Patents
Literature
122 results about "Key derivation function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
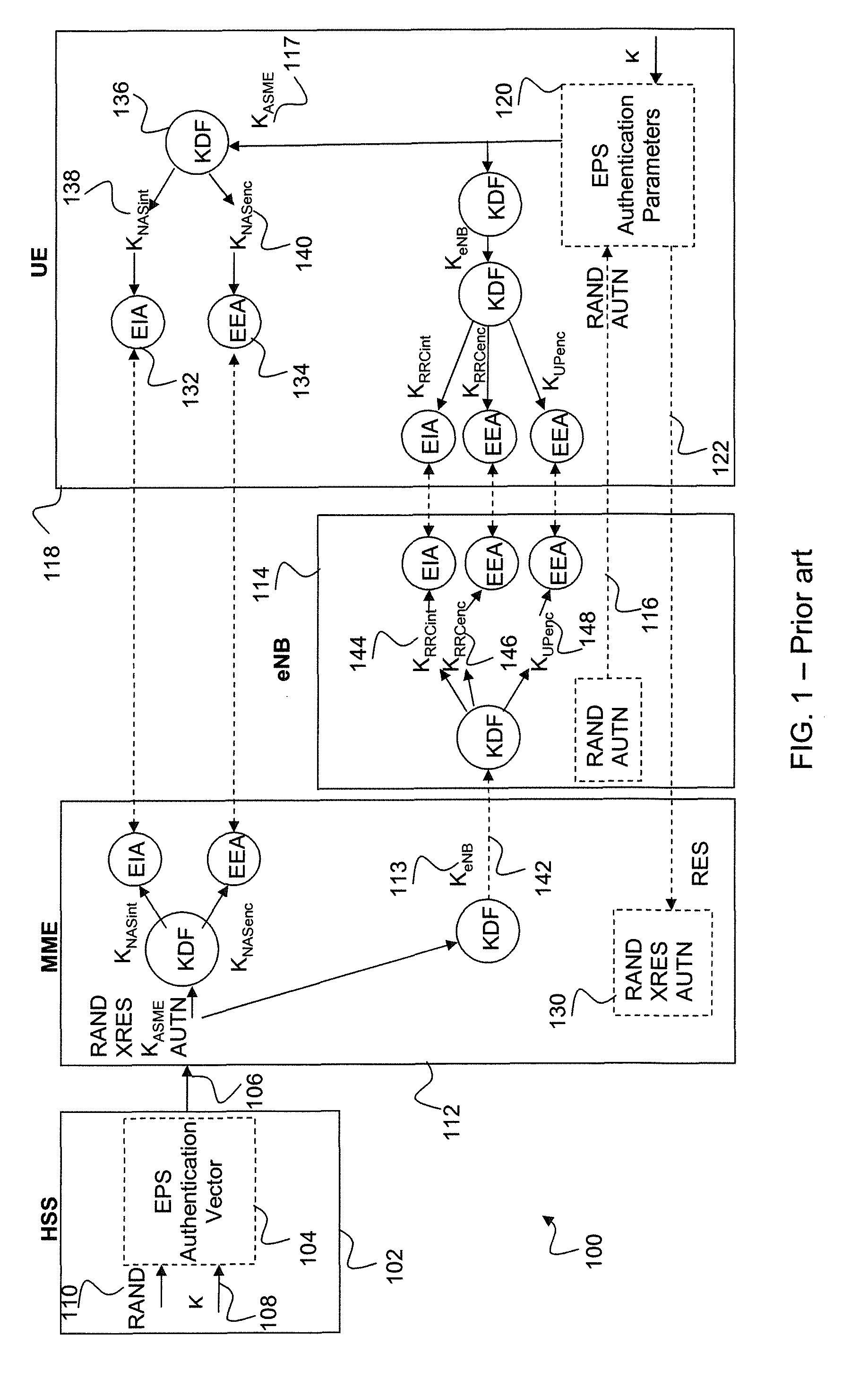
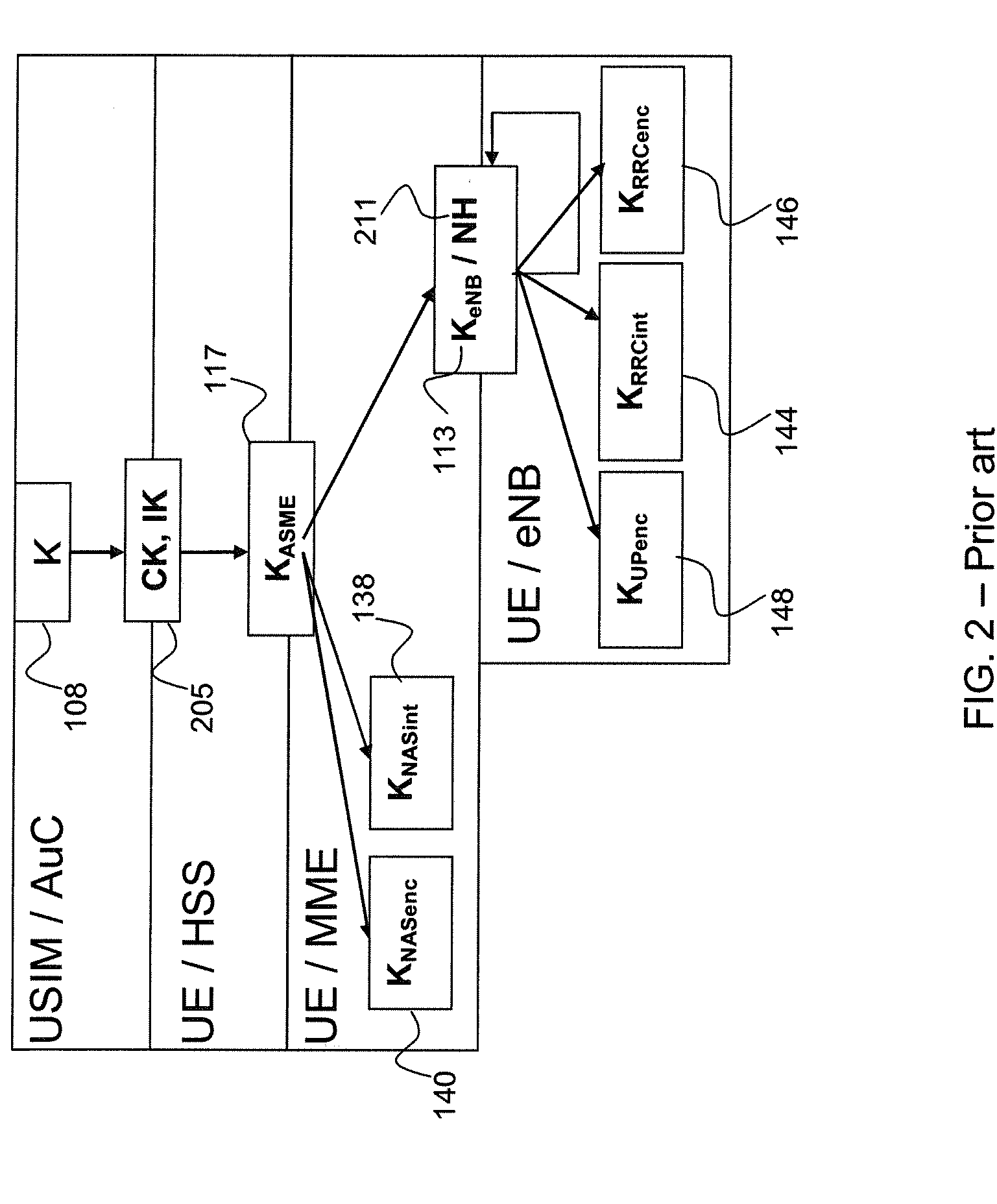
In cryptography, a key derivation function (KDF) derives one or more secret keys from a secret value such as a master key, a password, or a passphrase using a pseudorandom function. KDFs can be used to stretch keys into longer keys or to obtain keys of a required format, such as converting a group element that is the result of a Diffie–Hellman key exchange into a symmetric key for use with AES. Keyed cryptographic hash functions are popular examples of pseudorandom functions used for key derivation.
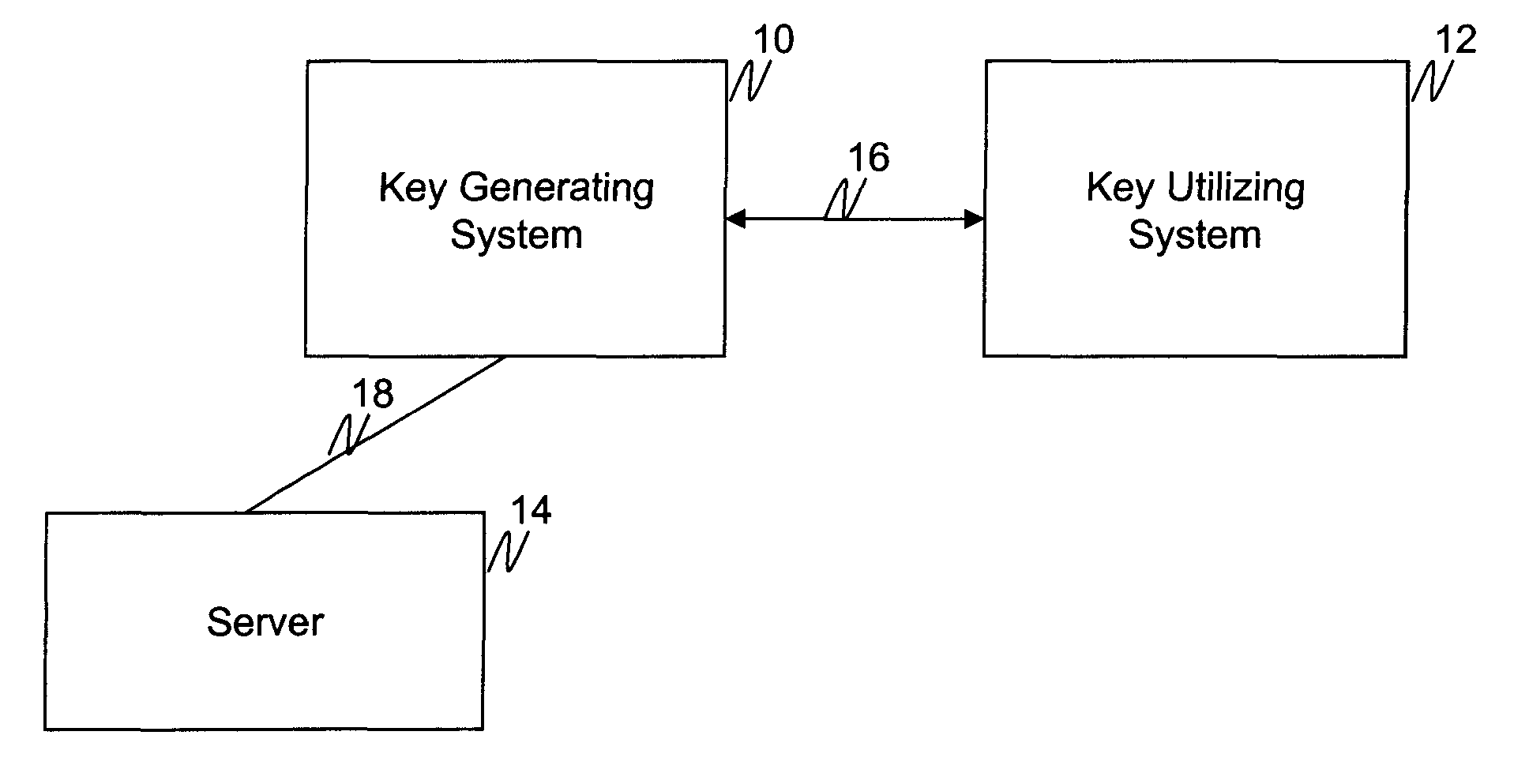
Efficient management of cryptographic key generations
InactiveUS20070127719A1Restricted accessEfficient storageKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptographic key generationEarly generation
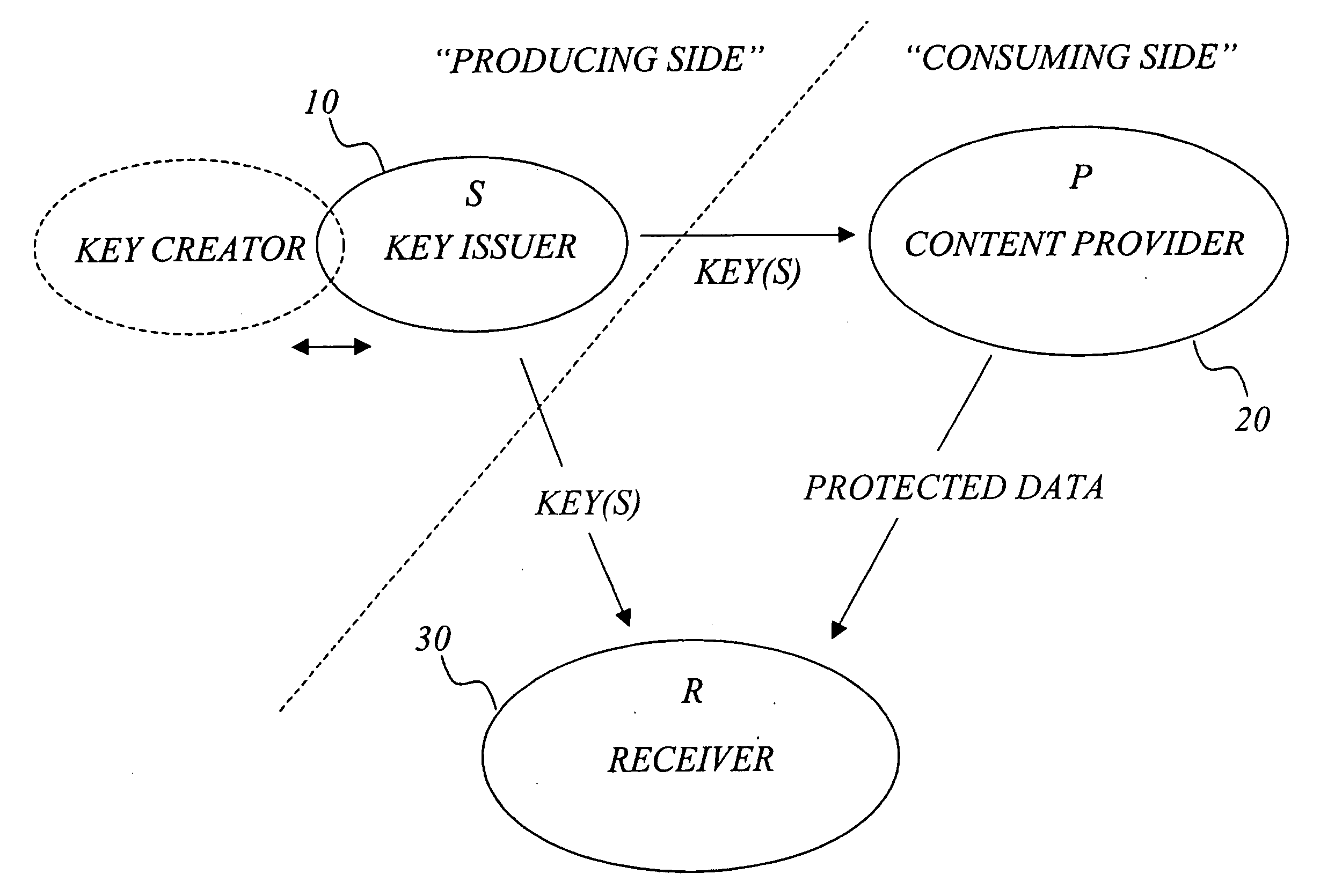
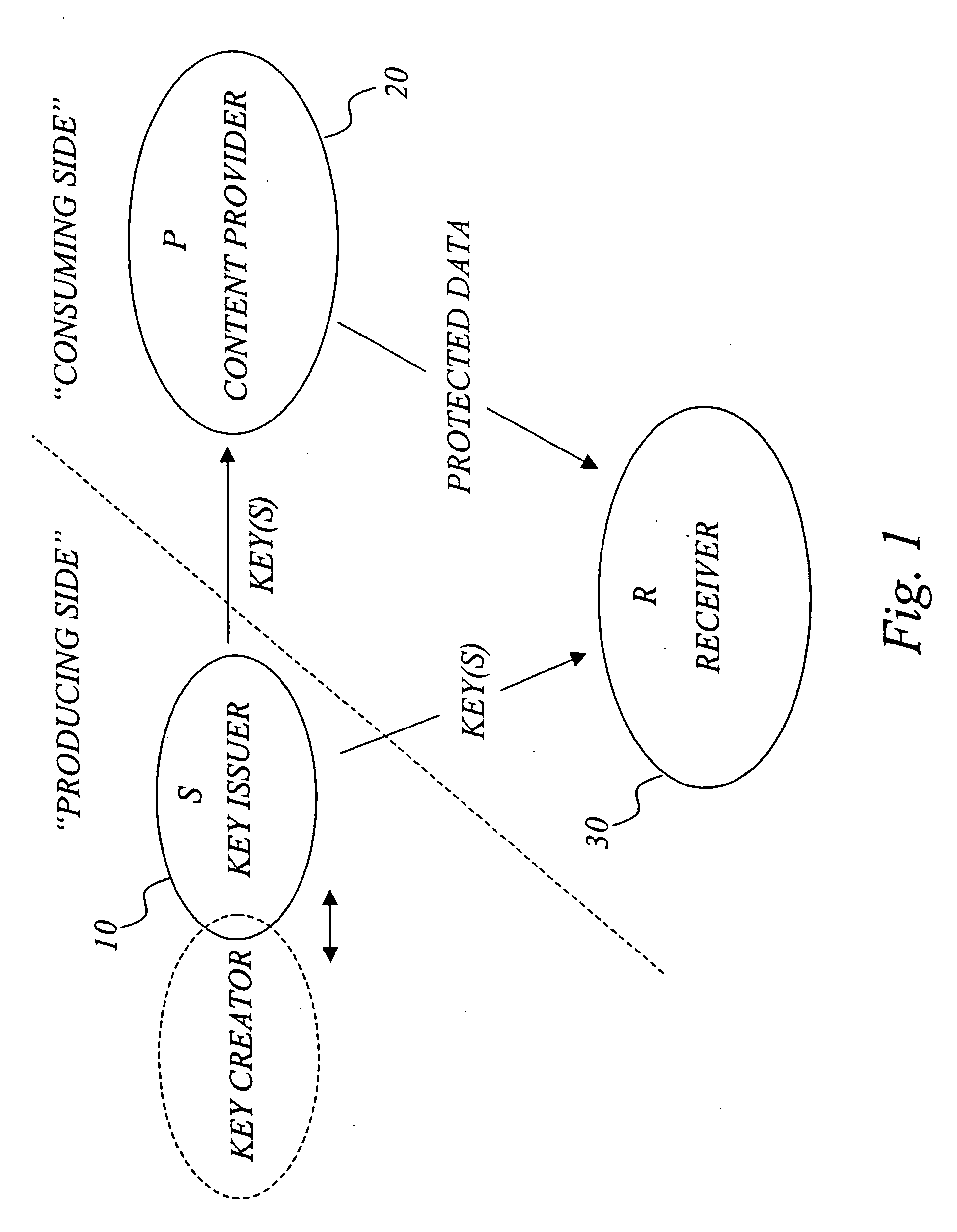
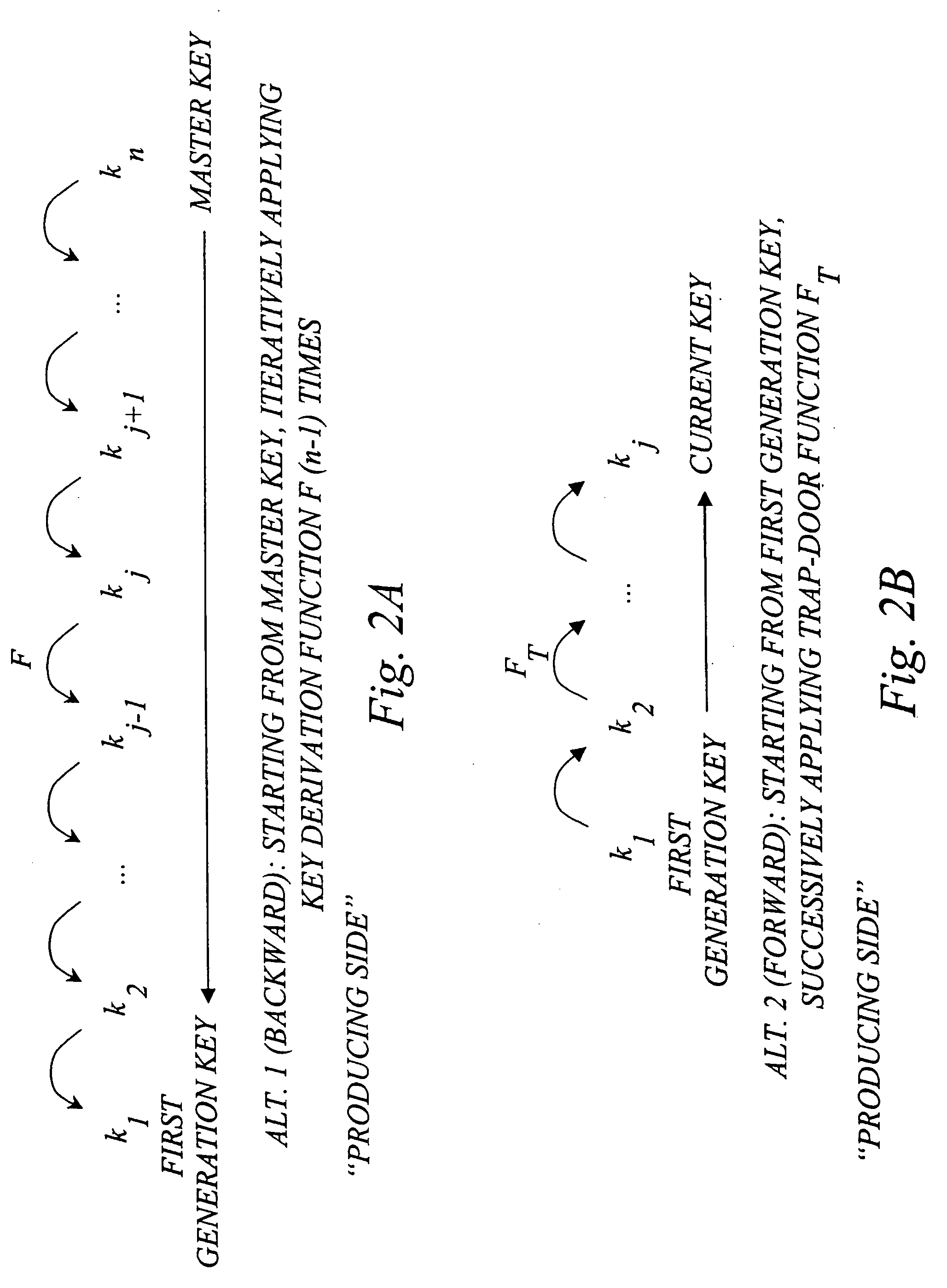
The invention generally relates to management of cryptographic key generations in an information environment comprising a key-producing side generating and distributing key information to a key-consuming side. A basic concept of the invention is to define, by means of a predetermined one-way key derivation function, a relationship between generations of keys such that earlier generations of keys efficiently may be derived from later ones but not the other way around. A basic idea according to the invention is therefore to replace, at key update, key information of an older key generation by the key information of the new key generation on the key-consuming side. Whenever necessary, the key-consuming side iteratively applies the predetermined one-way key derivation function to derive key information of at least one older key generation from the key information of the new key generation. In this way, storage requirements on the key-consuming side can be significantly reduced.
Owner:EMC CORP +1
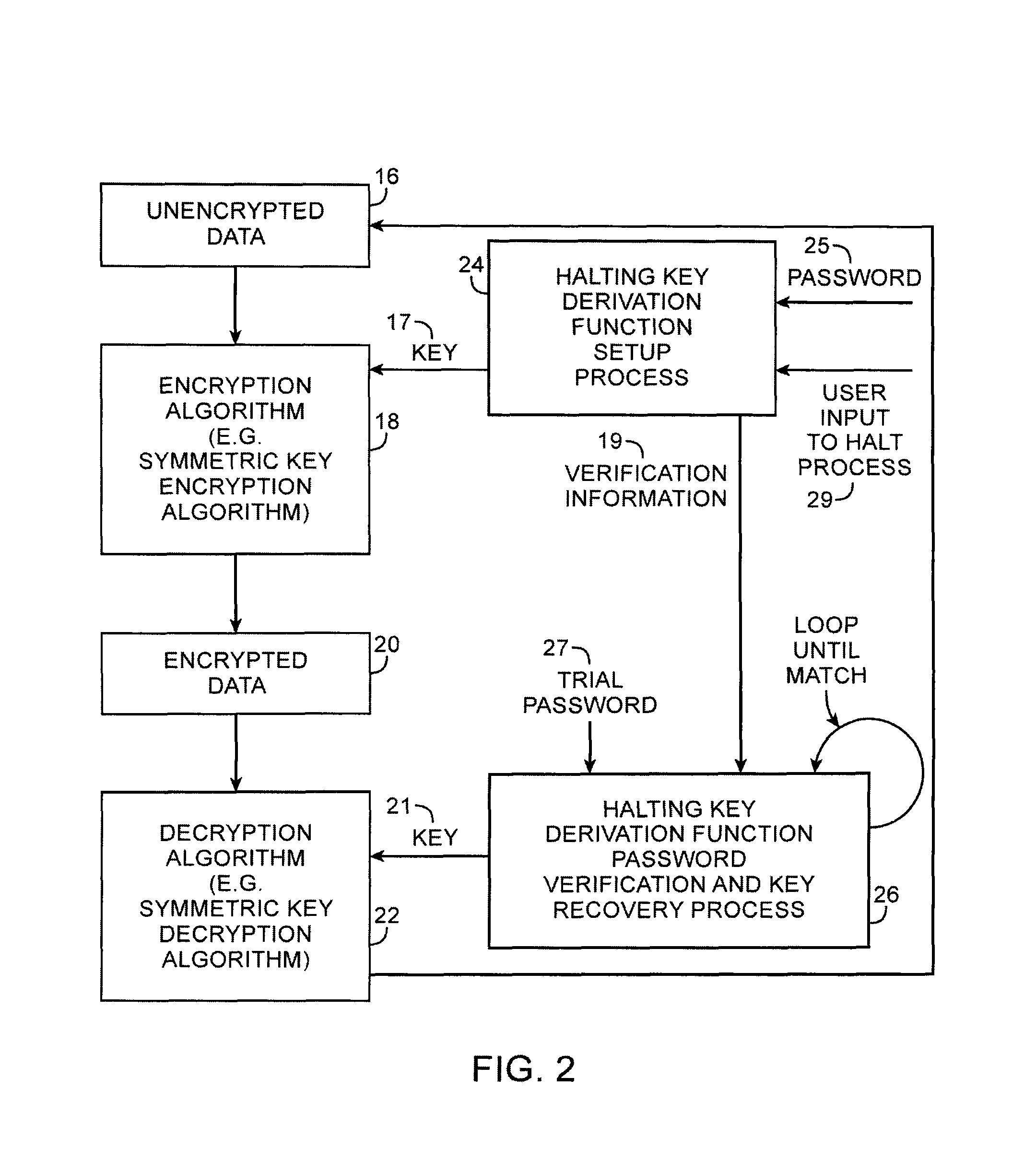
Cryptographic system with halting key derivation function capabilities
ActiveUS8254571B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsUser inputPassword
A halting key derivation function is provided. A setup process scrambles a user-supplied password and a random string in a loop. When the loop is halted by user input, the setup process may generate verification information and a cryptographic key. The key may be used to encrypt data. During a subsequent password verification and key recovery process, the verification information is retrieved, a user-supplied trial password obtained, and both are used together to recover the key using a loop computation. During the loop, the verification process repeatedly tests the results produced by the looping scrambling function against the verification information. In case of match, the trial password is correct and a cryptographic key matching the key produced by the setup process may be generated and used for data decryption. As long as there is no match, the loop may continue indefinitely until interrupted exogenously, such as by user input.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
Method and system for protecting signaling information
InactiveUS20080181411A1Key distribution for secure communicationOrthogonal multiplexAccess networkComputer hardware
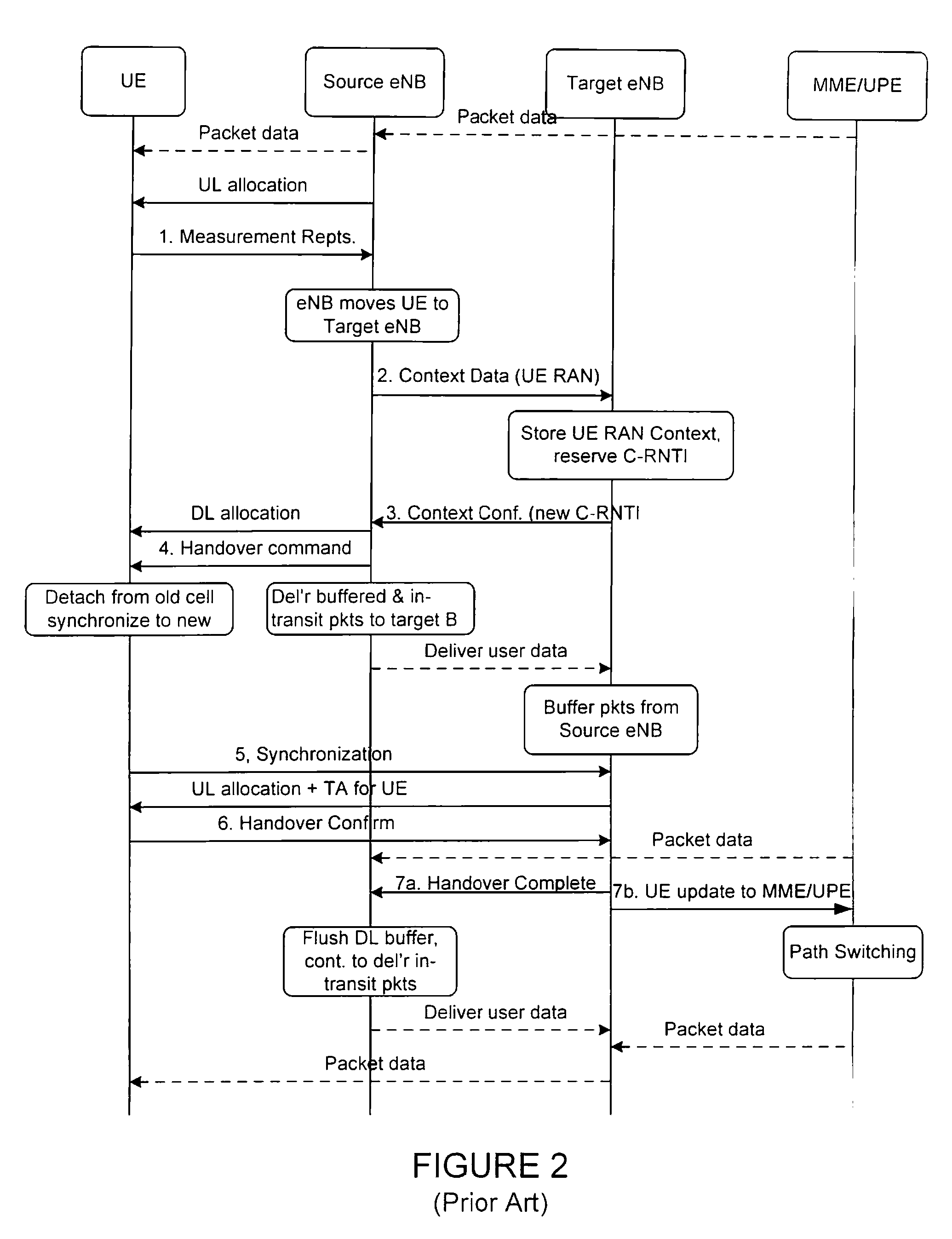
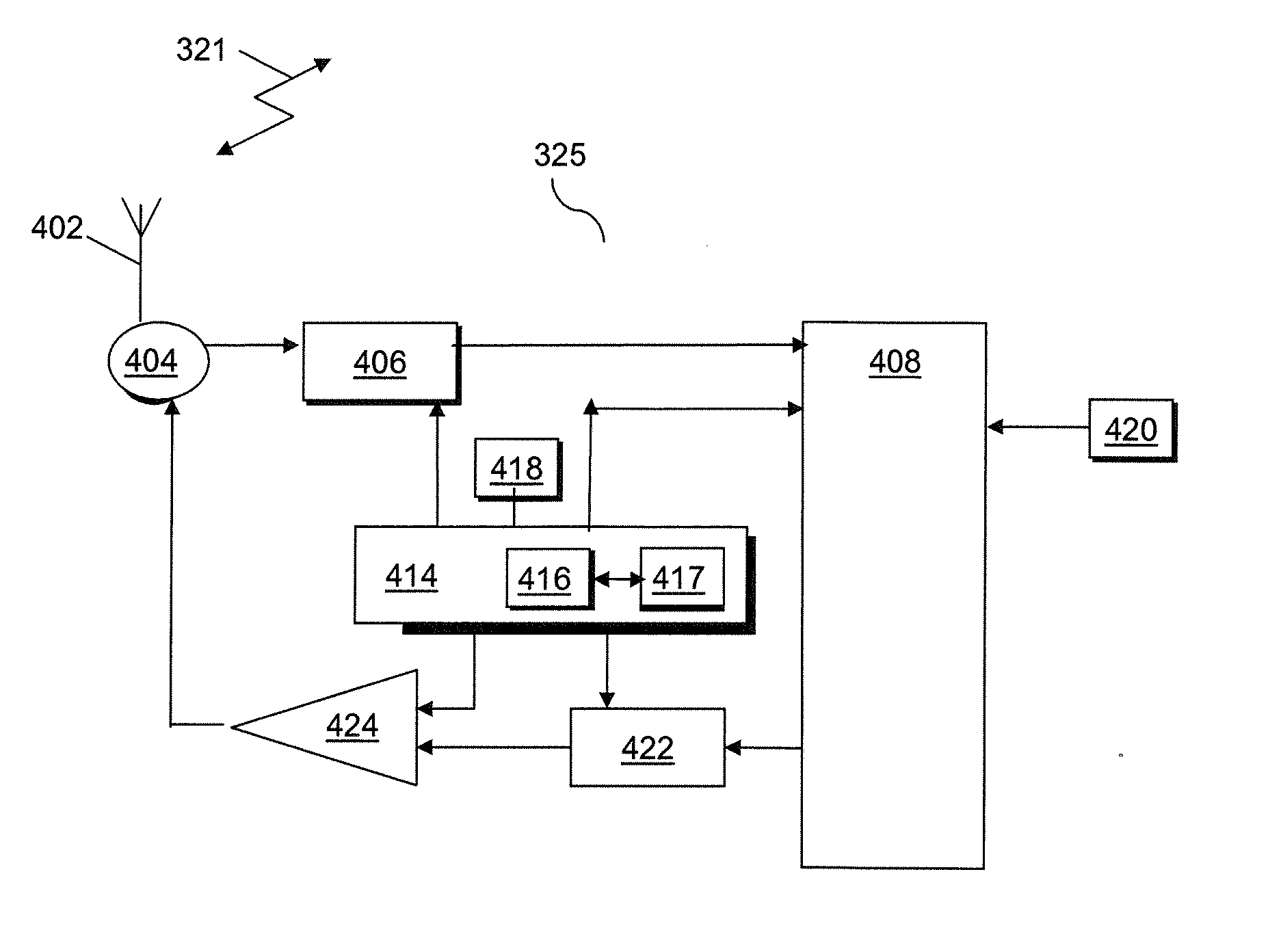
A path switch message in a mobile radio access network is protected as the message is sent over a user plane interface that may be insecure (e.g. lacks integrity and / or confidentiality protection). According to the invention a UE provides an AP with a fresh integrity key over an already existing and secure RAN channel enabling AP to use the integrity key to integrity protect information sent to a UPN. Specifically, UE derives locally at least a user plane key K1. The key derivation is done at authentication e.g. when performing an AKA procedure. On the network side CPN derives the same key K1 for delivery to UPN. At handover, the UE generates a fresh integrity key K3 by applying a Key Derivation Function (KDF) with at least the UP key K1 and a nonce, e.g. a sequence number.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
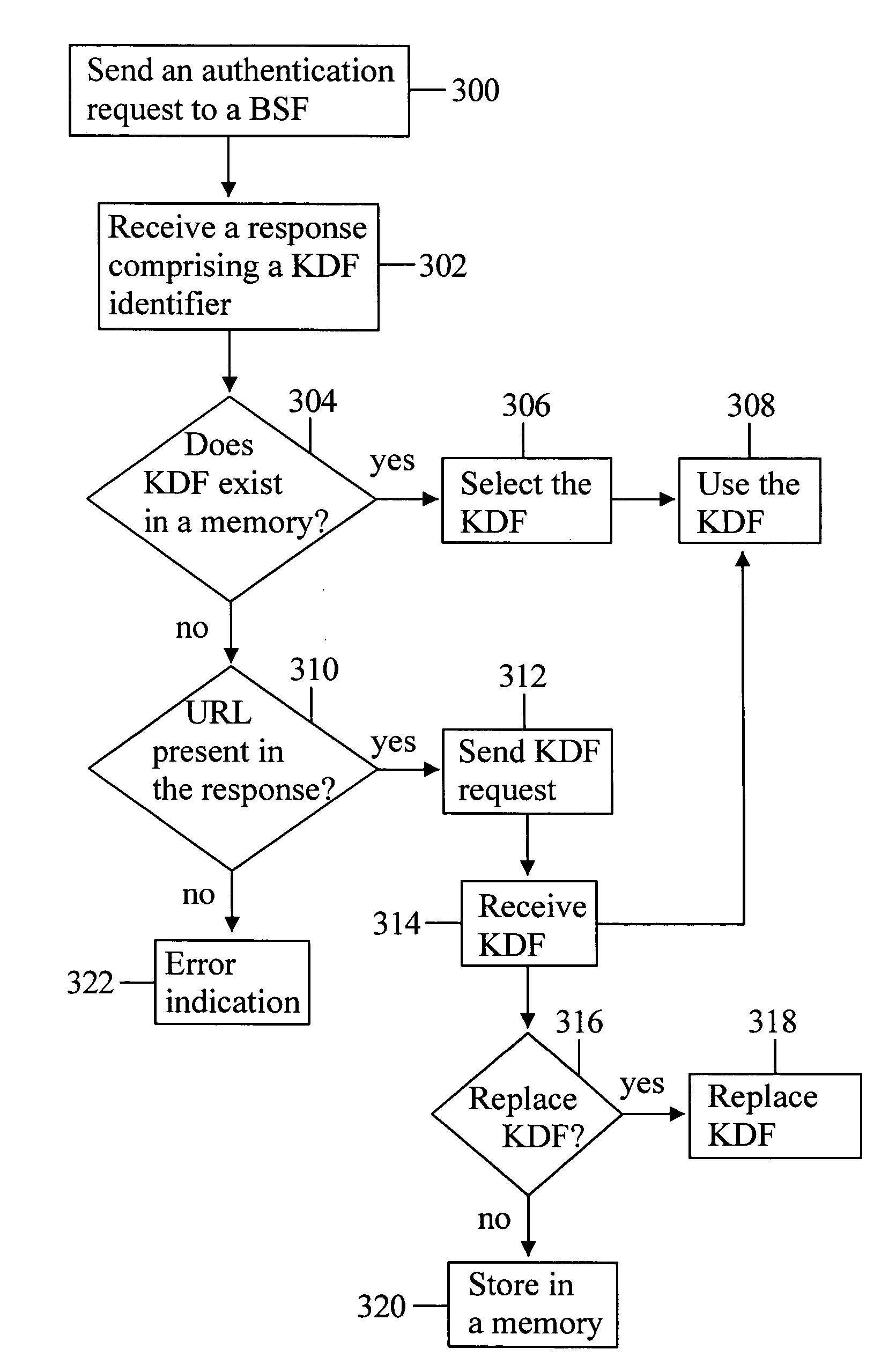
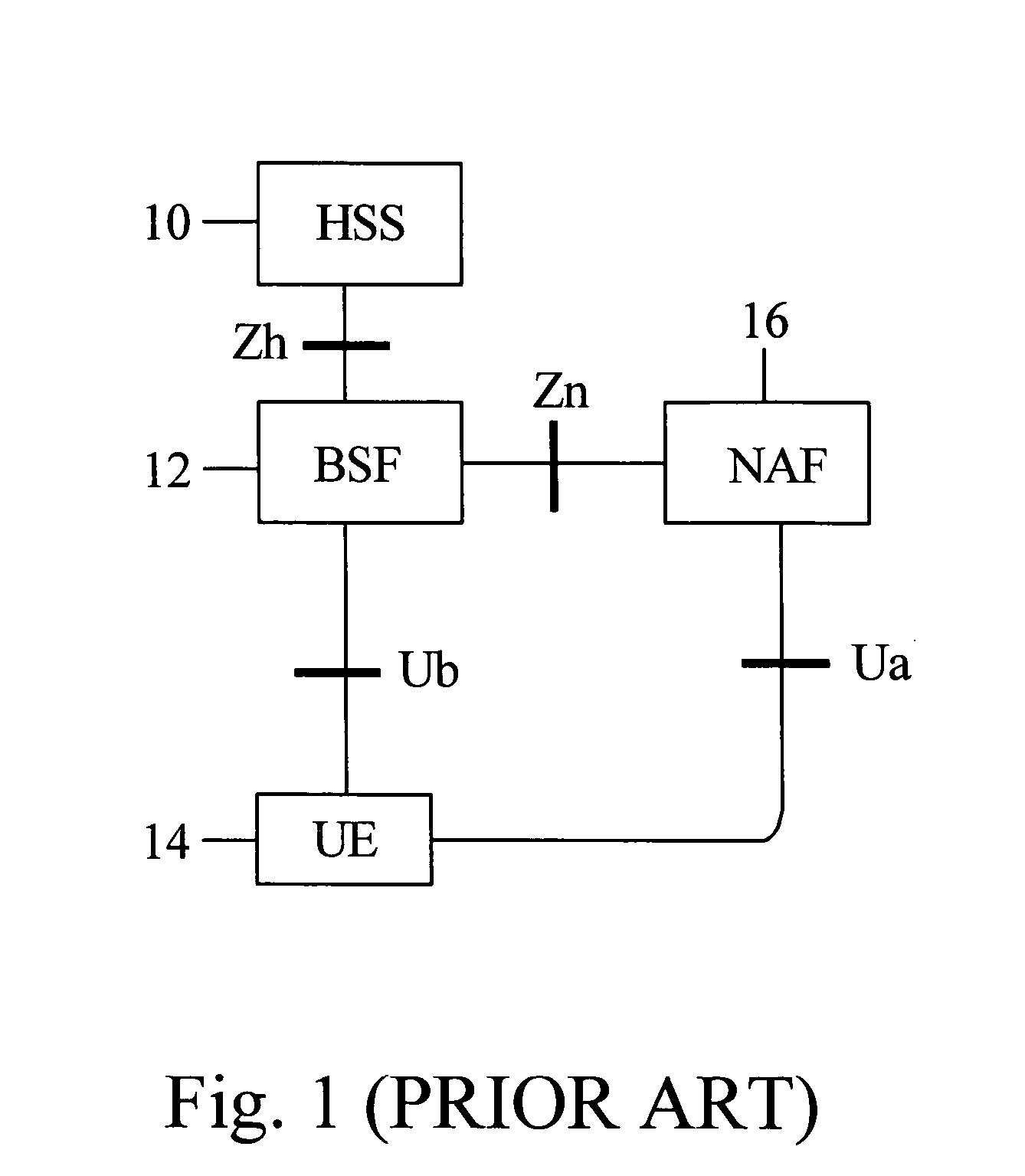
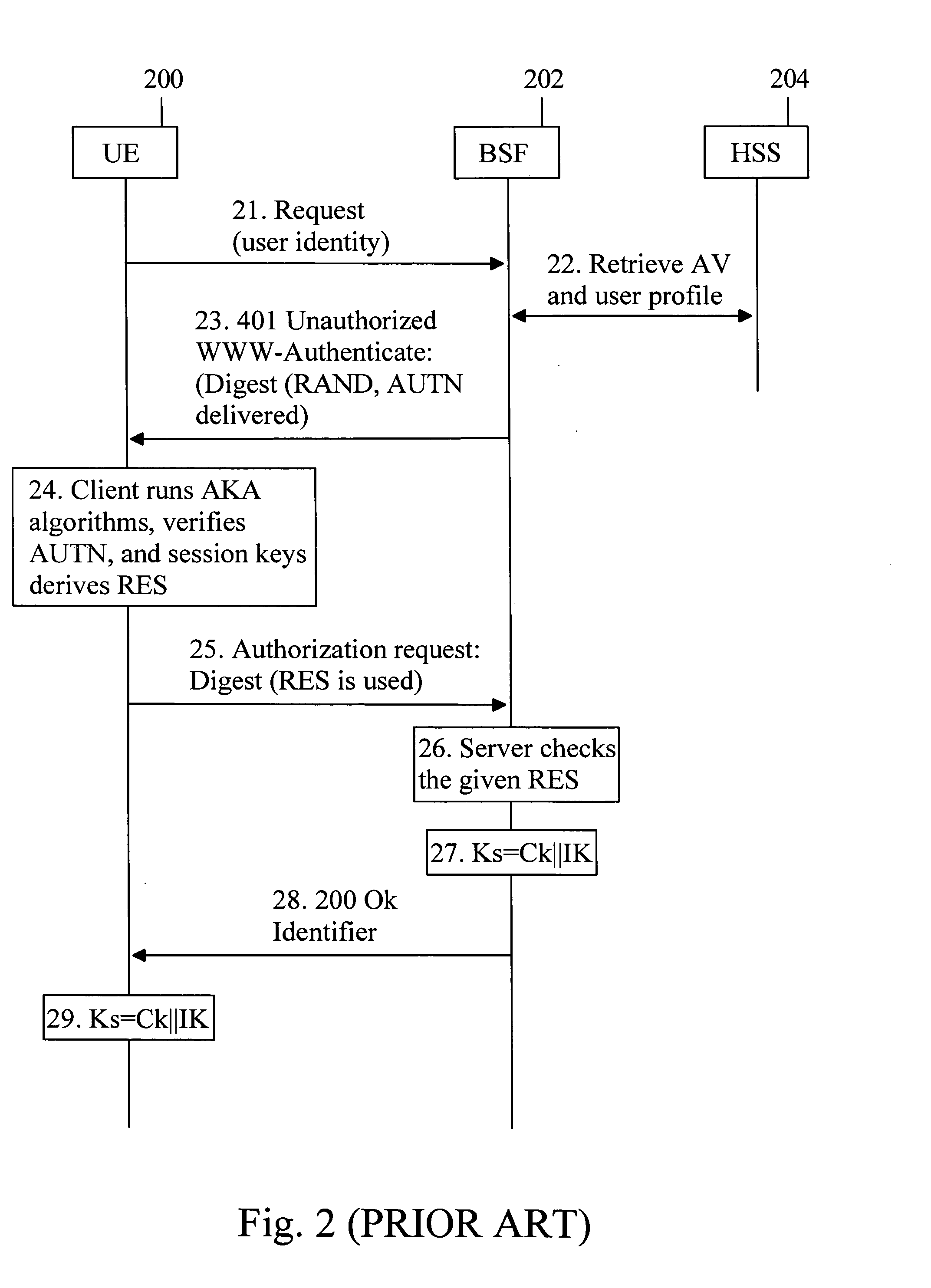
Determining a key derivation function
InactiveUS20060101270A1Easy to switchKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey derivation functionUser equipment
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System access using a mobile device
ActiveUS20200052905A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeComputer network
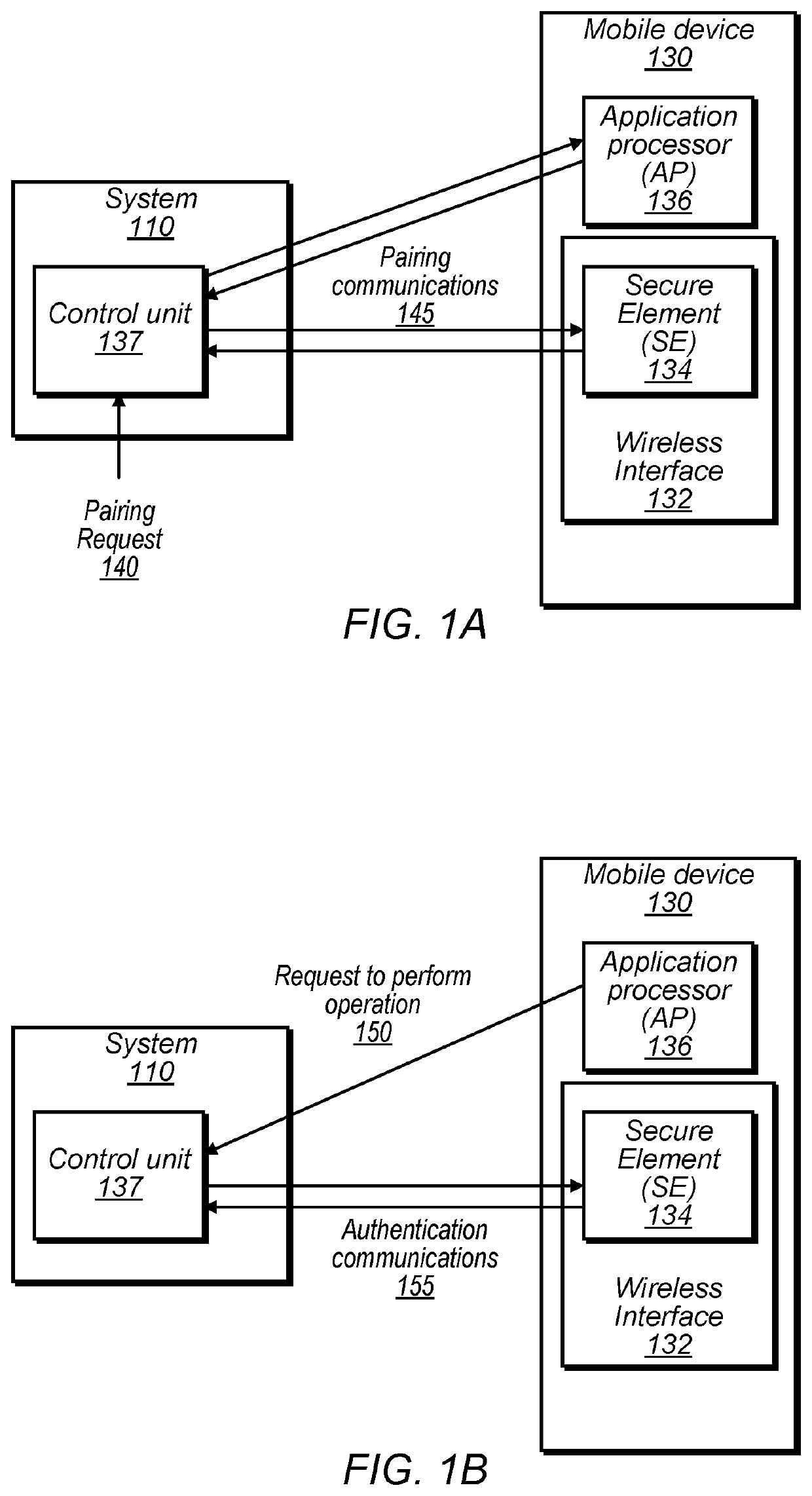
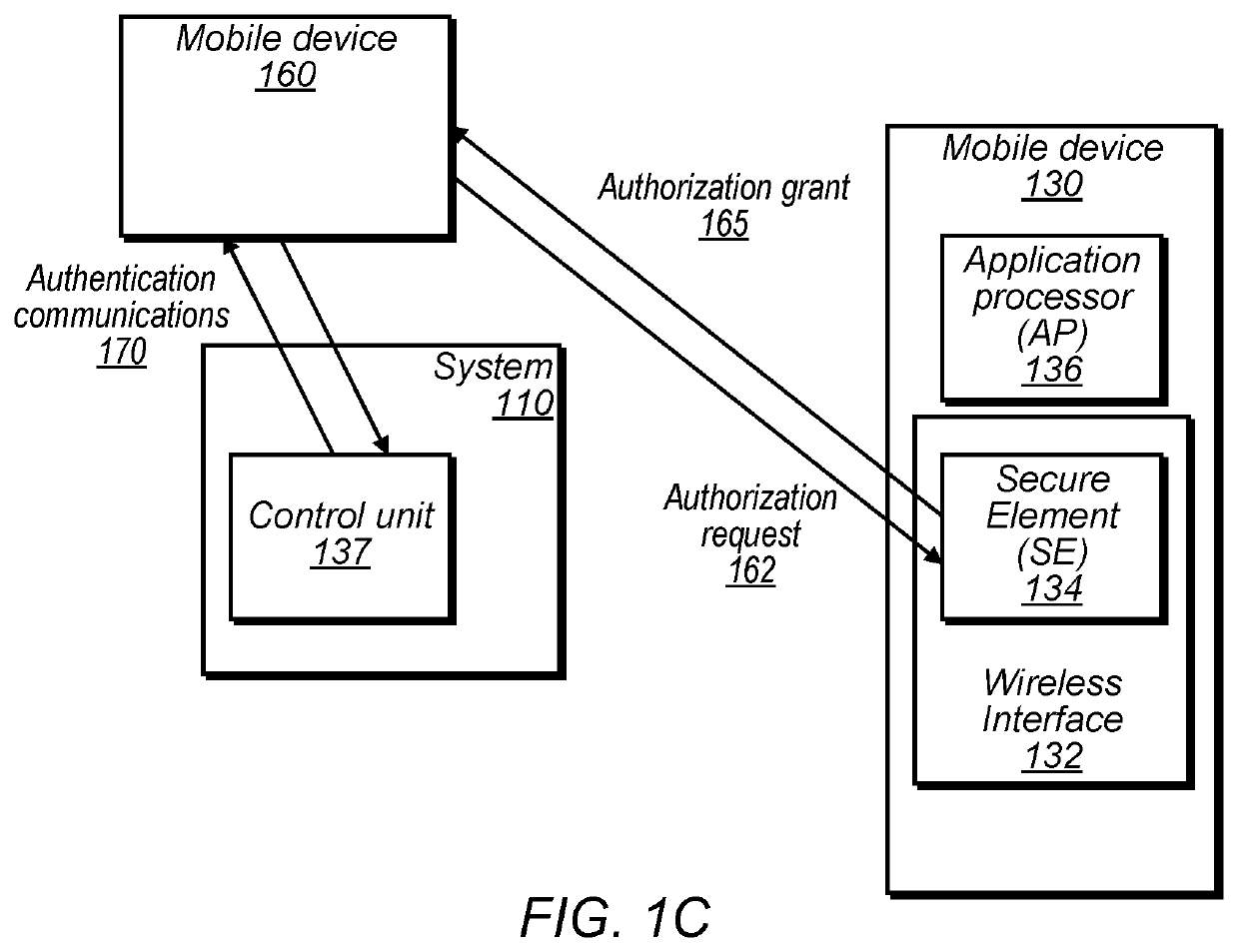
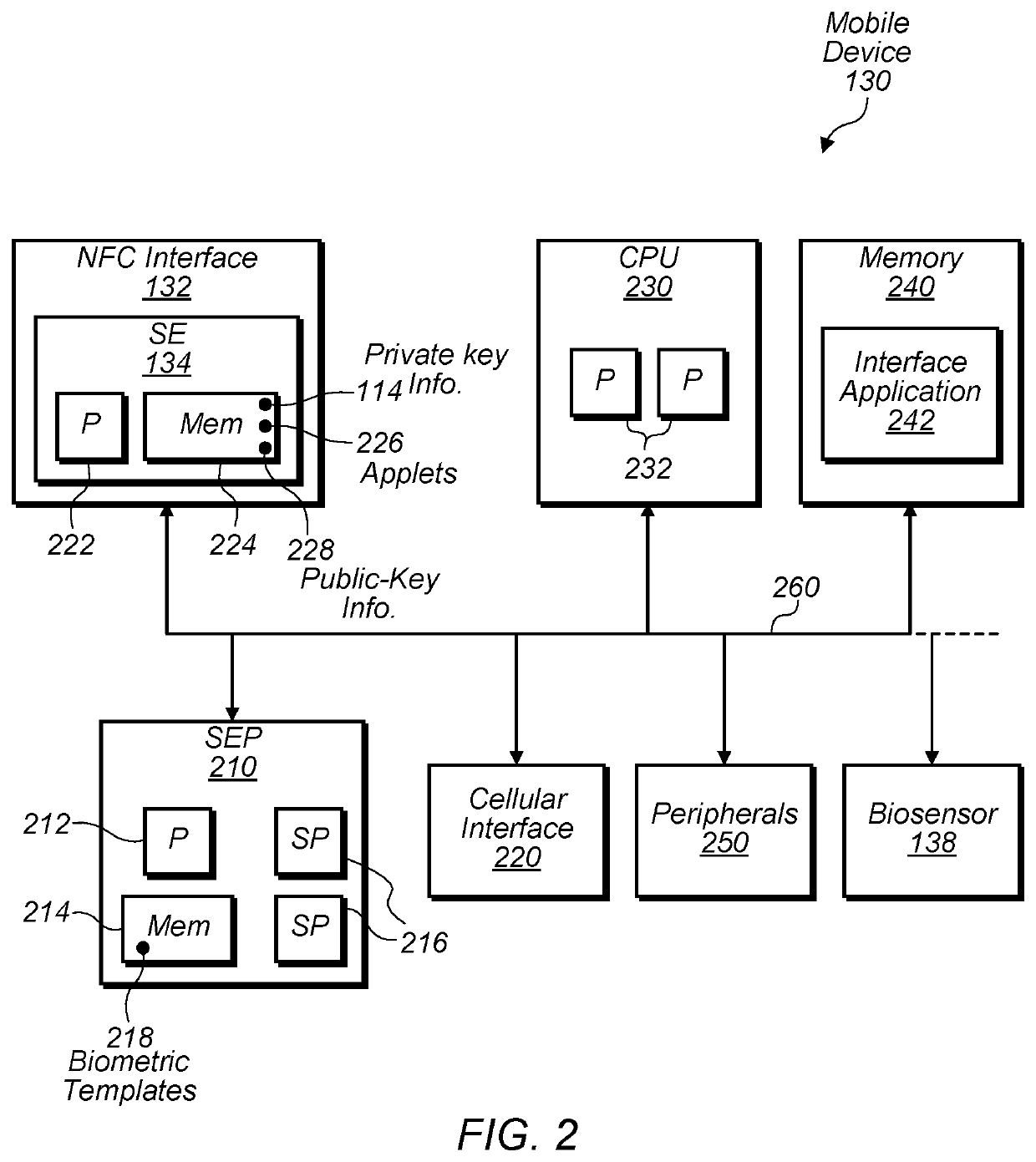
Techniques are disclosed relating to electronic security, e.g., for authenticating a mobile electronic device to allow access to system functionality (e.g., physical access to the system, starting an engine / motor, etc.). In some embodiments, a system and mobile device exchange public keys of public key pairs during a pairing process. In some embodiments, an asymmetric transaction process includes generating a shared secret using a key derivation function over a key established using a secure key exchange (e.g., elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman), and verifying a signature of the system before transmitting any information identifying the mobile device. In various embodiments, disclosed techniques may increase transaction security and privacy of identifying information.
Owner:APPLE INC
Semi-deterministic digital signature generation
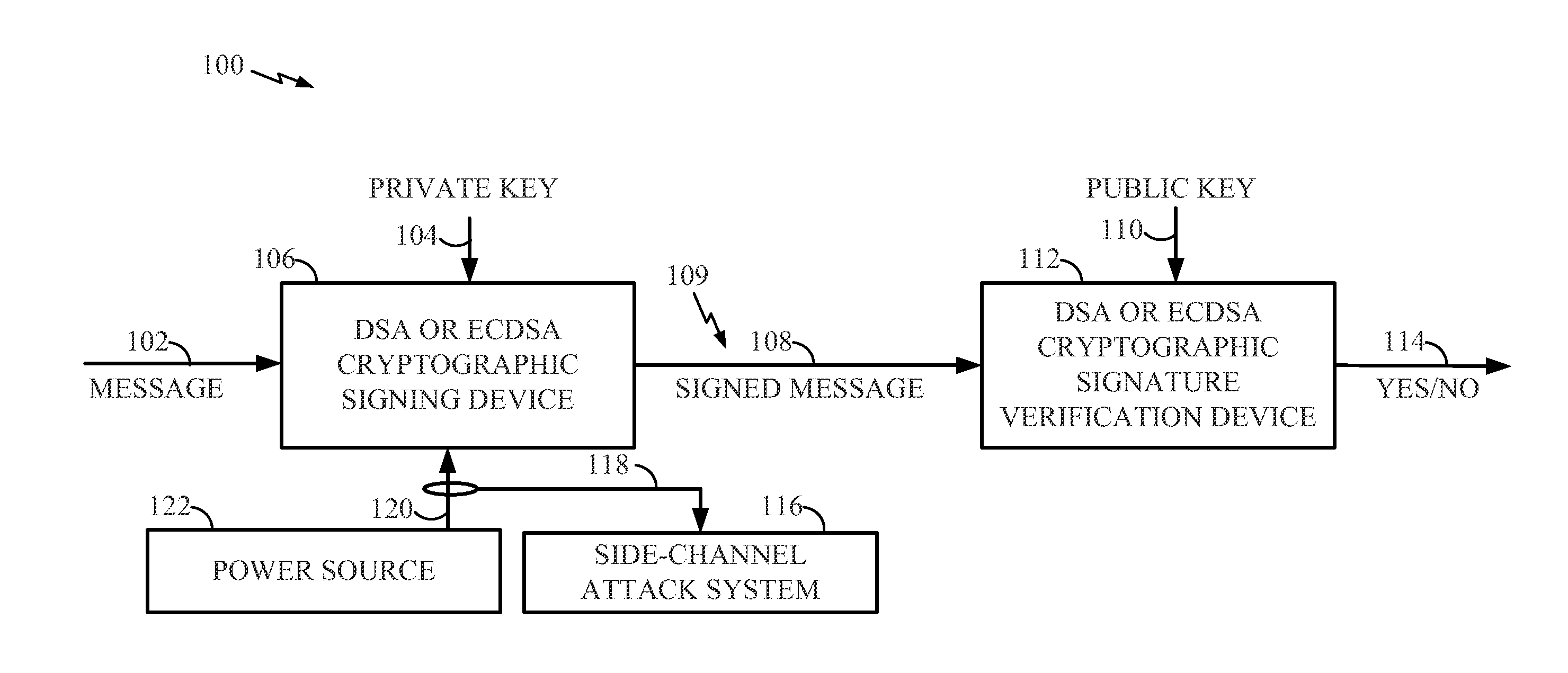
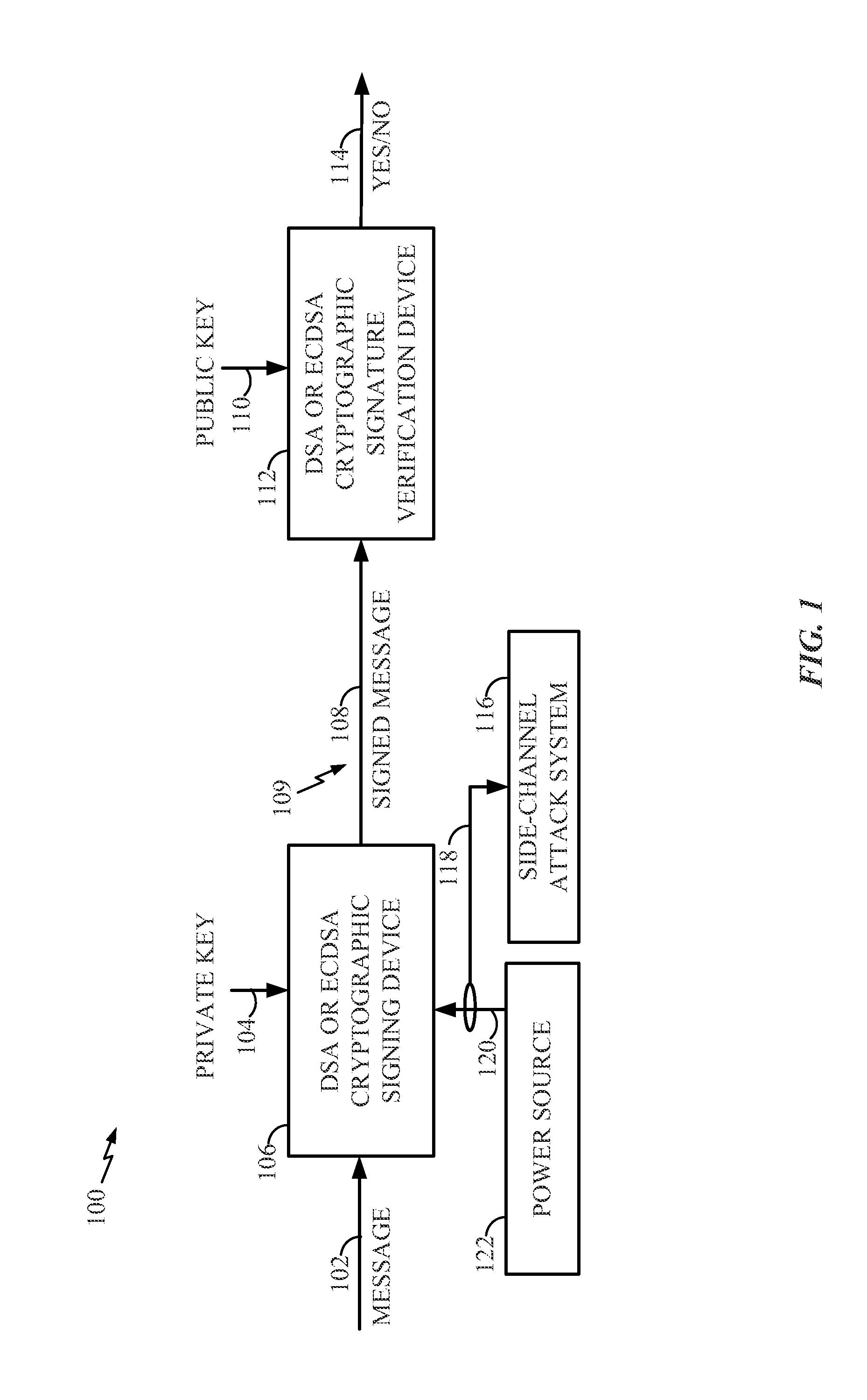
InactiveUS20150350171A1User identity/authority verificationCryptographic attack countermeasuresDigital signatureKey derivation function
Various features pertain to digital signatures for use in signing messages. In one aspect, a digital signature is generated based on a nonce derived using a per-message salt value, particularly a salt selected to provide a semi-deterministic nonce (i.e. a nonce that is neither fully deterministic nor completely random.) In one example, the nonce is generated by concatenating the salt value with a long-term private key and then applying the result to a key derivation function along with a hash of the message to be signed. The salt value may be, e.g., a counter, a context-specific message or may be randomly generated within a restricted range of values (relative to a full range of values associated with the particular digital signature generation protocol used to generate a digital signature from the nonce.)
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
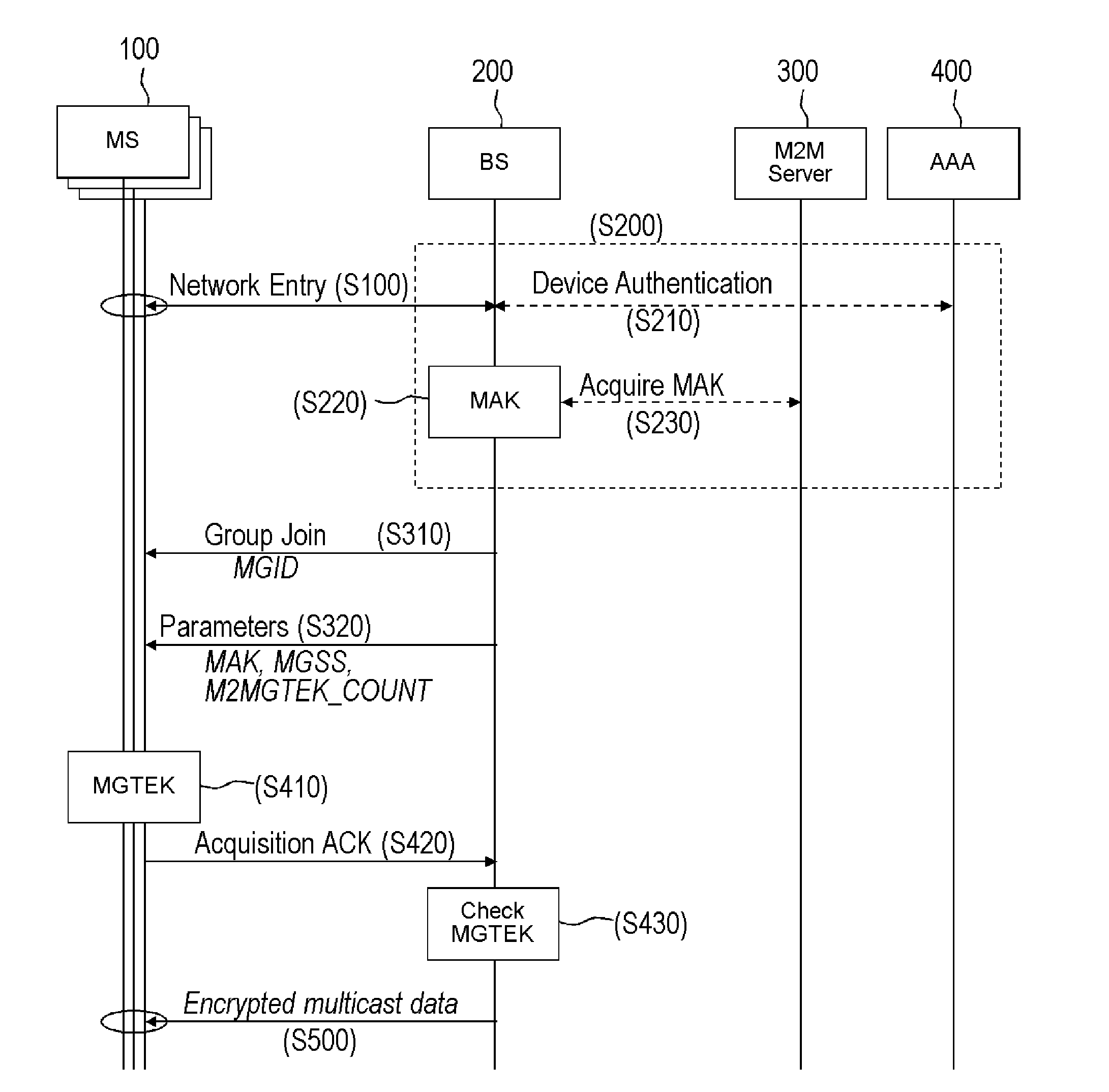
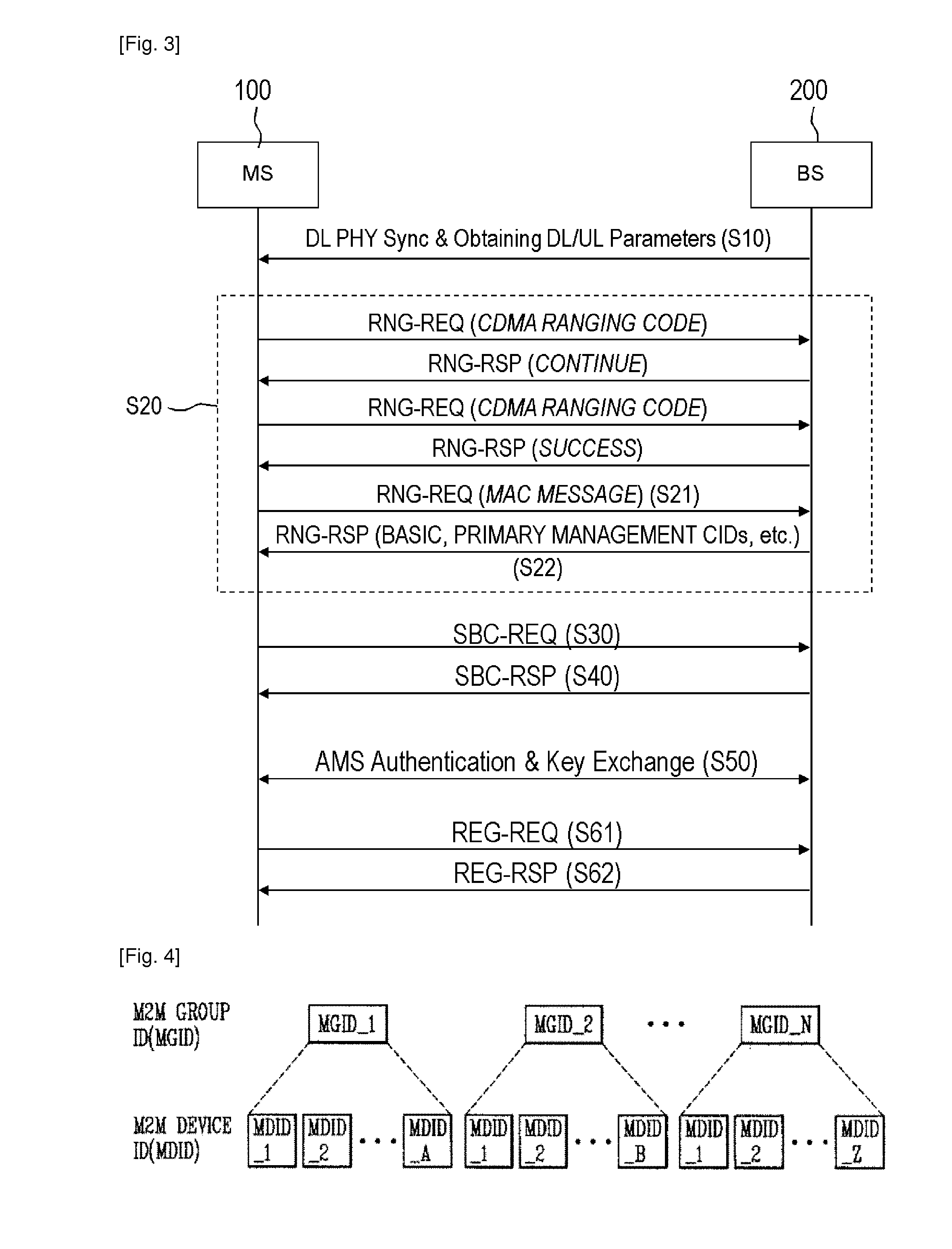
Traffic encryption key management for machine to machine multicast group
ActiveUS20130315389A1Broadcast service distributionSecret communicationTraffic capacityCommunications system
A method for decrypting multicast data by a mobile station in a wireless communication system is described. The method includes receiving an identifier of a group from a base station, receiving parameters for generating a group traffic key from the base station, wherein the parameters include an authentication key for the group, a group security seed and a counter, performing a key derivation function to generate the group traffic key based on the identifier and the parameters and decrypting multicast data using the group traffic key.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Secure channel establishment
ActiveUS20180026784A1Avoid attackKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageElliptic curve Diffie–HellmanKey derivation function
A method of establishing a secure channel for communication between a first computing device and a second computing device is described. The method uses an elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman protocol, wherein G is an elliptic curve generator point and the first computing device has a unique private key dc with a public key Qc=dc G certified by a party trusted by the second computing device. The first computing device generates (520) a blinding factor r and sends (540) a blinded public key R=r·Qc to the second computing device. The second computing device generates (510) an ephemeral private key dt and a corresponding ephemeral public key Qt=dt G and sends Qt to the first computing device. The first computing device generates (530) Kc=KDF (r dc·Qt) and the second computing device generates (550) Kt=KDF (dt·R), where KDF is a key derivation function used in both generation operations, to establish a secure channel between the first computing device and the second computing device. G is a point in the elliptic curve group E, wherein E is a group of prime order but E* is the quadratic twist of E and is a group of order m=z·m′ where m′ is prime and z is an integer, wherein r·dc is chosen such that z is a factor of r·dc. Suitable apparatus for performing the method is also described.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
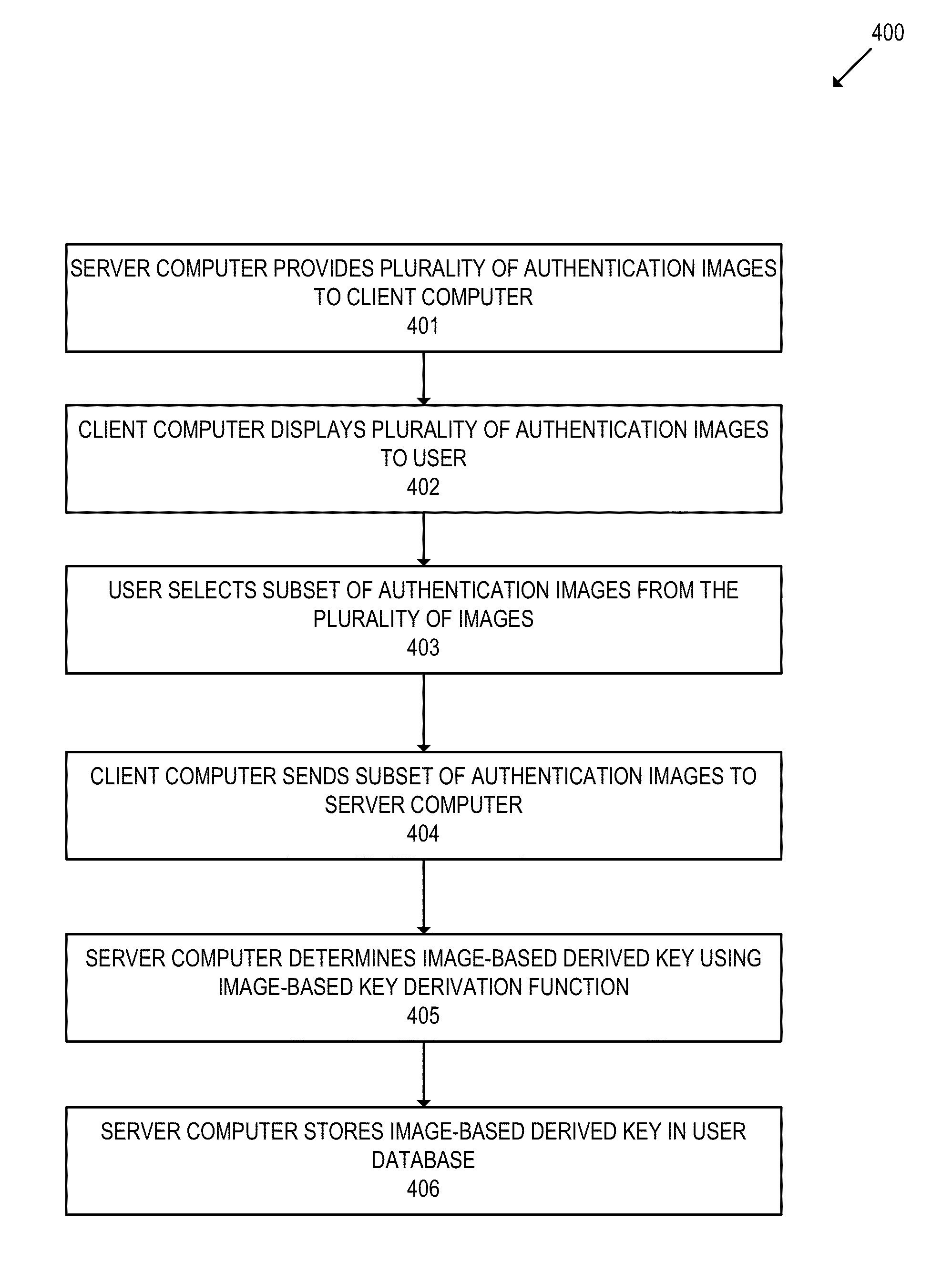
Image based key derivation function
ActiveUS20140372754A1Easy authenticationFacilitate data encryptionUser identity/authority verificationMechanically effected encryptionKey derivation functionUser authentication
Embodiments of the invention relate to methods of generating and using an image-based derived key. In various embodiments, the image-based derived key may be used to facilitate user authentication and data encryption. For some embodiments, a method is disclosed comprising determining an image-based derived key, wherein the image-based derived key is generated from a selection of authentication images chosen by a user, encrypting data using the image-based derived key, and transmitting the encrypted data.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Authentication and secure channel setup for communication handoff scenarios
Persistent communication layer credentials generated on a persistent communication layer at one network may be leveraged to perform authentication on another. For example, the persistent communication layer credentials may include application-layer credentials derived on an application layer. The application-layer credentials may be used to establish authentication credentials for authenticating a mobile device for access to services at a network server. The authentication credentials may be derived from the application-layer credentials of another network to enable a seamless handoff from one network to another. The authentication credentials may be derived from the application-layer credentials using reverse bootstrapping or other key derivation functions. The mobile device and / or network entity to which the mobile device is being authenticated may enable communication of authentication information between the communication layers to enable authentication of a device using multiple communication layers.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Highly secure ellipse curve encryption and decryption method and device
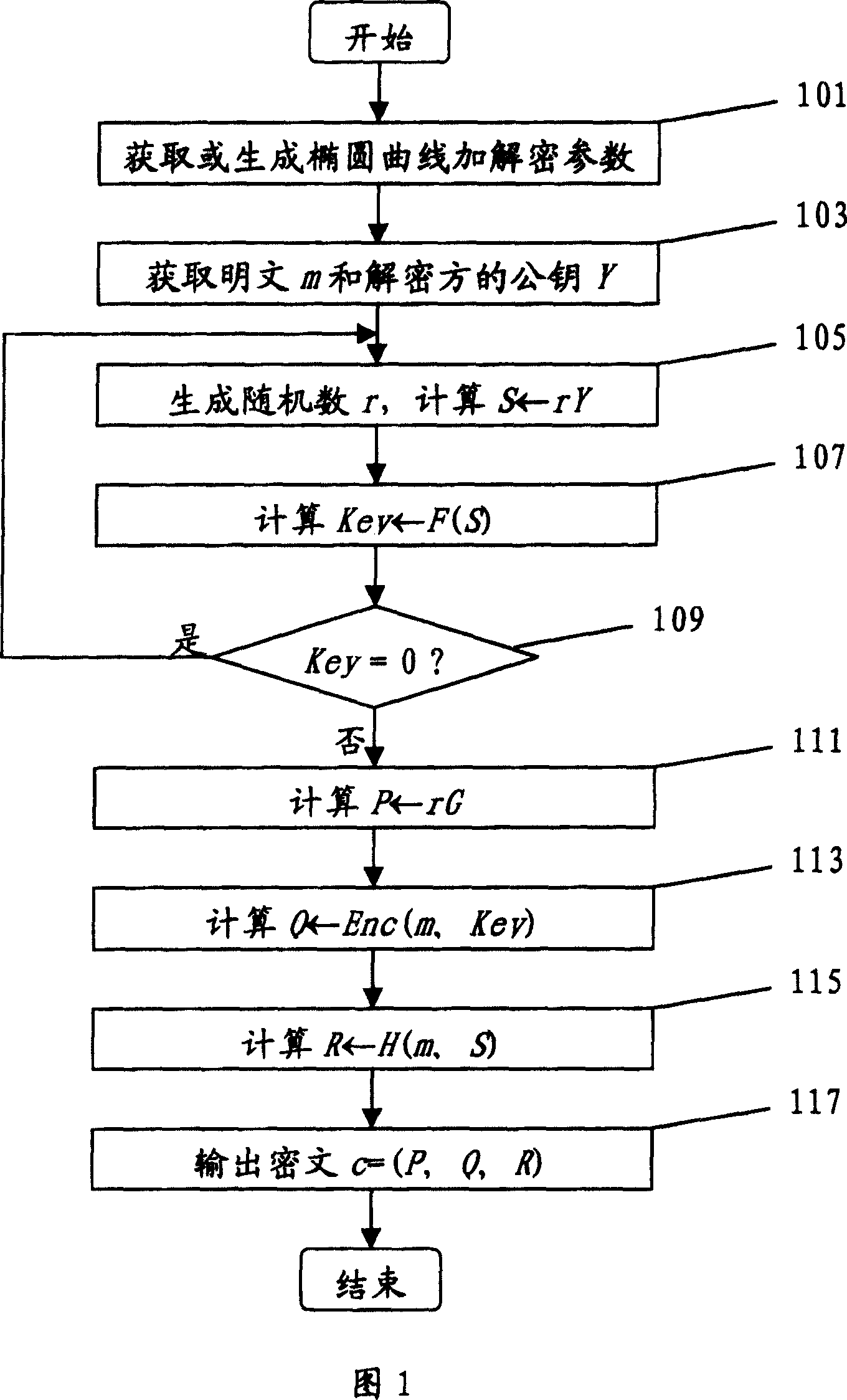
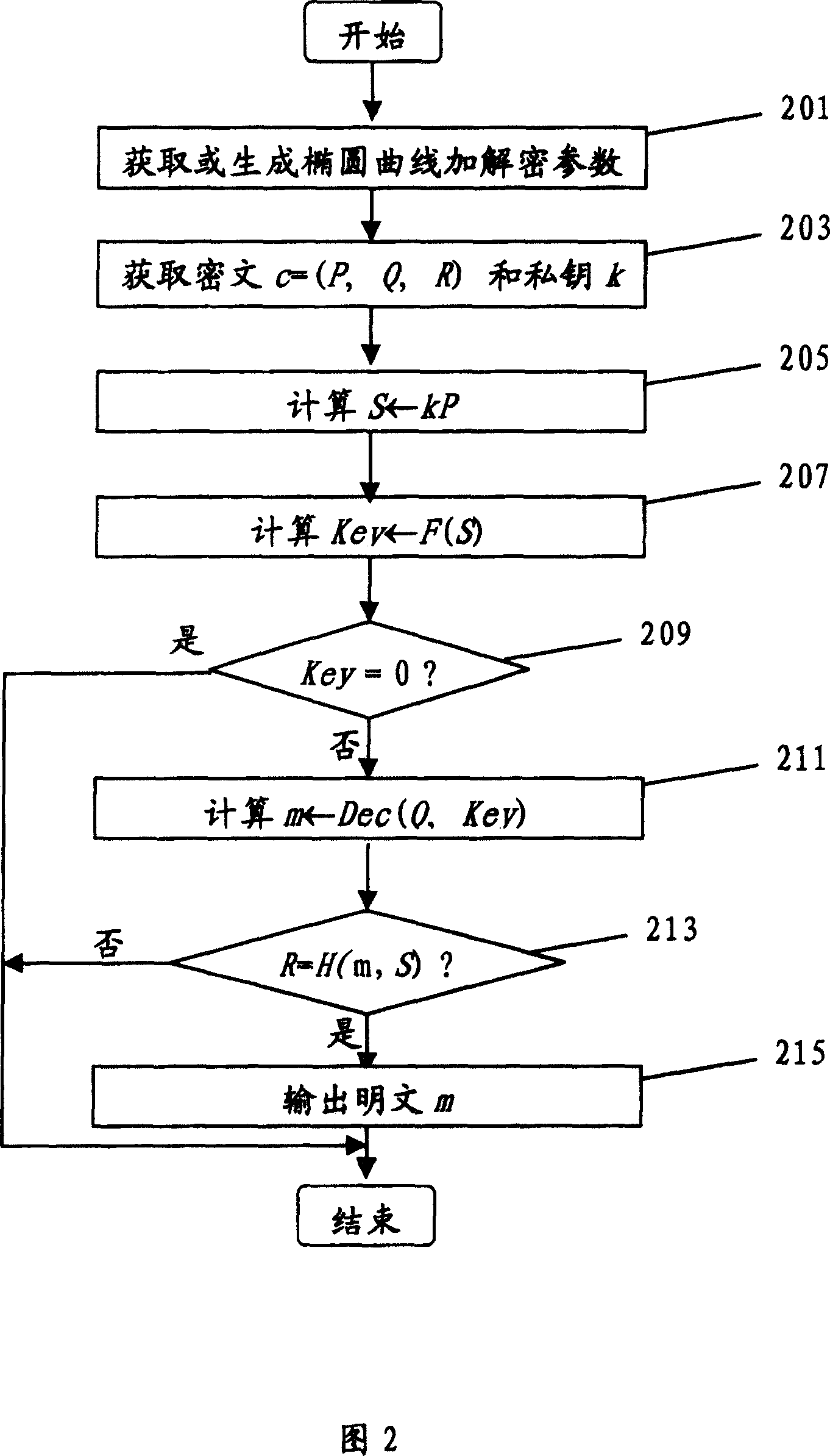
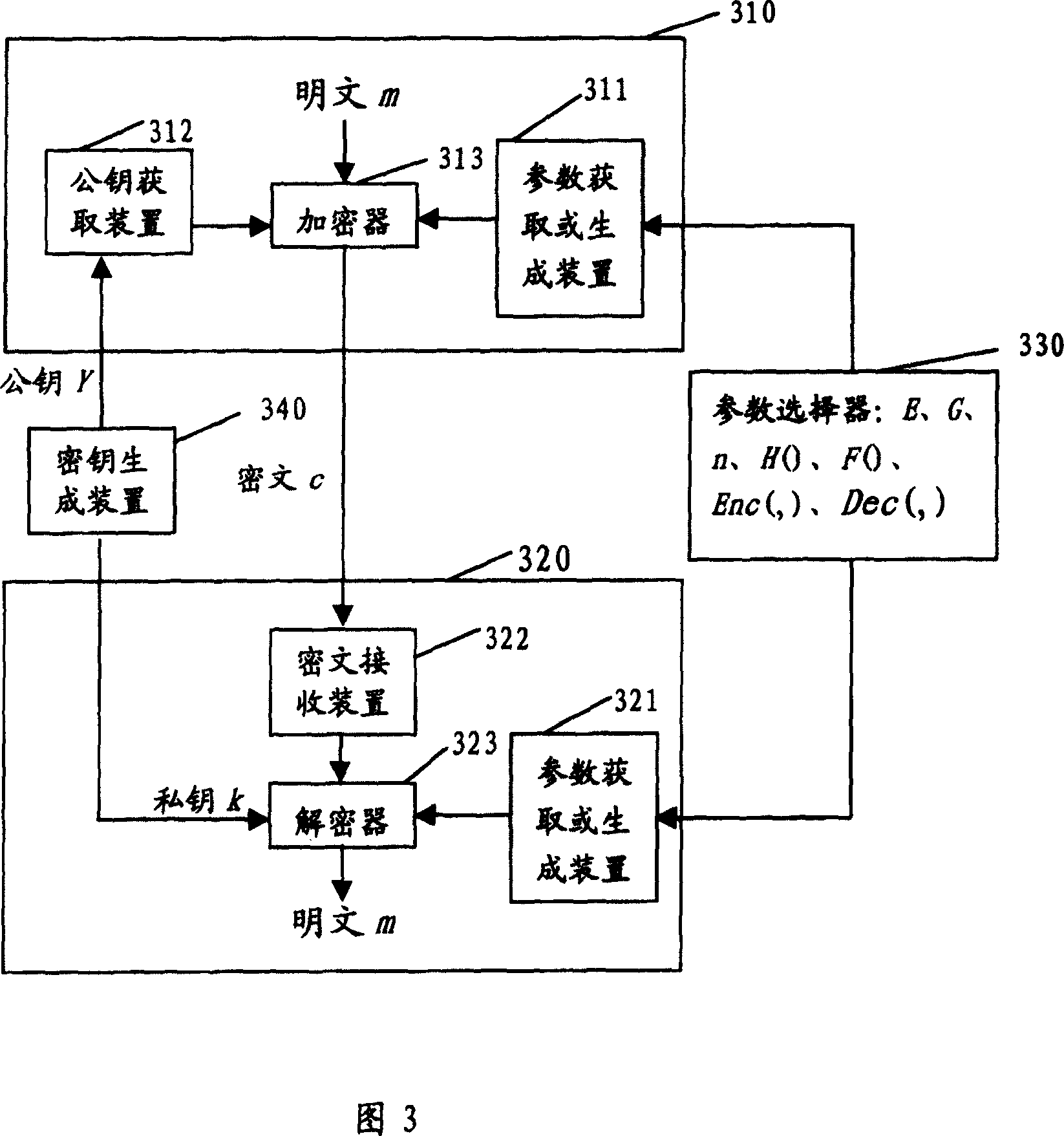
ActiveCN101079701AOvercoming security deficienciesPublic key for secure communicationDecoding methodsPlaintext
Owner:BEIJING HUADA INFOSEC TECH
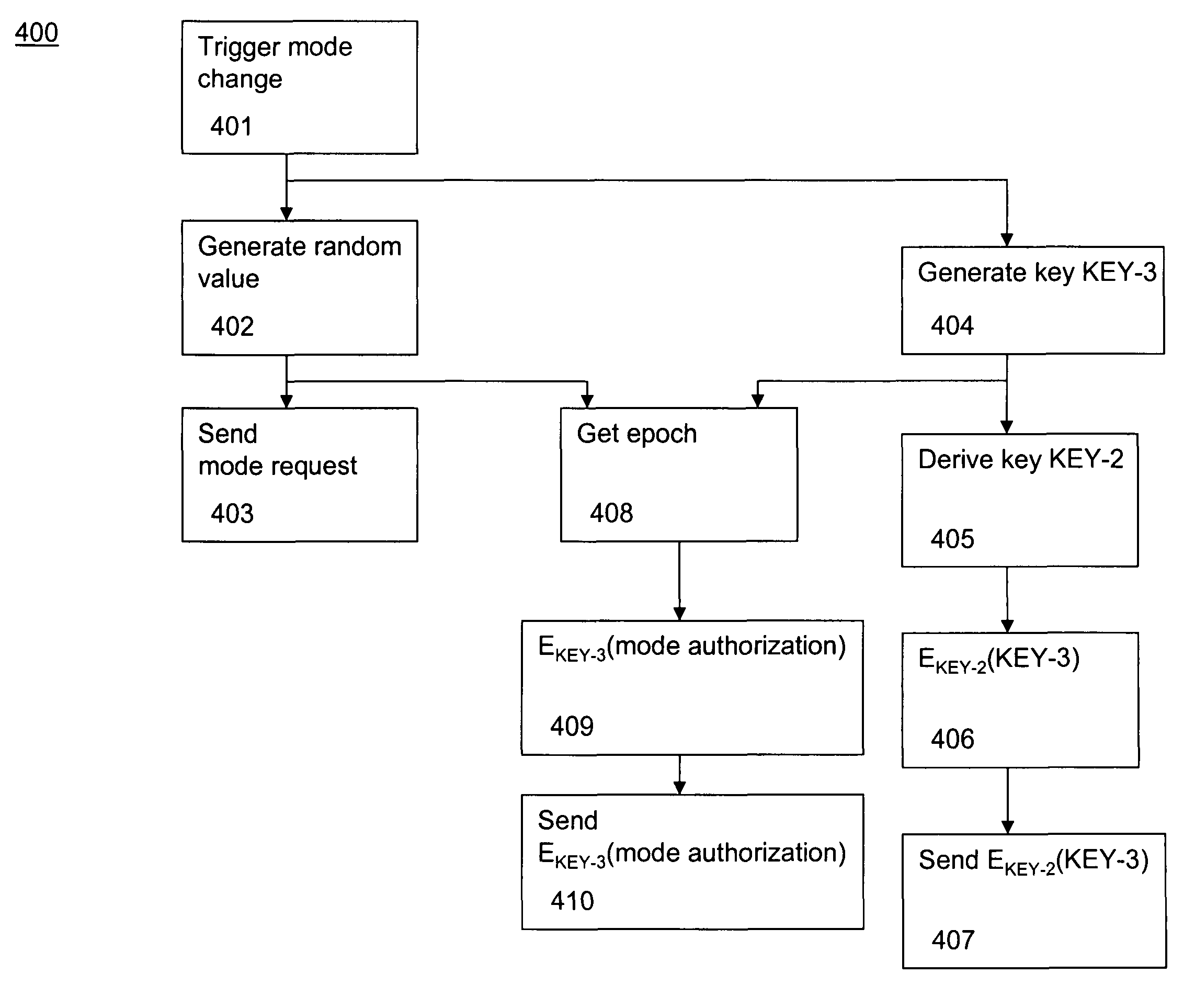
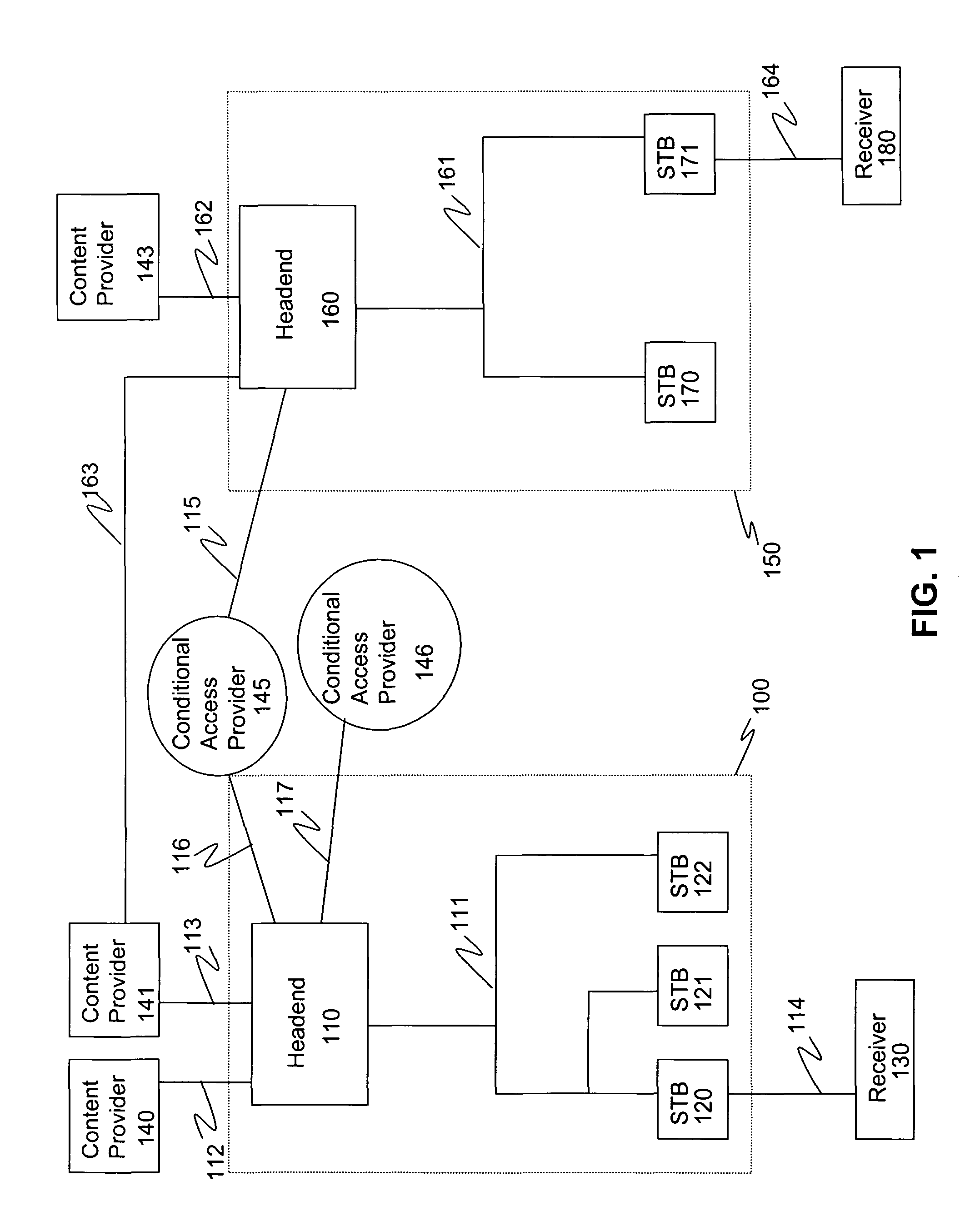
Authenticated mode control
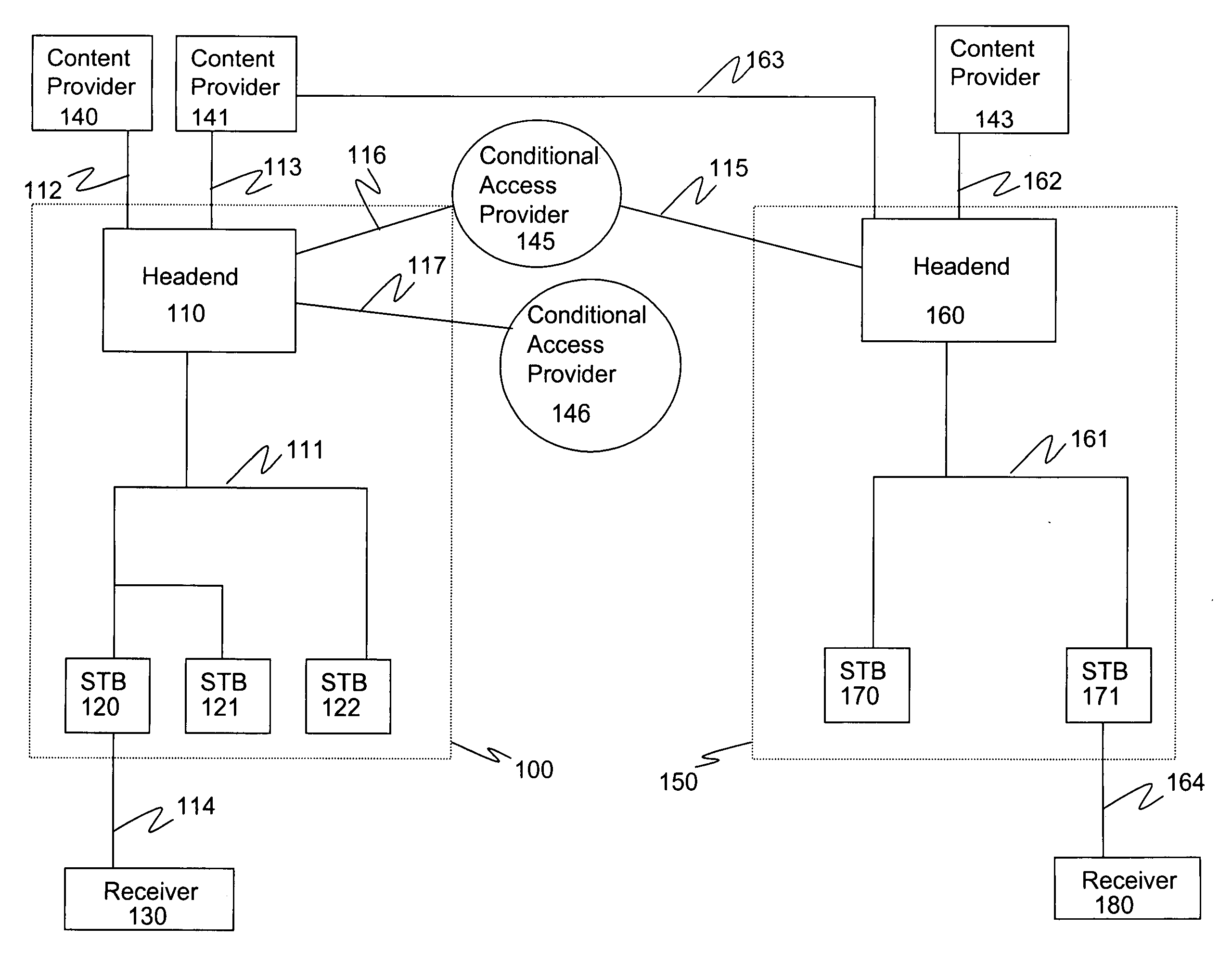
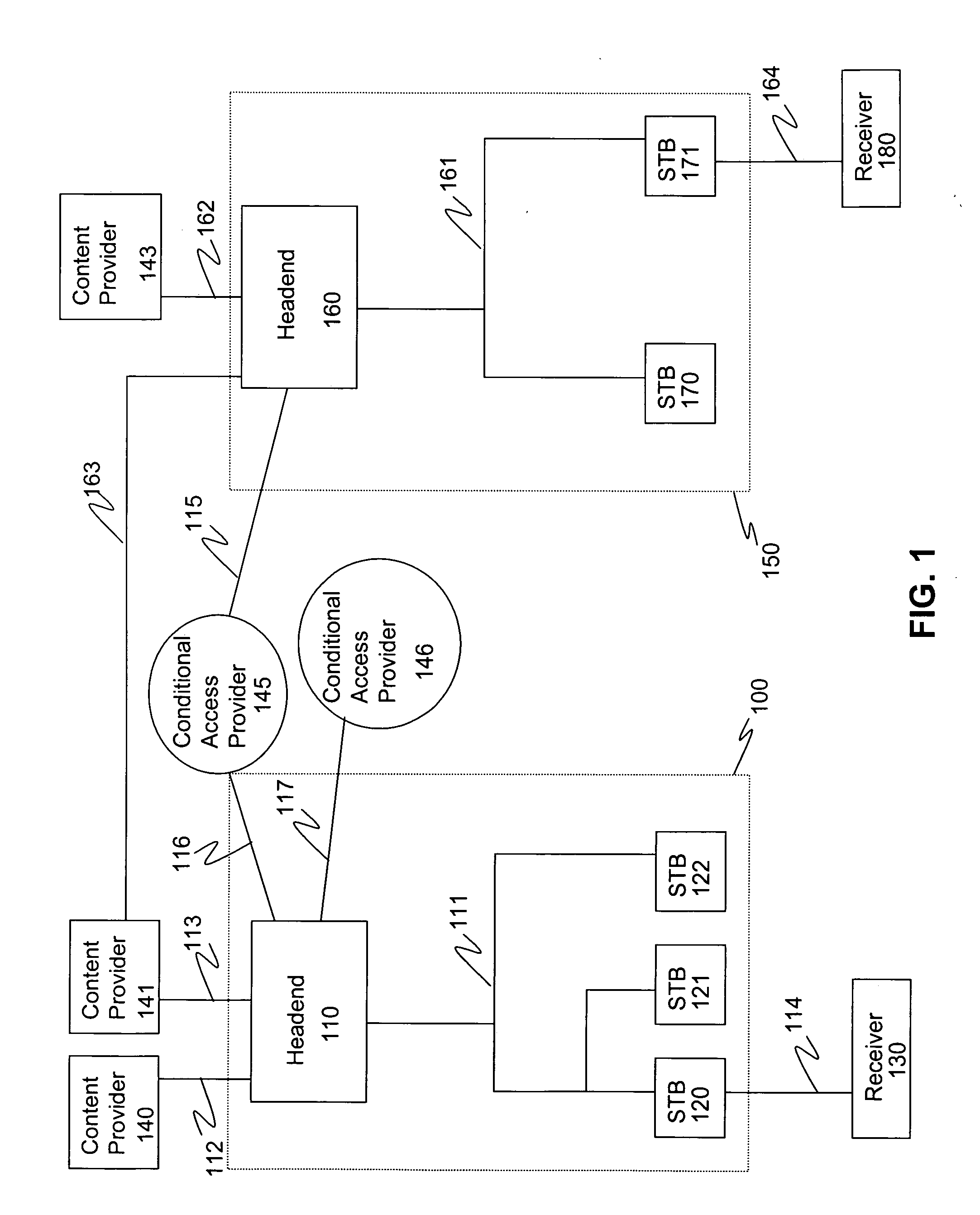
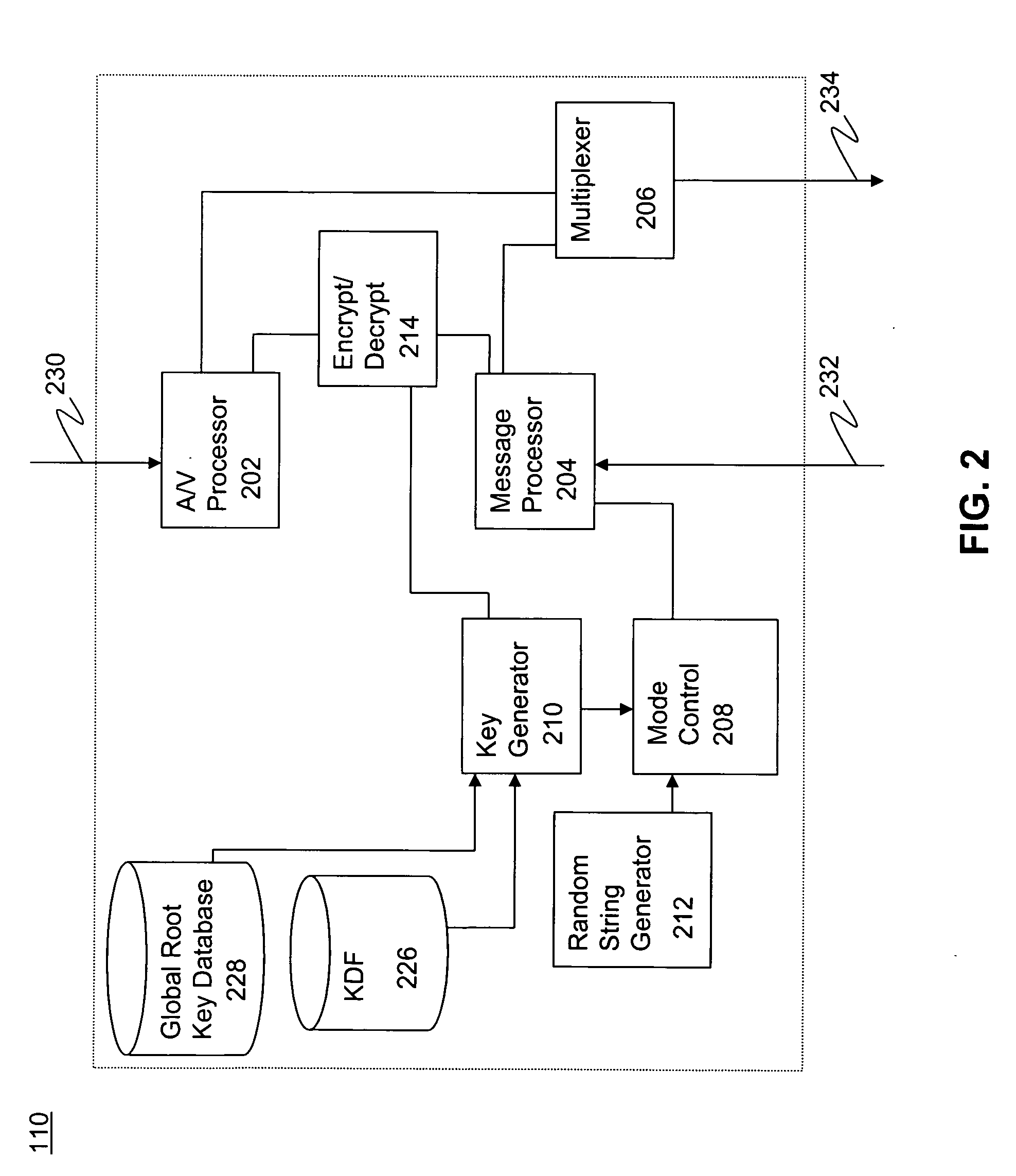
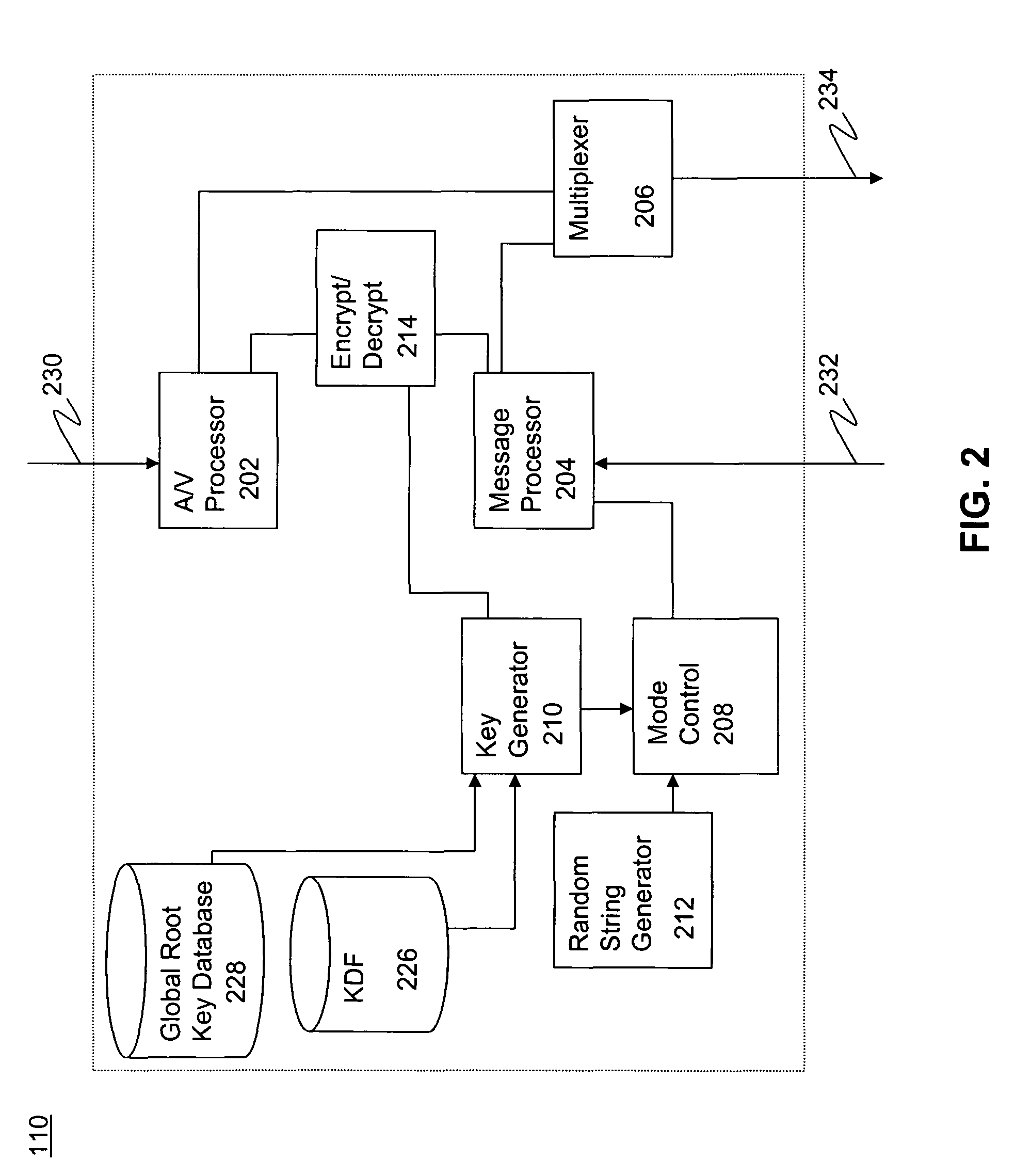
ActiveUS20100254536A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageMode controlConditional access
Methods and systems for authenticated mode control in controlled devices are disclosed. A method for changing a mode in a controlled device from a current mode includes selecting one of several available key derivation functions based on a target mode, generating a target mode specific root key using a global root key and the selected key derivation function, and the use of that root key to affect a change of the controlled device to a target mode. Corresponding devices and systems are also disclosed. In one embodiment, the methods are applicable to a cable television distribution system and the changing of the operating mode of a set top box from one conditional access provider to another.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
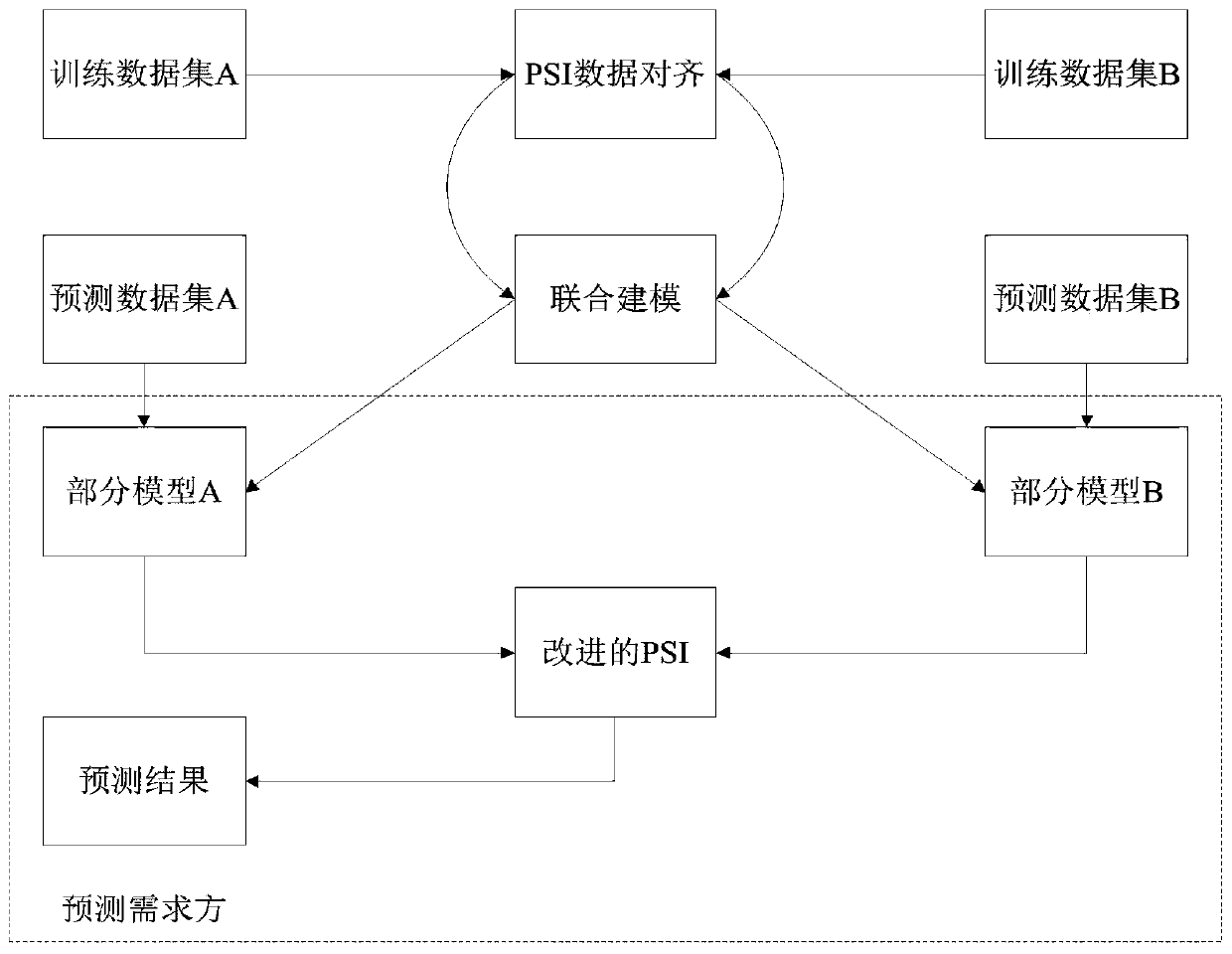
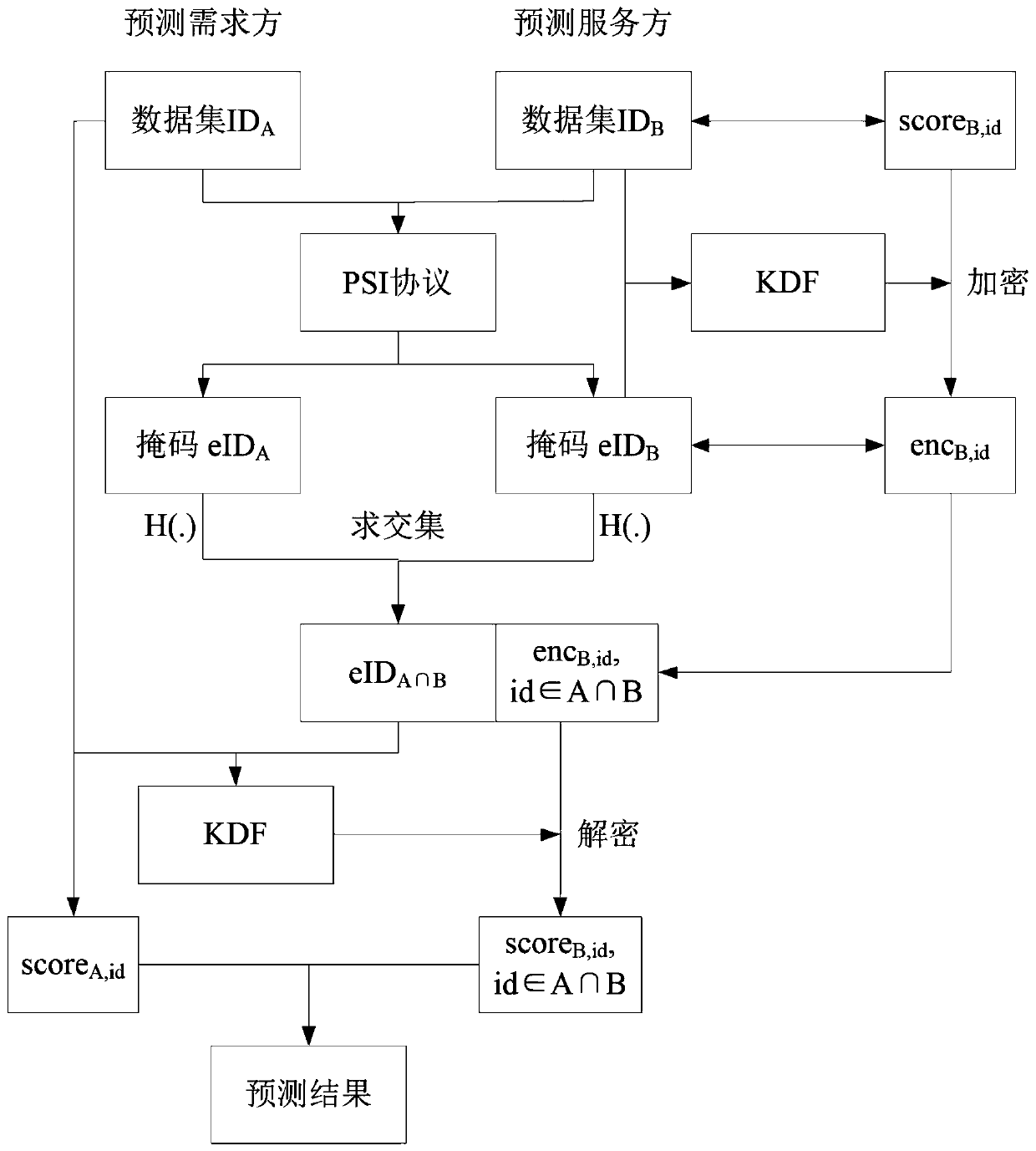
Method for protecting privacy in federated learning prediction stage based on PSI technology
ActiveCN111259443AEnsure safetyImprove forecast resultsDigital data protectionMachine learningData providerPrivacy protection
The invention discloses a method for protecting privacy in a federated learning prediction stage based on a PSI technology. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a prediction serviceparty calculates a prediction result of a model of the prediction service party, then the prediction service party and the prediction service party execute an improved PSI protocol, a part of model calculation results of the prediction service party are encrypted, a prediction demand party decrypts the calculation result of a data provider in combination with data of the prediction demand party, and finally a prediction result of a keyword id shared by the prediction service party and the prediction demand party is obtained. According to the method, the PSI technology is utilized, the data areencrypted through the key derivation function, the privacy protection requirement in the federated learning prediction stage is met, the last link of federated learning privacy security protection isbroken through, and landing of more application scenes of federated learning is promoted.
Owner:百融云创科技股份有限公司
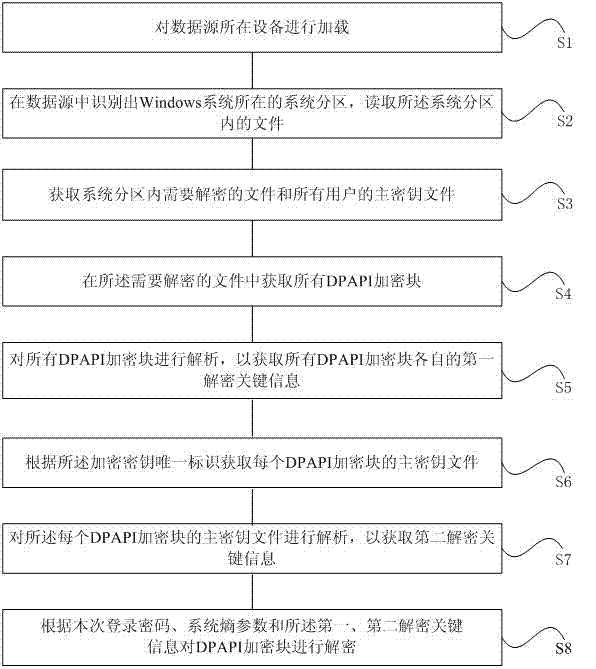
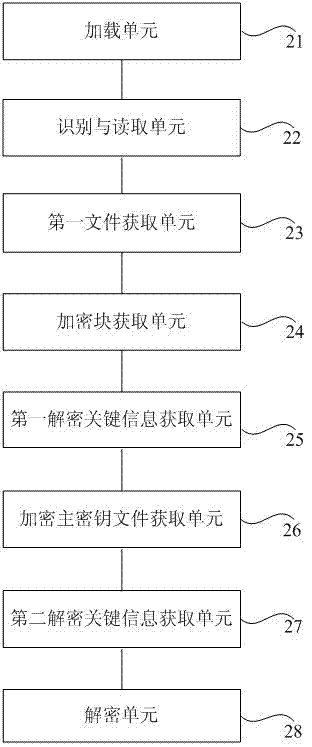
Deciphering method and system of data protection application programming interface (DPAPI) enciphered data
ActiveCN103116730AImplement offline decryptionMeet the read-only requirementEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data protectionComputer hardwareOperational system
The invention provides a deciphering method and system of data protection application programming interface (DPAPI) enciphered data. The method comprises the following steps: loading a device, wherein a data source is in the device, identifying a system partition from the data source and reading files in the system partition, wherein the Windows system is in the system partition, acquiring files which need to be deciphered and master key files of all users, acquiring all DPAPI enciphered blocks from the files which need to be deciphered, analyzing all the DPAPI enciphered blocks to acquire the first deciphering key information which comprises encipherment secret key unique identification, acquiring the master key files of each DPAPI enciphered block according to the encipherment secret key unique identification, analyzing the master key files to acquire the second deciphering key information which comprises a second annoyance value and a second secret key derive function iteration based on commands, and deciphering the DPAPI enciphered blocks according to a login password, system entropy parameters, the first deciphering key information and the second deciphering key information. The method and the system can achieve read only operation of the data source and meet the need of cross-platform without restriction of operating system.
Owner:XIAMEN MEIYA PICO INFORMATION
System and method for digital rights management using digital signatures
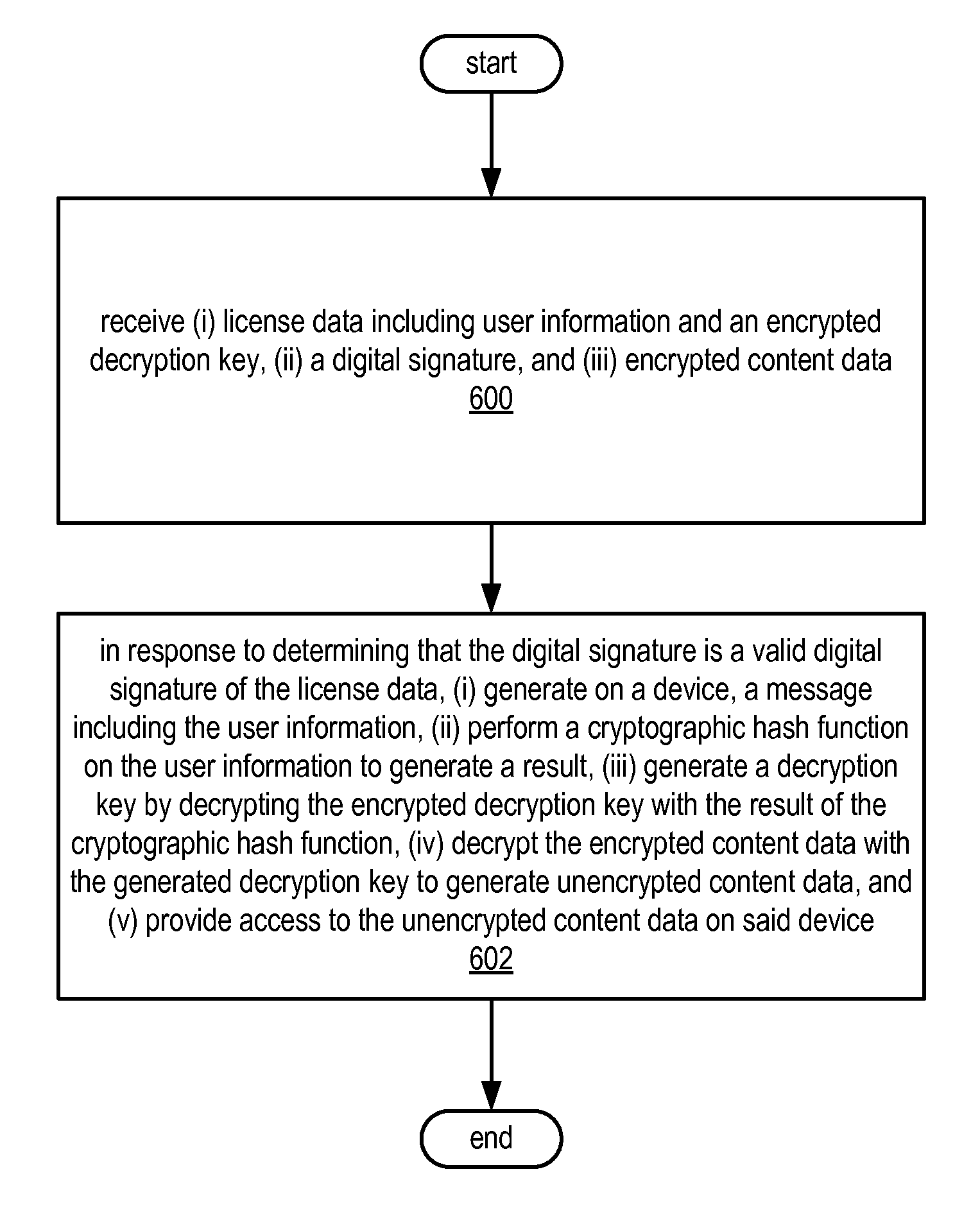
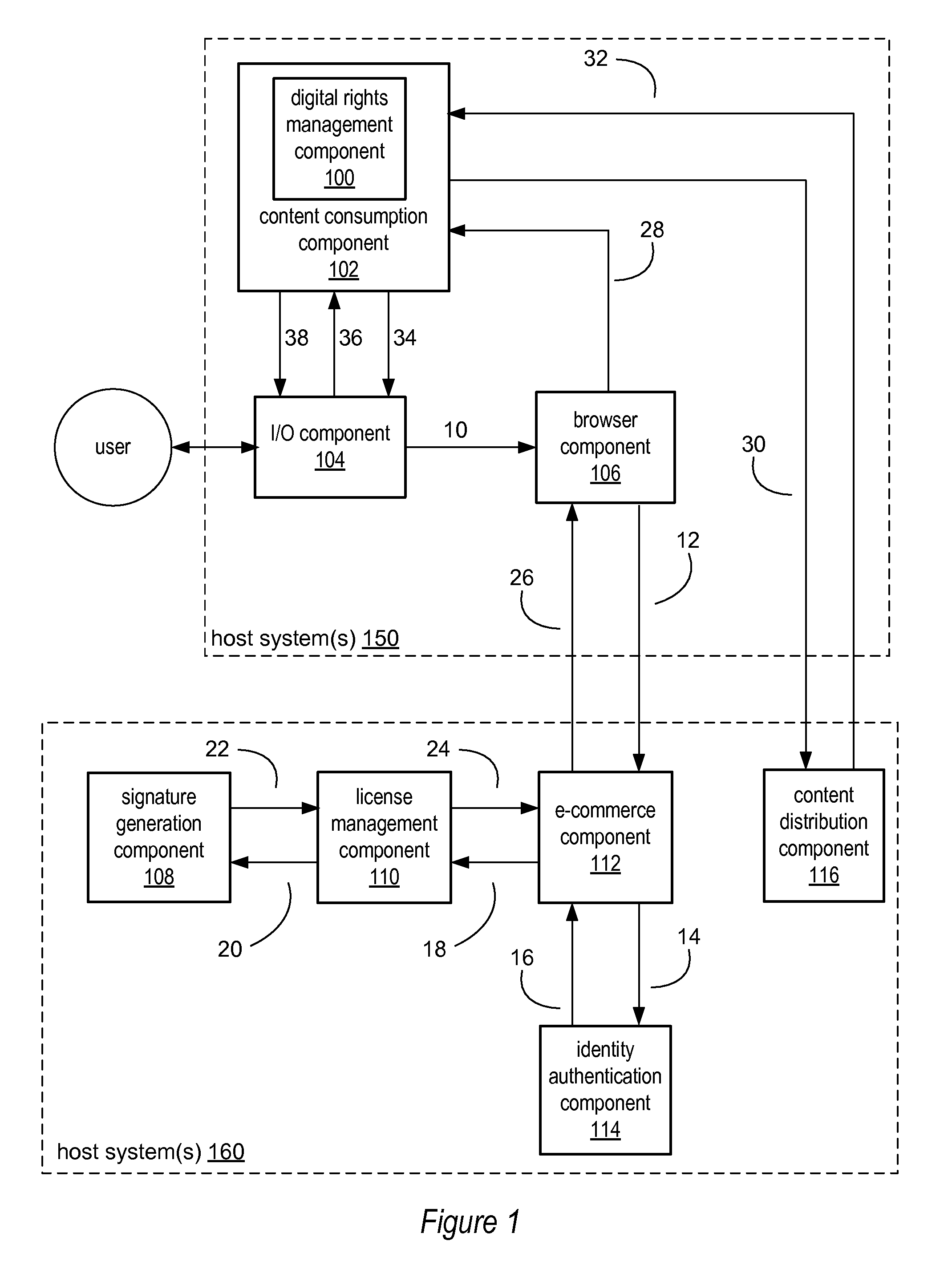
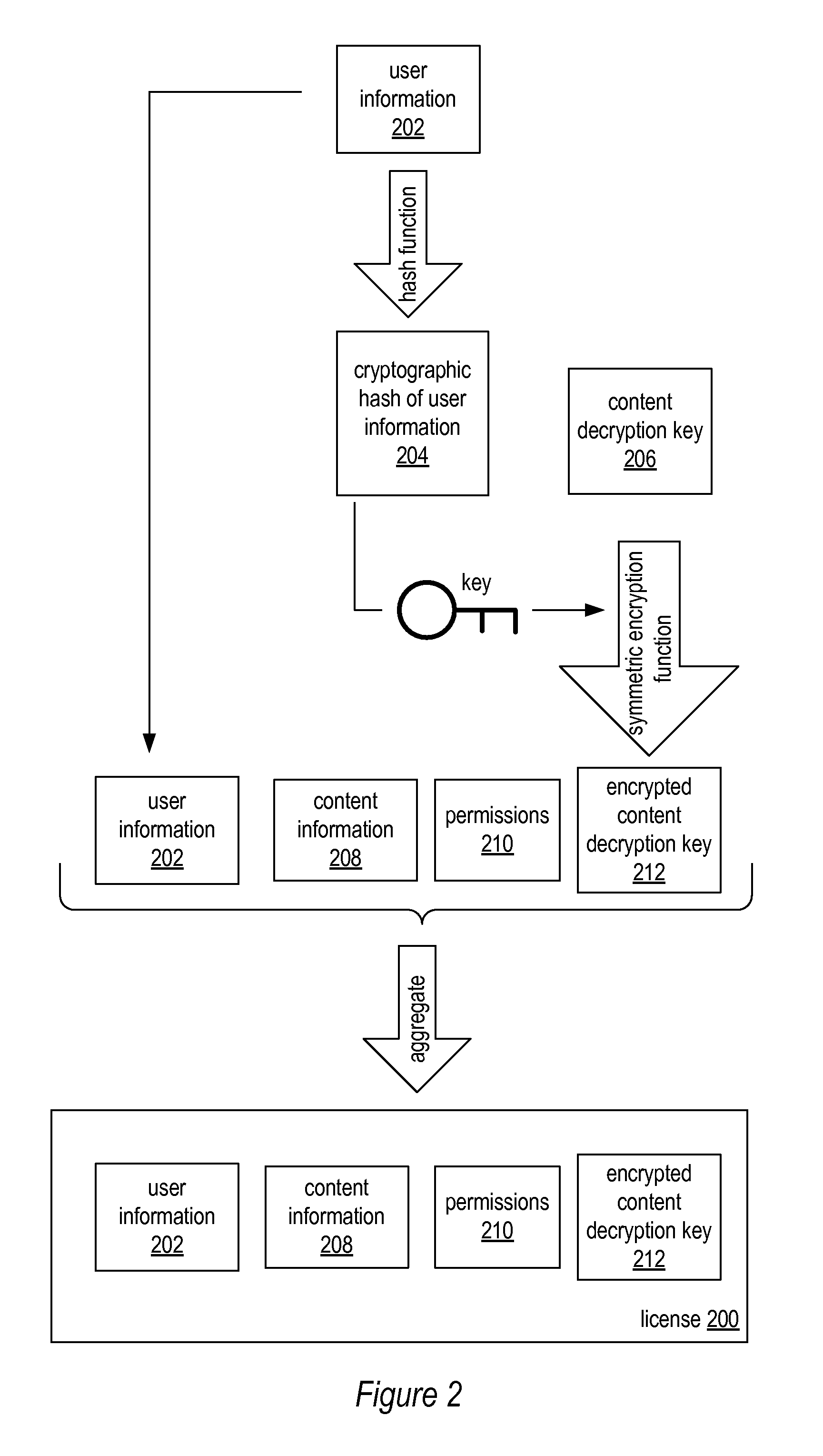
ActiveUS8359473B1User identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital signatureKey derivation function
Various embodiments of a system and method for digital rights management using digital signatures are described. Various embodiments may include a digital rights management component configured to receive license data including user information and an encrypted decryption key. The digital rights management component may also receive a digital signature and encrypted content data. The digital rights management component may, in response to determining that the digital signature is a valid digital signature of the license data, generate on a device, a message including the user information. The digital rights management component may also perform a key derivation function on the user information to generate a result, generate a decryption key by decrypting the encrypted decryption key with the result of the key derivation function, and decrypt the encrypted content data with the generated decryption key to generate unencrypted content data.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Apparatus and Methods for Key Generation
ActiveUS20140302820A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method for key generation at a terminal device supporting at least two communication modes of operation is described. The method comprises, at a terminal device comprising a key derivation function: receiving at least one input parameter from a first wireless communication system; generating a first key in the key derivation function using the received at least one input parameter and at least one first locally stored input parameter in order to transmit in a first mode of operation on the first wireless communication system; and generating a second key in the key derivation function solely using at least one second locally stored input parameter in order to transmit in a second mode of operation on a second wireless communication system; wherein the at least one second locally stored input parameter is arranged to enable the second key to be used as the first key.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
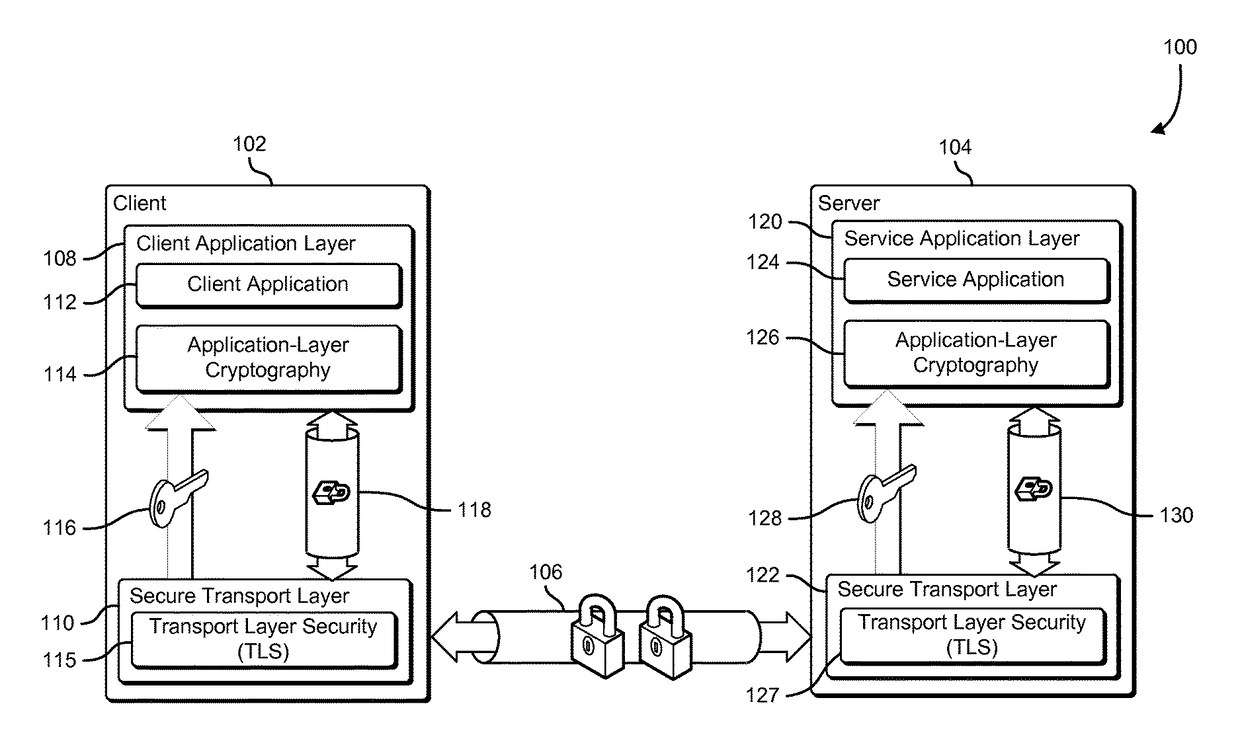
Leveraging transport-layer cryptographic material
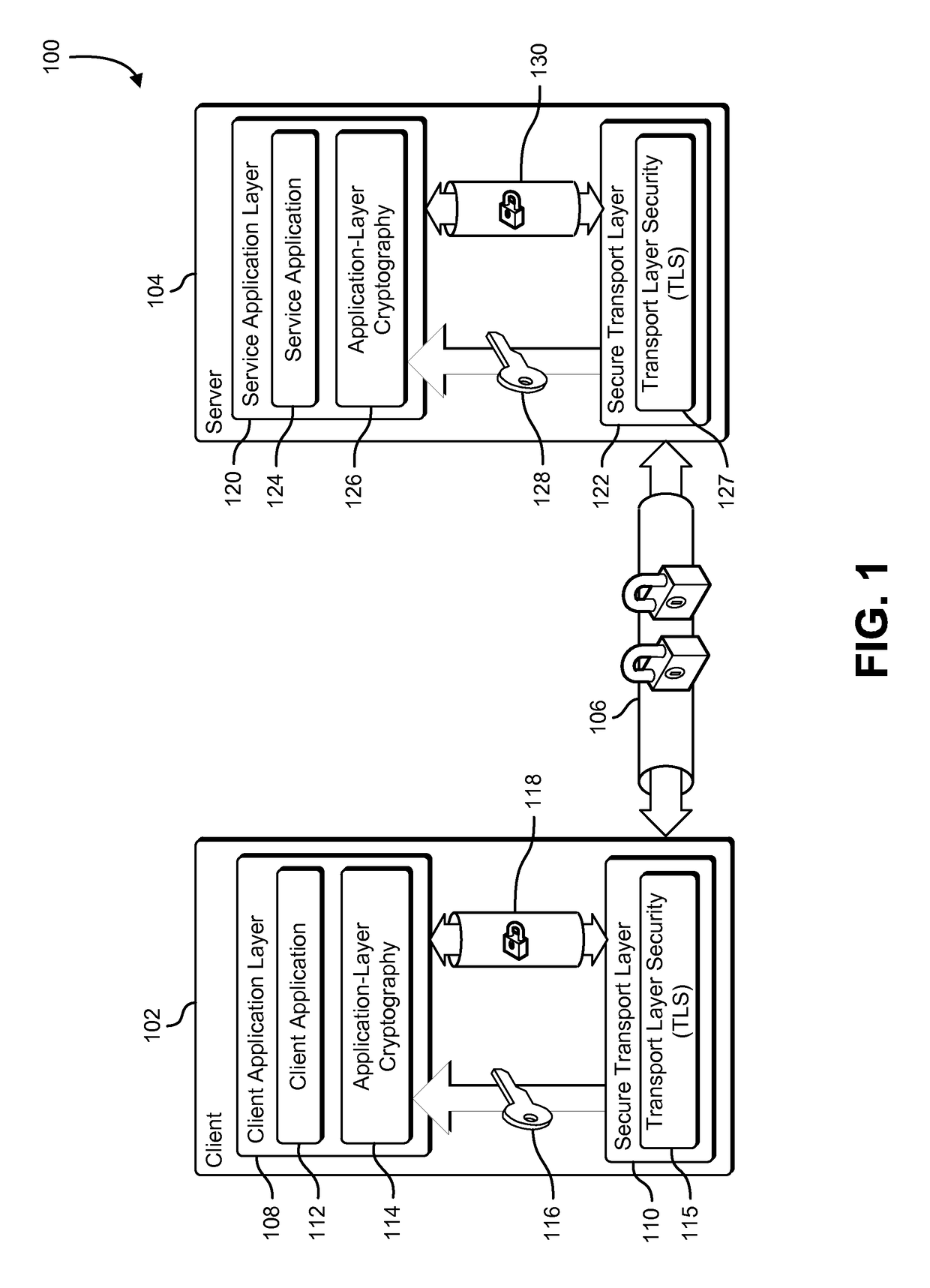
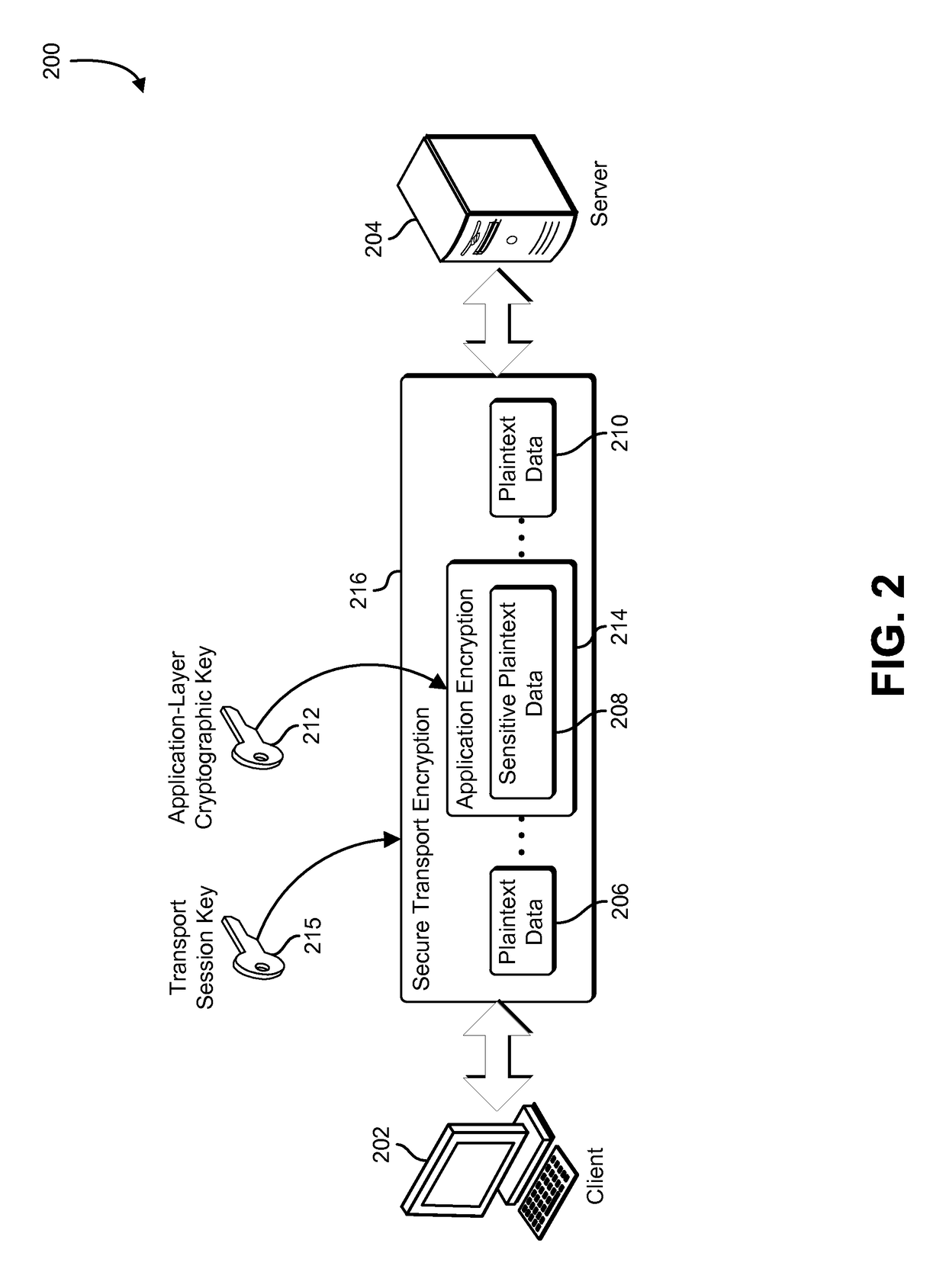
ActiveUS9781081B1User identity/authority verificationSecret communicationCryptographic hash functionTransport layer
A client application cryptographically protects application data using an application-layer cryptographic key. The application-layer cryptographic key is derived from cryptographic material provided by a cryptographically protected network connection. The client exchanges the cryptographically protected application data with a service application via the cryptographically protected network connection. The client and service applications acquire matching application-layer cryptographic keys by leveraging shared secrets negotiated as part of establishing the cryptographically protected network connection. The shared secrets may include information that is negotiated as part of establishing a TLS session such as a pre-master secret, master secret, or session key. The application-layer cryptographic keys may be derived in part by applying a key derivation function, a one-way function or a cryptographic hash function to the shared secret information.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Secure interface for versatile key derivation function support
ActiveUS8335317B2Easy to implementImprove usabilityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareKey derivation function
Improper re-use of a static Diffie-Hellman (DH) private key may leak information about the key. The leakage is prevented by a key derivation function (KDF), but standards do not agree on key derivation functions. The module for performing a DH private key operation must somehow support multiple different KDF standards. The present invention provides an intermediate approach that neither attempts to implement all possible KDF operations, nor provide unprotected access to the raw DH private key operation. Instead, the module performs parts of the KDF operation, as indicated by the application using the module. This saves the module from implementing the entire KDF for each KDF needed. Instead, the module implements only re-usable parts that are common to most KDFs. Furthermore, when new KDFs are required, the module may be able to support them if they built on the parts that the module has implemented.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Key management device and key management method
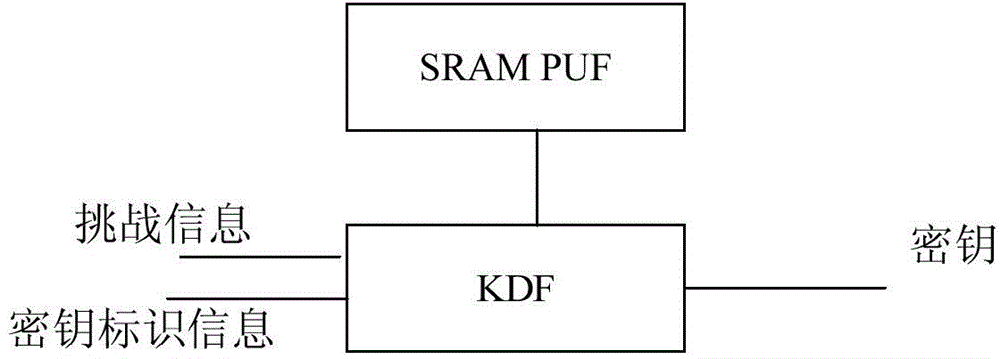
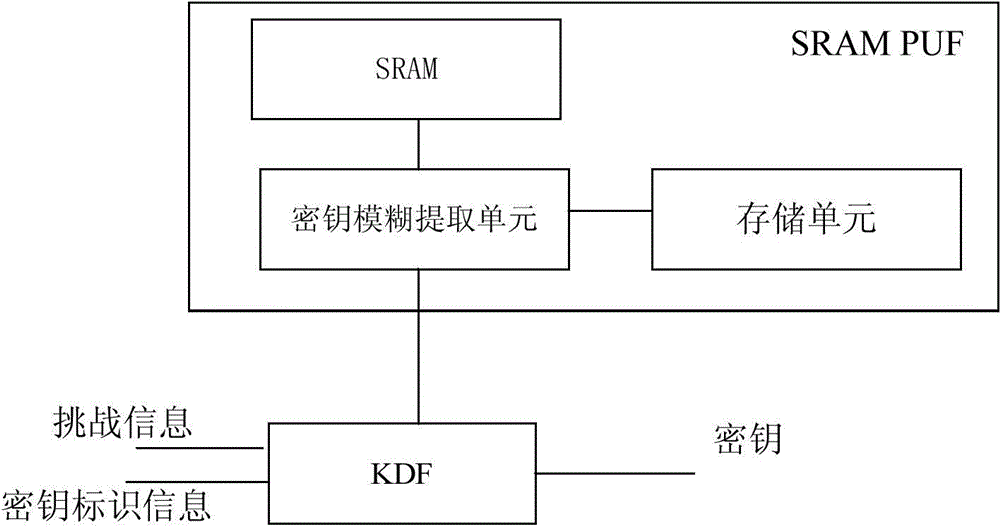
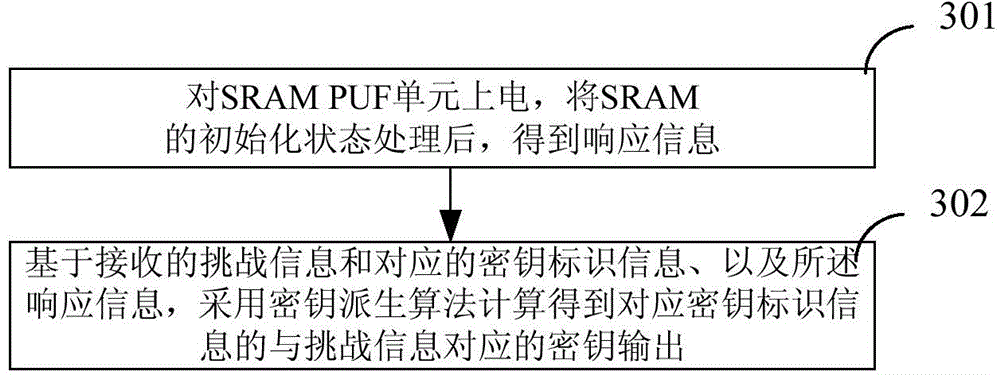
InactiveCN105337725AEnsure safetyReduce manufacturing costKey distribution for secure communicationStatic random-access memoryKey derivation function
The invention discloses a key management device and a key management method. A SRAM PUF (Static Random Access Memory Physically Unclonable Function) and a key derivation function (KDF) unit are set in the key management device; when the key management device is going to generate a key, challenge information, key identifier information and response of the SRAM PUF are taken together as input to be input into the KDF unit; the KDF unit obtains key output, corresponding to the challenge information, of corresponding key identifier information after executing calculation based on a key derivation algorithm. Since the key management device provided by the embodiment of the invention establishes strong PUF by only one SRAM PUF, cost of conventionally establishing the Strong PUF is saved.
Owner:DATA ASSURANCE & COMM SECURITY CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Multi-factor identity authentication method for preventing library collision attacks
ActiveCN105187382AAvoid Credential Stuffing AttacksImprove verification capabilitiesTransmissionBrute forcePassword
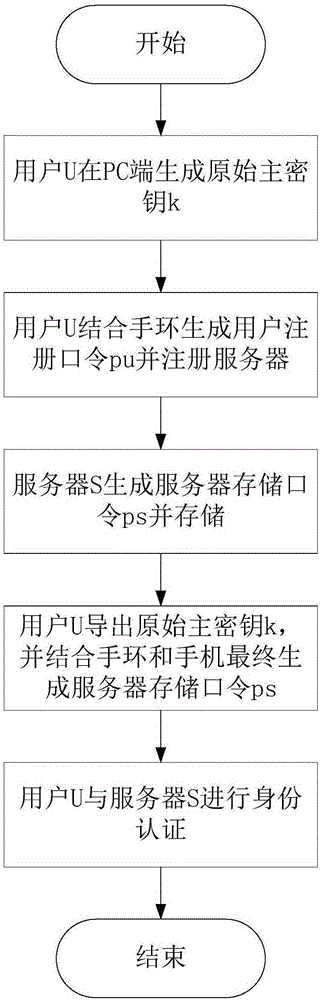
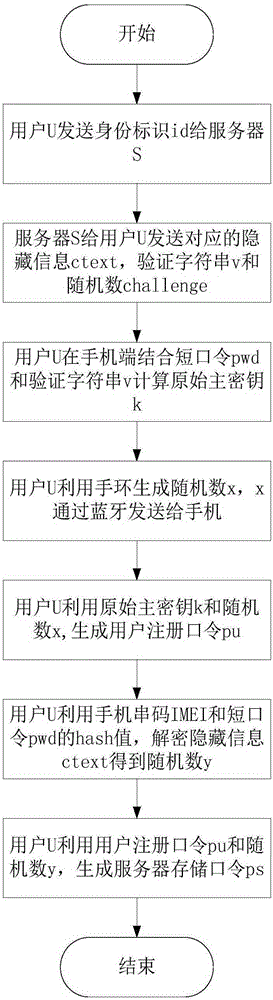
The invention discloses a multi-factor identity authentication method for preventing library collision attacks, which is mainly used for solving the problem that user passwords in the existing website login systems are vulnerable to brute force attacks and library collision attacks. The multiple factors in the multi-factor identity authentication method disclosed by the invention comprises a user password, a mobile phone and a bracelet, which are indispensable to complete the security authentication of user identity. The multi-factor identity authentication method comprises the steps of: (1) a user uses a short password to generate an original master key through a termination key derivation function and processes the original master key for twice in combination with two random numbers related to the bracelet and the mobile phone respectively to generate a server storage password, and stores the server storage password in a server; (2) the user successively derives the original master key and two different random numbers in combination with the bracelet and the mobile phone factors to generate the server storage password; and (3) the user uses the server storage password to carry out mutual authentication with the server. The multiple factors in the multi-factor identity authentication method disclosed by the invention is used for generating different original master keys for different websites and providing security protection to effectively avoid the risk that a single password is vulnerable to embezzlement for identity camouflage.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
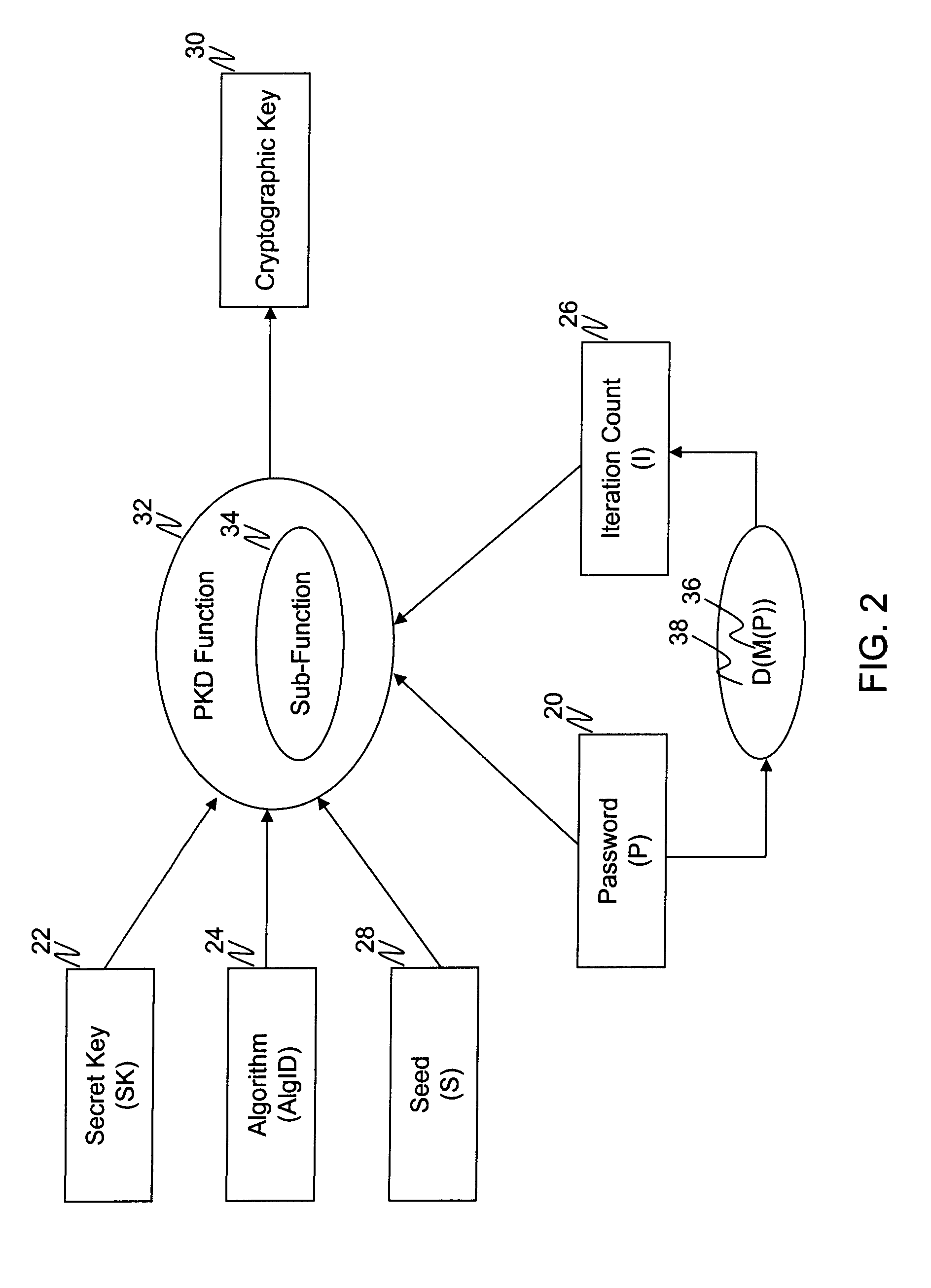
Password key derivation system and method
ActiveUS8238552B2Increase the number of iterationsReduce calculationMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionPasswordKey derivation function
A password-based key derivation function includes a sub-function that gets executed multiple times based on an iteration count. A key derivation module computes the iteration count dynamically with each entered password. The iteration count is computed as a function of the password strength. Specifically, the weaker the password, the higher the iteration count; but the stronger the password, the smaller the interaction count. This helps strengthen weaker passwords without penalizing stronger passwords.
Owner:OPEN TEXT HLDG INC
Apparatus and methods for key generation
ActiveUS9204296B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareCommunications system
A method for key generation at a terminal device supporting at least two communication modes of operation is described. The method comprises, at a terminal device comprising a key derivation function: receiving at least one input parameter from a first wireless communication system; generating a first key in the key derivation function using the received at least one input parameter and at least one first locally stored input parameter in order to transmit in a first mode of operation on the first wireless communication system; and generating a second key in the key derivation function solely using at least one second locally stored input parameter in order to transmit in a second mode of operation on a second wireless communication system; wherein the at least one second locally stored input parameter is arranged to enable the second key to be used as the first key.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
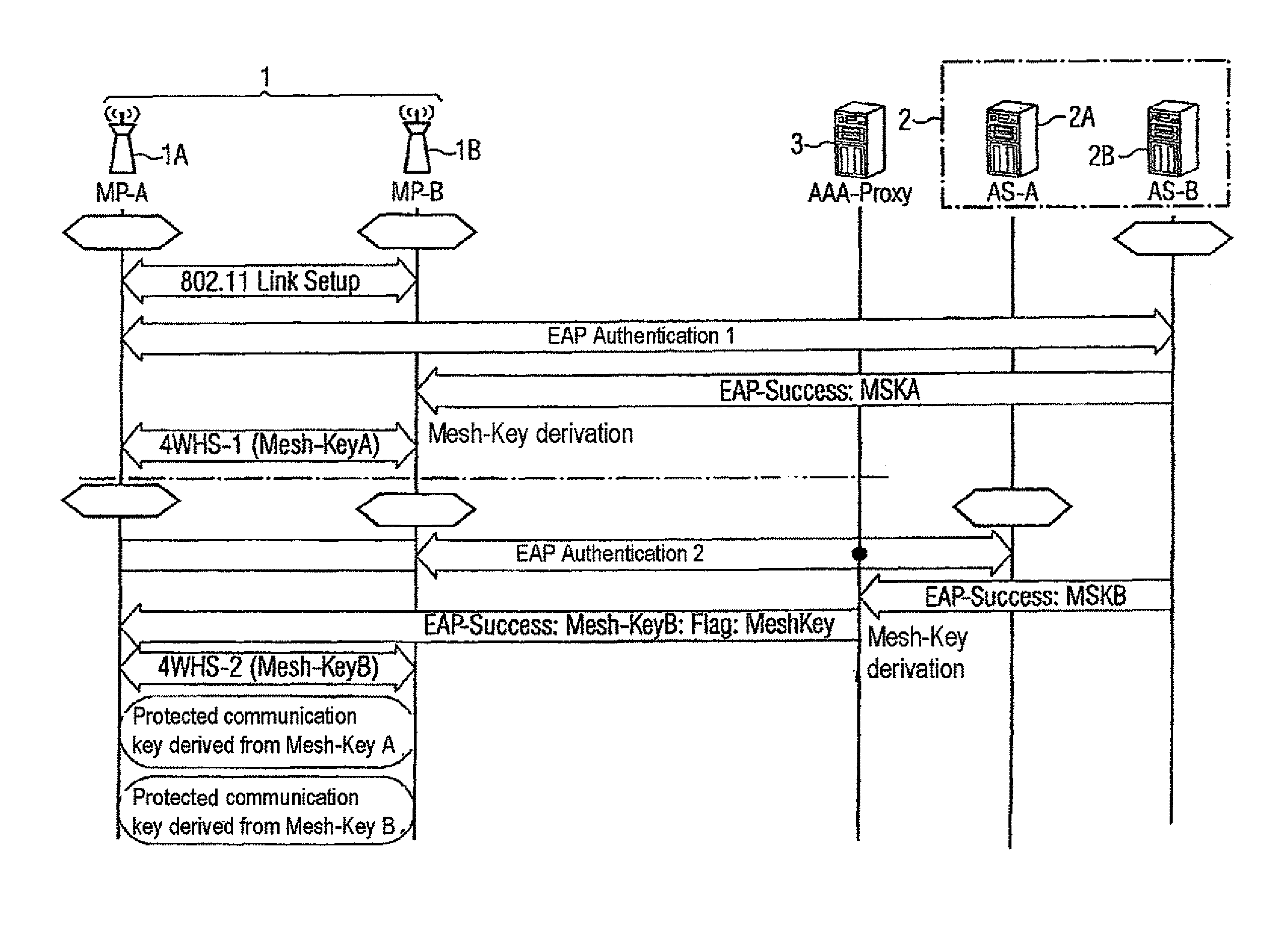
Method and system for providing a mesh key
InactiveUS8959333B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsKey derivation functionAuthentication server
Method for providing a mesh key which can be used to encrypt messages between a first node and a second node of a mesh network, wherein a session key is generated when authenticating the first node in an authentication server, the first node and the authentication server or an authentication proxy server using a predefined key derivation function to derive the mesh key from said session key, which mesh key is transmitted to the second node.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
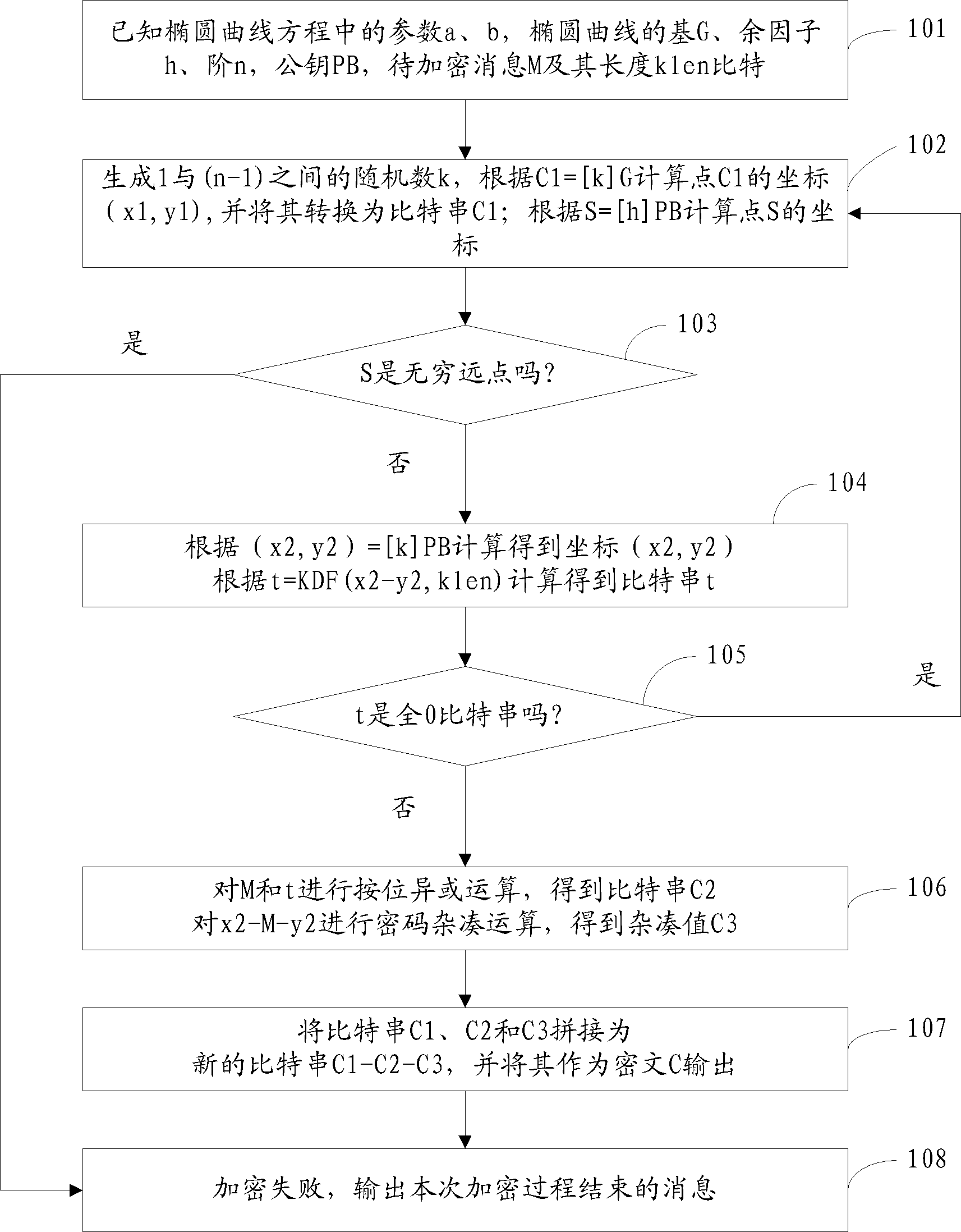
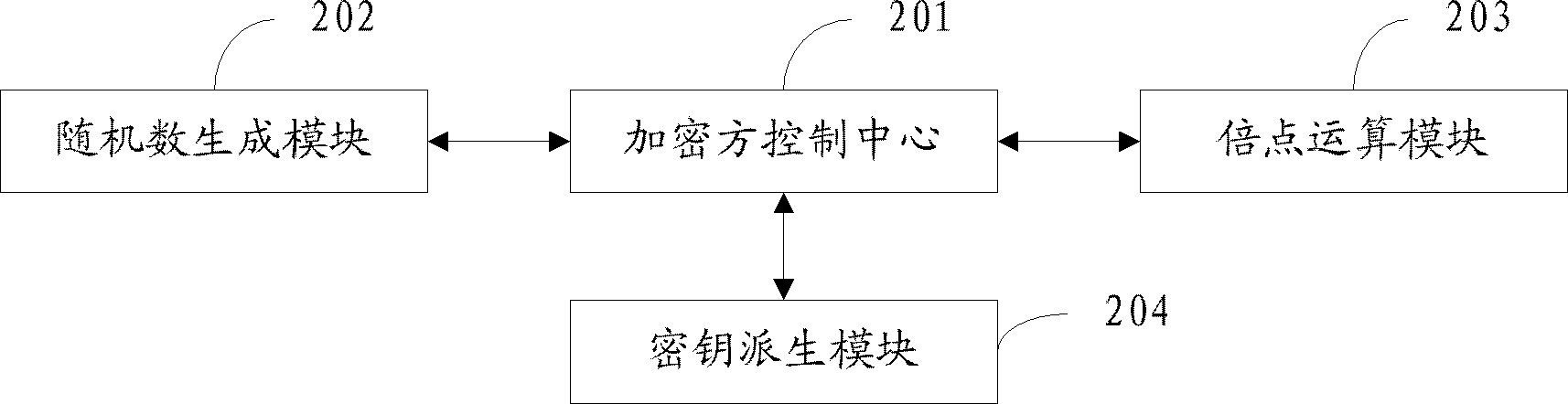
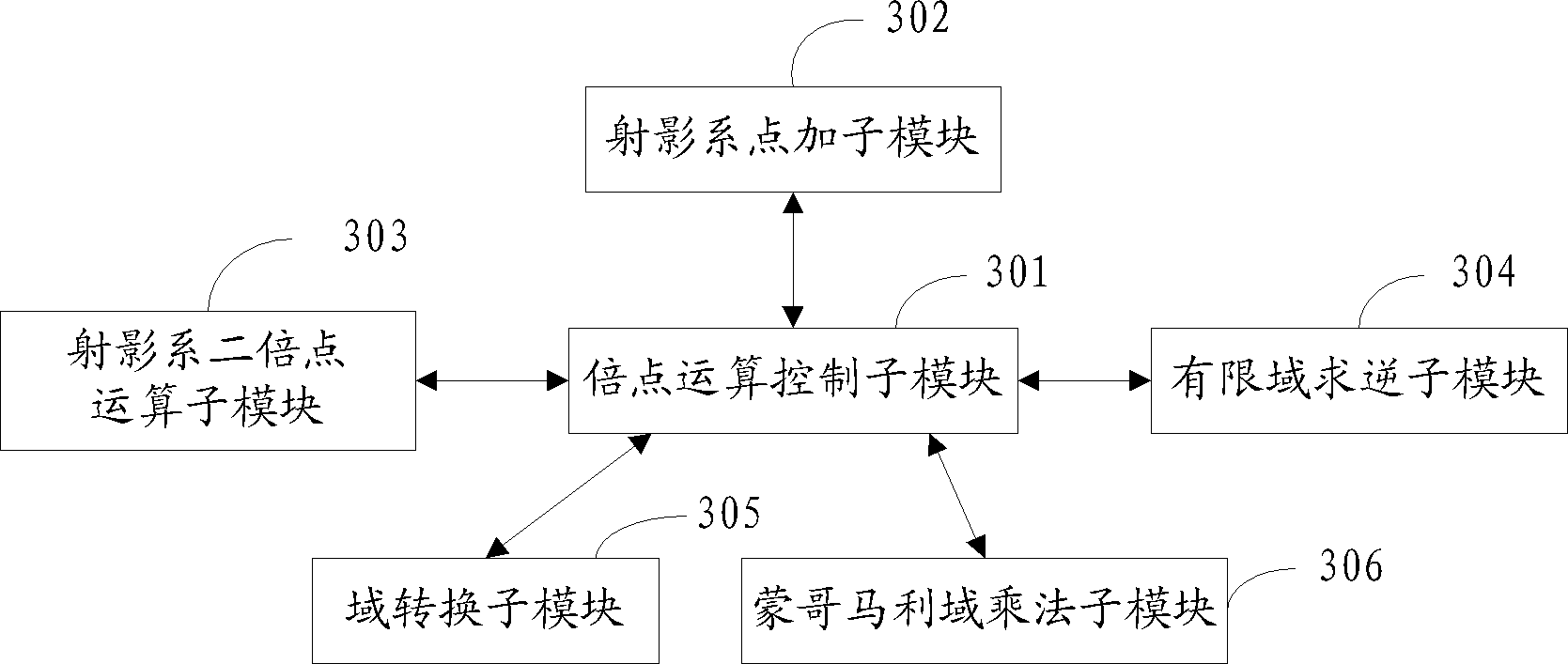
P-element domain SM2 elliptic curve public key encryption, decryption and encryption-decryption hybrid system
InactiveCN102761412AKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareHybrid system
The invention relates to a p-element domain SM2 elliptic curve public key encryption, decryption and encryption-decryption hybrid system. The system comprises an encryption party control center for performing judgment, bit string splicing, cryptographic hash and data exchange with other modules to control the working time sequence of other modules, a random number generation module for generating a random number, a point doubling module for performing a point doubling function and a key derivation module for performing a key derivation function, and all the modules are implemented by hardware. The system disclosed by the invention can implement a public key encryption algorithm in an SM2 elliptic curve public key cryptographic algorithm by hardware.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION
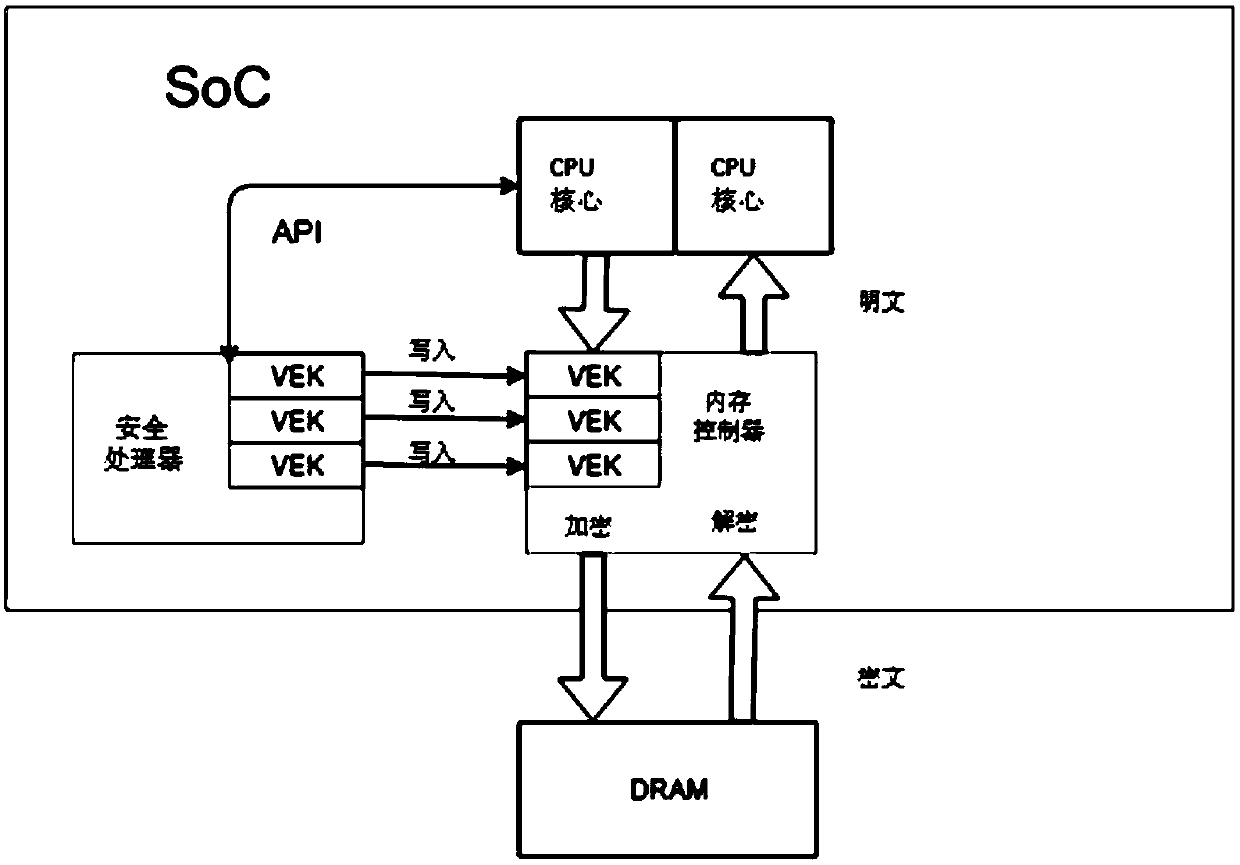
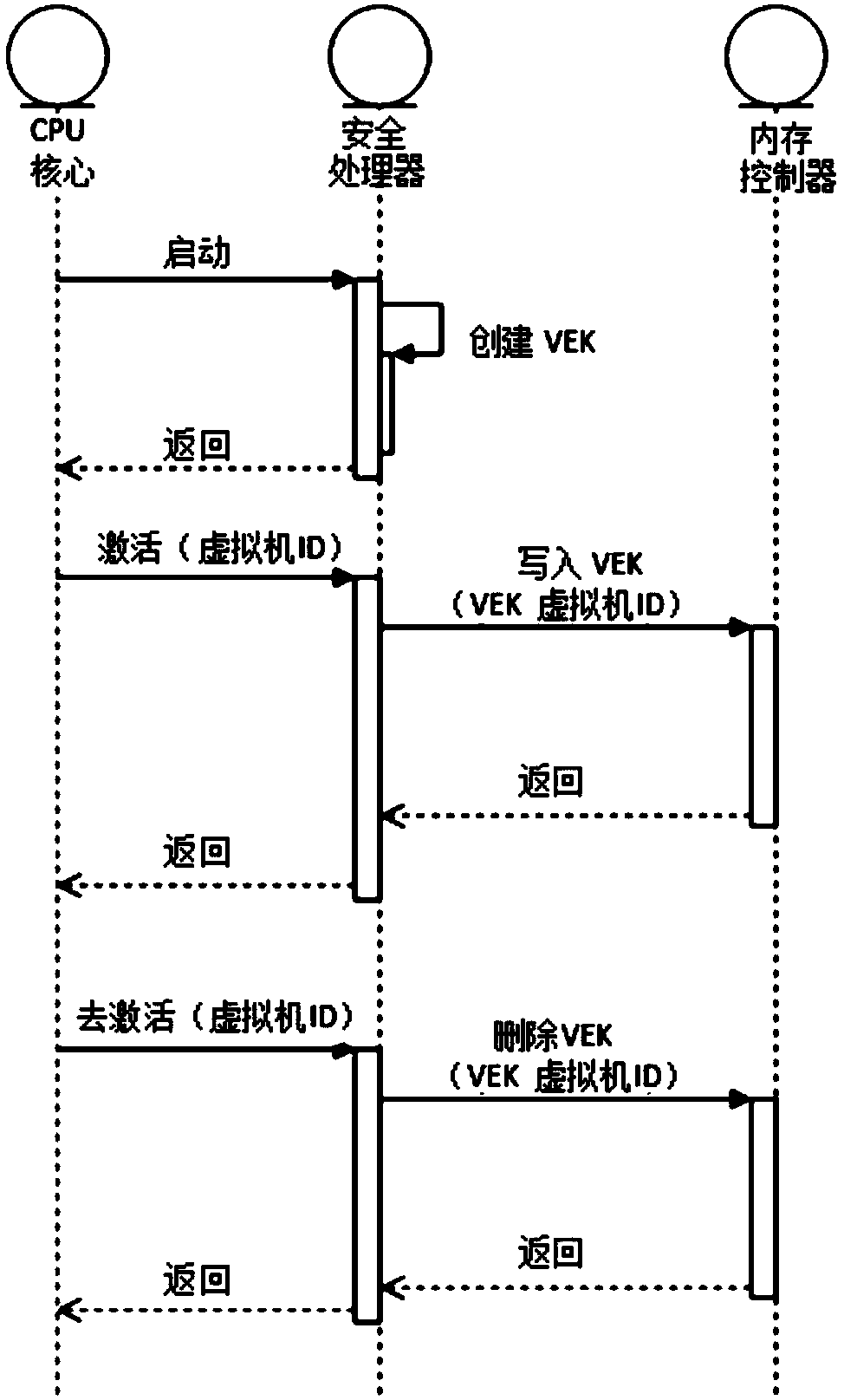
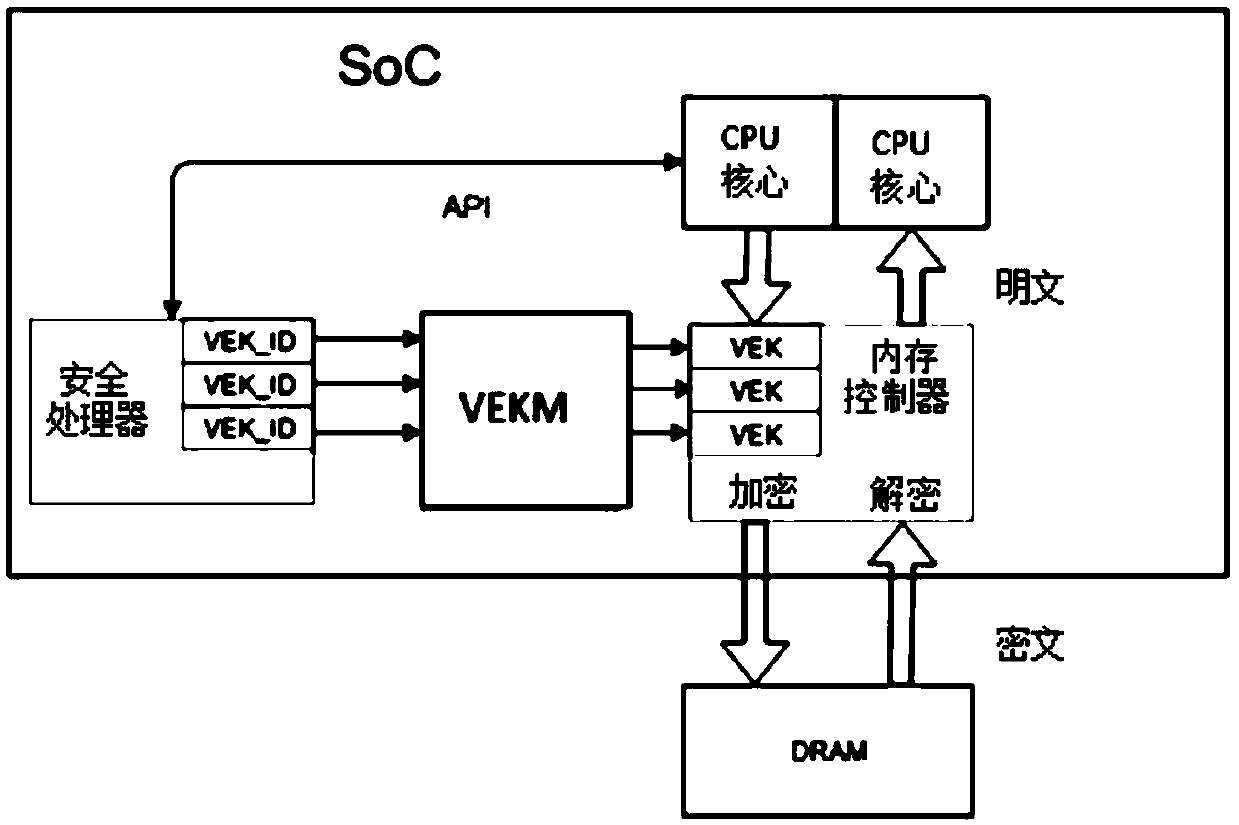
Virtual machine memory key generation device and method, encryption method and SoC system
ActiveCN109684030AImprove securityEnsure data securitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationProcessing coreKey derivation function
The invention discloses a virtual machine memory key generation system. The method is used for a SoC system comprising more than one processing core. The system comprises a security processor and a virtual machine memory key generation device, wherein the security processor generates a virtual machine memory key index based on a request from the processing core, and the virtual machine memory keygeneration device receives the virtual machine memory key index from the security processor and calculates and generates a memory key for the processing core through a specific algorithm. The memory key generation device includes: a random key generation unit that generates a random key; And a key derivation function circuit that generates the memory key by using the virtual machine memory key index and the random key through the specific algorithm. According to the method, the security of the memory key of the virtual machine in security virtualization is improved, and the data security of the virtual machine is better ensured.
Owner:HYGON INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
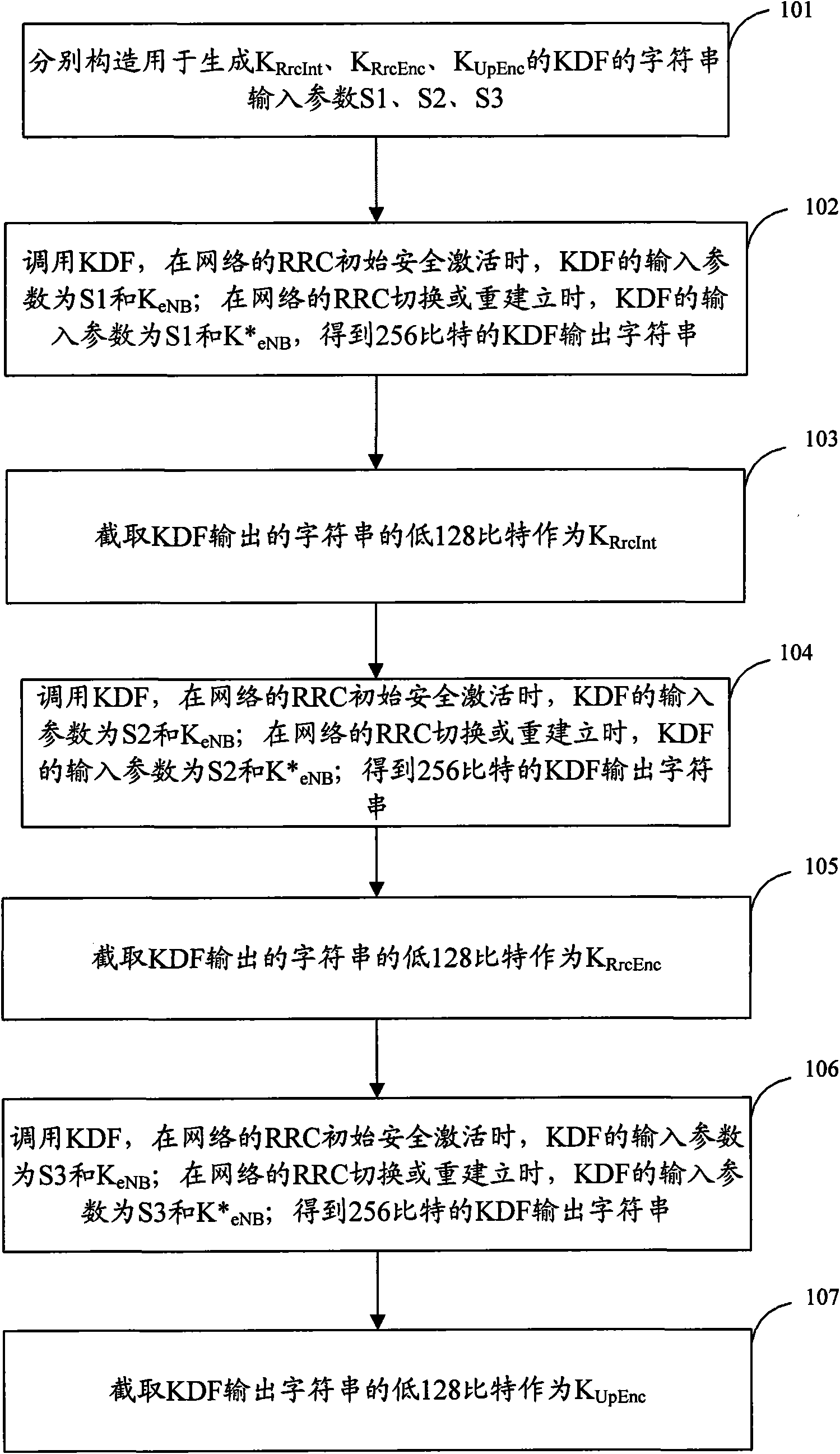
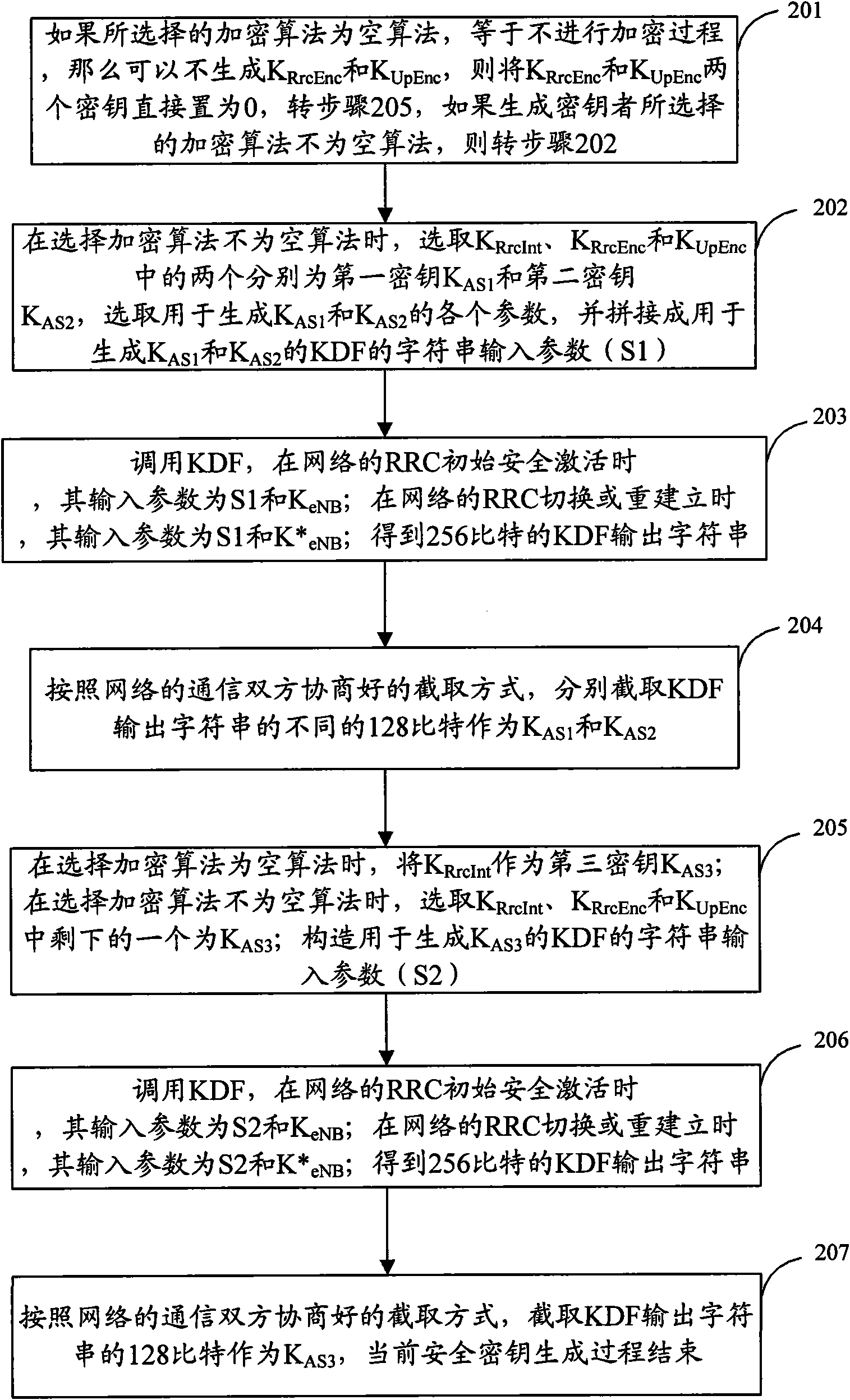
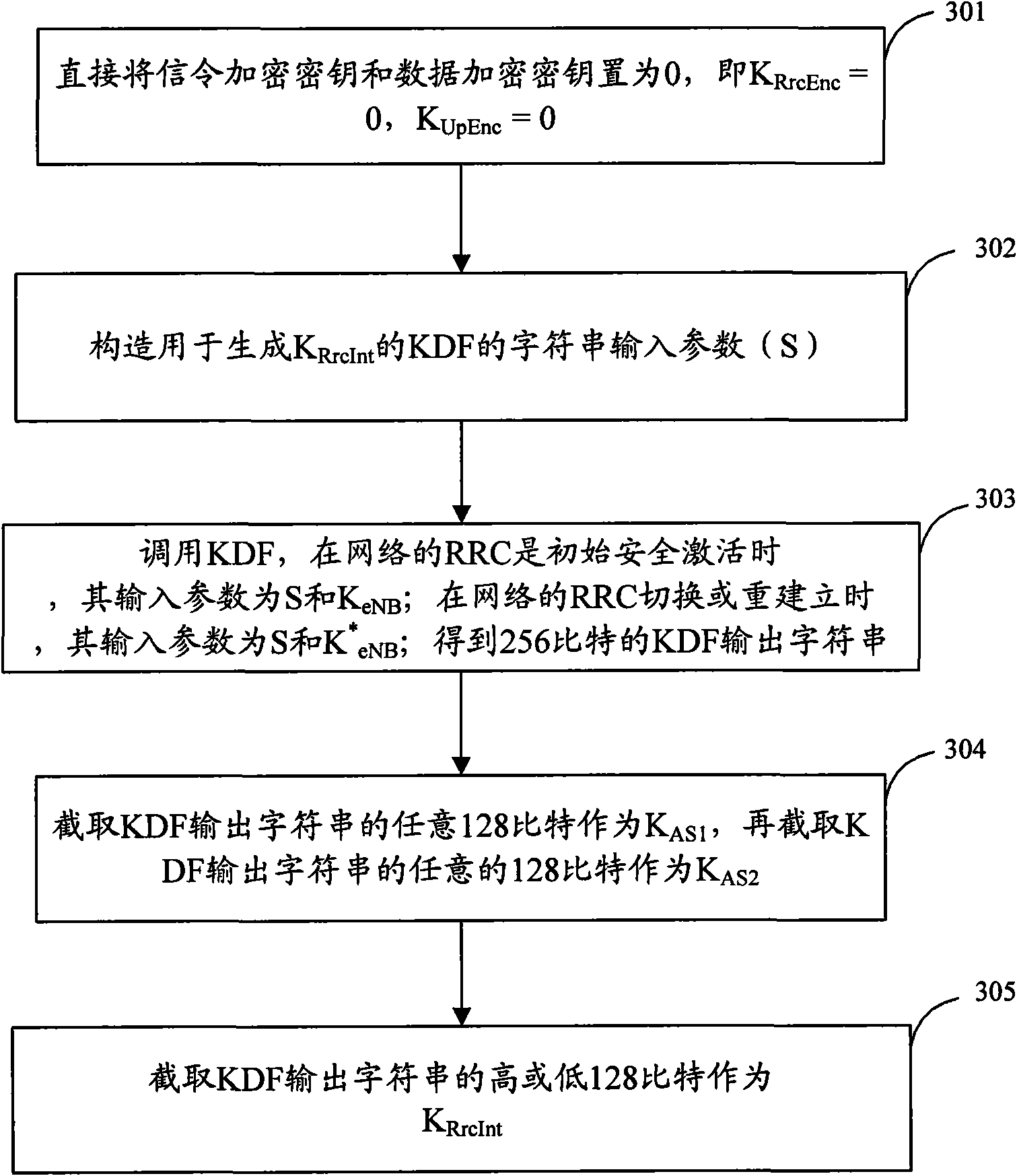
Generation method and device of safe keys
ActiveCN101938743AReduce latencySmall amount of calculationSecurity arrangementTime delaysKey derivation function
The invention discloses a generation method of safe keys. When the three safe keys of an AS (Access Layer) are generated: if an encryption algorithm is a null algorithm, a signaling integrity protection key is generated by only one calling of a KDF (Key Derivation Function), and a signaling encryption key and a user data encryption key are directly set as 0; if the encryption algorithm is not thenull algorithm, parameters for generating any two keys are combined, and in the process of once calling the KDF, the two keys can be obtained, thus, the three keys can be generated by only twice calling the KDF; and meanwhile, the invention discloses a generation device of the safe keys, and the utilization ratio of key generation resources can be improved and the time delay of the whole key generation system can be reduced through the method or the device.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Secure interface for versatile key derivation function support
ActiveUS20070076866A1Easy to implementImprove usabilityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareKey derivation function
Improper re-use of a static Diffie-Hellman (DH) private key may leak information about the key. The leakage is prevented by a key derivation function (KDF), but standards do not agree on key derivation functions. The module for performing a DH private key operation must somehow support multiple different KDF standards. The present invention provides an intermediate approach that neither attempts to implement all possible KDP operations, nor provide unprotected access to the raw DH private key operation. Instead, the module performs parts of the KDF operation, as indicated by the application using the module. This saves the module from implementing the entire KDF for each KDF needed. Instead, the module implements only re-usable parts that are common to most KDFs. Furthermore, when new KDFs are required, the module may be able to support them if they built on the parts that the module has implemented.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
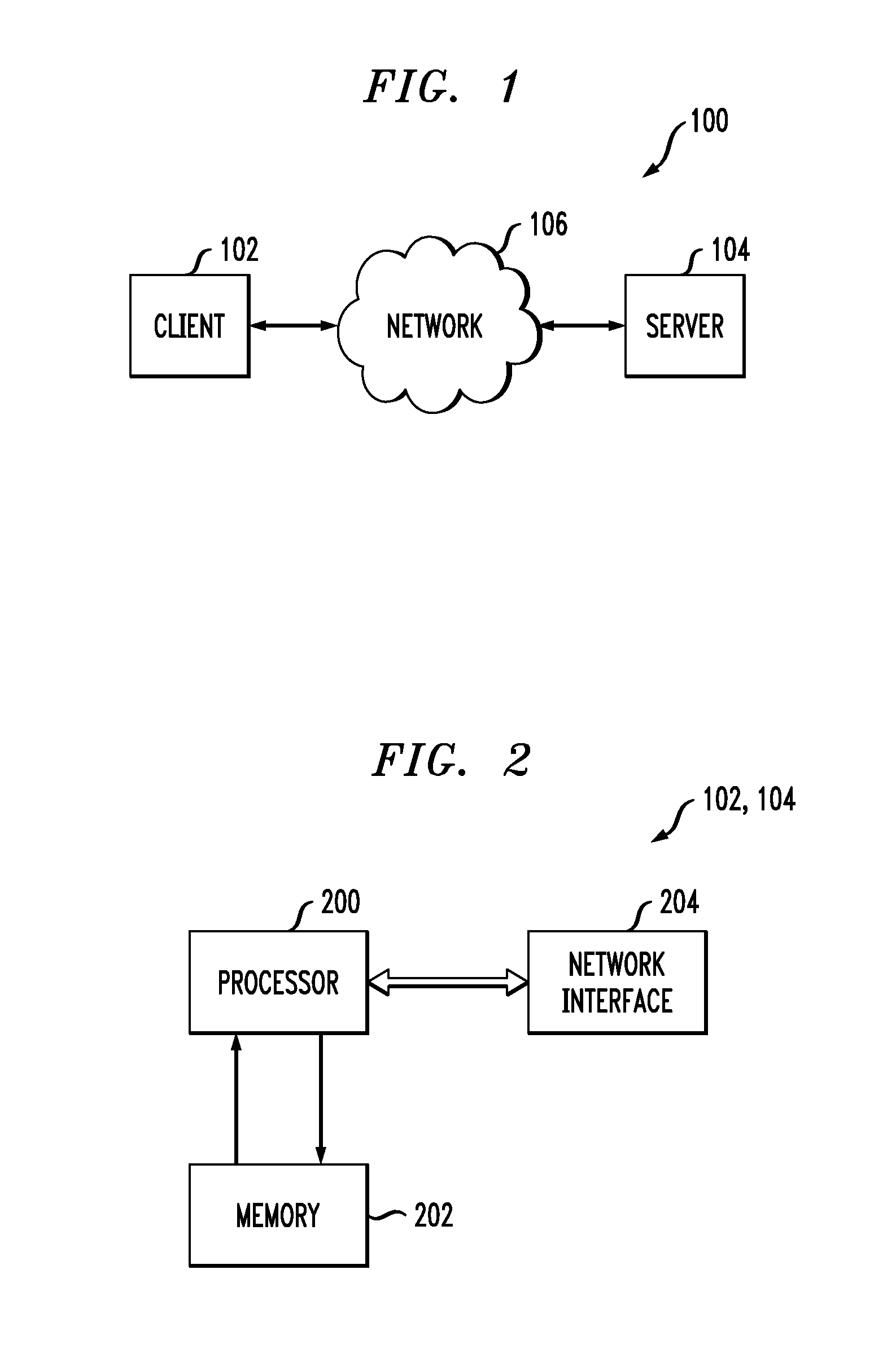
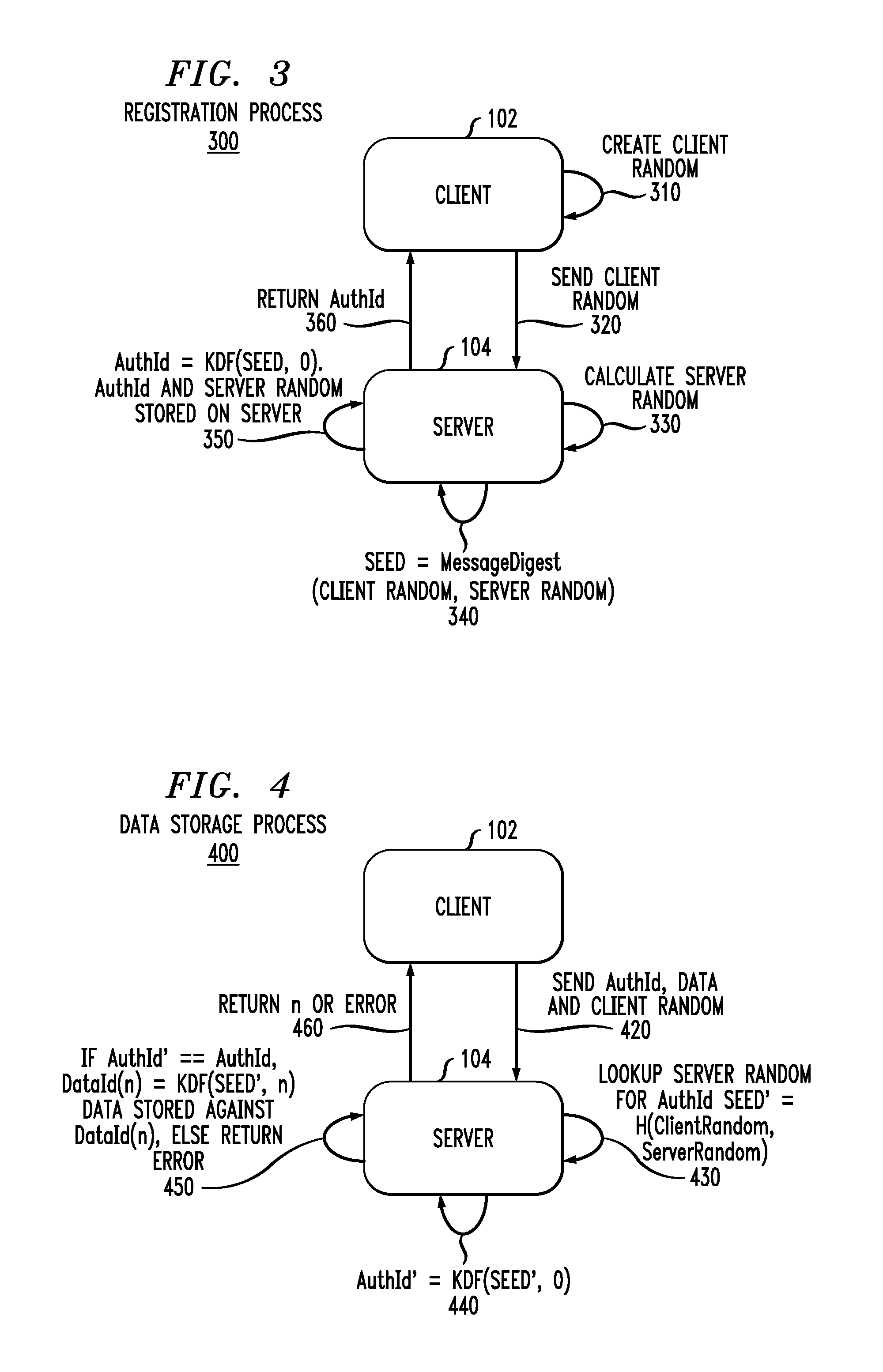
Cryptographically linking data and authentication identifiers without explicit storage of linkage
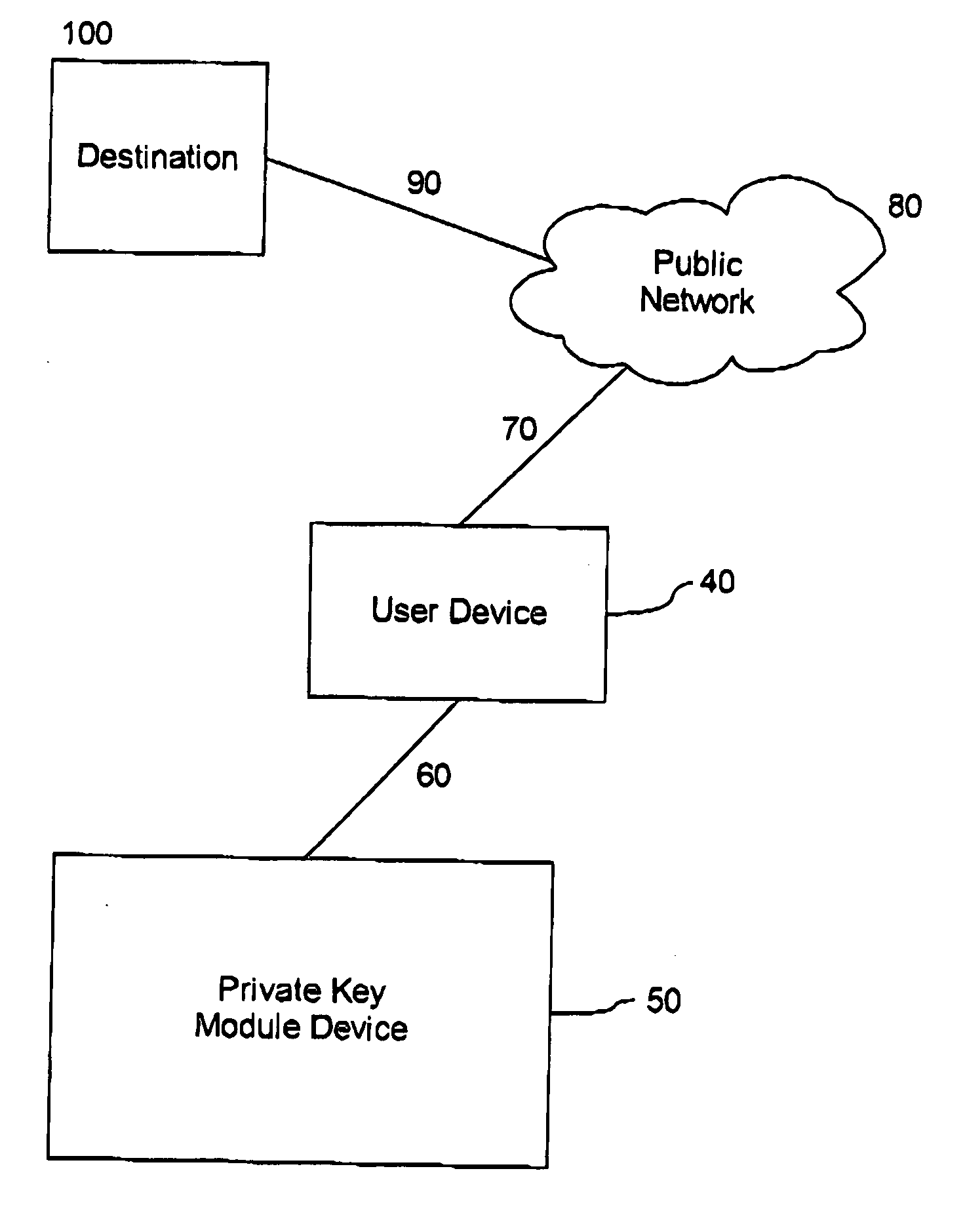
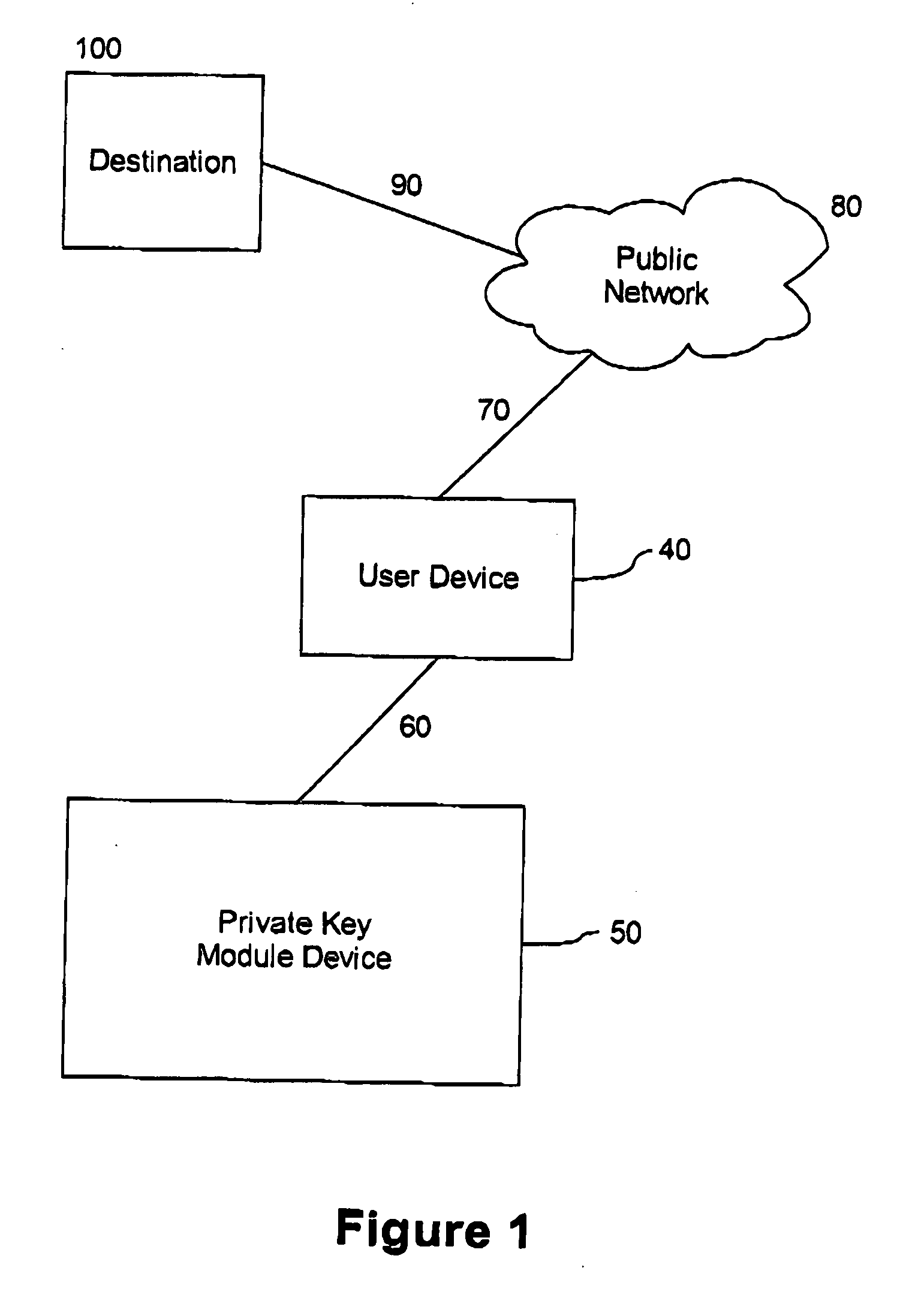
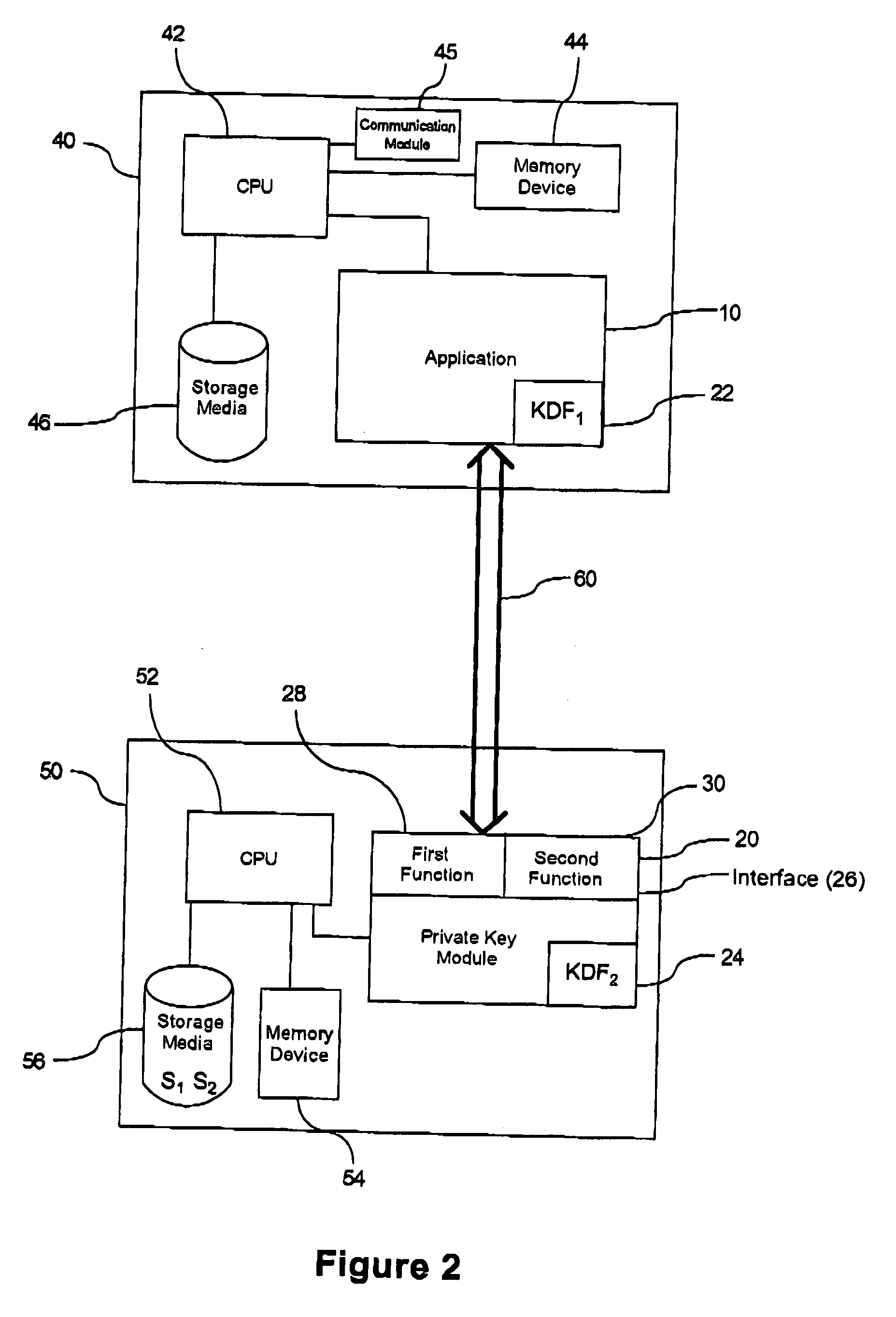
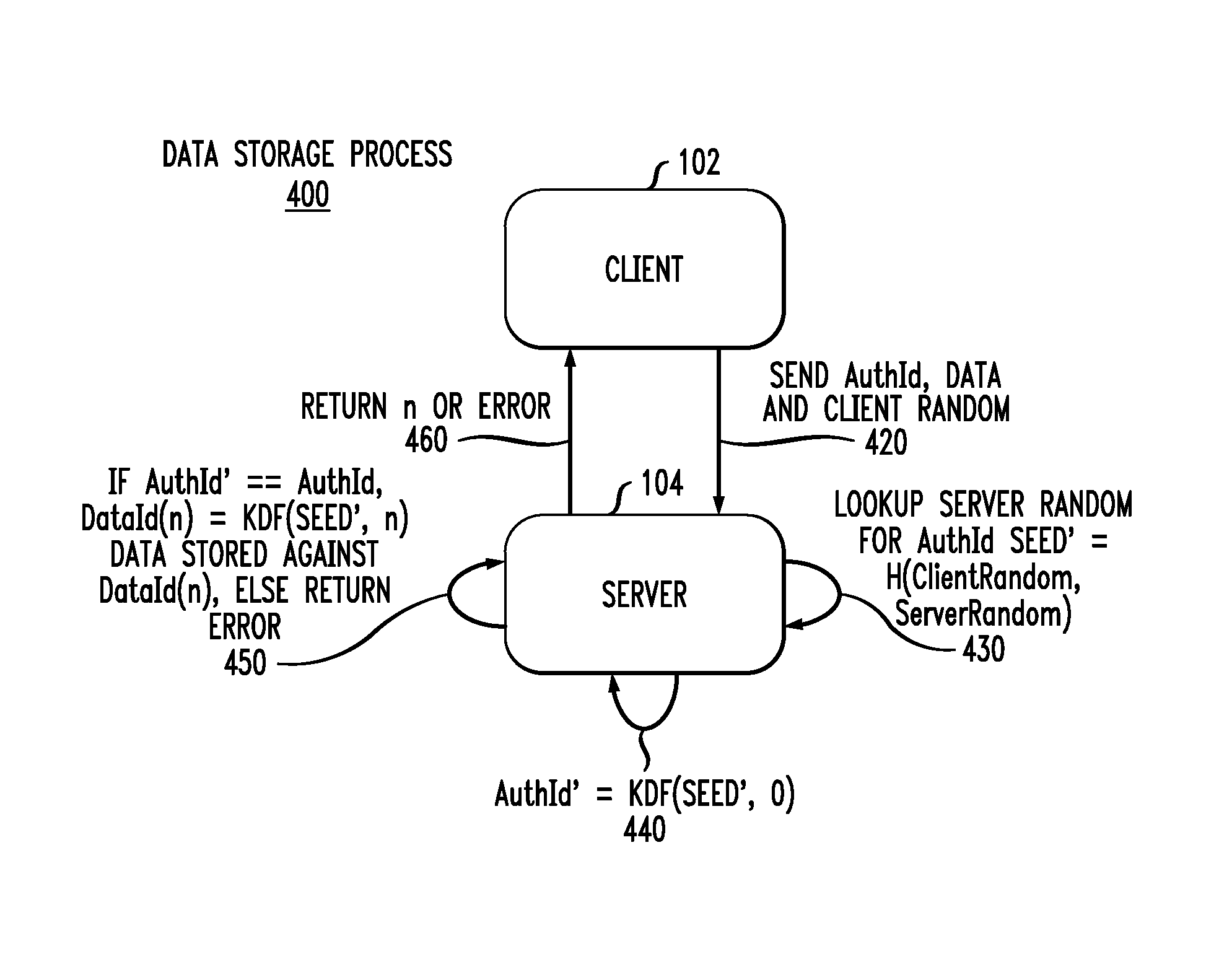
ActiveUS9288049B1Improve securityReadily apparentKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey derivation functionClient-side
Methods and apparatus are provided for cryptographically linking data identifiers and authentication identifiers without storing the association between the authentication and data secrets in the database of the server. A data secret of a client is provided to a server for storage with an authentication identifier (AuthId) and a pseudo-random client value. The server provides the client with a sequence number of the stored data secret that is associated with a data identifier (DataId) identifying the data secret obtained using a Key Derivation Function and a storage seed. The client registers with the server to obtain the authentication identifier (AuthId). Techniques are also provided for retrieving and updating the data secret.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Authenticated mode control
ActiveUS8160248B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageMode controlConditional access
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
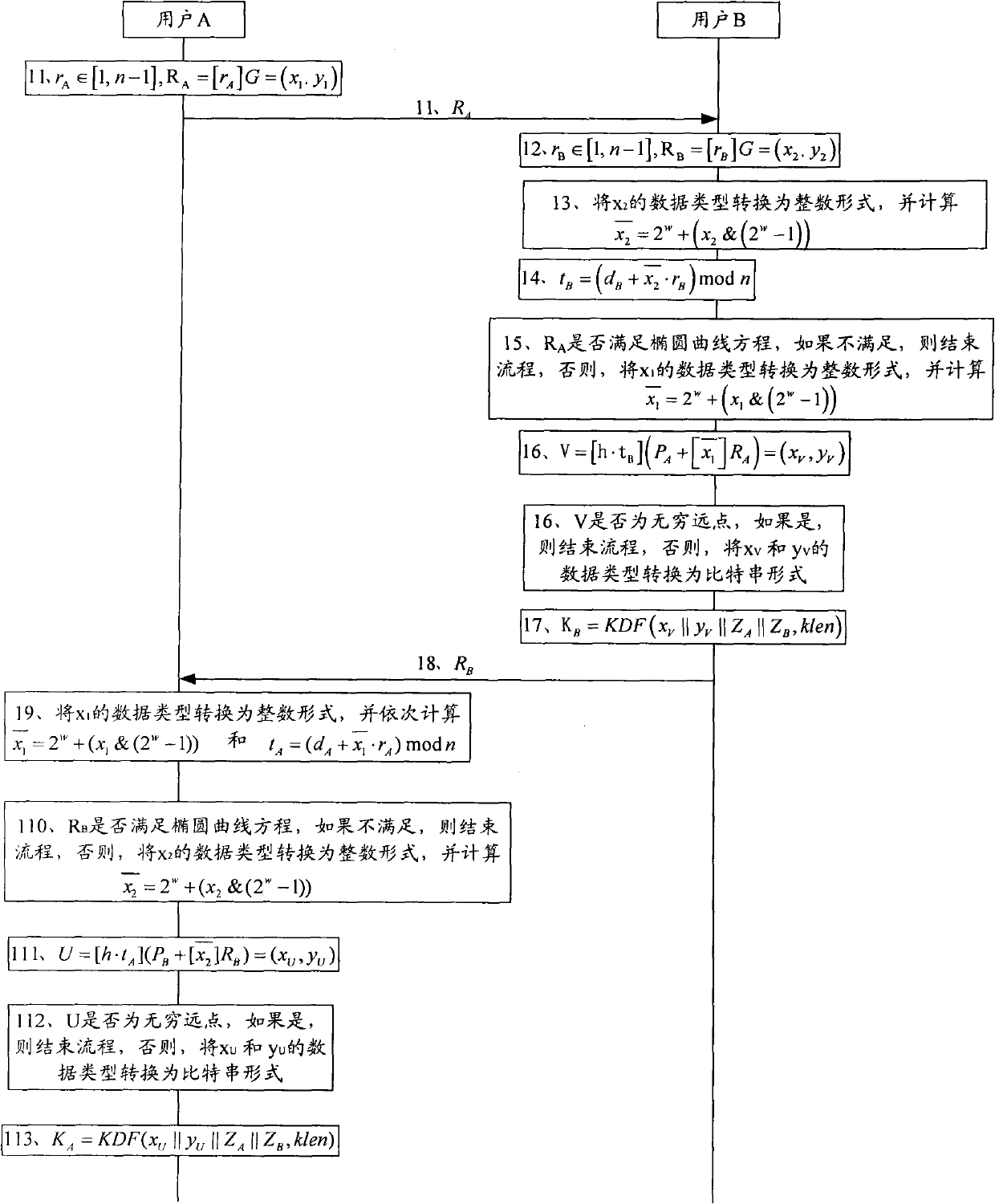
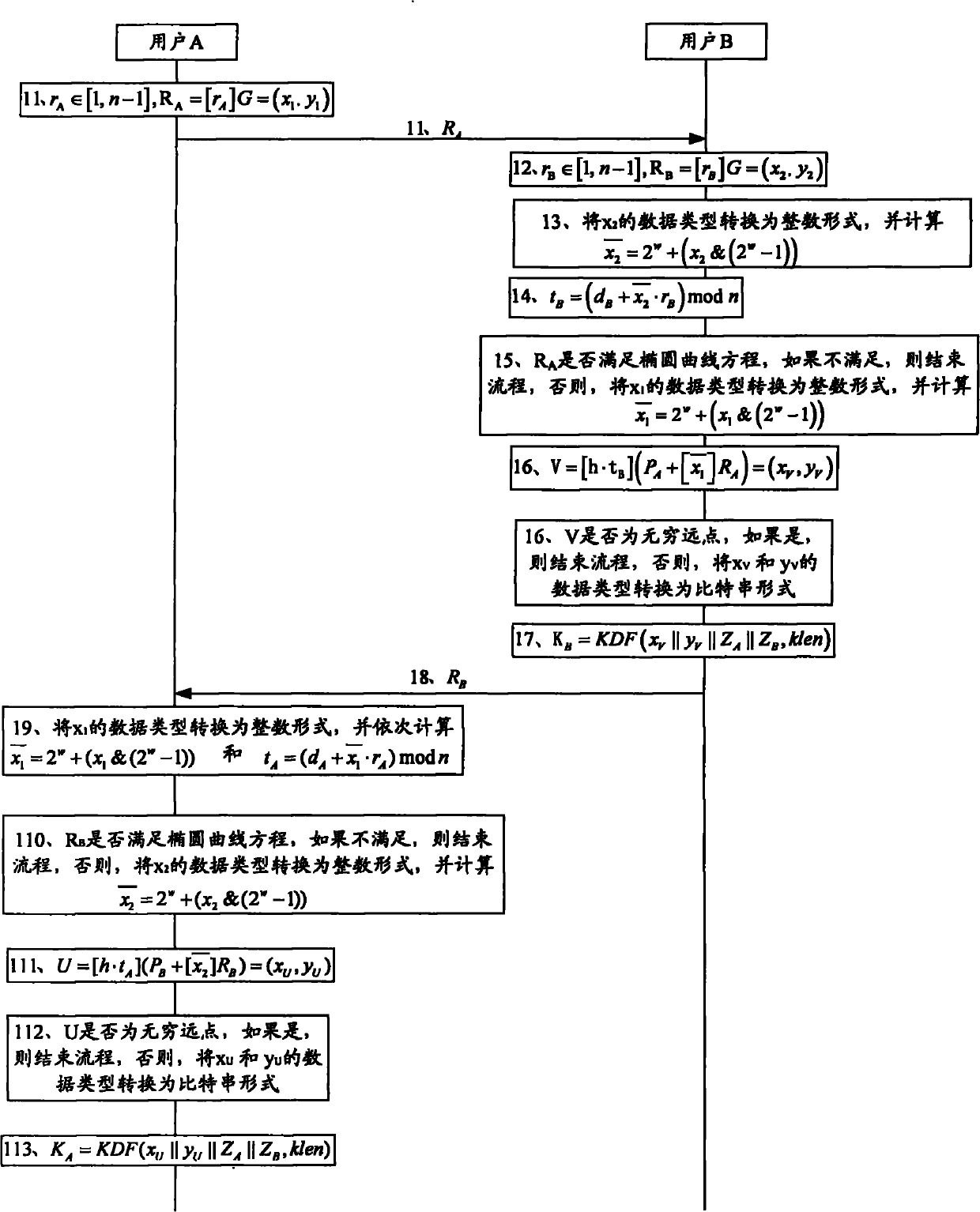
Elliptic curve-based key exchange method
ActiveCN102104481AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeKey derivation function
The invention provides an elliptic curve-based key exchange method. In the process of constructing a key generation function, user identity information, elliptic curve equation parameter information, public keys of a user and other information are fully considered, and a cofactor, a random number and other information are fully utilized in the process of calculating elliptic curve points. Therefore, compared with the prior art, the method can better improve the safety.
Owner:DATA ASSURANCE & COMM SECURITY CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com