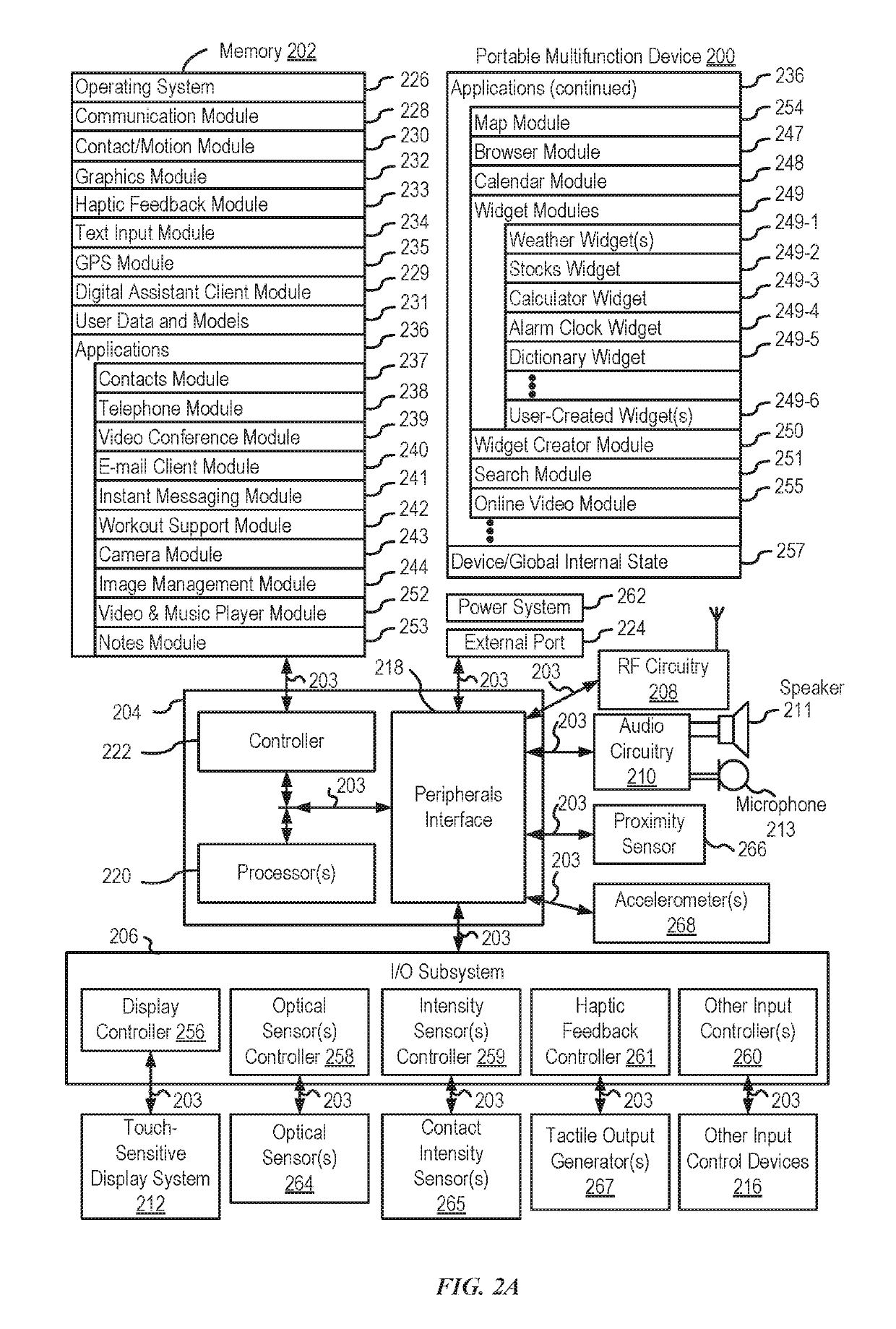
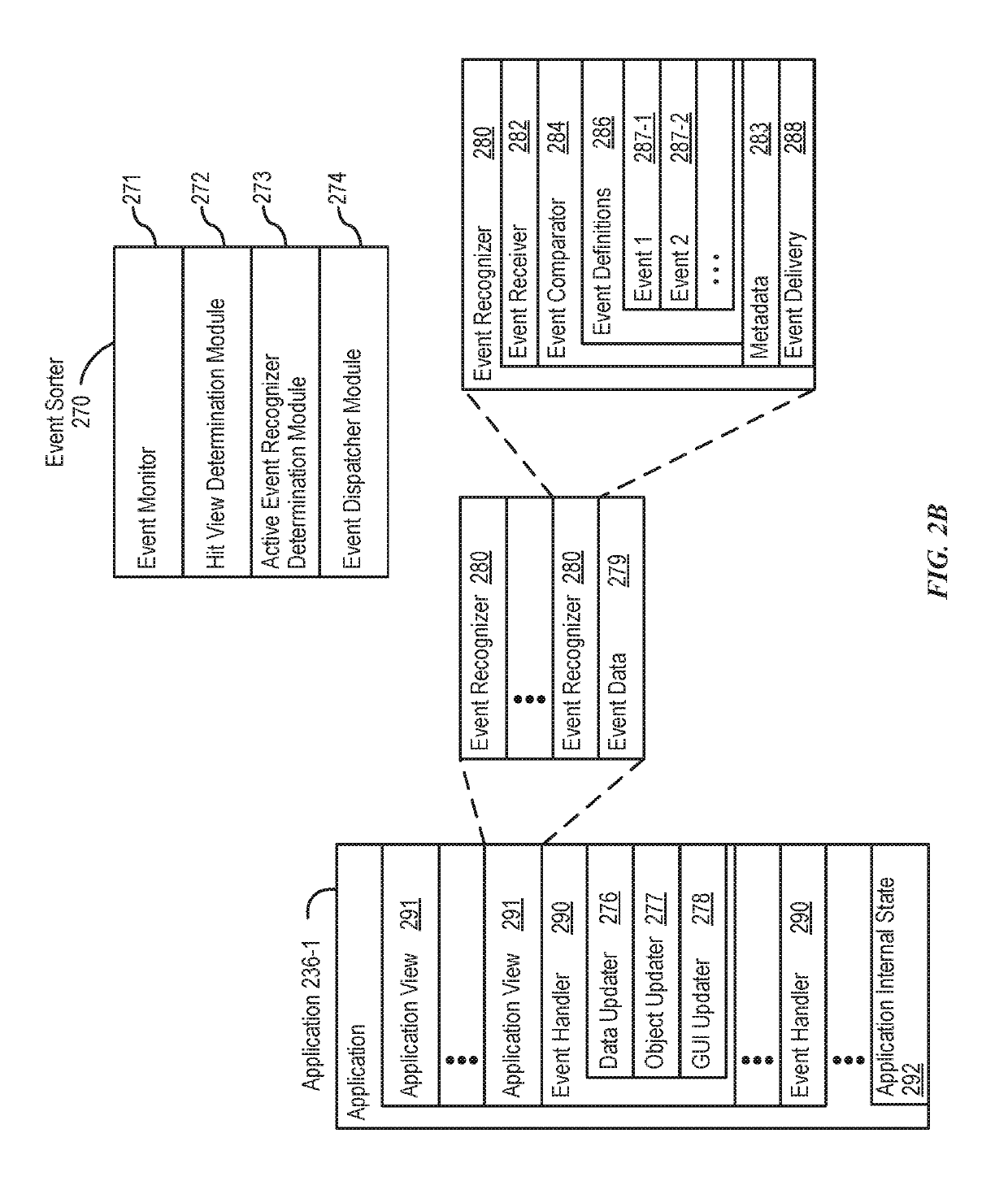
Patents
Literature
4268results about "Web data querying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
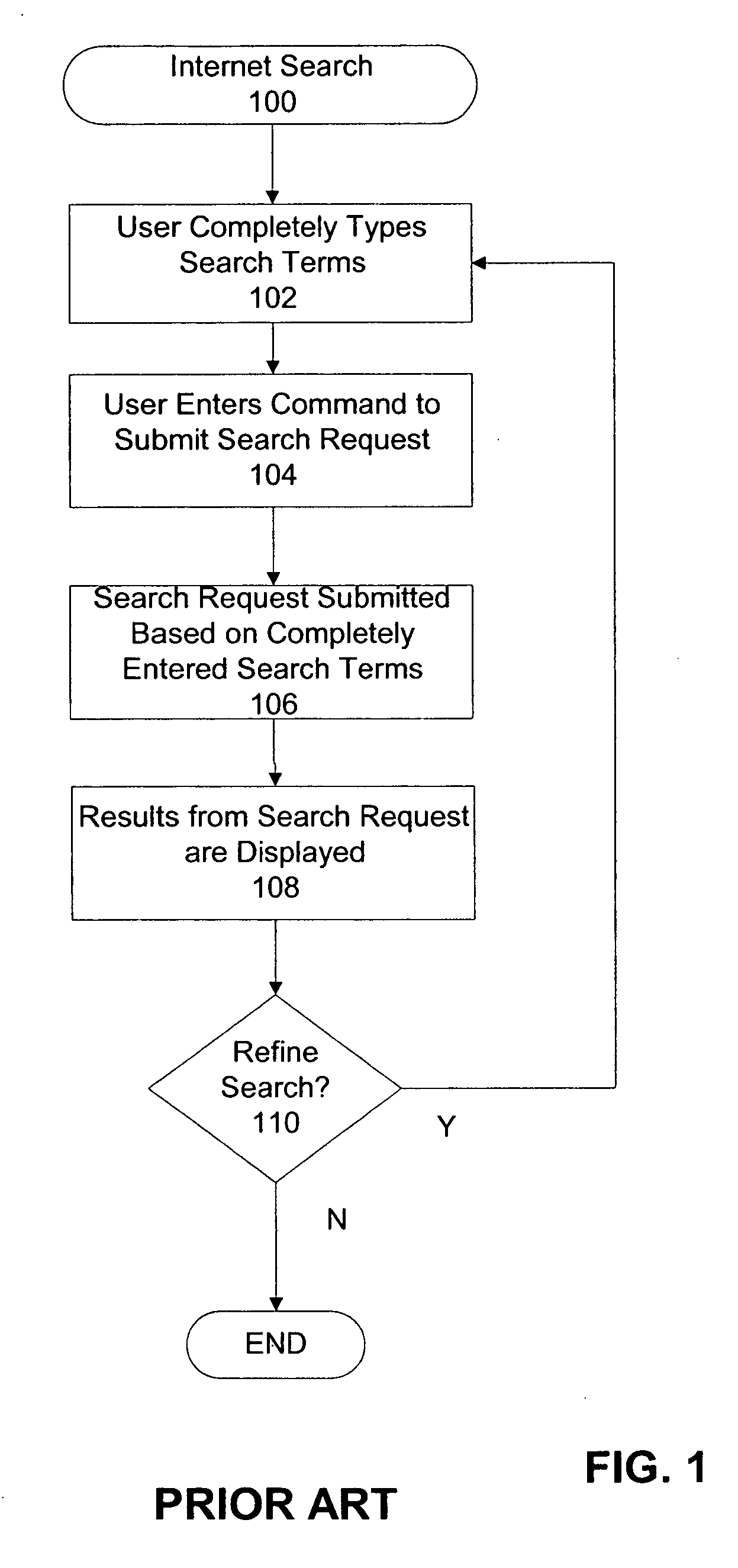
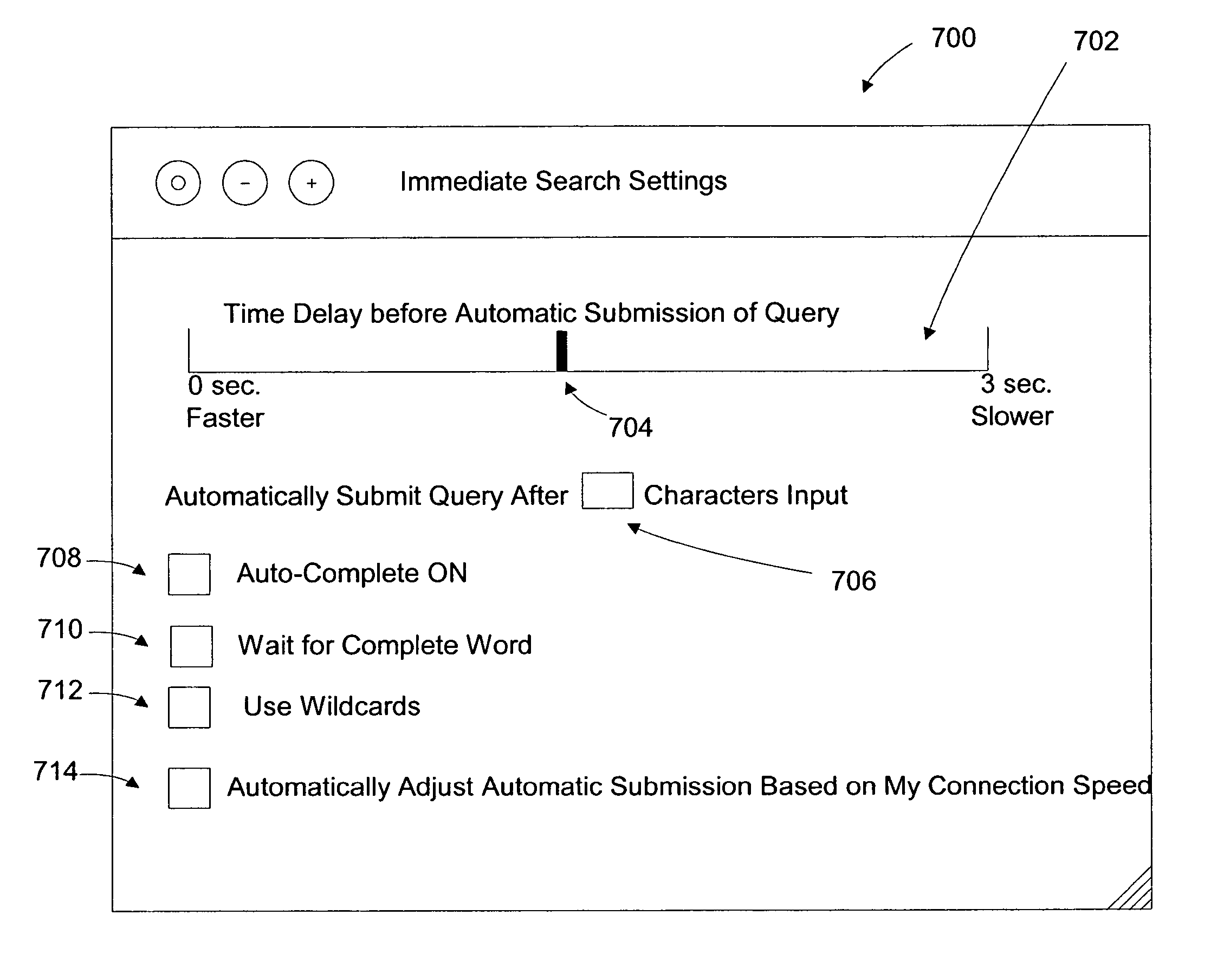
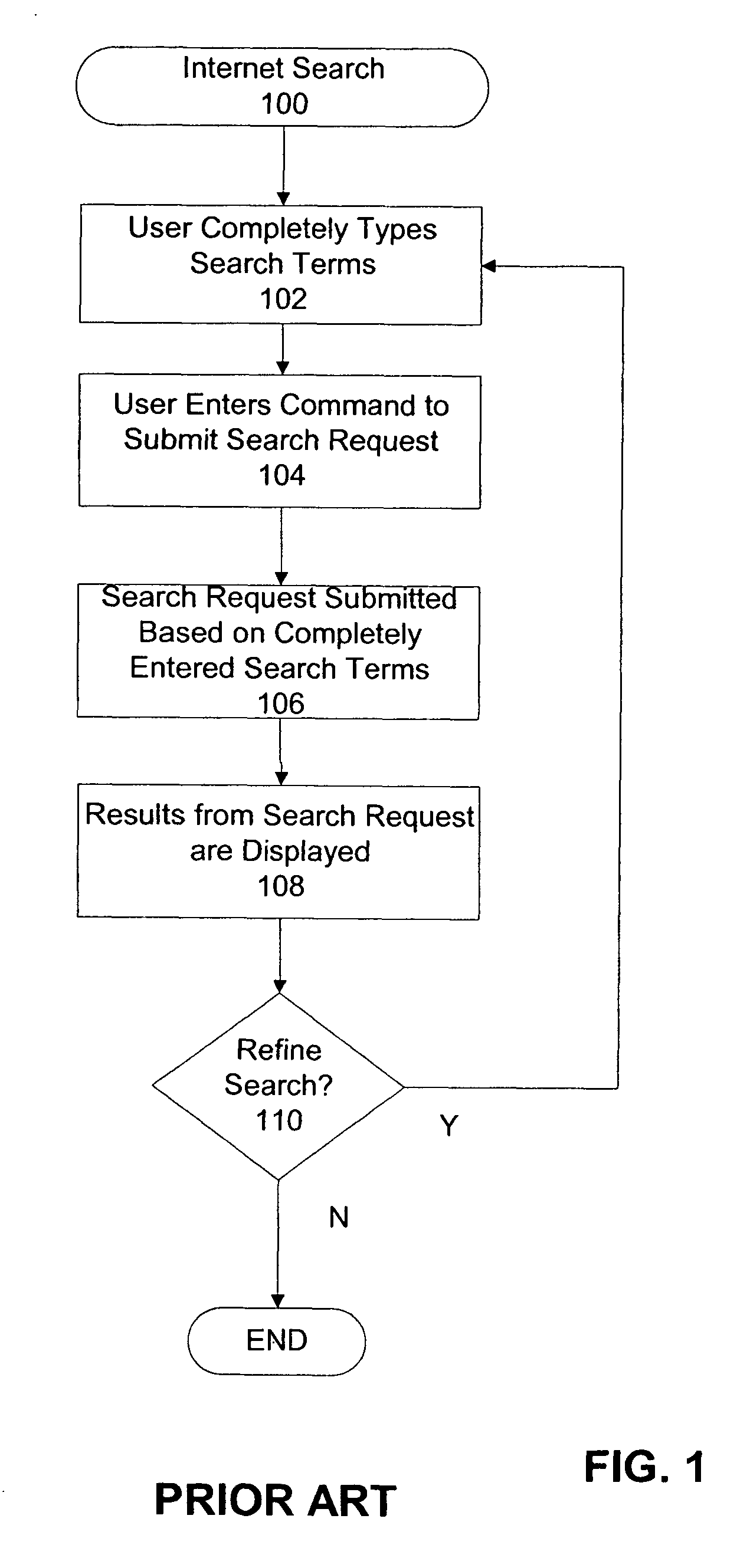
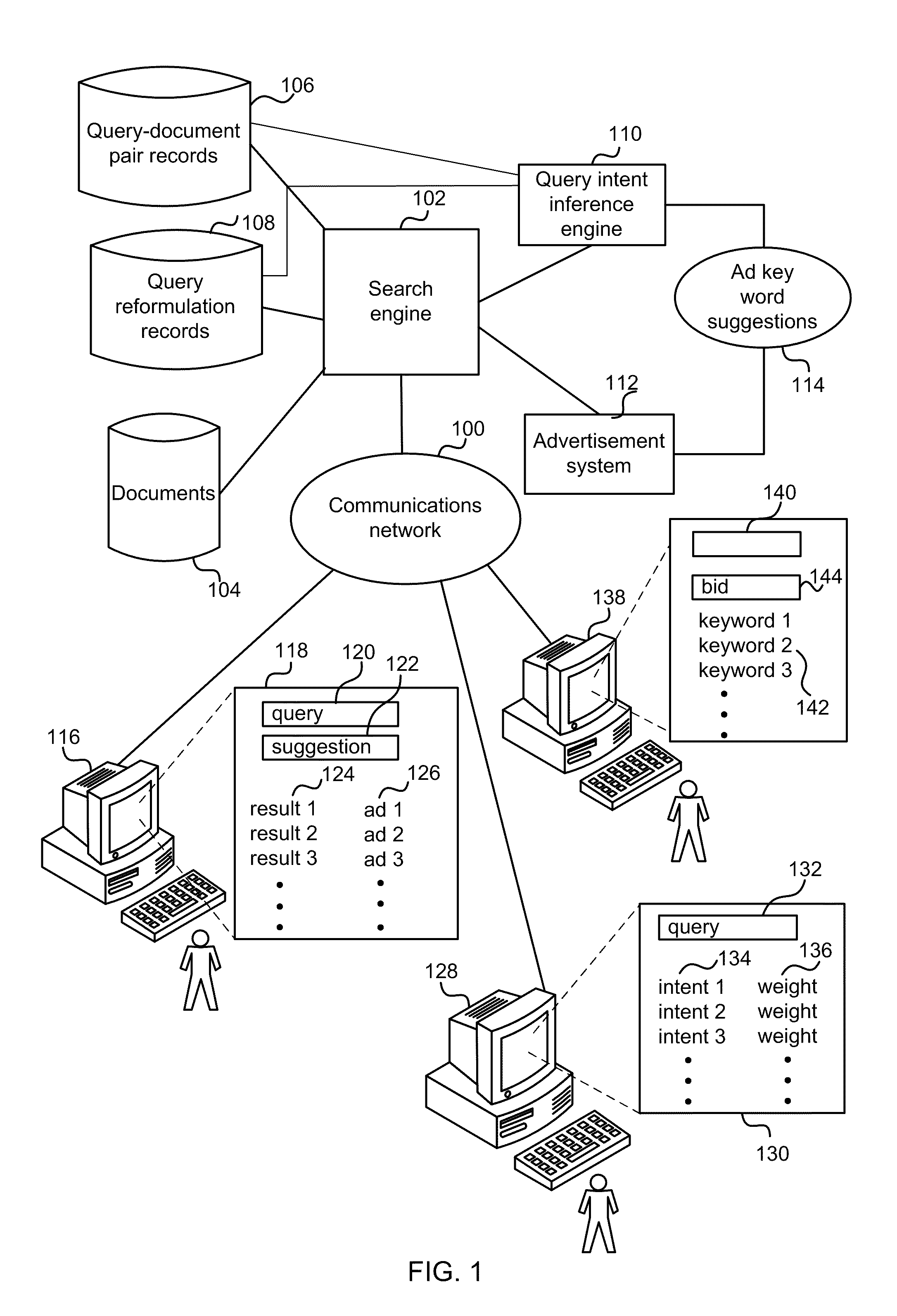
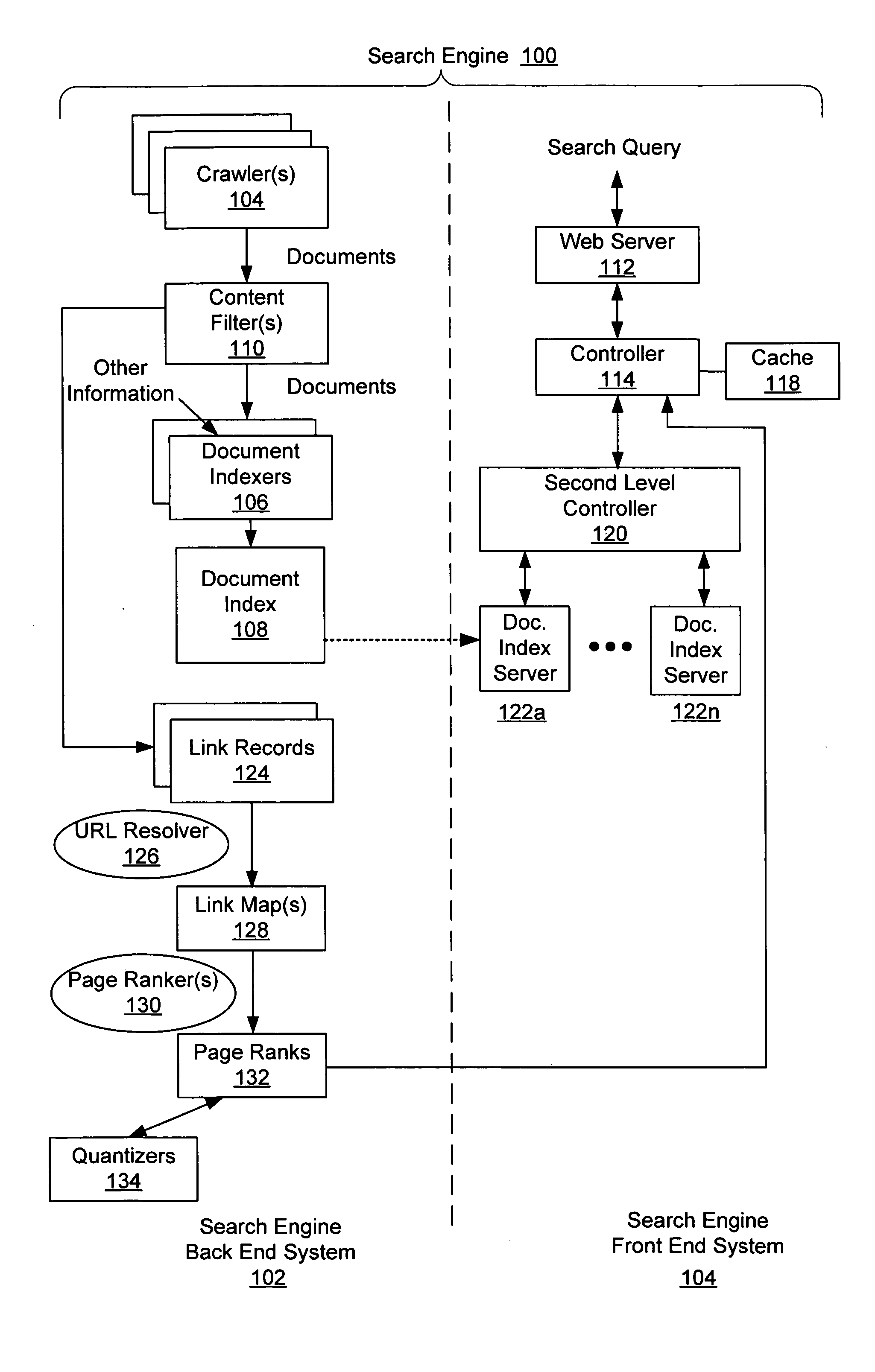
Immediate search feedback
Providing immediate search feedback is disclosed. Search input is received within a search field of a web browser application. Based on characteristics of the search input, a determination is made whether to automatically submit a query to a search engine. In one aspect, the query is automatically submitted to the search engine. The query is based on the received first search input. Results are displayed within the web browser application, the results web page returned from the query submitted to the search engine.
Owner:APPLE INC
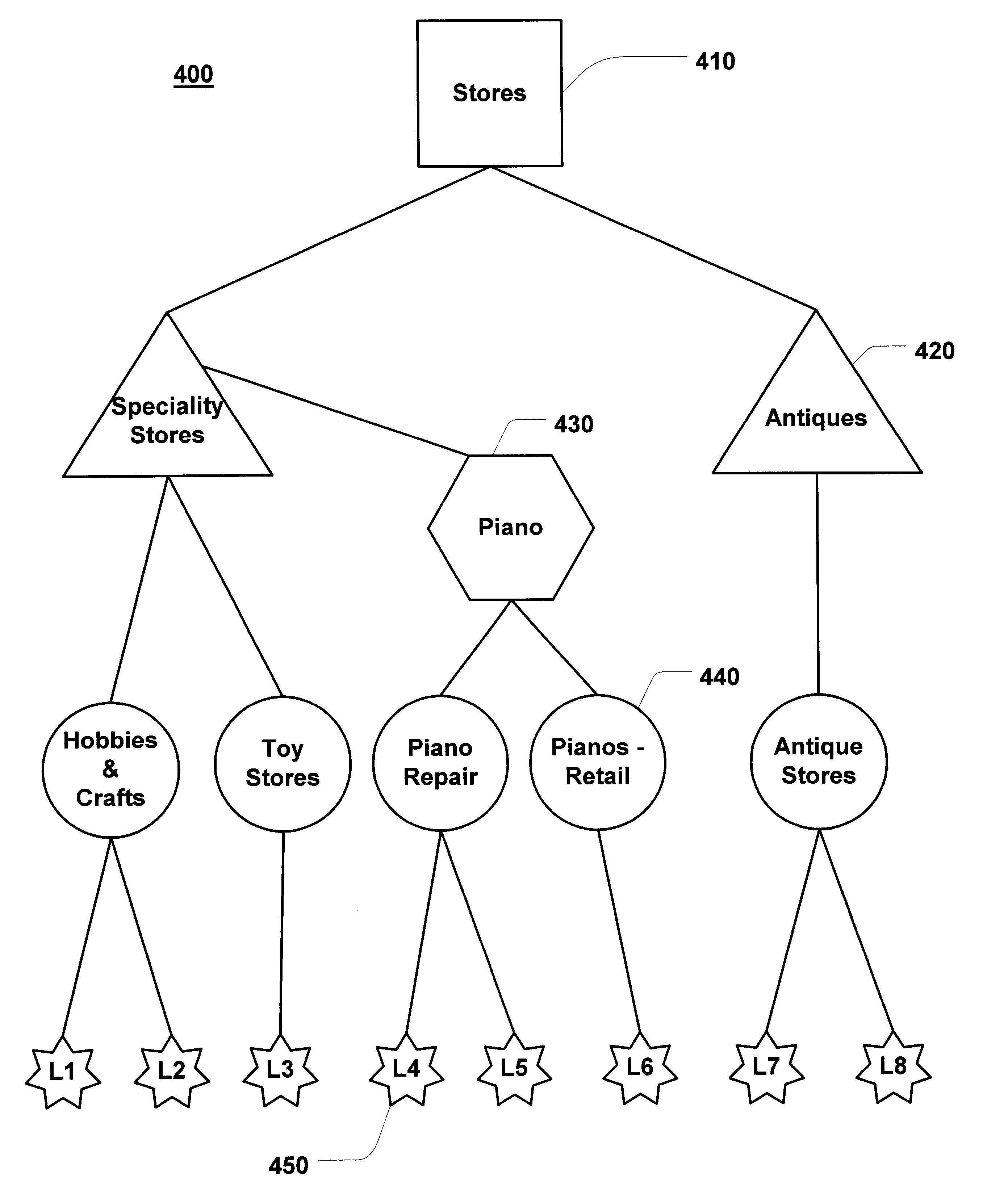
Business directory search engine
A system and method for efficiently searching directory listing information to obtain more relevant results is provided. In a computer system running a computing application, it is advantageous to provide search capabilities, in the form of a search engine, to operators to assist them in their effort of retrieving desired data. The search engine may cooperate with a data store having directory listing information to provide listings data to an operator. In an illustrative implementation, this search engine may be deployed on an Internet Web site that offers business listing information. The search system may comprise a user interface to enter search query information, a data store that houses a variety of directory listing information according to a predefined data taxonomy, and a means for displaying the search results. In operation, the search engine offers a variety of search options, such as, search by business name, by business categories levels, by geographic position of the user or the business, or a combination thereof. Depending on the search query entered, the search engine will perform either a bounded search (i.e. a search bounded to a specific geographic area), a proximity search (i.e. a search proximate to a computed centroid), or a combination of the two to find the most relevant directory listings. Using the inputted search qualifiers, the search engine polls the data store according to a predefined set of rules and instructions for the relevant directory listing information. These rules are directly related to the taxonomy of the data store.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
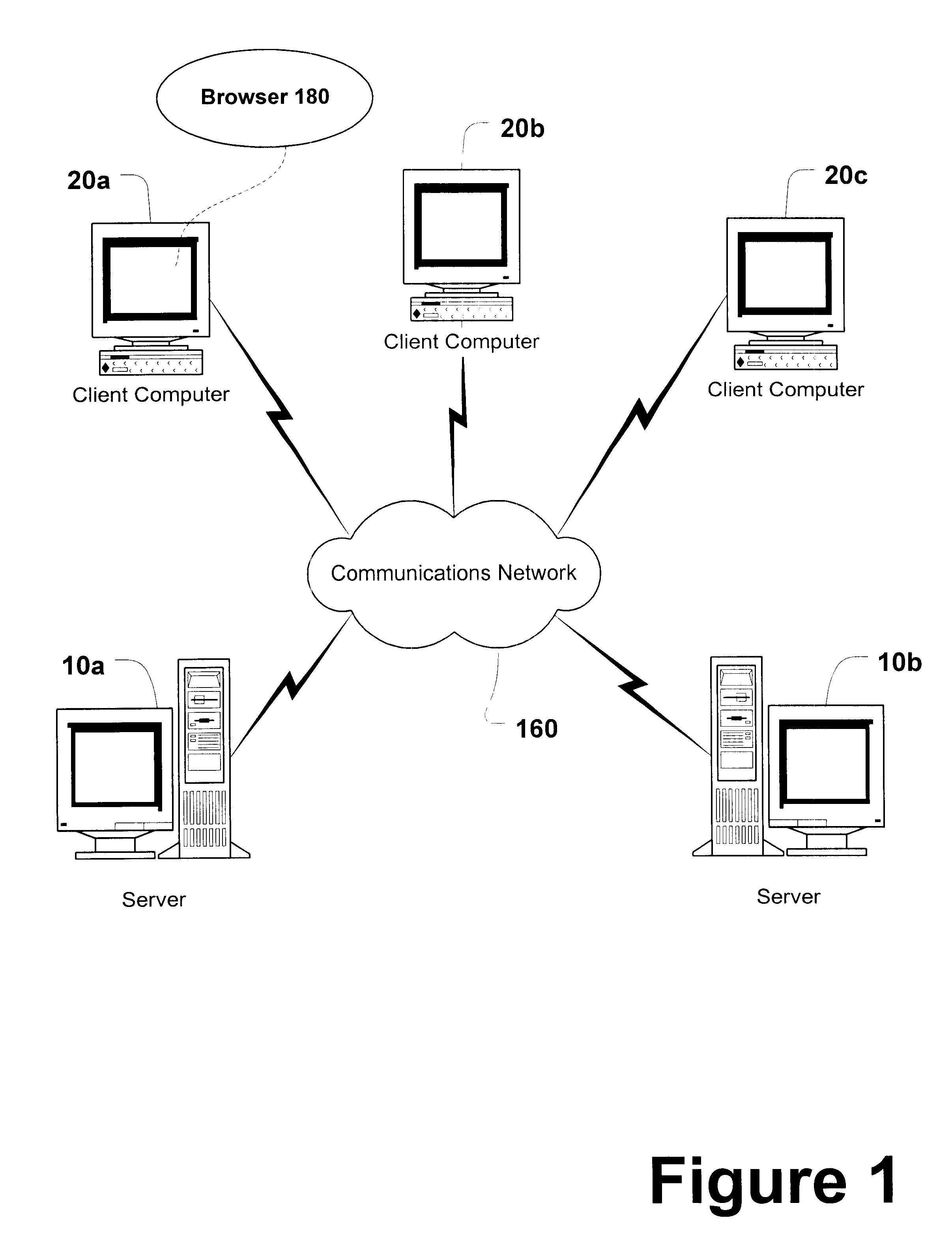
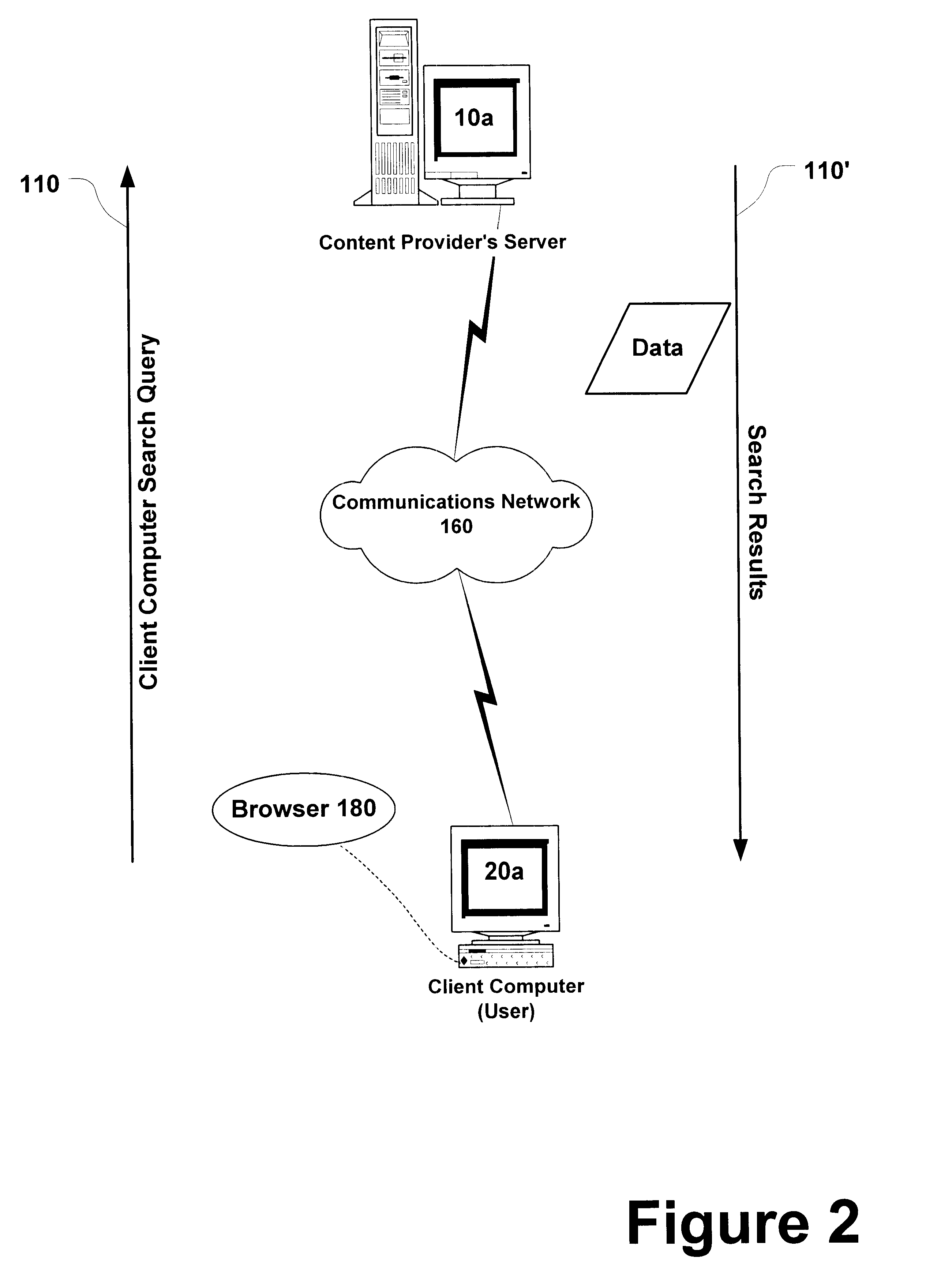
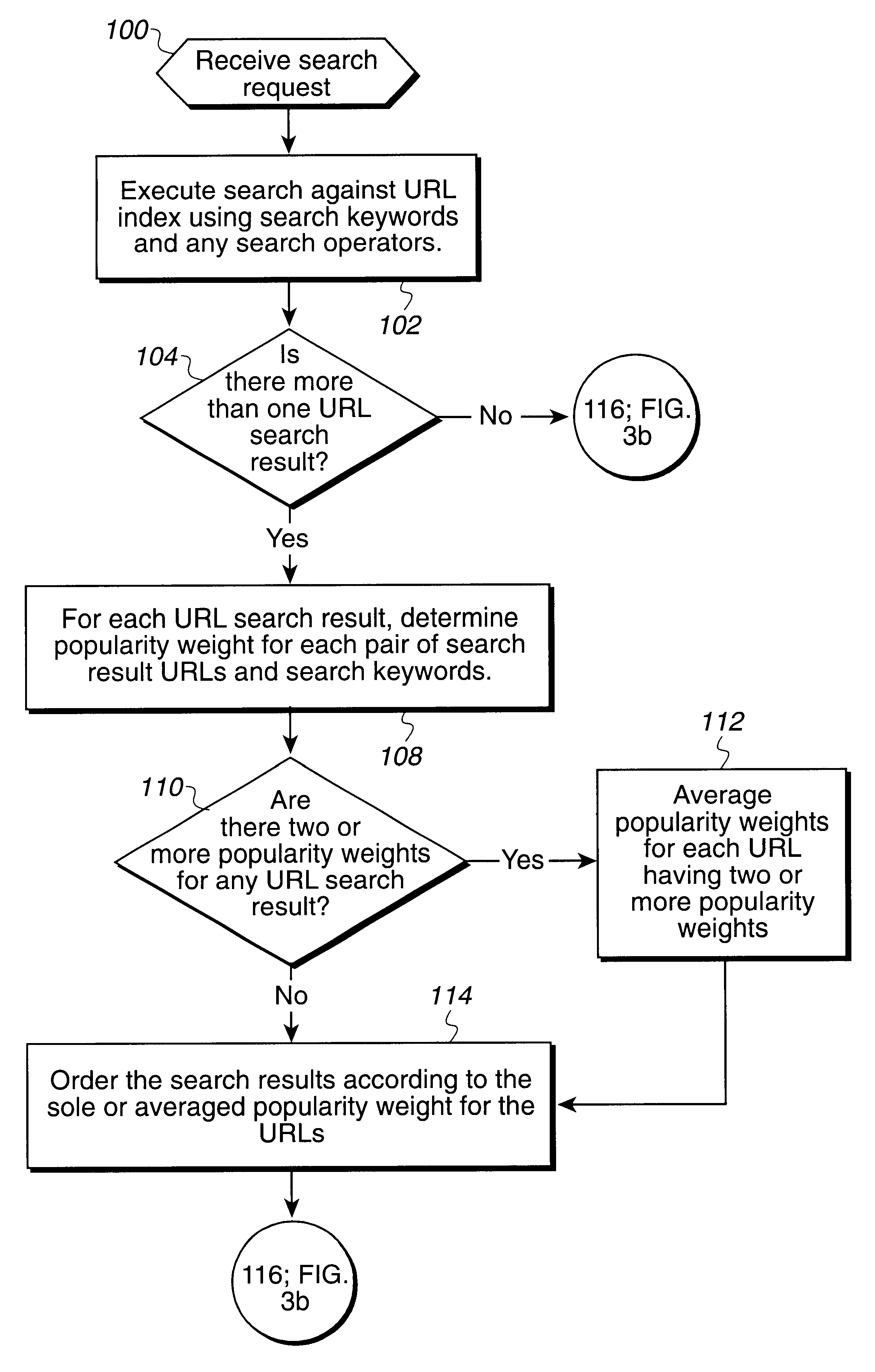
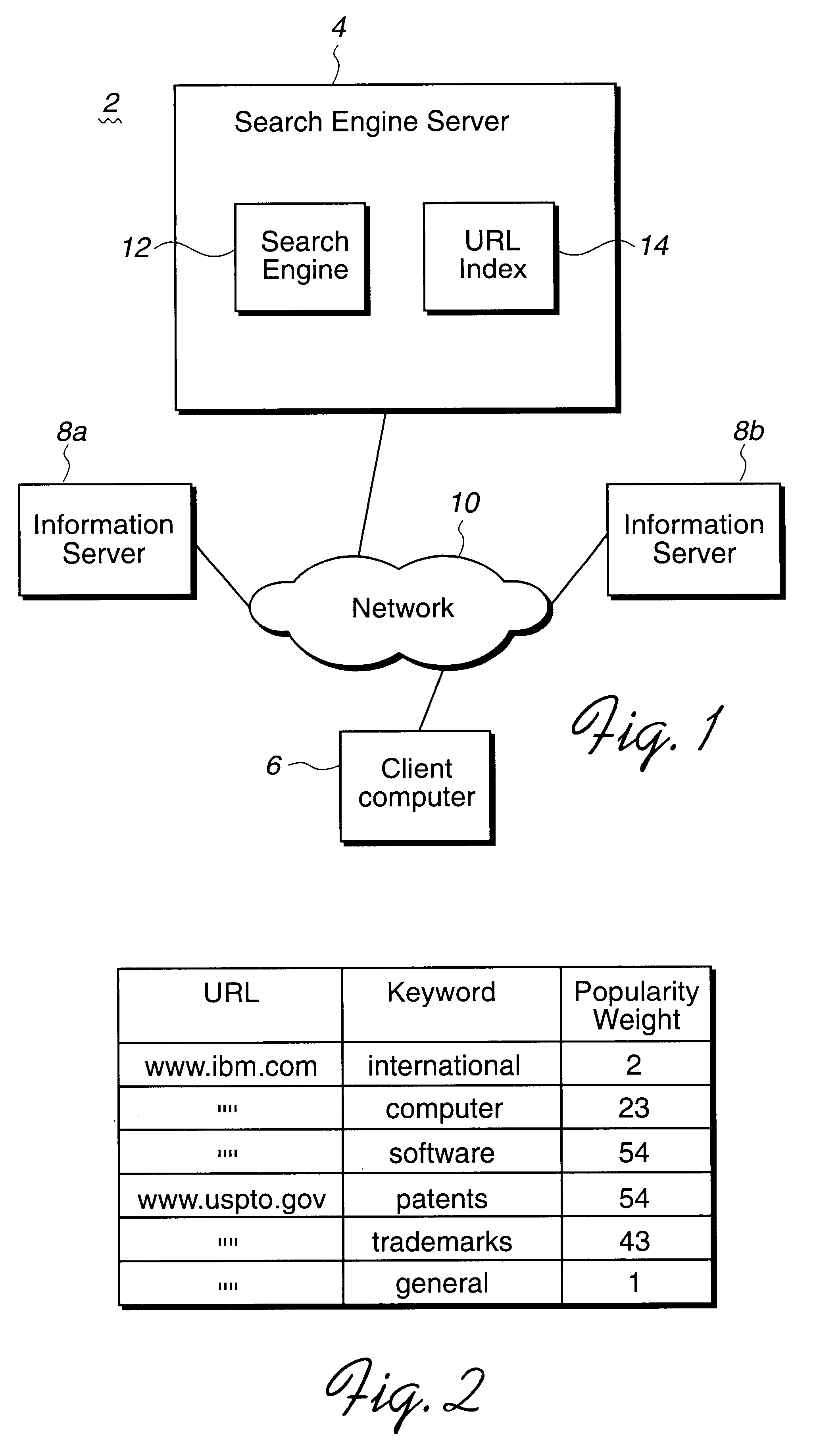
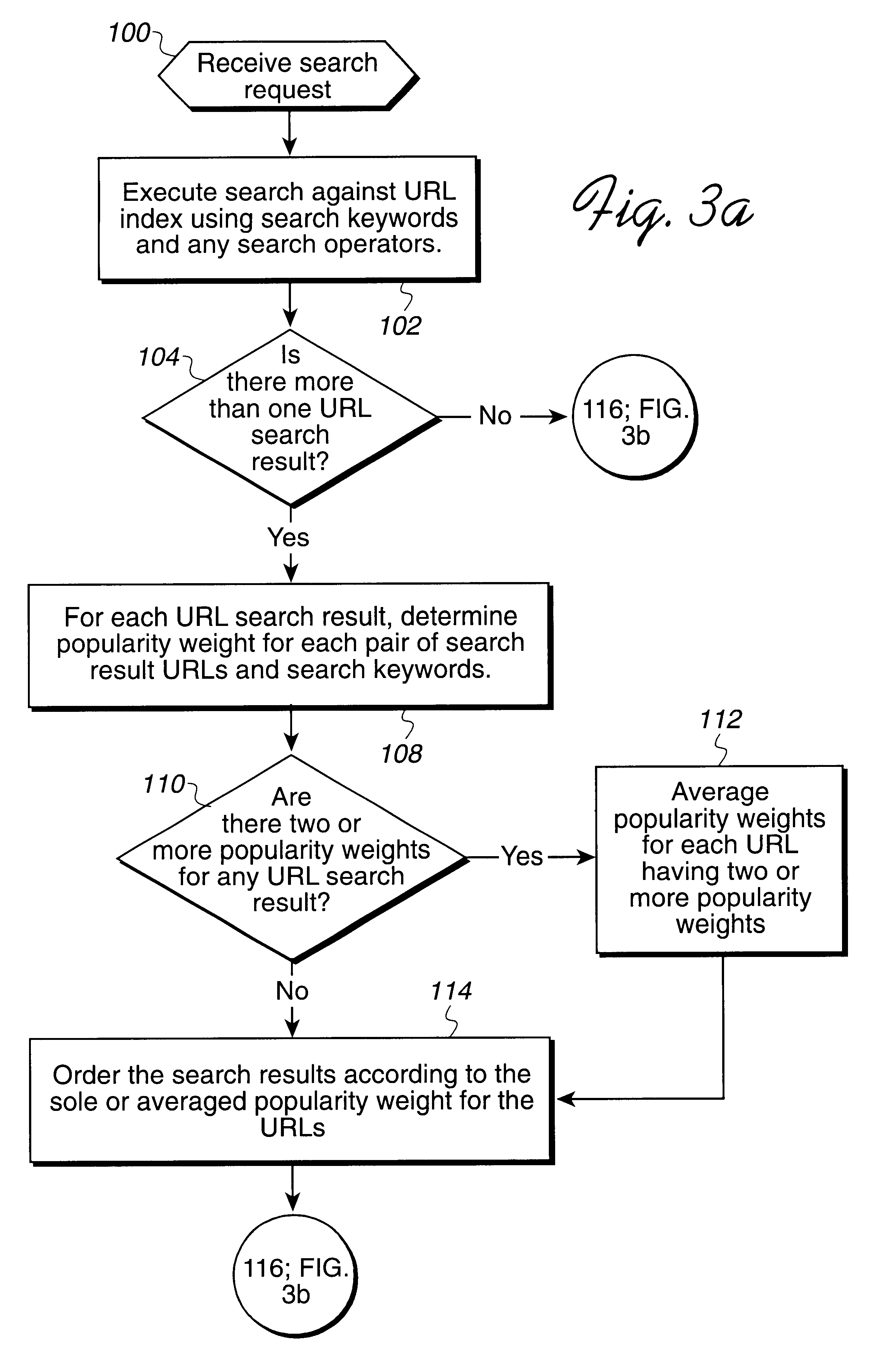
Method, system, and program for ordering search results using a popularity weighting
InactiveUS6480837B1Different popularityAccurately reflectData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDocument preparationUniform resource locator
Disclosed is a method, system, program, and data structures for ordering electronic files subject to searching. At least one keyword is associated with each file. A physical location of each file is identified by a file address, such as a URL. A popularity weight is associated with at least one file address and key word pair such that a file address is capable of having multiple associated keywords and one associated popularity weight for each file address and keyword pair. In response to executing a search query including search keywords, file address search results are received that have at least one associated keyword that matches at least one search keyword in response to executing the search query. The search results are ordered according to the popularity weight associated with each file address search result and keyword pair whose keyword matches the search keyword. A document is then coded to include the file address search results such that the document will display the file address search results according to the ordering.
Owner:LINKEDIN
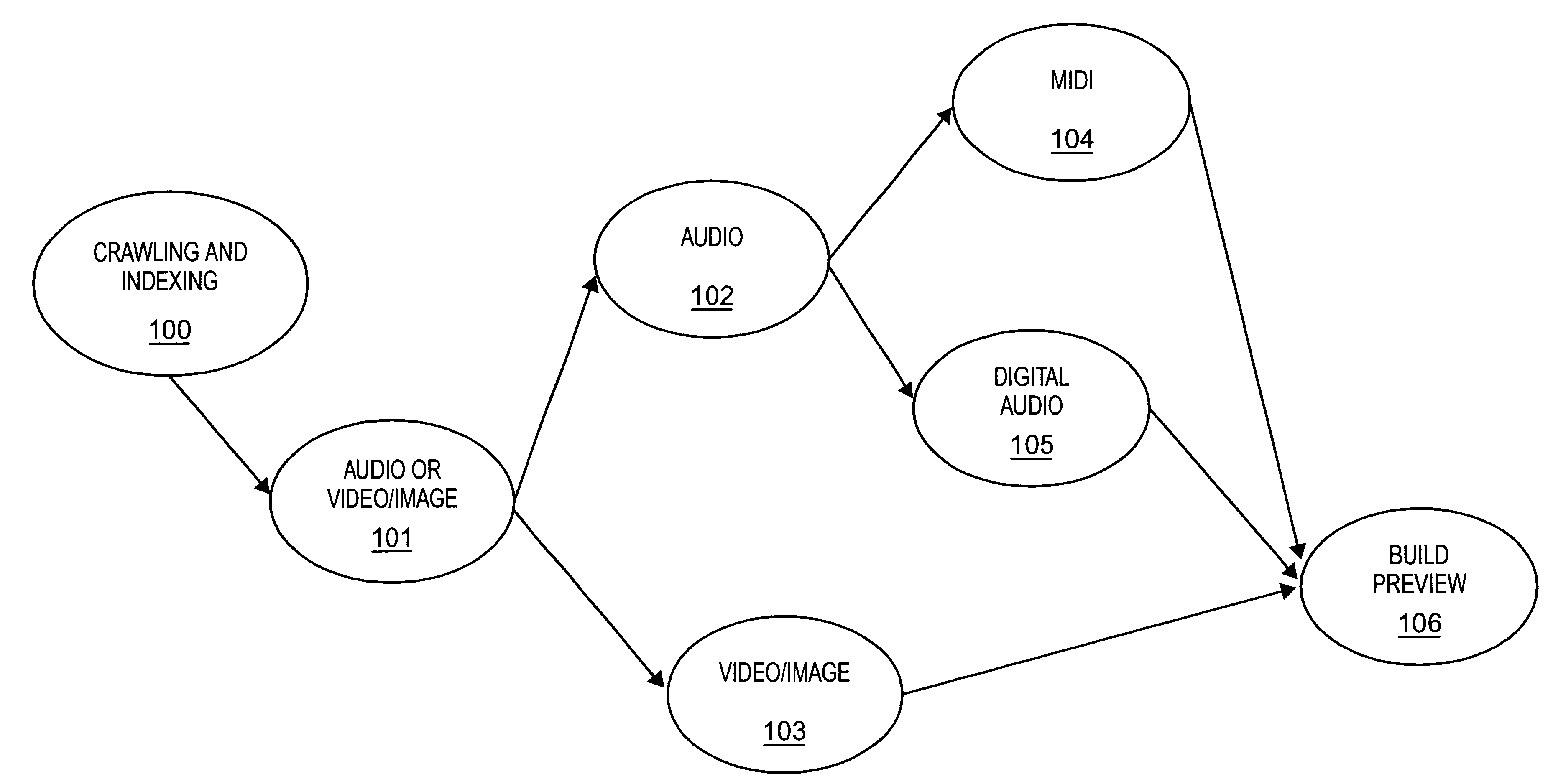
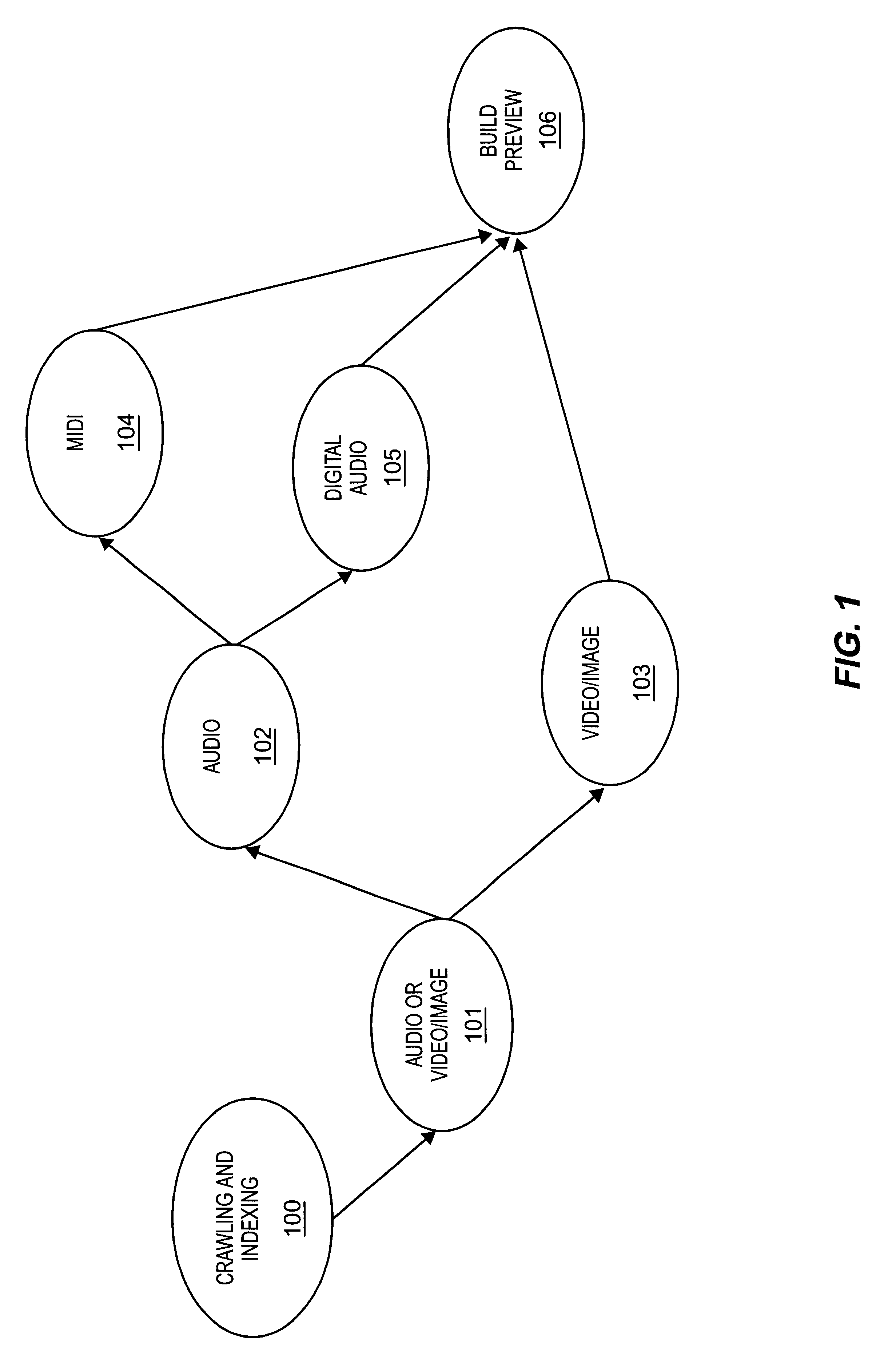
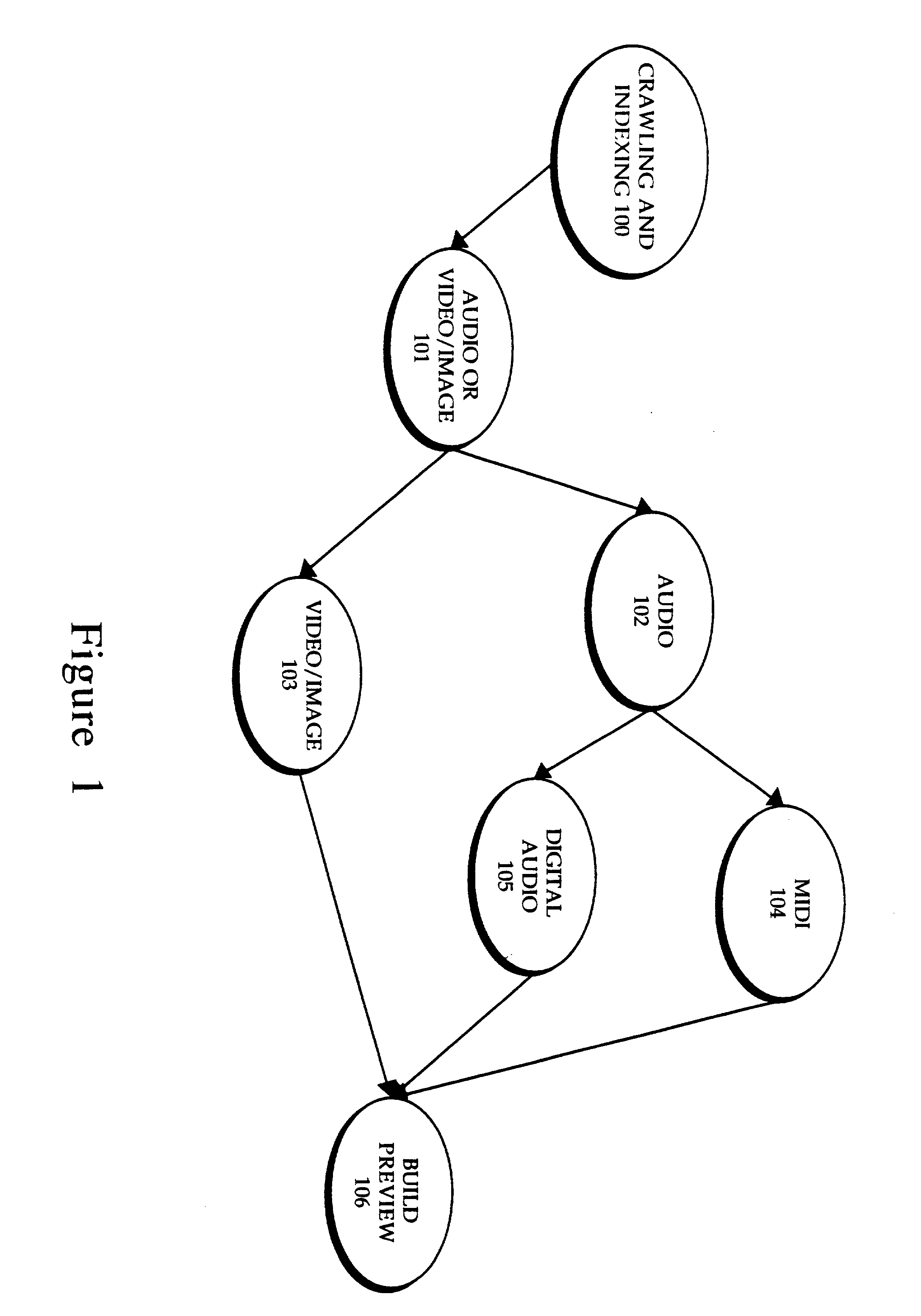
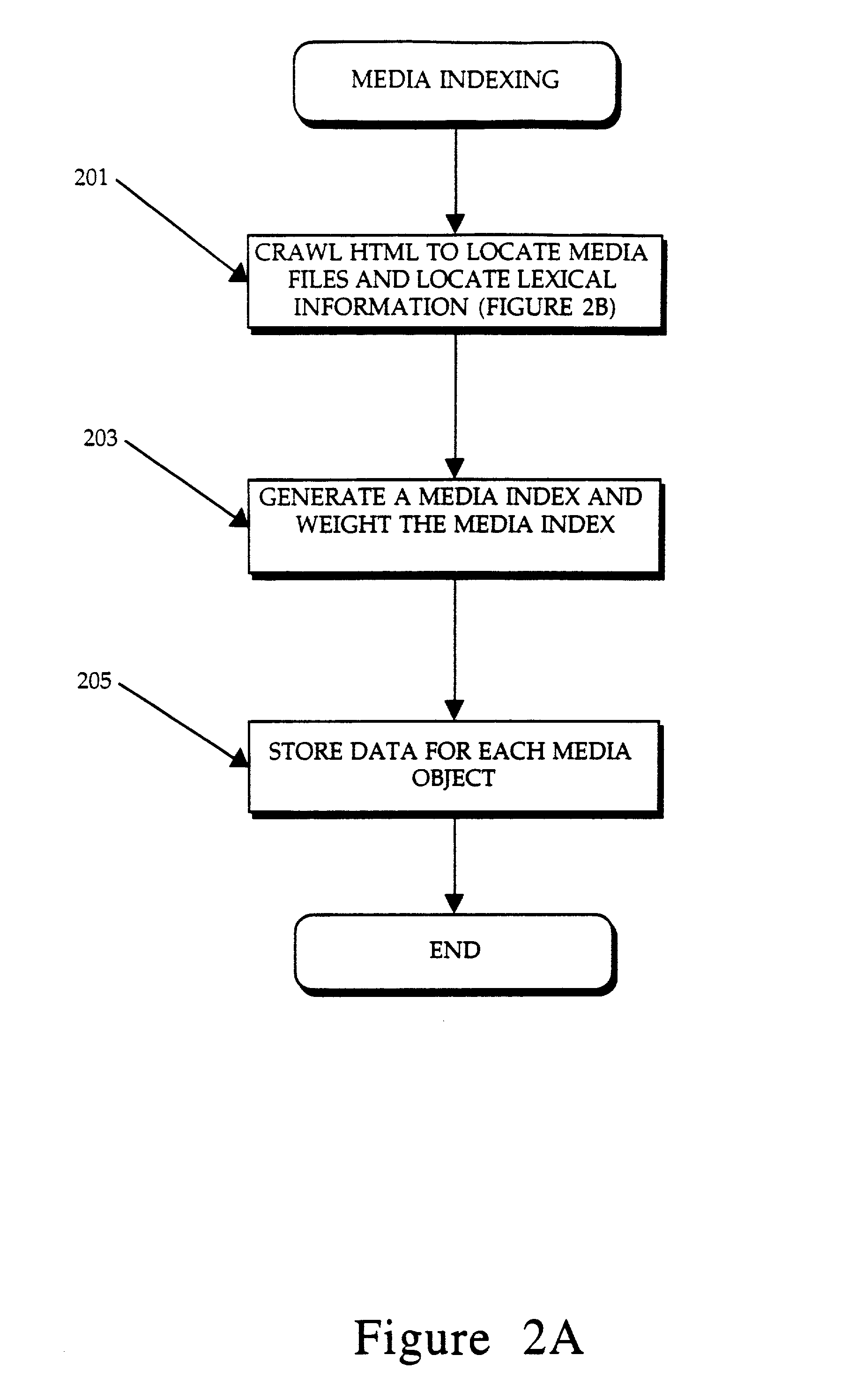
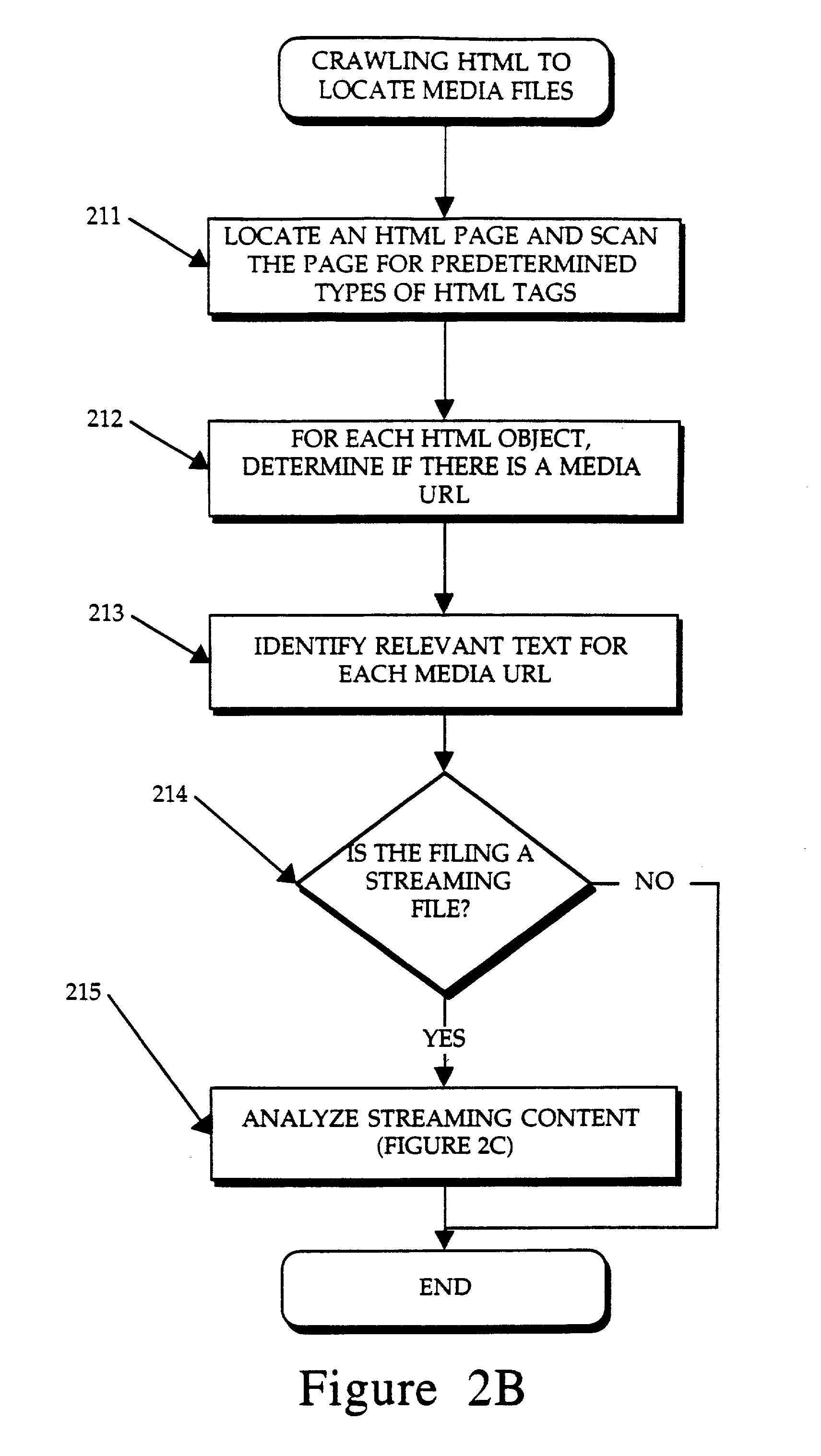
Display of media previews
A method and apparatus for searching for multimedia files in a distributed database and for displaying results of the search based on the context and content of the multimedia files.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Display of media previews
A method and apparatus for searching for multimedia files in a distributed database and for displaying results of the search based on the context and content of the multimedia files.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
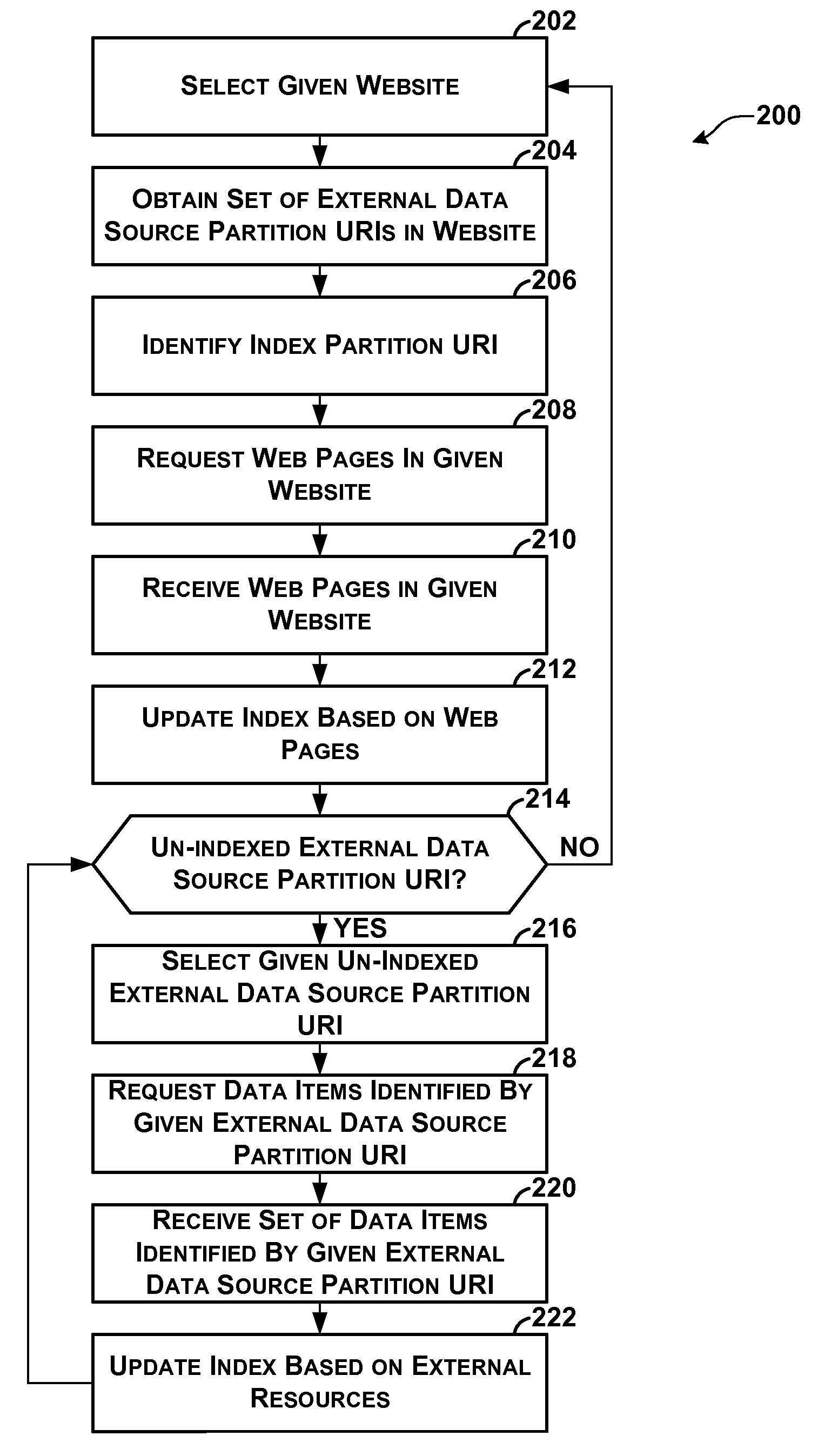
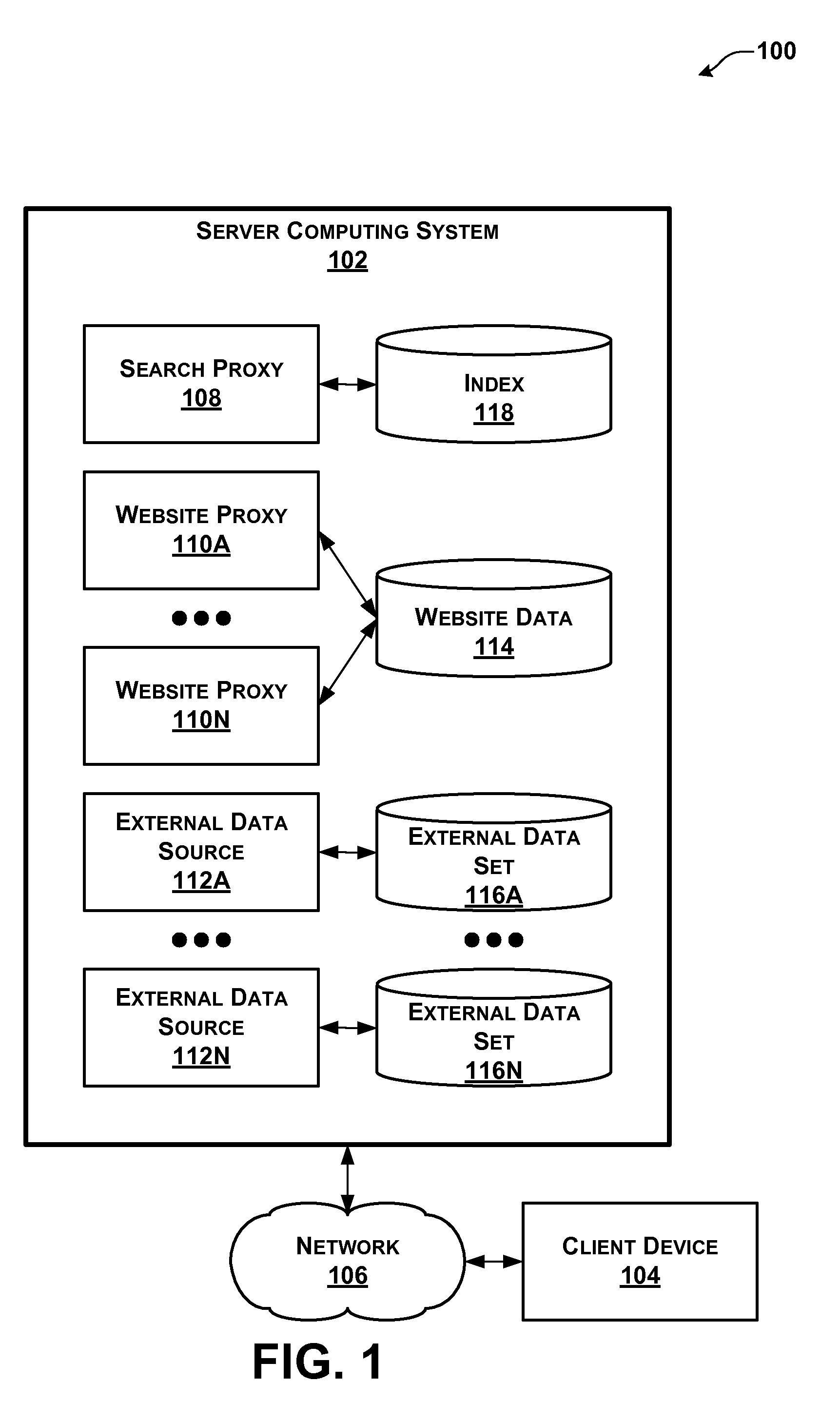
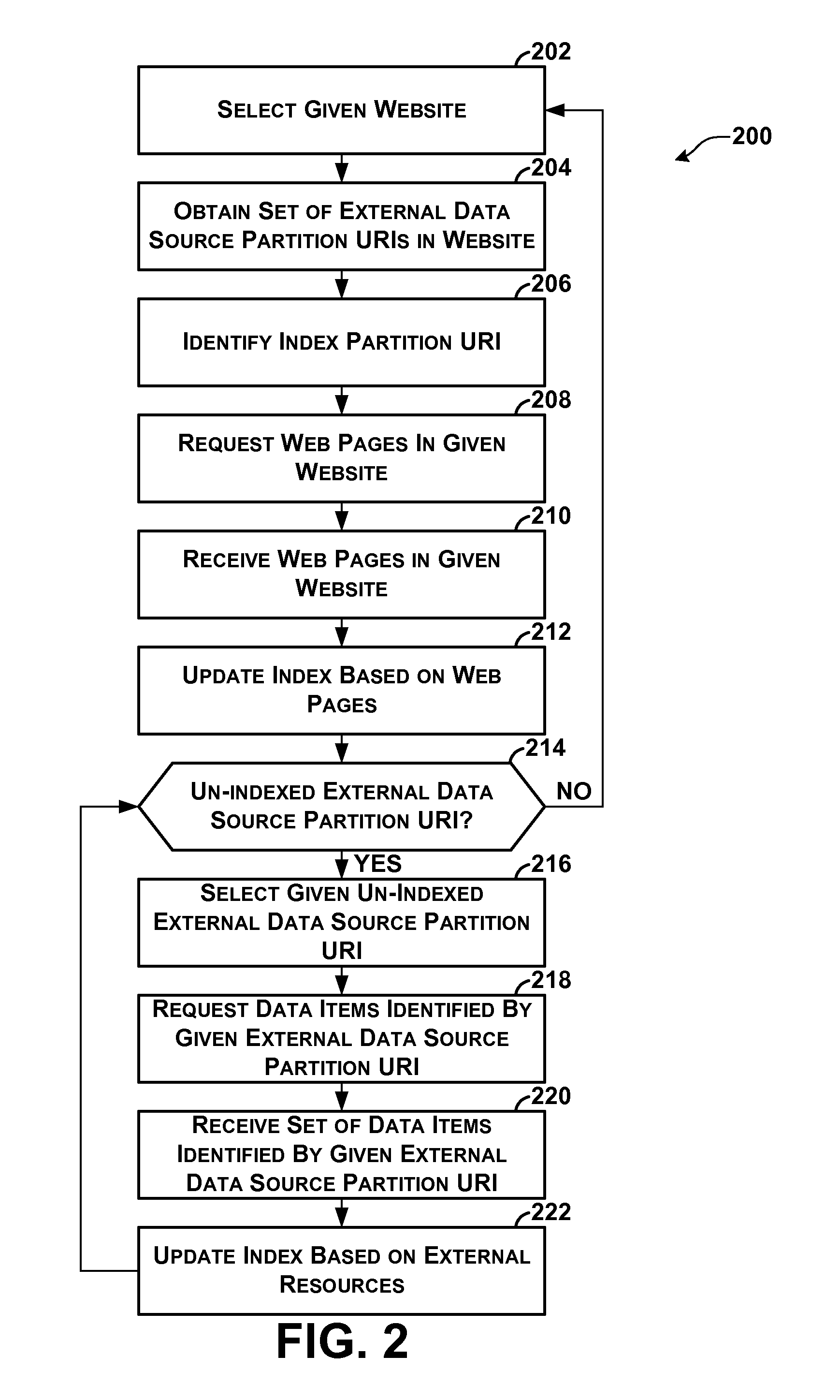
Indexing of Partitioned External Data Sources
ActiveUS20110022582A1Well formedWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsWeb siteExternal data
A computing system hosts a plurality of websites, a plurality of external data sources, and a search service. External resources in each of the external data sources are partitioned among a plurality of external partitions. The search service automatically generates an index comprising index entries. The index entries are partitioned among a plurality of index partitions, each associated with one or more of the websites. For each given index partition, the index entries in the given index partition map terms to resources in the given set of resources that contain the terms. The given set of resources includes web pages in a given set of websites associated with the given index partition and external resources in external partitions used by the given set of websites. The search service uses the index entries in given index partition to identify resources in the given set of resources containing query terms.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
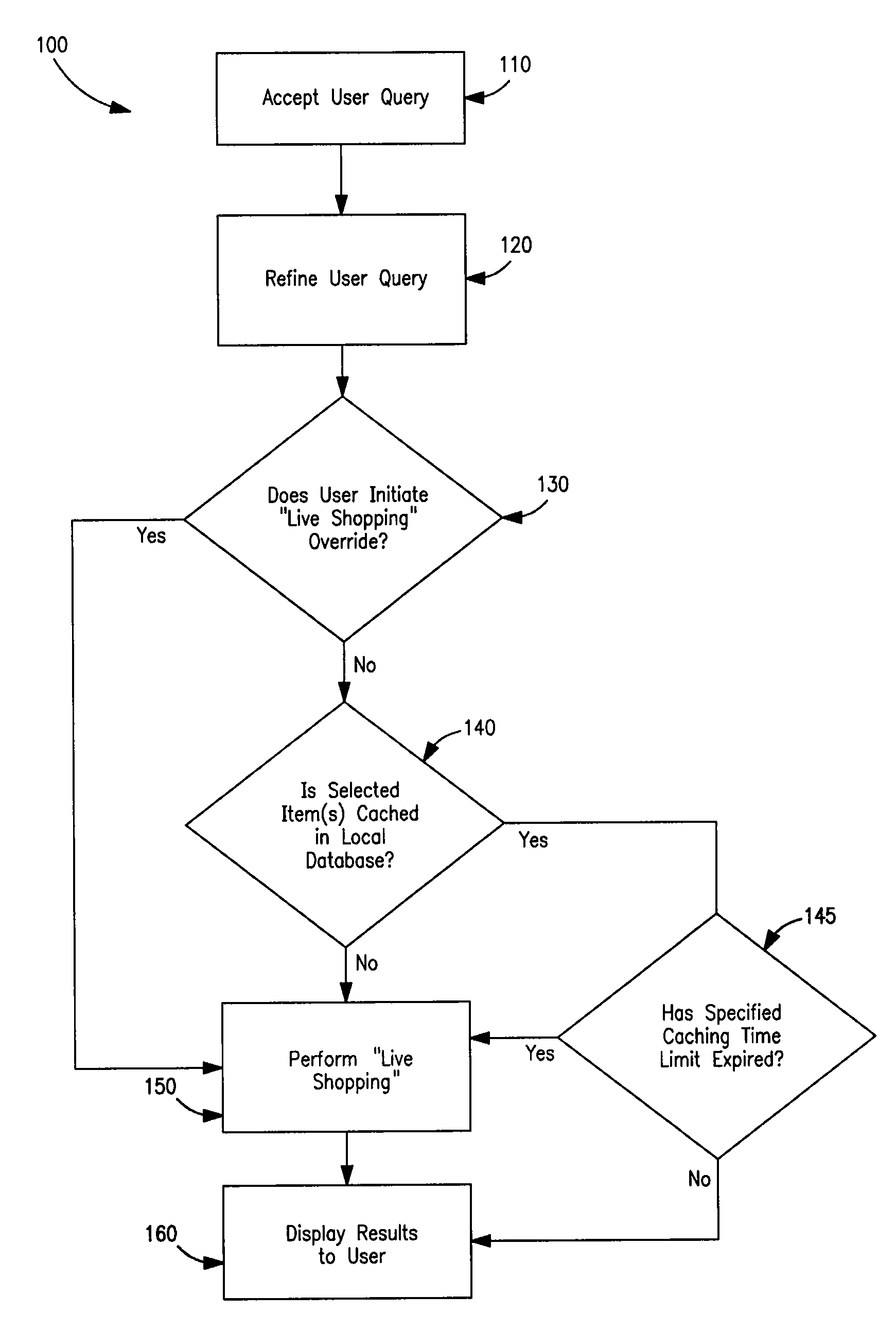
System, method and apparatus for interactive and comparative shopping
ActiveUS8255291B1Efficient queryShopping less confusing.Web data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsLibrary science
A method and system allows a user to aggregate product information or compare multiple products by a single query. A sales representative or end consumer is provided quick access to accurate detailed product information and comparison information, which can make shopping less confusing. The method involves generating a comparison report of two or more products, including detailed product information.
Owner:ANDERSON MERCHANDISERS
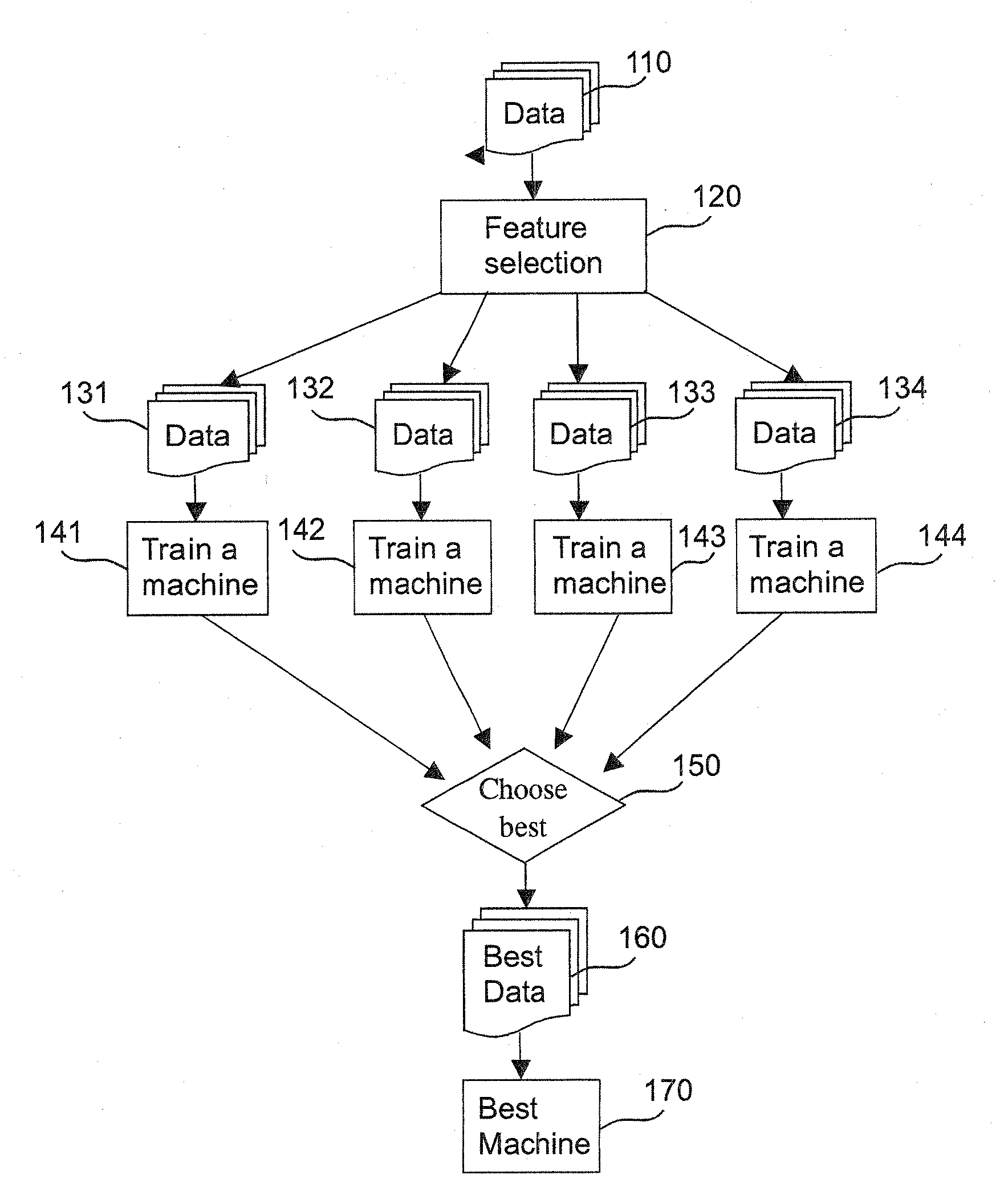
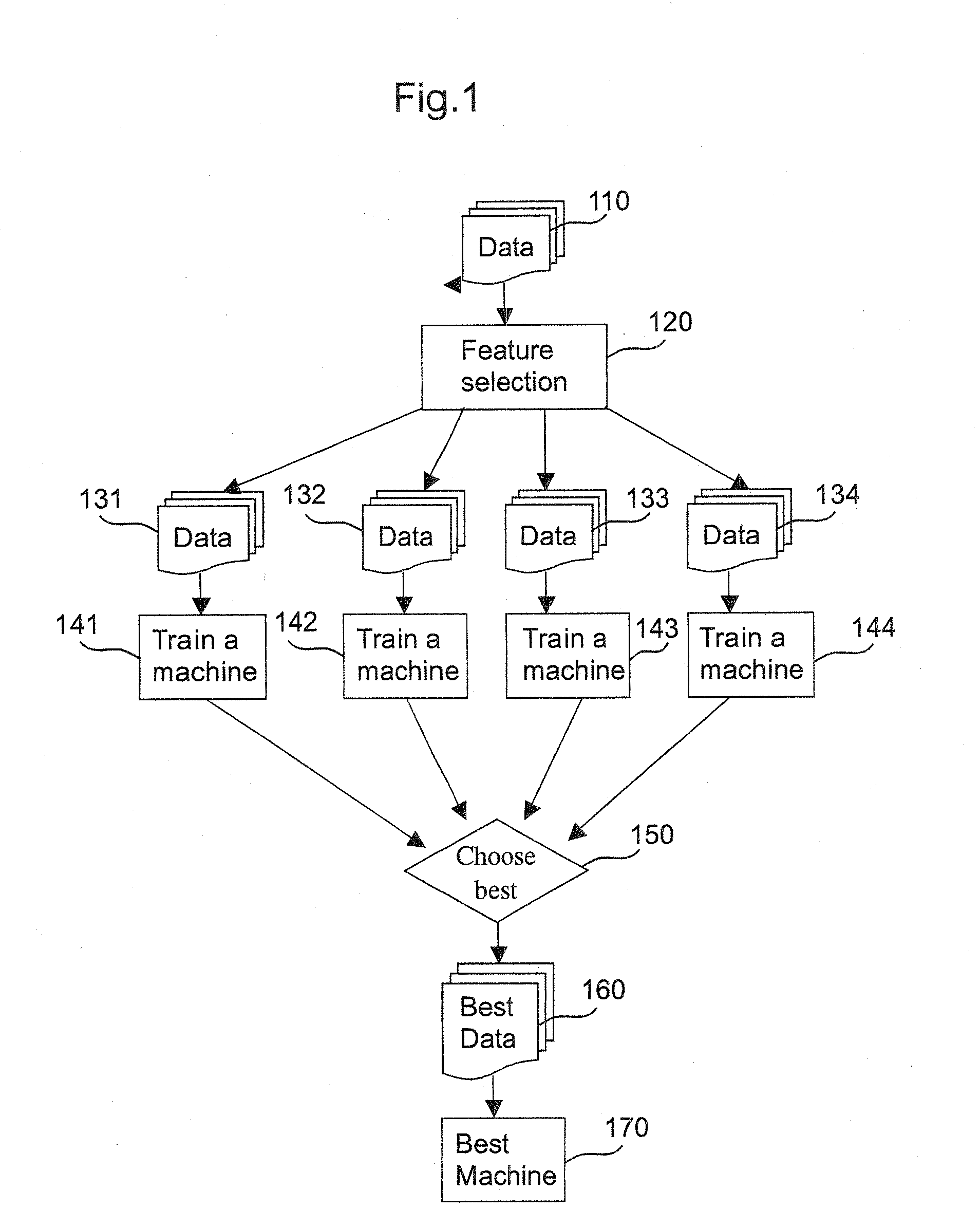
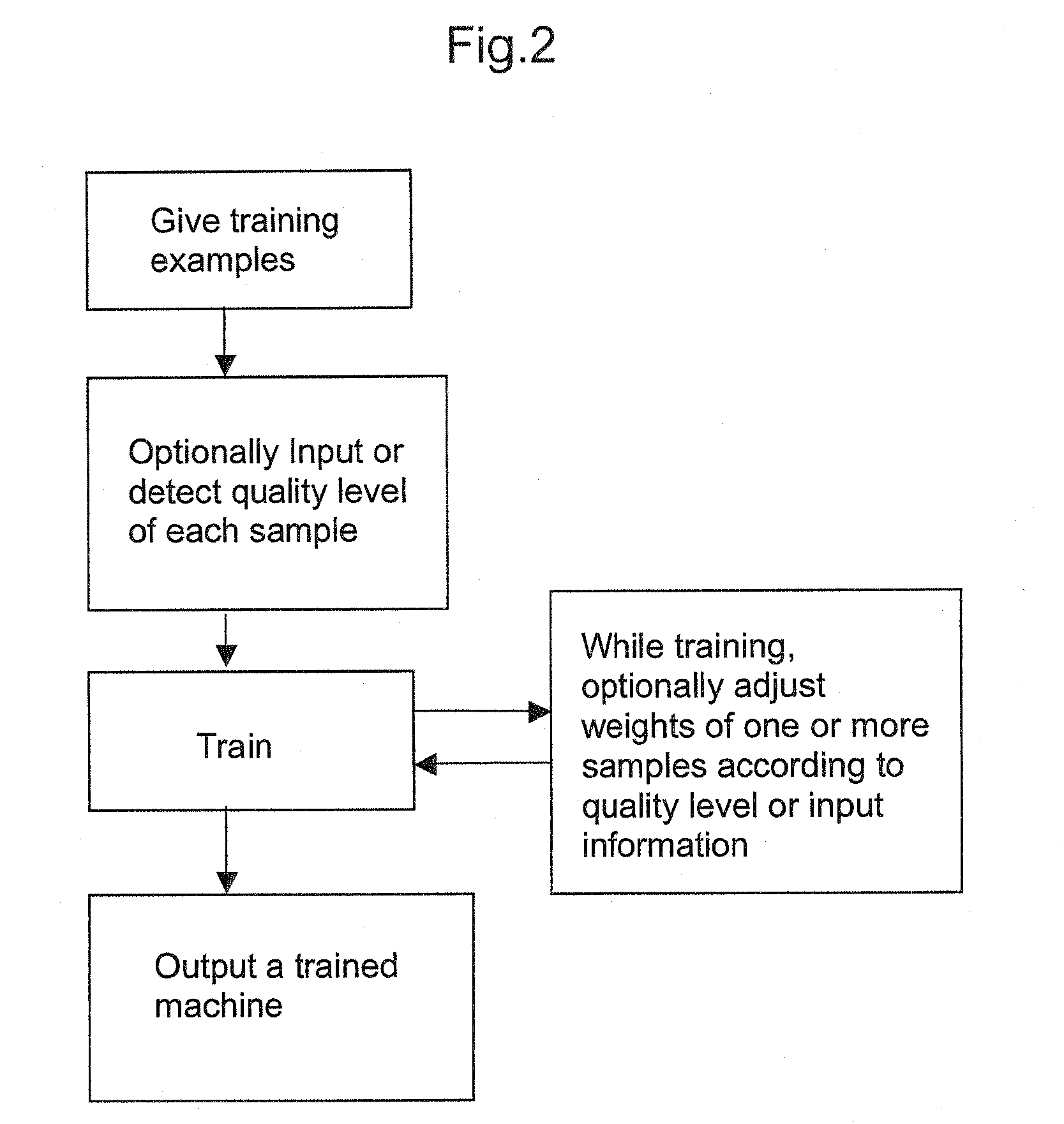
Machine learning methods and systems for identifying patterns in data
ActiveUS20100063948A1Reduce dimensionalityPromote resultsDigital data processing detailsKernel methodsData classSupport vector machine
Methods for training machines to categorize data, and / or recognize patterns in data, and machines and systems so trained. More specifically, variations of the invention relates to methods for training machines that include providing one or more training data samples encompassing one or more data classes, identifying patterns in the one or more training data samples, providing one or more data samples representing one or more unknown classes of data, identifying patterns in the one or more of the data samples of unknown class(es), and predicting one or more classes to which the data samples of unknown class(es) belong by comparing patterns identified in said one or more data samples of unknown class with patterns identified in said one or more training data samples. Also provided are tools, systems, and devices, such as support vector machines (SVMs) and other methods and features, software implementing the methods and features, and computers or other processing devices incorporating and / or running the software, where the methods and features, software, and processors utilize specialized methods to analyze data.
Owner:DIGITAL INFUZION
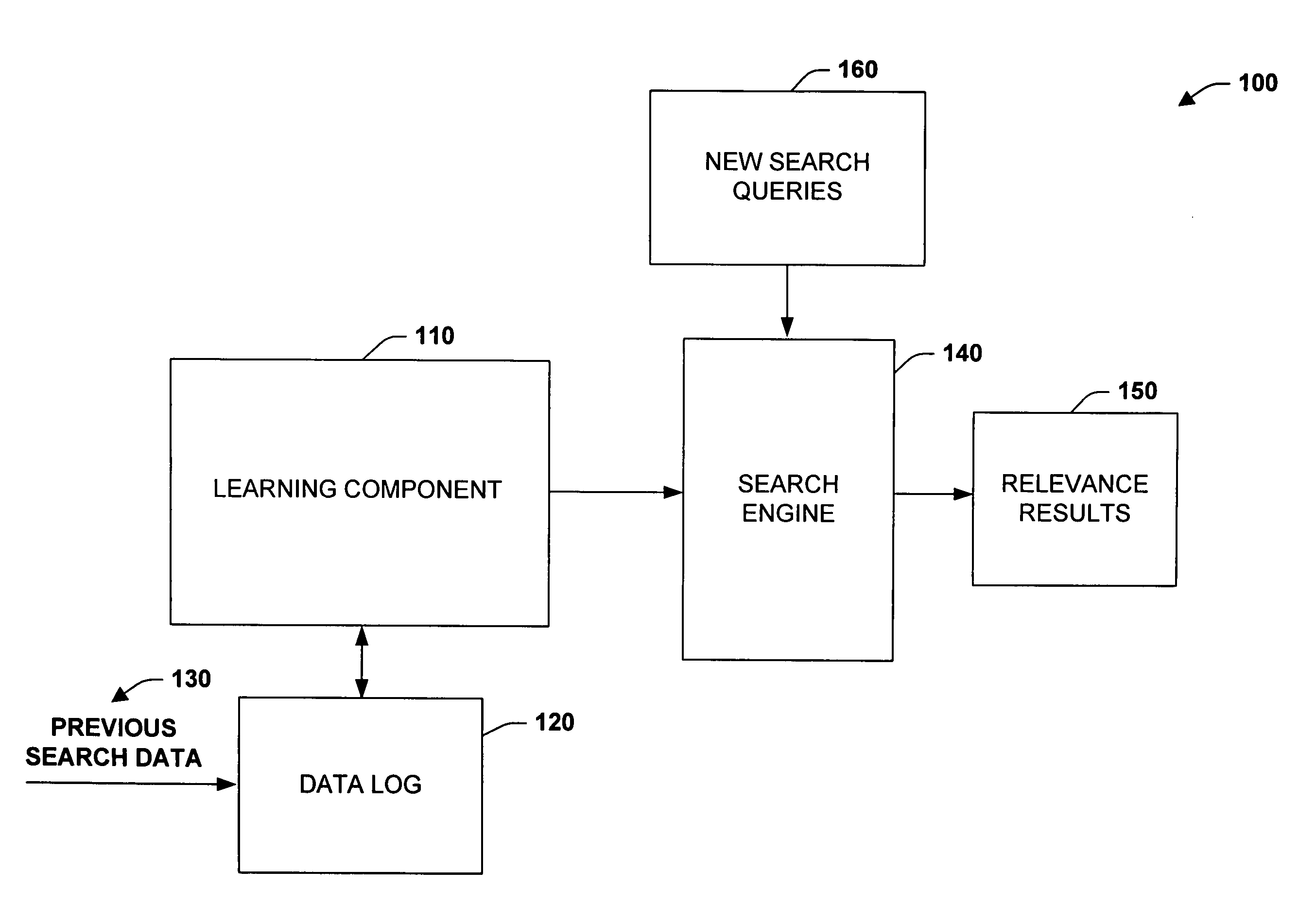
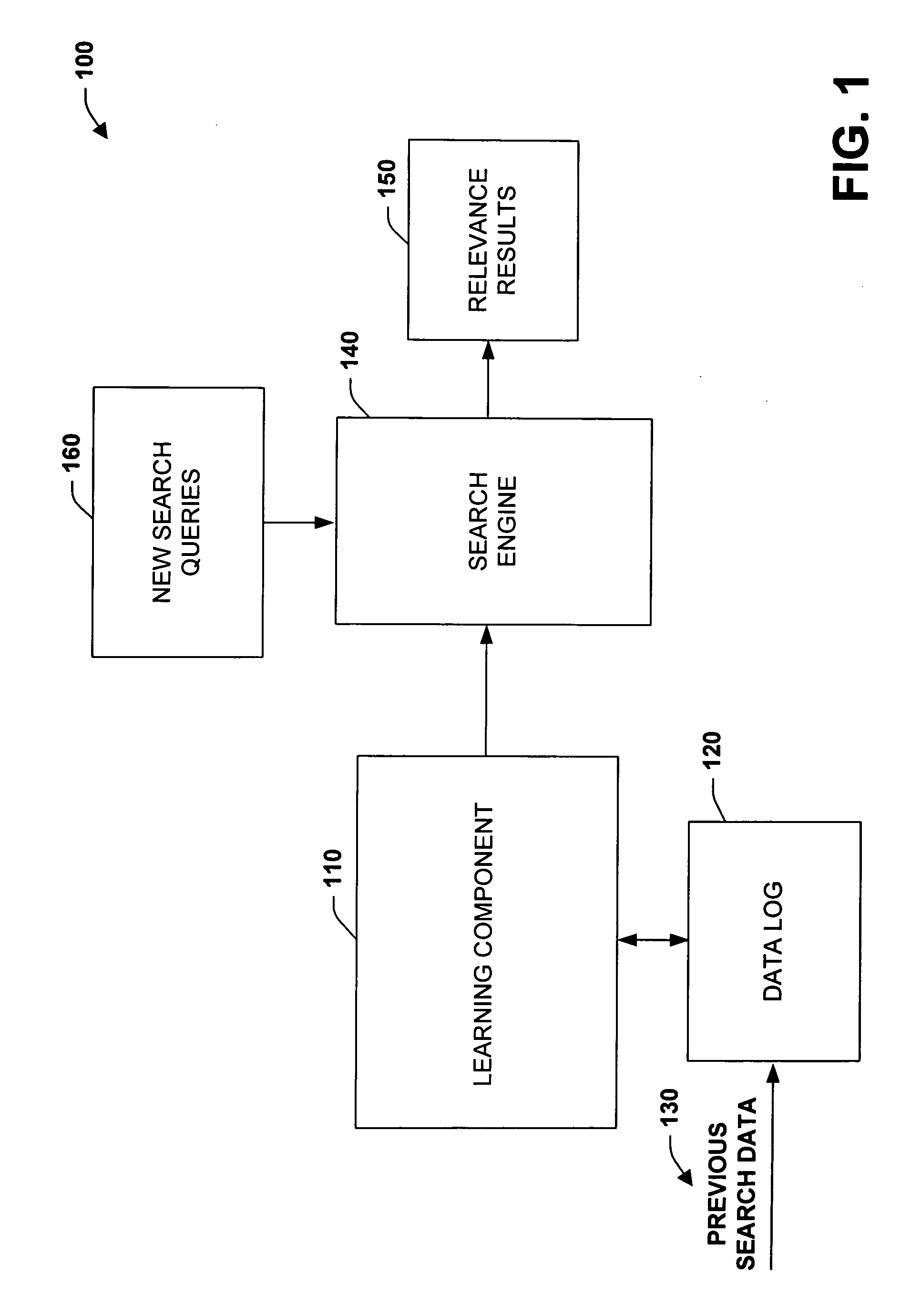
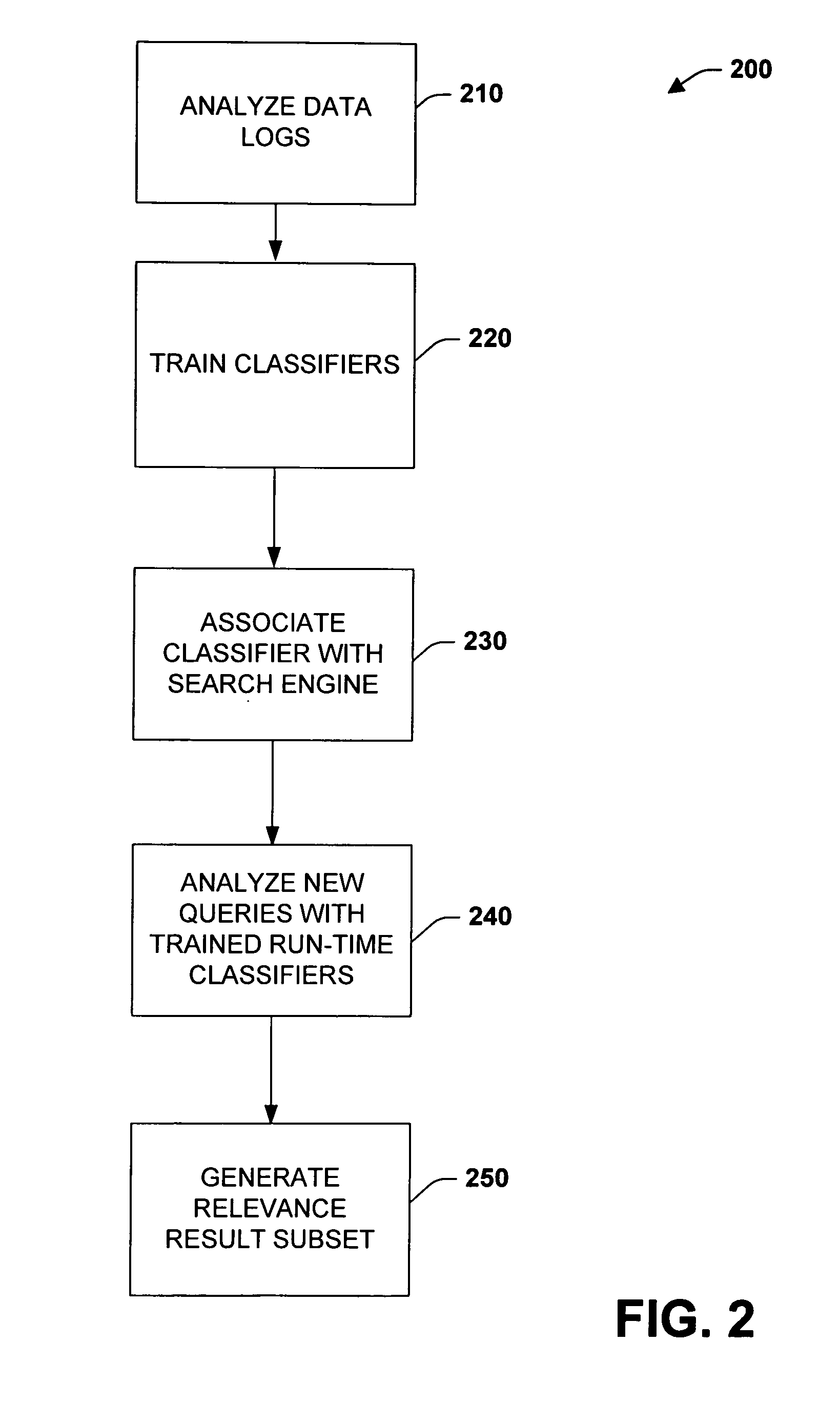
Data mining techniques for improving search engine relevance
InactiveUS20060224579A1Facilitate efficient searching and retrieval and analysisSimple processWeb data indexingSolid waste disposalLearning dataInformation retrieval
The subject invention relates to systems and methods that automatically learn data relevance from past search activities and apply such learning to facilitate future search activities. In one aspect, an automated information retrieval system is provided. The system includes a learning component that analyzes stored information retrieval data to determine relevance patterns from past user information search activities. A search component employs the learning component to determine a subset of current search results based at least in part on the relevance patterns, wherein numerous variables can be processed in accordance with the learning component to efficiently generate focused, prioritized, and relevant search results.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
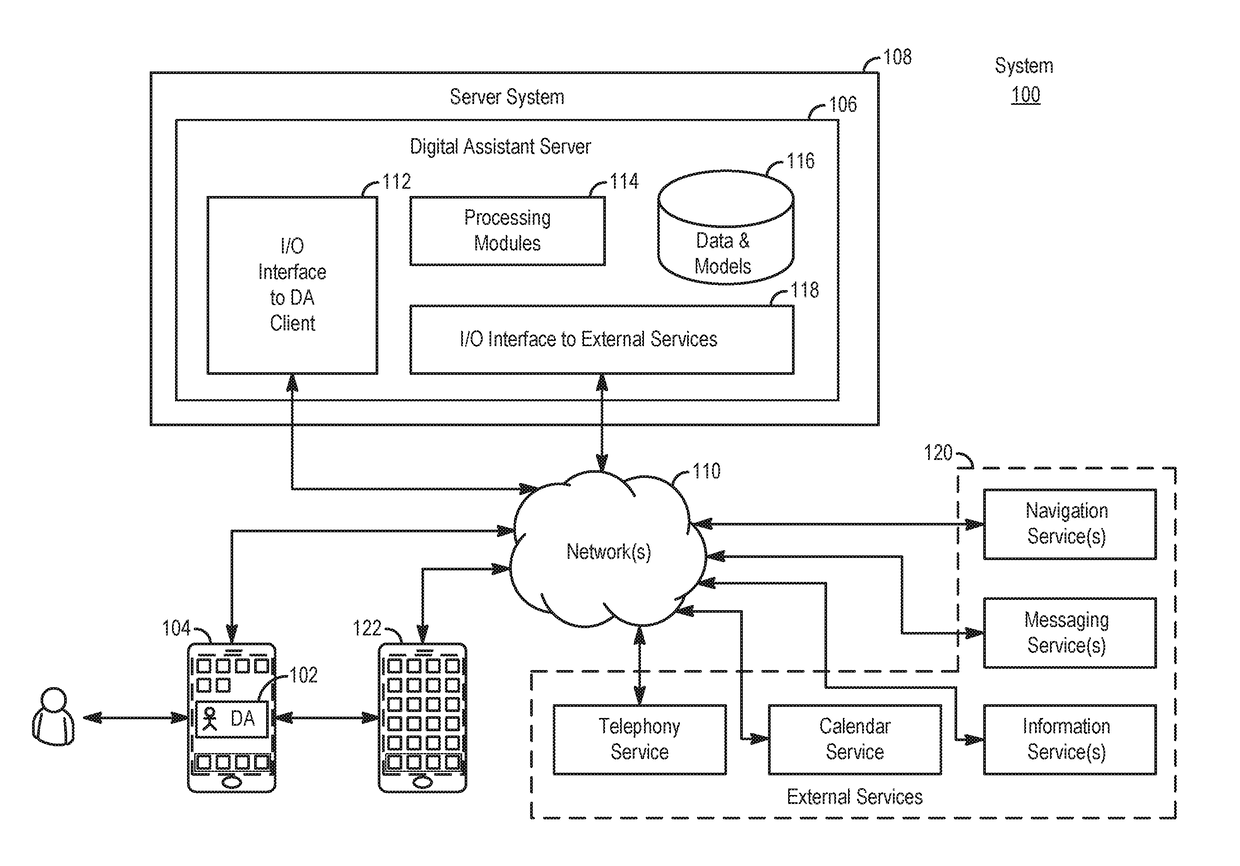
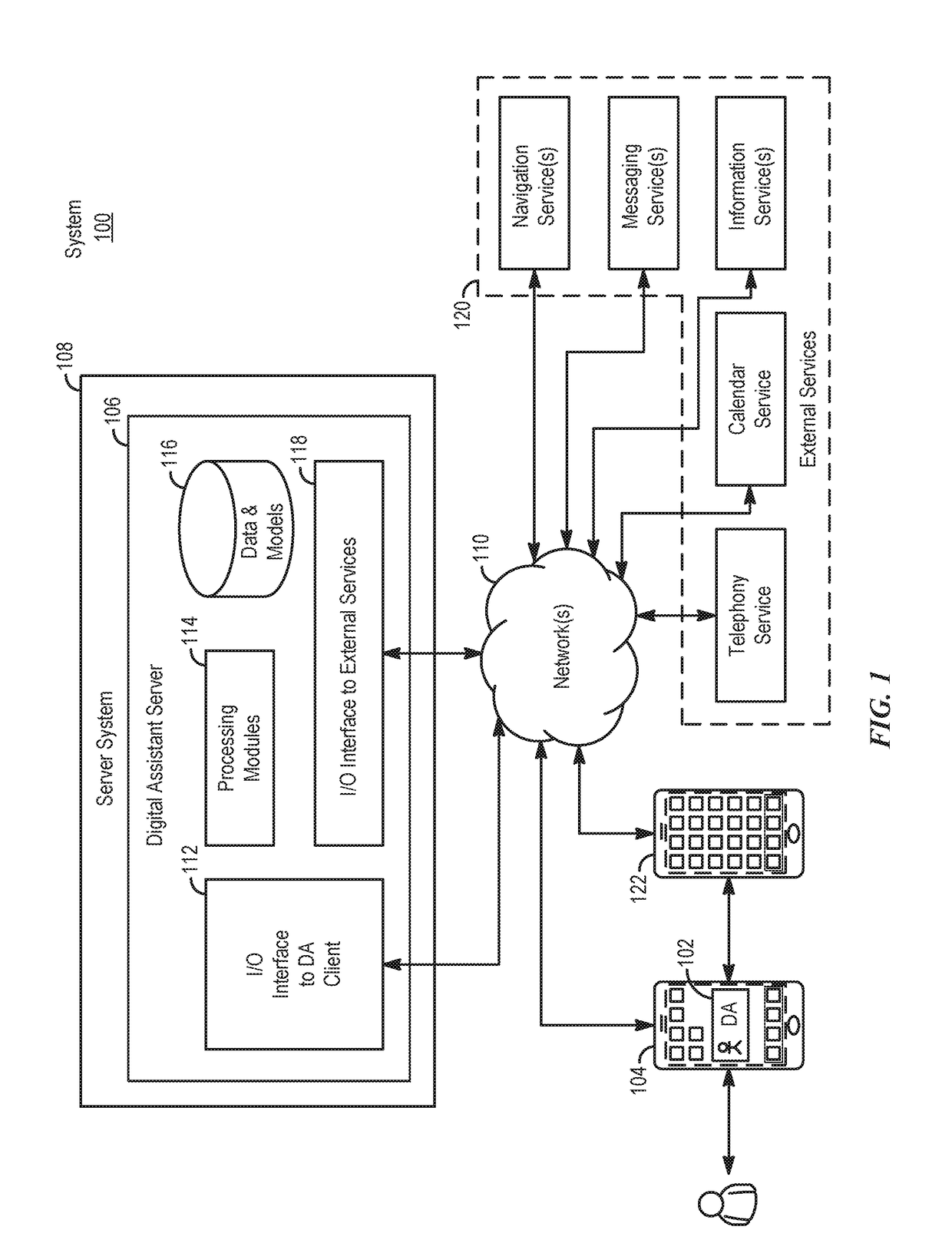
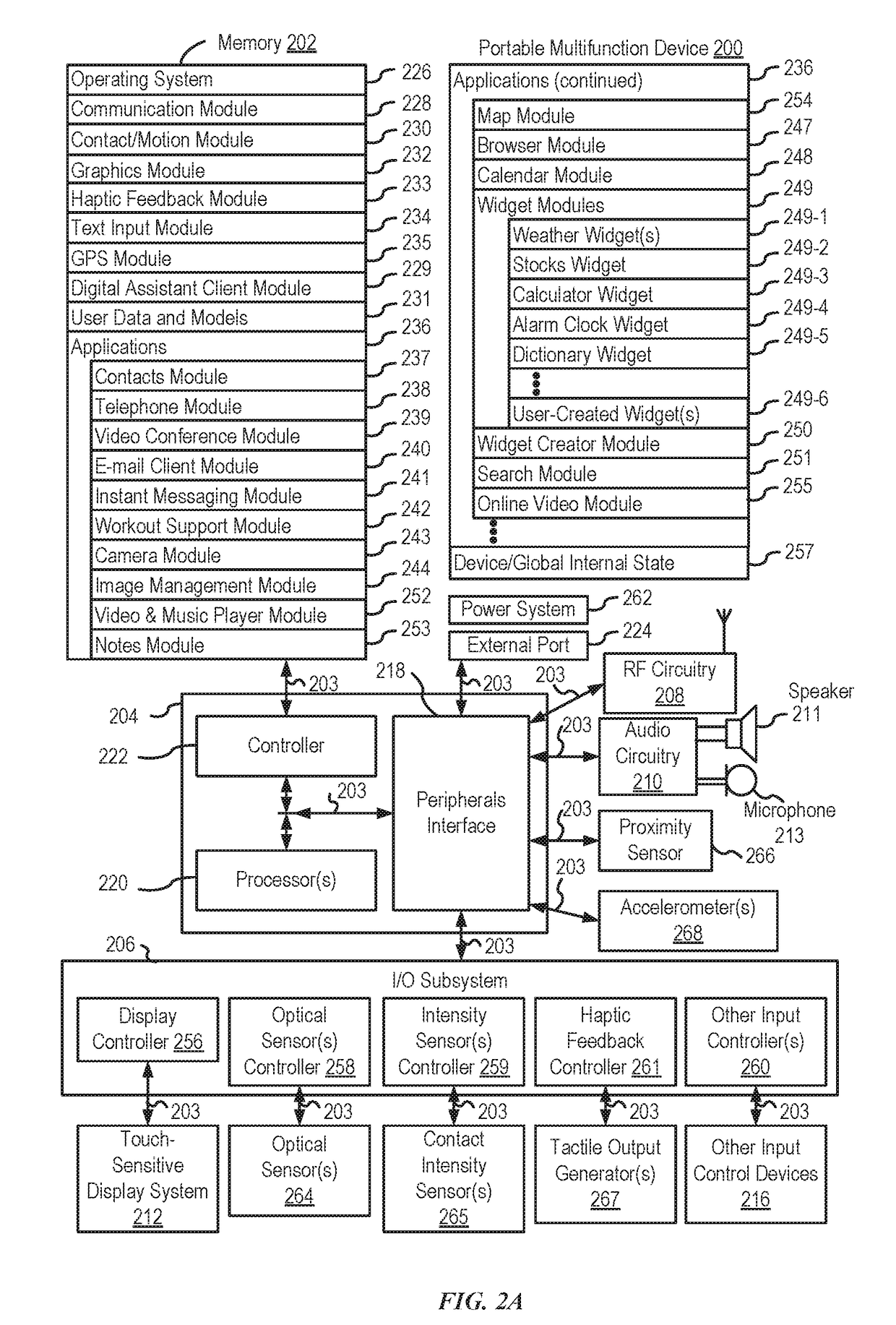
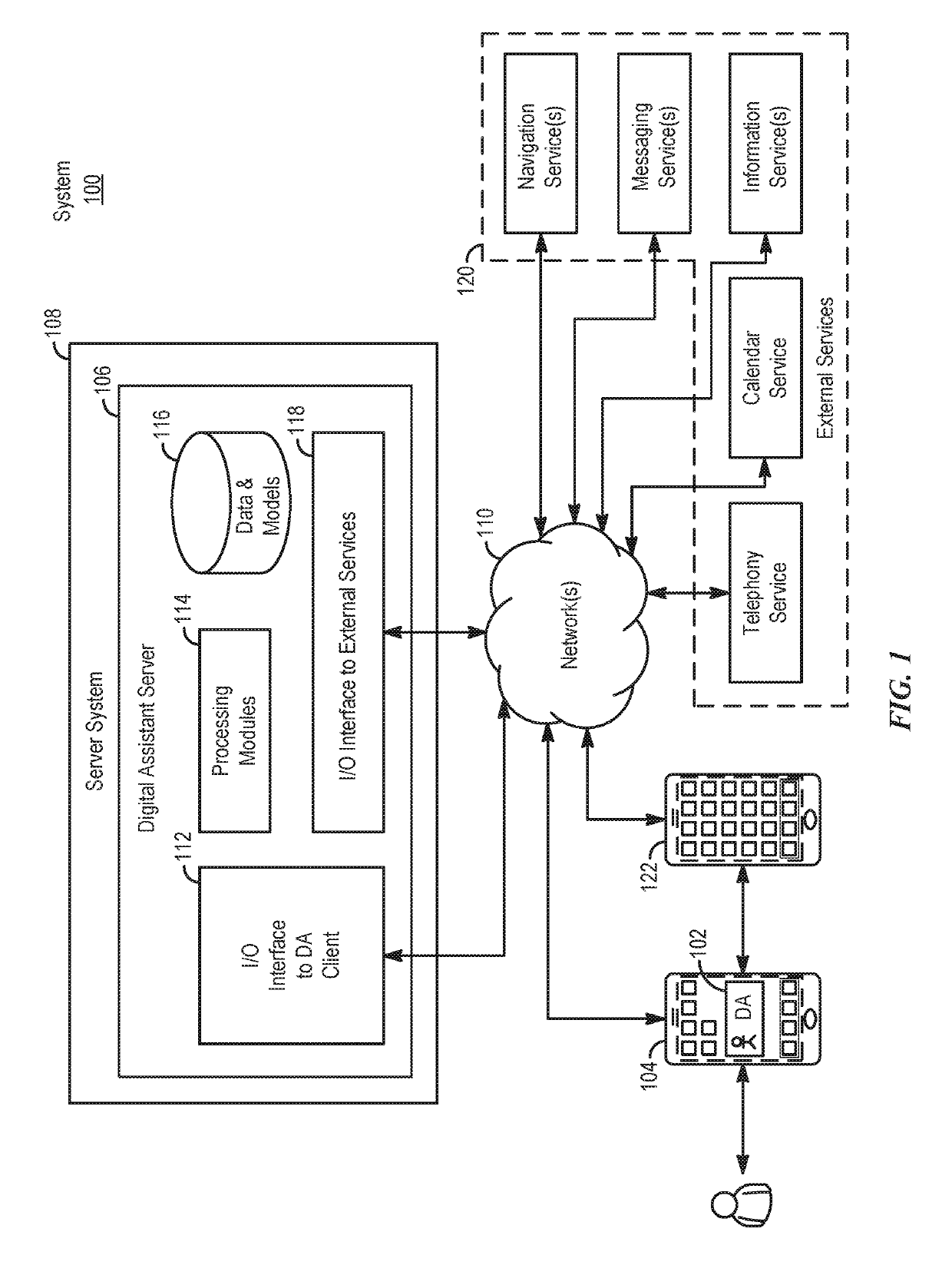
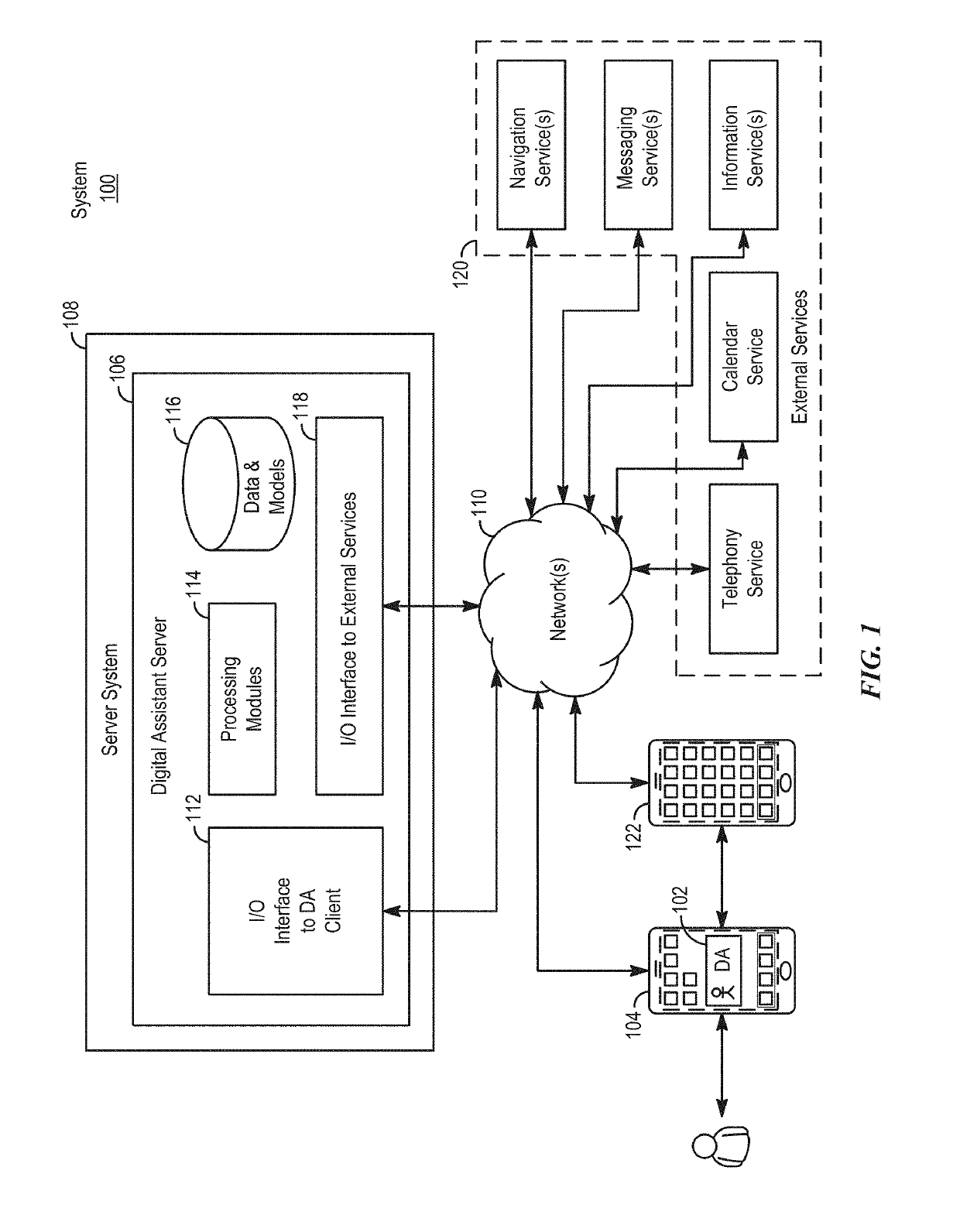
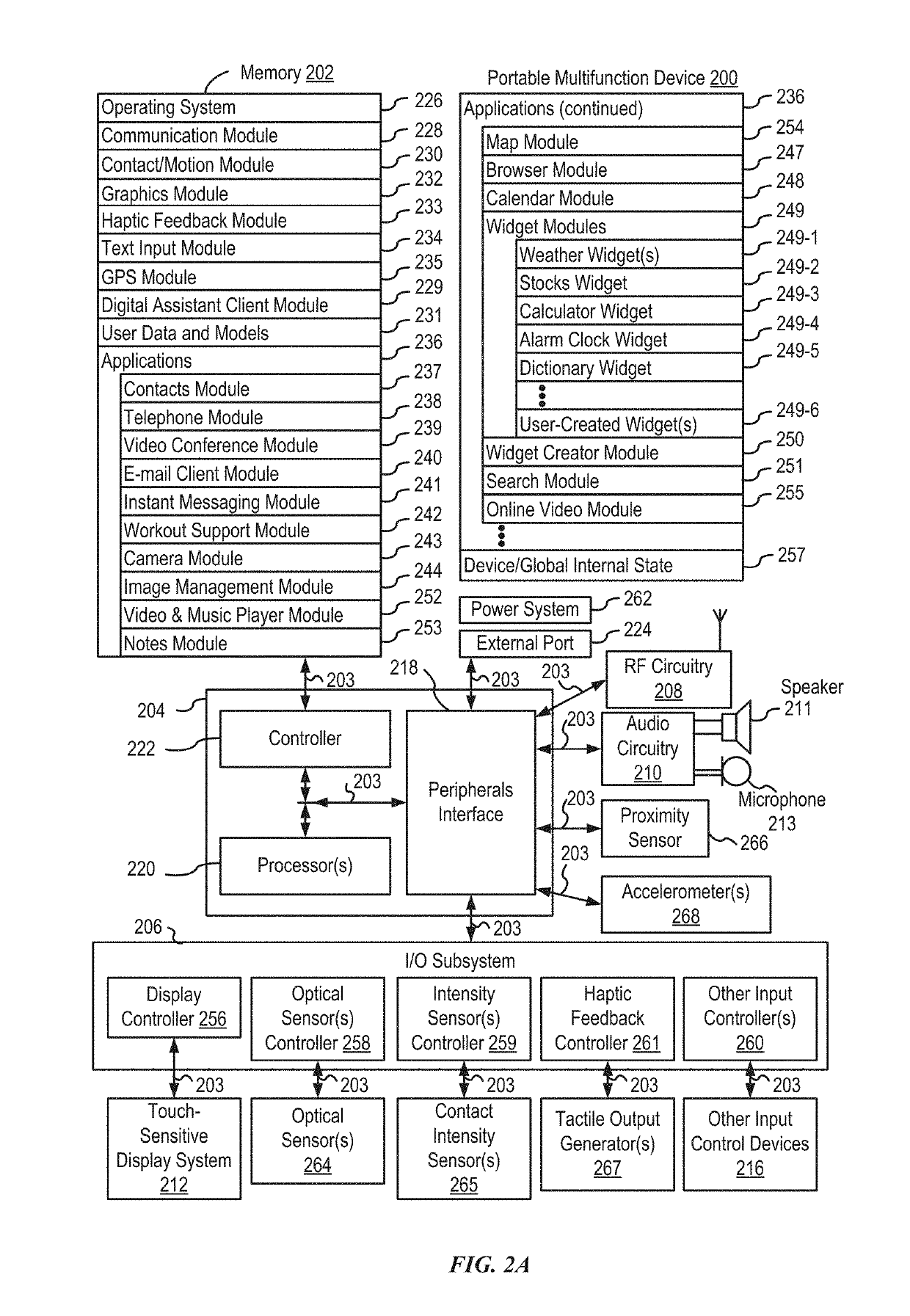
Application integration with a digital assistant
ActiveUS20170358303A1Software maintainance/managementNatural language data processingEnterprise application integrationUser input
Systems and processes for application integration with a digital assistant are provided. In accordance with one example, a method includes, at an electronic device having one or more processors and memory, receiving a natural-language user input; identifying, with the one or more processors, an intent object of a set of intent objects and a parameter associated with the intent, where the intent object and the parameter are derived from the natural-language user input. The method further includes identifying a software application associated with the intent object of the set of intent objects; and providing the intent object and the parameter to the software application.
Owner:APPLE INC
Learning data prototypes for information extraction
InactiveUS6714941B1Facilitate wrapper generationData processing applicationsWeb data indexingLearning dataData mining
Owner:IMPORT IO GLOBAL INC +1
Recommender system for on-line articles and documents
InactiveUS20090300547A1Increase engagementIncrease the number ofKnowledge representationMachine learningDocumentationUser interface
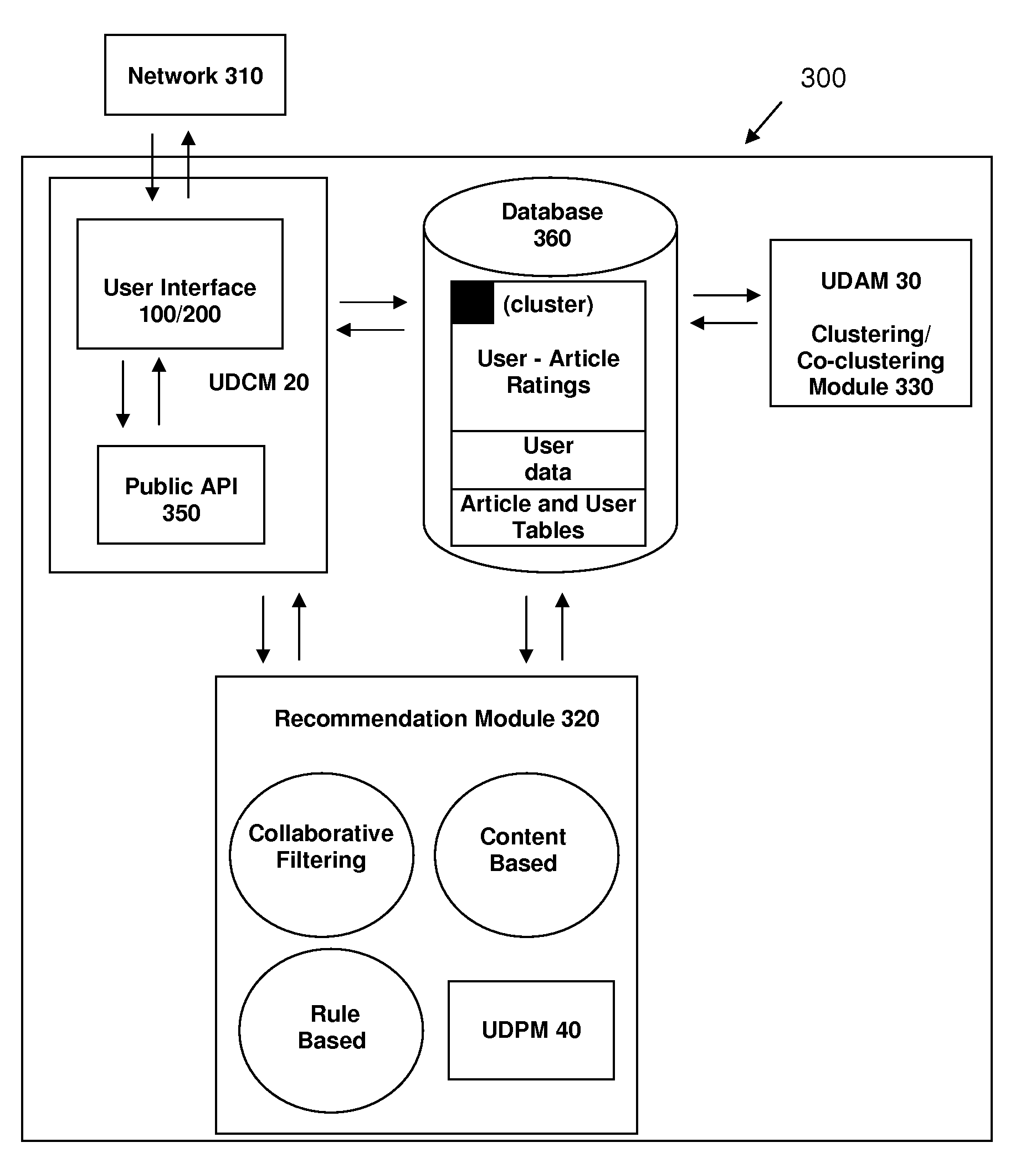
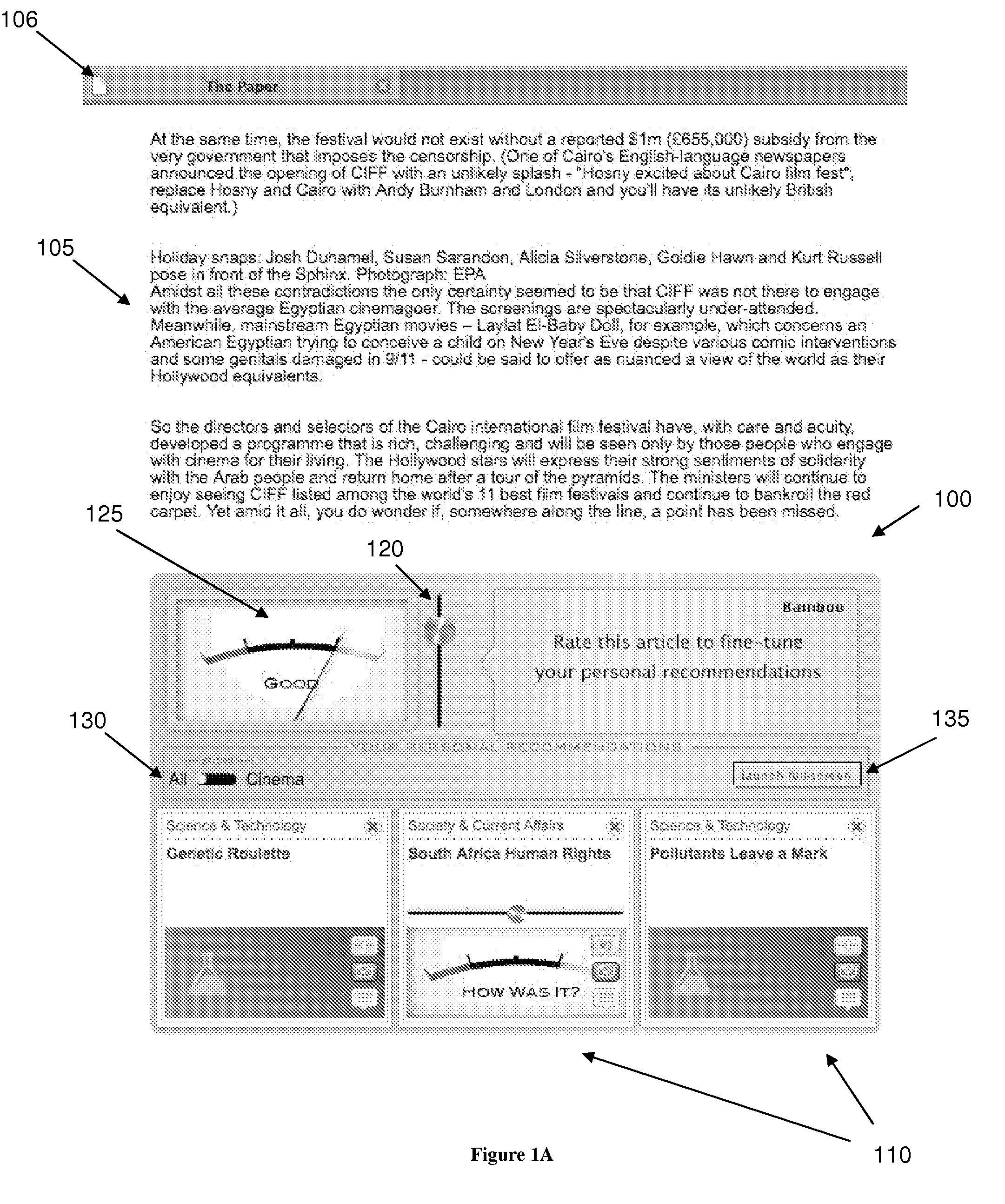
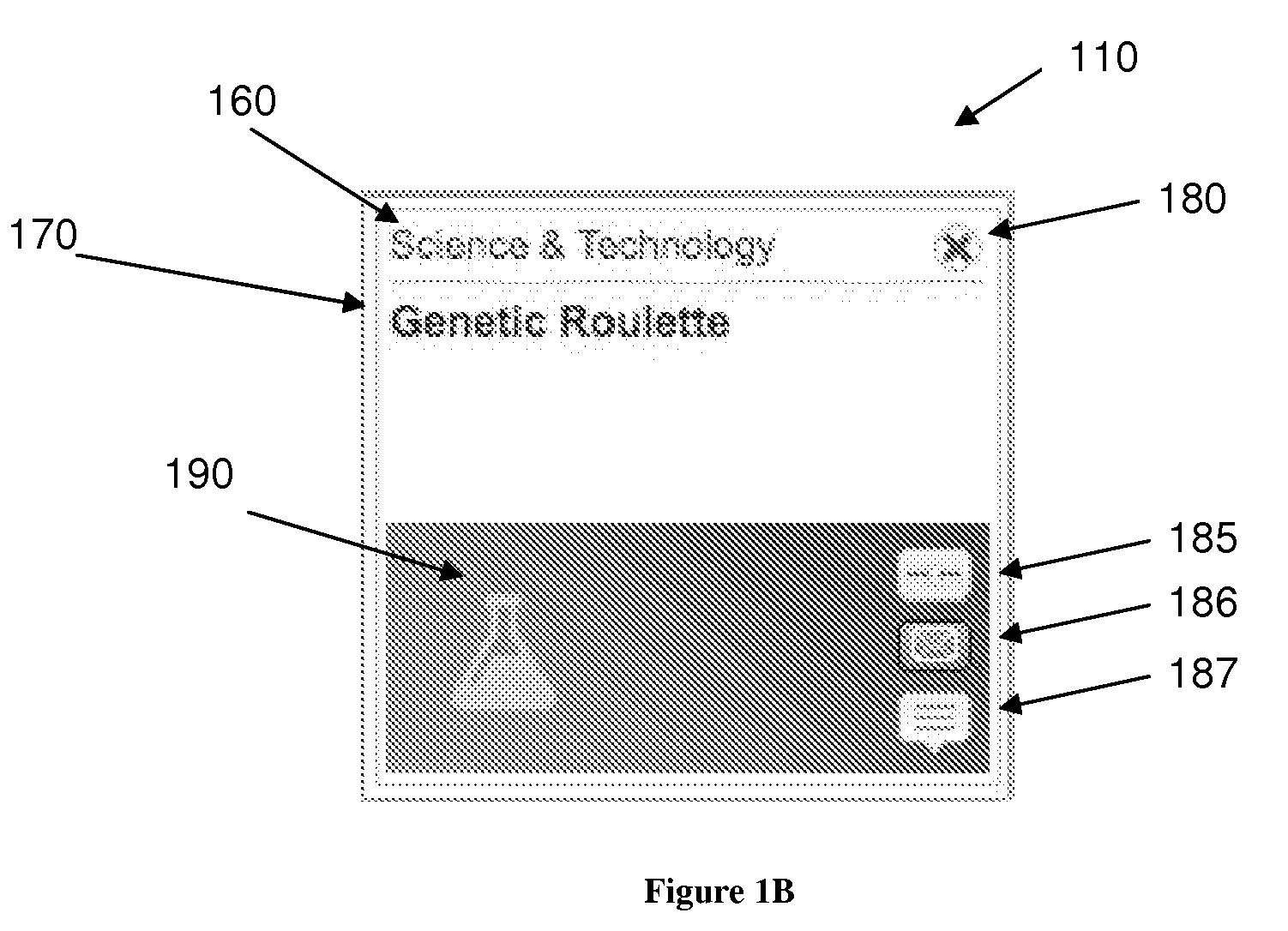
A system and method for recommending on-line articles and documents to users is disclosed. The method provides an article widget user interface and a full-screen widget user interfaces to allow a user to rate articles, to preview articles, to filter articles based on category, article length, or other characteristics. A recommender system is configured to provide a continually refreshing list of recommended articles to the user via the user interfaces. The system comprises a module configured to monitor the user's explicit and implicit interactions with the user interfaces, and provides a refreshed list of recommended articles accordingly. The recommender system may be configured to use a package of approaches including rule-based, content-based or collaborative filtering approaches including Slope, Co-Visitation, Mwinnow and Clustering / Co-clustering.
Owner:KIBBOKO
Application integration with a digital assistant
ActiveUS10297253B2Software maintainance/managementNatural language data processingEnterprise application integrationUser input
Systems and processes for application integration with a digital assistant are provided. In accordance with one example, a method includes, at an electronic device having one or more processors and memory, receiving a natural-language user input; identifying, with the one or more processors, an intent object of a set of intent objects and a parameter associated with the intent, where the intent object and the parameter are derived from the natural-language user input. The method further includes identifying a software application associated with the intent object of the set of intent objects; and providing the intent object and the parameter to the software application.
Owner:APPLE INC
Immediate search feedback
Providing immediate search feedback is disclosed. Search input is received within a search field of a web browser application. Based on characteristics of the search input, a determination is made whether to automatically submit a query to a search engine. In one aspect, the query is automatically submitted to the search engine. The query is based on the received first search input. Results are displayed within the web browser application, the results web page returned from the query submitted to the search engine.
Owner:APPLE INC
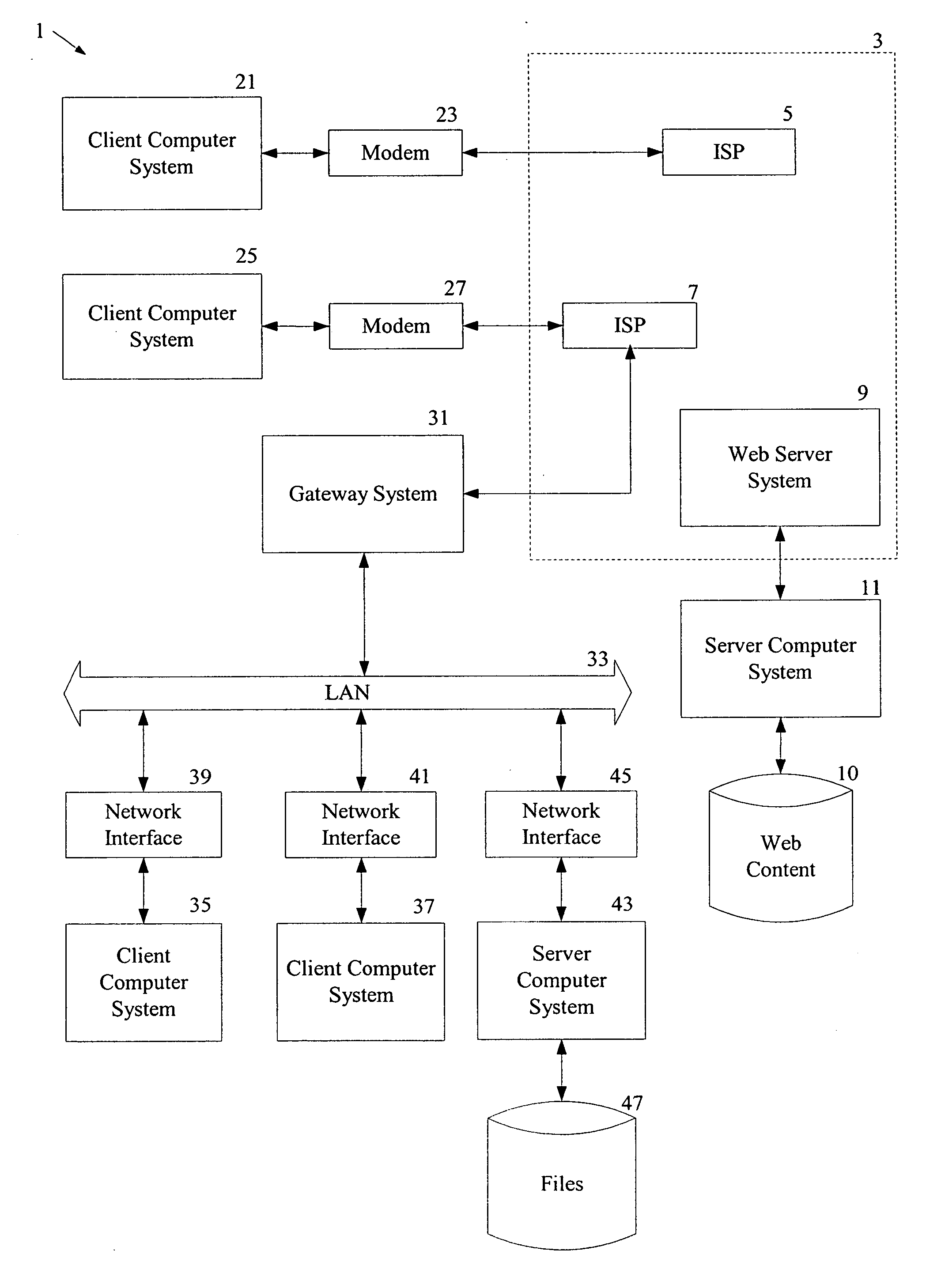
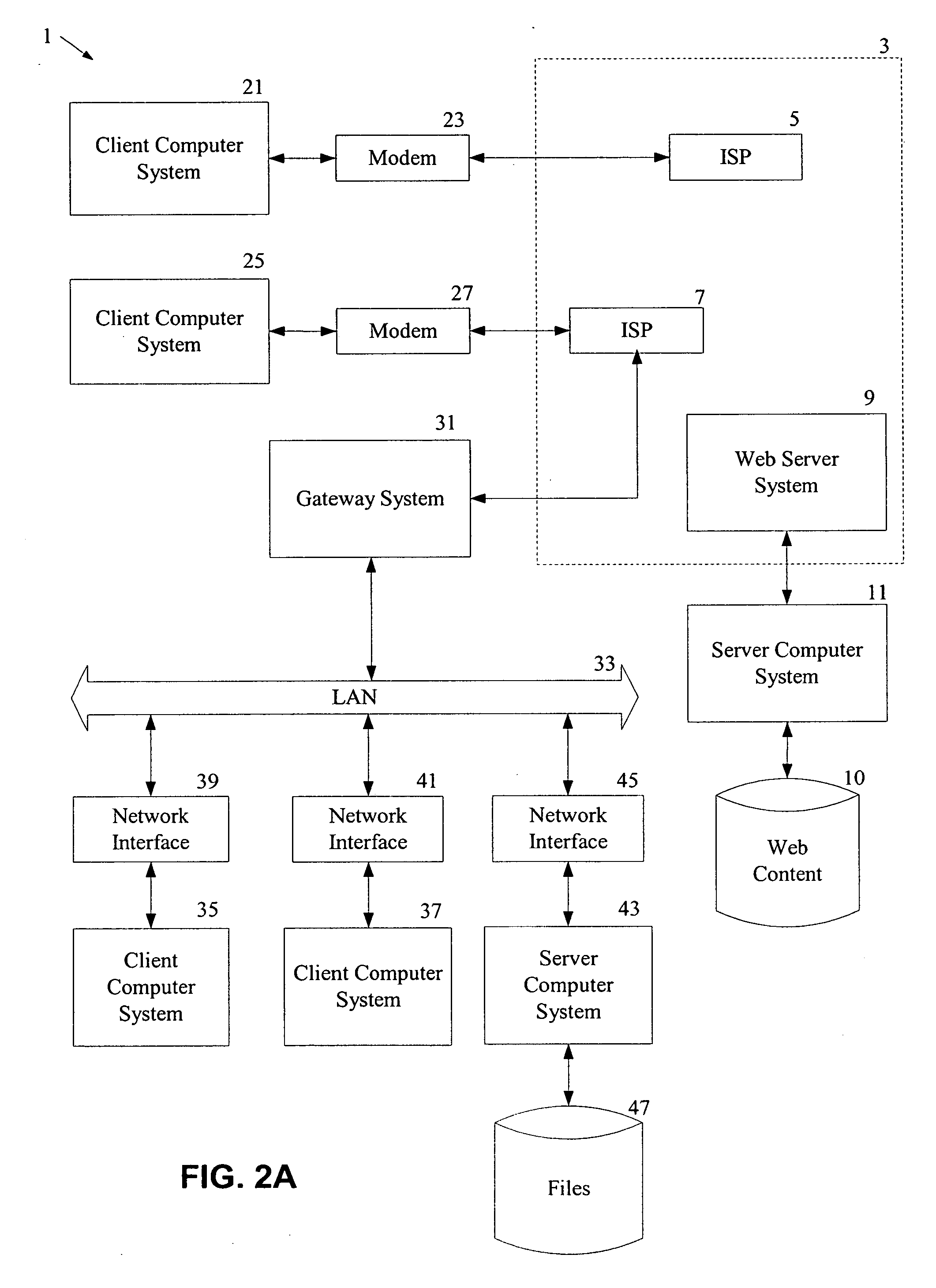
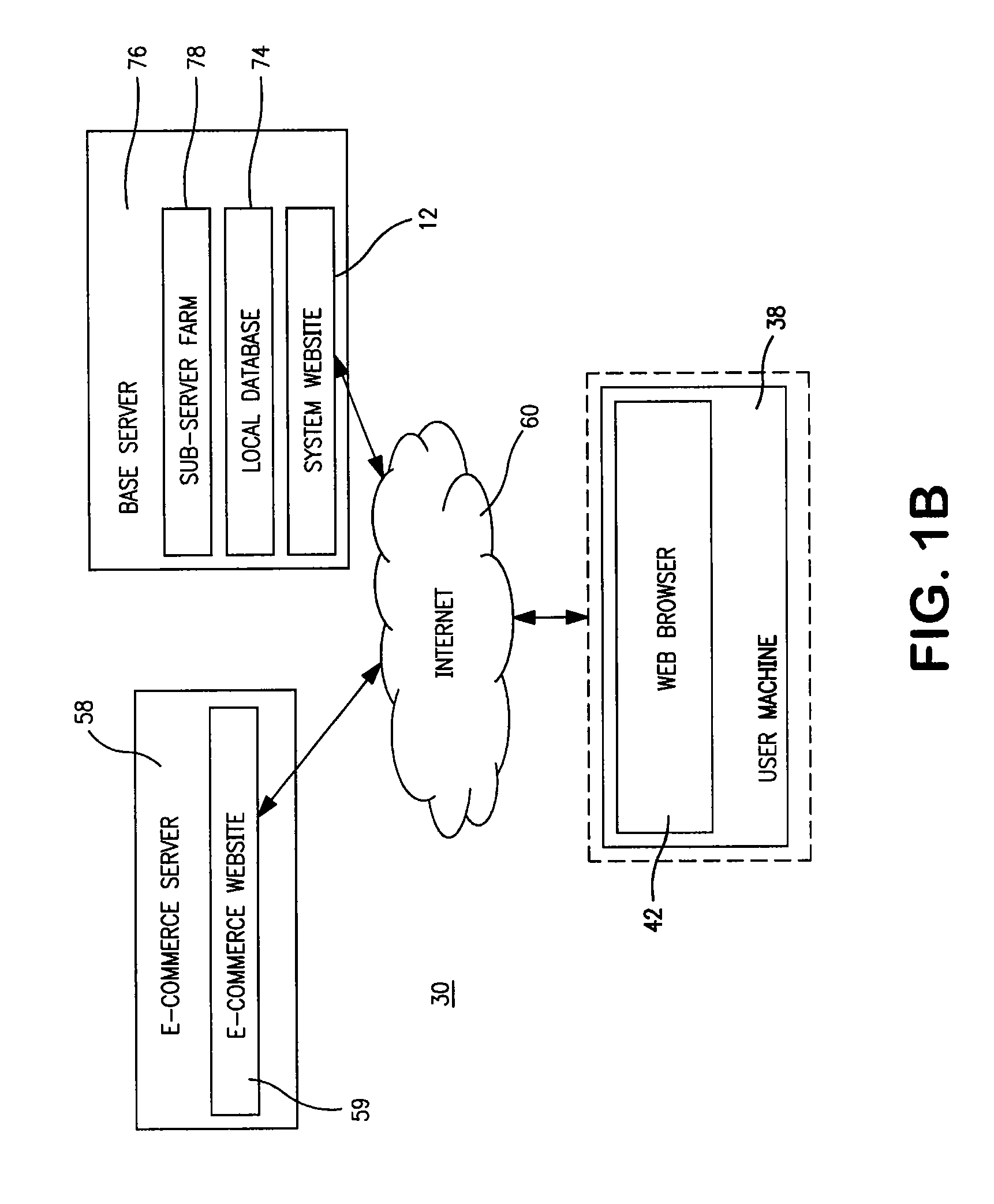
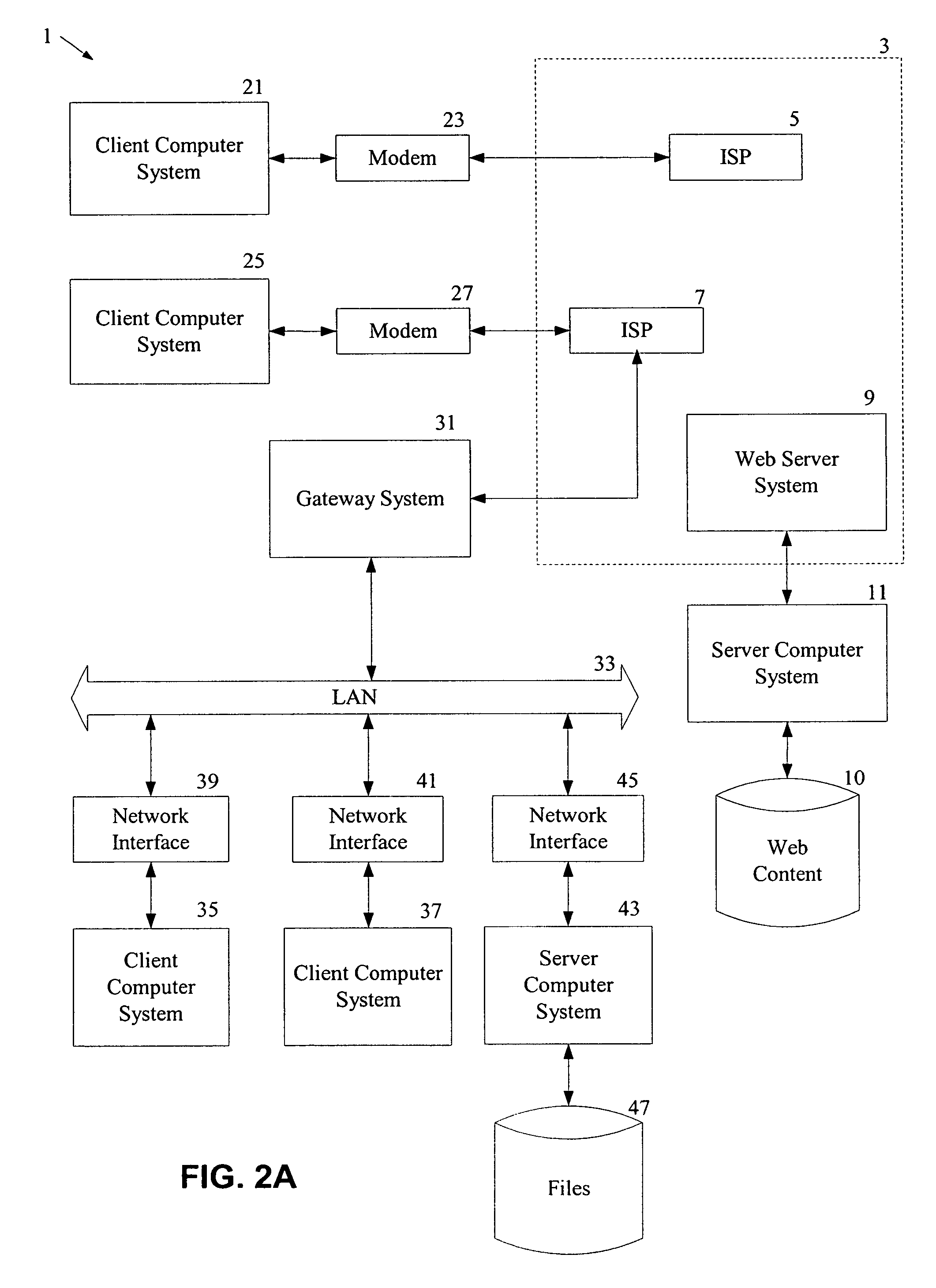
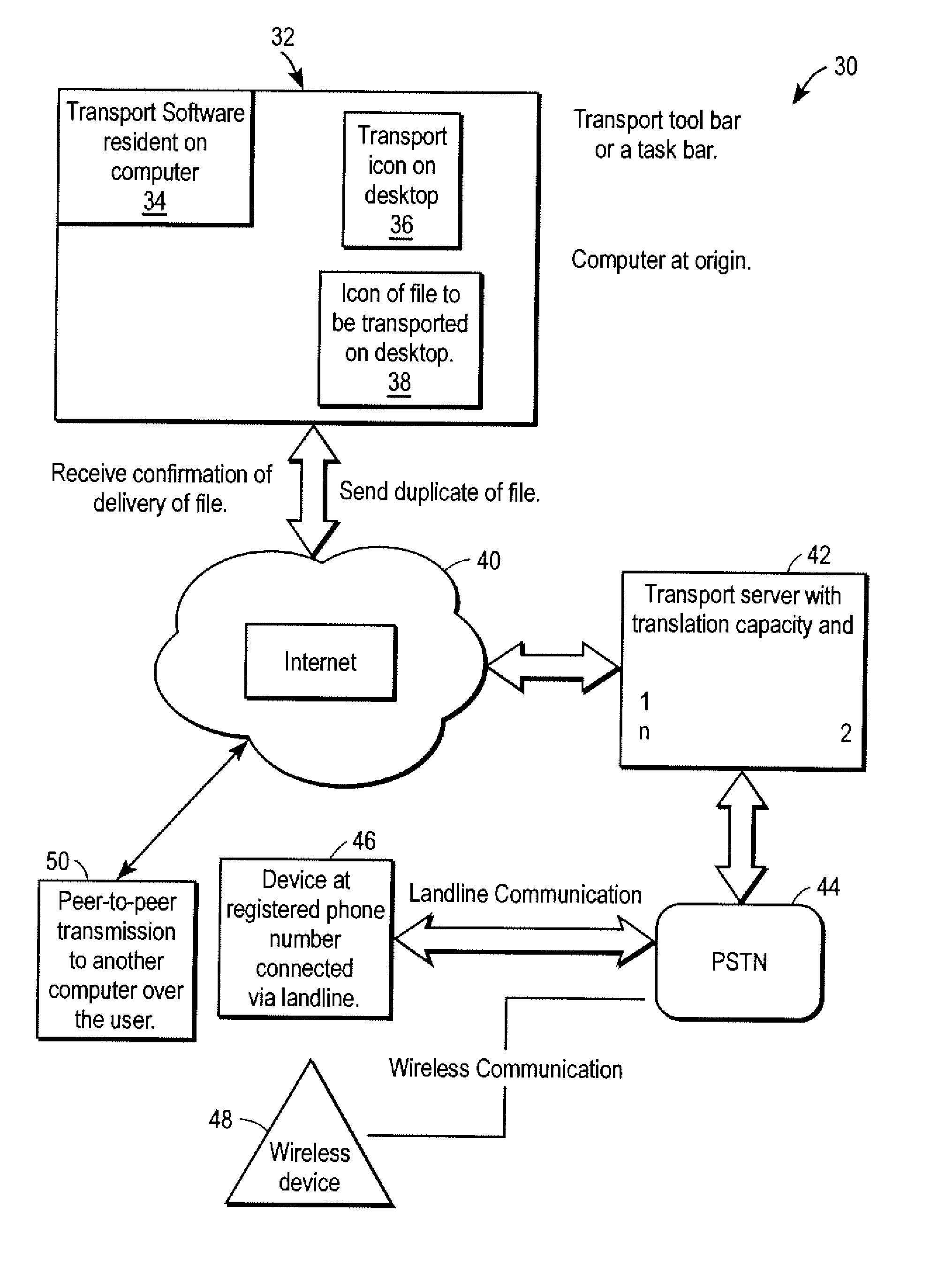
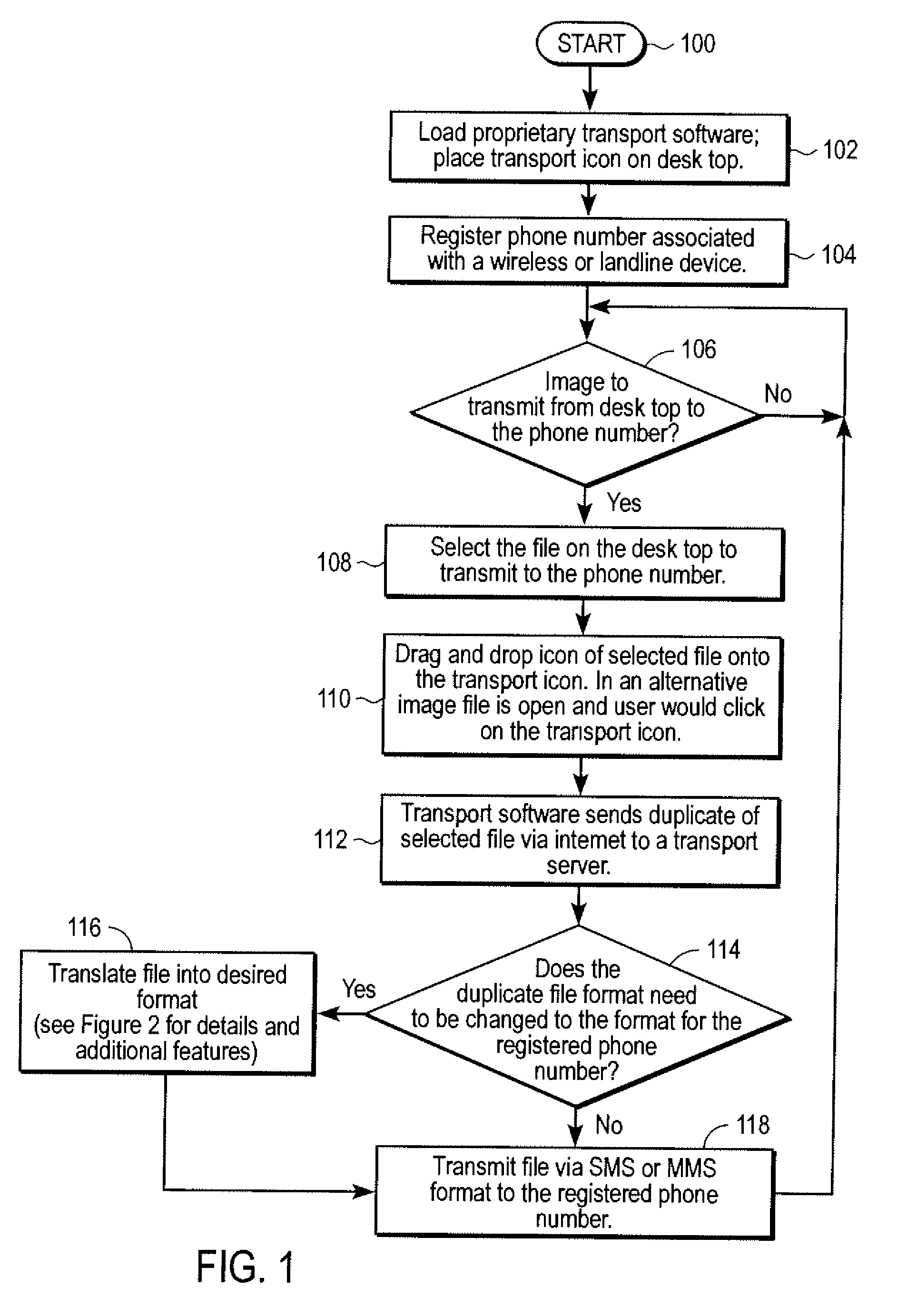
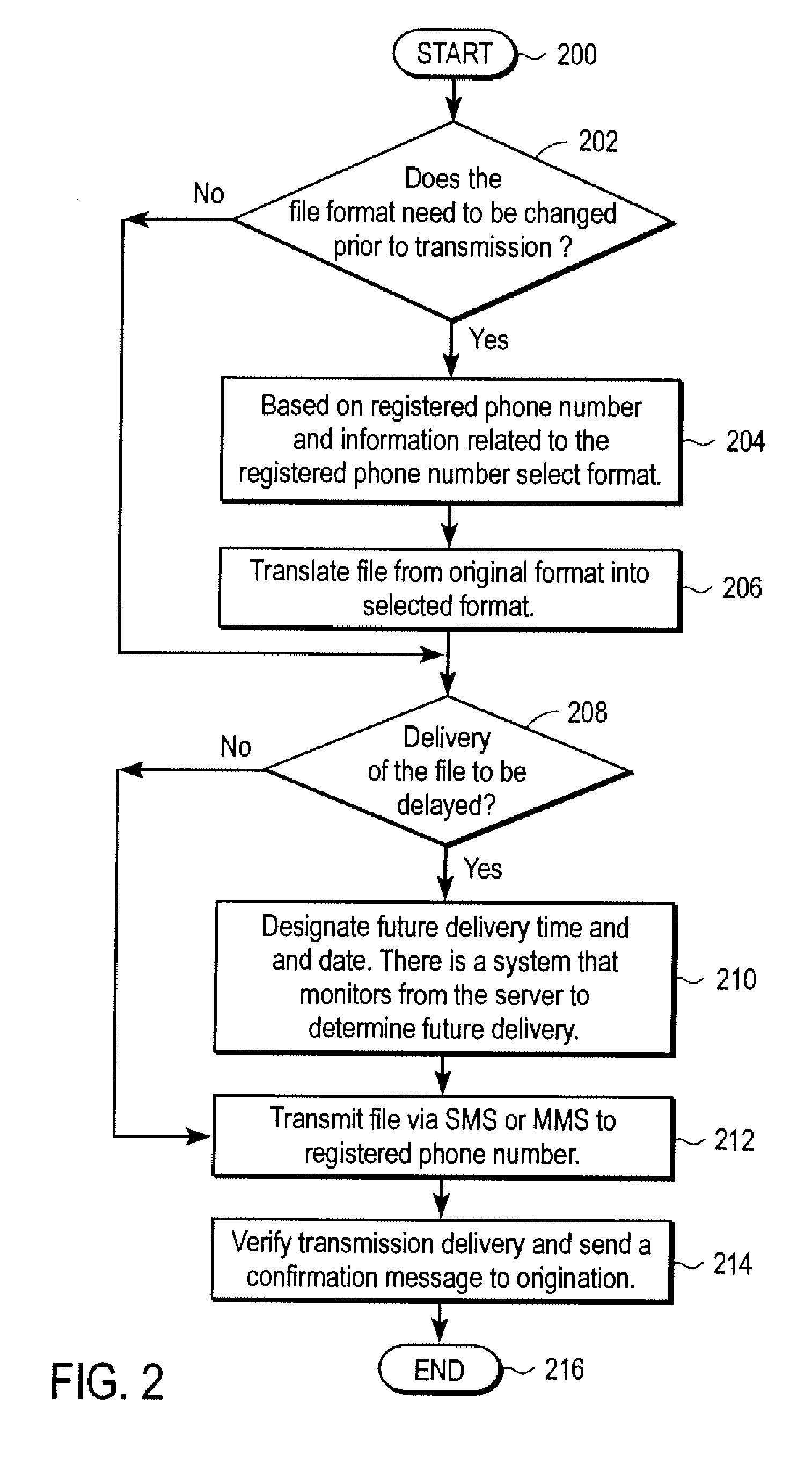
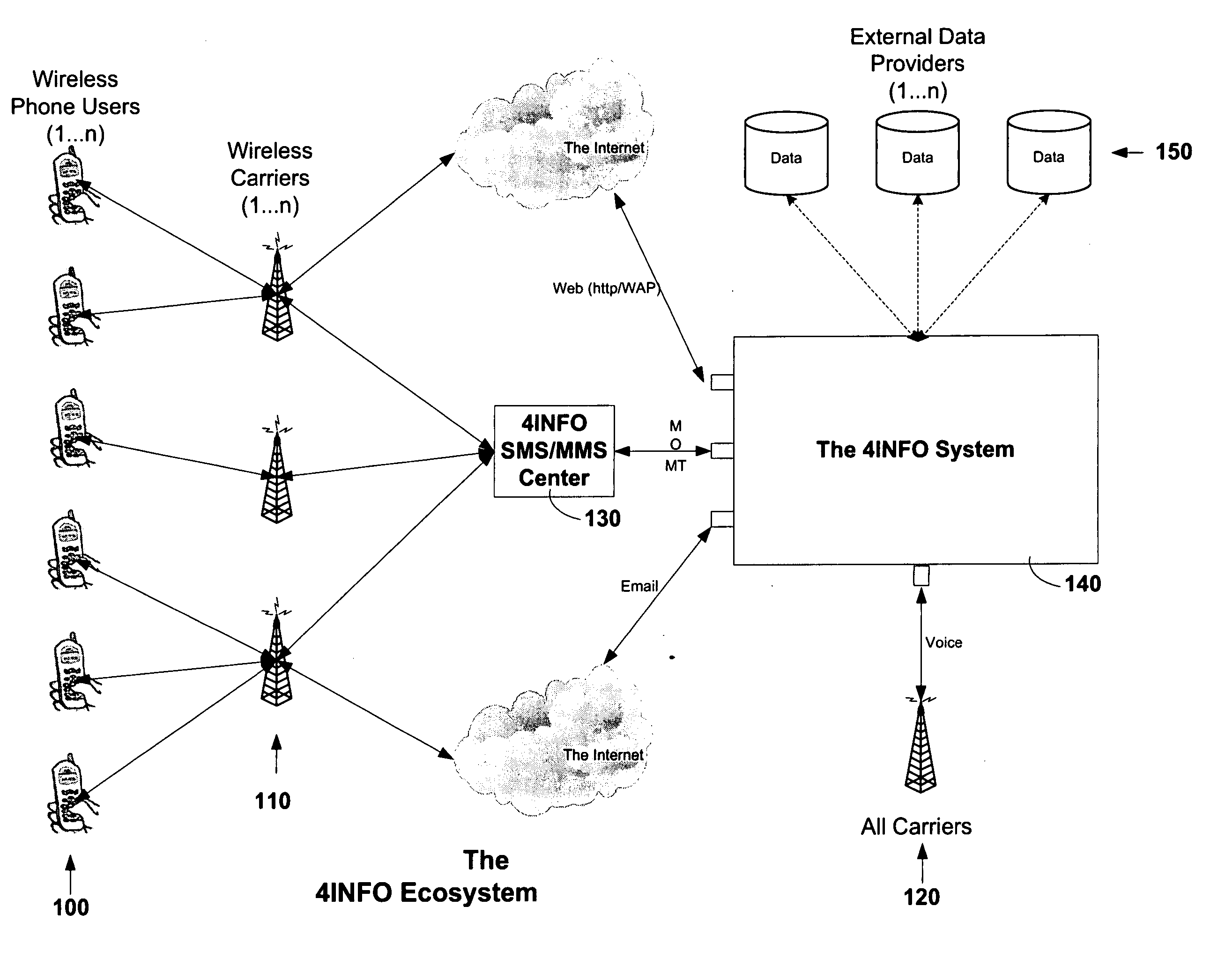
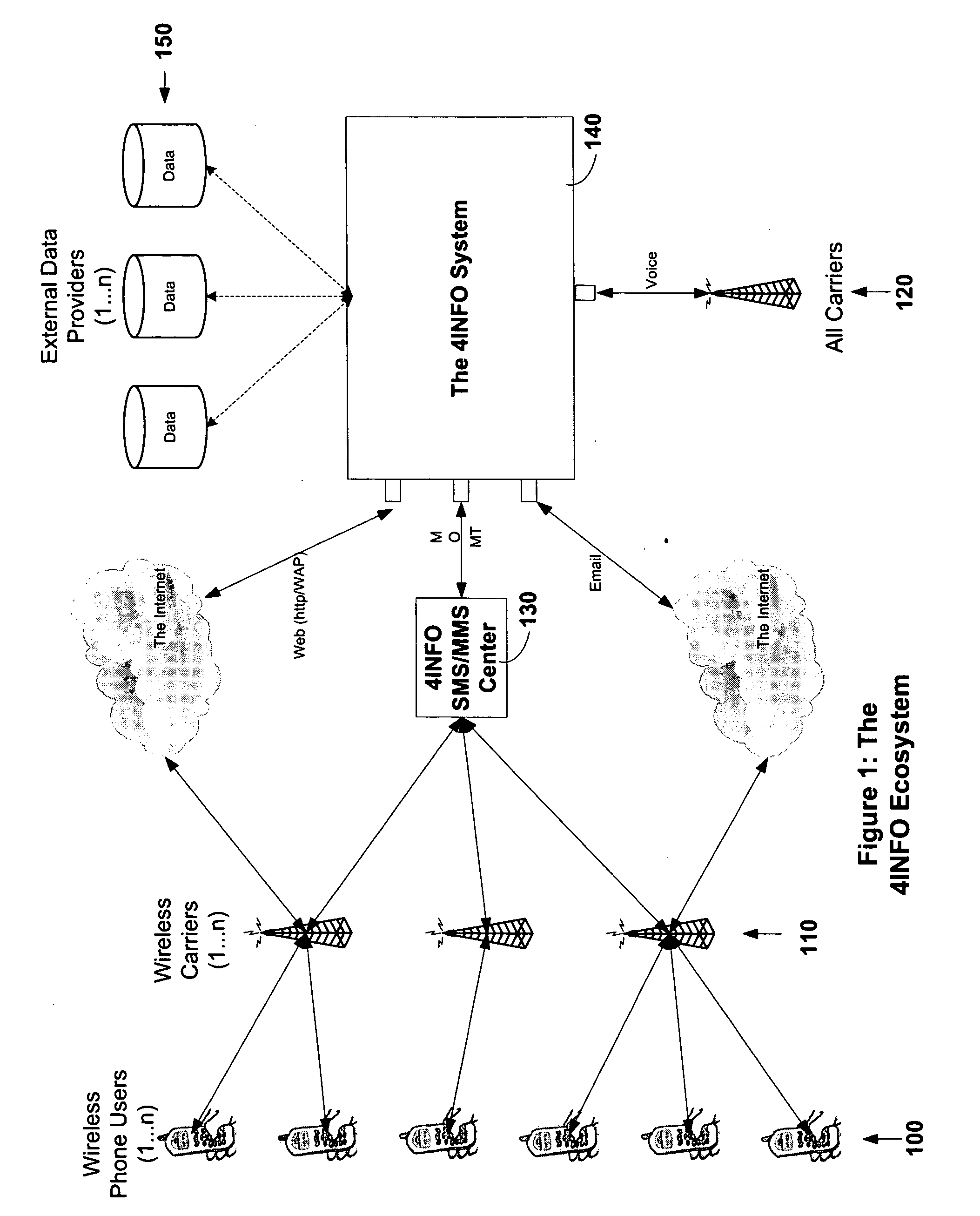
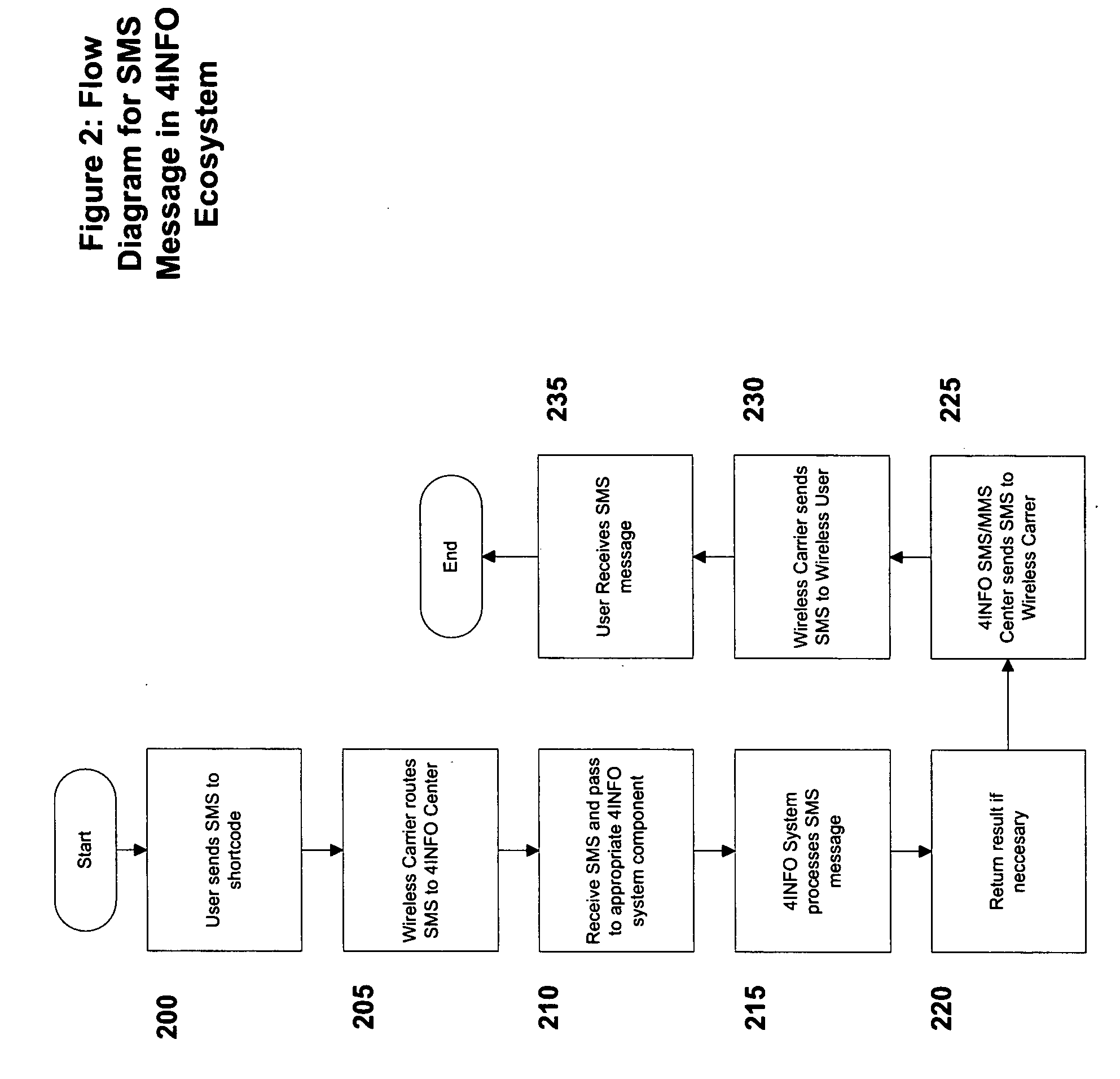
Automated transfer of data from PC clients
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for transferring a data object such as a data file from a PC client to a wireless device regardless of the format of the file and with minimum user intervention. A system is disclosed wherein the file is transferred from a PC client through the Internet to a server and ultimately to a device, which can be a wireless device, a peer-to-peer device, or any suitable device capable of receiving an over the air transmission.
Owner:4INFO
System and method for registering or searching in multiple relationship-searching hosts
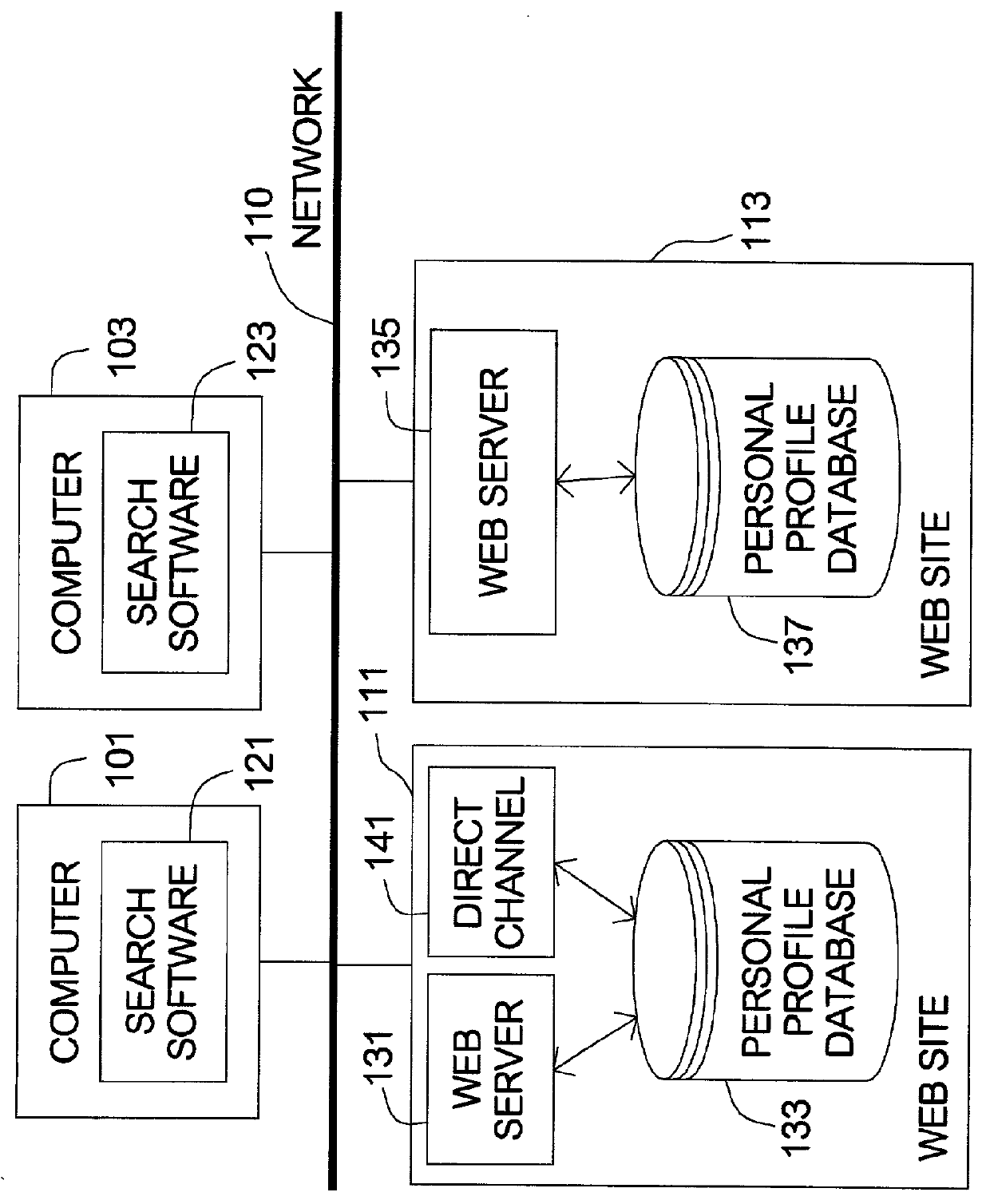
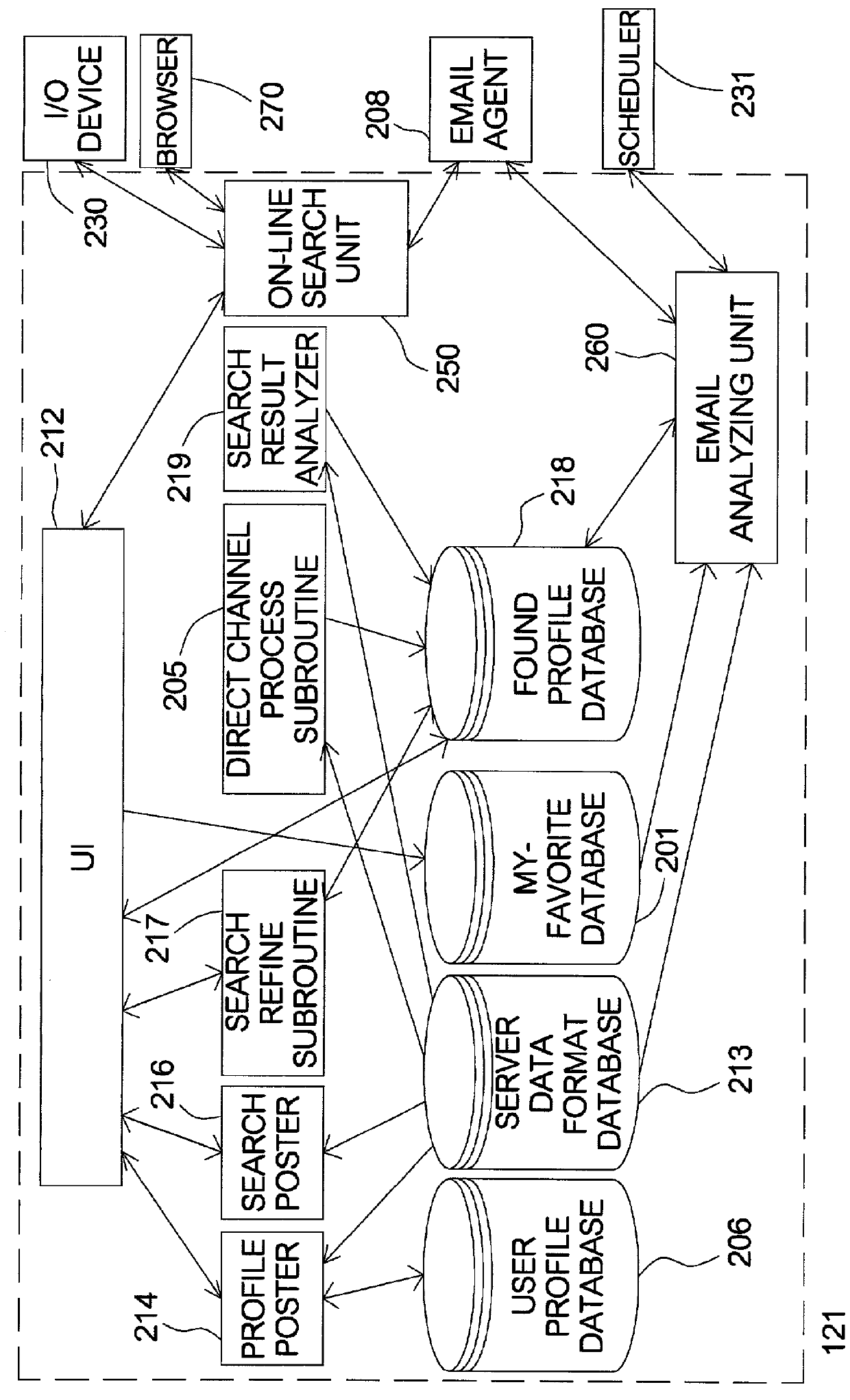
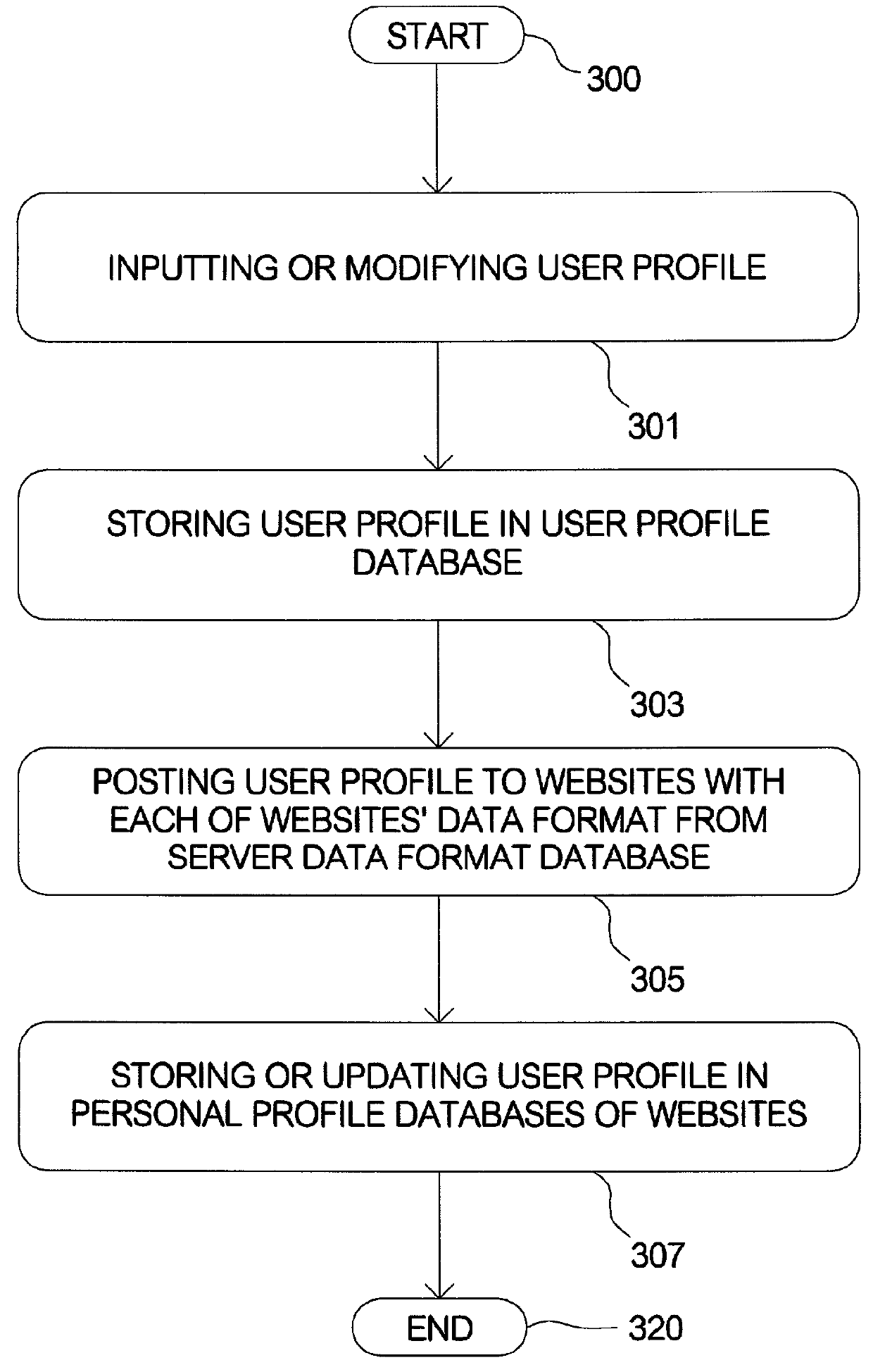
InactiveUS20010054041A1Conveniently obtainWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsData formatWorld Wide Web
A method for searching in multiple relationship-searching hosts. The method can be installed in a computer, wherein the computer comprises a user interface (UI) to access search conditions. Firstly the method begins with inputting the search conditions on the UI. Next, the search conditions are transmitted to the hosts with each of the hosts' data format retrieved from a server data format database in the computer. Then the hosts retrieve search results according to the search conditions and transmit the search results to the computer. Next, the search results are stored in a found profile database of the computer. The method makes a user be capable to register and search matched users in the multiple relationship-searching hosts, instead of repeatedly behavior of search in different hosts.
Owner:CHANG LAN
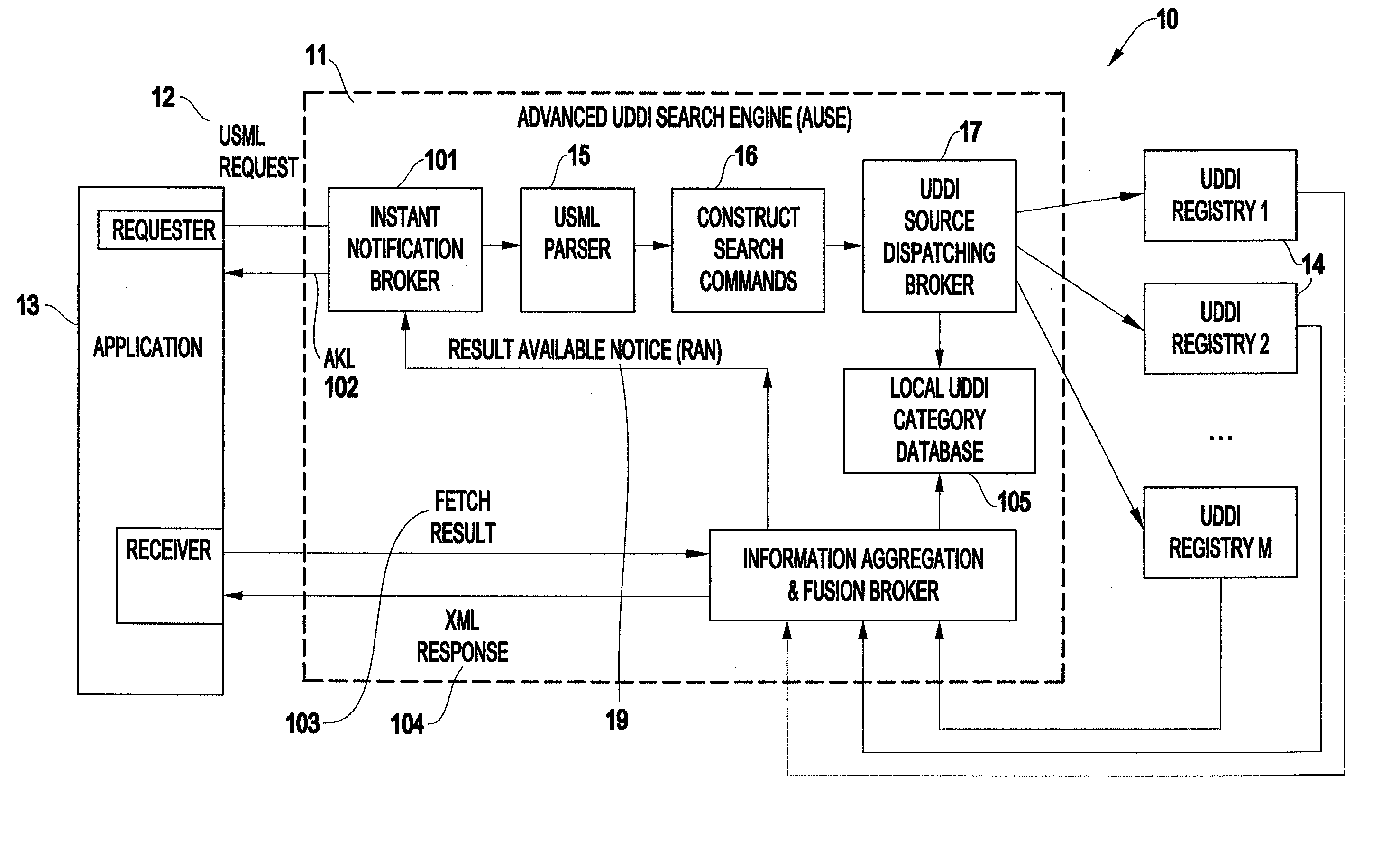
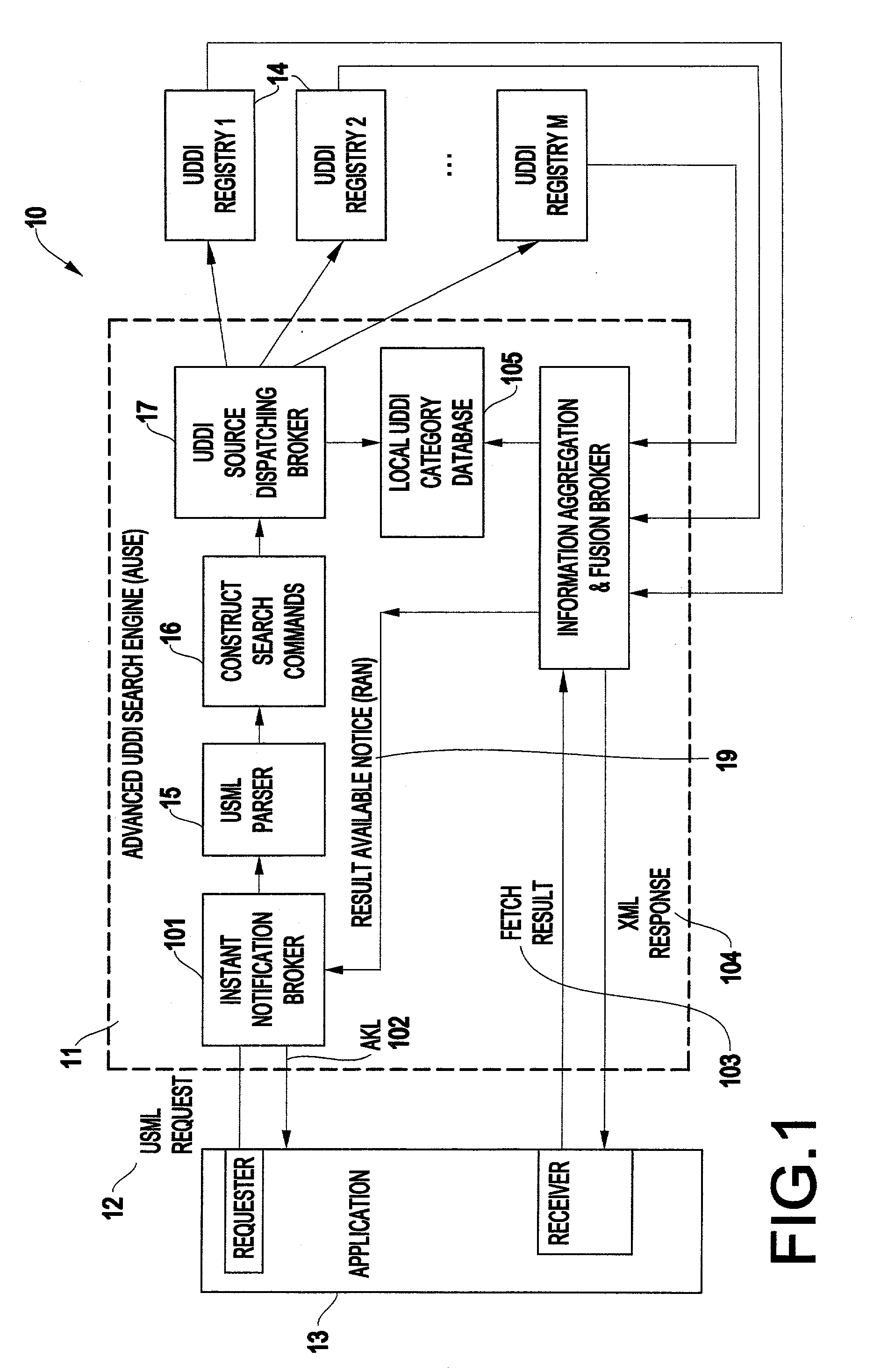
Method and structure for federated web service discovery search over multiple registries with result aggregation
InactiveUS20030187841A1Good reputationImprove efficiencyWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsWeb serviceData source
A method (and structure) of querying one or more Web-based data sources, includes receiving a compound query statement having at least one first-level query and at least one aggregation operator. An aggregation operator is determined which applies to each first-level query. Each aggregation operator can be either explicit or implicit. An implicit aggregation operator is an aggregation operator defining a default aggregate operation if no explicit aggregation operator is present.
Owner:IBM CORP
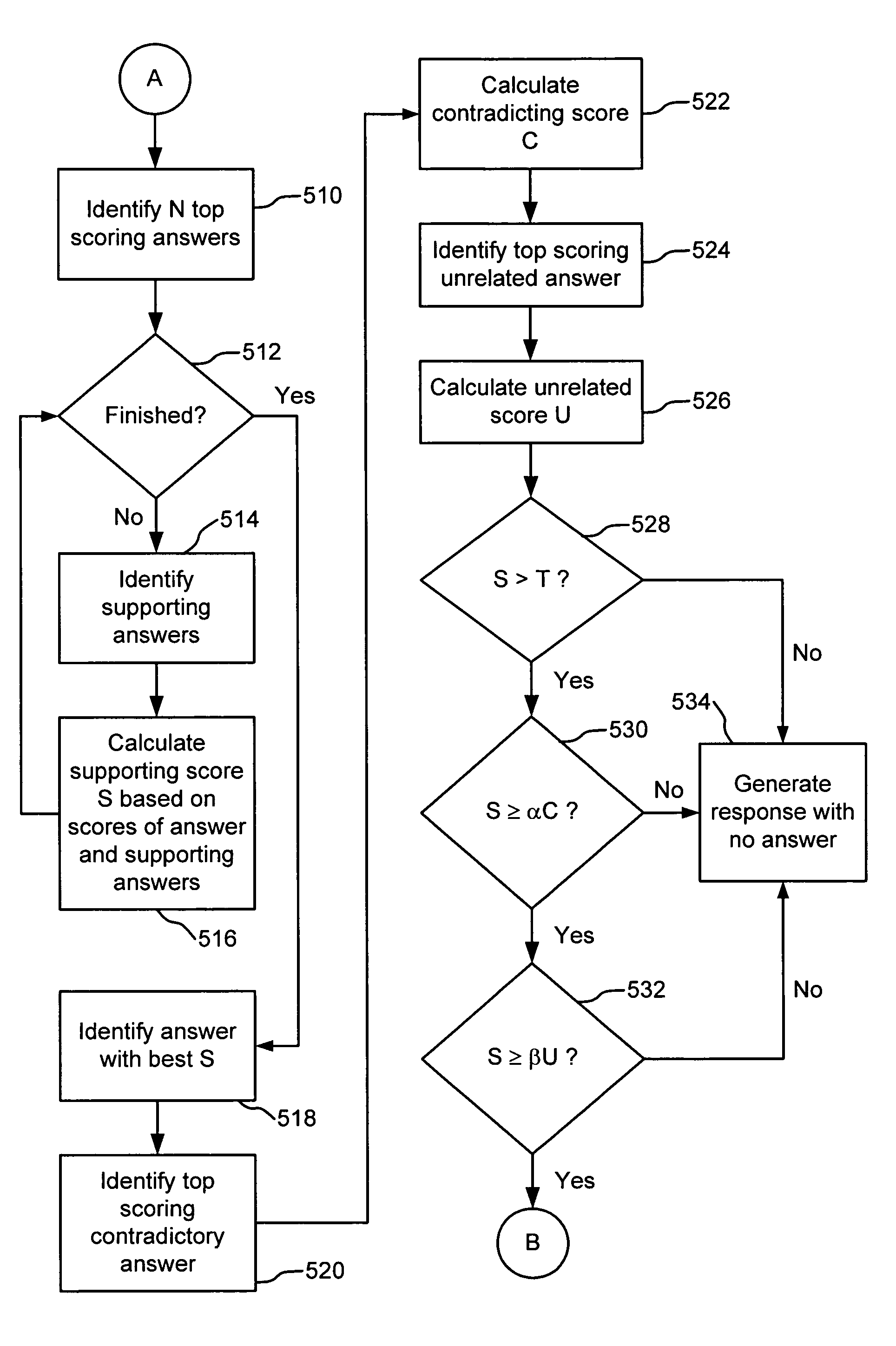
Selecting the best answer to a fact query from among a set of potential answers
A method and system for selecting a best answer to a factual query. Possible answers to a factual query are identified. The possible answers are scored and the best scoring possible answers are compared to other possible answers to determine how well they are supported. The most supported answer is chosen to be presented to the user.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
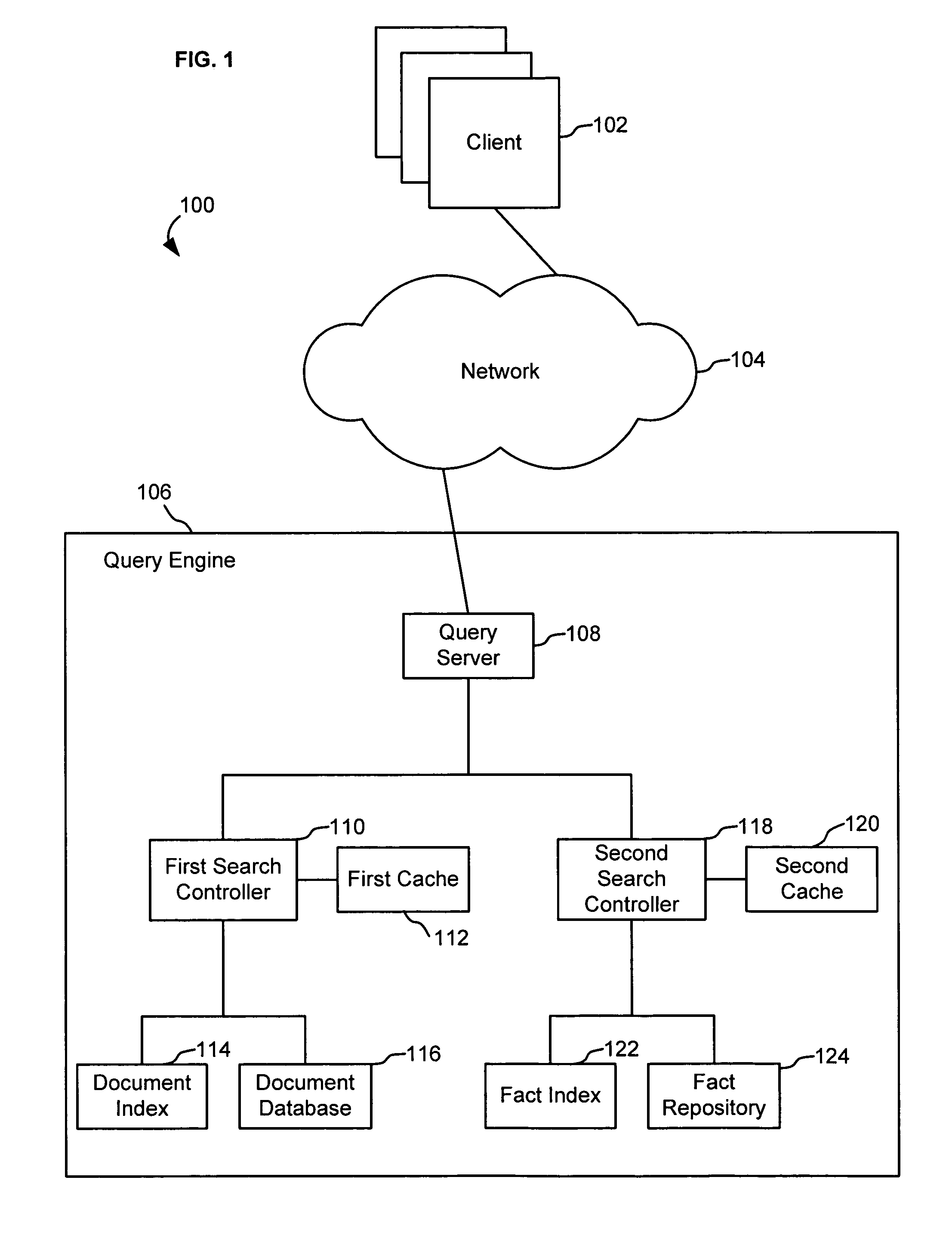
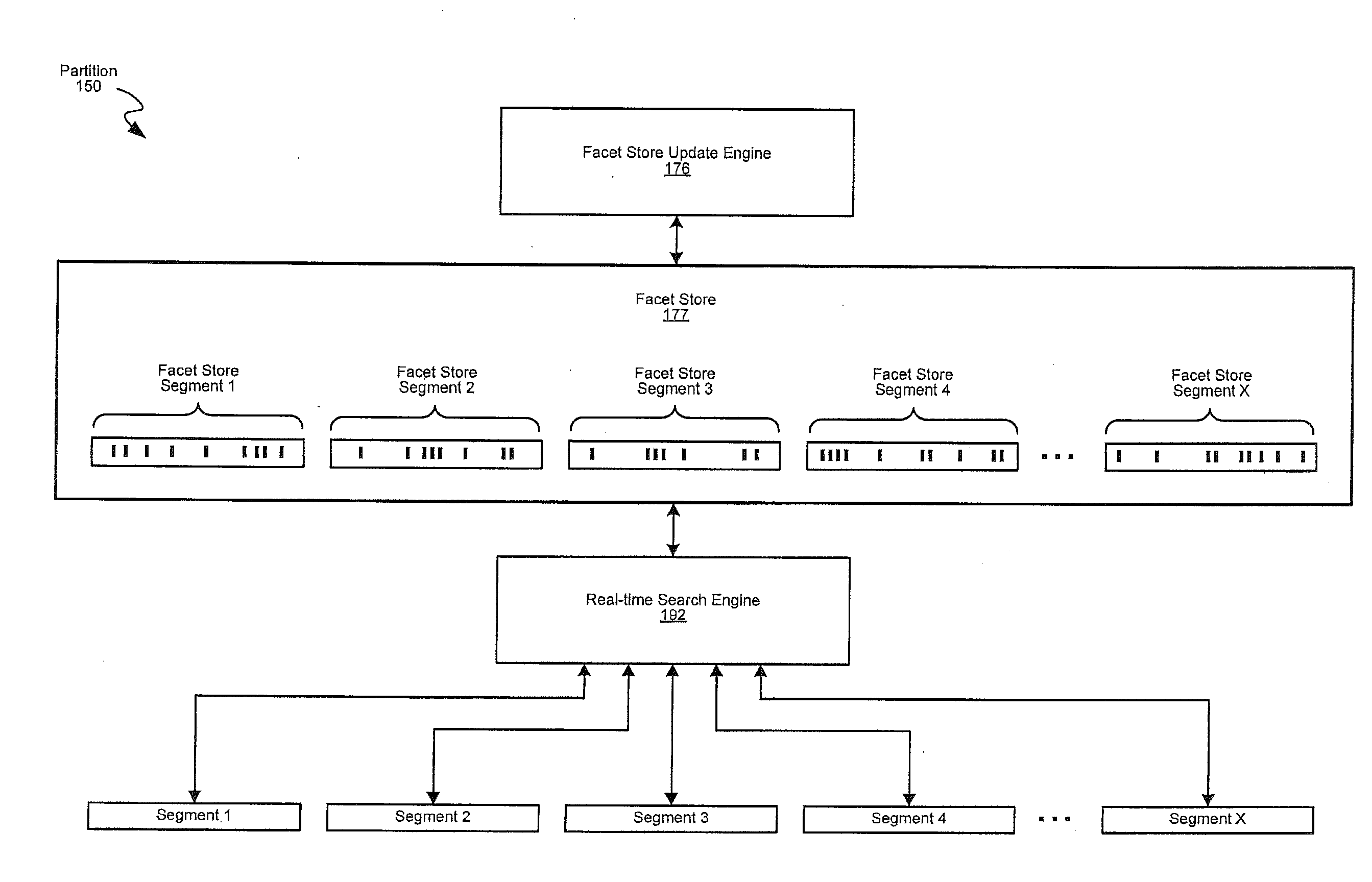
Search infrastructure
ActiveUS20150227624A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsDocument IdentifierChronological time
A system for real-time search, including: a set of partitions, each including a set of segments, each segment corresponding to a time slice of messages posted to the messaging platform, and a real-time search engine configured to receive a search term in parallel with other partitions in the set of partitions, and search at least one of the set of segments in reverse chronological order of the corresponding time slice to identify document identifiers of messages containing the search term; and a search fanout module configured to: receive a search query including the search term; send the search term to each of the set of partitions for parallel searching; and return, in response to the search query, at least one of the identified document identifiers of messages containing the search term.
Owner:TWITTER INC
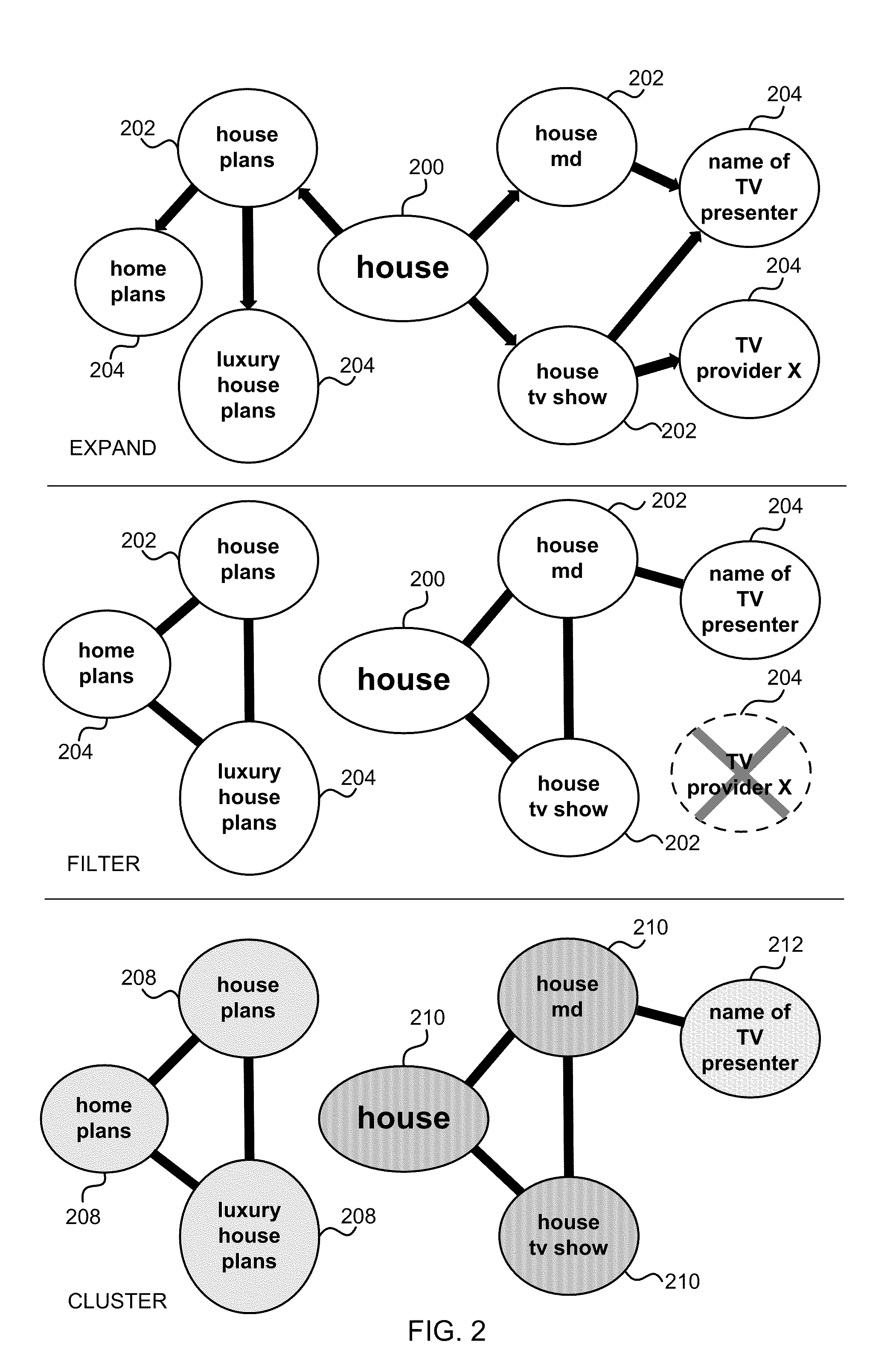
Query Intent in Information Retrieval
ActiveUS20110289063A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsDocument preparationArtificial intelligence
Inferring query intent in information retrieval is described. In an example reformulations of an initial query by a user are used to create a query neighborhood. In the example, the query neighborhood is used to identify a set of possibly related queries. First and higher order reformulations of the initial query may be used to expand the query neighborhood. In an example precision can be improved by reducing the query neighborhood to more closely related queries for example, two queries can be connected if they are often clicked for the same document. In an example two queries can be connected using a random walk and all pairs of queries that are not connected by a random walk of less than a fixed threshold are removed. The connected queries can be used to form clusters and weights can be applied in order to determine the most likely related queries.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Augmented processing of information objects in a distributed messaging framework in a computer network
InactiveUS6769032B1Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingInformation processingInformation object
Augmenting processing of information objects transferred among processors within a network. Processing is performed by a process, or processor, (called a "robot") at any point in the network where an information object is transferred, or where the object resides. By allowing processing at source, destination and at "interim" points between the source and destination, the ability to add functionality, services, control and management of objects and object transfers is greatly enhanced. The robots, can reside at any point in the system. A robot can be local to an end-user's computer, can reside on a content source server, or can be on another computer, processor, storage location or device on the network. Any type of processing can be performed by the robots. For example, access rights can be maintained so that certain attributes and values of information objects are restricted on a per user, per machine, chronological or other basis. Robots can use conditions which, when satisfied by attribute / value pairs within a specific object, or conditions which are satisfied by other, external, conditions, trigger specific processing. The processing can include one or more objects, other information processing, software or hardware control functions, etc. Information can be appended to objects. Statistics on object use, publication, subscription or transfers can be compiled. Groups of robots can operate in cooperation. Robots can share information.
Owner:EPIPHANY INC
Systems, methods, and media for utilizing electronic document usage information with search engines
Systems, methods and media for utilizing electronic document usage information are disclosed. More particularly, hardware and / or software utilizing electronic document usage information to respond to user search requests with search engines are disclosed. Embodiments include receiving a search request from a requesting user and receiving document utilization information associated with one or more electronic documents, where the document utilization information provides an indication of the usage of the electronic documents by one or more users. Further embodiments include generating search results based at least partially on the search request and the document utilization information and transmitting an indication of the search results to the requesting user. Further embodiments include generating statistical information regarding the search results for electronic documents and transmitting the generated statistical information.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
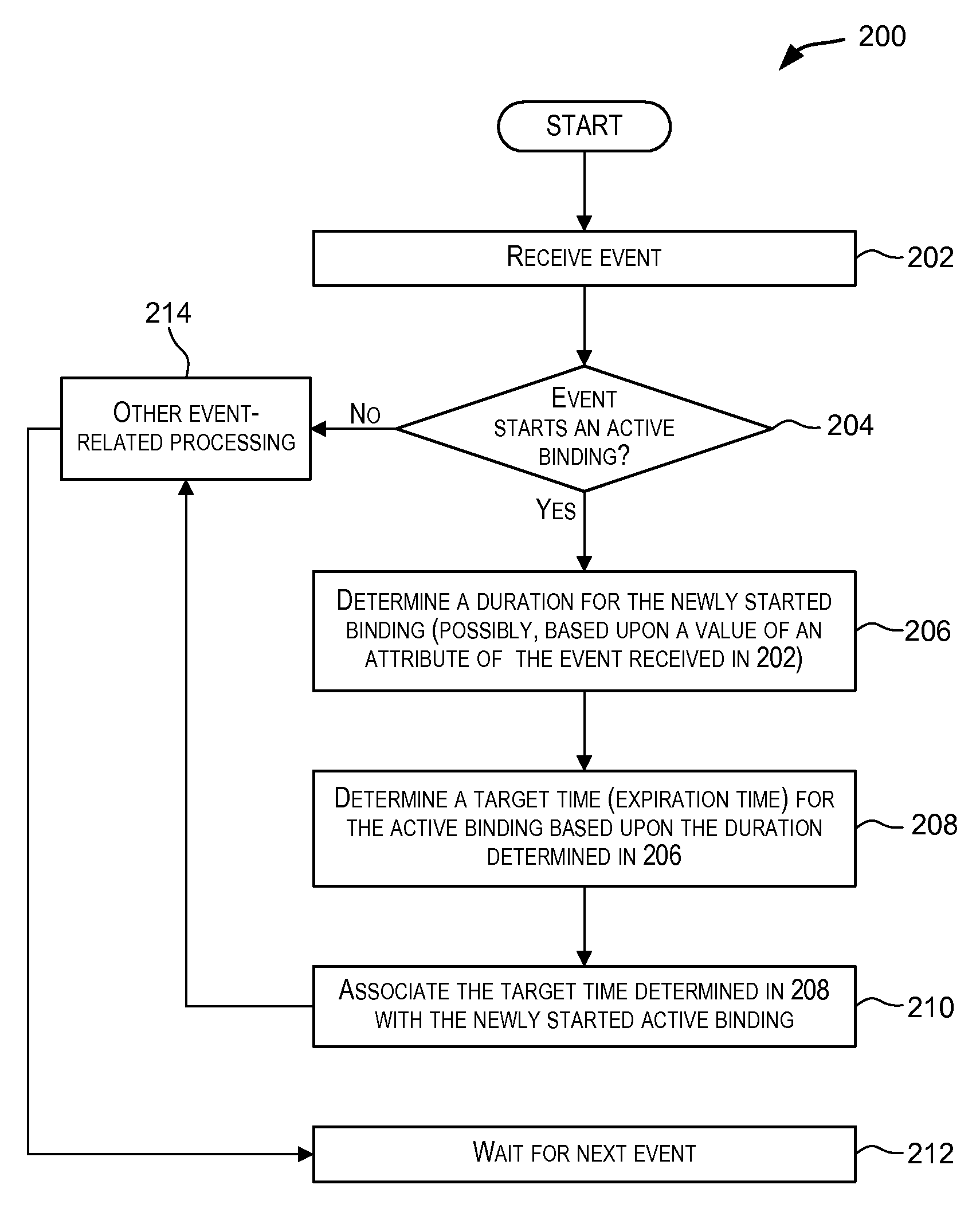
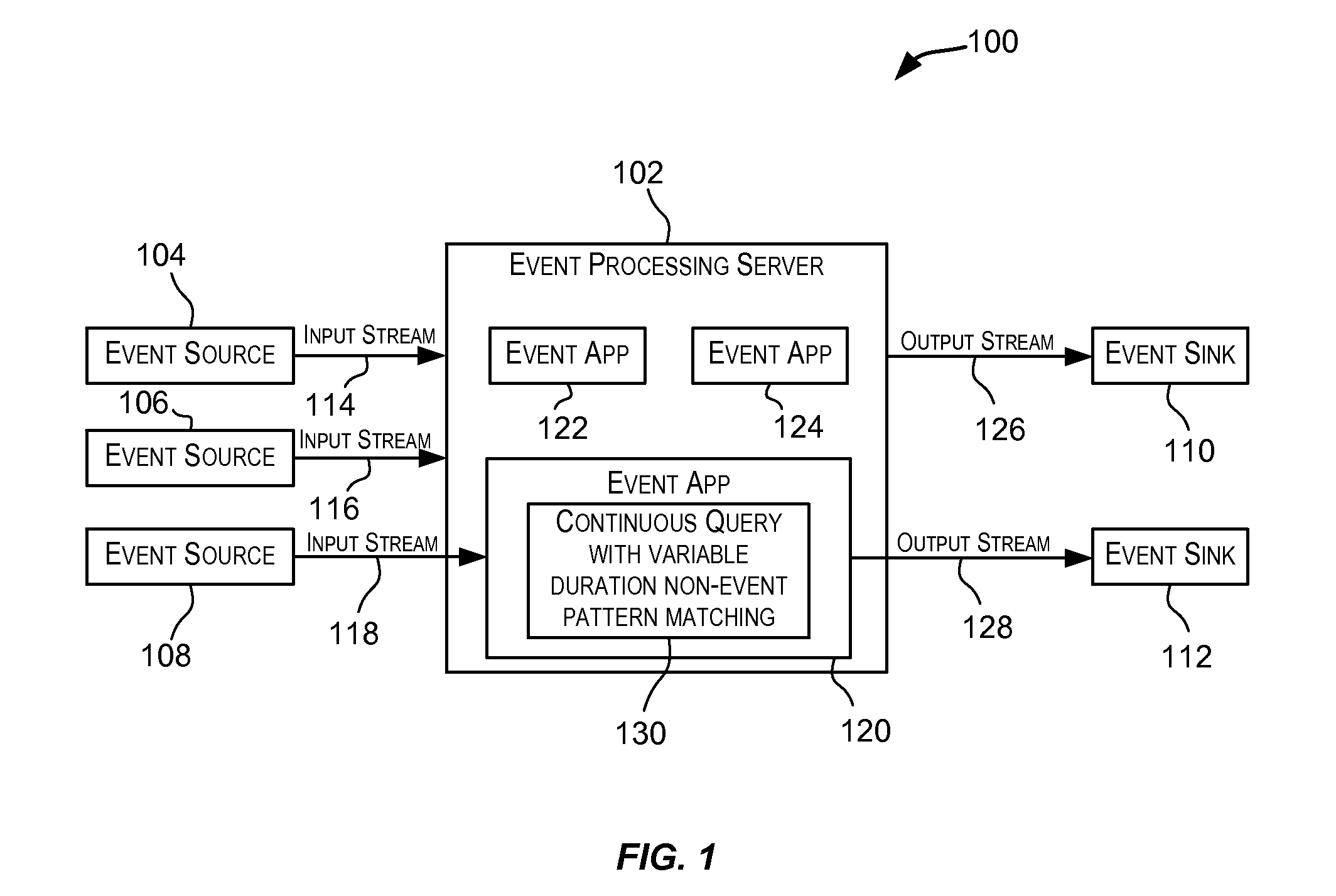
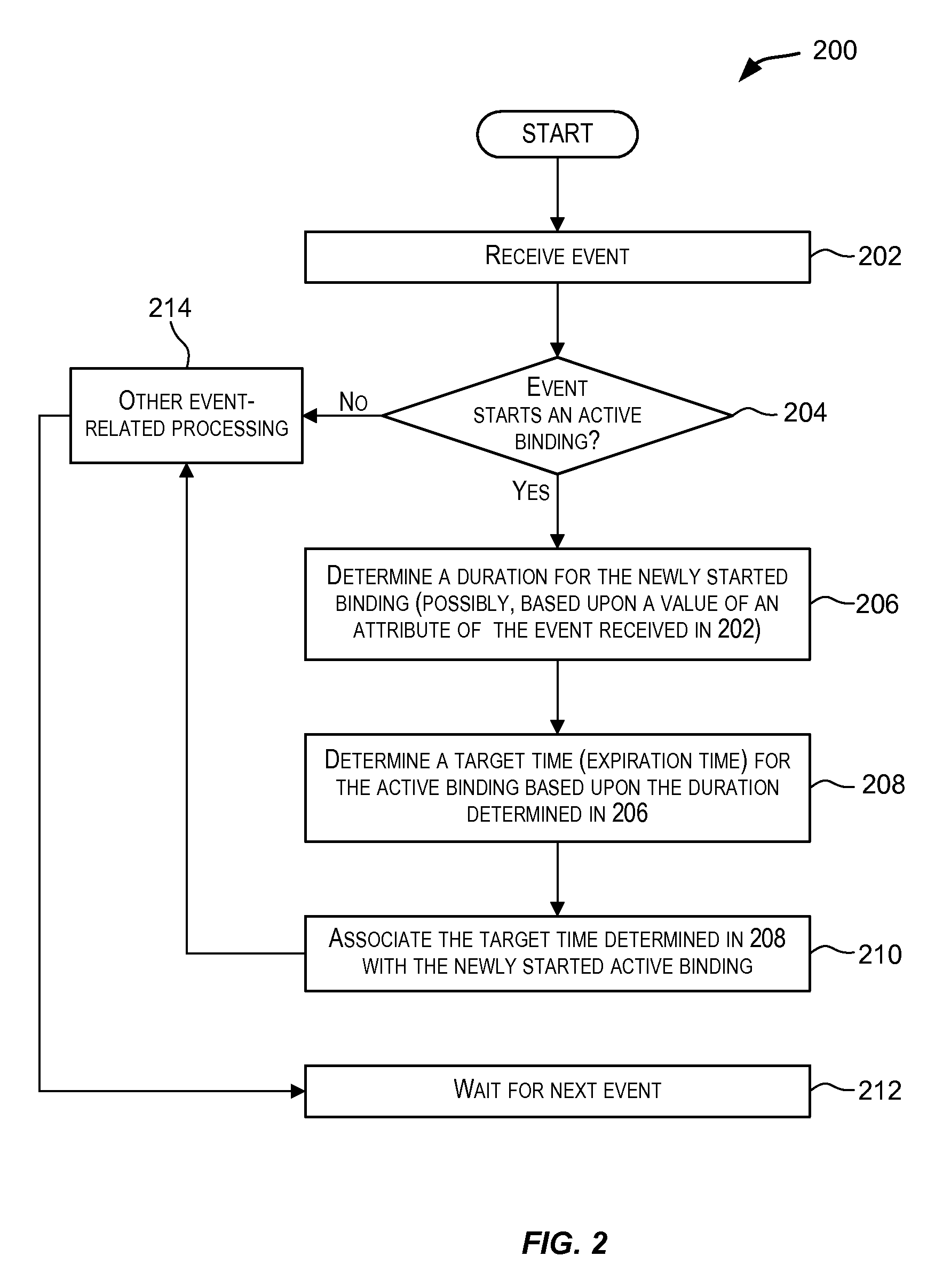
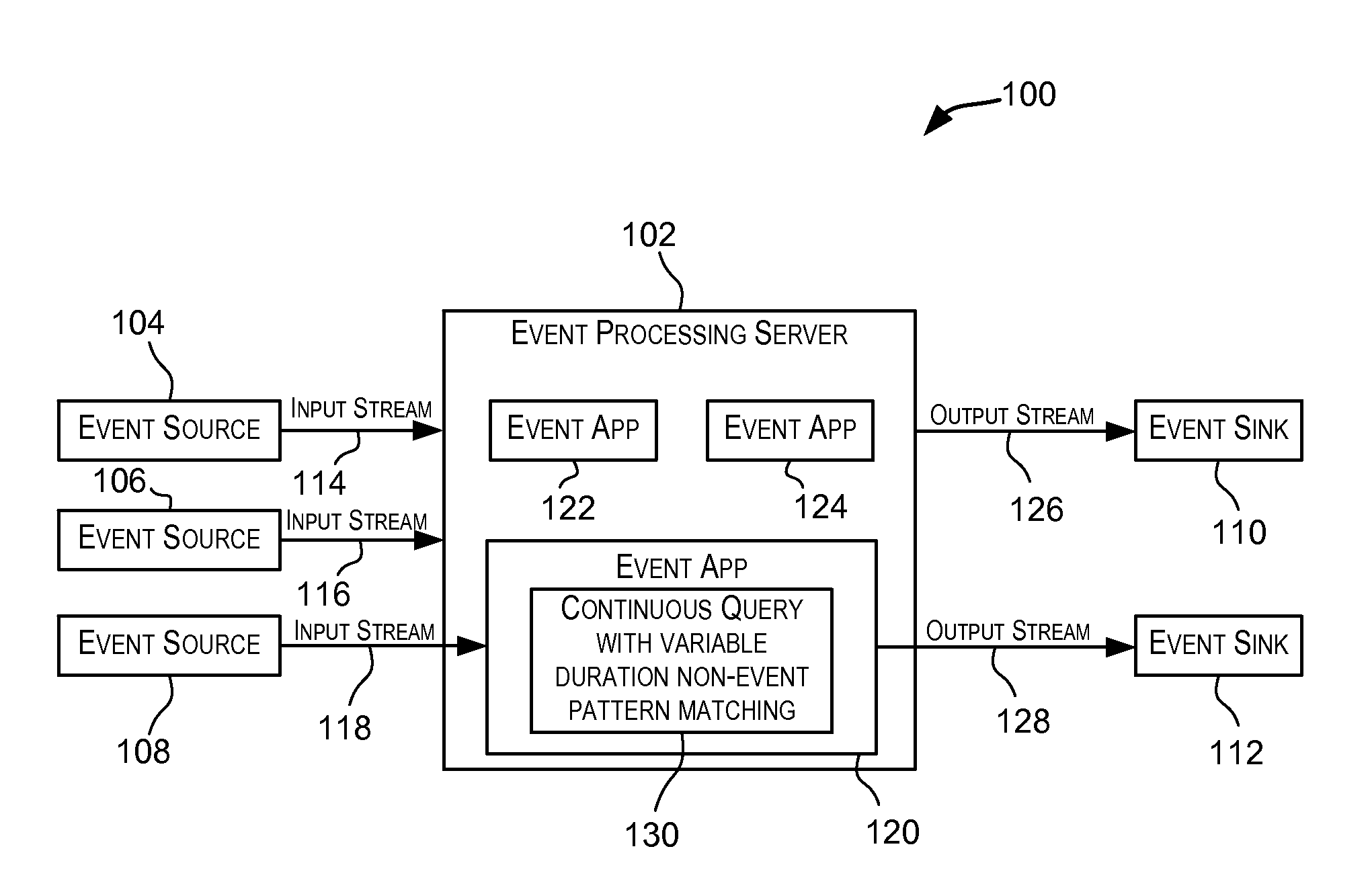
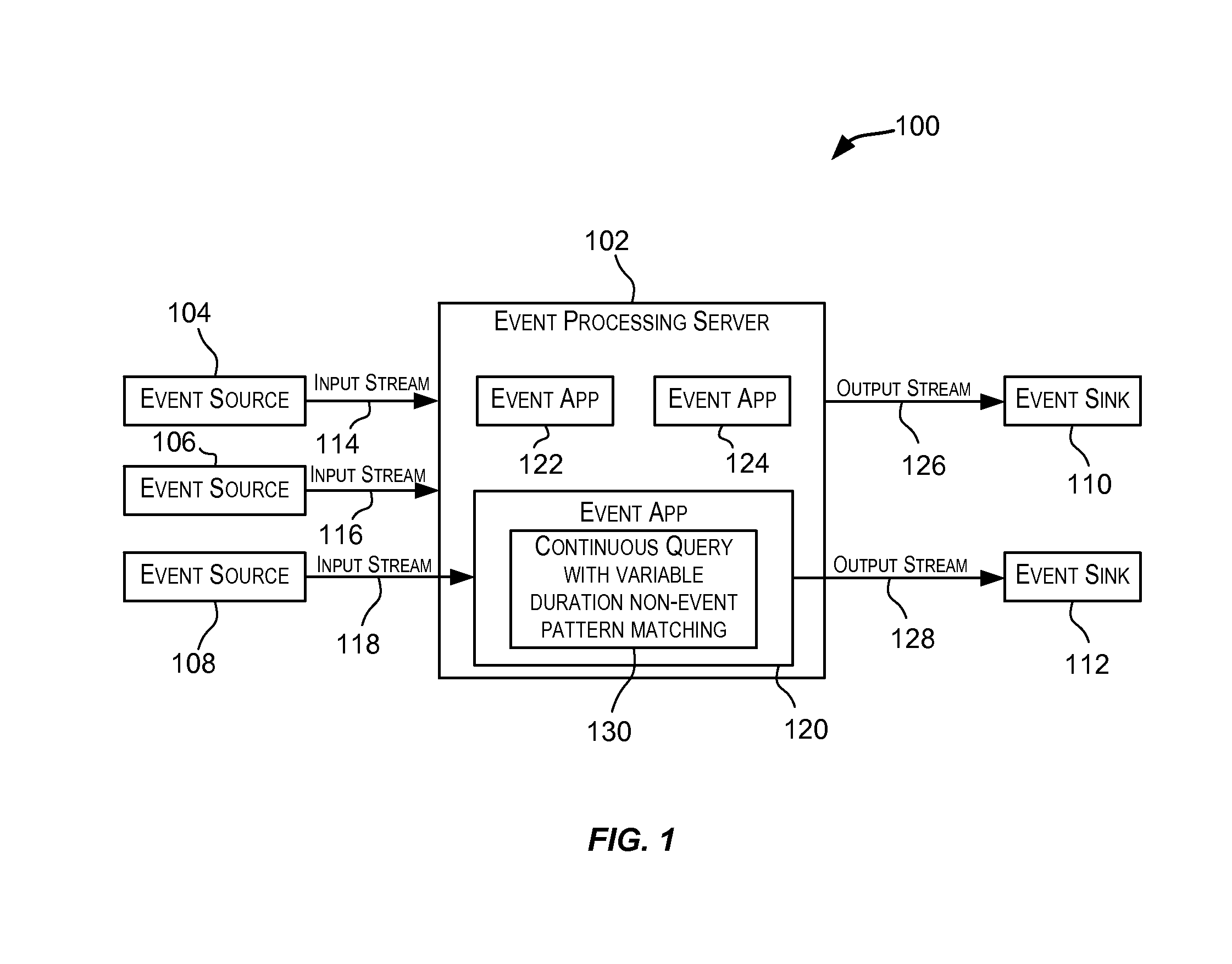
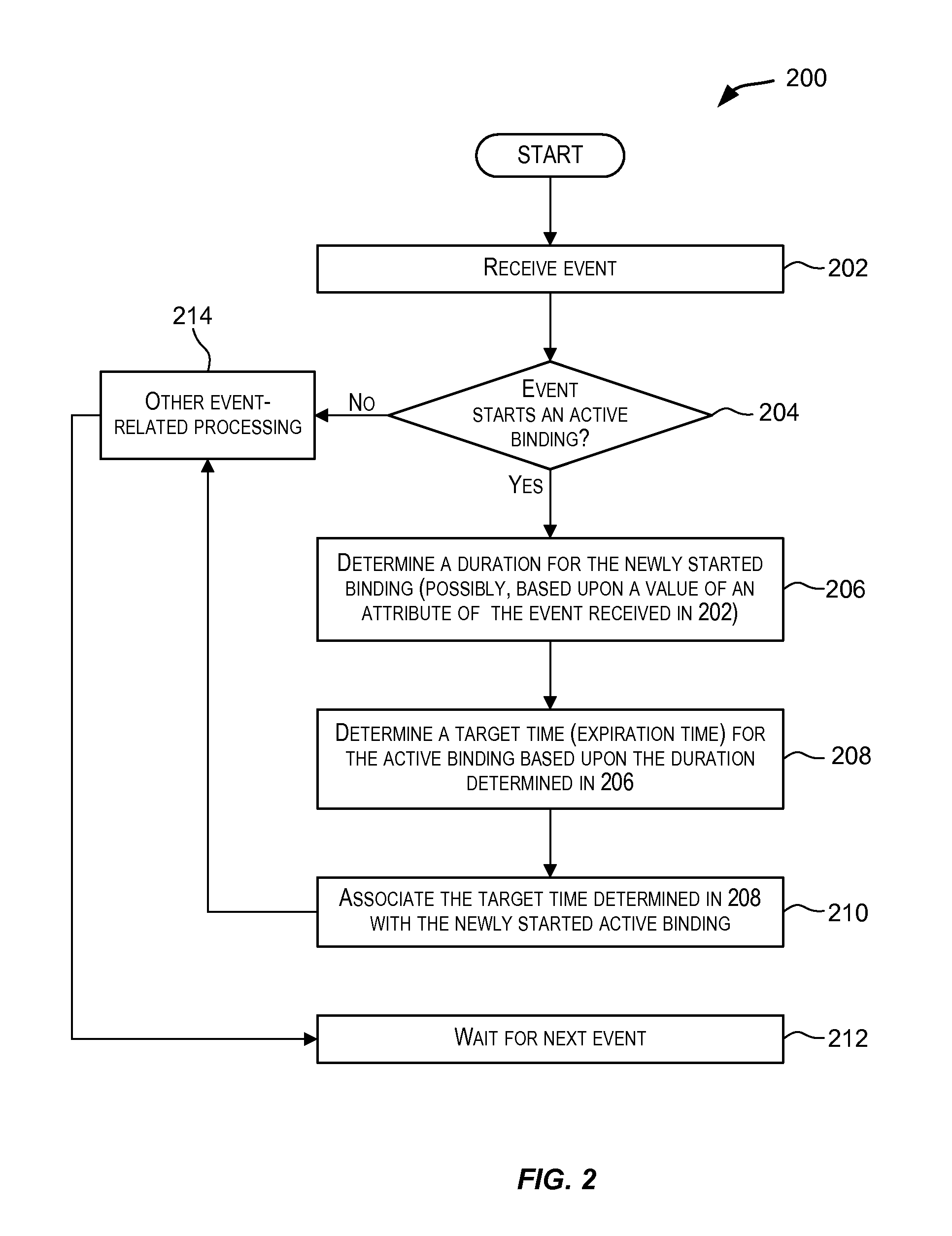
Variable duration non-event pattern matching
ActiveUS9098587B2Good flexibilityWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsPattern matchingAlgorithm
Techniques for performing non-event pattern matching on continuous event streams using variable duration. The duration value used in non-event pattern matching can be variable. Accordingly, a first pattern match candidate can have a different associated duration from a second pattern match candidate for matches arising from events received via an event stream. In certain embodiments, the duration for a candidate pattern match may be based upon one or more attributes of an event that started the candidate pattern match or based upon an expression (e.g., an arithmetic expression) involving one or more attributes of the event.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Application integration with a digital assistant
ActiveUS20190103112A1Software maintainance/managementNatural language data processingProgramming languageEnterprise application integration
Systems and processes for application integration with a digital assistant are provided. In accordance with one example, a method includes, at an electronic device having one or more processors and memory, receiving a natural-language user input; identifying, with the one or more processors, an intent object of a set of intent objects and a parameter associated with the intent, where the intent object and the parameter are derived from the natural-language user input. The method further includes identifying a software application associated with the intent object of the set of intent objects; and providing the intent object and the parameter to the software application.
Owner:APPLE INC
Variable duration non-event pattern matching
ActiveUS20140201225A1Good flexibilityWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmPattern matching
Techniques for performing non-event pattern matching on continuous event streams using variable duration. The duration value used in non-event pattern matching can be variable. Accordingly, a first pattern match candidate can have a different associated duration from a second pattern match candidate for matches arising from events received via an event stream. In certain embodiments, the duration for a candidate pattern match may be based upon one or more attributes of an event that started the candidate pattern match or based upon an expression (e.g., an arithmetic expression) involving one or more attributes of the event.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
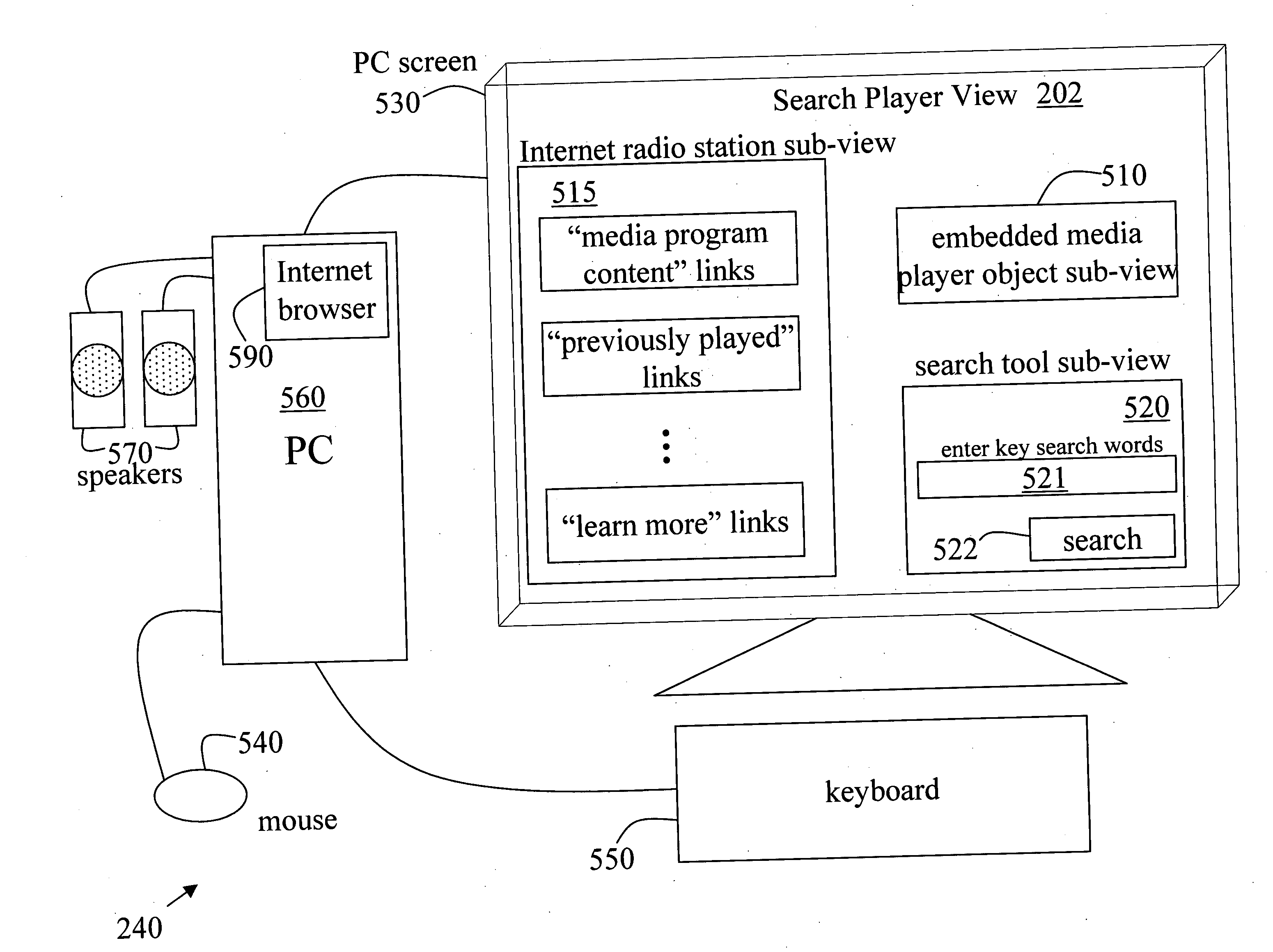
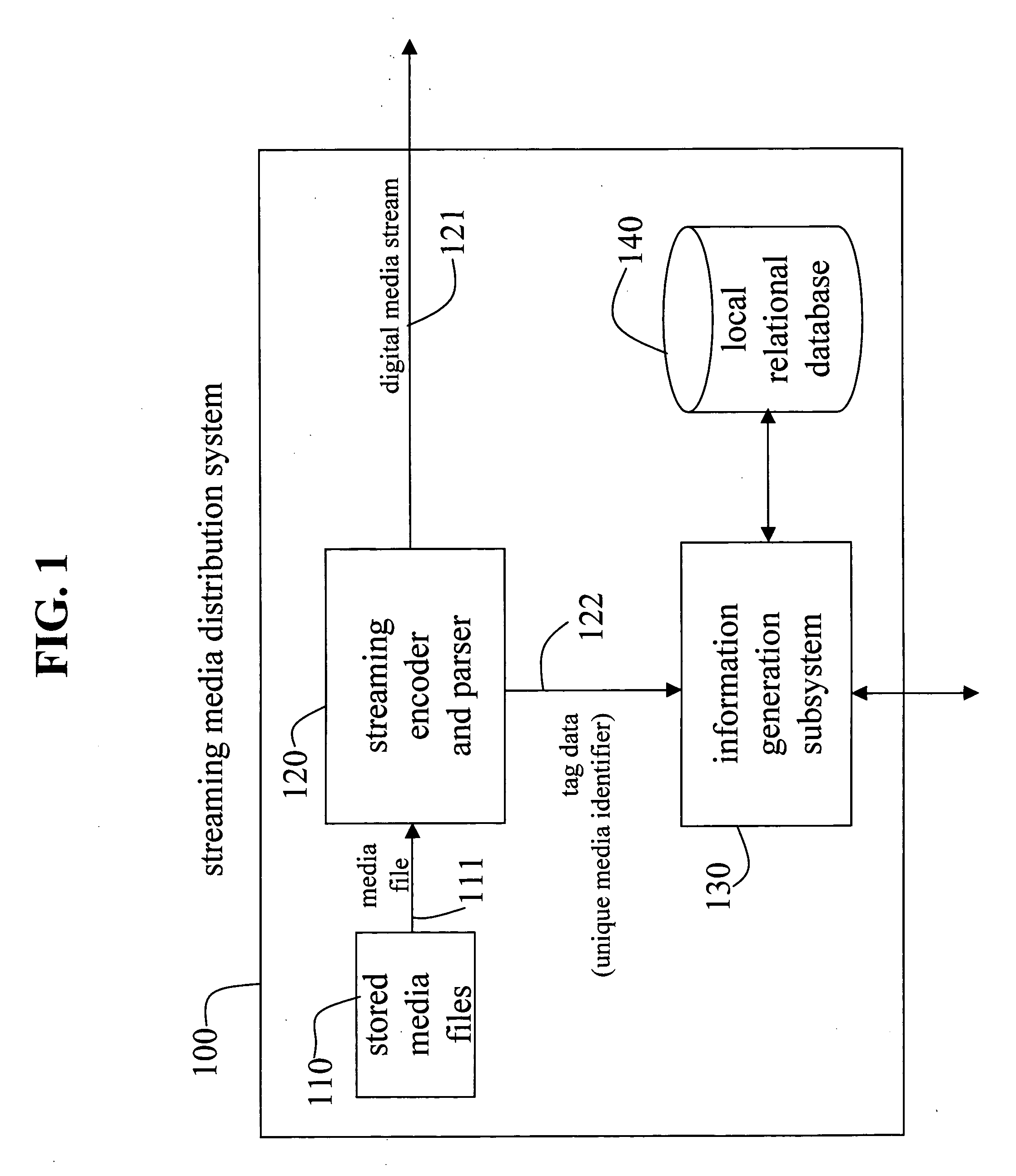
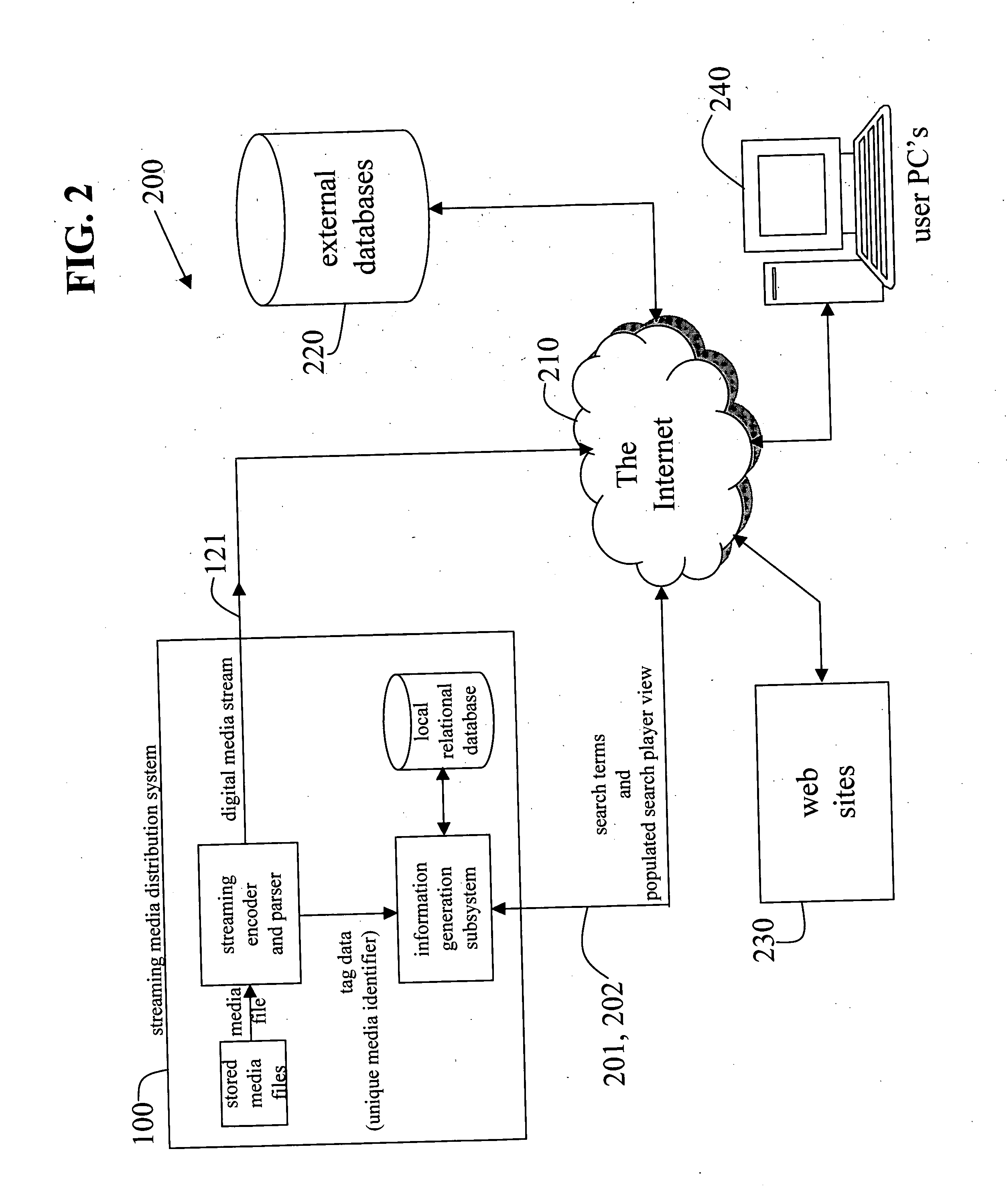
Systems and methods to provide internet search/play media services
InactiveUS20060173825A1Easily interfaceWeb data indexingMultimedia data browsing/visualisationInternet searchingWeb site
Owner:BLU VENTURES & IOMEDIA PARTNERS
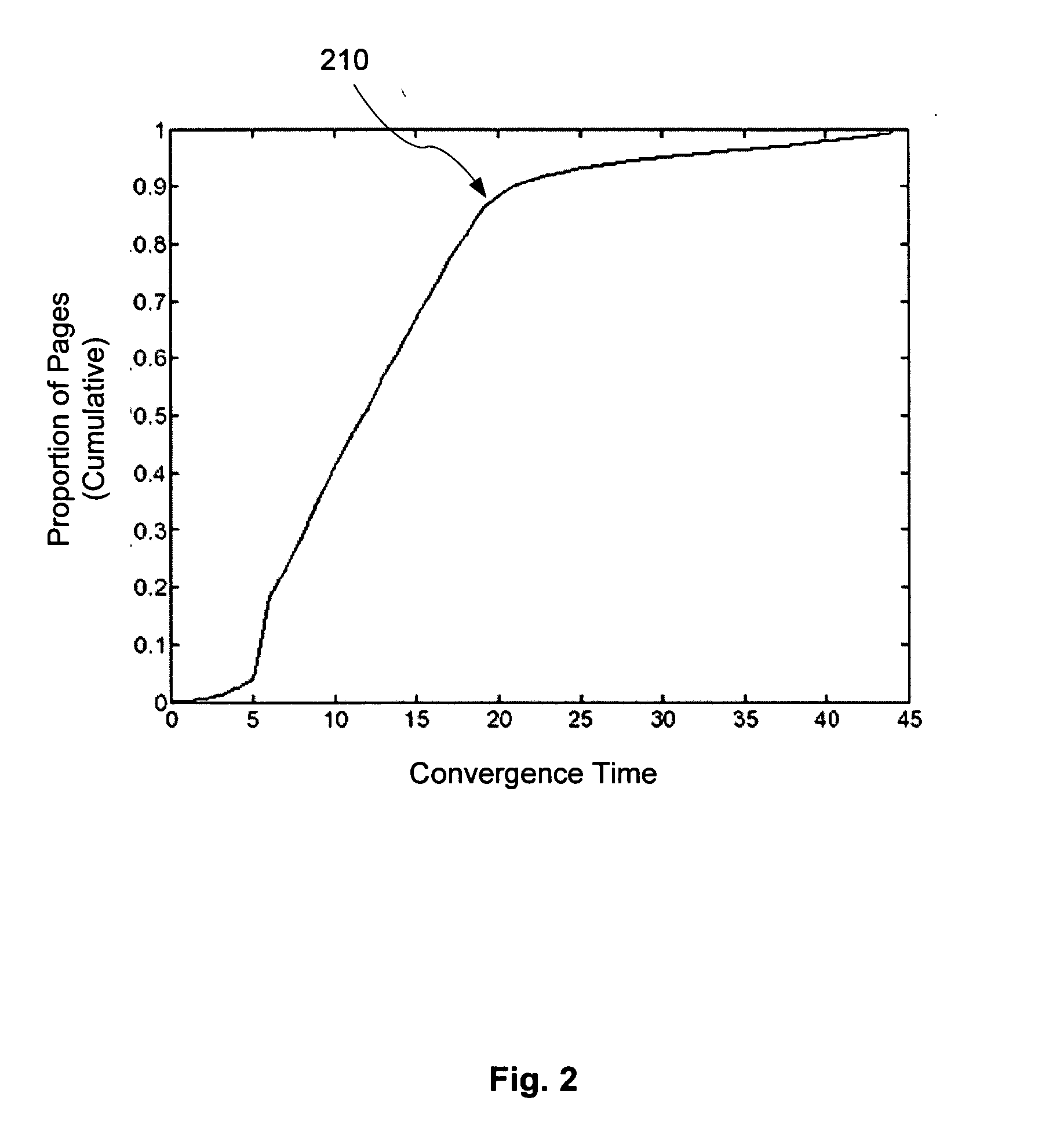
Adaptive computation of ranking
ActiveUS20050027685A1Reduce computing costData processing applicationsWeb data indexingPaper documentDocument preparation
A system and method is disclosed in which a ranking function for a set of document rank values is iteratively solved with respect to a set of linked documents until a first stability condition is satisfied. After such condition is satisfied, some of the ranks will have converged. The ranking function is modified to take into account these converged ranks so as to reduce the ranking function's computation cost. The modified ranking function is then solved until a second stability condition is satisfied. After such condition is satisfied more of the ranks will have converged. The ranking function is again modified and process continues until complete.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
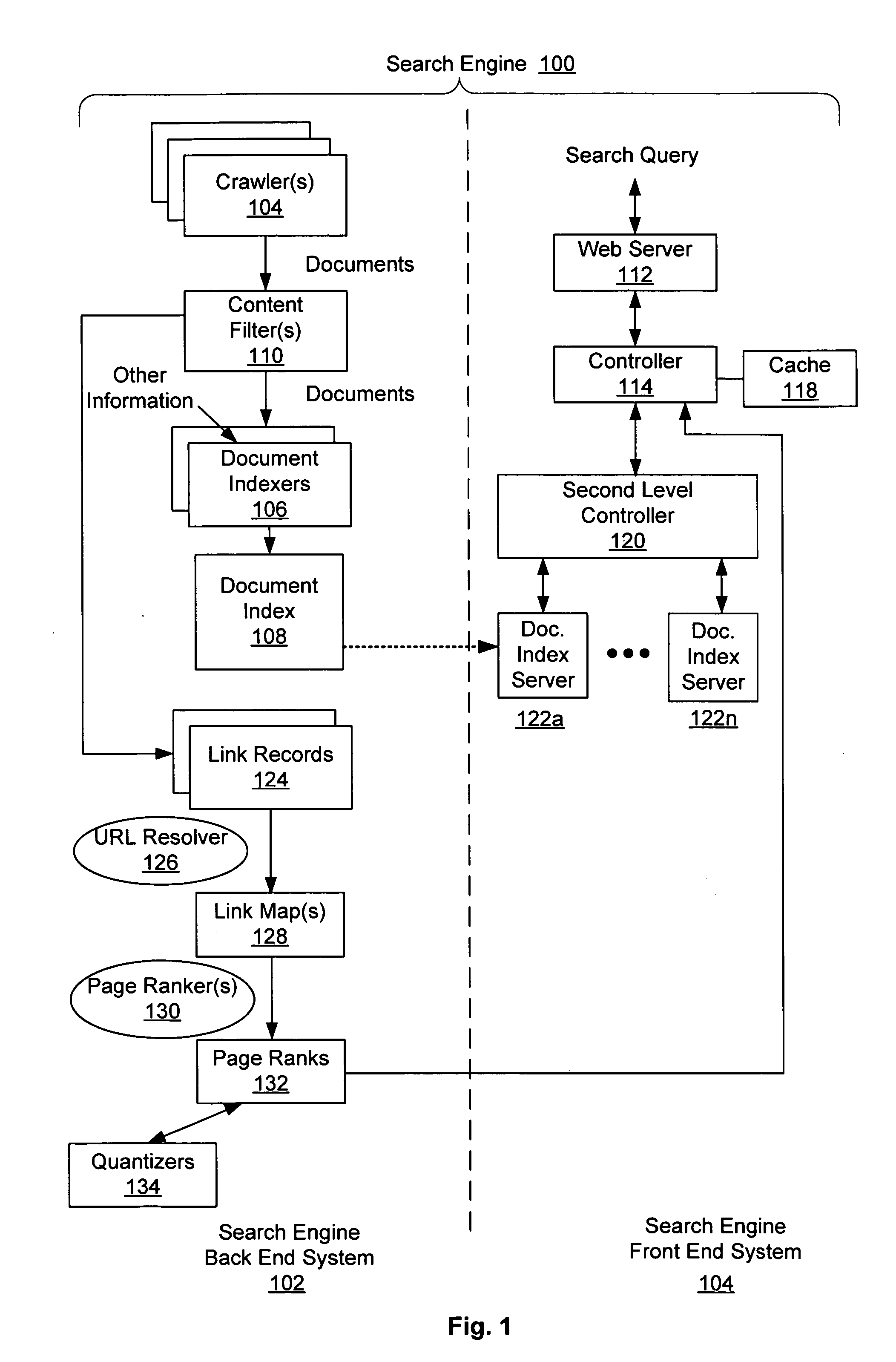
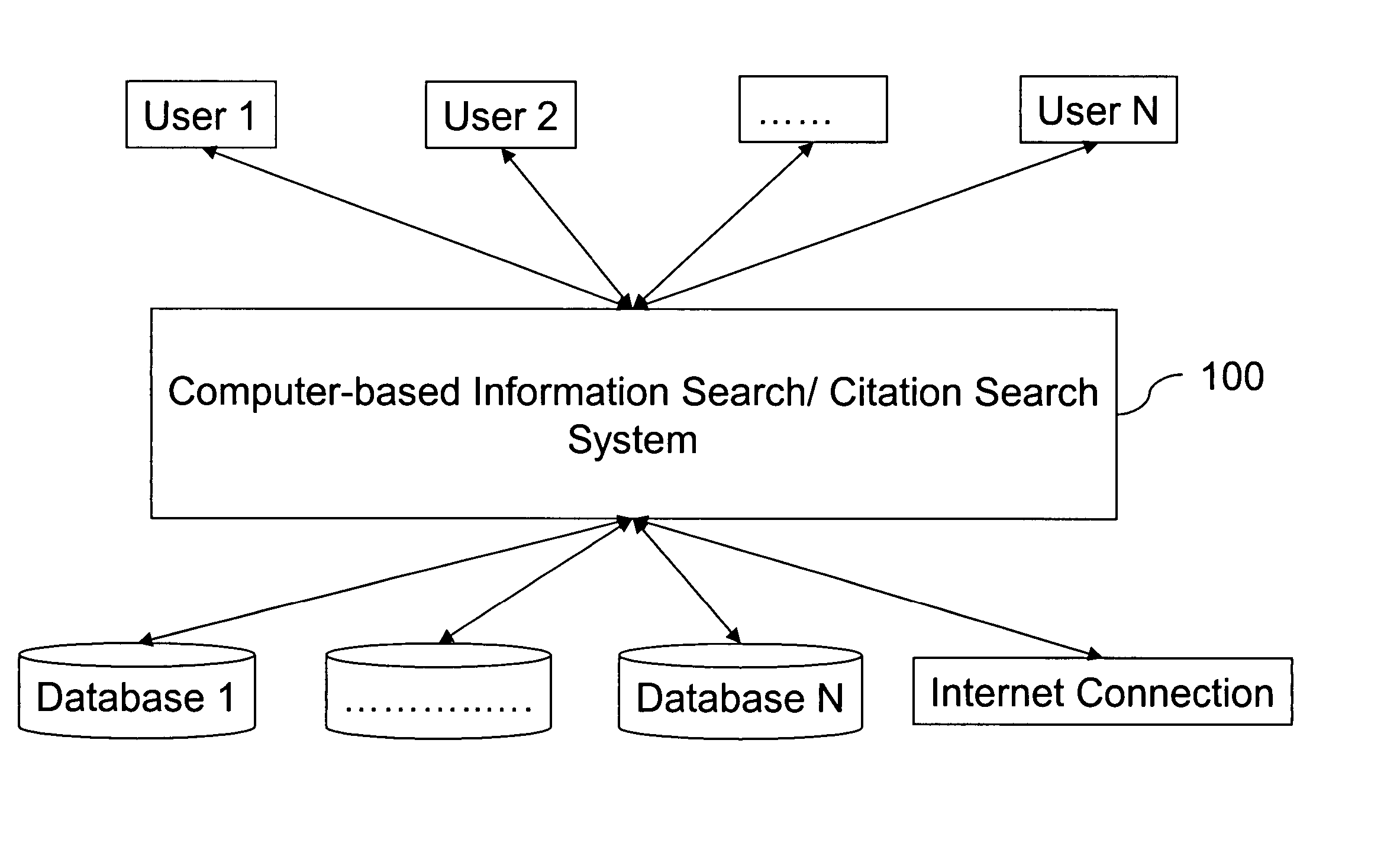
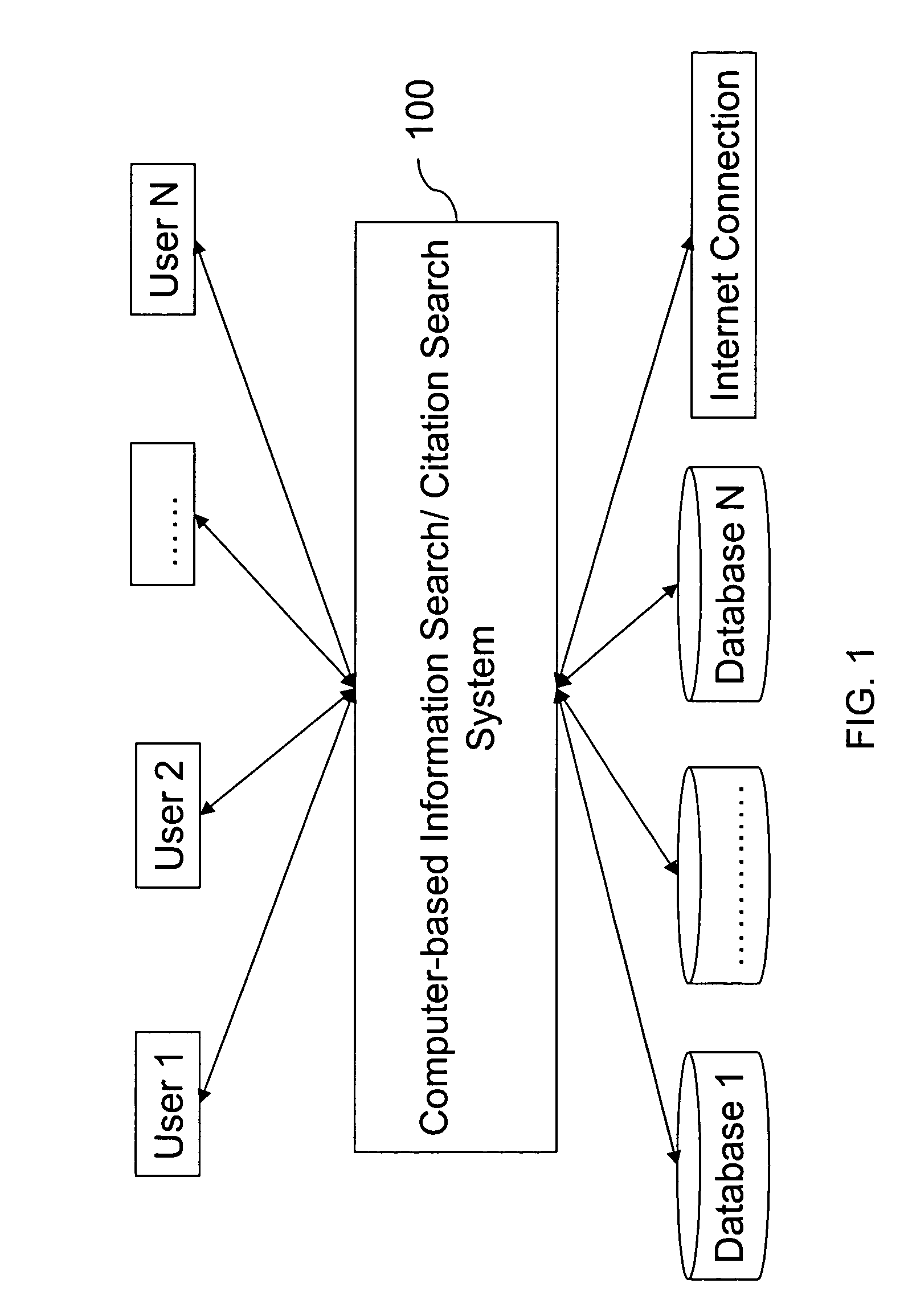
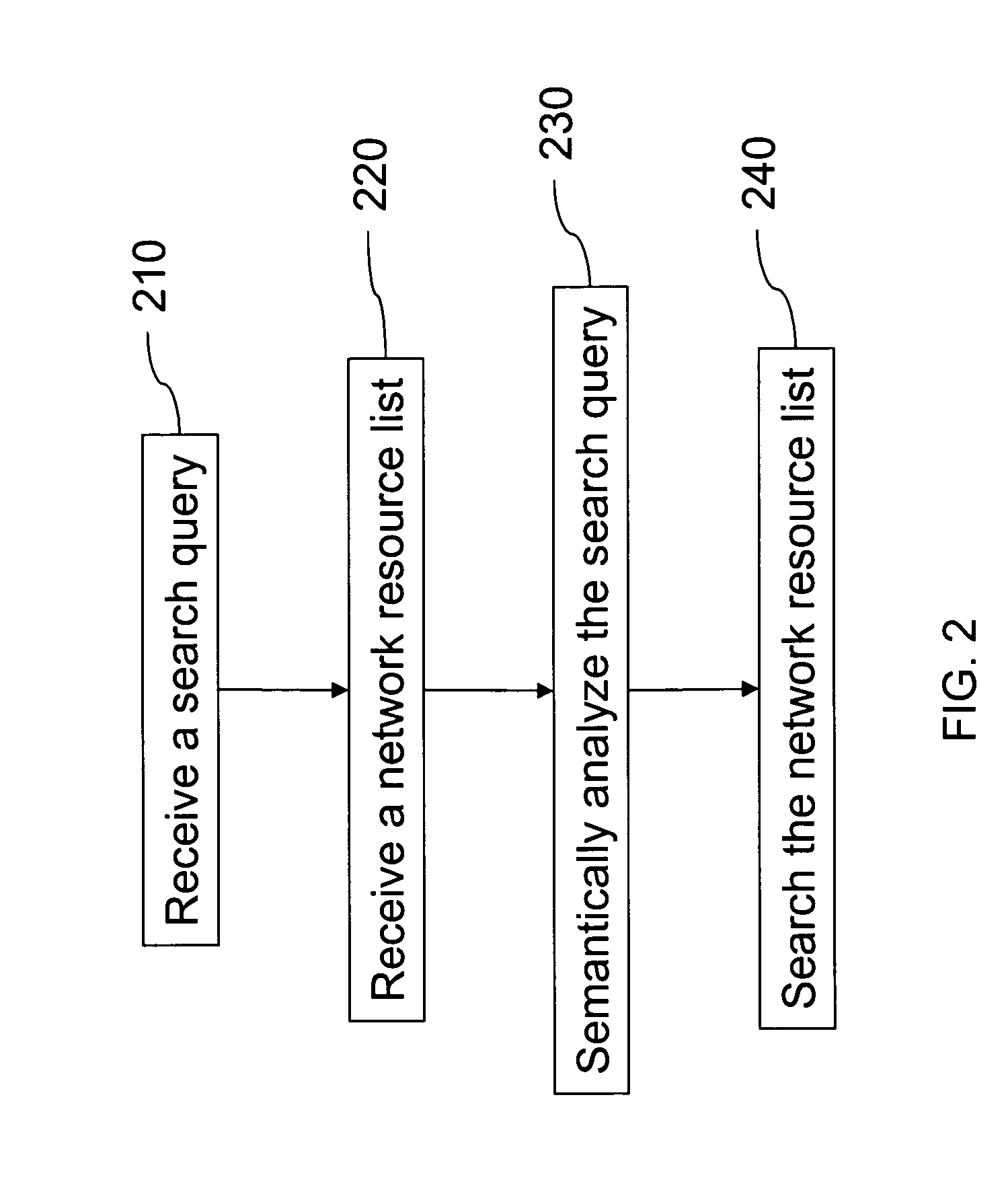
Methods for information search and citation search
InactiveUS20050010559A1Web data indexingDigital data processing detailsWeb siteInformation searching
A computer-based information search method comprises the steps of: receiving a search query, the search query comprising at least one term; receiving a network resource list, the list comprising at least one web site selected from a predetermined web site list; semantically analyzing the search query; and searching the network resource list for a response to the search query using a search engine. A computer-based citation search method comprises the steps of: receiving a search query, the search query comprising an patent identification condition; receiving a list of patent databases; searching the list of patent databases to collect at least one reference patent that cites patents or is cited by patents satisfying the condition of the search query; and producing a citation list, the list comprising at least an owner of the reference patent.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Short query-based system and method for content searching
InactiveUS20060184625A1Web data indexingNatural language data processingHigh probabilityWorld Wide Web
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for processing queries provided as short messages. Keywords can be extracted from short messages and specific meaning can be derived and attributed to the short messages based on various attributes and context associated with the message, time of day and a user. Responses are provided that comprise content from information sources identified as best-fit search result. Responses are provided that comprise a menu having options identifying plural high probability search results. An alert system is disclosed for generating and managing alerts based on search results. Based on search results, a user can be connected to an information service or a transactional system and can be provided with advertising, marketing and help information.
Owner:4INFO
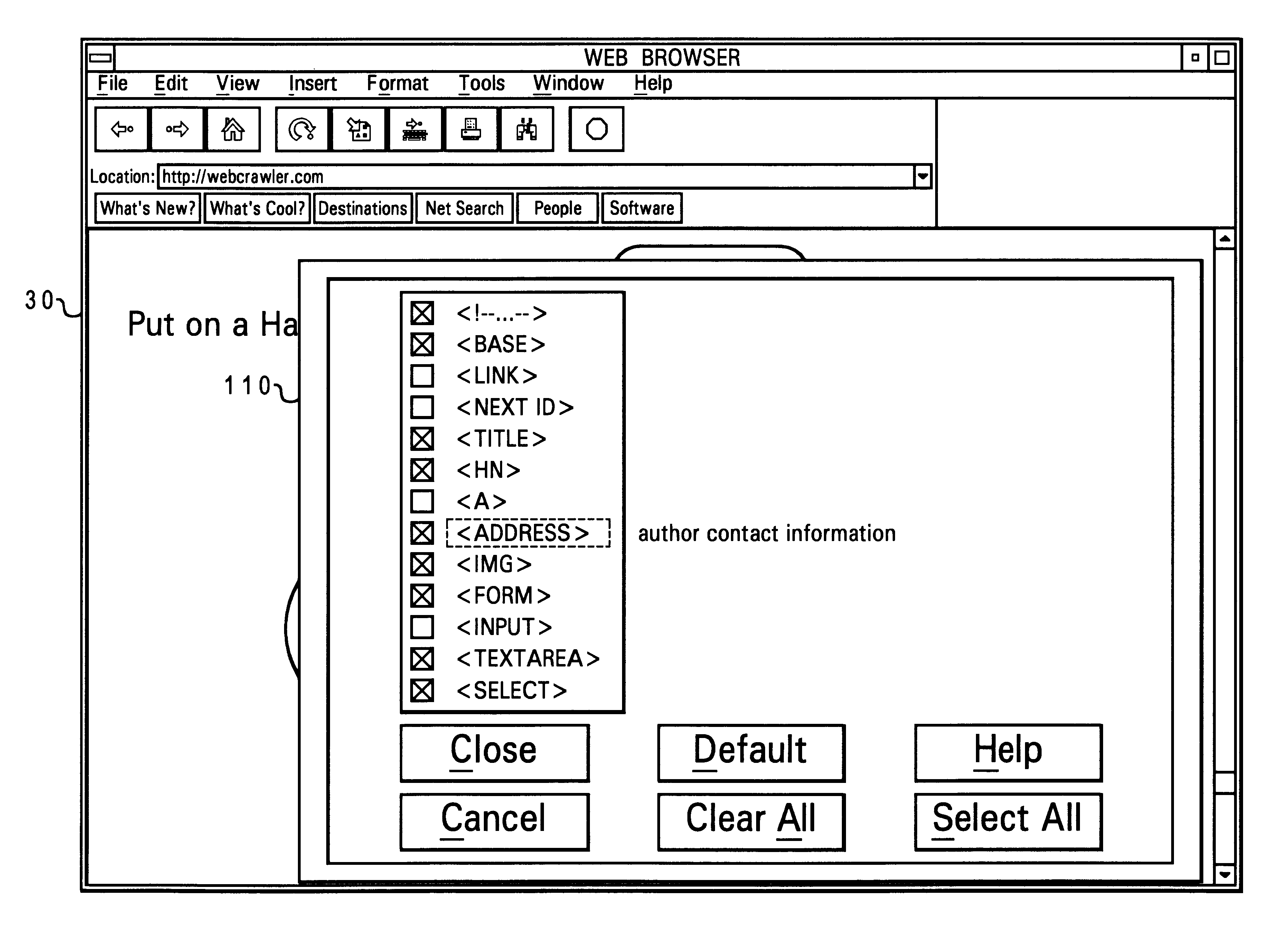
Search parameters
A method of searching for files located in a computer system, wherein each file has at least one of a plurality of fields, by creating a search query, selecting a subset of the fields for searching wherein the subset is selected independent of the search query, and processing the files by examining the content of only those fields included in the subset for matching against the query. The fields can be selected by using a default setting. Certain fields are ignored during the processing step. An illustrative embodiment is adapted for use with hypertext markup language (HTML) files that are transmitted along the Internet's World Wide Web. The user interface may include a pop-up window that displays a list of the tags which may be embedded in the files, and allows a user to individually select one or more tags so displayed for searching.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com