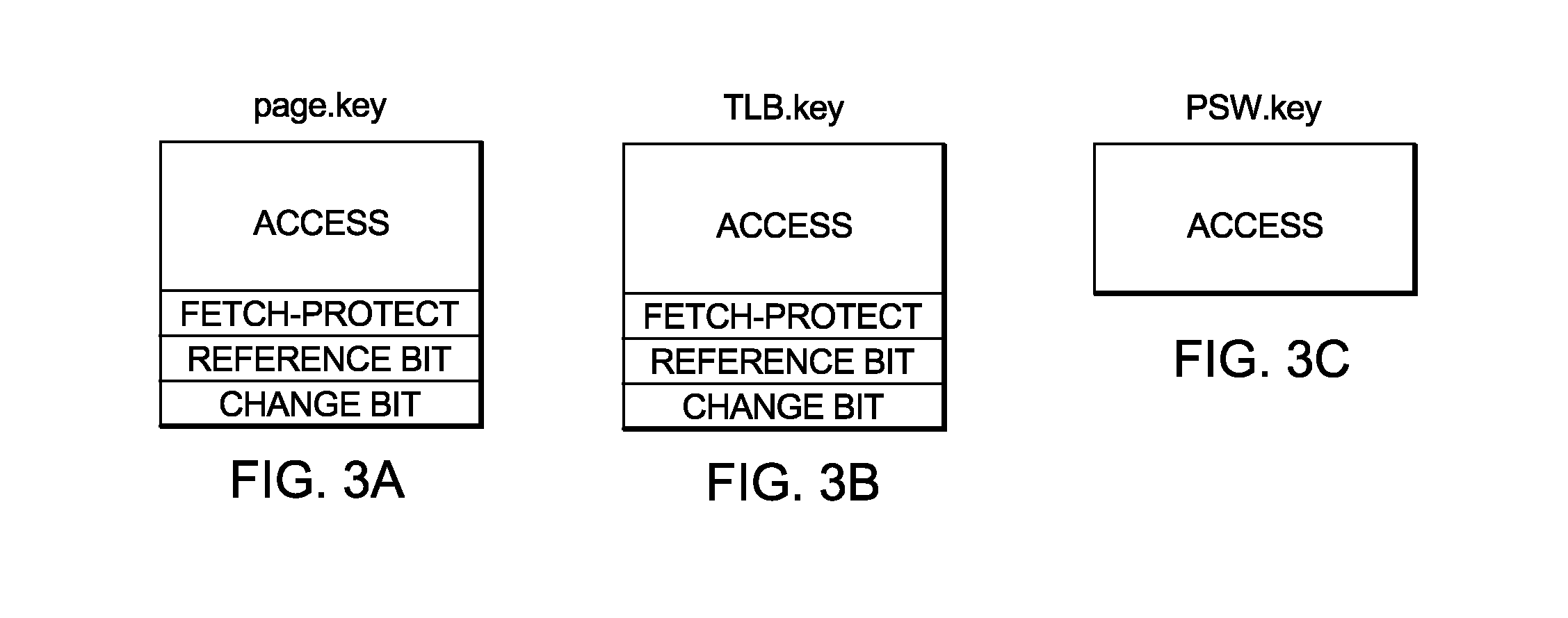
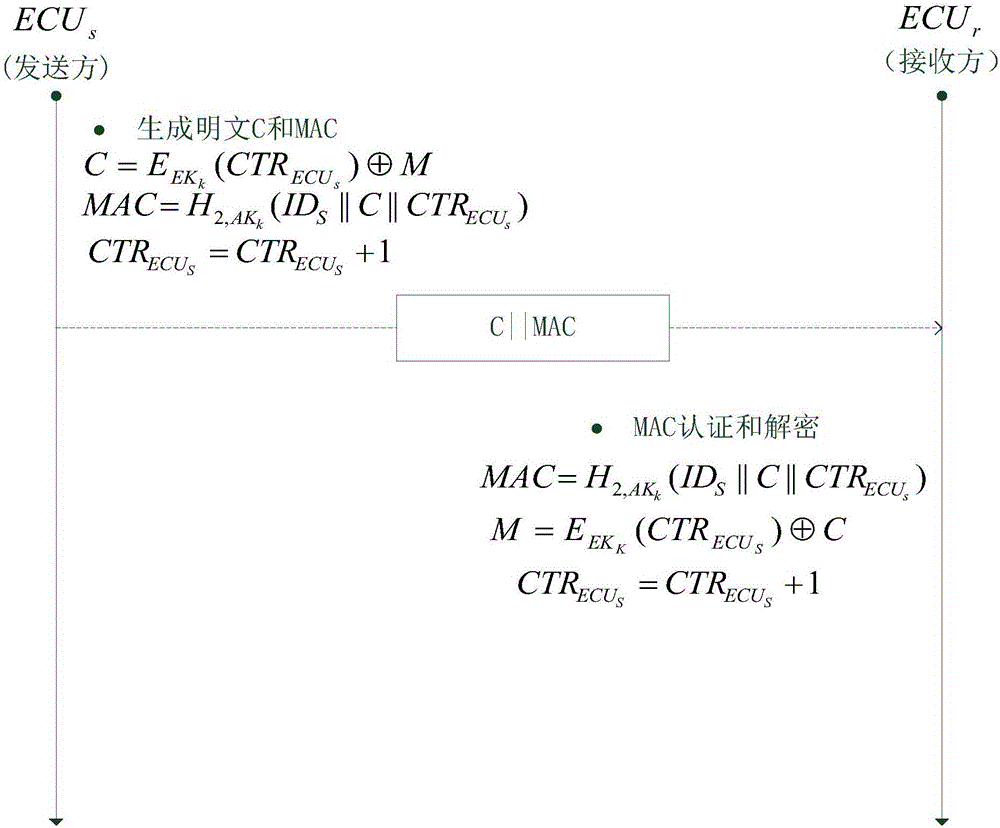Patents
Literature
191 results about "Rekeying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rekeying a lock is replacing the old lock pins with new lock pins.
Cryptographic key update management method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050018853A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMostly TrueRekeying
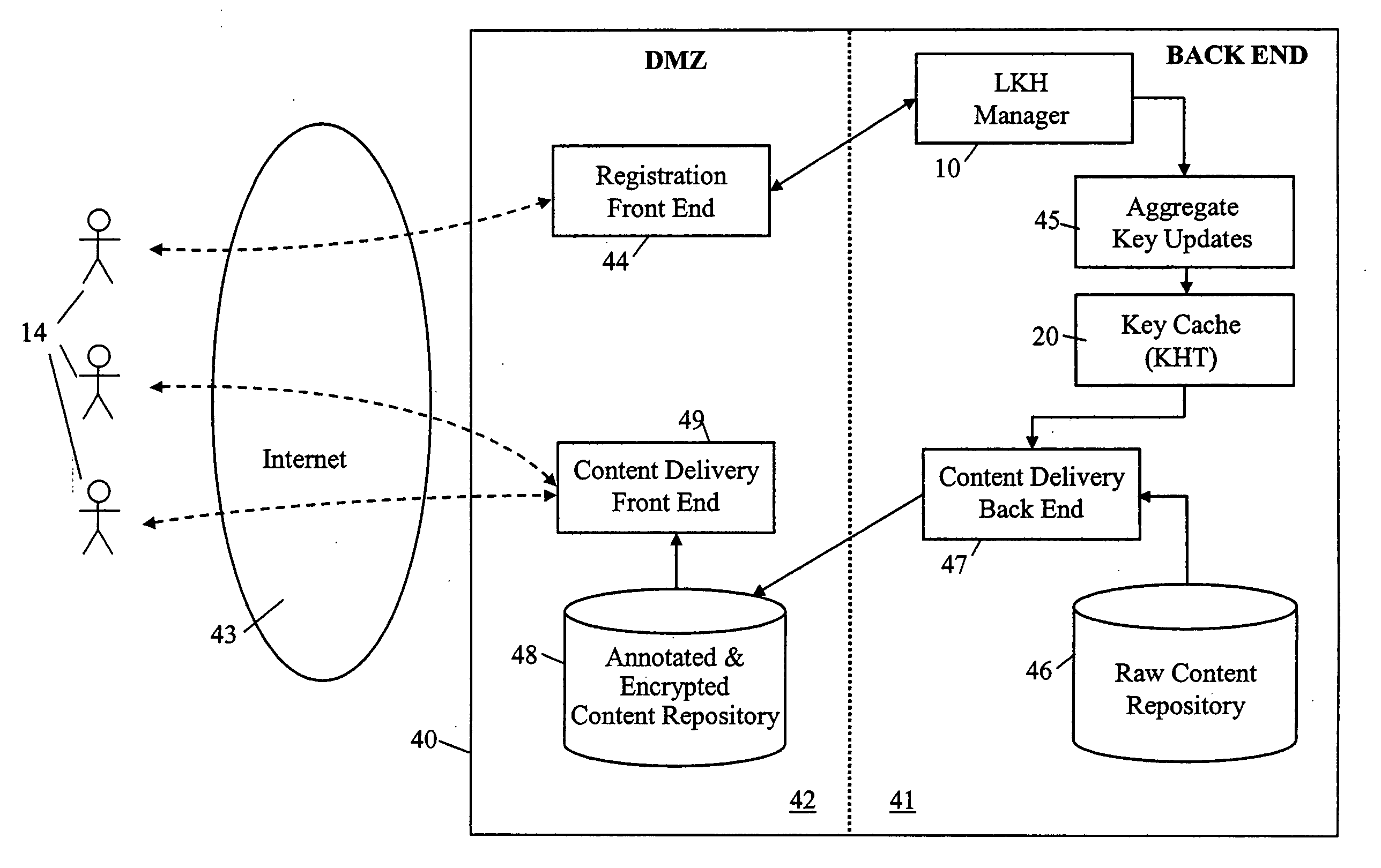
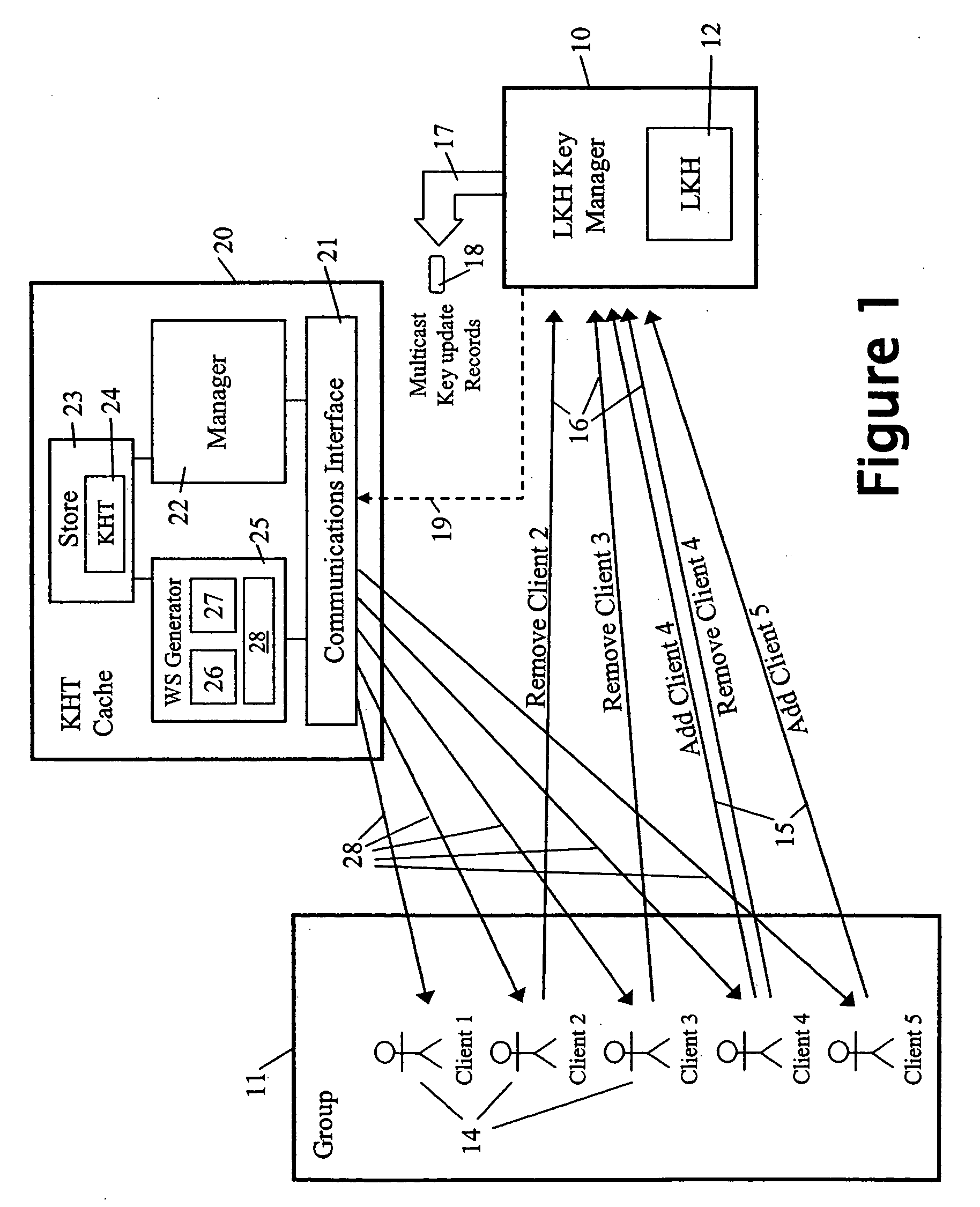
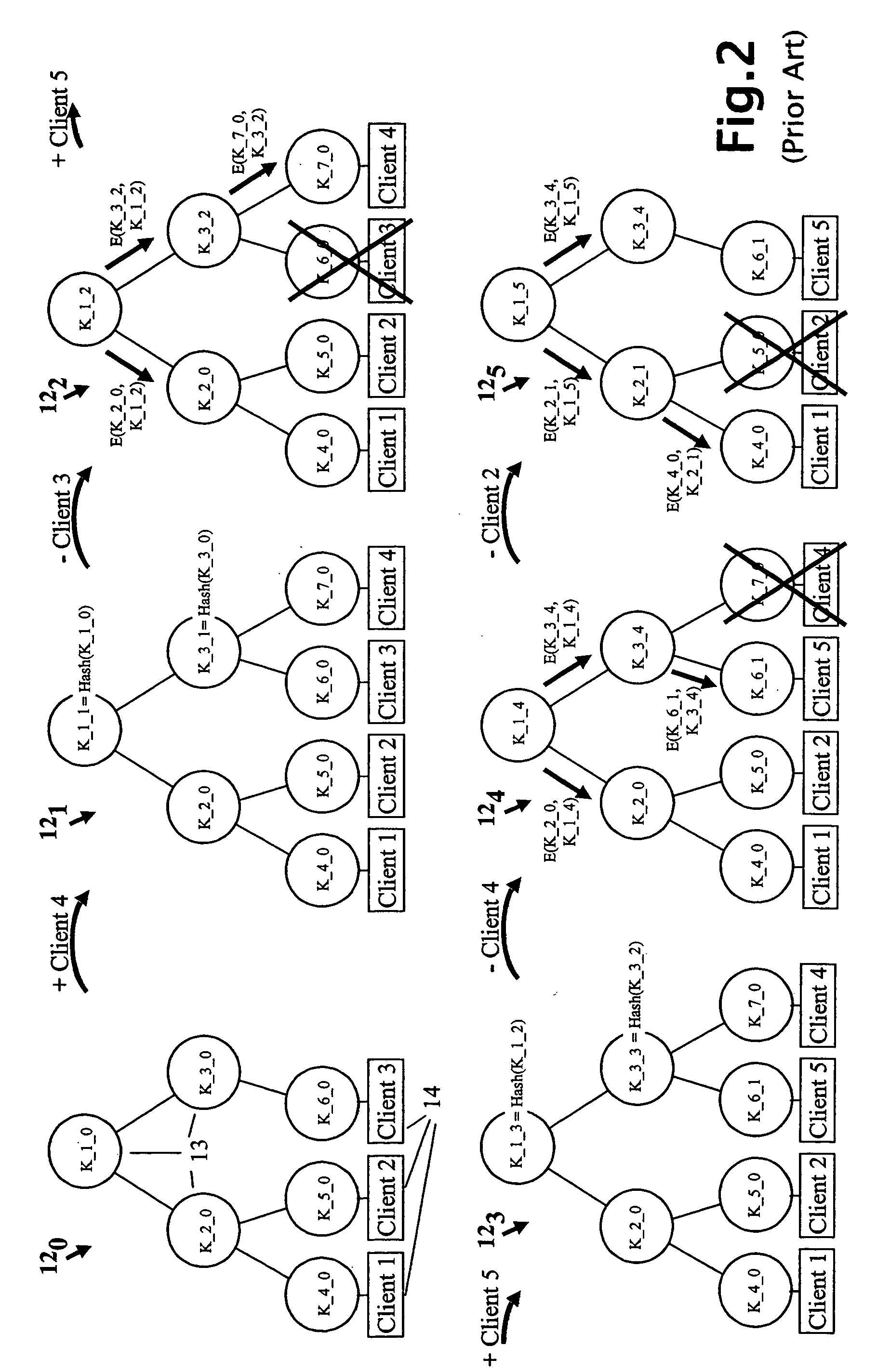
A method and apparatus is provided for consolidating cryptographic key updates, the consolidated update information enabling, for example, a returning member of a secure group who has been offline, to recover the current group key, at least in most cases. The unconsolidated key updates each comprise an encrypted key, corresponding to a node of a key hierarchy, that has been encrypted using a key which is a descendant of that node. The key updates are used to maintain a key tree with nodes in this tree corresponding to nodes in the key hierarchy. Each node of the key tree is used to store, for each encrypting key used in respect of the encrypted key associated with the node, the most up-to-date version of the encrypted key with any earlier versions being discarded. The key tree, or a subset of the tree, is then provided to group members.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
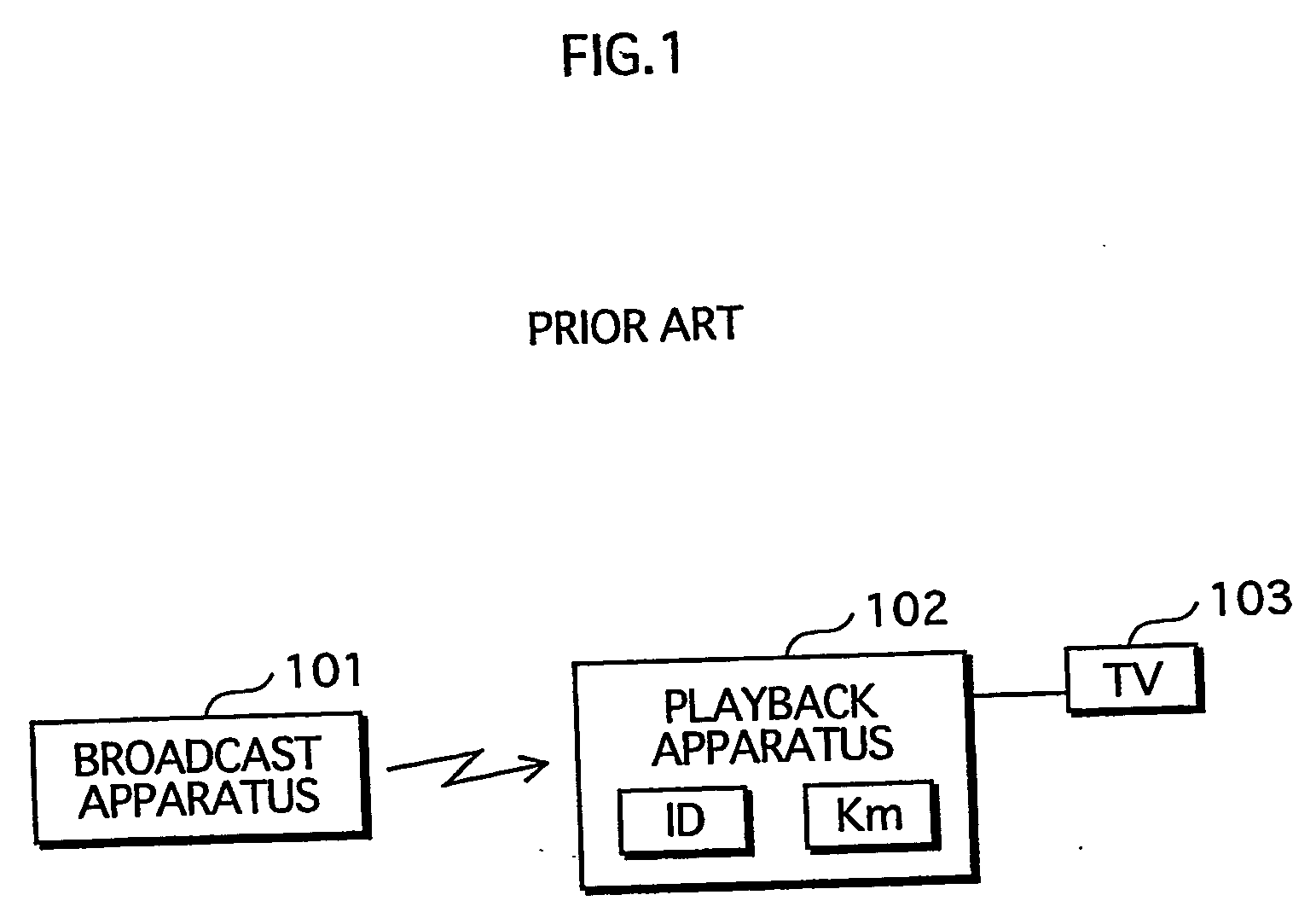
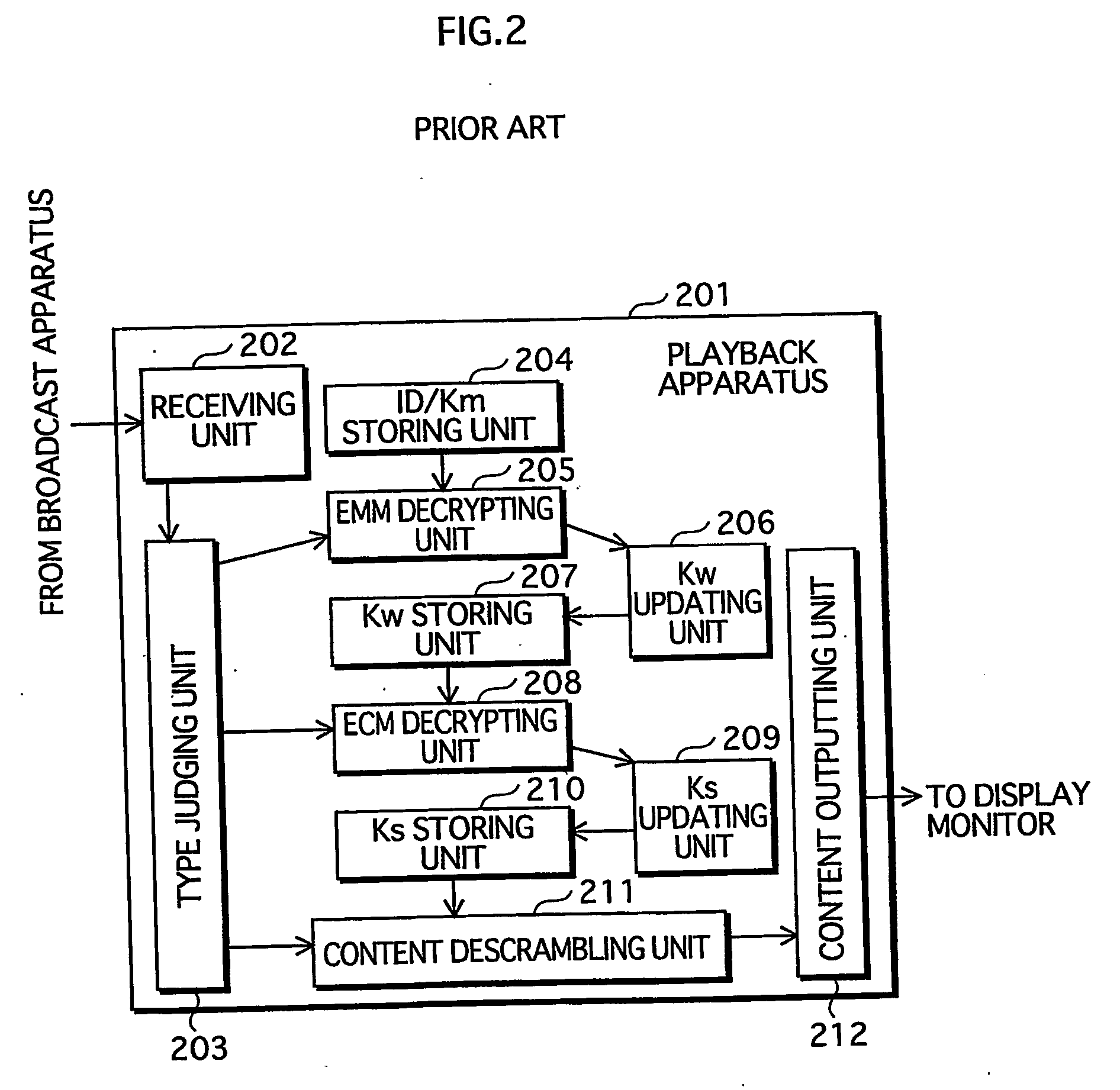
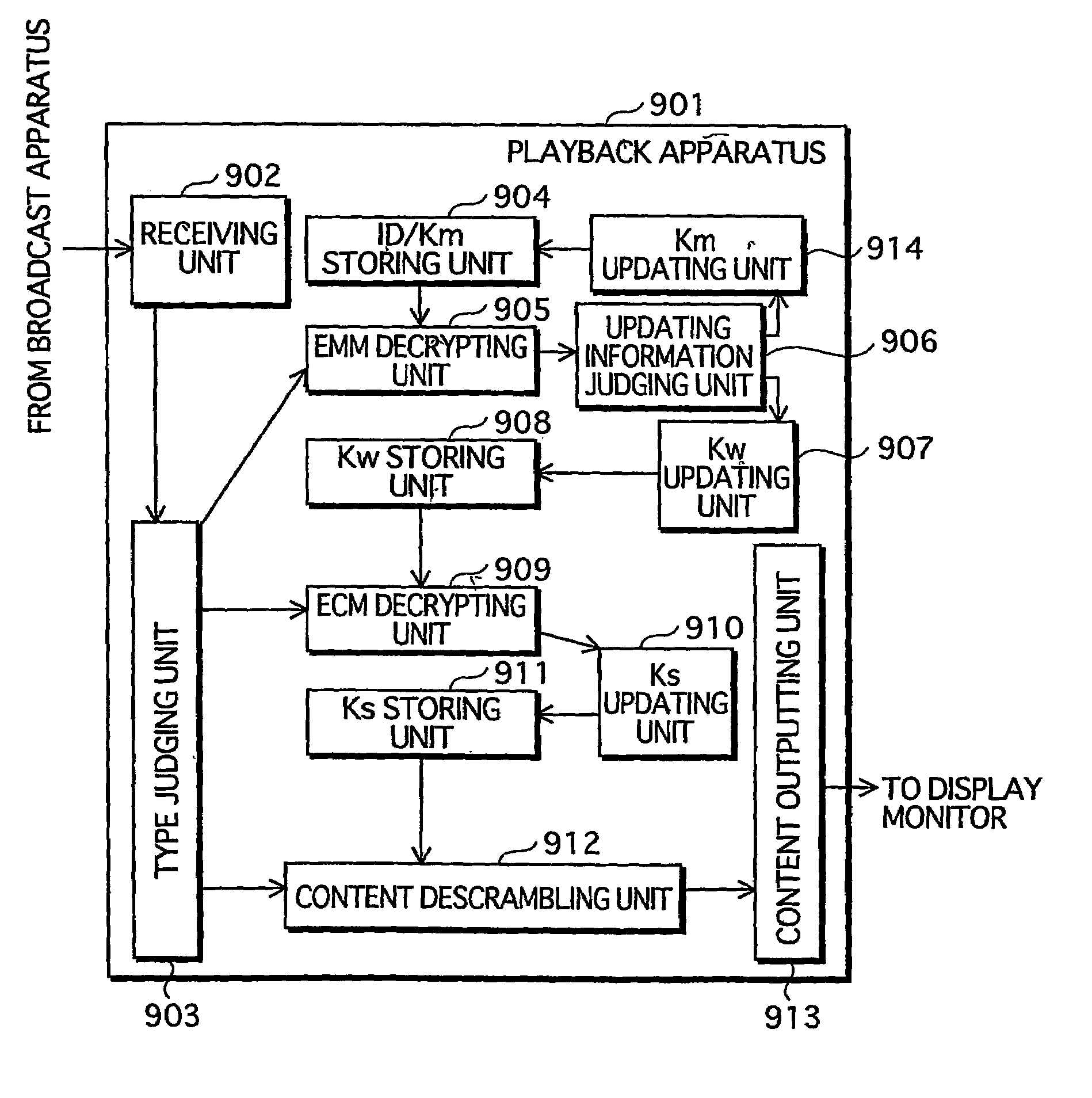
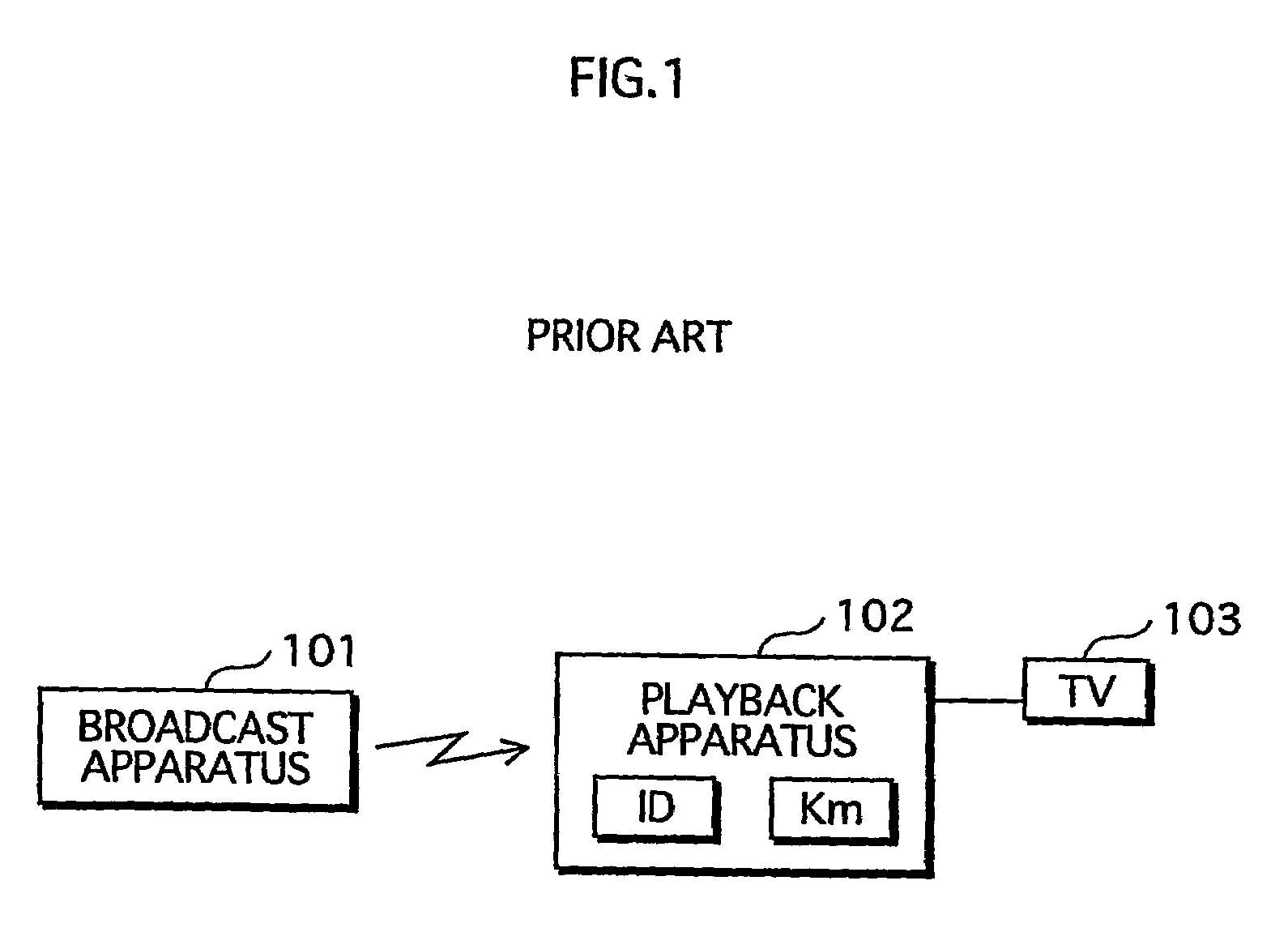
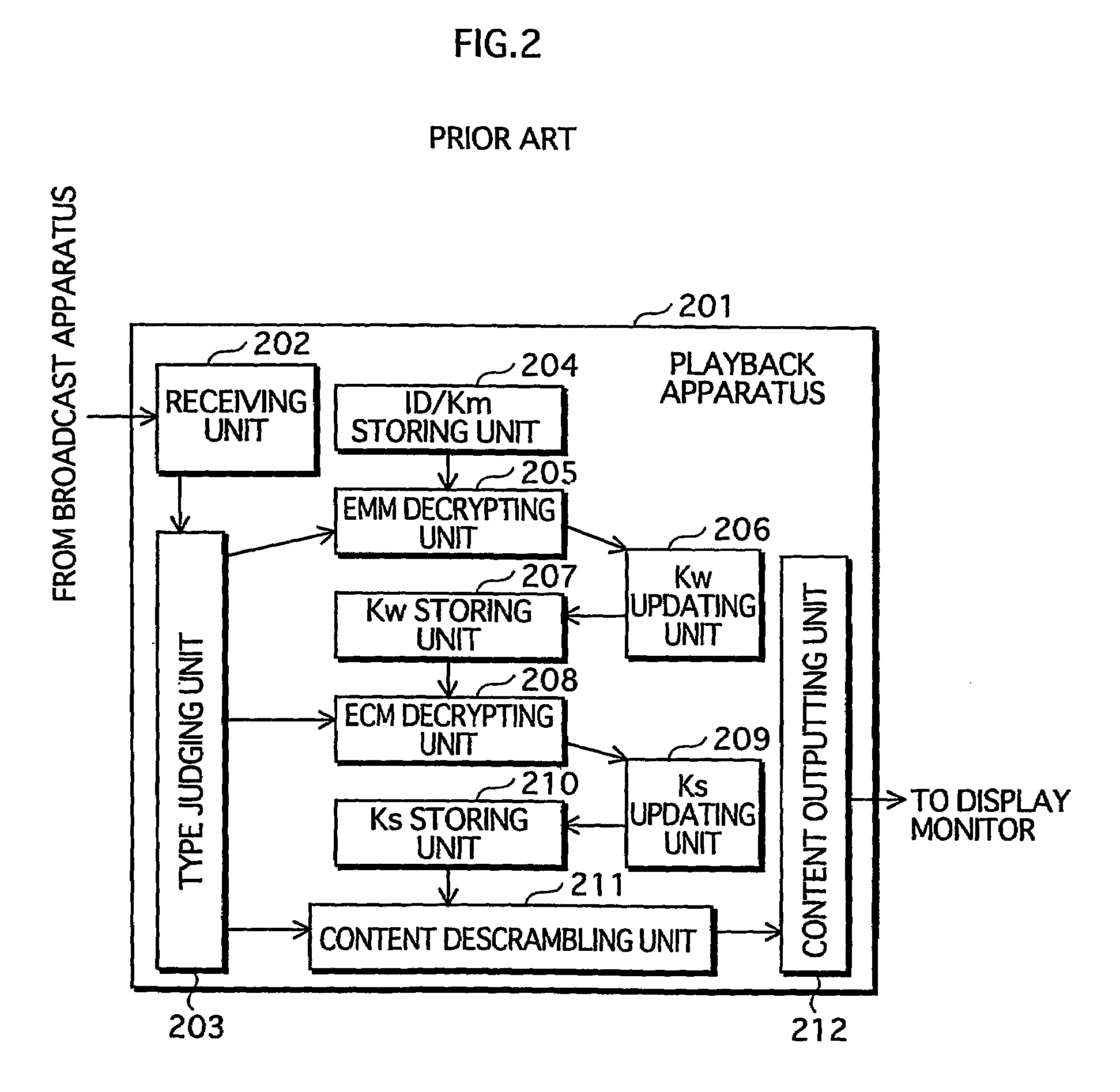
Content playback apparatus method and program and key management apparatus and system
InactiveUS20050021985A1Elimination contentTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareKey management
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Efficient management of cryptographic key generations
InactiveUS20070127719A1Restricted accessEfficient storageKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptographic key generationEarly generation
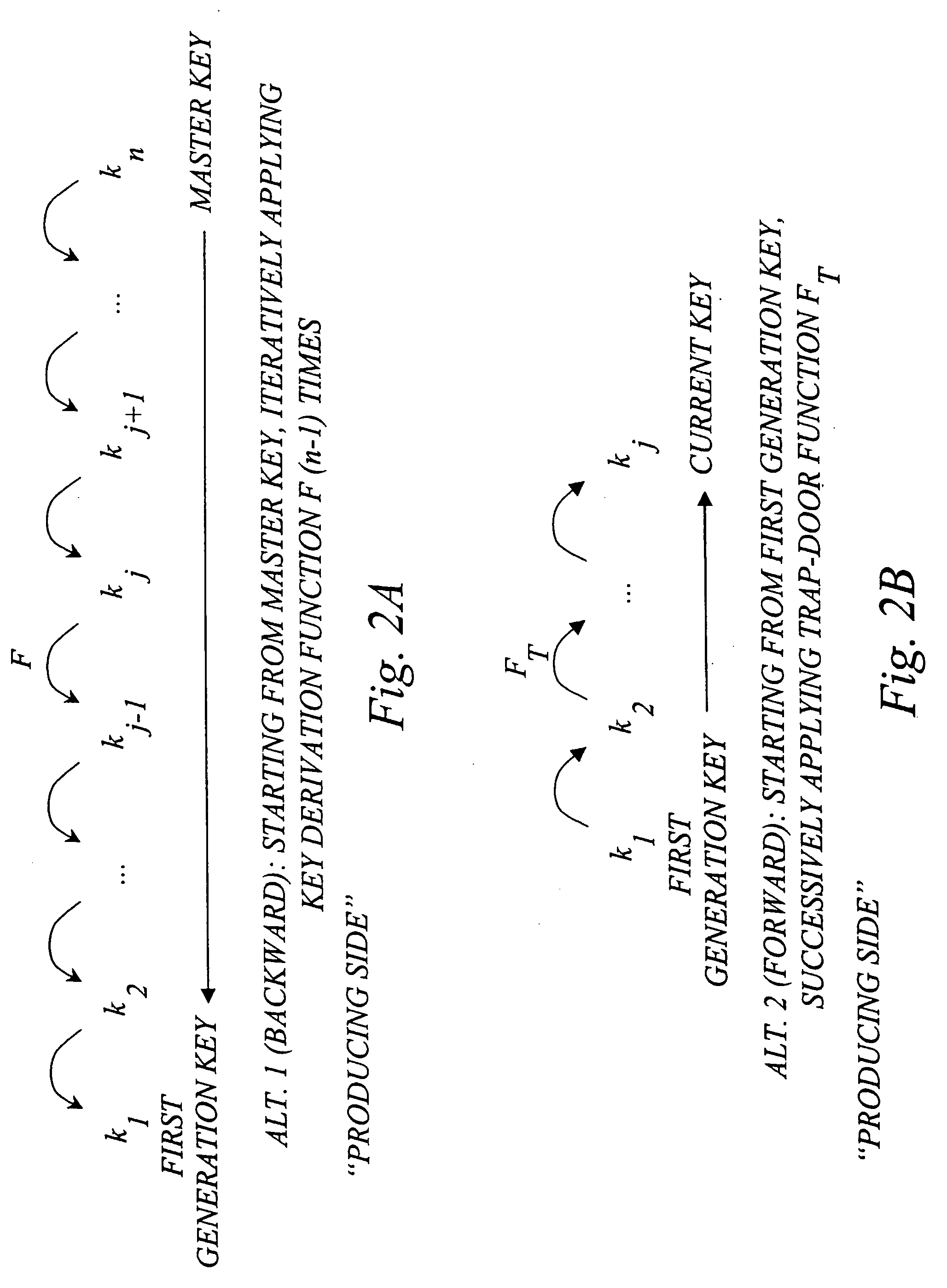
The invention generally relates to management of cryptographic key generations in an information environment comprising a key-producing side generating and distributing key information to a key-consuming side. A basic concept of the invention is to define, by means of a predetermined one-way key derivation function, a relationship between generations of keys such that earlier generations of keys efficiently may be derived from later ones but not the other way around. A basic idea according to the invention is therefore to replace, at key update, key information of an older key generation by the key information of the new key generation on the key-consuming side. Whenever necessary, the key-consuming side iteratively applies the predetermined one-way key derivation function to derive key information of at least one older key generation from the key information of the new key generation. In this way, storage requirements on the key-consuming side can be significantly reduced.
Owner:EMC CORP +1
Encryption method and apparatus with forward secrecy and random-access key updating method
InactiveUS7095850B1Generate efficientlyComputationally efficientData stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationOne-way functionRekeying
An encryption method and apparatus that provides forward secrecy, by updating the key using a one-way function after each encryption. By providing forward secrecy within a cipher, rather than through a key management system, forward secrecy may be added to cryptographic systems and protocols by using the cipher within an existing framework. A random-access key updating method can efficiently generate one or more future keys in any order. Embodiments are applicable to forward secret ciphers that are used to protect protocols with unreliable transport, to ciphers that are used in multicast or other group settings, and to protection of packets using the IPSec protocols.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
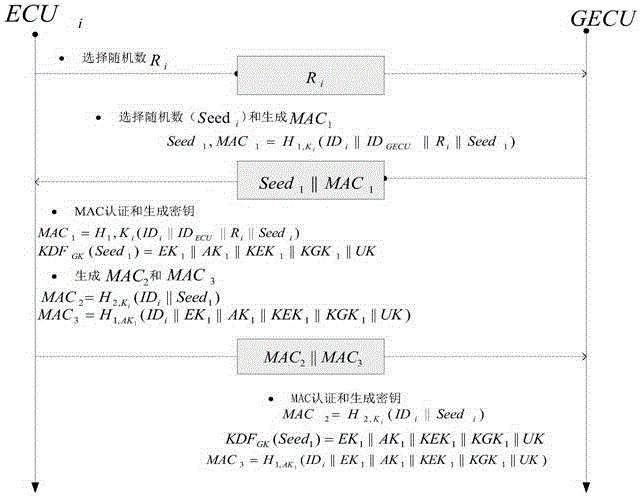
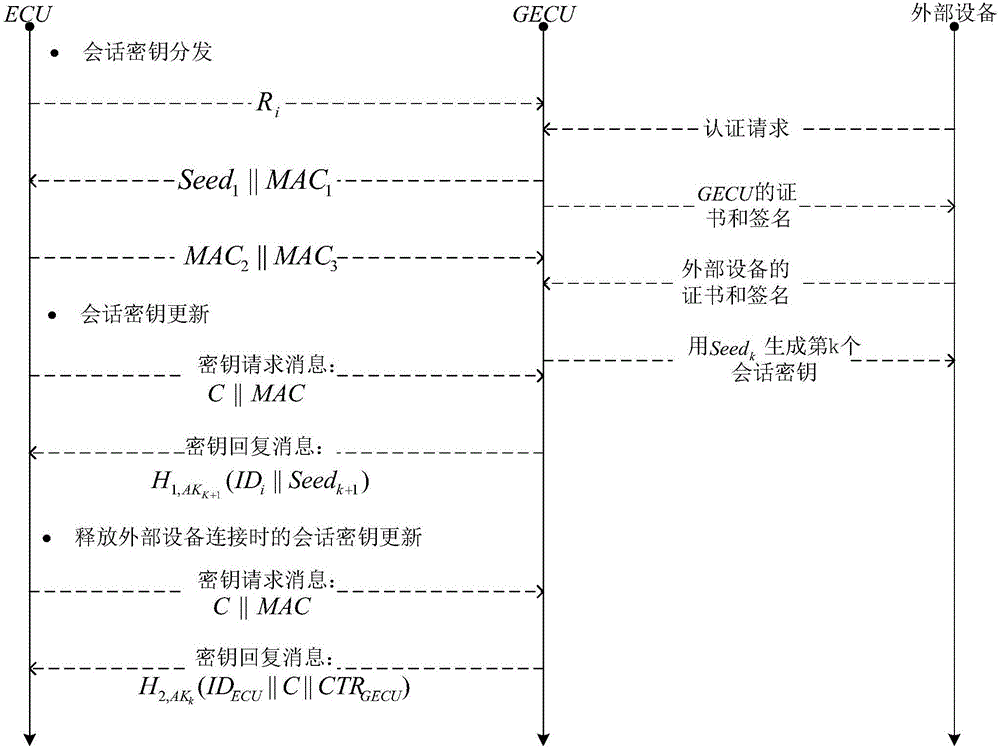
Method for safety communication of ECUs (Electronic Control Unit) in CAN (controller area network) bus
ActiveCN106790053AReduce computing costImprove efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesArea networkKey generation
The invention discloses a method for safety communication of ECUs (Electronic Control Unit) in a CAN (controller area network) bus, which comprises the steps that: 1, a system model is established; 2, an GECU (Gateway Electronic Control Unit) loads a session key into a safety storage of the GECU; 3, the GECU carries out session key distribution on each ECU in the CAN bus; 4, a receiver ECUr carries out authentication on an encrypted data frame sent by a sender ECUs; 5, the GECU updates an encryption key and an authentication key which are used for communication, wherein update is mainly divided into two stages of in-vehicle ECU key update and key update when a connection of external equipment is released; and 6, when a vehicle is connected with the external equipment, designing an additional authentication and key distribution method so as to ensure legality of the accessed external equipment. According to the method disclosed by the invention, calculation cost can be obviously reduced, and a load of the CAN bus is reduced; and optimization is carried out for a key distribution protocol in the in-vehicle CAN bus, a key update problem generated when the external equipment is connected and released is considered, a counter is used for generating a random number to change a parameter for key generation, and a relay attack is effectively prevented.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
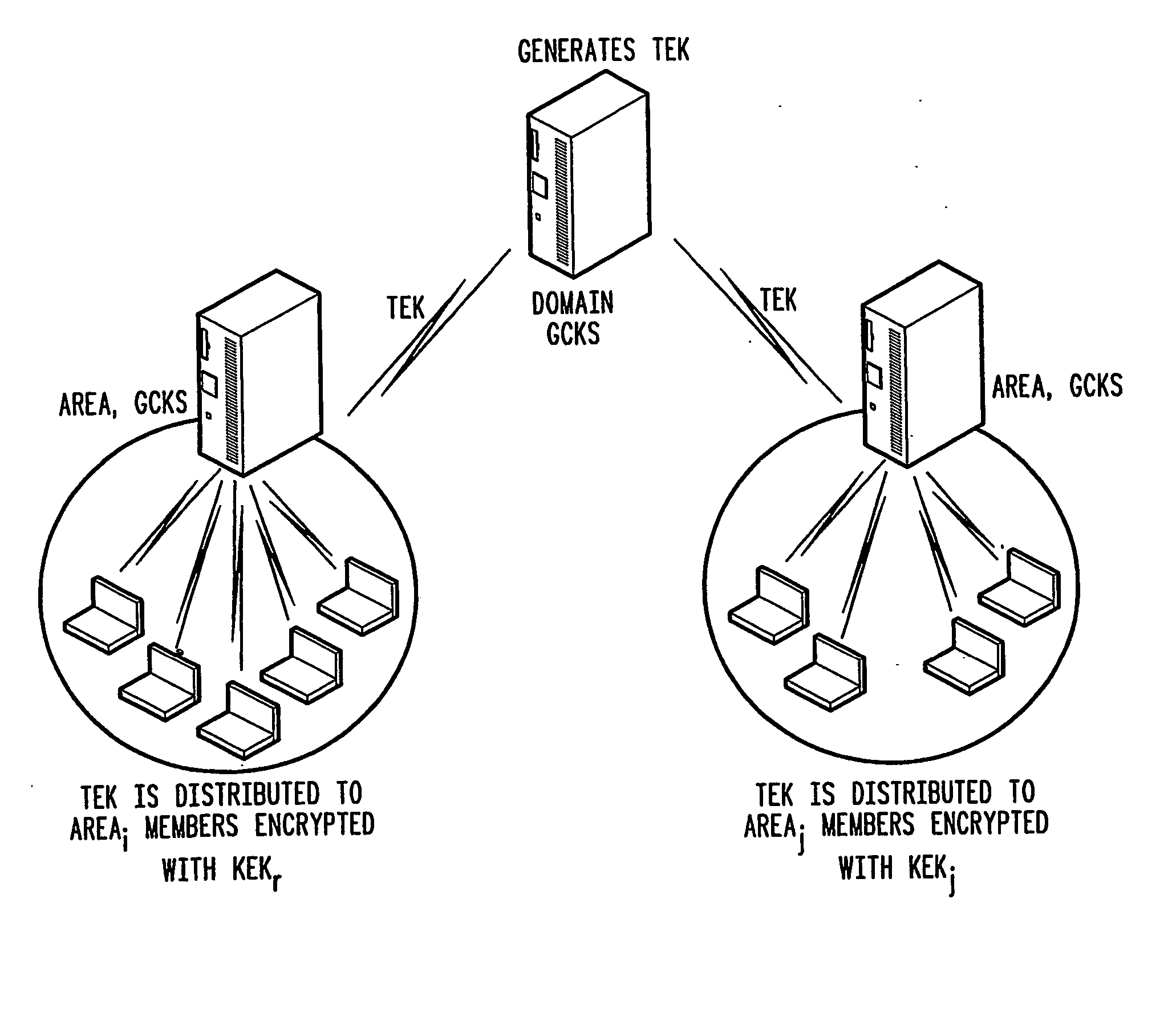
Rekeying in secure mobile multicast communications
InactiveUS20070143600A1Easy to calculateReduce the impactKey distribution for secure communicationKey serverGroup controller
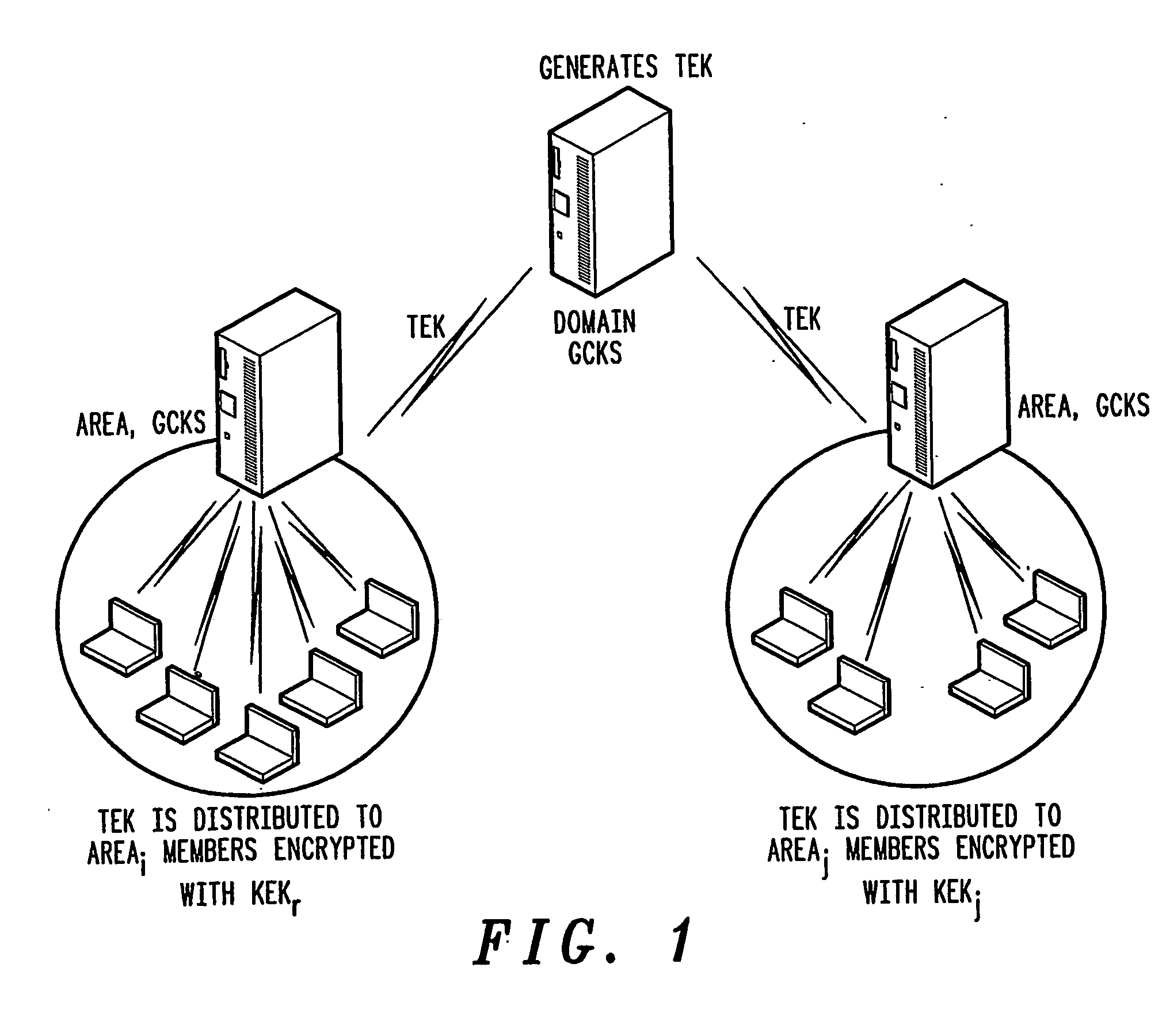
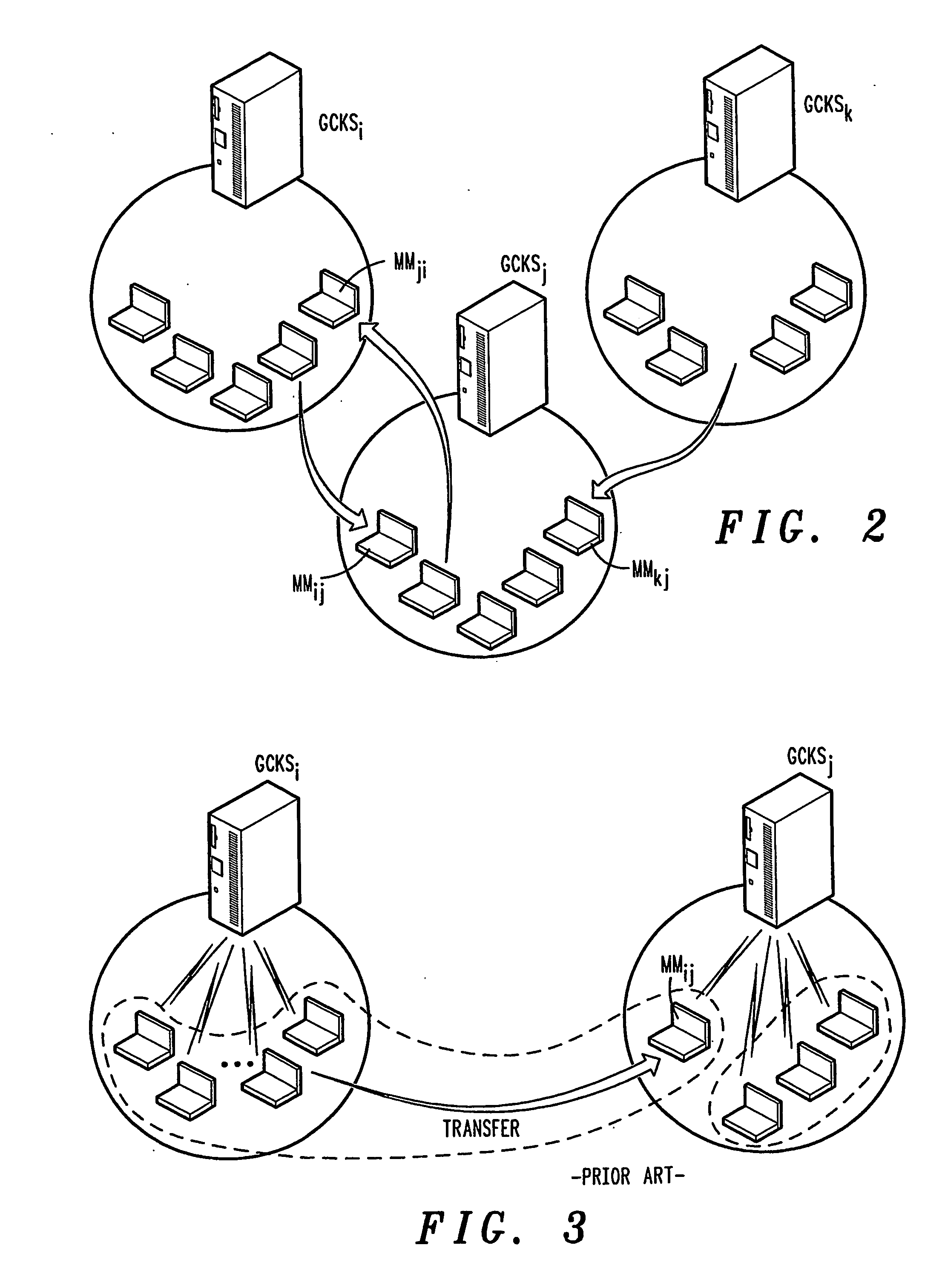
A method of inter-area rekeying of encryption keys in secure mobile muiticast communications, in which a Domain Group Controller Key Server (Domain GCKS) distributes Traffic Encryption Keys (TEK) to a plurality of local Group Controller Key Servers (local GCKS), and said local Group Controller Key Servers forward said Traffic Encryption Keys, encrypted using Key Encryption Keys (KEKi, KEKj) that are specific to the respective local Group Controller Key Server (local GCKSi, GCKSj), to group members, said local Group Controller Key Servers (GCKSi, GCKSj) constituting Extra Key Owner Lists (EKOLi, EKOLj) for group key management areas (areai, areaj) that distinguish group members (MMi, MMj) possessing Key Encryption Keys (KEKi, KEKj) and situated in the corresponding group key management area (areai, areaj) from group members (MMij) possessing Key Encryption Keys (KEKi) that were situated in the corresponding group key management area (areai) but are visiting another area (areaj).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
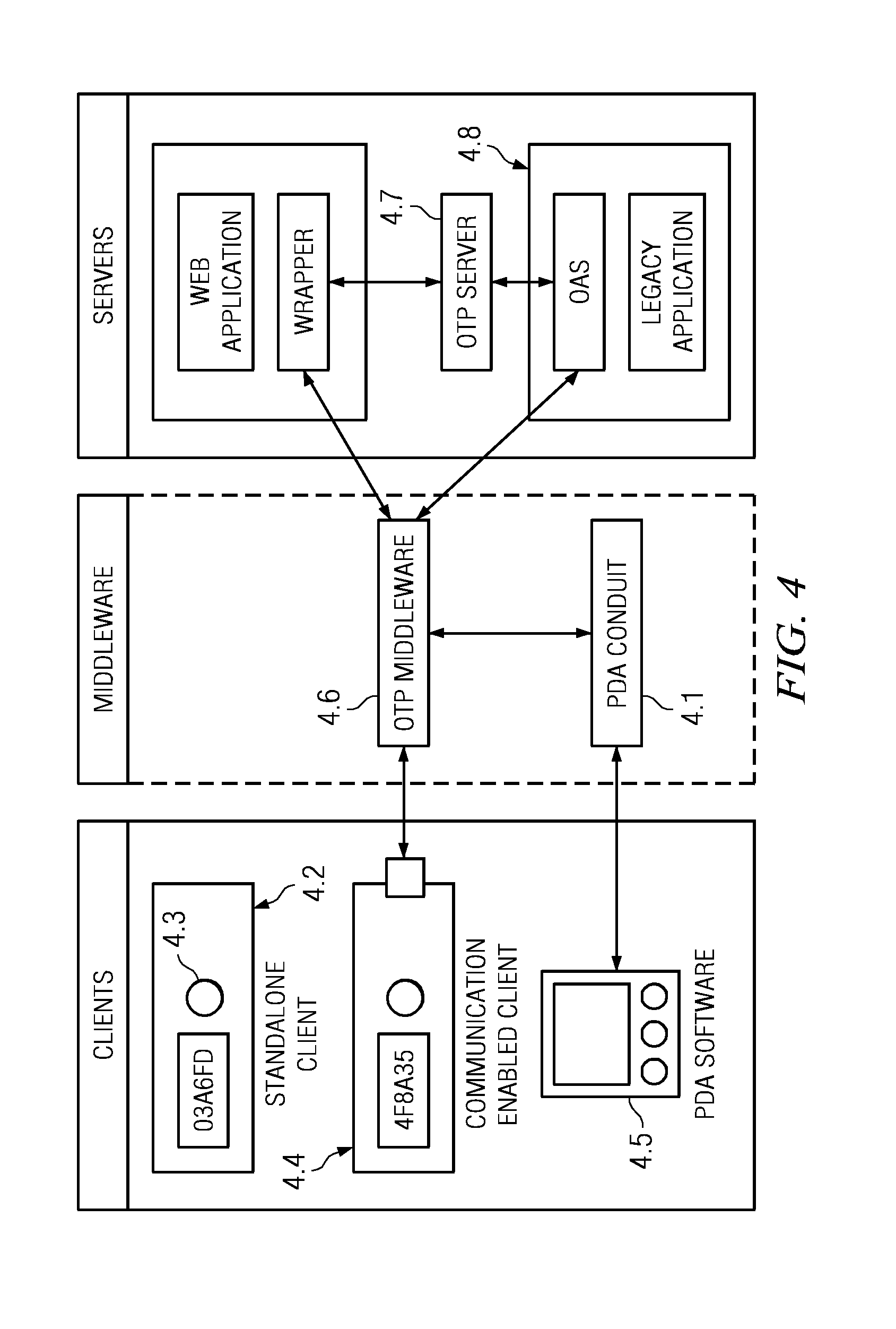
One time passcode system
InactiveUS7571489B2Mosaic printer telegraph systemDigital data processing detailsApplication serverUser input
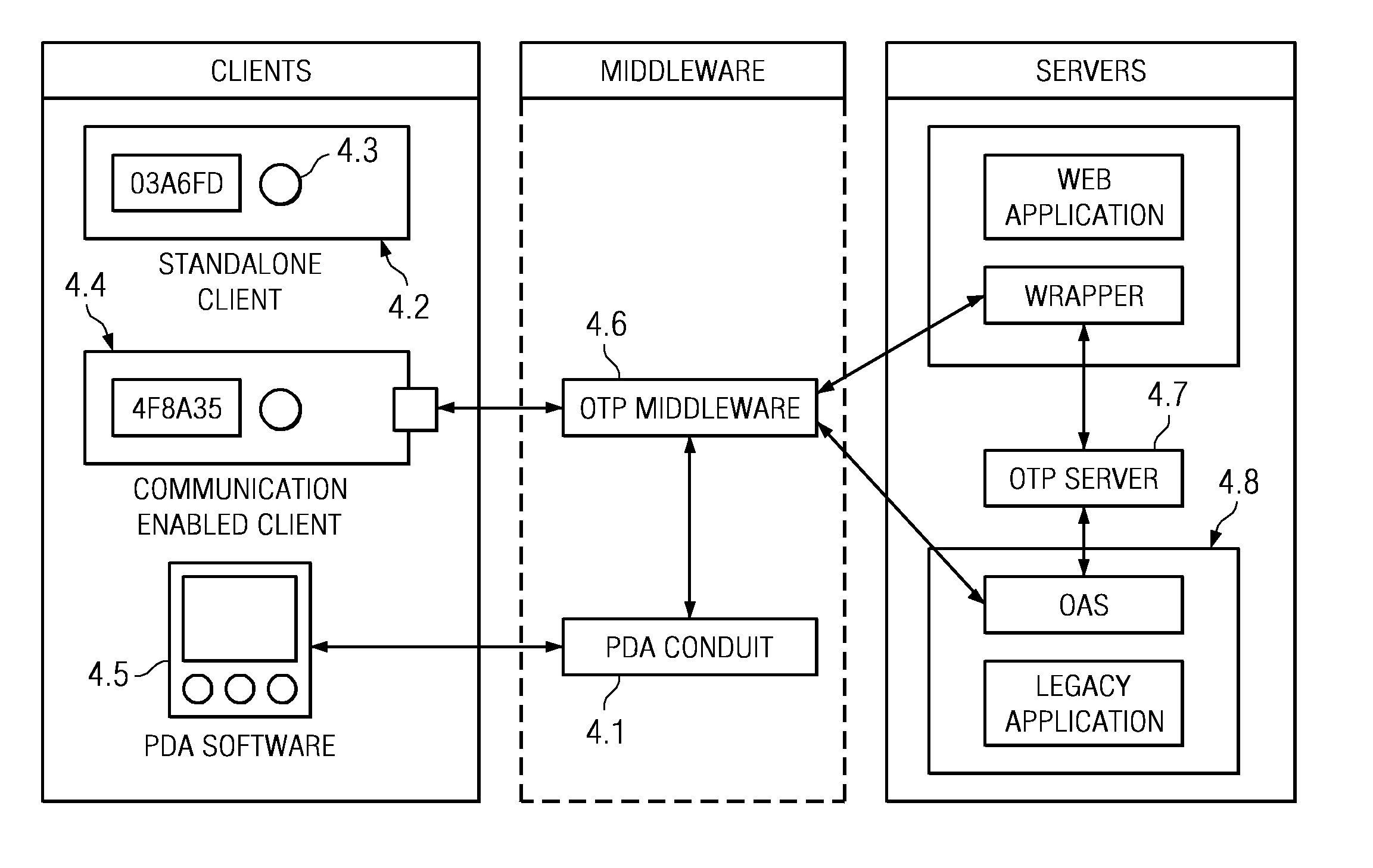
The invention relates to a system for securing access to resources or computer systems by means of a self modifying, single use password that limits access to a system and automatically changes each time it is used. Independent computer systems, or clients, are utilized by users to generate one time passcodes to prove their identity to one or more authentication servers. Servers are used to authenticate user inputted one time passcodes, to maintain and update the status of one time passcode clients, and perform rekeying and reset operations. Middleware, an optional component, allows for the interaction between one time passcode clients and servers. Middleware allows for client rekeying and resets as well as synchronisation between the client and server. The invention facilitates, inter alia, distribution of clients to users, maintaining and administering the status of clients on one or more servers, generation of a one time passcode (OTP), authentication of a one time passcode, rekeying of a one time passcode client, resetting of a one-time passcode client, Resetting of a one time passcode client, requesting for generation of a one time passcode on a communication enabled client through software or hardware interfaces, and authentication of one time passcodes by remote application servers.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
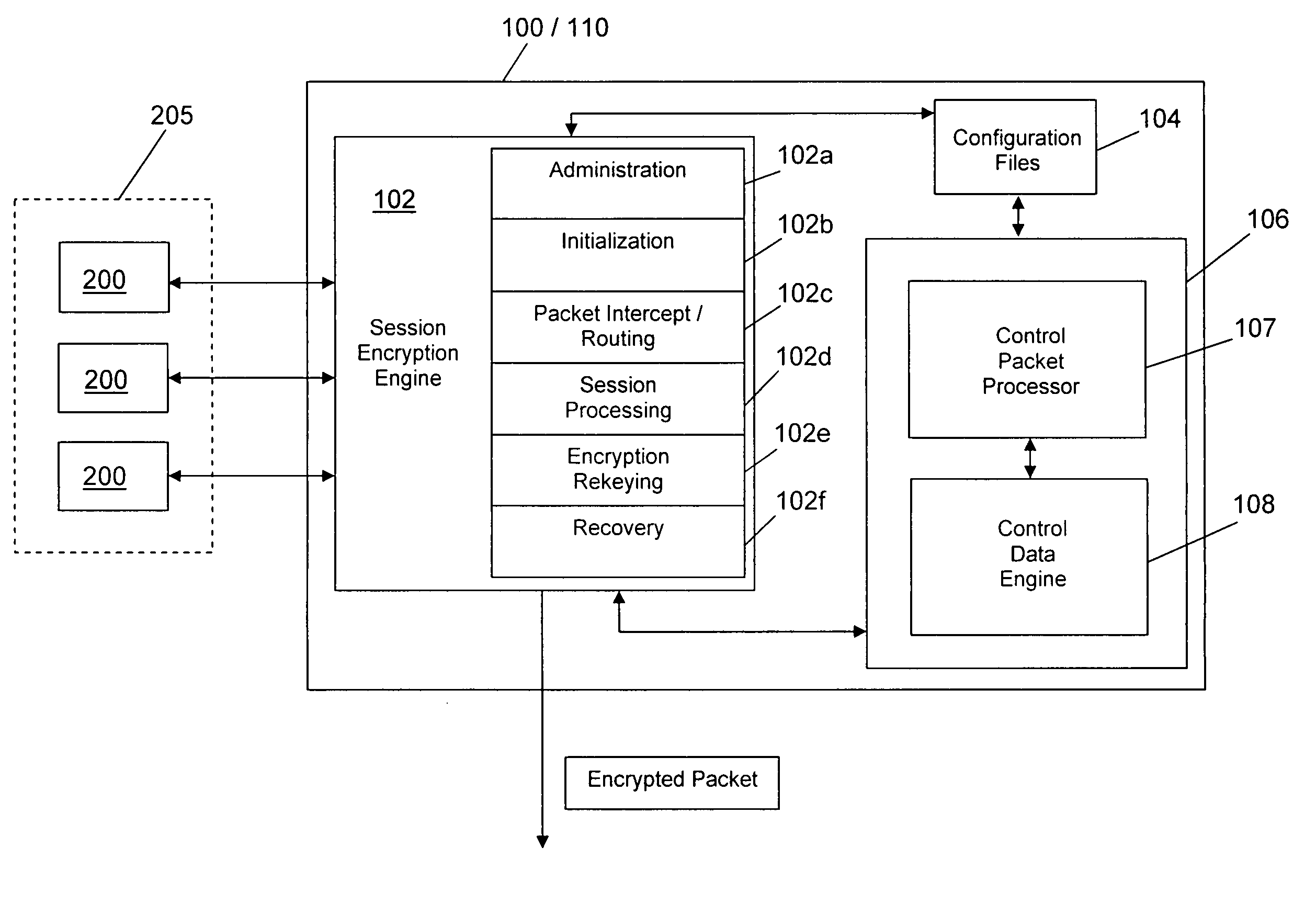
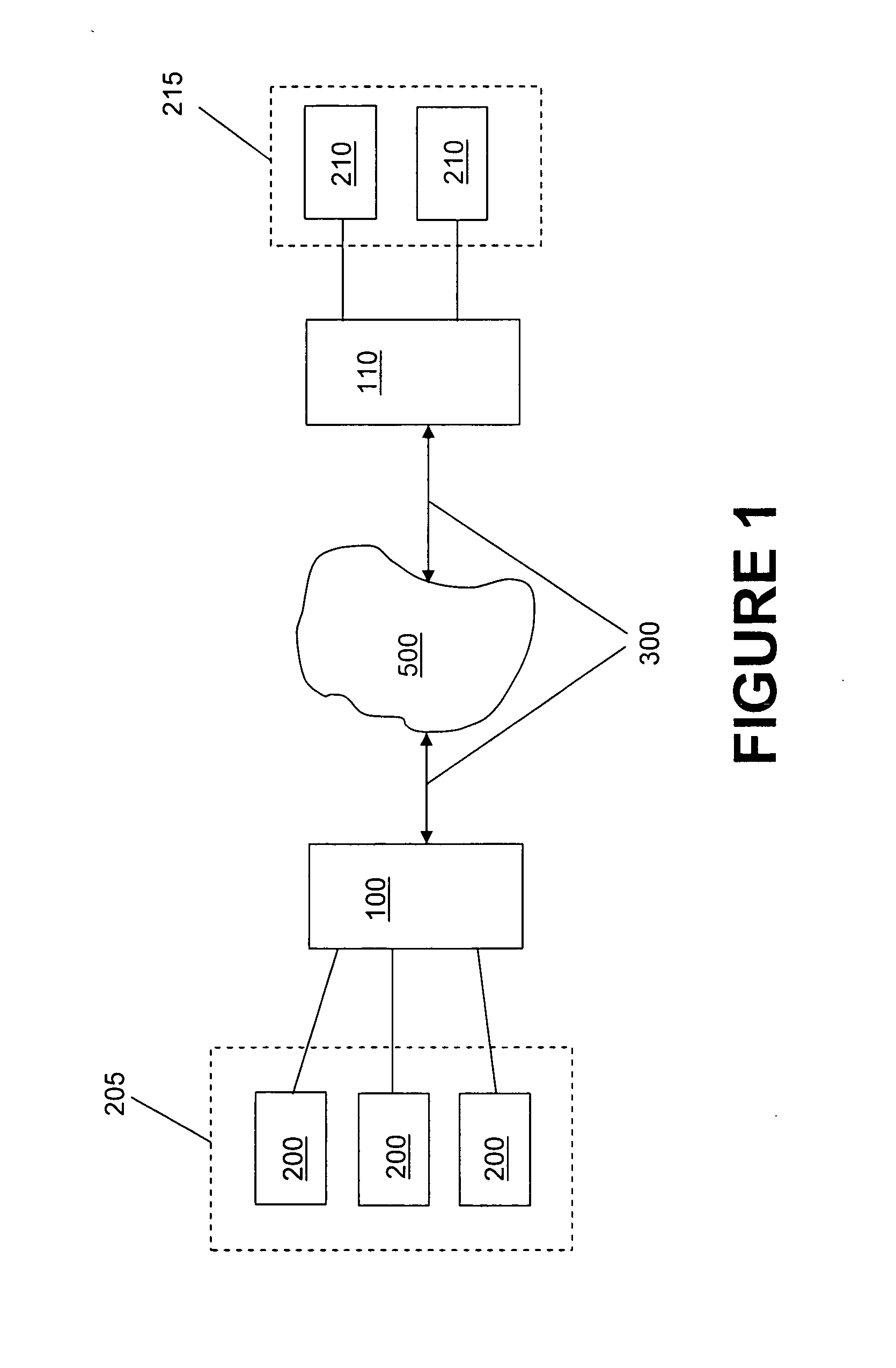
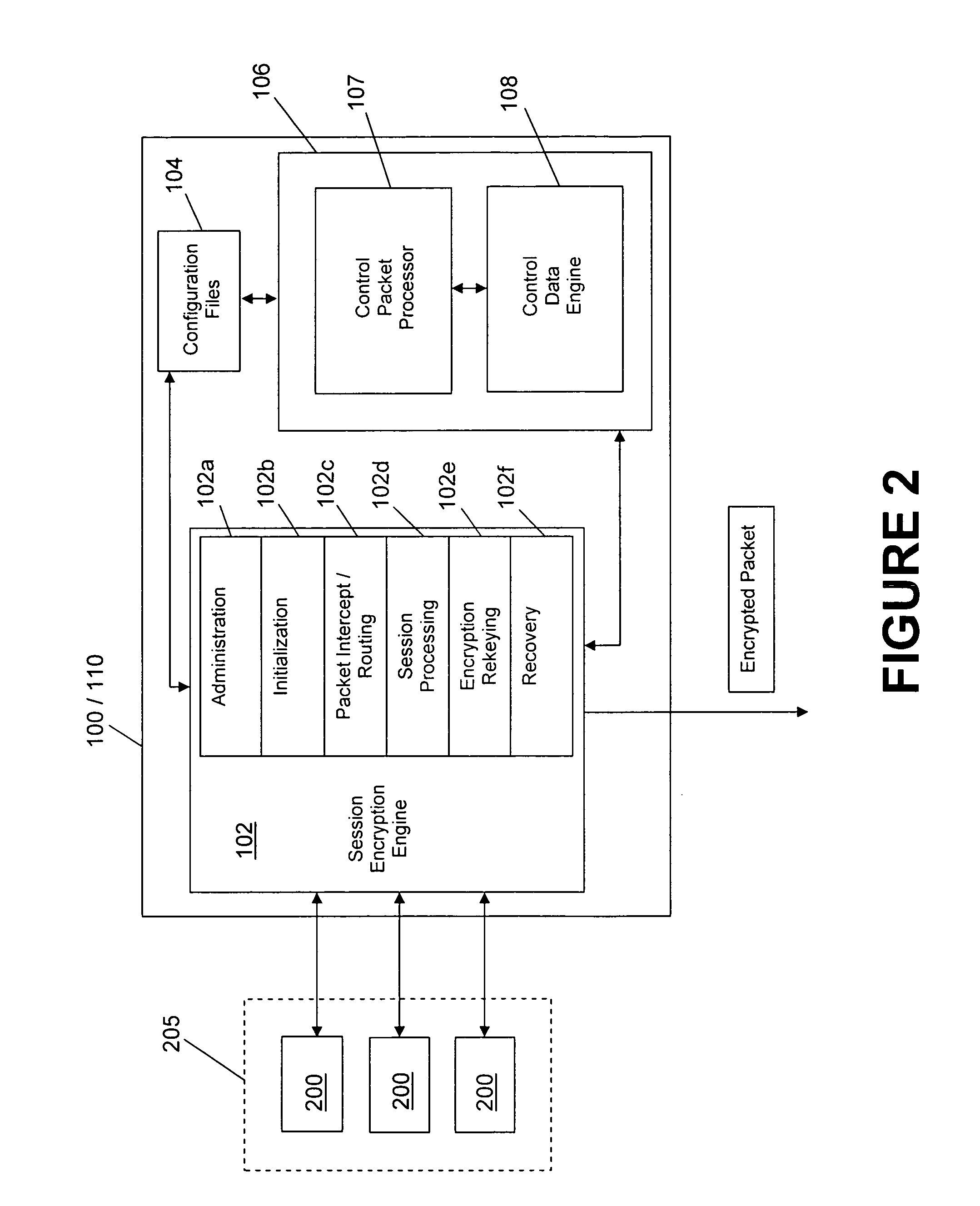
System and method for encryption rekeying
Disclosed is a system and method for maintaining a secure, encrypted networking session across a communications network by dynamically replacing encryption keys during the networking session and without terminating the session. A secure control channel is embedded within the general encrypted network connection and is used to transport encrypted control messages from one network endpoint to another. In order to hide that fact that such control messages are being transferred (as opposed to general network data traffic), the control message data packets are formatted in a way to simulate the standard general network data packets.
Owner:VELOCITE SYST
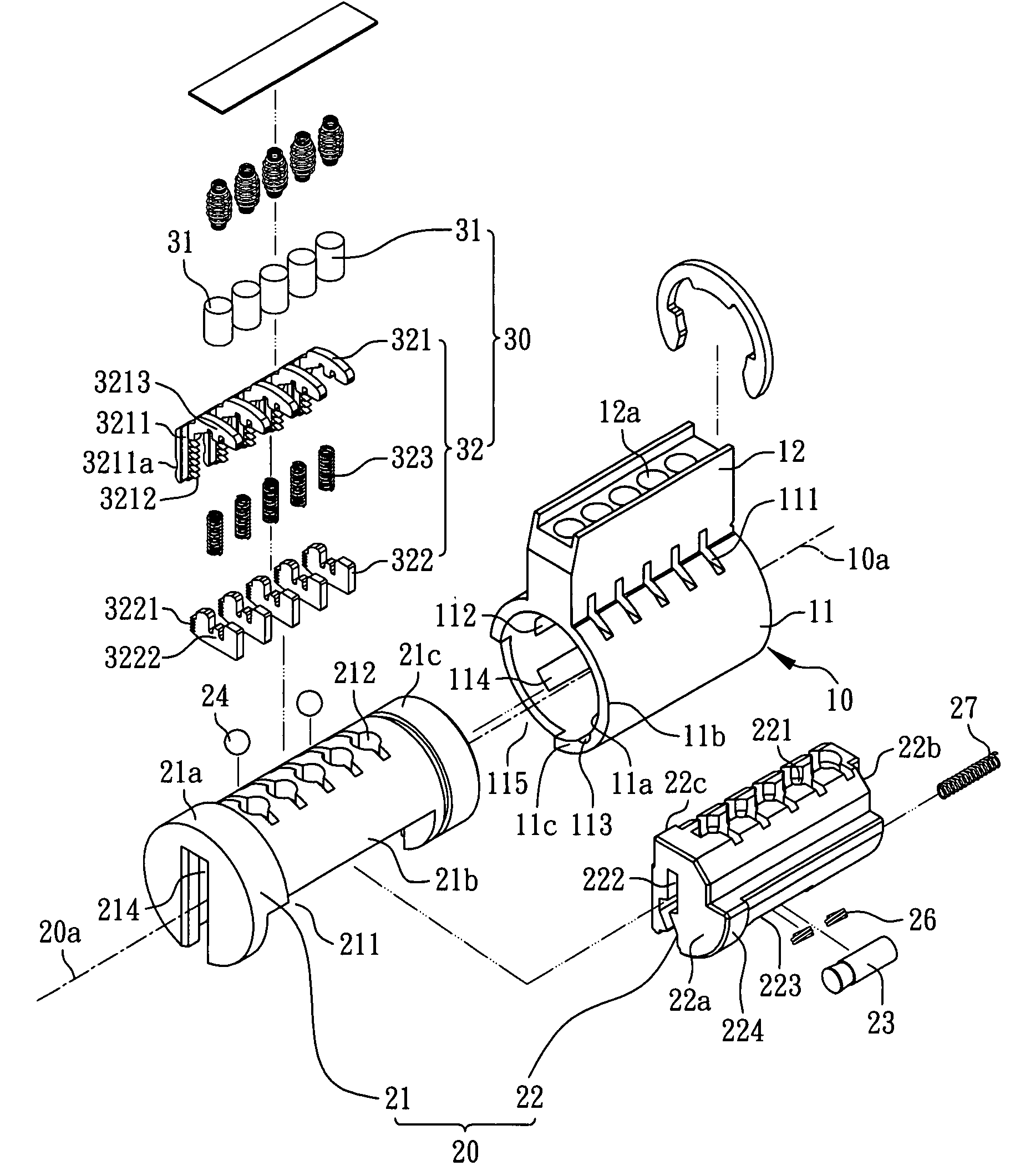
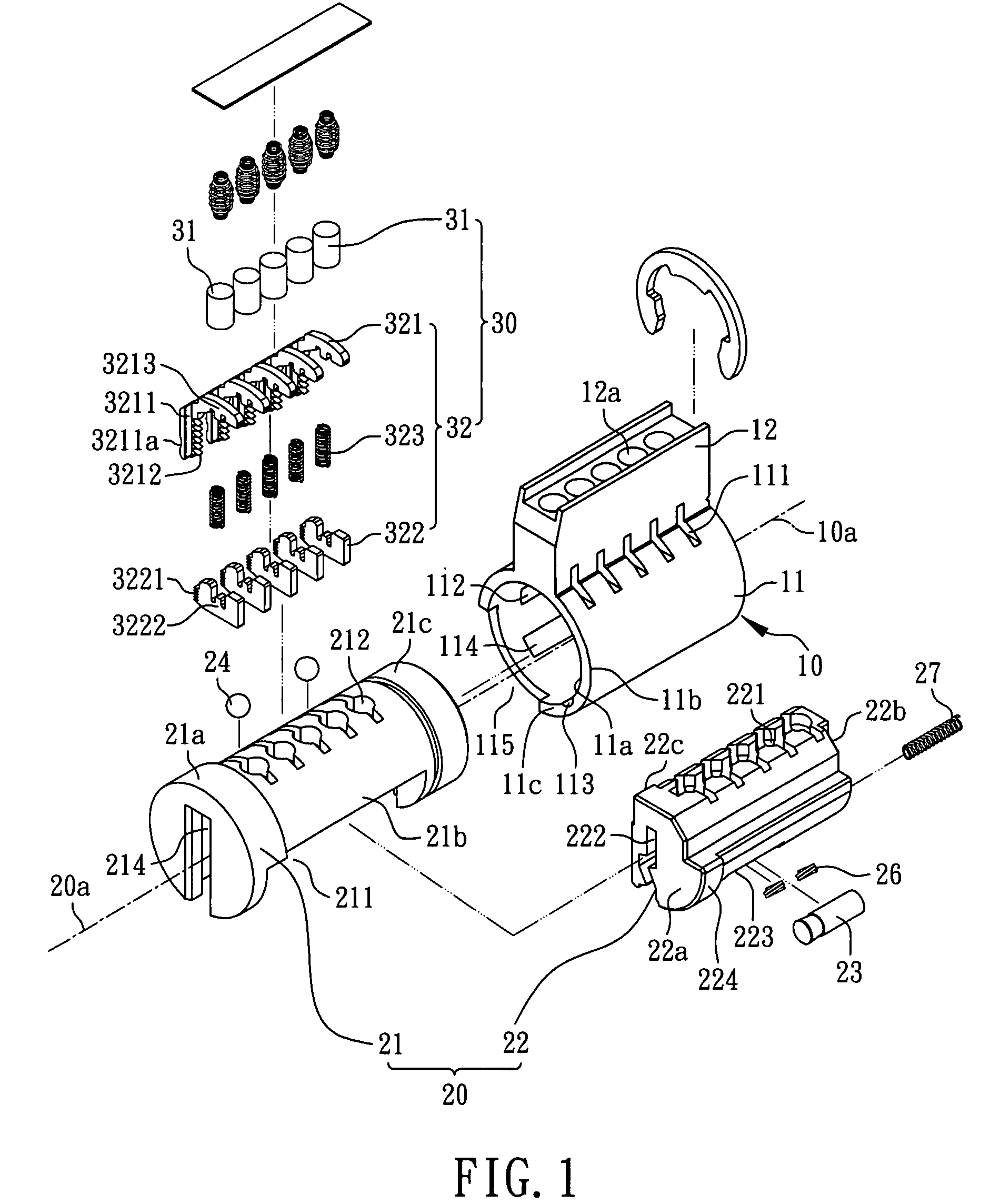
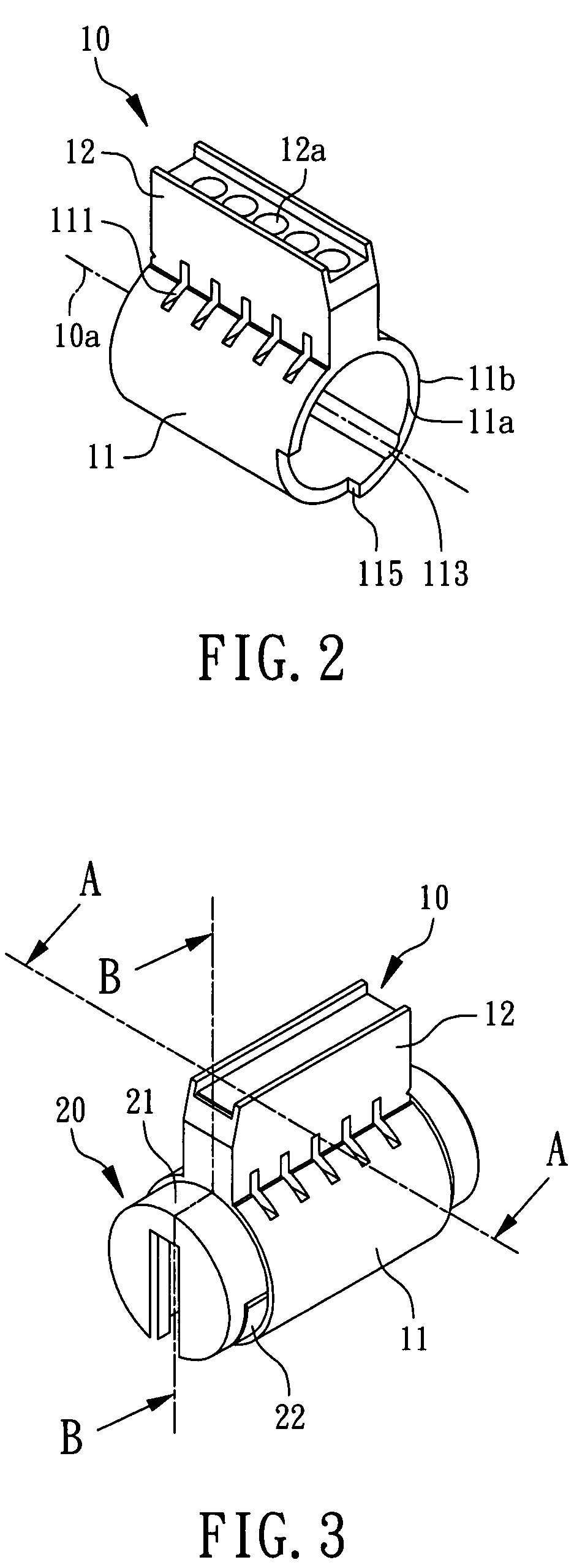
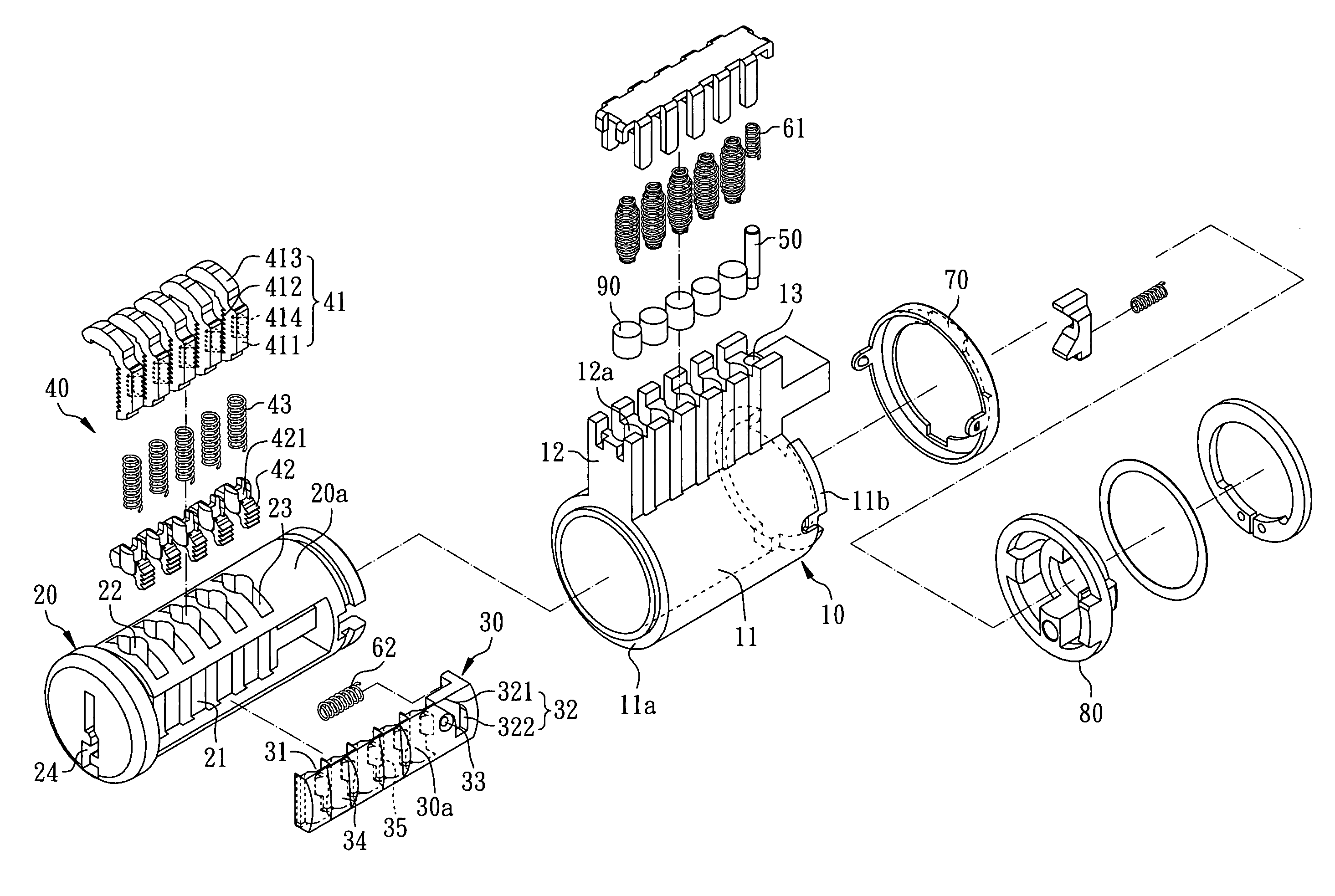
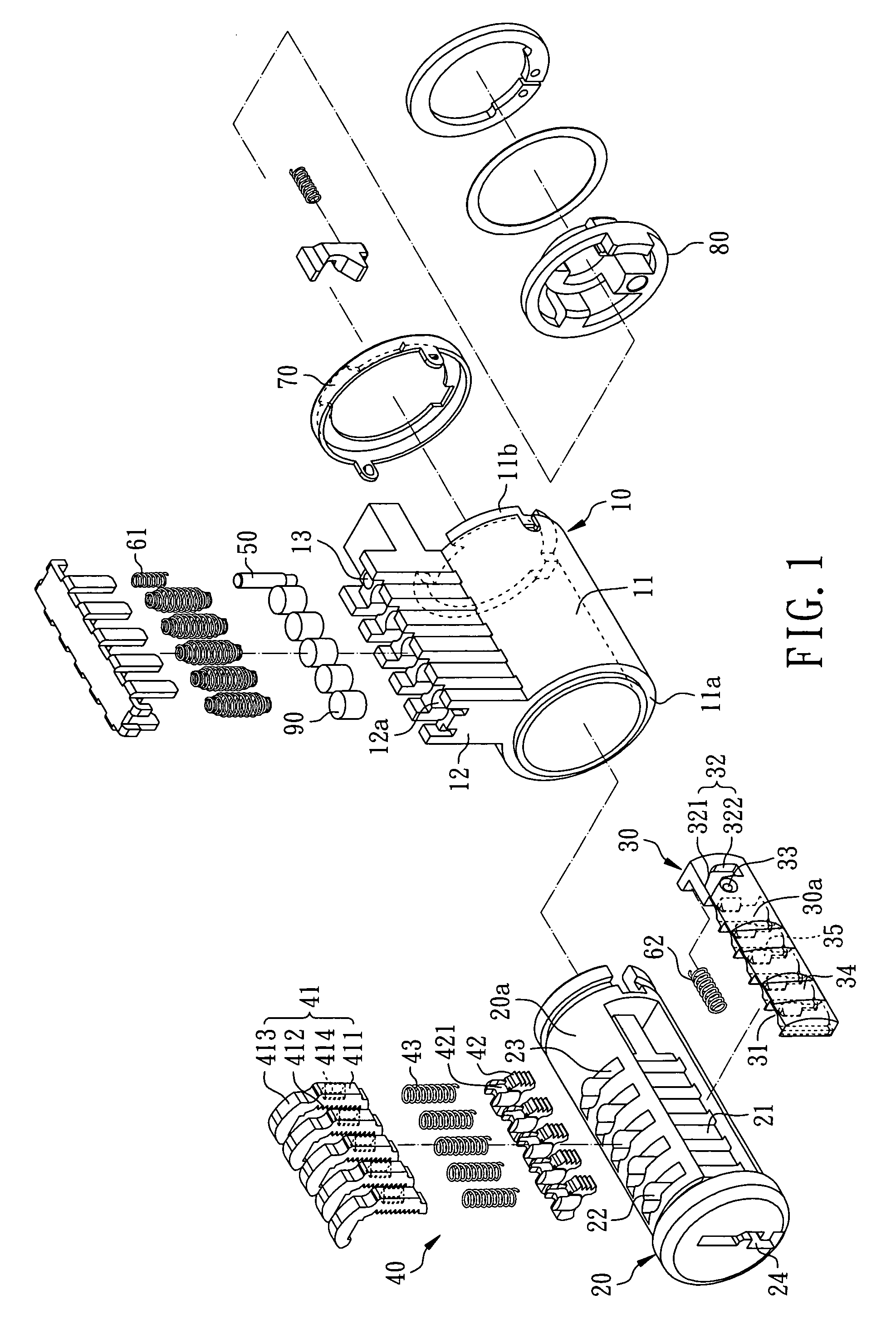
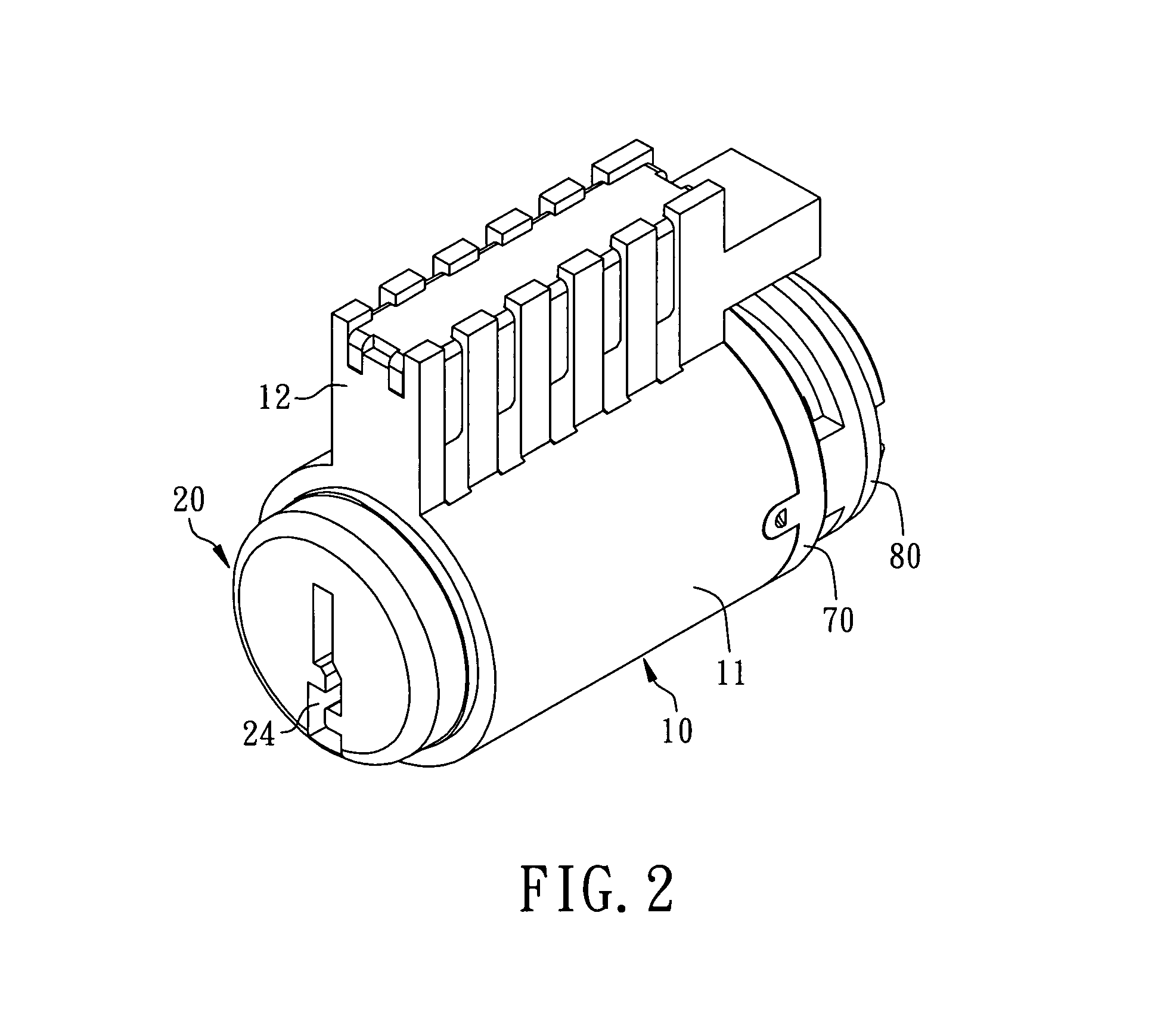
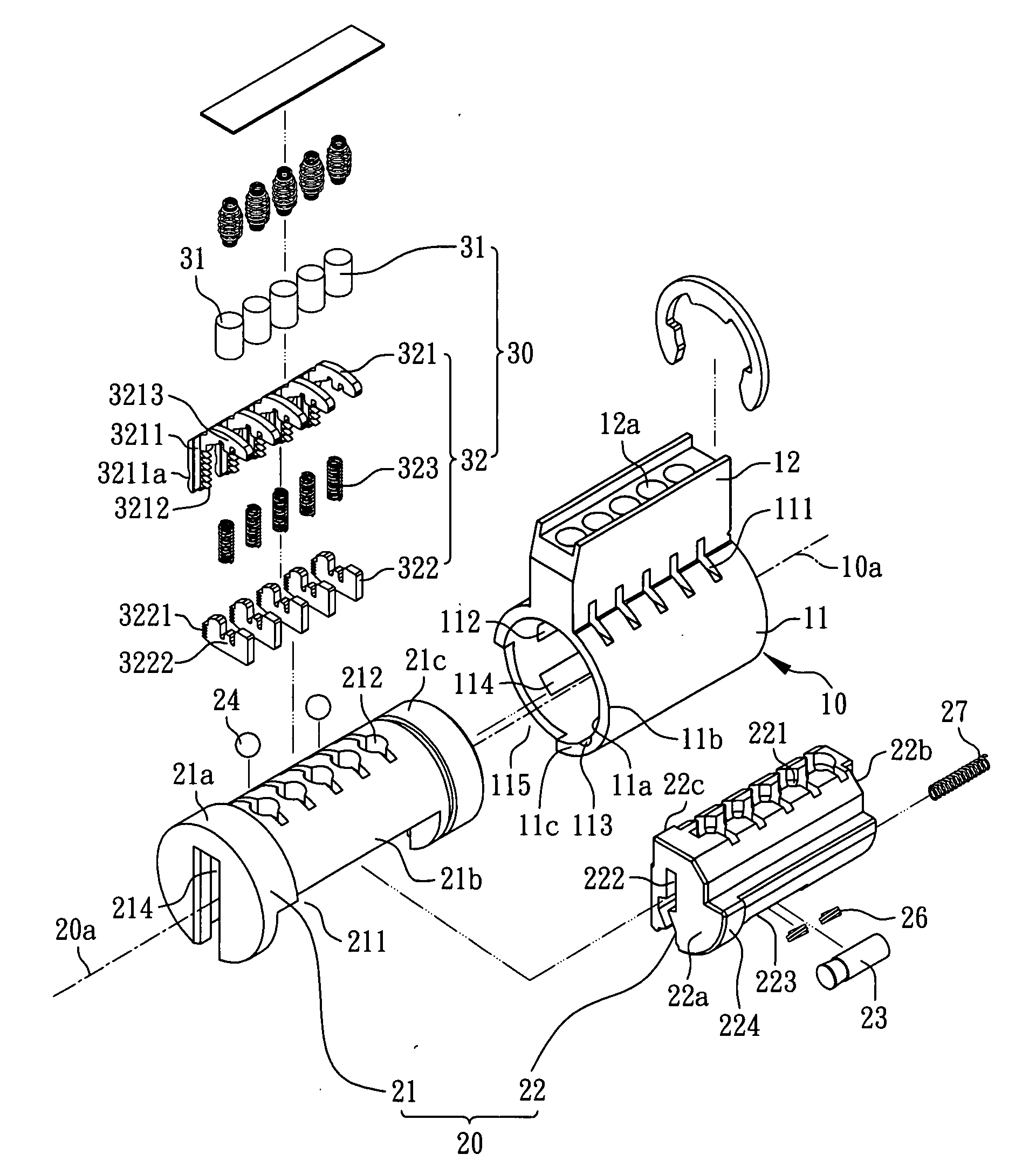
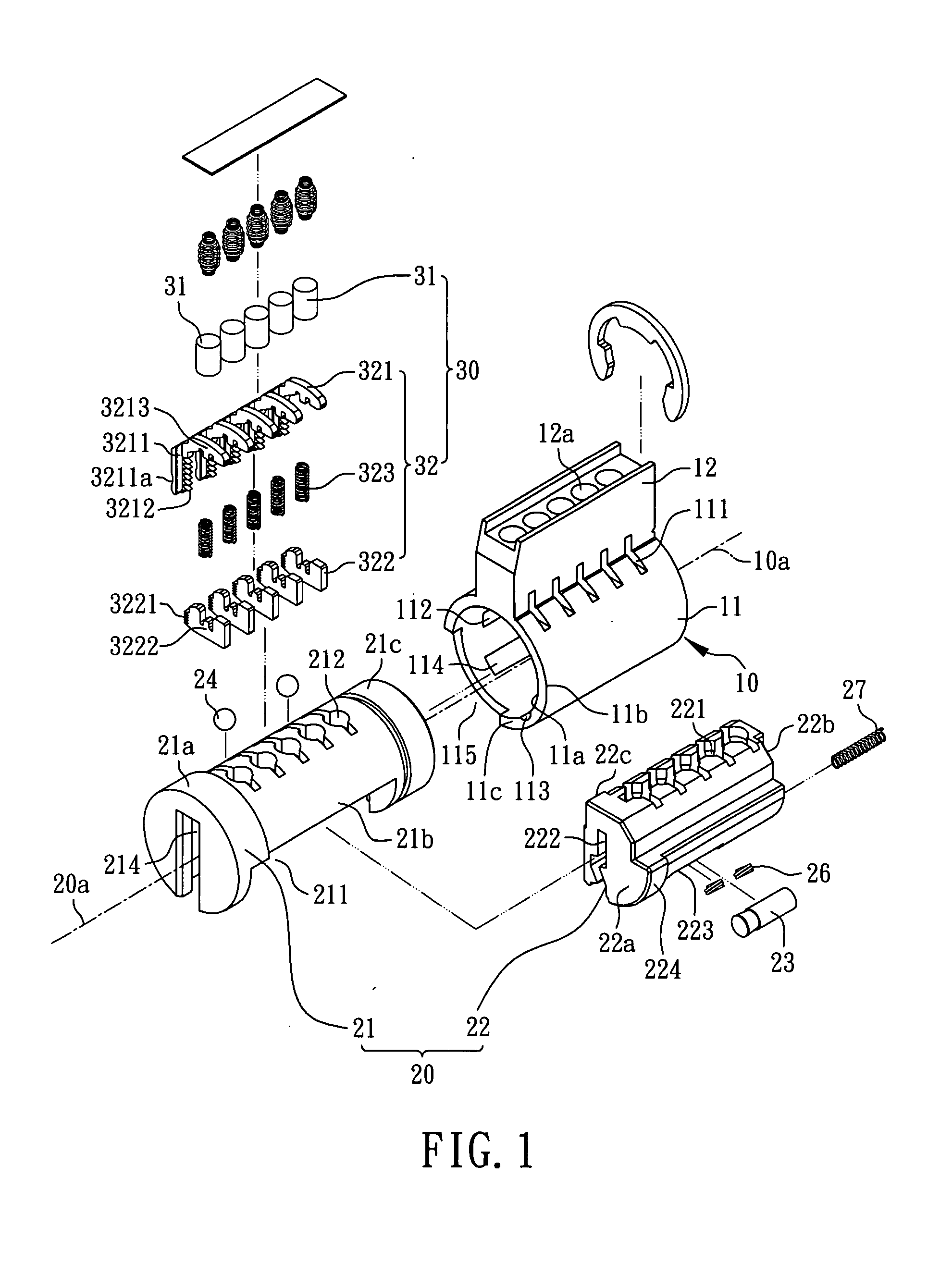
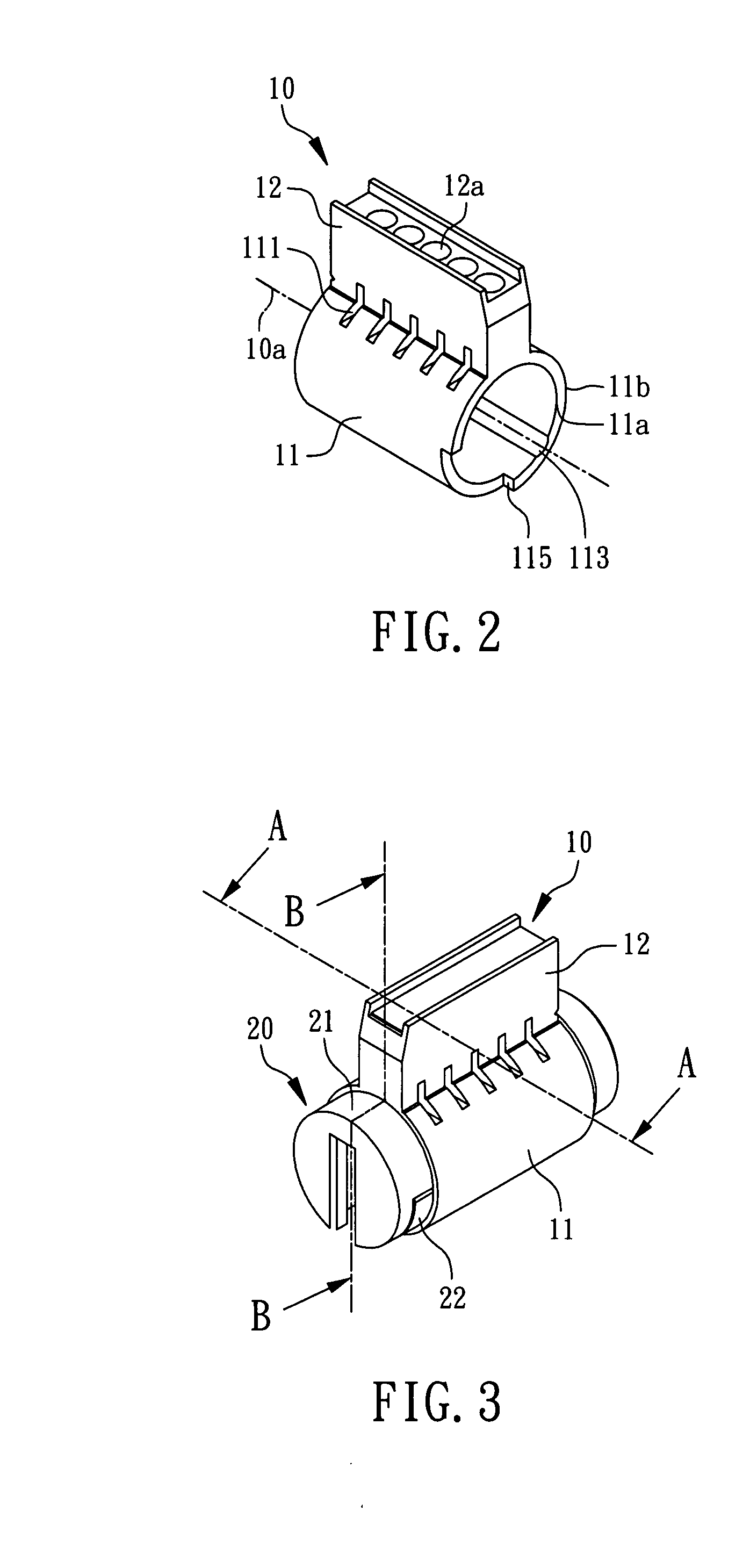
Method for rekeying a rekeyable lock cylinder
This invention is to provide a method for rekeying a rekeyable lock cylinder. The first step of entire rekeying process is to insert a first user key into a keyhole of a sliding block of a plug assembly and turn the first user key to rotate the plug assembly, then a thrust is added to the first user key to move the sliding block of the plug assembly, thereby disengaging a plurality of upper locking pieces and a plurality of lower locking pieces within a plurality of lower pin sets. Next, after pulling out the first user key from the keyhole, a second user key is inserted into the keyhole of the sliding block and turned to restore the sliding block as to reengage the upper locking pieces and the lower locking pieces. Finally, the second user key is pulled out to complete the entire rekeying process. Accordingly, the present invention may provide advantages of widely lowering rekeying cost and enhancing convenience in use, because lock replacement may be completed as soon as rekeying another user key only without replacing lock cylinder.
Owner:TAIWAN FU HSING INDAL
Encryption communication method and device
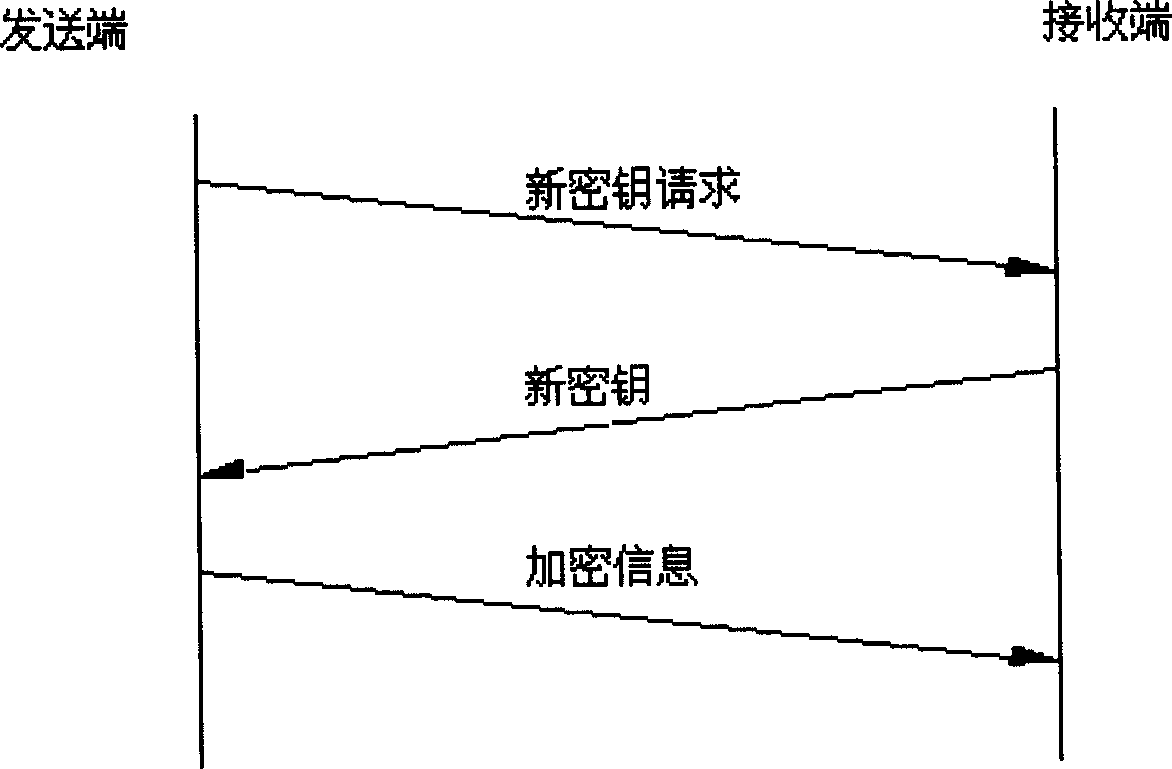
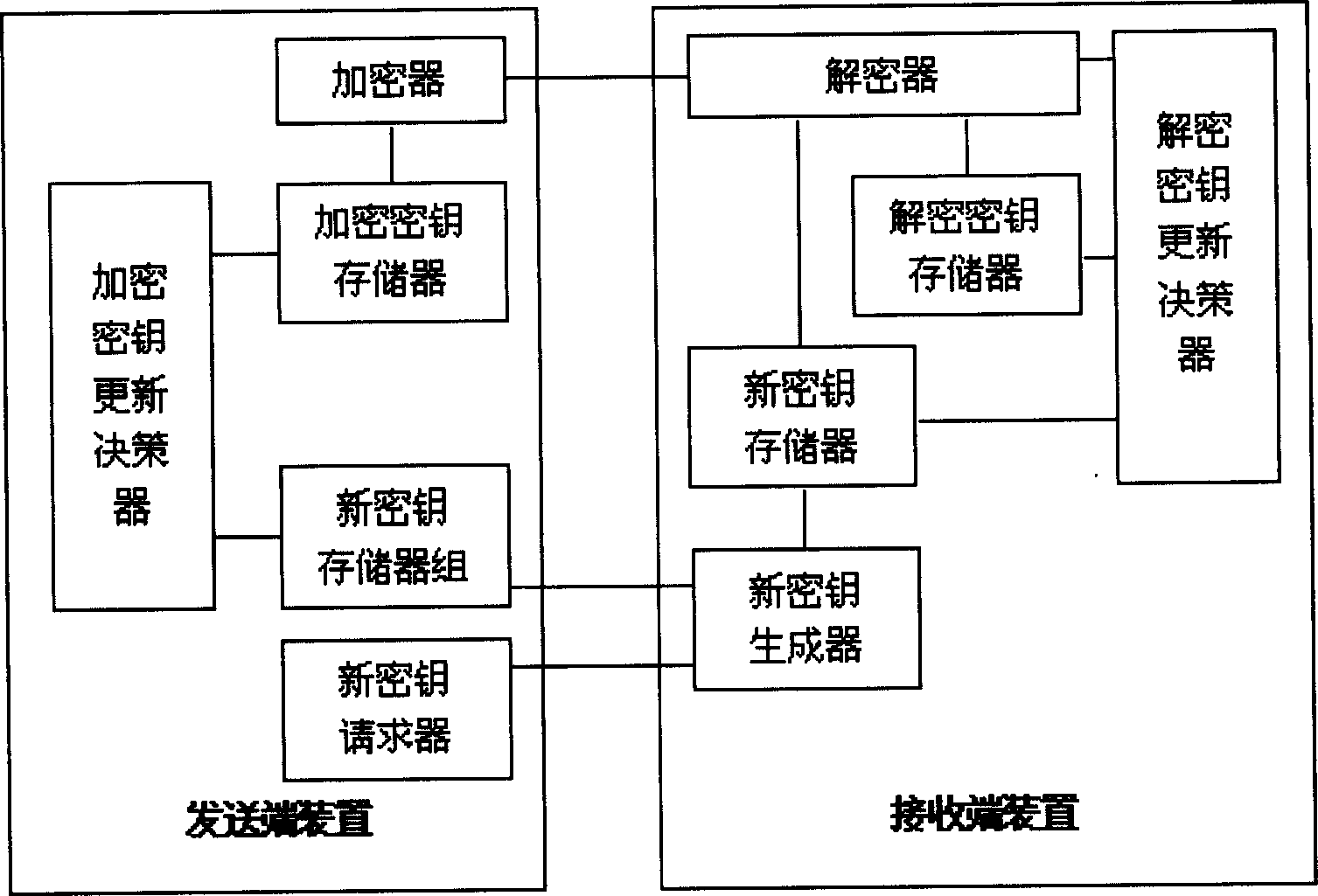
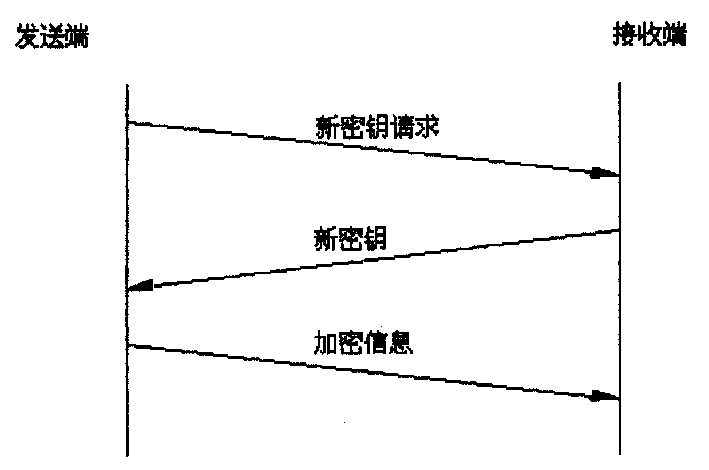
InactiveCN1494252ASimplified key update stepsImprove key update efficiencySynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey generatorDecision maker
The device includes sending end device and receiving end device. The former includes requester for new cipher key, storage group for new cipher key, storage for encryption key, renewal decision-maker for cipher key and encipherer. The latter includes creator for new cipher key, storage for new cipher key, storage for deciphered cipher key, decipherer; and renewal decision-maker for deciphered cipher key. The method includes following steps. Sending end sends request for new cipher key, and receiving end sends new cipher key. Sending end checks-up received new cipher key. If it is correct, the new cipher key is put into use, and needed encryption information is sent out in encryption mode. The receiving end deciphers the encryption information by using new and old cipher key. If tested result is correct, the new cipher key is put into use, and correct decryption information is output. The invention simplifies steps for updating cipher key, raises efficiency and lowers cost.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Encryption key updating for multiple site automated login
InactiveUS20050235345A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsExpiration TimeRekeying
A version number is associated with an encrypted key executable to allow real time updating of keys for a system which facilitates users signing on to multiple websites on different domains using an encrypted ticket. Two keys may be used at each site during updating of keys, each having an associated one digit Hex version tag. When a key is to be updated with a new key, the existing or old key is provided an expiration time. A second key is provided from the system in a secure manner with a new version number and made the current key which provides decryption of the encrypted ticket. The system tracks both keys while they are concurrent. After the existing key expires, only the second, or updated key is used to provide login services for users. The system periodically flushes old keys.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
WLAN session management techniques with secure rekeying and logoff
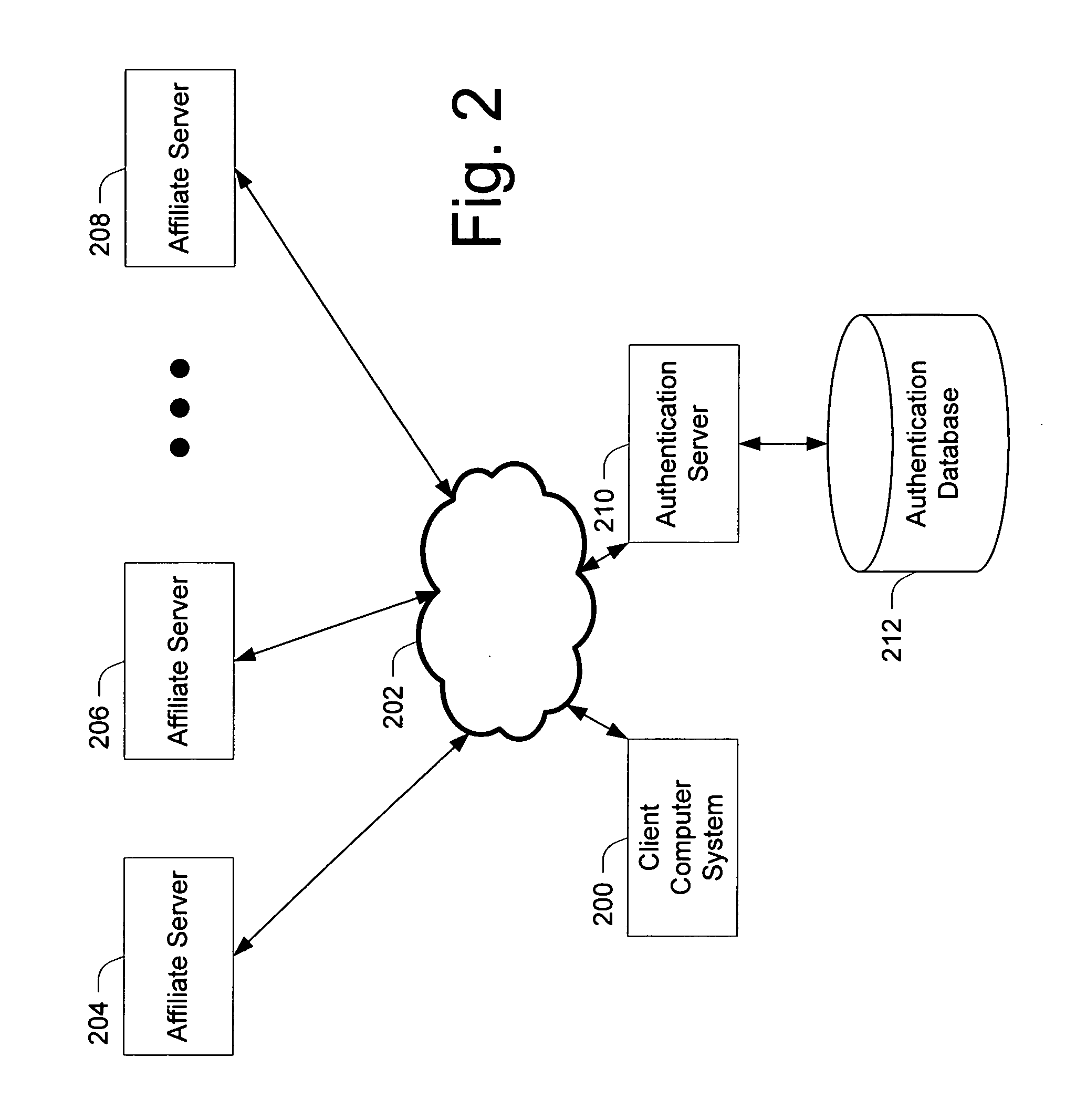
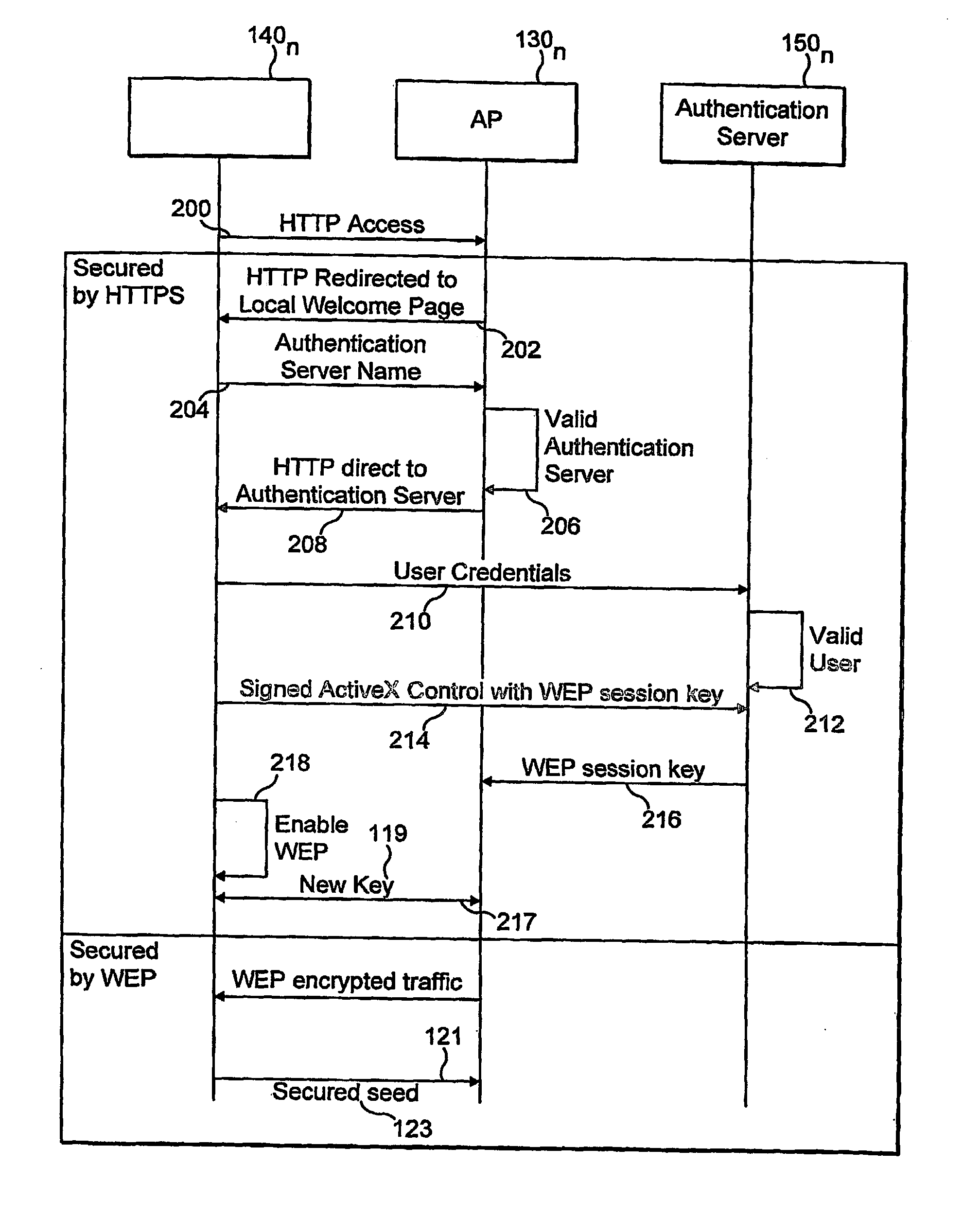
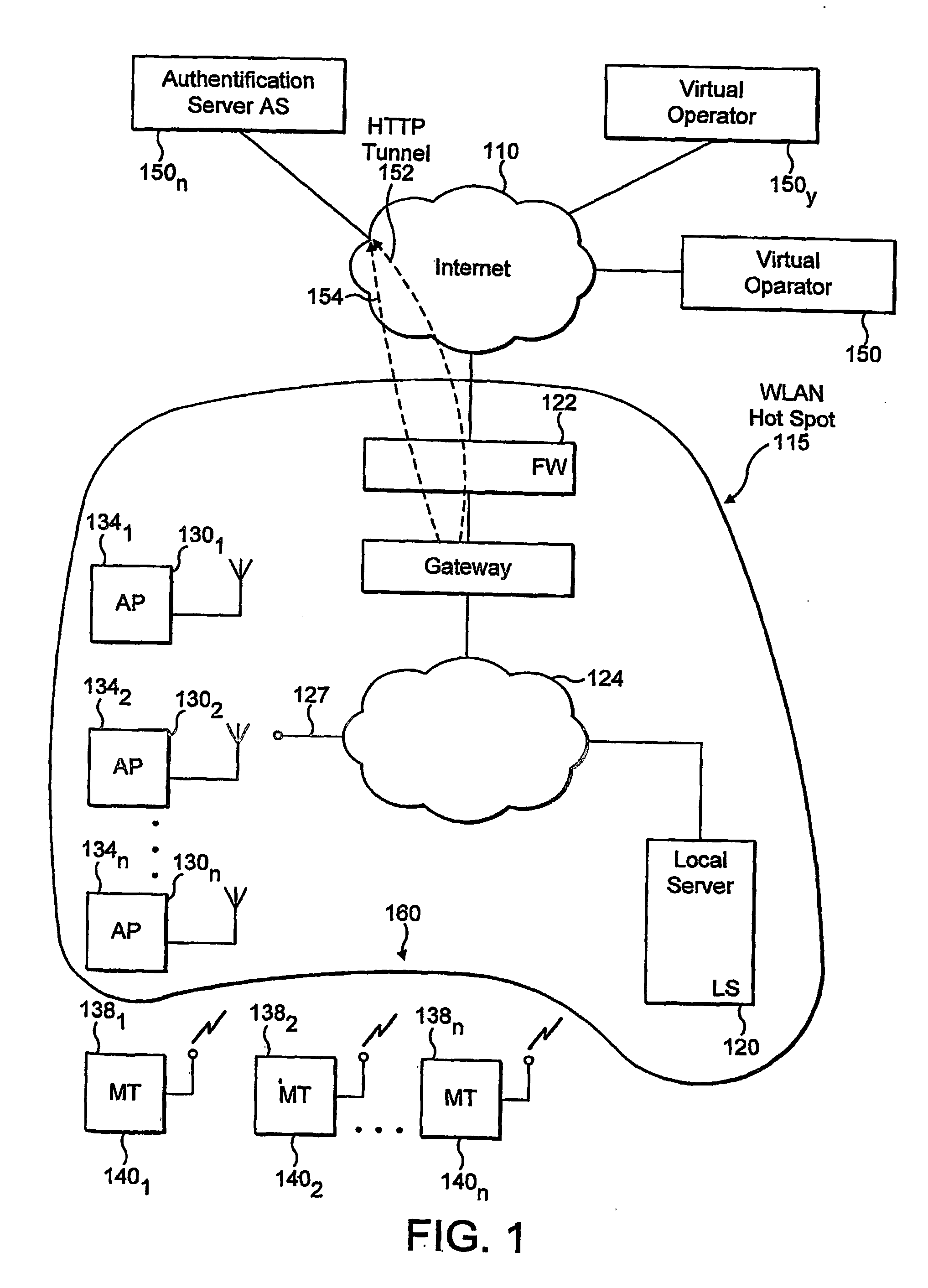
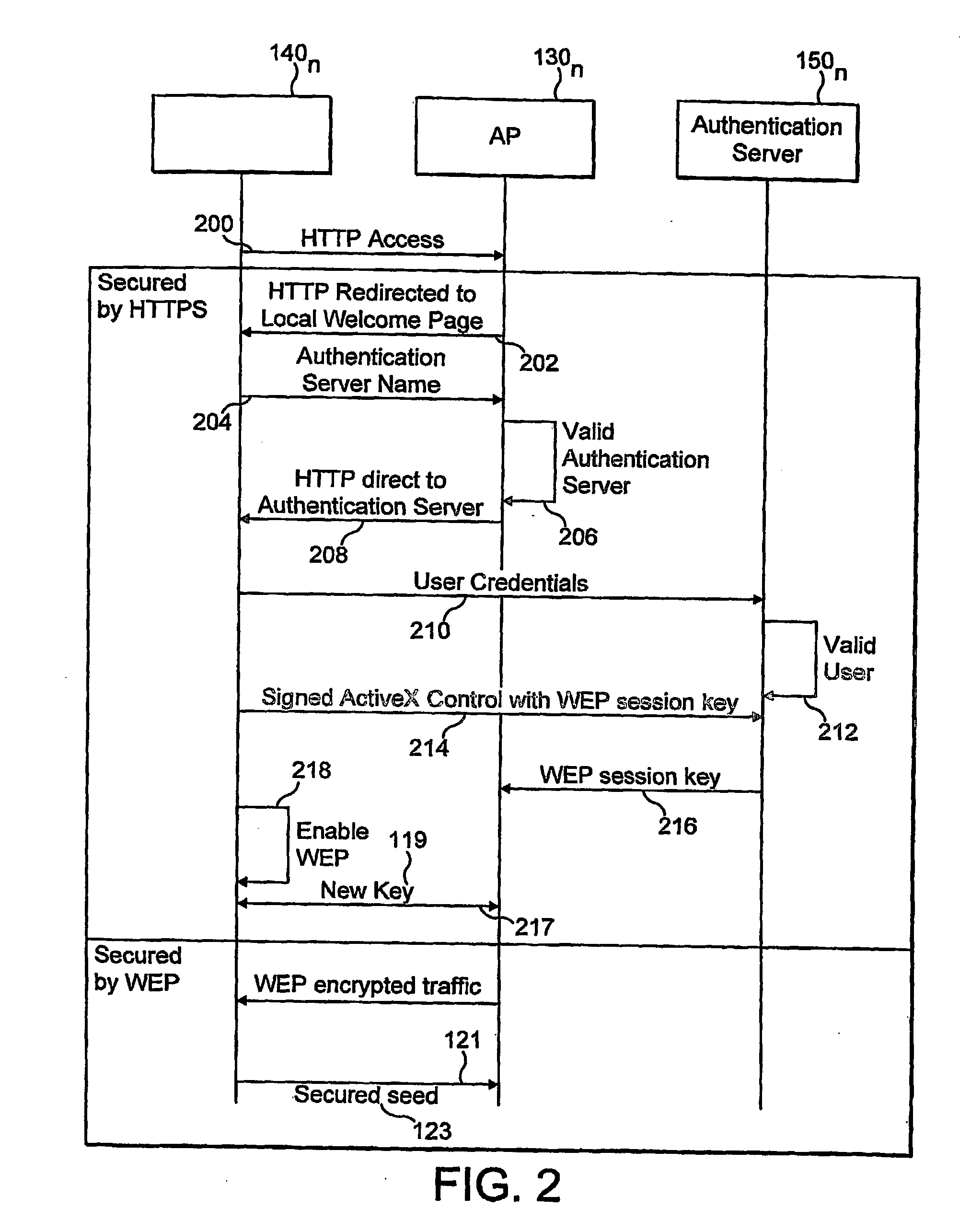
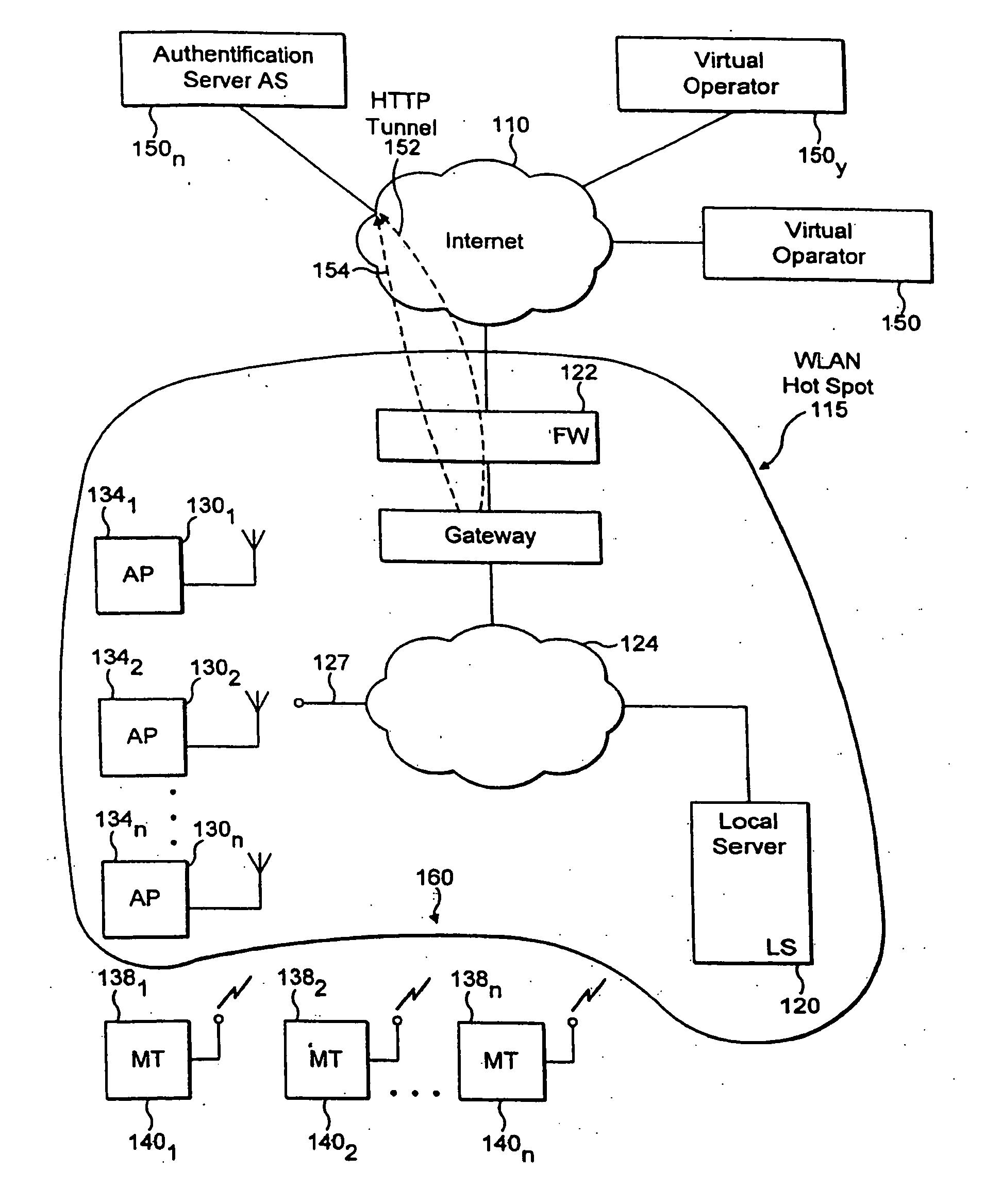
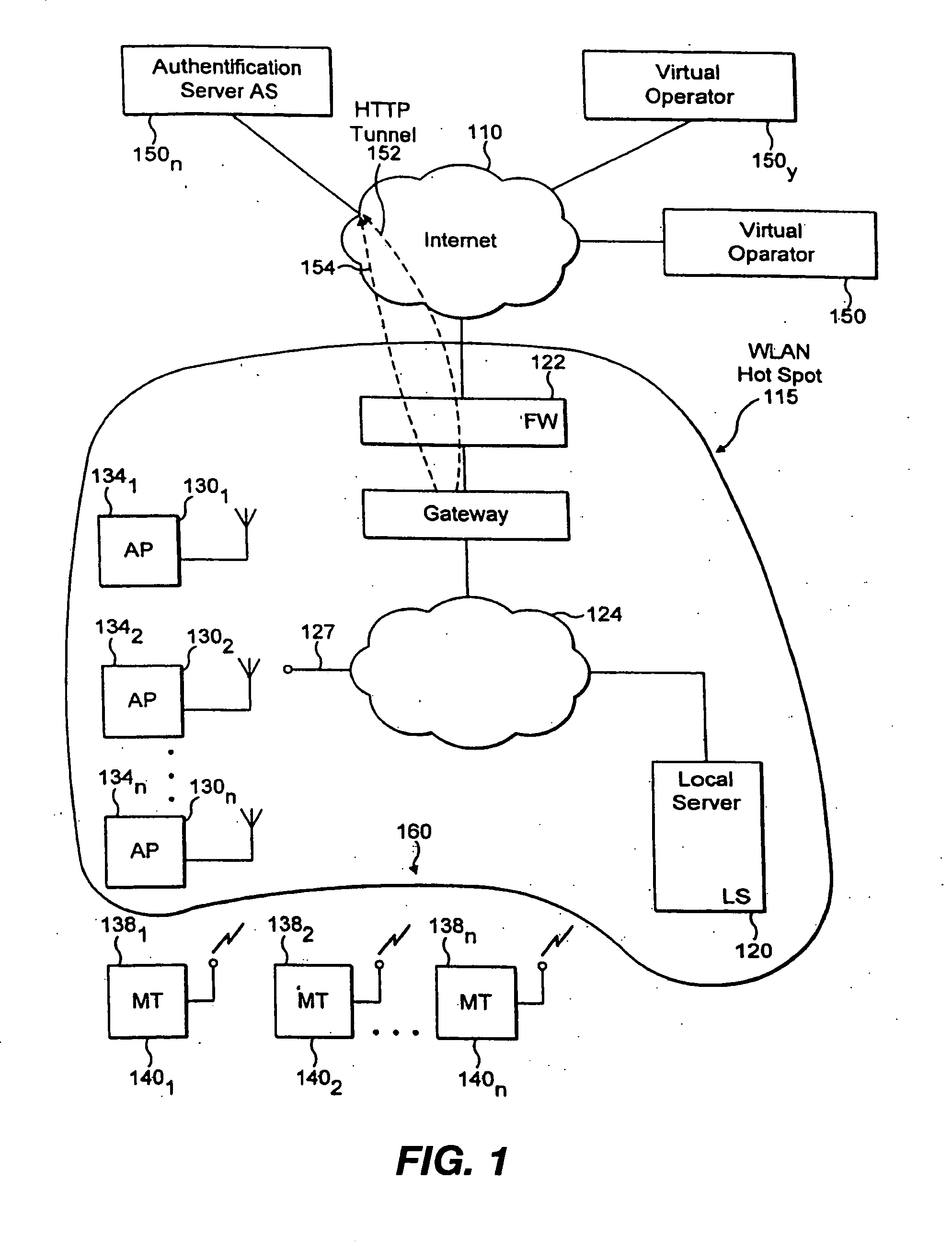
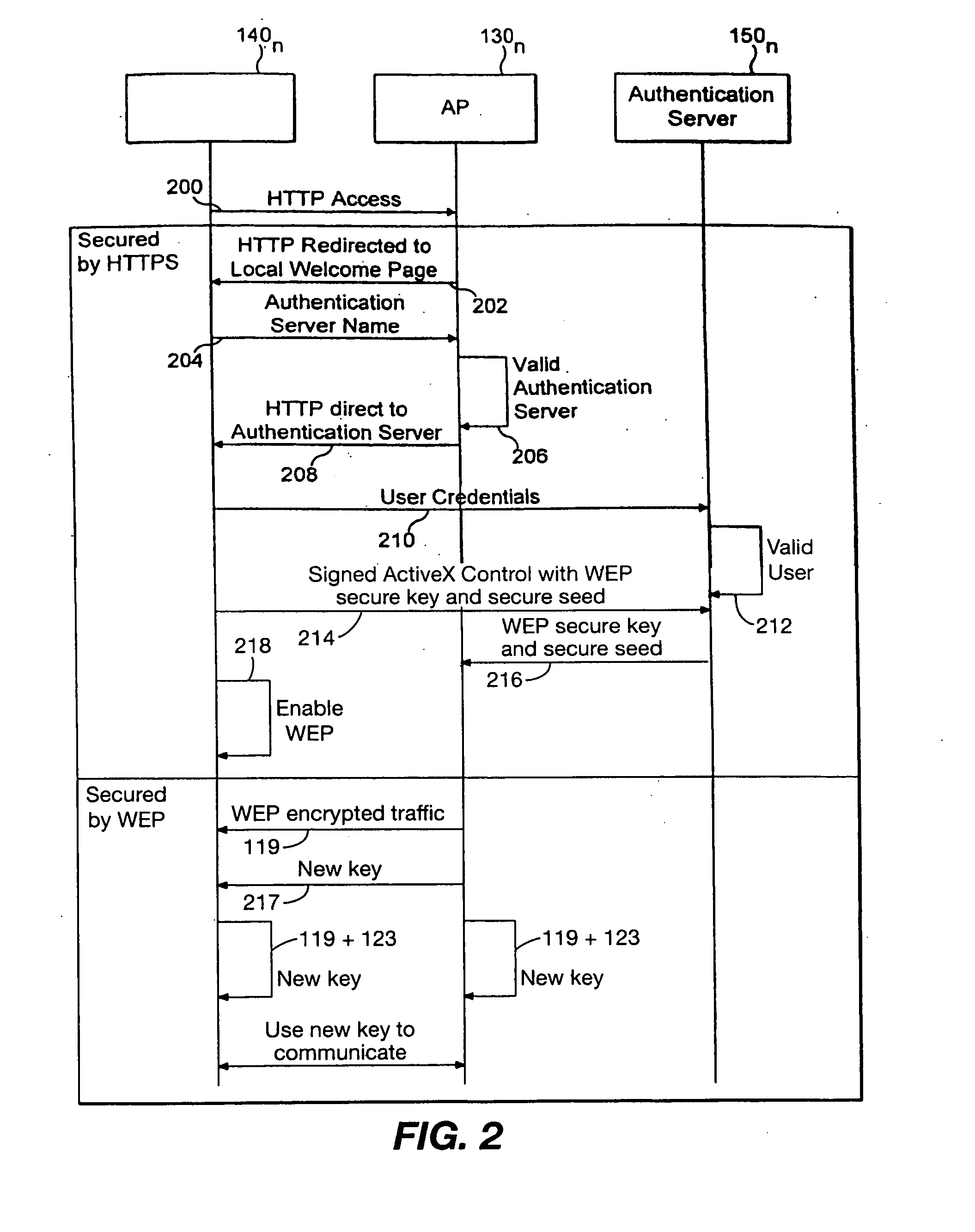
InactiveUS20060179305A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesSession managementUser authentication
The invention provides a method for improving the security of a mobile terminal in a WLAN environment by installing two shared secrets instead of one shared secret, the initial session key, on both the wireless user machine and the WLAN access point during the user authentication phase. One of the shared secrets is used as the initial session key and the other is used as a secure seed. Since the initial authentication is secure, these two keys are not known to a would be hacker. Although the initial session key may eventually be cracked by the would be hacker, the secure seed remains secure as it is not used in any insecure communication.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Ciphering key management and distribution in mbms
InactiveUS20060140411A1Shorten the timeReduce system loadKey distribution for secure communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInformation transmissionRekeying
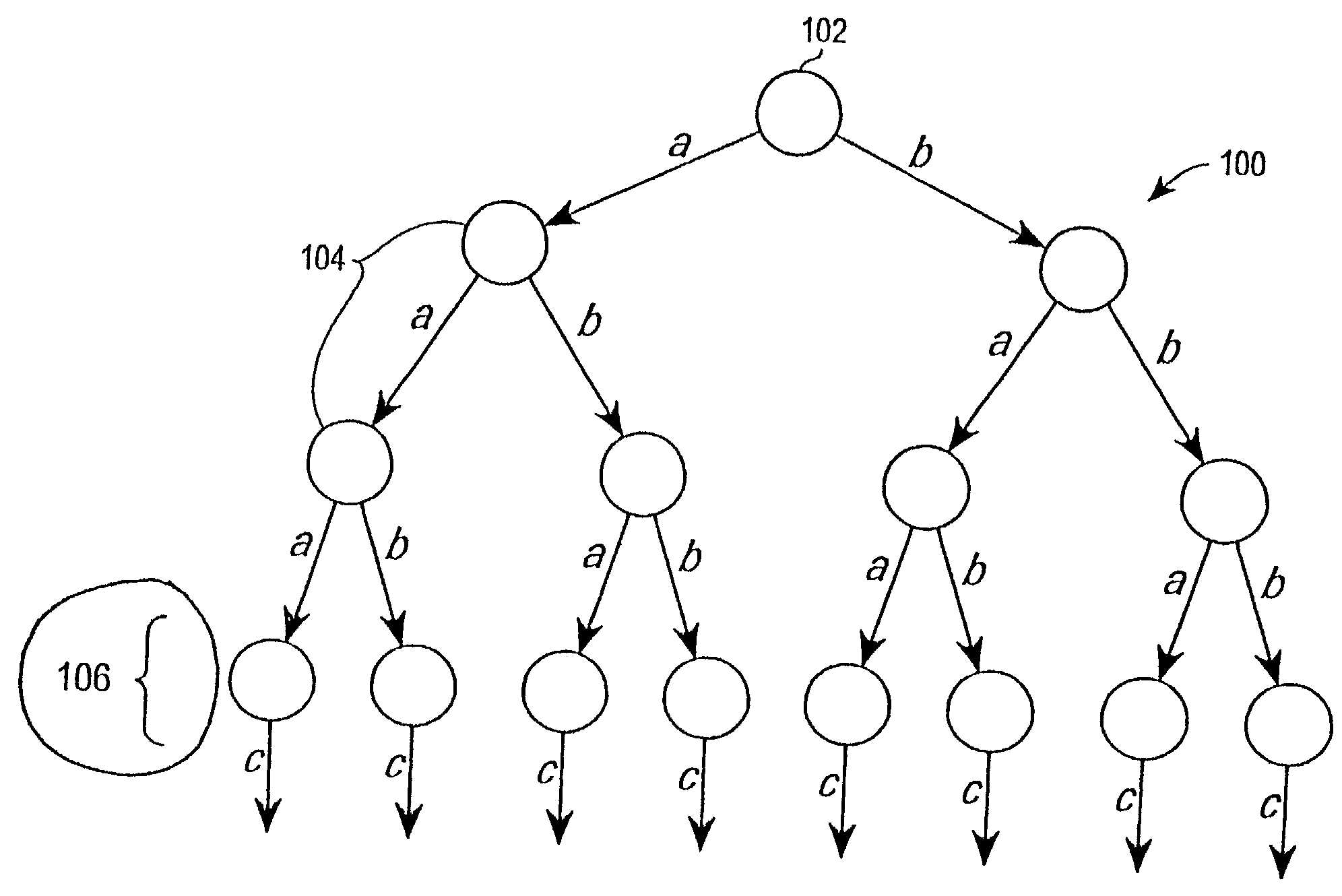
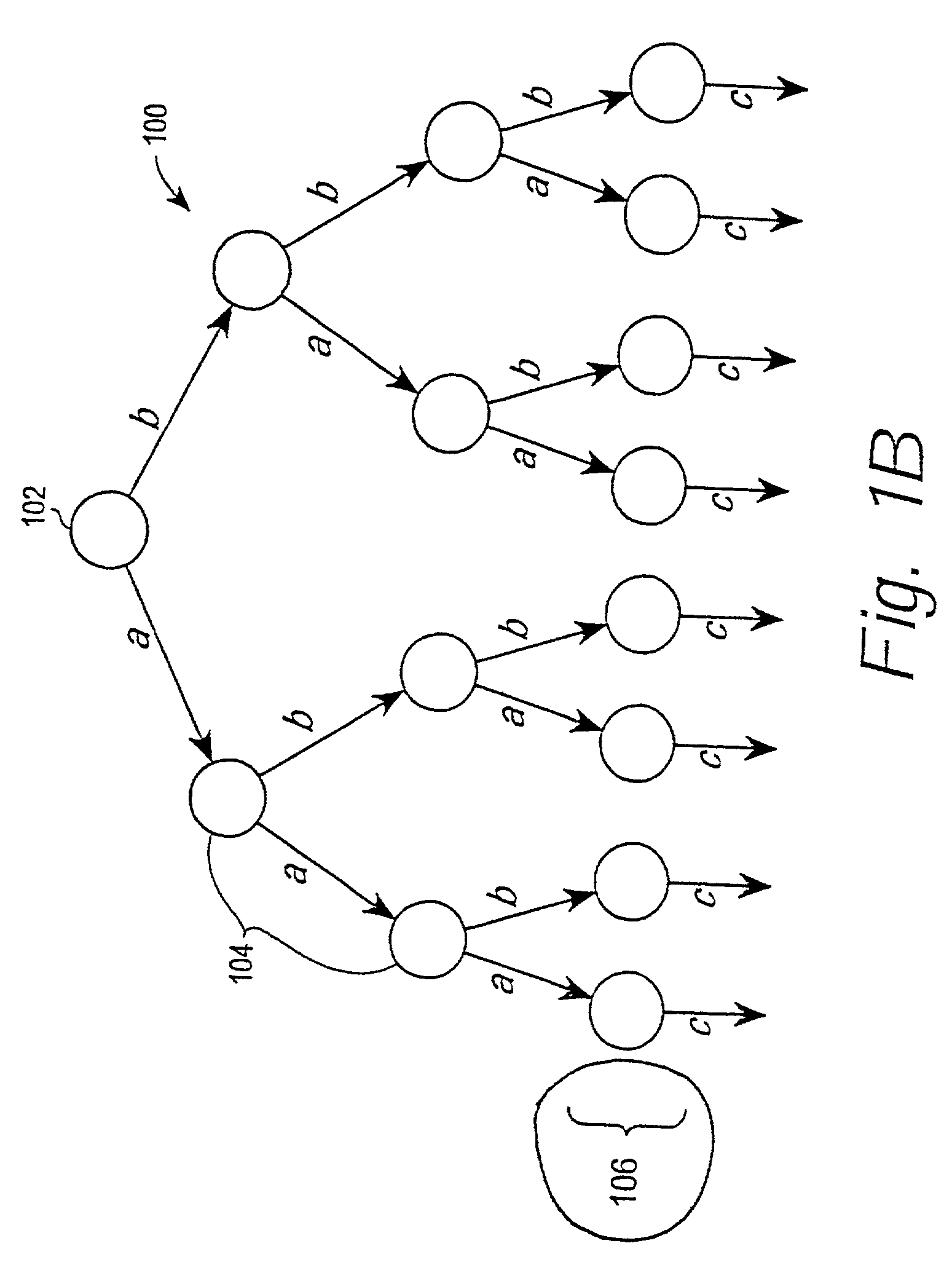
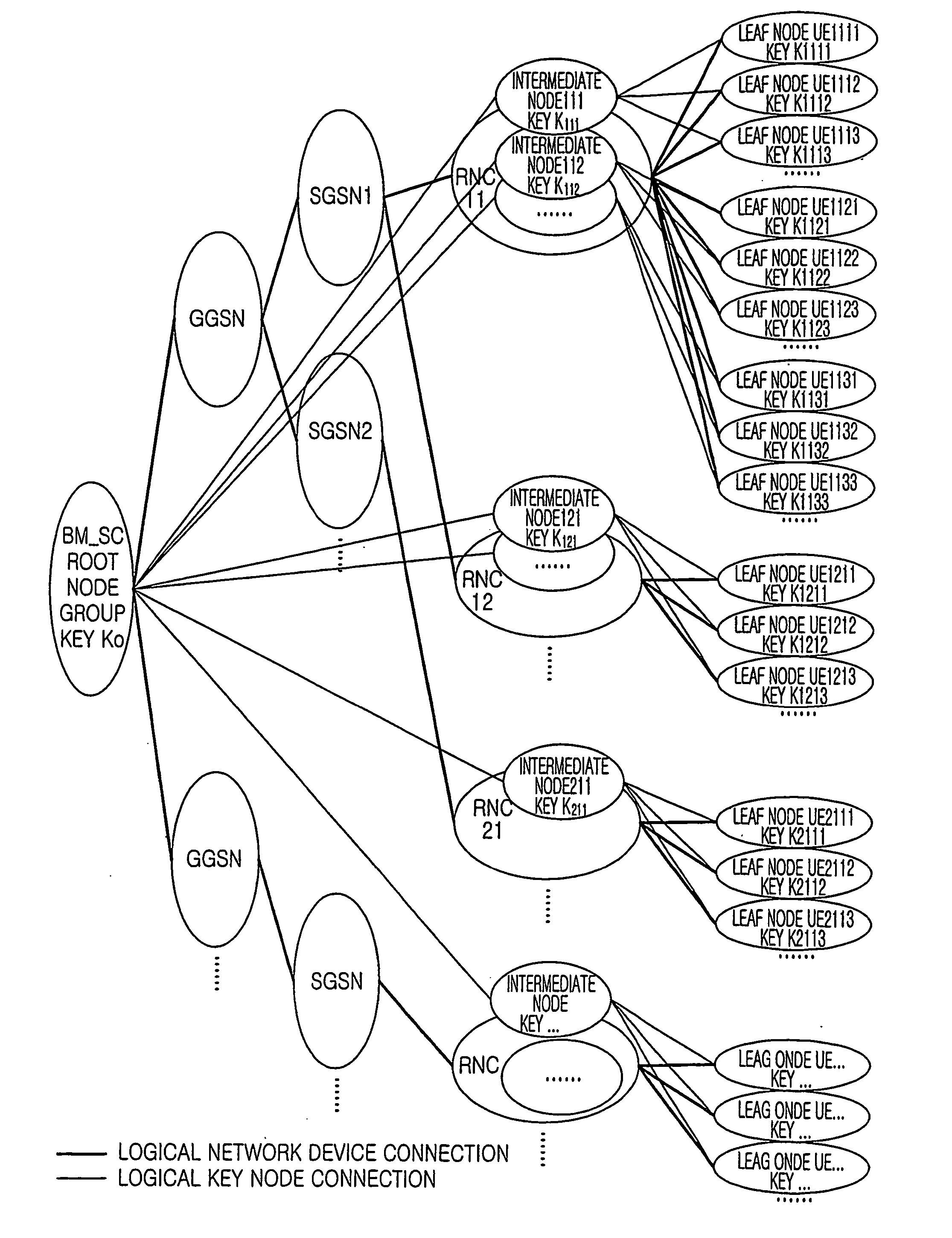
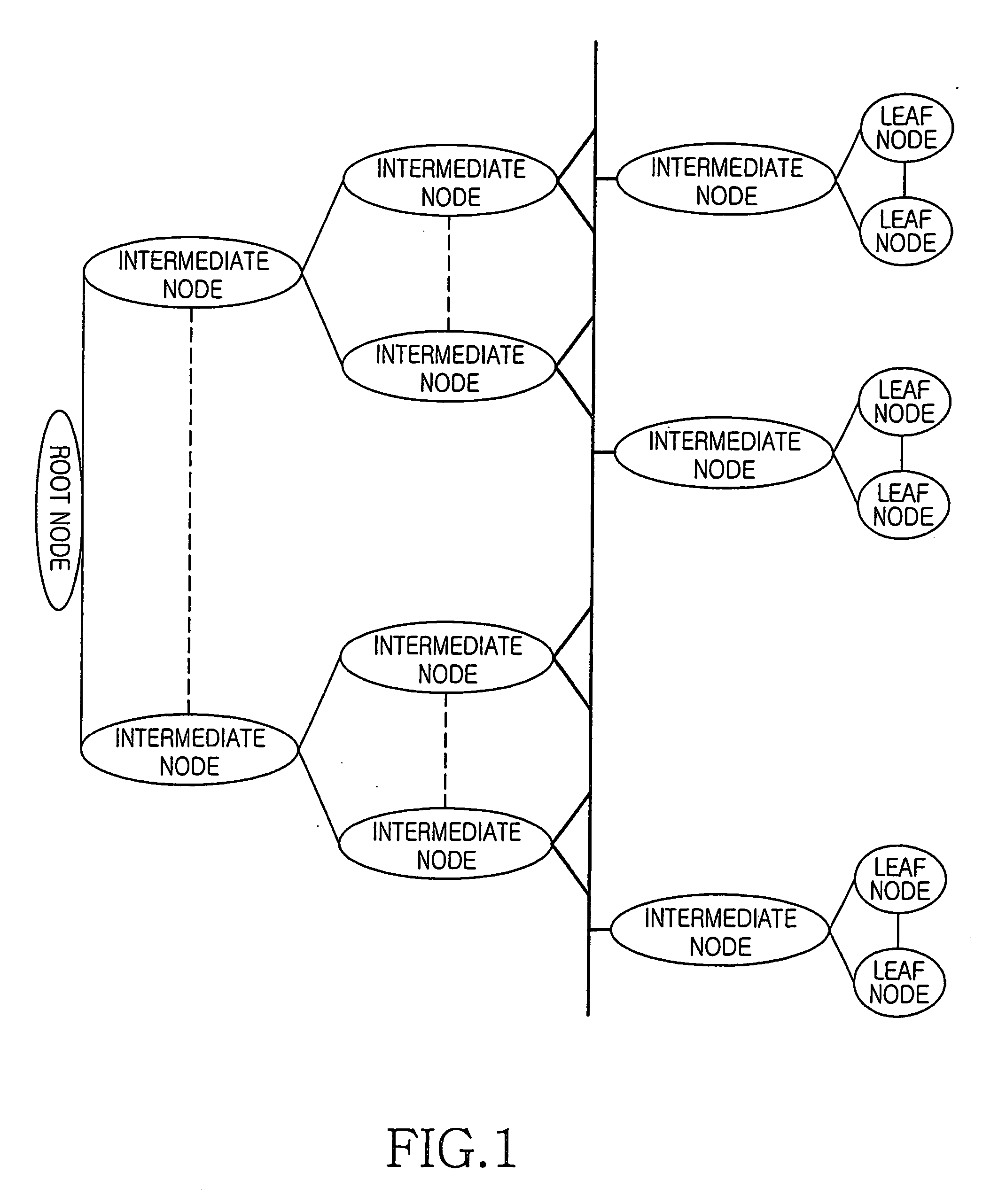
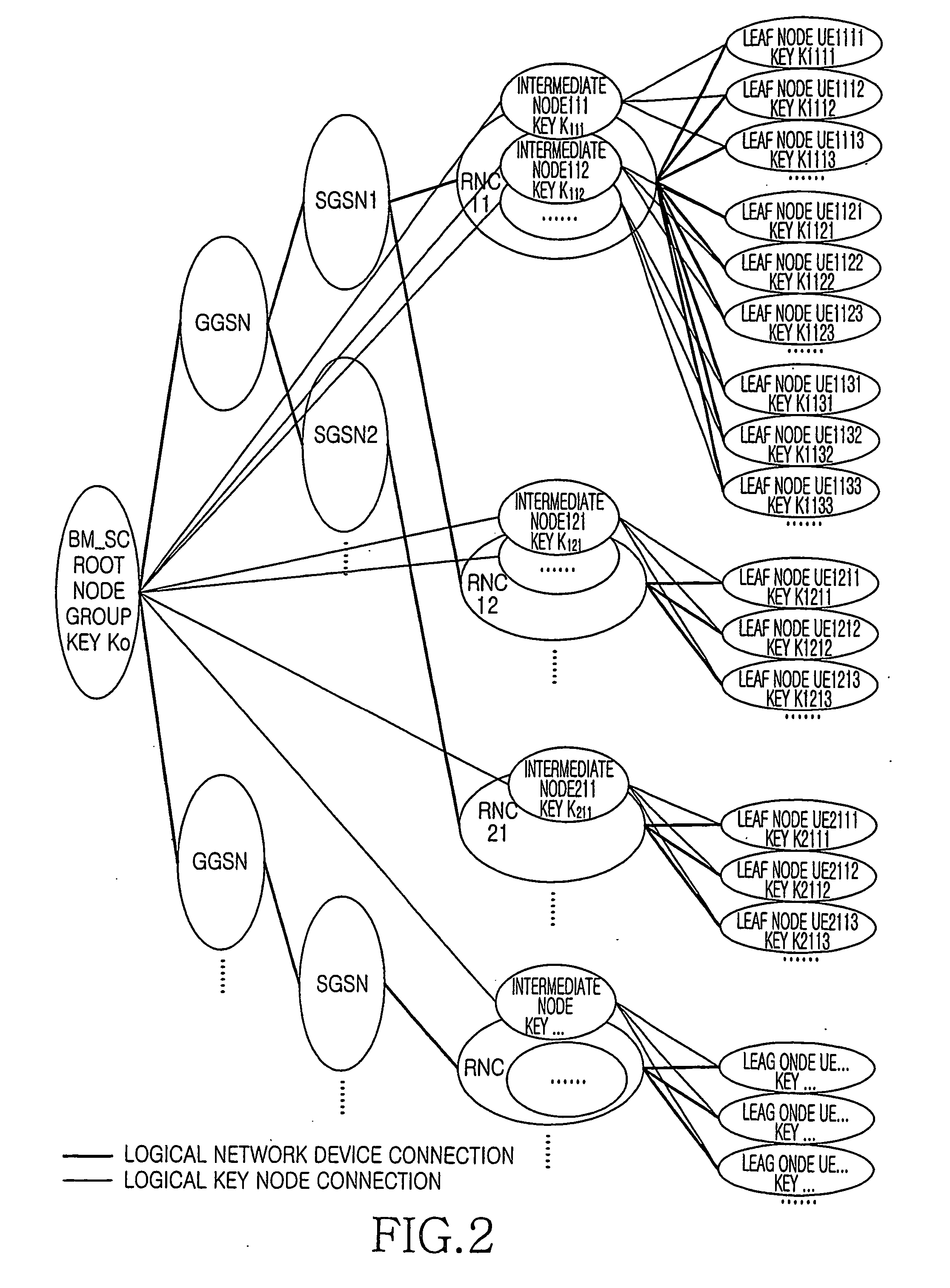
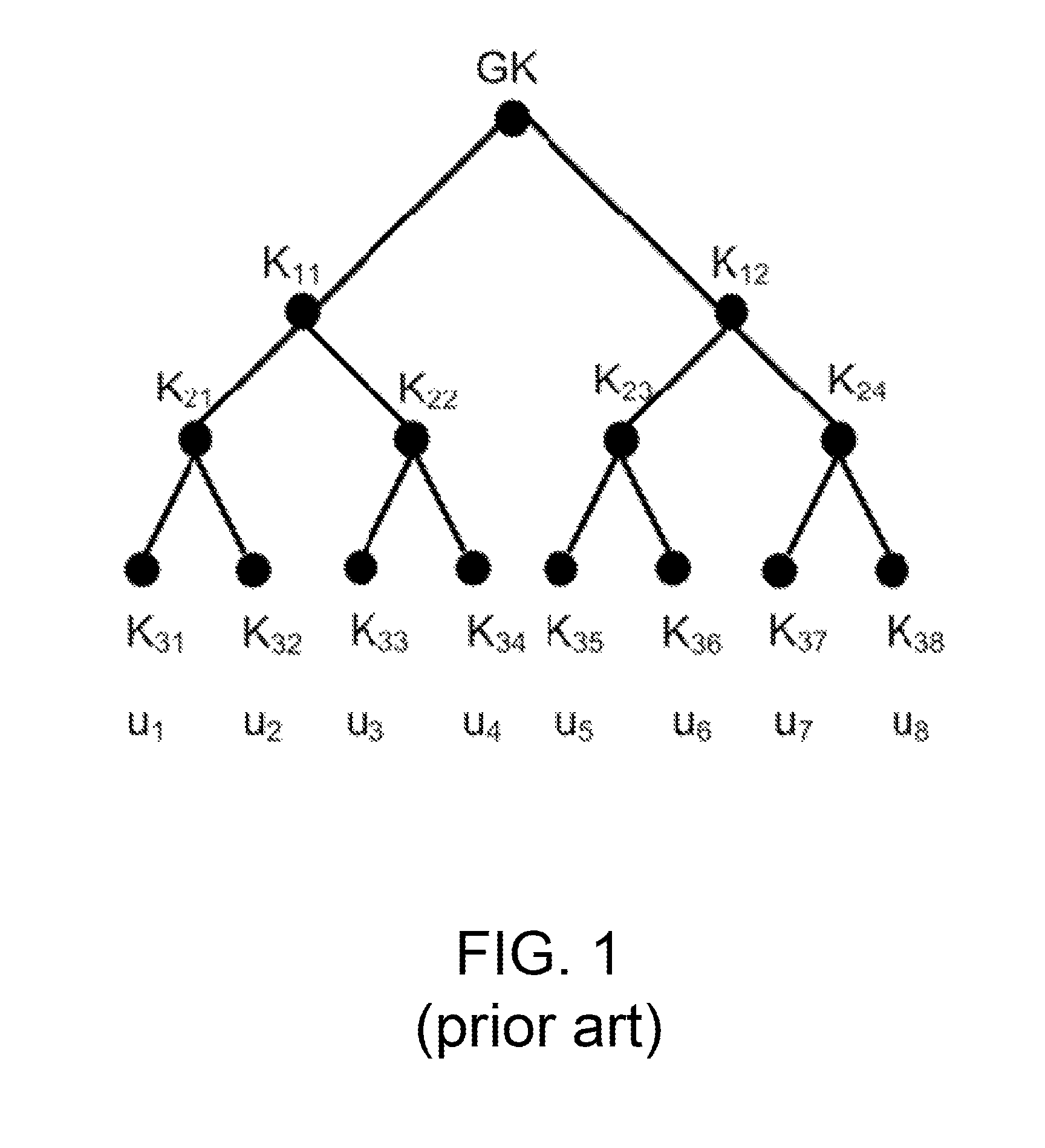
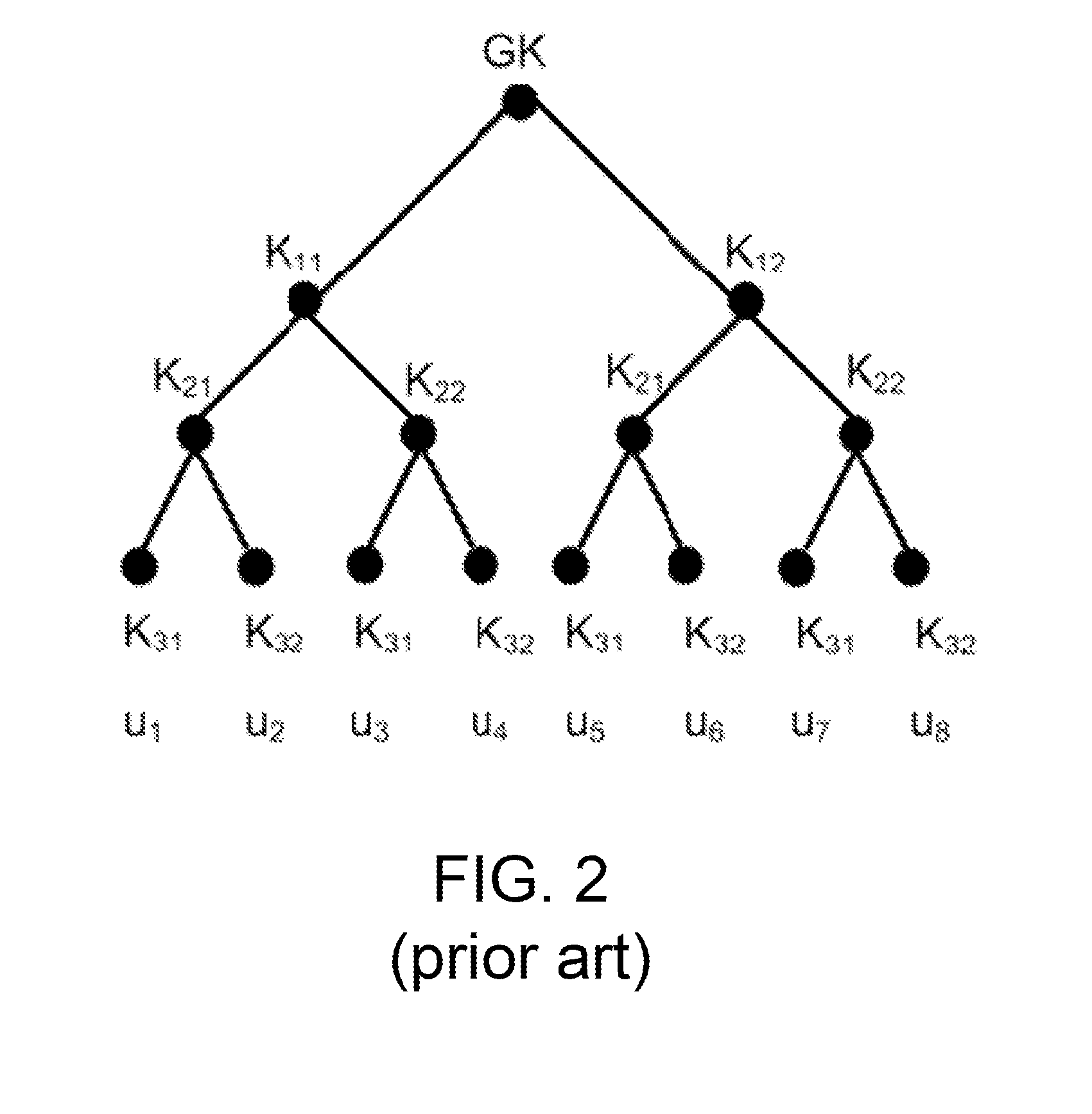
A method for key management and assignment in MBMS service, the method includes following steps: the group key locates in the root node on the highest layer, which only has child nodes and doesn't have parent nodes; private keys corresponding to users locate in leaf nodes; the described intermediate node that owns both one parent node and one or more child nodes holds it own key. This invention deploys the method of combining point-to-point mode and point-to-multipoint mode during the process of key update; compared with the key update method only deploying point-to-point mode, this method can reduce the times necessary for information transmission, reduce the system load as well as the time needed for one key update process. Compared with the key update method only deploying point-to-multipoint mode, this solves the security problem of key exposure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
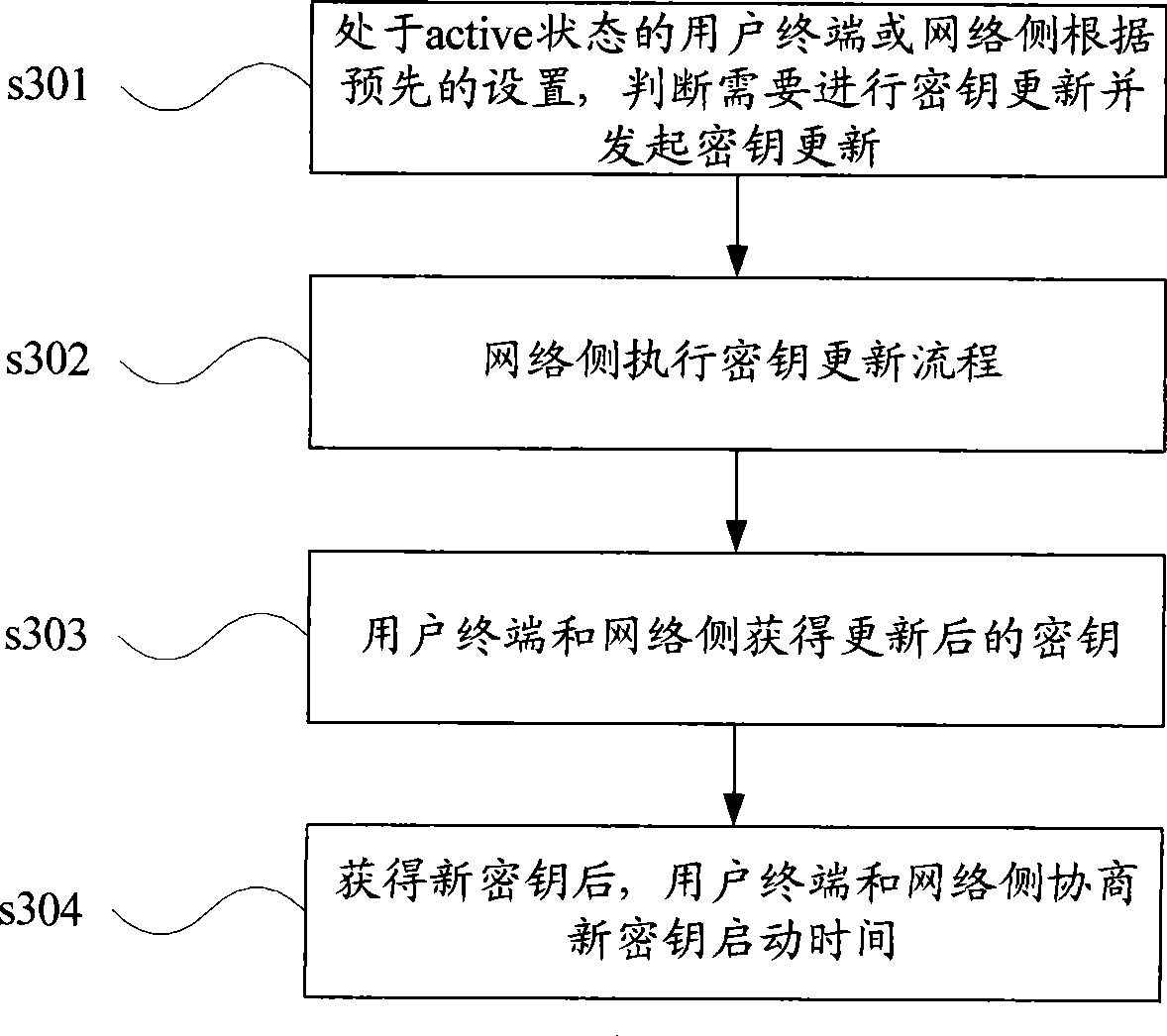
Cipher key updating method and device under active state
ActiveCN101400059AKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity arrangementComputer networkStart time
The invention discloses a secret key updating method under active state comprising following steps: user terminal under active state or network side starts a secret key updating when satisfying preset condition; the network side and user terminal update secret key and consult start time of new secret key. The invention also discloses a secret key updating device under active state. The user terminal and network side actively starts secret key updating procedure, and solves problem of secret key updating of session under active state.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Content playback apparatus method and program and key management apparatus and system
InactiveUS7401232B2Elimination contentTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationComputer networkEngineering
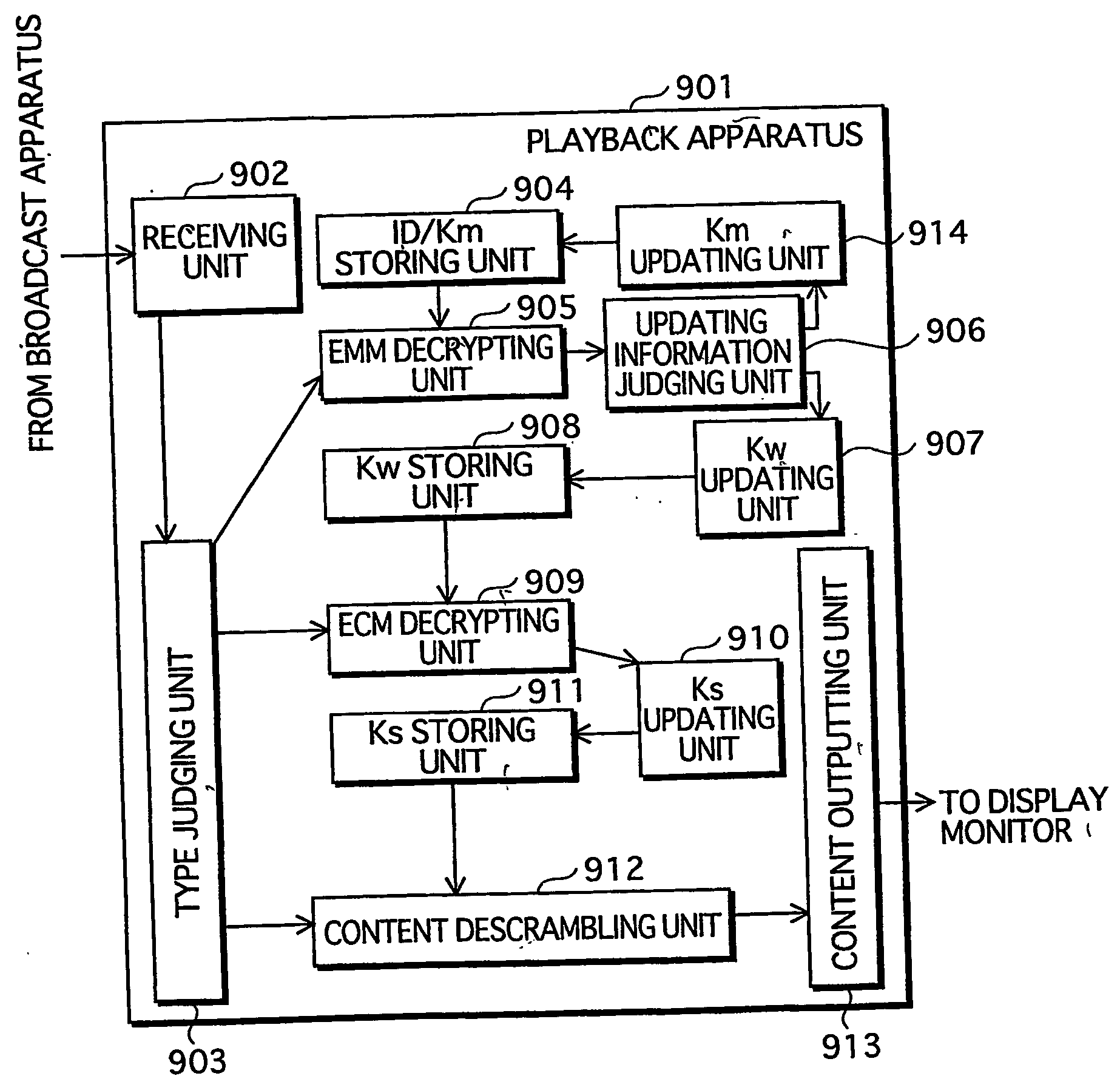
A key management apparatus which can be used to encrypt / decrypt content data in a content playback device includes a storing unit for storing a secret key, a key information decrypting unit for decrypting encrypted key information and an updating unit operable to update the secret key with an algorithm stored therein, when the decrypted key information is key-updating information. Seed information can be received for use with the algorithm to provide a new secret key, and preliminary trigger information can be used to poll a group of appliances to request key information to determine any duplication of appliances.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Encryption key updating for multiple site automated login
InactiveUS20050216773A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsExpiration TimeRekeying
A version number is associated with an encrypted key executable to allow real time updating of keys for a system which facilitates users signing on to multiple websites on different domains using an encrypted ticket. Two keys may be used at each site during updating of keys, each having an associated one digit Hex version tag. When a key is to be updated with a new key, the existing or old key is provided an expiration time. A second key is provided from the system in a secure manner with a new version number and made the current key which provides decryption of the encrypted ticket. The system tracks both keys while they are concurrent. After the existing key expires, only the second, or updated key is used to provide login services for users. The system periodically flushes old keys.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
WLAN session management techniques with secure rekeying and logoff
InactiveUS20070189537A1Improve securityNetwork topologiesSecret communicationSession managementUser authentication
The invention provides a method for improving the security of a mobile terminal in a WLAN environment by installing two shared secrets instead of one shared secret, the initial session key, on both the wireless user machine and the WLAN access point during the user authentication phase. One of the shared secrets is used as the initial session key and the other is used as a secure seed. Since the initial authentication is secure, these two keys are not known to a would be hacker. Although the initial session key may eventually be cracked by the would be hacker, the secure seed remains secure as it is not used in any insecure communication.
Owner:ZHANG JUNBIAO +2
Magnetic recording medium encryption
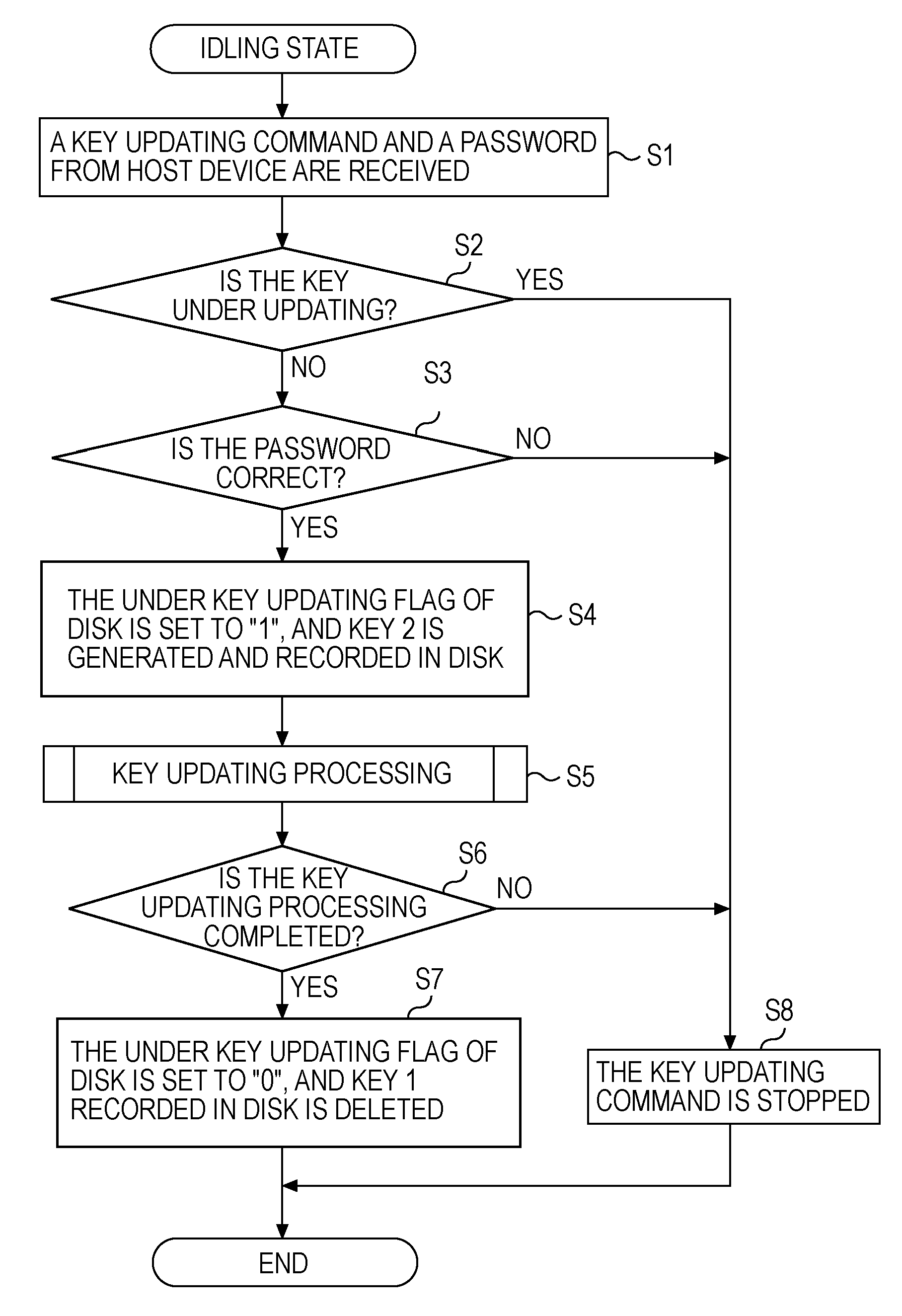
ActiveUS20080240428A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageUnauthorized memory use protectionEngineeringDatabase
Systems and methods for easily and at high speed re-encrypting data recorded on a magnetic recording medium when the data is encrypted using an encryption key and the encryption key is changed. A track where effective user data is not recorded is set as a first reserved track, then data is read out from the first updating source track and decrypted using a first encryption key KEY 1, which is reencrypted using a second encryption key KEY 2 and recorded in the first reserved track, next, the first updating source track is set as a second reserved track, and a second updating source track is set, and the encryption key is updated by repeating these steps until all tracks to be subjected to the key updating processing have been subjected to the key updating processing.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Reducing interprocessor communications pursuant to updating of a storage key
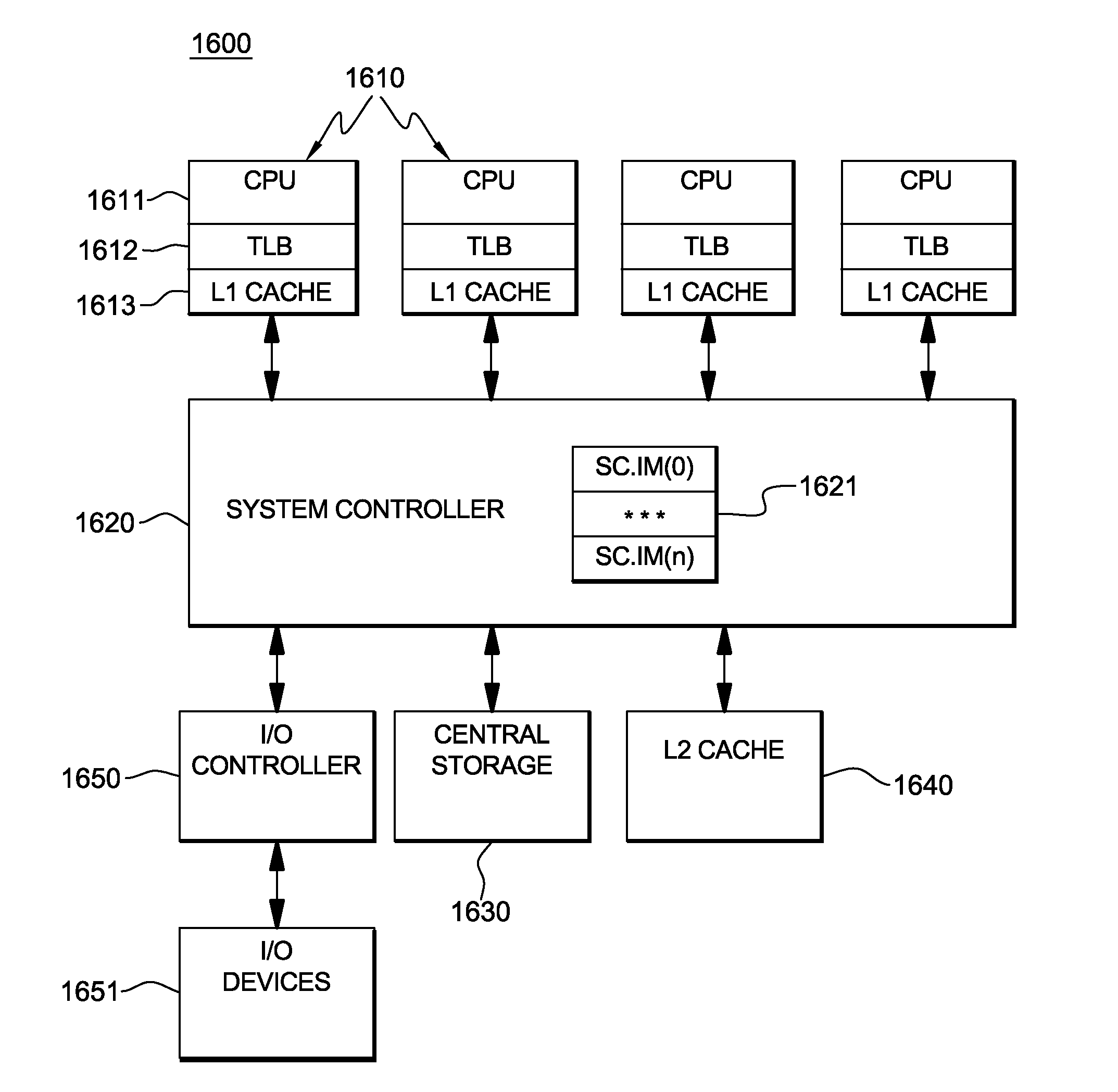
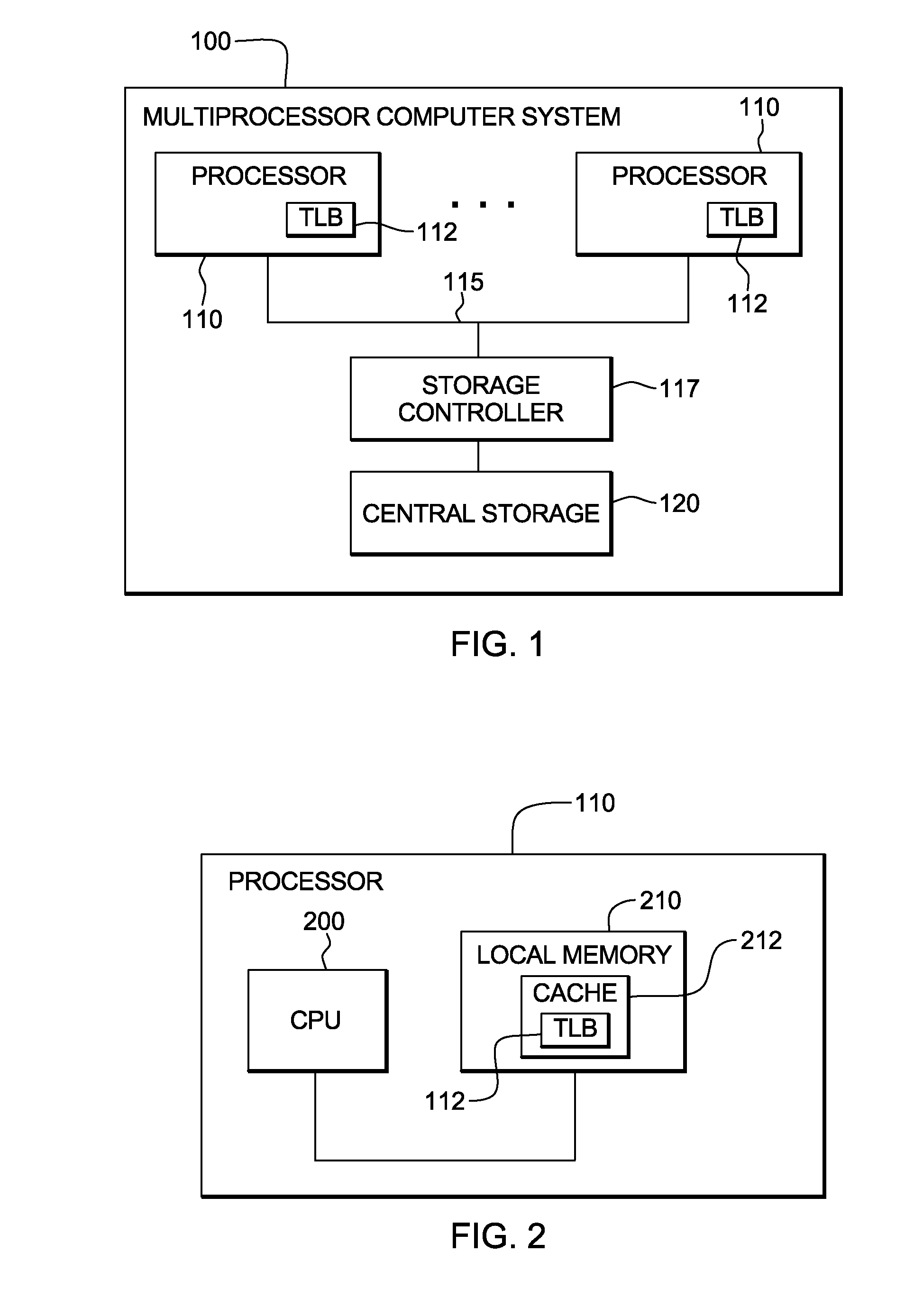
InactiveUS20110145510A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorInterprocessor communication
Processing within a multiprocessor computer system is facilitated by: deciding by a processor, pursuant to processing of a request to update a previous storage key to a new storage key, whether to purge the previous storage key from, or update the previous storage key in, local processor cache of the multiprocessor computer system. The deciding includes comparing a bit value(s) of one or more required components of the previous storage key to respective predefined allowed stale value(s) for the required component(s), and leaving the previous storage key in local processor cache if the bit value(s) of the required component(s) in the previous storage key equals the respective predefined allowed stale value(s) for the required component(s). By selectively leaving the previous storage key in local processor cache, interprocessor communication pursuant to processing of the request to update the previous storage key to the new storage key is minimized.
Owner:IBM CORP
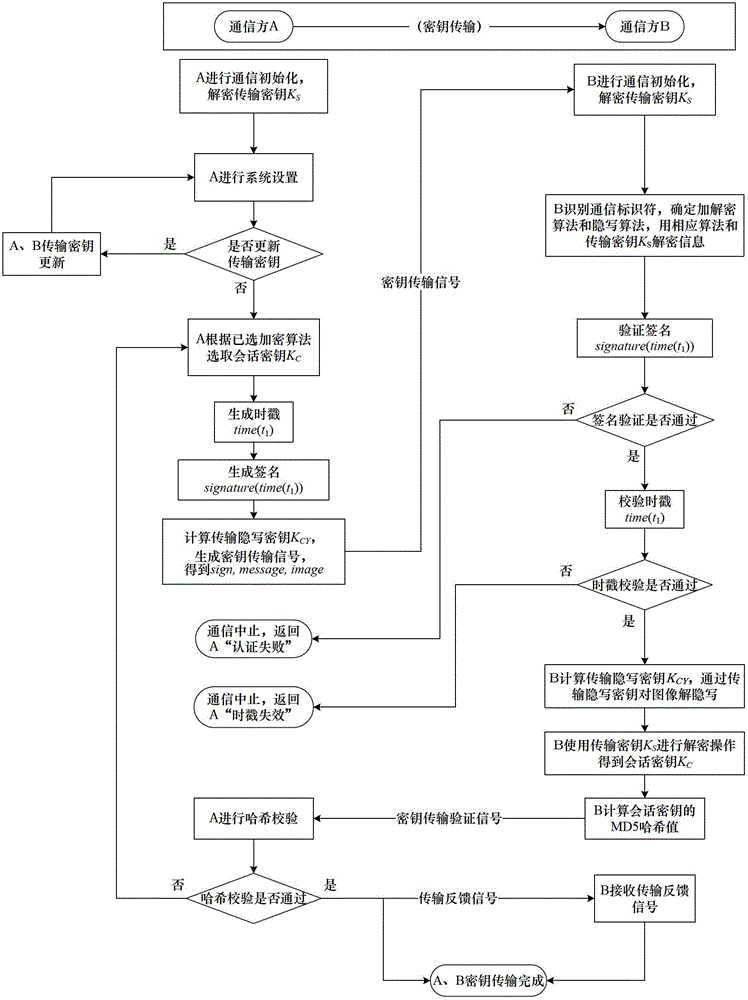
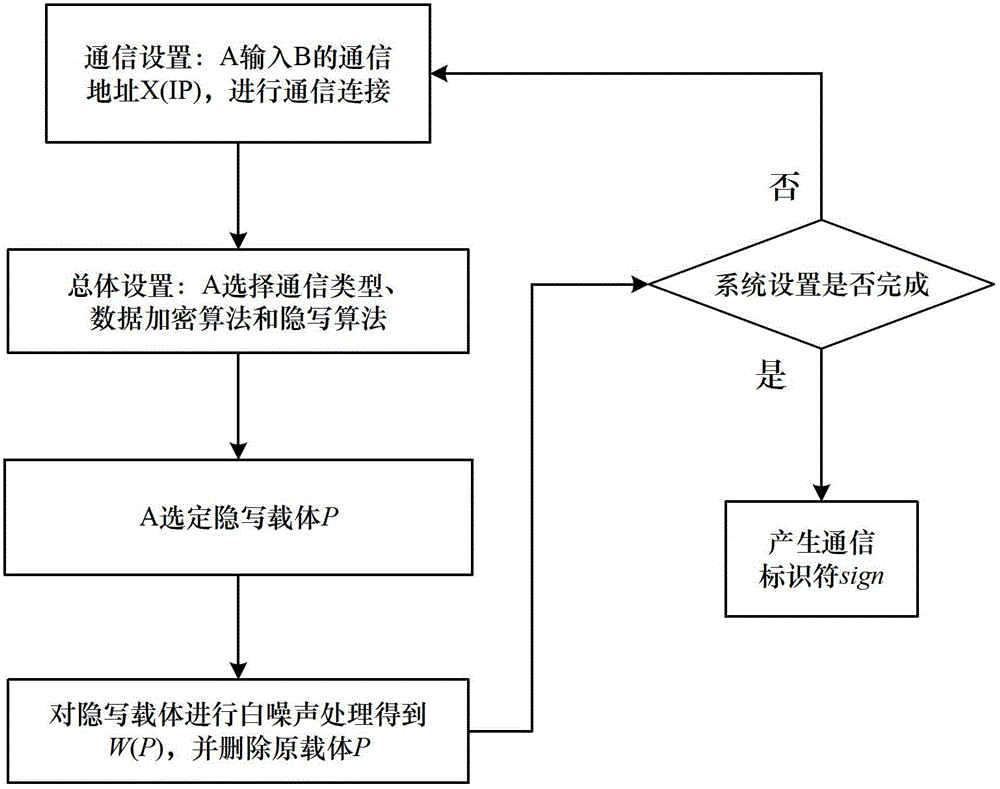
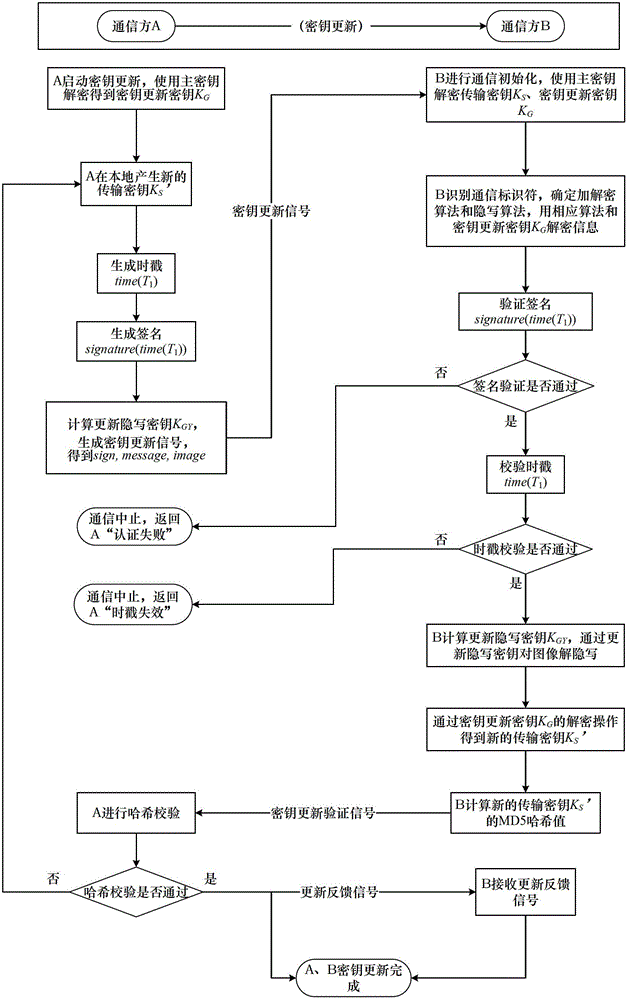
Steganography-based key transmission and key updating method
ActiveCN102724041AEffective verification of identity informationImprove authentication strengthEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationMultiple encryptionCiphertext
The invention provides a steganography-based key transmission and key updating method, which is applied to the field of information safety. The method comprises the steps that a communication party A sets a communication type, an encryption algorithm an steganography algorithm, selects a steganography carrier and generates a communication identifier and then performs the updating of a transmission key or the transmission process of a conversion key; a new transmission key is selected when in updating, a time stamp and a signature are generated to encrypt and steganograph the transmission key, the key updating information is generated to be transmitted to a communication party B, and the communication party B performs the verification, de-staganography and deciphering to obtain the transmission key; and the conversion key is selected in transmission to generate a time stamp and a signature so as to encrypt and steganograph the conversion key, the key transmission information is generated to be transmitted to the communication party B, and the communication party B performs the verification, de-steganography and deciphering to obtain the conversation key. The key is concealed by utilizing the steganography, so that an encrypted data format in the key transmission process and the key updating process can be effectively protected, and the safety transmission of multiple encryption and decryption algorithm conversation keys can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for optimal group key management for secure multicast communication
InactiveUS8837738B2Storage-communication optimalityConstant sizeKey distribution for secure communicationGroup controllerSecure multicast
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for optimal group key (OGK) management that may achieve non-colluding and / or the storage-communication optimality are disclosed. In some embodiments, a group controller (GC) is responsible for key generation and distribution and the group data are encrypted by a group key. When joining the group, in some embodiments, each group member (GM) is assigned a unique n-bit ID and a set of secrets, in which each bit is one-to-one mapped to a unique secret. Whenever GMs are revoked from the group, in some embodiments, the GC will multicast an encrypted key-update message. Only the remaining GMs may be able to recover the message and update GK as well as their private keys. The disclosed OGK scheme can achieve storage-communication optimality with constant message size and immune to collusion attack and also may outperform existing group key management schemes in terms of communication and storage efficiency.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Cloud storage data auditing method for preventing secret key from being revealed
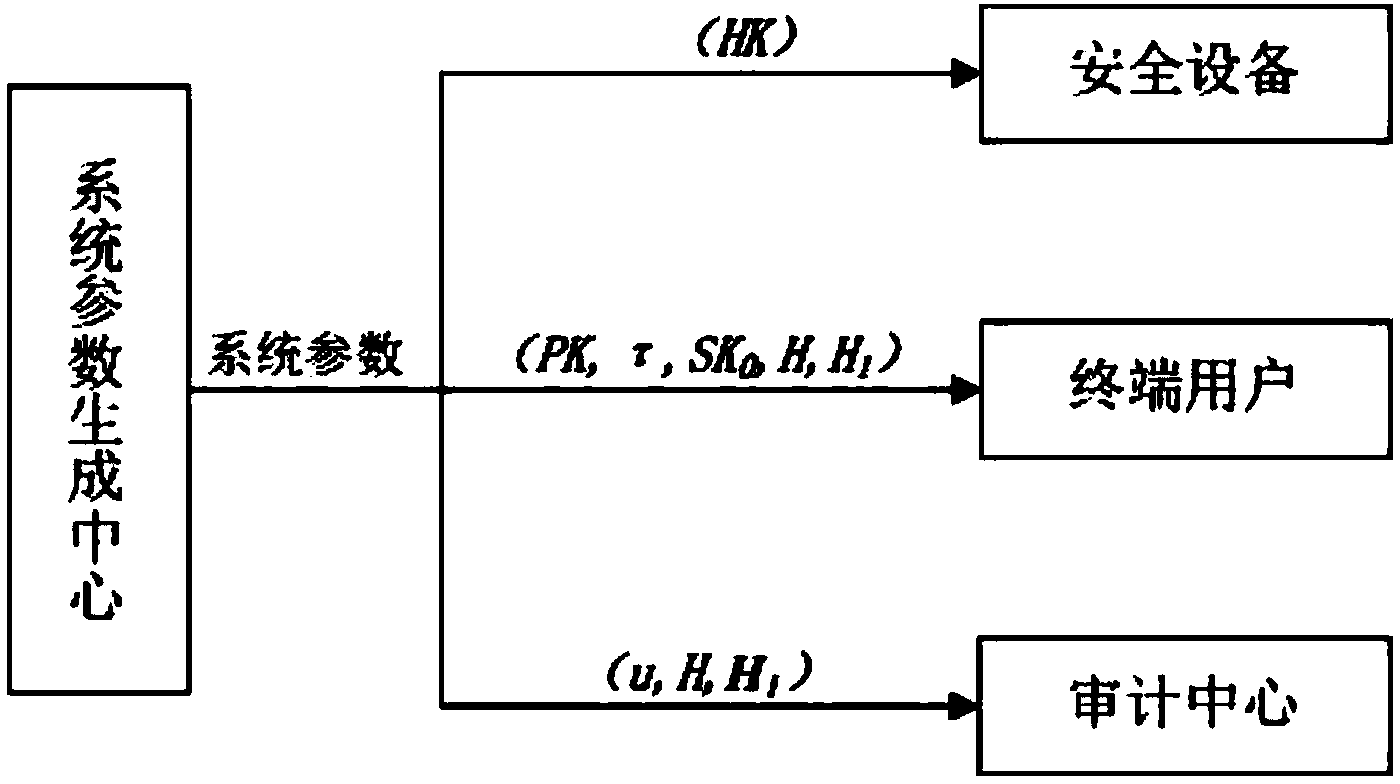
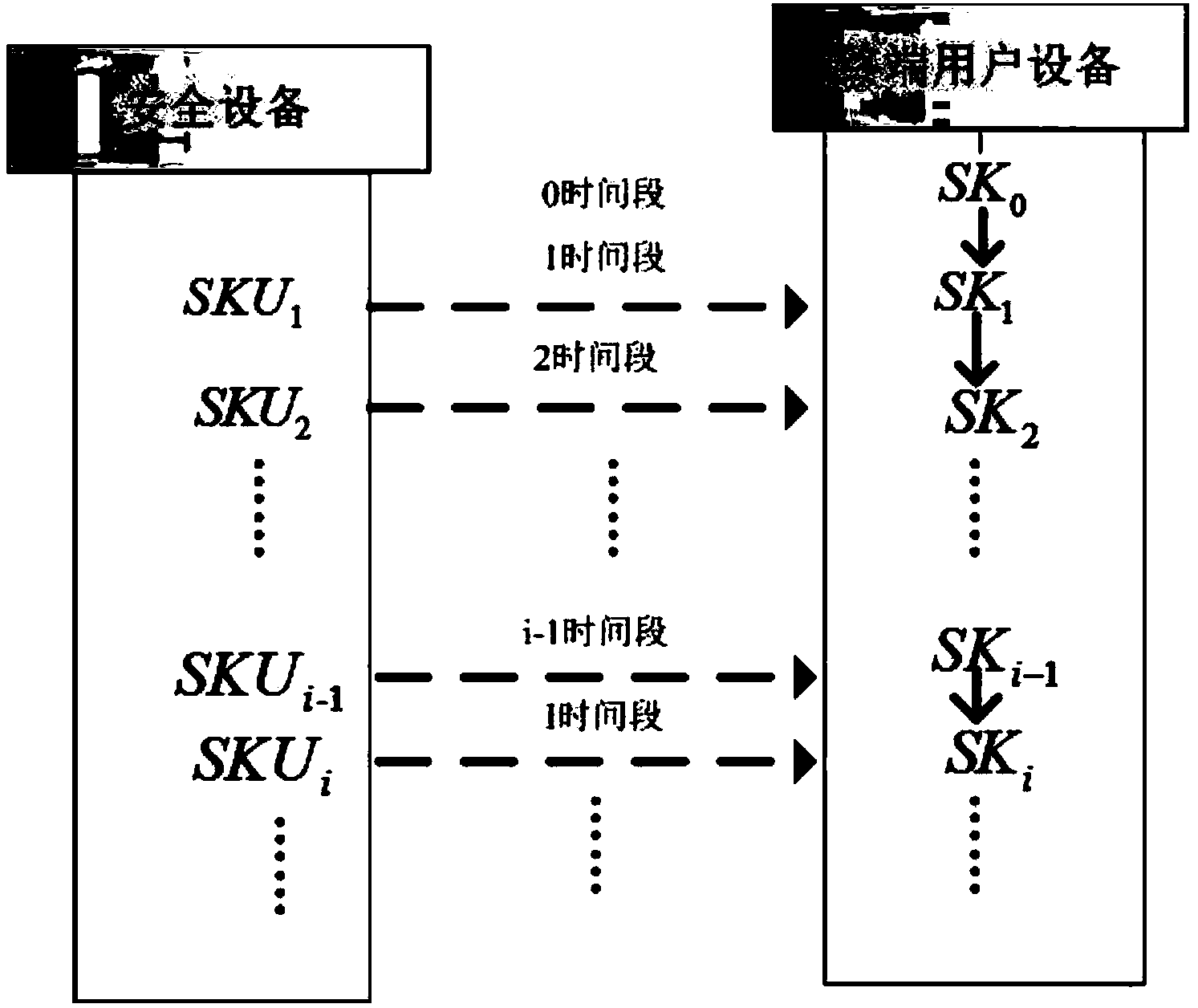
ActiveCN103986732AImprove audit efficiencyImprove efficiencyTransmissionPhysical securityTime segment
The invention provides a cloud storage data auditing method for preventing a secret key from being revealed. The method comprises the first step of system parameter generating, the second step of secret key updating and the third step of file uploading and auditing. According to the method, a physically safe safety device is introduced to help a user to periodically update the secret key, and therefore data auditing in other time periods is still safe even when an attacker attacks the user at one time period and obtains the user secret key at the time period.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHENGZHONG COMP NETWORK TECH CONSULTING
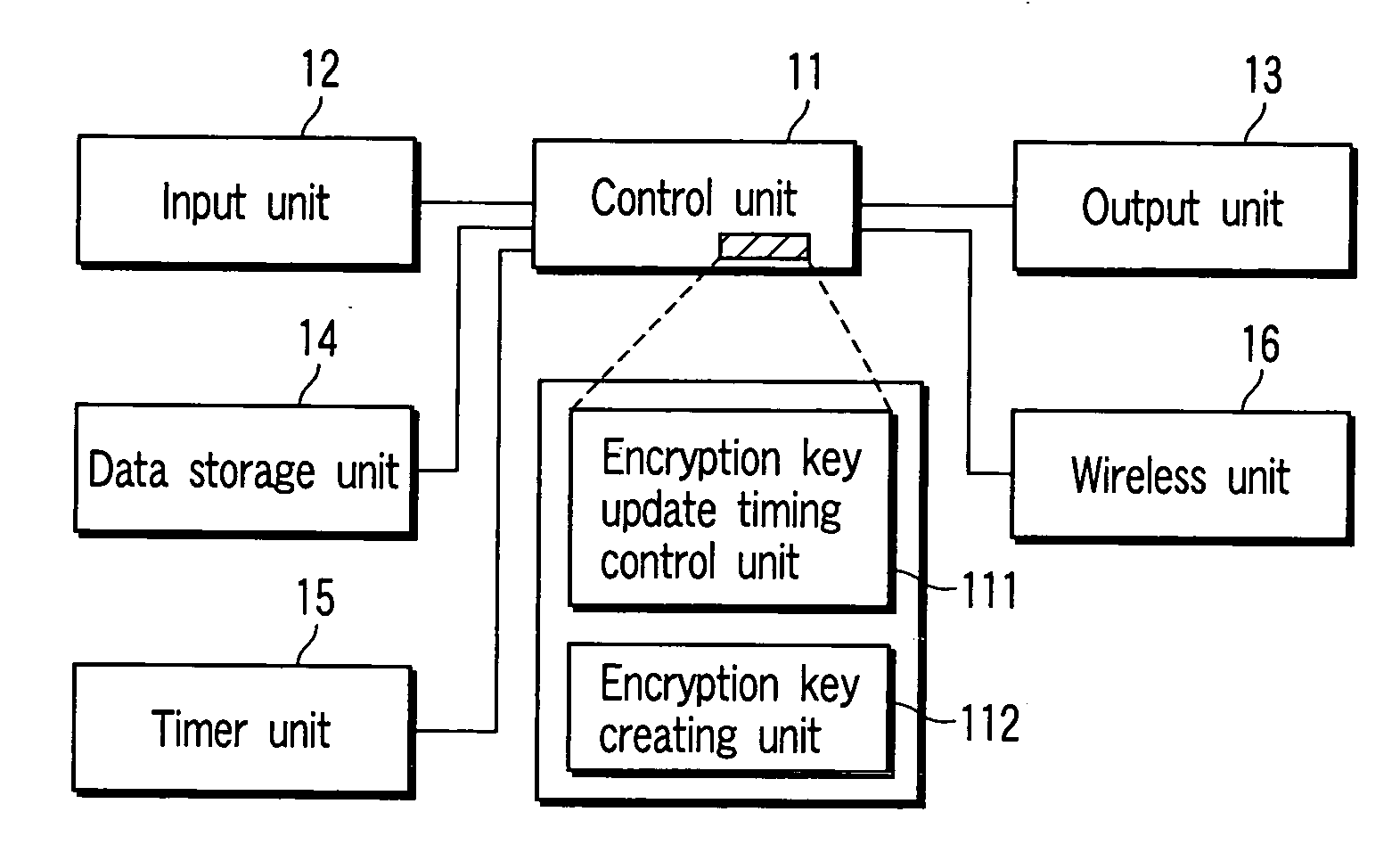
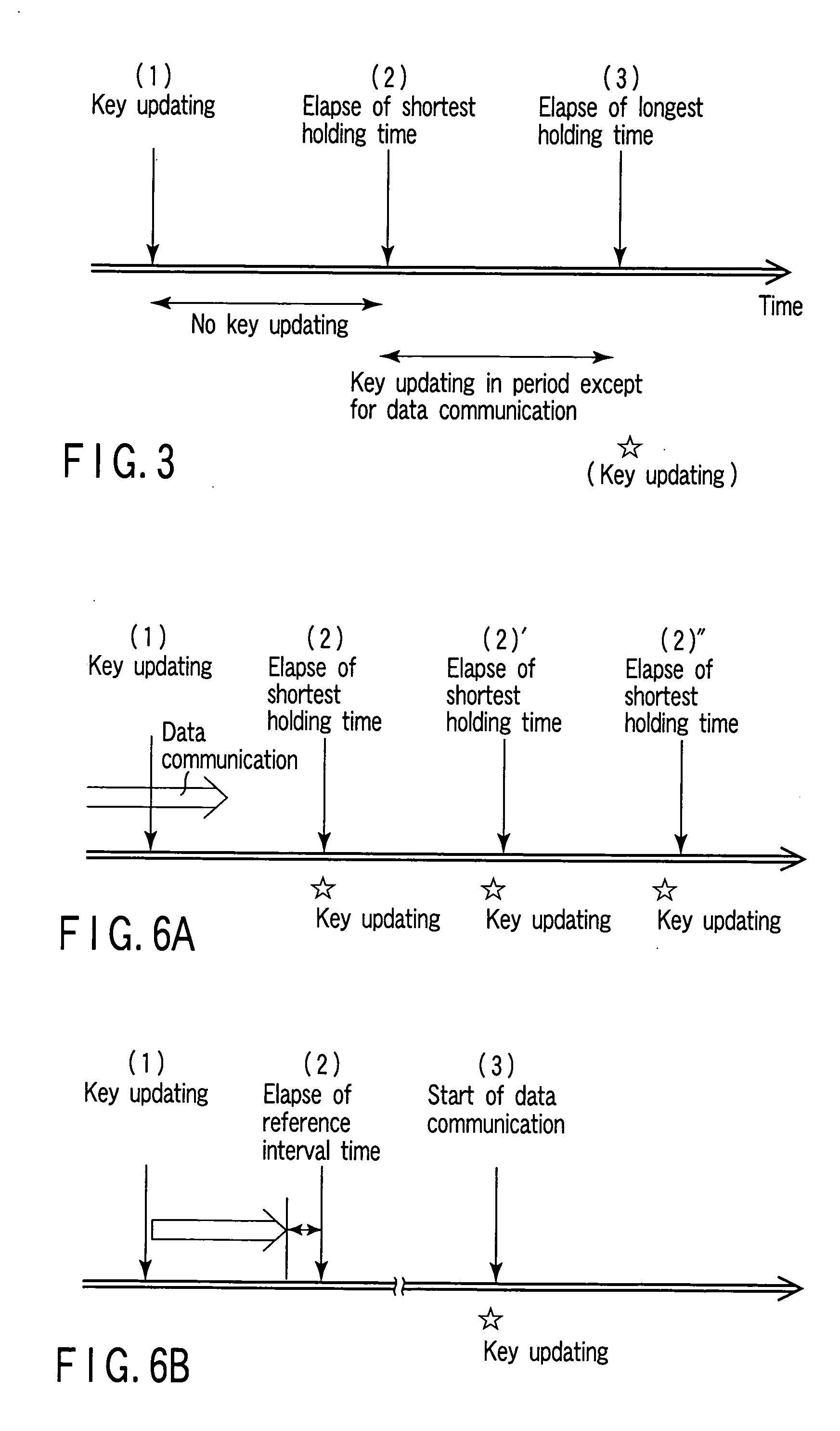
Electronic apparatus and encryption key updating
InactiveUS20050094814A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageNetwork topologiesComputer hardwareTime control
After an encryption key creating unit creates / updates an encryption key, an encryption key update timing control unit monitors whether or not the elapsed time since this time has reached the shortest holding time or longest holding time. If the shortest holding time has elapsed, the encryption key update timing control unit monitors whether or not wireless communication is being executed by a wireless unit. If a state wherein no wireless communication is being executed is detected, the encryption key creating unit is caused to create / update an encryption key at this timing. When the longest holding time has elapsed while this state is not detected, the encryption key update timing control unit gives a wireless unit an instruction to temporarily interrupt the wireless communication, and causes the encryption key creating unit to create / update an encryption key during interruption of wireless communication.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
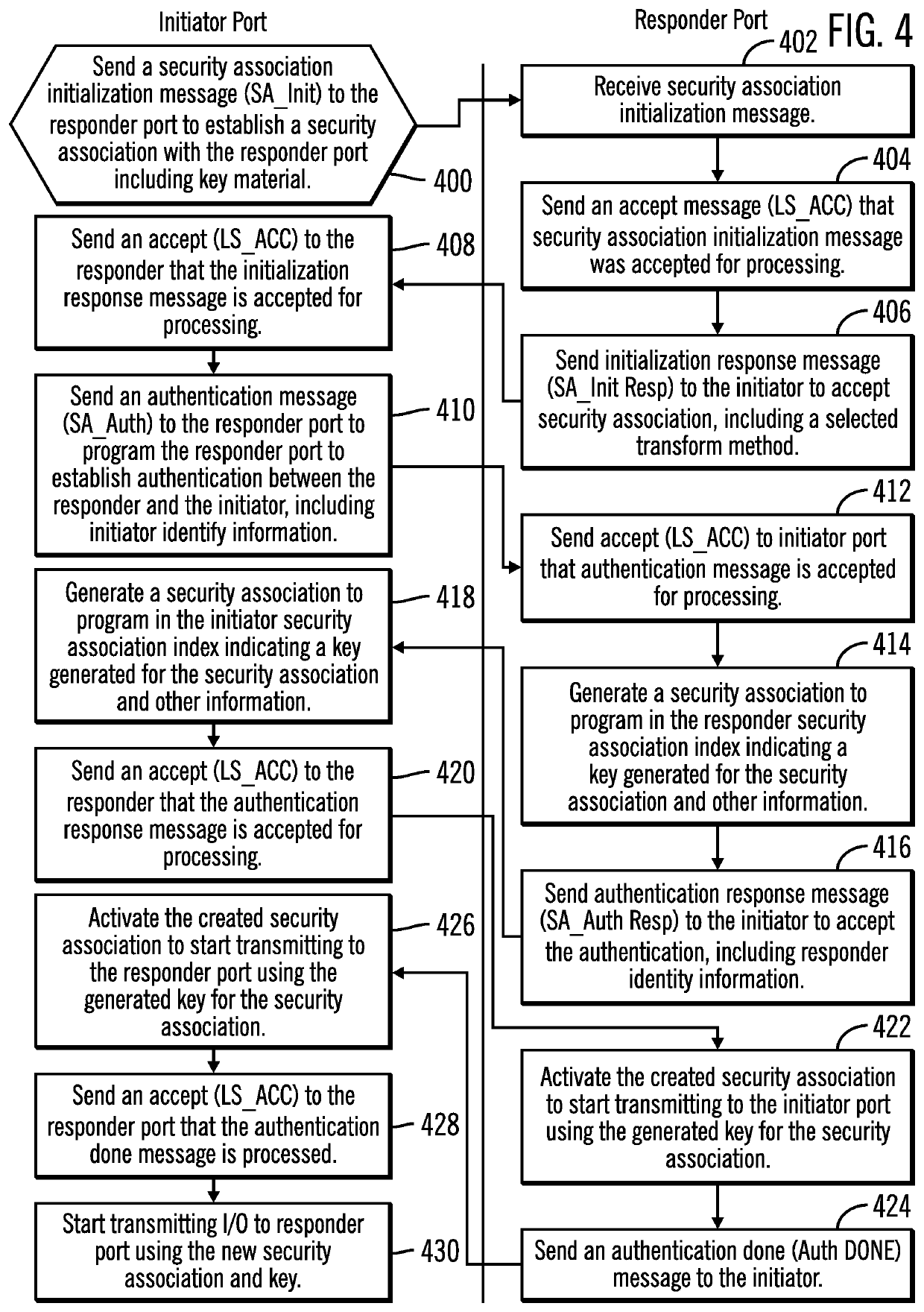
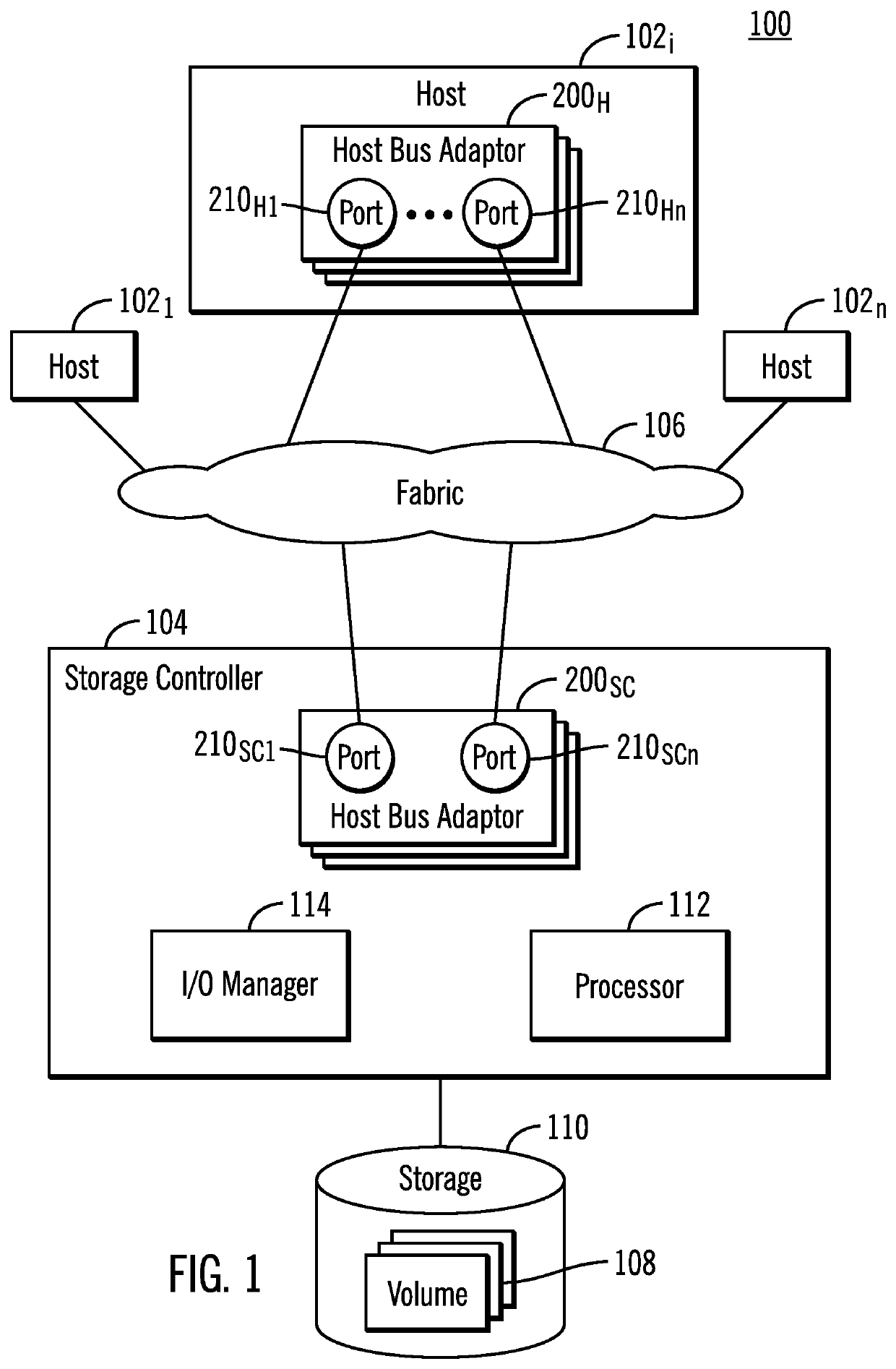
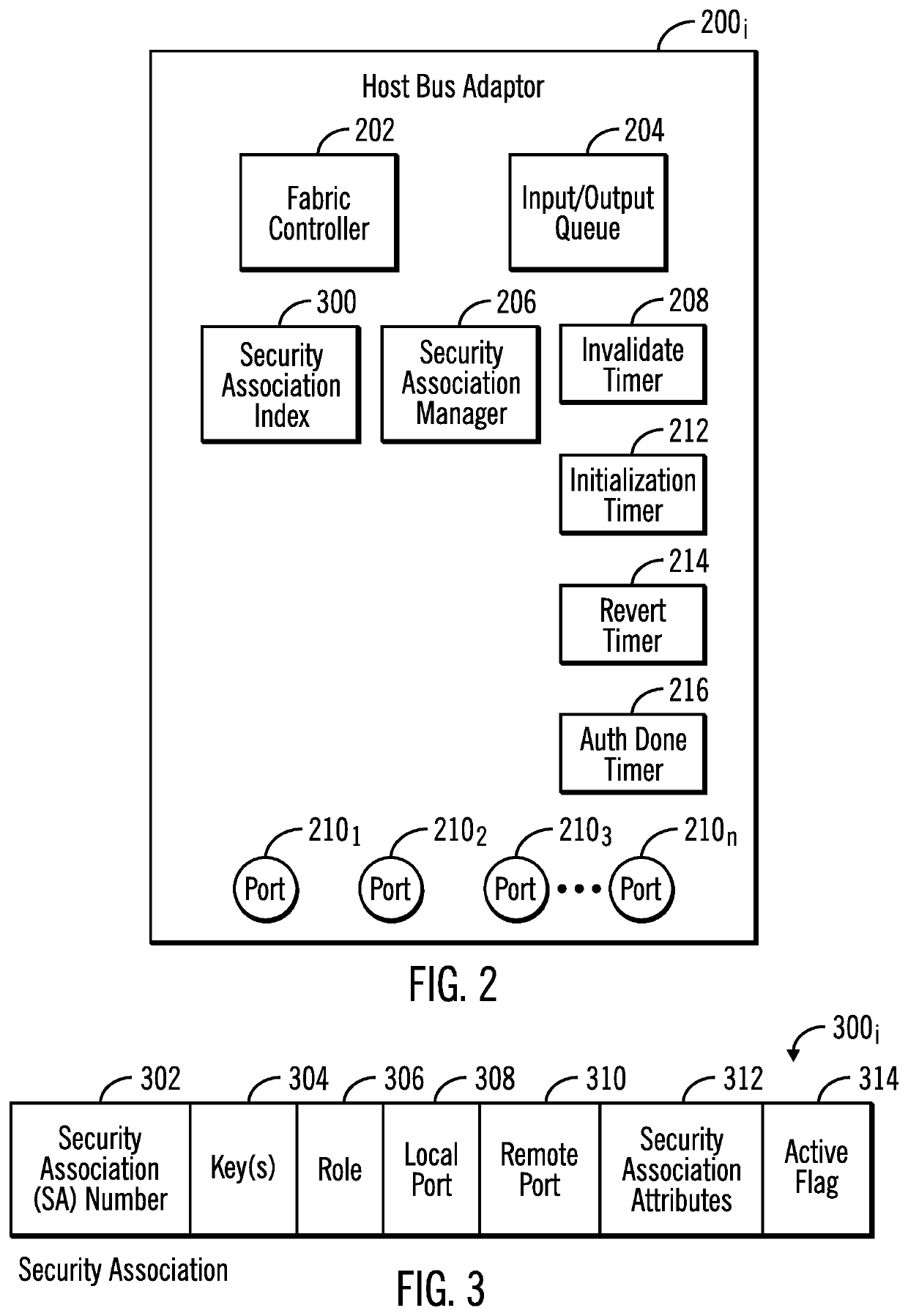
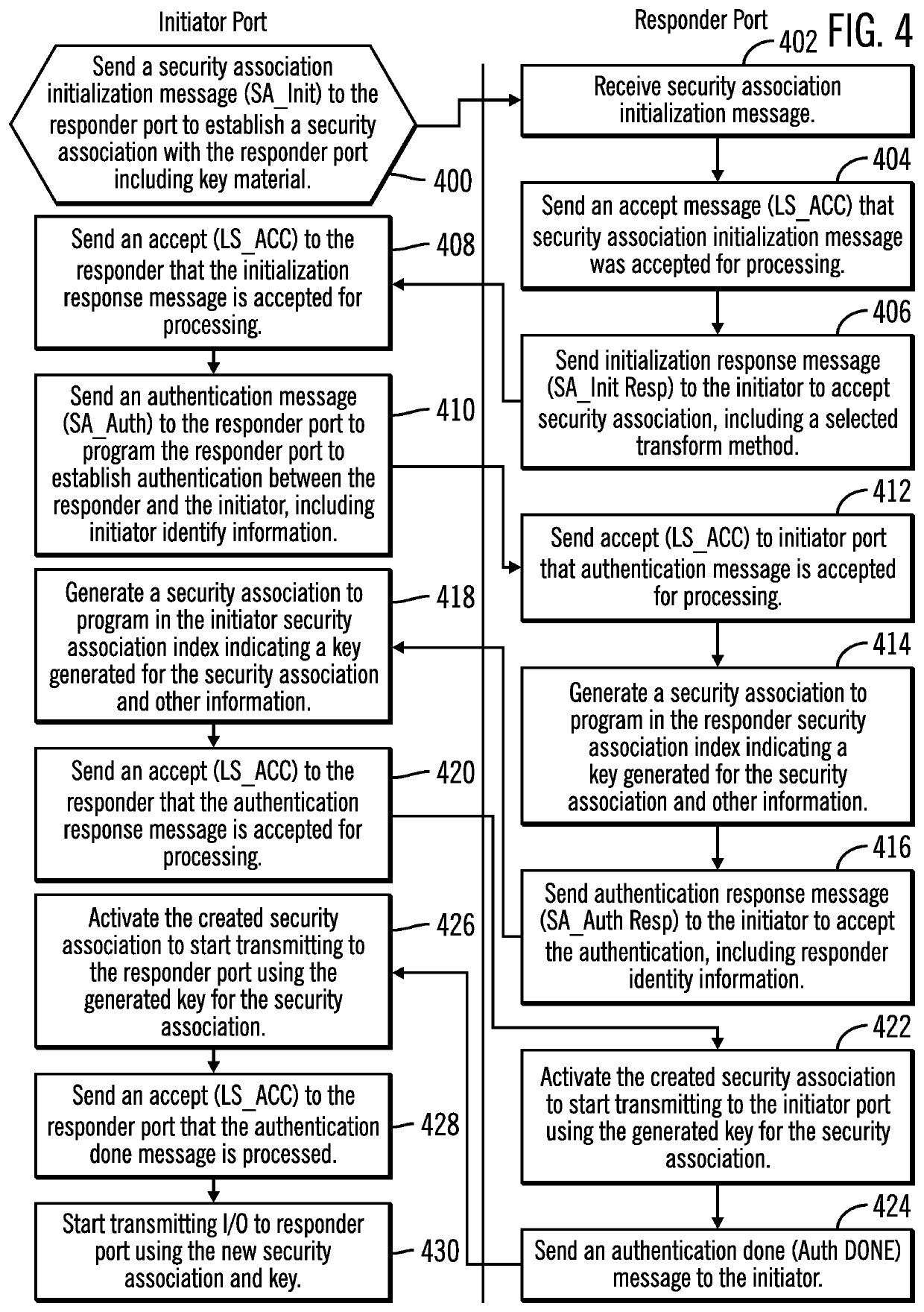
Reverting from a new security association to a previous security association in response to an error during a rekey operation
ActiveUS20210091943A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data authenticationComputer networkSecurity association
Provided are a computer program product, system, and method embodiments for reverting from a new security association to a previous security association in response to an error during a rekey operation. An initiator maintains a first security association with the responder having a first key to use to encrypt and decrypt data transmitted with the responder. The initiator initiates a rekey operation to establish a second security association with the responder using a second key. The initiator detects a failure of the rekey operation after the responder started using the second key for transmissions. A revert message is sent to the responder to revert back to using the first security association and first key in response to detecting the failure of the rekey operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Rekeyable lock cylinder and rekeying method thereof
Owner:TAIWAN FU HSING INDAL
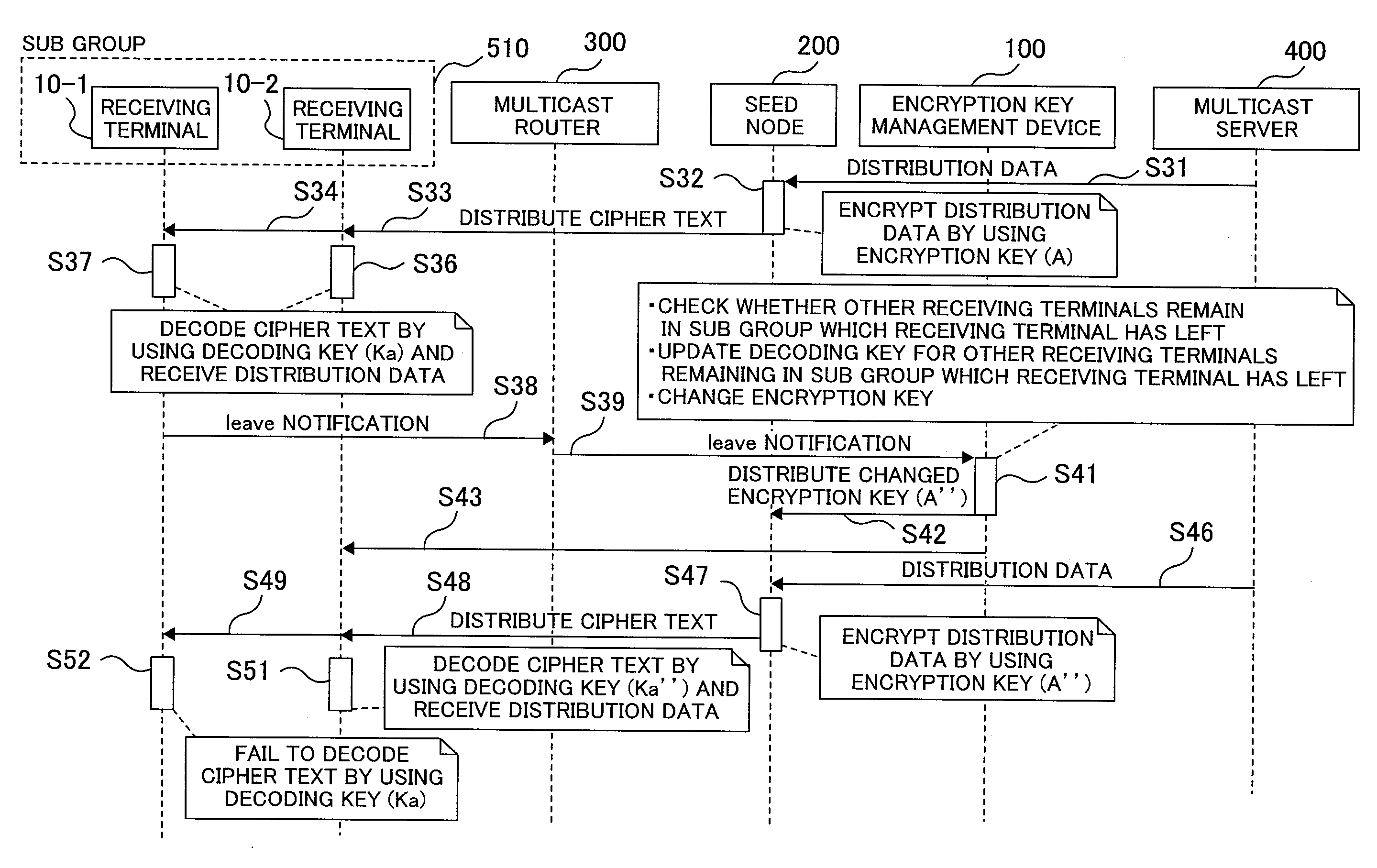
Data distribution system, key management device, and key management method
InactiveUS20100174899A1Reduce traffic problemsEfficient multicastingKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksNetwork connectionDistribution system
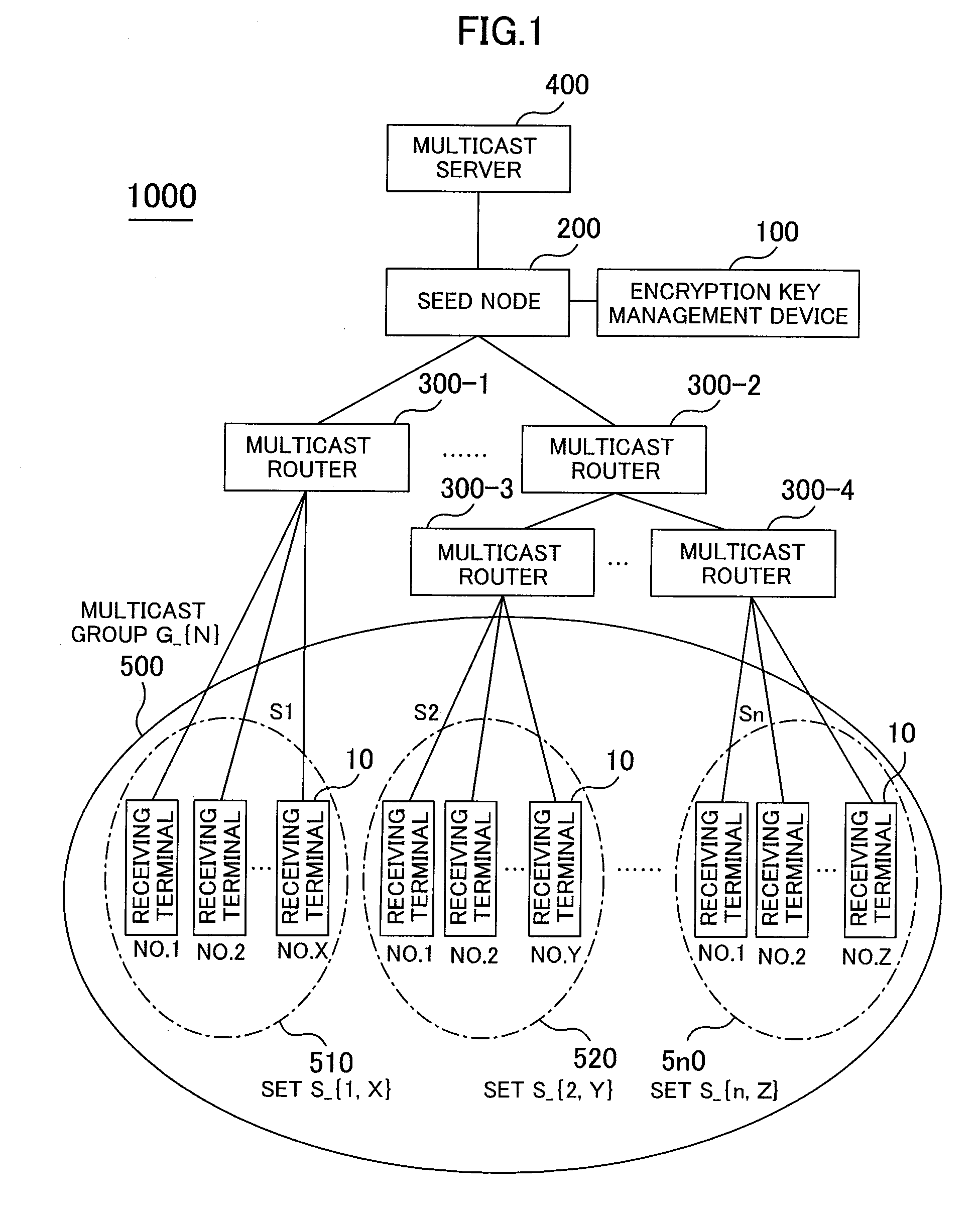
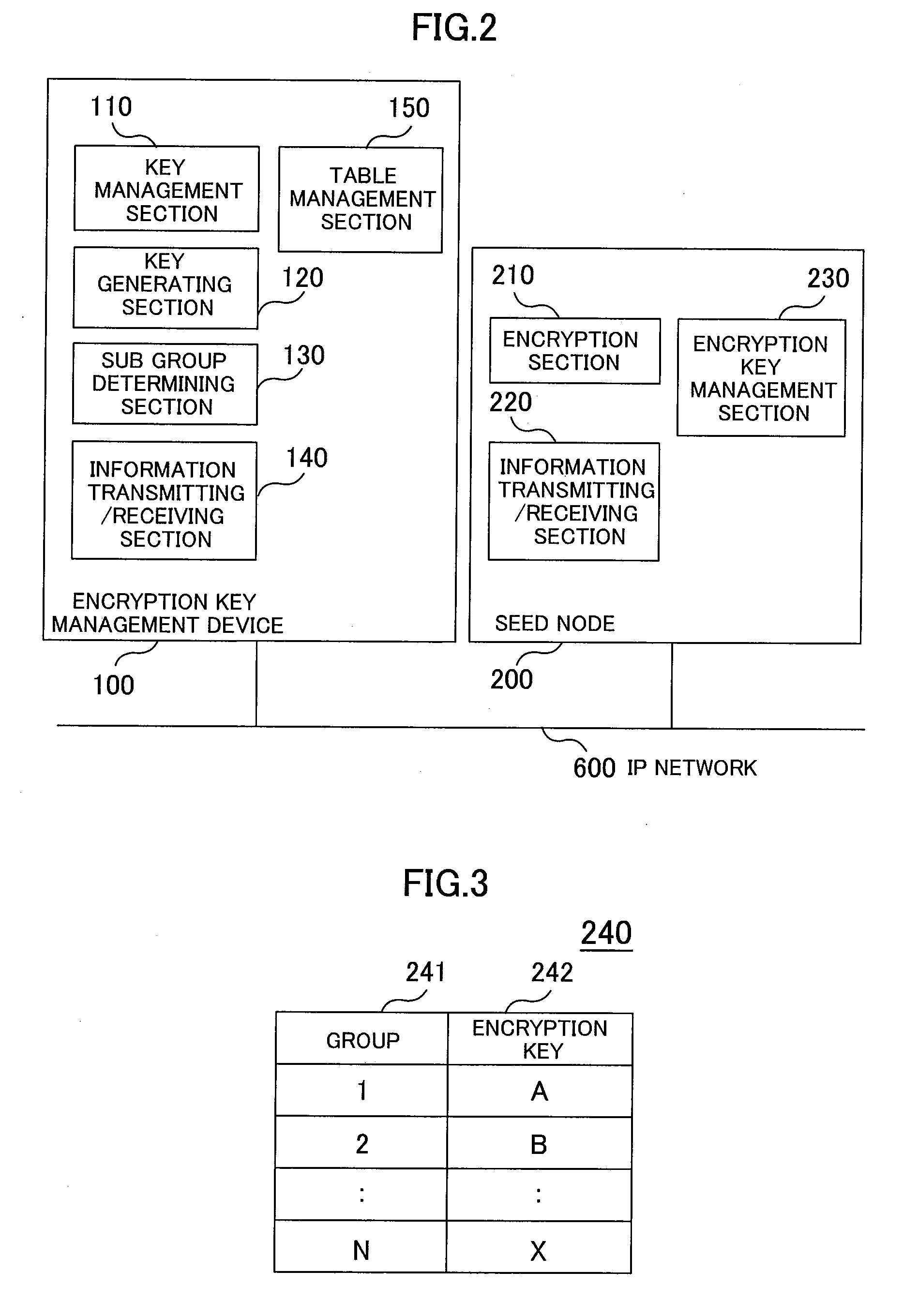
Receiving terminals joining a multicast group are divided into sub groups and rekeying is performed only on the sub group which one of the receiving terminals has left. An encryption key management system having an encryption method is provided in which a multicast server is connected via an IP network, a seed node carries out encryption multicast communications among receiving terminals by using an encryption key, the receiving terminals are properly divided into the sub groups, the single encryption key is used for data distribution of the multicast server, and the number of decoding keys is equal to the number of divided sub groups.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for rekeying a rekeyable lock cylinder
InactiveUS20090078012A1Lowering rekeying costImprove ease of useCylinder locksEngineeringMechanical engineering
This invention is to provide a method for rekeying a rekeyable lock cylinder. The first step of entire rekeying process is to insert a first user key into a keyhole of a sliding block of a plug assembly and turn the first user key to rotate the plug assembly, then a thrust is added to the first user key to move the sliding block of the plug assembly, thereby disengaging a plurality of upper locking pieces and a plurality of lower locking pieces within a plurality of lower pin sets. Next, after pulling out the first user key from the keyhole, a second user key is inserted into the keyhole of the sliding block and turned to restore the sliding block as to reengage the upper locking pieces and the lower locking pieces. Finally, the second user key is pulled out to complete the entire rekeying process. Accordingly, the present invention may provide advantages of widely lowering rekeying cost and enhancing convenience in use, because lock replacement may be completed as soon as rekeying another user key only without replacing lock cylinder.
Owner:TAIWAN FU HSING INDAL
Reverting from a new security association to a previous security association in response to an error during a rekey operation
ActiveUS20210091944A1Key distribution for secure communicationSecurity arrangementComputer networkSecurity association
Provided are a computer program product, system, and method embodiments for reverting from a new security association to a previous security association in response to an error during a rekey operation. The responder maintains a first security association with the initiator having a first key to use to encrypt and decrypt messages transmitted with the initiator. The responder receives a message from the initiator for a rekey operation to establish a second security association with the initiator using a second key. The responder queues Input / Output (I / O) for transmission using the second key after completing the rekey operation. After activating the second security association, the responder receives a revert message from the initiator to revert back to using the first security association and first key in response to a failure of the rekey operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
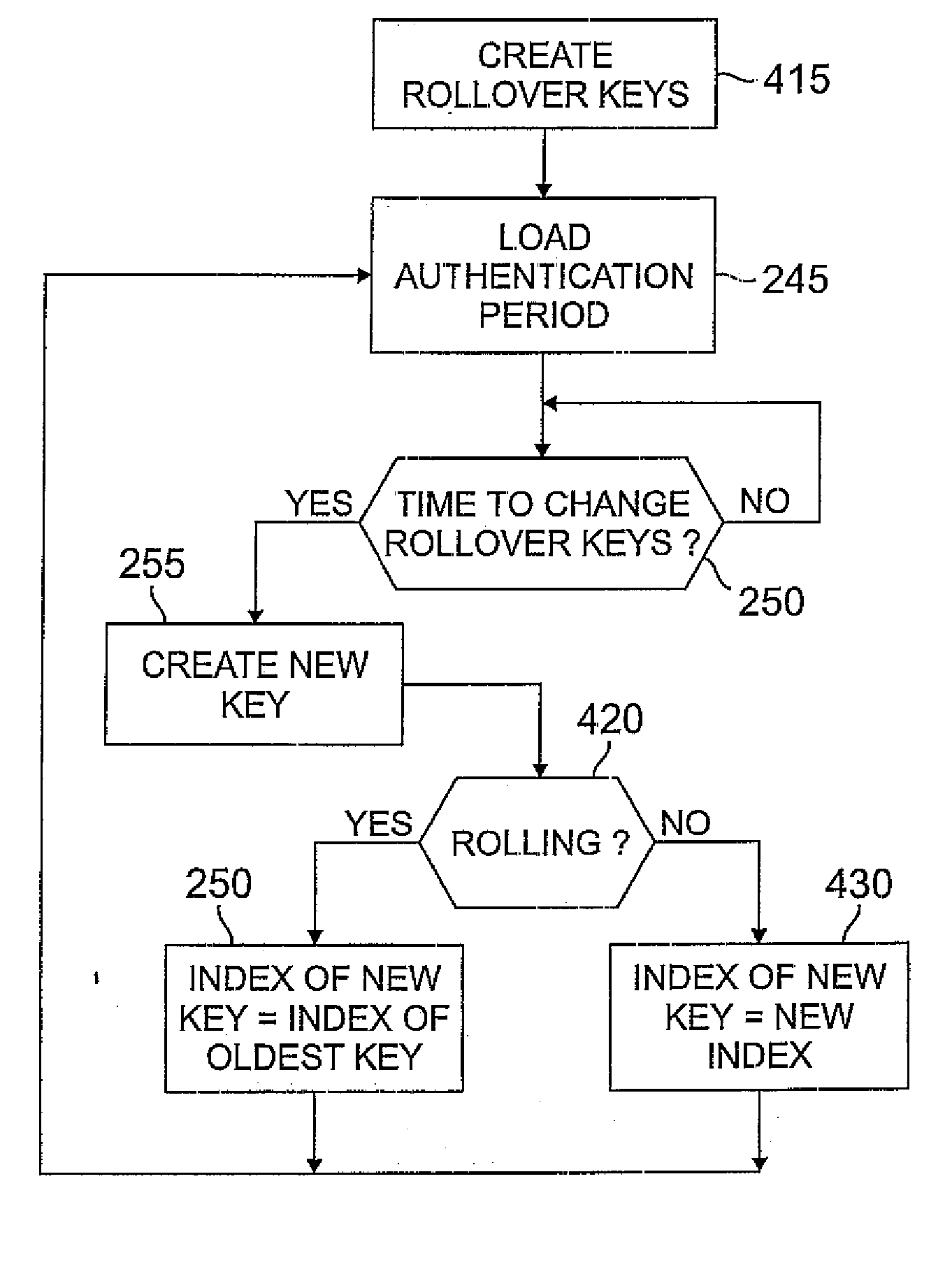
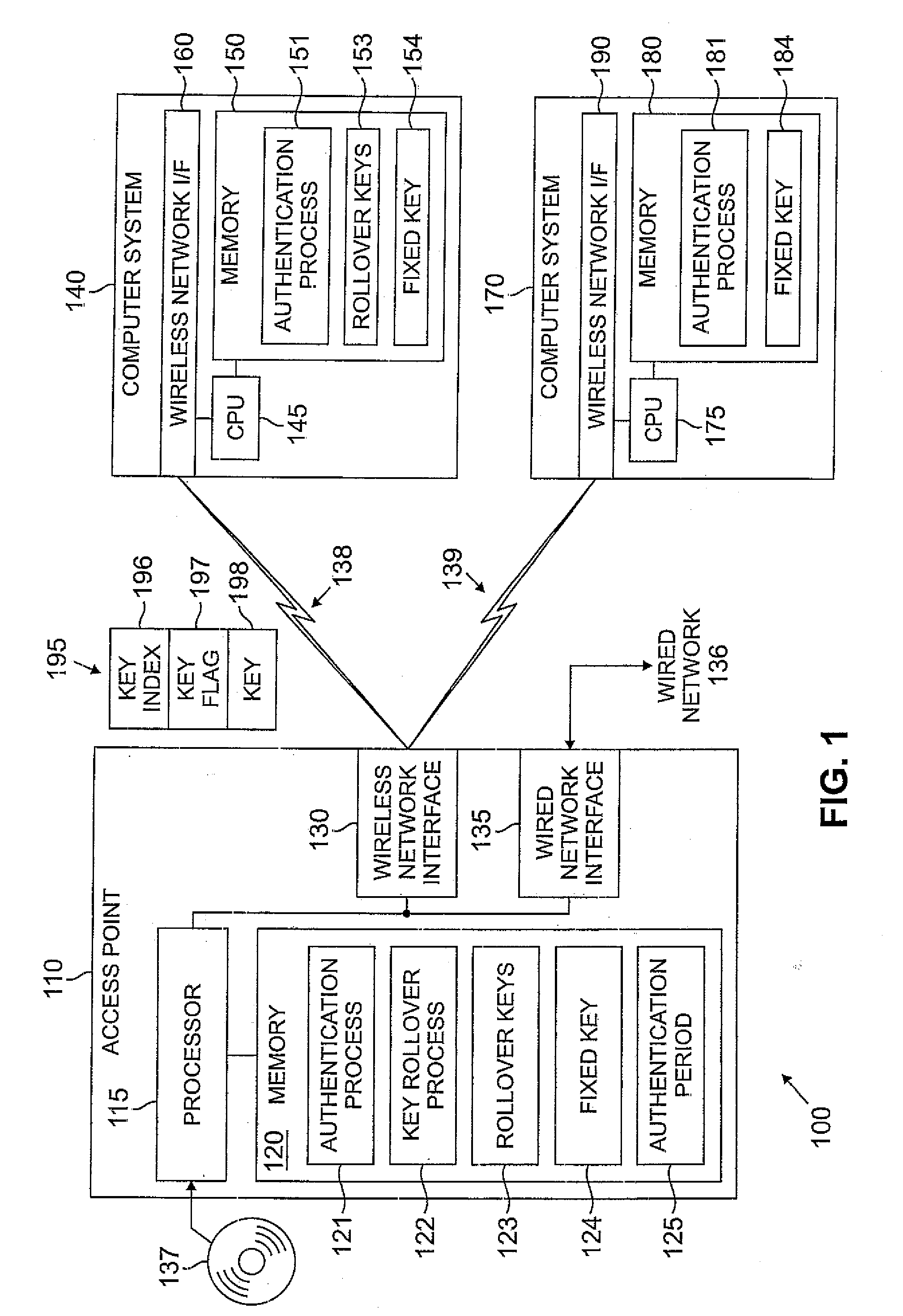
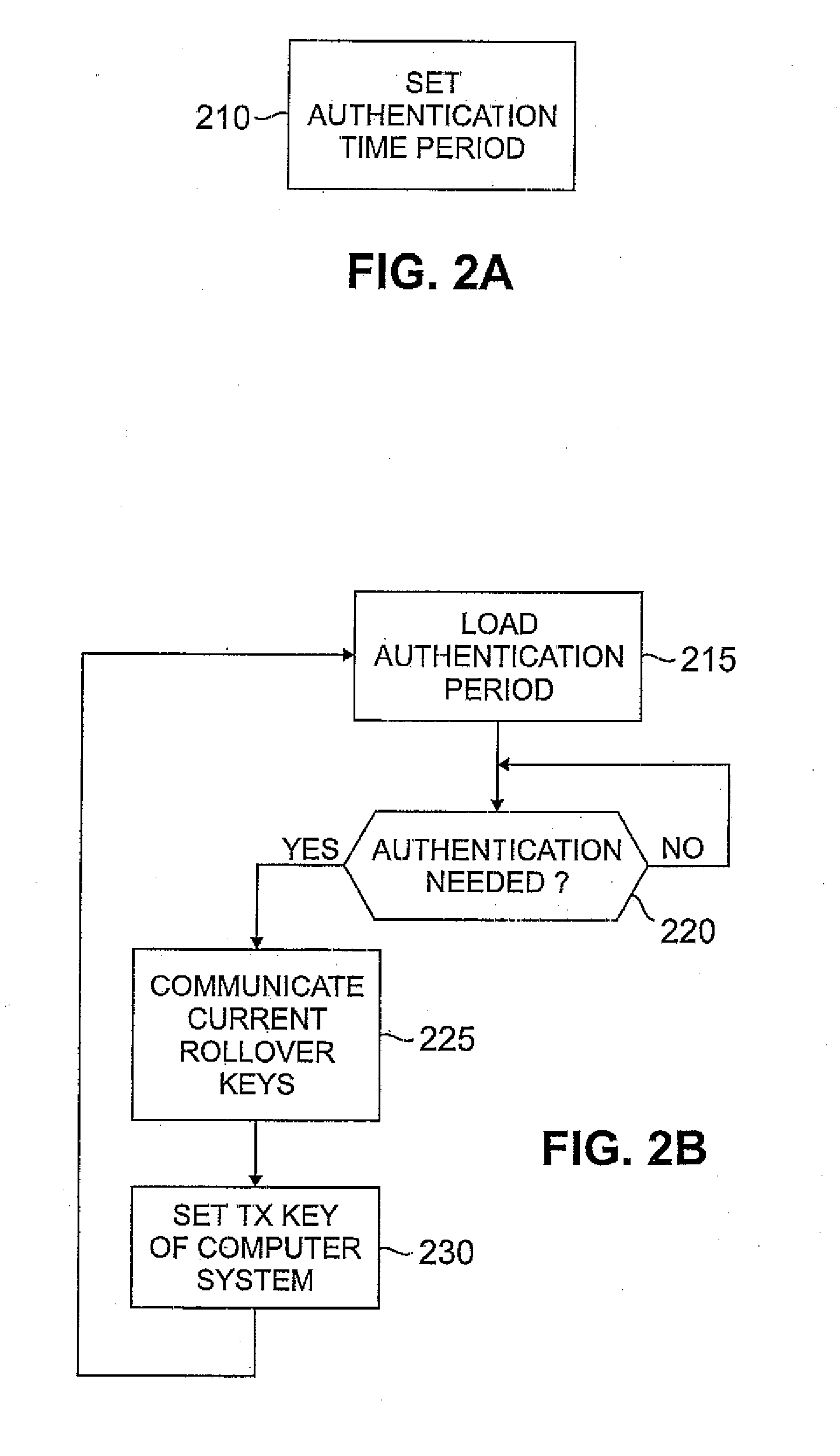
Security key distribution using key rollover strategies for wireless networks
InactiveUS20070183599A1Amount of data be minimalDifficult timeKey distribution for secure communicationNetwork traffic/resource managementRolloverKey distribution
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Secret key update method and system
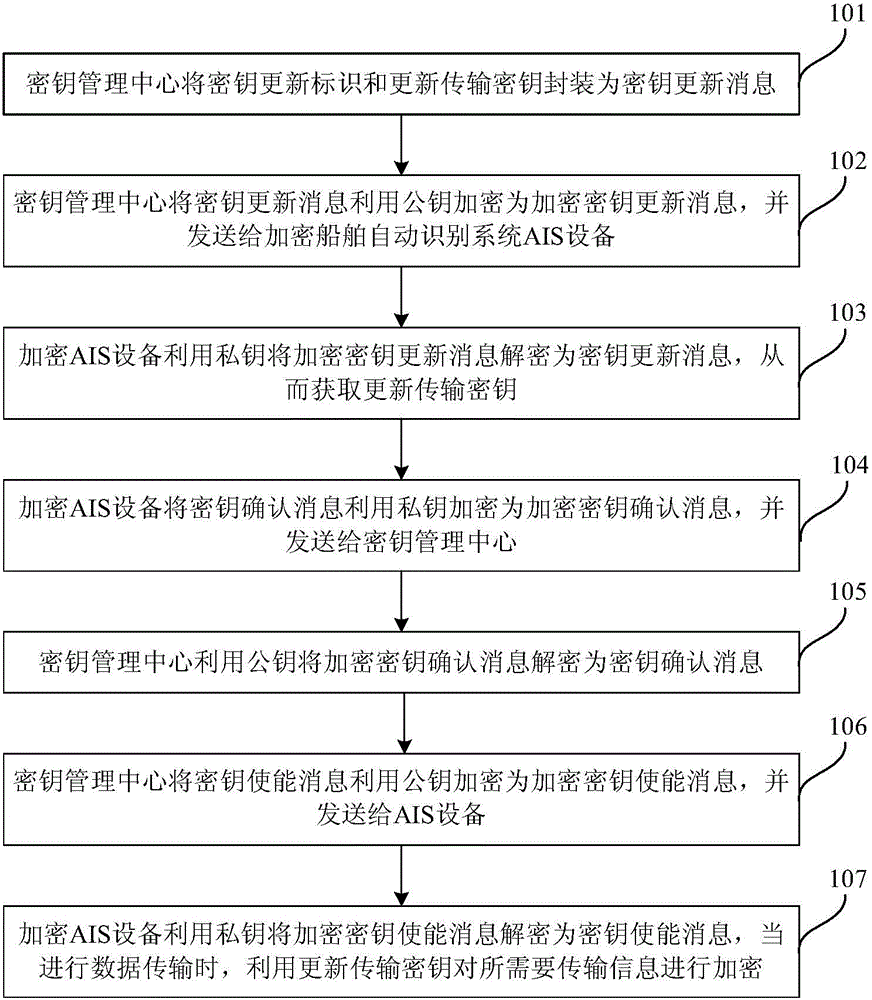
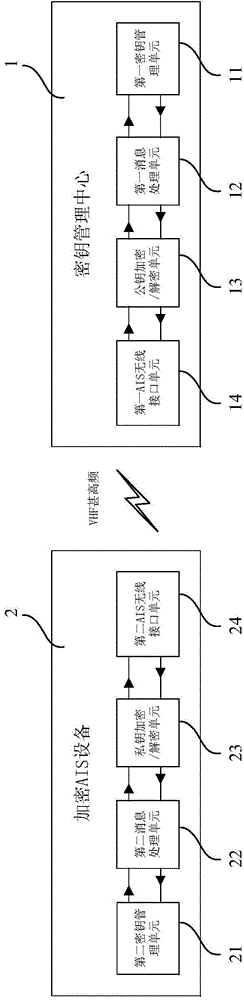
ActiveCN105101190AEasy and fast regular automatic updatesSecurity arrangementComputer hardwareData transmission
The invention relates to a secret key update method and a system. The method includes: a secret key update message is encrypted to an encryption key update message by the adoption of a public key and sent to encryption ship automatic identification system AIS equipment by a secret key management center; the encryption AIS equipment decrypts the encryption key update message to the secret key update message by the adoption of a private key and obtains an update transmission secret key; the encryption AIS equipment encrypts a secret key confirmation message to an encryption key confirmation message by the adoption of the private key and sends the message to the secret key management center; the secret key management center encrypts a secret key enablement message to an encryption key enablement message by the adoption of the public key and sends the message to the AIS equipment; and the encryption AIS equipment decrypts the encryption key enablement message to the secret key enablement message by the adoption of the private key, and transmitted information is encrypted by the adoption of the update transmission secret key during data transmission. According to the secret key update method and the system, regular automatic update of encryption keys of large-scale AIS equipment is conveniently and rapidly realized.
Owner:北京国基科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com