Patents
Literature
53 results about "Forward secrecy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, forward secrecy (FS), also known as perfect forward secrecy (PFS), is a feature of specific key agreement protocols that gives assurances that session keys will not be compromised even if the private key of the server is compromised. Forward secrecy protects past sessions against future compromises of secret keys. By generating a unique session key for every session a user initiates, the compromise of a single session key will not affect any data other than that exchanged in the specific session protected by that particular key. Forward secrecy further protects data on the transport layer of a network that uses common SSL/TLS protocols, including OpenSSL, which had previously been affected by the Heartbleed security bug. If forward secrecy is used, encrypted communications and sessions recorded in the past cannot be retrieved and decrypted should long-term secret keys or passwords be compromised in the future, even if the adversary actively interfered, for example via a man-in-the-middle attack.
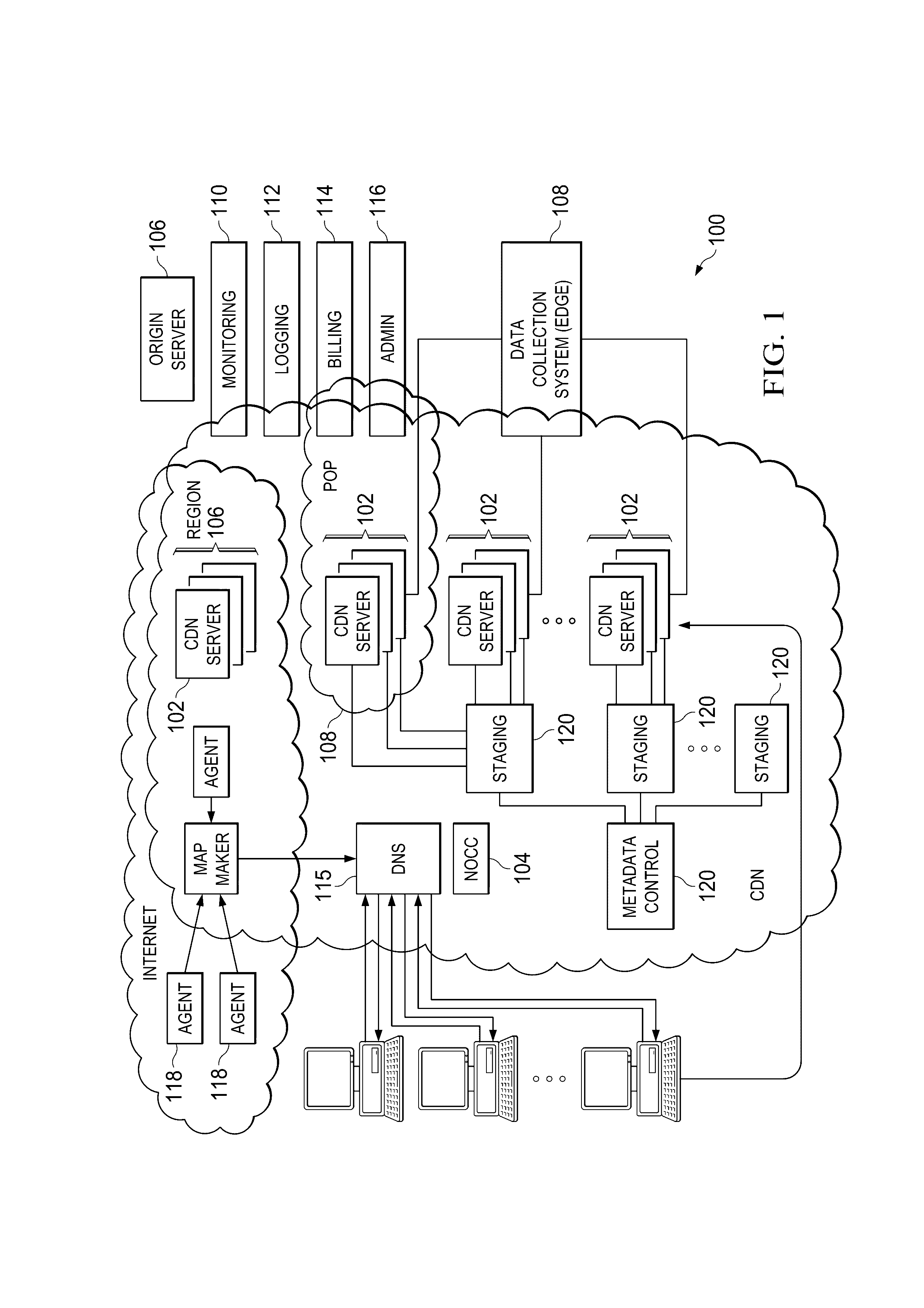
Encryption method and apparatus with forward secrecy and random-access key updating method
InactiveUS7095850B1Generate efficientlyComputationally efficientData stream serial/continuous modificationSecret communicationOne-way functionRekeying
An encryption method and apparatus that provides forward secrecy, by updating the key using a one-way function after each encryption. By providing forward secrecy within a cipher, rather than through a key management system, forward secrecy may be added to cryptographic systems and protocols by using the cipher within an existing framework. A random-access key updating method can efficiently generate one or more future keys in any order. Embodiments are applicable to forward secret ciphers that are used to protect protocols with unreliable transport, to ciphers that are used in multicast or other group settings, and to protection of packets using the IPSec protocols.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Providing forward secrecy in a terminating SSL/TLS connection proxy using ephemeral Diffie-Hellman key exchange
ActiveUS20150067338A1Promote exchangeKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageTerminal serverDigital signature
An infrastructure delivery platform provides a proxy service as an enhancement to the TLS / SSL protocol to off-load to an external server the generation of a digital signature, the digital signature being generated using a private key that would otherwise have to be maintained on a terminating server. Using this service, instead of digitally signing (using the private key) “locally,” the terminating server proxies given public portions of ephemeral key exchange material to the external server and receives, in response, a signature validating the terminating server is authorized to continue with the key exchange. In this manner, a private key used to generate the digital signature (or, more generally, to facilitate the key exchange) does not need to be stored in association with the terminating server. Rather, that private key is stored only at the external server, and there is no requirement for the pre-master secret to travel (on the wire).
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
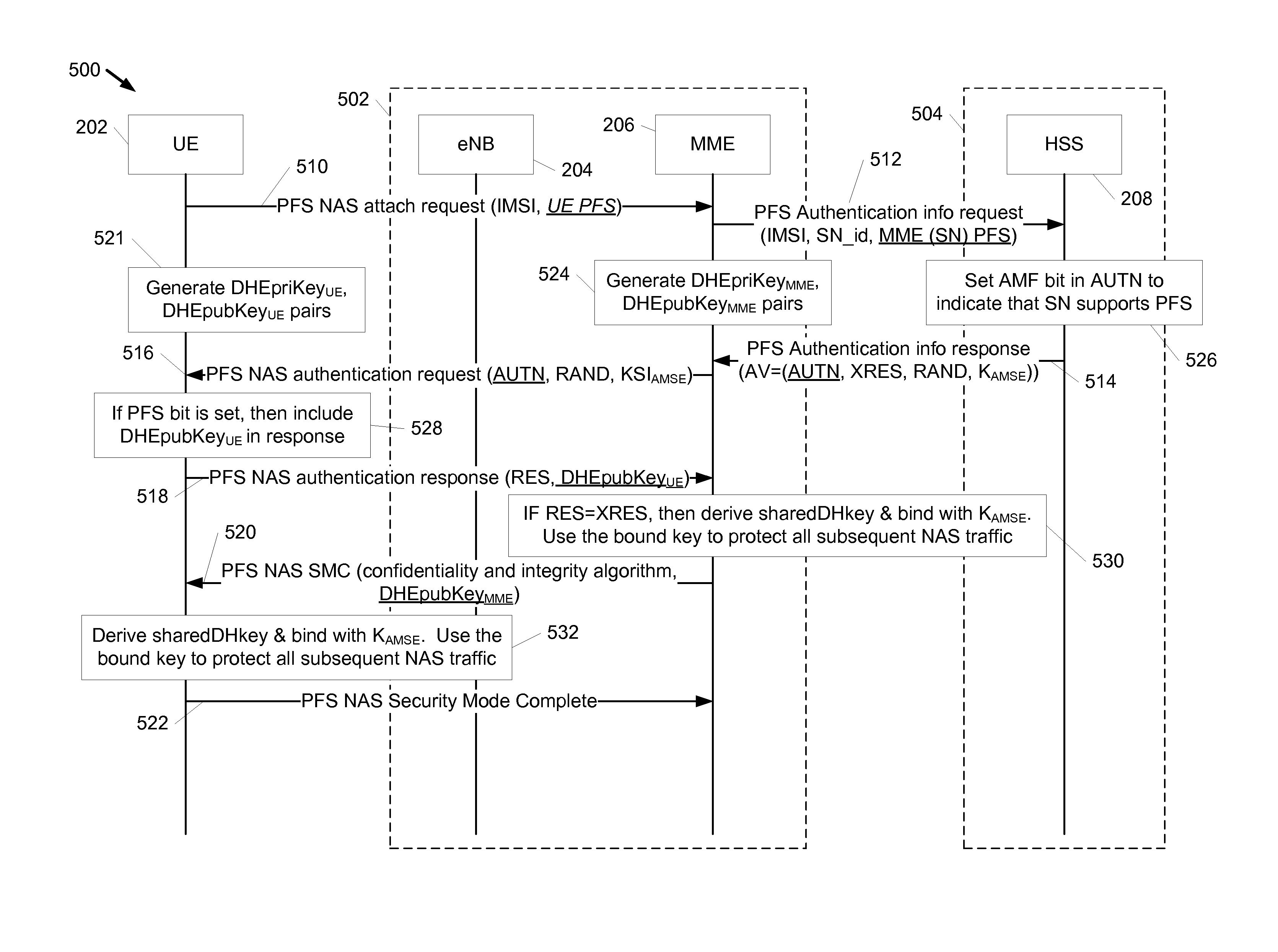
Authentication and key agreement with perfect forward secrecy
ActiveUS20170006469A1Reduce attackLower potentialKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Systems and methods for providing authentication key agreement (AKA) with perfect forward secrecy (PFS) are disclosed. In one embodiment, a network according to the disclosure may receive an attach request from a UE, provide an authentication request including a network support indicator to a network resource, receive an authentication token from the network resource, such that the authentication token includes an indication that a network supports PFS, provide the authentication token to the UE, receive an authentication response including a UE public key value, obtain a network public key value and a network private key value, determine a shared key value based on the network private key value and the UE public key value, bind the shared key value with a session key value to create a bound shared key value, and use the bound shared key value to protect subsequent network traffic.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
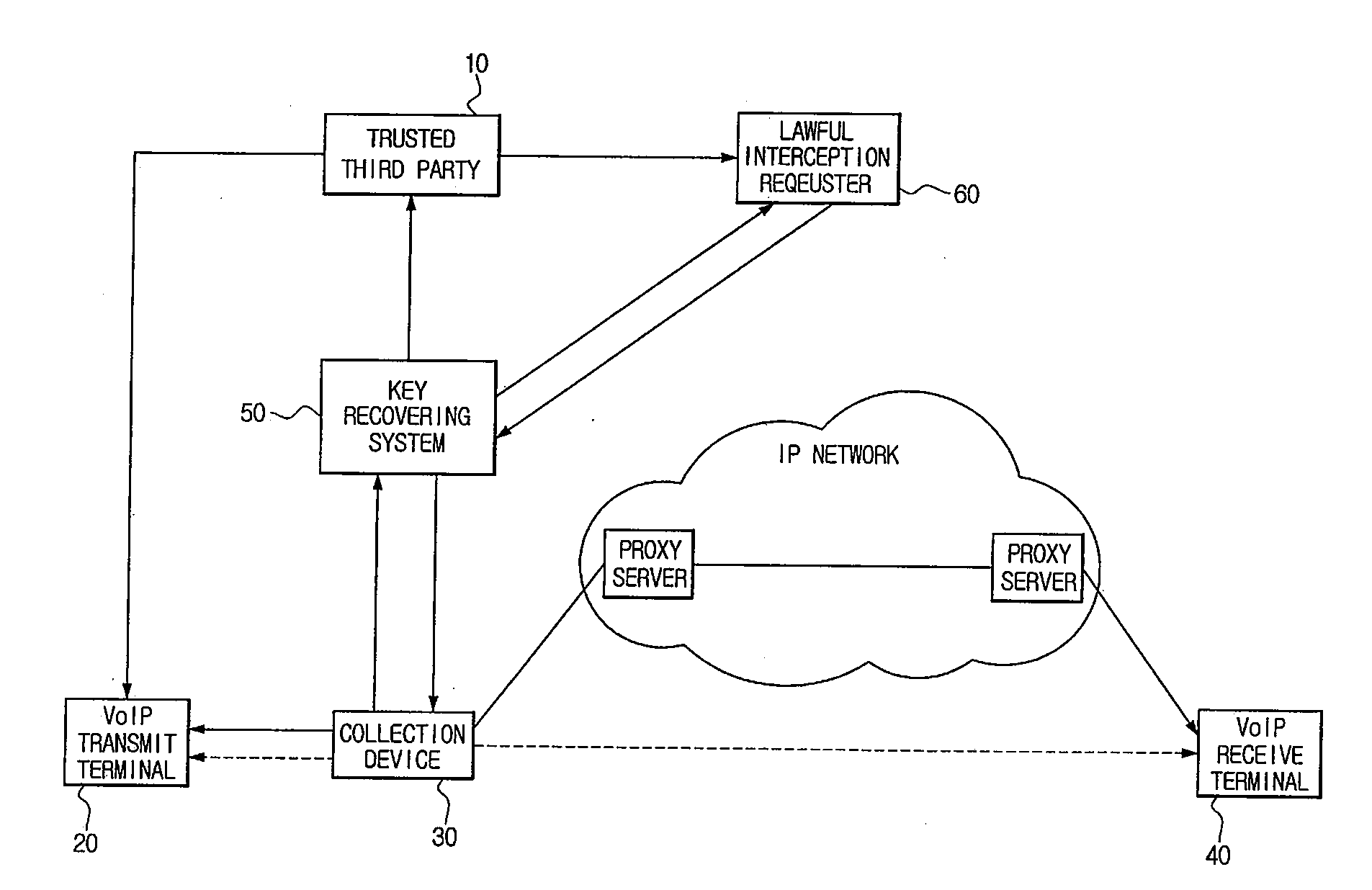
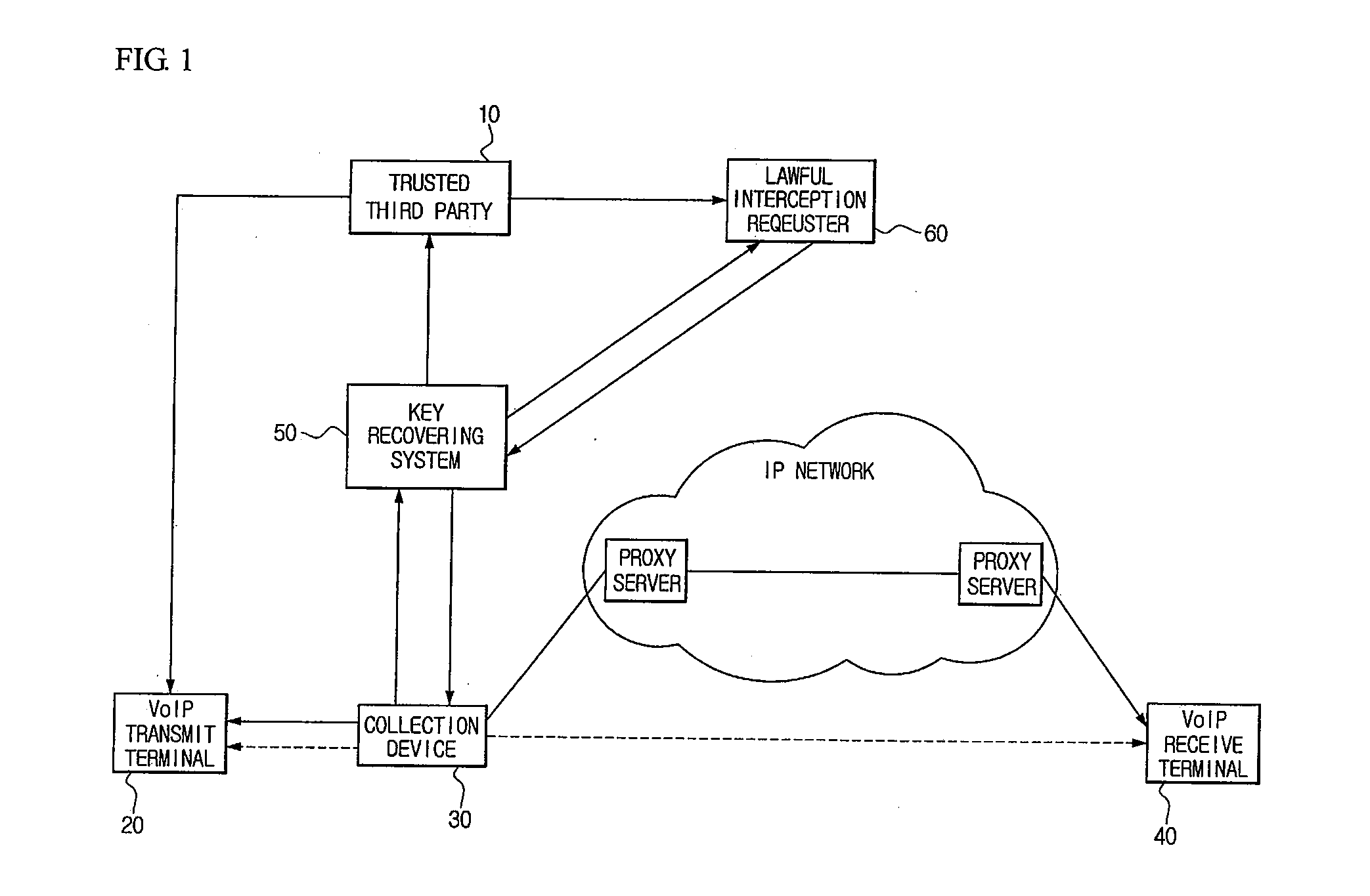
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LAWFUL INTERCEPTION USING TRUSTED THIRD PARTIES IN SECURE VoIP COMMUNICATIONS
InactiveUS20100002880A1Perfect forward secrecyKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationLawful interceptionMaster key
Disclosed is a system for lawful interception using a trusted third party in secure VoIP communication. A VoIP transmit terminal generates a secure packet using a master key received from a trusted third party and then communicates with a VoIP receive terminal. A collection device having received a lawful interception instruction from a key recovering system collects and transmits the secure packet to the key recovering system. The key recovering system decrypts the secure packet using the master key received from the trusted third party and provides the decrypted secure packet to a lawful interception requester or provides the master key received from the trusted third party and the secure packet to the lawful interception requester. It is possible to provide the perfect lawful interception in the secure VoIP communication environment, and to guarantee a perfect forward secrecy since the master key is changed for each call.
Owner:KOREA INTERNET & SECURITY AGENCY
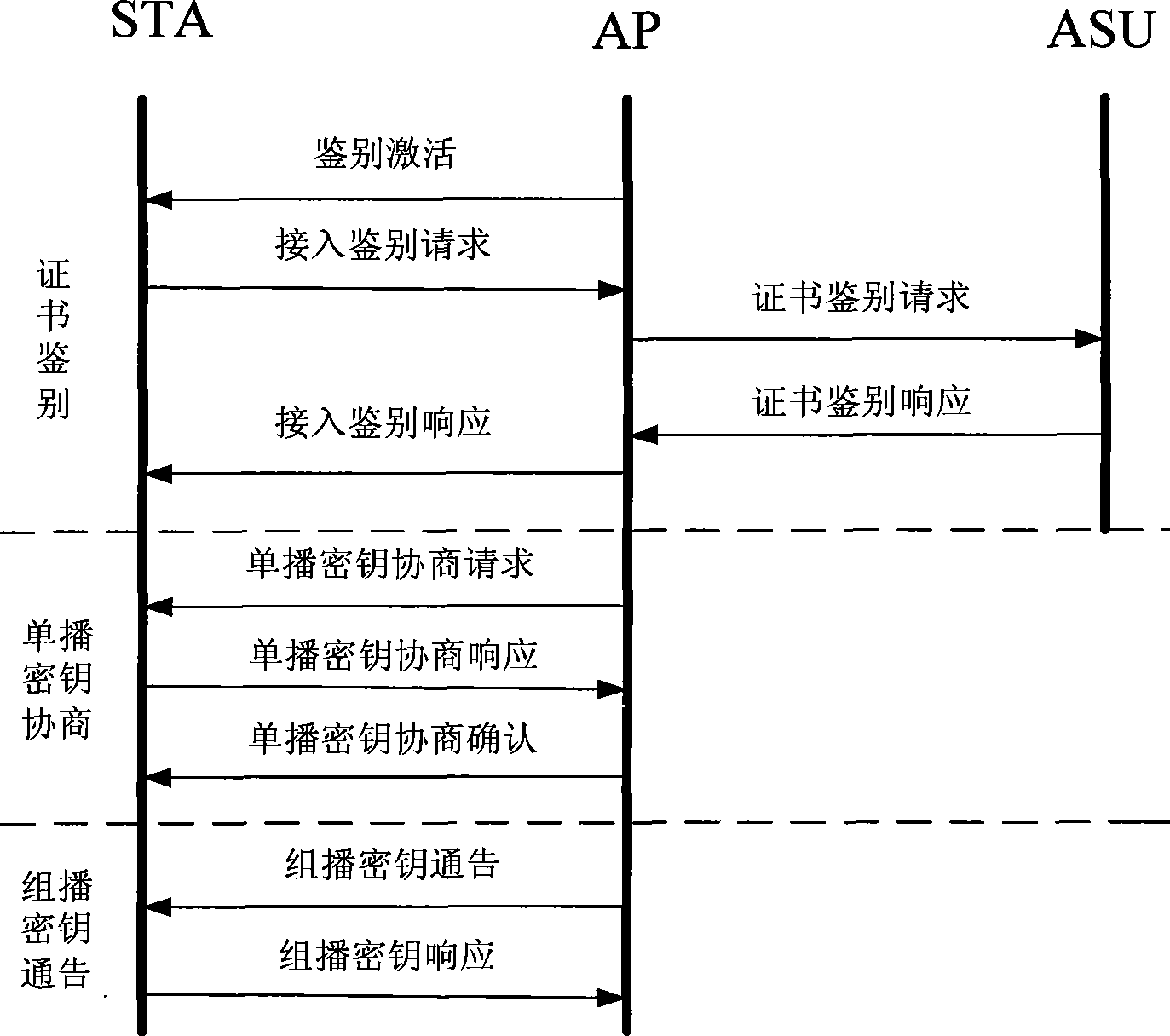
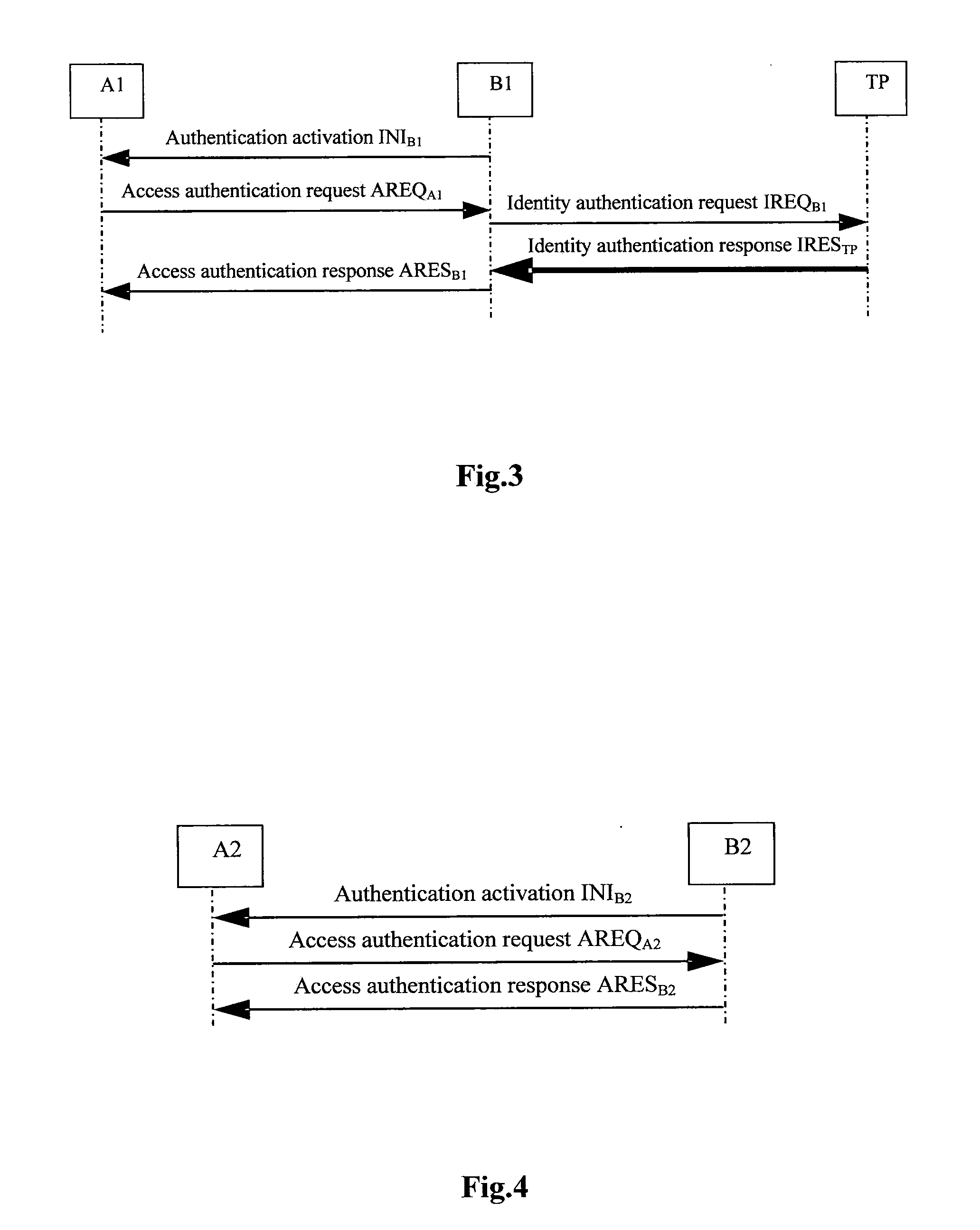
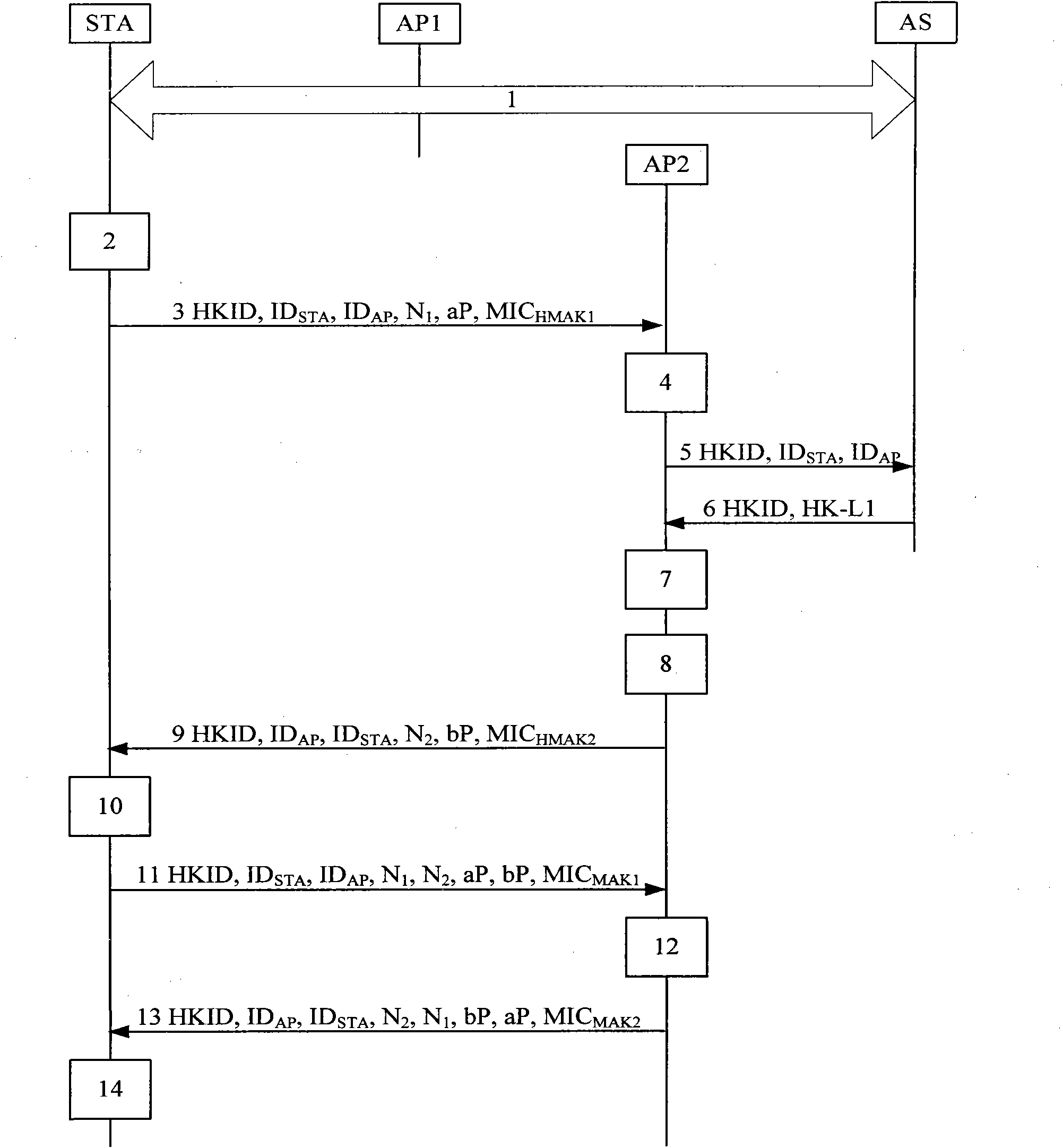
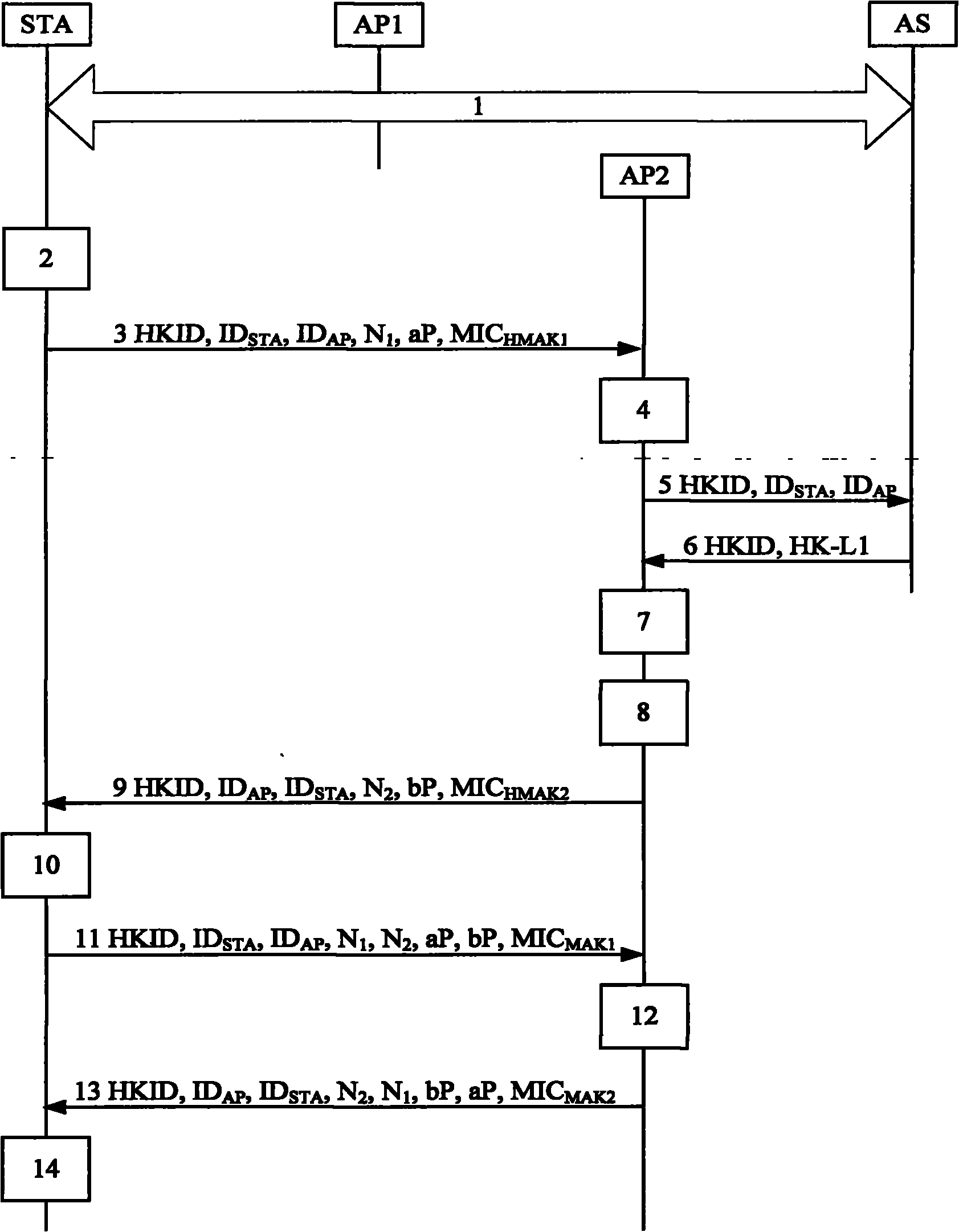
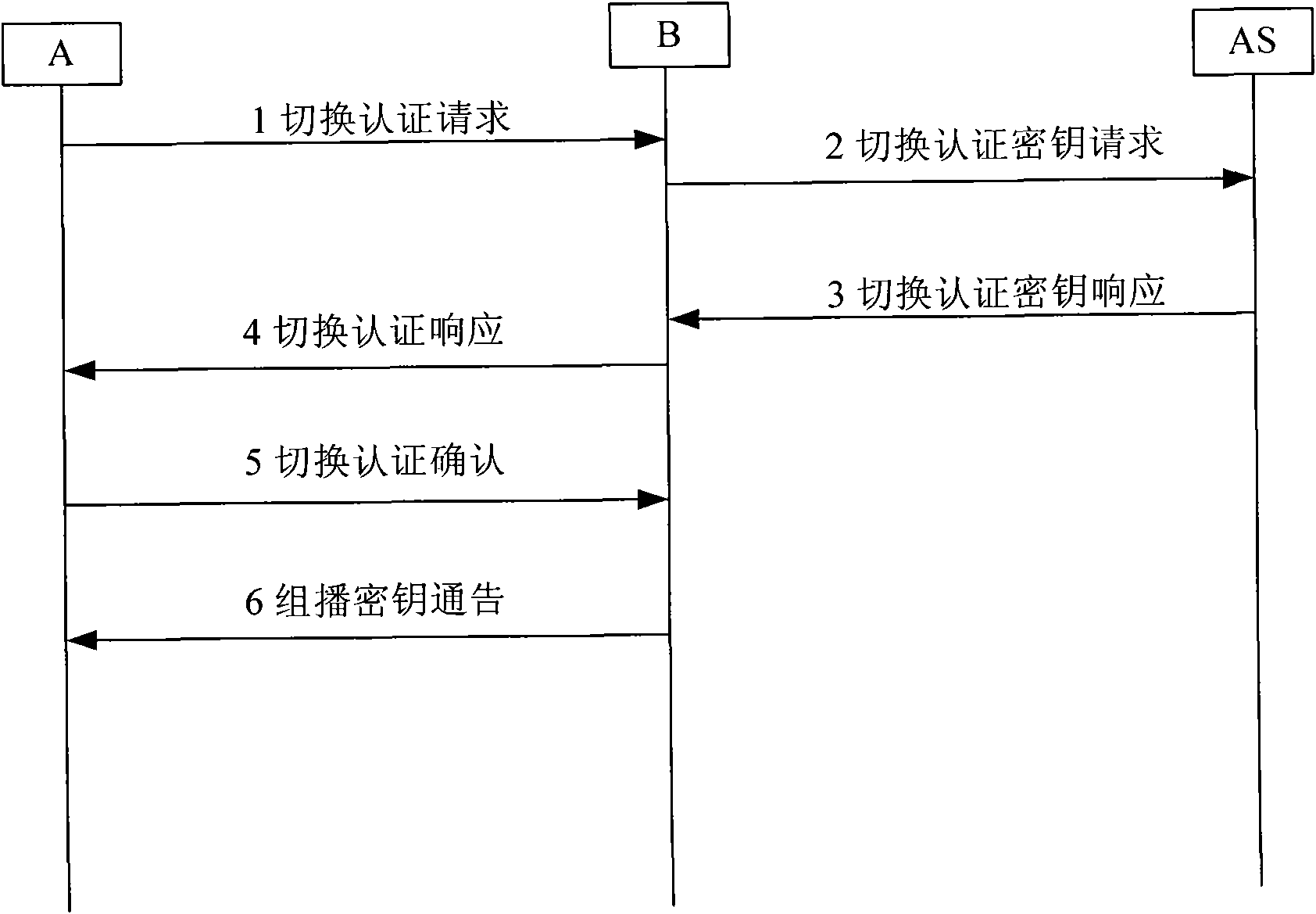
WAPI-XG1 access and fast switch authentication method
InactiveCN101420694AReduce complexitySolve the problem that fast switching is not supportedNetwork topologiesTransmissionClient-sideDictionary attack
The invention provides a method used for authentificating the access and quick switching over of WAPI-XG1, belonging to the field of wireless communication. The method comprises the steps as follows: an authentication protocol is accessed and used for establishing a connection between an STA and a first AP, the session key with the first AP is established, and keys used for quick switching over with an ASU are established; when the STA moves to the control domain of a second AP, a safety correlation establishing protocol and a unicall session key updating protocol under quick switching over are carried out. The method can solve the problems that the WAPI-XG1 can not support the quick switching over and the forward secrecy can not be ensured and the offline dictionary attack can not be resisted under a pre-shared key authentication mode; meanwhile, the method needs not change the authentication framework of the WAPI-XG1needs not changing, the two authentication modes based on the certificate and shared key are integrated into one authentication proposal; furthermore, when the switching over occurs on the client terminal, only the quick switching over safety correlation establishment protocol runs with the destination access point for the authentication mode based on the certificate, without re-authentication or pre-authentication.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
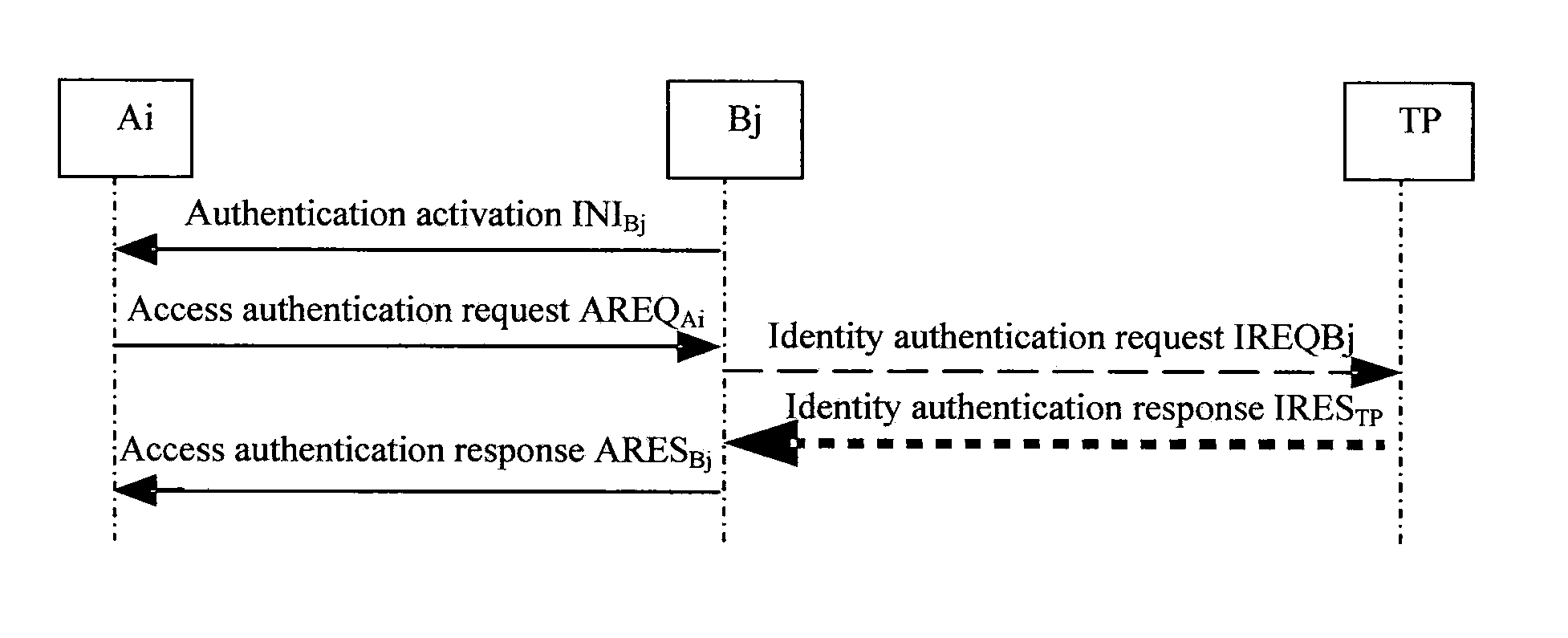
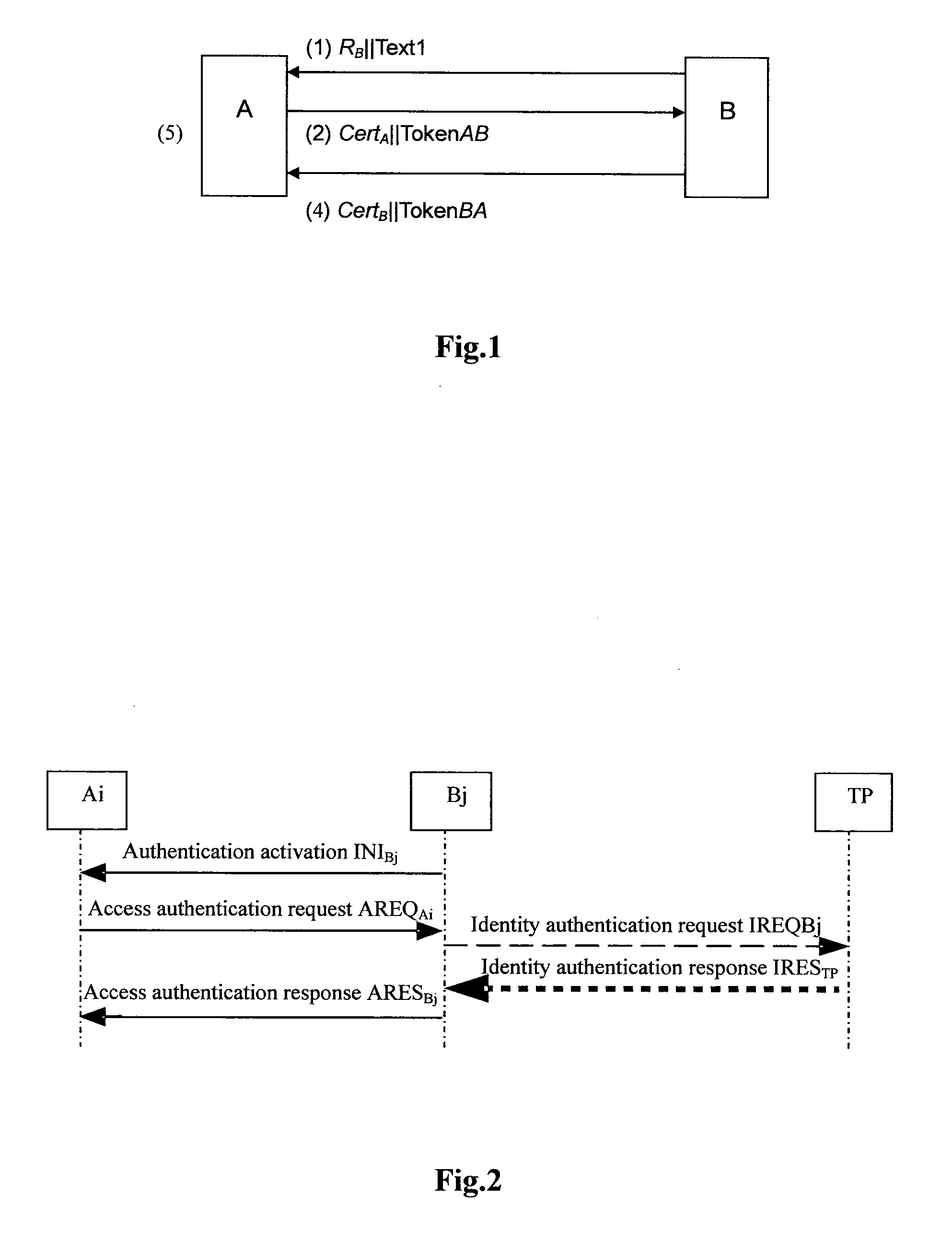
Entity bidirectional-identification method for supporting fast handoff
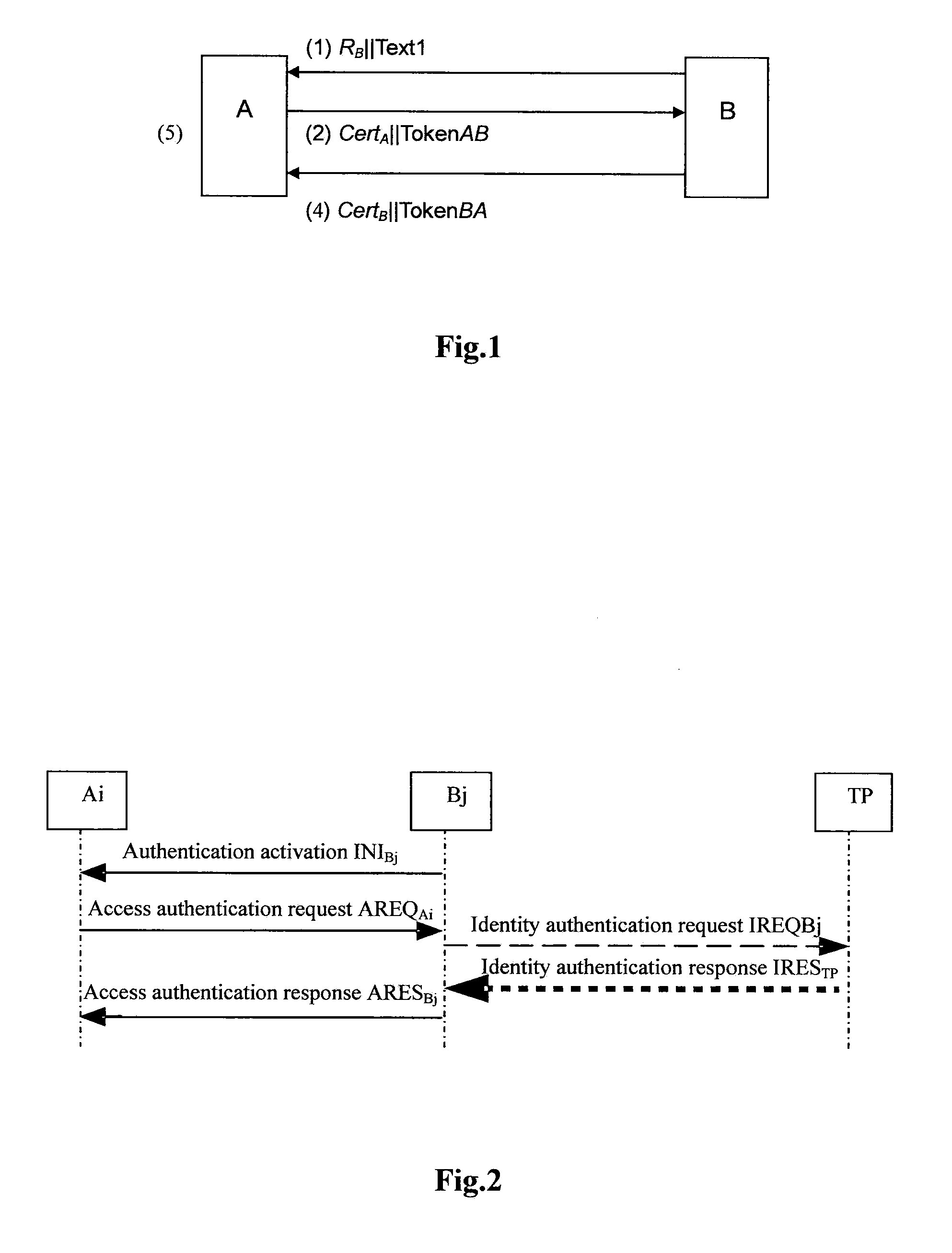
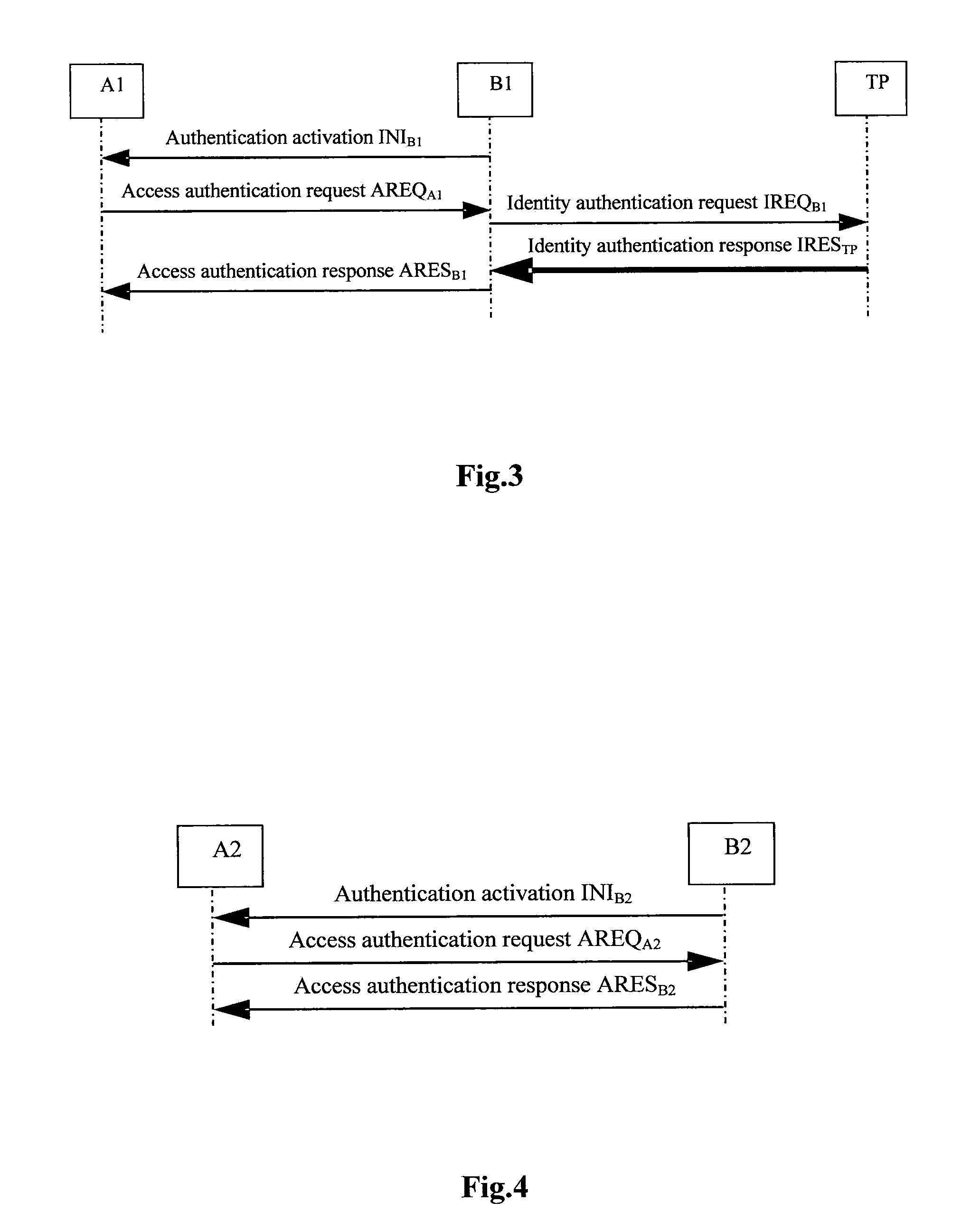
ActiveUS20110078438A1Reduce complexityShorten the time periodUser identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network AccessForward secrecy
An entity bidirectional-identification method for supporting fast handoff involves three security elements, which includes two identification elements A and B and a trusted third party (TP). All identification entities of a same element share a public key certification or own a same public key. When any identification entity in identification element A and any identification entity in identification element B need to identify each other, if identification protocol has never been operated between the two identification elements that they belong to respectively, the whole identification protocol process will be operated; otherwise, interaction of identification protocol will be acted only between the two identification entities. Application of the present invention not only centralizes management of public key and simplifies protocol operation condition, but also utilizes the concept of security domain so as to reduce management complexity of public key, shorten identification time and satisfy fast handoff requirements on the premises of guaranteeing security characteristics such as one key for every pair of identification entities, one secret key for every identification and forward secrecy.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
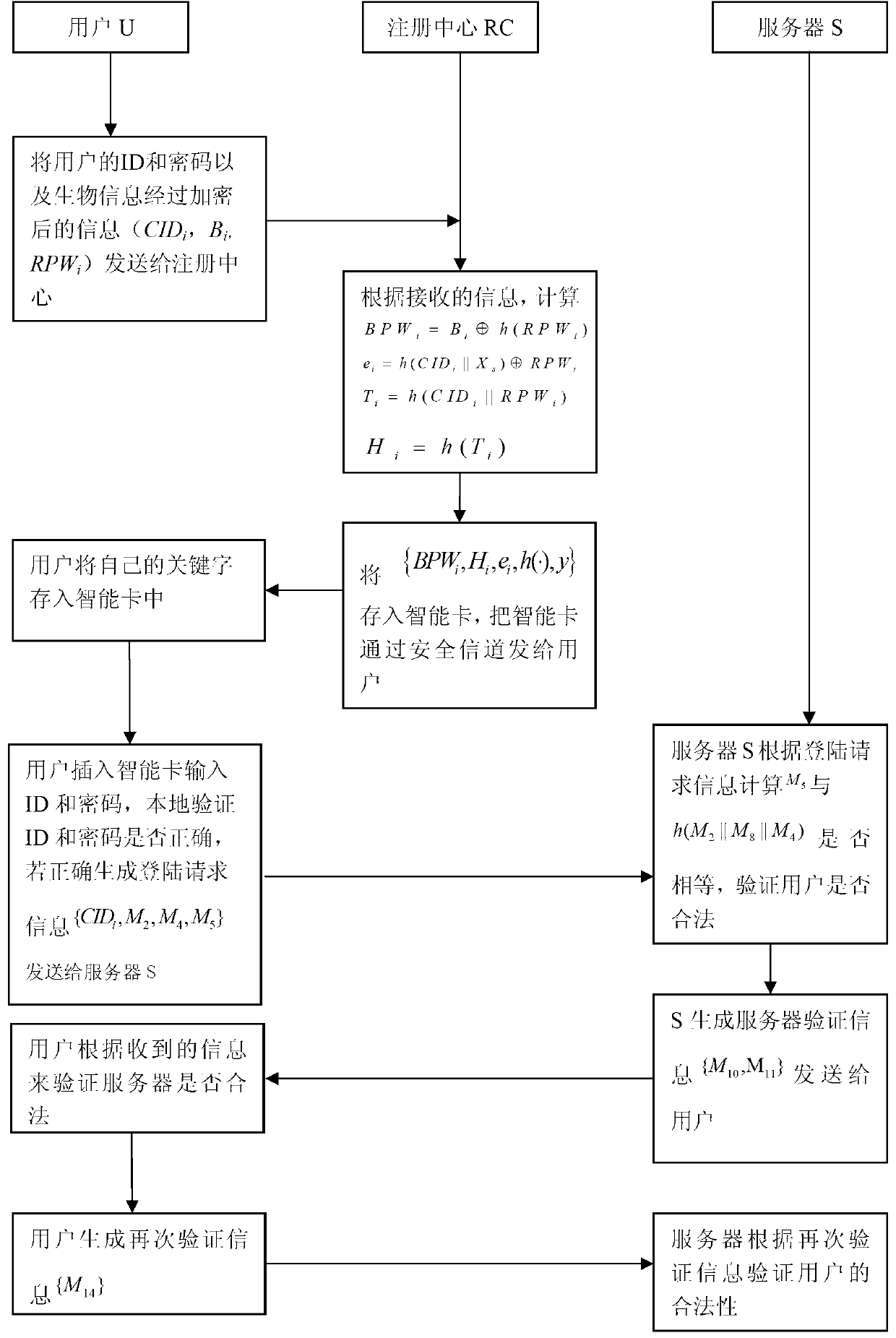
Remote identity authentication method based on password, smart card and biological features
ActiveCN103346888AAdd secondary verificationResist attackUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationPasswordSmart card
The invention a remote identity authentication method based on a password, a smart card and biological features. The method includes the step of registration, the step of logging in and the step of authentication. According to the method, a registration center generates a first parameter set and stores the first parameter set onto the smart card; the smart card verifies local legitimacy of the identity of a user, and if the identity of the user is legal, first verification data relevant to random numbers are generated and sent to a server; the server verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the user, and if the identity of the user is legal, second verification data used for verifying the identity of the server are generated and sent to the smart card; the smart card verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the server, and if the identity of the server is legal, third verification data are generated and sent to the server; the server verifies the identity of the user for the second time, and if the identity of the user is legal, the server and the smart card generate the same session key. The method can resist server denial attacks, verification table theft attacks, replay attacks and the problem of forward secrecy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
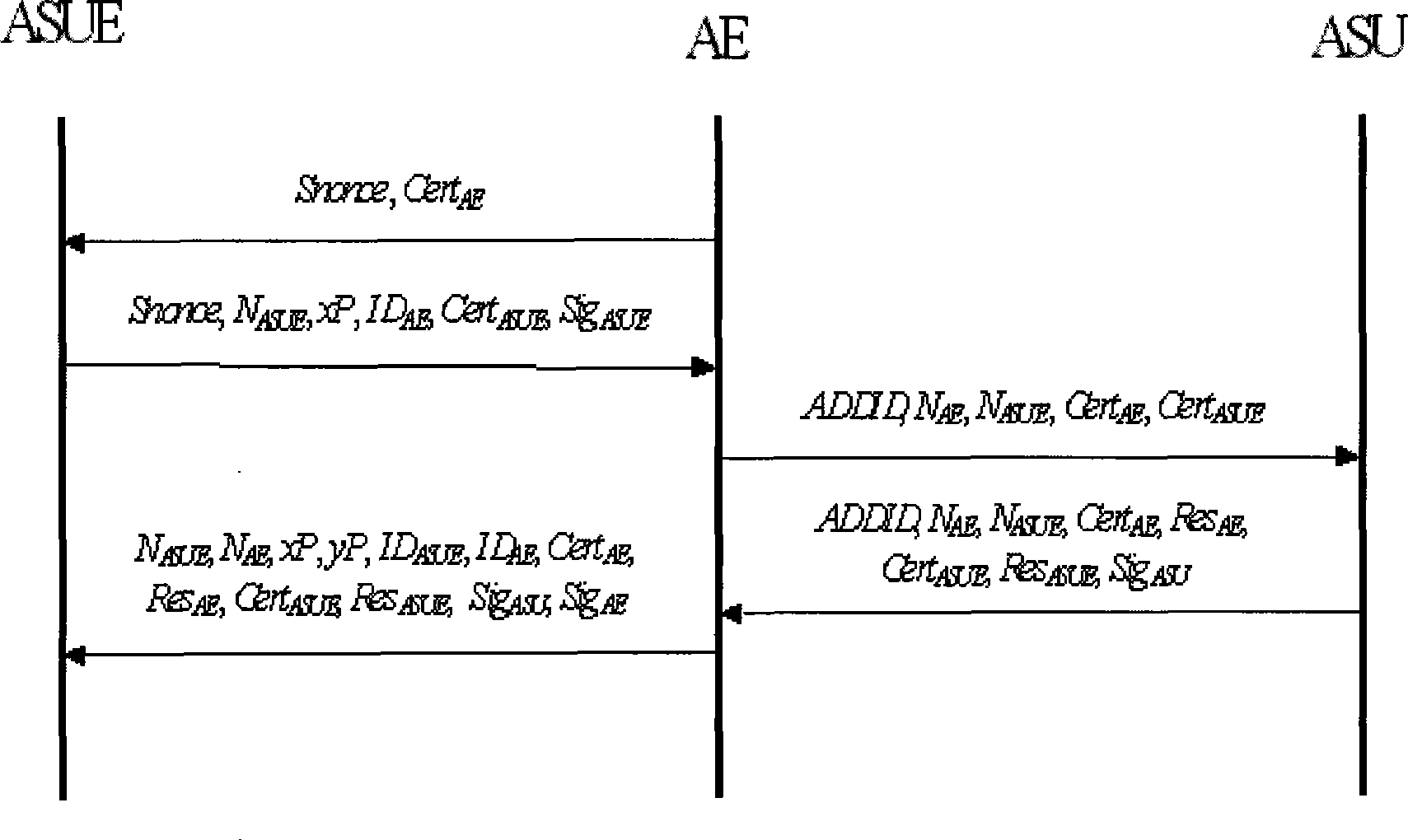
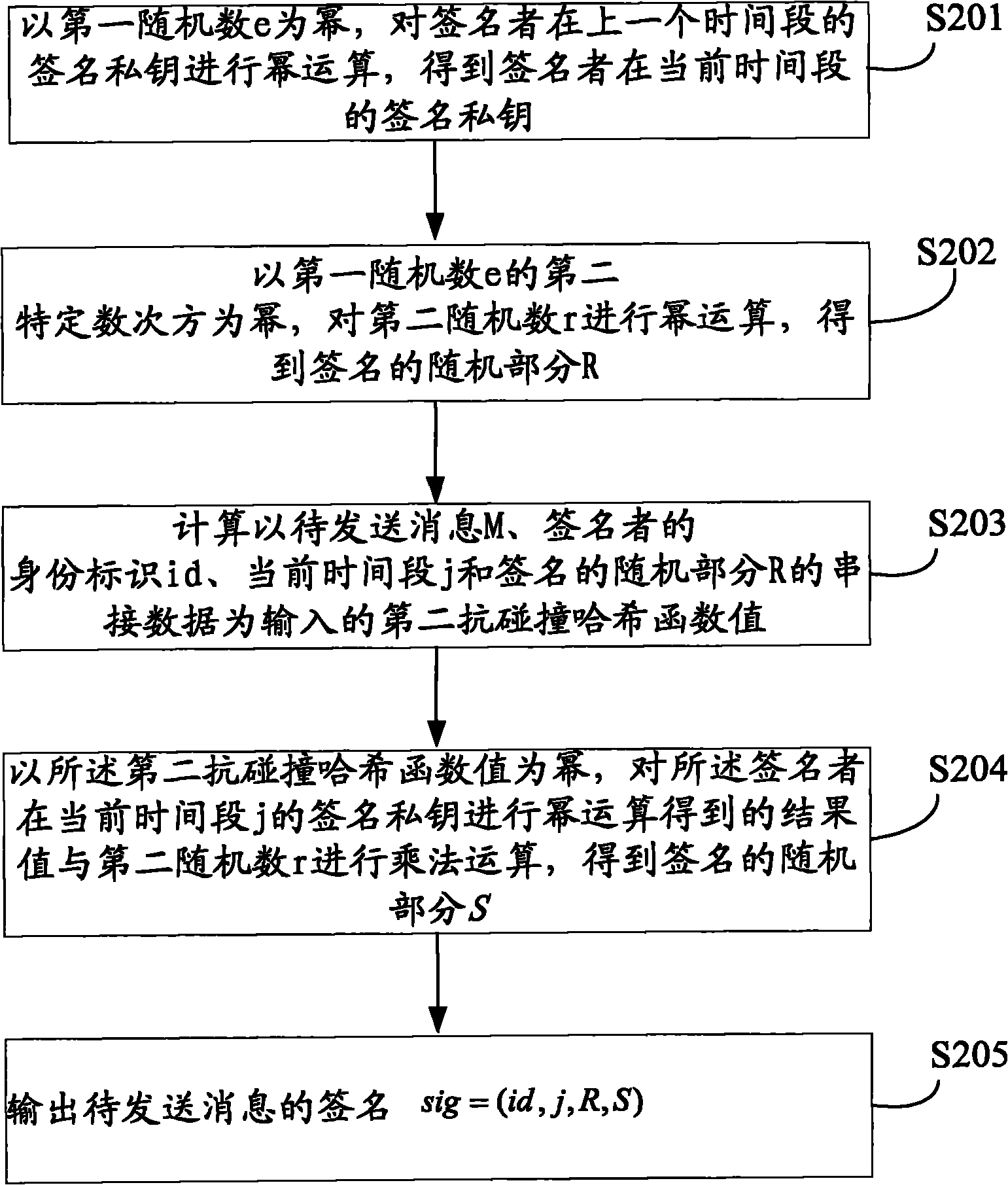
Digital signature method, device and system based on identity forward secrecy
InactiveCN101873307AShortened signature lengthDoes not compromise securityUser identity/authority verificationHash functionTime segment
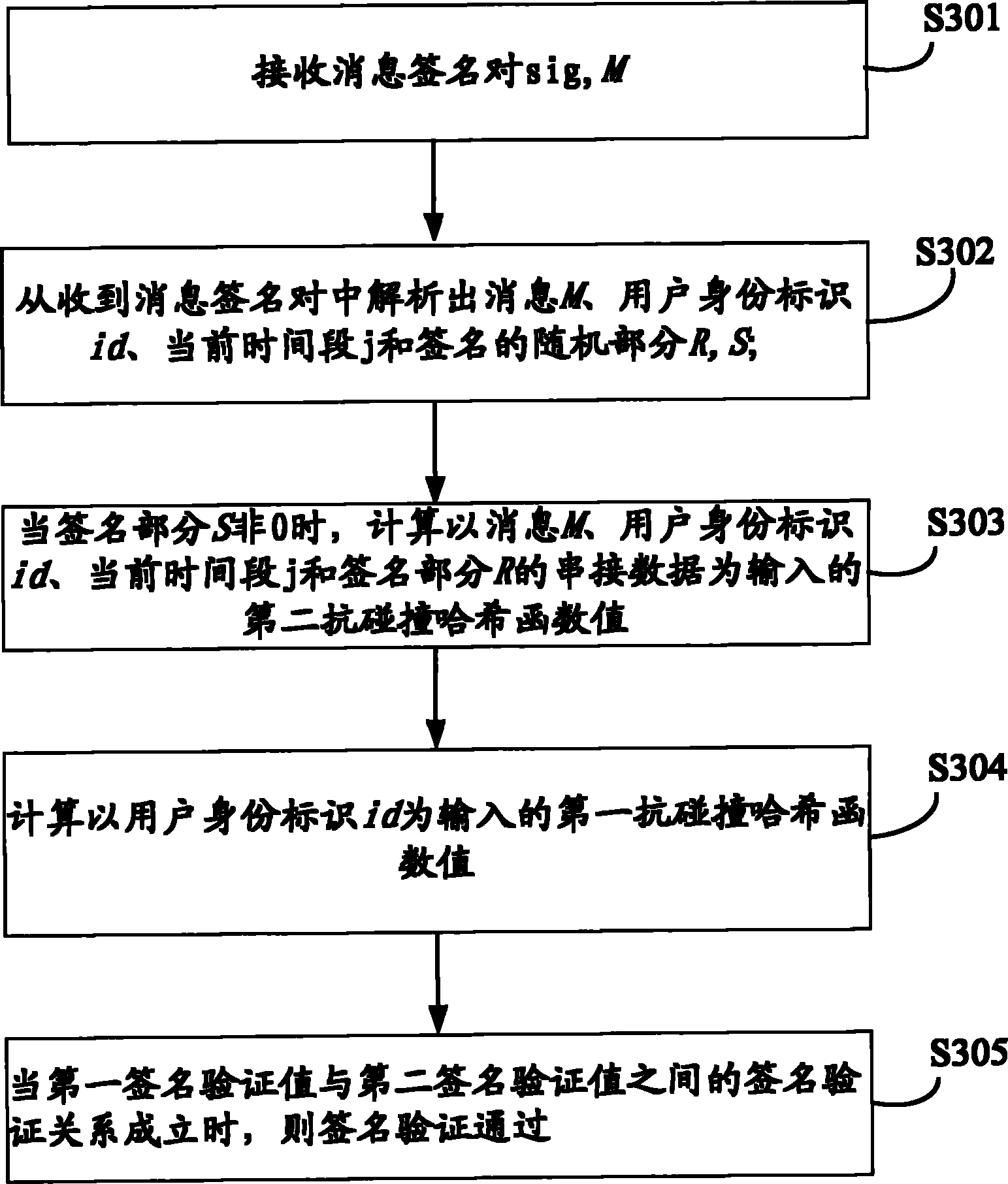
The embodiment of the invention discloses digital signature method, signature verification method, device and system based on identity forward secrecy. The signature method comprises the steps of: carrying out power operation on a second random number r by using a second specific number power of a first random number e in a system public parameter as a power to obtain a random part R of a signature; calculating cascading data of a message M to be sent, an identity identification id of a signer, the current time slot j and the random part R of the signature to be used as an input second collision resistant hash function value; multiplying a result value obtained by power calculation on a signature private key of the signer in the current time slot j with the second random number r by using the second collision resistant hash function value as the power to obtain a random part S of the signature, wherein the first random number e is used as the power in the signature private key of the signer in the current time slot j, and the signature private key of the signer in the current time slot j is obtained by power calculation on the signature private key of the signer in the last time slot; and outputting the signature sig=(id, j, R, S) of the message M. the safety of the identity forward signature plan is effectively realized while the signature length is shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Public key exchange with authenticated ecdhe and security against quantum computers
ActiveUS20200280436A1Solve insufficient capacityQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationKey exchangeKey (cryptography)
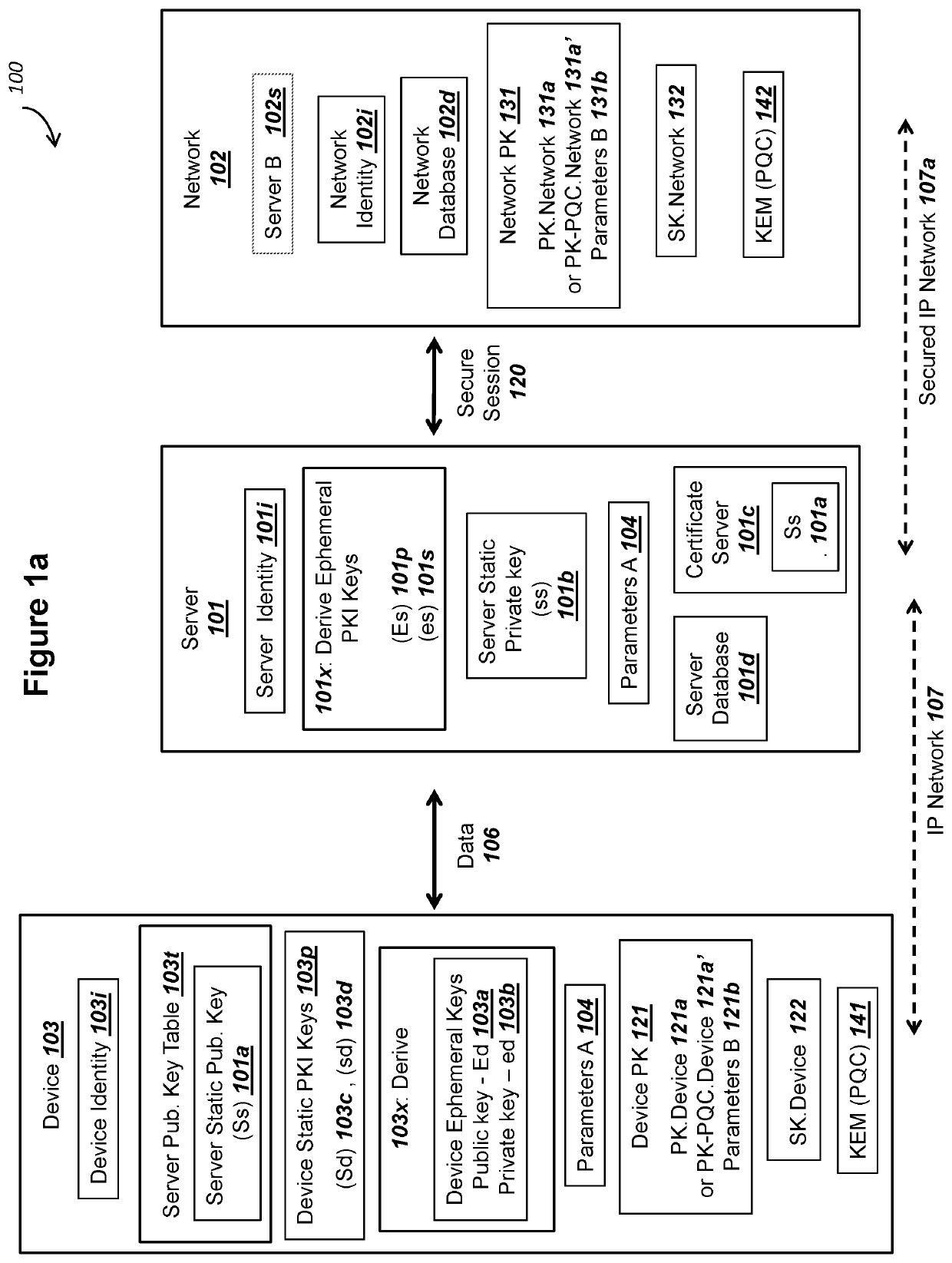
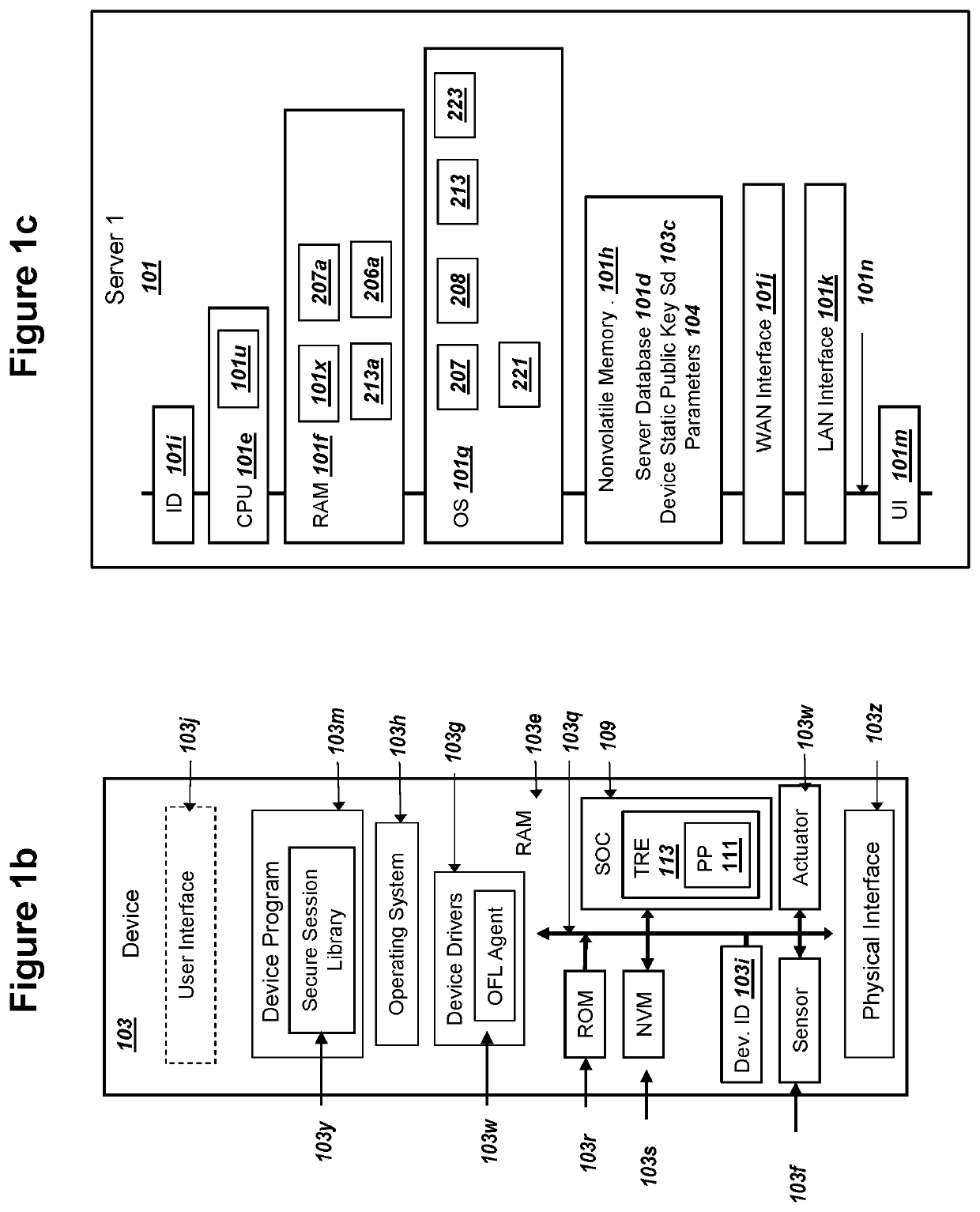
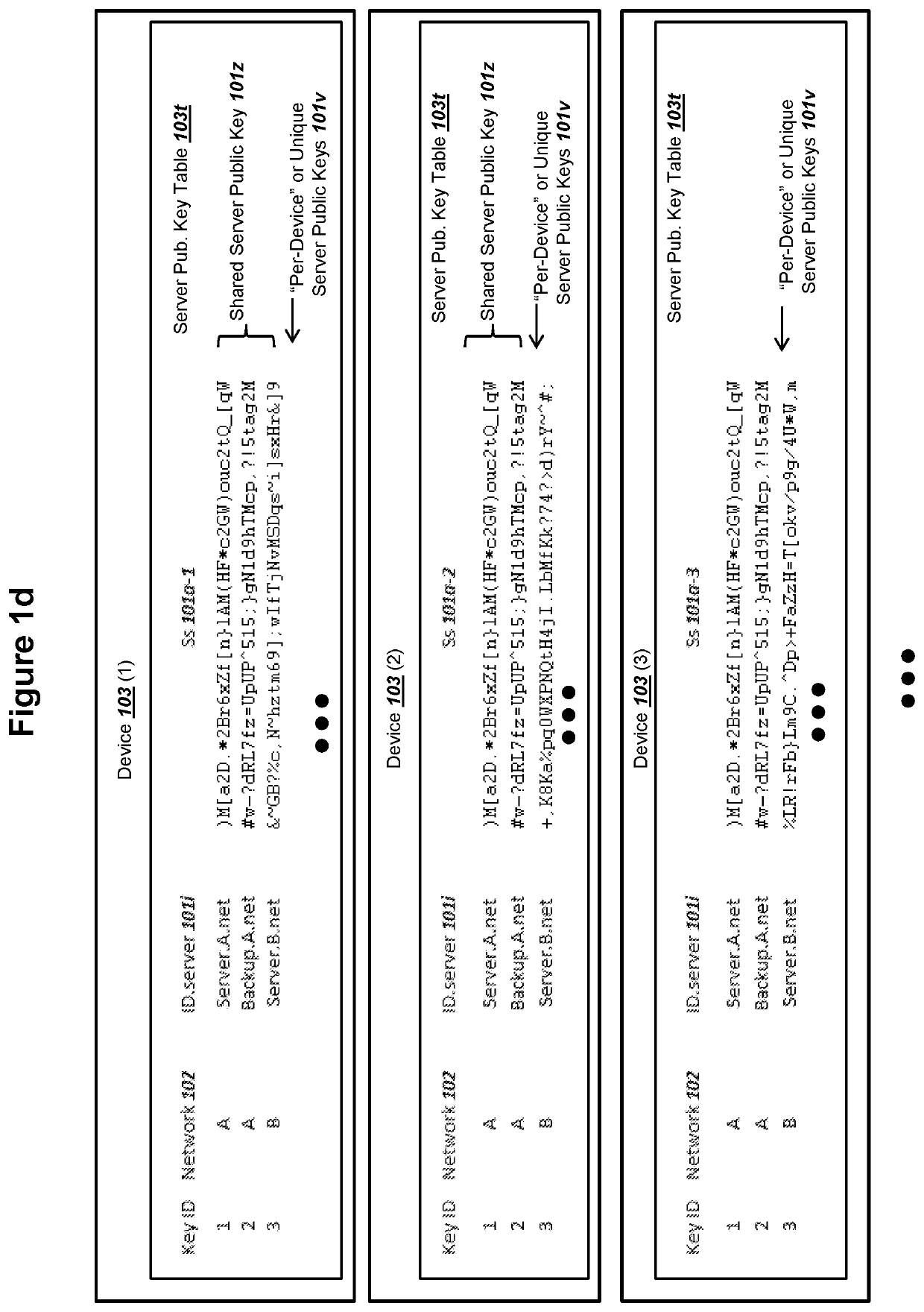
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) can provide security against quantum computers that could feasibly determine private keys from public keys. A server communicating with a device can store and use PKI keys comprising server private key ss, device public key Sd, and device ephemeral public key Ed. The device can store and use the corresponding PKI keys, such as server public key Ss. The key use can support all of (i) mutual authentication, (ii) forward secrecy, and (iii) shared secret key exchange. The server and the device can conduct an ECDHE key exchange with the PKI keys to mutually derive a symmetric ciphering key K1. The device can encrypt a device public key PK.Device with K1 and send to the server as a first ciphertext. The server can encrypt a server public key PK.Network with at least K1 and send to the device as a second ciphertext.
Owner:IOT & M2M TECH LLC
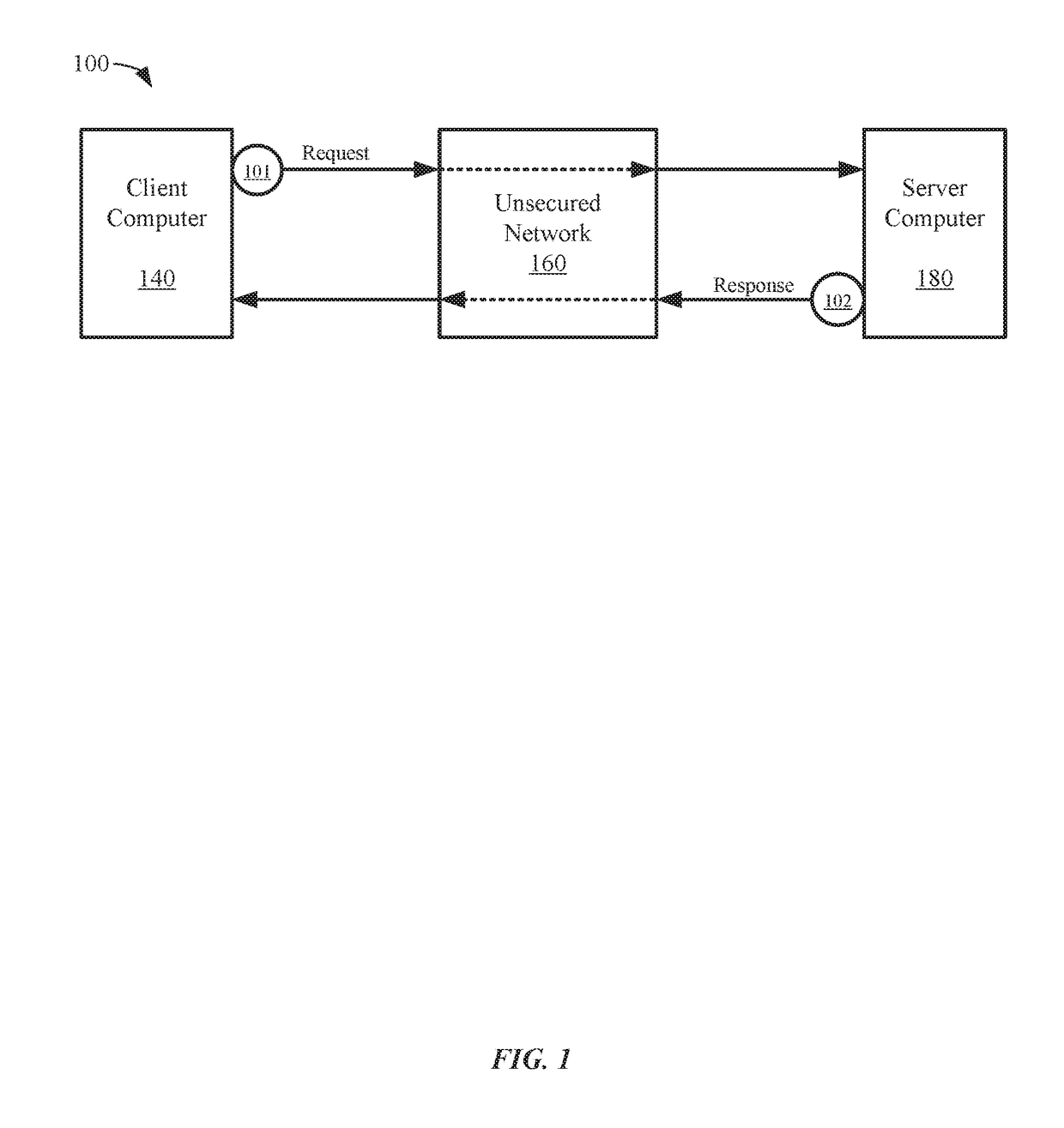
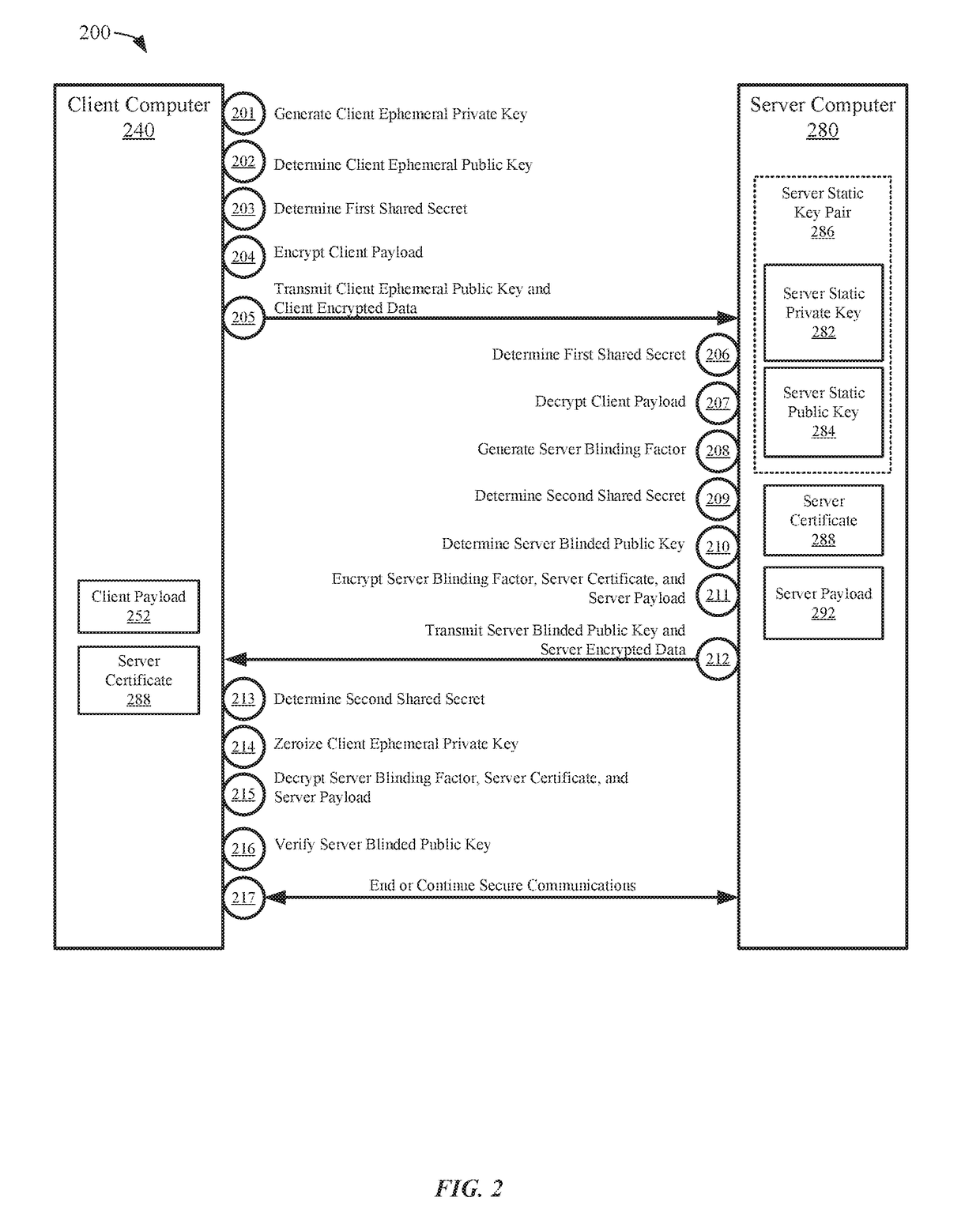
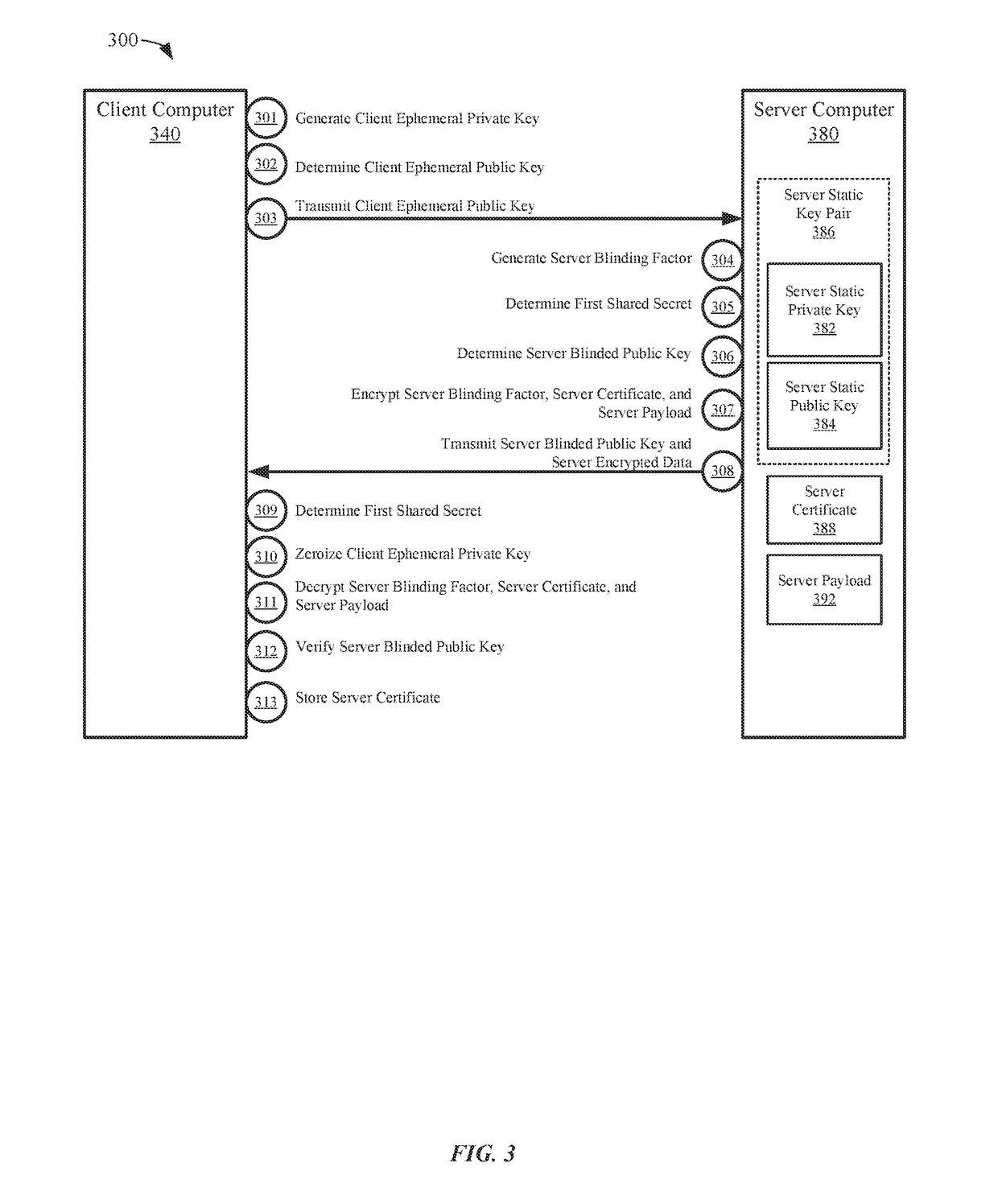
Secure communications providing forward secrecy
ActiveUS20180375663A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareSecure communication
Embodiments of the invention can establish secure communications using a single non-traceable request message from a first computer and a single non-traceable response message from a second computer. Non-traceability may be provided through the use of blinding factors. The request and response messages can also include signatures that provide for non-repudiation. In addition, the encryption of the request and response message is not based on the static keys pairs, which are used for validation of the signatures. As such, perfect forward secrecy is maintained.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
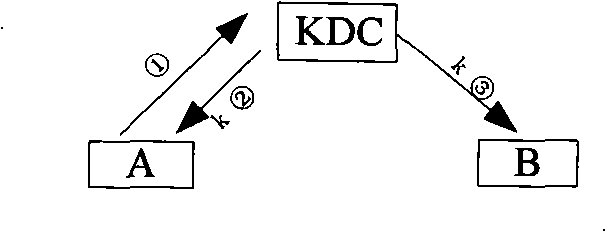
Method for distributing key
ActiveCN101282211AEnable secure distributionRealize dynamic updateKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCommunications systemNetworked system
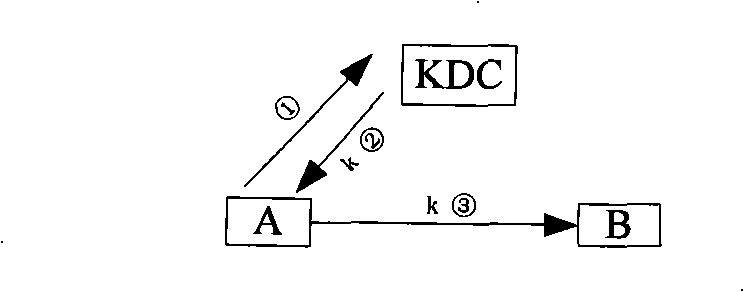
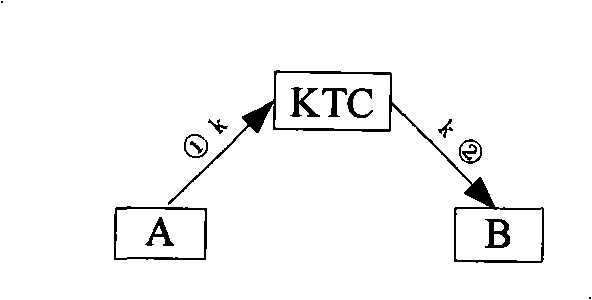
The present invention relates to a key distribution method which comprises the following steps: 1) respectively generating a pair of temporary public / private key pair by a first entity and a second entity which requires communication; and 2) through the public / private key pairs respectively generated by the first entity and the second entity, applying to a key distribution center to obtain a communication conversation key. The invention is based on a ternary equal identification (TePA) and adopts a public key cryptographic technique for distributing key to the entity which needs communication through the key distribution center KDC. The safe distribution and dynamic upgrading of the communication key are realized. A perfect forward security PFS is furthermore provided. The method settles the problems of considerable keys managed in the key distribution center, long storing period of the key by the user and no forward security of the communication key in the traditional method. The invention can be applied for the mobile communication network system and other communication system.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Key management and dynamic perfect forward secrecy
ActiveUS9698976B1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey managementComputer security
A pool of public keys, having a pool size, is received from a first device. The pool size reflects a target number of keys to be included in the pool. One of the received public keys included in the pool of keys is designated as a reserve key. A public key is selected from the pool of received public keys for use in conjunction with encrypting a communication to the first device. The selecting includes preferentially selecting a public key that is not designated as a reserve key, if at least one such key is present in the pool in addition to the reserve key. The size of the pool can be dynamically adjusted.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC +1
Secure time communication system
InactiveUS20190342101A1Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemMessage delay
Methods and apparatus for a Secure Time Communication System (10) are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention provides secure and non-interactive communication of clock information over an unsecured communications channel. This communication provides perfect forward secrecy, while detecting and blocking message spoofing, message replay, denial of service and cryptographic performance attacks. This mechanism also bounds the effect of message delay manipulation. The mechanism consists of two components, a filtered time encryptor (16) and a filtered time decryptor (28). The filtered time encryptor (16) produces a message in two parts; a time token followed by an encrypted message body. The time token is used as a filter to detect most attacks and to determine the message key.
Owner:BLUE ARMOR TECH LLC
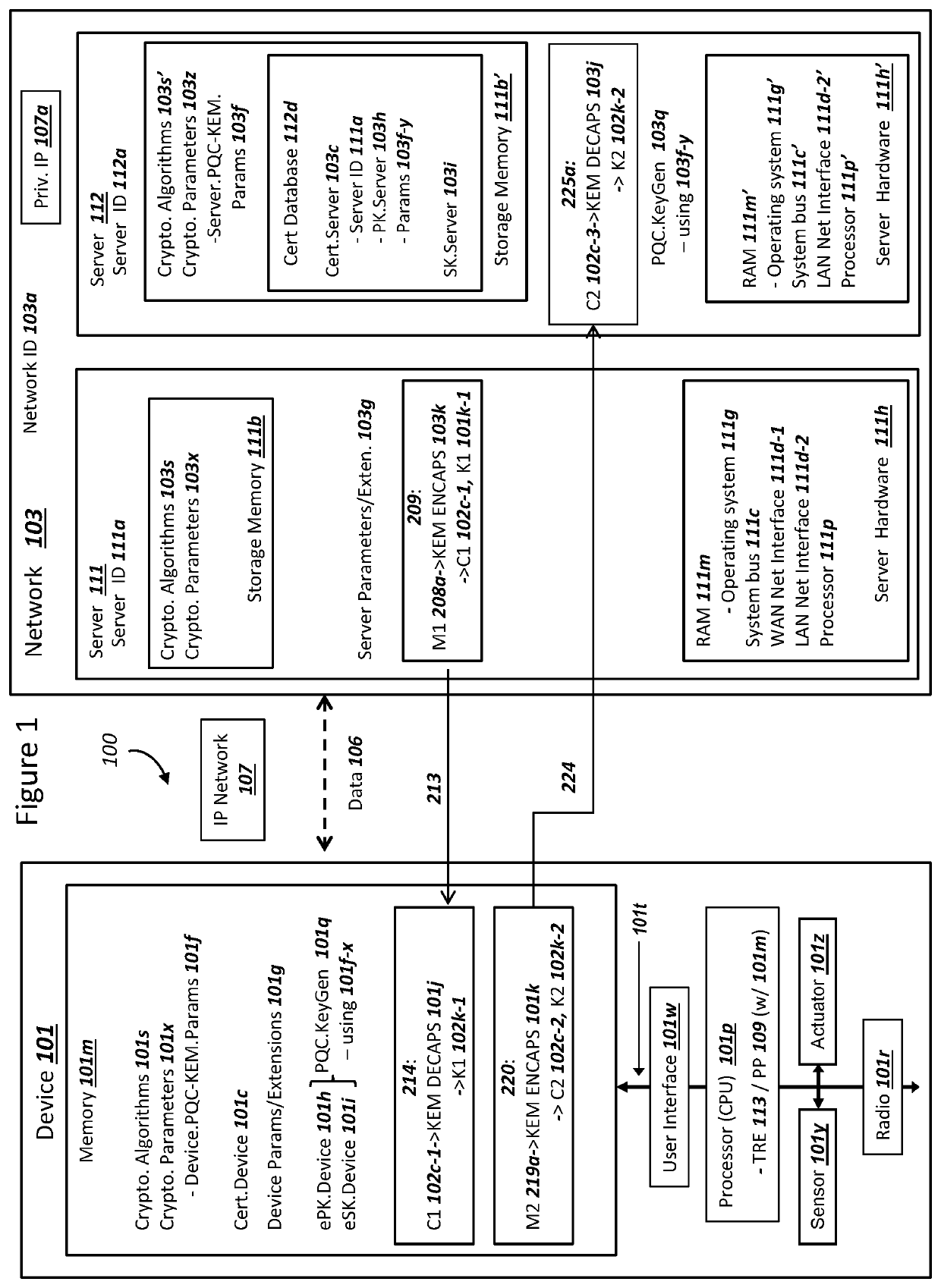
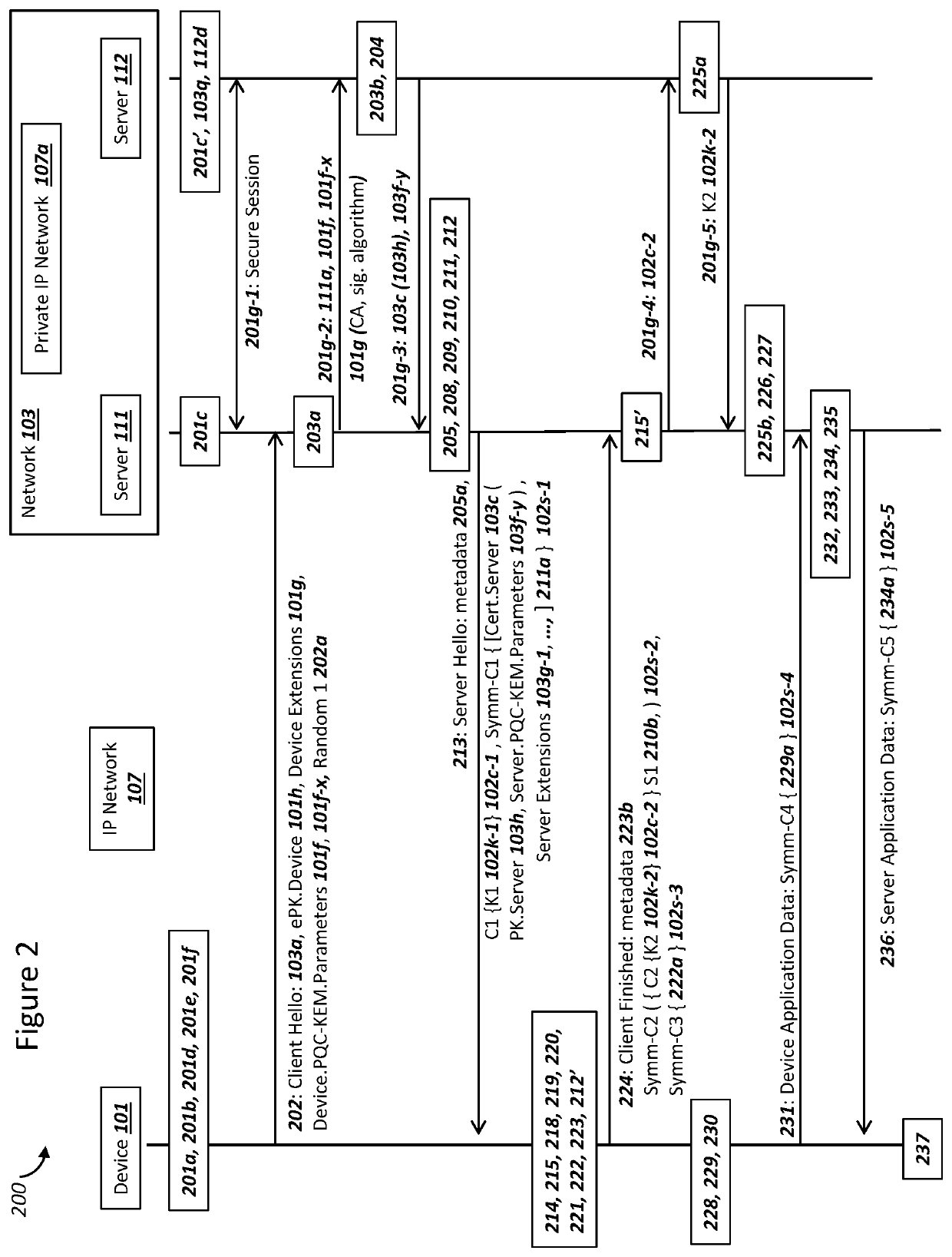
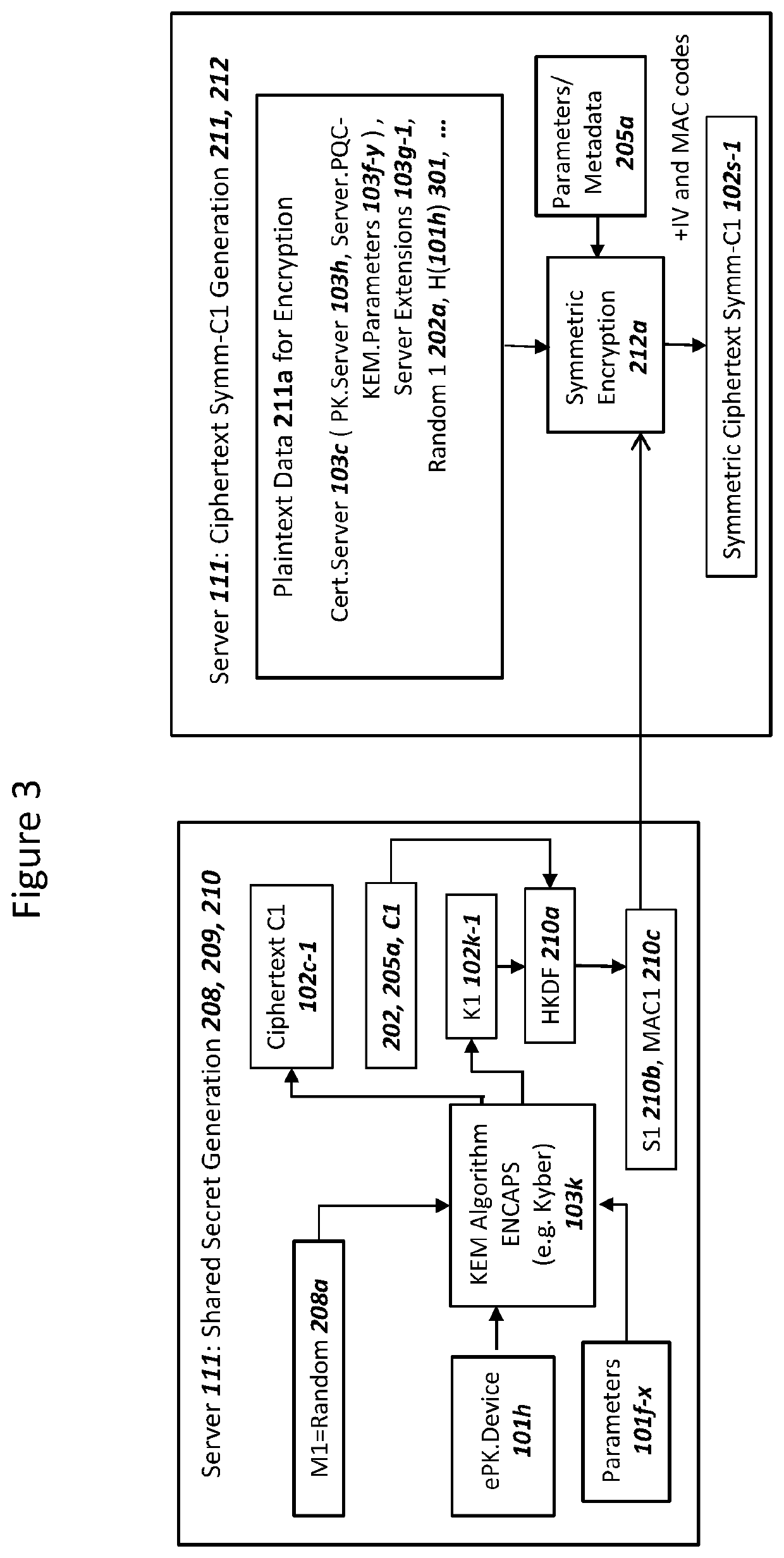
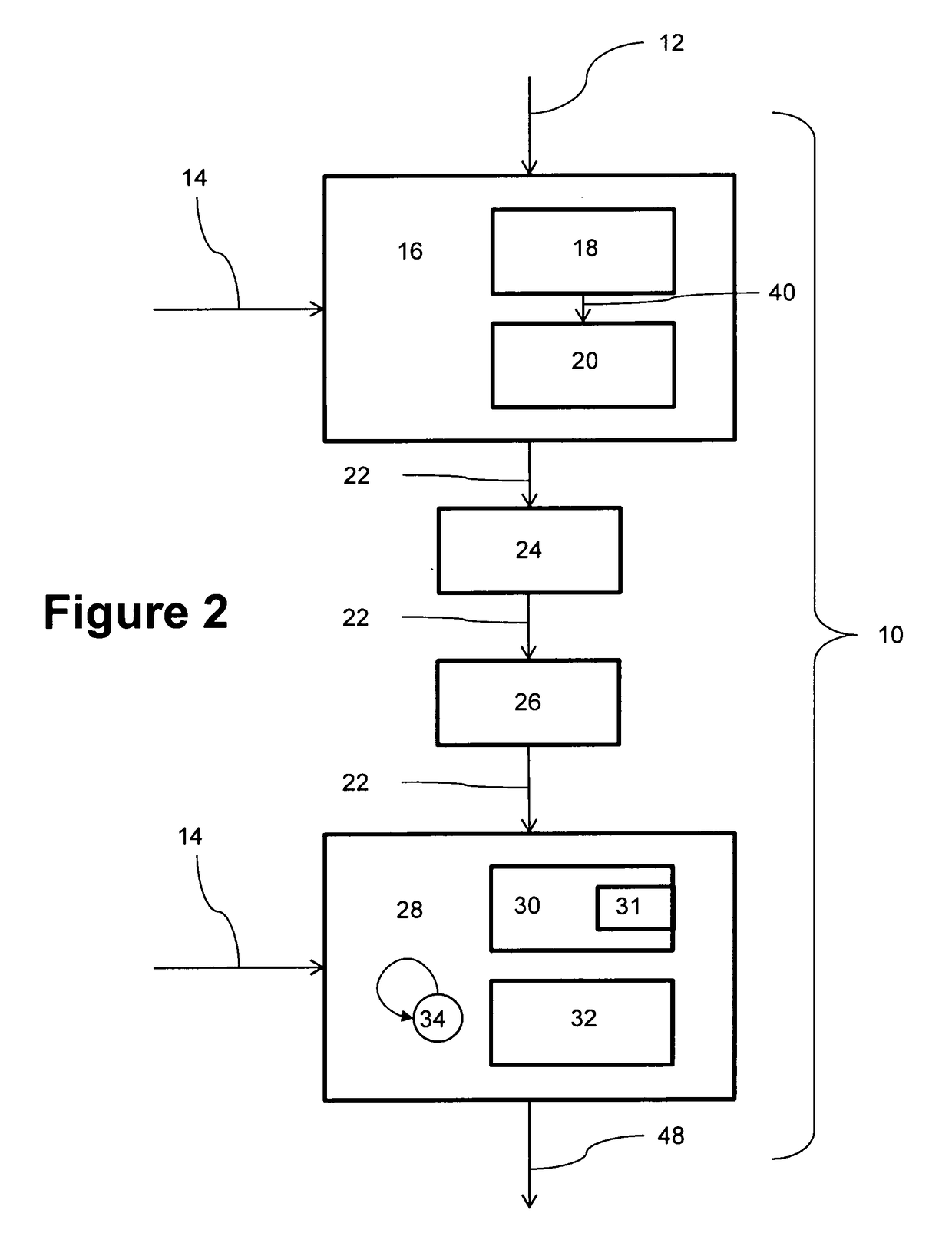
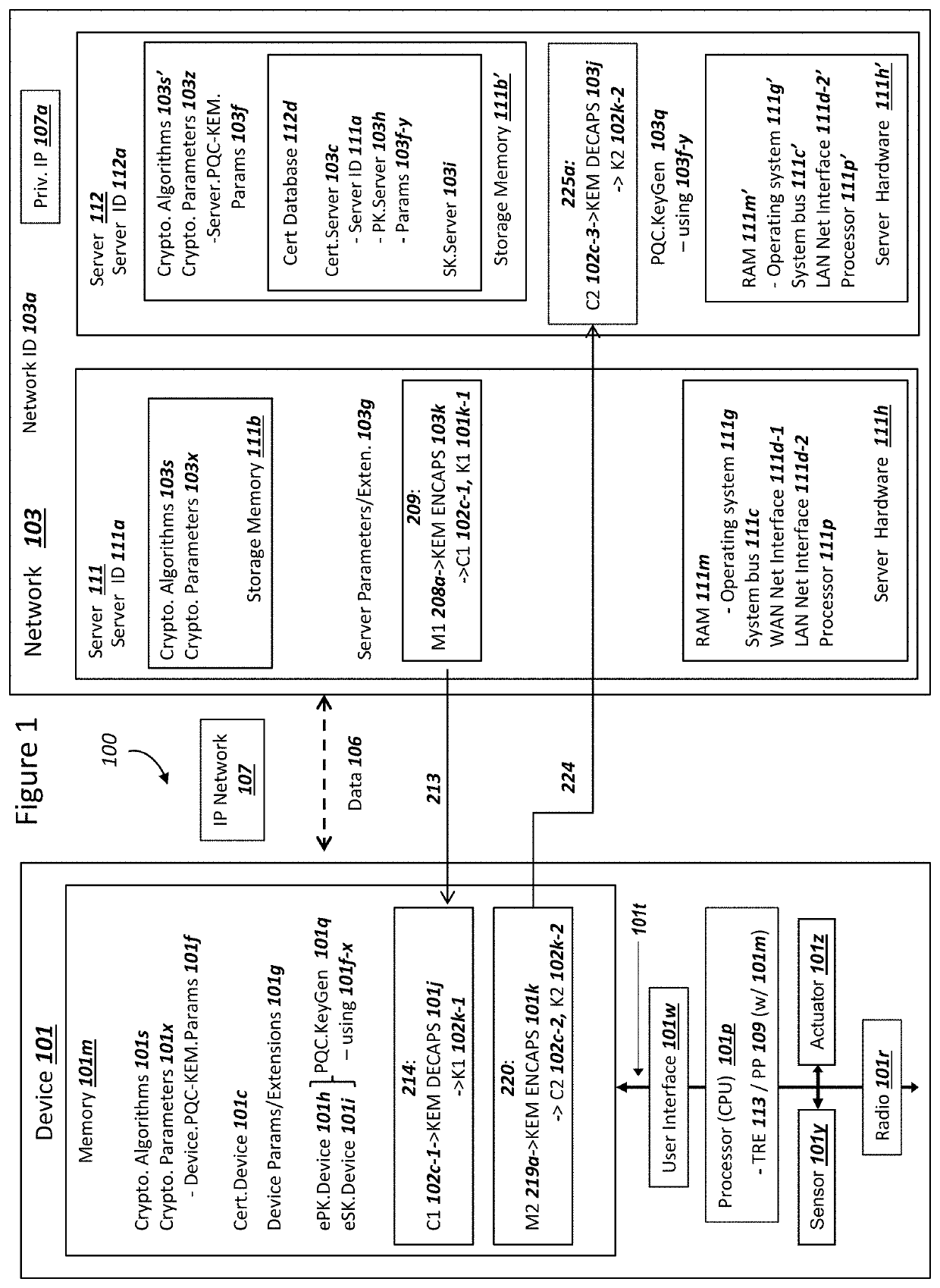
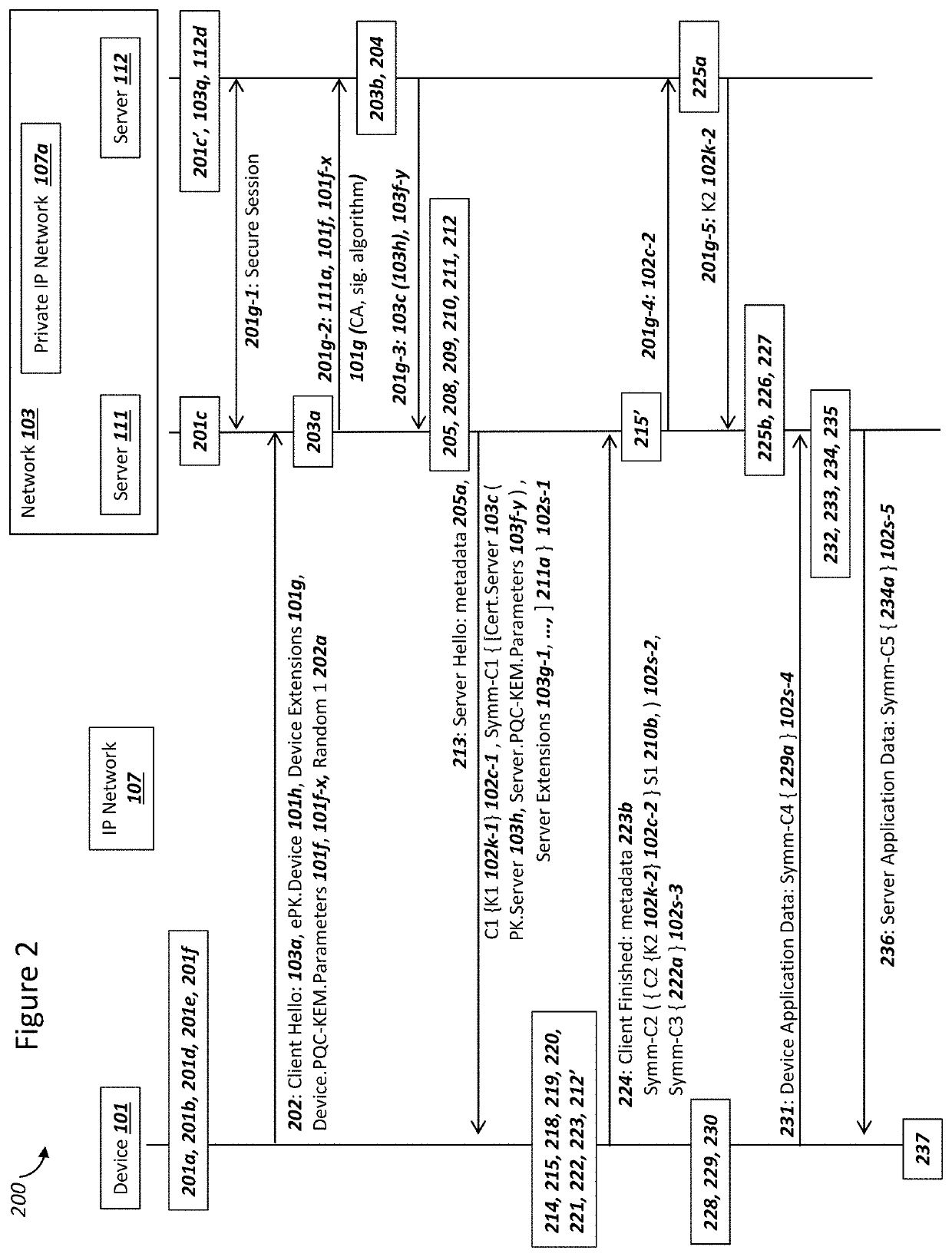
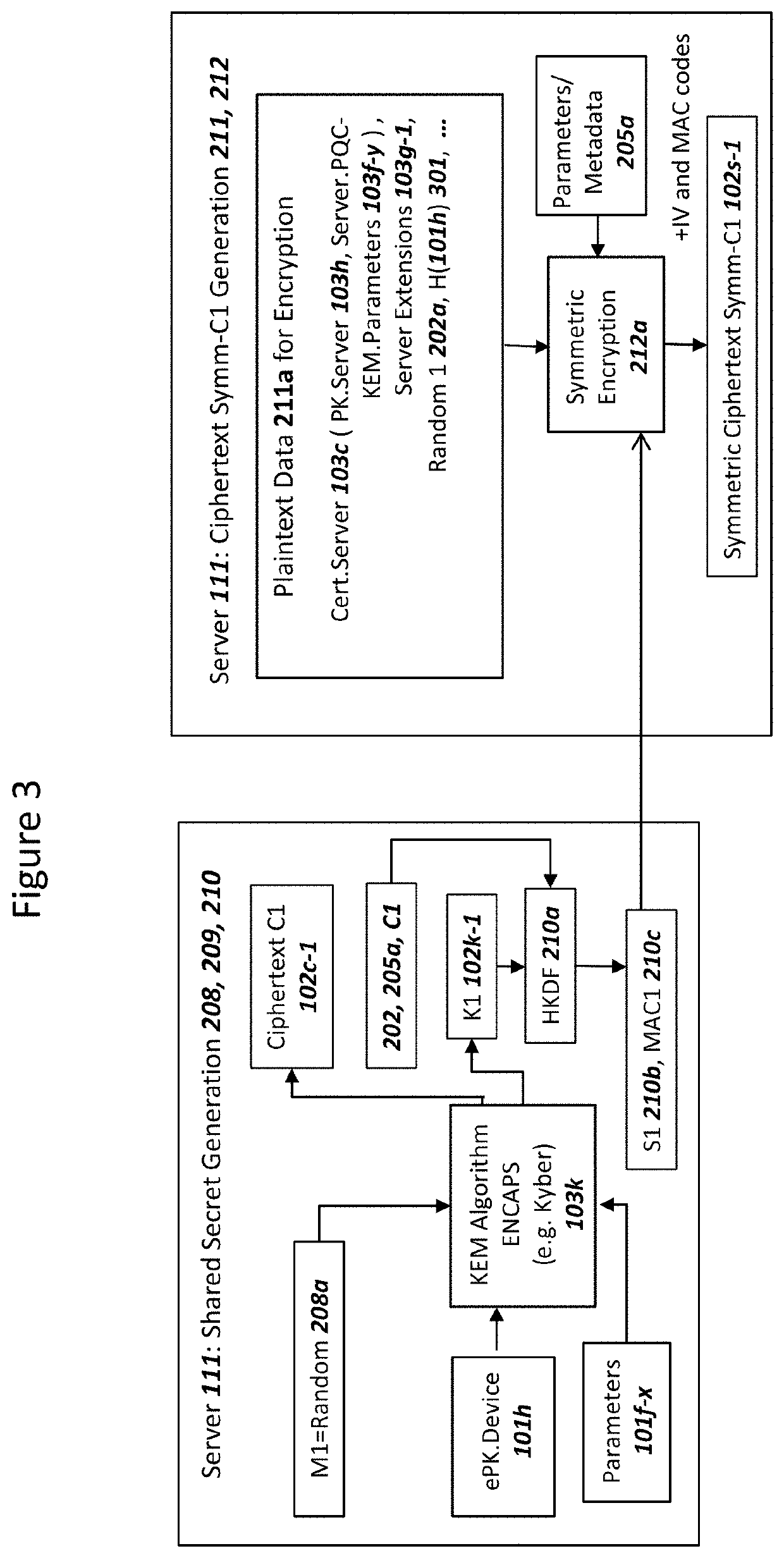
Network securing device data using two post-quantum cryptography key encapsulation mechanisms
ActiveUS11153080B1Less-long-term and detailed studyGuaranteed long-term securityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationKey (cryptography)Ciphertext
A network and a device can support secure sessions with both (i) a post-quantum cryptography (PQC) key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) and (ii) forward secrecy. The device can generate (i) an ephemeral public key (ePK.device) and private key (eSK.device) and (ii) send ePK.device with first KEM parameters to the network. The network can (i) conduct a first KEM with ePK.device to derive a first asymmetric ciphertext and first shared secret, and (ii) generate a first symmetric ciphertext for PK.server and second KEM parameters using the first shared secret. The network can send the first asymmetric ciphertext and the first symmetric ciphertext to the device. The network can receive (i) a second symmetric ciphertext comprising “double encrypted” second asymmetric ciphertext for a second KEM with SK.server, and (ii) a third symmetric ciphertext. The network can decrypt the third symmetric ciphertext using the second asymmetric ciphertext.
Owner:NIX JOHN A
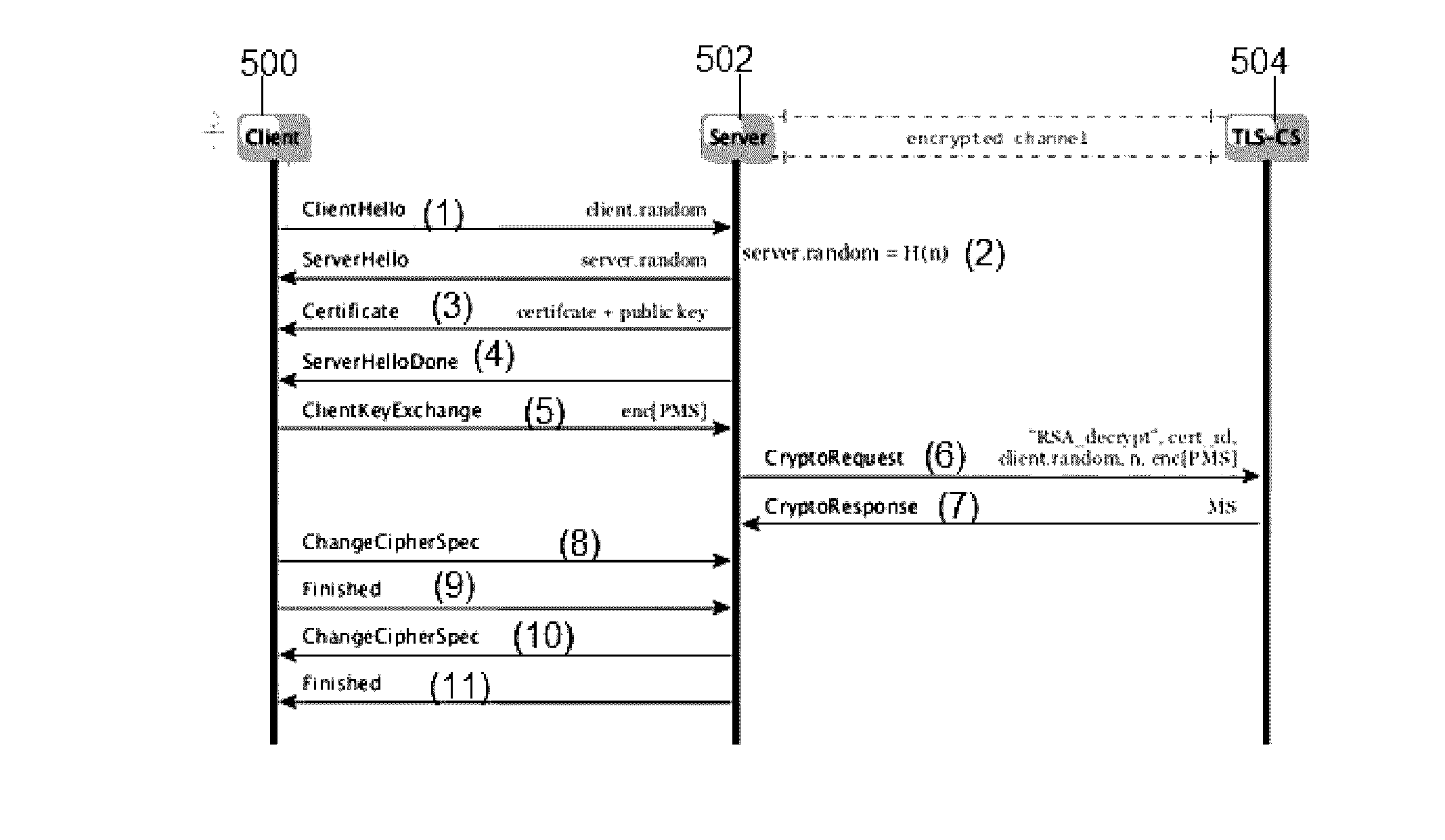
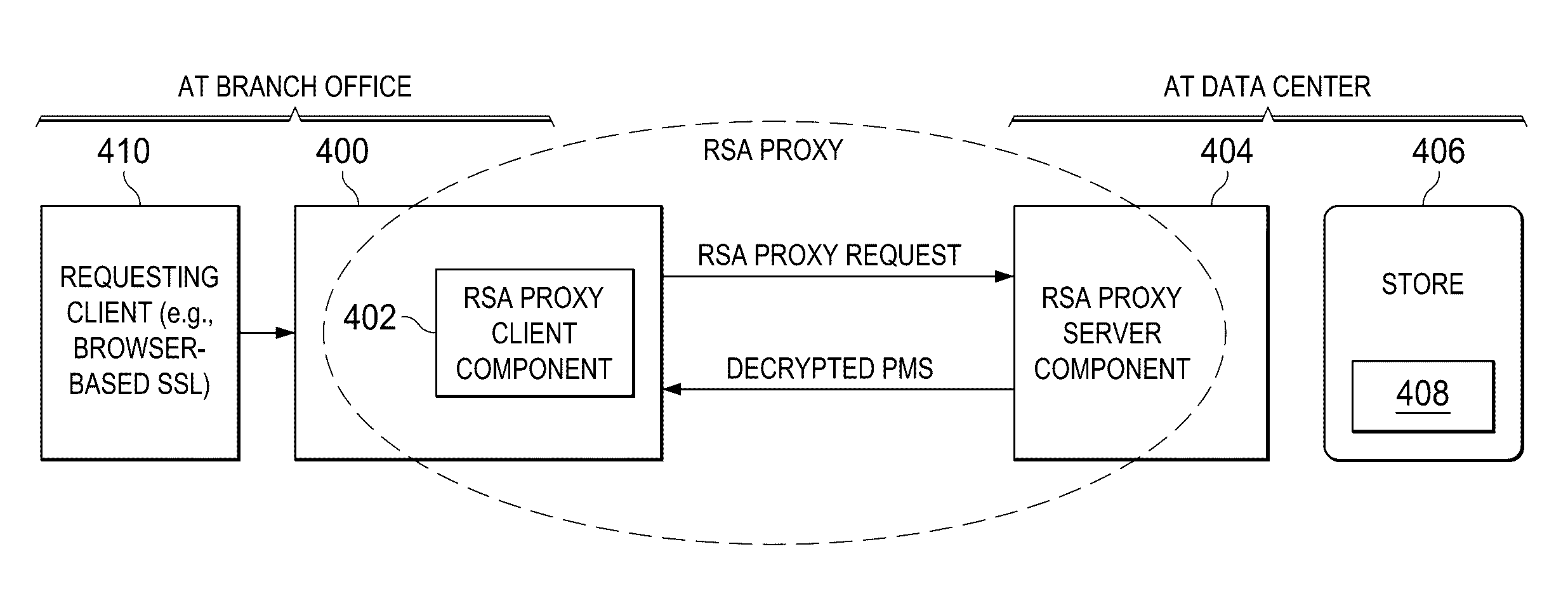
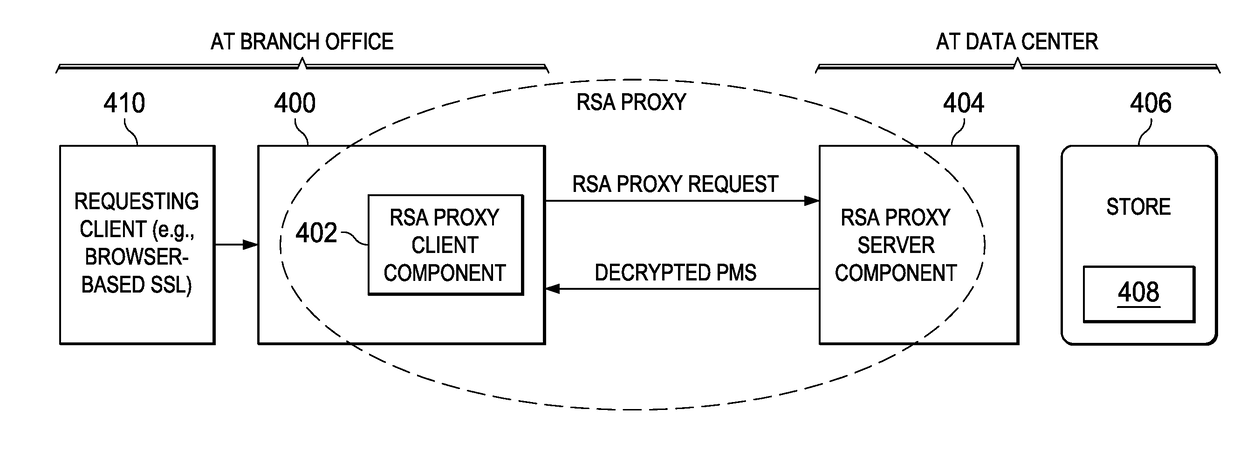
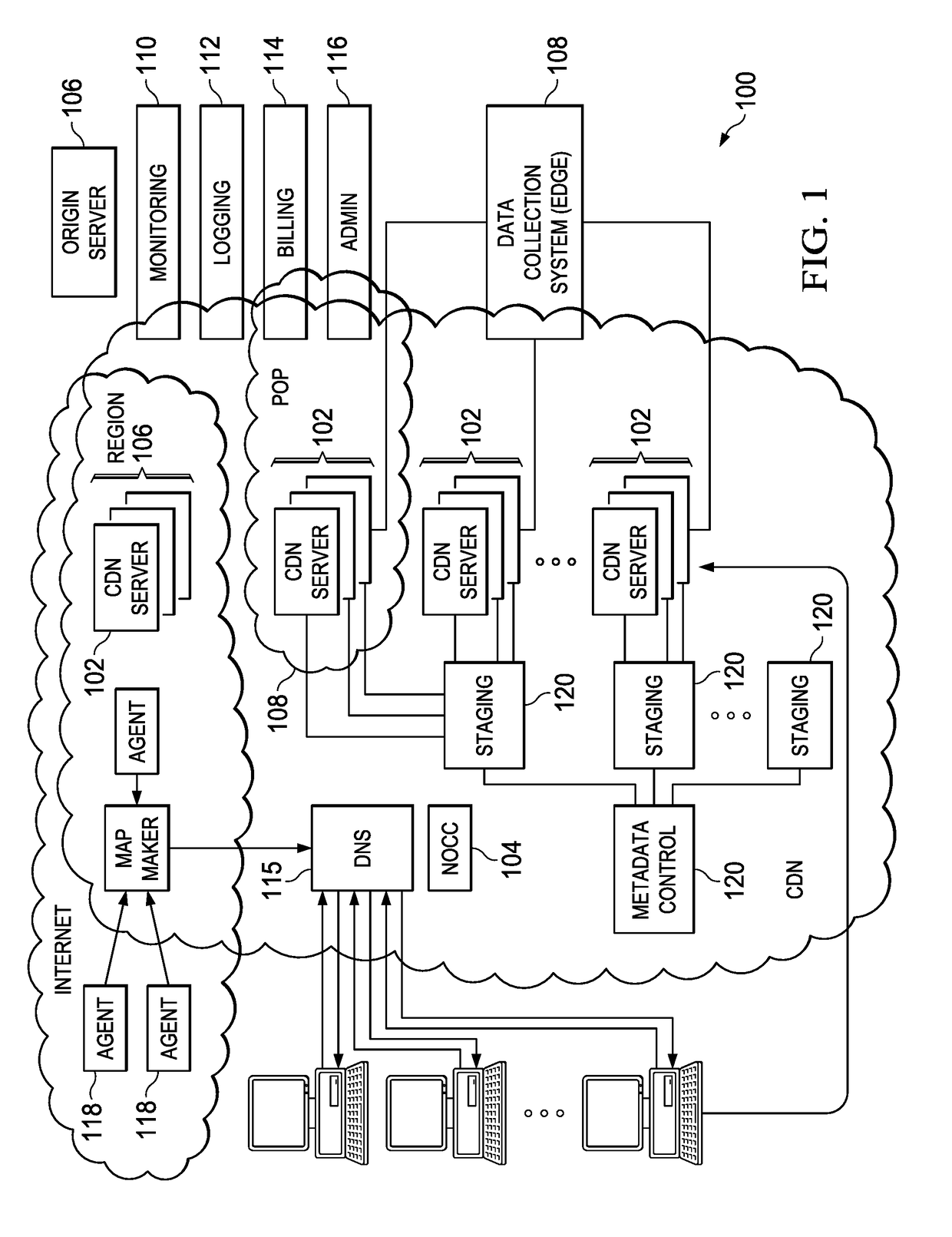
Providing forward secrecy in a terminating TLS connection proxy
ActiveUS9531691B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHash functionEdge server
An infrastructure delivery platform provides a RSA proxy service as an enhancement to the TLS / SSL protocol to off-load, from an edge server to an external cryptographic server, the decryption of an encrypted pre-master secret. The technique provides forward secrecy in the event that the edge server is compromised, preferably through the use of a cryptographically strong hash function that is implemented separately at both the edge server and the cryptographic server. To provide the forward secrecy for this particular leg, the edge server selects an ephemeral value, and applies a cryptographic hash the value to compute a server random value, which is then transmitted back to the requesting client. That server random value is later re-generated at the cryptographic server to enable the cryptographic server to compute a master secret. The forward secrecy is enabled by ensuring that the ephemeral value does not travel on the wire.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Method for enhancing fast handover authentication security of wireless local land area
InactiveCN101800982AImprove securityForward secrecySecurity arrangementNetwork deploymentFast handover
The invention provides a method for enhancing the fast handover authentication security of a wireless local land area, which mainly aims to solve the problem that the requirement of military application on high security cannot be met with a conventional standard. The method is implemented by the following steps that: a terminal negotiates a handover key with an authentication server in an initialaccess authentication stage; the authentication server calculates a corresponding handover sub-key when receiving a handover sub-key request transmitted by an access point, and transmits the handoversub-key to the access point; and in a handover process, the terminal and the access point utilize the handover sub-key to perform fast authentication and adopt elliptical-curve-based Diffie-Hellmn handover to generate a session key. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of forward confidentiality, capacity of resisting a part of denial of service attack, key management simplification and key exposure risk reduction, and can be used for the internal internet of emergency communication and a command station, an urban operation network and quick network deployment under a fieldoperation environment.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
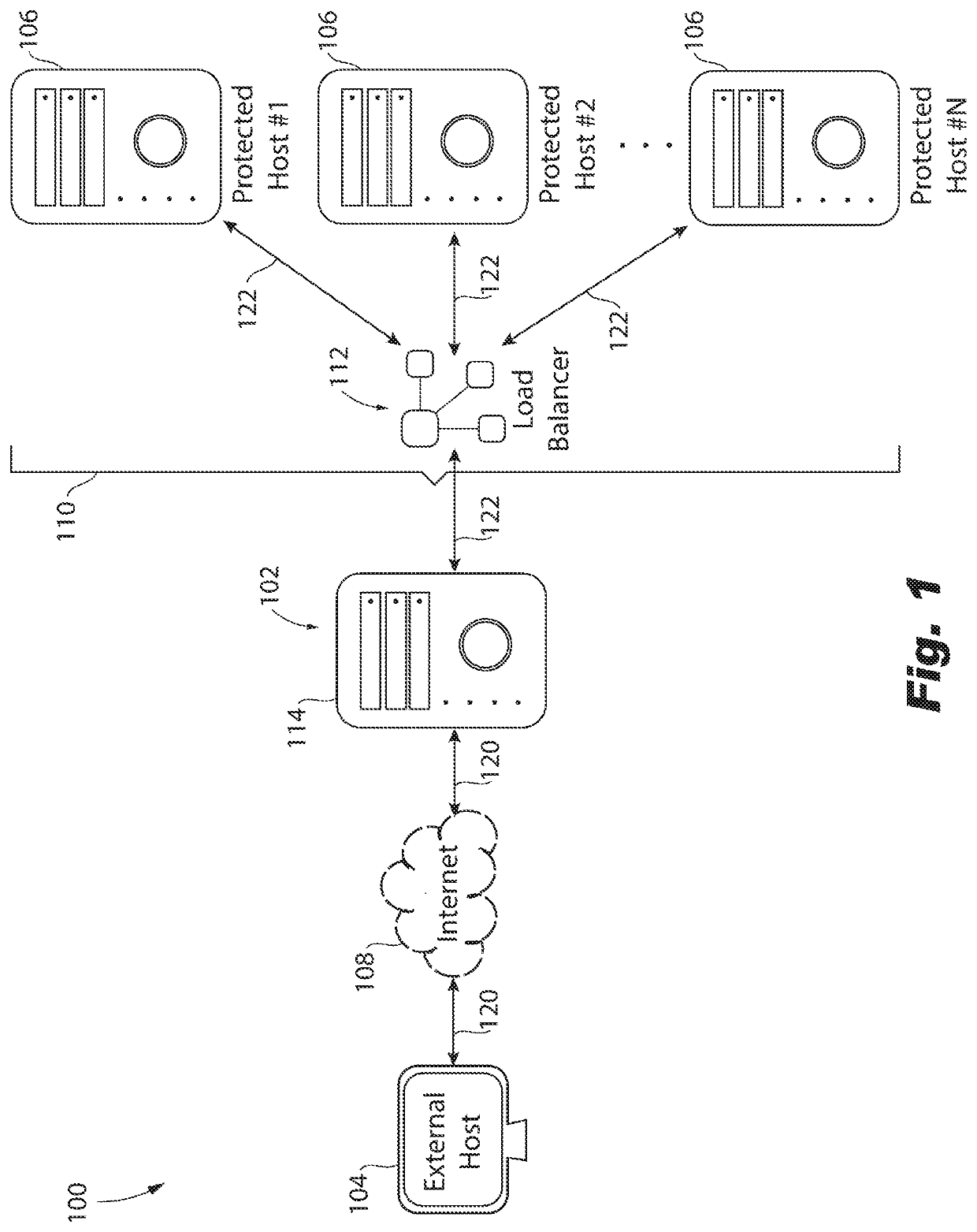
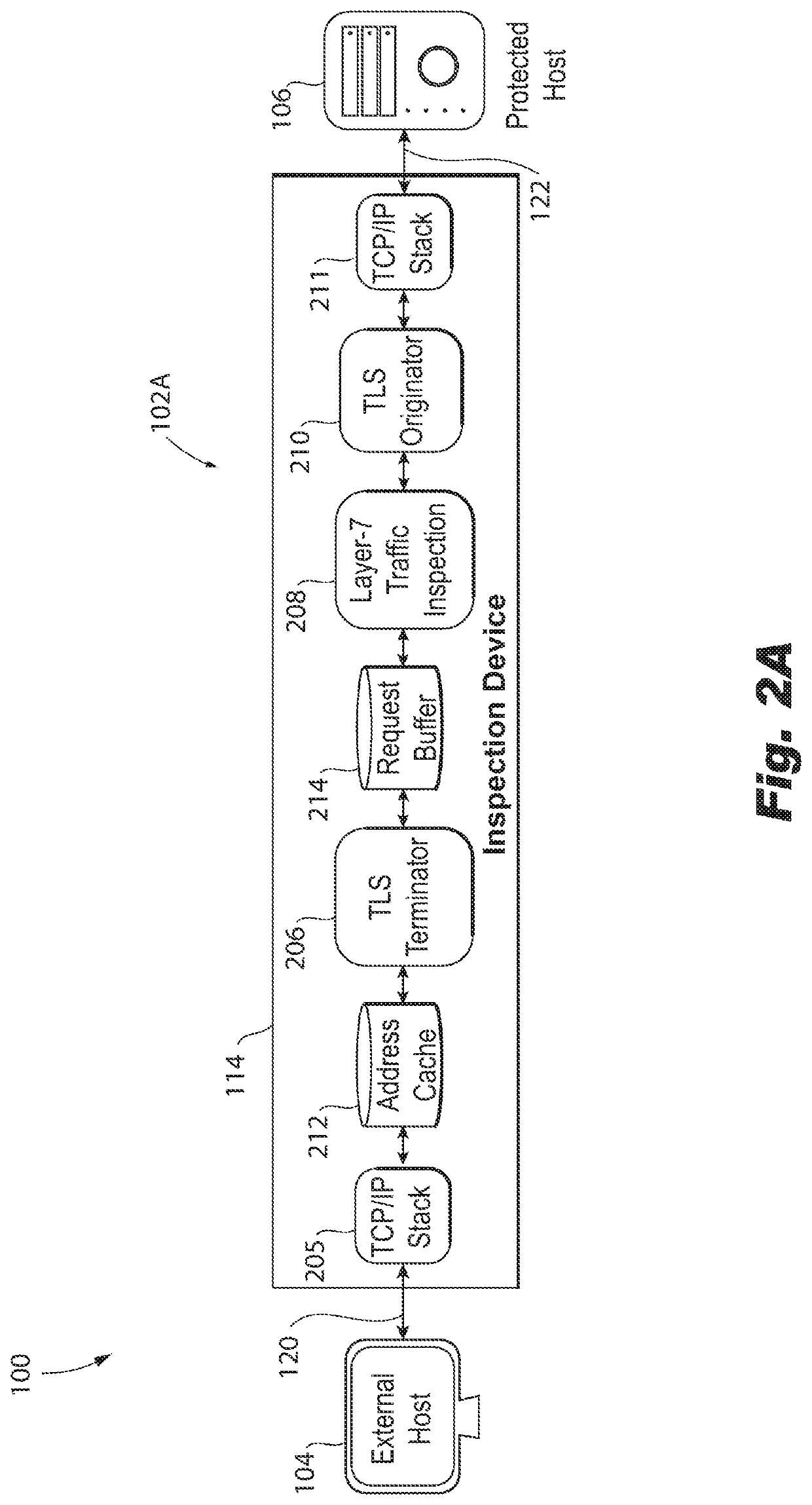
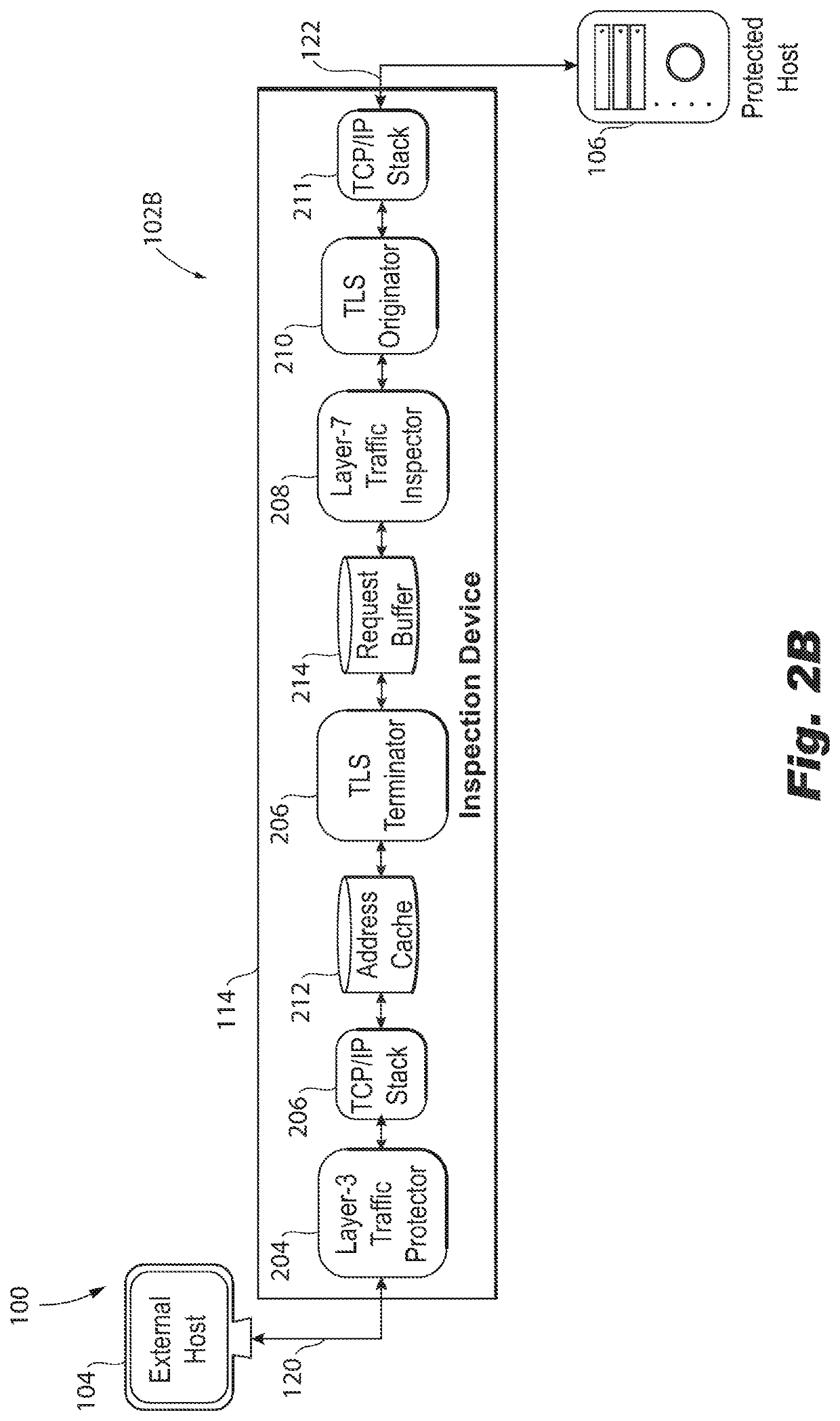
Transparent inspection of traffic encrypted with perfect forward secrecy (PFS)
A method is provided for inspecting network traffic. The method, performed in a single contained device, includes receiving network traffic inbound from an external host that is external to the protected network flowing to a protected host of the protected network, wherein the network traffic is transported by a secure protocol that implements ephemeral keys that endure for a limited time. The method further includes performing a first transmission control protocol (TCP) handshake with the external host, obtaining source and destination data during the first TCP handshake, the source and destination data including source and destination link and internet addresses obtained, caching the source and destination data, and using the cached source and destination data to obtain a Layer-7 request from the external host to the protected host and to pass a Layer-7 response from the protected host to the external host.
Owner:ARBOR NETWORKS
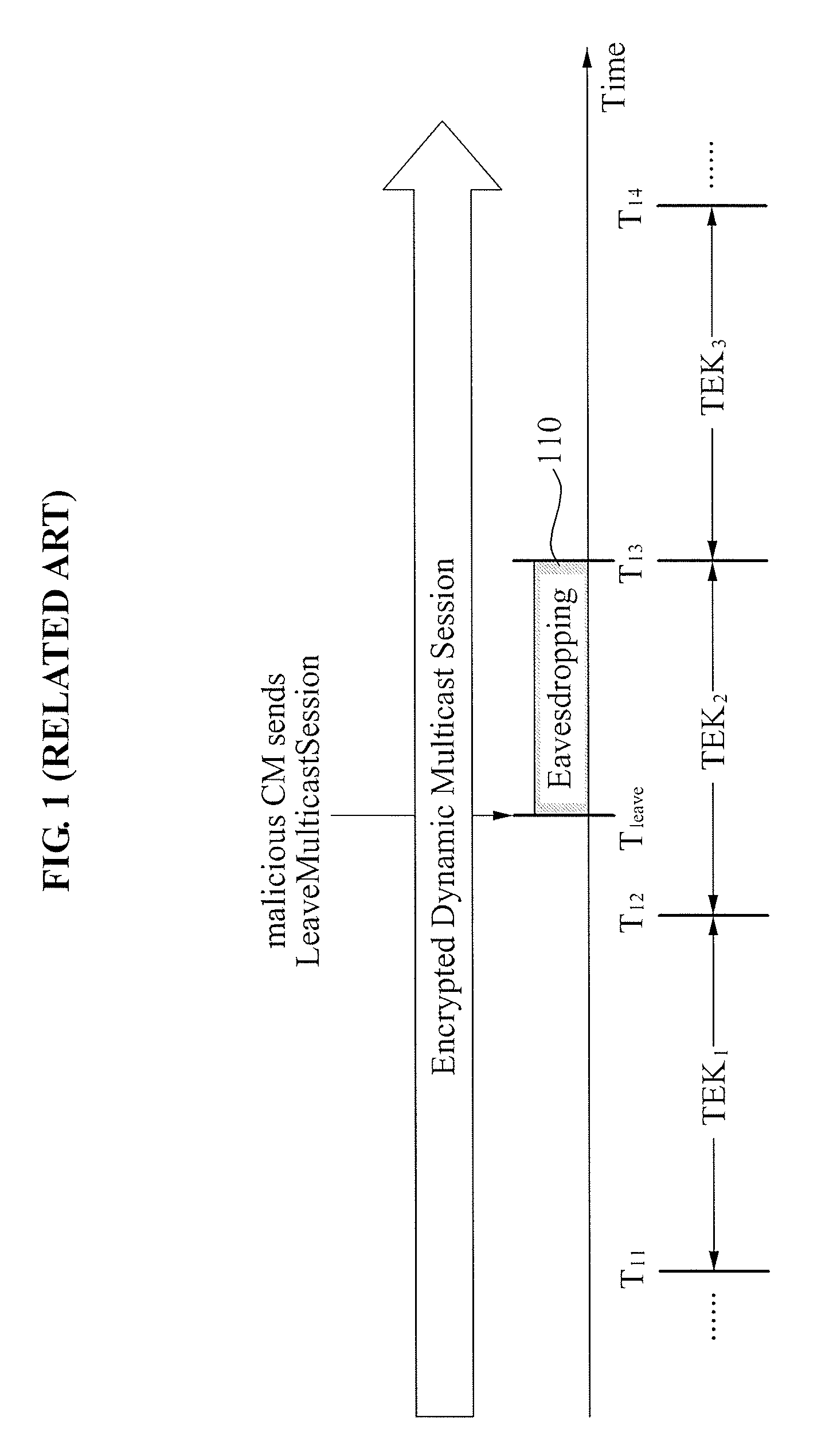
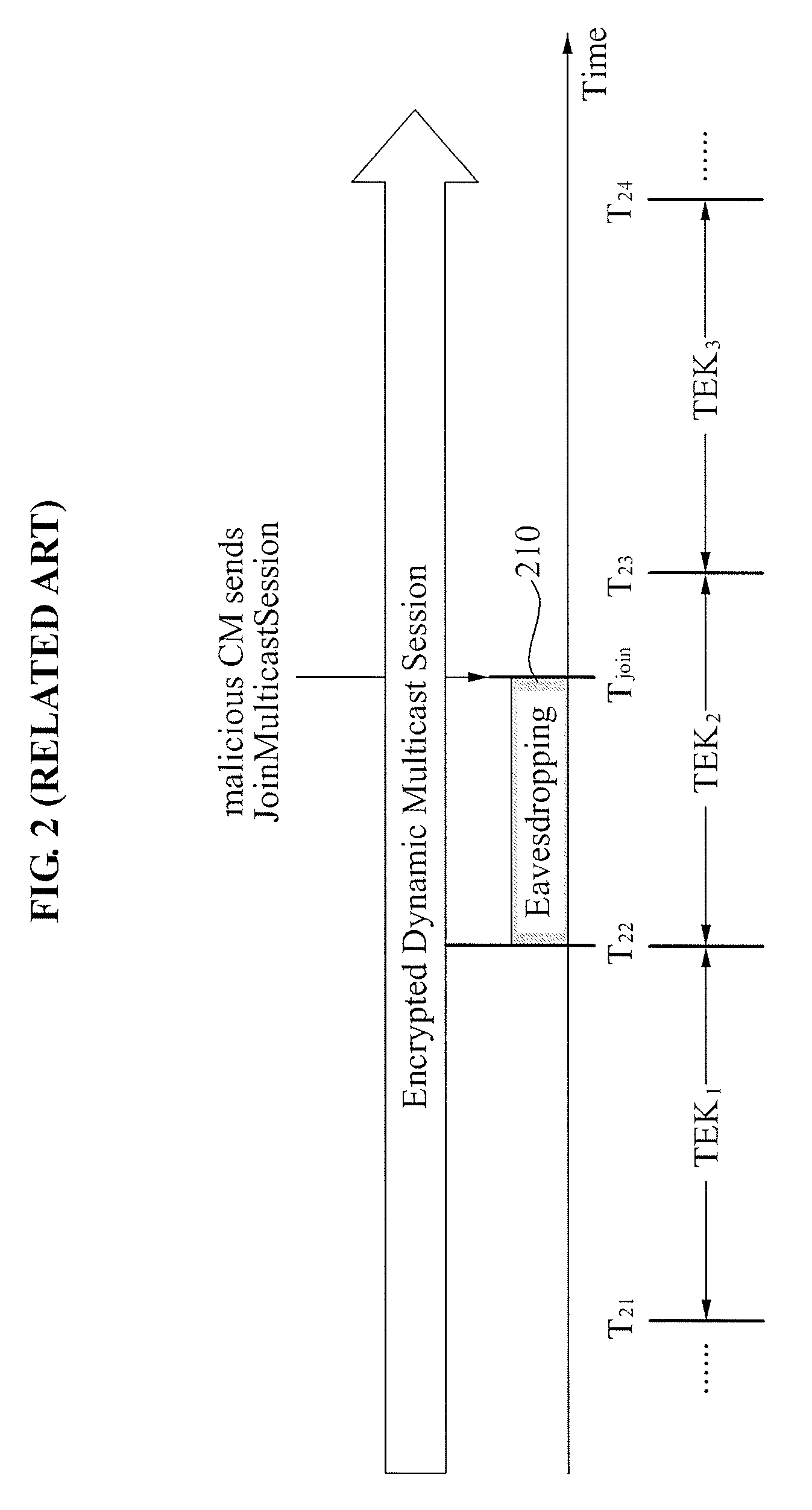
Cable network system and method for controlling security in cable network encrypted dynamic multicast session
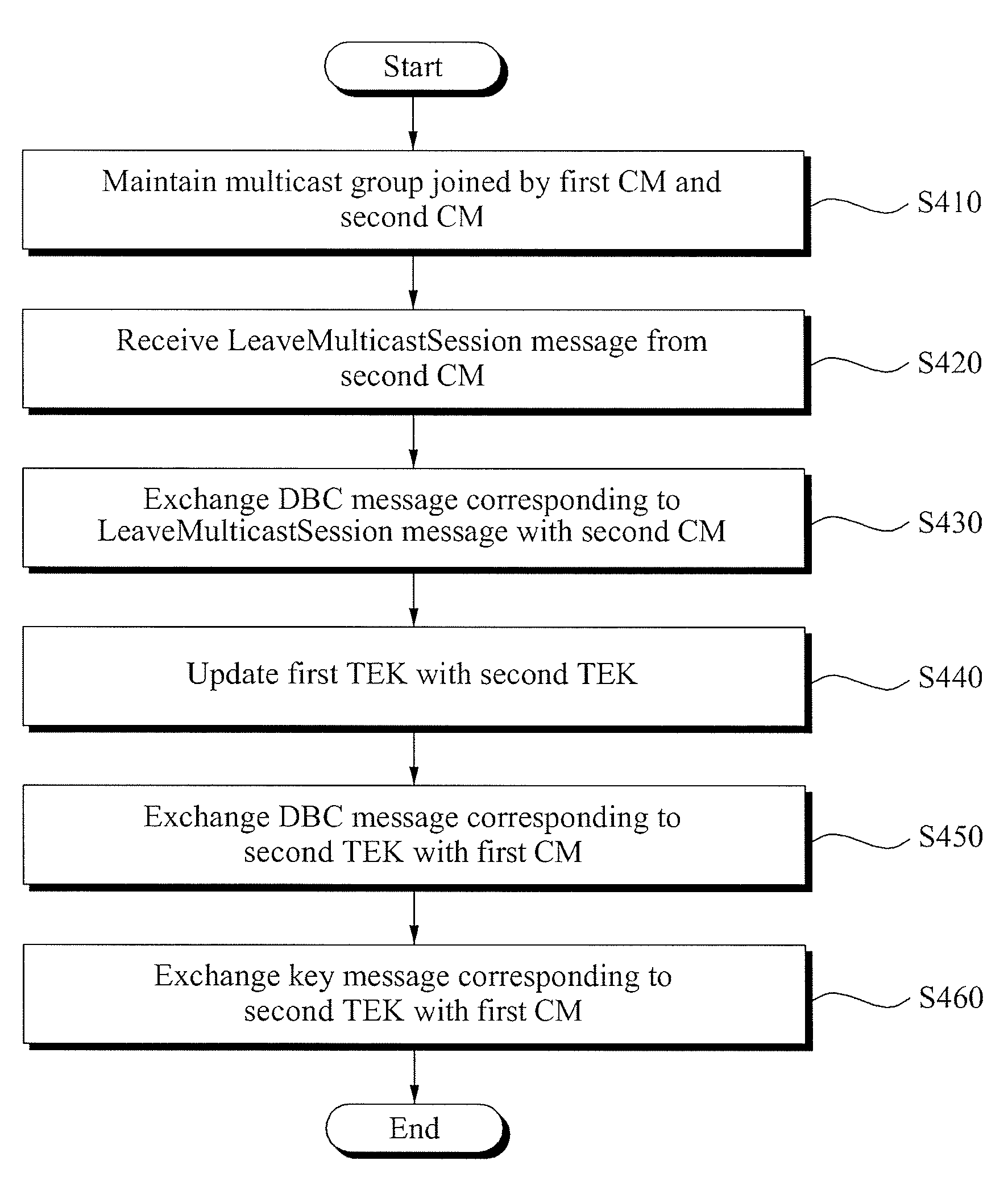
InactiveUS20090144544A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesData taking preventionModem deviceDBc
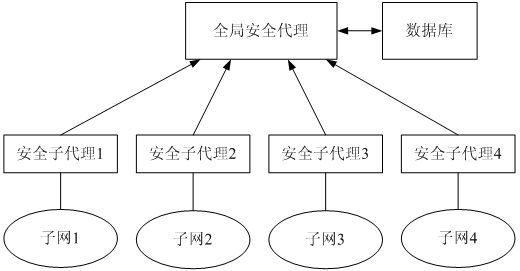
A security control method in a cable network dynamic multicast session, and more particularly, a method of controlling forward secrecy and backward secrecy in a Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) 3.0 network dynamic multicast session is provided. A security control method in a cable network dynamic multicast session, includes: maintaining a multicast group that is allocated with a first Downstream Service Identifier (DSID) and a first Security Association Identifier (SAID) and that is joined by a first cable modem and a second cable modem; receiving a LeaveMulticastSession message from the second cable modem; exchanging, corresponding to the LeaveMulticastSession message, a Dynamic Bonding Change (DBC) message for changing a multicast parameter with the second cable modem; and updating a first Traffic Encryption Key (TEK) corresponding to the first DSID with a second TEK.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Rapid authentication method for wireless Mesh network backbone node switching
InactiveCN101867930AReduce deliveryReduce communication loadSecurity arrangementKey exchangeWireless mesh network
The invention discloses a rapid authentication method for wireless Mesh network backbone node switching, which mainly solves the problem existing in the security of the rapid switching of a wireless Mesh backbone node which is not covered by the existing standard IEEE 802.11s, IEEE 802.11r and a series of China wireless local area network security standards. The authentication scheme is that when the backbone node is switched, a switching authentication request is transmitted to a switching target; a backbone node used as the switching target requests an authentication server for a switching authentication key; the authentication server generates a random key which is used as the switching authentication key and safely issues the switching authentication key to the backbone nodes involving in switching through a switching authentication key response message; and the two backbone nodes use the switching authentication key for rapid authentication in the switching process and adopt an elliptic curve key exchange algorithm to negotiate a session key. The invention has the advantages that the number of the transmitted messages is small, the forward secrecy is kept, the method can resist partial service denial attacks, and the method can be used for rapid network deployment for field operation, emergency command and emergency rescue and disaster relief.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Providing forward secrecy in a terminating SSL/TLS connection proxy using Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman key exchange
ActiveUS9531685B2Promote exchangeKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageServer agentKey exchange
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Dynamic certificate authentication key negotiation method for wireless sensor network
ActiveCN109600747AImprove computing efficiencyReduce computational complexityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHash functionConfidentiality
The invention discloses a dynamic certificate authentication key negotiation method for a wireless sensor network, belongs to the field of sensor network information security, and only adopts a Hash function as a construction block and provides mutual identity verification and perfect forward confidentiality attribute based on a new DAC. In the method, each node is configured with one new DAC, andonce the session key is successfully established based on the current key, the DAC is updated, so that specific DAC value is only limited to one session key. Thus, the compromised authentication keydoes not affect other previously established session keys. In addition to having basic security attributes (e.g., mutual authentication and PFS, etc.), the method may also detect previously simulatedattacks to a user / sensor by comparing its current DAC with respective DACs stored at a gateway node. In addition, according to the scheme, only the hash function and the XOR operation are used, so that the calculation efficiency of the method is comprehensively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Entity bidirectional-identification method for supporting fast handoff
ActiveUS8392710B2Reduce complexitySimple conditionsUser identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementRound complexitySecurity domain
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Method and Implementation for Information Exchange Using Markov Models
ActiveUS20100272256A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationThird partyTrust third party
The replacement of secret keys is a central problem in key management. Typical solutions exchange handshaking messages, involve complex computations, or require the cooperation of trusted third parties. Disclosed herein is a key replacement method that exploits the randomness of Markov models to efficiently provide fresh keys to users. Unlike other methods, the proposed method removes the need for extra communications, intensive computation, or third parties. It is demonstrated that the proposed method has perfect forward secrecy as well as resistance to known-key attacks.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND OFFICE OF TECH COMMLIZATION +1
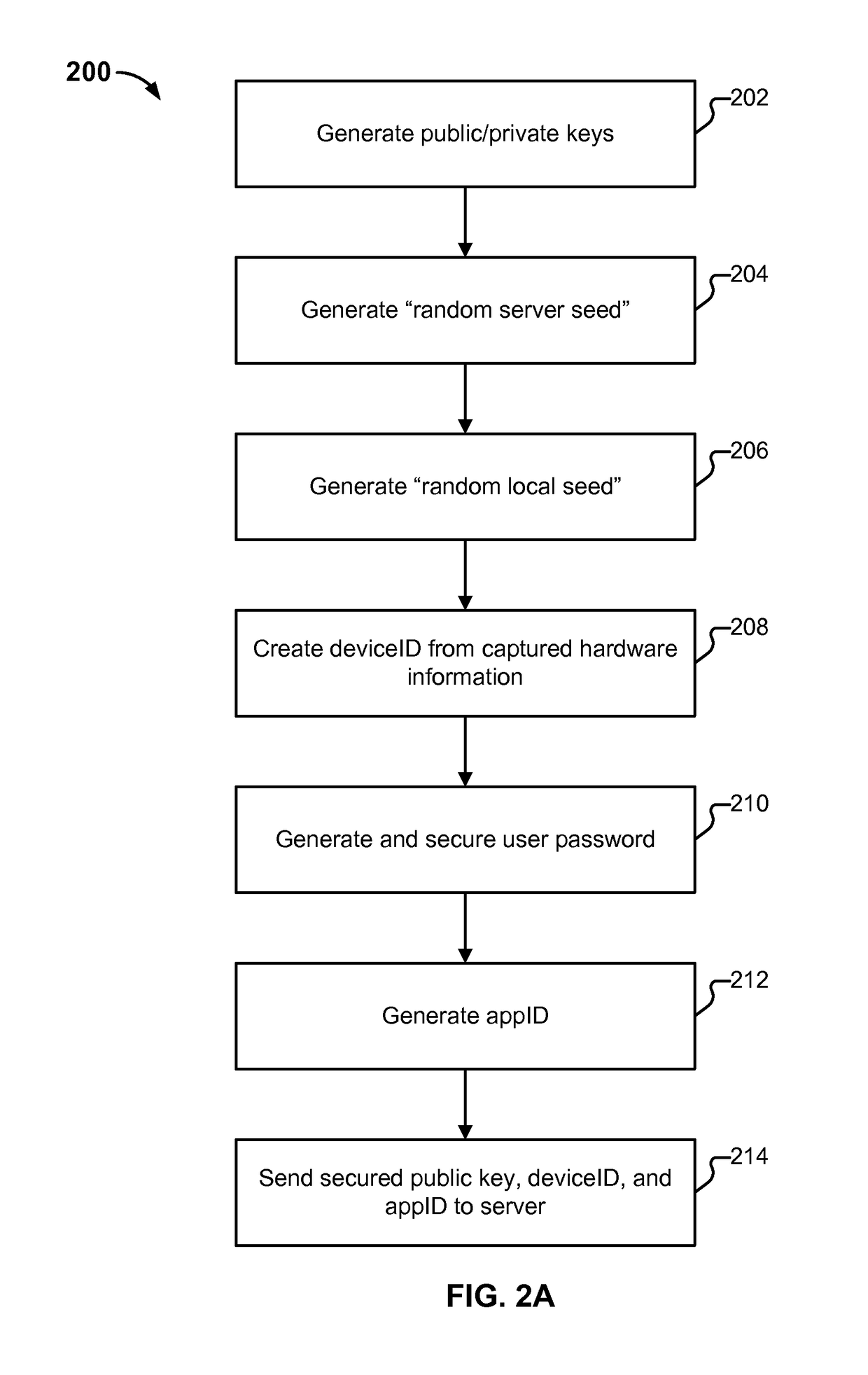
Method and apparatus for perfect forward secrecy using deterministic hierarchy
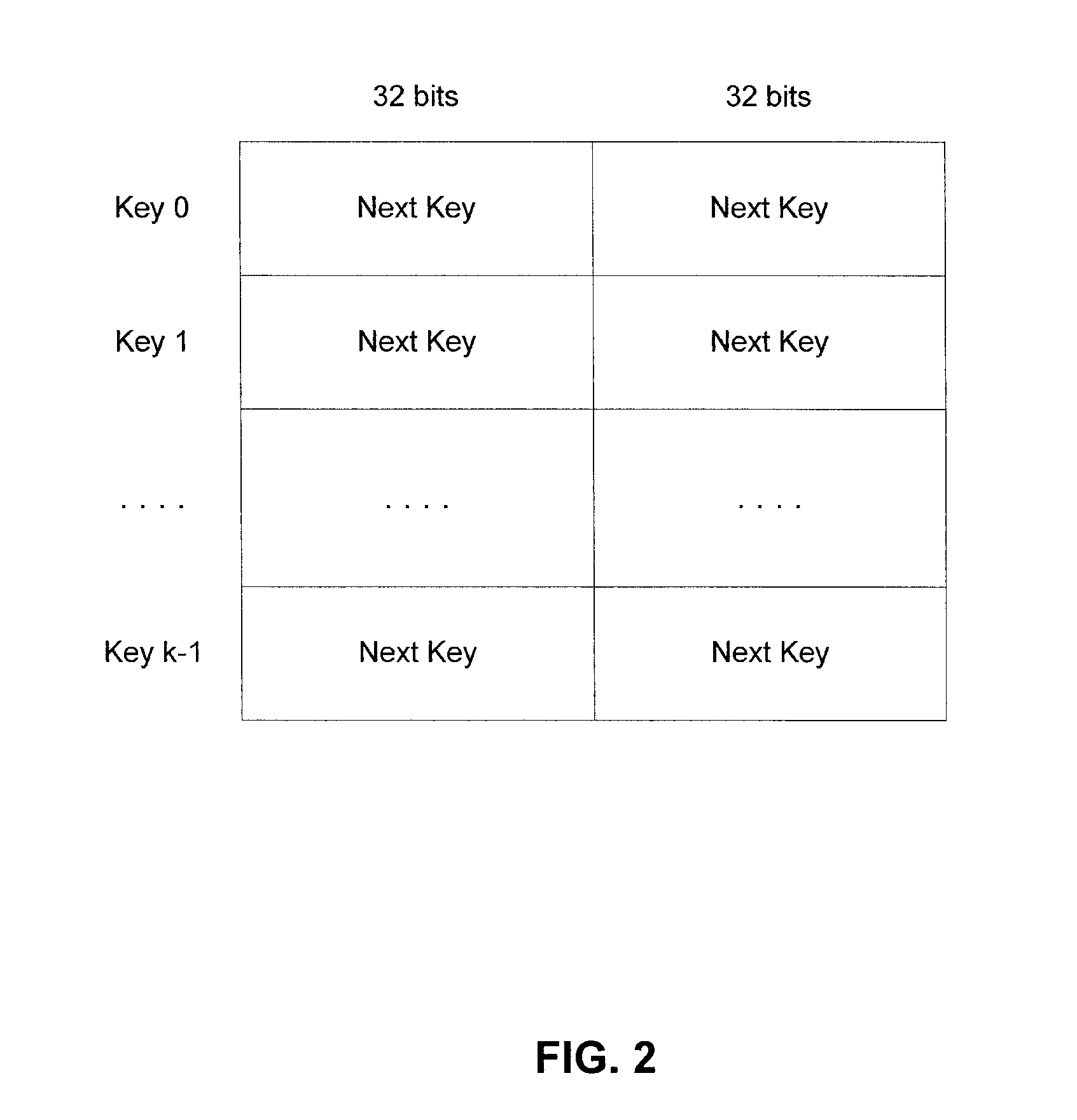
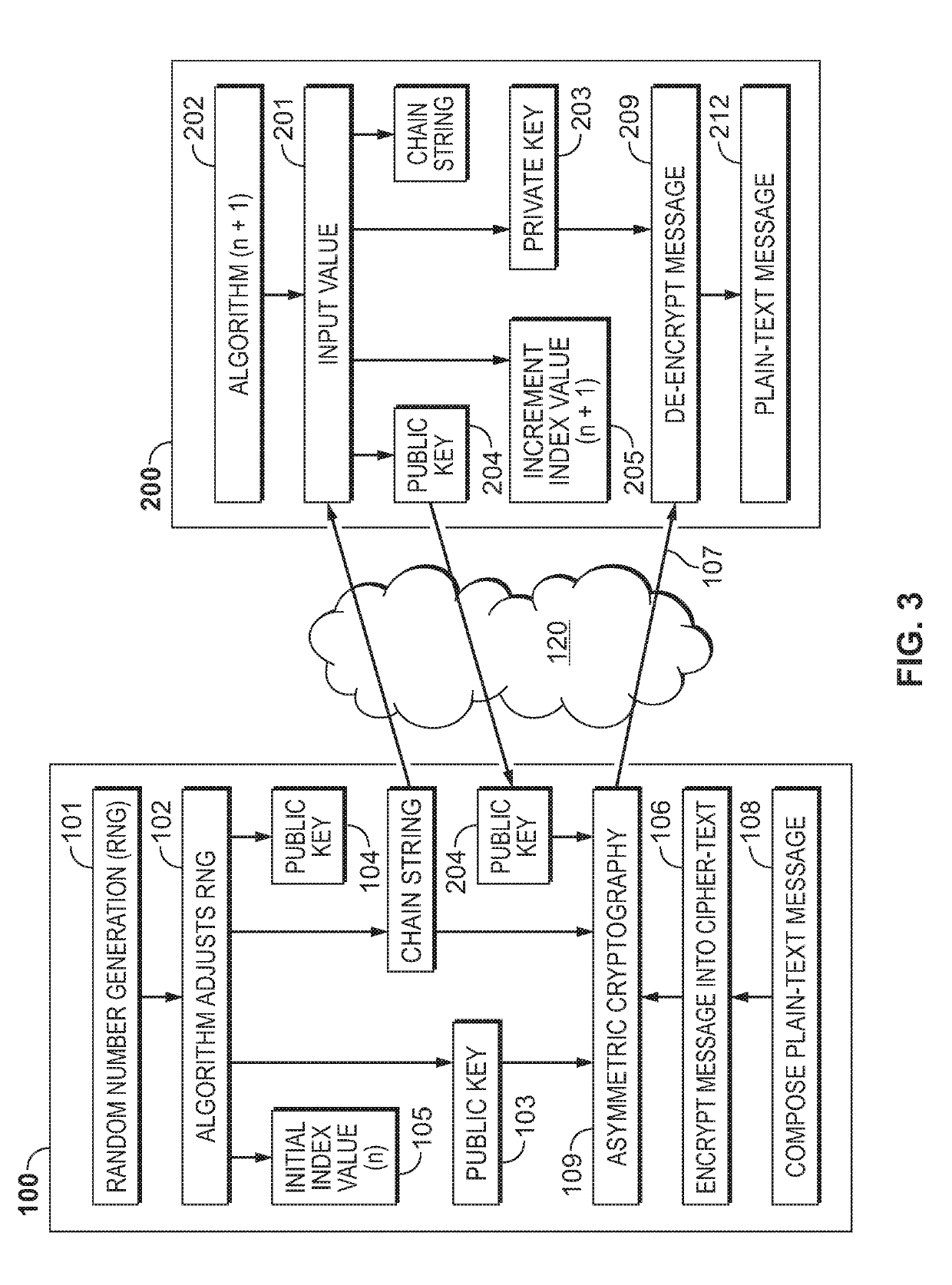
ActiveUS20190123897A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageMan-in-the-middle attackForward secrecy
Method and apparatus for a system to communicate via perfect forward secrecy. A deterministic hierarchy is used to generate public and private keys, offline, on distinct devices, for use with asymmetrical cryptography over an unsecure medium. Because each private key is not transmitted over the unsecure medium, but must be used to de-encrypt the communications, it is very difficult for man-in-the-middle attacks to de-encrypt the communications. Because each private key is generated according to a deterministic hierarchy, a master entity can recreate the private keys and passively monitor the communications while maintaining perfect forward secrecy.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
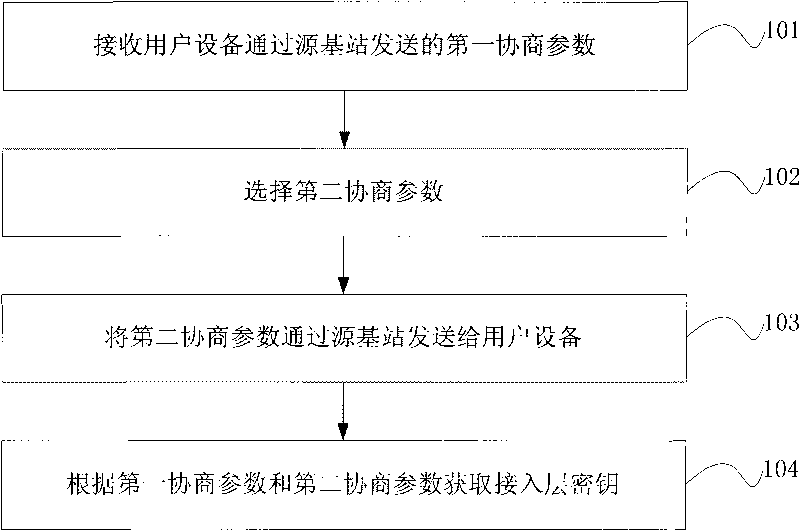
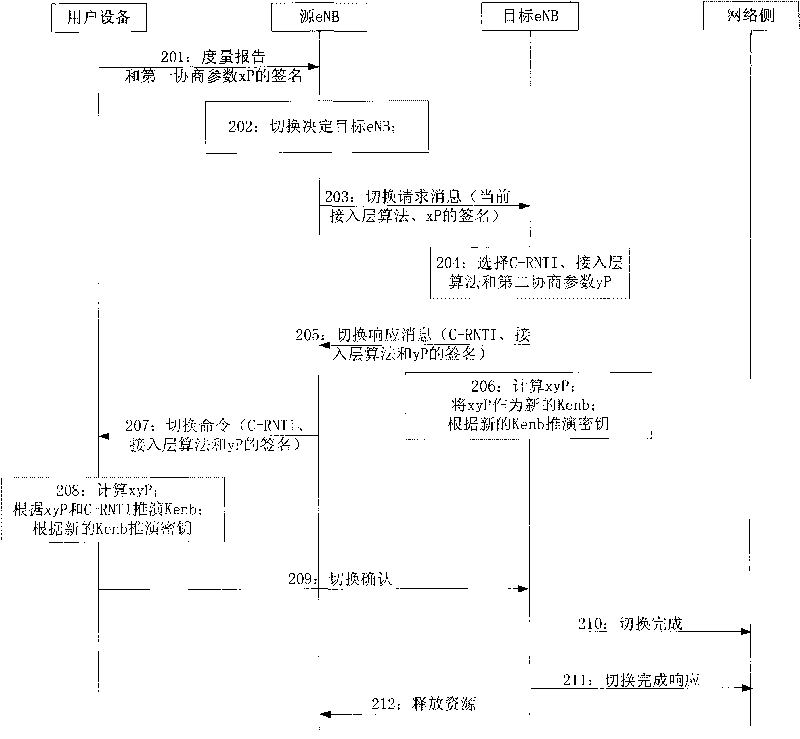
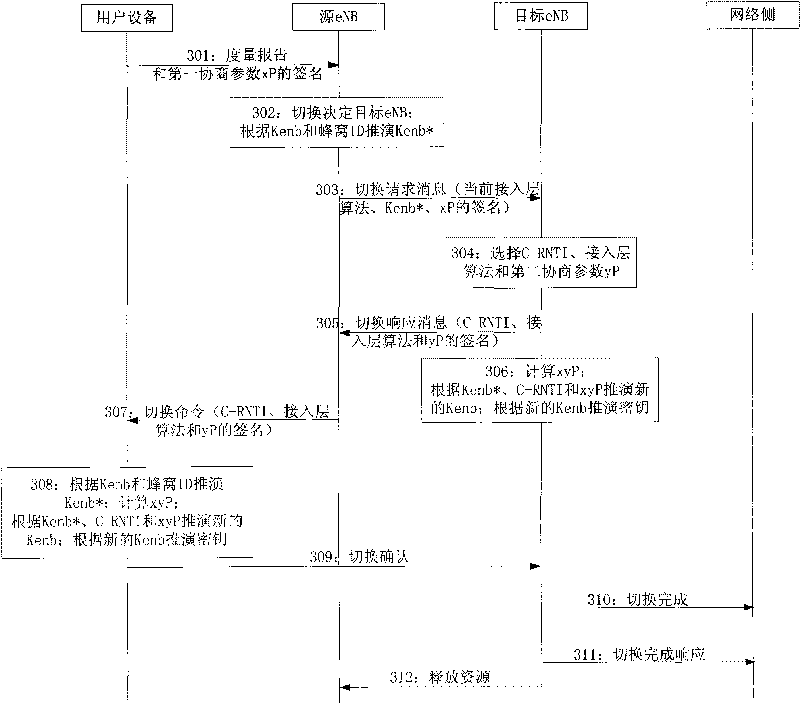
Method, network equipment, user equipment and communication system for ensuring forward security
ActiveCN101741551ASolve the forward insecurity problemSimple processPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemUser equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, network equipment, user equipment and a communication system for ensuring forward security. The method for ensuring the forward secrecy comprises the following steps of: receiving a first negotiation parameter sent by the user equipment through a source base station; selecting a second negotiation parameter; sending the second negotiation parameter to the user equipment through the source base station; and acquiring an access layer key according to the first negotiation parameter and the second negotiation parameter. The network equipment comprises a first receiving module, a selecting module, a sending module and an access layer key acquiring module. The user equipment comprises a generation module, a first sending module, a receiving module and an acquiring module. The communication system comprises the user equipment, the source base station and a target base station. The embodiment of the invention effectively solves the problem of forward insecurity in the process of the user equipment switching eNB and also simplifies the process of the traditional scheme.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
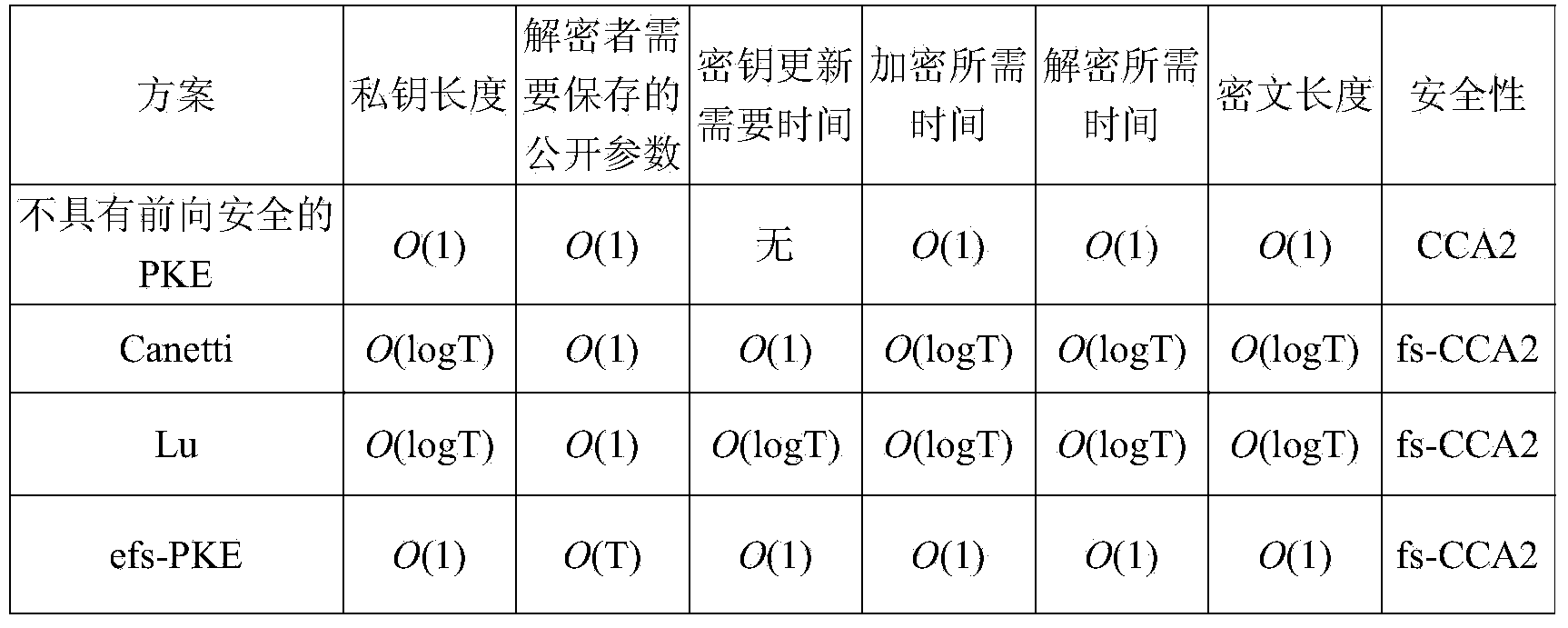
Method for efficient public key encryption with forward security
ActiveCN103684764AStrong security goalsConstant lengthPublic key for secure communicationPlaintextRandom oracle
The invention discloses a method for efficient public key encryption with forward security. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, system initialization is conducted and a PK and an initial SK1 of a user are calculated; step 2, the secret keys are updated; step 3, a plaintext m is encrypted through the PK so that a CT of the plaintext m at the current period i can be obtained; step 4, the CT is decrypted through an SK i at the current time period i so that the plaintext m can be obtained. The method has the advantages that an encryptor only needs to own one cluster element so that a public key of each time period can be obtained through public information. In addition, the public keys can be identity information. On the basis, an encryption scheme based on the identity can be converted into a public encryption scheme with forward security and an efficient public key encryption scheme with forward security which achieves adaptive selection ciphertext security under a random prediction machine model is obtained.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
Multicast security agent assembly and multicast encryption management method
InactiveCN102684875AEnsure safetyMulticast Security GuaranteeSpecial service provision for substationKey distribution for secure communicationAttackEngineering
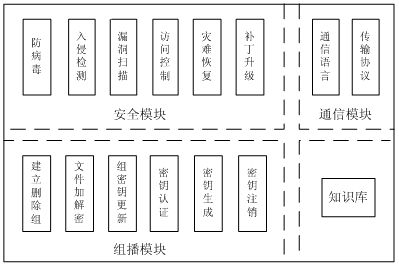
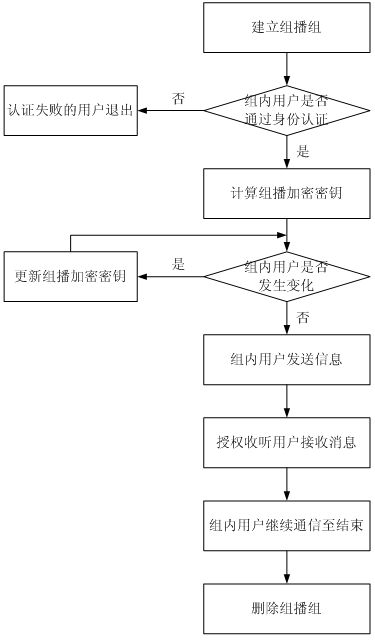
The invention relates to a multicast security agent assembly and a multicast encryption management method. File encryption and decryption submodules in a multicast module serve as specific execution modules for multicast users to encrypt / decrypt messages or files, an RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) algorithm is adopted as a multicast encryption / decryption algorithm, and private keys of the users are taken as decryption keys. After system authentication, if some users in an intranet need intra-group communication, a group key formed by a product of the private keys of all the members can ensure multicast security; and when new users participate in the intranet or the old users exit the intranet, the new users can not access communication contents before accessing and the exited users can not access the communication contents after exiting through updating the group key, therefore, the functions of encryption with one key and decryption with multiple keys in a multicast group are realized. When group members change, the keys (namely the private keys) of the other users in the group do not need to be updated, thereby realizing the encryption on the multicast information, and achieving important forward secrecy, backward secrecy, inner attack resistance and the like in security multicast.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Providing forward secrecy in a terminating TLS connection proxy
ActiveUS20170111334A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHash functionEdge server
An infrastructure delivery platform provides a RSA proxy service as an enhancement to the TLS / SSL protocol to off-load, from an edge server to an external cryptographic server, the decryption of an encrypted pre-master secret. The technique provides forward secrecy in the event that the edge server is compromised, preferably through the use of a cryptographically strong hash function that is implemented separately at both the edge server and the cryptographic server. To provide the forward secrecy for this particular leg, the edge server selects an ephemeral value, and applies a cryptographic hash the value to compute a server random value, which is then transmitted back to the requesting client. That server random value is later re-generated at the cryptographic server to enable the cryptographic server to compute a master secret. The forward secrecy is enabled by ensuring that the ephemeral value does not travel on the wire.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Secure time communication system
ActiveUS20180234393A1Key distribution for secure communicationGenerating/distributing signalsCommunications systemMessage delay
Methods and apparatus for a Secure Time Communication System (10) are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention provides secure and non-interactive communication of clock information over an unsecured communications channel. This communication provides perfect forward secrecy, while detecting and blocking message spoofing, message replay, denial of service and cryptographic performance attacks. This mechanism also bounds the effect of message delay manipulation. The mechanism consists of two components, a filtered time encryptor (16) and a filtered time decryptor (28). The filtered time encryptor (16) produces a message in two parts; a time token followed by an encrypted message body. The time token is used as a filter to detect most attacks and to determine the message key.
Owner:INVISINET TECH LLC
Device Securing Communications Using Two Post-Quantum Cryptography Key Encapsulation Mechanisms
ActiveUS20220038269A1Improve securityImprove security levelKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationKey (cryptography)Ciphertext
A network and a device can support secure sessions with both (i) a post-quantum cryptography (PQC) key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) and (ii) forward secrecy. The device can generate (i) an ephemeral public key (ePK.device) and private key (eSK.device) and (ii) send ePK.device with first KEM parameters to the network. The network can (i) conduct a first KEM with ePK.device to derive a first asymmetric ciphertext and first shared secret, and (ii) generate a first symmetric ciphertext for PK.server and second KEM parameters using the first shared secret. The network can send the first asymmetric ciphertext and the first symmetric ciphertext to the device. The network can receive (i) a second symmetric ciphertext comprising “double encrypted” second asymmetric ciphertext for a second KEM with SK.server, and (ii) a third symmetric ciphertext. The network can decrypt the third symmetric ciphertext using the second asymmetric ciphertext.
Owner:NIX JOHN A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com