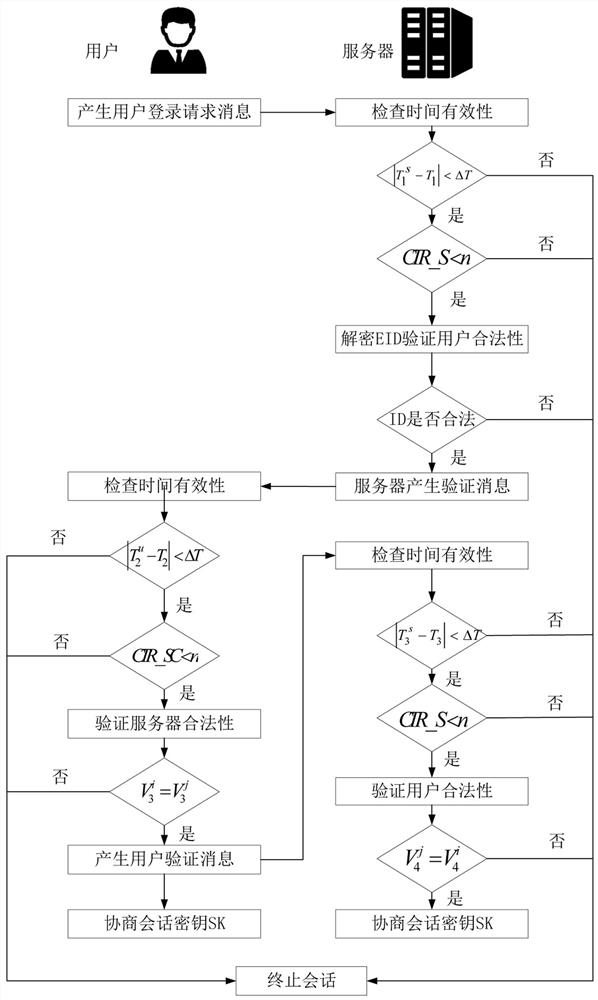
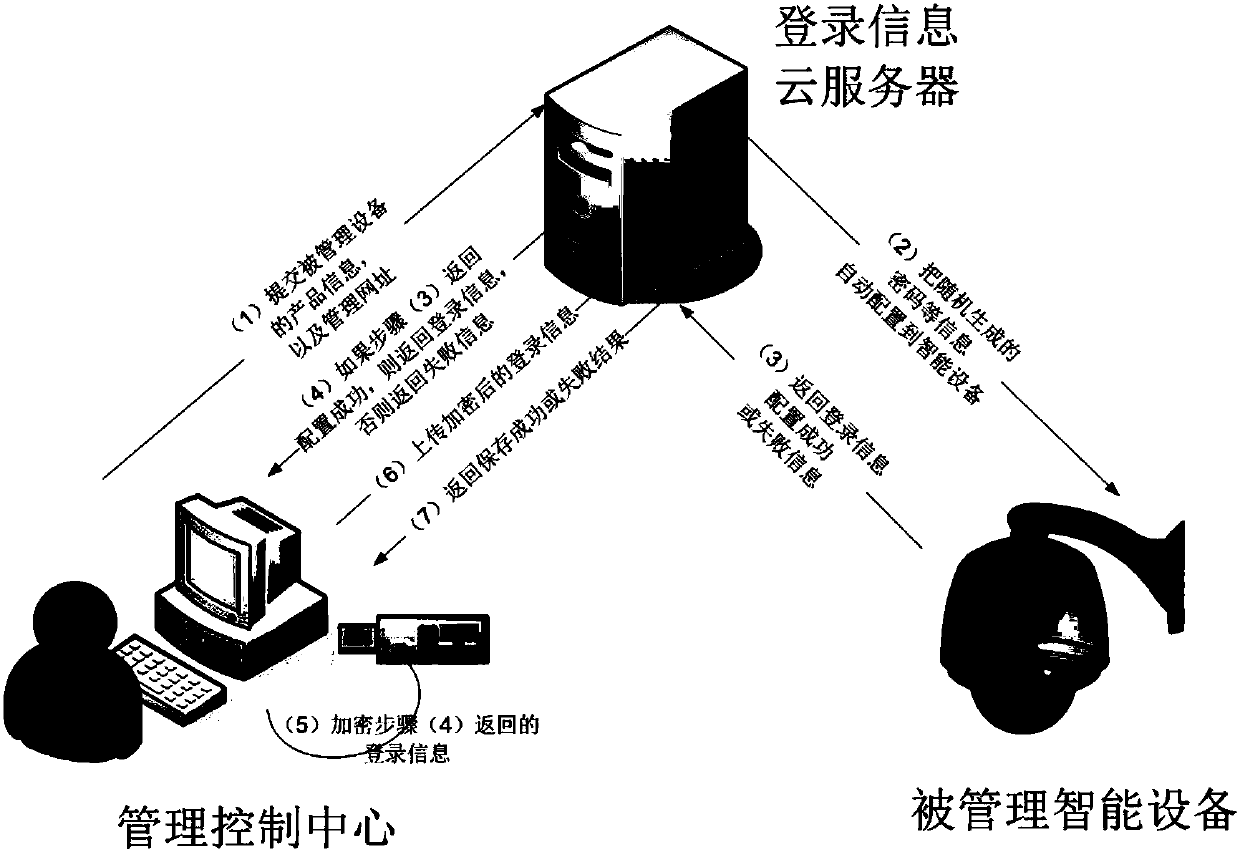
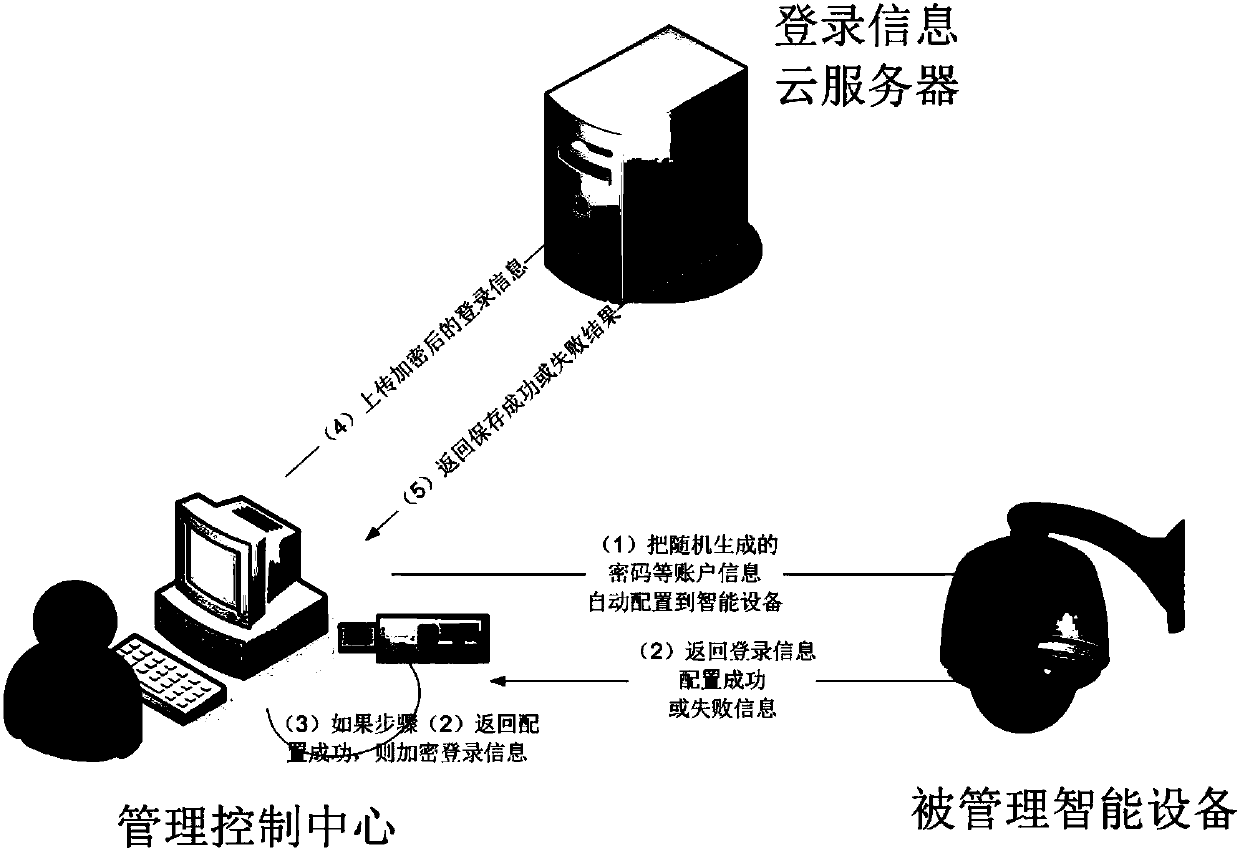
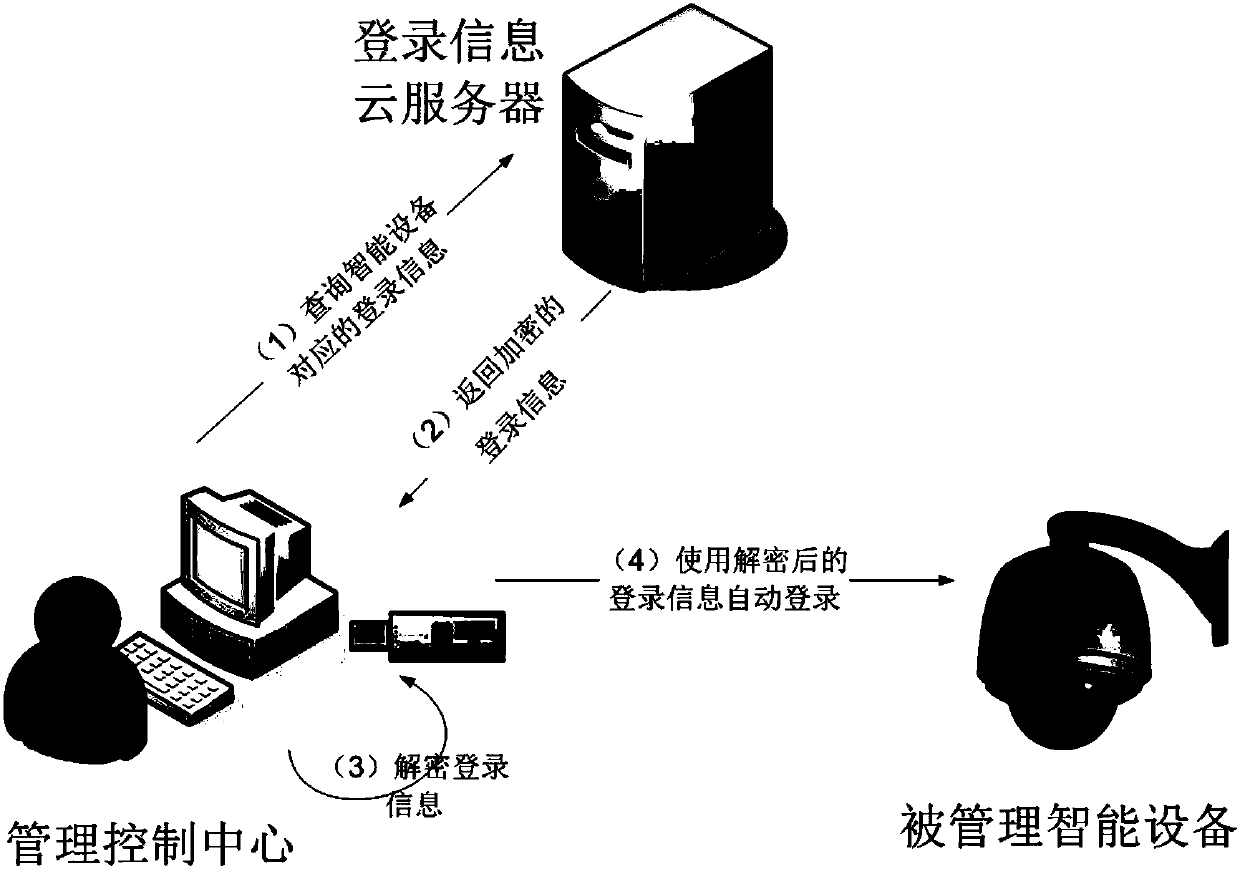
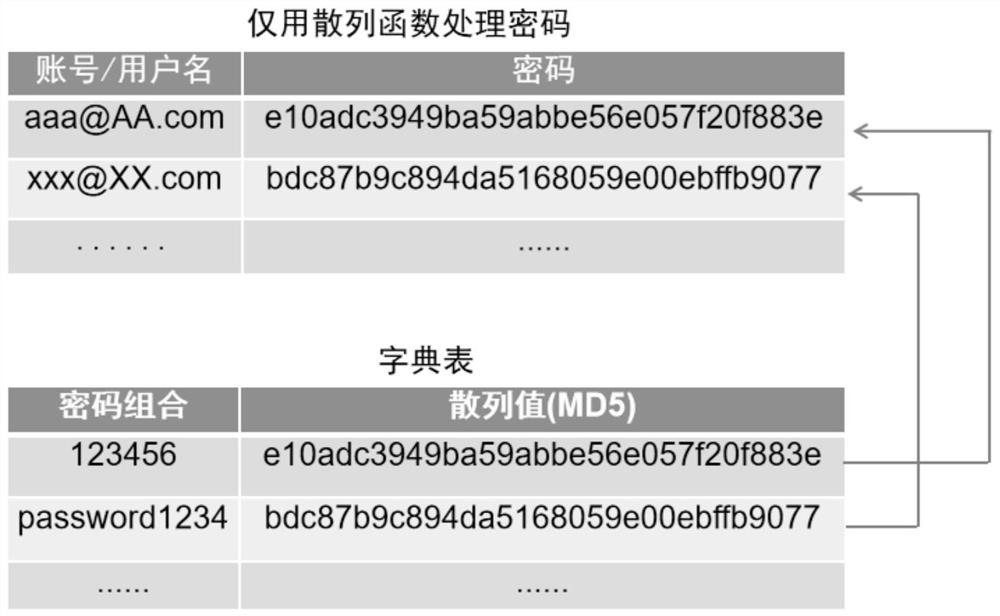
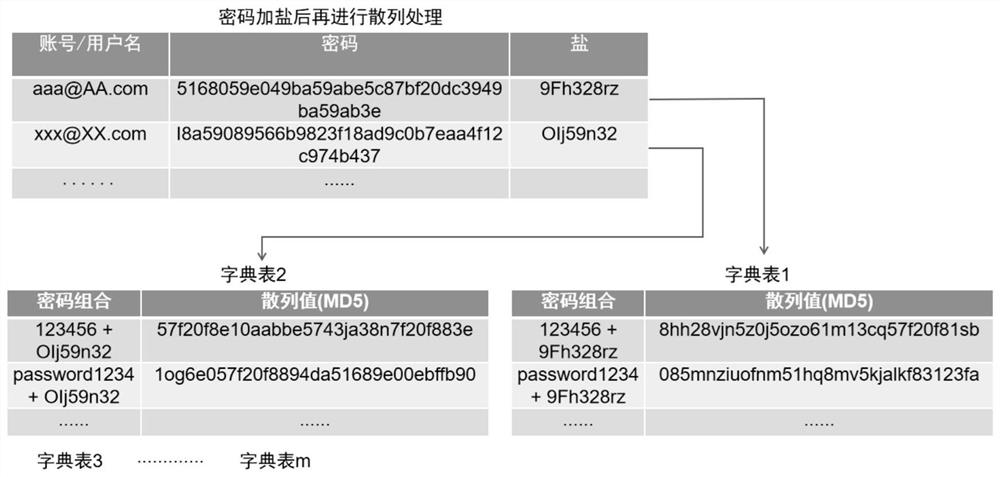
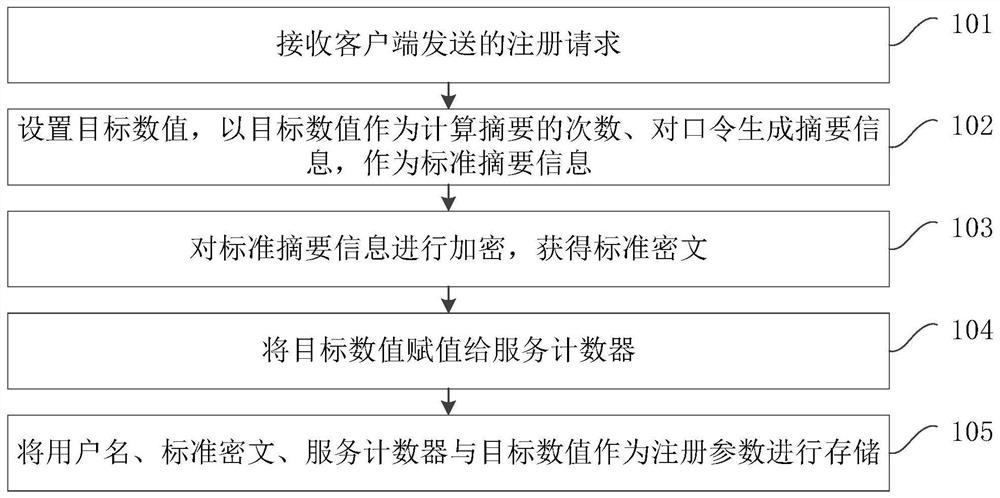
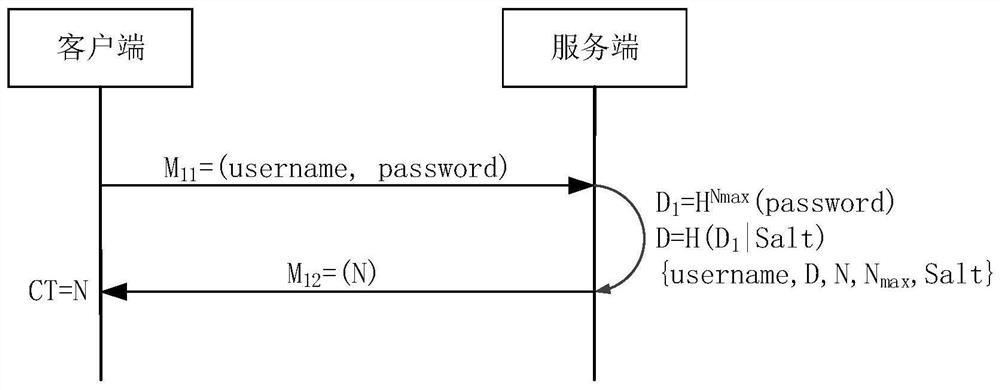
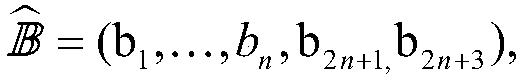Patents
Literature
45 results about "Dictionary attack" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
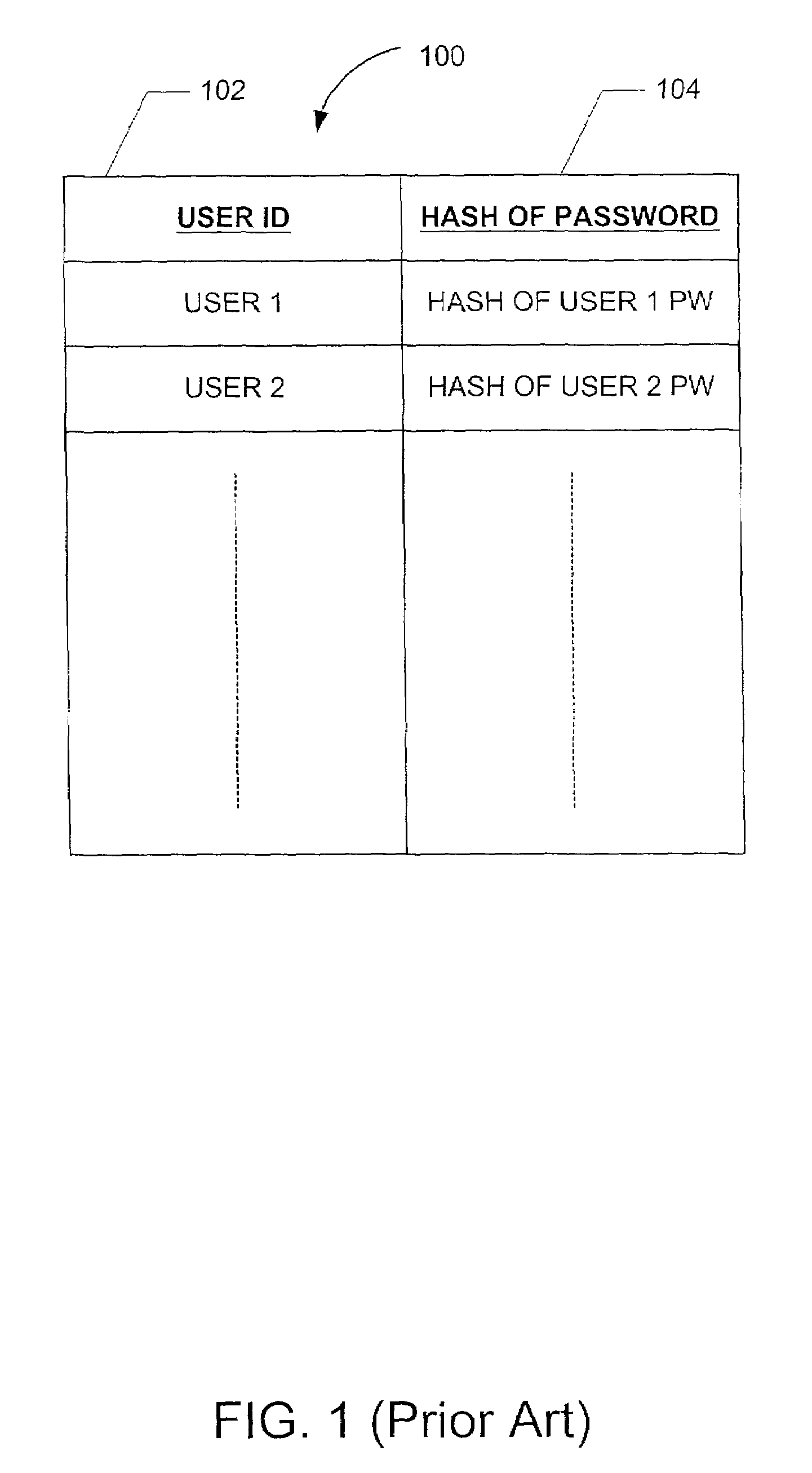
In cryptanalysis and computer security, a dictionary attack is a form of brute force attack technique for defeating a cipher or authentication mechanism by trying to determine its decryption key or passphrase by trying hundreds or sometimes millions of likely possibilities, such as words in a dictionary.
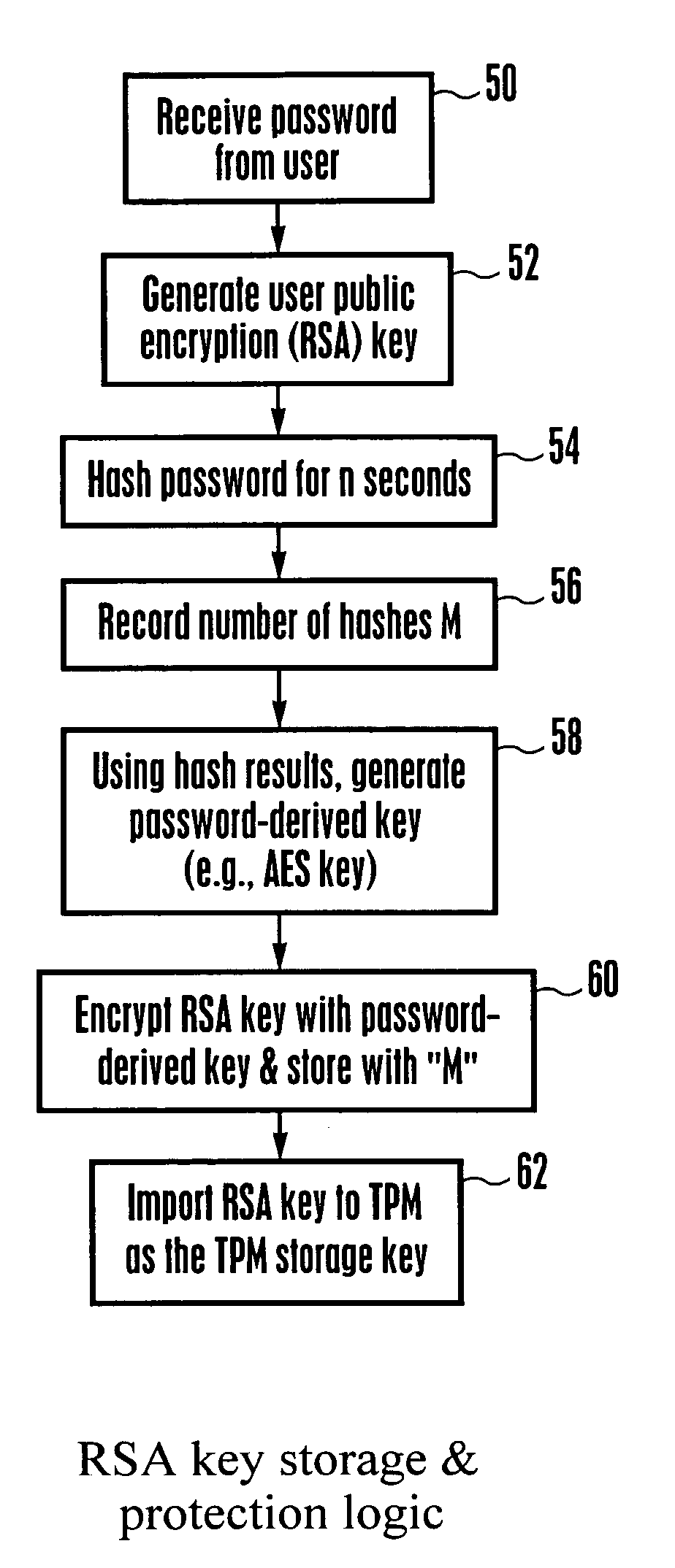
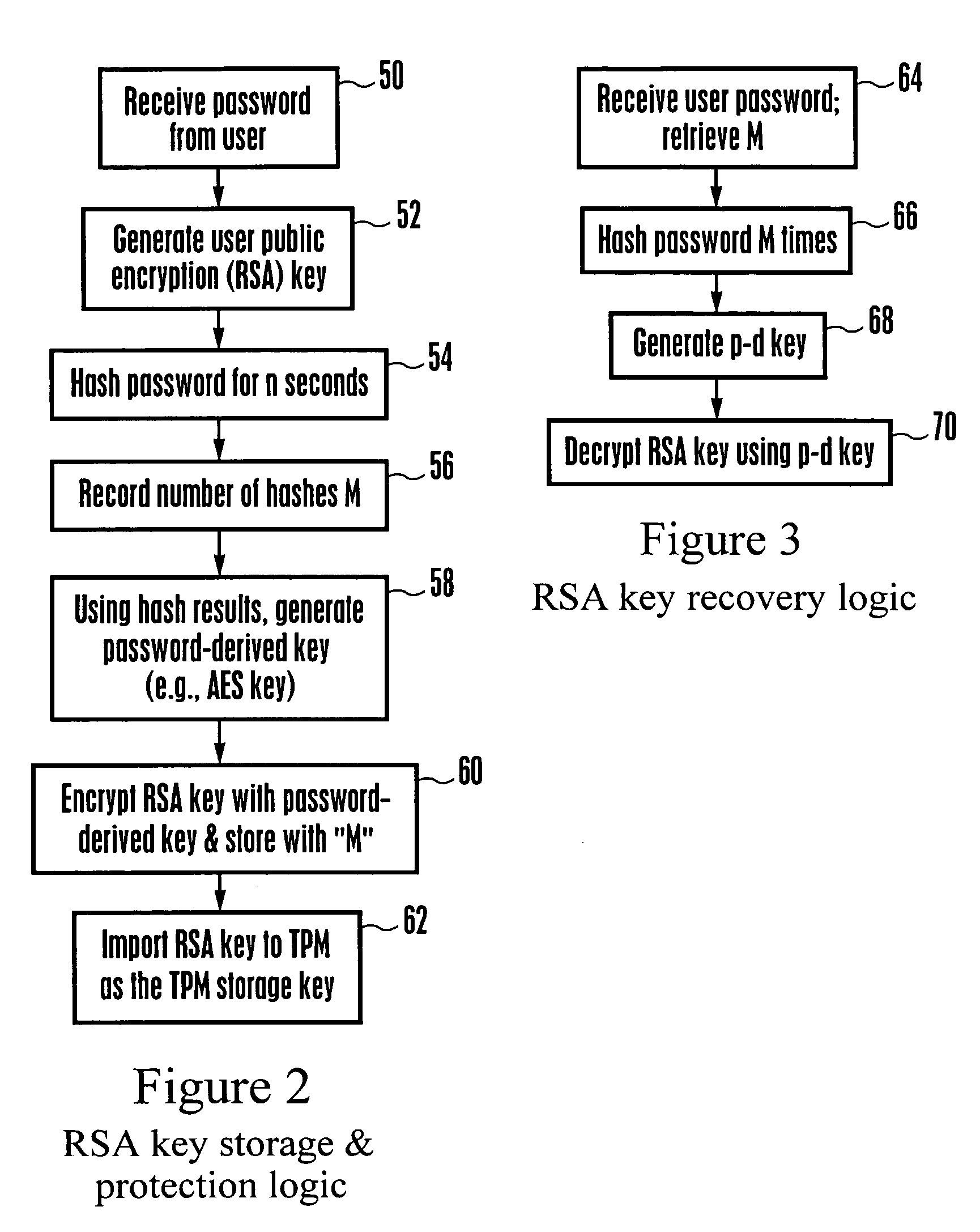
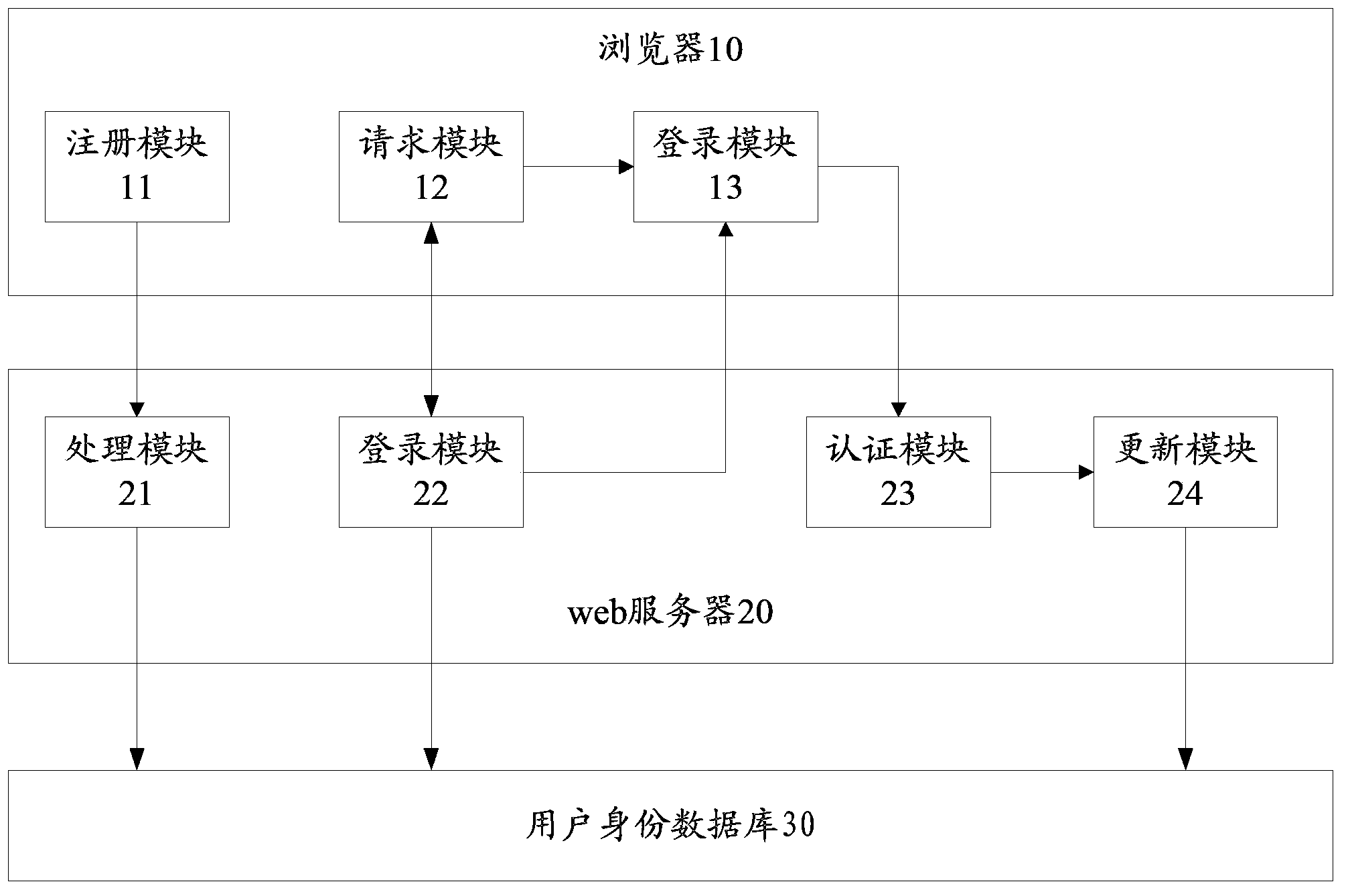
System and method for protecting against dictionary attacks on password-protected TPM keys
InactiveUS20070014416A1Key distribution for secure communicationCryptographic attack countermeasuresTrusted Platform ModuleUser input
A computer system that may include a trusted platform module (TPM) along with a processor hashes a user-supplied password for a predetermined time period that is selected to render infeasible a dictionary attack on the password. The results of the hash are used to render an AES key, which is used to encrypt an RSA key. The encrypted RSA key along with the total number of hash cycles that were used is stored and the RSA key is provided to the TPM as a security key. In the event that the RSA key in the TPM must be recovered, the encrypted stored version is decrypted with an AES key that is generated based on the user inputting the same password and hashing the password for the stored number of cycles.
Owner:IBM CORP
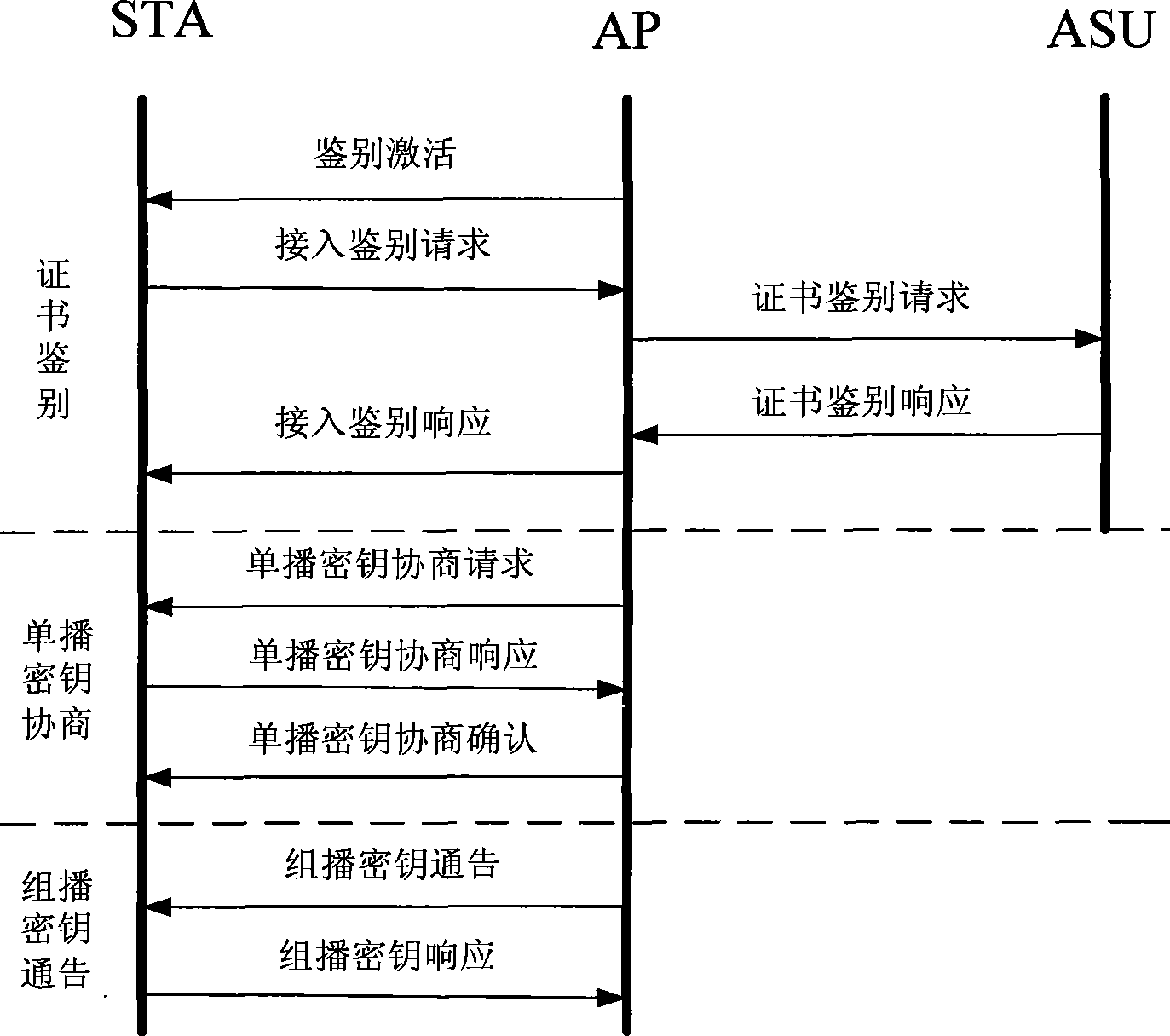
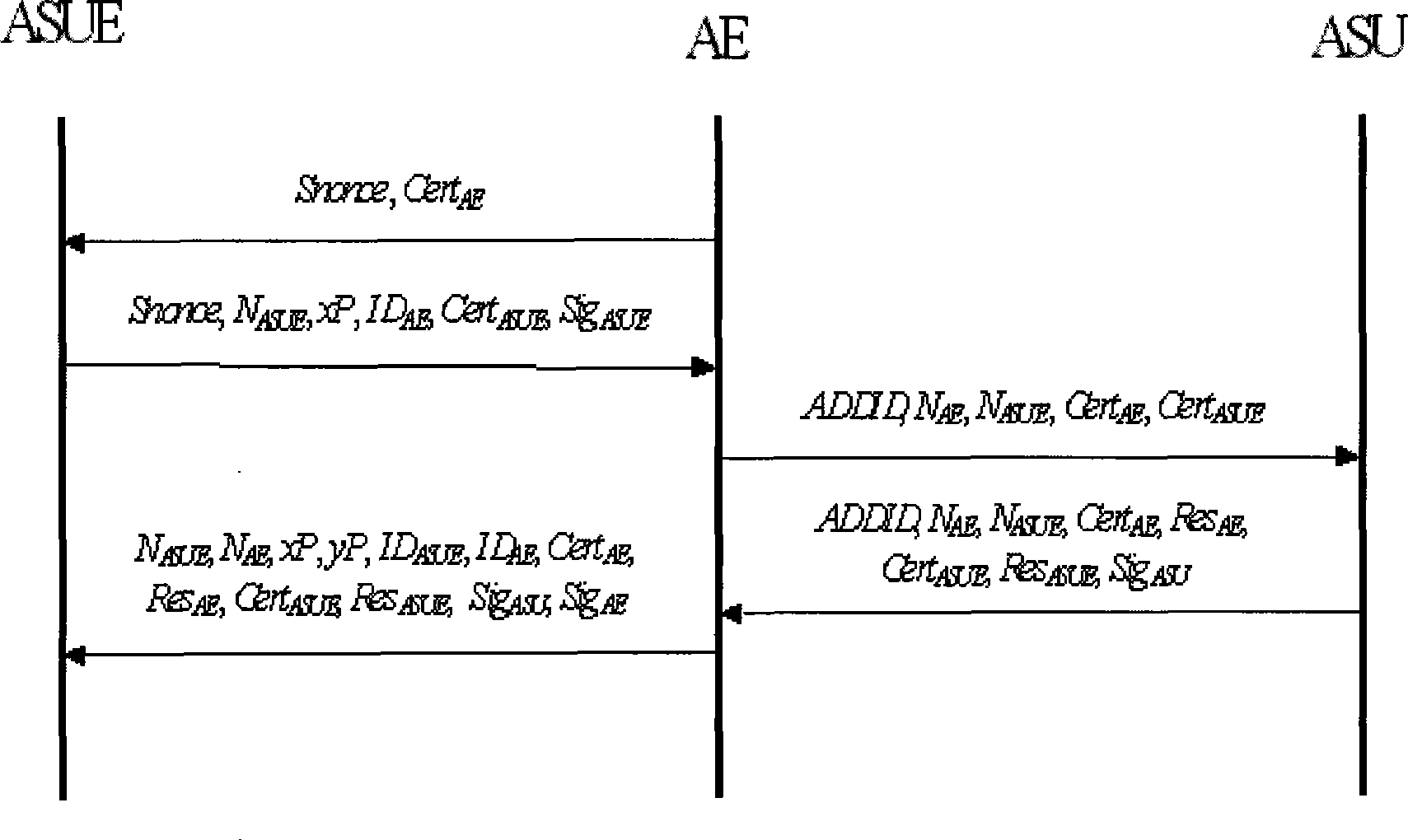
WAPI-XG1 access and fast switch authentication method
InactiveCN101420694AReduce complexitySolve the problem that fast switching is not supportedNetwork topologiesTransmissionClient-sideDictionary attack
The invention provides a method used for authentificating the access and quick switching over of WAPI-XG1, belonging to the field of wireless communication. The method comprises the steps as follows: an authentication protocol is accessed and used for establishing a connection between an STA and a first AP, the session key with the first AP is established, and keys used for quick switching over with an ASU are established; when the STA moves to the control domain of a second AP, a safety correlation establishing protocol and a unicall session key updating protocol under quick switching over are carried out. The method can solve the problems that the WAPI-XG1 can not support the quick switching over and the forward secrecy can not be ensured and the offline dictionary attack can not be resisted under a pre-shared key authentication mode; meanwhile, the method needs not change the authentication framework of the WAPI-XG1needs not changing, the two authentication modes based on the certificate and shared key are integrated into one authentication proposal; furthermore, when the switching over occurs on the client terminal, only the quick switching over safety correlation establishment protocol runs with the destination access point for the authentication mode based on the certificate, without re-authentication or pre-authentication.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
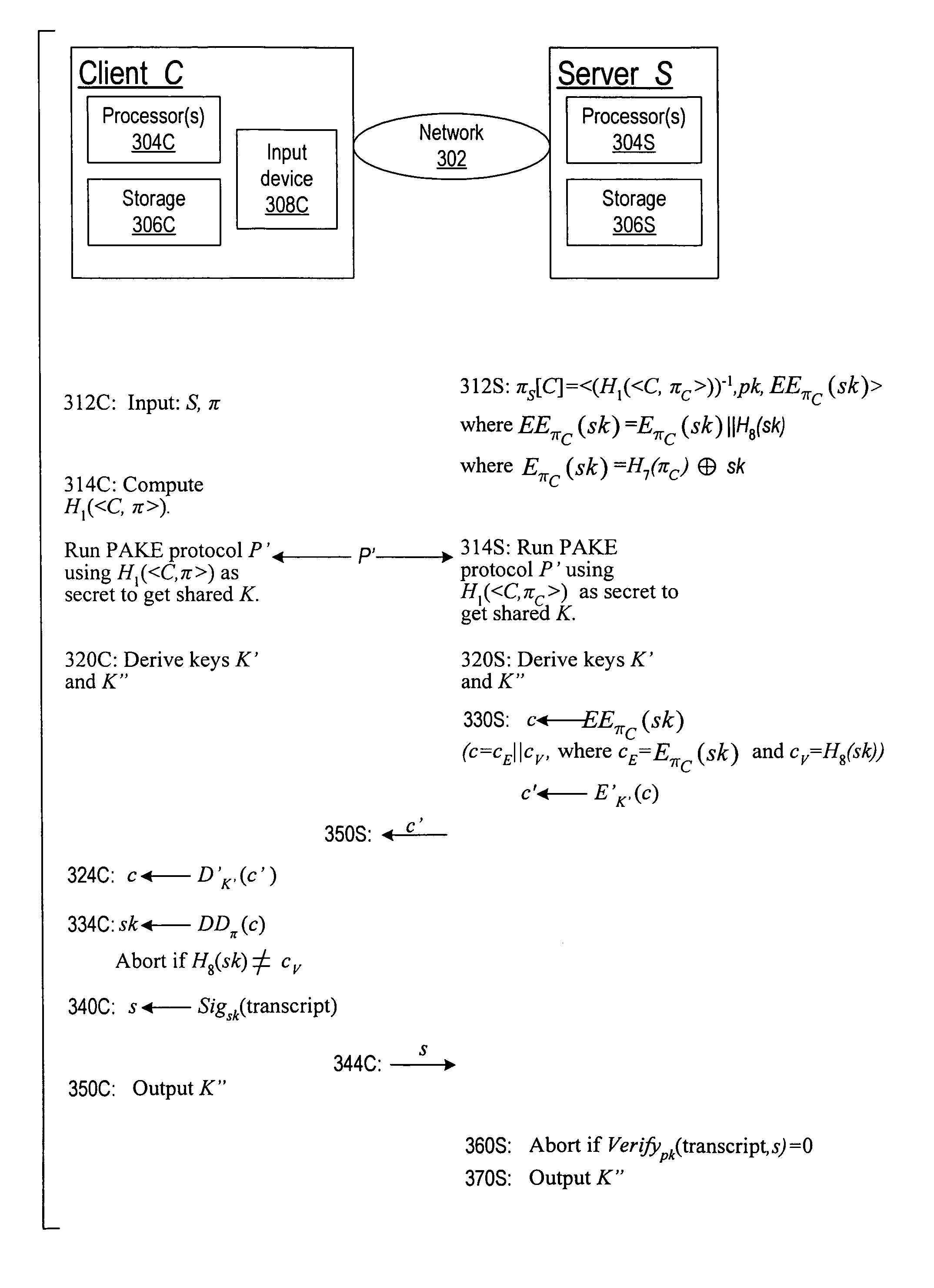
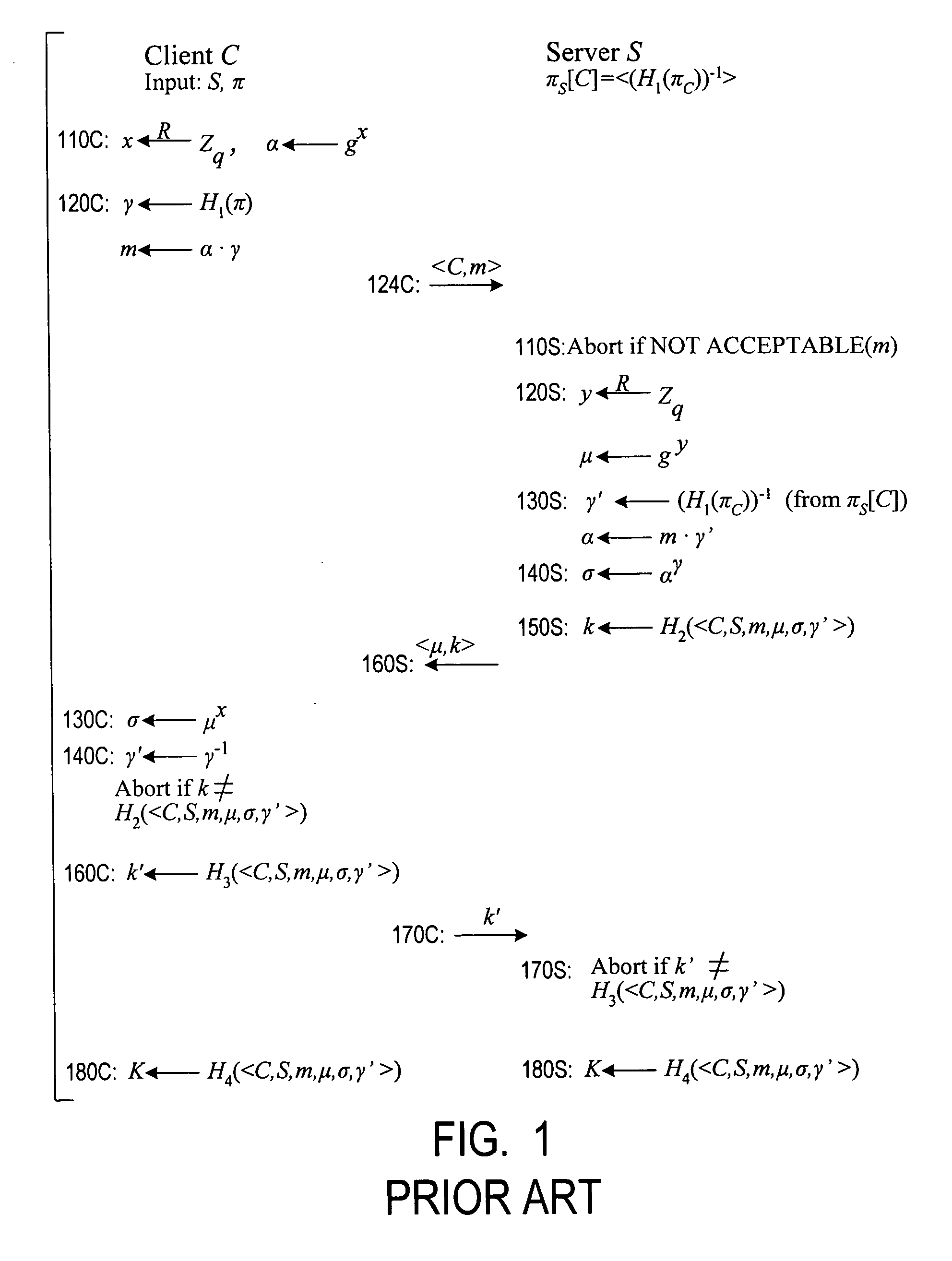
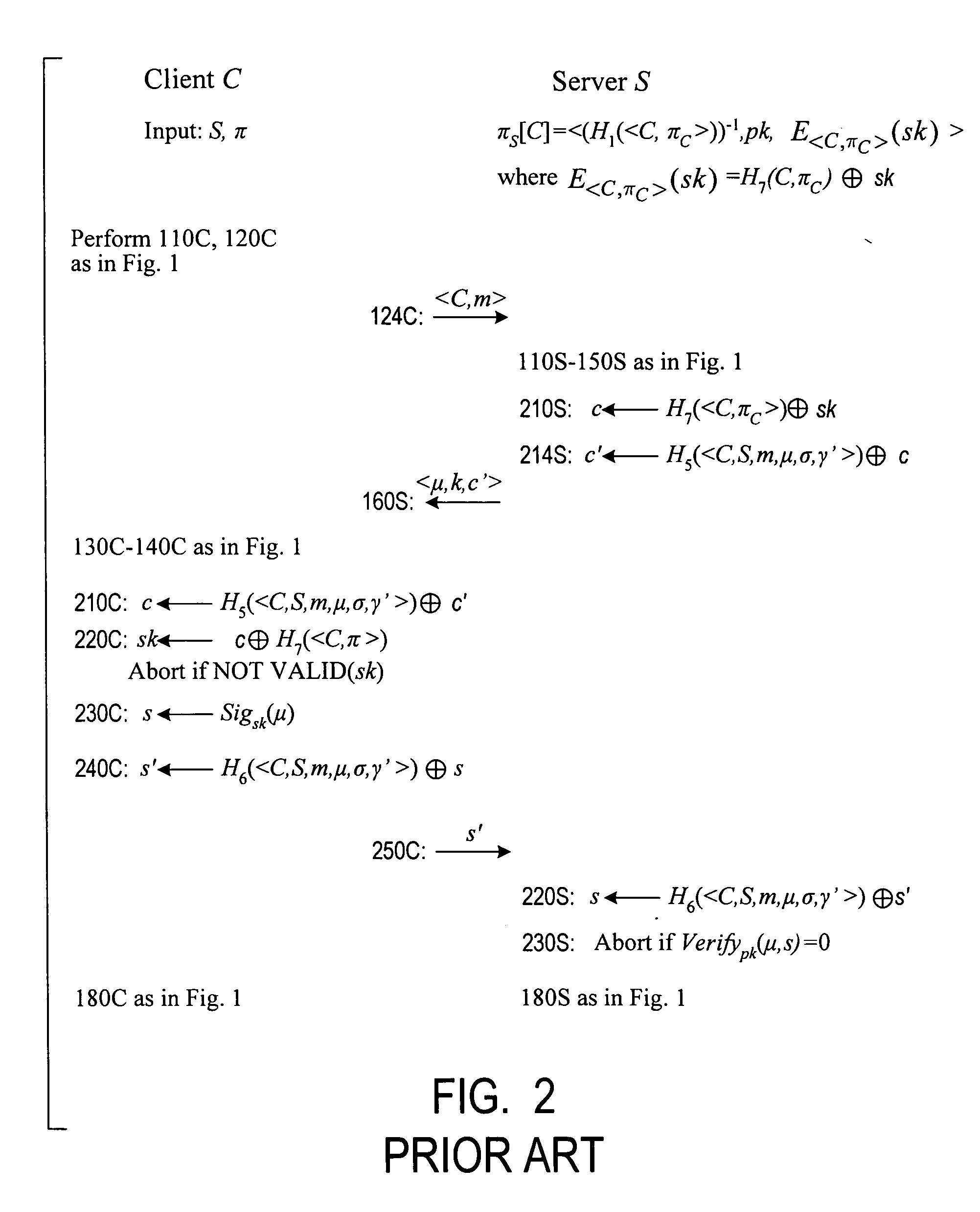
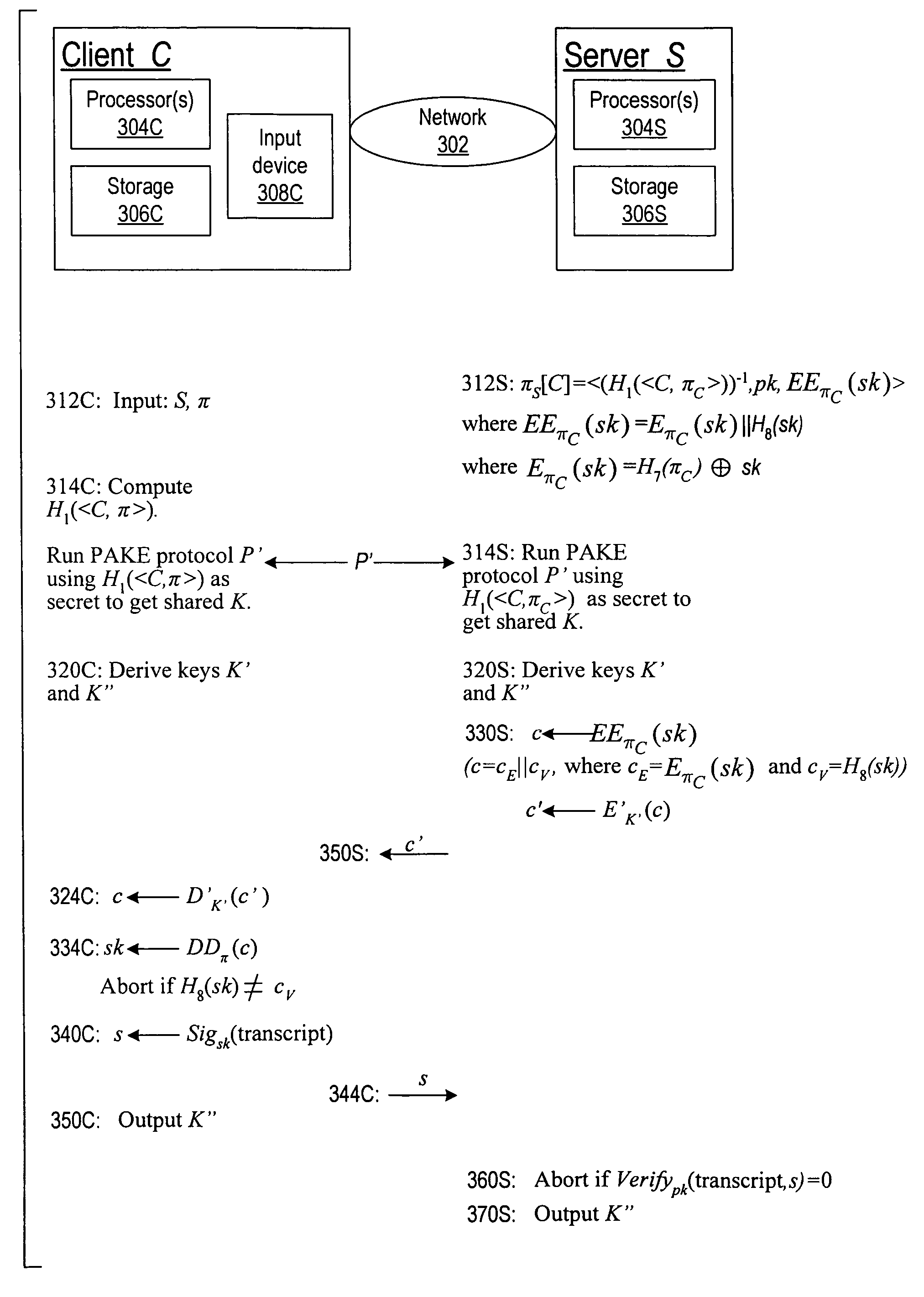
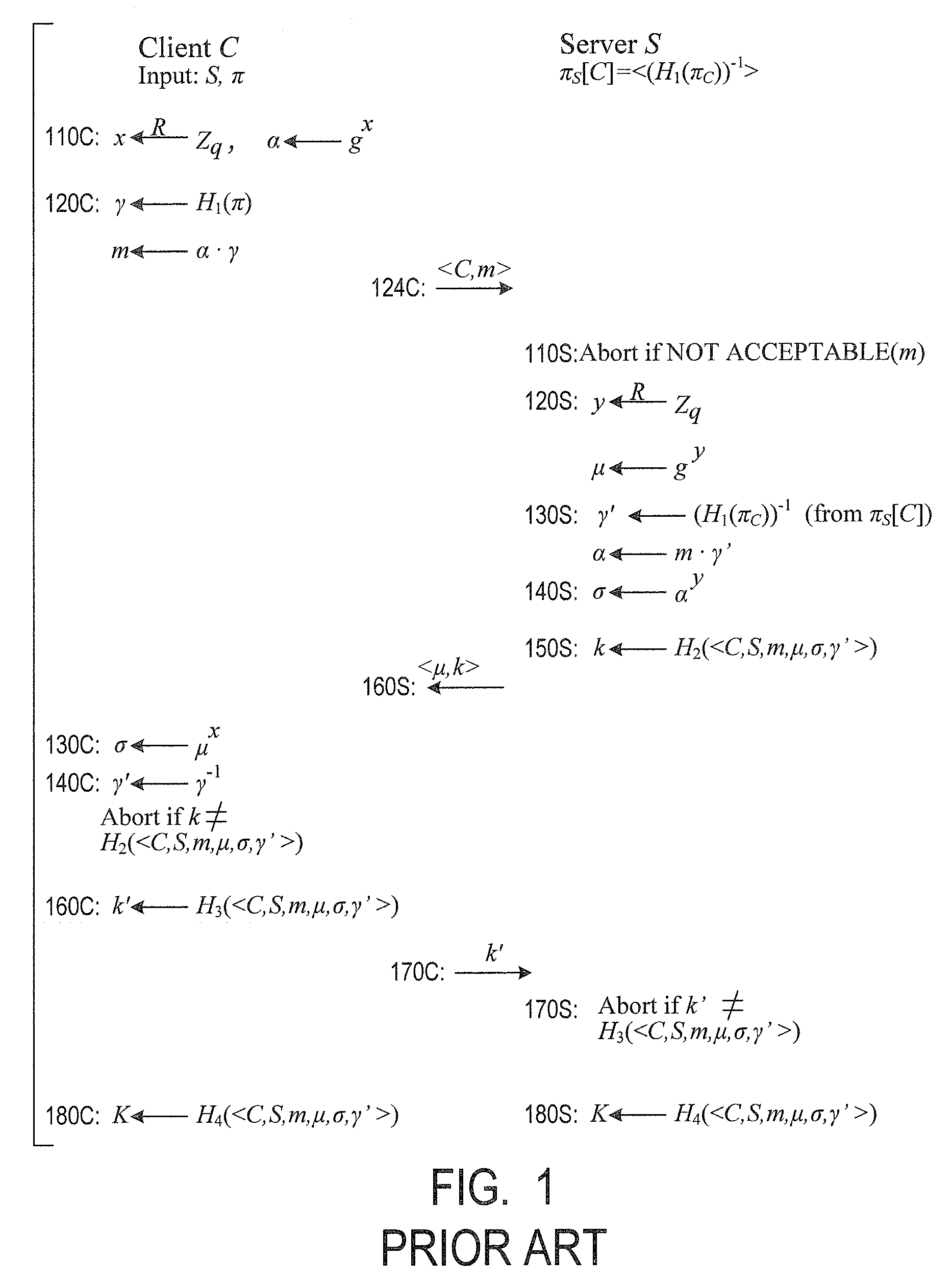
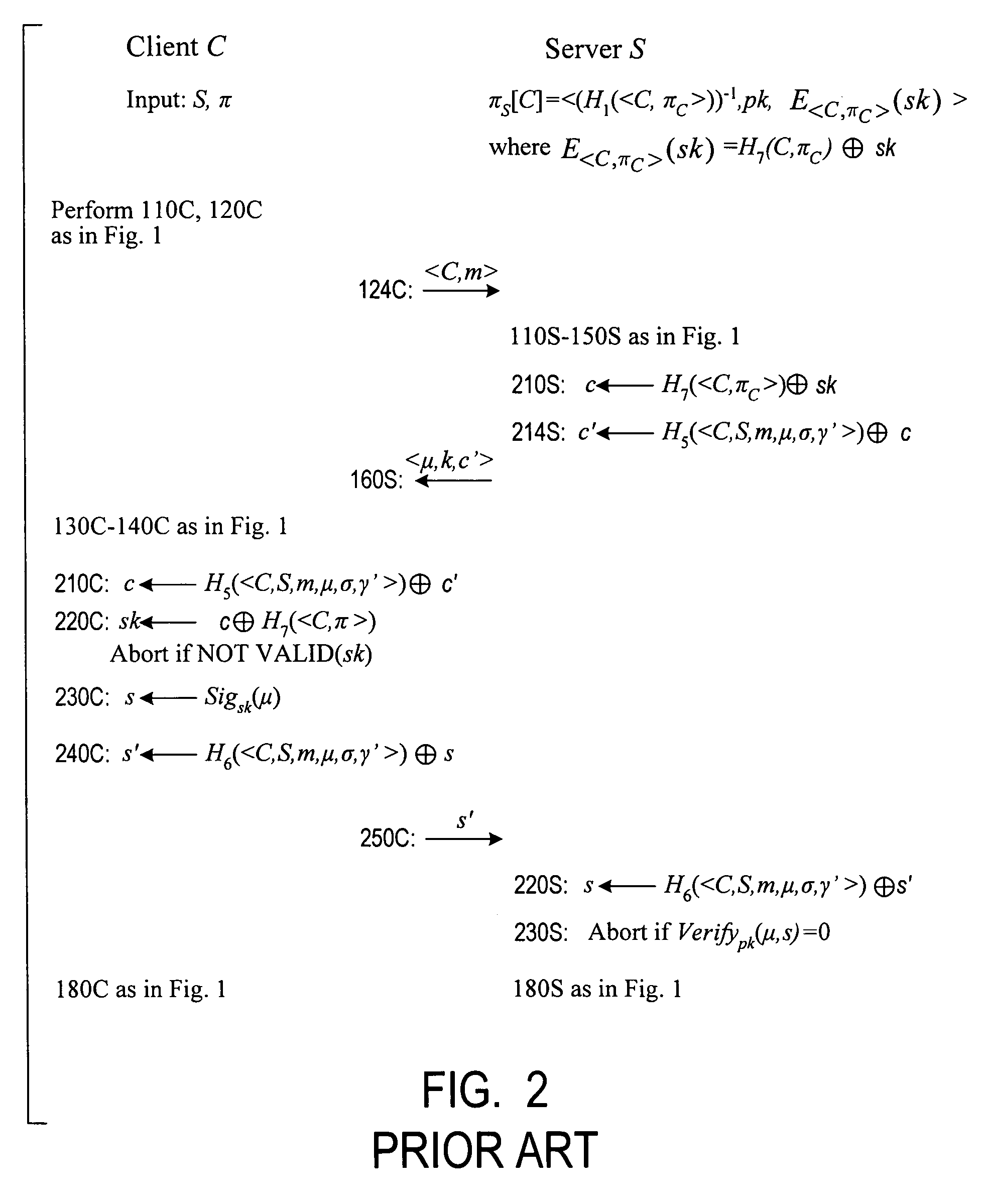
Cryptographic authentication, and/or establishment of shared cryptographic keys, using a signing key encrypted with a non-one-time-pad encryption, including (but not limited to) techniques with improved security against malleability attacks
InactiveUS20070067629A1Effective attackUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsOne-time passwordClient-side
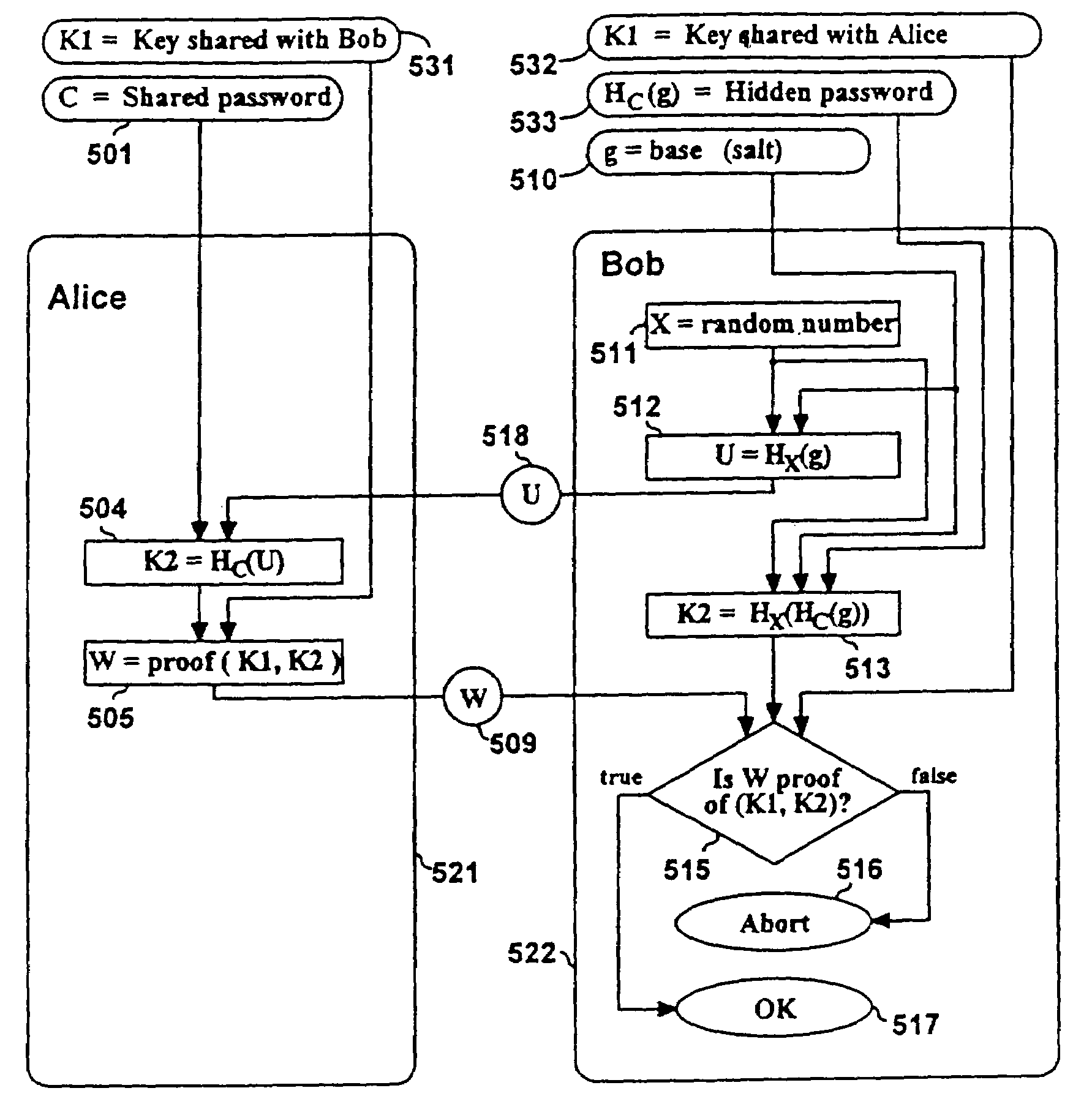
Using a password (π), a client (C) computes part (H1(<C,πC>) of the password verification information of a server (S), and together they use this information to authenticate each other and establish a cryptographic key (K′), possibly using a method resilient to offline dictionary attacks. Then over a secure channel based on that cryptographic key, the server sends an encryption (EE<C,π>(sk)) of a signing key (sk) to a signature scheme for which the server know a verification key (pk). The encryption is possibly non-malleable and / or includes a decryptable portion (E<C,π>(sk)) and a verification portion (H8(sk)) used to verify the decrypted value obtained by decrypting the decryptable portion. The signing key is based on the password and unknown to the server. The client obtains the signing key using the password, signs a message, and returns the signature to the server. The server verifies this signature using the verification key, hence getting additional proof that the client has knowledge of the password. The client and the server generate a shared secret key (K″), more secure than the password, for subsequent communication.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Cryptographic methods for remote authentication
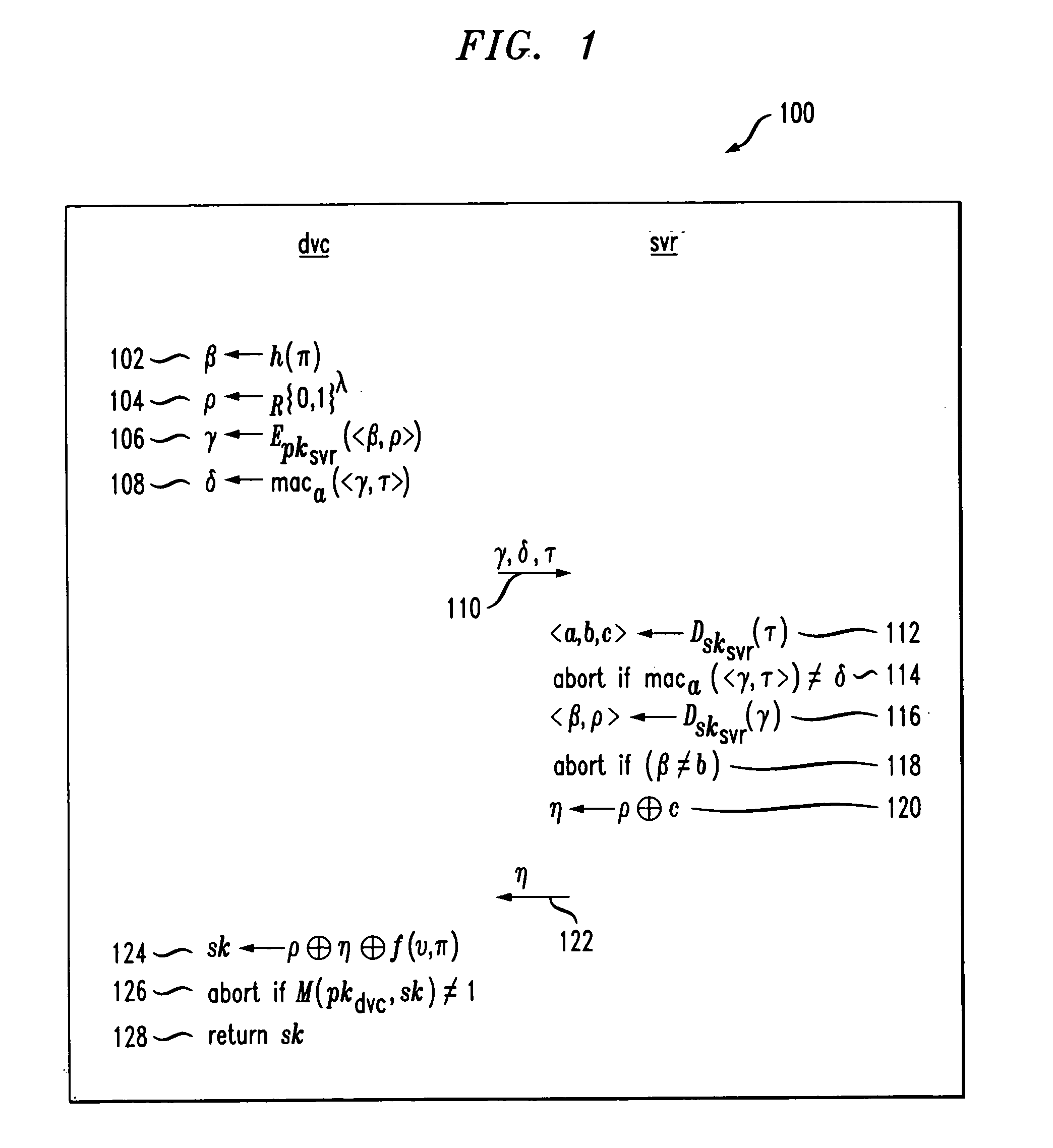
InactiveUS7010692B2Prevent replay attacksImprove the immunityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationAlice and BobKey exchange
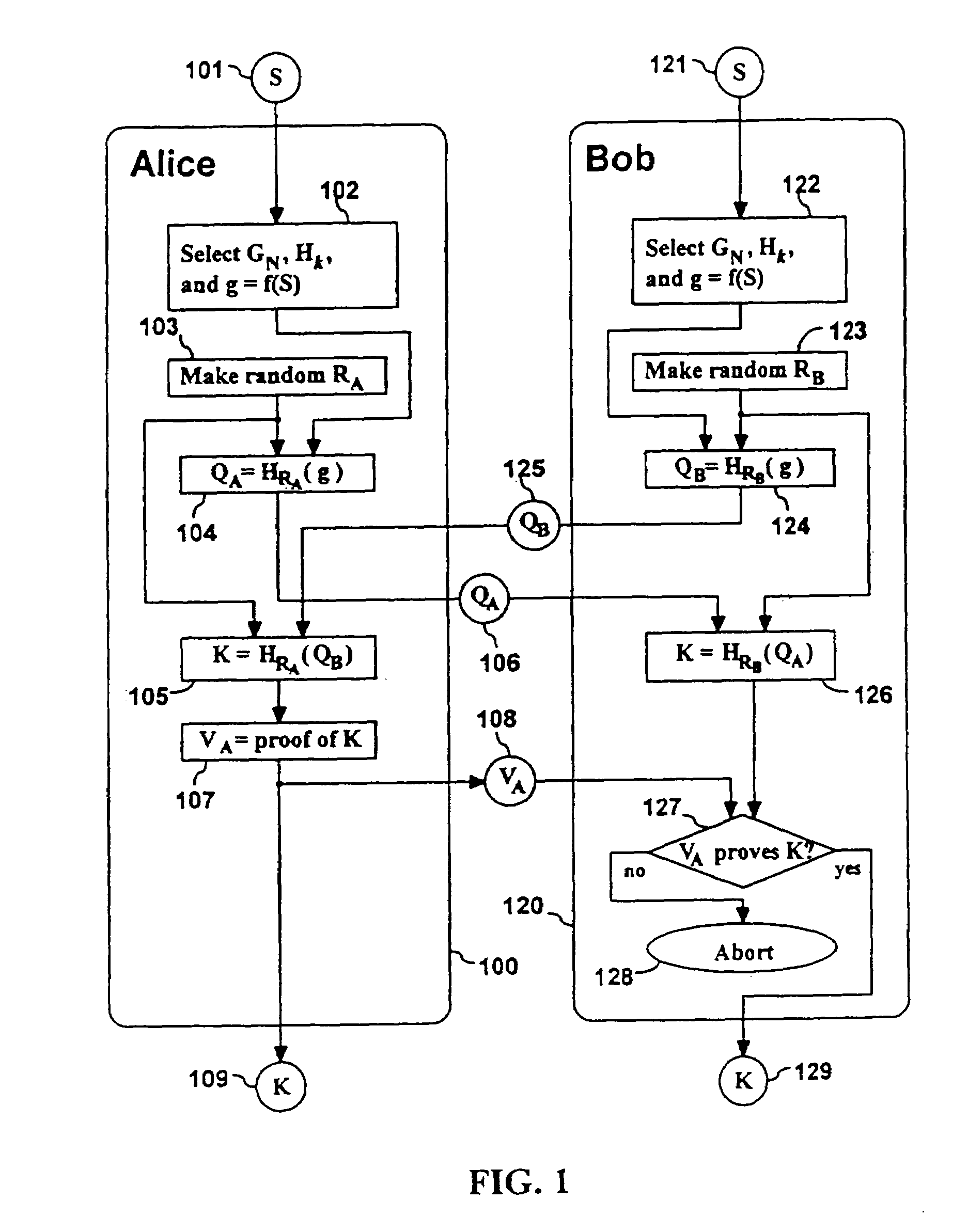
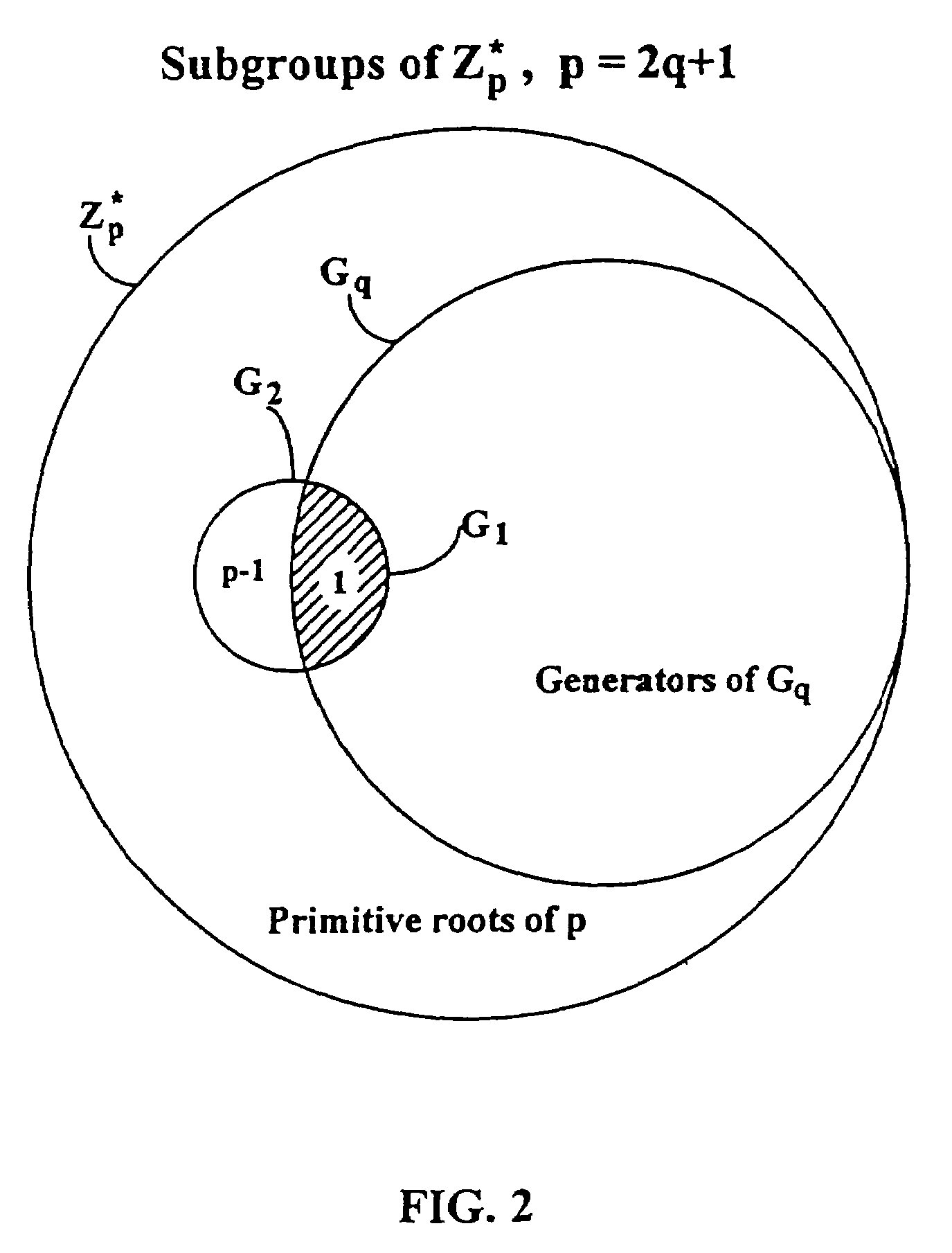
Methods are described for two parties to use a small shared secret (S) to mutually authenticate one another other over an insecure network. The methods are secure against off-line dictionary attack and incorporate an otherwise unauthenticated public key distribution system. One embodiment uses two computers Alice and Bob, and a Diffie-Hellman exponential key exchange in a large prime-order finite group. Both parties choose the same generator of the group (g) as a function of S. Alice chooses a random number RA, and sends gR<sub2>A < / sub2>to Bob. Bob chooses a random RB, sends gR<sub2>B < / sub2>to Alice. Both compute a shared key K=g(R<sub2>A< / sub2>R<sub2>B< / sub2>). Each party insures that K is a generator of the group, verifies that the other knows K, and then uses K as an authenticated key. Constraints are described to prevent passive and active attacks. An extension is described where Alice proves knowledge of S to Bob who knows only a one-way transformation of S. These methods establish a secure, authenticated network session using only an easily memorized password.
Owner:KINGLITE HLDG INC
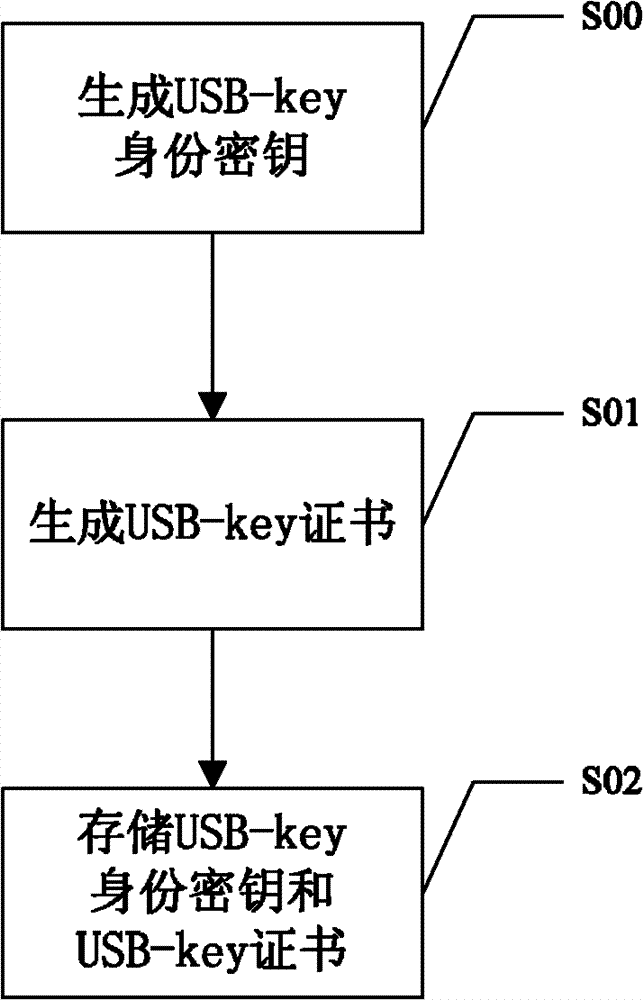
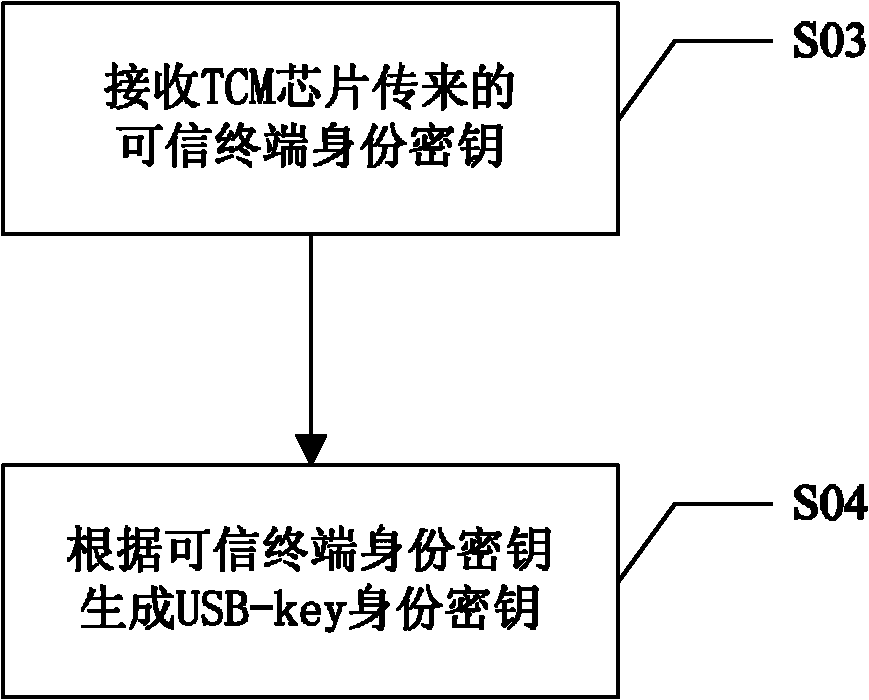
USB (universal serial bus)-key and application method thereof
ActiveCN102904719AImprove securityProtect against dictionary attacksKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPersonal identification numberUSB
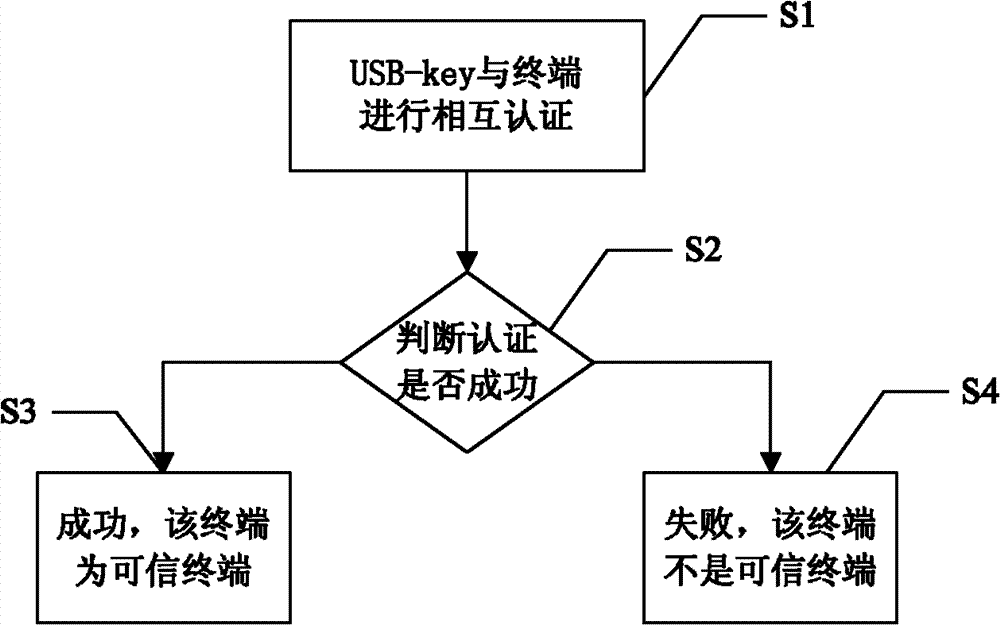
The invention discloses a USB (universal serial bus)-key and an application method thereof. The application method includes the following steps: performing mutual authentication between a USB-key and a terminal connected with the same; judging whether the authentication between the USB-key and the terminal succeeds or not; judging the terminal to be a trustable terminal on success so that the USB-key can work normally on the terminal; and judging the terminal to be an non-trustable terminal on failure so that the USB-key cannot be identified by the terminal. With the USB-key, an illegal user cannot use the USB-key on the non-trustable terminal if the USB-key of a user is lost, so that the illegal user has no chance to input a PIN (personal identification number) code on a present terminal, dictionary attack to the PIN code of the user from the illegal user can be prevented, and usage security of the USB-key for the user is improved.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for providing networked cryptographic devices resilient to capture
ActiveUS7149311B2Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsTamper resistanceDictionary attack
Techniques are provided by which a device that performs private key operations (e.g., signatures or decryptions) in networked applications, and whose local private key is activated with, for example, a password or PIN, can be immunized to offline dictionary attacks in case the device is captured. The techniques do not assume tamper resistance of the device, but rather exploit the networked nature of the device, in that the device's private key operations are performed using a simple interaction with a remote server. This server, however, is untrusted, i.e., its compromise does not reduce the security of the device's private key unless the device is also captured, and need not have a prior relationship with the device. Techniques are also provided for supporting key disabling, by which the rightful owner of a stolen device can disable the device's private key even if the attacker already knows the user's password.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
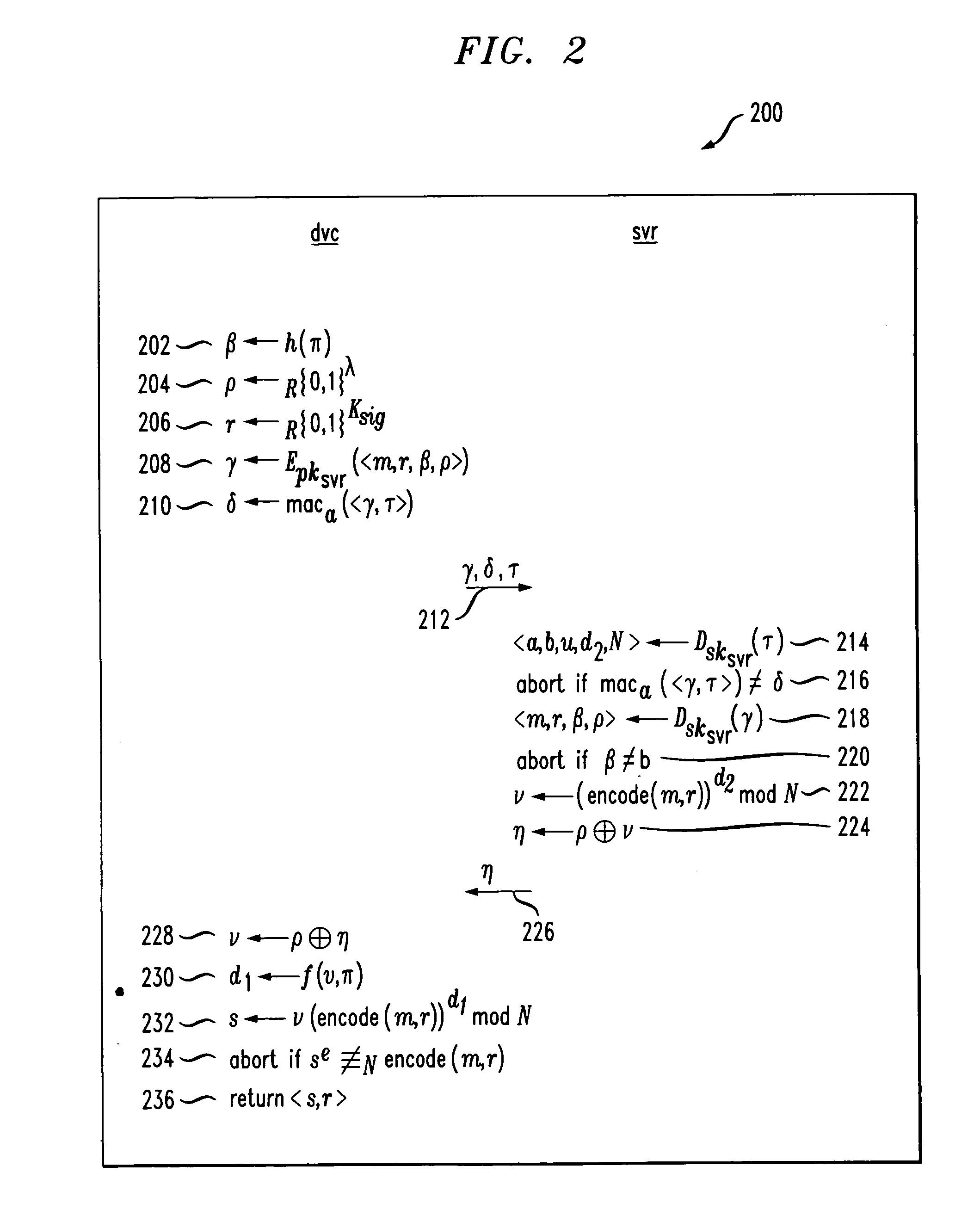
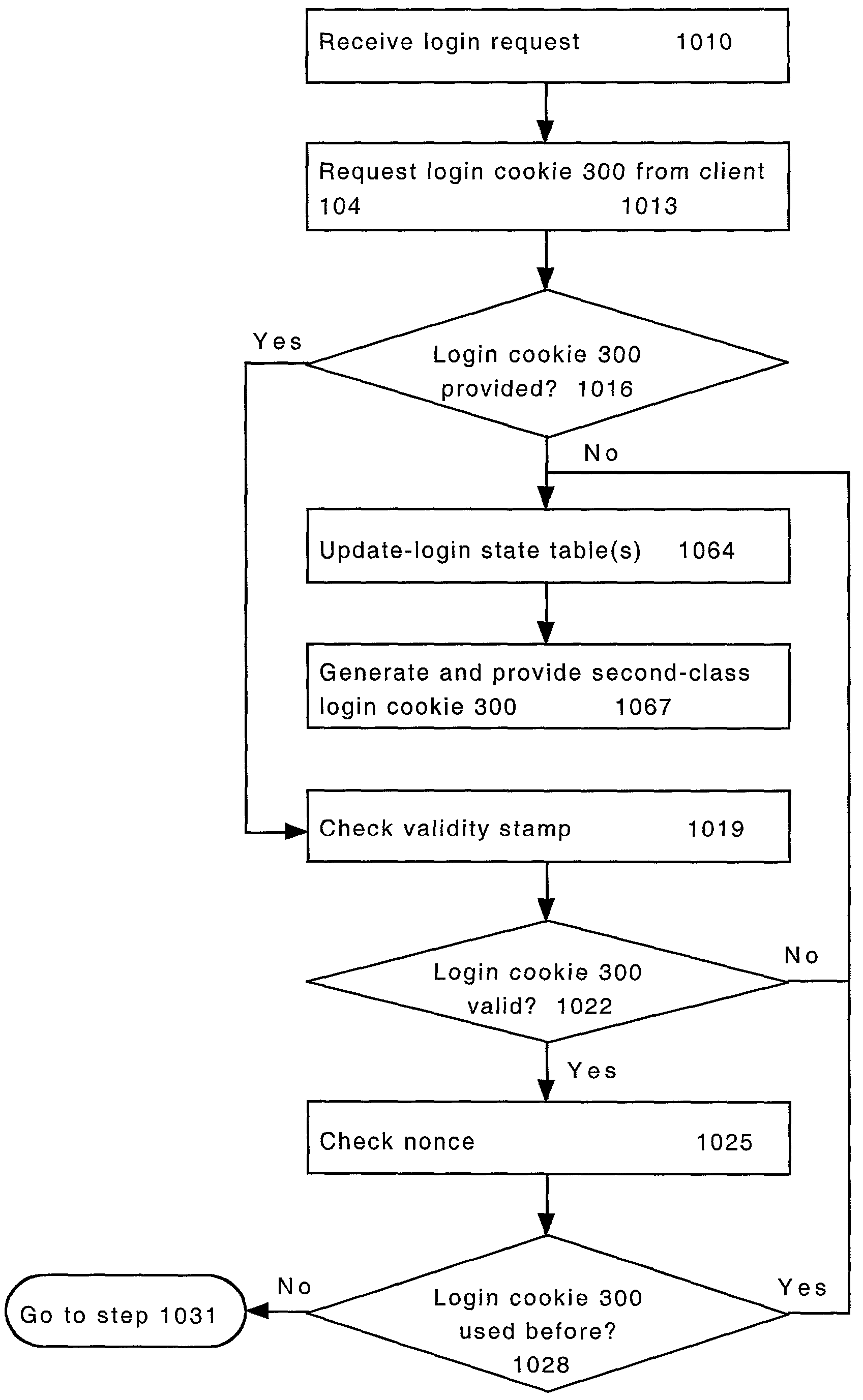
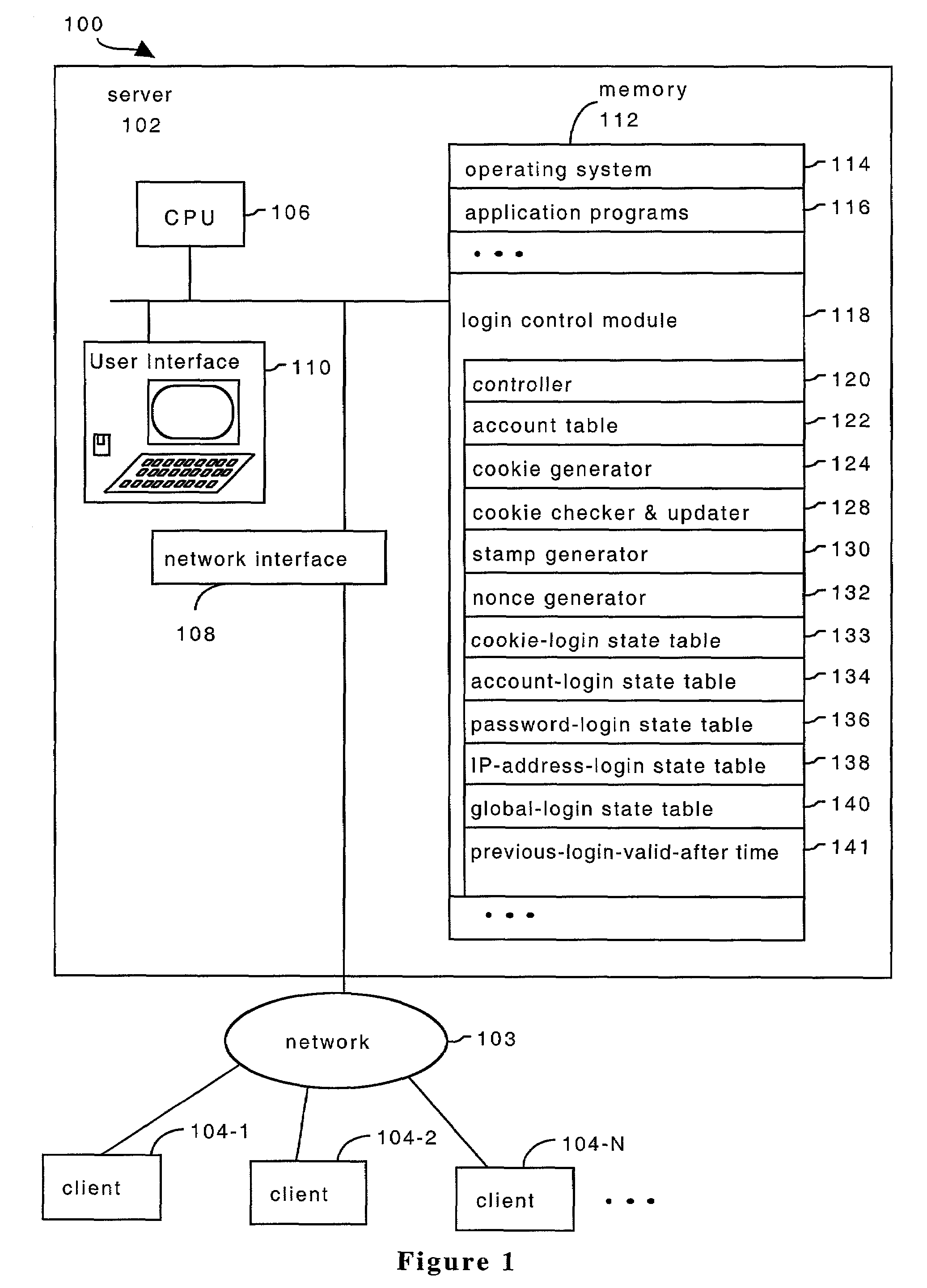
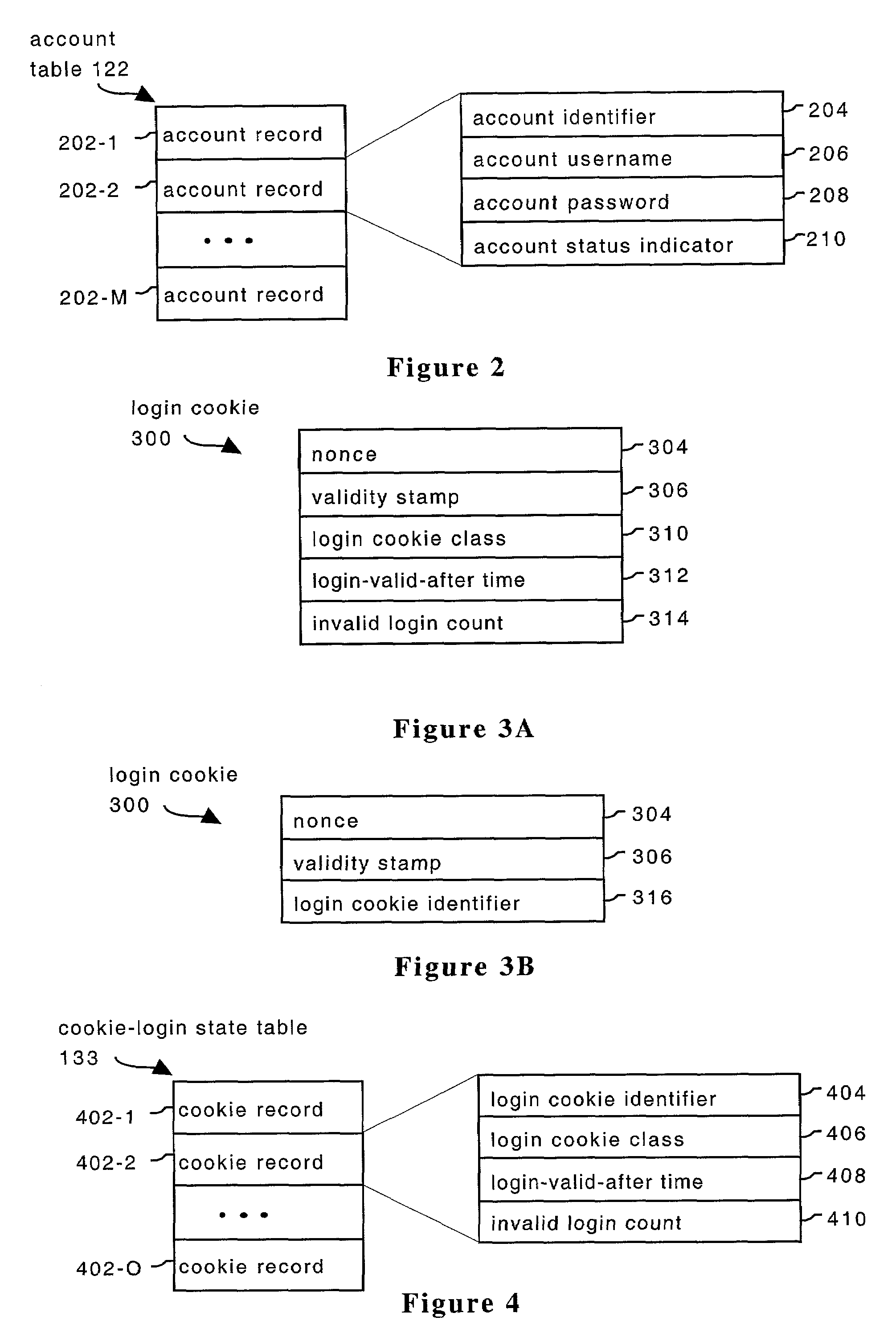
System and method for providing multi-class processing of login requests
InactiveUS7421733B2Minimize their effectivenessDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer scienceDictionary attack
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Password based threshold token generation
ActiveUS20210243026A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyEngineering
Embodiments disclosed herein are directed to methods and systems of password-based threshold authentication, which distributes the role of an authentication server among multiple servers. Any t servers can collectively verify passwords and generate authentication tokens, while no t−1 servers can forge a valid token or mount offline dictionary attacks.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Verifiable semantic security multi-keyword search method in cloud storage
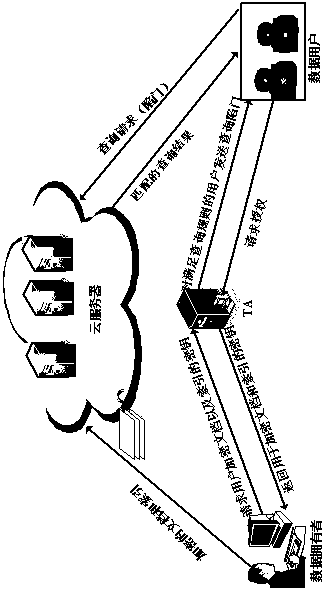
ActiveCN109450935AImplement join queriesAvoid join queriesPublic key for secure communicationWeb data queryingUser verificationPredicate encryption
The invention relates to a verifiable semantic security multi-keyword search method in cloud storage. The method comprises the following six steps: initializing the system, establishing a shared key between a TA and a data owner, encrypting the data document and its index by the data owner, generating a query trapdoor by the TA, performing security query by a cloud server, and querying a user verification query result. The method realizes the semantic security multi-keyword connection query of the encrypted index by inner product predicate encryption and dual system encryption, and implementsfine-grained authorization and overcomes the shortcomings of the traditional "0" or "1" authorization model by introducing a trusted TA. The TA verifies the query user's query qualification and sendsa query trapdoor for the authenticated user, which solves the problem that the data owner needs to be online always. The method, which can achieve fine-grained authorization, resist dictionary attacks, and verify the correctness of query results, is a semantic security multi-keyword search method.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of creating password list for remote authentication to services
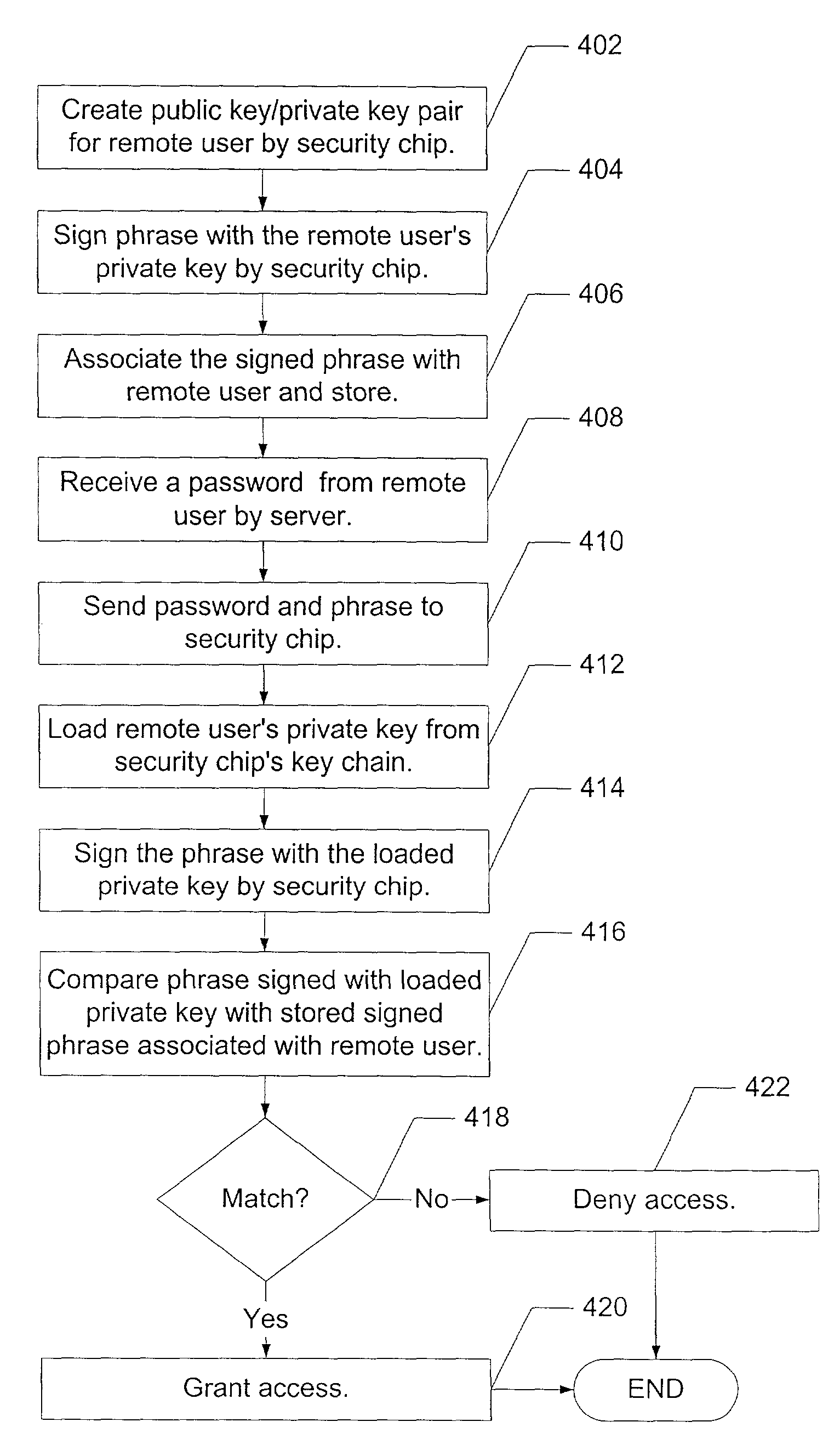
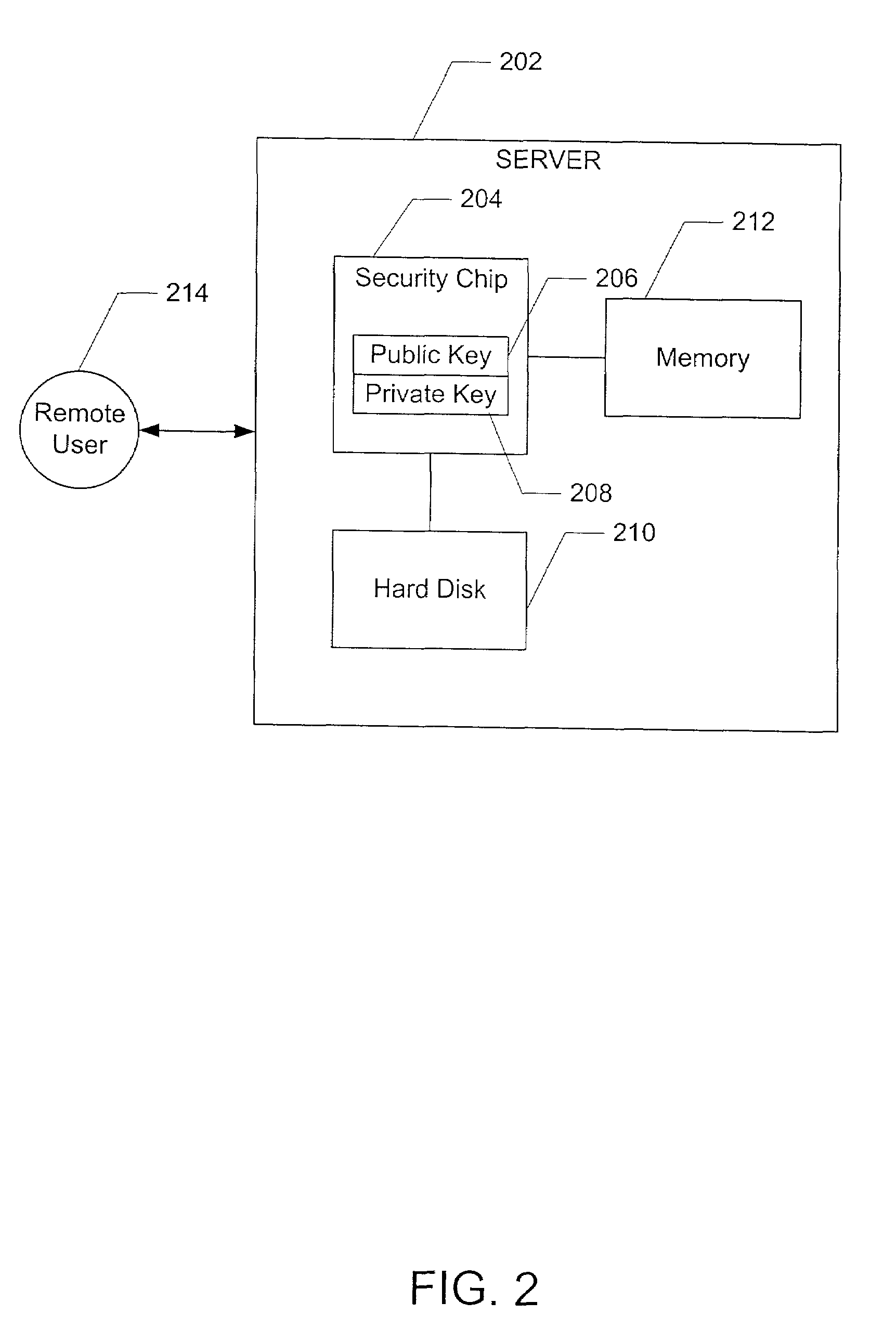
InactiveUS7194762B2Improve securityProvide securityKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageDictionary attackPhrase
A method for providing security in password-based access to computer networks, the network including a server and a remote user, includes: signing a phrase by a security chip of the server using an encryption key; associating the signed phrase with the remote user; signing the phrase with an encryption key obtained by the security chip when a request for access to the computer network is received from the remote user; comparing the phrase signed with the obtained encryption key with the signed phrase associated with the remote user; and granting access to the remote user if the phrase signed with the obtained encryption key is the same as the stored signed phrase associated with the remote user. The use of the encryption key protects against “dictionary attacks”. Use of the security chip protects against offline attacks. These provide greater security for the computer network.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Cryptographic authentication, and/or establishment of shared cryptographic keys, using a signing key encrypted with a non-one-time-pad encryption, including (but not limited to) techniques with improved security against malleability attacks
InactiveUS7814320B2Synchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesMultiple keys/algorithms usageClient-sideOne-time password
Using a password (π), a client (C) computes part (H1(<C,πC>) of the password verification information of a server (S), and together they use this information to authenticate each other and establish a cryptographic key (K′), possibly using a method resilient to offline dictionary attacks. Then over a secure channel based on that cryptographic key, the server sends an encryption (EE<C,π>(sk)) of a signing key (sk) to a signature scheme for which the server know a verification key (pk). The encryption is possibly non-malleable and / or includes a decryptable portion (E<C,π>(sk)) and a verification portion (H8(sk)) used to verify the decrypted value obtained by decrypting the decryptable portion. The signing key is based on the password and unknown to the server. The client obtains the signing key using the password, signs a message, and returns the signature to the server. The server verifies this signature using the verification key, hence getting additional proof that the client has knowledge of the password. The client and the server generate a shared secret key (K″), more secure than the password, for subsequent communication.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Point of sale (POS) personal identification number (PIN) security
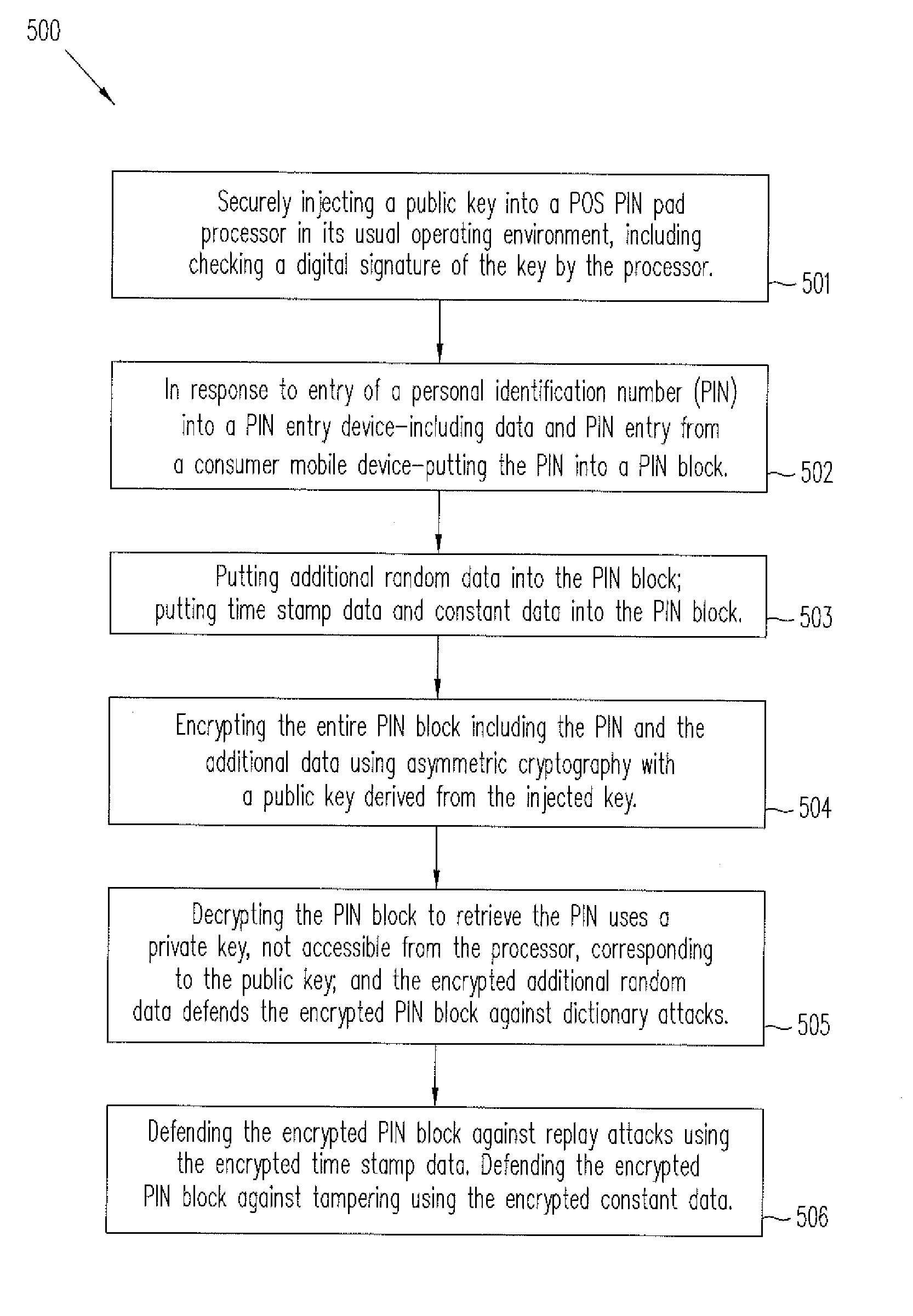
ActiveUS8819428B2Acutation objectsUser identity/authority verificationPersonal identification numberEngineering
A key is securely injected into a POS PIN pad processor in its usual operating environment. In response to entry of a personal identification number (PIN) into a PIN pad, the processor puts the PIN into a PIN block; puts additional random data into the PIN block; and encrypts the entire PIN block using asymmetric cryptography with a public key derived from the injected key residing in the PIN pad processor. The corresponding private key may be held securely and secretly by an acquirer processor for decrypting the PIN block to retrieve the PIN. The encrypted random data defends the PIN against dictionary attacks. Time stamp data and constant data encrypted with the PIN block enables a defense of the PIN against replay attacks and tampering. The method may also include accepting the PIN from a mobile phone in communication with the processor.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
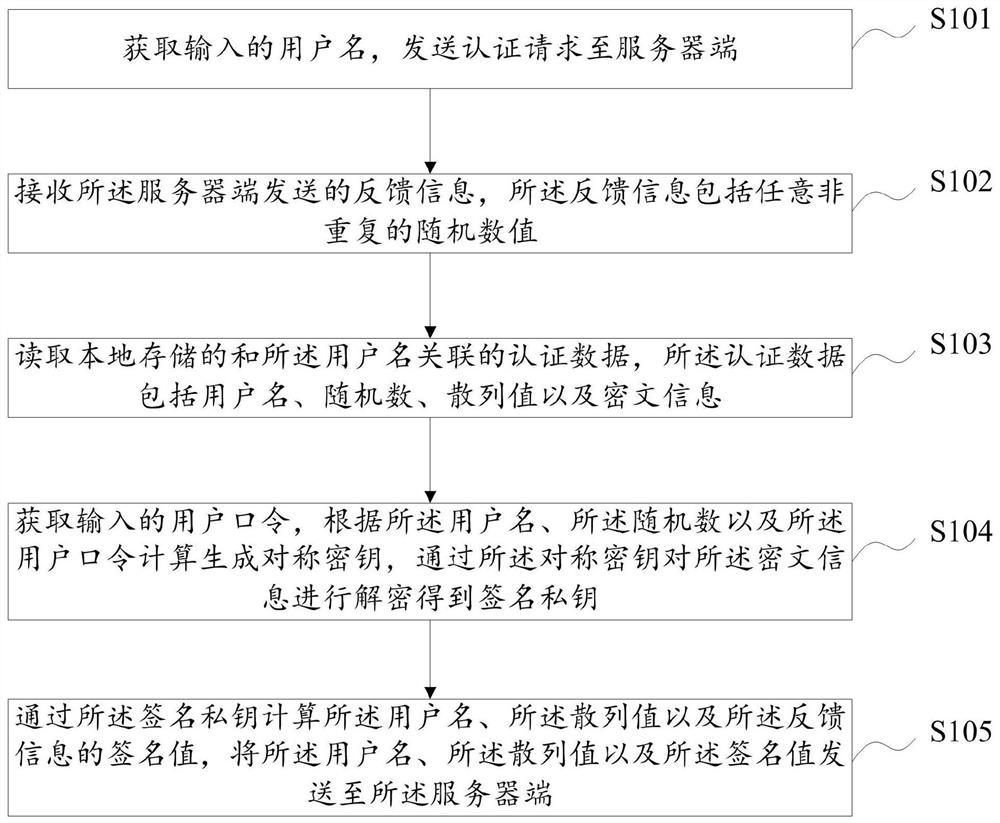
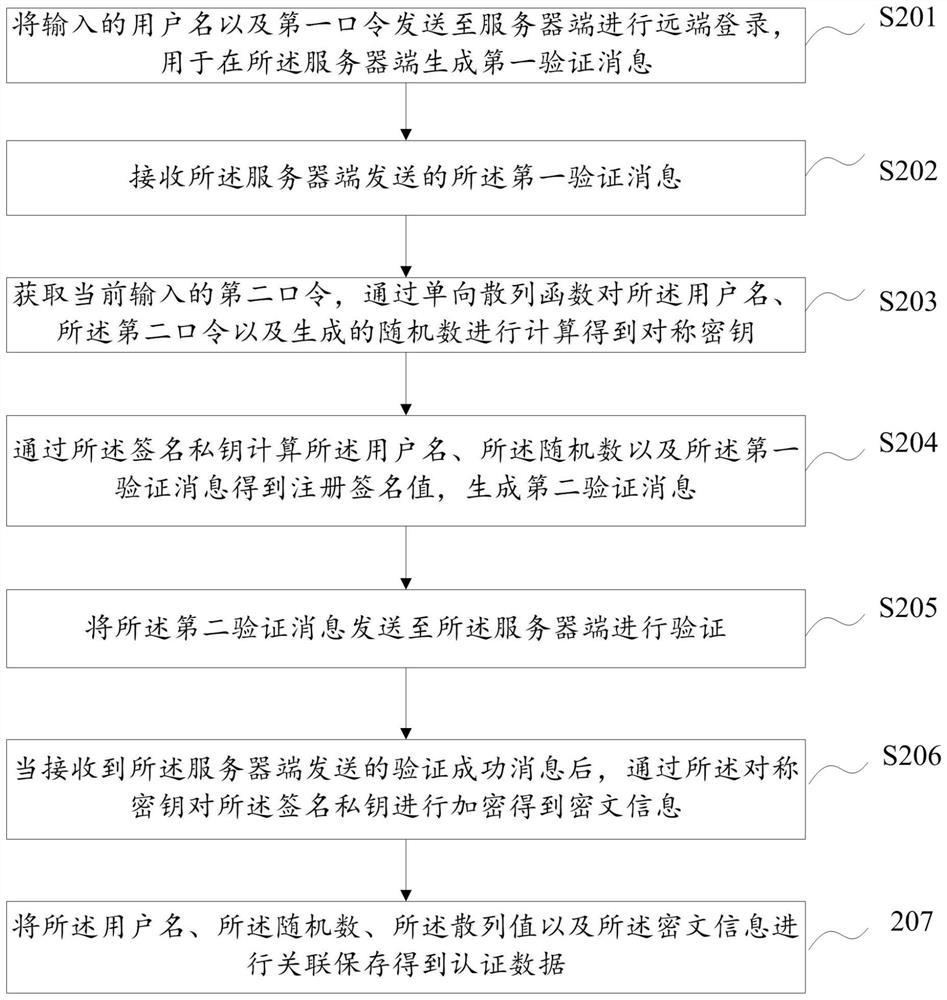
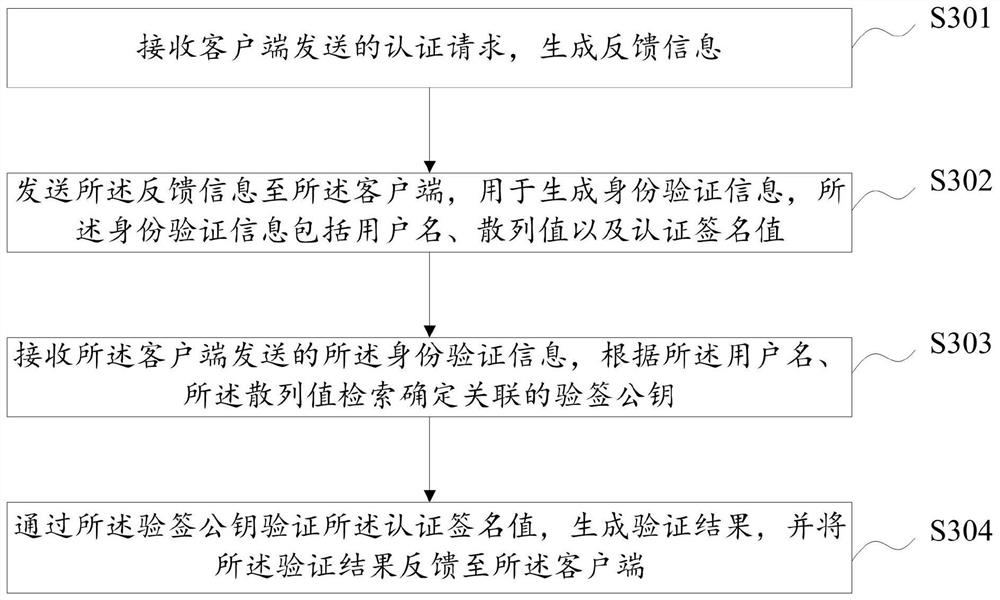
User identity authentication method, device and equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112637131APrevent replay attacksLow costUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextAttack
The embodiment of the invention discloses a user identity authentication method, device and equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an input user name, and sending an authentication request to a server; receiving feedback information sent by the server side; reading locally stored authentication data associated with the user name; obtaining an input user password, calculating and generating a symmetric key according to the user name, the random number and the user password, and decrypting the ciphertext information through the symmetric key to obtain a signature private key; and calculating the user name, the hash value and the signature value of the feedback information through the signature private key, and sending the user name, the hash value and the signature value of the feedback information to the server. In the scheme, the eavesdropping attack, the replay attack and the dictionary attack of the user password can be effectively prevented, no extra hardware equipment is added, and the cost overhead is reduced.
Owner:BIGO TECH PTE LTD
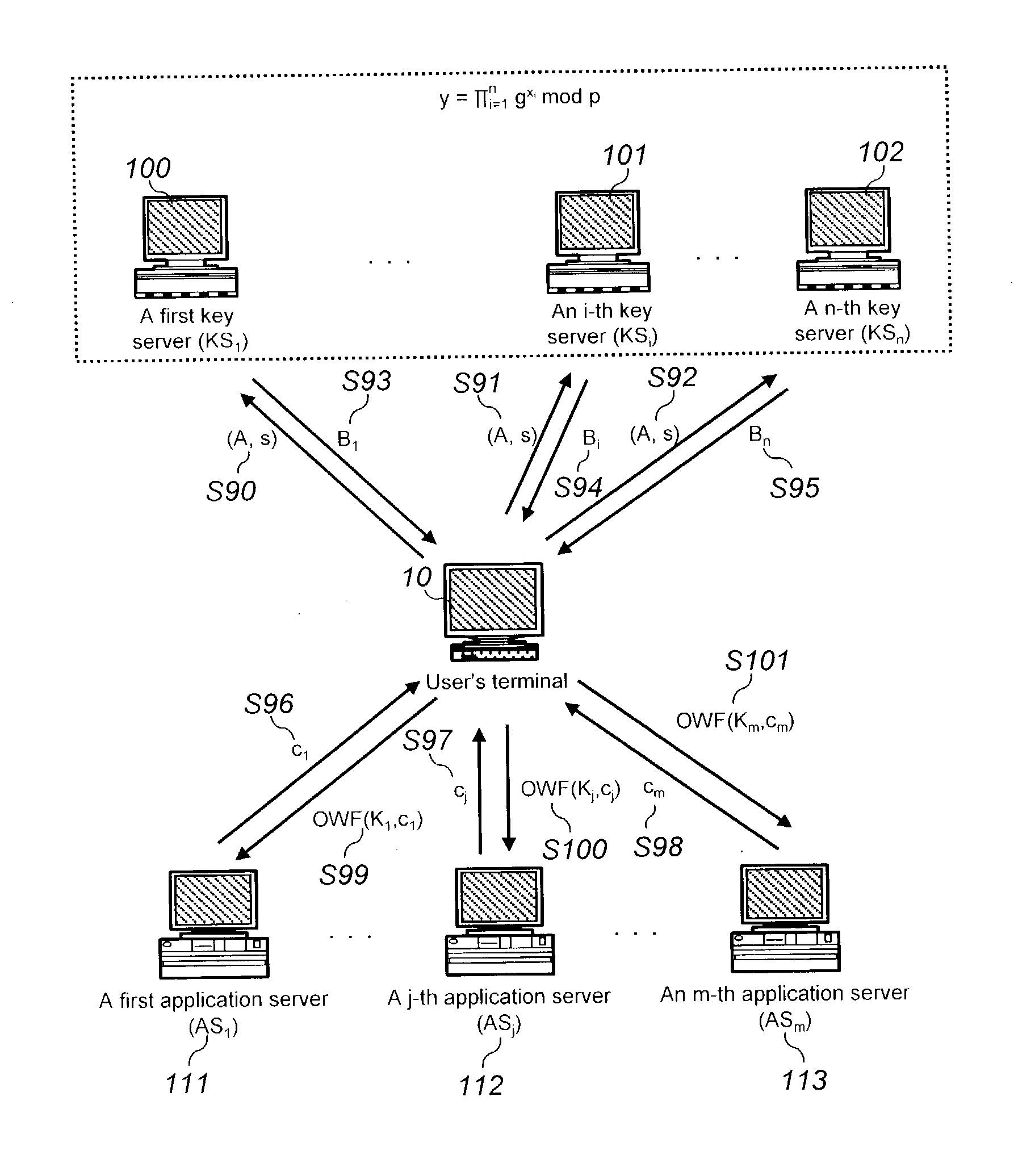
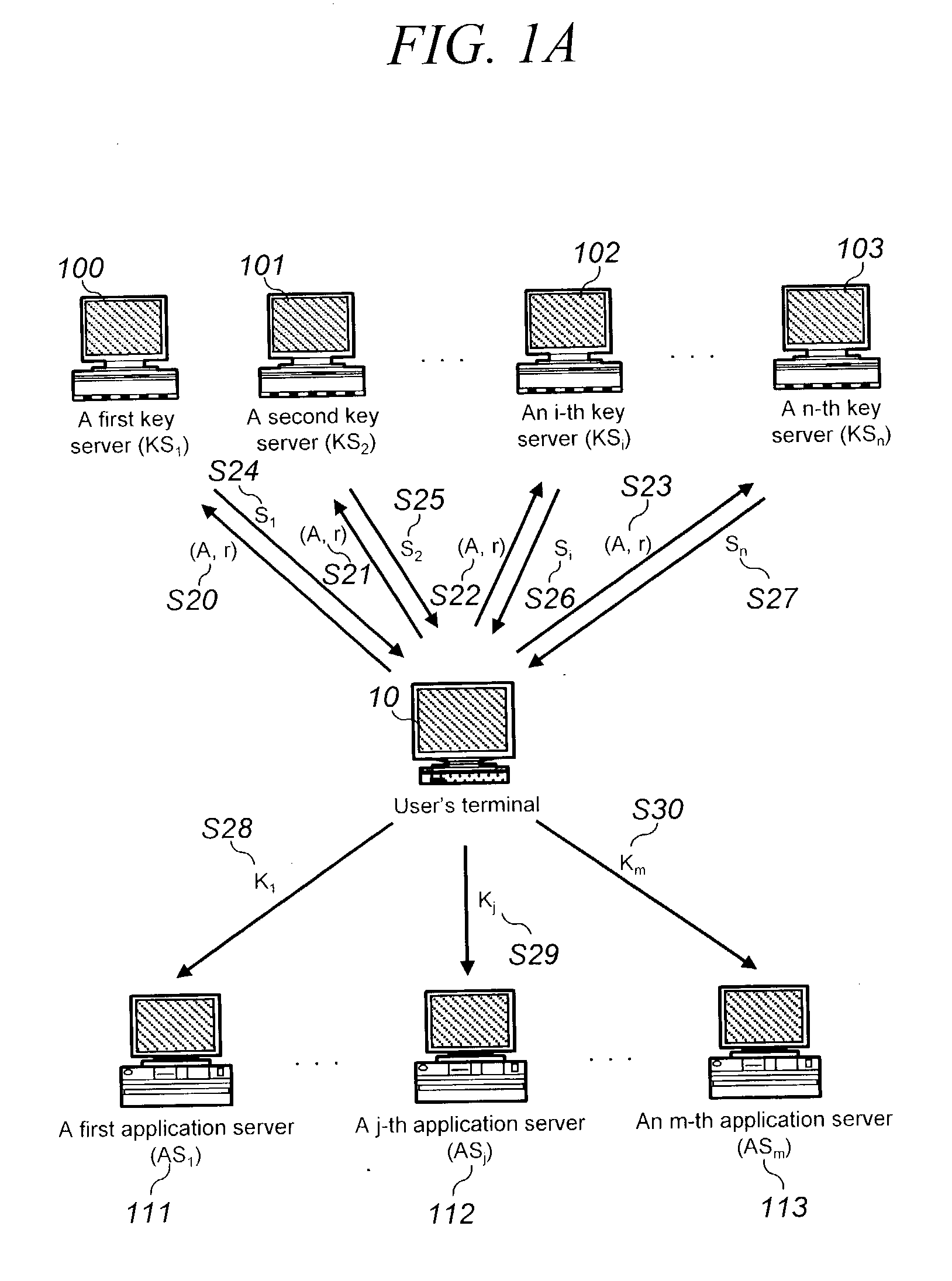
Password-based authentication protocol secure against server's dictionary attack
InactiveUS20030163698A1Improve computing efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey serverInternet privacy
The present invention discloses a password-based authentication protocol wherein an authentication key is generated with an individual private key of the key servers and a public key of the group of the key servers, which do not store the user's password, and thereby it is possible to protect against a camouflaging server's dictionary attack for accessing the user's password.
Owner:KOREA INTERNET & SECURITY AGENCY
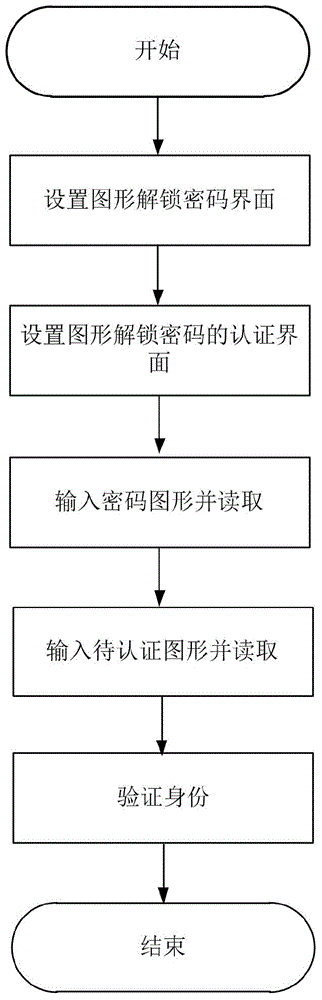
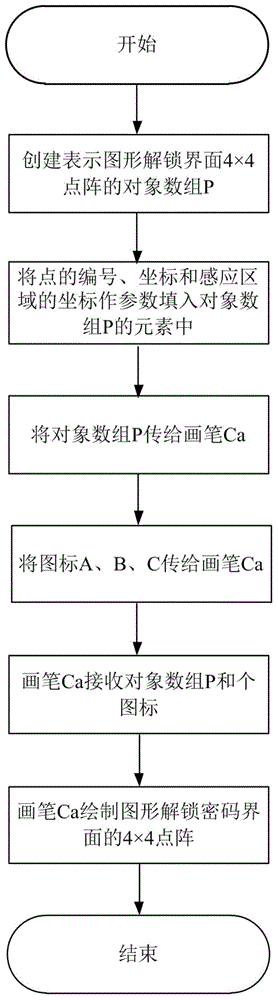
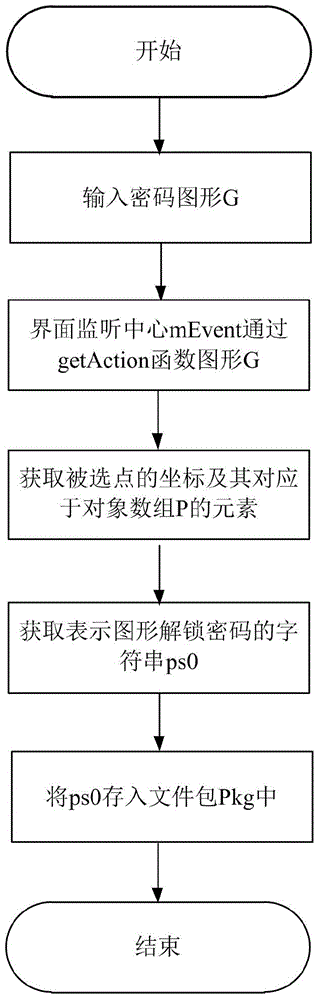
Identity authentication improving method for pattern puzzle password in Android system
ActiveCN104917773ALarge password spaceImprove securityDigital data authenticationTransmissionGraphicsBrute force
The invention discloses an identity authentication improving method for a pattern puzzle password in an Android system, and mainly aims to solve the problem of potential safety hazard due to revealing of the use habit of a user in practical application of existing Android pattern puzzle. An implementation scheme comprises the following steps: (1) setting a pattern puzzle password interface; (2) setting an authentication interface of the pattern puzzle password; (3) inputting a password pattern on the pattern puzzle password interface, and reading the character string representation form of the password pattern; (4) inputting a pattern to be authenticated on the pattern puzzle password interface or the authentication interface of the pattern puzzle password, and reading the character string representation form of the pattern to be authenticated; and (5) comparing whether or not the character string expression ways of the pattern to be authenticated and the password pattern are consistent in order to verify the identity. Through adoption of the identity authentication improving method, the password space is enlarged on the basis of the existing Android pattern puzzle; the security is enhanced; and the defense capability specific to dictionary attacks and brute force attacks is enhanced. The identity authentication improving method can be applied to identity authentication of graphical equipment such as smart phones.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for delegation of cryptographic servers for capture-resilient devices
InactiveUS7373499B2Remove threatKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDictionary attackCipher
Improved cryptographic techniques are provided by which a device that performs private key operations (e.g., signatures and / or decryptions), and whose private key operations are protected by a password, is immunized against offline dictionary attacks in case of capture by forcing the device to confirm a password guess with a designated entity or party in order to perform a private key operation, and by which the initiating device may dynamically delegate the password-checking function (i.e., confirmation of the password guess) from the originally designated entity or party to another designated entity or party.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
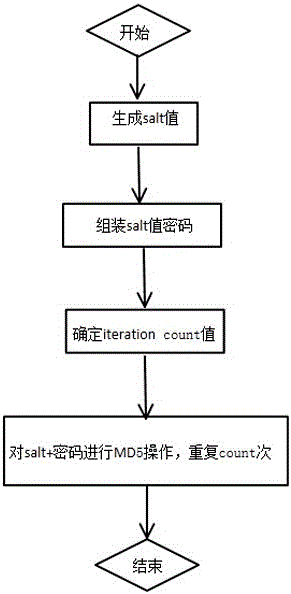
Method for encrypting SSR password
InactiveCN105959099APrevent brute forceImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesBrute forceDictionary attack
The invention discloses a method for implementing SSR password encryption. The method uses two methods of salt value encryption and iteration count encryption. The salt value encryption refers to adding a salt value before the user password. This value is randomly generated by the system. Only the system knows, and then perform MD5 encryption on the combination of the salt value and the password; the iteration count algorithm is an iterative digest algorithm, and continues to generate the digest repeatedly for the first generated digest, which is to perform count times of MD5 operations. The method of the invention can effectively prevent hackers from brute force cracking, Birthday attacks and dictionary attacks, greatly improves the security of password encryption, and the simple encryption algorithm greatly improves the security of SSR.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
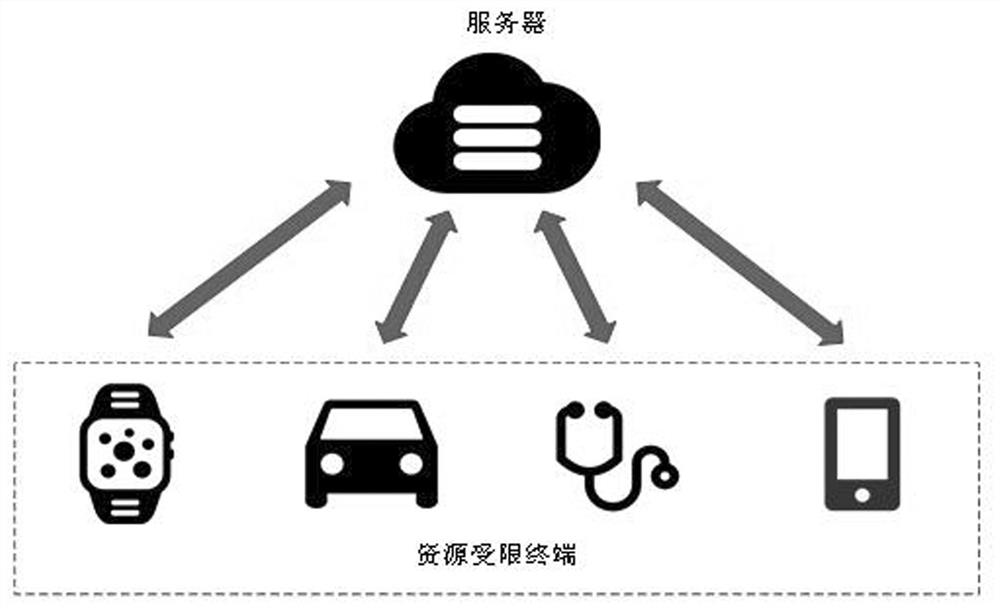
Lightweight identity authentication key negotiation method for resource-constrained terminal
ActiveCN113572765ATrue and valid identityPrevent malicious attacksKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey sizeProtocol design
The invention discloses a lightweight identity authentication key agreement protocol for a resource-constrained terminal. According to the method, a set of identity authentication and session key agreement service is provided between a resource-constrained terminal and a server. The method can ensure that the identities of the resource-limited terminal and the server are real and effective, and malicious attacks are avoided. The scheme comprises four stages: a registration stage, a login and authentication stage, a password modification stage and an intelligent card revocation stage. According to the method, an elliptic curve algorithm is introduced to encrypt key data in a login authentication process. A one-way Hash algorithm is introduced in the protocol design process, the risk of data plaintext transmission leakage is avoided on the basis that the intelligent card and password double factors serve as important links of identity authentication, and security vulnerabilities such as intelligent card loss attacks and offline dictionary attacks are resisted. Compared with other key negotiation protocols, the protocol is small in key size, system parameters and storage space, high in operation speed and suitable for terminal equipment with limited computing resources and storage resources.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH +1
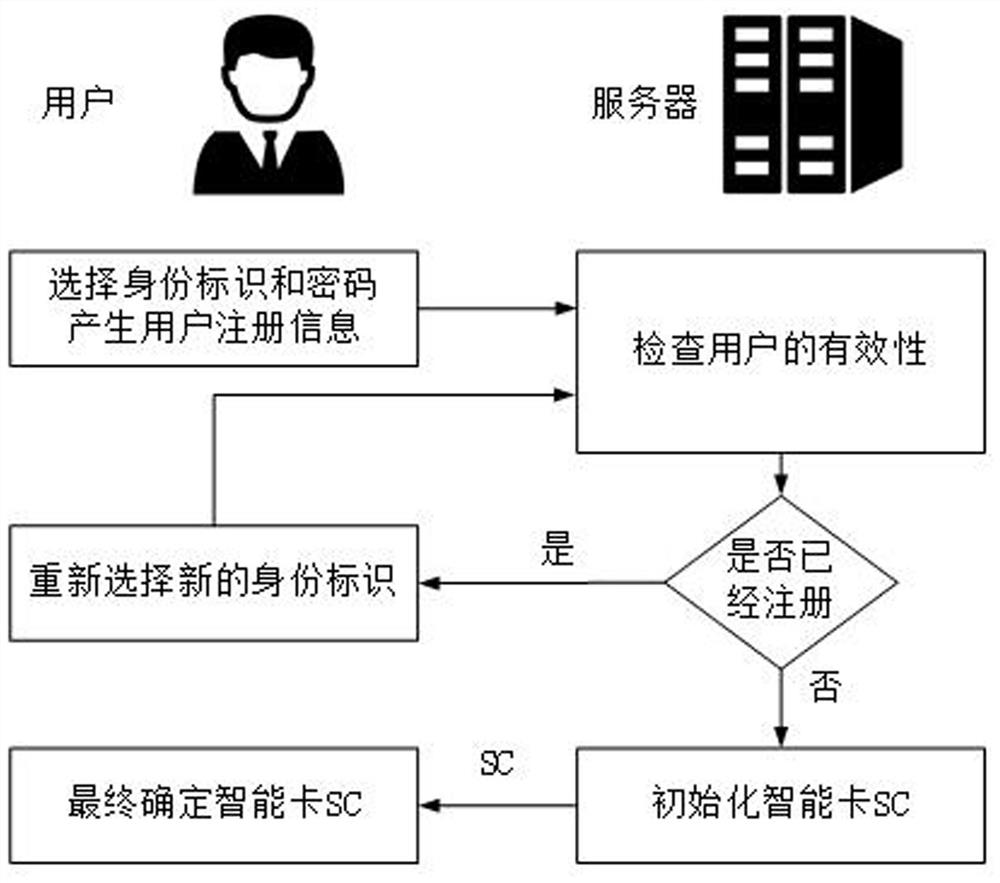
Safety automatic login management system
InactiveCN107819751AGood technical effectAvoid gettingKey distribution for secure communicationShort range communication serviceComputer moduleIntelligent equipment
The invention relates to the technical field of data safety, and discloses a safety automatic login management system. The safety automatic login management system comprises a configuration module, anencryption module and a decryption module; the configuration module comprises a cloud server configuration module and a management control center configuration module; the cloud server configurationmodule is used for receiving login information of intelligent equipment, which is added by a management control center; the management control center configuration module randomly generates a passwordby the management control center to configure to the intelligent equipment; the encryption module is used for carrying out encryption on the login information; and the decryption module is used for decrypting the login information. According to the invention, the safety password is automatically and randomly generated for a website or equipment, and account information is encrypted and saved by apublic key, so that a Hacker can be prevented from acquiring the account information by adopting a brute force attack or dictionary attack method, and safety of an account is greatly improved.
Owner:浙江码博士防伪科技有限公司 +1
Log-in authentication method and system on web application
ActiveCN103581121APrevent tamperingPrevent eavesdropping attacksTransmissionWeb applicationWeb service
The invention discloses a log-in authentication method on web application. The method includes the following steps that after a log-in request of a user is received, a browser obtains authentication information by means of two random numbers provided by a web server and sends the authentication information to the web server; the web server carries out log-in authentication according to the stored user information and the received authentication information. The invention further provides a log-in authentication system on the web application. According to the technical scheme, data tampering, intercepting attract, decimal attract, dictionary attack, replay attract and denial of service attack can be prevented.
Owner:ZICT TECH CO LTD
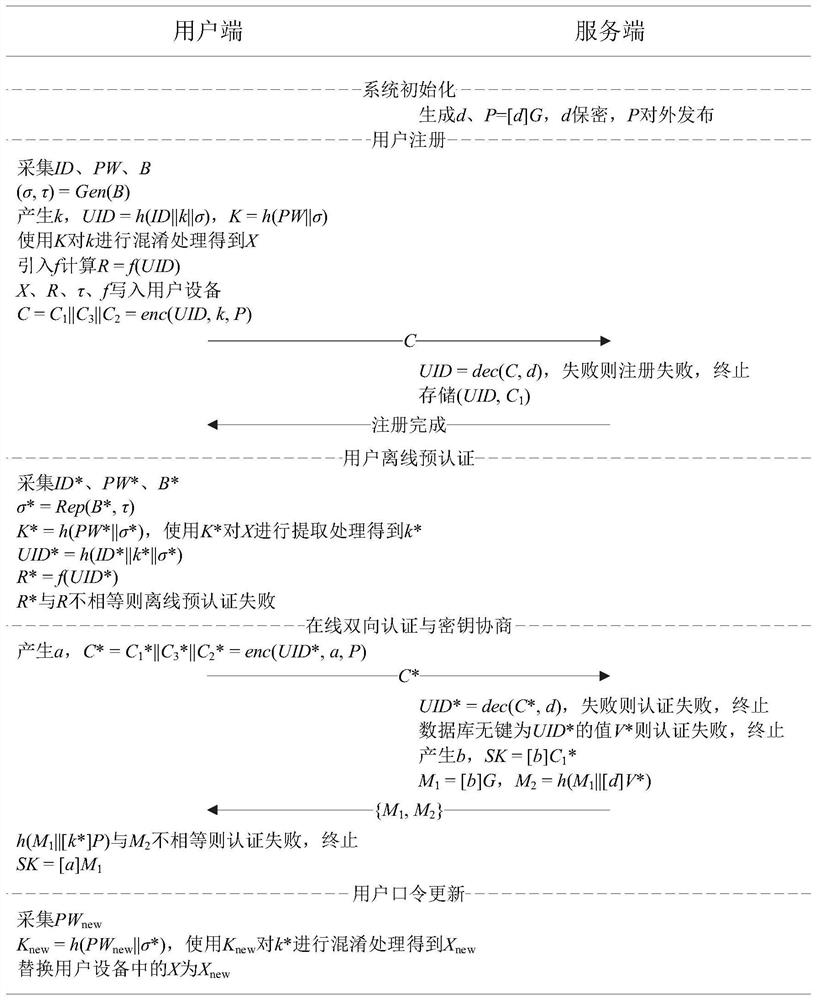
Method for realizing three-factor anonymous identity authentication based on SM2 algorithm
ActiveCN113486324AFix the leakSolving Offline Dictionary AttacksDigital data protectionDigital data authenticationAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention relates to a method for achieving three-factor anonymous identity authentication based on an SM2 algorithm. The method comprises the steps: system initialization: a server generates a private key d and a public key P, the private key d is kept secret, and the public key P is published to the outside; user registration; user offline pre-authentication; online bidirectional authentication and key negotiation; and updating of the user password. According to the method for realizing three-factor anonymous identity authentication based on the SM2 algorithm, mutual authentication and key negotiation security are realized by utilizing multiple means, so the problems of sensitive information leakage, offline dictionary attack, insufficient security strength of a cryptographic algorithm and the like in the prior art are solved.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
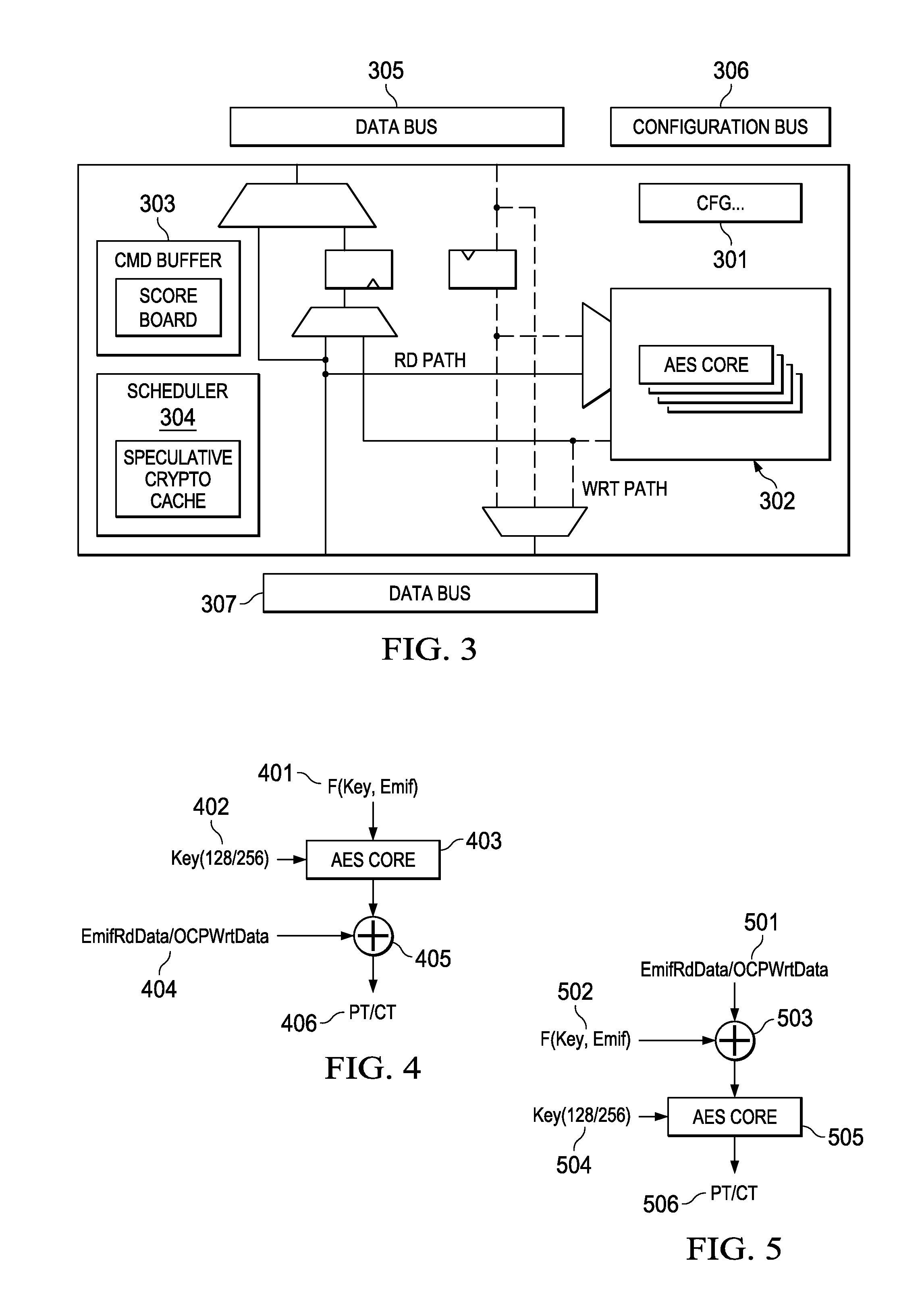
Hardware protection of inline cryptographic processor
PendingUS20150363332A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionExternal storageData integrity
A real time, on-the-fly data encryption system is shown operable to encrypt and decrypt the data flow between a secure processor and an unsecure external memory system. Multiple memory segments are supported, each with it's own separate encryption capability, or no encryption at all. Data integrity is ensured by hardware protection from code attempting to access data across memory segment boundaries. Protection is also provided against dictionary attacks by monitoring multiple access attempts to the same memory location.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
A method for generating and refreshing picture verification codes based on React
InactiveCN108959899APrevent requests for the same verification codeClear cacheDigital data authenticationWeb siteConfusion
The invention discloses a method for generating and refreshing picture verification codes based on React. Using the react framework, users can obtain pictures and verification codes directly from theserver through the operation of the user without storing data into session, so there will be no data confusion or time-consuming and unusable situations, the users can stay in operation for a certainperiod of time, the frequent operation of the users is reduced and the pressure of the server is reduced. The method improves the security of the website, and through the use of react, the picture isrefreshed in time, so that users have a better operation experience and feel that the system is formal trustworthy. The method can effectively prevent illegal users from malicious login programs to destroy, and is used to prevent dictionary attacks, machine registration and other issues.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
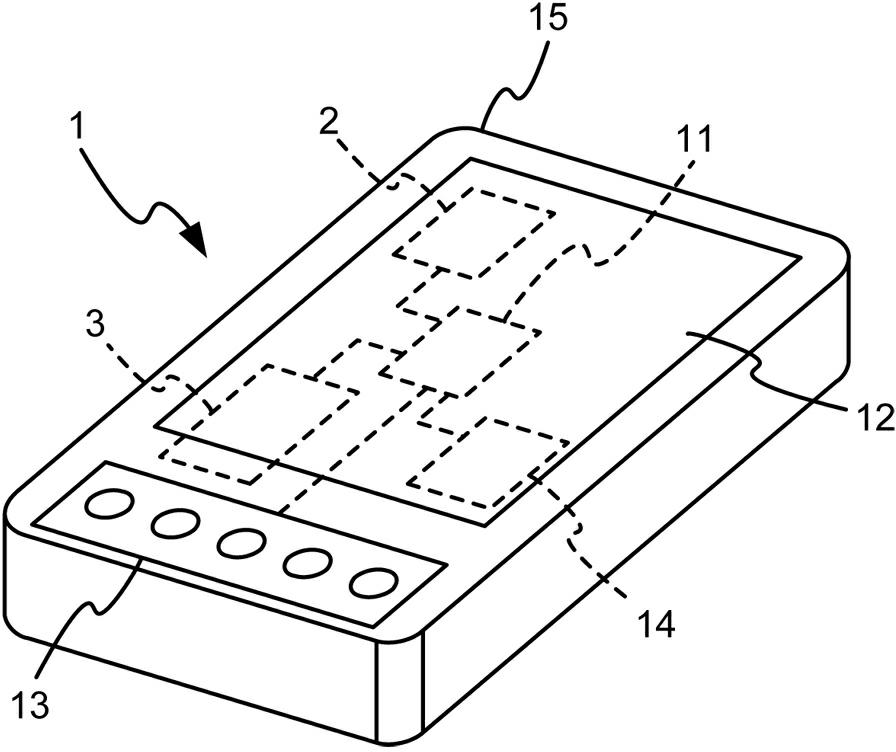
Towed authentication device
InactiveCN102385672AImprove securityReduce the risk of obtainingDigital data authenticationElectric power systemElectric power
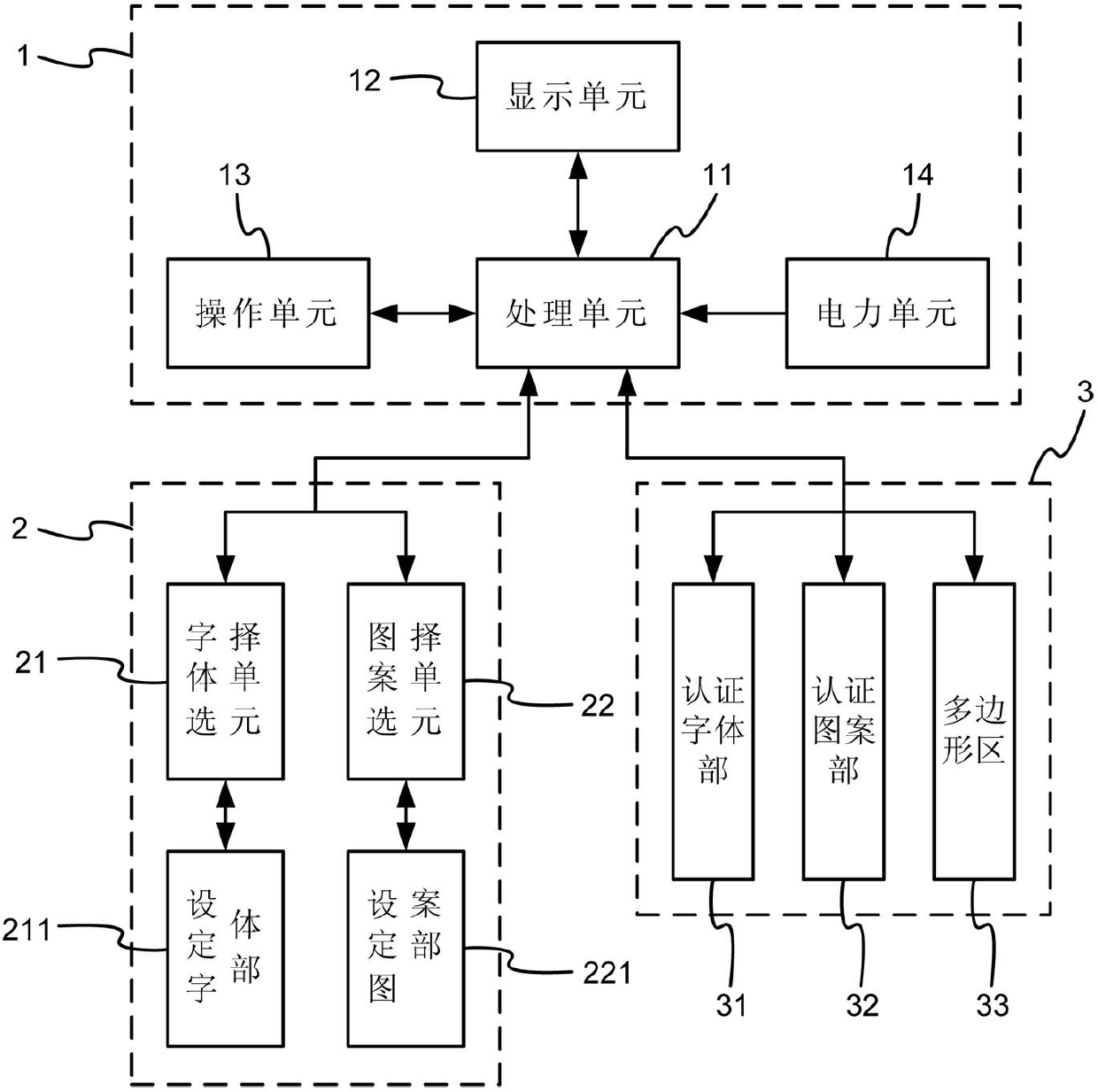
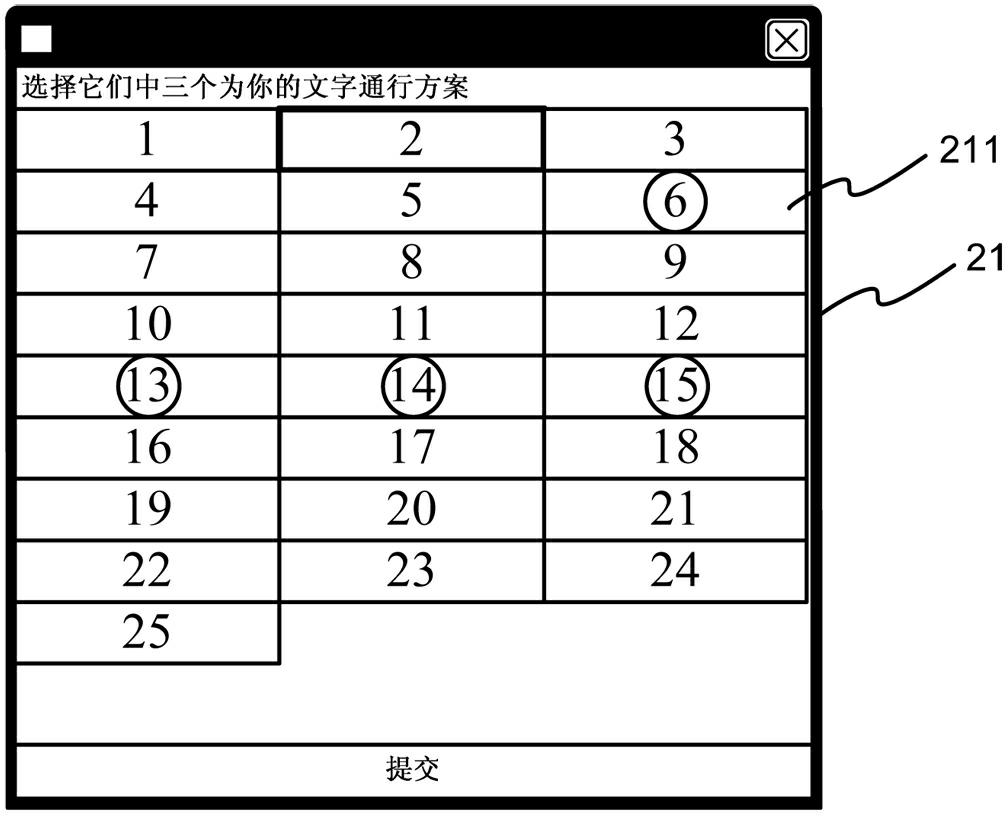
The invention discloses a towed authentication device which comprises an electronic apparatus, a setting mechanism and an authentication mechanism, wherein the electronic apparatus comprises a processing unit, a display unit, an operating unit and an electric power unit; the setting mechanism is connected with the processing unit, and comprises a first password selecting unit and a second password selecting unit for selecting related characters and patterns; and the authentication mechanism is connected with the processing unit, and comprises a plurality of alternatively displayed first password authentication parts and second password authentication parts, wherein each first password authentication part defines a polygonal region according to the password set in the first password selecting unit, and enables the polygonal region to be matched with each second password authentication part for authentication in a towed manner. Thus, the security of a user while logging in can be improved really, and logging attack and dictionary attack can be withstood effectively, thereby achieving the effects of reducing the risk that the password is stolen, and increasing the reliability.
Owner:杨丰源
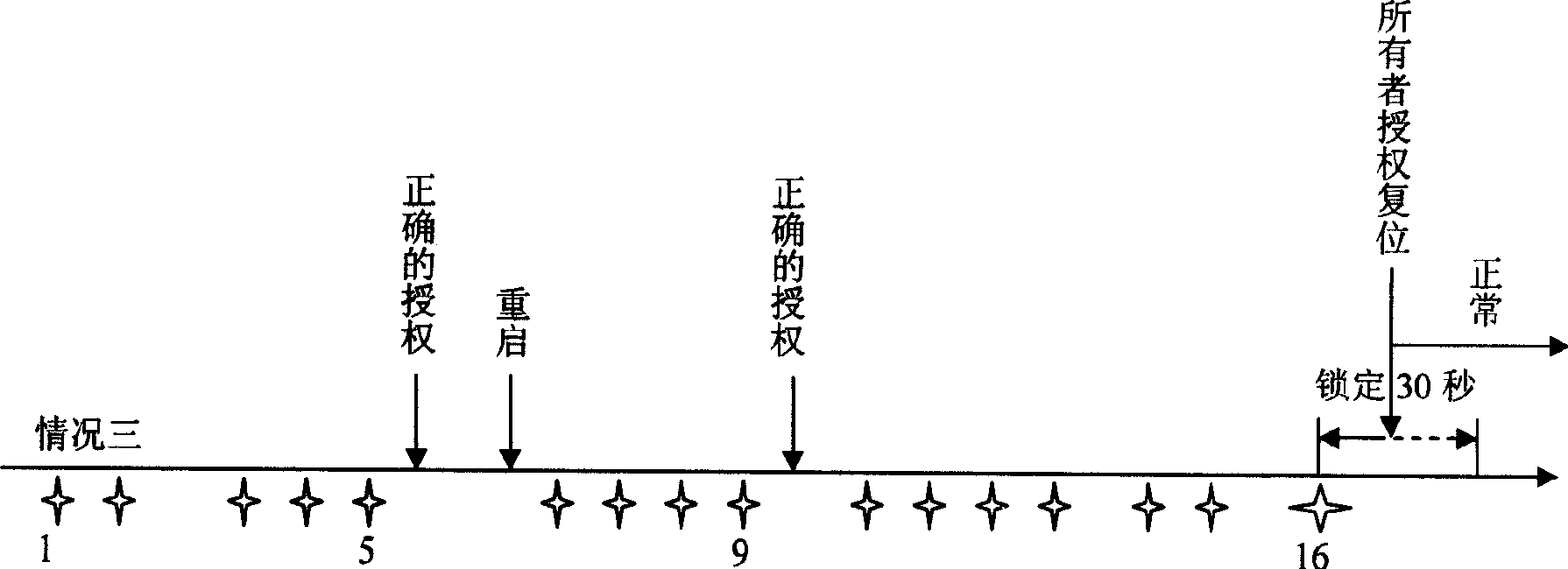
Method for avoiding dictionary attack
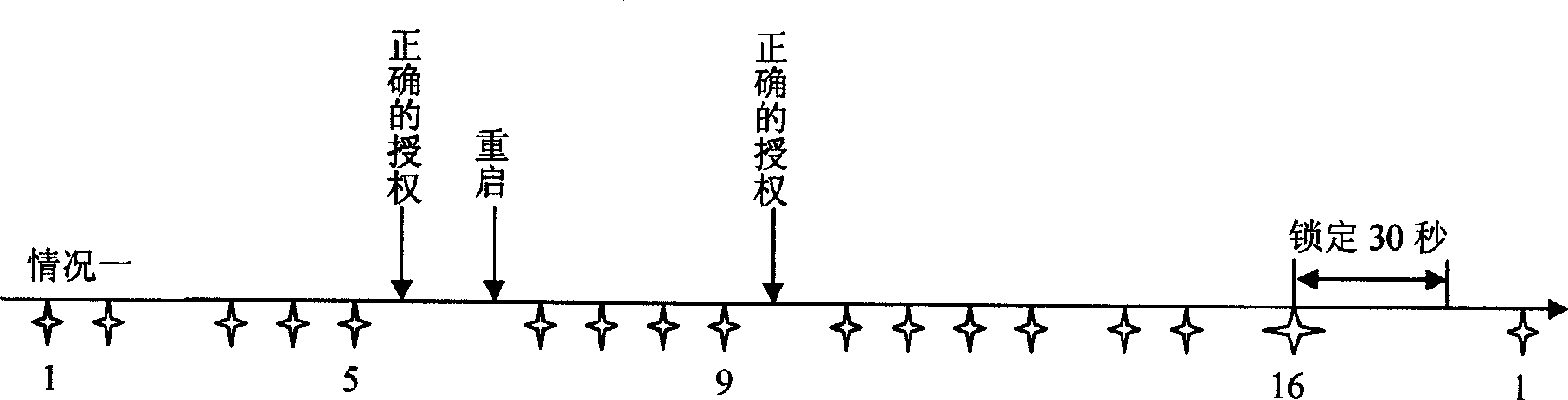
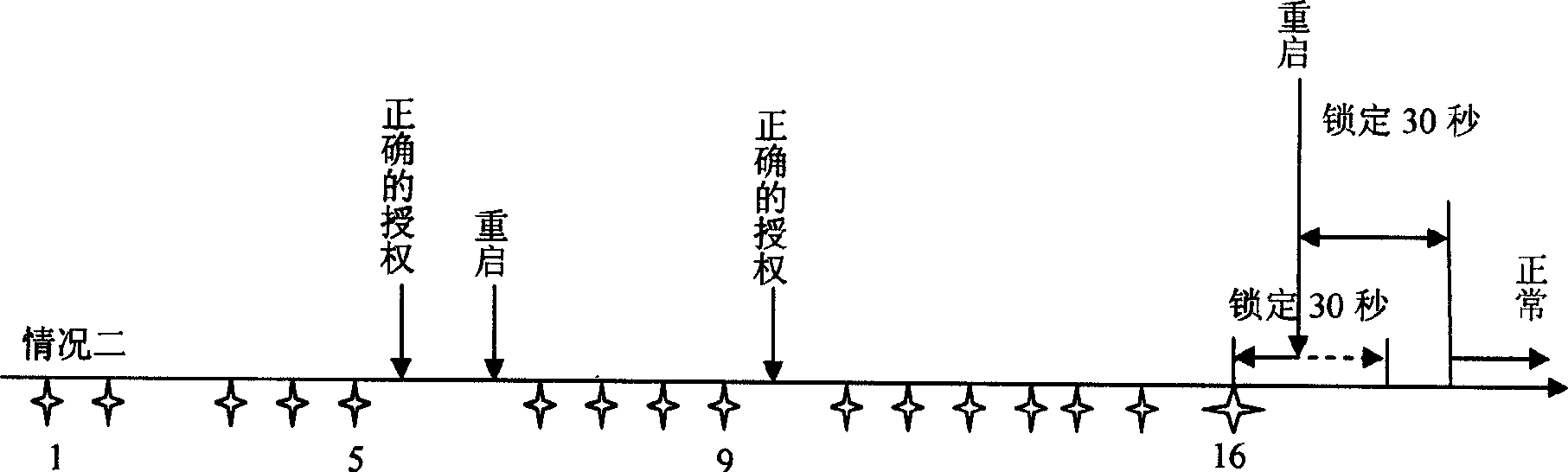
A method for avoiding attack on dictionary includes setting a nonvolatile storing region in computer for storing counting figure of failure authority test, locking time figure and locking mark; providing a timer by computer for timing lock time ; setting threshold for number of failure authority ; locking said computer when set threshold is exceeded by counting figure of failure authority test; only responding to starting up, self detection and reset request by computer as it is in locking period.
Owner:SHENZHEN SINOSUN TECH
Access authentication method of wireless local area network, server and authentication system
ActiveCN106713222ASolve the problem of attackTransmissionSecurity arrangementAuthentication systemUser equipment
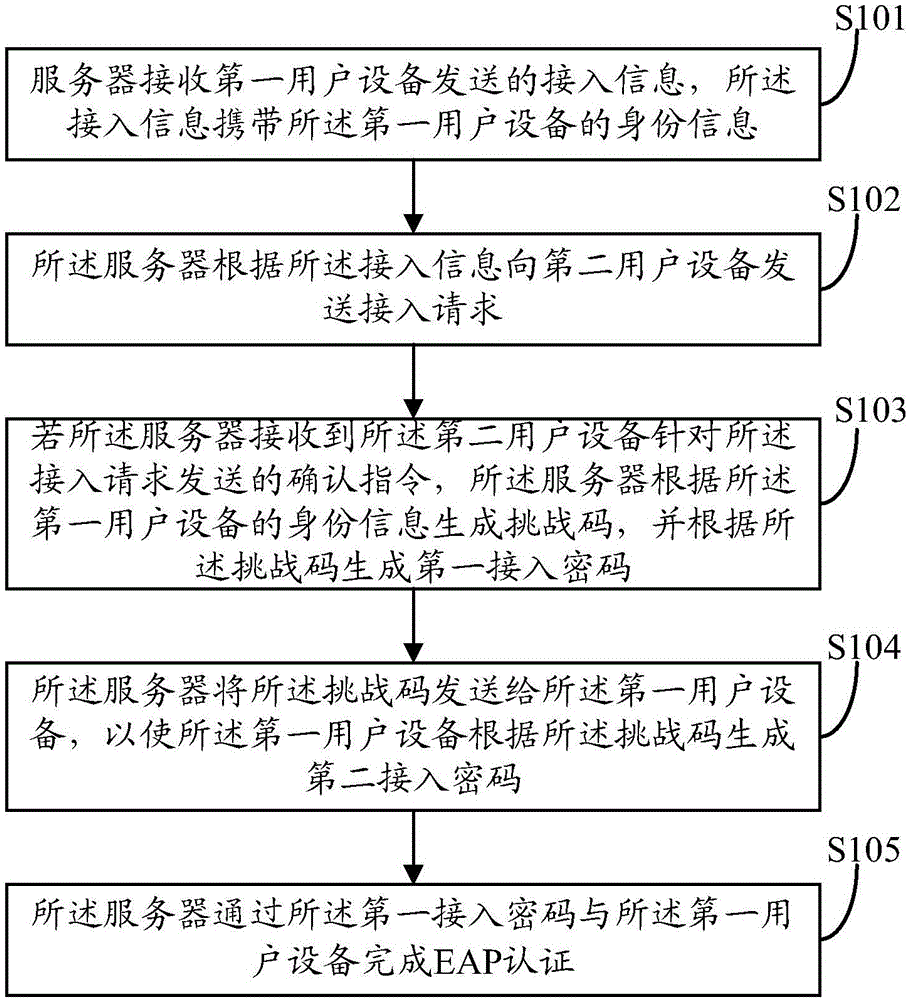
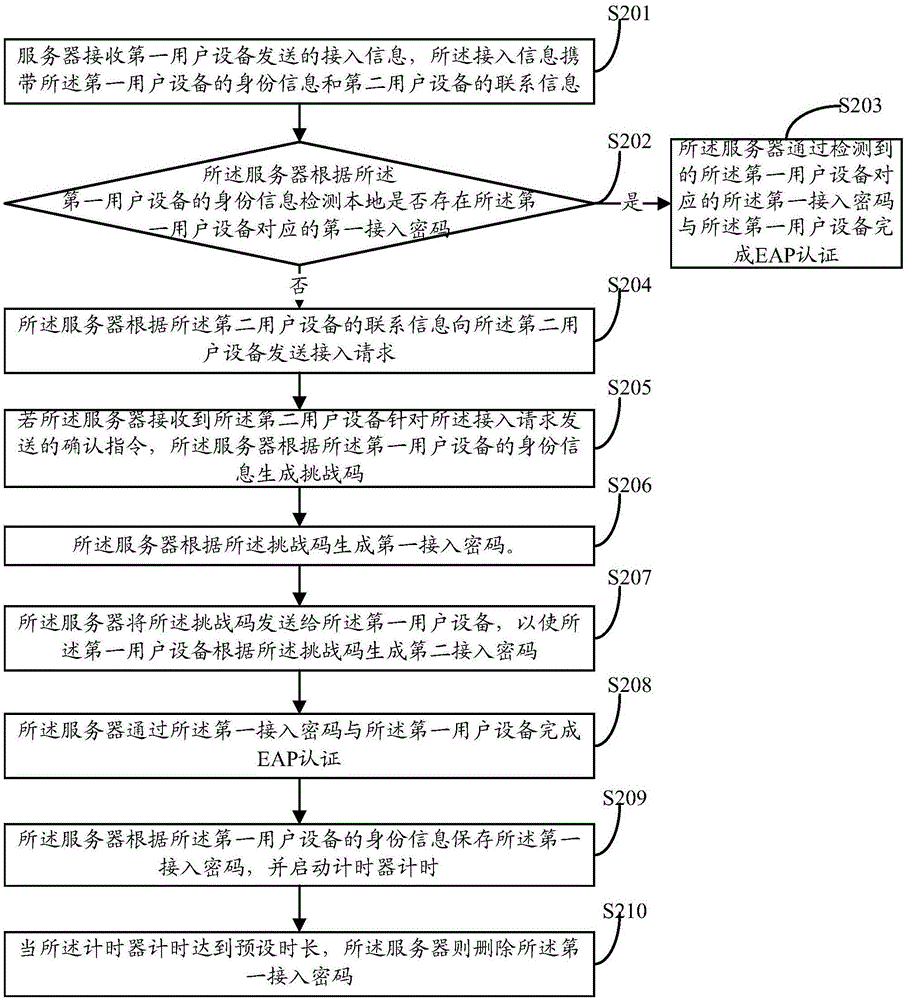
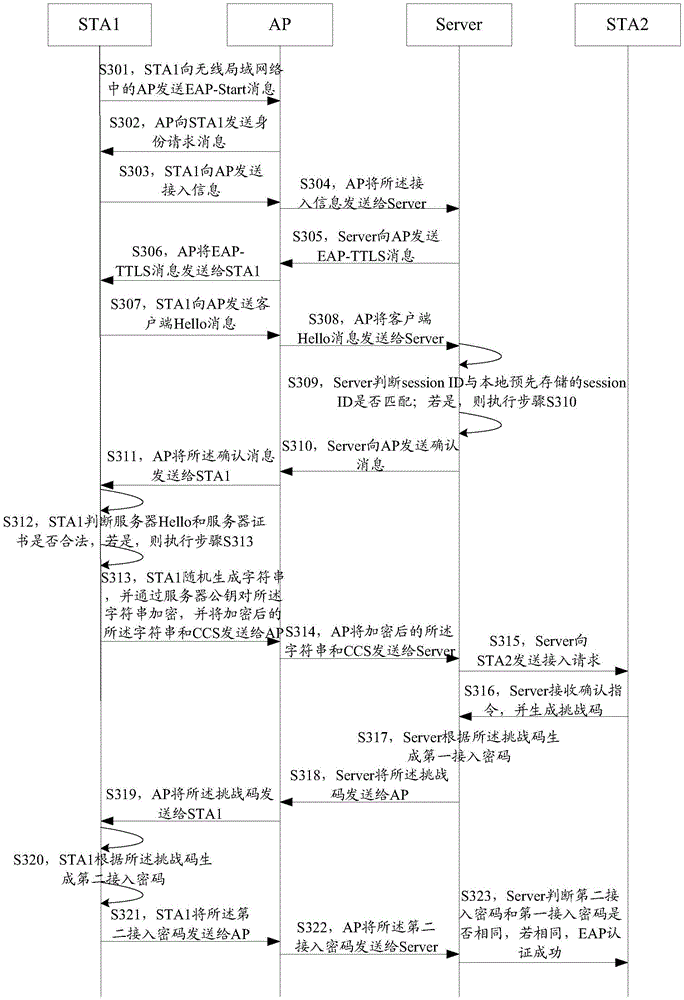
The invention discloses an access authentication method of a wireless local area network. The method comprises the steps that: a server receives access information sent by first user equipment, and the access information carries the identity information of the first user equipment; the server sends an access request to the second user equipment according to the access information; if the server receives a confirmation instruction sent by the second user equipment for the access request, the server generates a challenge code and generates a first access password according to the challenge code; the server sends the challenge code to the first user equipment such that the first user equipment generates a second access password according to the challenge code; and the server completes EAP certification through the first access password and the first user equipment. Correspondingly, the invention discloses the server and an authentication system. By using the access authentication method, the server and the authentication system, a problem of dictionary attack can be solved.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
User request permission method and device based on password confusion
PendingCN113630238AEnsure safetyReduce waiting timeKey distribution for secure communicationFinancePlaintextHash function
The invention provides a user request permission method and device based on password confusion. The method can be used in the technical field of finance. In a reasonable salting processing mode, confusion is carried out in combination with a hash function, so that the method has the characteristics of counterfeiting resistance, eavesdropping resistance, replay attack resistance, dictionary attack resistance after database leakage, incapability of acquiring a password plaintext in the whole process, infeasibility of violent exhaustion and reverse cracking of the password plaintext in cost calculation and the like, and the safety of a user logging in an account through a webpage is ensured to the greatest extent.
Owner:INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL BANK OF CHINA
Identity verification method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112055008APrevent replay attacksReduce the number of timesKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCiphertextAttack
The embodiment of the invention provides an identity verification method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: receiving a verification request sentby a client, the verification request comprising a user name, verification summary information and a user counter, and the verification summary information being summary information generated for a password by taking the user counter as the frequency of calculating a summary, searching registration parameters which are recorded during client registration and associated with the user name, the registration parameters comprising a service counter and a standard ciphertext, matching the user counter with the service counter to detect the consistency of the numerical value during identity verification, and if the user counter is successfully matched with the service counter, verifying the identity of the client according to the difference between the standard ciphertext and the verification abstract information, within 1RTT, the client completes password verification, the abstract calculation frequency of the password is decreased progressively, eavesdropping attacks and replay attacks ofthe password in the network transmission process can be prevented, and potential dictionary attacks are prevented.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIGUOYUAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and system for password protocols in the bounded retrieval mode with security dictionary attacks and intrusions
ActiveUS8528060B2Efficiently computableDifficult to invertDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHash functionRandom choice
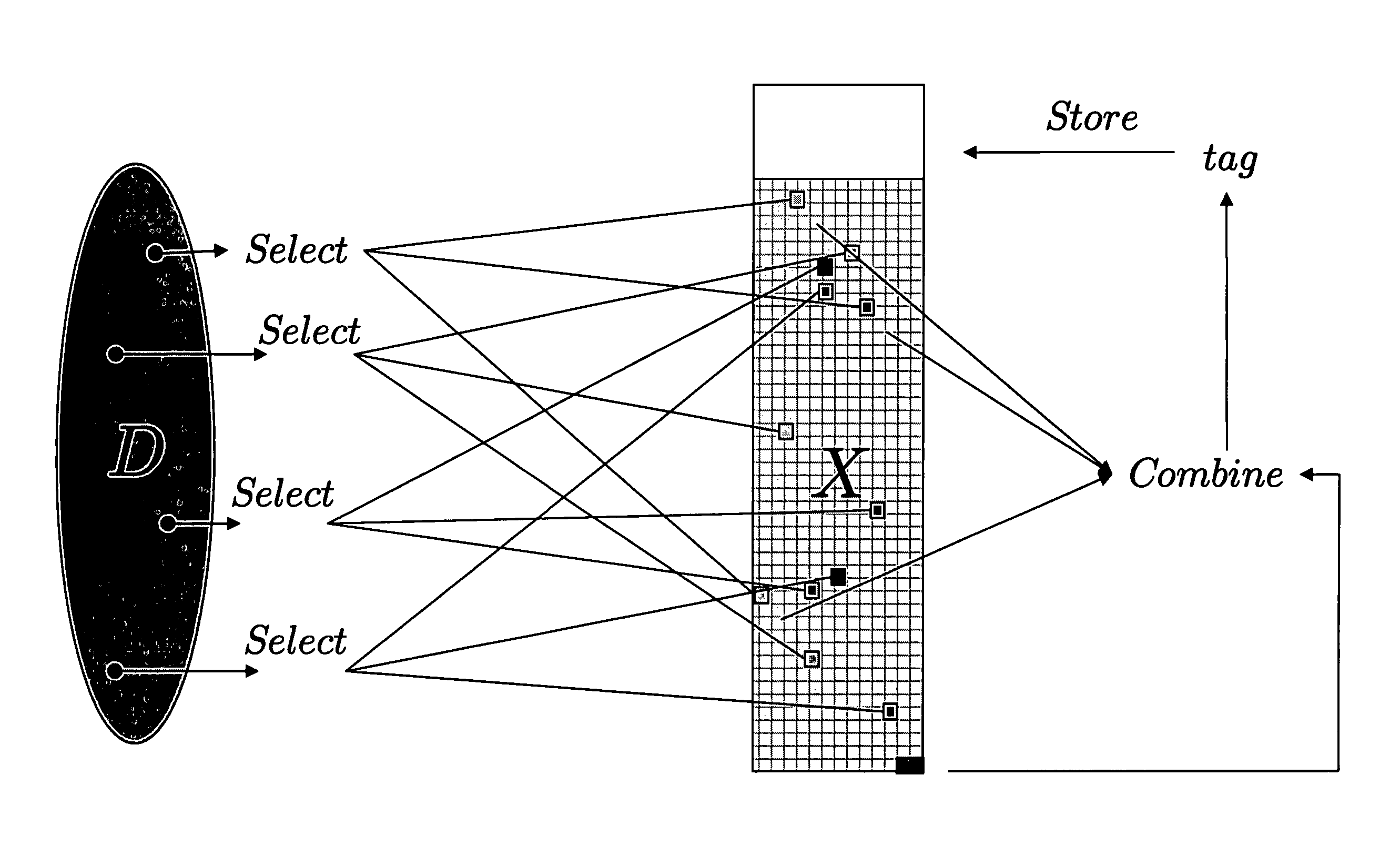
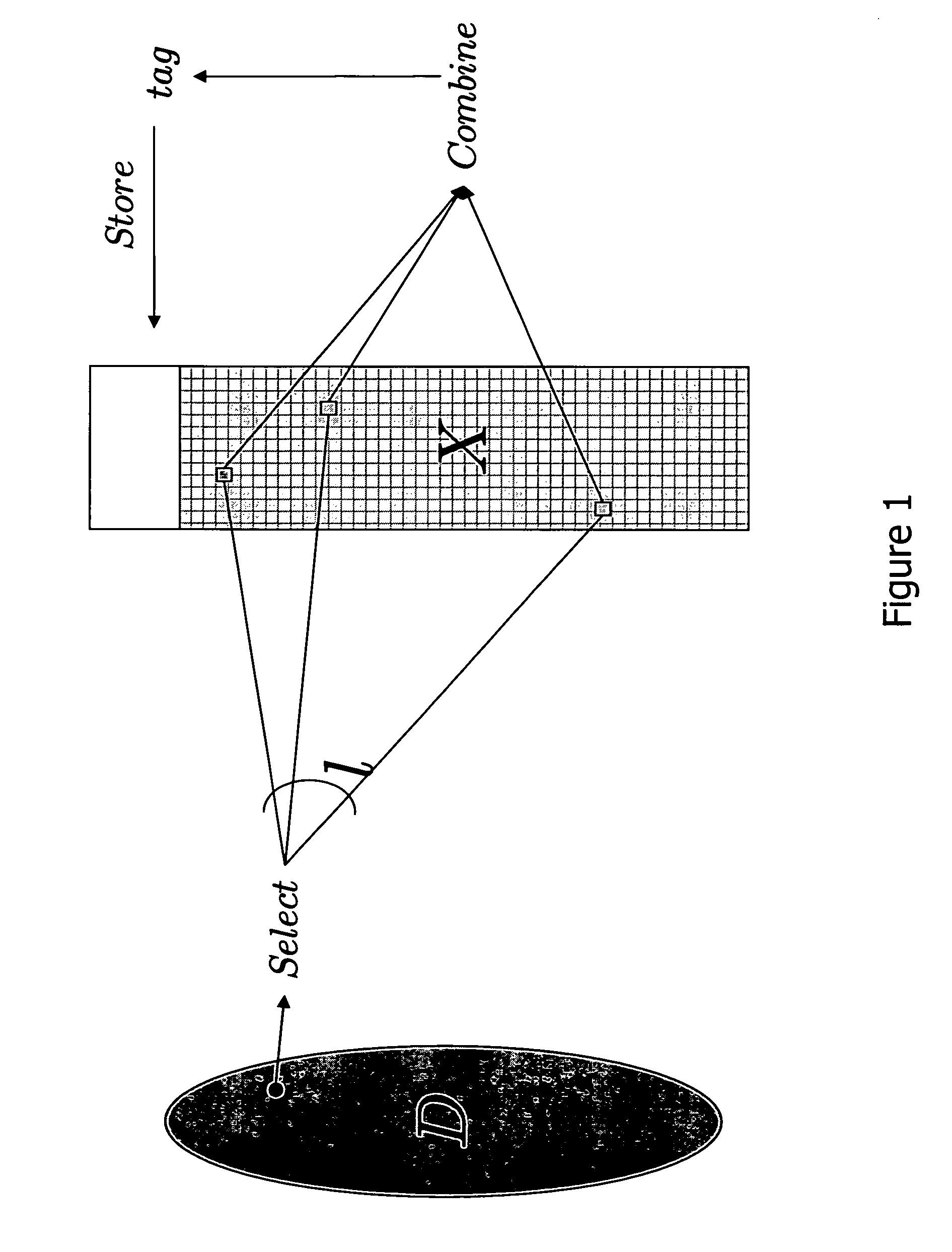
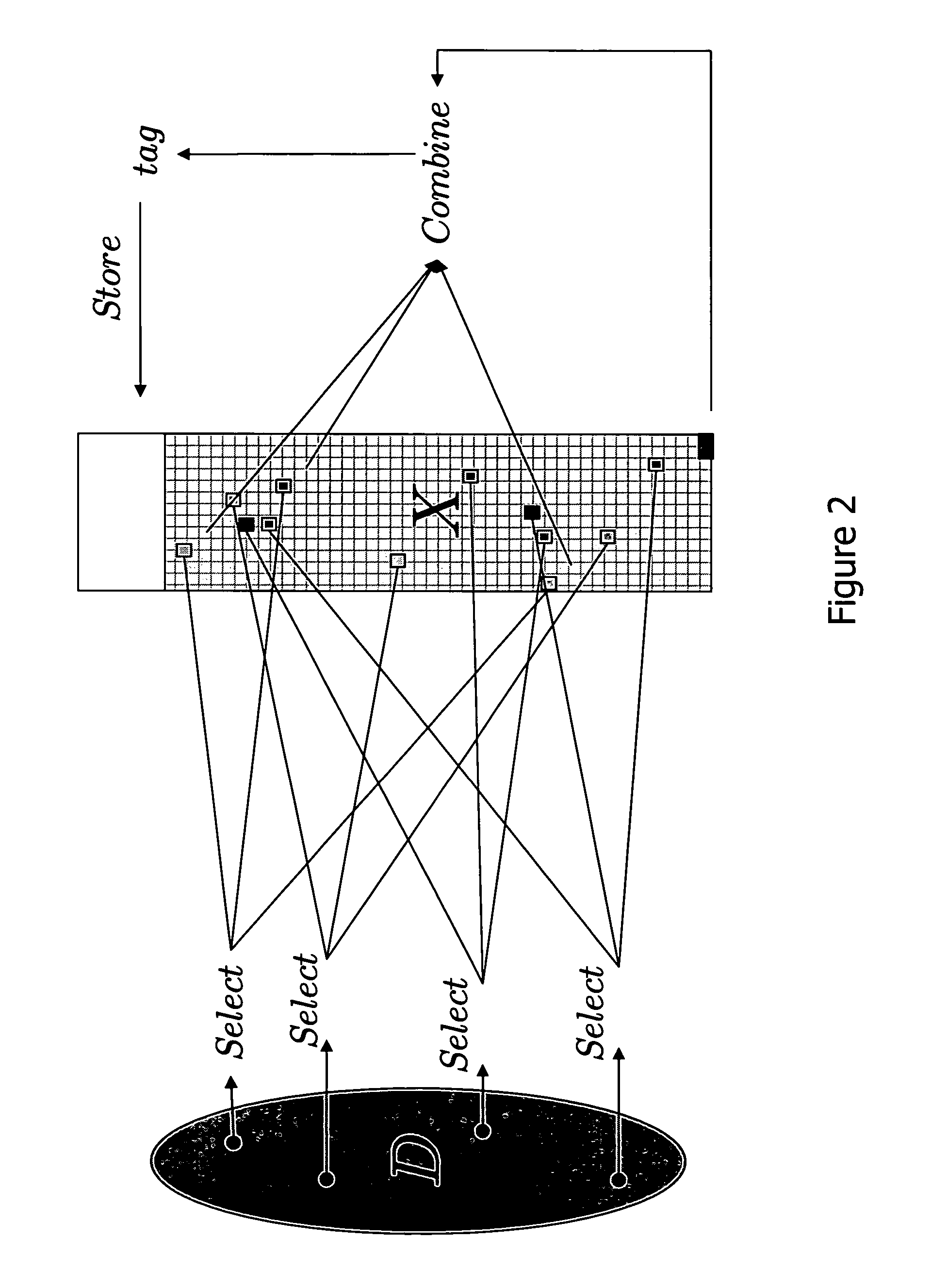
Efficient secure password protocols are constructed that remain secure against offline dictionary attacks even when a large, but bounded, part of the storage of a server responsible for password verification is retrieved by an adversary through a remote or local connection. A registration algorithm and a verification algorithm accomplish the goal of defeating a dictionary attack. A password protocol where a server, on input of a login and a password, carefully selects several locations from the password files, properly combines their content according to some special function, and stores the result of this function as a tag that can be associated with this password and used in a verification phase to verify access by users. Two main instantiations of our method are given; in one, a combination of mathematical tools, called dispersers and pairwise-independent hash functions is used to achieve security against adaptive intrusions (dispersers make sure that the password of each user depends on randomly chosen locations in a large password file, and pairwise-independent hash functions help in making this dependency sufficiently random); in a second one, a combination of mathematical tools, called k-wise independent hash functions and locally-computable and strong extractors (k-wise independent hash functions make sure that the locations chosen in the large password file from each password are sufficiently random, and locally-computable and strong extractors are used to combine the contents of these locations to generate a single long random value, which makes verification harder for the adversary to foil).
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Key generation method based on position uniqueness information
ActiveCN113225183AResist attackMake up for the shortcomingsKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHash functionTheoretical computer science
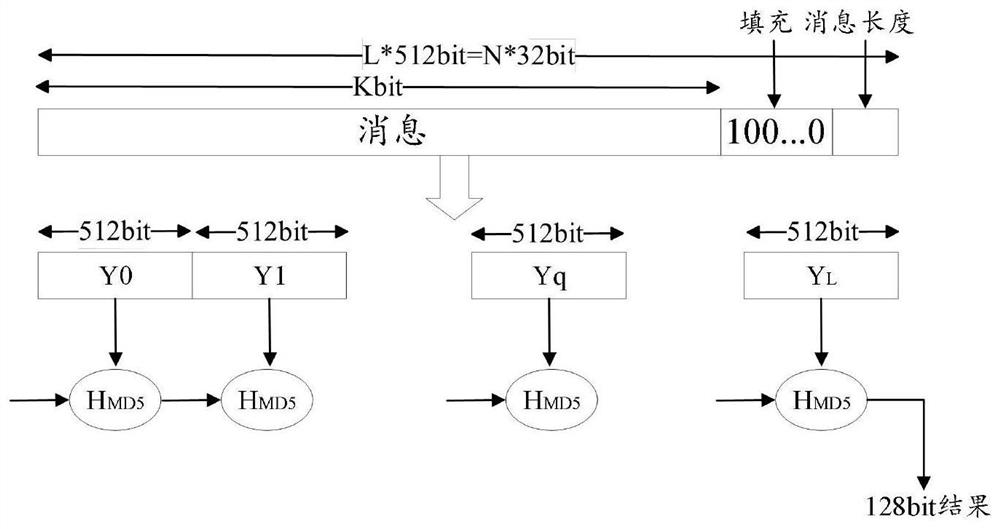
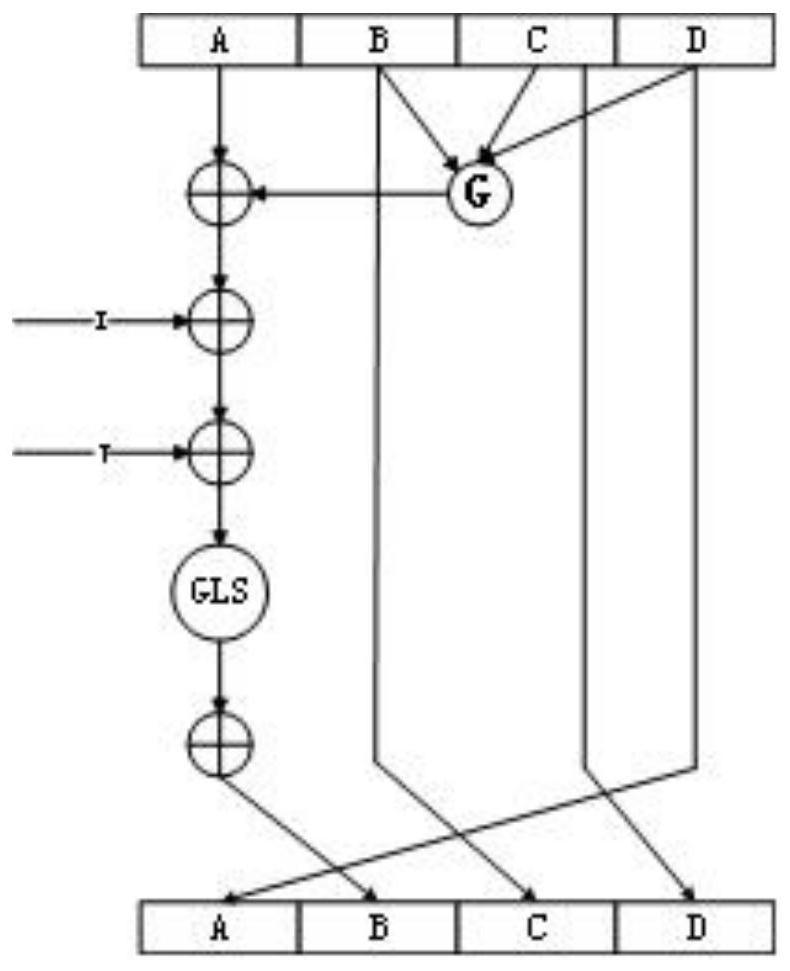
The invention provides a key generation method based on position uniqueness information, which is improved on the basis of a hash function, and when the hash function fills input information, a chaotic sequence is introduced, an MD buffer area is initialized, and messages are processed by taking groups as units. The information filled each time can be randomly changed along with the change of the input positioning information, so that the defect that a hash function is easily attacked by a dictionary is effectively avoided; meanwhile, a plurality of control parameters are introduced, the change space of a key is increased, and the security of a key generation algorithm and the randomness of the generated key are improved; according to the method, the structure of the MD5 algorithm is not changed too much, so that the properties of irreversibility, initial value sensitivity and the like of the original MD5 algorithm still exist, the complexity of the improved algorithm is not obviously improved, and the operation time is relatively short.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com