Patents
Literature
146results about How to "Save overhead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
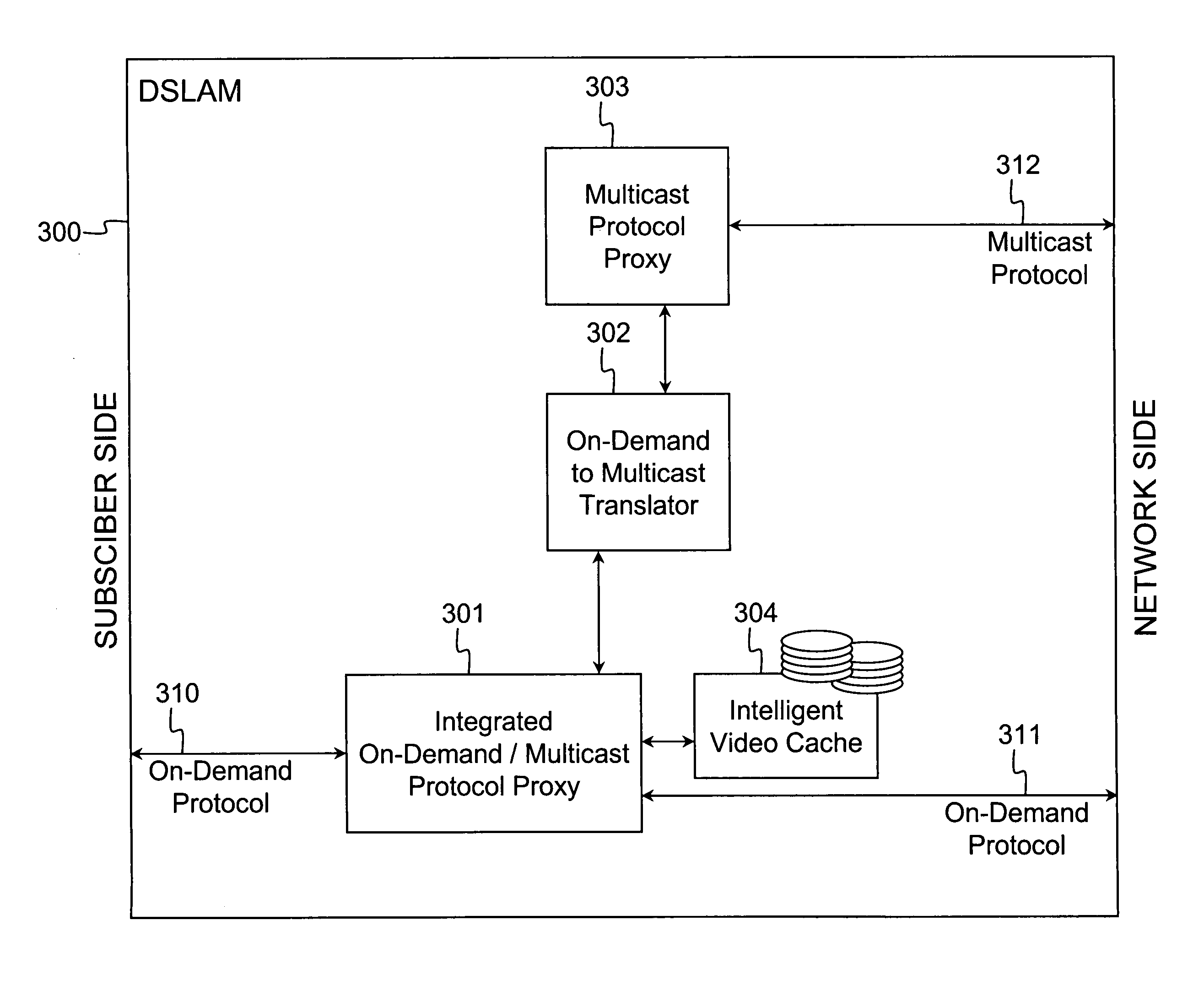
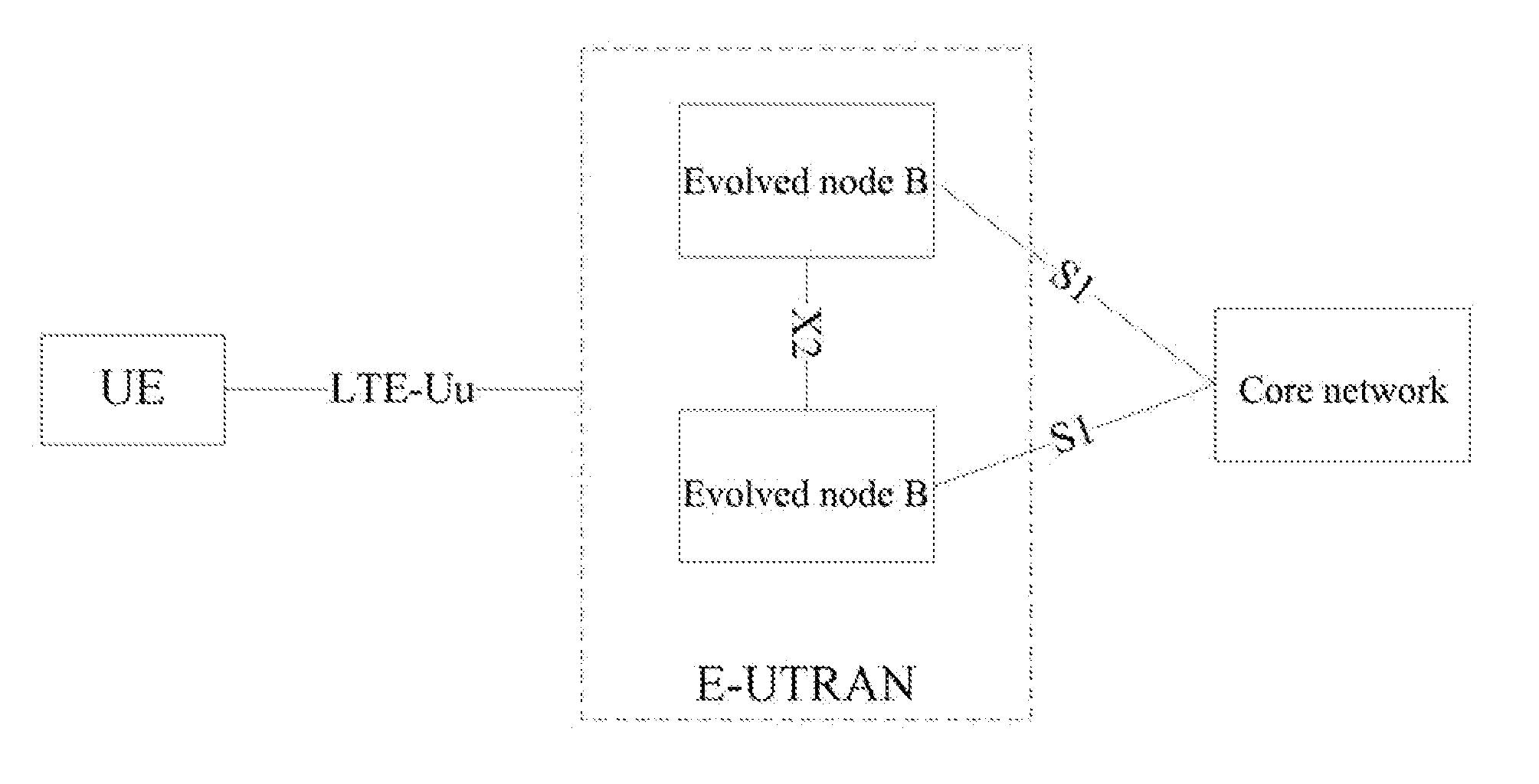
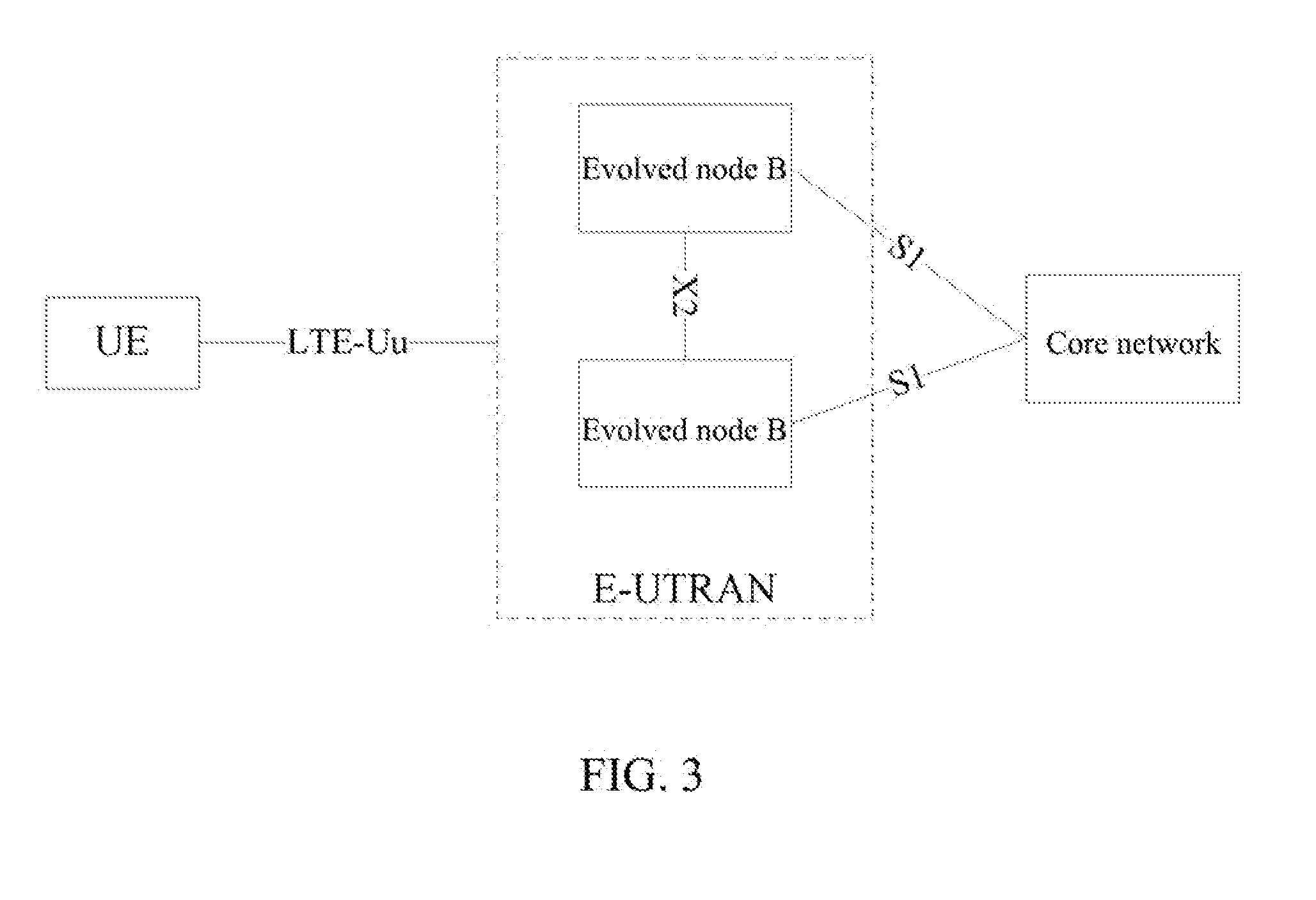
Access/edge node supporting multiple video streaming services using a single request protocol
ActiveUS20070101377A1Compact integrationReduce in quantityAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsClosed circuit television systemsEdge nodeService use
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS +2
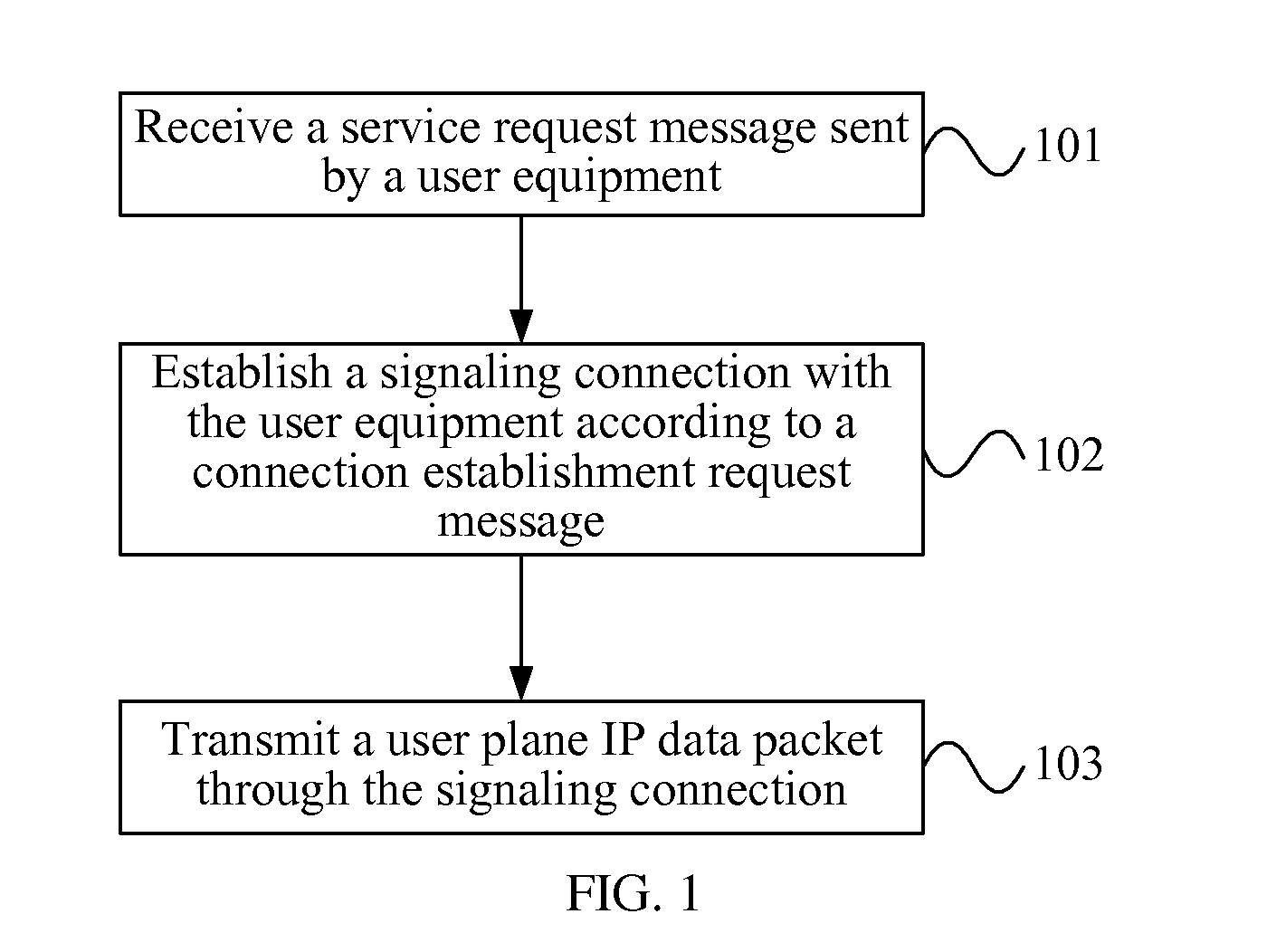
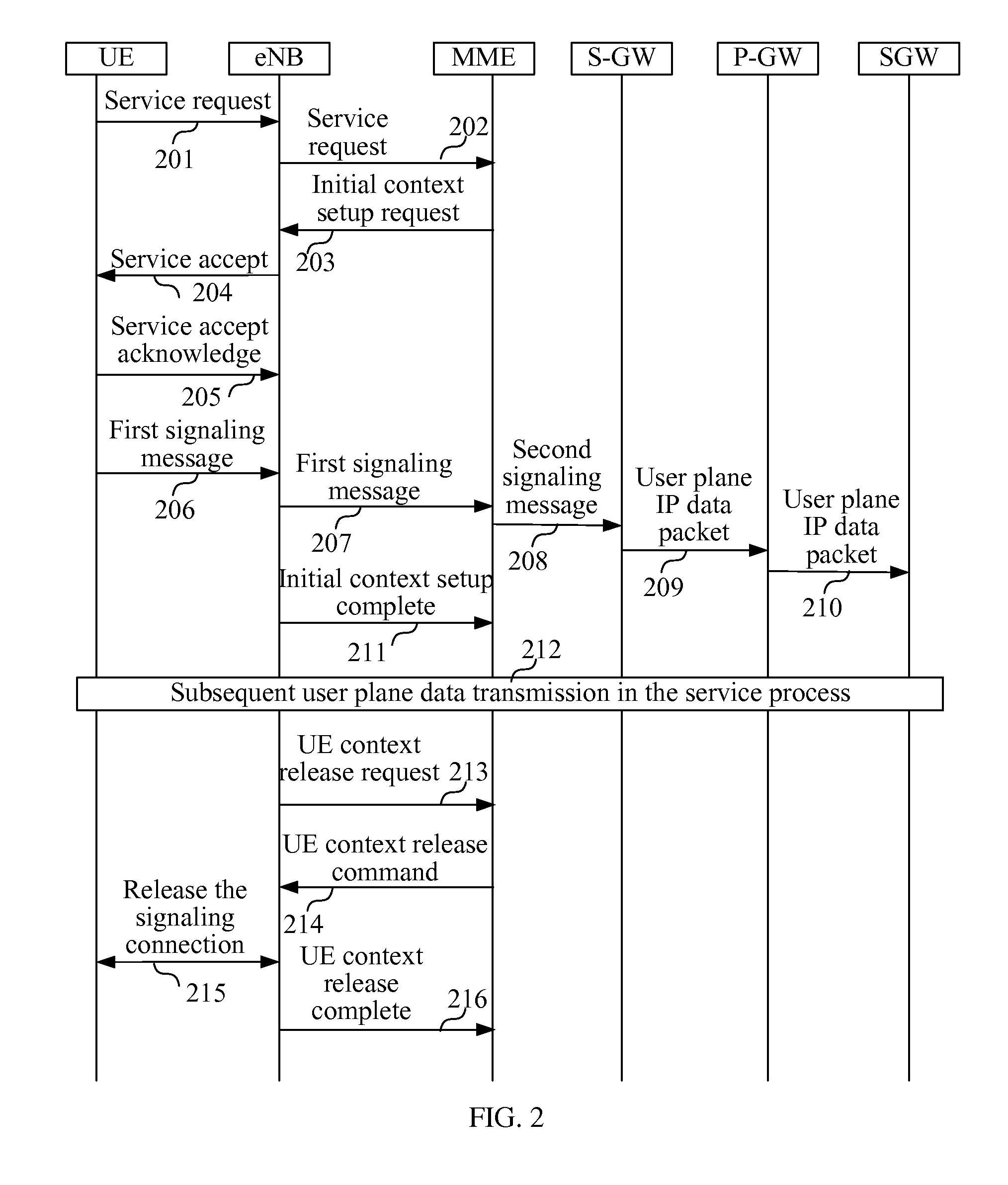
Method, Apparatus and System for Transmitting User Plane Data
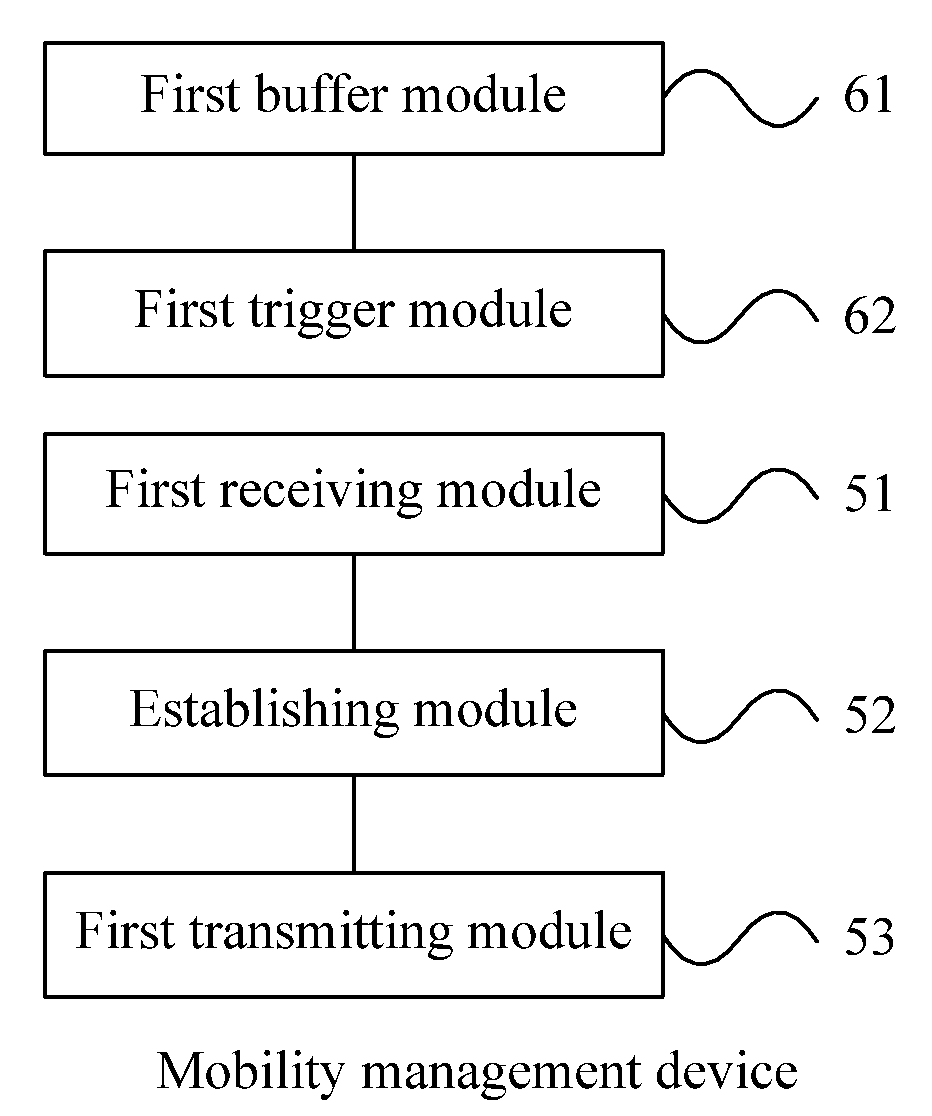
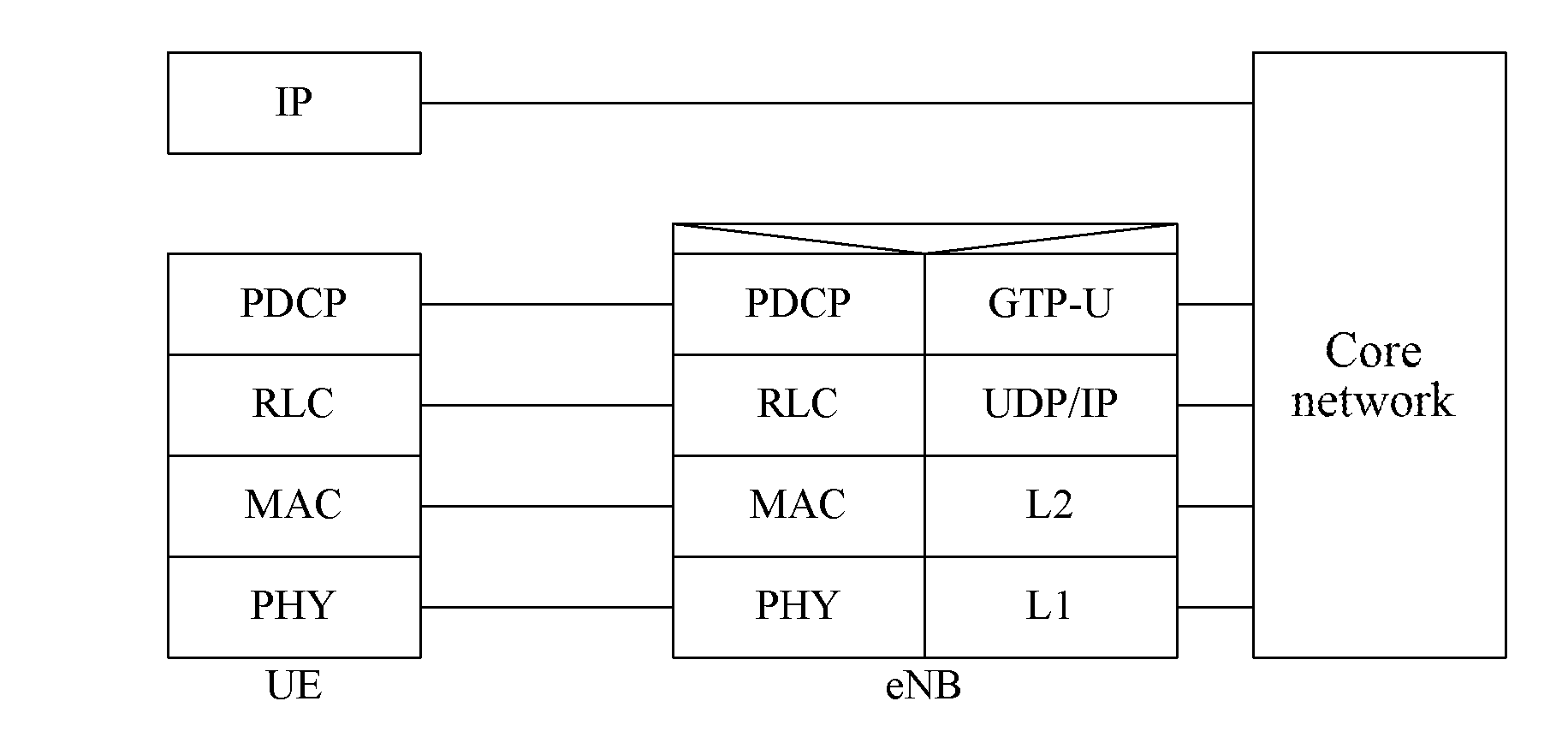
ActiveUS20120093086A1Save signaling overheadReduce network loadConnection managementWireless commuication servicesOperational costsNetwork packet
Receiving a connection establishment request message sent by a user equipment; establishing a signaling connection with the user equipment according to the connection establishment request message; and transmitting a user plane IP data packet through the signaling connection. After a signaling connection is established between a UE in an idle state and a mobility management device, an uplink user plane IP data packet or a downlink user plane IP data packet, is directly transmitted between the UE and the network side through the signaling connection, with no need to specifically establish (recover) an RAB between the UE and an S-GW, which can save the signaling overhead, thus reducing the network load and lowering the operating cost of an operator.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
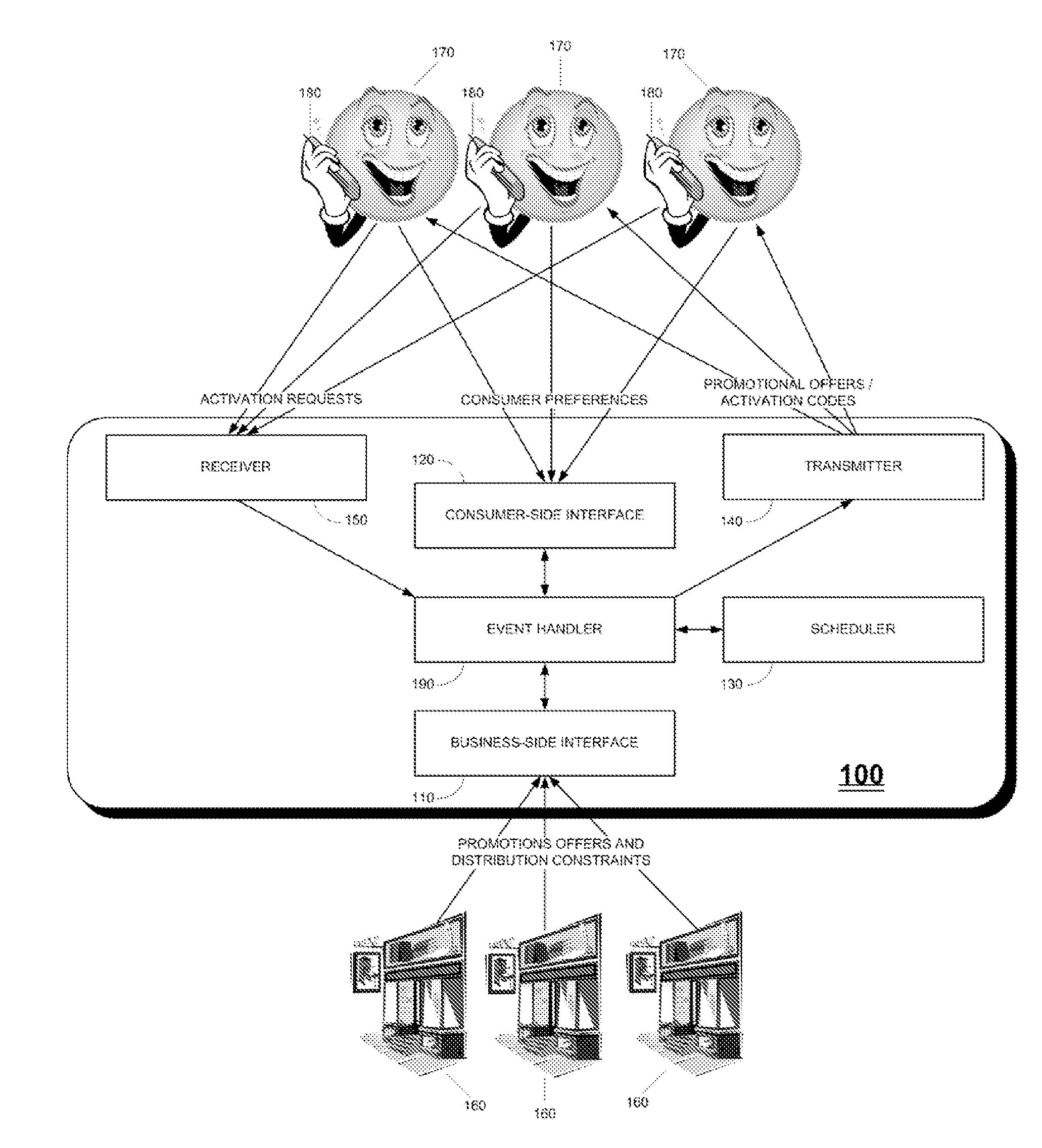
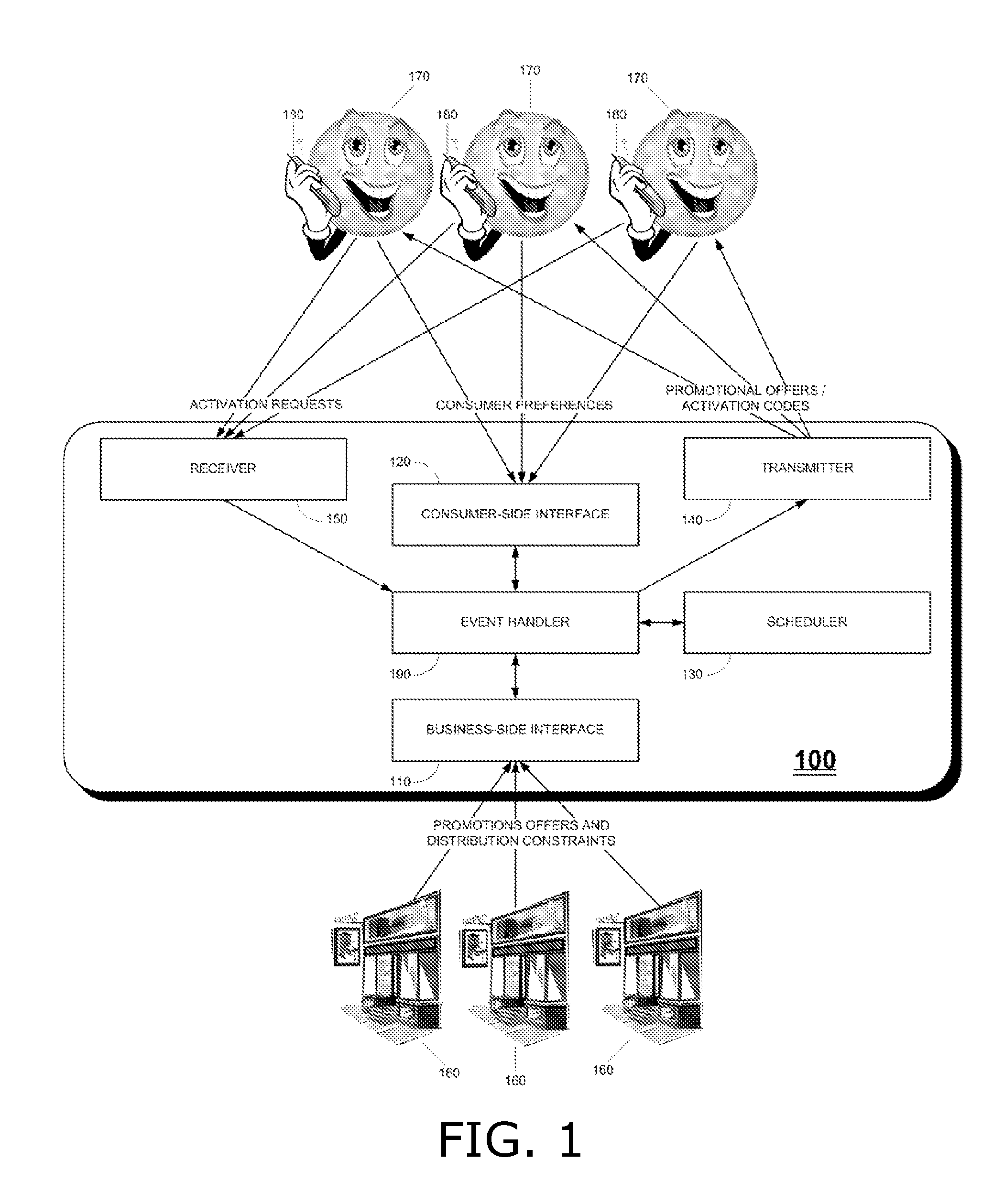
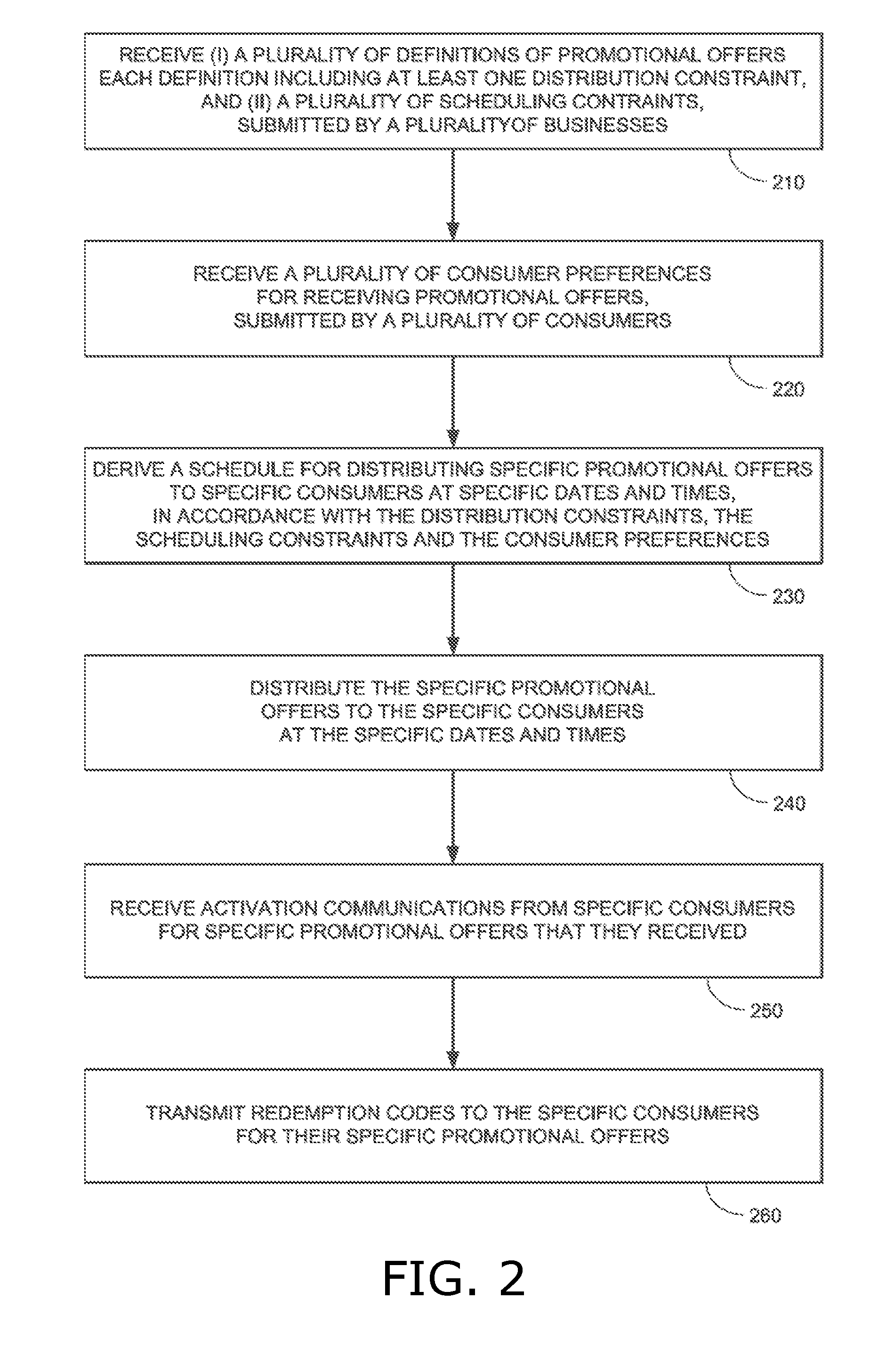
Managed distribution of business promotional offers to consumers
InactiveUS20130073381A1Overcomes drawbackIncreasing the sense of urgencyOffice automationMarketingTime scheduleOperating system
A system for managed distribution of business promotional offers, including a business-side interface for enabling each of a plurality of businesses to submit one or more definitions of promotional offers, each definition comprising at least one distribution constraint, and one or more scheduling constraints, a consumer-side interface for enabling each of a plurality of consumers to submit preferences for receiving promotional offers, a scheduler for deriving a schedule for distributing specific promotional offers to specific consumers at specific dates and times, in accordance with the distribution constraints, the scheduling constraints and the consumer preferences, and an event handler for invoking the scheduler in response to submissions by business and by consumers processed respectively by the business-side interface and the consumer-side interface. A method is also described and claimed.
Owner:MOBILIZEME
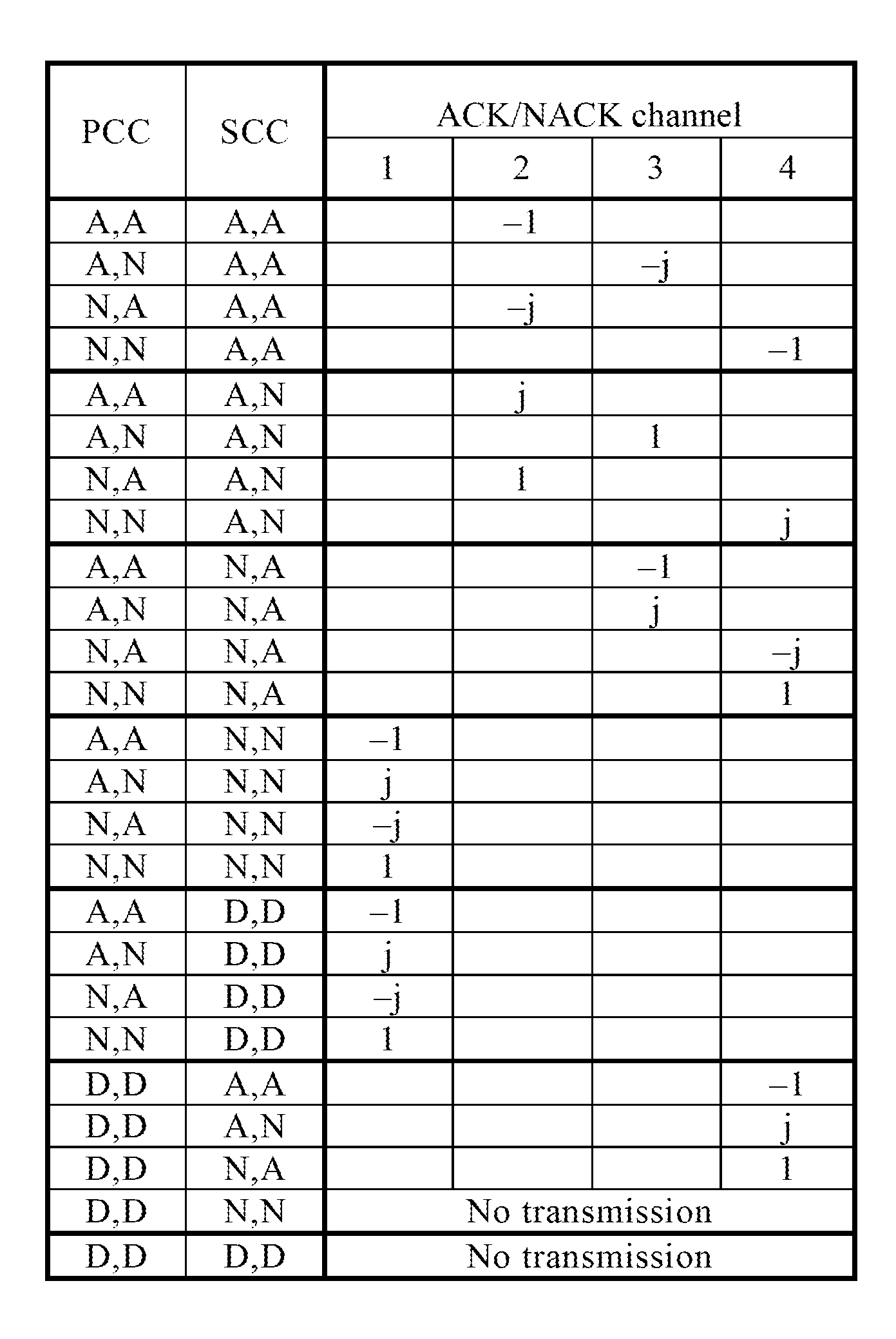
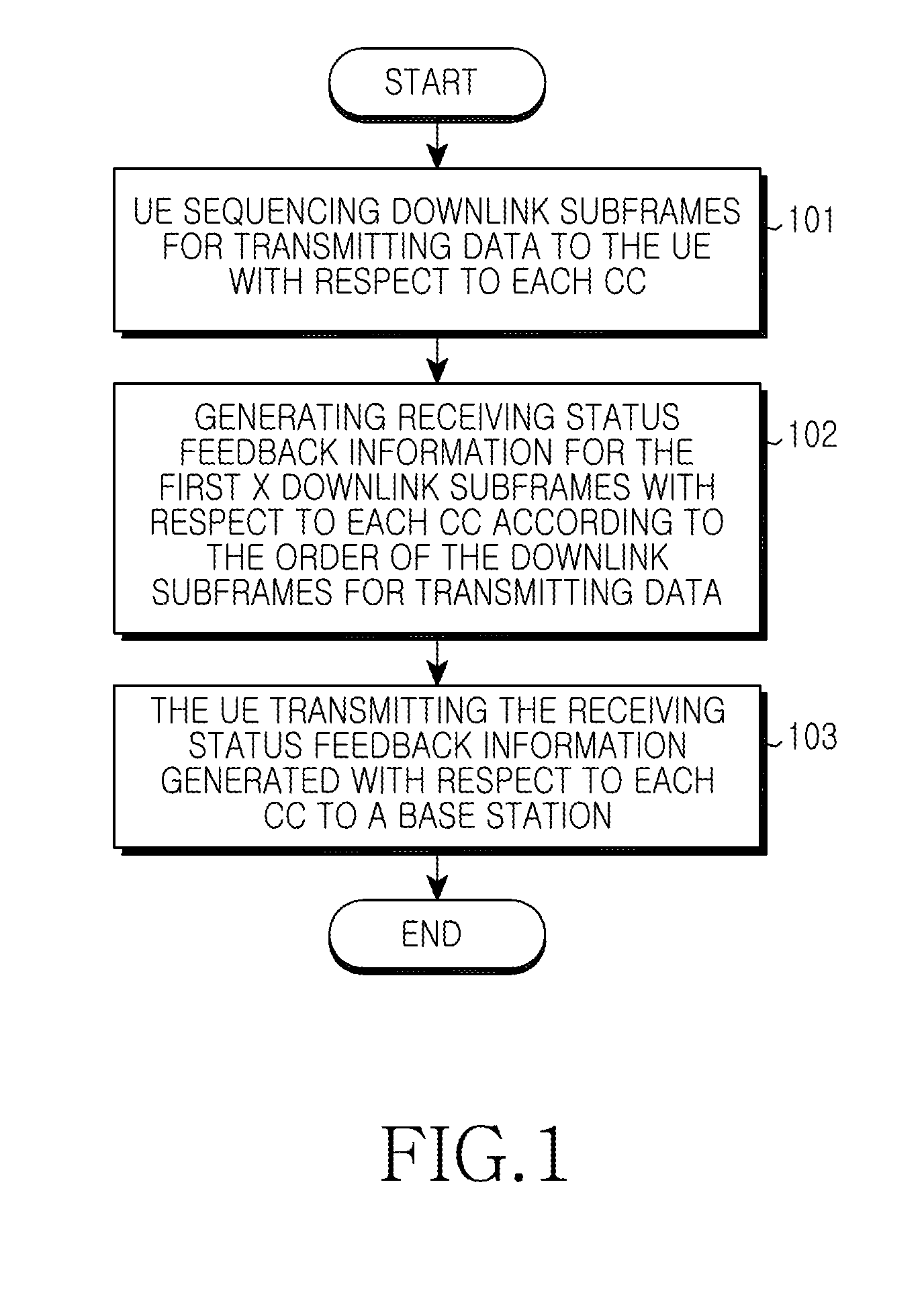
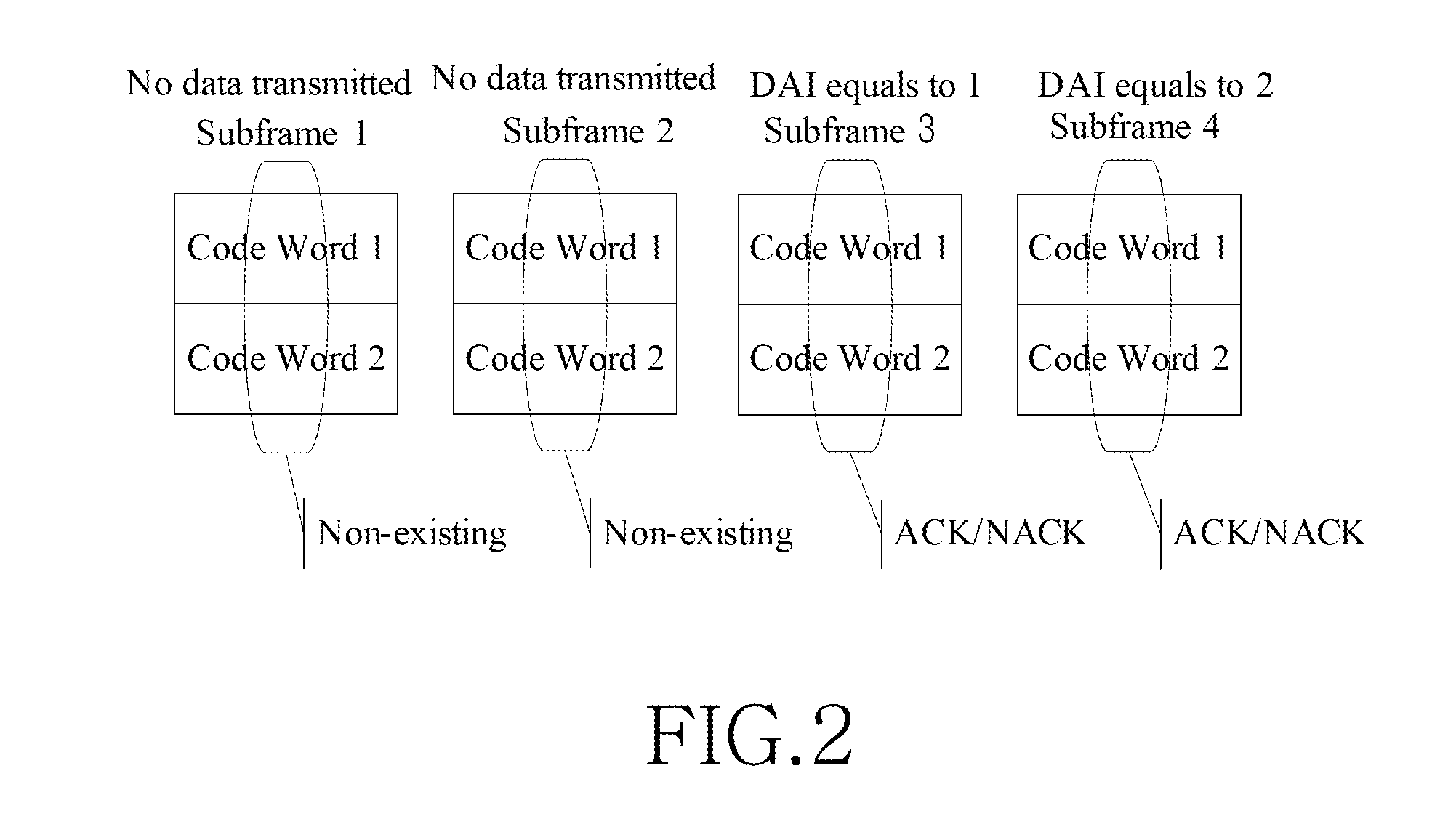
Apparatus and method for feeding back data receiving status
ActiveUS20110268059A1Reduce uplink overheadIncrease coverage areaError preventionSignal allocationCarrier signalAutomatic repeat request
An apparatus and a method for feeding back data receiving status, applied to a system, are provided. The method includes sequencing, by a User Equipment (UE), downlink subframes for transmitting data with respect to each Component Carrier (CC), generating receiving status feedback information for the first X downlink subframes with respect to each CC according to the result of the sequencing, where X≦M, wherein M is the number of downlink subframes on each CC, and transmitting the receiving status feedback information generated with respect to each CC to a base station. Accordingly, the UE will not misinterpret the receiving status for the downlink subframes due to inconsistencies with the base station between transmitting and receiving feedback. This affects the Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) transmission, saves the uplink overheads occupied by the receiving status feedback information, and increases the uplink coverage area.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
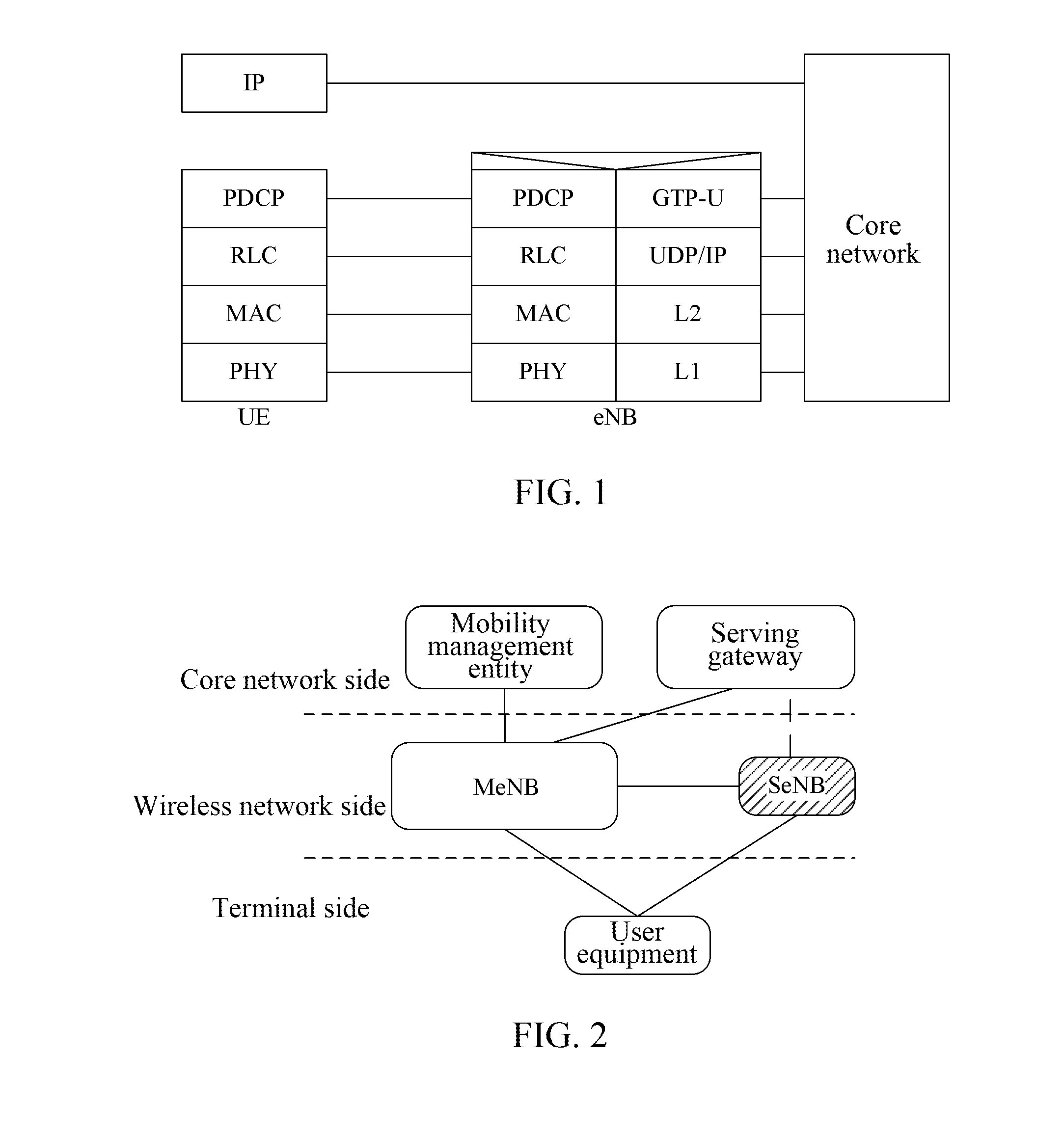
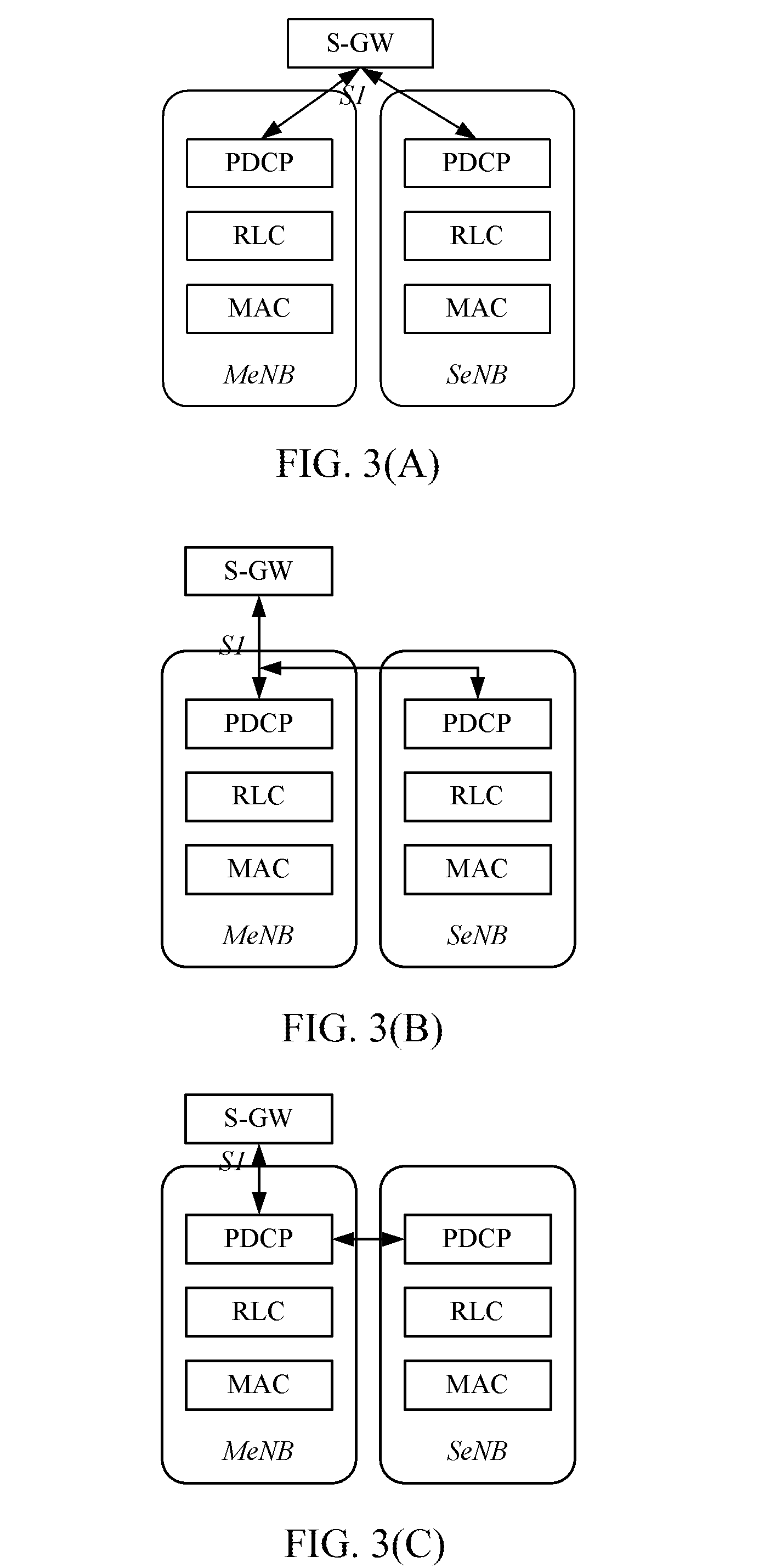
Handover Method, Master Base Station and Slave Base Station
ActiveUS20160192245A1Optimize and enhance handover performanceEnsure backward compatibilityNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesHandoverEnodeB
Disclosed are a handover method, a master evolved NodeB (MeNB) and a secondary evolved NodeB (SeNB), wherein, the method is applied to perform a handover on a MeNB for a user equipment (UE) in a multi-connection scenario in which the UE has connections with both a master evolved NodeB (MeNB) and a secondary evolved NodeB (SeNB), including: a source MeNB initiating a handover, and sending a handover command to the UE after receiving a corresponding response, instructing the UE to perform the handover on the MeNB via the handover command, and remaining a connection with the SeNB; after the UE successfully accesses a destination MeNB, the source MeNB or the destination MeNB sending a handover instruction message to the SeNB connected with the UE, the SeNB connected with the UE establishing an association with the destination MeNB according to the handover instruction message.
Owner:ZTE CORP
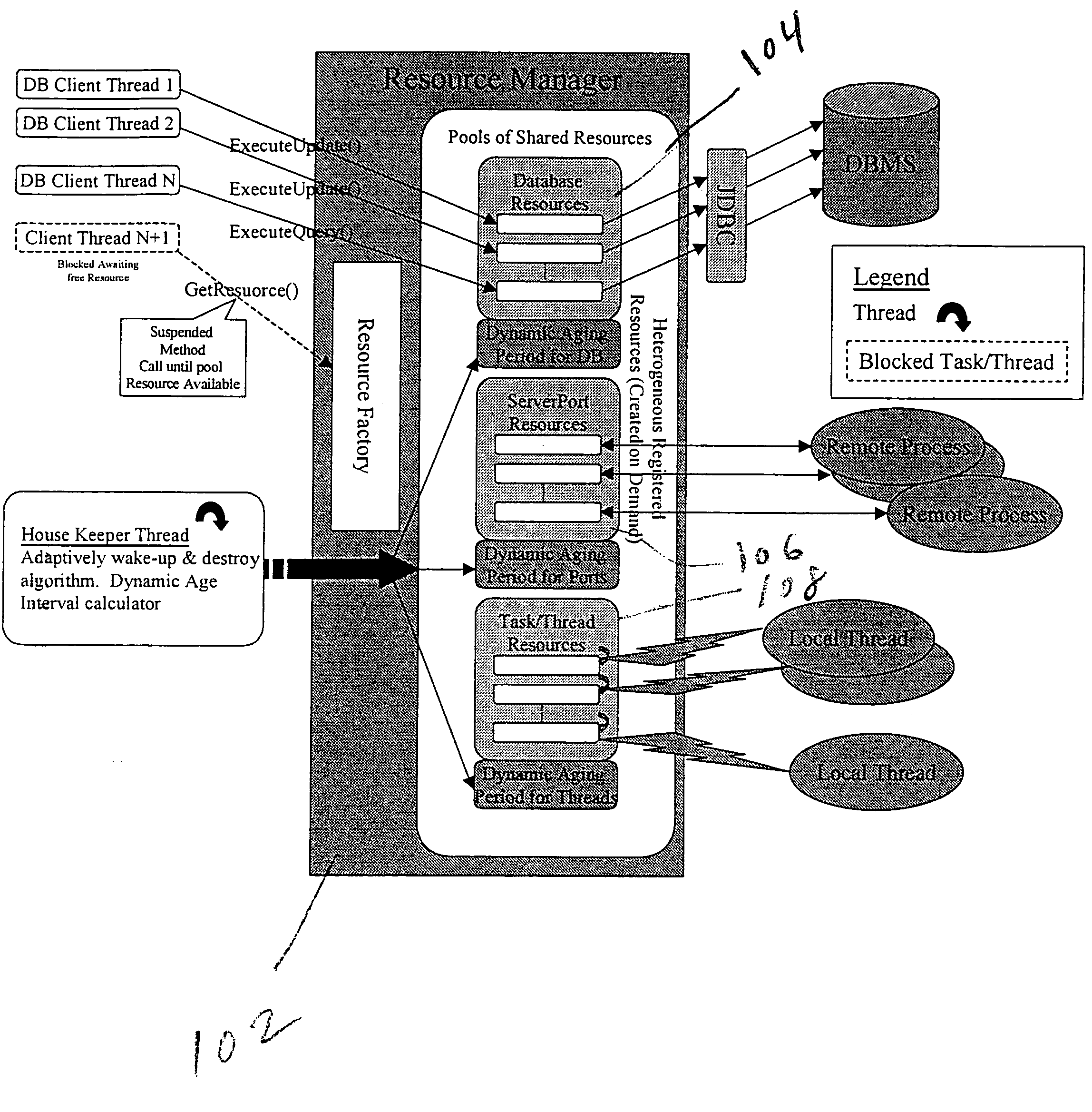
Flexible computer resource manager
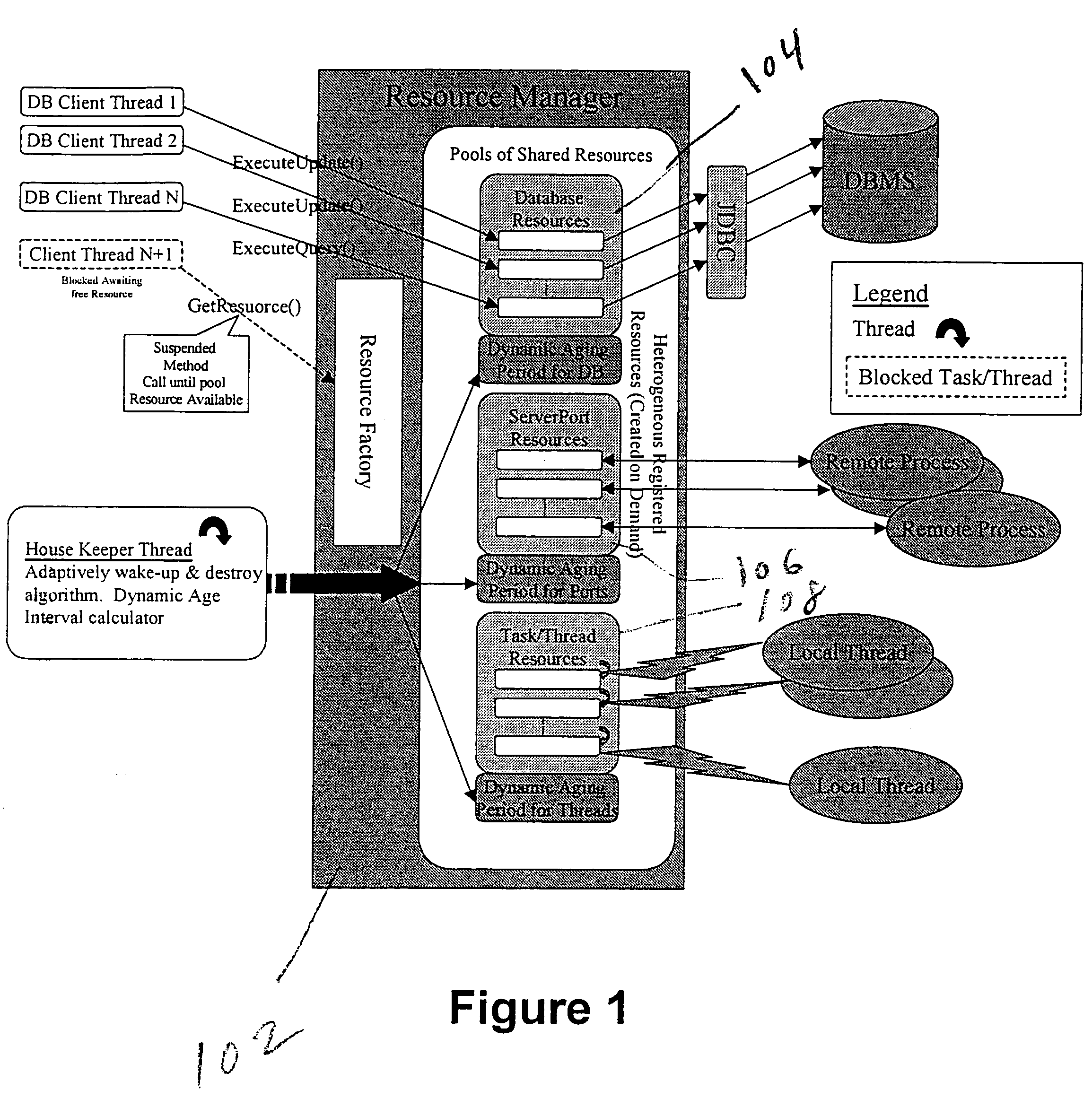
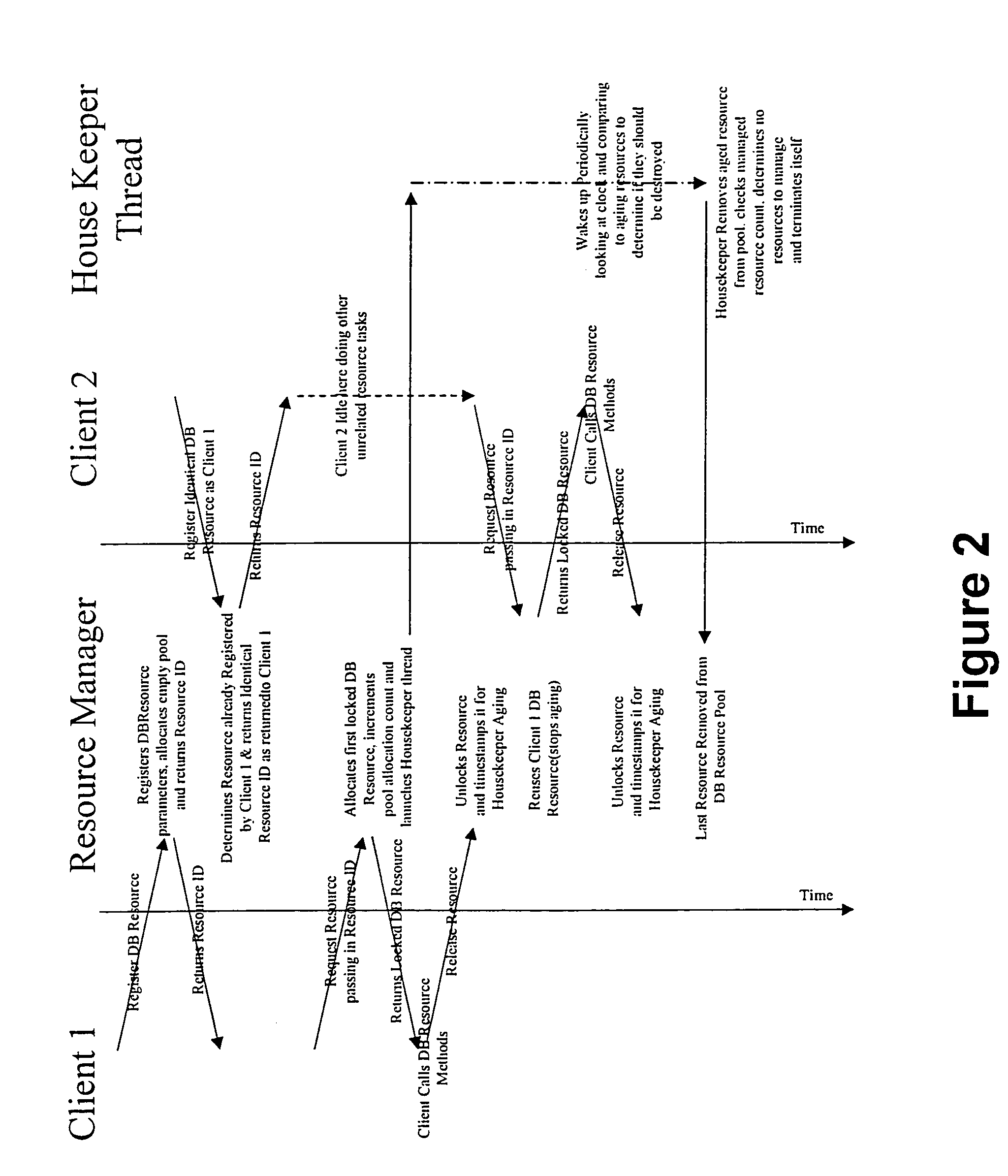
InactiveUS7007075B1Facilitates thread-safe accessConserving memory and processing overheadProgram synchronisationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer resourcesClient-side
A Flexible Resource Manager, or FRM, enables multiple clients to share disparate resources, including database connections, communication ports and tasks for multiple clients. The approach balances performance issues, such as the latency introduced by resource allocation, with the overhead of retaining unused resources, while providing for demand-based allocation, reuse of already allocated resources, and removal of resources under the control of an aging parameter. During registration, each resource object class and its corresponding constructor parameters are stored, and a resource pool is configured to contain a maximum and minimum number of instances. When registration completes, the FRM returns back a unique identifier that the application can use request instances of these resources in the future. Drivers or other dependent resources supporting the managed resource are only loaded when needed, thereby conserving memory and processing overhead.
Owner:E LYSIUM TRANSACTION SYST
Method and device for detecting downlink control information
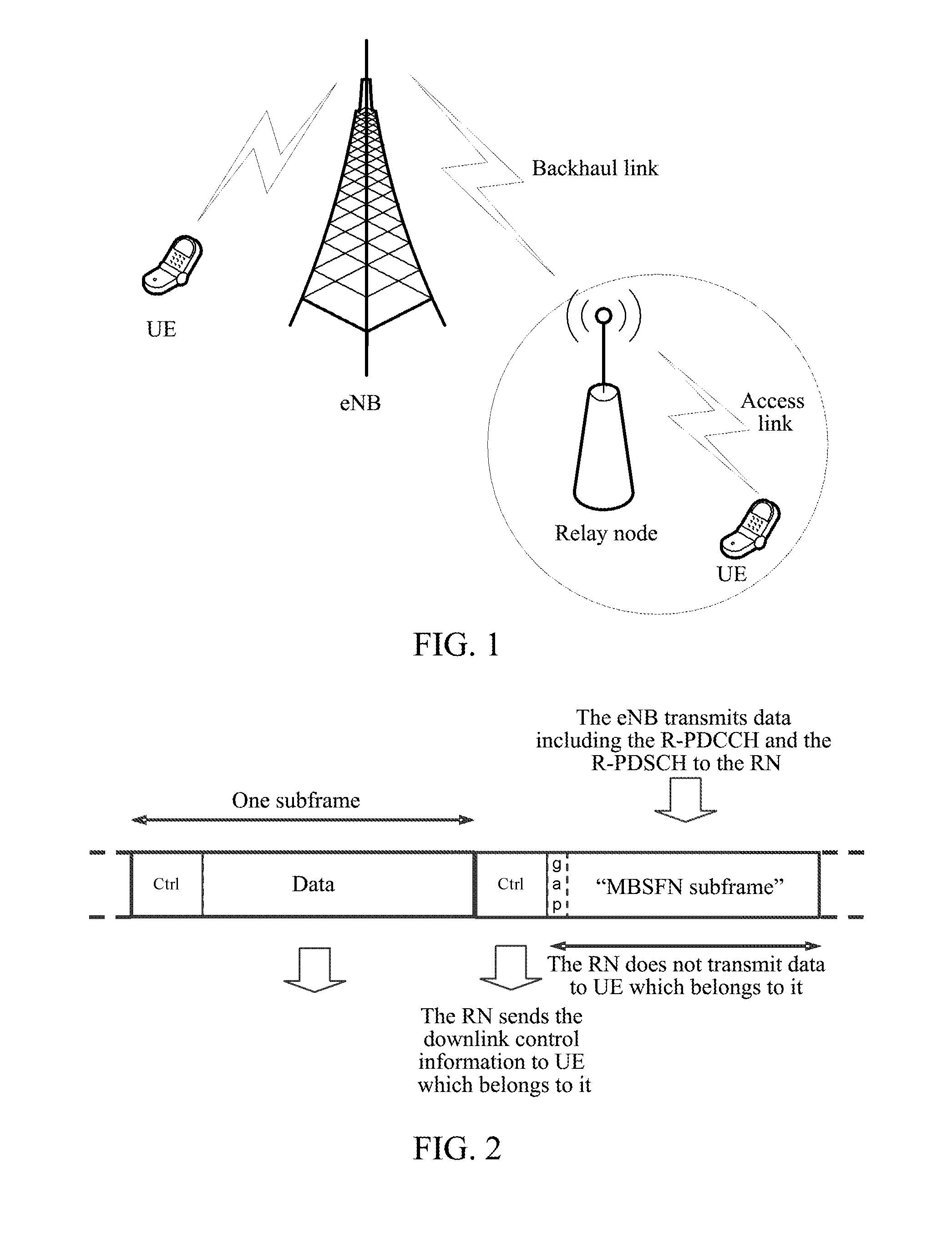
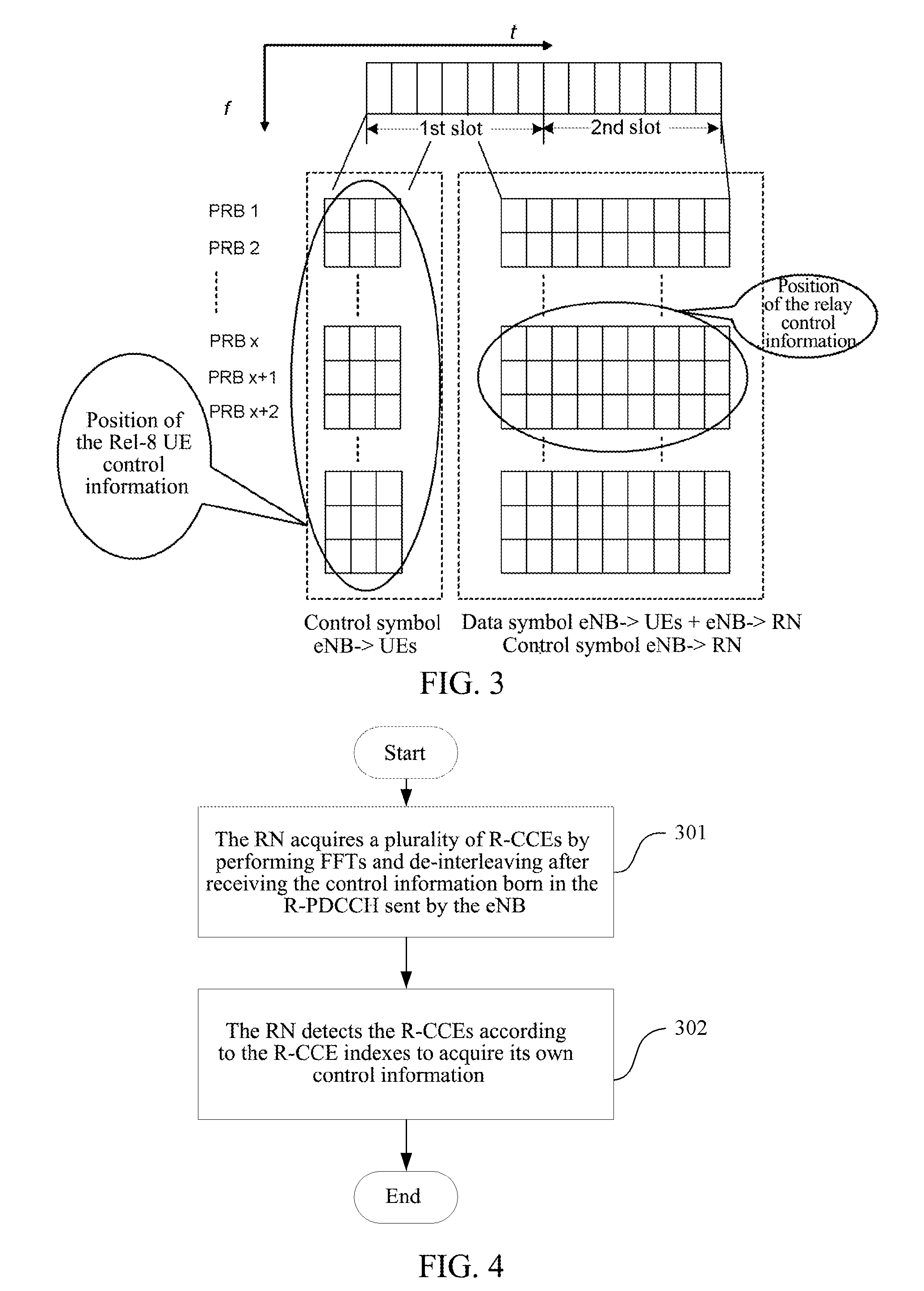
ActiveUS20120093063A1Simple performanceSave overheadFrequency-division multiplex detailsAssess restrictionComputer networkResource block
The present invention discloses a method and a device for detecting downlink control information. The method includes: a Relay Node (RN) receiving control information born in a Relay Physical Downlink Control Channel (R-PDCCH) sent by an evolved Node B (eNB) to acquire a control resource; the RN performing detection on the control resource according to an index of the control resource to acquire own control information; wherein the control resource is a Relay Control Channel Element (R-CCE) or a Physical Resource Block (PRB). The present invention can save system overhead and improve system transmission efficiency.
Owner:ZTE CORP
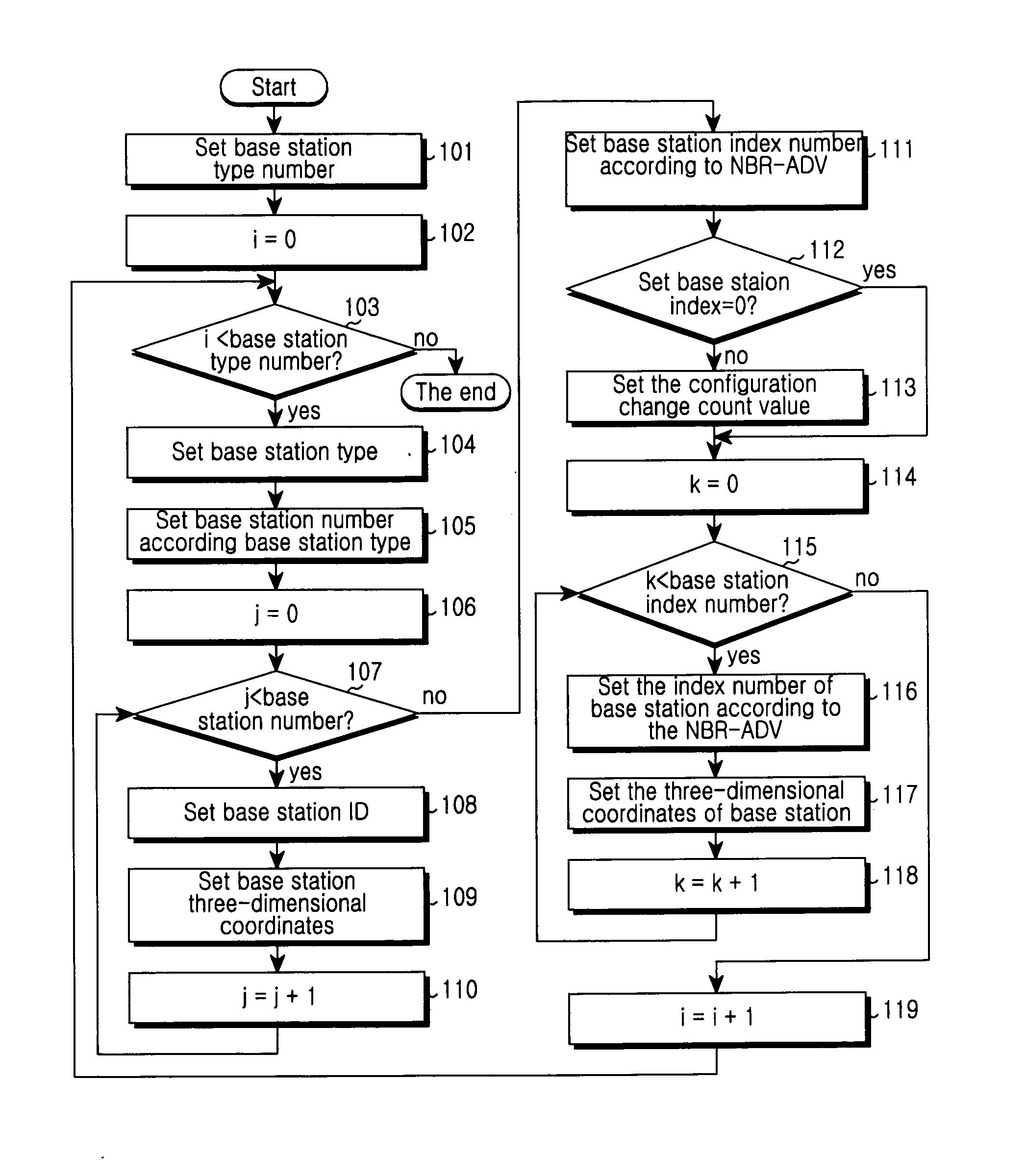
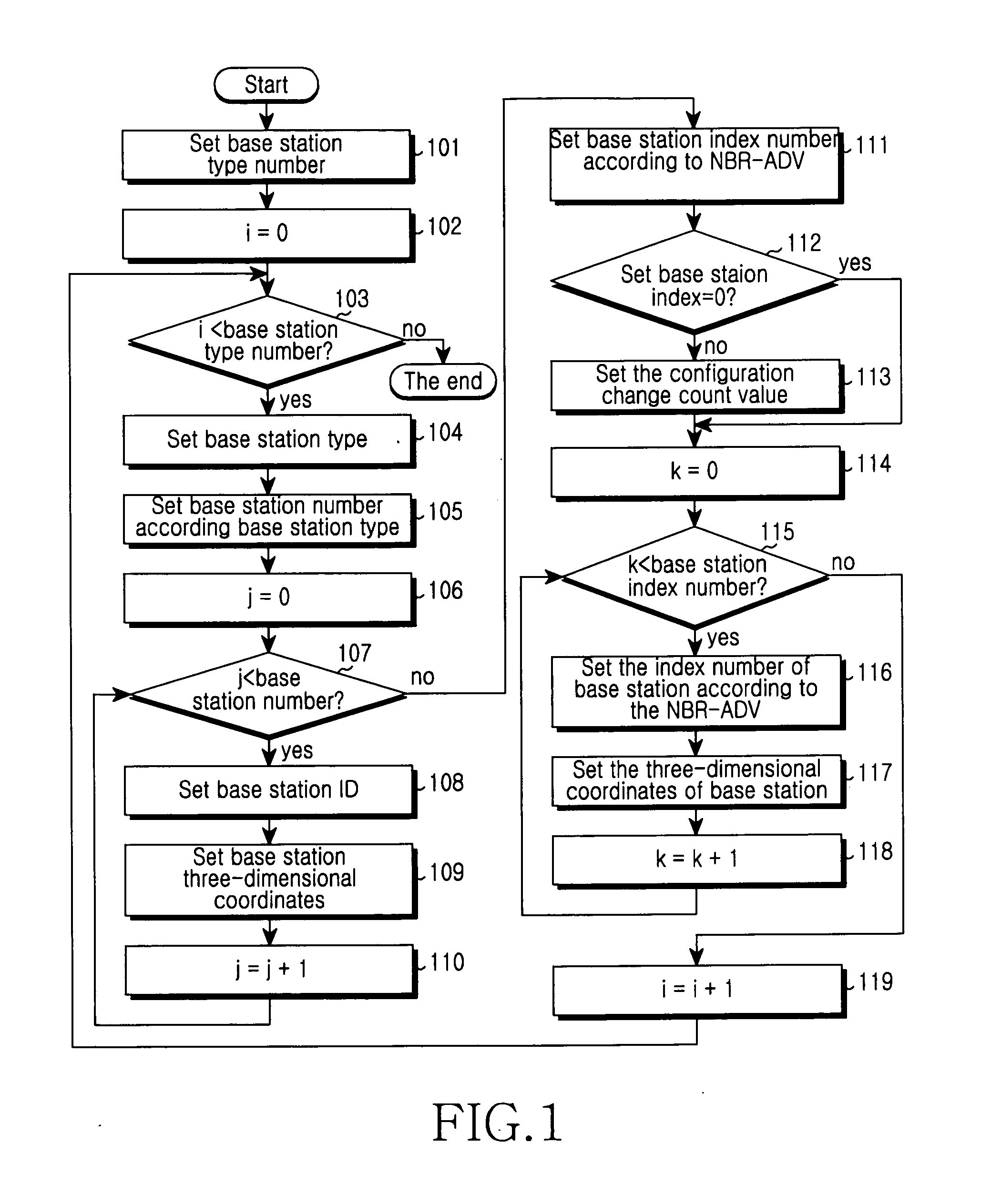
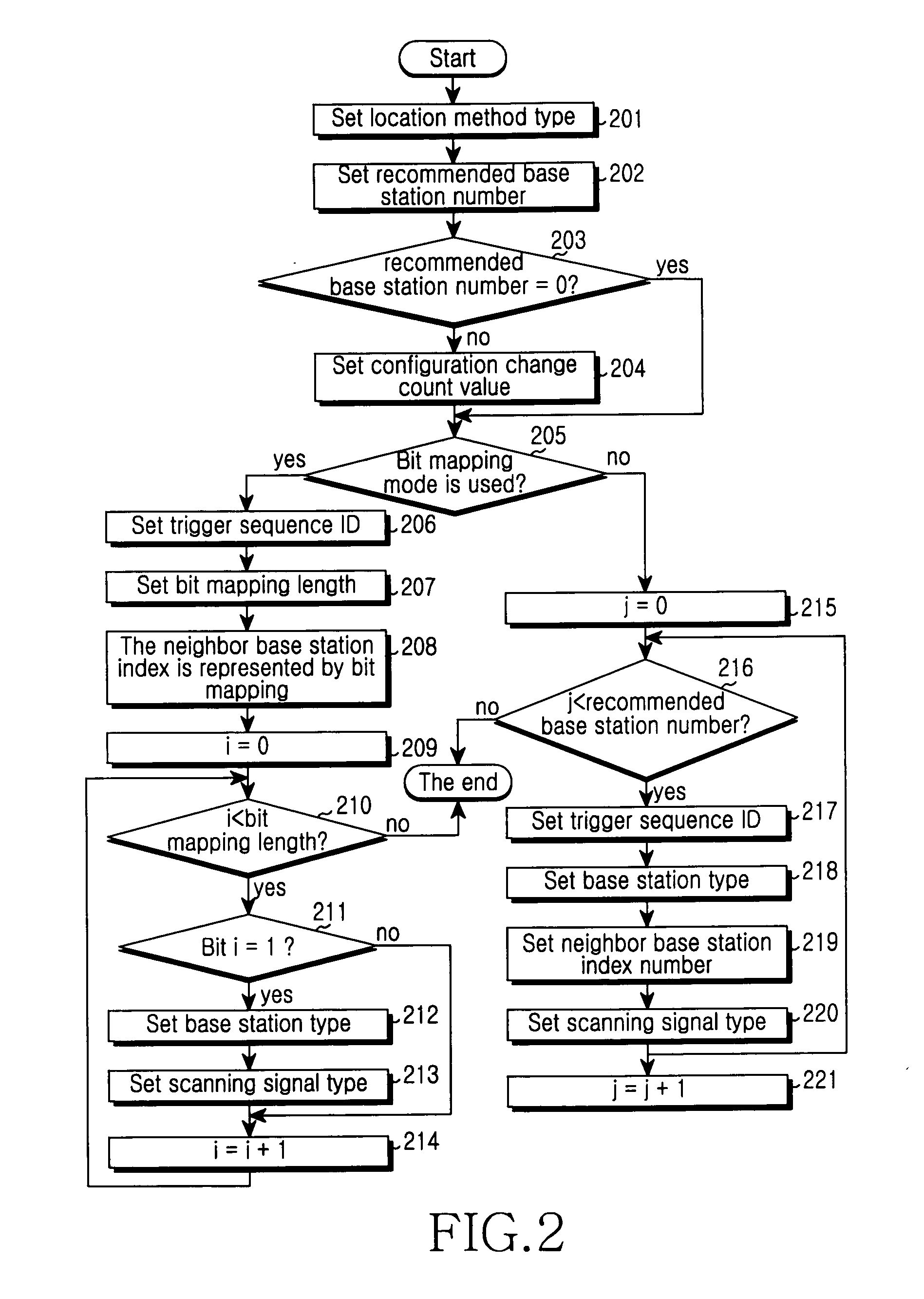
Method of implementing location, method of broadcasting position information of neighbor base station and method of negotiating location capability
InactiveUS20110053613A1Save signaling overheadReduce delaysLocation information based serviceLocator ParameterMobile station
A method of implementing the location includes determining the base stations participating in the location and parameters required in the location via the signaling interaction between a mobile station and a serving base station. Afterwards, the mobile station and the base stations participating in the location perform the location measuring according to the determined parameters required in the location; at last, performing the location calculation according to the measuring result of location measuring.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficient QoS signaling for mobile IP using RSVP framework
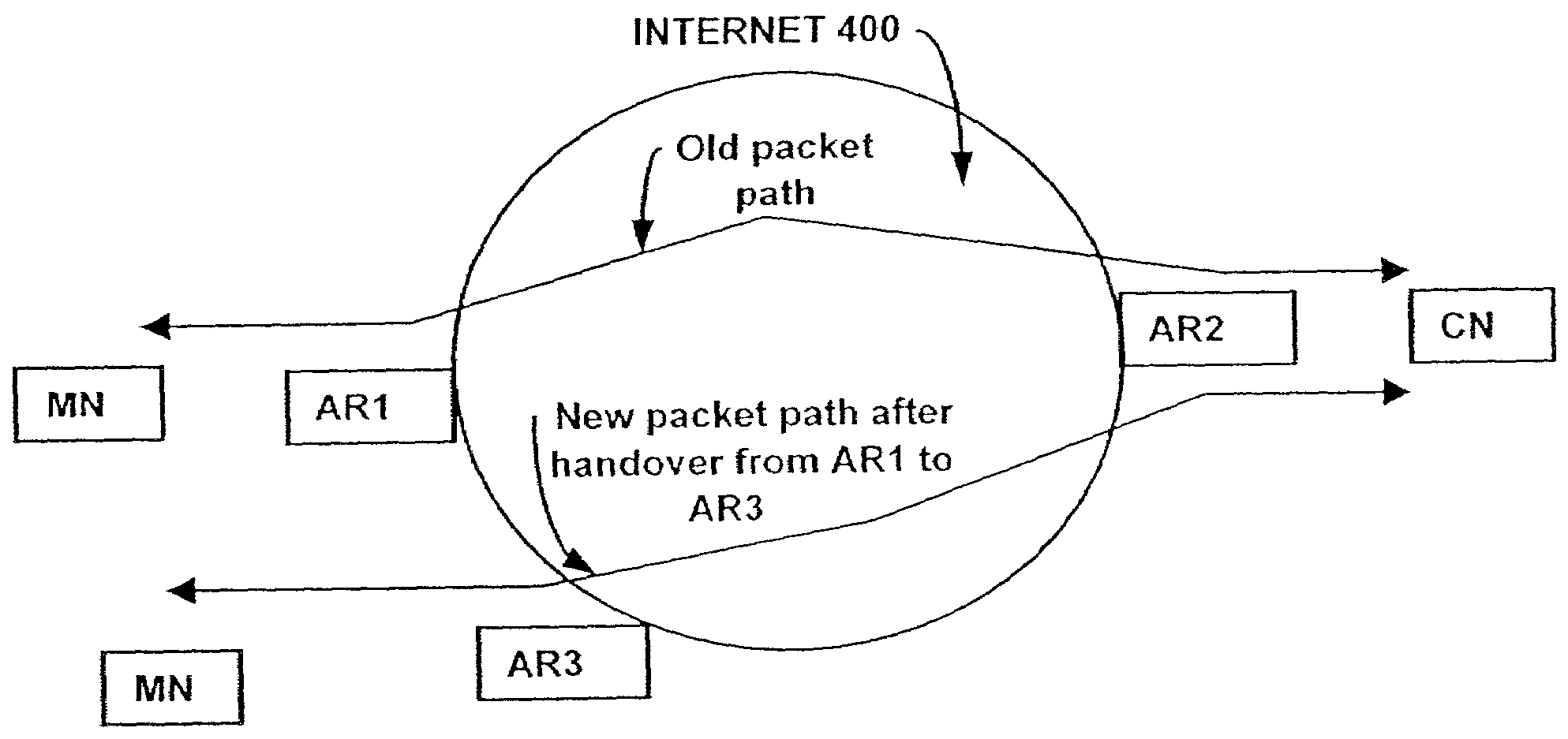
InactiveUS7123598B1Save overheadEliminate delaysNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer networkMobile IP
A system and method for efficient QoS signaling for mobile IP using RSVP framework in which mobile nodes are connected to correspondent nodes via plurality of intermediate nodes. The method has the steps of: programming in the mobile node for data packets propagating upstream data from a mobile node to correspondent node via intermediate nodes; initiating in the mobile node a first PATH message for upstream data; sending the first PATH message from the mobile node to the correspondent node via the intermediate nodes; programming in the correspondent node for data packets propagating downstream data from the correspondent node to the mobile node via the intermediate nodes; initiating in the correspondent node a first RSVP message for downstream data; sending the first RSVP message from the correspondent node to the mobile node via the intermediate nodes; and thereafter sending REFRESH messages only between intermediate nodes.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and device for feedback information transmission based on enhanced phich
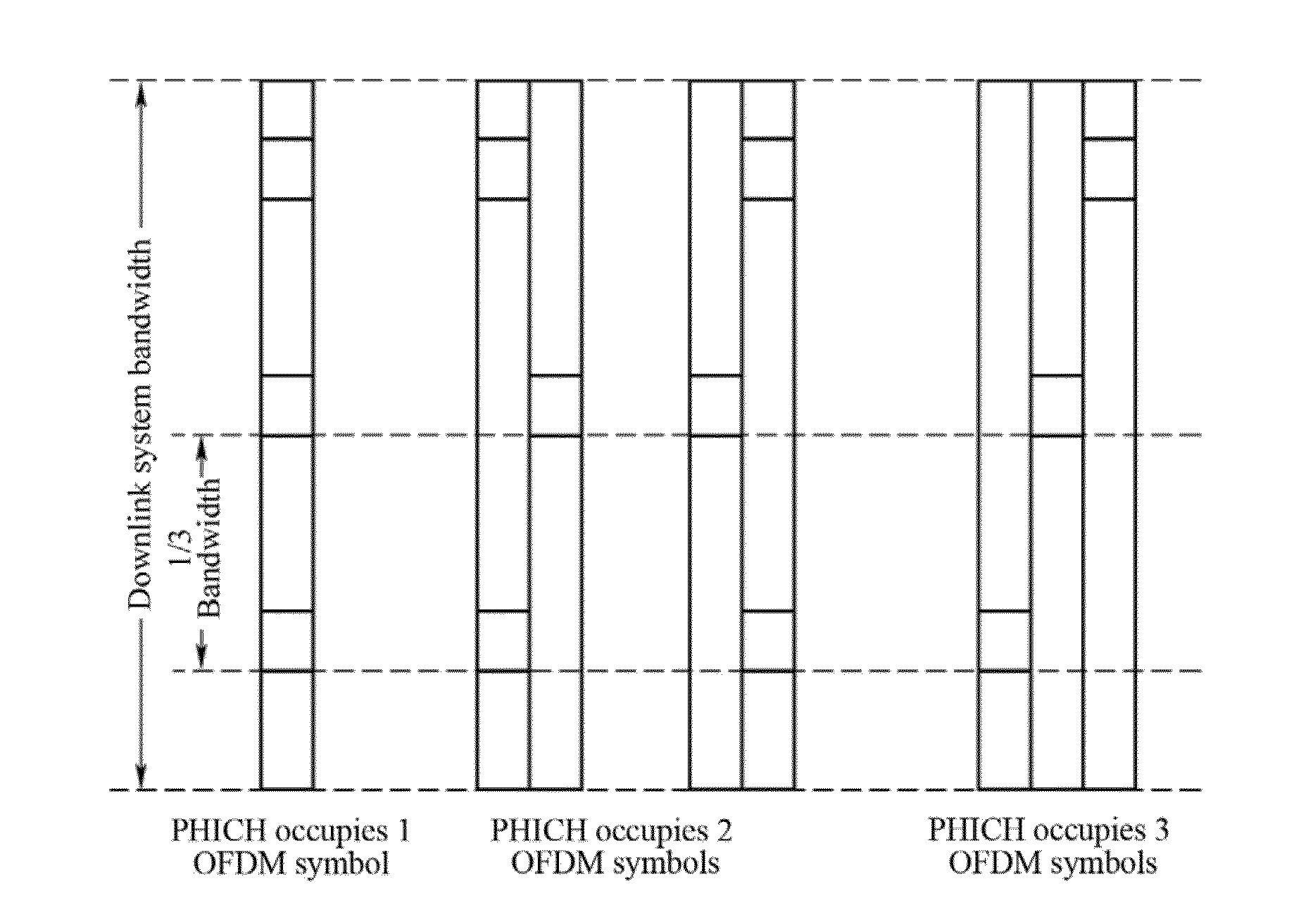
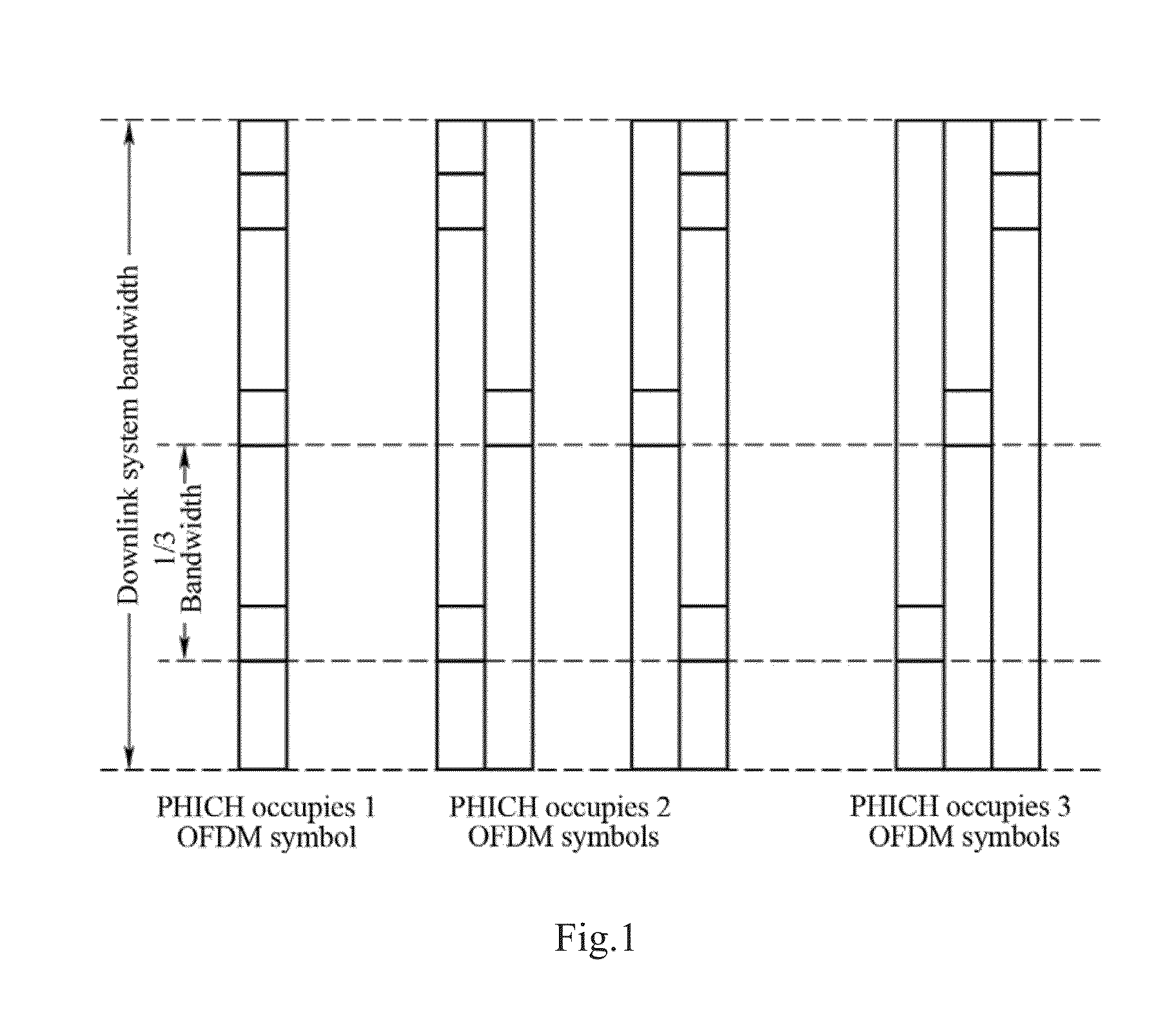
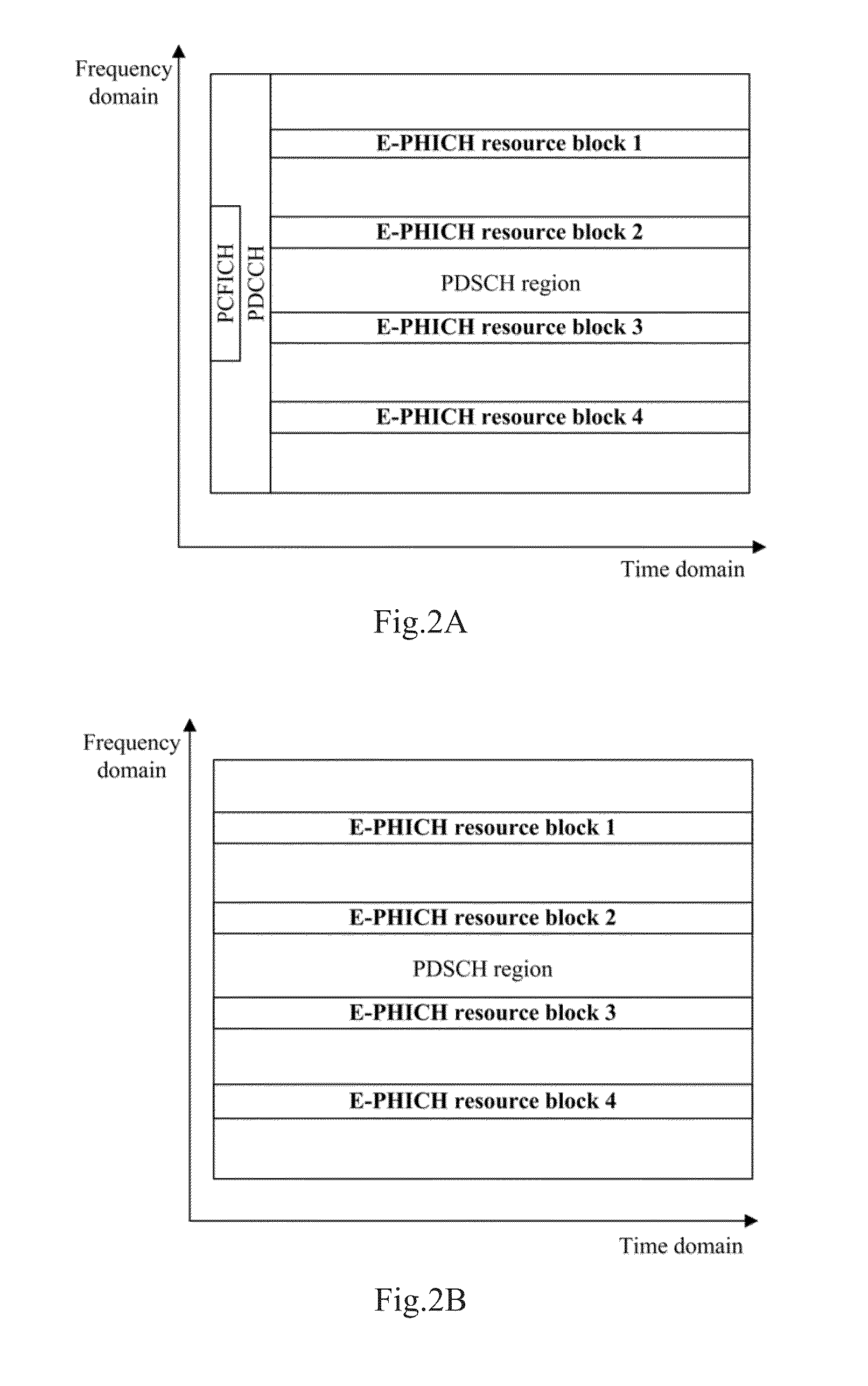
ActiveUS20150289234A1Increase in overheadSave overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationInformation transmissionCarrier signal
The present invention relates to the field of communications. Disclosed are a method and a device for feedback information transmission based on an enhanced PHICH. The method comprises transmitting ACK / NACK feedback information to a terminal through E-PHICH sources configured in a PDSCH area; therefore, on one hand, the problem that the PHICH cannot be transmitted in some scenarios, such as an ABS sub-frame of eICIC and a subsequent possibly-defined extended carrier, is solved; and on the other hand, the signaling overhead can be saved, so that the utilization rate of resources is improved, for example, the scheduling of retransmission of a PUSCH is prevented from being carried out by a system though a DCI format 0, therefore, the effects of improving the capacity of the PHICH and solving the problem of legacy PHICH resource contention are achieved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
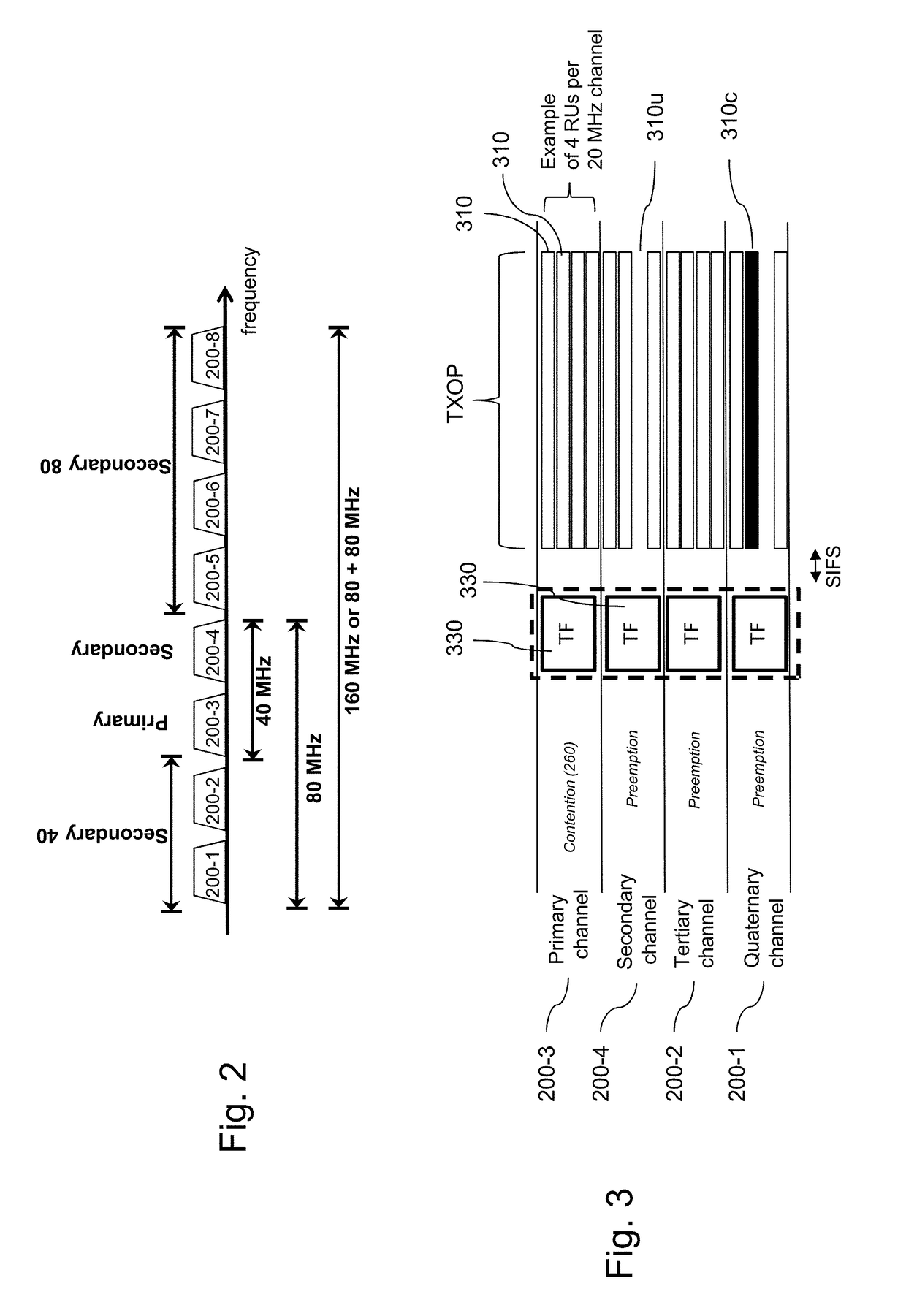
ACCESS MANAGEMENT TO MULTI-USER UPLINK RANDOM RESOURCE UNITS BY A PLURALITY OF BSSs
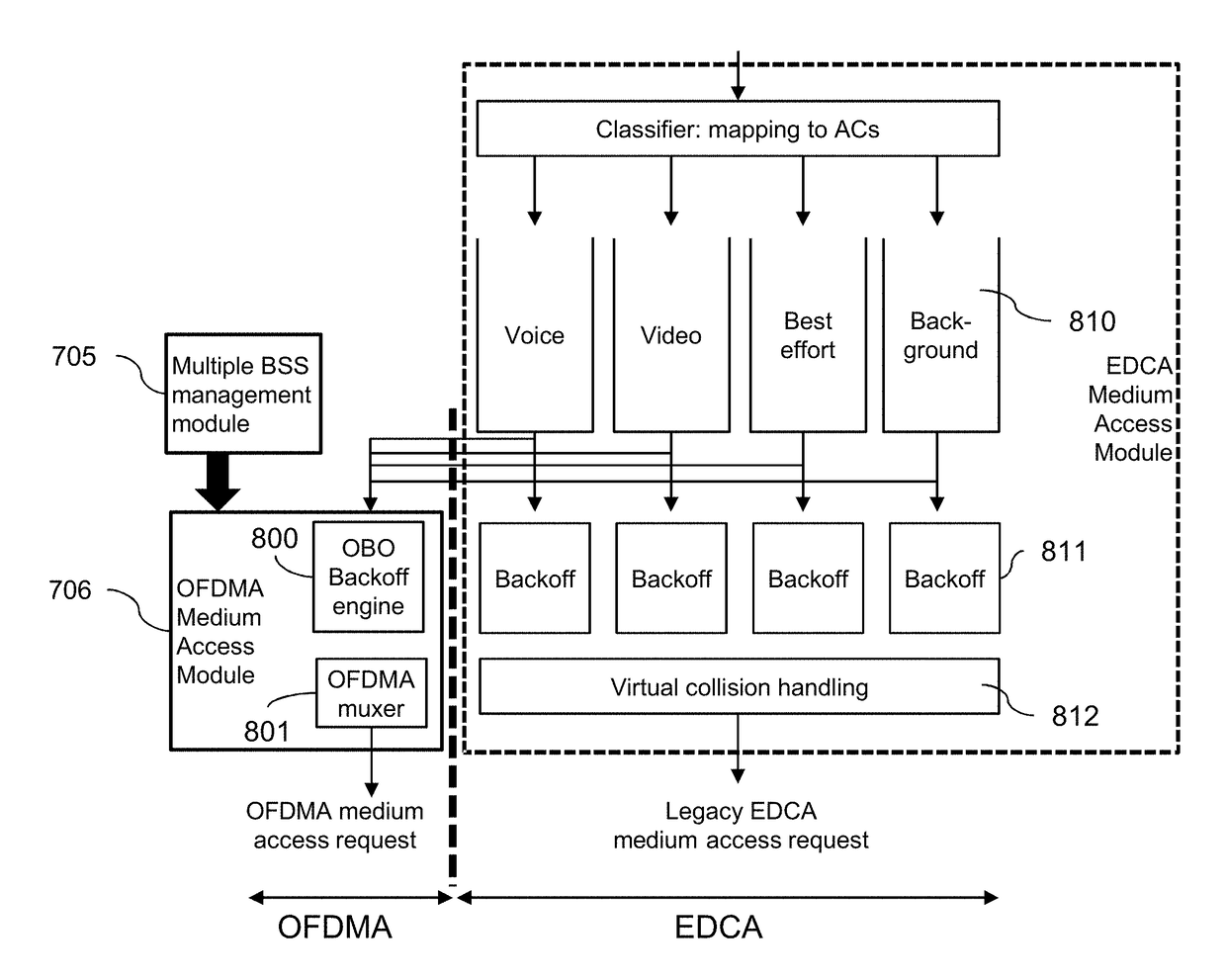
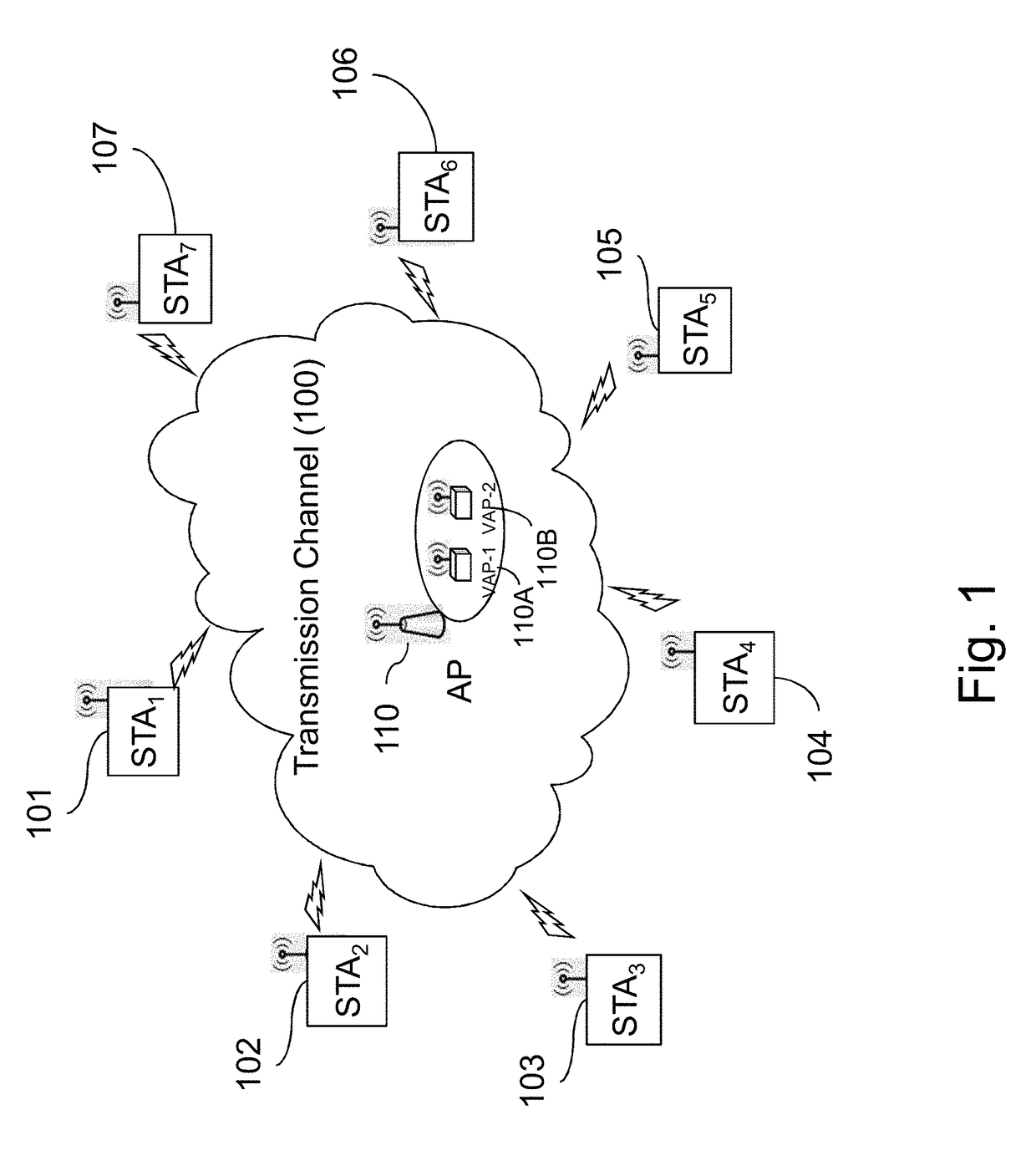
ActiveUS20180199271A1Improve situationEfficient useAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsRandom access
A physical Access Point (AP) manages a plurality of BSS groups through Virtual APs. The AP periodically sends beacon frames informing of the profile of each BSS of the plurality of BSSs. To improve channel utilization, the trigger frame identifies a plurality of BSS groups, stations of which are allowed to access the resources units to transmit data during the reserved TXOP. The AP receives, during the reserved TXOP, data from one station of a first group identified in the trigger frame and data from one station (separate from the first one) of a second and separate group identified in the trigger frame. First group and second group use the same joint set of random access parameters for the random access procedure, thus ensuring equivalent fairness in accessing the offered the resources units to transmit data during the reserved TXOP to several BSSs.
Owner:CANON KK
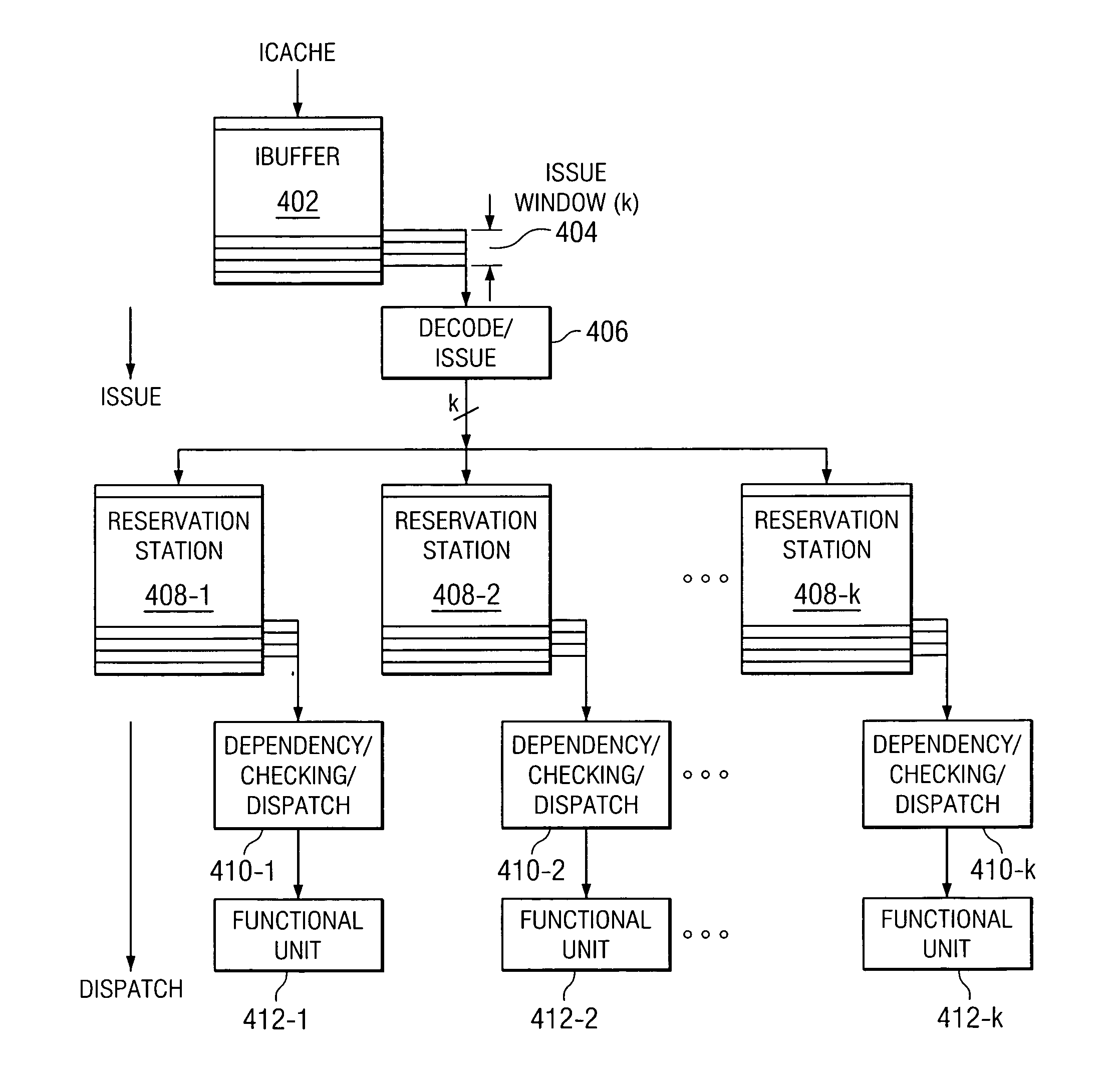
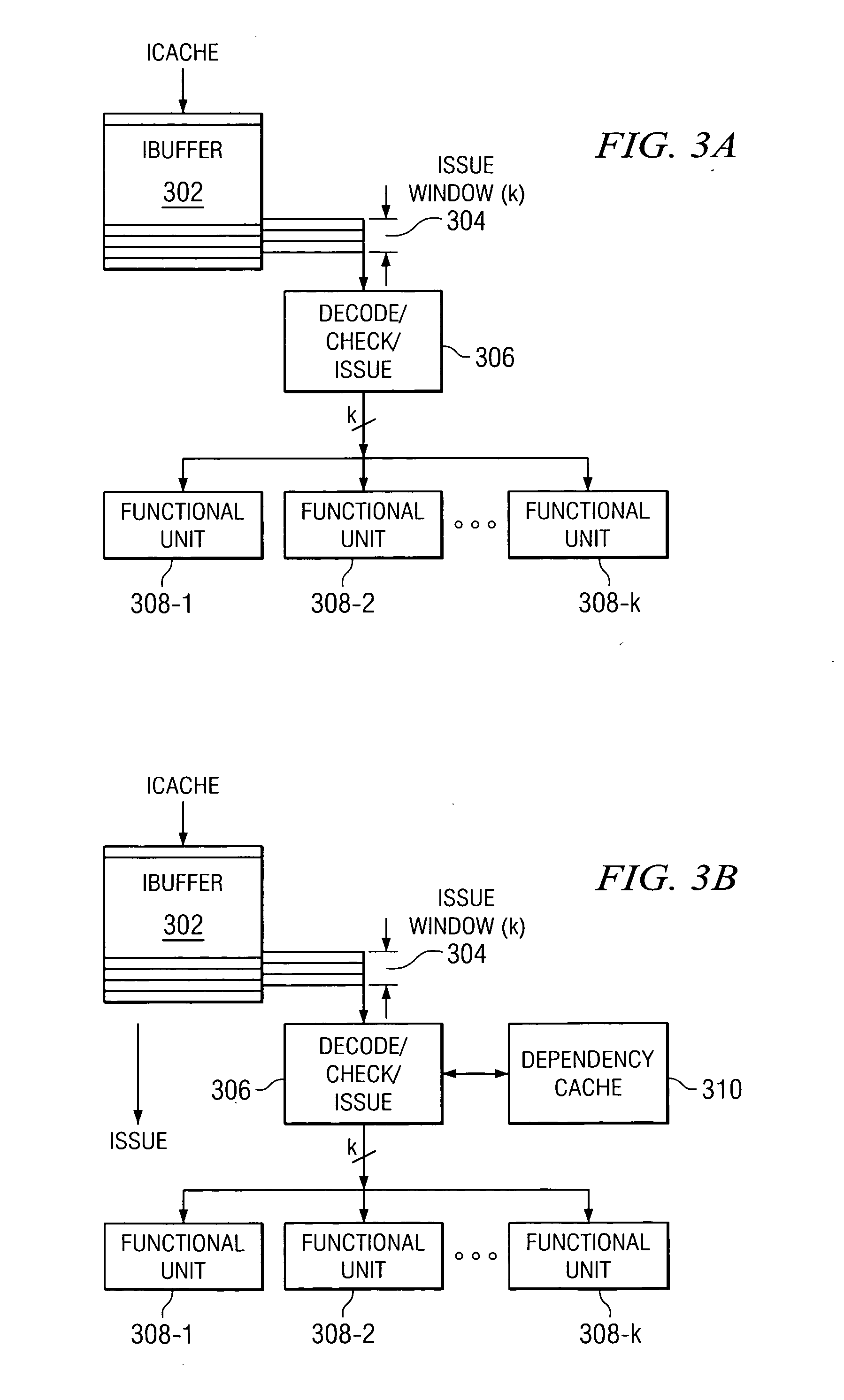
Method and apparatus for control signals memoization in a multiple instruction issue microprocessor
InactiveUS20060155965A1Save overheadDigital computer detailsMemory systemsControl vectorControl signal
A dynamic predictive and / or exact caching mechanism is provided in various stages of a microprocessor pipeline so that various control signals can be stored and memorized in the course of program execution. Exact control signal vector caching may be done. Whenever an issue group is formed following instruction decode, register renaming, and dependency checking, an encoded copy of the issue group information can be cached under the tag of the leading instruction. The resulting dependency cache or control vector cache can be accessed right at the beginning of the instruction issue logic stage of the microprocessor pipeline the next time the corresponding group of instructions come up for re-execution. Since the encoded issue group bit pattern may be accessed in a single cycle out of the cache, the resulting microprocessor pipeline with this embodiment can be seen as two parallel pipes, where the shorter pipe is followed if there is a dependency cache or control vector cache hit.
Owner:IBM CORP
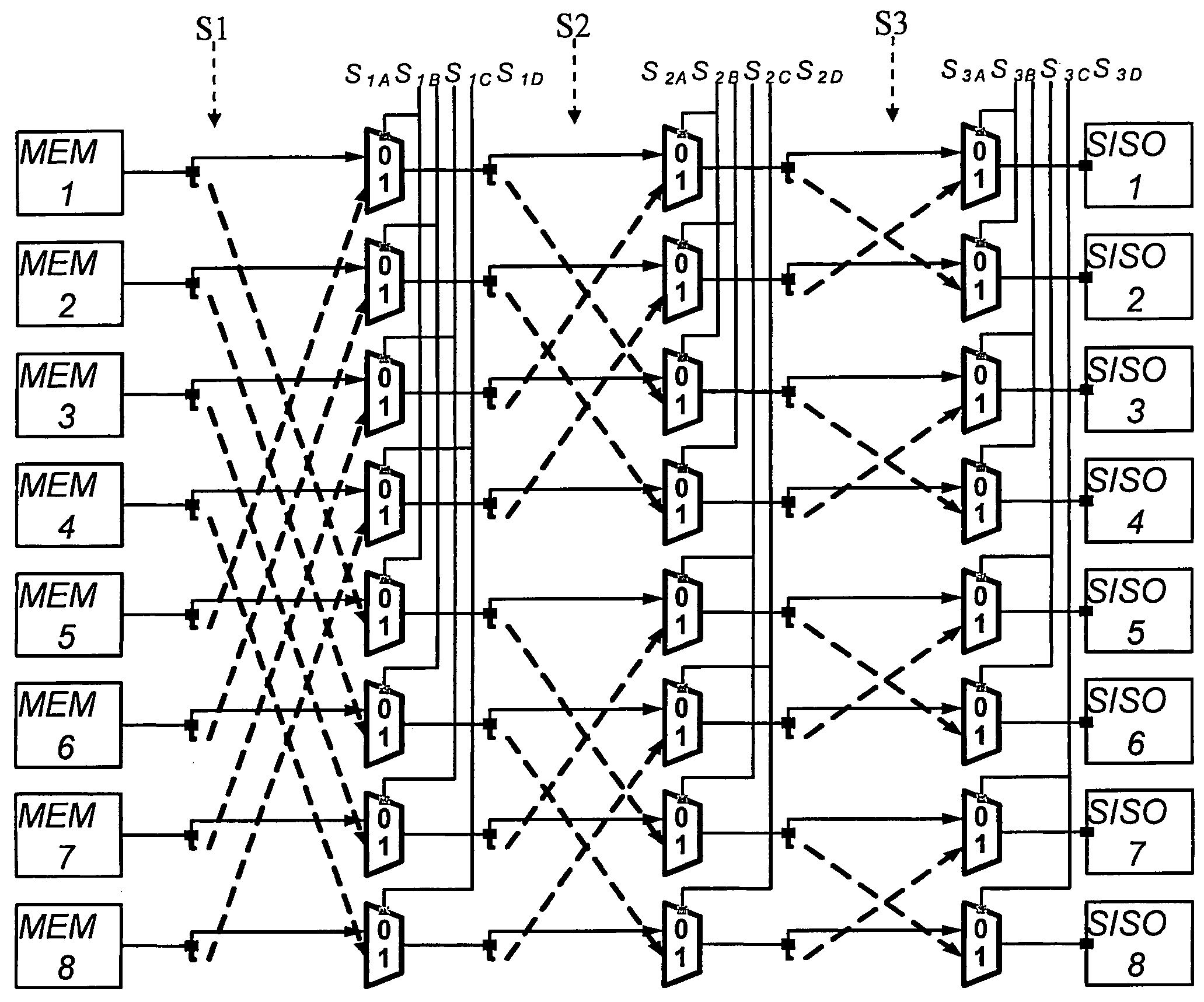
Apparatus of multi-stage network for iterative decoding and method thereof
An apparatus and method of multi-stage network for iterative network are disclosed. The apparatus has M stages, and each stage uses N multiplexers to transmit N codeword partitions simultaneously. Every starting terminal, either the output port of memories, soft-in soft-out decoders, or multiplexers, has two paths to couple with two different multiplexers at next stage. One path connects the source to the first data port of one multiplexer; the other connects the source to the second data port of another multiplexer. The two multiplexers will be controlled with the same 1-bit signal, so each source has only one valid path to next stage. The invention can guarantee that the transmission of N data blocks is free from contention.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
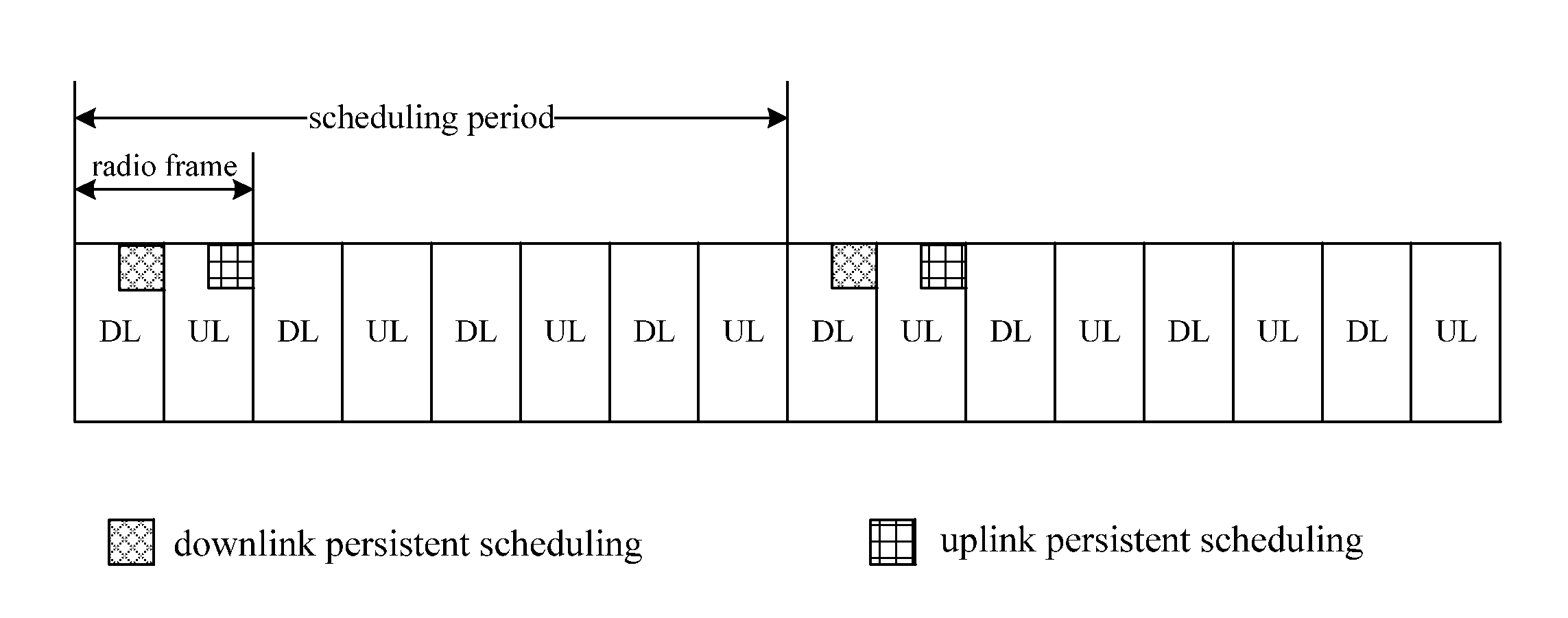
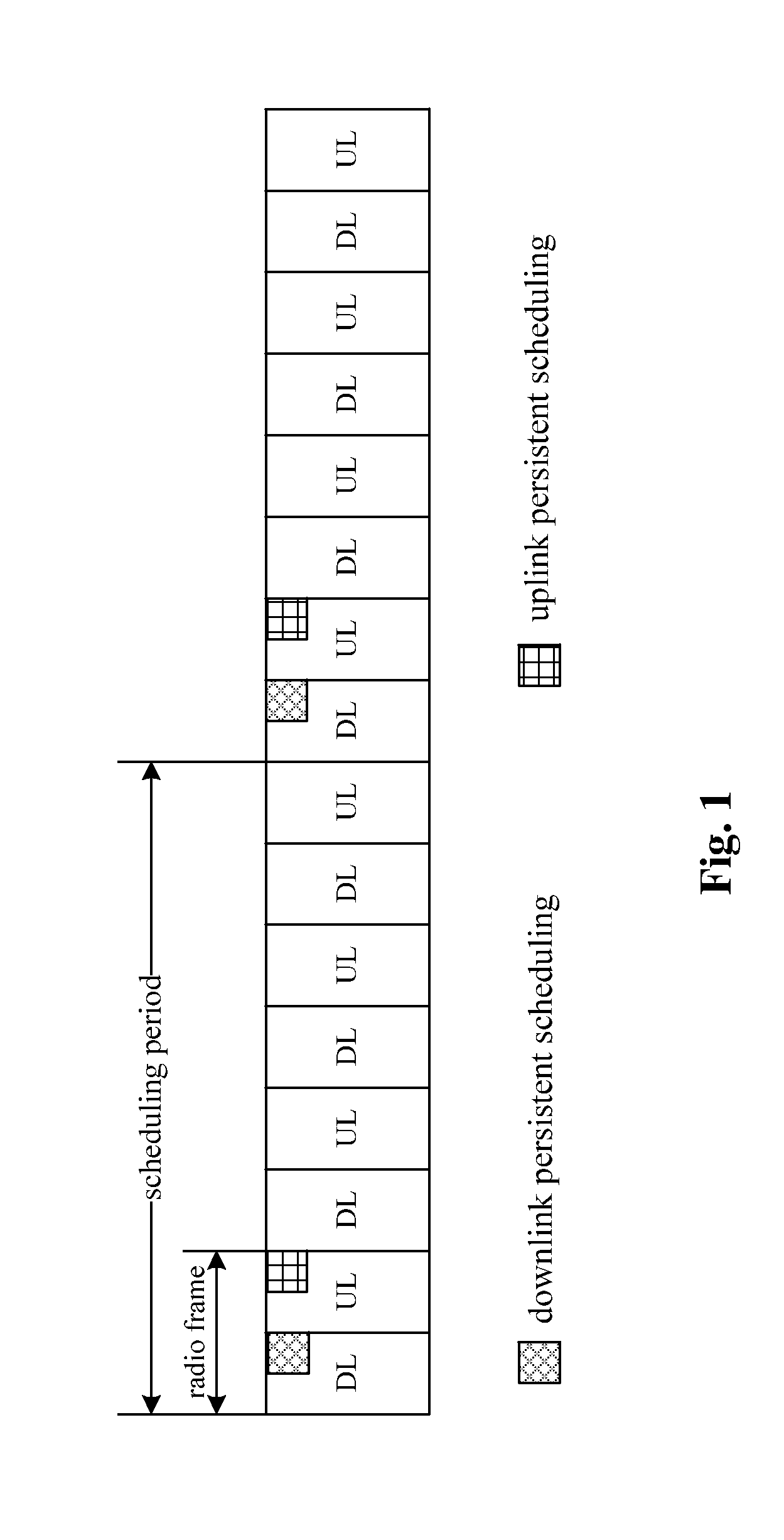
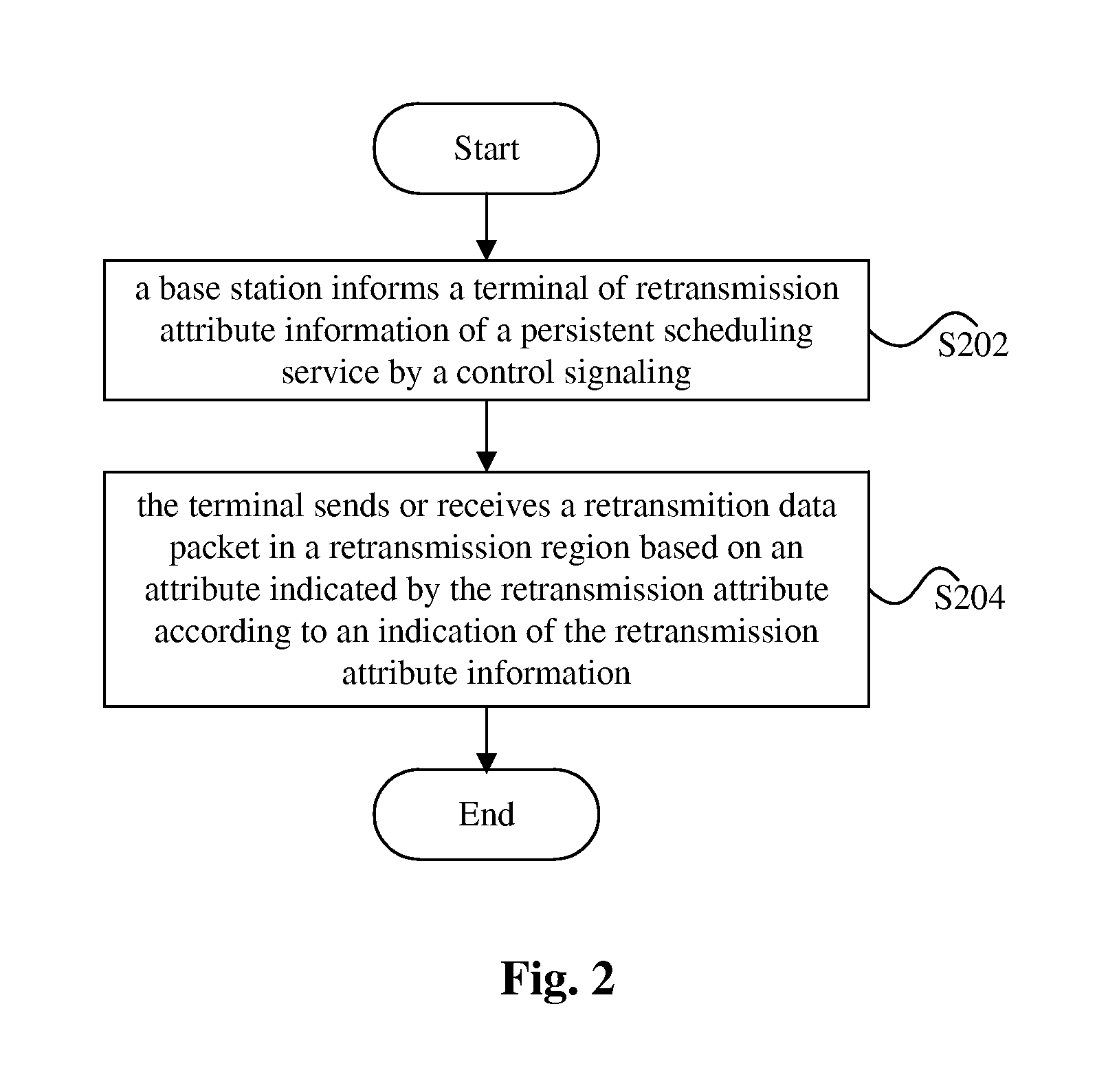
Method for Realizing Hybrid Automatic Retransmission Based on Persistent Scheduling
InactiveUS20120051305A1Save overheadError preventionTransmission path multiple useControl signalNetwork packet
The present invention discloses a method for retransmitting hybrid automatic based on persistent scheduling. The method includes: a base station sending retransmission attribute information of a persistent scheduling service to a terminal by a control signaling. An HARQ mechanism under a persistent scheduling mode is perfected by defining a retransmission region of the persistent scheduling service, and retransmission data packets are centralized to be transmitted in the retransmission region at a synchronization time, which, compared with the prior art, saves the overhead of resource indication information indicating each retransmission packet.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Transport of aggregated client packets
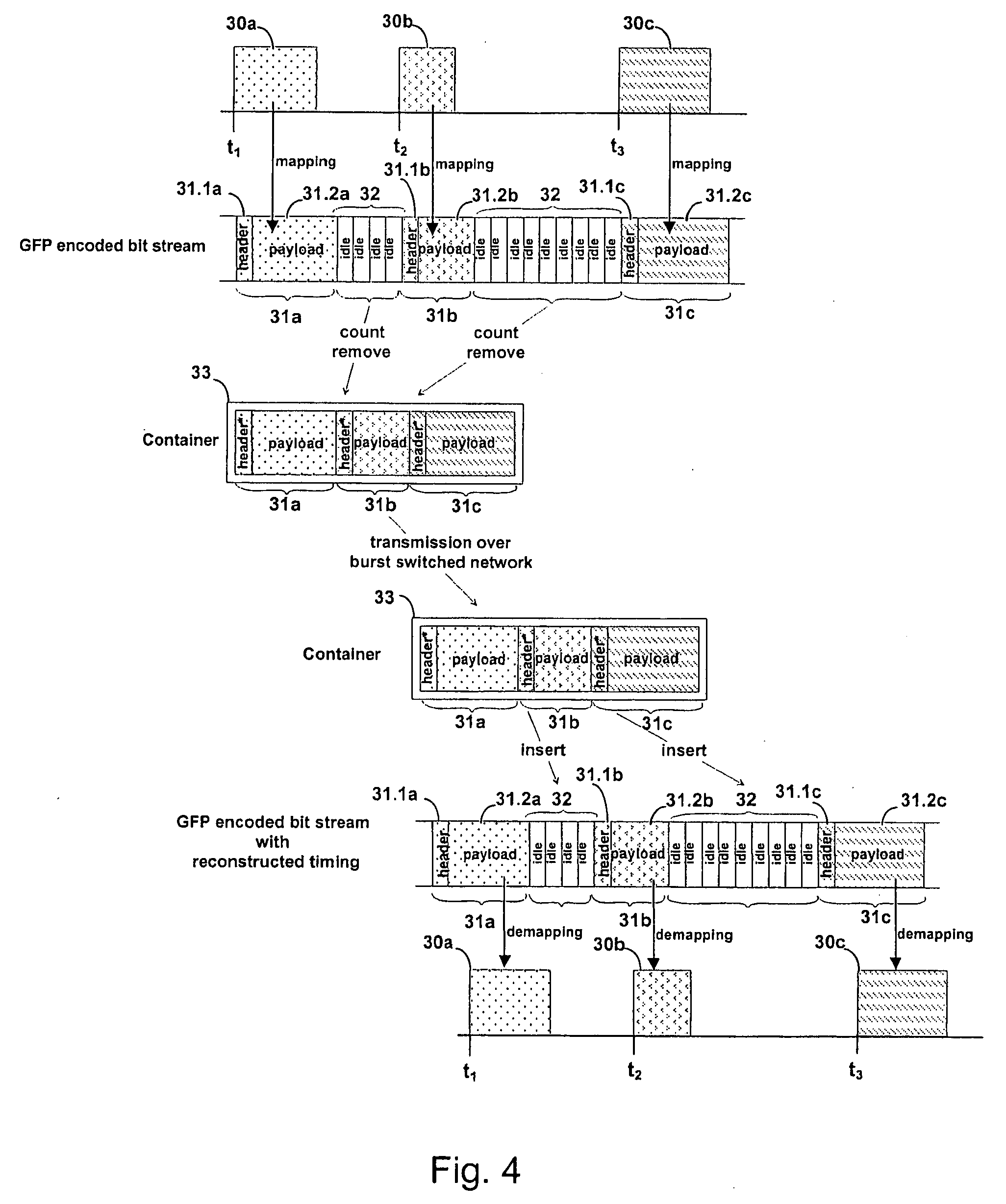
ActiveUS20090154475A1Improve liquidityRestoration timeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationClient-sideTime information
The invention relates to a method for transmitting one or more client signals via a packet transport network. According to the method, packets of the one or more client signals are received at an ingress node of the network. Timing information characterizing the timing of the received packets is determined and the received packets are mapped into a container. The container and the timing information are transmitted via the network. At an egress node of the network, the packets are extracted from the container and the packets are timed for further transmission based on the transmitted timing information.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Method of determining a channel state in coordinated multipoint transmission
InactiveUS20130322288A1Reduce overheadSave overheadSite diversityError preventionChannel state informationPrecoding
In order to reduce the feedback overhead of channel state information in Coordinated Multipoint (CoMP) transmission, the present invention provides a method of determining a channel state in the CoMP transmission, wherein the serving base station receives first channel state information with the serving base station and second channel state information with each of coordinated base stations, fed back by a user equipment; informing each coordinated base stations of the corresponding second channel state information; precoding a first reference signal according to the first channel state information, and sending the precoded first reference signal to the user equipment on the communication resource commonly used with the coordinated base station, wherein the first reference signal is superimposed with precoded second reference signals respectively sent by each of coordinated base stations; receiving third channel state information fed back by the user equipment according to the superimposed reference signal, and determining a channel state of the coordinated multipoint transmission corresponding to the user equipment, according to the first, second and third channel state information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
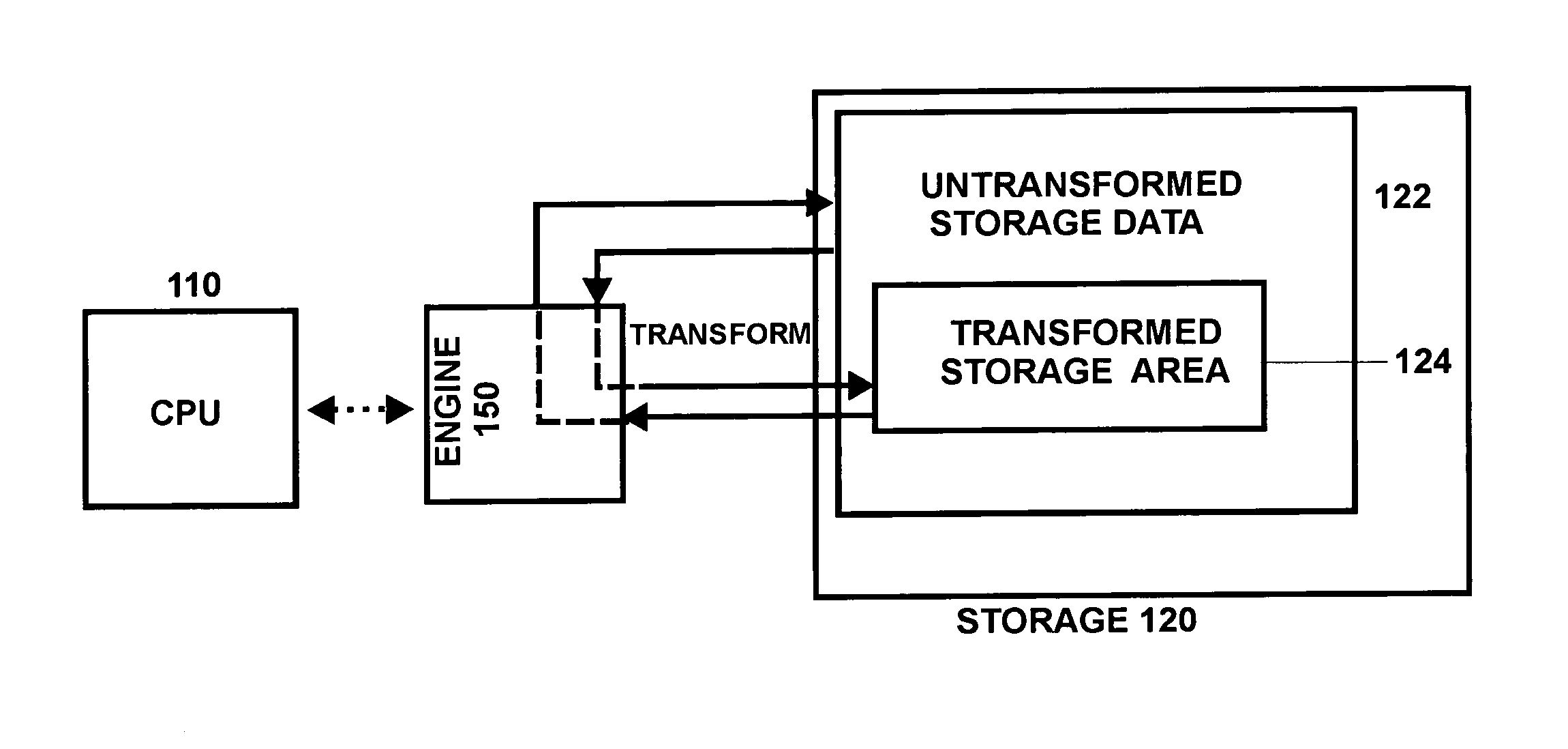
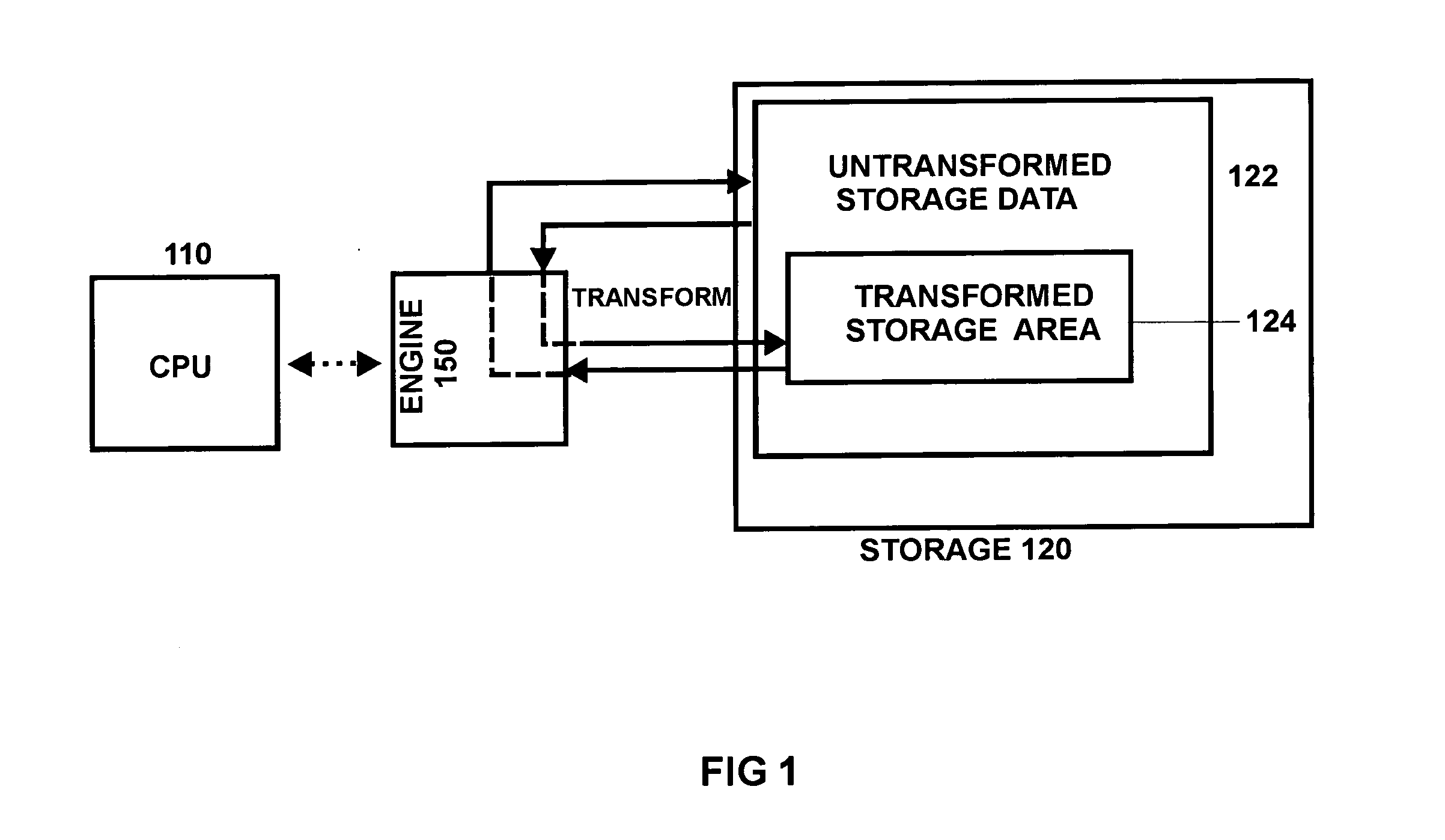
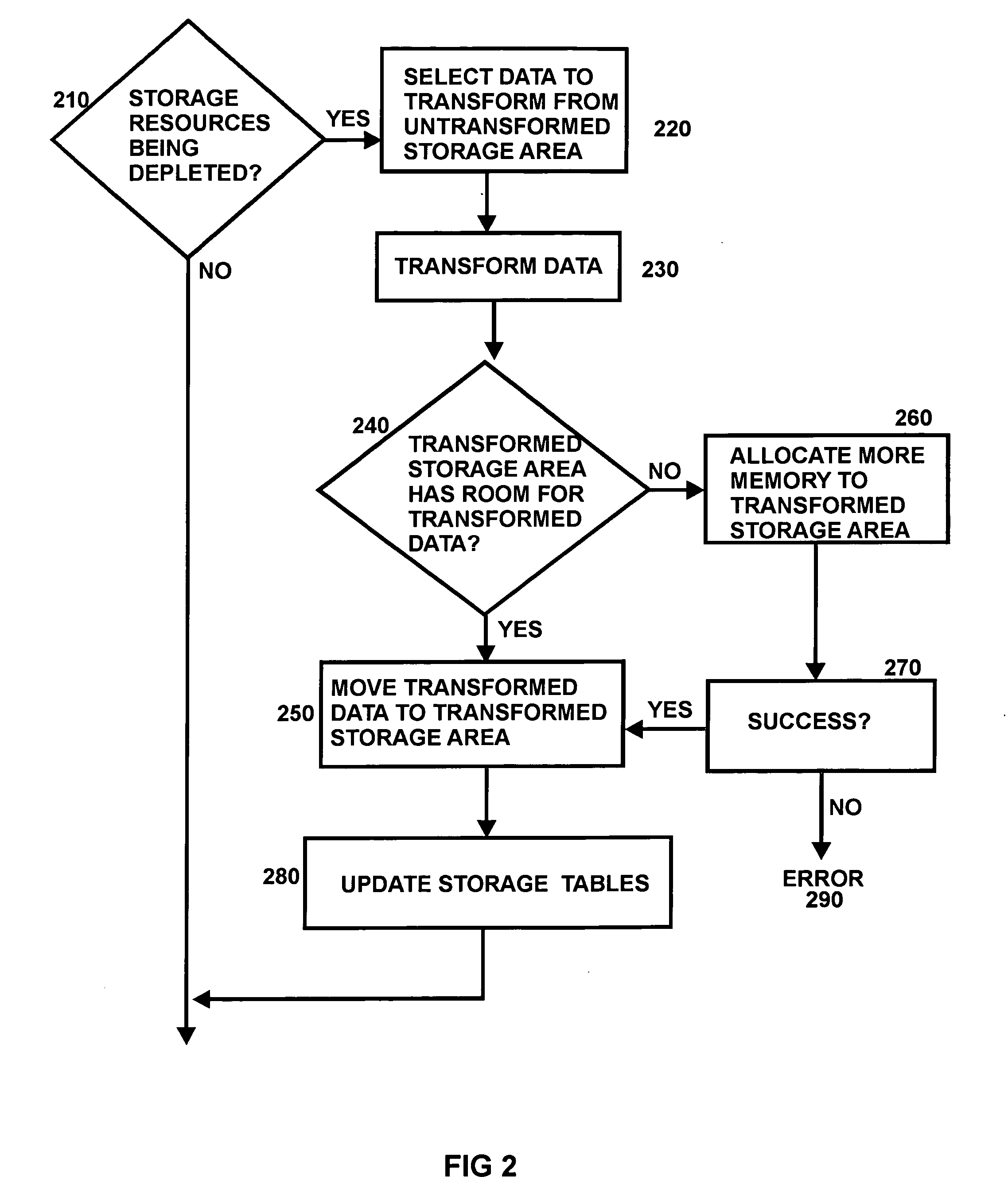
Storage architecture for embedded systems
InactiveUS20070005625A1Easy to compressFacilitates of dataMemory architecture accessing/allocationResource allocationComputer architectureStorage management
A storage management architecture is disclosed which is particularly advantageous for devices such as embedded systems. The architecture provides a framework for a compression / decompression system which advantageously is software-based and which facilitates the compression of both instruction code and writeable data.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Technique for performing arbitrary width integer arithmetic operations using fixed width elements
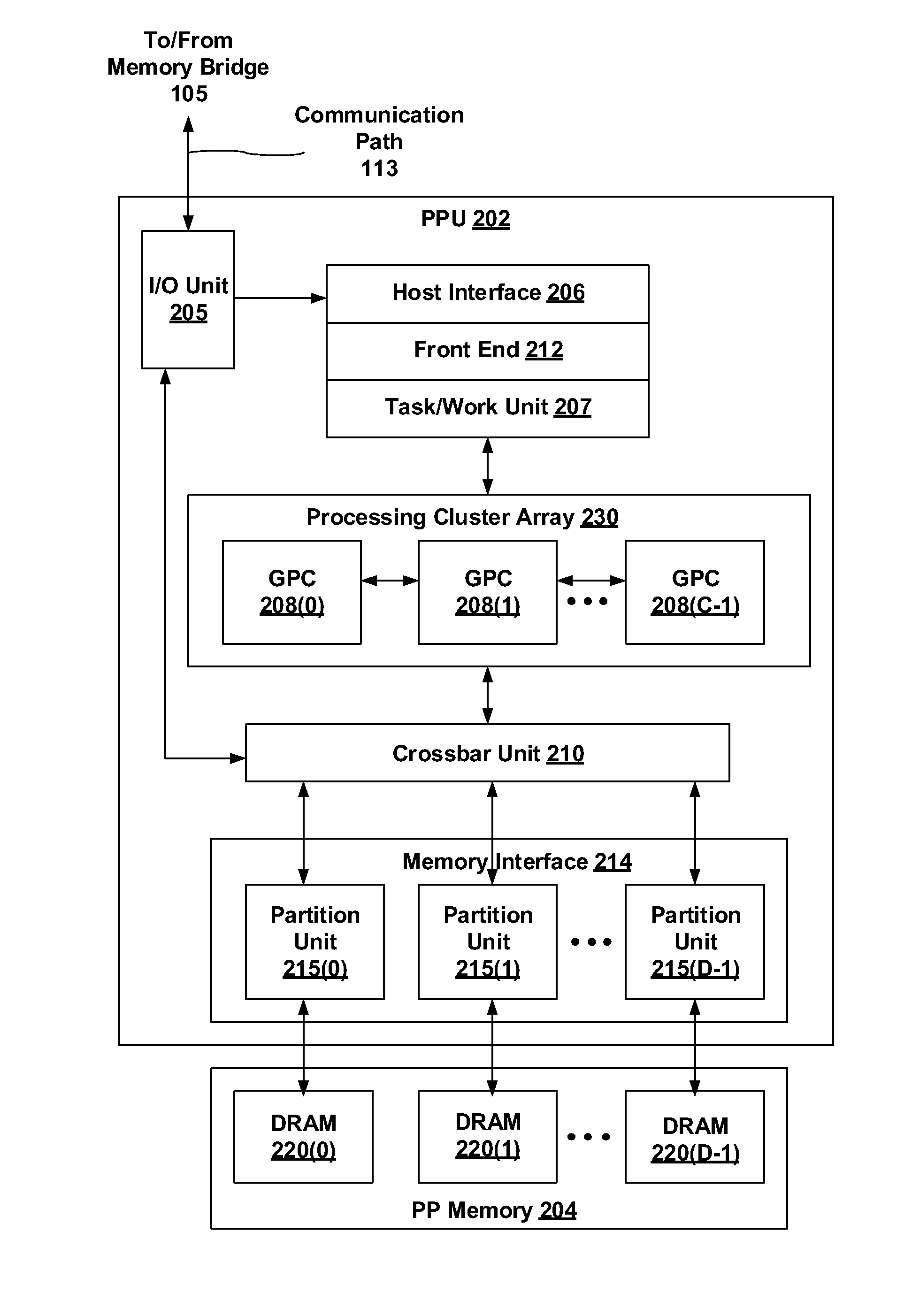
ActiveUS20150081753A1Improve abilitiesSave overheadComputation using denominational number representationOperandFloating point
One embodiment of the present invention includes a method for performing arithmetic operations on arbitrary width integers using fixed width elements. The method includes receiving a plurality of input operands, segmenting each input operand into multiple sectors, performing a plurality of multiply-add operations based on the multiple sectors to generate a plurality of multiply-add operation results, and combining the multiply-add operation results to generate a final result. One advantage of the disclosed embodiments is that, by using a common fused floating point multiply-add unit to perform arithmetic operations on integers of arbitrary width, the method avoids the area and power penalty of having additional dedicated integer units.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method, module of access controls and a ue comprising the same
InactiveUS20140329503A1Reduce modificationSave overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionTelecommunicationsMedia access control
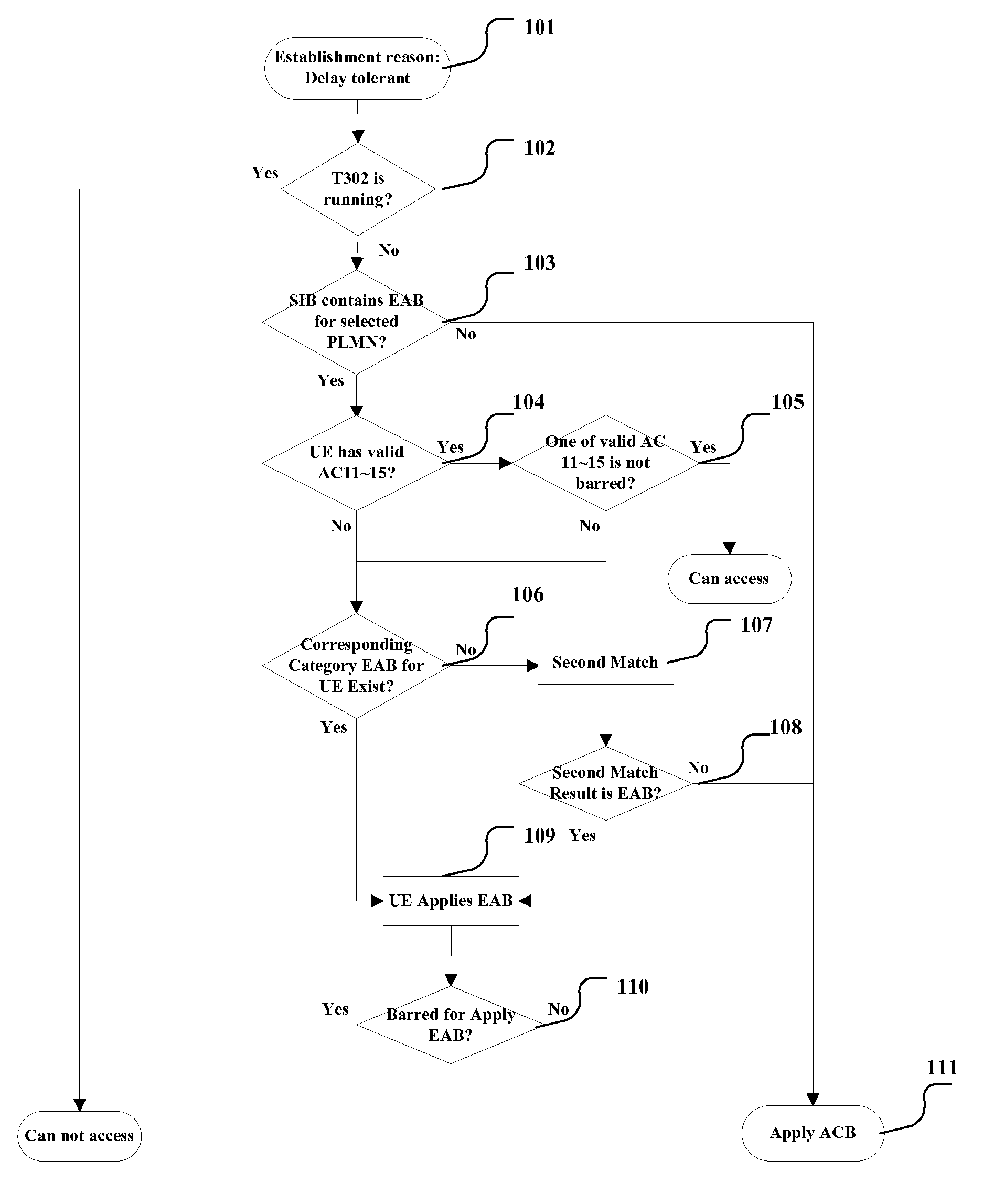
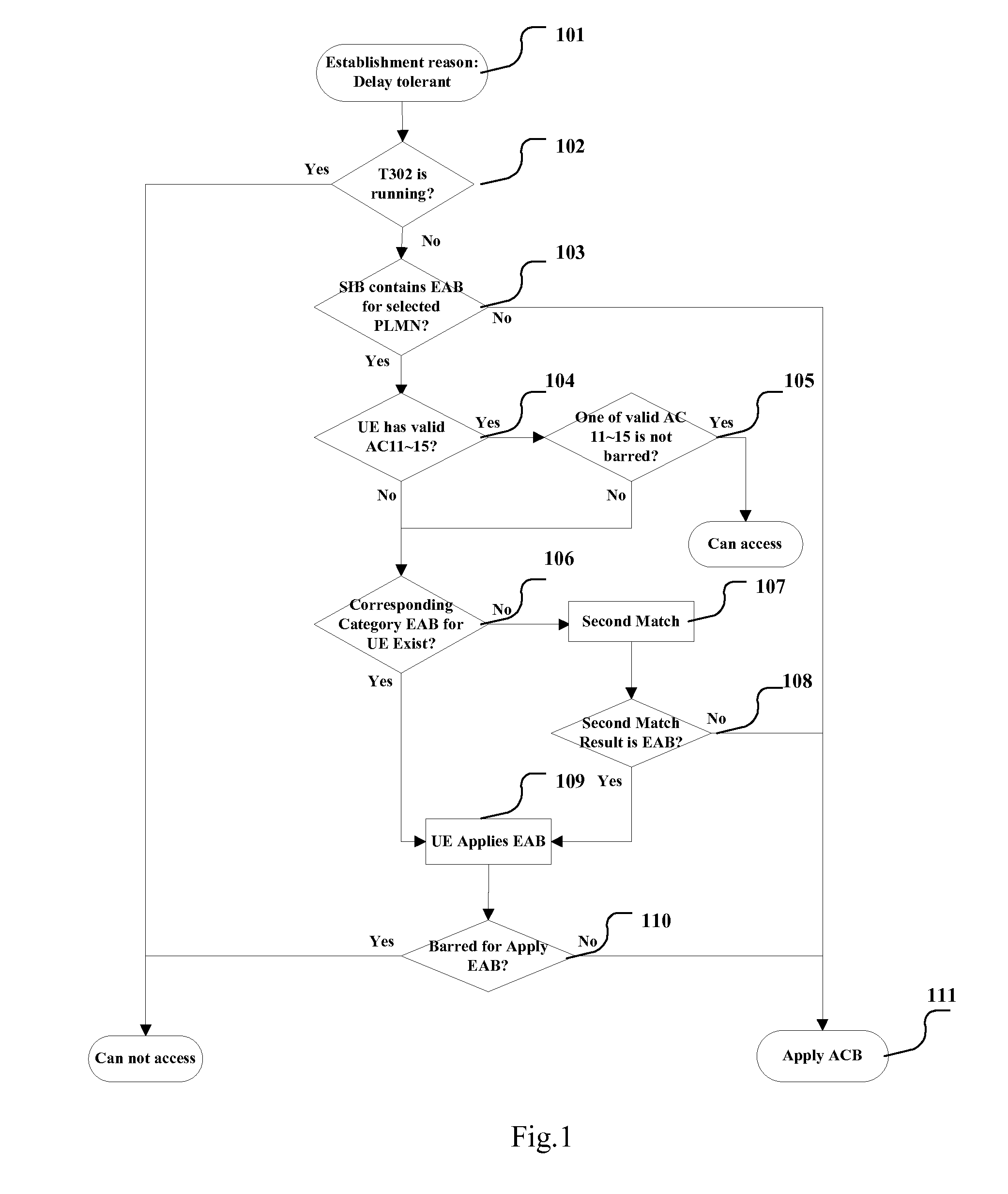
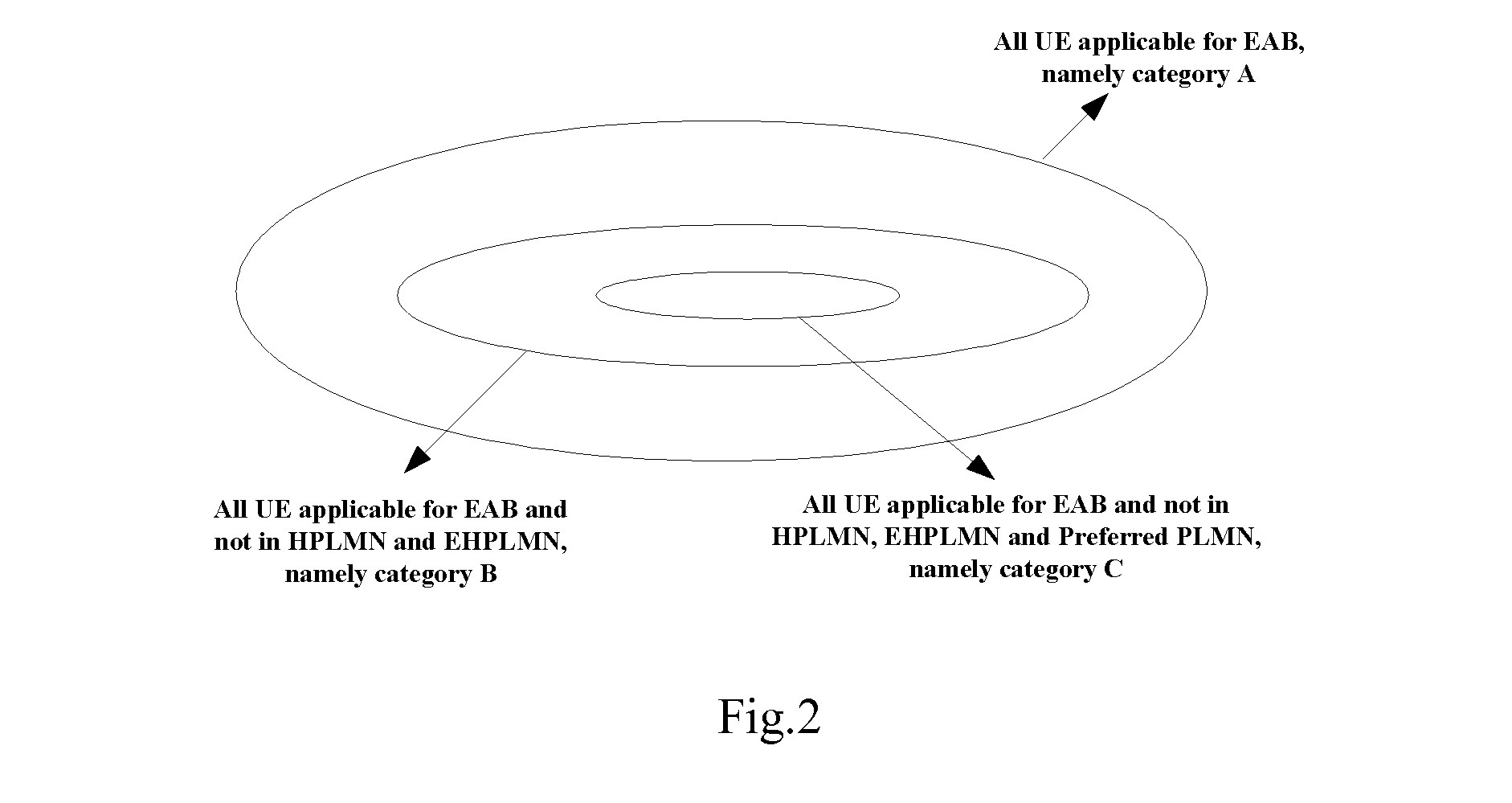
There is no detailed scheme implementing access controls using extended access barring (EAB) in the current technology. The invention provides a method, module and UE of implementing access controls, the method comprises the following steps: b. determining (104, 105) whether the UE has a special access level which is valid and not barred: when having, determining the UE can access a current cell; d. determining (103) whether a system information block comprises extended access barring (EAB) parameters of the UE, when comprising: e. determining (116-110) whether the UE can access the current cell based on extended access barring, according to the extended access barring (EAB) parameters of the UE. The invention provides a method of implementing access controls based on extended access barring.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for transmitting downlink control signaling, method for searching downlink control signaling and apparatus used for the same
InactiveUS20140119335A1Save overheadSignal allocationForward error control useCommunications systemControl channel
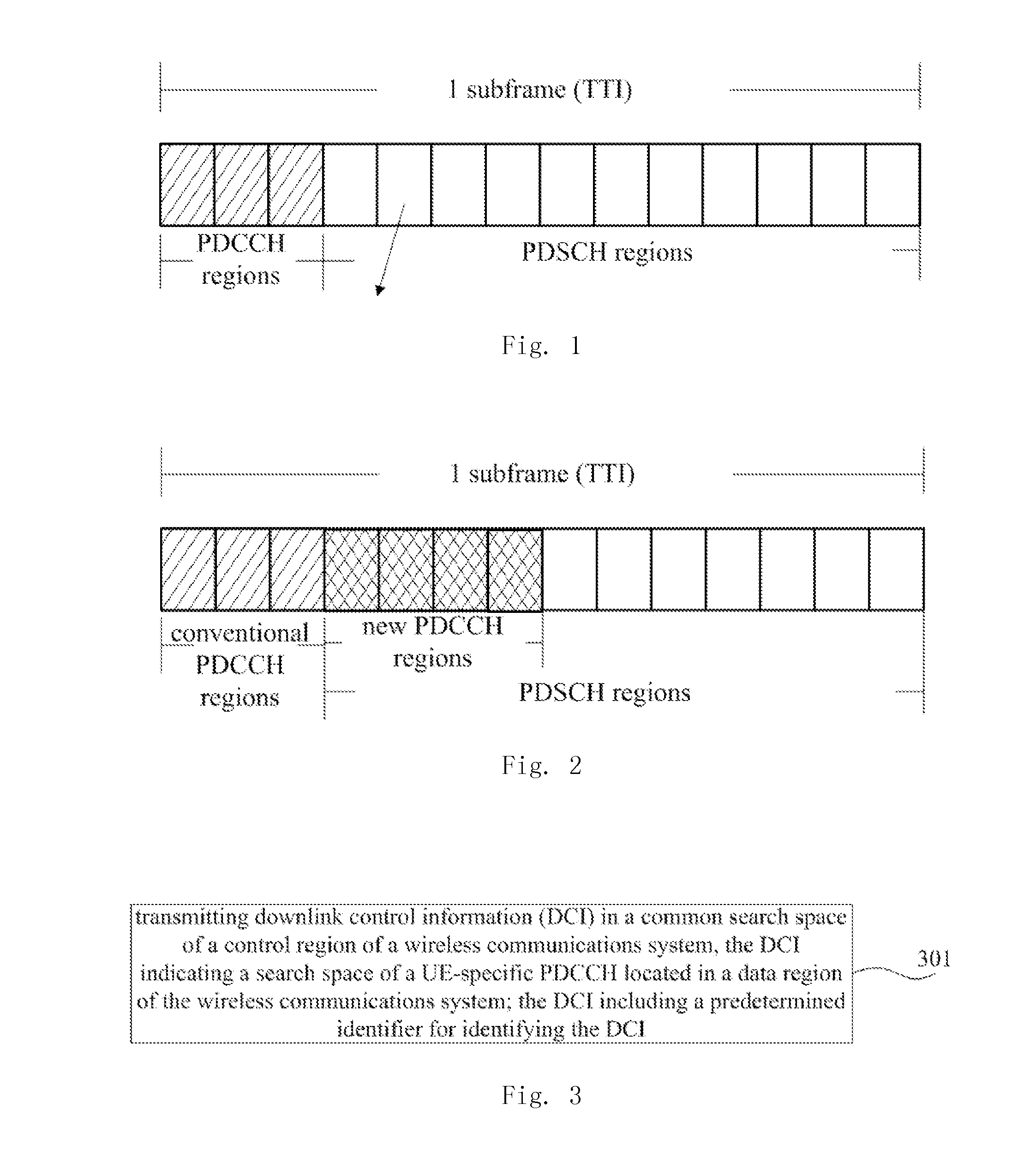
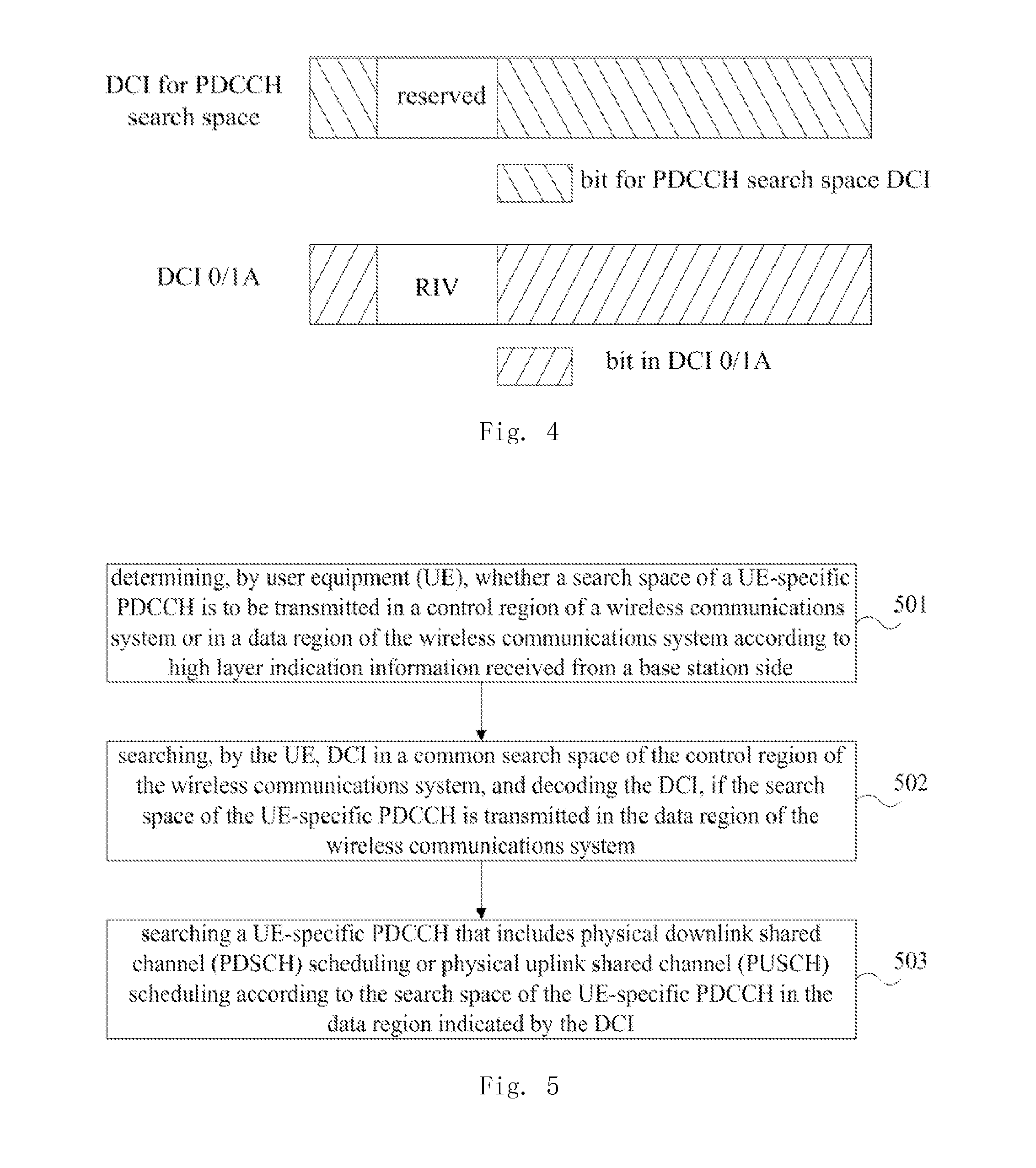
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method for transmitting downlink control signaling, a method for searching downlink control signaling and an apparatus used for the same. The method for transmitting includes: transmitting downlink control information (DCI) in a common search space of a control region of a wireless communications system, the DCI indicating a search space of a UE-specific physical downlink control channel (PDCCH) located in a data region of the wireless communications system, the DCI further including a predetermined identifier for identifying the DCI. With the methods and apparatuses of the embodiments of the present invention, the search space of the PDCCH may be dynamically adjusted, thereby saving signaling overhead, and avoiding inconsistence of the search space of the base station and that of the UE.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
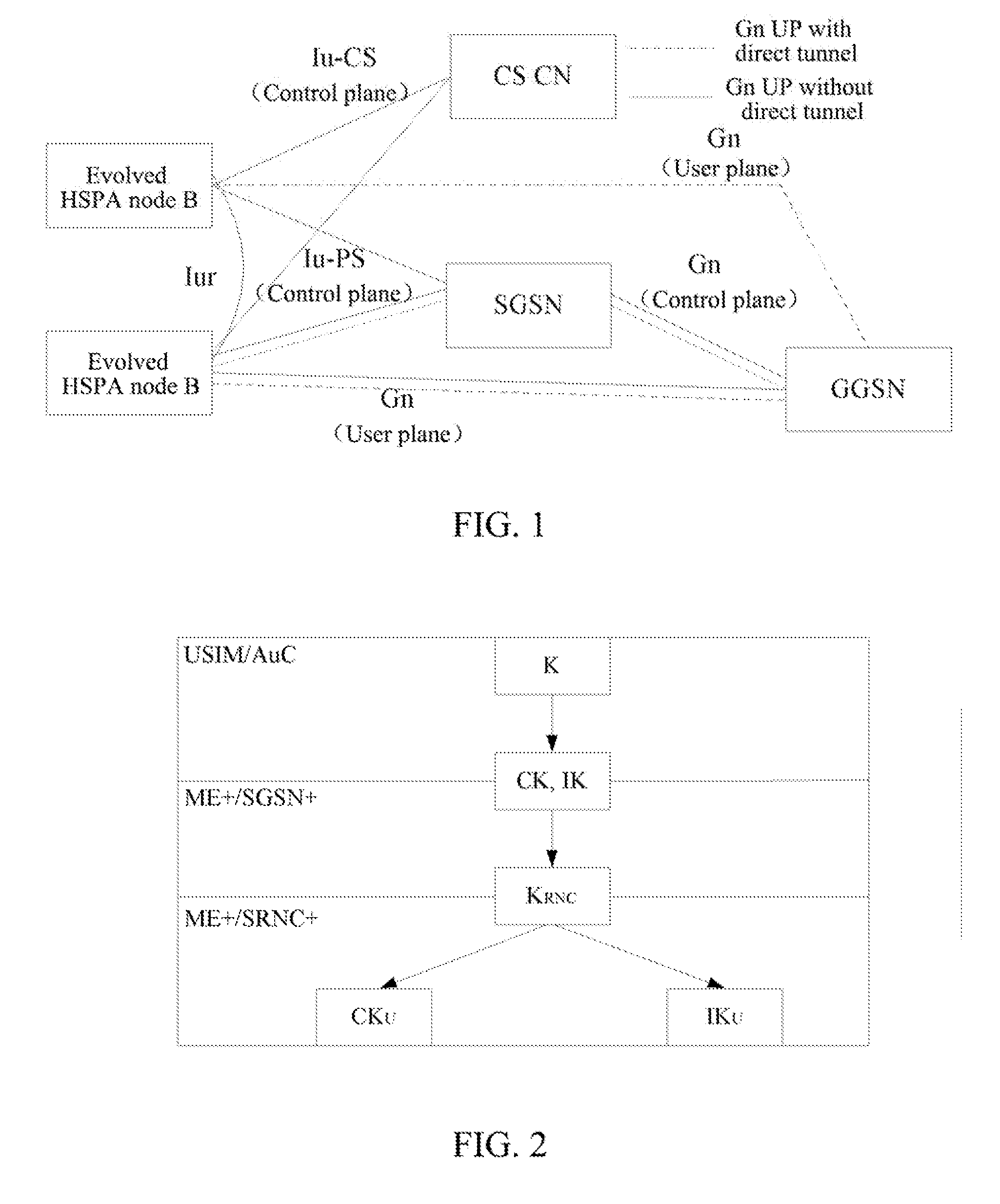
Method and System for Establishing Enhanced Key when Terminal Moves to Enhanced Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN)
ActiveUS20130028421A1Carry-out safelySave overheadSecret communicationSecurity arrangementComputer networkRadio access network
The present invention discloses a method and system for establishing an enhanced key when a terminal moves from an EUTRAN to an enhanced UTRAN, so as to ensure that the terminal can carry out normal communication safely in the enhanced UTRAN. The method includes: when the terminal moves from the EUTRAN to the enhanced UTRAN, a target enhanced serving GPRS support node (SGSN+) in the enhanced UTRAN deducing an intermediate key used in the UTRAN according to a mapped traditional key obtained from a source mobile management entity; and the terminal, after deducing the mapped traditional key, further deduces the intermediate key used in the enhanced UTRAN by using an algorithm which is the same as that of the target SGSN+ according to the mapped traditional key.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method of maintaining coherency of a precoding channel in a communication network and associated apparatus
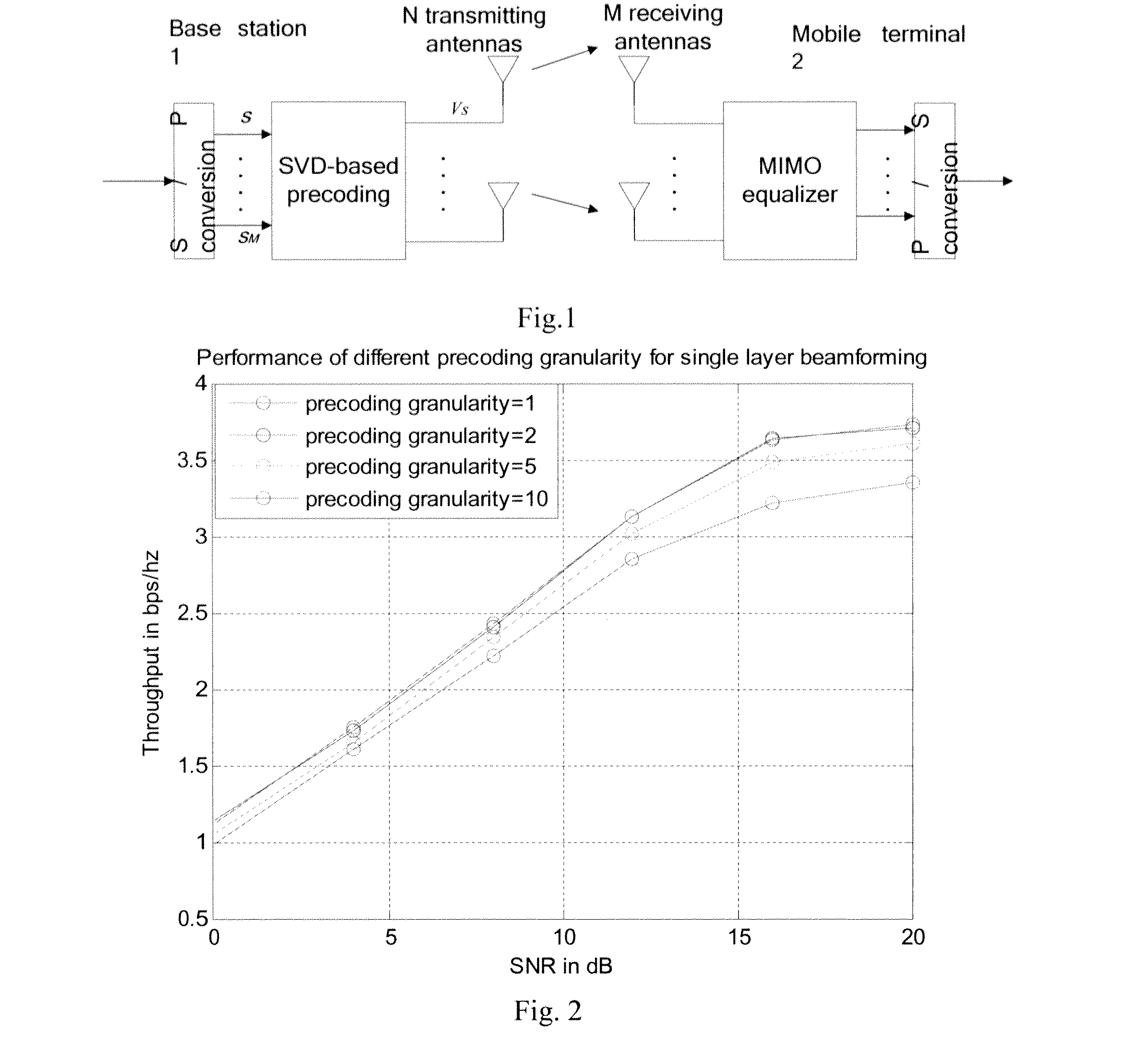
InactiveUS20120140851A1Increasing precoding gainImprove channel estimation performanceReceivers monitoringSpatial transmit diversitySystem capacityResource block
In prior art, selection of precoding granularity is affected by two inter-restricting factors, i.e., precoding accuracy and channel estimation at a mobile terminal. To solve this problem, the present invention provides a method of maintaining coherency of a precoding channel in a communication network and an associated apparatus. During precoding, this method takes into account both channel coherency and system capacity. A base station adjusts phase and / or amplitude of a precoding matrix corresponding to each precoded unit to maintain coherency of associated information of the overall precoding channel. The associated information of the precoding channel includes, for example, CSI or eigenvalue matrix of the precoding channel. Afterwards, a mobile terminal performs channel estimation based on reference signals of multiple precoded units, thereby eliminating the limitation in prior art that a mobile terminal can perform channel estimation only within one or more resource block limited by a precoding granularity.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
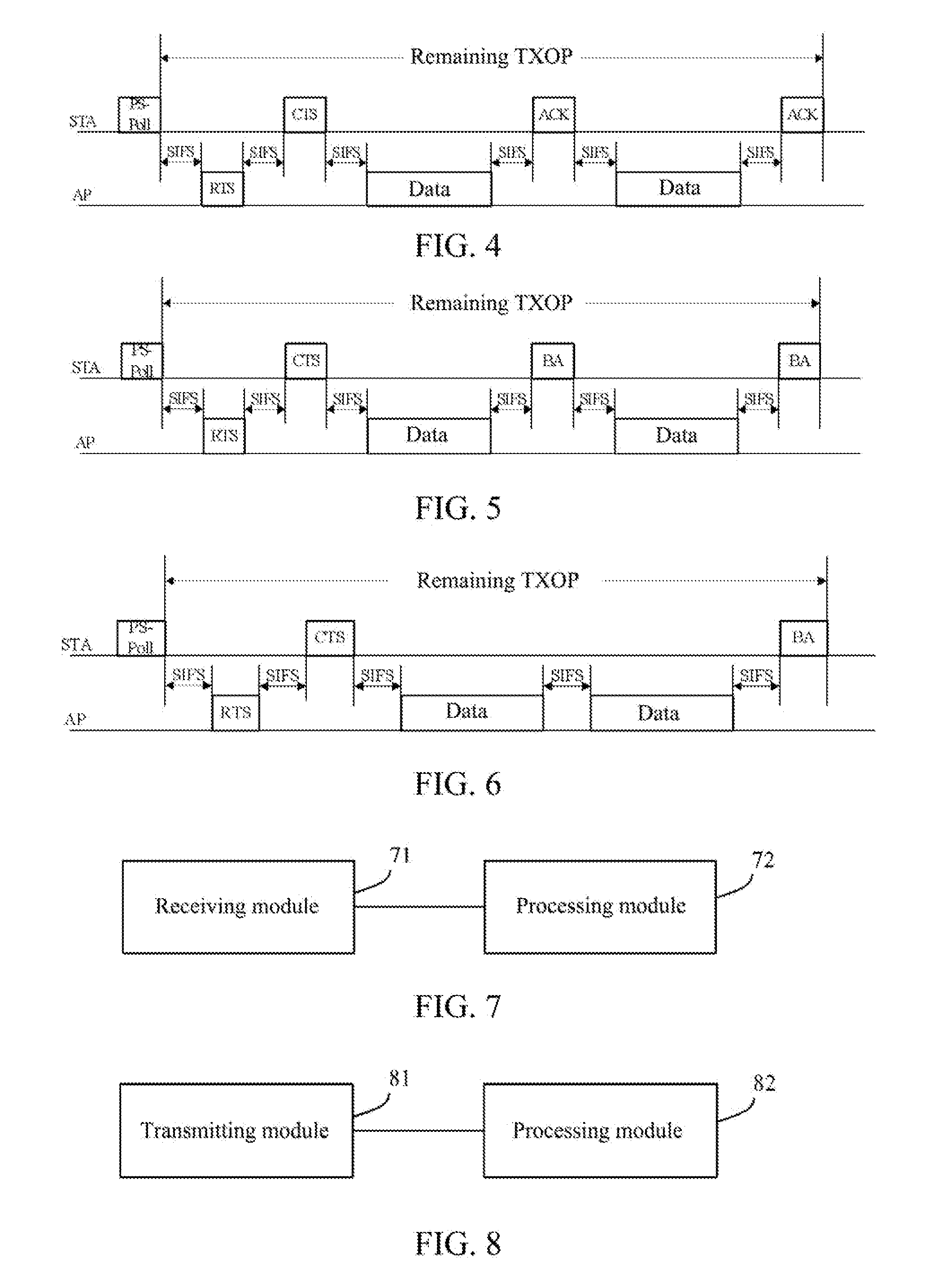
Downlink Data Collision Avoidance Method, Access Point and Station
ActiveUS20150055577A1Saving link overheadAvoid collisionPower managementError preventionPaper documentReal-time computing
The present document provides a method for avoiding downlink data collision, an Access Point (AP) and a Station (STA). The method for avoiding downlink data collision includes: an AP receiving a radio frame for inquiring whether the AP has a Bufferable Unit (BU) of an STA transmitted by the STA; and after determining that there is a BU of the STA and the BU is larger than a predetermined threshold, the AP exchanging radio frames with the STA to reserve a channel, and transmitting the BU to the STA after succeeding in reserving the channel. The method can guarantee the fairness among various STAs and the reasonable utilization of channel resources, thus avoiding the collision; furthermore, the channel reservation frame transmitted by the AP can reserve a longer period of time, i.e. a plurality of BUs can be transmitted to the STA at a time, thus saving the link overhead.
Owner:ZTE CORP
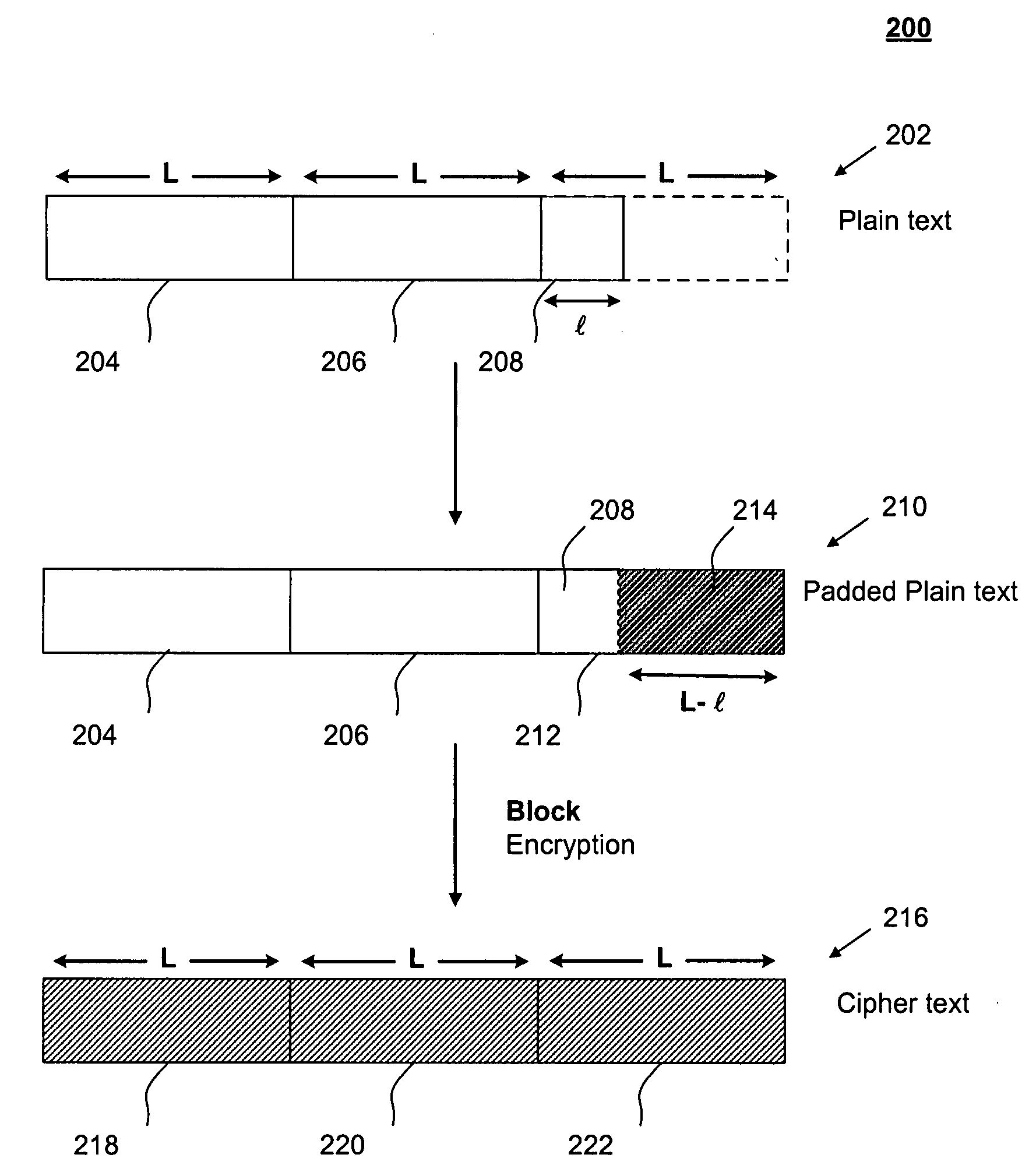
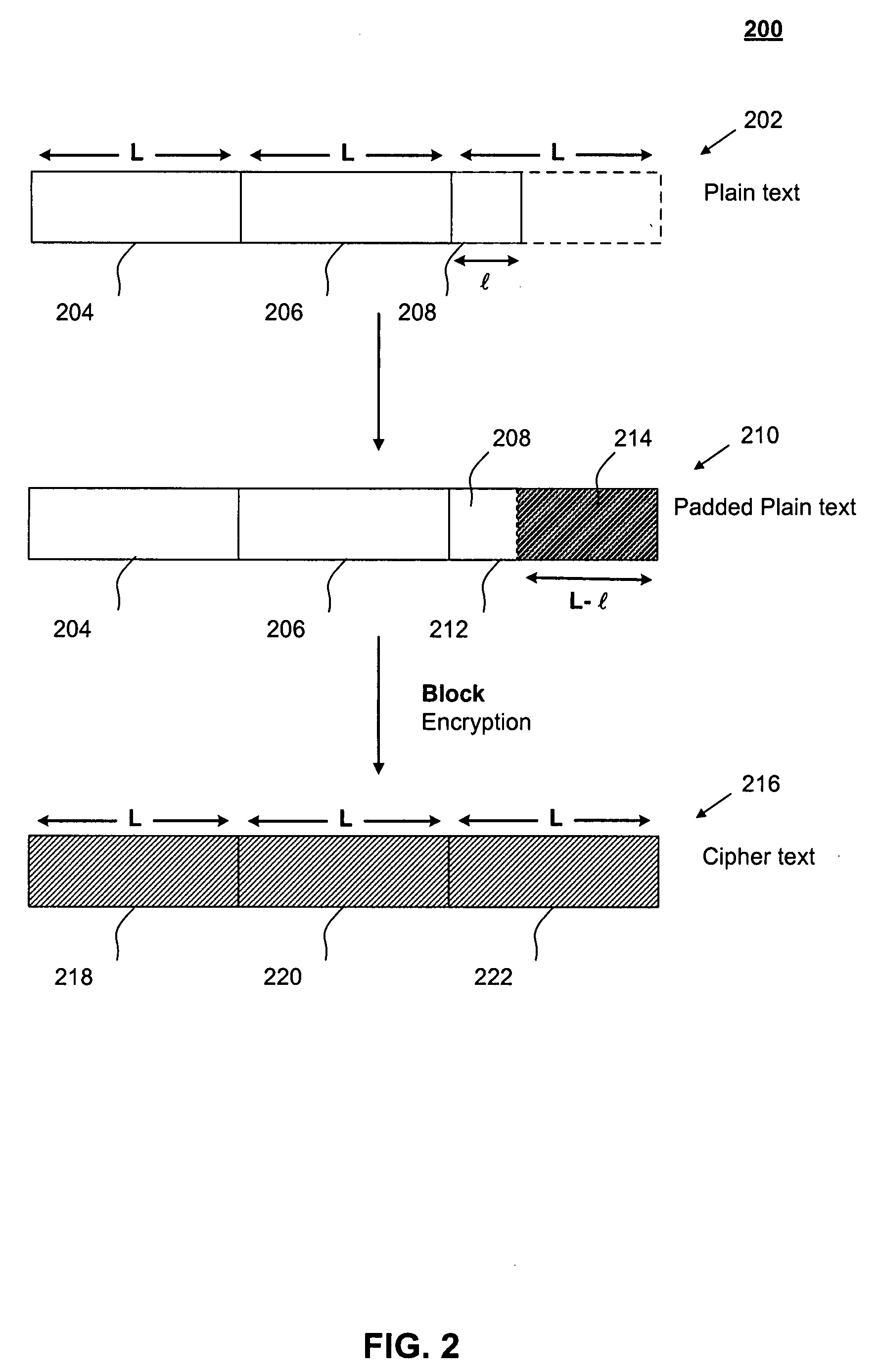
Data encryption without padding
InactiveUS20080192924A1Encryption overhead savingAvoid paddingSecret communicationSecuring communicationPlaintextBlock cipher
The present invention relates generally to data encryption. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of block cipher encryption and decryption. Embodiments of the present invention avoid padding in encrypting plain text messages having lengths that are non-integral multiples of a pre-determined block size. As such, encryption overhead savings can be achieved. Further, security from side-channel attacks can be increased.
Owner:SYBASE INC
Methods and devices for notifying and determining patterns of common reference signals
ActiveUS20140211695A1Effectively perfectingSave overheadSite diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission pointTelecommunications
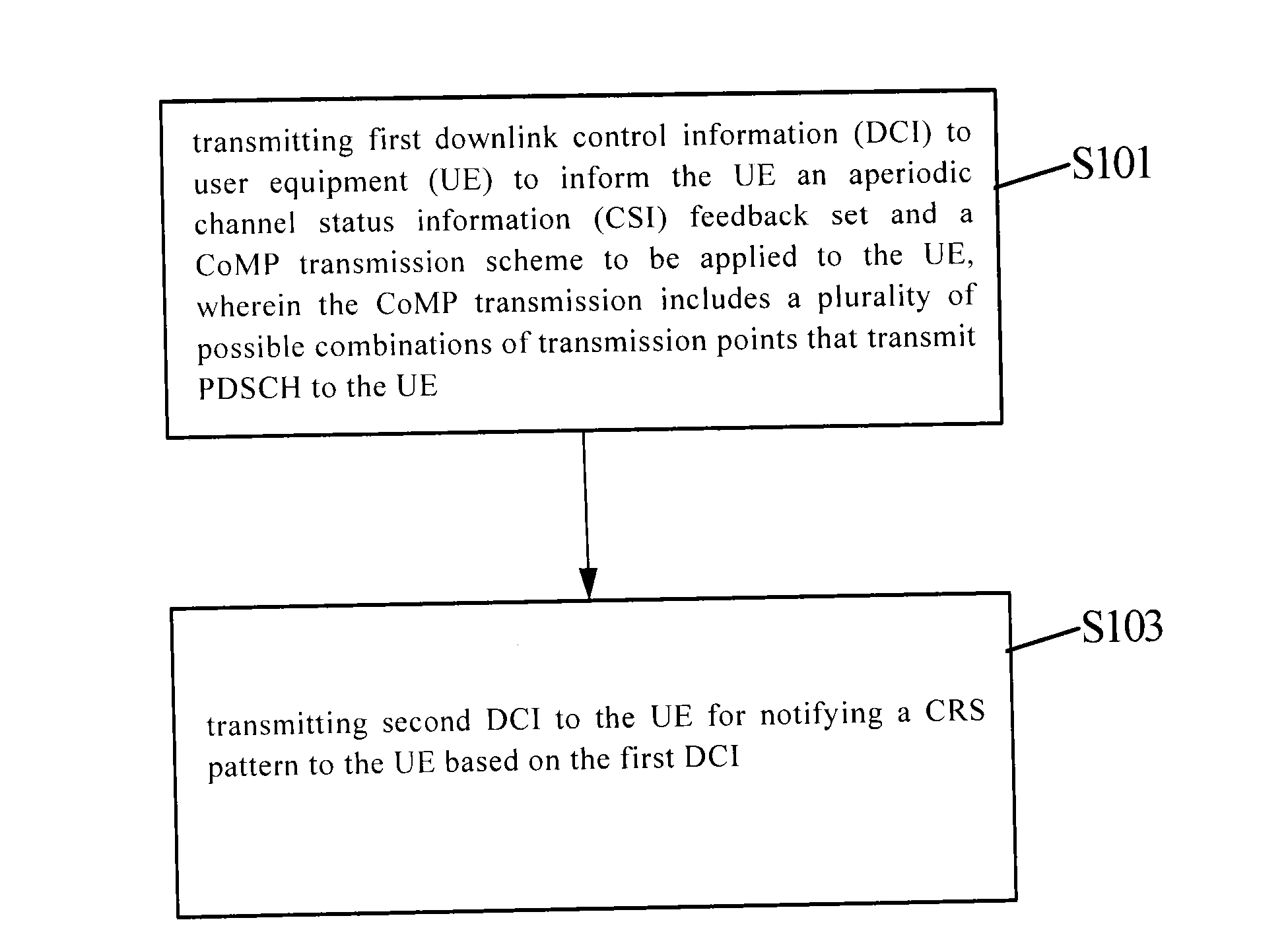
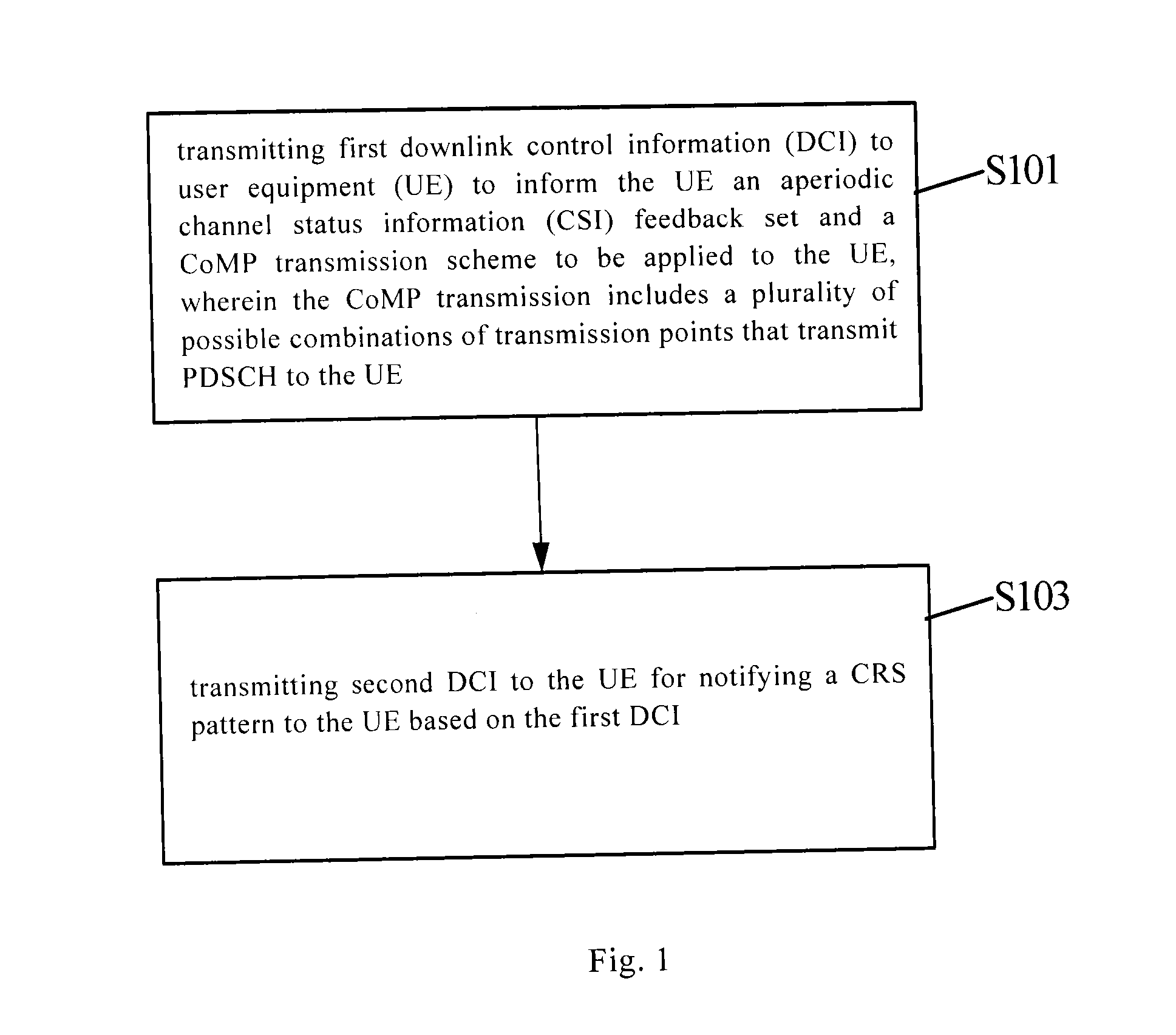
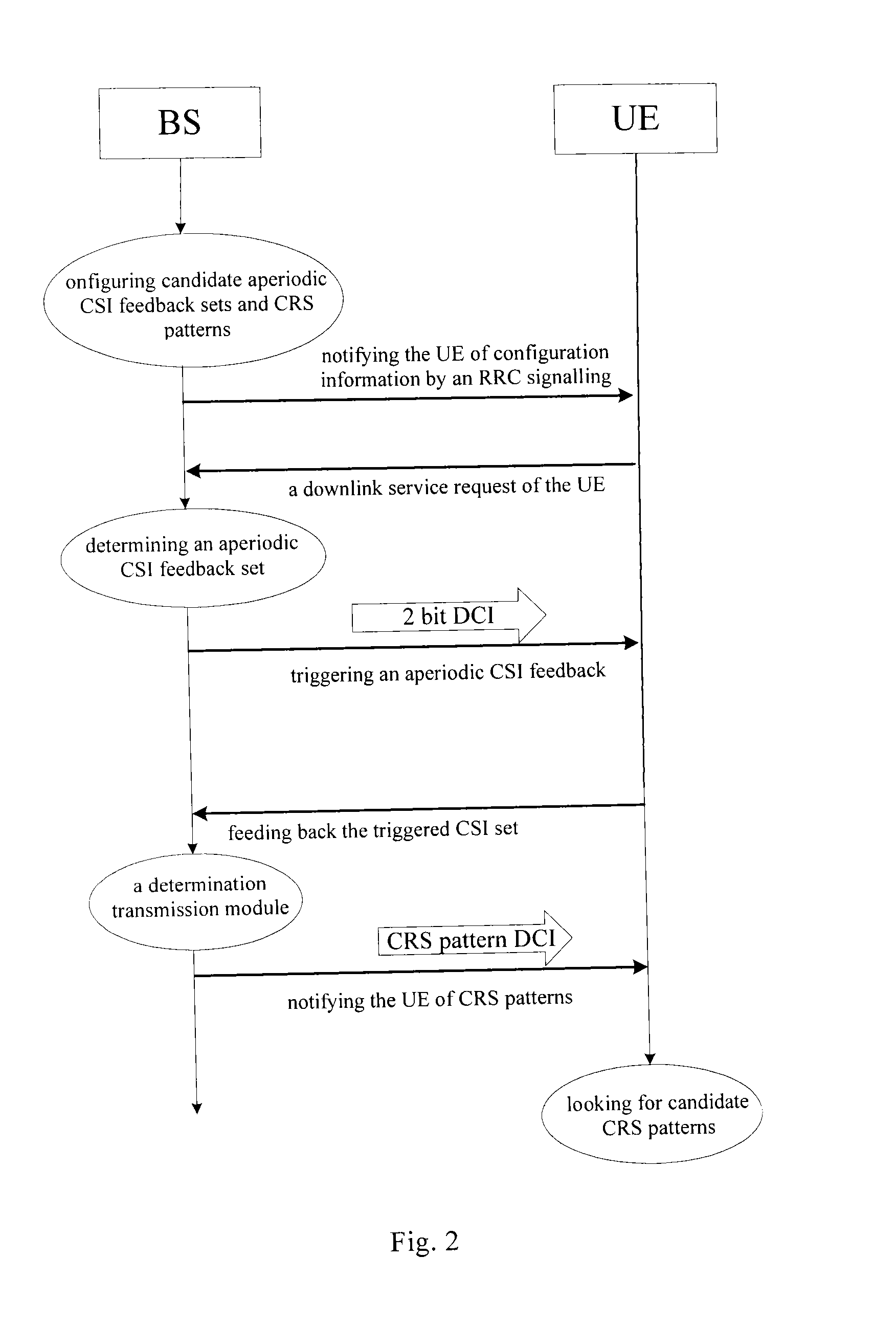
The disclosure relates to methods and devices for notifying and determining common reference signal (CRS) patterns. The notification method comprises the steps of transmitting first downlink control information (DCI) to user equipment (UE) to inform the UE an aperiodic channel status information (CSI) feedback set and a CoMP transmission scheme to be applied to the UE, wherein the CoMP transmission includes a plurality of possible combinations of transmission points that transmit PDSCH to the UE; and transmitting second DCI to the UE for notifying transmission parameter to the UE based on the first DCI. In the disclosure, all CoMP transmission schemes and notifications of all CRS patterns therein can be supported, thus effectively perfecting notifications of the CRS patterns, saving signaling overheads, and significantly improving the flexibility.
Owner:SONY CORP
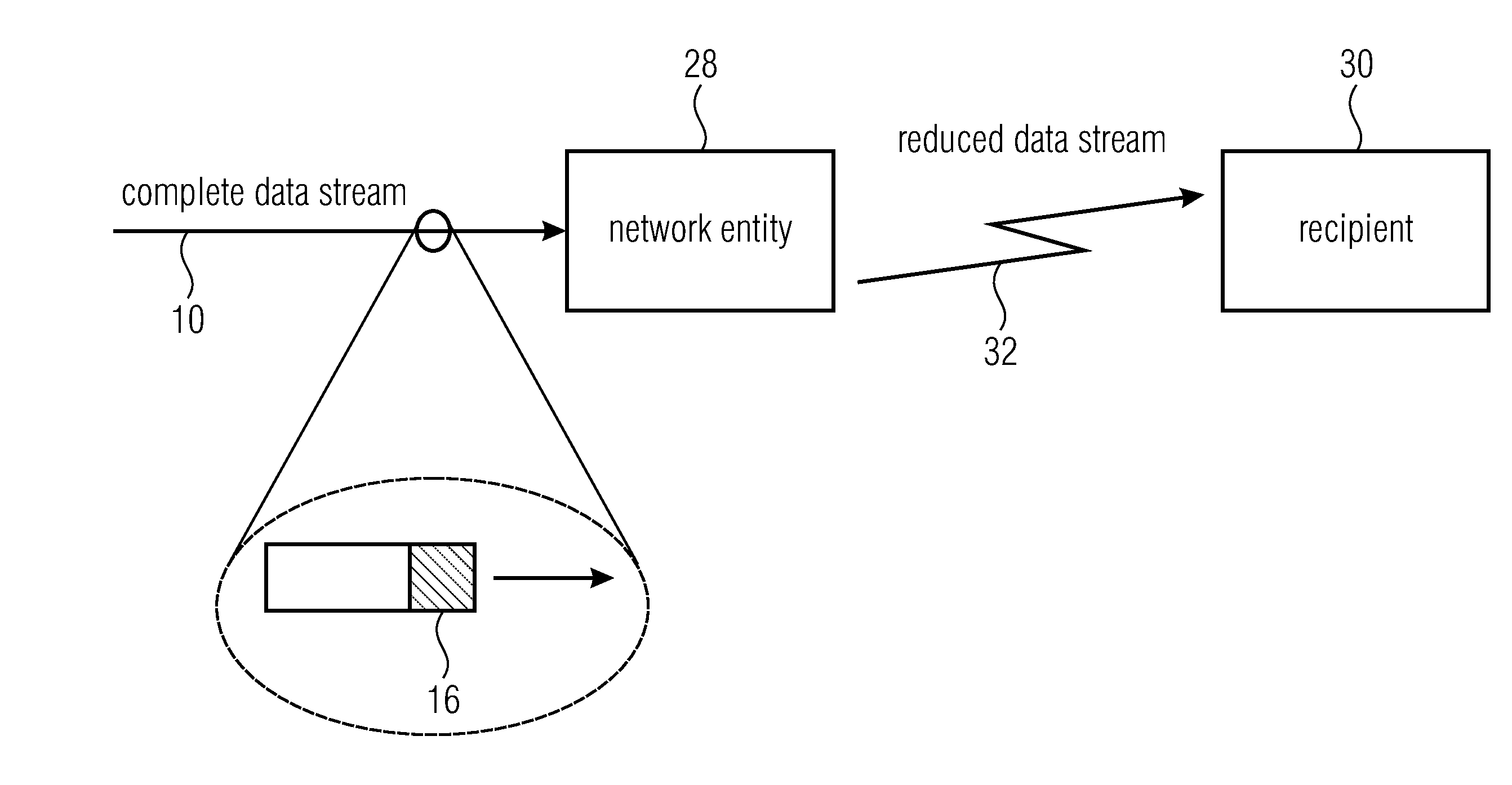
Scalable data stream and network entity
ActiveUS20150023434A1Reduce amount of dataScalable data streamColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSyntaxOperating point
The handling of scalable data streams by network entities is rendered less complex by, in the data stream, accompanying packets which actually carry data by packets of a different packet type which have a scalability axes descriptor defining the number of scalability axes and a semantic meaning thereof. In another aspect, the handling of scalable data streams by network entities is rendered more efficient by conveying level and / or profile descriptors using packets other than the data carrying packets, with profile and / or level descriptors being divided up into a first set explicitly signaling the definition of the available coding option set and / or available syntax element value range for a respective operation point, and a second set of profile and / or level descriptors which signal the definition of the available coding option set and / or available syntax element value range for their respective operation points by reference another profile and / or level descriptor.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
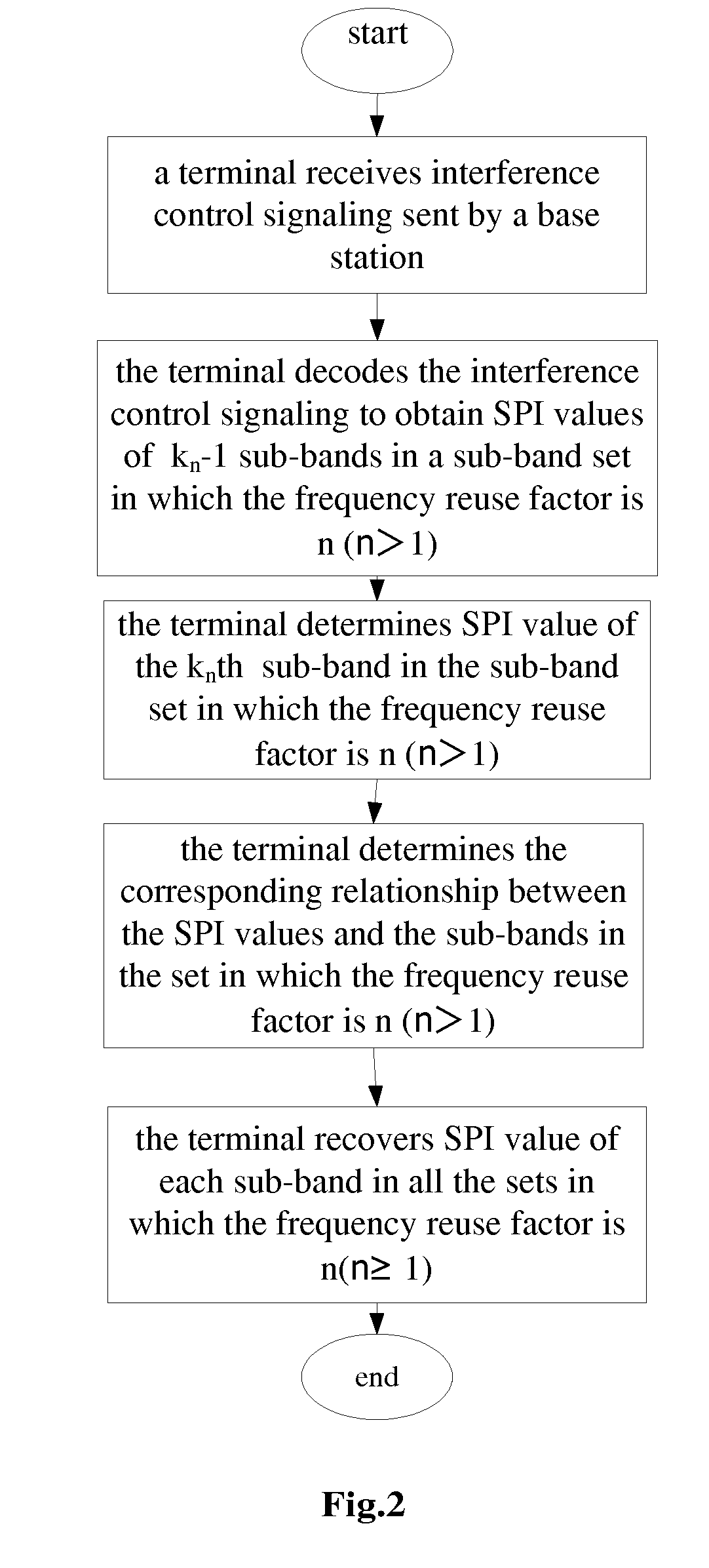
Method for transmitting and receiving interference control signaling in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20110171911A1Saving system overheadFacilitates terminal 's analyzing SPI valuePower managementSignalling characterisationCommunications systemFrequency reuse
A method for transmitting and receiving interference control signaling in the wireless communication system is provided by the present invention, wherein the transmitting method includes: a base station firstly selecting SPI values of a part of sub-bands in a sub-band set in which the frequency reuse factor is Reuse=n>1 according to SPI value selecting regulation of sub-bands, then forming interference control signaling, and finally transmitting the interference control signaling to all the terminals under the base station through a downlink channel. The SPI values of a part of sub-bands may be either SPI values of kn−1 sub-bands in a sub-band set in which the frequency reuse factor is Reuse=n>1, or SPI values of sub-bands corresponding to Ln−1 transmission power levels in a sub-band set in which frequency reuse factor is Reuse=n>1. Through the present invention, the system overhead can be effectively saved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
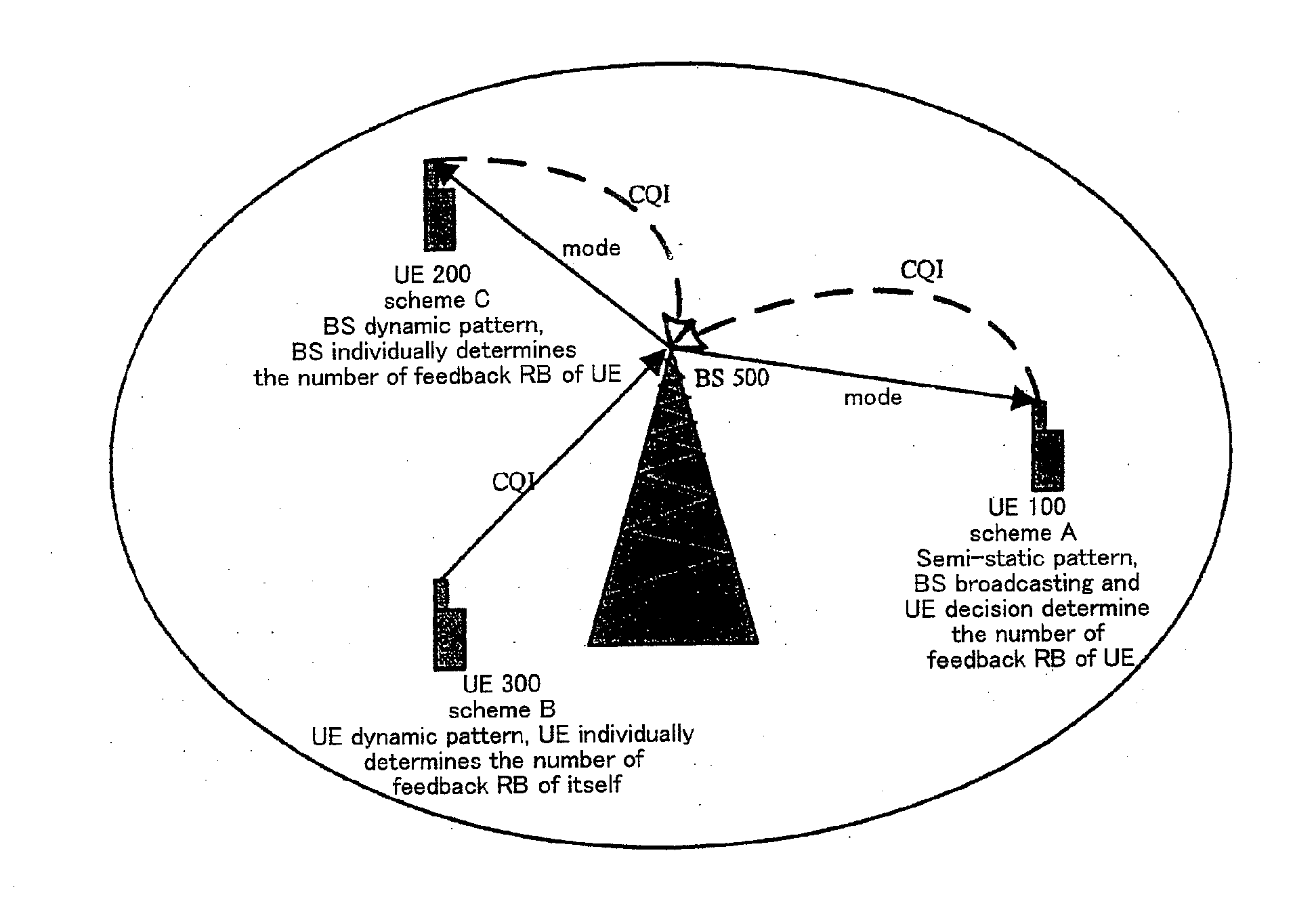
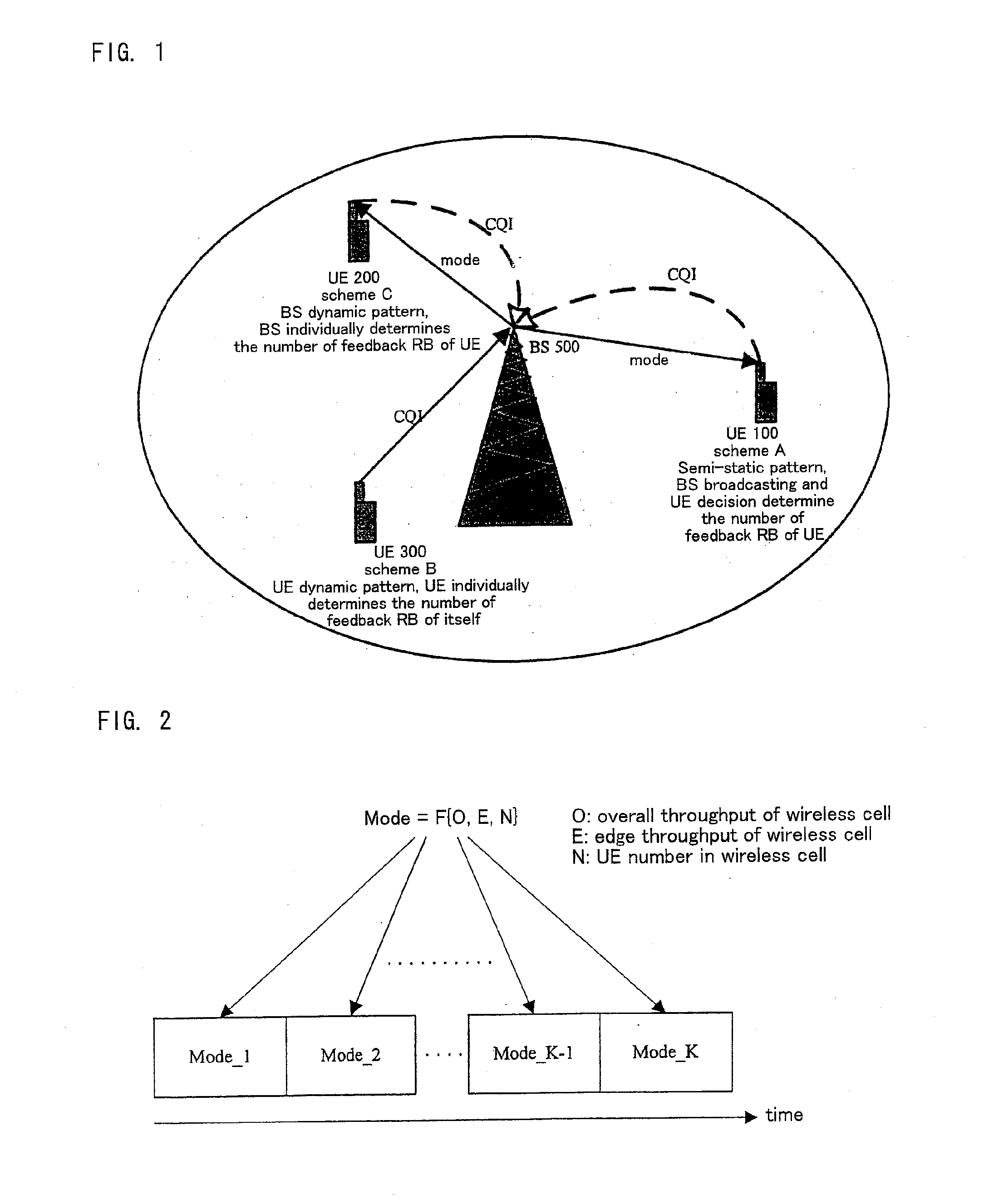
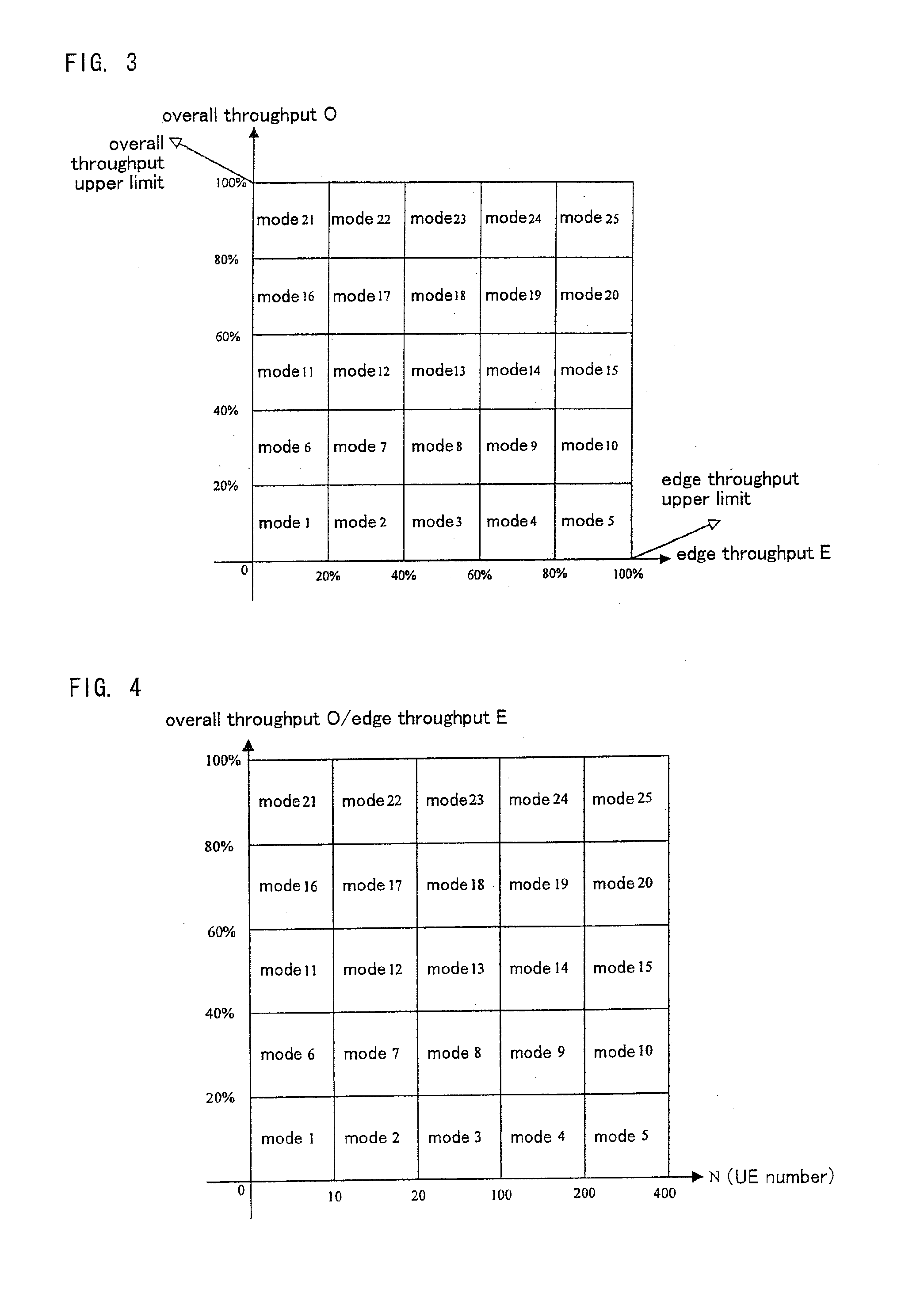
Mobile communication system, base station, user equipment, and communication method
ActiveUS20110007643A1Improve efficiencyEasy to implementTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsResource blockMobile communication systems
A method for adaptively deciding number of feedback resource blocks in a downlink which comprises that a base station (500) determines a mode corresponding to the number of the feedback resource blocks which a user equipment feeds back by monitoring performance of a wireless cell and number of the user equipments (100) and transmits the mode to the user equipments (100) through signaling; the user equipments (100) listens to the mode and adaptively decides the number of feedback resource blocks by conditions of itself and feeds back downlink channel quality indicator information to the base station (500) according to Best channel quality indicator number or Threshold based feedback algorithm; and the base station (500) performs resource scheduling according to the feedback information. The present invention provides a method for adaptively deciding the number of feedback resource blocks based on base station signaling and user equipment decision, with respect to Best channel quality indicator number or Threshold based feedback algorithm in downlinks, thus insuring the performance of the wireless cell.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and device for notifying and determining dmrs ports or mapping relationship
ActiveUS20190013910A1Channel estimation performanceSave signaling overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelConnection managementMimo transmissionPhysical layer
A method and device for notifying and determining DMRS ports or a mapping relationship is provided. The method includes a sending end sending indication information to a receiving end in a TM, and the sending end indicates allocation information about DMRS ports or a mapping relationship according to the indication information, and the indication information includes at least one of the following: RRC signaling, physical layer NDI bit, and DMRS pilot scrambler configuration information nscid. A problem of influence on a performance of a MU-MIMO system caused by lower channel estimation performance due to limited orthogonal DMRS ports for MU-MIMO transmission and high MUI after increment of a total number of MU-MIMO transmission layers is solved.
Owner:XIAN ZHONGXING NEW SOFTWARE
Method for Implementing Link Self-Adaptation, Network Device and Terminal Device
ActiveUS20140286246A1Save system resourcesSave signaling overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumTransfer mode
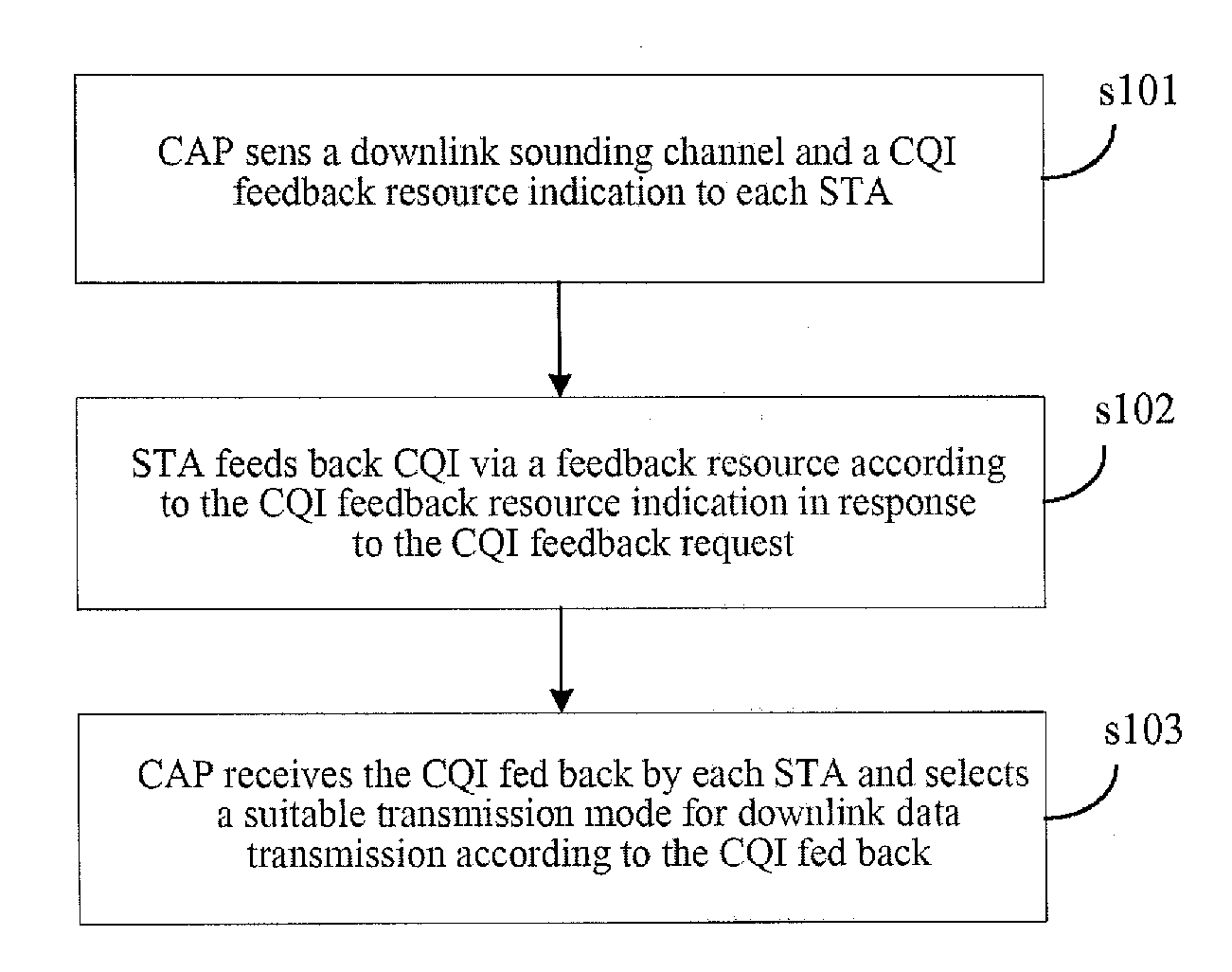
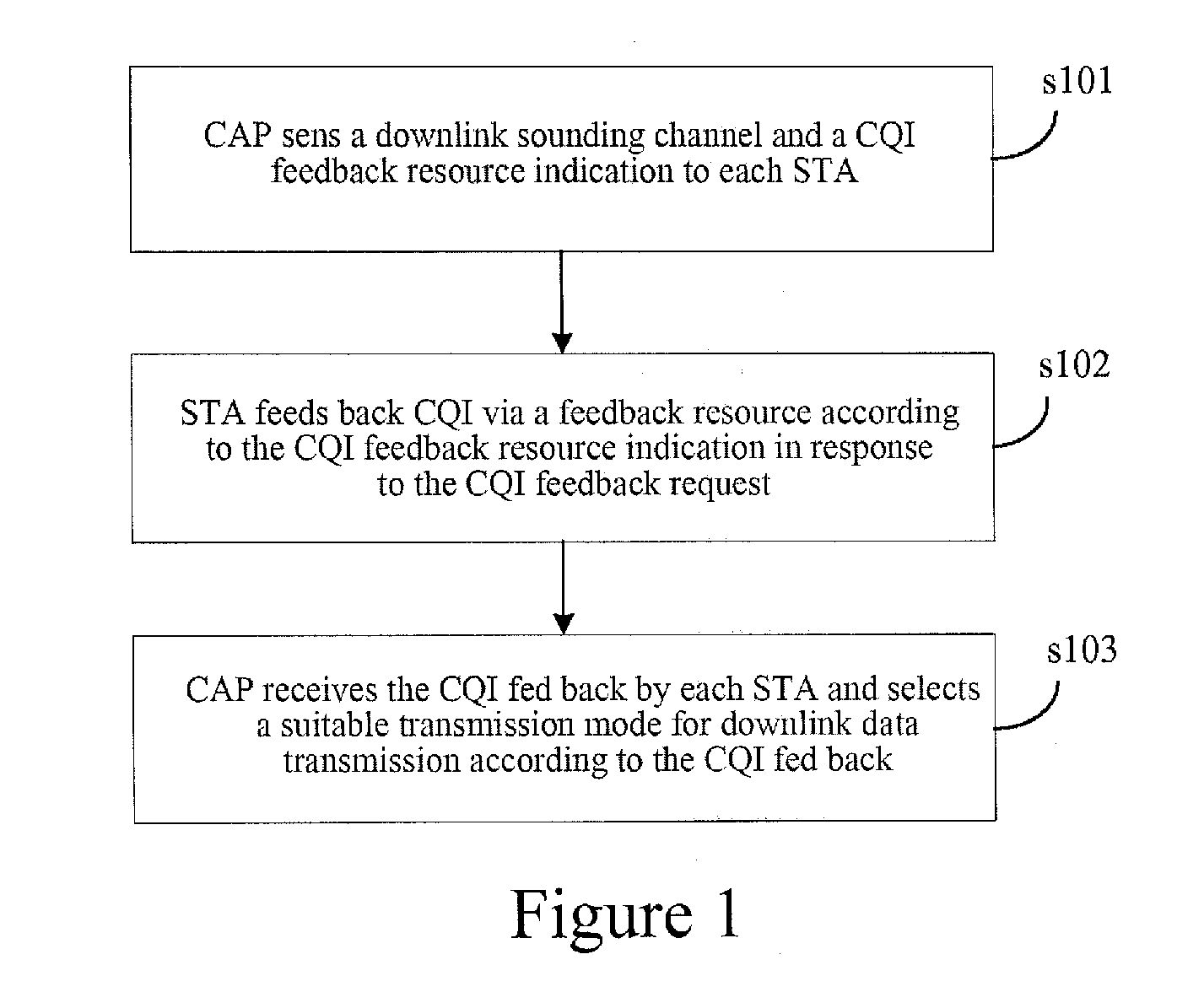
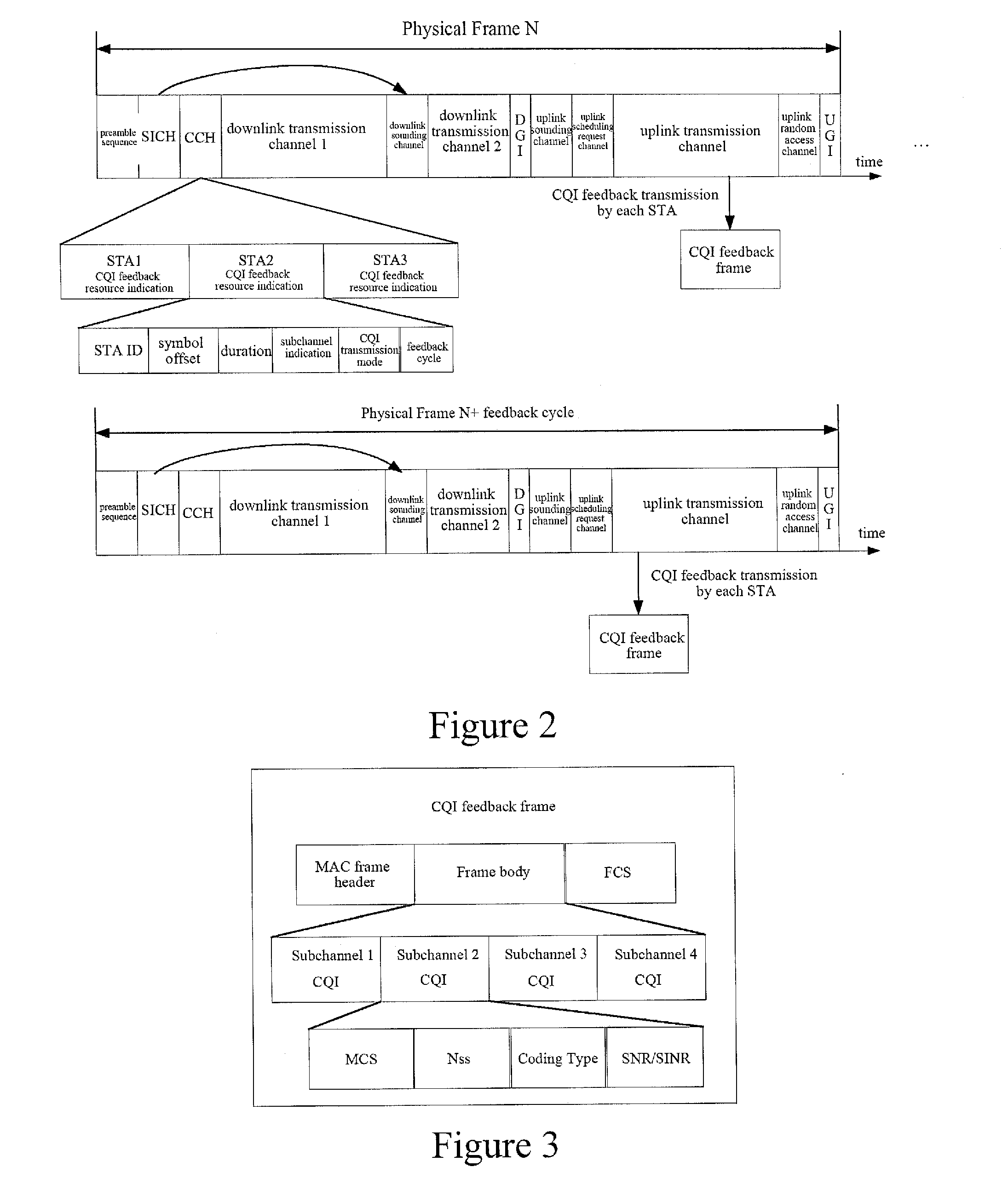
Disclosed is a method for implementing link self-adaptation, comprising: sending a downlink sounding channel and a channel quality information CQI feedback resource indication; and receiving CQI information, and selecting a suitable transmission mode for downlink data transmission according to the CQI information. Further disclosed are a network device and a terminal device. By using the method and devices provided in the present invention, the spectrum utilization rate and system performance can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING NUFRONT MOBILE MULTIMEDIA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com