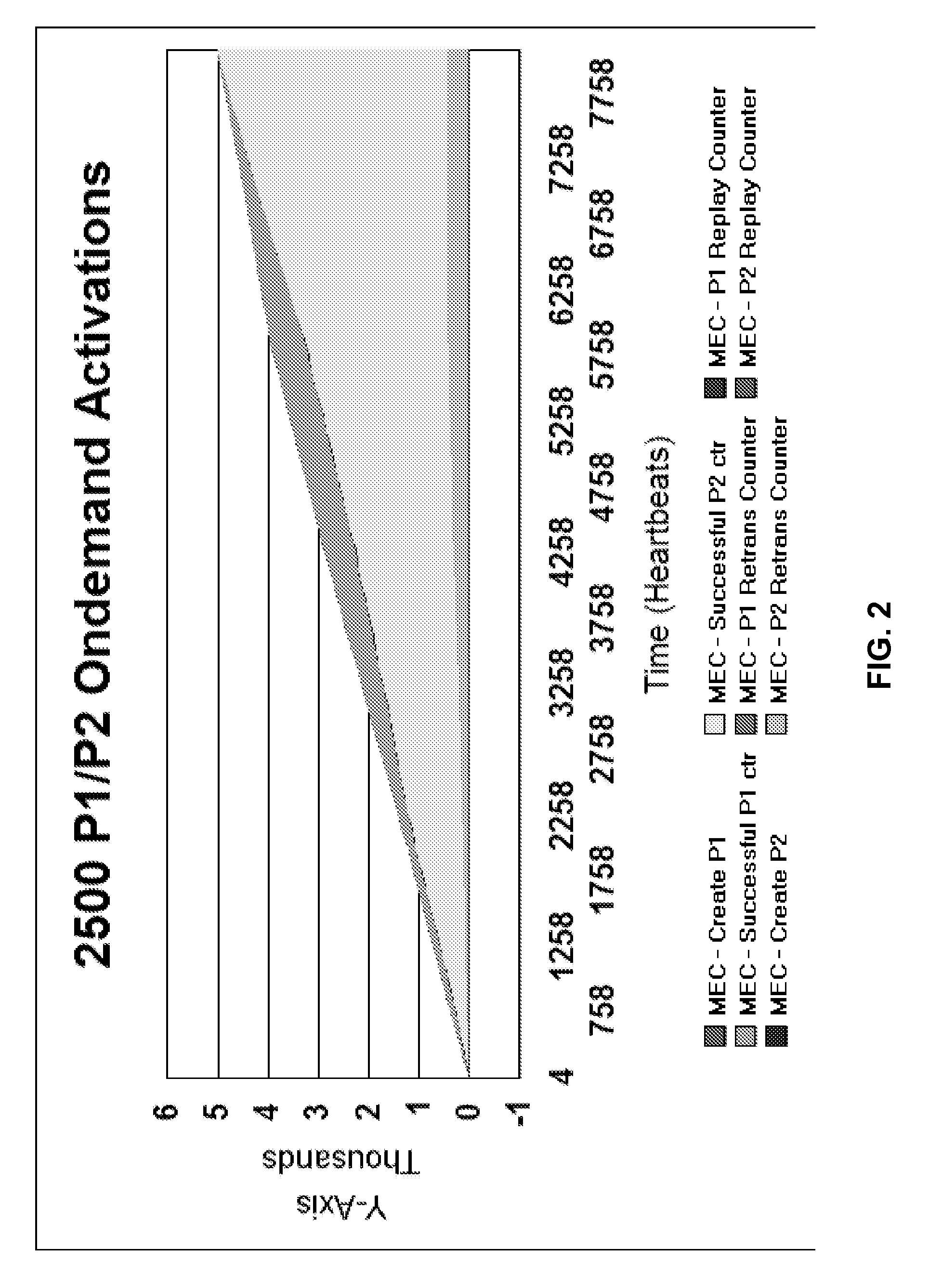
Patents
Literature
166 results about "Internet Key Exchange" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
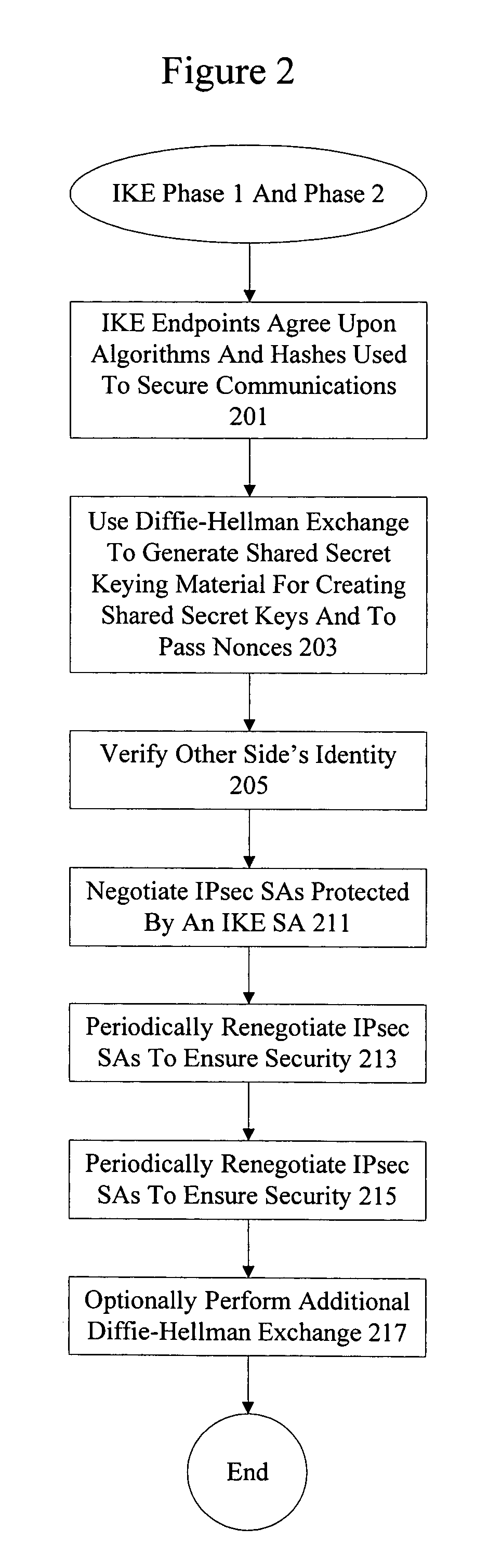
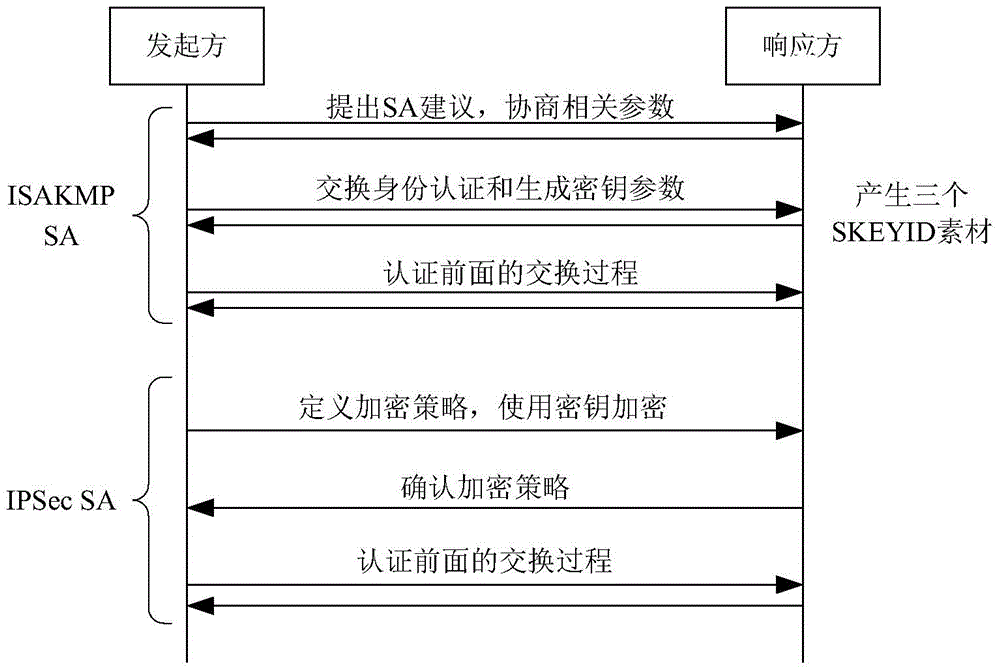
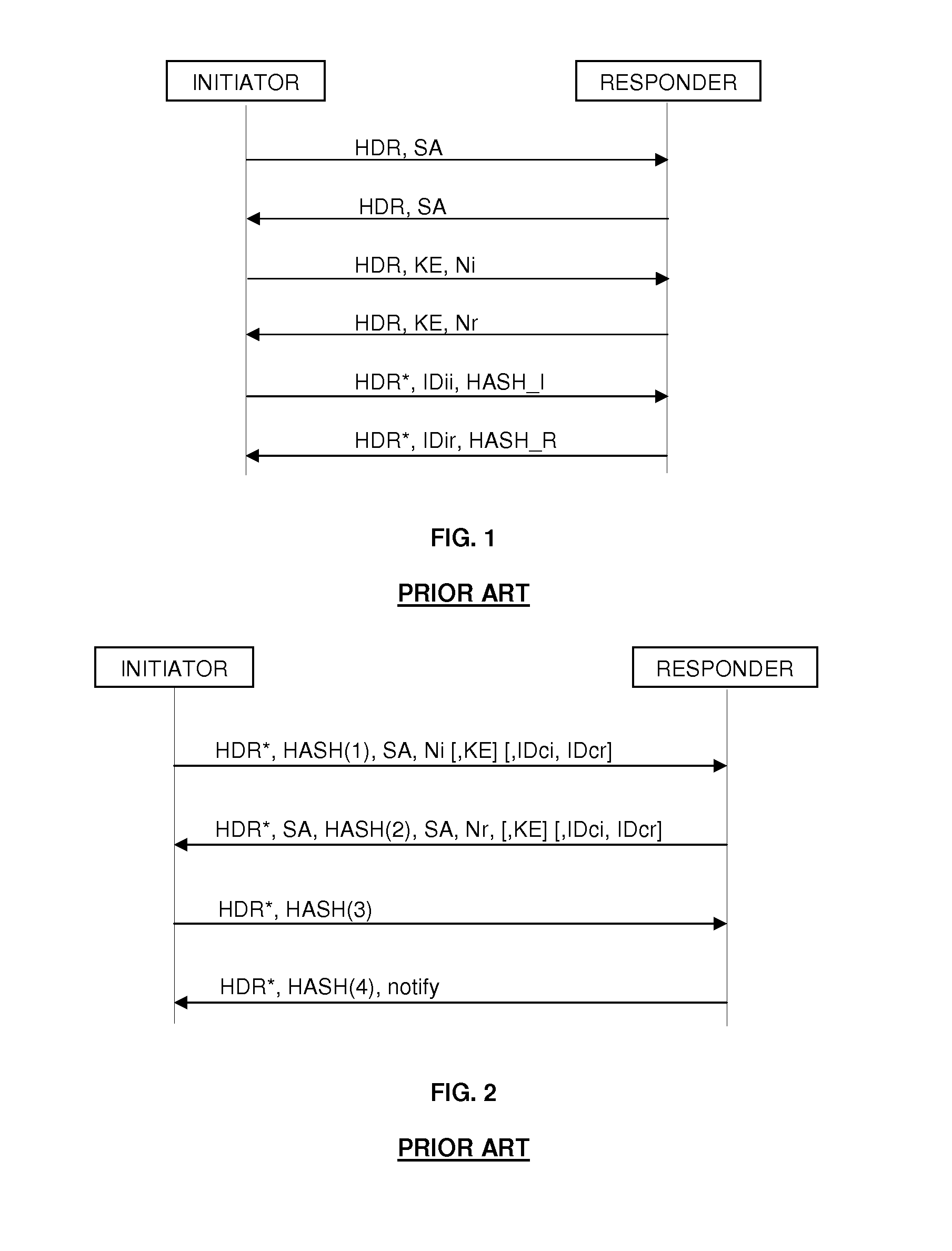
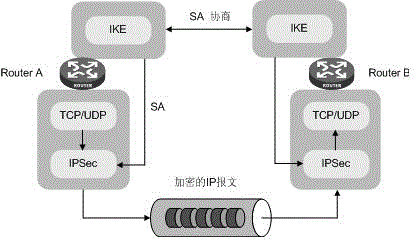
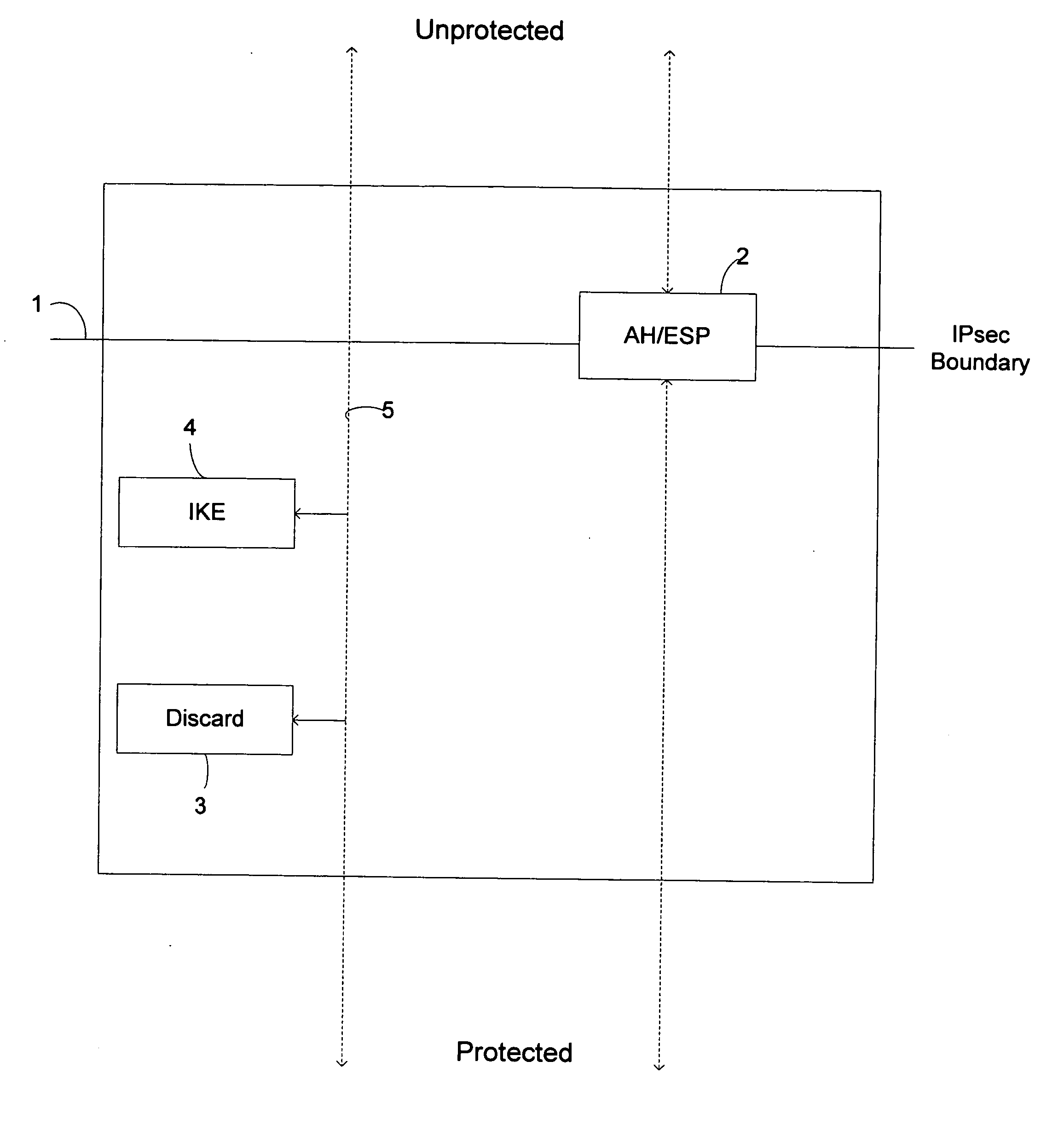
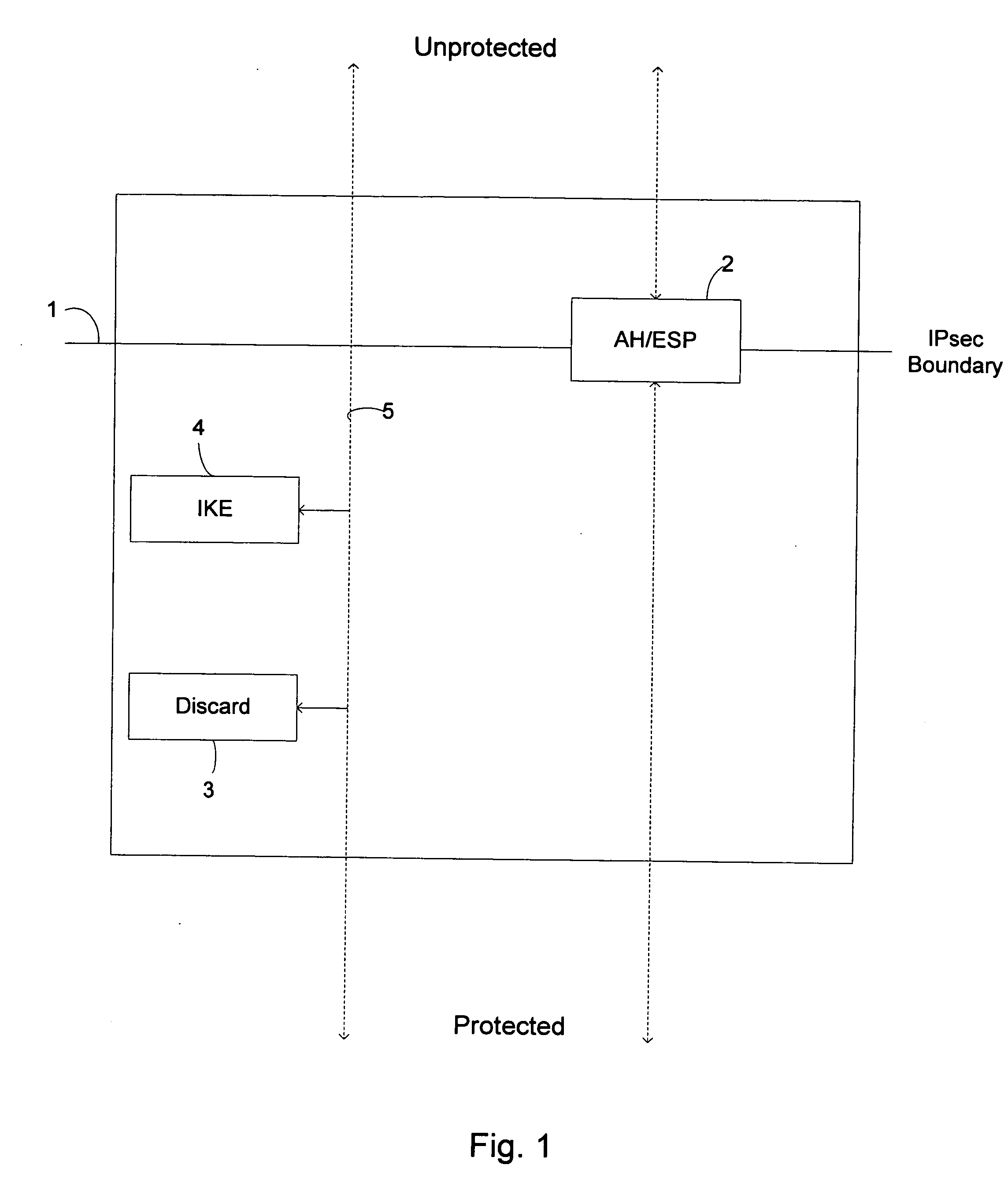
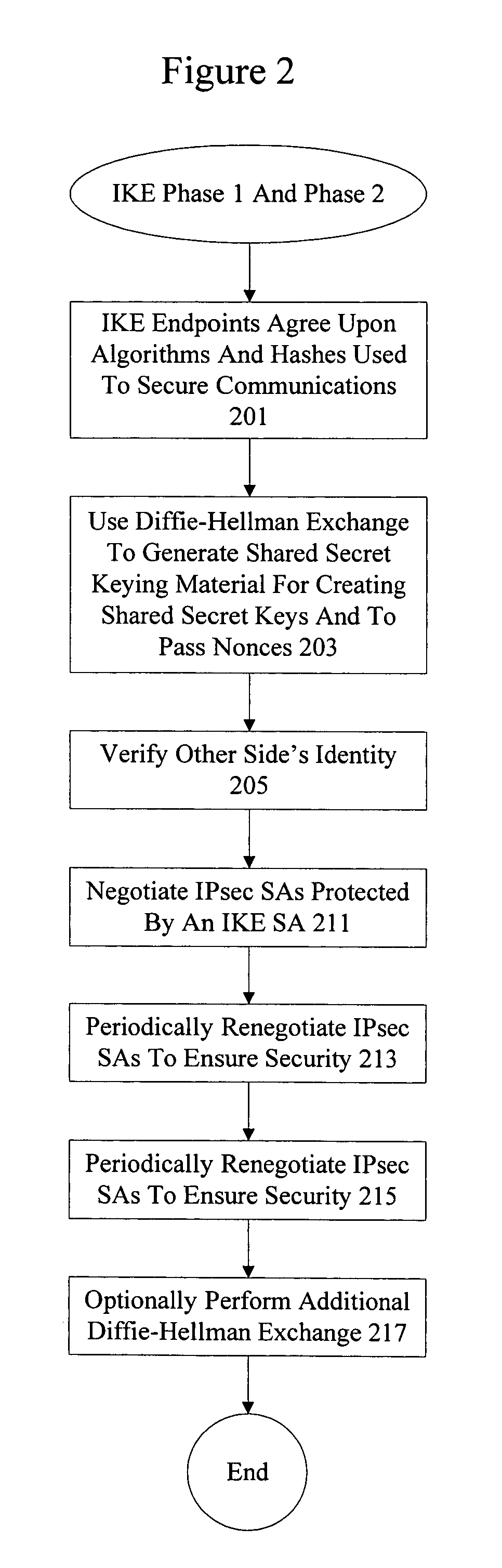
In computing, Internet Key Exchange (IKE, sometimes IKEv1 or IKEv2, depending on version) is the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec protocol suite. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and ISAKMP. IKE uses X.509 certificates for authentication ‒ either pre-shared or distributed using DNS (preferably with DNSSEC) ‒ and a Diffie–Hellman key exchange to set up a shared session secret from which cryptographic keys are derived. In addition, a security policy for every peer which will connect must be manually maintained.
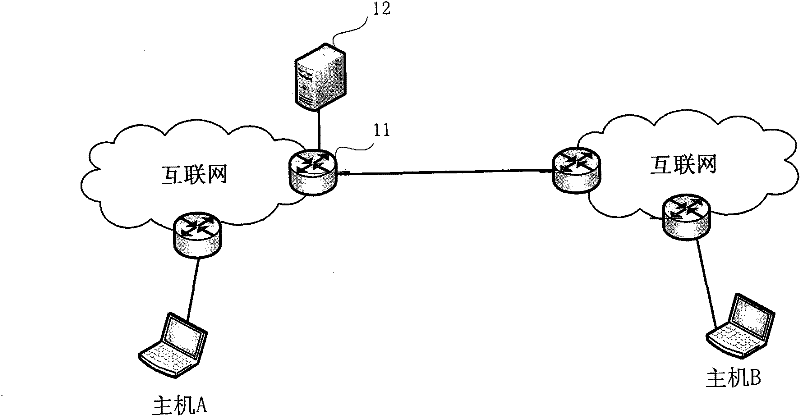
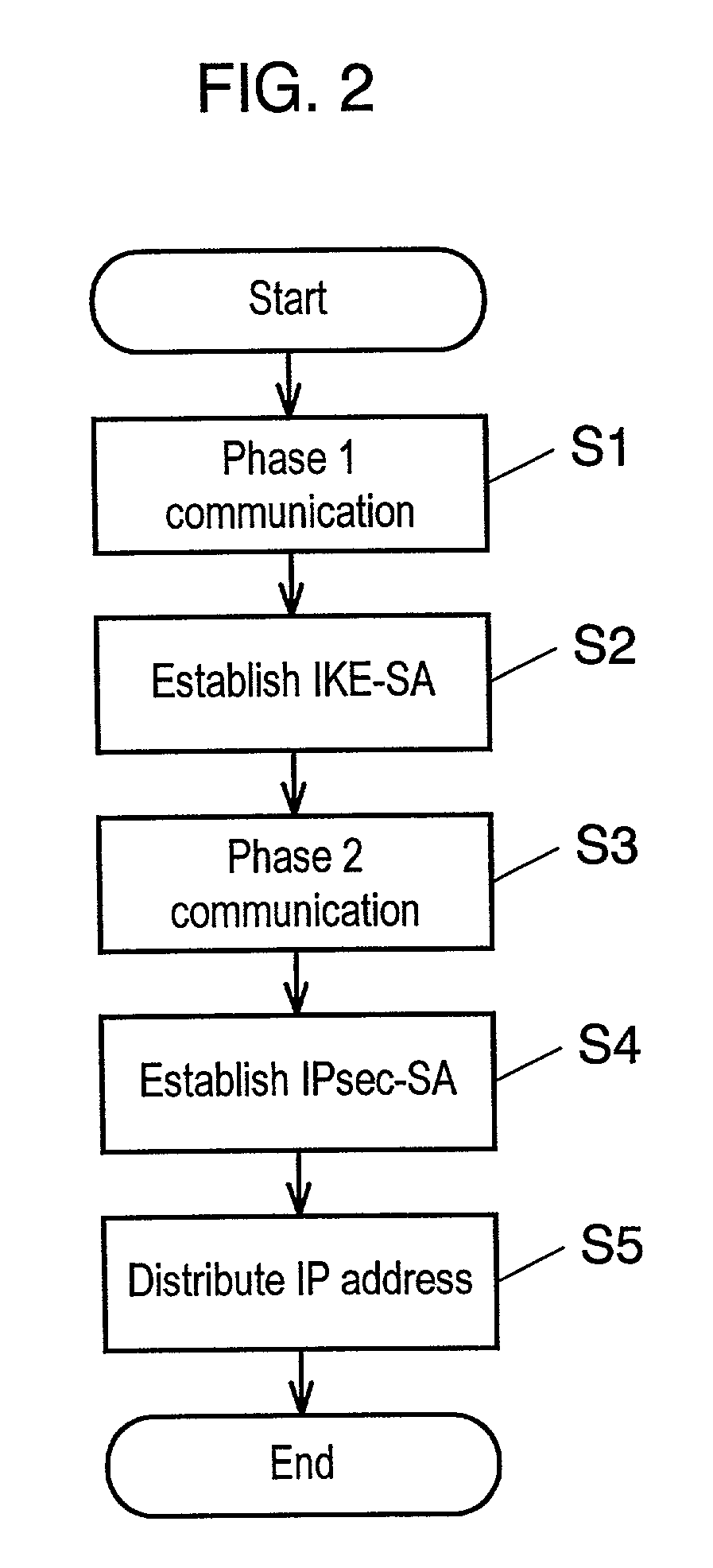
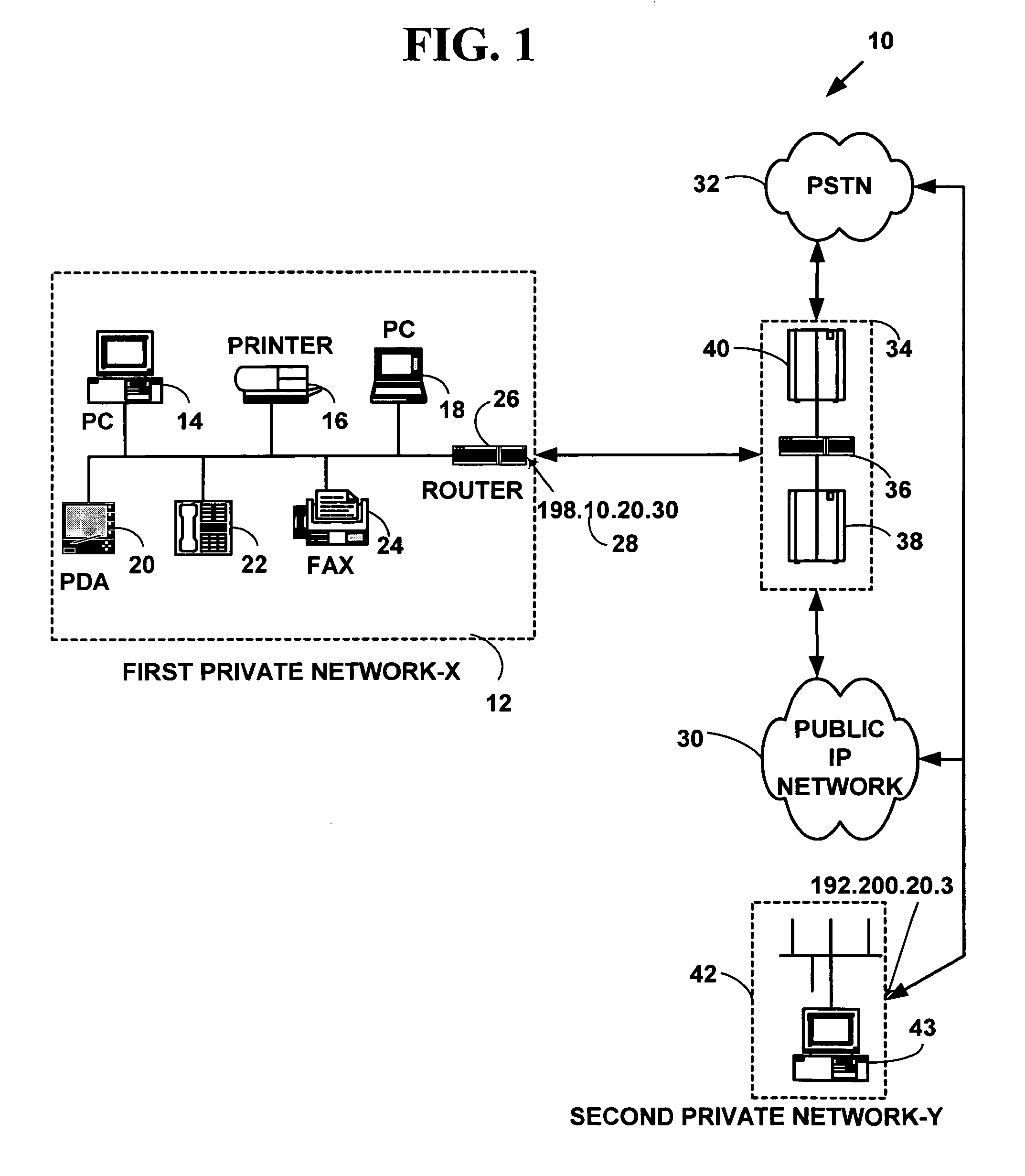
Establishing consistent, end-to-end protection for a user datagram
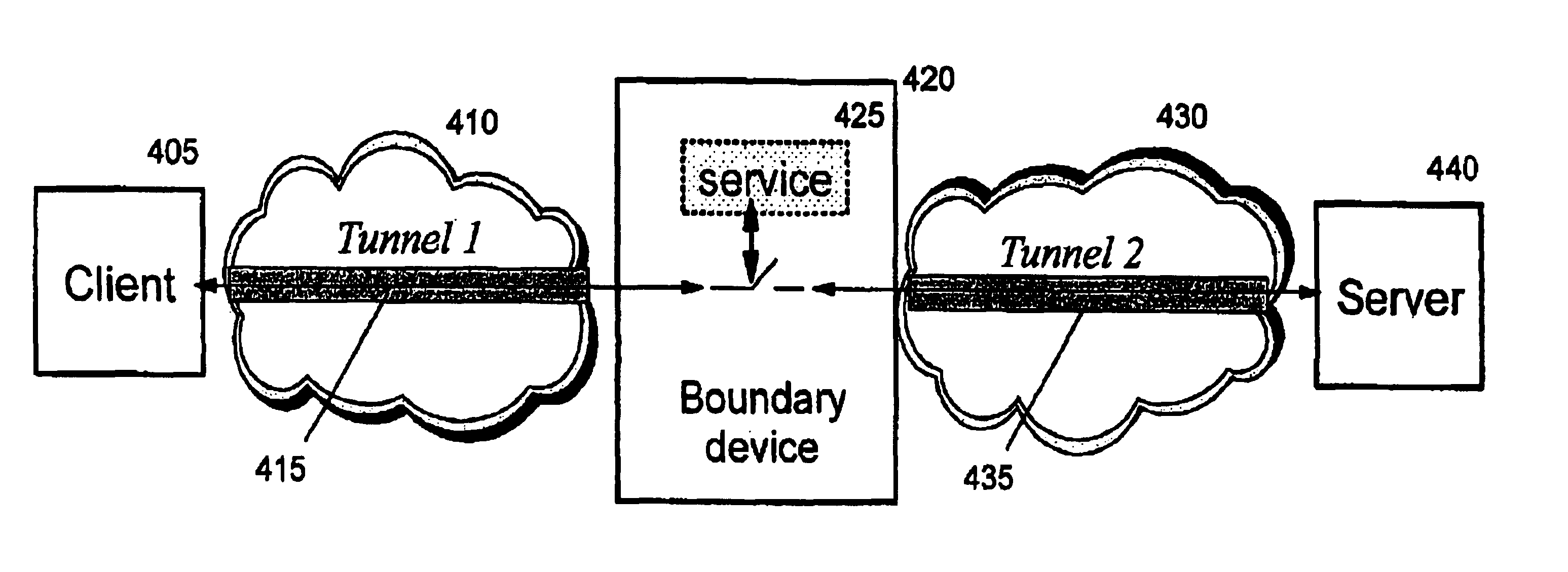
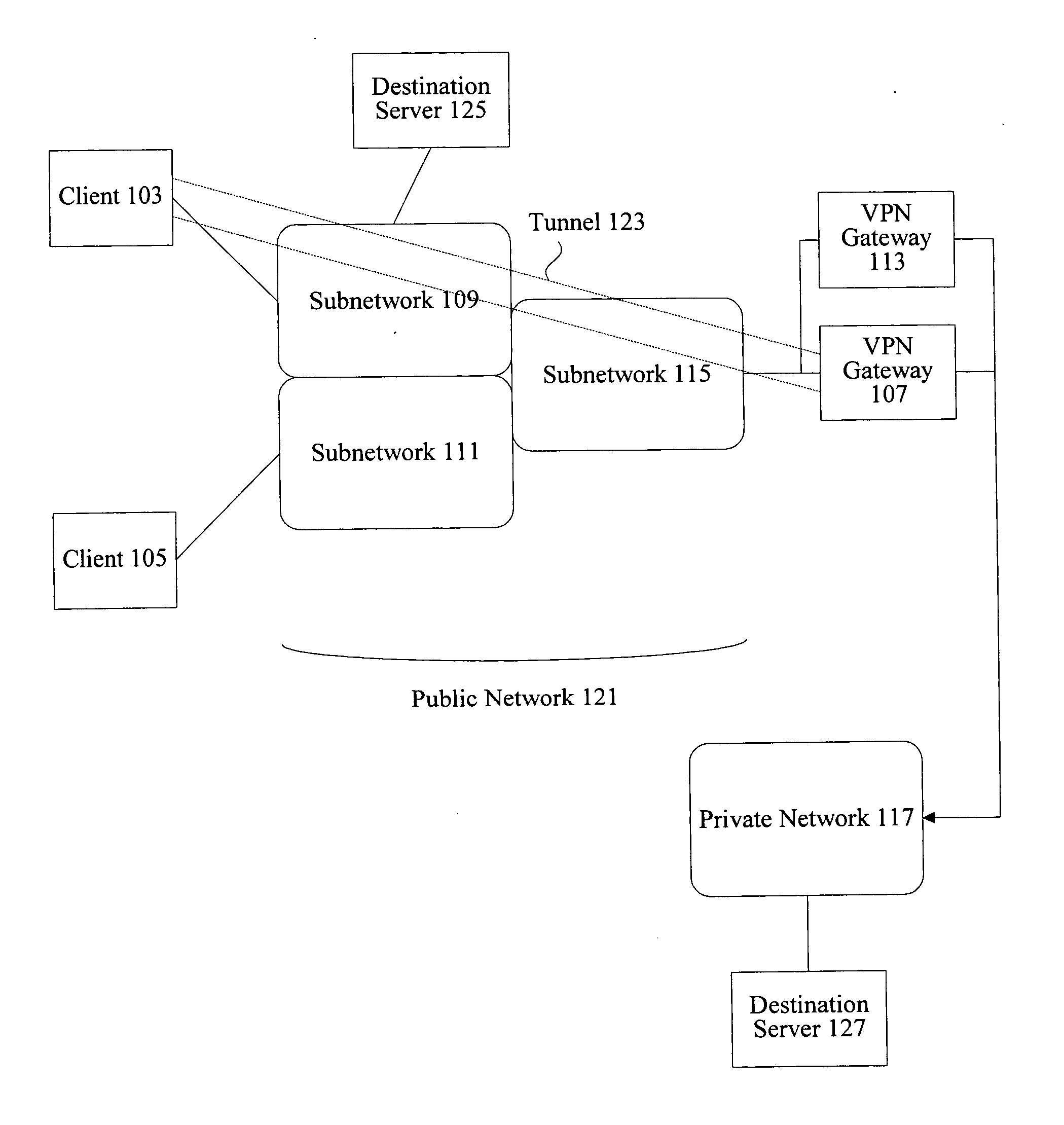
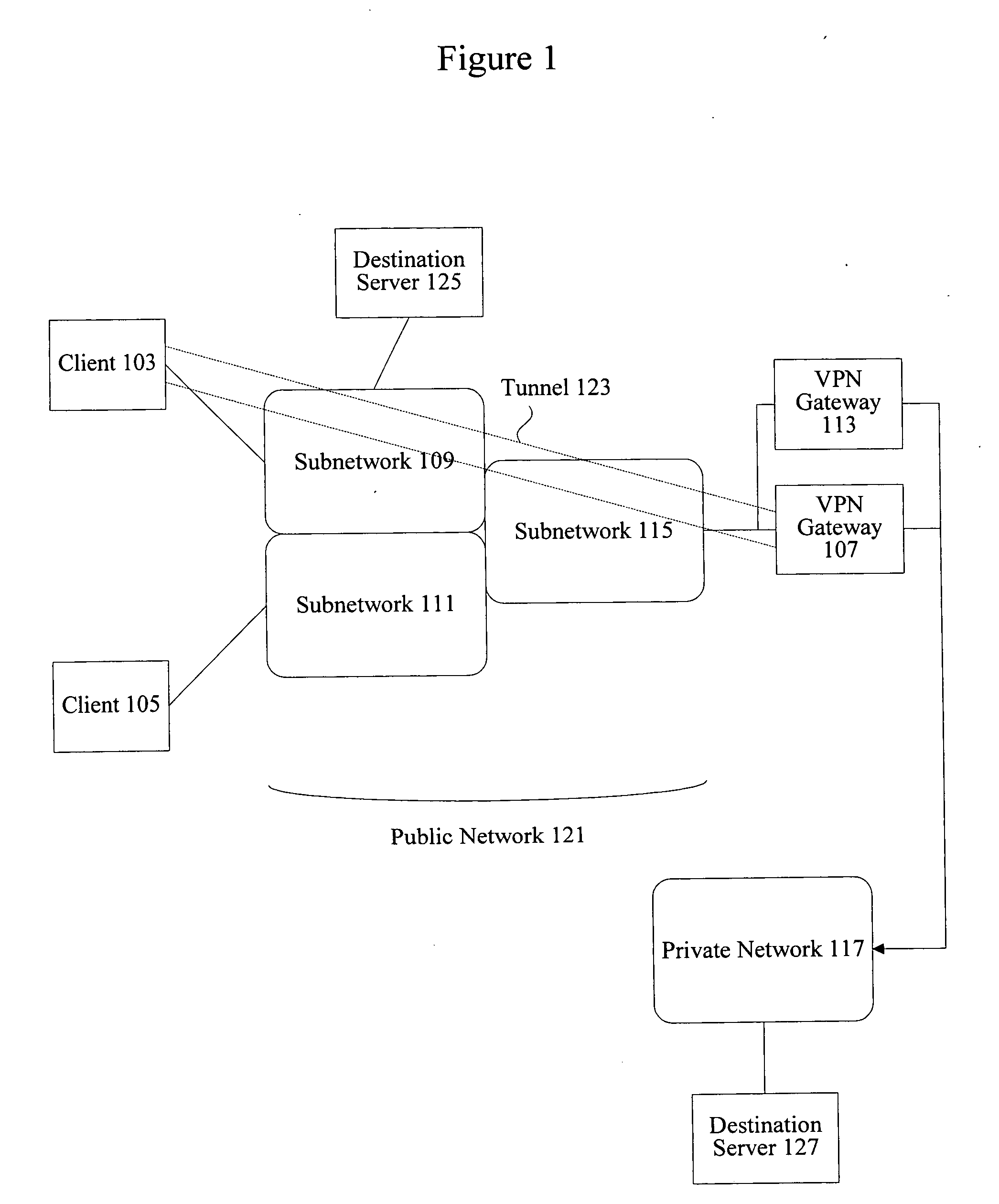
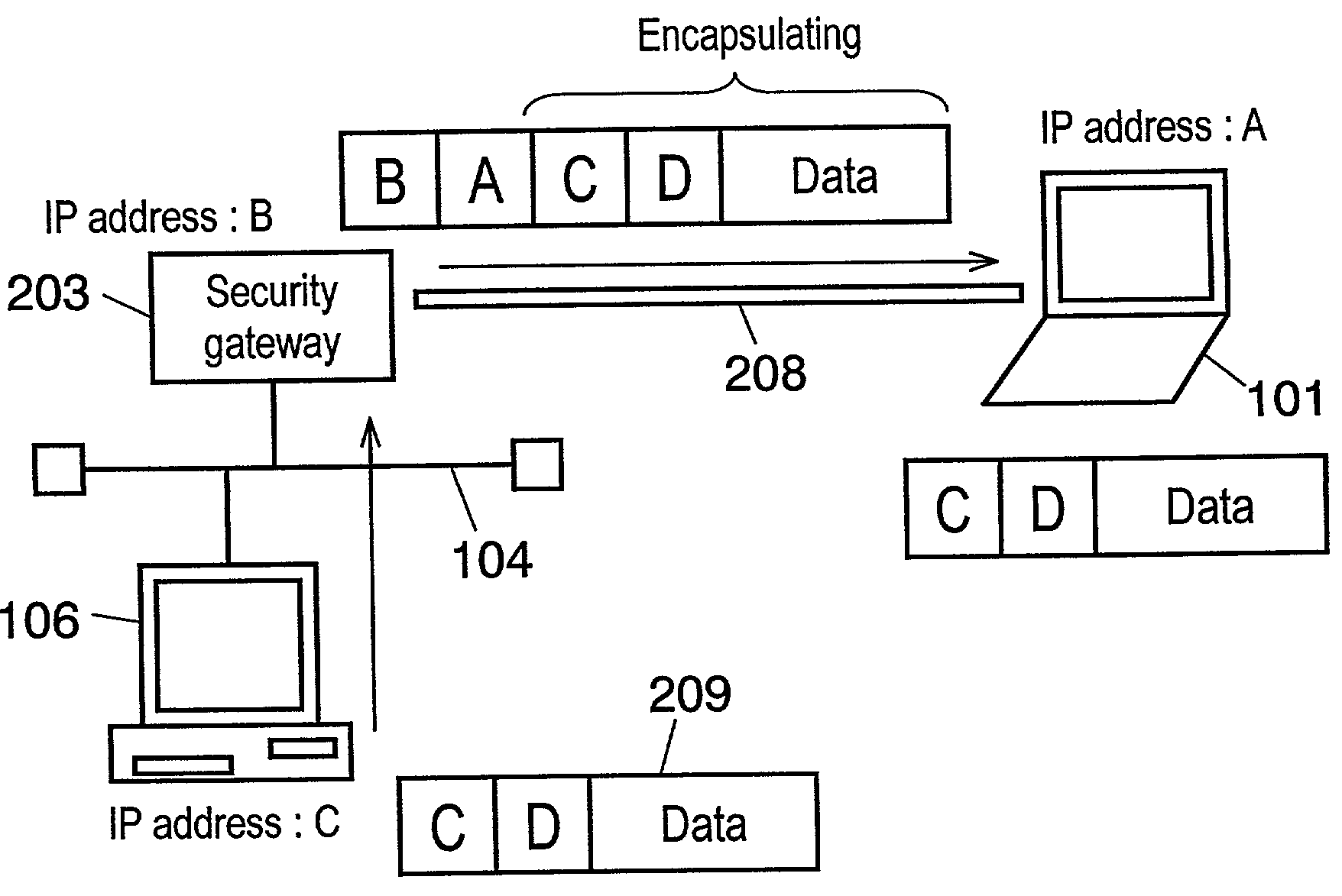
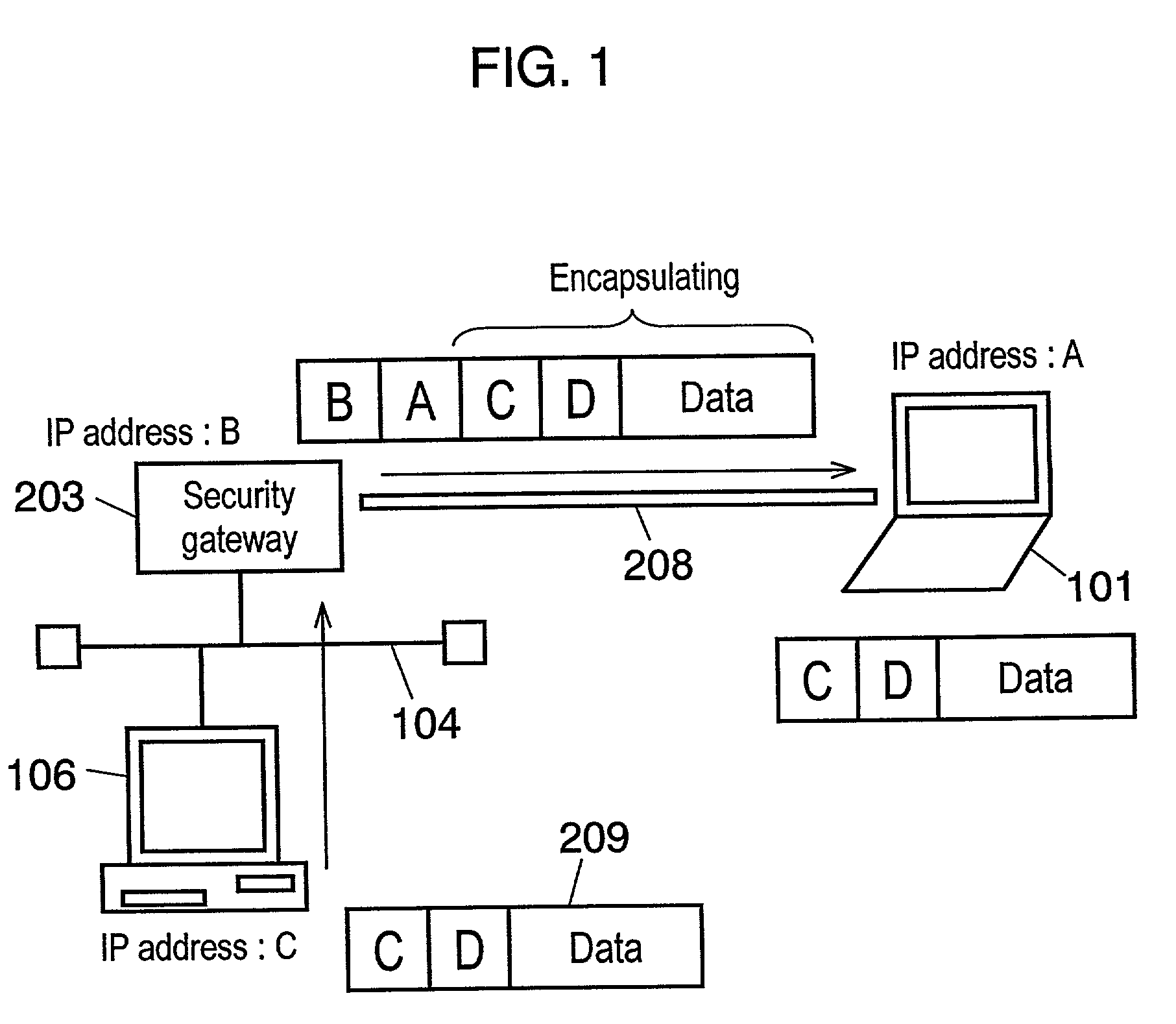
A method, system, and computer program product for providing consistent, end-to-end protection within a computer network for user datagrams (i.e. packets) traveling through the network. The network may comprise network segments that are conventionally assumed to be secure (such as those found in a corporate intranet) as well as network segments in non-secure networks (such as the public Internet or corporate extranets). Because security breaches may in fact happen in any network segment when datagrams are unprotected, the present invention discloses a technique for protecting datagrams throughout the entire network path by establishing cascaded tunnels. The datagrams may be exposed in cleartext at the endpoints of each tunnel, thereby enabling security gateways to perform services that require content inspection (such as network address translation, access control and authorization, and so forth). The preferred embodiment is used with the “IPSec” (Internet Protocol Security Protocol) and “IKE” (Internet Key Exchange) protocols, thus providing a standards-based solution.
Owner:IBM CORP
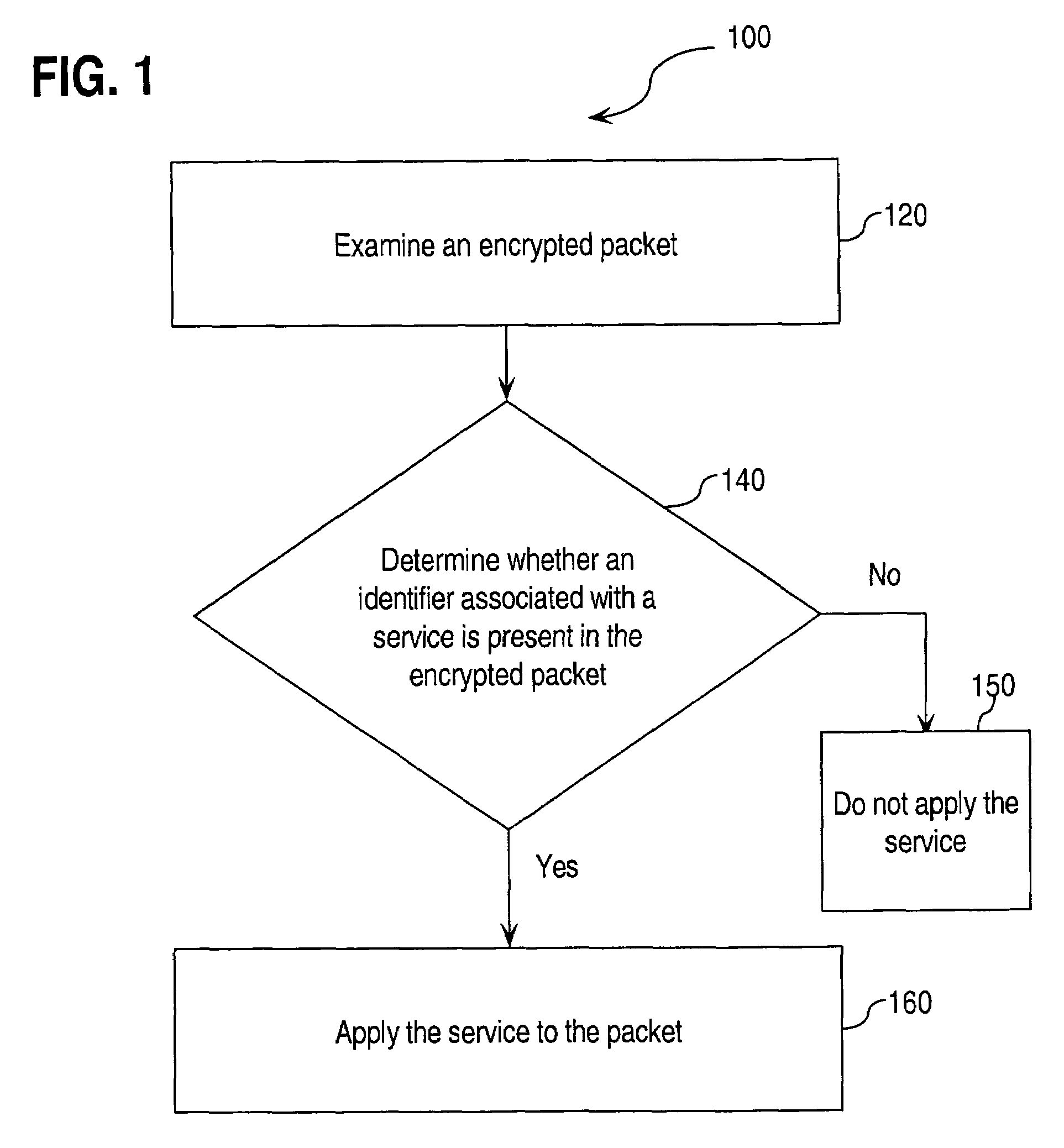
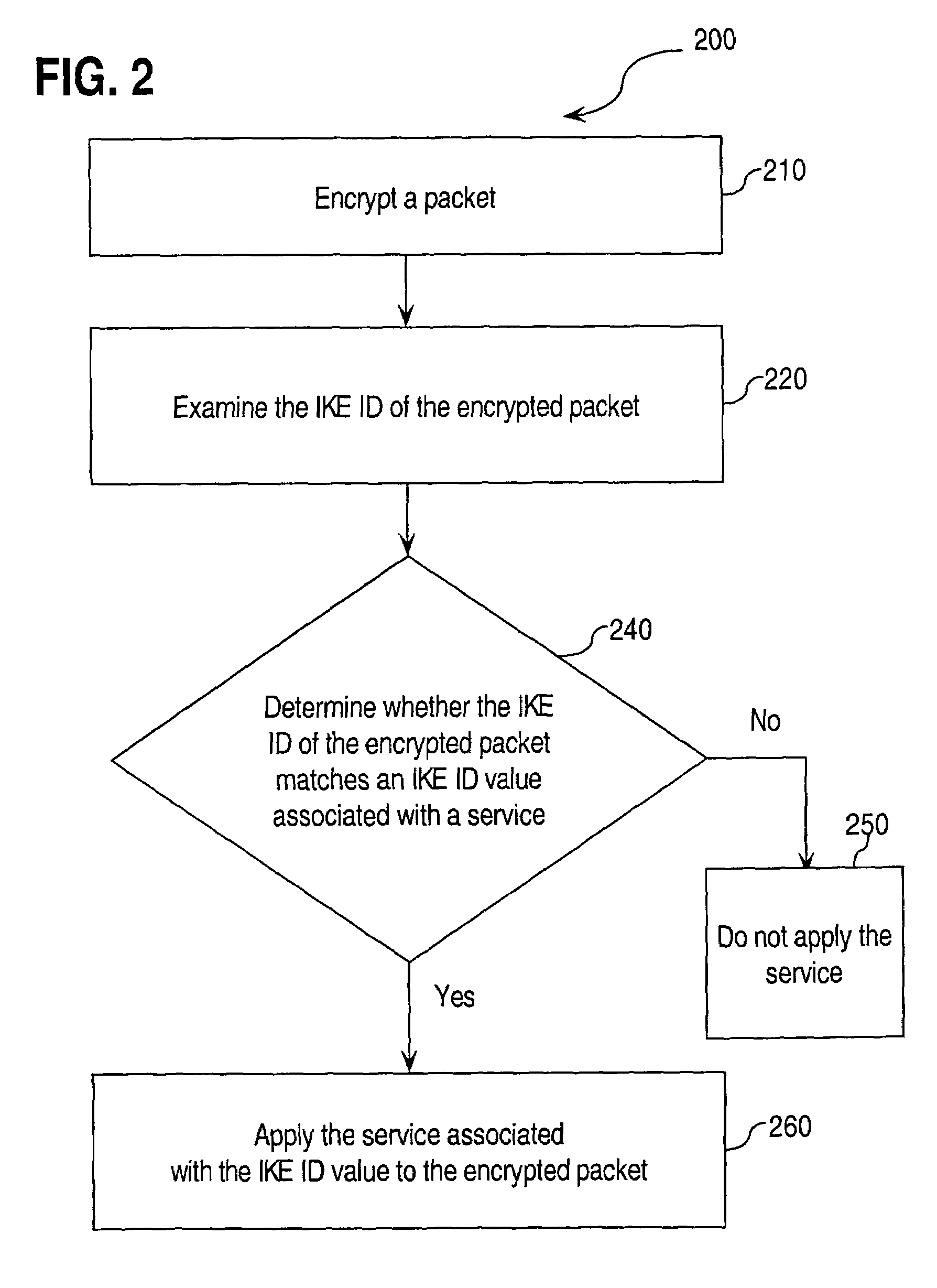
Approaches for applying service policies to encrypted packets
InactiveUS7562213B1Avoiding and reducing relianceSecuring communicationKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
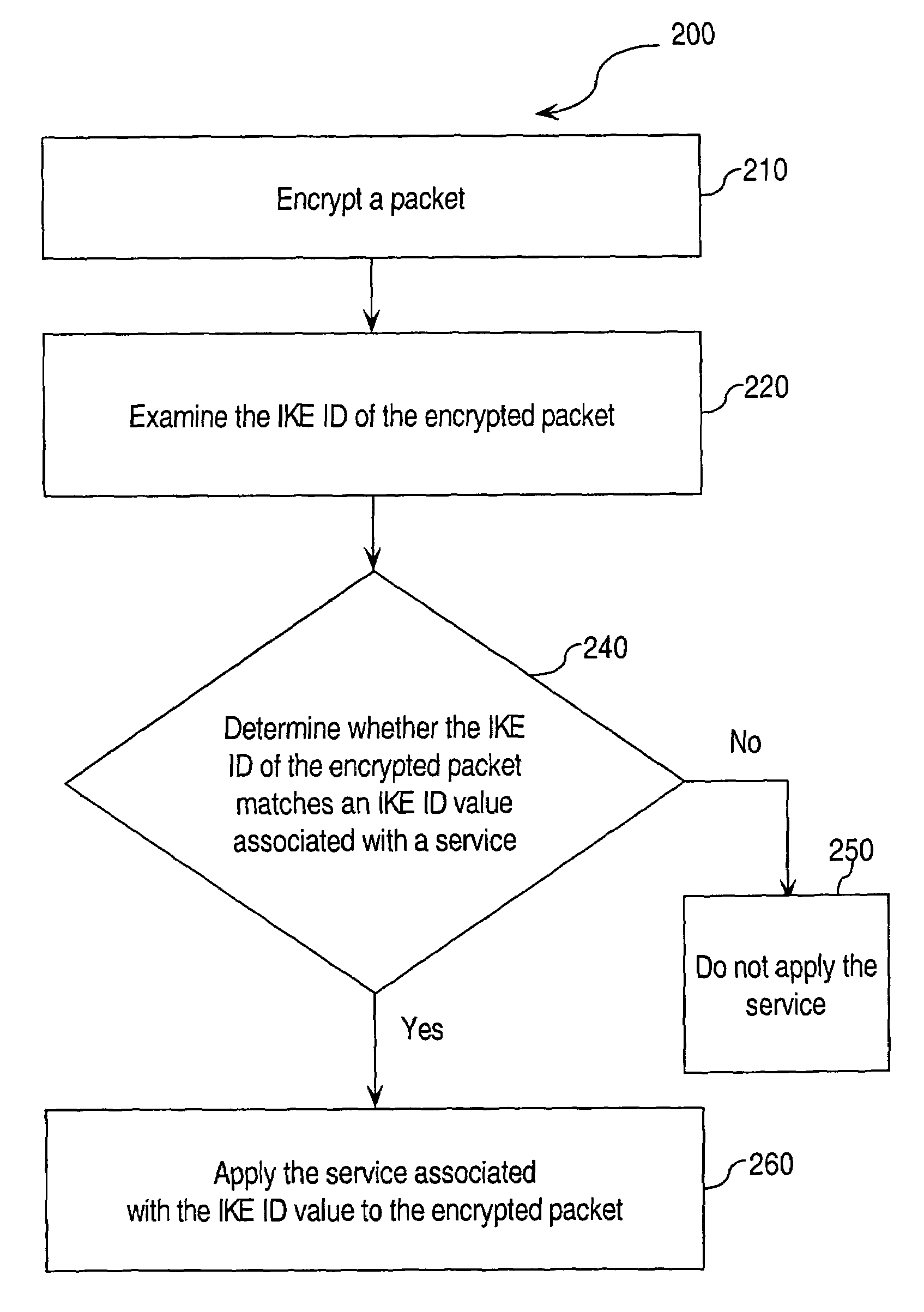
Approaches for applying service polices to encrypted packets are disclosed. One approach comprises examining an encrypted packet, determining whether an identifier associated with a service is present in an encrypted packet, and if it is determined that the identifier is present in the encrypted packet, applying the service to the encrypted packet. In an embodiment, the identifier is the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) ID of the encrypted packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
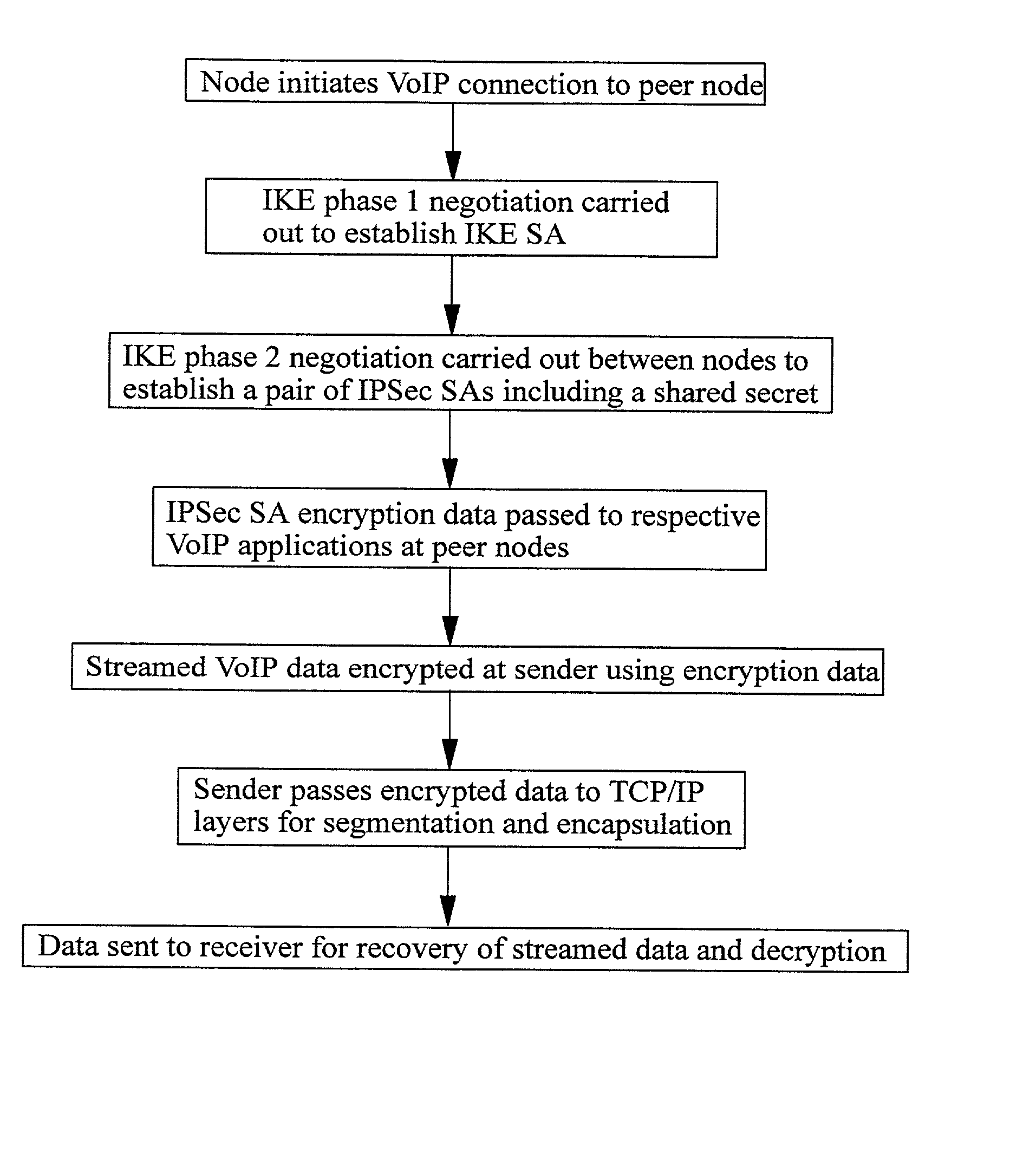
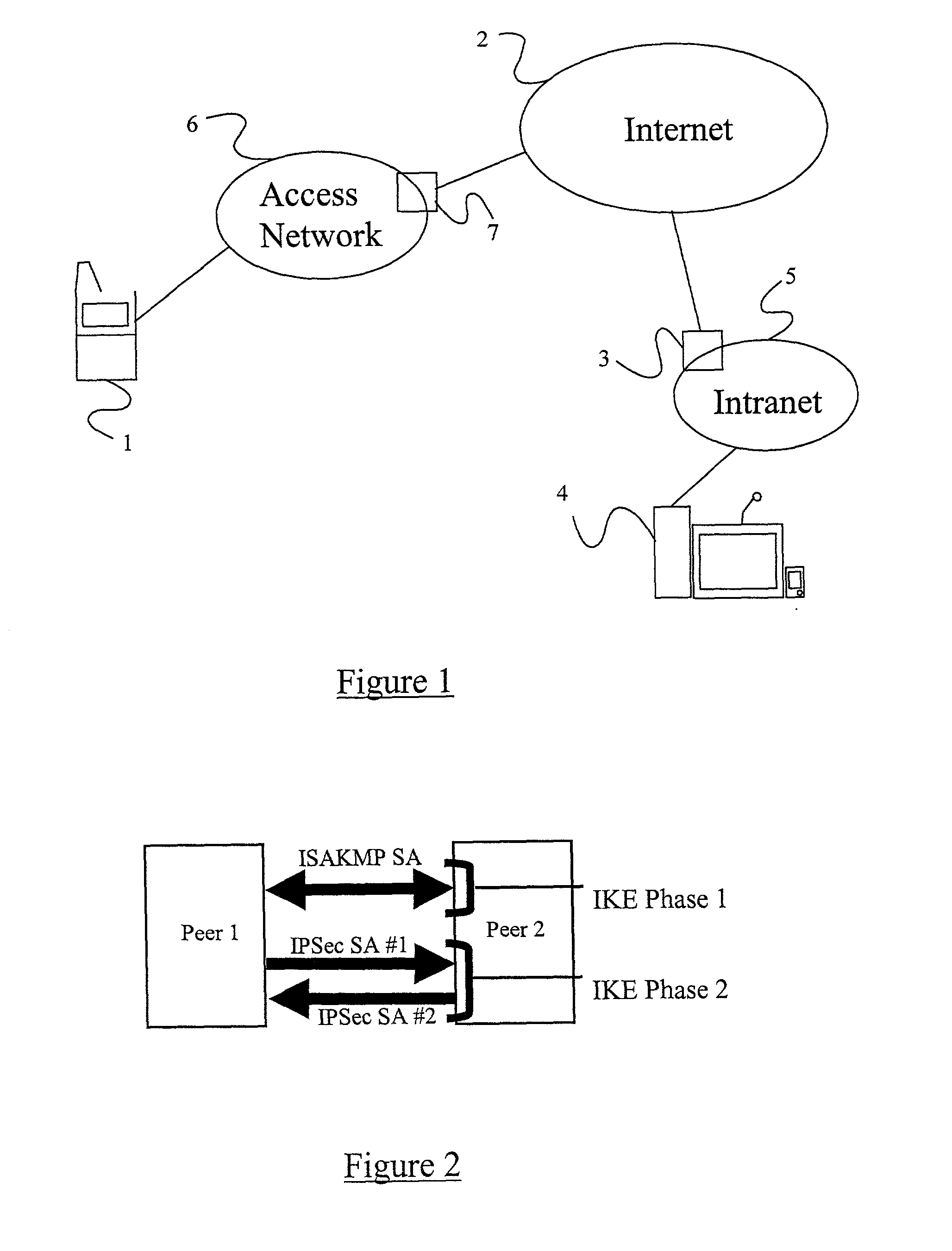
Securing Voice over IP traffic
A method of sending streamed data over an IP network from a first node 1 to a second node 4, the method comprising using Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to establish an IKE security association (SA) between the first and second nodes 1,4. A shared secret is established between the first and second nodes using the IKE SA, and the streamed data encrypted at the first node 1 with a cipher using the shared secret or a key derived using the shared secret. IP datagrams are constructed containing in their payload, segments of the encrypted streamed data, the datagrams not including an IPSec header or headers. The IP datagrams are then sent from the first node 1 to the second node 4.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for improved network security
InactiveUS6915437B2Improve performanceImprove securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTraffic capacityInternet Key Exchange
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for providing adaptive VPN to enable different security levels in virtual private networks (VPNs)
ActiveUS7478427B2Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableIp address
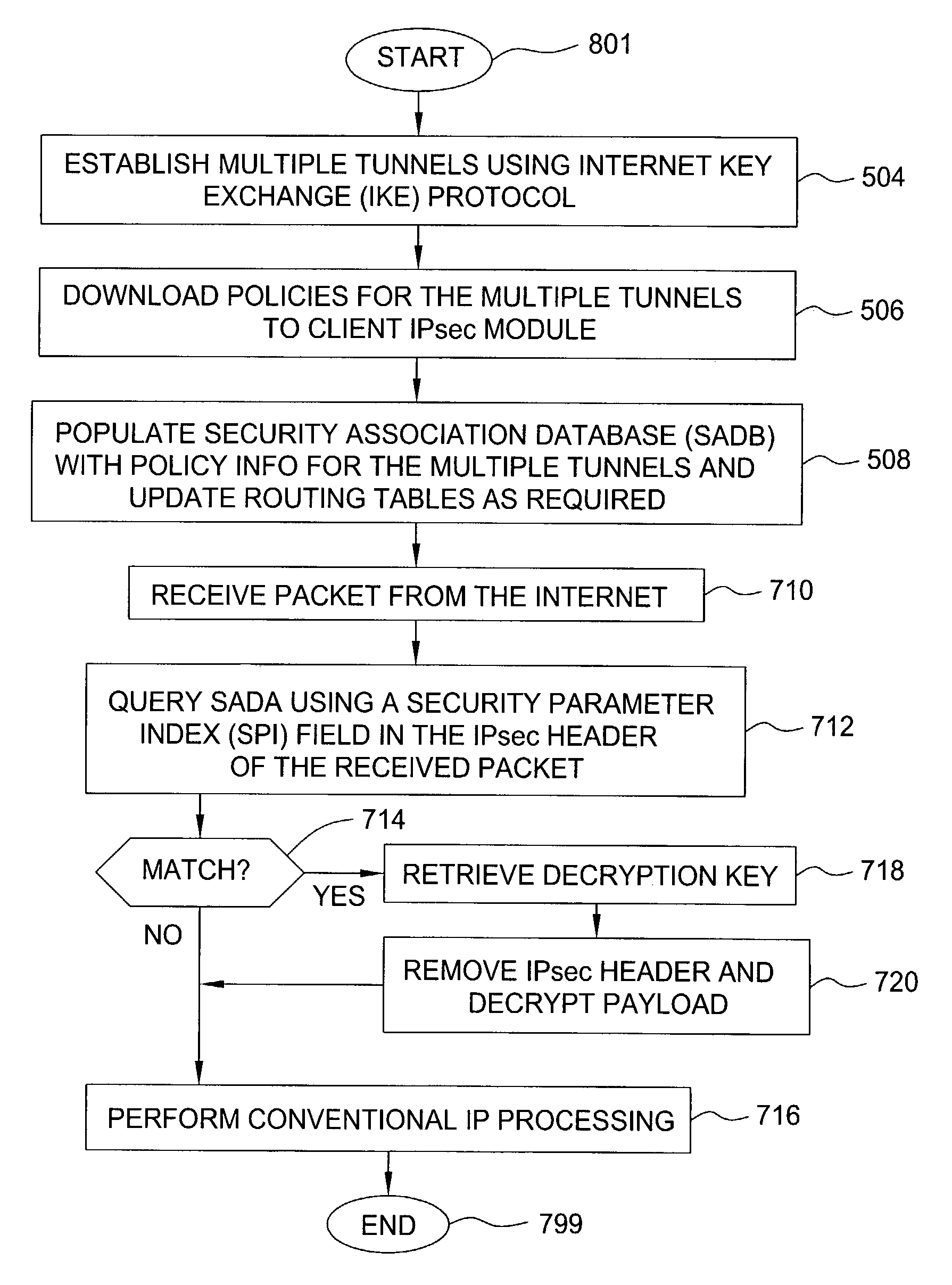
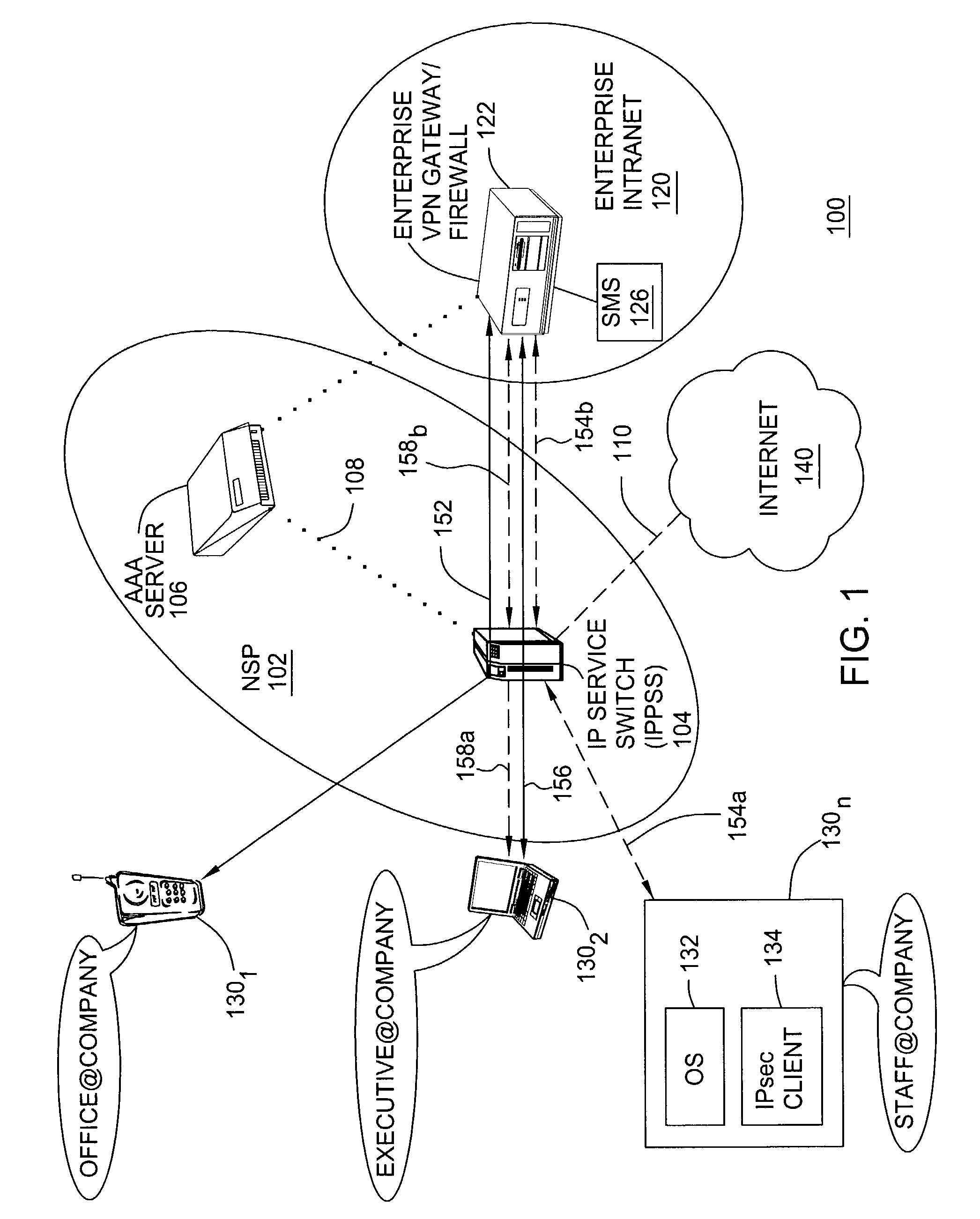
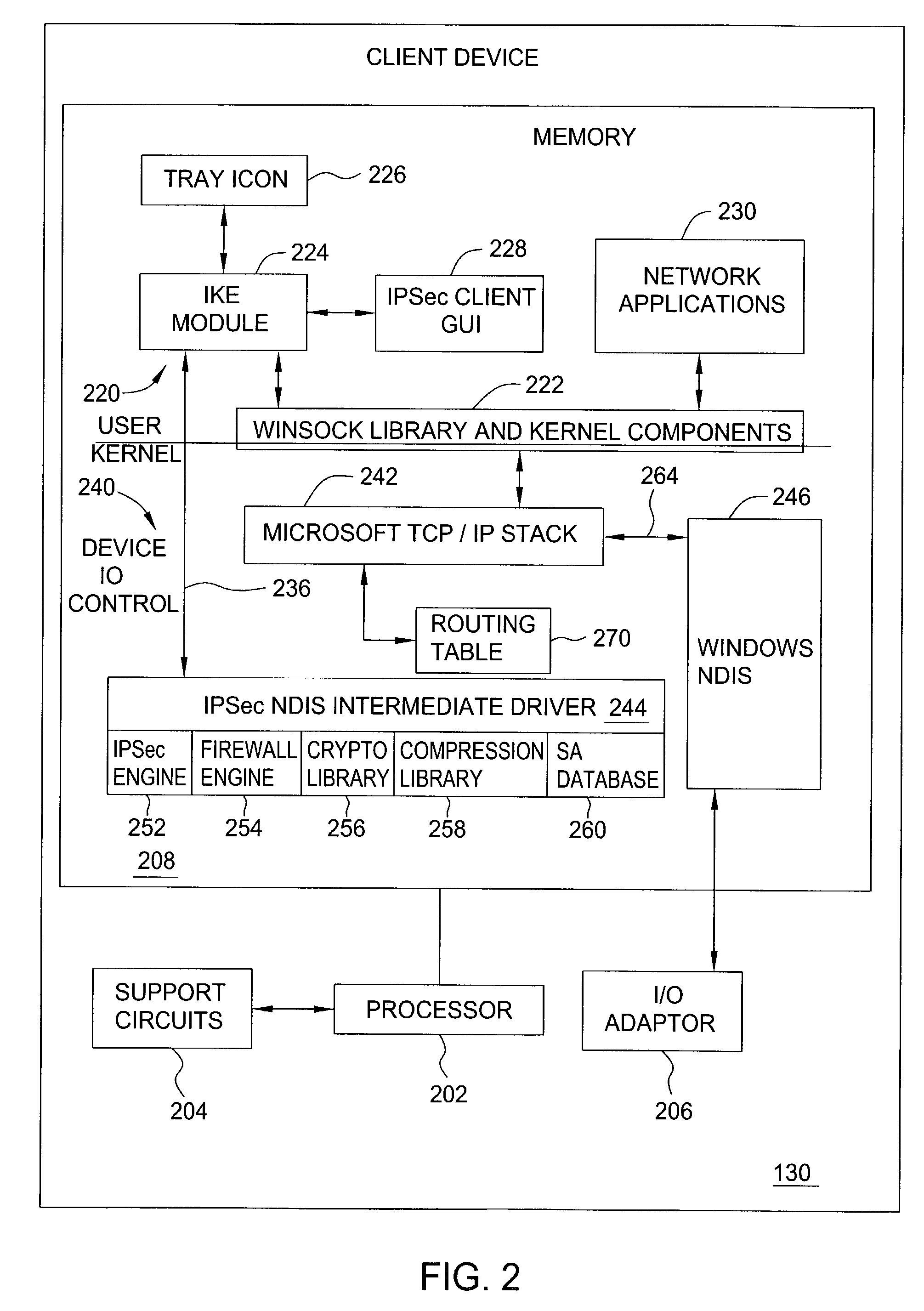
A method and apparatus for providing at least two virtual private network VPN tunnels from a client device in a VPN network having an enterprise gateway and a network VPN gateway. The method and apparatus includes a client device having an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) module for establishing the at least two tunnels using an IKE protocol wherein a first tunnel is an end-to-end VPN tunnel to the enterprise gateway, and a second tunnel is a network-based tunnel to the network VPN gateway. An IPsec Network Driver Interface interfaces with the IKE module, which includes a security authentication database (SADB) that stores downloaded enterprise security policies respectively for each of the at least two tunnels. A routing table stores IP addresses of local presences and hosts respectively associated with the at least two tunnels, whereby packets are routed over the at least two tunnels based on the downloaded policies.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
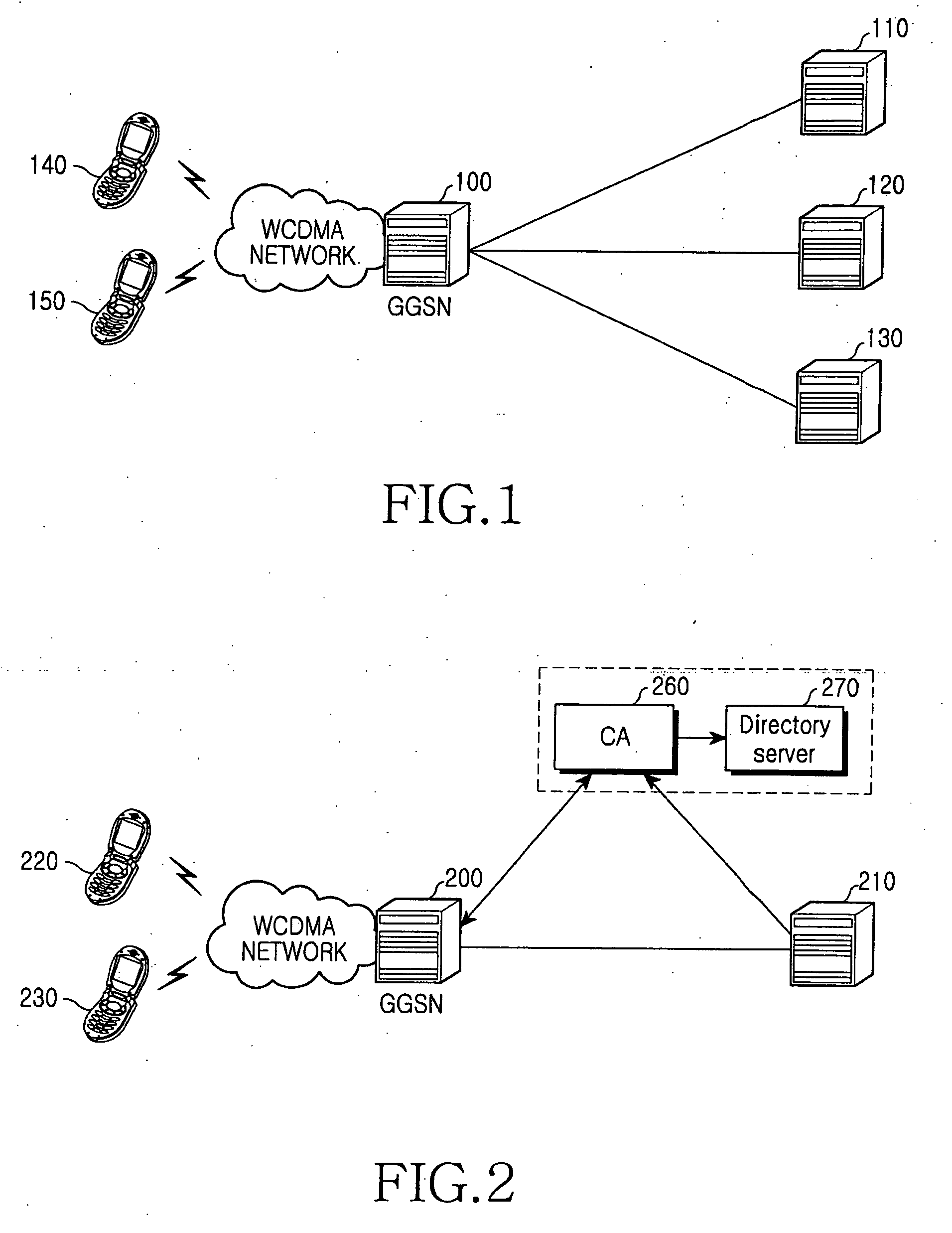
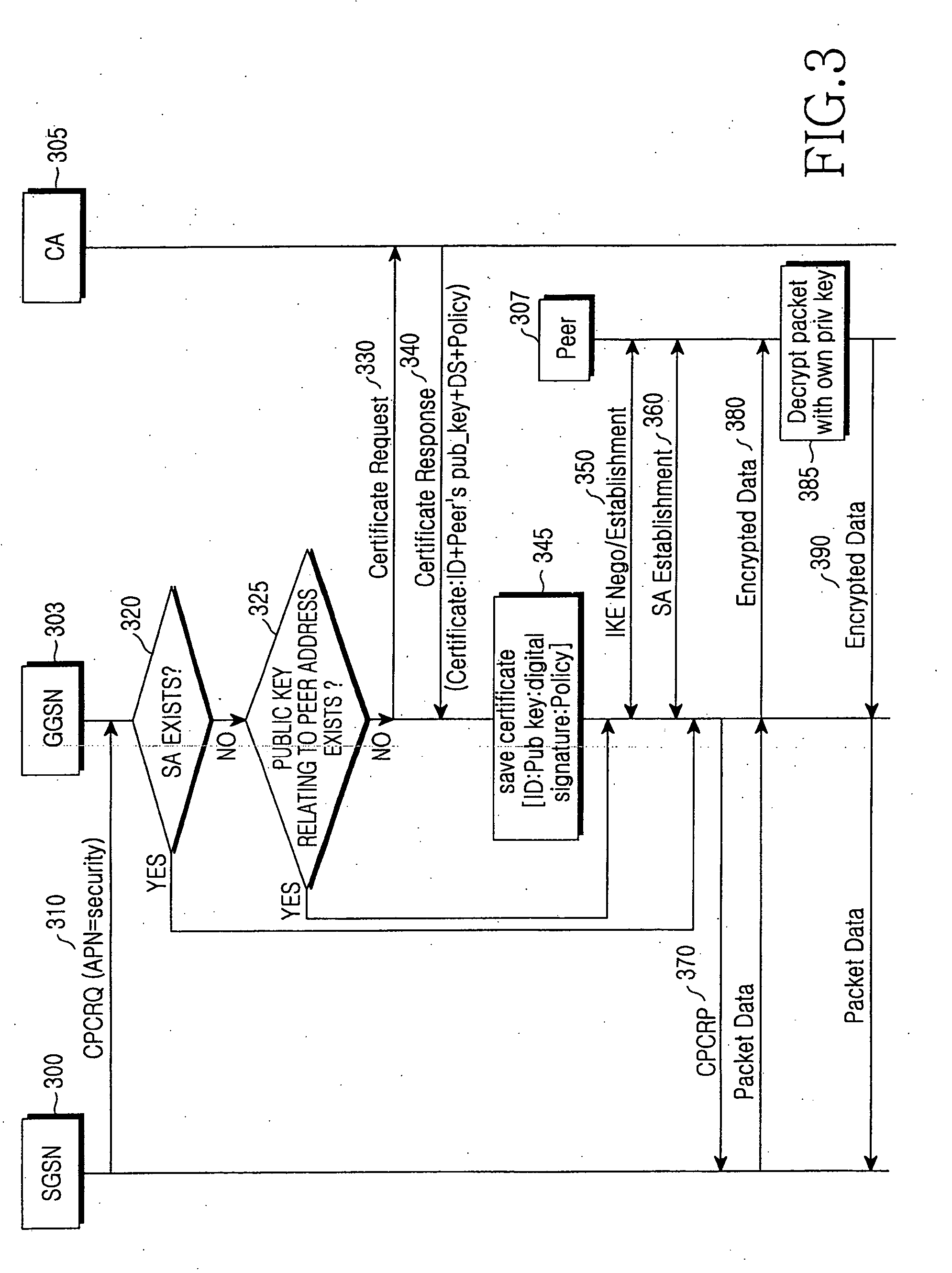
Method and apparatus for security of IP security tunnel using public key infrastructure in mobile communication network
InactiveUS20060105741A1Applied load reductionUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
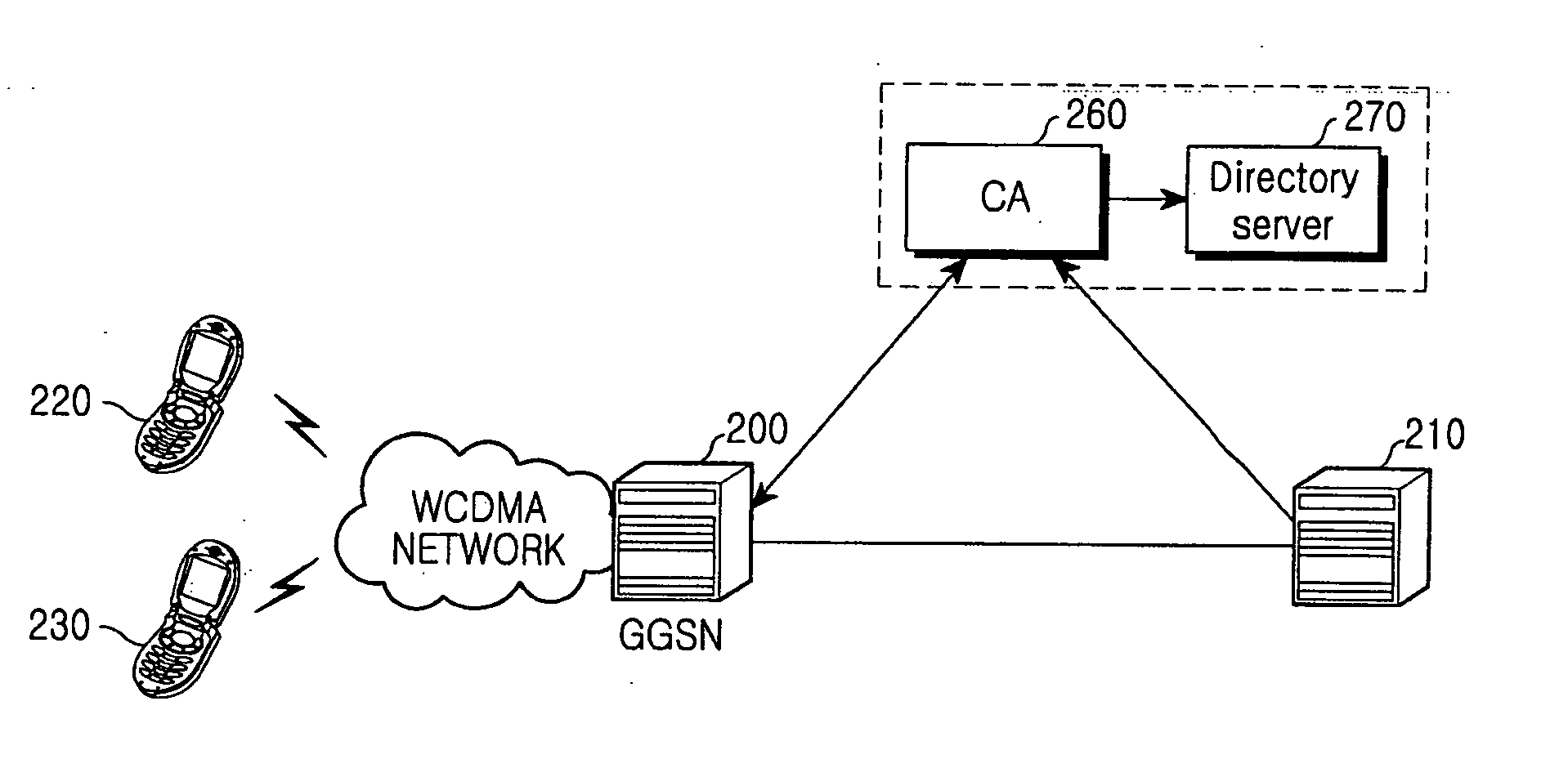
A method and apparatus is provided for security of an IP security tunnel using public key infrastructure, including the steps of receiving a request message which relates to a security service requested by a mobile node, determining if there is security association (SA) for the security service and determining if there is a public key related to a peer address when the SA does not exist, sending a certificate request message to a certificate authority (CA) when the public key does not exist and receiving a certificate response message which has a certificate that includes a public key. The method further includes the steps of performing an internet key exchange and SA establishment procedure with a peer corresponding to the peer address by using the certificate, completing the internet key exchange and the SA establishment, and encrypting a packet received from the mobile node, transmitting the encrypted packet to the peer, decrypting a packet received from the peer, and transmitting the decrypted packet to the mobile node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
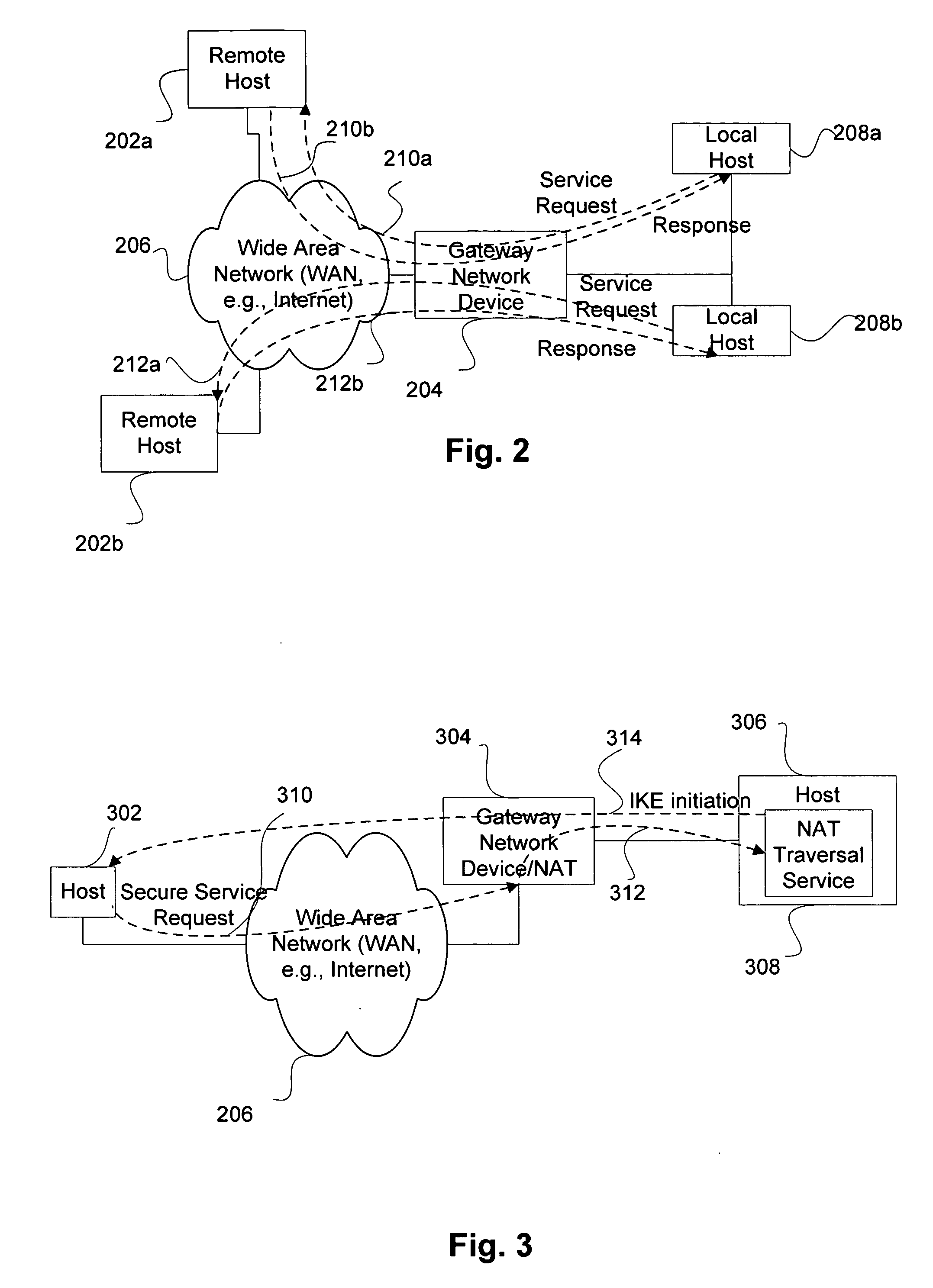
Service for NAT traversal using IPSEC
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for methods and apparatus for facilitating a secure connection between a first and a second node in a computer network where one or both of the nodes may or may not reside behind a network address translation (NAT) enabled gateway. Embodiments of the present invention provide a seamless integration by providing a uniform solution for establishing secure connections, such as IPSEC, between two nodes irrespective of whether they are behind a NAT-enabled gateway or not. In general, a gateway is operable to receive a request from a remote host for a secure connection to a local host that within the home network of the gateway. The gateway then forwards this received request to a NAT traversal service. The NAT traversal service receives the request and then automatically sends an initiation message to set up a secure session, e.g., performing authentication and exchanging keys. In a specific aspect, the setup data utilizes an IKE (Internet Key Exchange) initiation message that is sent to the originator of the request via the gateway. Upon receipt of this initiation message, the gateway is then able to set up a two way connection to allow other setup data to flow between the remote and local hosts to complete the setup session and then secure data to flow between the remote and local hosts in a secure communication session, such as in IPSec or VPN session.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
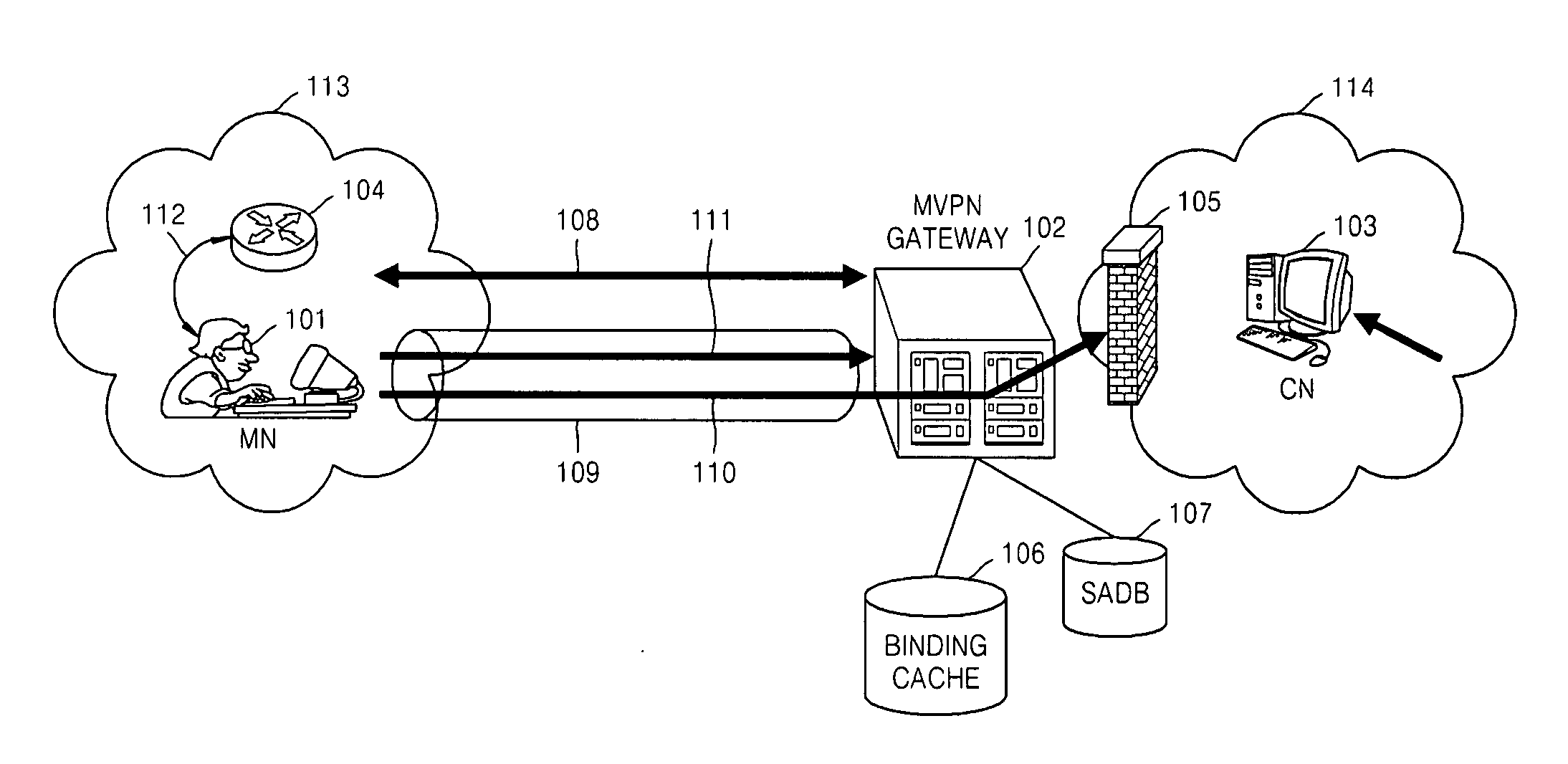
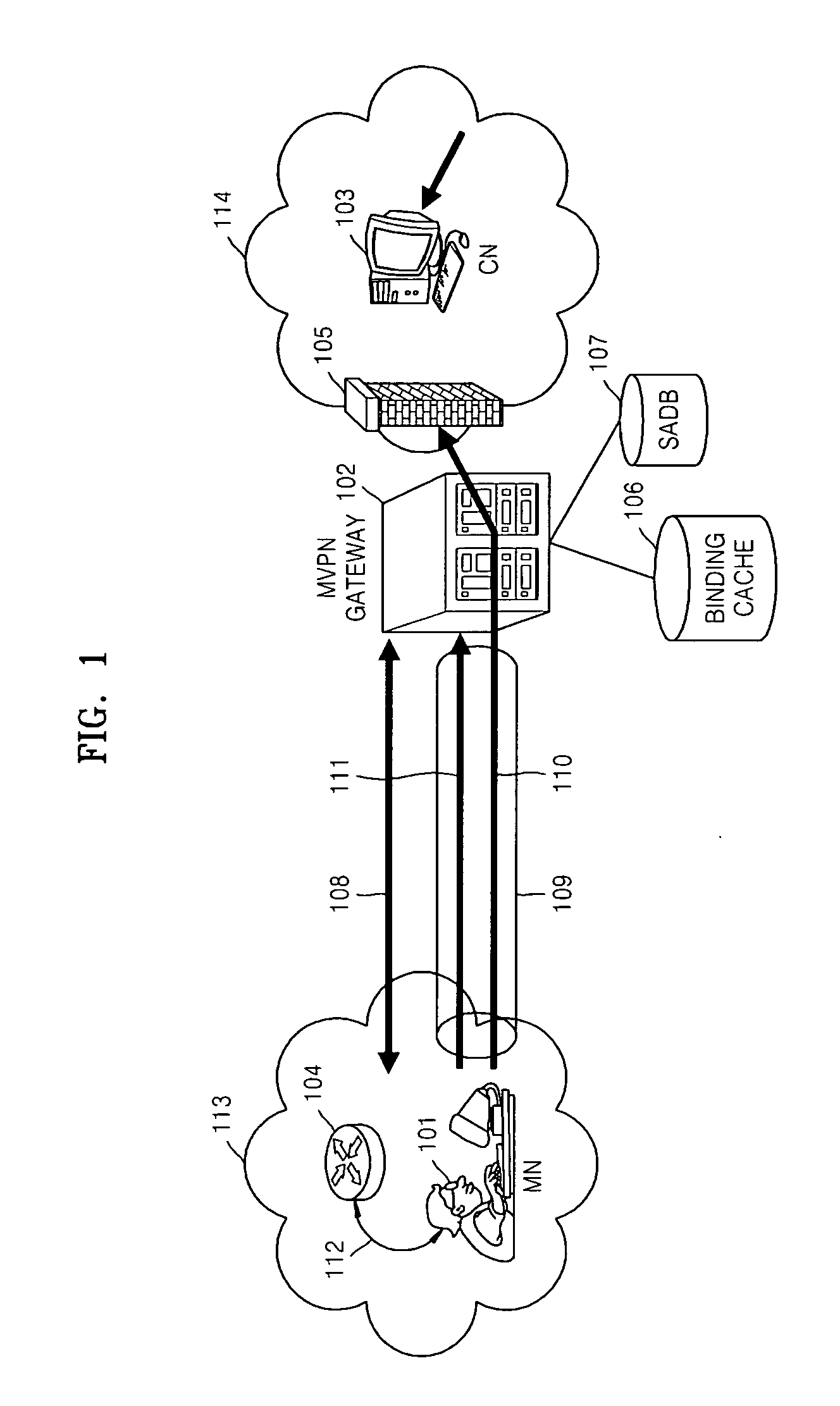
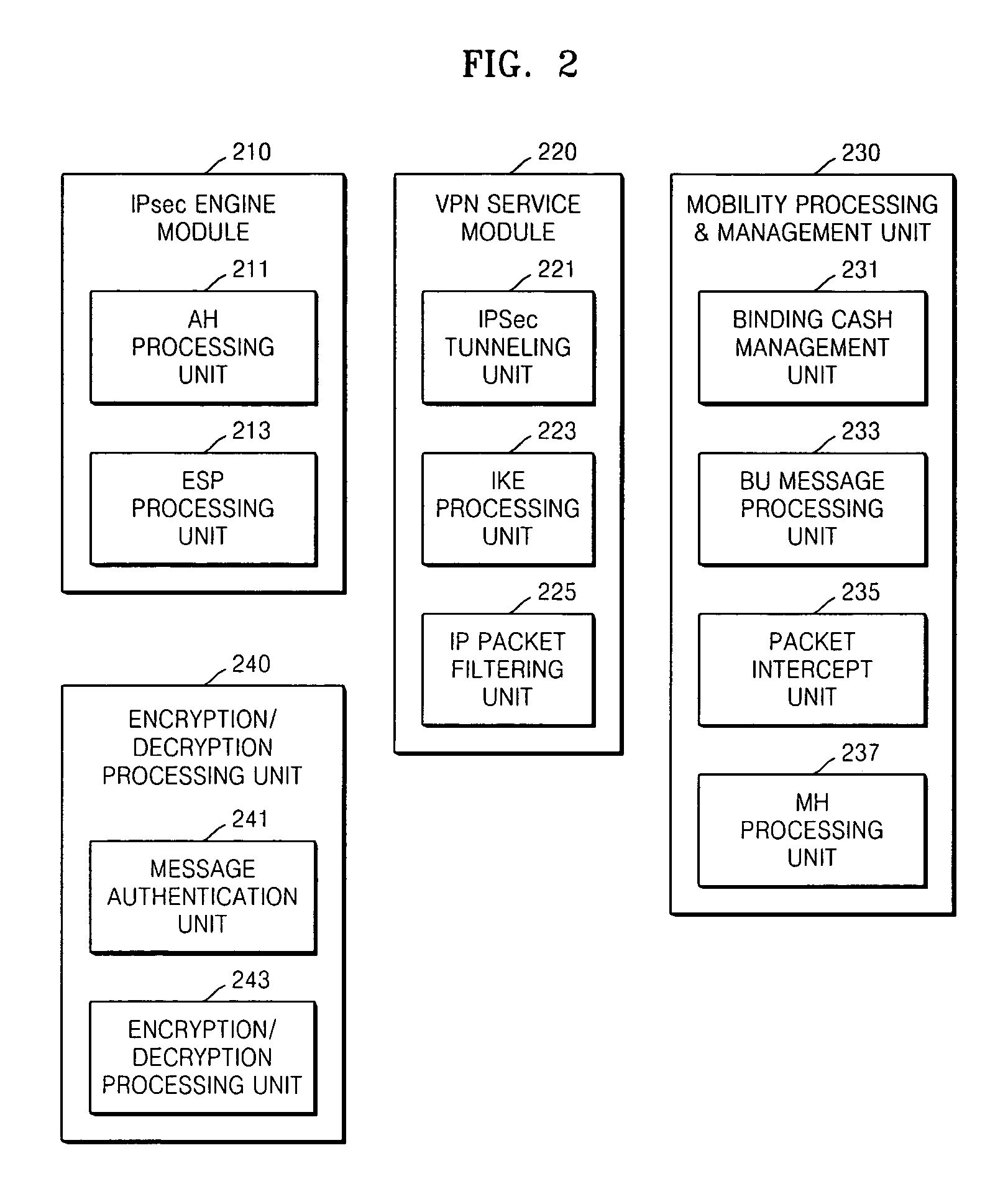
Method for providing virtual private network services to mobile node in IPv6 network and gateway using the same
InactiveUS20070177550A1Support mobilityUser identity/authority verificationWireless network protocolsInternet Key ExchangeSecurity association
Provided are a method for providing virtual private network (VPN) services to a mobile node (MN) in an IPv6 network and a gateway using the same. The method includes: performing IKE (Internet key exchange) negotiation with an MN (mobile node) which has performed handover, acquiring SA (security association) and then authenticating a terminal of the MN; receiving a BU (binding update) message from the MN and verifying the BU message, storing new position information of the MN, transmitting a BA (binding acknowledgement) message and performing mobility processing; if the mobility processing is completed, performing IPsec processing on packets which the MN transmits to a CN (correspondent node), and transmitting the packets; and re-configuring and transmitting packets so that packets which the CN transmits to a home address of the MN can be transmitted to a CoA (Care-of-Address) of the MN. A function performed by a home agent (HA) of Mobile IPv6 is performed so that IP mobility in VPN services can be provided and both mobility inside a VPN domain of the MN and mobility outside the VPN domain can be supported.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Secure extended authentication bypass
ActiveUS20070192842A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
Methods and apparatus are provided to allow Internet Key Exchange (IKE) phase 1 keying materials to be periodically refreshed in a secure manner without requiring user interaction. A client and server perform authentication and key exchange during set up of a secure connection. A token is passed to the client by the server during or after the initial user authentication phase. The token is stored both at the client and at the server. Instead of requiring user credentials, the token can be used to securely prove the identity of the client.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
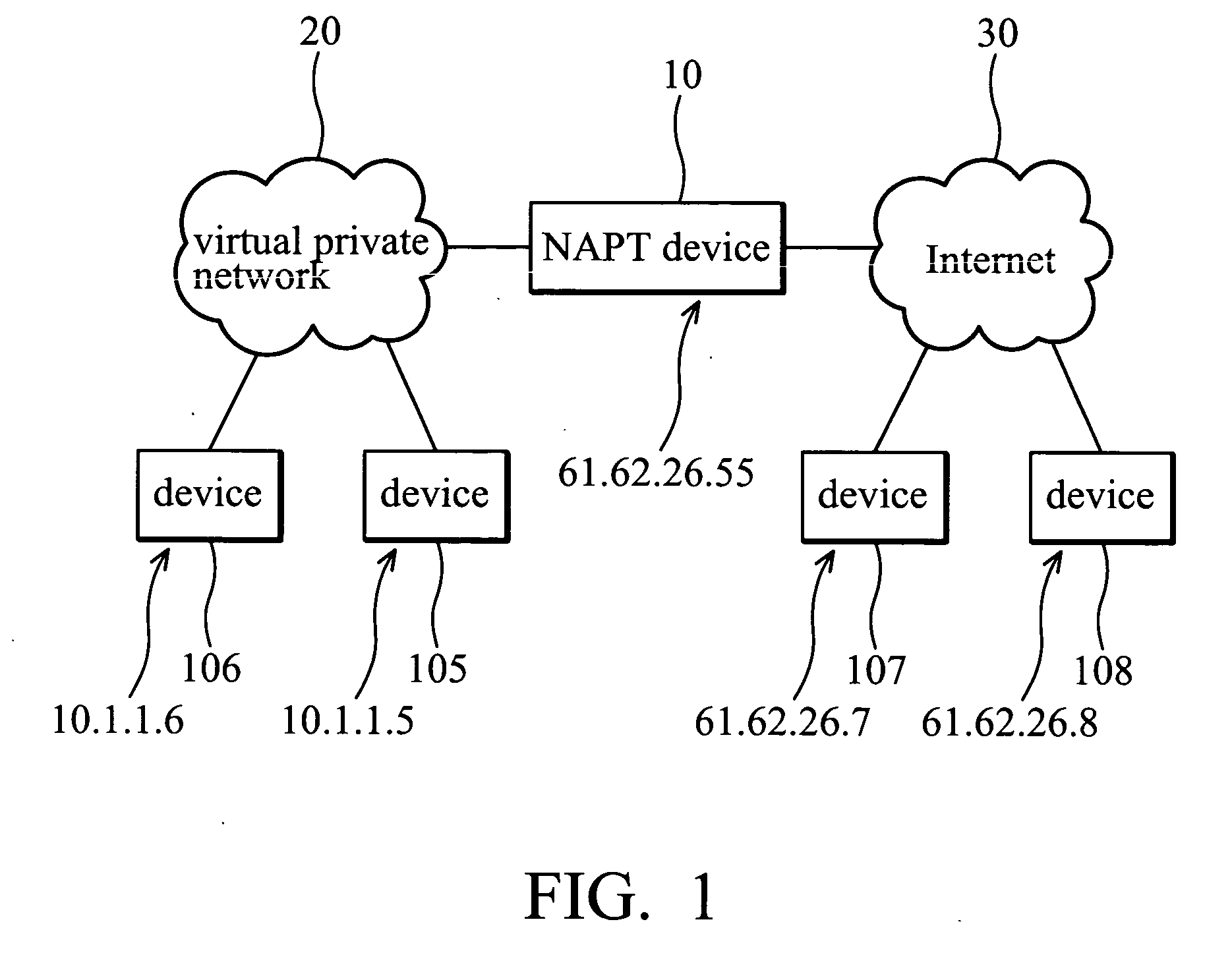
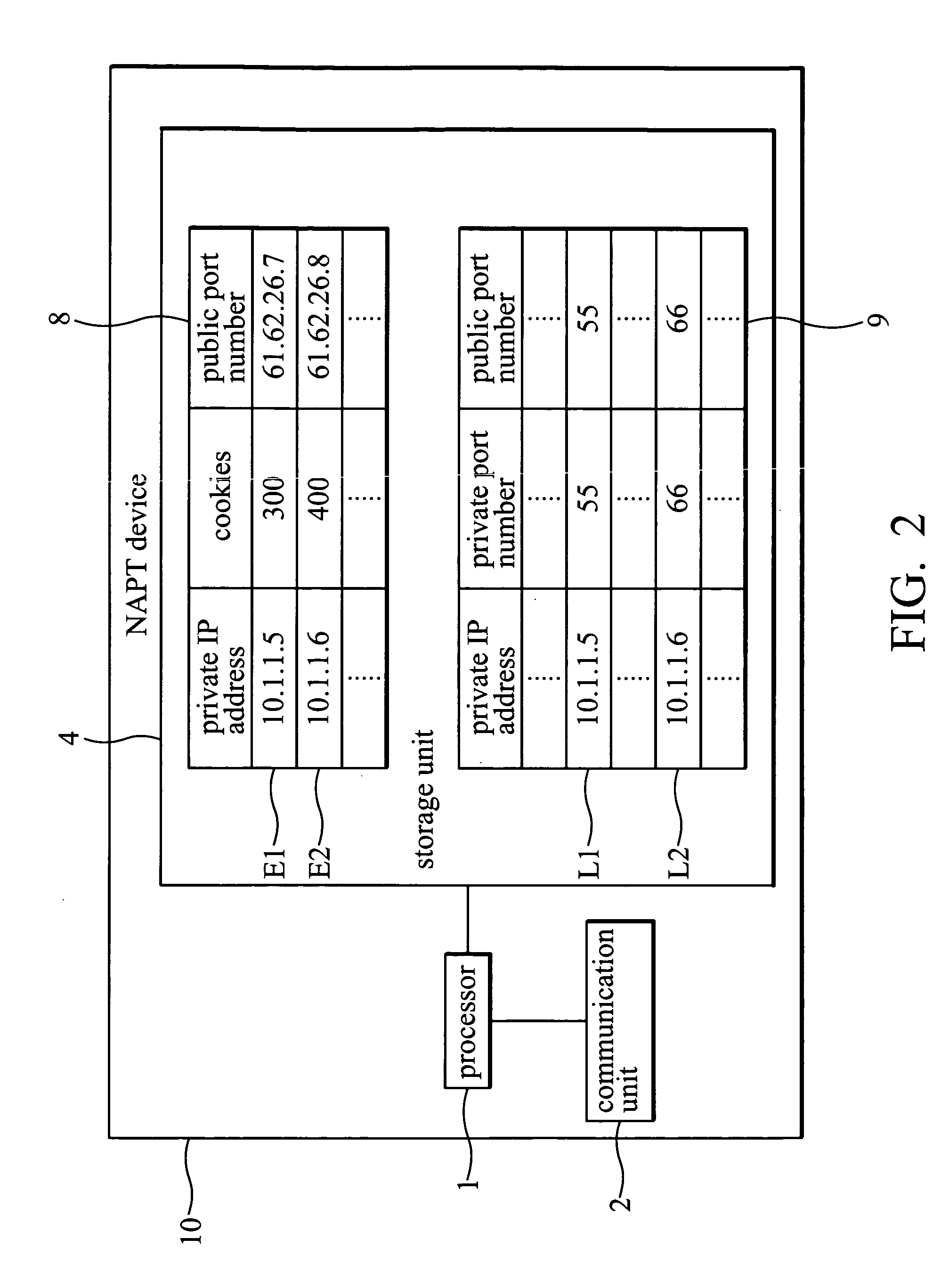
System and method for IPSEC-compliant network address port translation
A system for IPsec-compliant network address port translation. The system comprises a communication unit, a storage device, and a processor. The communication unit receives an outgoing first Internet Key Exchange (IKE) packet and a first incoming Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) packet. The IKE packet comprises an IP header specifying a private source IP address and a first destination IP address. The ESP packet comprises a first source IP address and a second destination IP address, wherein the first source IP address equals the first destination IP address. The storage device stores the private source IP address and the first destination IP address in corresponding fields of a first table. The processor, connected to the communication unit and the storage device, retrieves the first source IP address of the first ESP packet, searches the first table for a match of the first source IP address, and substitutes the searched match for the second destination IP address of the ESP packet.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
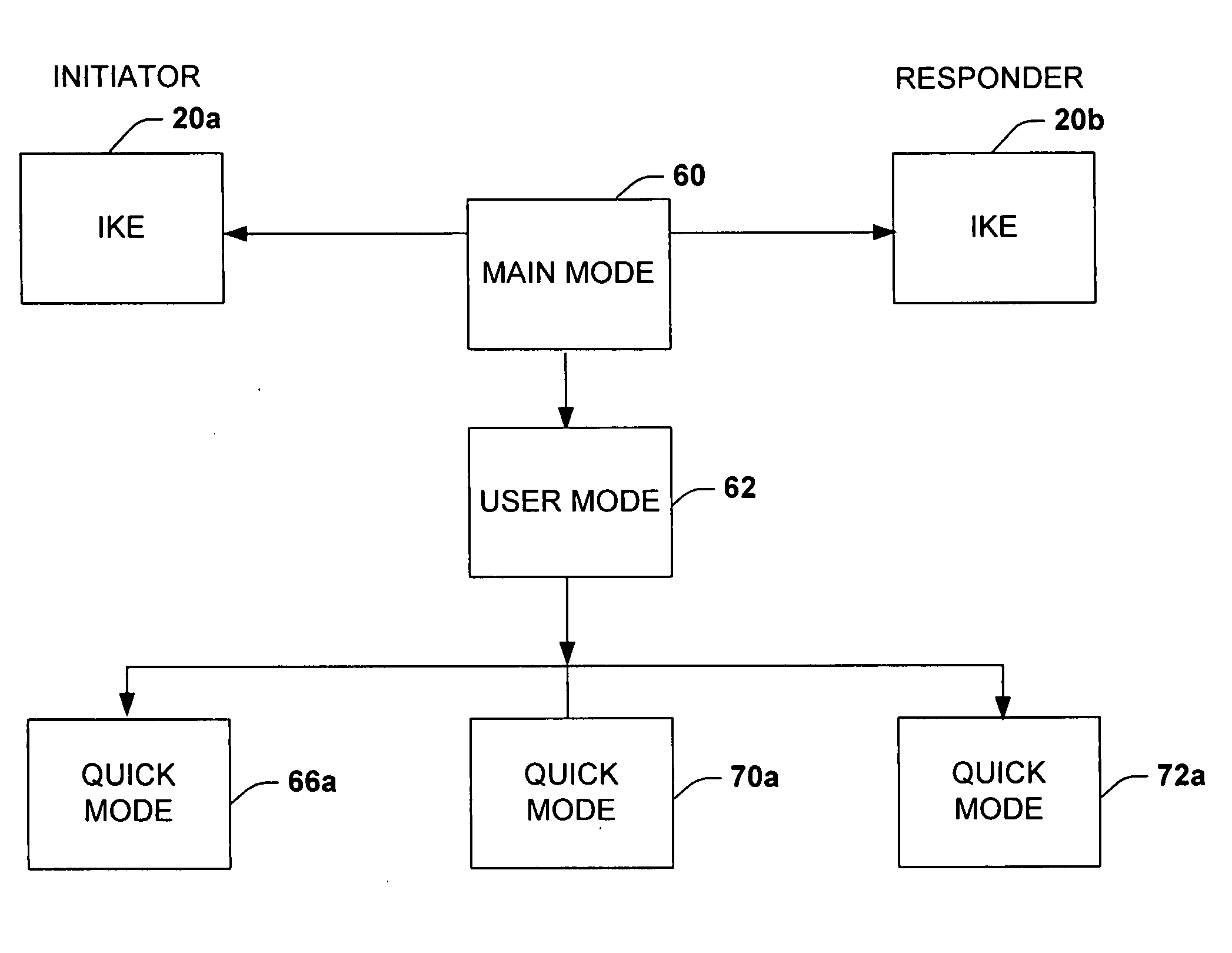
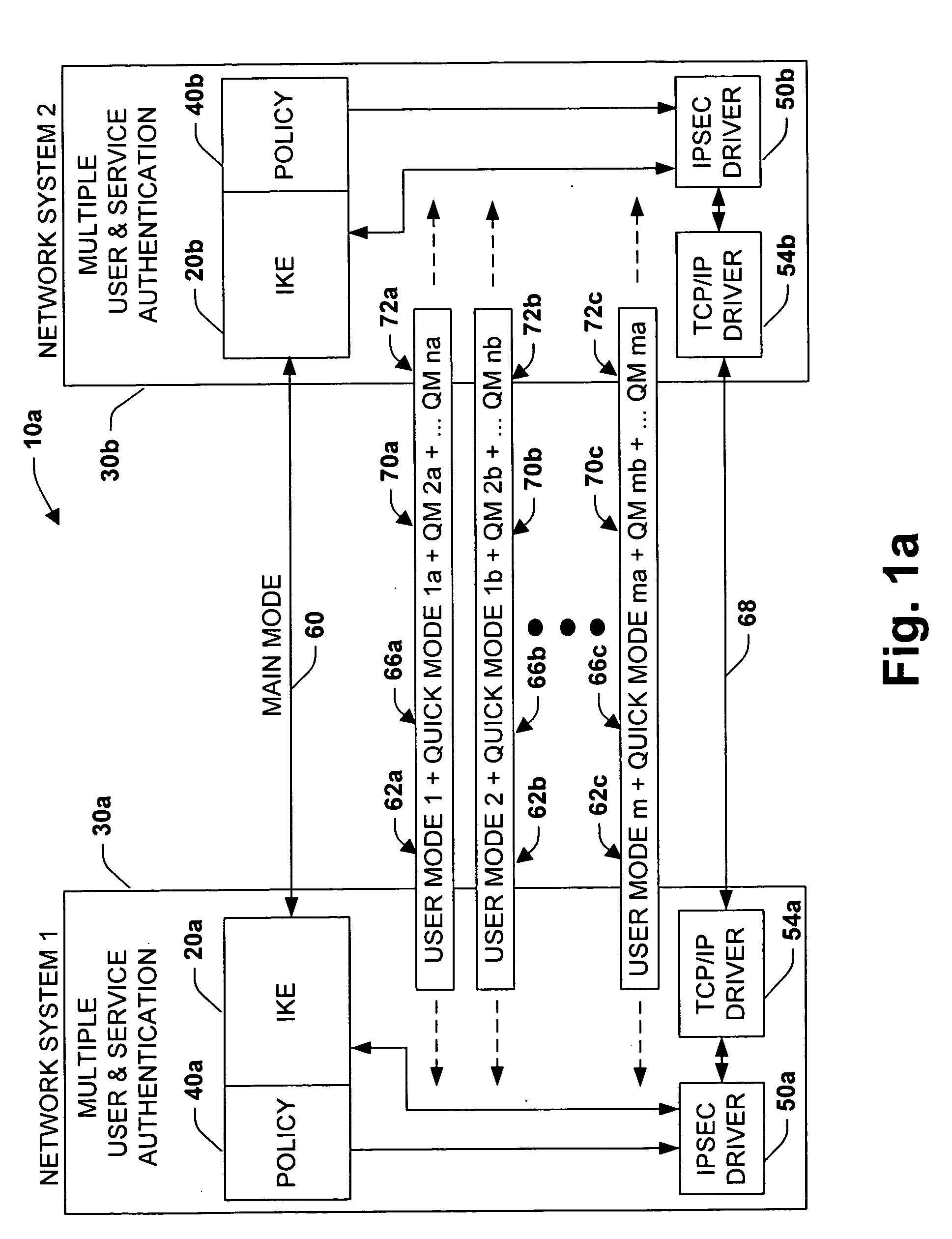
System and method for improved network security
InactiveUS20050091527A1Improve network securityImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInternet Key ExchangeSecurity association
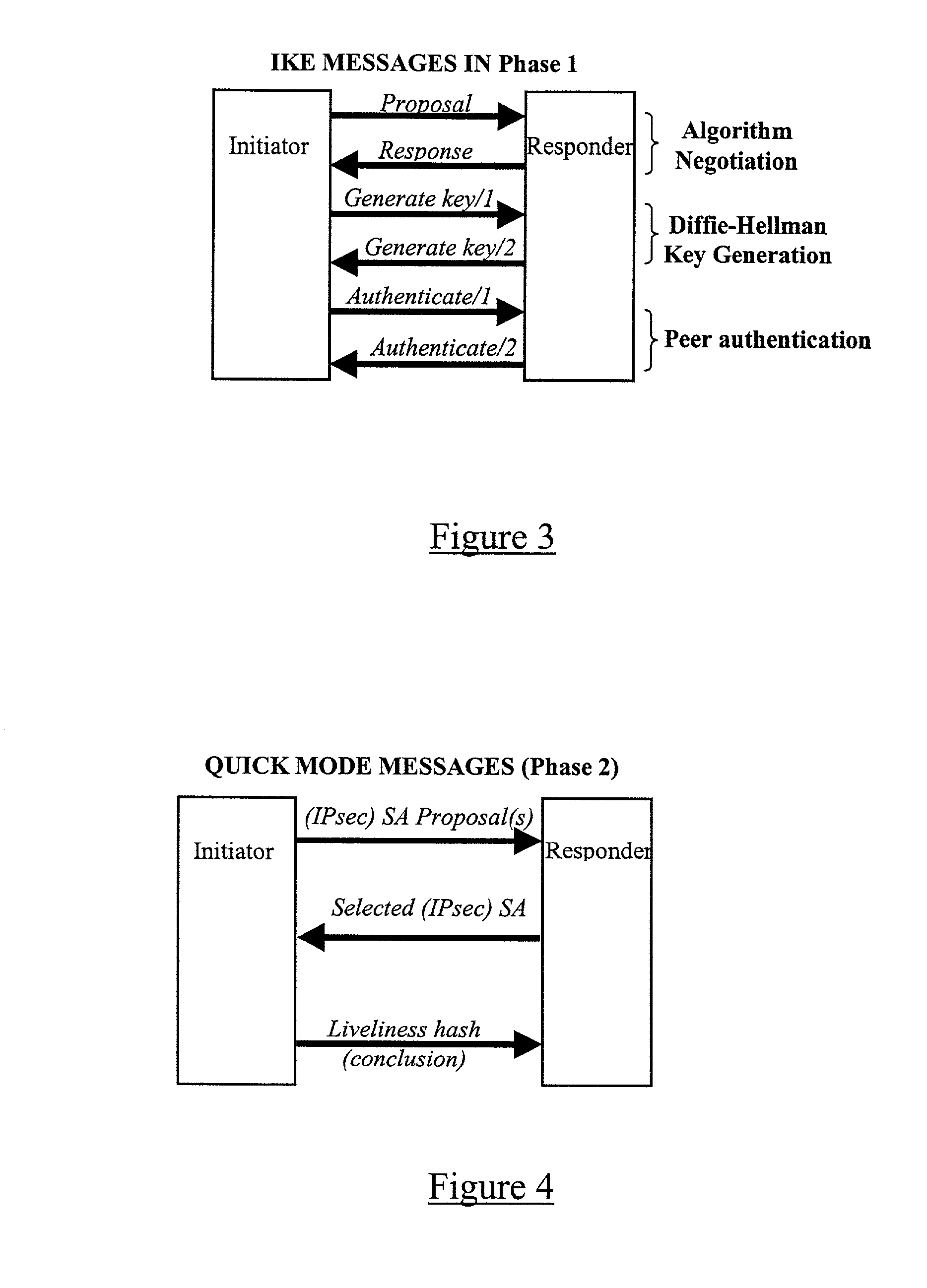
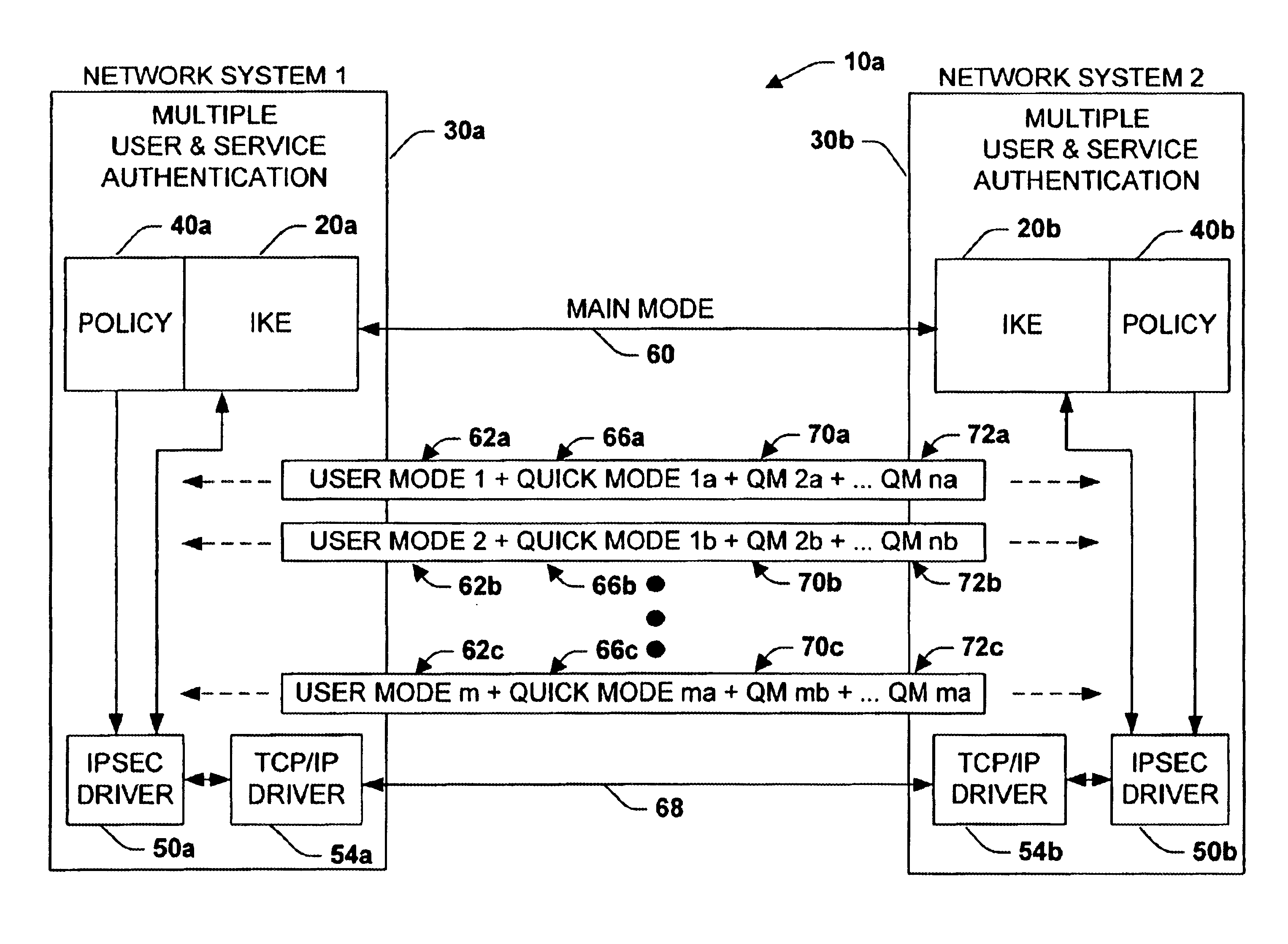
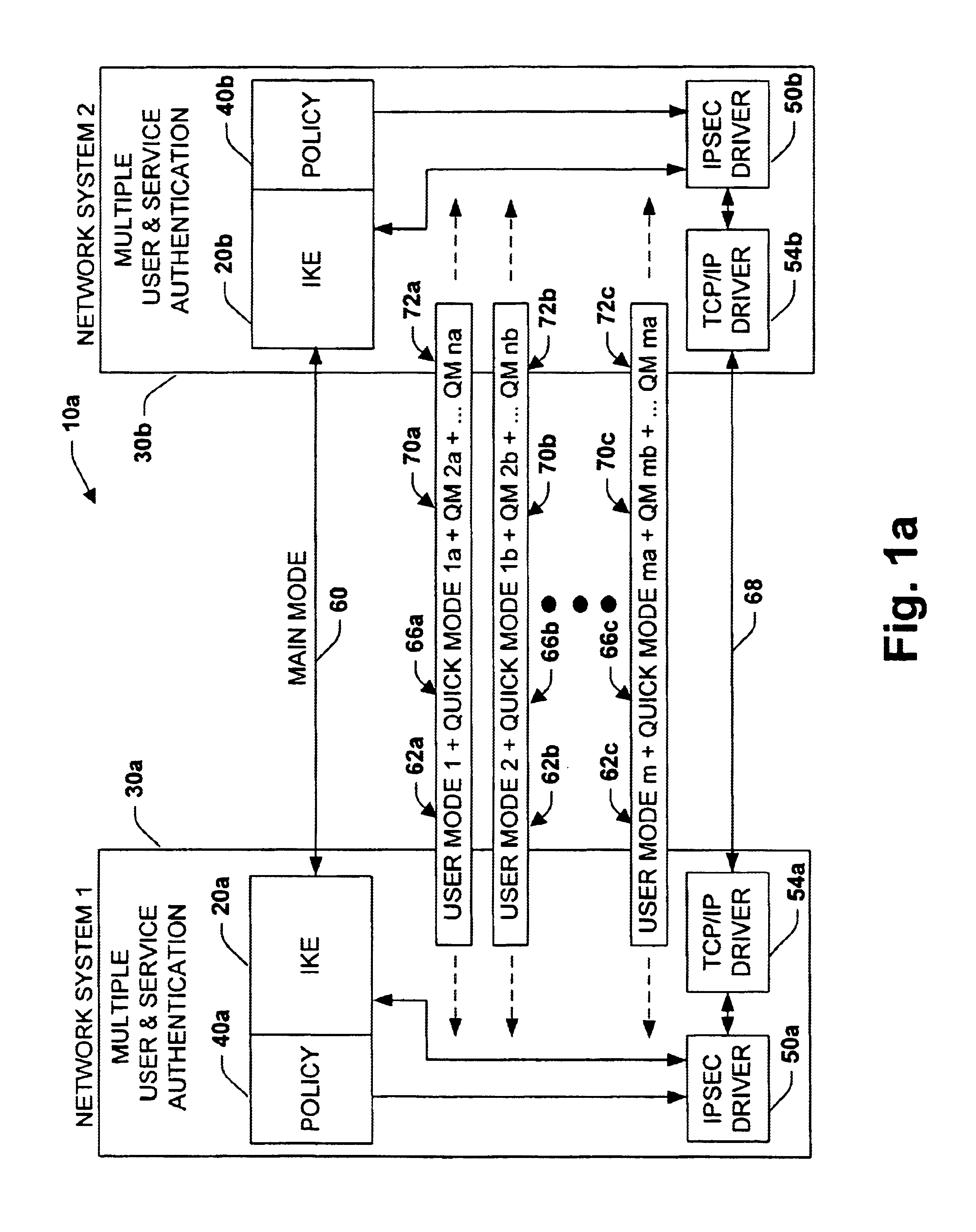
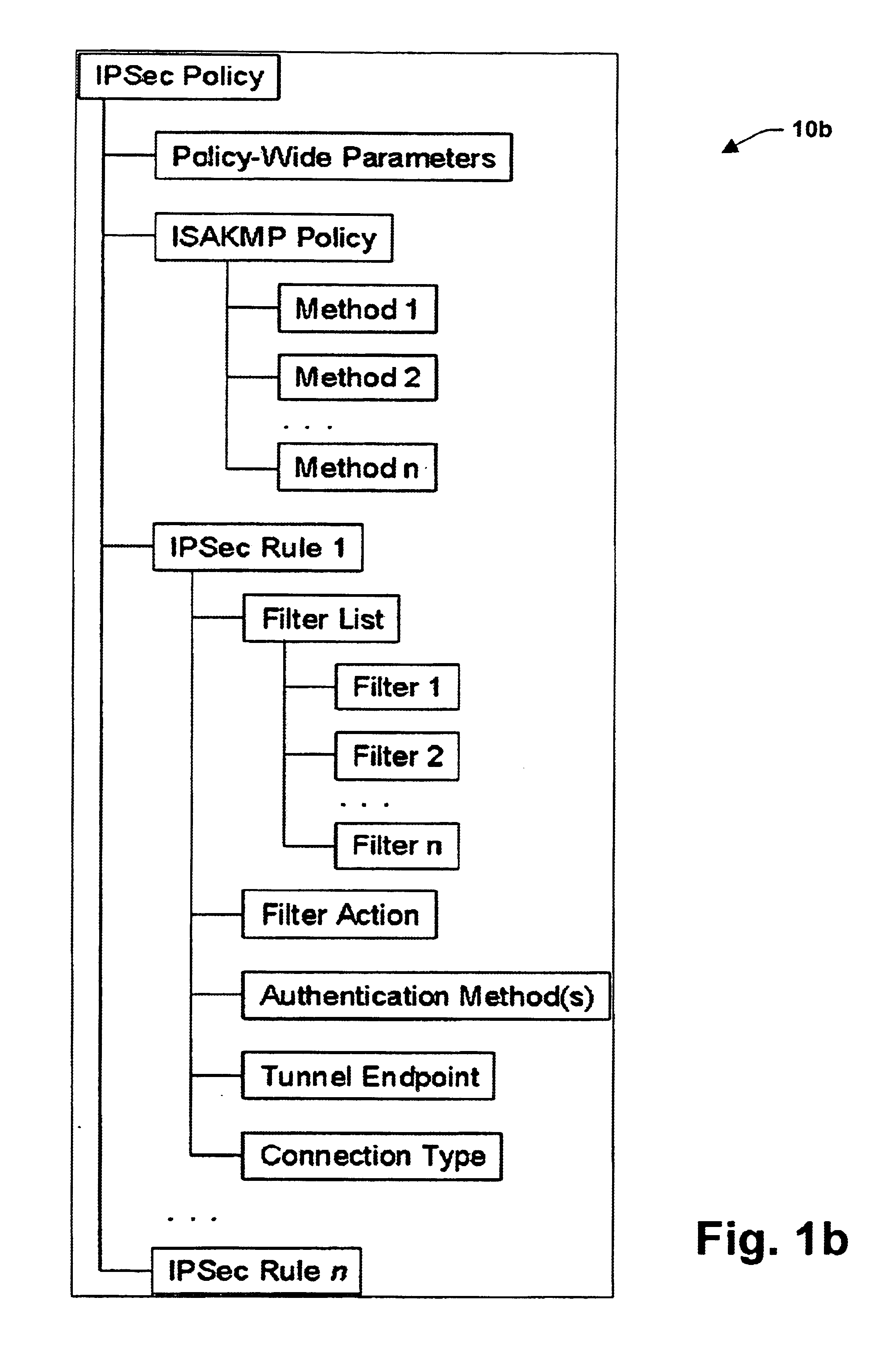
A system is provided for establishing a secure link among multiple users on a single machine with a remote machine. The system includes a subsystem to filter traffic so that traffic from each user is separate. The subsystem generates and associates a Security Association (SA) with at least one filter corresponding to the user and the traffic, and employs the SA to establish the secure link. An Internet Key Exchange module and a policy module may be included to generate and associate the security association, wherein the policy module is configured via Internet Protocol Security (IPSEC).
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for control of security protocol negotiation
ActiveUS7120930B2Add significant overheadMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlPlaintextPrivate network
Method and apparatus for enhanced security for communication over a network, and more particularly to control of security protocol negotiation to enable multiple clients to establish a virtual private network connection with a same remote address, is described. A mapping table accessible by a gateway computer is used to form associations between a local address for the client and a destination address for a peer and a Security Parameters Index associated with IPSec-protected traffic from the peer. When a packet is received at the gateway from a client it is checked to determine if it is an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) packet, whether an IKE session has already been recorded from this client in the mapping table for the destination address in the IKE packet, whether a Security Parameters Index has been observed in the clear from a remote computer associated with the destination address.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
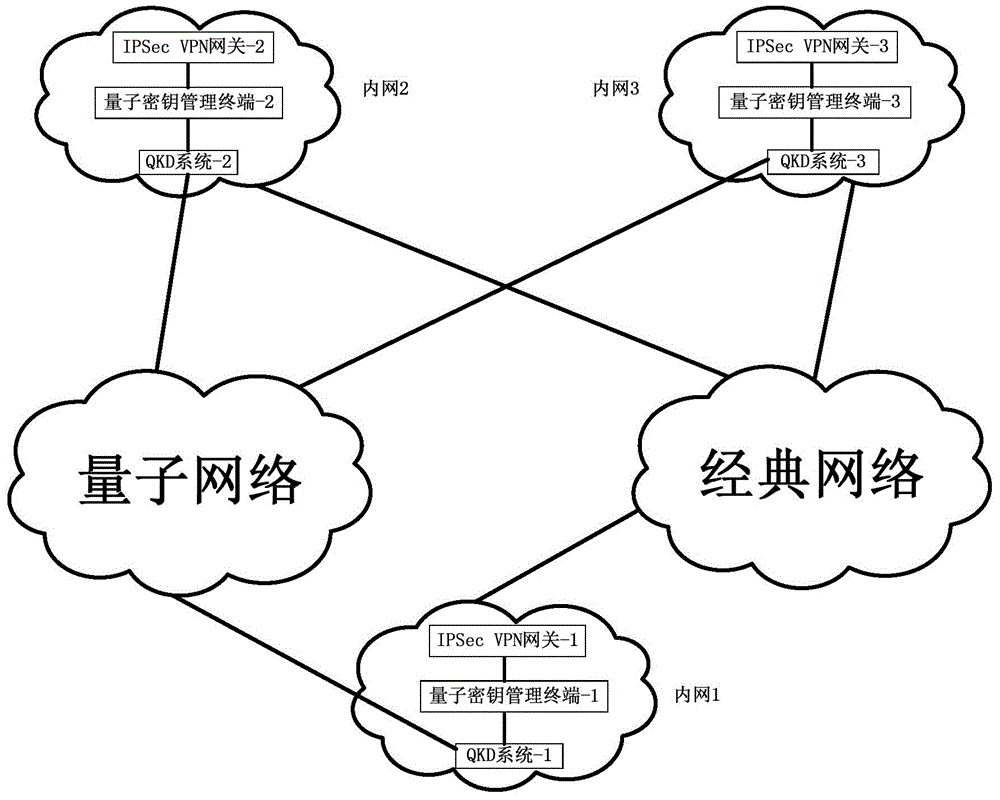
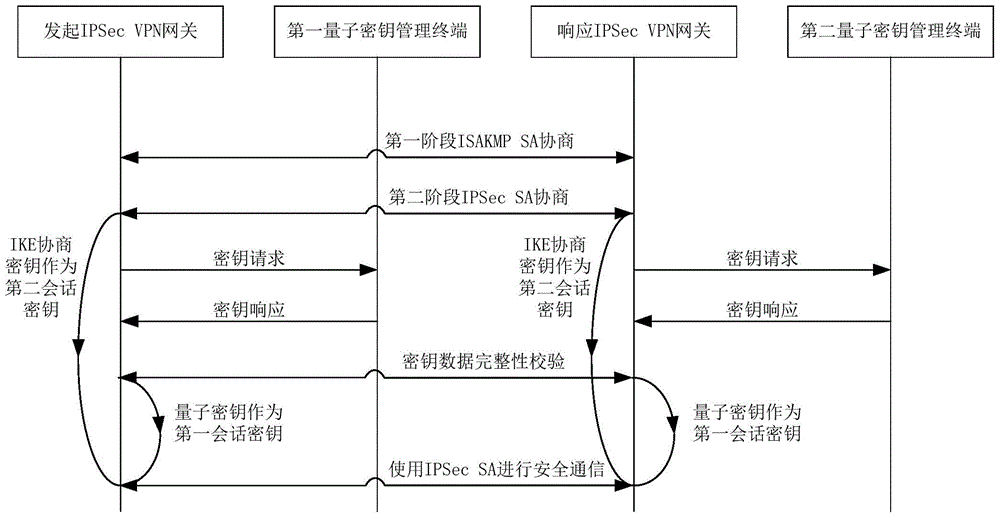
Method and system for extended use of quantum keys in IPSec VPN (internet protocol security-virtual private network)
ActiveCN104660603ANovel structureIncrease update frequencyKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksSession keyKey management
The invention discloses a method and a system for extended use of quantum keys in an IPSec VPN (internet protocol security-virtual private network) system. The IPSec VPN system comprises at least two IPSec VPN gateways including an initiating IPSec VPN gateway and a responding IPSec VPN gateway as well as corresponding quantum key management terminals. The method comprises steps as follows: through parallel processing of negotiation of the quantum keys and IKE (internet key exchange) negotiated keys, the quantum keys are taken as first session keys for preferential use, and the IKE negotiated keys are taken as second session keys for safety communication. Besides, the invention further provides the corresponding IPSec VPN gateway, the quantum key management terminals and the IPSec VPN system. The quantum keys are taken as the session keys through extended use, so that the session key updating frequency is greatly increased and the safety communication performance of conventional IPSec VPN is guaranteed under the condition that an original IPSec VPN is compatible.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF QUANTUM SCI & TECH +1
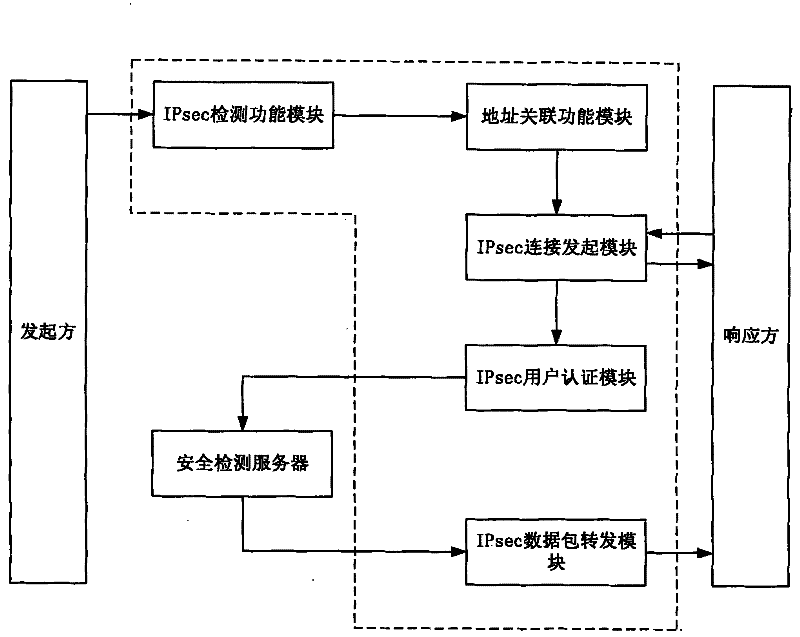
Flow rate security detection method, equipment and system
ActiveCN102347870AEnsure safetyRealize regulationData switching networksTraffic capacityInternet Key Exchange
The invention discloses an Internet protocol security (IPSec) flow rate security detection method, equipment and a system. The method comprises the following steps that: when an initiation party initiates an Internet key exchange (IKE) request of the IPsec communication to a response party through gateway equipment, and the gateway equipment intercepts and captures the IKE request, extracts the source address of the request and the corresponding target address of the response party and stores the source address of the request and the corresponding target address of the response party into a local data list; the encryption consultation is respectively carried out with the initiation party and the response party, and in addition, IPsec security channels with the initiation party and the response party are respectively built; the initiation party encrypts a data packet to be sent to the response party by a gateway equipment consultation encryption method and sends the data packet to the gateway equipment through the IPsec security channel built with the gateway equipment; after the gateway equipment receives the data packet, the deep packet detection is carried out after the data packet is decrypted by an encryption method negotiated with the initiation party; when the deep packet detection is passed, the gateway equipment encrypts the data packet by the encryption method negotiated with the response party, and the data packet is sent to the response party through the IPsec security channel built with the response party.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Method of virtual private network communication in security gateway apparatus and security gateway apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7028337B2Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet Key ExchangePrivate network
A method of the Virtual Private Network (VPN) communication employed for a security gateway apparatus and the security gateway apparatus using the same, which allow a personal computer outside a local area network (LAN) to access, via a WAN, to a terminal on the LAN, virtually regarding the outside PC as a terminal on the LAN. The communication method is employed for a security gateway apparatus to connect, through concentration and conversion process, between a LAN and a WAN including a public network. Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol (IPsec) establishes VPN with an outside PC having a dialup connection to the WAN. During an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) communication that is performed prior to the IPsec communication, the security gateway apparatus integrates a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) communication option into an IKE data, and designates the IP address of the outside PC from a tunneled IP packet.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
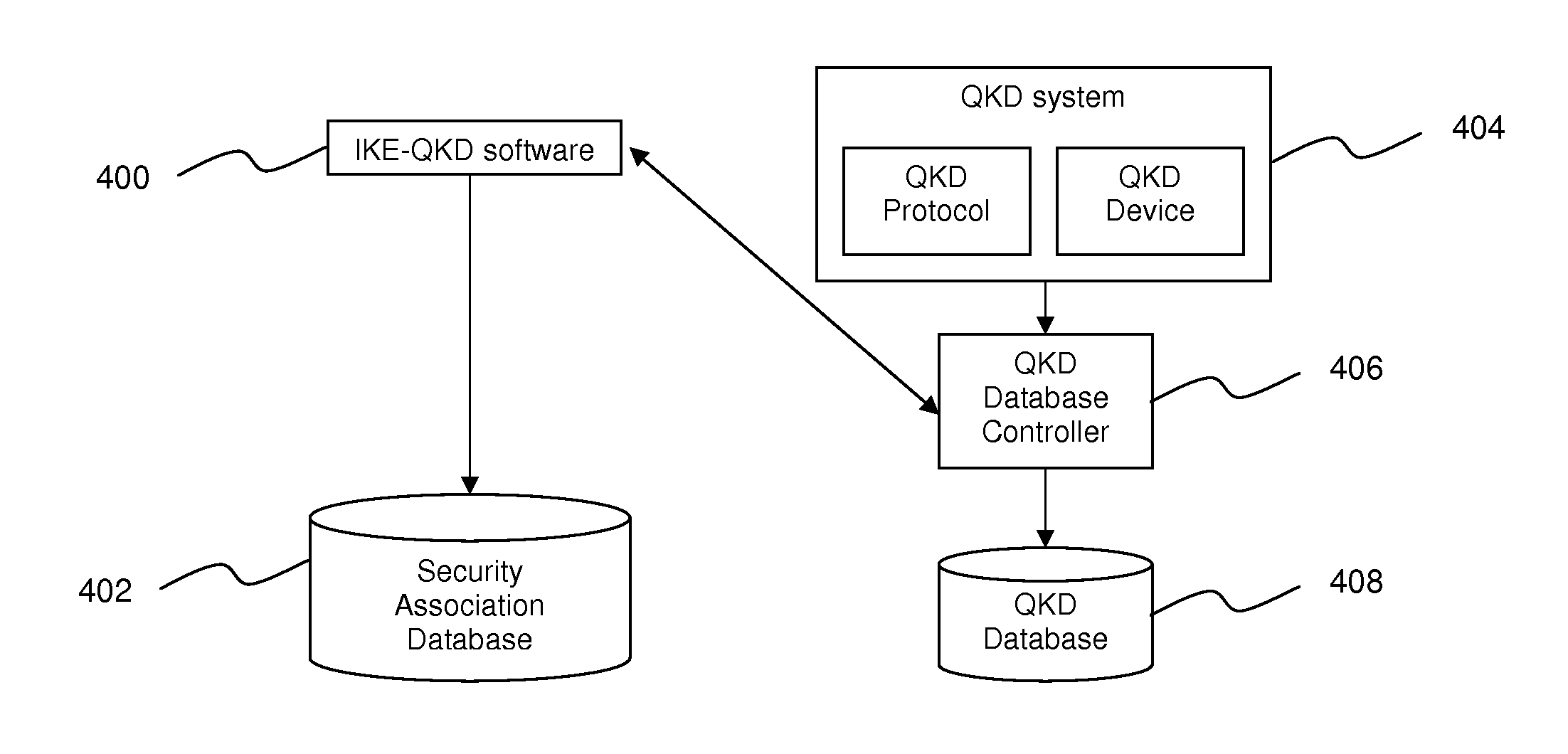
Method of integrating QKD with IPSec
ActiveUS20060212936A1Increase in sizeFast key flippingKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet Key ExchangeSecurity association
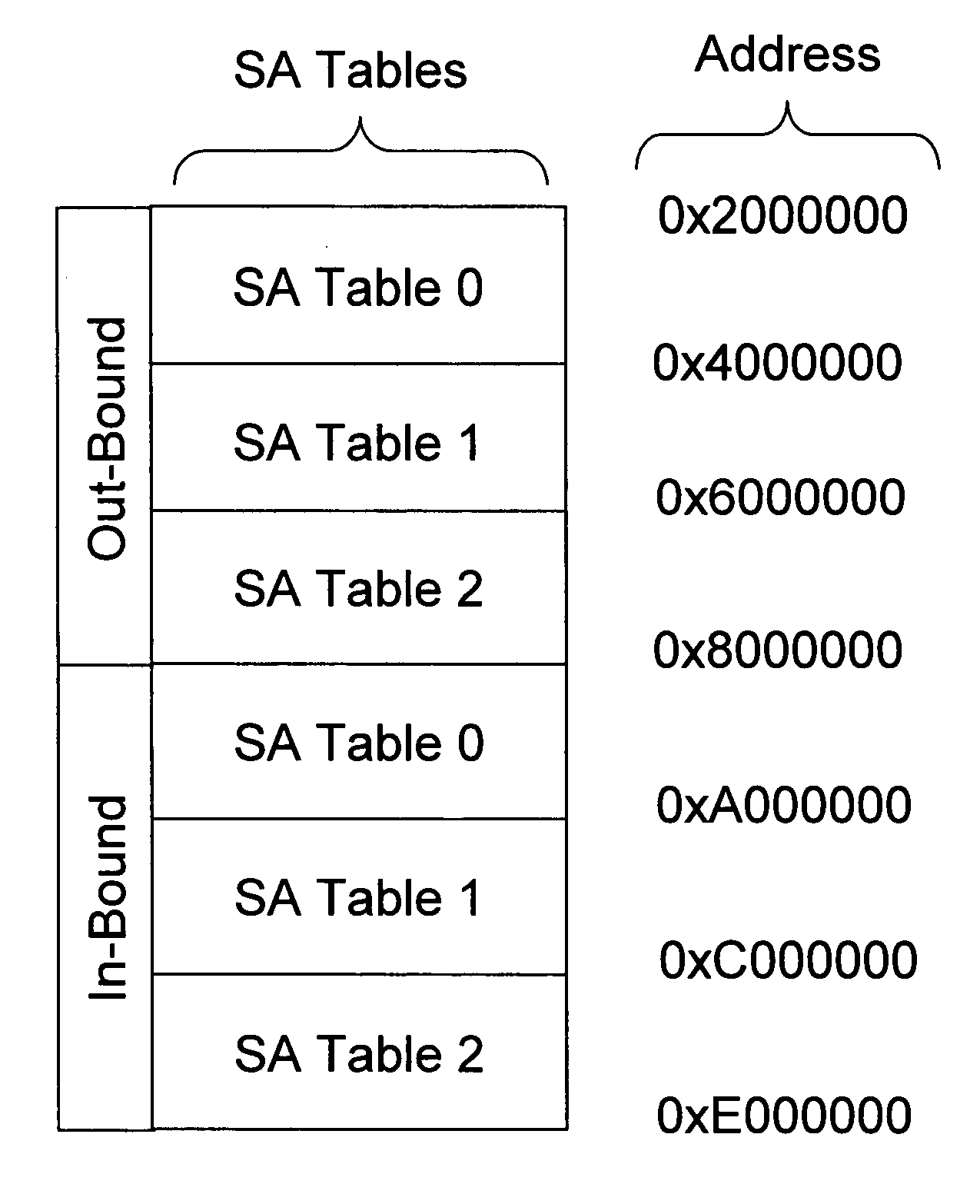
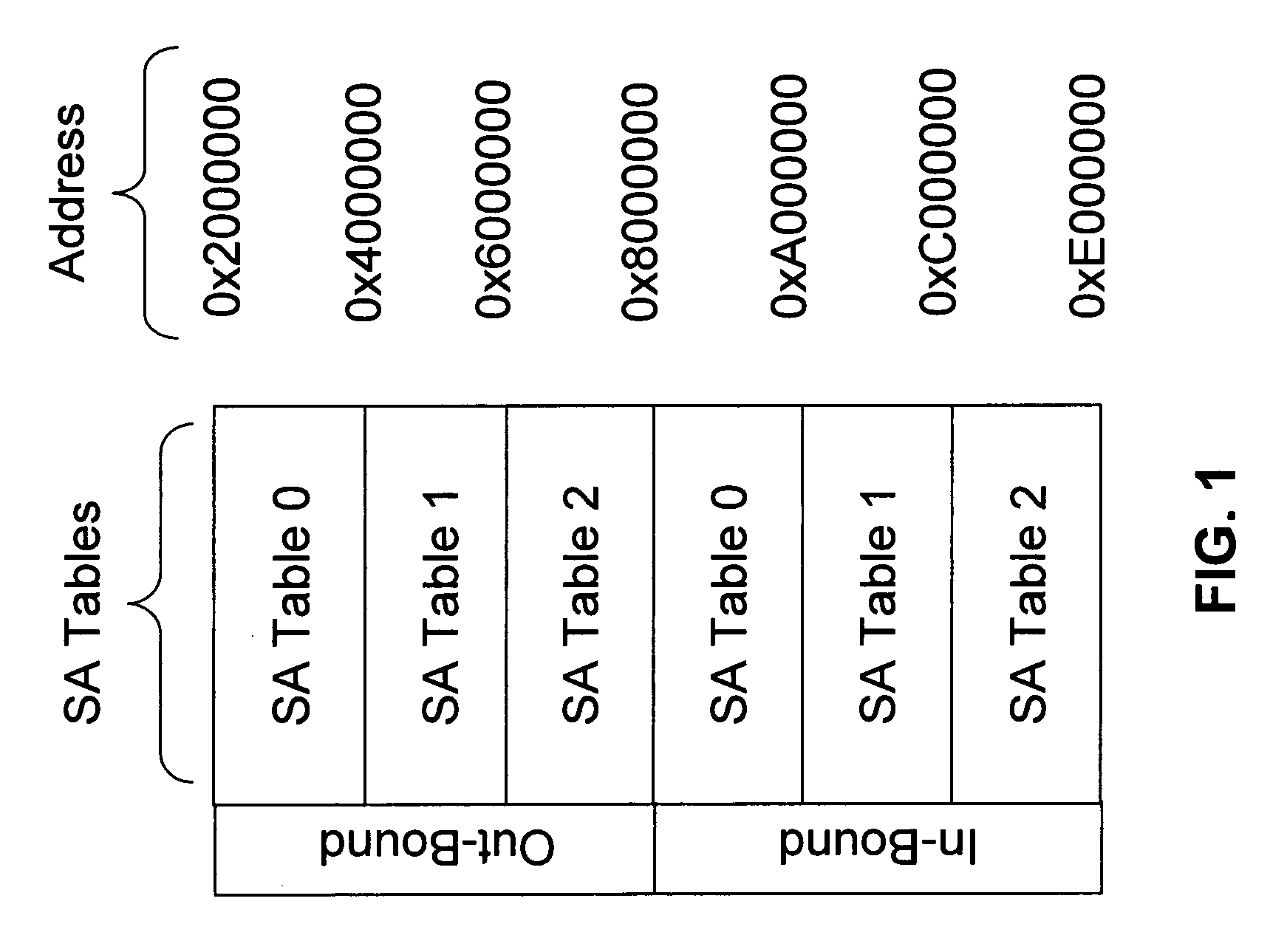
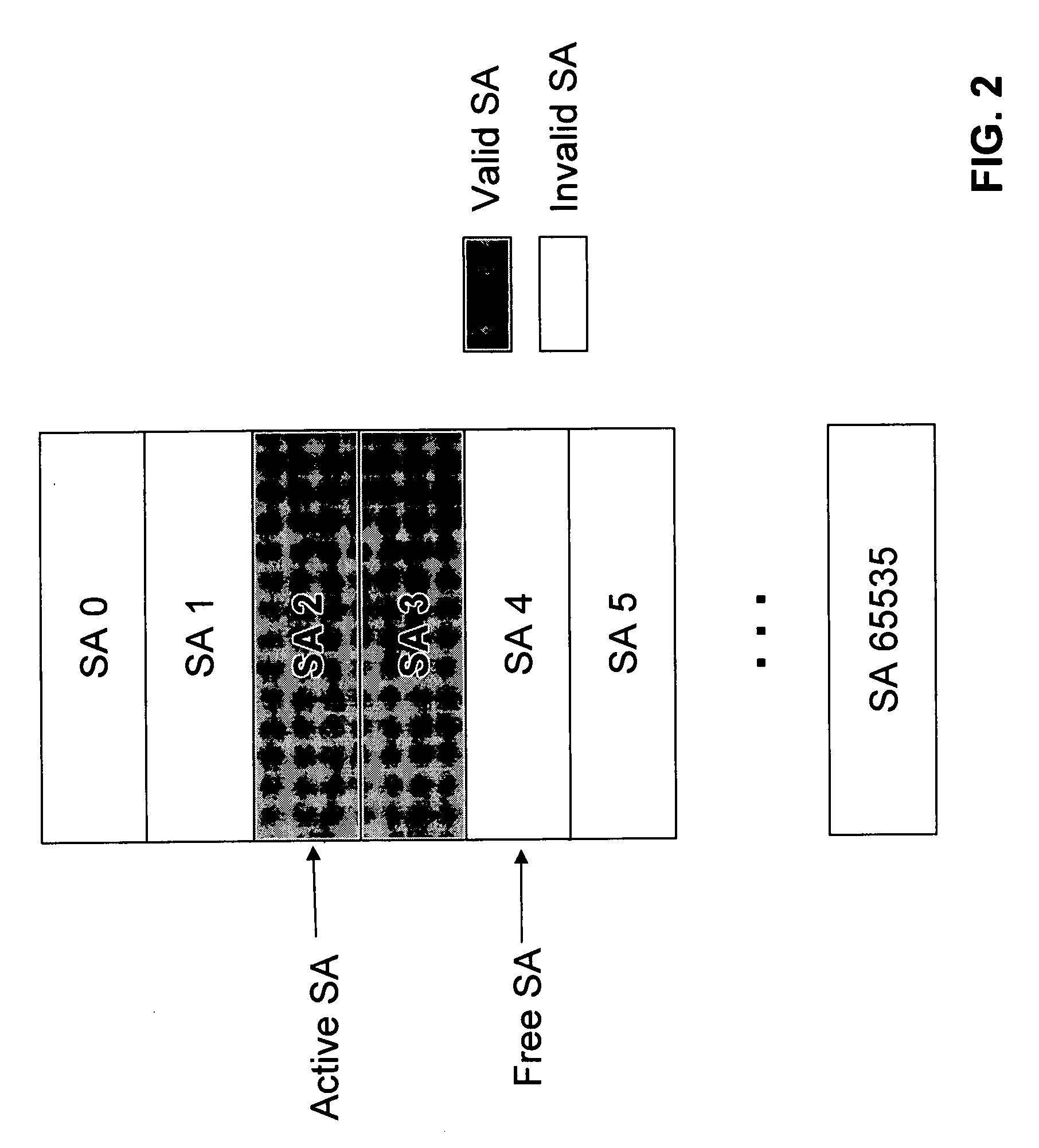
A method of integrating quantum key distribution (QKD) with Internet protocol security (IPSec) to improve the security of IPSec. Standard IPSec protocols impose limits on the frequency at which keys can be changed. This makes efforts to improve the security of IPSec by employing quantum keys problematic. The method includes increasing the size of the Security Association (SA) Table in a manner that enables a high key change rate so that the quantum keys can be combined with the classical keys generated by Internet Key Exchange (IKE). The invention includes a method of creating the SA Table by combining quantum keys generated by the QKD process with classical keys generated by the IKE process, thereby enabling QKD-based IPSec.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Method of integrating quantum key distribution with internet key exchange protocol
InactiveUS20110188659A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
A method of integrating quantum key distribution with Internet key exchange protocol, wherein the method comprises exchanging quantum-shared secret index from a cryptographic key database in Phase 1 of the Internet key exchange protocol between an initiator and a responder (100), integrating a number of quantum-shared secret from the cryptographic key database with classic shared secret using a predetermined operation mode in Phase 2 of the Internet key exchange protocol (200) to generate an array of security associations to be used by the initiator and the responder during a single Internet key exchange session, and managing inbound and outbound of the array of security associations in a security association database (402) using a database structure.
Owner:MIMOS BERHAD
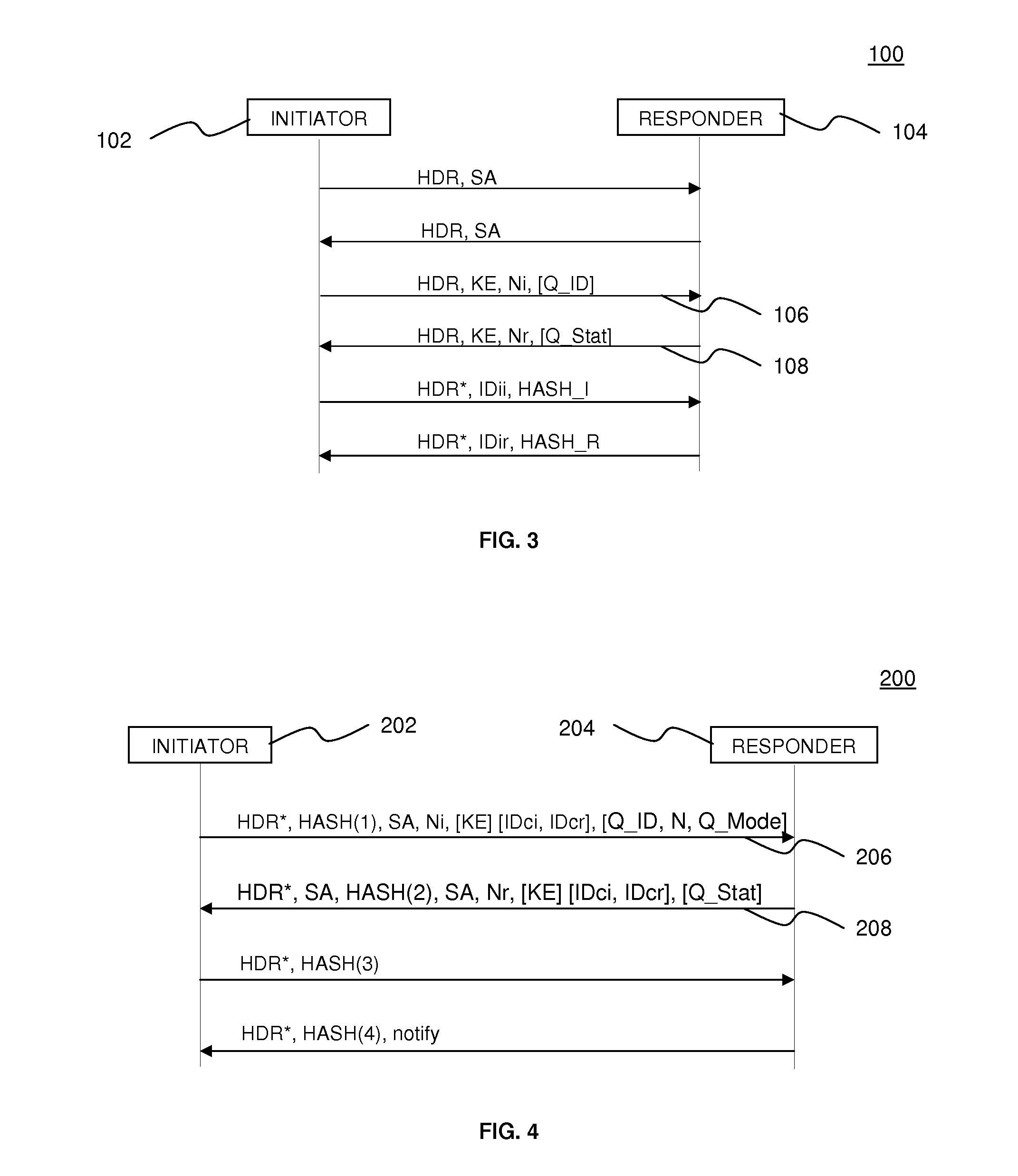
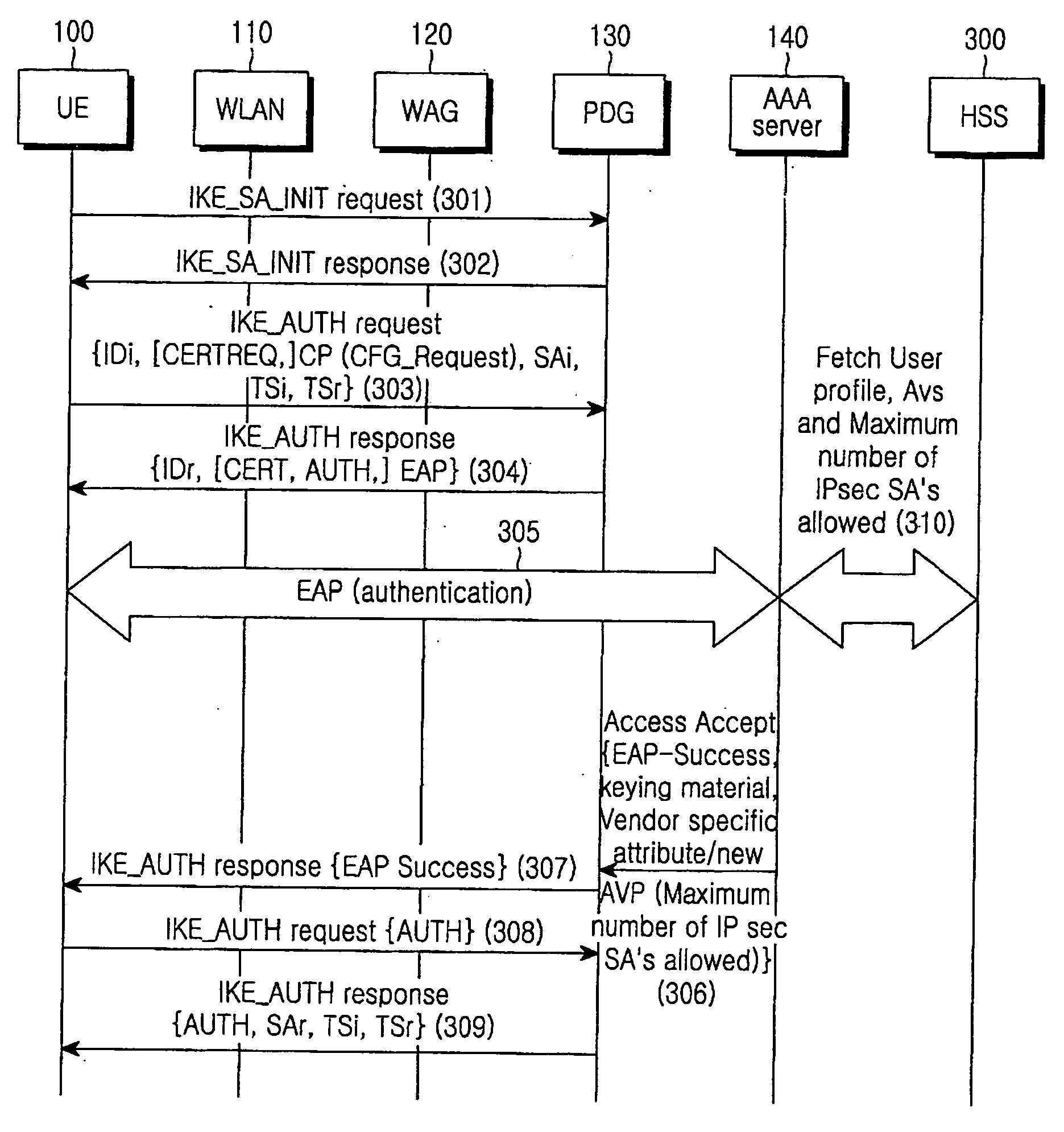
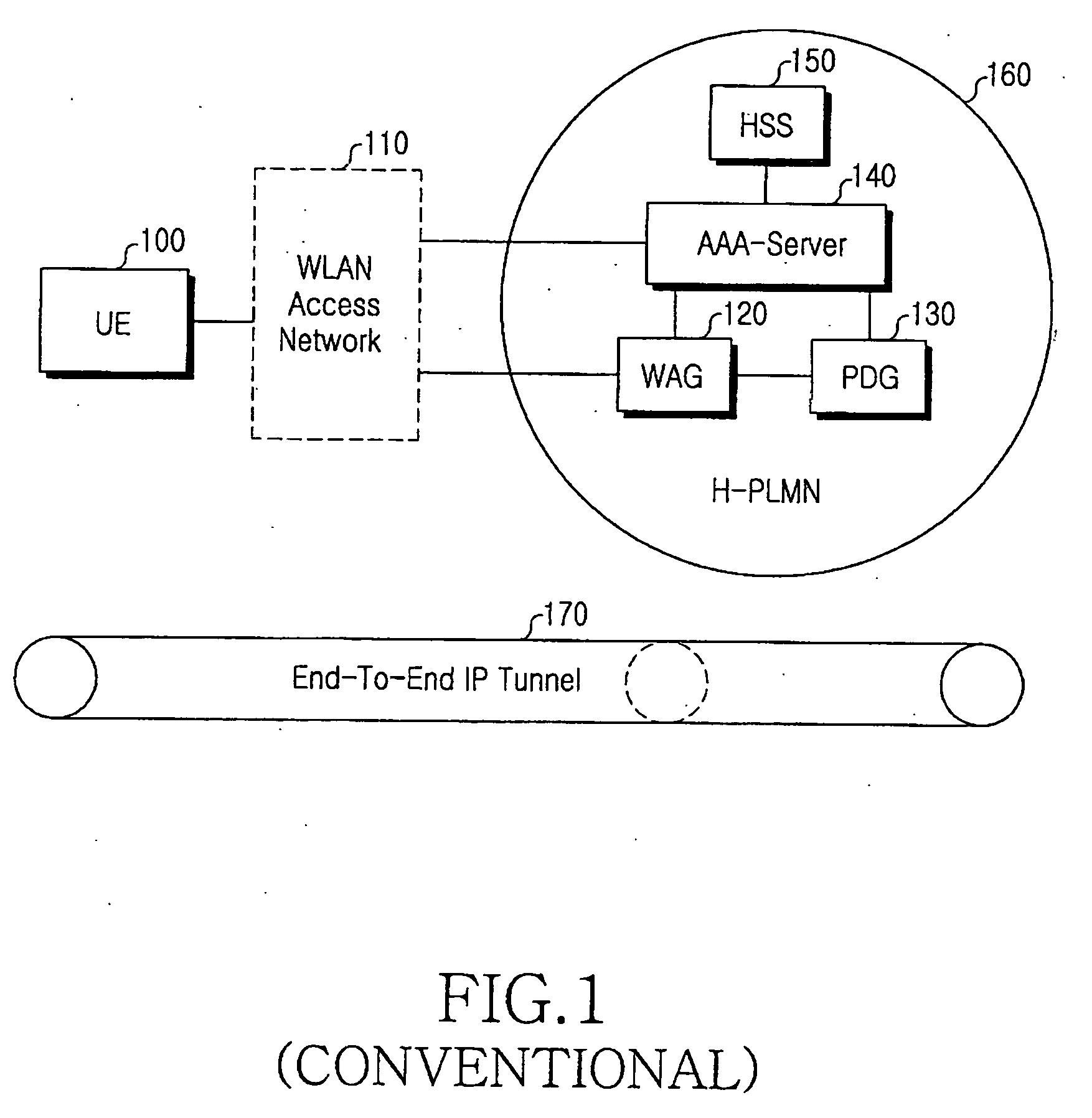
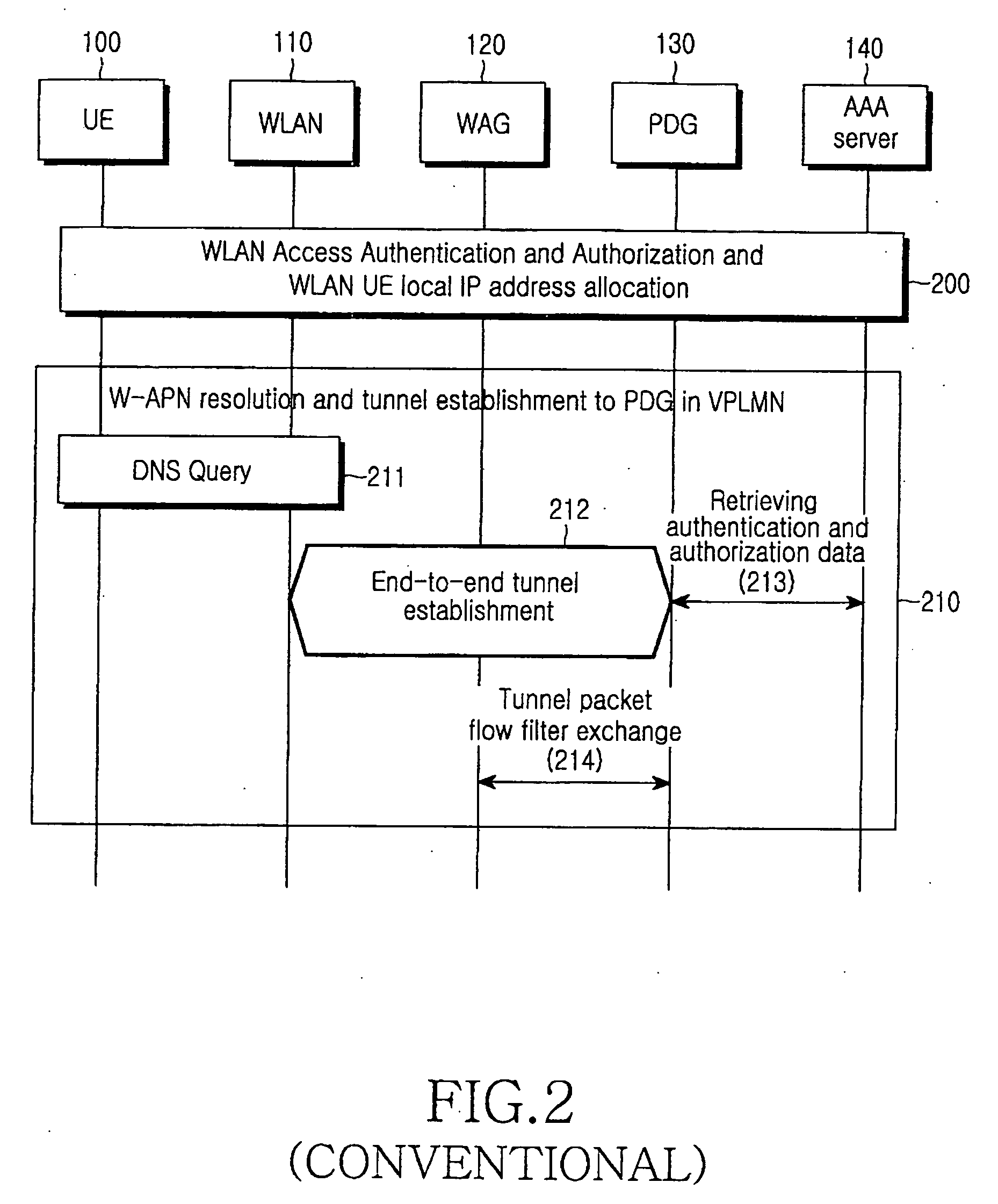
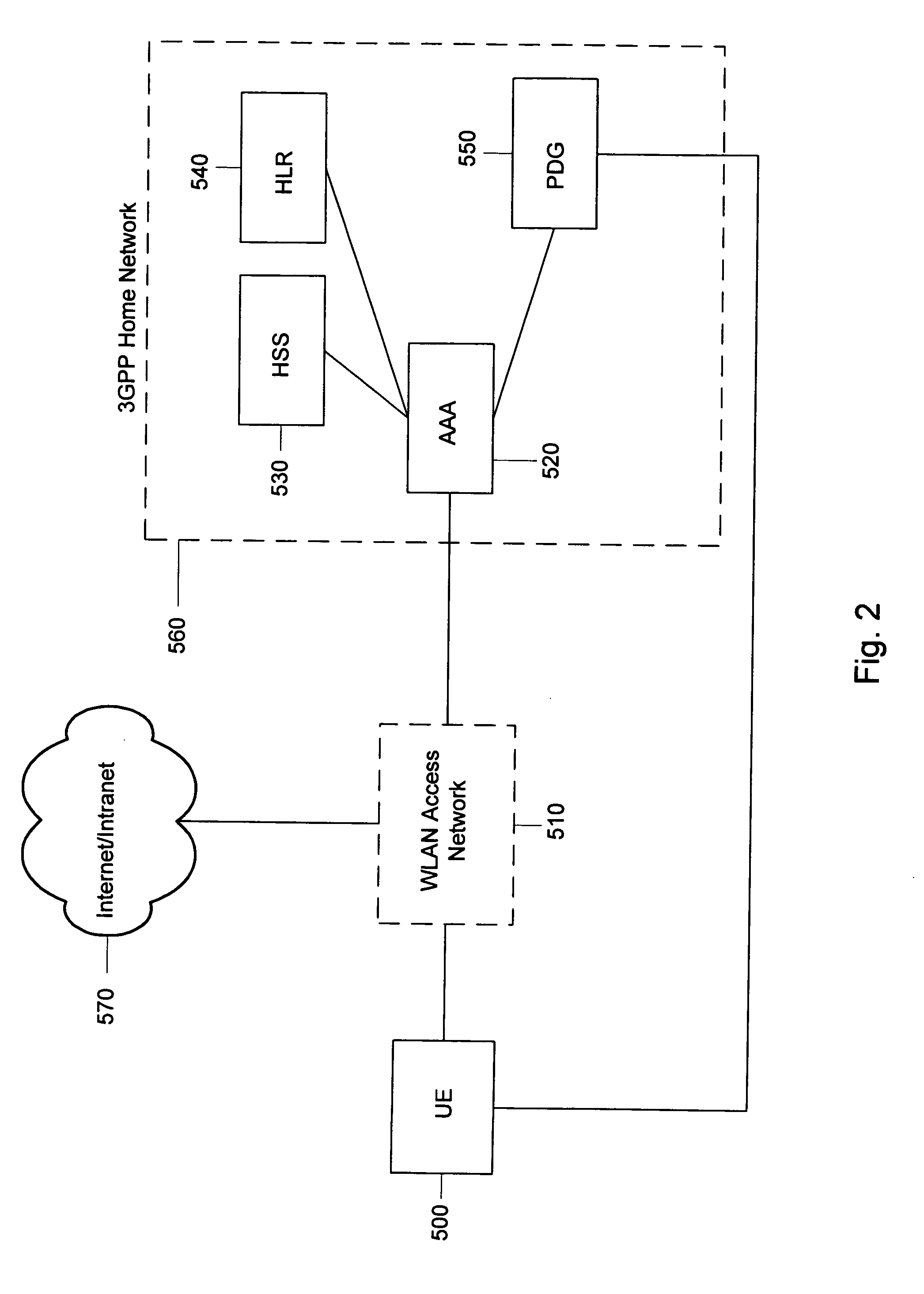
System and method for tunnel management over a 3G-WLAN interworking system
InactiveUS20060294363A1Security arrangementSecuring communicationInternet Key ExchangeSecurity association
Method and system for facilitating tunnel management in the 3G-WLAN interworking systems providing dynamic configuration of maximum number of IP Security Protocol (IPsec) tunnels allowed per Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Security Association (SA) at the Packet Data Gateway (PDG) during the initial tunnel establishment procedure. Authentication Authorization and Accounting (AAA) server is notified of the new IPsec tunnel established between the user equipment (UE) and the PDG.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
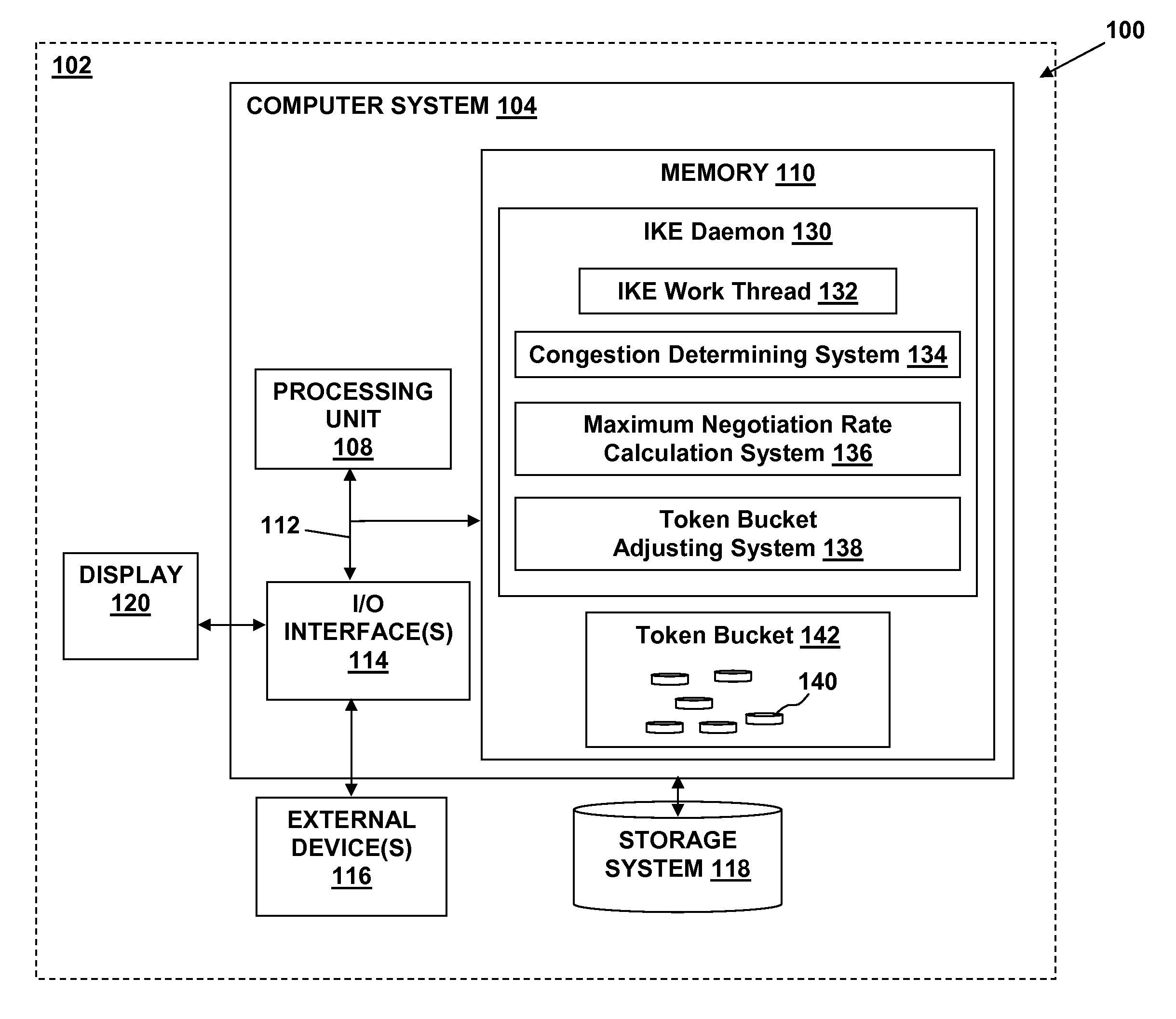
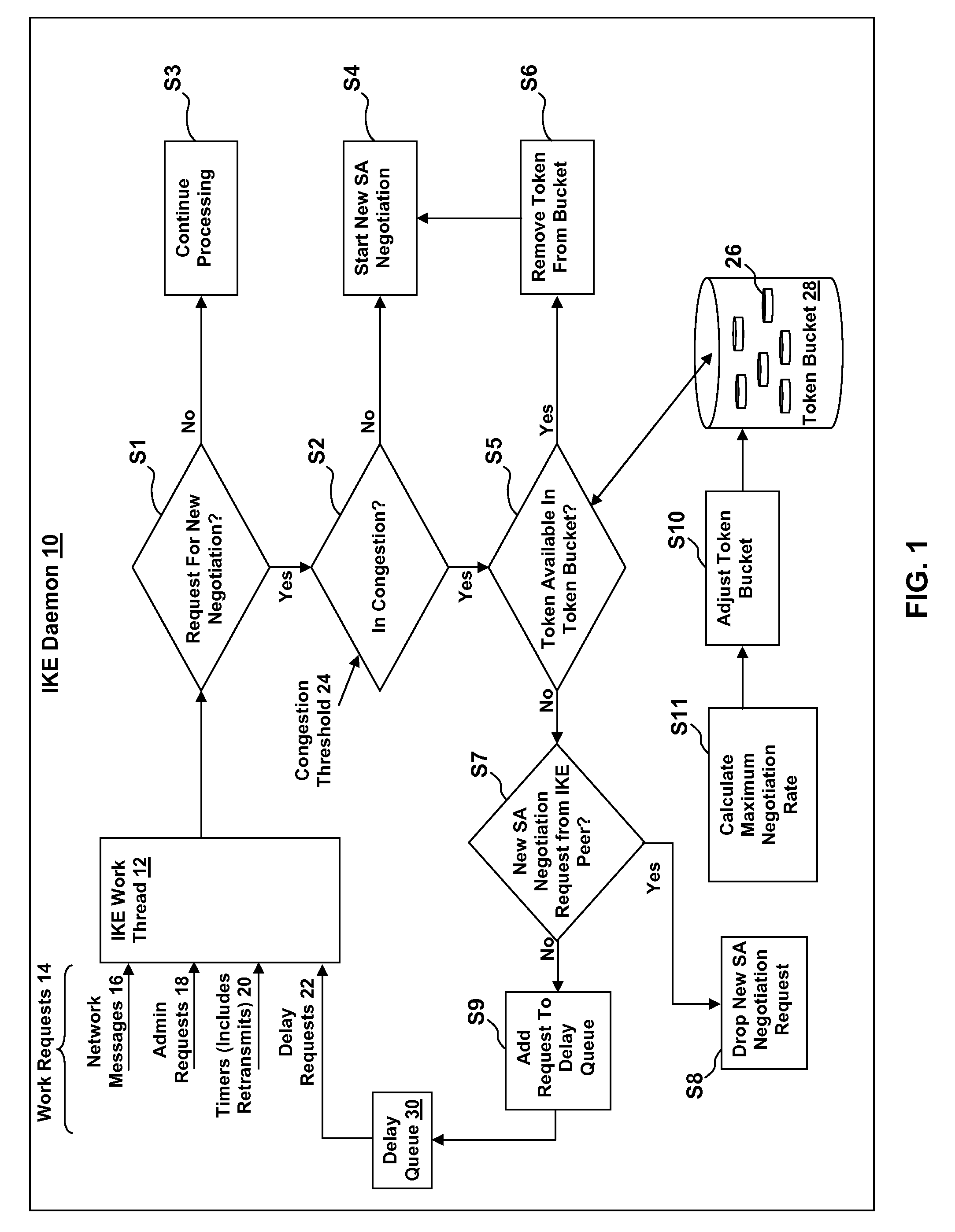
Ike daemon self-adjusting negotiation throttle
InactiveUS20070277232A1Minimizing retransmission processingMaximizing numberDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer networkInternet Key Exchange
The present invention provides an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) daemon self-adjusting negotiation throttle for minimizing retransmission processing during Security Association (SA) negotiation requests. A method in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention includes: receiving a request for a new negotiation to be performed by a negotiation system; determining if the negotiation system is in congestion; and if the negotiation system is determined to be in congestion: determining if a token is available in a token bucket; and if a token is available in the token bucket, removing the token from the token bucket; and performing the new negotiation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for resilient IP security/internet key exchange security gateway
ActiveUS20080155677A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlInternet Key ExchangeIPsec
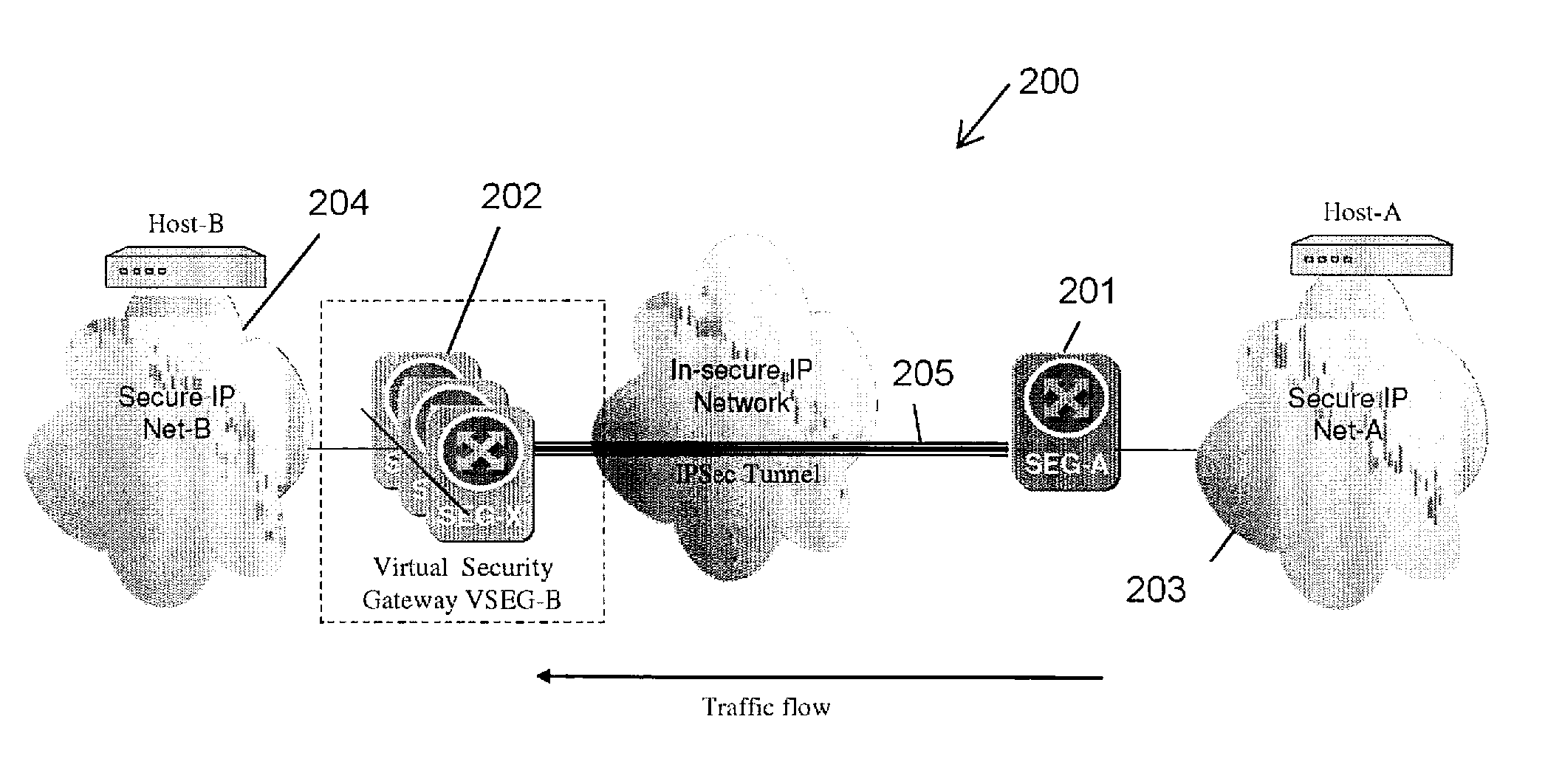
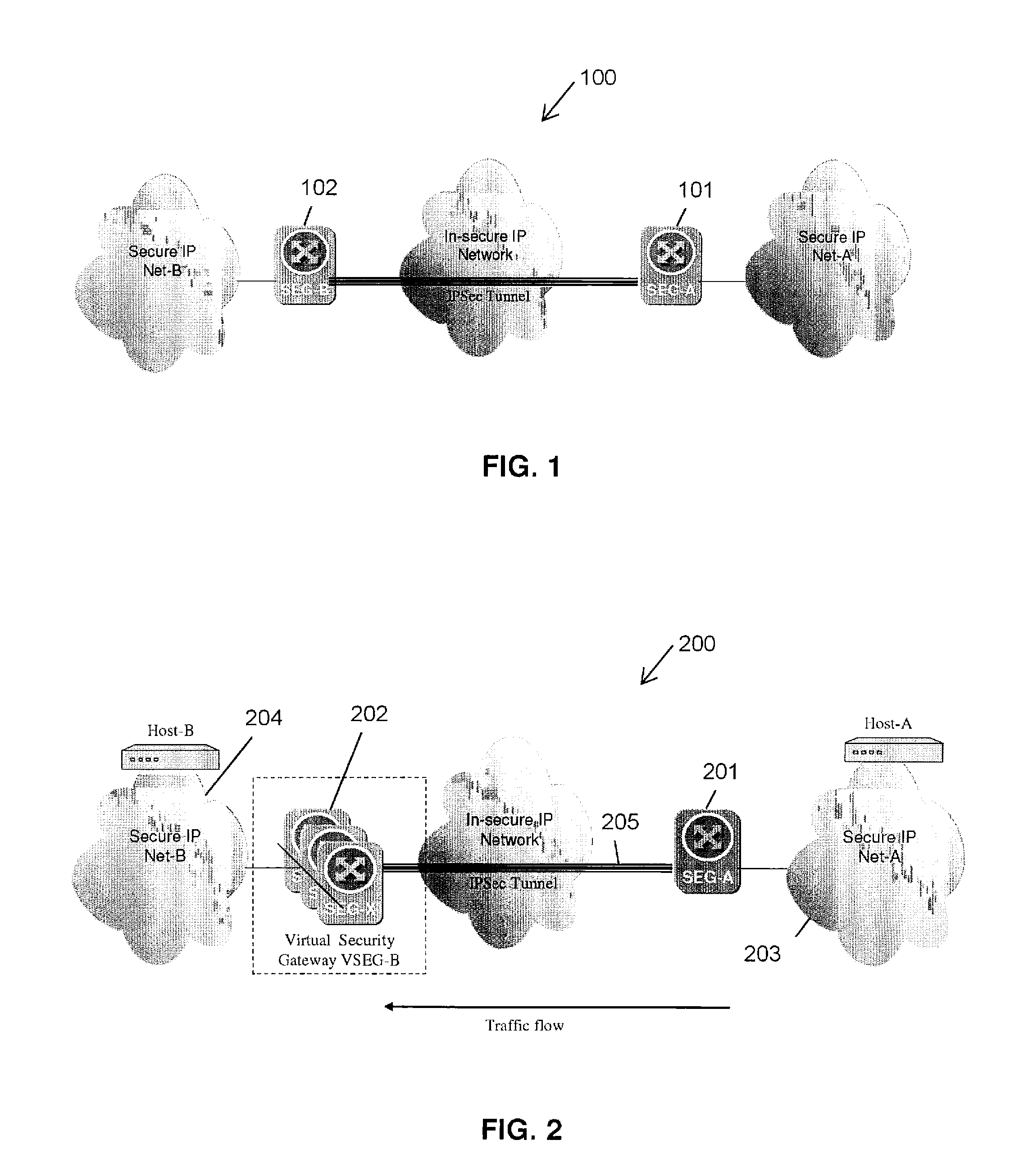
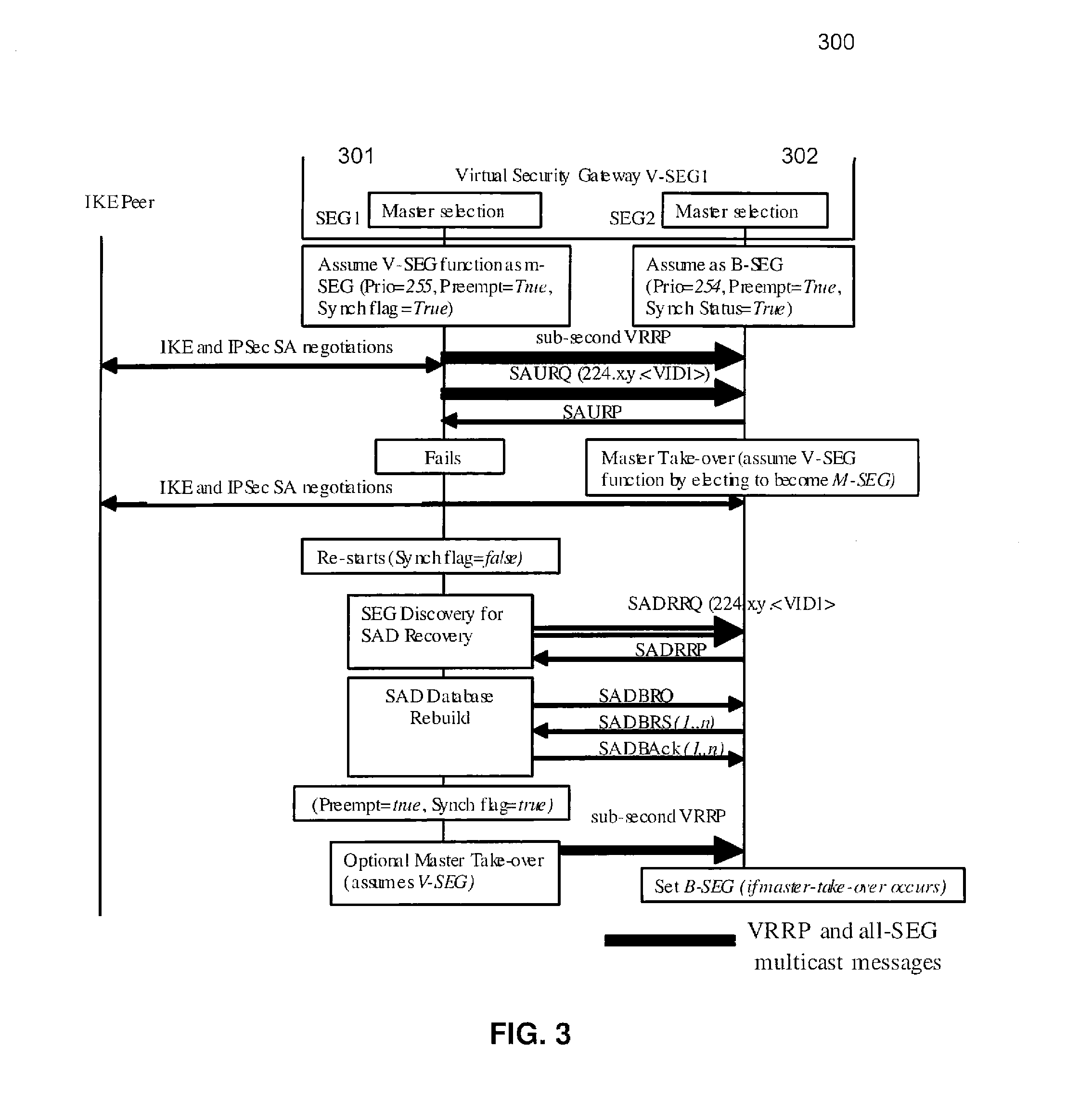
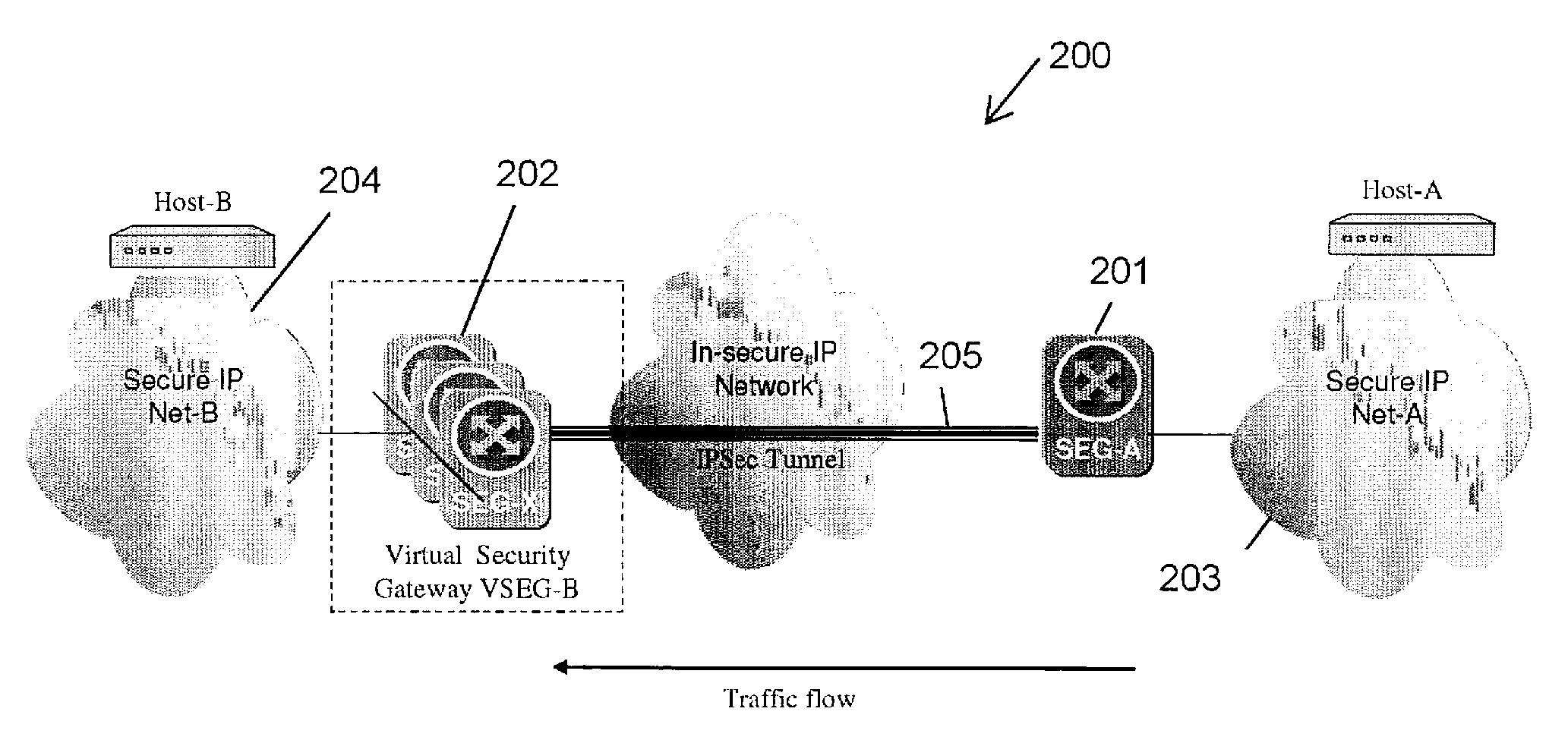
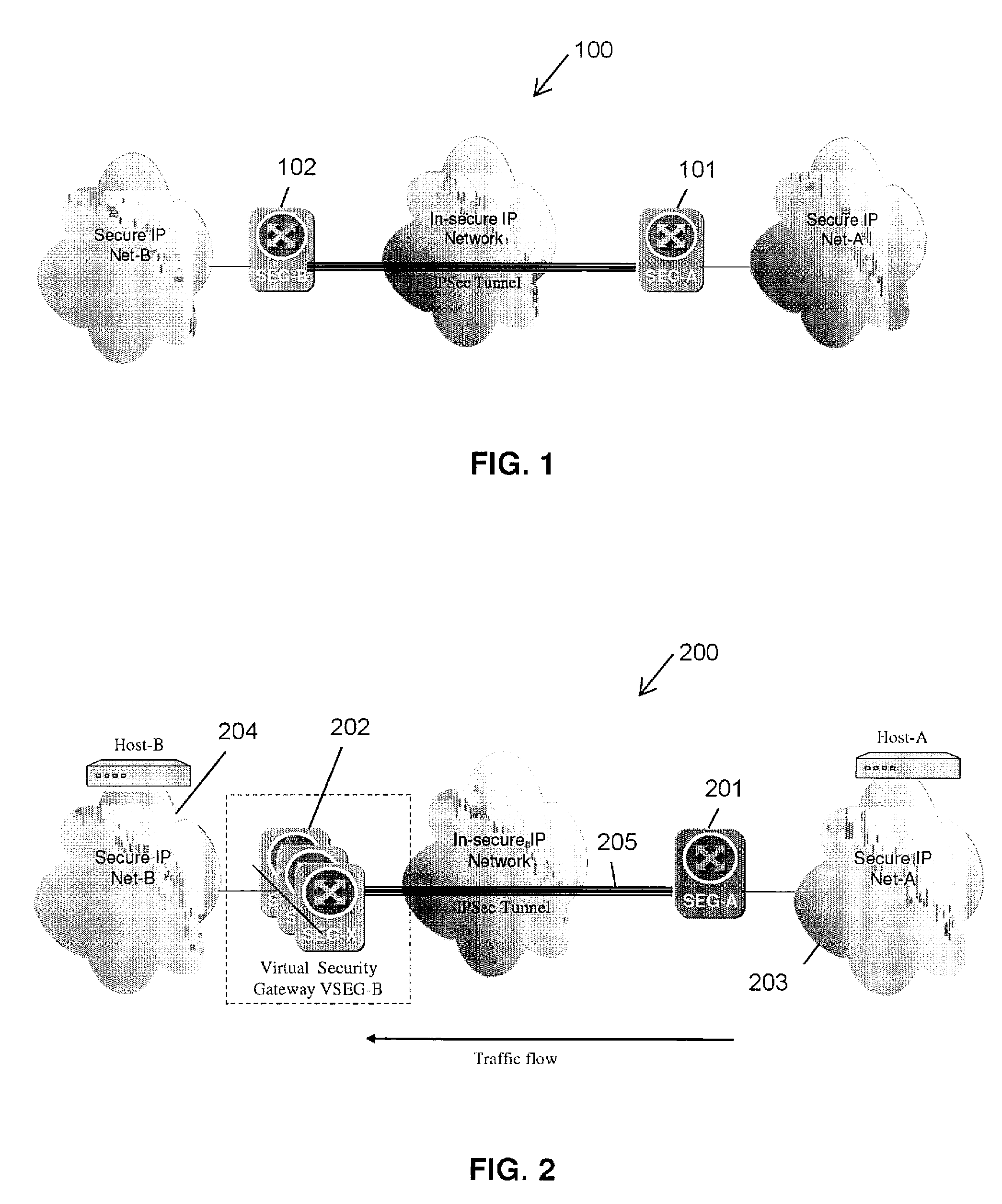
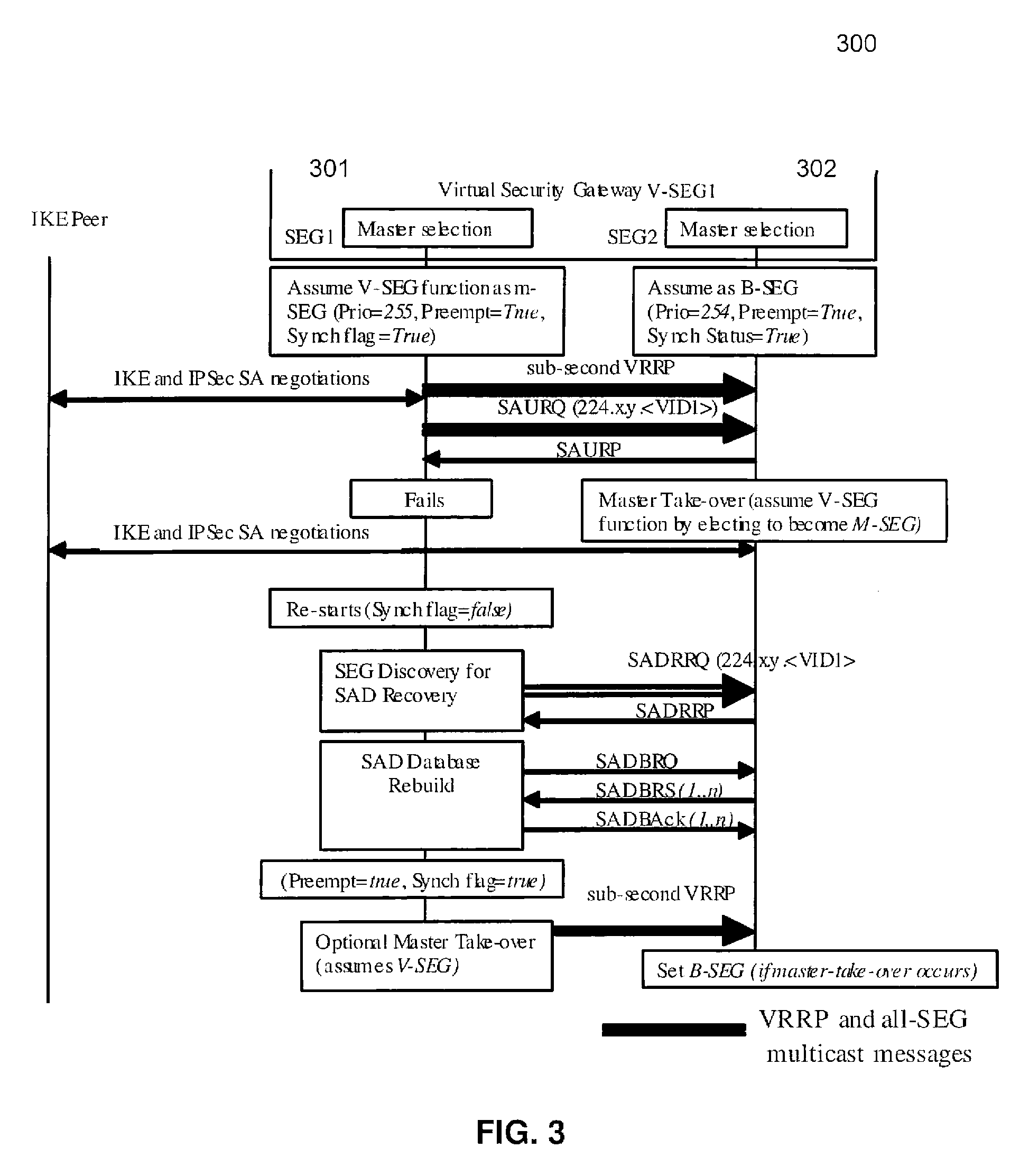
A method and apparatus adapting a Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) between a set of physical SEGs that realize a V-SEG function towards a remote IPsec / IKE peer. In tandem with the VRRP, a new protocol, referred to herein as the IPsec / IKE SA Transfer Protocol (SATP), is introduced to exchange IKE and IPsec SA information between VRRP capable SEGs. SATP synchronizes all participating SEGs with respect to dynamic IPsec state information in near real time. Thus, in the event of a master VRRP SEG failure, one of the hot-standby SEGs takes over the V-SEG function. This allows the V-SEG function to remain functional despite the possible failure of one or more participating SEGs.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
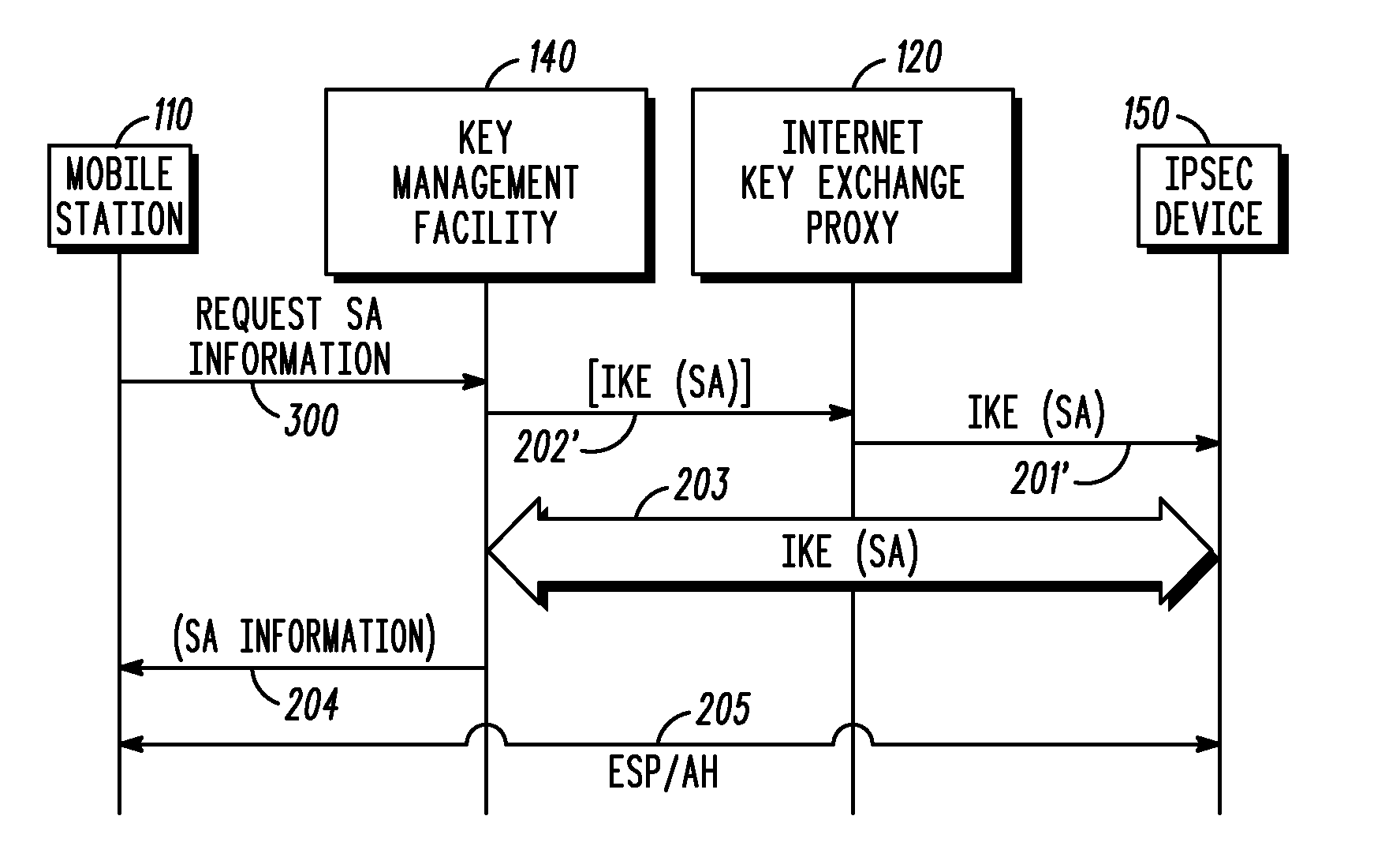
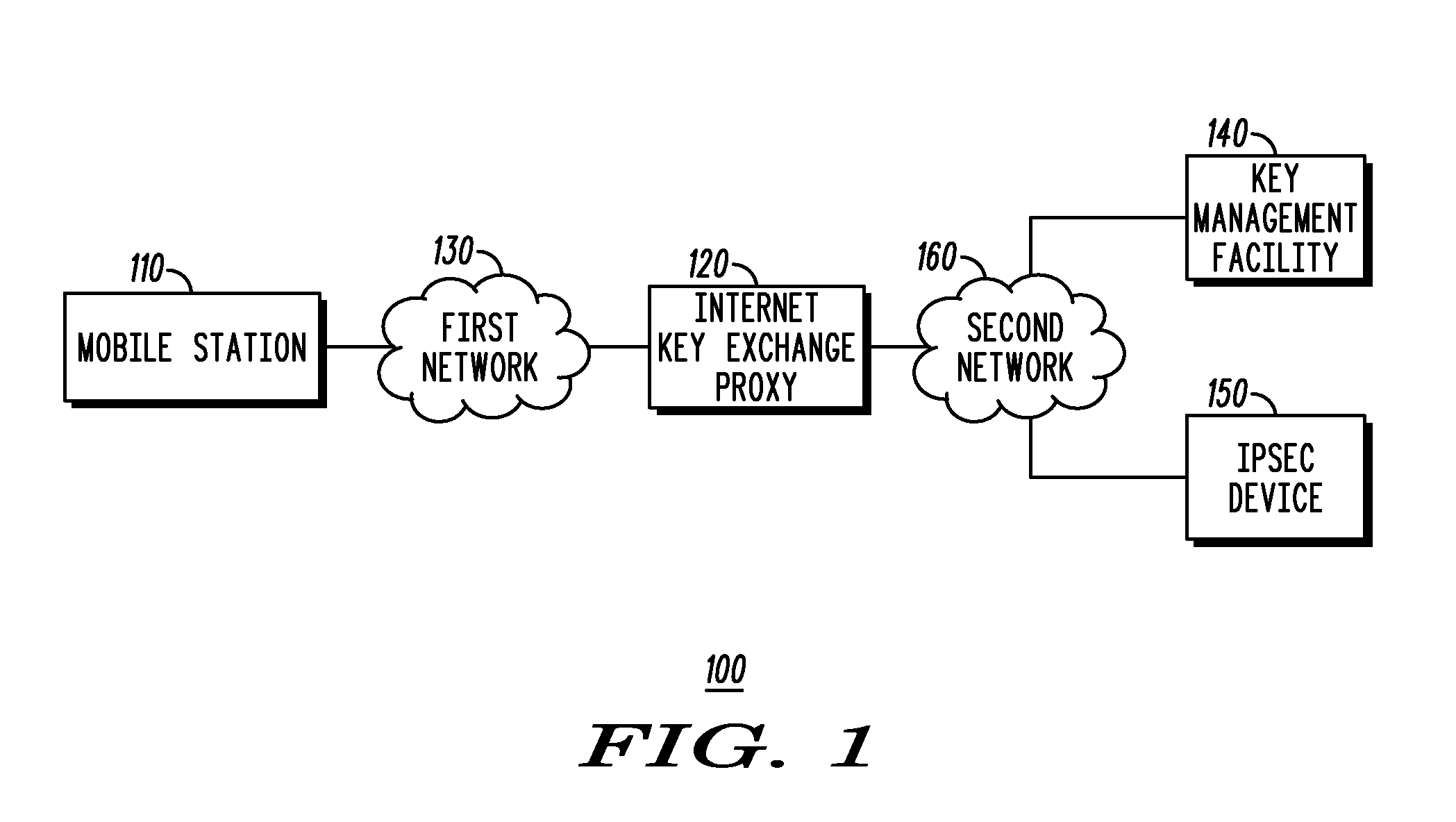
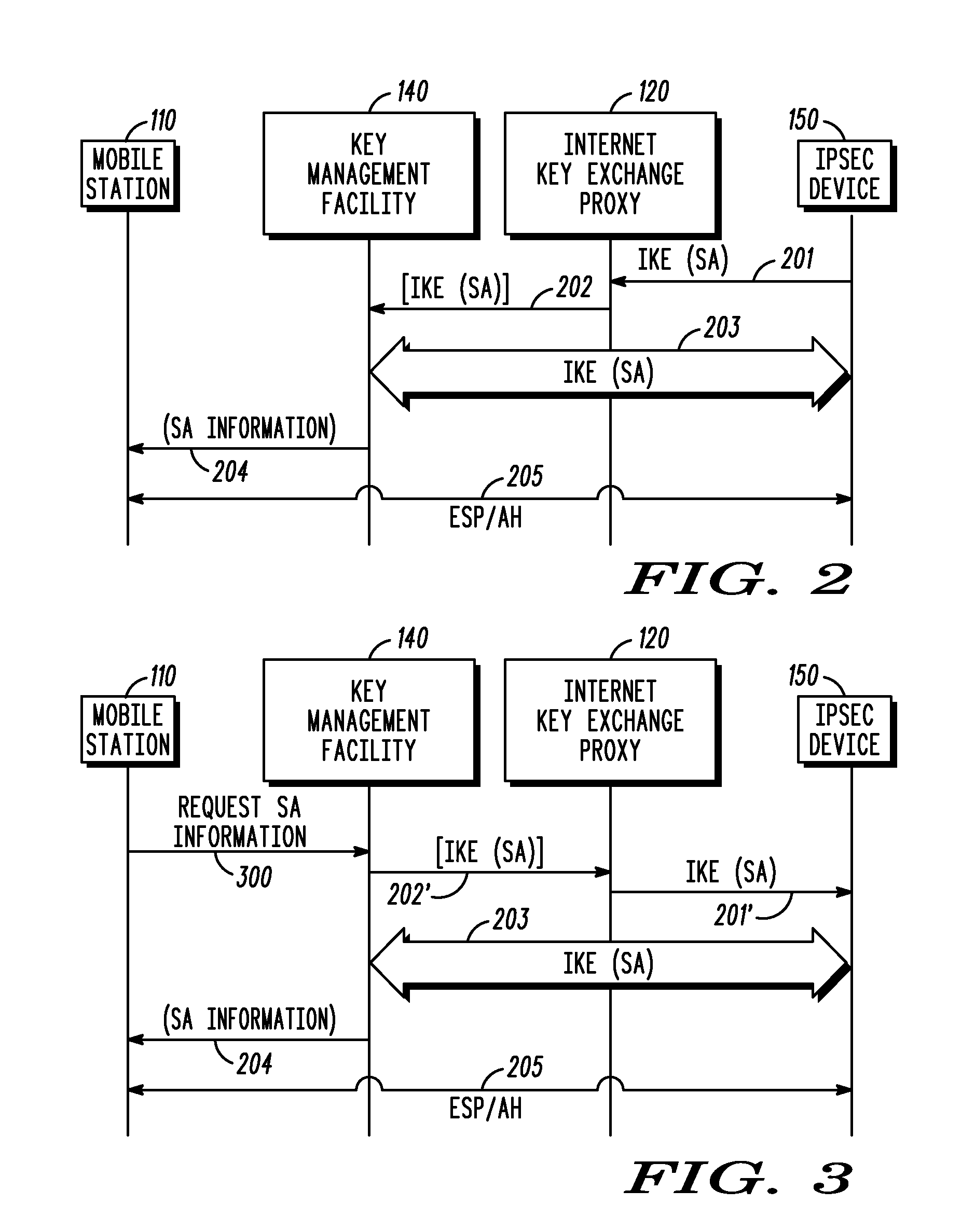
Method and system for using a key management facility to negotiate a security association via an internet key exchange on behalf of another device
InactiveUS20080137863A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageSecret communicationManagement toolCommunications system
A key management facility for a communication network masquerades as a first device within the communication system during an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) negotiation with a second device within the communication system. The key management facility establishes, on behalf of the first device, a security association with the second device using IKE. After the negotiation is complete, the key management device provides information regarding the security association to the first device such that the first device can engage in an Internet Protocol Security-protected communication with the second device.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
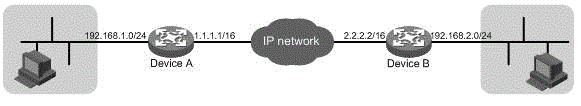
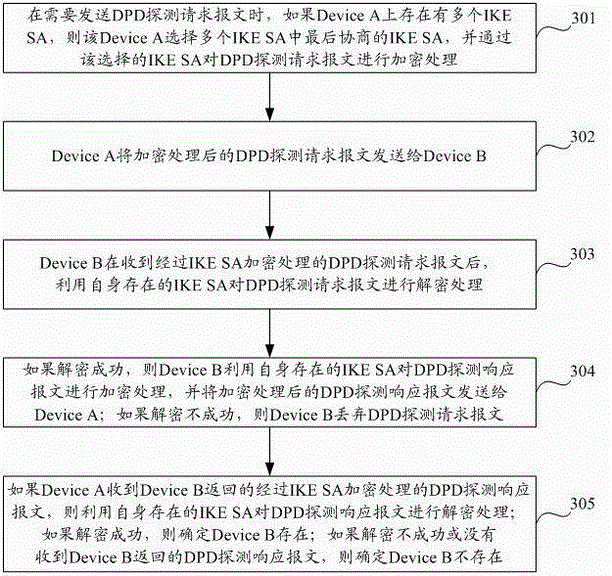
DPD method and equipment based on IPsec
The invention discloses a DPD (Dead Peer Detection) method and equipment based on IPsec (Internet Protocol Security). The method comprises the steps that detecting equipment selects a finally negotiated IKESA (Internet Key Exchange Security Association) from a plurality of IKESAs when the IKESAs corresponding to detected equipment exist on the detecting equipment, conducts encryption processing on a DPD request message by the selected IKESA, and sends the DPD request message to the detected equipment; if the detecting equipment receives a DPD response message, the detecting equipment conducts decryption processing on the DPD response message; if the decryption is successful, the detected equipment exists; and if the decryption is unsuccessful or no DPD response message is received, the detected equipment does not exist. With the adoption of the method and the equipment, CPU (Central Processing Unit) resources can be saved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
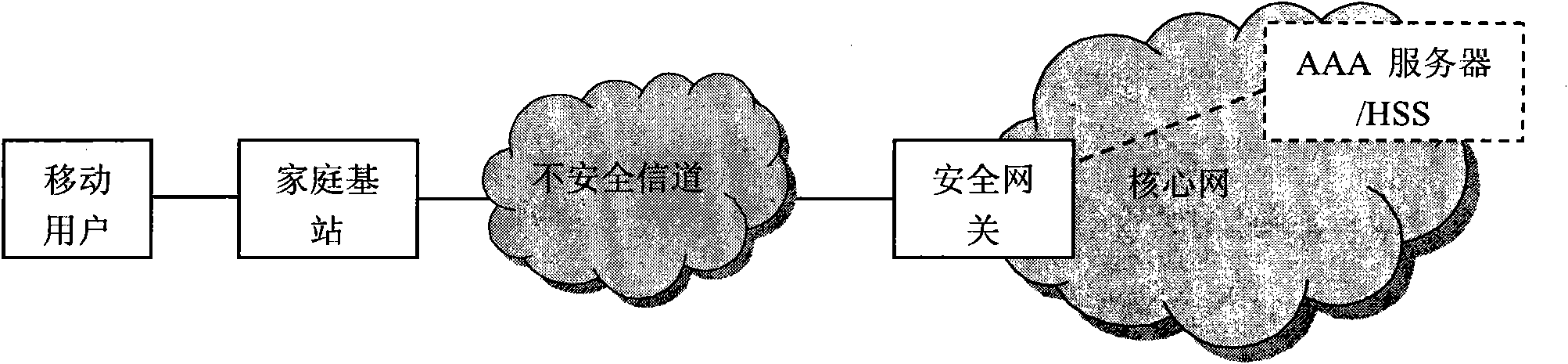
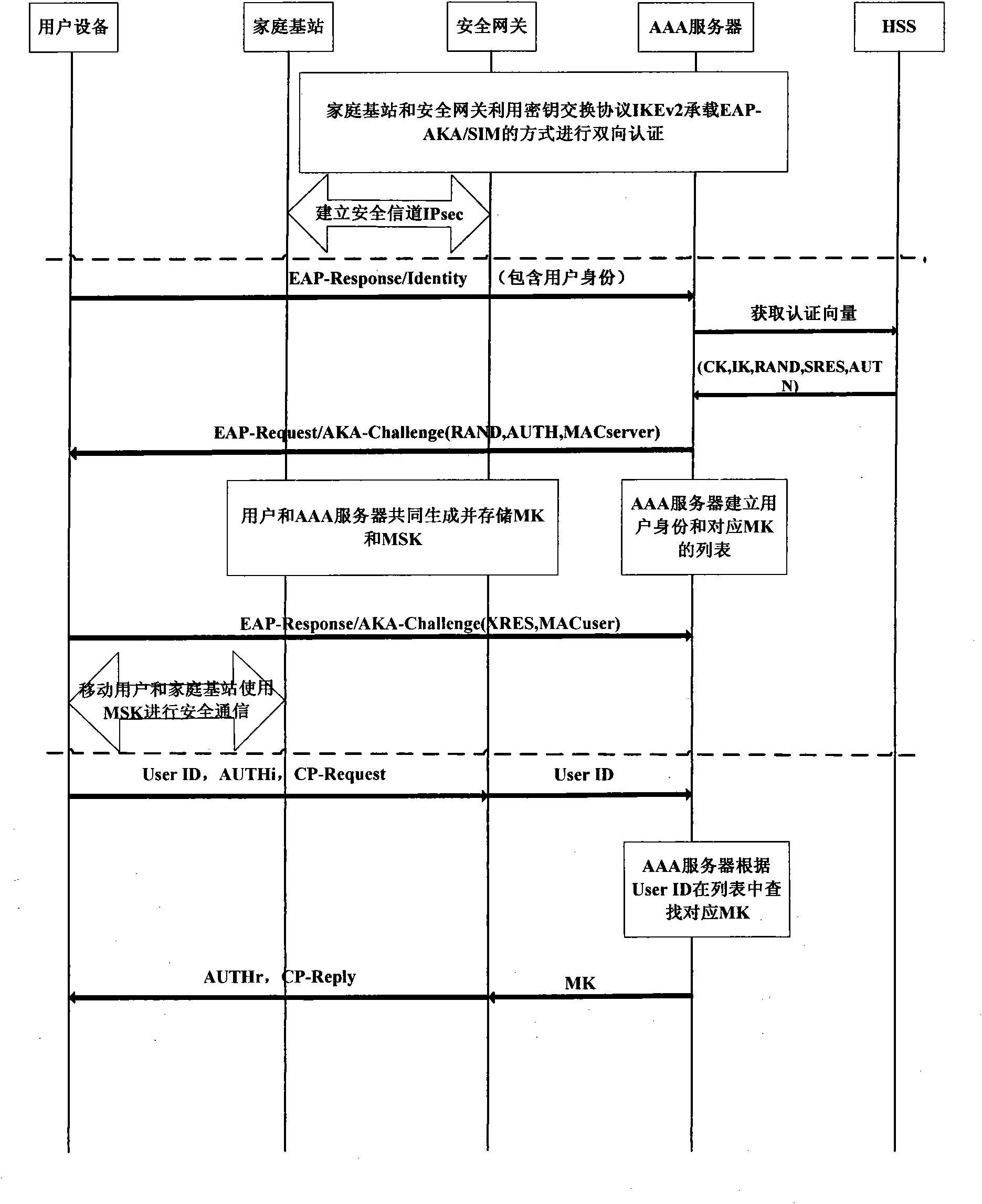
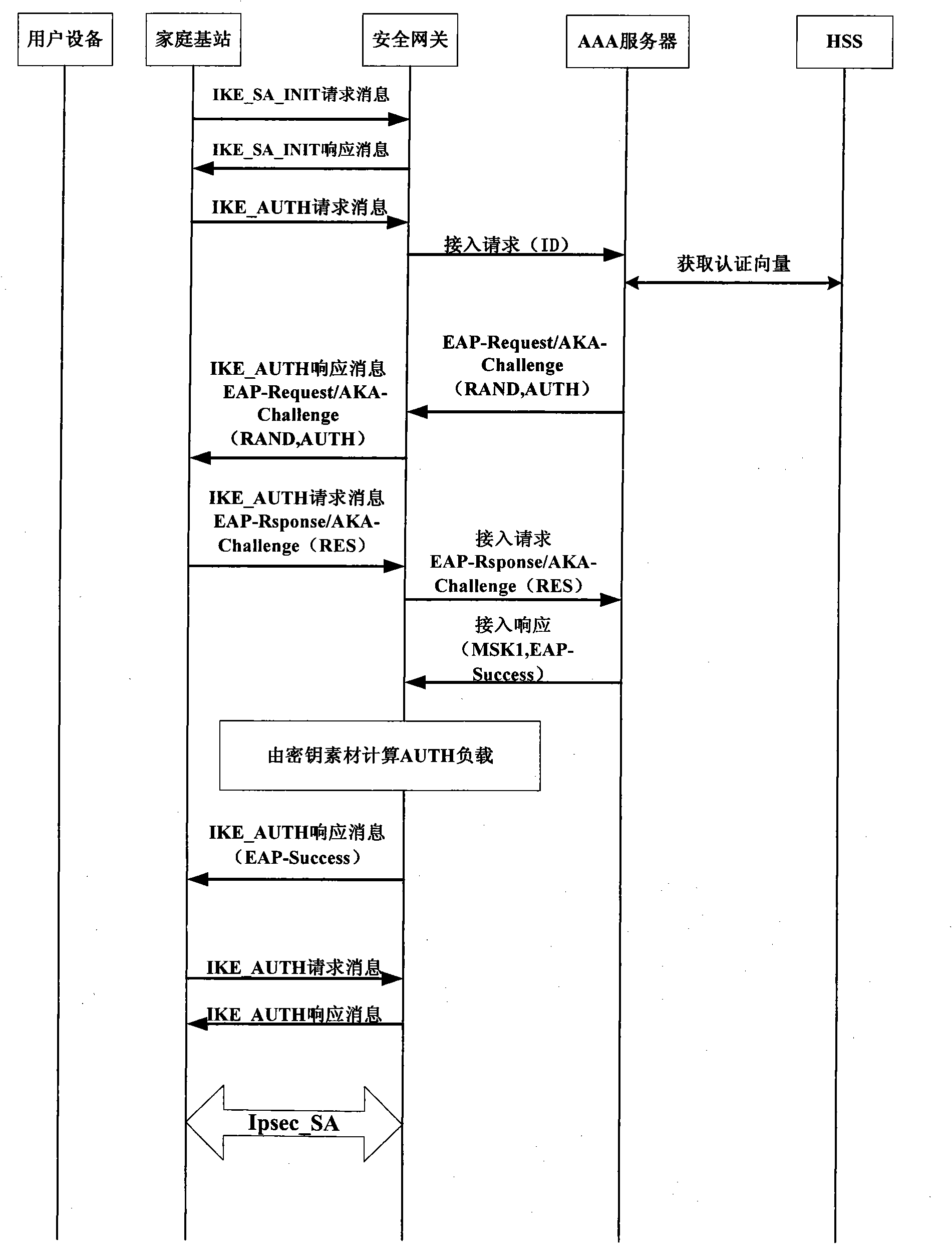
Authentication method for accessing mobile subscriber to core network through femtocell
InactiveCN101867928AEnsure safetyReduce transmissionTransmissionSecurity arrangementKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
The invention discloses an authentication method for accessing a mobile subscriber to a core network through a femtocell, which mainly makes up for the defect that a complete authentication method for accessing the mobile subscriber to the core network is not provided in the 3GPP standard. Under the condition of not changing network equipment in the 3GPP standard, the conventional extensible authentication protocol and key agreement EAP-AKA and internet key exchange IKEv2 are improved. The authentication method comprises that: (1) a secure channel IPsec is established between the femtocell and a secure gateway; (2) the mobile subscriber is subjected to access authentication and pre-generates an important authentication parameter MK for a step (3); and (3) the mobile subscriber and the core network perform bidirectional authentication by using the IPsec established by the step (1) and the MK pre-generated by the step (2). Compared with the traditional authentication method using the EAP-AKA and the IKEv2, the authentication method optimizes authentication steps under the condition of not reducing security, reducing authentication overhead, has the advantages of security and quickness, and is suitable for scenes that the mobile subscriber accesses the core network through the femtocell.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
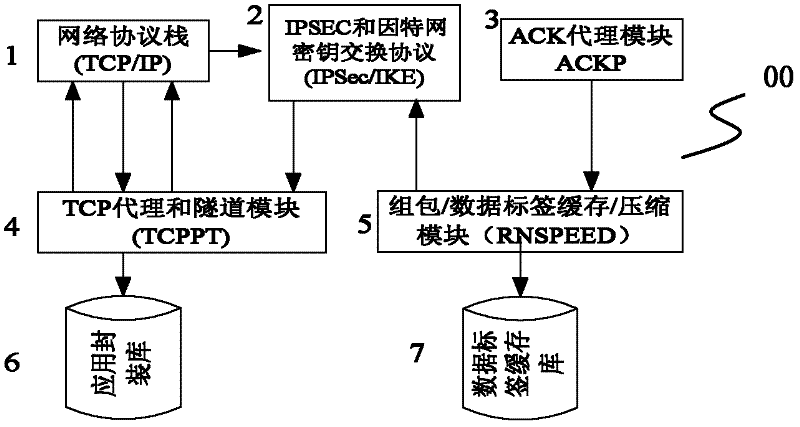
Wide area network vpn acceleration gateway and its acceleration communication system and method
InactiveCN102263687ANo data issuesImprove reliabilityNetworks interconnectionData compressionPacket communication
The invention relates to a technique for recombining, replacing, compressing and encapsulating network communication messages, in particular to a wide area network VPN accelerating gateway and its accelerating communication system and method. The WAN VPN acceleration gateway is: network protocol stack, IPSec and Internet key exchange protocol module, TCP agent and tunnel module and network protocol stack call in turn to form a closed-loop system, while TCP agent and tunnel module call the application package library module one-way Functions provided; ACK proxy module, package / data label cache / compression module, IPSec and Internet key exchange protocol modules are called sequentially, while package package / data label cache / compression module calls data label cache library one-way function function. The invention reduces the transmission of repeated data, greatly improves the link data transmission rate, and greatly enhances the high speed and reliability of the network.
Owner:武汉思为同飞网络技术股份有限公司
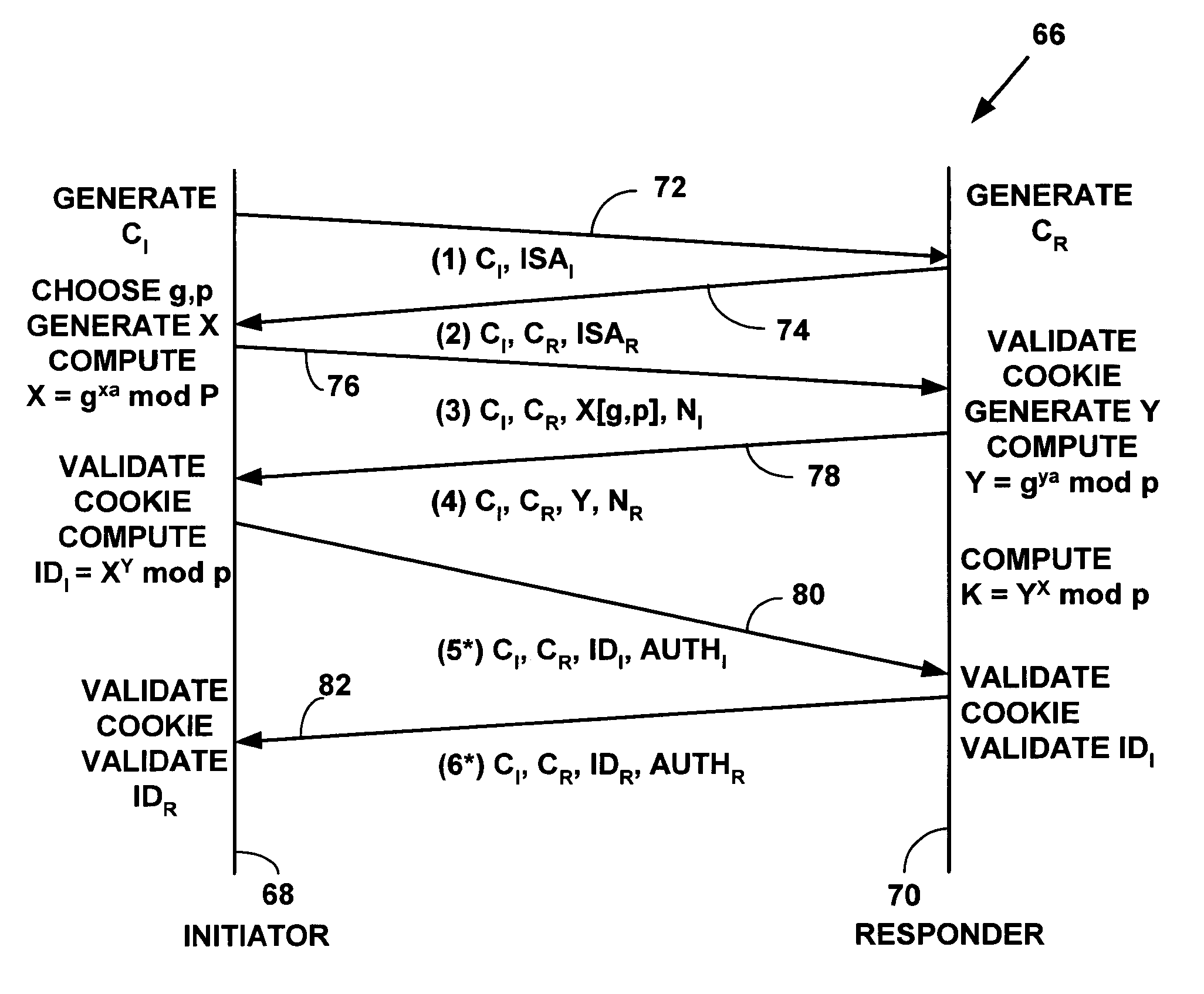
Method and system for distributed generation of unique random numbers for digital tokens
InactiveUS6948074B1User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsInternet Key ExchangeCryptographic protocol
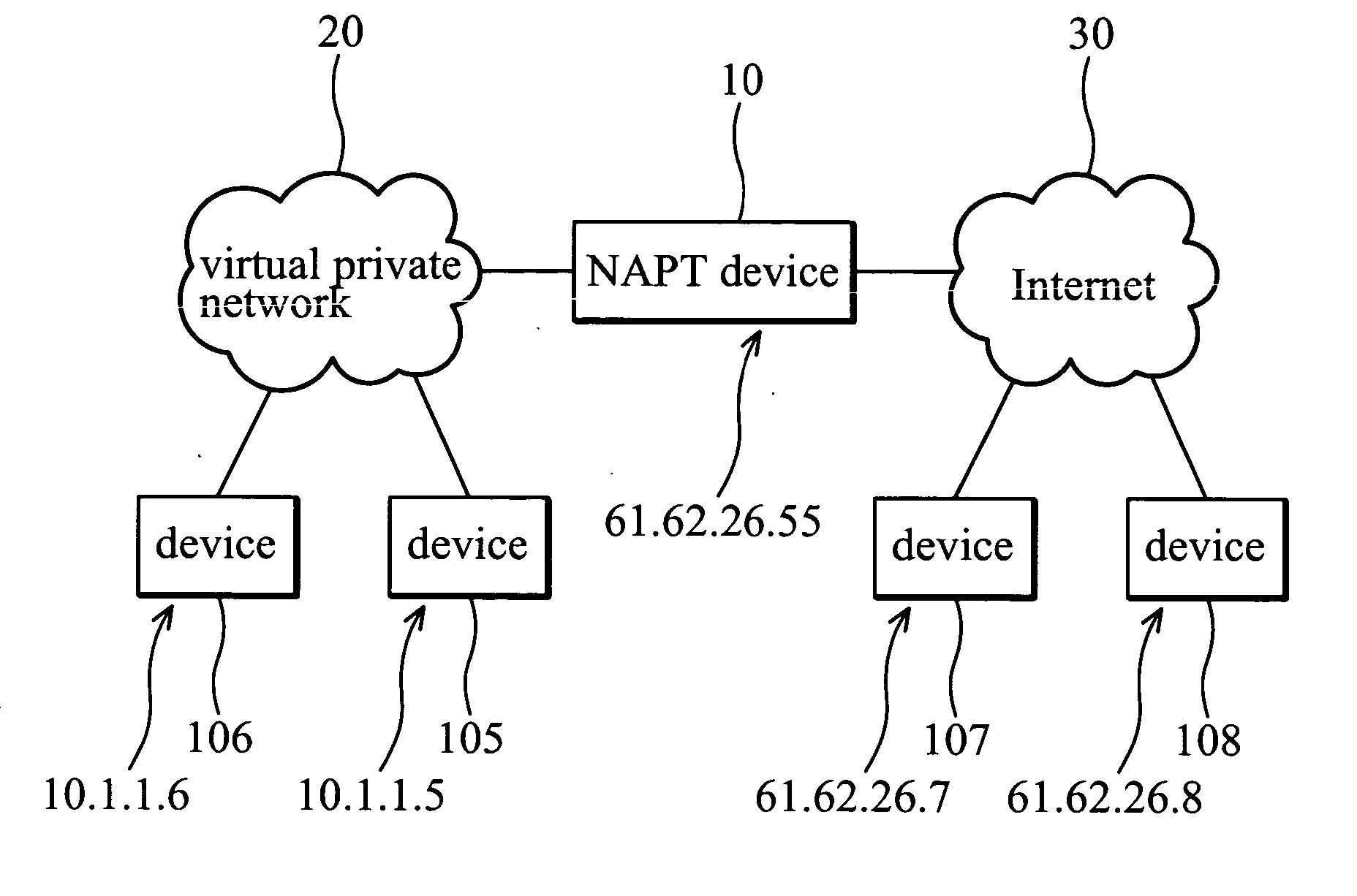
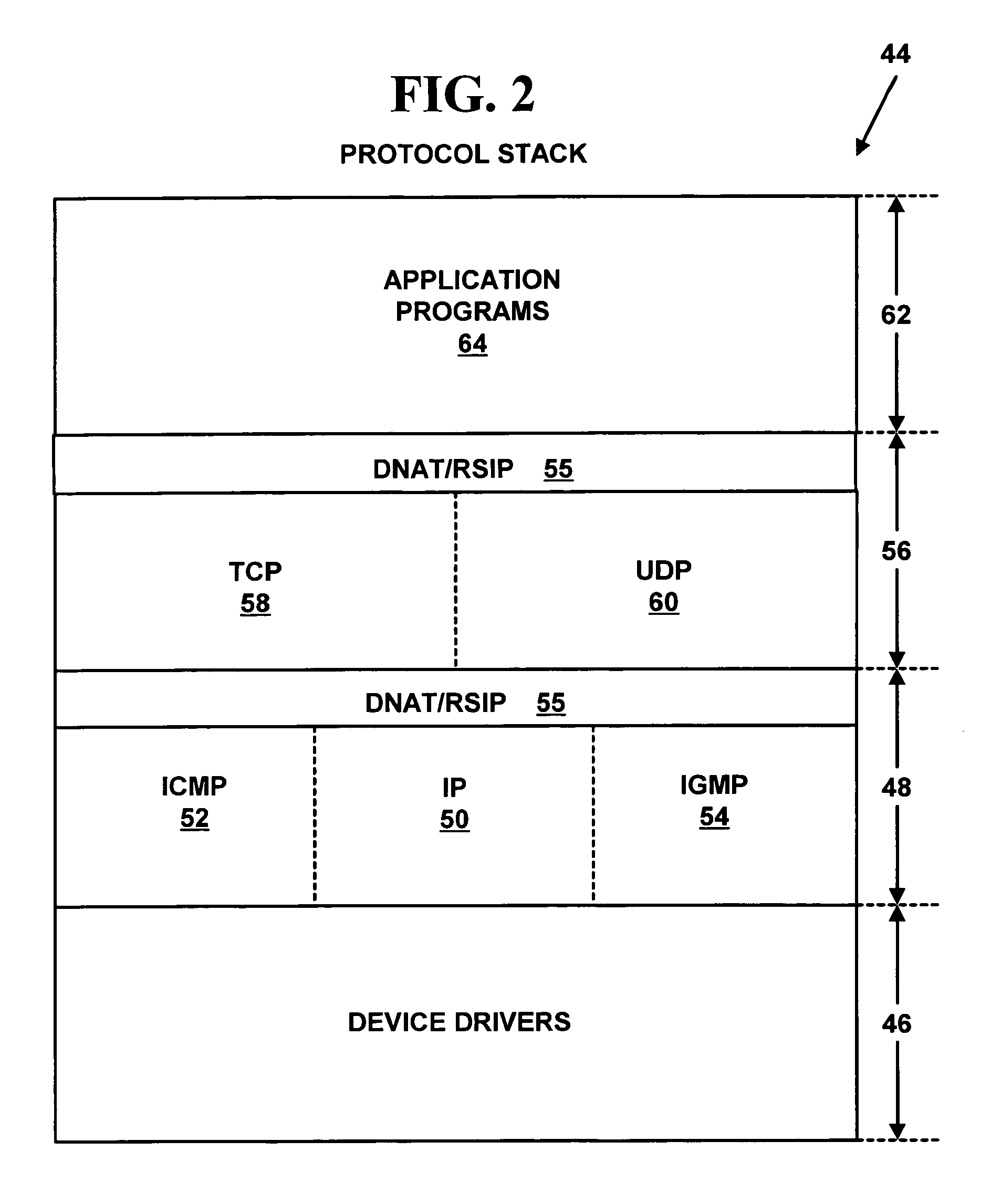
A method and system for distributed generation of unique random numbers. The unique random number can be used to create digital cookies or digital tokens. A first network device (e.g., a computer) on a computer network receives an x-bit bit mask template from a second network device on the computer network (e.g., a gateway). The first network device generates a first portion of an x-bit digital cookie. The first network device requests a second portion of the x-bit digital cookie from the second network device. The request includes the first portion of the x-bit digital cookie. The first network device generates a complete x-bit digital cookie using the first portion of the x-bit digital cookie generated by the first network device and the second portion of the x-bit digital cookie generated by the second network device. The generated complete x-bit digital cookie is not in use on the computer network because the second network device has selected the second portion of the bit mask so the complete x-bit digital cookie including the first portion generated on the first network device and the second portion generated on the second network device is not use on the computer network. The method and system can be used on a Distributed Network Address Translation (“DNAT”) or a Realm Specific Internet Protocol (“RSIP”) subnet to allow a network device (e.g., a computer) to create a complete x-bit digital cookie with help from a DNAT / RSIP gateway. The complete x-bit digital cookie can be used as a 64-bit anti-clogging cookie for security protocols such as Internet Key Exchange (“IKE”) protocol exchanges used with Internet Protocol security (“IPsec”).
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Controlling the number of internet protocol security (IPsec) security associations
ActiveUS20070157305A1Increase the number ofMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlInternet protocol suiteInternet Key Exchange
The invention provides a system and method for controlling the number of Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) security associations per Internet Key Exchange (IKE) security association for a single user. The limit on the number of security association (SA) tunnels per key management protocol SA may be stored in a server. A user equipment sends a request, to the server, to set up a new SA. The server, upon receiving the request, checks whether the limit on the number of SA tunnels per key management protocol has been reached. The request is accepted when the limit has not yet been reached.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Apparatus and method for resilient IP security/internet key exchange security gateway
A method and apparatus adapting a Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) between a set of physical SEGs that realize a V-SEG function towards a remote IPsec / IKE peer. In tandem with the VRRP, a new protocol, referred to herein as the IPsec / IKE SA Transfer Protocol (SATP), is introduced to exchange IKE and IPsec SA information between VRRP capable SEGs. SATP synchronizes all participating SEGs with respect to dynamic IPsec state information in near real time. Thus, in the event of a master VRRP SEG failure, one of the hot-standby SEGs takes over the V-SEG function. This allows the V-SEG function to remain functional despite the possible failure of one or more participating SEGs.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method, device and system for negotiating business bearing tunnels
ActiveCN102055733AImprove processing efficiencyReduce transmission delayNetworks interconnectionCommunications systemInternet Key Exchange
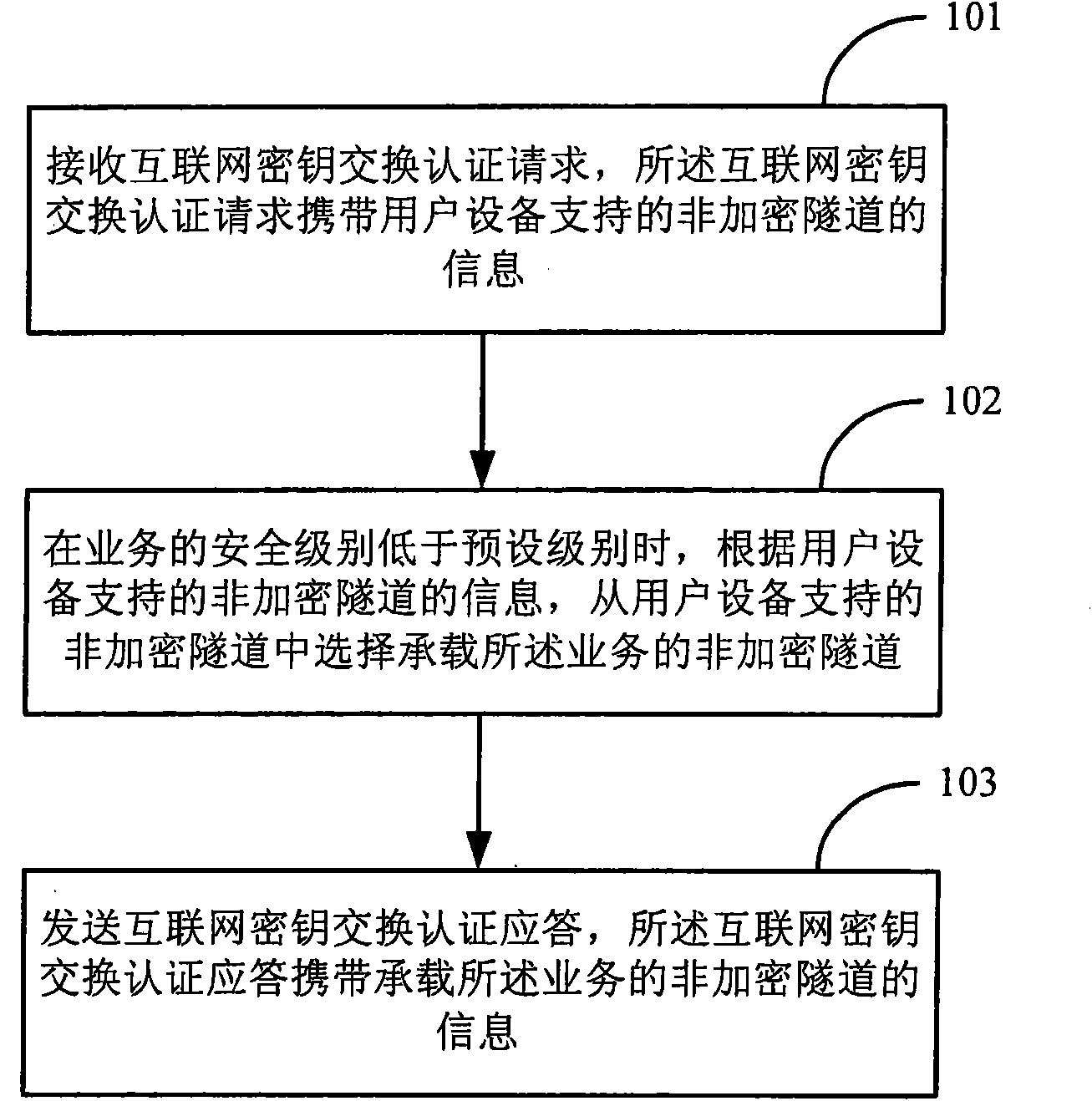
The invention discloses a method for negotiating business bearing tunnels, which comprises the following steps: receiving an internet key exchange (IKE) authentication request, wherein the IKE authentication request carries information of non-encrypted tunnels supported by user equipment; when the security level of the business is lower than the preset level, according to the information of the non-encrypted tunnels supported by the user equipment, selecting the non-encrypted tunnels for bearing the business from the non-encrypted tunnels supported by the user equipment; and sending an IKE authentication response, wherein the IKE authentication response carries the information of the non-encrypted tunnels for bearing the business. The invention also discloses a grouping gateway device, the user equipment and a communication system. In the method, the non-encrypted tunnel for bearing the business can be negotiated, so that the encryption / decryption treatment and / or the consistency check are not carried out when the subsequent business bearing is performed, thus reducing the transmission delay of the messages and the device cost.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Secure extended authentication bypass
ActiveUS8201233B2Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsKey exchangeInternet Key Exchange
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for recovering from the failure or reset of an IKE node
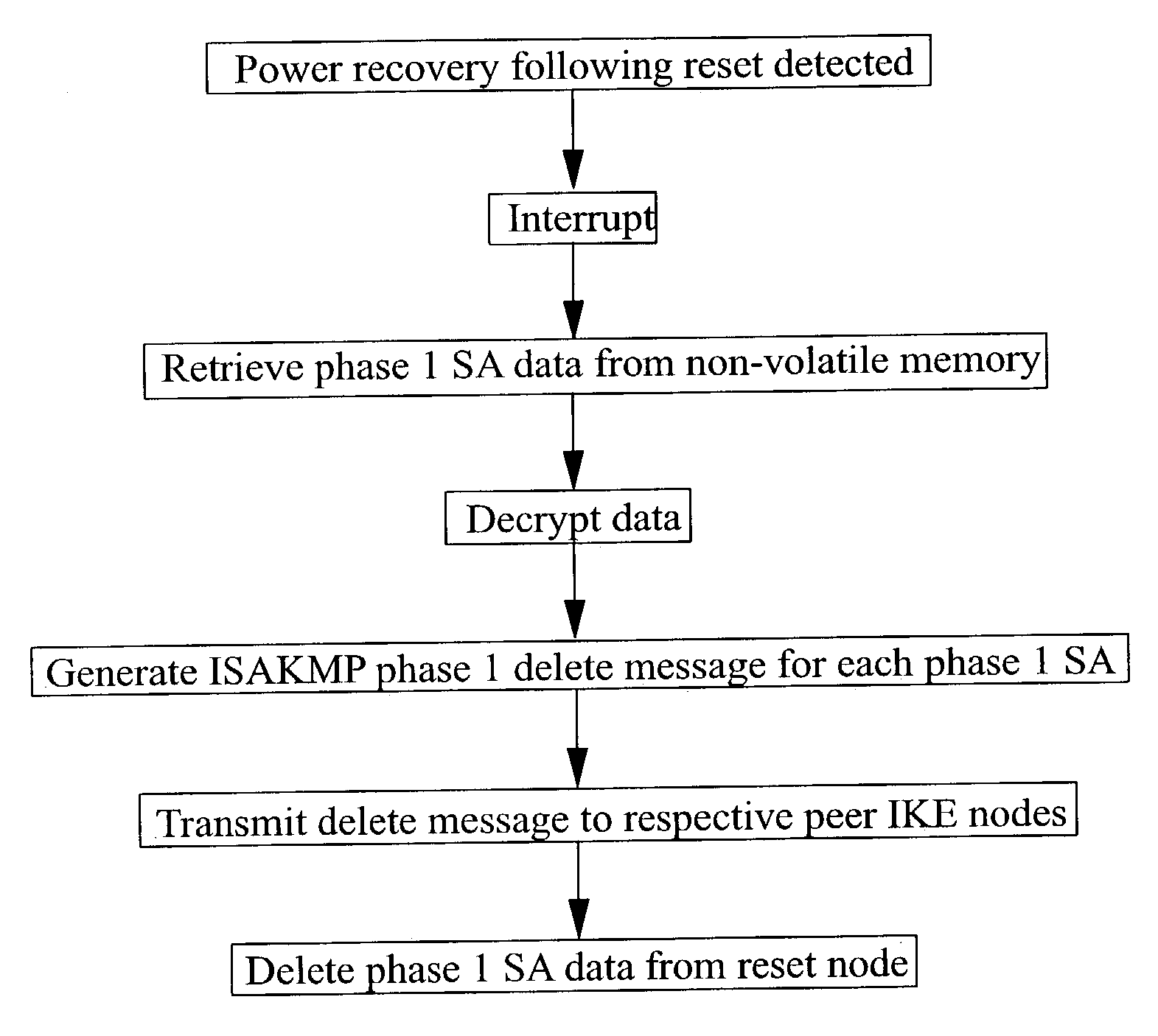
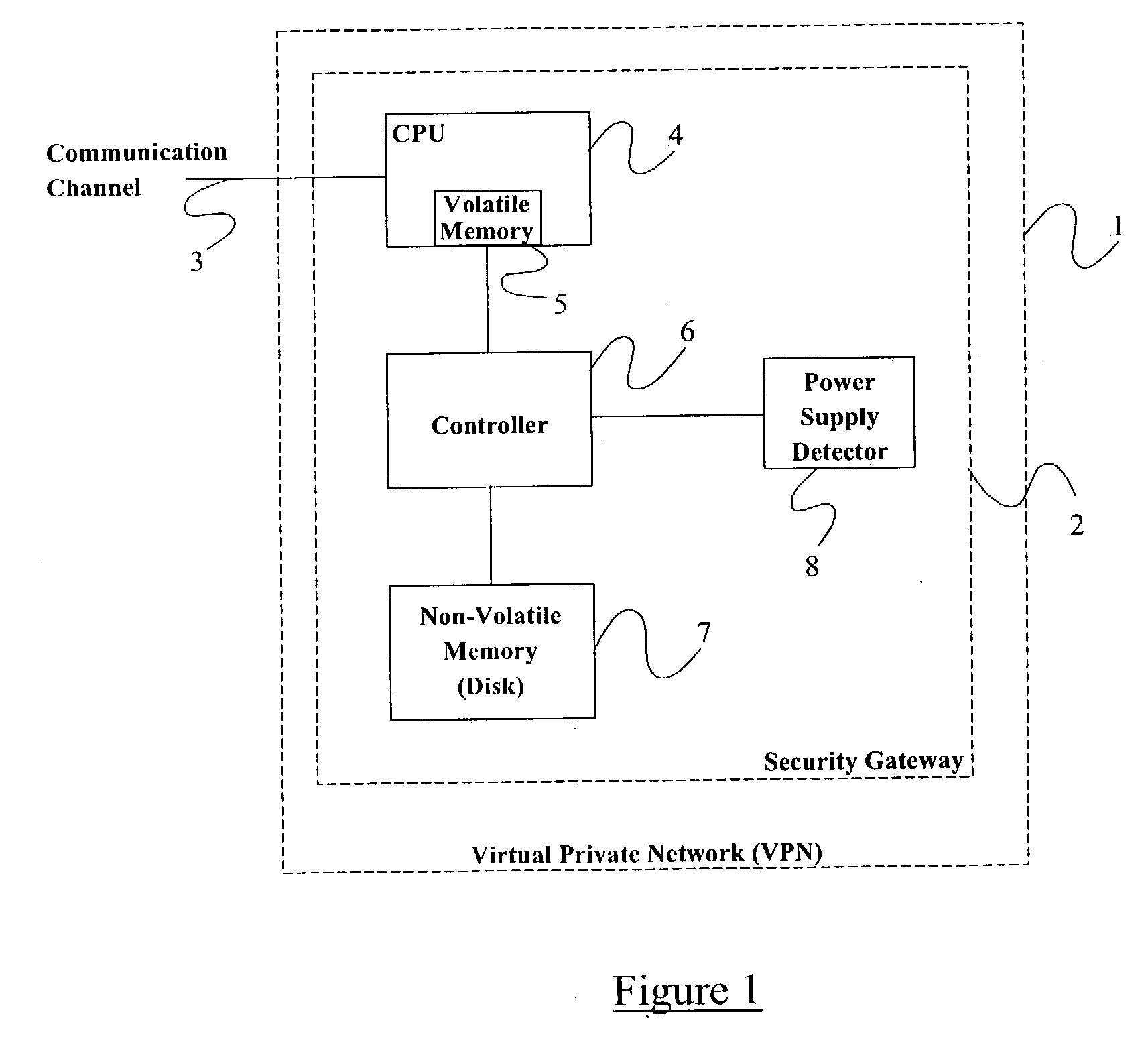
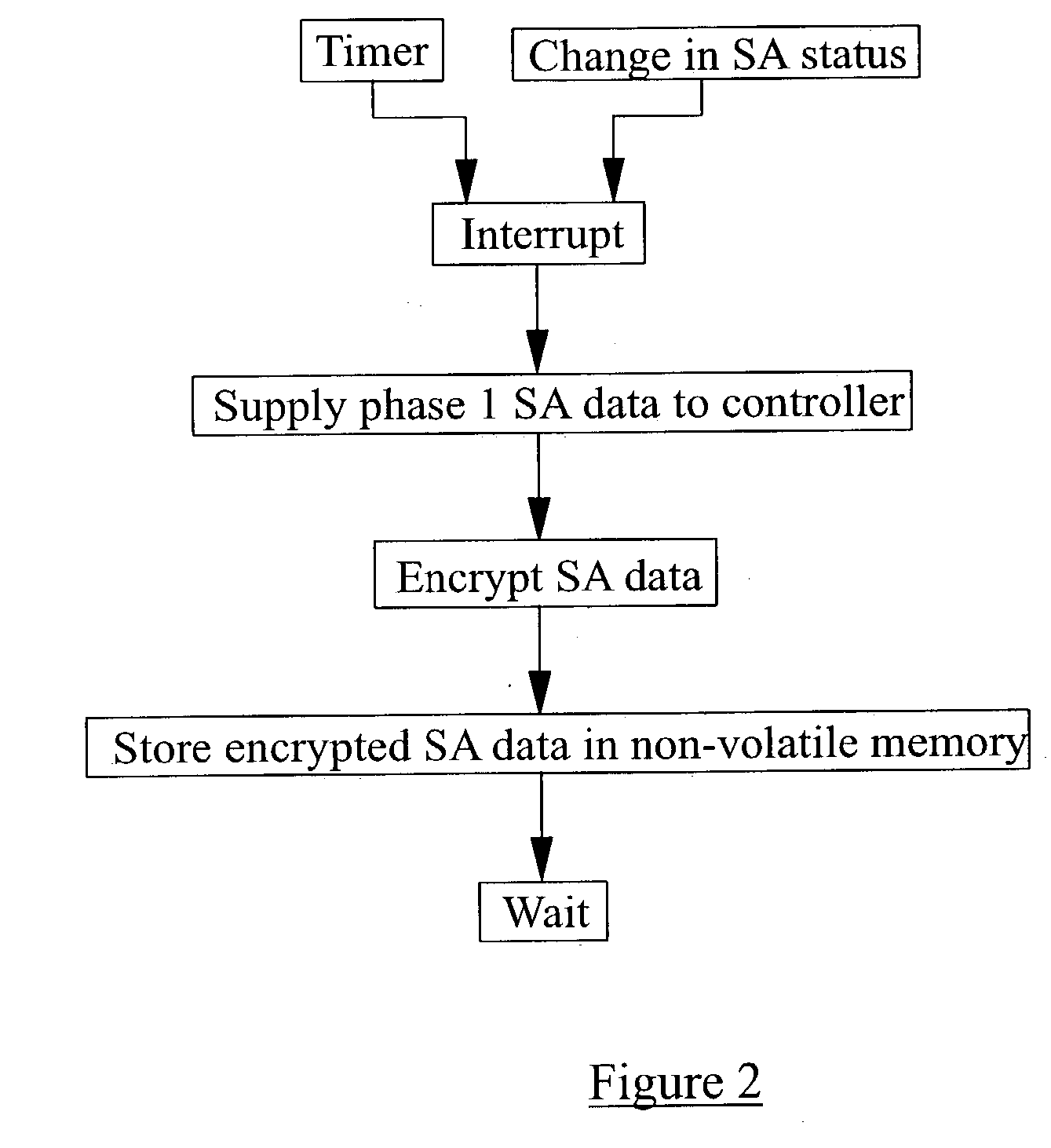
InactiveUS20030237003A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlInternet Security Association and Key Management ProtocolComputer network
Methods and apparatus adapted to recover from the reset of an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) node involved in secure IPSec communication with one or more peer IKE nodes. For each phase 1 Security Association (SA) established prior to reset, an Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) phase 1 SA delete message is generated. Each delete message is transmitted to the one or more peer IKE nodes, whereby the peer IKE nodes delete each local phase 1 SA corresponding to each of the phase 1 SAs established prior to the reset.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com