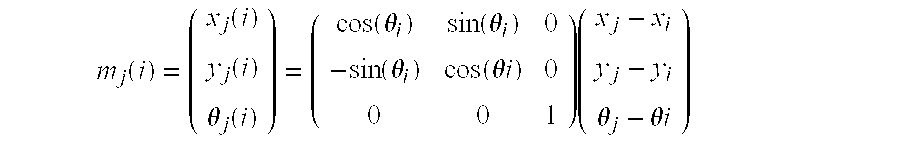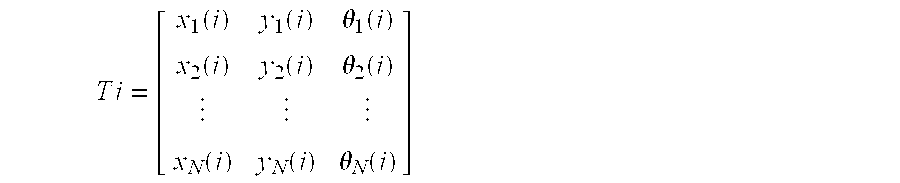Patents
Literature
261 results about "Cryptographic nonce" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cryptography, a nonce is an arbitrary number that can be used just once in a cryptographic communication. It is similar in spirit to a nonce word, hence the name. It is often a random or pseudo-random number issued in an authentication protocol to ensure that old communications cannot be reused in replay attacks. They can also be useful as initialization vectors and in cryptographic hash functions.
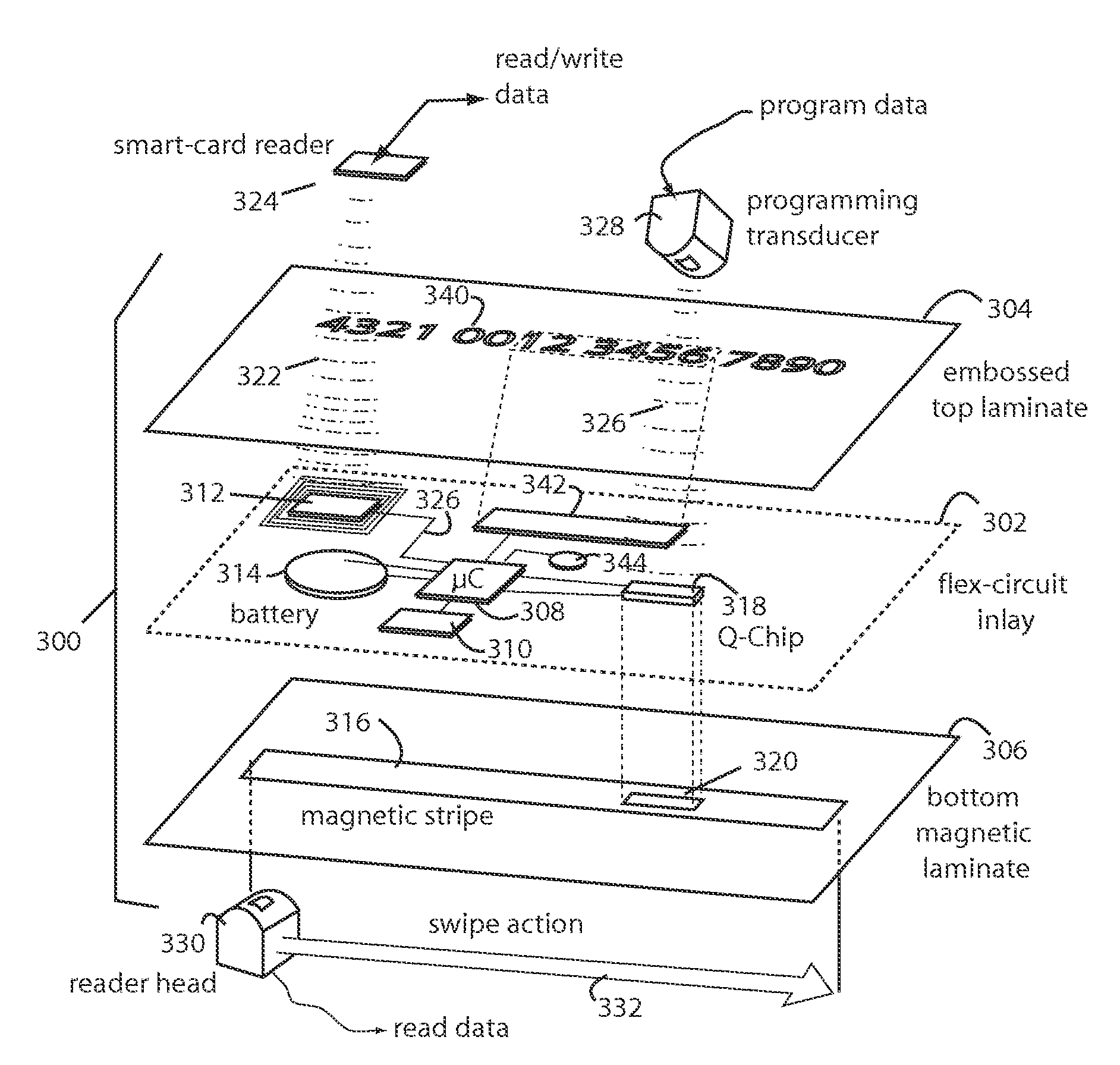
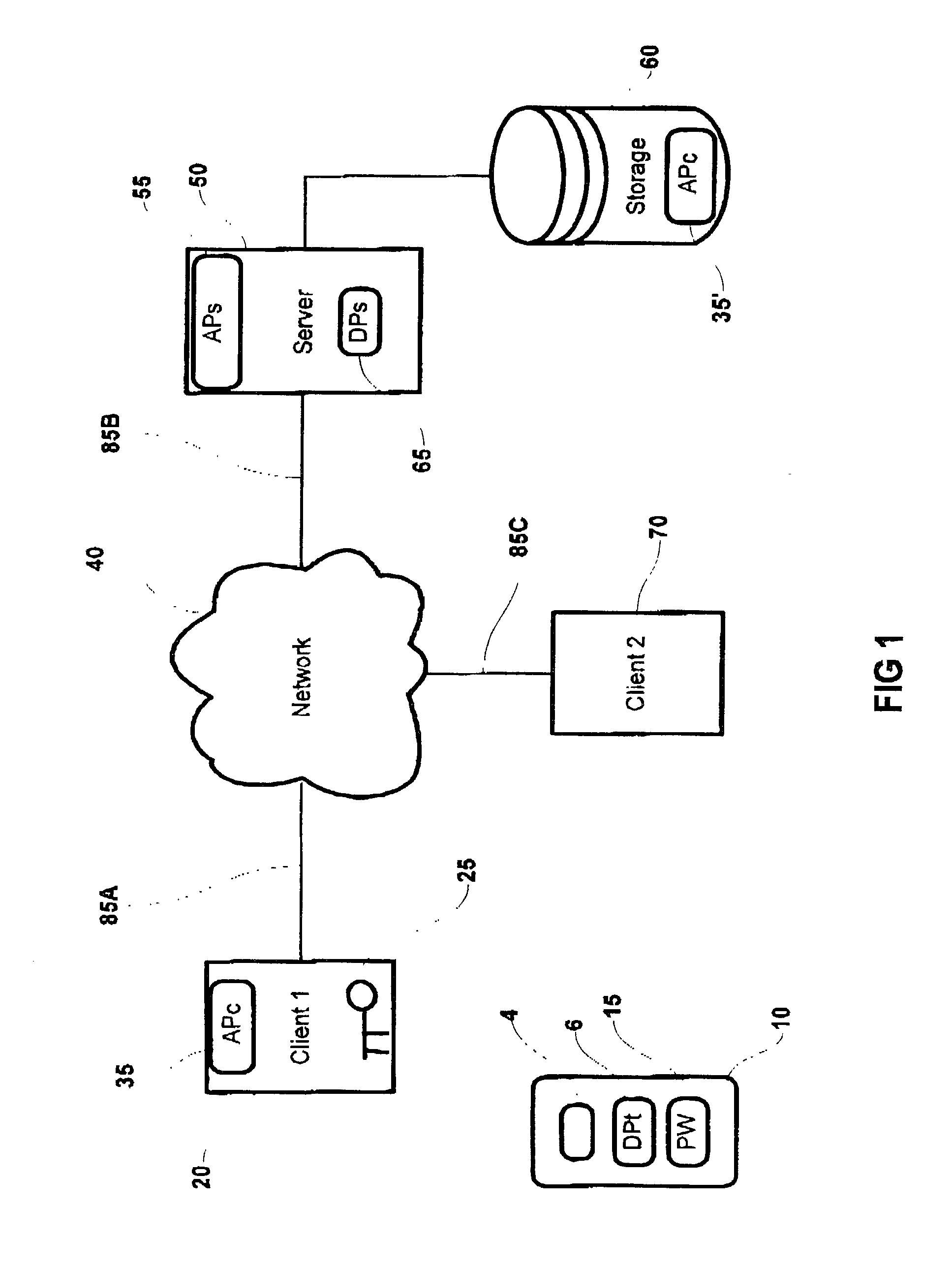
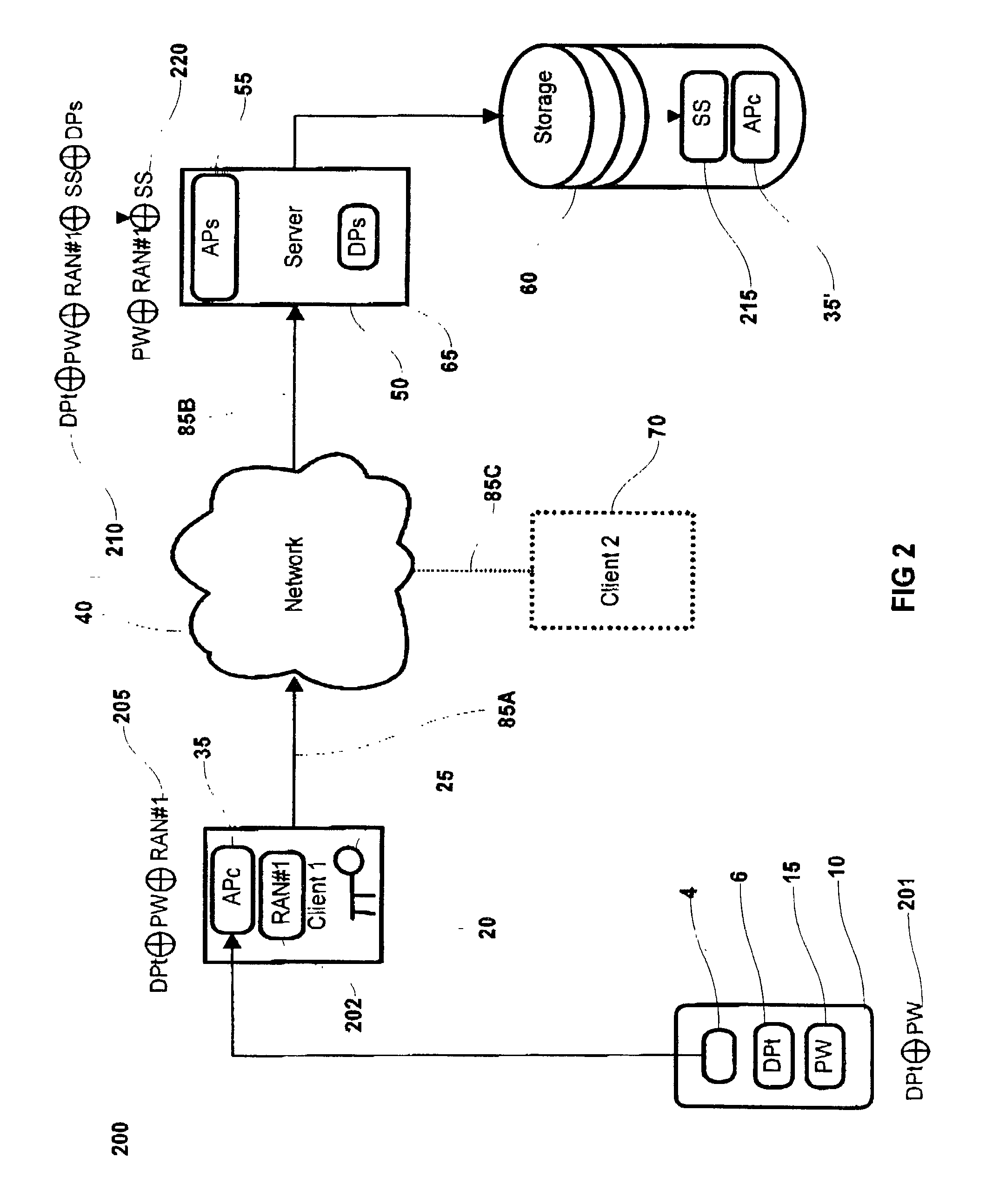
Payment card financial transaction authenticator
InactiveUS20080201264A1Sufficient dataAcutation objectsFinanceCryptographic nonceFinancial transaction
A payment card financial transaction authenticates for providing overall financial network security computes a number of results from a cryptographic key that match values that were selectively used to personalize individual payment cards with their individual user identification and account access codes. An account access code is later presented daring a financial transaction involving at least one of those individual payment cards. A dynamic portion is included in a merchant's magnetic reading of the payment card. Then authenication can proceed by matching it with values computed from the cryptographic key.
Owner:FITBIT INC
Authentication in a secure computerized gaming system
InactiveUS6962530B2Straightforward and easy to manageData processing applicationsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareData set
An architecture and method for a gaming-specific platform are disclosed that features secure storage and verification of game code and other data, provides the ability to securely exchange data with a computerized wagering gaming system, and do so in a manner that is straightforward and easy to manage. Some embodiments provide the ability to identify game program code as certified or approved, such as by the Nevada Gaming Regulations Commission or other regulatory agency. The disclosed embodiments provides these and other functions by encrypting a random number, storing the encrypted random number, and hashing the random number and a casino game data set to provide a first bit string, and storing the first bit string.
Owner:IGT
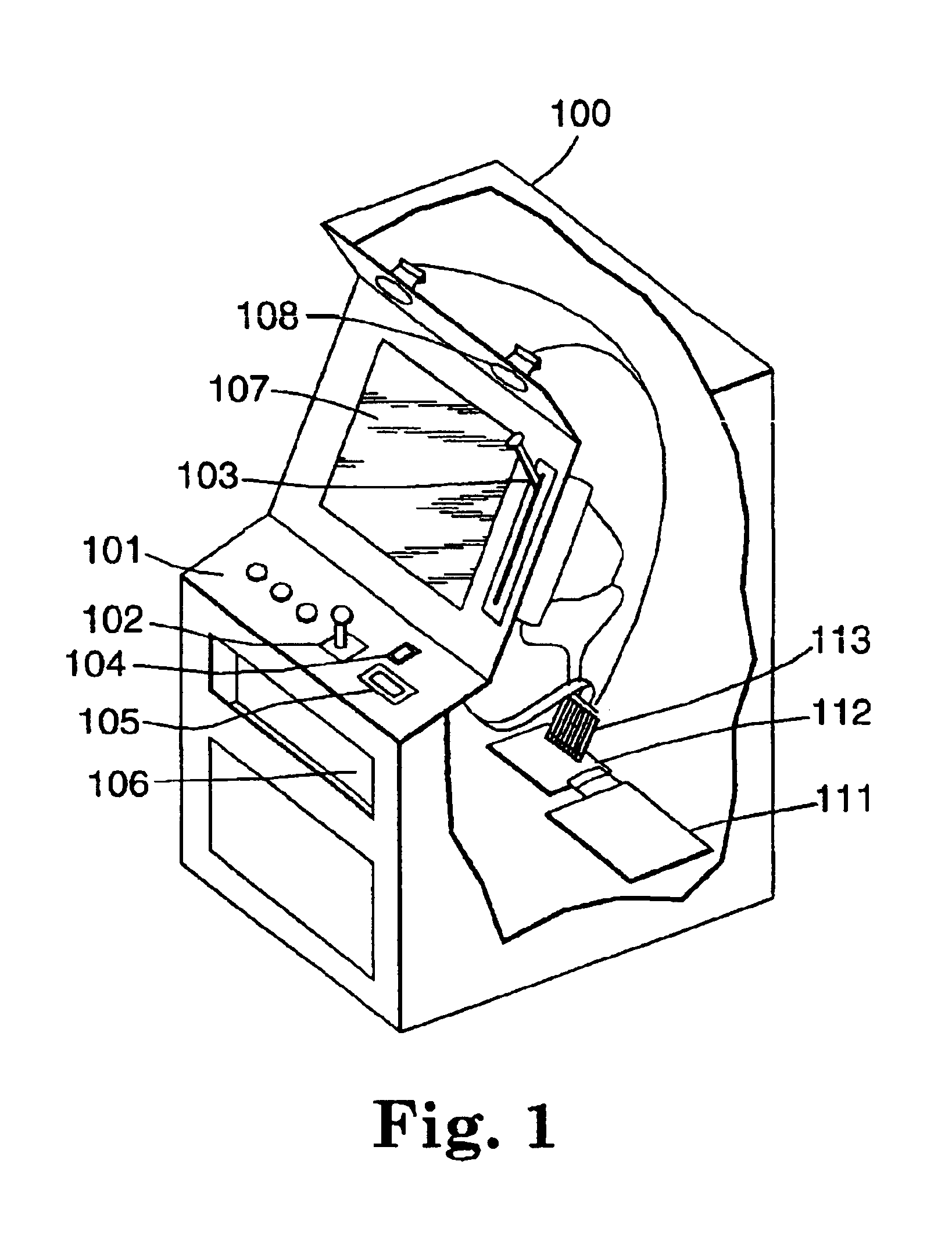
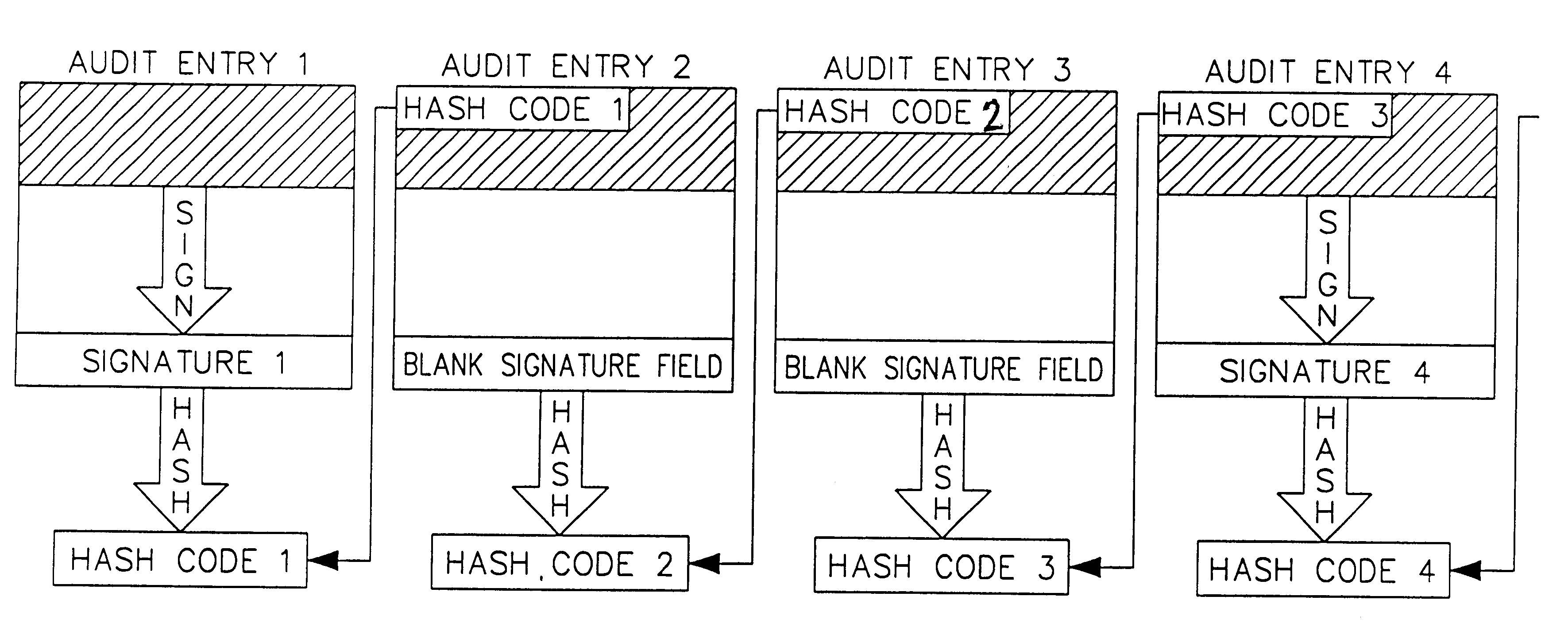
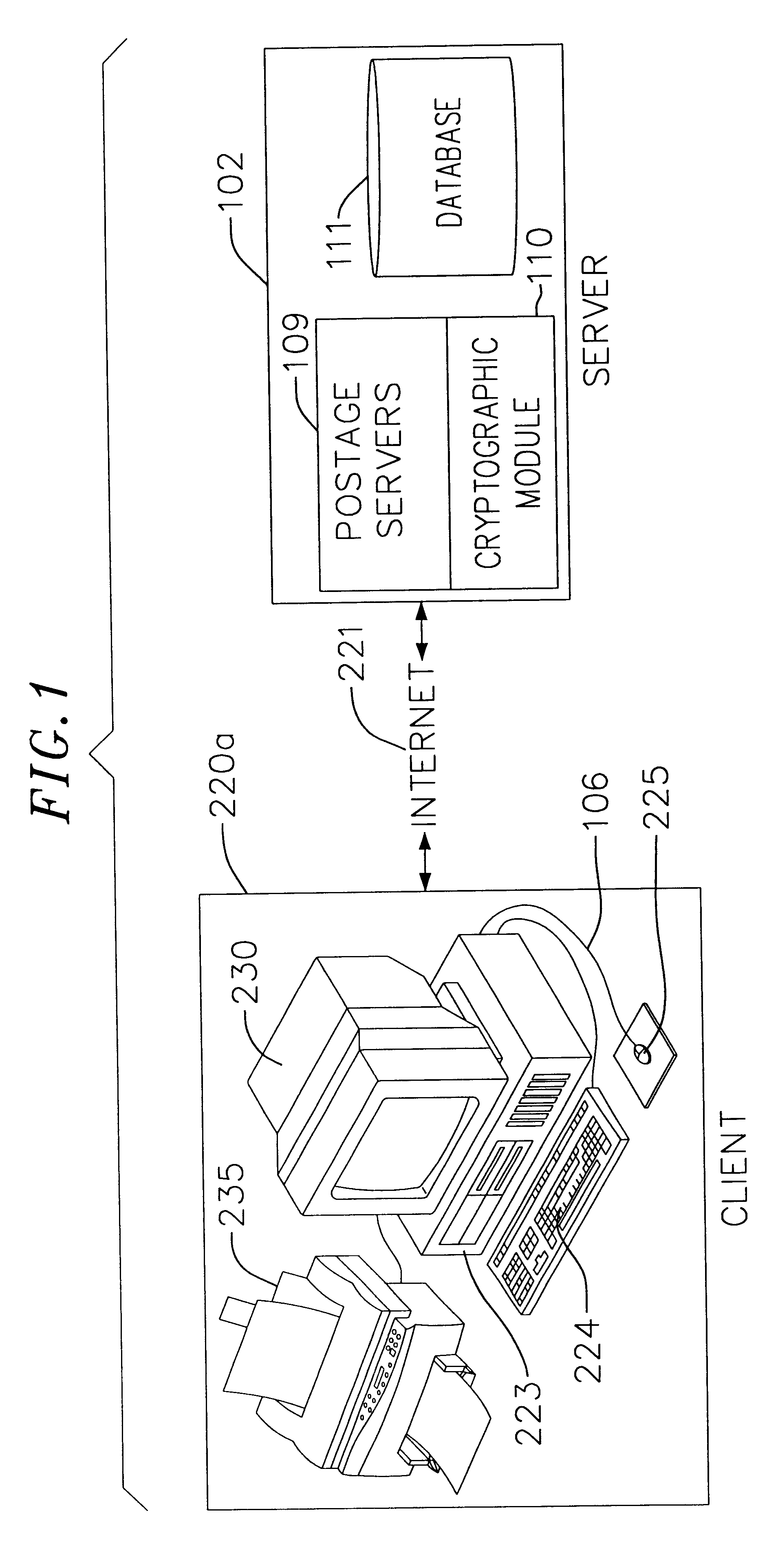
Auditing method and system for an on-line value-bearing item printing system
InactiveUS6868406B1Avoid accessPrevent unauthorized accessPayment architectureFranking apparatusCryptographic nonceCentral database
An on-line value bearing item (VBI) printing system that includes one or more cryptographic modules and a central database is disclosed. The cryptographic modules are capable of implementing the USPS Information Based Indicia Program Postal Security Device Performance Criteria and other required VBI standards. The modules encipher the information stored in the central database for all of the on-line VBI system customers and are capable of preventing access to the database by unauthorized users. Additionally, each cryptographic module is capable of providing audit support functions that enable secure logging of all sensitive actions.
Owner:STAMPS COM
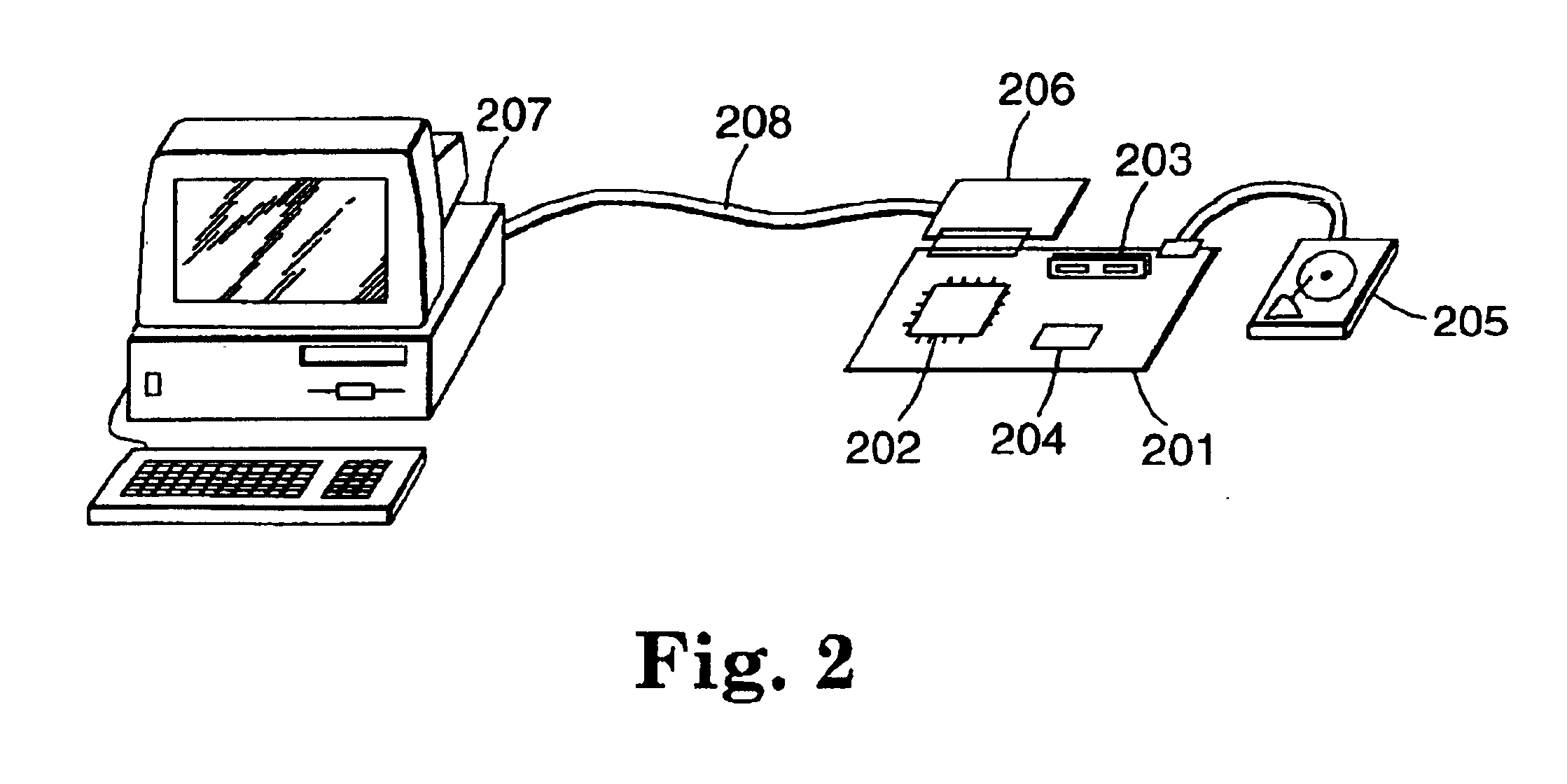
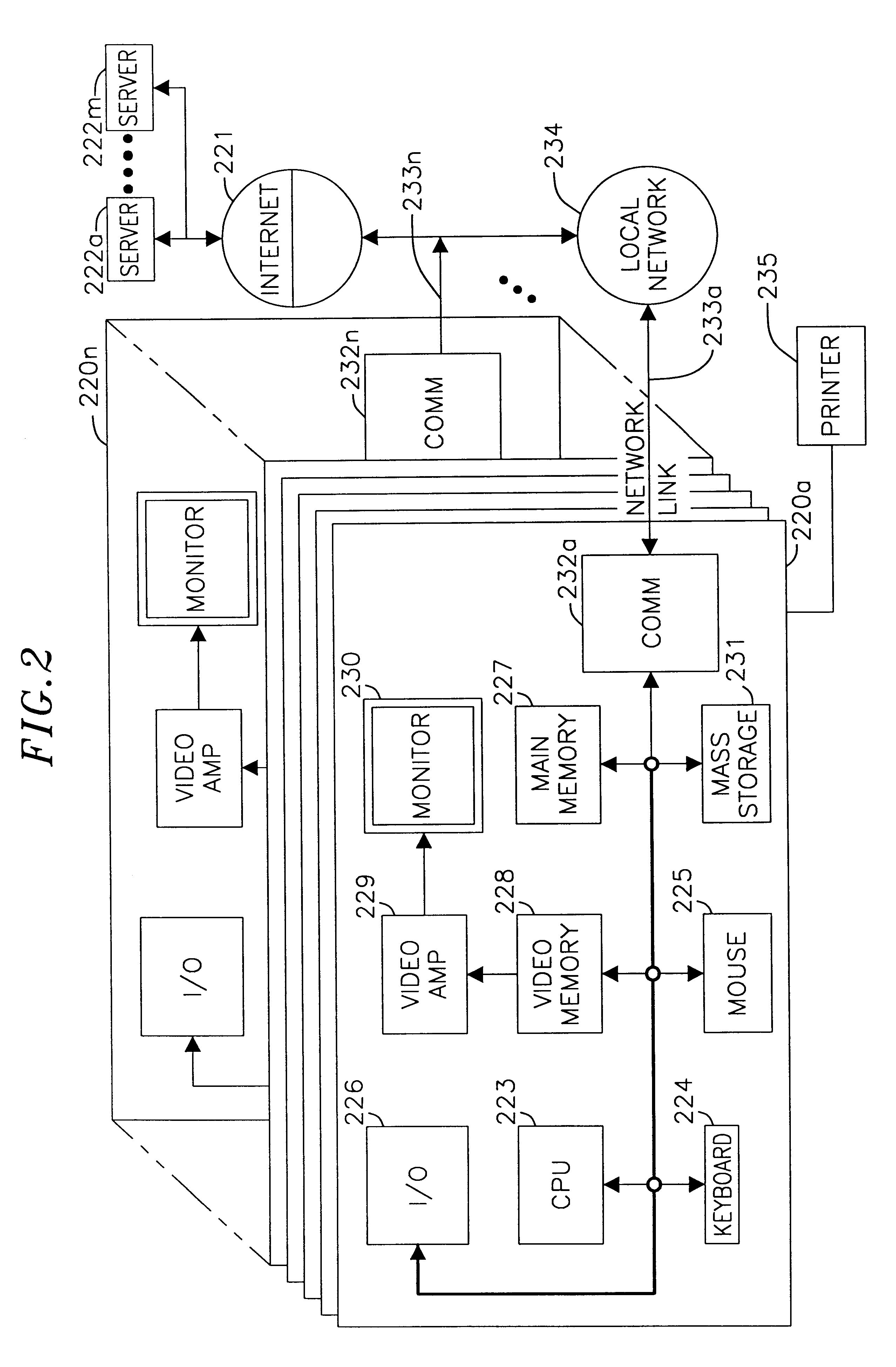
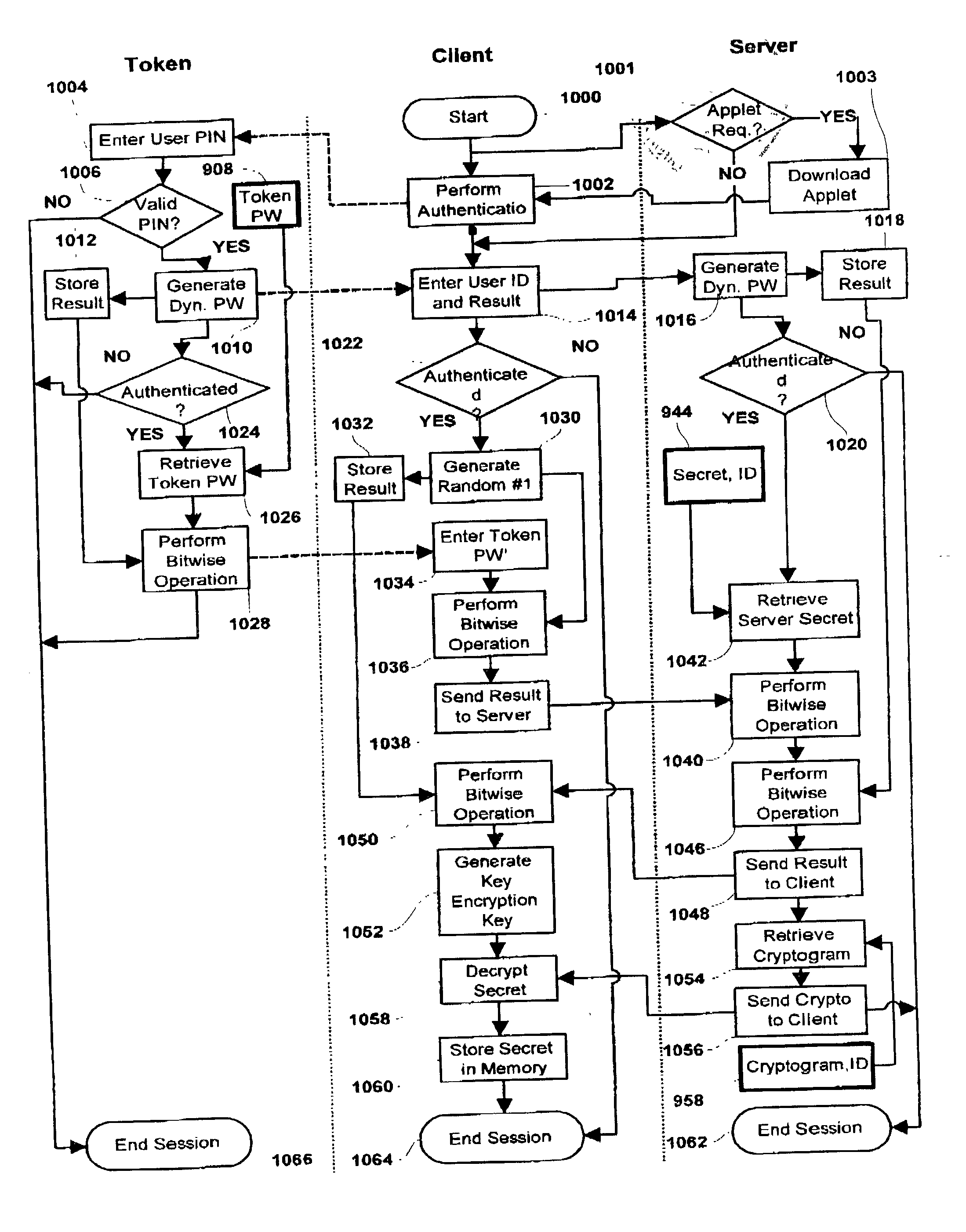
System and method for storage and retrieval of a cryptographic secret from a plurality of network enabled clients
InactiveUS20030204732A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationData processing systemPassword
This patent application describes a data processing system and method for securely storing and retrieving a cryptographic secret from a plurality of network-enabled clients. The cryptographic secret is encrypted using a split key arrangement where a first key component is generated and stored inside a hardware security token and a second key component is generated and stored on a server. Random variables and dynamic passwords are introduced to mask the key components during transport. In order to gain access to the first password, the user is required to enter his or her PIN. The key encryption key is generated by performing a series of XOR operations, which unmasks the first and second key components on a client allowing generation of a symmetric key The symmetric key is used to encrypt the cryptographic secret at the user's normal client and decrypt the cryptogram at another client lacking the cryptographic secret. The applications performing the cryptographic functions are intended as browser applets, which remains in transient memory until the user's session has ended. At which time, the key encryption key and cryptographic secret are destroyed.
Owner:ACTIVCARD
Cryptographic key, encryption device, encryption/decryption device, cryptographic key management device, and decryption device
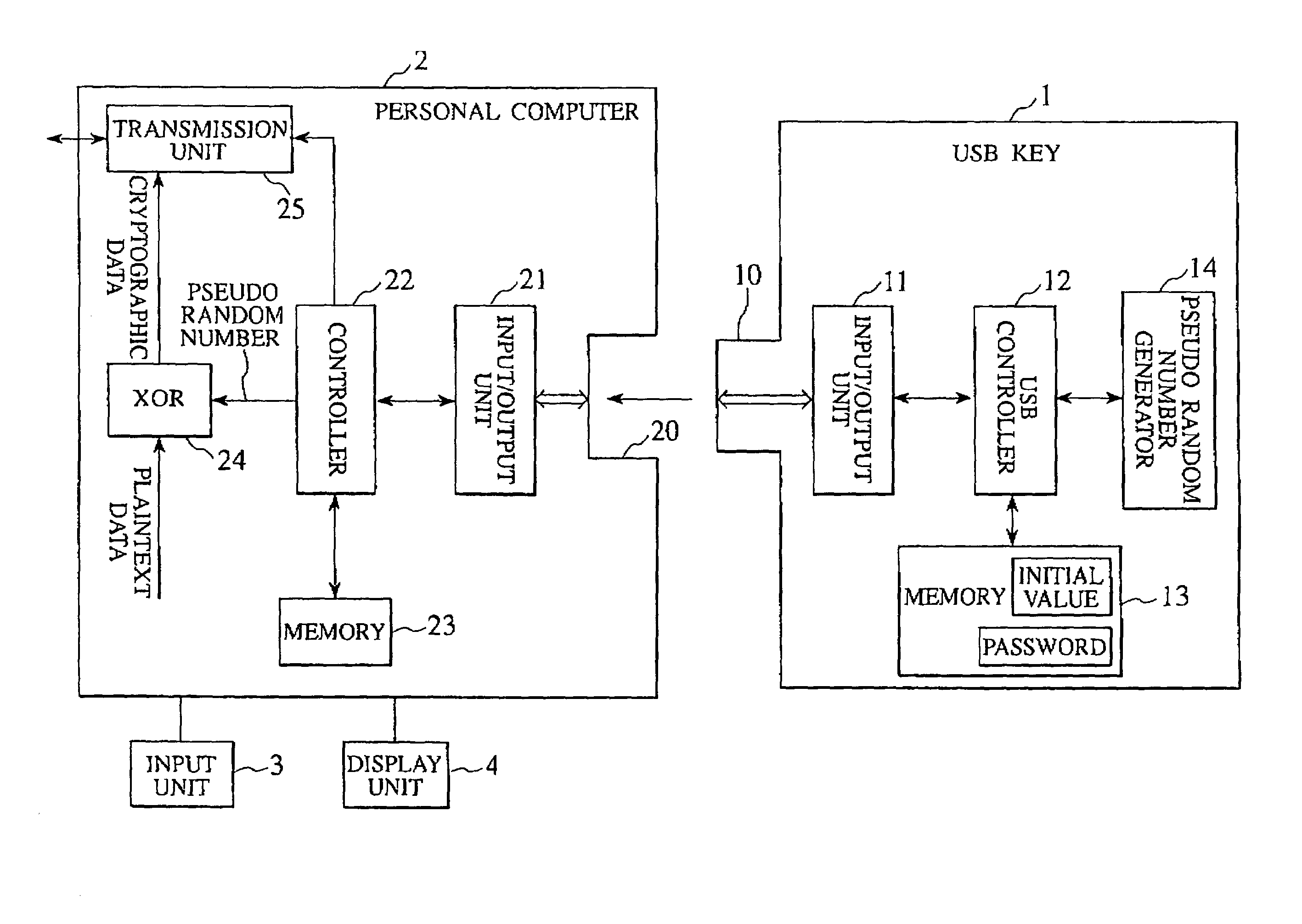
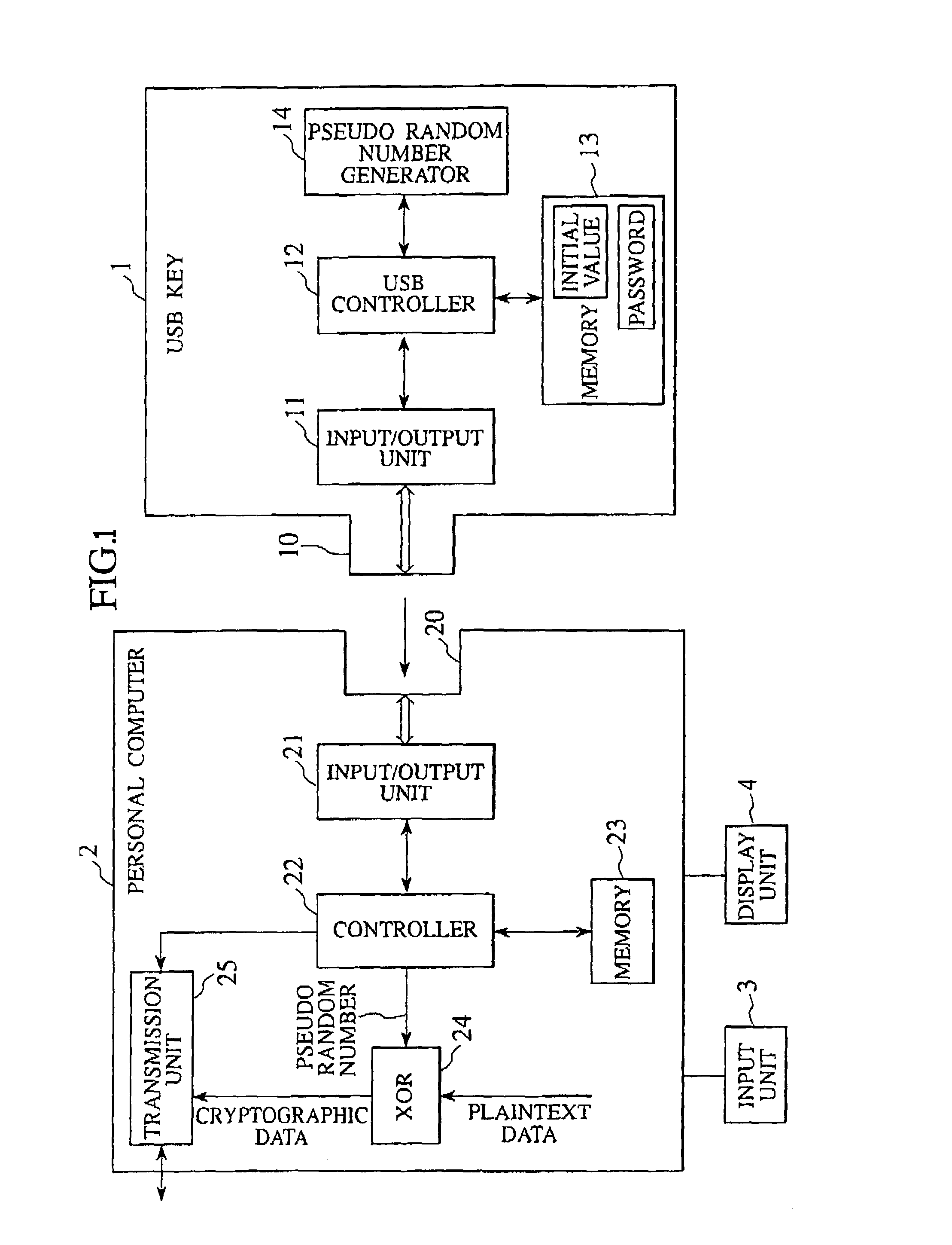
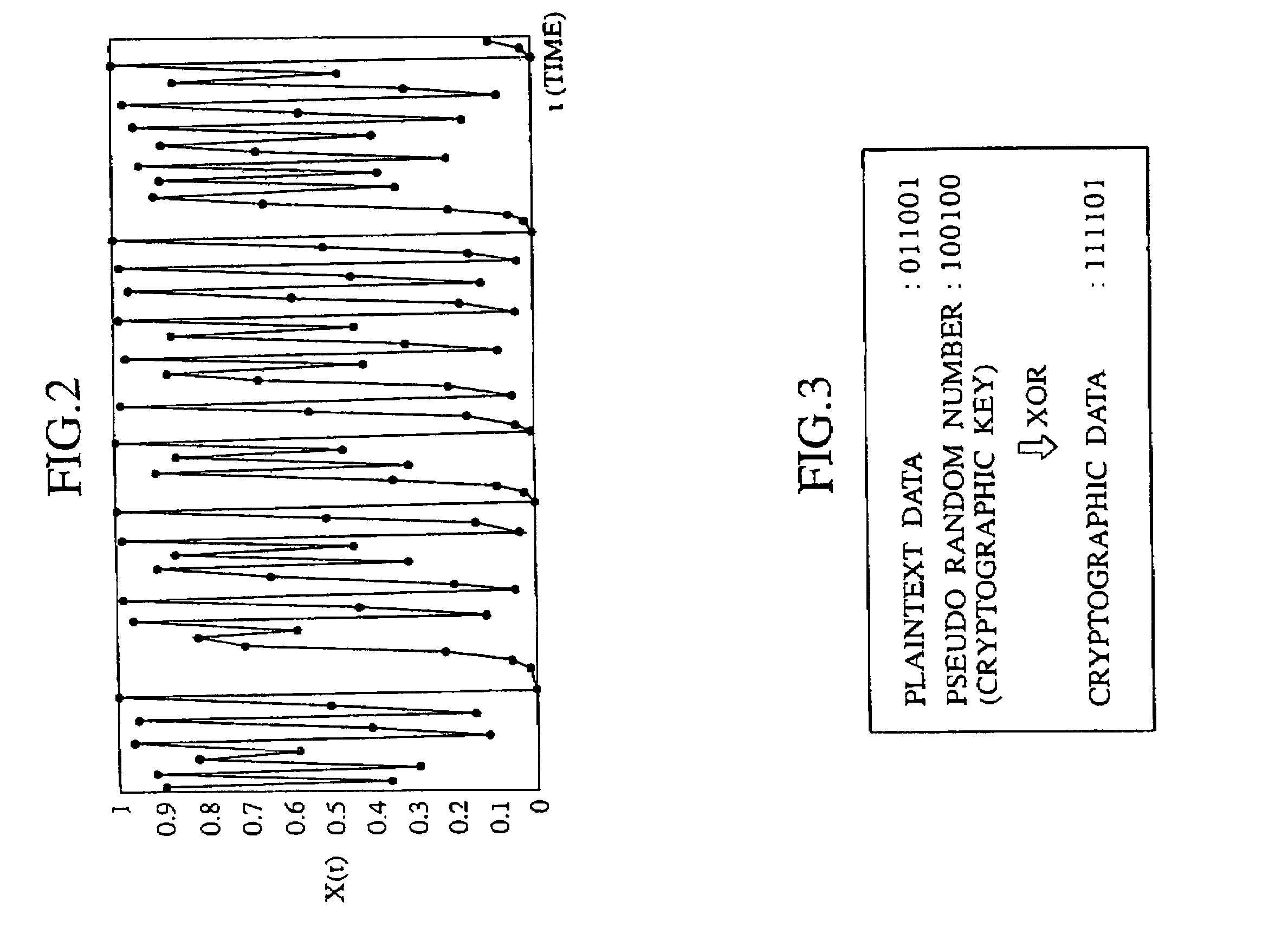
ActiveUS7269258B2Random number generatorsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsComputer hardwareCryptographic nonce
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Implicit certificate verification
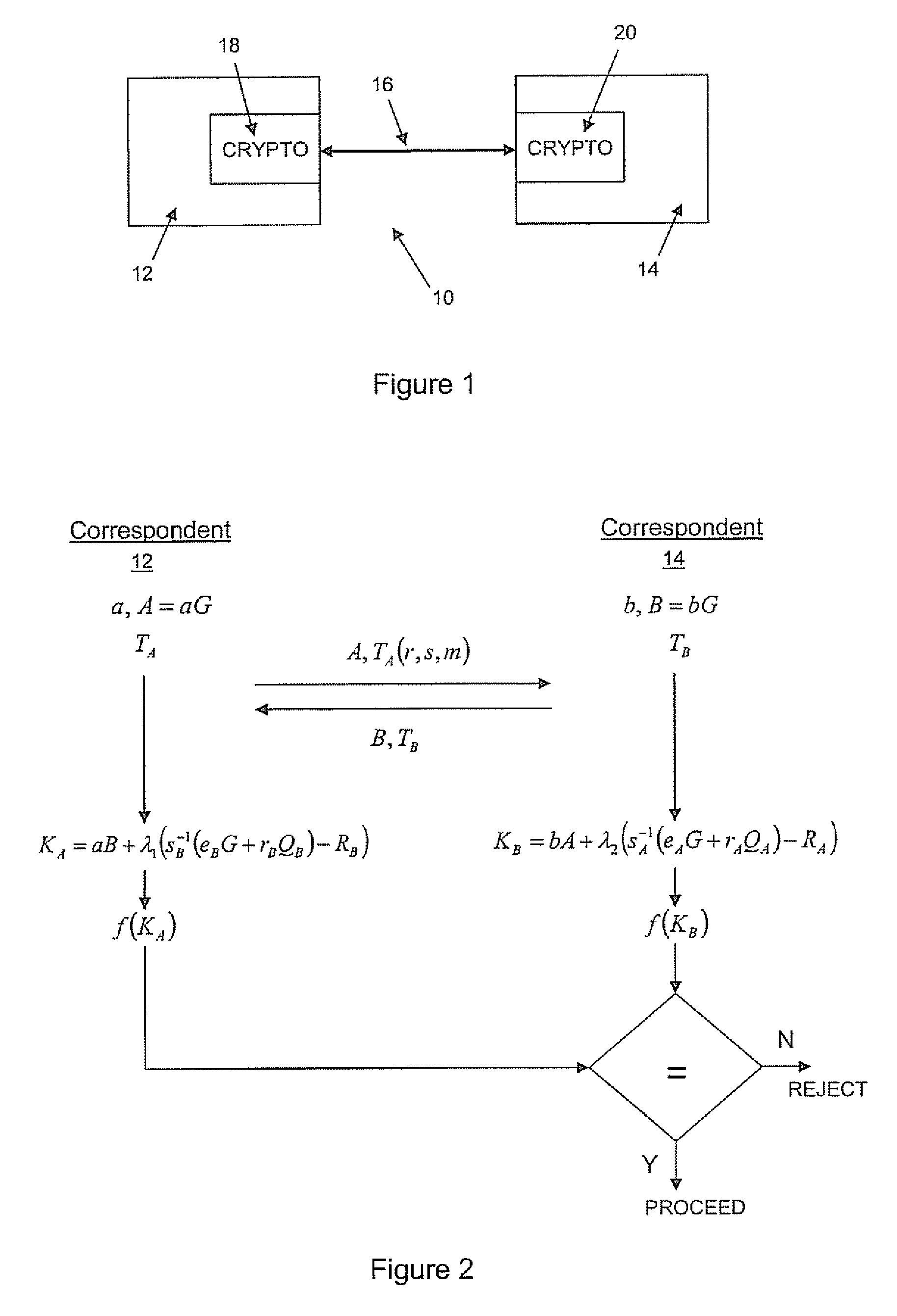
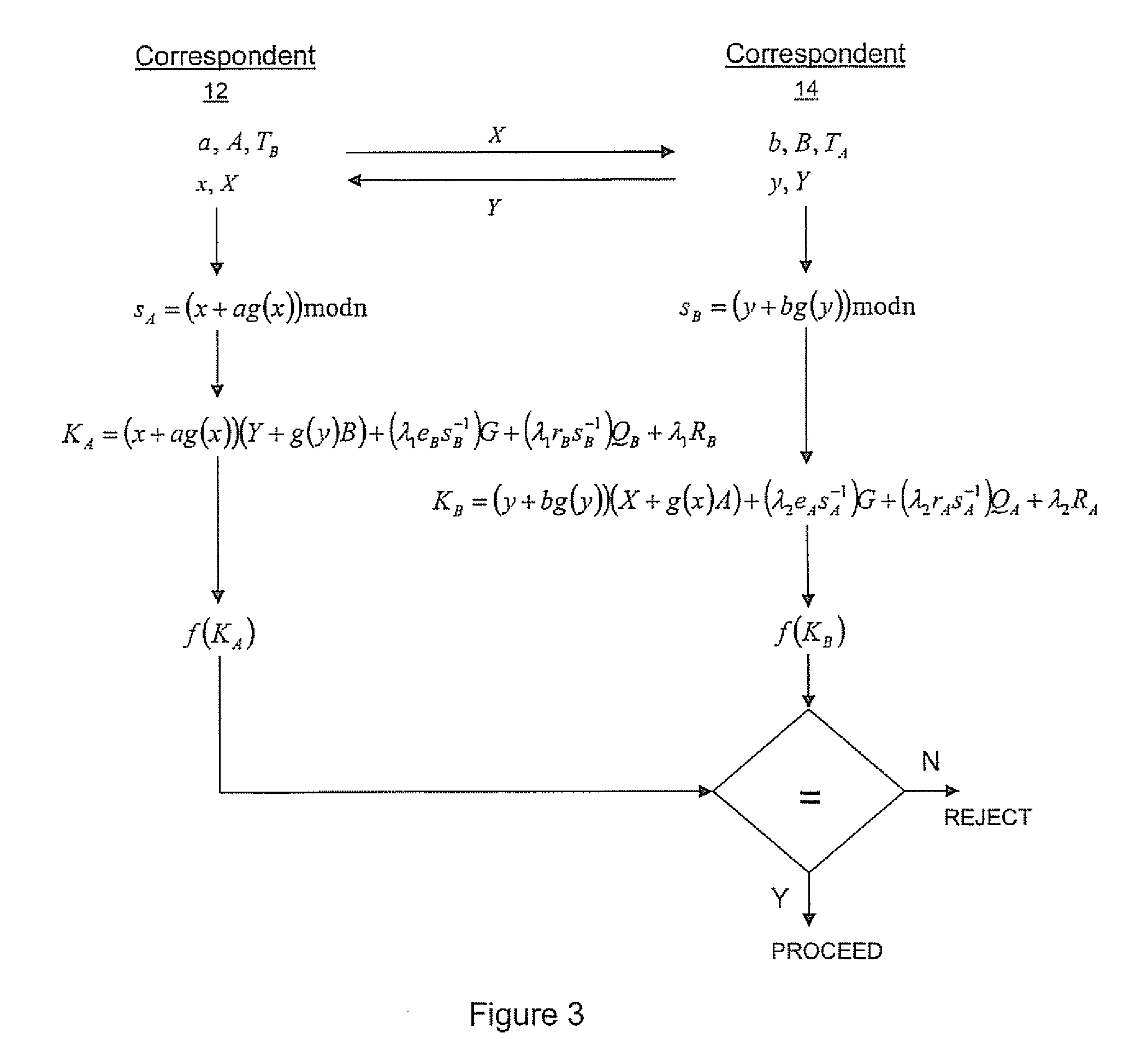
ActiveUS20100023771A1Heavy calculationPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsCryptographic key typesCryptographic nonce
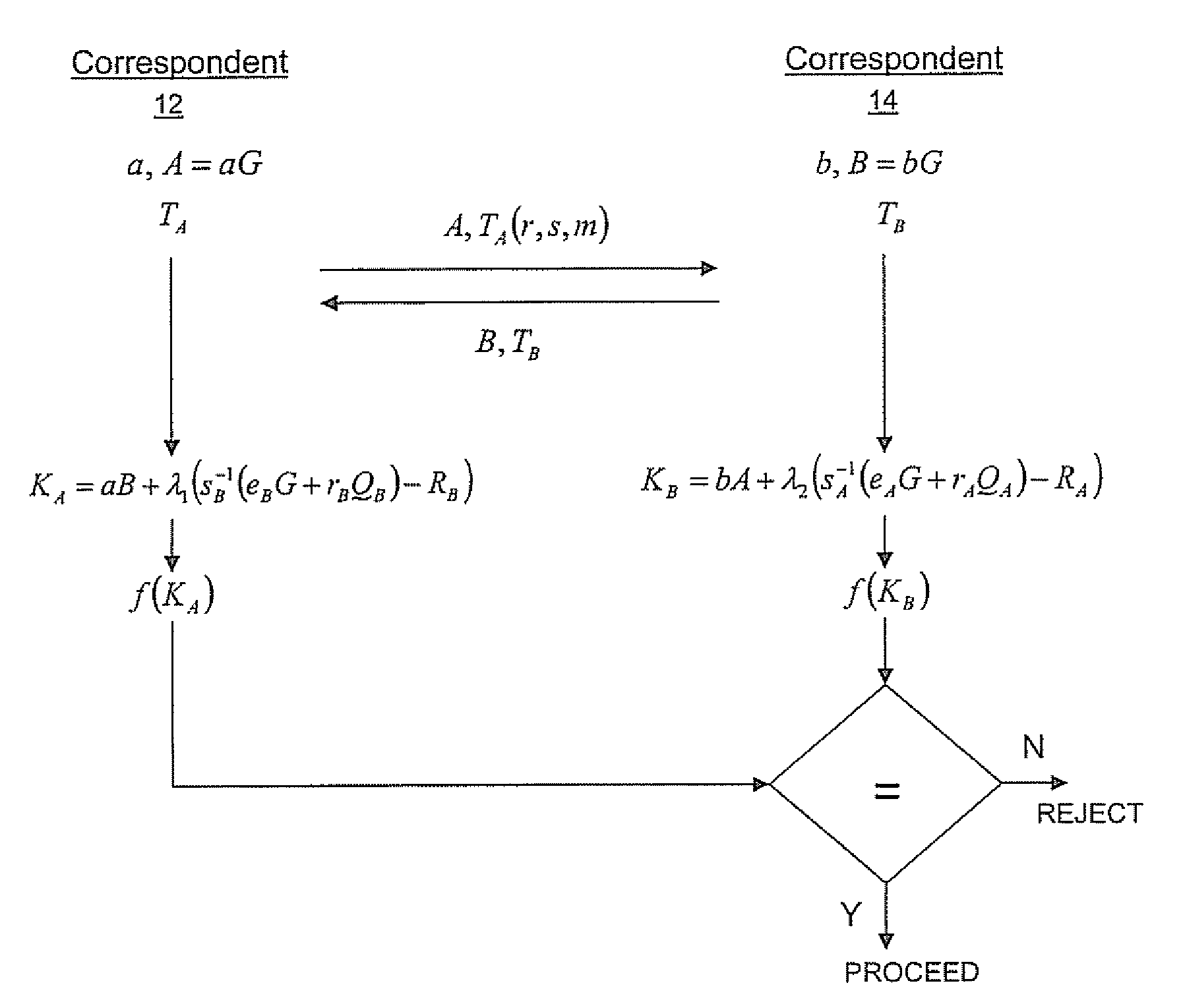
A method of computing a cryptographic key to be shared between a pair of correspondents communicating with one another through a cryptographic system is provided, where one of the correspondents receives a certificate of the other correspondents public key information to be combined with private key information of the one correspondent to generate the key. The method comprises the steps of computing the key by combining the public key information and the private key information and including in the computation a component corresponding to verification of the certificate, such that failure of the certificate to verify results in a key at the one corespondent that is different to the key computed at the other correspondent.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
System for establishing a cryptographic key depending on a physical system
ActiveUS20120072737A1Reduction of informationReduce decreaseKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareCryptographic nonce
In systems for establishing a cryptographic key depending on a physical uncloneable function (PUF) it may be a problem that internal information correlated with the cryptographic key is leaked to the outside of the system via a side-channel. To mitigate this problem a cryptographic system for reproducibly establishing a cryptographic key is presented. The system comprises a physical system comprising a physical, at least partially random, configuration of components from which an initial bit-string is derived. An error corrector corrects deviations occurring in the initial bit-string. Through the use of randomization the error corrector operates on a randomized data. Information leaking through a side channel is thereby reduced. After error correction a cryptographic key may be derived from the initial bit-string.
Owner:INTRINSIC ID
Method and apparatus for streaming data using rotating cryptographic keys
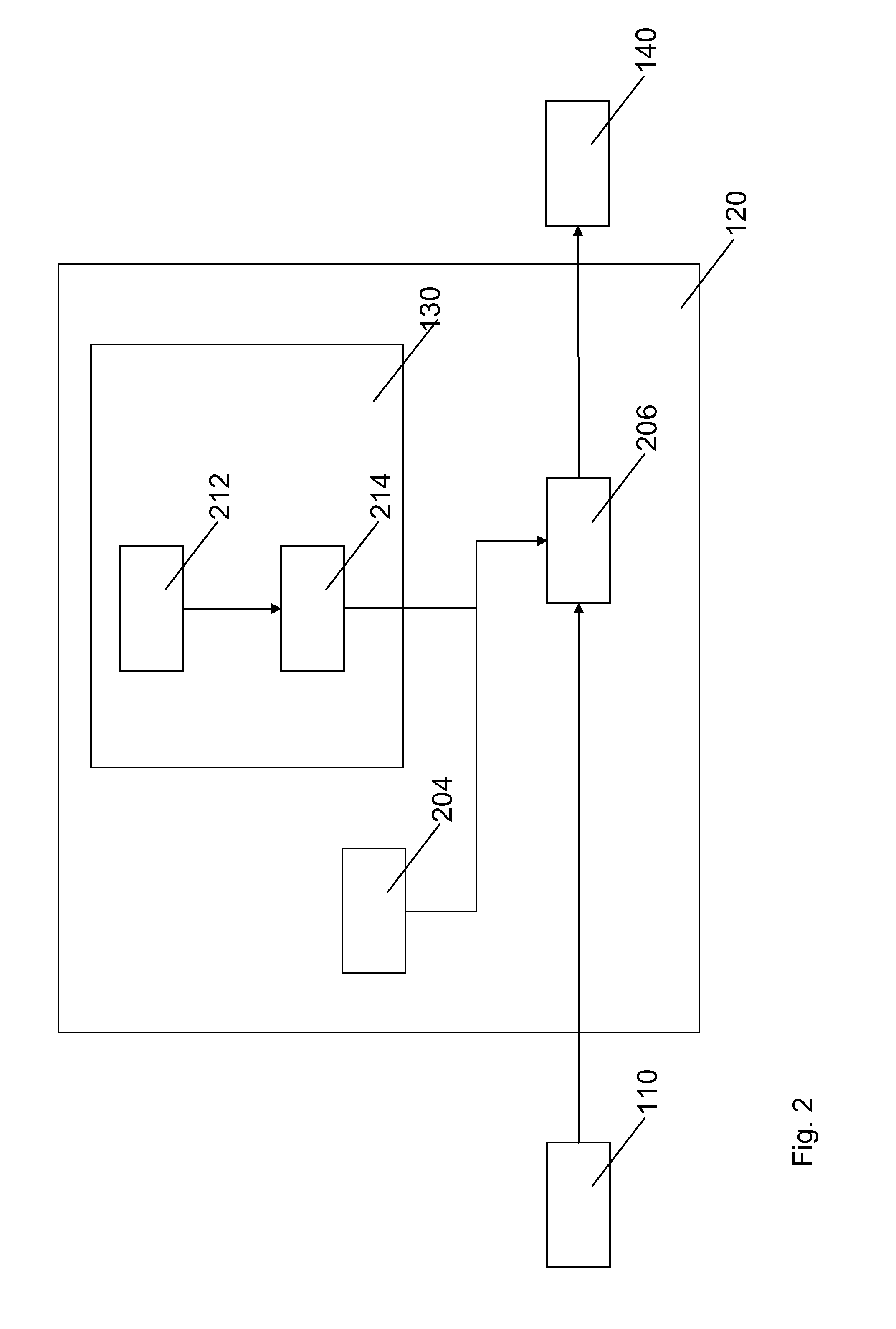
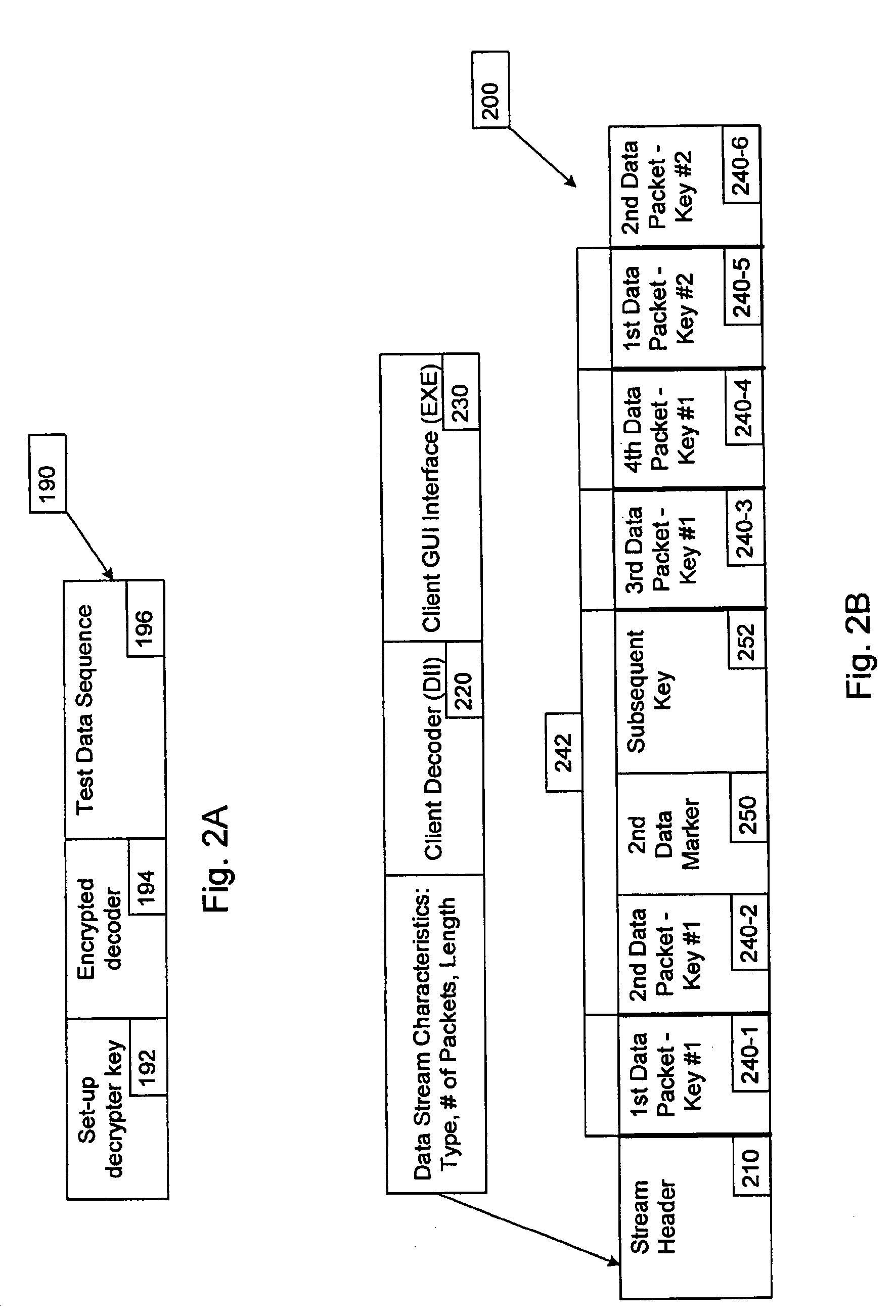
InactiveUS7050583B2Easy to copyData stream serial/continuous modificationComputer security arrangementsDigital dataStreaming data
A method of producing a stream of digital data. The method includes determining a plurality of portions within the stream of digital data, such that a portion of the stream of digital data is encrypted with an encryption key that is capable of being decrypted by a decryption key and the portion including therein another decryption key capable of decrypting a subsequent portion of the stream of digital data, and the subsequent portion of the stream of digital data is encrypted with another encryption key that is capable of being decrypted by the another decryption key. The method also includes transmitting the stream of digital data, including the portion and the subsequent portion.
Owner:ETREPPID TECH
Method for generating cryptographic key from biometric data
InactiveUS20090310779A1Secret key can be re-generated efficientlyCharacter and pattern recognitionSecuring communicationBiometric dataTheoretical computer science
Data from biometric images such as minutiae of a fingerprint are represented in coordinates x- and y-, and the direction of the ridge flow of the minutia θ; in vector sets of (x1, y1, θ1) are used in generating a 256-bit secret key in a secure manner in enrolling the fingerprint in the Enrolment Phase. The key generation algorithm includes random key generation, threshold signature scheme using polynomial functions, generating random fake minutiae vector sets to form a locked representation of the fingerprint. In the Query Phase, the fingerprint image used to re-generate the secret key is matched against the locked template representation through automatic alignment process using geometric hash table to compare the enrolled minutiae (genuine and fake) with the vector set extracted from the query minutiae sets, and adjustable transform equation is used for adjusting for the minutiae direction, etc.
Owner:PRIVYLINK PRIVATE
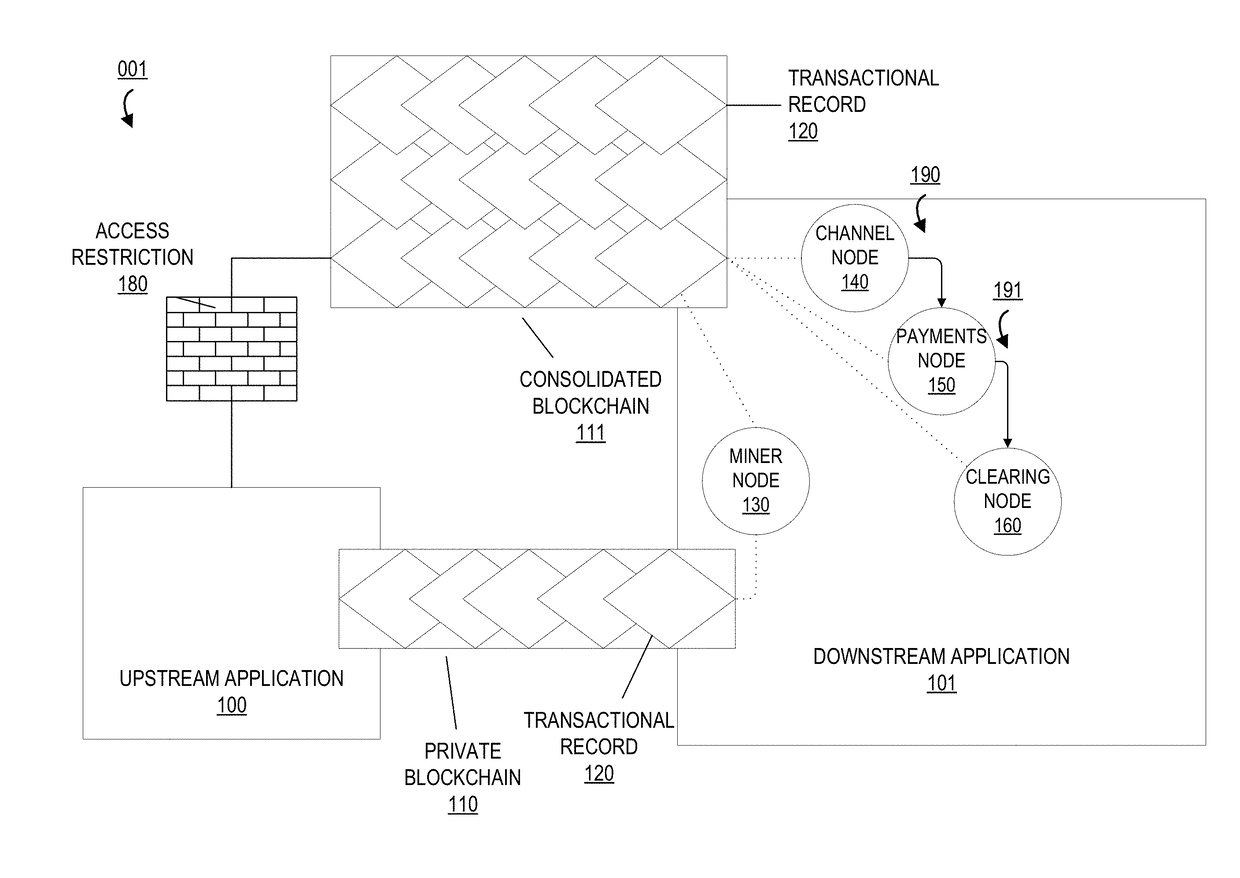
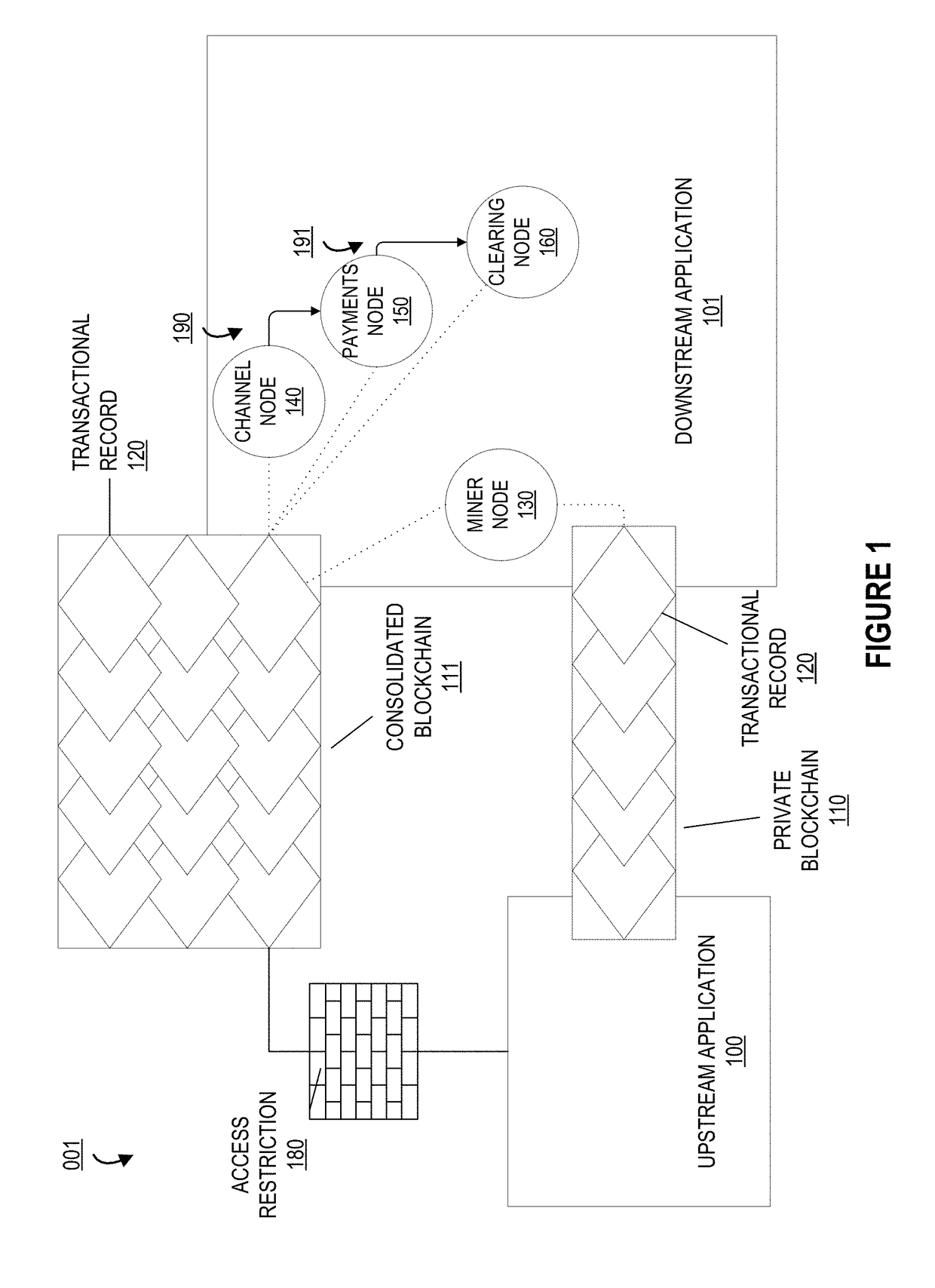
Automated data authentication and service authorization via cryptographic keys in a private blockchain
ActiveUS20180103042A1Well formedPublic key for secure communicationData validationCryptographic nonce
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system for authenticating records belonging to an individual or entity and providing authorized access of said records to service providers. Embodiments of the invention utilize a private blockchain to store various types of records to be conveyed to the service providers. In this way, the individual or entity may securely store on the blockchain all records relevant to service providers, then provide the service providers with secured access to said records such that the providers may access only the specific records for which they are authorized, e.g. a healthcare provider may access only the healthcare records on the blockchain.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
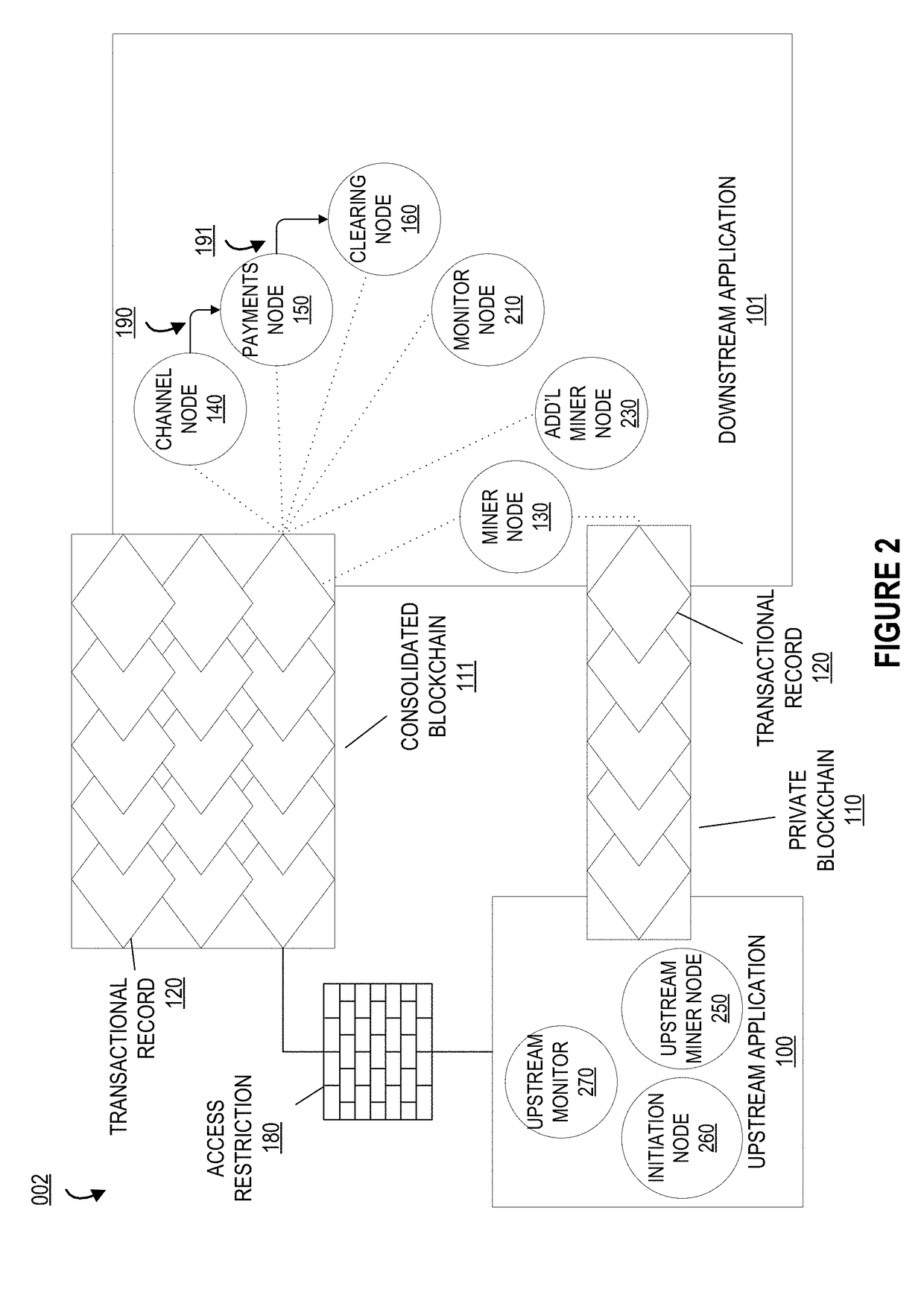
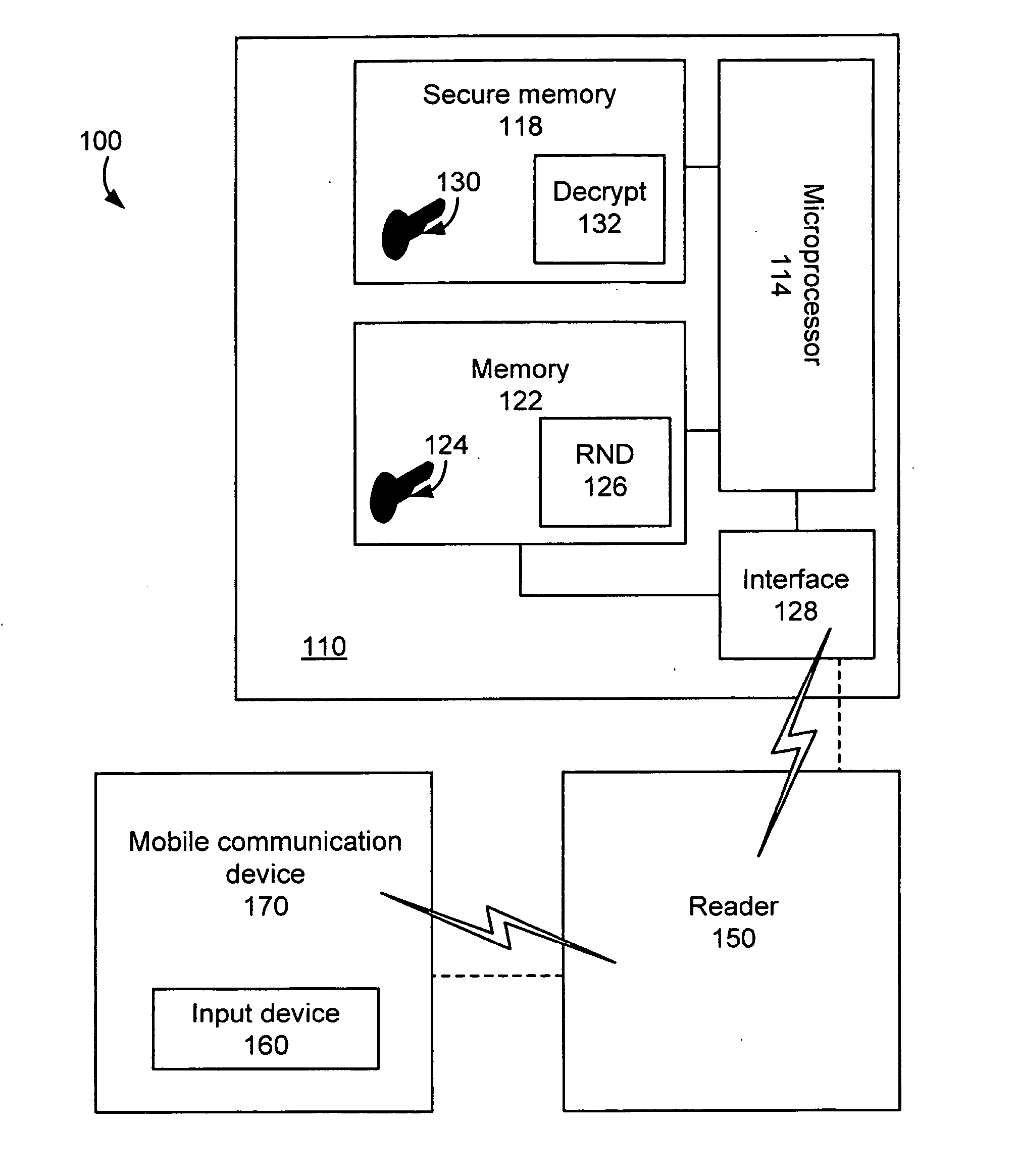
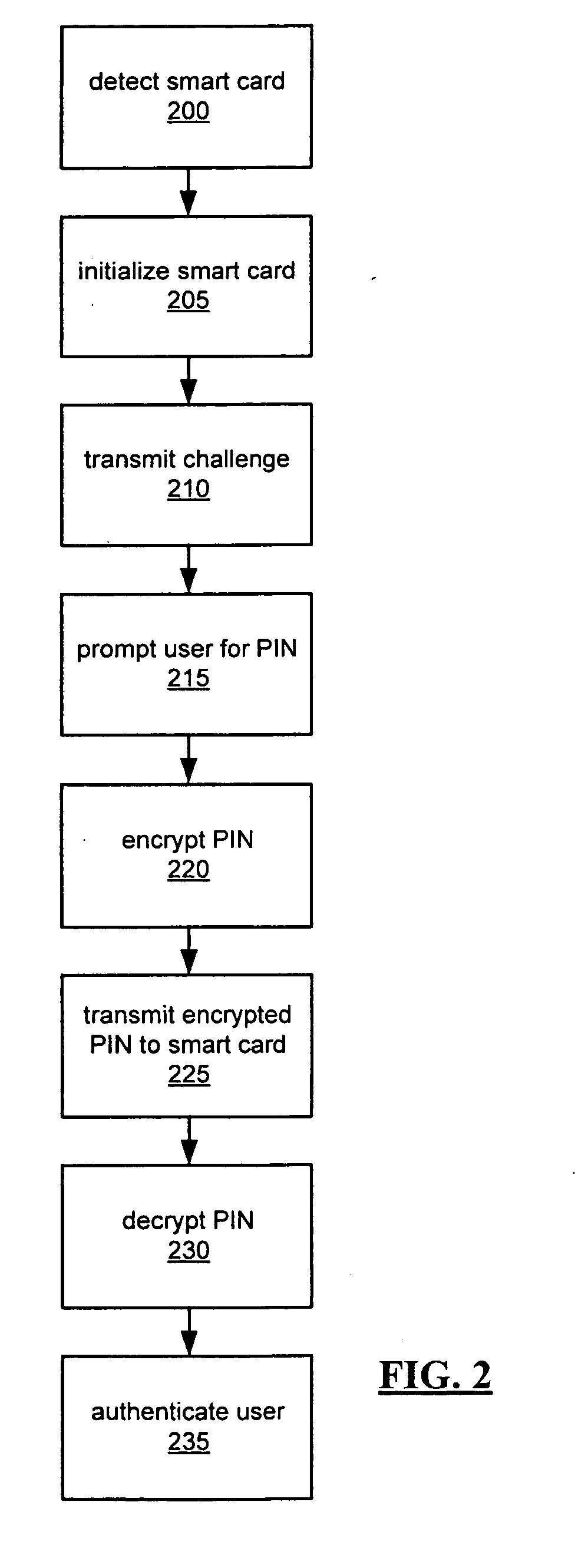
System and method for encrypted smart card pin entry
A smart card, system, and method for securely authorizing a user or user device using the smart card is provided. The smart card is configured to provide, upon initialization or a request for authentication, a public key to the user input device such that the PIN or password entered by the user is encrypted before transmission to the smart card via a smart card reader. The smart card then decrypts the PIN or password to authorize the user. Preferably, the smart card is configured to provide both a public key and a nonce to the user input device, which then encrypts a concatenation or other combination of the nonce and the user-input PIN or password before transmission to the smart card. The smart card reader thus never receives a copy of the PIN or password in the clear, allowing the smart card to be used with untrusted smart card readers.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Cryptographic communications using in situ generated cryptographic keys for conditional access
InactiveUS7149308B1Improve securityFacilitate communicationKey distribution for secure communicationComputer security arrangementsCryptographic key generationCommunication interface
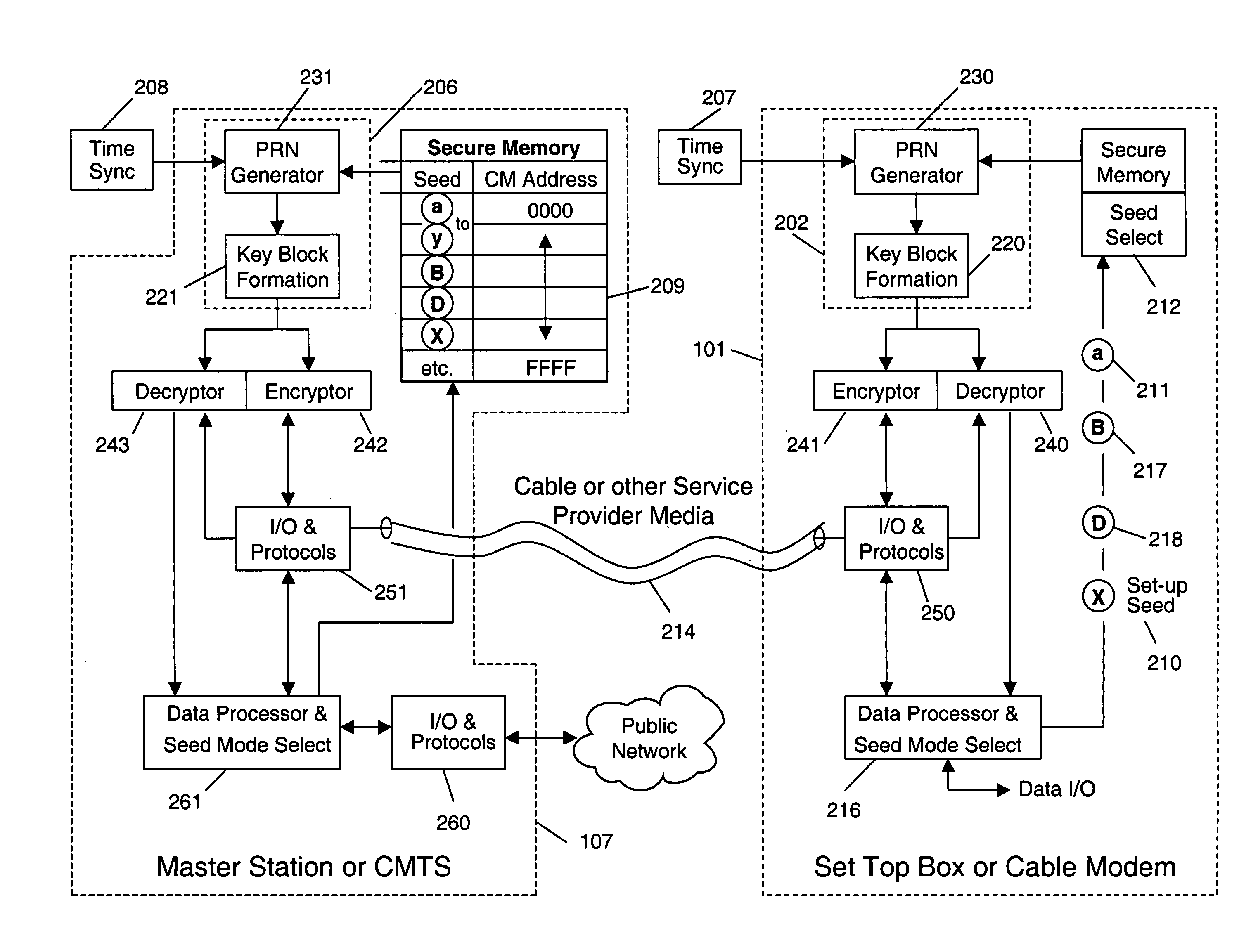
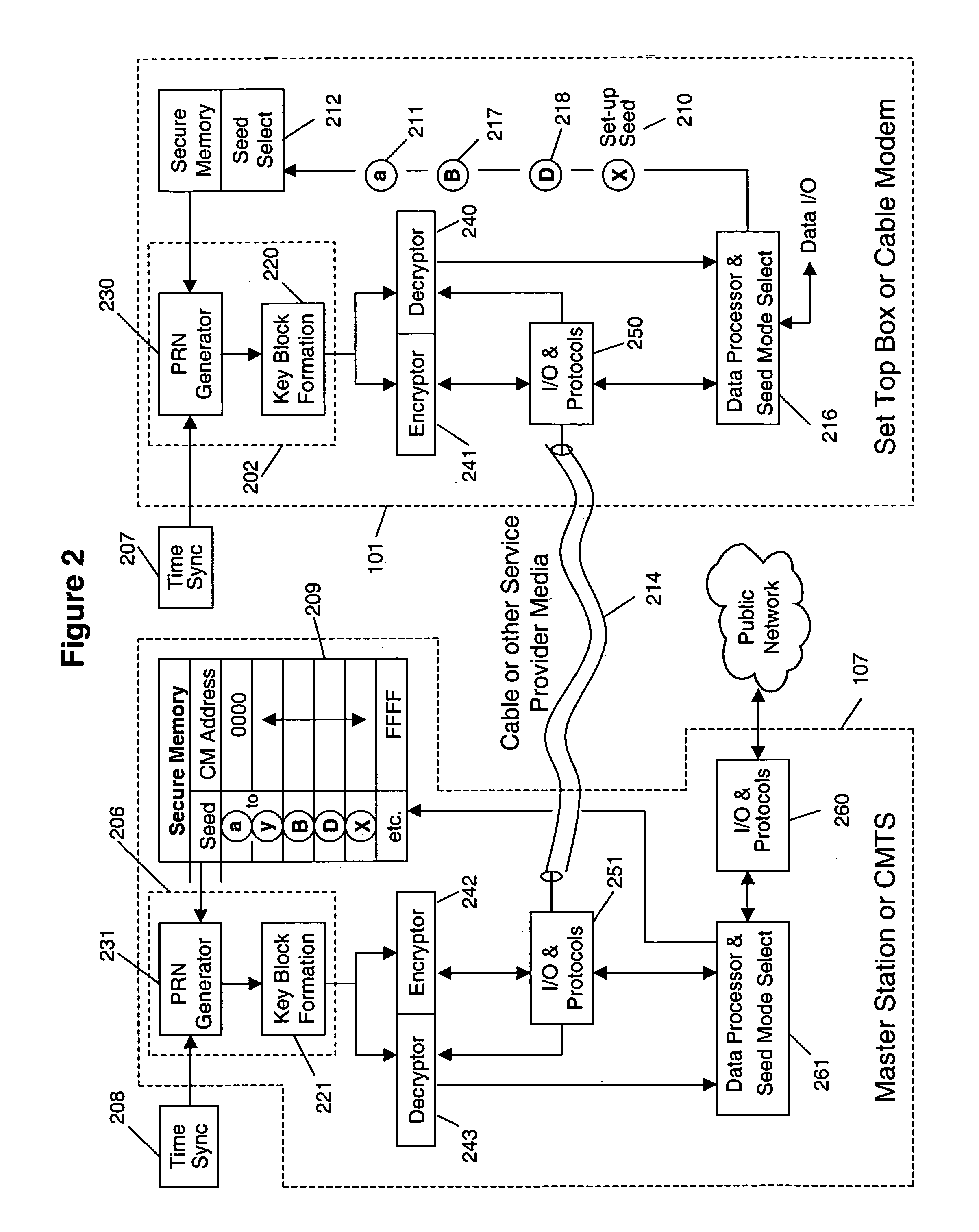
A system and method for cryptographic communication among multiple users and a central service provider using in situ generated cryptographic keys. Each user communicates with the central service provider preferably using a user communication interface that includes an in situ key generator, which, after initialization with the user's own individual seed value, generates a unique cryptographic key. By distributing different user individual seeds unique to each user, each user's in situ key generator generates a unique set of keys. The central service provider also possesses an in situ key generator, and also preferably possesses a copy of all the individual seeds assigned to authorized users. The central service provider preferably communicates in a secure encrypted fashion with each user using cryptographic keys generated from that user's individual seed. Distribution of additional seed values common to more than one user, via encrypted communication using said unique individual cryptographic key generations, then permit secure conditional access to said users via signal encryption using key generations resulting from a seed value common to the intended group of users.
Owner:STEALTHKEY
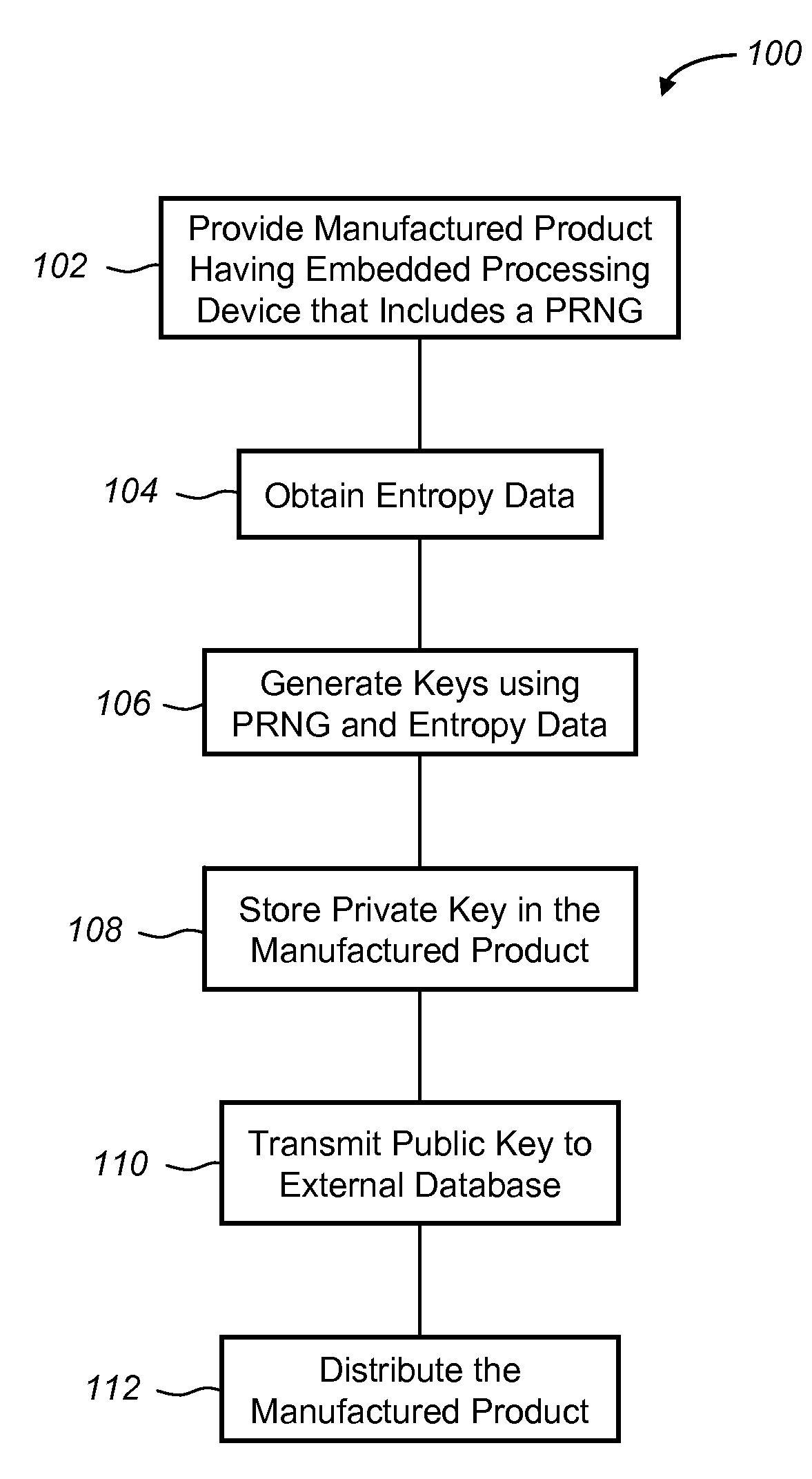
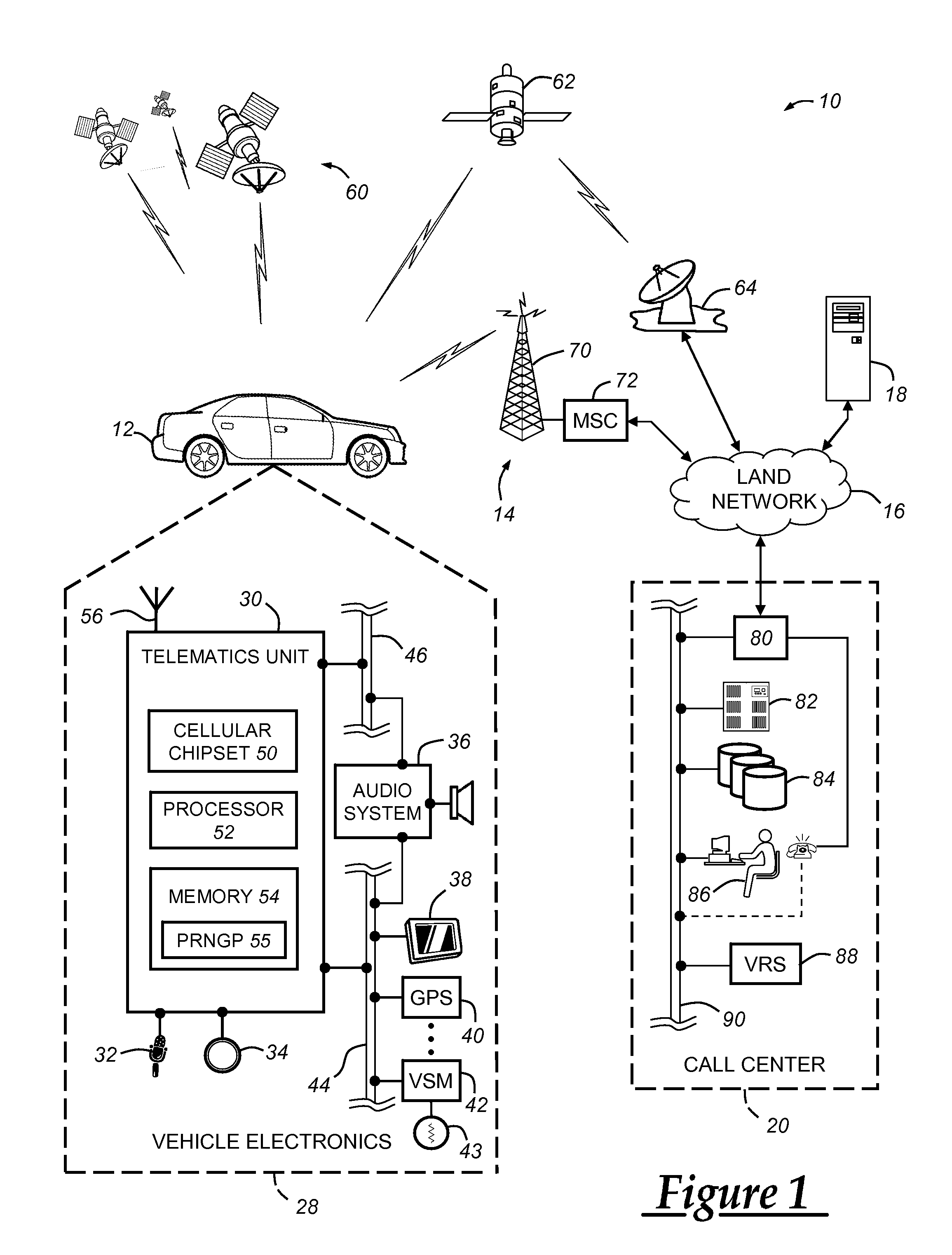
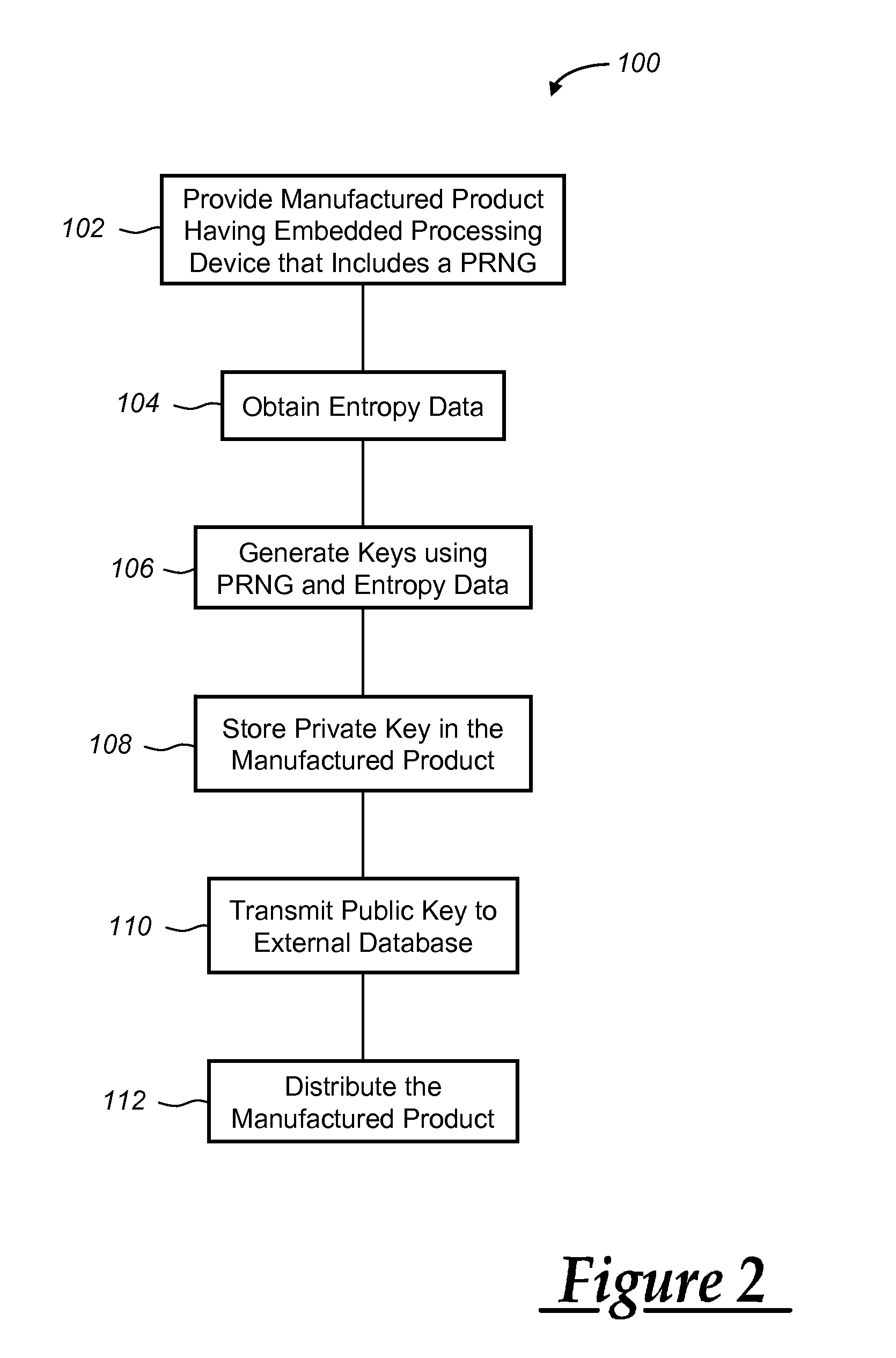
Production of cryptographic keys for an embedded processing device
ActiveUS20090323967A1Avoid dataKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationUnique identifierCryptographic nonce
A system and method for producing cryptographic keys for use by an embedded processing device within a manufactured product. A pseudo random number generator is seeded with entropy data gathered by the embedded device, and the result is used to generate a public-private key pair. The process can be carried out during manufacturing so that the public key of each manufactured product can be stored in a database along with a unique identifier for the embedded device associated with the key. In one particular example, a vehicle having an installed telematics unit uses the key generating process to self-generate keys using entropy data available to the vehicle.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
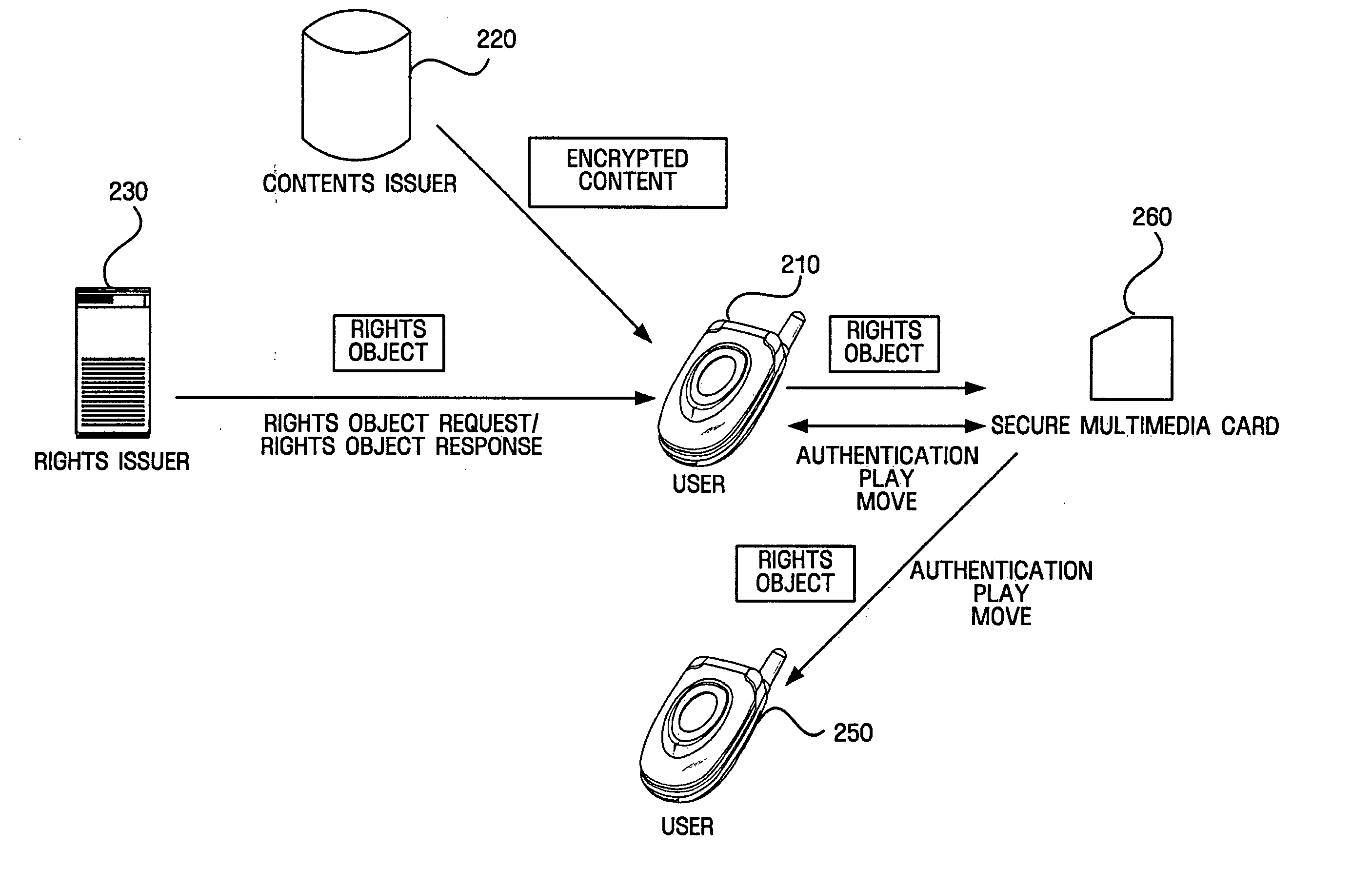
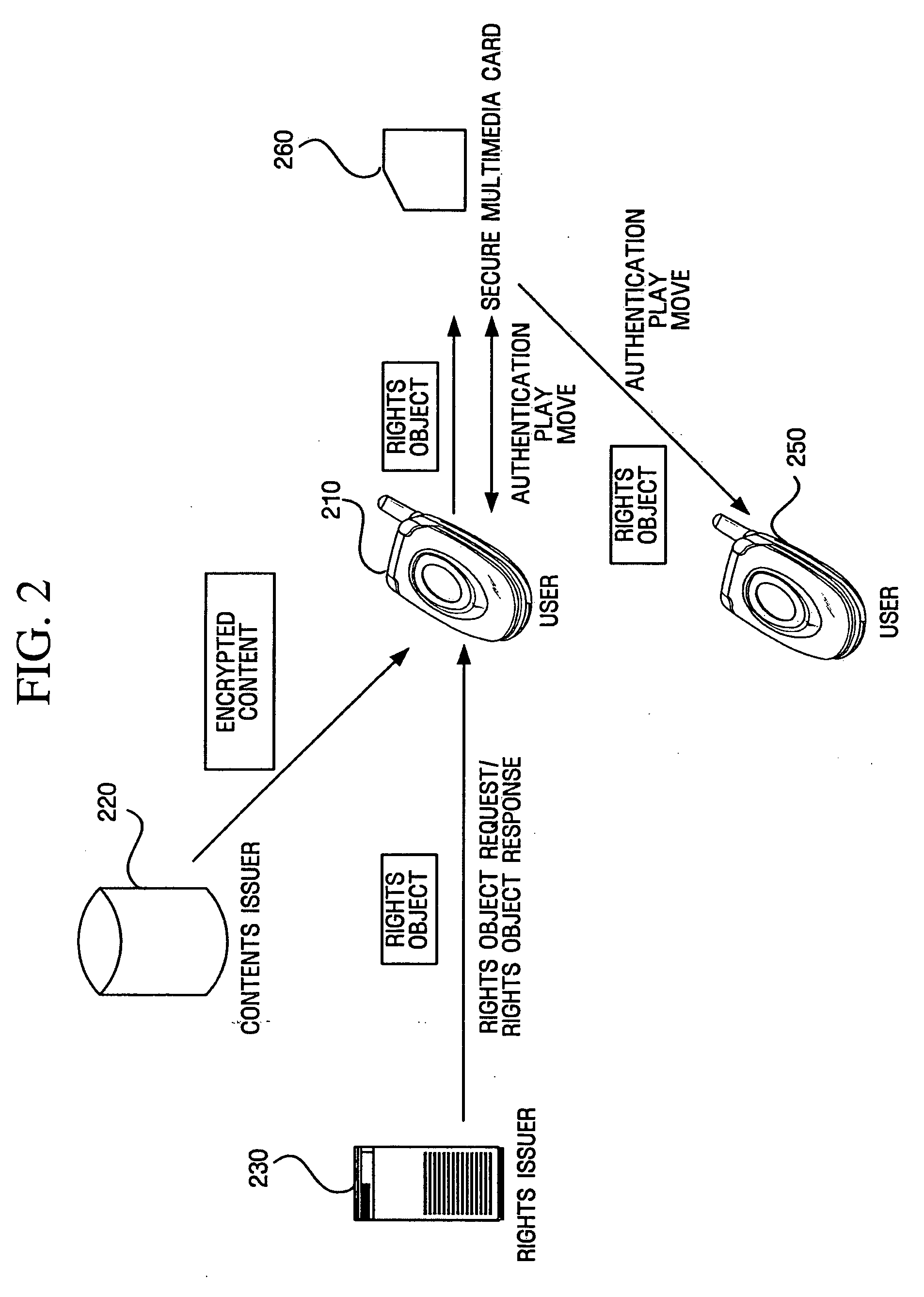
Authentication between device and portable storage
InactiveUS20050210279A1Authentication securityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareCryptographic nonce
For digital rights management (DRM), a method for performing authentication between a device and a portable storage, which is performed by the device, includes transmitting a first key to the portable storage, receiving a third key and a first encrypted random number obtained by encrypting a first random number using the first key from the portable storage and decrypting the first encrypted random number using a second key related with the first key, generating a second encrypted random number by encrypting a second random number using the third key and transmitting the second encrypted random number to the portable storage, and generating a session key using the first random number and the second random number. The technique guarantees secure authentication between the device and the portable storage for DRM.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
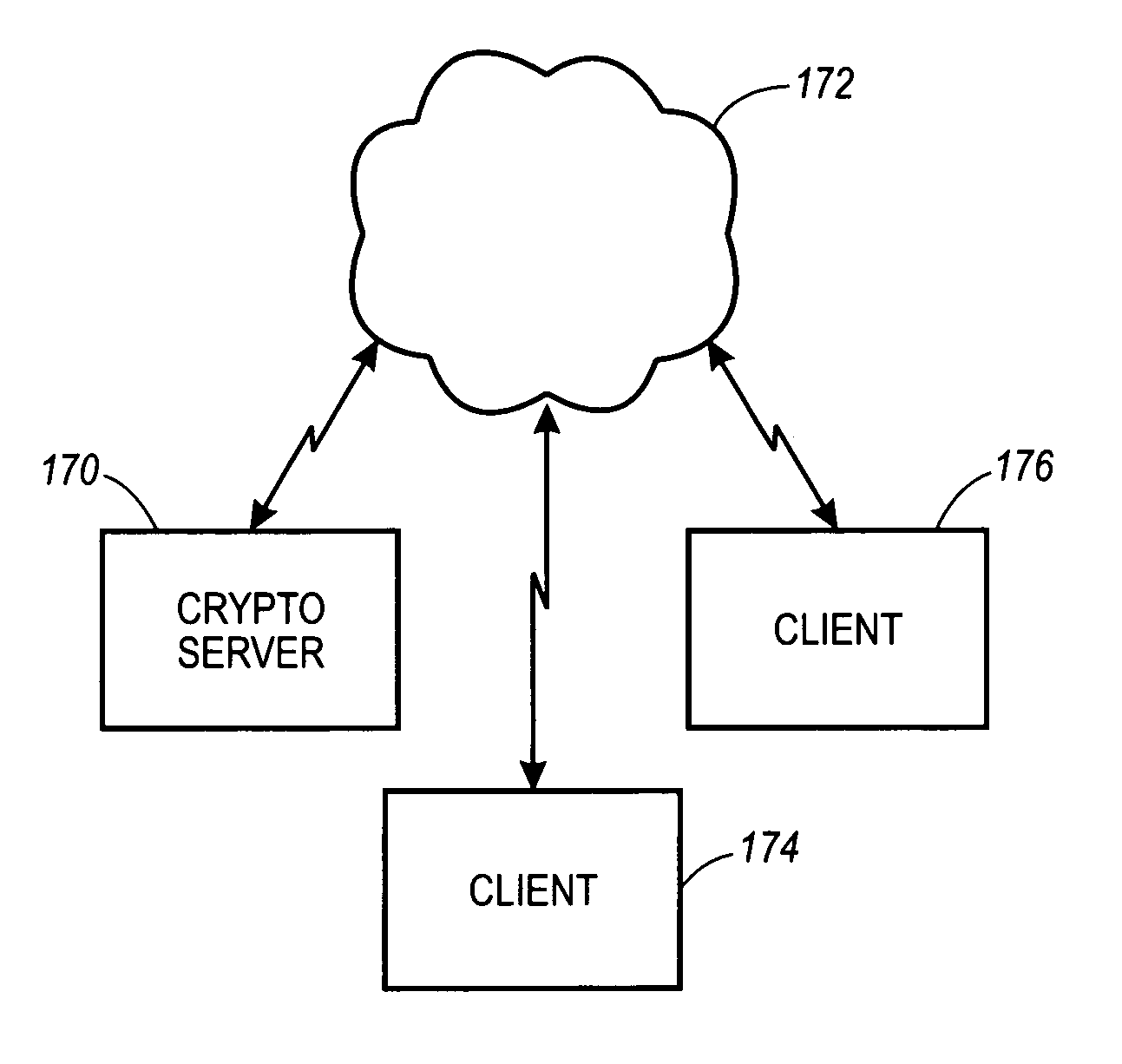
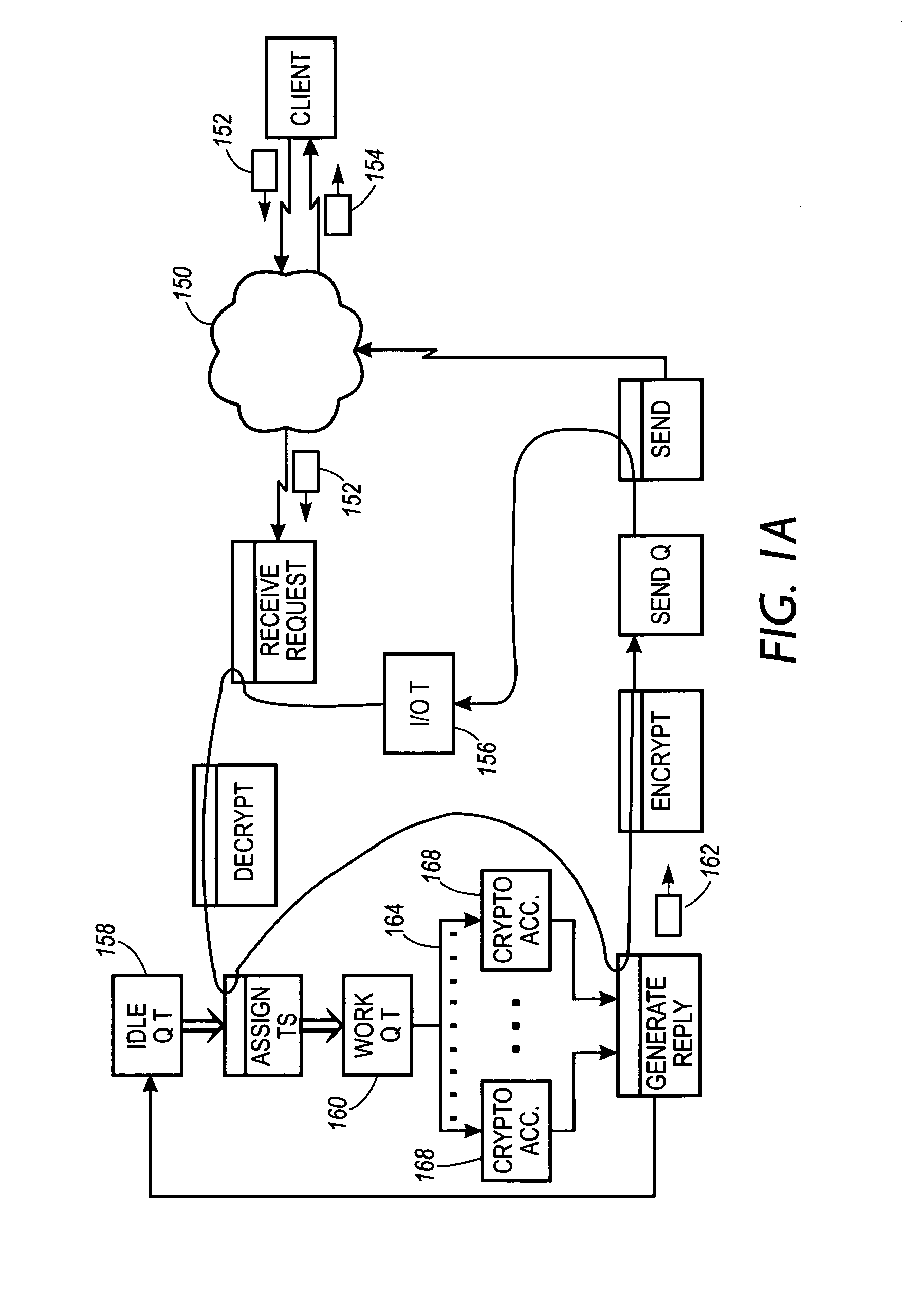
System, method and article of manufacture for providing cryptographic services utilizing a network
InactiveUS7051199B1Faster turn around timeCost-effectiveKey distribution for secure communicationCryptographic nonceClient-side
A system, method and article of manufacture are provided for affording a cryptographic service utilizing a server on a network. Initially, a client is identified utilizing the network. A first key is established, and a tunnel is generated on the network. Thereafter, information is received at the server from the client utilizing the tunnel. Such information is encrypted by the client using the first key. At the server, cryptographic work is performed using the first key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Cryptographic key management in communication networks
InactiveUS20080095362A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageAccess networkCryptographic nonce
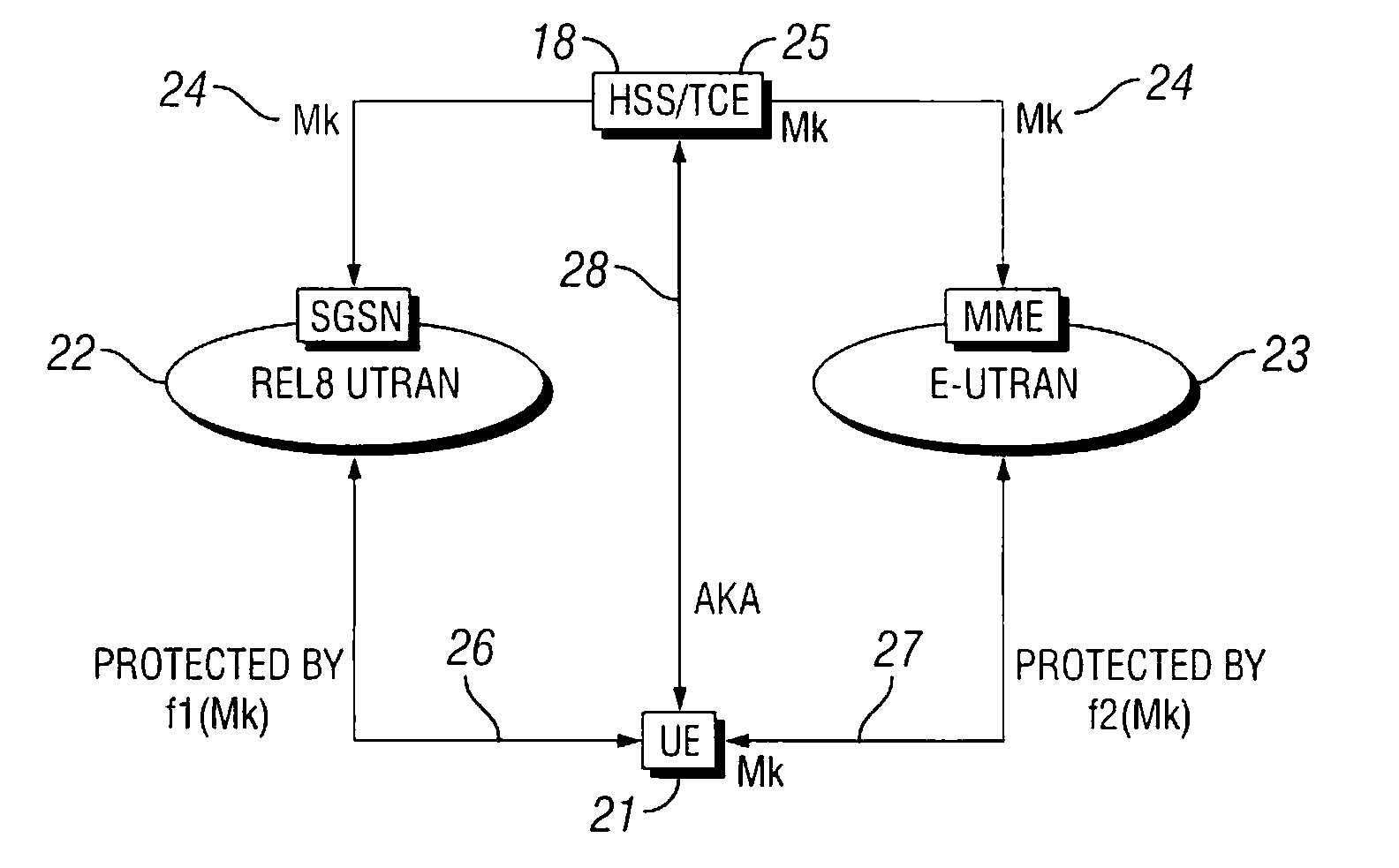
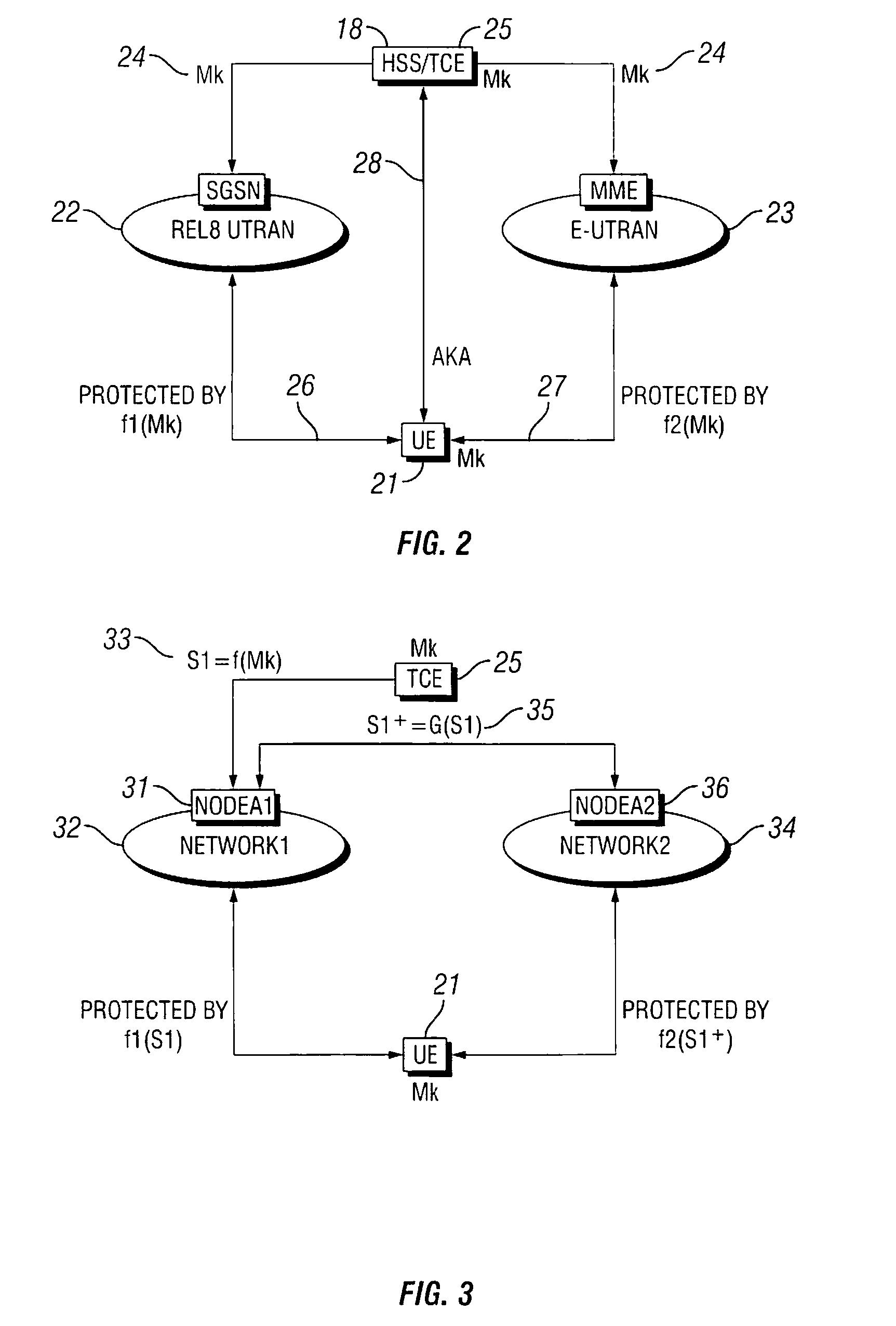
An authentication server and a system and method for managing cryptographic keys across different combinations of user terminals, access networks, and core networks. A Transformation Coder Entity (TCE) creates a master key (Mk), which is used to derive keys during the authentication procedure. During handover between the different access types, the Mk or a transformed Mk is passed between two nodes that hold the key in the respective access networks when a User Equipment (UE) terminal changes access. The transformation of the Mk is performed via a one-way function, and has the effect that if the Mk is somehow compromised, it is not possible to automatically obtain access to previously used master keys. The transformation is performed based on the type of authenticator node and type of UE / identity module with which the transformed key is to be utilized. The Mk is never used directly, but is only used to derive the keys that are directly used to protect the access link.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Securing Encrypted Virtual Hard Disks
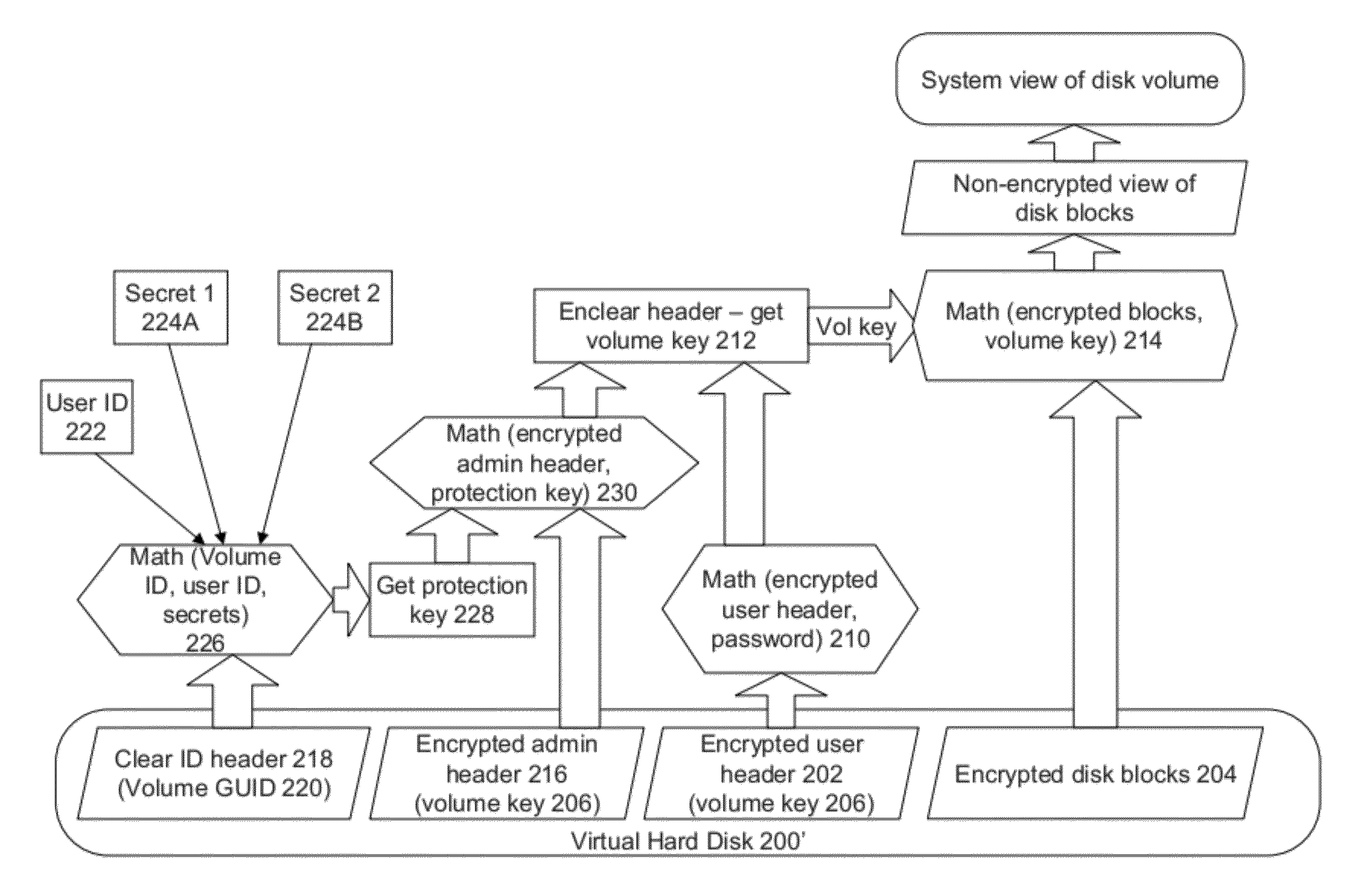
ActiveUS20120297206A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageUnauthorized memory use protectionCryptographic nonceUser identifier
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
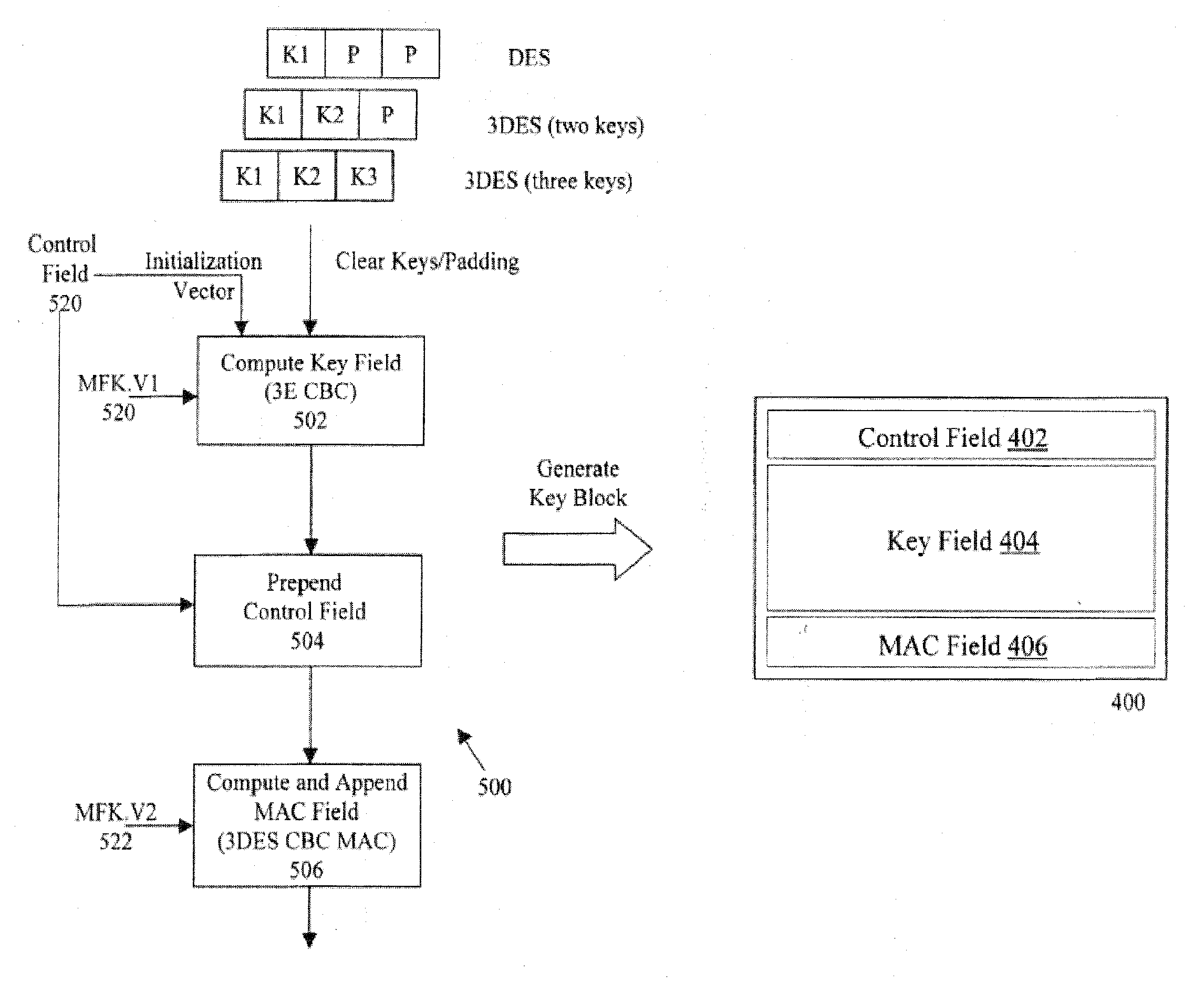
Method and system for secure storage, transmission and control of cryptographic keys
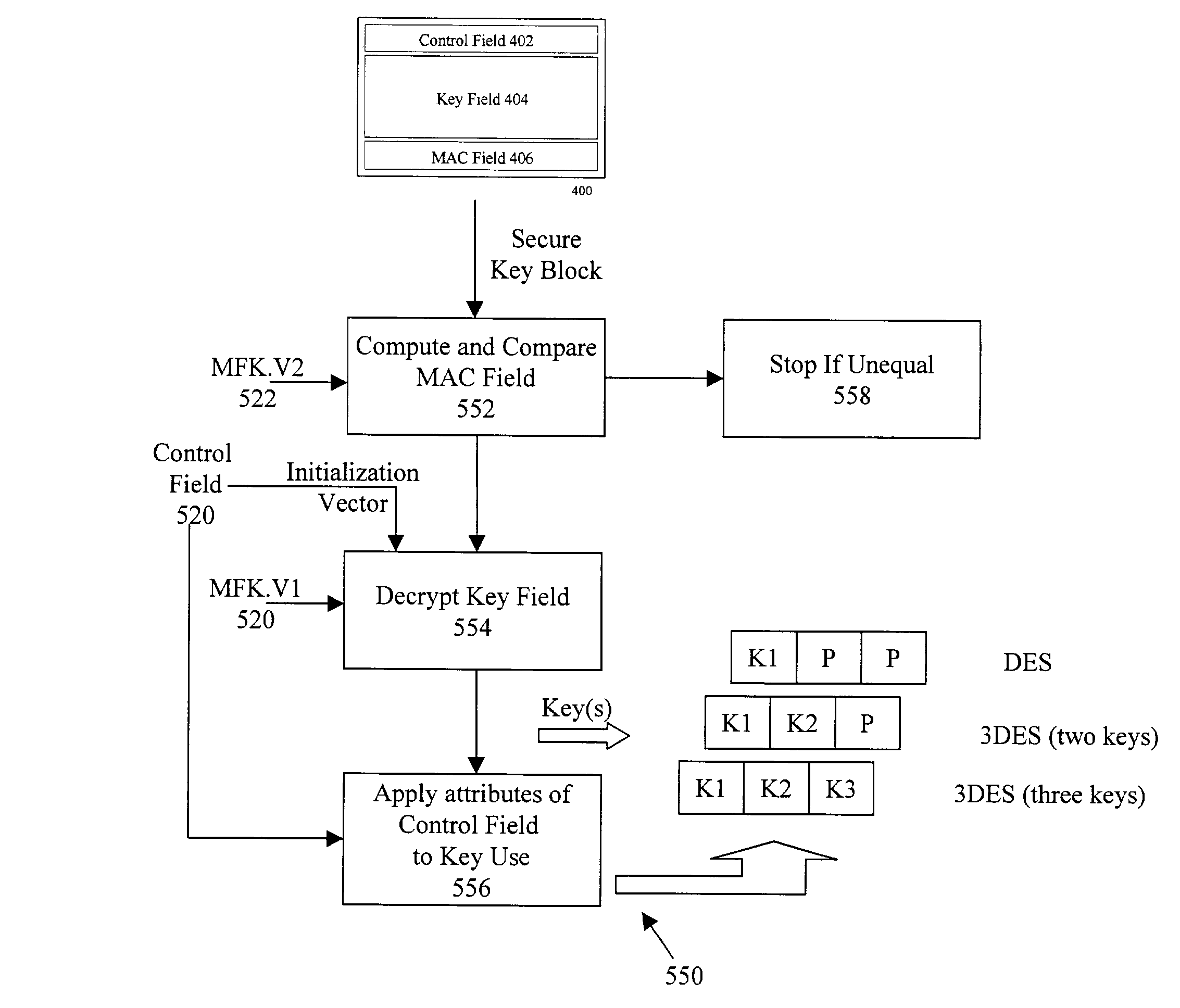
InactiveUS7392384B2Equal and great cryptographic strengthKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCryptographic nonceComputer security
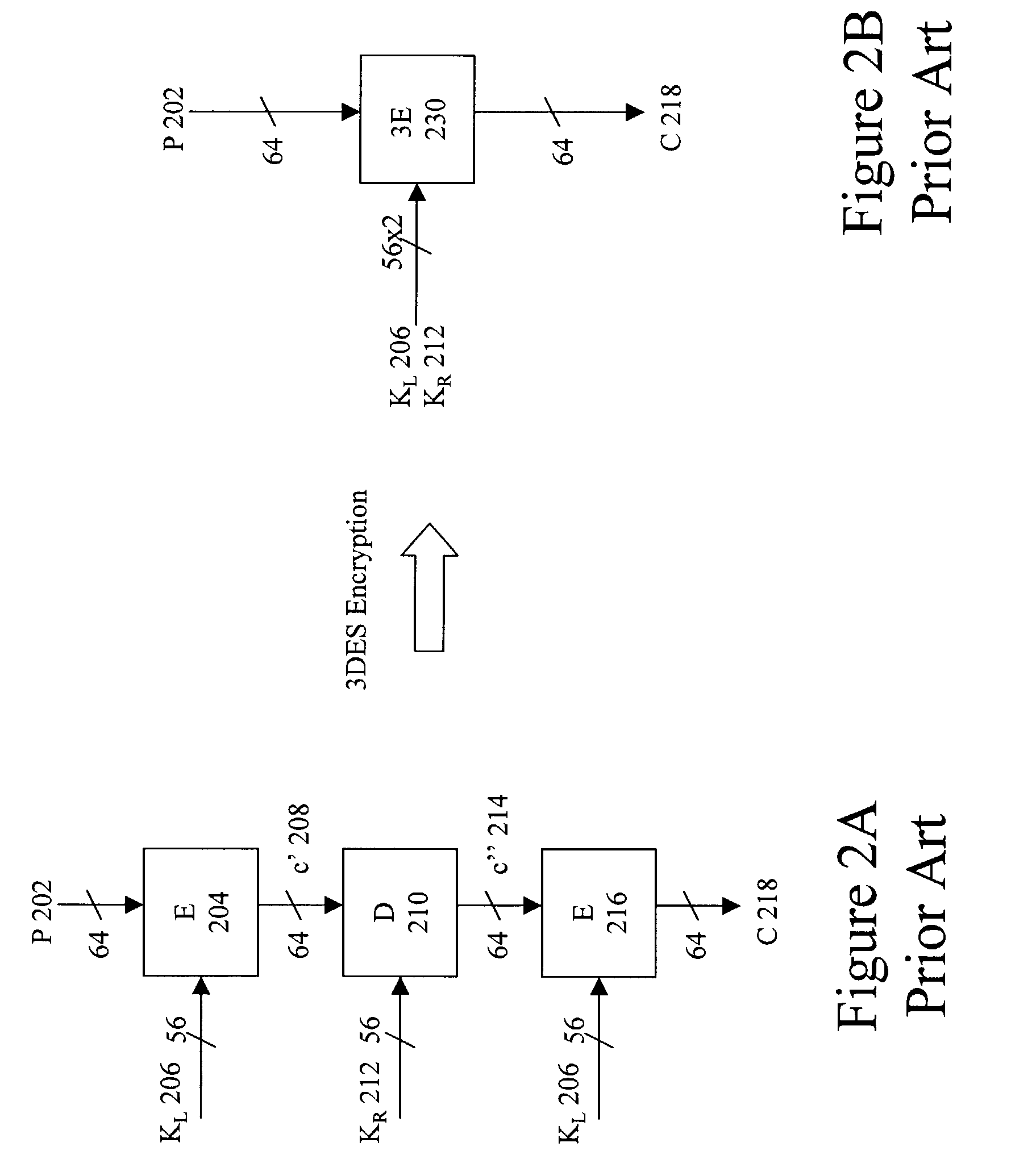
A system and method are described supporting secure implementations of 3DES and other strong cryptographic algorithms. A secure key block having control, key, and MAC fields safely stores or transmits keys in insecure or hostile environments. The control field provides attribute information such as the manner of using a key, the algorithm to be implemented, the mode of use, and the exportability of the key. A MAC algorithm is applied across the key and control for generating a MAC field that cryptographically ties the control and key fields together. Improved security is provided because tampering with any portion of the key block results in an invalid key block. The work factor associated with any manner of attack is sufficient to maintain a high level of security consistent with the large keys and strong cryptographic algorithms supported.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
Method and device for managing cryptographic keys in secret communications network
ActiveUS20090316910A1Managed easily and stablyKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareCryptographic nonce
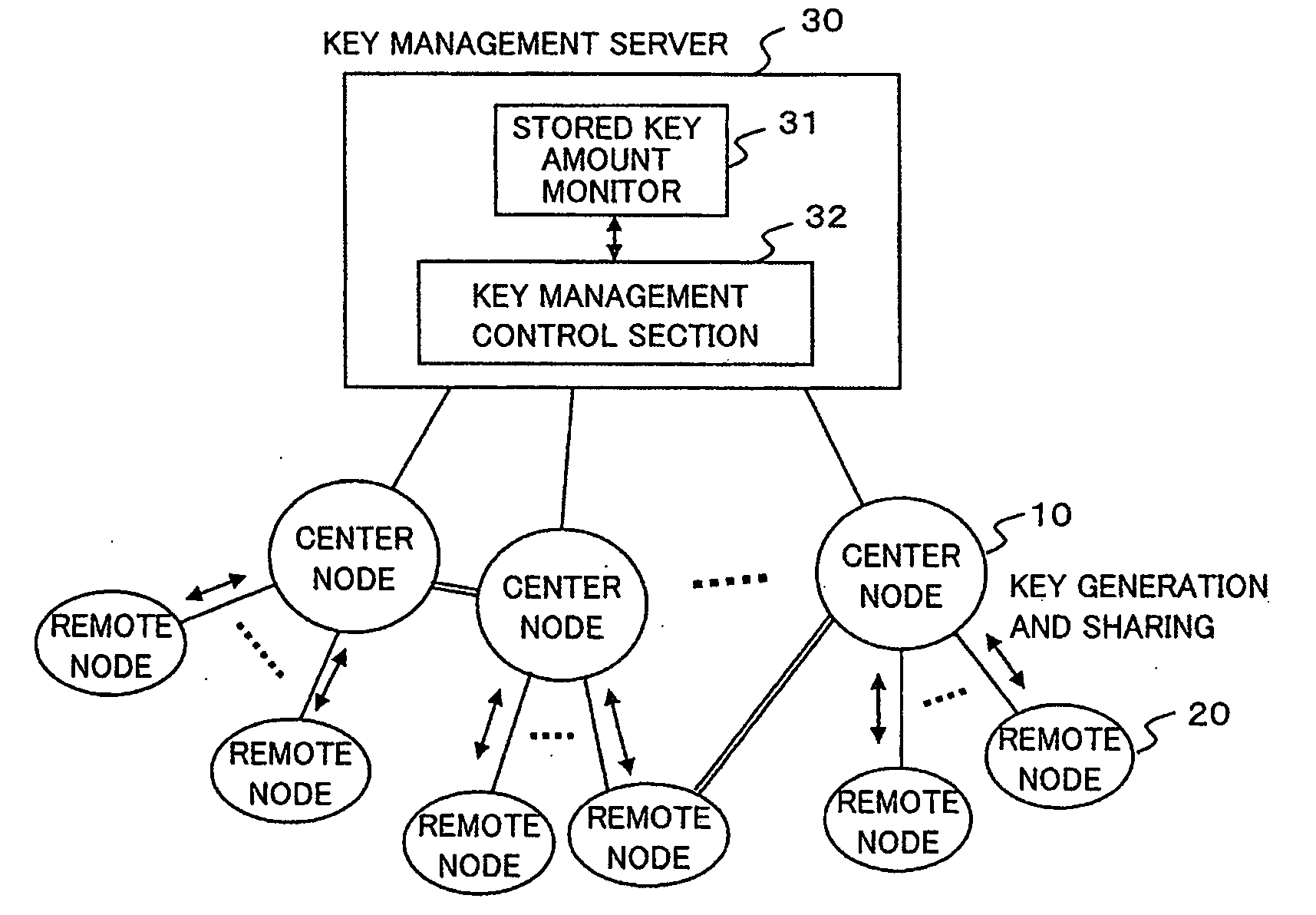
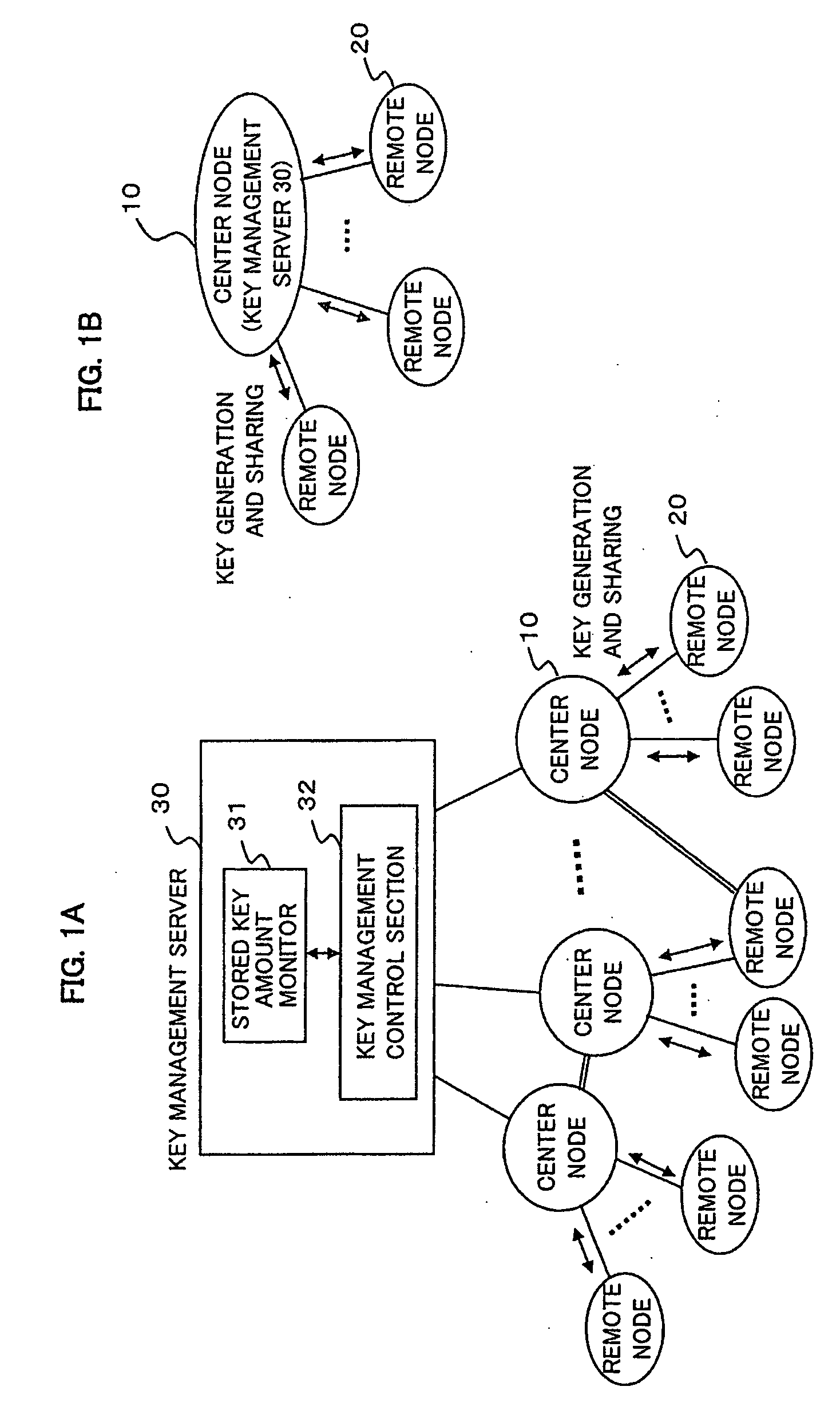
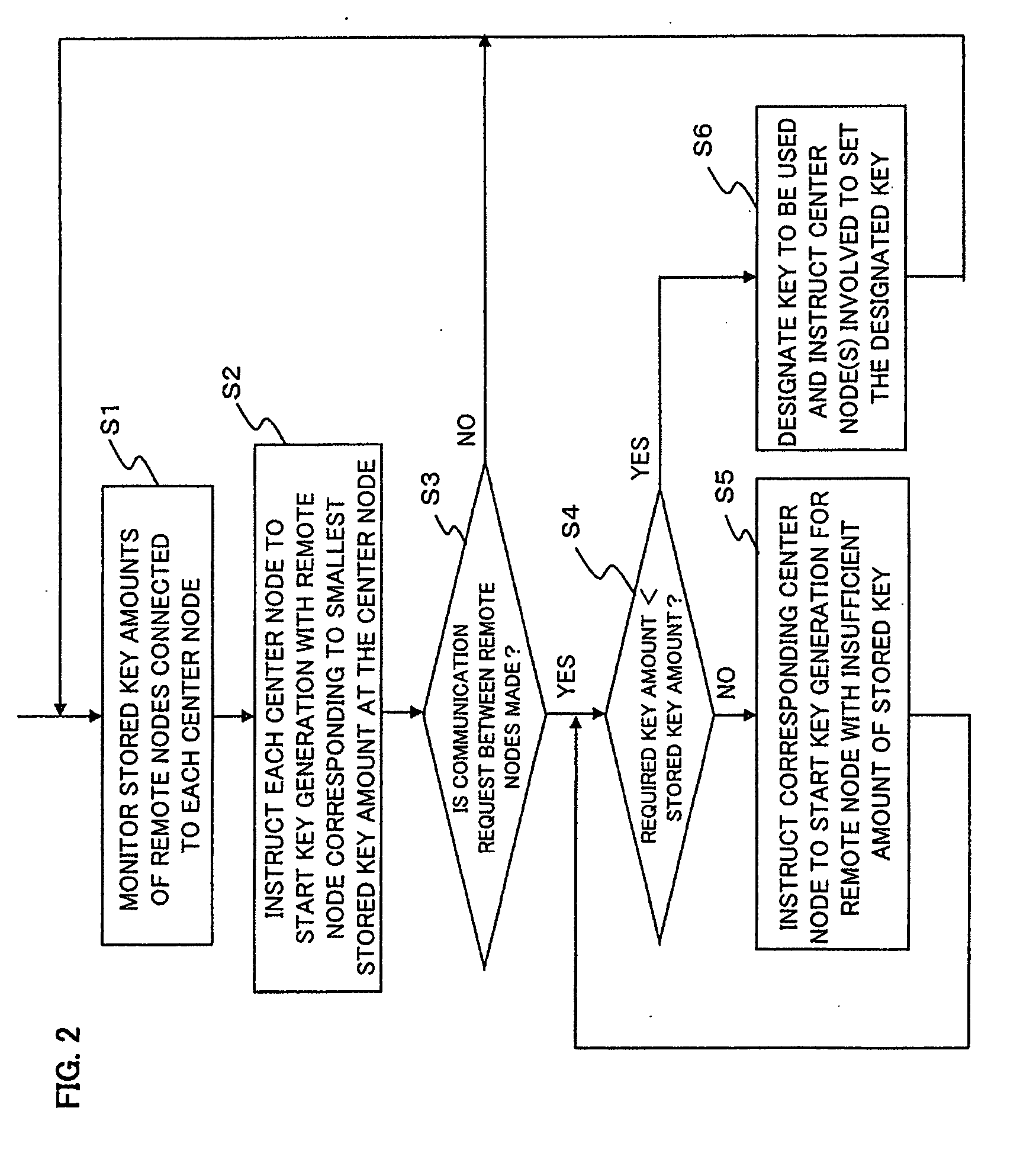
A cryptographic key management method and device are provided by which cryptographic keys of multiple nodes can be managed easily and stably. A system includes at least one first node and a plurality of second nodes connected to the first node, and the first node individually generates and consumes a cryptographic key with each of the second nodes connected to the first node itself. A cryptographic key management device in such a system has a monitor that monitors the stored key amounts of cryptographic keys of the individual second nodes, stored at the first node, and a key management control section that performs key generation control on the first node, based on the stored key amounts.
Owner:NEC CORP
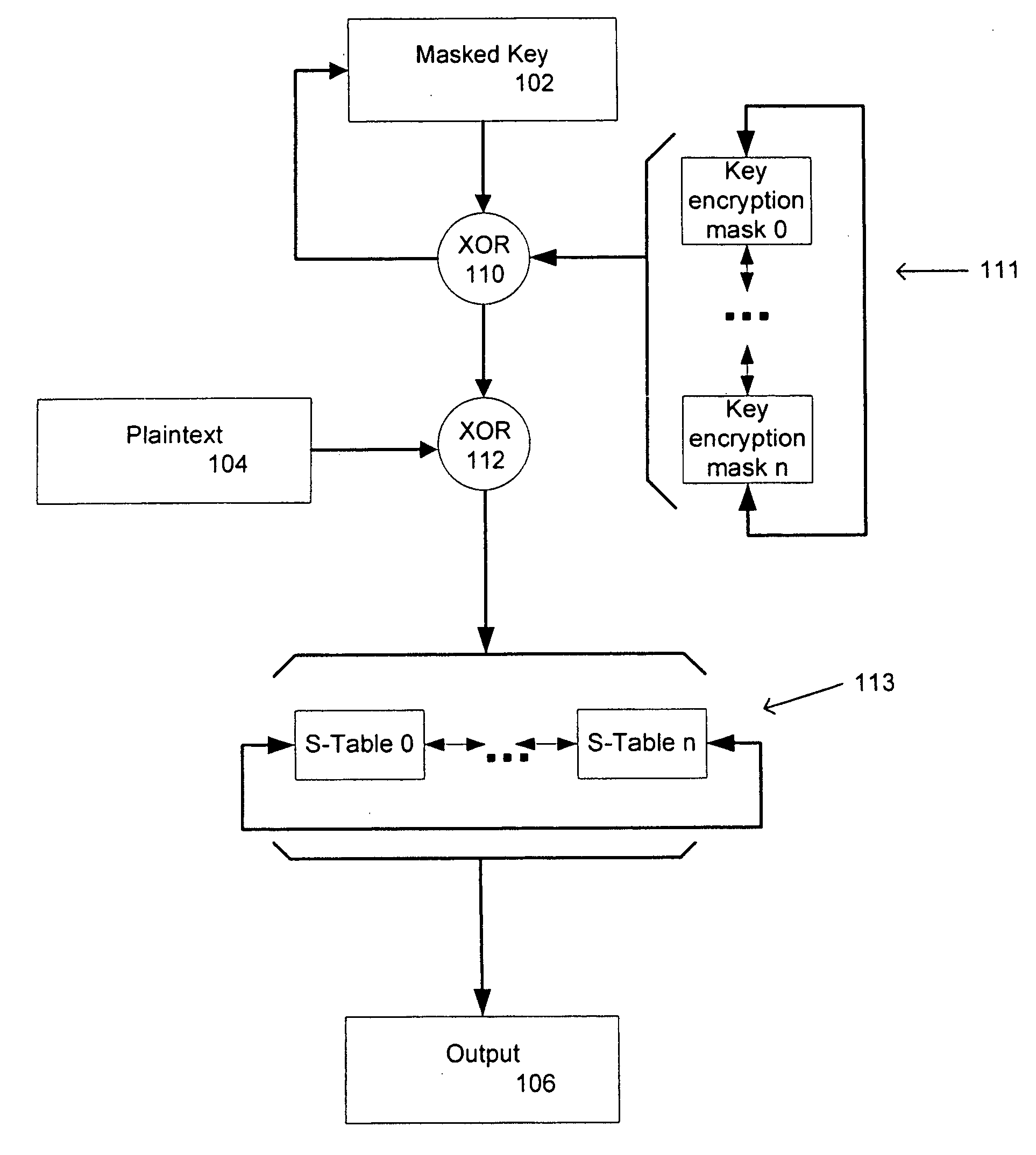
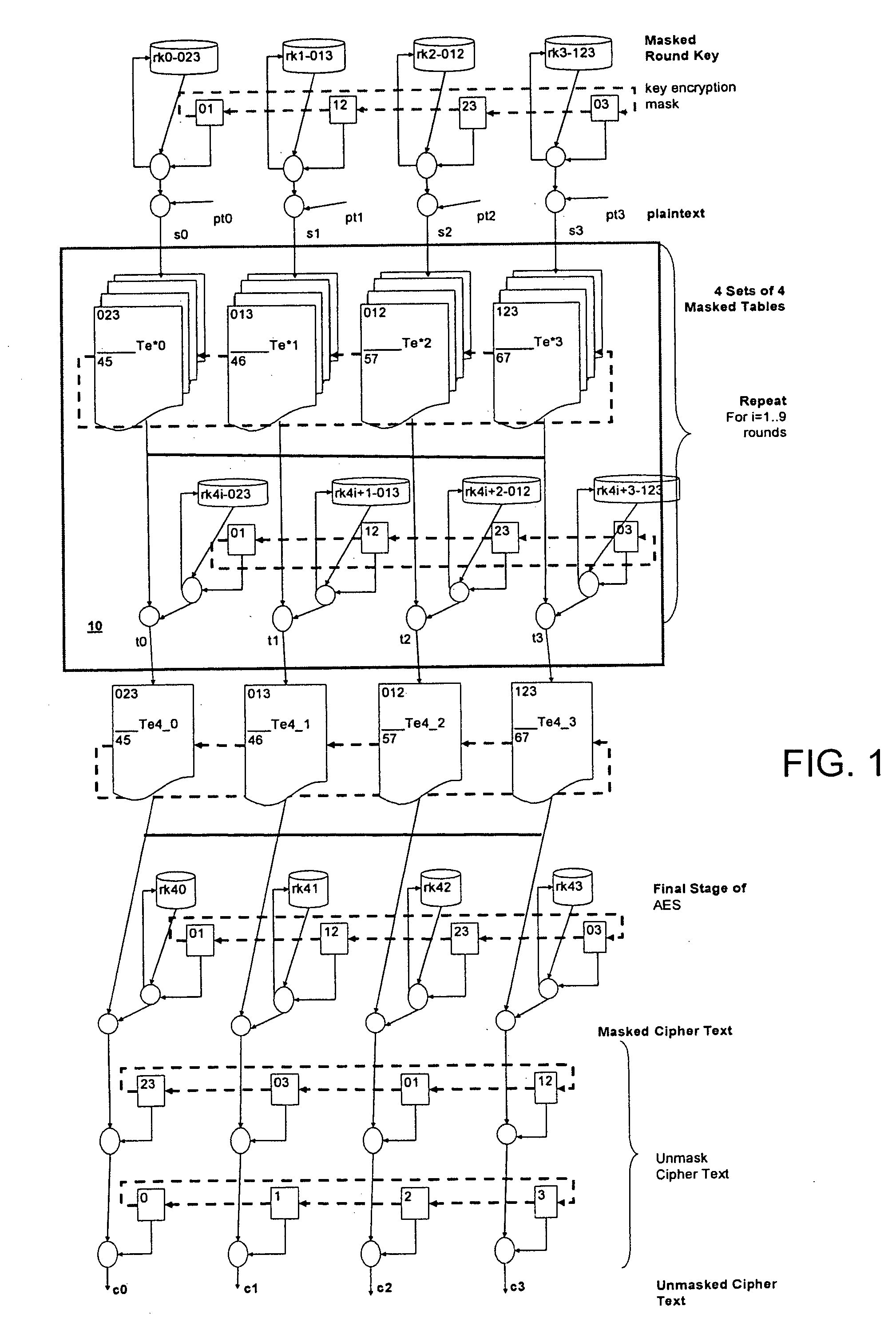
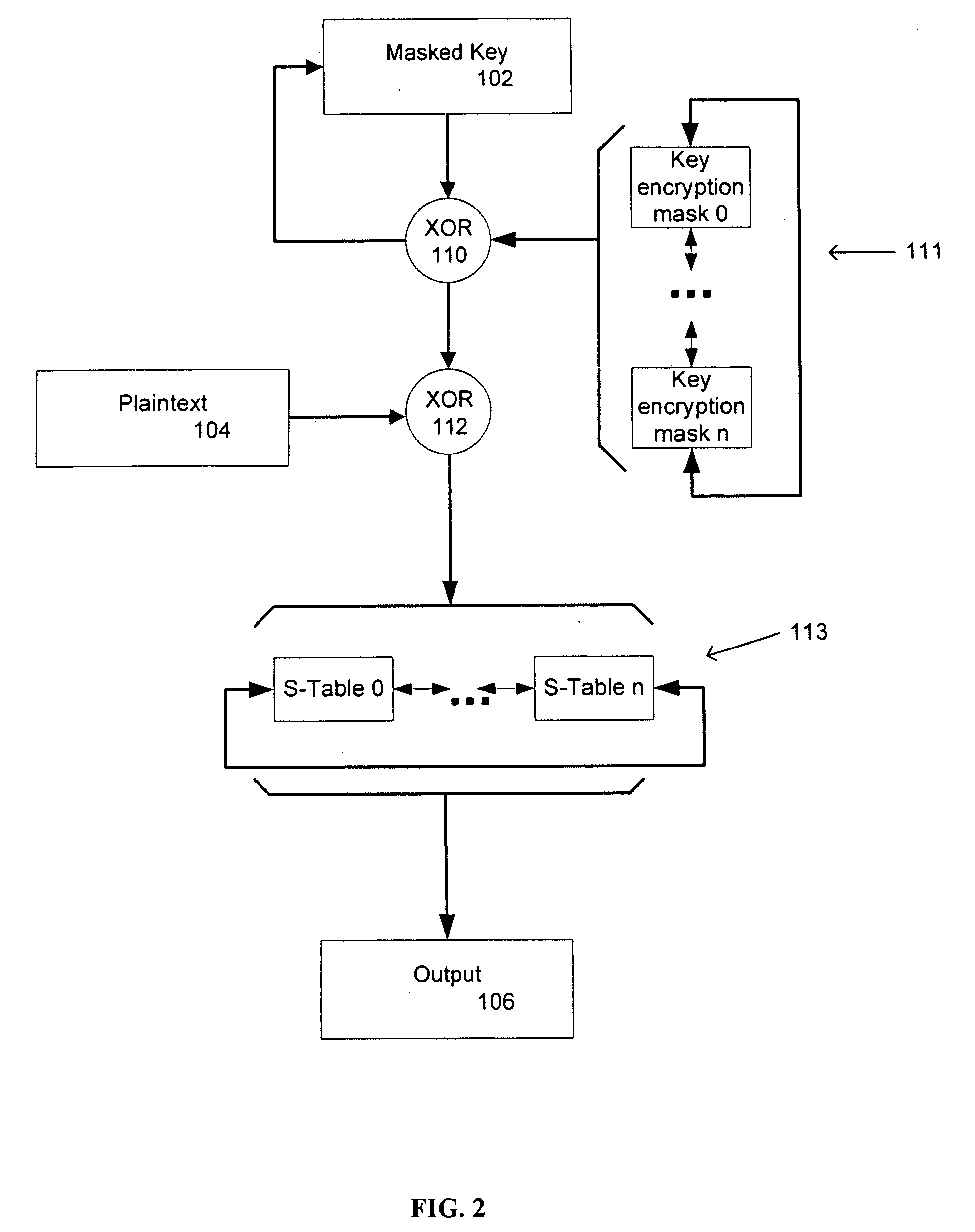
Key masking for cryptographic processes
ActiveUS20060256963A1User identity/authority verificationSecret communicationCountermeasureCryptographic protocol
Countermeasures for differential power or electromagnetic analysis attacks are provided with the definition and use of key encryption masks and masked substitution tables in a cryptographic process. Different key encryption masks and masked substitution tables are applied to different portions of masked keys used in the cryptographic process and are rotated as the cryptographic operations are carried out. The rotation of the key encryption masks and the masked substitution tables is non-uniform. Input and output masking for the substitution tables is provided.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
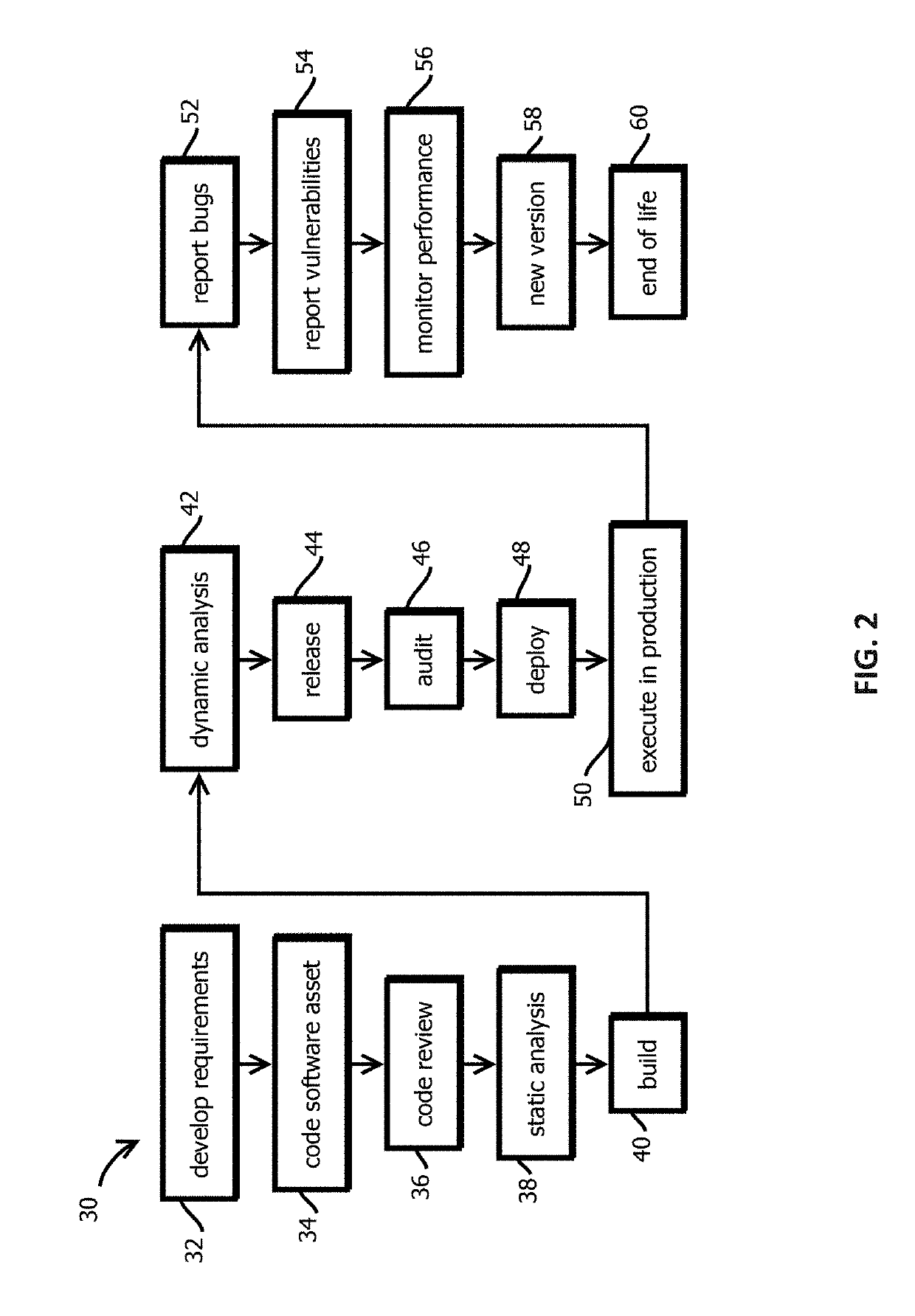
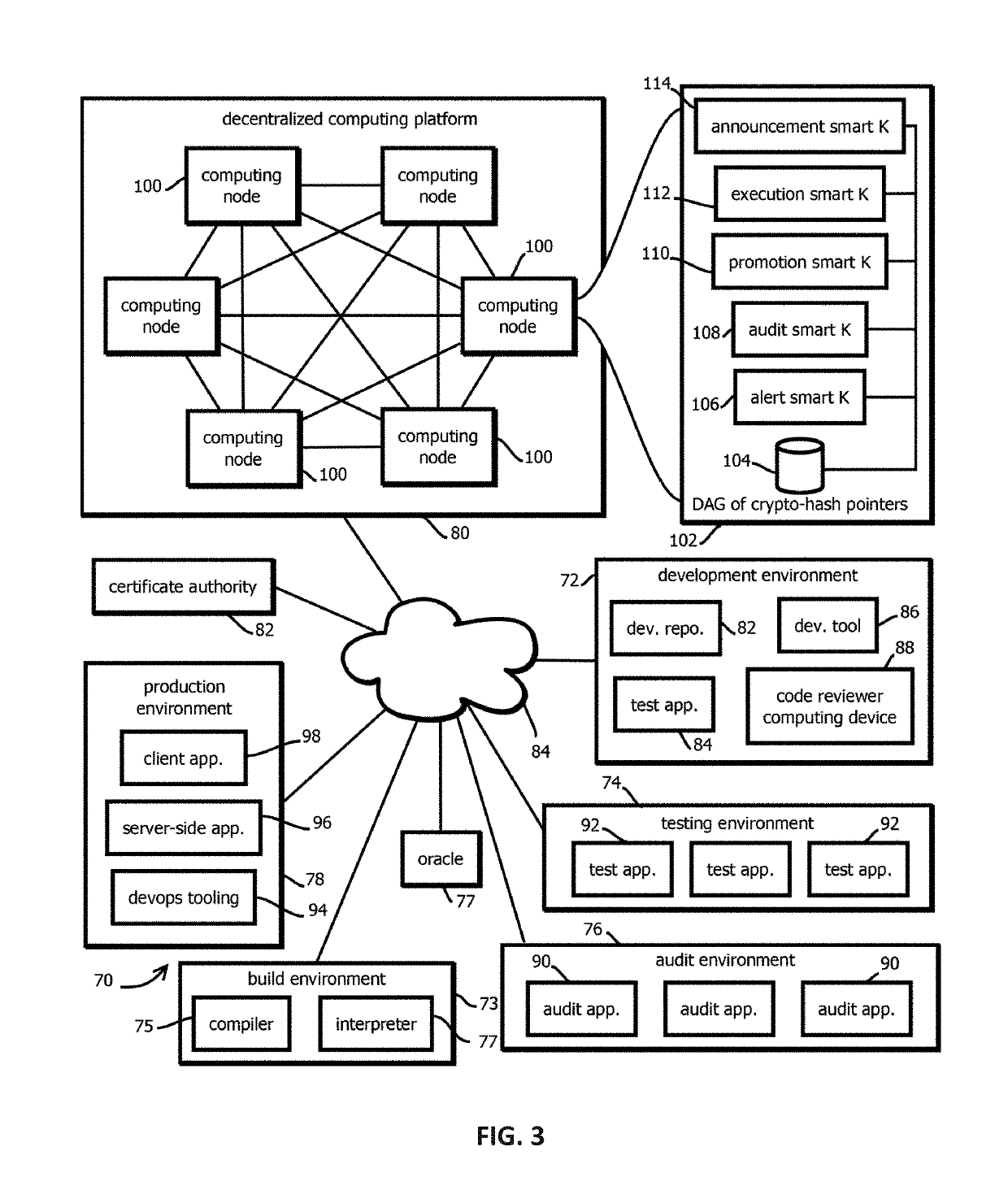
Announcement smart contracts to announce software release
InactiveUS20190305959A1User identity/authority verificationVersion controlDocumentation procedureCryptographic nonce
Provided is a process that includes: calling a program executed on a decentralized computing platform configured to persist state to a blockchain, the call requesting the program to release the software asset to the production environment, wherein: respective instances of the program are configured to publish release documentation by which provenance of the software asset is verifiable to the blockchain, respective instances of the program are configured to verify a cryptographic signature associated with the software asset, the cryptographic signature establishes that the software asset being released has not been tampered with subsequent to signing, the cryptographic signature establishes that the releasing entity or a proxy of the releasing entity has access to a cryptographic key by which the cryptographic signature was formed, and the decentralized computing platform is configured to reach a consensus verification determination among verification results from the replicated instances of the program.
Owner:CA TECH INC
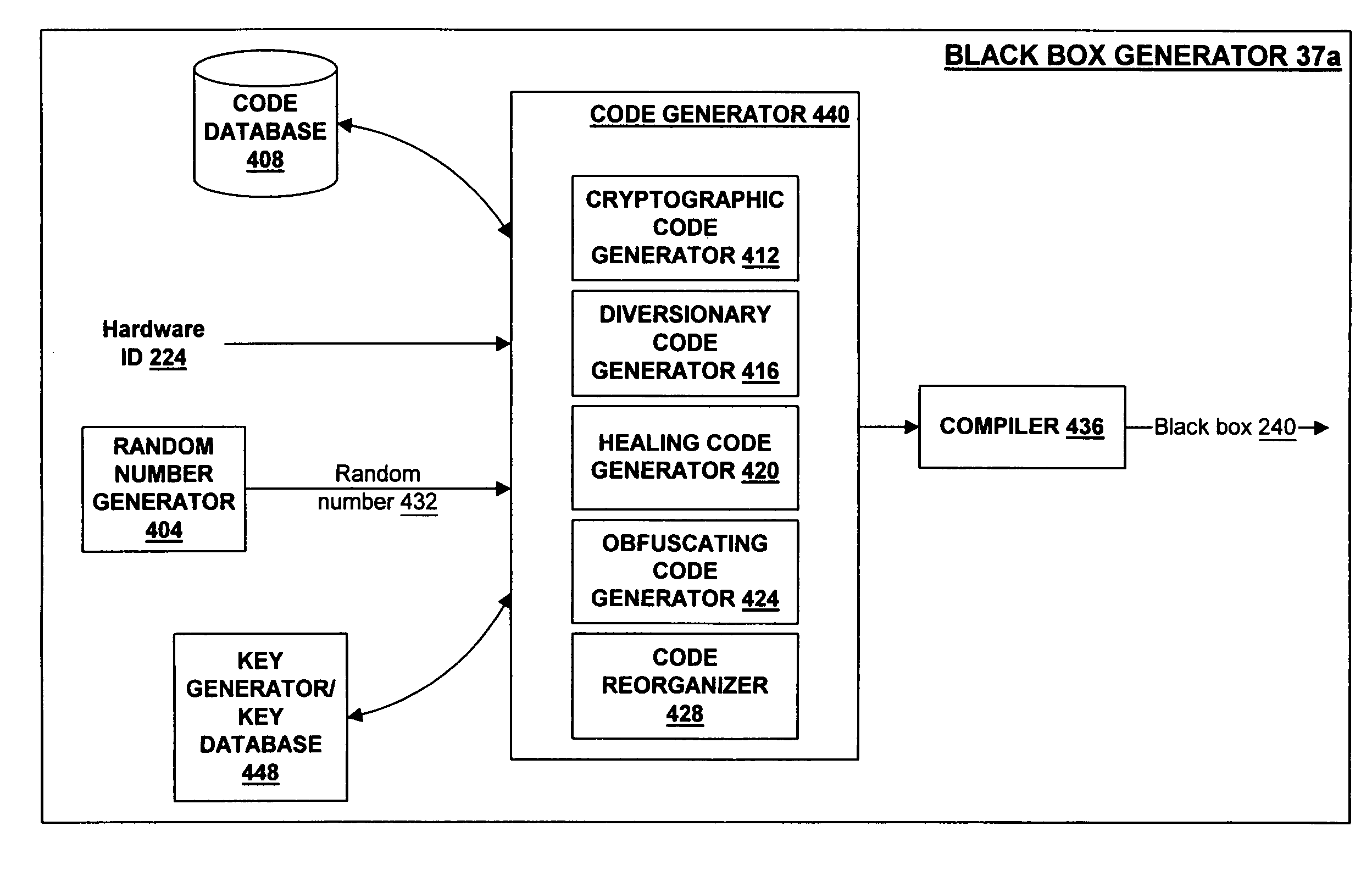
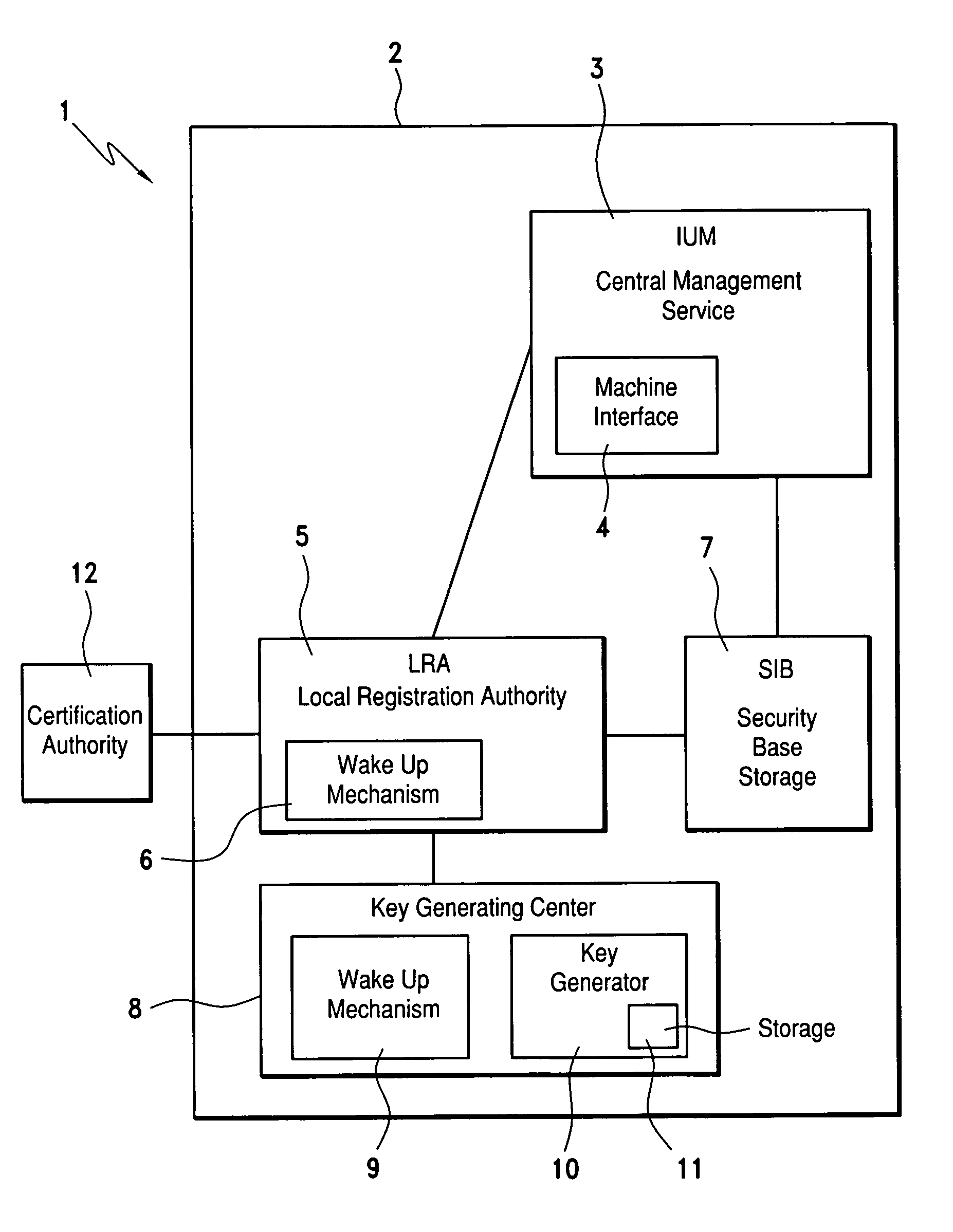
Secure repository with layers of tamper resistance and system and method for providing same
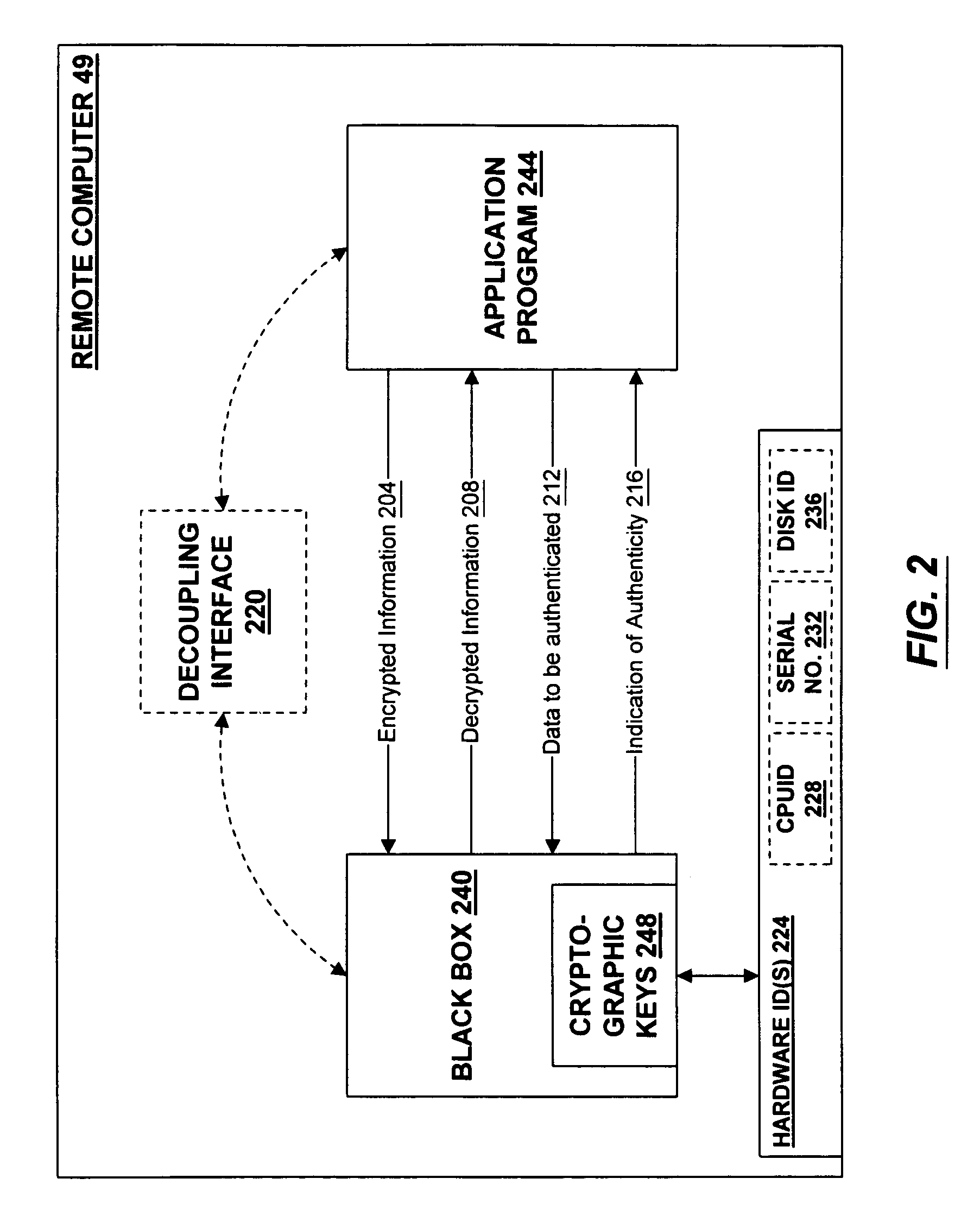
InactiveUS7539875B1Operational safetyDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionPersonalizationTamper resistance
A secure repository individualized for a hardware environment and a method and system for providing the same. The secure repository includes a hidden cryptographic key and code that applies the key without requiring access to a copy of the key. The code that implements the secure repository is generated in a manner that is at least partly based on a hardware ID associated with the hardware environment in which the secure repository is to be installed, and may also be based on a random number. Cryptographic functions implemented by the secure repository include decryption of encrypted information and validation of cryptographically signed information. The secure repository may be coupled to an application program, which uses cryptographic services provided by the secure repository, by way of a decoupling interface that provides a common communication and authentication interface for diverse types of secure repositories. The decoupling interface may take the form of a single application programmer interface (API) usable with multiple dynamically linkable libraries.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
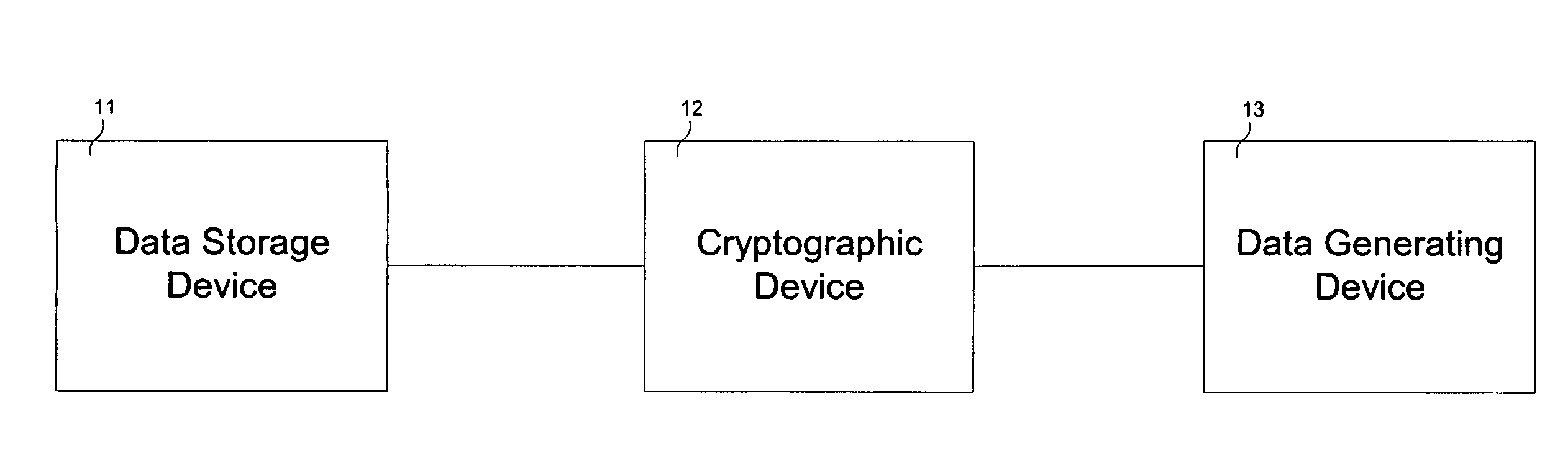
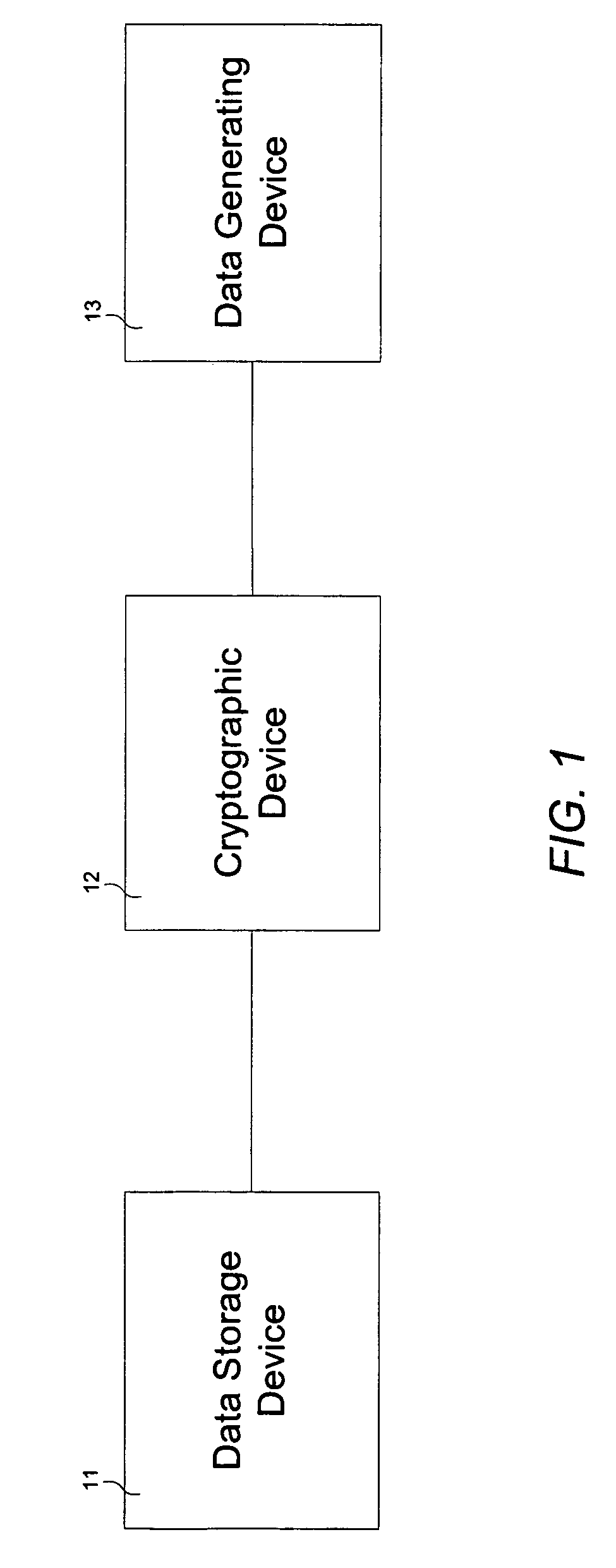
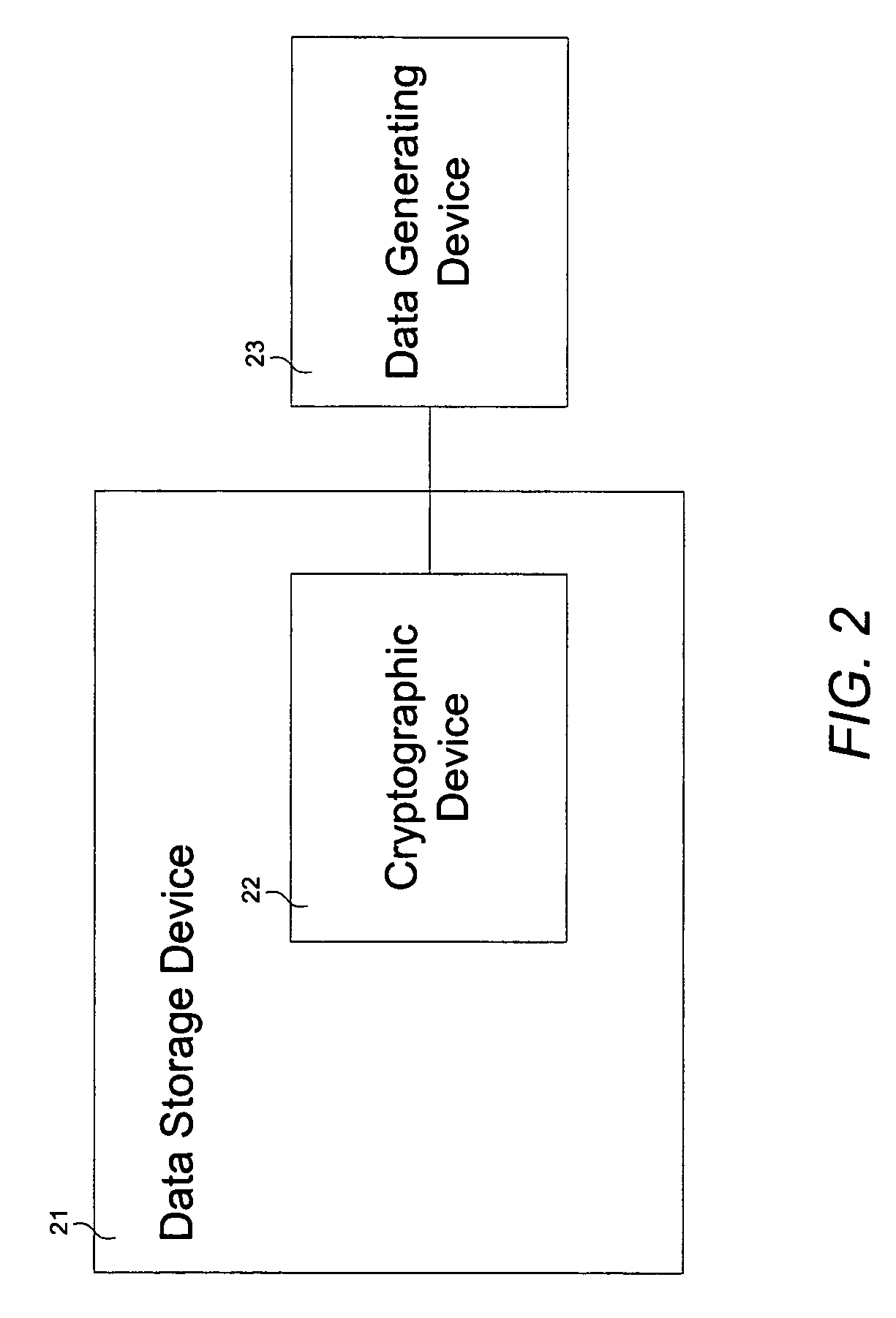
Cryptographic device
InactiveUS7136995B1Without compromising overall system performanceData stream serial/continuous modificationUnauthorized memory use protectionData streamControl store
A cryptographic device comprises a data stream interceptor, a main controller receiving input from the data stream interceptor, and a pair of data generating and storage controllers adapted to perform data transfer protocols with corresponding peer controllers of a data generating device and a data storage device, respectively, on command from the main controller. The cryptographic device further comprises a cipher engine programmed to transparently encrypt and decrypt data streams flowing between the data generating device and data storage device on command from the main controller. The cryptographic device does not utilize system resources associated with the data generating and storage devices during operation.
Owner:ENOVA TECH
Revocation of cryptographic keys in the absence of a trusted central authority
ActiveUS20160254910A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityCryptographic nonce
A method and apparatus is presented for revoking cryptographic keys within a distributed ledger system in which no central trusted authority is available, consisting of sending a key revocation message by a network connected device to other network connected devices over a peer-to-peer network for inclusion in a ledger. In one embodiment the revocation message is signed using a private key of a public / private key pair to be revoked. In another embodiment an authorization for future revocation of the public / private key pair by a plurality of other public / private keys is sent for inclusion in the ledger, and subsequently the key revocation message is signed with one of the private keys of the plurality of public / private key pairs before sending the key revocation message. Once a valid key revocation message is included in the ledger, any future request to include a message signed by the revoked cryptographic key is rejected.
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
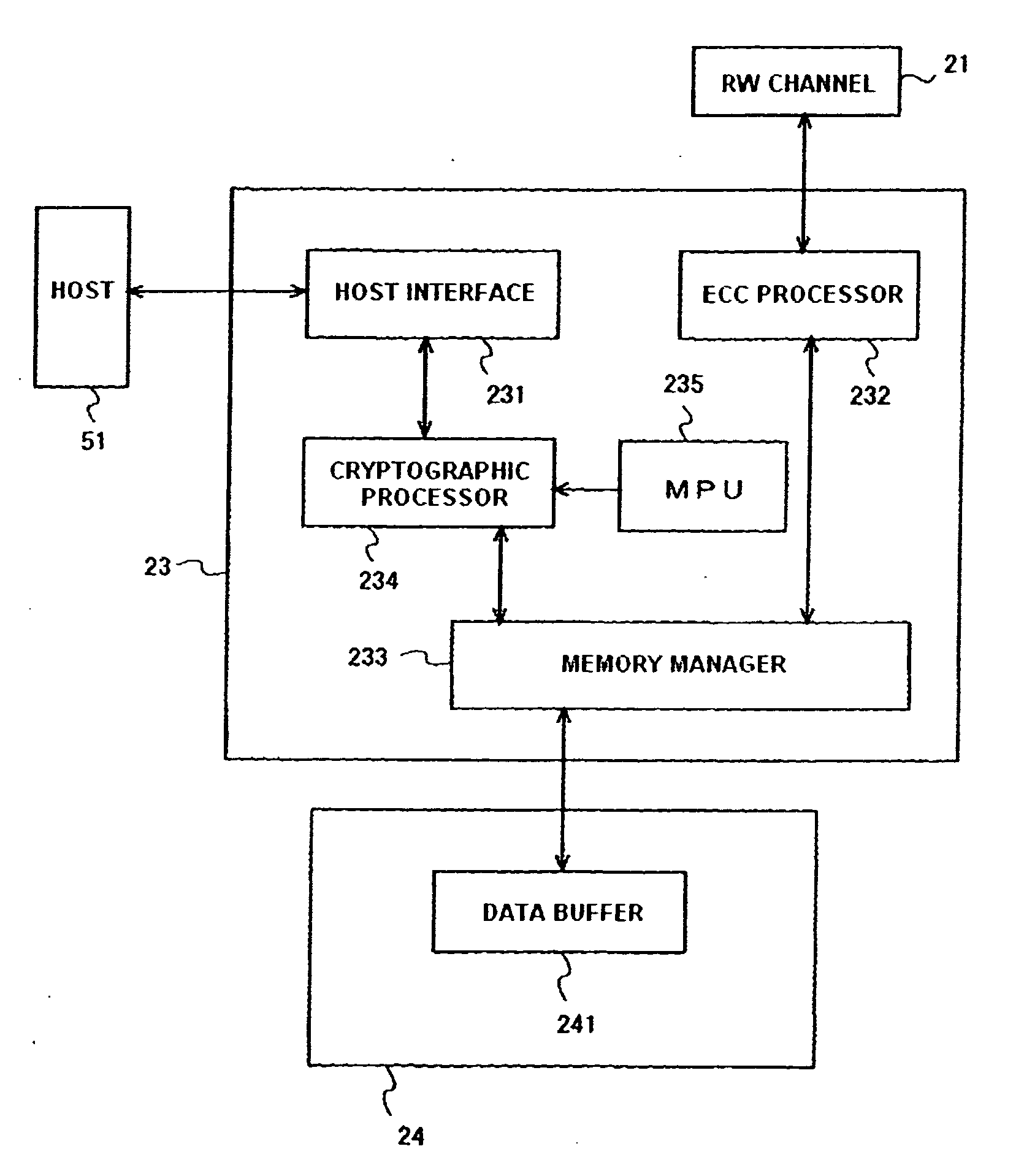
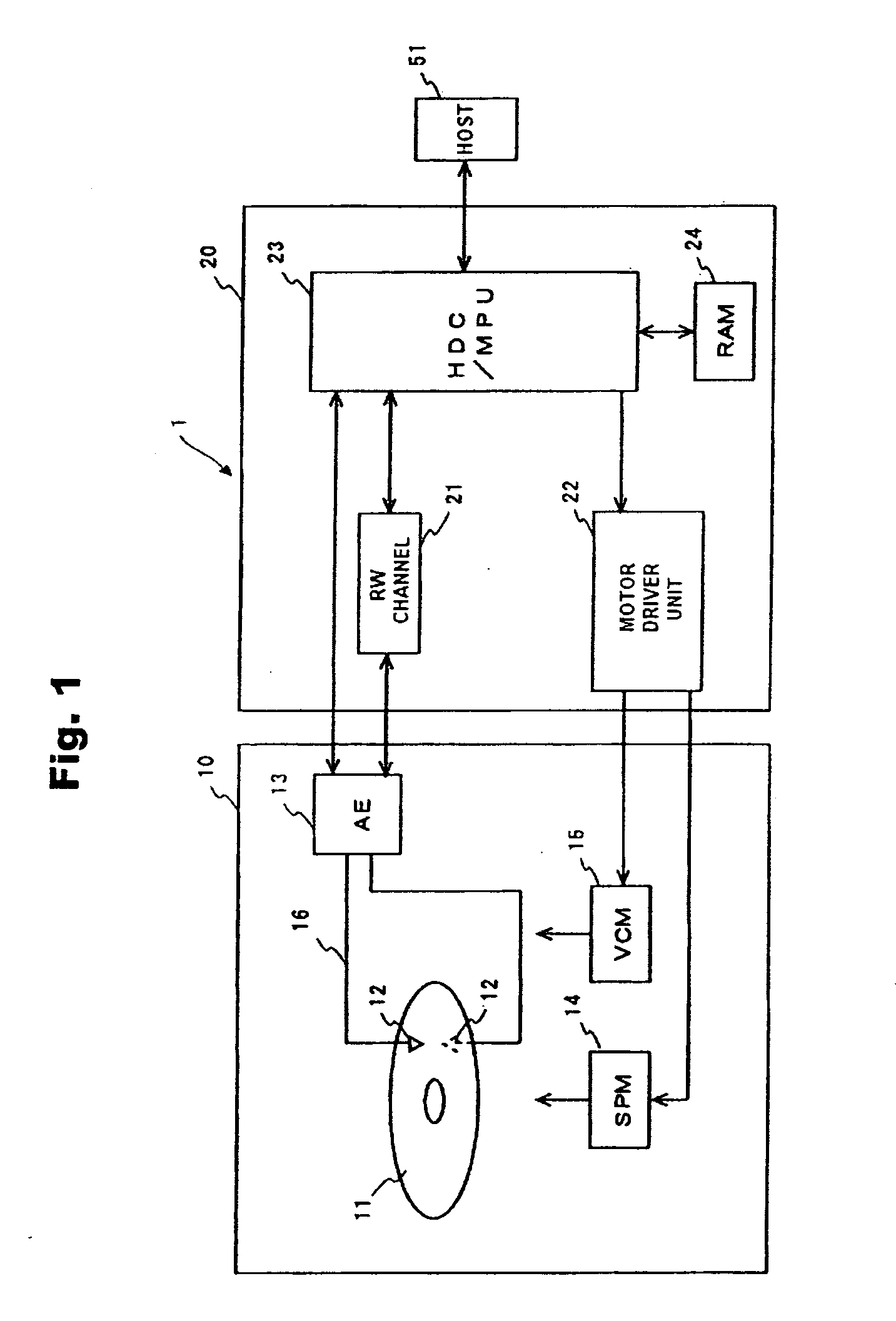
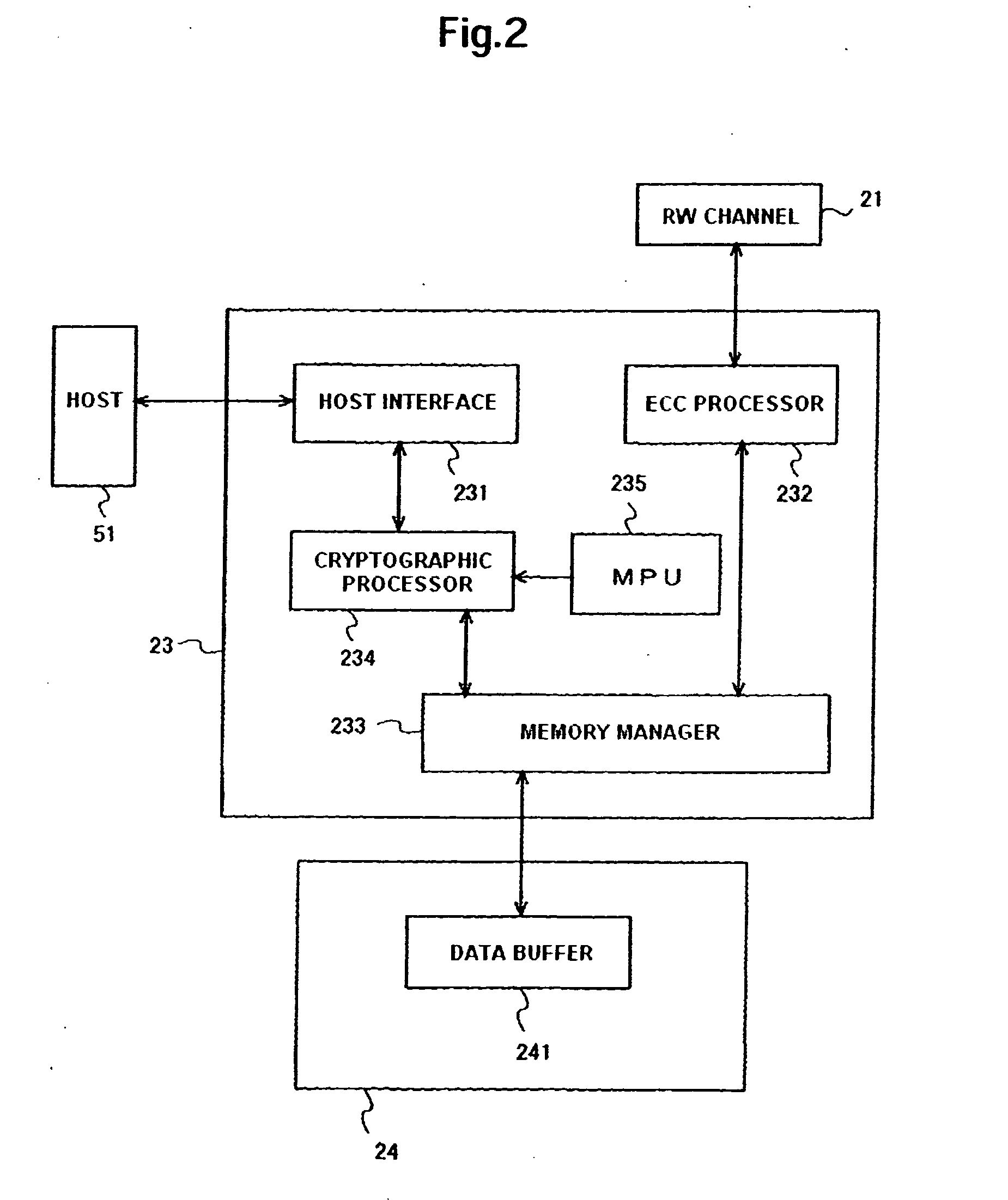
Data storage device and management method of cryptographic key thereof
ActiveUS20100031061A1More securityUnauthorized memory use protectionRecord information storageHard disc drivePassword
Embodiments of the present invention help to securely manage a data cryptographic key in a data storage device. In an embodiment of the present invention, a cryptographic processor for encrypting and decrypting data is located between a host interface and a memory manager. In parts of the hard disk drive (HDD), except for the host interface, the HDD handles user data in an encrypted state. A data cryptographic key which the cryptographic processor uses to encrypt and decrypt the user data is encrypted and stored in a magnetic disk. A multiprocessing unit (MPU) decrypts the data cryptographic key using a password and a random number to supply it to the cryptographic processor. Using the password and the random number, the HDD can manage the data cryptographic key with more security.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
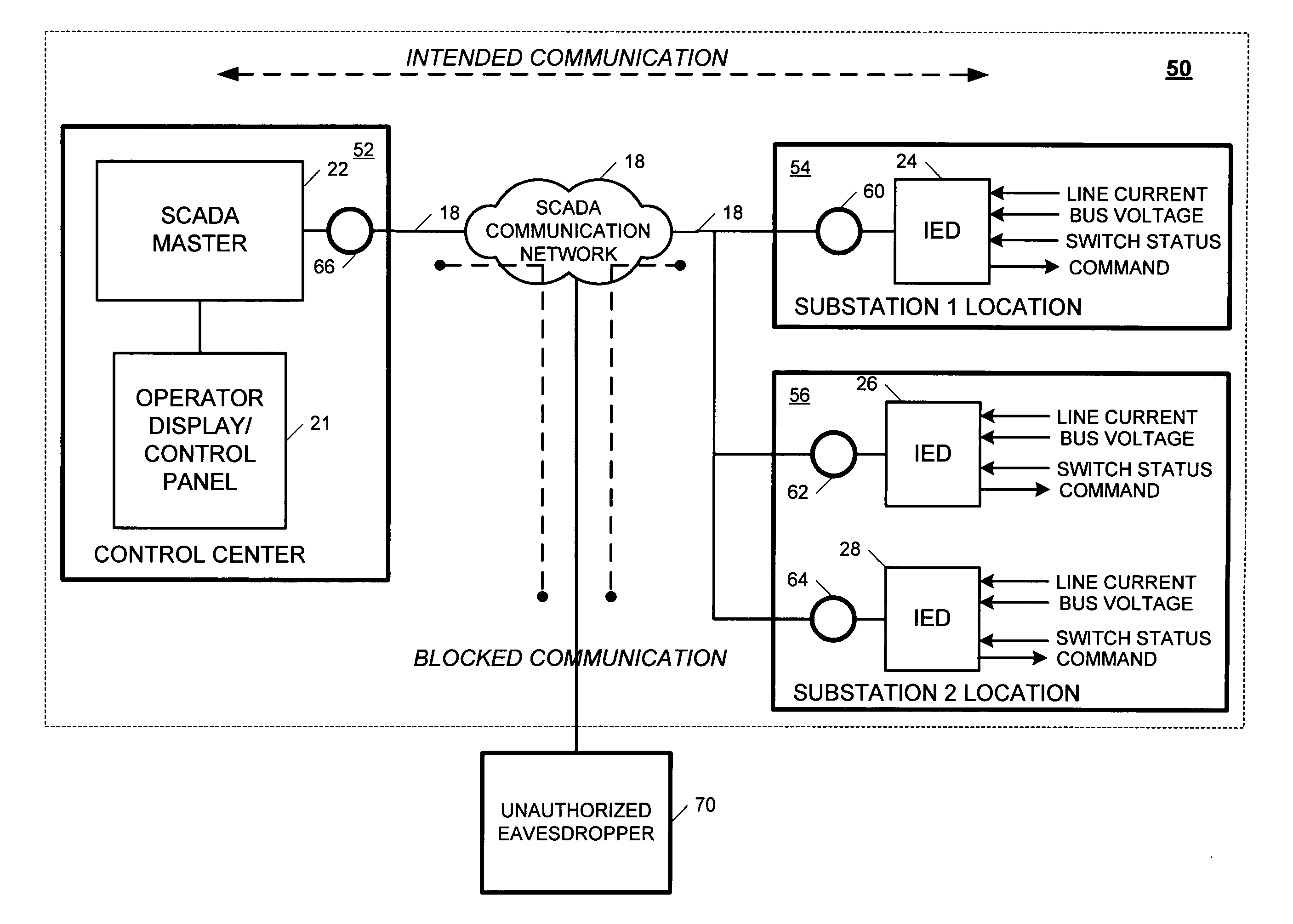
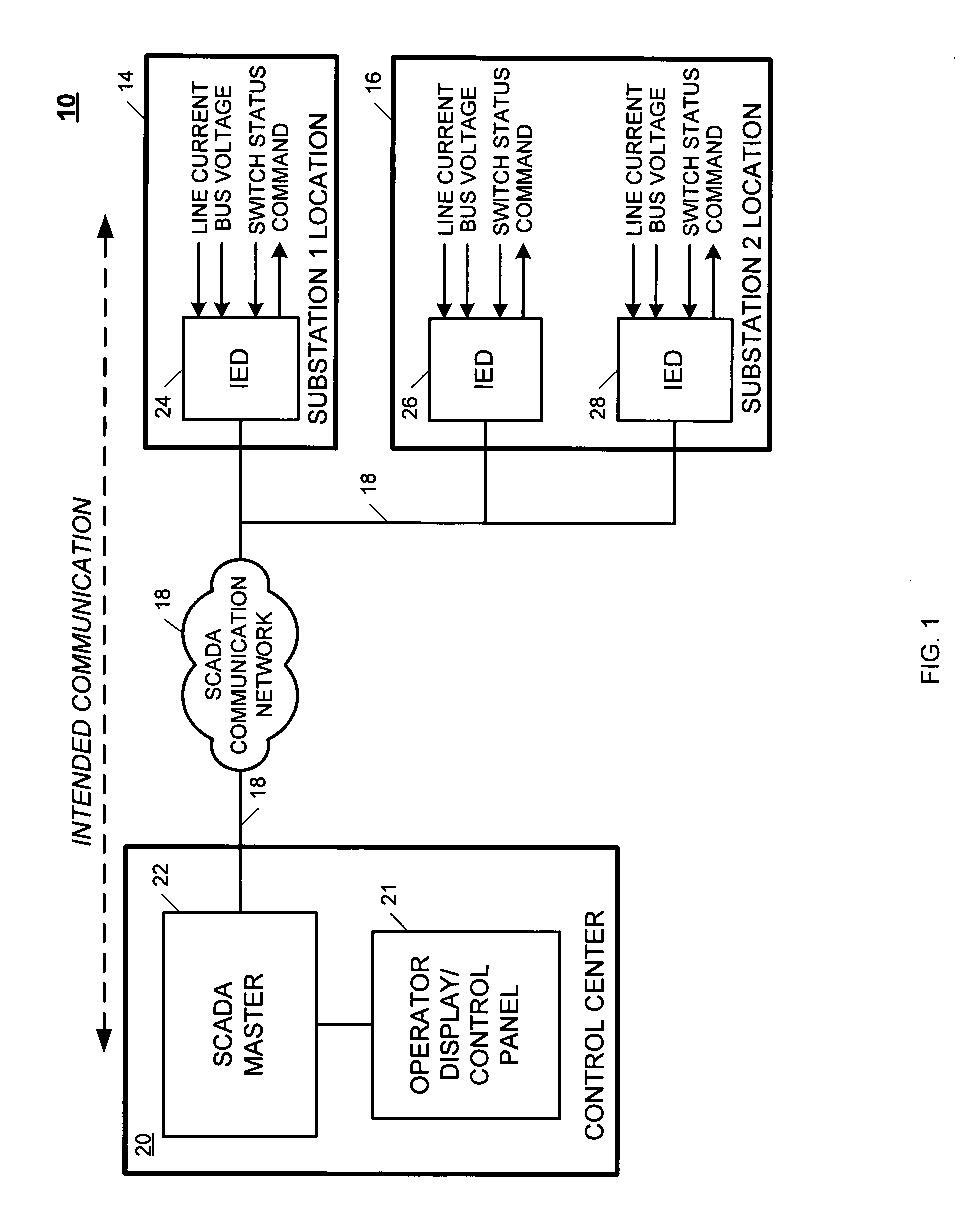
Method and apparatus for reducing communication system downtime when configuring a cryptographic system of the communication system
ActiveUS20100002879A1Reducing communication system downtimeReduce downtimeSecret communicationTransmissionComputer hardwareCommunications system
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for reducing communication system downtime when enabling cryptographic operation of a cryptographic system of the communication system where the cryptographic system includes a first cryptographic device operatively coupled to a plurality of second cryptographic devices via a communication network of the communication system. The method includes causing a pass-through mode of the second cryptographic devices to be suspended, sequentially determining a state of each of the second cryptographic devices, causing the second cryptographic devices and the first cryptographic device to substantially simultaneously operate in a secure mode if each of the second cryptographic devices is determined to have a first state, and causing the second cryptographic devices and the first cryptographic device to operate in the pass-through mode if at least one of the plurality of second cryptographic devices is determined to have a second state.
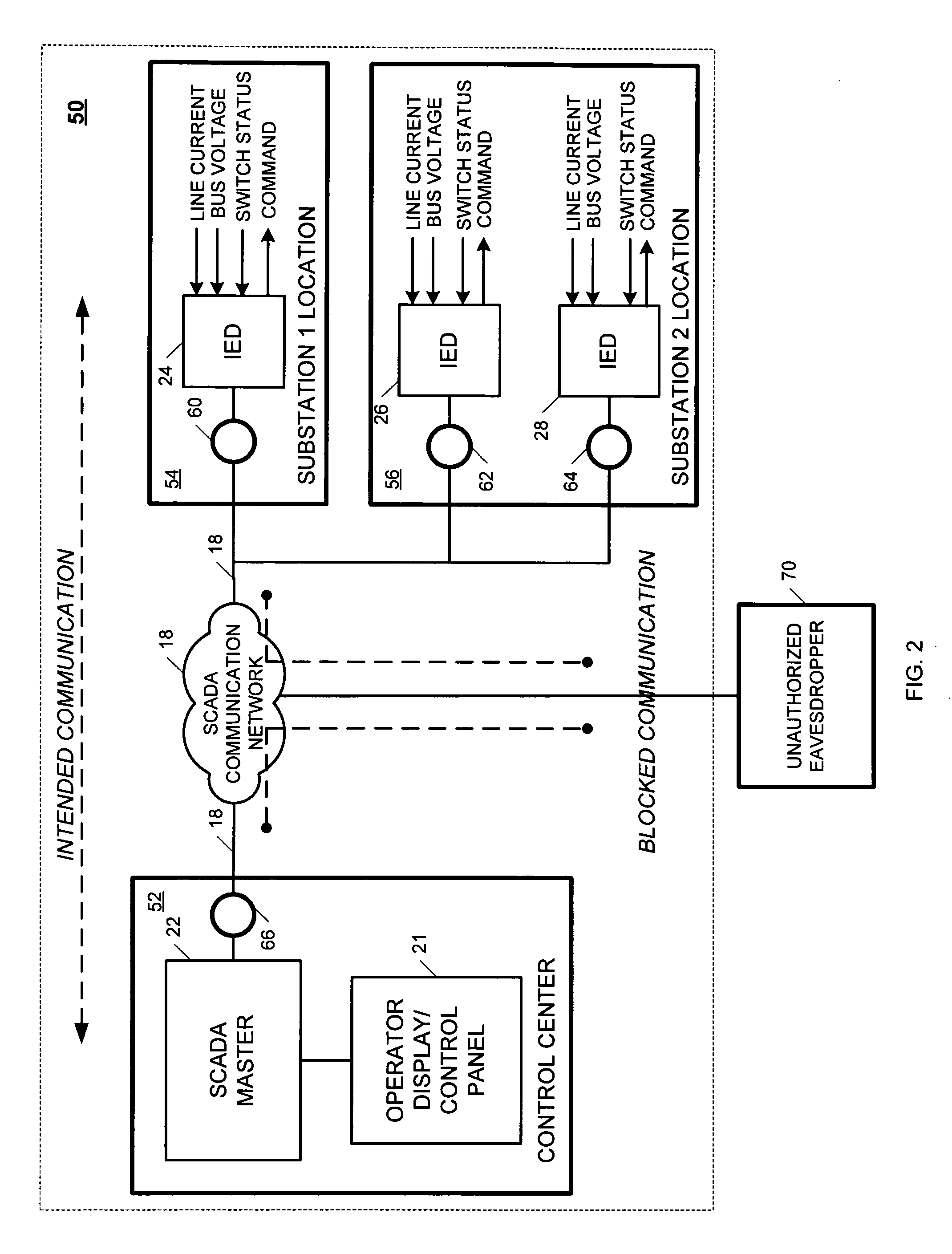
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Cryptographic key distribution using key folding
Owner:VADIUM TECH INC
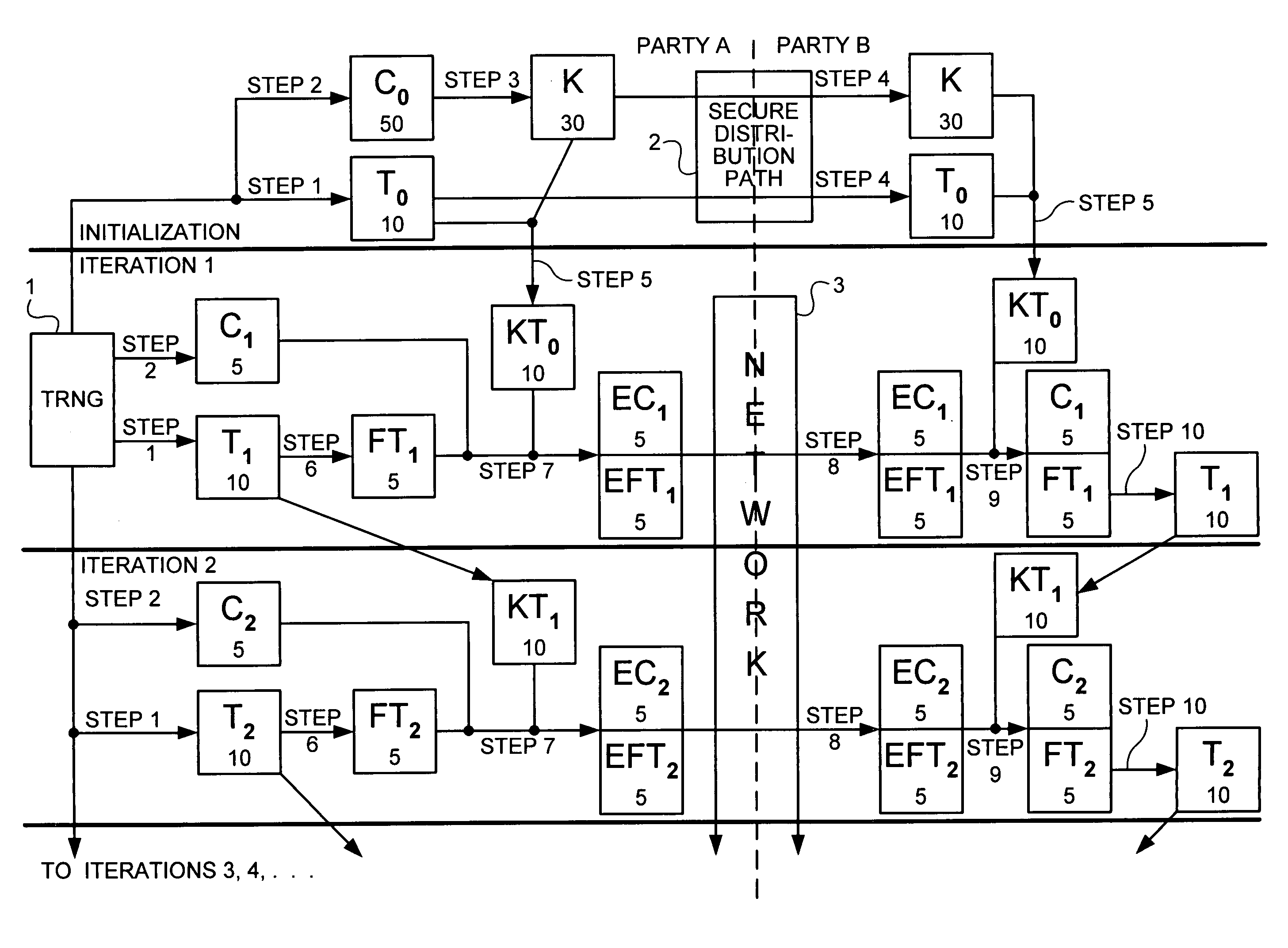
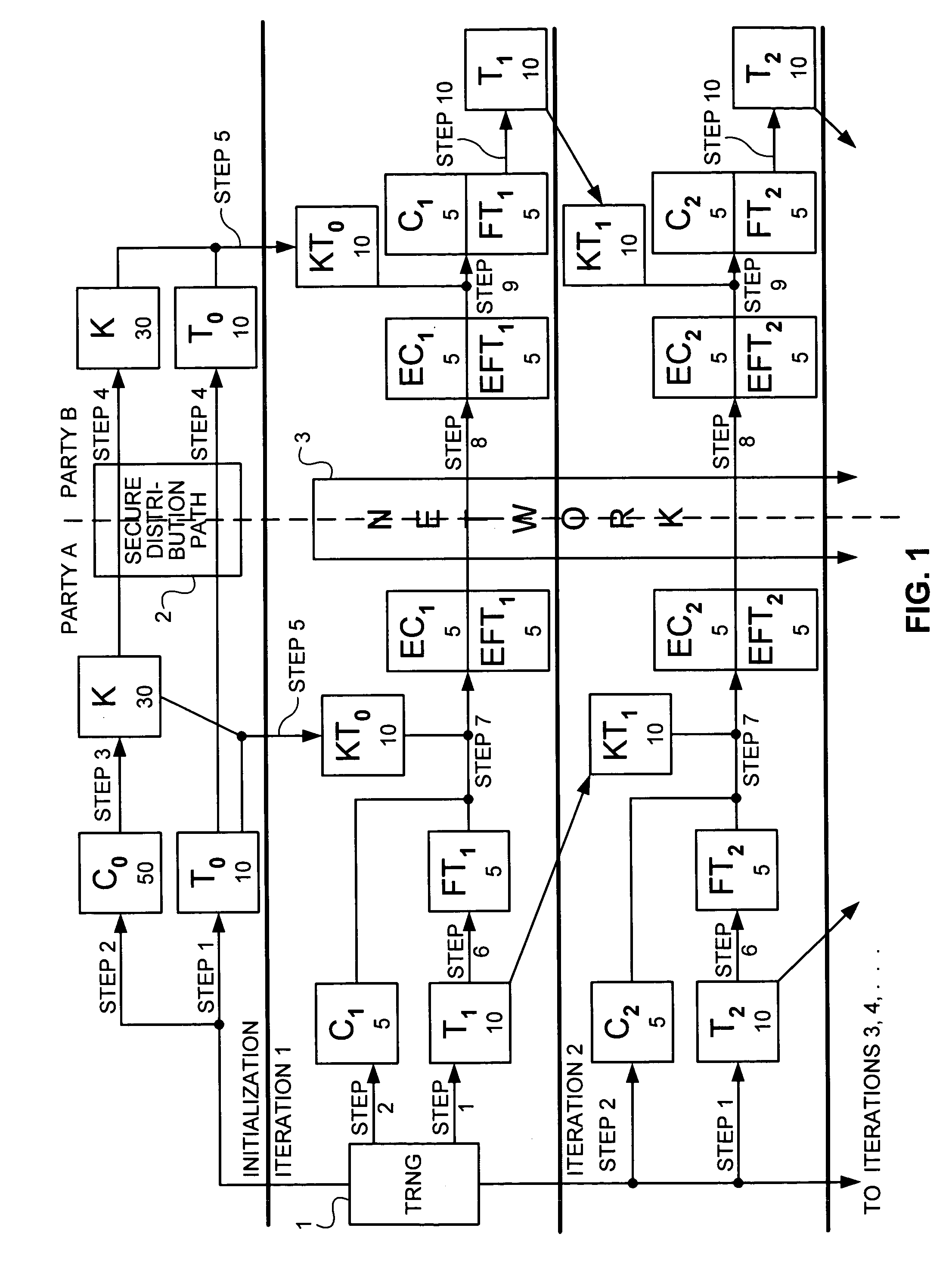
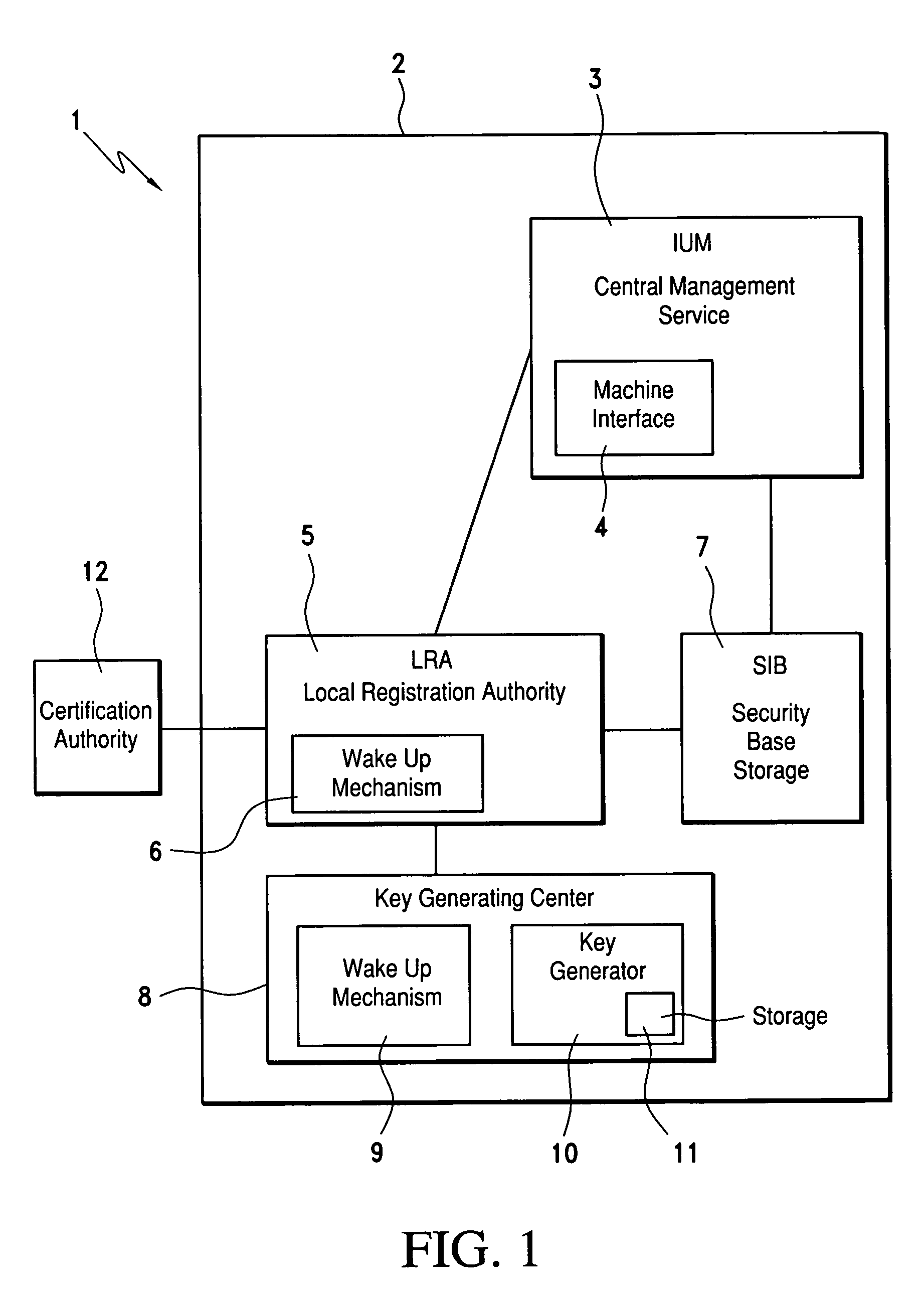
Process for creating and managing at least one cryptographic key, and system for its implementation
InactiveUS7209563B1Easy to updateKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCryptographic nonceComputerized system
A process for creating and managing pairs of asymmetrical cryptographic keys and / or certificates associated with the pairs of keys, each pair of keys and associated certificates being intended for an object managed by a computer system. The process includes creating an individual request for creating and / or certifying at least one pair of keys for an object of the system that lacks a pair of keys or a certificate for its pair of keys.
Owner:EVIDAN
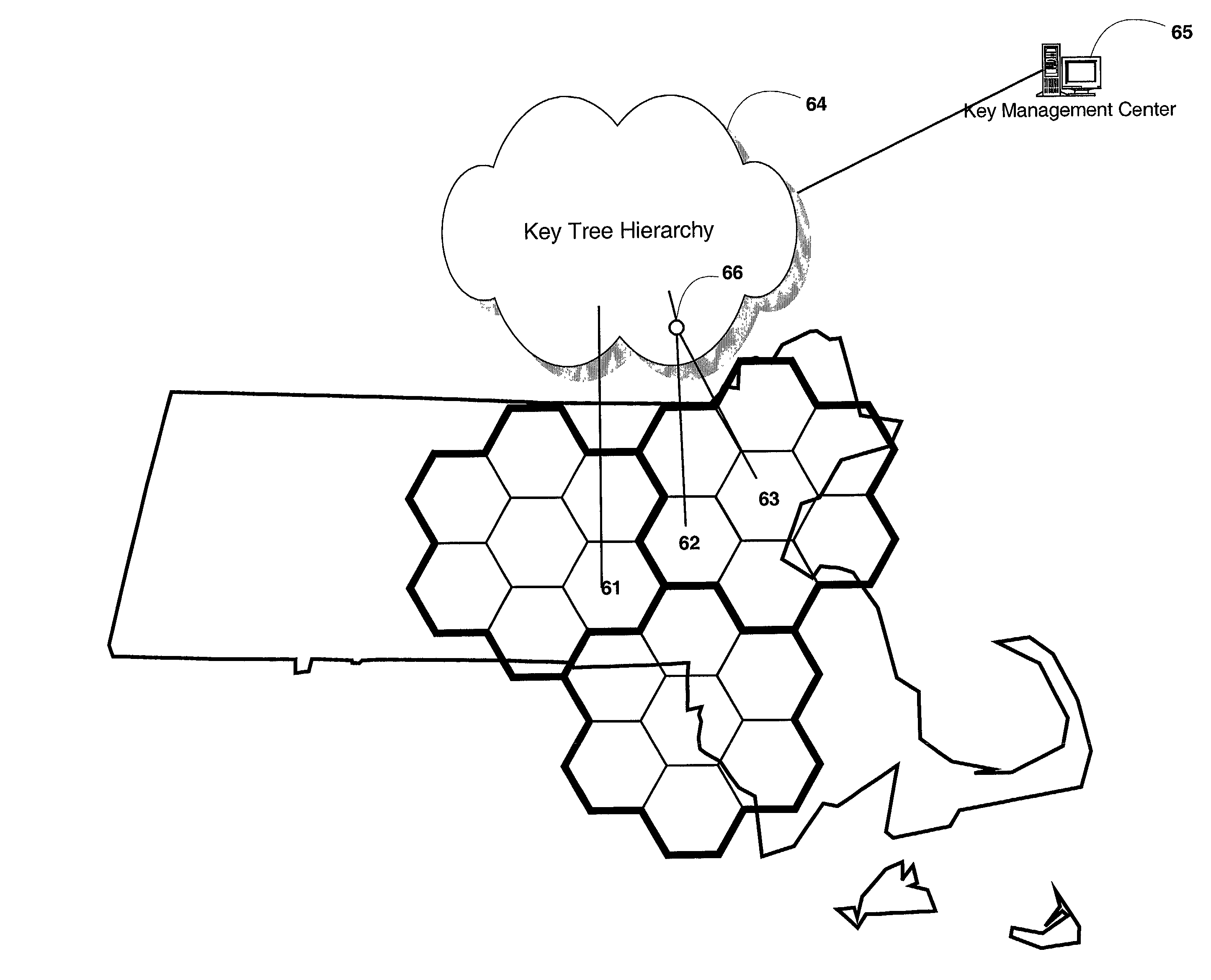
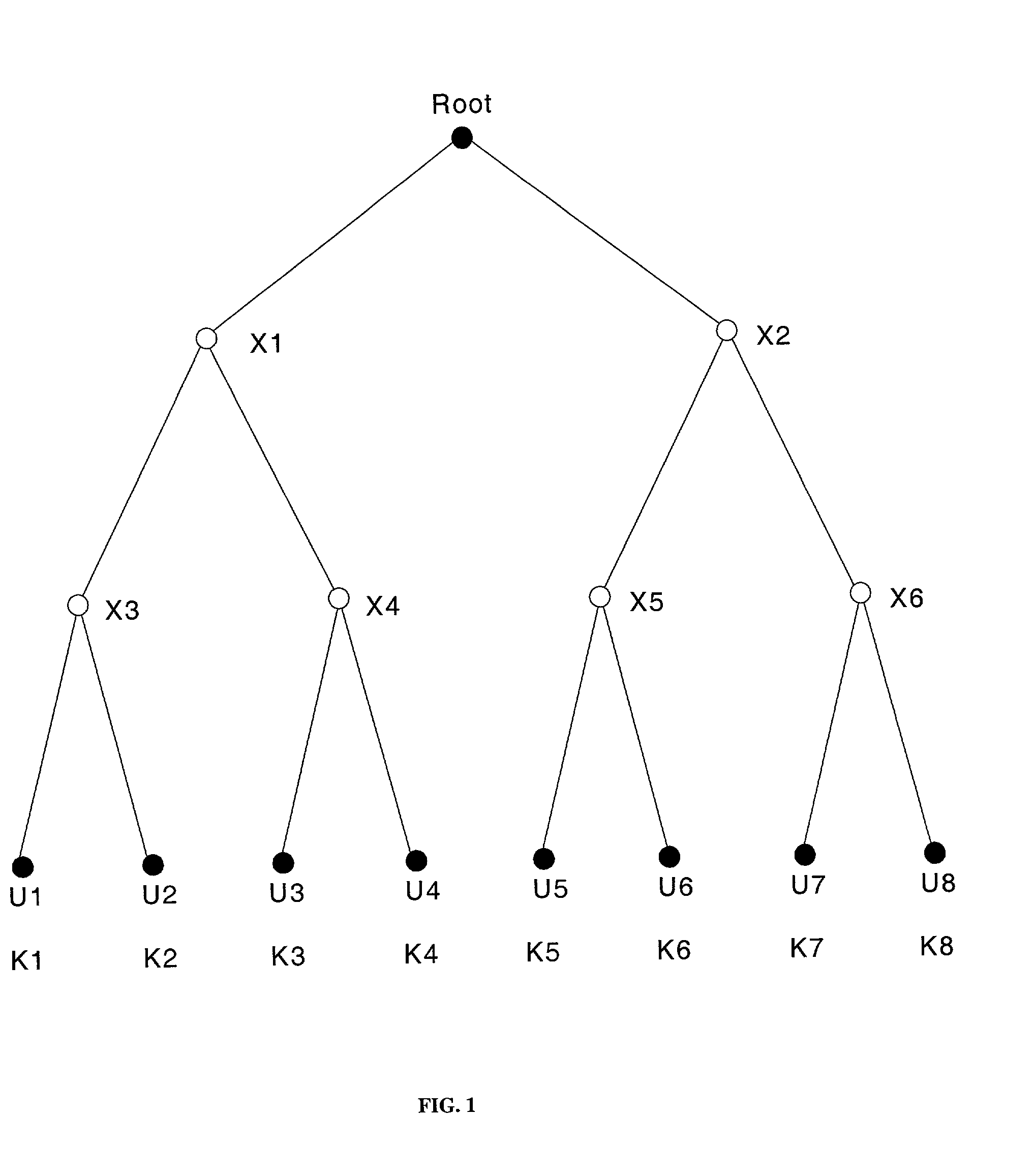
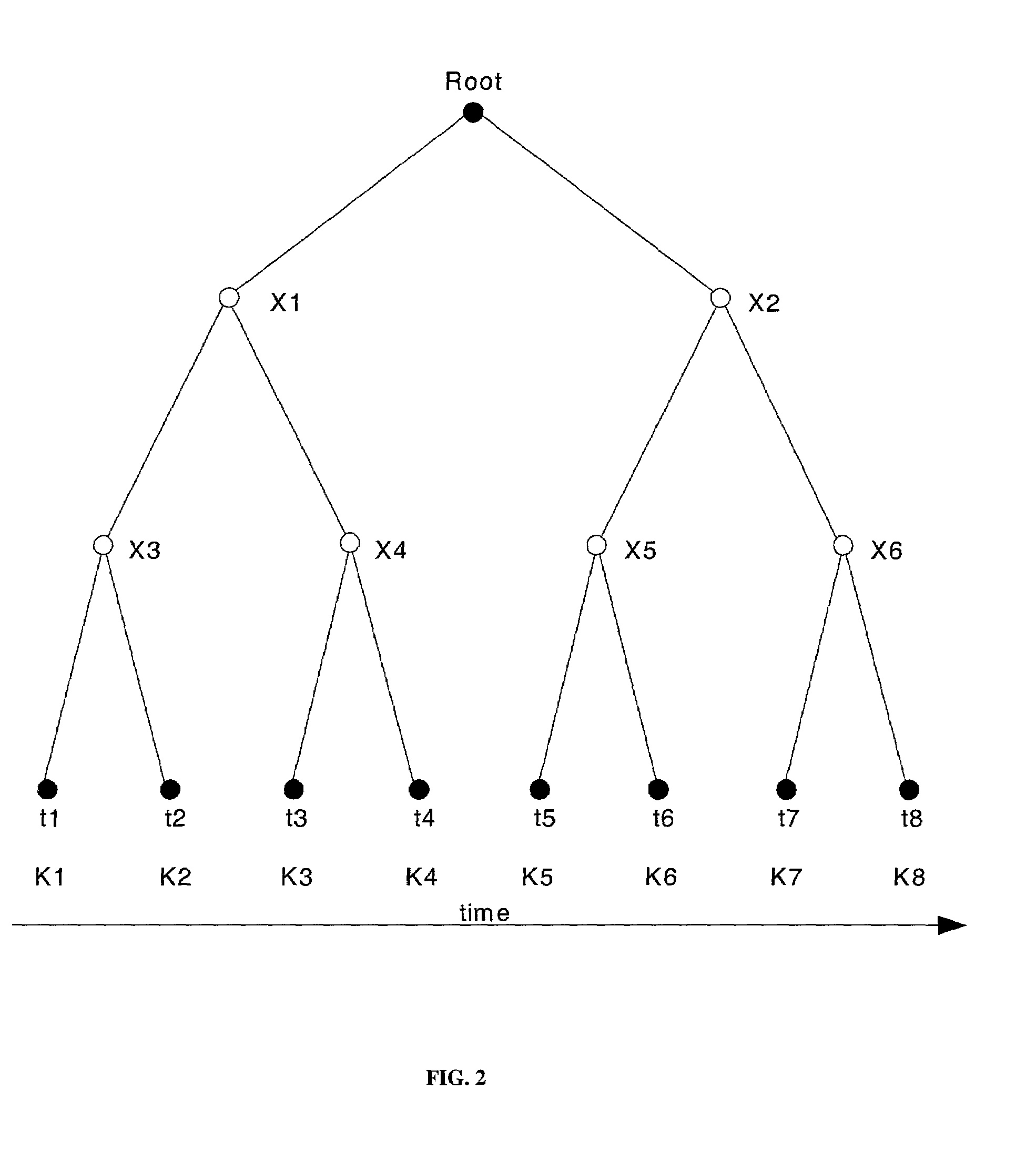
Spatial key trees for key management in wireless environments
InactiveUS6993138B1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecure communicationCurrent cell
A system, method, and program code are given for secure communication. Multiple geographic cells are arranged in a hierarchical tree having a root node and internal nodes. The root node and each internal node in the tree have an associated node cryptographic key for secure communication with lower nodes in the tree. Each cell is associated with a leaf node of the tree and a cell cryptographic key for secure communications with devices located within the cell. A key management center is at the root node for determining an anticipated cell path of a mobile device from a current cell to a destination cell. The key management center distributes to the mobile device a set of cryptographic keys from the tree. This set contains a minimum number of cryptographic keys necessary to permit secure communications for the mobile device within each cell along the anticipated cell path, but no other cells.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and system for secure storage, transmission and control of cryptographic keys
InactiveUS20100158247A1Equal and great cryptographic strengthKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCryptographic nonceComputer security
A system and method are described supporting secure implementations of 3DES and other strong cryptographic algorithms. A secure key block having control, key, and hash fields safely stores or transmits keys in insecure or hostile environments. The control field provides attribute information such as the manner of using a key, the algorithm to be implemented, the mode of use, and the exportability of the key. A hash algorithm is applied across the key and control for generating a hash field that cryptographically ties the control and key fields together. Improved security is provided because tampering with any portion of the key block results in an invalid key block. The work factor associated with any manner of attack is sufficient to maintain a high level of security consistent with the large keys and strong cryptographic algorithms supported.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com