Patents
Literature
87 results about "Ingress router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
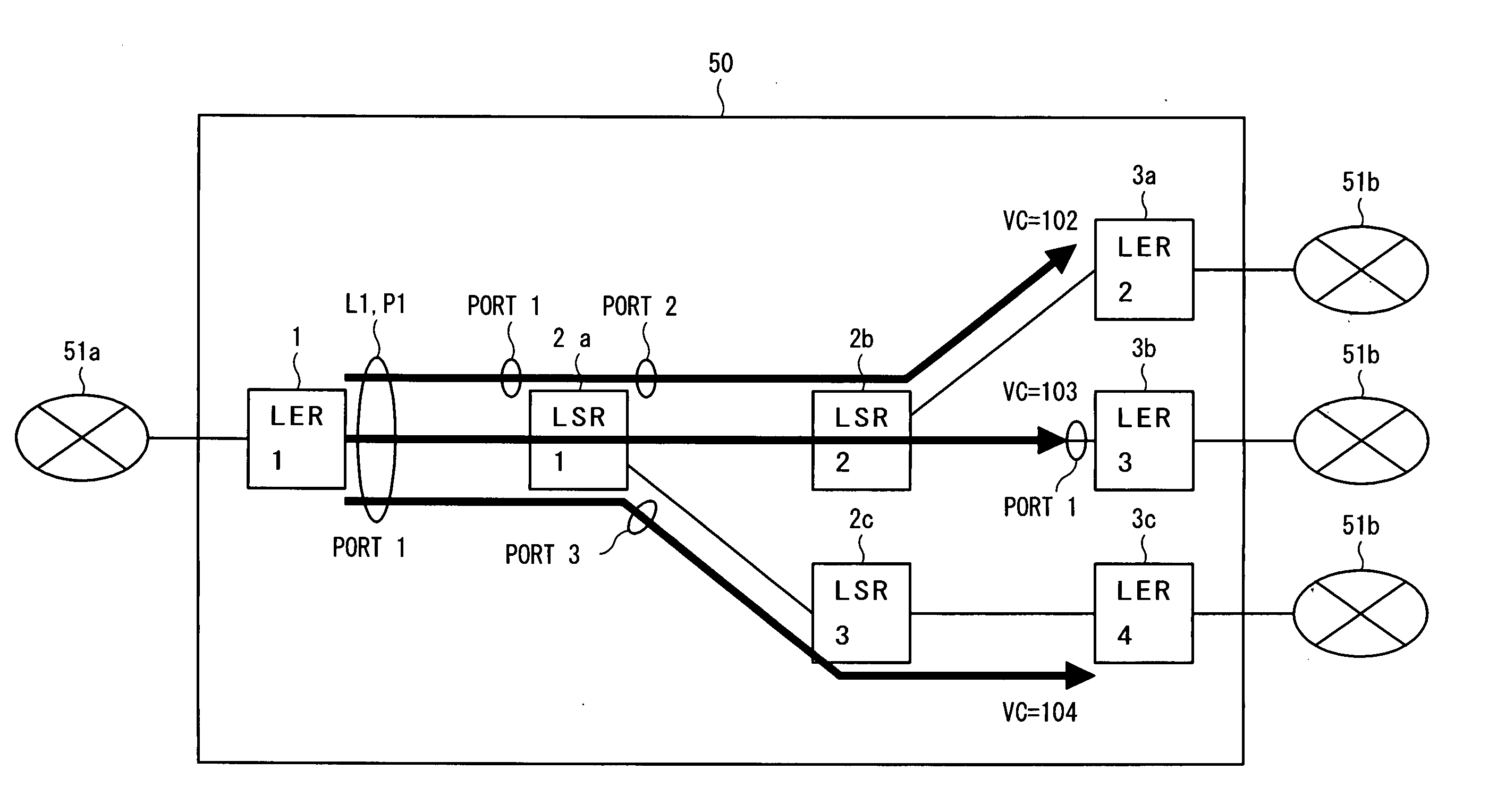
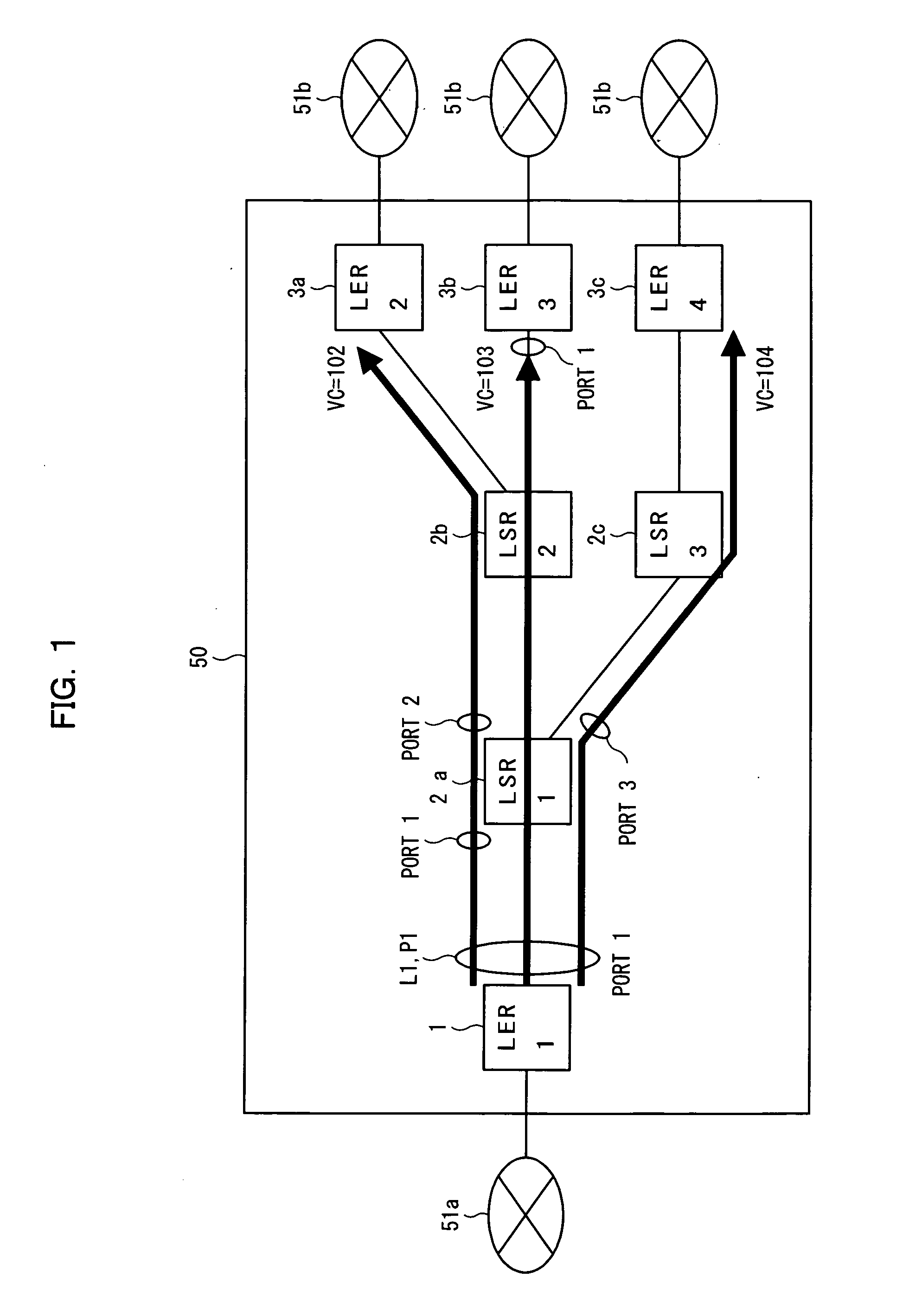
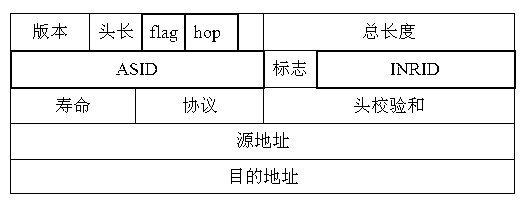
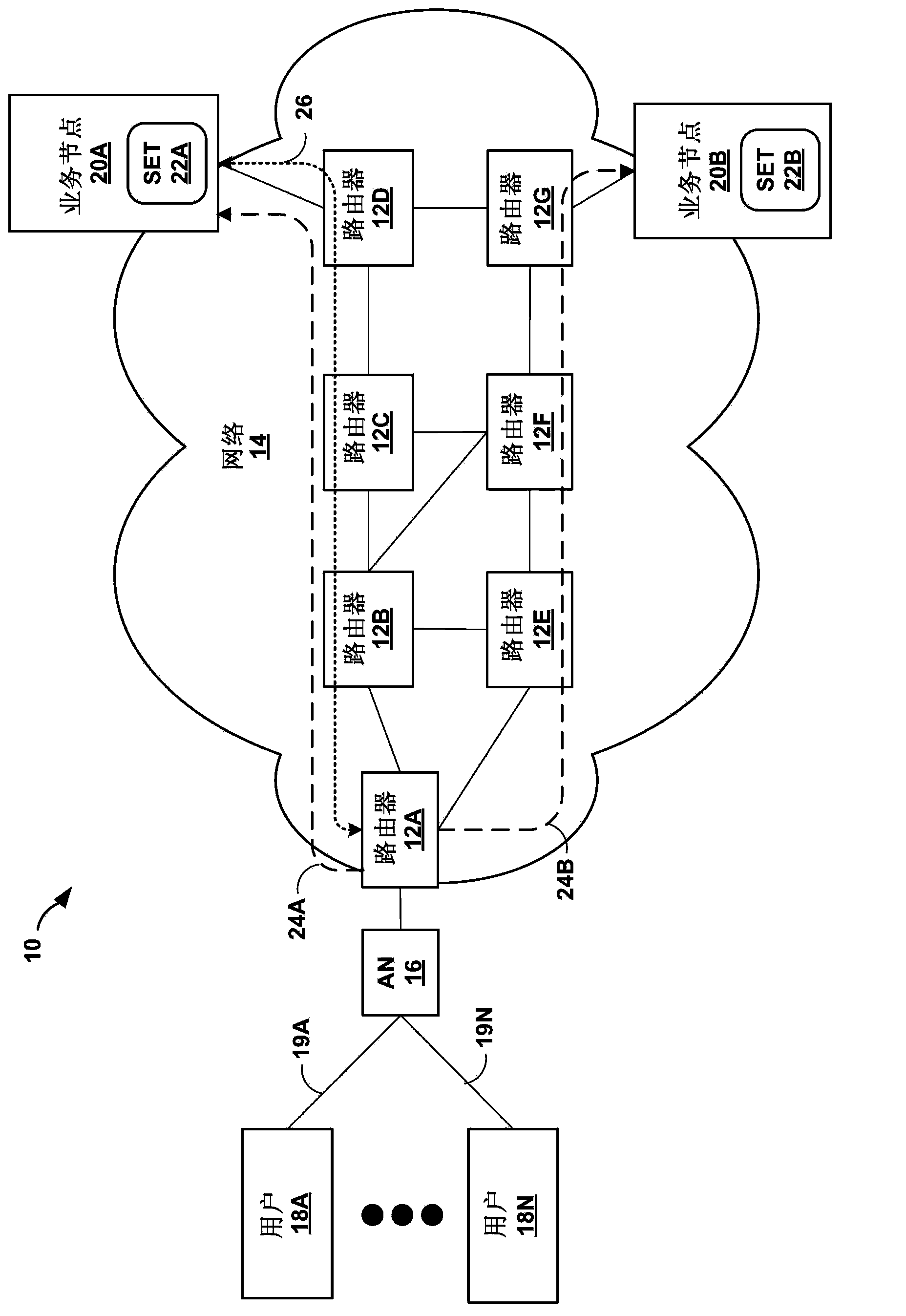
An "ingress router" is a Label Switch Router that is a starting point (source) for a given Label Switched Path (LSP). An ingress router may be an egress router or an intermediate router for any other LSP(s). Hence the role of ingress and egress routers is LSP specific. Usually, the MPLS label is attached with an IP packet at the ingress router and removed at the egress router, whereas label swapping is performed on the intermediate routers. However, in special cases (such as LSP Hierarchy in RFC 4206, LSP Stitching and MPLS local protection) the ingress router could be pushing label in label stack of an already existing MPLS packet (instead of an IP packet). Note that, although the ingress router is the starting point of an LSP, it may or may not be the source of the under-lying IP packets.
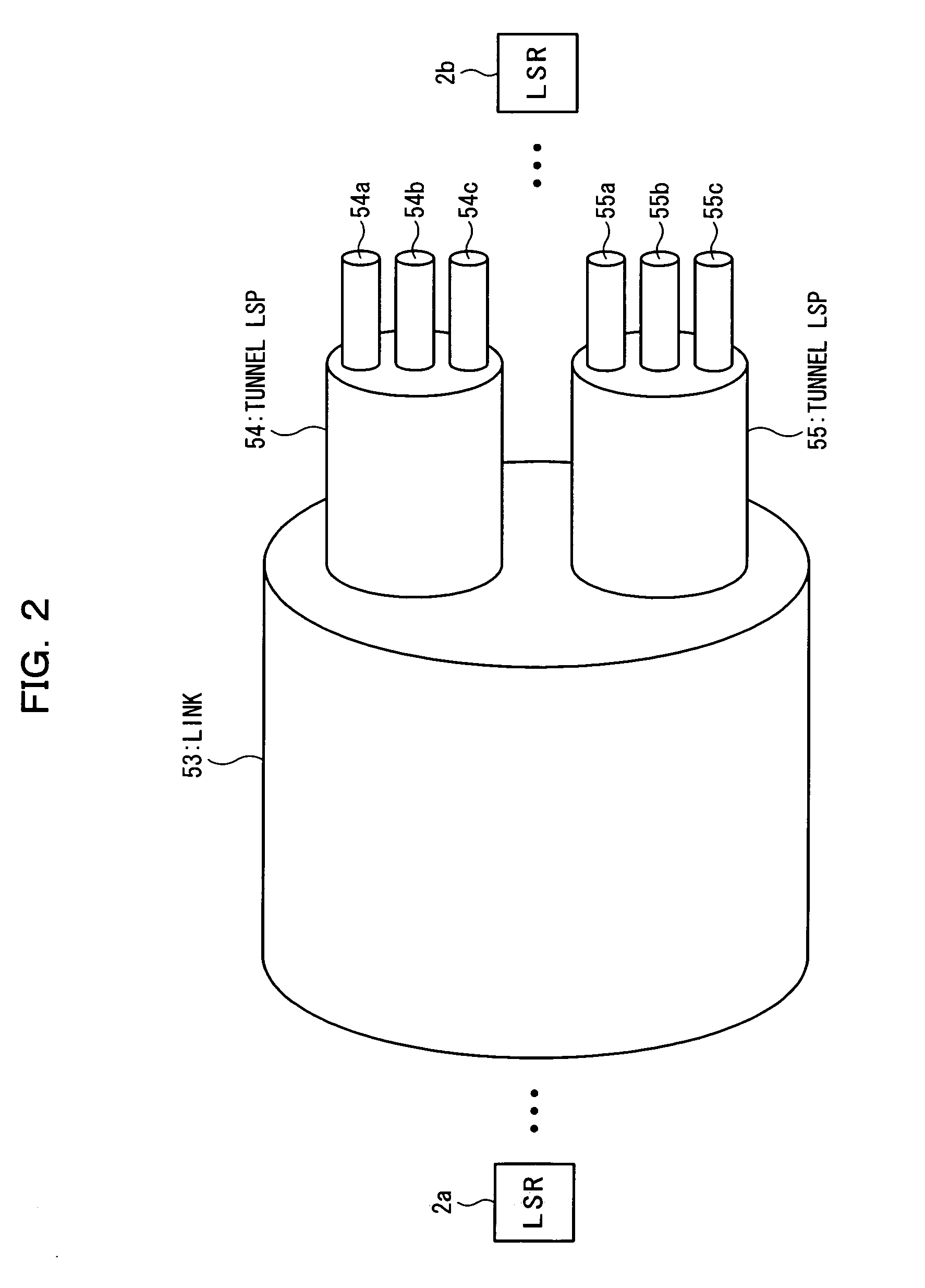
Router, frame forwarding method, and lower layer frame virtual forwarding system
InactiveUS20050169270A1Avoid loadEasy to useTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionPhysical addressLabel switching
In an MPLS network, multicast, broadcast and address learning belonging to the layer 2 functions are realized. An ingress router comprises a frame receiving unit, a determining unit, a first frame transmitting unit, a physical address table for multicast, a label switching unit, a tunnel label table, a VCID giving unit, a L2 header creating unit and a second frame transmitting unit. The load on the network is suppressed, the band is efficiently used, and wasteful frame duplication and frame forwarding between edge routers are avoided.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Methods and apparatus for implementing bi-directional signal interfaces using label switch paths
InactiveUS7061921B1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationCommunications systemEgress router
Methods and apparatus for implementing bi-directional logical signal interfaces (LSIs) in communications systems which use uni-directional label switched paths (LSPs), e.g., MPLS networks, are described. To implement an LSI, two uni-directional LSPs between the same end points, e.g., routers, and extending in opposite directions, are associated together. The association of LSPs may be done by setting LSI configuration information in the routers at both ends of an LSI. Each router at the end of an LSI serves as an egress router for one of the LSPs associated with the LSI and an ingress router for the other LSP associated with the LSI. To enable an egress router to determine which, if any, LSI a packet or message corresponds to, a real as opposed to a null label is used when sending packets over an LSI LSP to an LSI LSP egress router.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
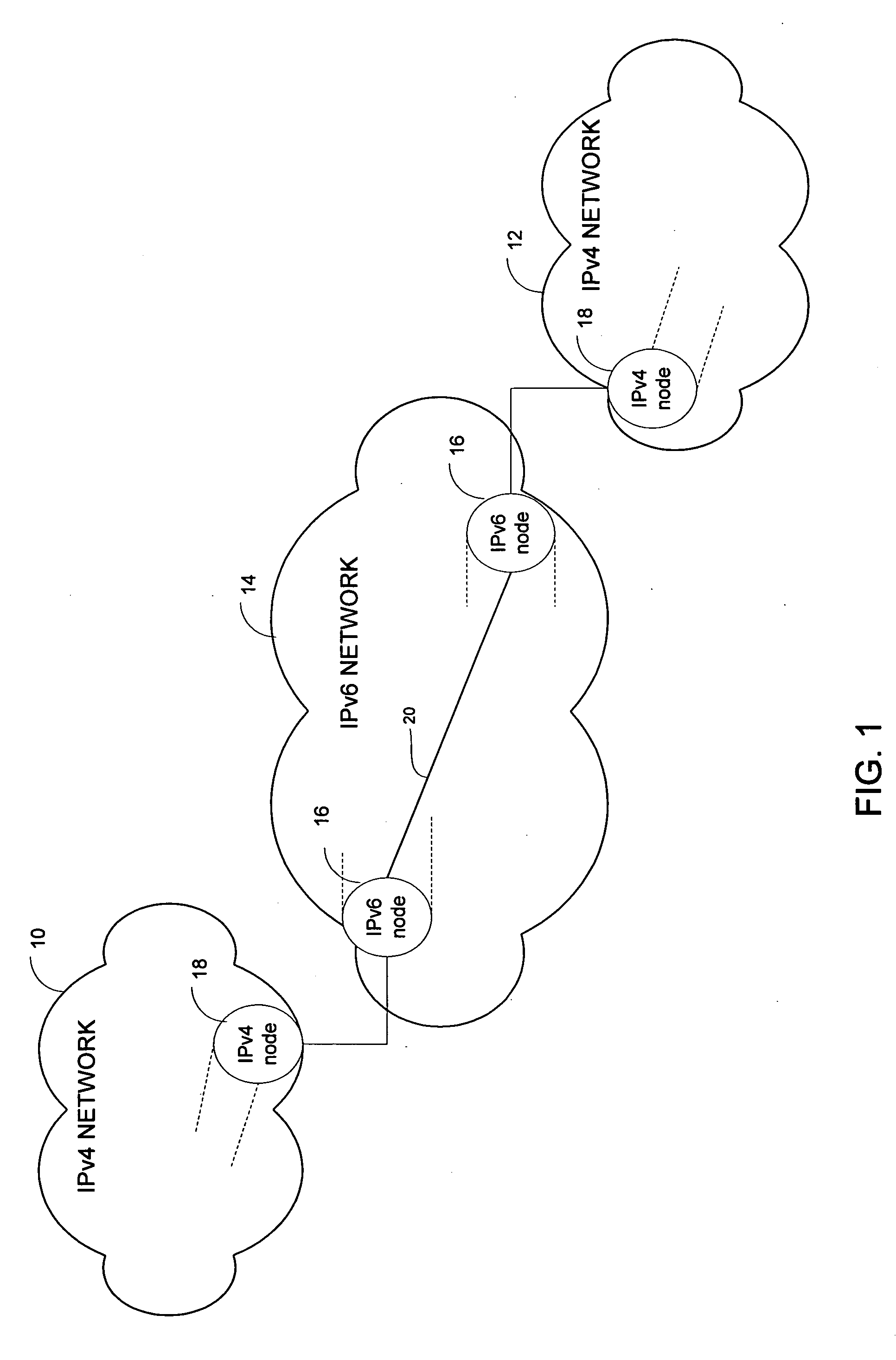
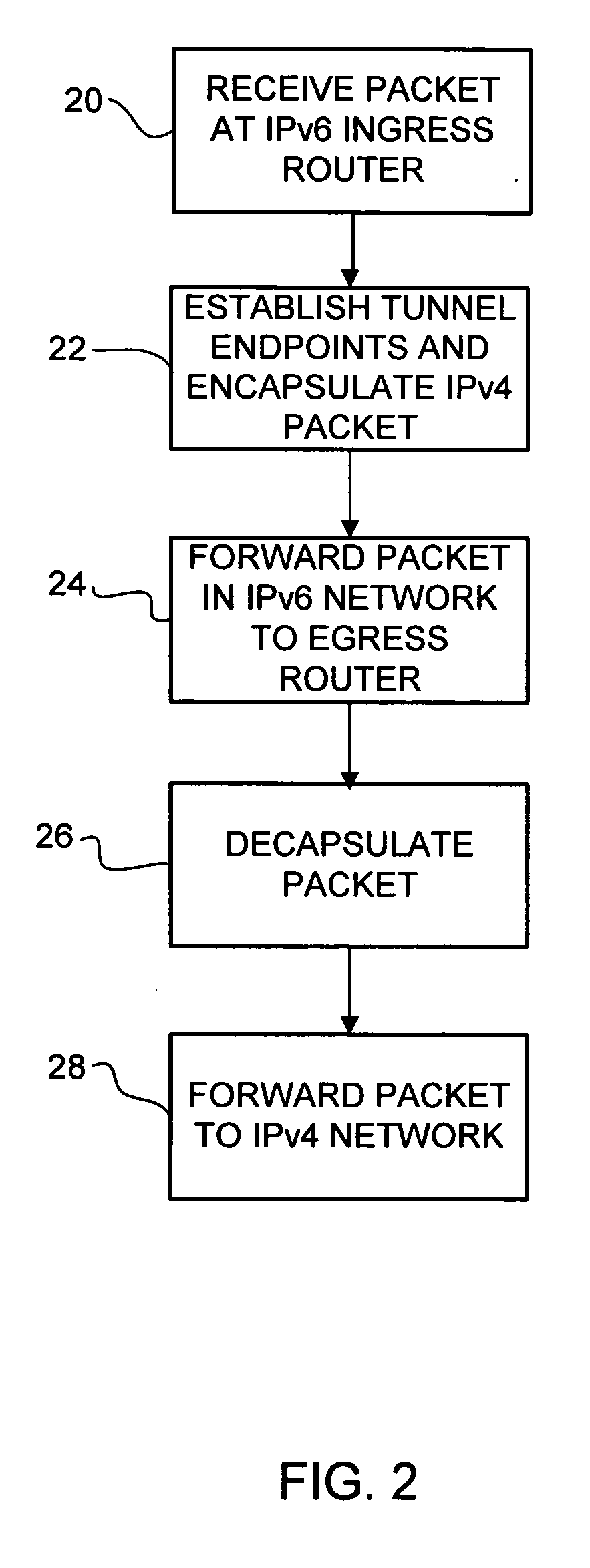
Method and system for automatically interconnecting IPv4 networks across an IPv6 network
InactiveUS20060209885A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIPv6 packetEgress router
A method and system for automatically interconnecting IPv4 networks across an IPv6 network are disclosed. The method includes receiving an IPv4 packet at an ingress router in the IPv6 network and finding the longest match IPv4 routing entry for IPv4 addresses in the received packet to identify an egress router in the IPv6 network. The IPv4 packet is encapsulated to create an IPv6 packet, wherein destination and source addresses of the encapsulated packet identify a subnet router anycast corresponding to the ingress router and the egress router in the IPv6 network. The encapsulated packet is forwarded to the egress router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Content based data packet routing using labels
InactiveUS20060165053A1Fast and efficientImprove performanceData switching by path configurationRouting tableEgress router
Disclosed is a content based router, system and method of operation. Upon receipt of a data packet at in ingress router, the ingress router matches the content of the data packet against stored user subscriptions. In one embodiment, the content is described using XML data and the user subscriptions are defined by XML queries. The router assigns a routing label to the data packet based on the matching, and transmits the data packet to a second network router. Intermediate routers along the packets path then use the assigned label in combination with stored routing tables in order to determine next hop routing. Upon receipt at an egress router, the content of the message is matched against user subscriptions for those users serviced by the egress router, and the egress router provides the data packet to those end users whose subscriptions match the content. The assigned routing labels may define routing paths or routing trees.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
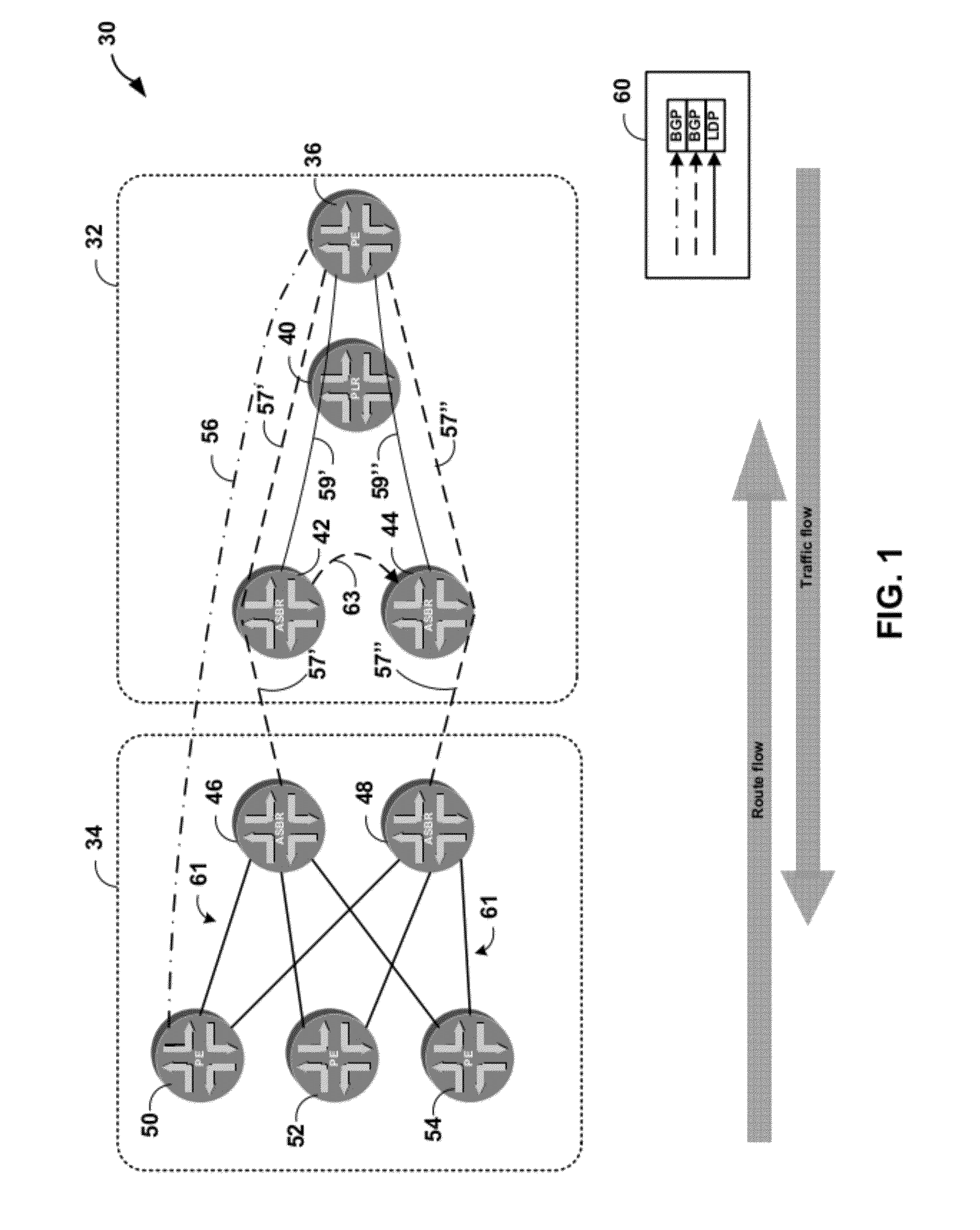
Egress protection for label switched paths
ActiveUS8259564B1Protection to failError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsIp addressEgress router
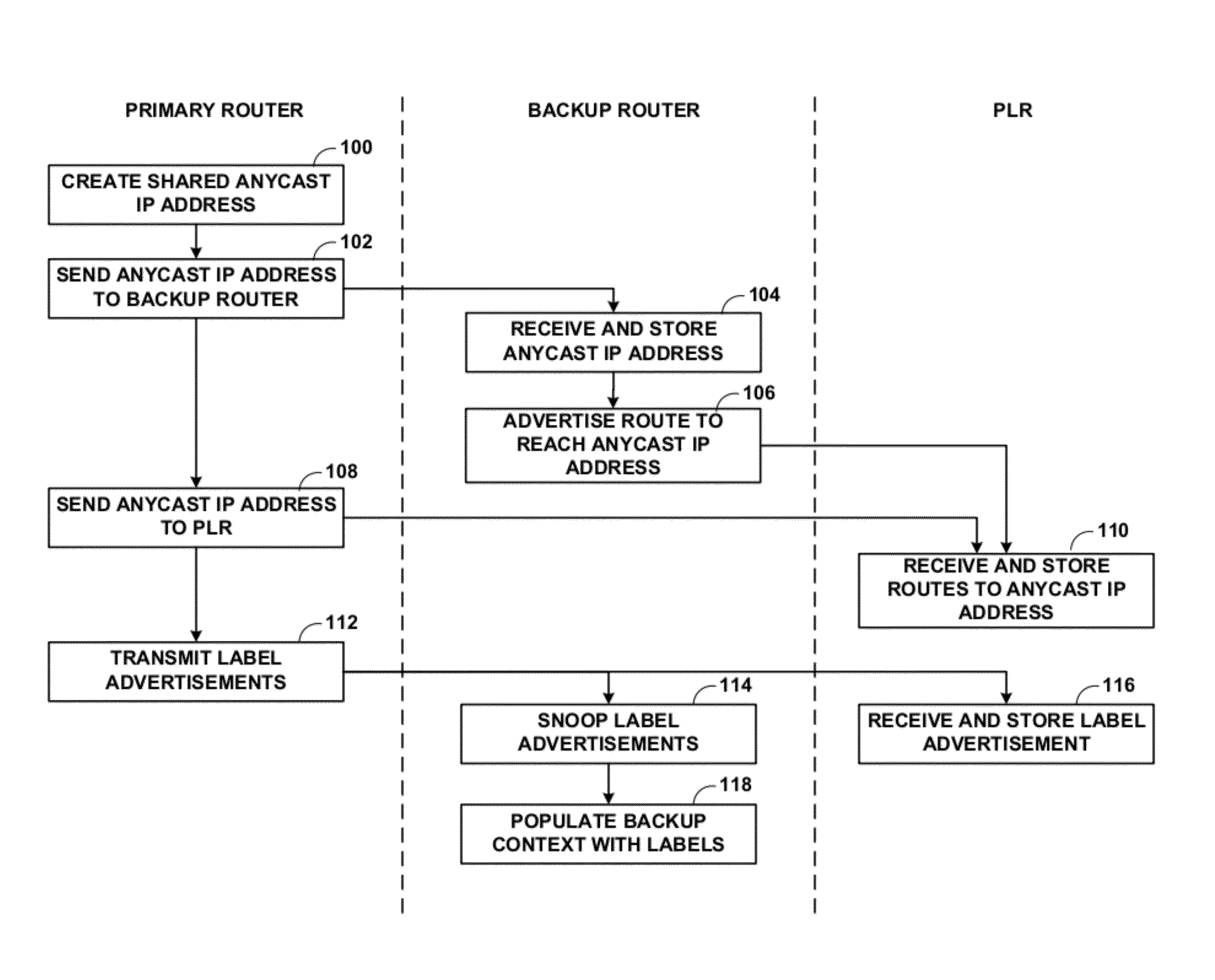
This disclosure describes techniques for protecting an endpoint of a label switched path. In one embodiment, a system includes an ingress router, a primary egress router, backup router, and a point of local repair (PLR) router. The ingress router, the PLR router, and the first egress router form a first label switched path. The backup router provides protection for the primary egress router such that the backup router provides routing services for the first egress router when the first egress router is not available. The primary egress router and the backup router share an anycast IP address. The backup router advertises a route to reach the primary egress router, but upon receiving a packet intended for the primary egress router, the backup router identifies the destination of the packet and forwards the packet to the destination instead of the primary egress router along a different route.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method and system for forwarding data units
InactiveUS20050068933A1SaveSave bandwidthTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCommunications systemForwarding equivalence class
A method and system for forwarding data units in a communications system, that comprises: ingress routers (901) capable of forwarding data units and containing a Forwarding Equivalence Class table (911) that contains mapping information, intermediate routers (905, 907, 909) capable of forwarding data units, egress routers (903) capable of forwarding data and containing a Forwarding Equivalence Class table (919) that contains mapping information. The method comprising the steps of: assigning a first label on data unit and a second label on data unit based on mapping information, sending data unit in to egress router via one or more intermediate router (905, 907, 909), receiving (903) data unit, identifying data unit based on mapping information on Forwarding Equivalence Class table (919) and based on second label. The method further comprises the steps of: creating a Forwarding Equivalence Class for radio access network specific data units; and storing information about Forwarding Equivalence Class in Forwarding Equivalence class table (FEC).
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
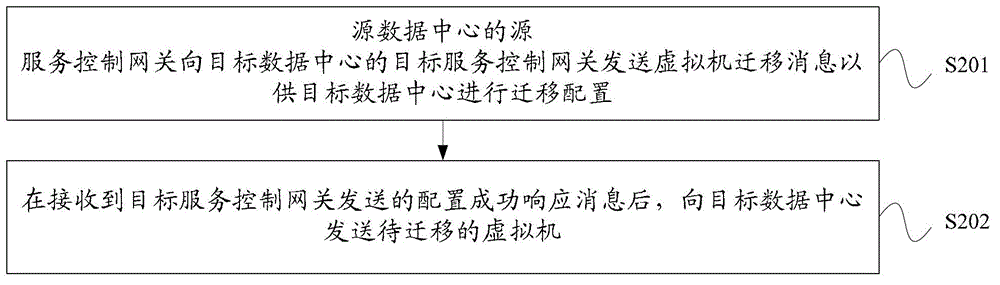
Cross-data-center virtual machine migration method, service control gateway and cross-data-center virtual machine migration
ActiveCN102884763AImplement automatic installationNo human intervention requiredNetworks interconnectionAuto-configurationService control
Embodiments of the invention provide a cross-data-center virtual machine migration method, a service control gateway and a cross-data-center virtual machine migration. The migration method comprises: a target service control gateway of a target data center receives virtual machine migration information sent by a source service control gateway of a source data center; the target service control gateway configures a response strategy, an internal data channel between an ingress router of the target data center and a target switch, and an external data channel between the target data center and a user on the target switch; the target service control gateway sends configuration success information to the source service control gateway; and the target service control gateway installs an virtual machine to be migrated on the target server and provides service for the user. According to the embodiments of the invention, the strategy of the target switch can be automatically installed, the external data channel from the user to the target data center can be automatically installed, and the internal data channel between the ingress router of the target data center and the target switch can be automatically installed, thereby achieving the automatic virtual machine migration across data centers.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
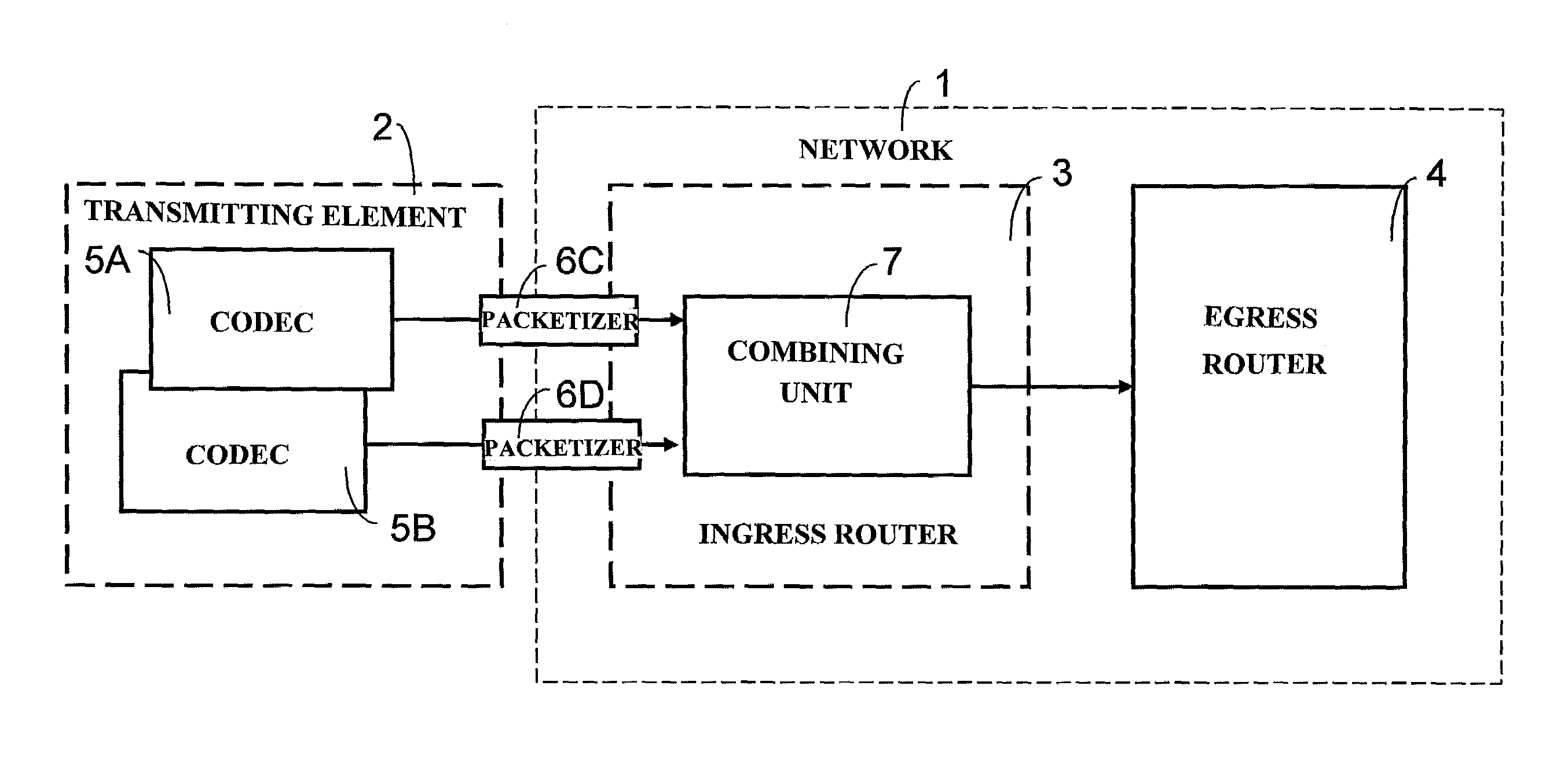
Method for optimizing the use of network resources for the transmission of data signals, such as voice, over an IP-packet supporting network
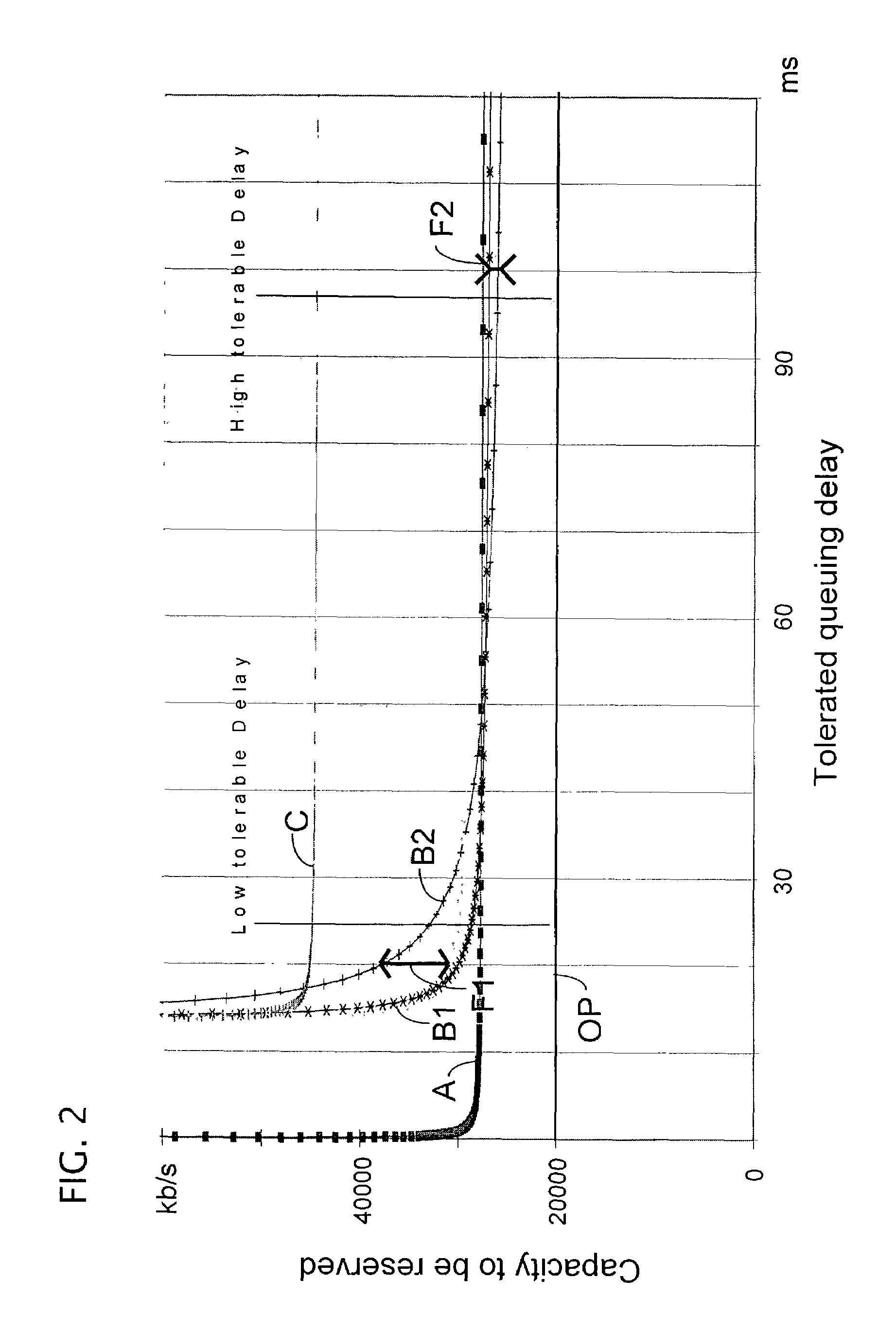
ActiveUS7486661B2Efficient use of bandwidthHigh resource reservationNetwork traffic/resource managementSpeech analysisMultiplexingComputer network
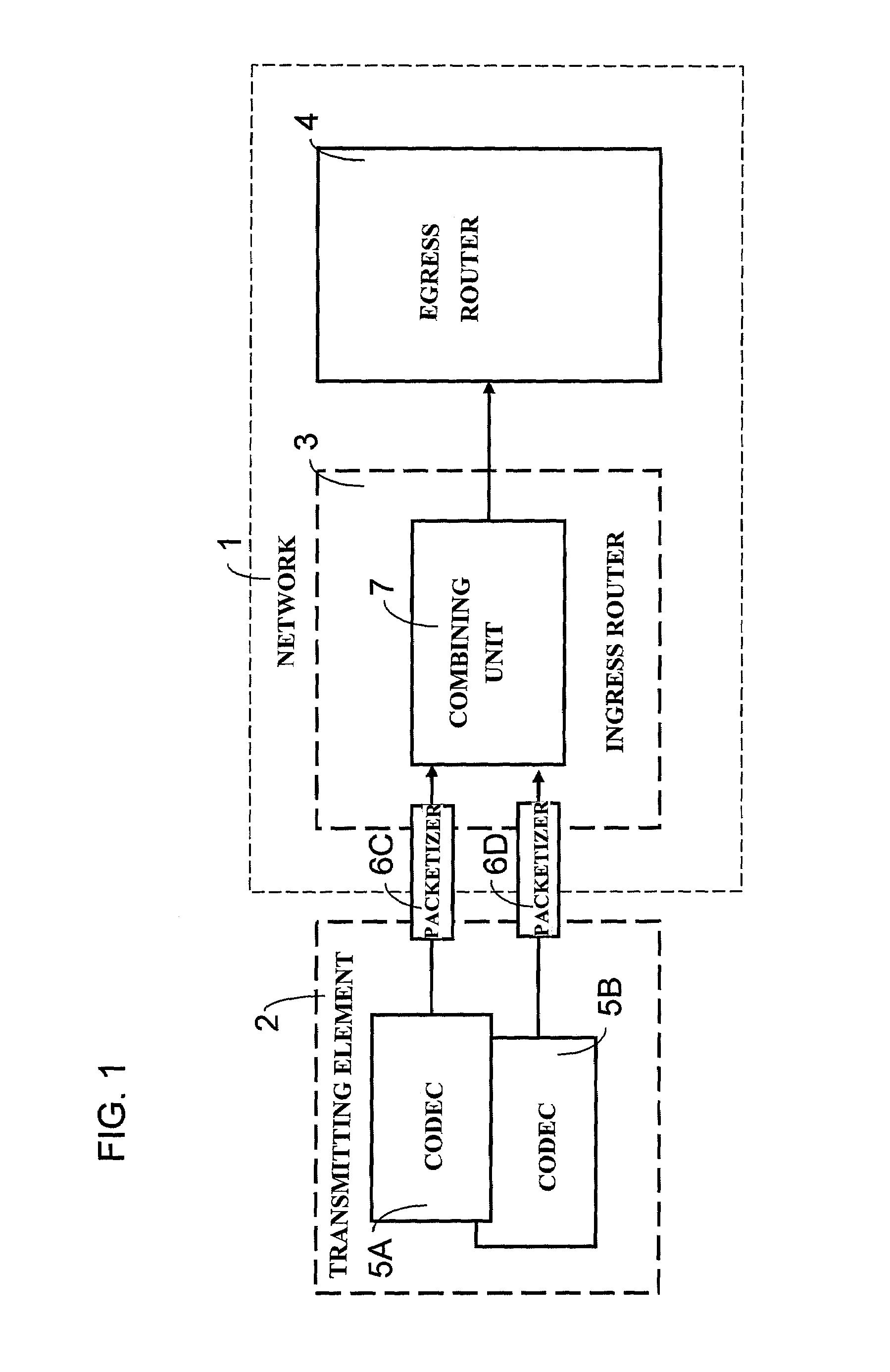
A method for optimizing the use of network resources for the transmission of data signals, such as voice frames, between network units over an IP-packet supporting network. The data frames are obtained using codecs, which may have a different mouth-to-ear transmission delay, from data samples, e.g. voice samples, that are formatted and to which a data frame header is added. The method includes attributing codec categories to each of the data or voice frames according to the codecs by means of which the data samples are generated, each codec category corresponding to a different mouth-to-ear delay budget range for the data frames; sorting the data frames according to their codec categories; generating multiplexed cells from data frames of a same codec category, each multiplexed cell being obtained by multiplex aggregation of a predetermined number of voice samples; and transporting the multiplexed cells from an ingress router to an egress router in the IP-network.
Owner:RPX CORP
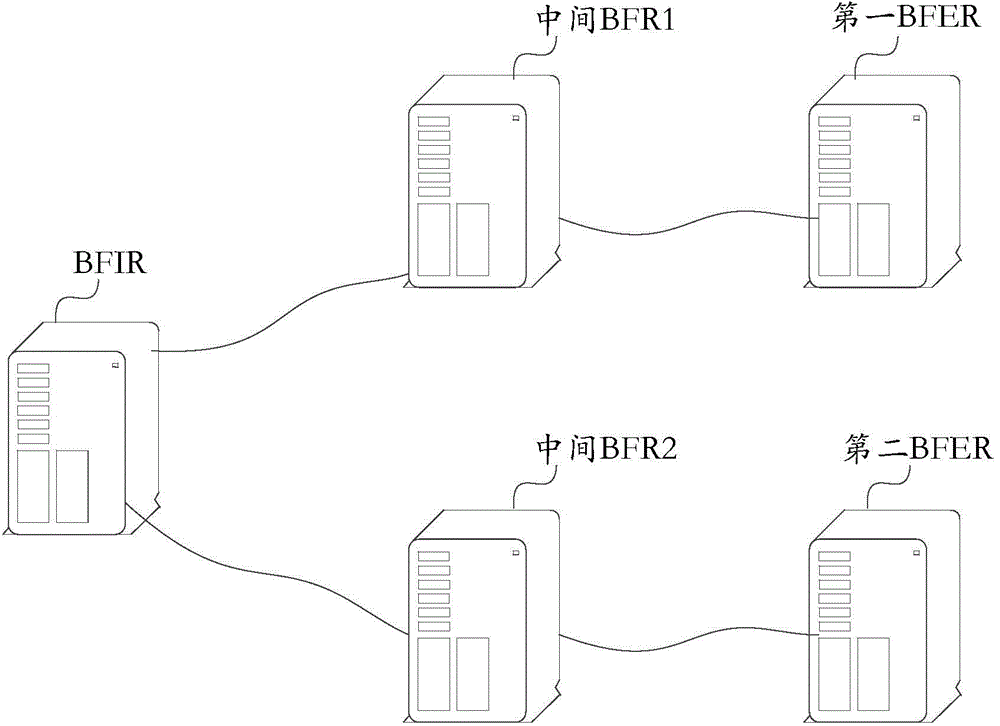
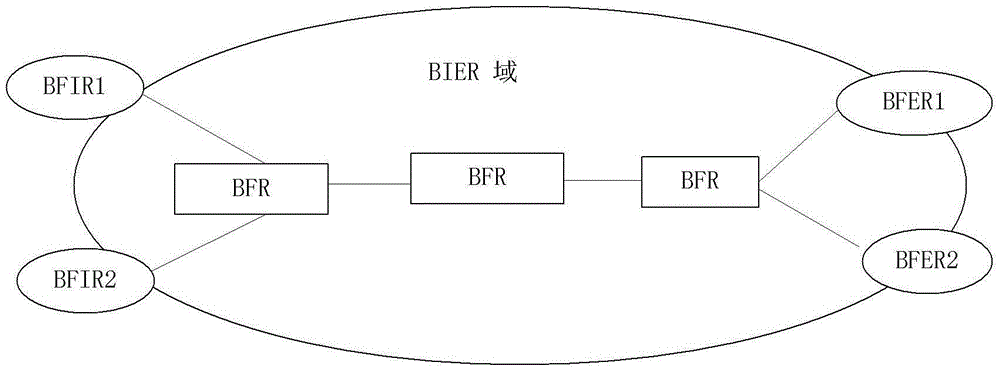
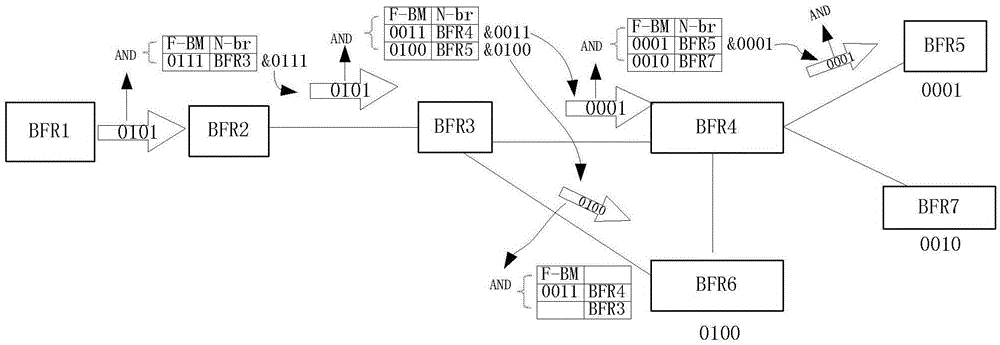
Bit-forwarding ingress router, bit-forwarding router and operation administration maintenance detection method
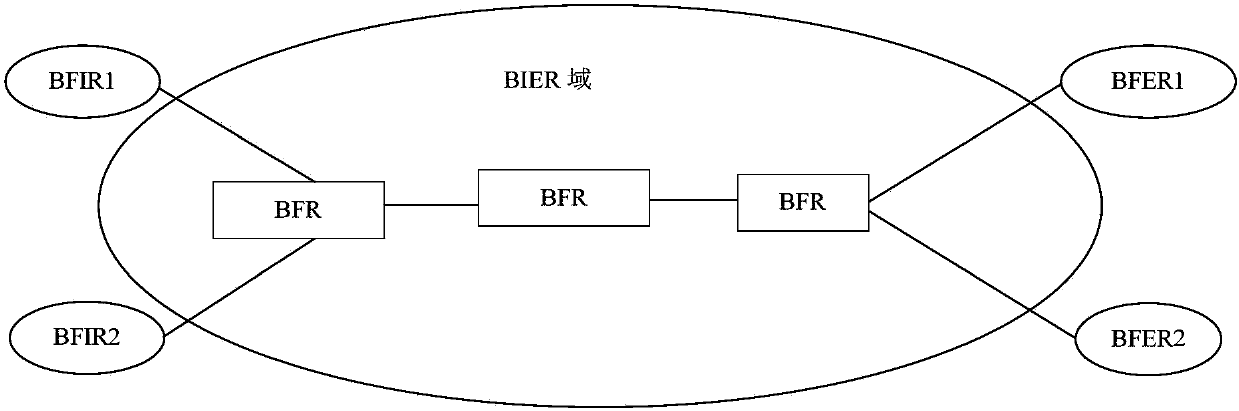
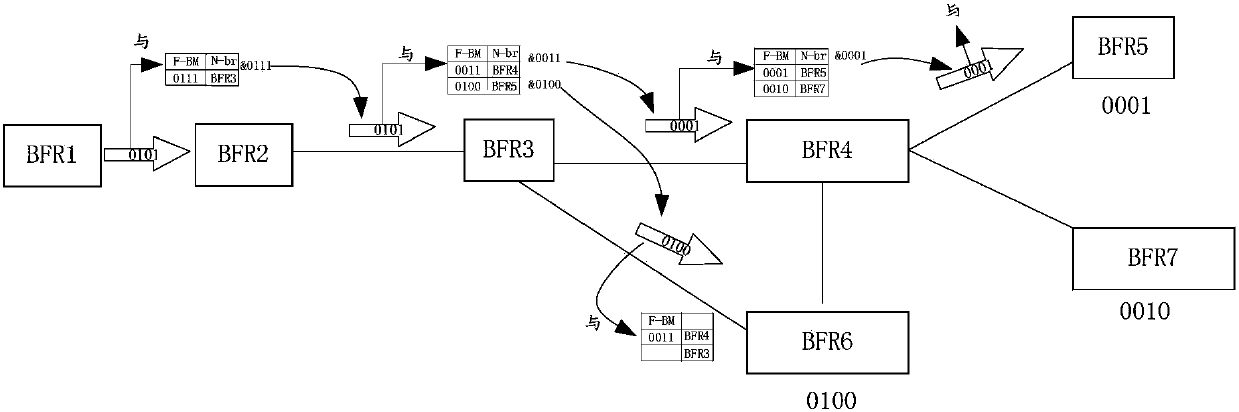
ActiveCN105812197ASave resourcesImprove detection efficiencySpecial service provision for substationMulticast networkEgress router
The invention provides a bit-forwarding ingress router (BFIR), a bit-forwarding router (BFR) and an operation administration maintenance (OAM) detection method and belongs to the multicast network field. An OAM request message from the BFIR is received through a first BFR; a target BFR corresponding to the OAM request message is determined by the first BFR to be the first BFR according to the OAM request message; a first OAM response message is acquired by the first BFR according to the ID of the BFIR, and the first OAM response message is sent to the BFIR. Through the method and the device, a problem that a transmission fault generated in a transmission process of a multicast message can not be diagnosed or processed by the BFIR can be solved, connectivity detection can be facilitated through the OAM message, and detection on multiple bit-forwarding egress routers (BFER) can be realized.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Assured delivery message system and method
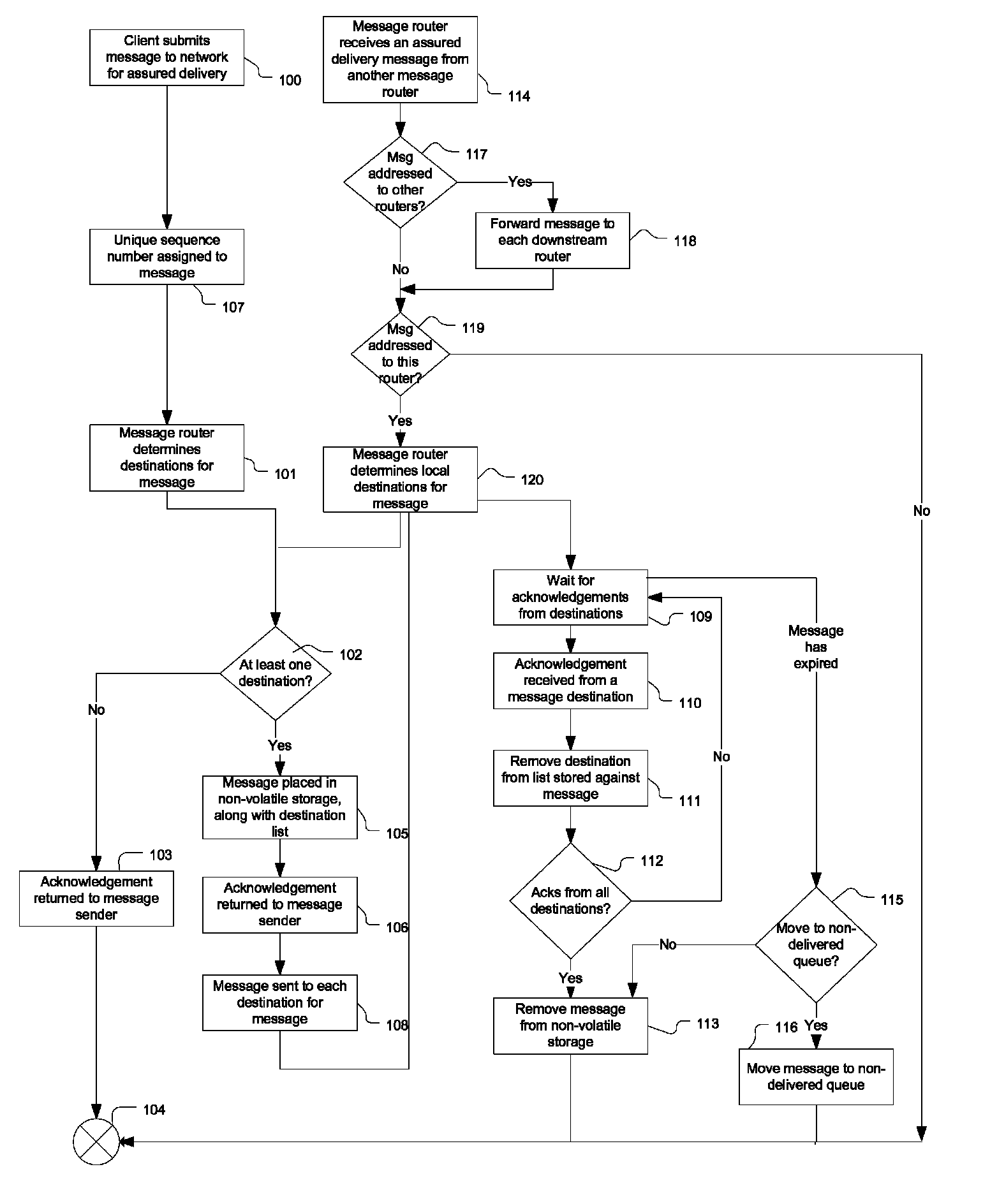
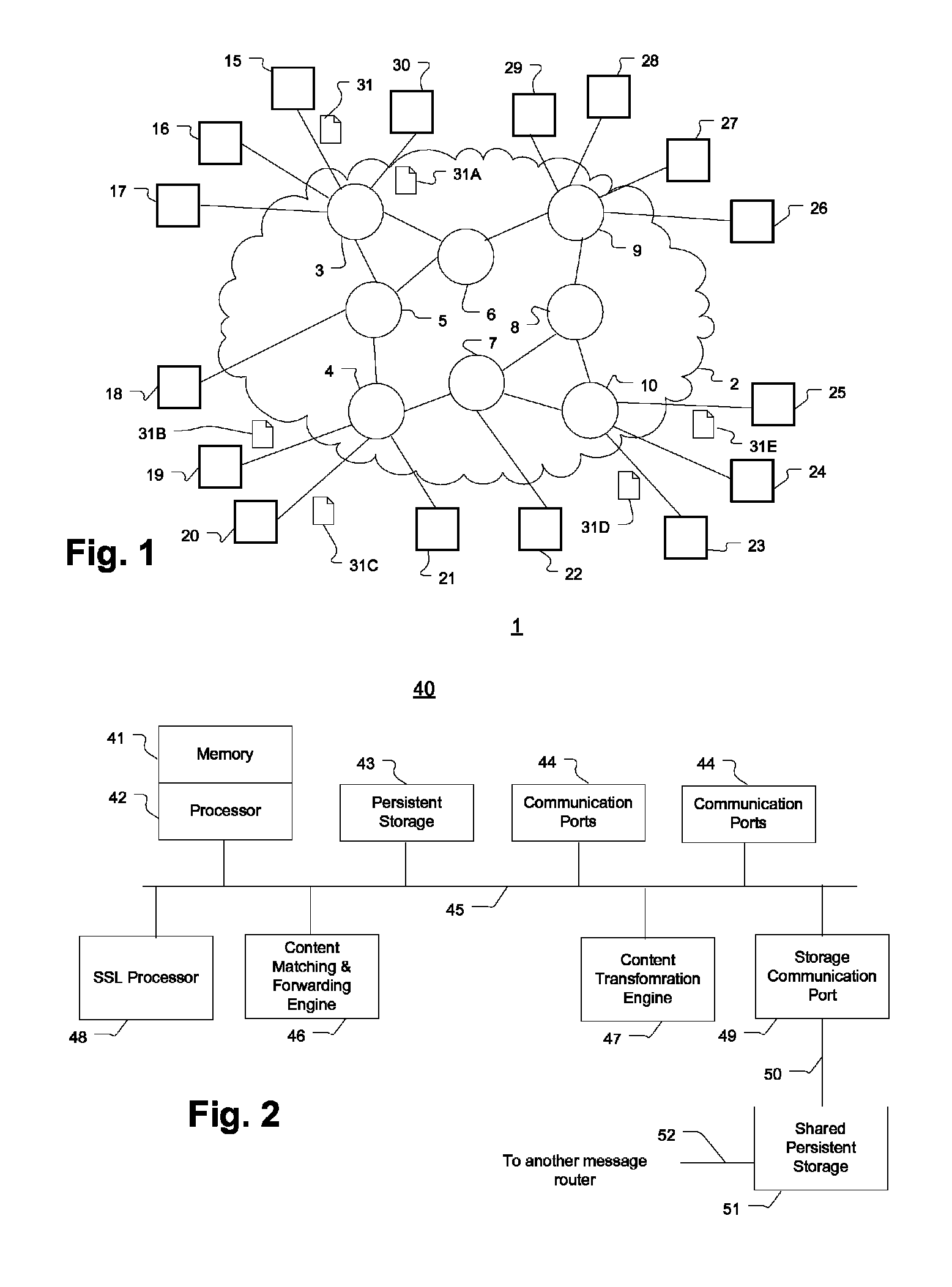
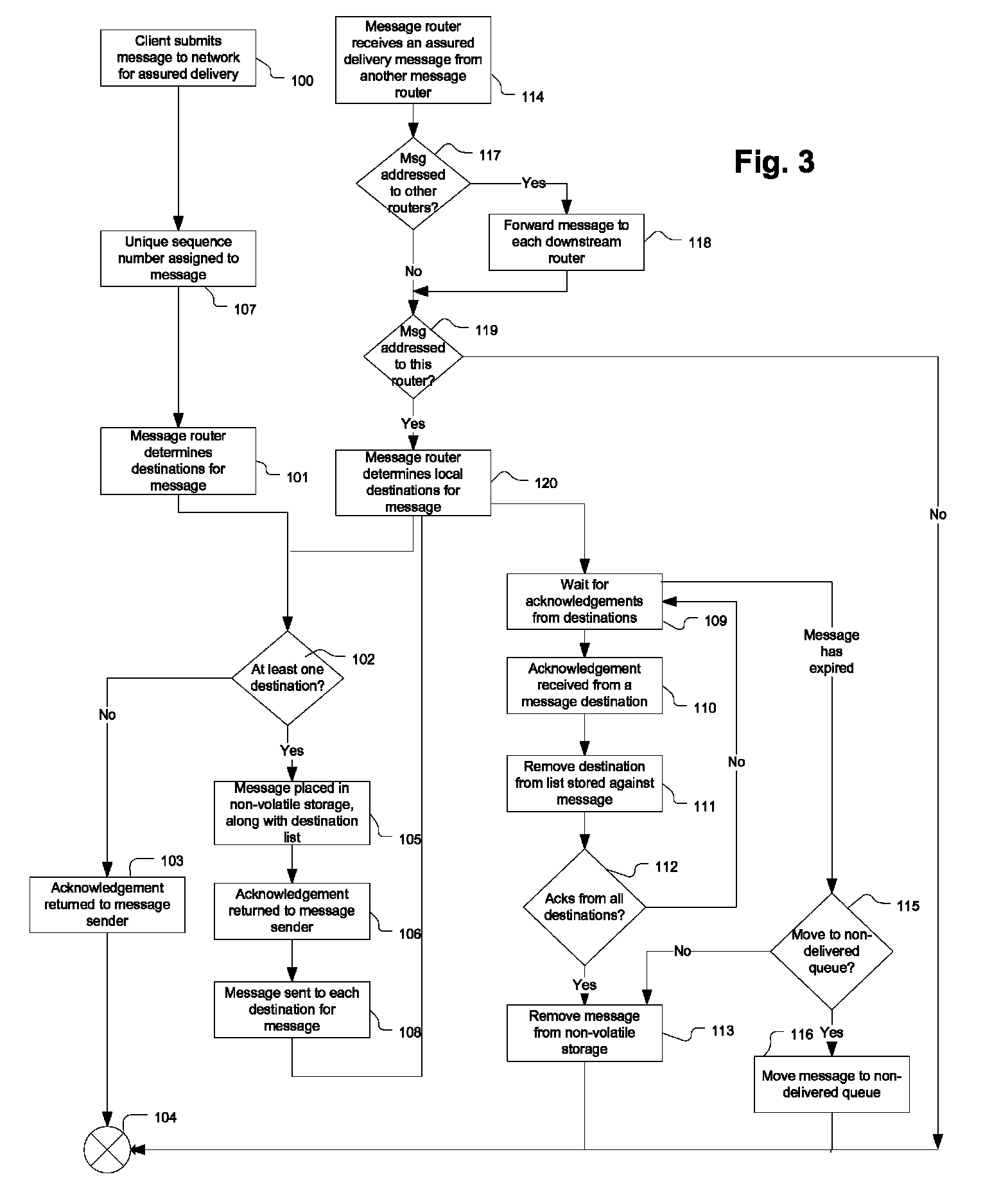
ActiveUS8144714B1Delay minimizationResourceError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityMessage delivery
In method of providing assured message delivery across a distributed message delivery system with low delivery latency and network traffic, a set of destinations is first identified for a set of destinations for a message received at an ingress router to the network. The received message is stored in persistent storage along with meta-data about each destination for the message before the message is routed to each identified destination. The message is only removed from persistent storage when an acknowledgement has been received from each destination indicating that the message has been successfully received.
Owner:SOLACE CORP
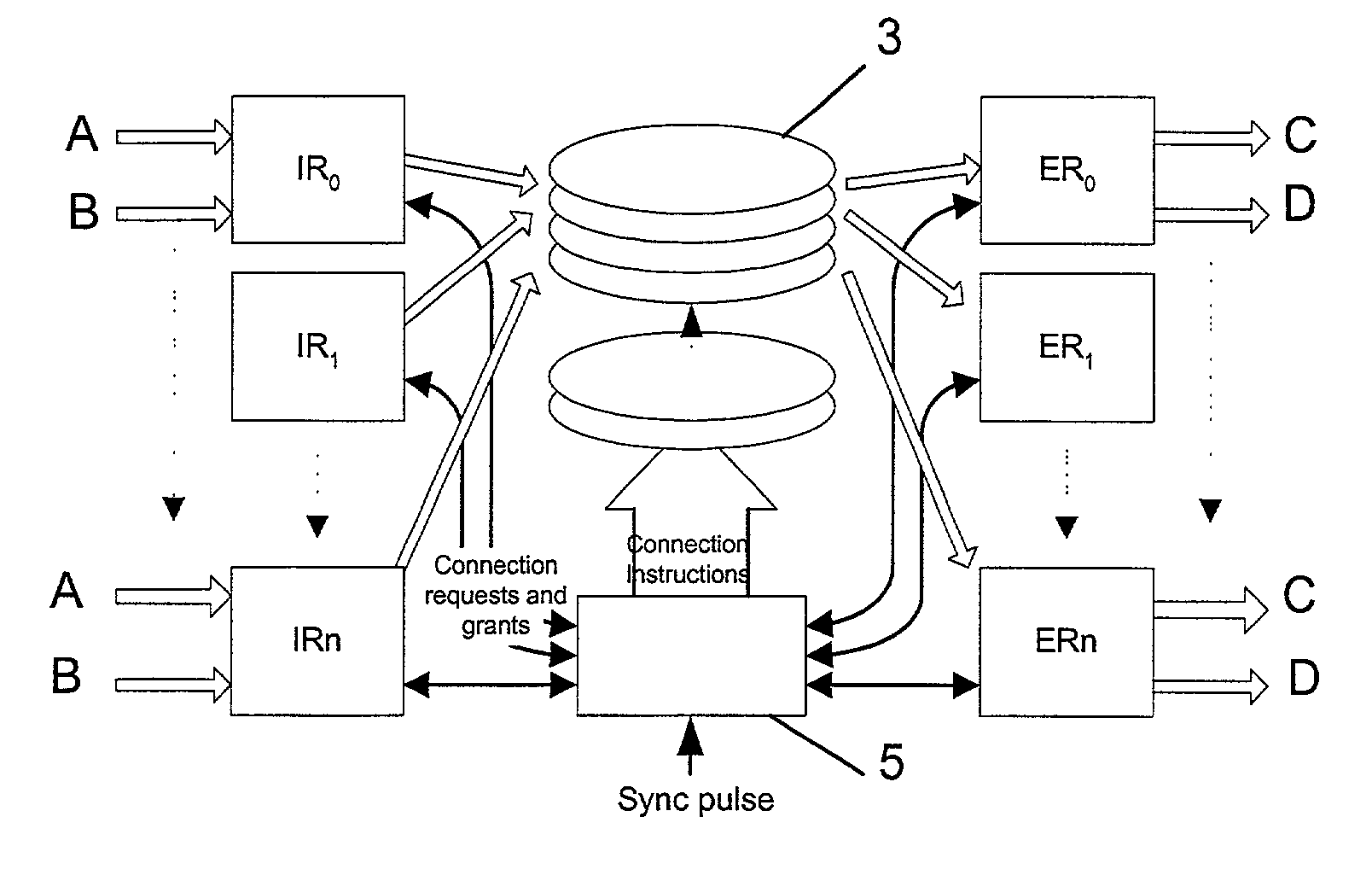
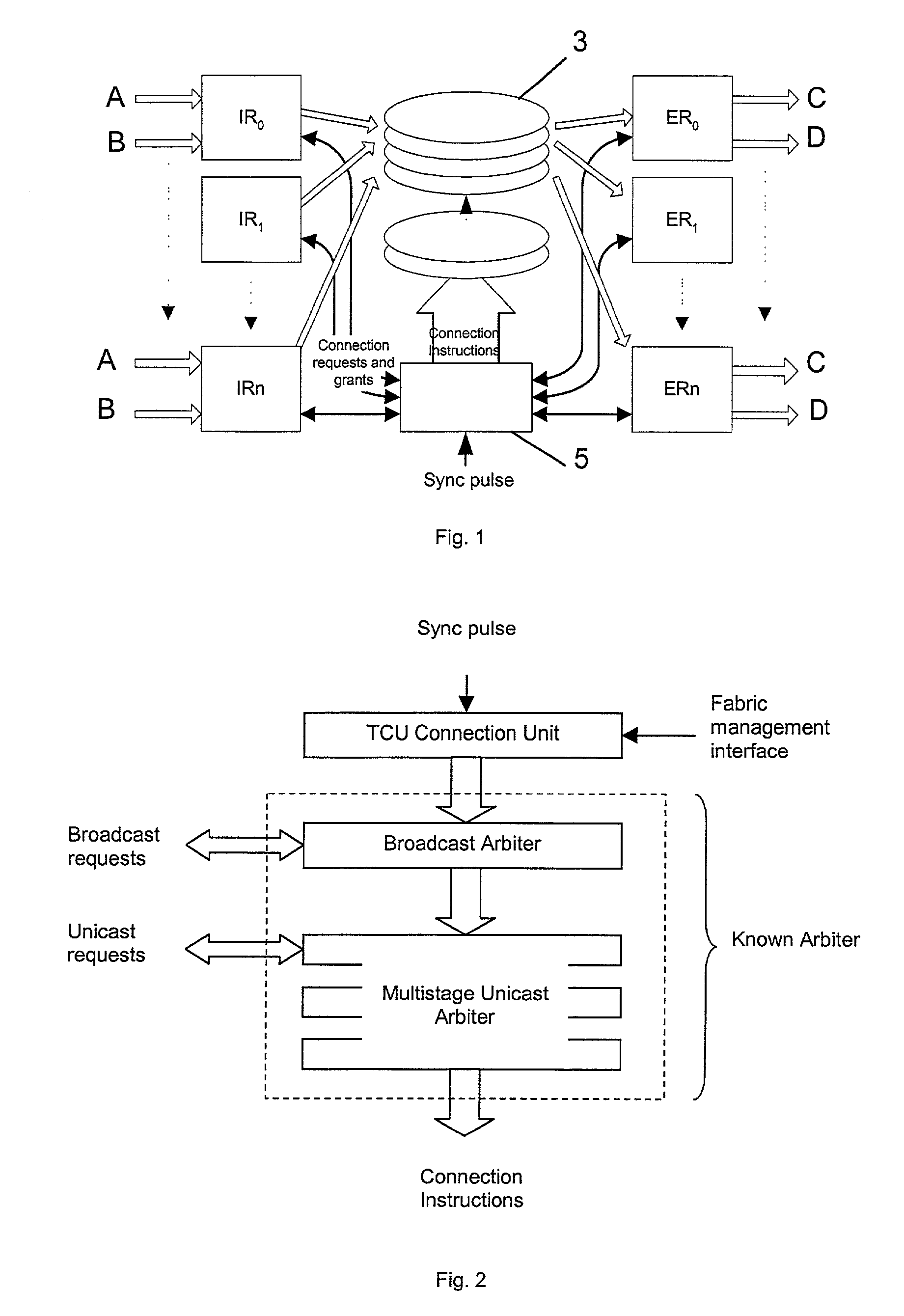
Switching system
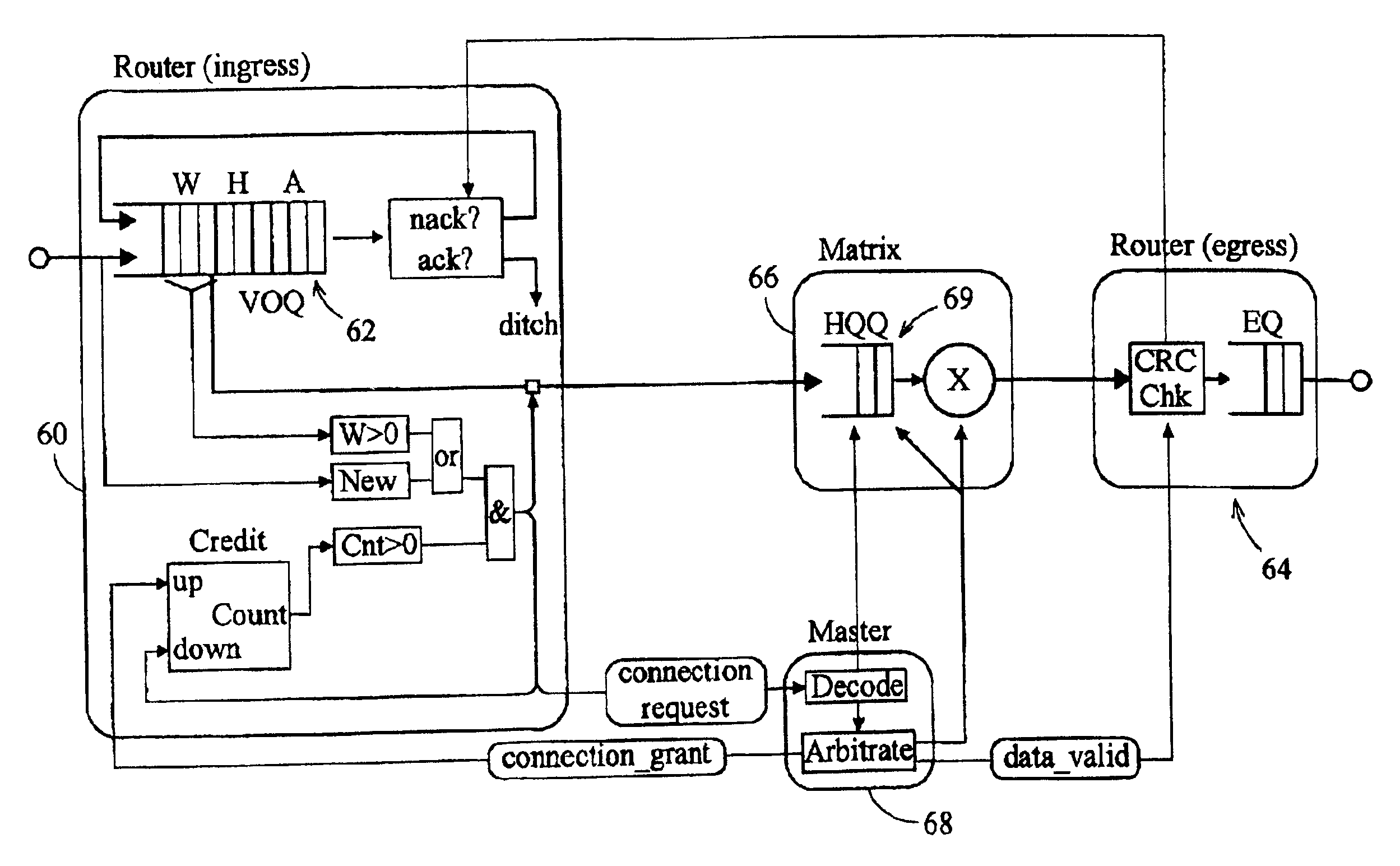
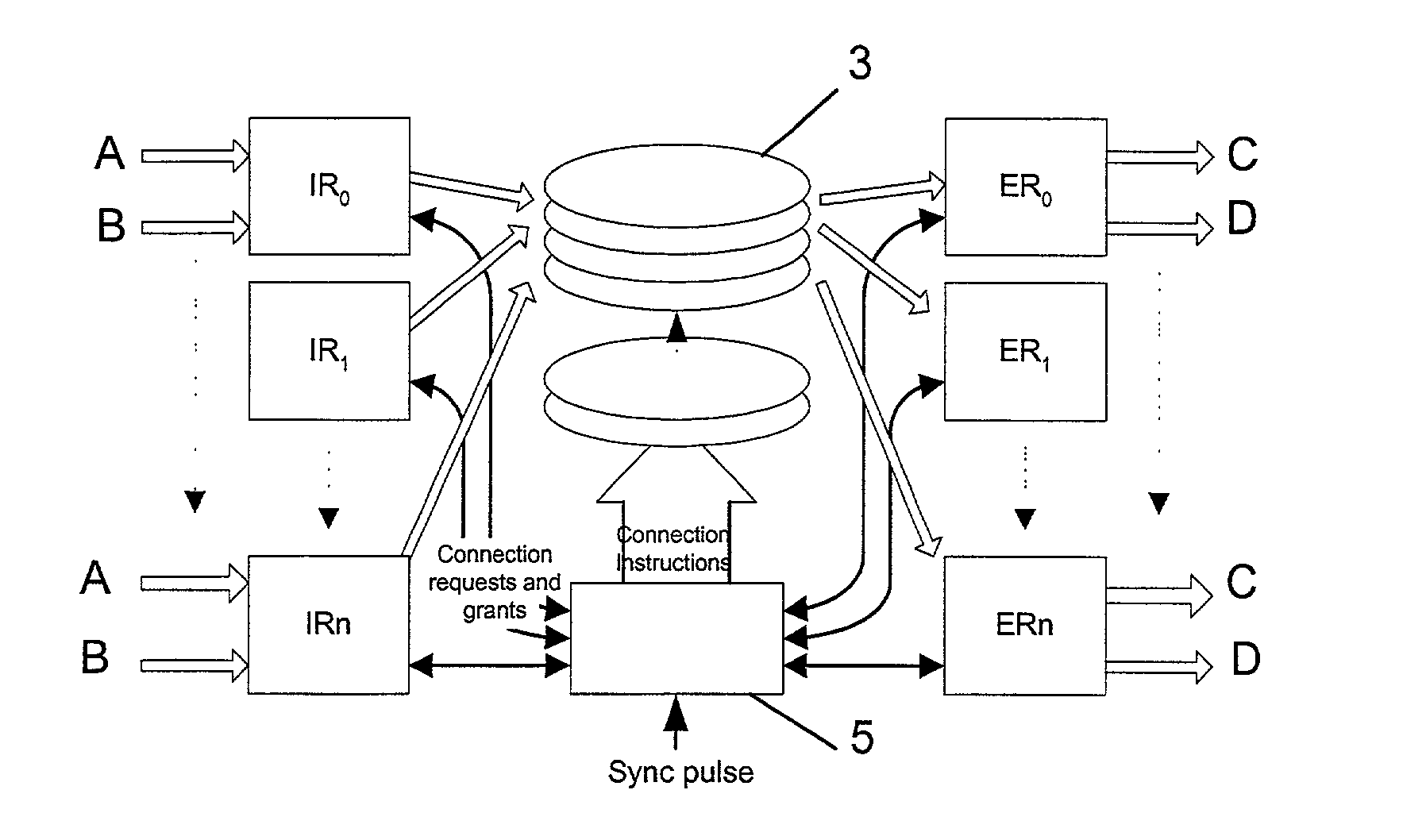
InactiveUS6876663B2Data switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionEgress routerData interchange
A data switching device has ingress routers and egress routers interconnected by a switching matrix controlled by a controller. Each ingress router maintains one or more virtual output queues for each egress router. The switching matrix itself maintains a head-of queue buffer of cells which are to be transmitted. Each of these queues corresponds to one of the virtual output queues, and the cells stored in the switching matrix are replicated from the cells queuing in the respective virtual output queues. Thus, when it is determined that a connection is to be made between a given input and output of the switching matrix, a cell suitable for transmission along that connection is already available to the switching matrix. Upon receipt of a new cell by one of the ingress routers, the cell is stored in one of the virtual output queues of the ingress router corresponding to the egress router for the cell, and also written the corresponding head of queue buffer, if that buffer has space. If not, the cell is stored, and written to the head of queue buffer when that buffer has space for it.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Data switch and a method for controlling the data switch
ActiveUS20020141397A1Reduce, or even eliminate, variation in the latency of the throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexControl dataEgress router
A data switch is proposed of the type having virtual queue ingress routers interconnected with egress routers by way of a memoryless switching matrix controlled by a control unit which performs an arbitration process to schedule connections across the switch. This scheduling is performed to ensure that data cells which arrive at the ingress routers at unpredictable times are transmitted to the correct egress routers. Each ingress router further includes a queue for time division multiplex traffic, and at times when such traffic exists, the control unit overrides the arbitration process to allow the time division multiplex traffic to be transmitted through the switch.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Message sending method and apparatus and message cross-domain forwarding network architecture
InactiveCN107592262ASolve technical problems that occupy more network resourcesSave network resourcesData switching networksNetwork architectureEgress router
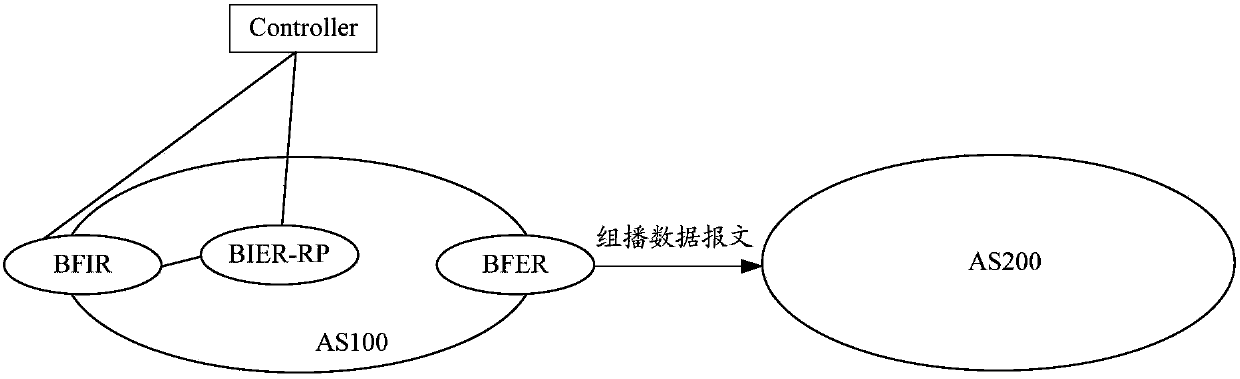
The invention provides a message sending method and apparatus and a message cross-domain forwarding network architecture. The message sending method comprises steps: a bit indexed explicit replication-rendezvous point (BIER-RP) device of a first domain announces an address of a cross-domain multicast group to a controller; and after a bit-index forwarding ingress router (BFIR) of the first domainreceives a multicast data message requesting to be transmitted across a domain to a second domain, the BFIR transmits the multicast data message to a bit-index forwarding egress router (BFER) of the first domain, and the BFER forwards the multicast data message to the second domain. The technical problem that many network resources need to be occupied when the multicast data message is transmittedin a related technology can be solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Transmission method, apparatus and system of BIER control information
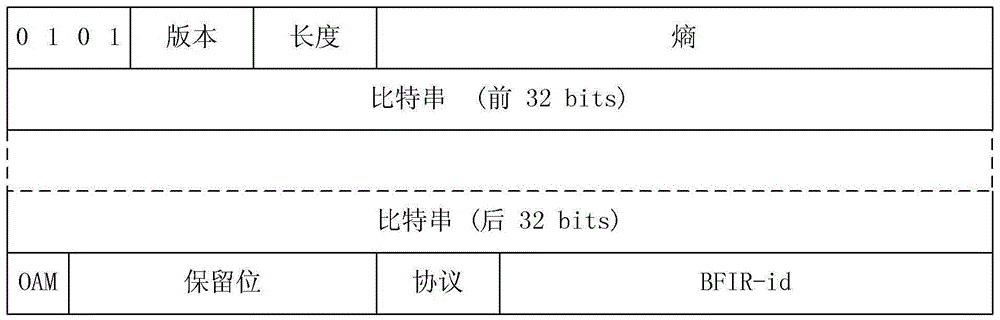
InactiveCN106656524APrevent leakageShorten the timeSpecial service provision for substationMemory footprintEgress router
The invention discloses a transmission method, apparatus and system of BIER (Bit Indexed Explicit Replication) control information, which can transmit control information in an easy and highly efficient manner and prevent control information overload. The method includes the following steps: a bit forwarding ingress router (BFIR) constructs a BIER datagram, a datagram header carries indication information used for indicating that the BIER datagram carries control information, and a datagram body carries the control information. A system comprises a bit forwarding ingress router (BFIR) and a bit forwarding egress router (BFER). The BFIR comprises a first construction module and a second construction module. The BFER comprises a receiving module and a de-packaging module. Through the scheme of the embodiment of the invention, access information related to mlticasting is only sensed at boundary nodes, the memory occupaion processing time and mechanism of intermediate forwarding nodes is saved, and information leakage at unrelated nodes is prevented.
Owner:ZTE CORP
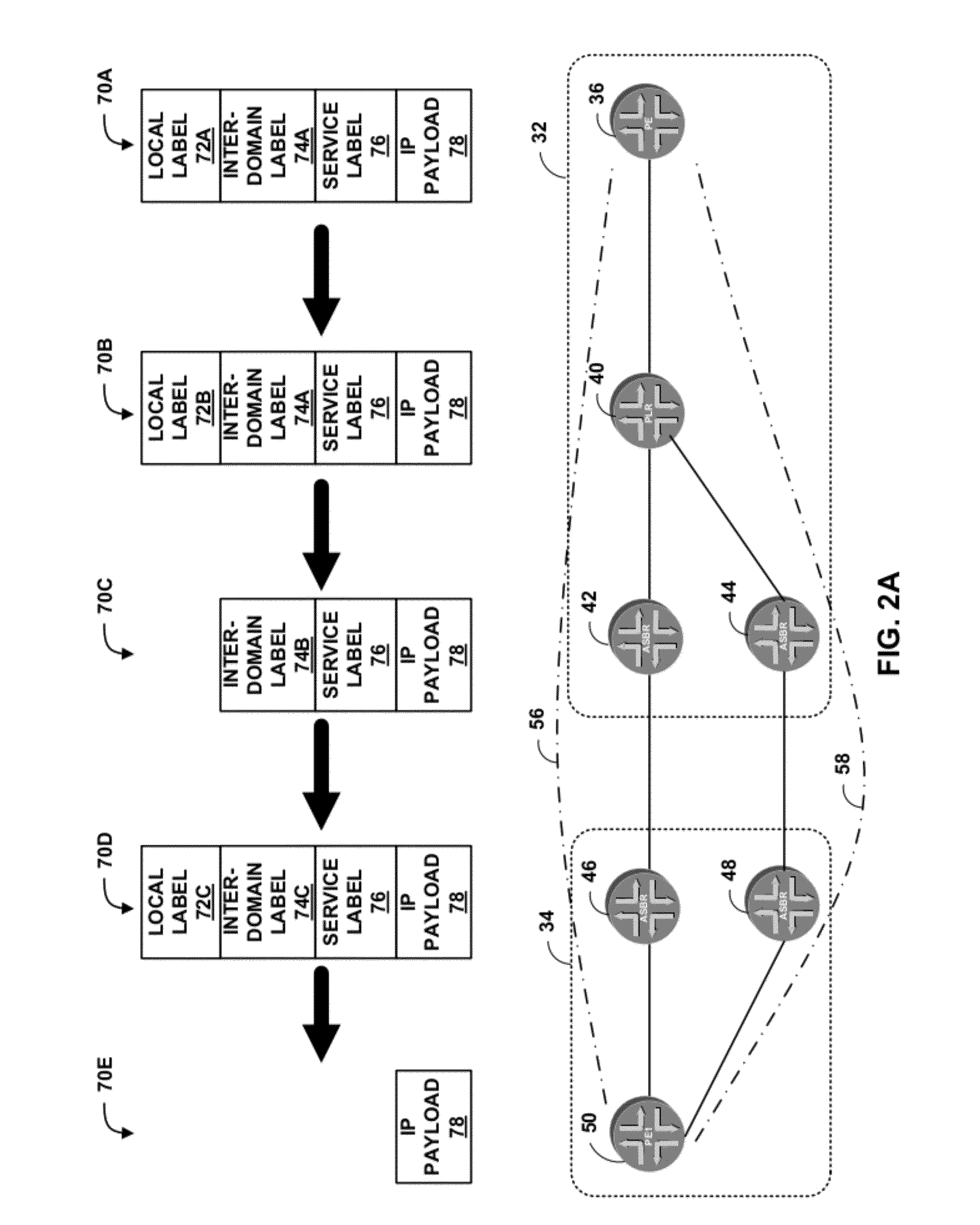
Method and system for supporting a dedicated label switched path for a virtual private network over a label switched communication network
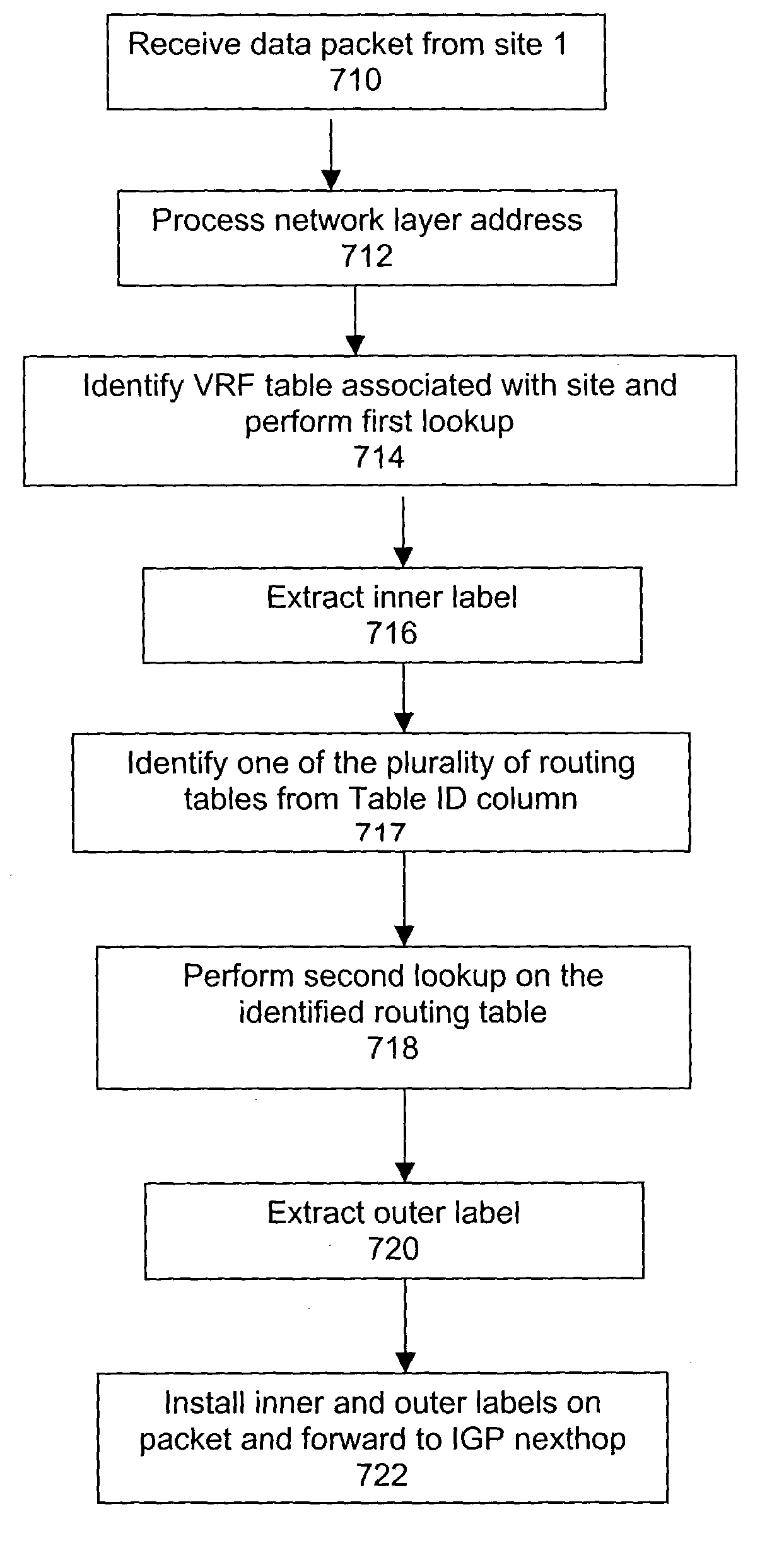
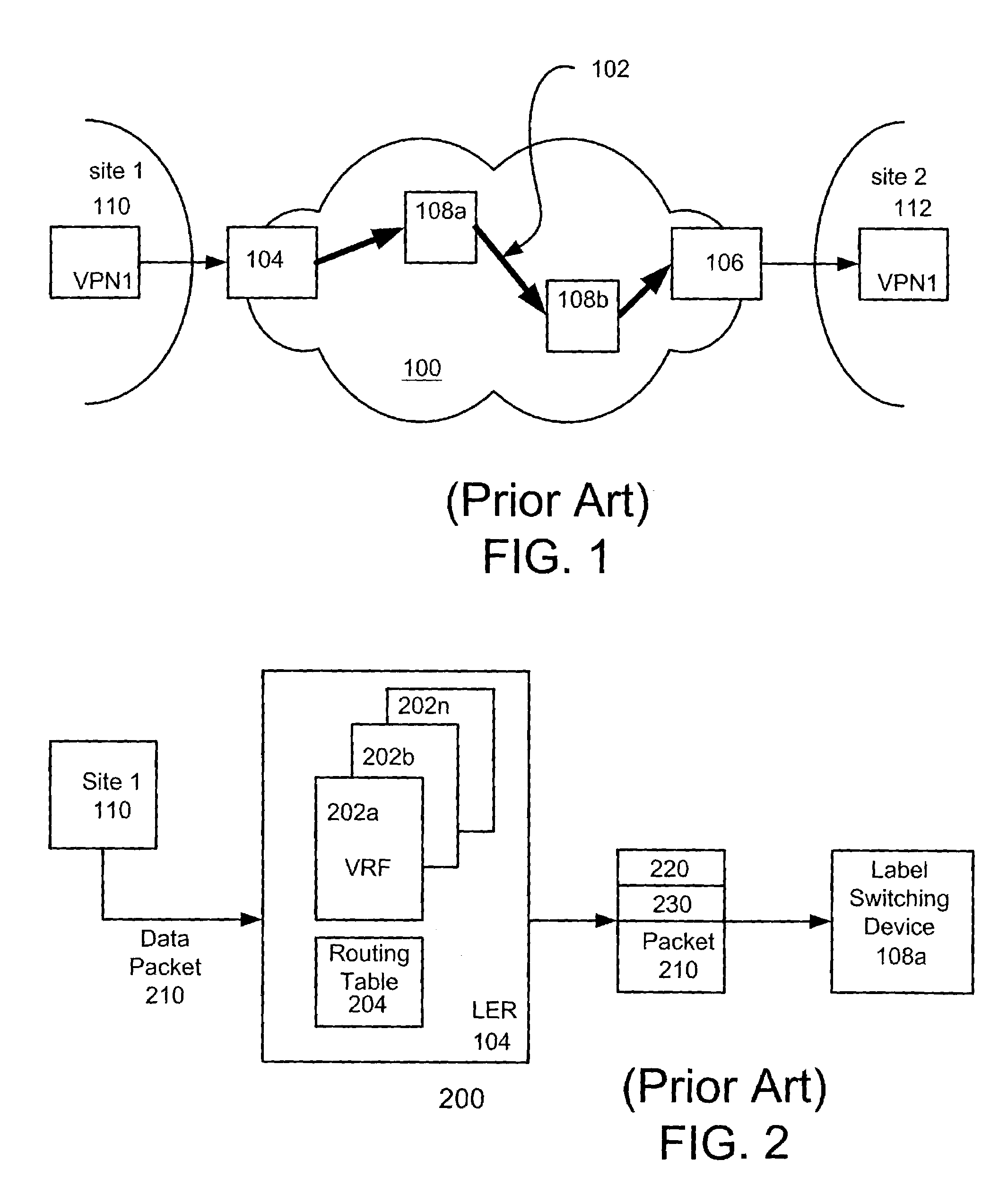
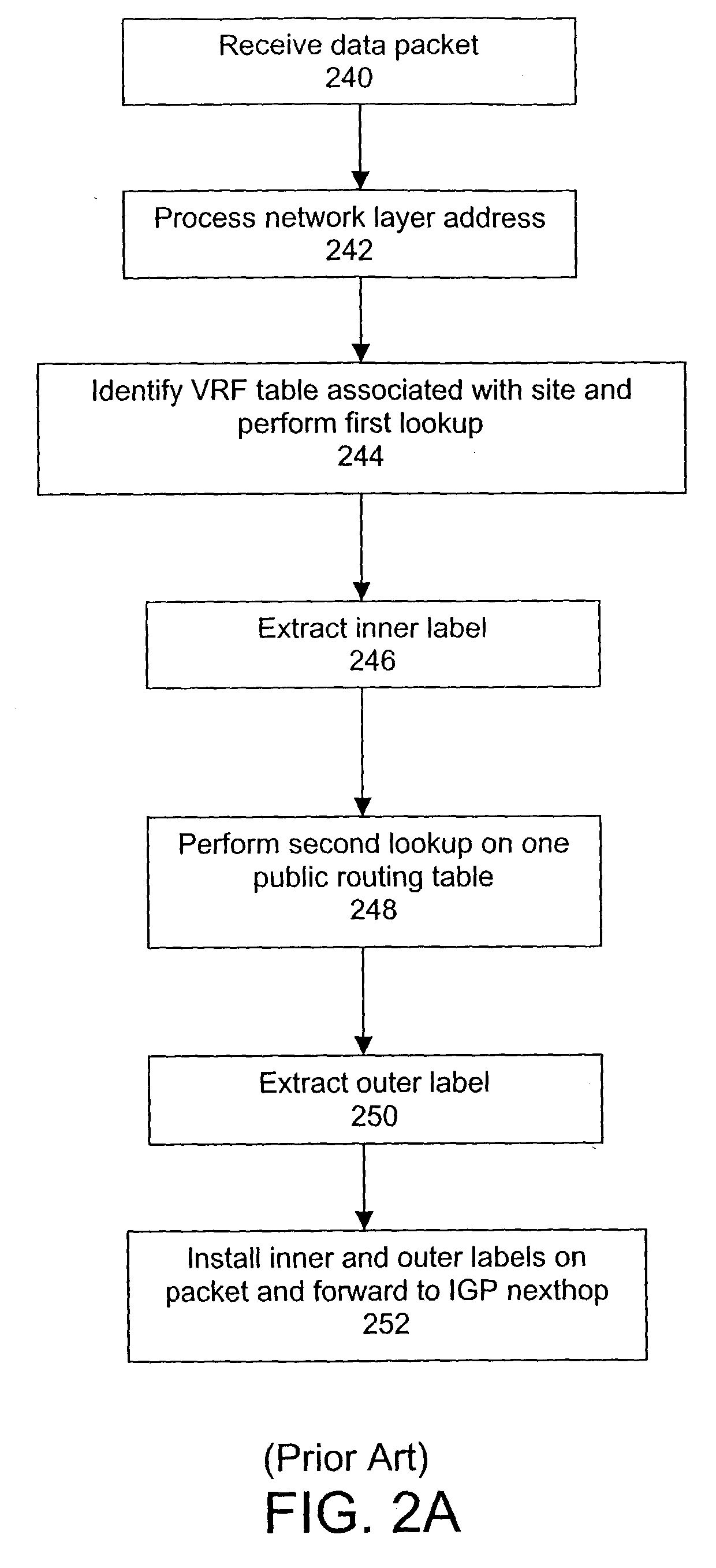
A system and method for transmitting data from a first site to a second site over a shared Multi-Protocol Label Switched (MPLS) network comprising a plurality of routers, including an ingress router in communication with the first site and an egress router in communication with the second site, includes configuring a plurality of label switching paths between the ingress router and the egress router over a plurality of label switching devices. The method further includes performing a first lookup on one of at least one virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) table stored in the ingress router, whereby the first lookup identifies one routing table from a plurality of routing tables stored in the ingress router, each routing table being associated with one of the plurality of label switched paths, and performing a second lookup on the one routing table, wherein the routing table defines the associated label switched path between the ingress router and the egress router for a virtual private network (VPN) between the first site and the second site.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
Packet protection technique
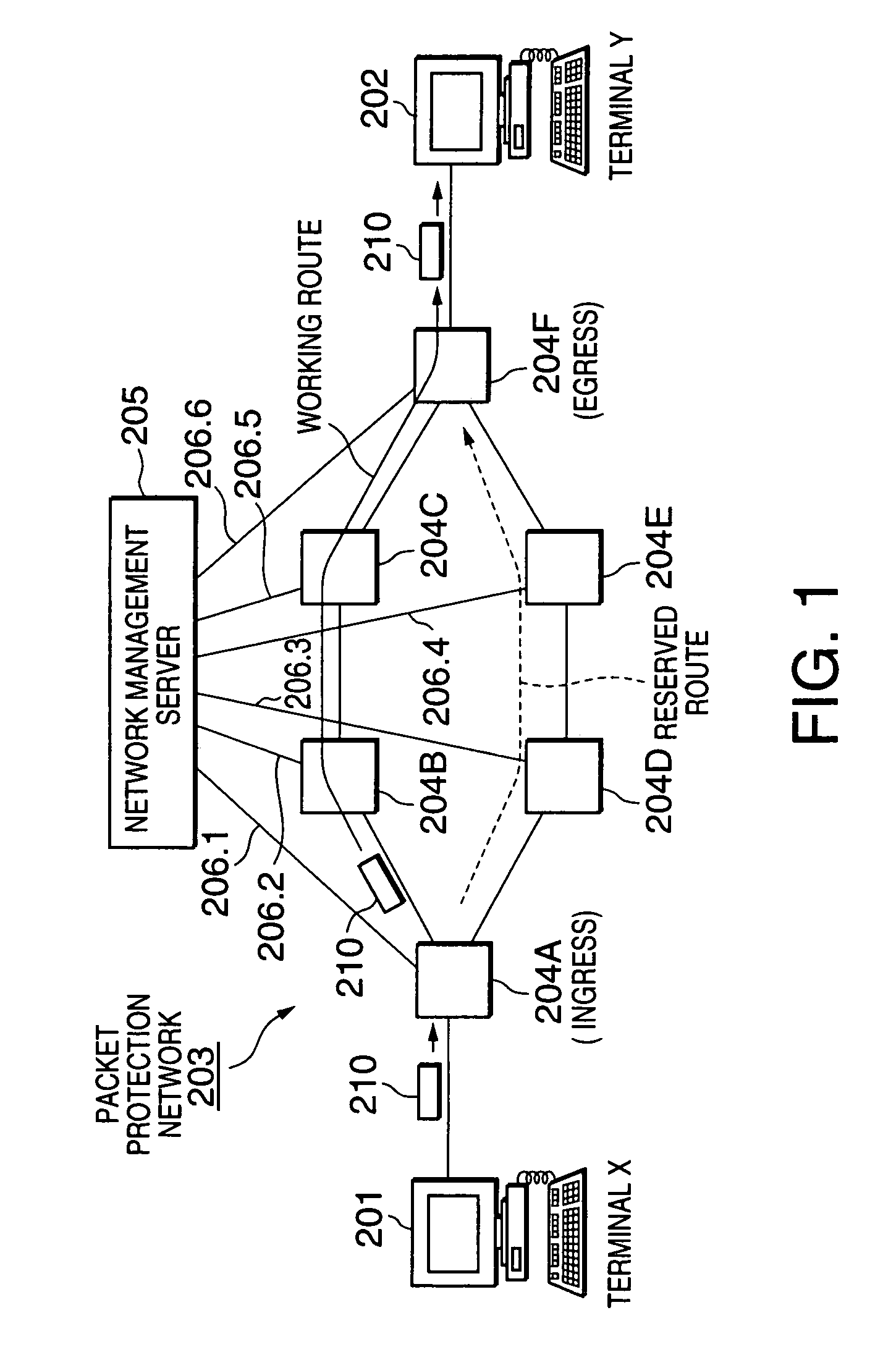
InactiveUS7075889B2Promote recoveryLow efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsFault occurrenceIngress router
A packet protection method allowing rapid restoration in case of fault occurrence without undesired reduction in efficiency on the use of network bandwidth is disclosed. In a packet protection network having a working route and a reserved route set therein, when a failure occurs, a router on the working route sends an incoming packet to be protected back to the ingress router. The ingress router forwards the packet to be protected to the reserved route so that the packet to be protected travels through the reserved route around the failure.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and device for multicast forwarding
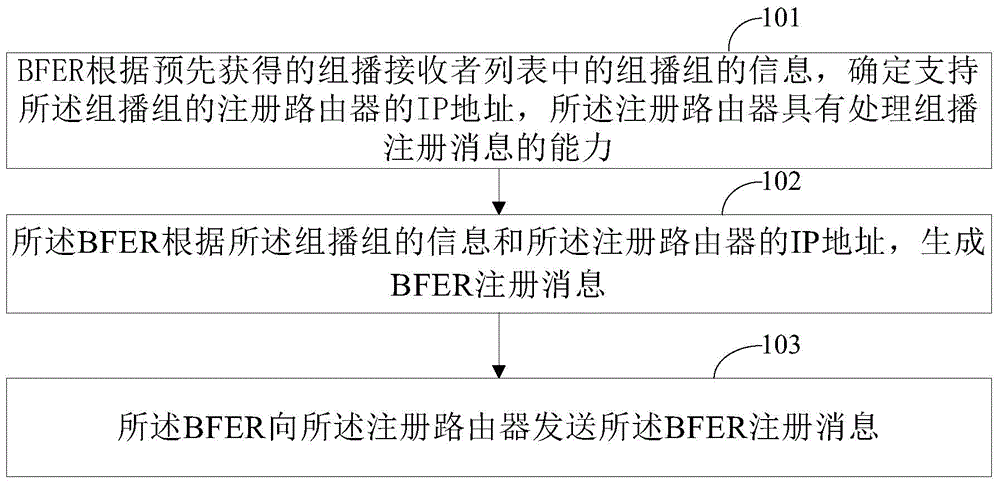
ActiveCN105871565ARealize interconnectionRapid deploymentSpecial service provision for substationIp addressMulticast network
The invention discloses a method and a device for multicast forwarding, which can enable a BFIR (bit-forwarding ingress router) to acquire BFER (bit-forwarding egress router) information included in a multicast group and enable a BIER (bit index explicit replication) multicast network to be quickly deployed. The BFER in the BIER network can determine an IP address of a registered router supporting the multicast group according to information of the multicast group in a pre-acquired multicast receiver list; according to the information of the multicast group and the IP address of the registered router supporting the multicast group, the BFER generates a BFER registration message, wherein the BFER registration message comprises the information of the multicast group, the destination IP address of the BFER registration message is the IP address of the registered router, and the source IP address of the BFER registration message is the IP address of the BFER; the BFER sends the BFER registration message to the registered router; and after the registered router in the BIER network receives the BFER registration message sent by the BFER, a BFER table entry is acquired according to the BFER registration message, wherein the BFER table entry comprises the information of the multicast group and the IP address of the BFER.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
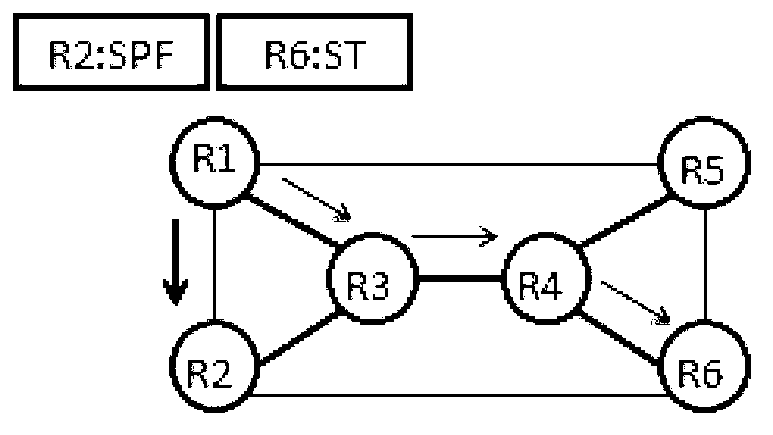
Shortest path tree and spanning tree combined energy-saving routing method
The invention discloses a shortest path tree and spanning tree combined routing method and belongs to the technical field of network topology. The method is characterized in that on the basis of a standard link state routing protocol, a dormant state is added to each link which is connected with a router node in a network, a shared spanning tree is selected on a given network topology, links on the spanning tree are in a working state all the time so as to guarantee network connectivity, other links which are not on the spanning tree enter into dormant states if no flow passes, each router stores a shortest path routing list of the whole network path and a routing list of a corresponding spanning tree, as for a data packet, an ingress router determines that the data packet uses a path therein according to current link loads, a label identification is added, and a non ingress router selects a corresponding routing list according to a label to perform forwarding.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and System For Computing Multicast Traffic Matrices
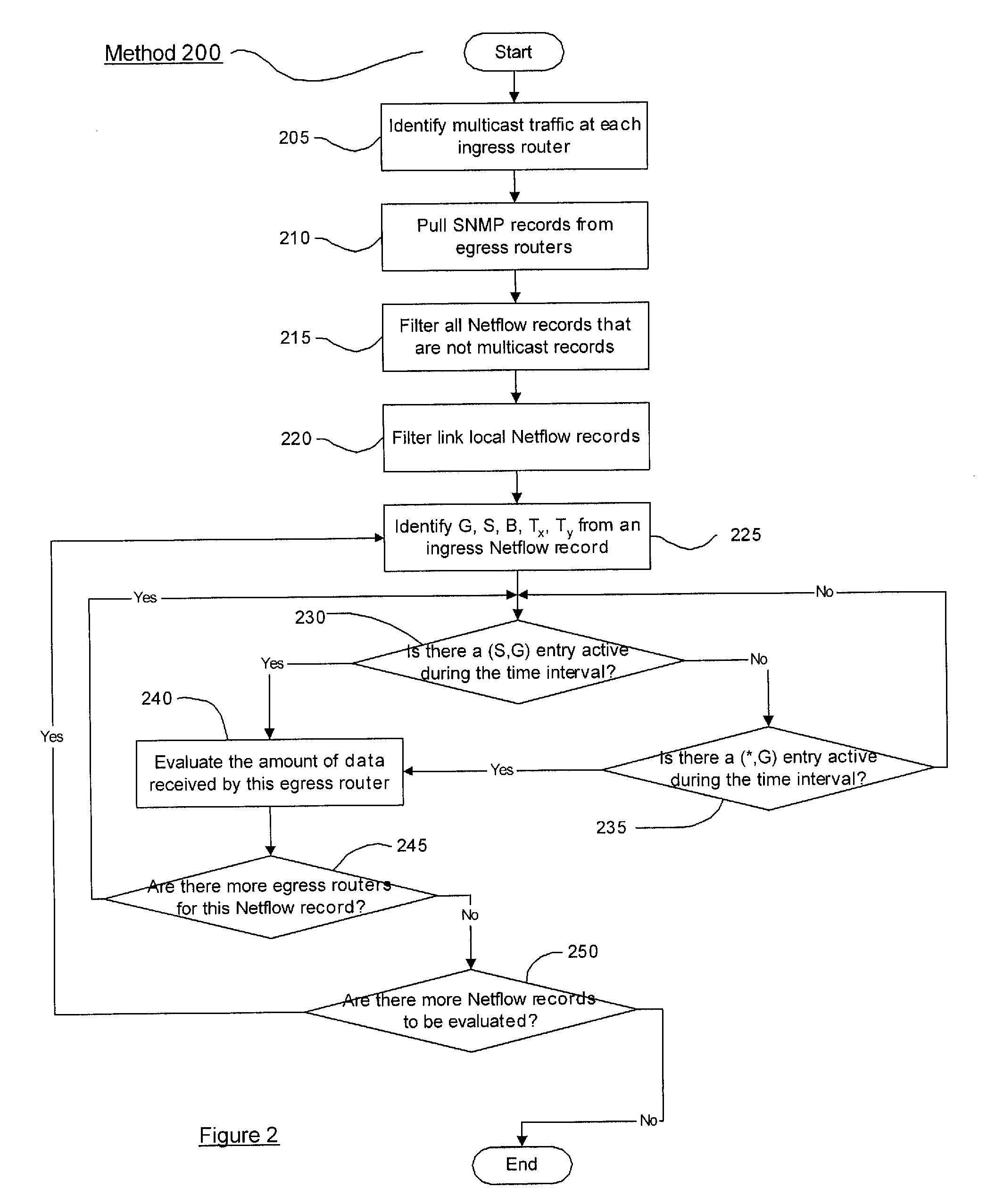
InactiveUS20090161673A1Broadcast transmission systemsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityEgress router
A system and method for receiving, from one or more ingress routers, a first set of records including data corresponding to network traffic, receiving, from one or more egress routers, a second set of records including data corresponding to network traffic and creating a multicast traffic matrix using at least a portion of the data included in the first and second sets of records.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
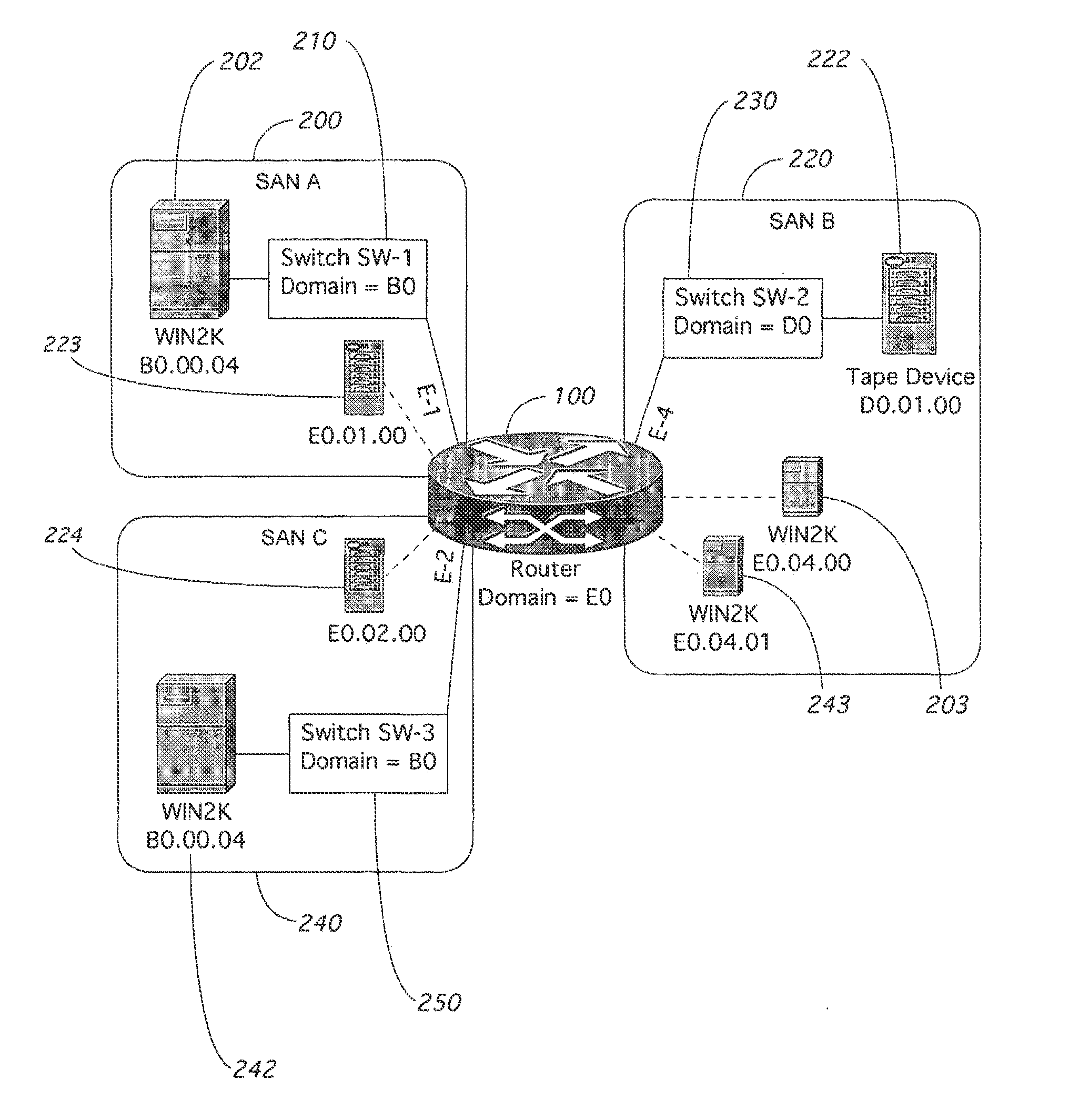
Inter-Fabric Routing
A method and apparatus is shown for communicating Fibre Channel frames between distinct fabrics. A proxy zone is established in each fabric with a physically present local device and a remote fabric device. A router creates a proxy device in each fabric for every device not physically connected to the fabric. The proxy devices appear to be directly attached to the router. The router handles all address translations between proxy and physical addresses. When multiple routers are encountered, the ingress router does all address translation. No routing or encapsulation headers are used except when routing between two routers. The source ID and the originator exchange identifier are stored at the egress router for all link requests that require special handling. When replies pass through that router, the destination ID and originator exchange identifier are compared with the stored information. On a match, the reply is specially handled.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
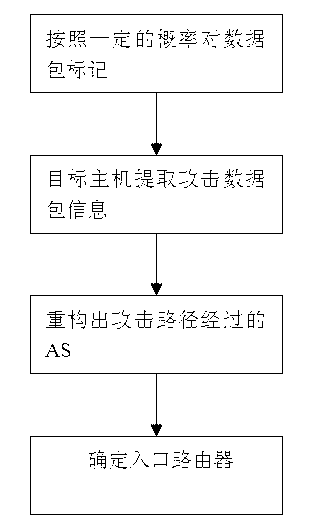
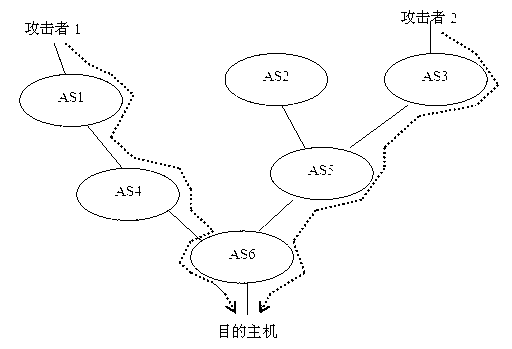
DDoS attacker tracing method based on autonomous system
The invention discloses a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack source tracing method for an autonomous system and belongs to the technical field of network security. The technical scheme is that firstly, an ingress router marks a data packet according to a certain probability, then a target host extracts the attacked data packet for bath configuration to obtain the AS (Autonomous System) through which an attack path passes, and finally, the ingress router is determined. The DDoS attack source tracing method is mainly used for searching the autonomous system where the attack source is positioned and finding out the attacked ingress router in case of a DDoS attack, so that the attack is suppressed at the attack source.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
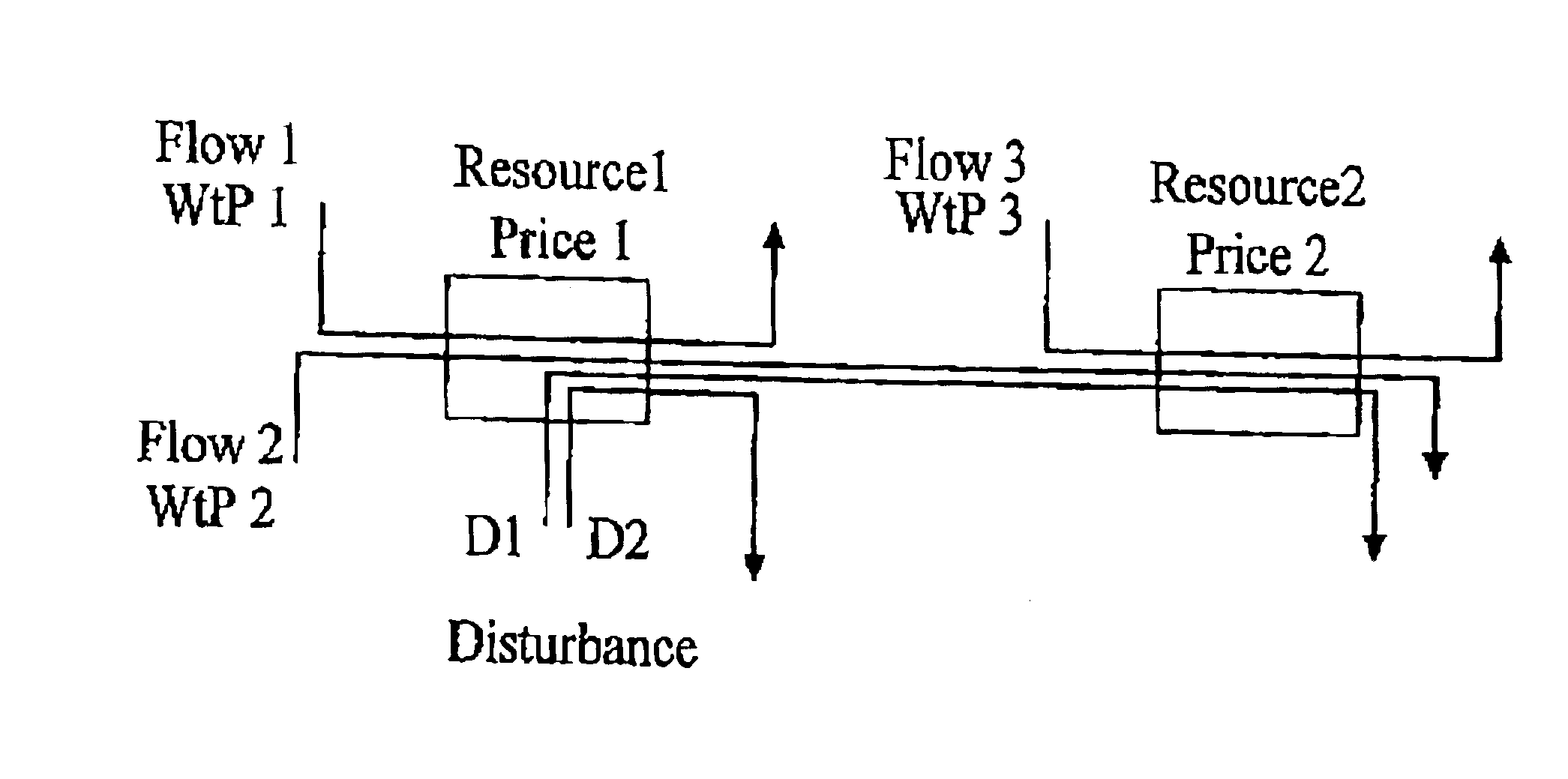
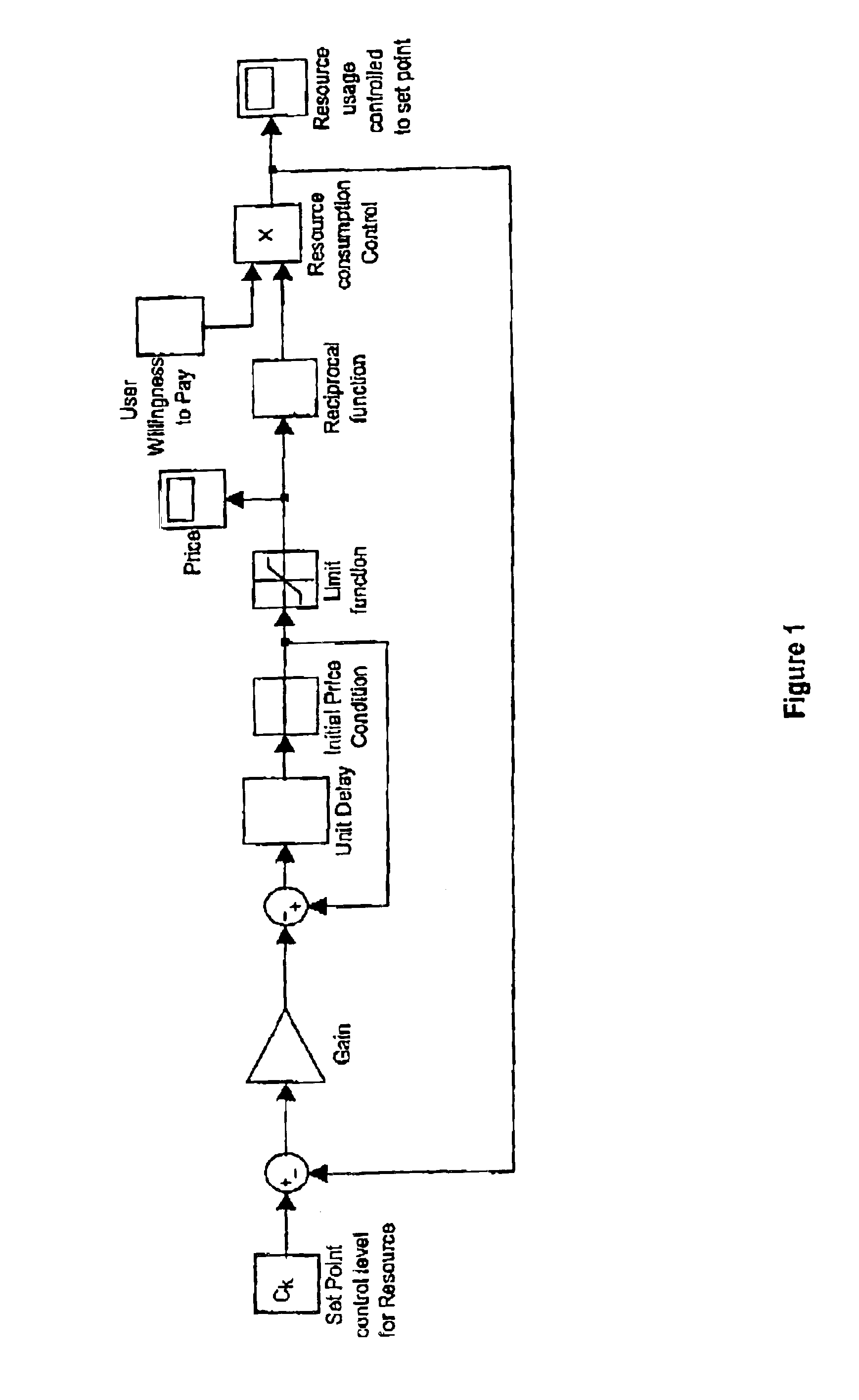
Dynamic resource control in telecommunications networks
InactiveUS6928053B1Control flowMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsError preventionFactor baseTelecommunications link
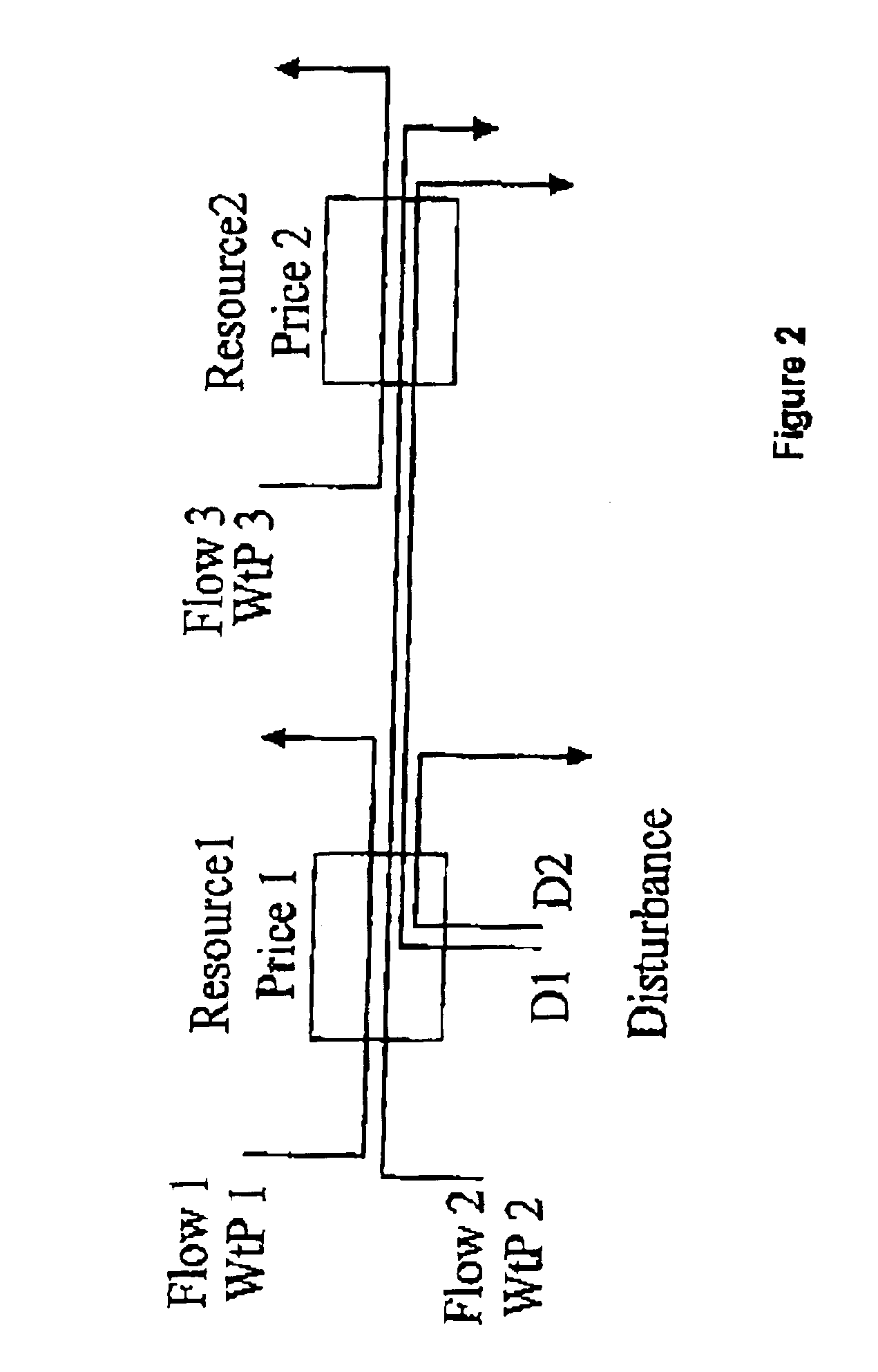
A method of managing resources in a switched network including the steps of assigning a respective willingness to pay WtP value to each of a plurality of network users, assigning respective set point values for a network performance parameter for each of a plurality of routers in the network, assigning a respective initial price value to each router which is associated with the network performance parameter at the router, and operating a first control loop which is operable to receive respective measures of the actual network performance at each of the routers, calculate for each router, a plurality of difference values which are the respective differences between the actual performance and the set point for each router, adjust the price value for each router by a factor based on the respective difference value, generate a flow price value for each user by summing the price values for each of the routers in the path of the respective user's desired data flow through the network, allocate a resource share value for each user which represents the value of the respective VtP value divided by the respective flow price value, and cause the ingress router for each user to restrict flow into the network ingress from each user in accordance with each user's allocated resource share value, whereby the actual network performance at each router is made to converge to the set point value for the respective router by automatic admission control adjustment at the network ingress routers.
Owner:CIENA
Data switch and a method for controlling the data switch
ActiveUS7016350B2Reduce, or even eliminate, variation in the latency of the throughput of time division multiplexed trafficMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexControl dataEgress router
A data switch is proposed of the type having virtual queue ingress routers interconnected with egress routers by way of a memoryless switching matrix controlled by a control unit which performs an arbitration process to schedule connections across the switch. This scheduling is performed to ensure that data cells which arrive at the ingress routers at unpredictable times are transmitted to the correct egress routers. Each ingress router further includes a queue for time division multiplex traffic, and at times when such traffic exists, the control unit overrides the arbitration process to allow the time division multiplex traffic to be transmitted through the switch.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
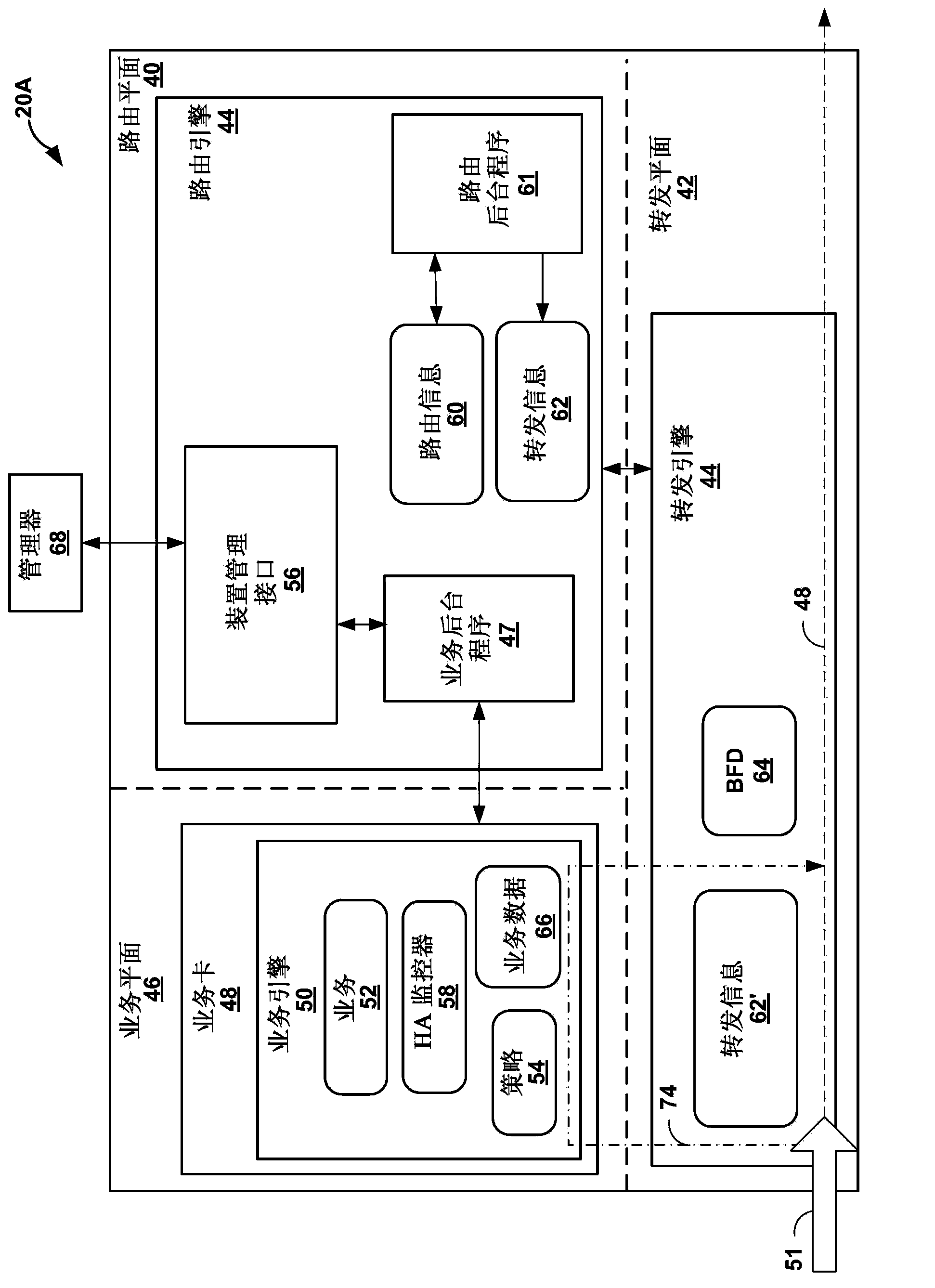
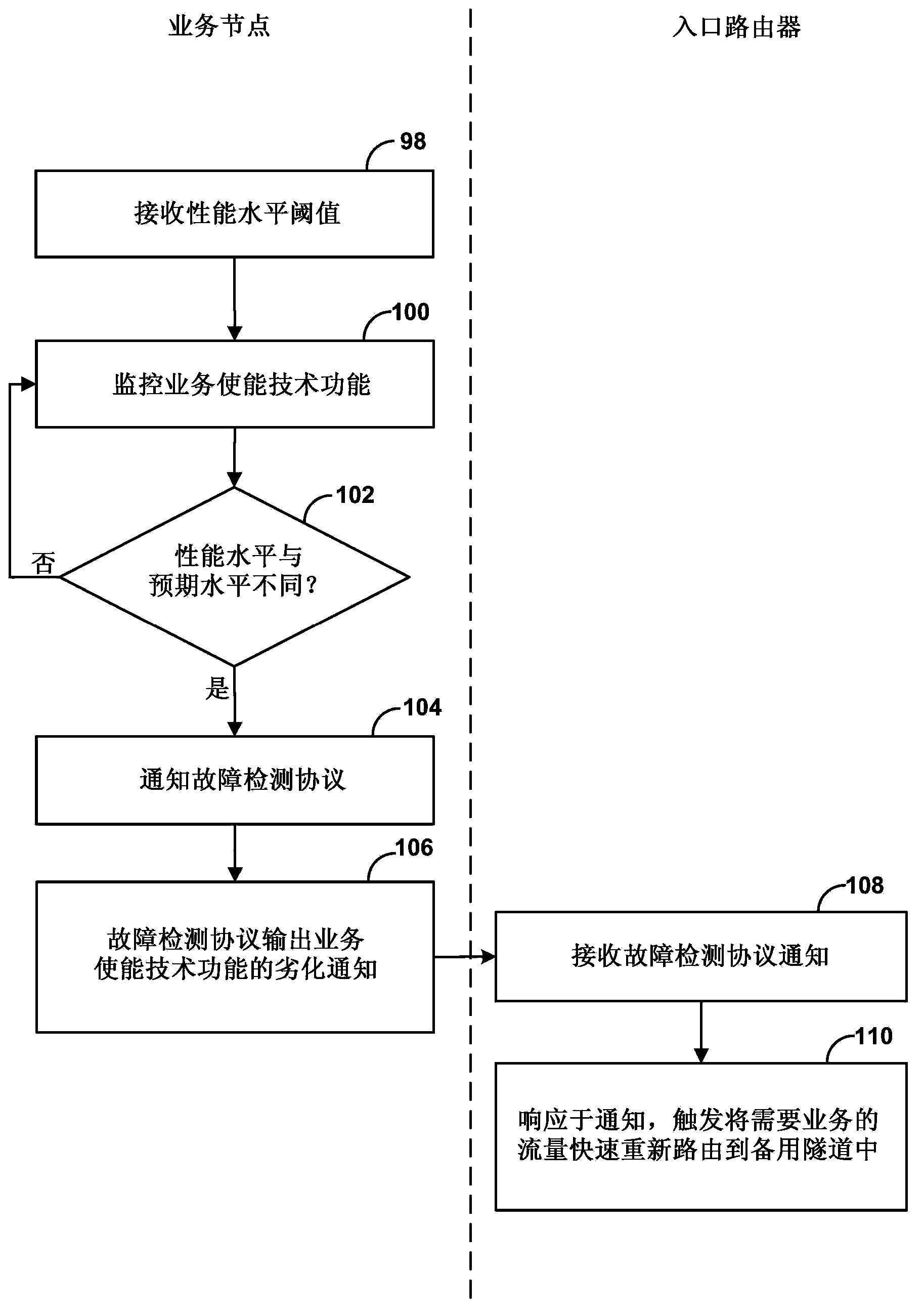
Service plane triggered fast reroute protection
Techniques are described for detecting failure or degradation of a service enabling technology function independent from an operational state of a service node hosting the service enabling technology function. For example, a service node may provide one or more service enabling technology functions, and service engineered paths may be traffic-engineered through a network to service node network devices that host a service enabling technology function. A monitor component at the service layer of the service node can detect failure or degradation of one or more service enabling technology functions provided by the service node. The monitor component reports detection of failure or degradation to a fault detection network protocol in a forwarding plane of the service node. The fault detection network protocol communicates with an ingress router of a service engineered path to trigger fast reroute by the ingress of traffic flows to bypass the affected service enabling technology function.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
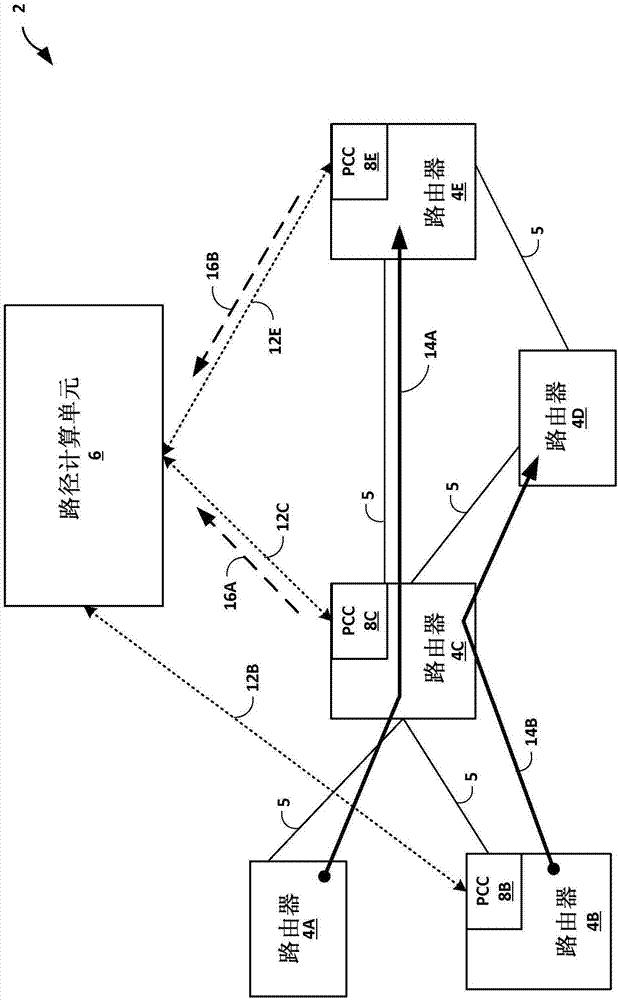
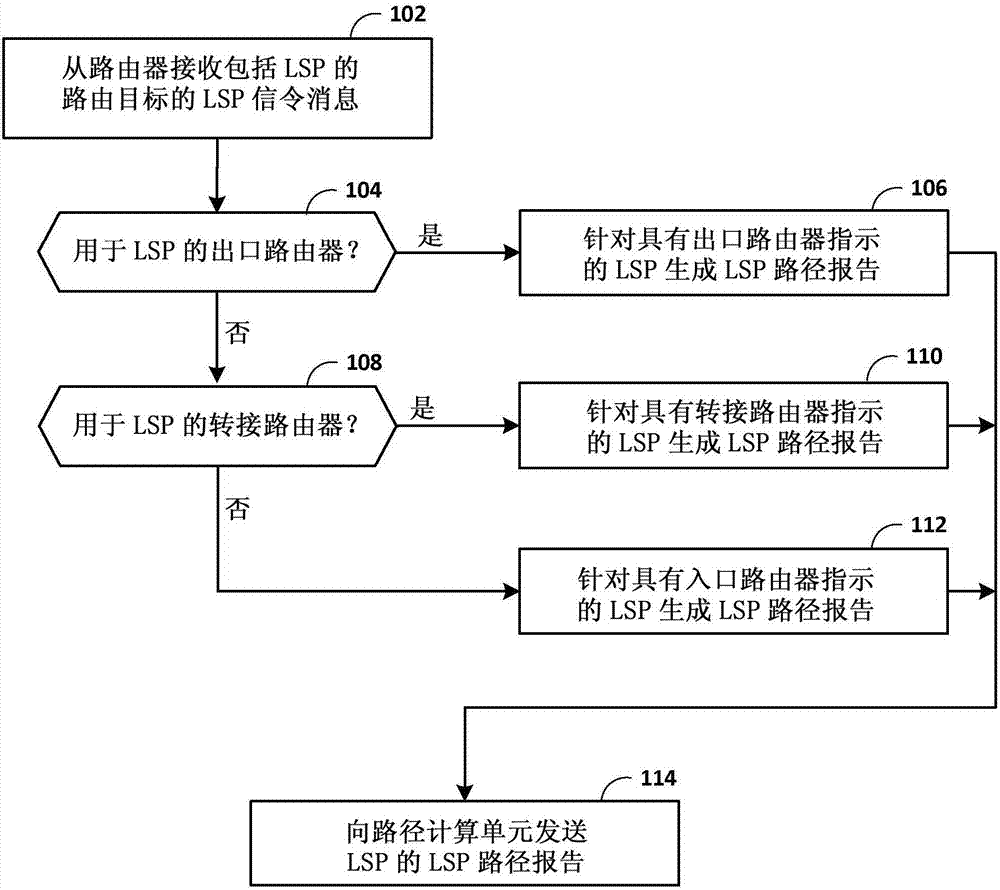
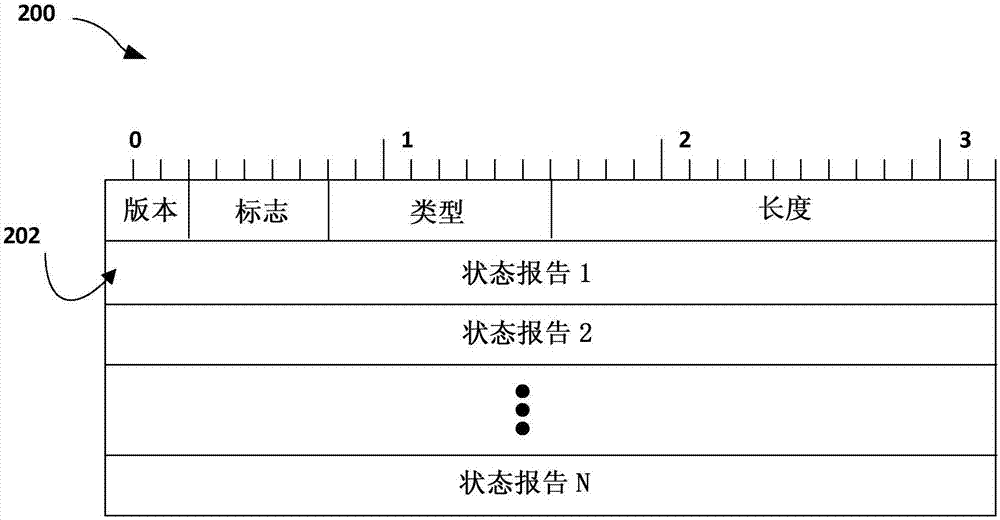
Label switched path reporting
The invention relates to label switched path reporting. Techniques are described for reporting, by non-ingress routers for traffic engineering label switched paths (TE LSPs) and to a path computation element, actual paths taken by the TE LSPs through the network. A first network device: receives, from a second network device, an LSP path signaling message that includes a route object having a first indication of at least a sub-path of a path for TE LSP through a network, wherein the first network device is not an ingress label edge router for the TE LSP; generates, in response to the LSP path signaling message and based at least in part on the route object, an LSP path report message that includes a second indication of the at least the sub-path of the path for the TE LSP; and sends, to a path computation element, the LSP path report message to notify the PCE.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
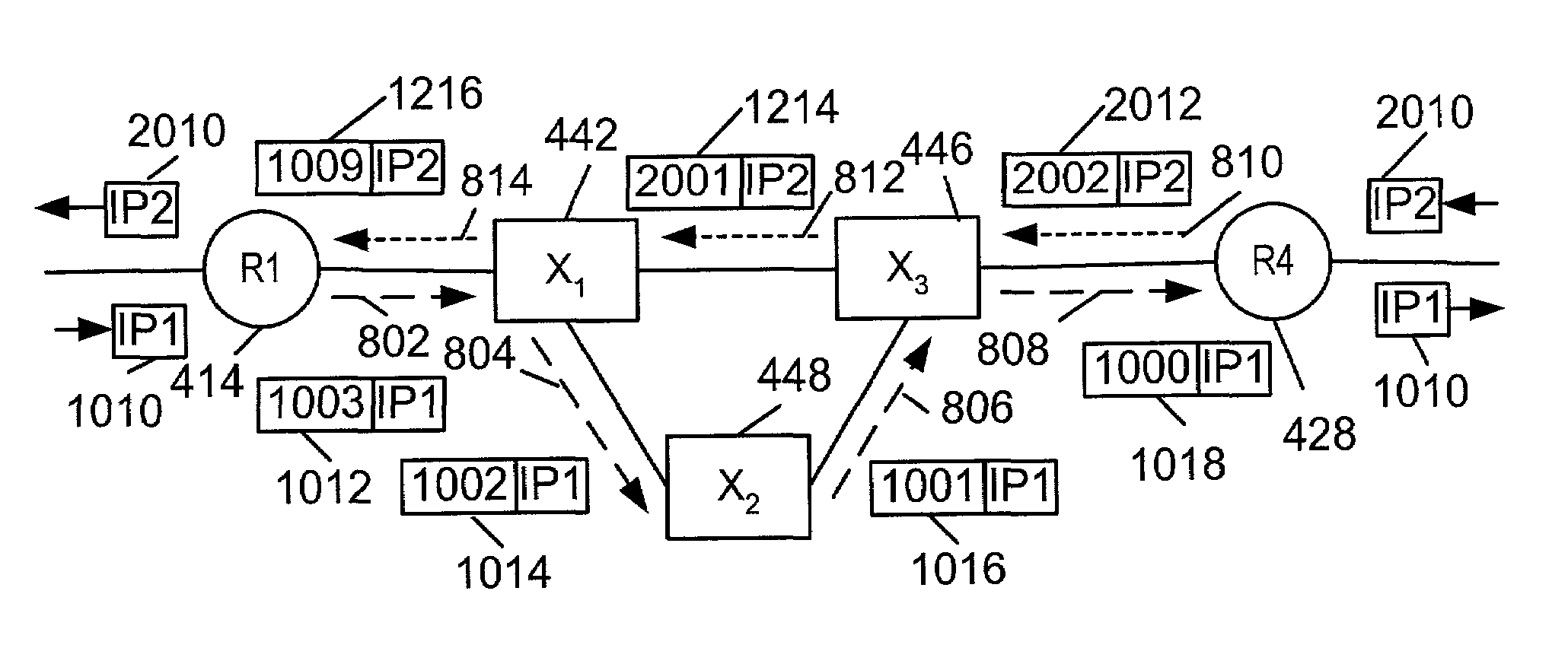
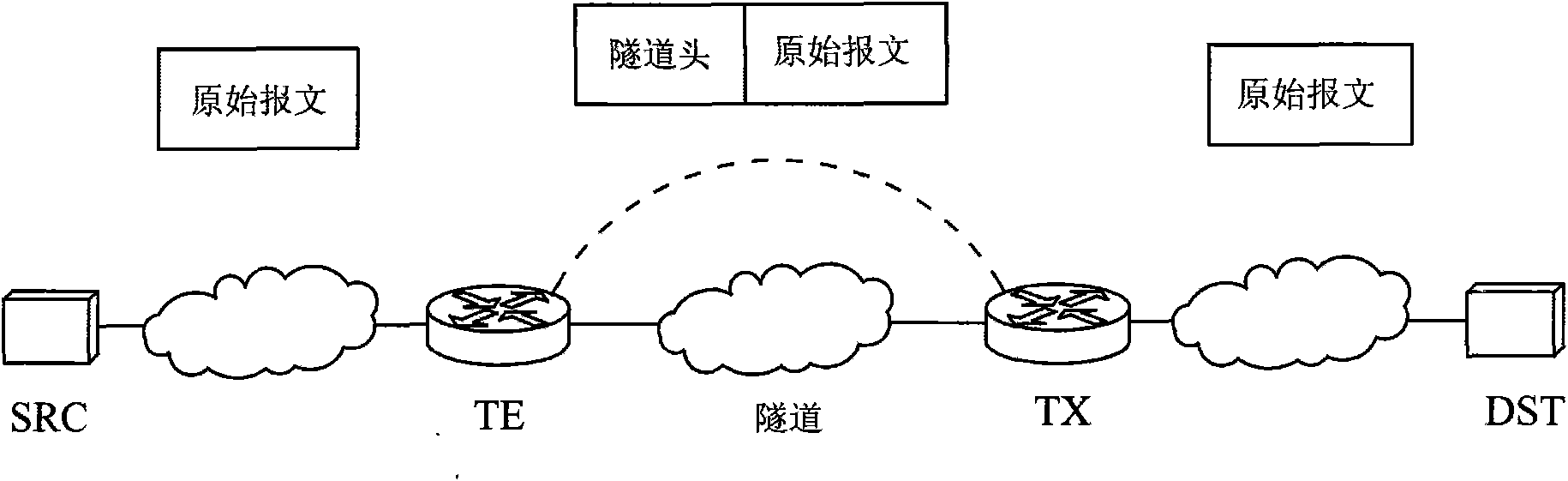
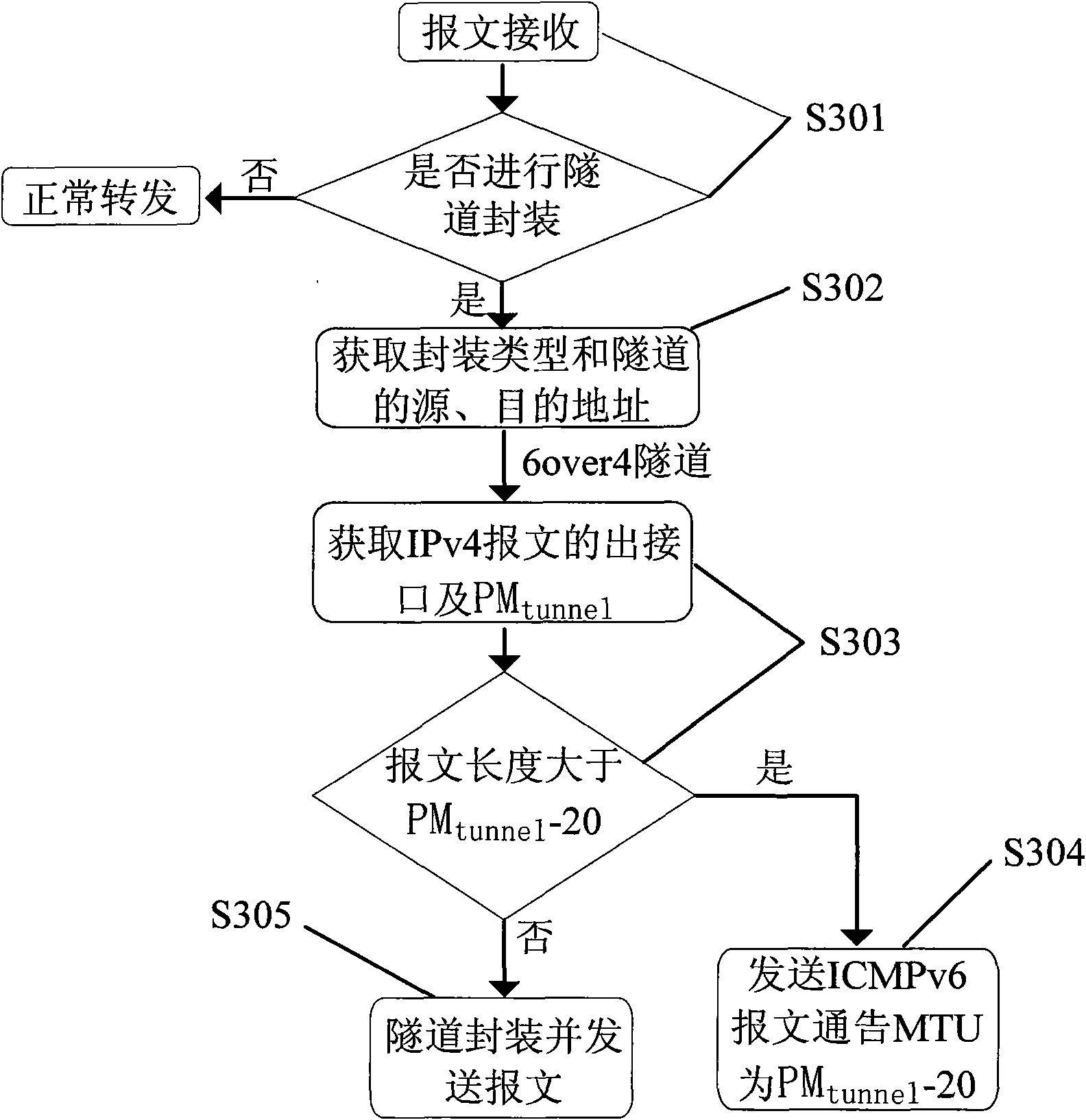
Method for avoiding message recombination in 6over4 tunnel and system therefor
InactiveCN101640635AAvoid fragmentationAvoid reorganizationNetworks interconnectionRouting tableEgress router
The invention discloses a method for avoiding message recombination in a 6over4 tunnel and a system therefor, and more particularly relates to a method for avoiding message recombination at a tunnel exit in the 6over4 tunnel, and a system therefor. The method comprises: a tunnel entrance router can be used for looking up a routing table according to the destination address of the tunnel, so as toacquire an outgoing interface of the message; the tunnel entrance router also can search a tunnel path maximum transmission unit PM tunnel according to the destination address of the tunnel and the outgoing interface, and obtain the tunnel encapsulation length L t-head at the same time according to the encapsulation type; then, whether the length of the original message is more than maximum sharding length PM tunnel-L t-head is judged; if yes, error information is sent to a message sending unit, the fact that the length of the original message is more than maximum sharding length is notified,the maximum sharding length is notified to be PM tunnel-L t-head, and the original message is discarded; if not, tunnel encapsulation is carried out on the original message, an IPv4 routing table is looked up, and the message is transmitted into a tunnel exit router after the tunnel encapsulation. The invention can avoid message sharding and recombination in the 6over4 tunnel, and the experiment proves that the invention can greatly improve the performance of tunnel communication.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
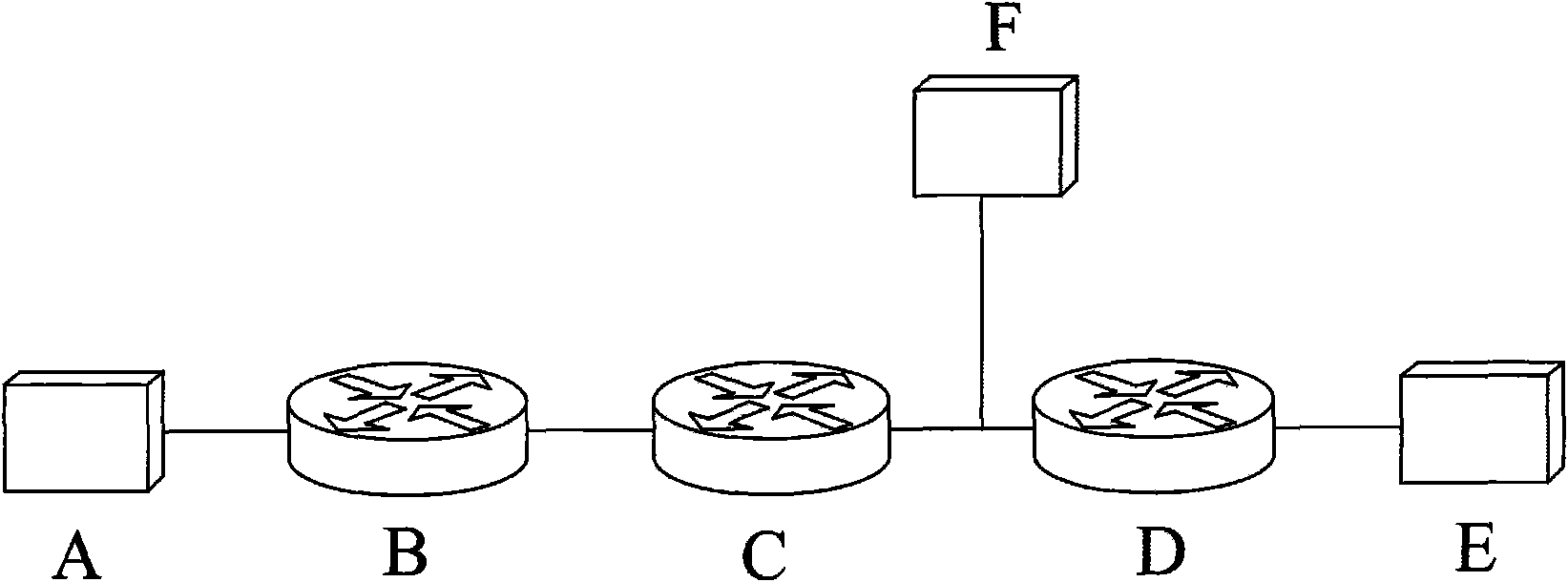
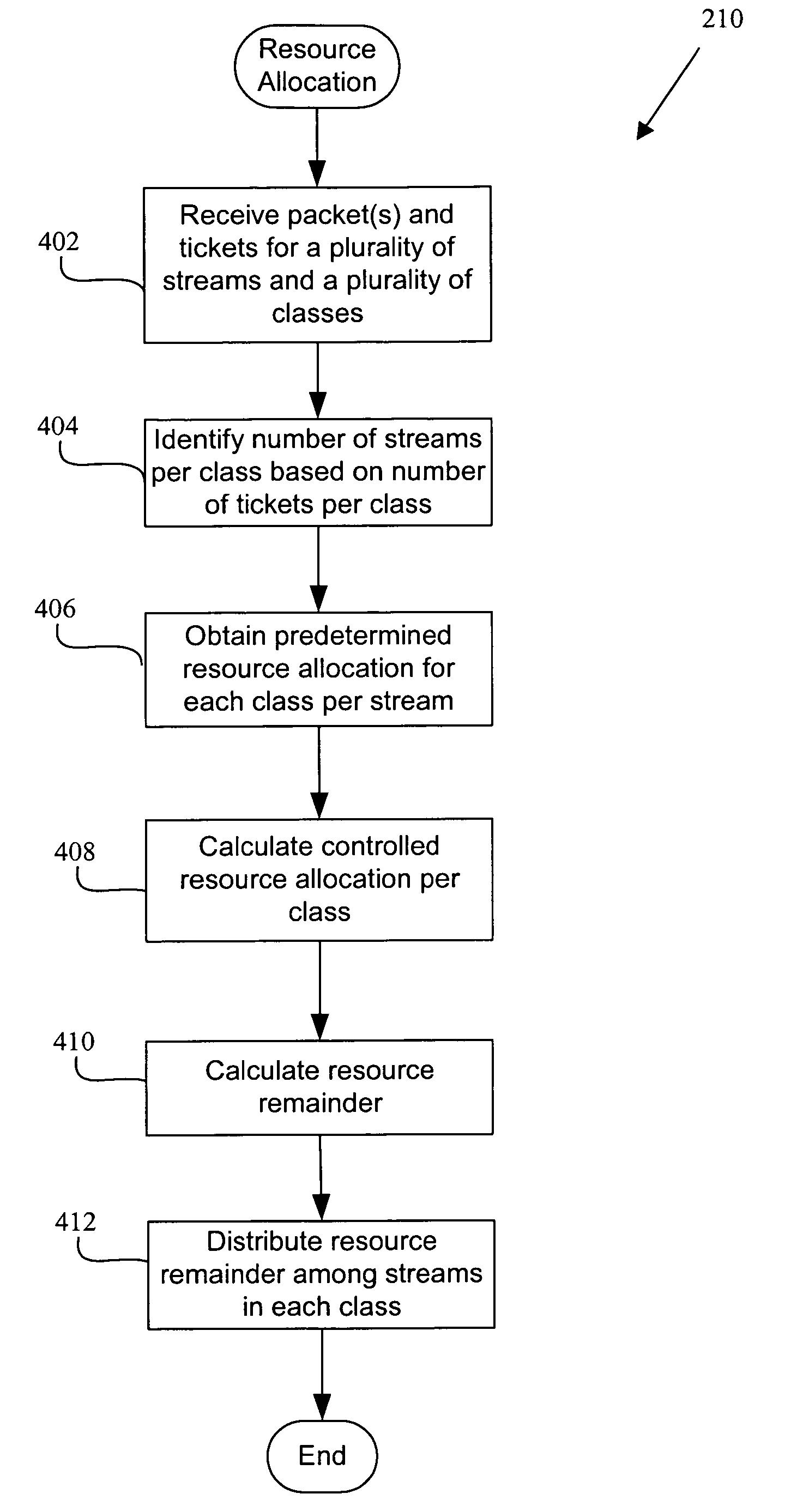
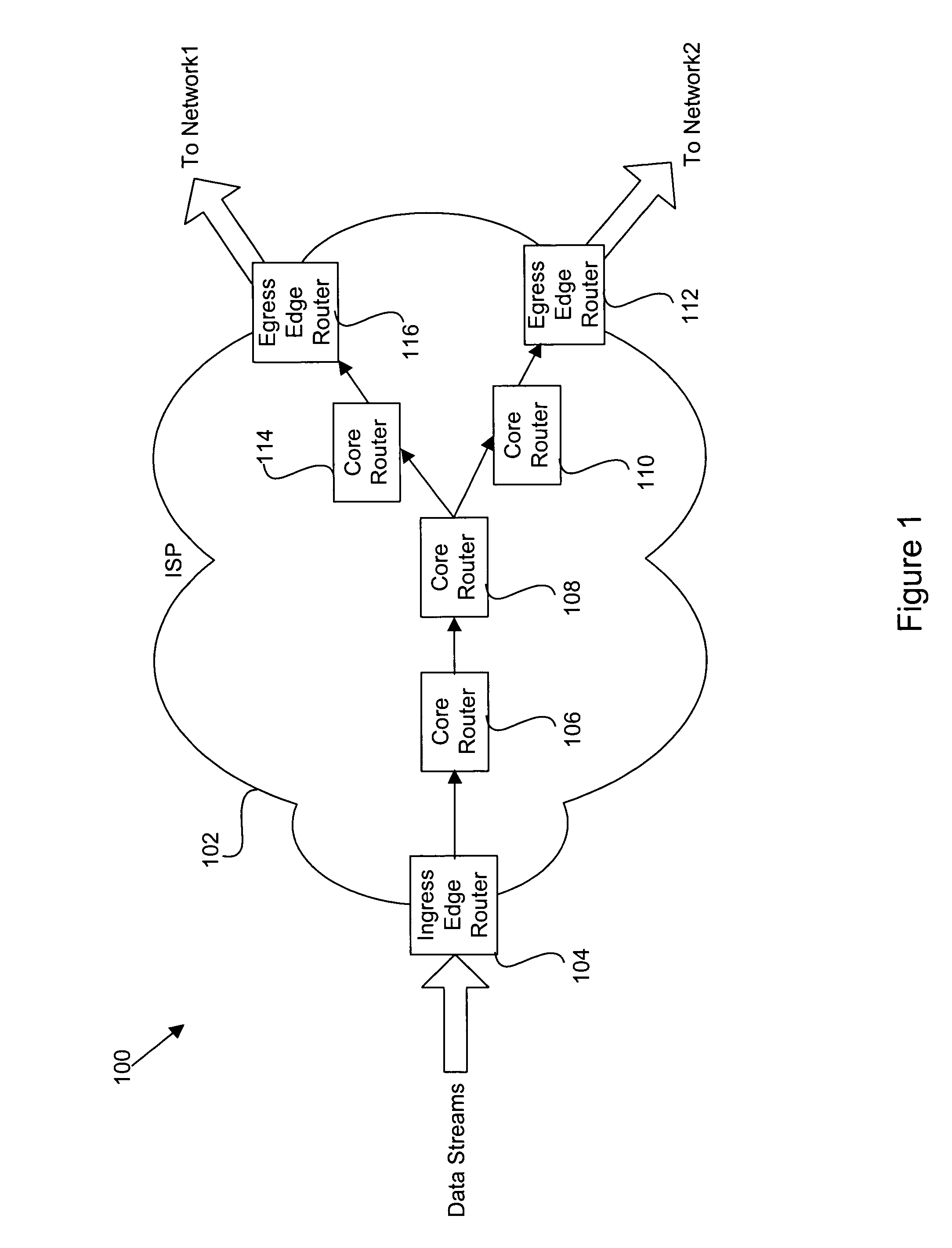
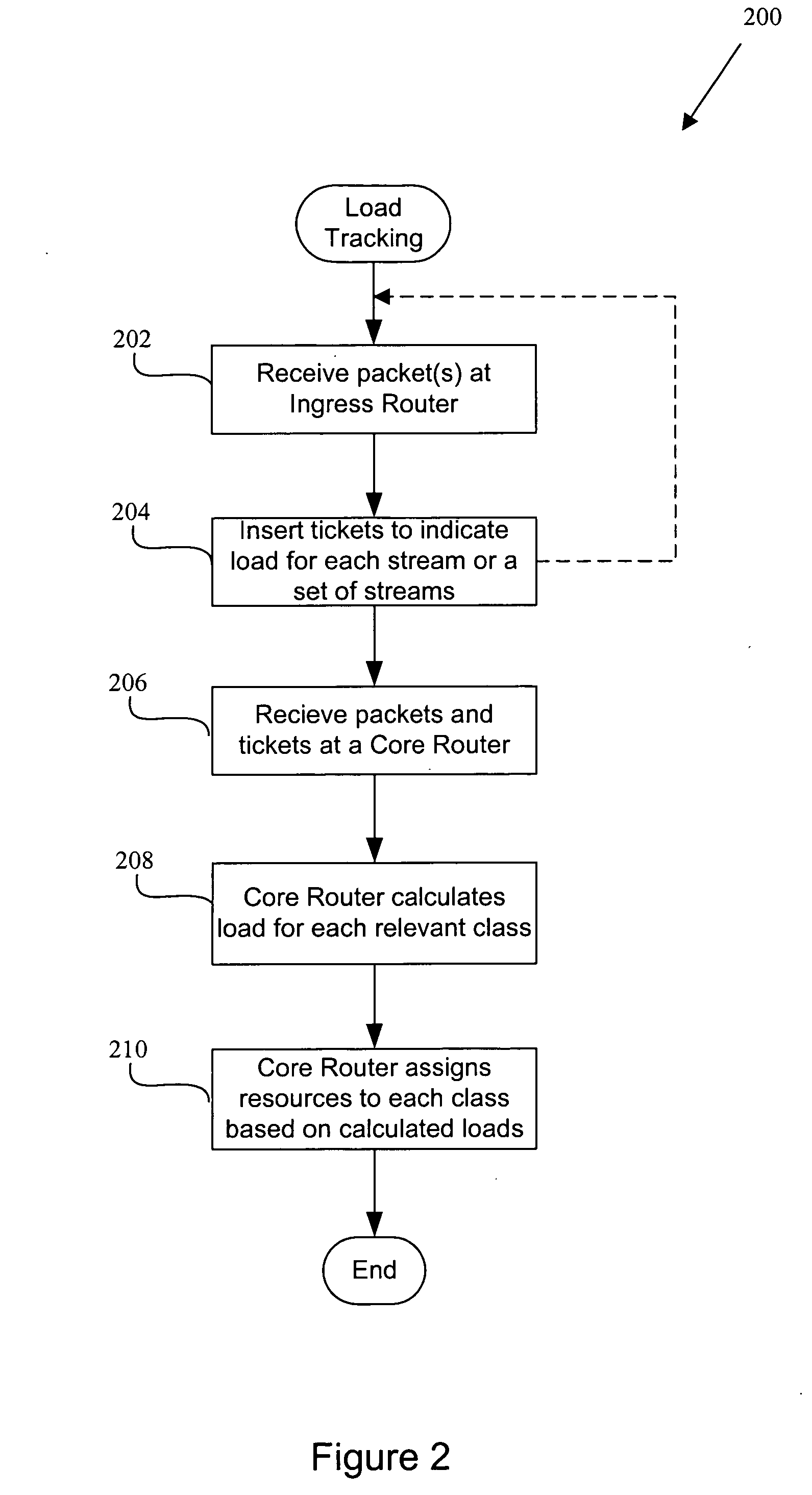
Ticket insertion: load information for assured forwarding classes
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for providing load information for one or more data streams within a network having a plurality of ingress routers, a plurality of core routers, and a plurality of egress routers is disclosed. a plurality of packets are received into a selected ingress router. Each packet belongs to one of several service classes, and the packets are being transmitted to a particular destination. A load value is metered for each service class and the particular destination of at least one of the packets. One or more tickets are periodically transmitted to the destination to indicate the load value for each of the one or more service classes. This load information is then utilized to dynamically allocate load for each service class at the destination.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Intelligent routing selection method based on flow analysis and node trust degree
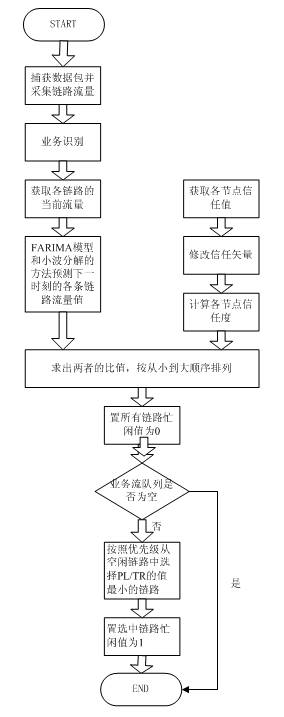
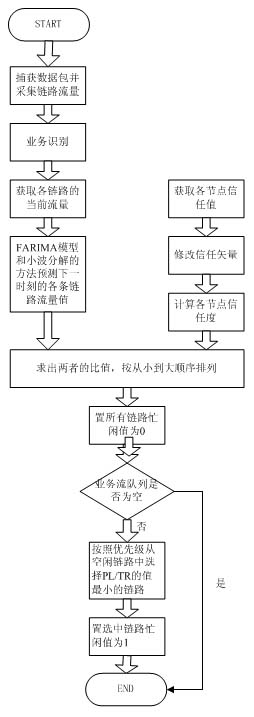
InactiveCN101958843AAchieve distinctionGuaranteed service qualityData switching networksDifferentiated servicesTraffic prediction
The invention discloses an intelligent routing selection method based on flow analysis and node trust degree, which belongs to the technical field of networks and is suitable for the situation that a plurality of routings exist between an inlet router node and a target node and each routing only passes one intermediate node. The method comprises the steps of: implementing differentiation service among different businesses through business identification and marking, and then selecting a link with smaller load and higher trust degree through link flow prediction and the trust degree of an evaluation node. The method guarantees the safety at the same time of realizing load balance, thereby realizing the real-time, intelligent and dynamic routing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com