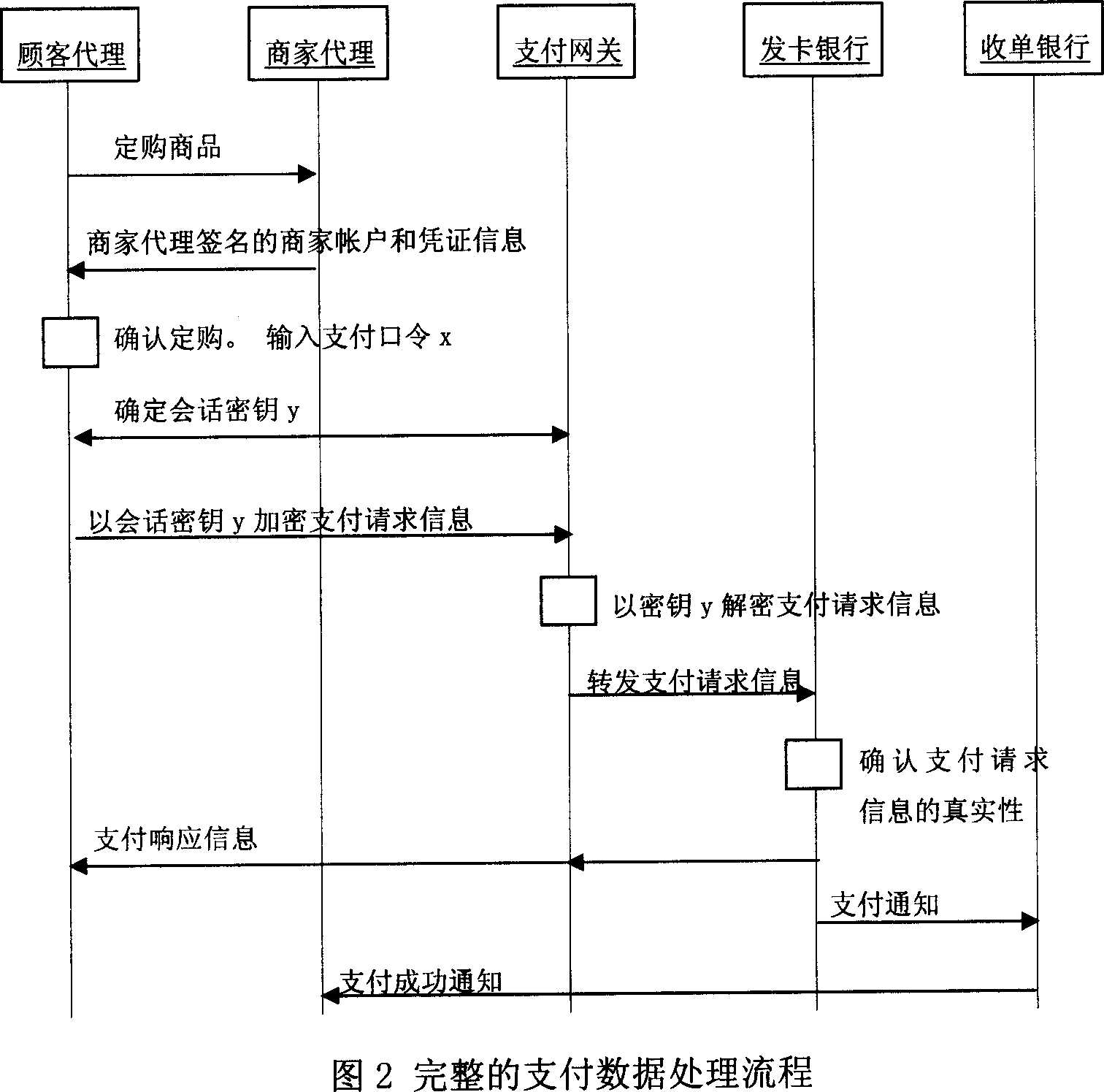
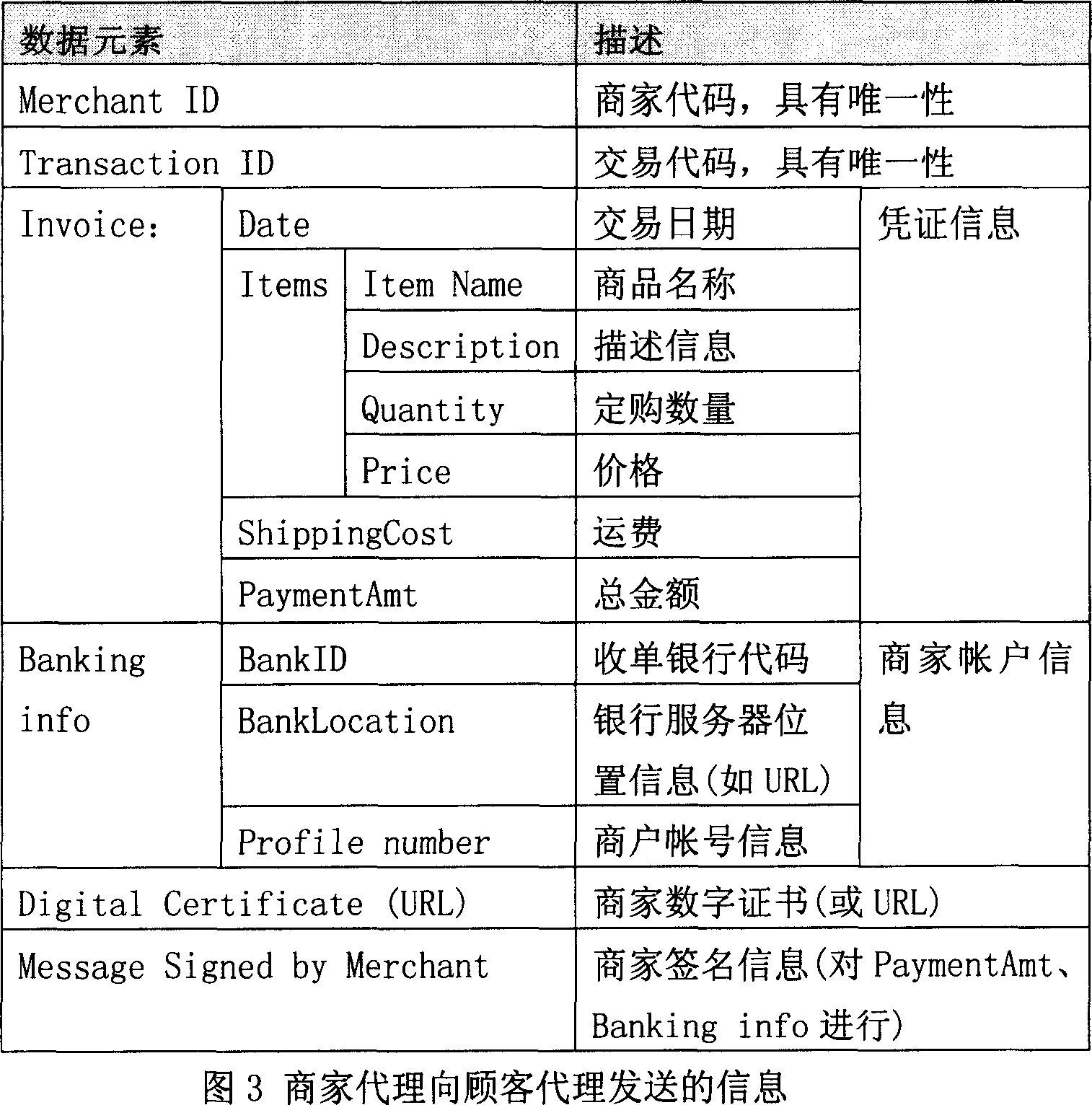
Safe mobile macro-payment data processing system
InactiveCN101059853ALow costPayment architectureTransmissionData processing systemEnd to end security
The invention relates to a safety mobile payment data processing system, in particular to a system for remote mobile macro payment data processing. The inventive system comprise four portions as a customer proxy, payment gateway, a supplier proxy, a supplier bank, and a receive bank. The inventive system uses the bank card or other virtual account as payment account, without mounting WPKI digit certificate on mobile terminal, and the supplier check is based on general PKI, via simple guide process to improve the end-to-end safety of WAP channel on the mobile terminal based on check key exchange and encrypt algorism, and confirm the calculation efficiency of the mobile terminal, to flexibly apply various mobile payment service modes.
Owner:赵壮 +1
Automated security provisioning protocol for wide area network communication devices in open device environment
An automated security provisioning protocol is provided for wide area network communication devices in an open device environment, such as cellular communication devices in a machine-to-machine (M2M) environment. For example, a method for performing a security provisioning protocol between a first communication device and a second communication device over at least one wide area communication network comprises the following steps from the perspective of the first communication device. The first communication device automatically uses access information not previously provisioned in the wide area communication network to gain access to the wide area communication network for an initial purpose of communicating with the second communication device. The first communication device, upon gaining access to the wide area communication network, automatically performs an authenticated key exchange operation with the second communication device over the wide area communication network and establishes a secure communication key as a result of the authenticated key exchange operation for subsequent use by the first communication device for secure communications. The wide area communication network is operated by a first entity and the second communication device is operated by a second entity.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Securing arbitrary communication services
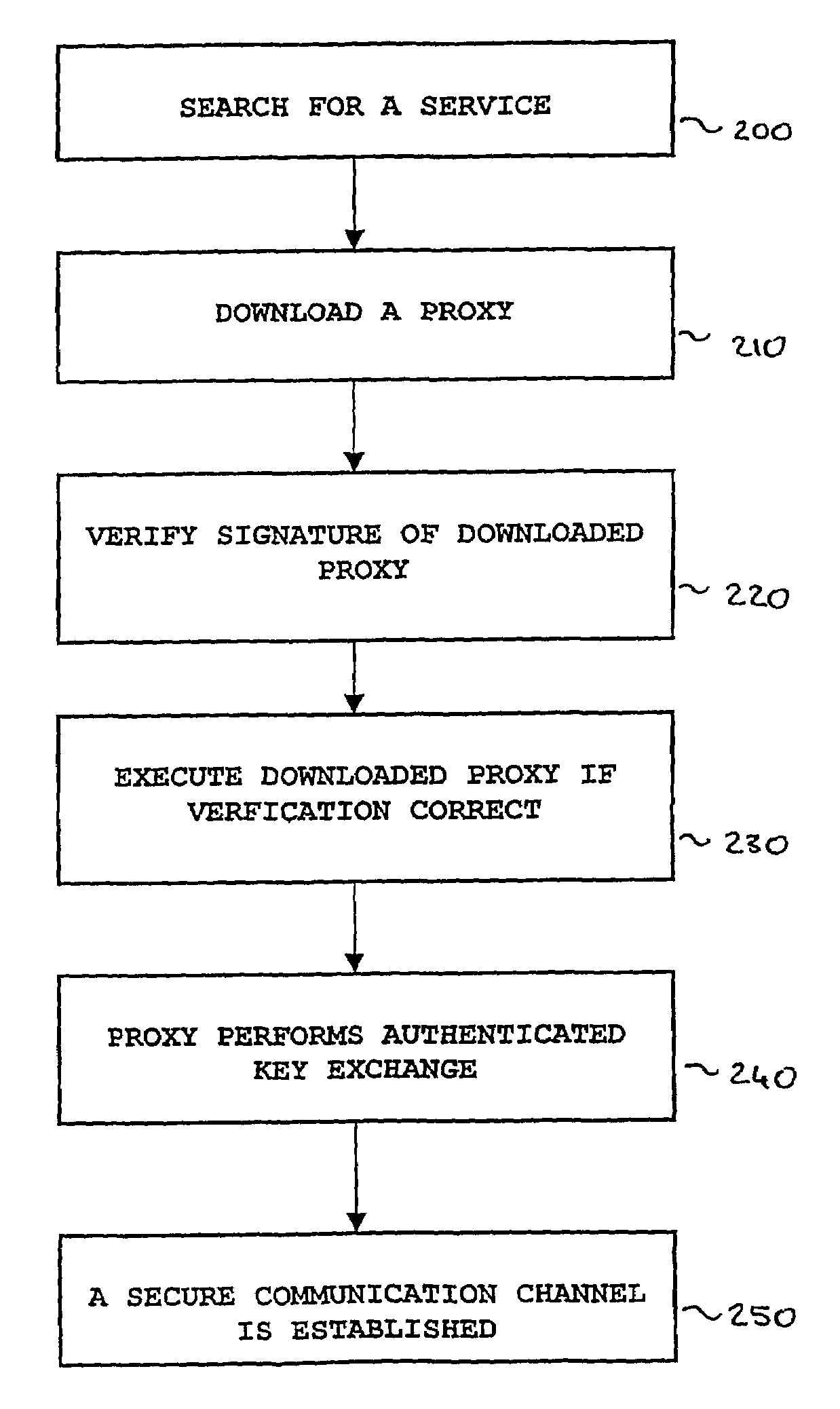
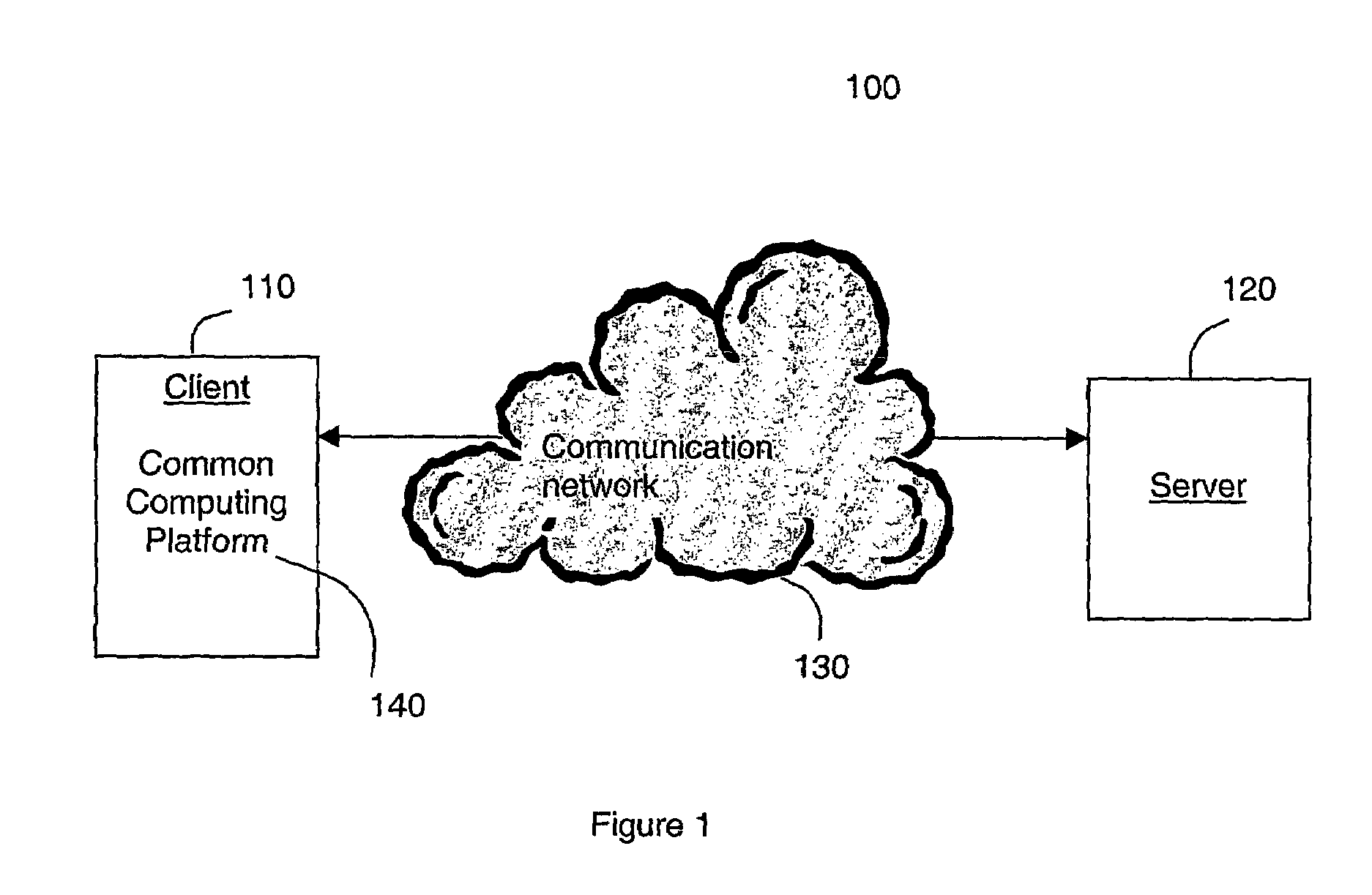
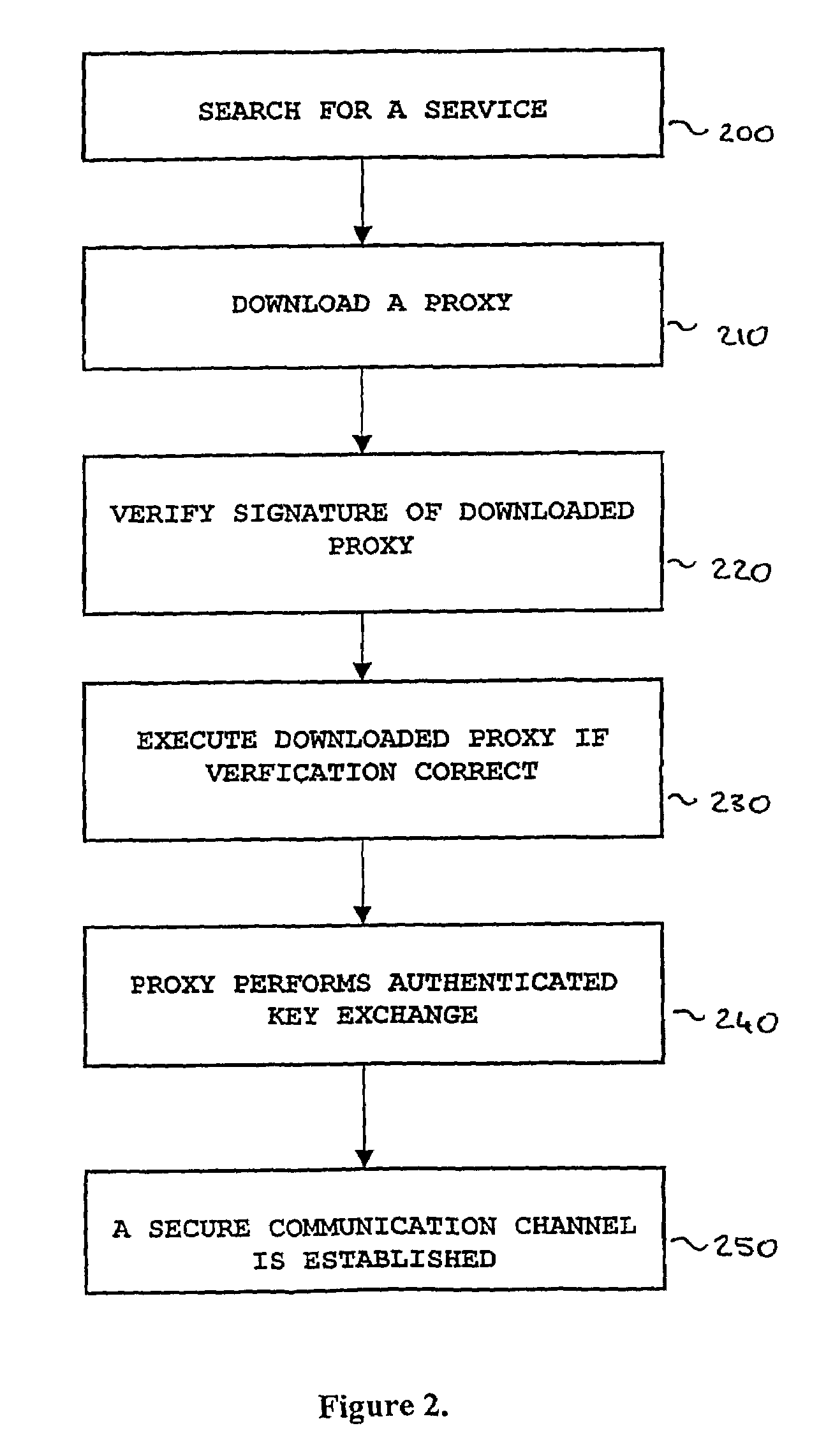
InactiveUS7457956B2Key exchange is made efficientEasy to updateDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHash functionConfidentiality
The present invention relates to securing information in open systems and more particularly to a method and a system for providing authentication, confidentiality and integrity protection of arbitrary communication services. A client that wishes to communicate with a particular service downloads a signed program code from that service containing code necessary for doing authenticated key exchange with that service. The client is assumed to support only two basic cryptographic functions: signing of arbitrary data by using a public key algorithm together with a one way hash function, and verifying a public key signature of arbitrary data. By allowing the security protocol needed for key exchange and data communication protection to be downloaded the number of predefined security functions that a client or server needs to support is limited. This also makes it much easier to update the communication protection since only the server program needs to be updated.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Cryptographic authentication and/or establishment of shared cryptographic keys, including, but not limited to, password authenticated key exchange (PAKE)
ActiveUS20100257362A1Small probabilitySolve the real problemDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordCryptographic nonce
A server (120) uses a password (π) to construct a multiplicative group (ZN*) with a (hidden) smooth order subgroup (<x′>), where the group order (Pπ) depends on the password. The client (110) uses its knowledge of the password to generate a root extraction problem instance (z) in the group and to generate data (y) allowing the server to construct a discrete logarithm problem instance (y′) in the subgroup. The server uses its knowledge of the group order to solve the root extraction problem, and solves the discrete logarithm problem efficiently by leveraging the smoothness of the subgroup. A shared key (sk) can be computed as a function of the solutions to the discrete logarithm and root extraction problem instances. In some embodiments, in an oblivious transfer protocol, the server queries the client (at 230) for data whose position in a database (210) is defined by the password. The client provides (240) such data without knowing the data position associated with the server's query. The client obtains the data position independently from the password. The data positions and / or the respective data are used for authentication and shared secret key generation. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Three-party password-based authenticated key exchange protocol in no need of smart card
InactiveCN107592197AImprove performanceImprove efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInternet communicationPassword
The invention discloses a three-party password-based authenticated key exchange protocol in no need of a smart card. The method comprises the following steps: A, in an initialization stage, a server Sinitializes certain parameters and publishes the parameters {p, alpha, h1(.), IDS and Ts(alpha)}, wherein Ts(alpha) is used as the public key of the S, the s is used as the private key of the S and the two keys are stored in a database, and the protocol does not need a smart card; B, in a registration stage, is a legal user Ui wants to register the self information to the server S, a registrationrequest is firstly initiated; C, authenticated key exchange is carried out; and D, in a password exchange stage, when a user A feels that the current password may be or is already leaked out, a new password needs to be exchanged in order to reduce unnecessary losses. The unsafe problems, such as disclosure and theft of information between two parties in the Internet communication, can be solved,the authenticated key exchange purposes are realized in the communication process with no need of assistance of the smart card, and the higher performance and the higher efficiency are realized in a similar safety protocol.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
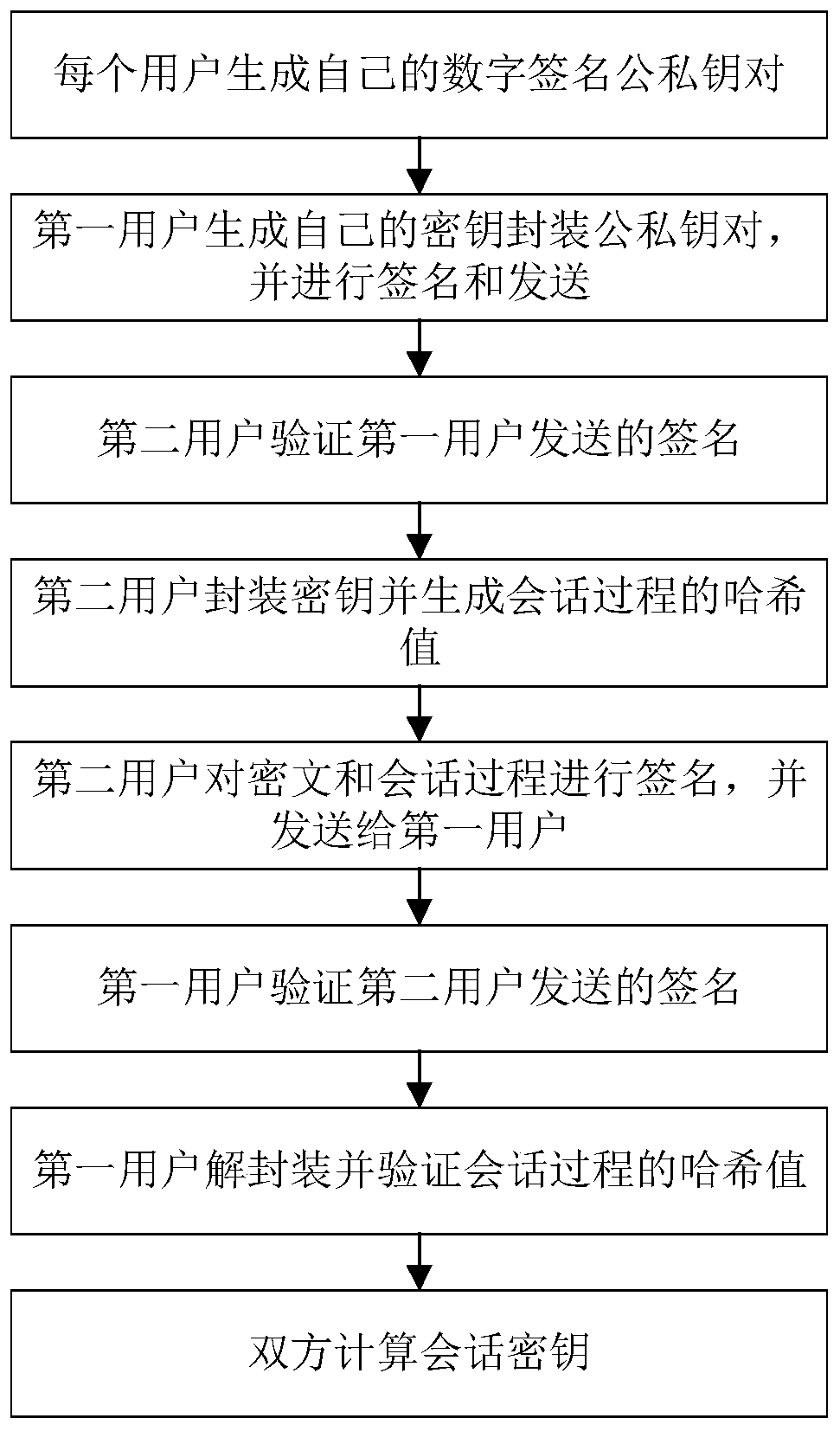
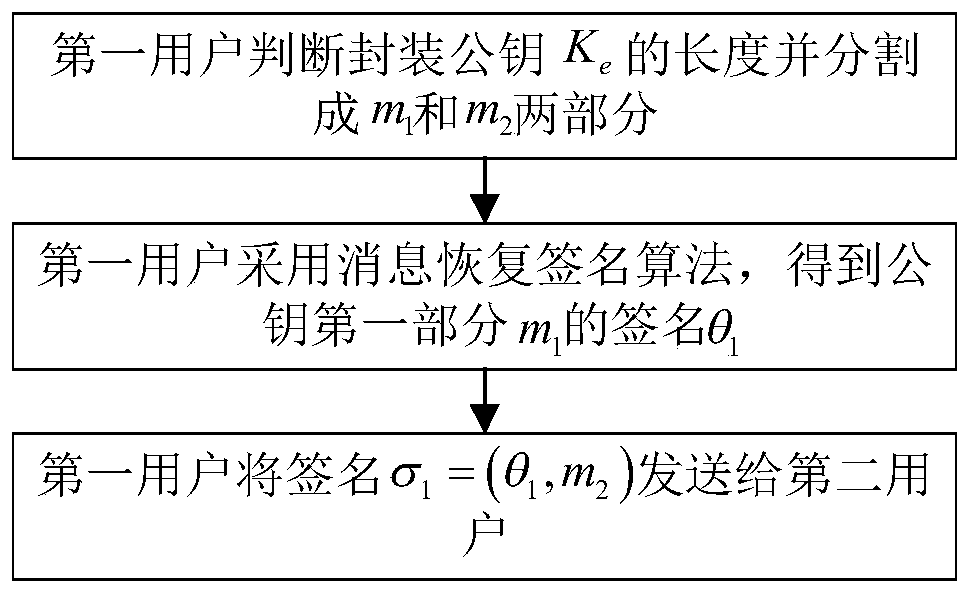
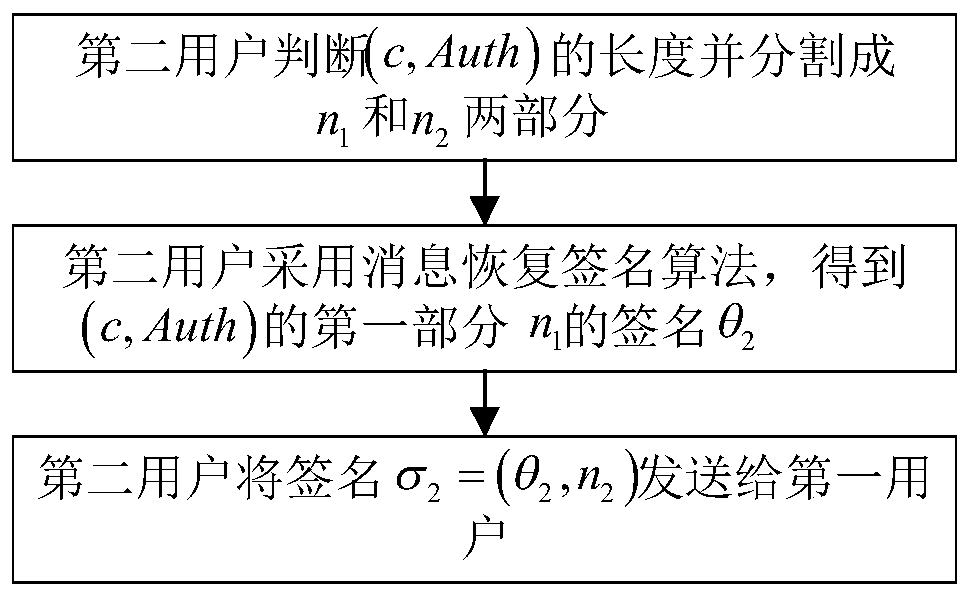
Authentication key exchange method based on message recovery signature
ActiveCN109995509AReduce trafficReduce overheadKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser verificationDigital signature
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-factor password-authenticated key exchange
ActiveUS8776176B2Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsPasswordAuthentication
Apparatus, methods, and computer program products are disclosed that enable a first computer and a second computer to mutually authenticate each other over a network. A first computer sends first authentication evidence to a second computer. The first authentication evidence is used to prove to the second computer that the first computer has access to a first plurality of authentication secrets without exposing the first plurality of authentication secrets. In addition, the second computer sends second authentication evidence to the first computer. The second authentication evidence is used to prove to the first computer that the second computer has access to a second plurality of authentication secrets without exposing the second plurality of authentication secrets. The first plurality of authentication secrets is related to the second plurality of authentication secrets. Thus, the first computer is authenticated to the second computer and the second computer is authenticated to the first computer.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Read and write optimization for protected area of memory
InactiveUS8775827B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputerized systemDigital memory
Owner:MEDIA IP
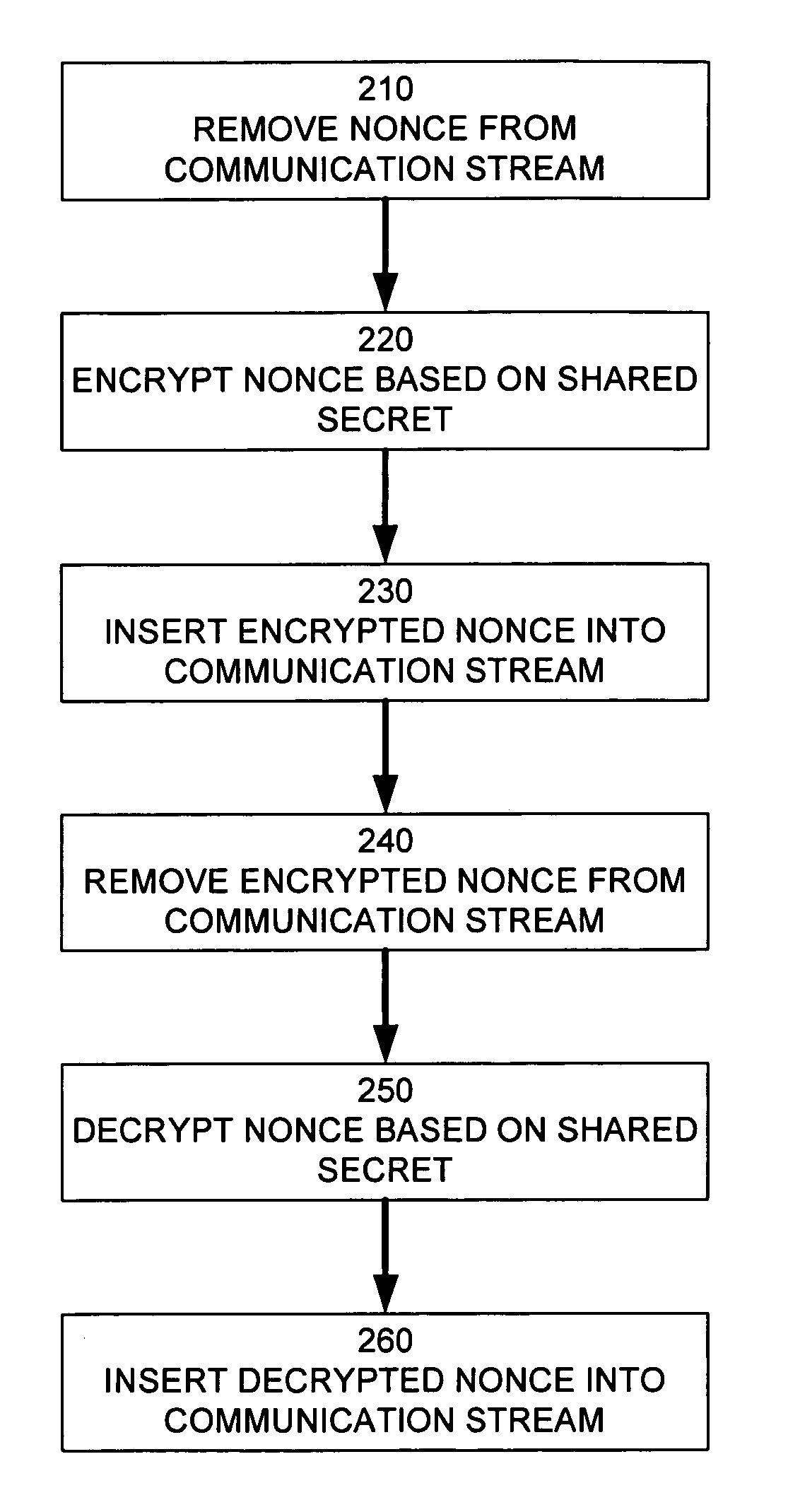
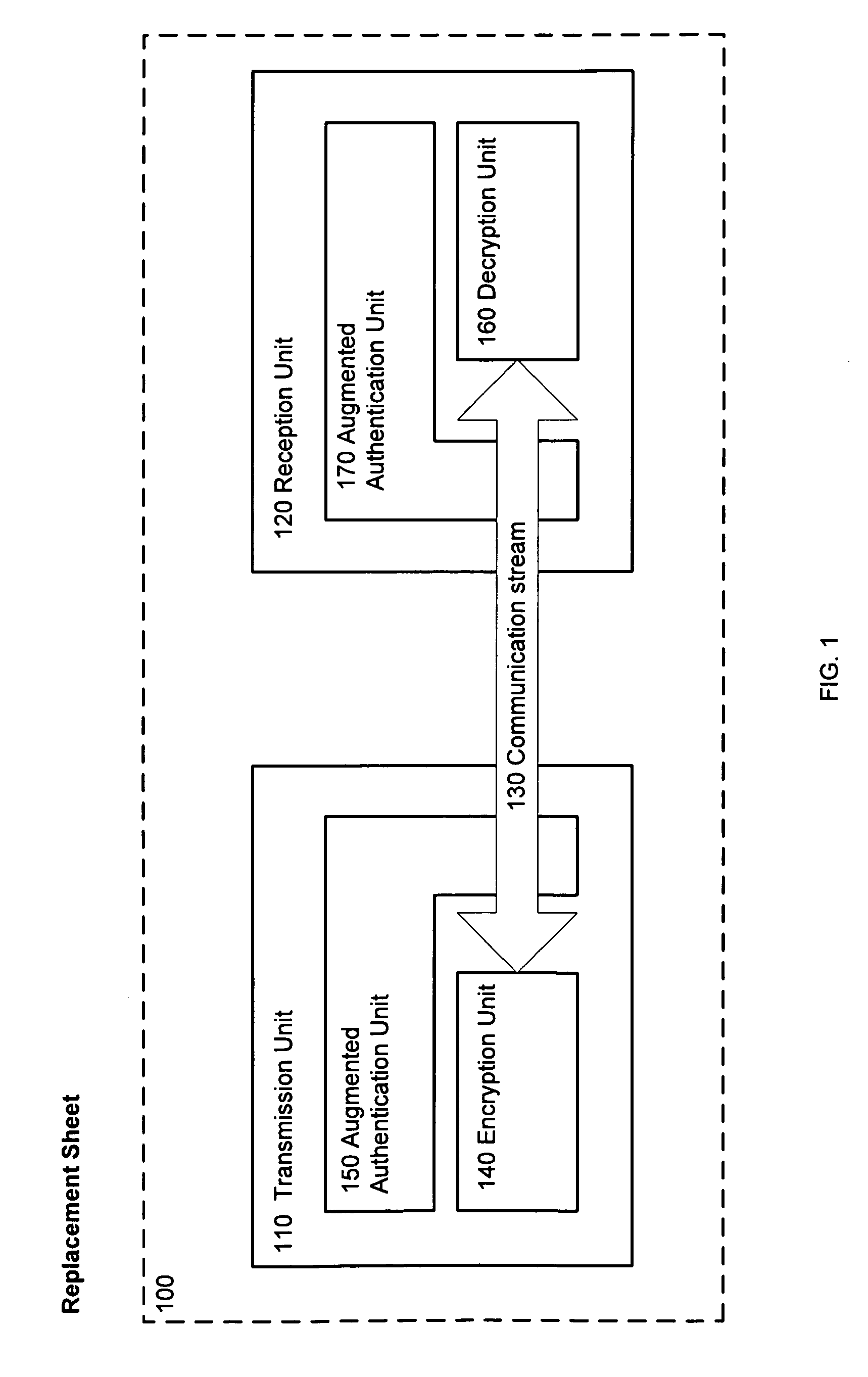
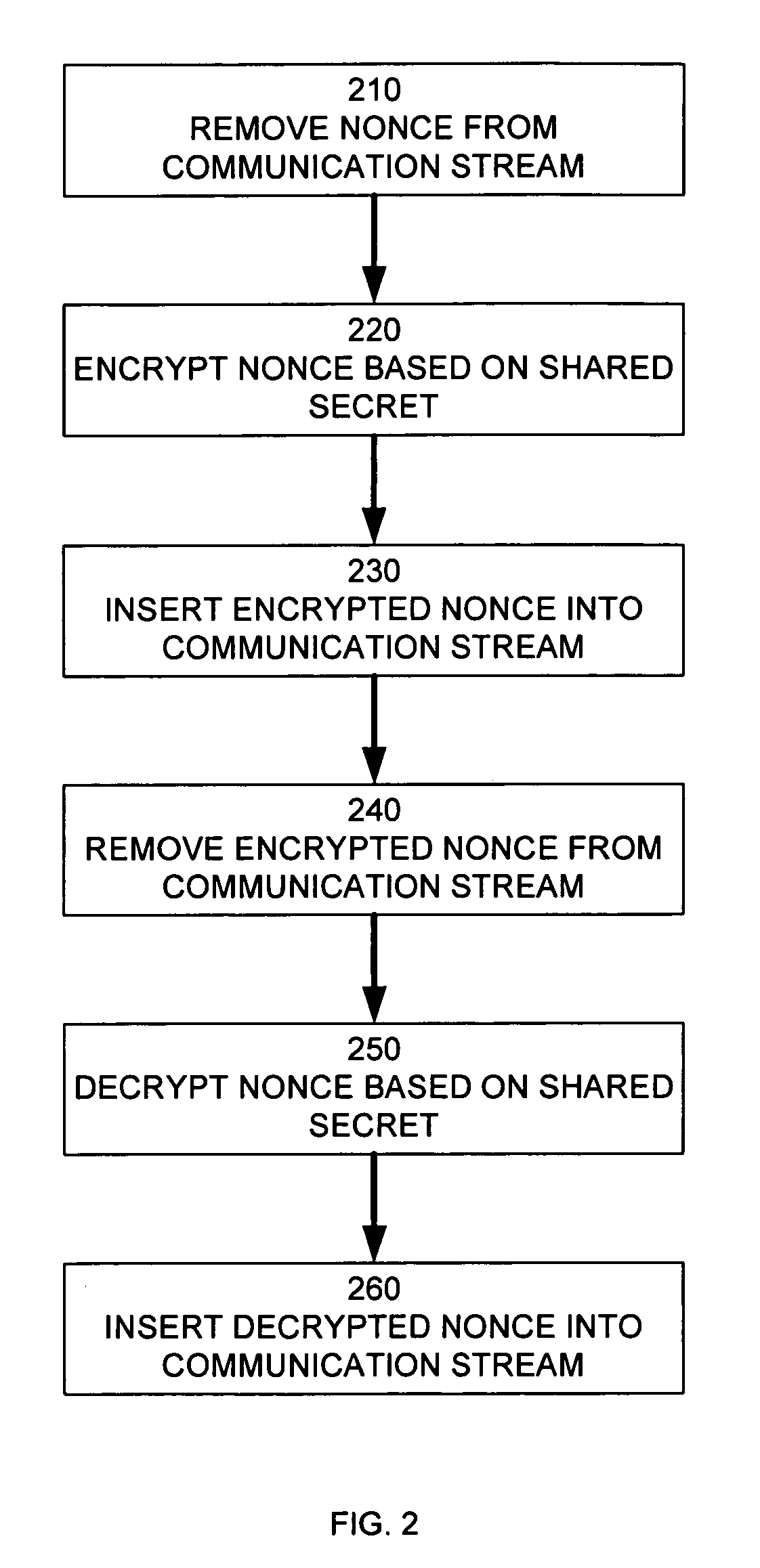
Method and apparatus for augmenting authentication in a cryptographic system
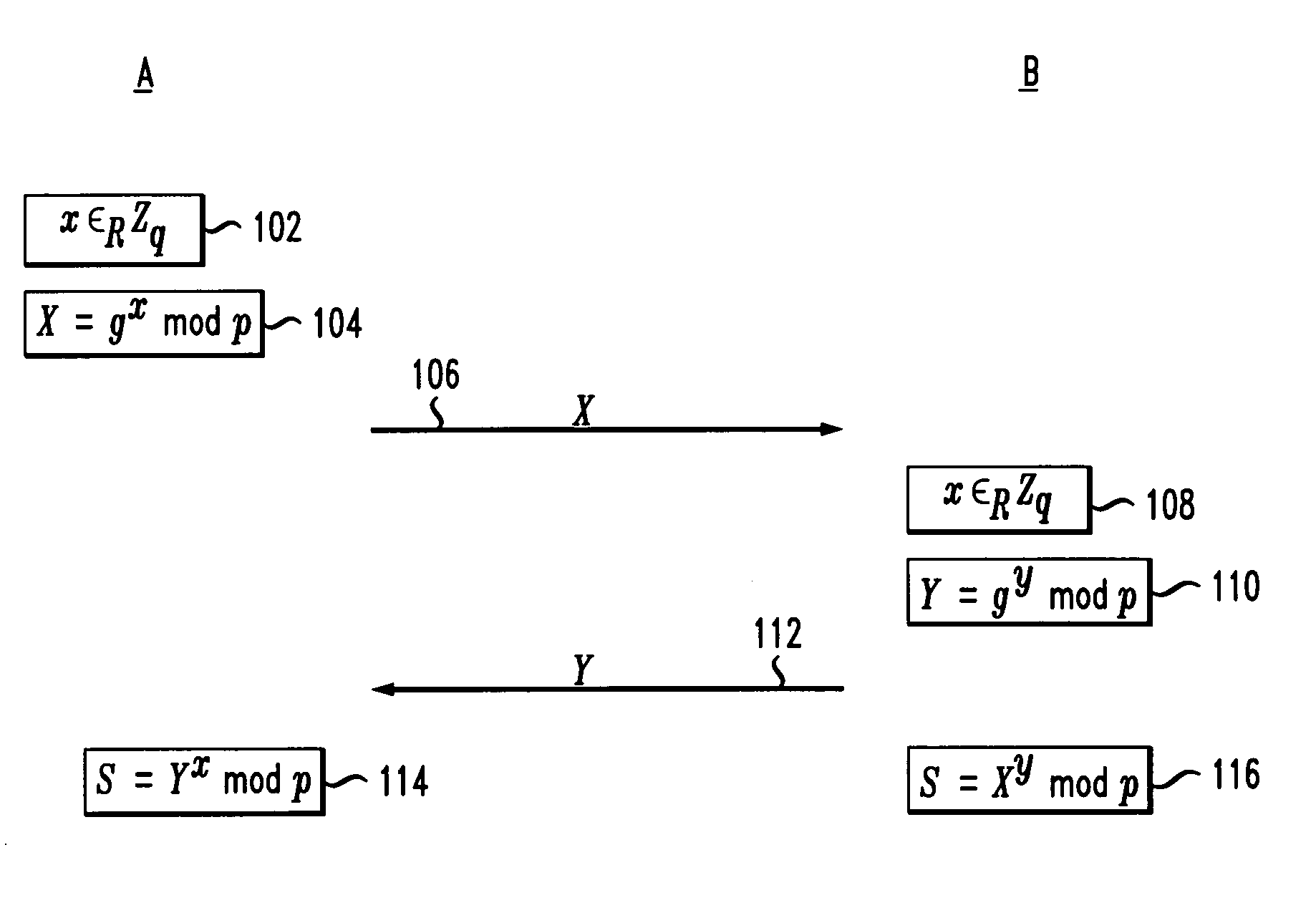
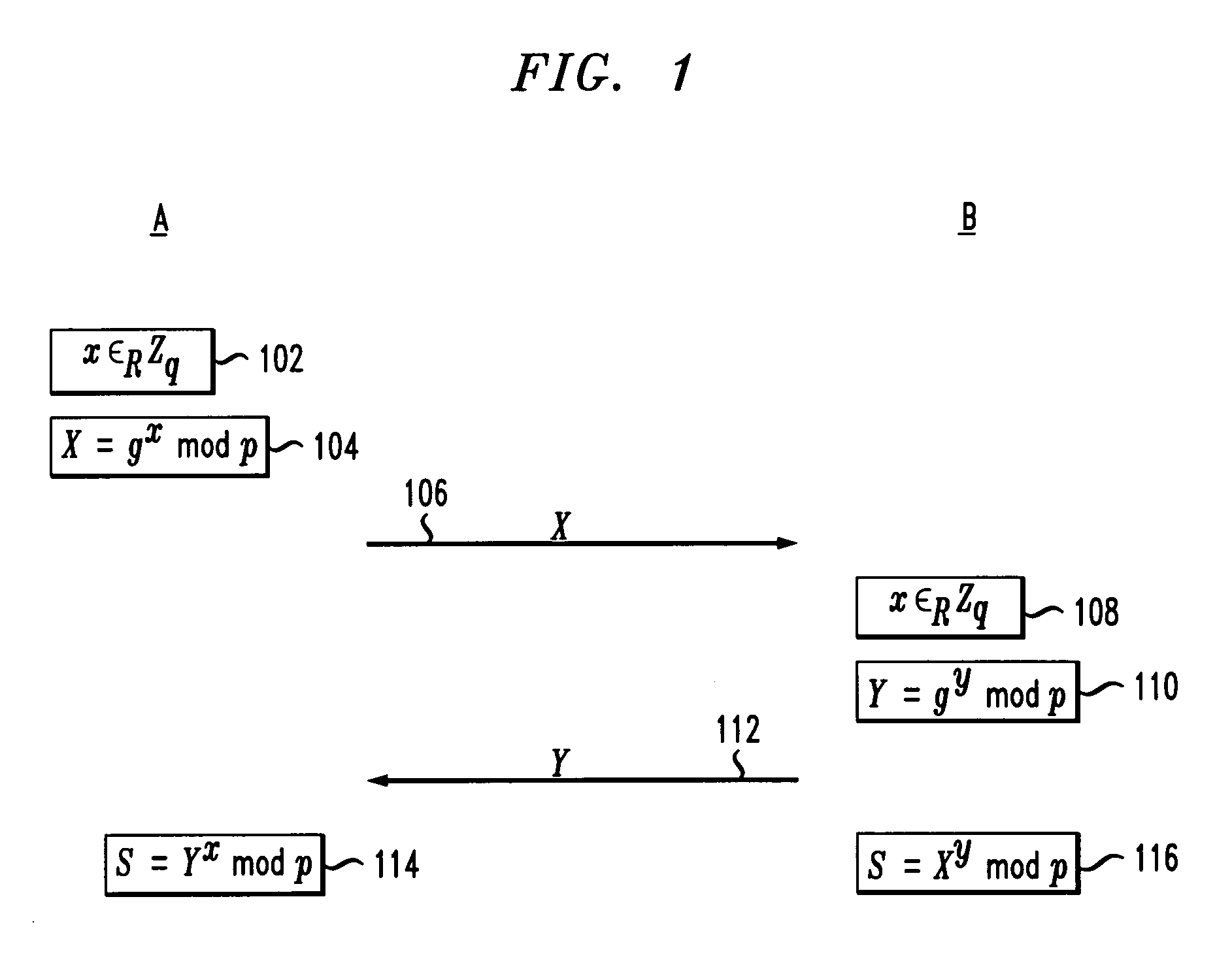
ActiveUS7600118B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDiffie–Hellman key exchangeCryptographic nonce
In a cryptographic system, a nonce is removed from a communication stream. The nonce is encrypted based on a shared secret. The encrypted nonce is inserted into the communication stream. The encrypted nonce is removed from the communication stream. The encrypted nonce is decrypted based on the shared secret formed by an authenticated key exchange. The decrypted nonce is inserted into the communication stream. The nonce may be an An value generated by a HDCP function. The authenticated key exchange may use Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange.
Owner:INTEL CORP
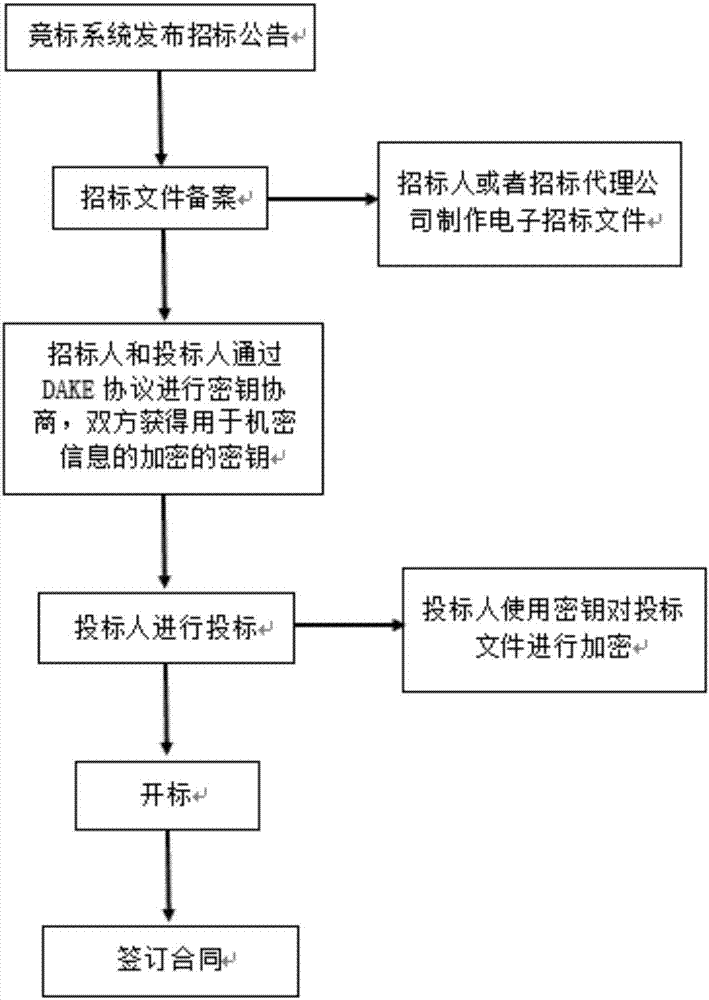
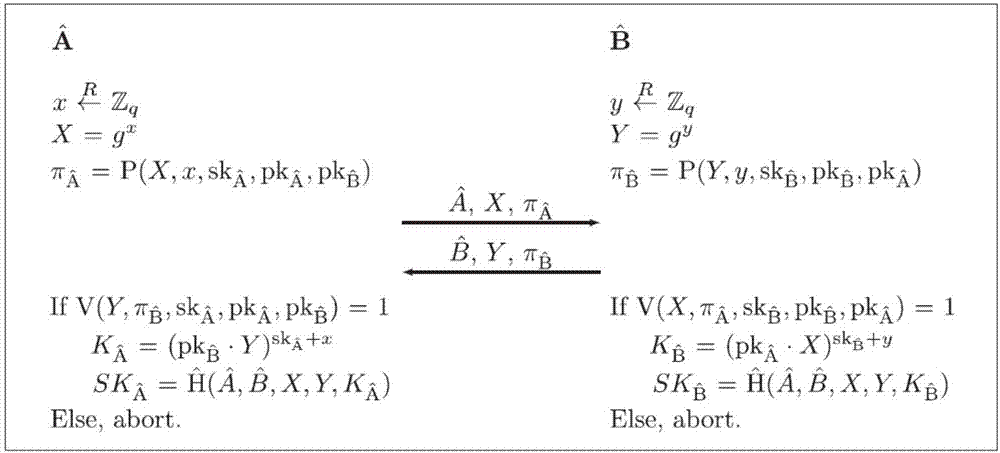
Realization method of perfect forward security deniable key exchange protocol of online bidding system
InactiveCN107547199AMeet the application requirements of deniable forward securityCompleteKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDependabilityProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The invention discloses a realization method of a perfect forward security deniable key exchange protocol of an online bidding system. The realization method comprises the following steps: S1, defining a non-interactive specified verifier knowledge certificate which has completeness, special reliability, self-adaptive zero knowledge, unforgeability and symmetry, wherein a constructed protocol is provided with the perfect forward security and the complete deniability through the unforgeability and the symmetry; S2, constructing a non-interactive specified verifier knowledge certificate scheme;S3, constructing a round of deniable authentication key exchange protocol through a Diffie-Hellman type protocol, wherein the deniable authentication key exchange protocol is provided with the perfectforward security and the complete deniability at the same time. Through the realization method disclosed by the invention, the round of authentication key exchange protocol with completely deniable forward security is constructed, a good combination is achieved on the security and the efficiency, and a demand of the current electronic bidding system is satisfied.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for transforming unauthenticated key exchange protocol into authenticated key exchange protocol
The invention discloses a method for transforming an unauthenticated key exchange protocol into an authenticated key exchange protocol. DSig=(Gen, Sig,Ver) is set as a standard digital signature algorithm by a digital signature method, wherein Gen is a key generation algorithm; Sig is a signature algorithm; Ver is a signature verification algorithm; and Gen generates a pair of signature / verification key pair for a user Ui. Simultaneously, the invention is an authenticated key exchange protocol and is used for fulfilling the aim of sharing one common conversion key among unacquainted members in a published network through interaction. The method for transforming the unauthenticated key exchange protocol into the authenticated key exchange protocol makes up security flaws of the conventional method and has higher security, and simultaneously compared with the conventional method, the method has the advantages of improvement on the calculation amount and communication traffic, and better application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
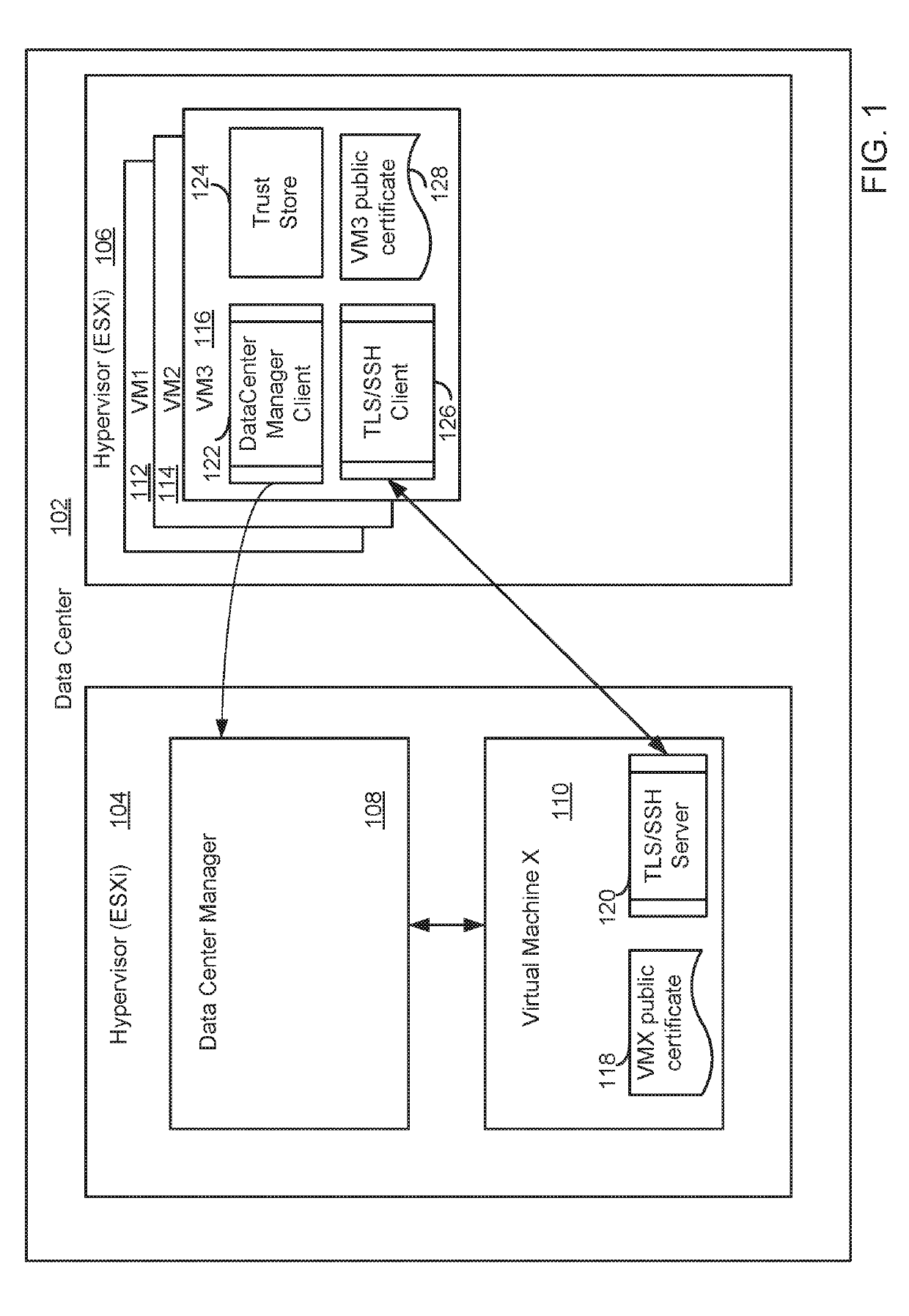
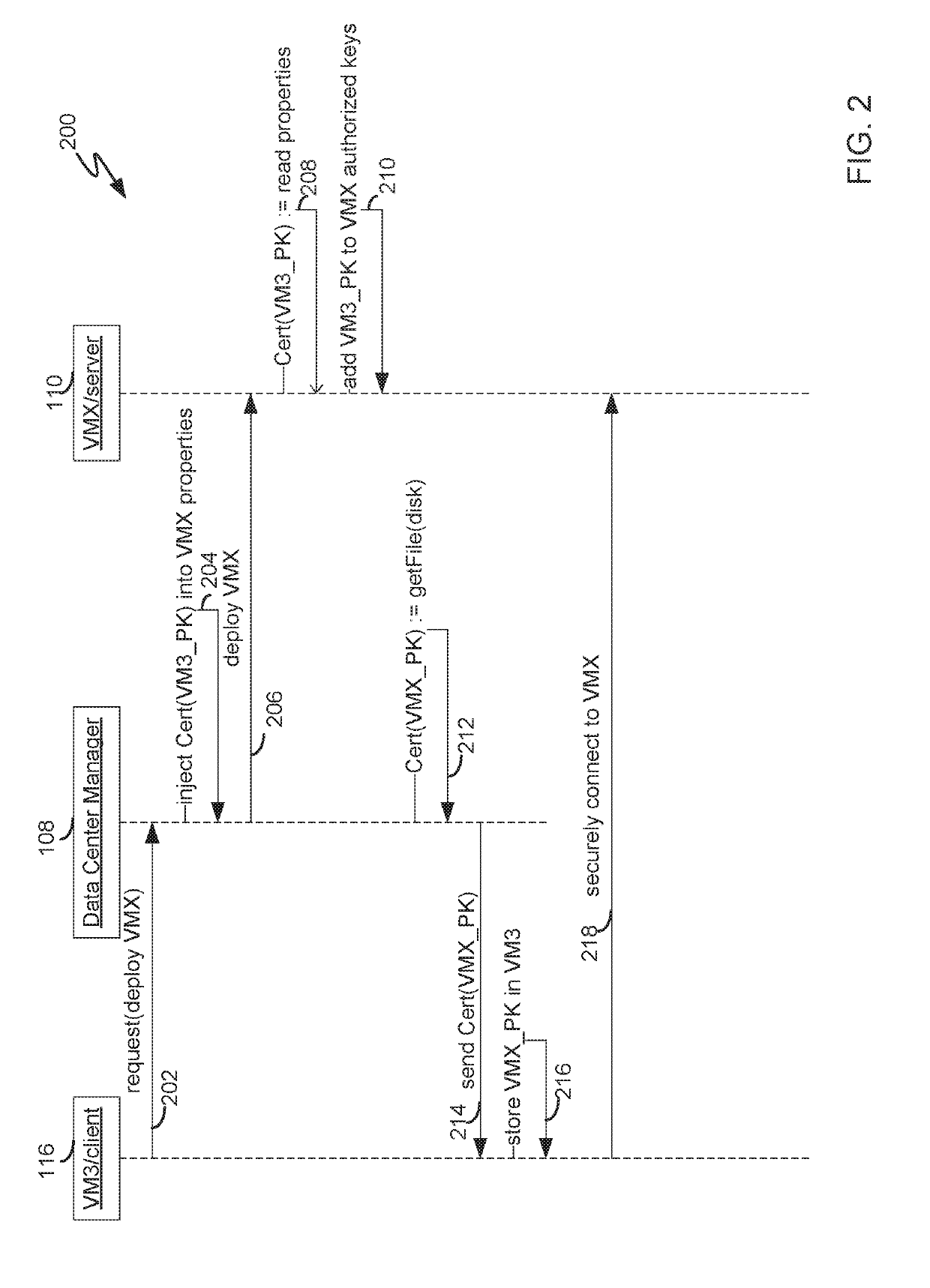
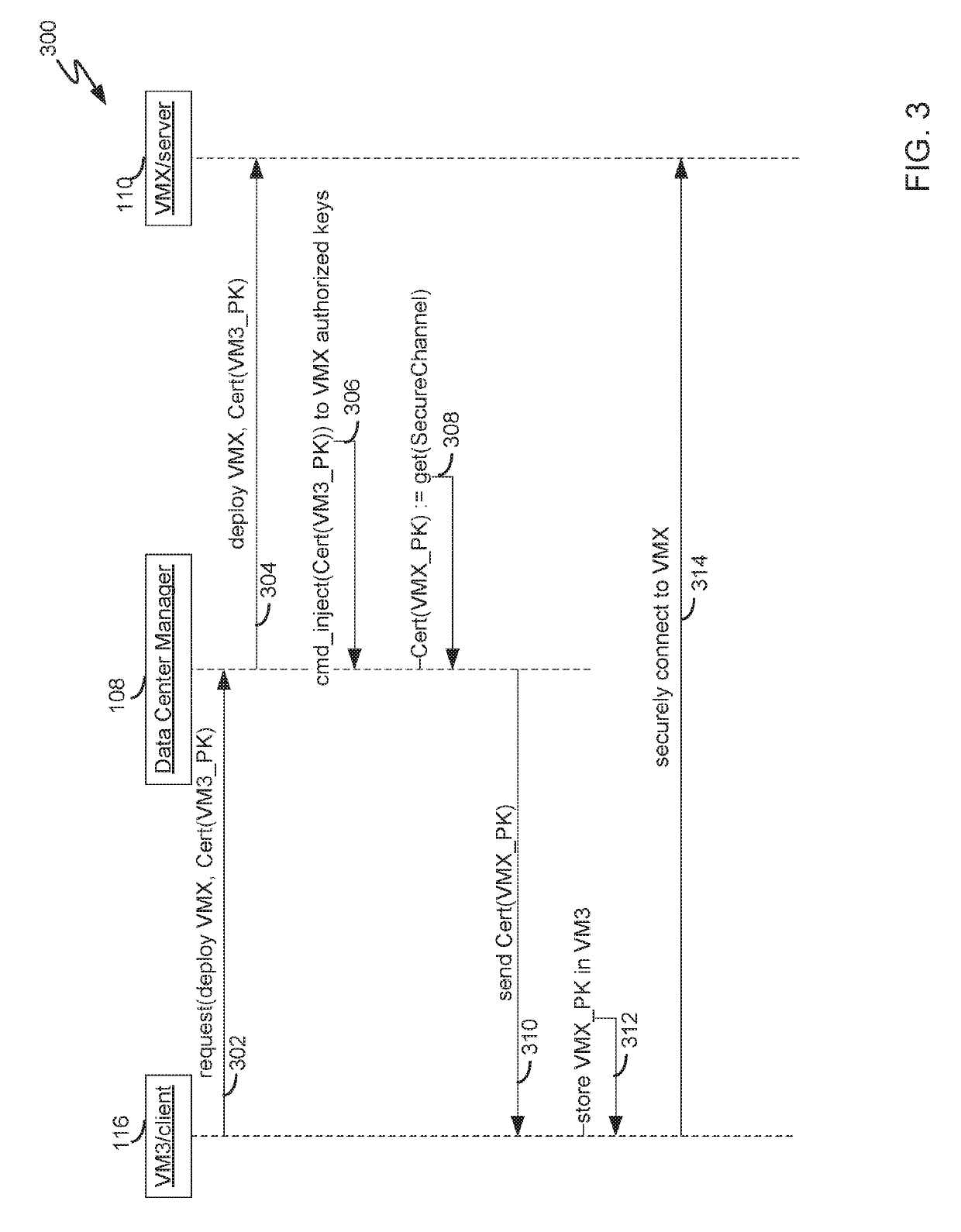
Automating establishment of initial mutual trust during deployment of a virtual appliance in a managed virtual data center environment
System and method for securely deploying a virtual machine in a data center is disclosed. In one embodiment, public keys are established between the requesting virtual machine and the deployed virtual machine, so that authentication and communication between the machines can occur using the public keys. In another embodiment, a secret private key is established between the requesting virtual machine and the deployed virtual machine using a password authenticated key exchange protocol. Authentication and communication between the machines is then established using the secret private key.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com